Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
127results about How to "Packet loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
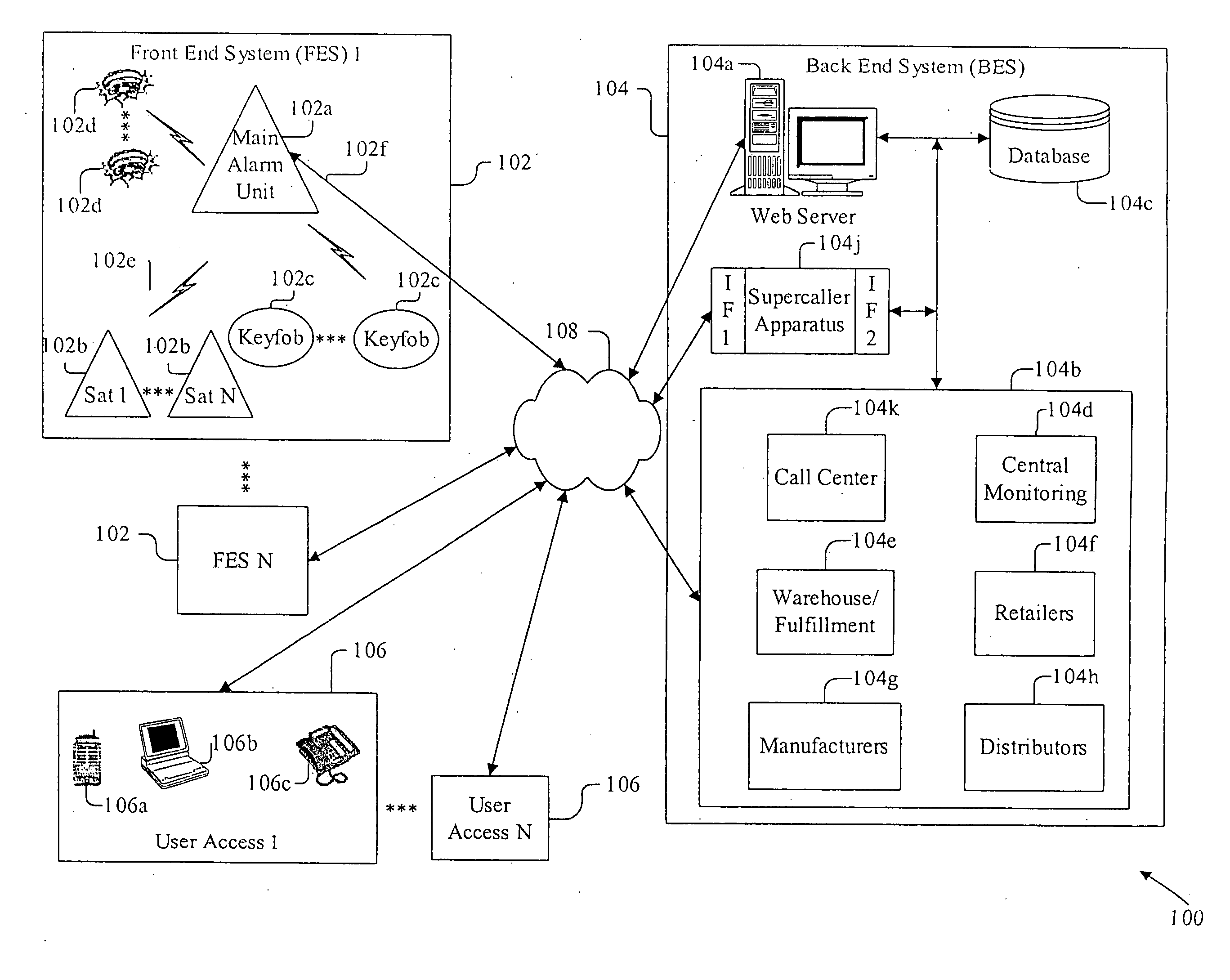
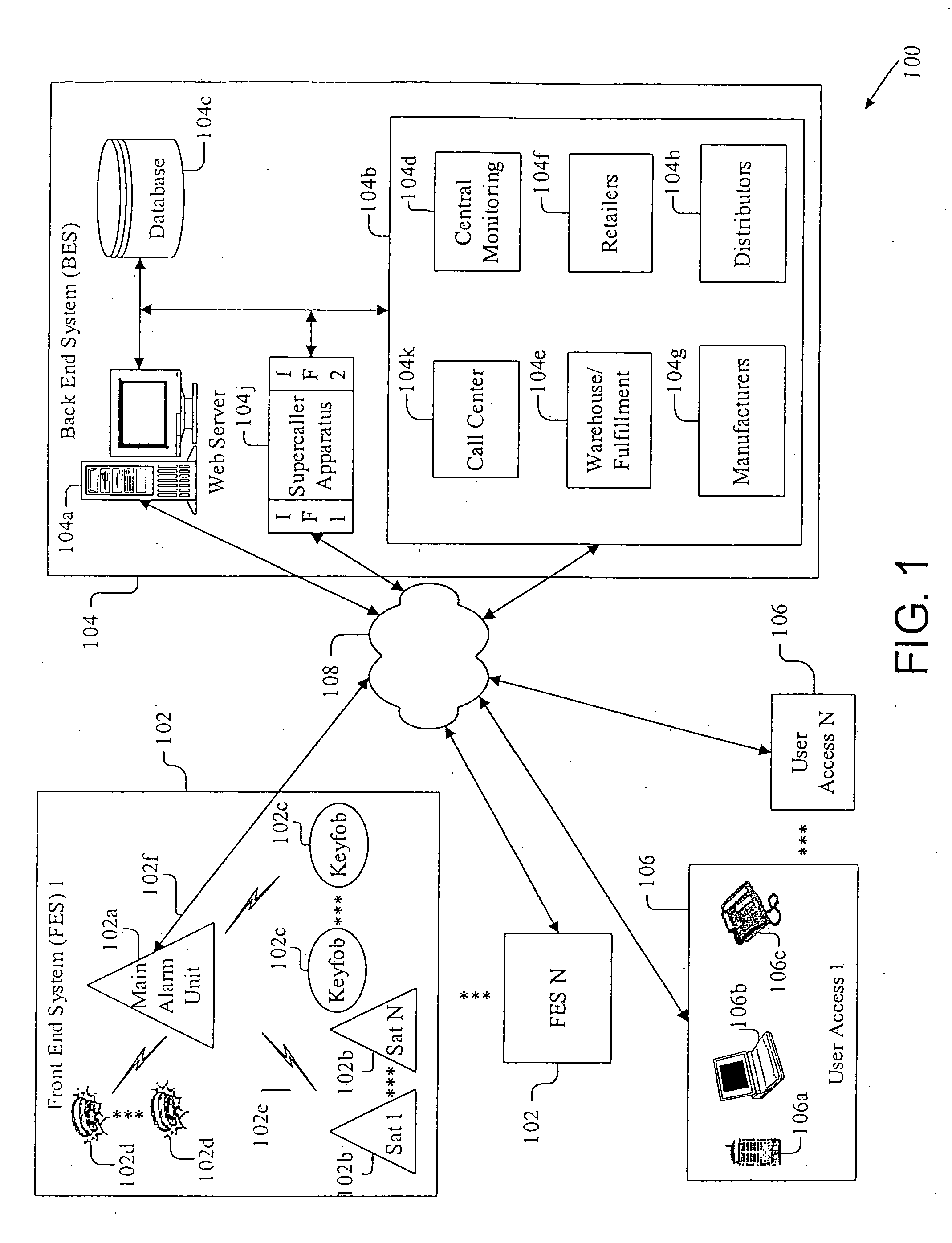
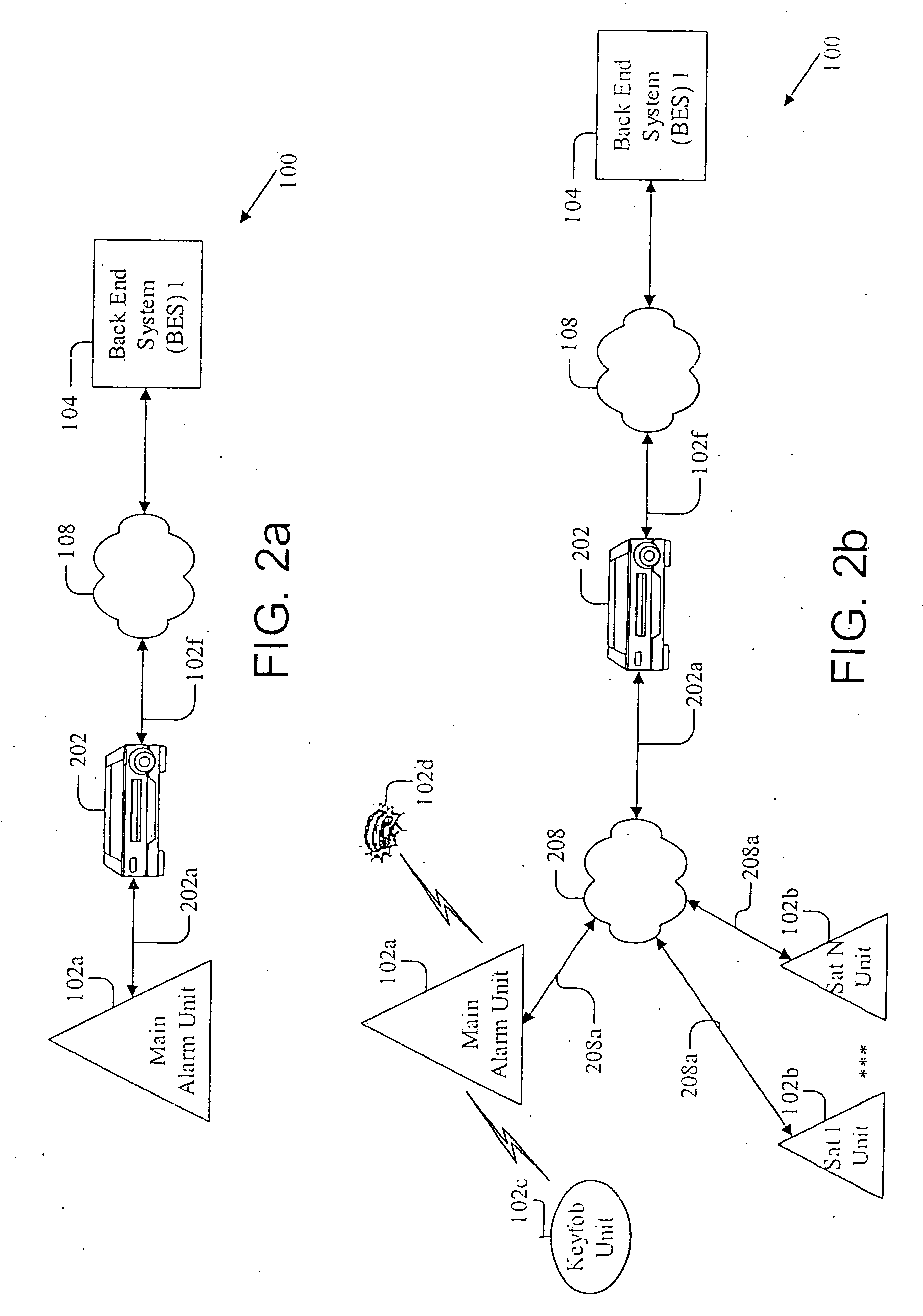
Apparatus, system, and method for alarm systems
InactiveUS20060176167A1Packet lossMinimizing inputFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelephonic communicationComputer hardwareAlarm device
An alarm system (100), including ease of programming of a family or group of interoperating alarm devices (102) via a learn mode that detects new devices and provides reliable accounting of the group via state dumps to an external system (104). Reliable communications with the external system (104) are provided via a set of protocols. Disabling of the alarm system is prevented, by transmitting a pre-alarm signal prior to expiration of an entry delay, and by verifying communications with an external device, prior to an alarm-triggering event. Multi-priority message code assignment, including error tolerance, employs n-bit codes with maximized error tolerance. Message transmissions include multiple levels of error protection. The group of monitored alarm devices (102) can be easily set up, purchased and activated by a consumer, and do not become permanent fixtures.
Owner:LASERSHIELD SYST
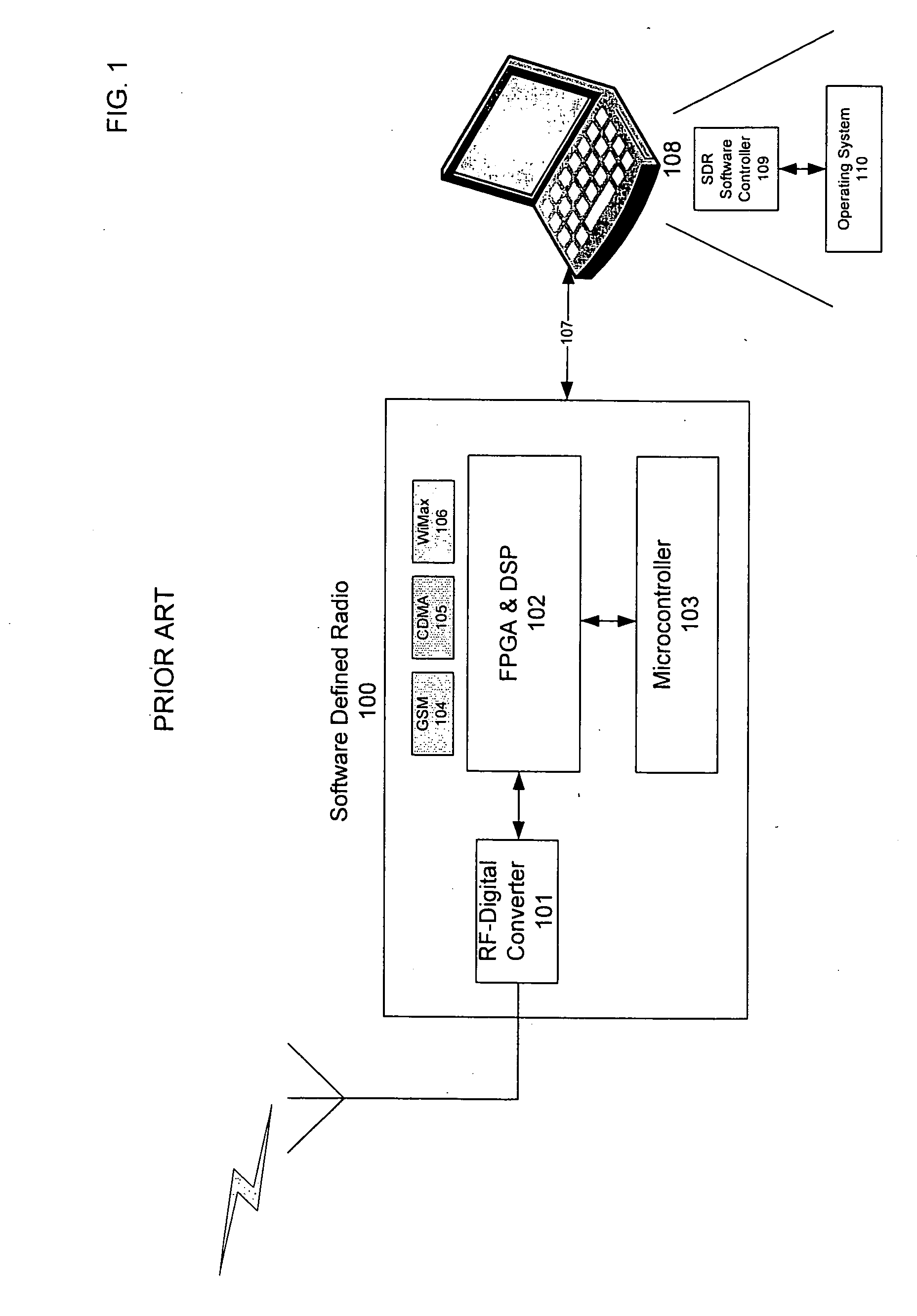
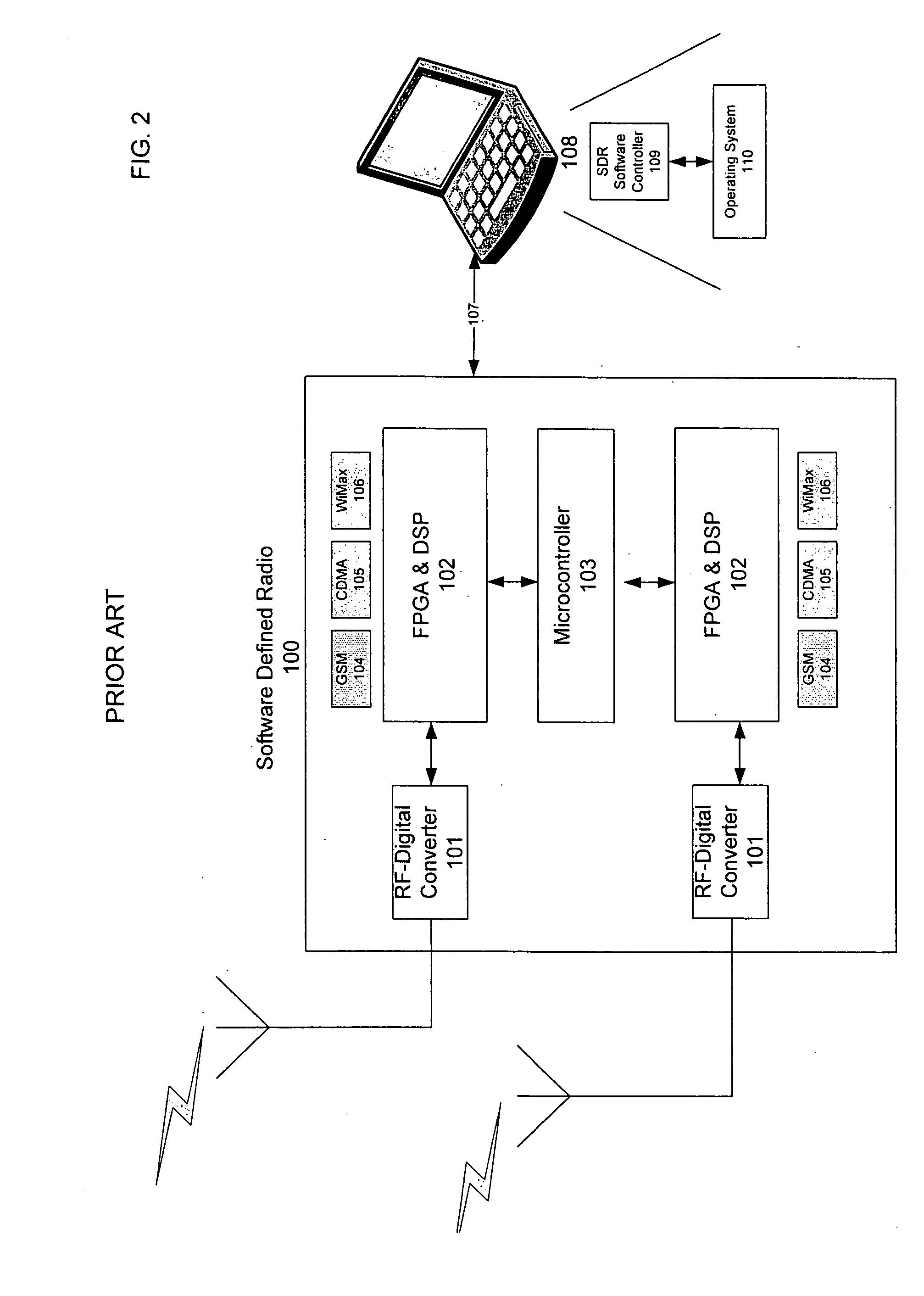
Multi-network seamless roaming through a software-defined-radio
InactiveUS20060046716A1Minimize packet lossPacket lossAssess restrictionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSoftware define radioCommunication device
A method is provided for seamless roaming over multiple dissimilar wireless networks leveraging a set of one or more SDRs, and possibly some traditional radio communication devices. The method includes determining whether alternate networks are available regardless of whether the SDR has only a single transmitter and receiver or multiple transmitters and receivers. In addition, if the SDR provides multiple transmitters and receivers, or if multiple distinct SDRs are available to the mobile computing device, the method will be able to better optimize the seamless roaming experience for the user while still utilizing the set of SDRs, in part, to determine whether alternate networks are available. The method further includes managing the transitions of an SDR between various modulation algorithms according to a variety of states and settings of the SDR or of the set of SDRs as a whole.
Owner:MOBILE SONIC INC
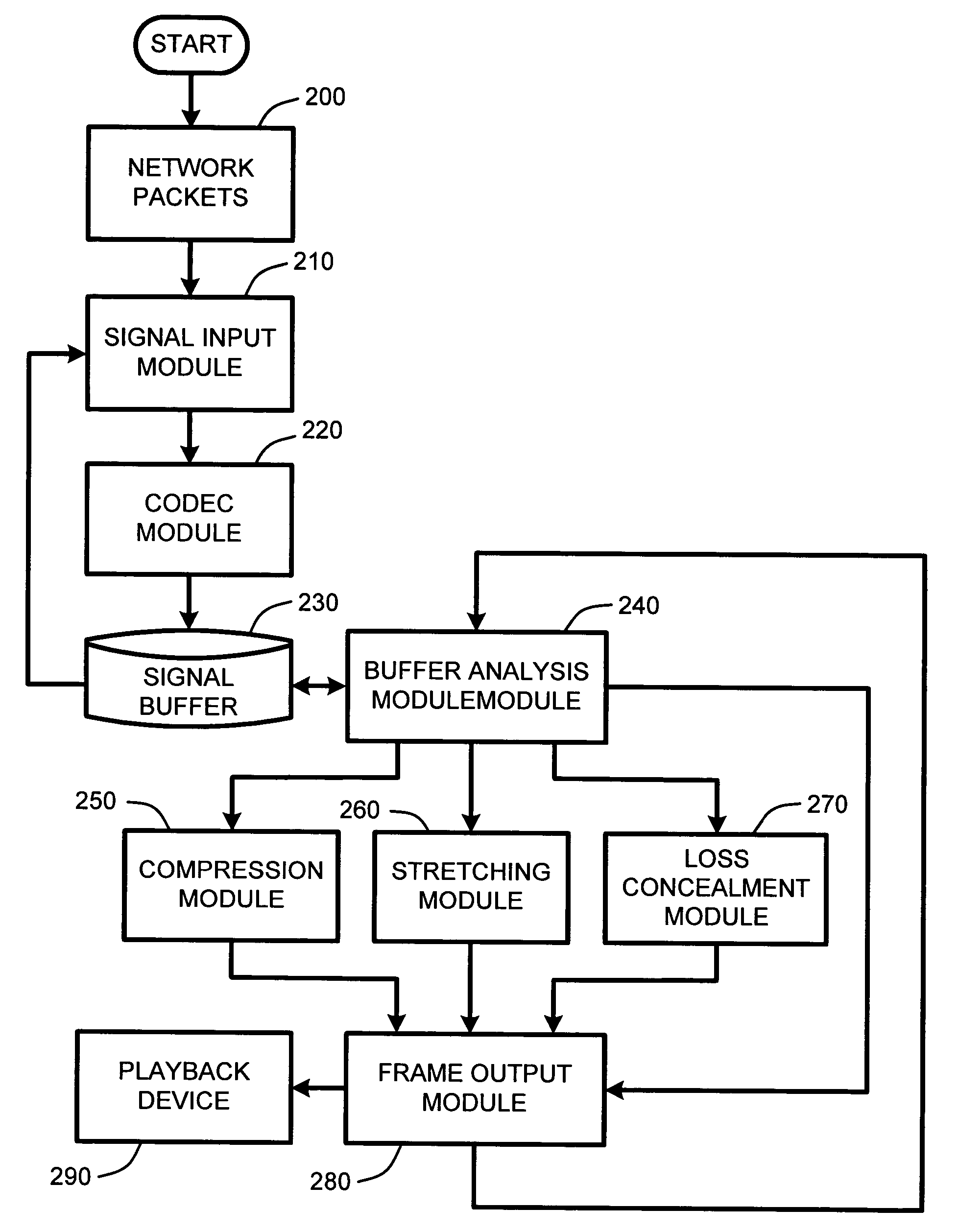
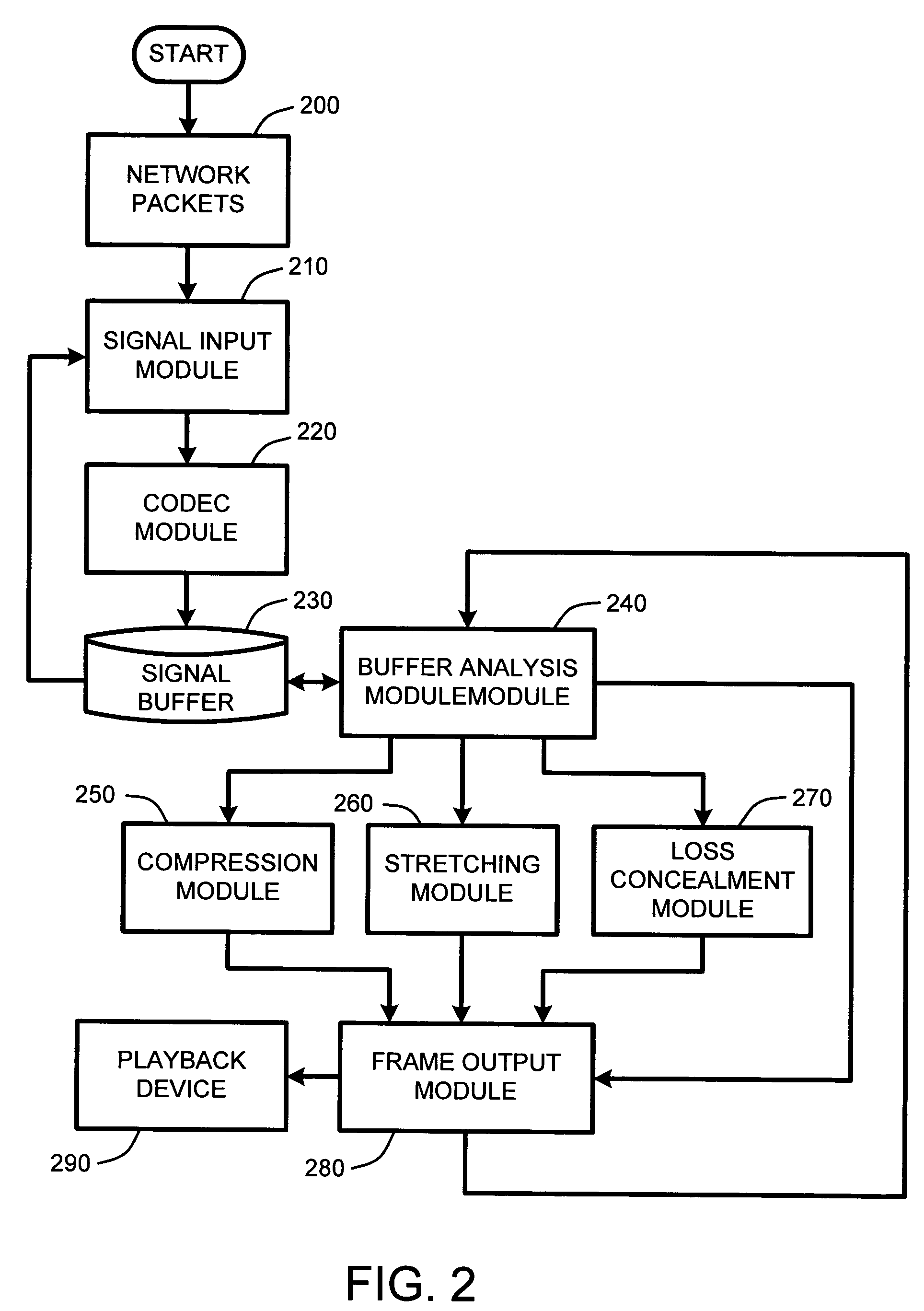
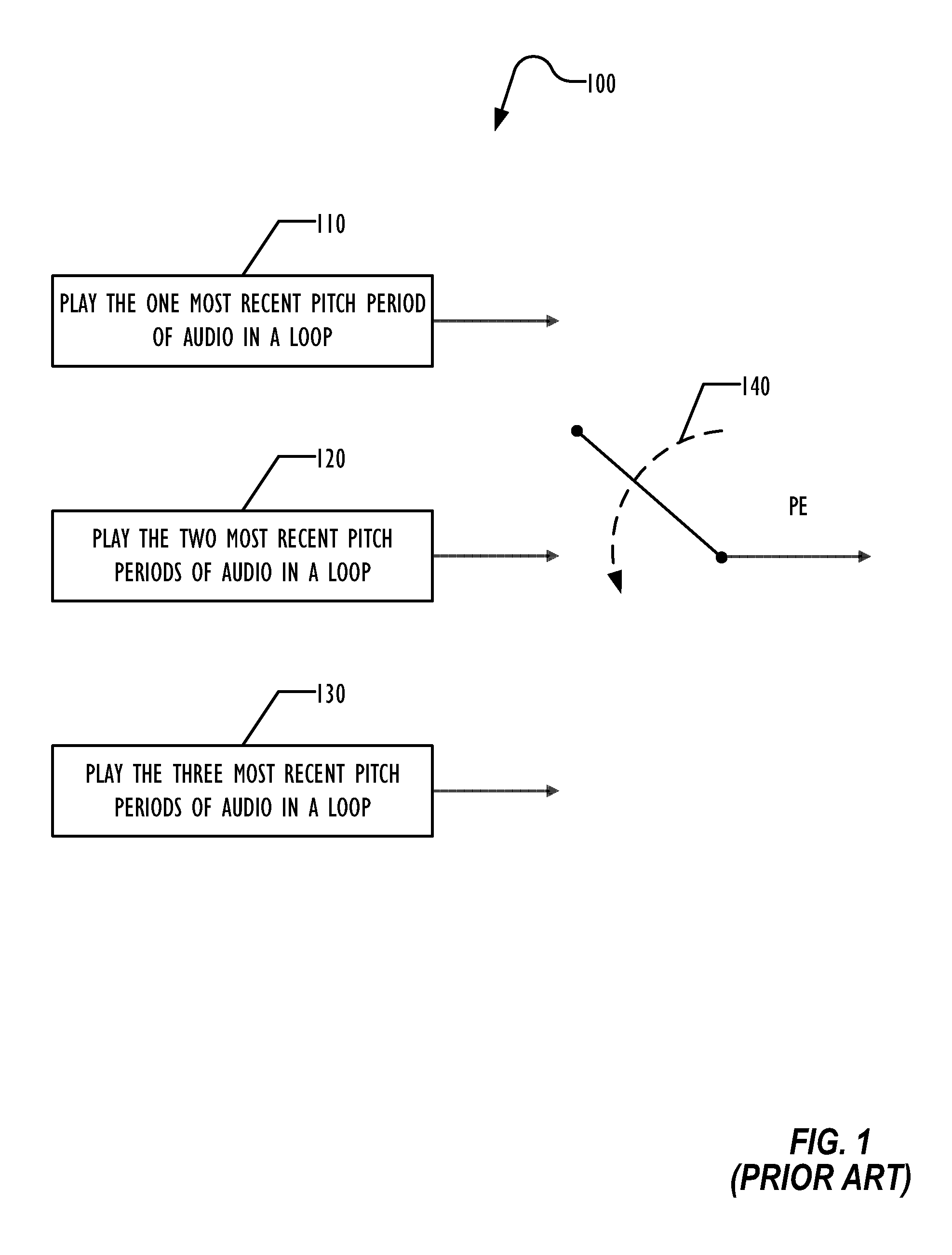
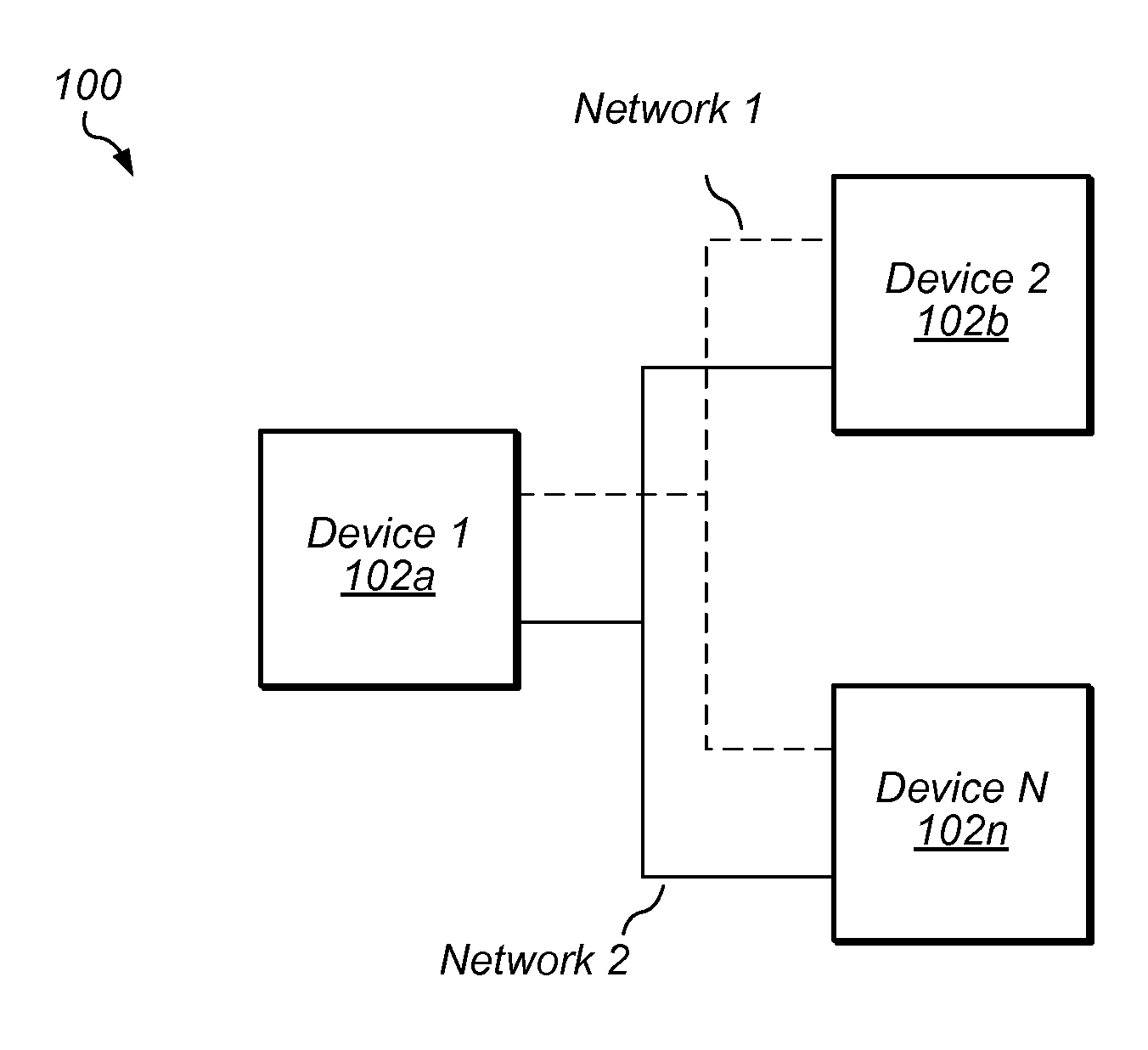
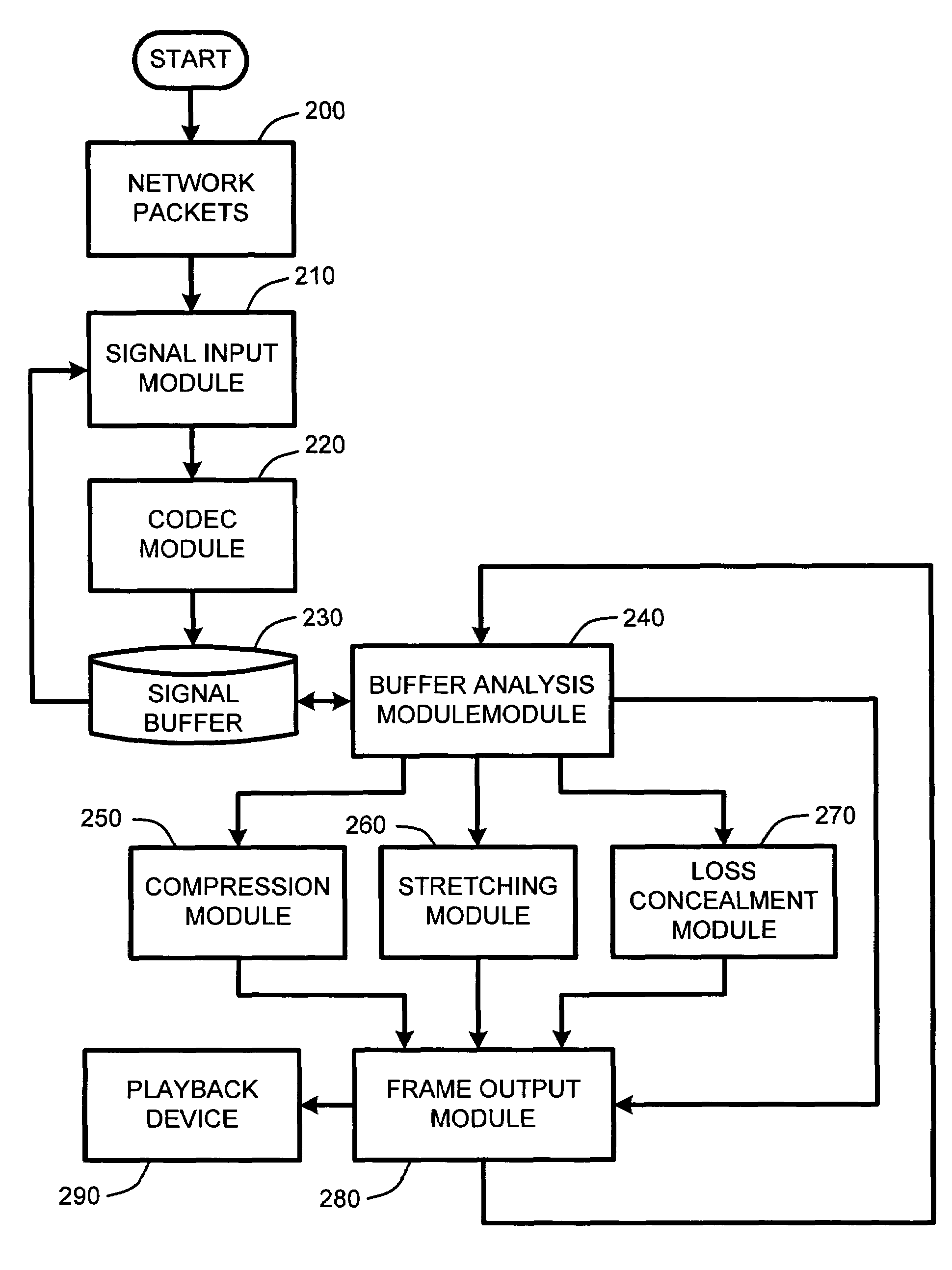
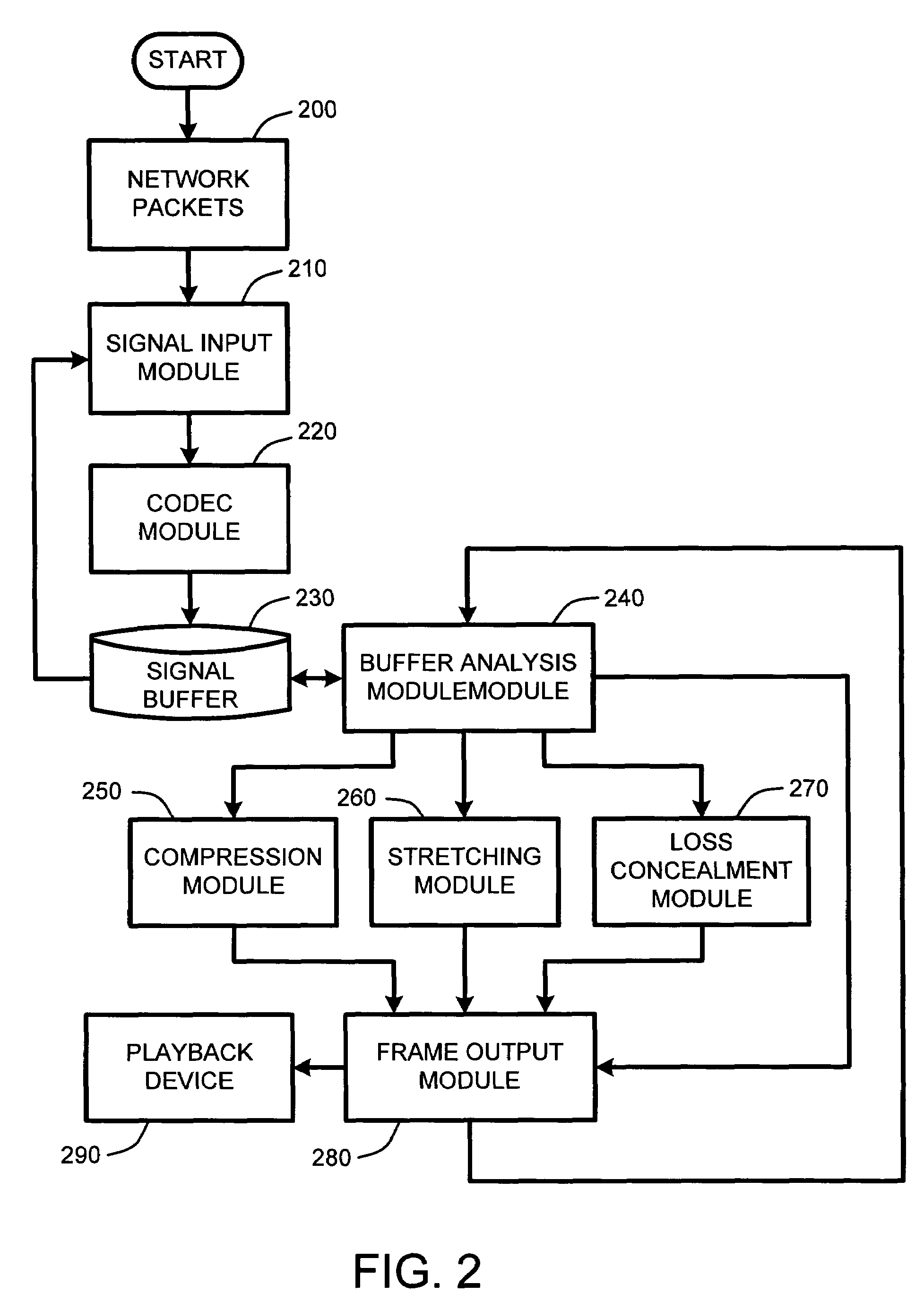
System and method for real-time jitter control and packet-loss concealment in an audio signal
InactiveUS20050058145A1Improve signal qualityImprove quality performanceSpeech analysisTime-division multiplexSelf adaptiveEngineering
An “adaptive audio playback controller” operates by decoding and reading received packets of an audio signal into a signal buffer. Samples of the decoded audio signal are then played out of the signal buffer according to the needs of a player device. Jitter control and packet loss concealment are accomplished by continuously analyzing buffer content in real-time, and determining whether to provide unmodified playback from the buffer contents, whether to compress buffer content, stretch buffer content, or whether to provide for packet loss concealment for overly delayed or lost packets as a function of buffer content. Further, the adaptive audio playback controller also determines where to stretch or compress particular frames or signal segments in the signal buffer, and how much to stretch or compress such segments in order to optimize perceived playback quality.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
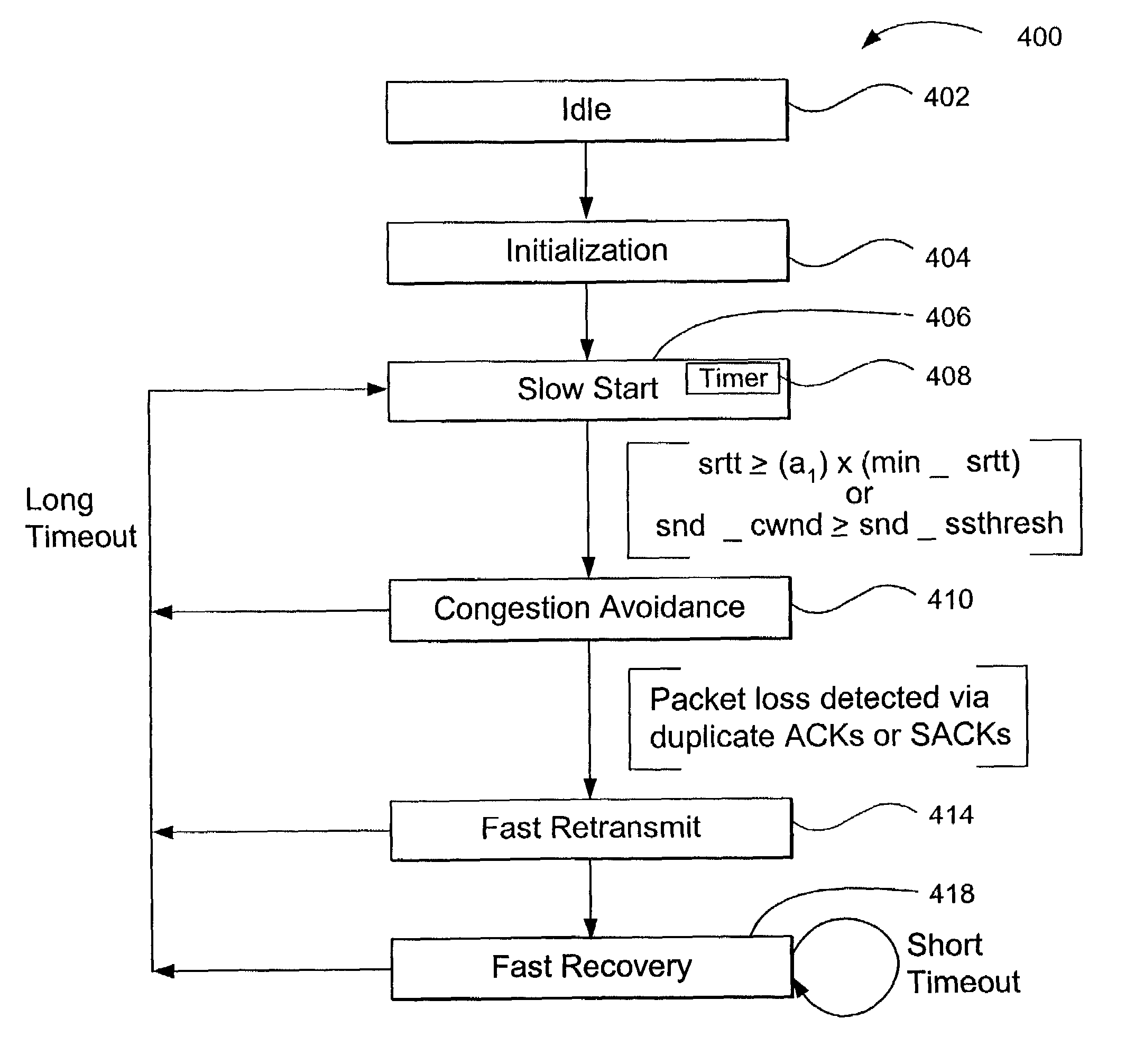
Data transport acceleration and management within a network communication system
ActiveUS7099273B2Good estimateReduce and eliminate bursty transmission of dataEnergy efficient ICTError prevention/detection by using return channelCongestion windowPacket loss
Improved data transport and management within a network communication system may be achieved by utilizing a transmit timer incorporated within the sender device and exploiting host-level statistics for a plurality of connections between a sender and receiver. The period of the transmit timer may be periodically adjusted based on a ratio of the smoothed round-trip time and the smoothed congestion window, thereby reducing or eliminating bursty data transmission commonly associated with conventional TCP architectures. For applications having a plurality of connections between a sender and a receiver that share a common channel, such as web applications, the congestion window and smoothed round trip time estimates for all active connections may be used to initialize new connections and allocate bandwidth among existing connections. This aspect of the present invention may reduce the destructive interference that may occur as different connections compete with one another to maximize the bandwidth of each connection without regard to other connections serving the same application. Error recovery may also be improved by incorporating a short timer and a long timer that are configured to reduce the size of the congestion window and the corresponding transmission rate in response to a second packet loss with a predefined time period in order to increase resilience to random packet loss.
Owner:OPTIMORPHIX INC
Packet-Based Aggregation of Data Streams Across Disparate Networking Interfaces While Providing Robust Reaction to Dynamic Network Interference With Path Selection and Load Balancing
ActiveUS20130132604A1Packet lossConnection managementMultiple digital computer combinationsData packData stream
System and method for load-balancing a plurality of transmission media. A first plurality of packets of a first stream may be transmitted to a second device on a first transmission medium. It may be determined that current medium utilization of the first transmission medium exceeds a first threshold. The first stream may be selected for transmission on both of the first transmission medium and a second transmission medium based on said determining that current medium utilization of the first transmission medium exceeds the first threshold. A second plurality of packets of the first stream may then be transmitted to the second device using both the first transmission medium and the second transmission medium. A first portion of the second plurality of packets may be transmitted on the first transmission medium and a second portion of the second plurality of packets may be transmitted on the second transmission medium.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
System and method for error-control for multicast video distribution
InactiveUS7224702B2Packet lossReduce traffic overheadSpecial service provision for substationError prevention/detection by using return channelPacket lossControl system
An embodiment of the invention includes an efficient error-control system and method for recovering packet losses, especially losses in distributing multicast video over broadband residential networks. Preferably, unlike most existing error-control algorithms designed for Internet multicast, the system and method does not employ substantial feedback suppression. Preferably, the system and method does not employ substantial multicasted retransmission. Preferably, the system and method does not employ substantial parity retransmission. Preferably, the system and method does not employ substantial local loss recovery. The system and method integrates two existing classes of error-control algorithms: Automatic Repeat Request (ARQ) and Forward Error Correction (FEC), to reduce traffic overhead and achieve scalability.
Owner:SONY CORP +2
Method for supporting scalable and reliable multicast in tdma/tdd systems using feedback suppression techniques
InactiveUS20060198325A1Reduce delaysImprove scalabilitySpecial service provision for substationError prevention/detection by using return channelCollision detectionReliable multicast
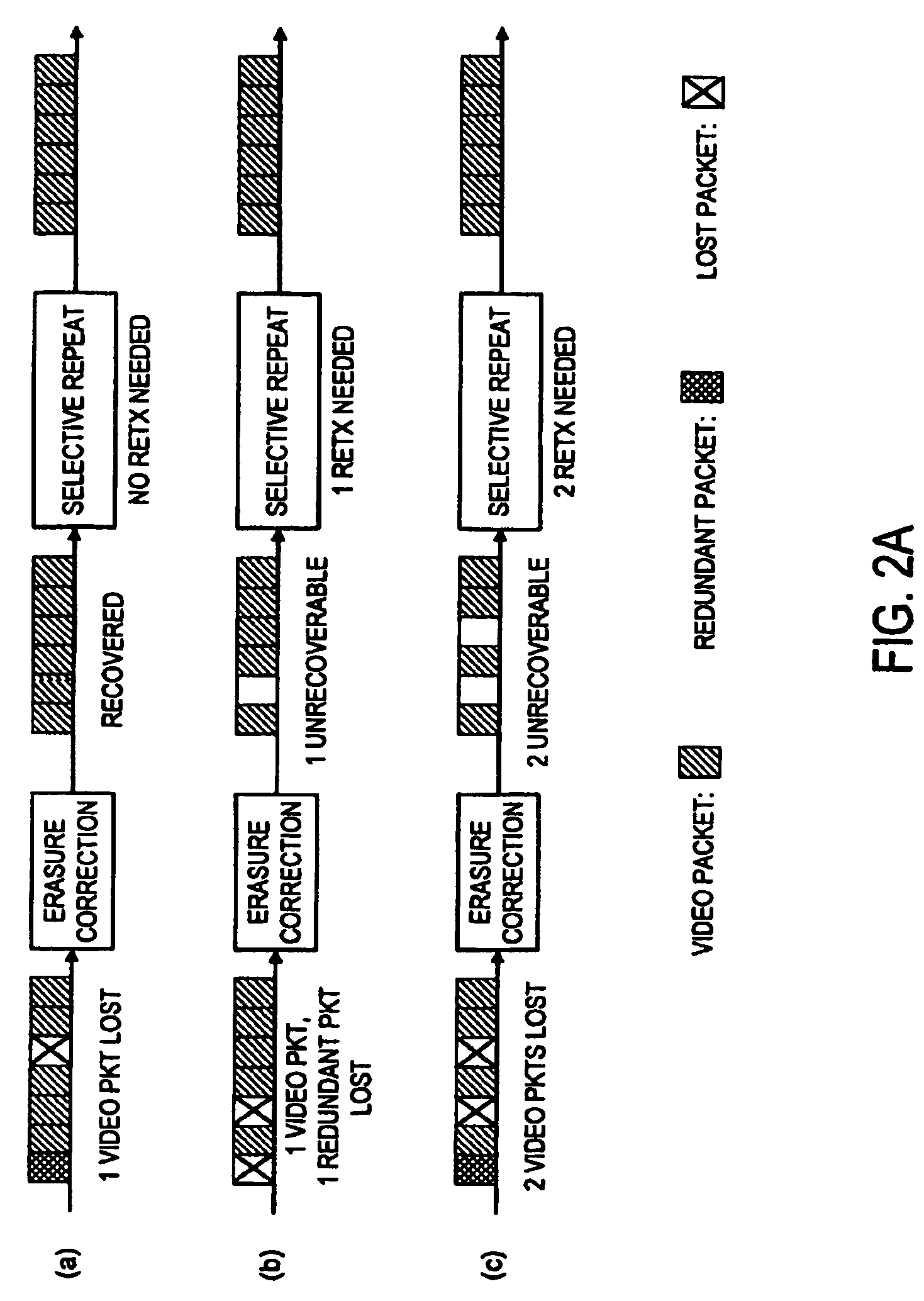
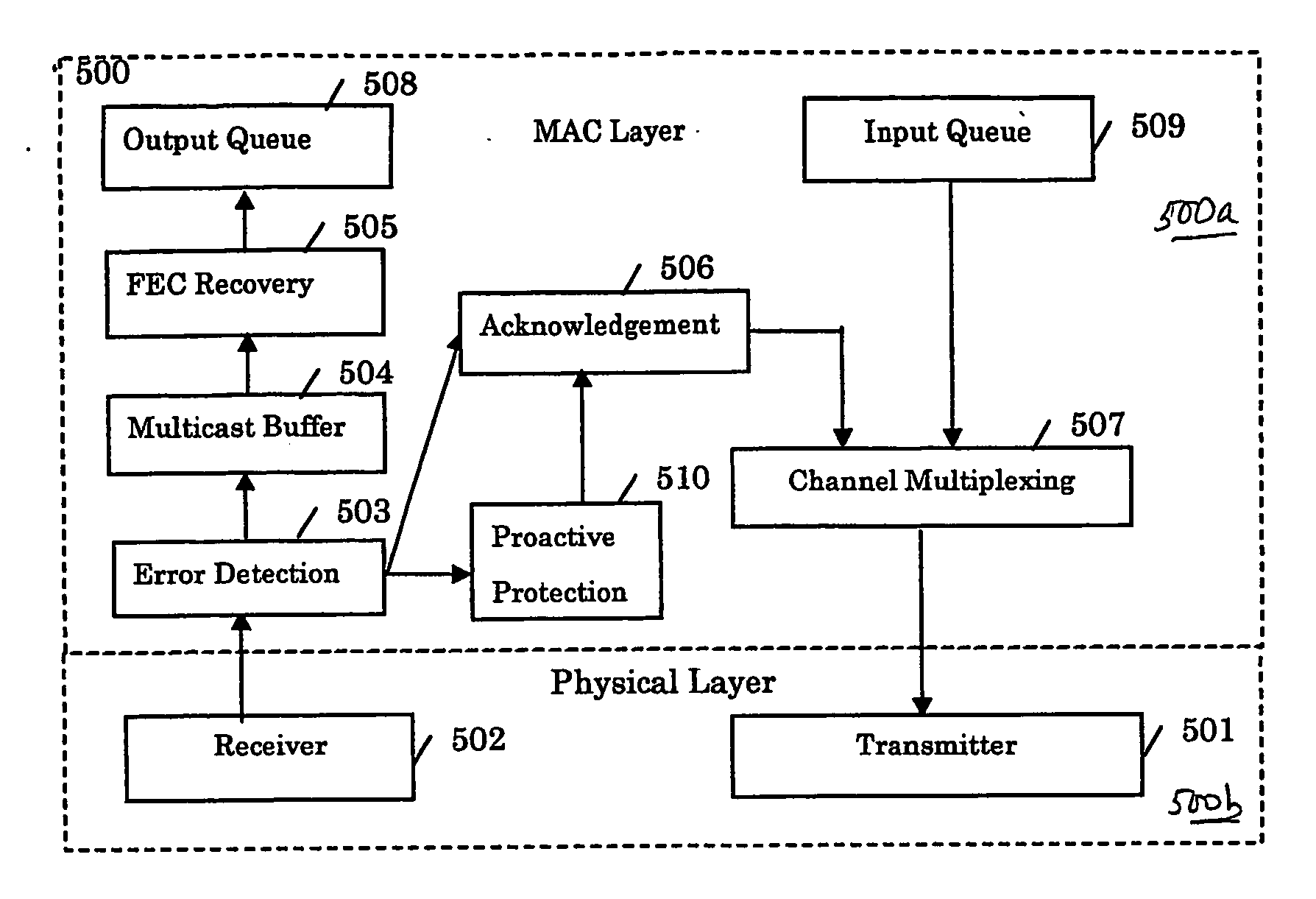
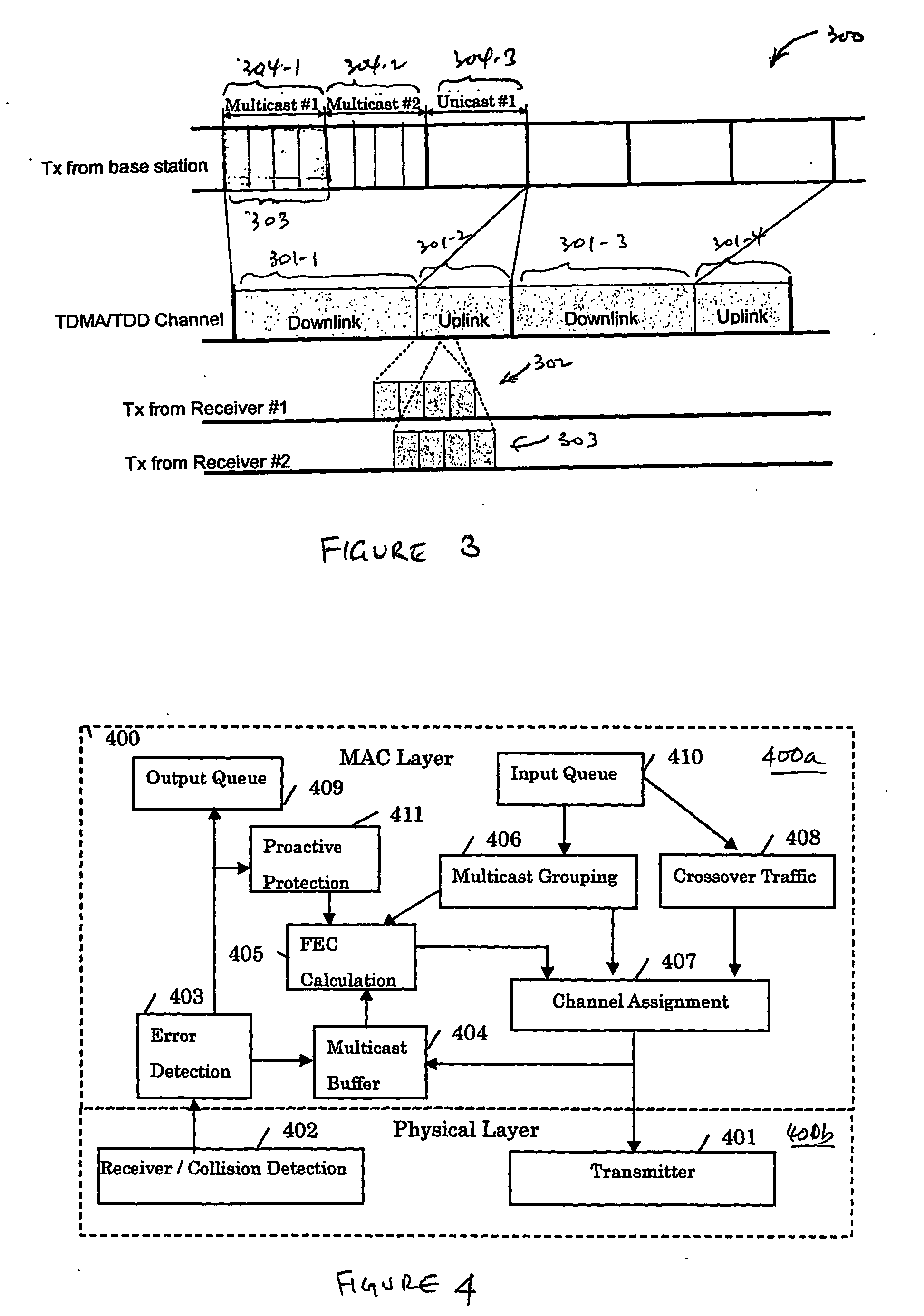
A method supports scalable and reliable multicast in a wireless network with a large bandwidth-delay product. In this method, acknowledgement packets from different receivers experiencing the same number of data packets lost are assigned the same time slots. This method can be combined with other loss recovery techniques, such as forward error correction (FEC) recovery, proactive protection, feedback suppression and collision detection. Scalability is achieved as bandwidth usage relates only to the number of packets transmitted, rather than the number of receivers.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
System and method for error-control for multicast video distribution
InactiveUS20020114283A1Packet lossReduce traffic overheadSpecial service provision for substationError prevention/detection by using return channelExtensibilityTraffic capacity
<heading lvl="0">Abstract of Disclosure< / heading> An embodiment of the invention includes an efficient error-control system and method for recovering packet losses, especially losses in distributing multicast video over broadband residential networks. Preferably, unlike most existing error-control algorithms designed for Internet multicast, the system and method does not employ substantial feedback suppression. Preferably, the system and method does not employ substantial multicasted retransmission. Preferably, the system and method does not employ substantial parity retransmission. Preferably, the system and method does not employ substantial local loss recovery. The system and method integrates two existing classes of error-control algorithms: Automatic Repeat Request (ARQ) and Forward Error Correction (FEC), to reduce traffic overhead and achieve scalability.
Owner:SONY CORP +2
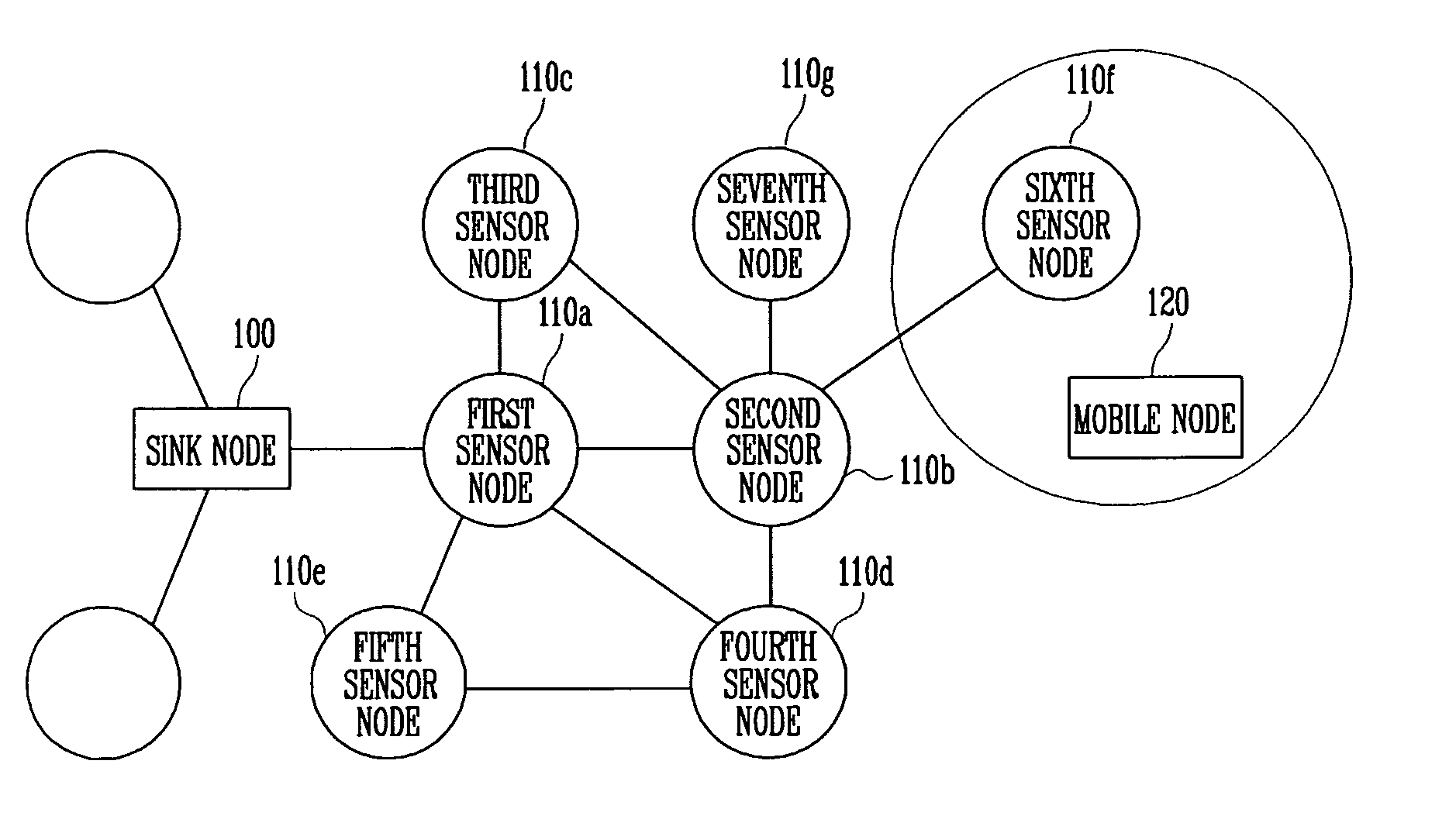
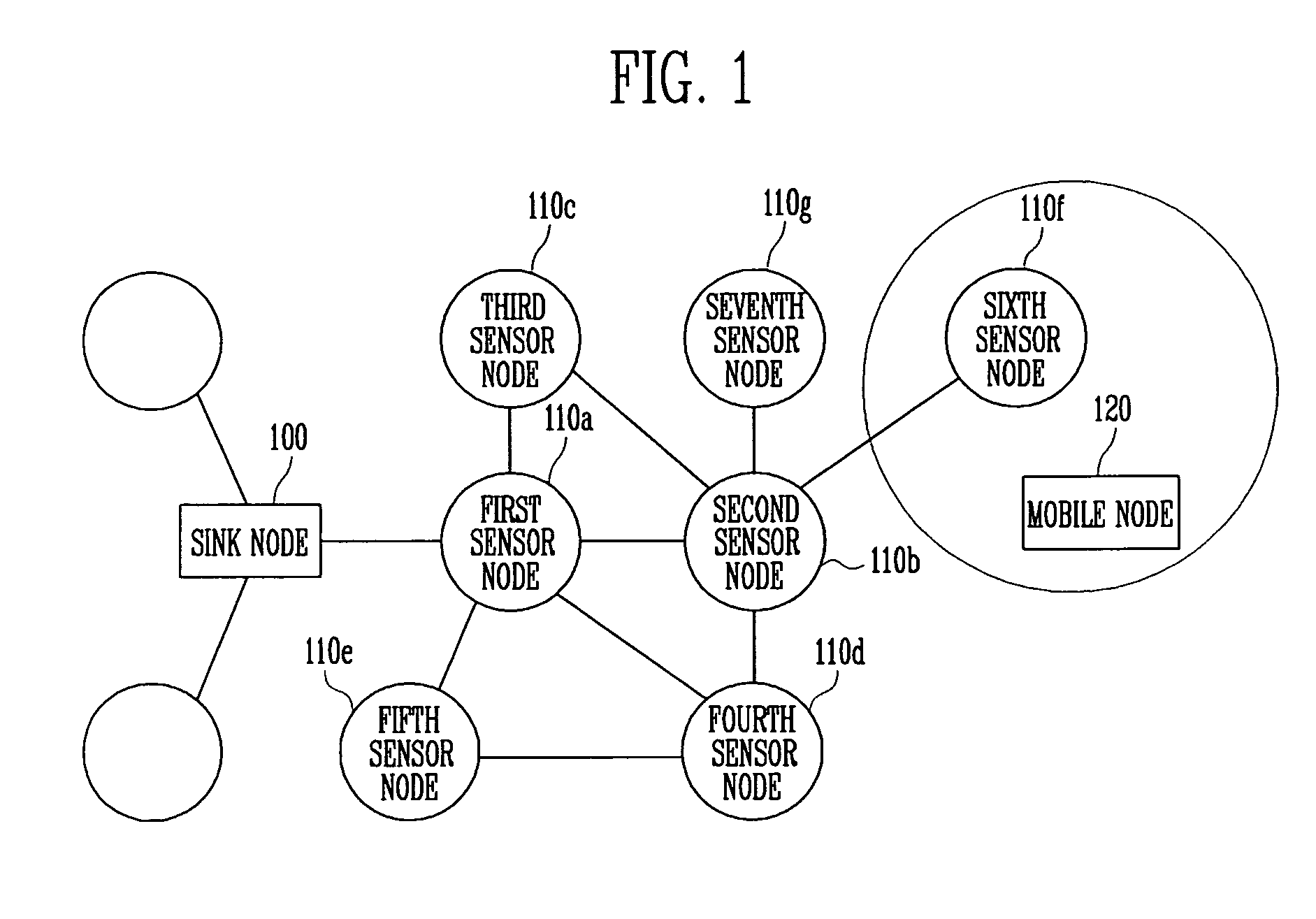
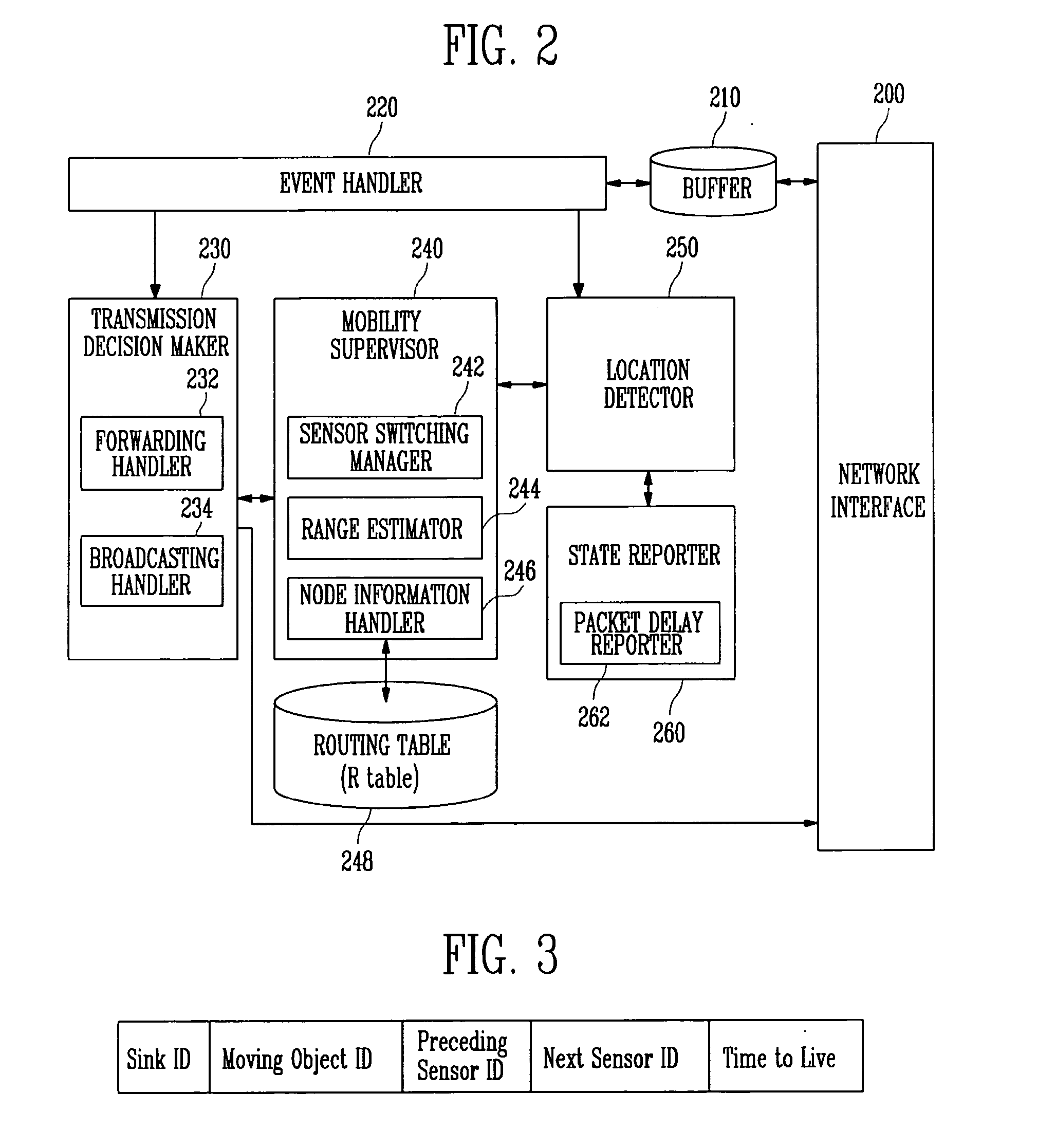
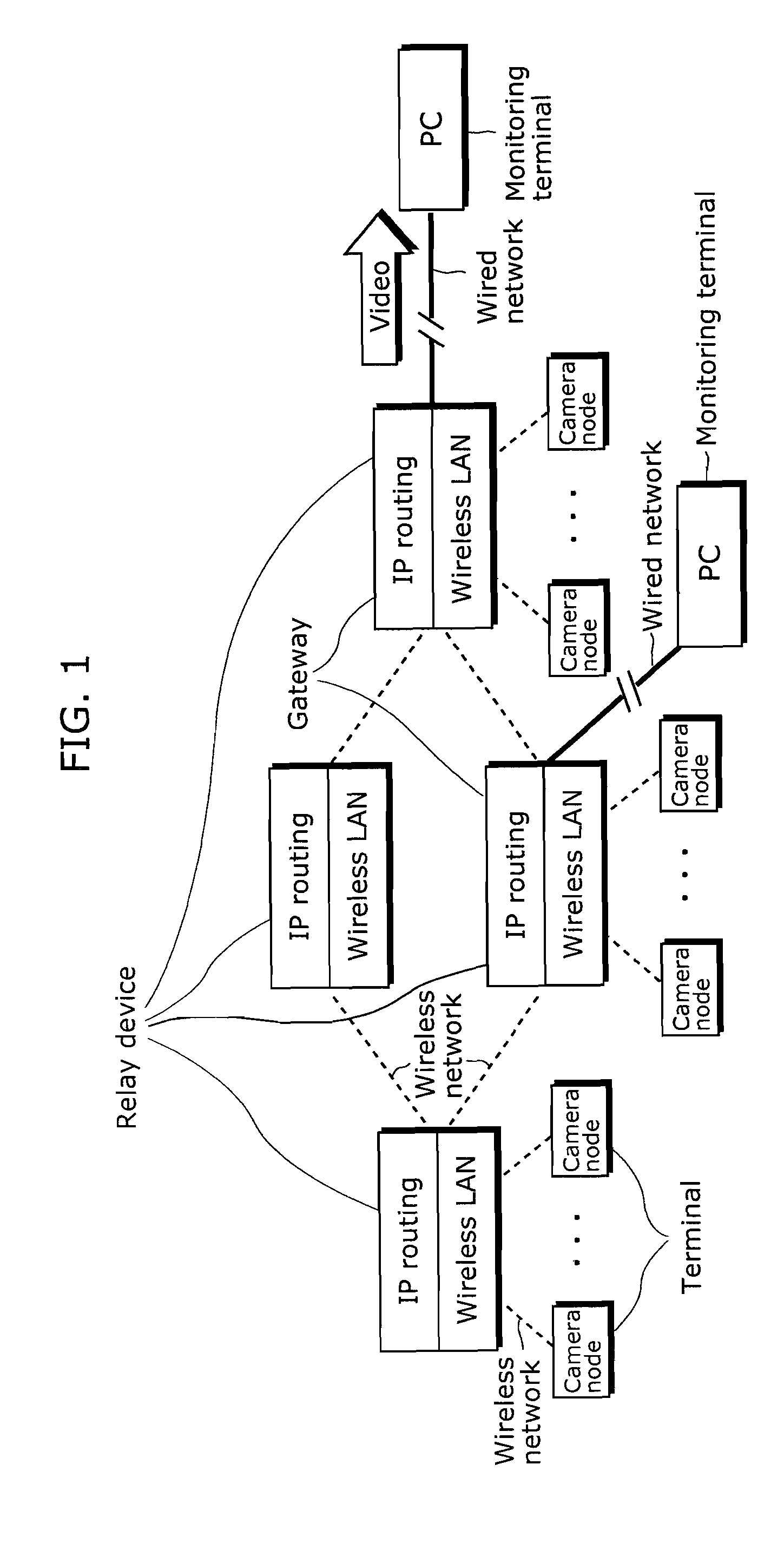
Sensor node device and method for supporting mobility of mobile node in sensor network
InactiveUS20070133469A1Minimizes packet lossPacket lossAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesDecision makerTransfer mode
Provided are a sensor node device and method for supporting mobility of a mobile node in a sensor network. The sensor node device includes: a network interface for communicating with a sink node, at least one neighboring sensor node, and the mobile node; a mobility supervisor for detecting a location of the mobile node, and deciding a sensor node for a service of a data packet received through the network interface on the basis of the detected location; a transmission decision maker for deciding a transmission mode for the data packet received through the network interface according to the location of the mobile node; and a state reporter for reporting a transmission state of the data packet through the sensor node device. When the mobile node moves to a place where radio wave propagation areas of sensor nodes overlap each other, the radio wave intensity of each sensor node is detected to perform a handoff to the sensor node of the area having the strongest radio wave intensity. Thus, a ping-pong problem caused by unnecessary repeated handoff, and a delay problem caused by too slow handoff, can be prevented.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
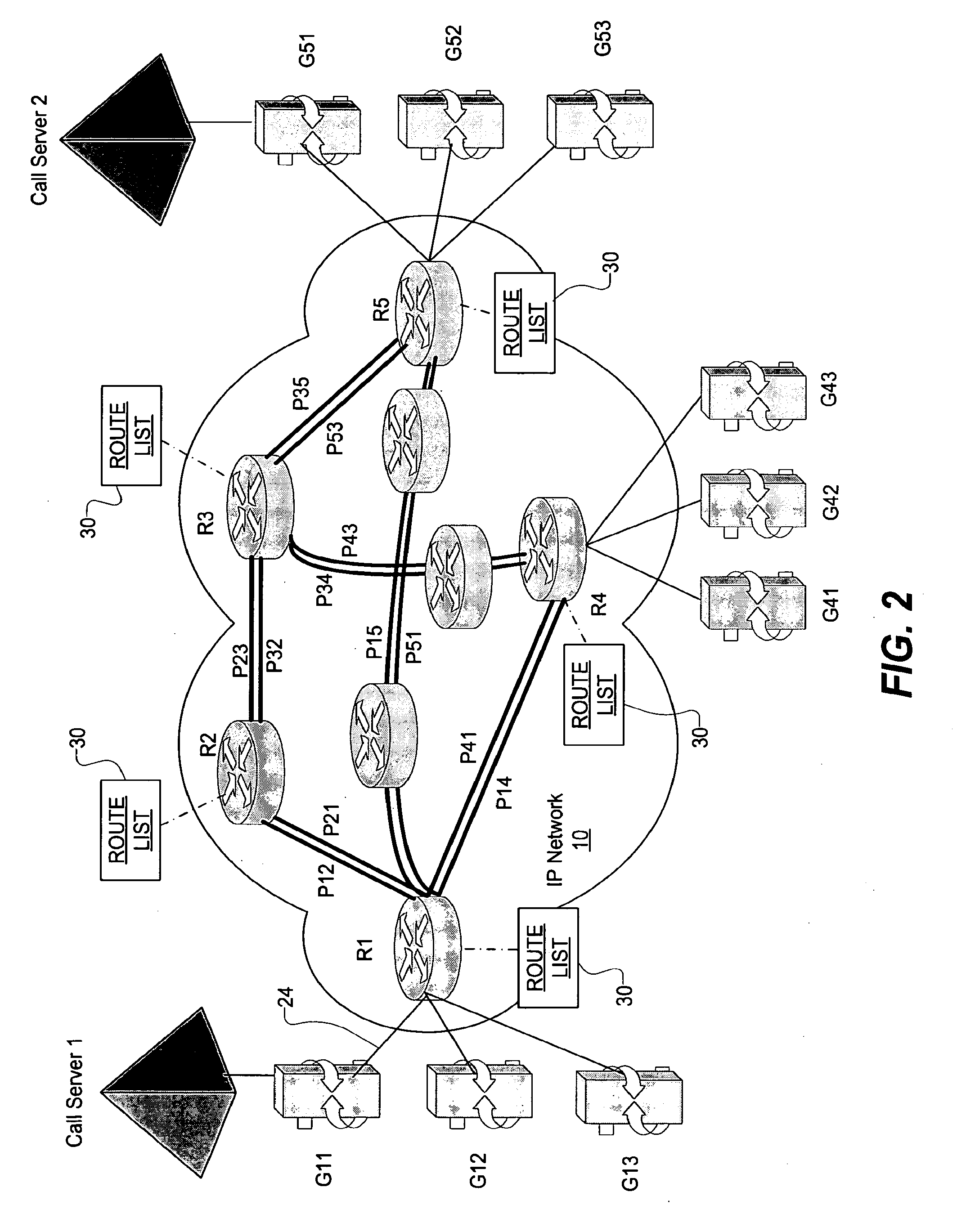
Adaptive call routing in IP networks
InactiveUS20150003240A1Improve network utilizationPacket lossInterconnection arrangementsError preventionTelecommunicationsSelf adaptive
A method of adaptively routing voice packets in an IP network receiving a request for a new call at a voice gateway, determining a destination gateway for the new call, determining an availability of at least one route for routing the new call across the IP network to the destination gateway, and deciding whether to admit the new call into the IP network based on whether a route is available over which voice packets for the new call can be routed. A call admission decision is made based on whether a direct, single-path route or a two-path route is available, where each path is an LSP tunnel whose availability is determined using a token bucket technique. If no route is available, the voice gateway does not admit the call into the IP network.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
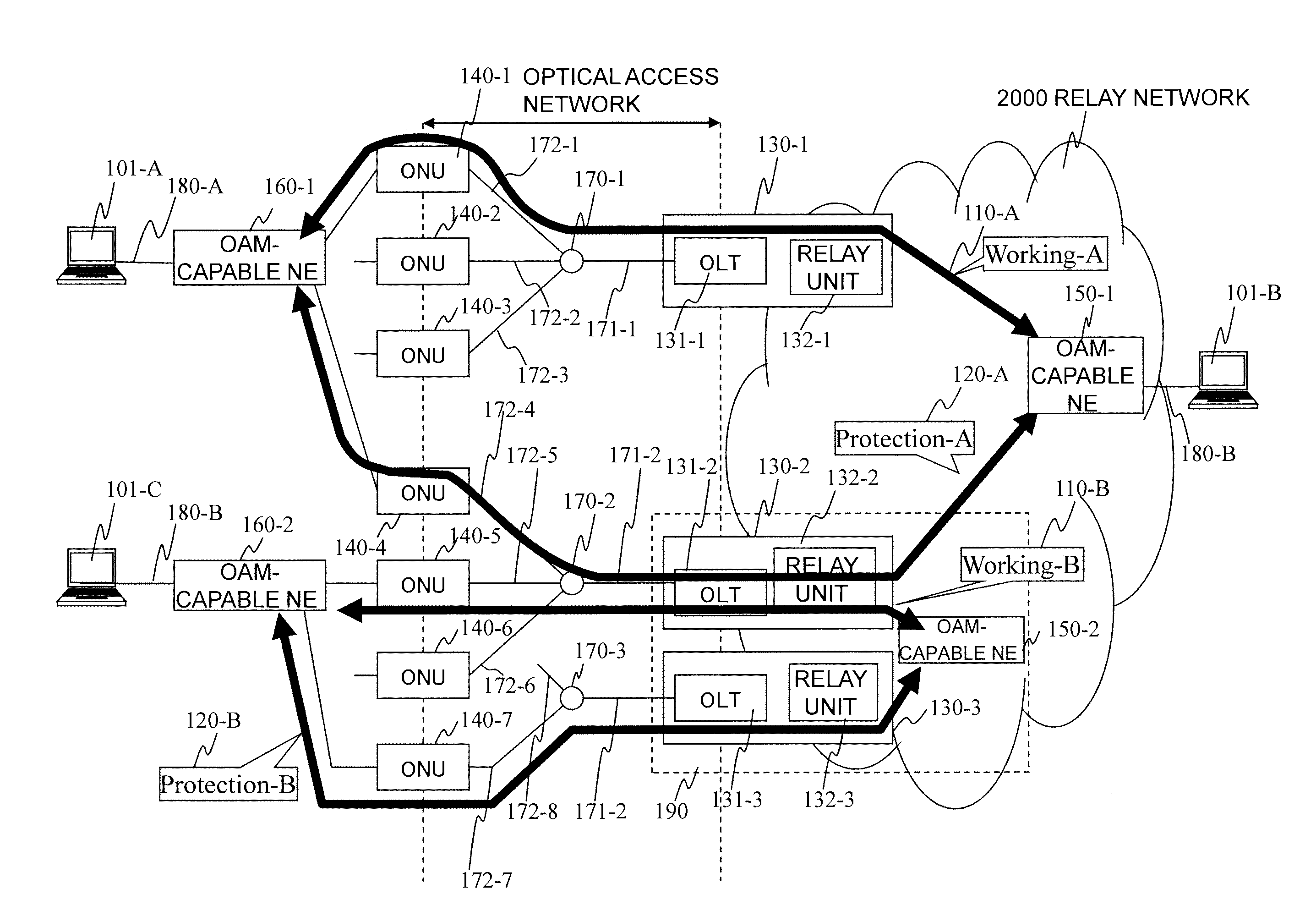
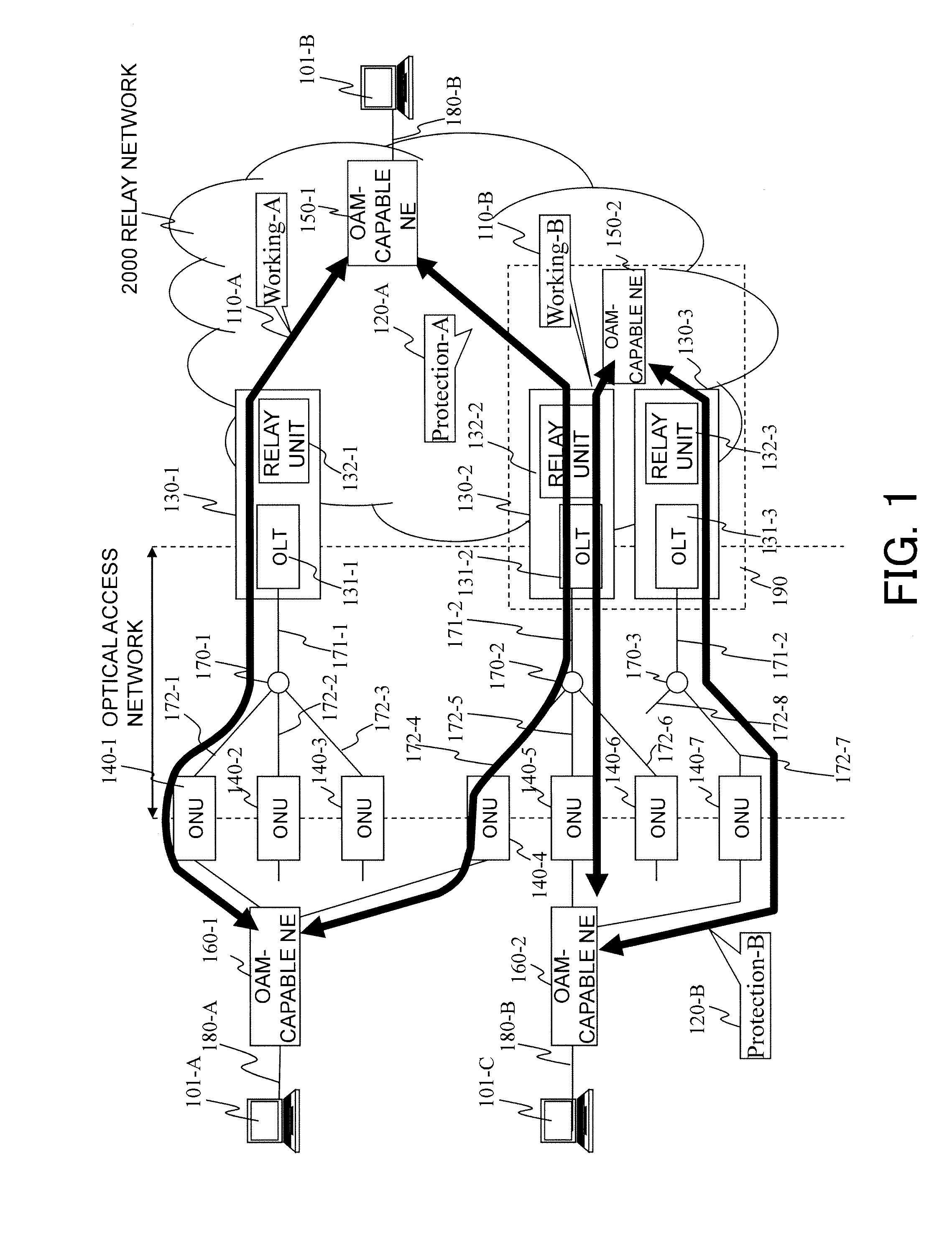
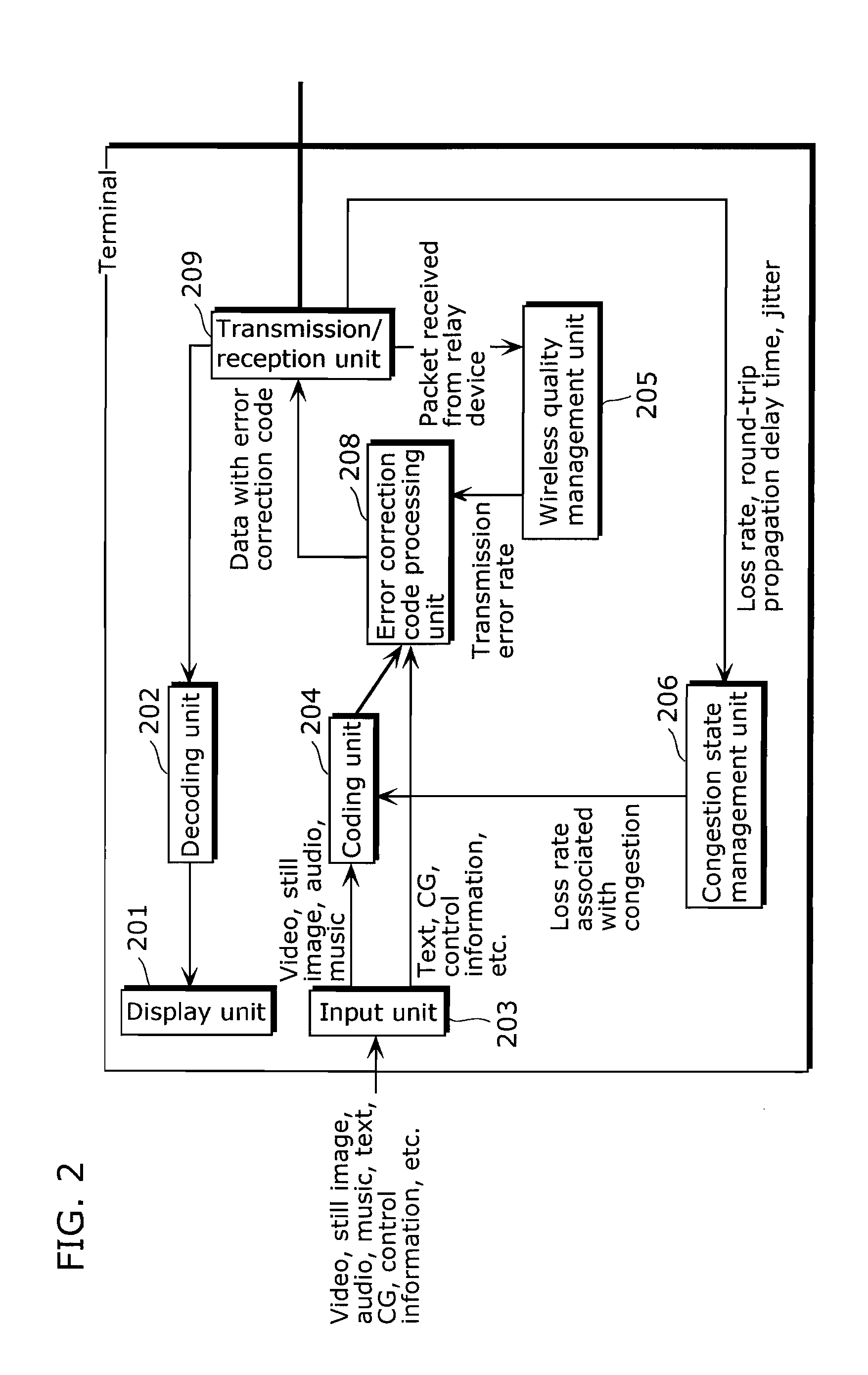
Communication system, subscriber accommodating apparatus and communication method
InactiveUS20110268435A1Packet lossReduce the packet lossMultiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsCommunications systemReal-time computing
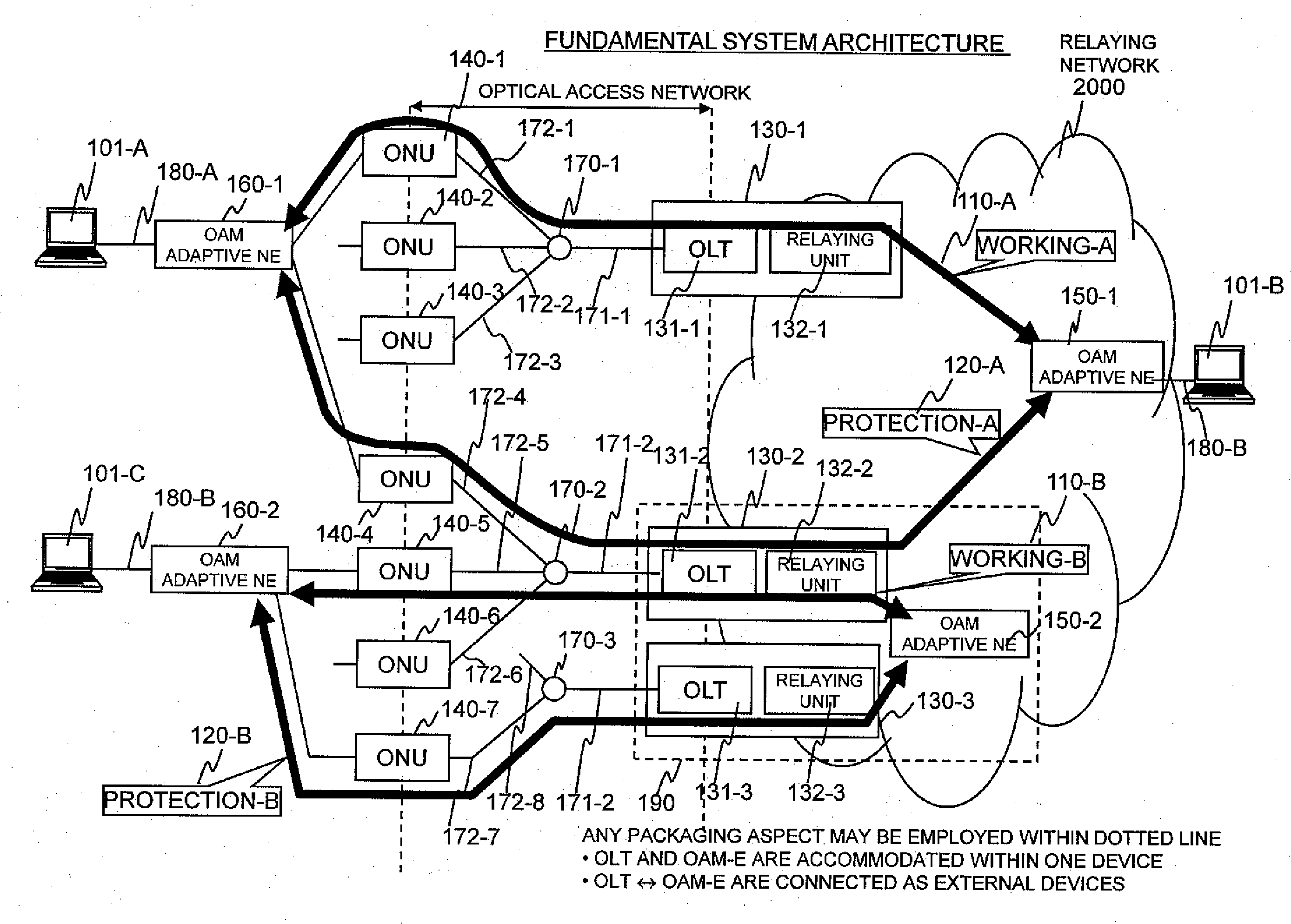
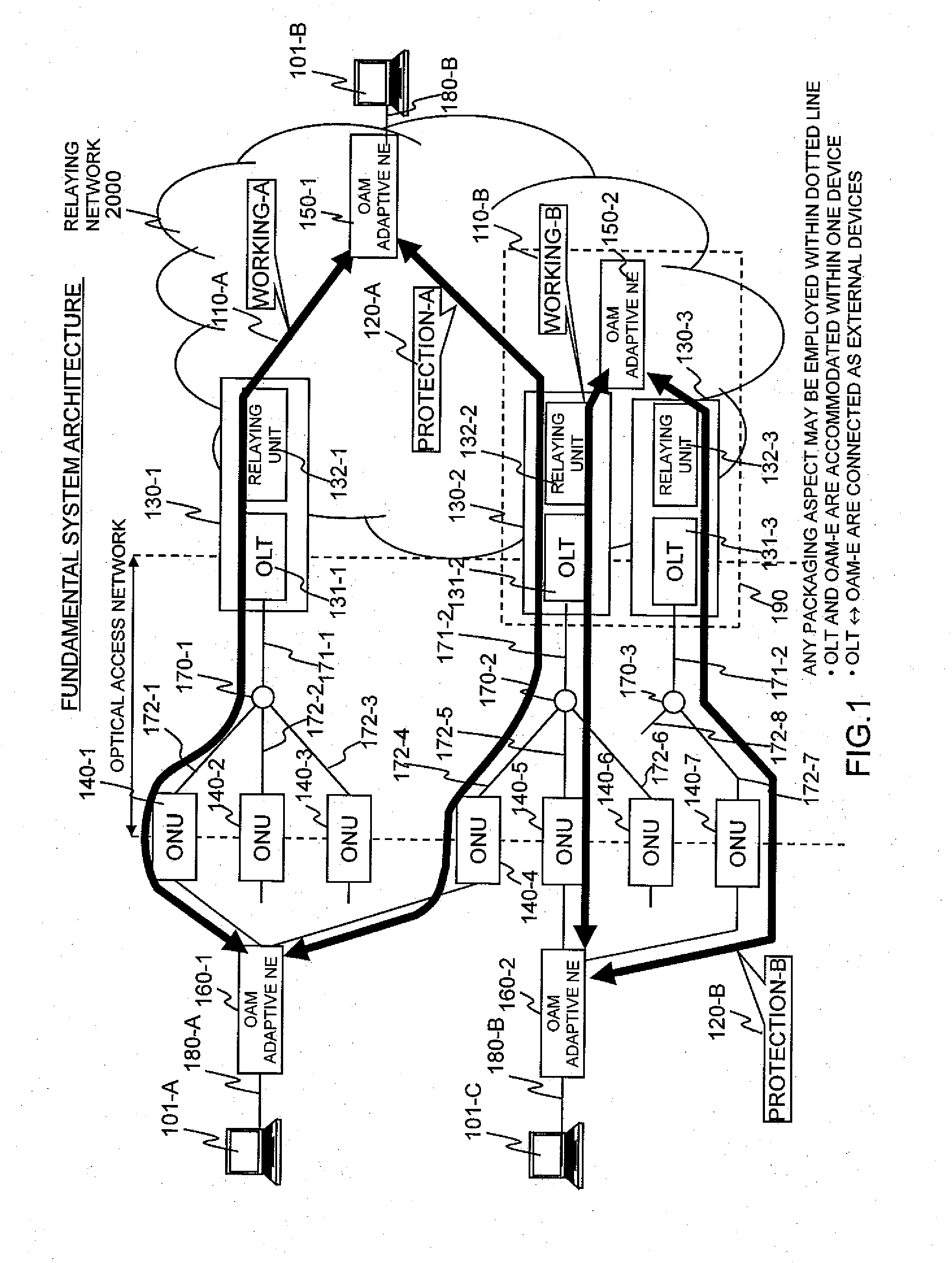
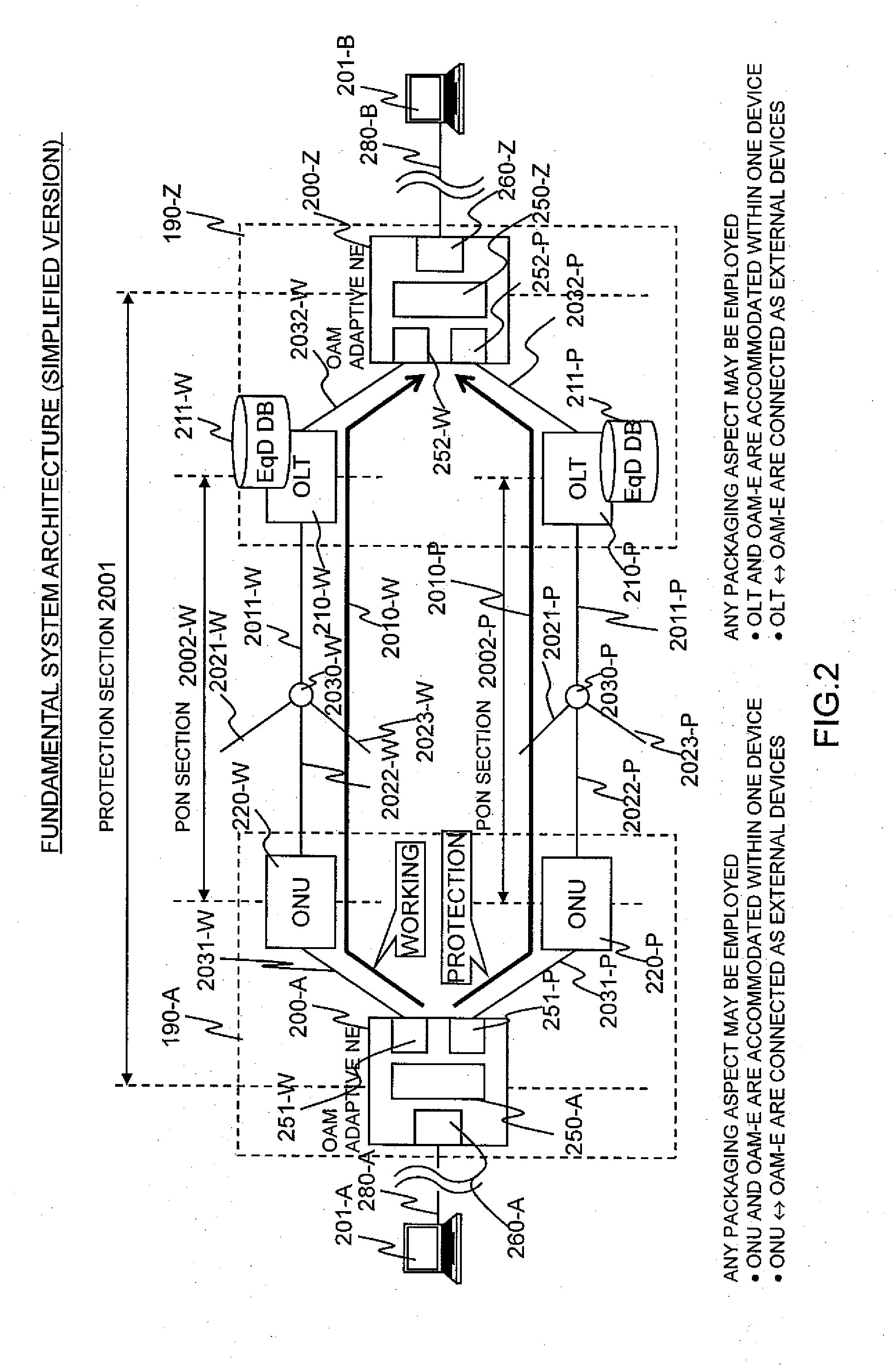
Switching process at the occurrence of a path trouble is performed more quickly to reduce the number of packet discards during a traffic transition from a currently used system path to a standby system path within a section to be protected. An OLT (210-W) refers to the DBA information of a PON section and, if receiving no CCM frame at a timing at which the same should be received, then determines that some trouble has occurred on the path (S801) and transmits, to an OAM-compliant NE (200-Z), an application-for-switching frame (1501) to notify the OAM-compliant NE (200-Z) of the abnormal condition. The OAM-compliant NE (200-Z) monitors the occurrence of the trouble within the PON section nearly in real time, starts a switching process (S802) and generates and transmits a standby-system delivery request (321) (S302, S803). An OAM-compliant NE (200-A) switches the communication path to the standby-system passing through an OLT (210-P).
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method for high speed rerouting in multi protocol label switching network
InactiveUS6904018B2Minimize packet lossFast trafficMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionTraffic capacityPacket loss
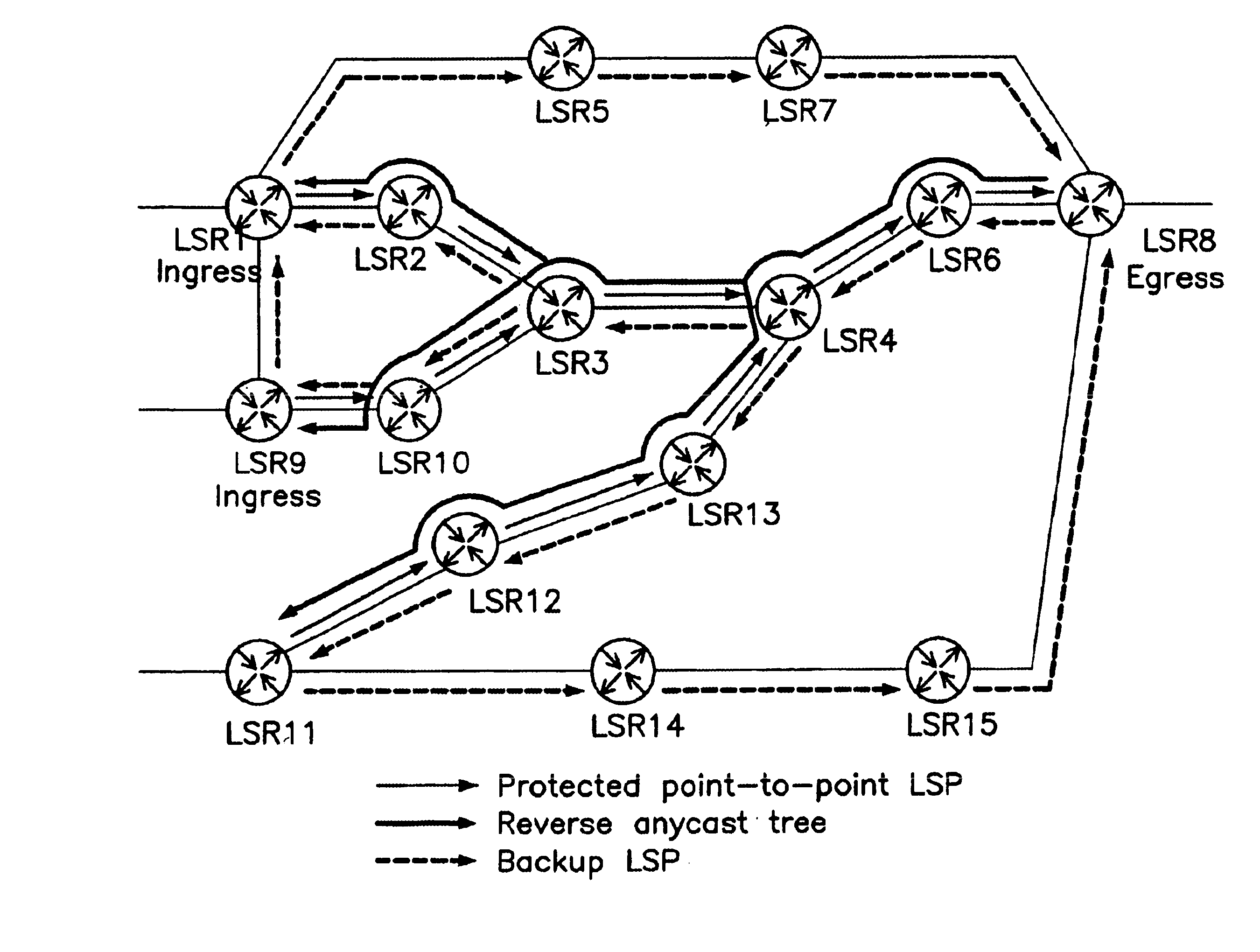
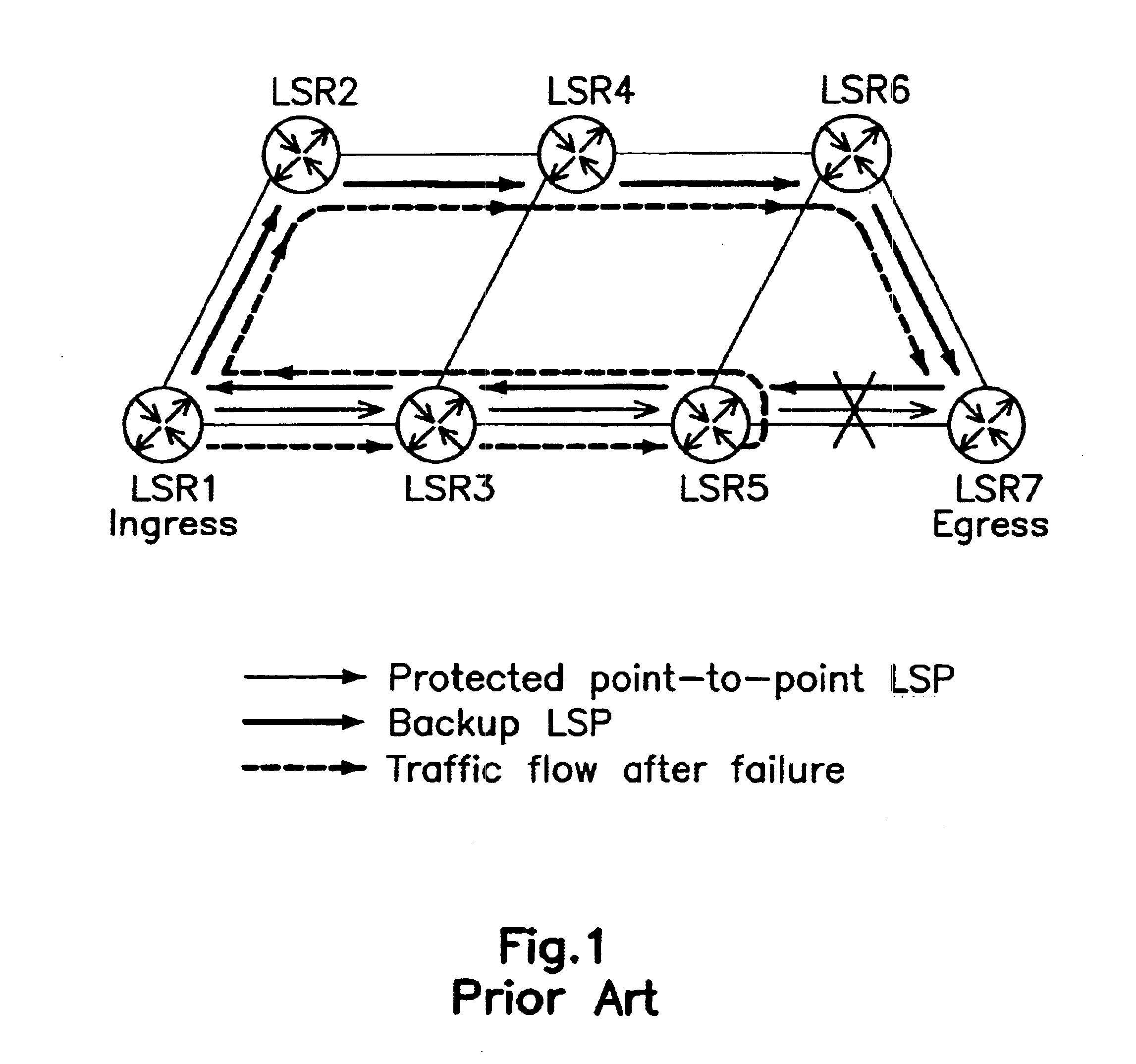
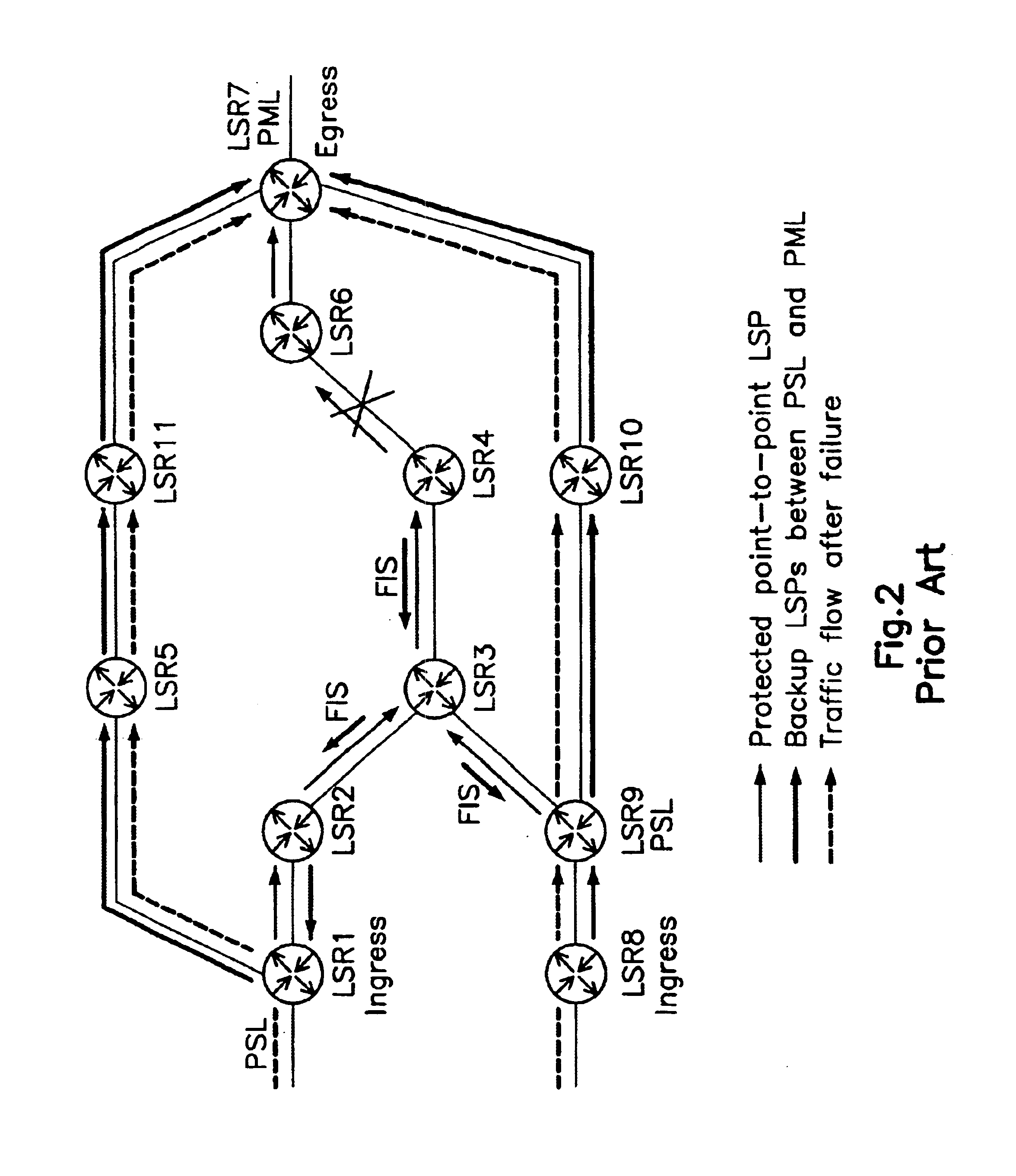
Disclosed is a method for high speed rerouting in a multi protocol label switching (MPLS) network which can minimize a packet loss and enable a fast rerouting of traffic so as to protect and recover a multi point to point LSP occupying most LSPs in the MPLS network. The method for high speed rerouting in a multi protocol label switching (MPLS) network, the method comprising the steps of controlling a traffic stream to flow in a reverse direction in a point where a node or link failure occurs by using a backup Label Switched Path (LSP) comprising an Explicitly Routed (ER) LSP having a reverse tree of a protected multi point to point LSP and an ingress LSR through an egress LSR.
Owner:KOREA TELECOMM AUTHORITY
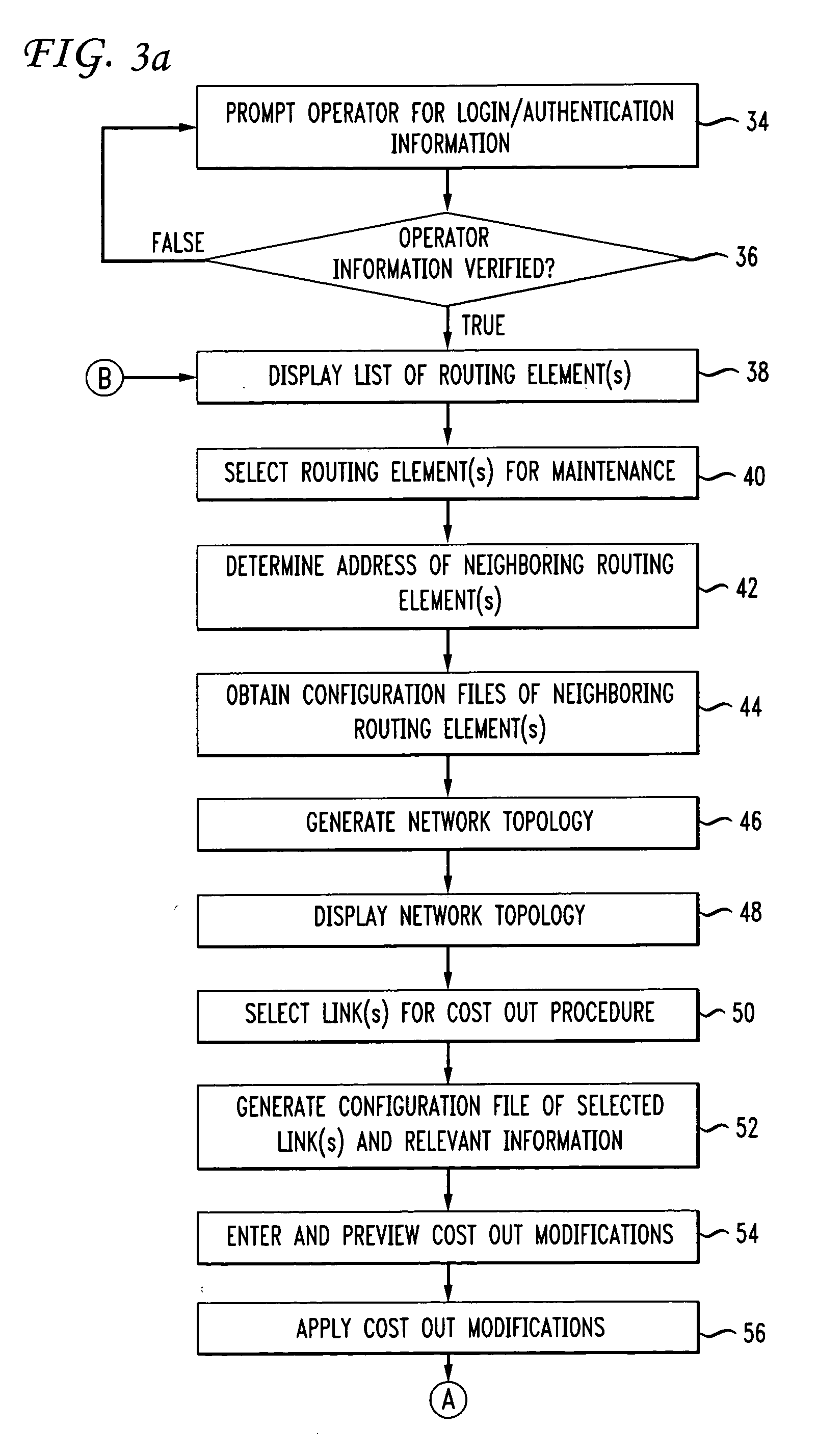
Method and apparatus for determining neighboring routing elements and rerouting traffic in a computer network
InactiveUS20060056411A1Easy to optimizeFacilitates taskData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityNetwork topology
A method and apparatus for rerouting traffic in a computer network select a routing element, apply a subnet mask to an interface address of the routing element to generate subnet addresses, determine the address of neighboring elements from the subnet addresses, and obtain configuration information from the neighboring elements. Network topology is determined from the configuration information, a link in the network topology is selected, and a cost associated with the link is modified. The modified cost renders the link less desirable for routing. A method and apparatus for determining the address of neighboring routing elements in a computer network, combine a subnet mask and interface address associated in a bitwise AND operation to generate subnet addresses, disregard the highest and lowest subnet addresses and the address of the selected routing element from the subnet addresses, and identify the remaining subnet address as associated with the neighboring routing element.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
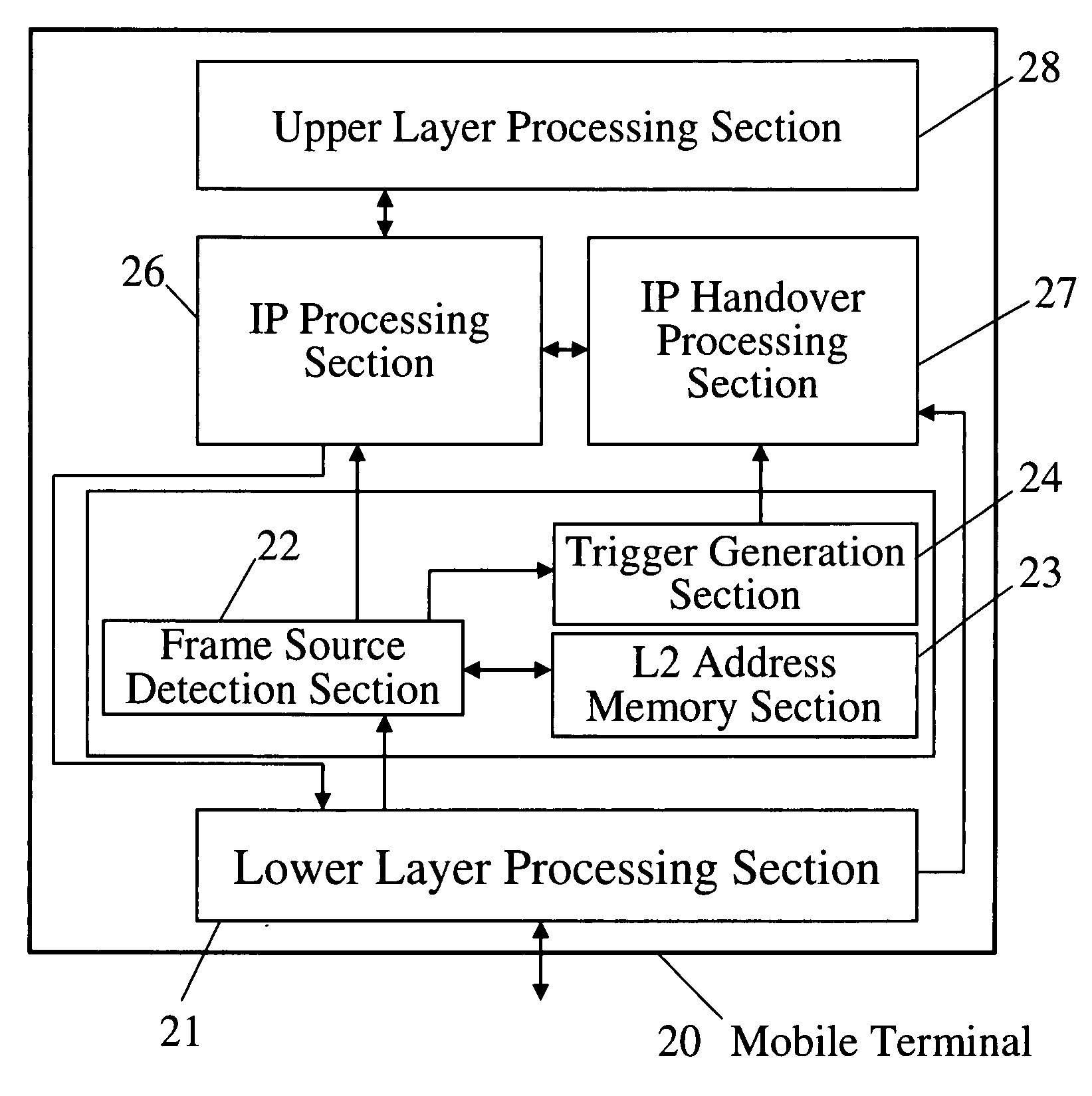
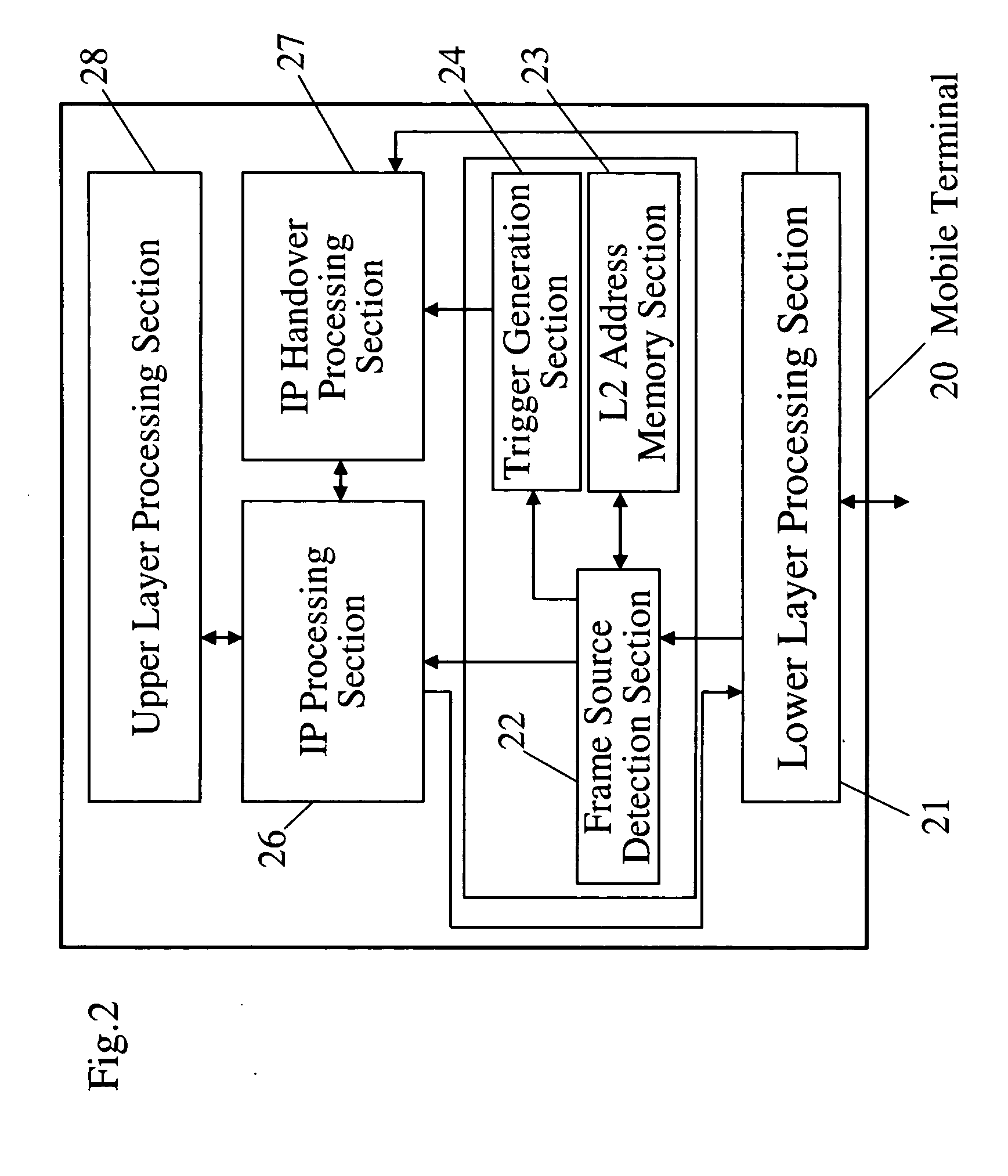
Movement detection method and a mobile terminal
InactiveUS20050083885A1Shorten handover timeShorten the timeTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationHandoverIp layer
In accordance with a movement detection method, a mobile terminal in moving among access router devices all set at the same frequency, stores the link layer address of the currently reachable access router device. When receiving a Layer 2 frame from a new access router device, the mobile terminal issues a trigger for requesting to implement a part of IP handover processing. By so doing, it allows IP handover processing to be initiated at higher speed than in the case of the conventional IP layer, thus enabling to reduce the total time of handover processing.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method of dynamically adapting the size of a jitter buffer
InactiveUS20070206645A1Easy to handleSpeech quality will be good—particularlyTime-division multiplexHybrid transportCommunications systemSpeech sound
The present invention relates to a receiver system in a communication system supporting packet-based communicatior (e.g., an IP-network), including a receiver, speech decoder (40) and a jitter buffer (20) for handling delay variations in the reception of a speech signal consisting of packets containing frames with encoded speech. A jitter buffer controller (50) is provided for keeping information about the functional size of the jitter buffer (20) and for providing the speech decoder (40) with control information, such that the speech decoder (40), based on that information. provides a dynamic adaptation of the size of the jitter buffer (20) using the received encoded, packetized speech signal. The invention also relates to a method of adapting the functional size of the jitter buffer of a receiver system.
Owner:SUNDQVIST JIM +4
Wireless streaming of an audio signal to multiple audio receiver devices
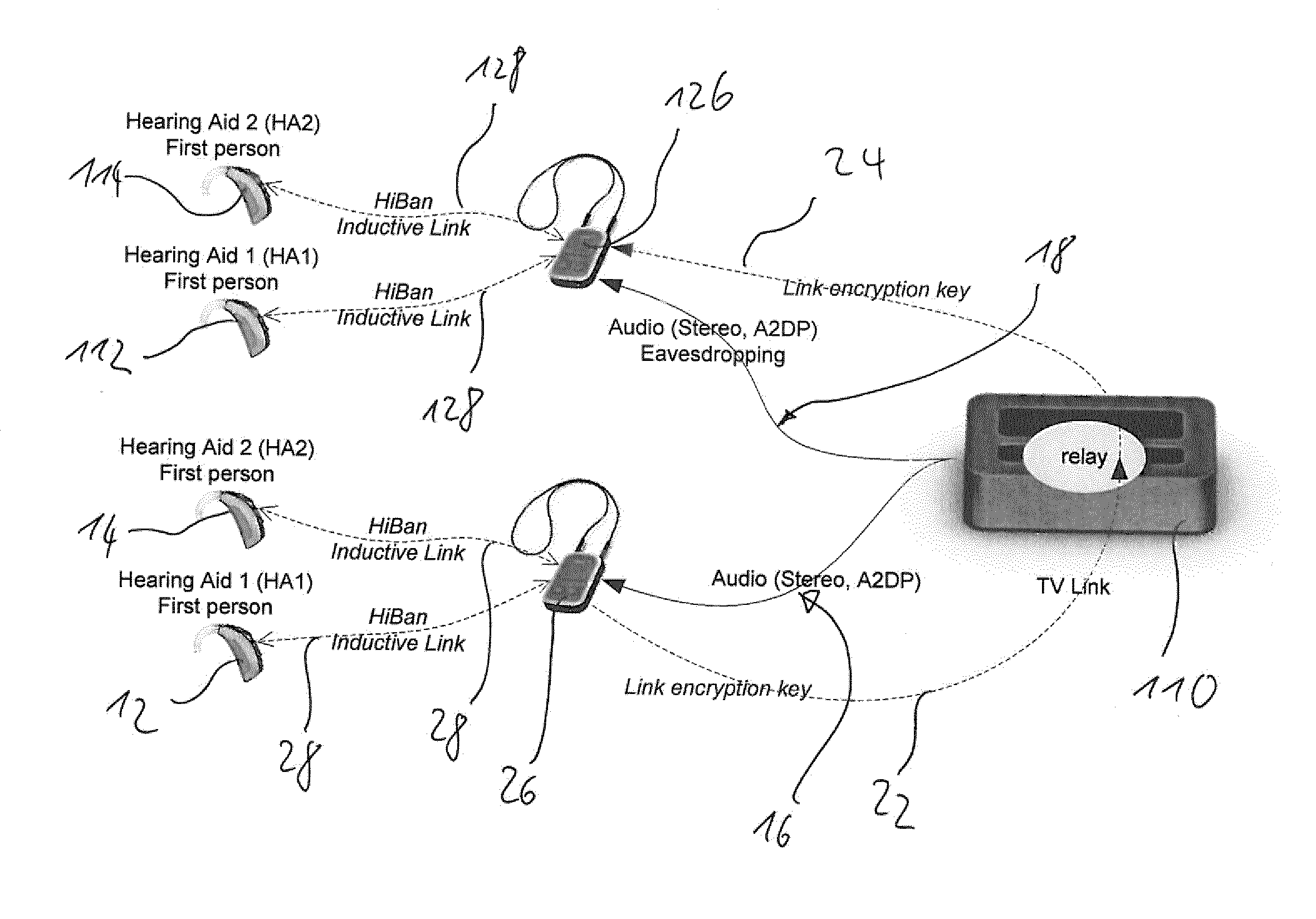
ActiveUS20150319557A1Reliable audio signal receiptPacket lossSynchronisation arrangementHearing device energy consumption reductionComputer hardwareBluetooth
A method of streaming an audio signal from an audio transmission device to first and second audio receiver devices via a Bluetooth link using a protocol that requires an audio data packet to be retransmitted if a positive packet receipt is not received. The first audio receiver device is synchronized to the audio transmission device to enable the first audio receiver device to receive an audio signal stream from the audio transmission device, the second audio receiver device is synchronized to the audio transmission device to enable the second audio receiver device to eavesdrop the audio signal stream to the first audio receiver device. When a positive packet receipt acknowledgement is not transmitted from the first audio receiver device to the audio transmission device, the audio transmission device repeats transmission of that audio data packet irrespective of whether the packet has been correctly received by the first audio receiver device.
Owner:SONOVA AG
Secure Network Coding for Multi-Resolution Wireless Video Streaming
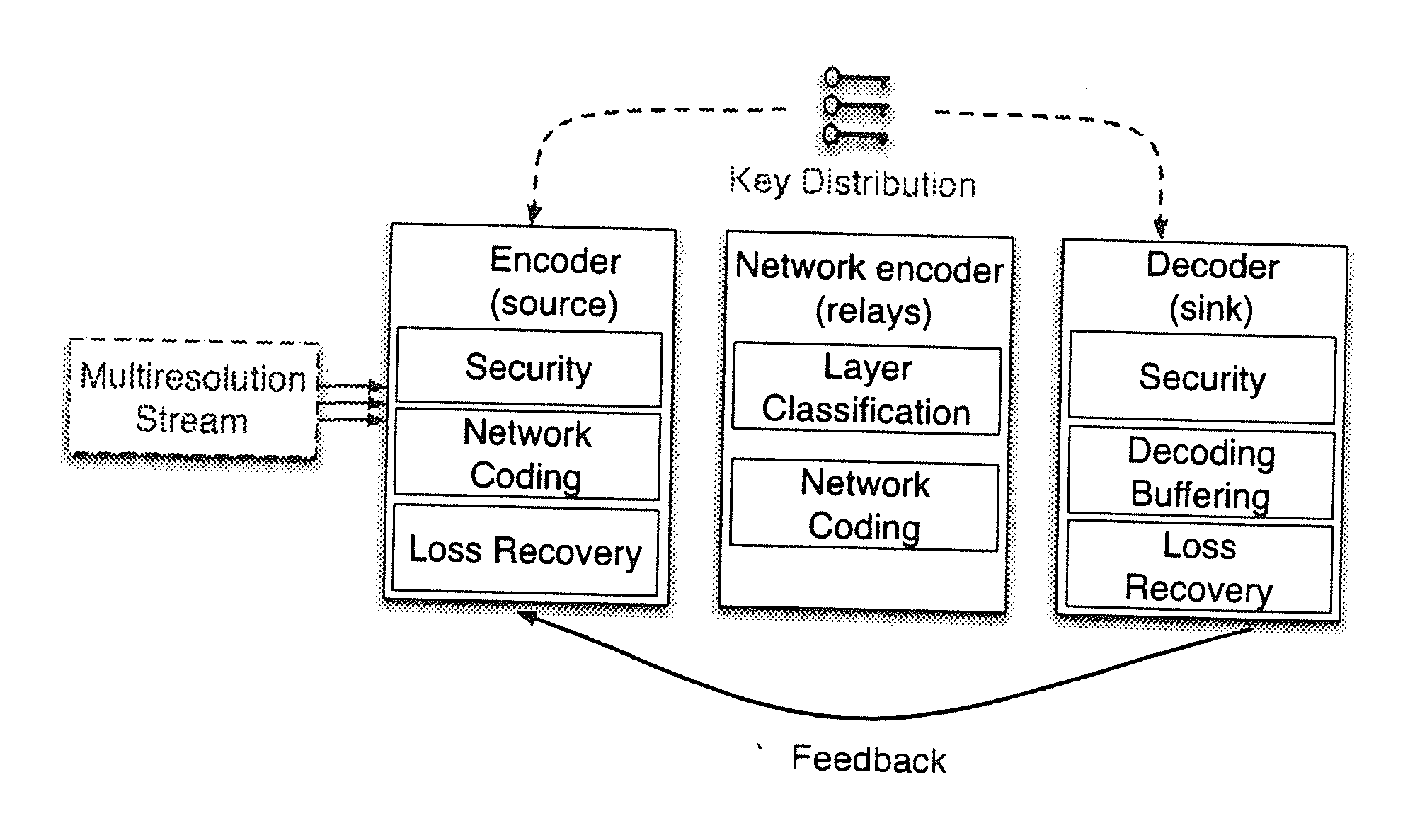
ActiveUS20110243324A1Increasing throughput and robustnessBenefitTime-division multiplexTelevision systemsPacket lossWireless video
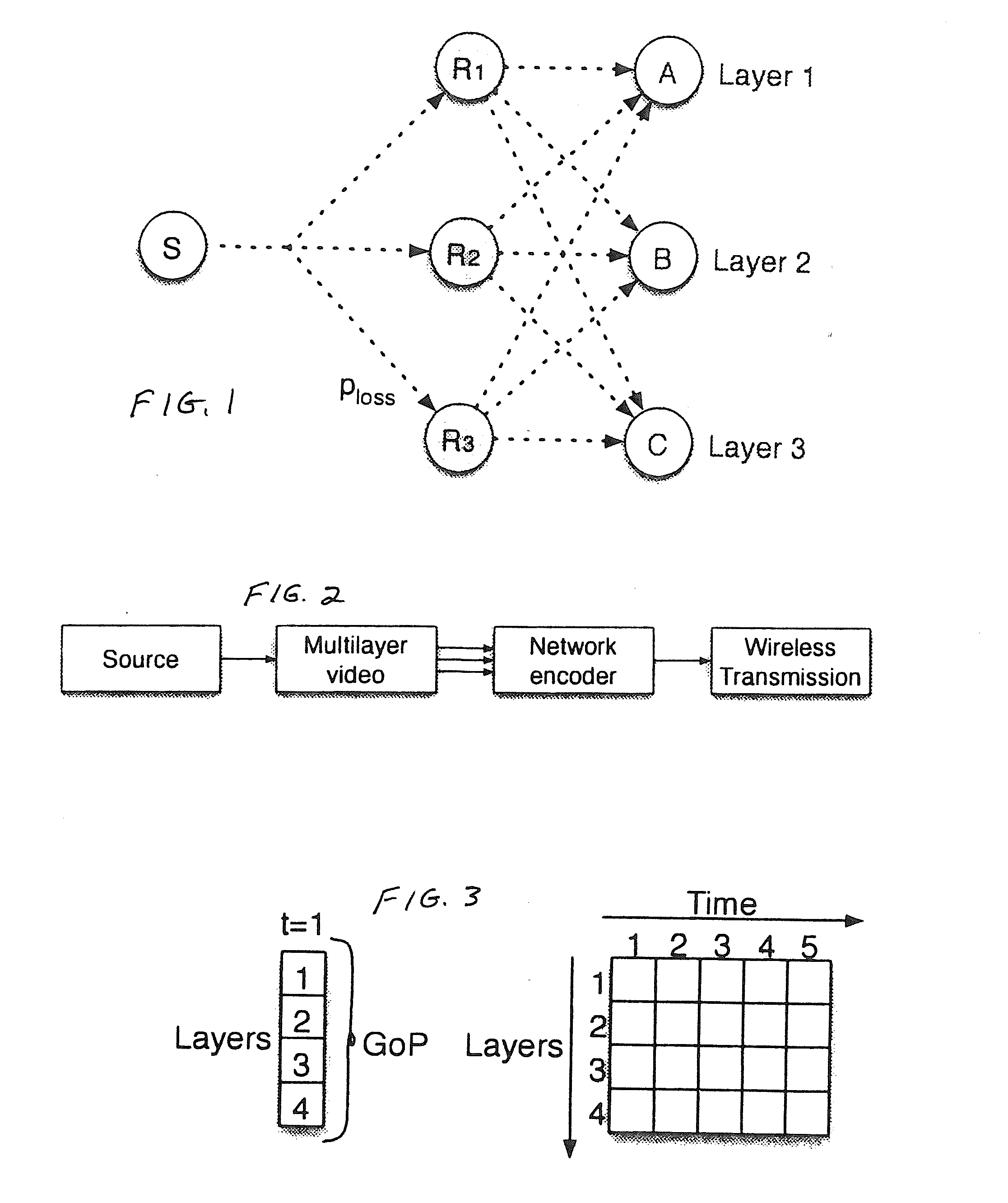
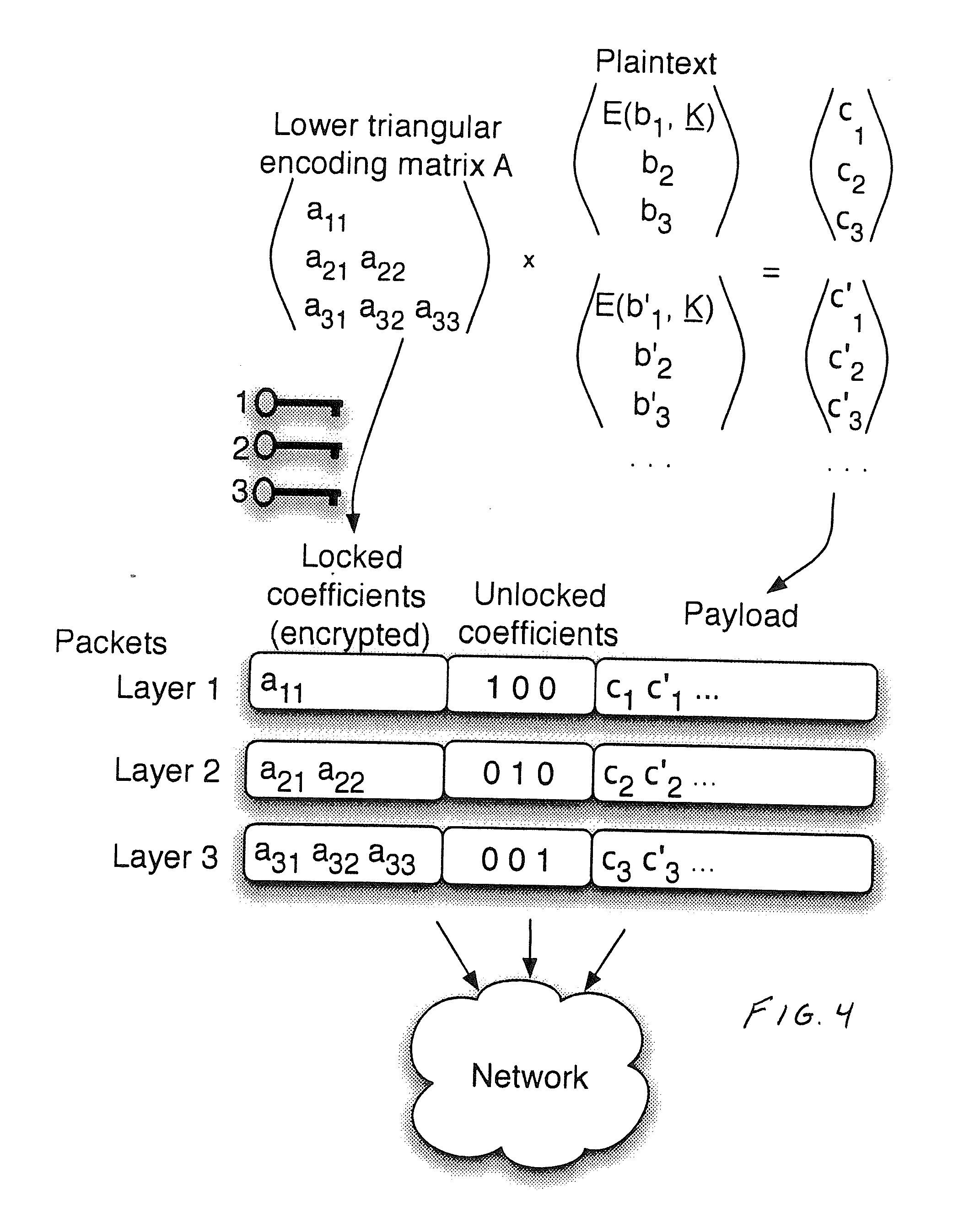
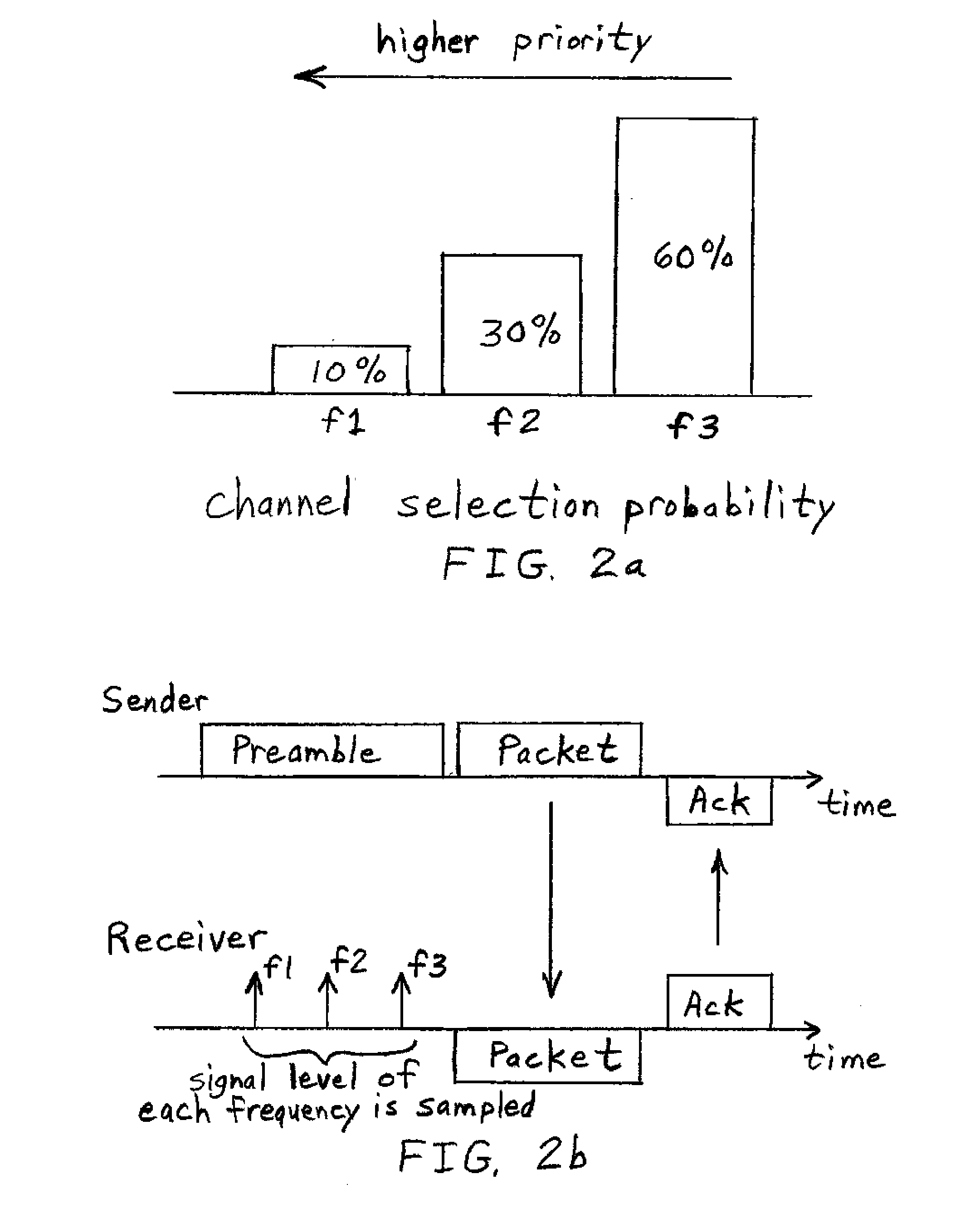
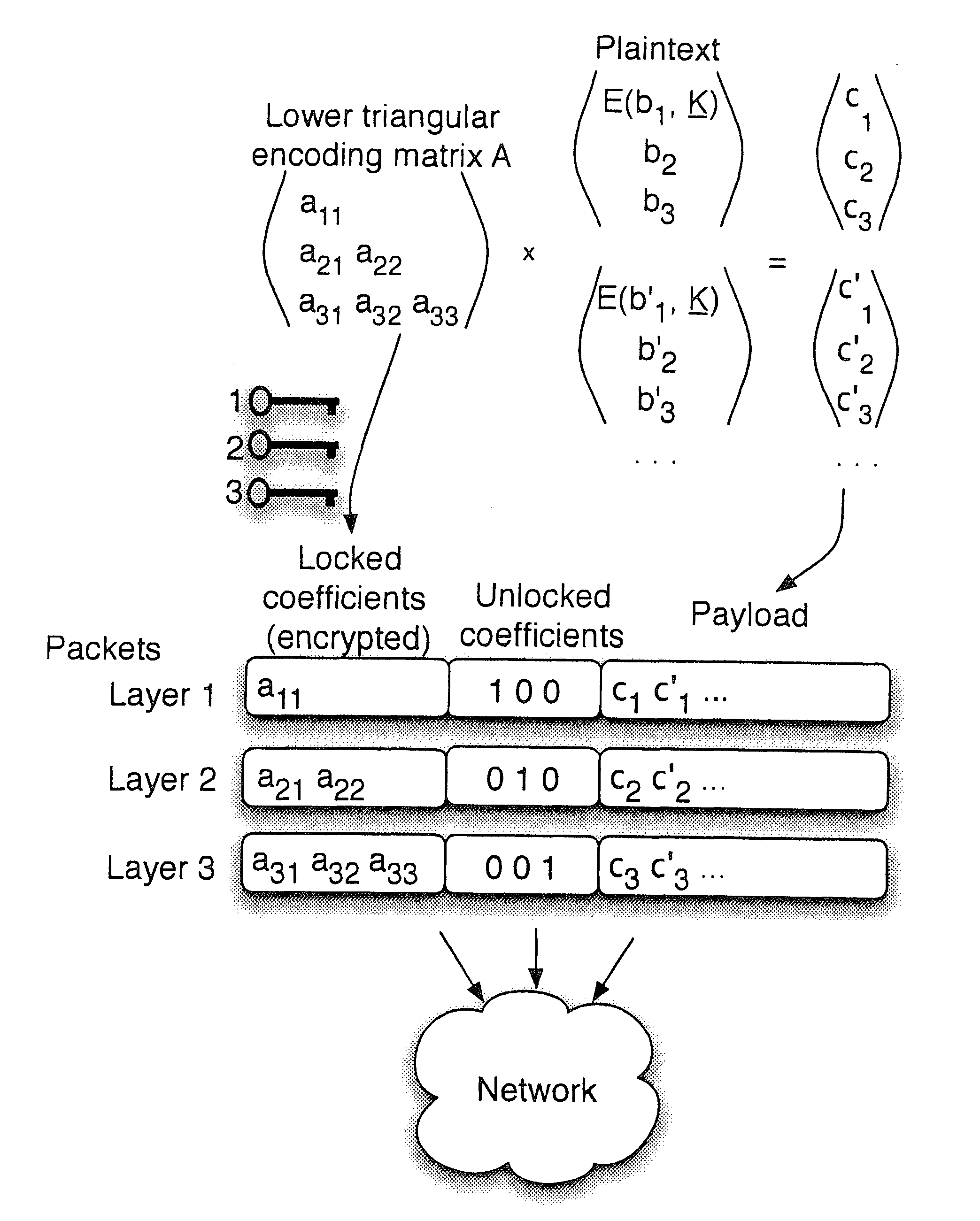
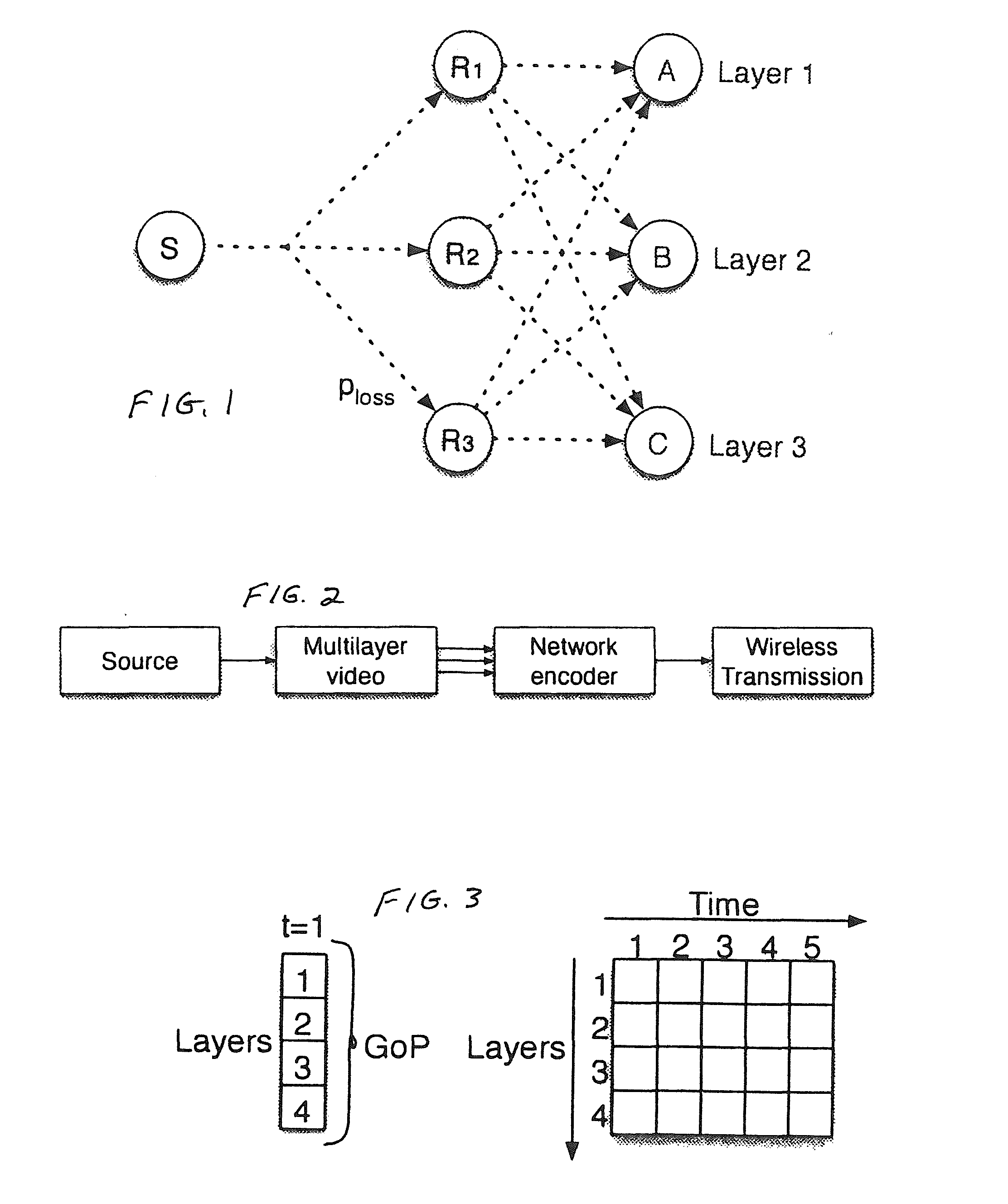
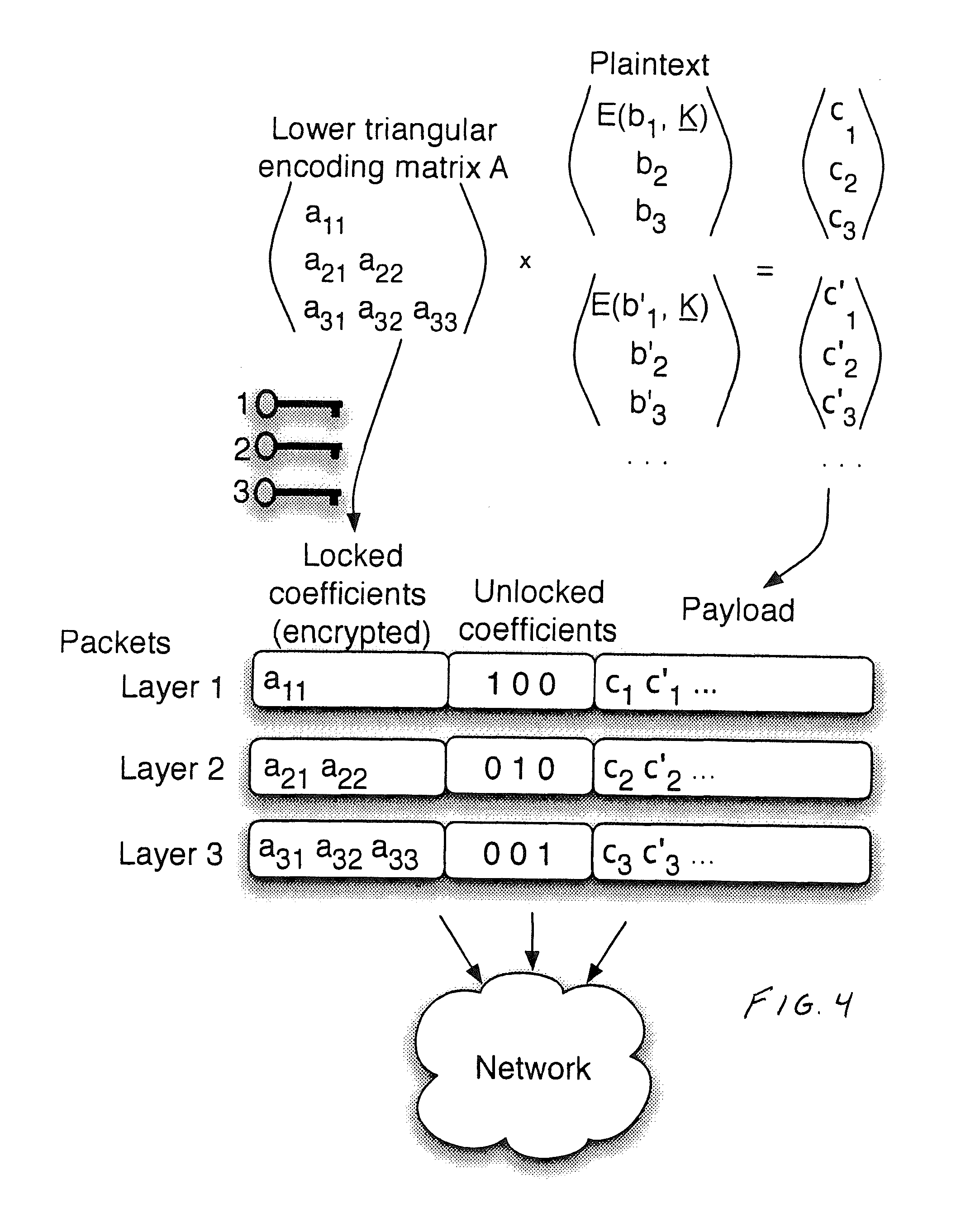
Described herein is a method and system for hierarchical wireless video with network coding which limits encryption operations to a critical set of network coding coefficients in combination with multi-resolution video coding. Such a method and system achieves hierarchical fidelity levels, robustness against wireless packet loss and efficient security by exploiting the algebraic structure of network coding.
Owner:UNIV DO PORTO +2
Hybrid Networking Path Selection and Load Balancing to Provide Robust High Bandwidth Availability in Home Networks
InactiveUS20130128738A1Packet lossError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsHigh bandwidthMix network
System and method for selecting a transmission medium on which to transmit a first stream. At least one of the plurality of transmission media may be substantially dynamic in nature. Path characteristics of each of a plurality of transmission media may be determined. A first transmission medium may be selected from the plurality of transmission media for the first stream based on the determined path characteristics. A first plurality of packets of the first stream may be transmitted on the first transmission medium.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
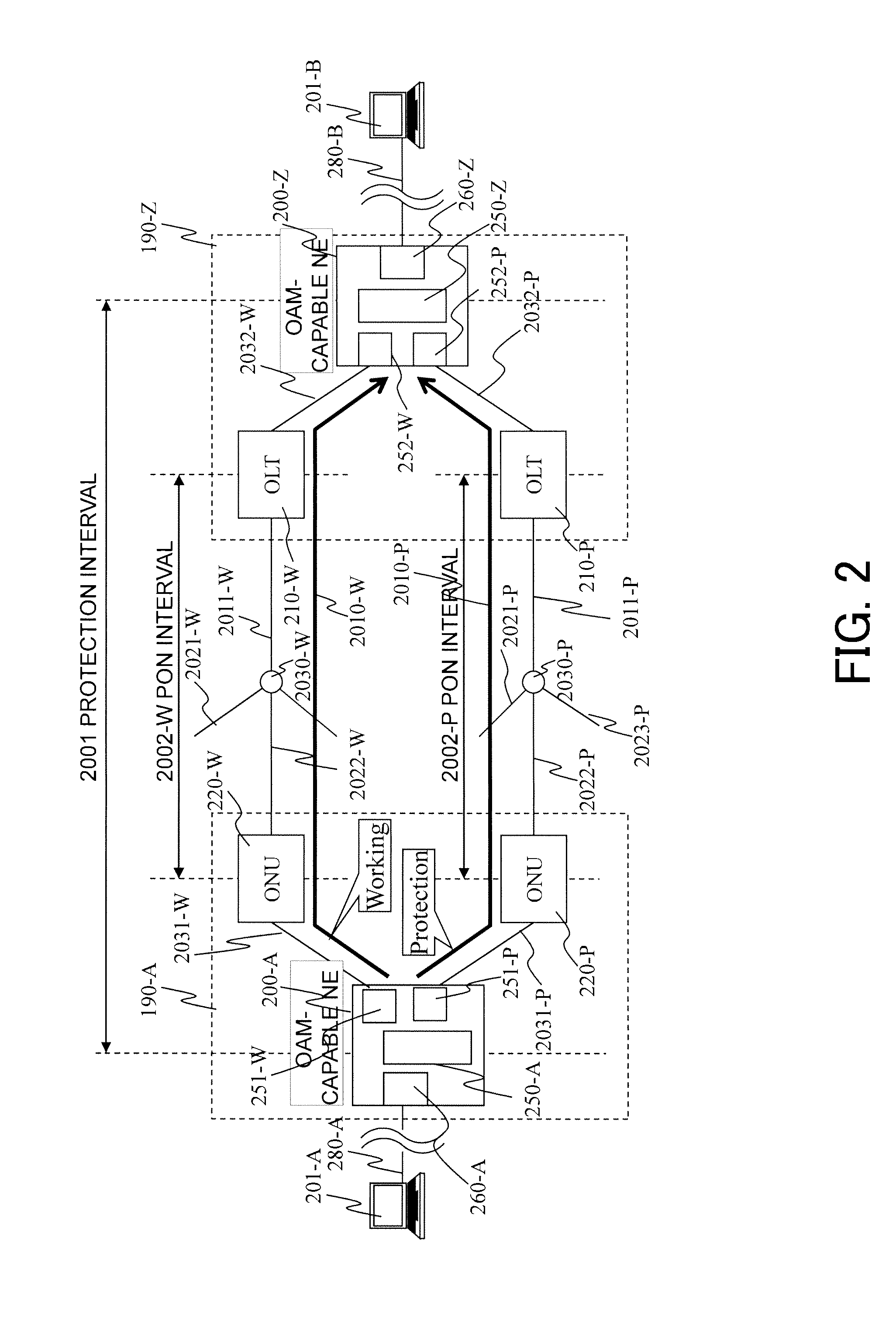
Communication System and Communication Apparatus
InactiveUS20100002591A1Decrease packet lossHigh bandwidthMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionPacket communicationCommunications system
Communication time period measuring frames are simultaneously sent from an OAM adaptive device on a transmission side, to both a working path and a protection path. In an OAM adaptive device on a reception side, reception times of the frames having arrived from both the paths are checked so as to measure a time period difference between both the paths. The time period difference is fed back to a logic distance adjustment function of each PON section to determine required communication time periods of the PON sections respectively included in a working system and a protection system. Communication time periods of the working system and the protection system in a packet communication network are arbitrated in order to decrease a packet loss at line switching in a packet relaying network.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
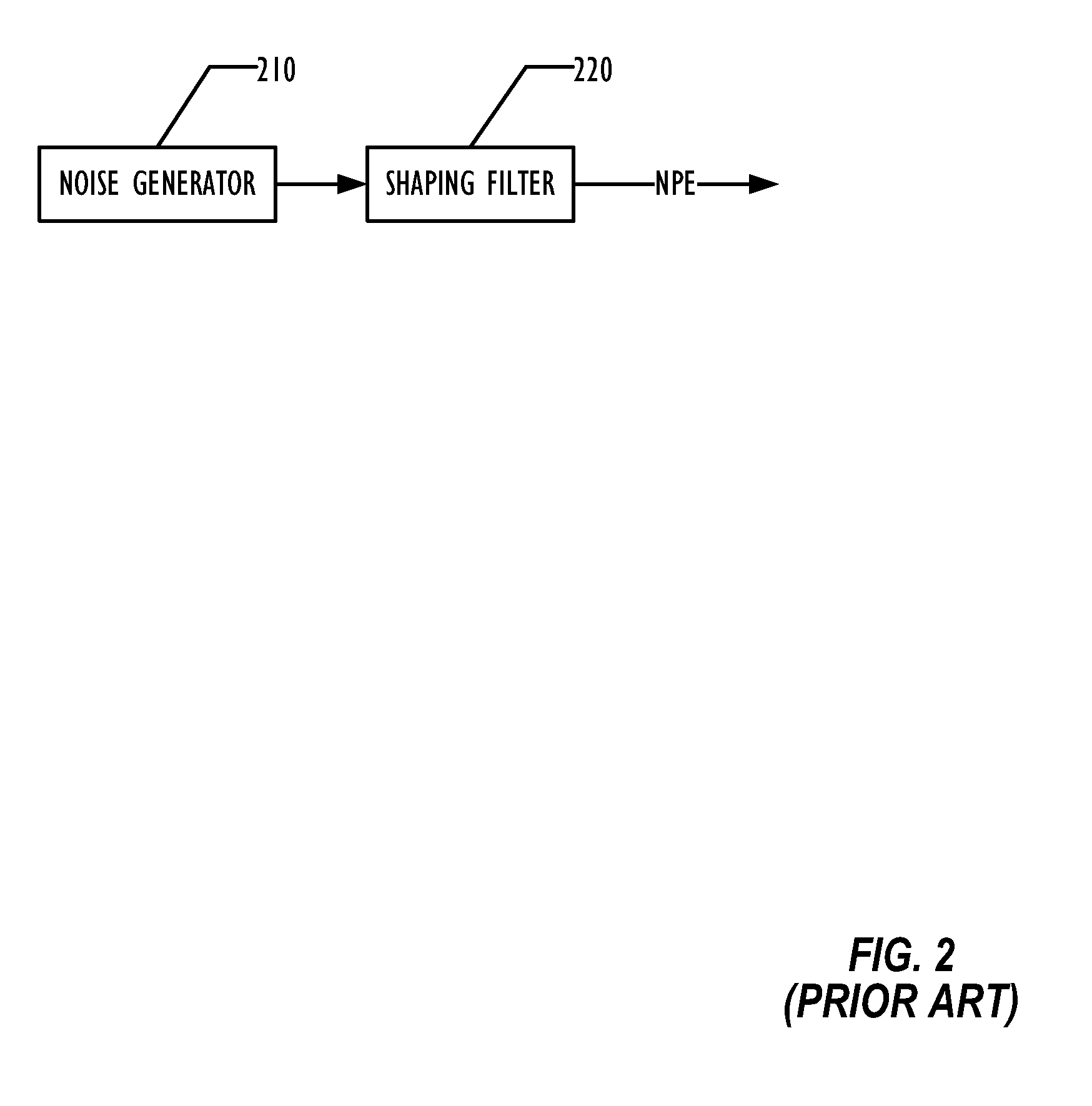
Artifact Reduction in Packet Loss Concealment
ActiveUS20120101814A1Improving packet loss concealmentReduce artifactsSpeech analysisUltrasound attenuationPacket loss concealment
Various techniques are disclosed for improving packet loss concealment to reduce artifacts by using audio character measures of the audio signal. These techniques include attenuation to a noise fill instead of attenuation to silence, varying how long to wait before attenuating the extrapolation, varying the rate of attenuation of the extrapolation, attenuating periodic extrapolation at a different rate than non-periodic extrapolation, and performing period extrapolation on successively longer fill data based on the audio character measures, adjusting weighting between periodic and non-periodic extrapolation based on the audio character measures, and adjusting weighting between periodic extrapolation and non-periodic extrapolation non-linearly.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Relay transmission device and relay transmission method
ActiveUS7852764B2Congestion in an ad hoc network is suppressedImprove transmission qualityFrequency-division multiplex detailsActive radio relay systemsTransmission bandwidthSelf-optimization
A relay transmission device can achieve high-quality transmission by suppressing congestion in an ad hoc network, even when a network environment changes or performance of a relay device to be communicated with changes. The relay transmission device includes: an optimization coefficient storage unit (1608) that stores, for each cooperative relay device, a self-optimization coefficient for weighting an amount of data determined by a self-optimization flow control unit (1603) and a total optimization coefficient for weighting an amount of data determined by a total optimization flow control unit (1604); and a balance adjustment unit (1605) that compares, for each cooperative relay device, an influence of congestion caused by transmission bandwidth allocation contention on the relay transmission device and an influence of congestion caused by transmission bandwidth allocation contention on the cooperative relay device, and adjusts the self-optimization coefficient and the total optimization coefficient based on a result of the comparison.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
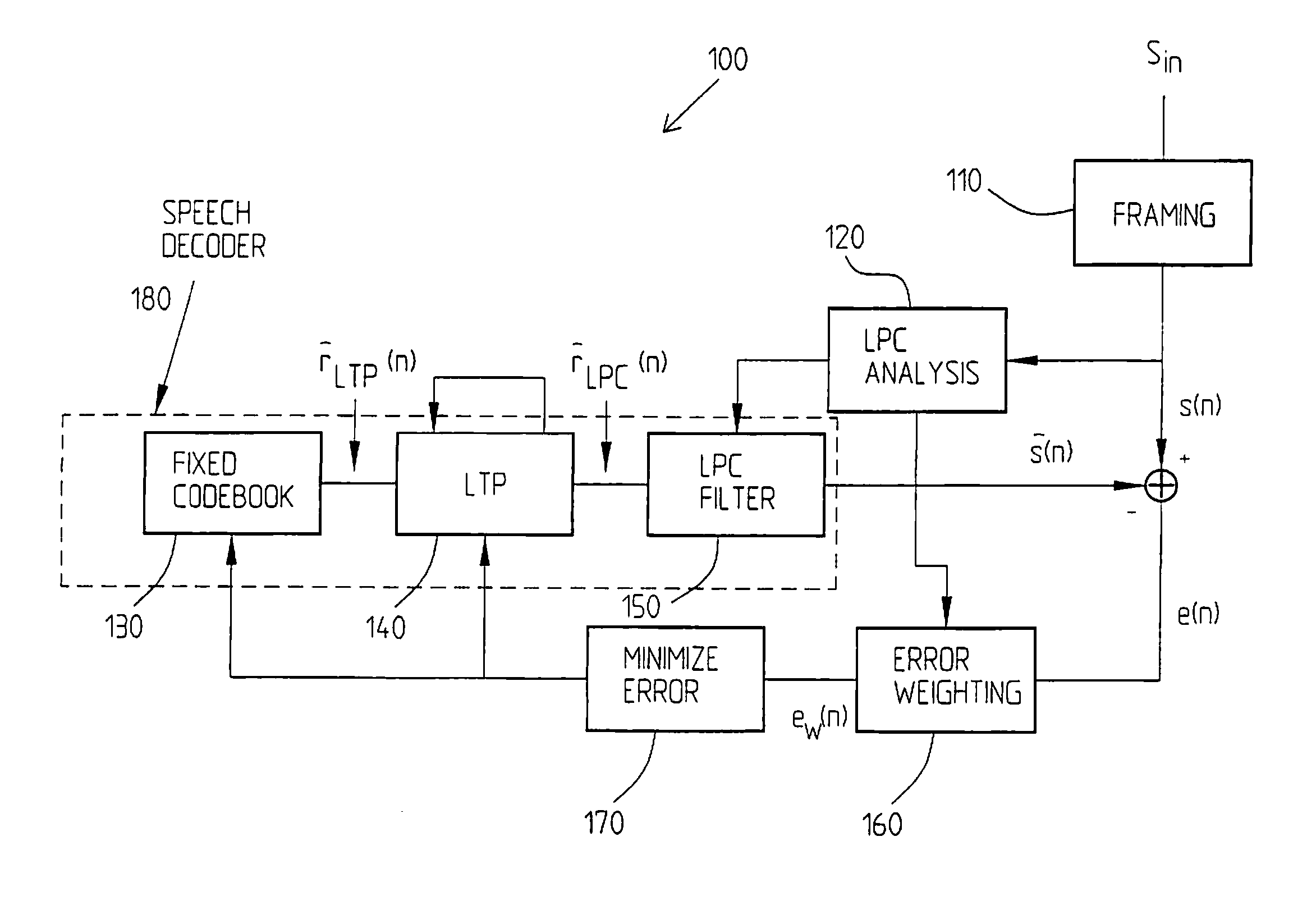
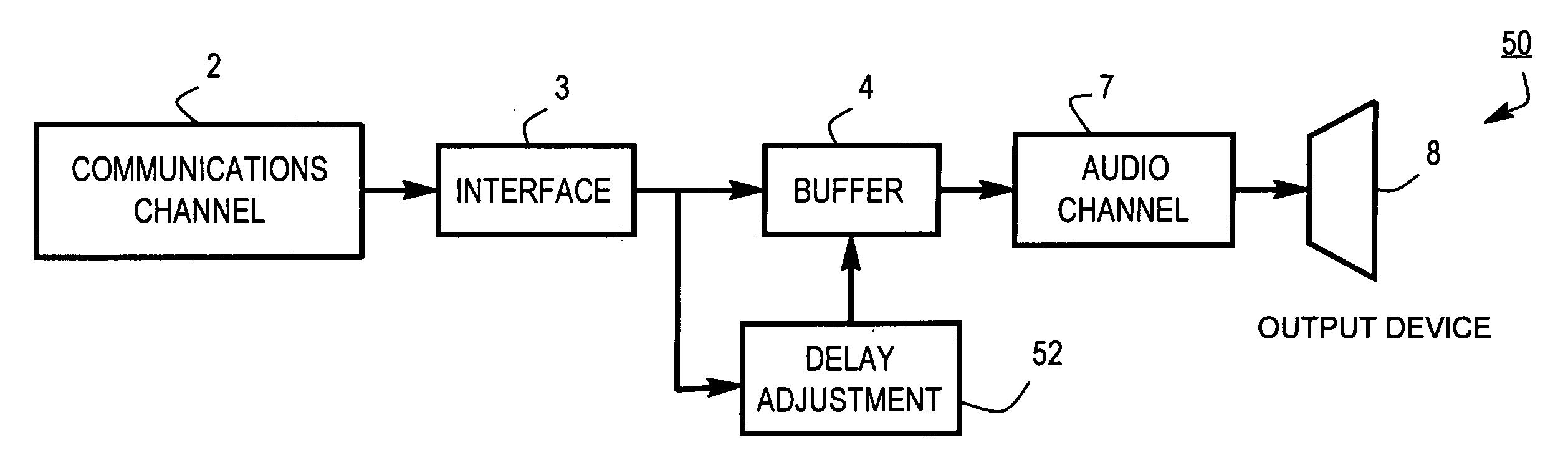
System for handling variations in the reception of a speech signal consisting of packets
InactiveUS7246057B1Efficiently handlePacket lossSpeech analysisHybrid transportData bufferReal-time computing
The present invention relates to a receiver system in a communication system supporting packet-based communication (e.g., an IP-network), including a receiver, speech decoder and a jitter buffer for handling delay variations in the reception of a speech signal consisting of packets containing frames with encoded speech. A jitter buffer controller is provided for keeping information about the functional size of the jitter buffer and for providing the speech decoder with control information, such that the speech decoder, based on that information, provides a dynamic adaptation of the size of the jitter buffer using the received encoded, packetized speech signal. The invention also relates to a method of adapting the function size of the jitter buffer of a receiver system.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
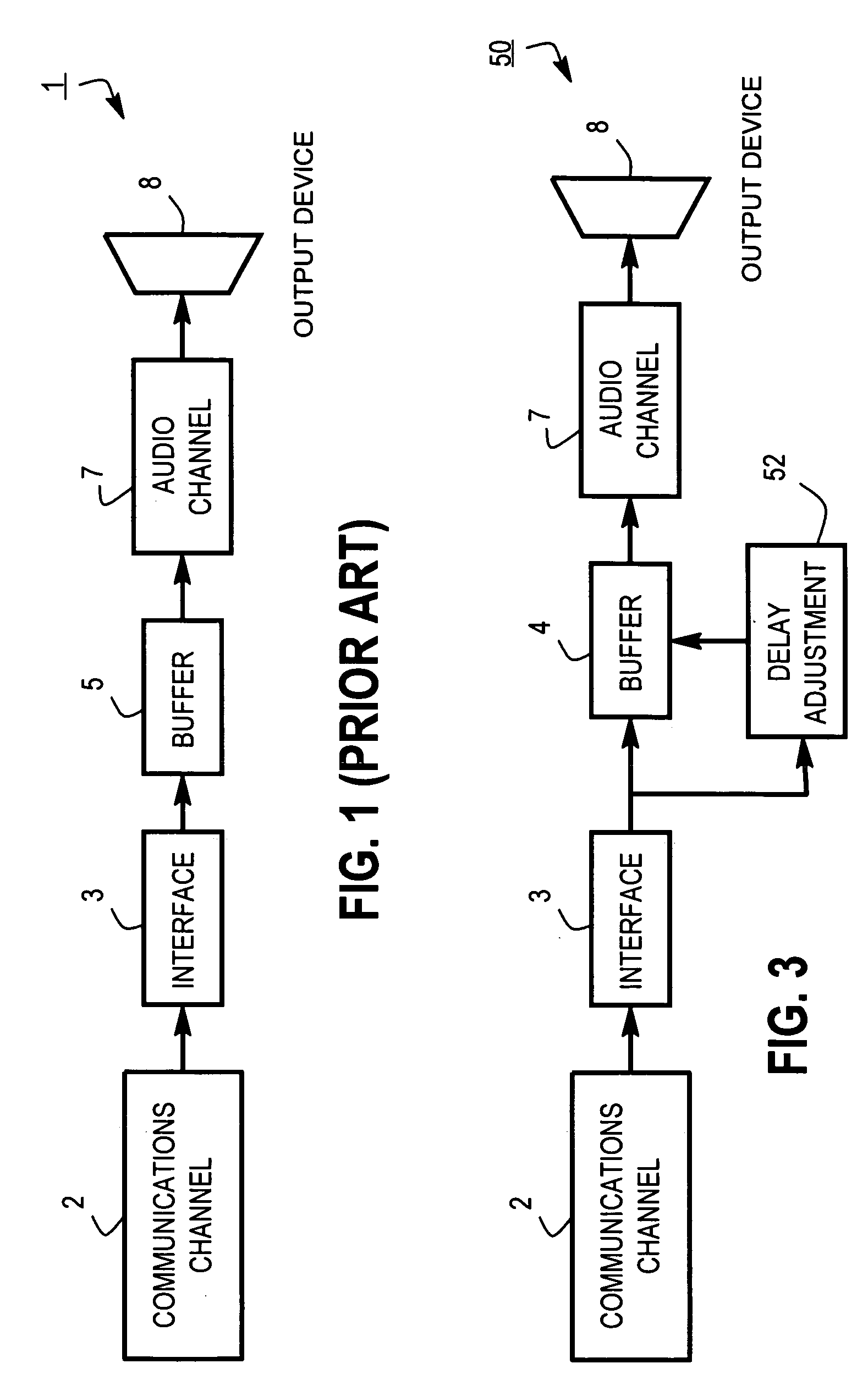
Audio receiver having adaptive buffer delay
InactiveUS20060092918A1Buffer delay be increaseIncreasing and decreasing buffer delayError preventionTransmission systemsInterval delaySelf adaptive
Generally speaking, there are provided systematic techniques for increasing and decreasing jitter buffer delay. The disclosed techniques typically utilize various combinations of: evaluating received data over a specified interval, increasing a recommended buffer delay if the interval delay exceeds a first threshold and decreasing the recommended buffer delay if the interval delay is less than a second threshold, causing the recommended buffer delay to decrease over time until an underflow condition is identified, and / or increasing the recommended buffer delay in response to identifying the underflow condition.
Owner:PIVOT VOIP
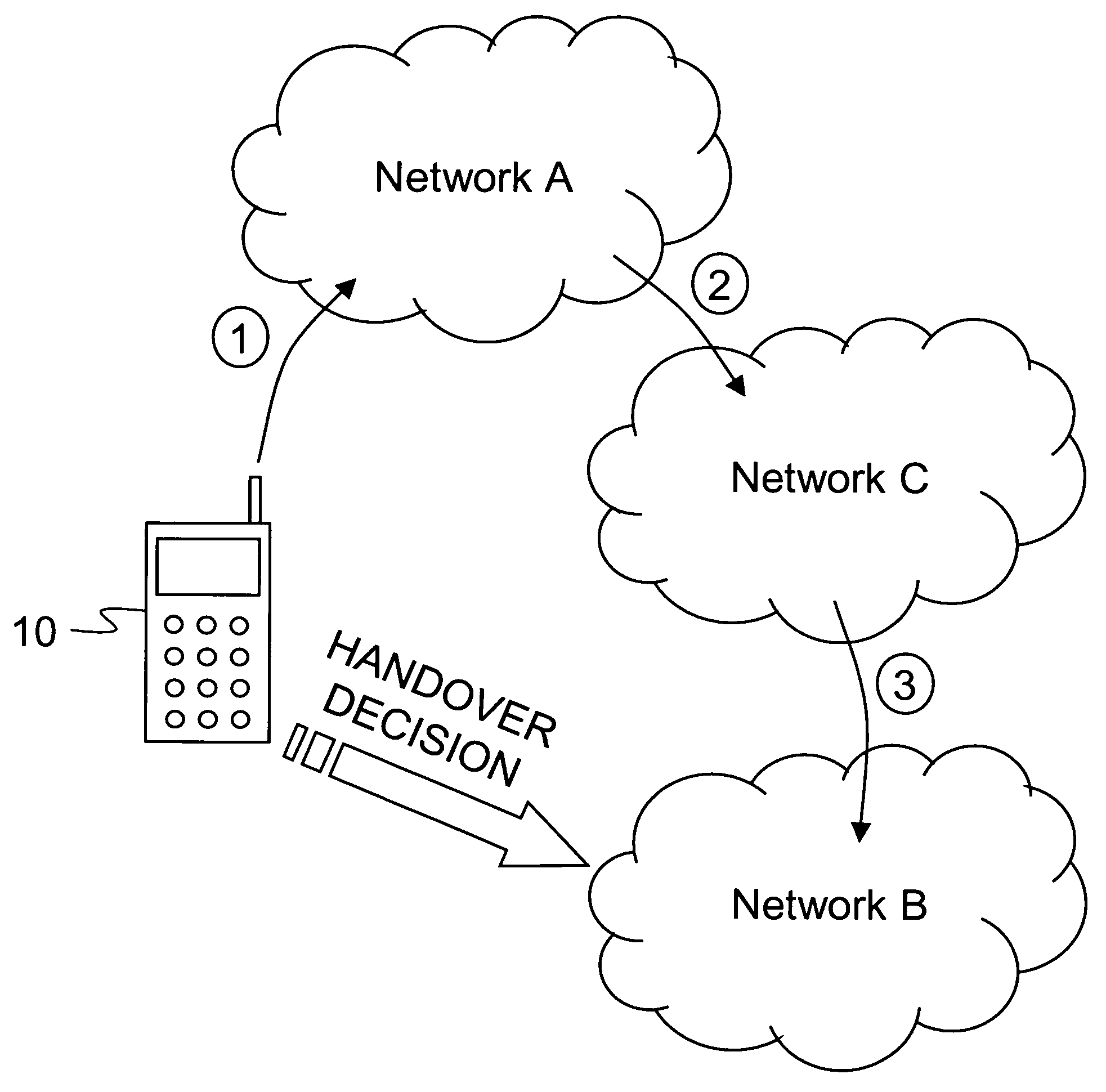
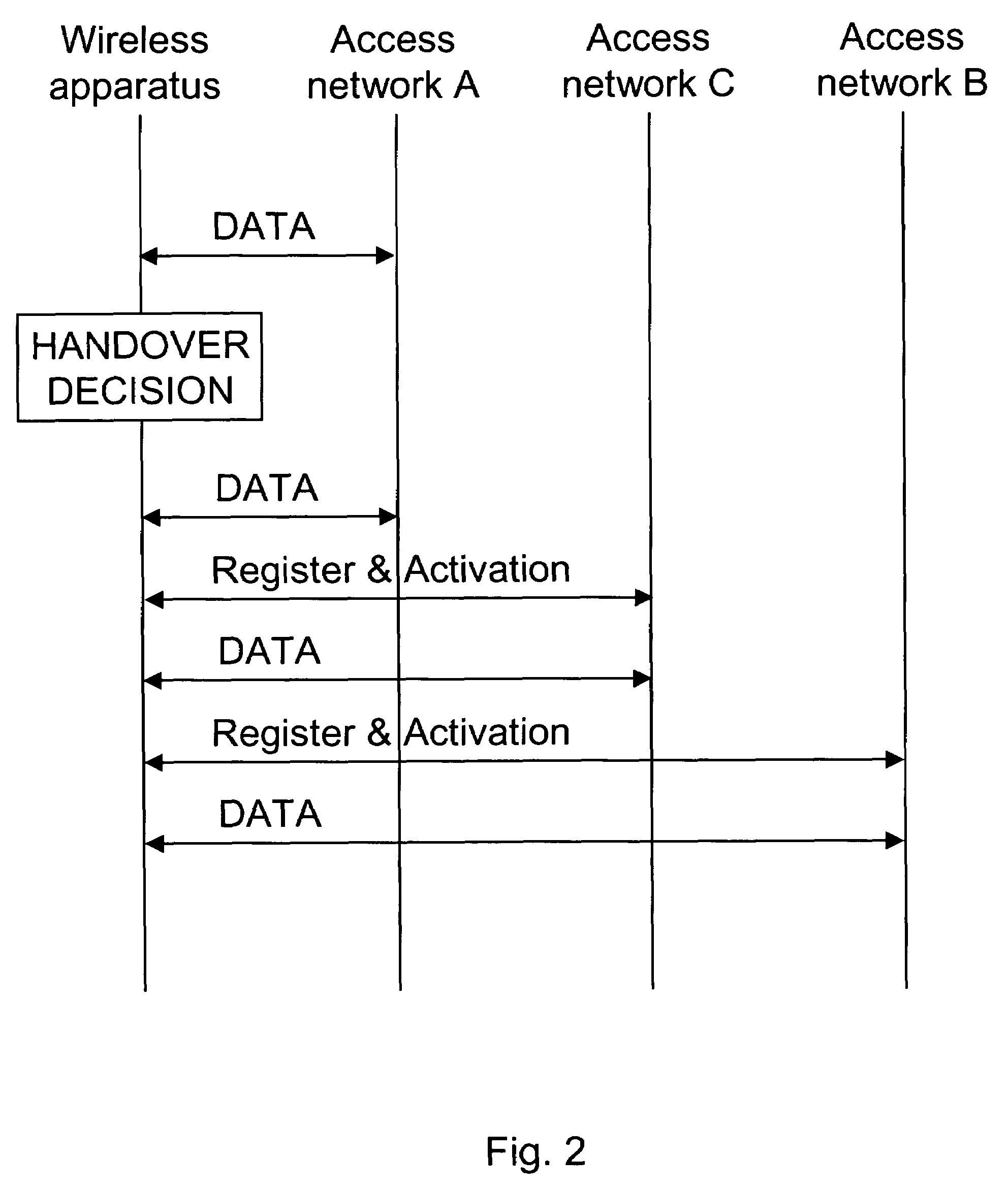
Vertical handover
ActiveUS20080064401A1Decrease delayPacket lossRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesAccess networkVertical handover
A vertical handover decision to perform a seamless vertical handover of a wireless apparatus from a current access network to a target access network is established. When deciding to perform the vertical handover from the current access network to the target access network it can be considered whether an intermediate access network could be used. It can be decided that first a seamless vertical handover is performed from the current access network to an intermediate access network, and subsequently a seamless vertical handover from the intermediate access network to the target access network is performed.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
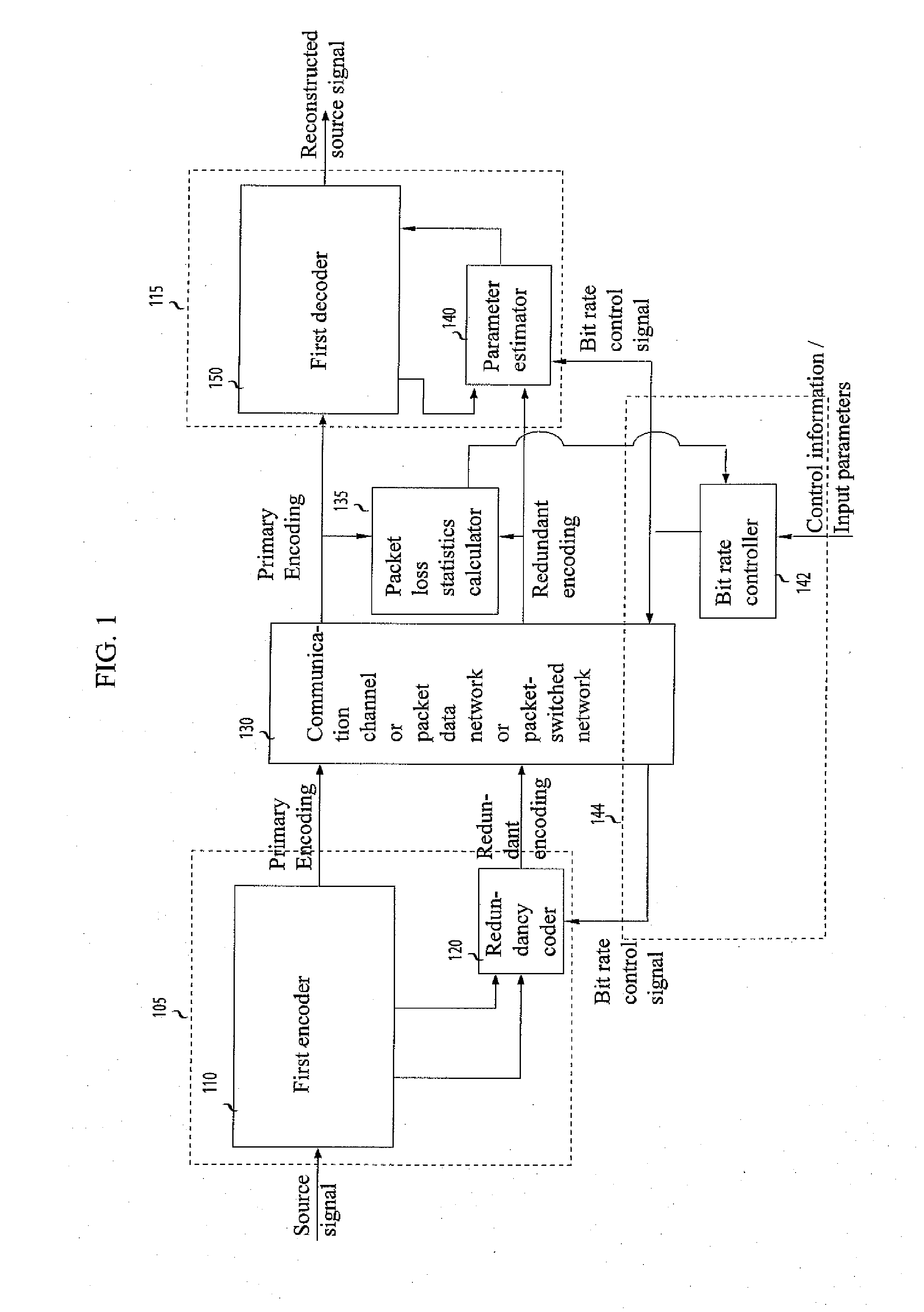
Adaptive, scalable packet loss recovery
InactiveUS20100054279A1Facilitates signal reconstructionAvoid network congestionError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsLossy source codingPacket loss rate
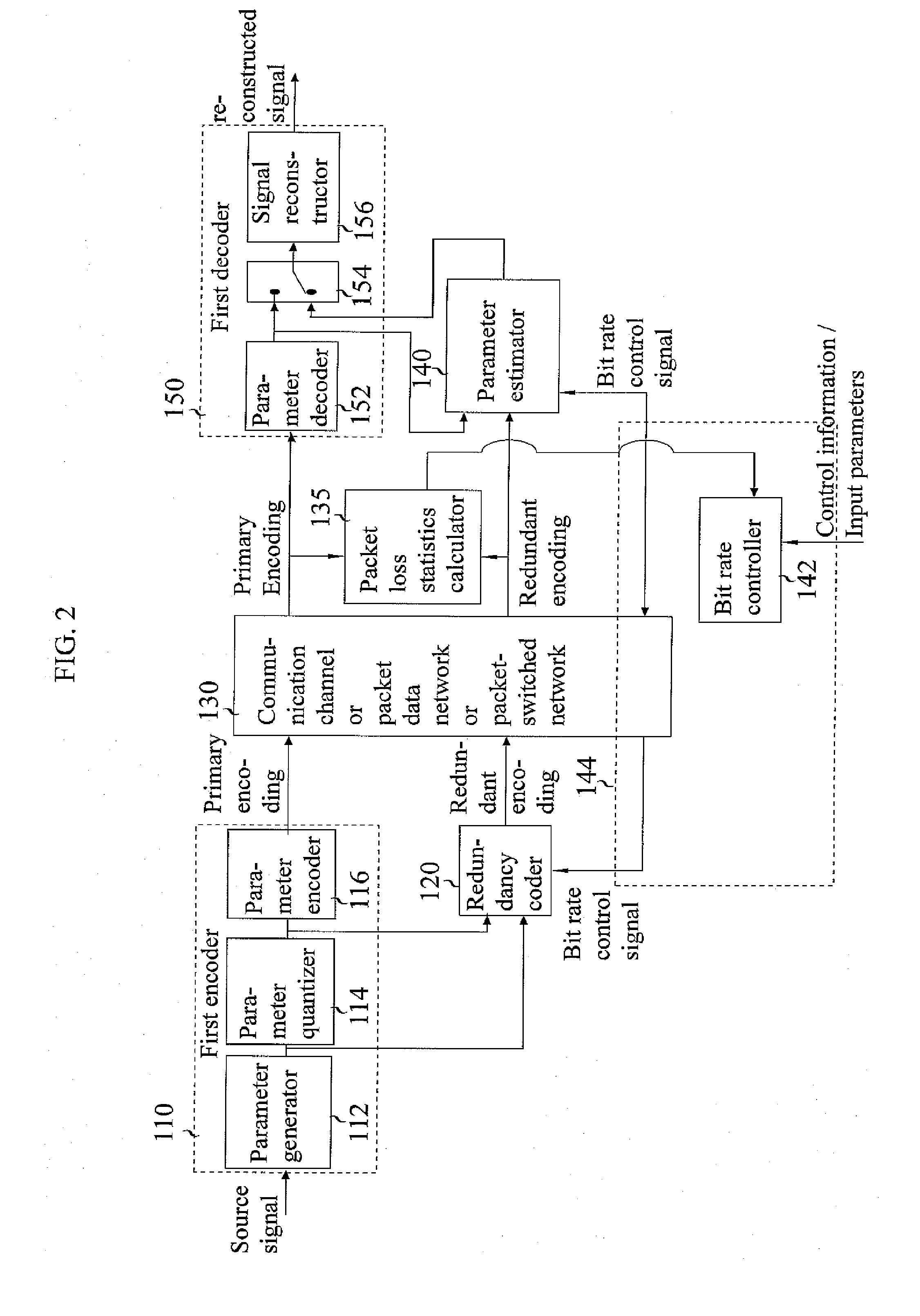
A system for transmitting data packets representing a source signal across a packet data network is provided. The encoder comprises a first encoder (110) and a redundancy encoder (120). The redundancy encoding is generated with a bit rate continuously scalable, the bit rate being provided by a bit rate controller (142) that uses input from the network (130) and packet-loss rate information. At the decoder, recovery is performed by a parameter estimator based in part on information transmitted from the first encoder using information from previous and / or future blocks and in addition on redundant information. The method may be added to existing lossy source coding systems or may be used to enhance the quality of the reconstructed source signal even in scenarios without packet loss.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method for encoding signals, related systems and program product therefor
ActiveUS20070047650A1Not complicate network topologyReduce resolutionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer hardwareImage resolution
A method for encoding video signals subjects the signals to unbalanced multiple description coding. The unbalanced multiple description coding codes a video signal in a first high resolution packet and a second low resolution packet and represents, respectively a first high resolution description and a second low resolution description. The unbalanced multiple description coding step includes using different intra refresh periods for the first and second high resolution descriptions, with an intra refresh period for the second low resolution description shorter than the intra refresh period of the first high resolution description.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Method of operating an event-driven, delay-critical wireless sensor network
ActiveUS20100085954A1Robust to interferenceReduce delayNetwork topologiesFrequency-division multiplexWireless sensor networkingWireless sensor network
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Secure network coding for multi-resolution wireless video streaming
ActiveUS8571214B2Increasing throughput and robustnessBenefitTime-division multiplexTelevision systemsPacket lossWireless video
Described herein is a method and system for hierarchical wireless video with network coding which limits encryption operations to a critical set of network coding coefficients in combination with multi-resolution video coding. Such a method and system achieves hierarchical fidelity levels, robustness against wireless packet loss and efficient security by exploiting the algebraic structure of network coding.
Owner:UNIV DO PORTO +2
Hybrid Networking System with Seamless Path Switching of Streams
InactiveUS20130132603A1Packet lossError preventionMultiple digital computer combinationsPath switchingReal-time computing
System and method for switching a stream to a new transmission medium. A first stream may be received. A first plurality of packets of the first stream may be transmitted to a second device on a first transmission medium. The first plurality of packets may include one or more index marker packets. It may be determined that at least a portion of the first plurality of packets may not have been received by the second device. A second plurality of packets of the first stream may be transmitted to the second device on a second transmission medium. The second plurality of packets may include at least a subset of the first plurality of packets and at least a subset of the one or more index marker packets. The one or more index marker packets may be configured for use by the second device to detect and discard duplicate packets.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
System and method for real-time jitter control and packet-loss concealment in an audio signal
InactiveUS7596488B2Improve signal qualityImprove performanceSpeech analysisTime-division multiplexNetwork packetPacket loss concealment
An “adaptive audio playback controller” operates by decoding and reading received packets of an audio signal into a signal buffer. Samples of the decoded audio signal are then played out of the signal buffer according to the needs of a player device. Jitter control and packet loss concealment are accomplished by continuously analyzing buffer content in real-time, and determining whether to provide unmodified playback from the buffer contents, whether to compress buffer content, stretch buffer content, or whether to provide for packet loss concealment for overly delayed or lost packets as a function of buffer content. Further, the adaptive audio playback controller also determines where to stretch or compress particular frames or signal segments in the signal buffer, and how much to stretch or compress such segments in order to optimize perceived playback quality.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com