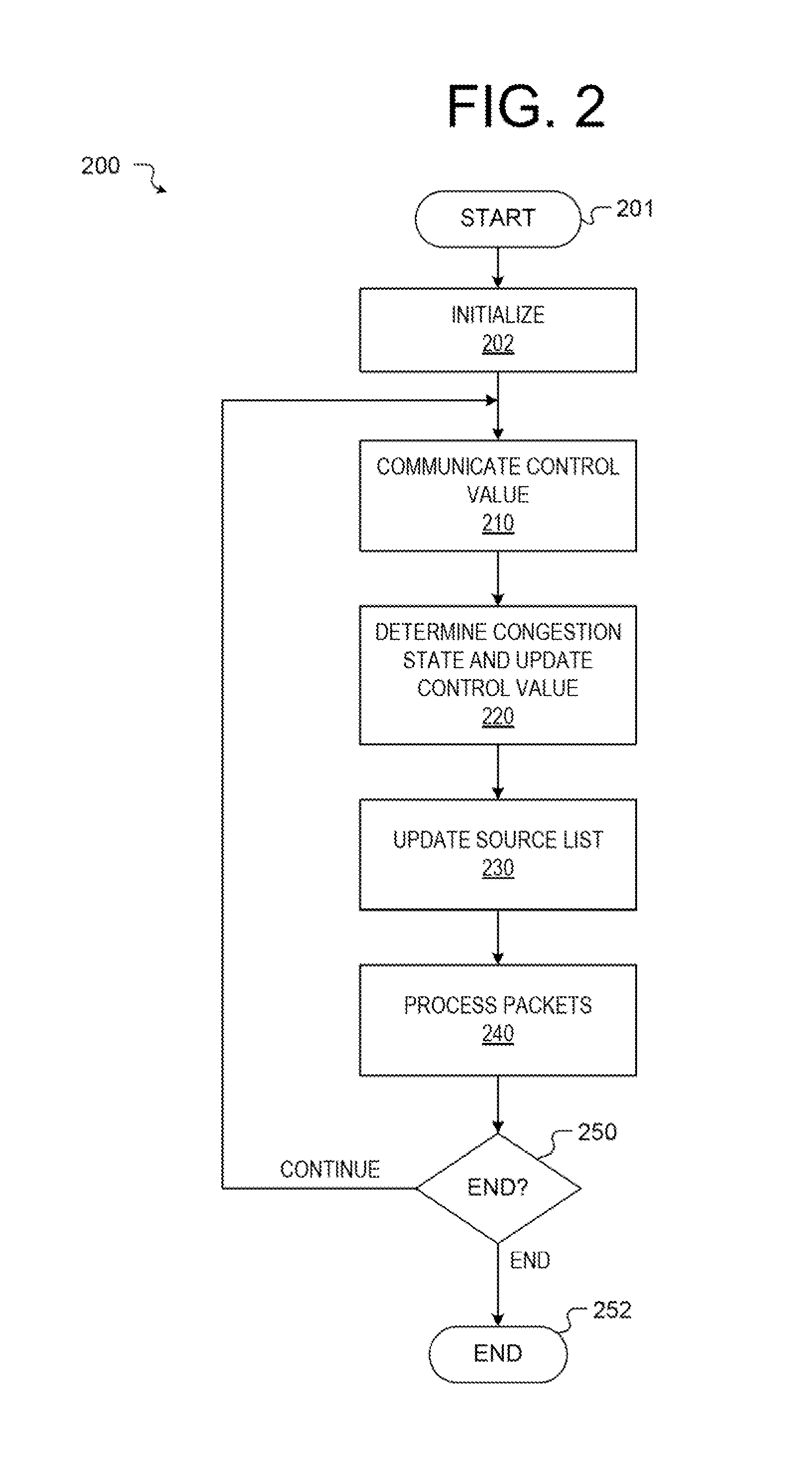
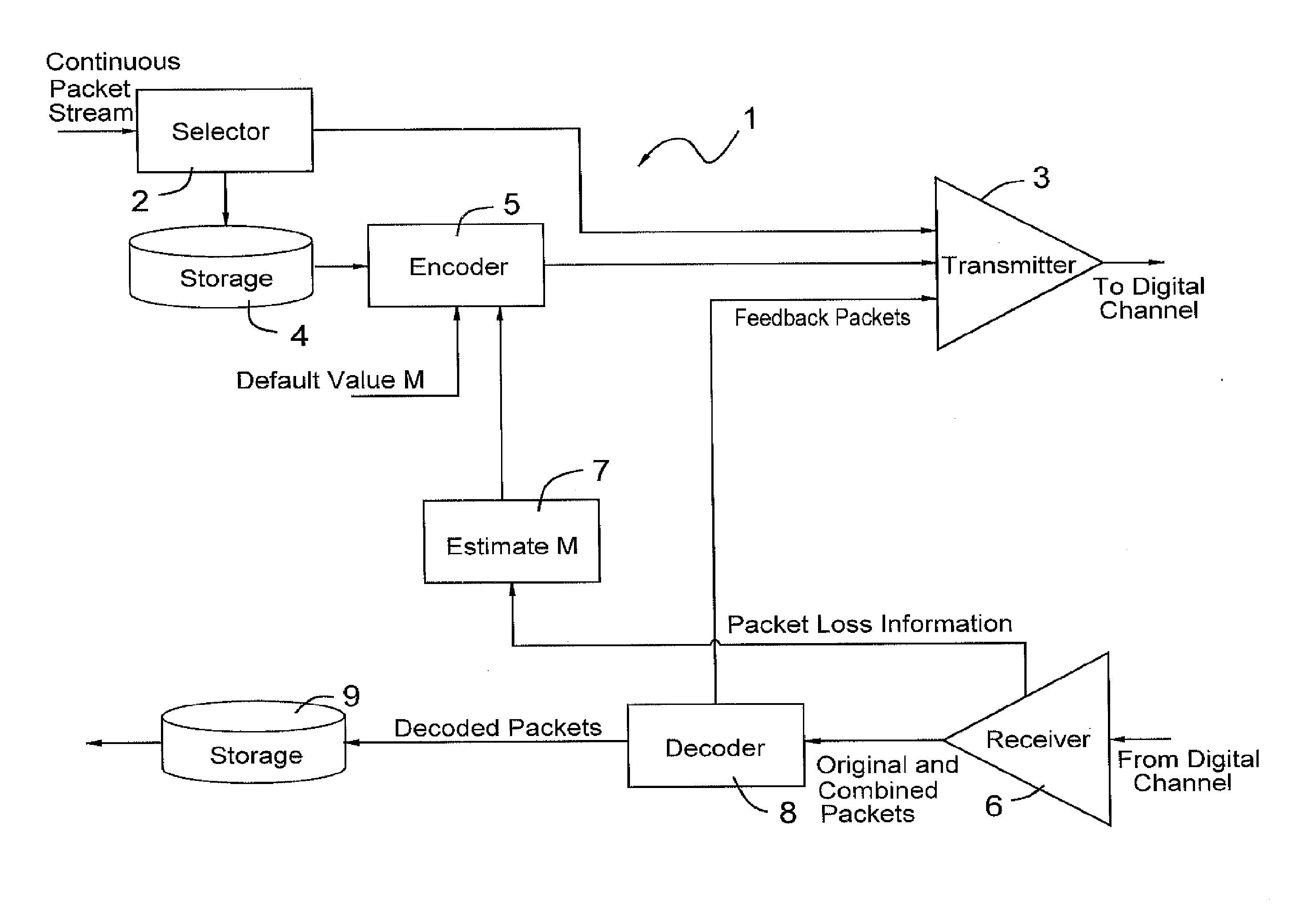
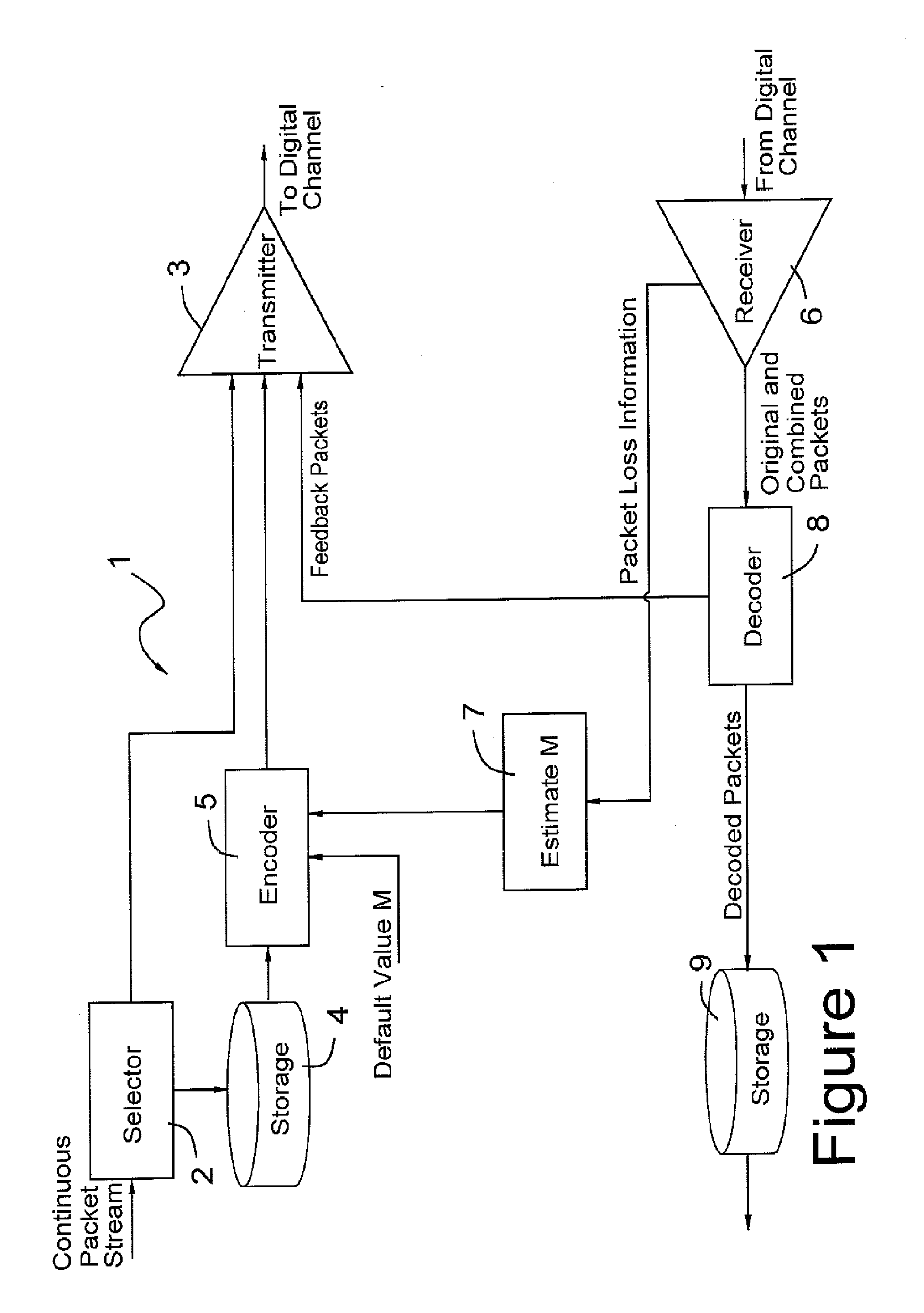
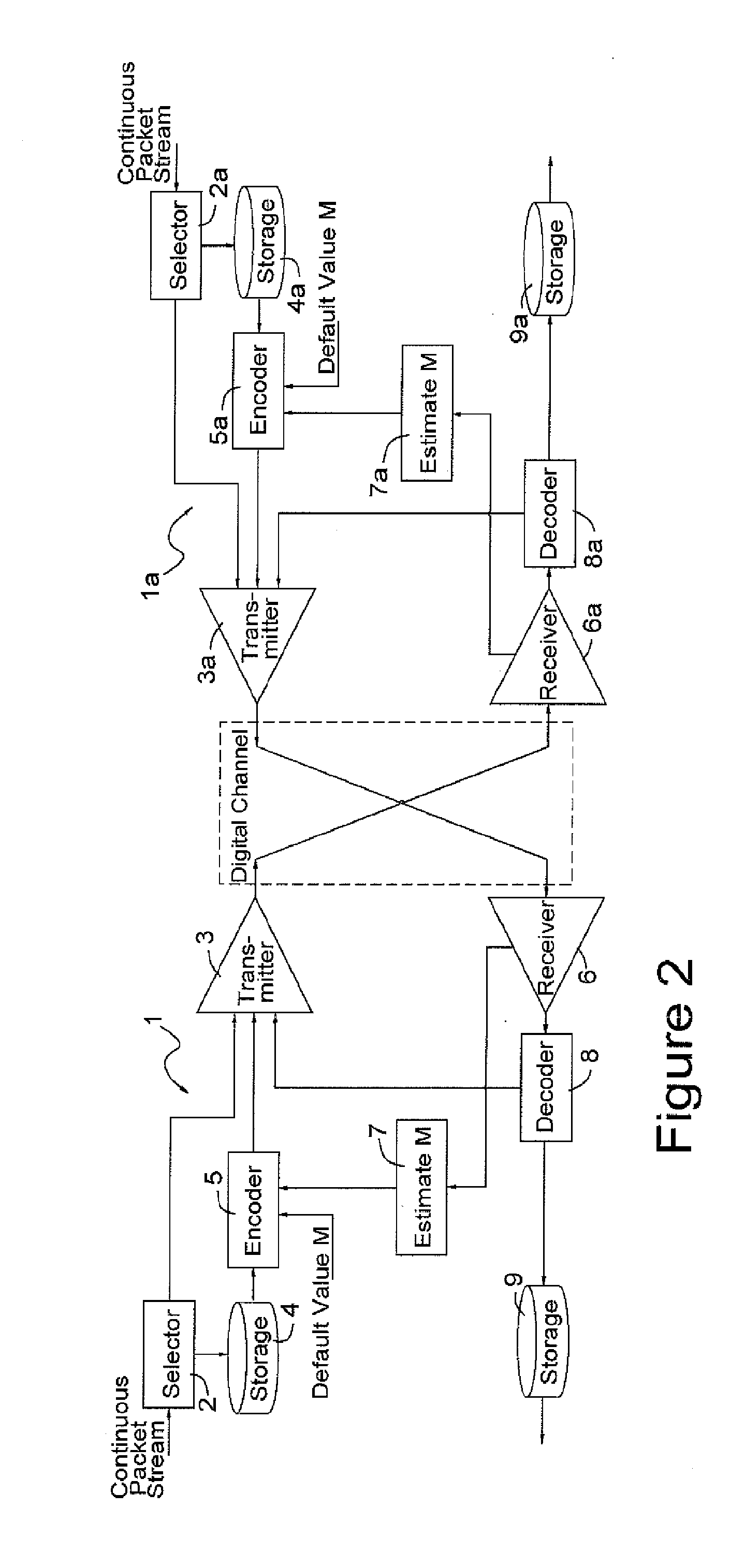
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
196 results about "Congestion management" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Congestion Management Process (CMP) is the name used nationally to describe an ongoing, systematic method of managing congestion that provides information about both system performance and potential alternatives for solving congestion-related problems. Addressing the costs of congestion is a recurring topic in...
Technique for providing end-to-end congestion control with no feedback from a lossless network
InactiveUS7035220B1Improve creditError preventionTransmission systemsEnd to end congestion controlDistributed computing
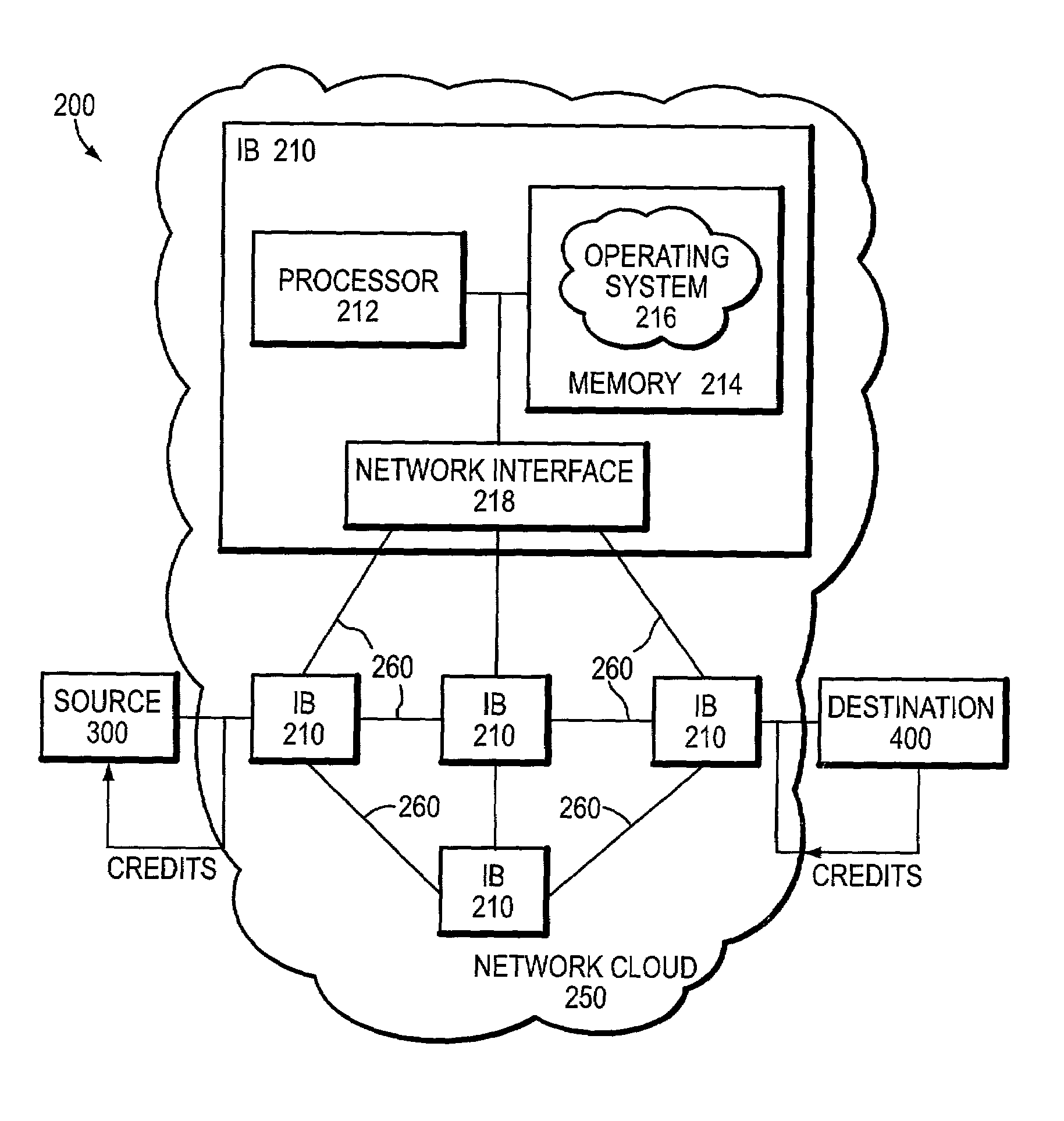
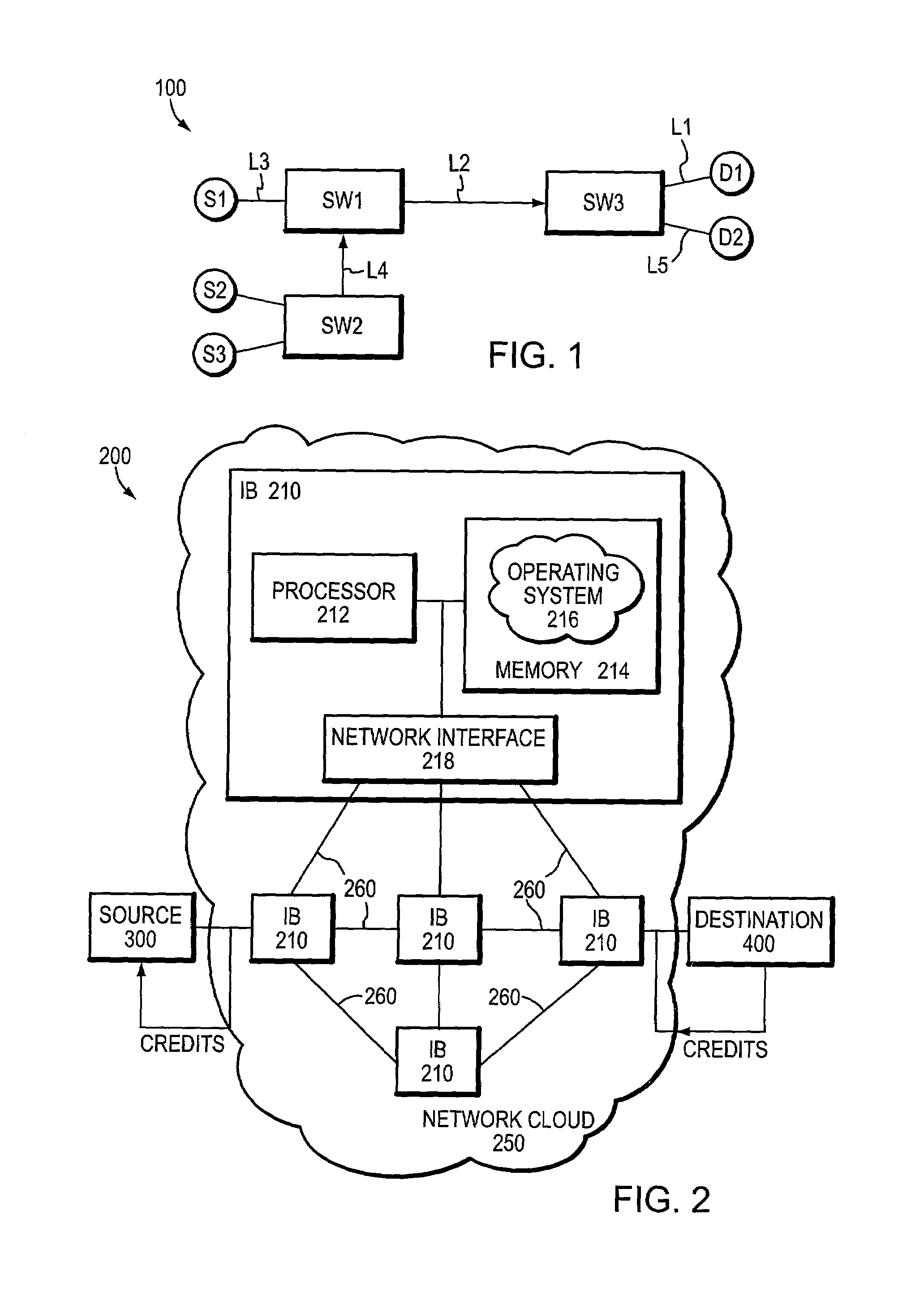
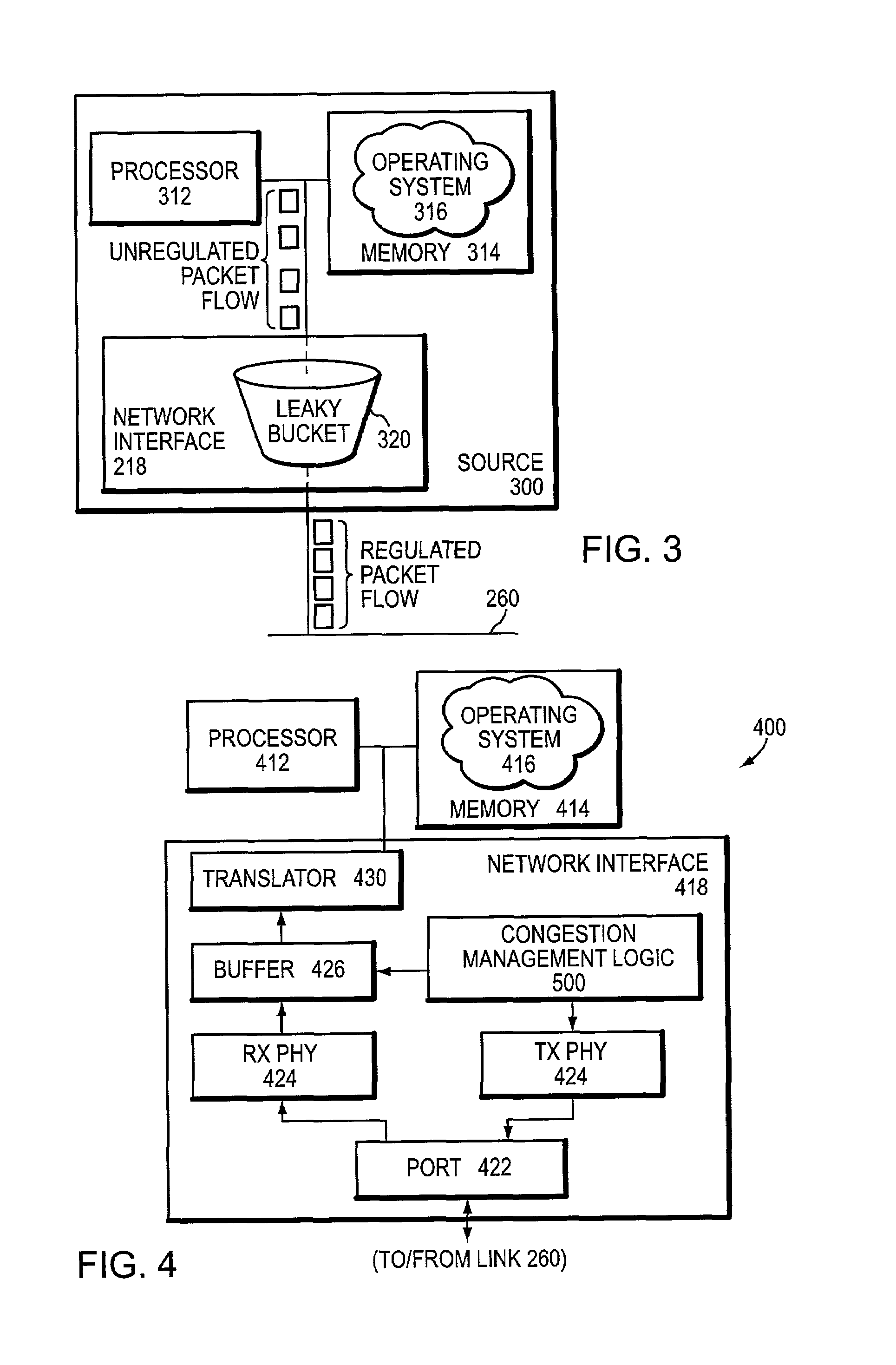
A congestion management technique achieves an end-to-end data flow rate that is supported by a lossless communications network. The end-to-end rate extends from a source end node to destination end node of the network and is preferably at or slightly below a bottleneck rate of the network. The destination end node determines, on its own and without any help from network elements, a supportable rate of activity in the network and provides feedback to the source end node. By achieving such a rate, data transmitted by the source end node can flow through the network without loss of packets and without the use of substantial buffering.
Owner:INFINISWITCH CORP +1
User-plane congestion management
Methods, apparatuses and systems for user-plane congestion management are provided. Among these method, apparatuses and systems is a method, implementable by a base station (and / or a serving gateway), for mitigating user plane congestion. The method may include sending a congestion indication to a core network; receiving a general packet radio system (GPRS) tunneling protocol (GTP) packet including an first internet protocol (IP) packet associated with a first flow within a bearer; obtaining, from a header of the GTP packet, an indicator indicative of a priority of the IP packet, wherein the indicator was inserted into the header of the GTP packet by the core network responsive to the congestion indication; and dropping any of the GTP packet and the first IP packet on condition that a priority of a second IP packet associated with second flow within the bearer takes precedence over the priority of the first IP packet.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
Method and Apparatus For Computer Network Bandwidth Control and Congestion Management
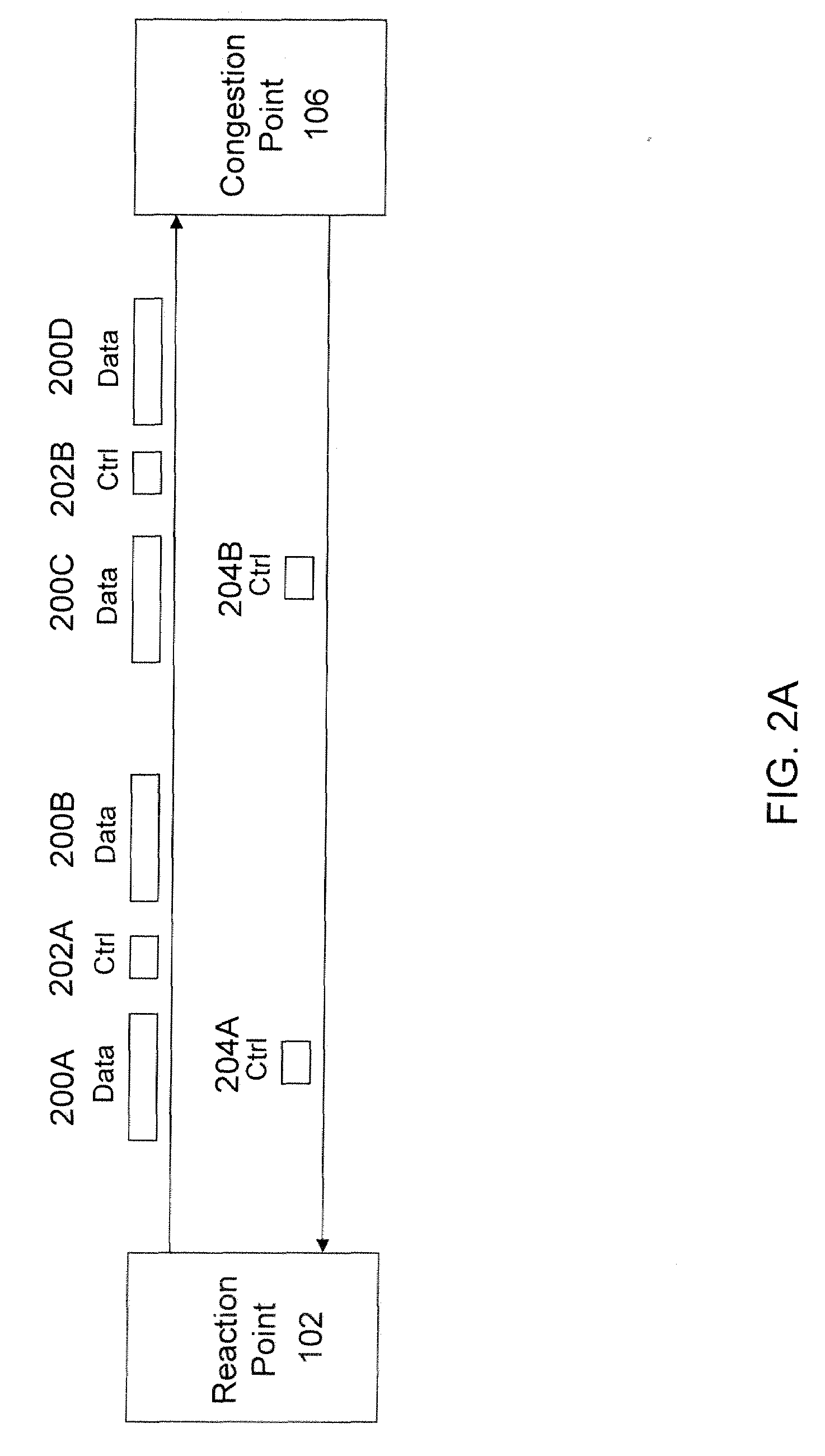
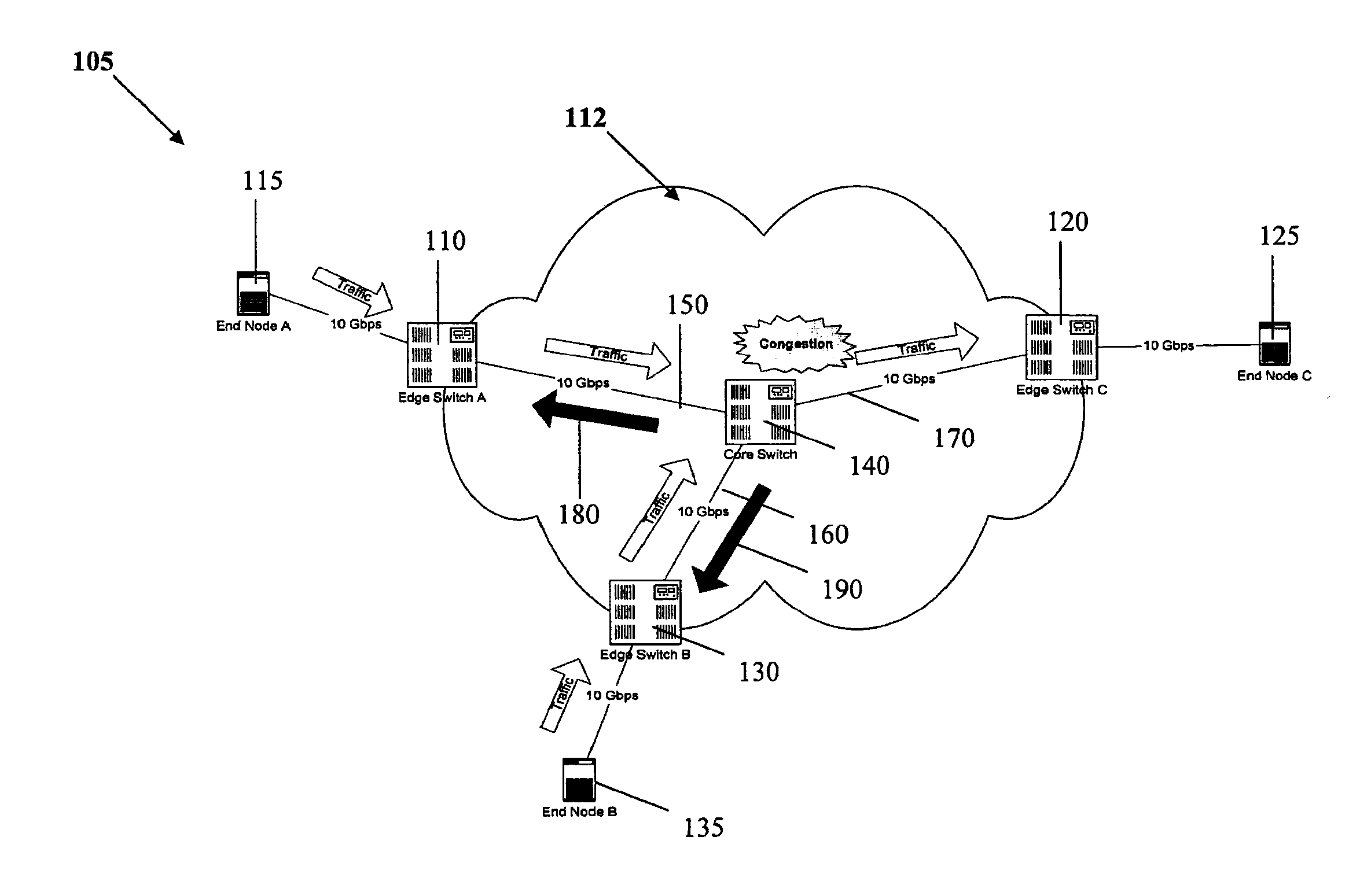
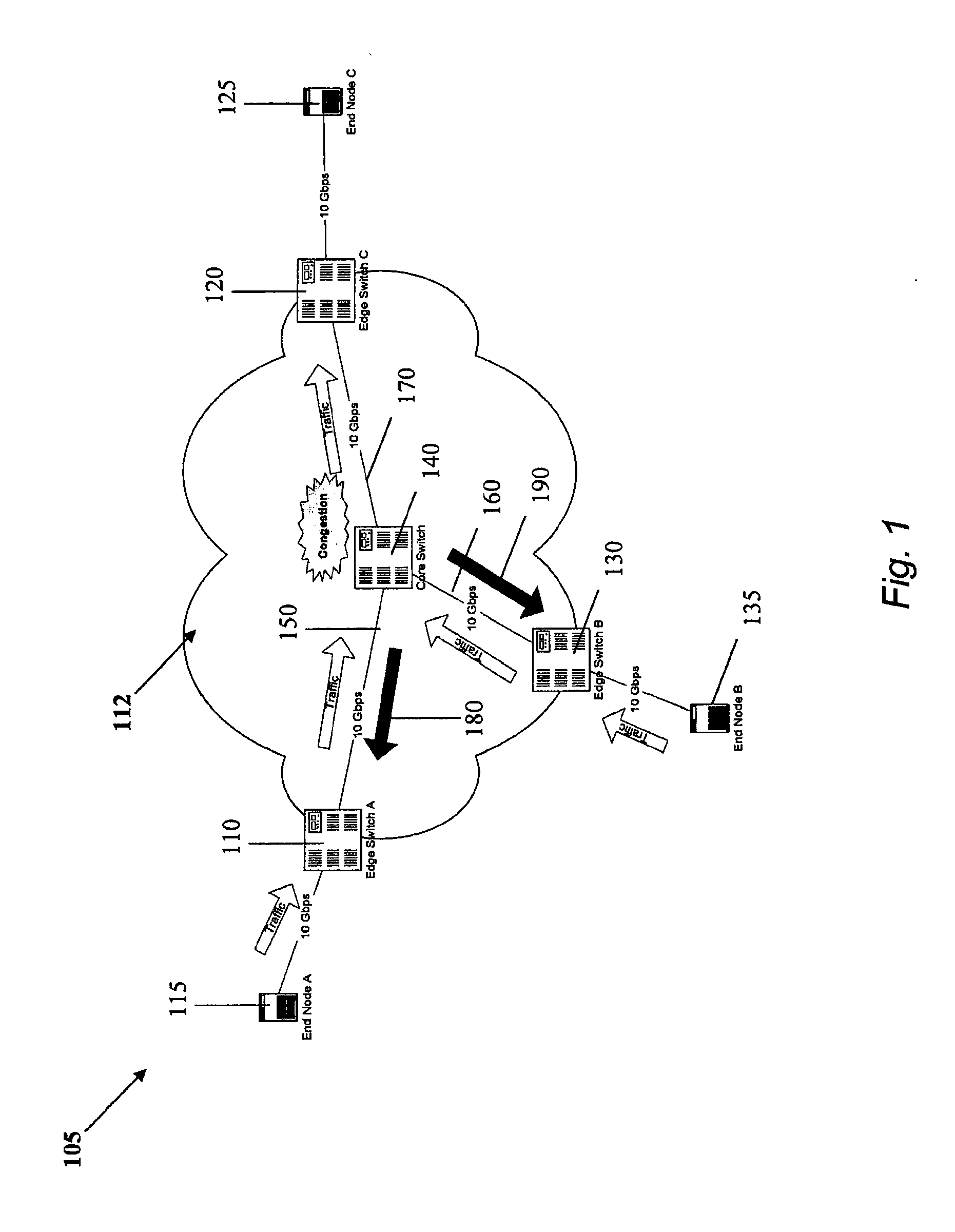
In one embodiment, a network switch includes first logic for receiving a flow, including identifying a reaction point as the source of the data frames included in the flow. The network switch further includes second logic for detecting congestion at the network switch and associating the congestion with the flow and the reaction point, third logic for generating congestion notification information in response to congestion, and fourth logic for receiving control information, including identifying the reaction point as the source of the control information. The network switch further includes fifth logic for addressing the congestion notification information and the control information to the reaction point, wherein the data rate of the flow is based on the congestion notification information and the control information. The content of the data frames included in the flow is independent of the congestion notification information and the control information in a first mode of the network switch.
Owner:TEAK TECH
Method and system for congestion management in a fibre channel network
ActiveUS20090116381A1Facilitates congestion managementAvoid network congestionMultiplex system selection arrangementsEnergy efficient ICTFiberChannel network
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that facilitates congestion management in a Fibre Channel (FC) network. During operation, the system determines a threshold data rate on an outgoing link coupled to an FC switch. The system further determines the number of sources that send data to the outgoing link and an aggregate arrival rate of data for the outgoing link. Next, the system determines an injection data rate for a respective source based on the threshold data rate on the outgoing link, the number of sources transmitting data to the outgoing link, and the aggregate arrival data rate for the outgoing link. Subsequently, the system communicates the injection data rate to the source, thereby allowing the source to throttle its data injection in the FC network to prevent network congestion.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
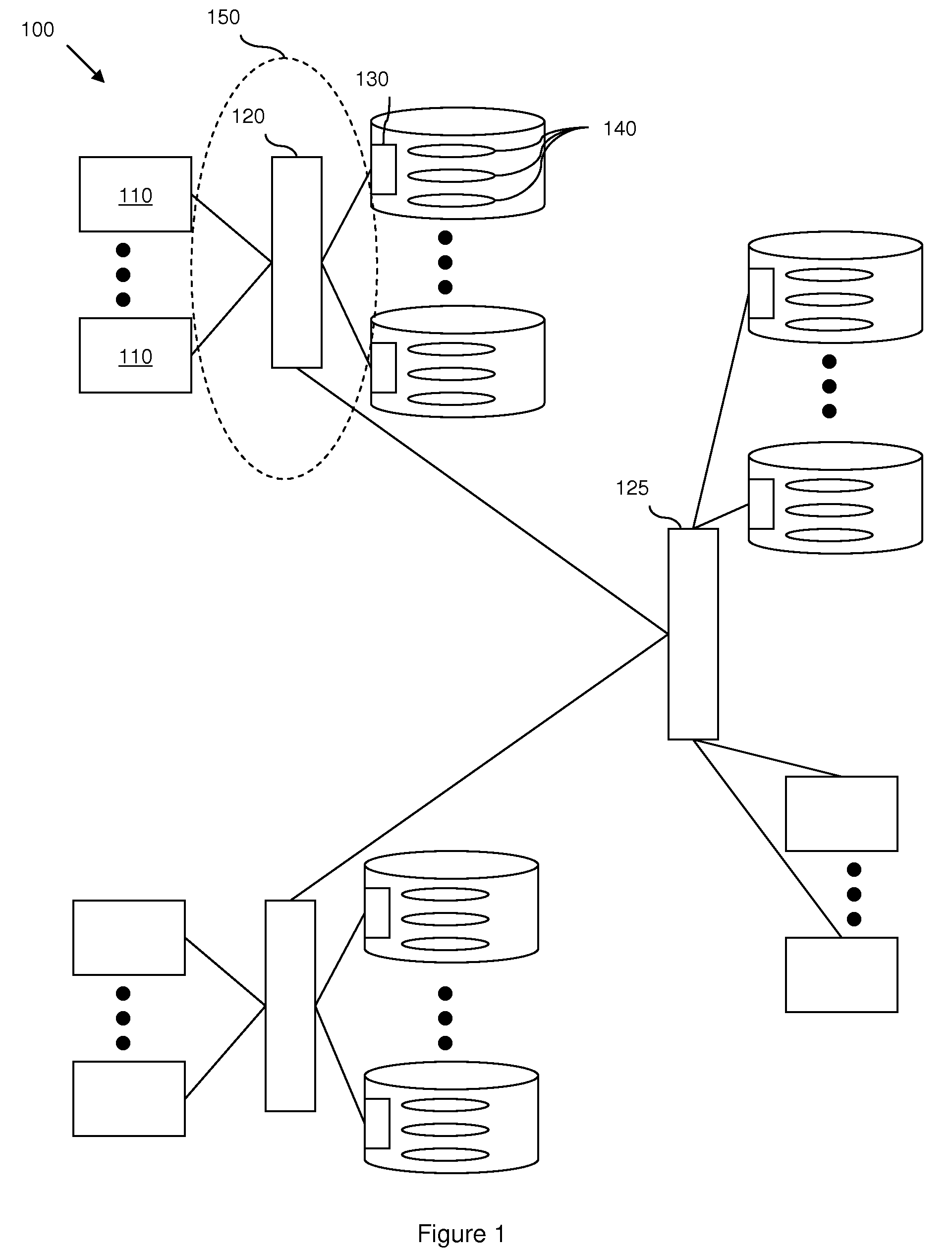
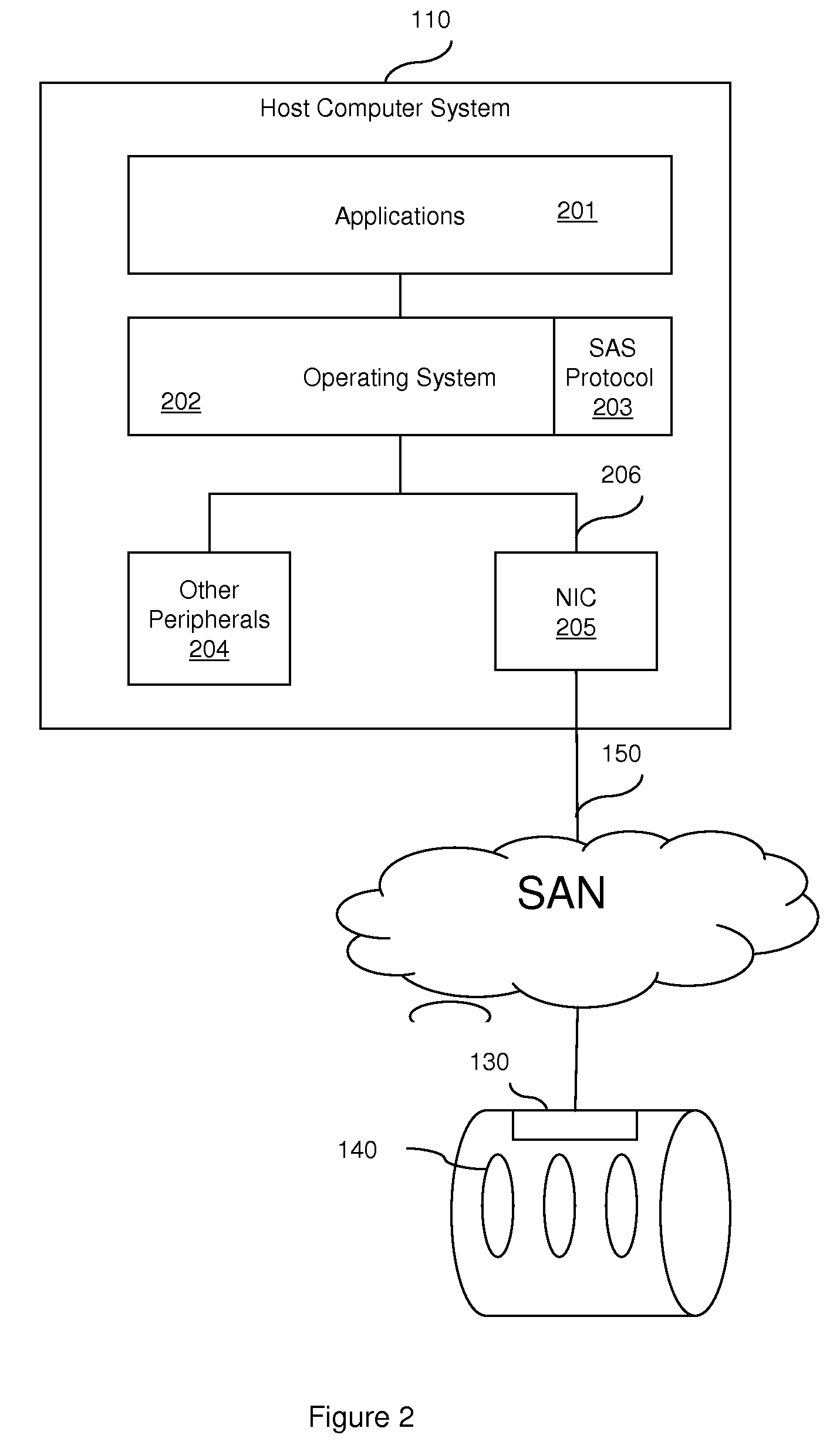
Layering serial attached small computer system interface (SAS) over ethernet
ActiveUS20080228897A1Solve insufficient capacityOvercome distanceMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionStorage area networkData center
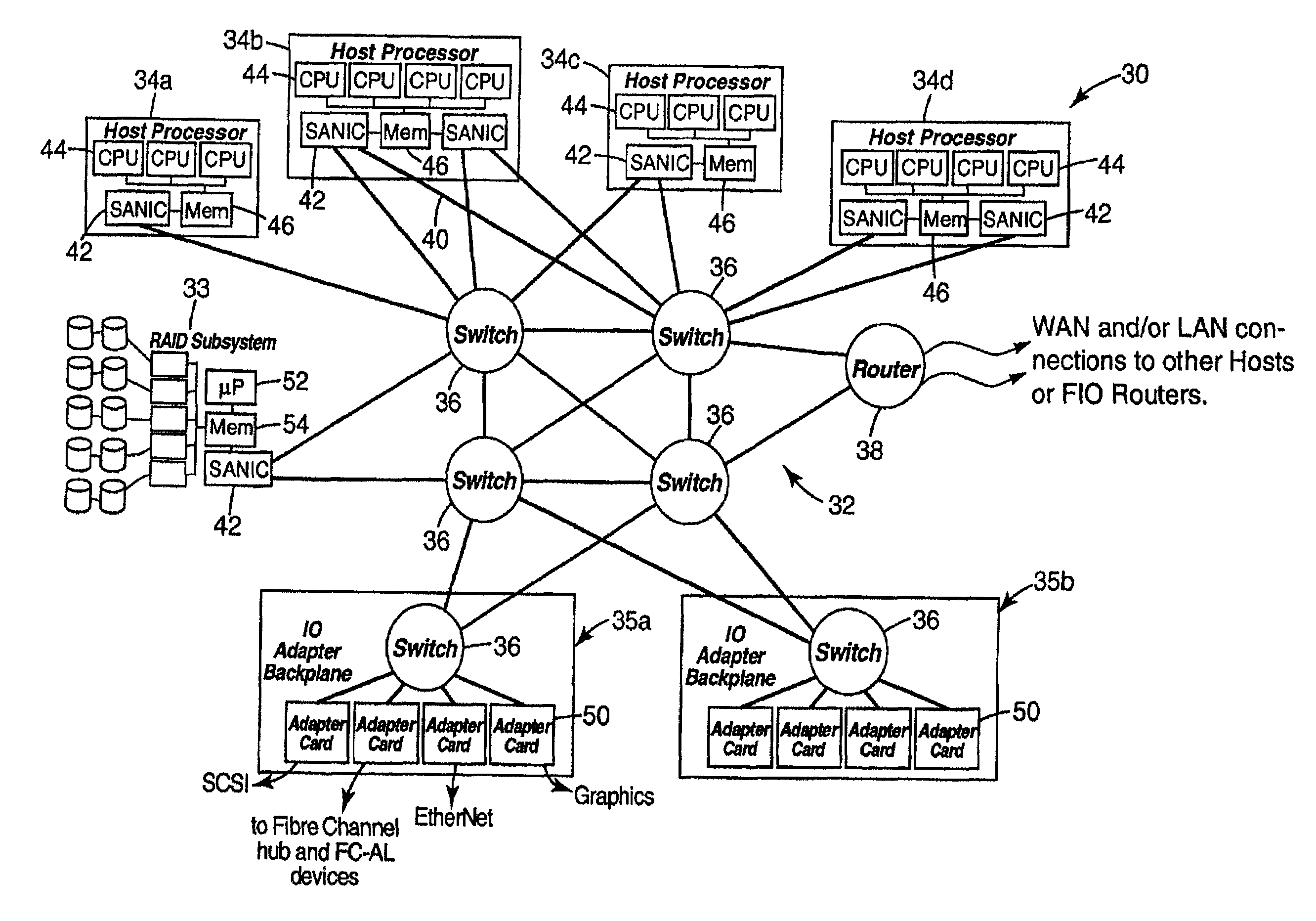
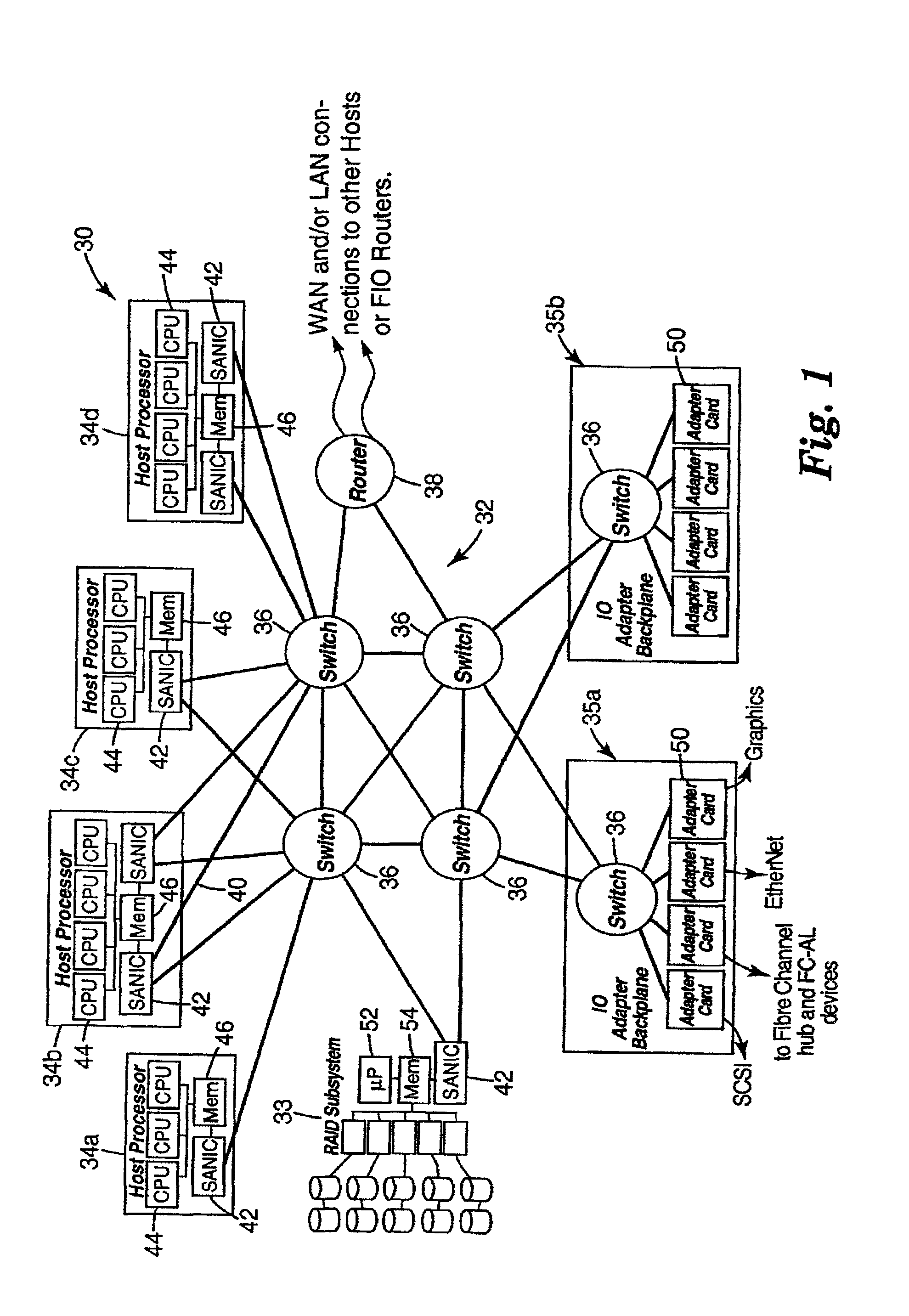
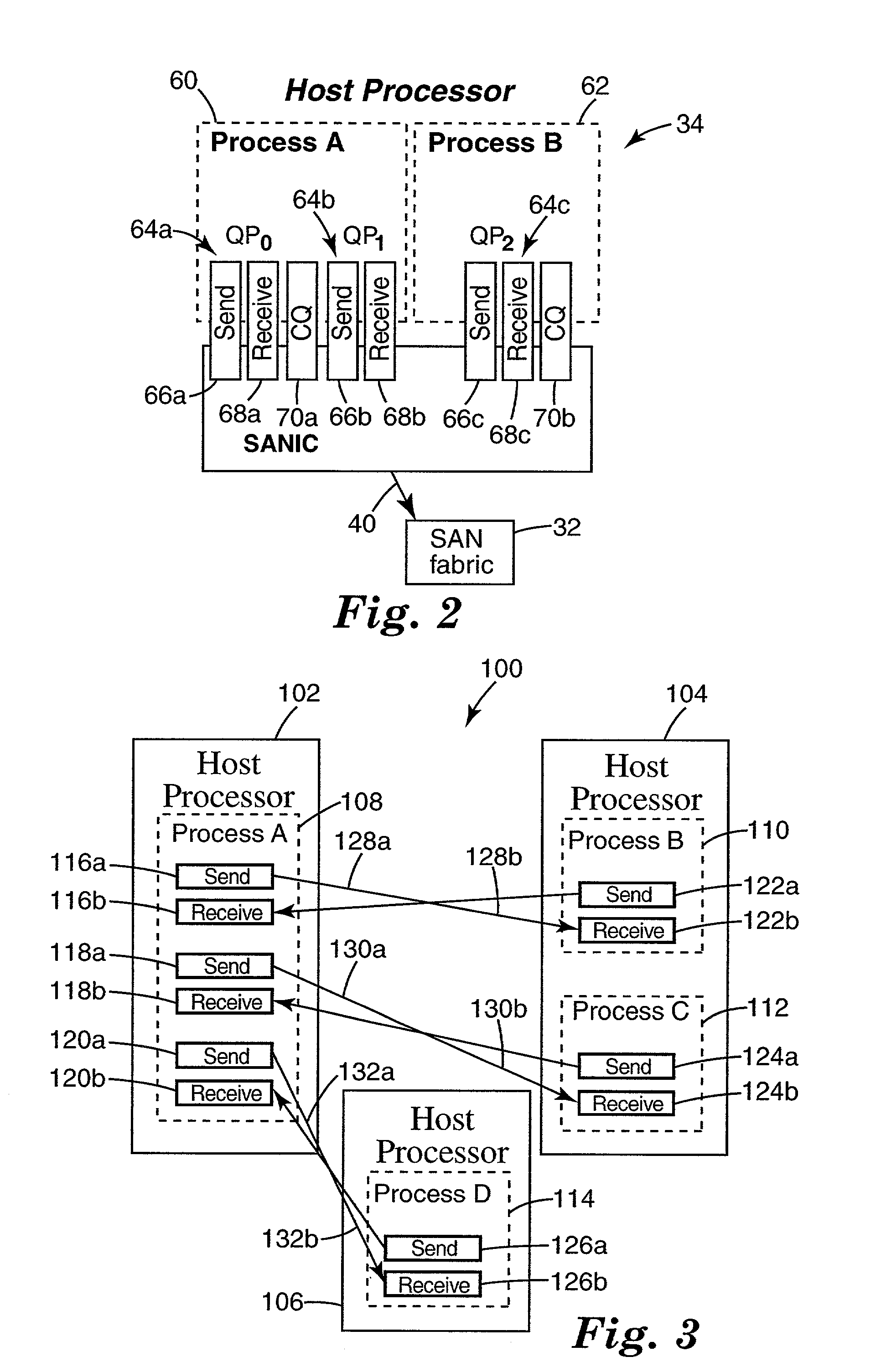
Disclosed are embodiments of a storage area network (SAN), a network interface card and a method of managing data transfers. These embodiments overcome the distance limitation of the Serial Attached Small Computer System Interface (SAS) physical layer so that SAS storage protocol may be used for communication between host systems and storage controllers. Host systems and storage controls are connected via an Ethernet interface (e.g., a legacy Ethernet or enhanced Ethernet for datacenter (EED) fabric). SAS storage protocol is layered over this Ethernet interface, providing commands and transport protocol for information exchange. Since the Ethernet interface has its own physical layer, the SAS physical layer is unnecessary and, thus, so is the SAS distance limitation. If legacy Ethernet is used, over-provisioning is used to avoid packet drops, or alternatively, TCP / IP is supported in order to recover from packet drops. If EED is used, congestion management as well as priority of service functions are provided by the EED protocols
Owner:DAEDALUS BLUE LLC
Method and system for path based network congestion management
InactiveUS20090300209A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionForward algorithmData stream
Aspects of a method and system for path based network congestion management are provided. In this regard, an indication of conditions, such as congestion, in a network may be utilized to determine which data flows may be affected by congestion in a network. A path table may be maintained to associate conditions in the network with flows affected by the conditions. Flows which are determined as being affected by a condition may be paused or flagged and transmission of data belonging to those flows may be deferred. Flows affected by a condition such as congestion may be identified based on a class of service with which they are associated. Transmission of one or more of the plurality of flows may be scheduled based on the determination. The determination may be based on one or both of a forwarding table and a forwarding algorithm of the downstream network device.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
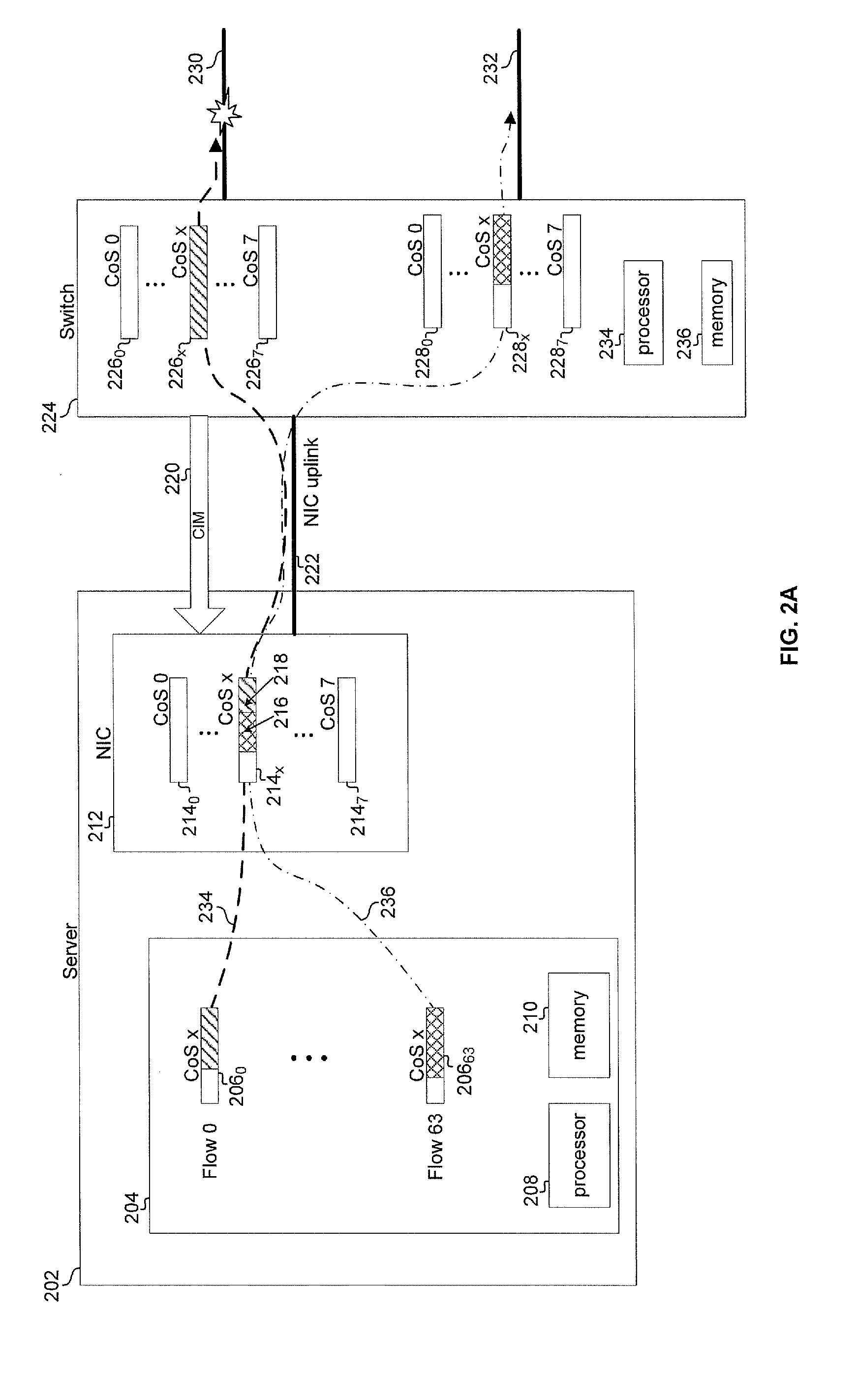
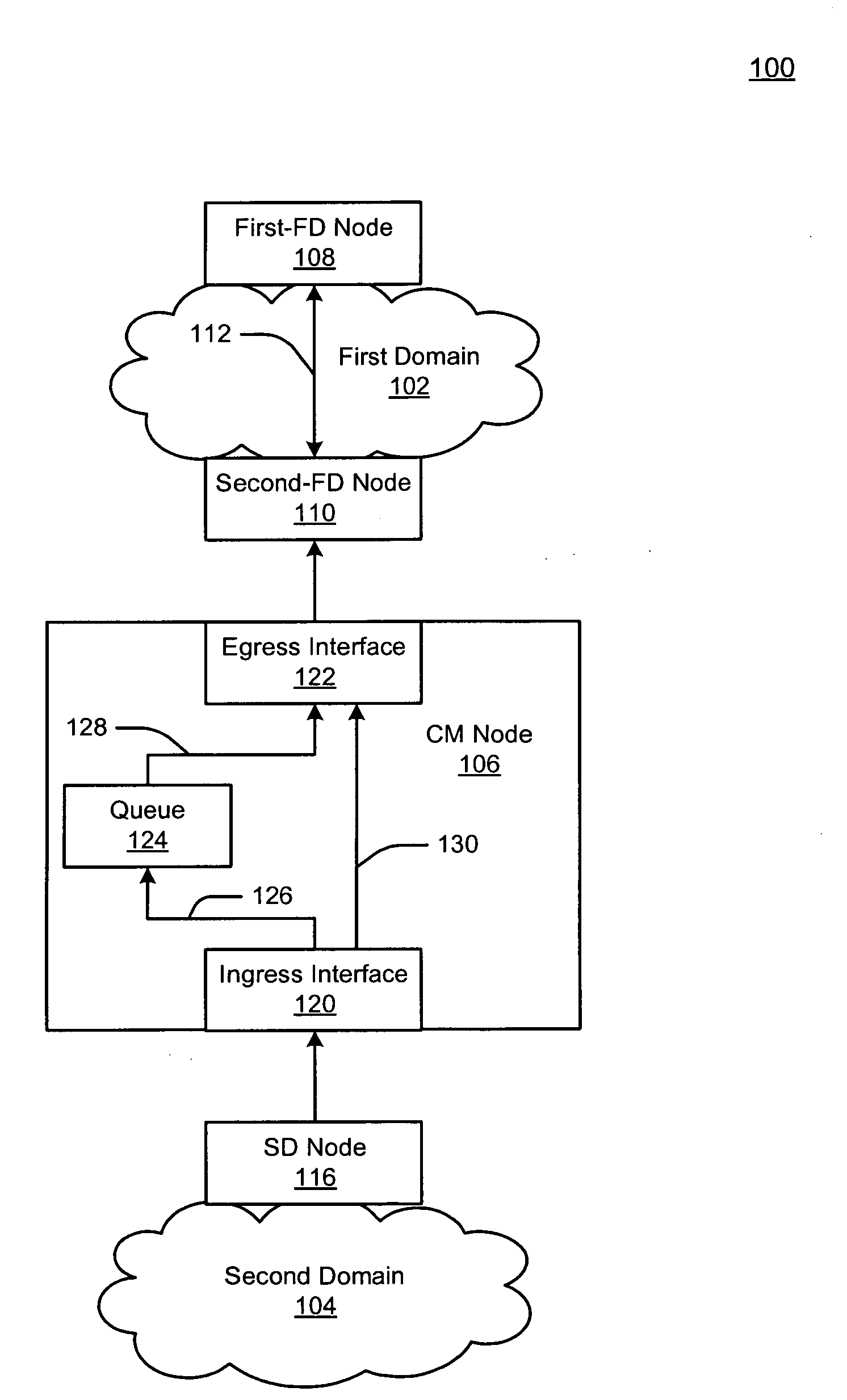
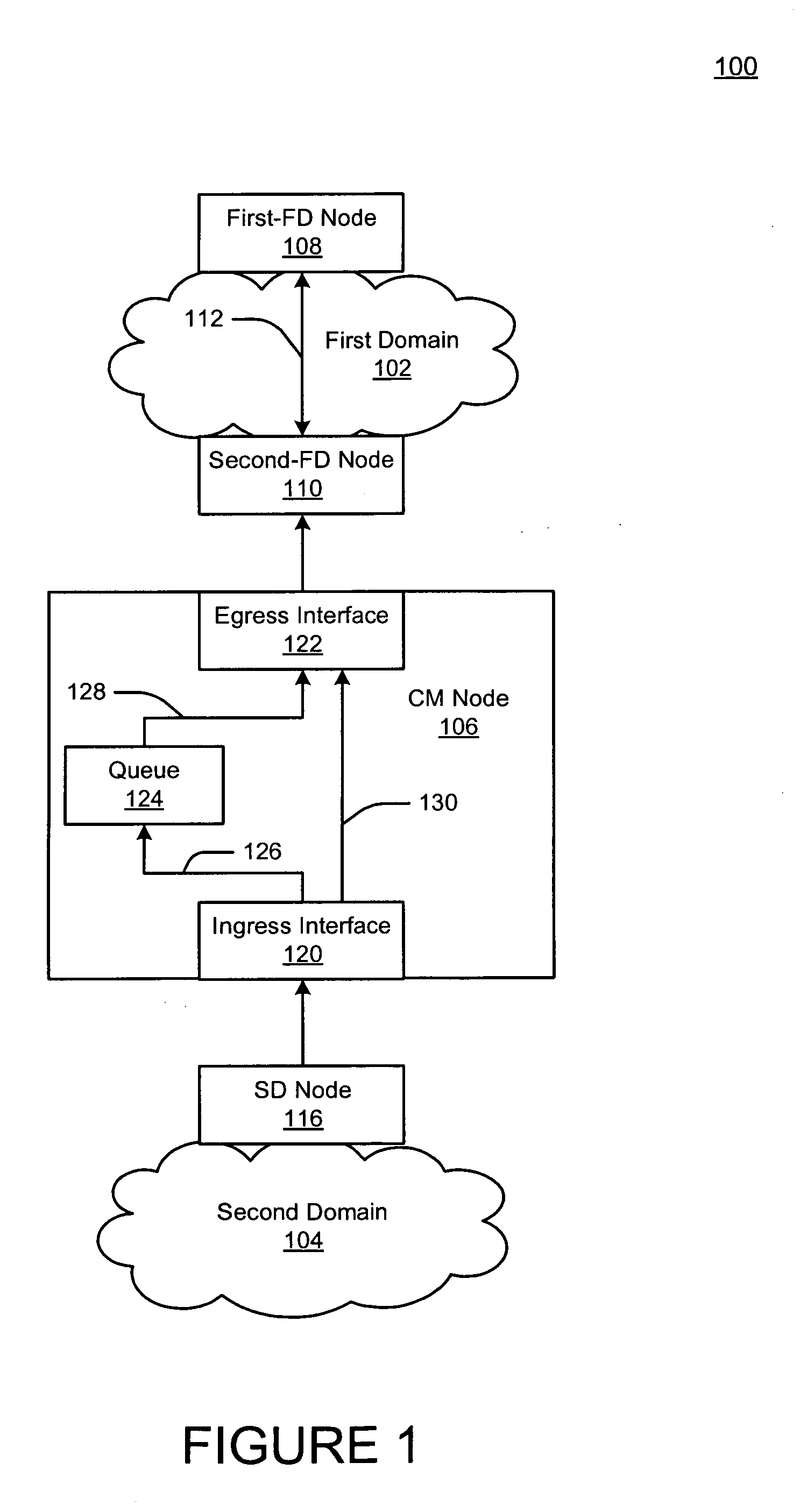
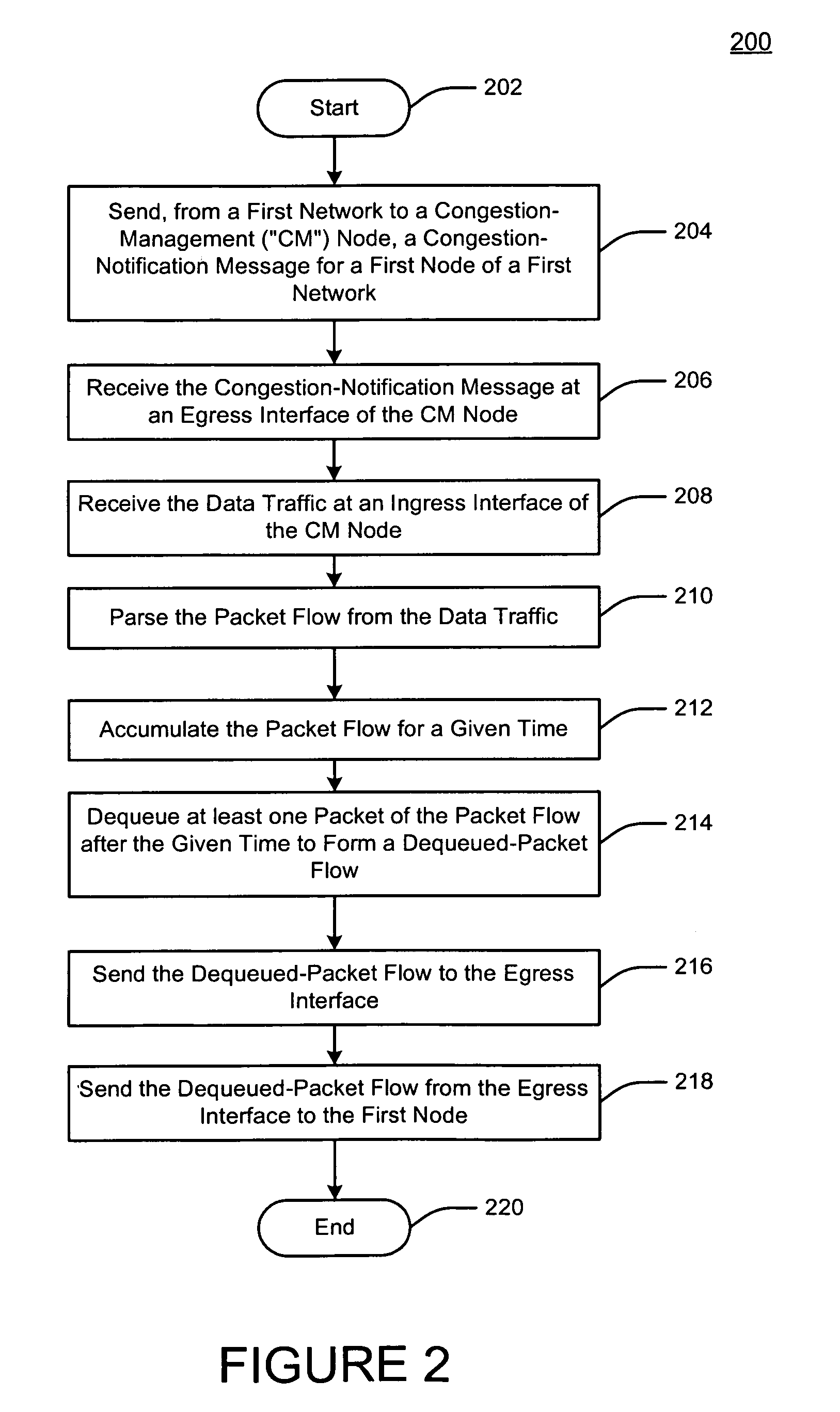
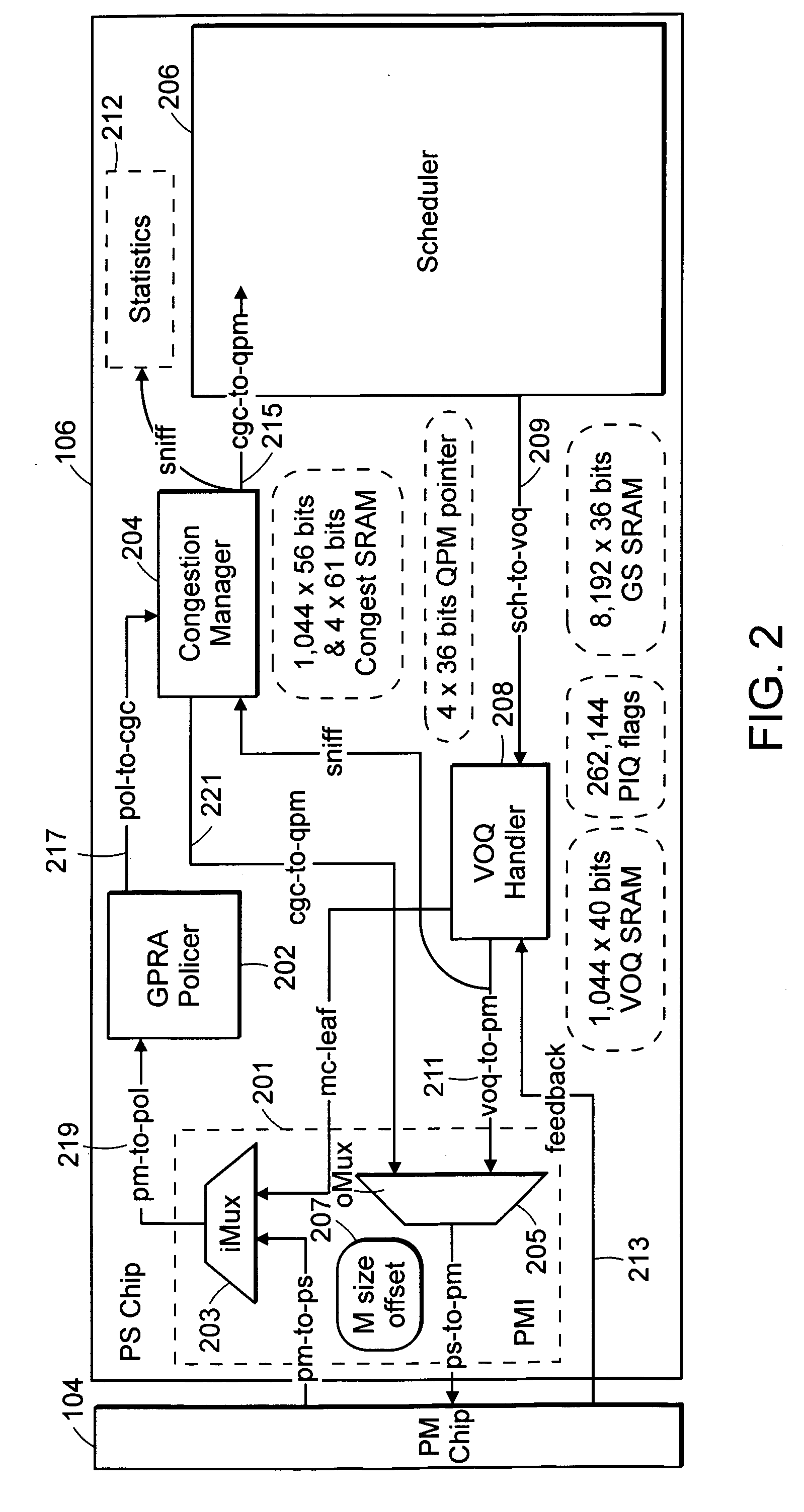
Method and apparatus for a network queuing engine and congestion management gateway
A method, apparatus, and queuing engine implement congestion management. The method may include receiving, via a first interface of the apparatus, data traffic for forwarding to a node of a network. The method may also include receiving, at a second interface of the apparatus, a notification that indicates that congestion is affecting communication with the node, and responsive to the notification, accumulating the data traffic into the queue for a given time period. The method may further include dequeuing the data traffic from the queue after the given time period; and sending the portion of the data traffic to the node via the second interface.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Backward congestion notification
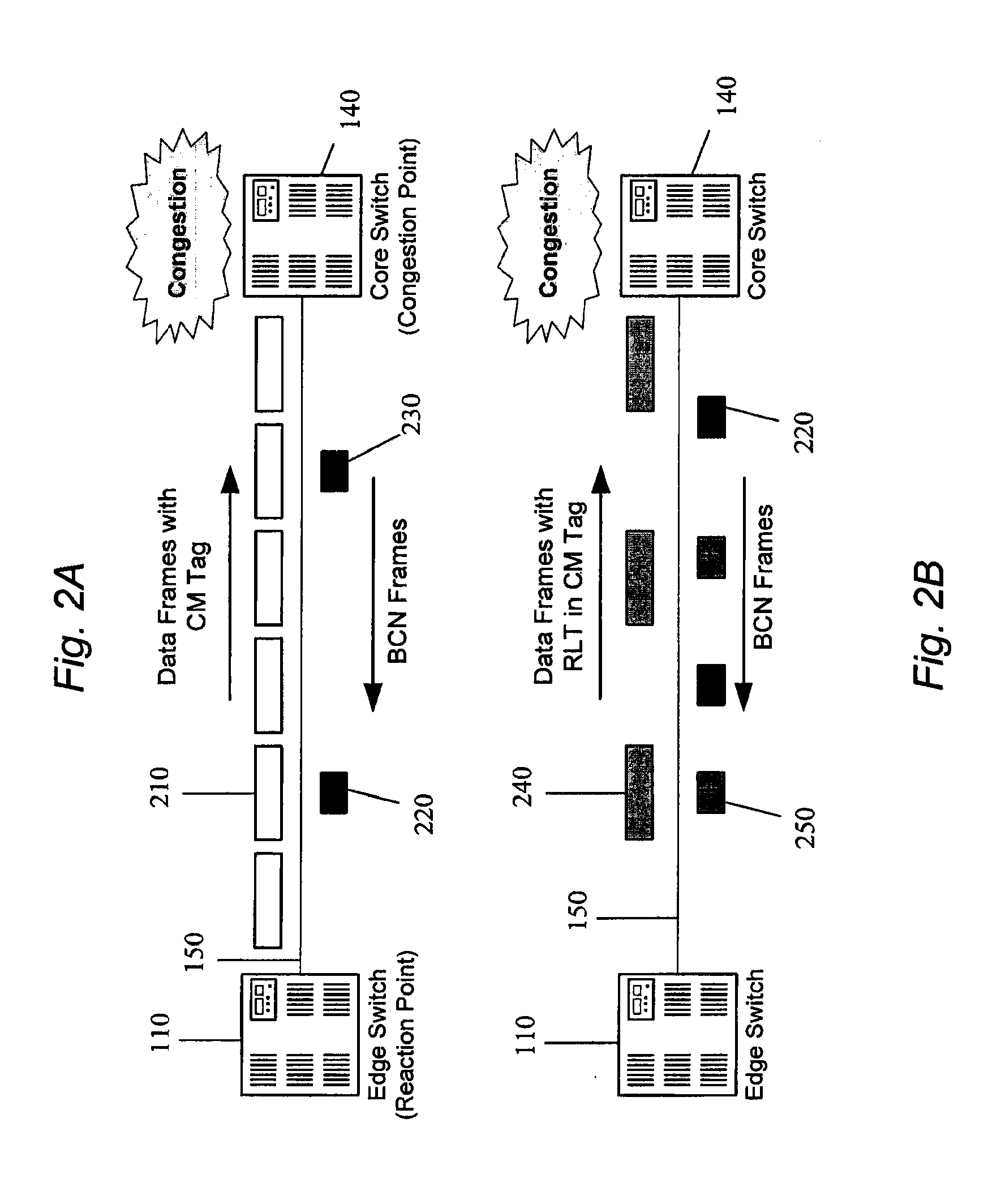
In one embodiment, an apparatus comprises a network interface system having at least one input port configured for receiving frames and a logic system comprising at least one logic device. The logic system may be configured to perform the following functions: determining a source address and a destination address of a frame received at an ingress port; calculating a flow hash based at least upon the source address and the destination address; forming a congestion management (“CM”) tag that includes the flow hash; inserting the CM tag in the frame; and forwarding the frame to the destination address.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
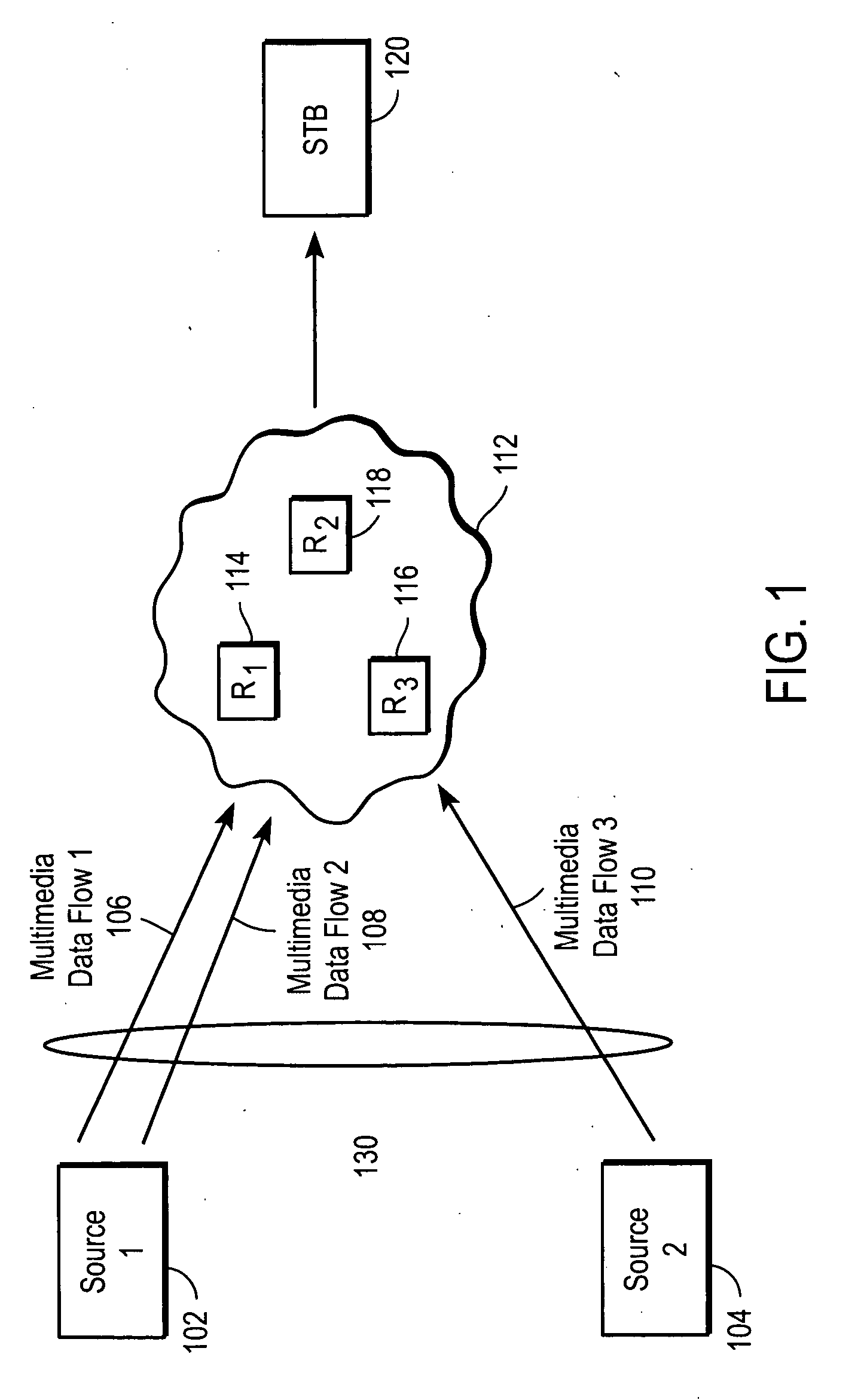
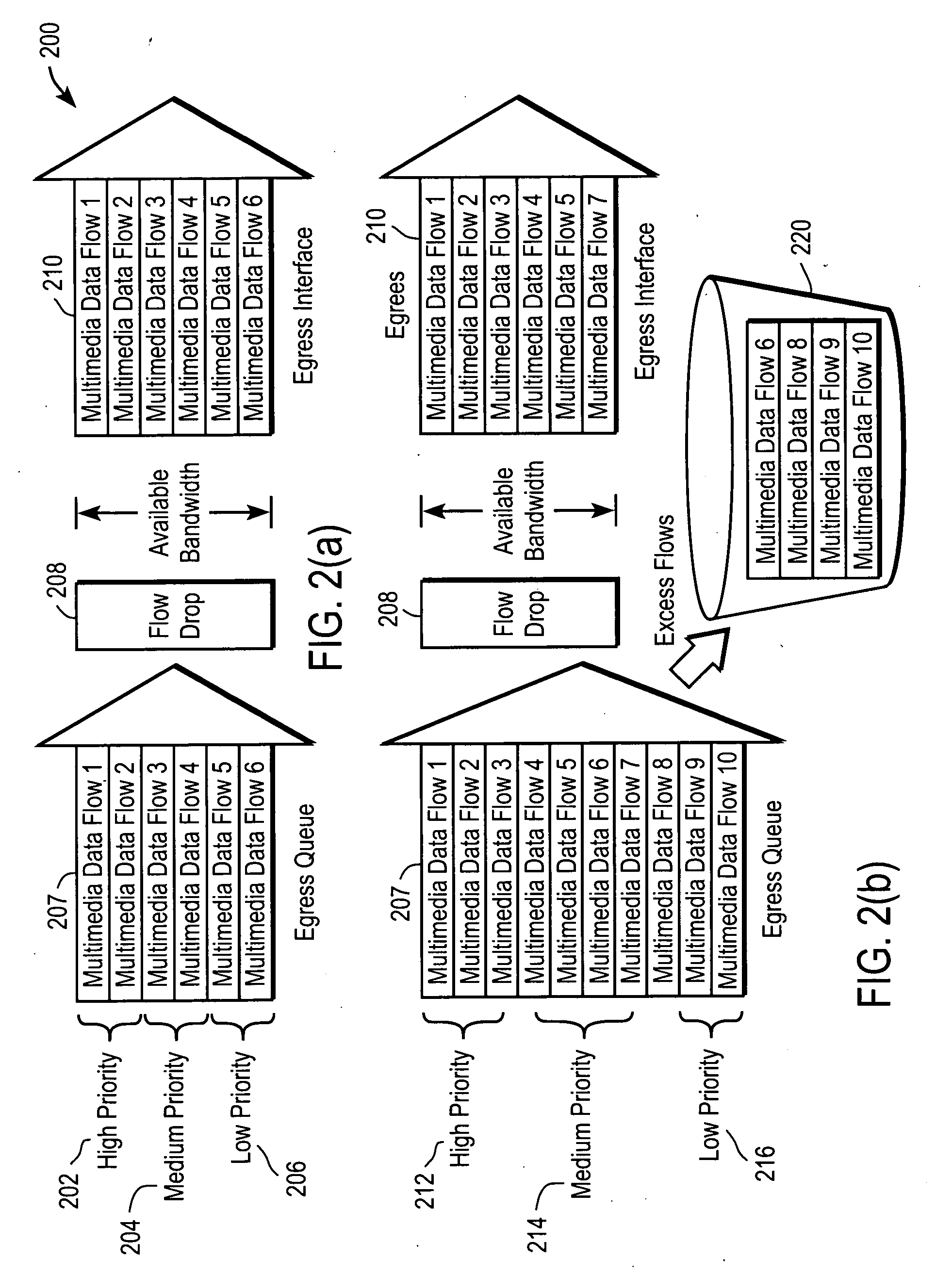
Multimedia data flow dropping
ActiveUS20070076604A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMultimedia data streamsDrop method
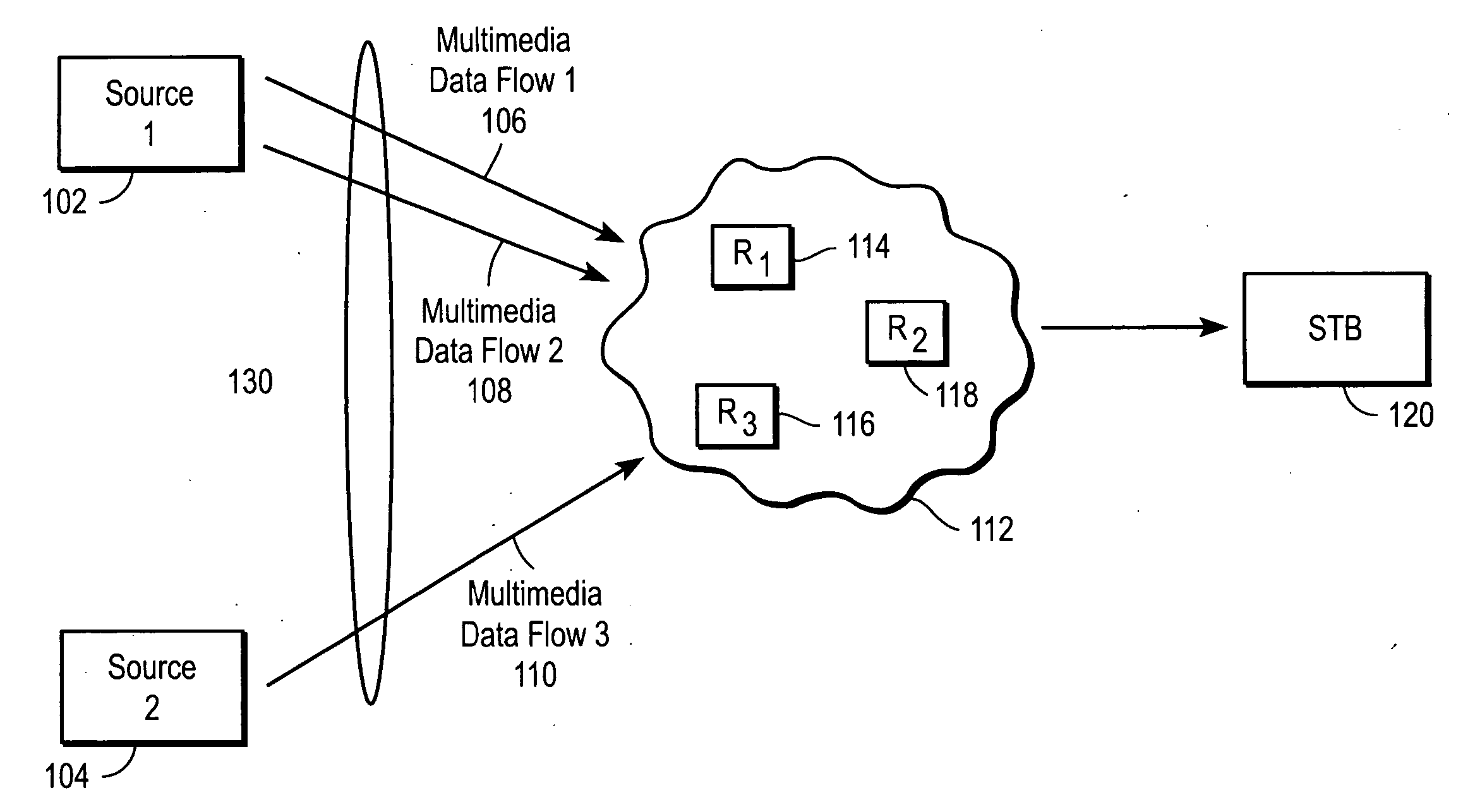
The present invention introduces a congestion control mechanism for constant bit rate (CBR) multimedia data flows in cable operator IP networks. A flow drop method within a congestion control unit of the present invention chooses a subset of multimedia data flows to drop, in whole, to alleviate a congestion condition. After the congestion condition is detected and the congestion control unit begins dropping multimedia data flows, the remaining multimedia data flows are no longer degraded for the end user, as compared to conventional congestion management systems.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
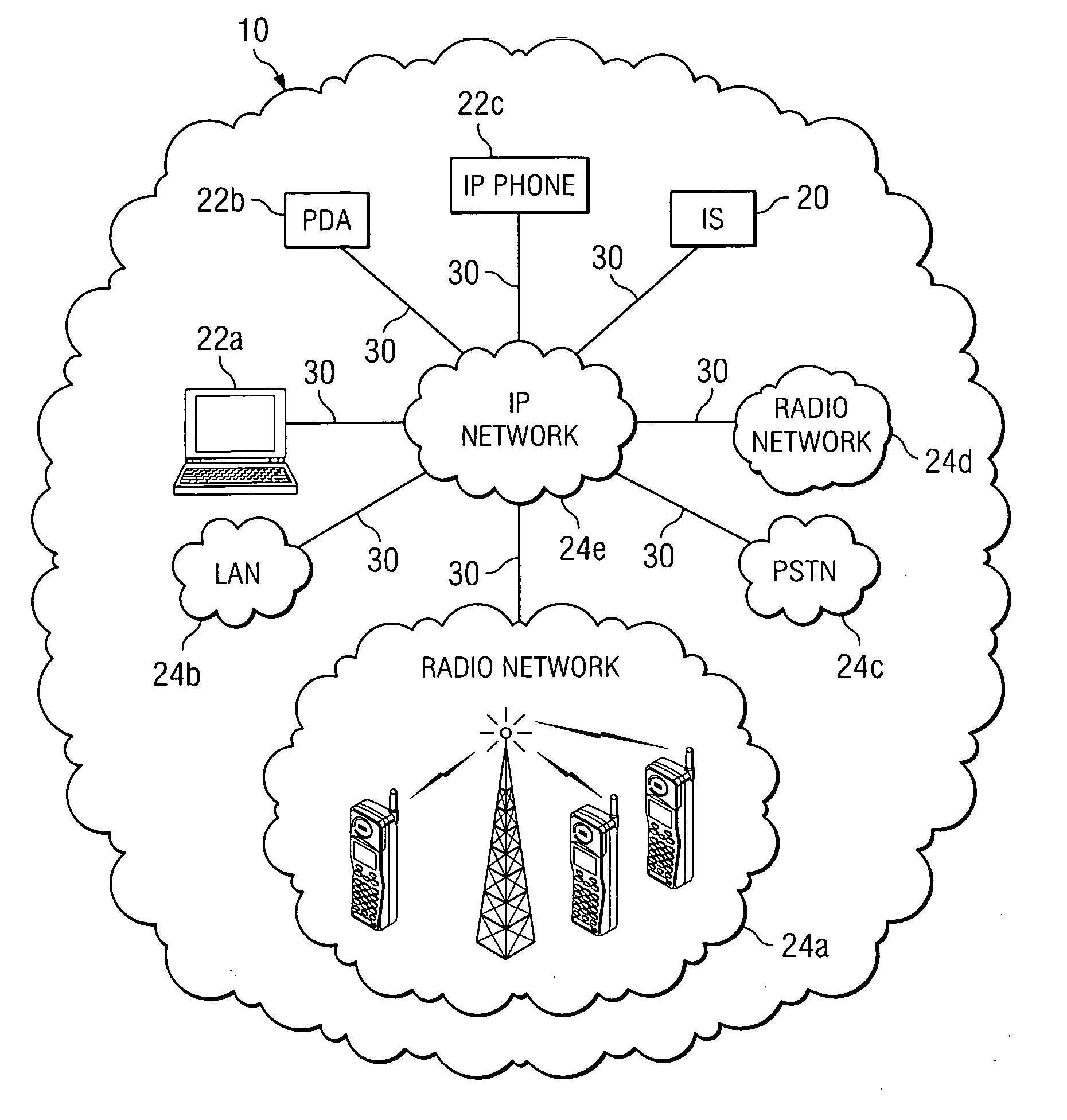
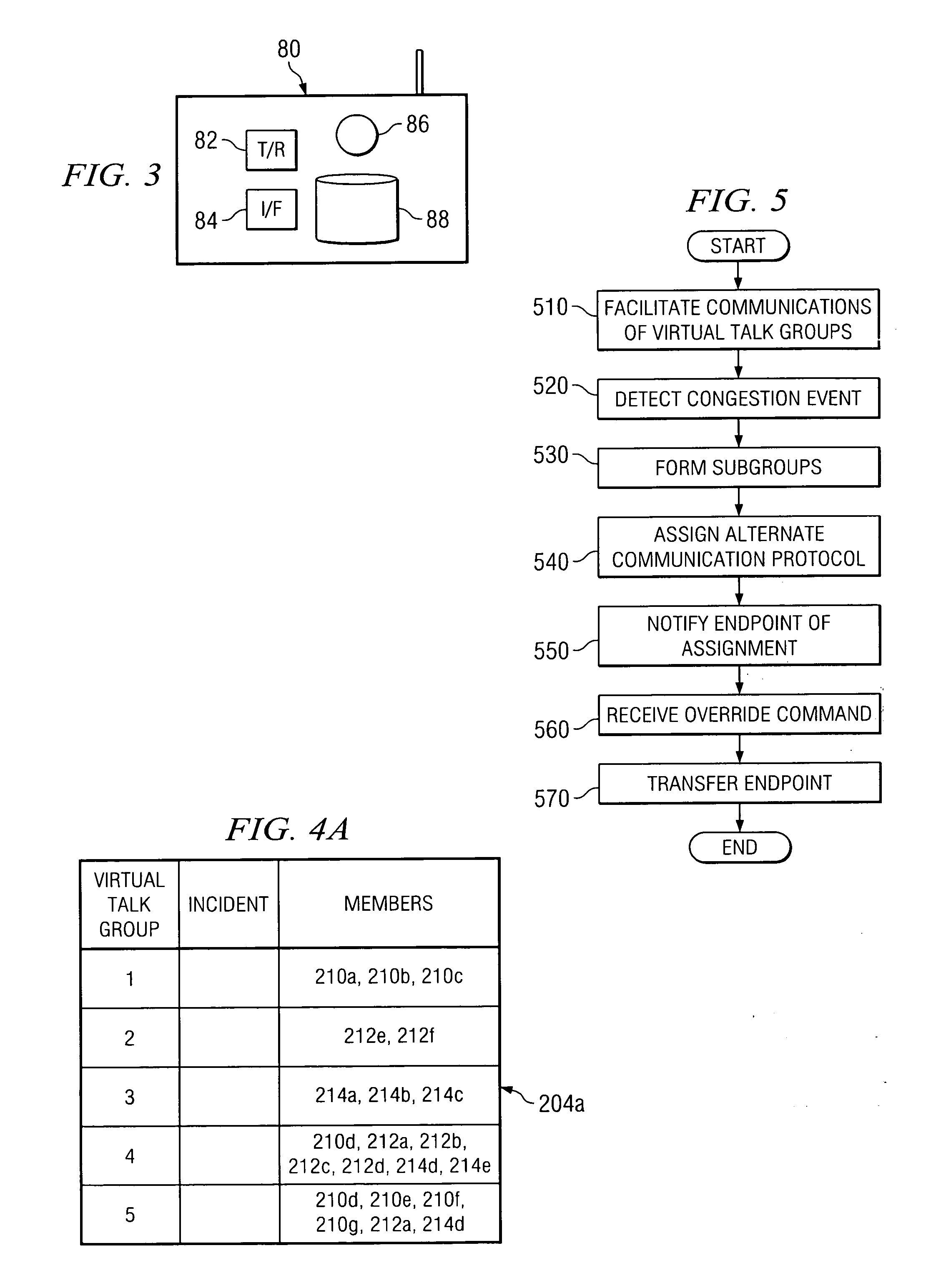
Method and System for Providing Congestion Management within a Virtual Talk Group
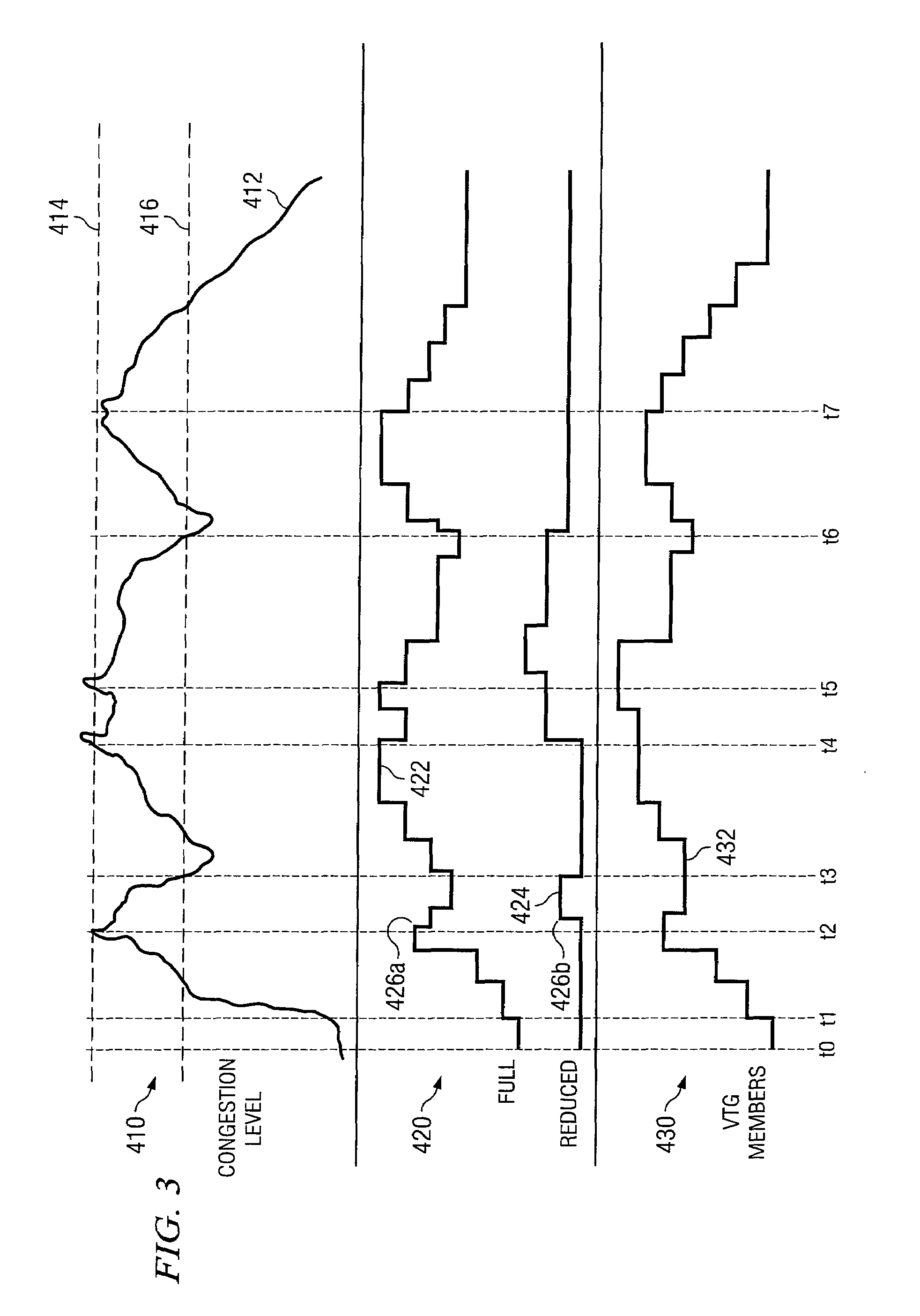
ActiveUS20080159128A1Eliminates and reduces of disadvantageEliminates and reduces of and problemError preventionTransmission systemsDistributed computingFacilitated communication
A method for providing congestion management within a virtual talk group includes facilitating communication within a virtual talk group between a plurality of endpoints of different communication networks. The method also includes monitoring a communication congestion level within the virtual talk group and tracking at least one priority characteristic for at least one endpoint of the plurality of endpoints within the virtual talk group. The method further includes detecting that the communication congestion level exceeds a congestion threshold and reducing the congestion level by executing at least one policy based on the at least one priority characteristic of the at least one endpoint.
Owner:STA GRP LLC
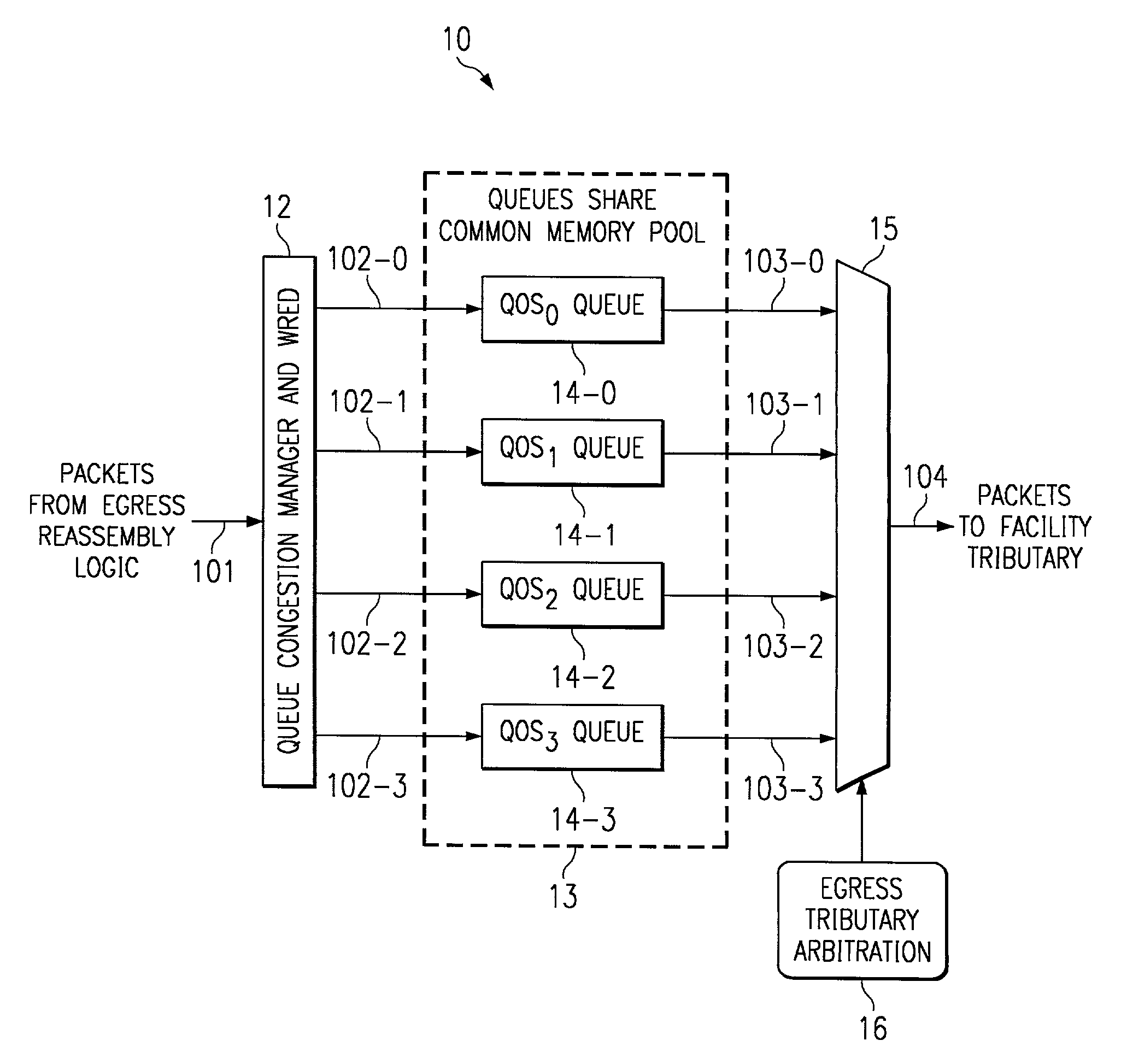
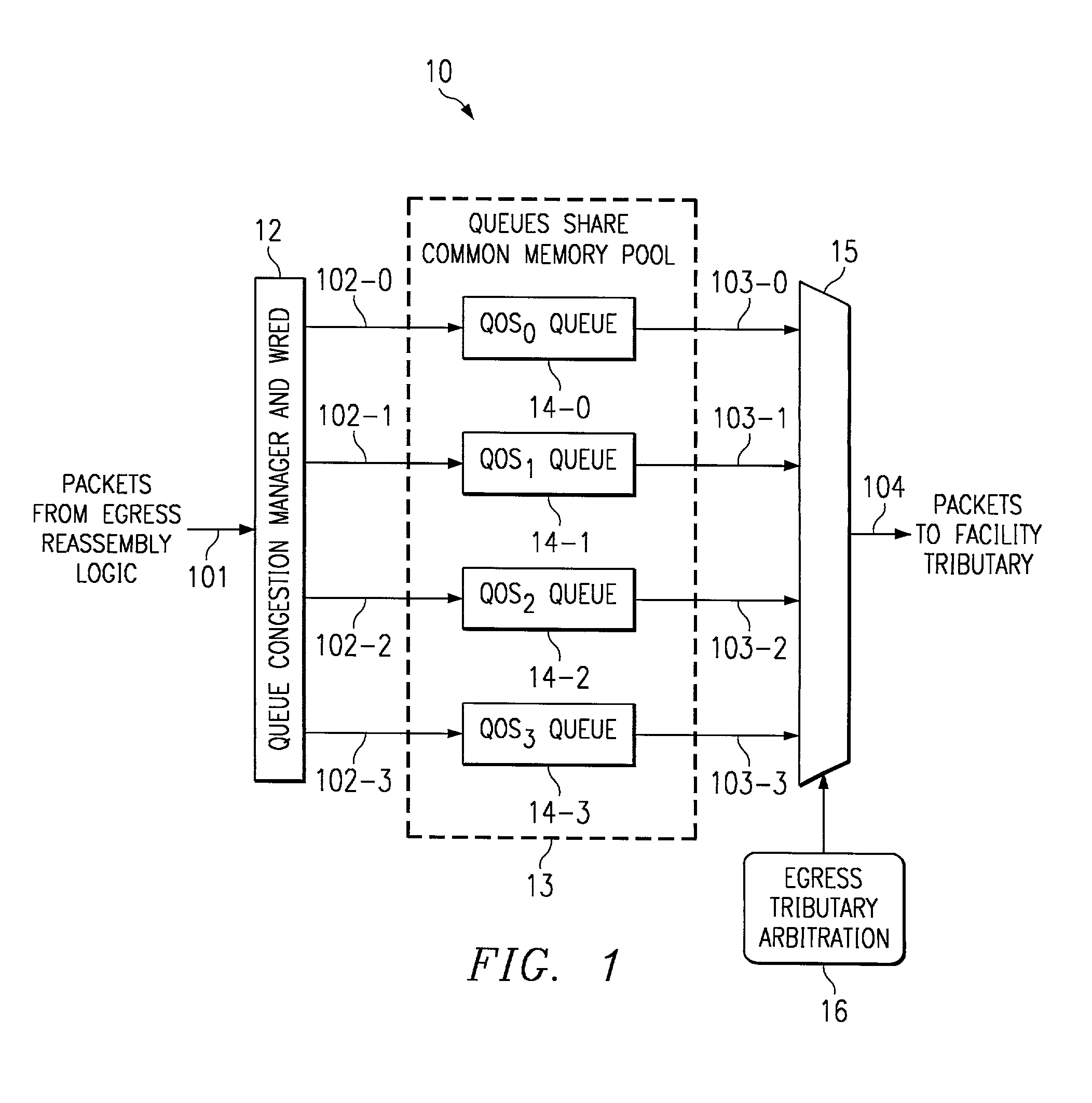
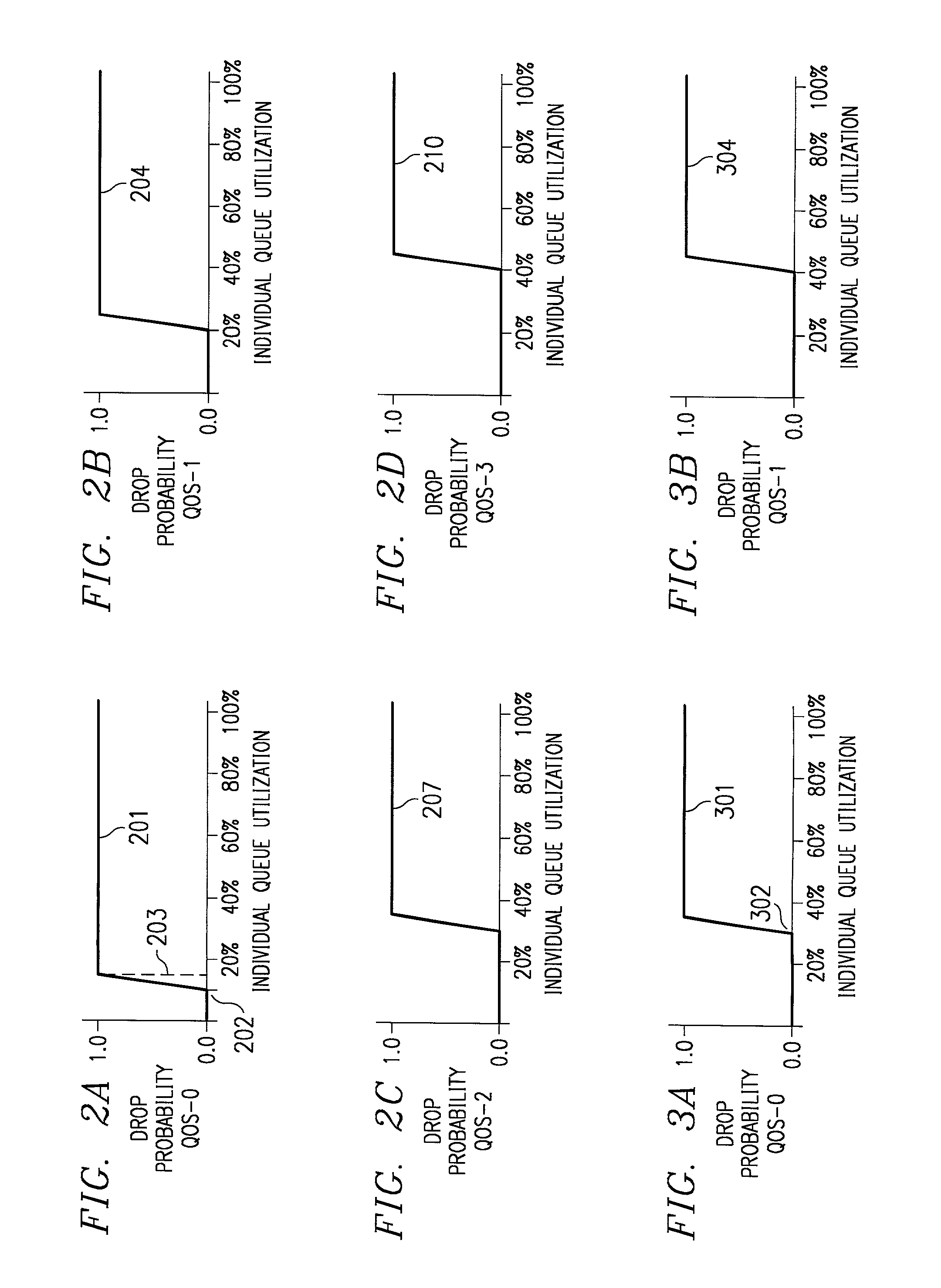
System and method for router queue and congestion management
In a multi-QOS level queuing structure, packet payload pointers are stored in multiple queues and packet payloads in a common memory pool. Algorithms control the drop probability of packets entering the queuing structure. Instantaneous drop probabilities are obtained by comparing measured instantaneous queue size with calculated minimum and maximum queue sizes. Non-utilized common memory space is allocated simultaneously to all queues. Time averaged drop probabilities follow a traditional Weighted Random Early Discard mechanism. Algorithms are adapted to a multi-level QOS structure, floating point format, and hardware implementation. Packet flow from a router egress queuing structure into a single egress port tributary is controlled by an arbitration algorithm using a rate metering mechanism. The queuing structure is replicated for each egress tributary in the router system.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Traffic lane management system
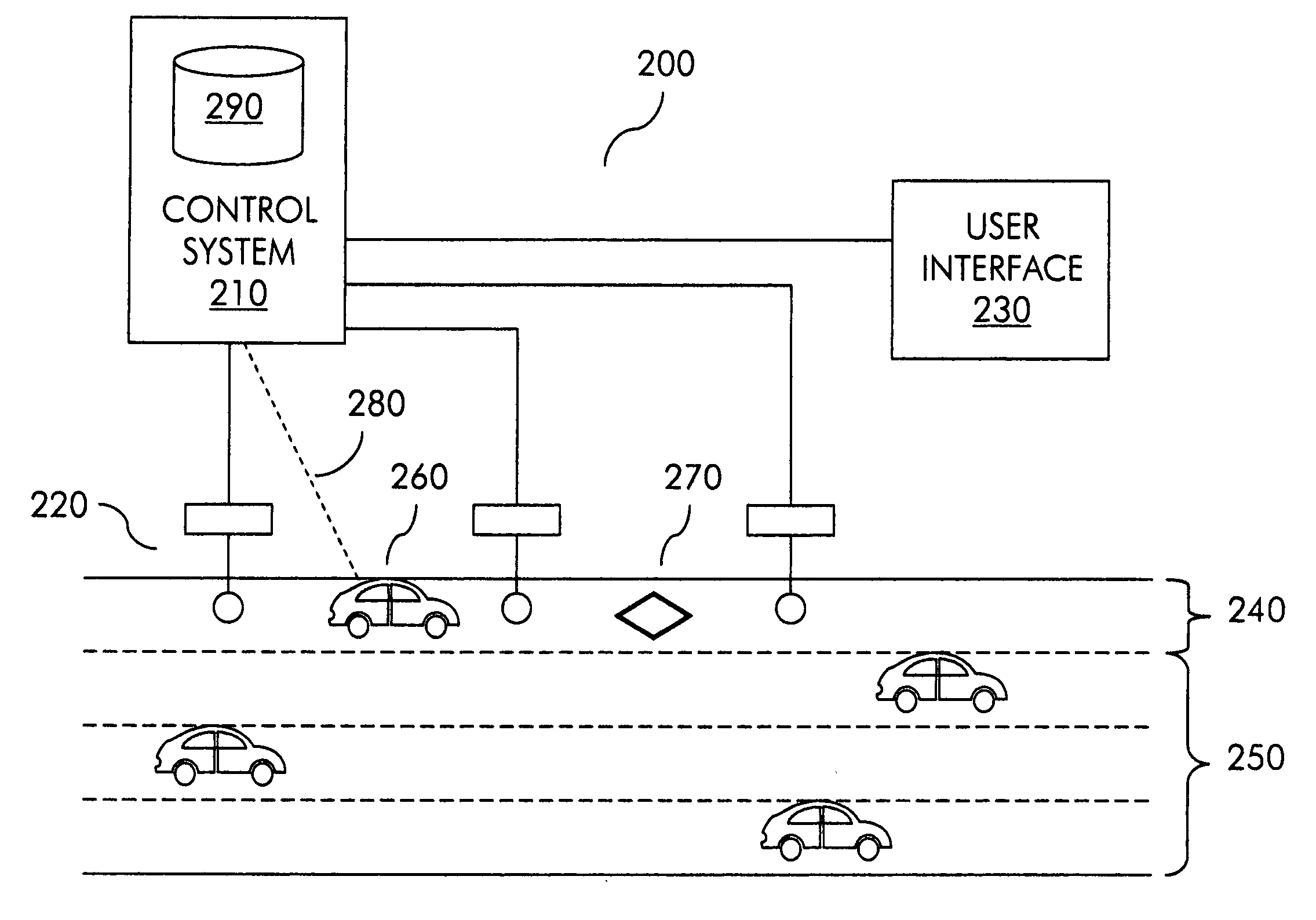
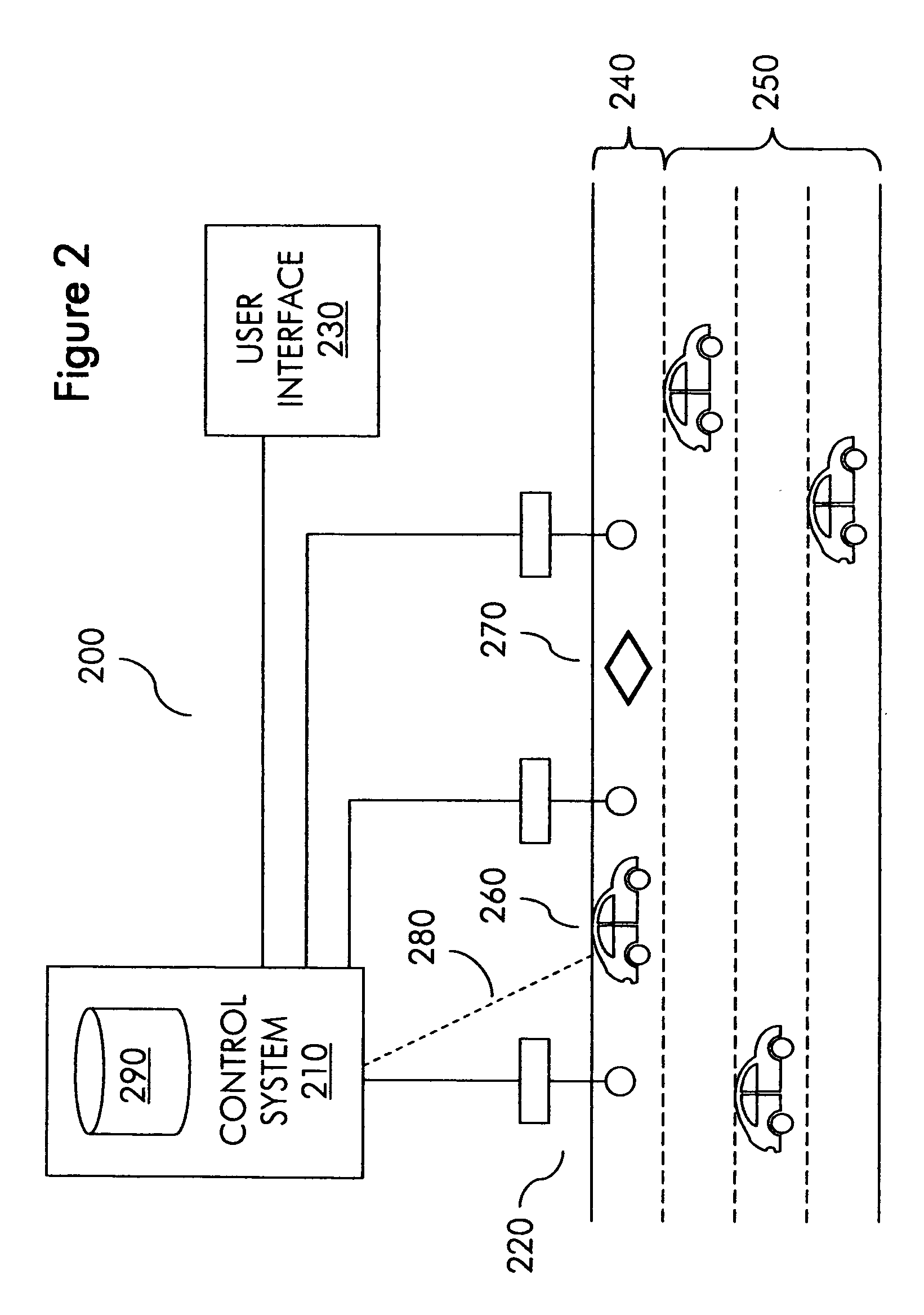
InactiveUS20080300776A1Analogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficEngineeringManagement system
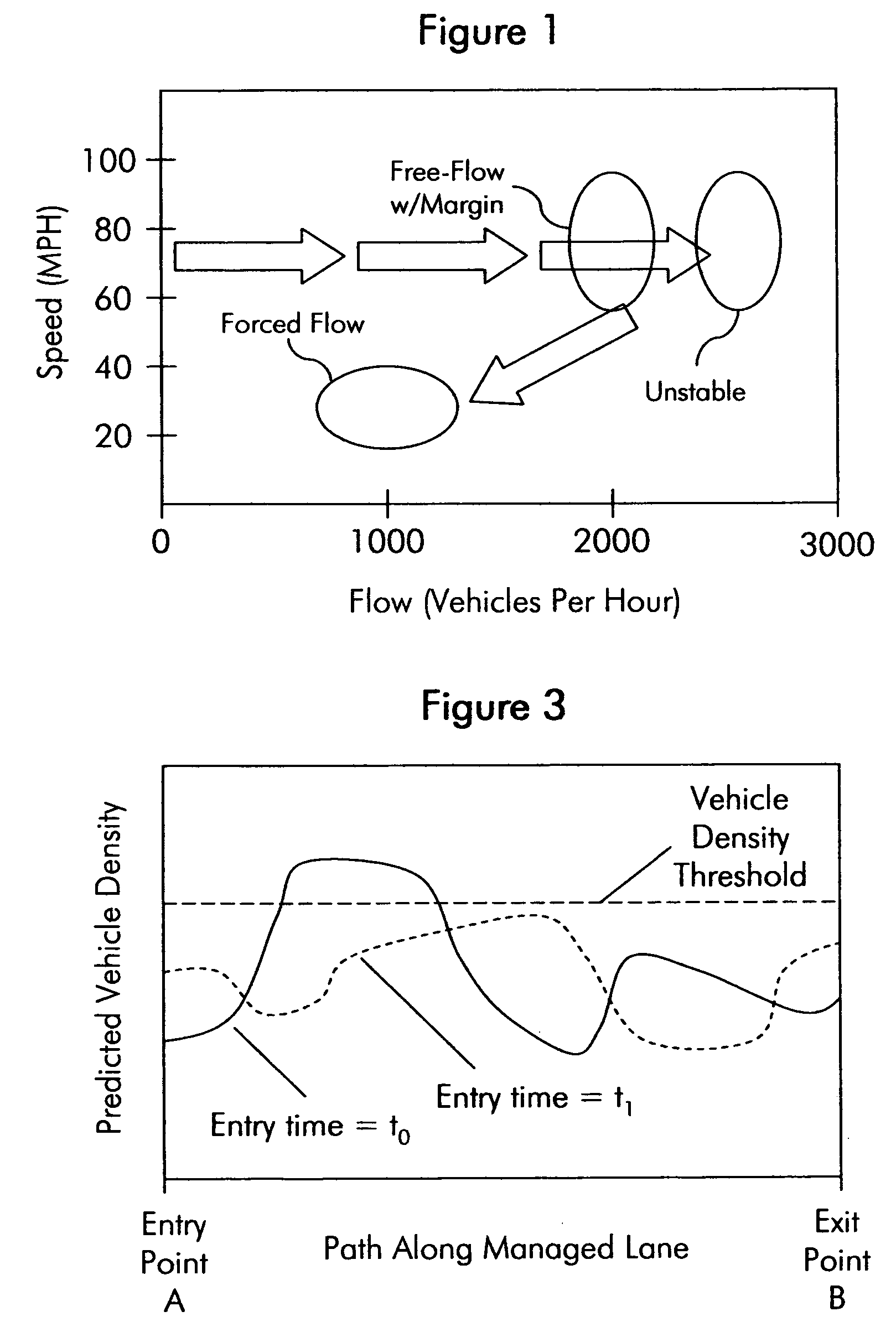
A management system for a traffic lane achieves congestion management objectives by dynamically predicting future vehicle density in a traffic lane and assigning to a requesting user a time slot for entering the traffic lane selected independent of any user requested time and based at least in part on a current prediction about future vehicle density in the traffic lane. The current prediction is based at least in part on predicted trajectories of vehicles, which are determined in turn based at least in part on actual trajectories of vehicles.
Owner:ORIGIN TECH LTD
Congestion management in a distributed computer system multiplying current variable injection rate with a constant to set new variable injection rate at source node
InactiveUS7016971B1Reduce the injection rateReduce rateMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionComputerized systemInjection rate
A distributed computer system includes links and routing devices coupled between the links and routing frames between the links. Each of the routing devices includes a congestion control mechanism for detecting congestion at the routing device and responding to detected congestion by gradually reducing an injection rate of frames routed from the routing device.
Owner:PMC-SIERRA +3
Navigation device assisting road traffic congestion management
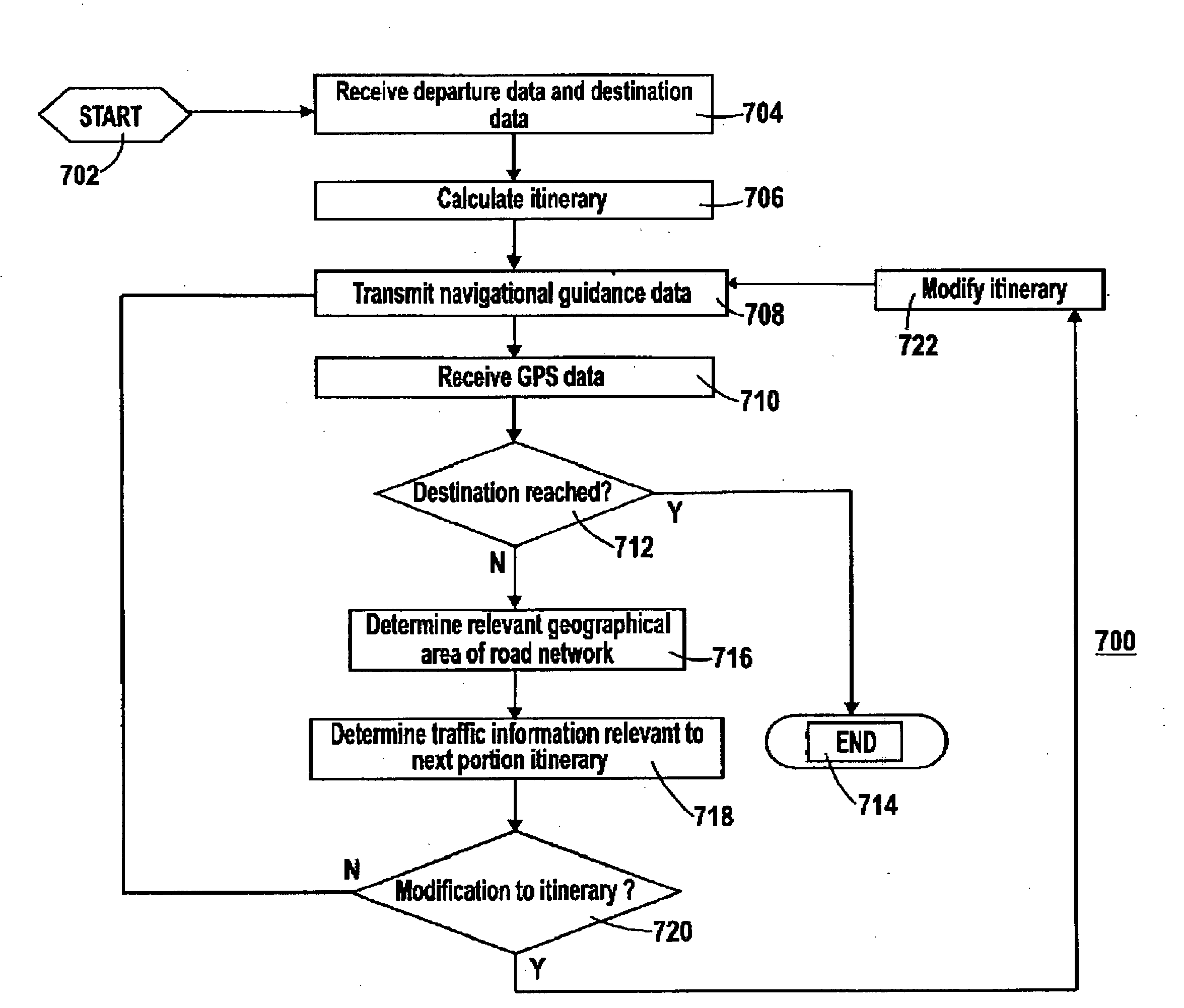
ActiveUS20080234921A1Improving navigational guidanceFacilitate traffic managementAnalogue computers for vehiclesInstruments for road network navigationTime informationTraffic flow
A navigation device has a GPRS receiver for receiving real-time information about slow traffic flow or slow average speed on a stretch of motorway, indicating congestion. The device calculates a new itinerary to avoid the congestion, based on historically recorded speeds on secondary roads weighed by the current average speed in the congestion area.
Owner:TOMTOM INT BV
Configuration of congestion thresholds for a network traffic management system
InactiveUS20070237074A1Improve performancePrevent fallingError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityCommunications system
A hierarchical congestion management system improves the performance of traffic through a communications system. In one embodiment of the invention, a first subset of thresholds is configured so as to guarantee the passage of a certain high-priority or other selected communications traffic. Further, a second subset of thresholds is configured to control interference among independent flows of traffic that are competing to pass through the system. As a result of these configurations, traffic flows that cause congestion at the output are isolated to prevent dropping other traffic, and high-priority traffic is ensured passage.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
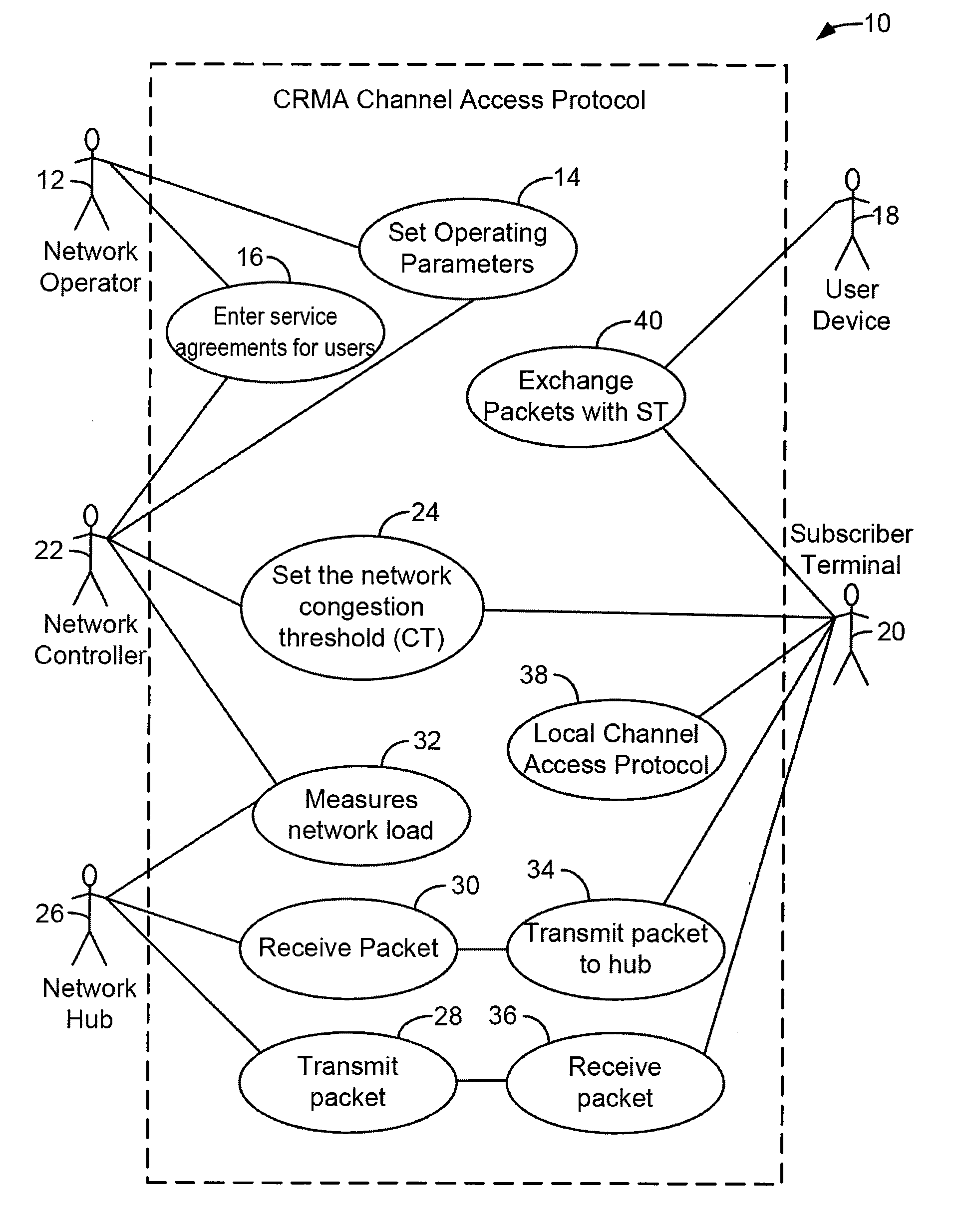
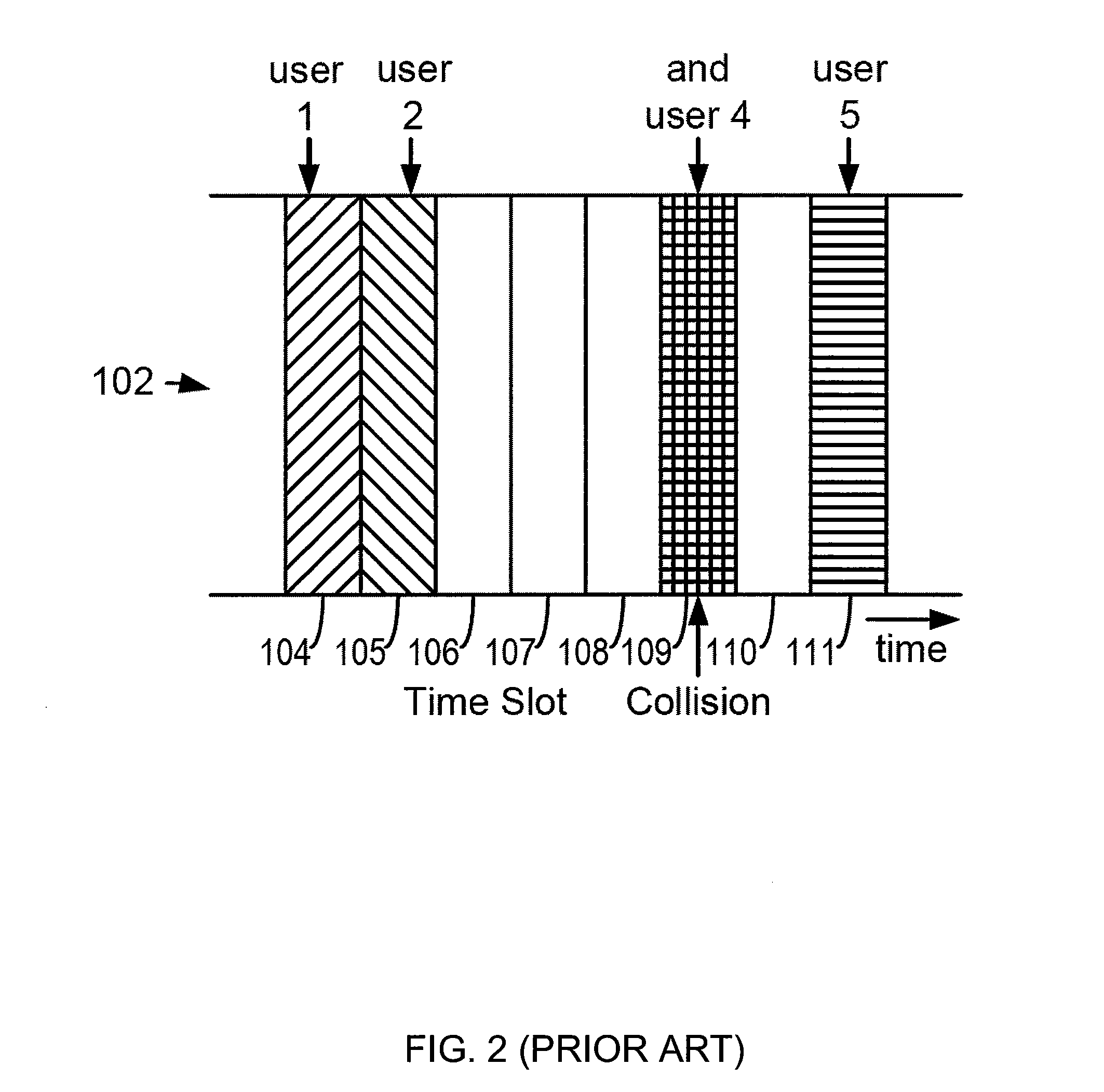
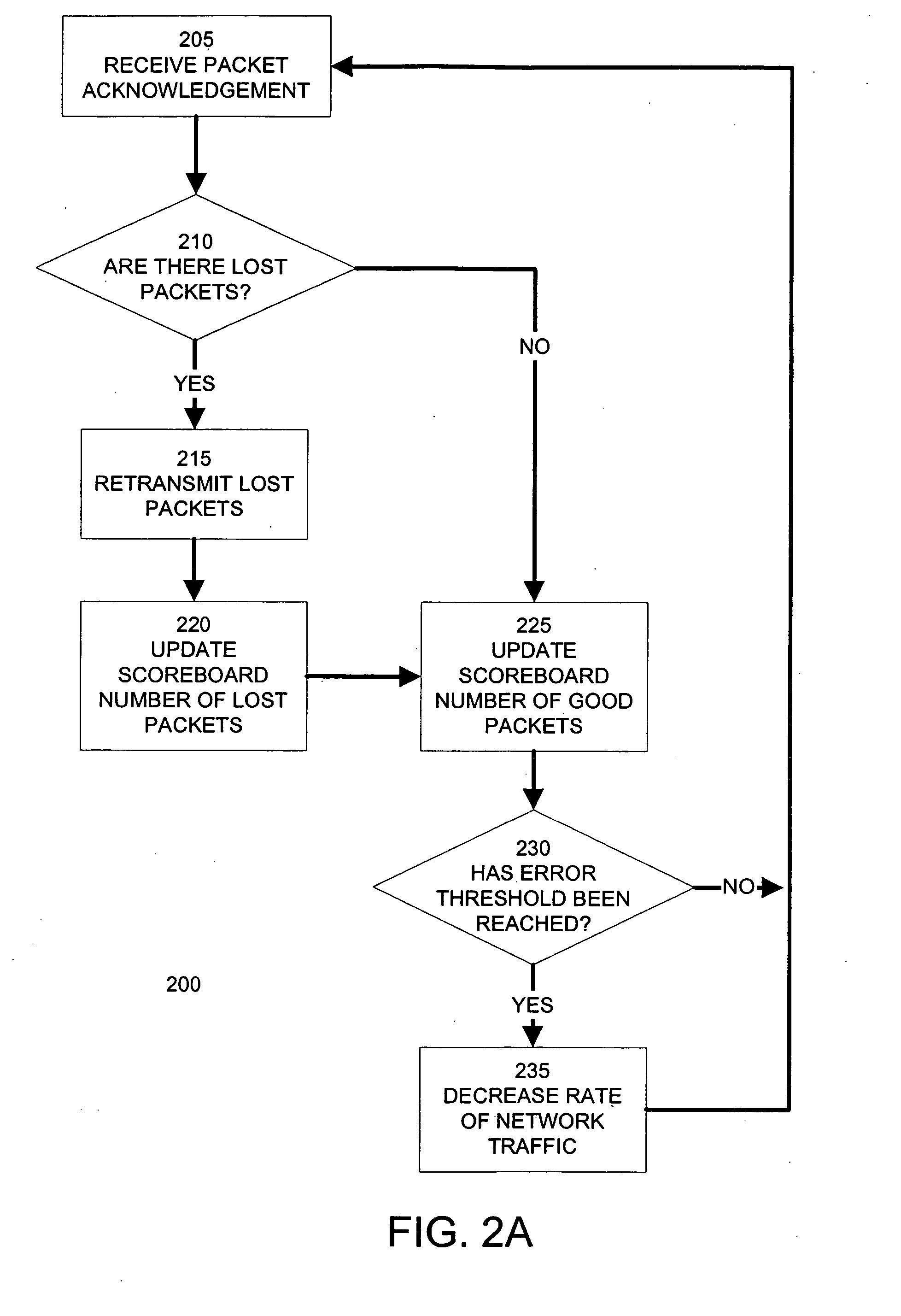
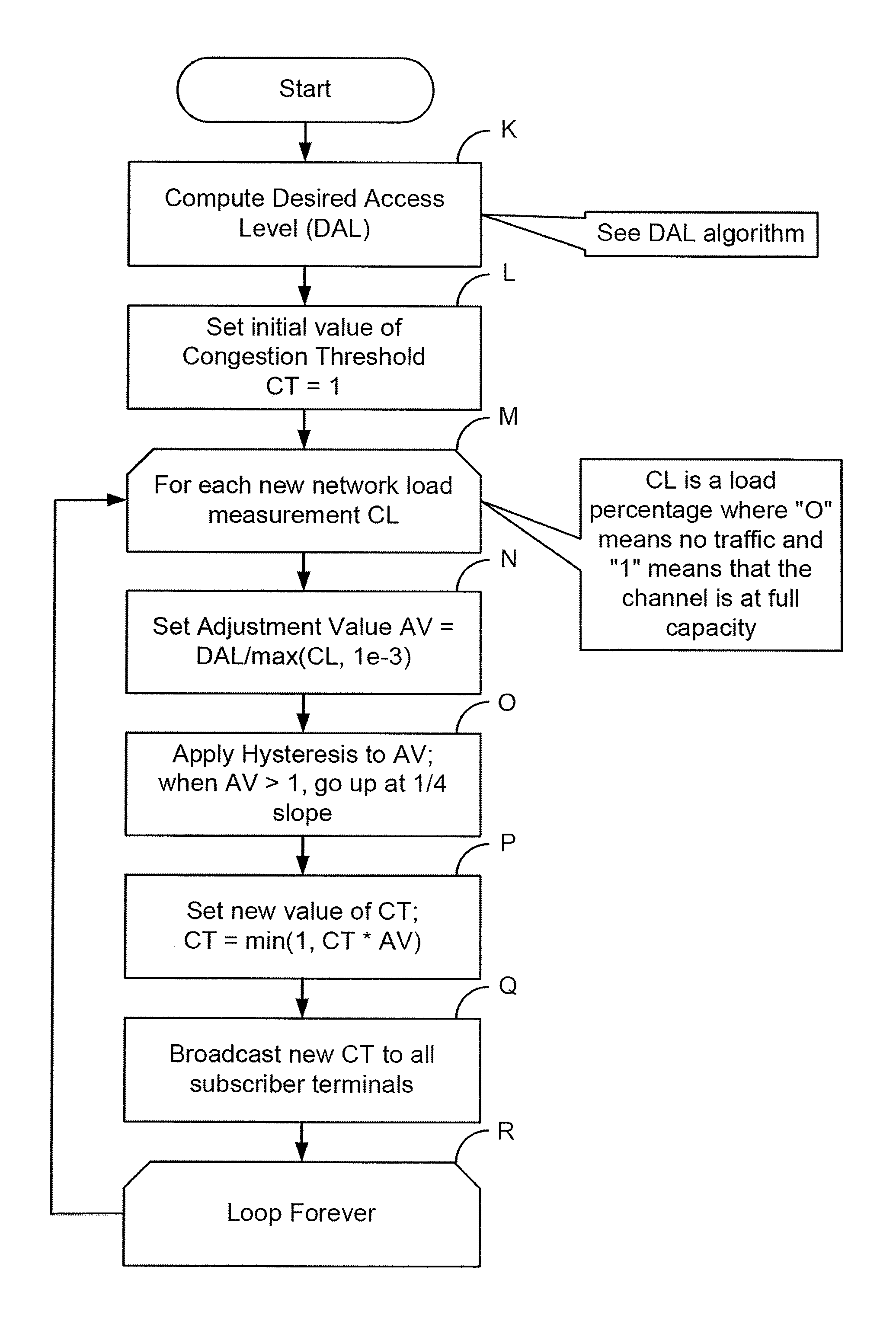
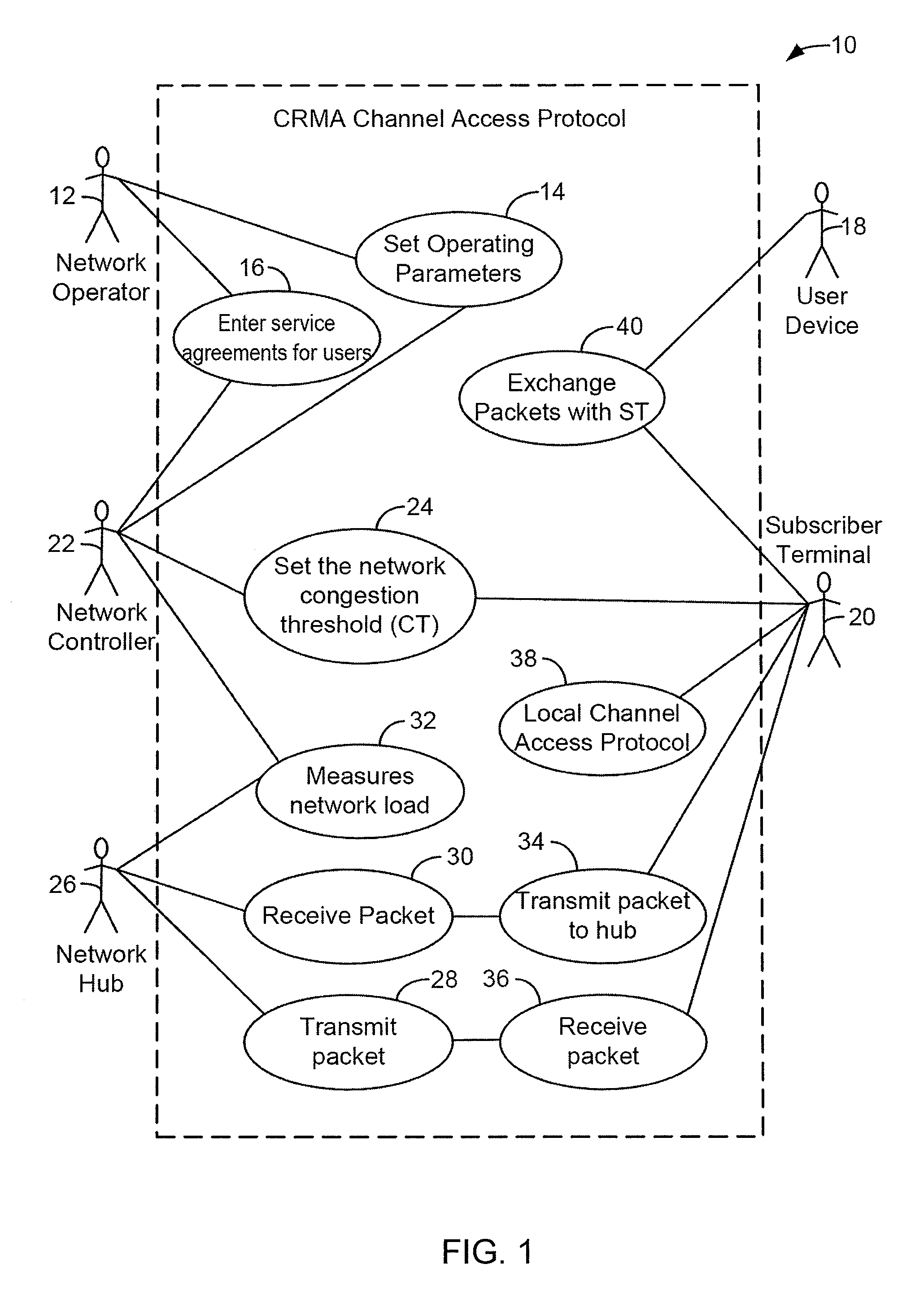
Method For Channel Congestion Management
ActiveUS20070110098A1Useful operationReduce cloggingTime-division multiplexMultiple digital computer combinationsNumber generatorData traffic
A method for managing data traffic in a multi-user multiple-simultaneous-access (MUMSA) environment, for example in a code reuse multiple access (CRMA) environment or other physical environment having true random access with more than one transmission present at the same time, the method including estimating channel load for multiple users, then using the estimate of channel load to calculate a congestion threshold on an ongoing basis, at each terminal performing an experiment using that congestion threshold value and a random number generator to determine if a packet is eligible to be transmitted, transferring downstream virtual channel traffic and redistributing user terminals to affiliate with the proper downstream virtual channel.
Owner:VIASAT INC
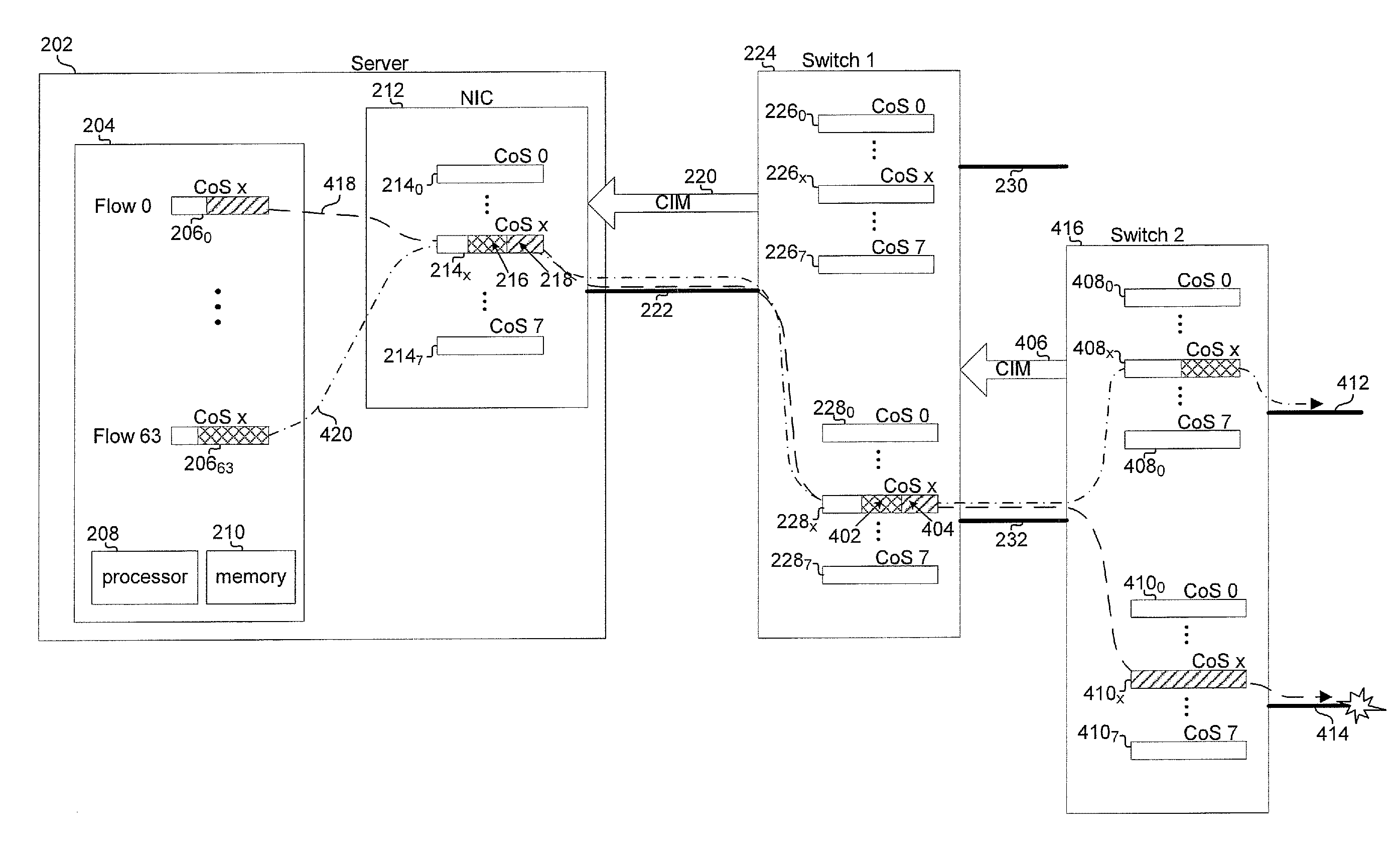
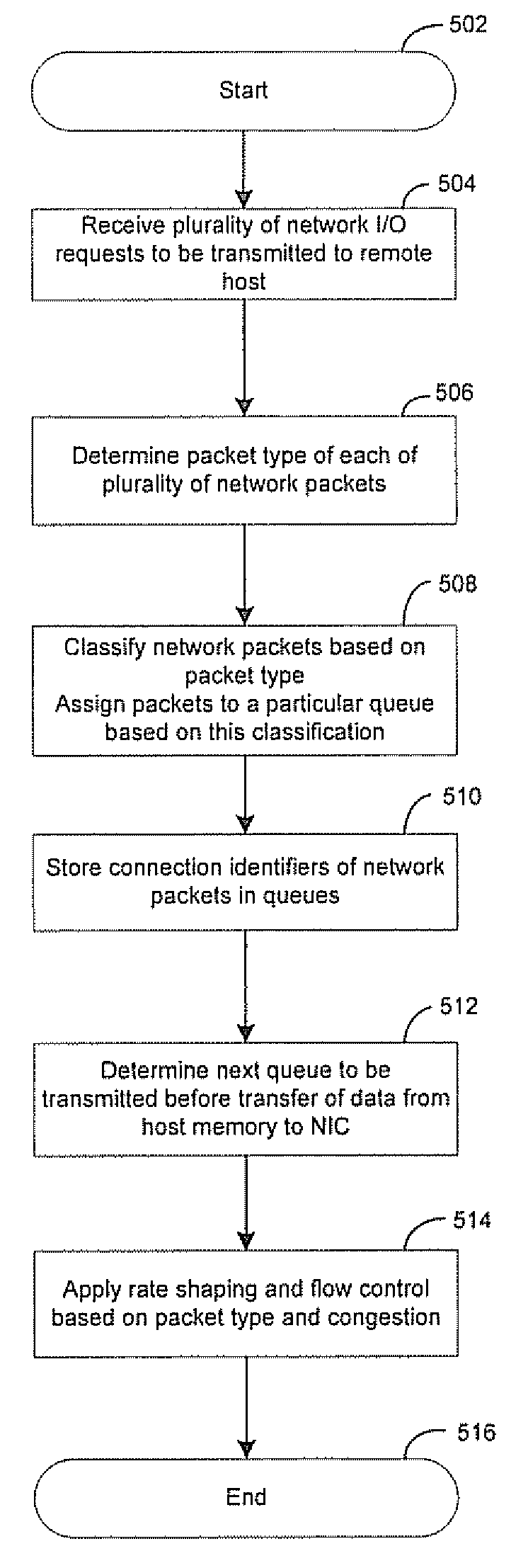
Method and system for quality of service and congestion management for converged network interface devices
Certain aspects of a method and system for quality of service and congestion management for converged network interface devices are disclosed. Aspects of a method may include processing at least one of: input / output (I / O) requests and network packets in a converged network interface card (CNIC) based on a class associated with each of the I / O requests and network packets by storing on the CNIC, information that identifies the I / O requests and network packets, without storing on the I / O requests and network packets on the CNIC
Owner:BROADCOM ISRAEL R&D
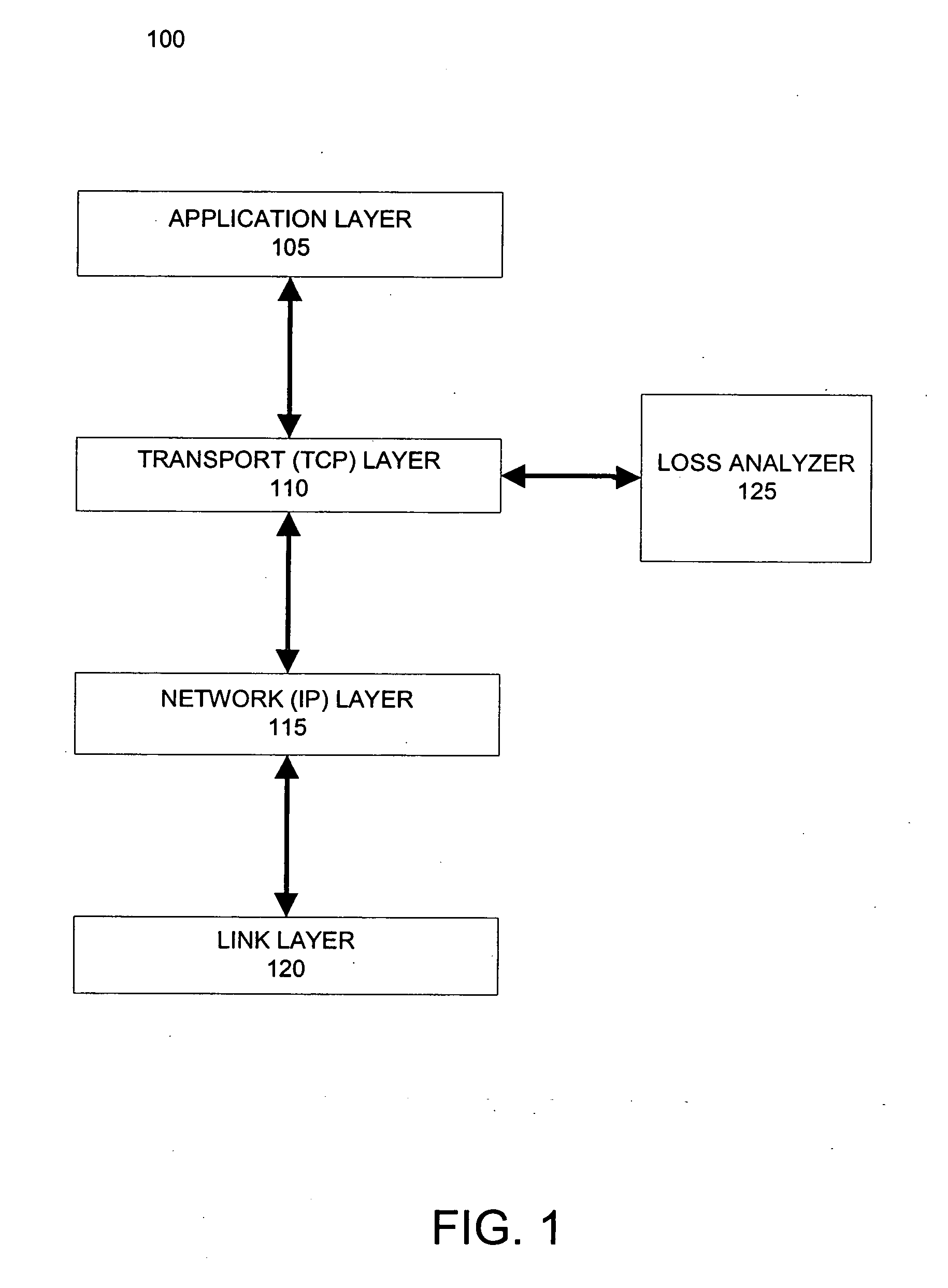
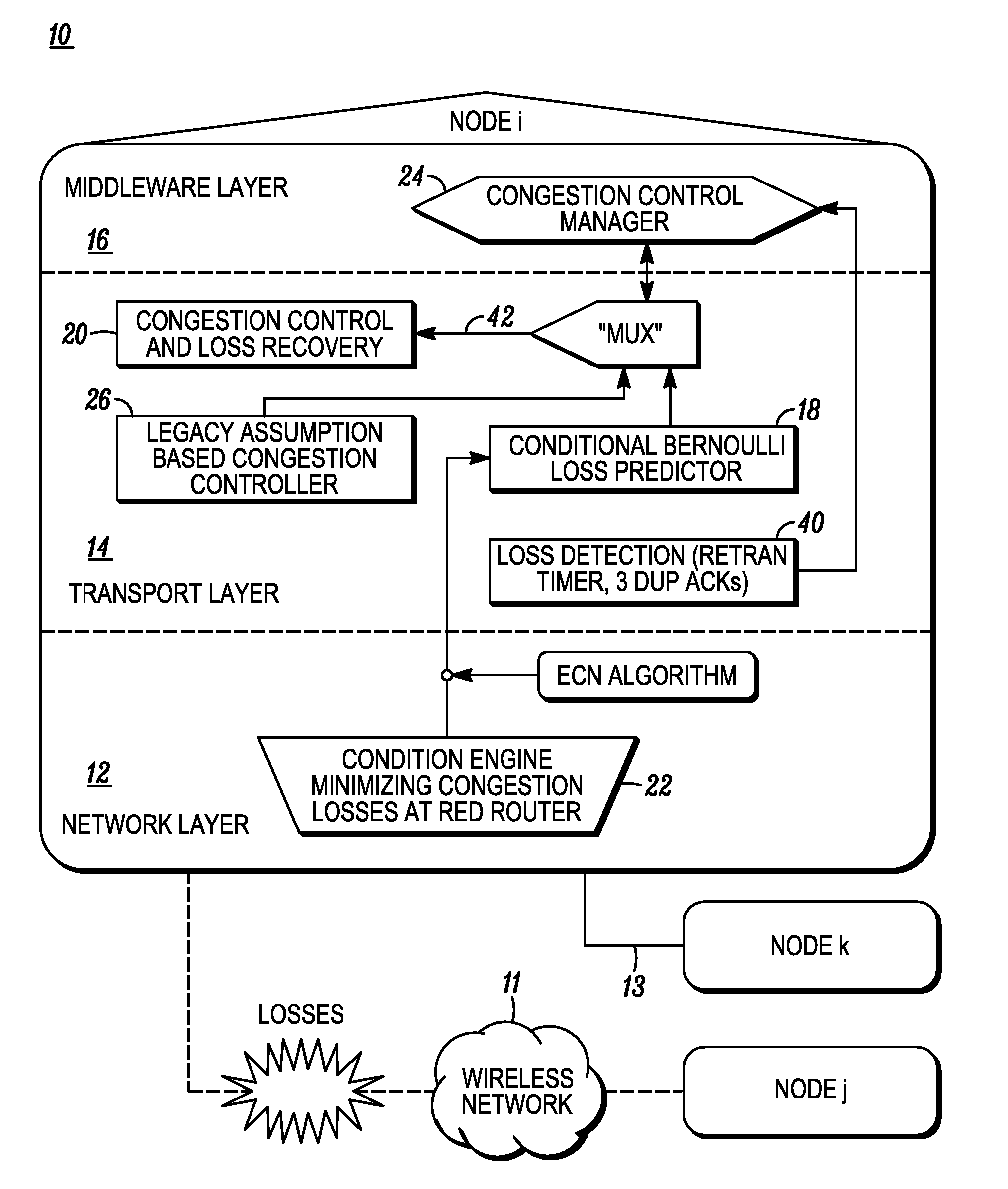
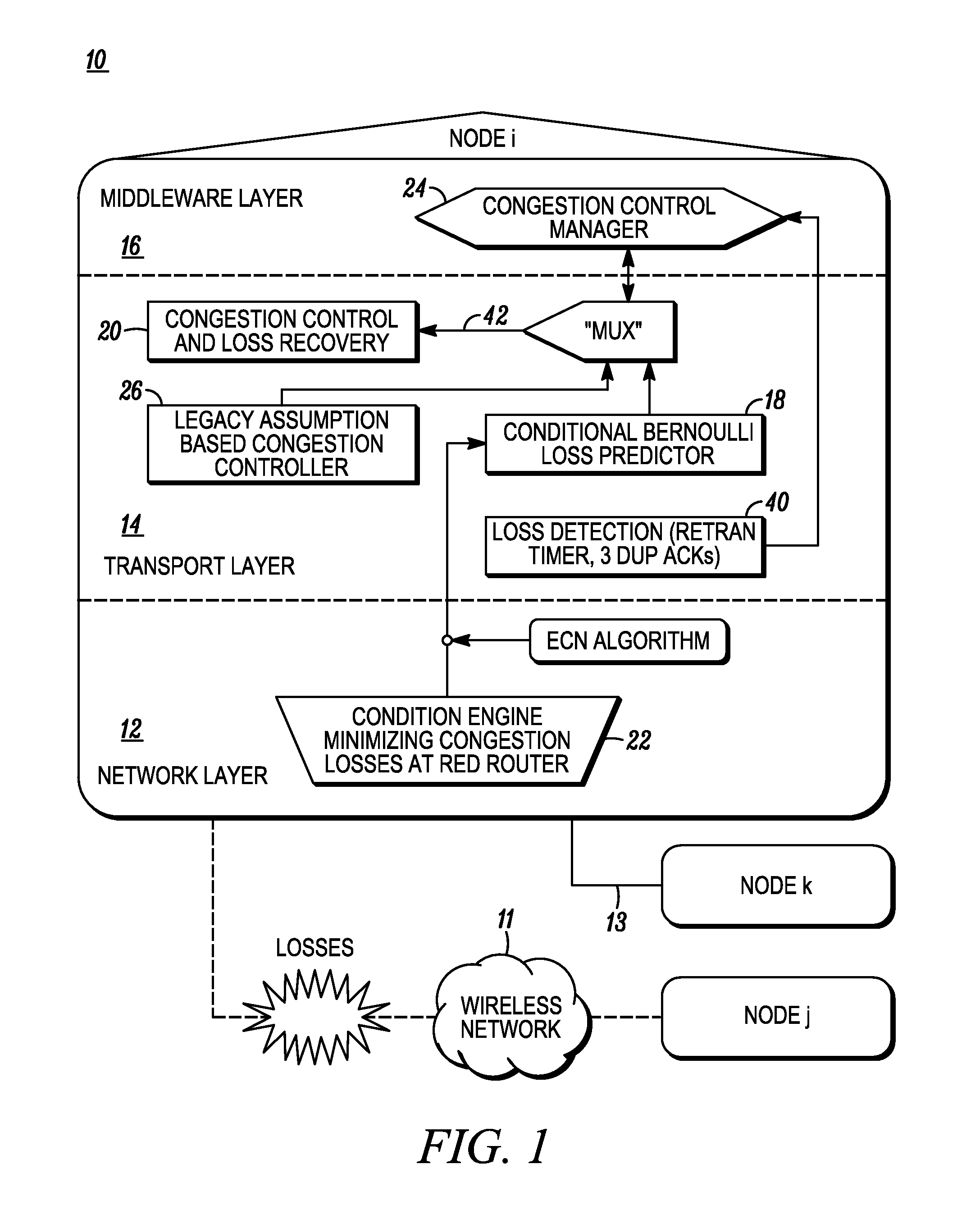
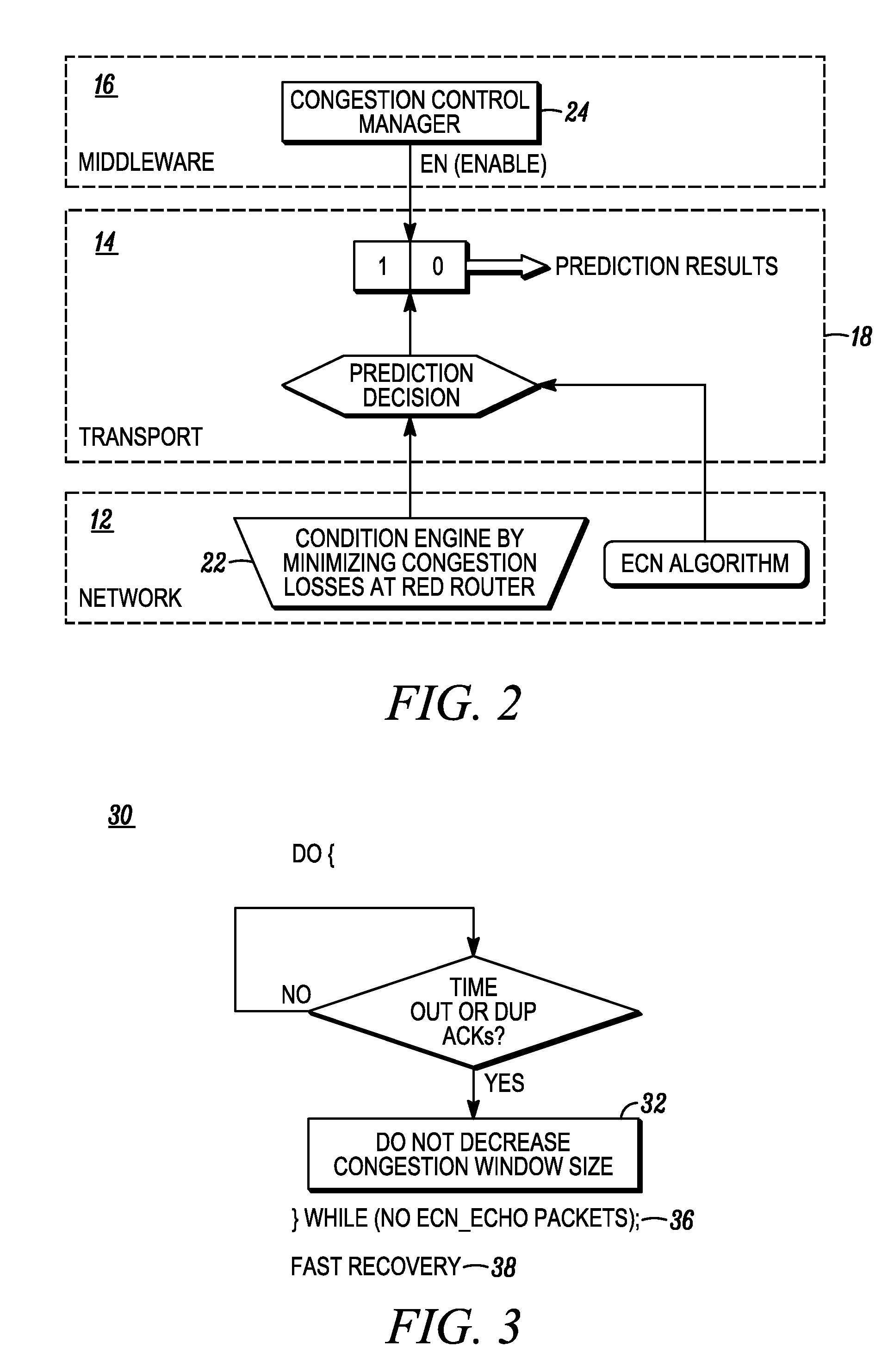
Congestion management over lossy network connections
ActiveUS20070086335A1Small sizeLow data rateTransmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsPacket lossNetwork connection
A network stack includes a packet loss analyzer that distinguishes between packet losses due to congestion and due to lossyness of network connections. The loss analyzer observes the packet loss patterns for comparison with a packet loss model. The packet loss model may be based on a Forward Error Correction (FEC) system. The loss analyzer determines if lost packets could have been recovered by a receiving network device, if FEC had been used. If the lost packets could have been corrected by FEC, the loss analyzer assumes that no network congestion exists and that the packet loss comes from the lossy aspects of the network, such as radio interference for wireless networks. If the loss analyzer determines that some of the lost packet could not have been recovered by the receiving network device, the loss analyzer assumes that network congestion causes these packet losses and reduces the data rate.
Owner:RIVERBED TECH LLC
Method for channel congestion management
ActiveUS7650379B2Reduce cloggingReduce channel congestionError preventionTransmission systemsNumber generatorData traffic
A method for managing data traffic in a multi-user multiple-simultaneous-access (MUMSA) environment, for example in a code reuse multiple access (CRMA) environment or other physical environment having true random access with more than one transmission present at the same time, the method including estimating channel load for multiple users, then using the estimate of channel load to calculate a congestion threshold on an ongoing basis, at each terminal performing an experiment using that congestion threshold value and a random number generator to determine if a packet is eligible to be transmitted, transferring downstream virtual channel traffic and redistributing user terminals to affiliate with the proper downstream virtual channel.
Owner:VIASAT INC
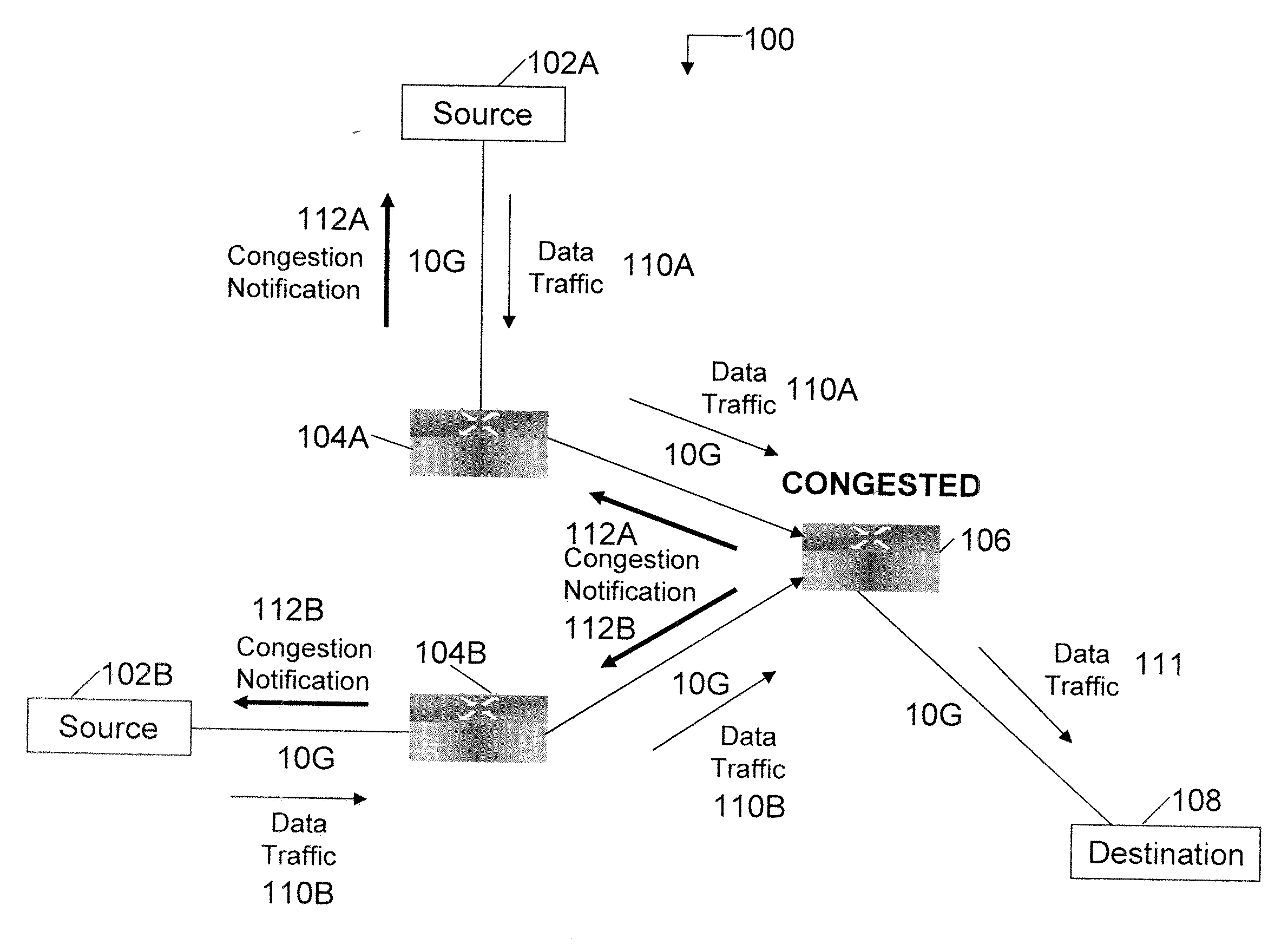
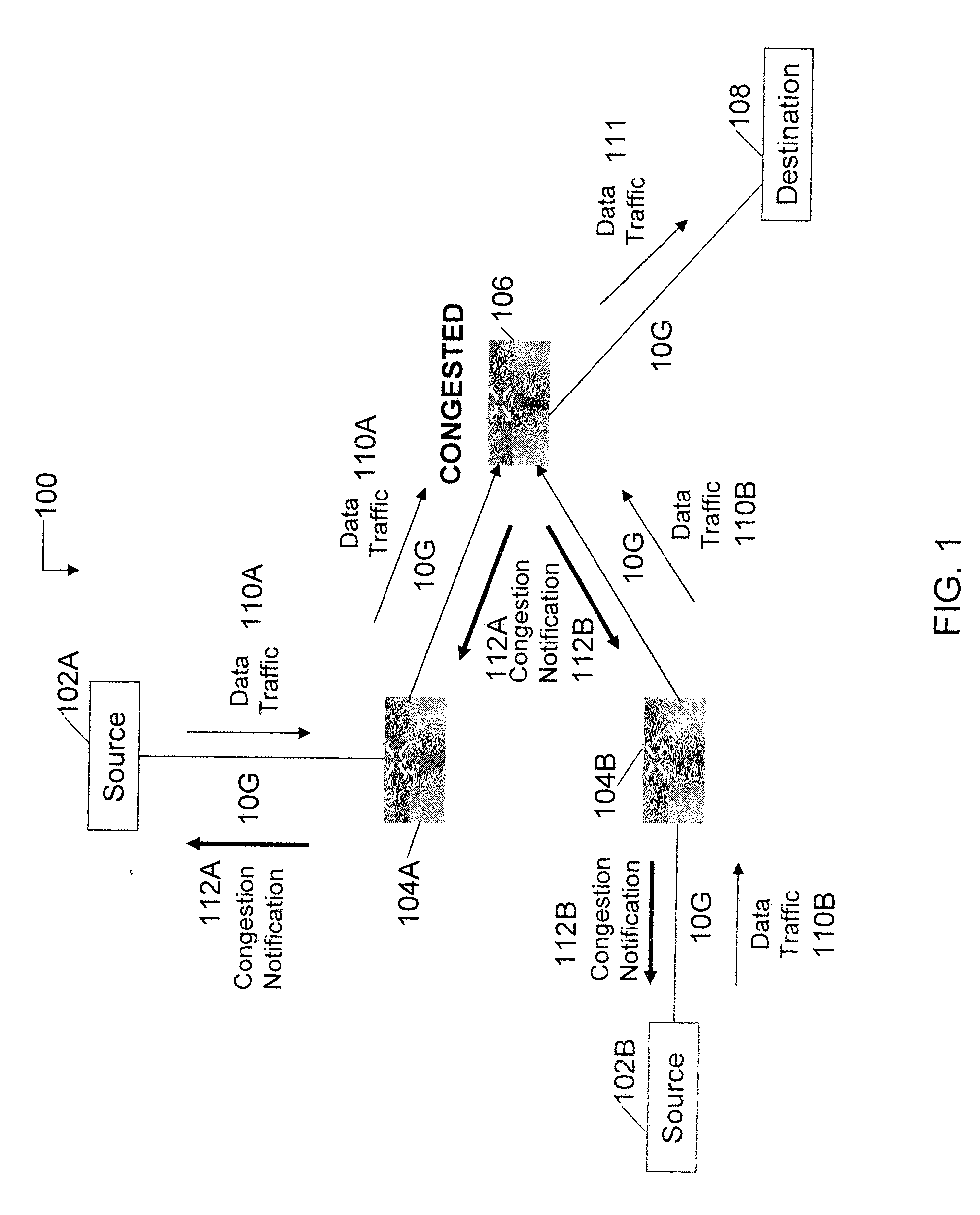
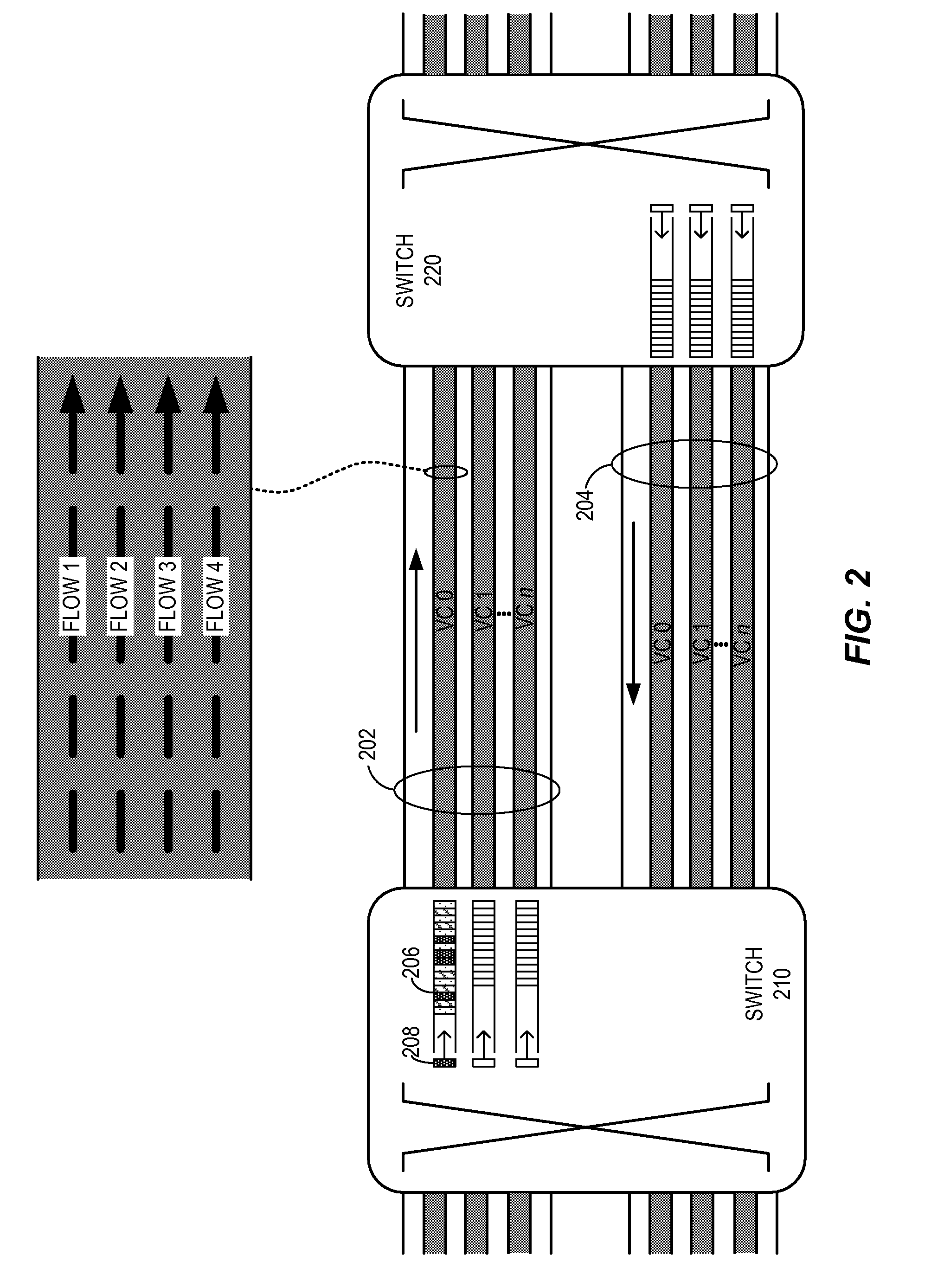
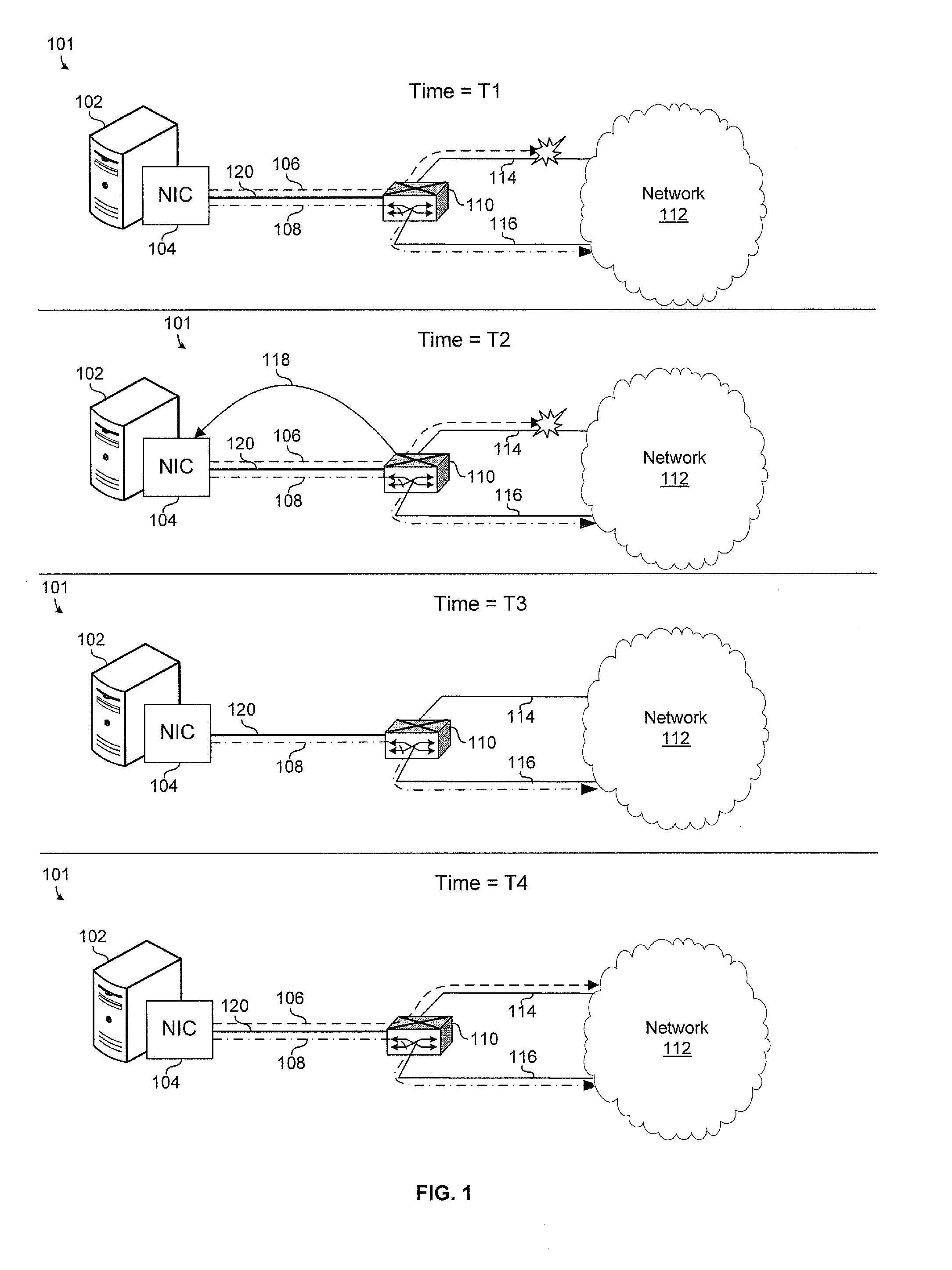
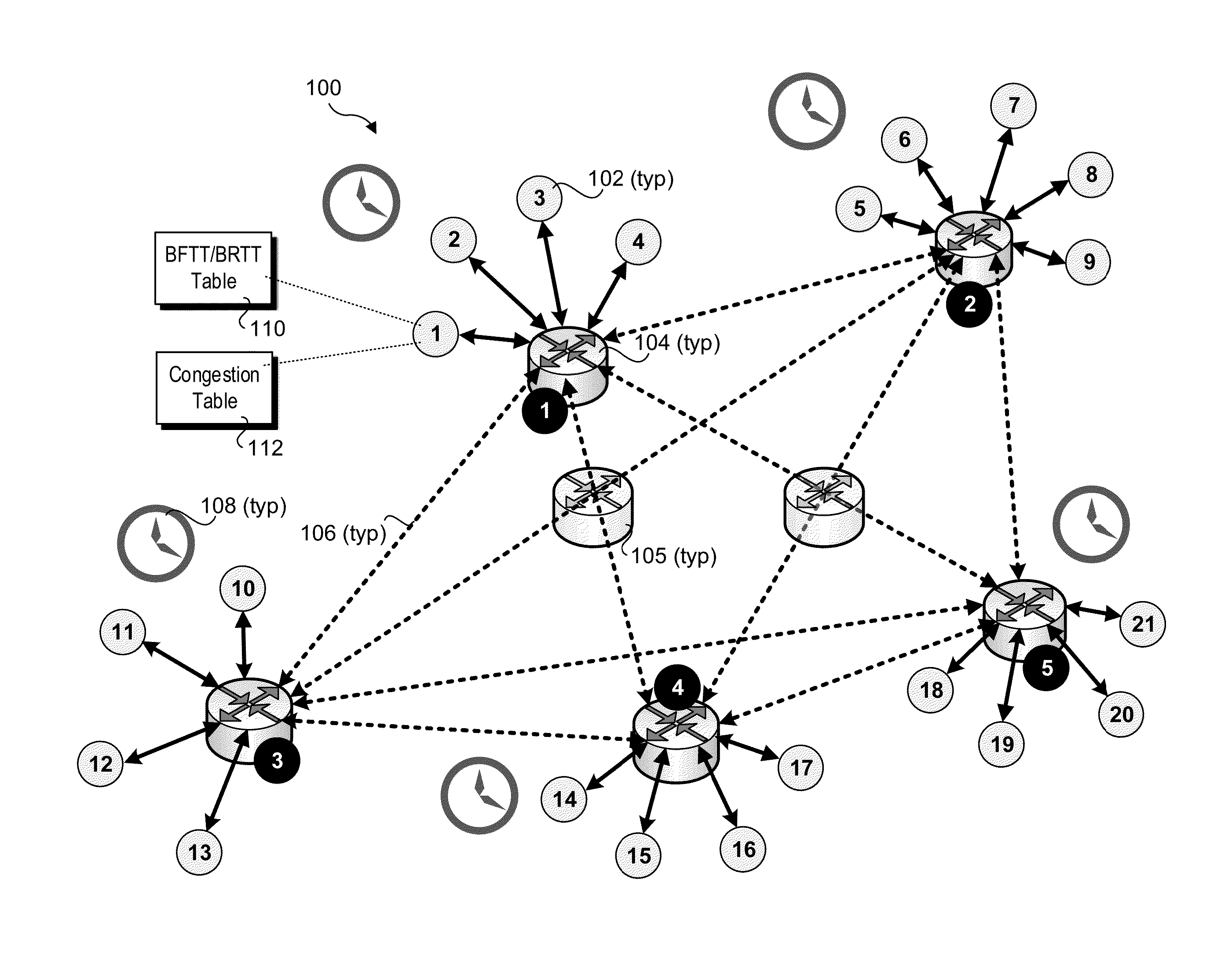
System and method to identify and communicate congested flows in a network fabric
ActiveUS20050270974A1Comprehensive and elegant solutionError preventionTransmission systemsExchange networkNetwork structure
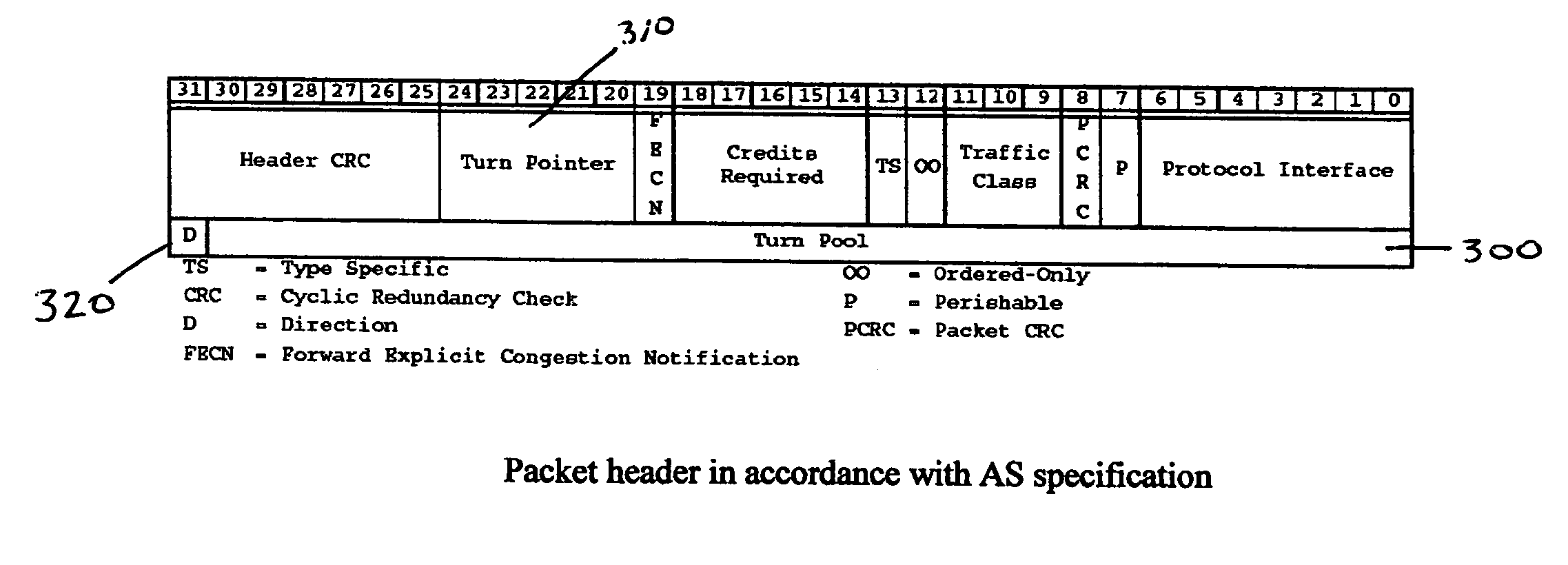
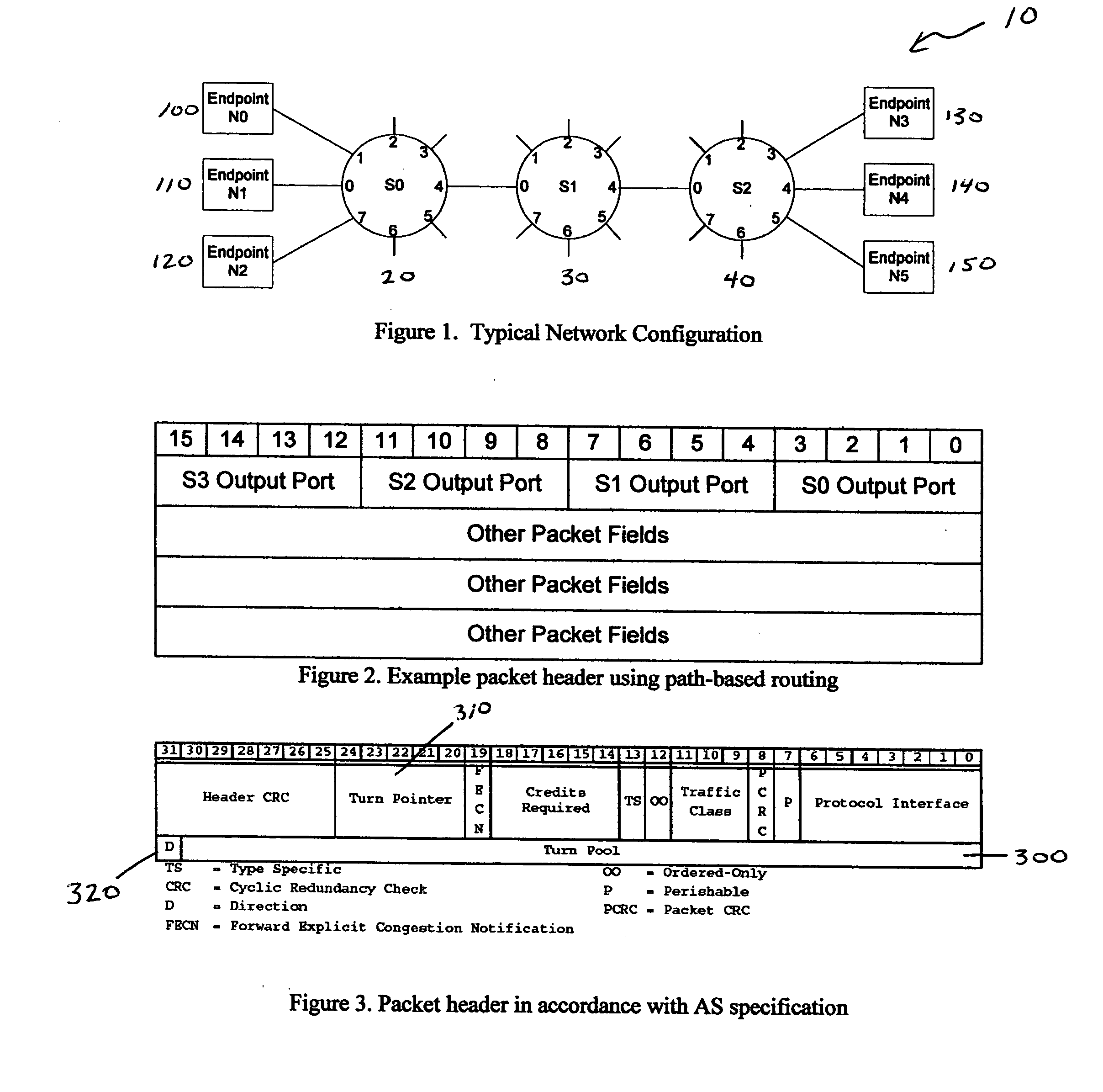
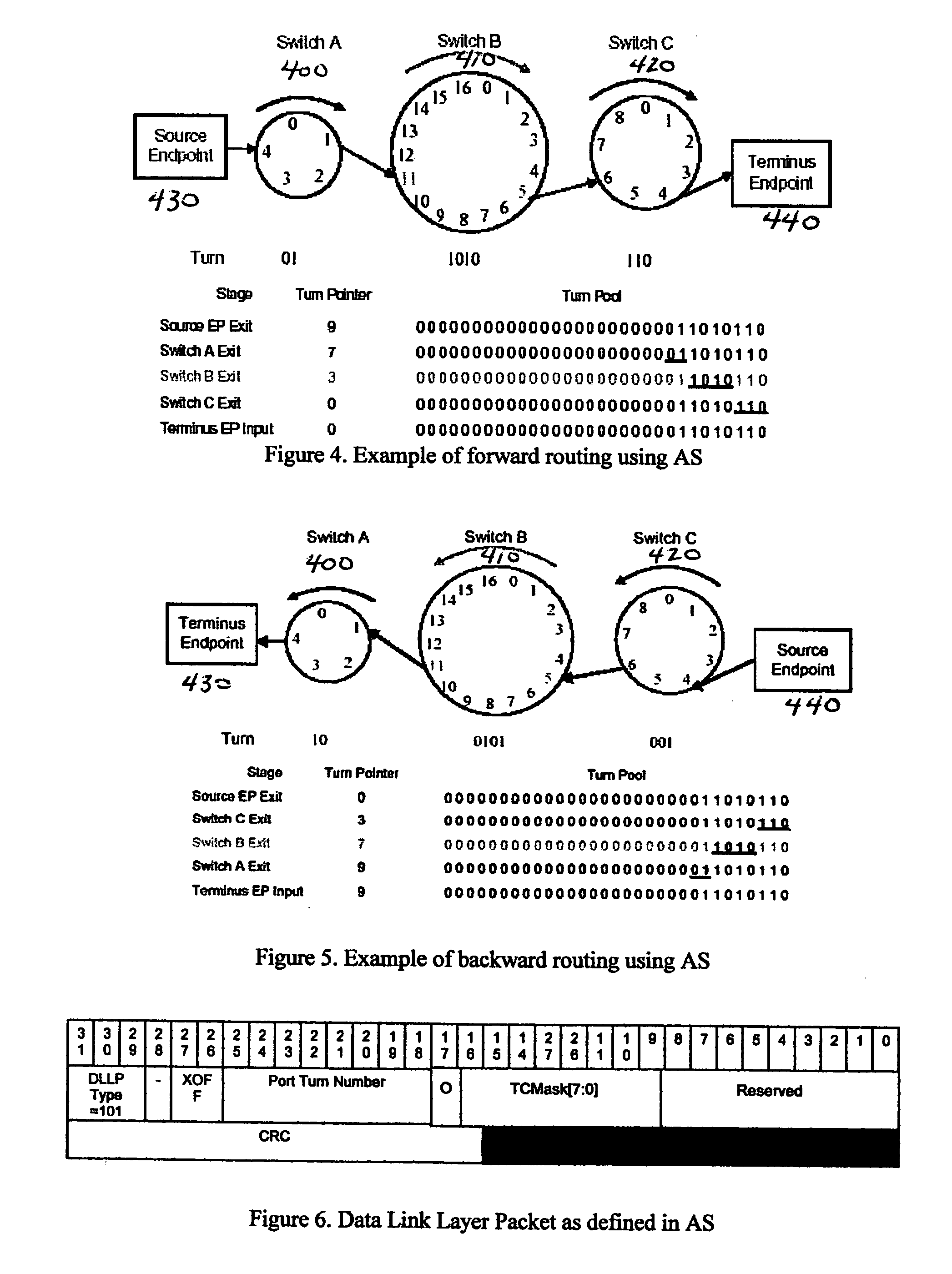
The invention provides a system and method for identifying and communicating congested paths throughout a network fabric. Briefly, the present invention augments the congestion management mechanism defined in ASI to allow for the communication of congested paths through the fabric, rather than the simple congested output port notification supported today through the use of DLLPs. Further, it also uses the communication mechanisms already defined in the ASI specification to implement this additional capability. Specifically, the present invention uses Transaction Layer Packets (TLPs) to communicate the information concerning congested flows throughout the network. This packet type allows the inclusion of much more information than DLLPs, allowing a more comprehensive and elegant solution to the issue of congestion management in an Advanced Switching network fabric.
Owner:CALLAHAN CELLULAR L L C
Method and apparatus for minimizing congestion in gateways
InactiveUS20080239953A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCongestion windowCommunications system
Methods and apparatus are provided to reduce data congestion and thus improve data throughput in gateways used in a wireless, wireline or a combination wireless and wireline communication system. The congestion management system optimally resizes, or not, congestion window (or buffer) sizing and threshold for the communication gateways based upon mathematical models. Application of the inventive congestion management method optimizes data recovery and throughput in communication networks, particularly those networks having lossy data links.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA +1
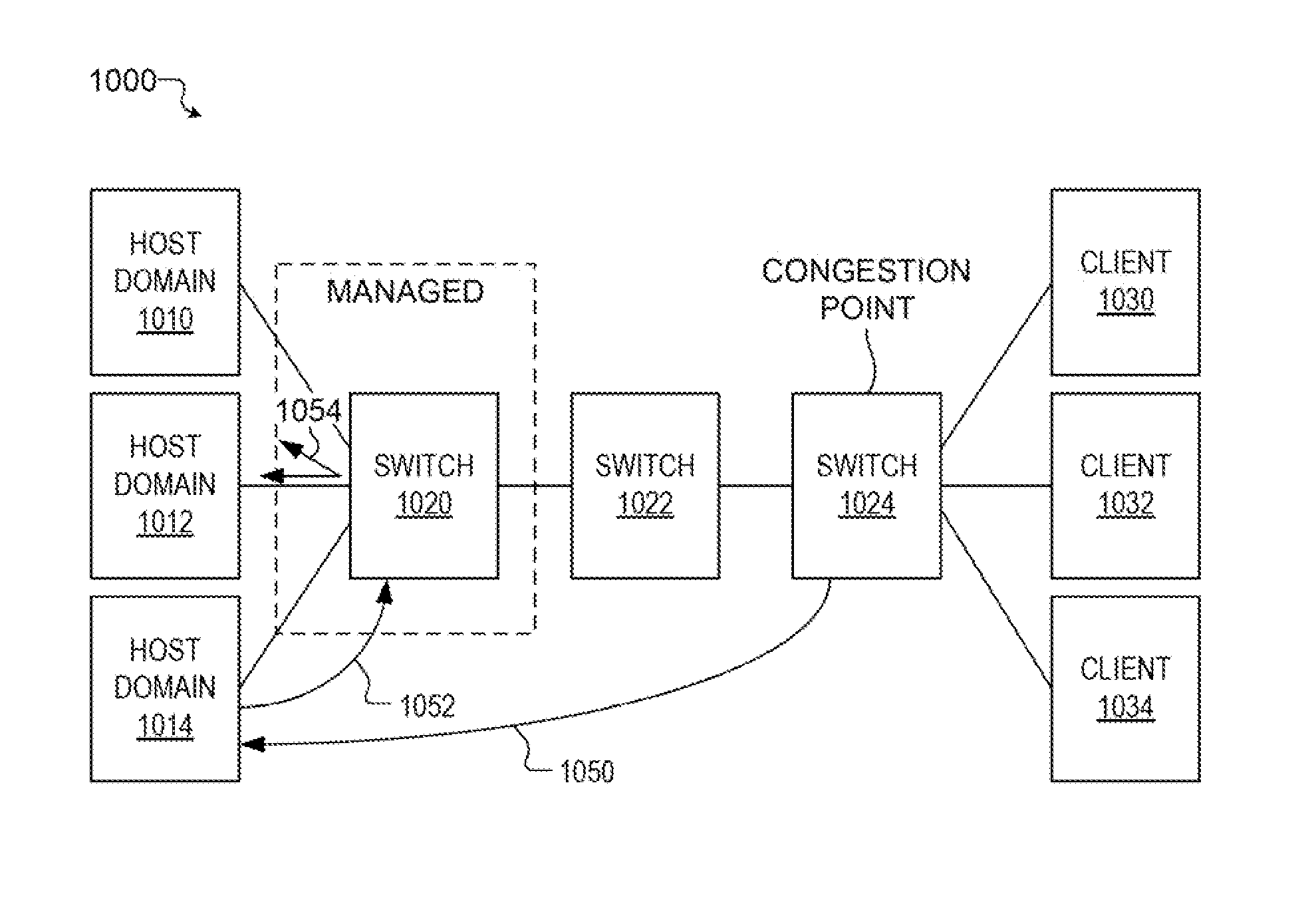
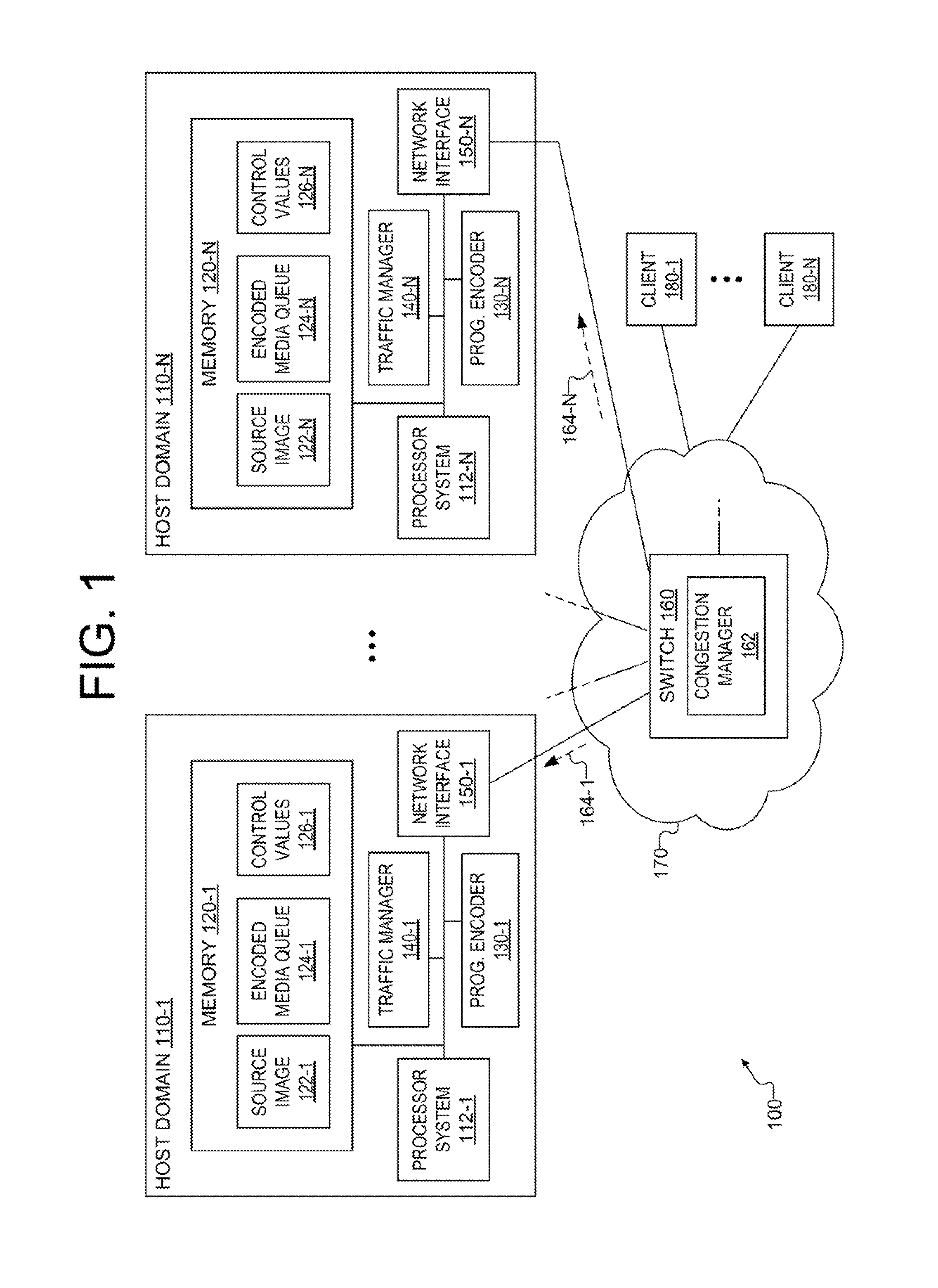
Switch-initiated congestion management method
ActiveUS9049271B1Selective content distributionData switching networksComputer scienceCongestion management
A method for managing media communications. In one embodiment, the method comprises establishing a session to a computer over a network and through a switch; generating first and second frames of an image stream; identifying updated regions of the first and the second frames, wherein the updated region of the first frame has a first size and the updated region of the second frame has a second size different from the first size; compressing, based on a value from a congestion manager, the updated regions of the first and the second frames to generate a first and a second encoding, respectively; transmitting the first encoding over the session at a first rate determined from the first size and the value; and transmitting the second encoding over the session at a second rate determined from the second size and the value, wherein the second rate is different from the first rate.
Owner:TERADICI CORP
Method & apparatus for improving the performance of TCP and other network protocols in a communication network
ActiveUS20150100858A1Reduce overheadCode conversionWireless network protocolsMultiplexingTraffic capacity
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
Differentiated services using weighted quality of service (QoS)
ActiveUS20070253438A1Quick understandingData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityCode point
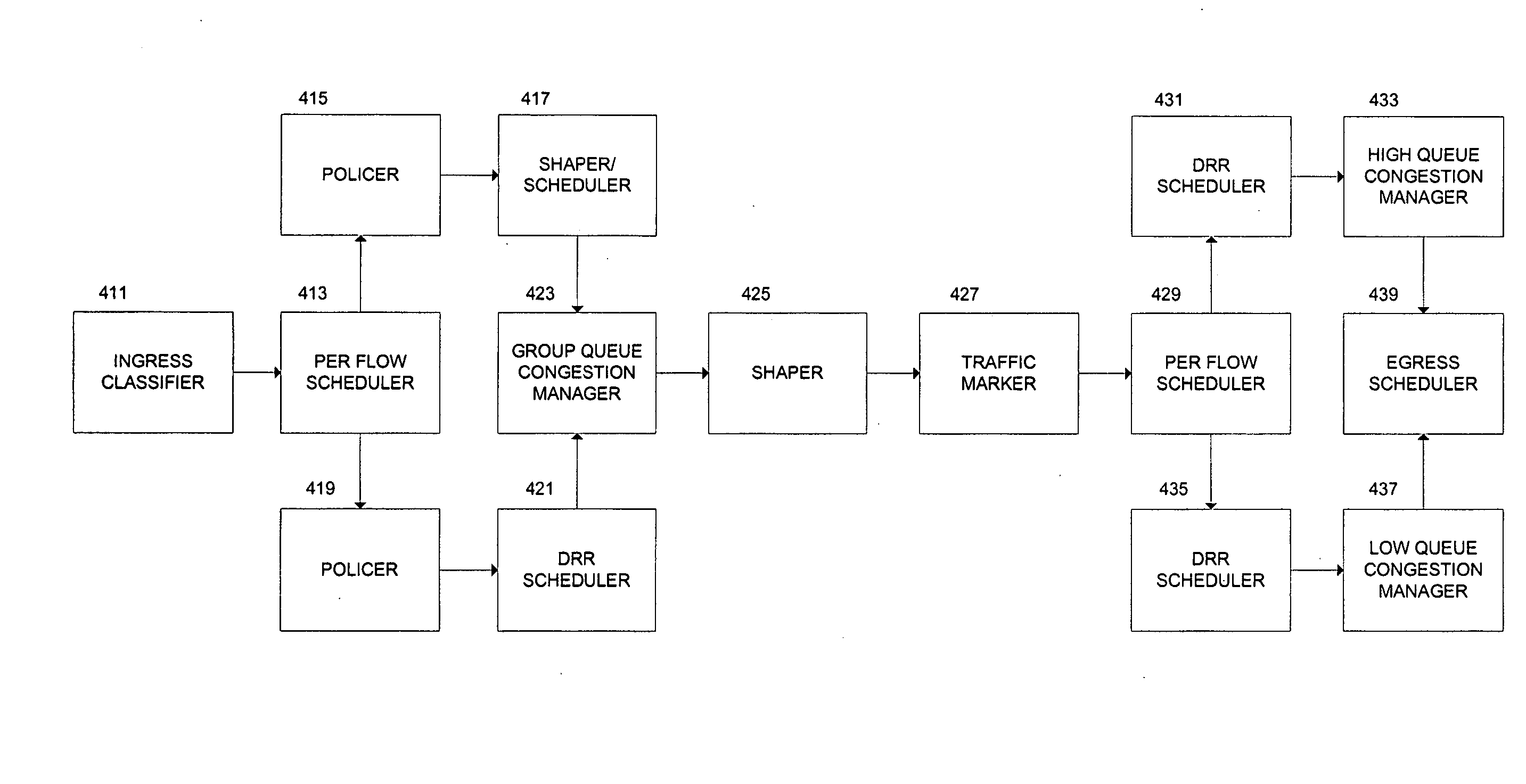
Differentiated services for network traffic using weighted quality of service is provided. Network traffic is queued into separate per flow queues, and traffic is scheduled from the per flow queues into a group queue. Congestion management is performed on traffic in the group queue. Traffic is marked with priority values, and congestion management is performed based on the priority values. For example, traffic can be marked as “in contract” if it is within a contractual limit, and marked as “out of contract” if it is not within the contractual limit. Marking can also include classifying incoming traffic based on Differentiated Service Code Point. Higher priority traffic can be scheduled from the per flow queues in a strict priority over lower priority traffic. The lower priority traffic can be scheduled in a round robin manner.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
Data center congestion management for non-tcp traffic
ActiveUS20150341273A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCongestion windowTraffic capacity
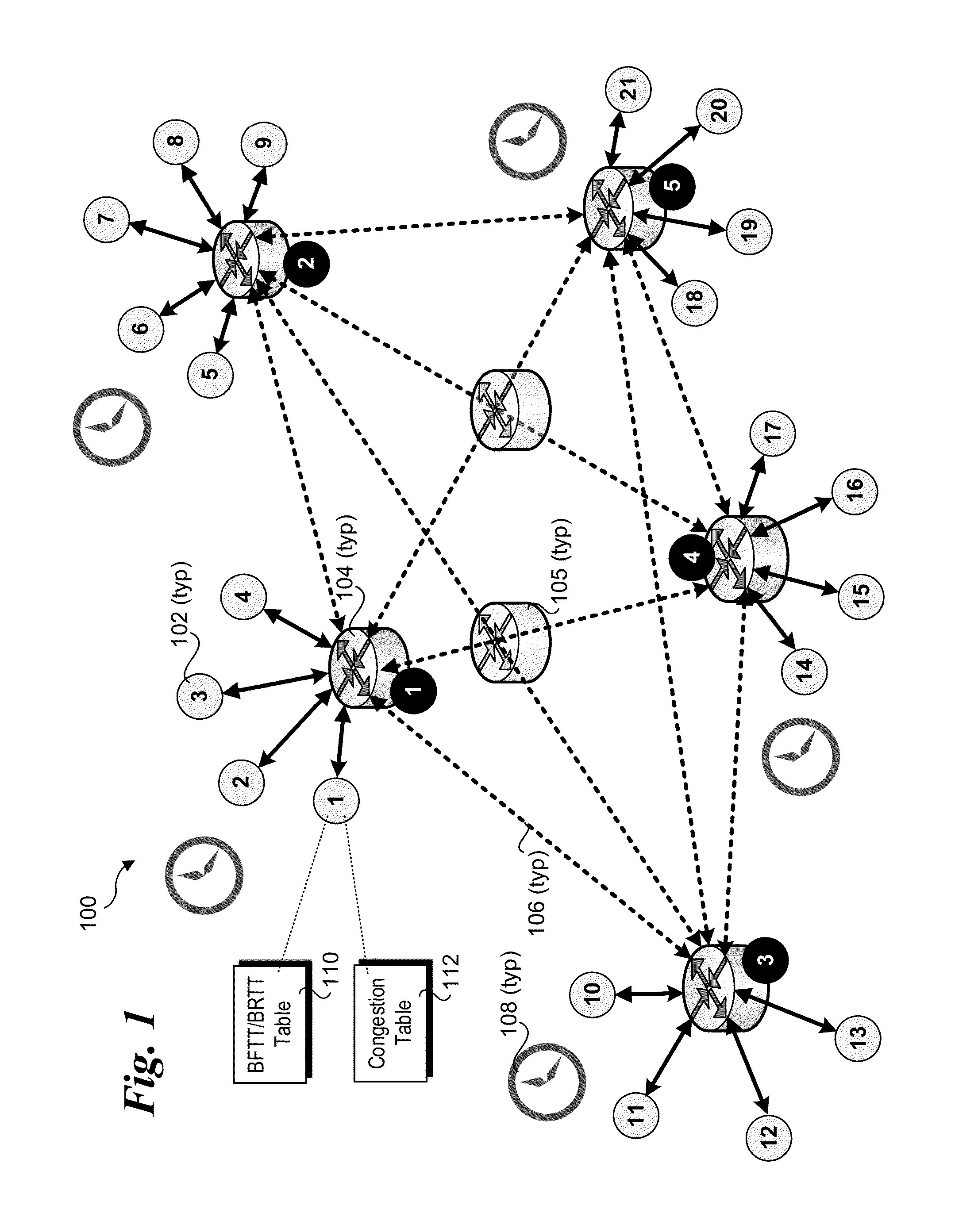
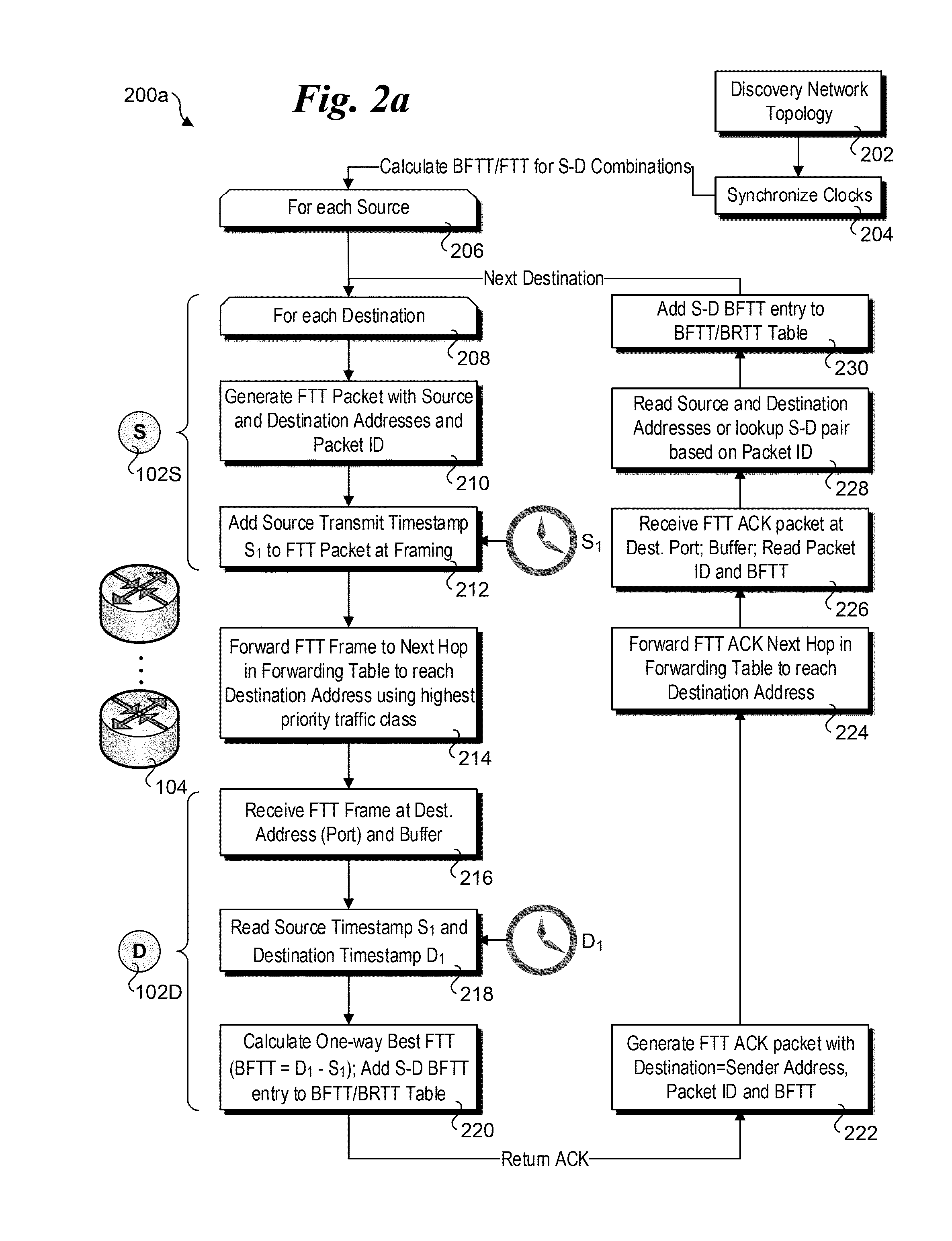
Methods, apparatus and software for implementing enhanced data center congestion management for non-TCP traffic. Non-congested transmit latencies are determined for transmission of packets or Ethernet frames along paths between source and destination end-end-nodes when congestion along the paths is not present or minimal. Transmit latencies are similarly measured along the same source-destination paths during ongoing operations during which traffic congestion may vary. Based on whether a difference between the transmit latency for a packet or frame and the non-congested transmit latency for the path exceeds a threshold, the path is marked as congested or not congested. A rate at which the non-TCP packets are transmitted along the path is then managed as function of a rate at which the path is marked as congested. In one implementation, non-TCP traffic is managed by mimicking a Data Center TCP technique, under which the congestion marking status of the path is substituted as an input to a DCTP algorithm in place of the normally-used ECN-Echo flag input. The congestion window output by the DCTCP algorithm is then used to manage the rate at which non-TCP packets to be forwarded via the path are transmitted from a source end-node.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and System for Ethernet Congestion Management
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Fair discard system
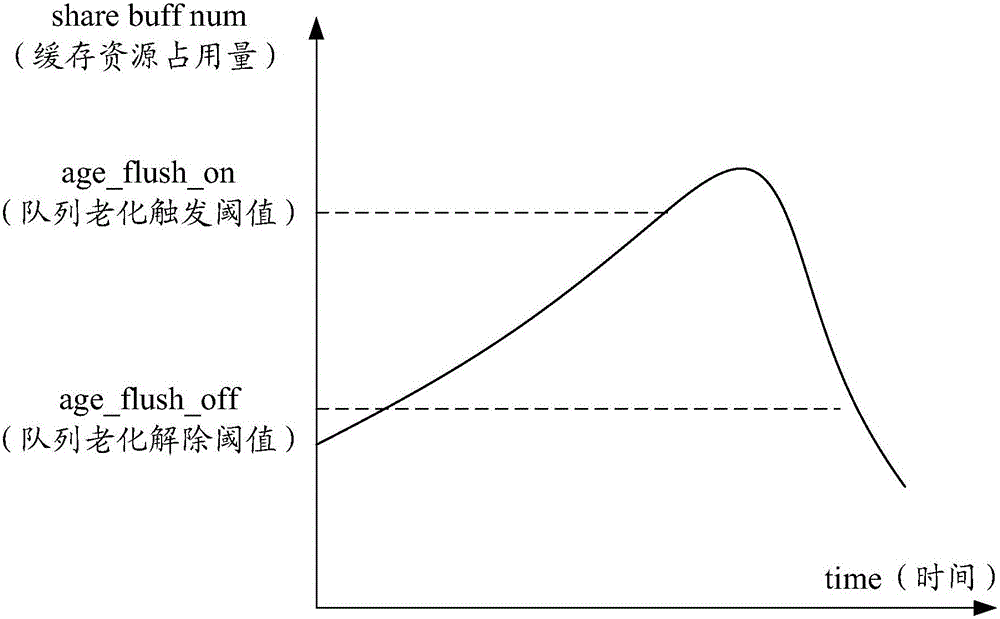
InactiveUS6717912B1Easy to useEffective distributionError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsClass of serviceMulti dimensional
The present invention is a shared buffer architecture that dynamically allocates buffer size to each of multiple sources depending on buffer pool utilization, estimated per-connection offered load, and the total number of connection established within a given class of service. When the buffer pool is almost empty, each source is allocated a large buffer space, proportional to its estimated offered load. When the buffer pool is more full each source is allocated a reduced buffer space, while maintaining the proportional weighting relationship. The invention keeps track of the amount of input per source and dynamically allocates a proportionate amount of buffer space in the buffer memory for that source. The dynamic allocation is made as a function of the fullness of the memory allocation for all sources. Additionally, thresholds are modulated dynamically as the number of established connections within a given class modulates, providing a predictive aspect to the system, with respect to congestion control. The main objective is to fairly allocate buffer space depending on the amount of traffic and the amount of buffer space taken up by each source. In operation, the memory allocation is readjusted depending on the total number of cells in the buffer memory, the estimated offered load, and the total number of connection established within each class of service, providing a highly dimensional solution to the multi-dimensional problem of congestion management in communication network nodes.
Owner:RIBBON COMM OPERATING CO INC
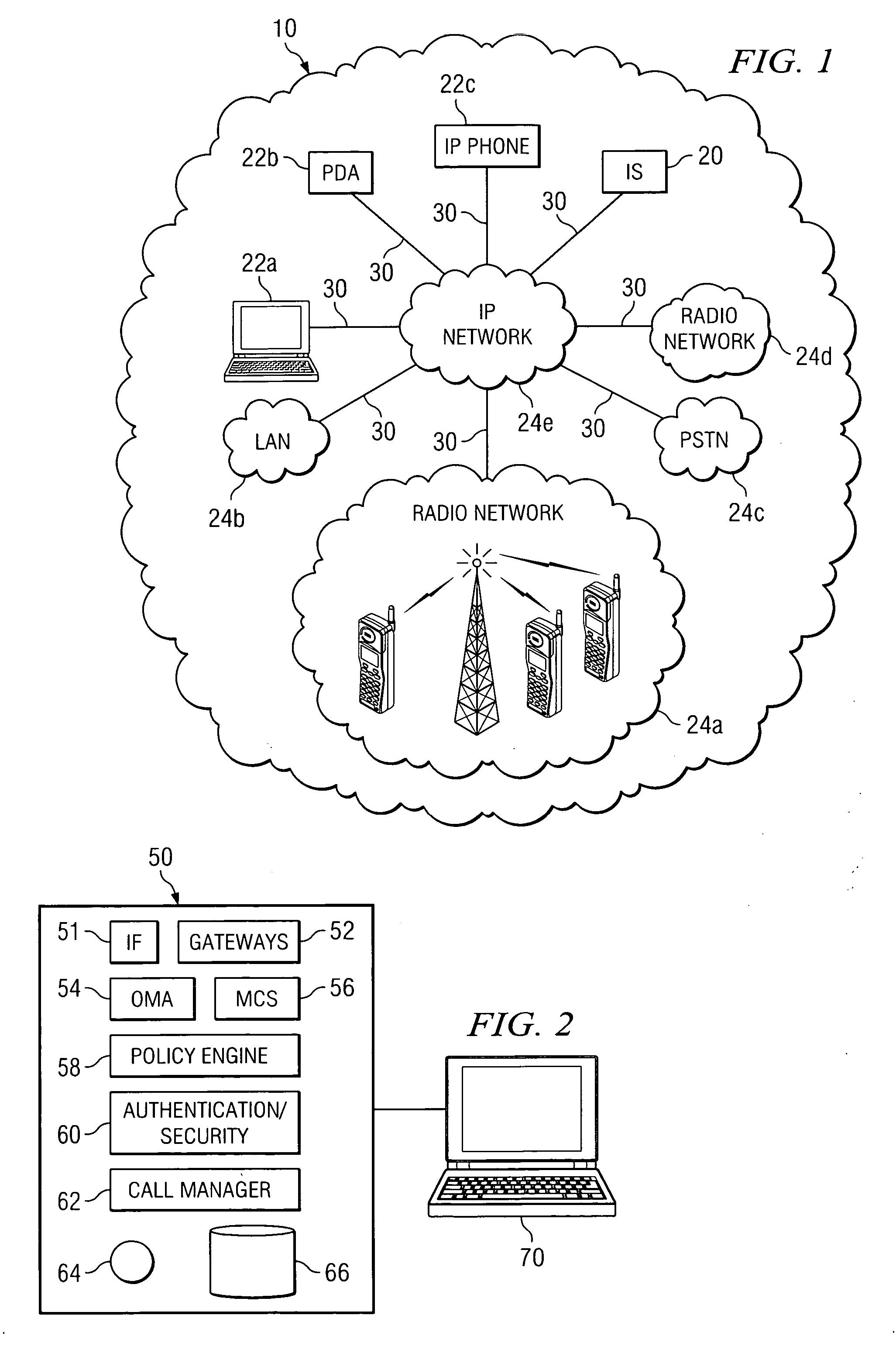
Method and system for providing interoperable communications with congestion management
ActiveUS20070202907A1Eliminates and reduces of disadvantageEliminates and reduces of and problemError preventionTransmission systemsComputer scienceDistributed computing
A method for providing interoperable communications with congestion management includes facilitating communications of a plurality of virtual talk groups. Each virtual talk group comprises a plurality of endpoints of different communication networks communicating using a respective communication channel. The method includes detecting, for a first virtual talk group of the plurality of virtual talk groups, a congestion event and, in response to detecting the congestion event, forming from the first virtual talk group one or more subgroups, each subgroup comprising at least two endpoints from the first virtual talk group. The method also includes assigning to each subgroup a respective alternate communication protocol for use by the plurality of endpoints of the subgroup.
Owner:STA GRP LLC
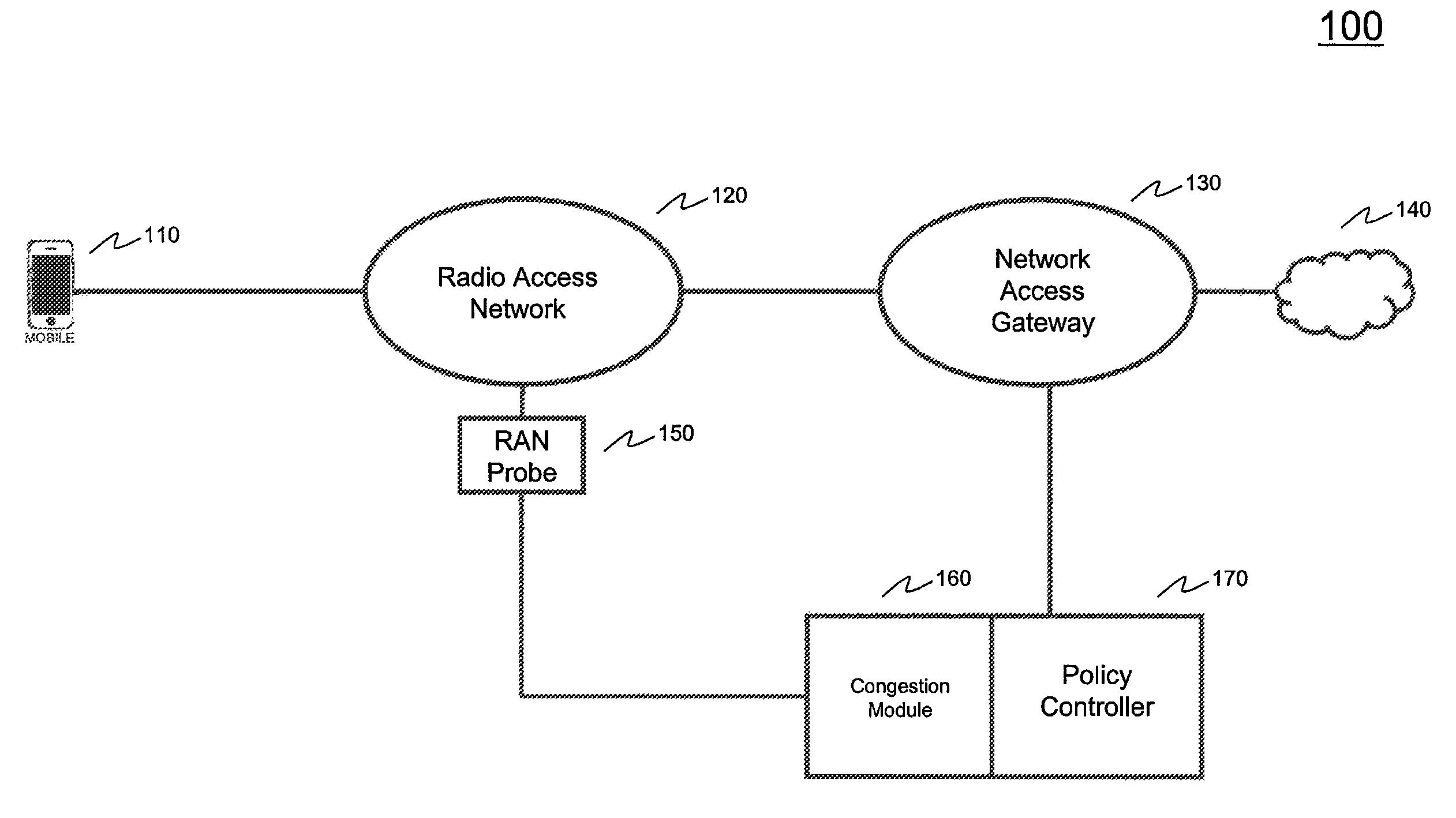
Systems and methods for network congestion management using radio access network congestion indicators
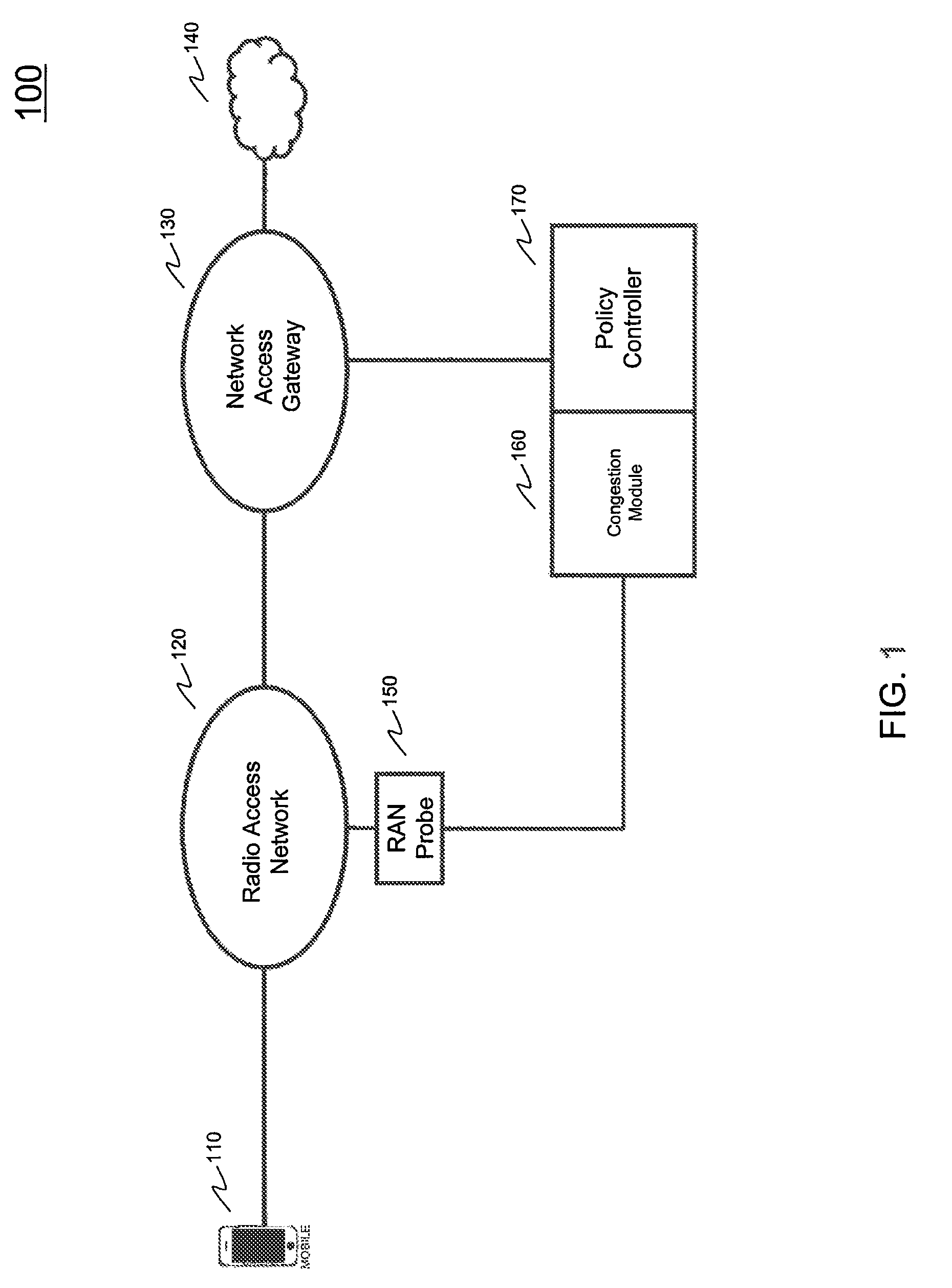
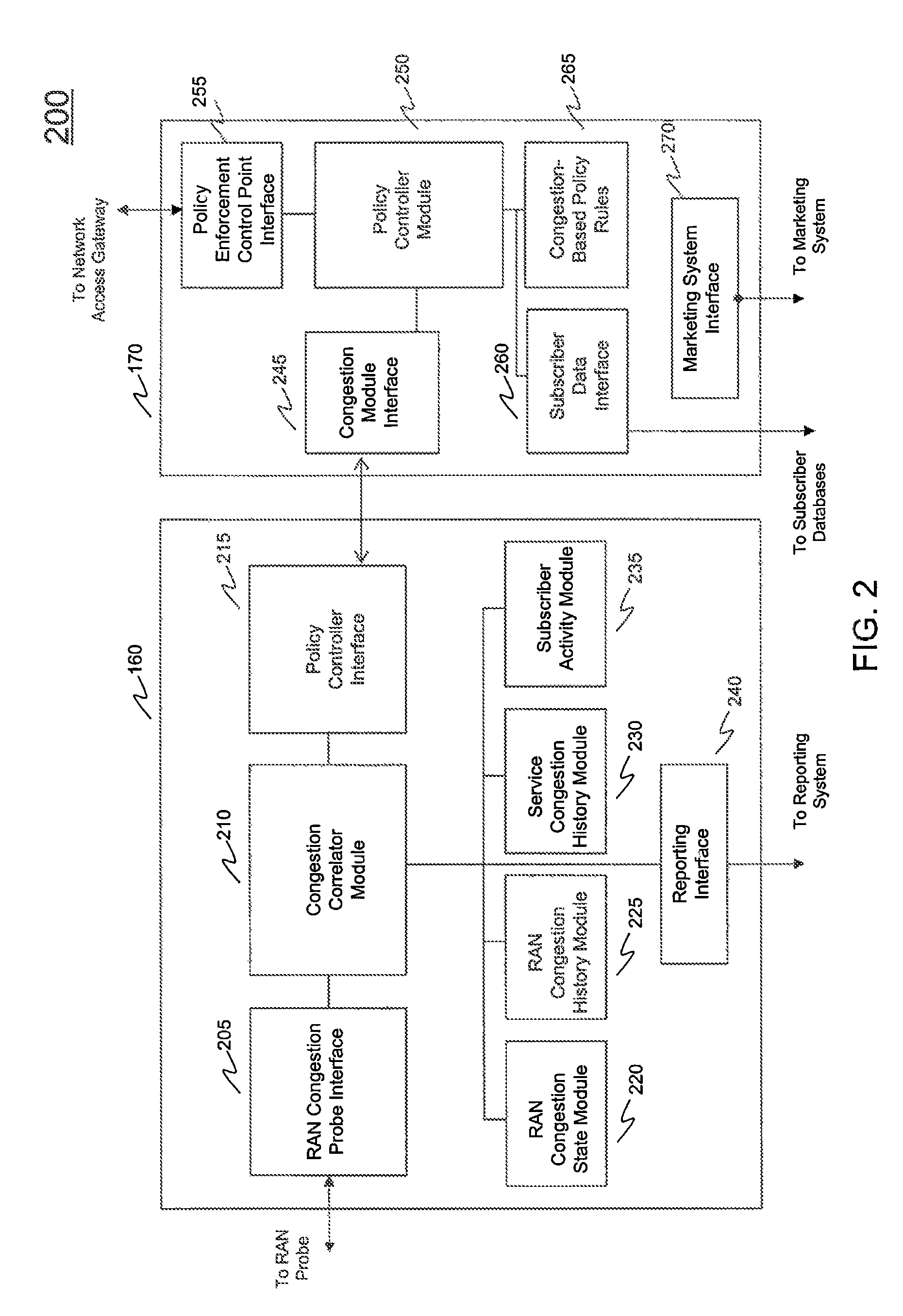
Owner:AMDOCS CANADIAN MANAGED SERVICES INC +1
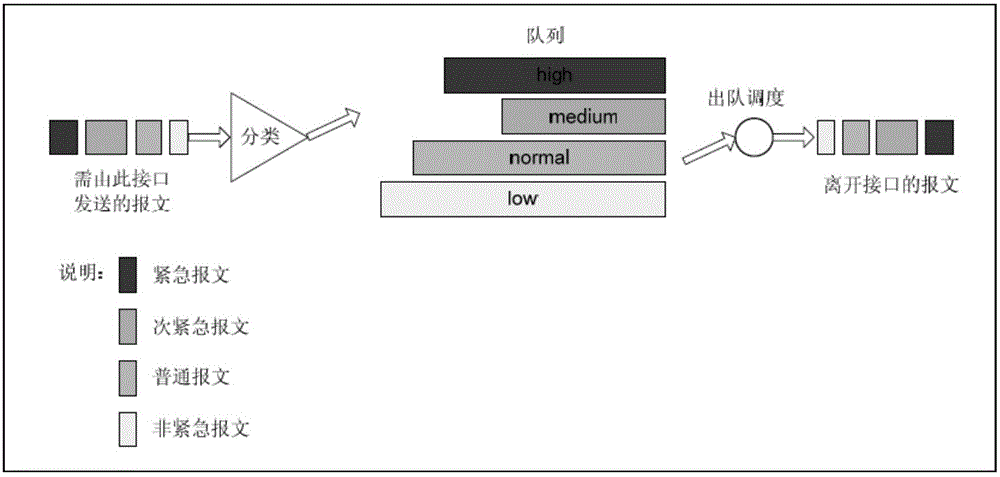
Port congestion management method and device
InactiveCN105812285ANot easy to discardGuaranteed entryData switching networksDistributed computingLower priority
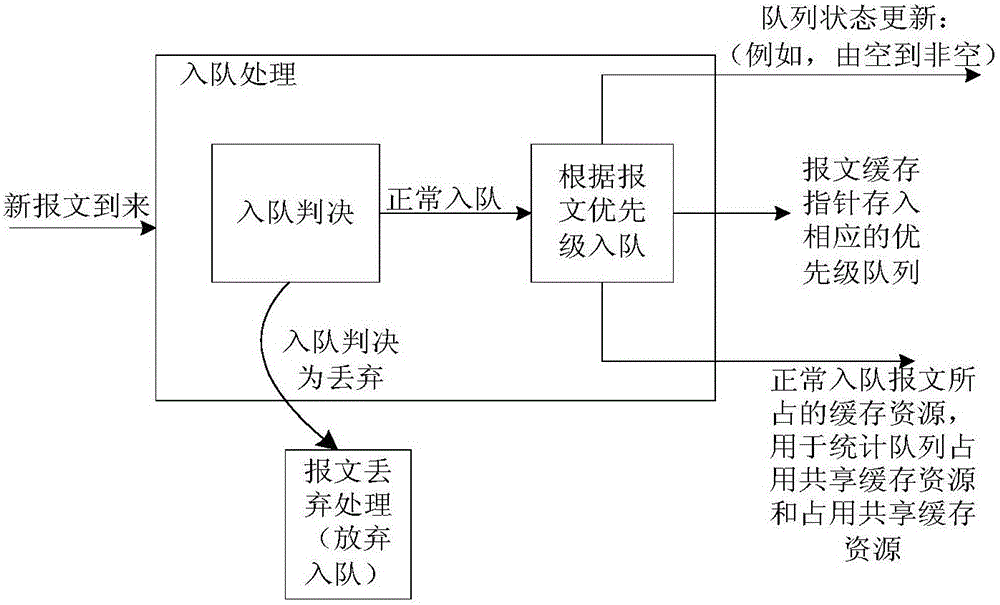
Embodiments of the invention disclose a port congestion management method and device, which solve a problem that buffering of high-priority packets cannot be greatly guaranteed. The port congestion management method comprises the steps: monitoring the size of idle buffering resources in a shared buffering resource aiming at a port, and when the size of the idle buffering resources is smaller than a buffering congestion threshold, determining at least one non-empty queue corresponding to the port; according to the priority respectively corresponding to the at least one non-empty queue, sorting the at least one non-empty queue, thereby obtaining a non-empty queue sorting result; according to the non-empty queue sorting result, screening at least one target queue from the at least one non-empty queue from low priority to high priority; and releasing a buffering resource respectively occupied by the at least one message included in each target queue.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com