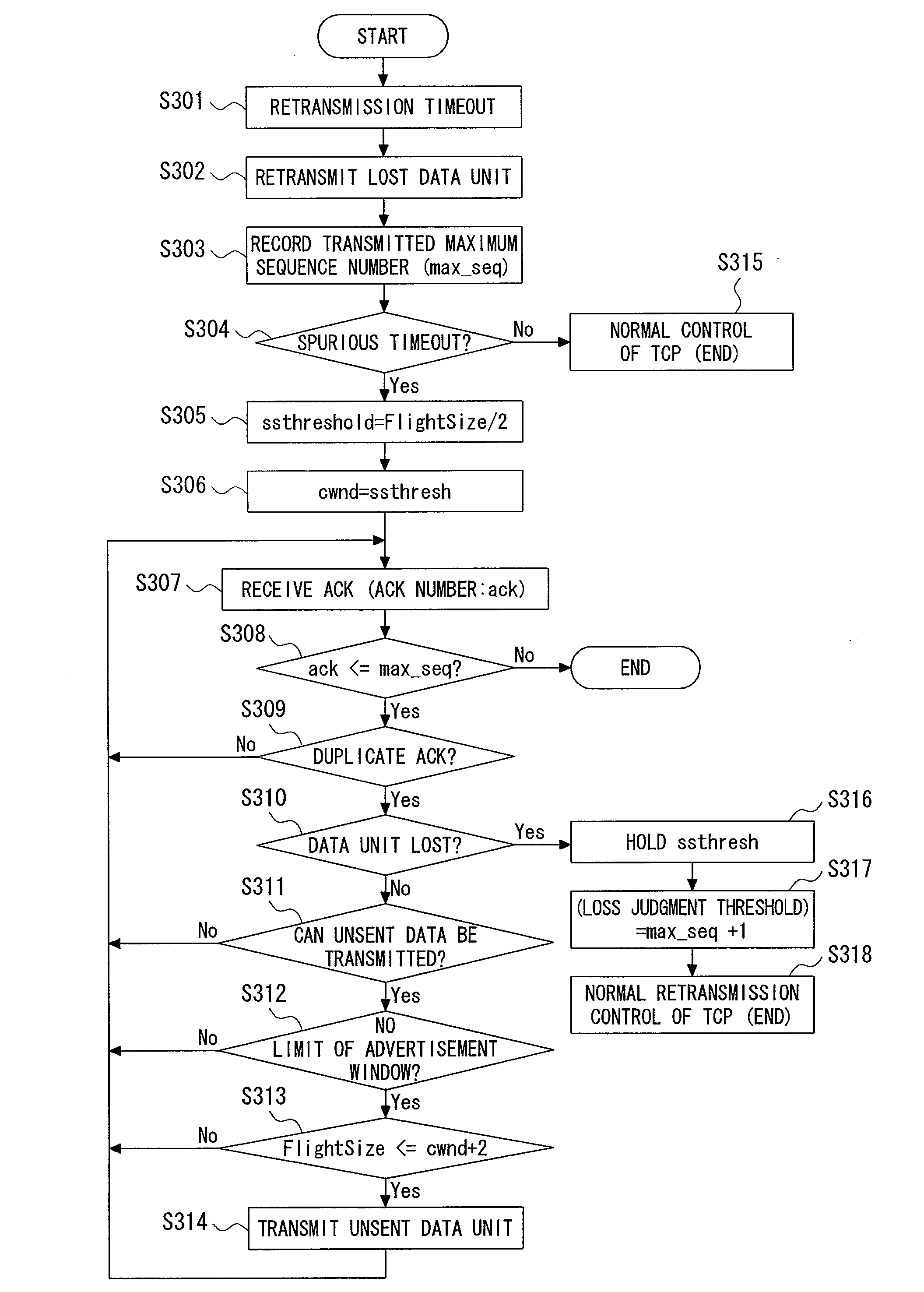
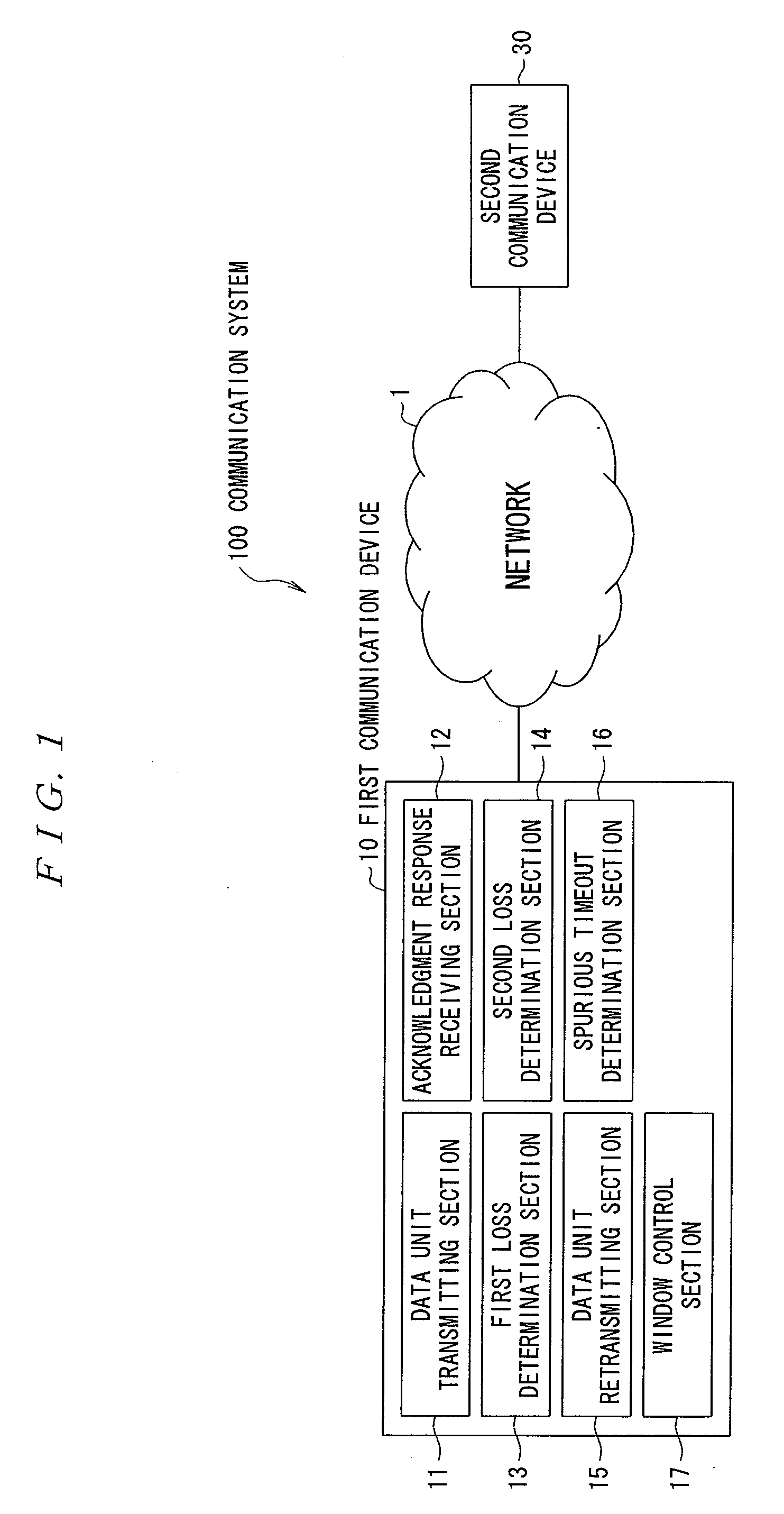
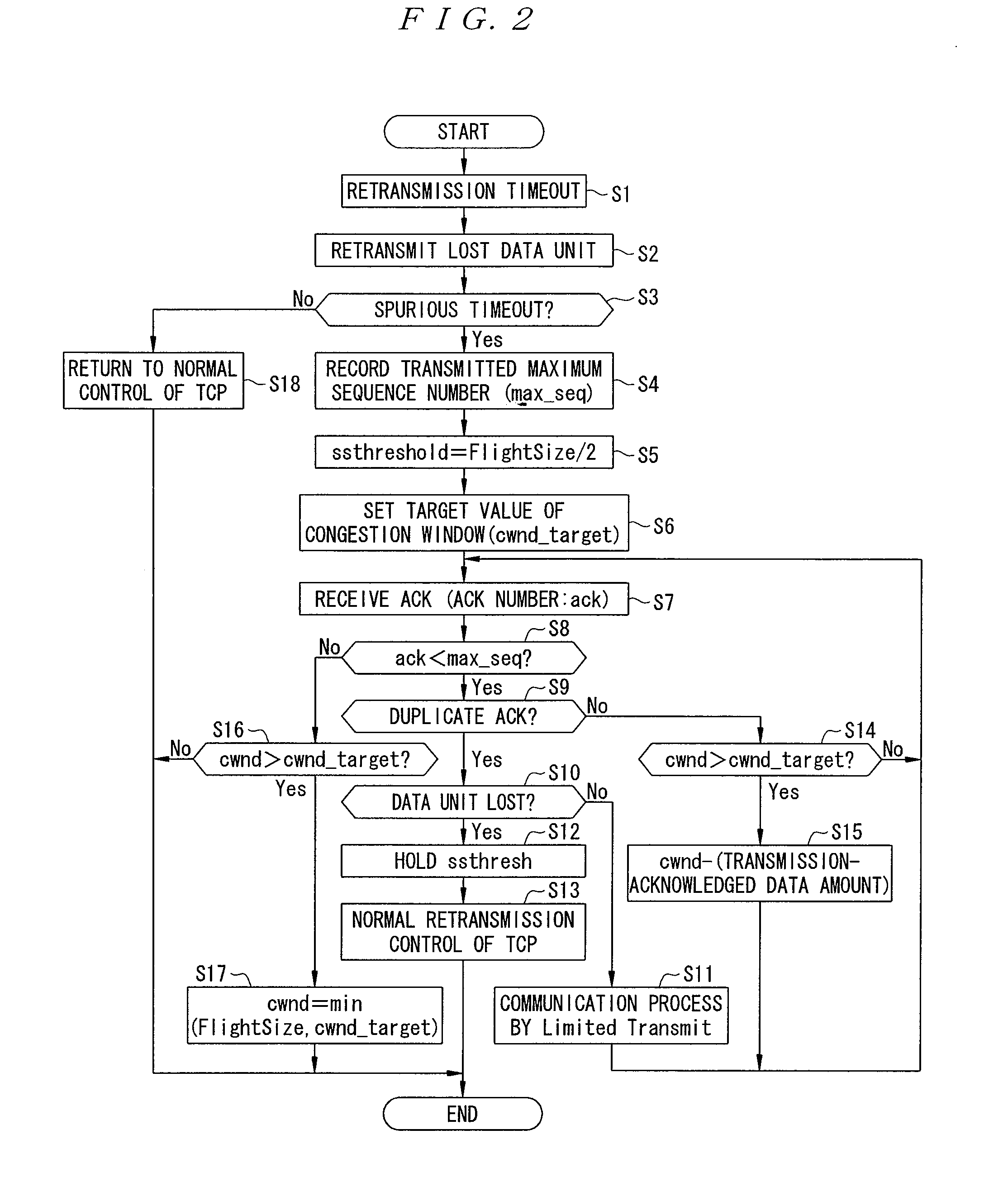
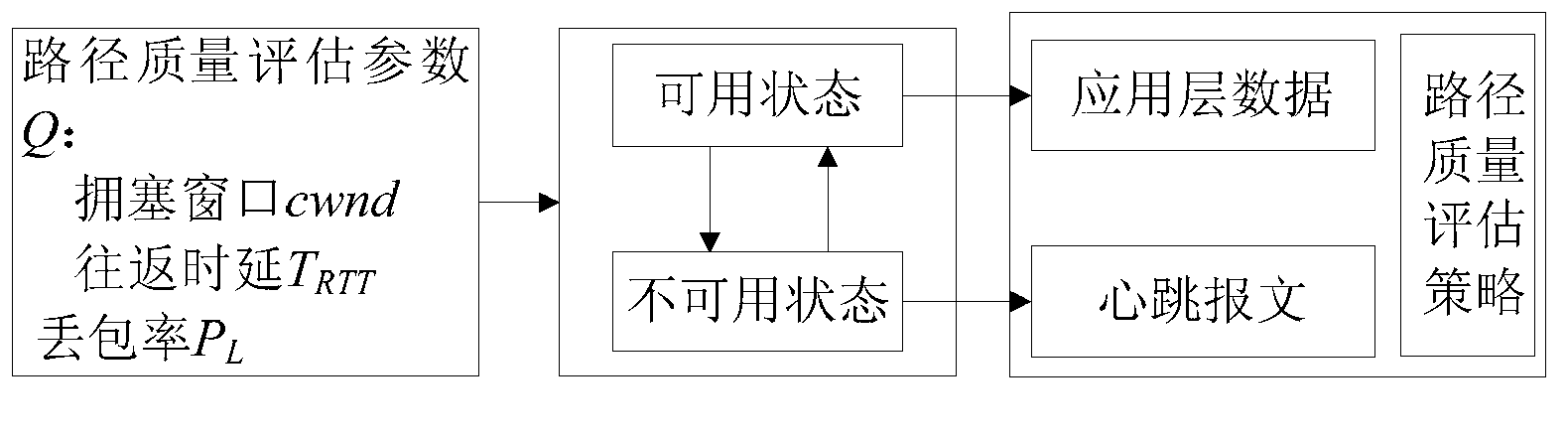
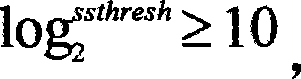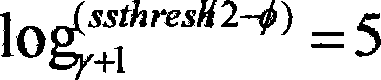Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
360 results about "Congestion window" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
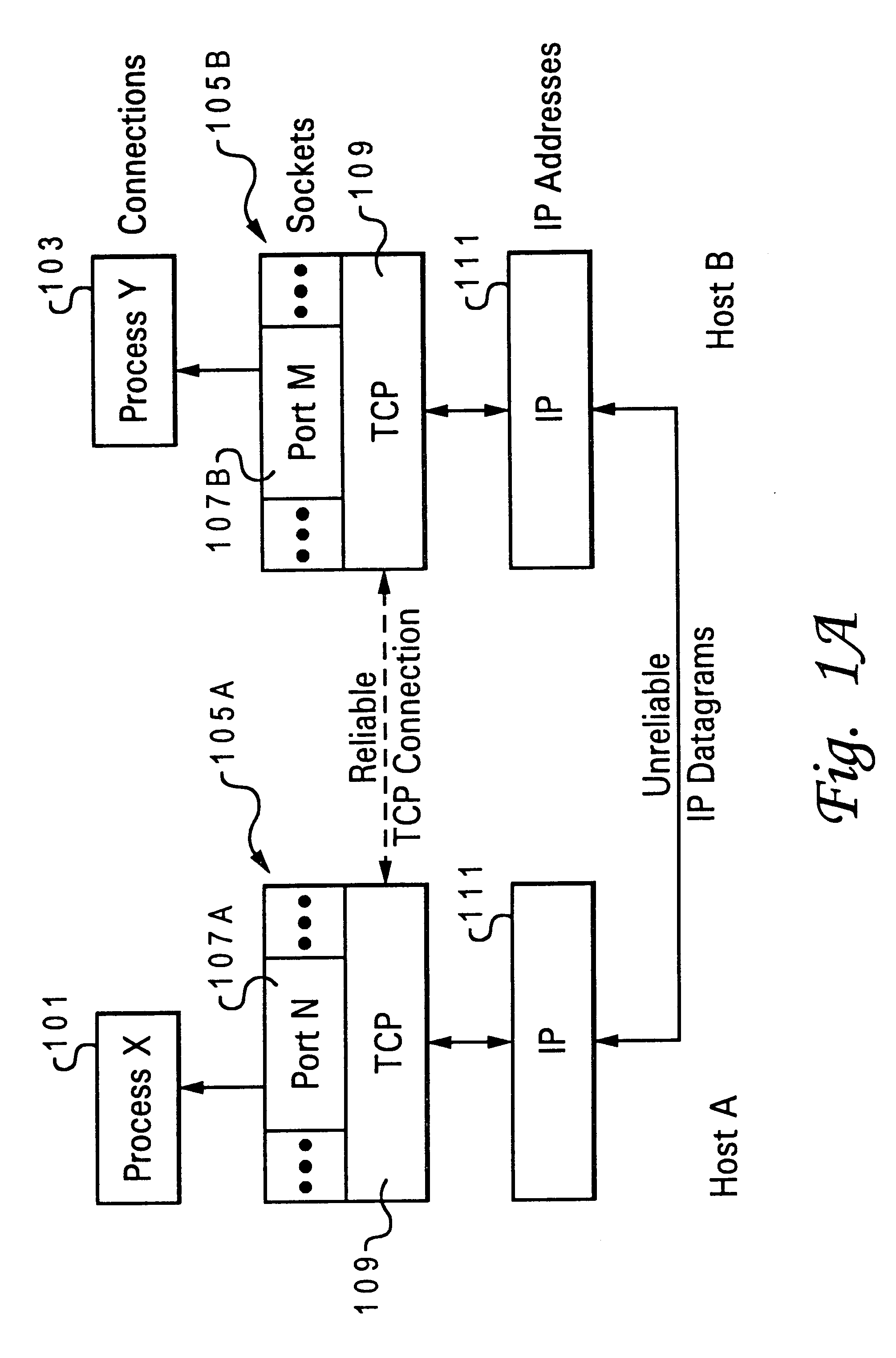
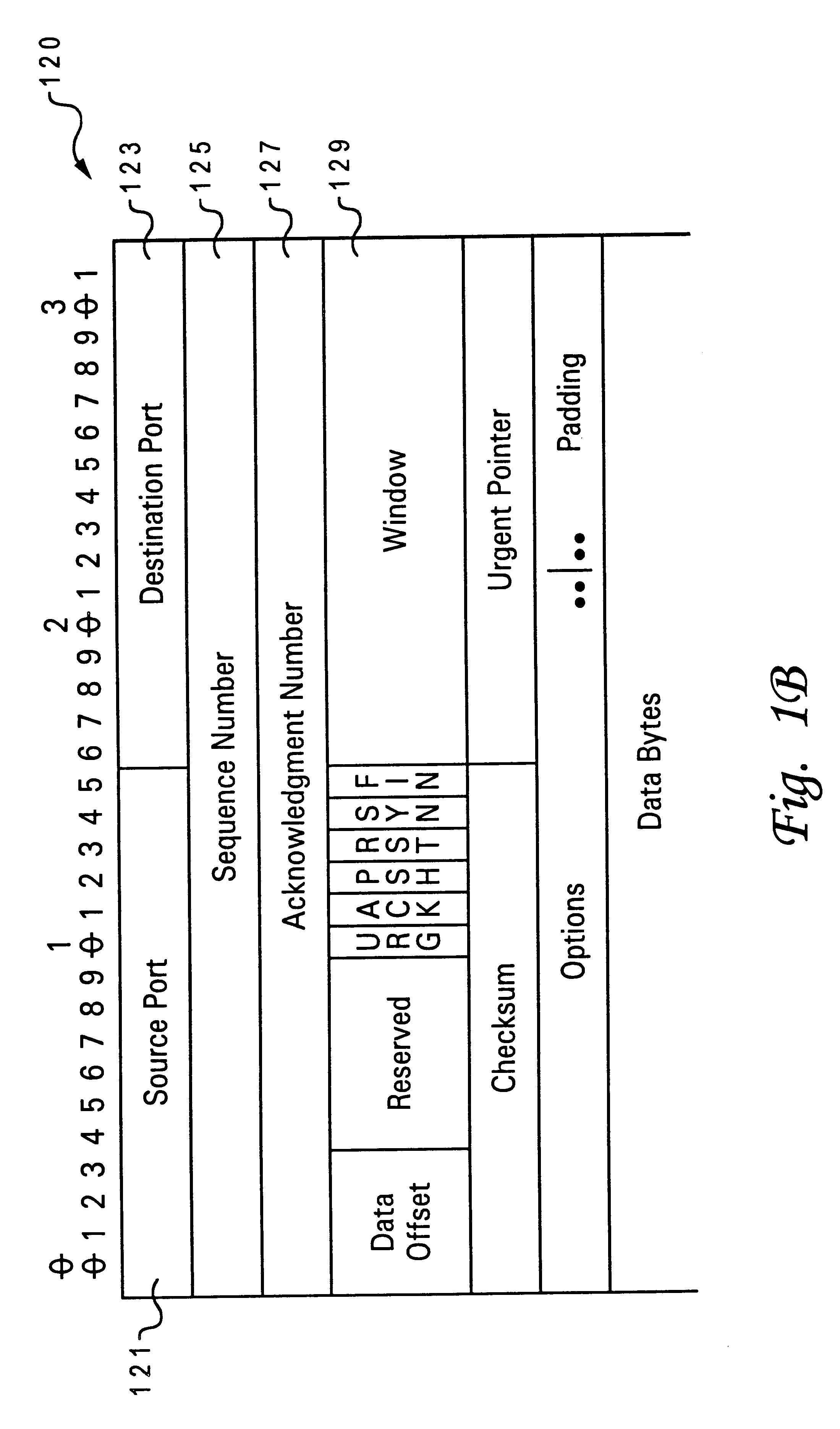
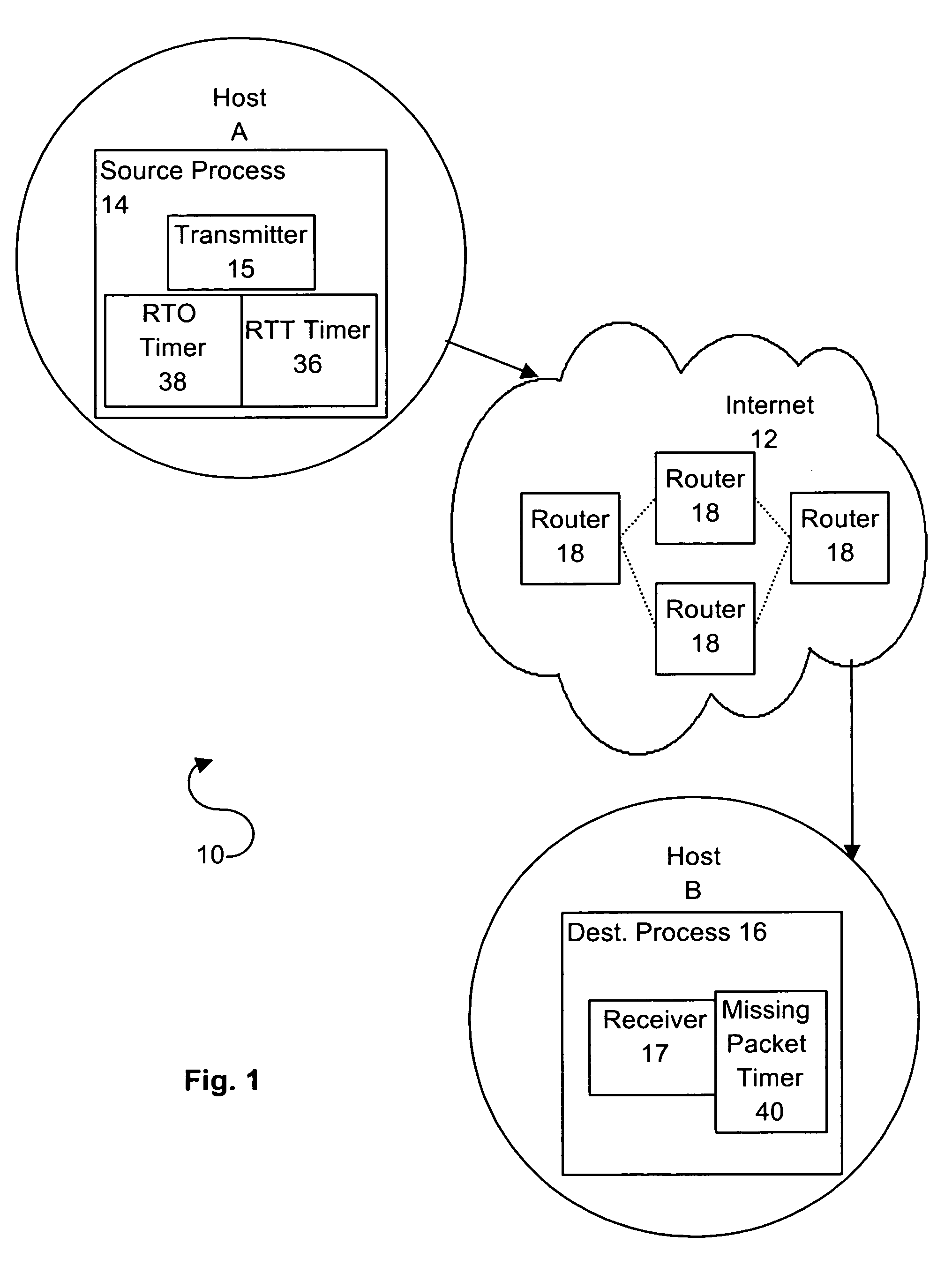
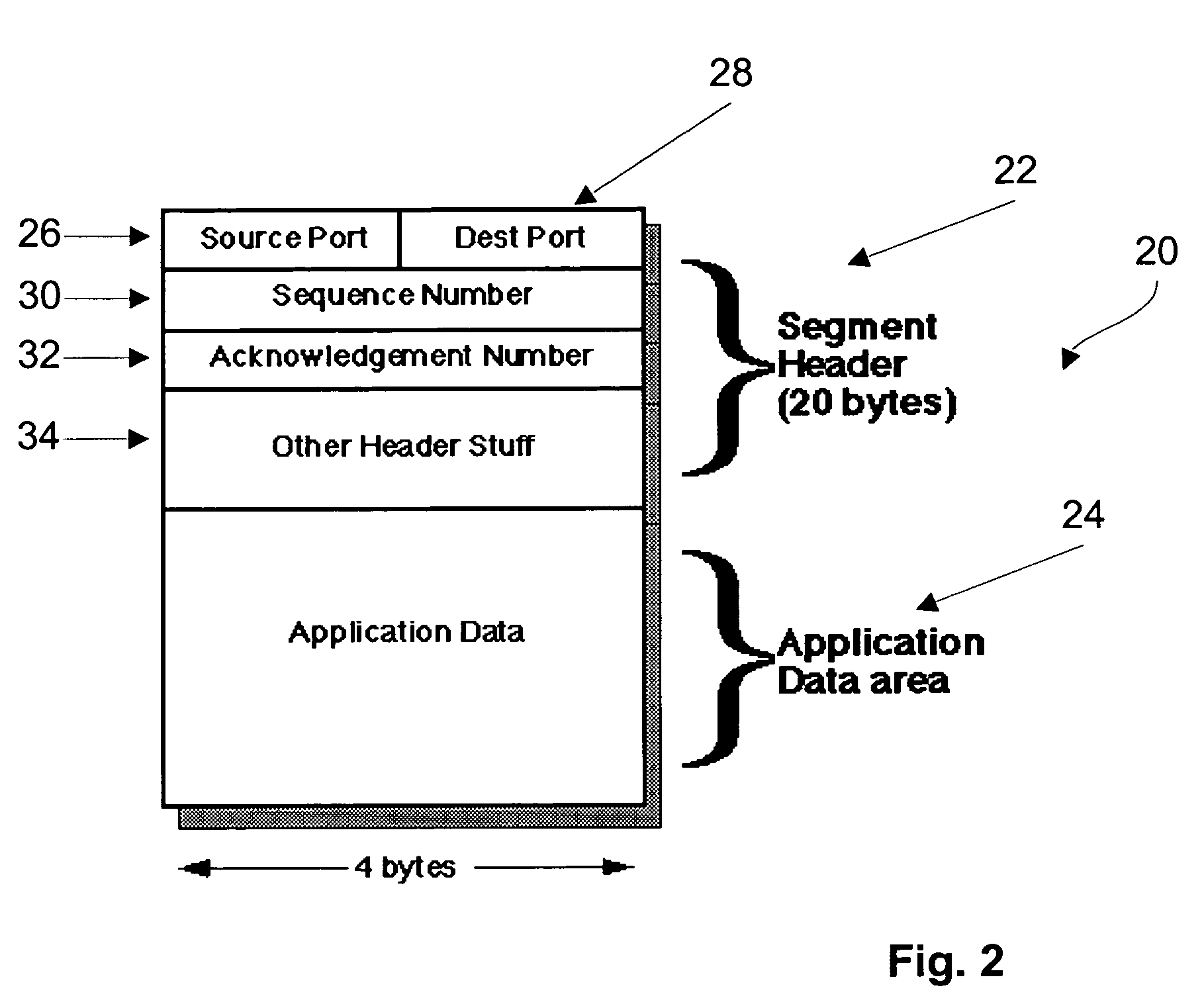
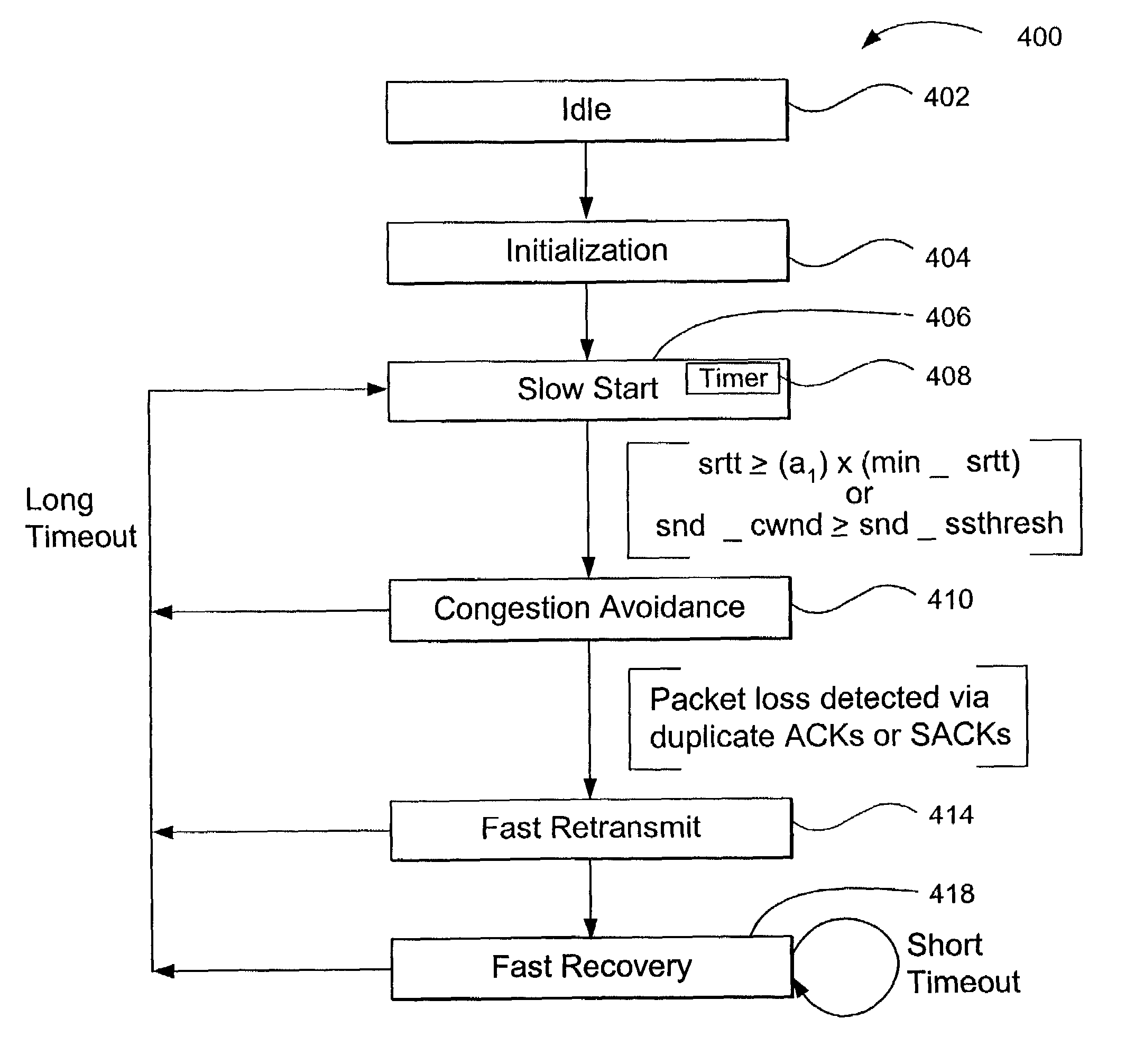
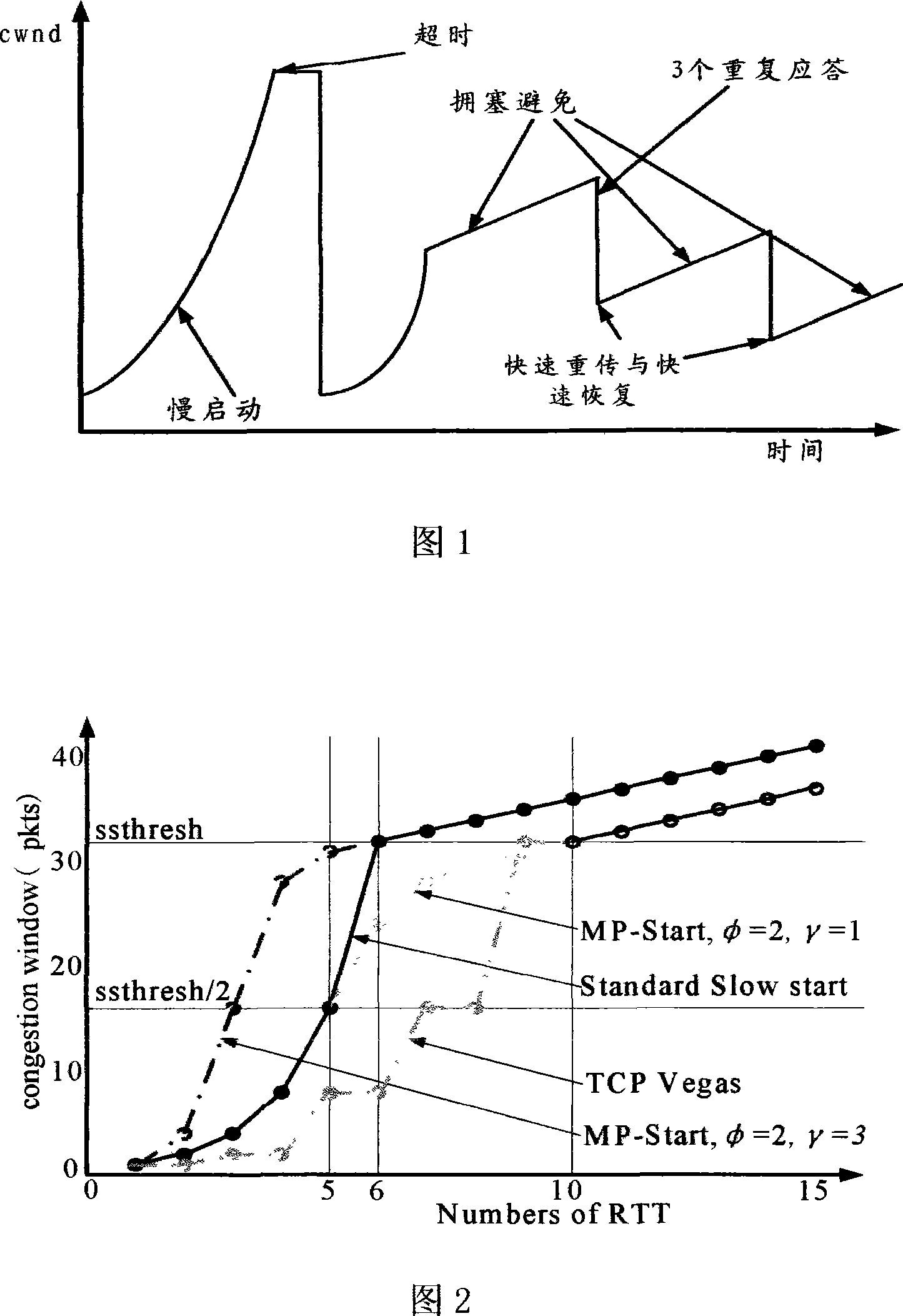
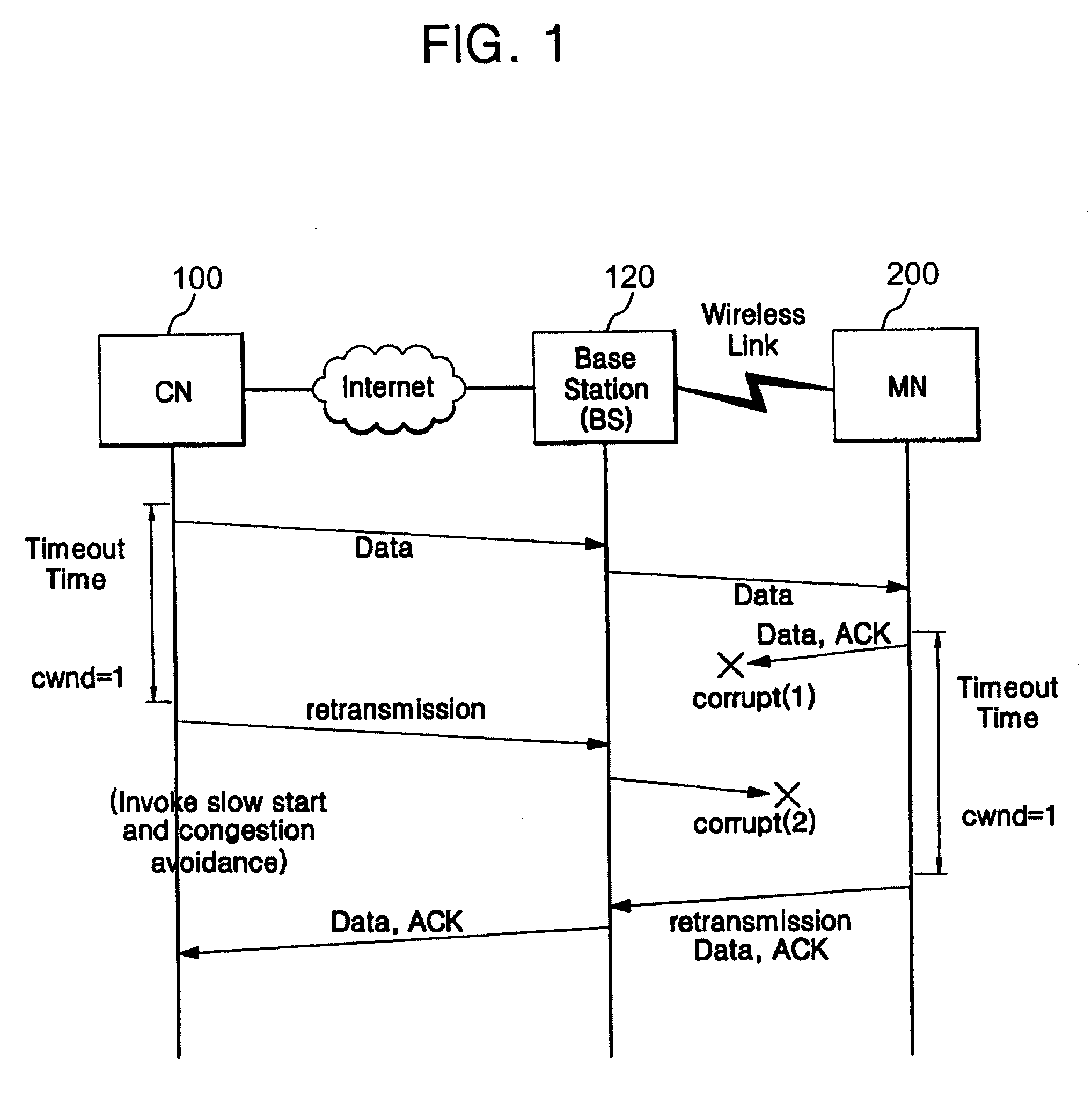
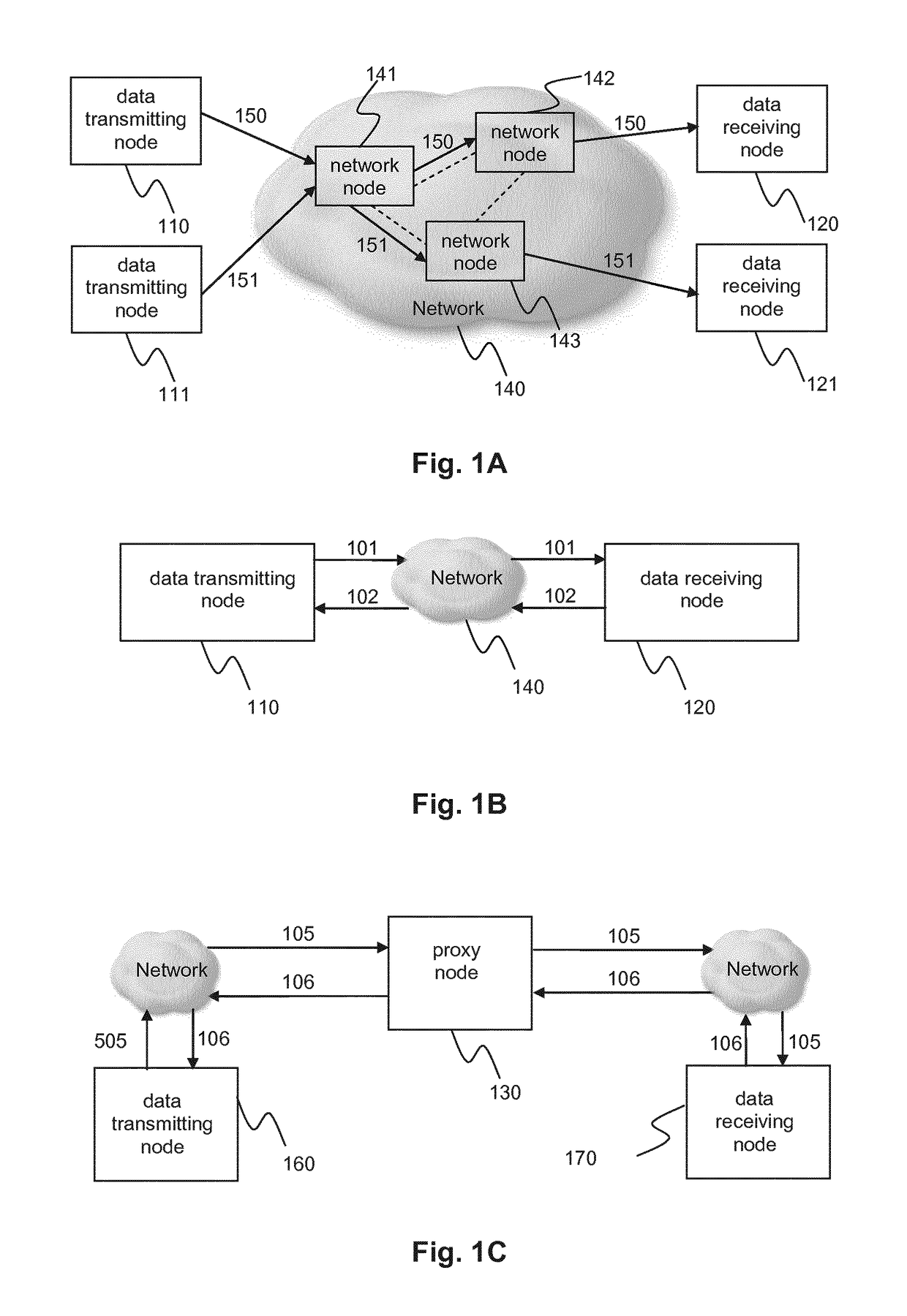
In Transmission Control Protocol, the congestion window is one of the factors that determines the number of bytes that can be outstanding at any time. This is not to be confused with the TCP window size which is maintained by the receiver. This is a means of stopping the link between two places from getting overloaded with too much traffic. The size of this window is calculated by estimating how much congestion there is between the two places. The sender maintains the congestion window. When a connection is set up, the congestion window, a value maintained independently at each host, is set to a small multiple of the maximum segment size allowed on that connection. Further variance in the congestion window is dictated by an Additive Increase/Multiplicative Decrease approach. This means that if all segments are received and the acknowledgments reach the sender on time, some constant is added to the window size. The window keeps growing exponentially until a timeout occurs or the receiver reaches its limit. After this the congestion window increases linearly at the rate of 1/packets on each new acknowledgement received. On timeout:
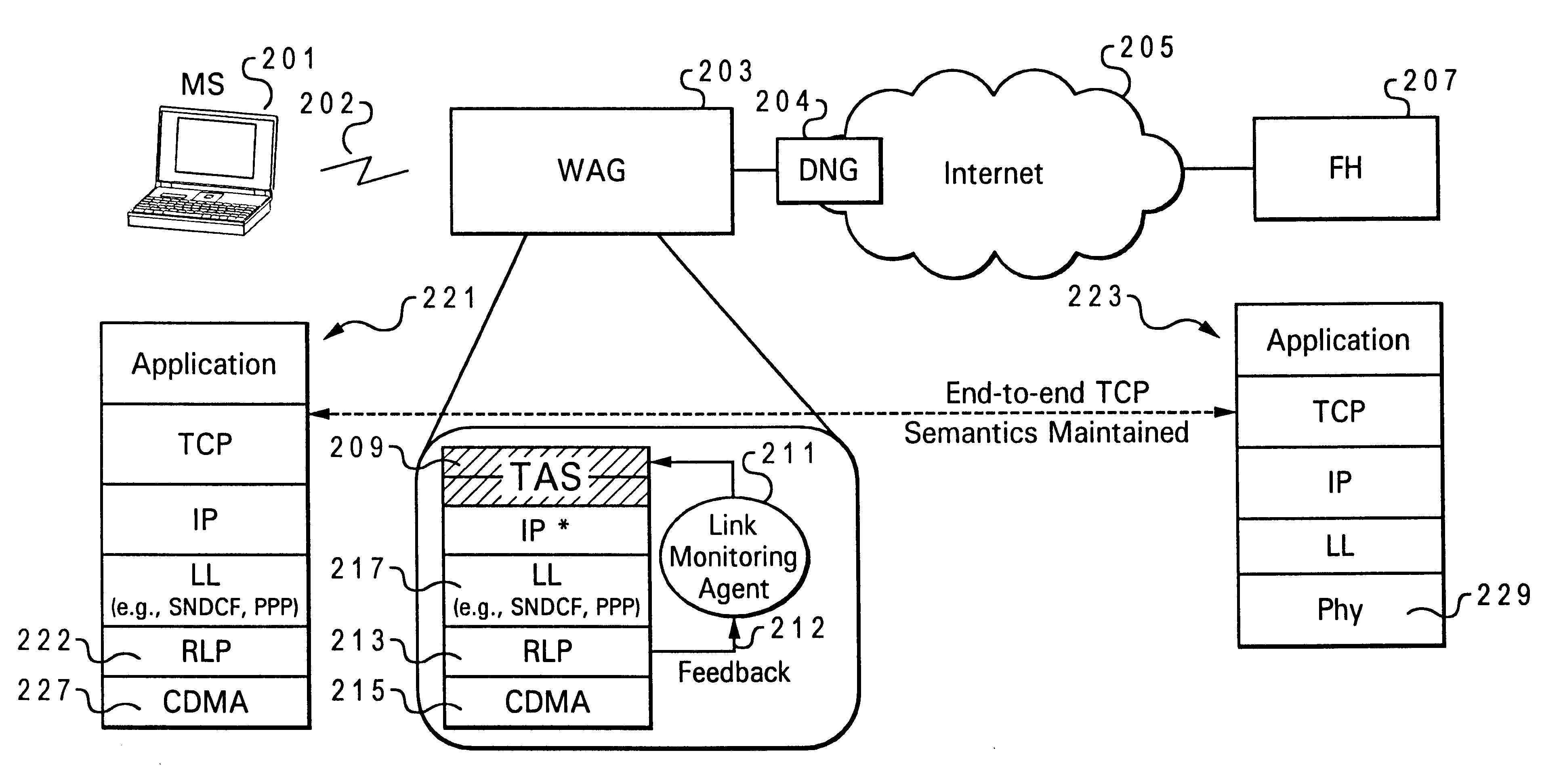
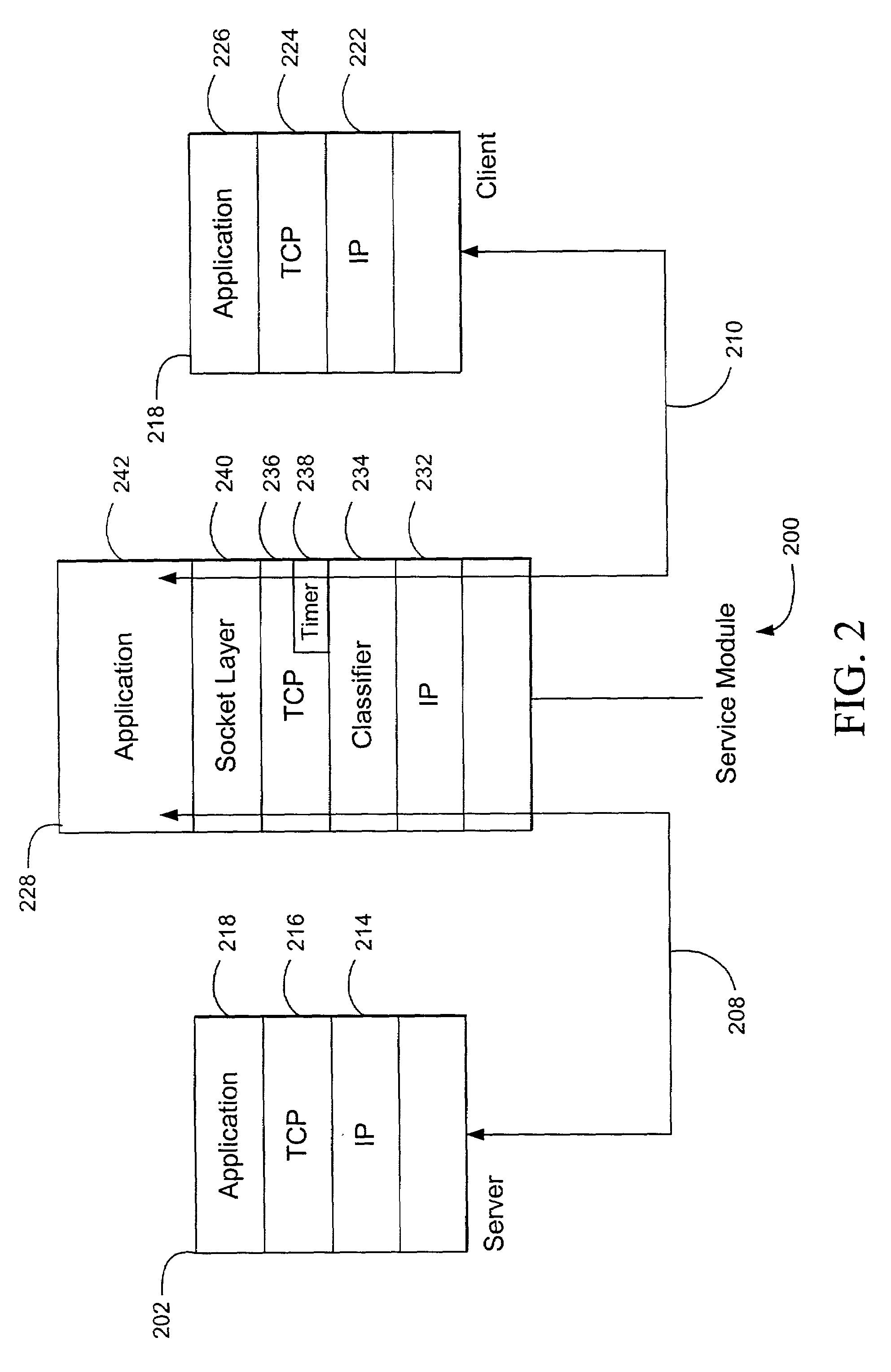
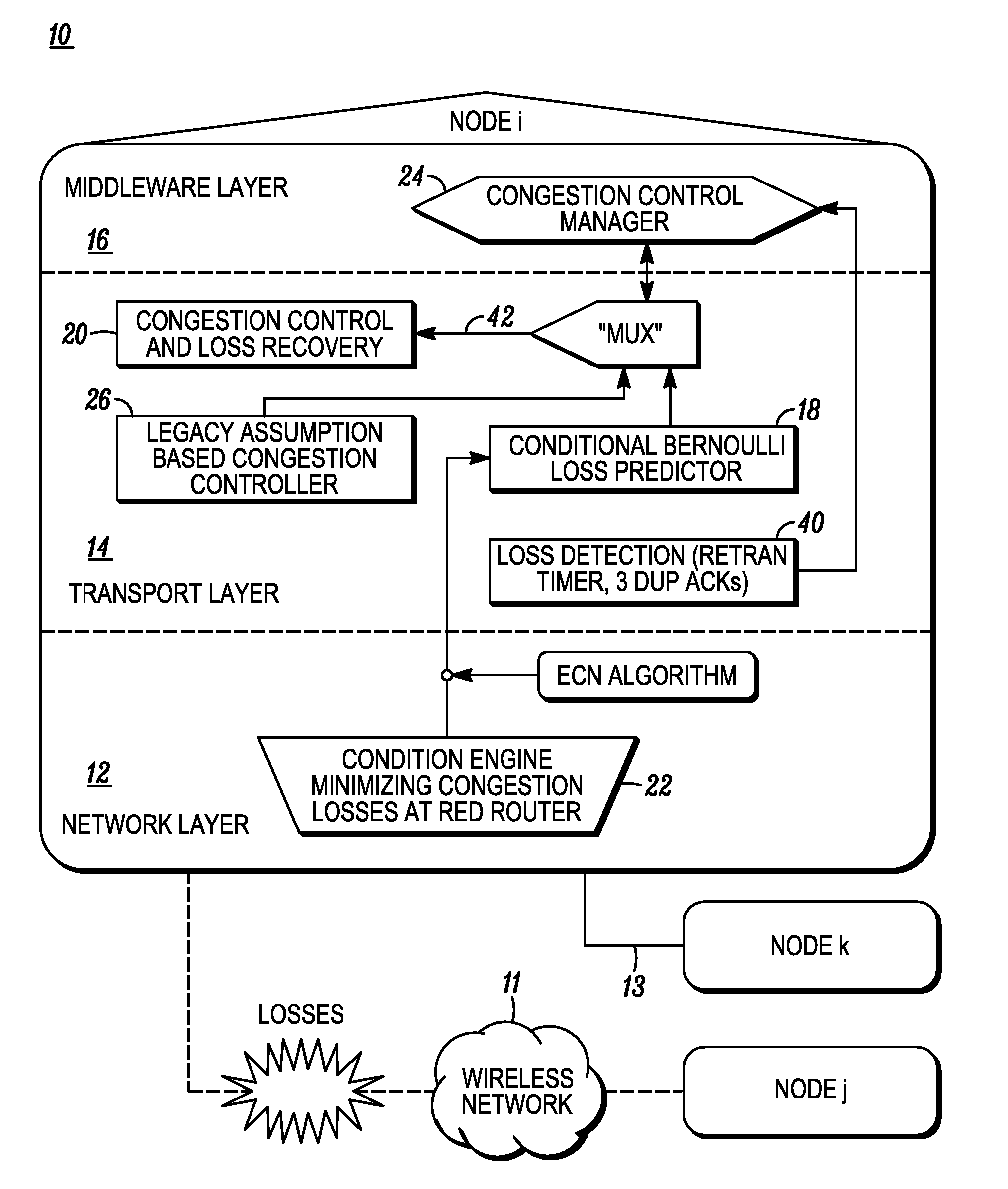
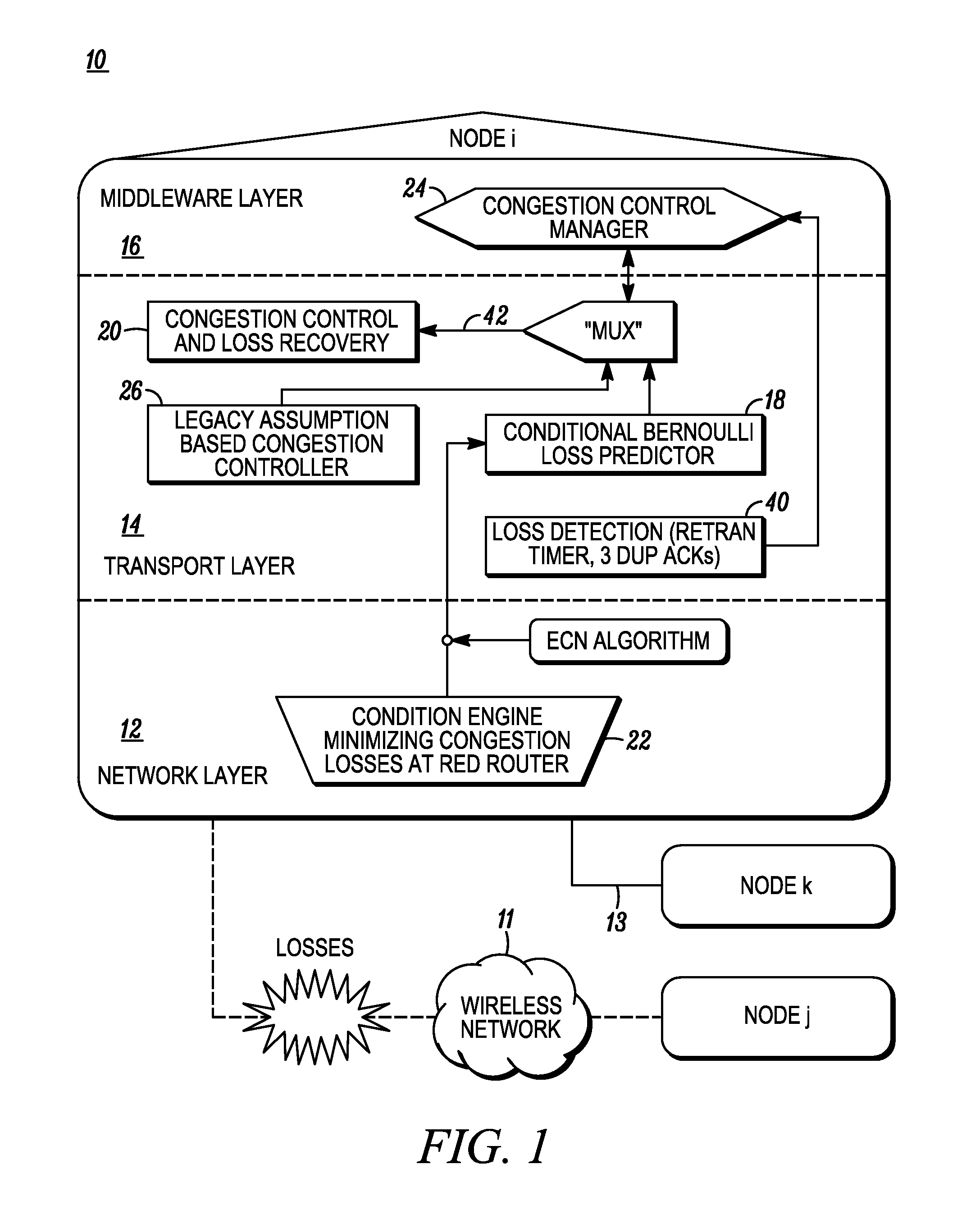
TCP-aware agent sublayer (TAS) for robust TCP over wireless
InactiveUS6208620B1Improve performanceMinimize impactError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsCongestion windowTransport control protocol
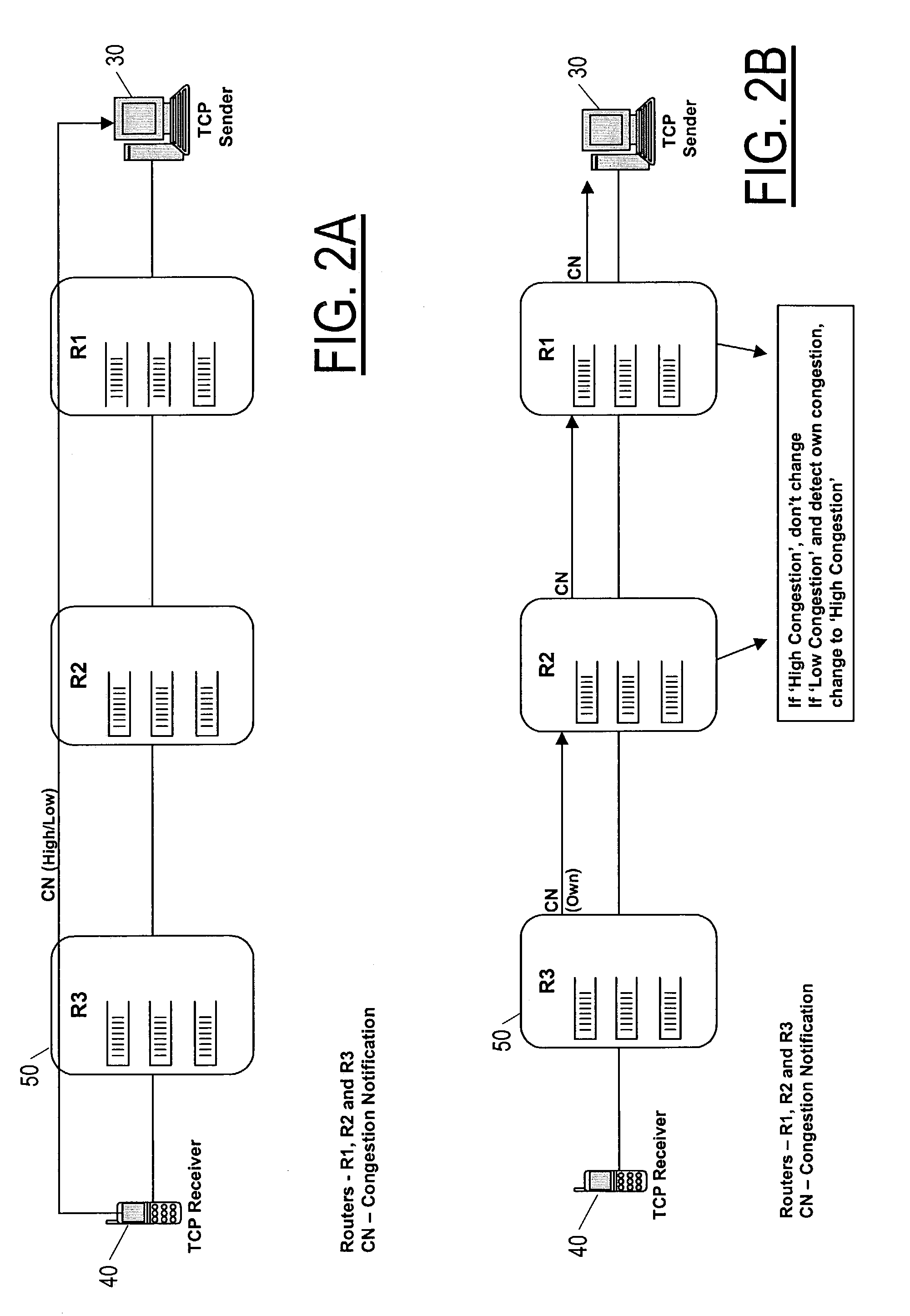
Disclosed is a system for minimizing the effects of faults over an air link of a wireless transmission channel utilizing Transport Control Protocol (TCP). The system includes a TCP-Aware Agent Sublayer (TAS) in a protocol stack, which has a mechanism for caching both TCP packets during forward transmission and acknowledgment (ACK) return packets. The caching mechanism is located near a wireless link of the wireless transmission channel. The system also includes a link monitoring agent coupled to the TAS. The link monitoring agent monitors the condition of the wireless transmission channel for an occurrence of a predefined fault. Once a predefined fault is detected, a system response is implemented based on the type of fault encountered. When the fault is an air link packet loss, an associated packet is immediately retransmitted from the cache, and when the fault is a temporary disconnect, a congestion window of the TCP source is closed.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
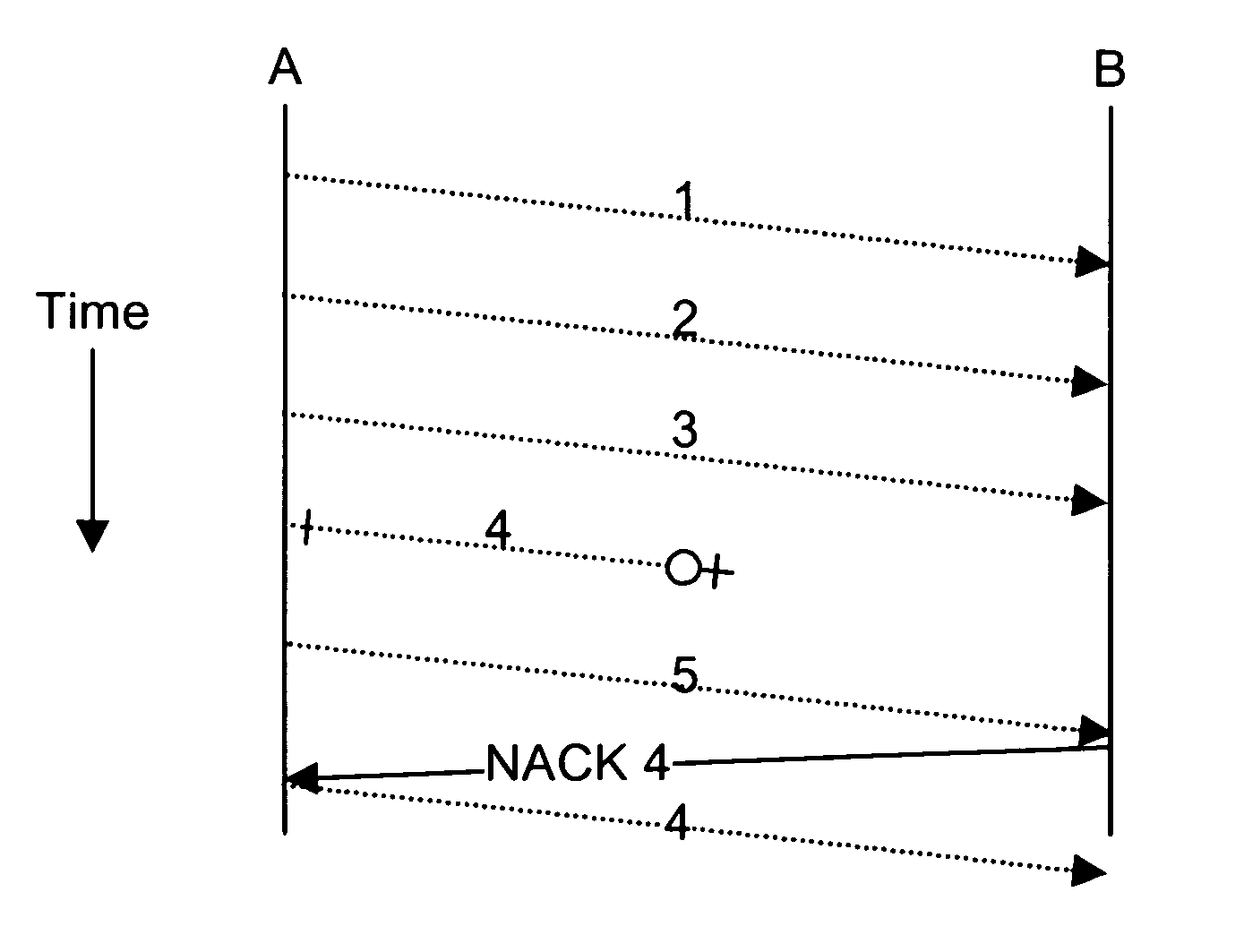
System and method for a negative acknowledgement-based transmission control protocol
InactiveUS7035214B1Shorten the lengthError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsCongestion windowTraffic capacity
A system and method for transmitting data in a data communications network, using a transmission control protocol, to provide reduced acknowledgment control traffic, error recovery and congestion control. A communications link is established between a transmitter and a receiver. Setting the communications link includes setting a network congestion window to an initial length. A sequence, or stream, of data packets is sent from the transmitter to the receiver. The receiver detects any missing packets, by examining the sequence numbers of the incoming packets, and sends negative acknowledgments, generally no more than four, to the transmitter identifying the missing data packet. When the transmitter receives a negative acknowledgment, it decreases the length of the congestion window, and re-transmits the missing packet. Detection and use of round-trip time, re-transmission time-out are provided.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Communication system
ActiveUS20050286416A1Low costEfficient use ofError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsCongestion windowCommunications system
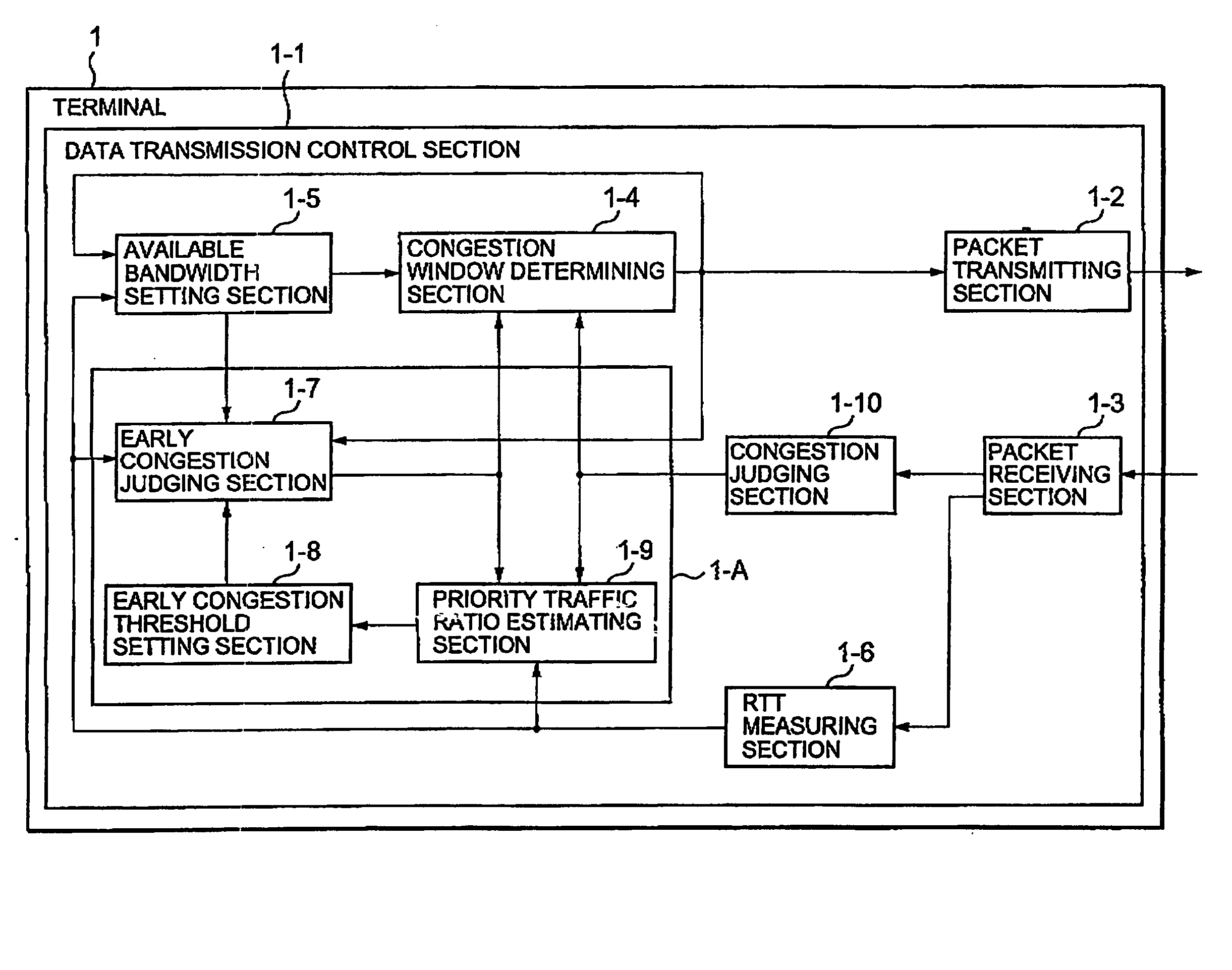
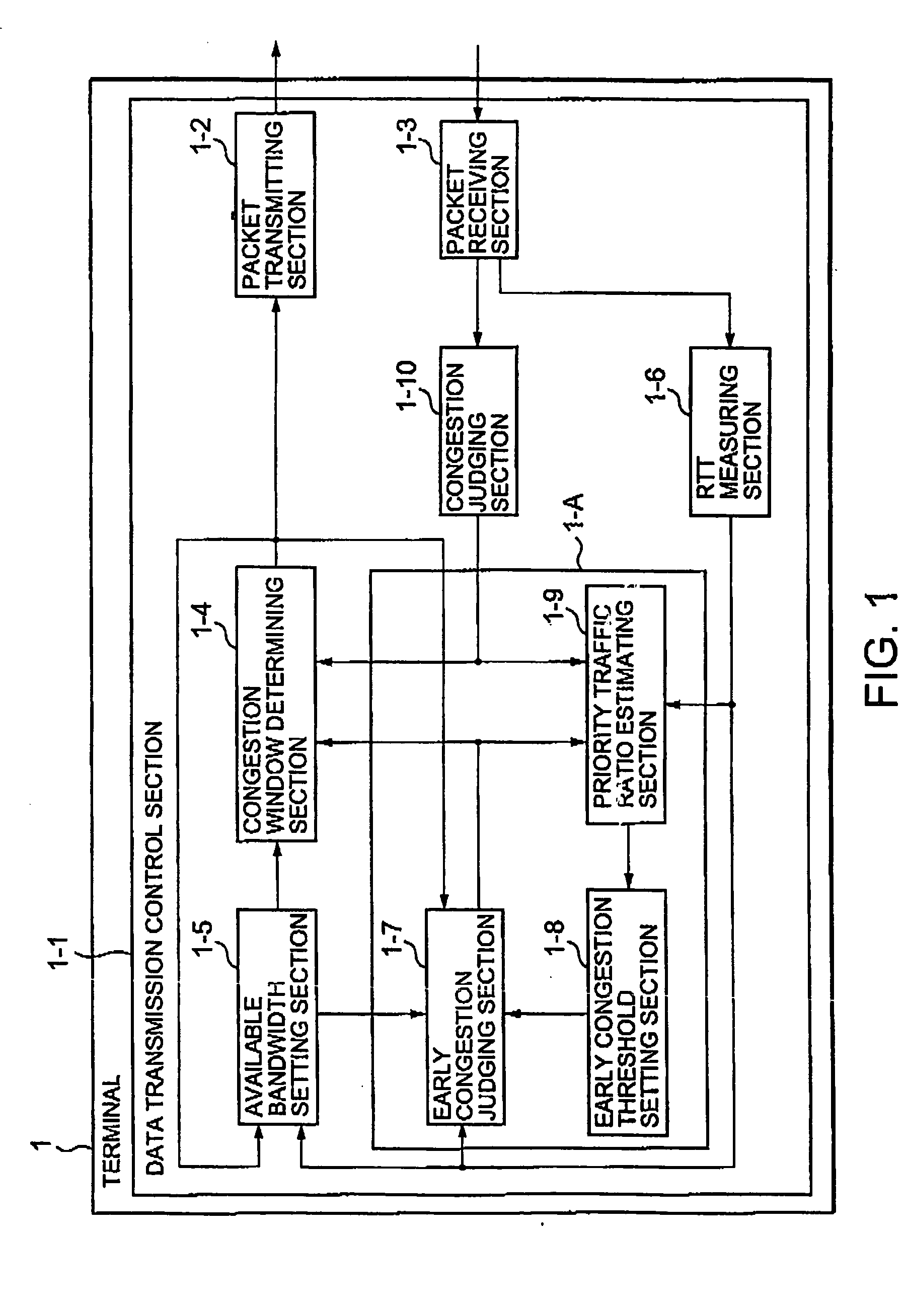
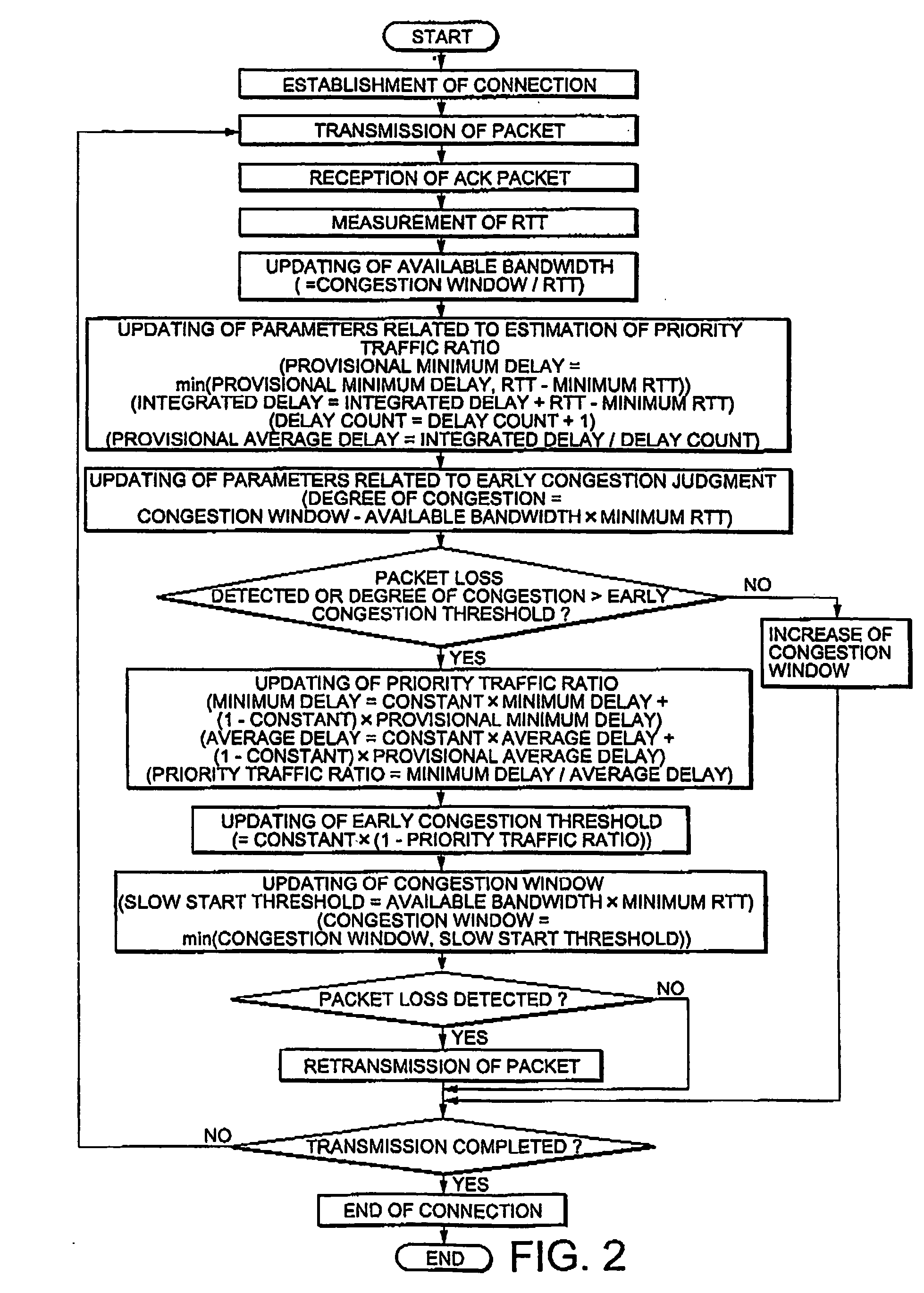
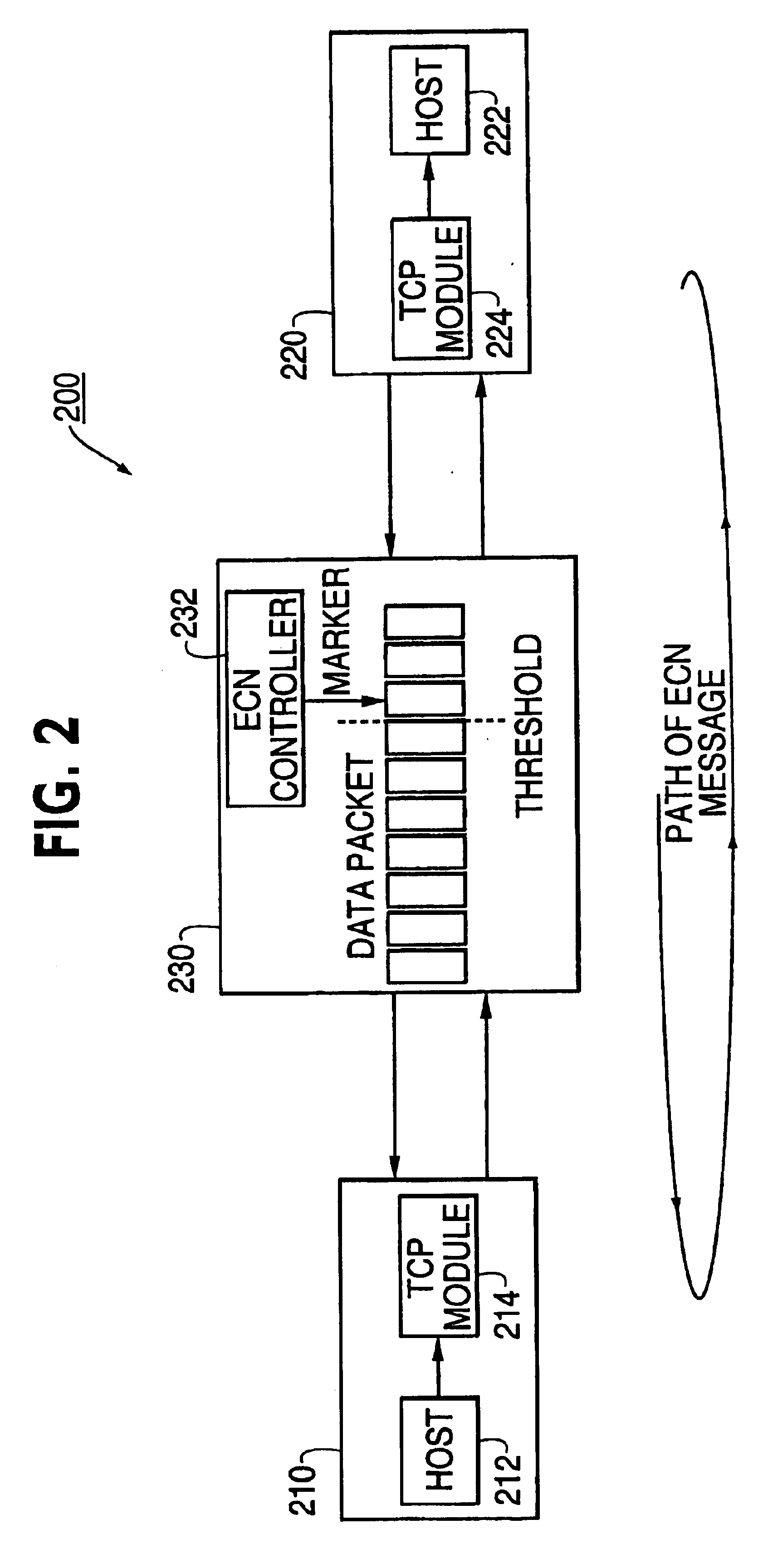
A communication terminal (1) on a transmission side comprises means (1-10) for detecting congestion, means (1-7) for detecting a sign of congestion with reference to an ideal congestion window size and a current congestion window size, means for estimating a ratio of priority traffic with respect to traffic within a network, and means (1-6) for dynamically changing a threshold value for detection of the sign of congestion in response to the estimated ratio. When the congestion or the sign of congestion is detected, a congestion window size is changed into the idea congestion window size.
Owner:NEC CORP +1
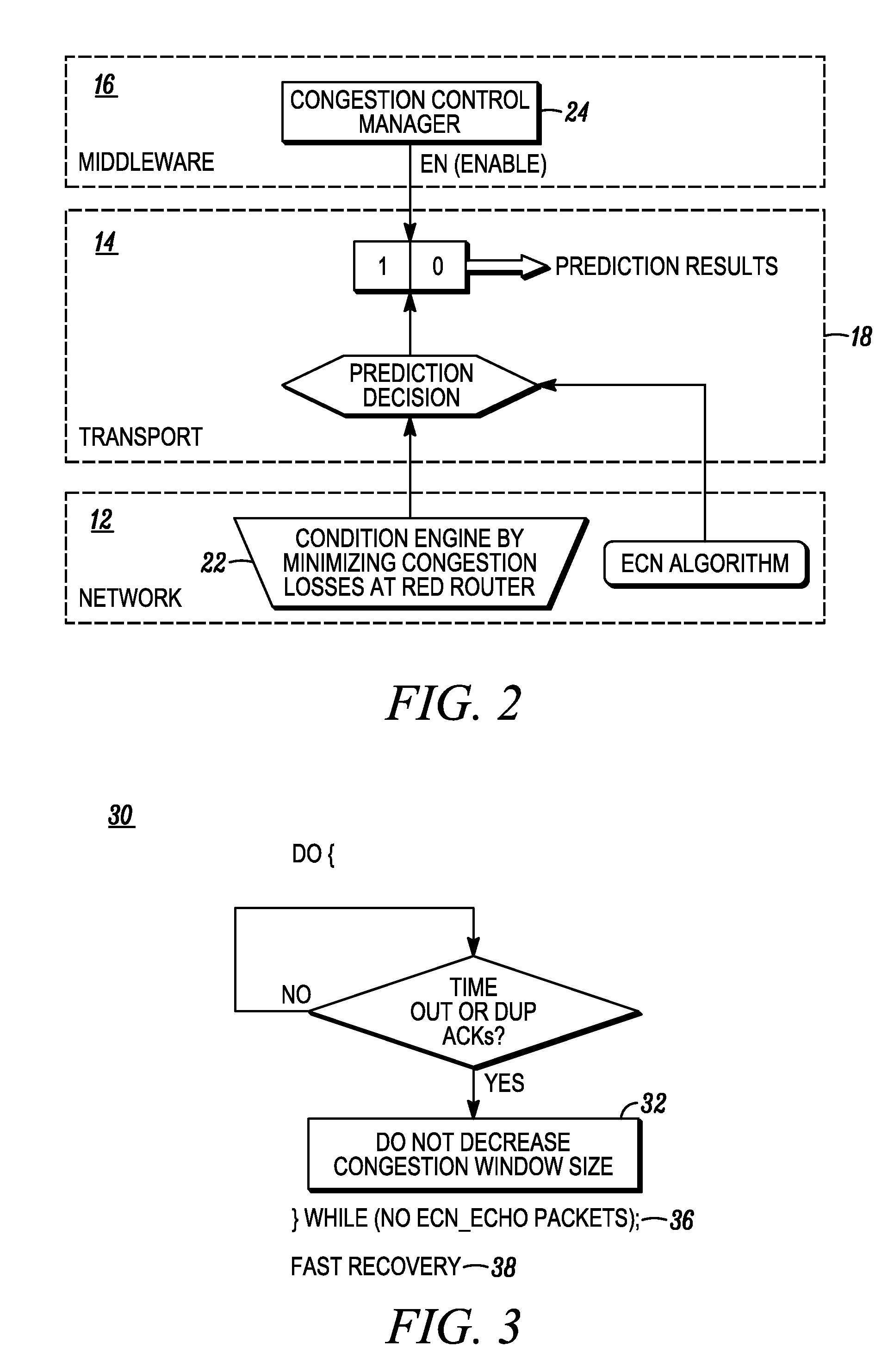
Enhancement of explicit congestion notification (ECN) for wireless network applications
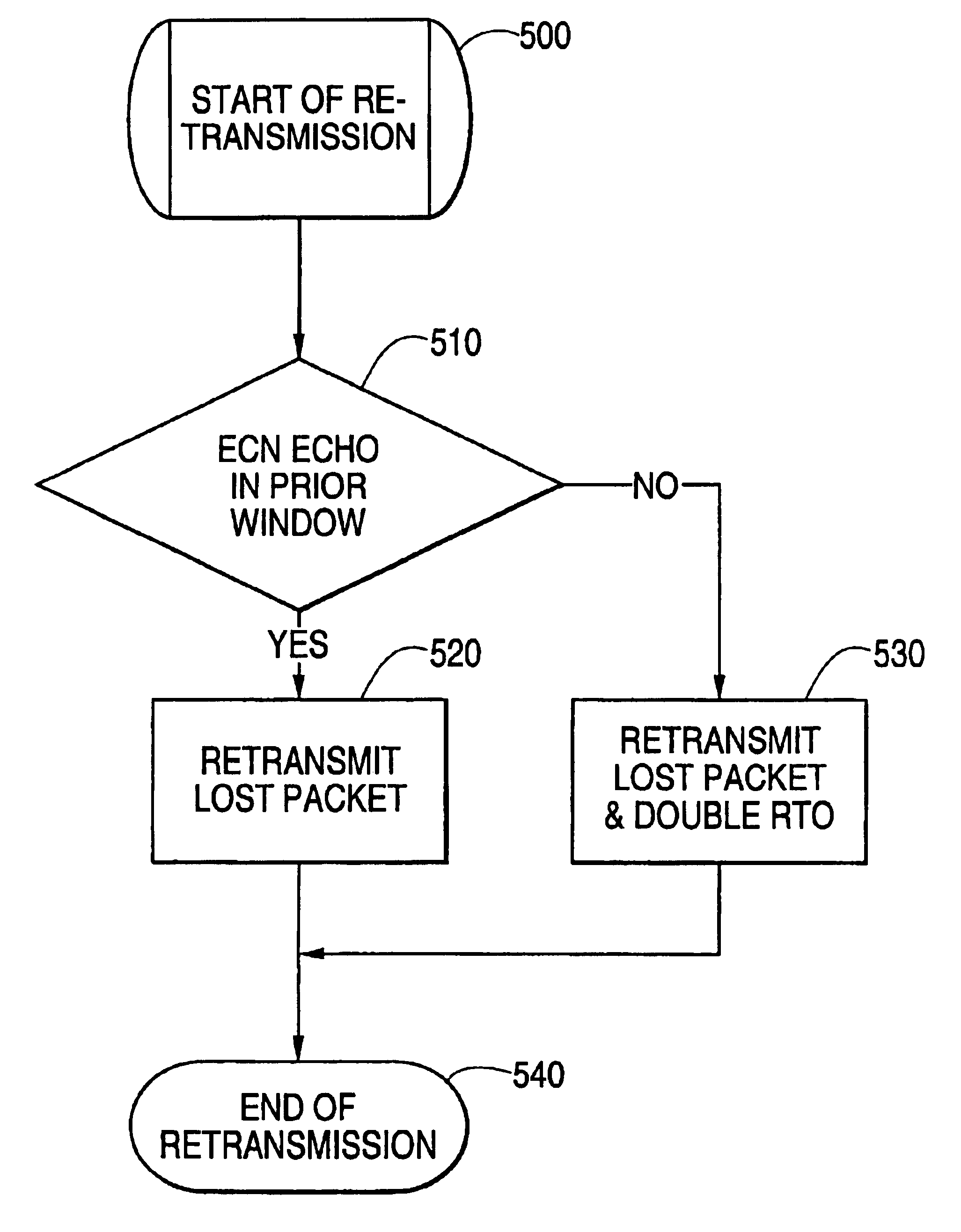
An Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN) method is disclosed for wireless applications to avoid network congestion in a TCP / IP packet-switched network. Such method comprises transmitting, at a source node, data packets to a destination node, via at least an intermediate node; determining, at the intermediate node, if an incipient congestion is encountered, setting a Congestion Experienced (CE) flag in each data packet to notify congestion; sending, at the destination node, an ECN-Echo acknowledgment packet back to the source node to inform congestion; reducing, at the source node, a congestion window and a transmission rate to avoid congestion; if the packet loss is due to congestion, re-transmitting, at the source node, only a lost packet to the destination node; alternatively, if the packet loss is due to transmission error, re-transmitting, the lost packet to the destination node, while increasing a round-trip timeout but maintaining the same congestion window.
Owner:VRINGO INFRASTRUCTURE +2
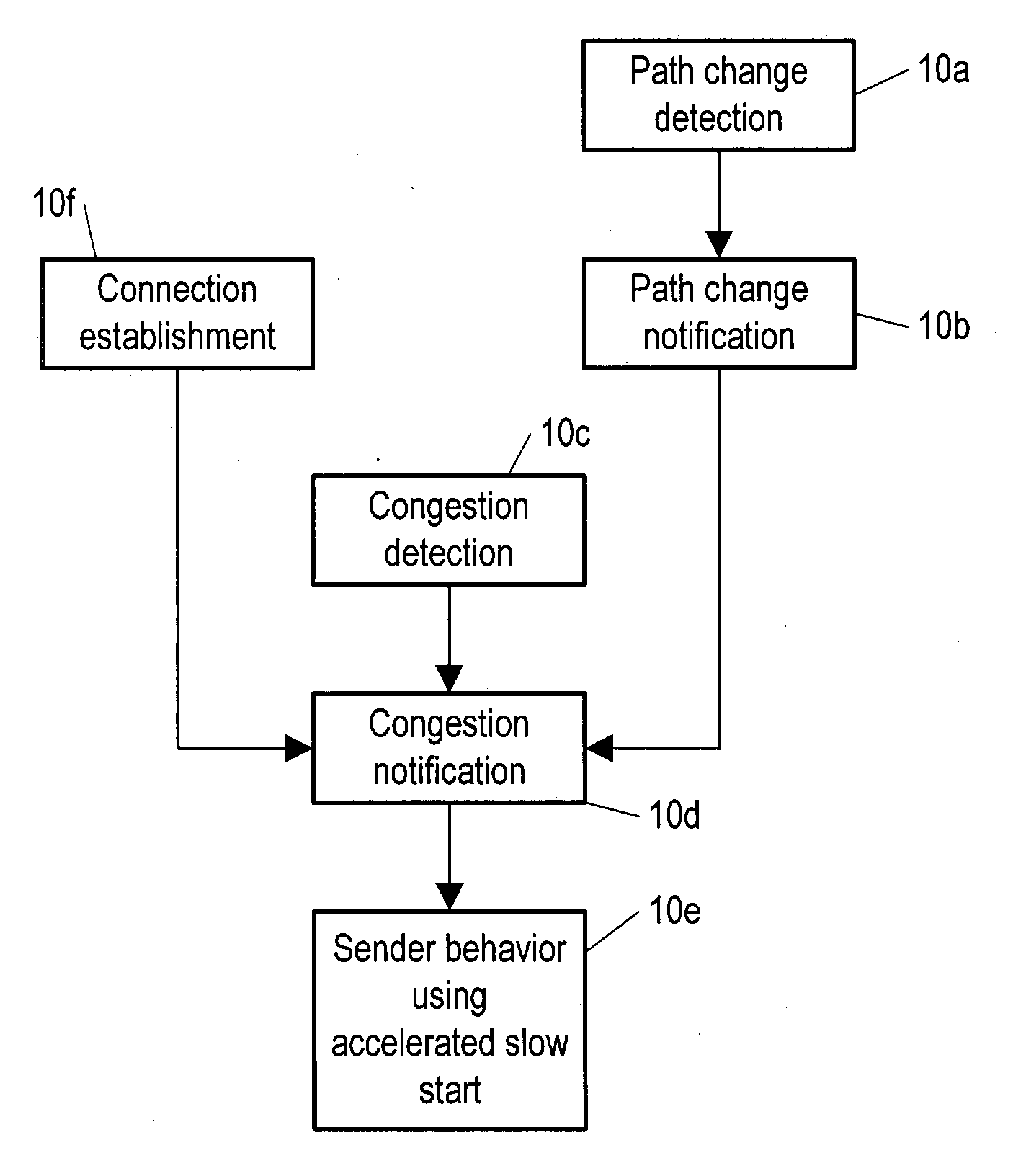
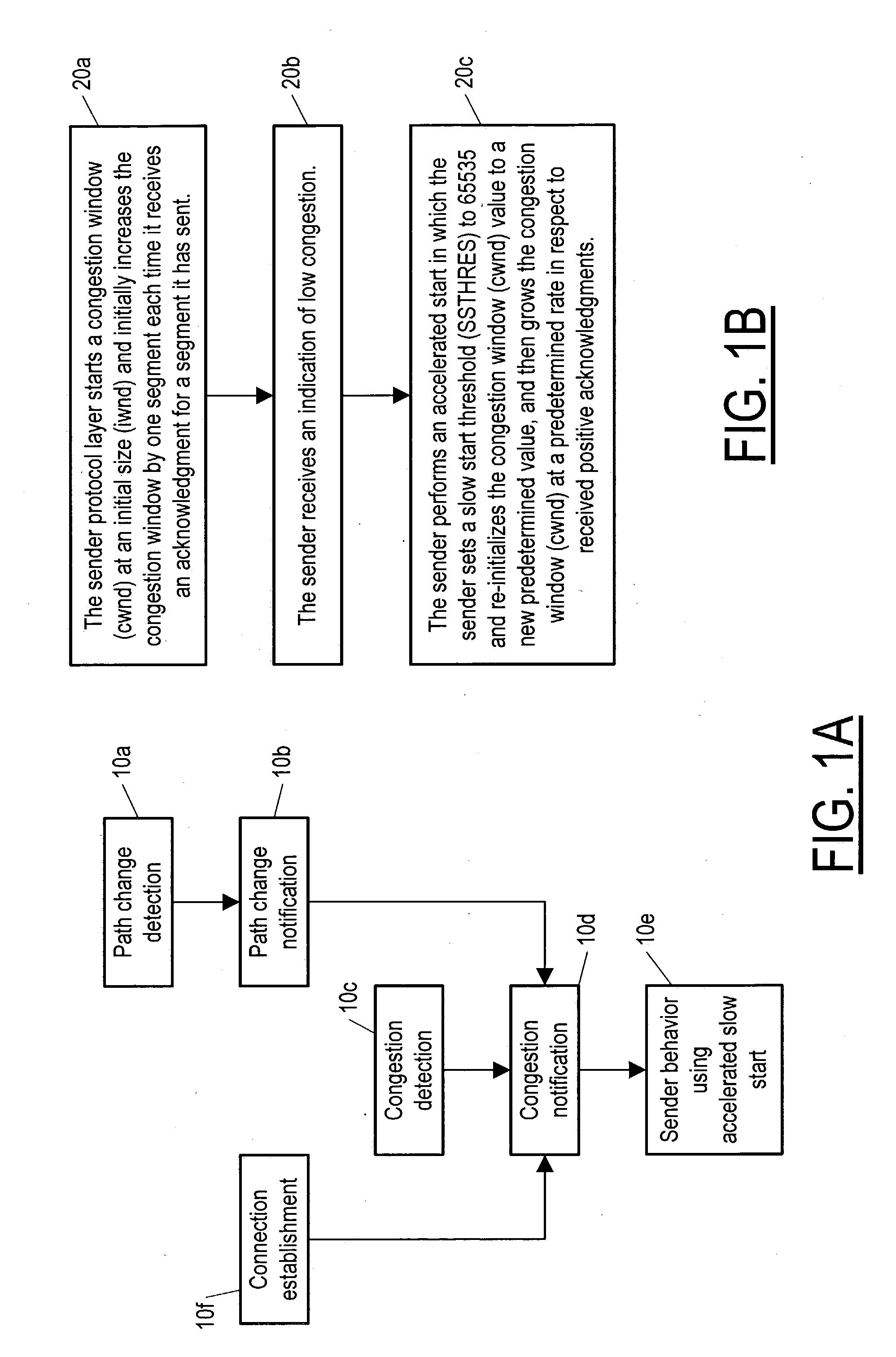
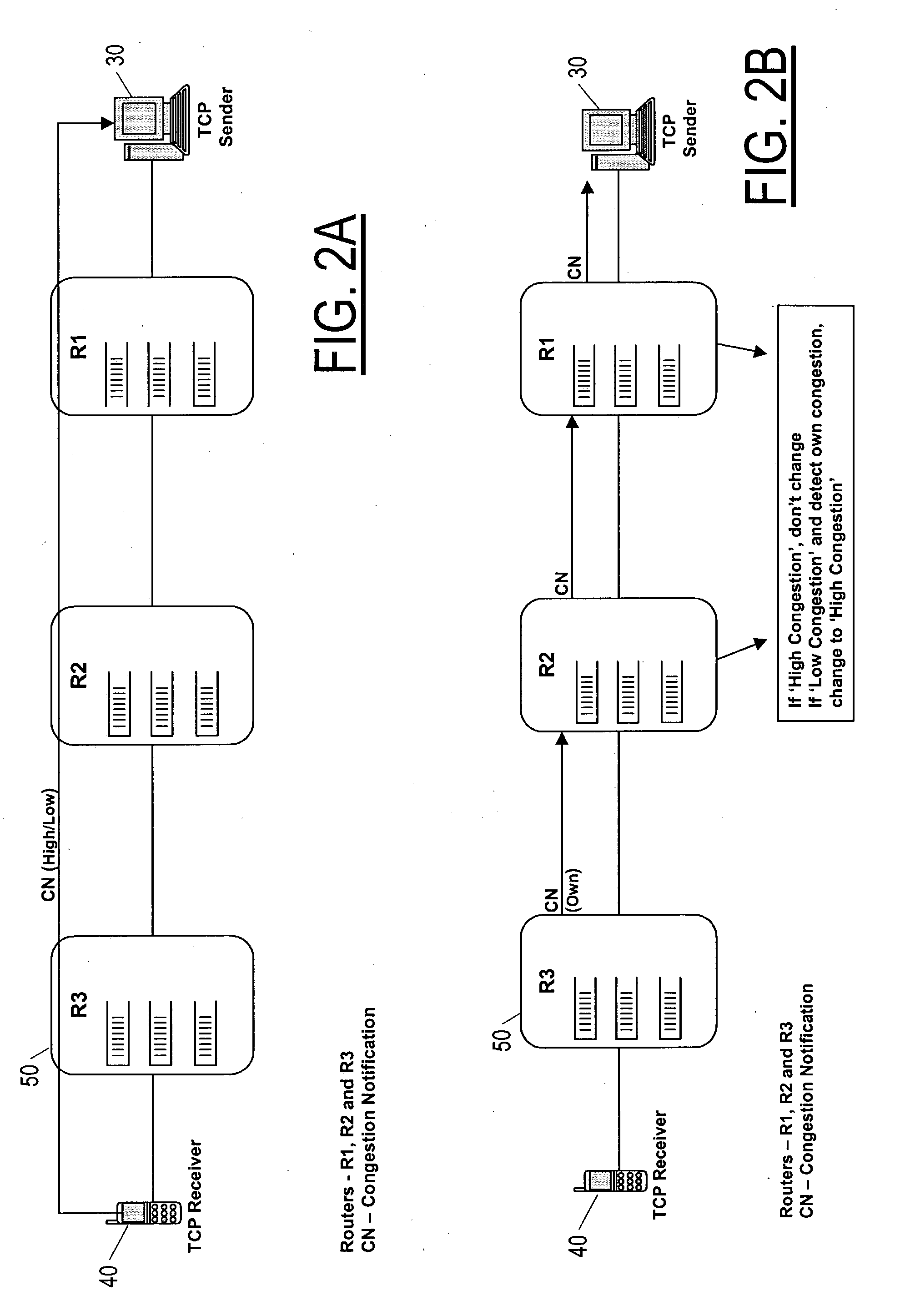
Method and apparatus for accelerating throughput in a wireless or other telecommunication system
ActiveUS7263067B2Frequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork traffic/resource managementCongestion windowSlow-start
Owner:RPX CORP
Method, system and article for improved TCP performance during packet reordering
InactiveUS20050036511A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCongestion windowNetwork link
TCP congestion avoidance is implemented upon retransmission of a packet and is reverted back to the original congestion state upon receipt of an early acknowledgement (ACK), indicating reordering of packets, thereby eliminating a needless restriction on TCP bandwidth. Upon receiving an ACK to a retransmitted packet, it is determined if the ACK resulted from receipt of the original reordered packet or the retransmitted packet, based on the arrival time of the ACK at the sender. If the round-trip-time (RTT) for the retransmitted packet is much lower than the average or current calculated RTT for the network link between sender and receiver, then the retransmission occurred as a result of a reordering event, and the congestion window is restored back to its value prior to the retransmission, thereby permitting the network link to continue operating at its original increased throughput.
Owner:IBM CORP
Data transport acceleration and management within a network communication system
ActiveUS7099273B2Good estimateReduce and eliminate bursty transmission of dataEnergy efficient ICTError prevention/detection by using return channelCongestion windowPacket loss
Improved data transport and management within a network communication system may be achieved by utilizing a transmit timer incorporated within the sender device and exploiting host-level statistics for a plurality of connections between a sender and receiver. The period of the transmit timer may be periodically adjusted based on a ratio of the smoothed round-trip time and the smoothed congestion window, thereby reducing or eliminating bursty data transmission commonly associated with conventional TCP architectures. For applications having a plurality of connections between a sender and a receiver that share a common channel, such as web applications, the congestion window and smoothed round trip time estimates for all active connections may be used to initialize new connections and allocate bandwidth among existing connections. This aspect of the present invention may reduce the destructive interference that may occur as different connections compete with one another to maximize the bandwidth of each connection without regard to other connections serving the same application. Error recovery may also be improved by incorporating a short timer and a long timer that are configured to reduce the size of the congestion window and the corresponding transmission rate in response to a second packet loss with a predefined time period in order to increase resilience to random packet loss.
Owner:OPTIMORPHIX INC
Method and apparatus for accelerating throughput in a wireless or other telecommunication system
ActiveUS20050013245A1Transmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsCongestion windowSlow-start
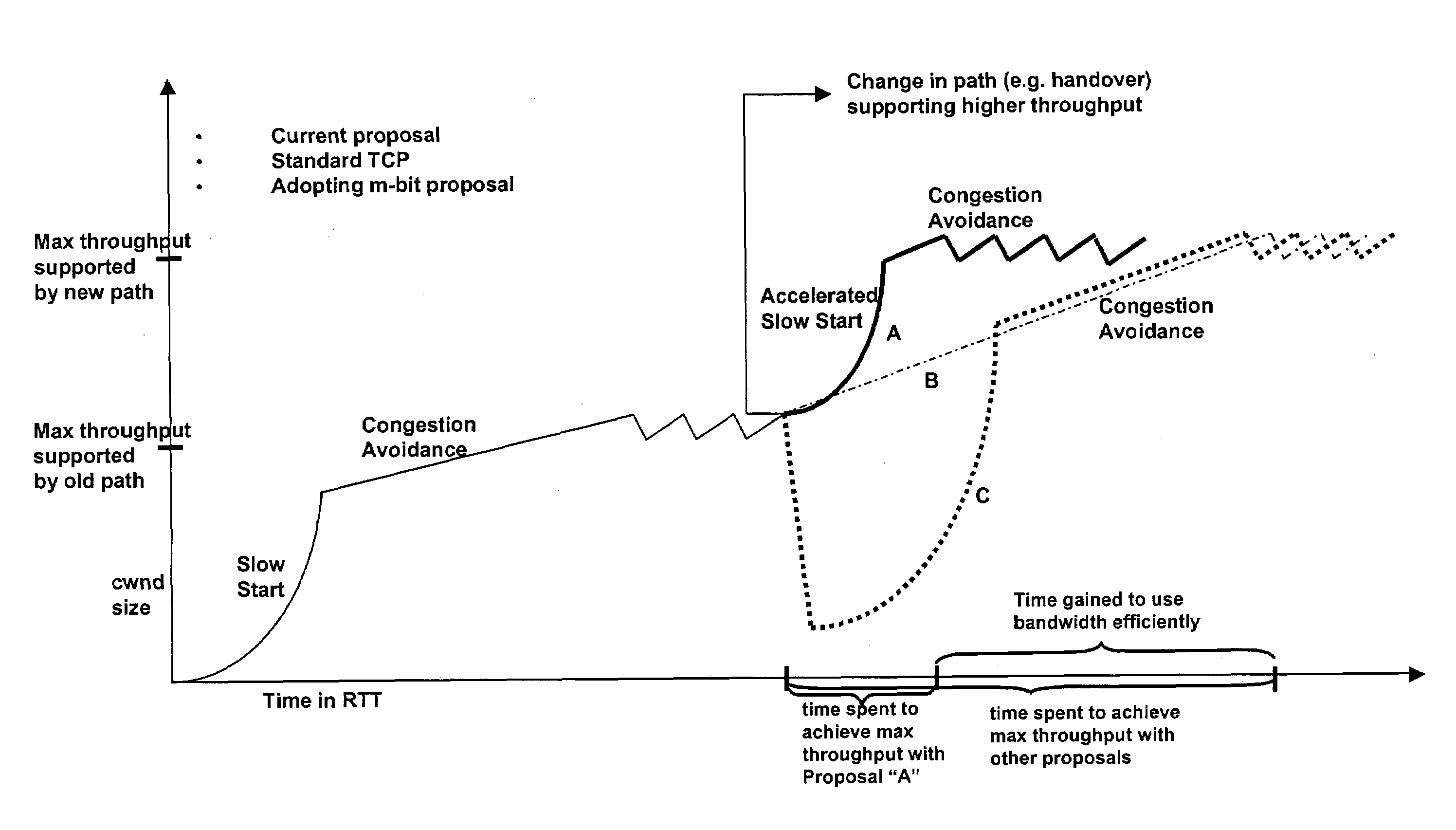
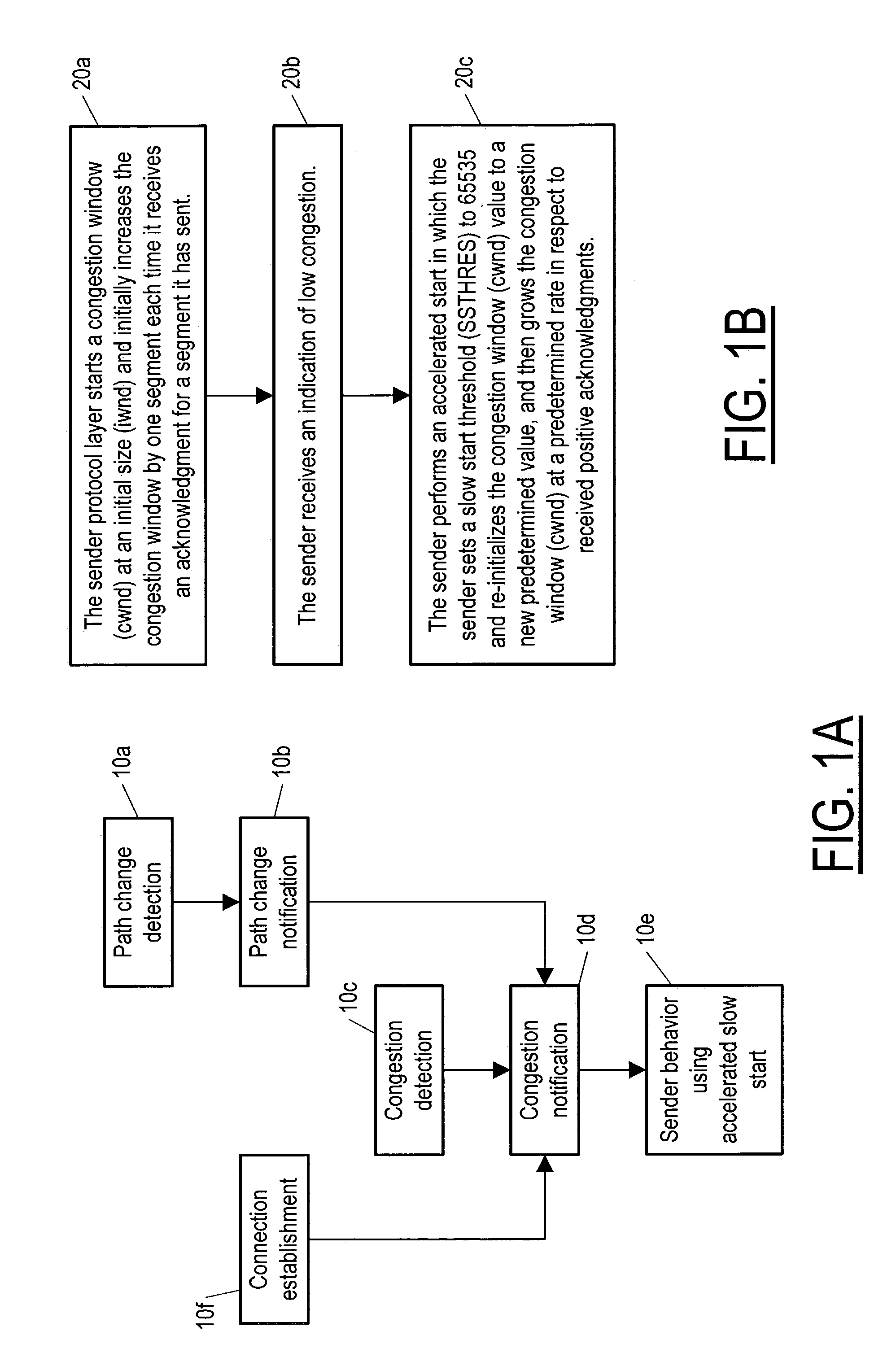
A method and equipment for accelerating throughput of communication segments from a sender (30) to a receiver (40) each of which include a protocol layer (30a 40a) for providing such segments, the method in case of TCP including a first step (20a) in which the sender protocol layer (30a) initializes a congestion window (cwnd) to some initial size (iwnd) and increases the congestion window by one segment each time it receives an ACK, but upon receiving an indication of low congestion, performs a step (20c) of accelerated start in which it sets a slow start threshold (SSTHRES) to a standard initial value (typically 65535) and re-initializes cwnd to a new value, and the sender protocol layer (30a) then increments cwnd at one or another predetermined rate—depending on whether the start immediately follows a new connection or instead follows a transfer of an existing connection to a new path—in respect to received ACKs.
Owner:RPX CORP
Staged, slowly-started transmission control method based on measurement of network state
InactiveCN101094047AEffectively get statusNot easy to shieldError prevention/detection by using return channelCongestion windowLoss rate
Via real time online bandwidth measurement, this method confirms the threshold value ssthresh. When the congestion window (CW) is less than a half of the threshold, the rule of exponent gain is followed. Otherwise CW gains each time a value of a half of difference of the threshold and CW (ssthresh-cwnd) to approach gradually the threshold. Until the difference is less than the regulation factor phi (ssthresh / 2>= phi >=2). Then CW is set as the threshold value to enter the stage of avoiding congestion. This invention can reduce the happening of loss of several texts in a window at the slowly start stage, reduce the package loss rate and raise the net transferring ability.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Packet size control technique
InactiveUS6934251B2Shorten the time periodImprove data transfer throughputTransmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsCongestion windowData link layer
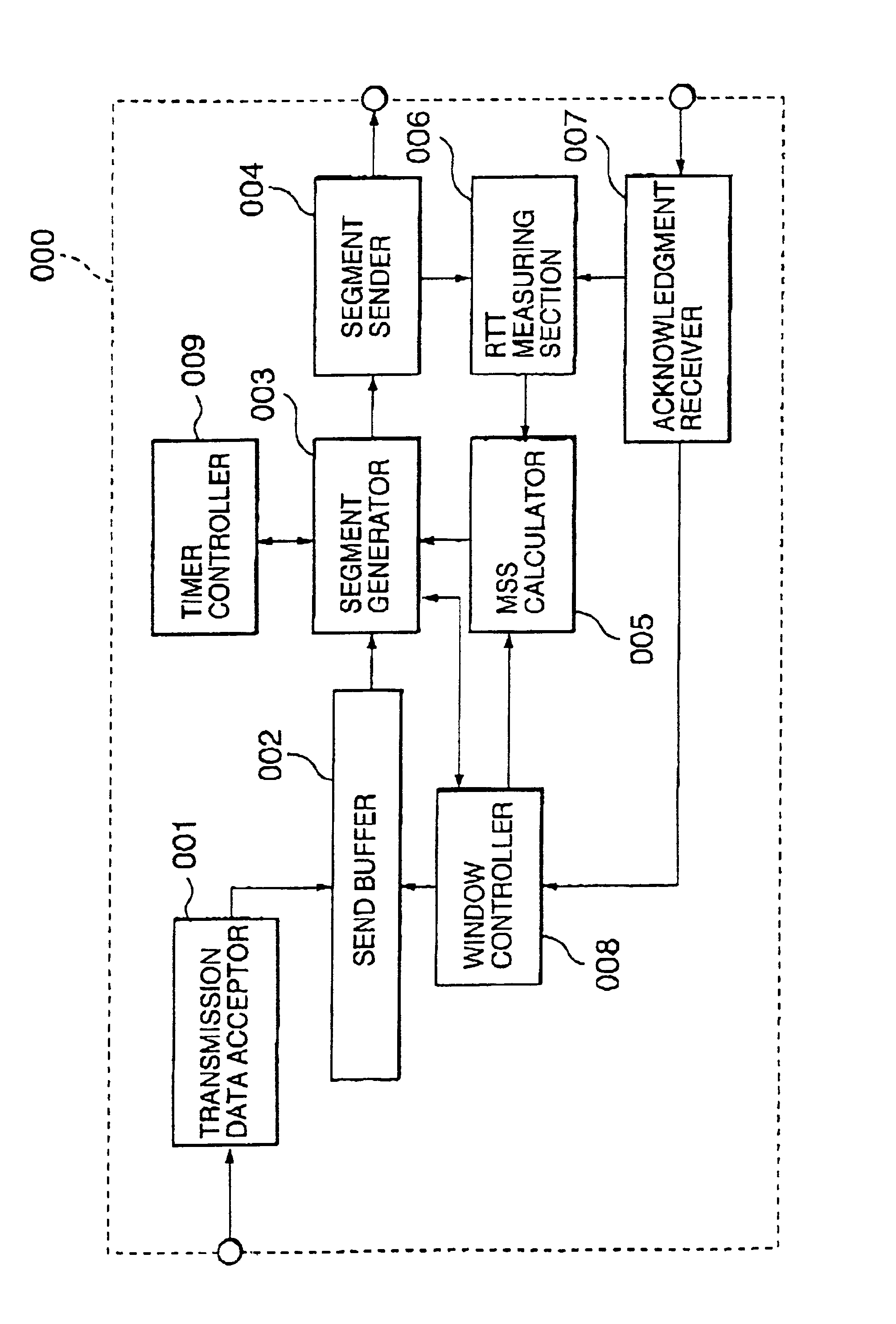
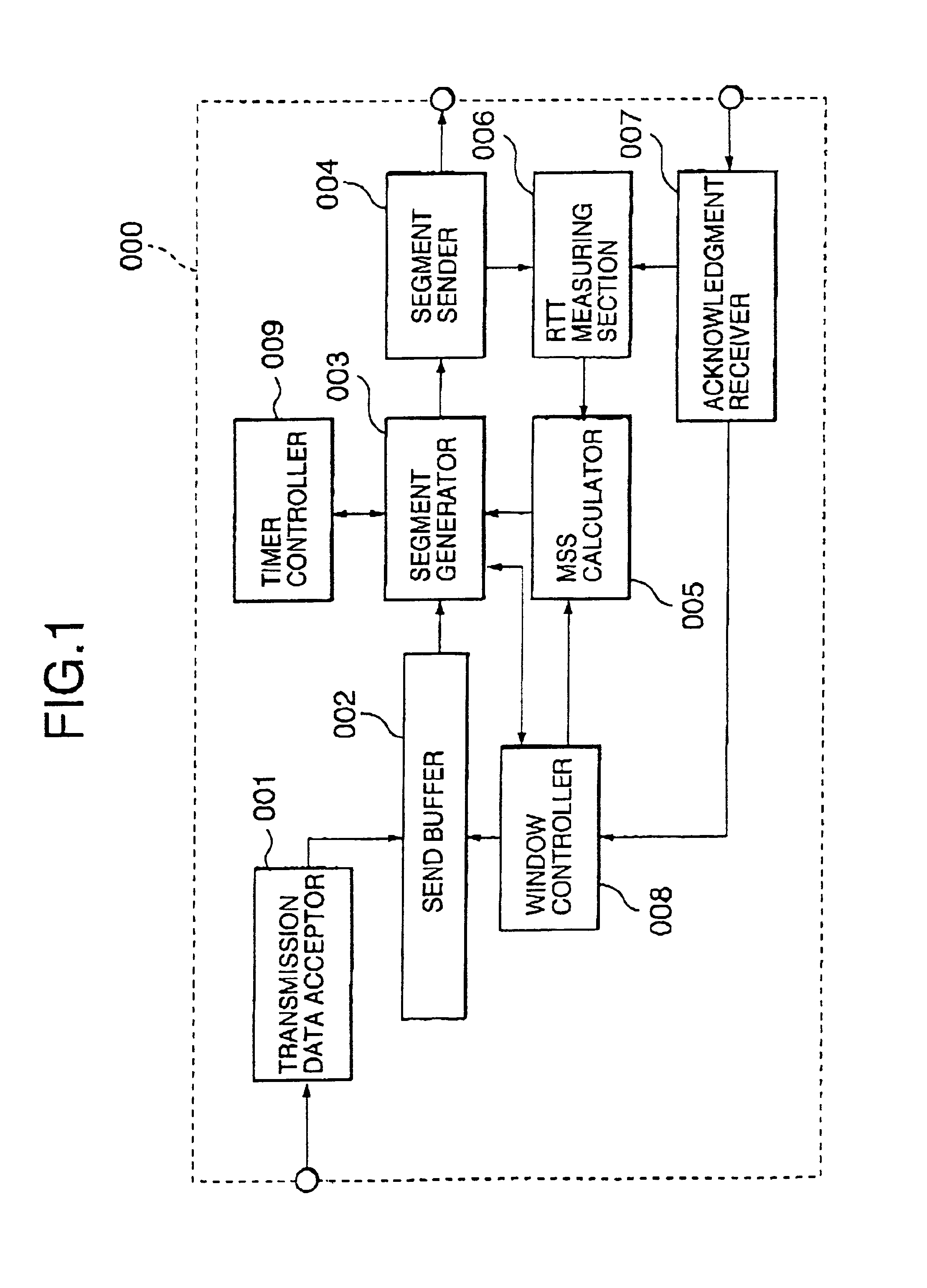
A packet size control method allowing reduction in the period of time during which transmission is in a blocked state is disclosed. The size of a packet to be sent is determined depending on a measured round trip time (RTT), a current bandwidth of the data link layer, and a current congestion window size. First, a maximum segment size (MSS) is obtained based on the measured RTT and the current bandwidth of the data link layer using a table obtained by data transfer simulation. Thereafter, the obtained MSS is corrected using the current congestion window size. And the correct MSS is used to determine the final segment of data to be sent.
Owner:NEC CORP
Network protocol with damage loss resilient congestion control algorithm
ActiveUS7821937B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCongestion windowNetworking protocol
Various embodiments of a network protocol that utilizes a congestion control algorithm that distinguishes between congestion loss and damage loss are described. In response to a packet loss on a network, a delay-based detection algorithm may be performed based on RTT (Round-Trip Time) information to determine whether the network is congested. If the delay-based detection algorithm does not determine that the network is congested then a consistency-based detection algorithm may be performed based on packet loss rate information. If either the delay-based detection algorithm or the consistency-based detection algorithm determine that the network is congested then the rate of data transmission may be reduced, e.g., by reducing a congestion window size.
Owner:VERITAS TECH
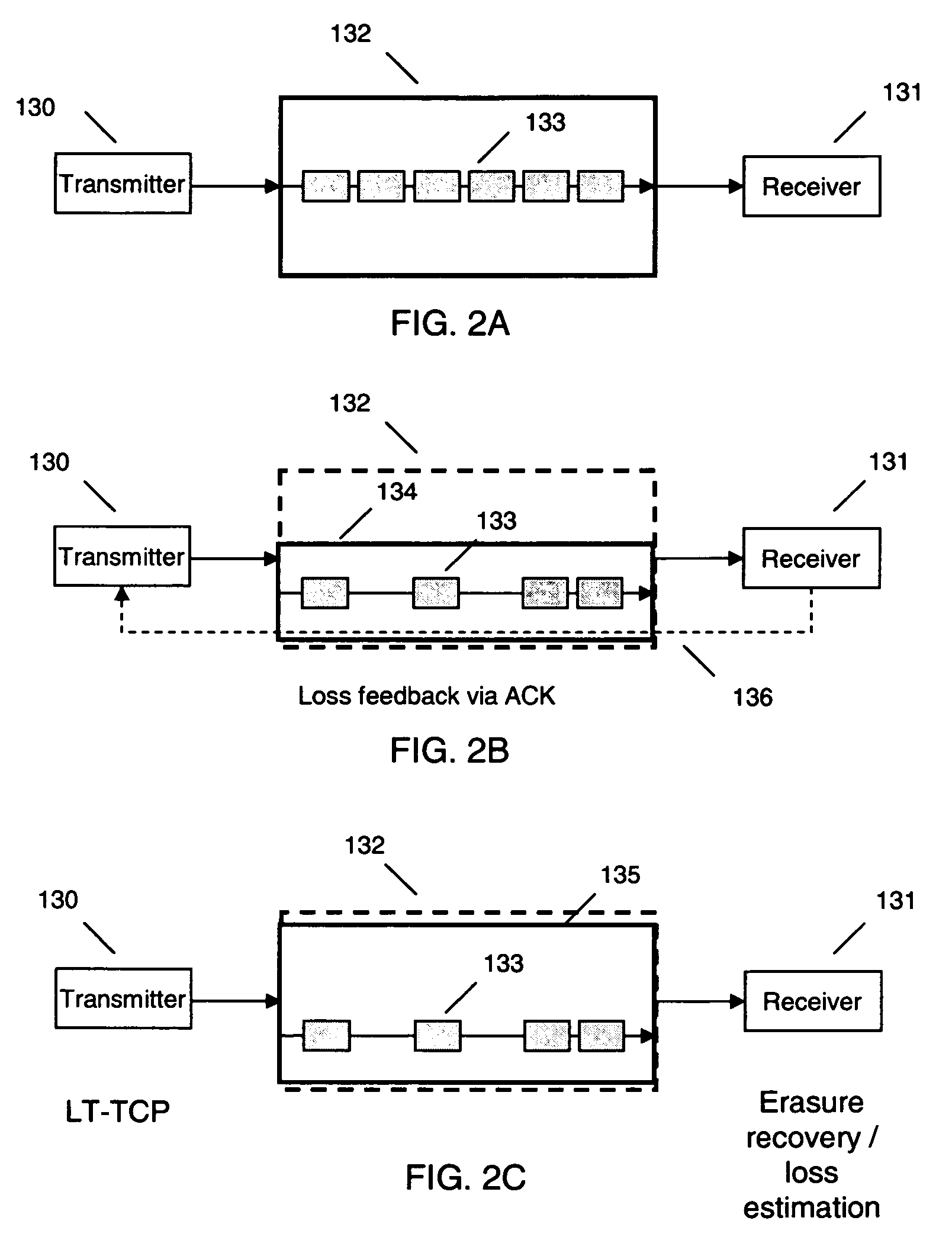
Loss tolerant transmission control protocol
ActiveUS20060251011A1Reduction of congestion windowReduce window sizeTransmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission protocolCongestion window
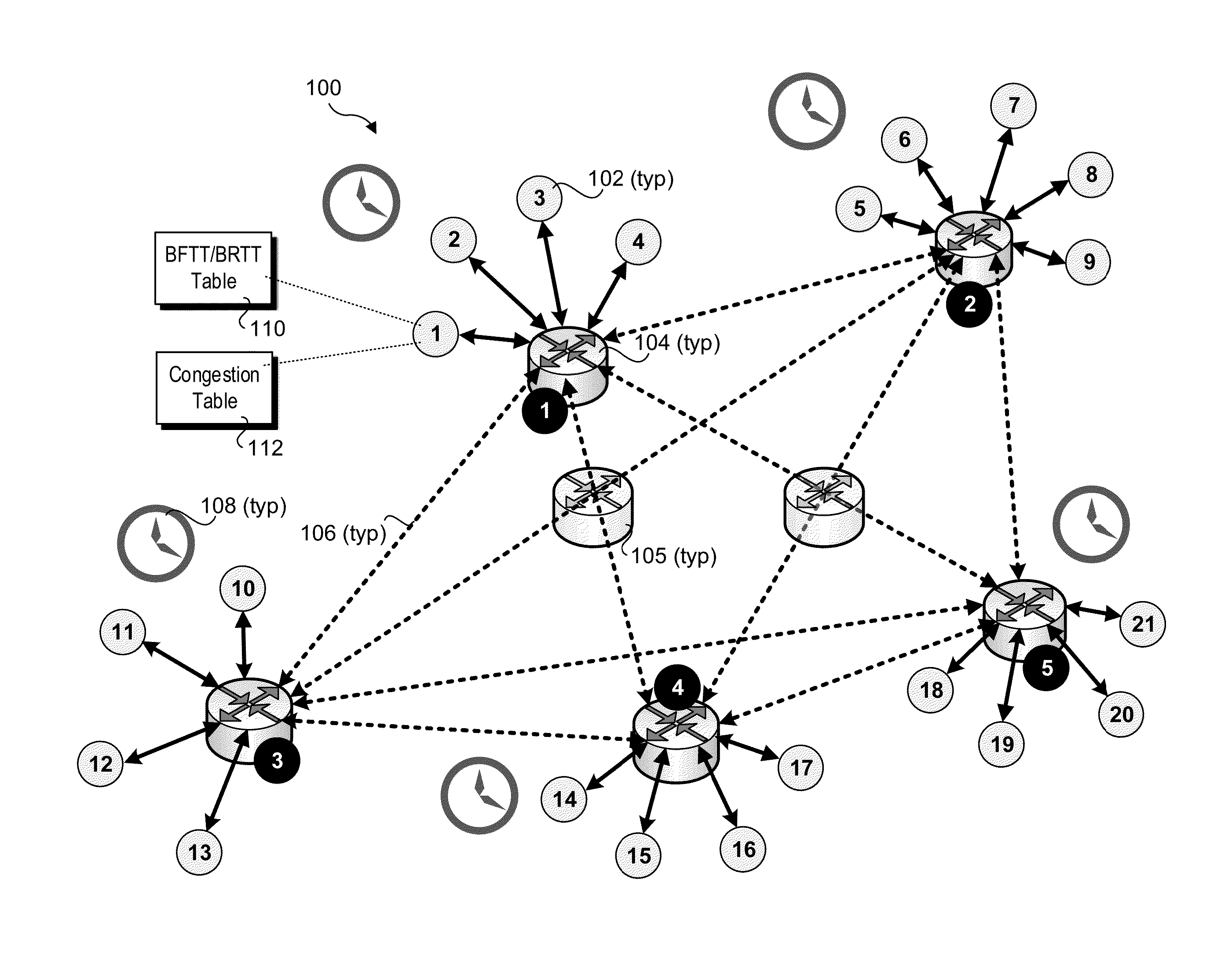
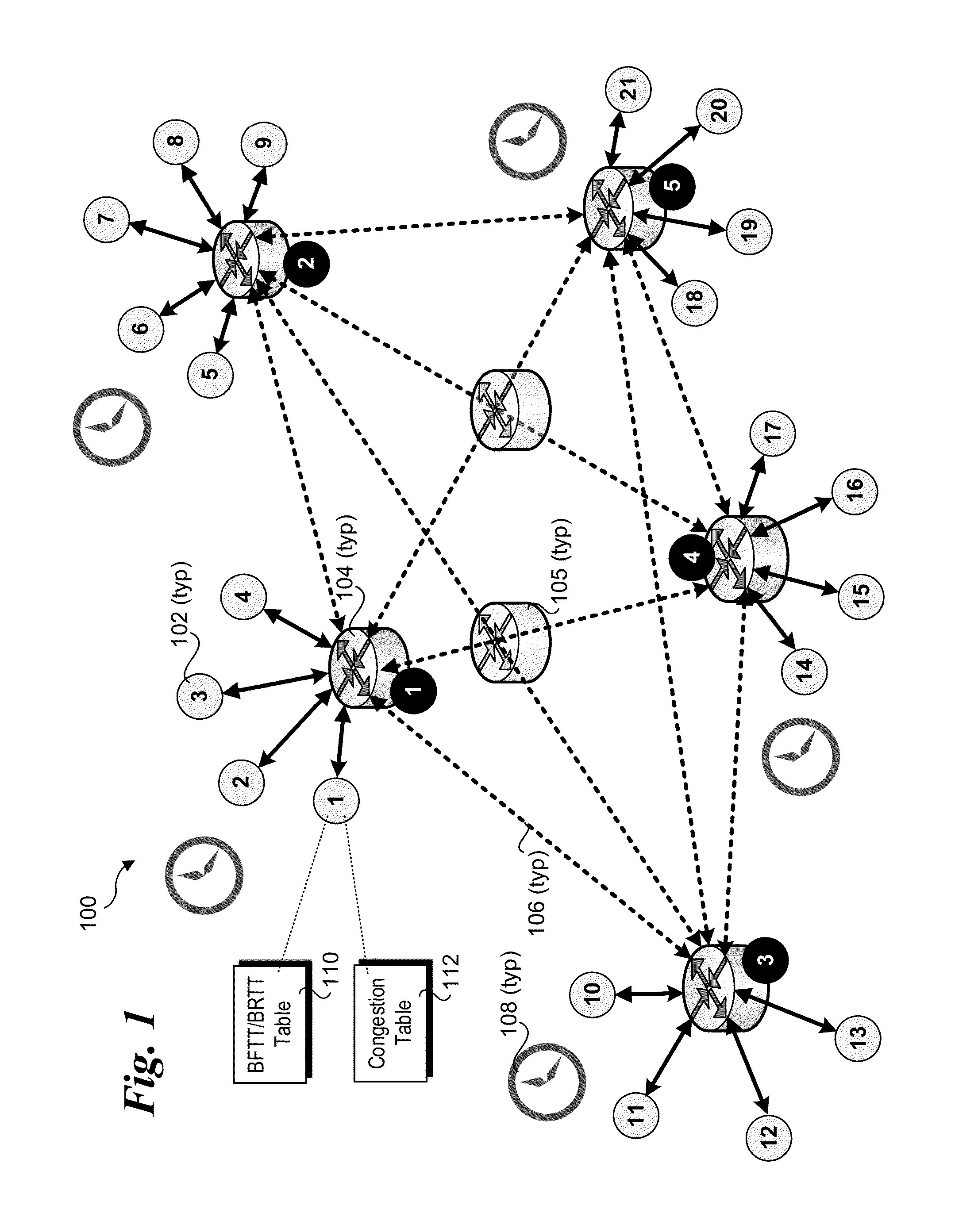
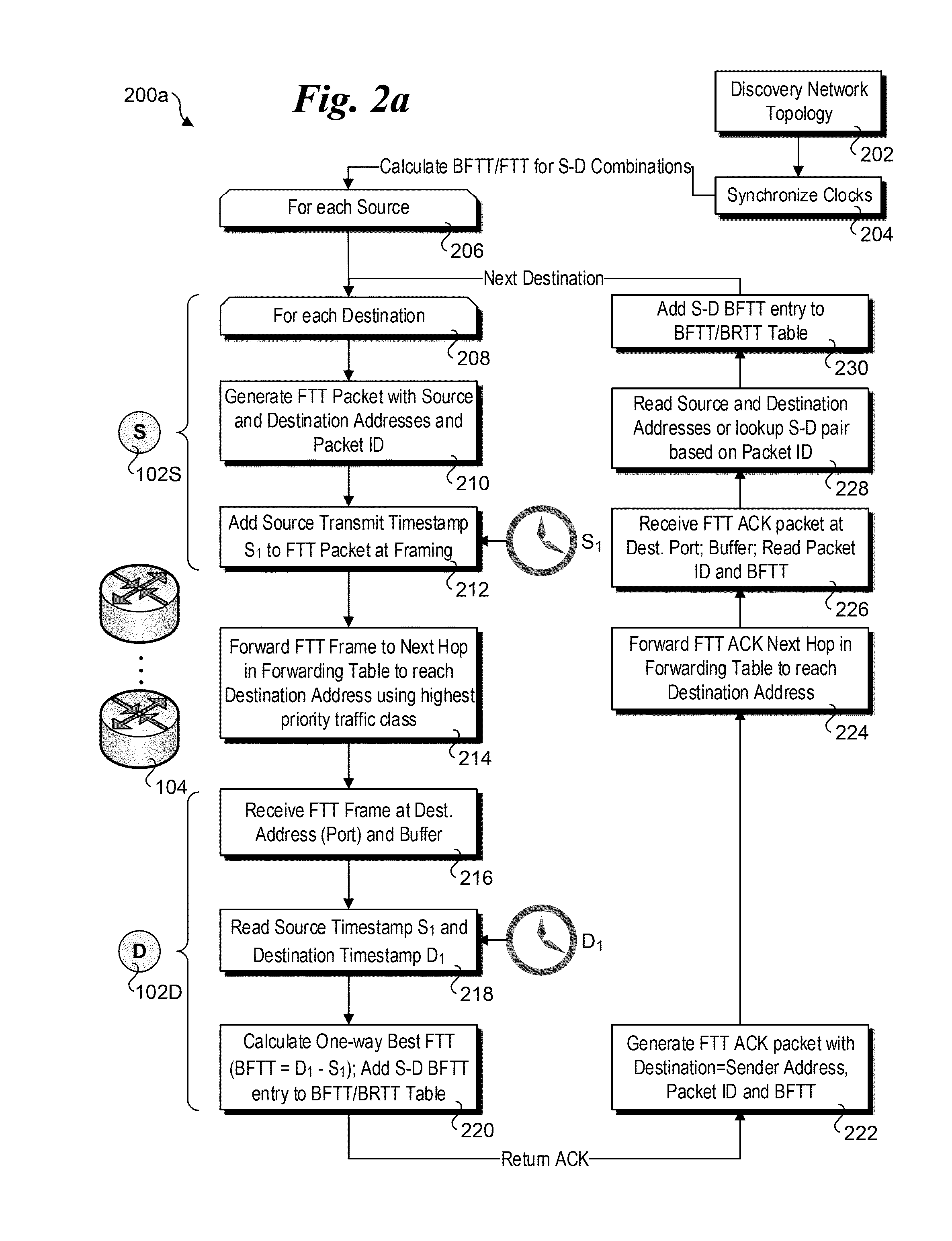
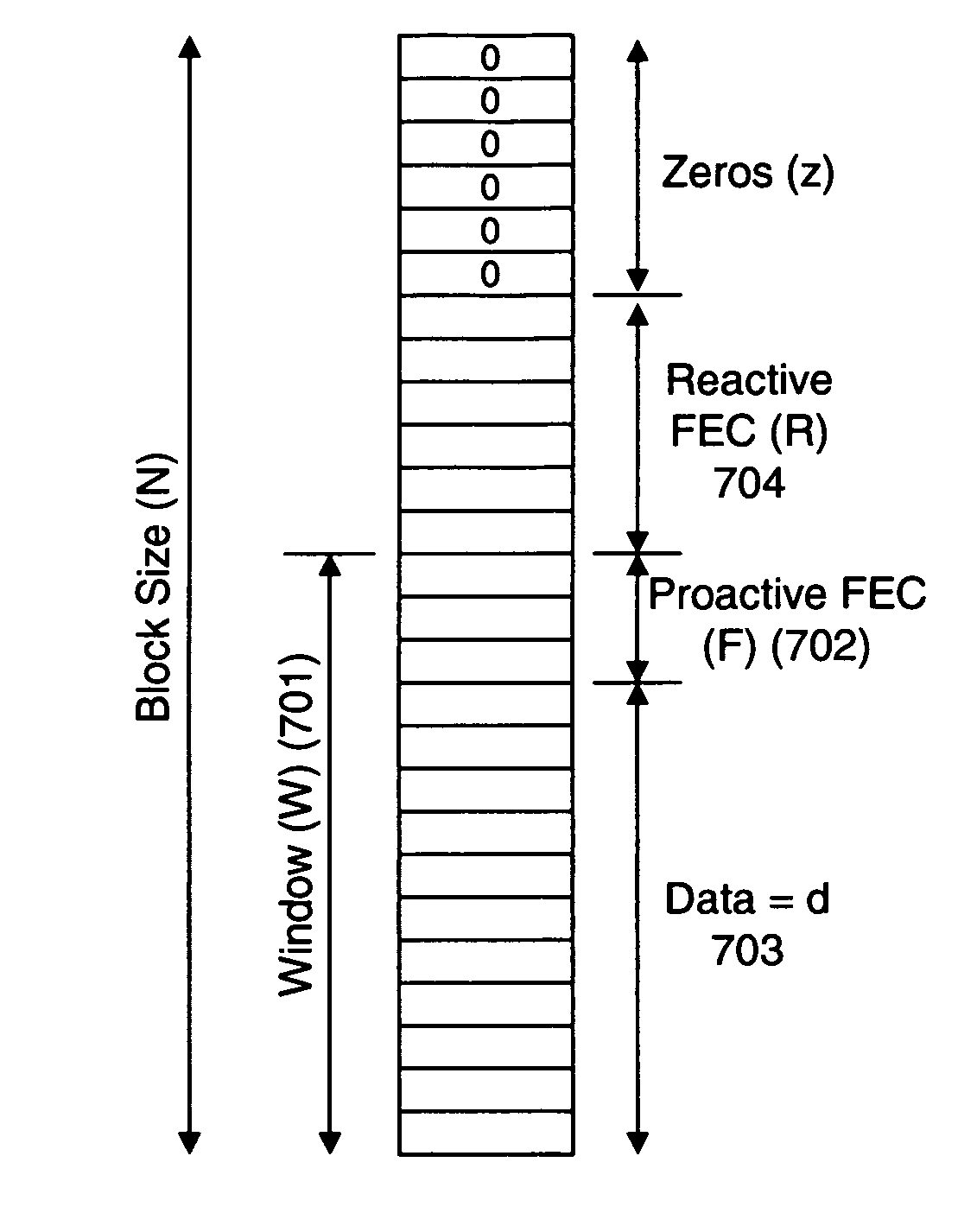
Provided are apparatuses and methods for transmitting or receiving data packets in a data block in a communication network with a transport protocol. In one example, a loss tolerant TCP protocol is used in which a maximum segment size (MSS) may be adapted to a minimum granularity of a congestion window. Also, proactive forward error correction (FEC) packets may be added to a window of the data block. The number of proactive FEC packets may be determined, for example, based on an estimate erasure rate. In addition, reactive FEC packets may be added to the data block. Also, a receiver may receive data packets in a data block and process a selective acknowledgment (SACK) responsive to the data packets received.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST +1
Methods and systems for automatic transport path selection for multi-homed entities in stream control transmission protocol
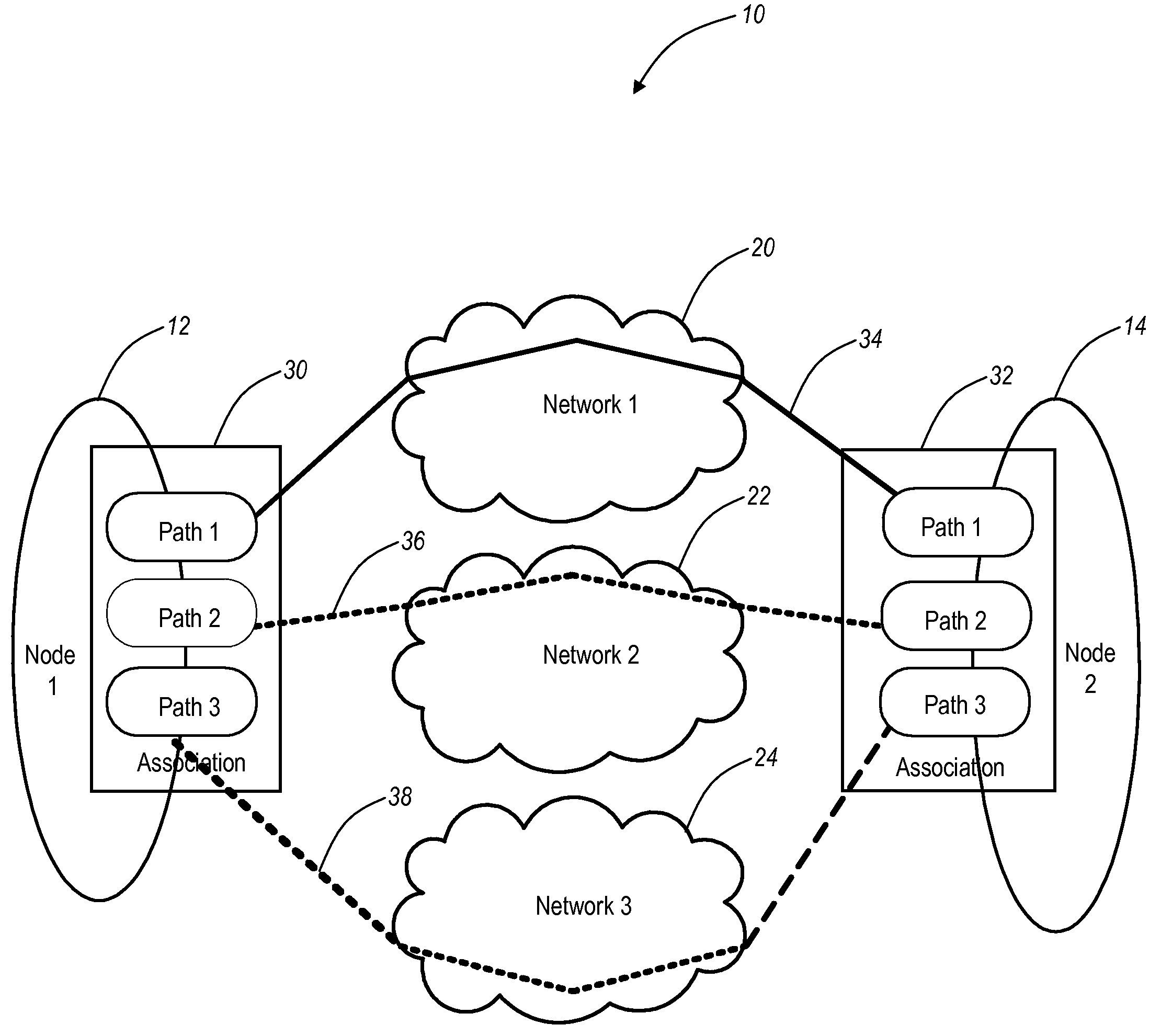
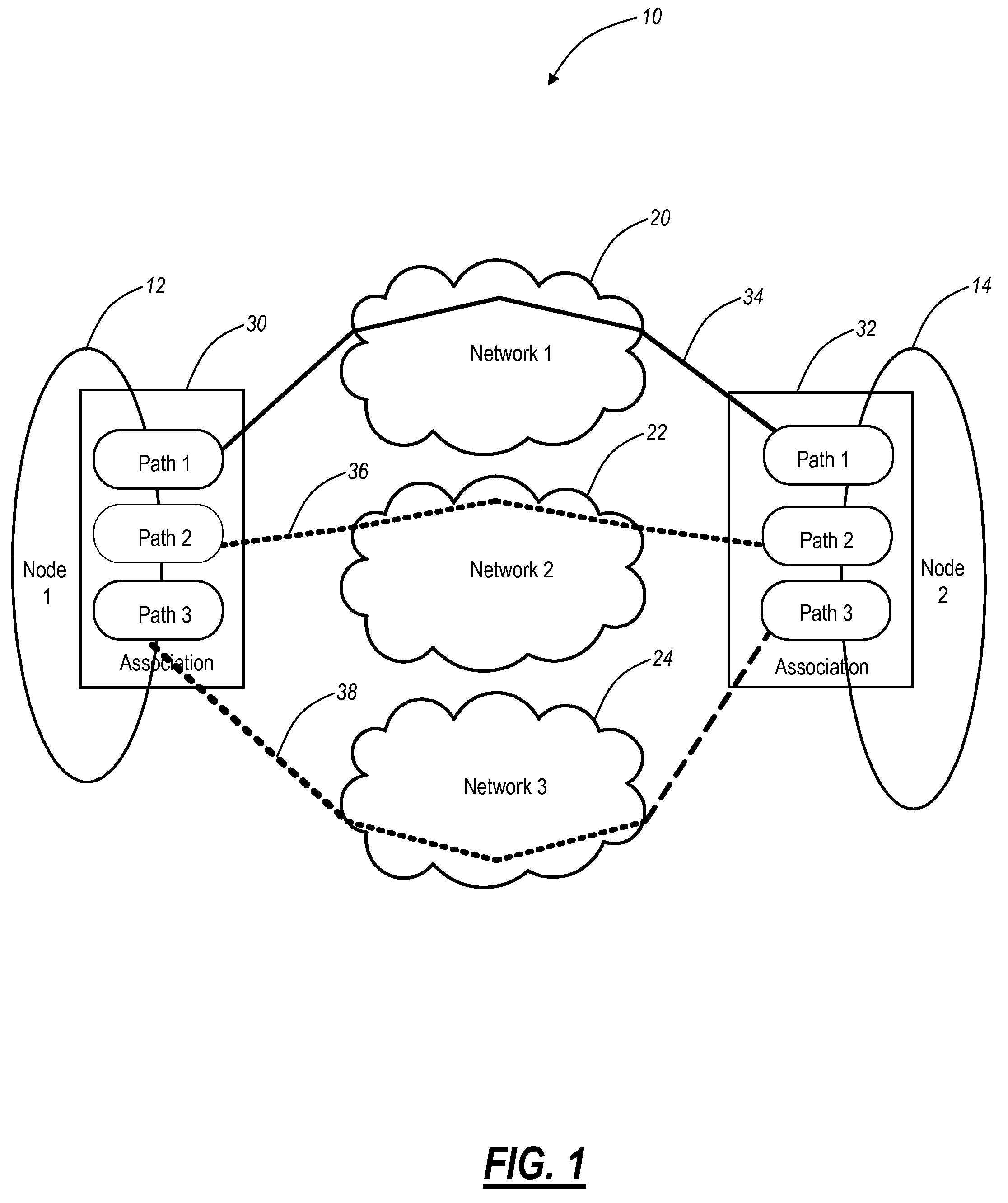
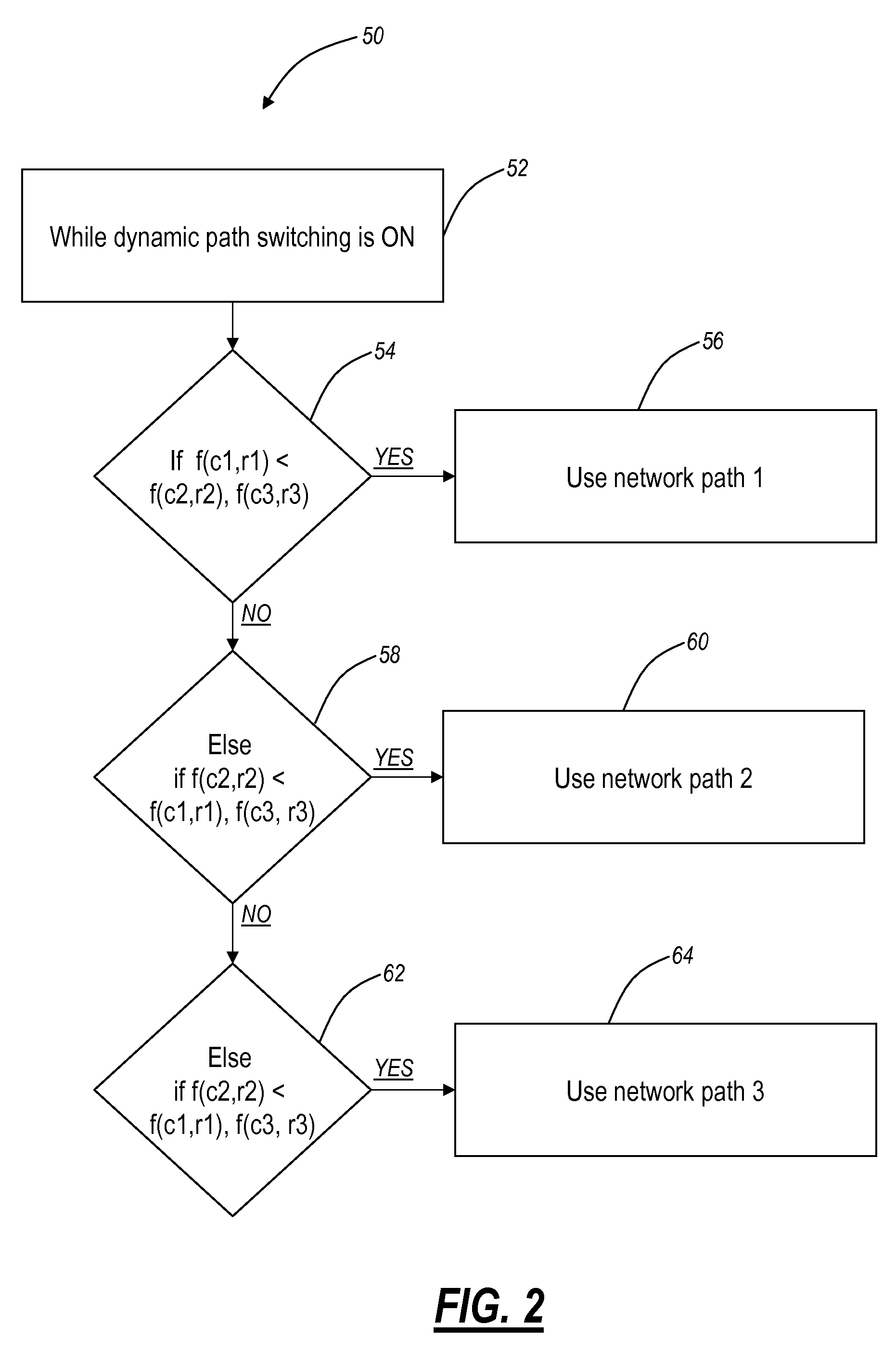
The present disclosure provides methods and systems for automatic transport path selection for multi-home entities in Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP). The present invention provides systems and methods for directing data transfer between applications and devices residing on different computers or devices using a dynamic path selection algorithm for multi-homed network entities (using SCTP). When an application or device requests to transfer data to another application or device, the dynamic path selection algorithm selects the most efficient path for data transfer. The decision to select the best network path is based upon the dynamic network conditions, such as, for example, congestion window (CWND), round trip time (RTT), and the like, and / or provisioning information.
Owner:CIENA
System, method and computer program product for increasing throughput in bi-directional communications
InactiveUS20050068894A1Reduce delaysImprove throughputError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsCongestion windowDistributed computing
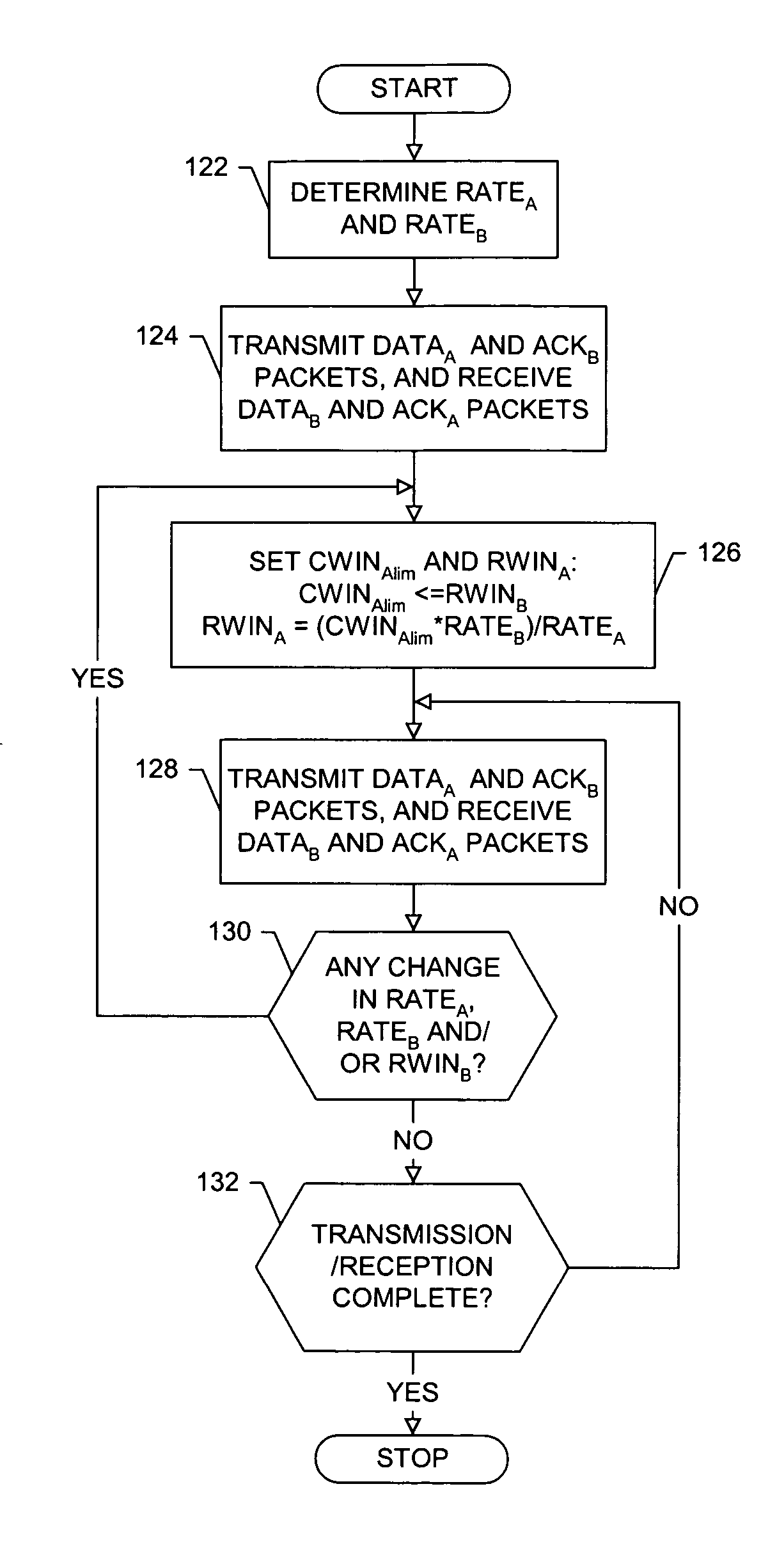
A system, method, and computer program product are provided for bi-directional communication. The system includes a first host capable of transmitting multiplexed data at a first transmission rate and operating with a first congestion window. The first host is also capable of receiving multiplexed data at a second transmission rate from a second host capable of operating with a second congestion window. The first host can be capable of configuring at least one of a size of the first congestion window and a size of the second congestion window based upon first transmission rate, the size of the second congestion window, the second transmission rate and the size of the first congestion window.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
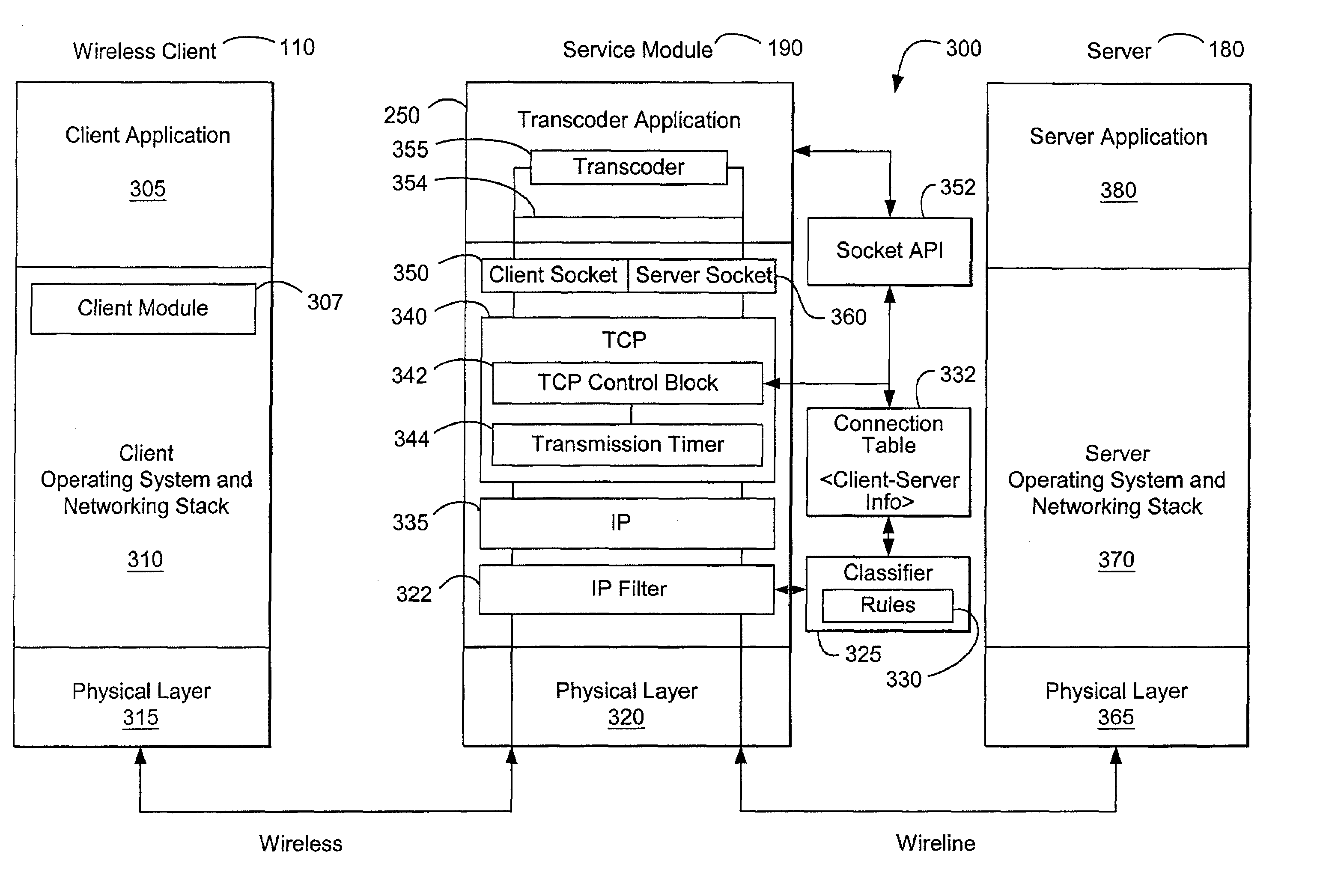
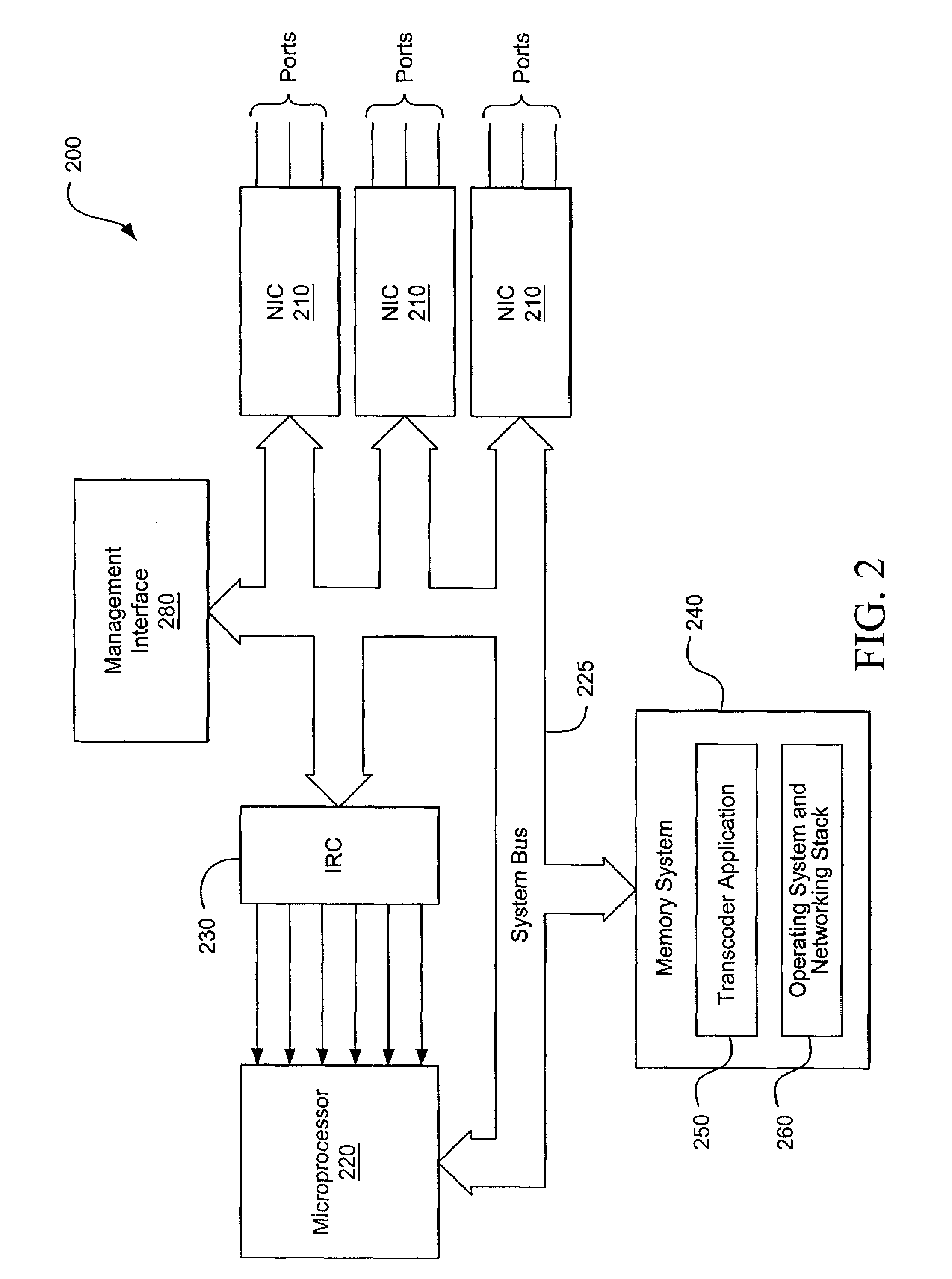
Transcoding multimedia information within a network communication system
ActiveUS7444418B2Reduce and eliminate bursty transmissionReduce decreaseInformation formatContent conversionCongestion windowCommunications system
Multimedia information communicated between a transmitter and a receiver may be transcoded by intercepting the multimedia information within a network communication system. The available transmission rate of the downlink channel may be estimated by, for example, calculating a ratio of the smoothed round trip time of packets communicated to the receiver and a smoothed congestion window associated with the downlink channel. If the transmission rate at which the multimedia information is encoded is greater than the available transmission rate, the multimedia information may be transcoded to conform the multimedia information to the available transmission rate. The transcoded multimedia information may then be transmitted to the receiver over the downlink channel using a transmission timer.
Owner:OPTIMORPHIX INC
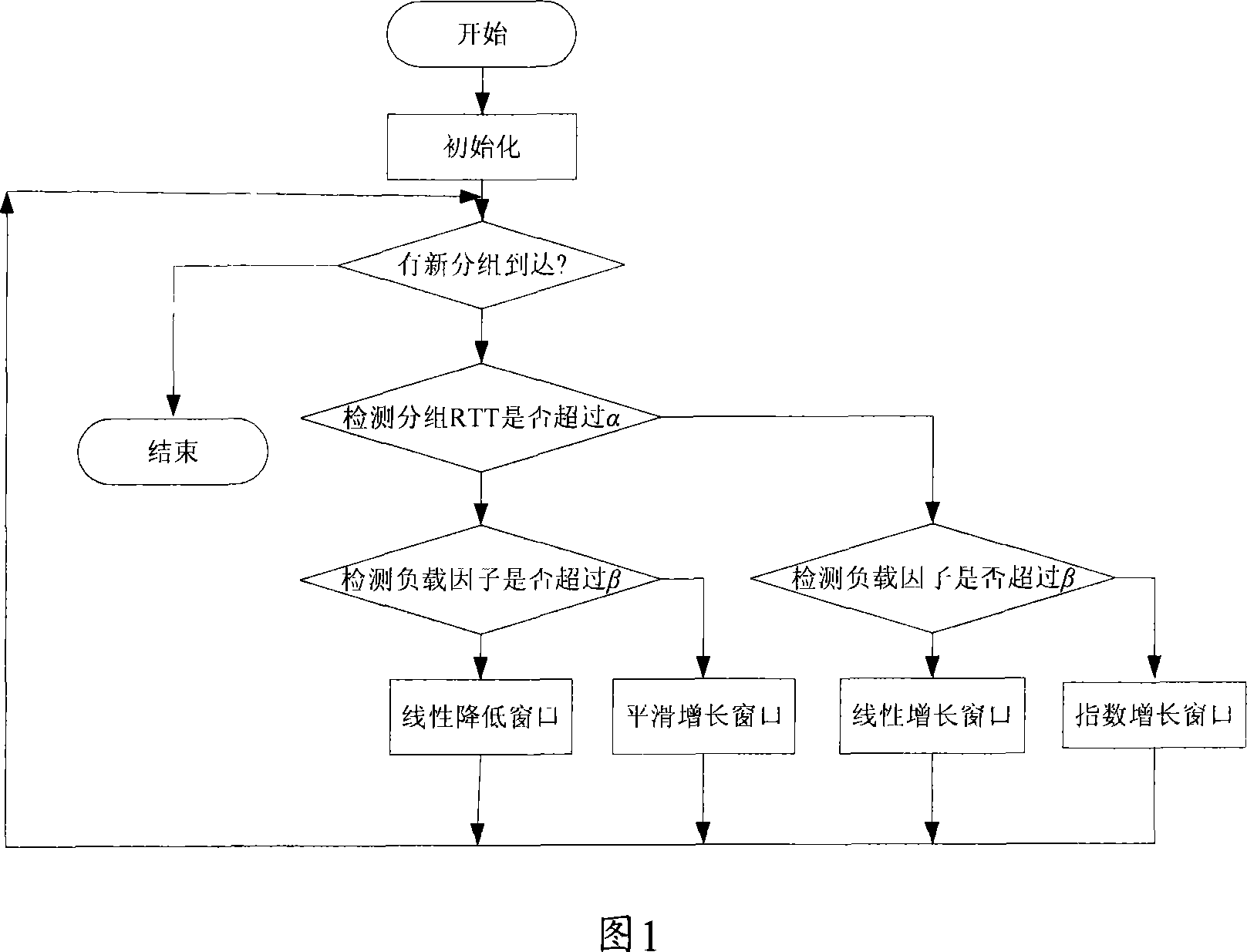
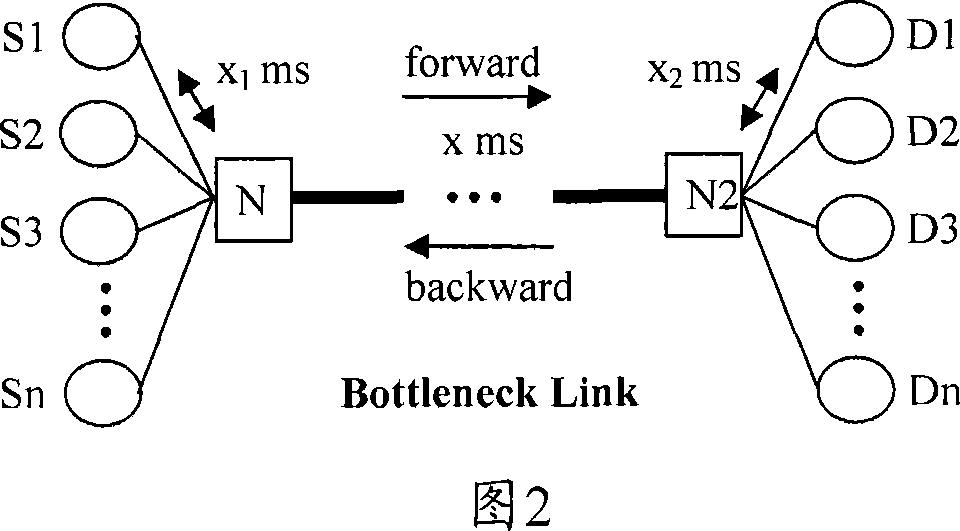
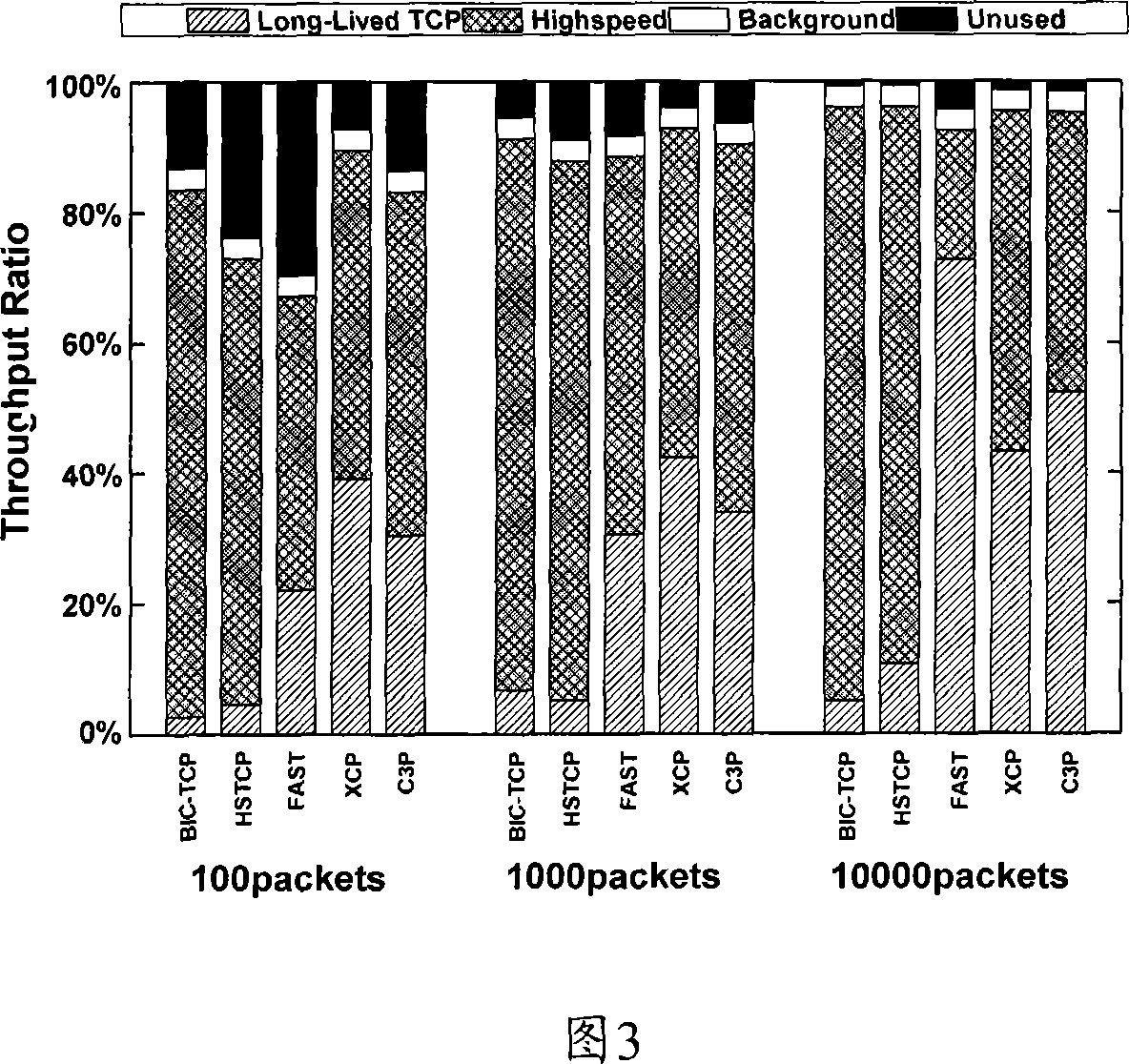
A collaborative congestion control method for high-speed network
InactiveCN101056259AReflect the real stateAvoid Misjudgment InformationData switching by path configurationCongestion windowDirect effects
The invention discloses a collaborative work congestion control method in the high-speed network, the transmitter detects the RTT delay information and 1-bit prediction information from the router to determine the network congestion status and the congestion window is the self-adapted and adjustable. The method of the invention combines the load factor of the network path and number of the data packets in the buffers of all routers connected in the path to adjust the congestion window of the high-speed network which can effectively adapt to the transfer characteristic of the high-speed network to guarantee the better link utilization rate of the network, friendly TCP and fair of the streaming. These two congestion information mechanisms can be fused to avoid the mistaken determination of single congestion detection mode under certain environment and reduce the direct influences of the unilateral information error on the reliability of the method.
Owner:中科博华信息科技有限公司
Method for transmitting data in mobile ad hoc network and network apparatus using the same
ActiveUS20050259577A1Improve throughputUrinalsError prevention/detection by using return channelCongestion windowData rate
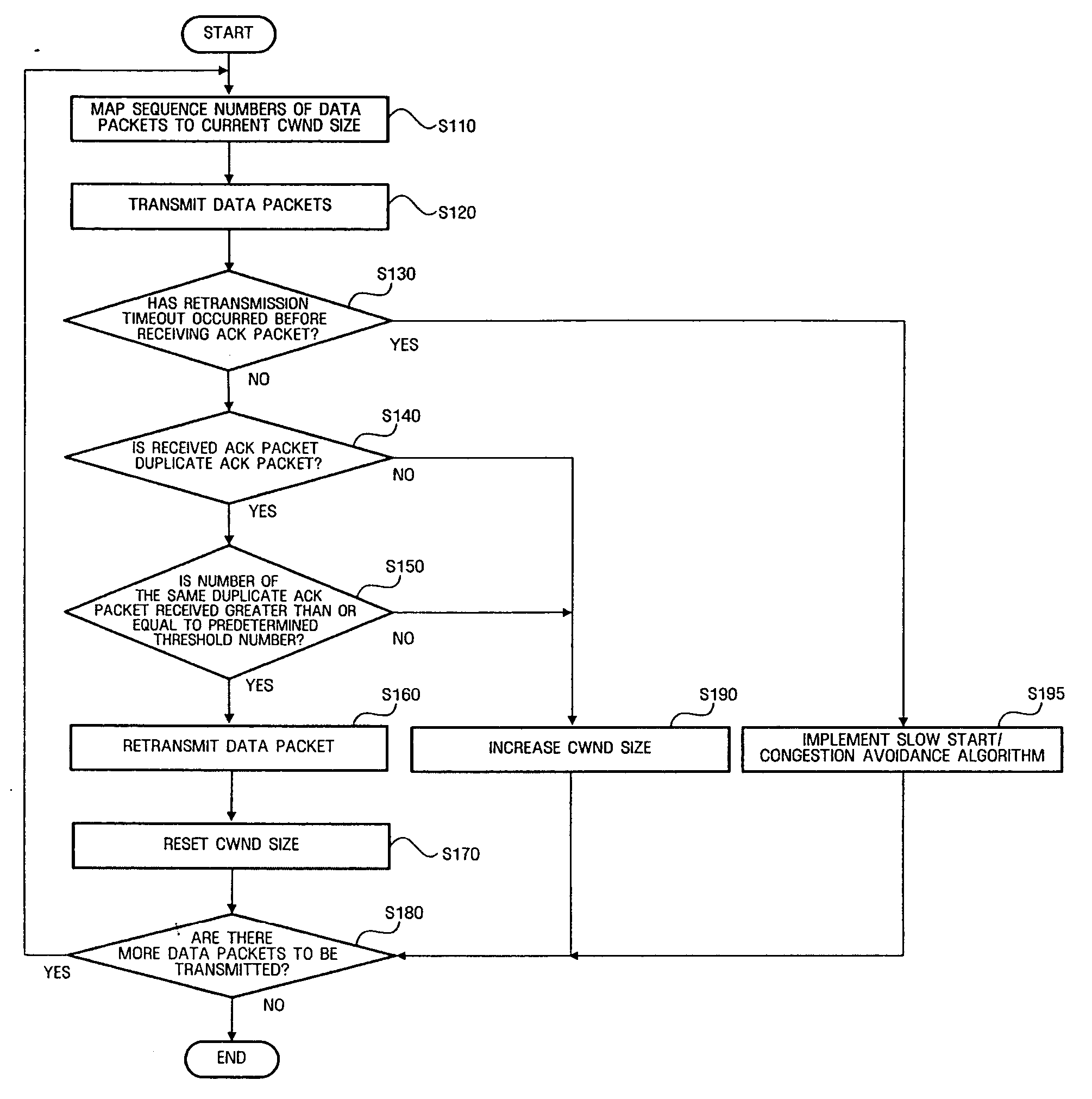
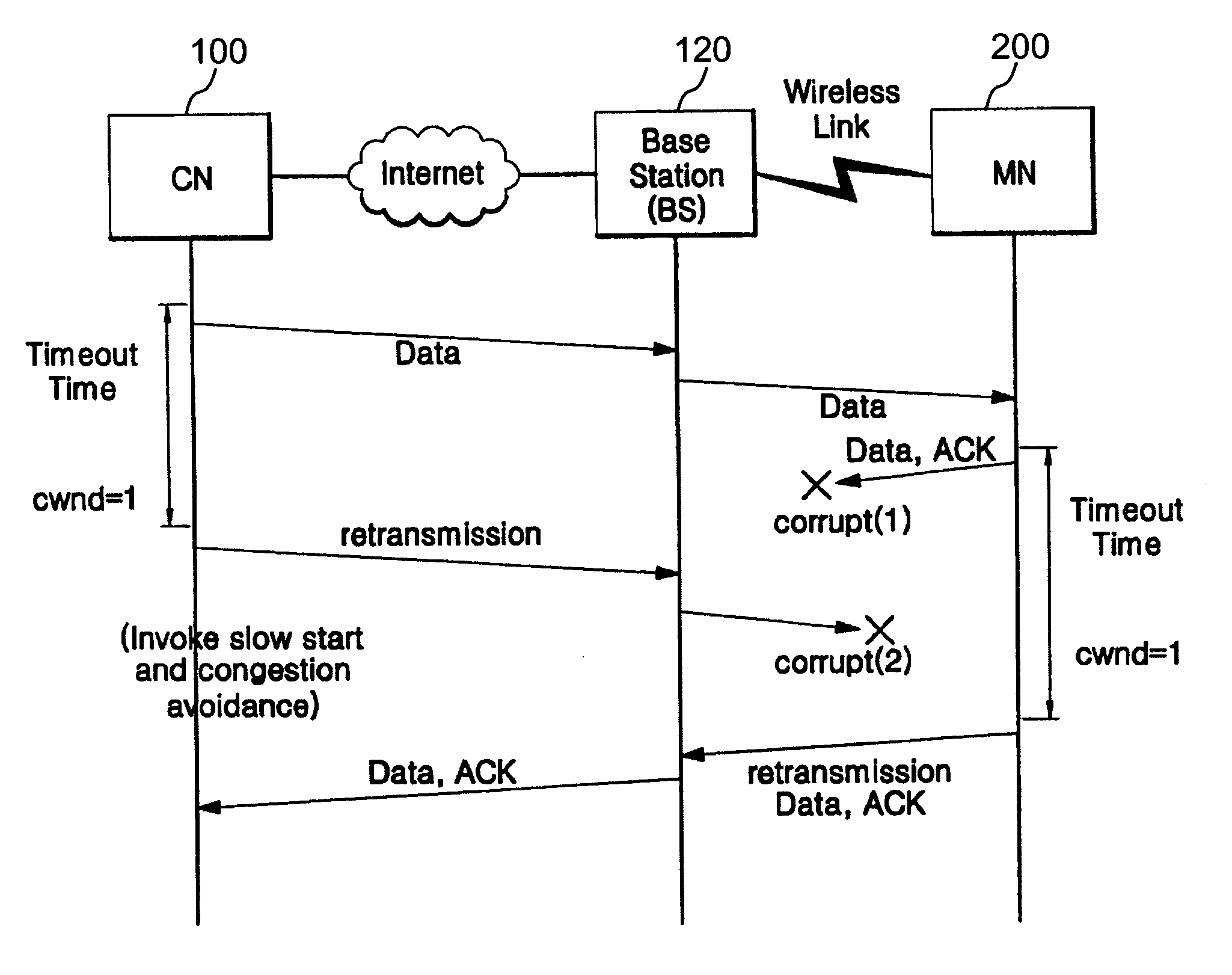
Provided are a method for transmitting data in a mobile ad hoc network in which the quantity of data transmitted is adjusted by adjusting the size of a congestion window when network duplicate ACK packets are received, and a network apparatus using the same. The method includes mapping sequence numbers of data packets to be transmitted to congestion window sizes during transmission of the data packets, determining whether there is a lost data packet or not, and if there is a lost data packet, retransmitting the lost data packet and adjusting a congestion window size to the congestion window size mapped to the sequence number of the lost data packet. Accordingly, a data rate throughput over a wireless ad hoc network can be increased.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Transmission control protocol (TCP) congestion control using multiple TCP acknowledgments (ACKs)
InactiveUS20060182025A1Increase valueSimply and effectively compensateError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsCongestion windowPacket loss
A method of Transport Control Protocol (TCP) congestion control using multiple TCP AKCs in an integrated network including wireless links, the method including: receiving a packet retransmitted from a correspondent upon a mobile node having a packet loss in a received packet; calculating the number of acknowledgment messages to be transmitted by the mobile node; generating multiple acknowledgment messages according to the calculated number and transmitting the multiple acknowledgment messages to a transmitting node; and increasing a congestion window value corresponding to the multiple acknowledgment messages received by the transmitting node, and executing the TCP transmission.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Congestion control method and system based on deep reinforcement learning
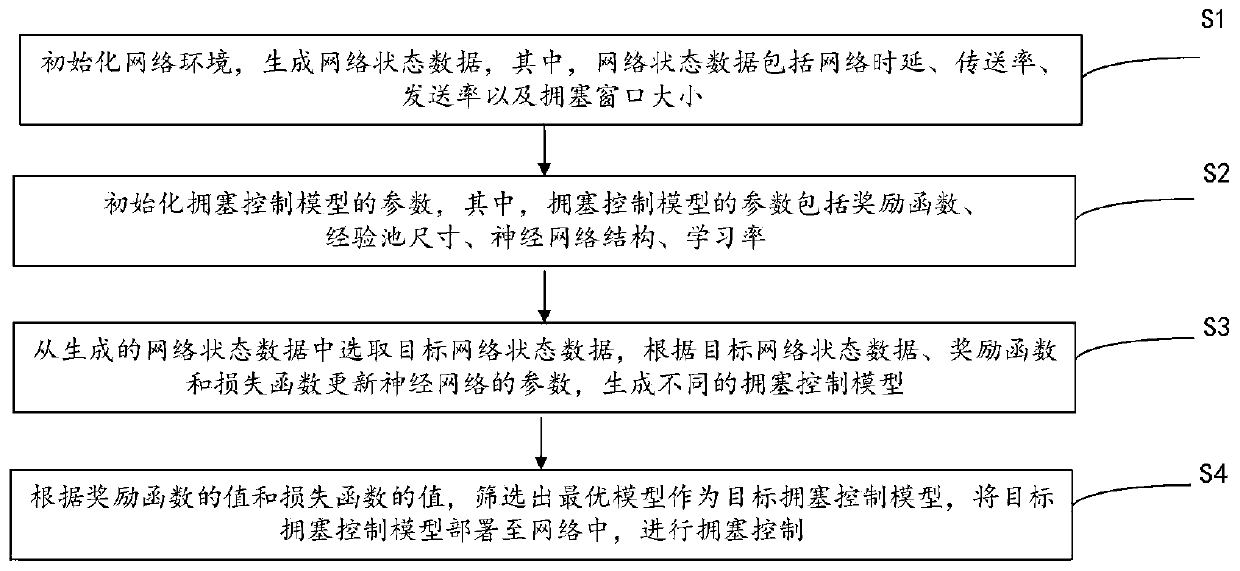
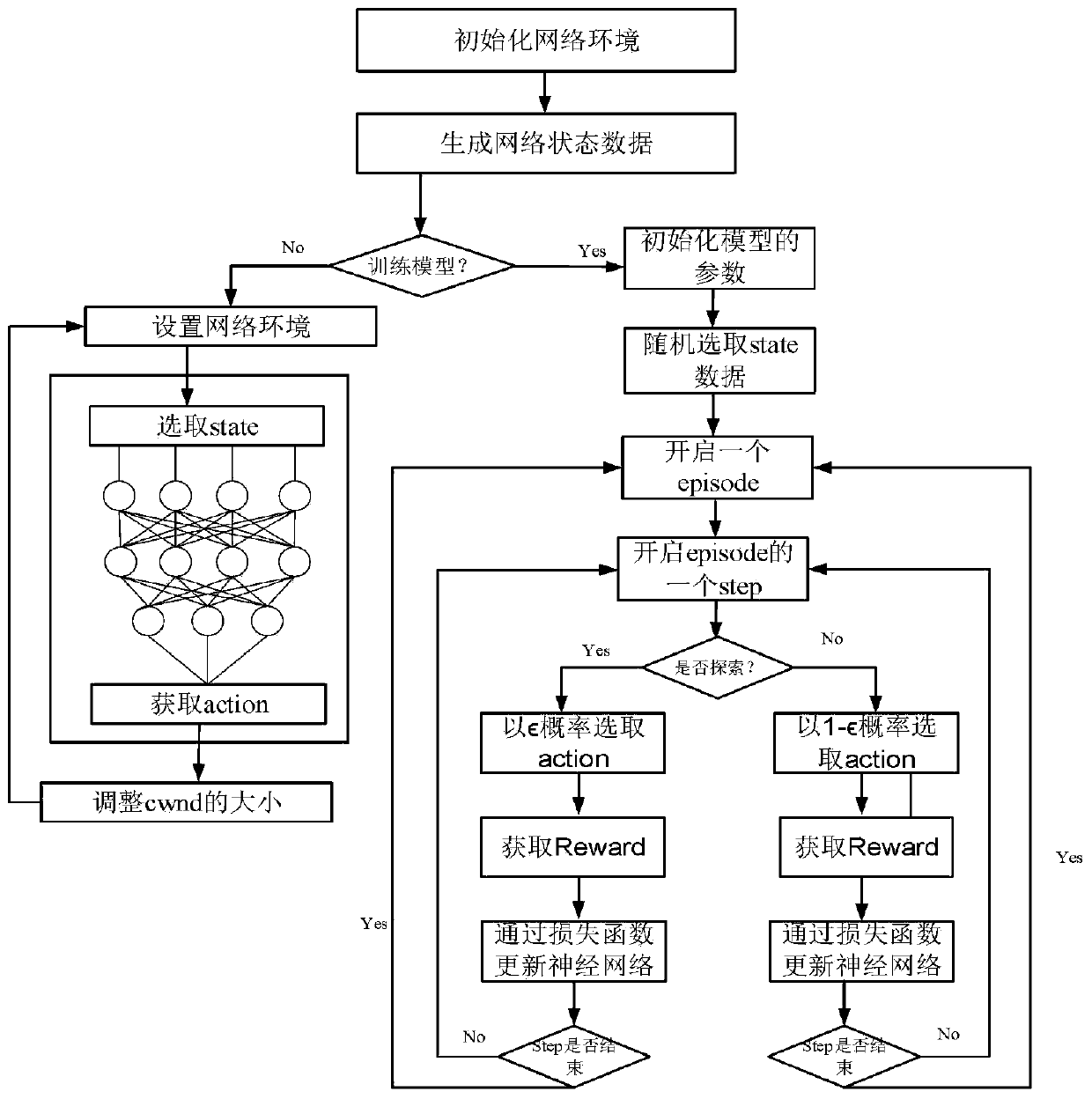
ActiveCN110581808AImprove performanceReduce controlData switching networksCongestion windowModel parameters
The invention discloses a congestion control method and system based on deep reinforcement learning. The congestion control method includes: firstly, initializing the environment and model parametersof a network; and training a congestion control model by utilizing the collected current window, the throughput, the time delay, the data transmission rate and the like in the network, selecting the congestion control model with the minimum model loss function value and the maximum reward function value according to a training result, and deploying the model into the network to perform congestioncontrol. According to the method, the size of the congestion window is dynamically adjusted according to the current network throughput, round-trip time delay and data packet loss rate, so that the data transmission rate is controlled, the network throughput is improved, the data transmission delay and the data packet loss rate are reduced, the network congestion is reduced, and the aim of optimizing the network performance is fulfilled.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method and apparatus for minimizing congestion in gateways
InactiveUS20080239953A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCongestion windowCommunications system
Methods and apparatus are provided to reduce data congestion and thus improve data throughput in gateways used in a wireless, wireline or a combination wireless and wireline communication system. The congestion management system optimally resizes, or not, congestion window (or buffer) sizing and threshold for the communication gateways based upon mathematical models. Application of the inventive congestion management method optimizes data recovery and throughput in communication networks, particularly those networks having lossy data links.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA +1
Communication system, communication device, and communication method
InactiveUS20100011270A1Reduce network loadImprove network performanceError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementCongestion windowCommunications system
A first loss determination section 13 of a first communication device 10 determines that a data unit is lost if an acknowledgment response for the transmitted data unit from a second communication device 30 is not received within a predetermined time and retransmits the data unit when the determination is made. When a determination section 16 determines that a spurious timeout has occurred, a window control section 17 sets a target value for decreasing the size of a congestion window and then gradually decreases the size of the congestion window to the target value when the acknowledgment response is received. Therefore, in a case of executing a response algorithm for changing a slow start threshold and the congestion window, if a segment loss occurs subsequent to the spurious timeout, an efficient loss recovery is achieved and the throughput is improved.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
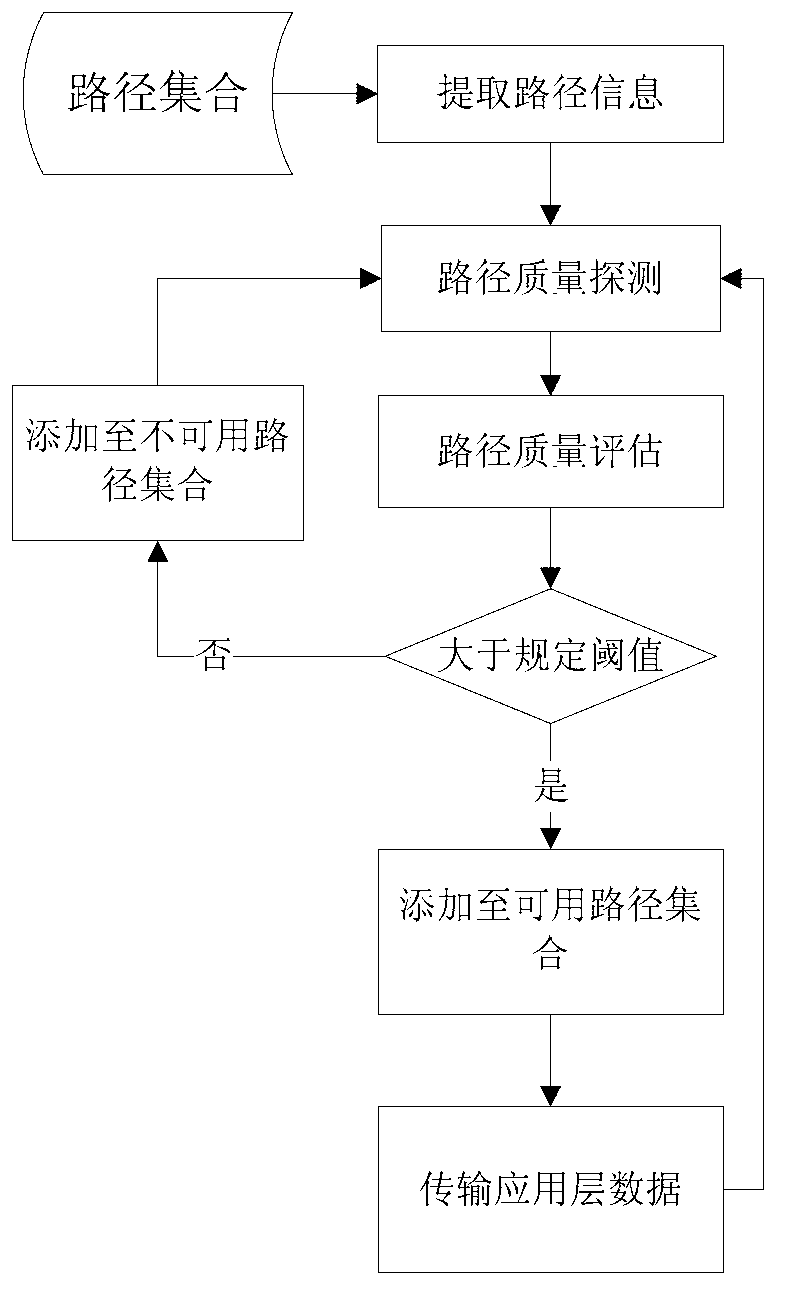
Path estimating method and device
ActiveCN102843257AAccurate adjustment effectImprove data transmission qualityData switching networksCongestion windowPacket loss
The invention discloses a path estimating method which comprises the steps of: calculating a path quality estimating parameter according to a round-trip-delay, a packet loss probability and a congestion window of a path; dividing the path into an available path and an unavailable path according to the path quality estimating parameter; transmitting data on the available path and calculating the round-trip-delay, the packet loss probability and the congestion window of the path in a process of transmitting the data; and sending a heartbeat message in the unavailable path for calculating the round-trip-delay, the packet loss probability and the congestion window of the path. According to the invention, the path quality can be detected in real time, the path quality can be accurately calculated according to the simple parameter and the data transmission path is regulated and selected in real time, therefore the quality of the data transmission path is ensured, and the data is reliably transmitted. The path quality can be effectively estimated, and the transmission quality of streaming media data is improved.
Owner:WUXI BUPT SENSING TECH & IND ACADEMY +1
Reliable transmission acceleration method facing networks with high error rate and long delay characteristics
ActiveCN101645765AImprove bandwidth utilizationImprove transmission performanceError prevention/detection by using return channelData switching networksCongestion windowReliable transmission
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
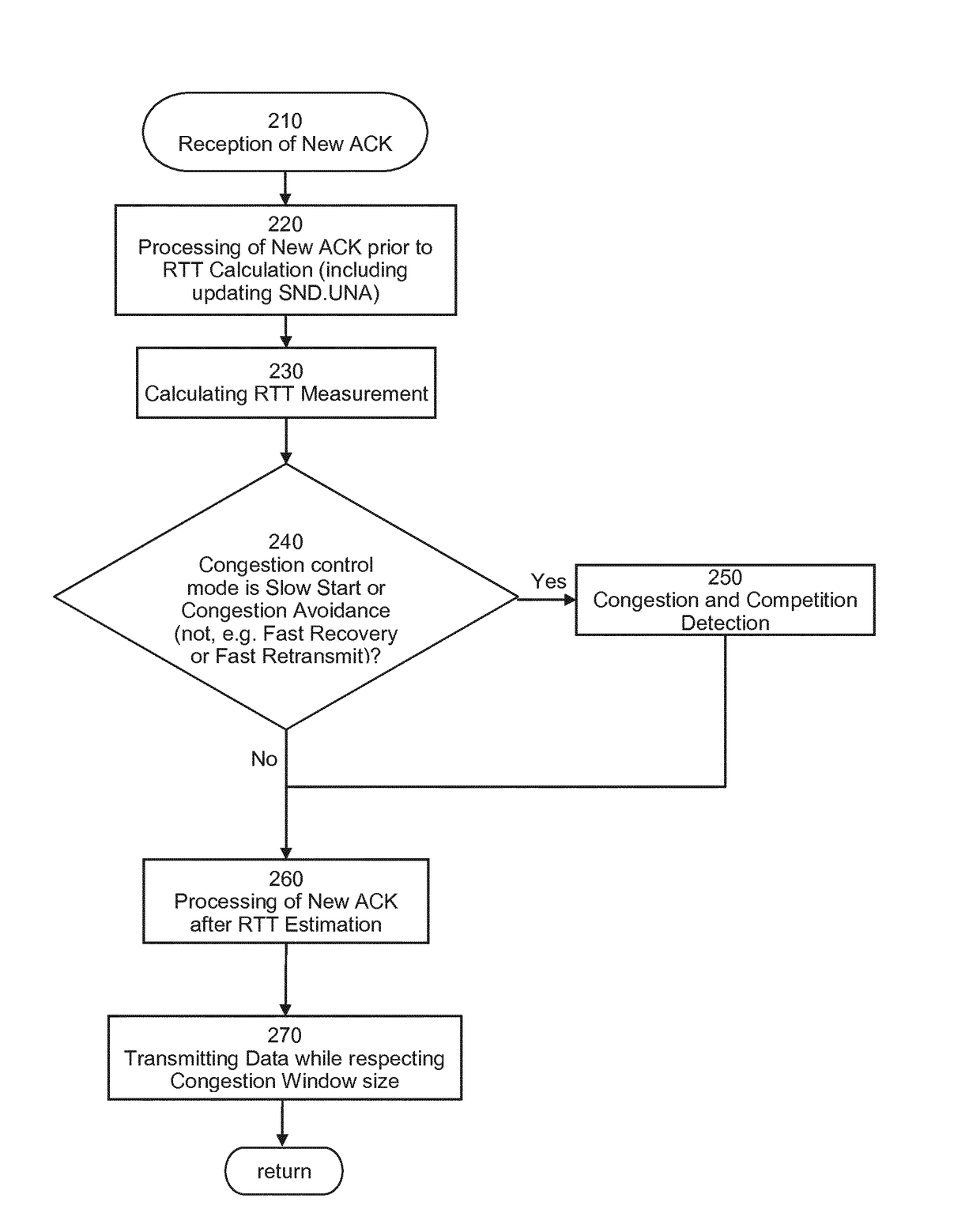
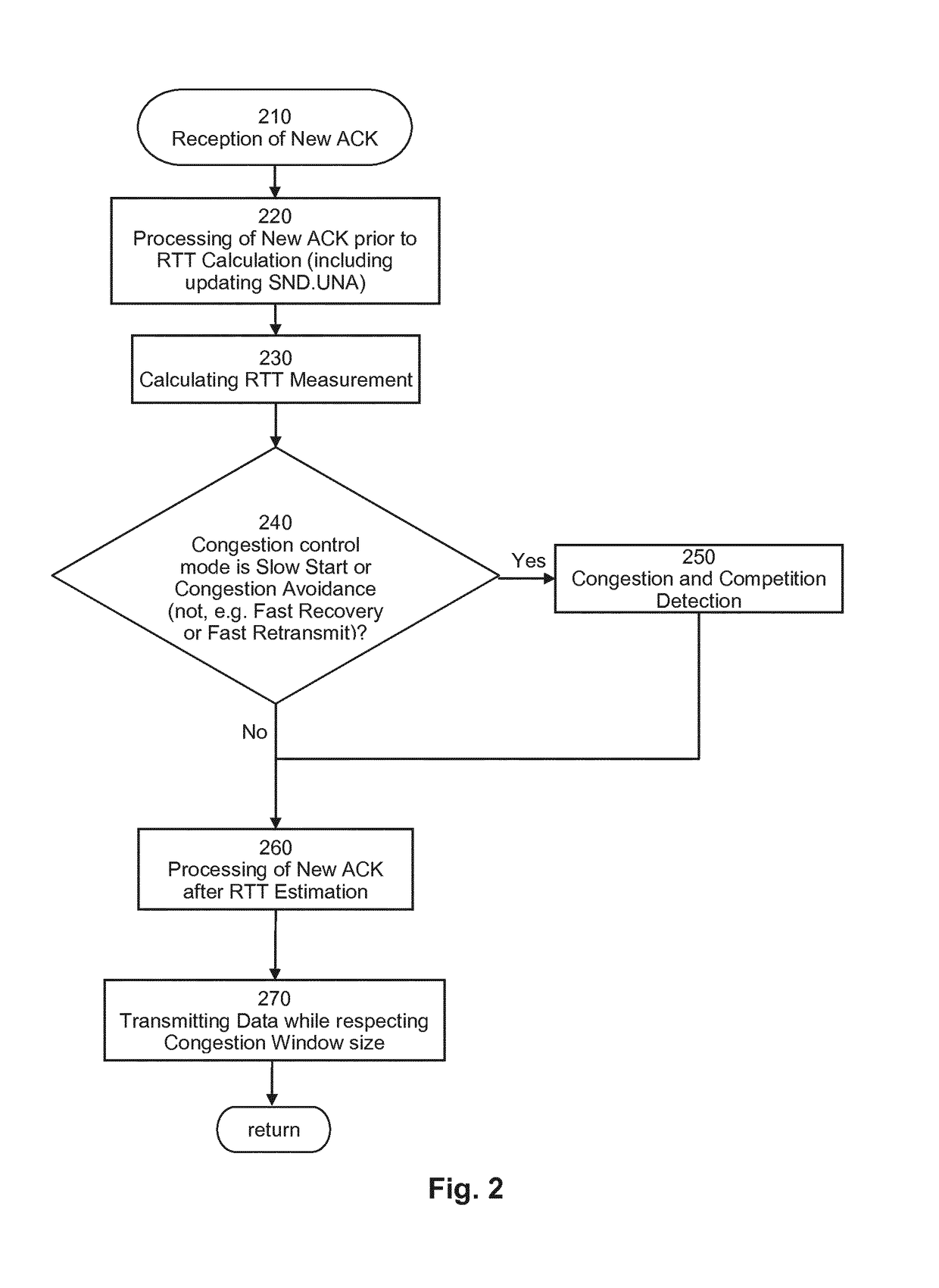
Method and Apparatus for Network Congestion Control Based on Transmission Rate Gradients
ActiveUS20170195231A1Reliable detectionEasy to handleData switching networksNetwork data managementCongestion windowCongestion detection
A method and apparatus for congestion control for acknowledged communication over networks detects congestion based on trends of flight size and transmission rate in order to adapt a congestion window in accordance with a detection result. Such congestion detection enables, for example, distinguishing between the congestion with or without unfair competition. Moreover, the measured transmission rate or its trend can be filtered to compensate for time variations. An end node or a proxy can be used for congestion control.
Owner:BEQUANT
Data center congestion management for non-tcp traffic
ActiveUS20150341273A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCongestion windowTraffic capacity
Methods, apparatus and software for implementing enhanced data center congestion management for non-TCP traffic. Non-congested transmit latencies are determined for transmission of packets or Ethernet frames along paths between source and destination end-end-nodes when congestion along the paths is not present or minimal. Transmit latencies are similarly measured along the same source-destination paths during ongoing operations during which traffic congestion may vary. Based on whether a difference between the transmit latency for a packet or frame and the non-congested transmit latency for the path exceeds a threshold, the path is marked as congested or not congested. A rate at which the non-TCP packets are transmitted along the path is then managed as function of a rate at which the path is marked as congested. In one implementation, non-TCP traffic is managed by mimicking a Data Center TCP technique, under which the congestion marking status of the path is substituted as an input to a DCTP algorithm in place of the normally-used ECN-Echo flag input. The congestion window output by the DCTCP algorithm is then used to manage the rate at which non-TCP packets to be forwarded via the path are transmitted from a source end-node.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Apparatus for Arq Controlling in Wireless Portable Internet System and Method Thereof
InactiveUS20080101290A1Flexible controlRetransmission be relatively fastNetwork traffic/resource managementConnection managementService flowCongestion window
The present invention relates to an ARQ control apparatus and method. According to the present invention, a subscriber station performs initialization by communicating with a base station, and receives wireless link channel quality information; stores an SDU in an SDU buffer when the SDU is transmitted from an upper block, and establishes a connection with the base station for a corresponding service flow; receives QoS information on the service flow, ARQ information, and a CINR, and transmits them to the uplink scheduler; detects a TCP header of the SDU and stores TCP sequence number information; and performs a DSC for controlling an MAC ARQ window size with reference to the QoS information, ARQ information, CINR, and TCP congestion window size.
Owner:KT CORP +4
Loss tolerant transmission control protocol
ActiveUS7889654B2Reduce congestionReduce window sizeFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork traffic/resource managementCongestion windowTransmission protocol
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST +1
Method for accelerating TCP flows in communication networks with dynamic control
Predictions of congestion conditions for a traffic stream in a communication network are applied to modify an initial congestion window size for the traffic stream; and dynamic bandwidth control is thereafter applied to the traffic stream. This dynamic bandwidth control may include modulating inter-packet bandwidths of the traffic stream according to a capacity of a bottleneck in a communication path through which the traffic stream passes in the communication network. The predictions of congestion conditions may be based on monitoring packet losses and / or round trip times within the communication network for a selected period of time. The monitoring may be performed on at least one of a traffic stream-by traffic stream basis, a connection-by-connection basis, a link-by-link basis, or a destination-by-destination basis.
Owner:RIVERBED TECH LLC
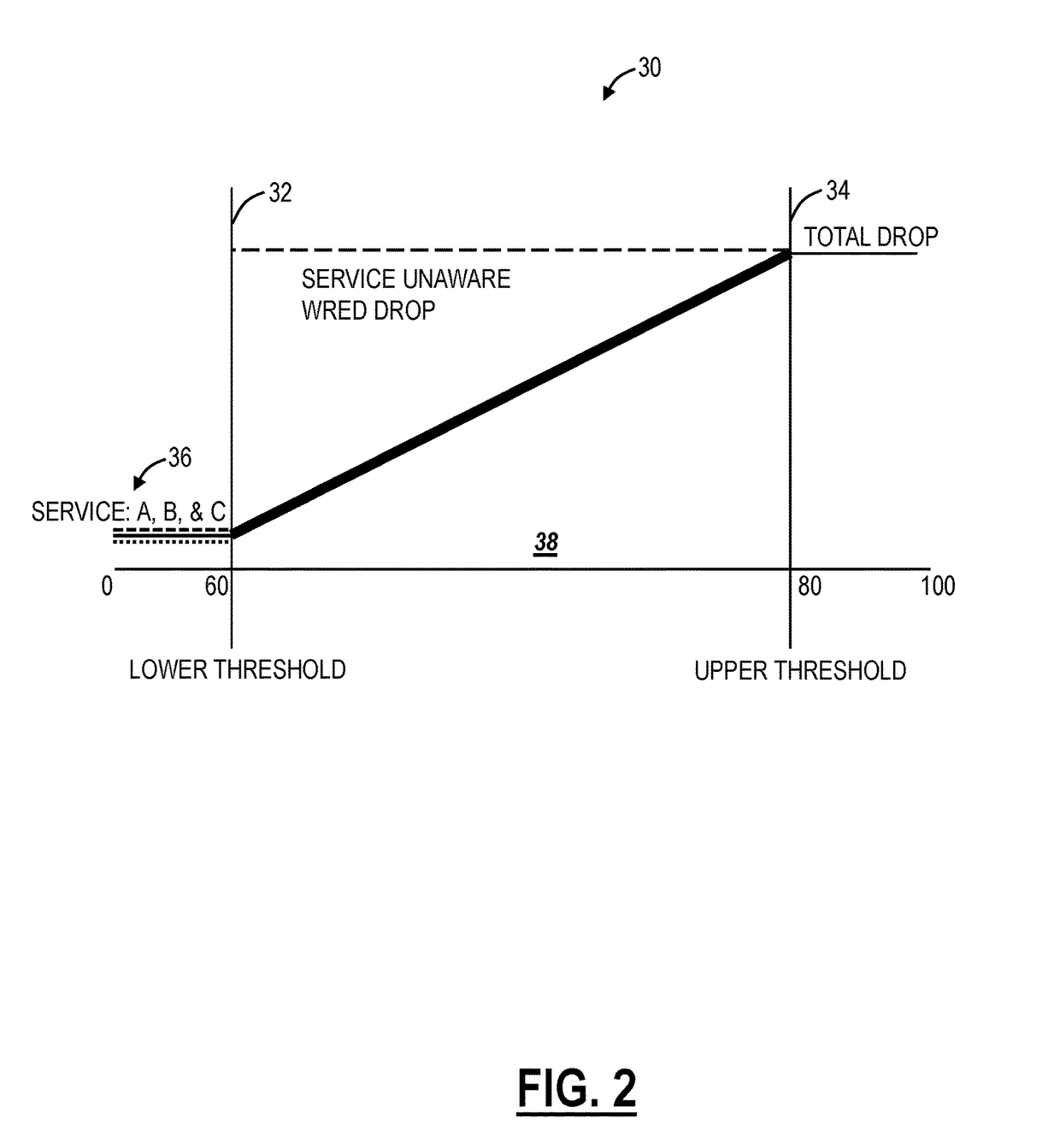
Per queue per service differentiation for dropping packets in weighted random early detection
Systems and methods for per service differentiation for congestion avoidance through dropping packets based on service priority include receiving an ingress packet; responsive to no congestion, providing the ingress packet to a queue of one or more queues; and, responsive to congestion, during a congestion window, one of providing the ingress packet to the queue and dropping the packet based on a packet dropping capability and service priority of a service associated with the packet.
Owner:CIENA
System and Method for Transmission Control Protocol Slow-Start
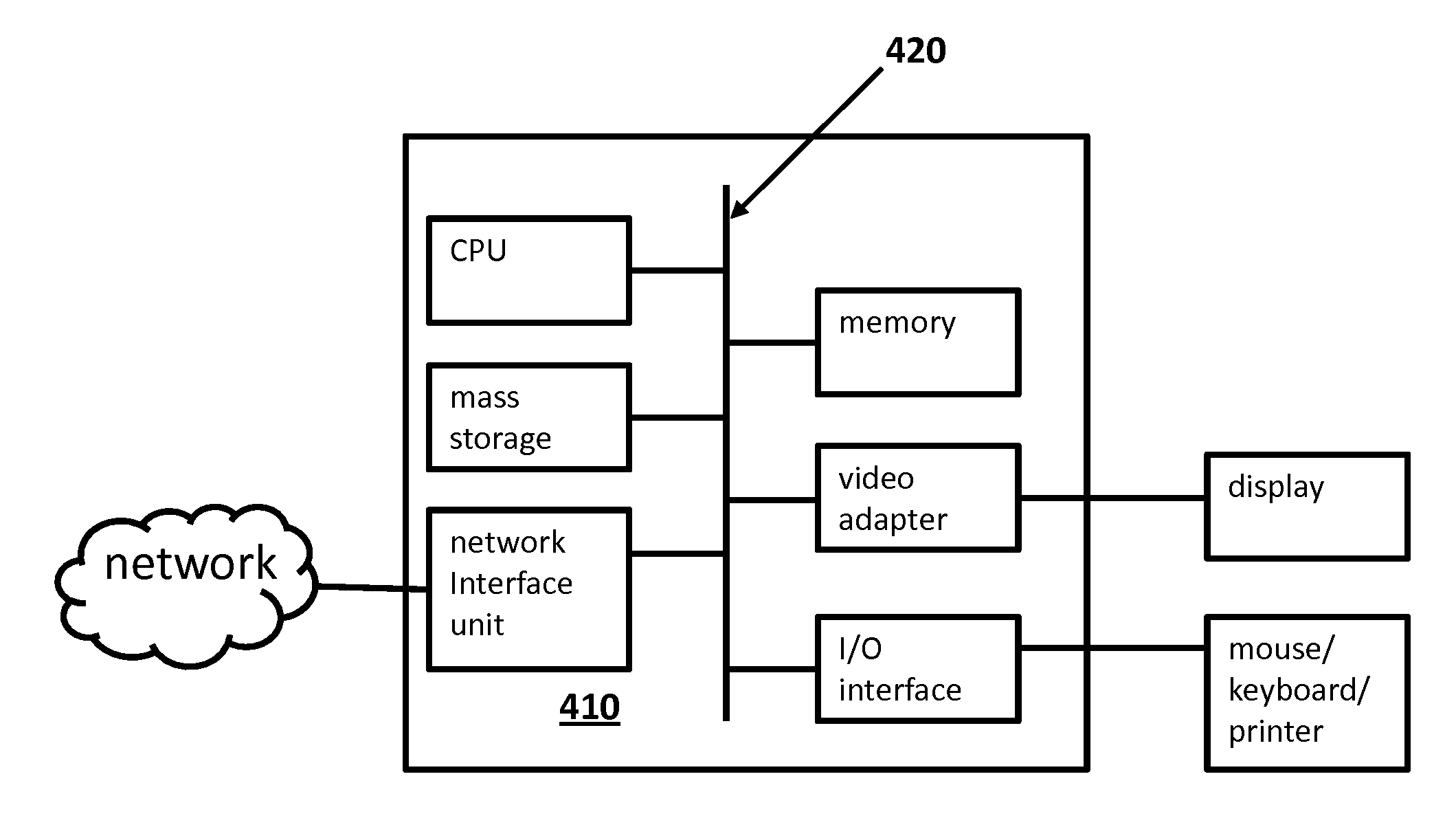
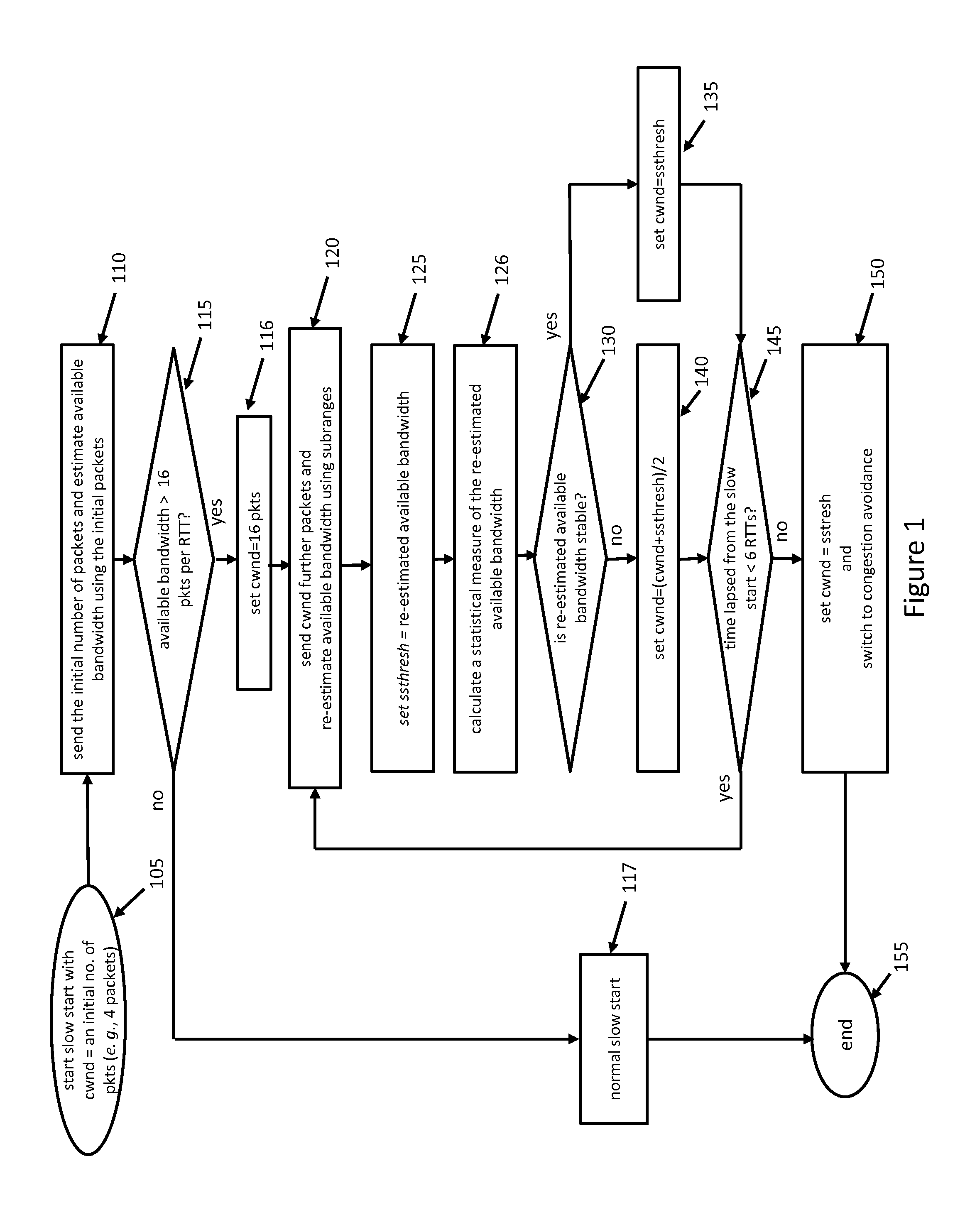
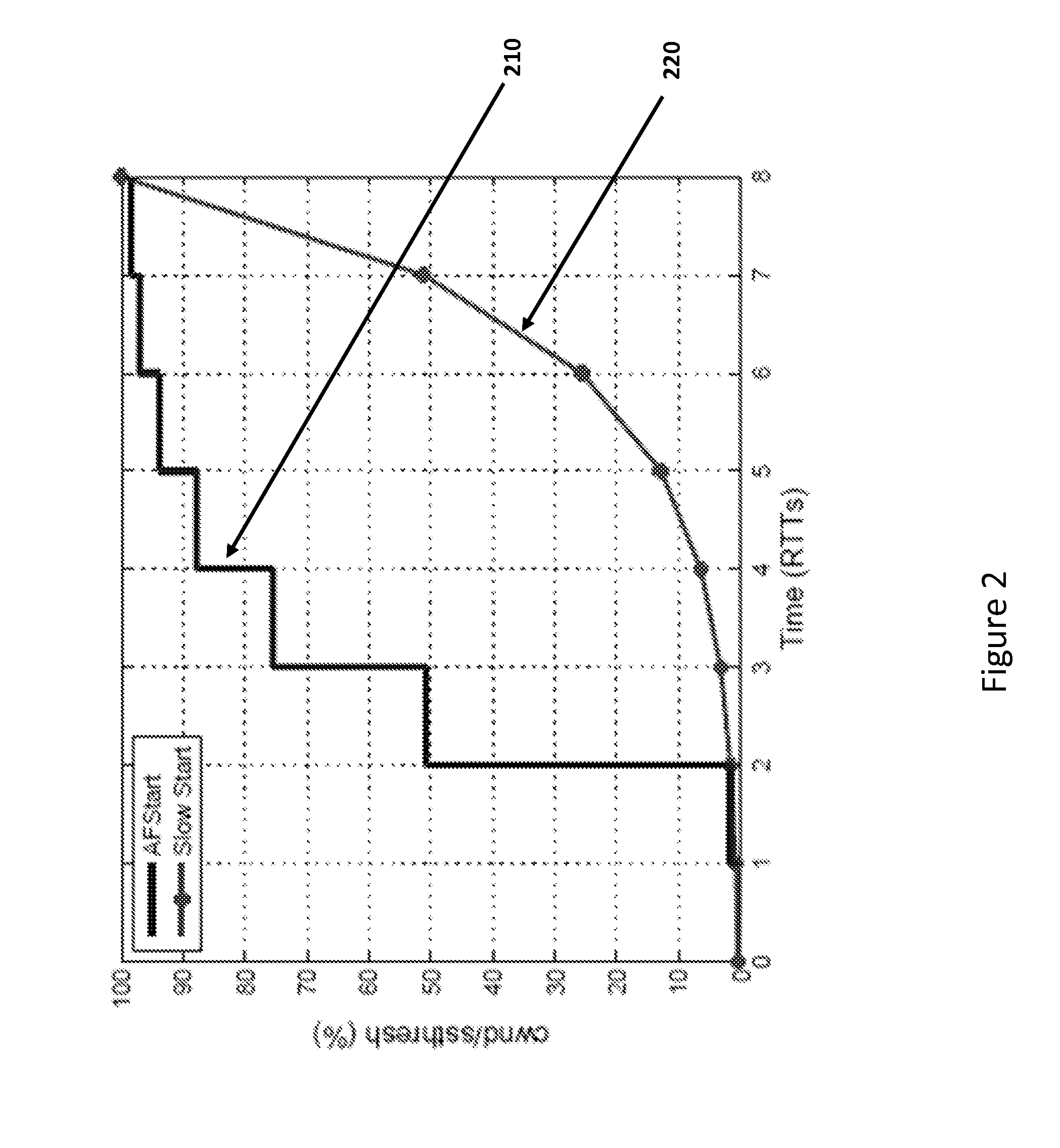
ActiveUS20130044598A1Set evenlyImprove efficiencyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCongestion windowSlow-start
An embodiment of a system and method that uses inline measurements to probe available bandwidth for a transmission control protocol, and adaptively sets a slow-start threshold according to the available bandwidth. The method includes initializing a congestion window “cwnd,” sending cwnd packets, estimating an available bandwidth for the cwnd packets. The congestion window cwnd is set to a higher number, and the higher number of further packets is sent if the available bandwidth is greater than a first threshold level. The available bandwidth is re-estimated for the higher number of the further packets, and a soft start threshold “ssthresh” is set to the re-estimated available bandwidth. A statistical measure is calculated for the re-estimated available bandwidth, and the congestion window cwnd is set equal to ssthresh if a ratio of the statistical measure to the re-estimated available bandwidth is less than a second threshold level.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com