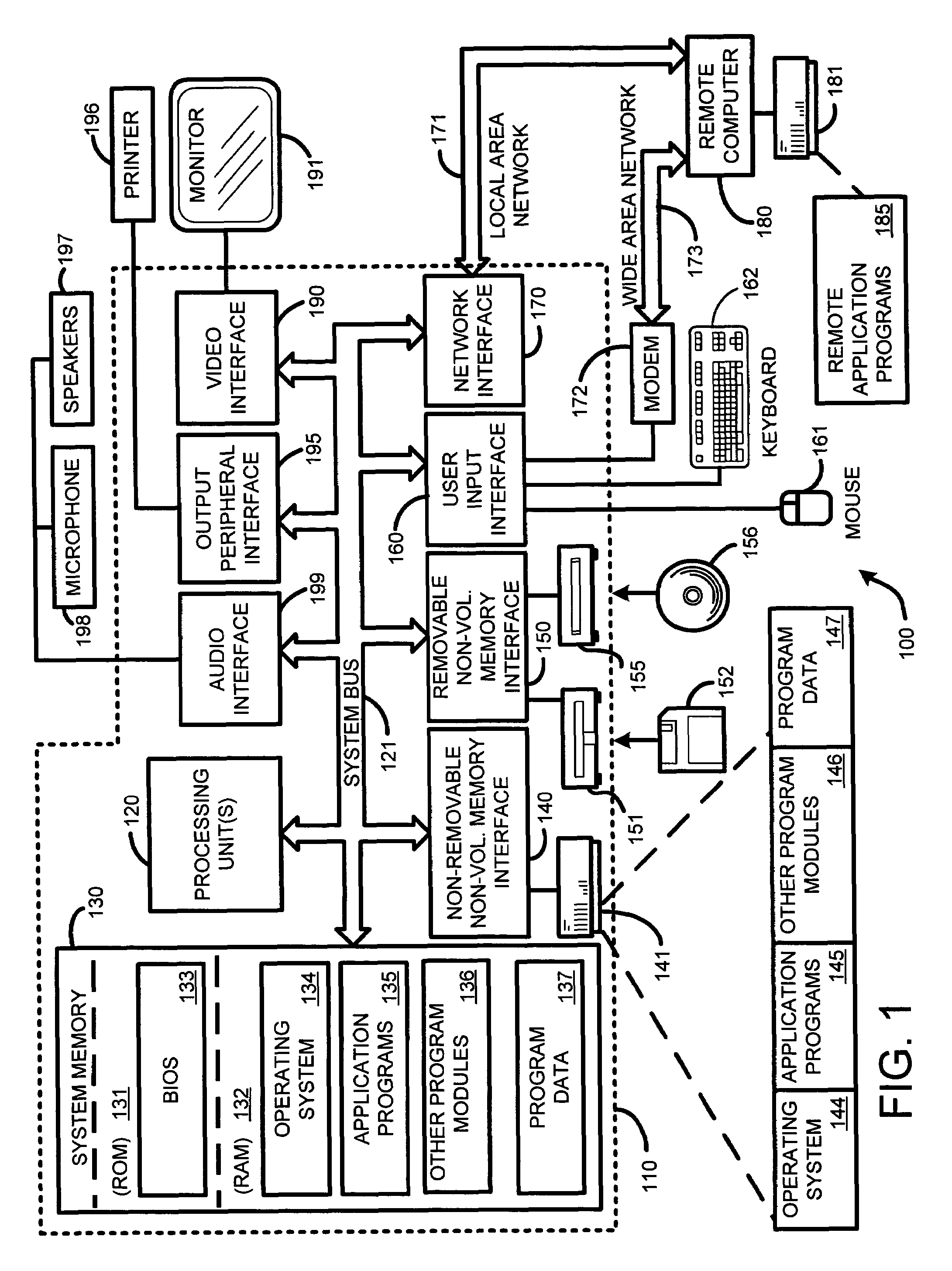
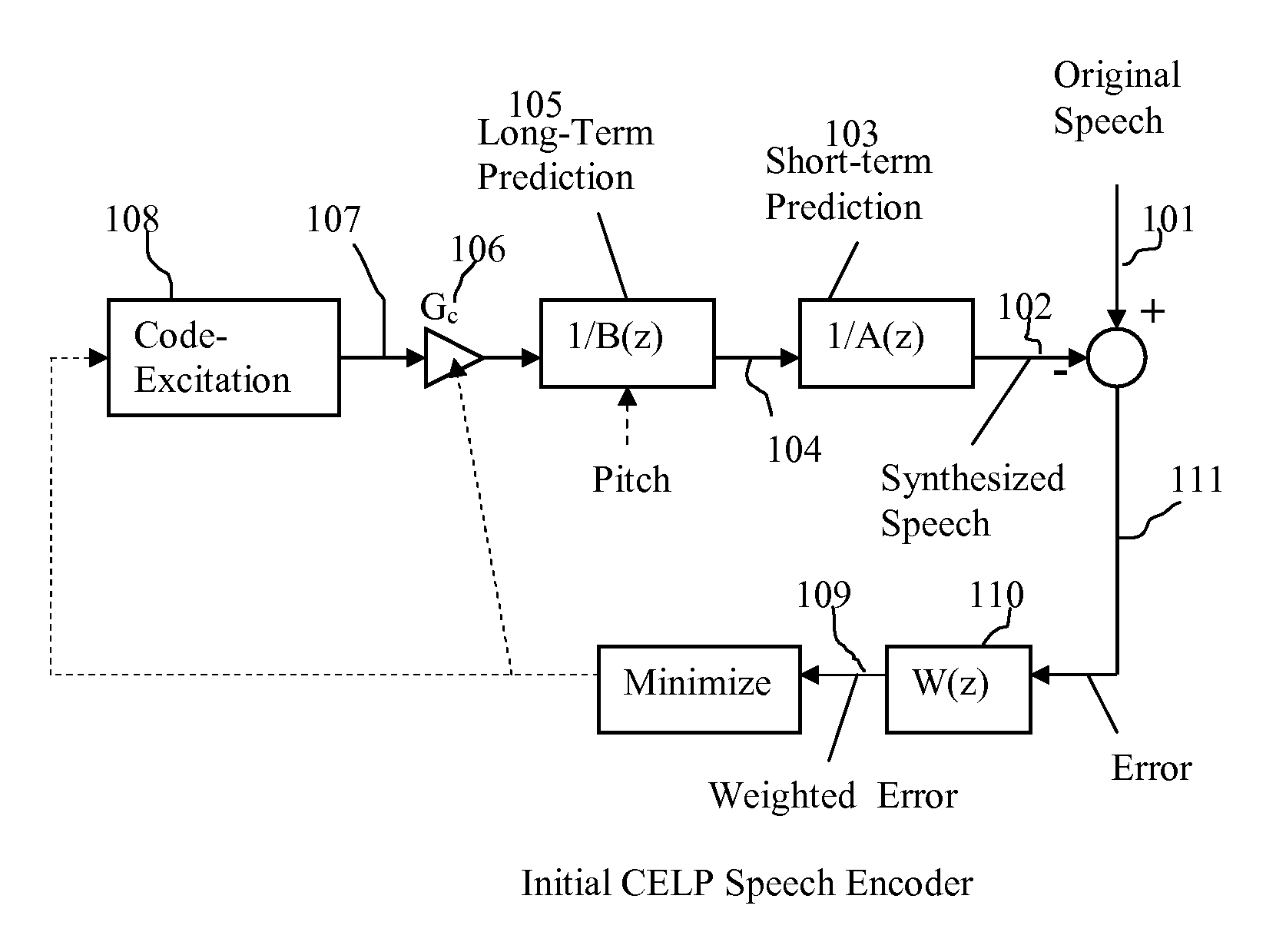
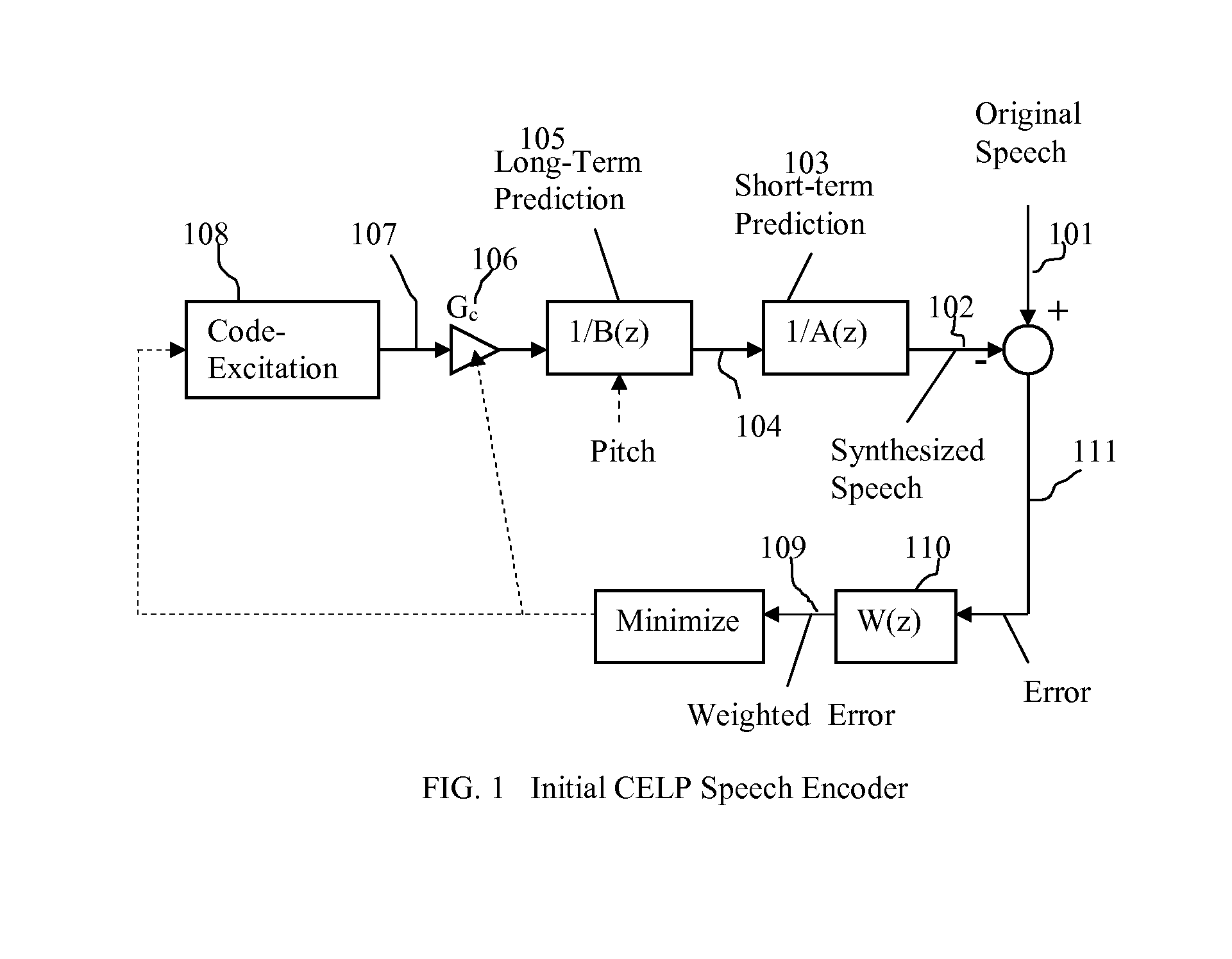
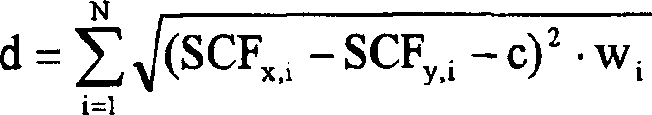Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
107 results about "Packet loss concealment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
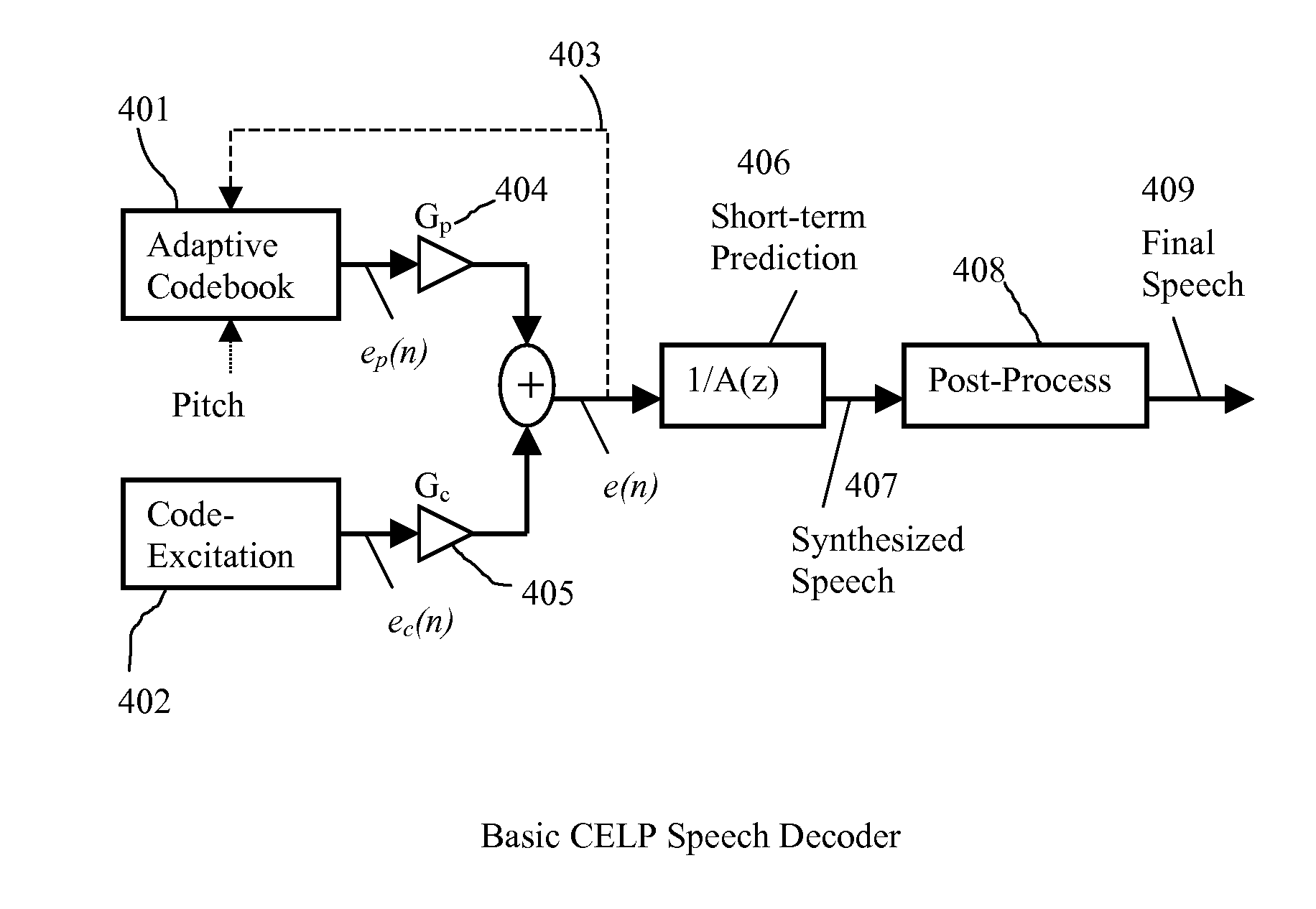
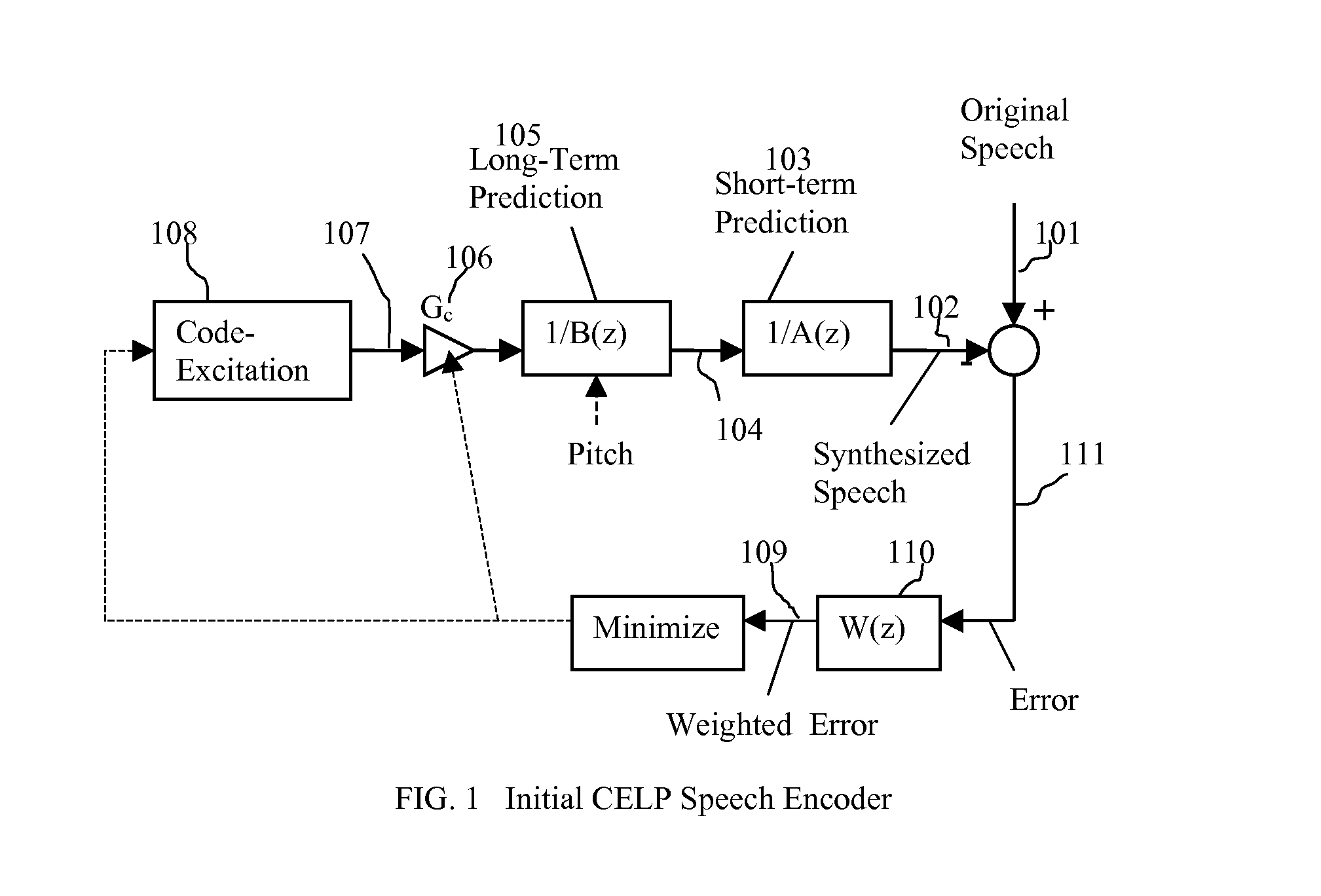
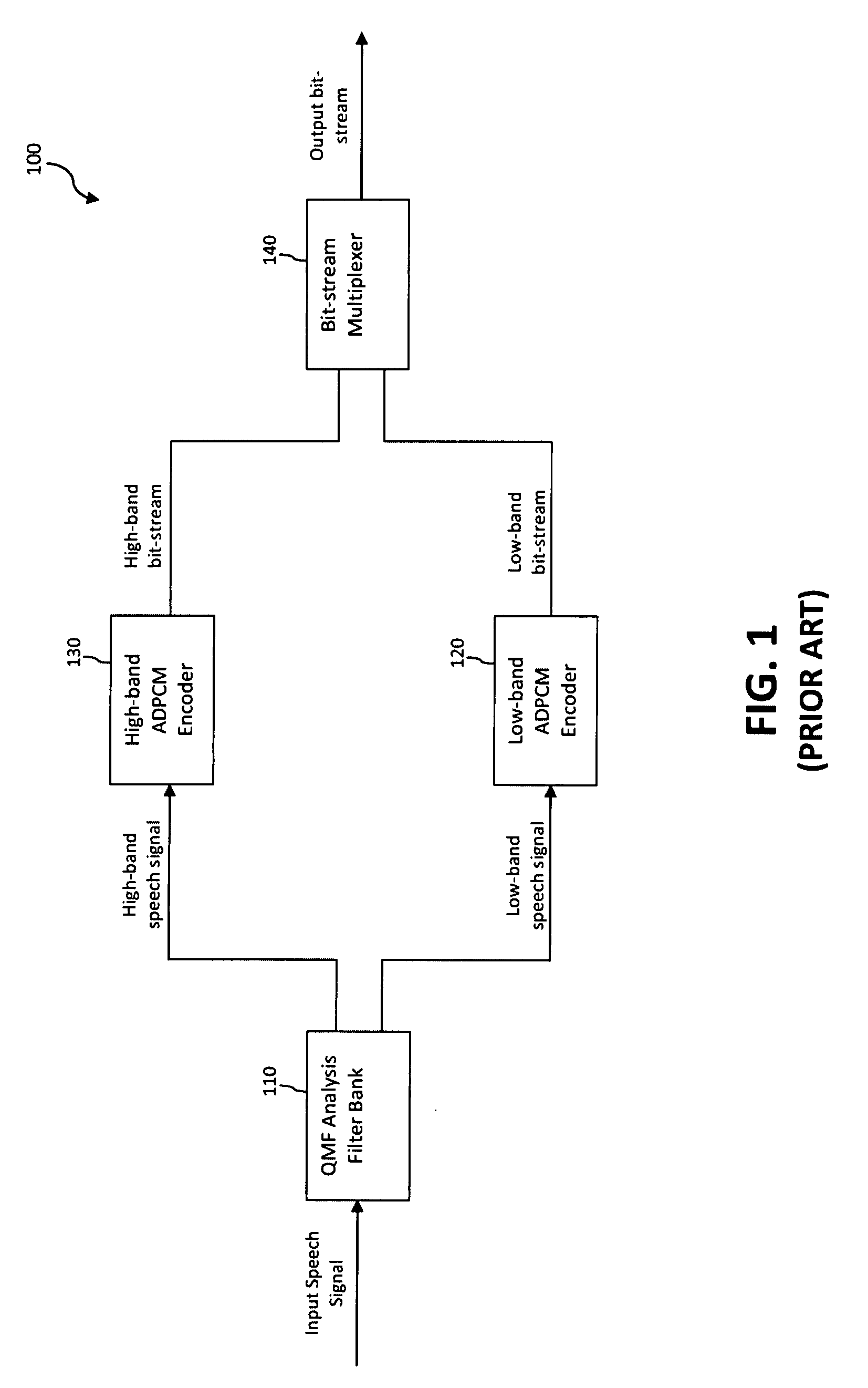
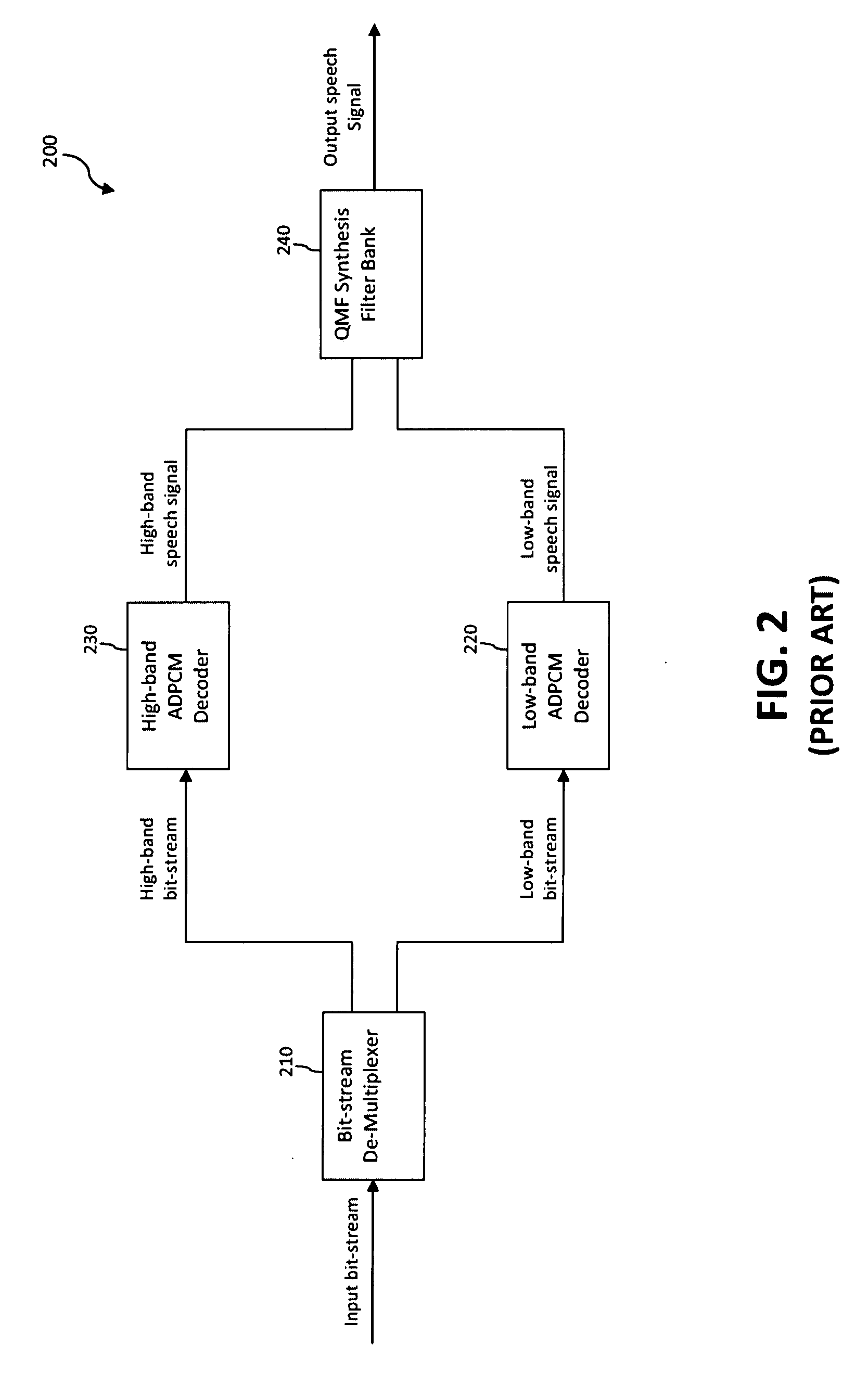
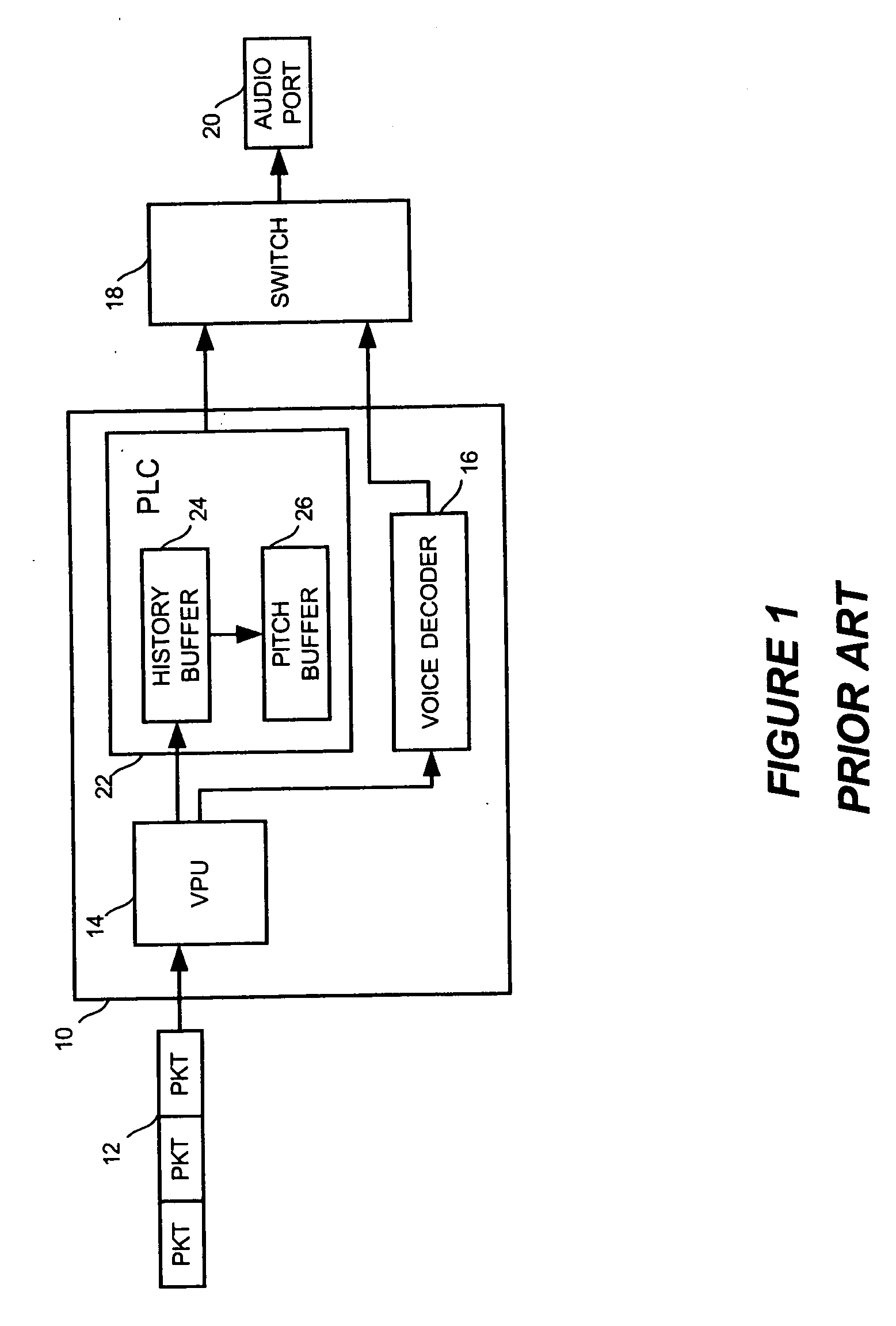
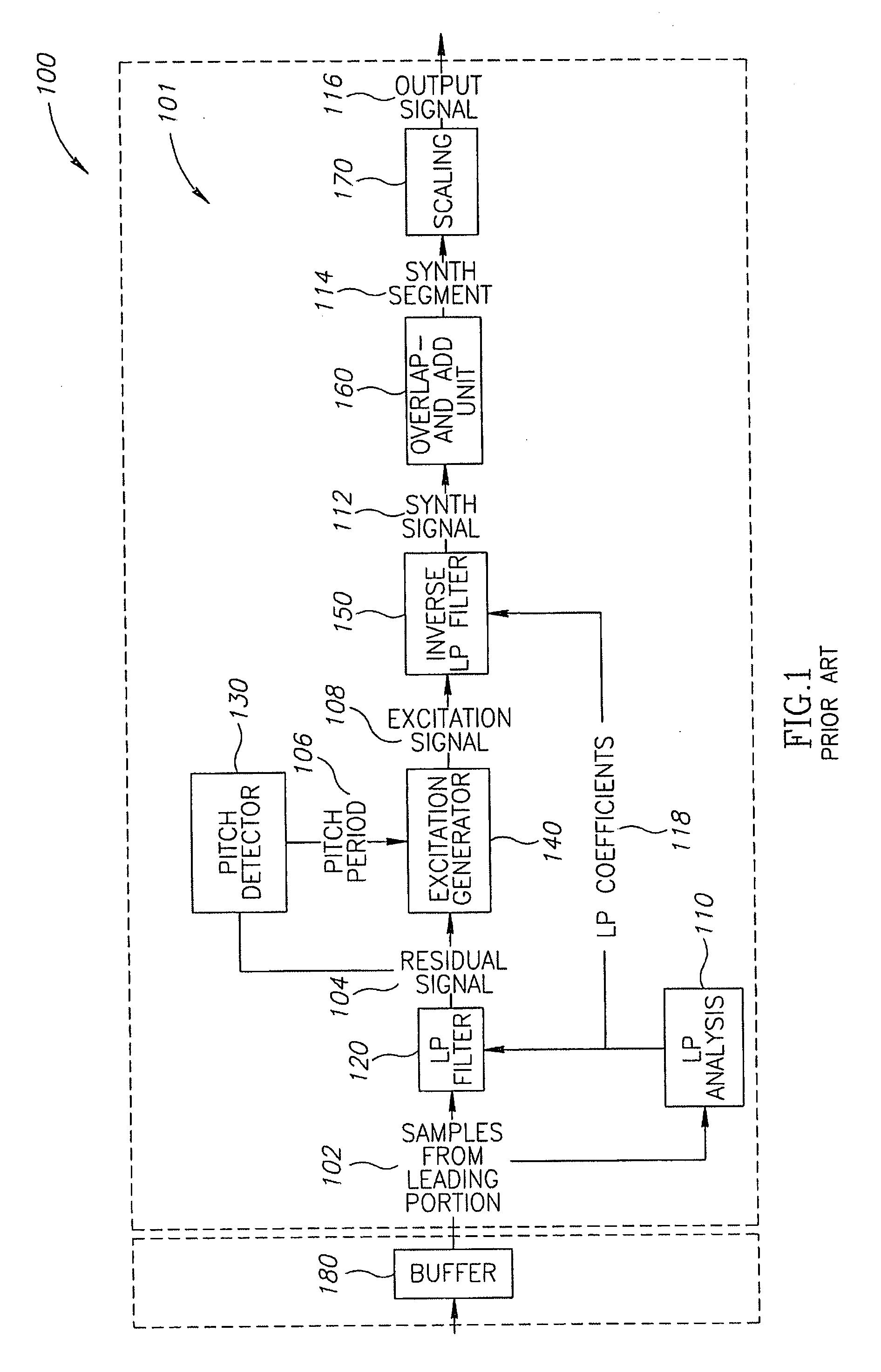
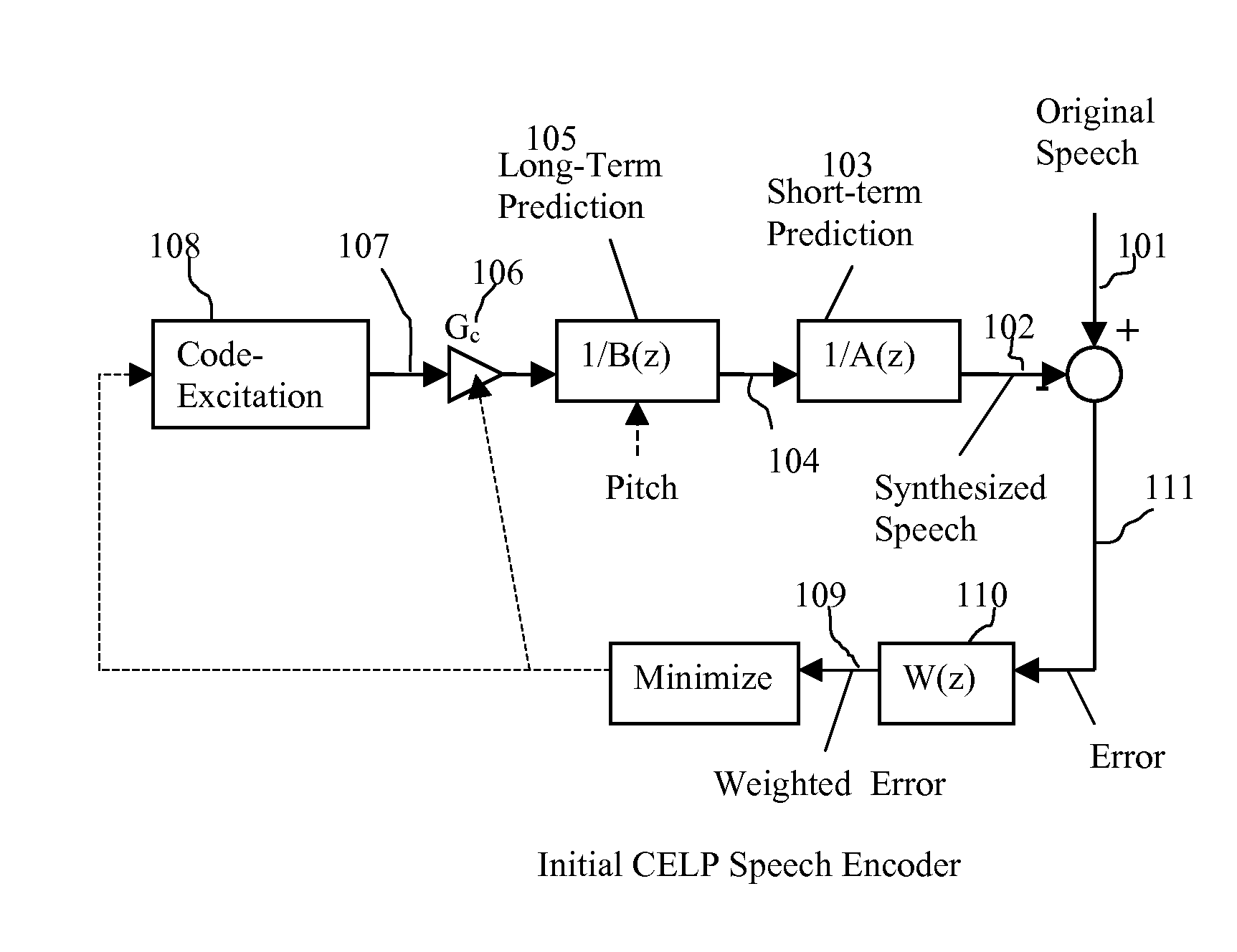
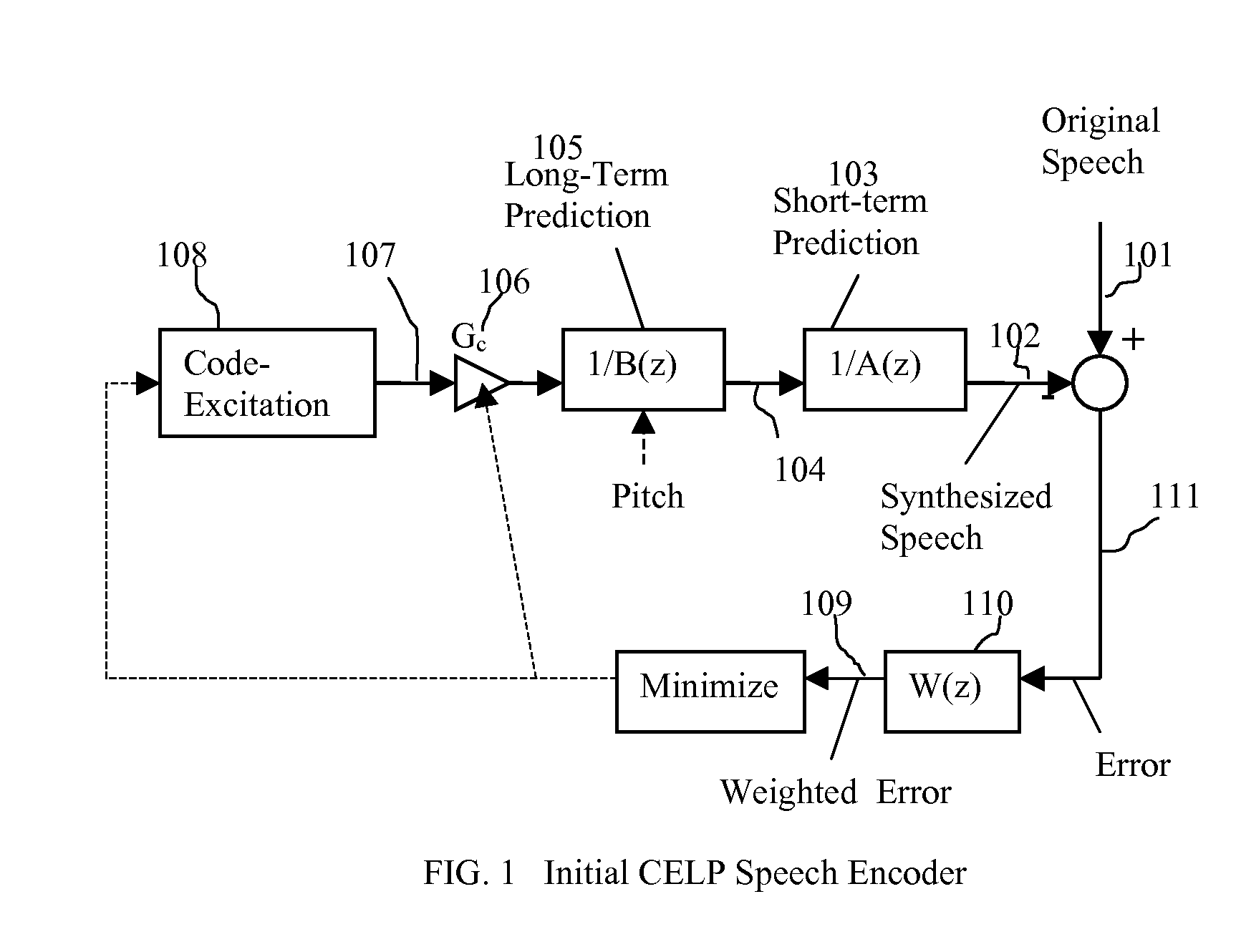
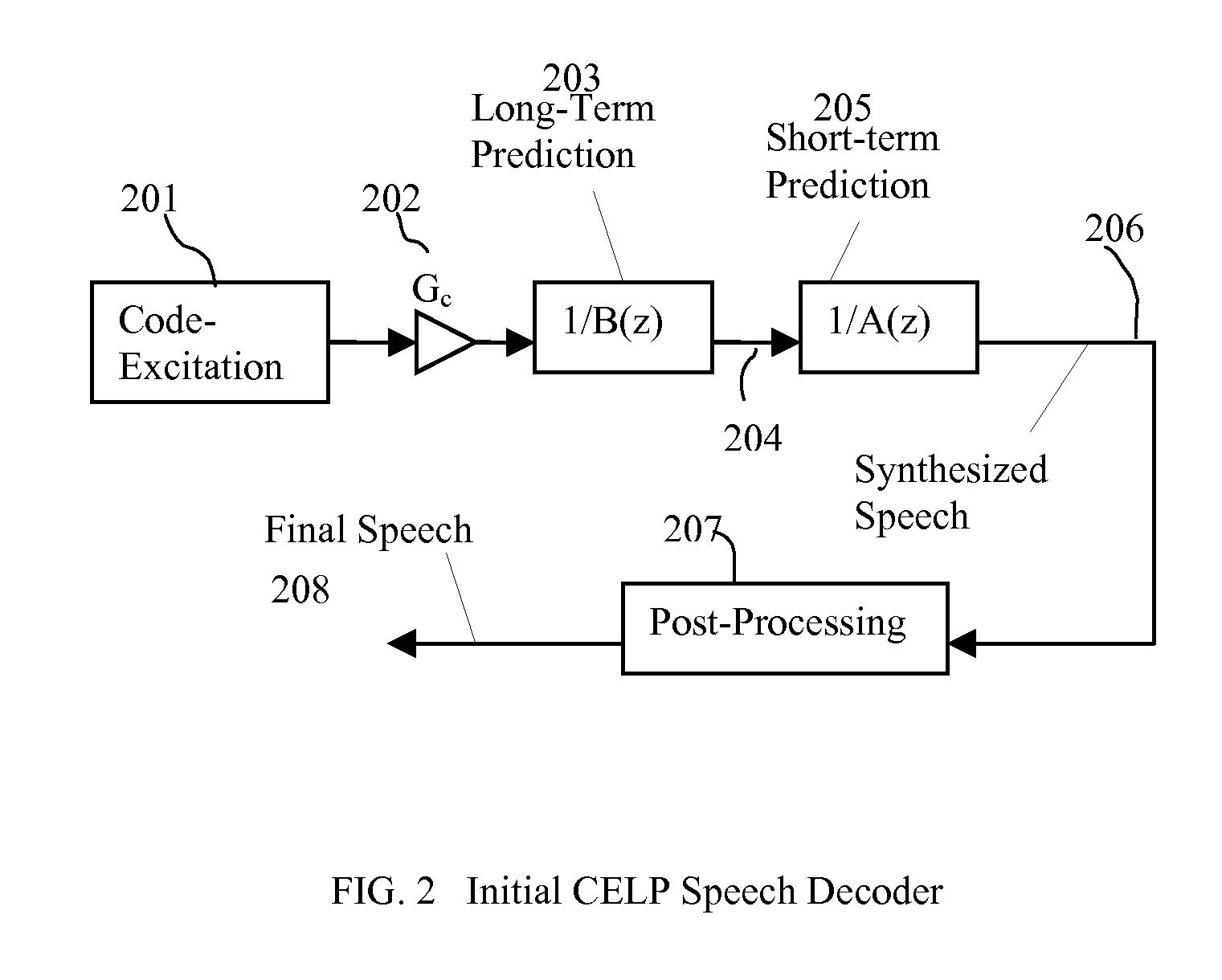
Packet loss concealment (PLC) is a technique to mask the effects of packet loss in voice over IP (VoIP) communications. When the voice signal is sent as VoIP packets on a TCP/IP network, the packets may (and likely will) travel different routes. A packet therefore might arrive very late, might be corrupted, or simply might not arrive at all. One example case of the last situation could is when a packet is rejected by a server which has a full buffer and cannot accept any more data. Other cases include network congestion resulting in significant delay. In a VoIP connection, error-control techniques such as automatic repeat request (ARQ) are not feasible and the receiver should be able to cope with packet loss. Packet loss concealment is the inclusion in a design of methodologies for accounting for and compensating for the loss of voice packets.
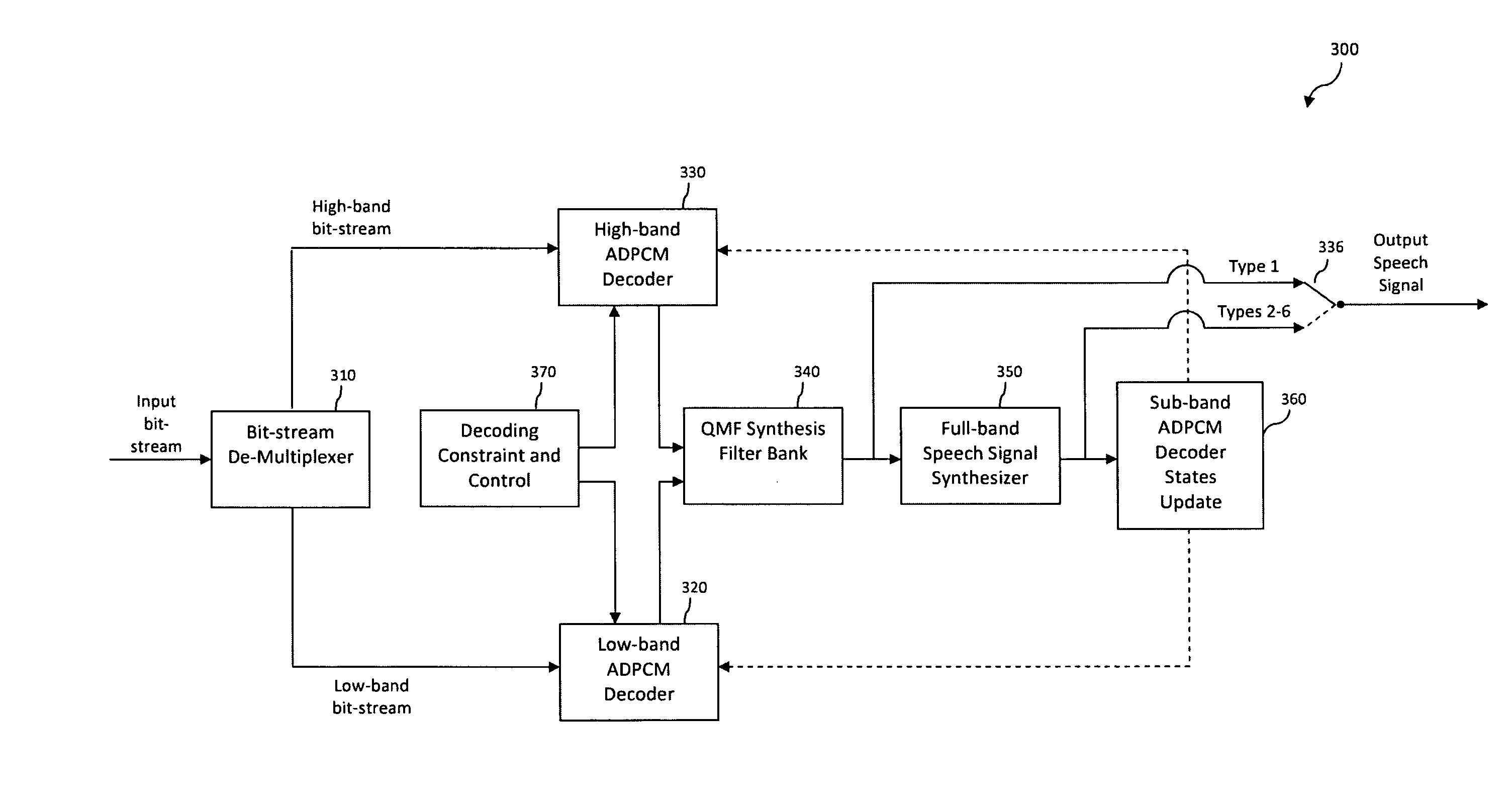
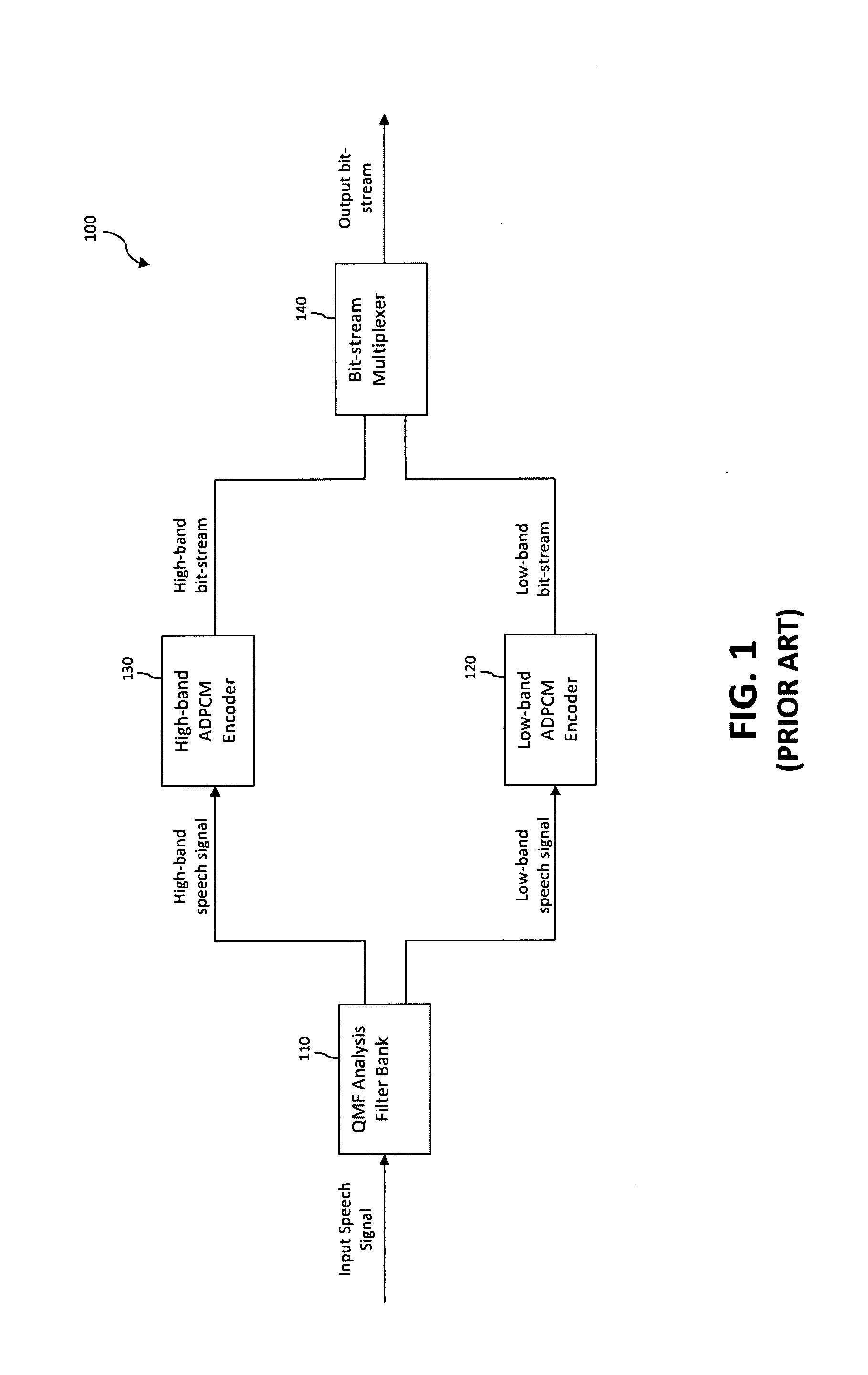
Packet Loss Concealment for Sub-band Predictive Coding Based on Extrapolation of Full-band Audio Waveform
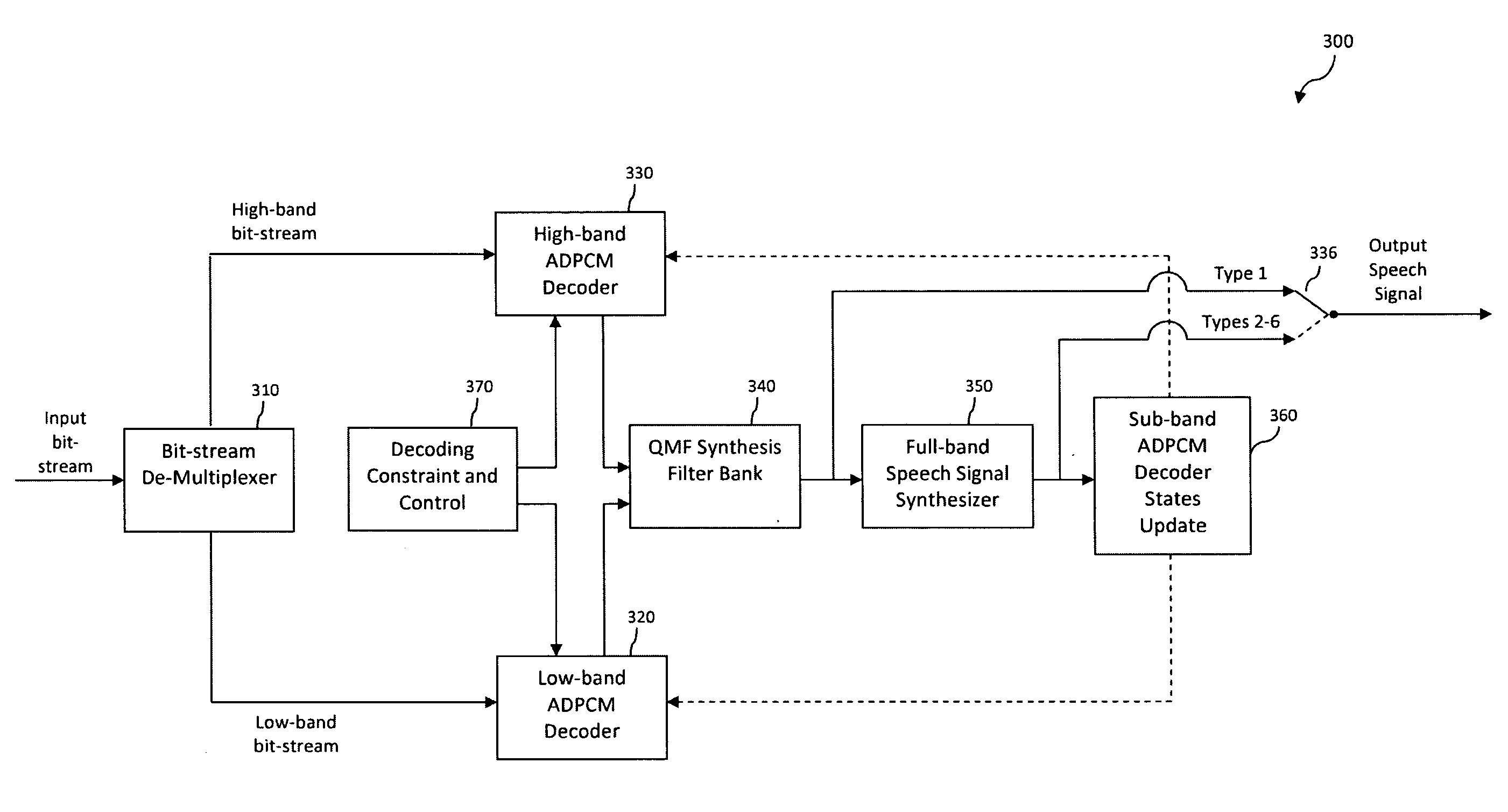
A technique for concealing the effect of a lost frame in a series of frames representing an encoded audio signal in a sub-band predictive coding system is provided. In accordance with the technique, one or more received frames in the series of frames are decoded to generate a full-band output audio signal, wherein the full-band output audio signal comprises a combination of at least a first sub-band decoded audio signal and a second sub-band decoded audio signal. The full-band output audio signal corresponding to the one or more received frames is stored. Then, a full-band output audio signal corresponding to the lost frame is synthesized, wherein synthesizing the full-band output audio signal corresponding to the lost frame comprises performing waveform extrapolation based on the stored full-band output audio signal corresponding to the one or more received frames.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Packet prioritization and associated bandwidth and buffer management techniques for audio over IP
ActiveUS7359979B2Raise priorityReduce the possibilityMultiple digital computer combinationsSpeech recognitionVoice communicationVoice activity
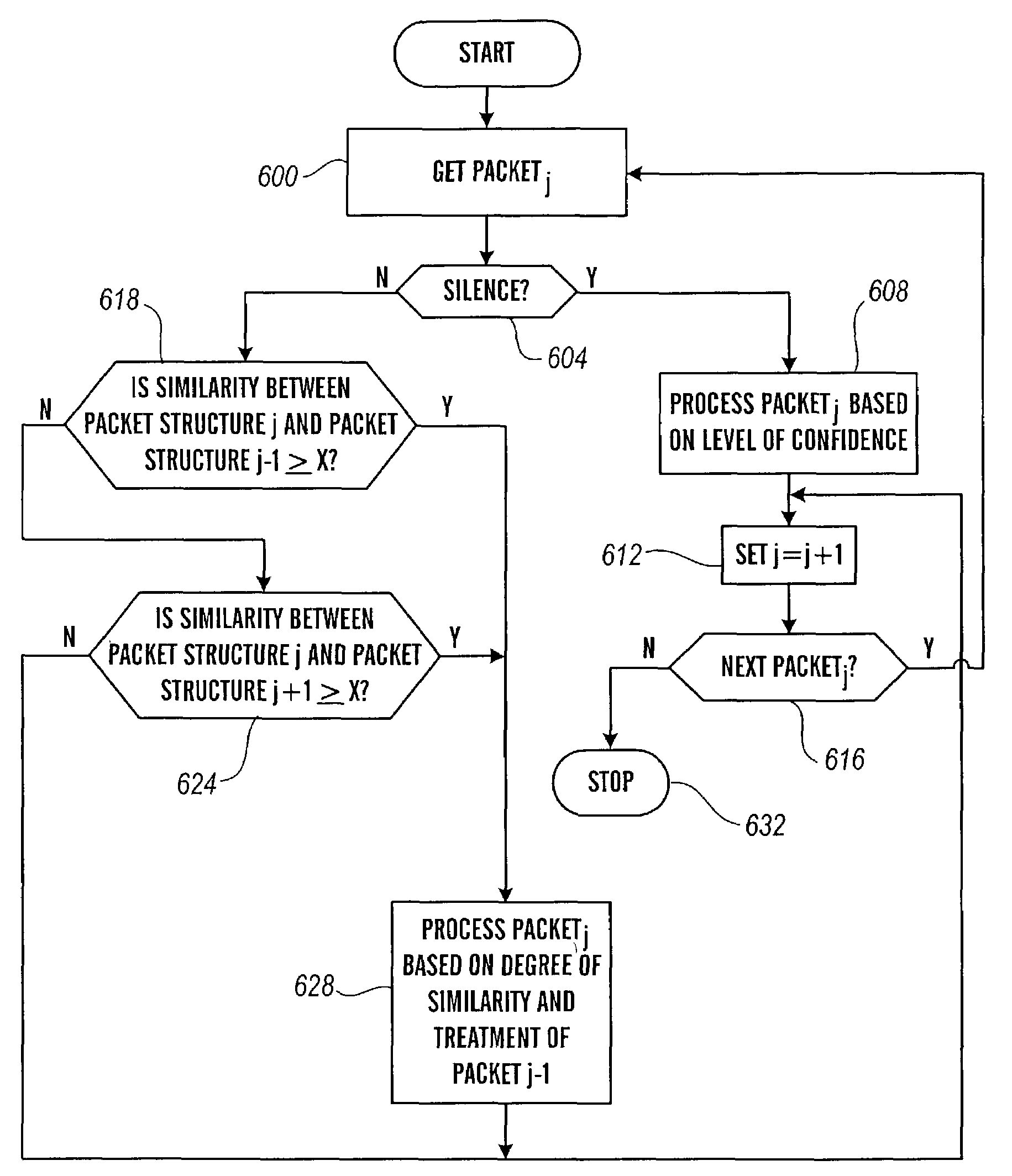
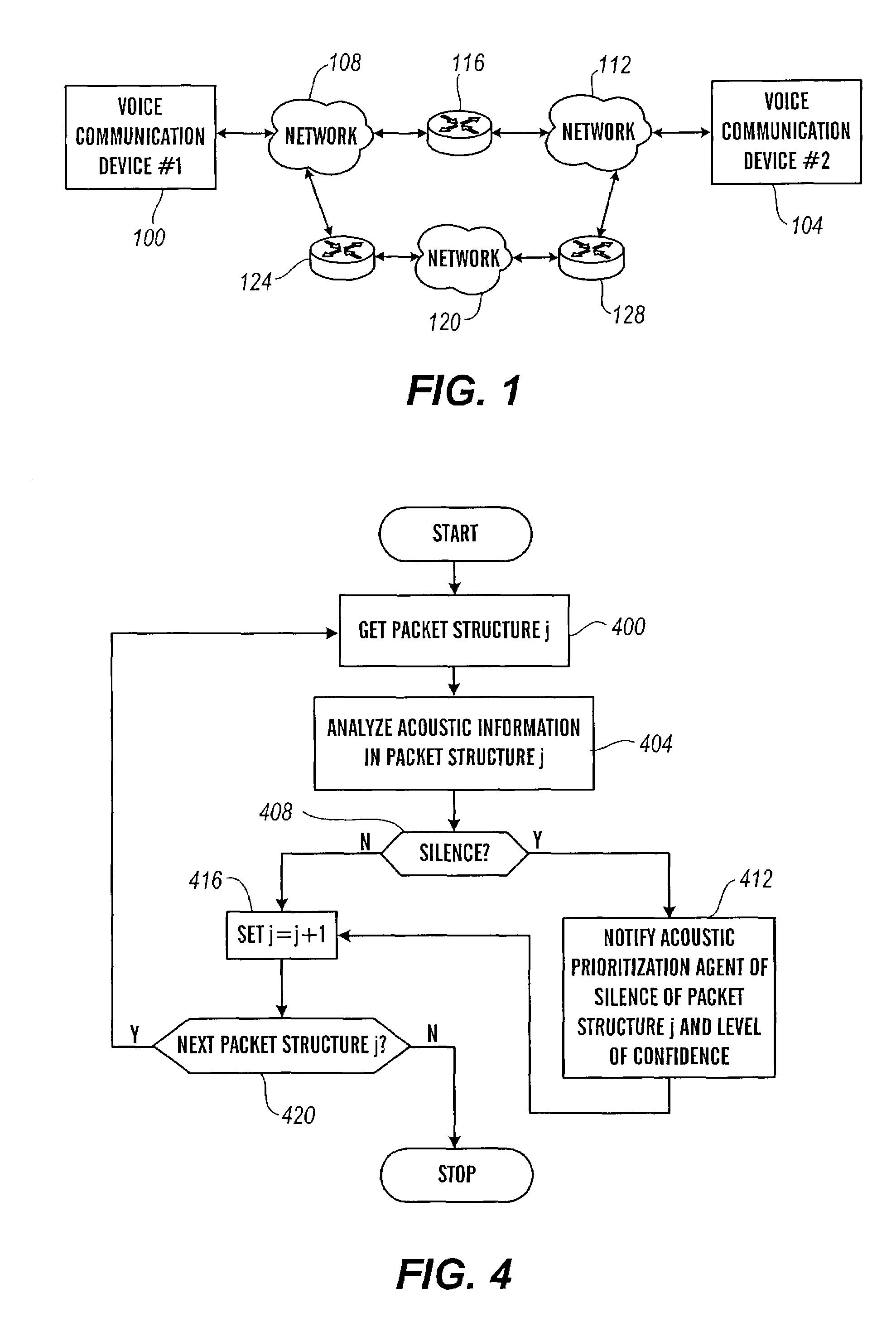
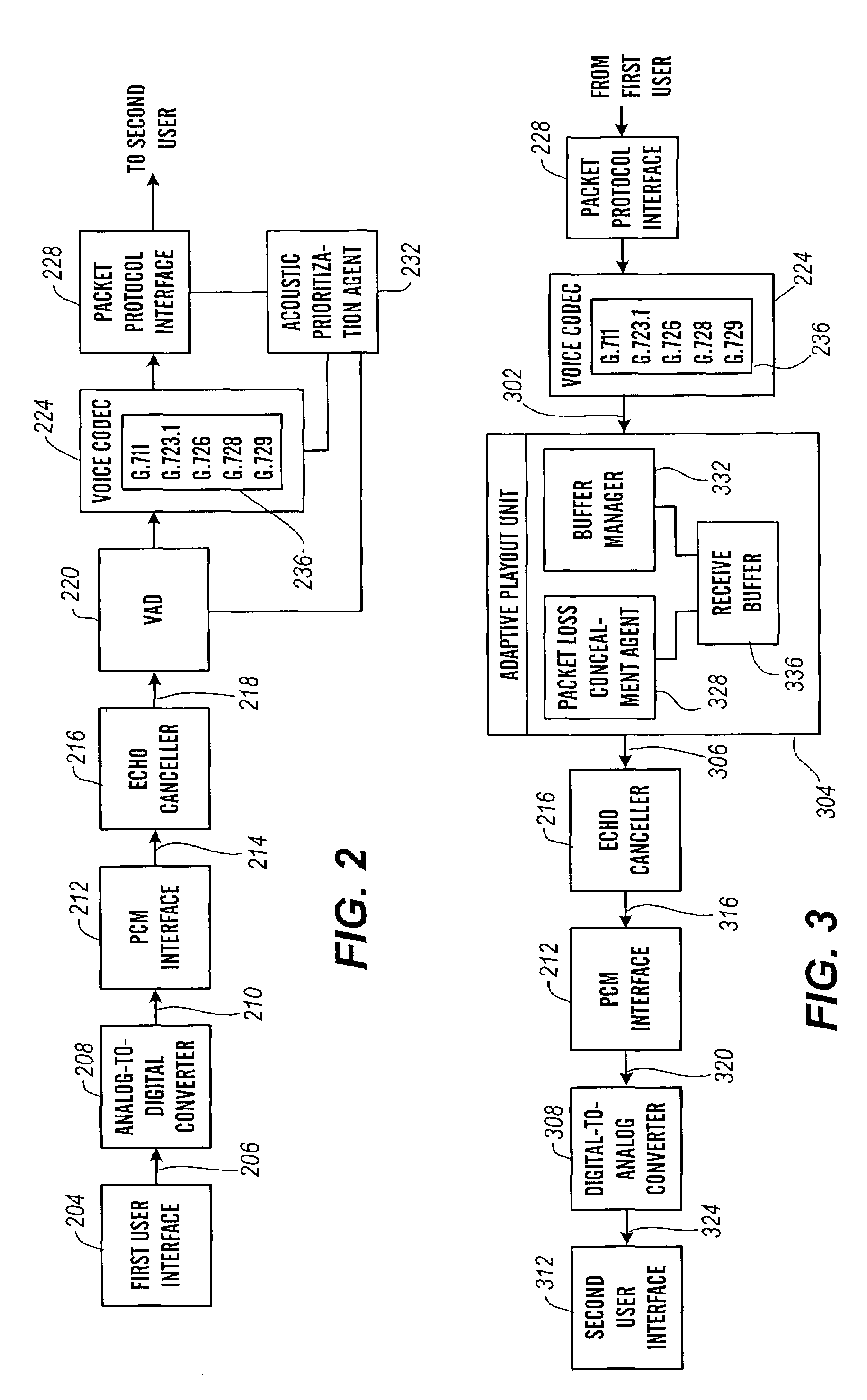
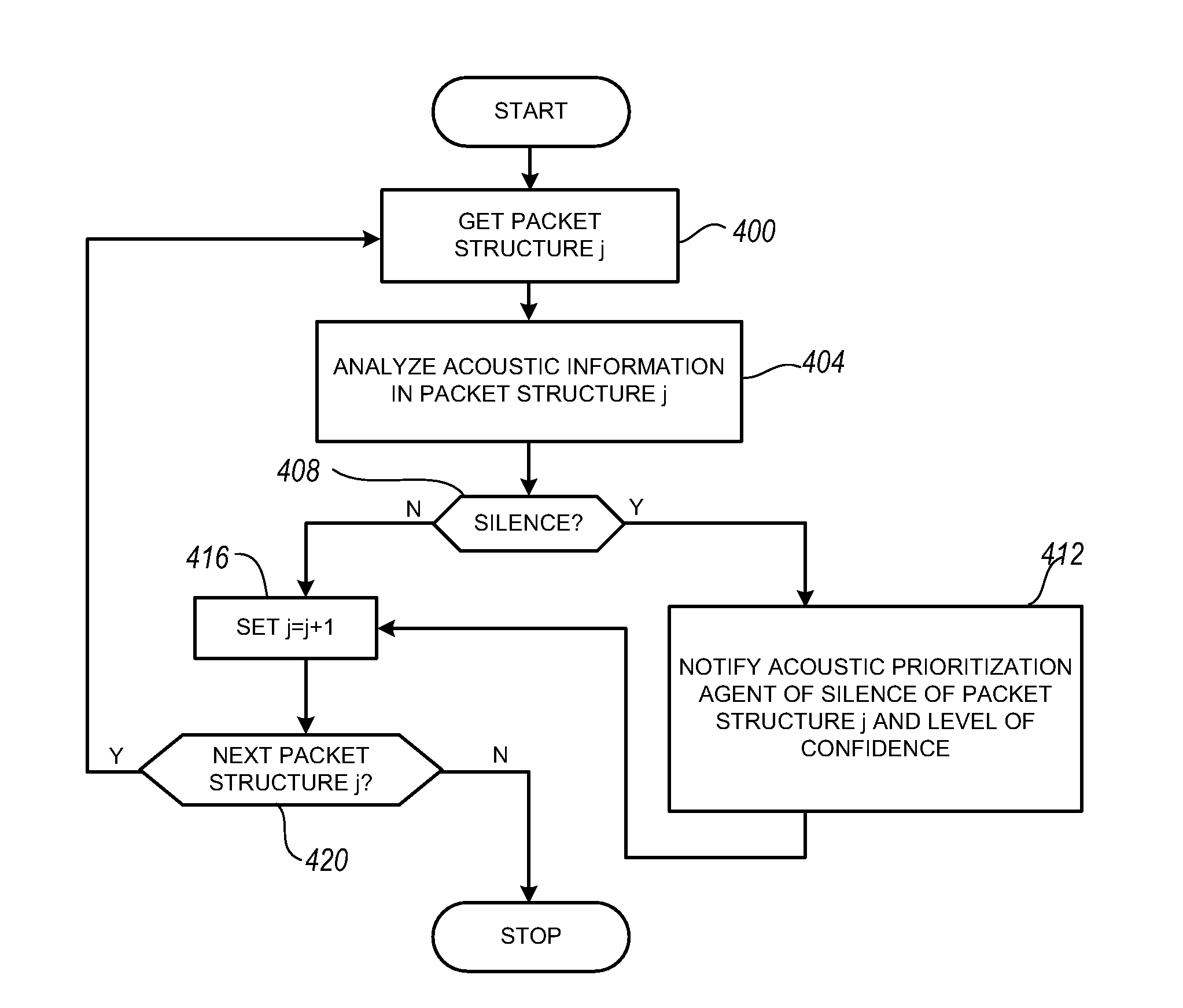
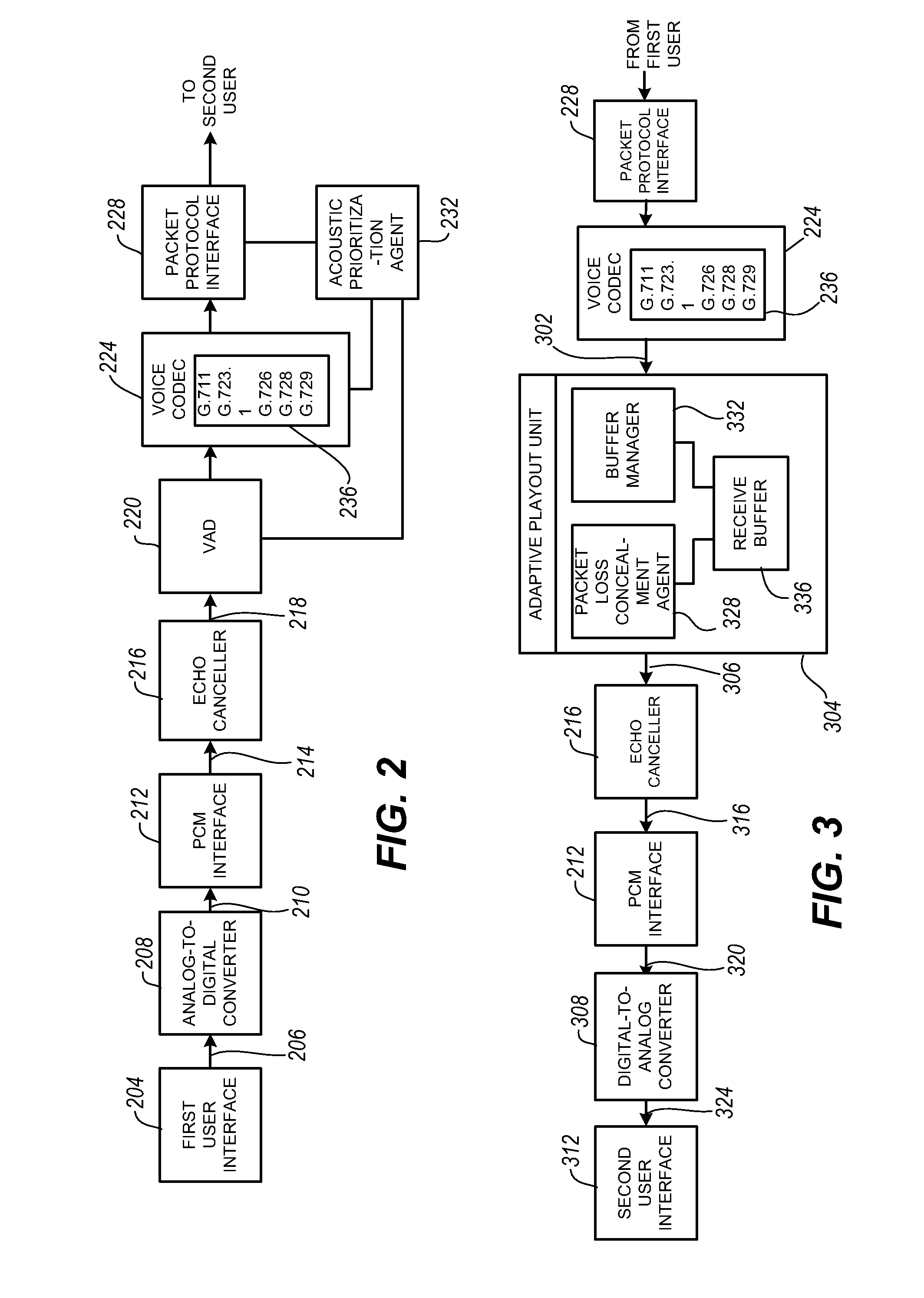
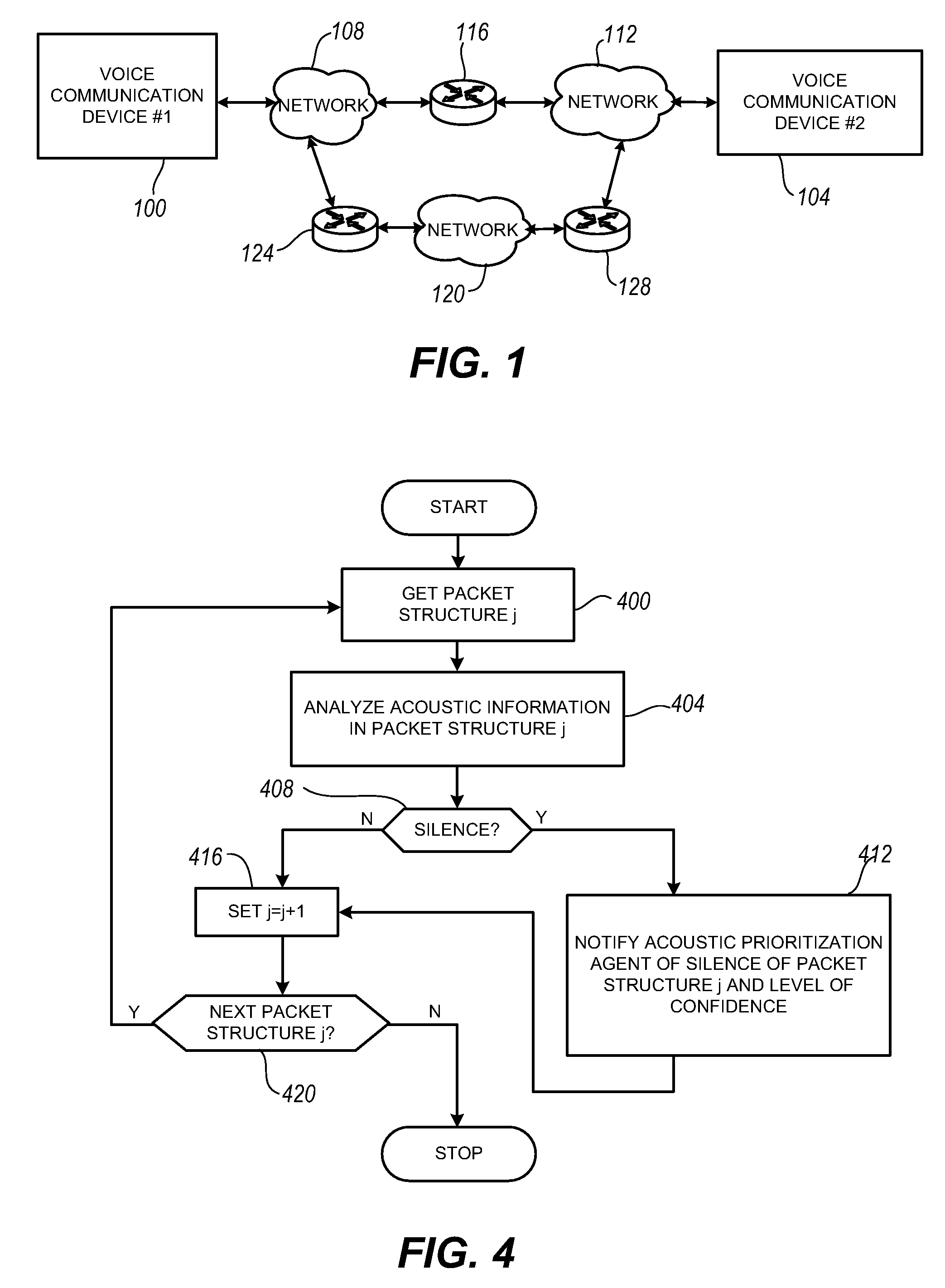
The present invention is directed to voice communication devices in which an audio stream is divided into a sequence of individual packets, each of which is routed via pathways that can vary depending on the availability of network resources. All embodiments of the invention rely on an acoustic prioritization agent that assigns a priority value to the packets. The priority value is based on factors such as whether the packet contains voice activity and the degree of acoustic similarity between this packet and adjacent packets in the sequence. A confidence level, associated with the priority value, may also be assigned. In one embodiment, network congestion is reduced by deliberately failing to transmit packets that are judged to be acoustically similar to adjacent packets; the expectation is that, under these circumstances, traditional packet loss concealment algorithms in the receiving device will construct an acceptably accurate replica of the missing packet. In another embodiment, the receiving device can reduce the number of packets stored in its jitter buffer, and therefore the latency of the speech signal, by selectively deleting one or more packets within sustained silences or non-varying speech events. In both embodiments, the ability of the system to drop appropriate packets may be enhanced by taking into account the confidence levels associated with the priority assessments.
Owner:AVAYA INC
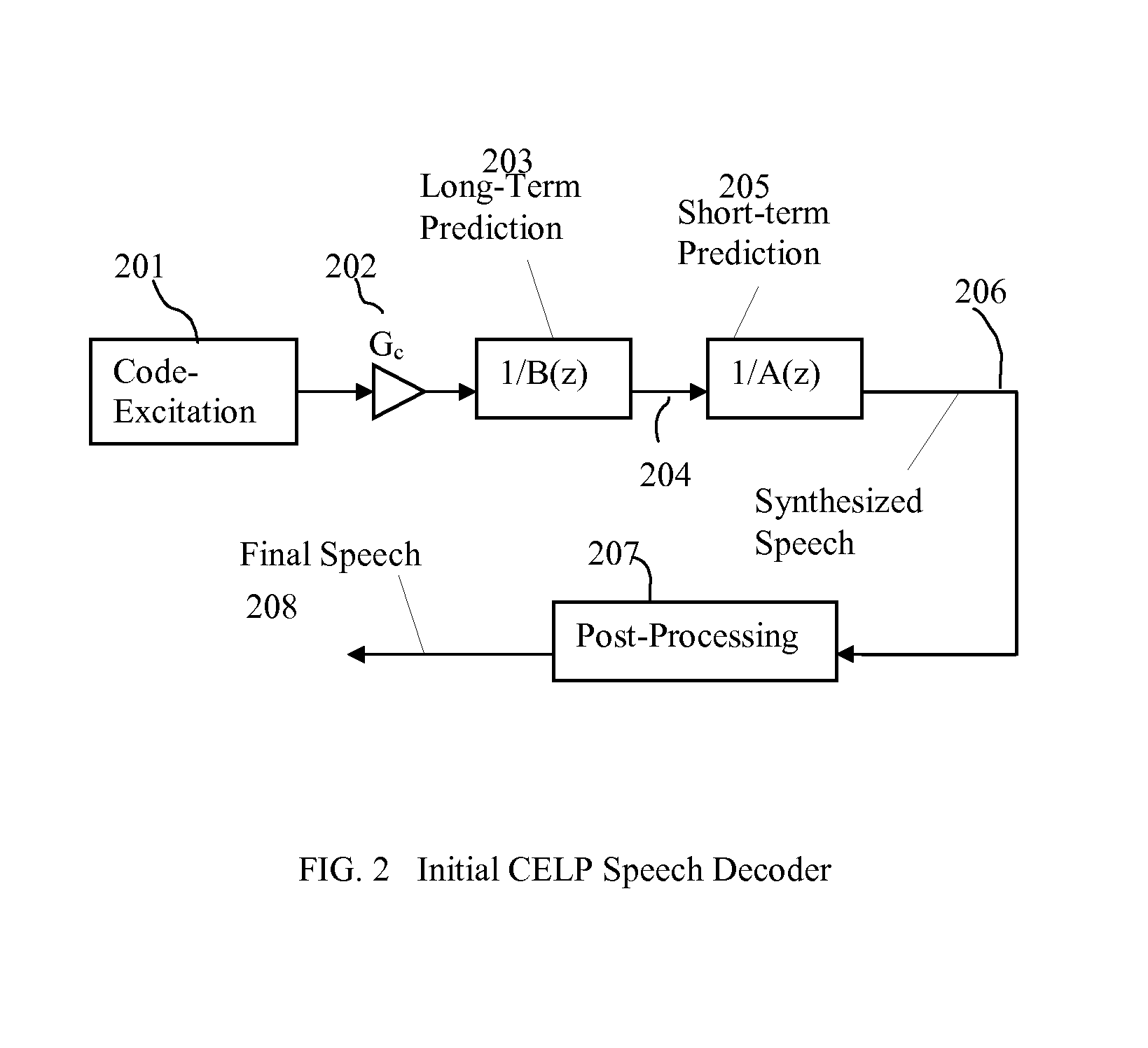
Speech Coding System to Improve Packet Loss Concealment
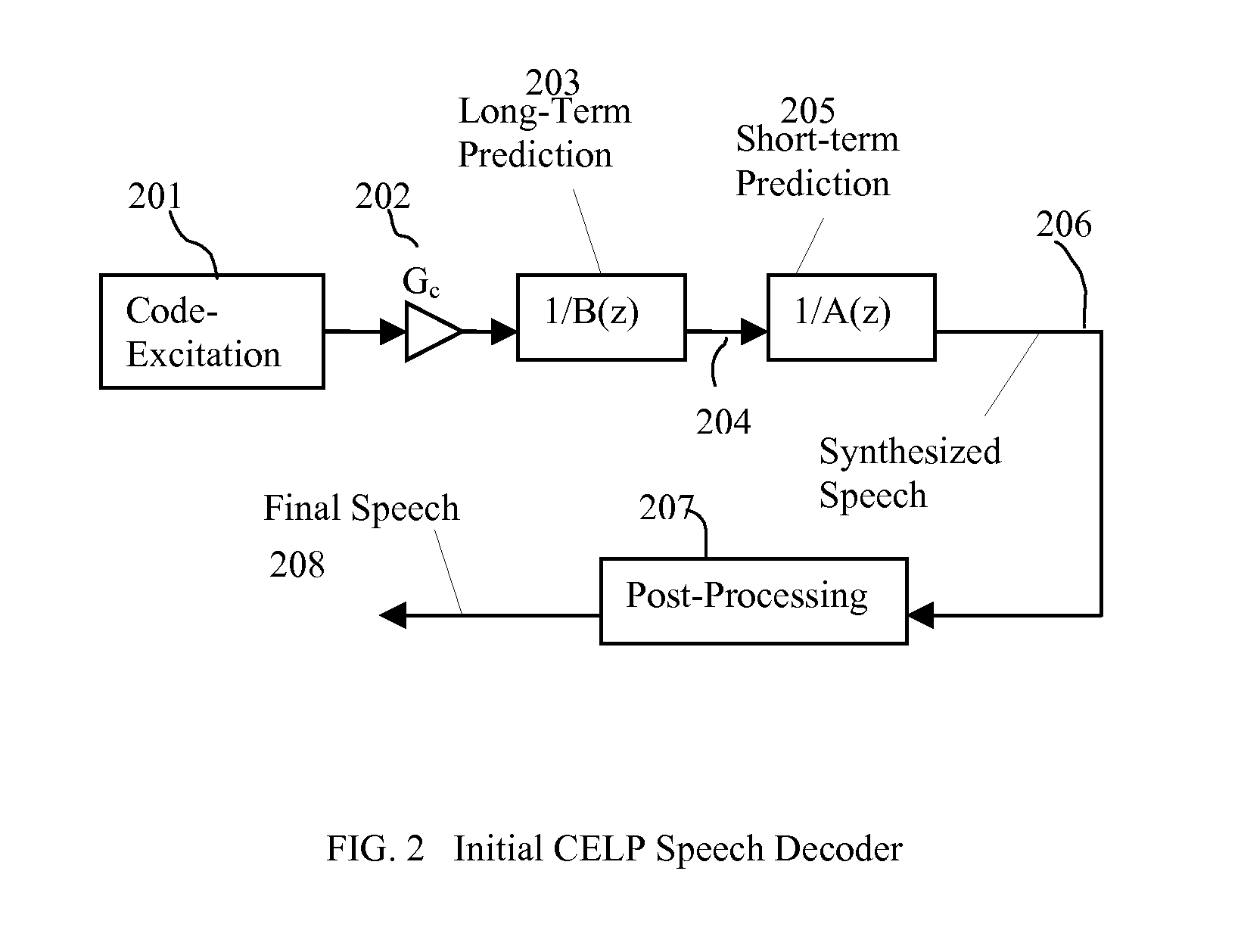
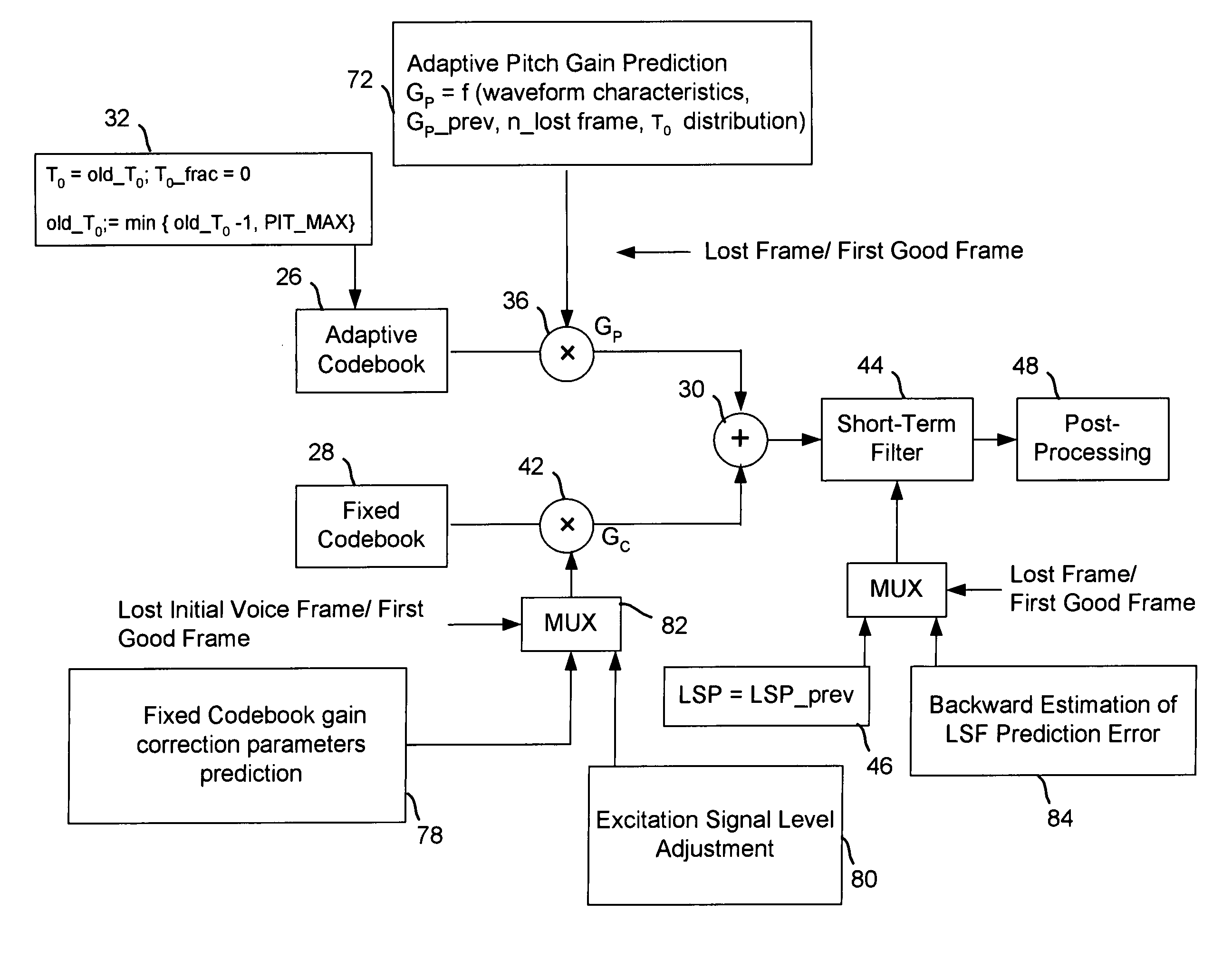
A method of significantly reducing error propagation due to voice packet loss, while still greatly profiting from long-term pitch prediction, is achieved by adaptively limiting the maximum value of the pitch gain for the first pitch cycle within one frame. A speech coding system for encoding a speech signal, wherein said a plurality of speech frames are classified into said a plurality of classes depending on if the first pitch cycle is included in one subframe or several subframes. The pitch gain is set to a value significantly smaller than 1 for the subframes covering first pitch cycle; wherein the pitch gain reduction is compensated by increasing the coded excitation codebook size or adding one more stage of excitation for the subframes covering the first pitch cycle.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and device for compressed-domain packet loss concealment
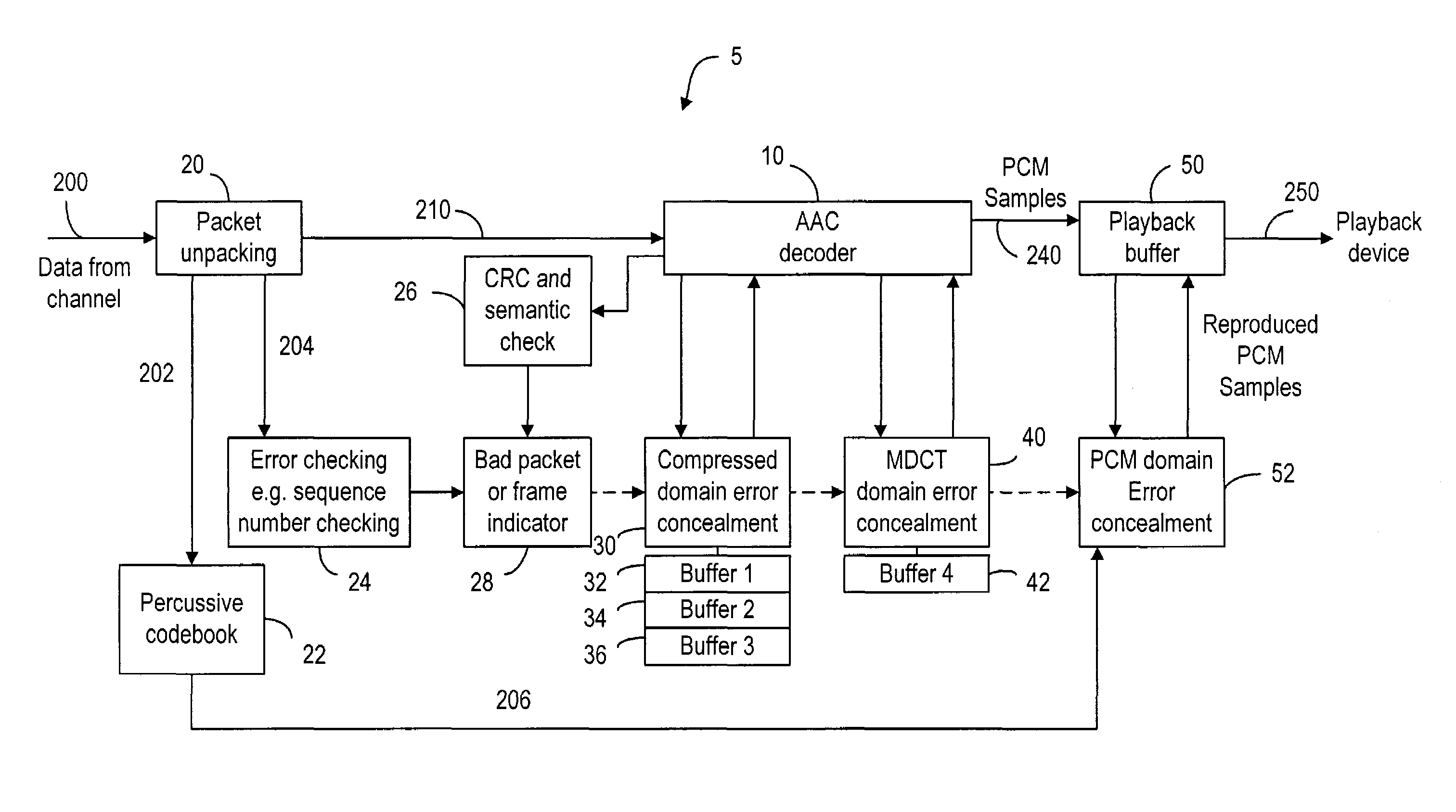
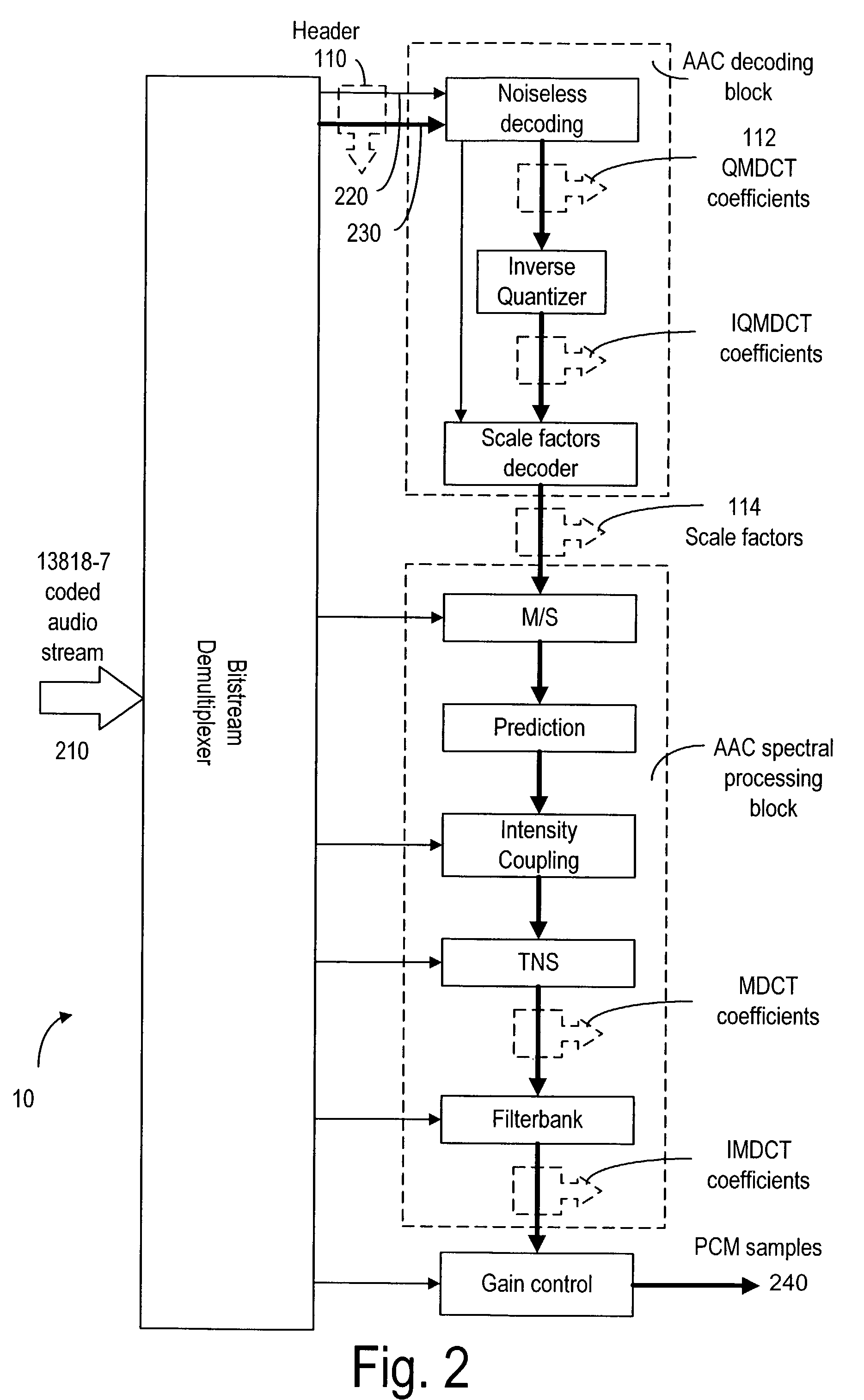
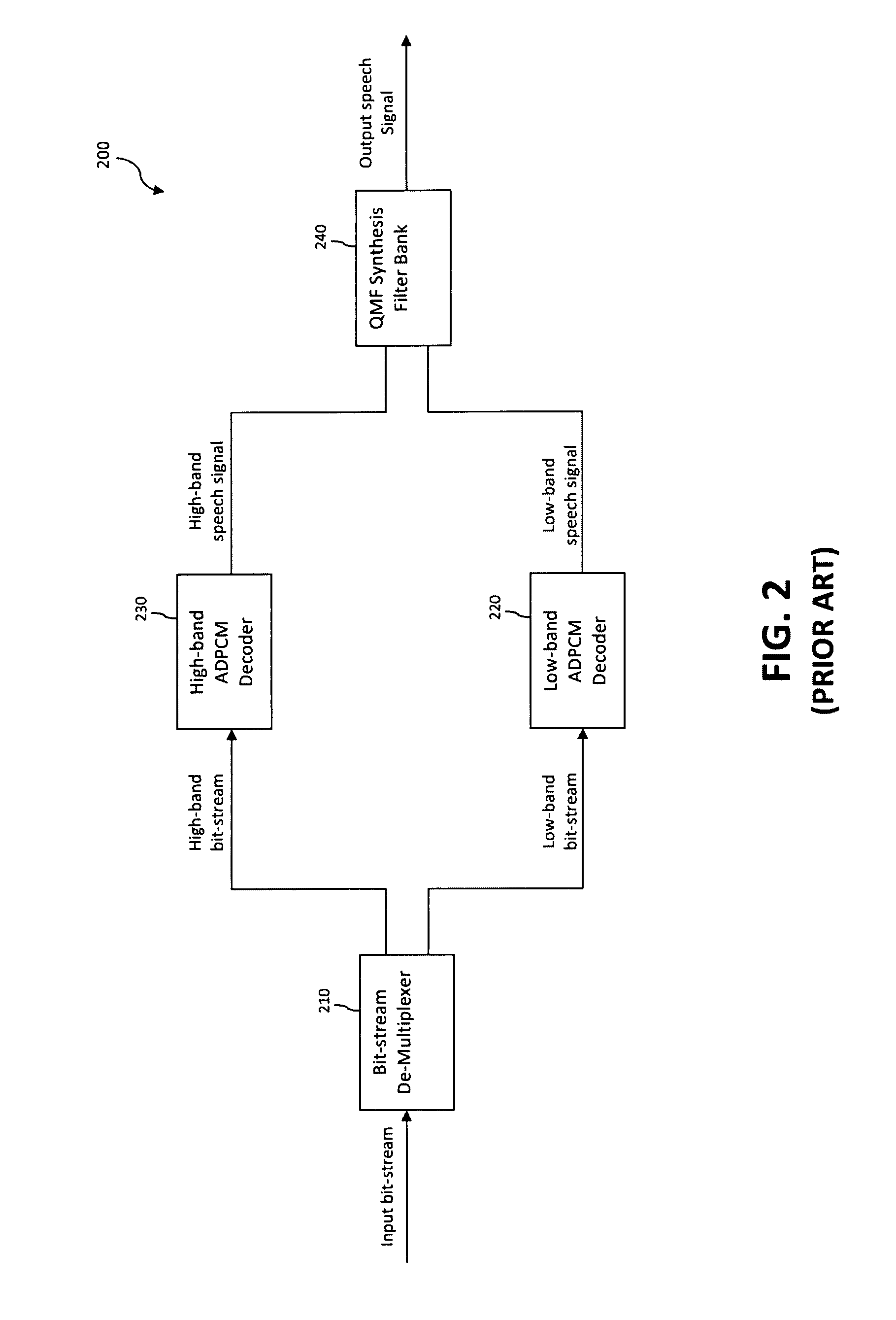
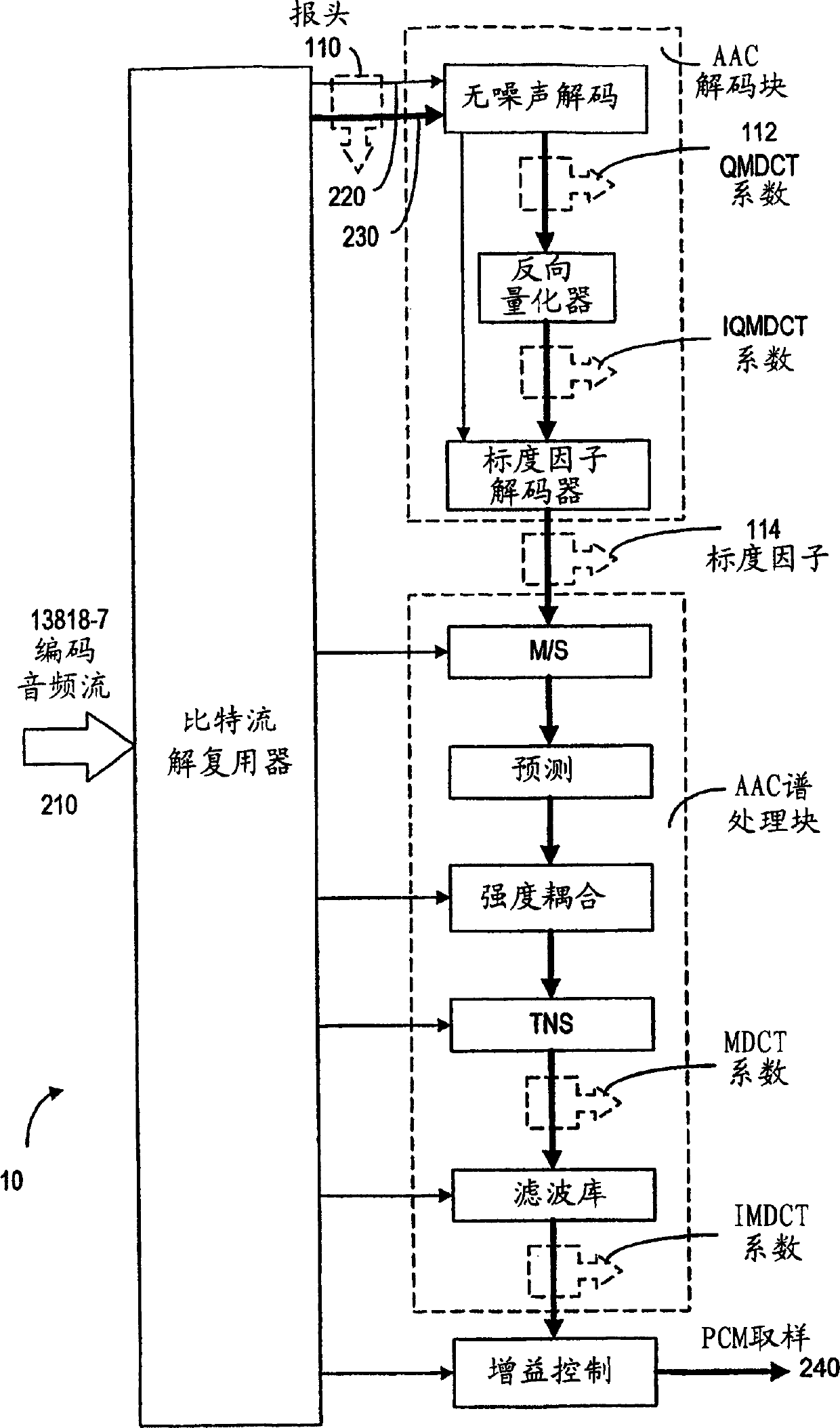
An error concealment method and device for recovering lost data in the AAC bitstream in the compressed domain. The bitstream are partitioned into frames each having a plurality of data parts including the header / global gain, scale factors and QMDCT coefficients. The data parts are stored in a plurality of buffers, so that if one or more data parts of a current frame is corrupted or lost, the corresponding data part in the neighboring frames is used to conceal the errors in the current frame.
Owner:RPX CORP
Packet loss concealment for a conjugate structure algebraic code excited linear prediction decoder
InactiveUS20070282601A1Speech analysisAlgebraic code-excited linear predictionClassification methods
A method to improve packet loss concealment for generation of a synthetic speech signal in a algebraic code excited linear prediction decoder for a voice over packet network. One method improves features for coding gains in the decoder and for post-filtering of the signals. An alternative method uses a classification method for the signal based on the bitstream in the decoder.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
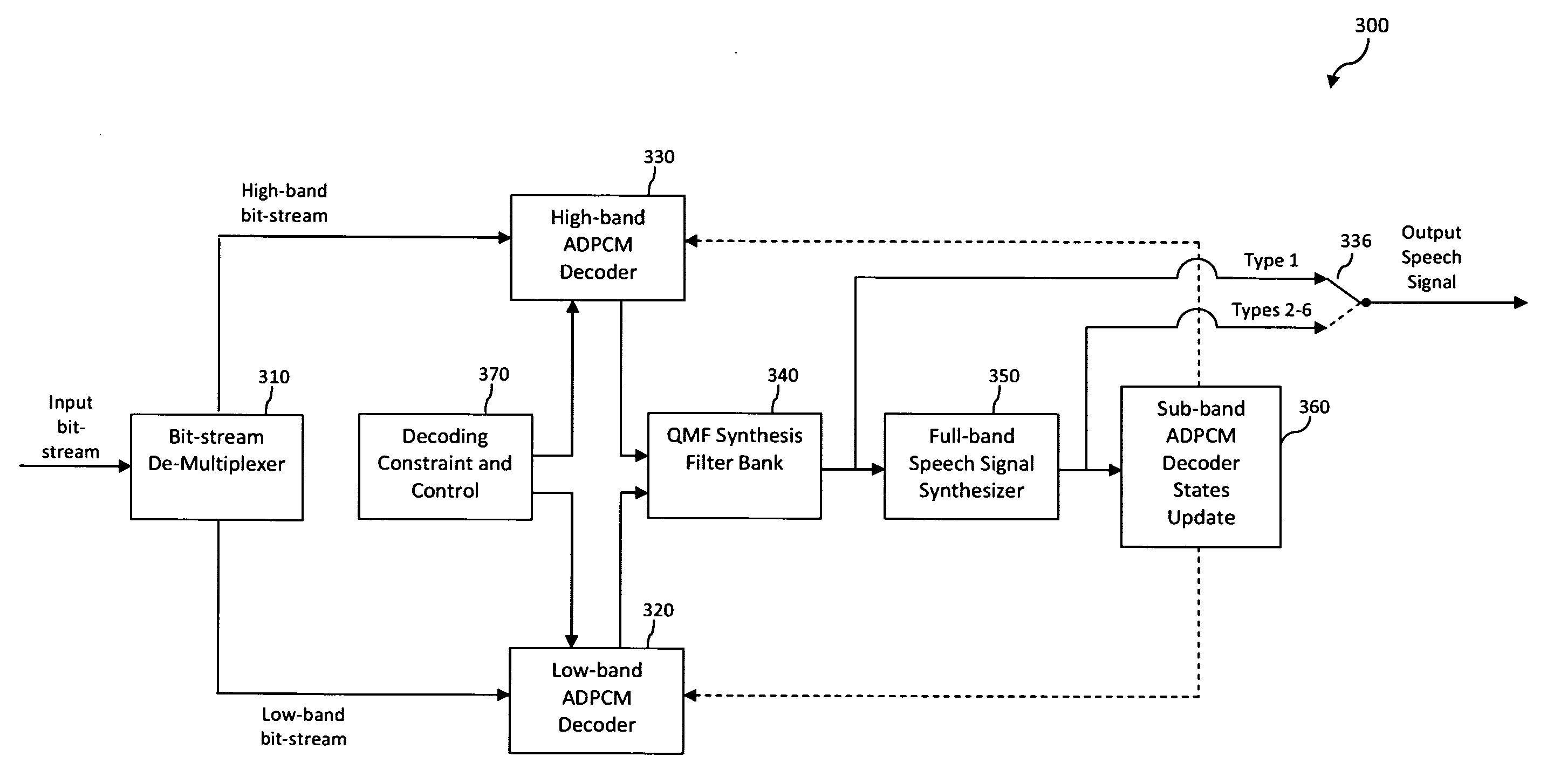
Updating of Decoder States After Packet Loss Concealment
A technique is described herein for updating a state of a decoder in a predictive coding system after synthesizing an audio output signal corresponding to a lost frame in a series of frames representing an encoded audio signal. In accordance with the technique, an audio signal associated with the synthesized output audio signal is re-encoded in an encoder to generate an encoder state, wherein the encoder is simplified with respect to an encoder used to generate the encoded audio signal. The state of the decoder is then updated based on the generated encoder state.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
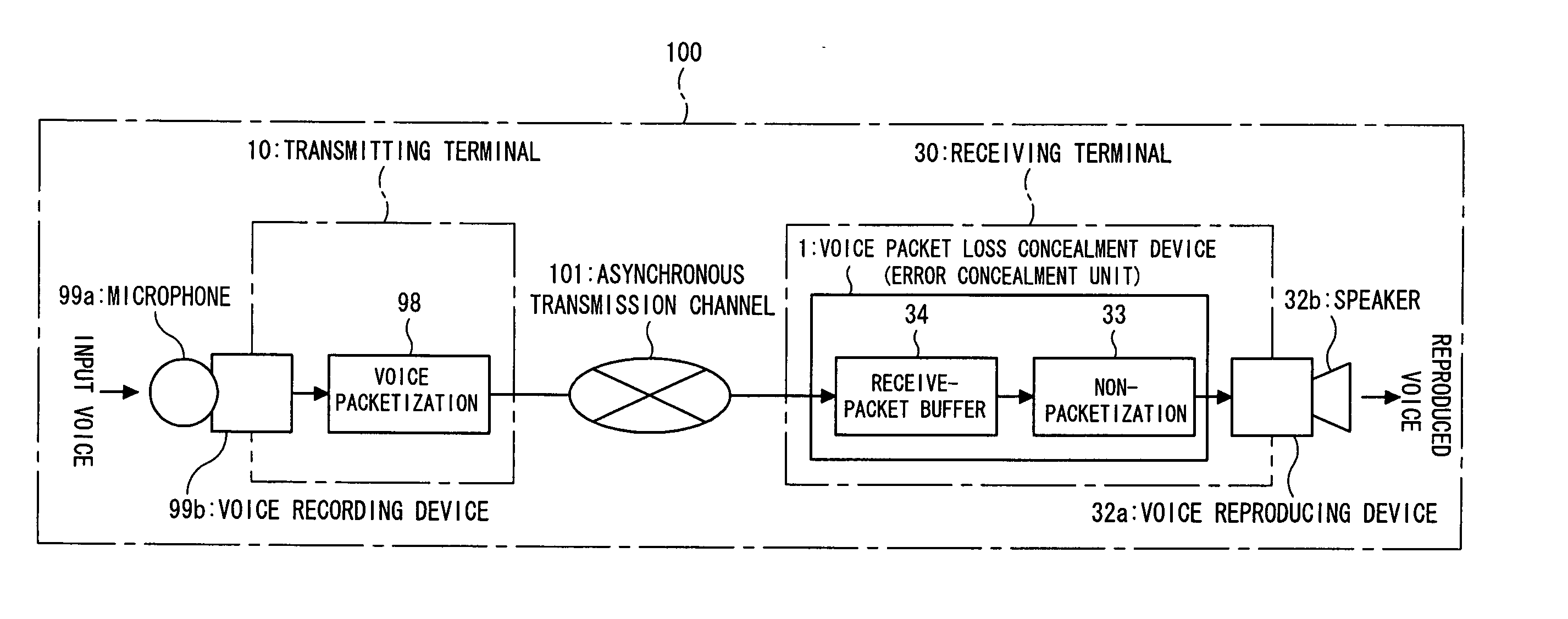
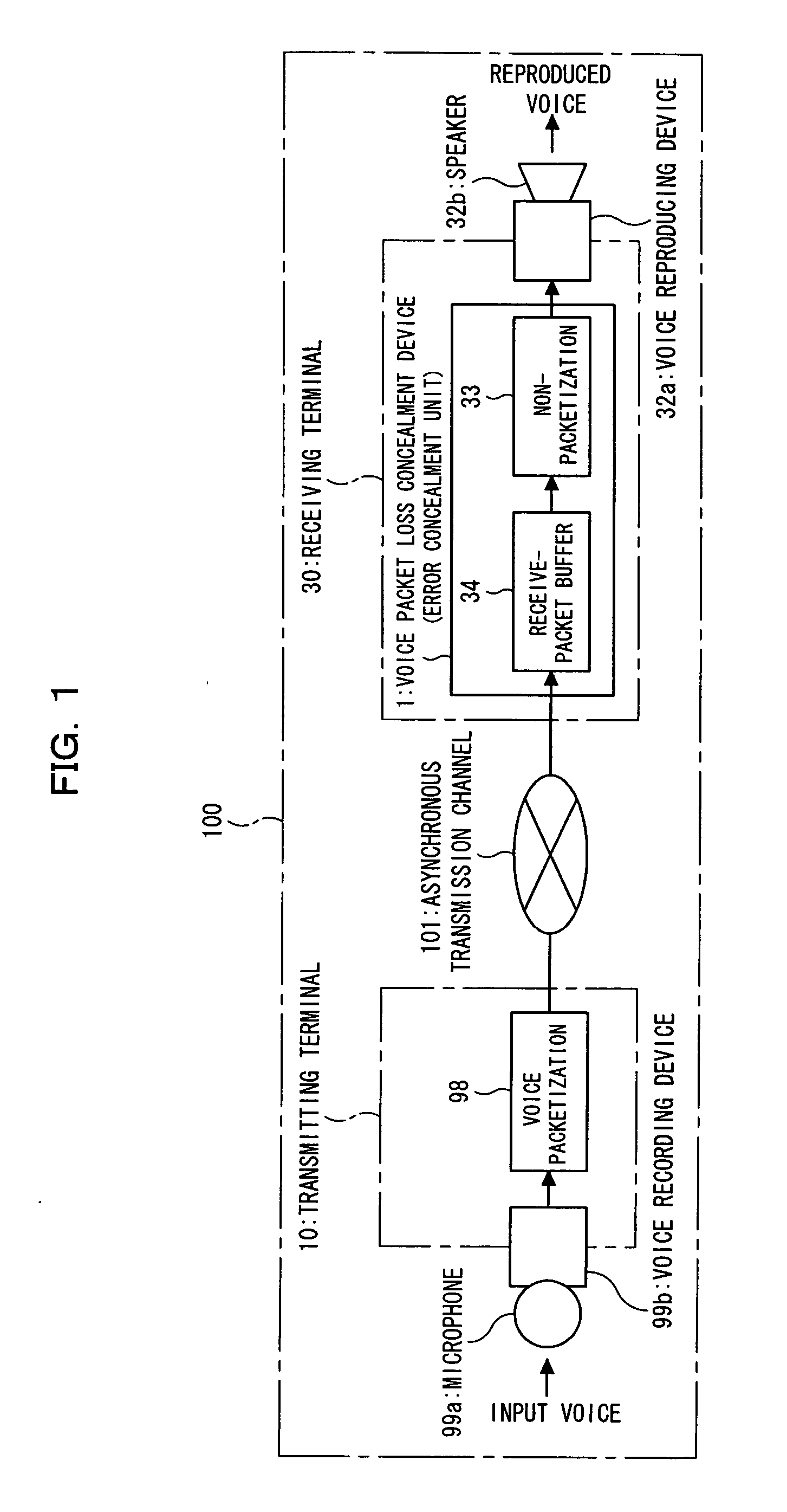
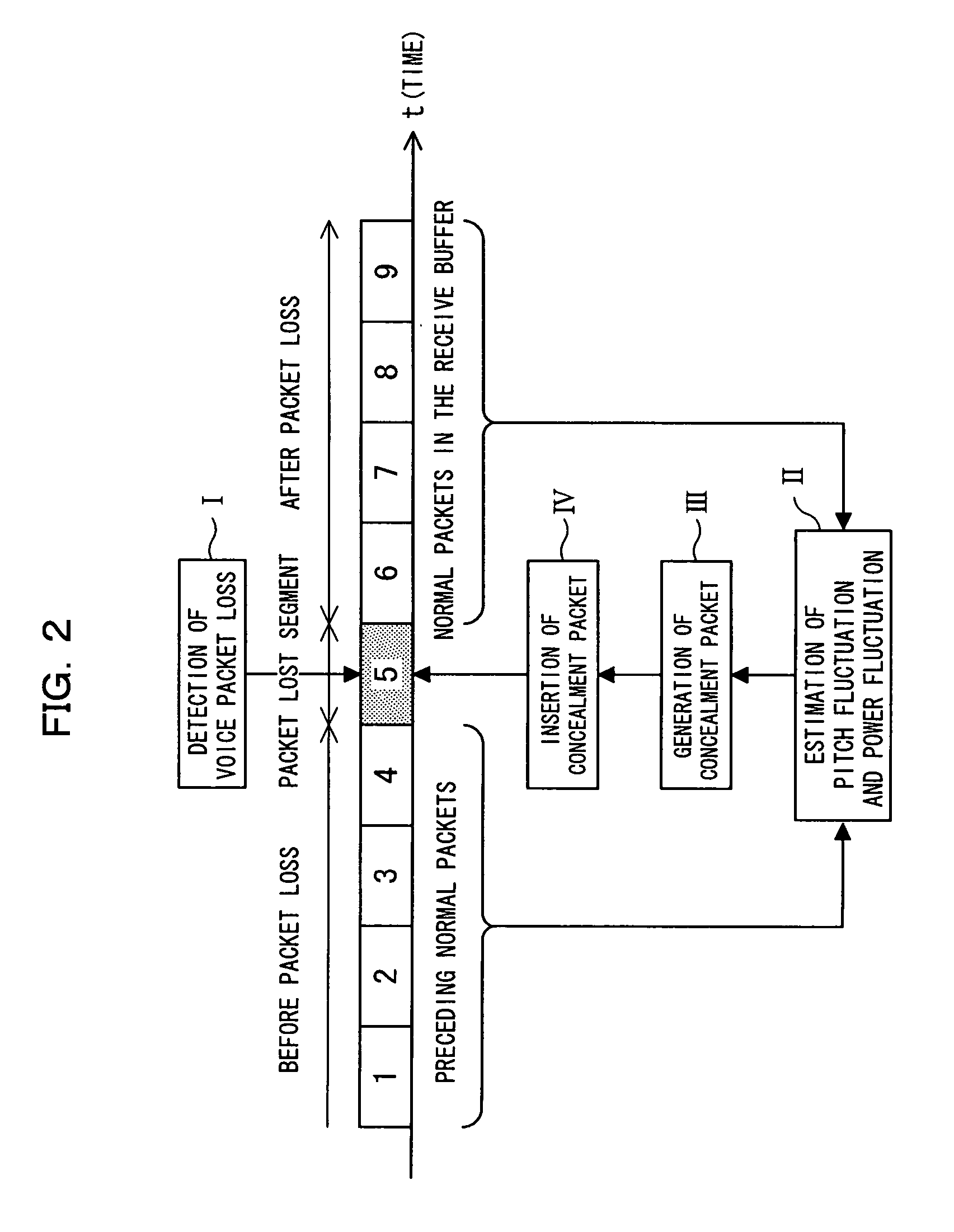
Voice packet loss concealment device, voice packet loss concealment method, receiving terminal, and voice communication system
InactiveUS20050166124A1Suppression of abnormal noiseDeterioration of continuitySpeech analysisCode conversionPacket communicationGroup communication systems
In a voice packet communication system, a voice packet loss concealment device compensates for the deterioration of voice quality due to voice packet loss. In the device, a detecting section detects a loss of a voice packet and outputting information; an estimating section estimates the voice characteristics of the lost segment using a pre-loss voice packet received before the lost segment or a post-loss voice packet received after the lost segment; a pitch signal generating section generates a pitch signal having the voice characteristics; and a lost packet generating section outputs the pitch signal generated by the pitch signal generating section, with the voice characteristics estimated by the estimating section, which allows abnormal noise and feeling of mute, subjective deterioration of naturalness and continuity to be improved, and the voice packet loss concealment to be further improved.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Artifact Reduction in Packet Loss Concealment
ActiveUS20120101814A1Improving packet loss concealmentReduce artifactsSpeech analysisUltrasound attenuationPacket loss concealment
Various techniques are disclosed for improving packet loss concealment to reduce artifacts by using audio character measures of the audio signal. These techniques include attenuation to a noise fill instead of attenuation to silence, varying how long to wait before attenuating the extrapolation, varying the rate of attenuation of the extrapolation, attenuating periodic extrapolation at a different rate than non-periodic extrapolation, and performing period extrapolation on successively longer fill data based on the audio character measures, adjusting weighting between periodic and non-periodic extrapolation based on the audio character measures, and adjusting weighting between periodic extrapolation and non-periodic extrapolation non-linearly.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
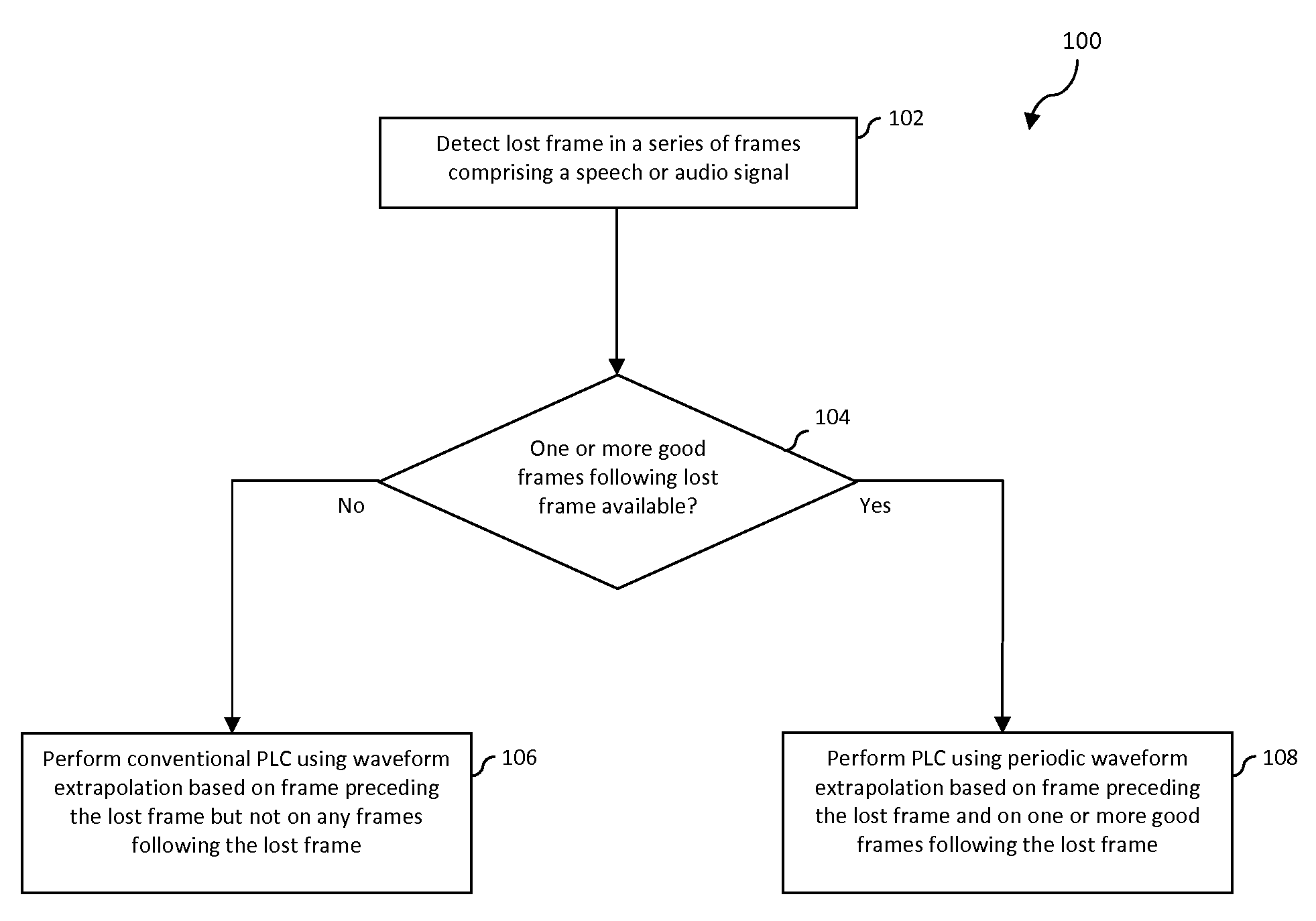
Packet Loss Concealment Based On Forced Waveform Alignment After Packet Loss
ActiveUS20080046235A1Reduce and eliminate destructive interferenceReduce and eliminate interferenceSpeech analysisPacket loss concealmentSpeech sound
A packet loss concealment method and system is described that attempts to reduce or eliminate destructive interference that can occur when an extrapolated waveform representing a lost segment of a speech or audio signal is merged with a good segment after a packet loss. This is achieved by guiding a waveform extrapolation that is performed to replace the bad segment using a waveform available in the first good segment or segments after the packet loss. In another aspect of the invention, a selection is made between a packet loss concealment method that performs the aforementioned guided waveform extrapolation and one that does not. The selection may be made responsive to determining whether the first good segment or segments after the packet loss are available and also to whether a segment preceding the lost segment and the first good segment following the lost segment are deemed voiced.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
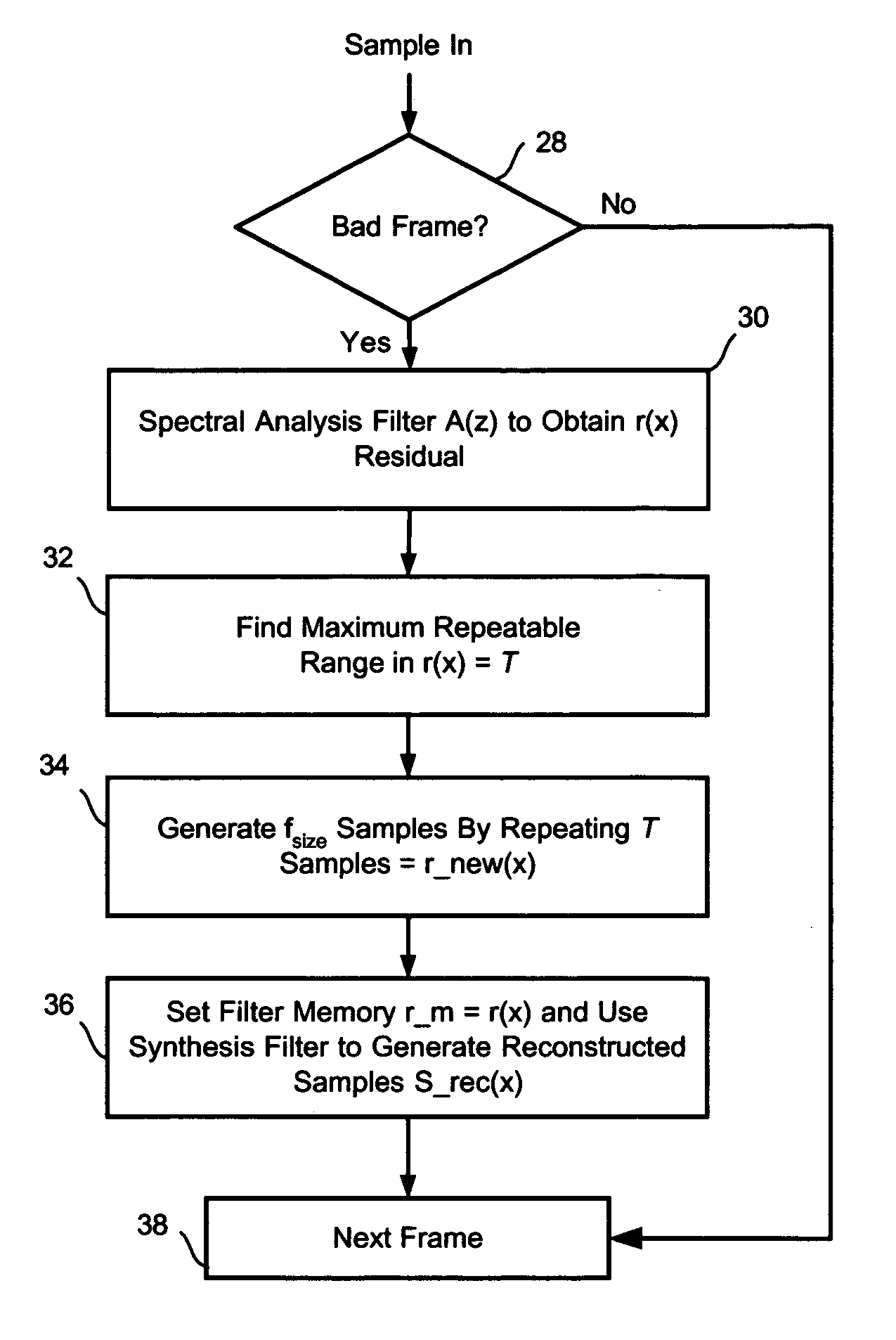
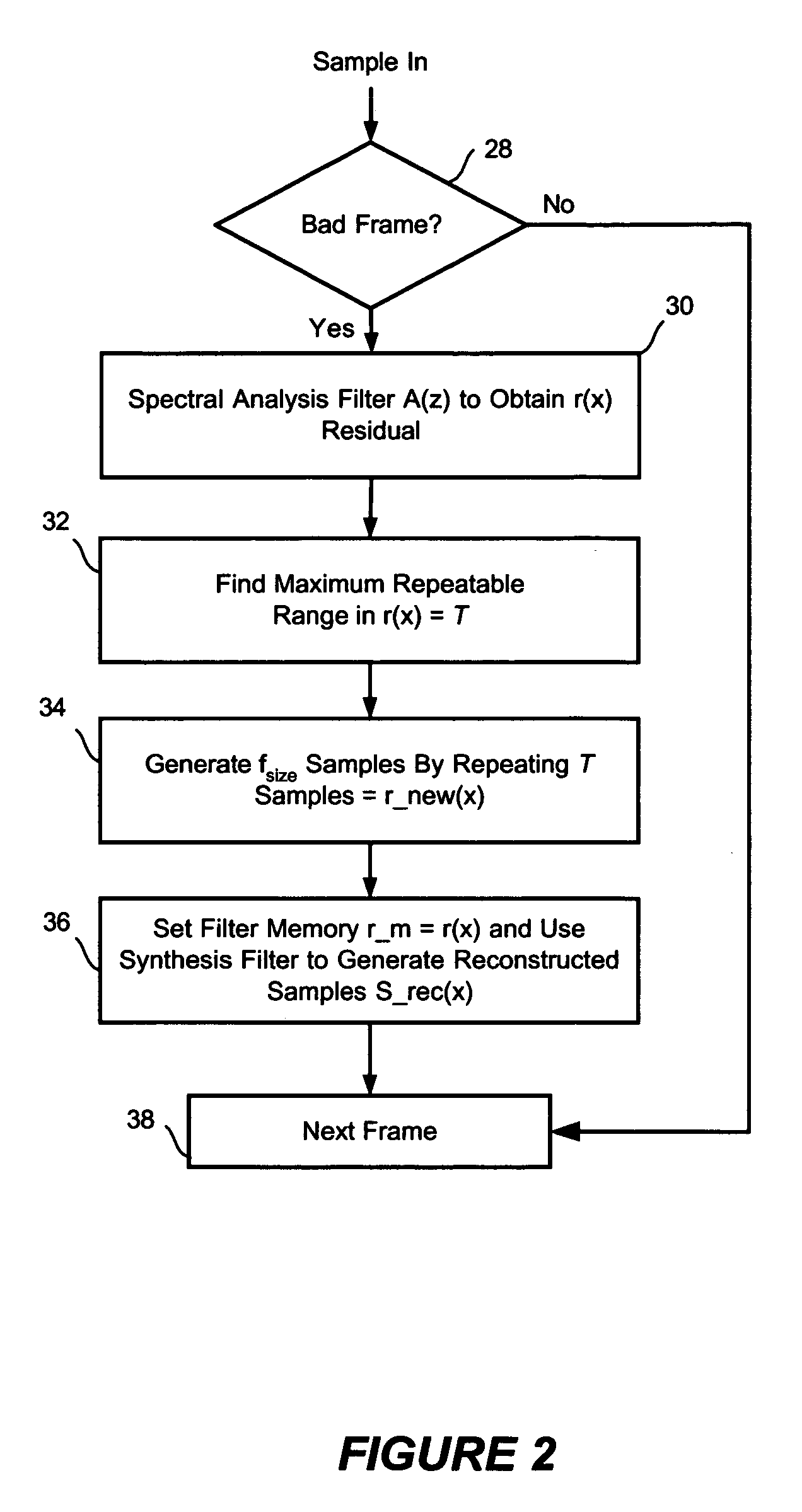
Packet loss concealment for voice over packet networks
ActiveUS20060171373A1Few processing resourceLess resourcesSpeech analysisTime-division multiplexRepeating waveformsPulse-code modulation
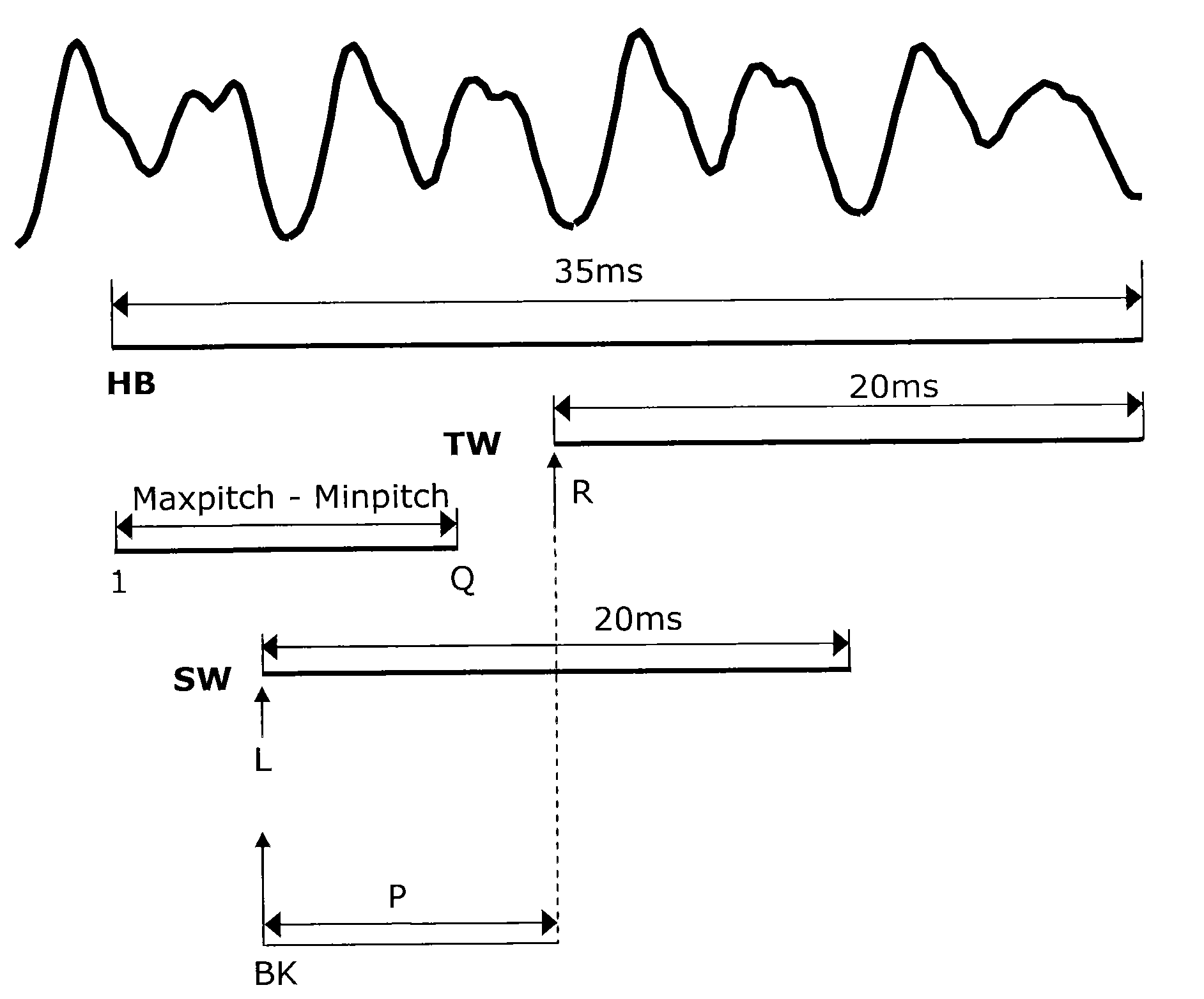
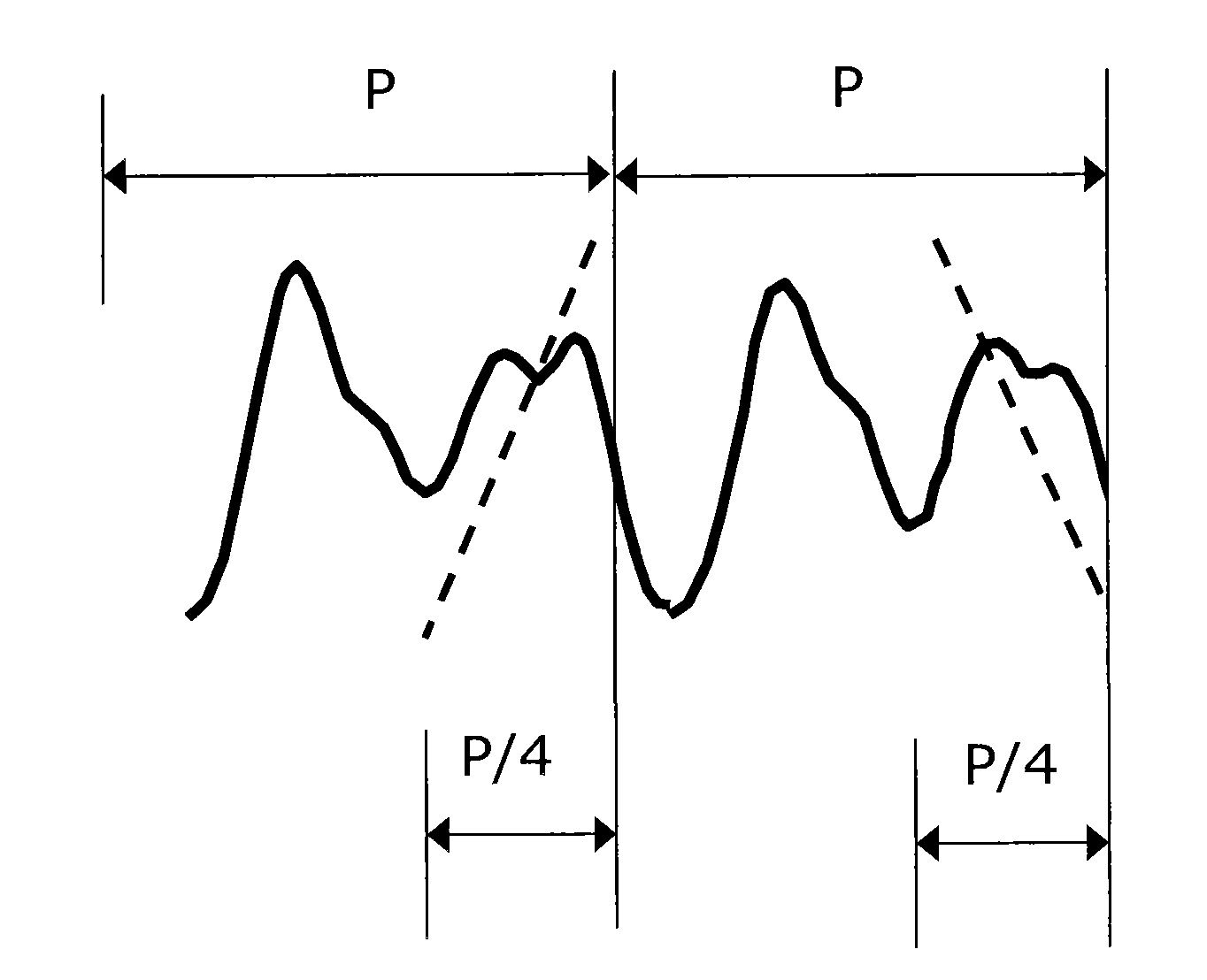
A method to reduce memory requirements for a packet loss concealment algorithm in the event of packet loss in a receiver of pulse code modulated voice signals. Packet losses are concealed by using the spectral analysis filter memory to smooth a signal gap and by using a technique for determining a maximum repeatable waveform range instead of using the pitch period to reproduce lost packets. The invention uses fewer processing resources and results in improved performance compared to a packet loss concealment algorithm under G.711 Appendix I standards.
Owner:TELOGY NETWORKS
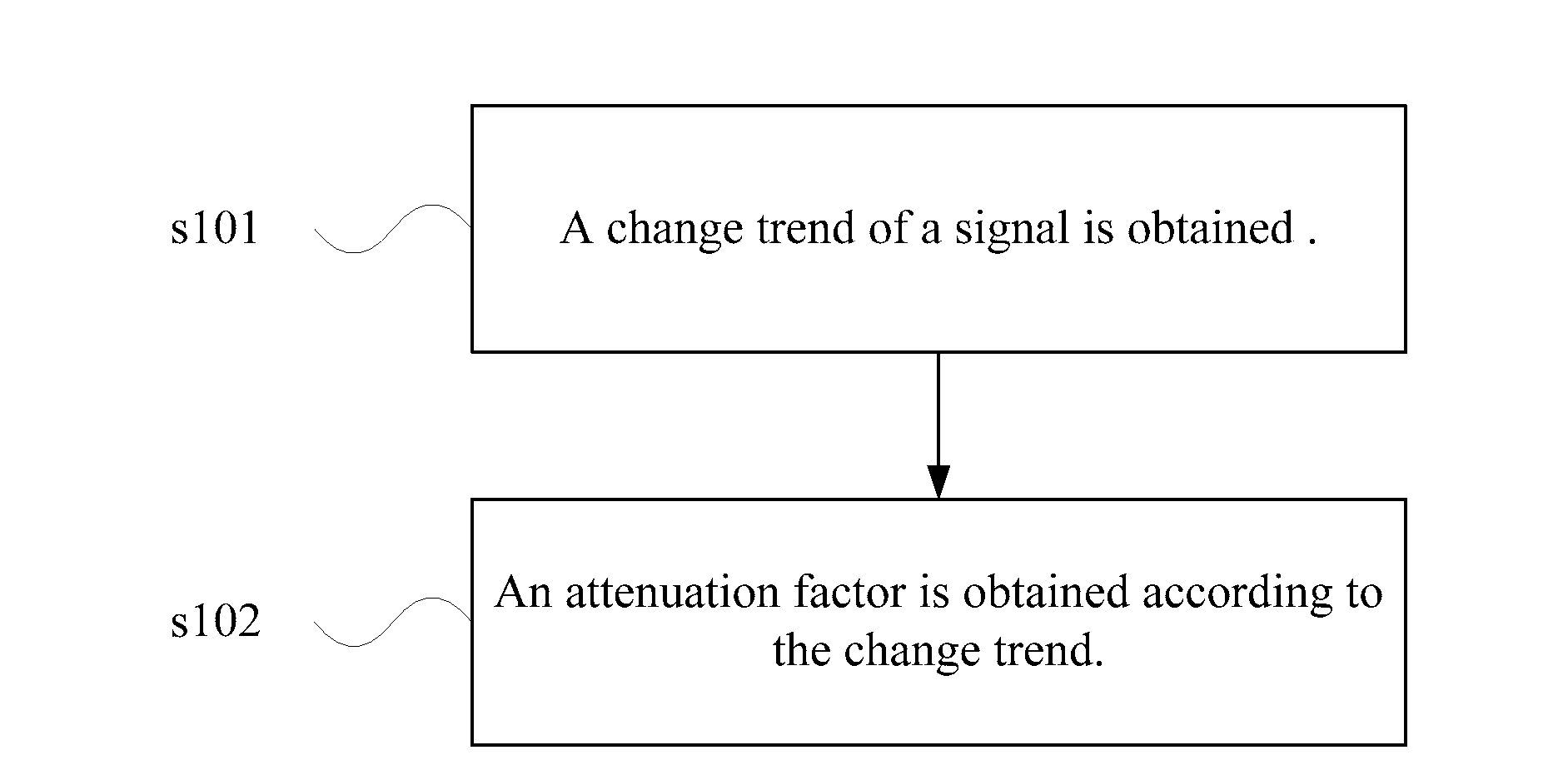
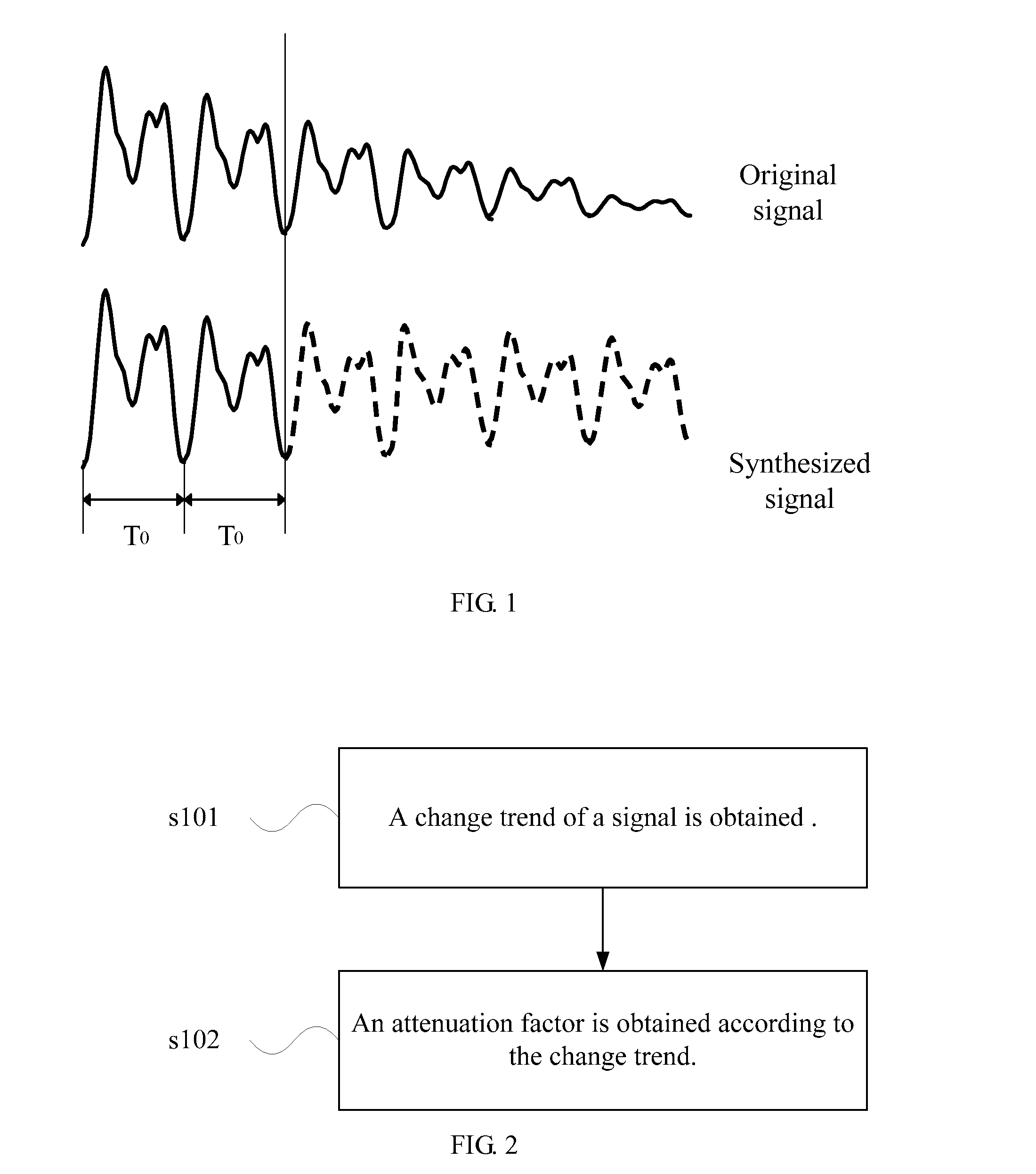
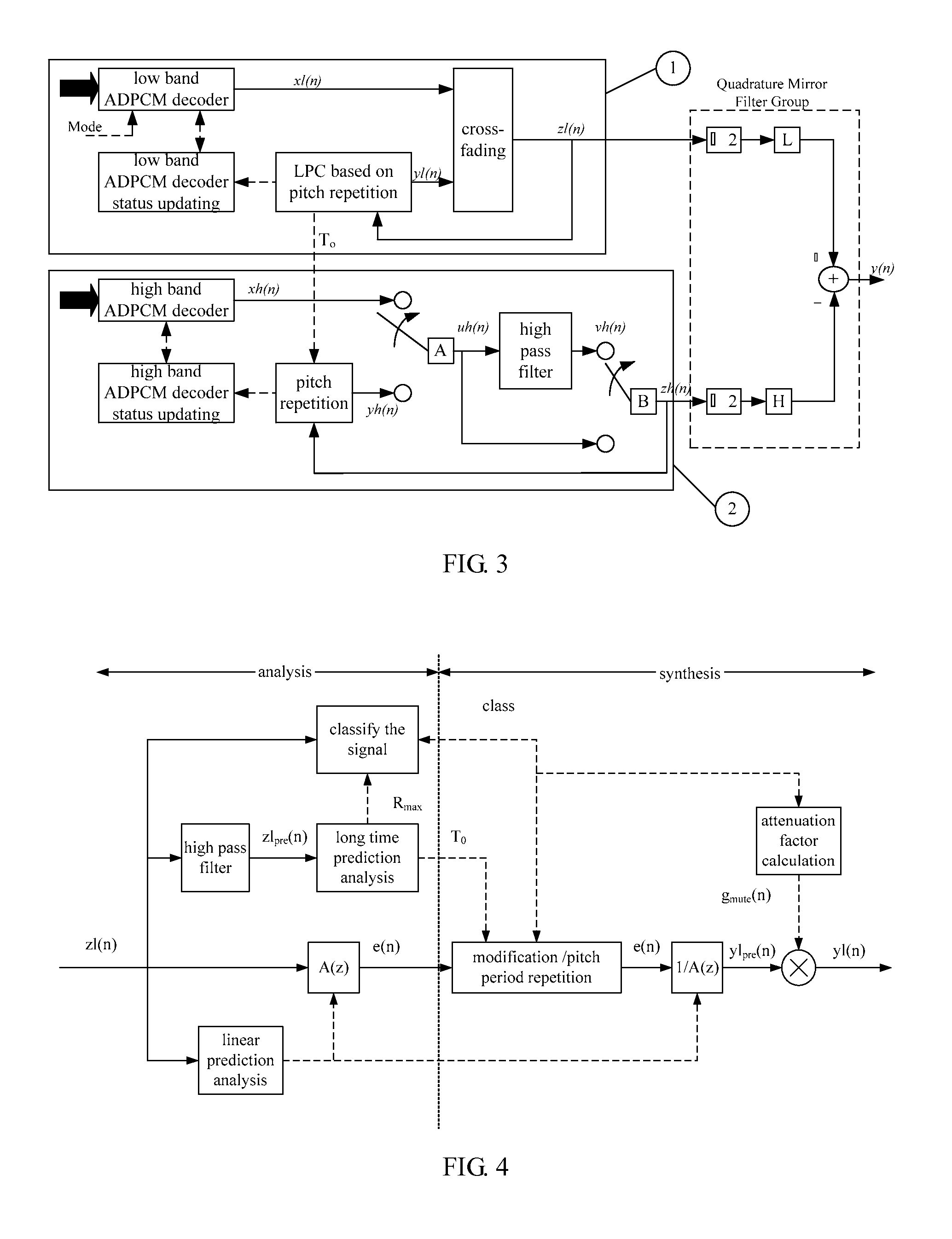
Method and apparatus for obtaining an attenuation factor
ActiveUS20090316598A1Smooth transitionError preventionTransmission systemsAttenuation coefficientUltrasound attenuation
The present invention discloses a method for obtaining an attenuation factor. The method is adapted to process the synthesized signal in packet loss concealment, and includes: obtaining a change trend of a pitch of a signal; obtaining an attenuation factor, according to the change trend of the pitch of the signal. The present invention also discloses an apparatus for obtaining an attenuation factor. A self-adaptive attenuation factor is adjusted dynamically by using the latest change trend of a history signal by using the present invention. The smooth transition from the history data to the data last received is realized so that the attenuation speed is kept consistent between the compensated signal and the original signal as much as possible for adapting to the characteristic of various human voices.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Packet loss concealment for overlapped transform codecs
InactiveUS20060209955A1Error minimizationMinimizes a model-based energy criterionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningPacket loss concealmentUnderdetermined system
Real-time packet-based audio communications over packet-based networks frequently results in the loss of one or more packets during any given communication session. The real-time nature of such communications precludes retransmission of lost packets due to the unacceptable delays that would result. Consequently, packet loss concealment methods are employed to “hide” lost packets from the listener. Unfortunately, conventional loss concealment methods, such as packet repetition or stretch / overlap methods, do not fully exploit information available from partially received samples. Therefore, when a single frame of N coefficients is lost, 2N samples are only partially reconstructed, thereby degrading the reconstructed signal. To address this problem, an optimized packet loss concealment solution is identified for particular lost packets by solving an underdetermined system of linear equations representing partially received samples while minimizing a computed error based on a model of the signal obtained from neighboring blocks or frames received by the decoder.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and device for realizing packet loss concealment
ActiveCN101833954AImprove relevanceImprove continuitySpeech analysisPacket loss concealmentVoice data
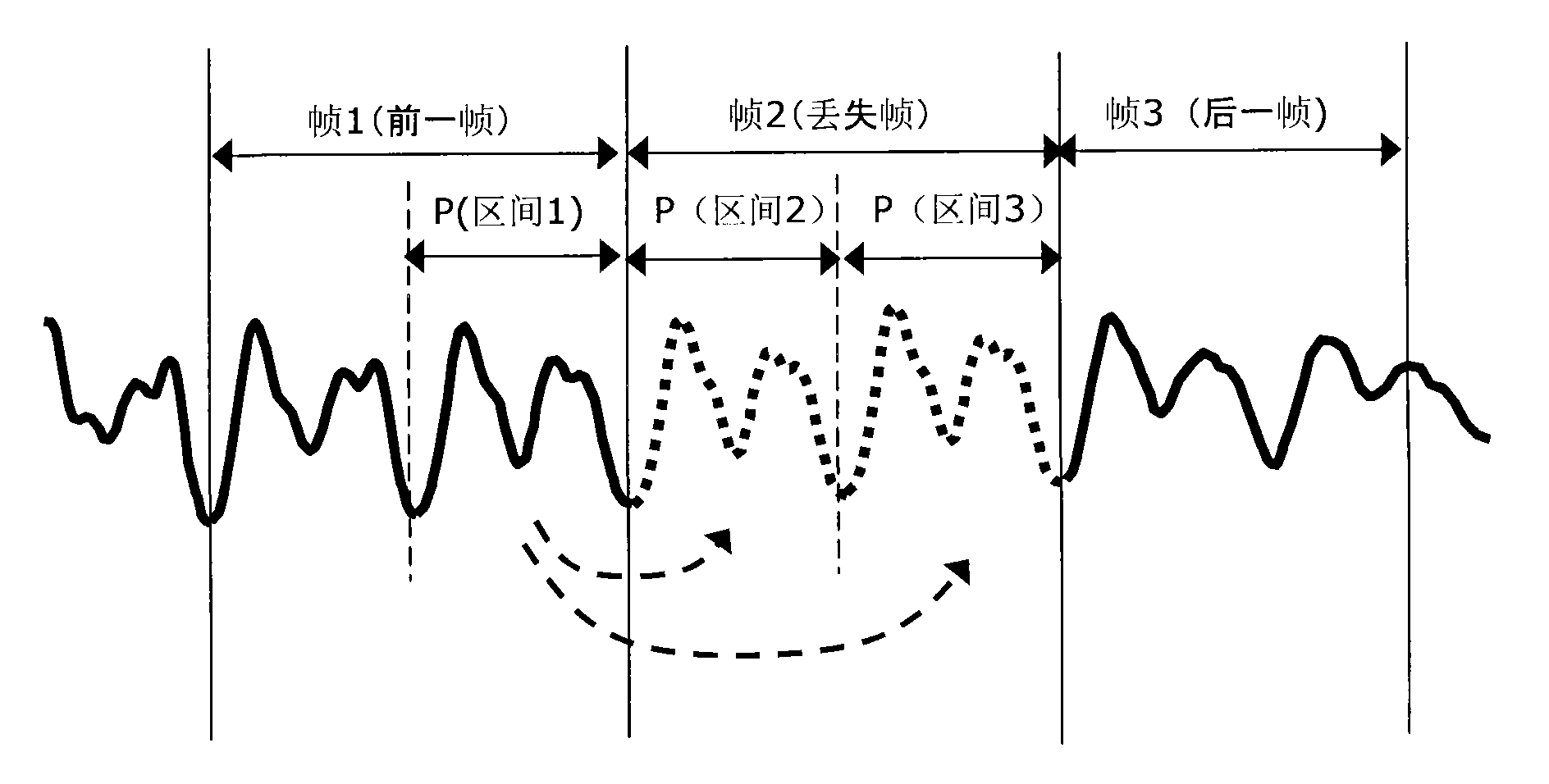
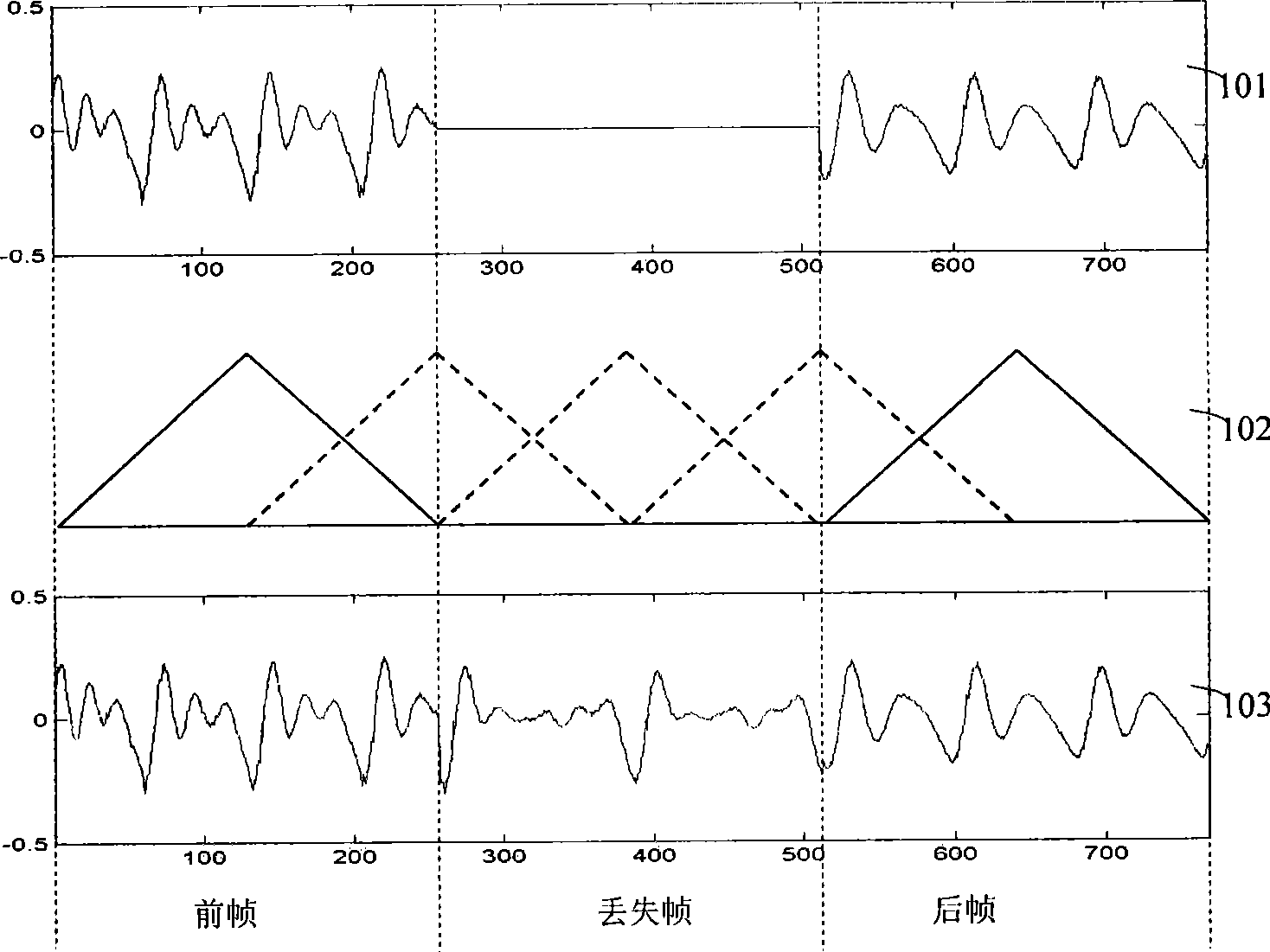
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method and a device for realizing packet loss concealment. Correlation between recovered lost frame data and data after frame loss is enhanced by the technical scheme for recovering lost frames by combining the data before the frame loss with the data after the frame loss so as to improve the continuity of phases between the recovered lost frame data and the data after the frame loss and improve the quality of voice data.
Owner:HUAWEI DEVICE CO LTD
Packet Loss Concealment for Sub-band Predictive Coding Based on Extrapolation of Sub-band Audio Waveforms
A technique is described for concealing the effect of a lost frame in a series of frames representing an encoded audio signal in a sub-band predictive coding system. In accordance with the technique, a first synthesized sub-band audio signal is synthesized, wherein synthesizing the first synthesized sub-band audio signal comprises performing waveform extrapolation based on a stored first sub-band decoded audio signal. A second synthesized sub-band audio signal is also synthesized, wherein synthesizing the second synthesized sub-band audio signal comprises performing waveform extrapolation based on the stored second sub-band decoded audio signal. The first synthesized sub-band audio signal and the second synthesized sub-band audio signal are combined to generate a synthesized full-band output audio signal corresponding to a lost frame.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
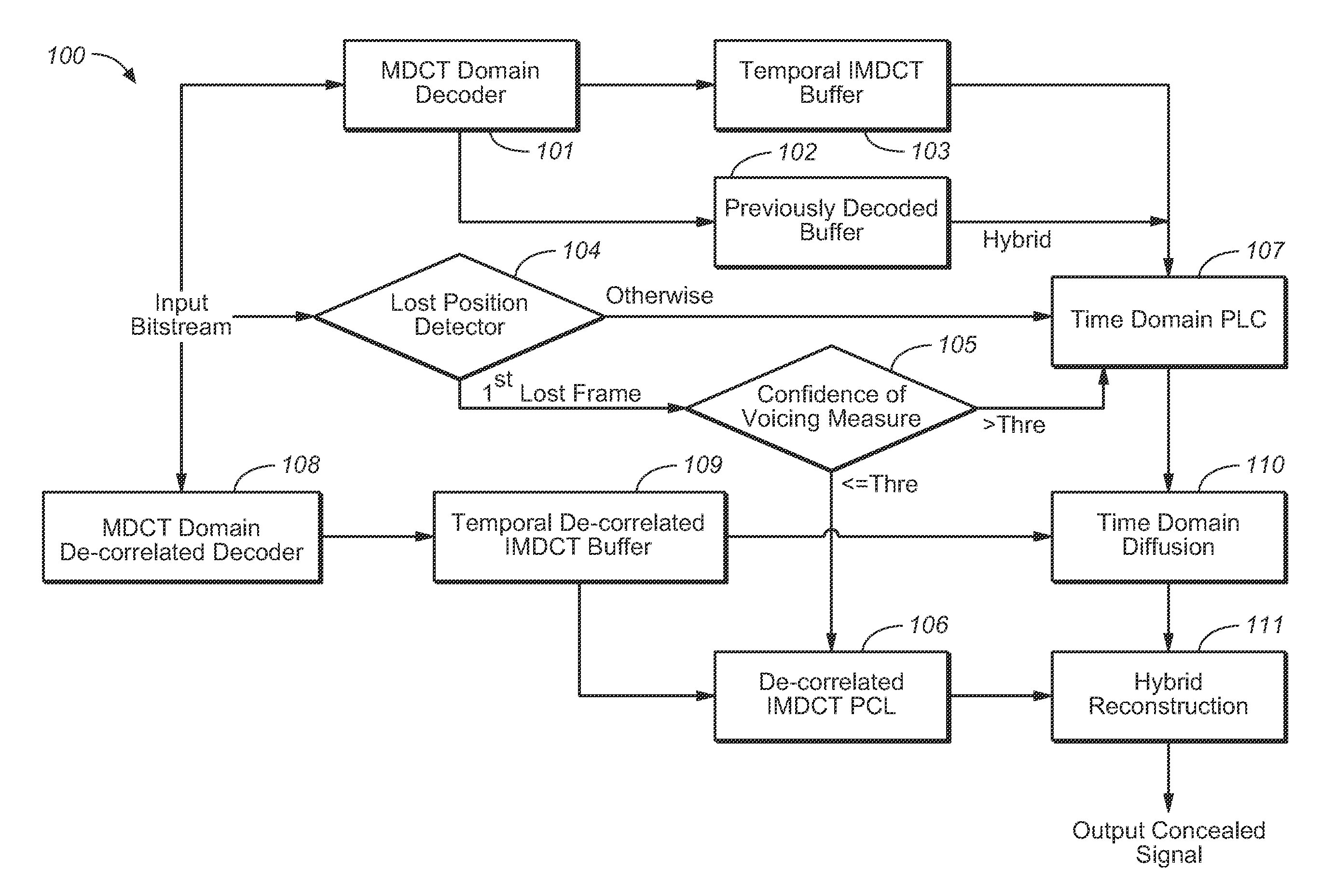
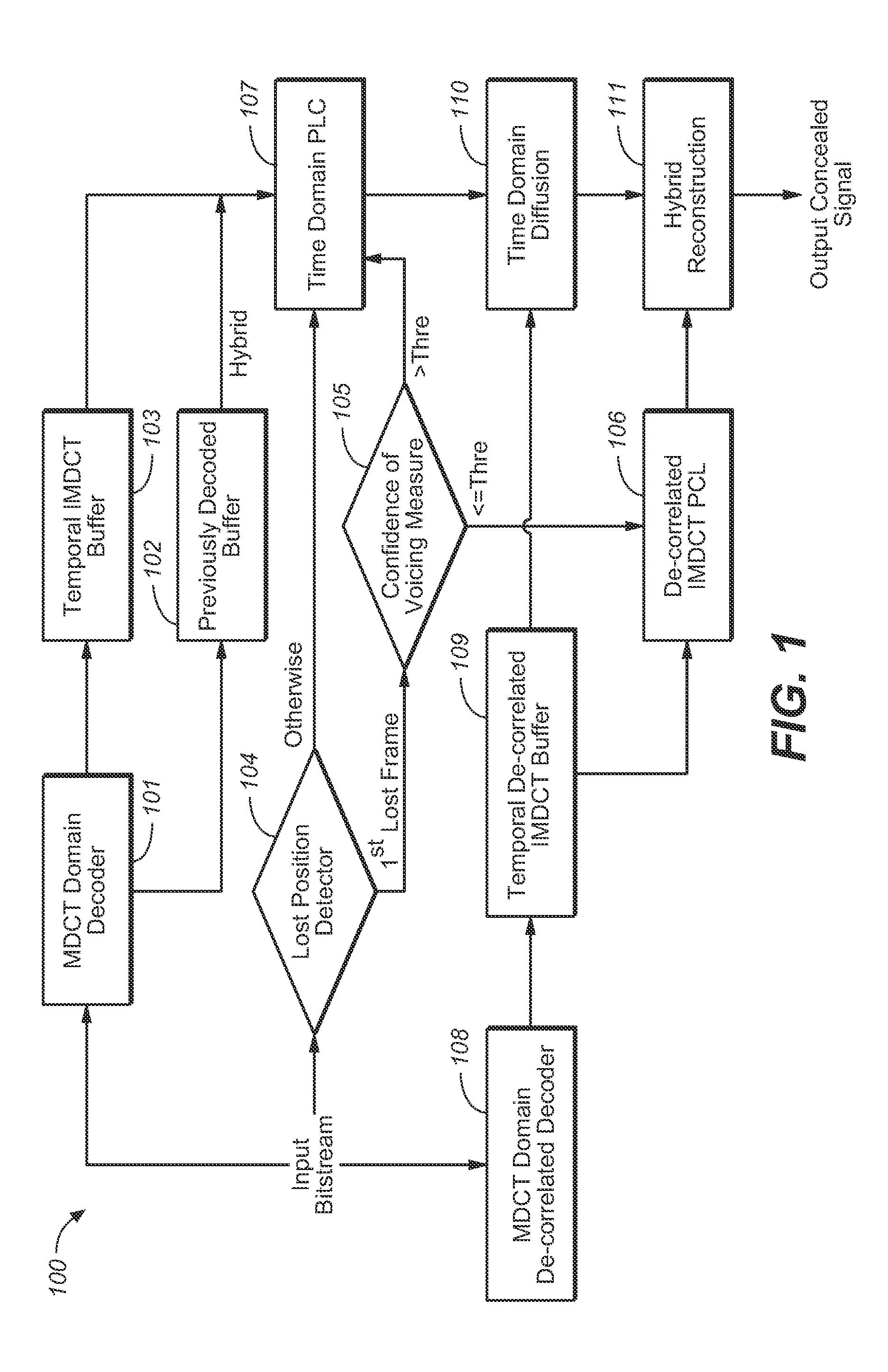
Position-Dependent Hybrid Domain Packet Loss Concealment
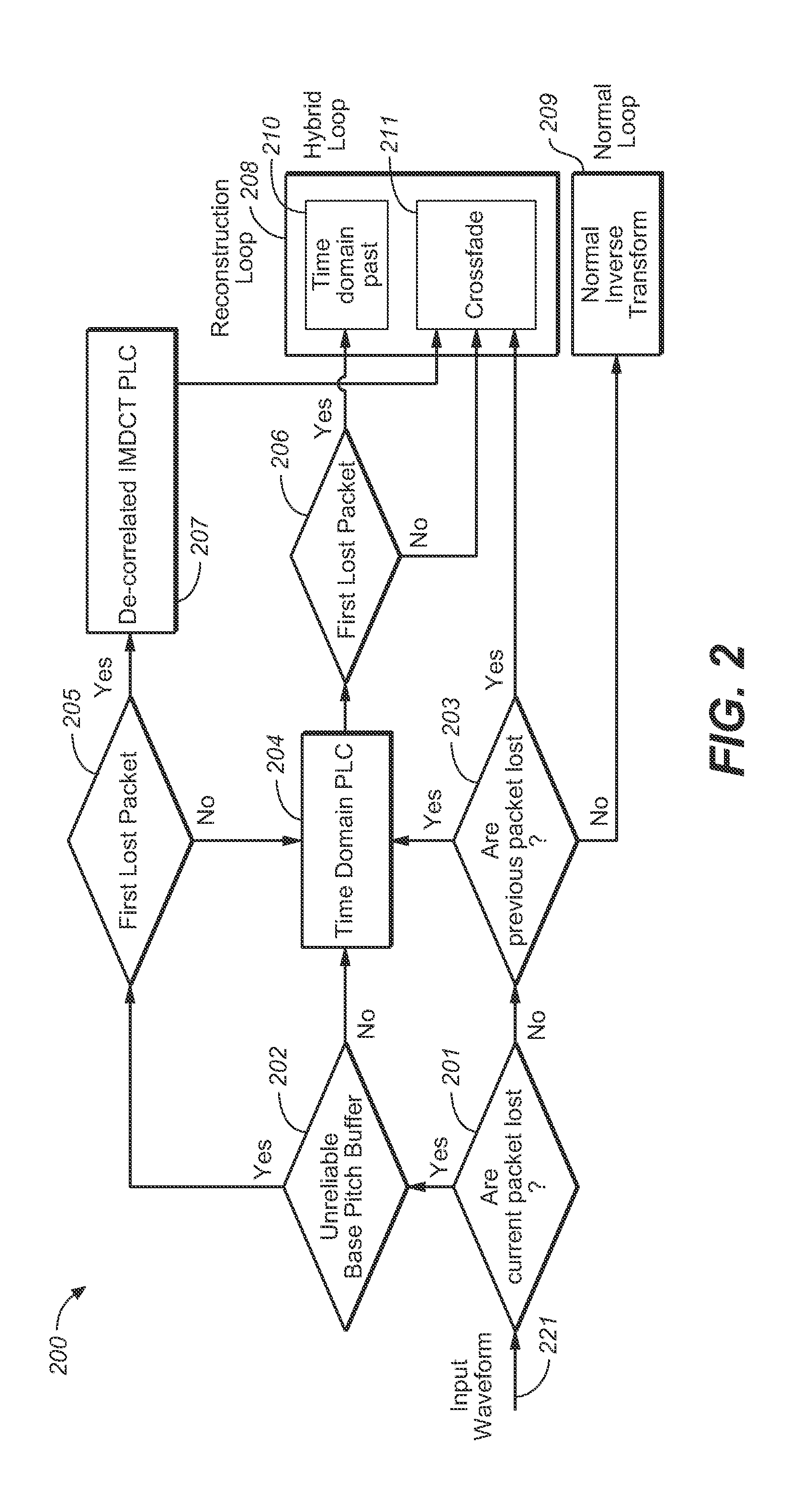
The present document relates to audio signal processing in general, and to the concealment of artifacts that result from loss of audio packets during audio transmission over a packet-switched network, in particular. A method (200) for concealing one or more consecutive lost packets is described. A lost packet is a packet which is deemed to be lost transform-based audio decoder. Each of the one or more lost packets comprises a set of transform coefficients. A set of transform coefficients is used by the transform-based audio decoder to generate a corresponding frame of a time domain audio signal. The method (200) comprises determining (205) for a current lost packet of the one or more lost packets a number of preceding lost packets from the one or more lost packets; wherein the determined number is referred to as a loss position. Furthermore, the method comprises determining a packet loss concealment, referred to as PLC, scheme based on the loss position of the current packet; and determining (204, 207, 208) an estimate of a current frame of the audio signal using the determined PLC scheme (204, 207, 208); wherein the current frame corresponds to the current lost packet.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Packet loss concealment for sub-band predictive coding based on extrapolation of sub-band audio waveforms
ActiveUS20090240492A1Analogue conversionSpeech analysisPacket loss concealmentLinear predictive coding
A technique is described for concealing the effect of a lost frame in a series of frames representing an encoded audio signal in a sub-band predictive coding system. In accordance with the technique, a first synthesized sub-band audio signal is synthesized, wherein synthesizing the first synthesized sub-band audio signal comprises performing waveform extrapolation based on a stored first sub-band decoded audio signal. A second synthesized sub-band audio signal is also synthesized, wherein synthesizing the second synthesized sub-band audio signal comprises performing waveform extrapolation based on the stored second sub-band decoded audio signal. The first synthesized sub-band audio signal and the second synthesized sub-band audio signal are combined to generate a synthesized full-band output audio signal corresponding to a lost frame.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
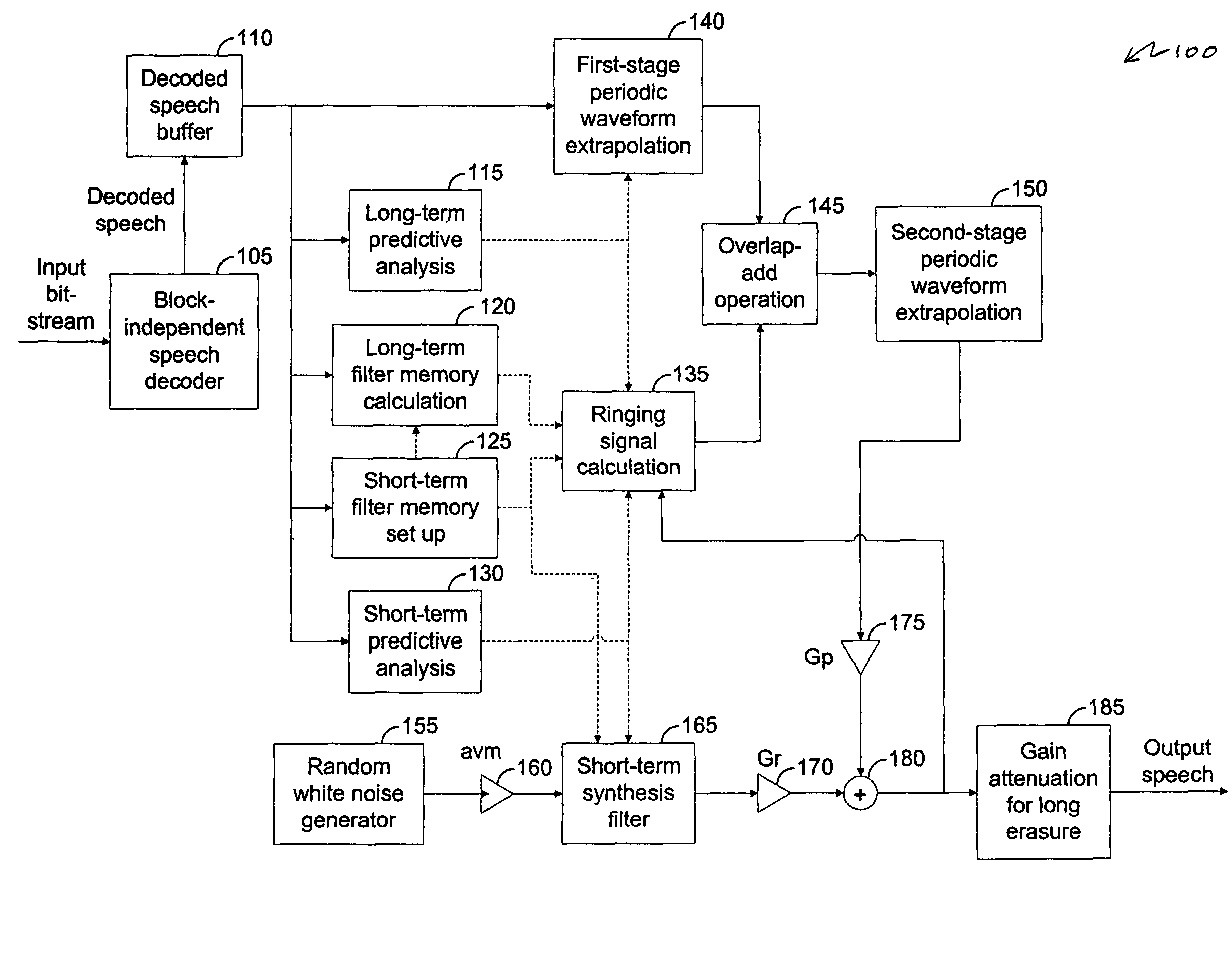
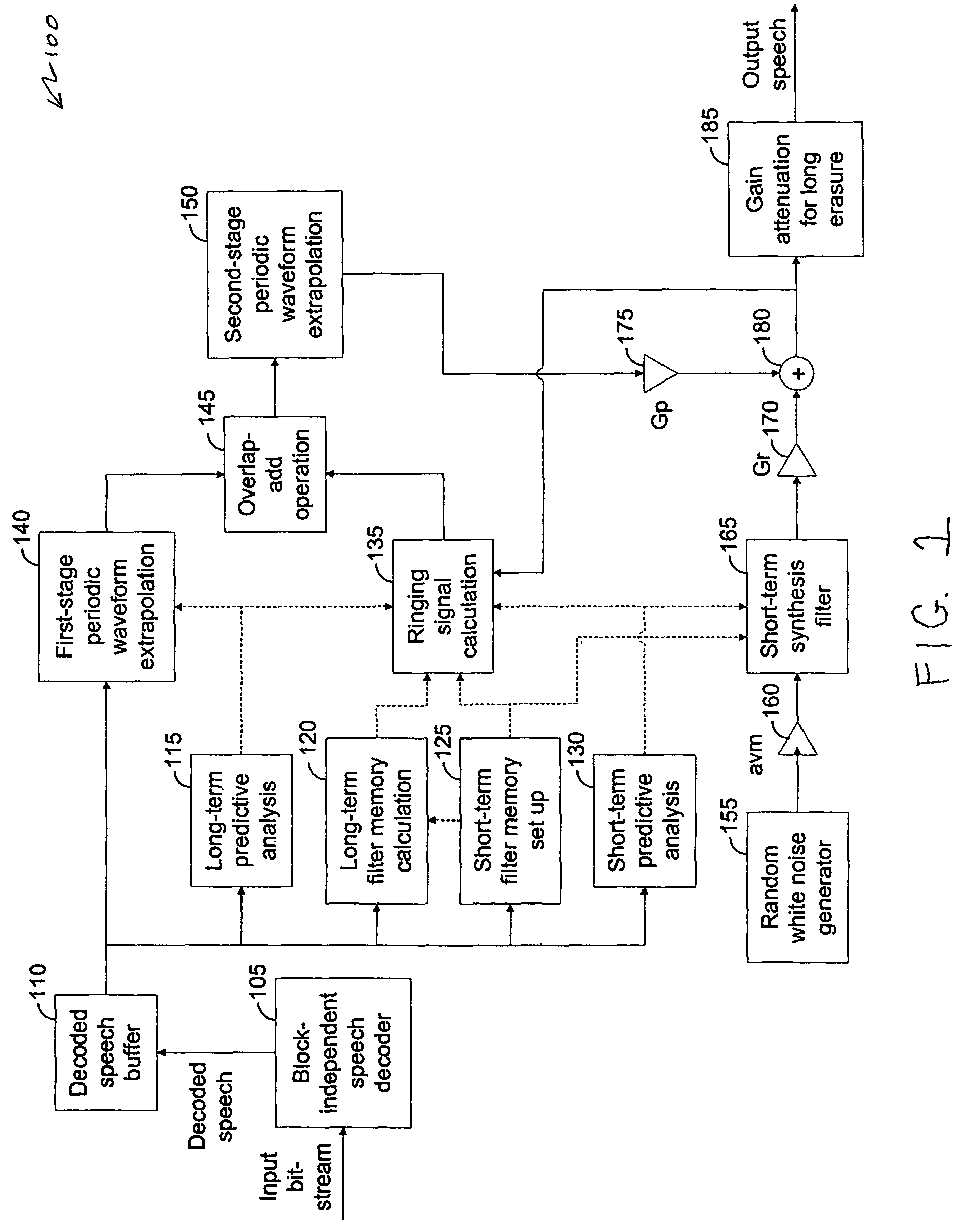
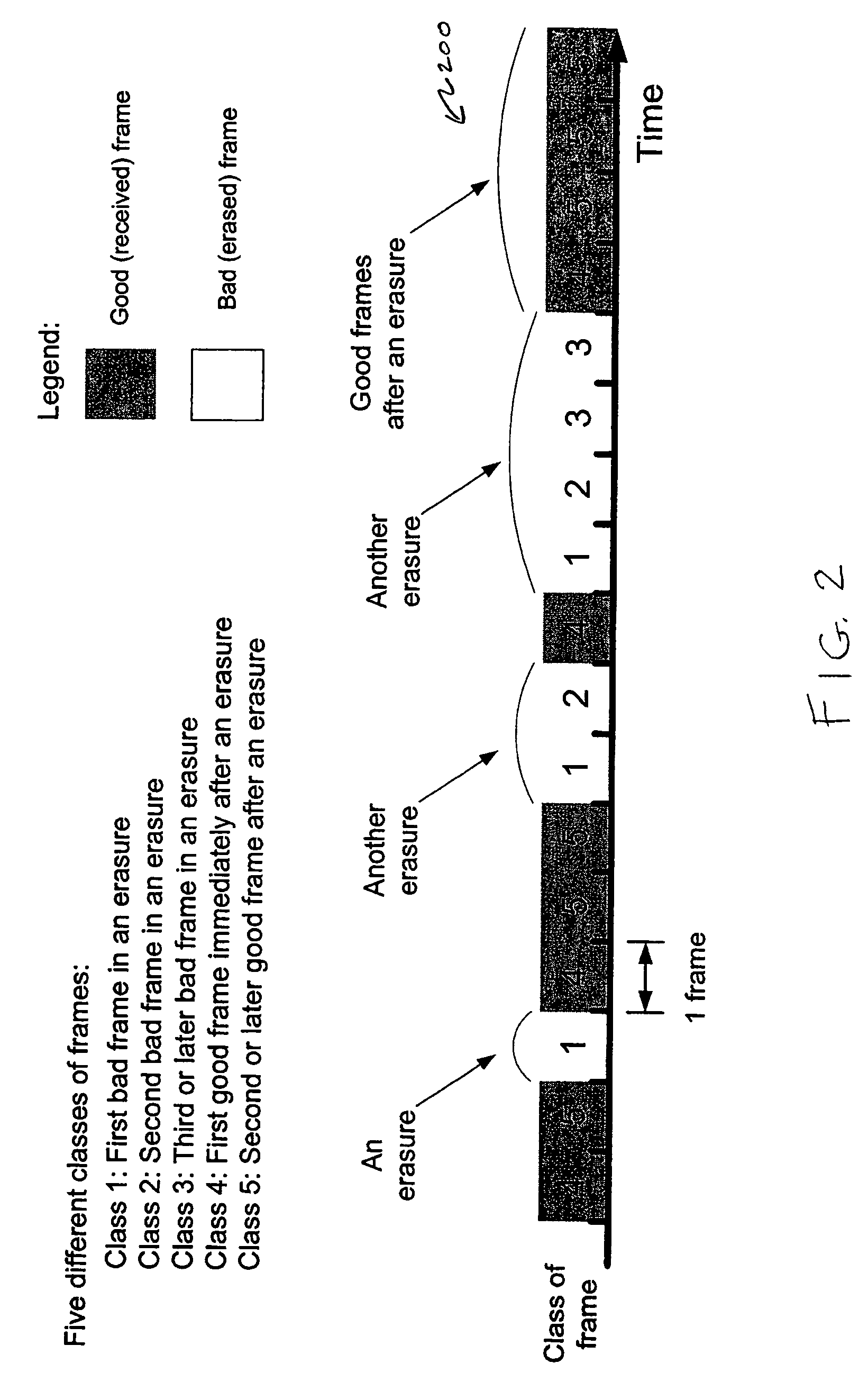
Packet loss concealment for block-independent speech codecs
A technique for performing frame erasure concealment (FEC) in a speech decoder. One or more non-erased frames of a speech signal are decoded in a block-independent manner. When an erased frame is detected, a short-term predictive filter and a long-term predictive filter are derived based on previously-decoded portions of the speech signal. A periodic waveform component is generated using the short-term predictive filter and the long-term predictive filter. A random waveform component is generated using the short-term predictive filter. A replacement frame is generated for the erased frame. The replacement frame may be generated based on the periodic waveform component, the random waveform component, or a mixture of both.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
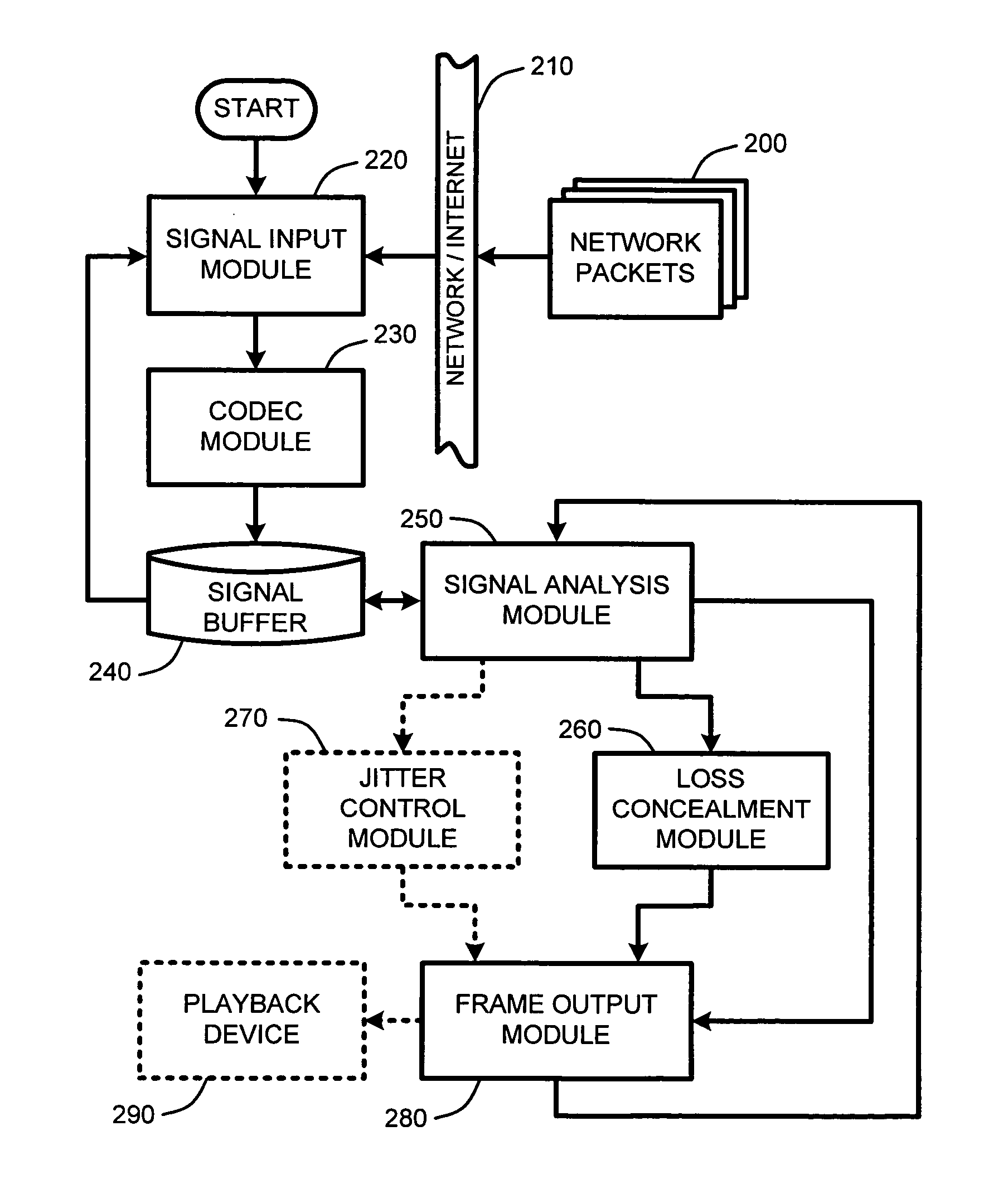
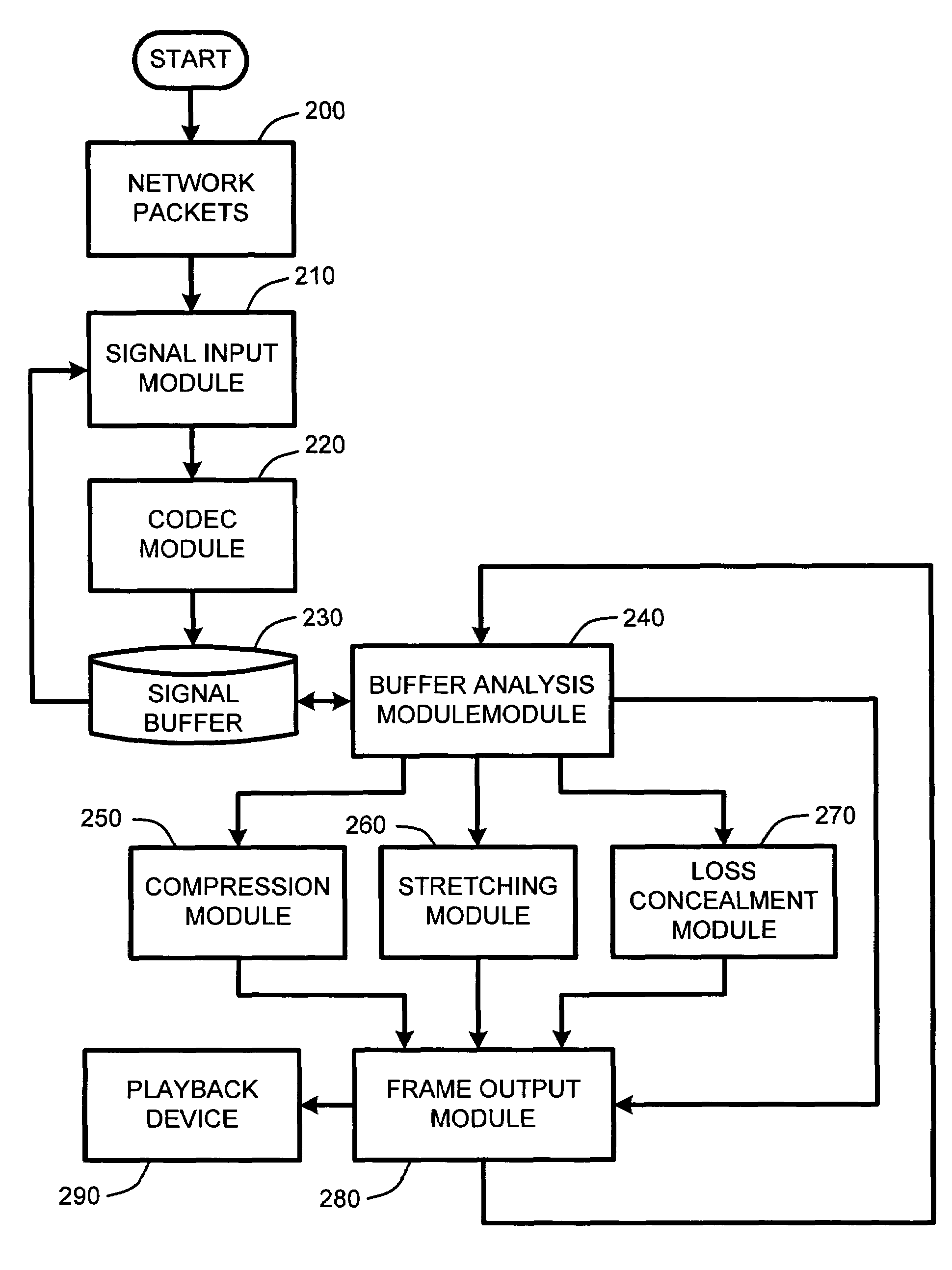
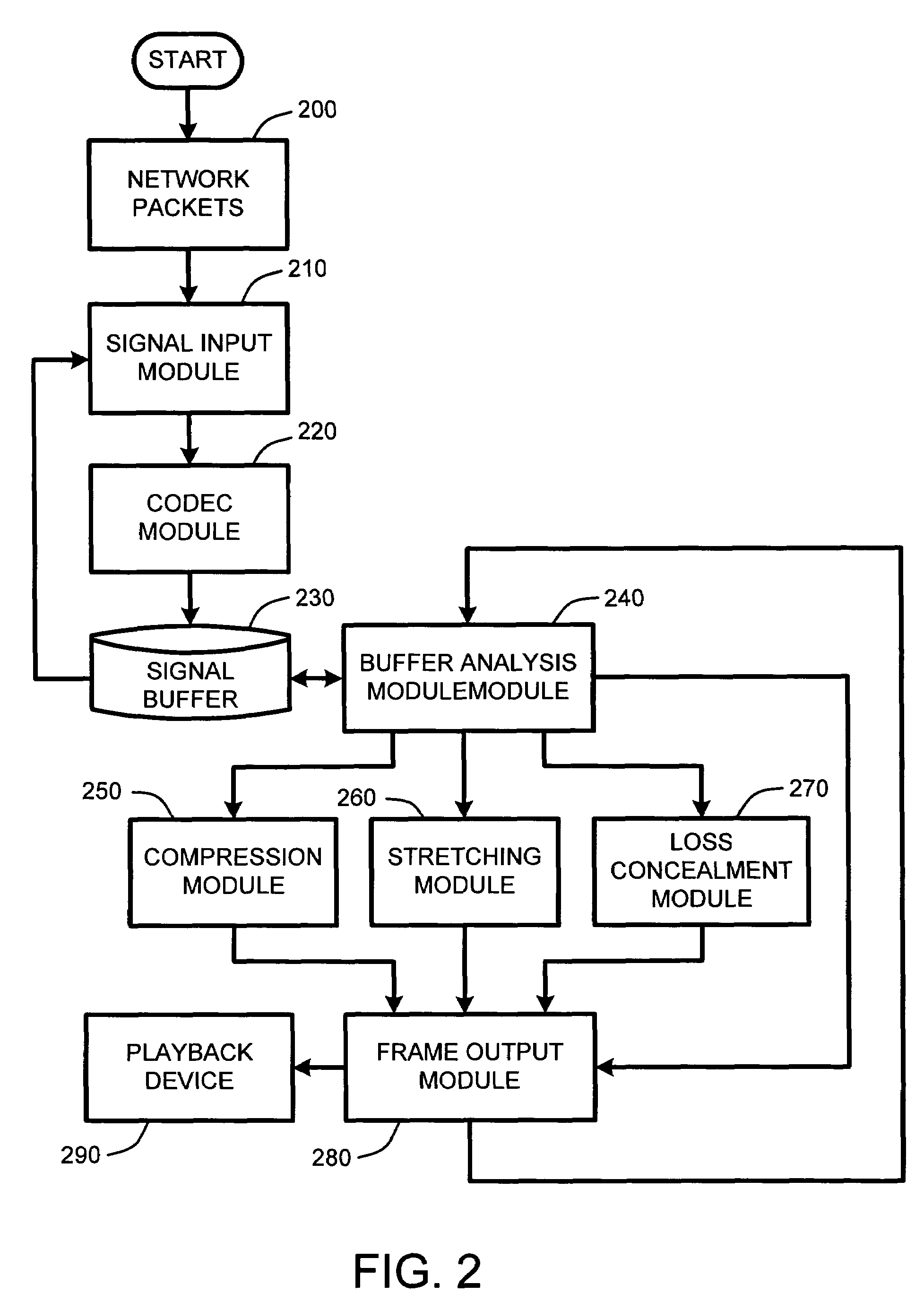
System and method for real-time jitter control and packet-loss concealment in an audio signal
InactiveUS7596488B2Improve signal qualityImprove performanceSpeech analysisTime-division multiplexNetwork packetPacket loss concealment
An “adaptive audio playback controller” operates by decoding and reading received packets of an audio signal into a signal buffer. Samples of the decoded audio signal are then played out of the signal buffer according to the needs of a player device. Jitter control and packet loss concealment are accomplished by continuously analyzing buffer content in real-time, and determining whether to provide unmodified playback from the buffer contents, whether to compress buffer content, stretch buffer content, or whether to provide for packet loss concealment for overly delayed or lost packets as a function of buffer content. Further, the adaptive audio playback controller also determines where to stretch or compress particular frames or signal segments in the signal buffer, and how much to stretch or compress such segments in order to optimize perceived playback quality.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Packet Loss Concealment for Speech Coding
ActiveUS20120323567A1Improving packet loss concealmentReducing and limiting energySpeech analysisSpeech codePacket loss concealment
A speech coding method of significantly reducing error propagation due to voice packet loss, while still greatly profiting from a pitch prediction or Long-Term Prediction (LTP), is achieved by limiting or reducing a pitch gain only for the first subframe or the first two subframes within a speech frame. The method is used for a voiced speech class; a pitch cycle length is compared to a subframe size to decide to reduce the pitch gain for the first subframe or the first two subframes within the frame. Speech coding quality loss due to the pitch gain reduction is compensated by increasing a bit rate of a second excitation component or adding one more stage of excitation component only for the first subframe or the first two subframes within the speech frame.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
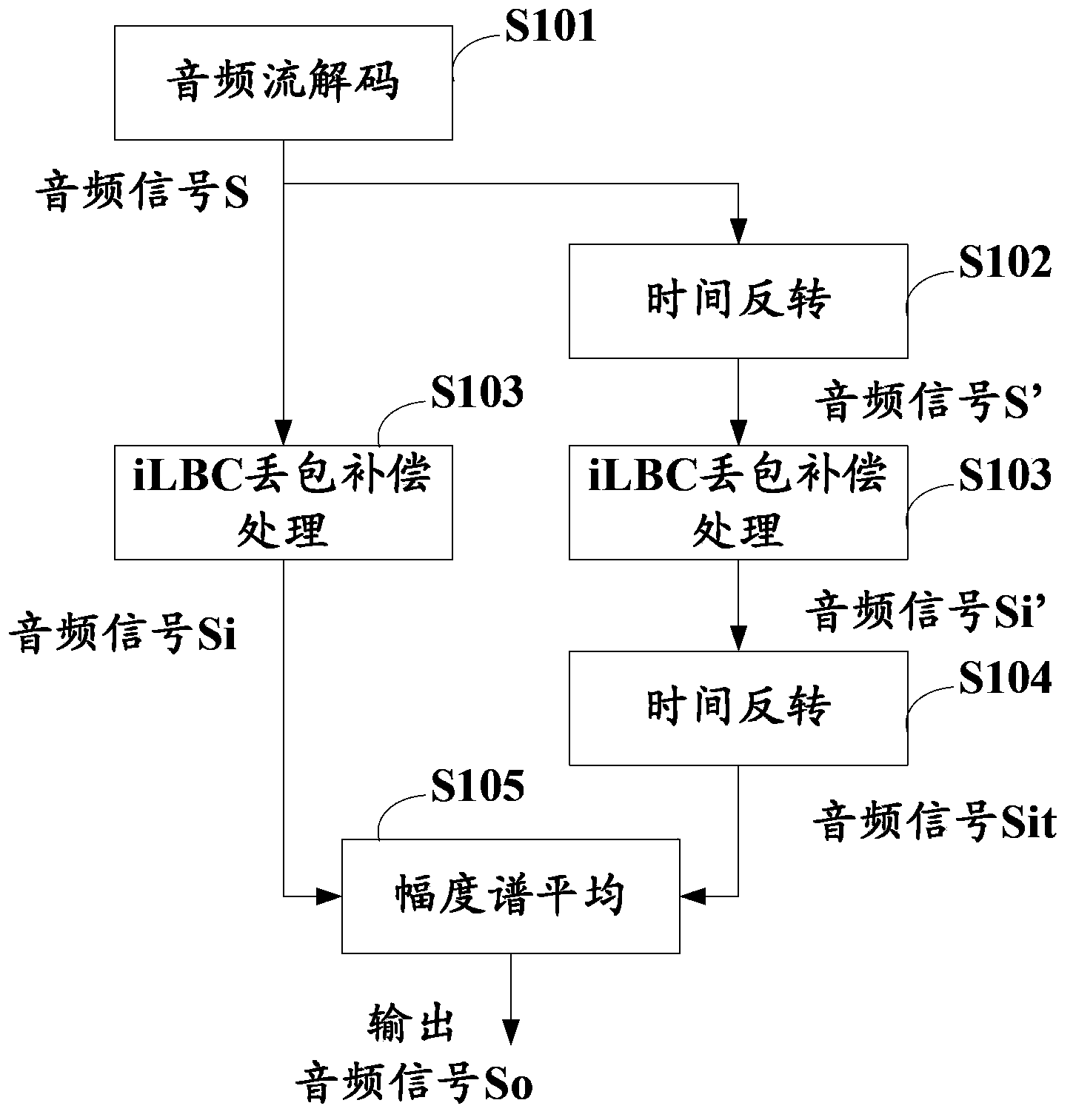
Network audio packet loss concealment method and device
ActiveCN104347076AImprove audio qualityClear voice effectSpeech analysisError concealmentPacket loss rate
The invention discloses a network audio packet loss concealment method and device, relating to the field of audio transmission. The method comprises the steps of decoding an audio stream subjected to packet loss, reversing audio signals obtained through decoding, then, carrying out packet loss compensation on the audio signals and the reversed audio signals respectively, reversing the compensated reversed audio signals again, and finally, carrying out magnitude average on the compensated audio signals of two channels, so as to obtain output signals. By the bidirectional-prediction error concealment technology, the quality of audio can be further improved, and particularly, a relatively clear voice effect can be obtained in the network environment that the packet loss rate is relatively high.
Owner:CHINA TELECOM CORP LTD
Packet prioritization and associated bandwidth and buffer management techniques for audio over IP
InactiveUS20080151921A1Raise priorityReduce the possibilityData switching by path configurationVoice communicationVoice activity
The present invention is directed to voice communication devices in which an audio stream is divided into a sequence of individual packets, each of which is routed via pathways that can vary depending on the availability of network resources. All embodiments of the invention rely on an acoustic prioritization agent that assigns a priority value to the packets. The priority value is based on factors such as whether the packet contains voice activity and the degree of acoustic similarity between this packet and adjacent packets in the sequence. A confidence level, associated with the priority value, may also be assigned. In one embodiment, network congestion is reduced by deliberately failing to transmit packets that are judged to be acoustically similar to adjacent packets; the expectation is that, under these circumstances, traditional packet loss concealment algorithms in the receiving device will construct an acceptably accurate replica of the missing packet. In another embodiment, the receiving device can reduce the number of packets stored in its jitter buffer, and therefore the latency of the speech signal, by selectively deleting one or more packets within sustained silences or non-varying speech events. In both embodiments, the ability of the system to drop appropriate packets may be enhanced by taking into account the confidence levels associated with the priority assessments.
Owner:AVAYA INC
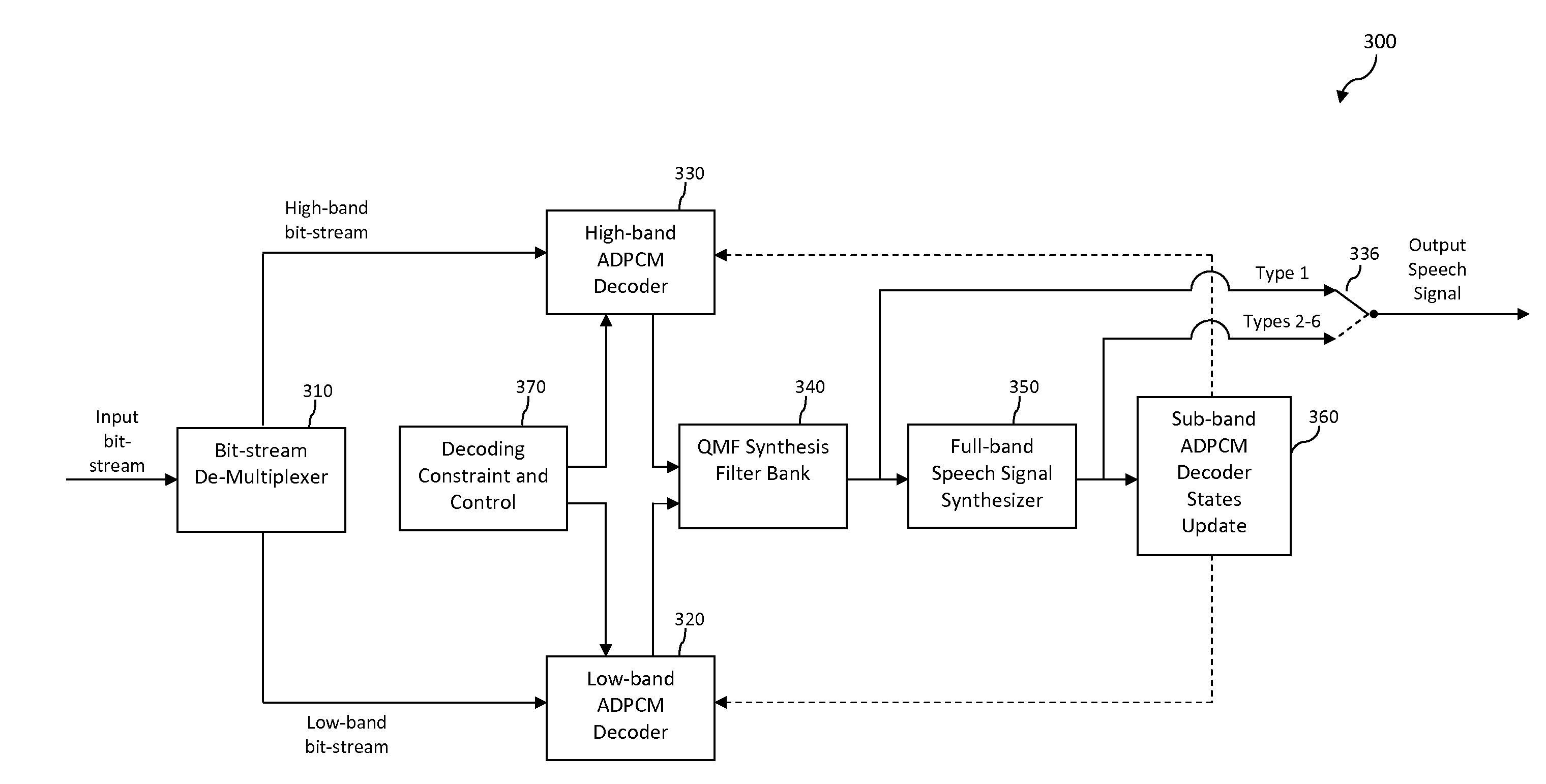
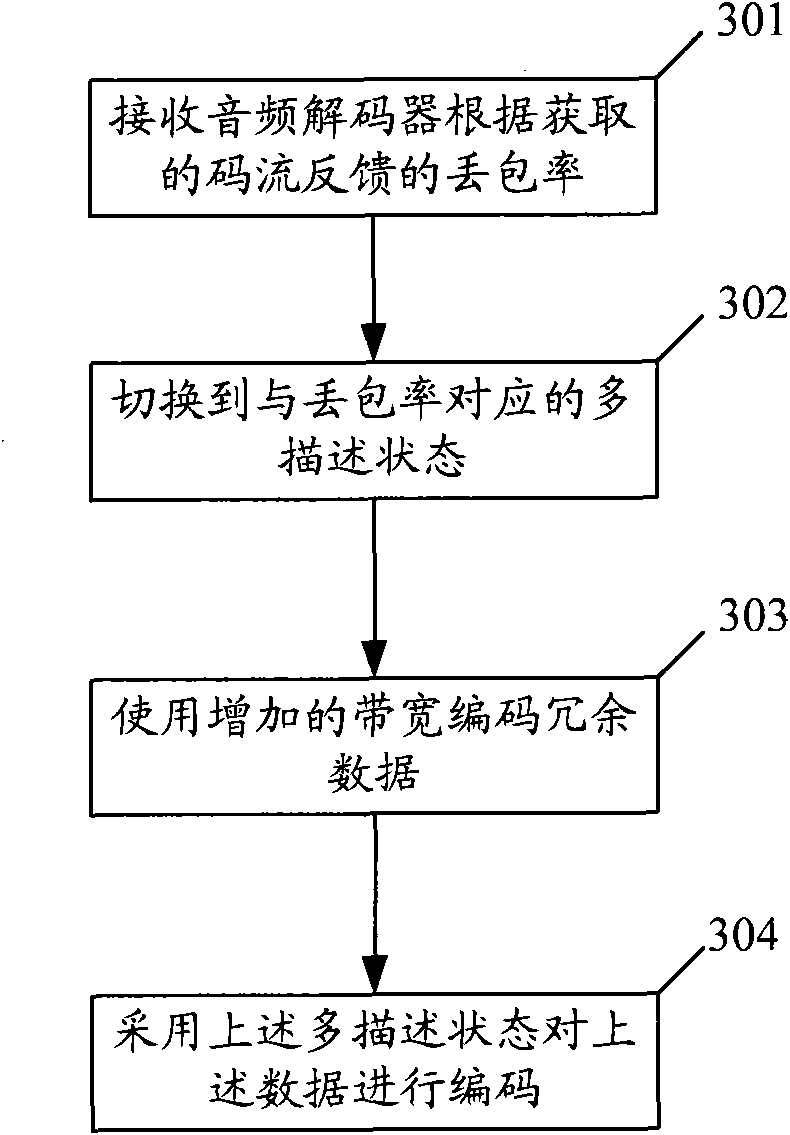
Audio encoding method, audio decoding method, related device and communication system
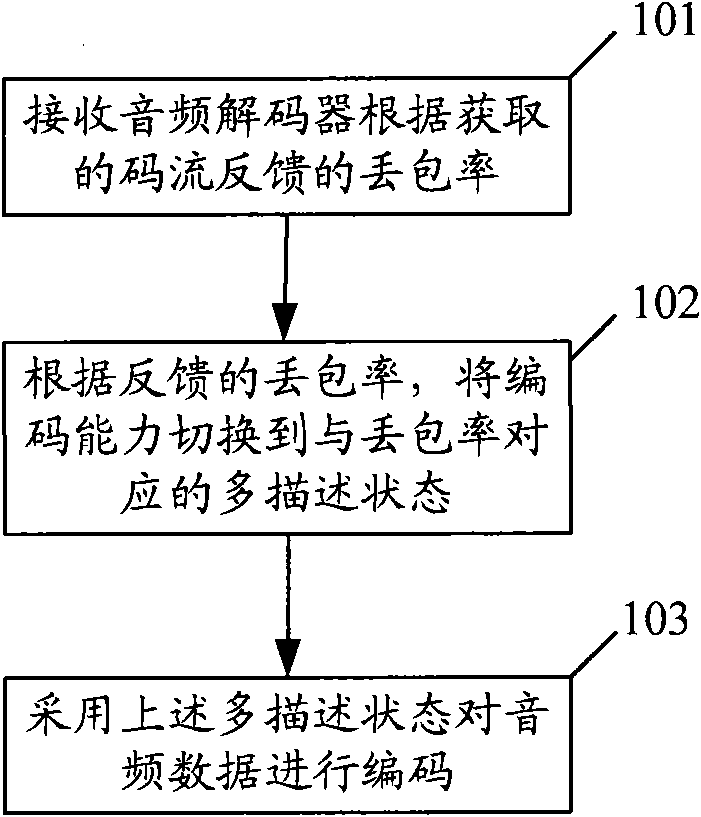
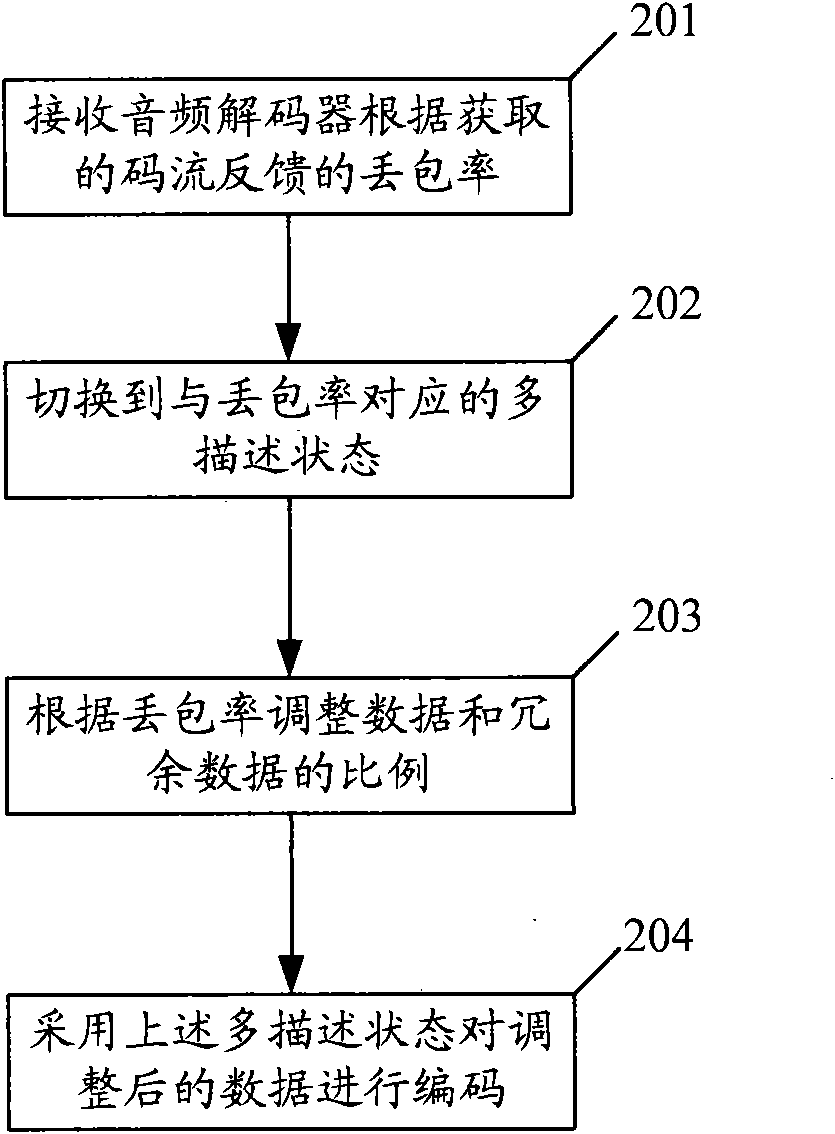
ActiveCN101777960AOccupies less bandwidthGood output stream qualityError prevention/detection by using return channelSpeech analysisDecoding methodsComputer hardware
The embodiment of the invention discloses an audio encoding method, an audio decoding method, a related device and a communication system. The audio encoding method comprises the steps of receiving packet loss rate fed back by an audio decoder according to acquired code streams, switching encoding capacity to a multiple description state corresponding to the packet loss rate according to the packet loss rate fed back and encoding audio data by the multiple description state. The audio decoding method comprises the steps of acquiring multiple description packets sent by the audio encoder, increasing the value of a counter of the multiple description packet which contains multiple description quantity and packet description number by 1, acquiring the numerical value of the packet loss packet, and calling packet loss concealment when determining the numerical value of the counter of the multiple description packet or when the packet description number is not smaller than the multiple description quantity and the numerical number of the packet loss counter is not smaller than the multiple description quantity. The embodiment of the invention adjusts the packet loss resisting capacity of encoding code streams according to actual condition and reduces bandwidth occupied by invalid redundant information, thereby acquiring better output code stream quality.
Owner:HUAWEI DEVICE CO LTD
Modem architecture for joint source channel decoding
ActiveUS20130191706A1Code conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresSignal qualityModem device
A modem architecture that supports the application of joint source channel decoding (JSCD). The modem architecture includes two channel decoders, one of which is modified to provide improved signal quality. The modem architecture further includes transparent network layers that enable the passage of data from one layer to another layer. For example, the modem architecture enables the passage soft bits, when available, from a physical layer to an application layer. The soft bits may be utilized for JSCD, packet loss concealment, or other applications. The modem architecture enables encryption and decryption of data to incorporate extrinsic information in operating JSCD.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
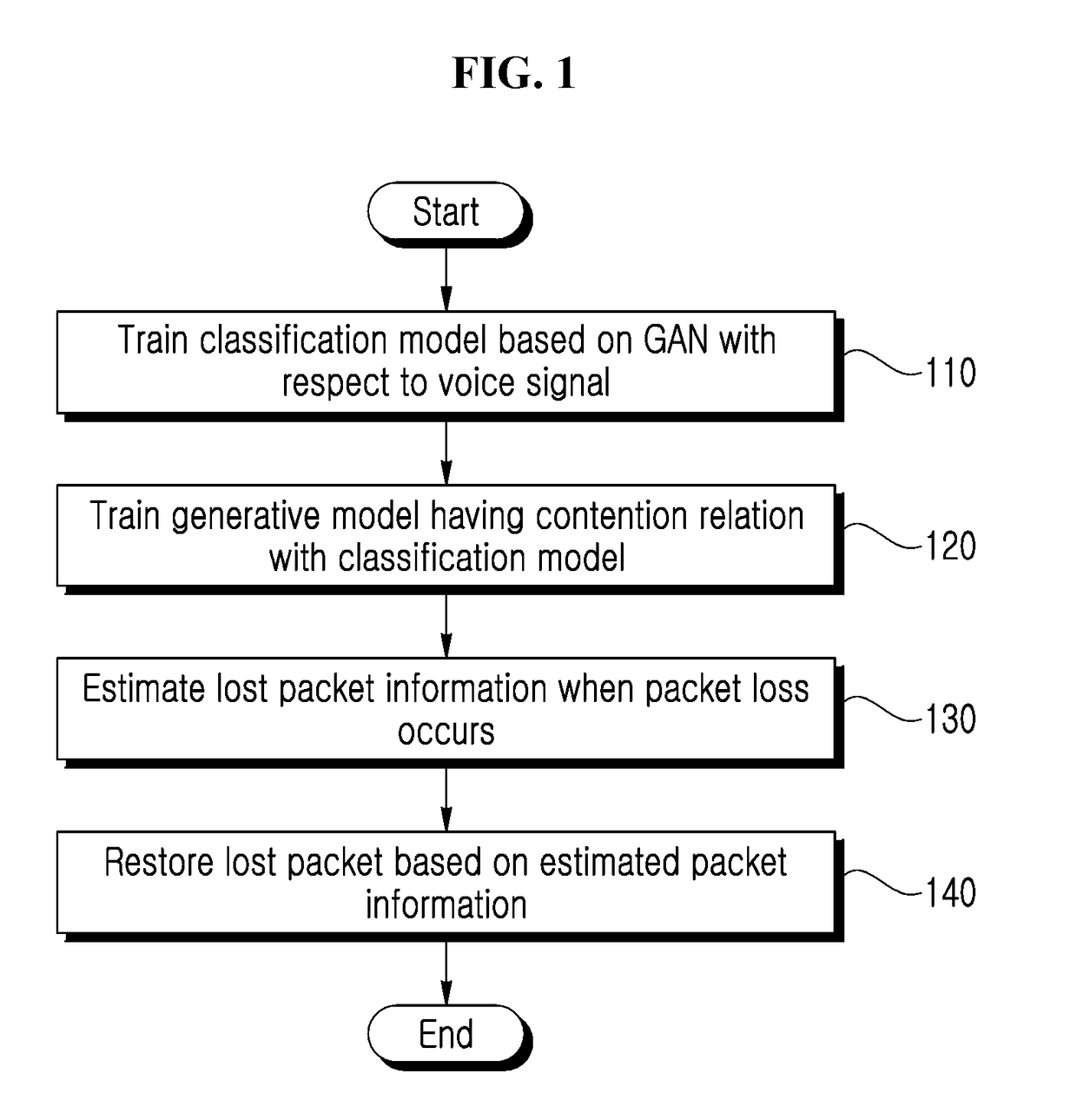
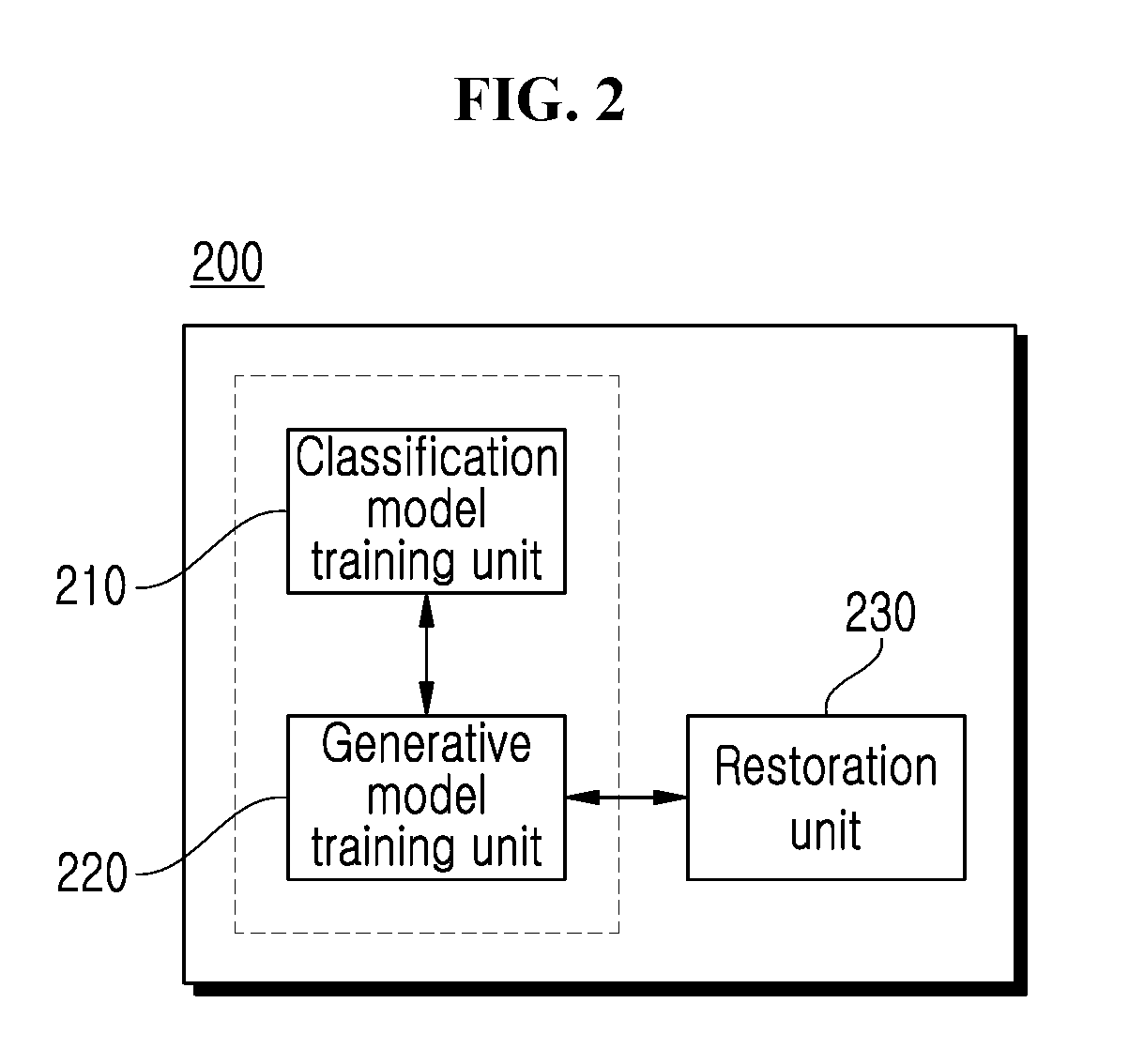
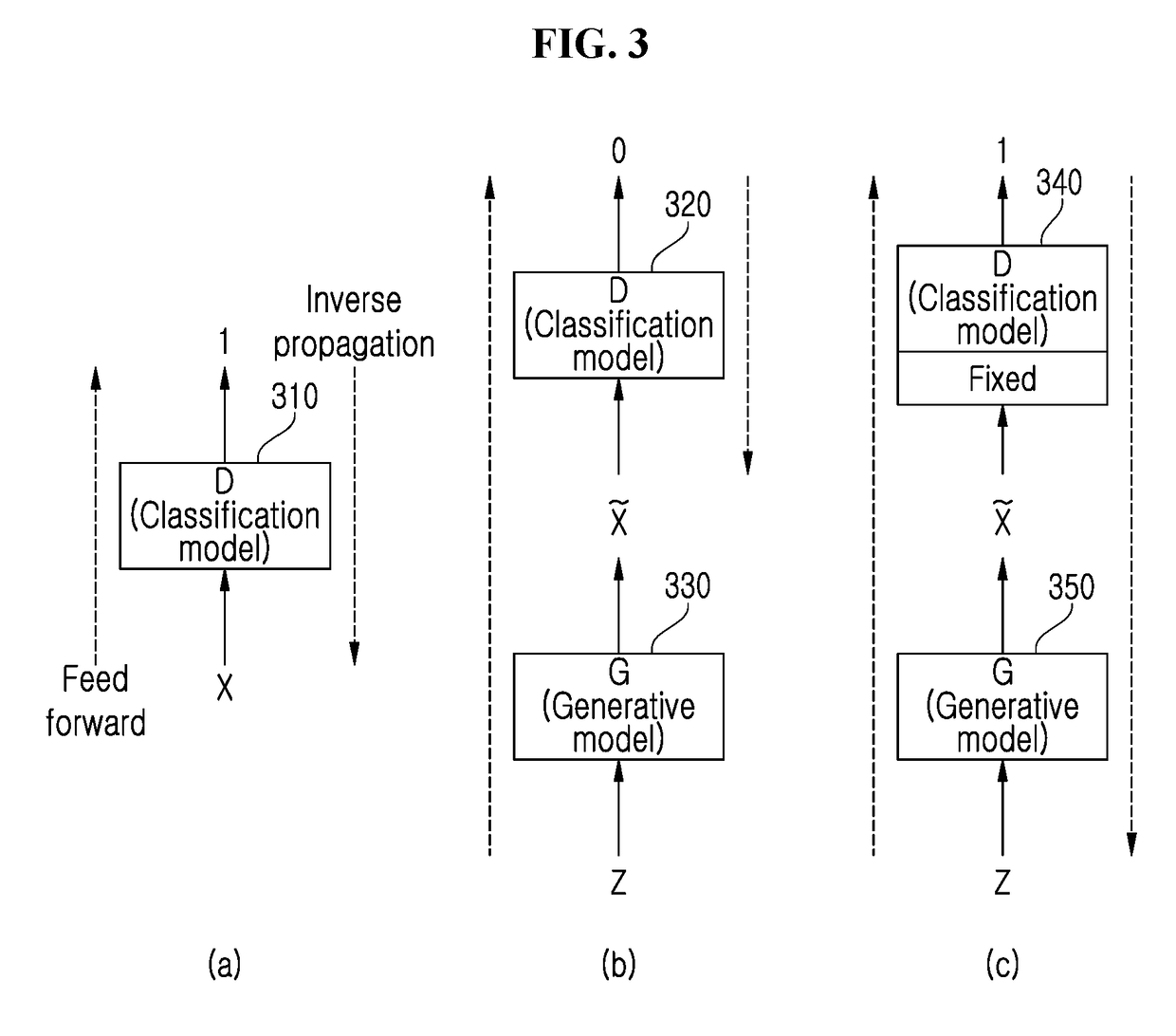
Method and apparatus for packet loss concealment using generative adversarial network
Disclosed are a packet loss concealment method and apparatus a using a generative adversarial network. A method for packet loss concealment in voice communication may include training a classification model based on a generative adversarial network (GAN) with respect to a voice signal including a plurality of frames, training a generative model having a contention relation with the classification model based on the GAN, estimating lost packet information based on the trained generative model with respect to the voice signal encoded by a codec, and restoring a lost packet based on the estimated packet information.
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUNDATION HANYANG UNIV)
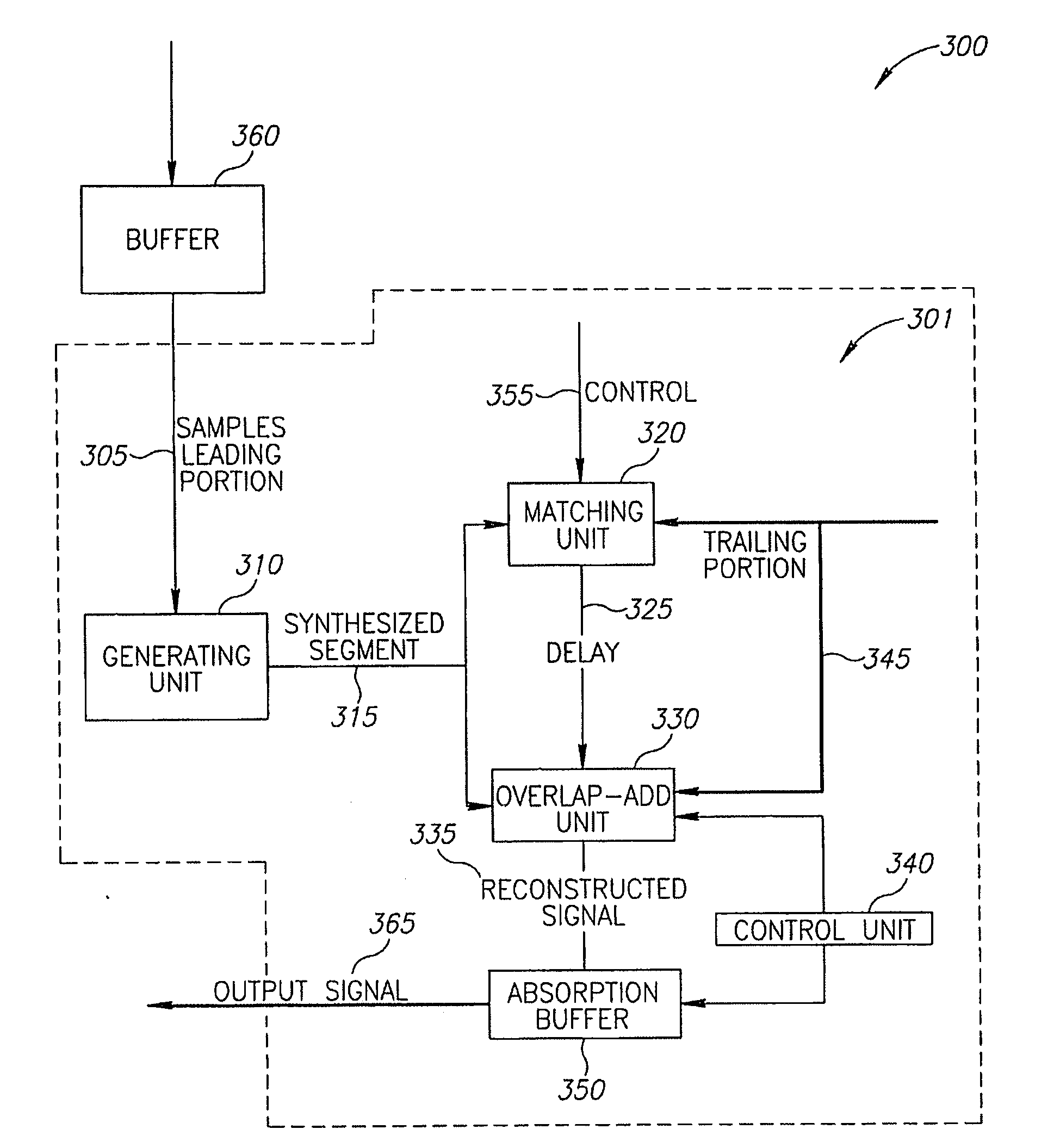
Packet loss concealment
InactiveUS20080294428A1Quality improvementReduction of audio qualitySpeech analysisNetwork connectionsPacket loss concealmentComputer science
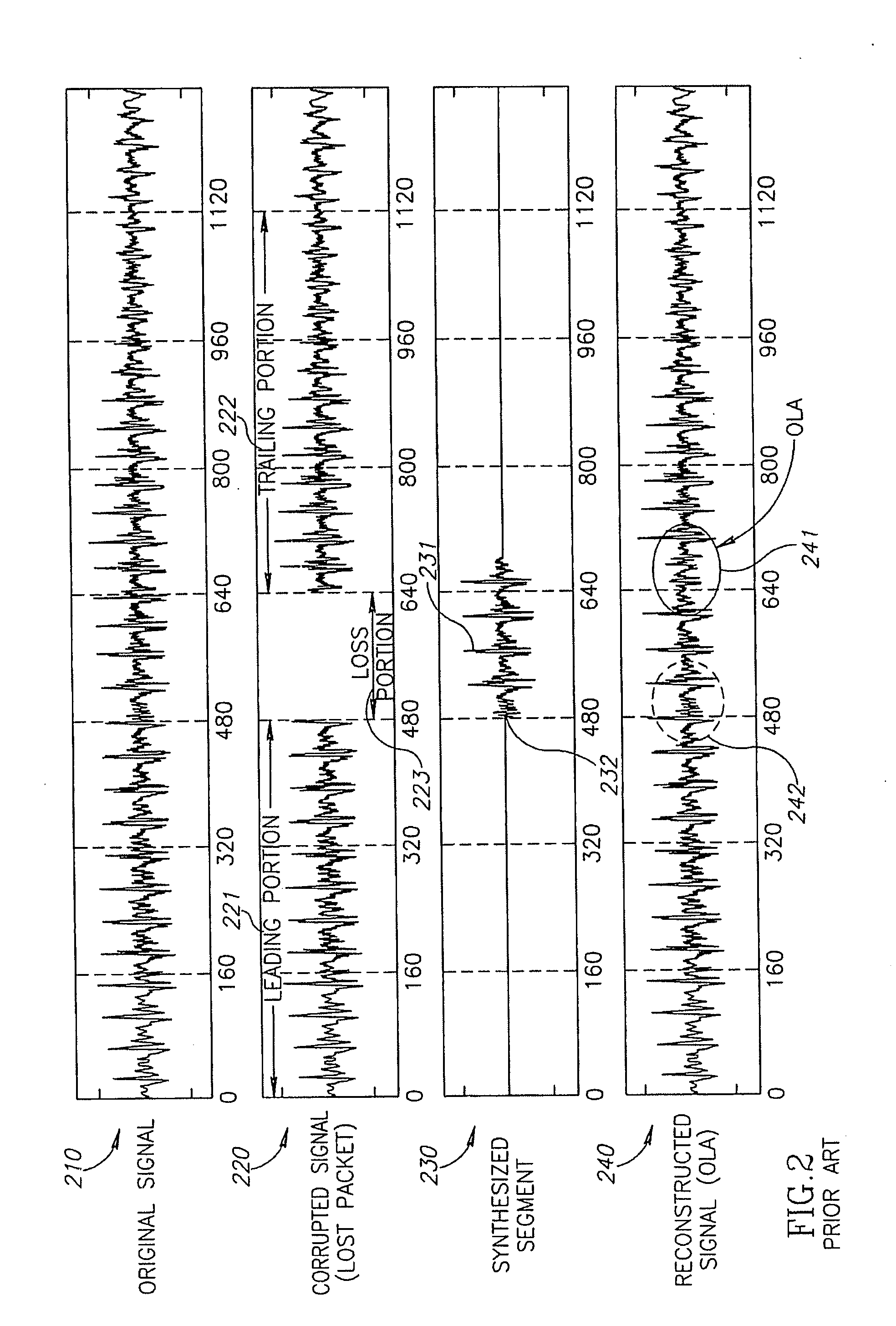
A method for using a waveform segment in place of a missing portion of an audio waveform generated in response to a packet stream encoding portions of the audio waveform, the method comprising: phase matching a trailing portion of the waveform segment with a trailing portion of the audio waveform that follows the missing portion; and adding the phase matched waveform segment to the audio waveform.
Owner:AUDIOCODES LTD
Method for hiding loss package and system thereof
ActiveCN101437009AImprove matching accuracyImprove accuracySpeech analysisHybrid transportTime domainPacket loss concealment
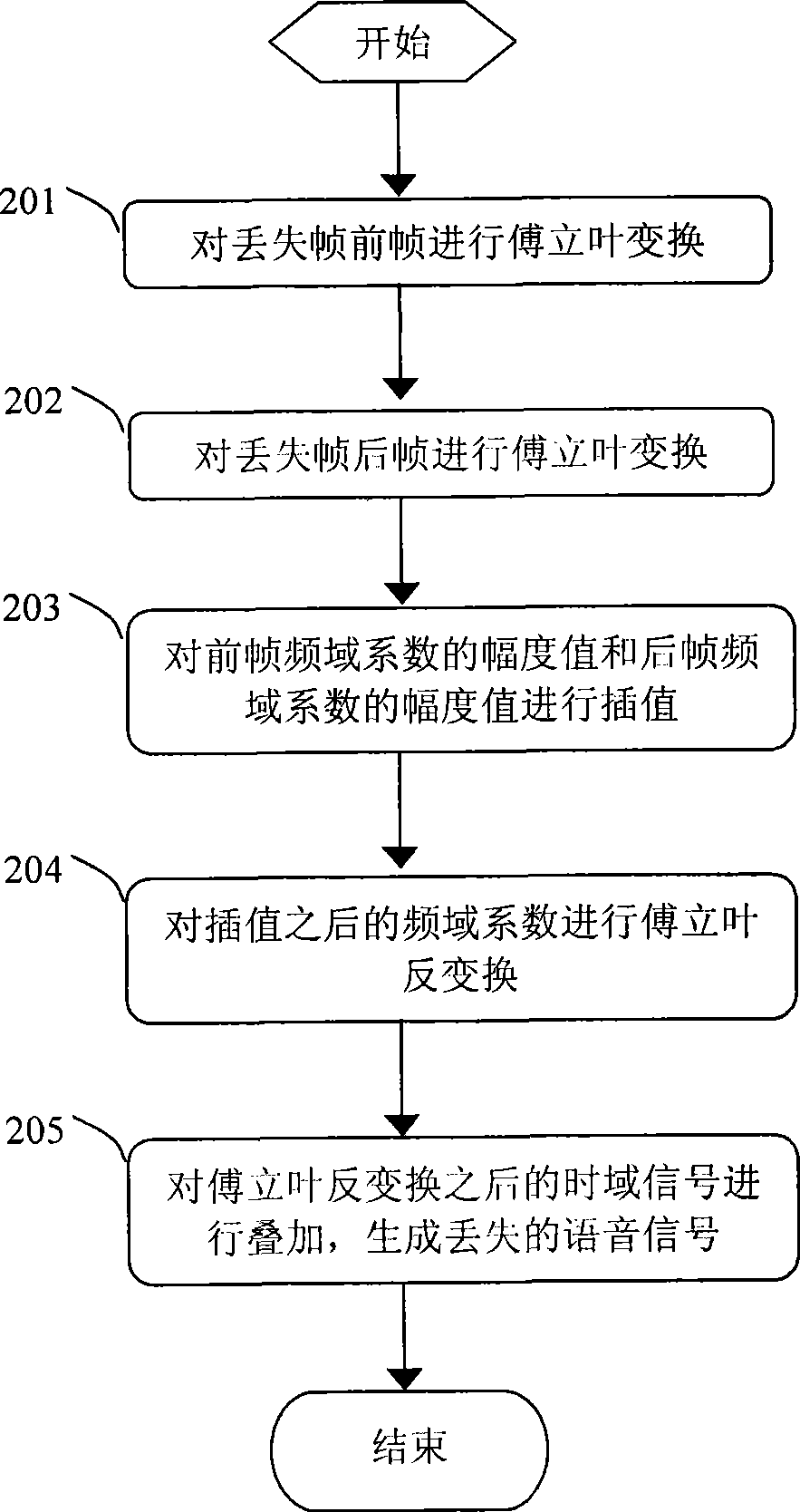
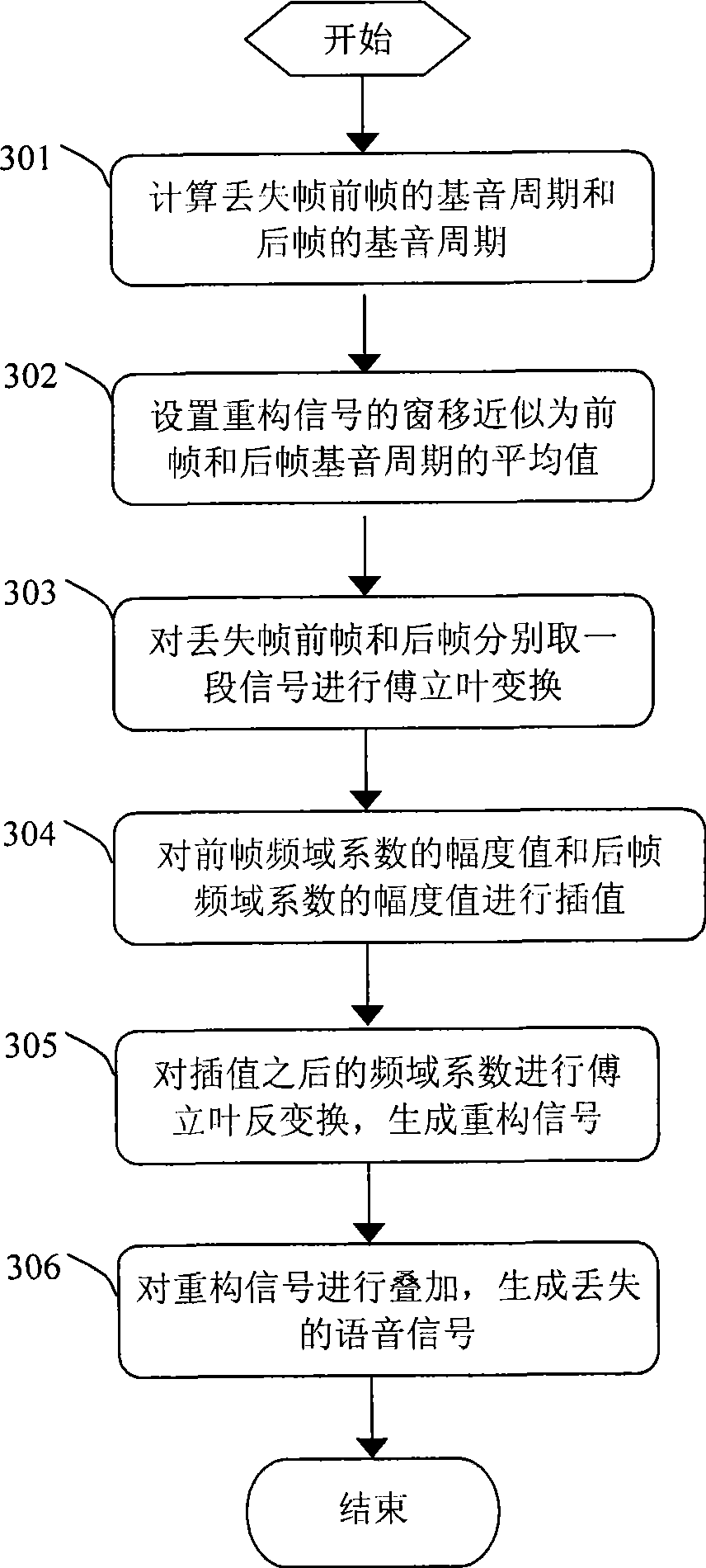
The invention discloses a method for packet loss concealment and a system therefor. The method comprises the following steps: according to the periodicity of a pitch and a phase of a signal, a section of time domain signal is taken in a previous frame and a later frame of a lost signal respectively for the conversion from time domain to frequency domain to obtain a previous frame frequency domain coefficient and a later frame frequency domain coefficient; amplitude values of the previous frame frequency domain coefficient and the later frame frequency domain coefficient are interpolated to obtain amplitude values of frequency domain coefficients of a plurality of reconstruction signals; phases which are most similar to those of the reconstruction signals are taken in the previous frame or the later frame respectively to serve as phase values of the frequency domain coefficients of the reconstruction signals; the conversion from frequency domain to time domain is performed according to the amplitude values of the frequency domain coefficients of the reconstruction signals to obtain time domain signals of the reconstruction signals, and time domain signals of the reconstruction signals are superposed to restore the lost signal. The adoption of the method can improve the accuracy of the period of the reconstruction signals and the matching precision of the phase.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Speech coding system to improve packet loss concealment
A speech coding method of significantly reducing error propagation due to voice packet loss, while still greatly profiting from a pitch prediction or Long-Term Prediction (LTP), is achieved by limiting or reducing a pitch gain only for the first subframe or the first two subframes within a speech frame. The method is used for a speech class decided by a classification algorithm; the classification algorithm is designed, depending on at least one pitch cycle length compared to one subframe size. Speech coding quality loss due to the pitch gain reduction is compensated by increasing a coded excitation codebook size or adding one more stage of excitation only for the first subframe or the first two subframes within the speech frame.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
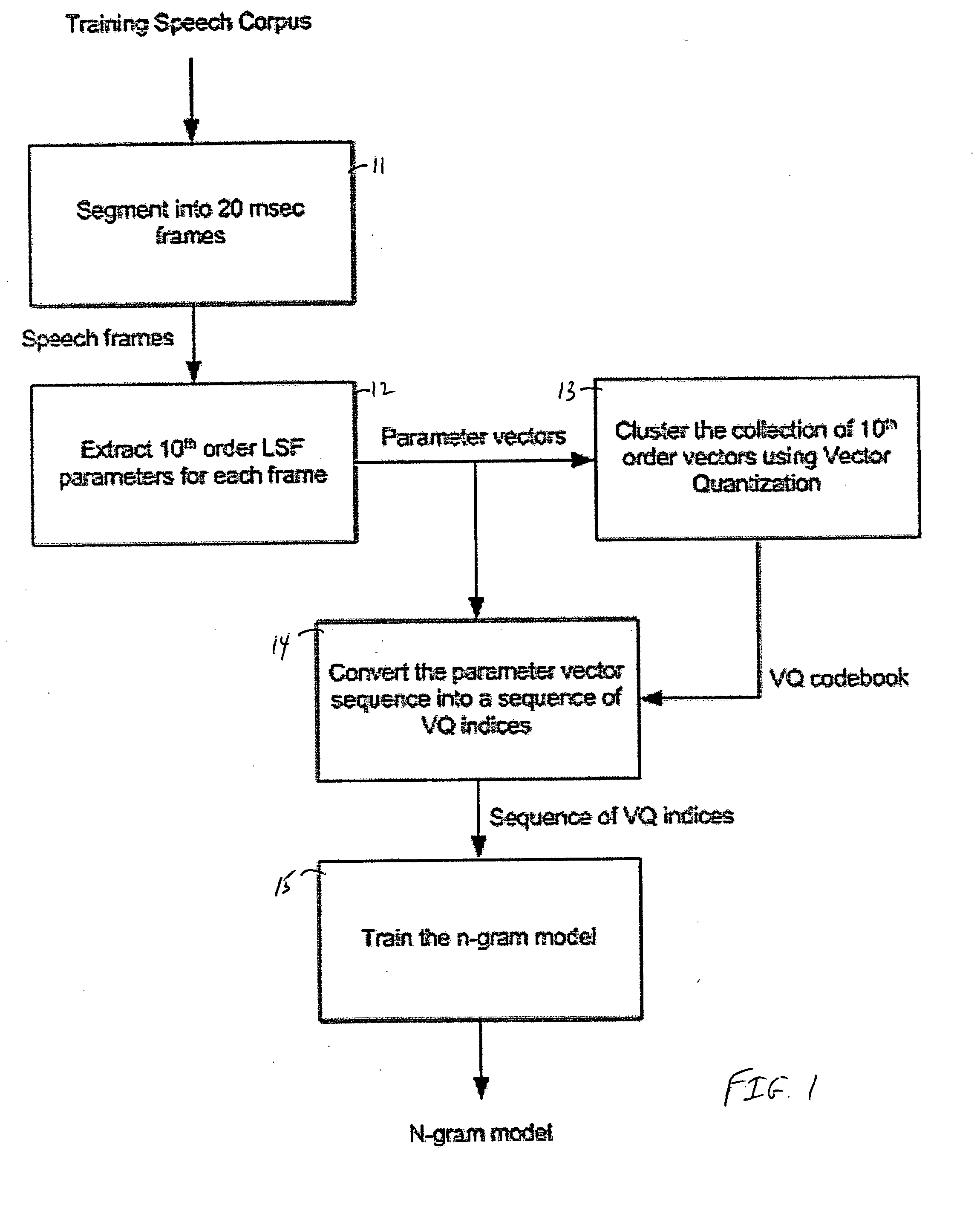
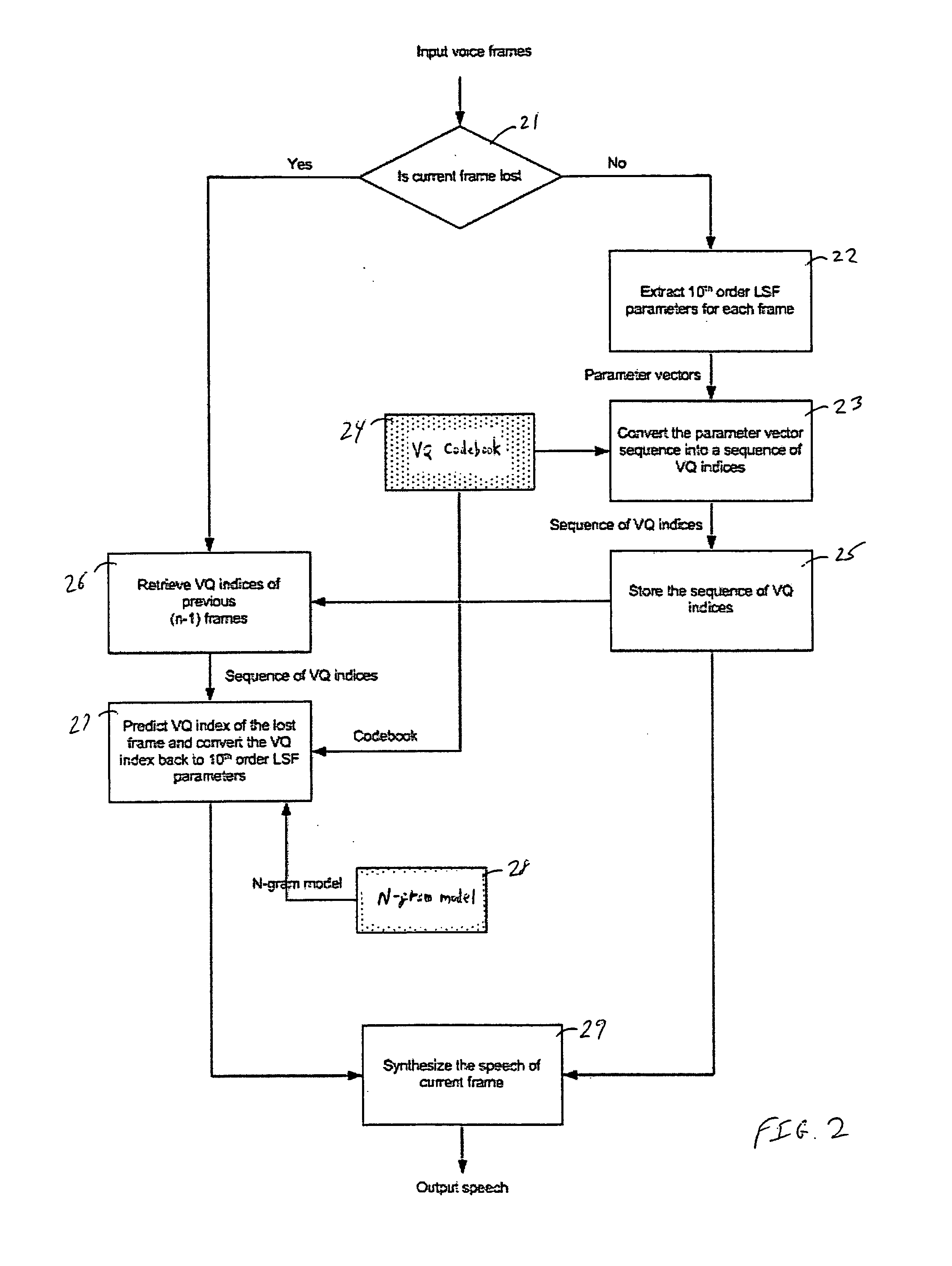
Packet loss concealment based on statistical n-gram predictive models for use in voice-over-IP speech transmission
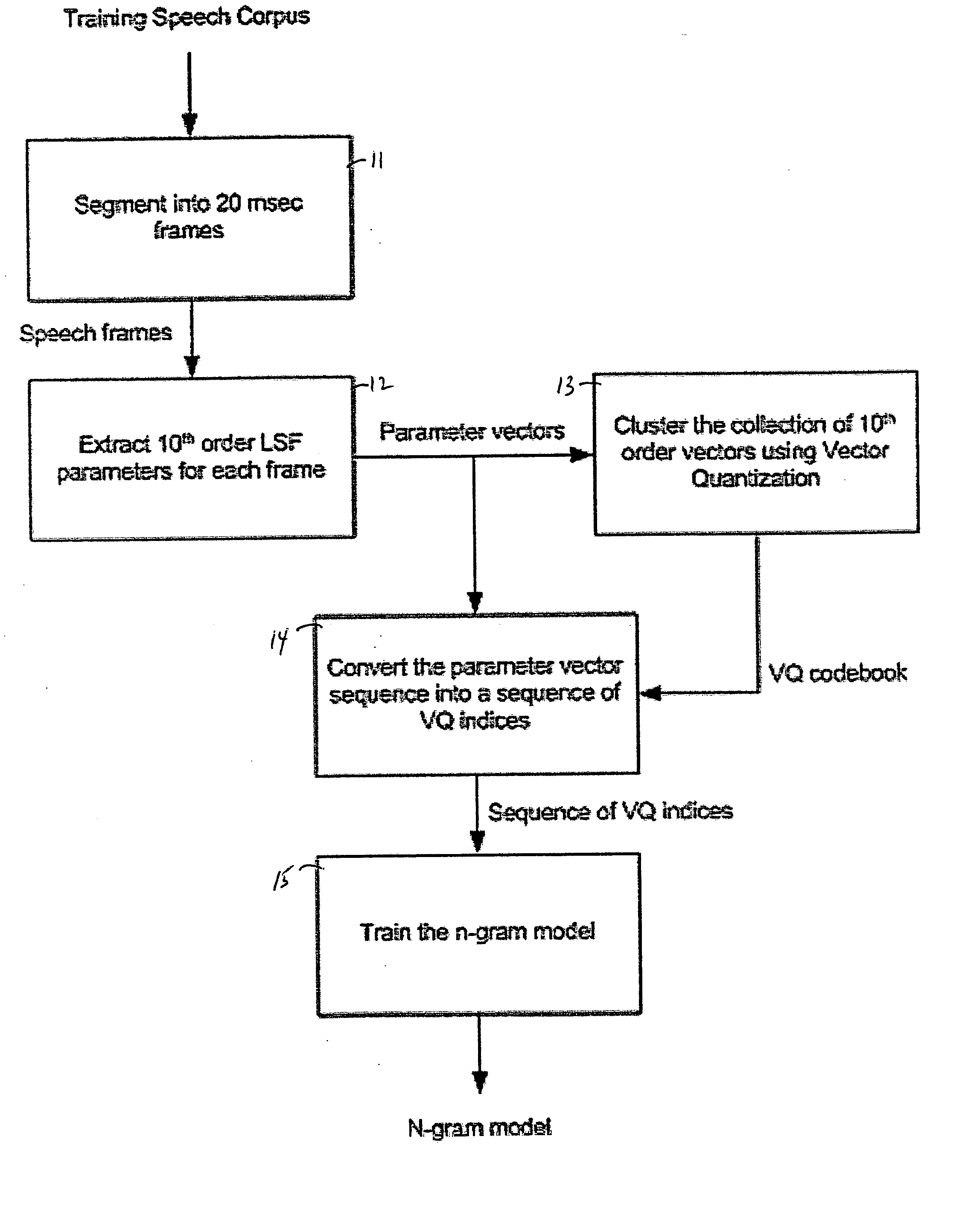
InactiveUS20050276235A1Improved packet loss concealment (PLC) algorithmSpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsStatistical correlationAlgorithm
A method for performing packet loss concealment of lost packets in Voice over IP (Internet Protocol) speech transmission. Statistical n-gram models are initially created with use of a training speech corpus, and then, packets lost during transmission are advantageously replaced based on these models. In particular, the existence of statistical patterns in successive voice over IP (VoIP) packets is advantageously exploited by first using conventional vector quantization (VQ) techniques to quantize the parameter data for each packet with use of a corresponding VQ index, and then determining statistical correlations between consecutive sequences of such VQ indices representative of the corresponding sequences of n packets. The statistic n-gram predictive models so created are then used to predict parameter data for use in representing lost data packets.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
Method and device for compressed-domain packet loss concealment
An error concealment method and device for recovering lost data in the AAC bitstream in the compressed domain. The bitstream are partitioned into frames each having a plurality of data parts including the header / global gain, scale factors and QMDCT coefficients. The data parts are stored in a plurality of buffers, so that if one or more data parts of a current frame is corrupted or lost, the corresponding data part in the neighboring frames is used to conceal the errors in the current frame.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Packet prioritization and associated bandwidth and buffer management techniques for audio over IP
InactiveUS20080151886A1Raise priorityReduce the possibilityData switching by path configurationVoice communicationVoice activity
The present invention is directed to voice communication devices in which an audio stream is divided into a sequence of individual packets, each of which is routed via pathways that can vary depending on the availability of network resources. All embodiments of the invention rely on an acoustic prioritization agent that assigns a priority value to the packets. The priority value is based on factors such as whether the packet contains voice activity and the degree of acoustic similarity between this packet and adjacent packets in the sequence. A confidence level, associated with the priority value, may also be assigned. In one embodiment, network congestion is reduced by deliberately failing to transmit packets that are judged to be acoustically similar to adjacent packets; the expectation is that, under these circumstances, traditional packet loss concealment algorithms in the receiving device will construct an acceptably accurate replica of the missing packet. In another embodiment, the receiving device can reduce the number of packets stored in its jitter buffer, and therefore the latency of the speech signal, by selectively deleting one or more packets within sustained silences or non-varying speech events. In both embodiments, the ability of the system to drop appropriate packets may be enhanced by taking into account the confidence levels associated with the priority assessments.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com