Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
585 results about "Token bucket" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
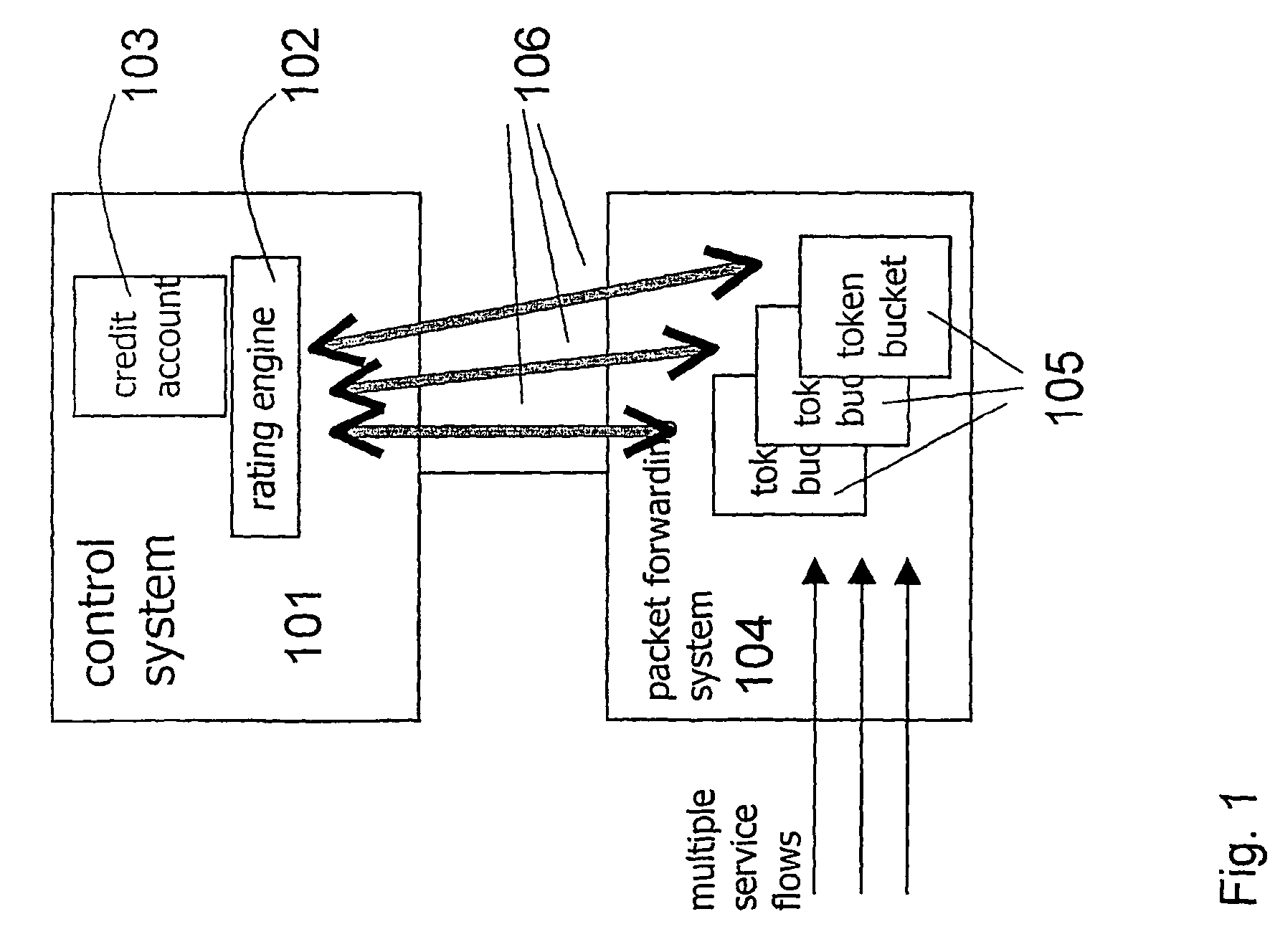
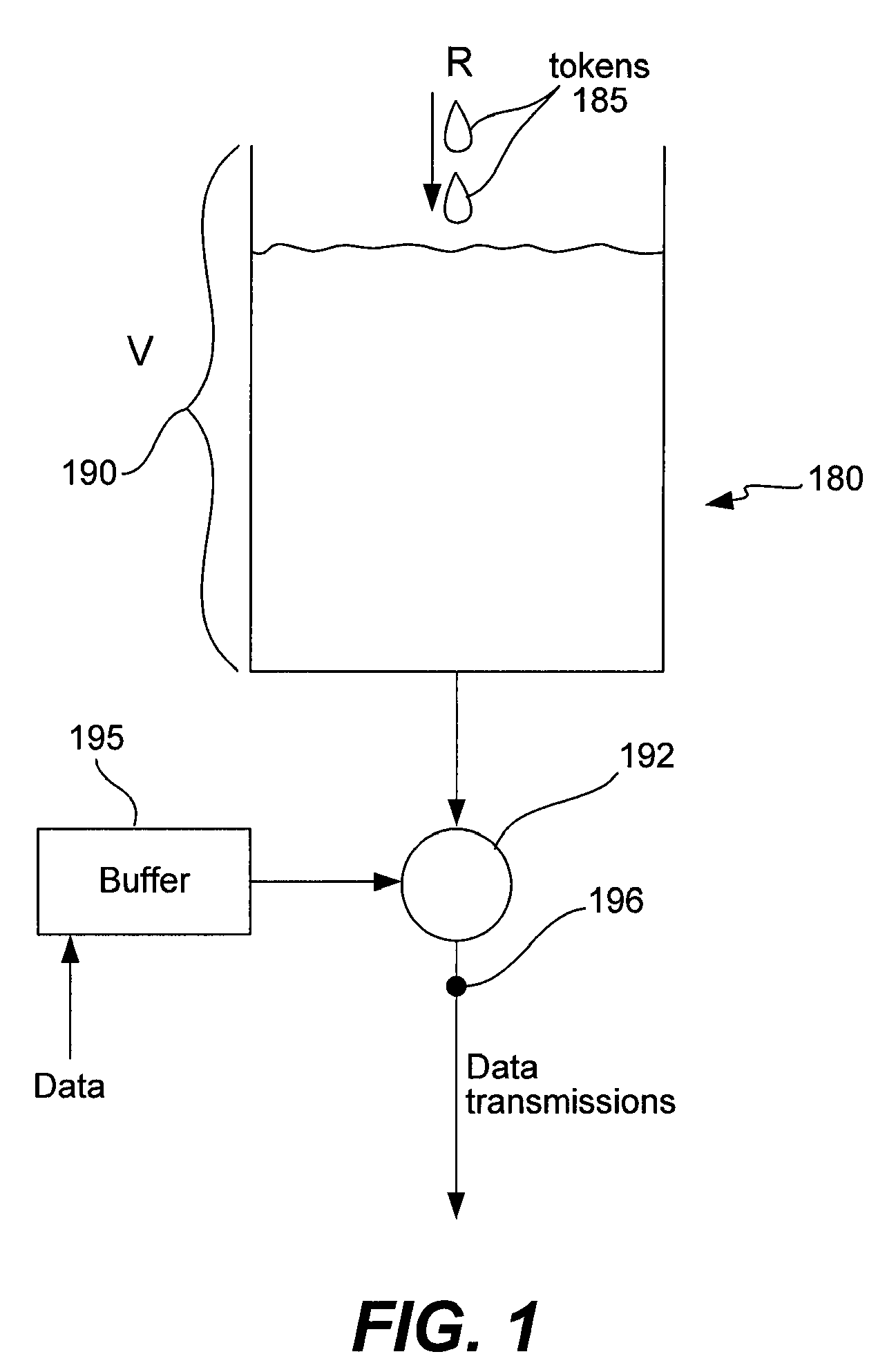
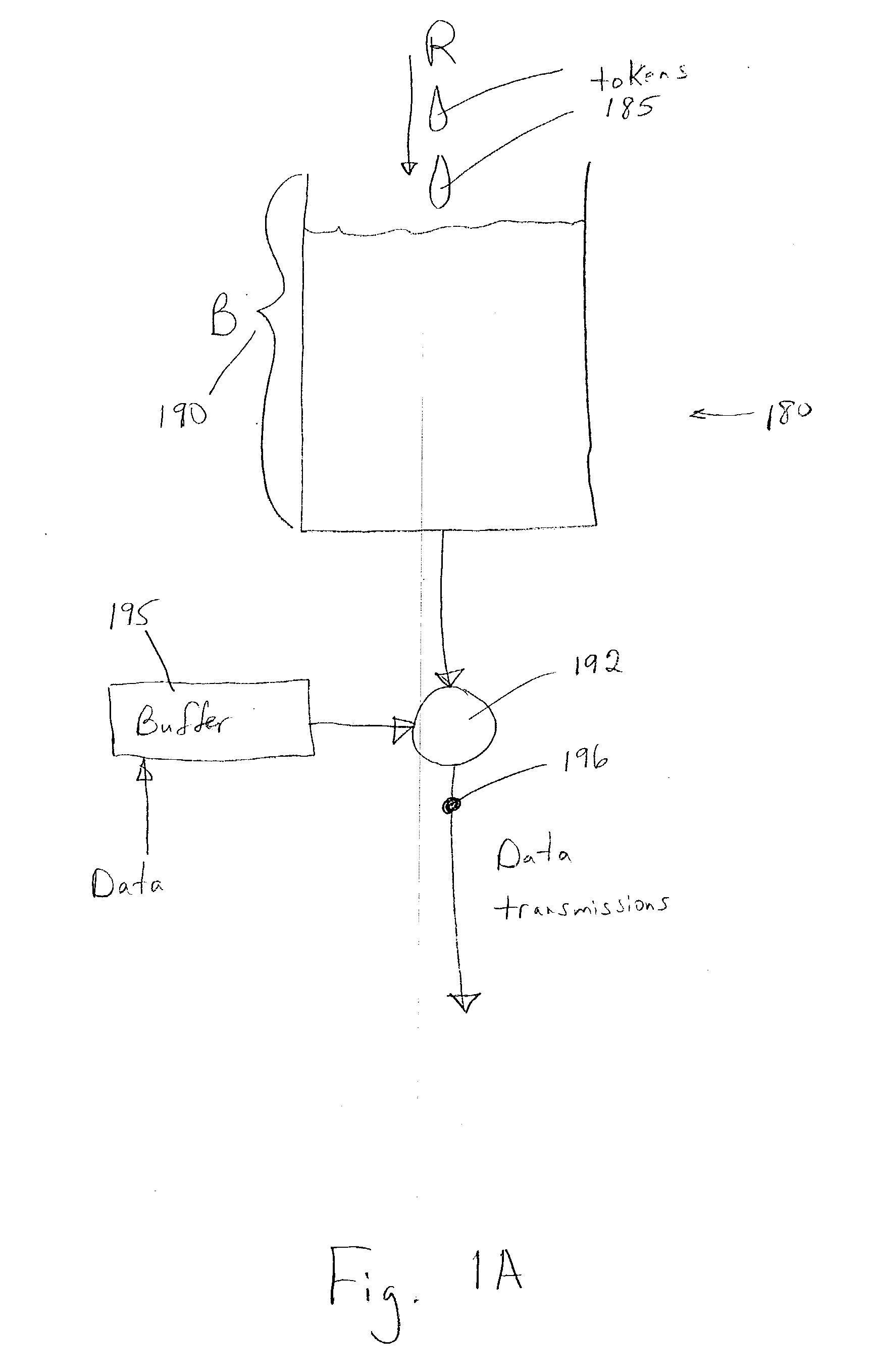
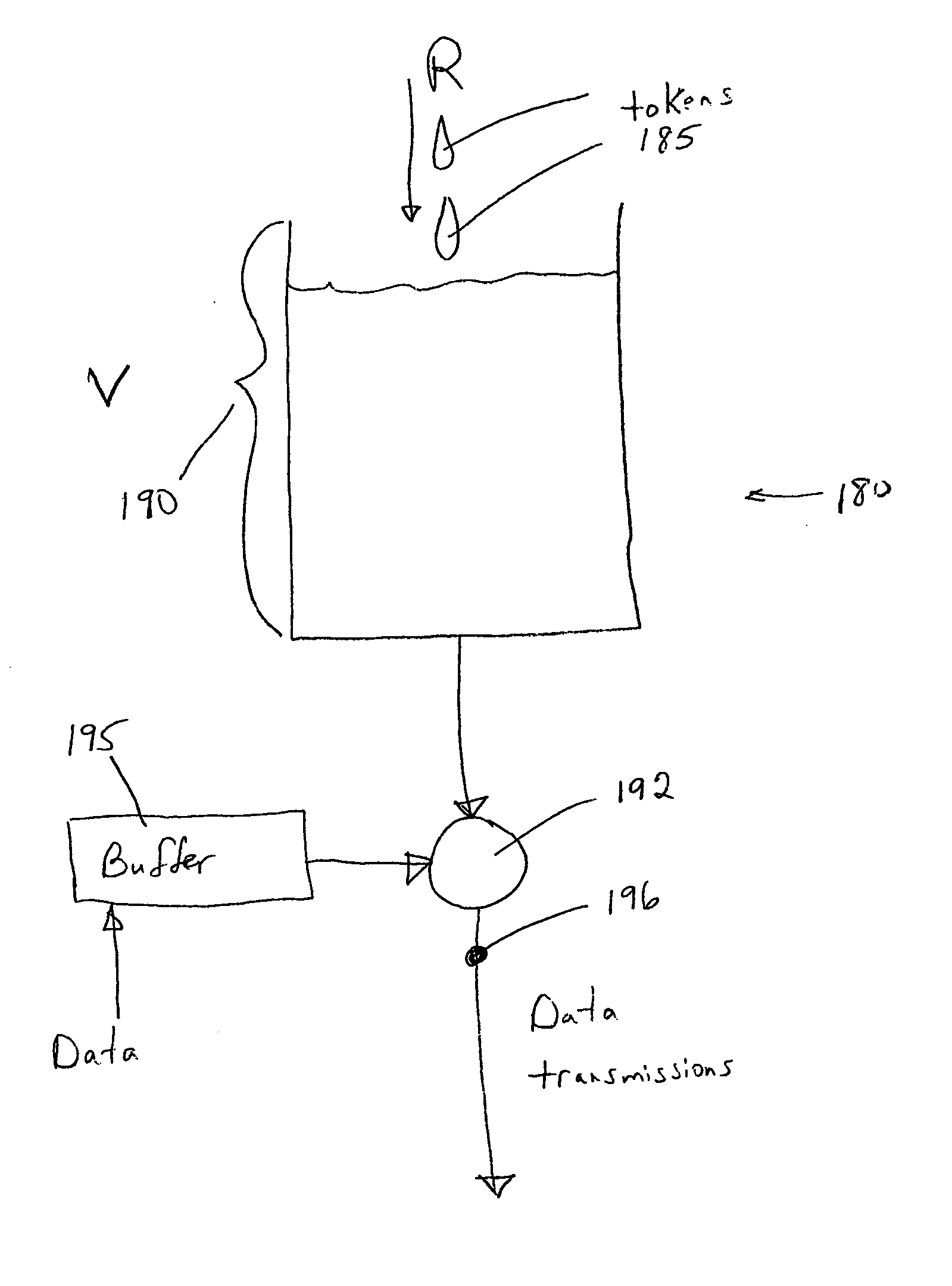
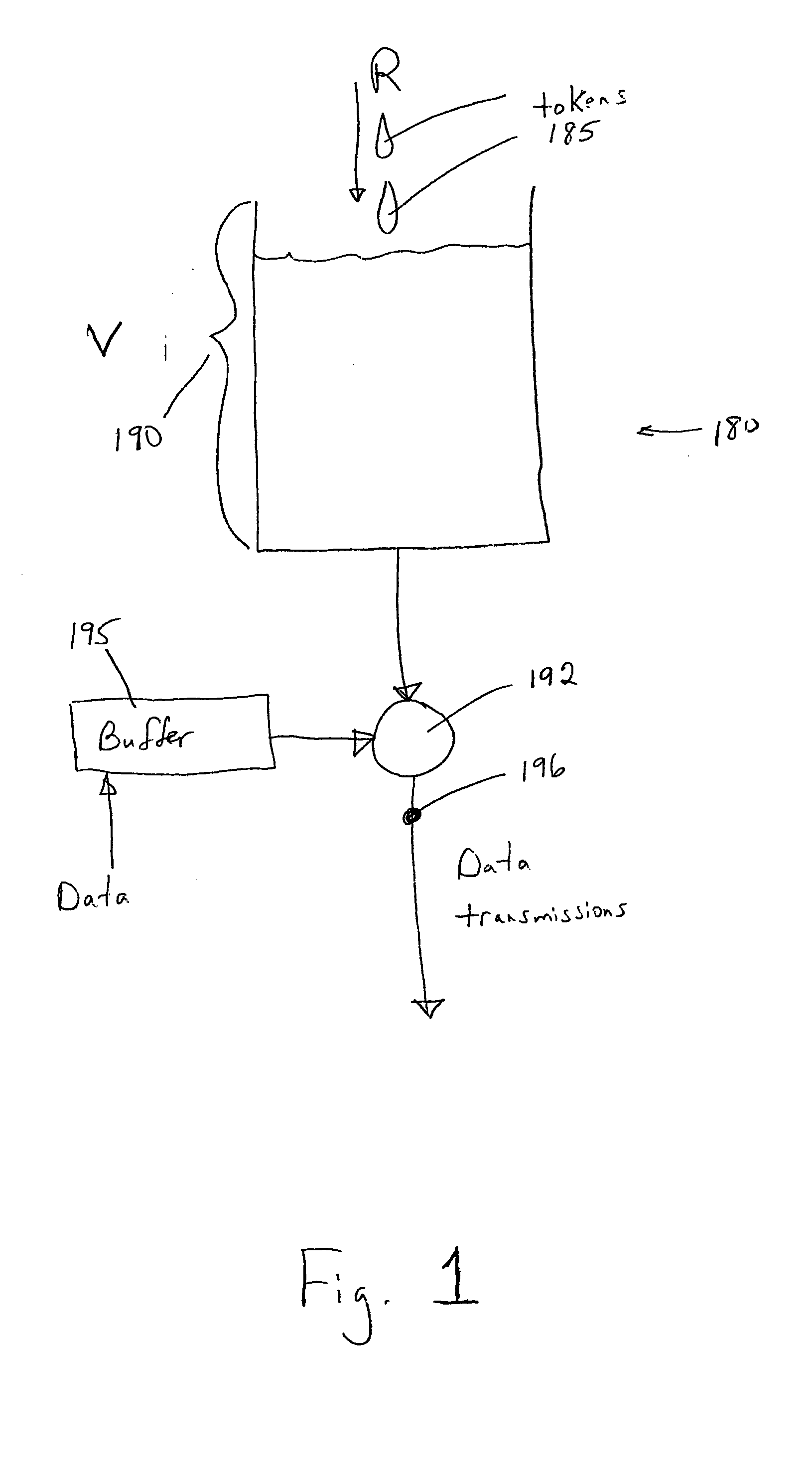
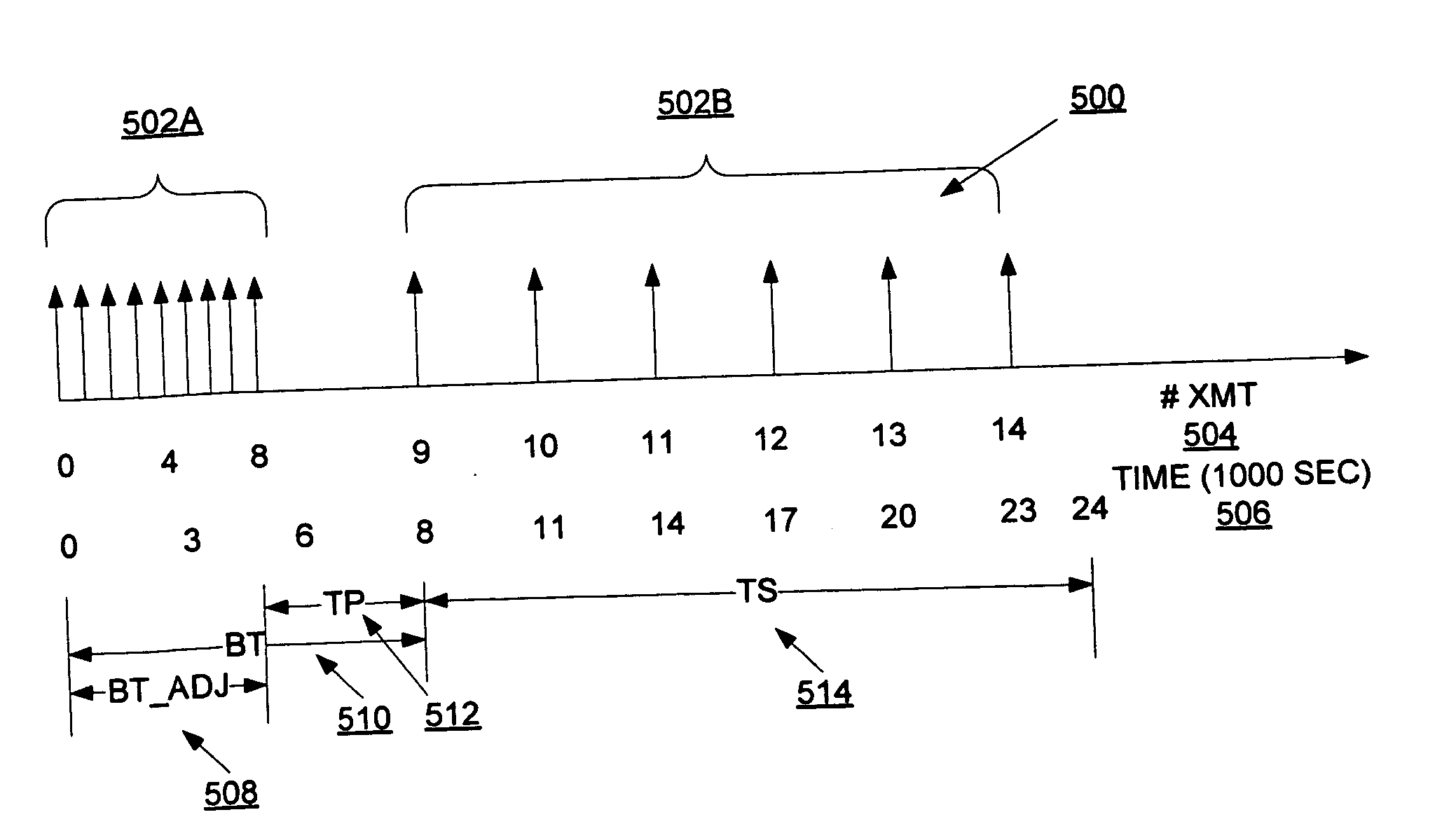
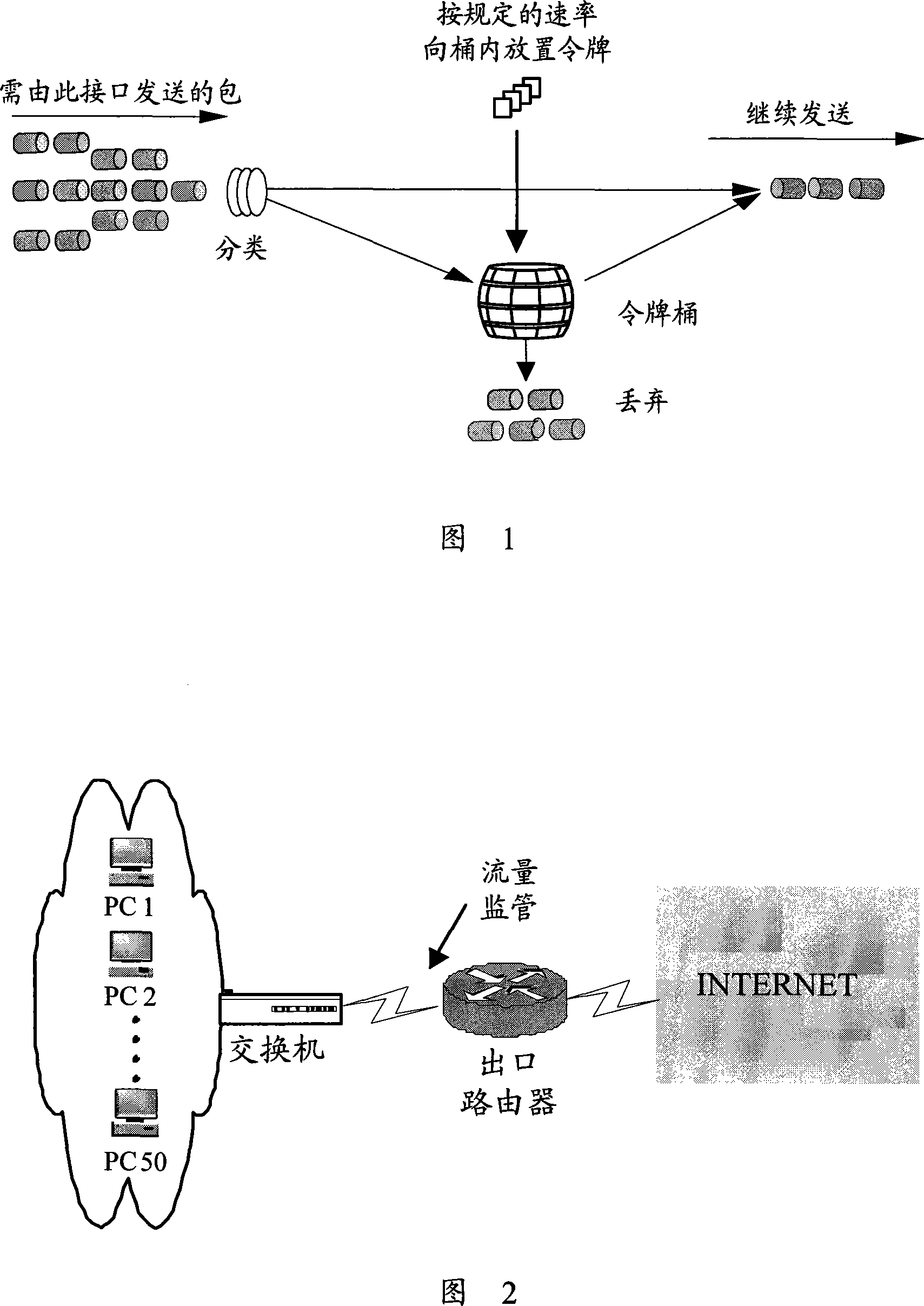
The token bucket is an algorithm used in packet switched computer networks and telecommunications networks. It can be used to check that data transmissions, in the form of packets, conform to defined limits on bandwidth and burstiness (a measure of the unevenness or variations in the traffic flow). It can also be used as a scheduling algorithm to determine the timing of transmissions that will comply with the limits set for the bandwidth and burstiness: see network scheduler.
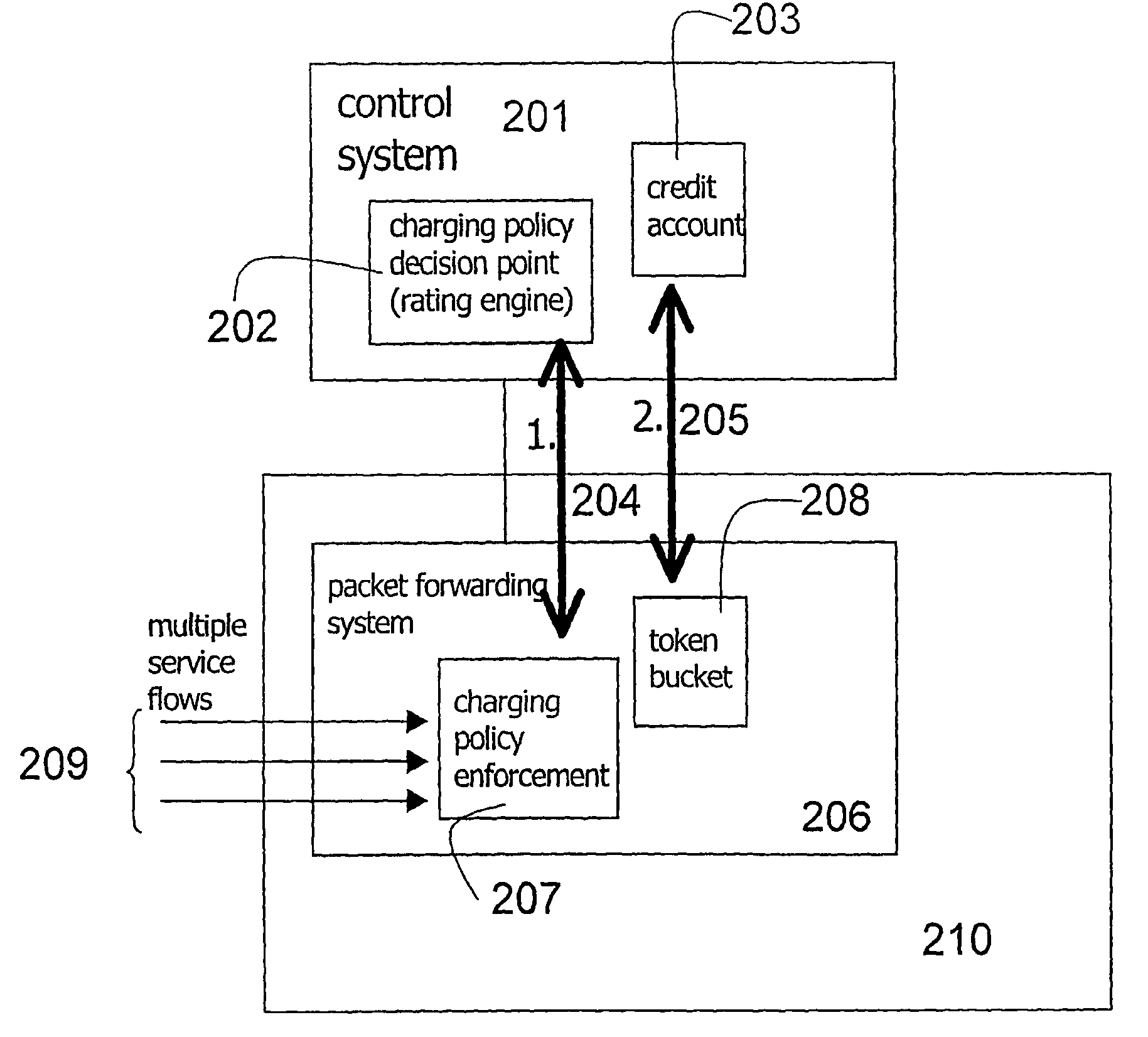
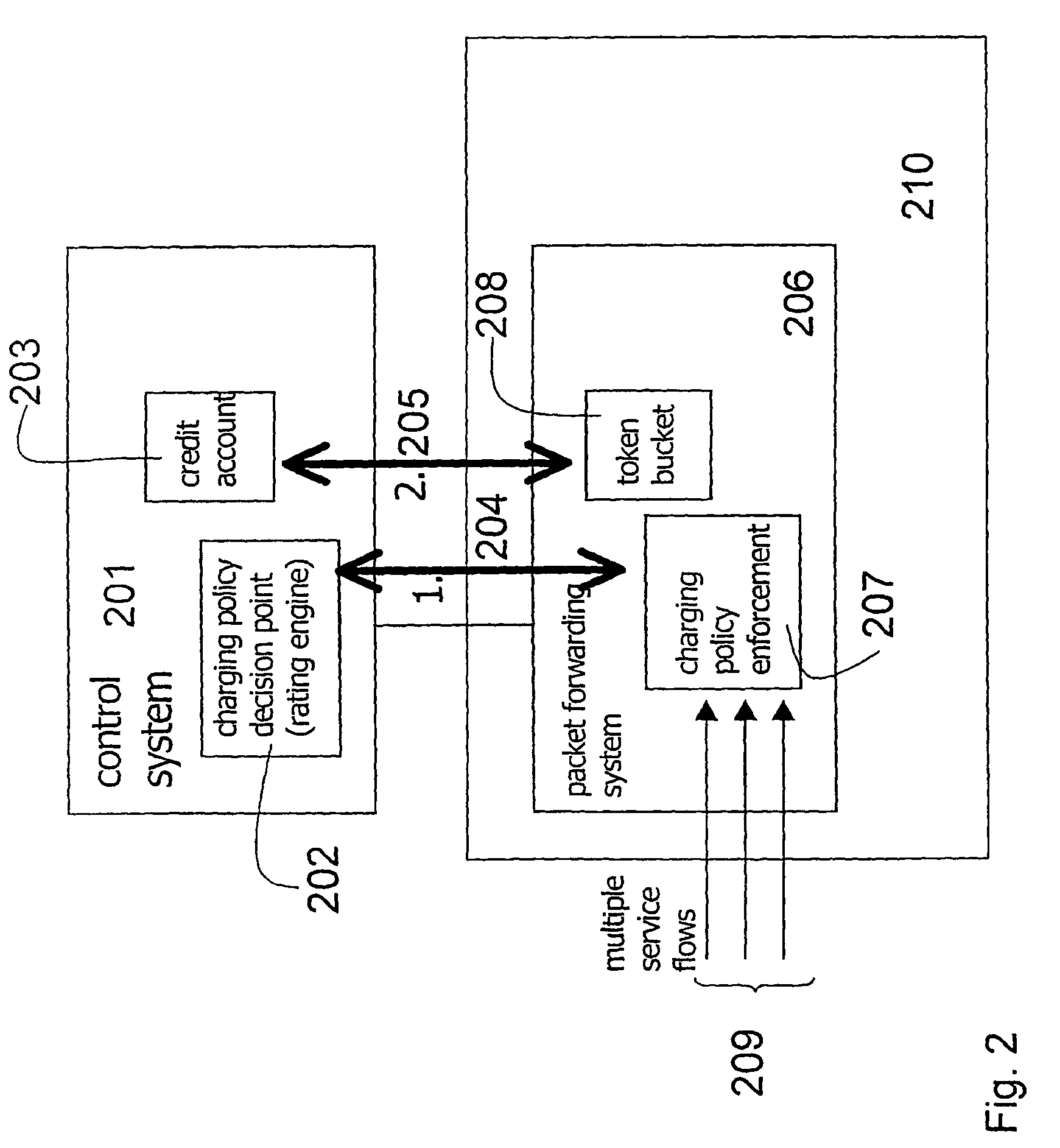
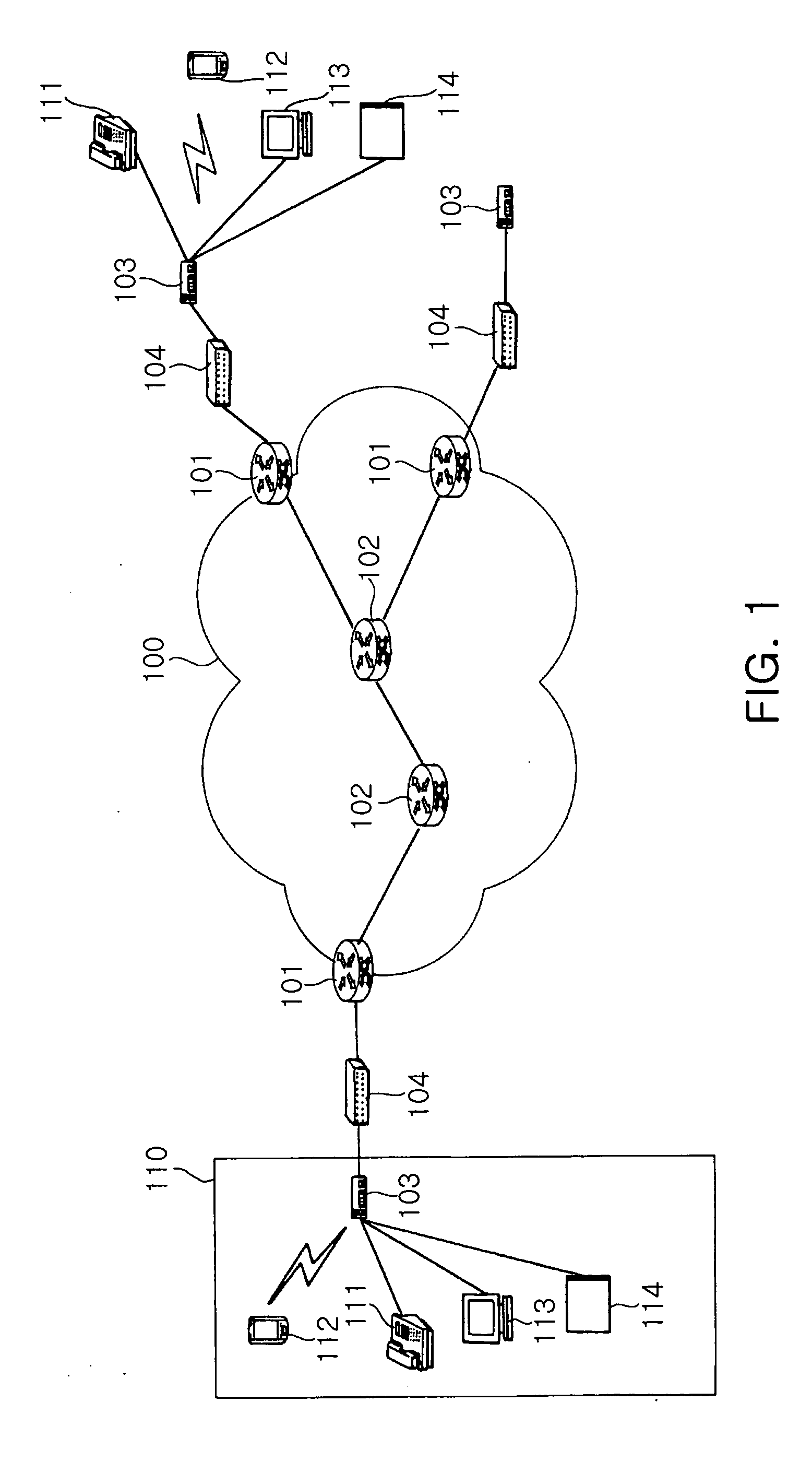
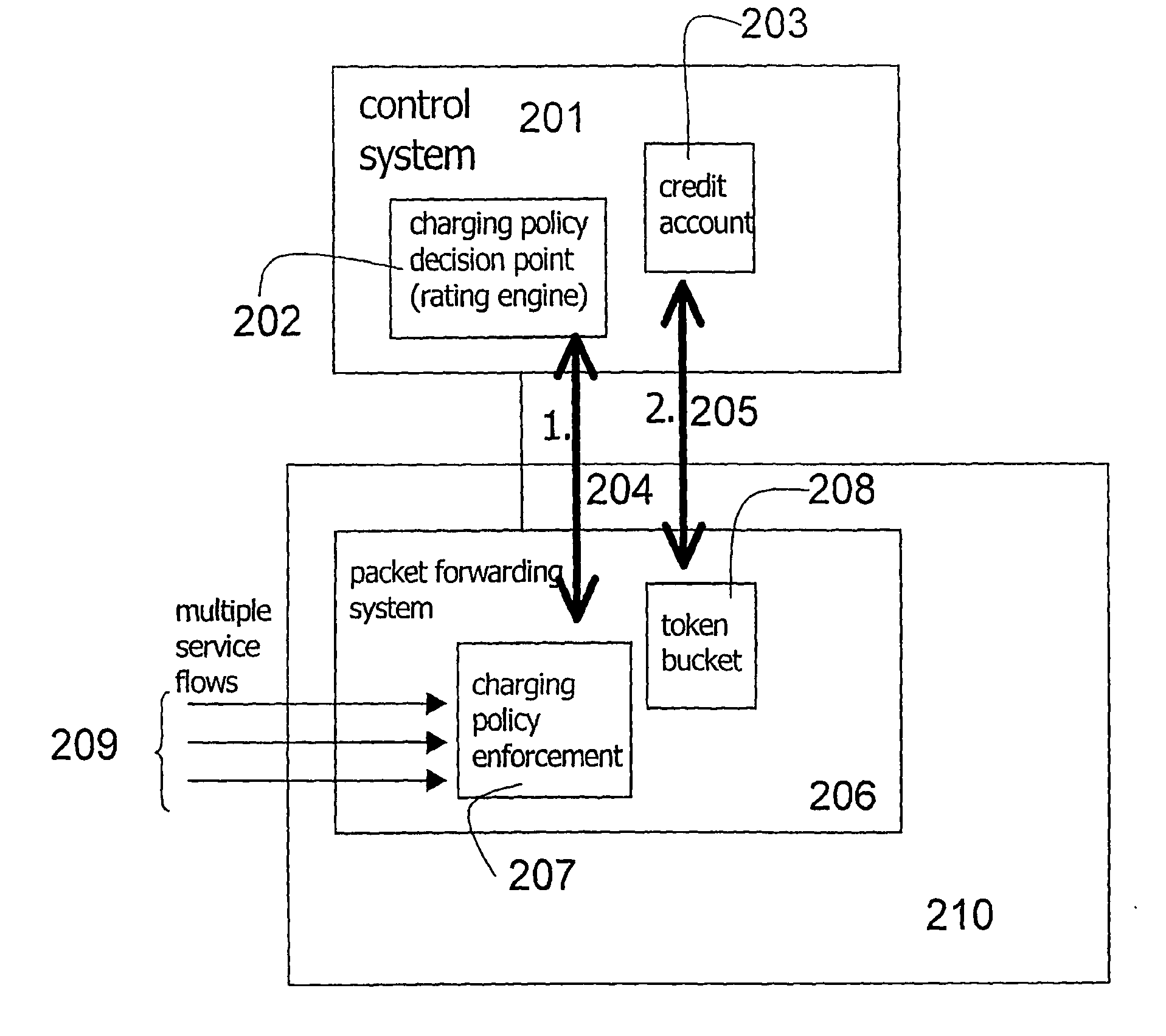
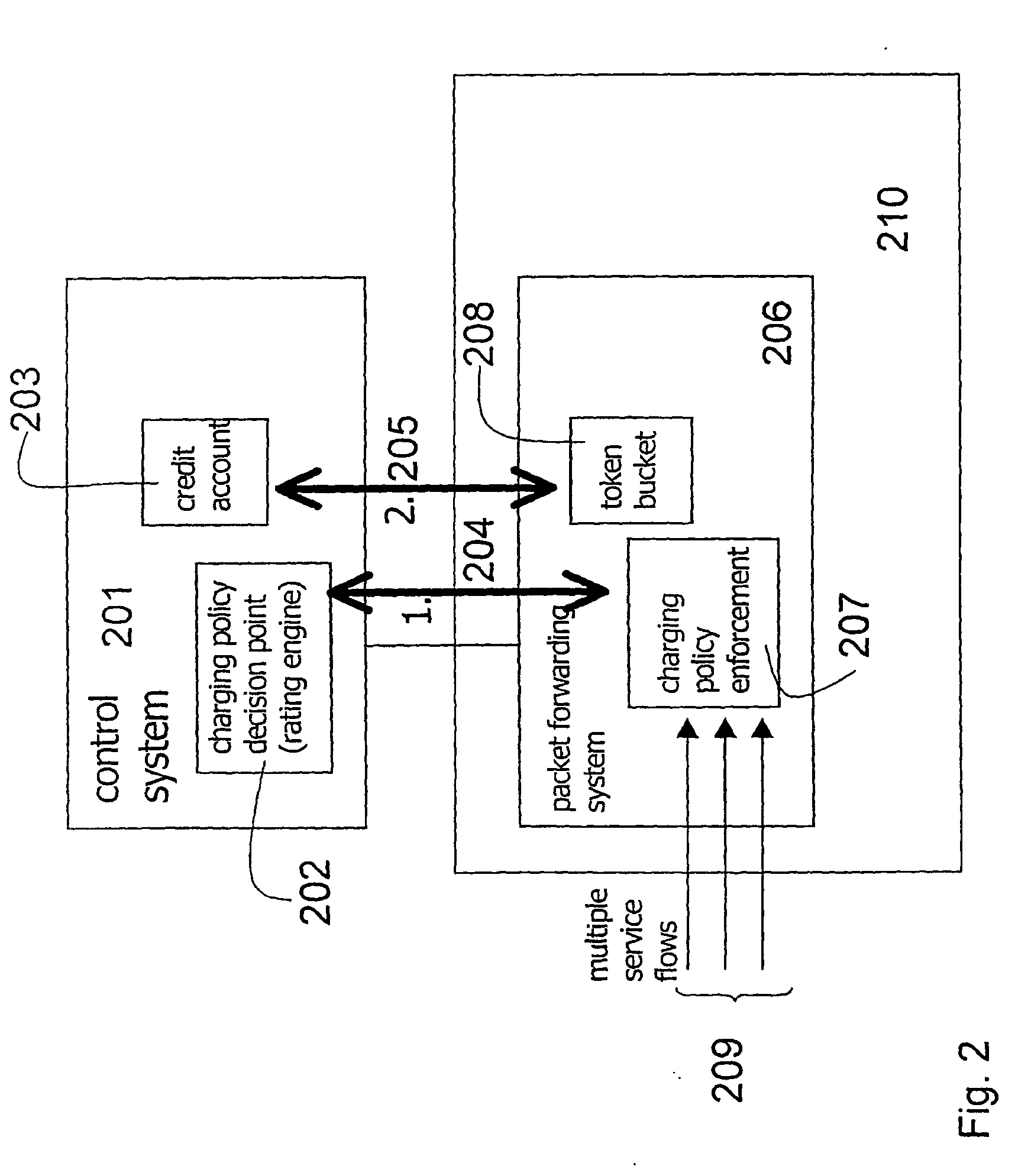
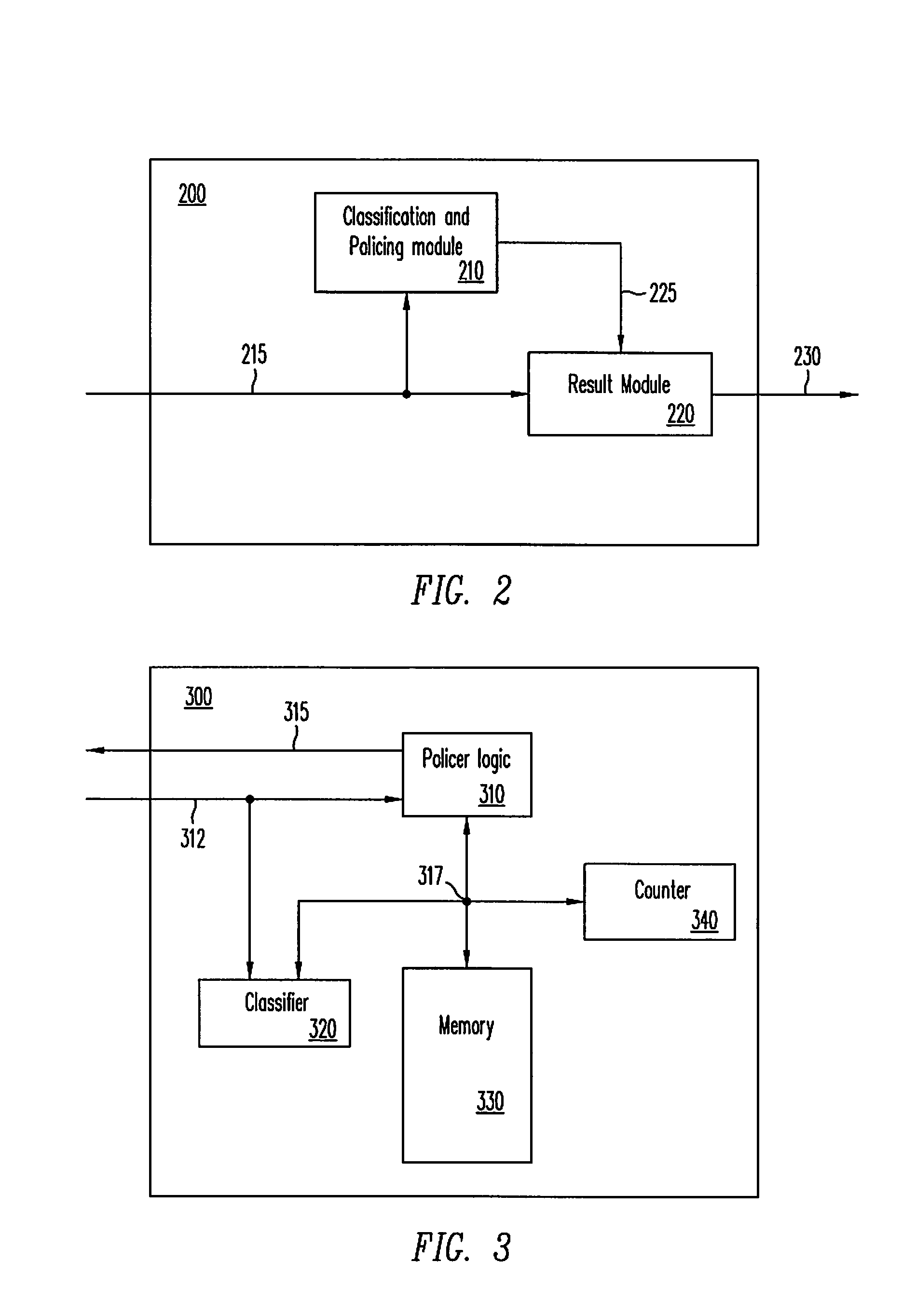
System for providing flexible charging in a network
ActiveUS7450591B2Reduce signaling loadReduce reservationMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsData switching by path configurationService flowPolicy decision
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
System and method for guaranteeing quality of service in IP networks
InactiveUS20050135243A1Guaranteed reliabilityReduce loadError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDifferentiated servicesData pack
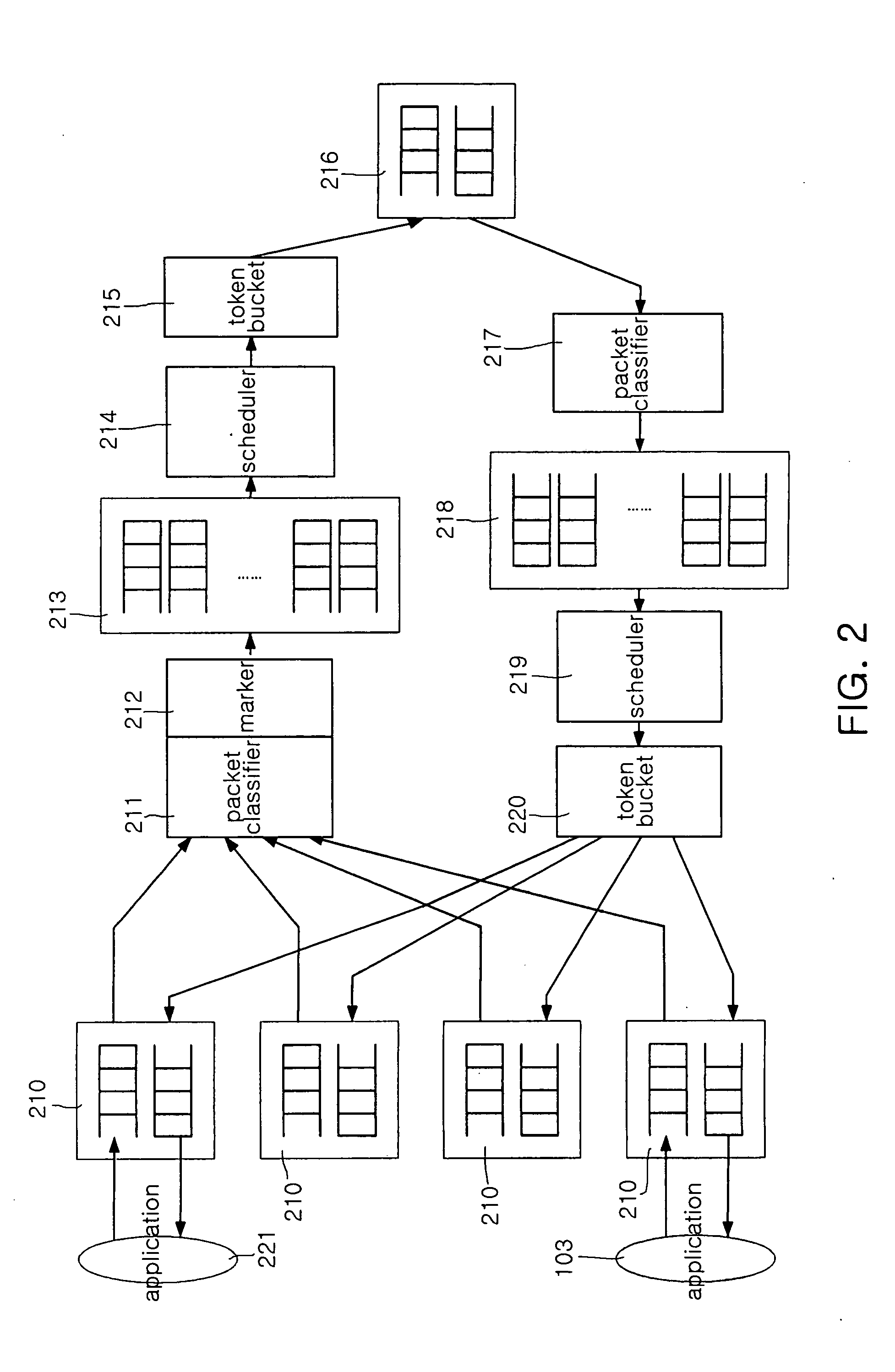
The system of the present invention guarantees quality of service with respect to packets transmitted / received between an external network capable of providing differentiated services and a home network. The system includes a packet classifier, a marker, a priority class queue, a scheduler and a token bucket. The packet classifier classifies the packets according to addresses and traffic types. The marker allocates information on priorities to packets transmitted from the home network to the external network. The priority class queue has a plurality of queues classified according to the priorities. The scheduler services packets stored in the priority class queue according to the priorities. The token bucket drops packets, bandwidths of which are above a preset maximum bandwidth, when the packets are generated.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
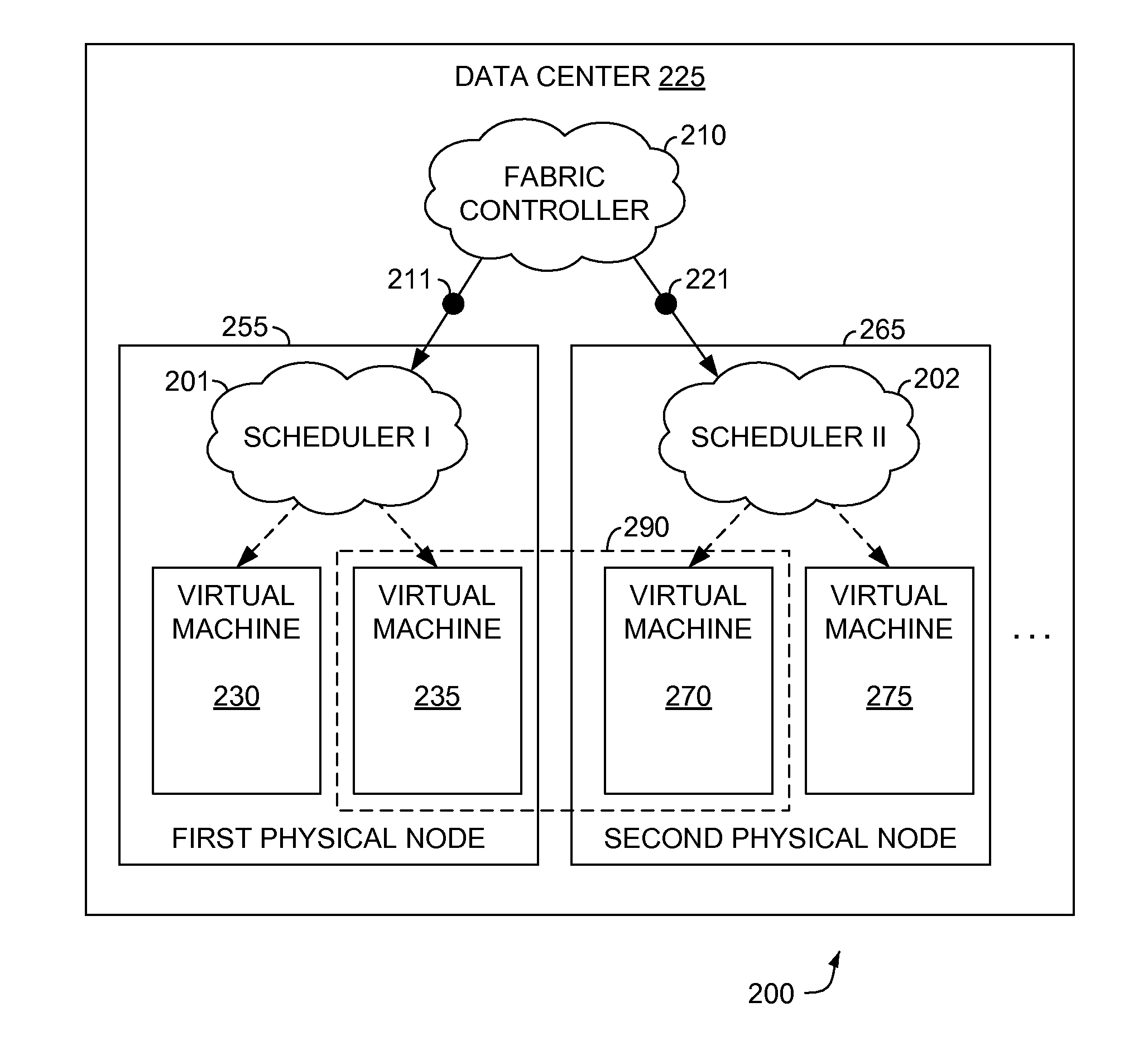
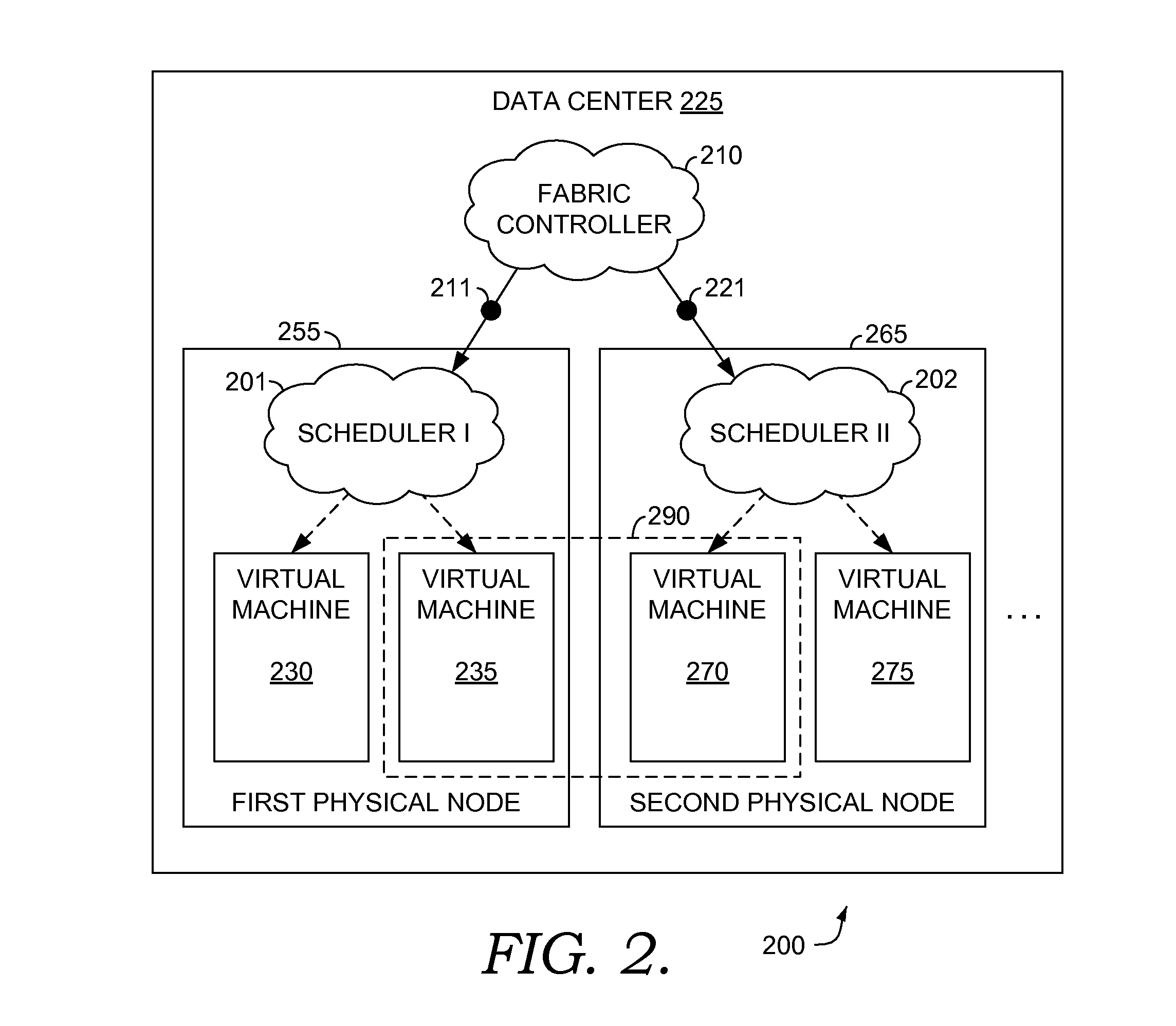
Applying Policies to Schedule Network Bandwidth Among Virtual Machines
ActiveUS20110292792A1Maintain fairnessMaximize throughputError preventionTransmission systemsResource consumptionDistributed computing
Computerized methods, systems, and computer-storage media for allowing virtual machines (VMs) residing on a common physical node to fairly share network bandwidth are provided. Restrictions on resource consumption are implemented to ameliorate stressing the network bandwidth or adversely affecting the quality of service (QoS) guaranteed to tenants of the physical node. The restrictions involves providing a scheduler that dynamically controls networking bandwidth allocated to each of the VMs as a function of QoS policies. These QoS policies are enforced by controlling a volume of traffic being sent from the VMs. Controlling traffic includes depositing tokens into token-bucket queues assigned to the VMs, respectively. The tokens are consumed as packets pass through the token-bucket queues. Upon consumption, packets are held until sufficient tokens are reloaded to the token-bucket queues.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
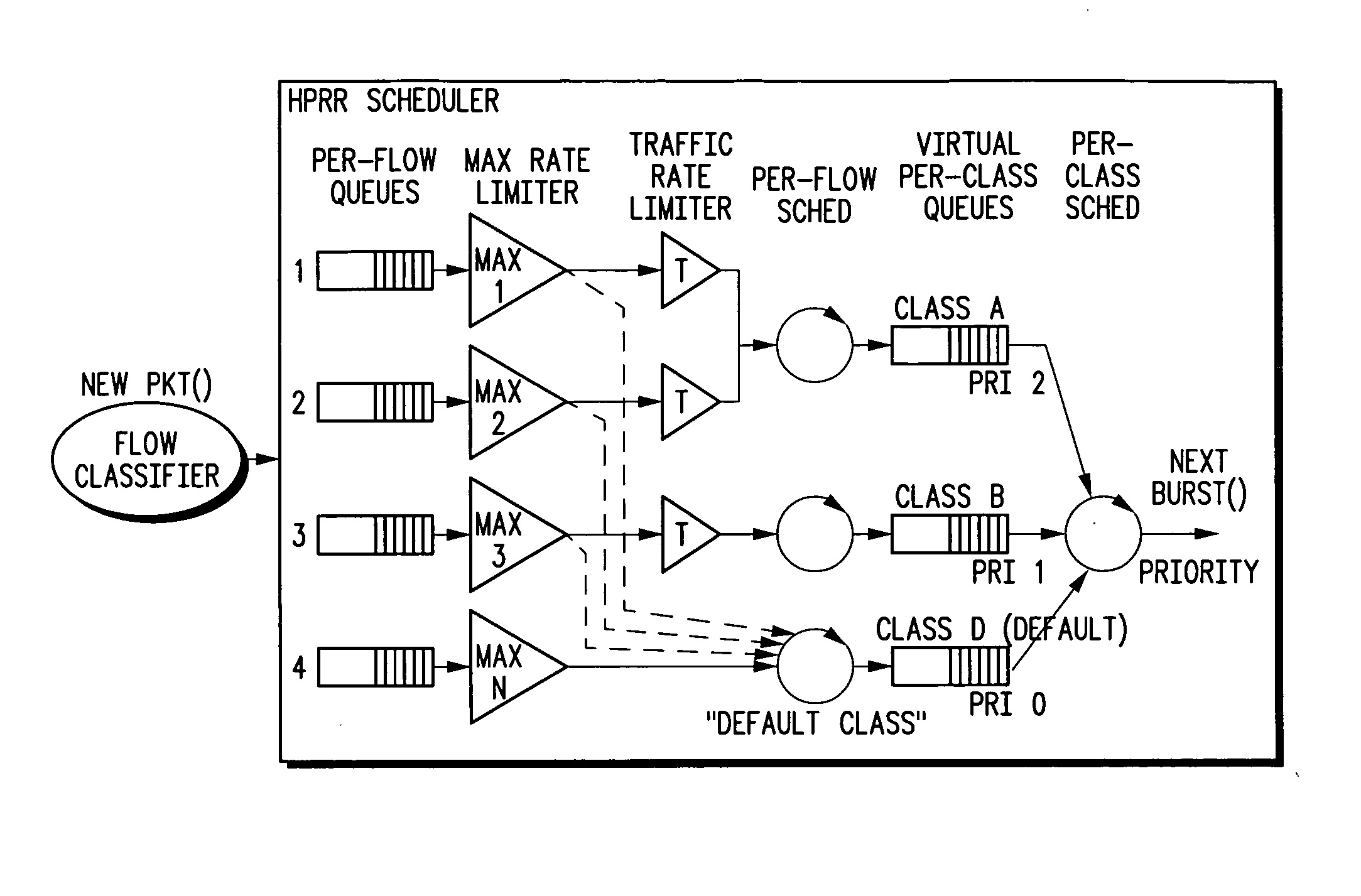
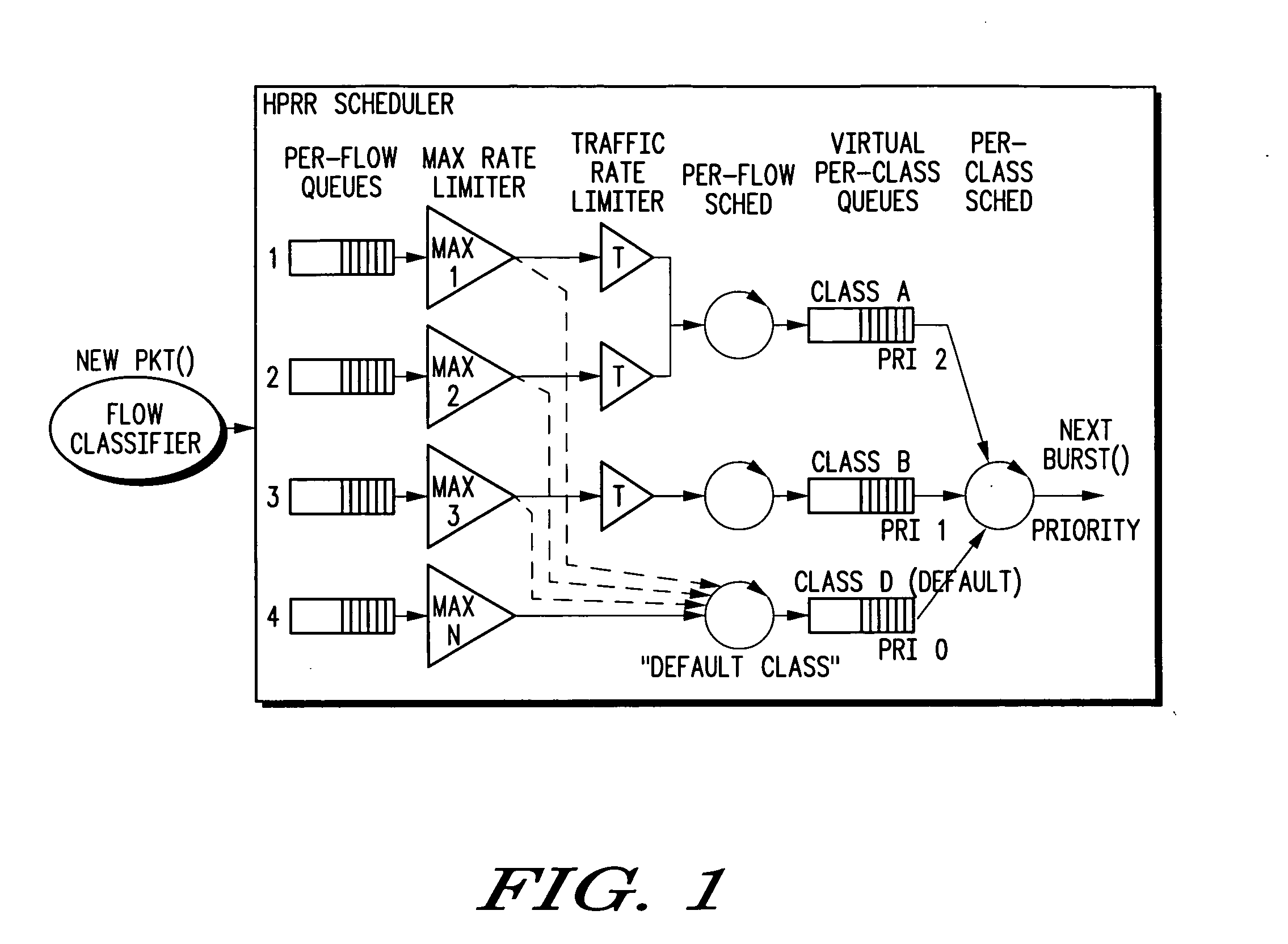
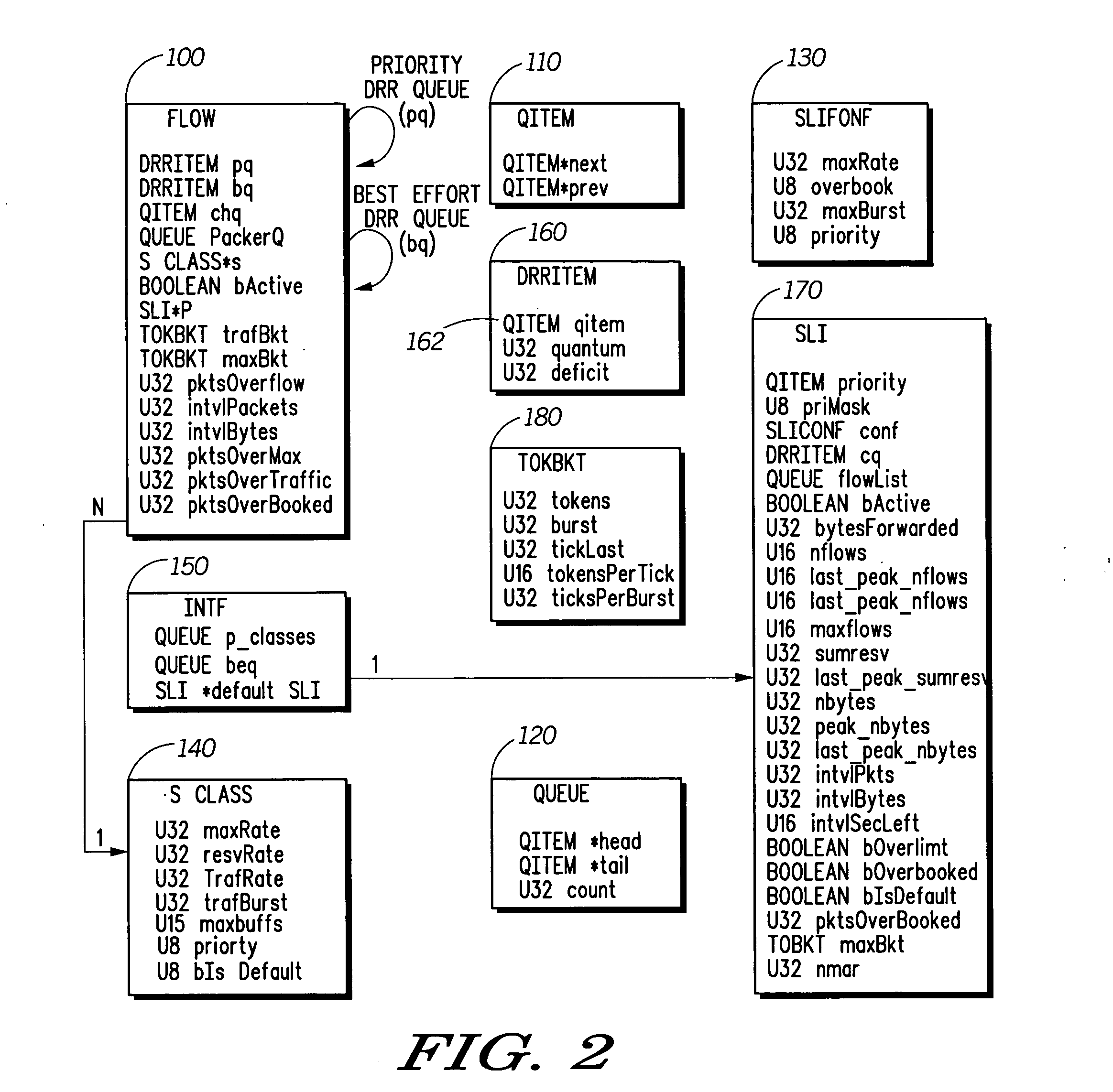
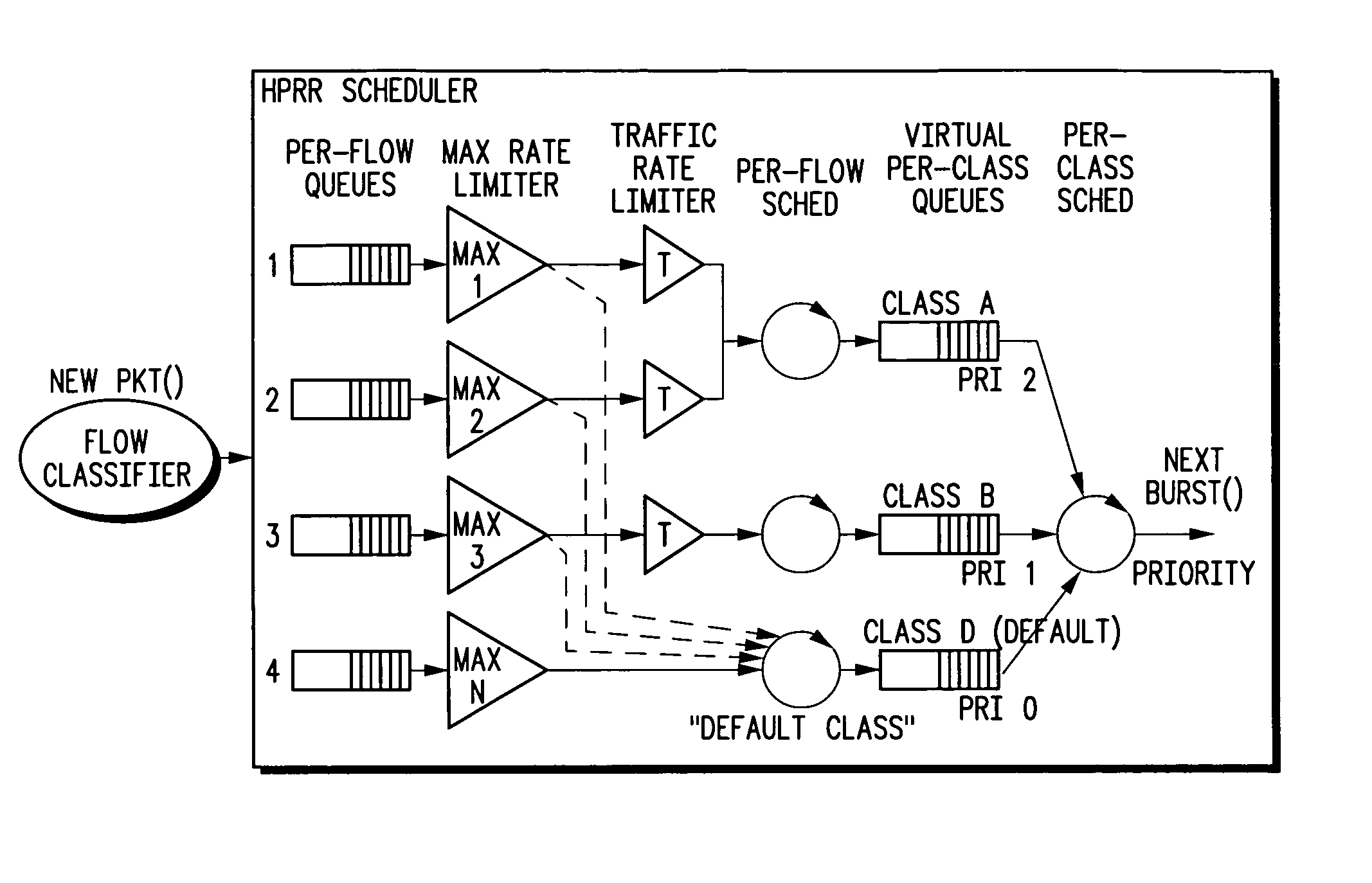
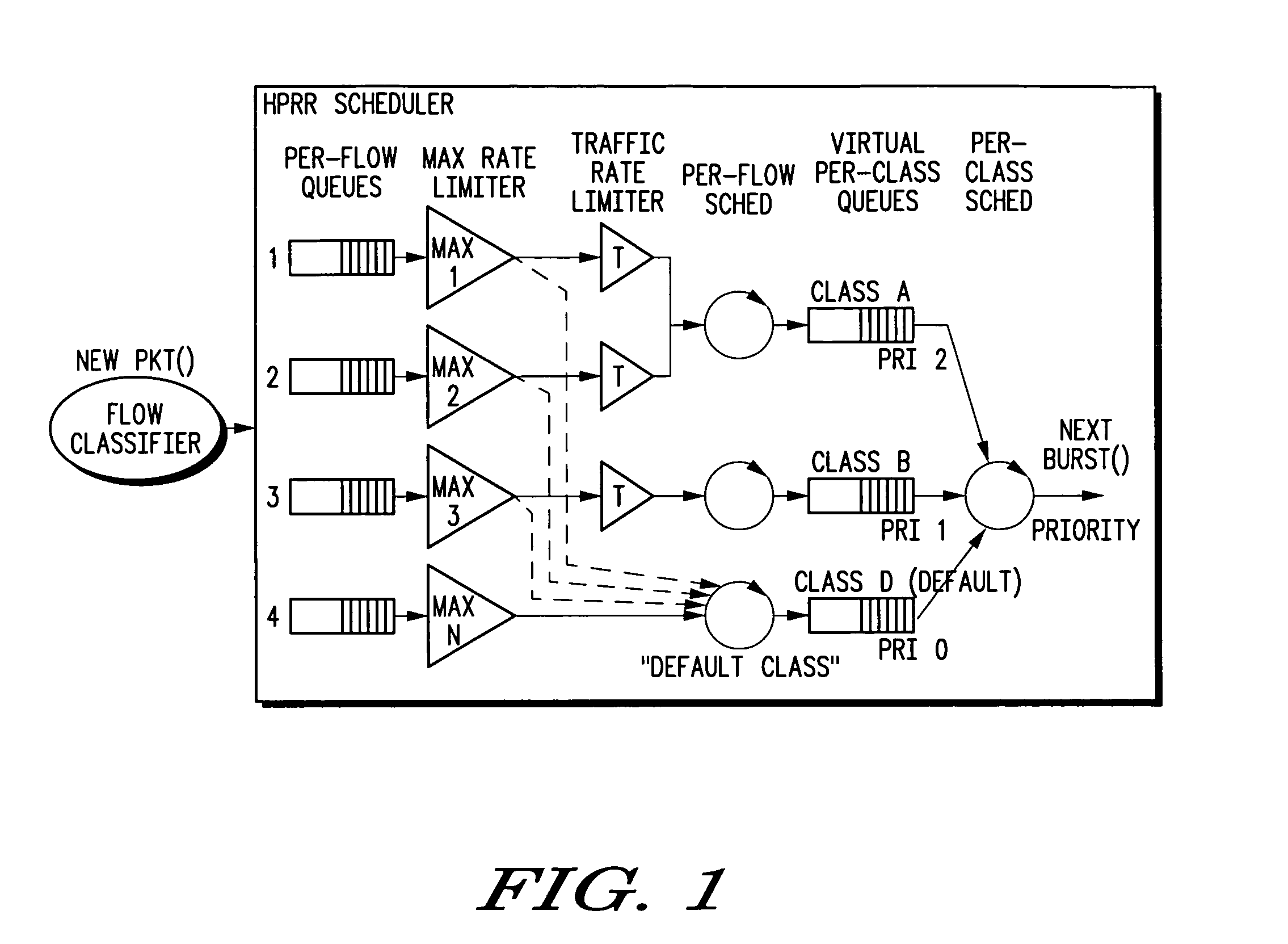
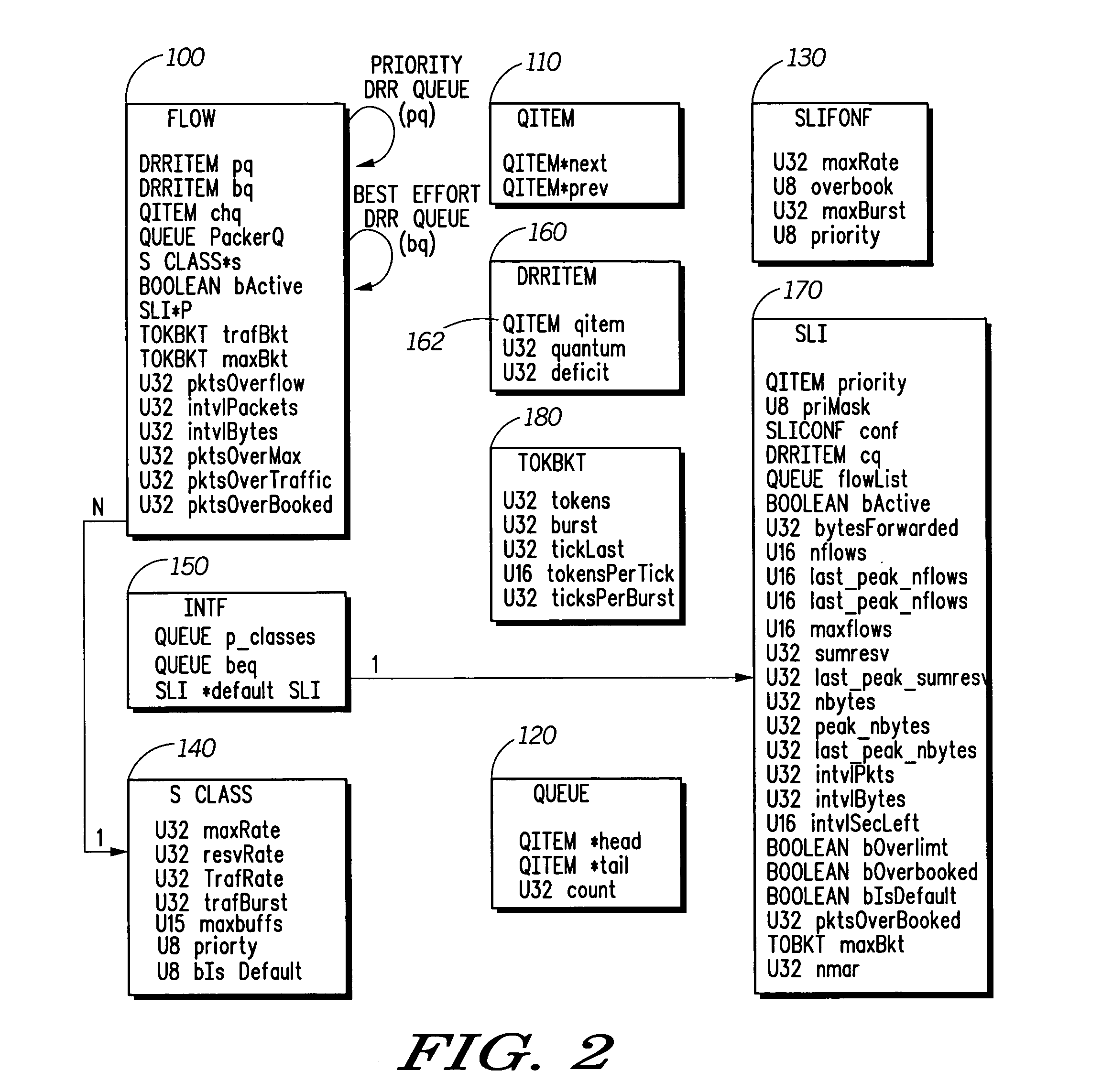
Hierarchical prioritized round robin (HPRR) scheduling
ActiveUS20050175014A1Simple algorithmIncrease delayData switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsDistributed computingToken bucket
The HPRR method uses “token bucket” rate classifiers to mark each individual packet as conforming or not conforming to a traffic specification for the flow. Flows are considered to be in a single service class. One such class is distinguished as a default “best effort” service class. Each service class is assigned a weight corresponding to its fraction of bandwidth granted to the class when all classes are active. The HPRR method allows a packet from a flow to be forwarded in one of two ways, either as part of its class's allocated bandwidth or as part of the “best effort” bandwidth. By always providing two paths for a flow to send its packets, a flow is always given its “fair share” of two different classes: its primary or configured class and the best effort class. An overbooked class will have each of its flows compete for the inadequate bandwidth allocated to the class, but because each flow can use the best effort bandwidth it also gets a fair share of that bandwidth to allow the classes bandwidth guarantees to be when other classes are inactive.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
Bandwidth allocation method and apparatus
System for bandwidth assignment to manage congestion over a network bottleneck, comprises a regulation point being set up downstream of the bottleneck in the network to manage congestion in data packets arriving from various sources via the bottleneck. For each of the sources, a priority level assigner assigns priority levels to respective data packets. A token bucket assigns tokens at a limiting rate to the prioritized data packets, the tokens allowing passage of packets to which they are assigned. The token bucket is a multi-priority token bucket, meaning it has at least two thresholds corresponding to the priority levels assigned to the packets. The token bucket only assigns a token to an arriving packet having a respective priority level if there are sufficient tokens currently in the bucket to reach the threshold corresponding to the packet's priority level.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
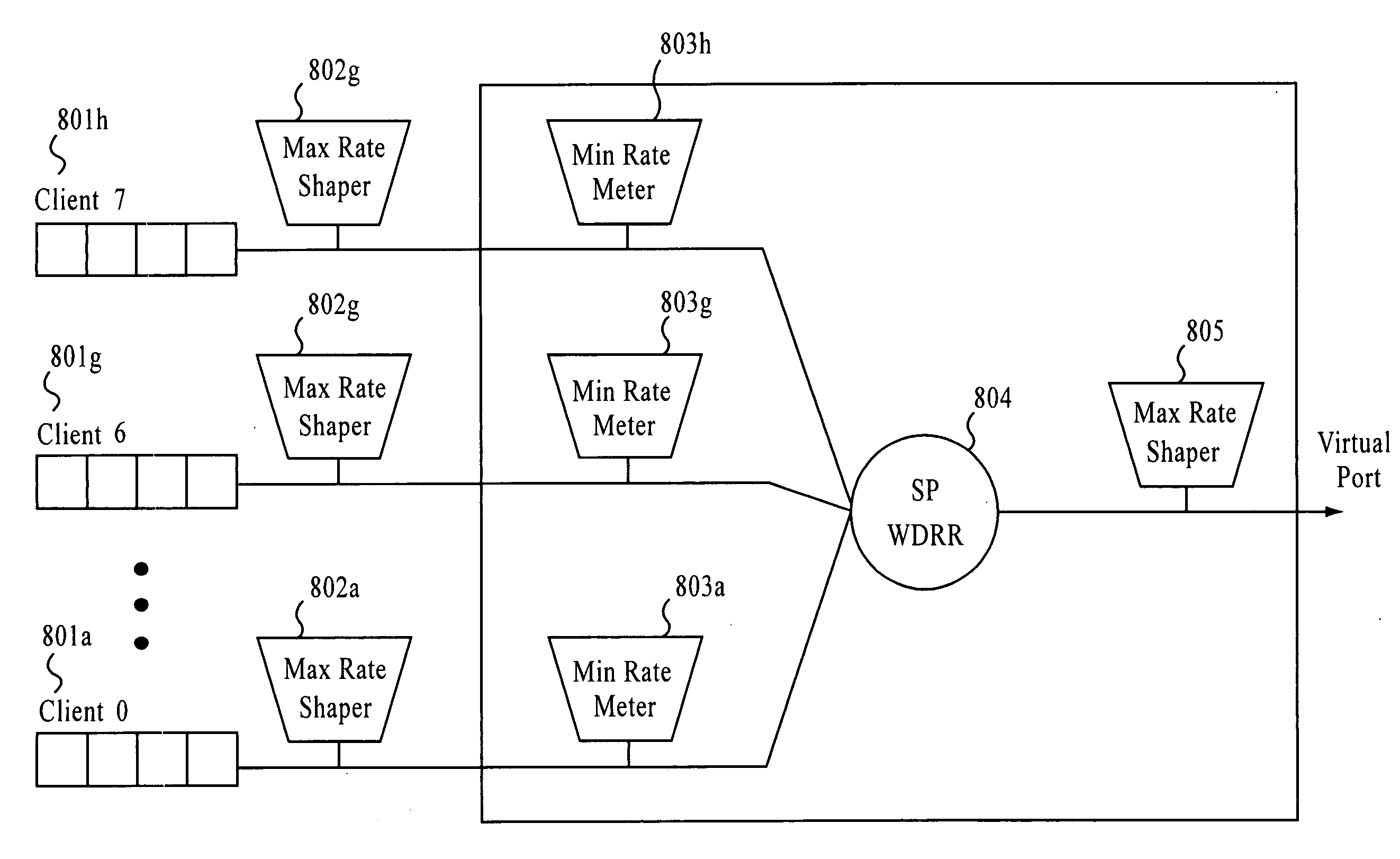
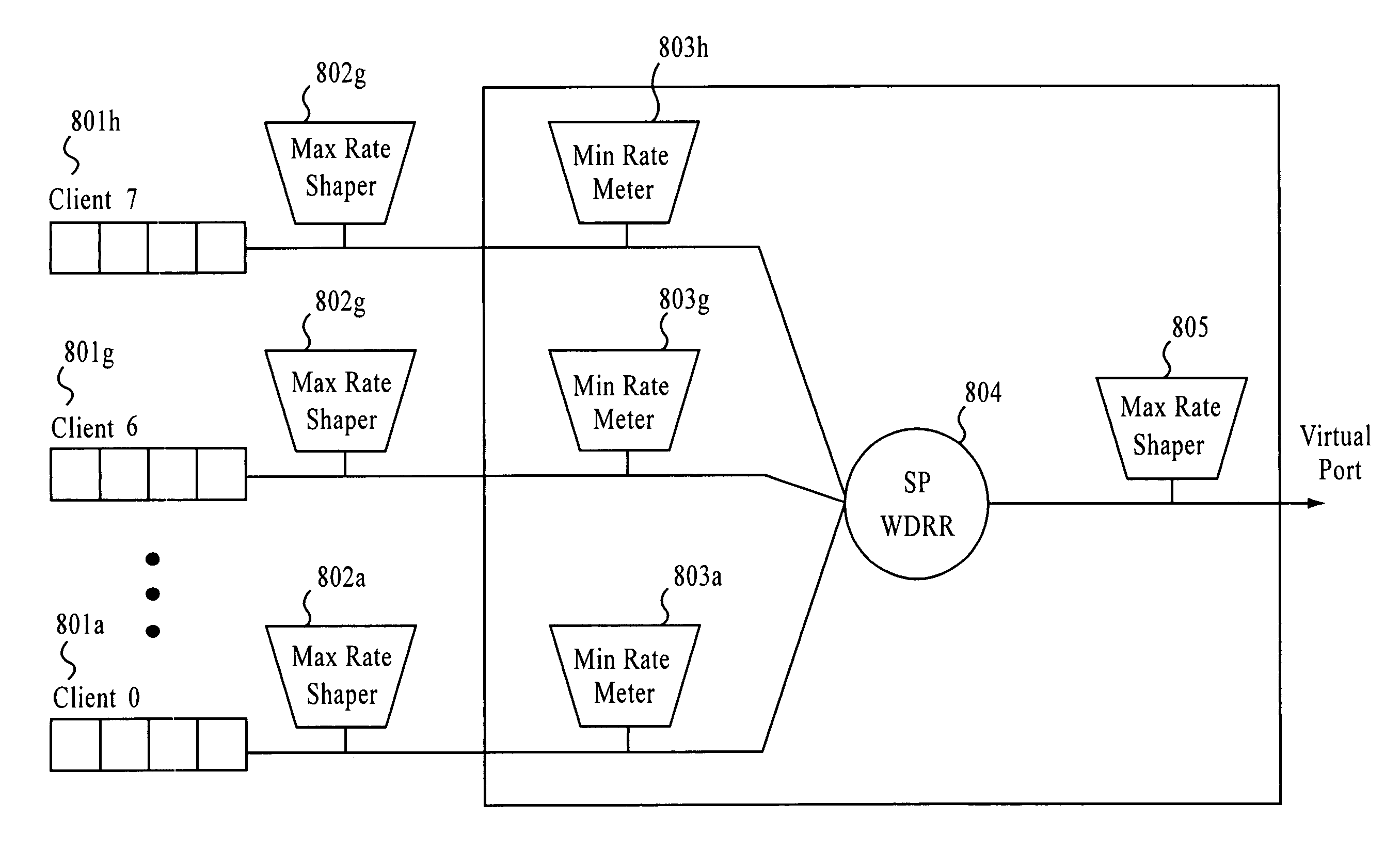
Hierarchical queue shaping
InactiveUS20070153697A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDeficit round robinDynamic bandwidth allocation
A network device and method include token buckets, each token bucket associated with one of clients and virtual ports and configured to process information based on a predefined bandwidth and a strict priority / weighted deficit round robin. A maximum rate shaper module and a minimum rate meter module shape and meter whether any of the clients or virtual ports have exceeded a predefined threshold. A scheduler is configured to schedule services of the clients and to calculate a new bandwidth allocation for at least one of the clients or virtual ports when the at least one of the clients or virtual ports has exceeded the predefined threshold, the new bandwidth allocation replacing the predefined bandwidth and being proportional to the predefined bandwidth for each of the clients or virtual ports.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Controlling traffic congestion
ActiveUS20050157723A1Prevent excessive traffic transferMaintaining stable and smooth traffic processingData switching by path configurationTraffic characteristicTraffic capacity
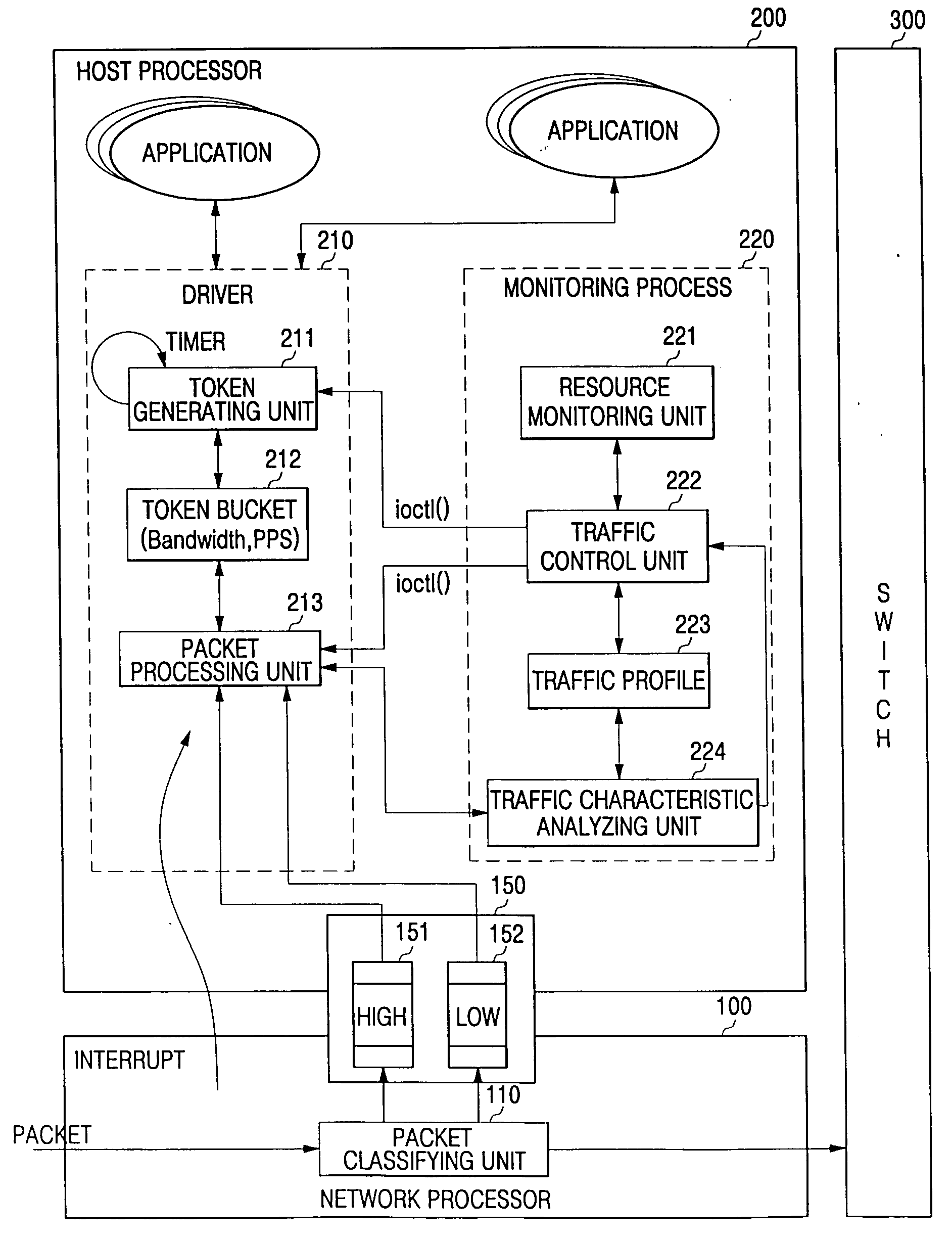
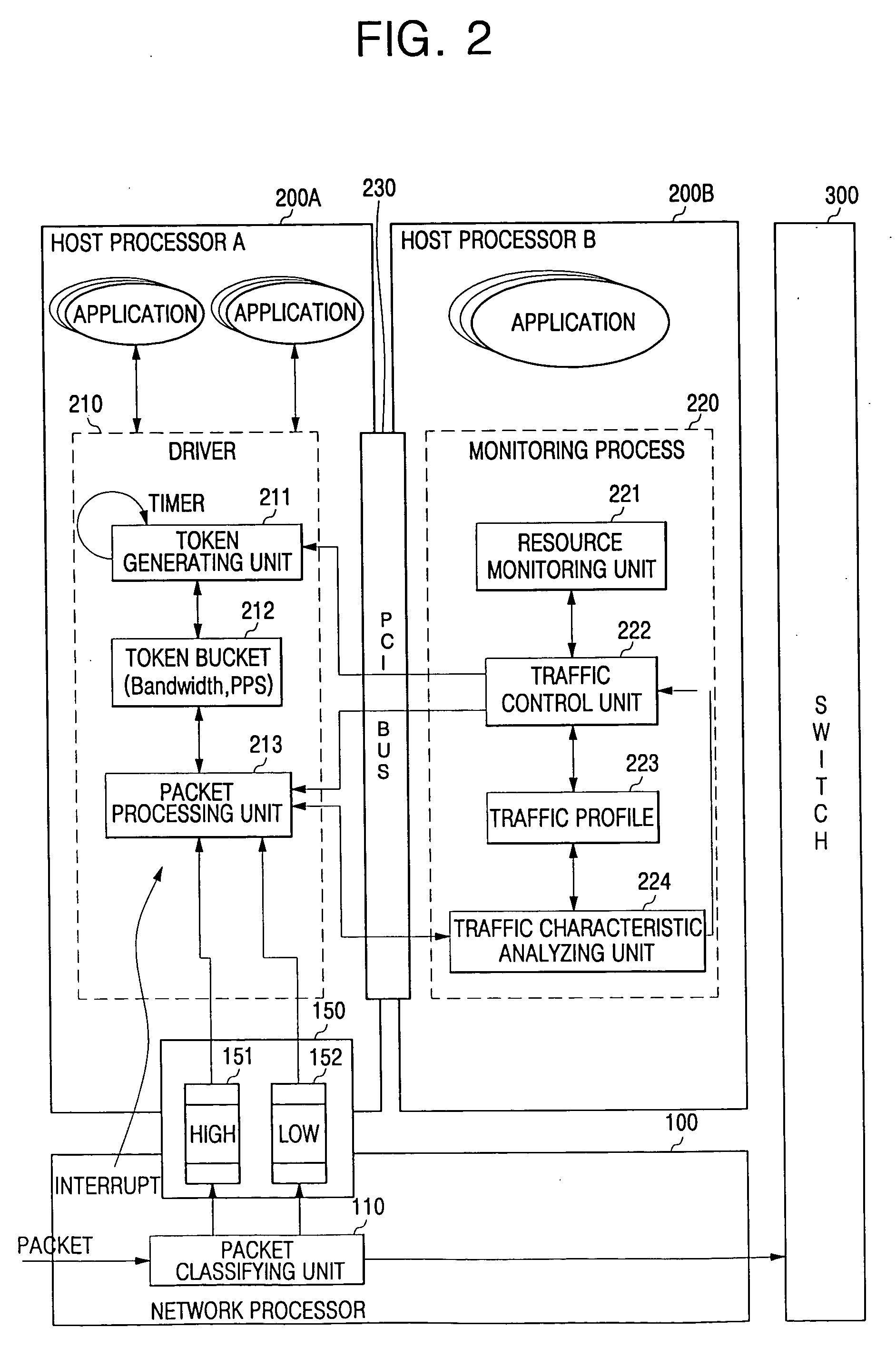
An apparatus for controlling traffic congestion includes: a transmitting processor including a packet classifying unit adapted to classify packets to be processed in a receiving processor and packets to be forwarded via the transmitting processor, the transmitting processor and the receiving processor having different traffic processing speeds; a buffer adapted to store the packets to be forwarded from the packet classifying unit to the receiving processor; and the receiving processor including a token driver adapted to output the packets stored in the buffer in accordance with a token bucket algorithm in response to an interrupt signal of the transmitting processor and to transmit the packets to a corresponding application, and a monitoring unit adapted to analyze and monitor a resource occupancy rate and a traffic characteristic used by the token driver to set an amount of tokens.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
System for providing flexible charging in a network
ActiveUS20060008063A1Reduce signaling loadReduce reservationMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsError preventionService flowPolicy decision
The present invention relates to arrangements for charging in a packet switched network. Packets are charged differently dependent on which service flow the packets belong to. The charging system comprises a control system and a serving element residing in a packet forwarding system wherein said control system comprises an account function adapted to manage an account of at least one user and a charging policy decision point arranged to calculate a charging policy for allowed services for the at least one user. Moreover, said serving element comprises a token bucket per user adapted to store reservations received from the account function of the user associated with the token bucket and a charging policy enforcement point arranged to perform charging for a plurality of the allowed services by reducing the stored reservation of the token bucket according to the calculated charging policy.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Methods and devices for flexible bandwidth allocation
Method and devices are provided for allocating network resources in a flexible manner. In some implementations, a customer's unused resources for a particular type of service are assigned to another type of service. In other implementations, a first customer's unused resources are assigned to a second customer, e.g., in exchange for a relatively lower service charge to the first customer. The unused bandwidth may be assigned on a hierarchical or a non-hierarchical basis. In preferred embodiments, resources are allocated using a token bucket methodology. Preferably, high-priority resources are not compromised by the allocation scheme. The discipline or manner in which resources or bandwidth are shared may be specified in a static fashion or information regarding the state of congestion in the network maybe used to generate a dynamic (time varying) specification.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
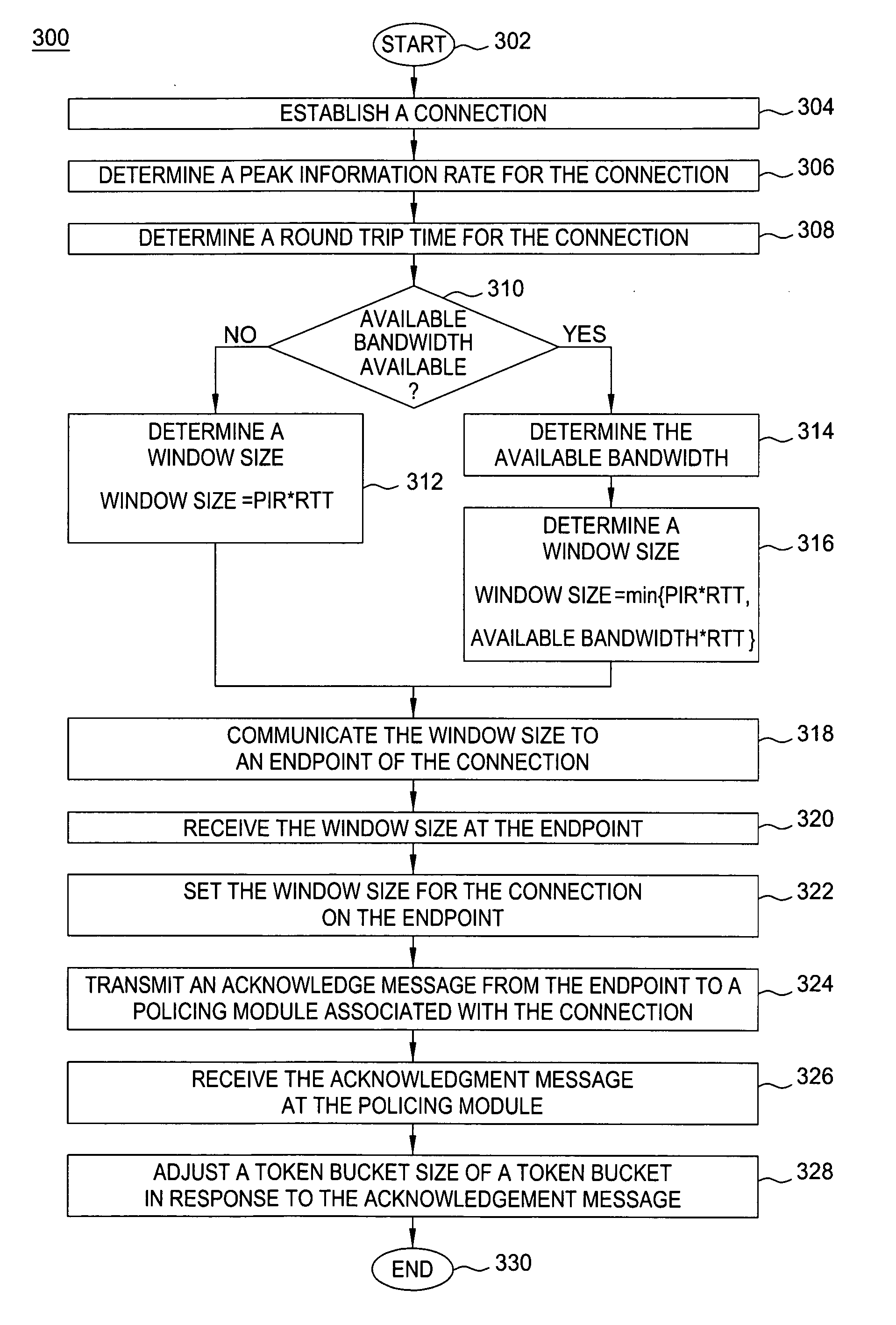
Method for policing-based adjustments to transmission window size
InactiveUS20070076621A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPeak information rateComputer module
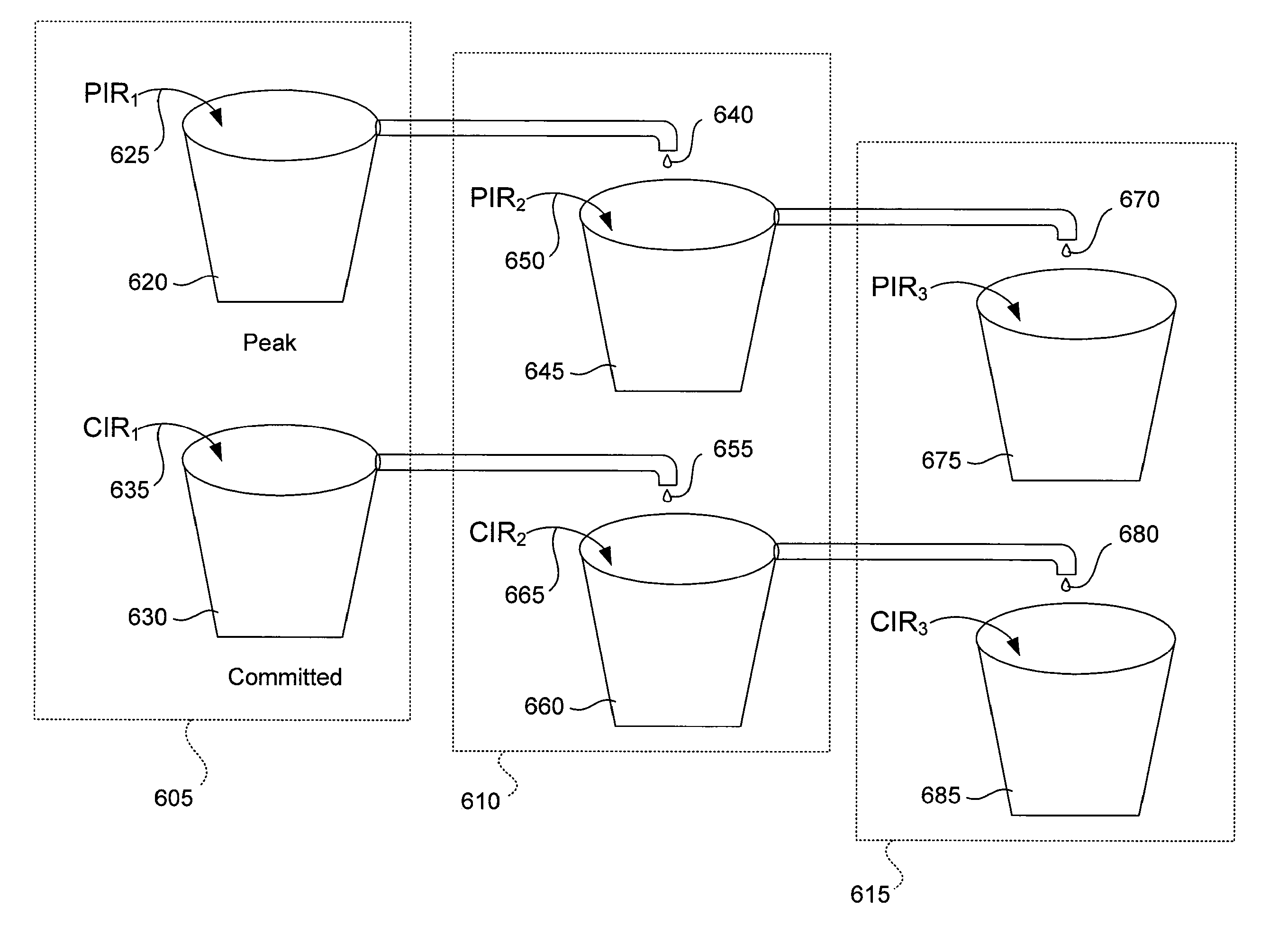
The invention includes a method for determining a window size for a connection. One method according to the invention includes determining a peak information rate for the connection, determining a round trip time for the connection, and determining the window size using the peak information rate and the round trip time. Another method includes determining a token bucket size of a token bucket in response to detecting a condition associated with the token bucket and determining the window size using the token bucket size. Another method includes determining a plurality of connection window sizes for each of a plurality of connections. In this embodiment, the connection window sizes are determined by distributing a total window size across the plurality of connections. A determined window size may be communicated to at least one of a sender of the connection, a receiver of the connection, and a policing module.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
Methods and devices for regulating traffic on a network
InactiveUS20040221032A1Increase chanceDigital computer detailsData switching networksTraffic capacityEngineering
Methods and devices are provided for regulating traffic on a network. According to some aspects of the invention, if a subscriber's upstream traffic exceeds a predetermined level over a first period of time, the subscriber's quality of service is adjusted without requiring the subscriber to re-register. According to some embodiments, a first token bucket is used to determine whether the subscriber's upstream traffic exceeds the predetermined level over the first period of time. In some such embodiments, the first token bucket is used to control the burst size of another token bucket, depending on the subscriber's upstream traffic during the first period of time.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Methods and devices for flexible bandwidth allocation
ActiveUS20050120102A1Reduce service chargesDigital computer detailsData switching networksShared resourceType of service
Method and devices are provided for allocating network resources in a flexible manner. In some implementations, a customer's unused resources for a particular type of service are assigned to another type of service. In other implementations, a first customer's unused resources are assigned to a second customer, e.g., in exchange for a relatively lower service charge to the first customer. The unused bandwidth may be assigned on a hierarchical or a non-hierarchical basis. In preferred embodiments, resources are allocated using a token bucket methodology. Preferably, high-priority resources are not compromised by the allocation scheme. The discipline or manner in which resources or bandwidth are shared may be specified in a static fashion or information regarding the state of congestion in the network maybe used to generate a dynamic (time varying) specification.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Hierarchical queue shaping
InactiveUS8130648B2Error preventionTransmission systemsDeficit round robinDynamic bandwidth allocation
A network device and method include token buckets, each token bucket associated with one of clients and virtual ports and configured to process information based on a predefined bandwidth and a strict priority / weighted deficit round robin. A maximum rate shaper module and a minimum rate meter module shape and meter whether any of the clients or virtual ports have exceeded a predefined threshold. A scheduler is configured to schedule services of the clients and to calculate a new bandwidth allocation for at least one of the clients or virtual ports when the at least one of the clients or virtual ports has exceeded the predefined threshold, the new bandwidth allocation replacing the predefined bandwidth and being proportional to the predefined bandwidth for each of the clients or virtual ports.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Hierarchical virtual queuing
InactiveUS20080159135A1Unwanted latencyFair sharingError preventionTransmission systemsData streamService planning
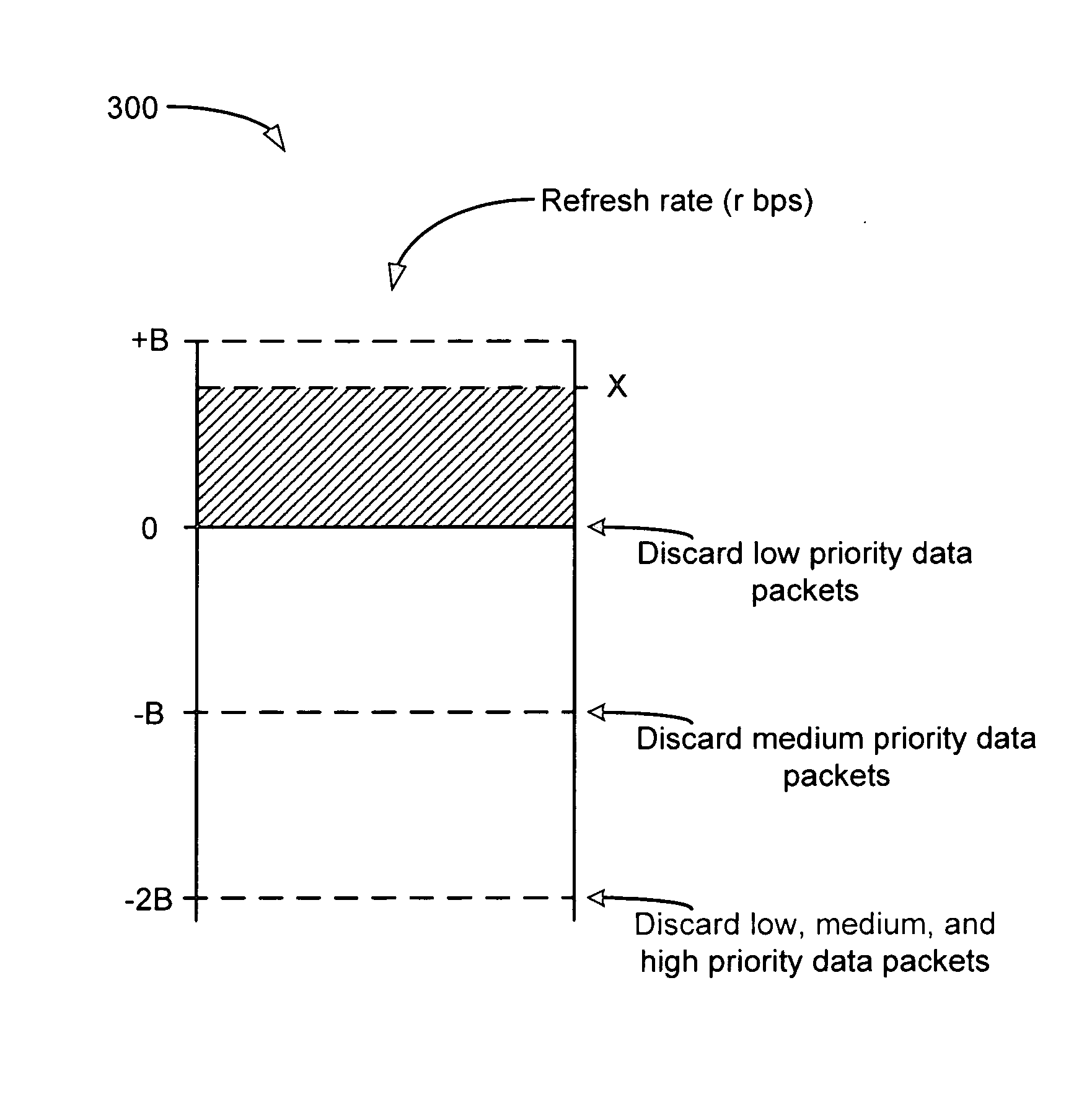
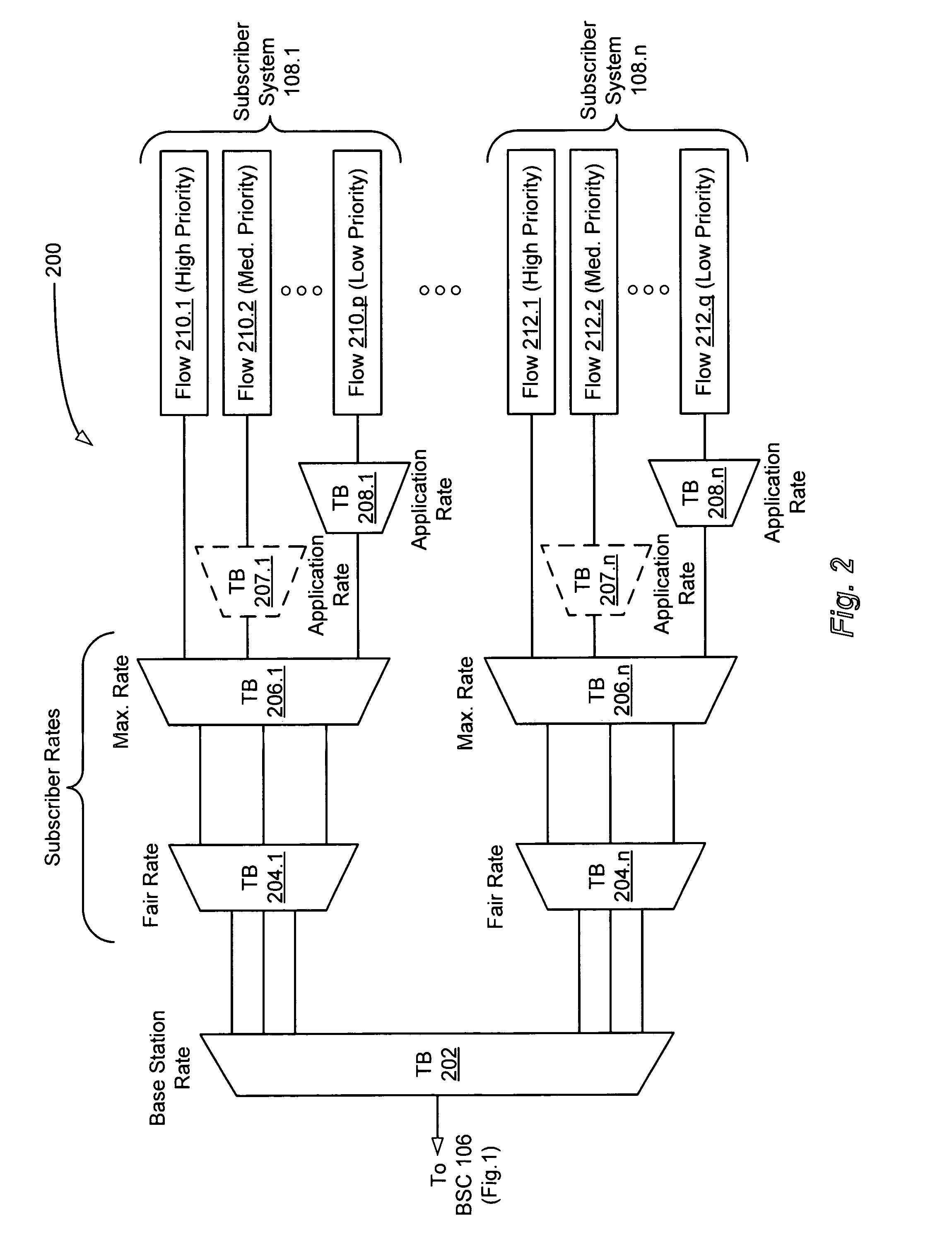
A system and method of providing high speed, prioritized delivery of data packets over broadband communications networks that avoids inducing unwanted latency in data packet transmission. The system employs a hierarchical, real-time, weighted token bucket prioritization scheme that provides for fair sharing of the available network bandwidth. At least one token bucket is employed at each level of the hierarchy to meter data flows providing service applications included in multiple subscribers' service plans. Each token bucket passes, discards, or marks as being eligible for subsequent discarding data packets contained in the data flows using an algorithm that takes into account the priority of the data packets, including strict high, strict medium, and strict low priorities corresponding to strict priority levels that cannot be overridden. The algorithm also takes into account weighted priorities of at least a subset of the low priority data packets. The priority levels of these low priority data packets are weighted to provide for fair sharing of the available network bandwidth among the low priority data flows, and to assure that none of the low priority data flows is starved of service.
Owner:ELLACOYA NETWORKS
Systems and methods for traffic shaping
InactiveUS6925055B1To offer comfortError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsByteControl logic
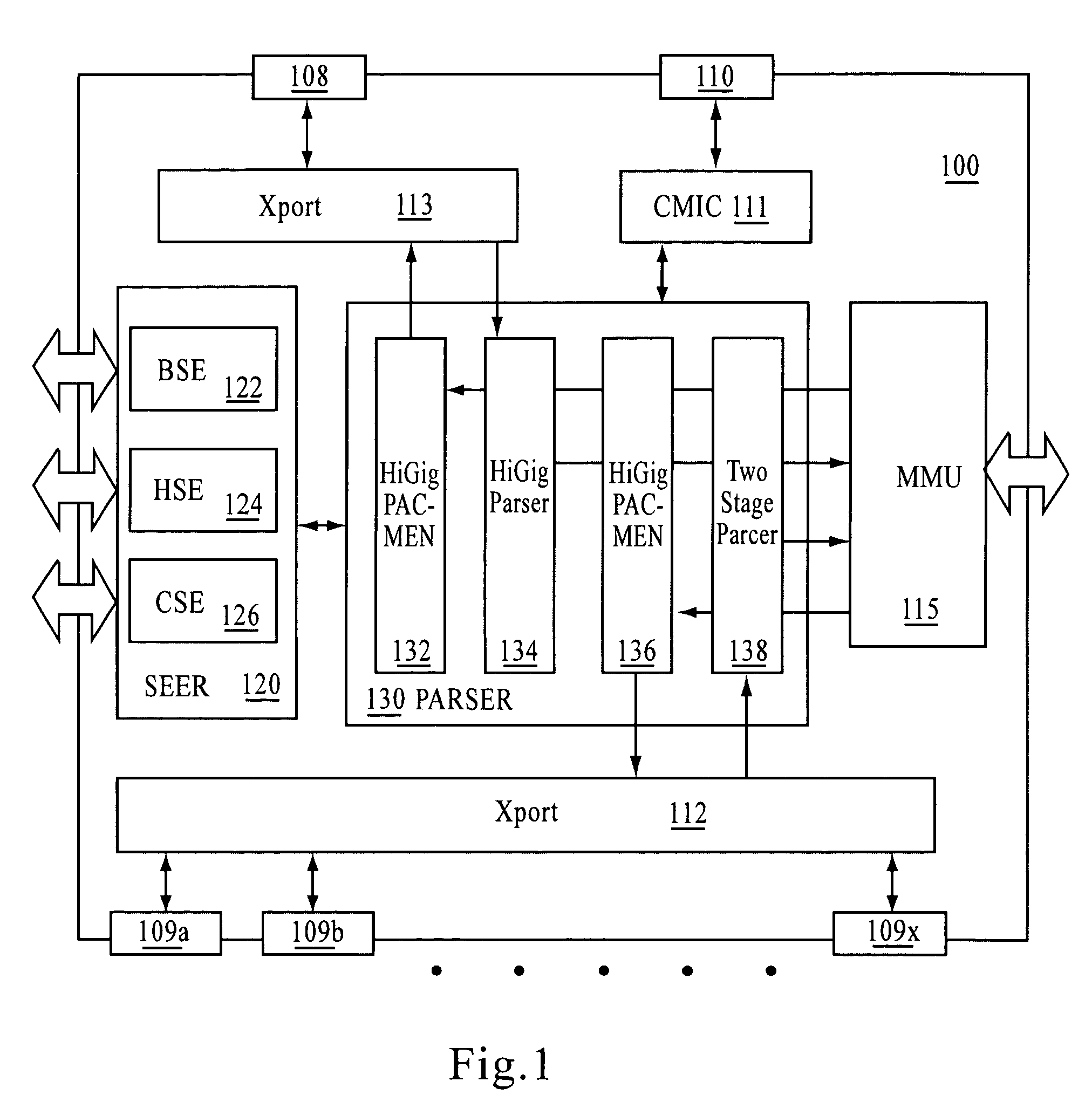
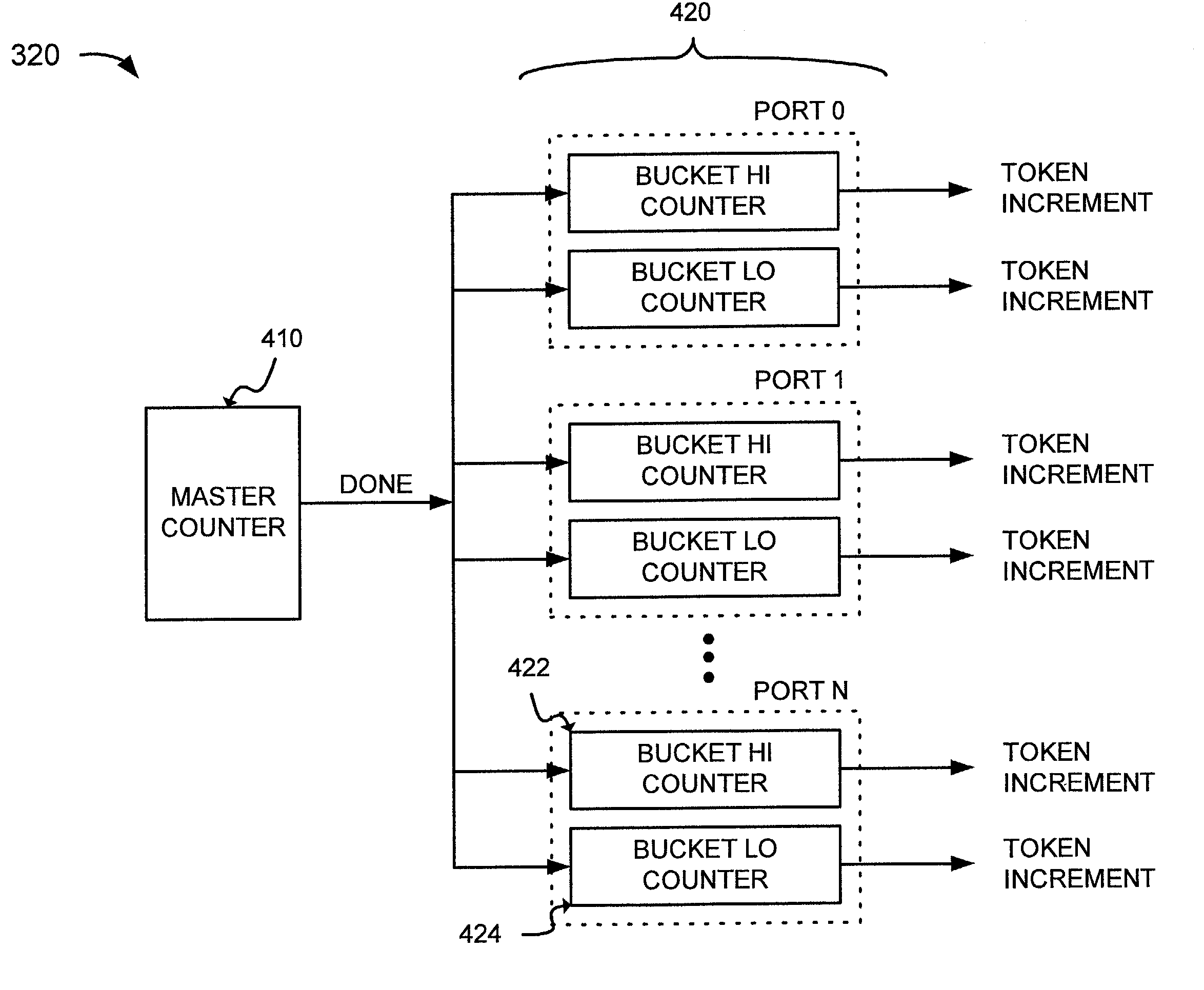
A system shapes traffic in a multiport network device. The system includes multiple token buckets and token bucket logic. The token buckets correspond to multiple priority queues of the multiple output ports of the network device and store one or more tokens. Each of the tokens corresponds to a byte of one or more received packets to be transmitted by the network device. The token bucket control logic generates the tokens for the token buckets. The token bucket control logic includes a master counter and multiple bucket counters. The master counter counts to a first count value and generates a done signal when the count reaches the first count value. The bucket counters, corresponding to the token buckets, receive the done signal, count to a second count value, and generate a token increment signal for storing a token in the corresponding token buckets when the count reaches the second count value.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Method and packet-level device for traffic regulation in a data network
ActiveUS20050083845A1Reducing effective data rateReduce rateError preventionTransmission systemsPacket communicationData pack
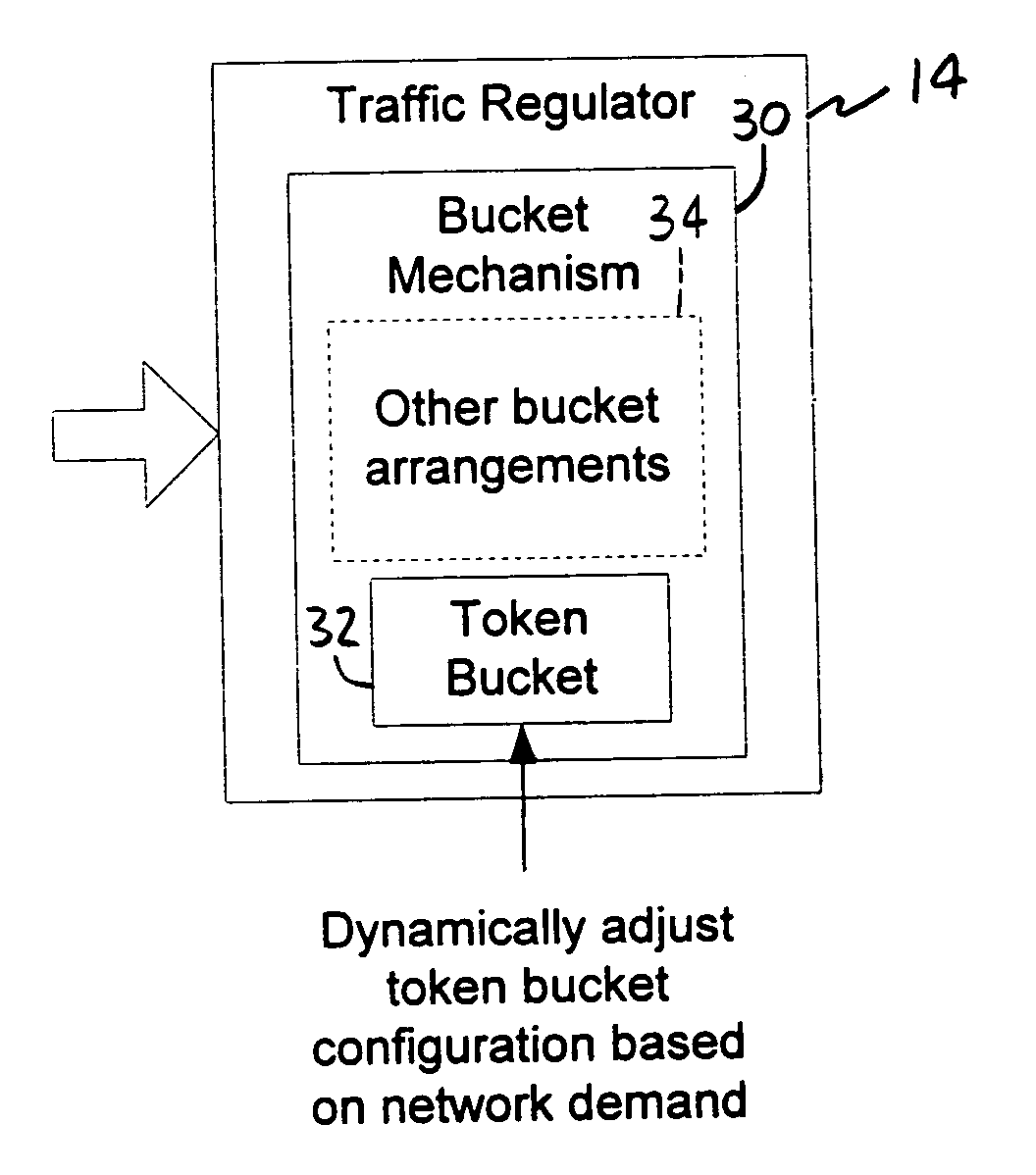
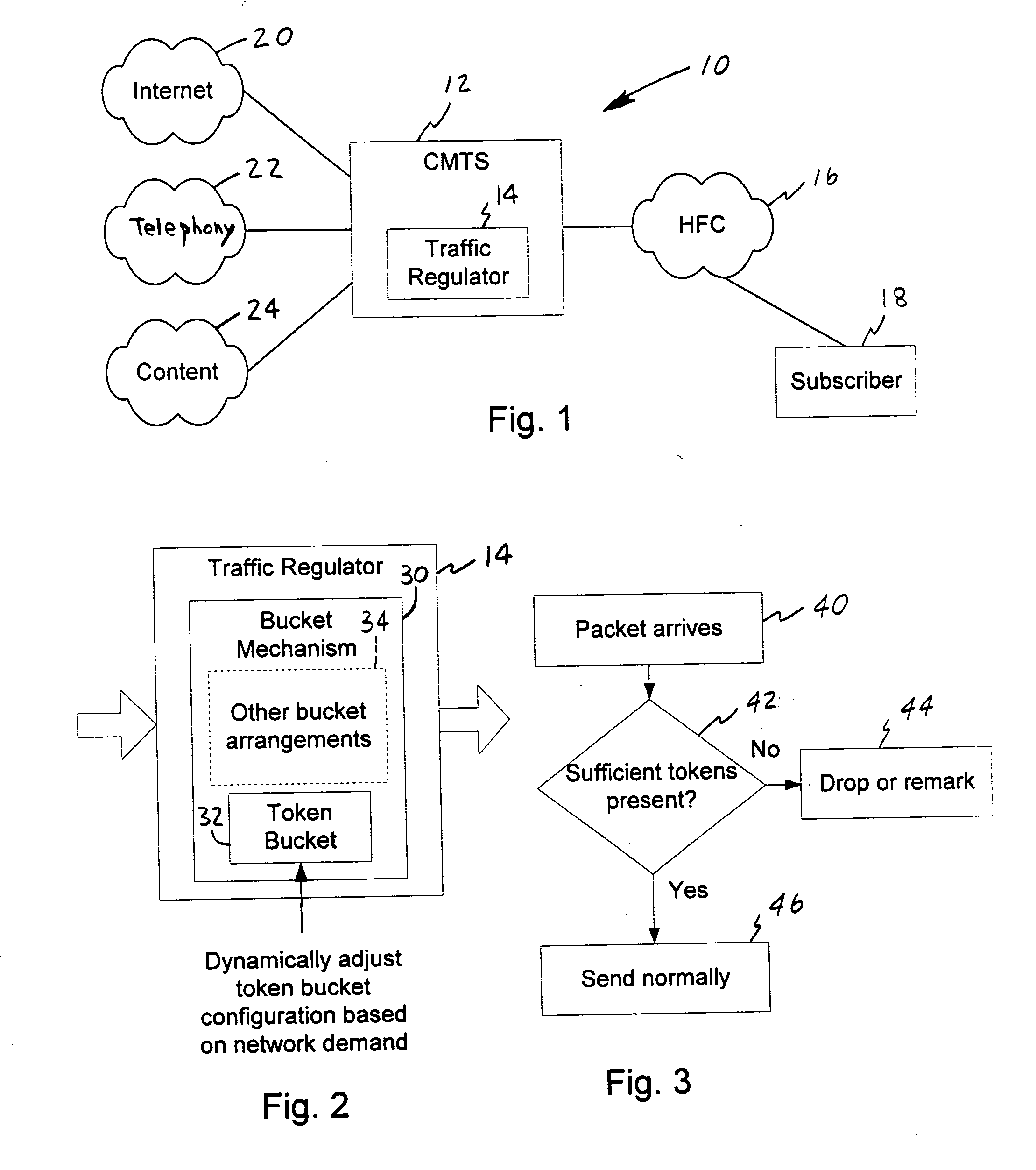
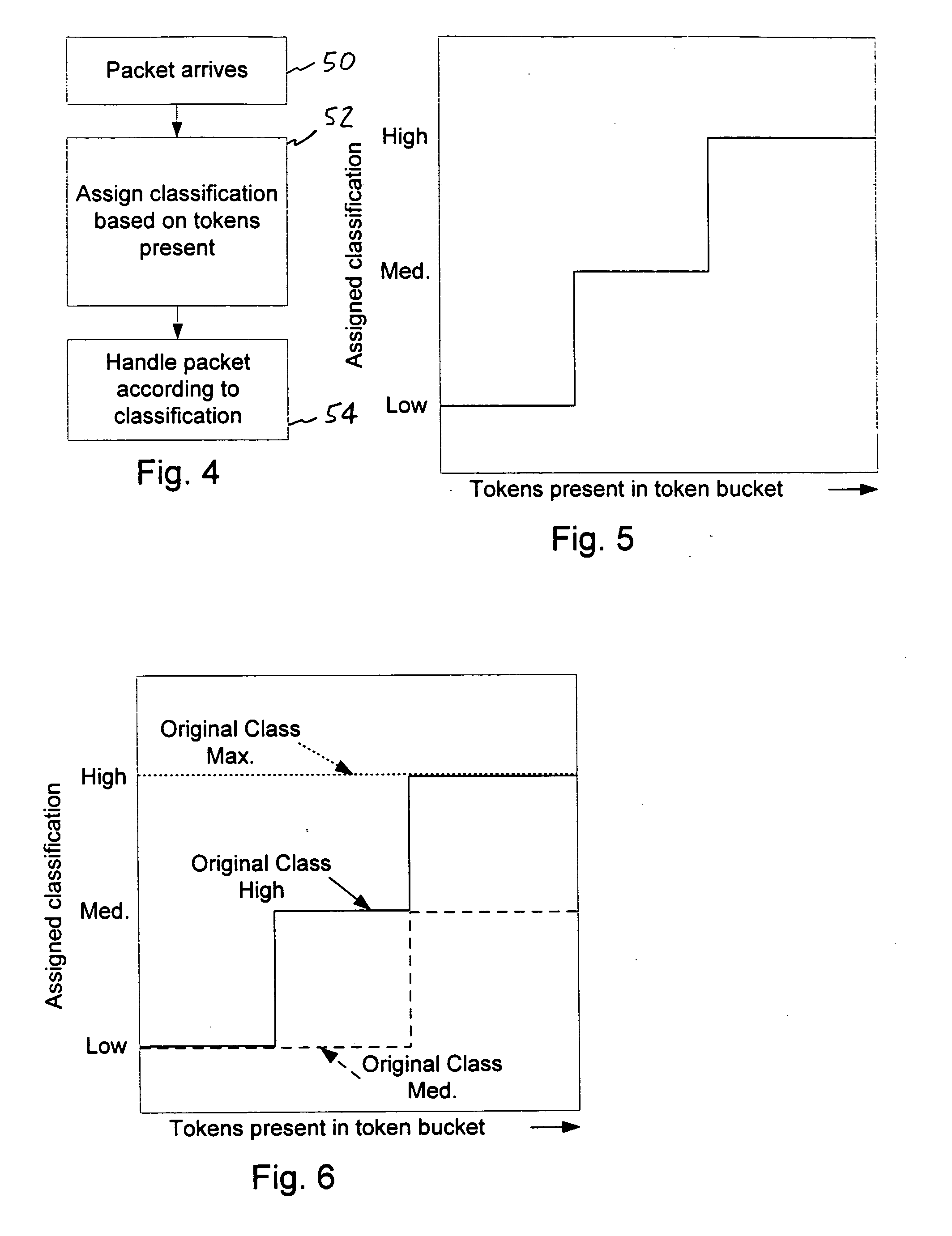
A method of traffic regulation in a packet communication network involves a token bucket associated with a subscriber. Packets arriving at the regulator are handled in accordance with the token bucket configuration. The method further involves measuring a demand placed on the packet communication network by the subscriber. The token bucket configuration for the subscriber is dynamically adjusted based on the demand. Another method of traffic regulation handles packets that arrive at the regulator in accordance with first and second token bucket configurations. The first token bucket regulates packet rate while the second token bucket regulates data rate. Another method of traffic regulation involves handling packets in accordance with a token bucket configuration, where the amount of tokens to be removed is based on the amount of the flow and is further based on a classification of the flow. Packet-level devices for traffic regulation are also contemplated.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM LLC
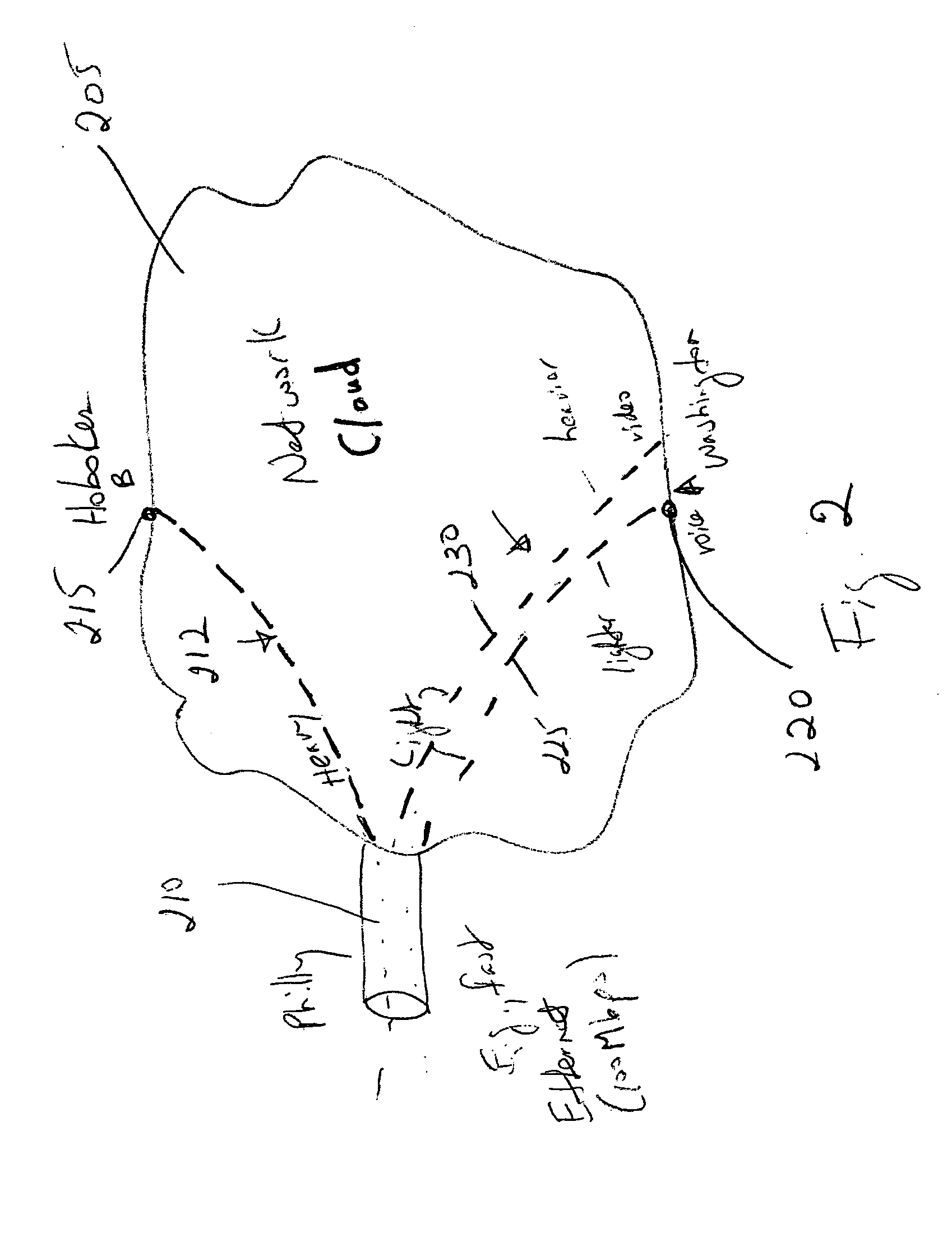
Adaptive call routing in IP networks
InactiveUS20150003240A1Improve network utilizationPacket lossInterconnection arrangementsError preventionTelecommunicationsSelf adaptive
A method of adaptively routing voice packets in an IP network receiving a request for a new call at a voice gateway, determining a destination gateway for the new call, determining an availability of at least one route for routing the new call across the IP network to the destination gateway, and deciding whether to admit the new call into the IP network based on whether a route is available over which voice packets for the new call can be routed. A call admission decision is made based on whether a direct, single-path route or a two-path route is available, where each path is an LSP tunnel whose availability is determined using a token bucket technique. If no route is available, the voice gateway does not admit the call into the IP network.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
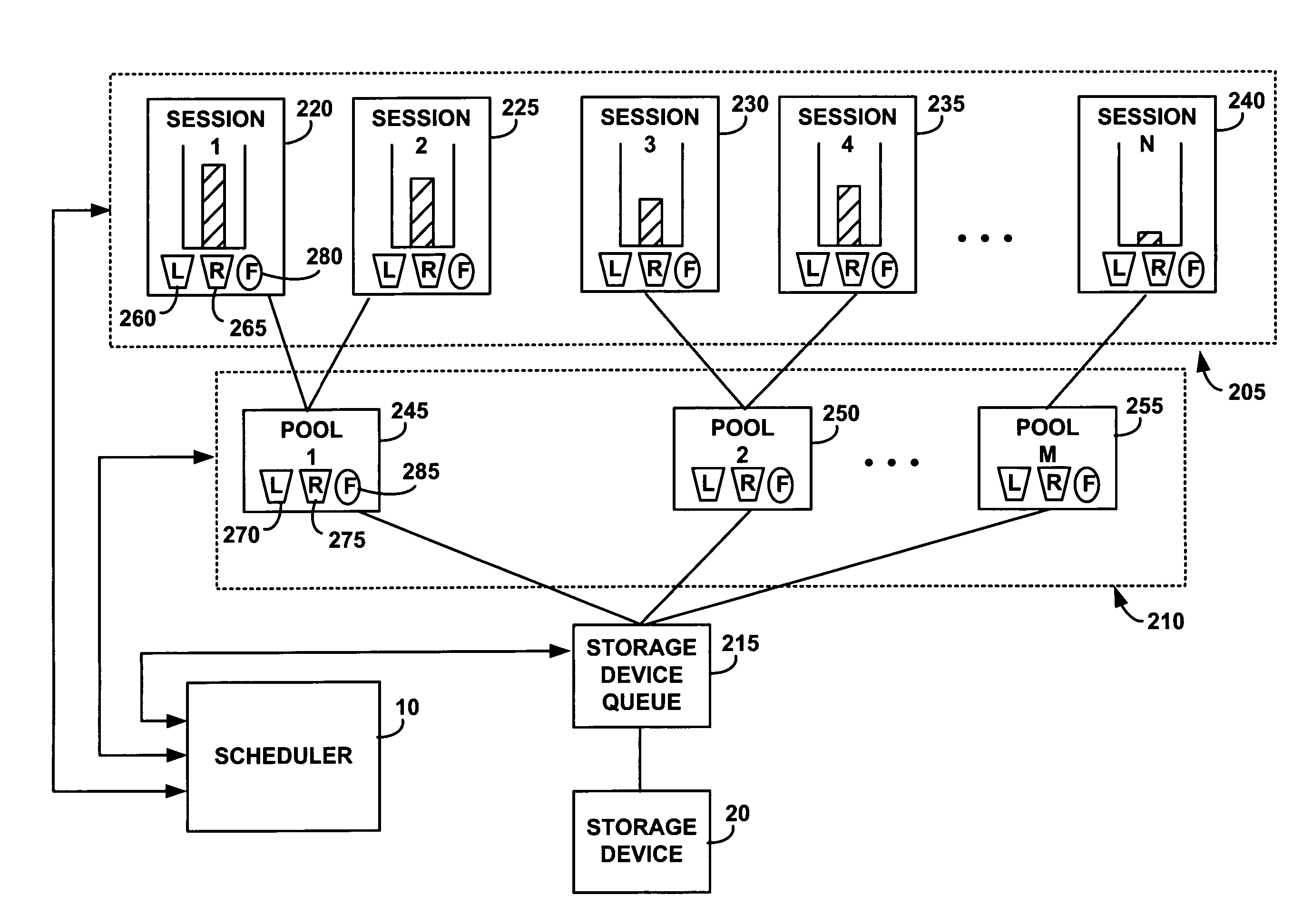
System and method for managing storage system performance as a resource
InactiveUS20070226332A1Multiple digital computer combinationsSpecial data processing applicationsRelease timeOperating system
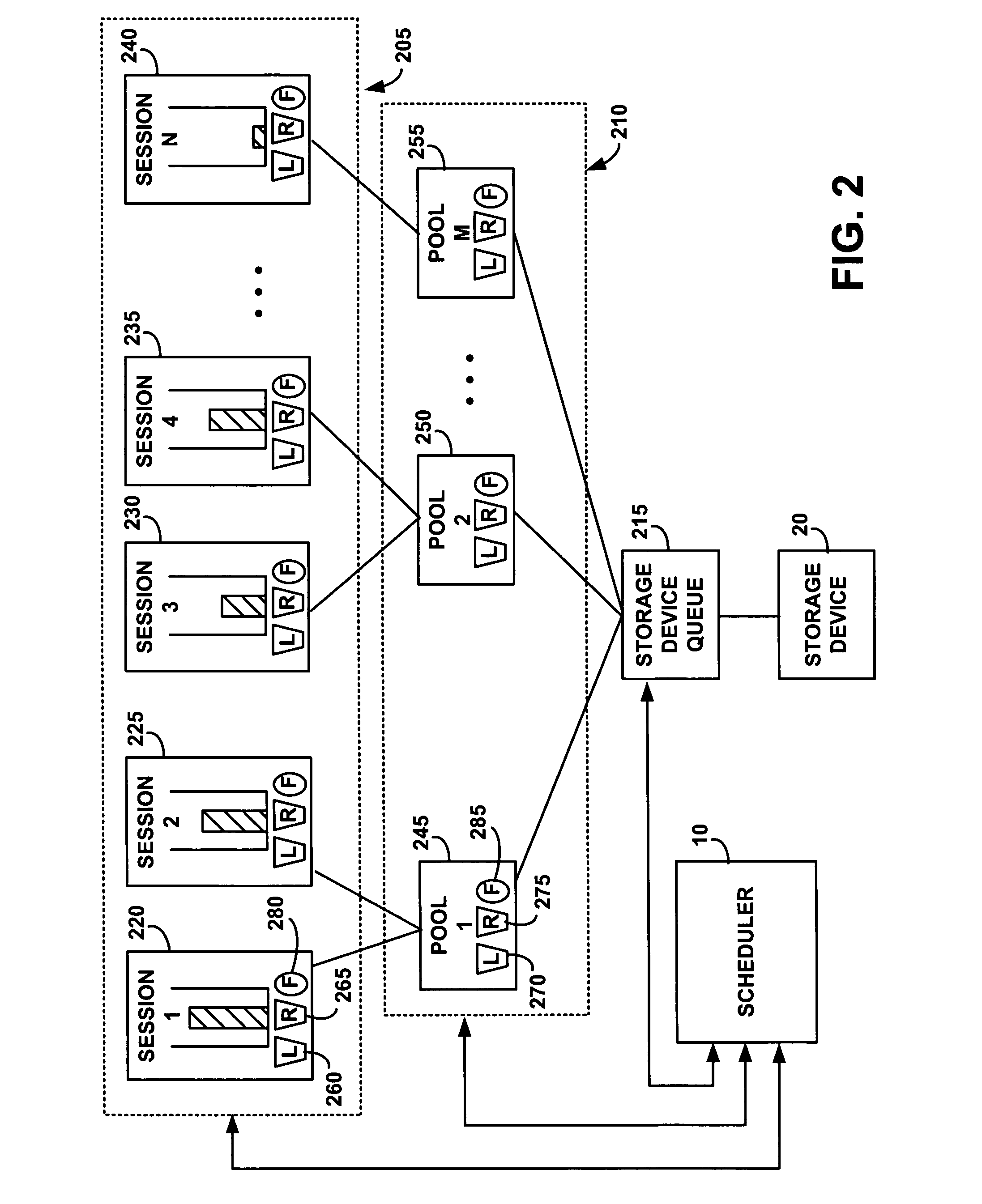
A scheduler selects an I / O from a session of a pool and updates token buckets associated with resource limits and reserves for the session and the pool and statistics used in determining fair sharing. To select an I / O, the scheduler identifies sessions with a non-empty queue, identifies head I / Os in the queues, computes for the head I / O a deadline using session and pool reserve buckets and a release time using session and pool limit buckets, and selects a head I / O with an earliest deadline that is past the release time. If the deadline of the selected candidate head I / O is in the past, the scheduler transfers the selected head I / O to the tail of the storage device queue. Otherwise, the scheduler selects the pool with the least amount of I / O traffic according to a session fair share estimator.
Owner:IBM CORP
Drive-level internal quality of service
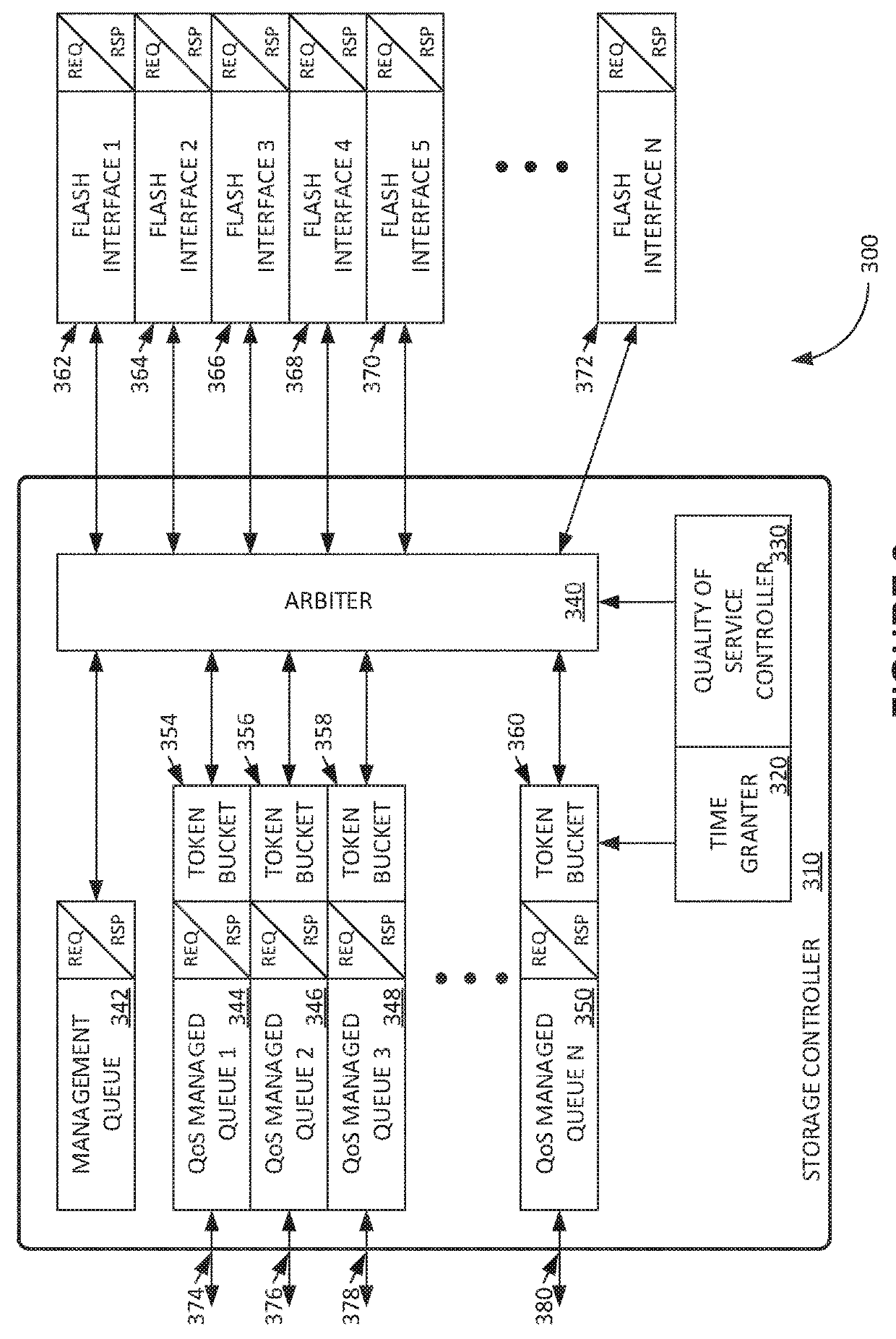
ActiveUS20180275923A1Input/output to record carriersData switching networksService-level agreementData stream
A storage controller is provided. The storage controller includes a host interface, a drive interface, and a quality of service control module coupled with the host interface and the drive interface. The QoS module includes read and write queues for each data stream, each queue associated with corresponding token buckets, and an arbiter, configured to receive requests from the read and write queues, and to service the read and write queues in an order at least partially determined by a quantity of tokens in each token bucket. The QoS module also includes a quality of service measurement module, configured to measure quality of service levels for each of the read and write queues, and a bandwidth allocation manager, configured to allocate tokens to each token bucket at a rate corresponding to the service level agreements and the measured quality of service level for each of the read and write queues.
Owner:BURLYWOOD LLC
Method and apparatus for traffic shaping
A method and apparatus for a traffic shaper that uses a traffic shaping algorithm based on a sustained rate token bucket and a constant rate emitter. The sustained rate token bucket uses a plurality of tokens based on the sustained rate and the sustained burst size. The constant rate emitter allows transmission of traffic at an adjusted transmission rate, where the adjusted transmission rate is derived from the peak rate, peak burst size, sustained rate and sustained burst size.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Differentiated service-based queue scheduling method
InactiveCN101964758AGuaranteed low latency requirementsGuaranteed Latency RequirementsData switching networksDifferentiated servicesQos quality of service
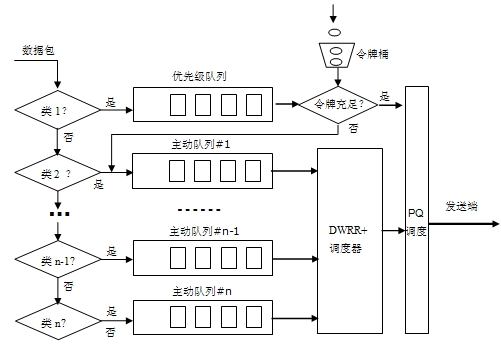
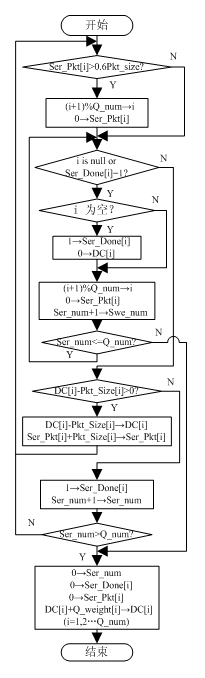
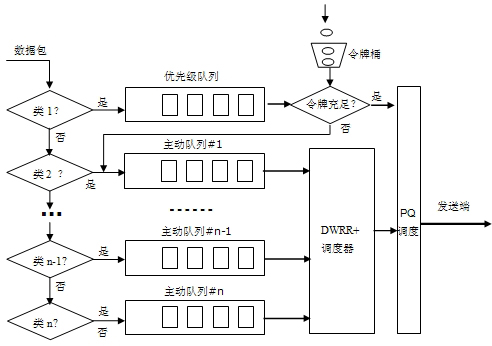
The invention discloses a differentiated service-based queue scheduling method Deficit Weighed Round Robin plus (DWRR+). In the method, the maximum byte count of a sent packet in once service is dynamically set according to the length of a packet in the current queue, so that the delay characteristic of a low-weight service is ensured, the relative fairness of bandwidth allocation is ensured, the defect that a low-priority queue may not be serviced for a long time is overcome, and the fact that a Deficit Weighed Round Robin plus (DWRR) algorithm cannot better met the requirement on the delay characteristic of the service is improved; a priority queue is set, and a token bucket algorithm is taken as a flow regulator, so that the priority of a real-time service is ensured; and the DWRR+ algorithm and a priority scheduling algorithm PQ are combined to serve as the scheduling strategy of a network node scheduler, so that on the premise of ensuring the priority of the real-time service and output bandwidths of other services, the time delay is reduced, and the service quality of different services can be ensured to a certain extent.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Unbiased token bucket
InactiveUS7369489B1Increase valueError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsData streamReal-time computing
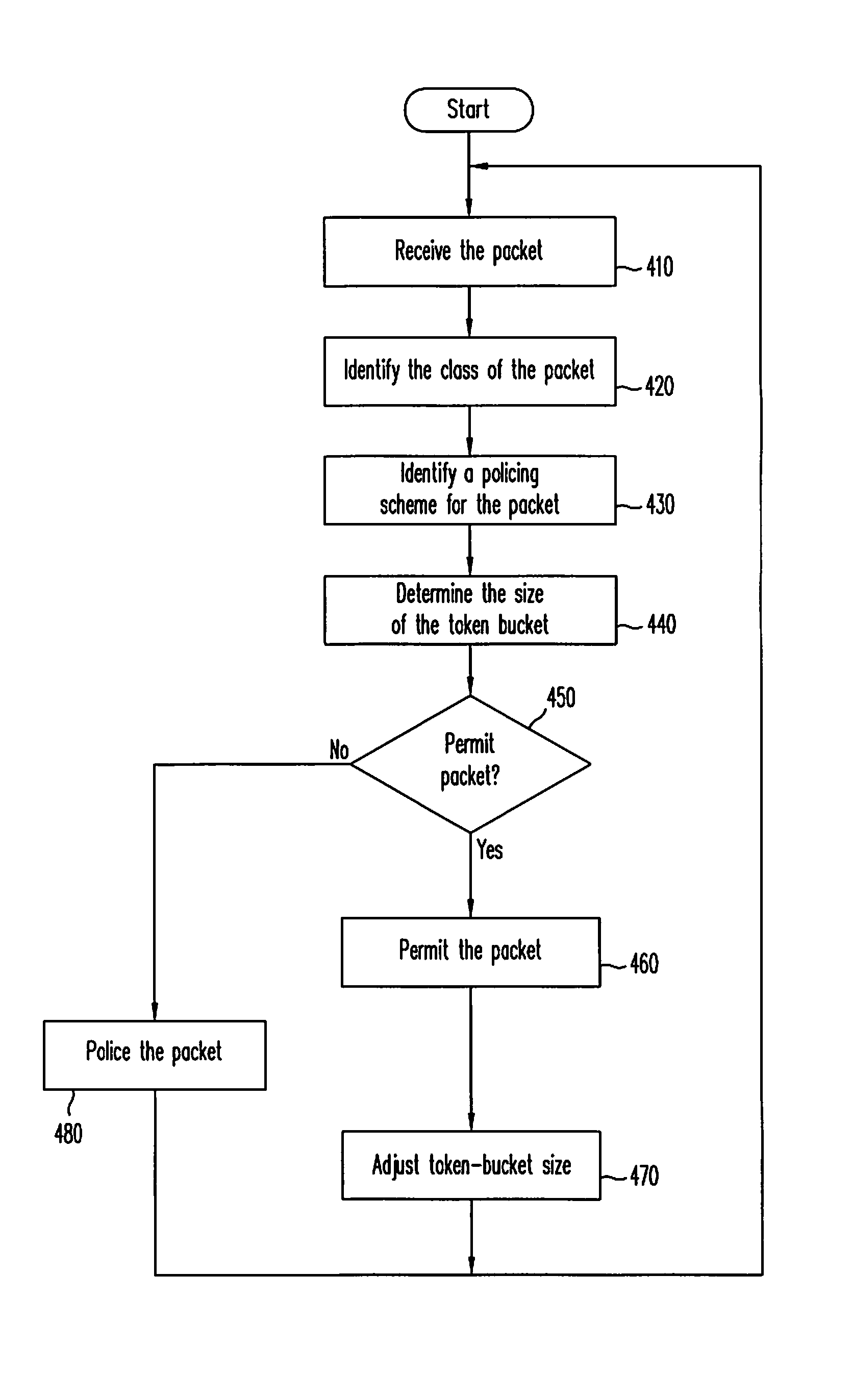
The present invention defines a method of unbiased policing of data flow in a network device. According to an embodiment of the present invention, the token bucket policer of the network device ‘permits’ (forwards) incoming packets even when the size of the token bucket is less than the size of the incoming packets. Permitting incoming packets that are larger than the token bucket ensures that incoming packets are not dropped because of the size of the incoming packets. Incoming packets are policed by TBP when the magnitude comparison of the token bucket and a predetermined constant value does not comply with the policing scheme defined for the incoming packets. When a packet is ‘permitted’ (forwarded), the size of the token bucket is reduced by an amount equal to the size of the packet.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
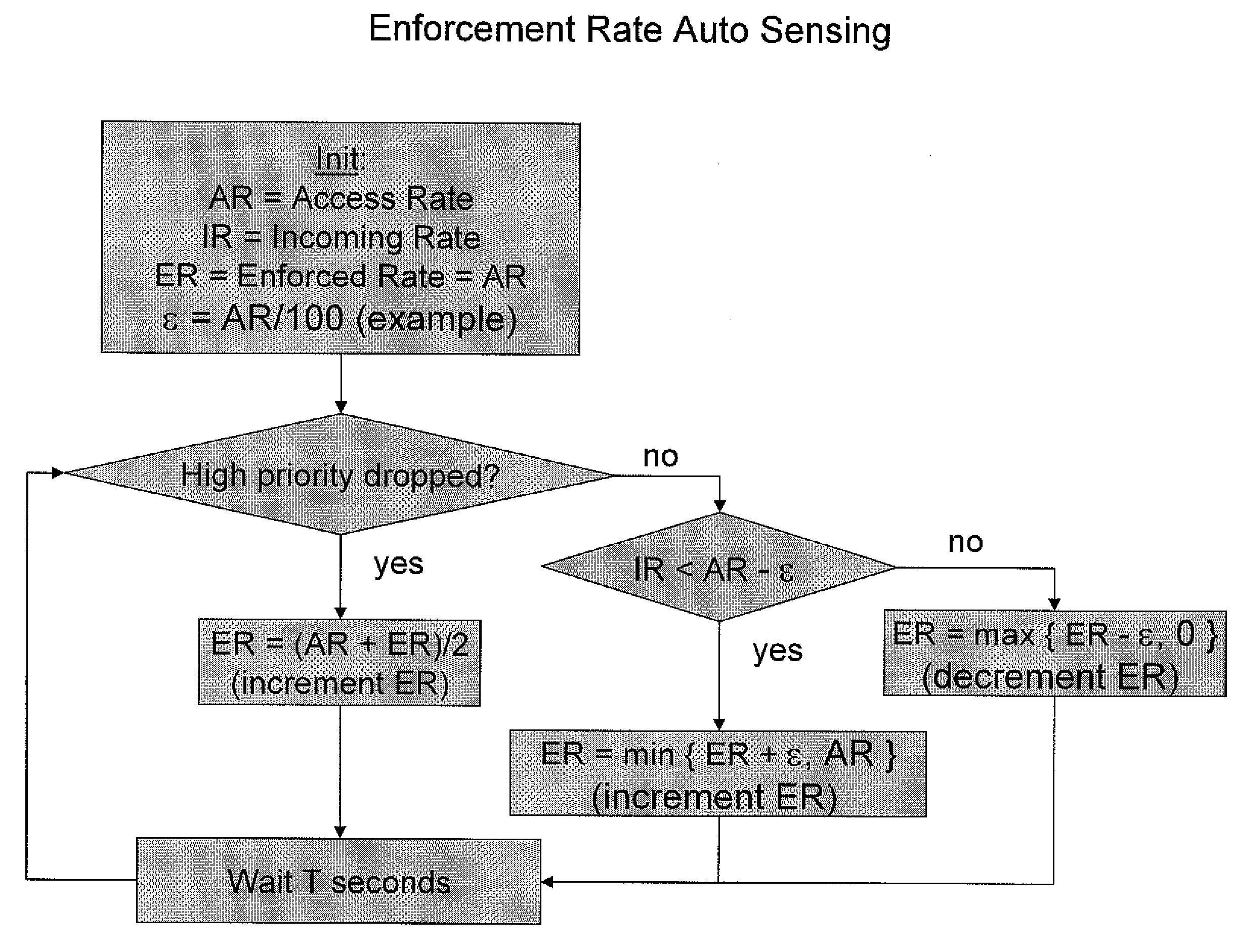
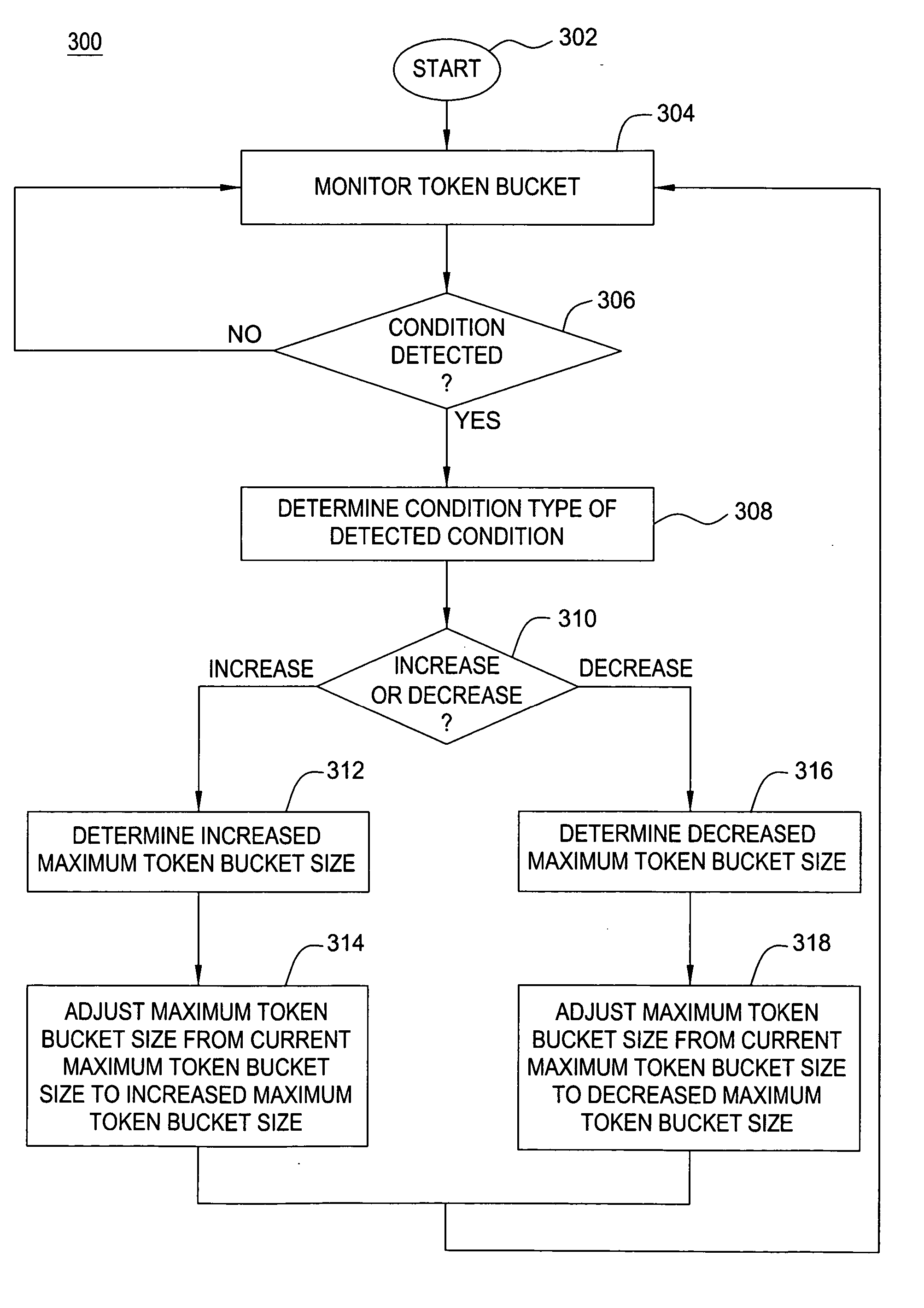
Method for dynamically adjusting token bucket sizes
The invention includes a method for determining a maximum size of a token bucket. One method includes detecting a condition and determining the maximum token bucket size in response to the condition. The condition may include one of a packet drop and a reduction of a current token bucket size, an actual information rate satisfying a rate threshold, or a current token bucket size satisfying a size threshold. Another method includes detecting a packet drop, detecting a reduction of a current token bucket size, and determining the maximum token bucket size in response to the packet drop and the reduction of the current token bucket size. Another method includes detecting a condition and performing an initial bucket size adaptation in response to the condition where the initial bucket size adaptation has an initial adaptation rate greater than a subsequent adaptation rate associated with a subsequent bucket size adaptation.
Owner:RPX CORP
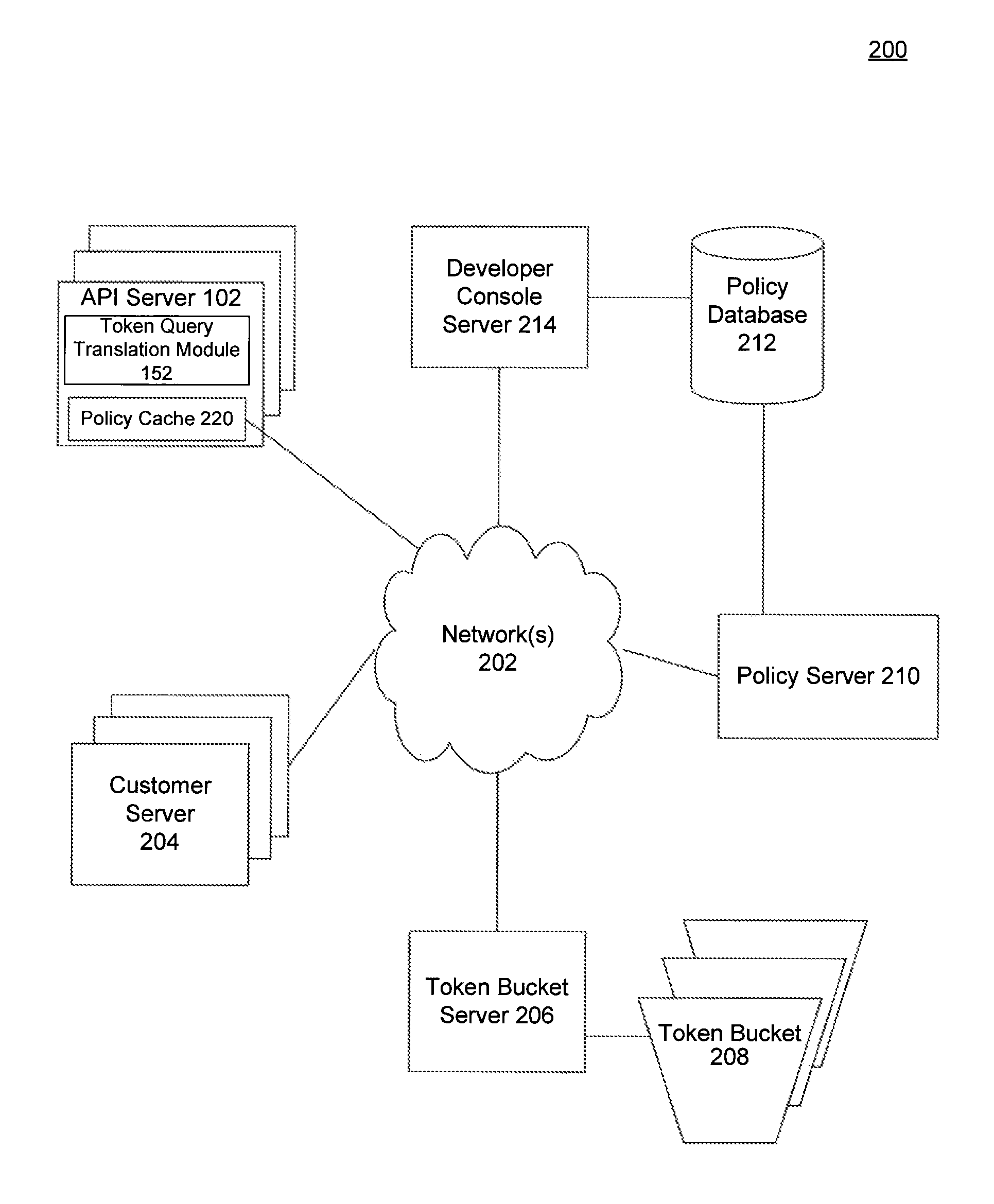
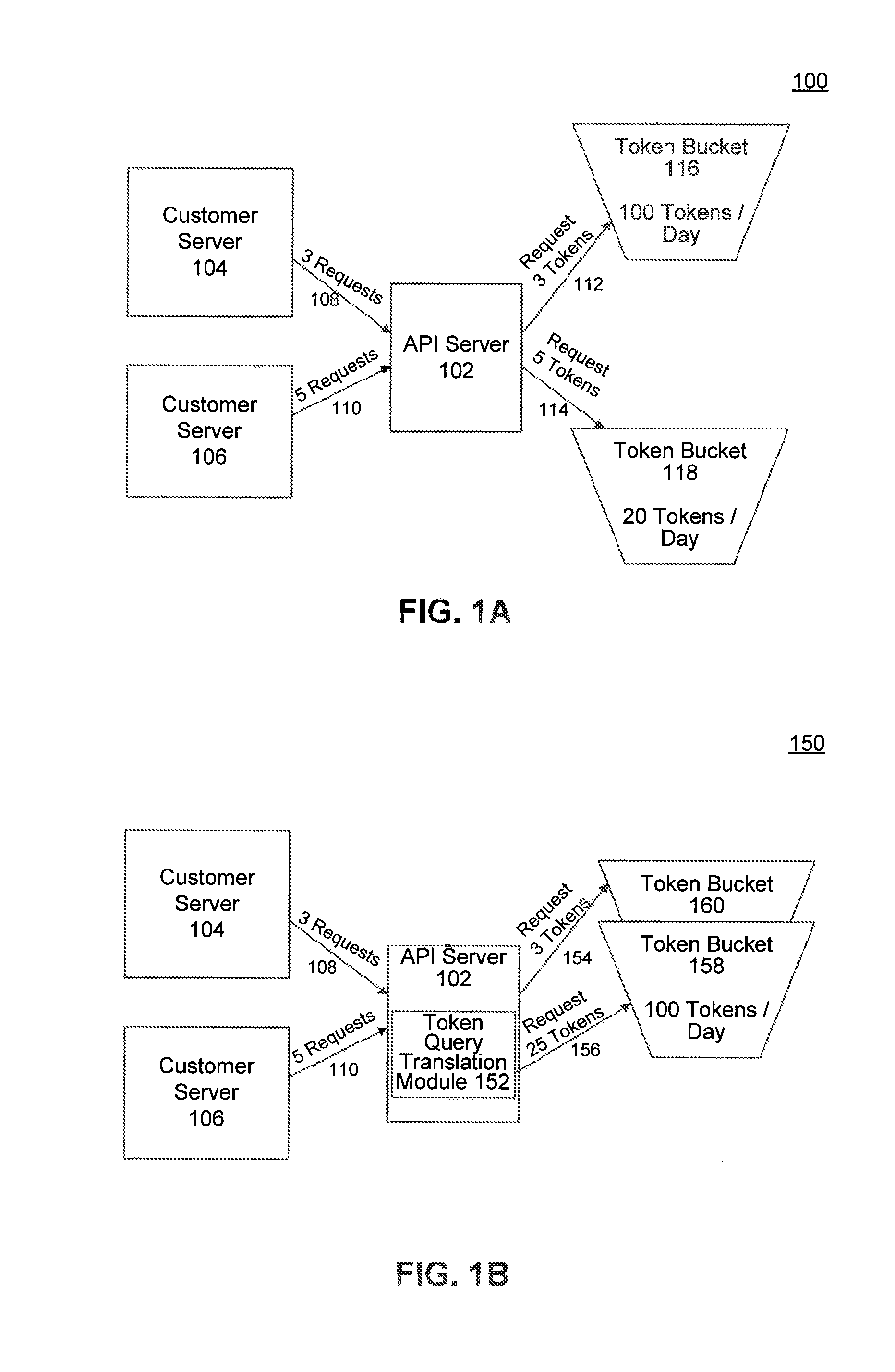
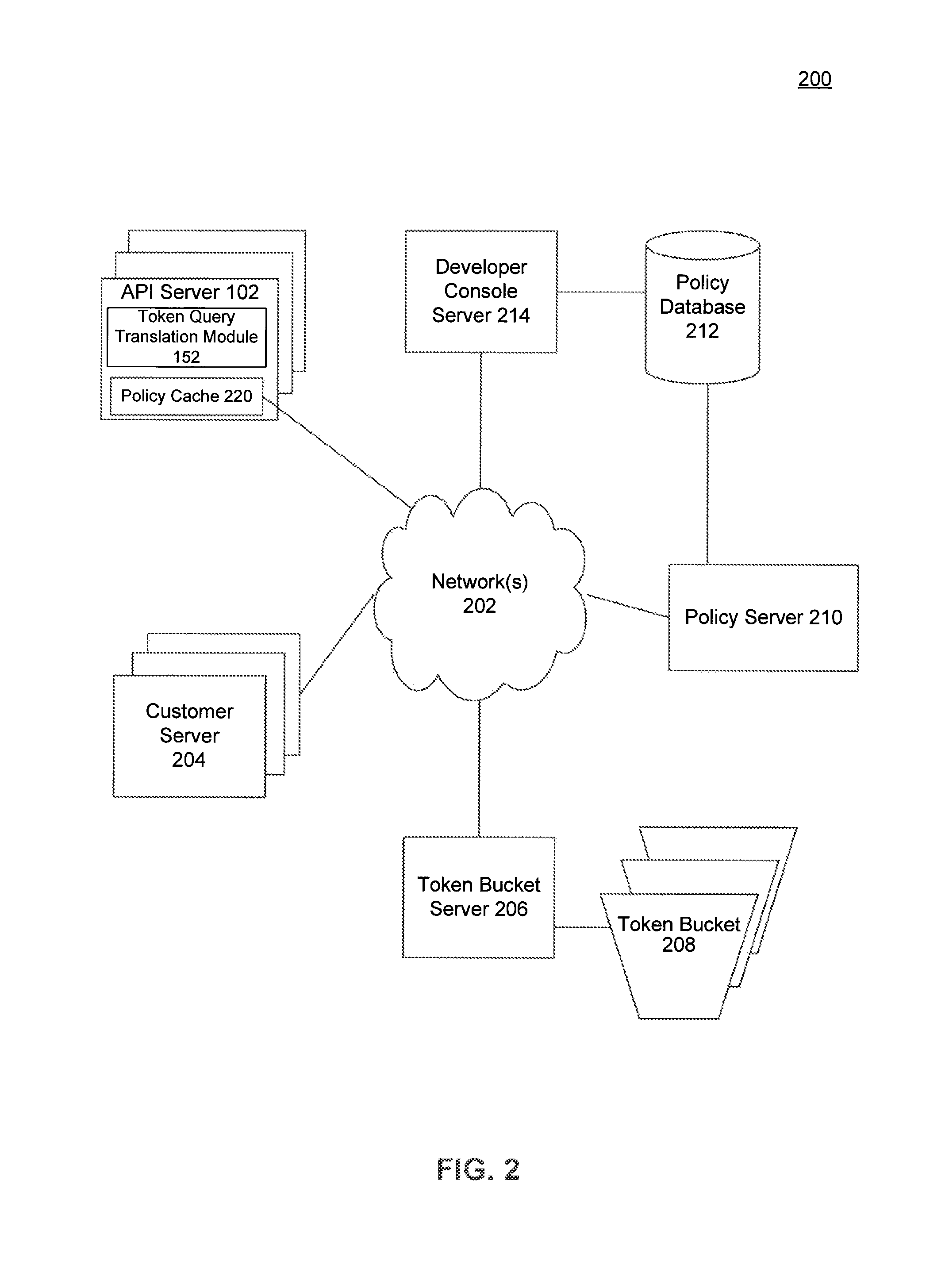
Configurable rate limiting using static token buckets, and applications thereof
ActiveUS8681630B1Control rateReduce in quantityError preventionTransmission systemsRate limitingProgramming language
A system disclosed rate limits API requests. The system includes an API server that receives an API request from a developer application at an API server and a token bucket to rate limit API requests from the developer application. A token query translation module determines a number of tokens needed to process the API request based on a rate configured in predefined policy data for the developer application and a replenish rate of the token bucket. The number of tokens inversely corresponds to the rate configured in the predefined policy data. A token request module instructs the API server to process the API request if the token bucket has sufficient tokens and reduces the number of tokens in the token bucket for the developer application by the number of tokens needed to process the API request. In this way, the disclosed system effectively simulates buckets having configurable replenish rates.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
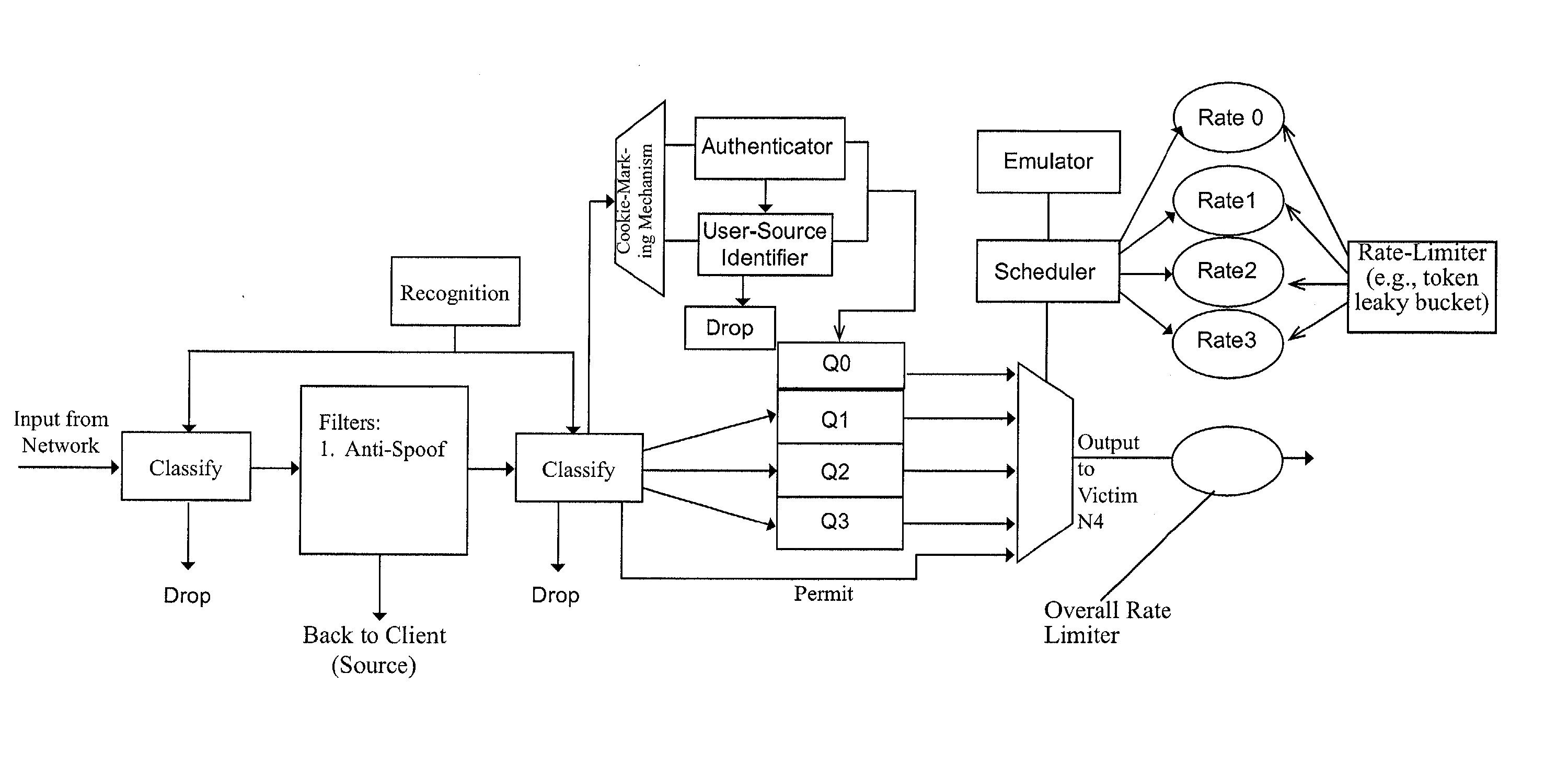
Weighted fair queuing-based methods and apparatus for protecting against overload conditions on nodes of a distributed network
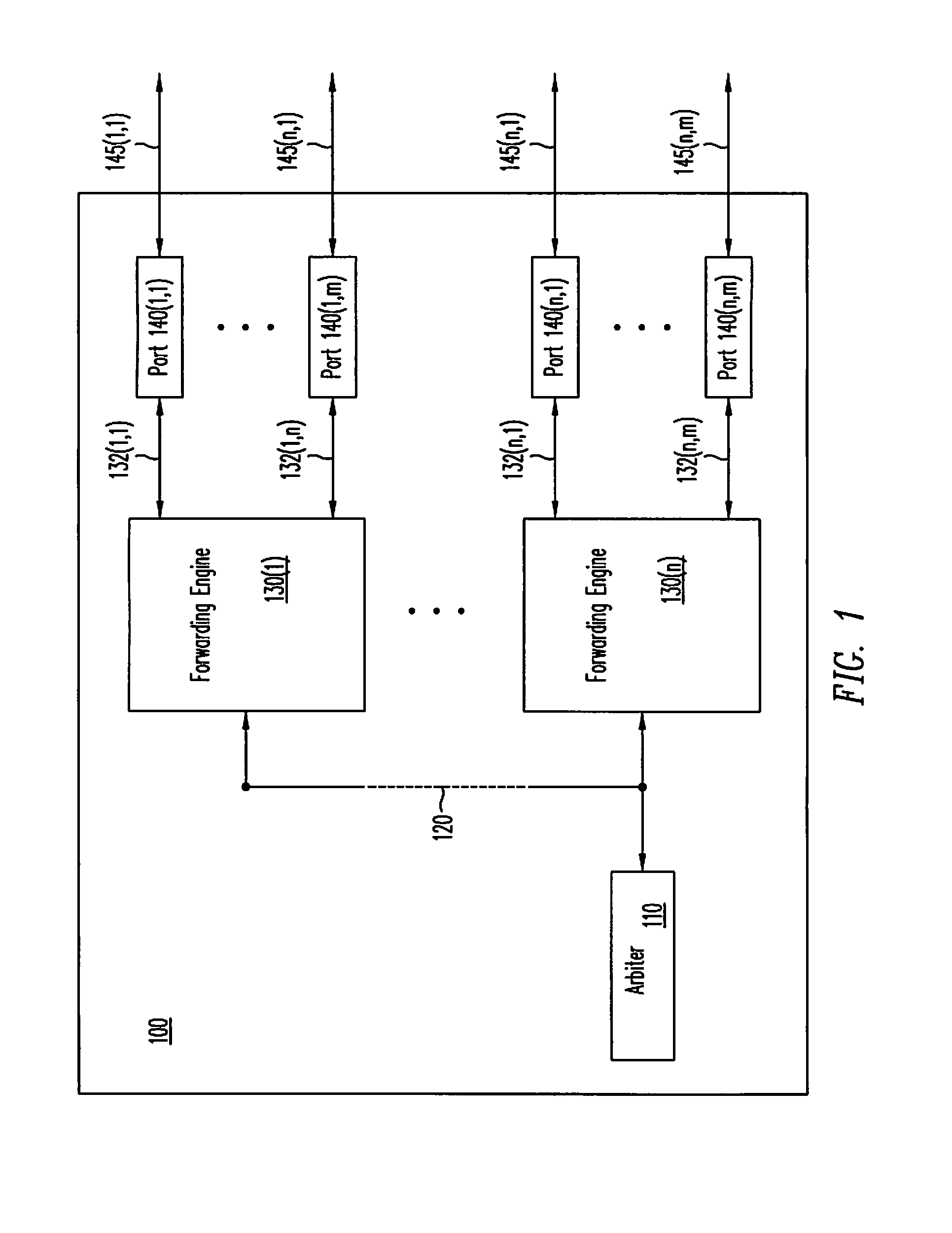
InactiveUS7342929B2Data switching by path configurationSecuring communicationComputer networkNetwork on
An improved network device that controls throughput of packets received thereby, e.g., to downstream devices or to downstream logic contained within the same network device. The network device comprises a scheduler that schedules one or more packets of a selected class for throughput as a function of a weight of that class and weights of one or more other classes. The weight of at least the selected class is dynamic and is a function of a history of volume of packets received by the network device in the selected class. An apparatus for protecting against overload conditions on a network, e.g., of the type caused by DDoS attacks, has a scheduler and a token bucket mechanism, e.g., as described above. Such apparatus can also include a plurality of queues into which packets of the respective classes are placed on receipt by the apparatus. Those packets are dequeued by the scheduler, e.g., in the manner described above, for transmittal to downstream devices (e.g., potential victim nodes) on the network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for implementing packet differential service
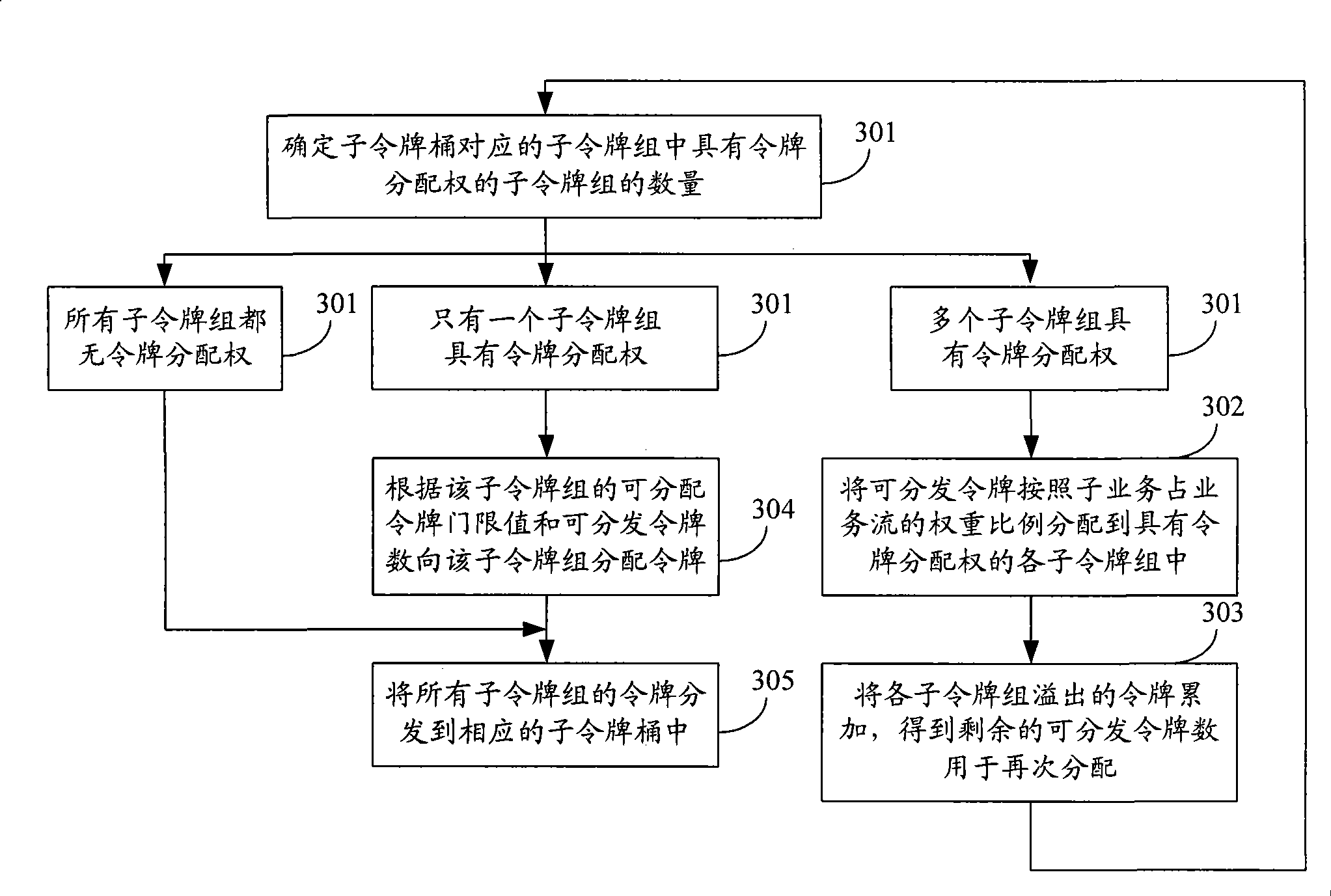
InactiveCN101478491AReduce complexityReduce difficultyData switching networksDifferentiated servicesTraffic capacity
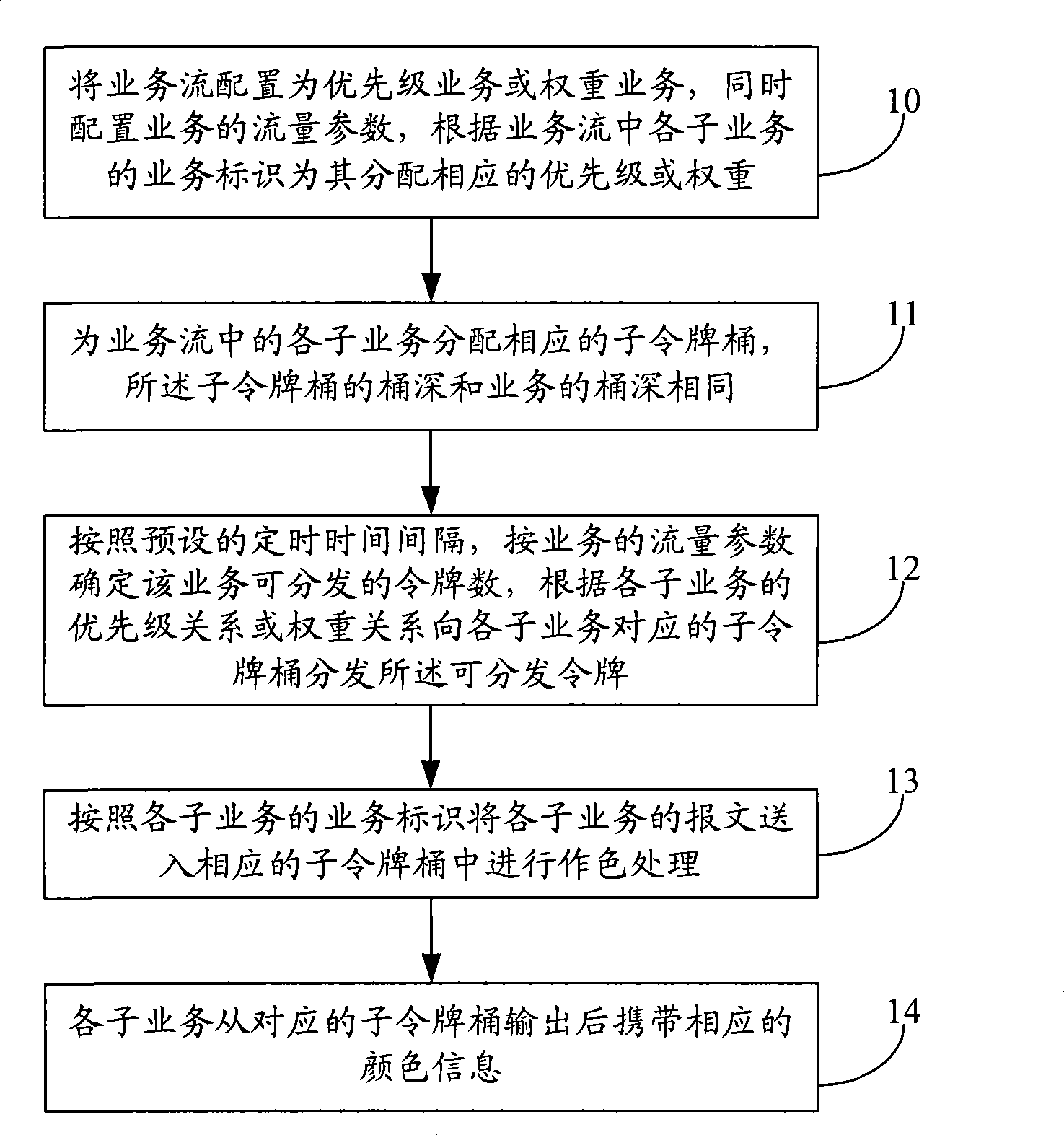
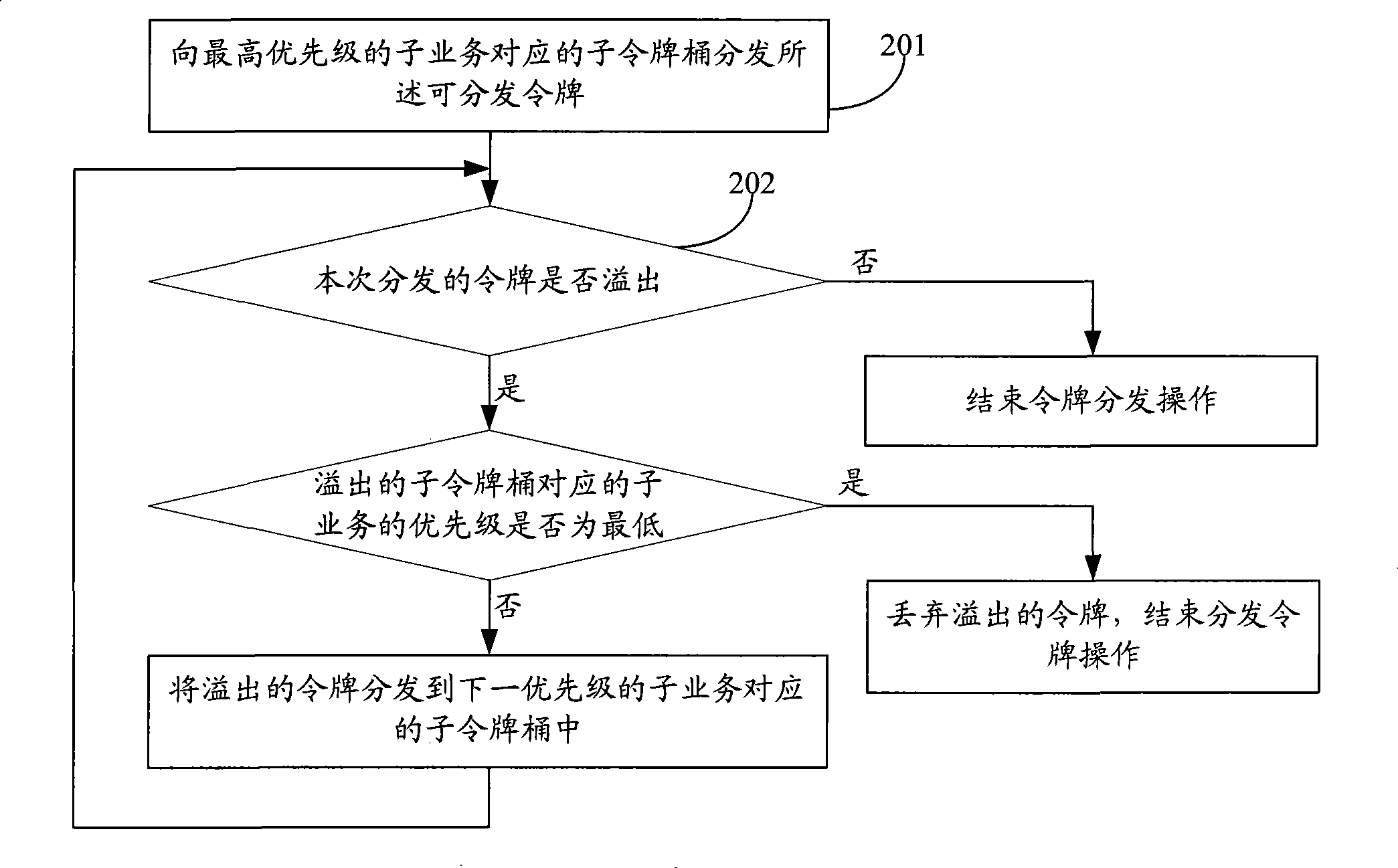
The invention discloses a method and a device for achieving differentiated service of packet service. The method comprises the following steps: configuring traffic parameters of a service, allocating corresponding priority or weight to each sub-service according to service identifies of the sub-services, and allocating corresponding sub-token bucket to each sub-service, wherein, the bucket depth of the sub-token bucket is equal to the bucket depth of the service; determining the available tokens of the service according to the traffic parameters of the service at a preset timing time interval; distributing the available tokens to the corresponding sub-token bucket of each sub-service according to the relationship of the priority or the weight of the sub-services; and transmitting messages of each sub-service to corresponding sub-token barrel according to the service identity of each sub-service to carry out dyeing treatment. The device comprises a priority or weight distribution module, a token distribution module, and a dyeing treatment module. The method and the device can realize bandwidth share and bandwidth control for forwarding messages based on priority or weight of the sub-services.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Hierarchical prioritized round robin (HPRR) scheduling
ActiveUS7457313B2Efficient and fair handlingEfficiently easily allocatesTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationDistributed computingToken bucket
The HPRR method uses “token bucket” rate classifiers to mark each individual packet as conforming or not conforming to a traffic specification for the flow. Flows are considered to be in a single service class. One such class is distinguished as a default “best effort” service class. Each service class is assigned a weight corresponding to its fraction of bandwidth granted to the class when all classes are active. The HPRR method allows a packet from a flow to be forwarded in one of two ways, either as part of its class's allocated bandwidth or as part of the “best effort” bandwidth. By always providing two paths for a flow to send its packets, a flow is always given its “fair share” of two different classes: its primary or configured class and the best effort class. An overbooked class will have each of its flows compete for the inadequate bandwidth allocated to the class, but because each flow can use the best effort bandwidth it also gets a fair share of that bandwidth to allow the classes bandwidth guarantees to be when other classes are inactive.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
I/O circuit and data transmission control method
ActiveUS20170163543A1Inefficient data transferEfficiently and fairly offer transmission priorityData switching networksElectric digital data processingComputer hardwareWaiting period
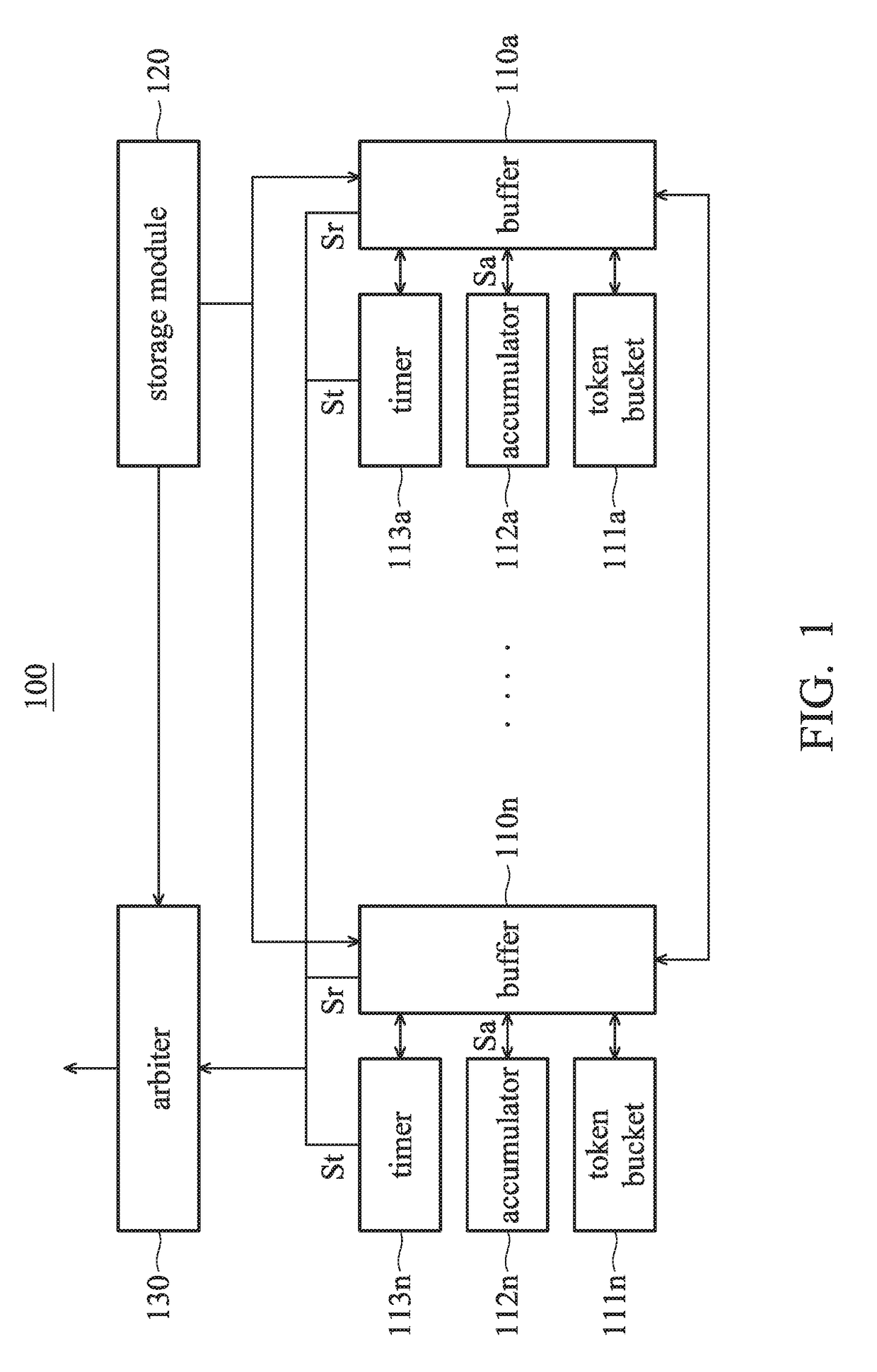
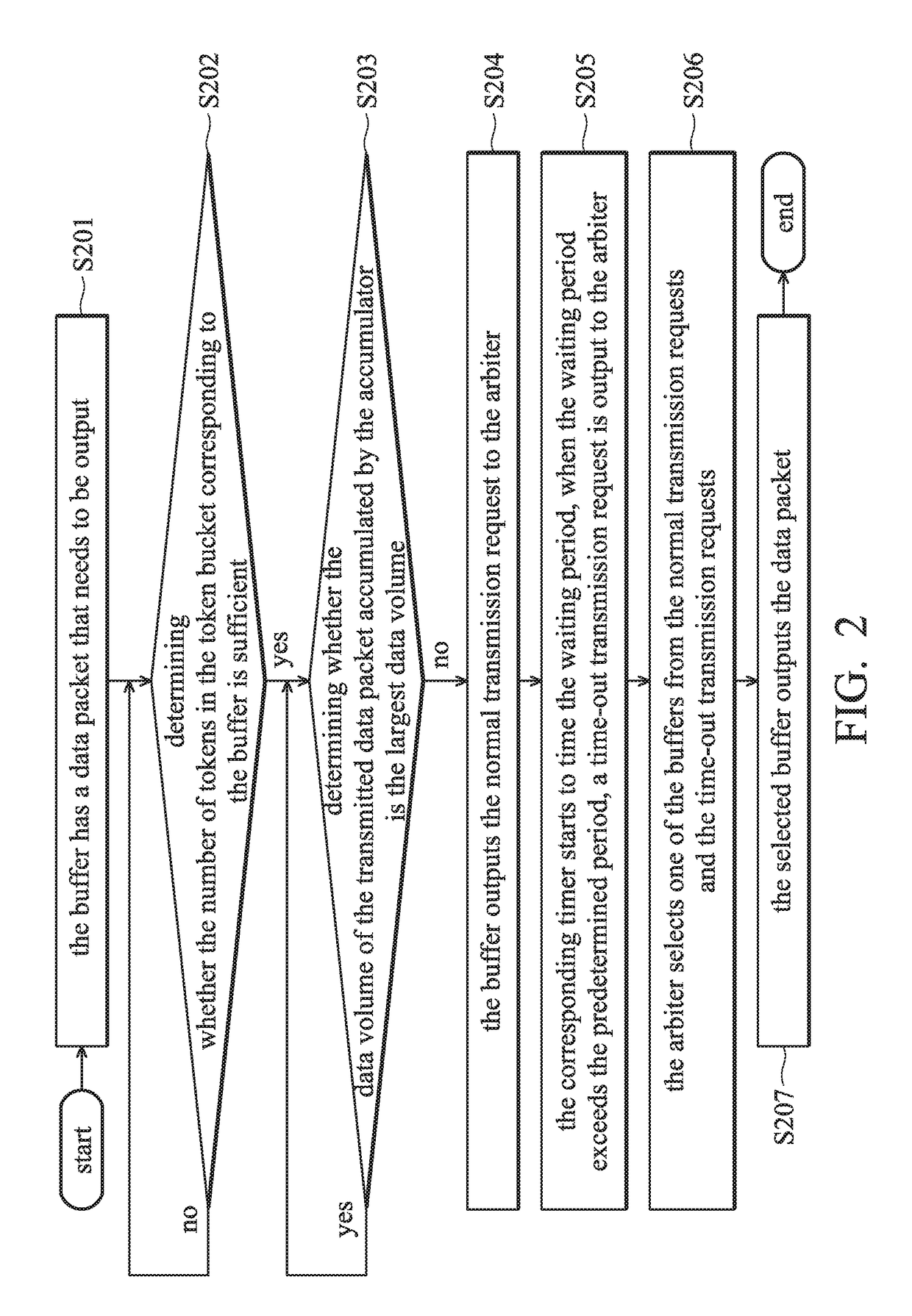
An I / O circuit includes buffers, a storage module, accumulators, timers, and an arbiter. Each buffer corresponds to a respective virtual channel. Each buffer corresponds to a respective token bucket, and outputs a normal transmission request according to the amount of tokens and an accumulating signal. The storage module stores a lookup table including a plurality of weightings. Each accumulator corresponds to a respective buffer, accumulates a data volume according to the corresponding weighting, and outputs the accumulating signal. Each timer corresponds to a respective buffer, times waiting period after the corresponding buffer outputs the normal transmission request, and outputs a time-out transmission request when the waiting period exceeds a predetermined period.The arbiter receives the time-out transmission requests and the normal transmission requests, and selects one of the buffers from all of the time-out transmission requests and the normal transmission requests.
Owner:VIA ALLIANCE SEMICON CO LTD
Multi-service scheduling method and system
ActiveCN101621457AGuaranteed base transfer rateFully consider QoS attributesData switching networksPacket lossDistributed computing
The invention discloses a multi-service scheduling method, which comprises the following steps: A, calculating a service transmission rate in a certain time period prior to a current scheduling time slot, counting packet loss of L2 packets and waiting time lengths of first packets of services, and then calculating scheduling priorities among the services; B, acquiring the service with the highest priority from a scheduling queue and allocating resources for the service through a GBR token bucket if the service is determined as a GBR service; and C, updating available resources, continuing allocating resources for the GBR service through an MBR token bucket if the available resources are determined to be not null, and combining the resources allocated for the service respectively through the GBR token bucket and the MBR token bucket. The invention simultaneously discloses a multi-service scheduling system. The method and the system fully consider the Quality of Service QoS attribute of the service, and meet the GBR requirement of the service at the same time of avoiding the occurrence of a 'hunger' situation.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Flow monitoring method and flow monitoring equipment
InactiveCN101227410AEfficient use ofAvoid wastingData switching networksResource utilizationMonitoring methods
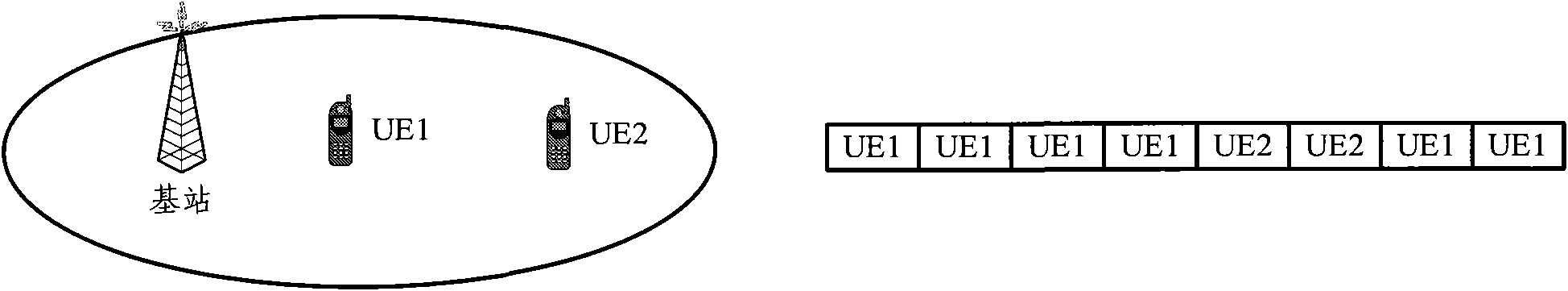
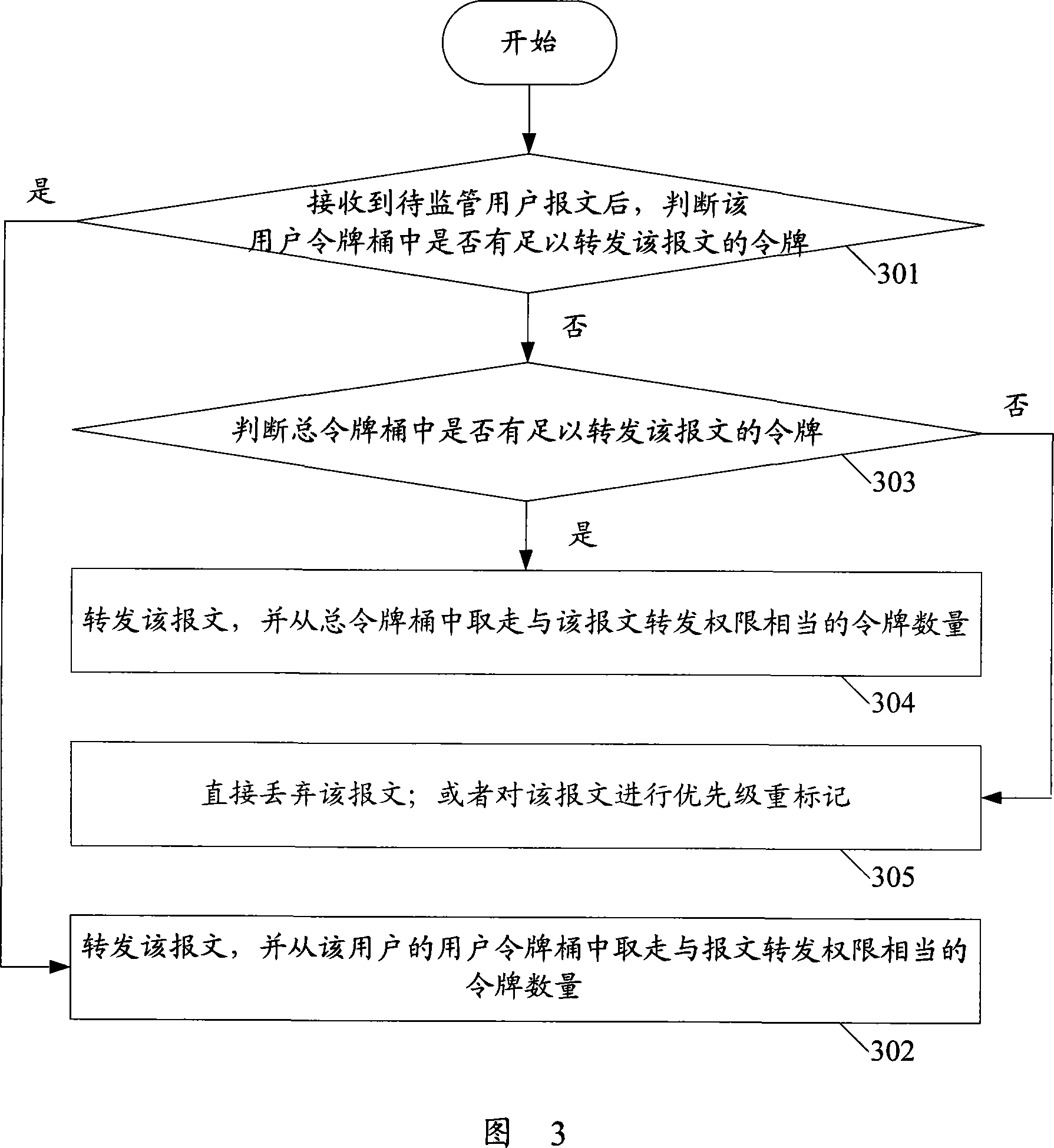
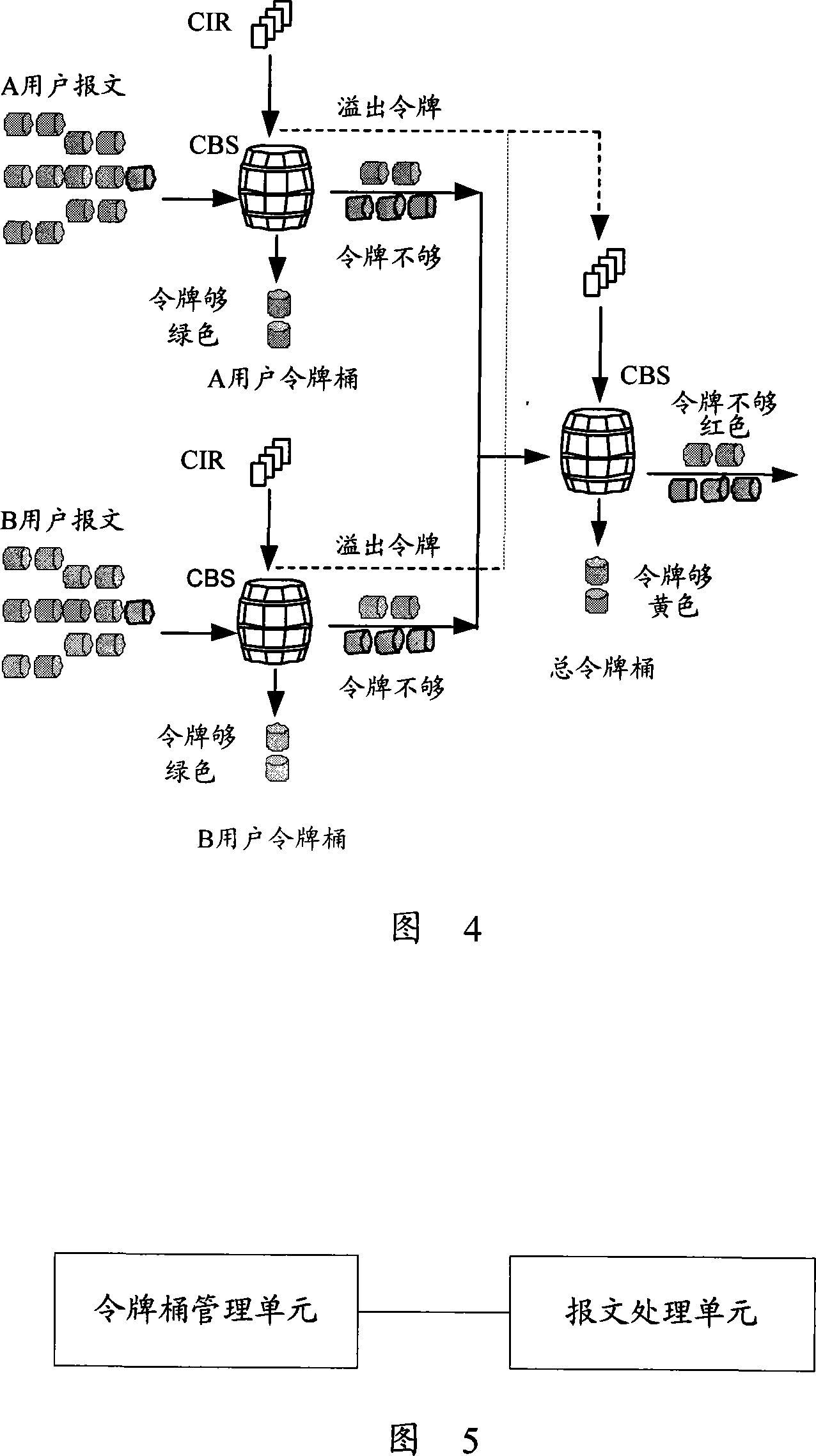
The invention provides a method for monitoring flow, the method comprises aiming at each user who is waiting to be monitored, respectively setting user token buckets, aiming at all users who are waiting to be monitored, setting a total token bucket, respectively adding tokens in each user token bucket, adding token which is overflowed from user token buckets in the total token bucket, judging whether a user token bucket of a user has enough buckets to transmit the message after receiving message of users which are waiting to be monitored, if has enough buckets, transmitting the message, taking out tokens whose number are equal to message transmitting authority from the user token bucket of the user, if not, judging whether tokes which are enough to transmit the message are existed in the total token bucket, if the tokes are enough, and then transmitting the message, and taking tokens whose number are equal to the message transmitting authority from the total token bucket. In addition, the invention also provides flow monitoring equipment. The invention can improve bandwidth resource utilization ratio.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com