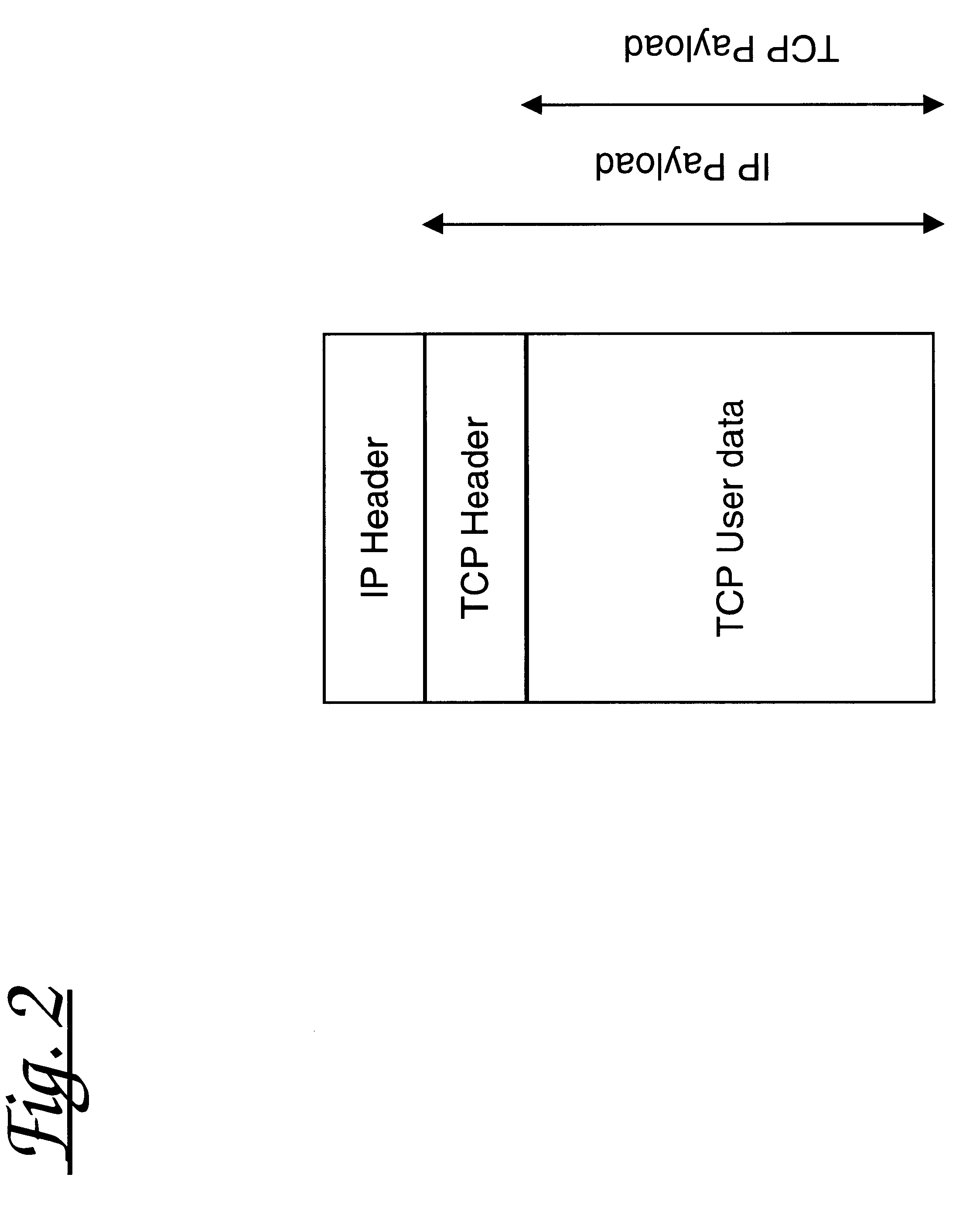
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
609 results about "Differentiated service" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
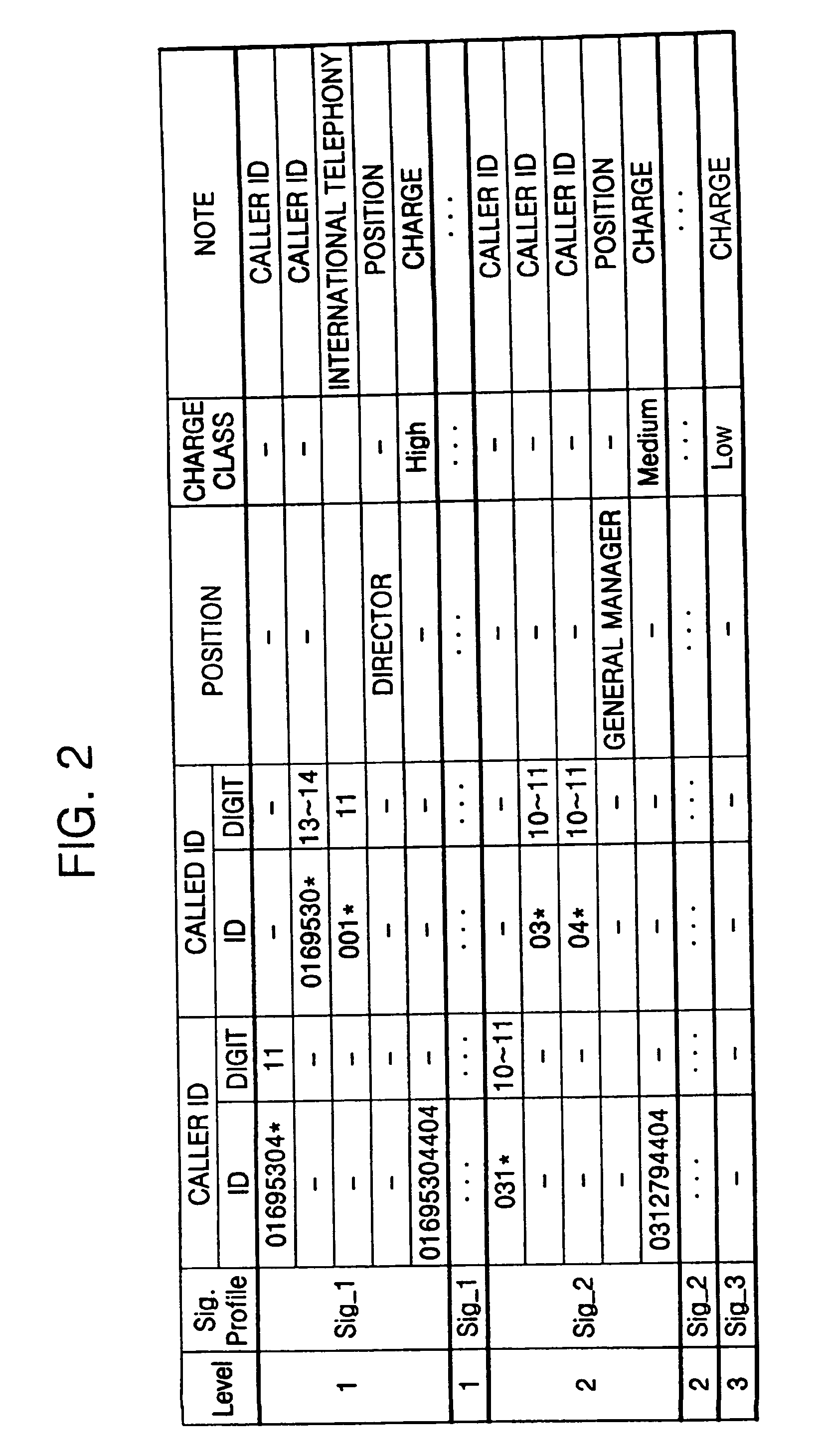
Differentiated service is a design pattern for business services and software, in which the service varies automatically according to the identity of the consumer and/or the context in which the service is used. Sometimes known as smart service or context-aware service.
Method of interference management for interference/collision avoidance and spatial reuse enhancement
InactiveUS20050058151A1Improve rendering capabilitiesImprove channel utilizationEnergy efficient ICTPower managementDifferentiated servicesDifferentiated service
A method called the evolvable interference management (EIM) method is disclosed in this patent for avoiding interference and collision and increasing network throughput and energy efficiency in wireless networks. EIM employs sensitive CSMA / CA, patching approaches, interference engineering, differentiated multichannel, detached dialogues, and / or spread spectrum techniques to solve the interference and QoS problems. EIM-based protocols can considerably increase network throughput and QoS differentiation capability as compared to IEEE 802.11e in multihop networking environments. Due to the improvements achievable by EIM, the techniques and mechanisms presented in this application may be applied to obtain an extension to IEEE 802.11 to better support differentiated service and power control in ad hoc networks and multihop wireless LANs. New protocols may also be designed based on EIM.
Owner:YEH CHIHSIANG
Method and apparatus for automatically establishing bi-directional differentiated services treatment of flows in a network
InactiveUS7050396B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDifferentiated servicesDifferentiated service
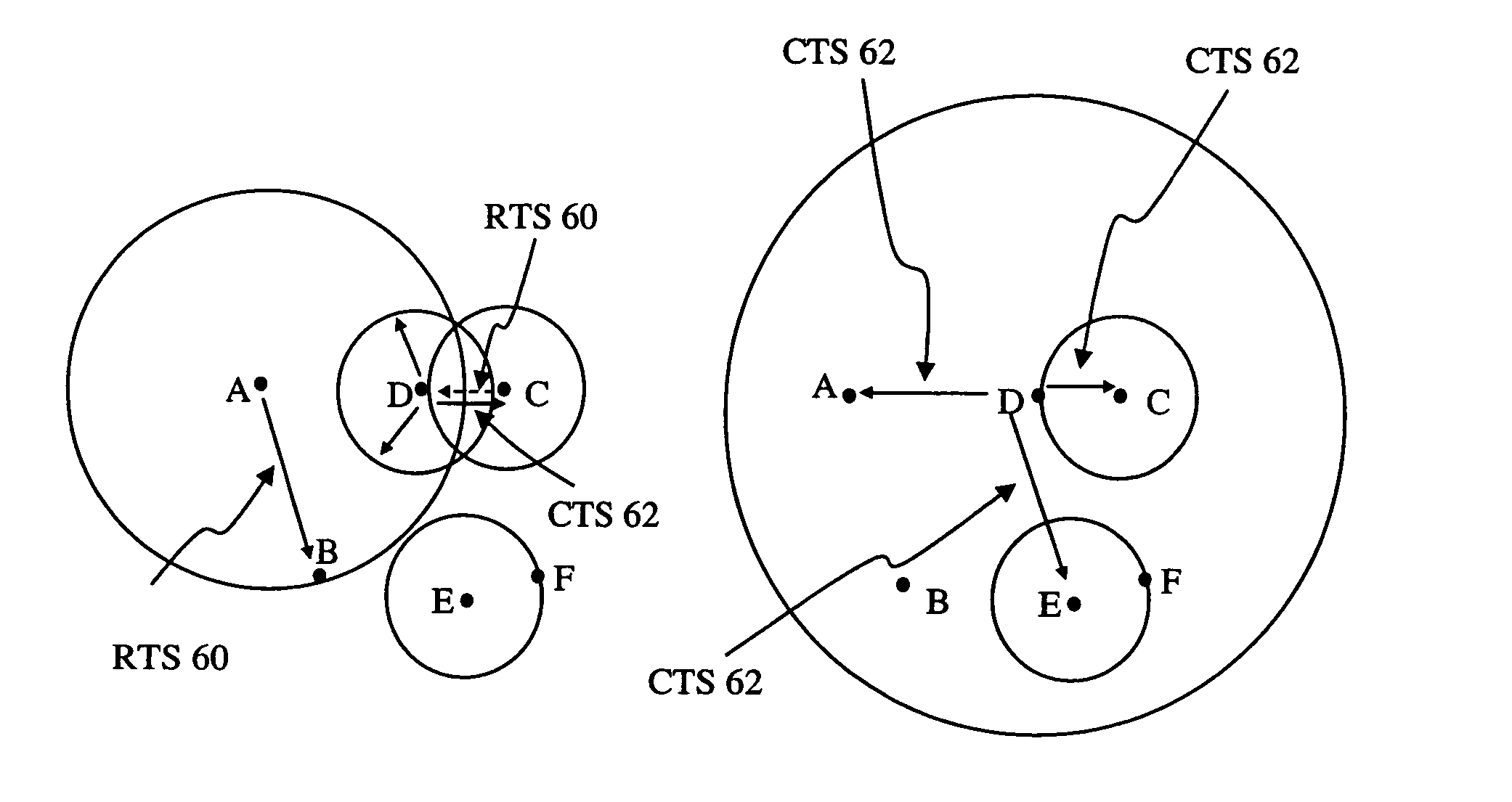
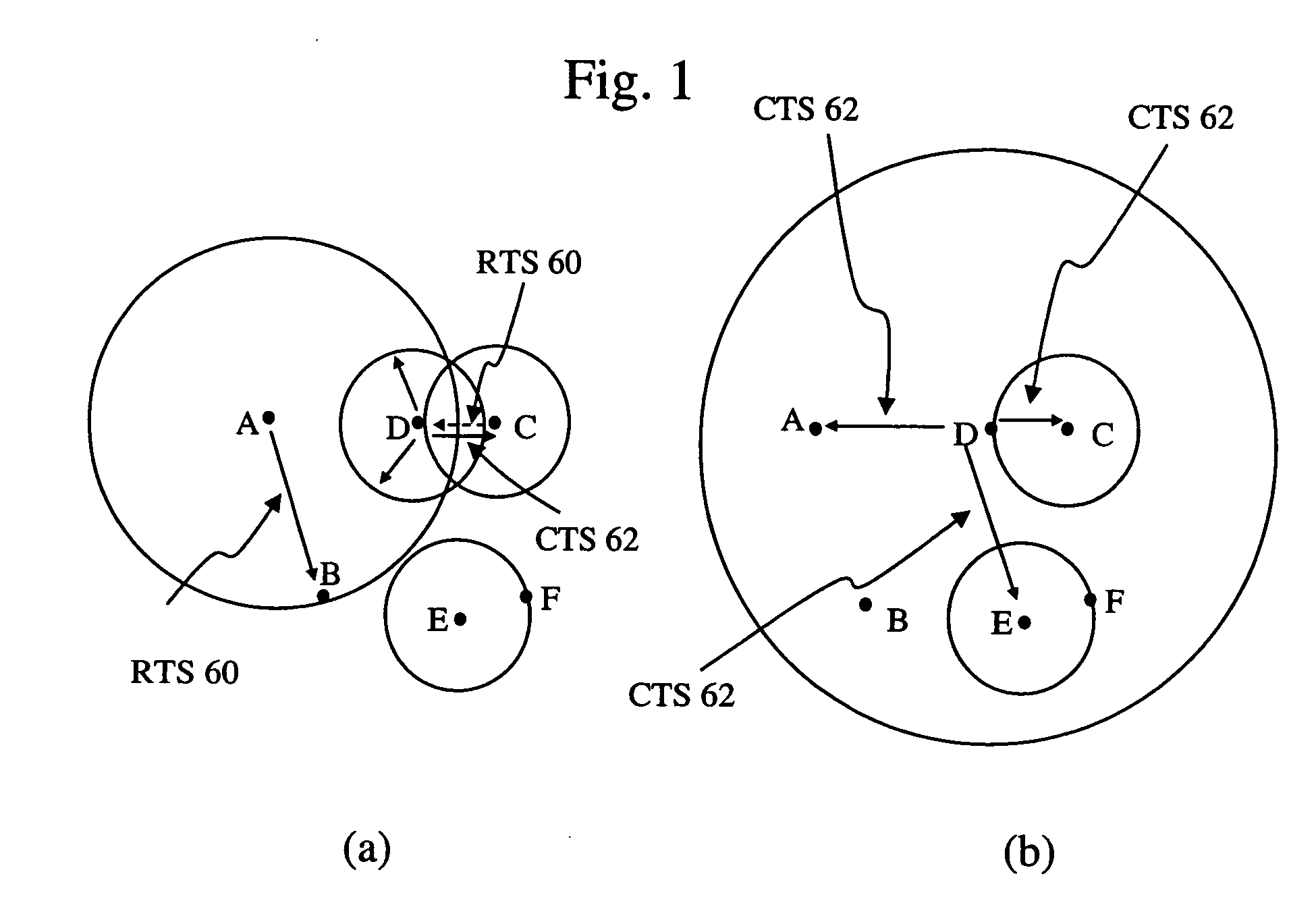
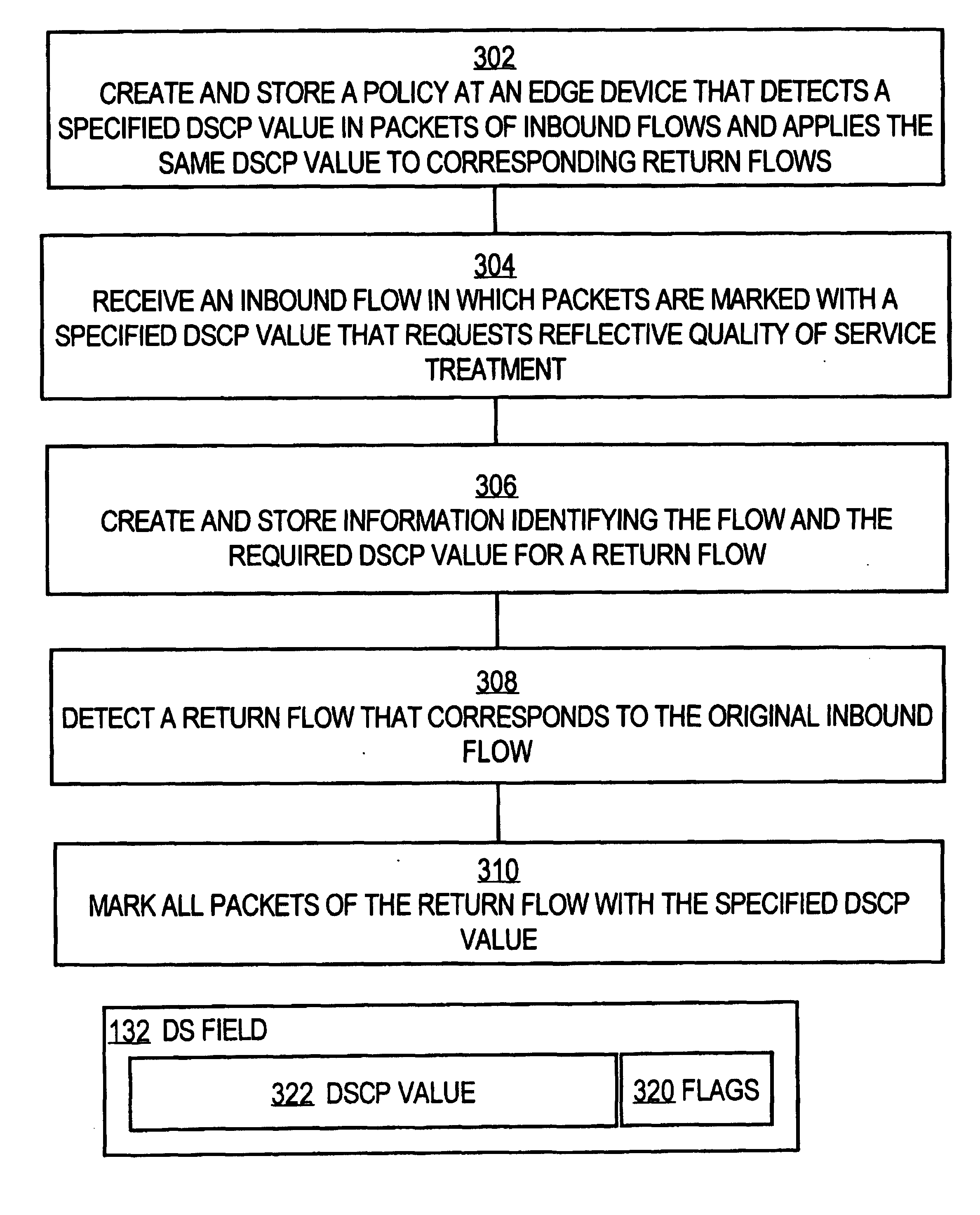
A method of automatically establishing differentiated services quality of service treatment for a return packet flow that is associated with an originating packet flow in a network is disclosed. The originating packet flow is received, and it is determined that one or more packets in the originating packet flow are marked with a DSCP value that matches a policy rule that instruct setting of a specified DSCP value to the return packet flow. In response, information identifying the originating packet flow and a second DSCP value for marking the return packet flow is created and stored. When a corresponding return packet flow is received and determined to be associated with the originating packet flow, packets of the return packet flow are automatically marked with the second DSCP value. Once the packet flow terminates, all stored information is removed.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Load balancing in mobile environment
InactiveUS20090163223A1Unbalanced loadImprove QoSRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless communicationResource utilizationHandover
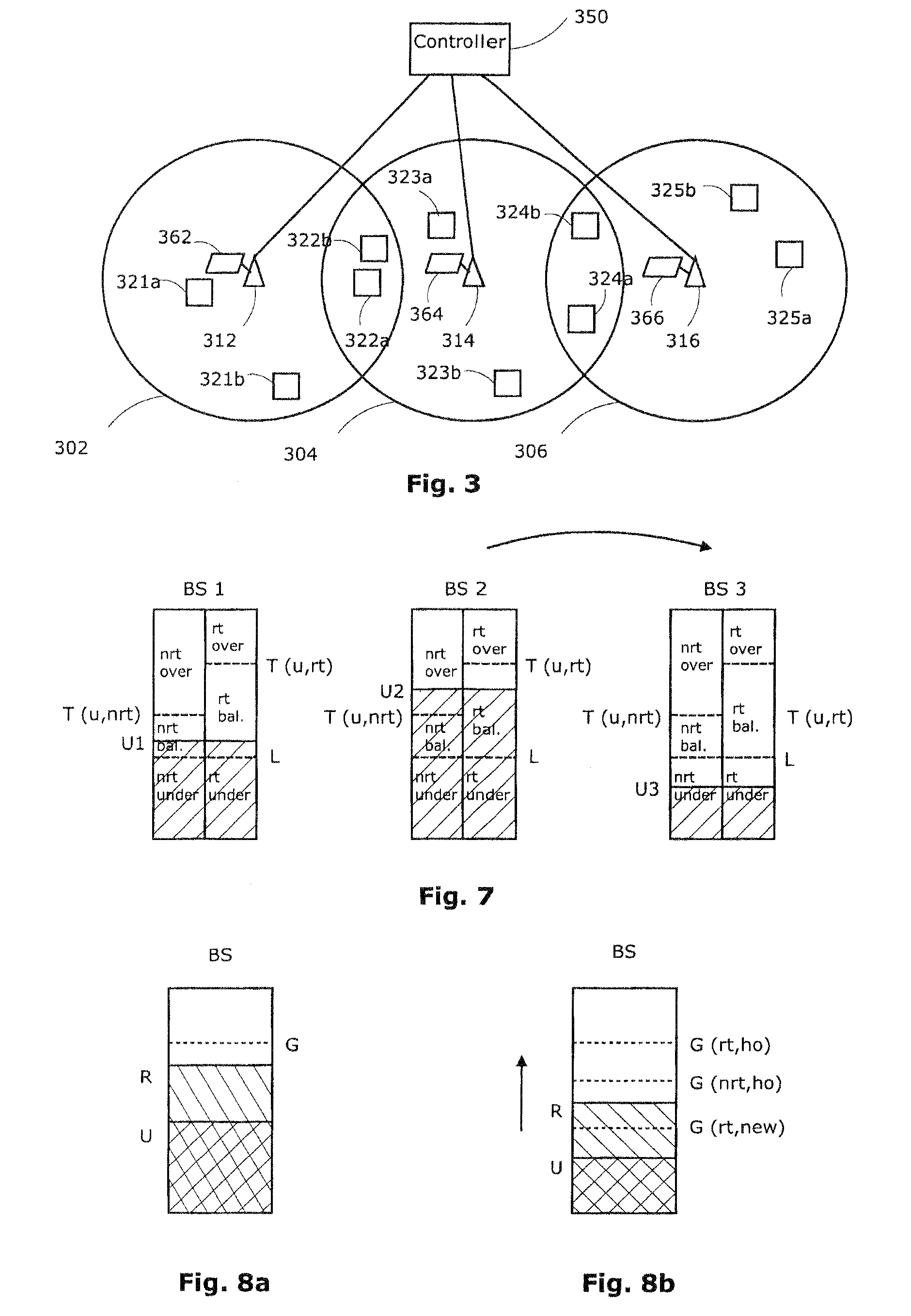
In next generation wireless networks such as a Mobile WiMAX traffic prioritization is used to provide differentiated quality of service (QoS). Unnecessary ping-pong handovers that result from premature reaction to fluctuating radio resources pose a great threat to the QoS of delay sensitive connections such as VoIP which are sensitive to scanning and require heavy handover mechanisms. Traffic-class-specific variables are defined to tolerate unbalance in the radio system in order to avoid making the system slow to react to traffic variations and decreasing system wide resource utilization. By setting thresholds to trigger load balancing gradually in fluctuating environment the delay sensitive connections avoid unnecessary handovers and the delay tolerant connections have a chance to react to the load increase and get higher bandwidth from a less congested BS. A framework for the resolution of static user terminals in the overlapping area within adjacent cells will be described.
Owner:ELEKTROBIT WIRELESS COMM LTD
System and method for guaranteeing quality of service in IP networks
InactiveUS20050135243A1Guaranteed reliabilityReduce loadError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDifferentiated servicesData pack
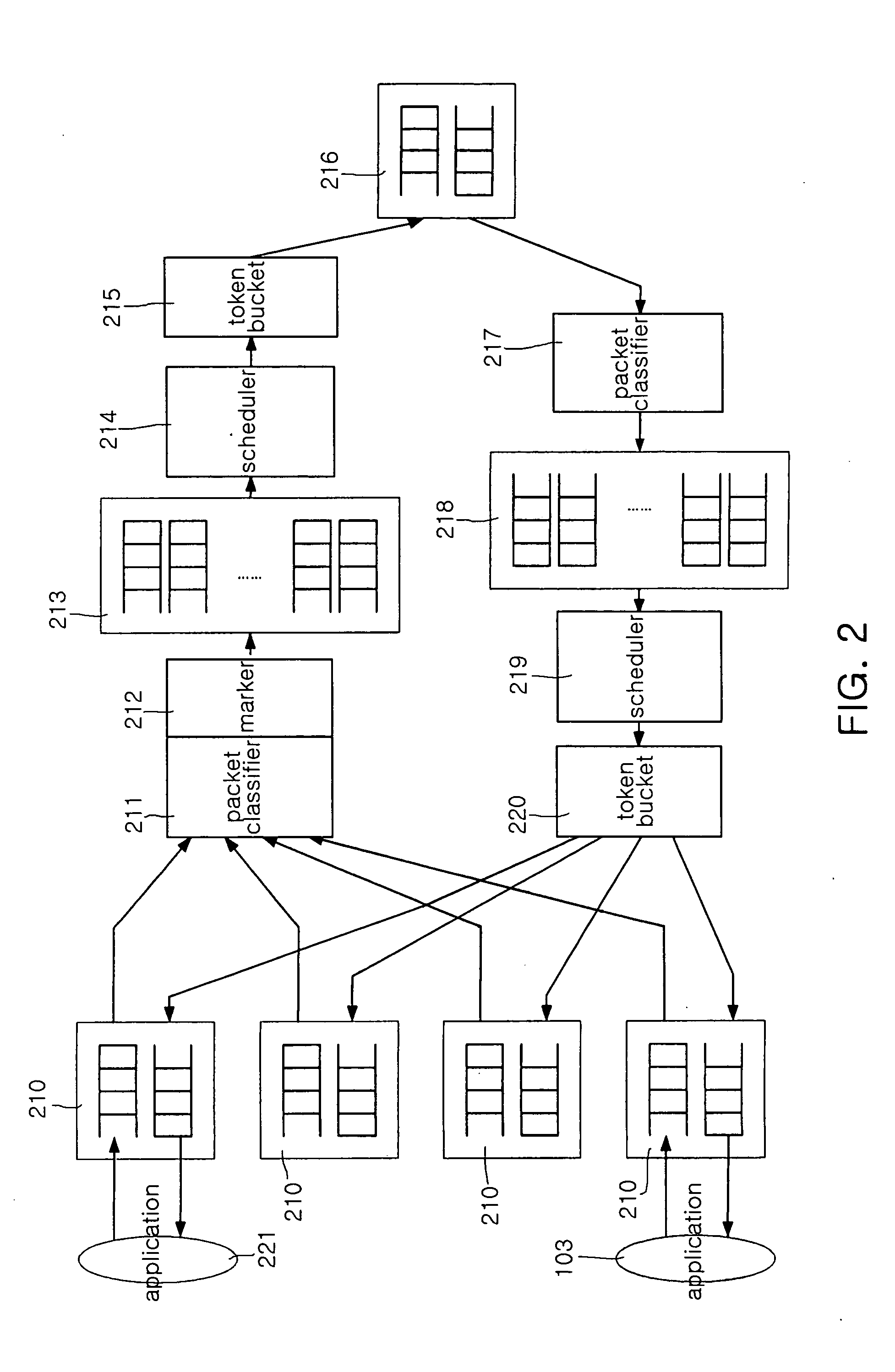
The system of the present invention guarantees quality of service with respect to packets transmitted / received between an external network capable of providing differentiated services and a home network. The system includes a packet classifier, a marker, a priority class queue, a scheduler and a token bucket. The packet classifier classifies the packets according to addresses and traffic types. The marker allocates information on priorities to packets transmitted from the home network to the external network. The priority class queue has a plurality of queues classified according to the priorities. The scheduler services packets stored in the priority class queue according to the priorities. The token bucket drops packets, bandwidths of which are above a preset maximum bandwidth, when the packets are generated.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
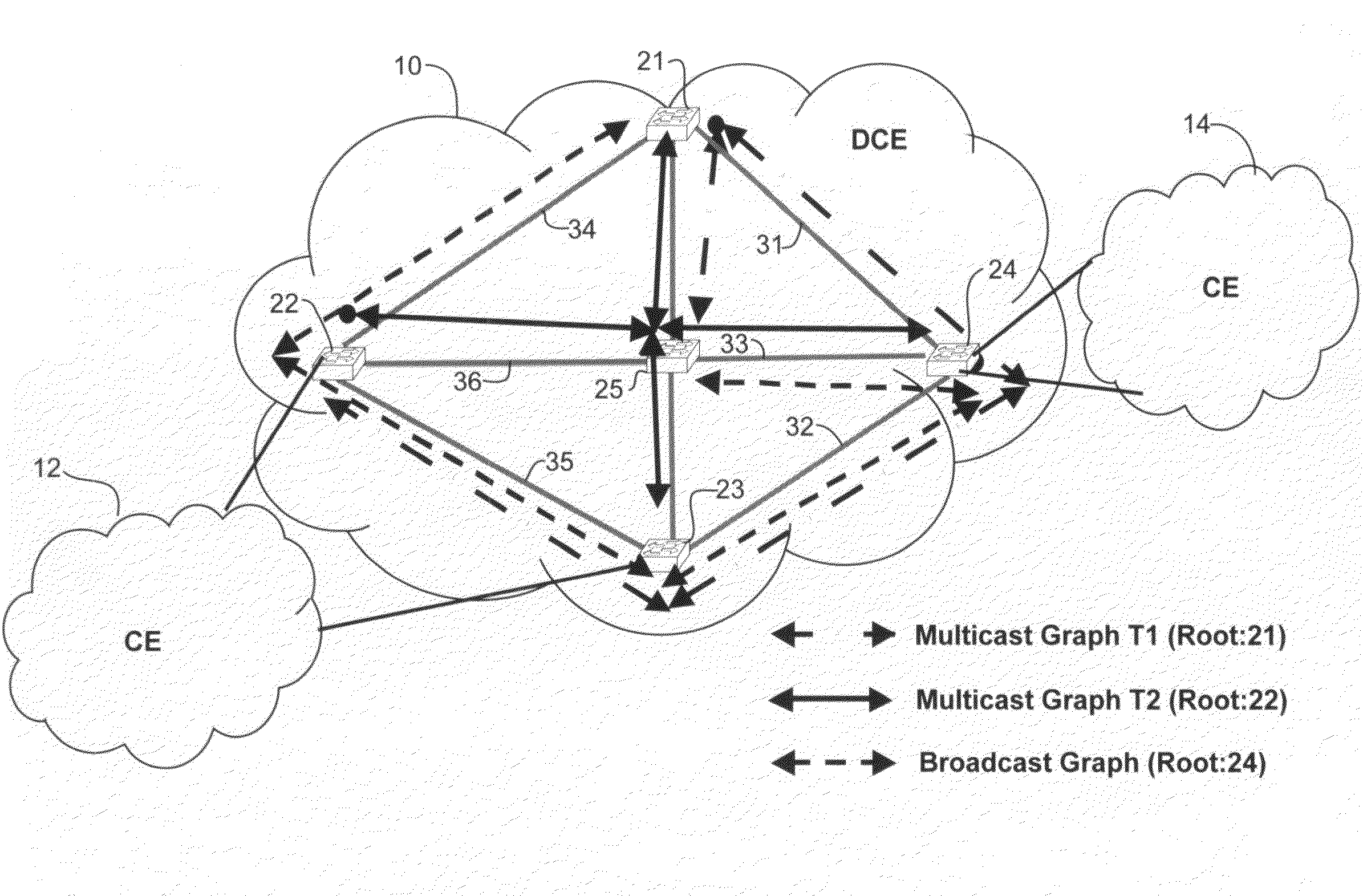
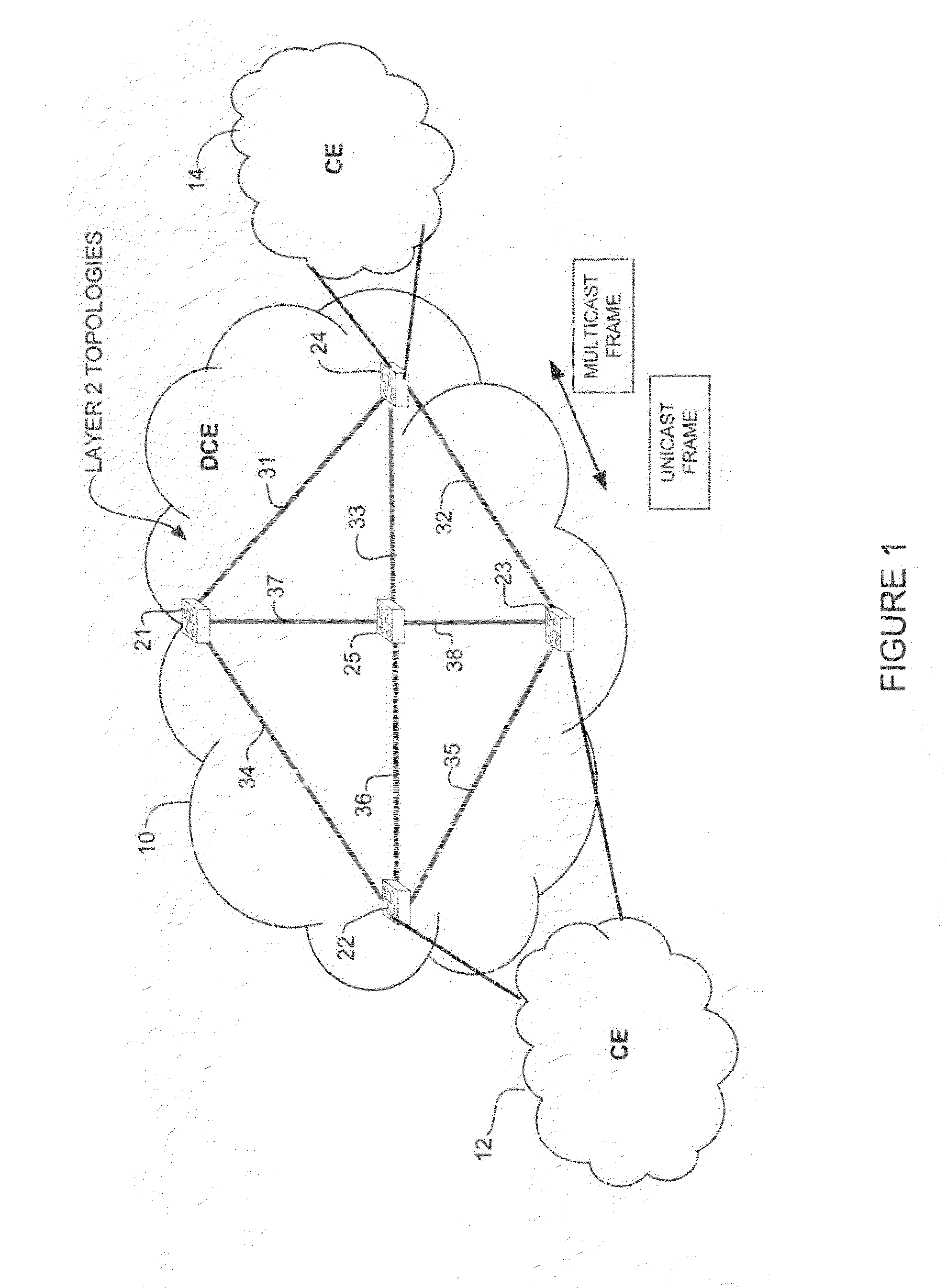
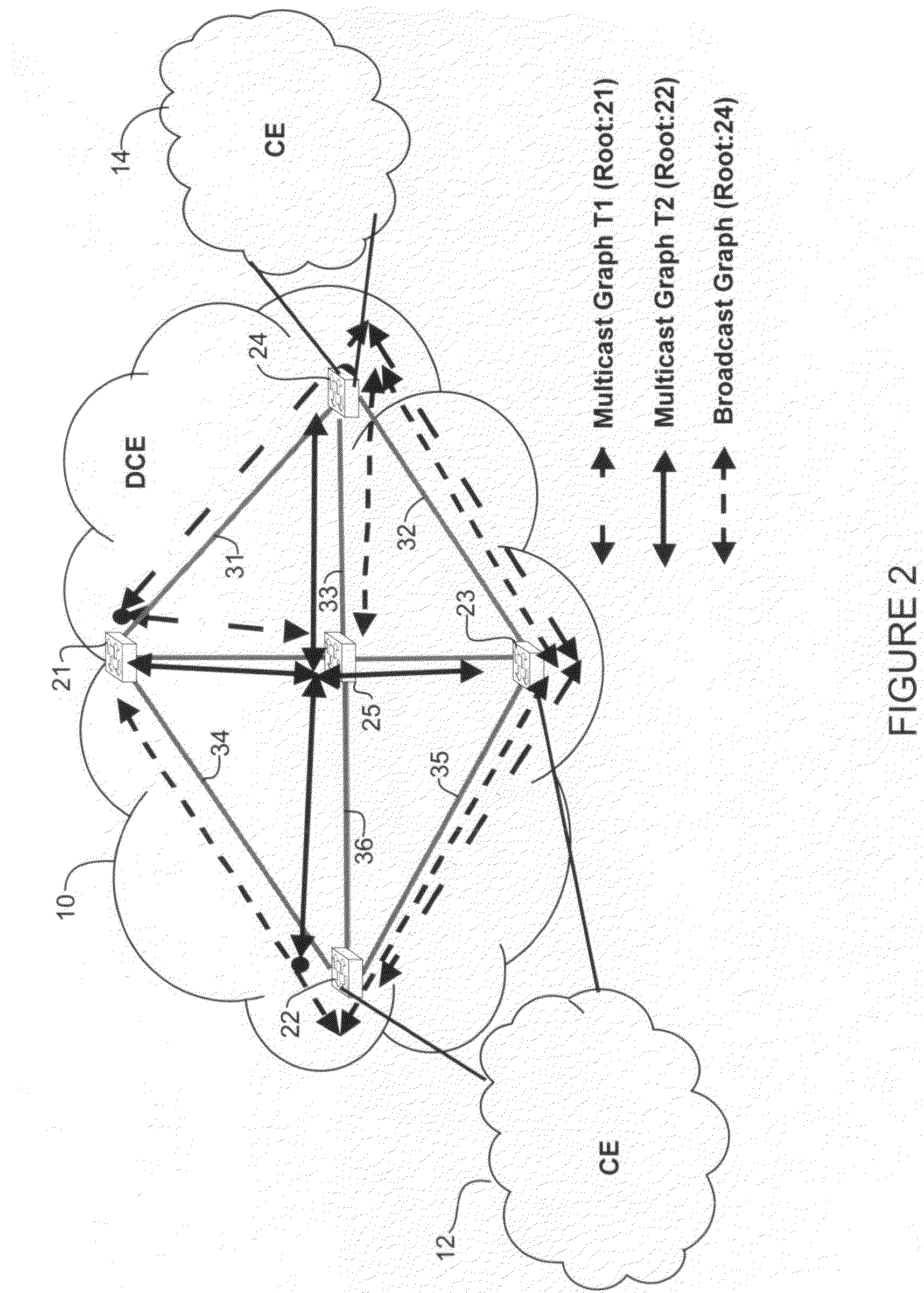
Differentiated services for unicast and multicast frames in layer 2 topologies
In one embodiment, a method includes receiving information on layer 2 topologies at a network device in a core network, mapping one or more Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) to the layer 2 topologies to provide differentiated services in said layer 2 topologies, defining multiple paths for each of the layer 2 topologies, and forwarding a packet received at the network device on one of the multiple paths. An apparatus for providing differentiated services in layer 2 topologies is also disclosed.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
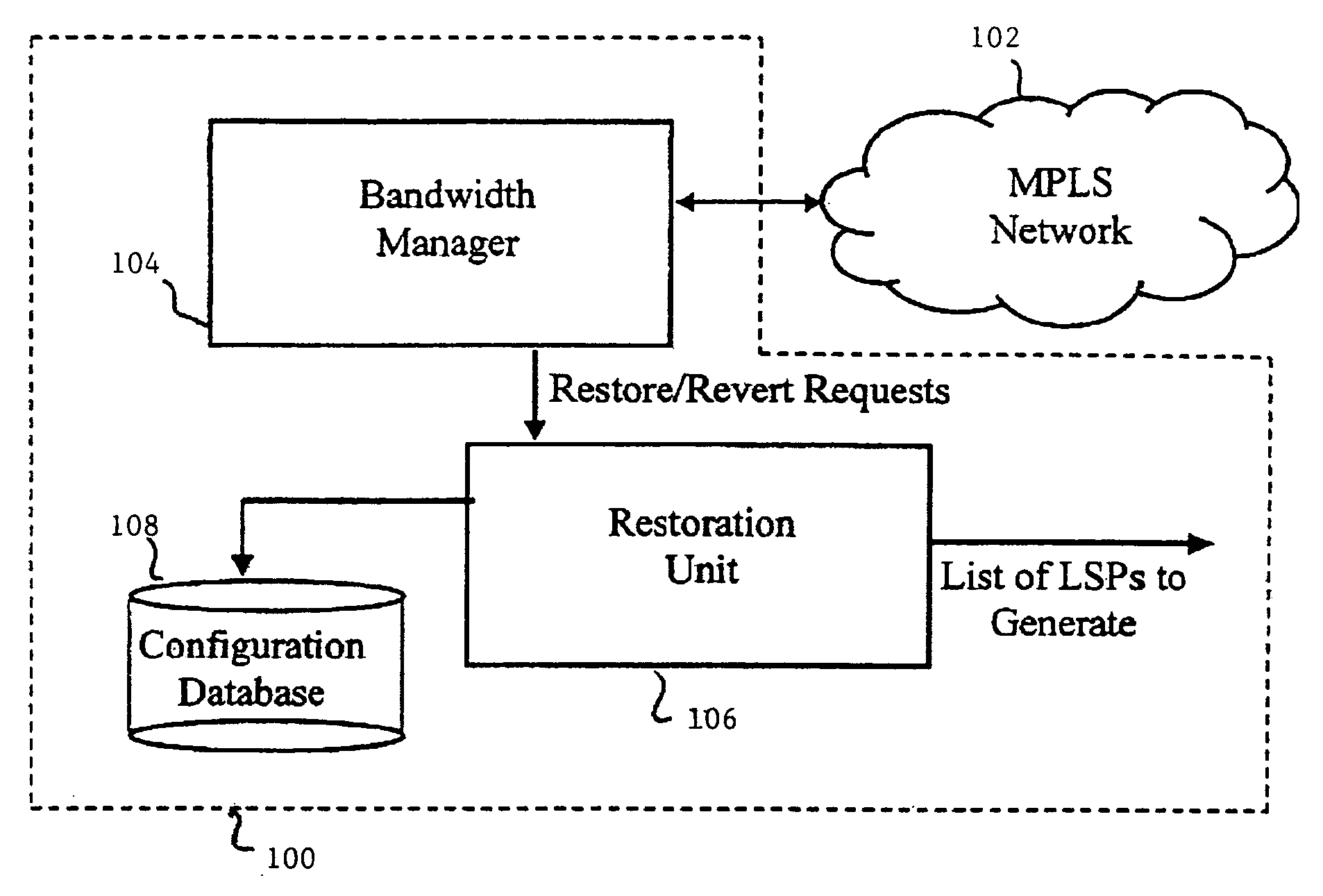
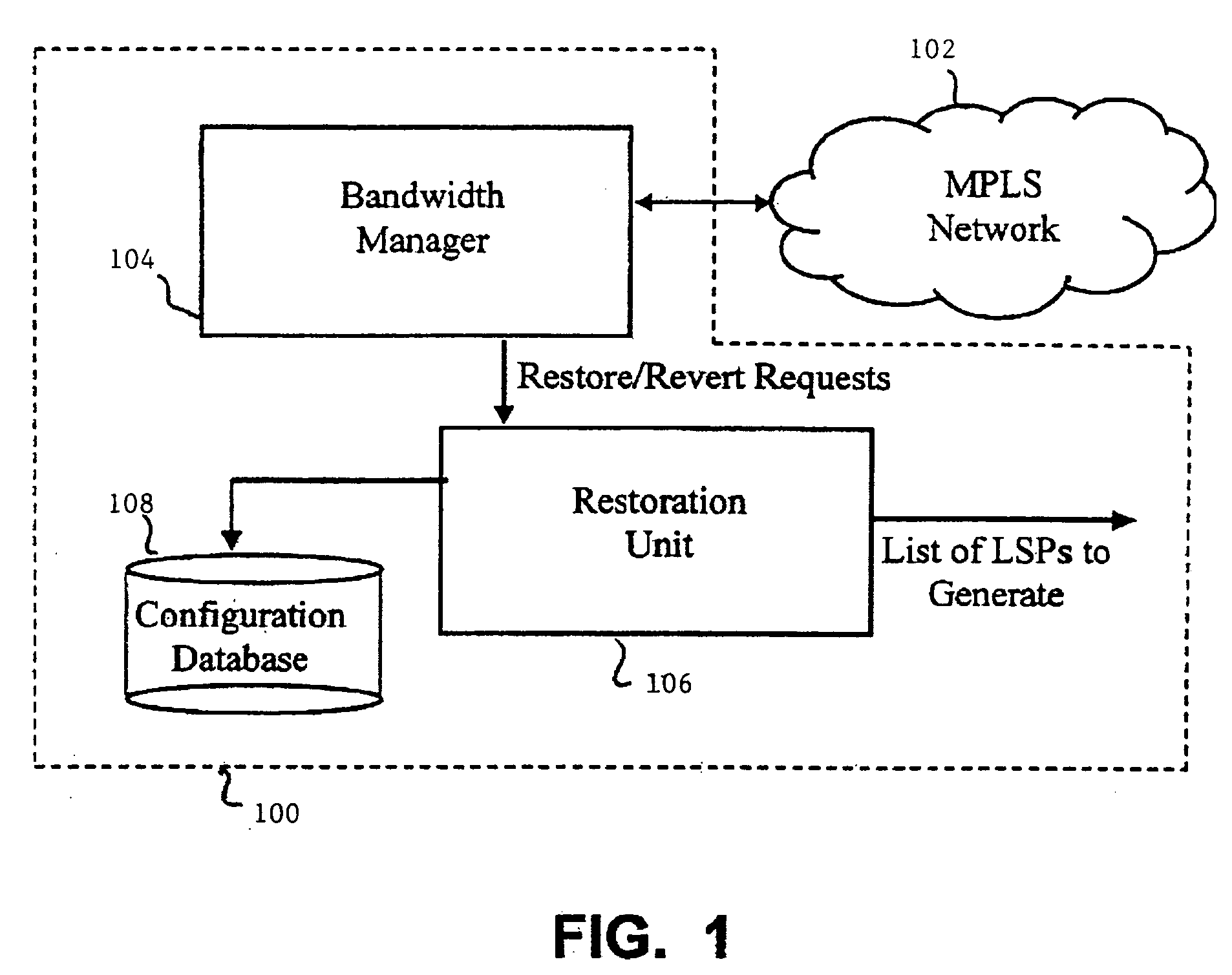
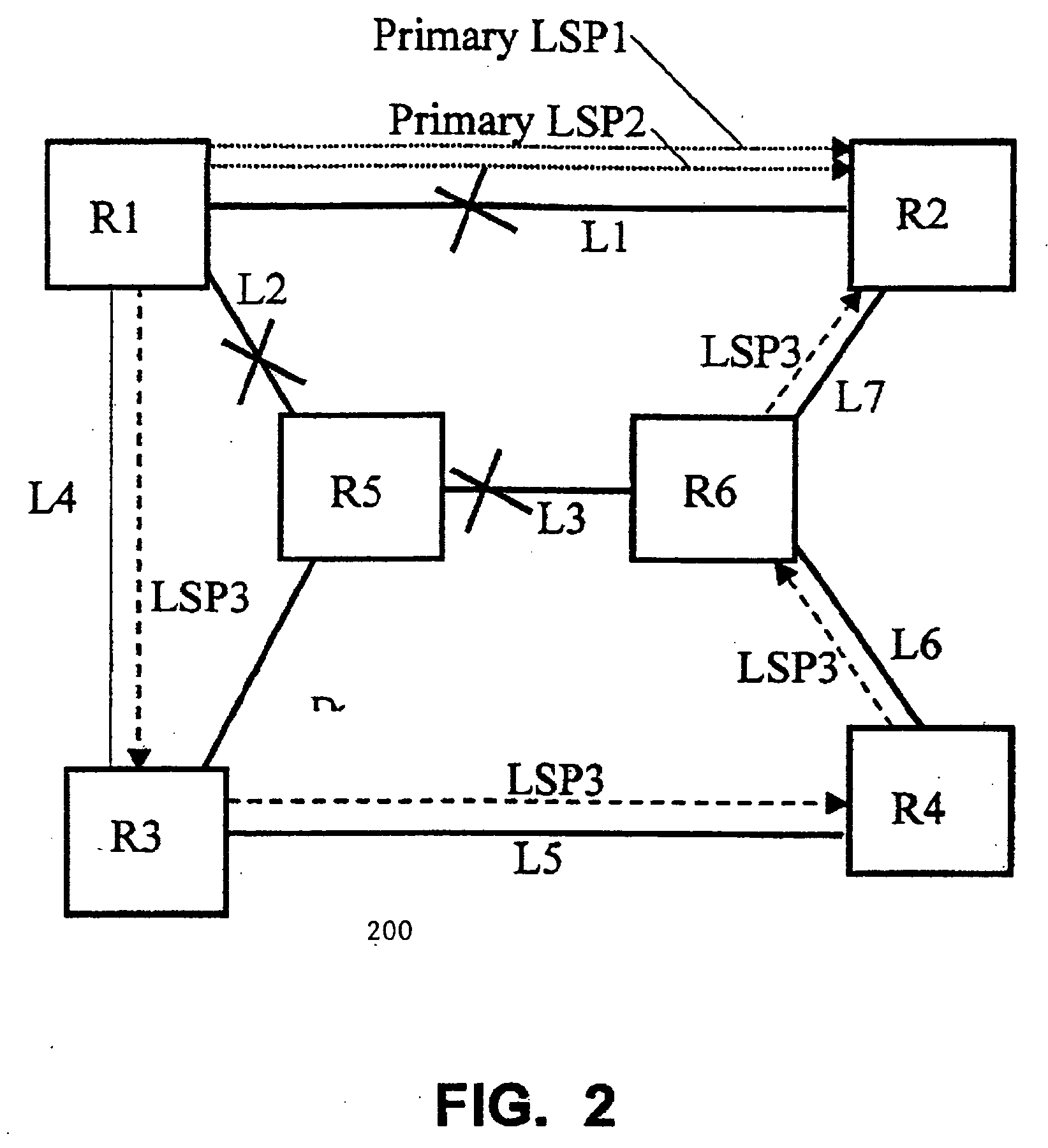
Dynamic traffic rearrangement and restoration for MPLS networks with differentiated services capabilities
InactiveUS20050259586A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDifferentiated servicesDifferentiated service
At least one substitute path is provided in place of a plurality of existing paths of a network to reallocate traffic carried by the plurality of existing paths. The total bandwidth needed to carry the traffic of the plurality of existing paths is determined. A proposed route is generated from the available links in the network. A portion of the bandwidth of a proposed route may be allocated to the needed bandwidth when the bandwidth of a proposed route is greater than or equal to the needed bandwidth. When the bandwidth of the proposed route is less than the needed bandwidth, at least one further route is generated, and the needed bandwidth is divided among the proposed route and the at least one further route such that a minimum number of further routes are generated.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
System and method for providing differentiated service levels to wireless devices in a wireless network
ActiveUS7720464B2Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsDifferentiated servicesTelecommunications
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
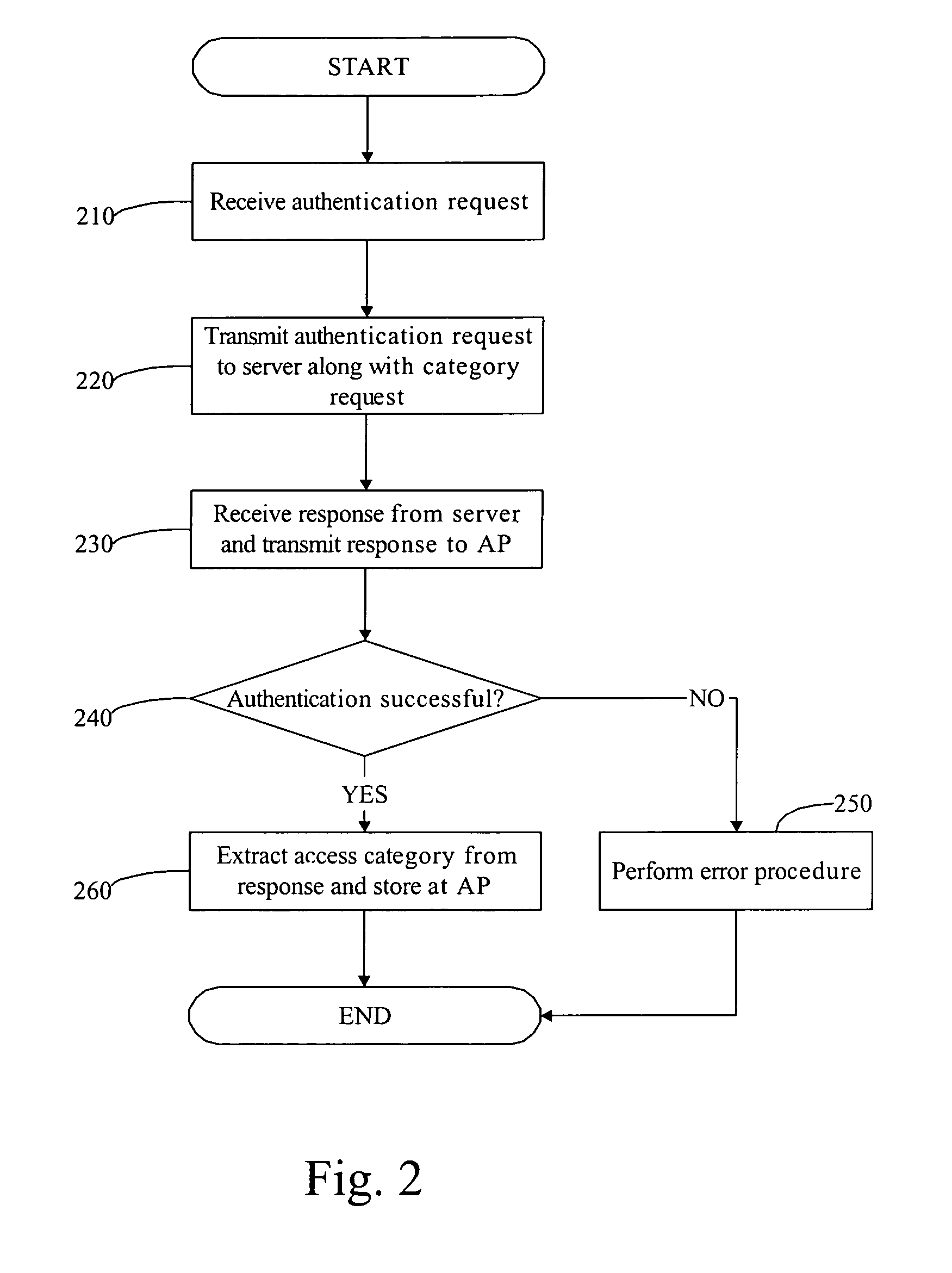
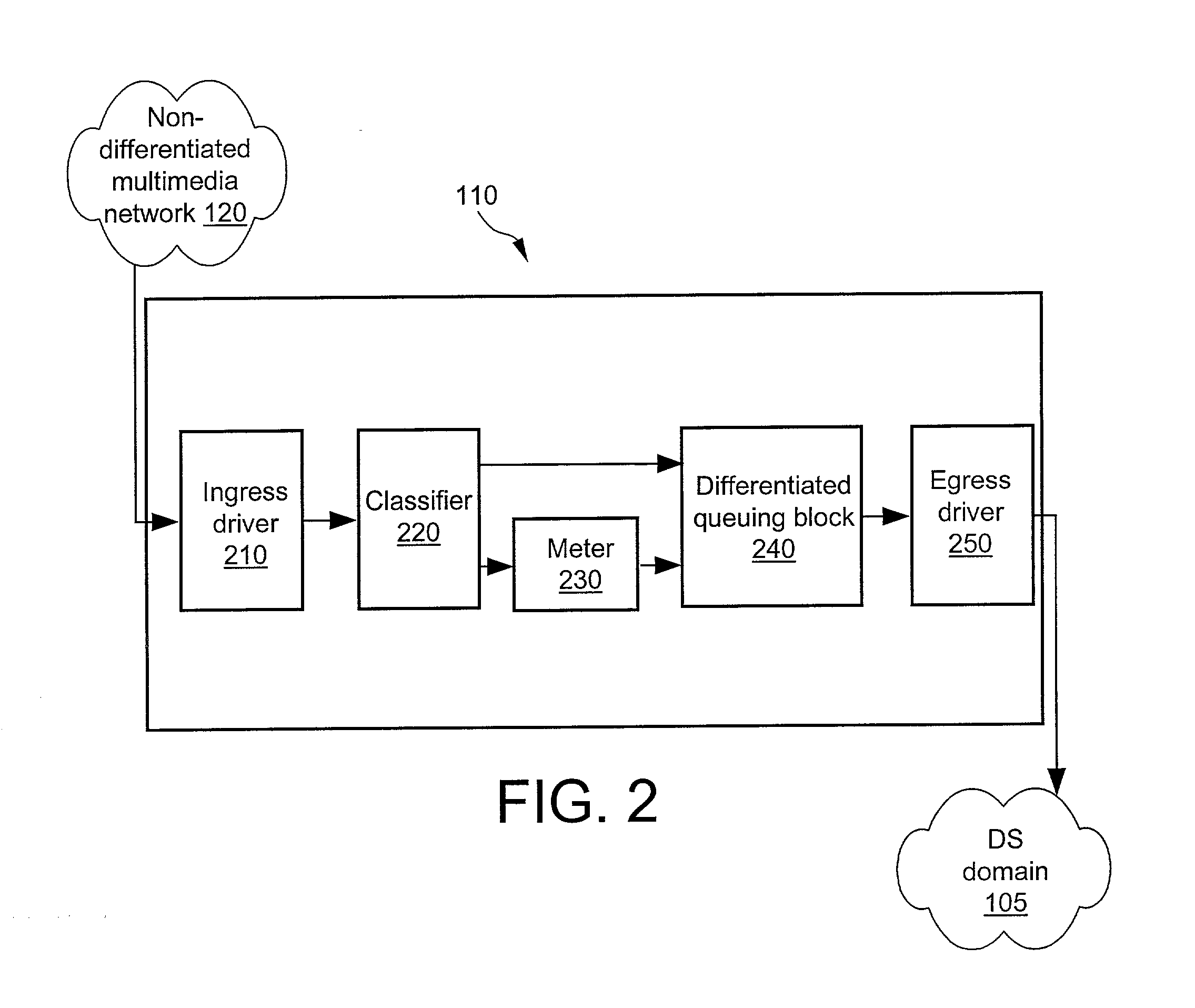
System for and method of differentiated queuing in a routing system
ActiveUS7020143B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDifferentiated servicesTraffic capacity
The invention relates to a method for routing Internet traffic. The method generally includes the steps of receiving a packet from multimedia network, allocating a message block header for the packet, wherein the header is used to hold behavior aggregate values for internal router mapping, and queuing and routing the packet to a differentiated services network domain in a manner that ensures a specific QoS.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
Marking network data packets with differentiated services codepoints based on network load
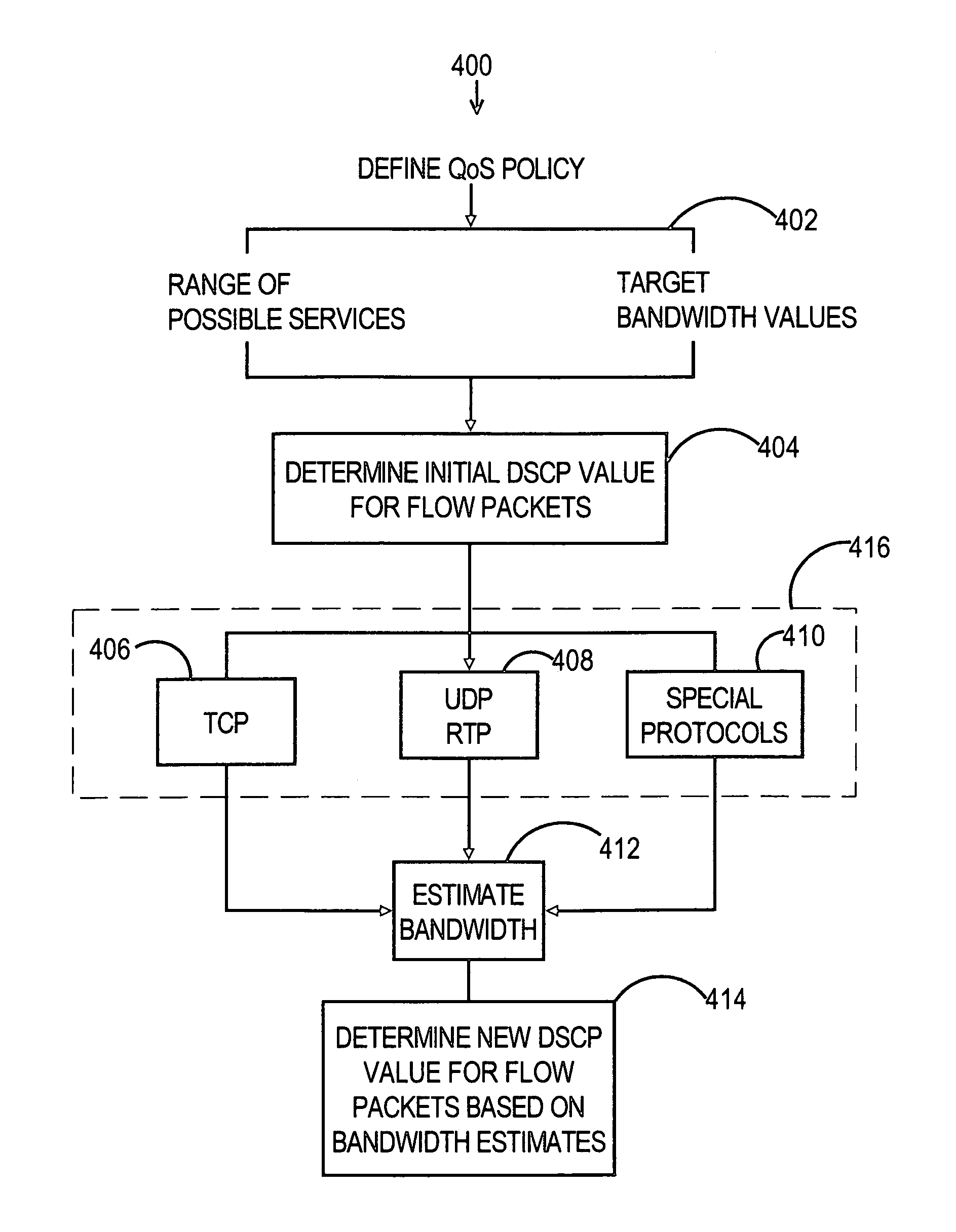
A method and apparatus for performing load-based packet marking within a network is described. In one aspect, a first group of one or more packets of a data flow are marked with a first behavioral treatment value that directs devices within the network to treat the first group of one or more packets with a first quality of service treatment. The bandwidth that is currently being achieved for the flow within the network is determined based on data traffic within the network. Based on the achieved flow bandwidth within the network a second behavioral treatment value is then determined. Thereafter, a second group of one or more packets of the data flow is marked with a second behavioral treatment value that directs devices within the network to treat the second group of one or more packets with a second quality of service treatment. The process of dynamically marking the packets for a particular data flow may be performed multiple times.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Internet differentiated services service for transaction applications
InactiveUS6483805B1Avoid abuseError preventionTransmission systemsDifferentiated servicesTelecommunications network
A method of monitoring telecommunications network traffic comprising the steps of: receiving a packet stream comprising packets each identified as belonging to one of at least three classes; calculating a difference between the numbers of packets received identified as belonging to a first and a second of said classes; and deriving a measure of traffic load on the network responsive to said difference. The invention also relates to a method for admission control based on the above method of monitoring and a method for overcoming admission control avoidance. It also relates to apparatus embodying these methods.
Owner:AVAYA INC
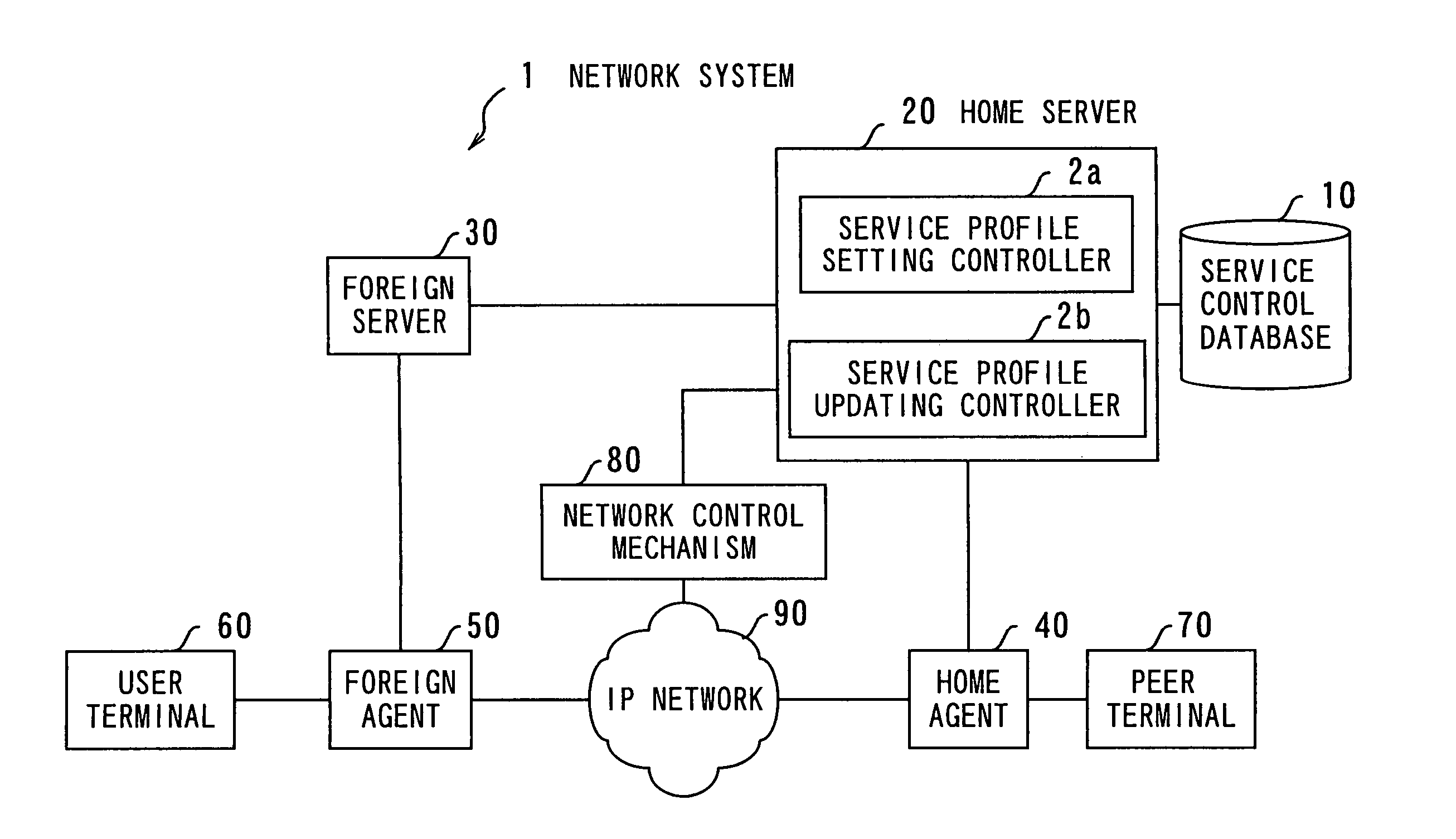
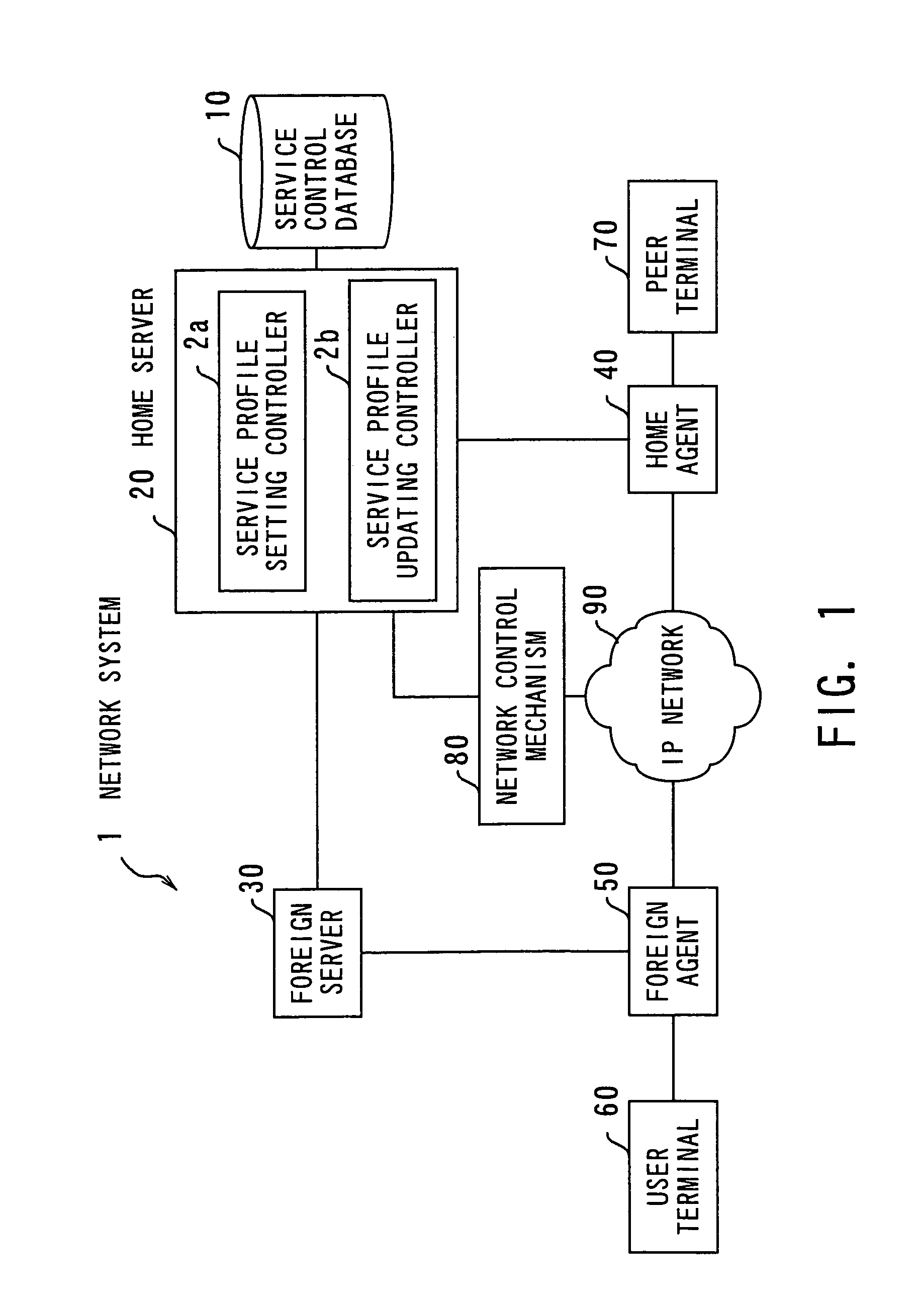
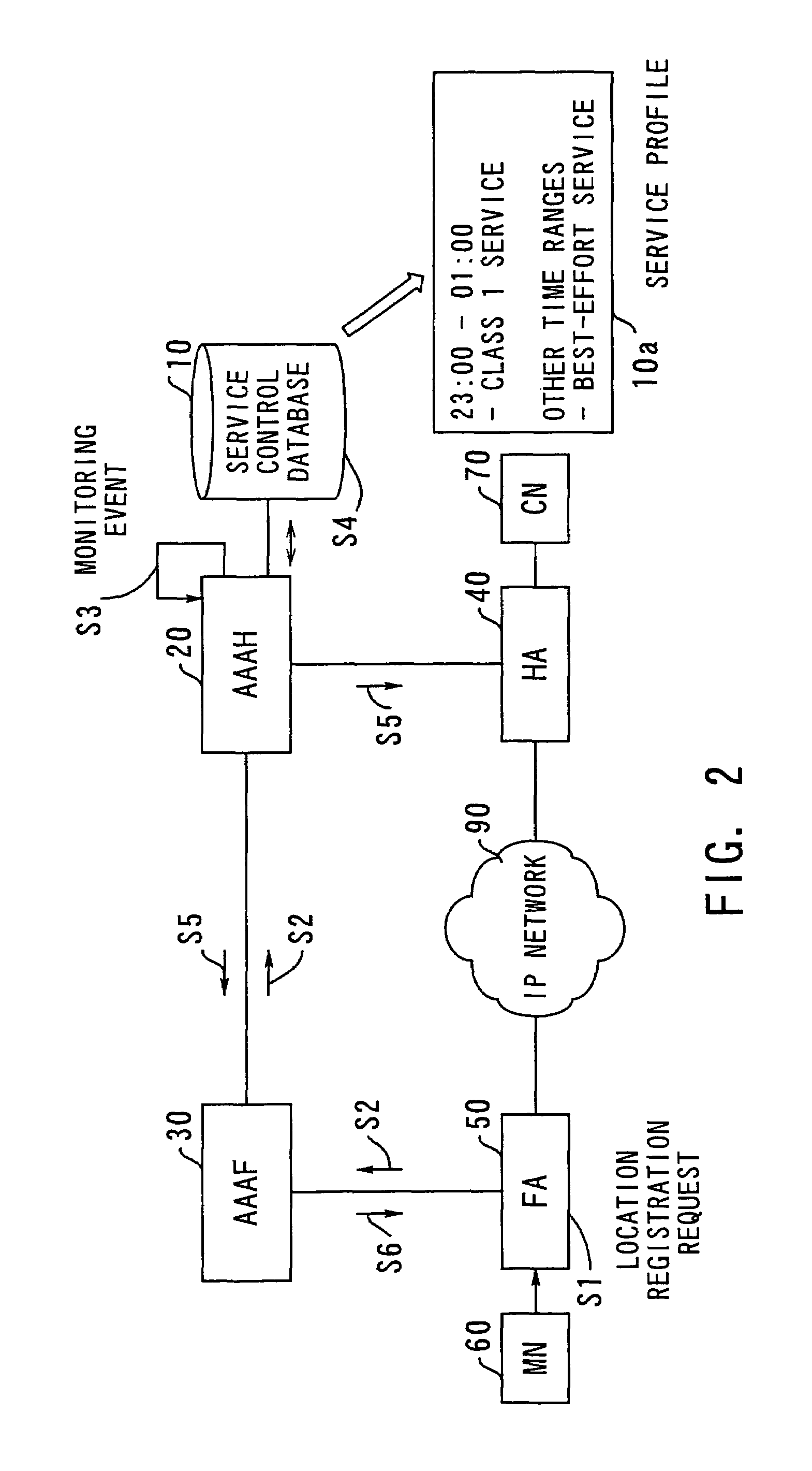
Network system with dynamic service profile updating functions
InactiveUS7277948B2Increase valueConnection managementMultiple digital computer combinationsDifferentiated servicesService profile
A network system which provides each terminal user with differentiated service, dynamically changing service profiles even in the middle of a communication session. A service control database maintains service profile definitions. When a mobile node registers with a foreign agent to initiate a conmiunication session, a service profile setting controller in the mobile node's home server sets up a service profile for the mobile user. When an event occurs within a service profile updating controller, it indicates that some control condition specified in the service profile is met. The service profile updating controller then makes access to the service control database to obtain a new service profile and the mobile node's foreign server forwards it to the foreign agent, to which the mobile node is attached. The service profile that has been established in relevant network nodes, including the home agent and foreign agent, is dynamically updated with the new one.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
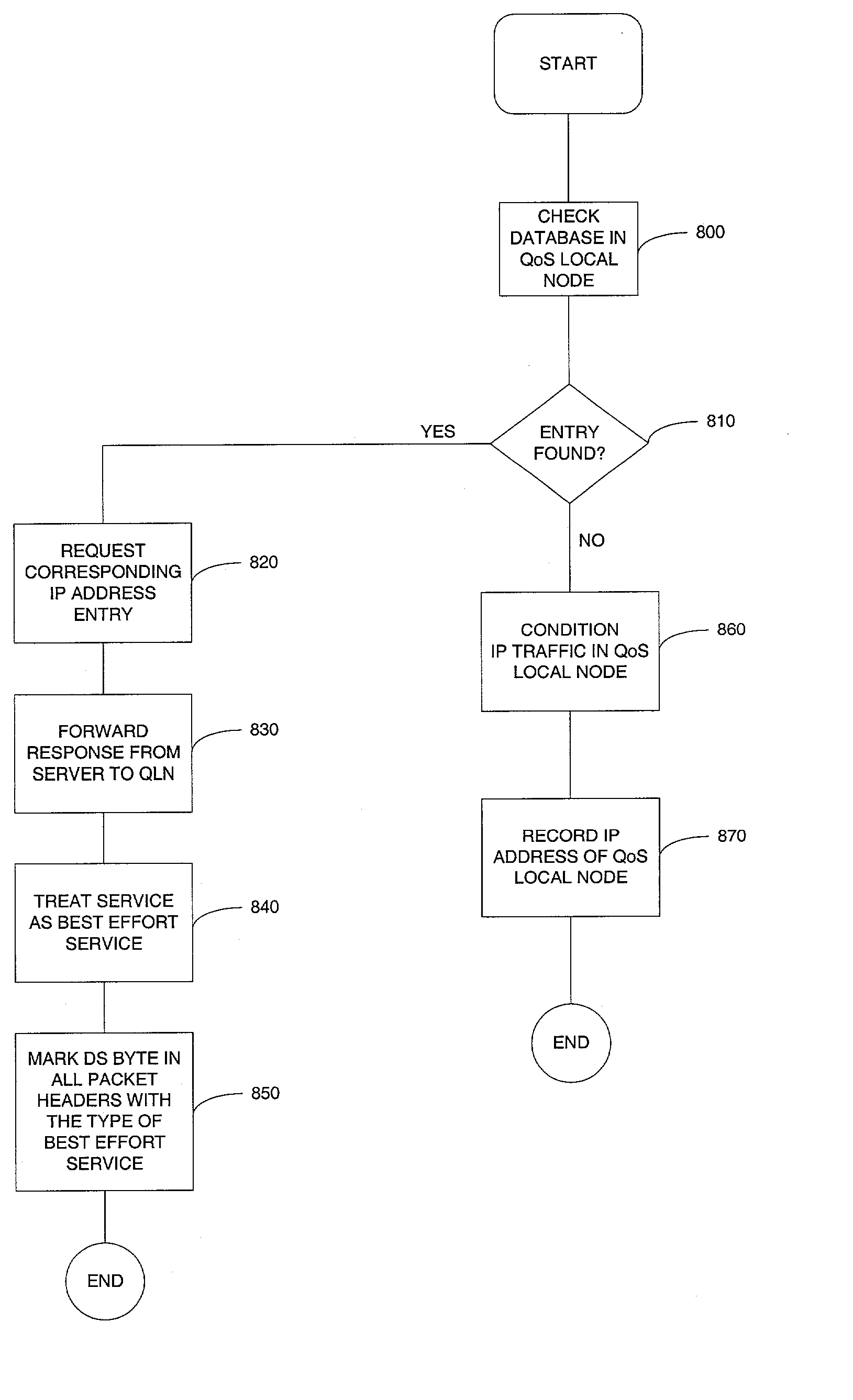
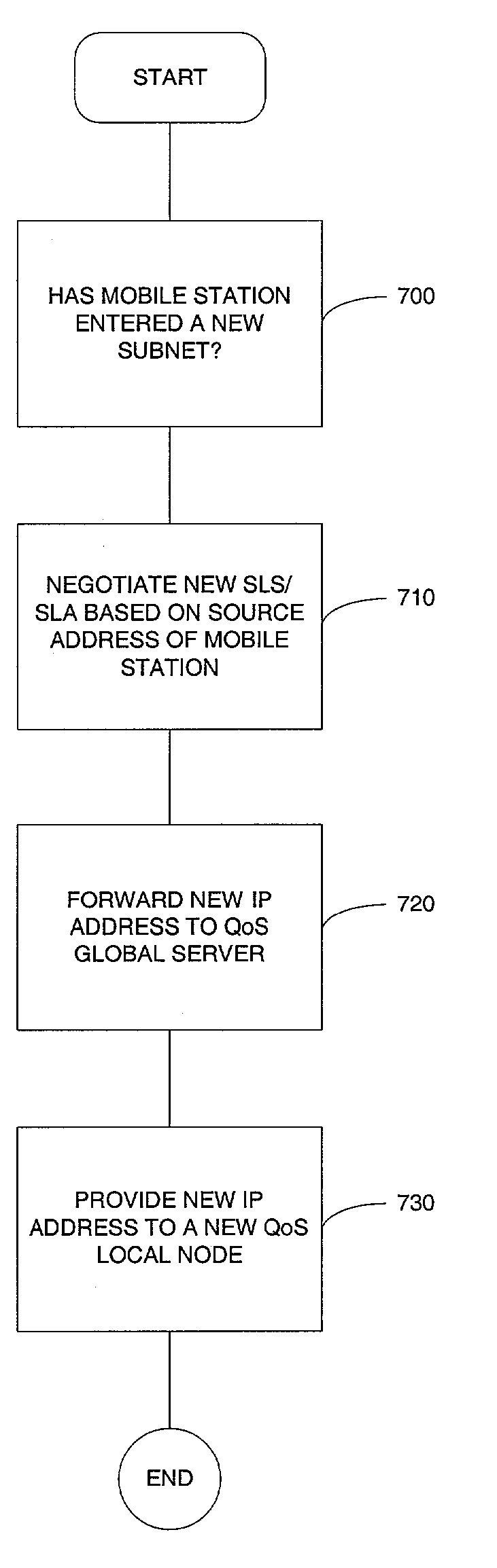
Method for distributing and conditioning traffic for mobile networks based on differentiated services
ActiveUS20030142681A1Data switching by path configurationWireless network protocolsDifferentiated servicesService-level agreement
A method for distributing and conditioning IP traffic for mobile networks based on differentiated services, wherein edge / border routers are only required to maintain QoS profiles for related mobile stations. A new IP address or a new service level subscription or service level agreement of an mobile station is only sent to related edge / border routers. As a result, unnecessary IP traffic is significantly reduced. The routers in accordance with methods of the invention disregard the contents of an IP payload and therefore all of the IP addresses that a mobile station may posse. A mobile station is permitted to enter into a domain and obtain a desired quality of service (e.g., Gold or Standard service) without the need to maintain the service while moving through the domain.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
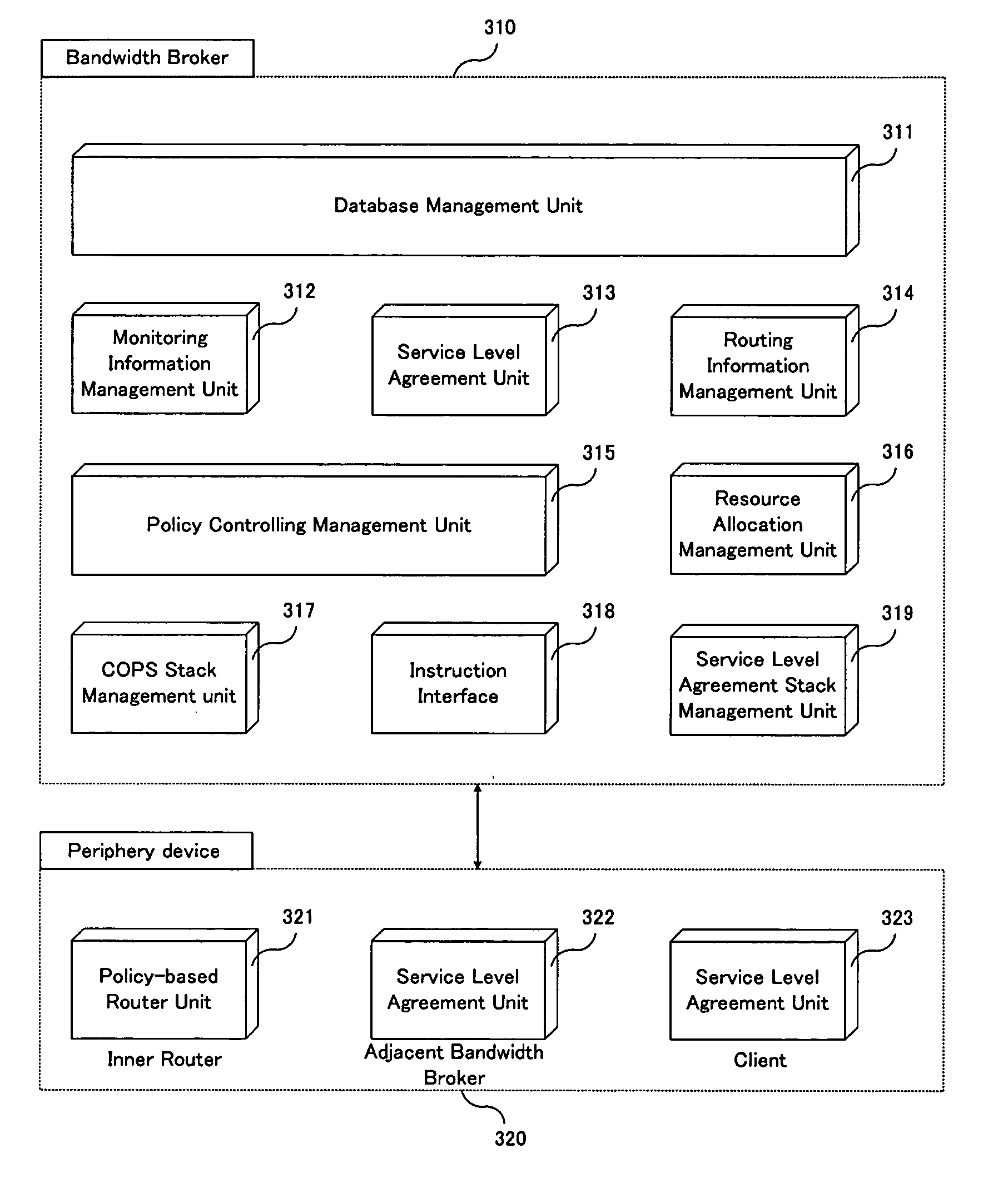
Resource allocation device for providing a differentiated service and a method thereof
InactiveUS20060171315A1Quick implementationEffective serviceError preventionTransmission systemsDifferentiated servicesService-level agreement
A resource allocation device includes a database of user and service information, a resource allocation management unit for determining whether a service request agrees with a service level agreement and whether it accepts a resource allocation request, a service level agreement unit for negotiating the service level agreement with the user, sending the received service request to the resource allocation management unit, acquiring the result of the resource allocation request, and transmitting the result of the resource allocation request to the user, a routing information management unit for obtaining a network configuring information, storing the network configuring information in the database, discovering the path to provide the service and storing the discovered path in the database to be reused and a policy control management unit for deciding a policy according to whether the service request and the resource allocation request are accepted.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method and apparatus for signaling VoIP call based on class of service in VoIP service system
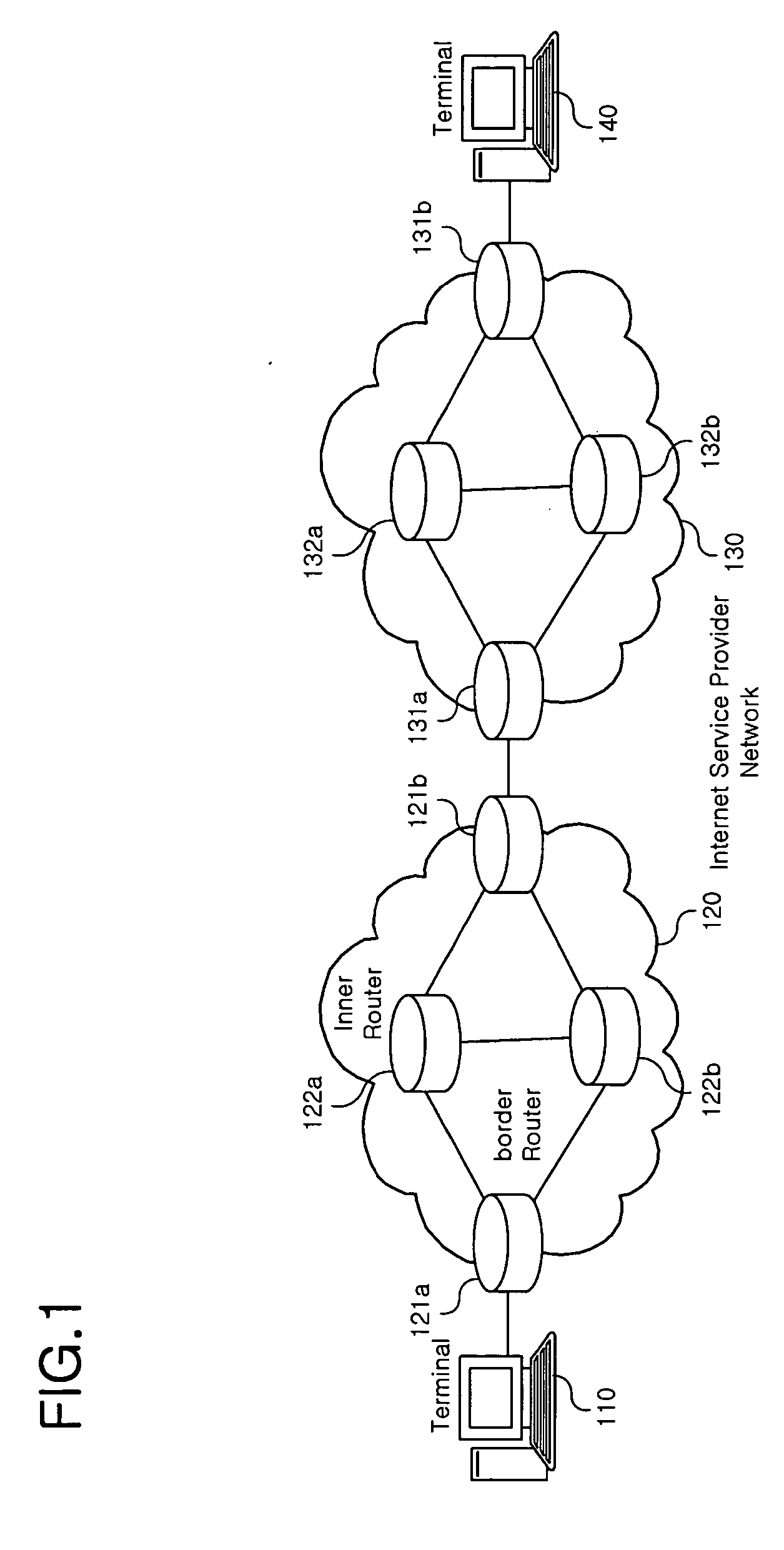
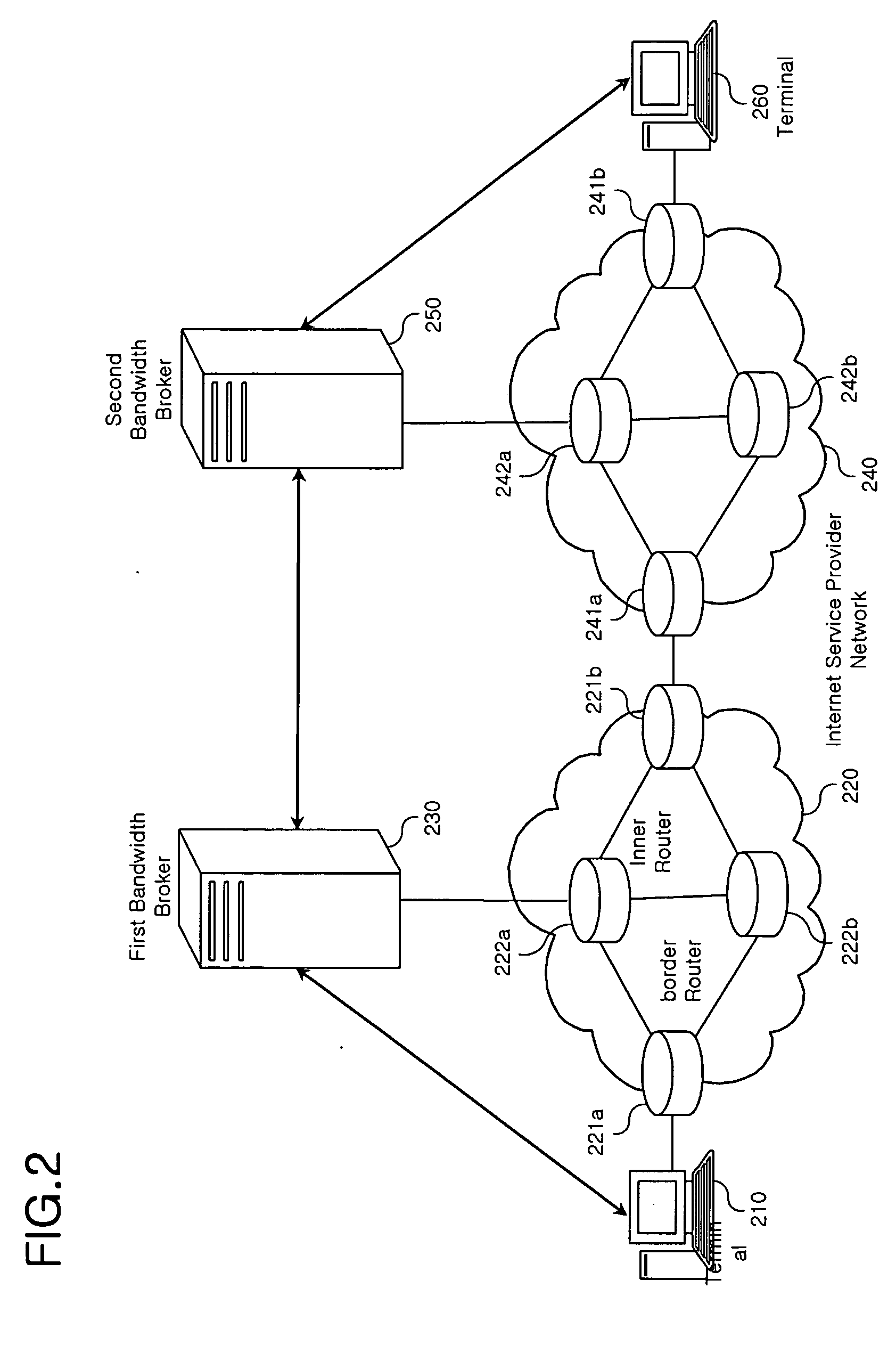
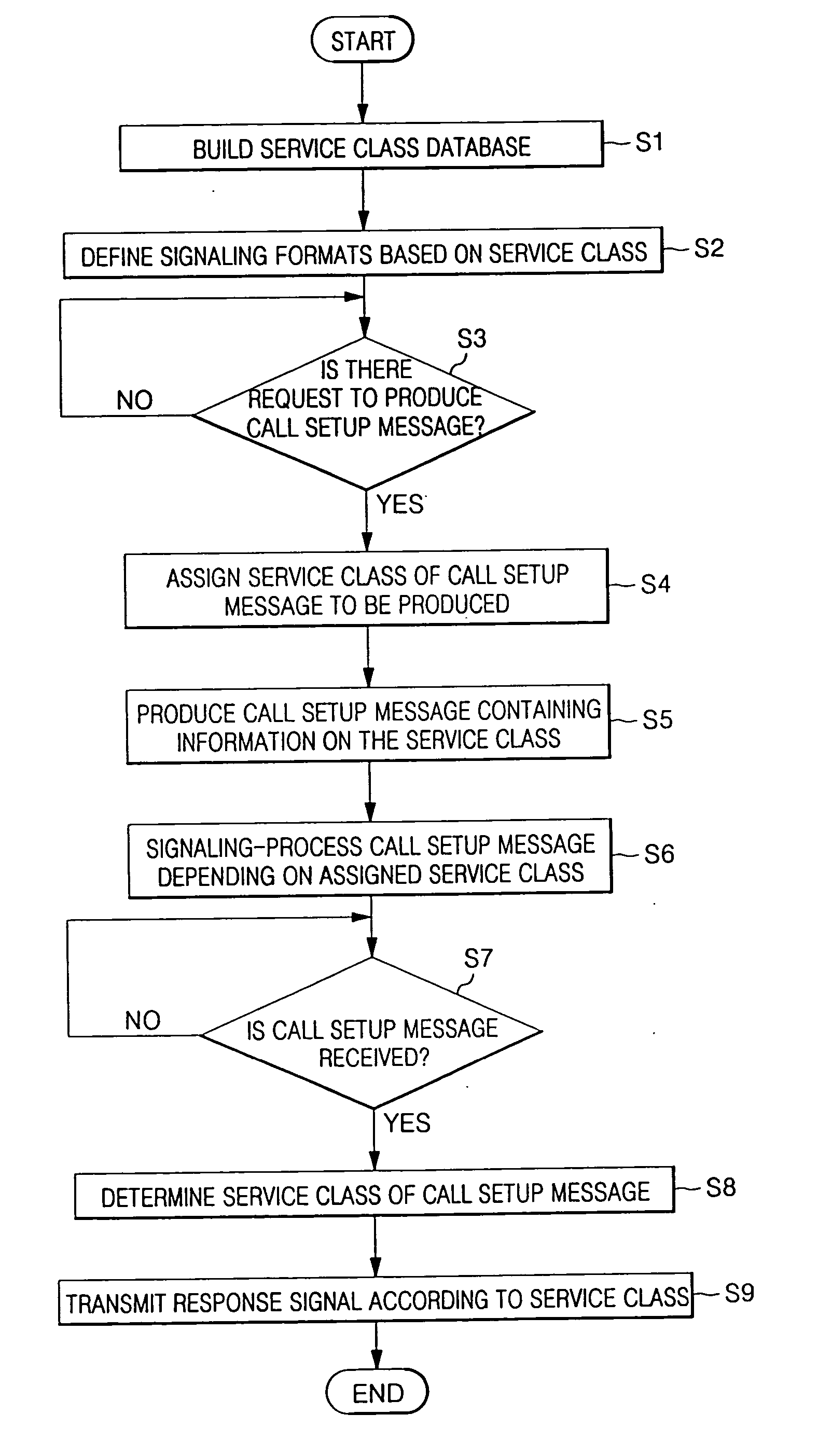
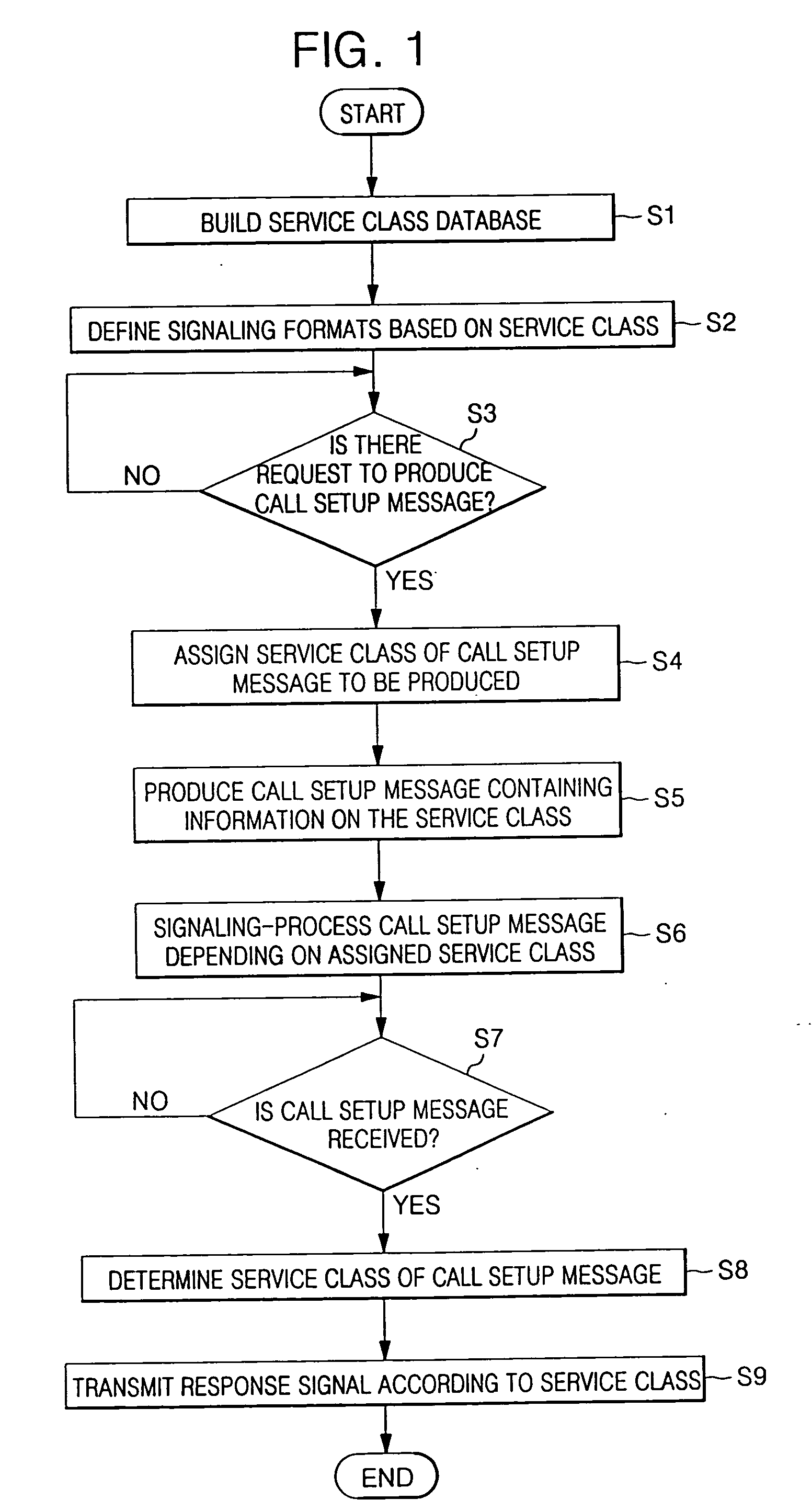
InactiveUS20060104264A1Improve efficiencyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDifferentiated servicesTelecommunications
In a method and apparatus for signaling a voice over Internet protocol (VoIP) call based on a class of service in a VoIP service system, a database which includes VoIP signaling information differentiated by the class of VoIP service is built, and the database is retrieved by a service class assignment condition to produce a call setup message. The call setup message includes information related to the service class. Accordingly, it is possible to perform dynamic VoIP signaling by setting a differentiated service class based on each user or a primary factor of each class of the VoIP service.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
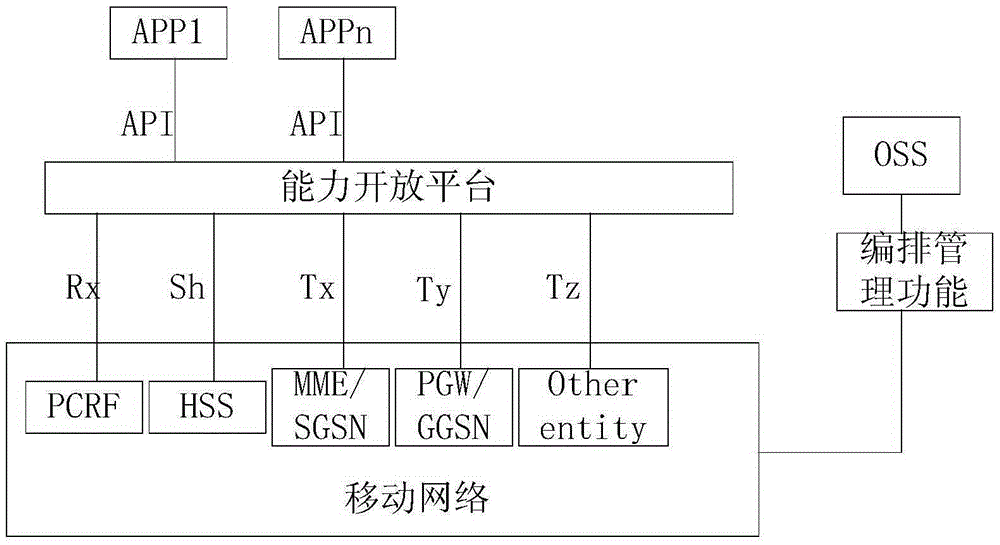
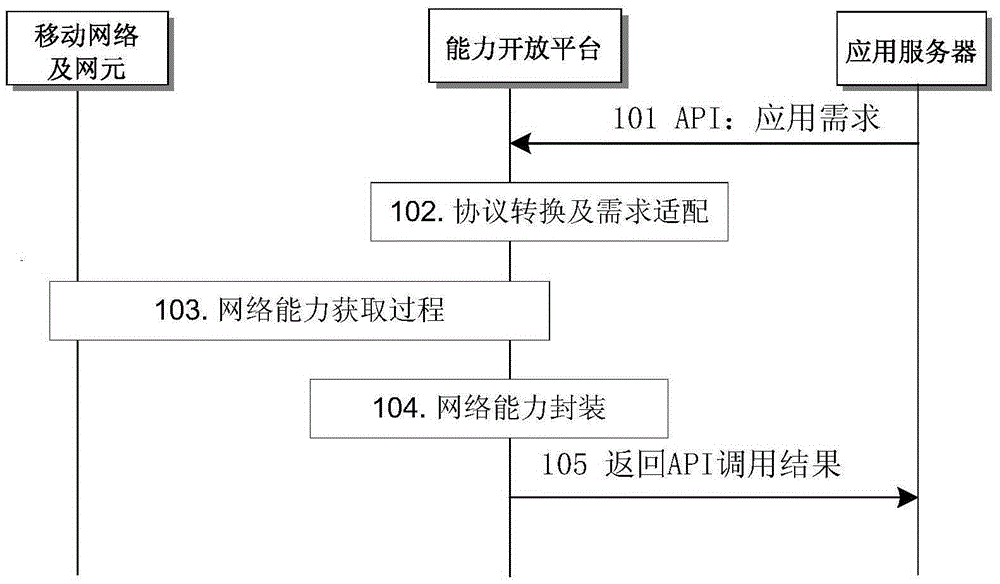
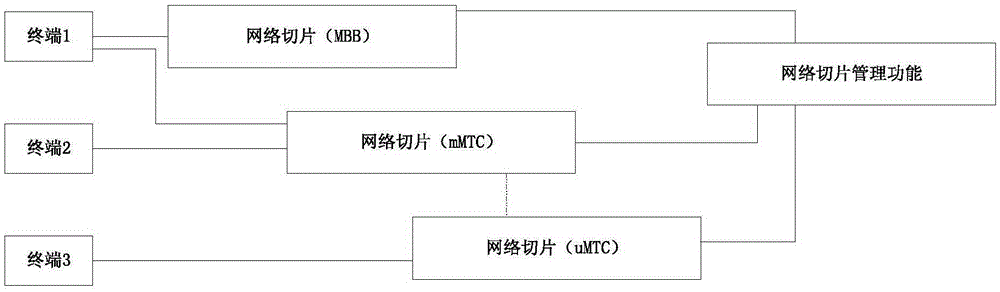
Network slice capability opening method, device and system
The application proposes a network slice capability opening method, device and system. The method includes the following steps: a network slice service request sent by a third-party service server is received; network slice information of a current network is obtained according to the network slice service request; and according to the network slice information of the current network and a service requirement of the network slice service request, a network slice service is provided to the third-party service server, a capability opening service of the network slice service of a future network can be provided, and the third party obtains related information of network slices through capability opening, and selects or requests creation of different network slices to provide differentiated services for third-party services.
Owner:ZTE CORP
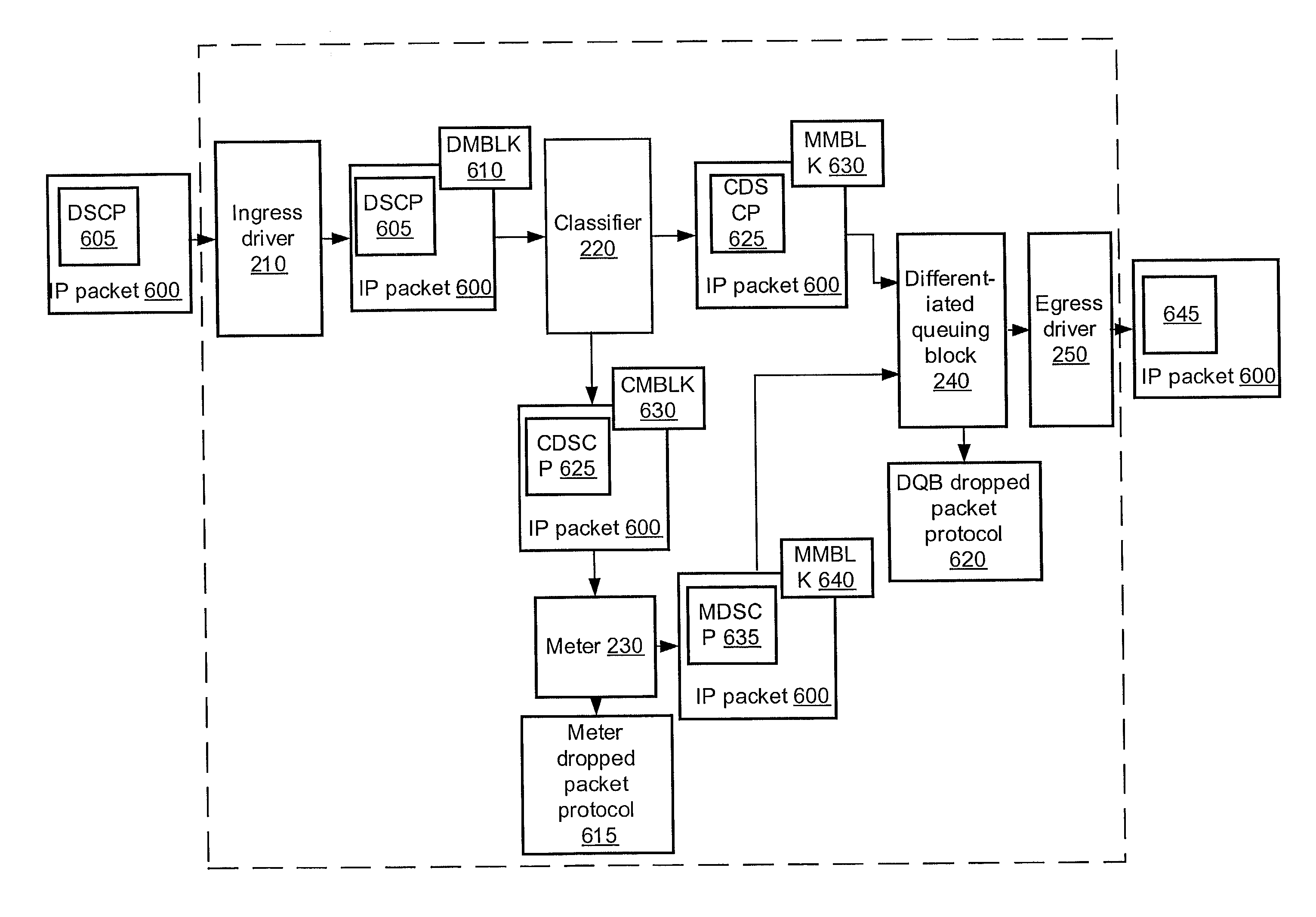
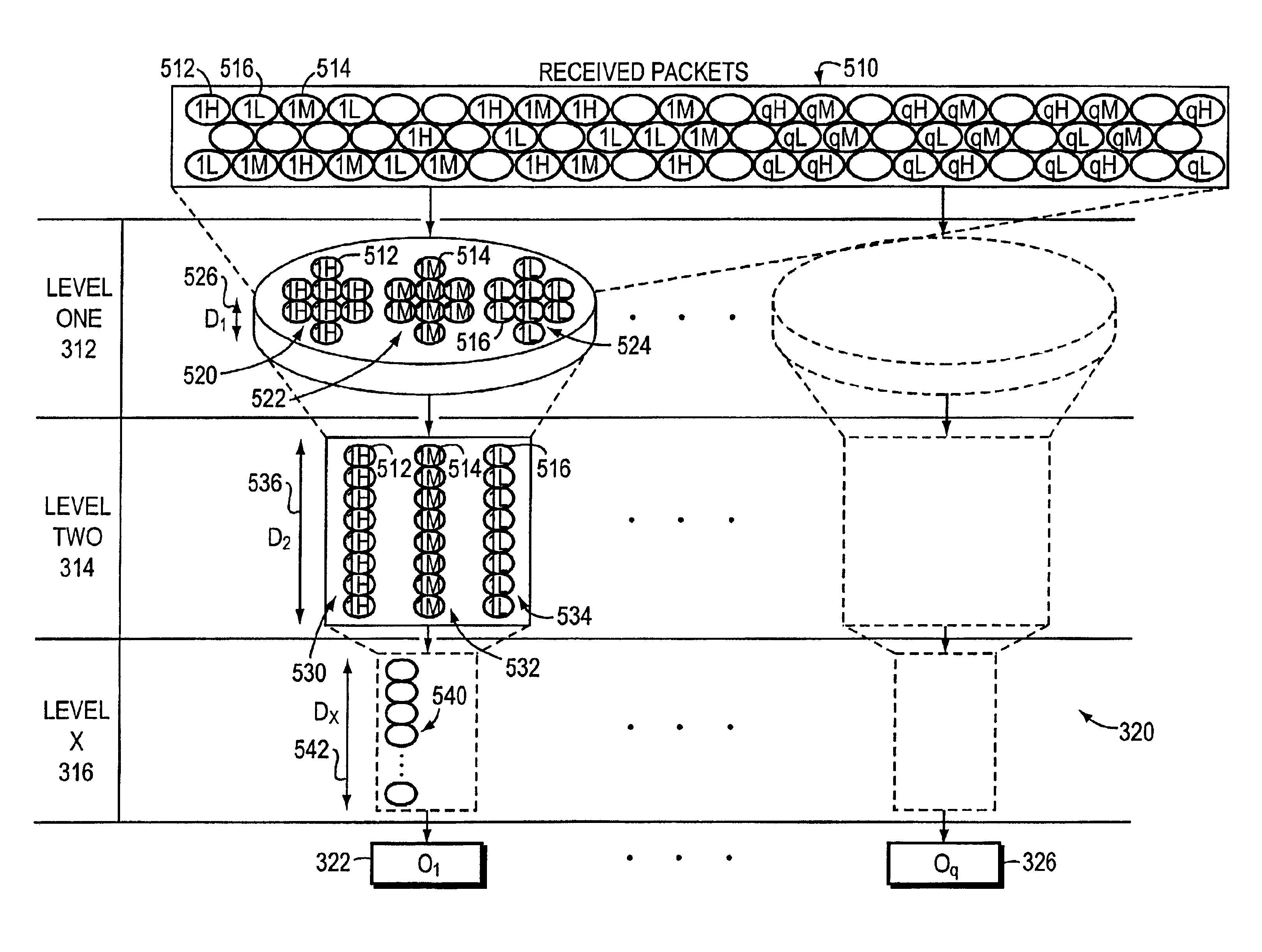
Hierarchical output-queued packet-buffering system and method
InactiveUS6850490B1High bandwidthIncrease speedError preventionTransmission systemsDifferentiated servicesCommunications system
The packet-buffering system and method of the present invention enables communication devices incorporating a full-mesh architecture to achieve bandwidth aggregation levels ordinarily associated with partial-mesh architectures. The packet-buffering invention uses a hierarchical memory structure having first and second packet-buffers to buffer packets between the input and output ports of the communication device. The received packets are organized by output port and priority level in the first packet buffer, which operates at the aggregate network rate of the communication device. The packets are then funneled to second packet buffers, having corresponding priority and output port assignments, at less than the aggregate network rate and which exhibit buffer depths that exceed that of the first packet buffer. The resulting hierarchical output-queued, packet-buffering system enables a communication system that exhibits a high degree of differentiated services with bandwidth guarantees and at high aggregation levels without experiencing head-of-line blocking.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
Method for distributing and conditioning traffic for mobile networks based on differentiated services
ActiveUS7161942B2Increase flexibilityReduce traffic problemsData switching by path configurationWireless network protocolsDifferentiated servicesService-level agreement
A method for distributing and conditioning IP traffic for mobile networks based on differentiated services, wherein edge / border routers are only required to maintain QoS profiles for related mobile stations. A new IP address or a new service level subscription or service level agreement of an mobile station is only sent to related edge / border routers. As a result, unnecessary IP traffic is significantly reduced. The routers in accordance with methods of the invention disregard the contents of an IP payload and therefore all of the IP addresses that a mobile station may posse. A mobile station is permitted to enter into a domain and obtain a desired quality of service (e.g., Gold or Standard service) without the need to maintain the service while moving through the domain.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
Method and apparatus for provisioning and monitoring internet protocol quality of service
InactiveUS6973033B1Minimum utilization of linkSimple processError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDifferentiated servicesDifferentiated service
An architecture, design, and realization for providing Quality of Service (QoS) to Internet Protocol (IP) networks based on a three-class differentiated service scheme where the service provider uses a resource management system and a schedule optimizer to enable the optimal use of bandwidth and buffer resources at each node or router along the various links between the ingress and egress points in a network. The resource reservation system checks to determine if sufficient bandwidth resources are available along the path requested by the customer for a particular class. The schedule optimizer ensures that sufficient buffer resource allocations and parameter settings are made to optimally reach the predetermined QoS criteria for each of the three classes. The system also contains a mechanism supporting resource reservations providing additional resources along alternative paths if the selected path links fail in the network.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Methods, systems and apparatus for managing differentiated service classes
InactiveUS20070206602A1Meet different requirementsData switching by path configurationDifferentiated servicesDifferentiated service
Differentiated service classes on a label switch path are managed by comparing at least one packet field value included in a packet of data to mapping field values of a mapping that correlates the mapping field values with queues. The packet is stored into one of the queues based on the comparing. A first subset of the queues is scheduled using a first queue scheduling algorithm and a second subset of the queues is scheduled using a second queue scheduling algorithm. The packet is transmitted onto the label switch path in accordance with a predefined scheduling order of the first subset of the queues and the second subset of the queues.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
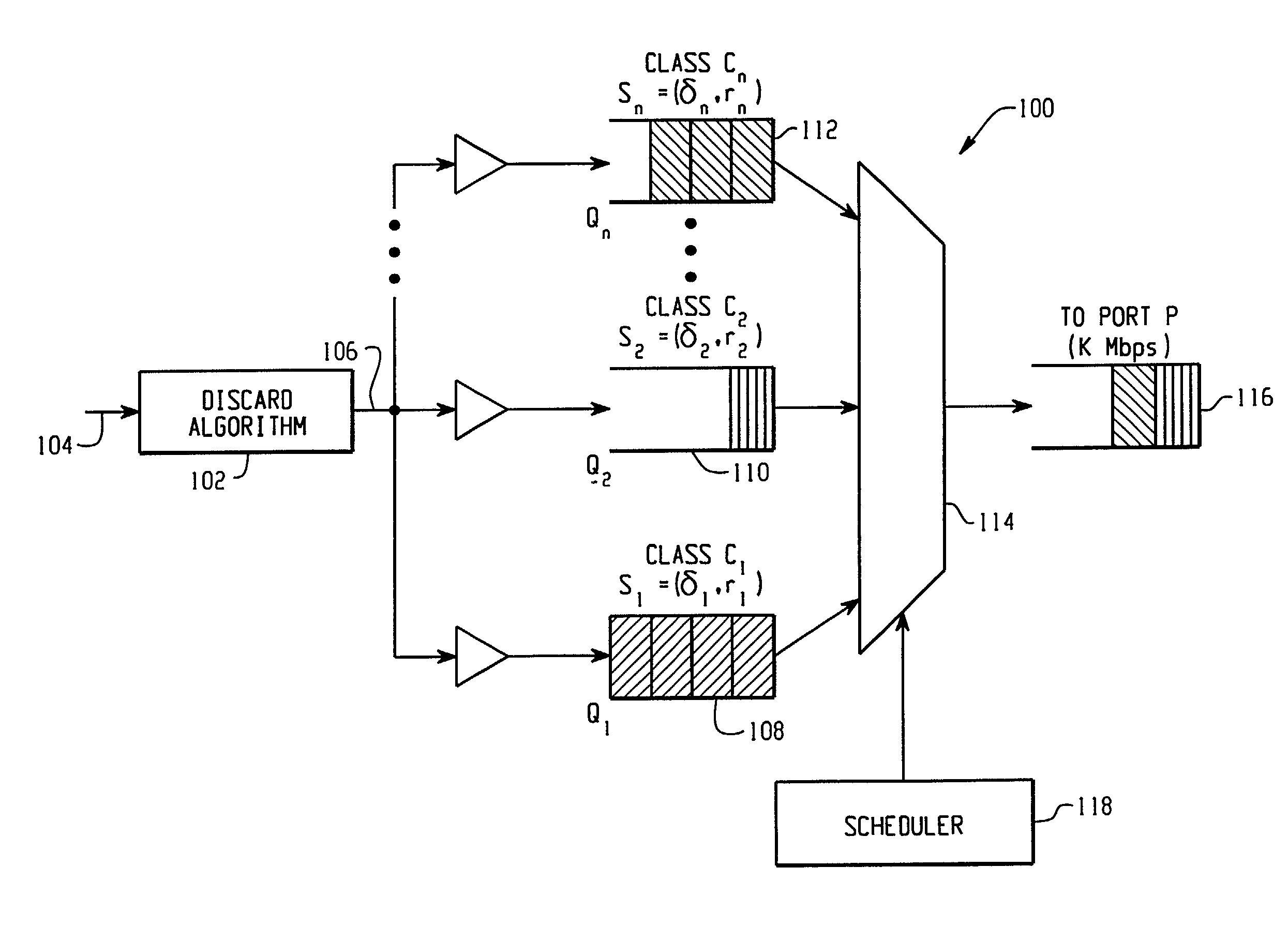
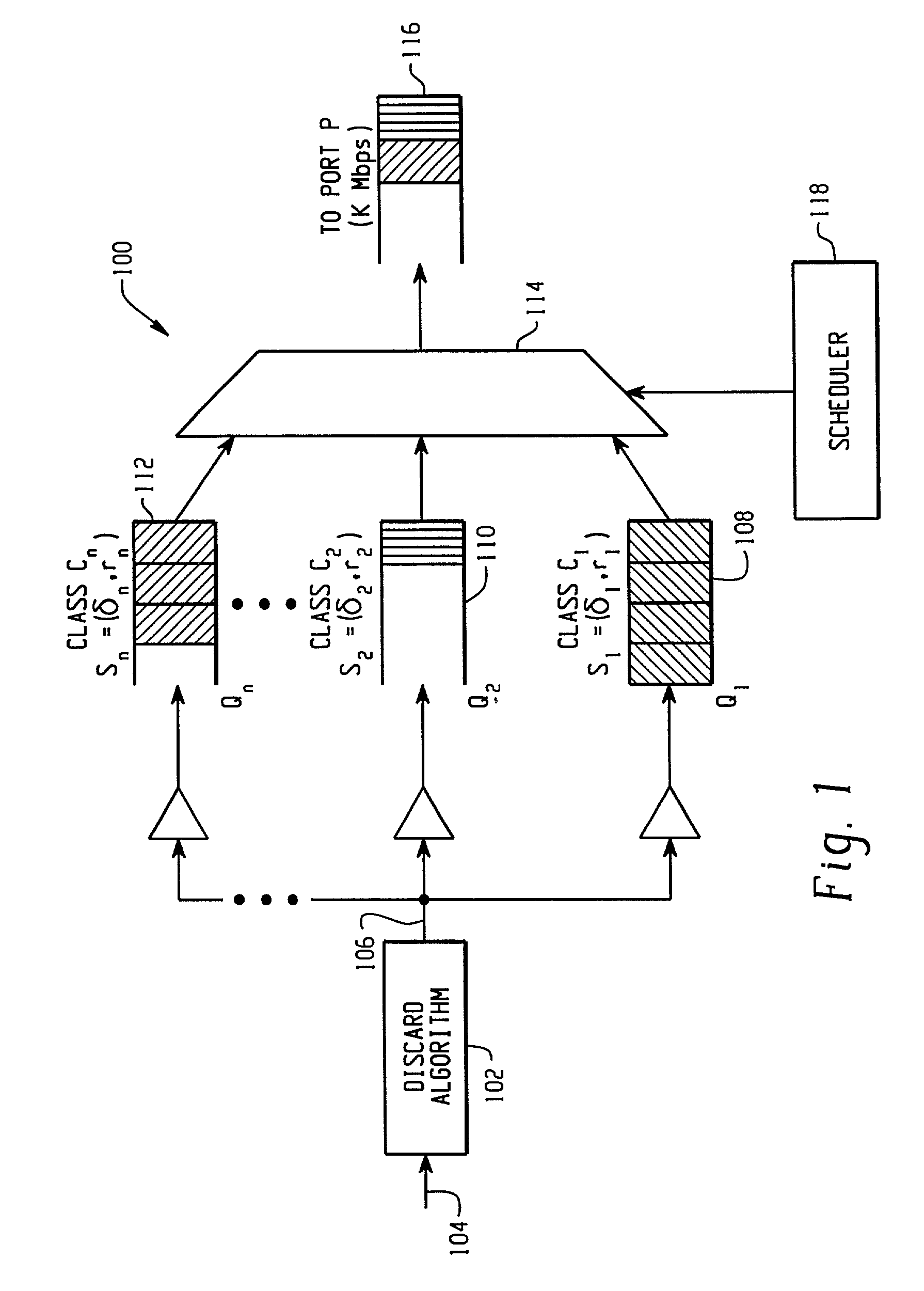
Unified algorithm for frame scheduling and buffer management in differentiated services networks
InactiveUS6990529B2Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksDifferentiated servicesDifferentiated service
A frame forwarding and discard architecture in a Differentiated Services network environment. The architecture comprises a discard logic for discarding a frame from a stream of incoming frames of the network environment in accordance with a discard algorithm, the frame being discarded if a predetermined congestion level in the network environment has been reached, and a predetermined backlog limit of a queue associated with the frame, has been reached. Scheduling logic is also provided for scheduling the order in which to transmit one or more enqueued frames of the network environment.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Method and apparatus to schedule packets through a crossbar switch with delay guarantees
ActiveUS20070280261A1Minimize delay jitterMeet bandwidth requirementsMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationCrossbar switchDifferentiated services
A method for scheduling cell transmissions through a switch with rate and delay guarantees and with low jitter is proposed. The method applies to a classic input-buffered N×N crossbar switch without speedup. The time axis is divided into frames each containing F time-slots. An N×N traffic rate matrix specifies a quantized guaranteed traffic rate from each input port to each output port. The traffic rate matrix is transformed into a permutation with NF elements which is decomposed into F permutations of N elements using a recursive and fair decomposition method. Each permutation is used to configure the crossbar switch for one time-slot within a frame of size F time-slots, and all F permutations result in a Frame Schedule. In the frame schedule, the expected Inter-Departure Time (IDT) between cells in a flow equals the Ideal IDT and the delay jitter is bounded and small. For fixed frame size F, an individual flow can often be scheduled in O(logN) steps, while a complete reconfiguration requires O(NlogN) steps when implemented in a serial processor. An RSVP or Differentiated Services-like algorithm can be used to reserve bandwidth and buffer space in an IP-router, an ATM switch or MPLS switch during a connection setup phase, and the proposed method can be used to schedule traffic in each router or switch. Best-effort traffic can be scheduled using any existing dynamic scheduling algorithm to fill the remaining unused switch capacity within each Frame. The scheduling algorithm also supports multicast traffic.
Owner:SZYMANSKI TED HENRYK
Network, system and method of differentiated security service
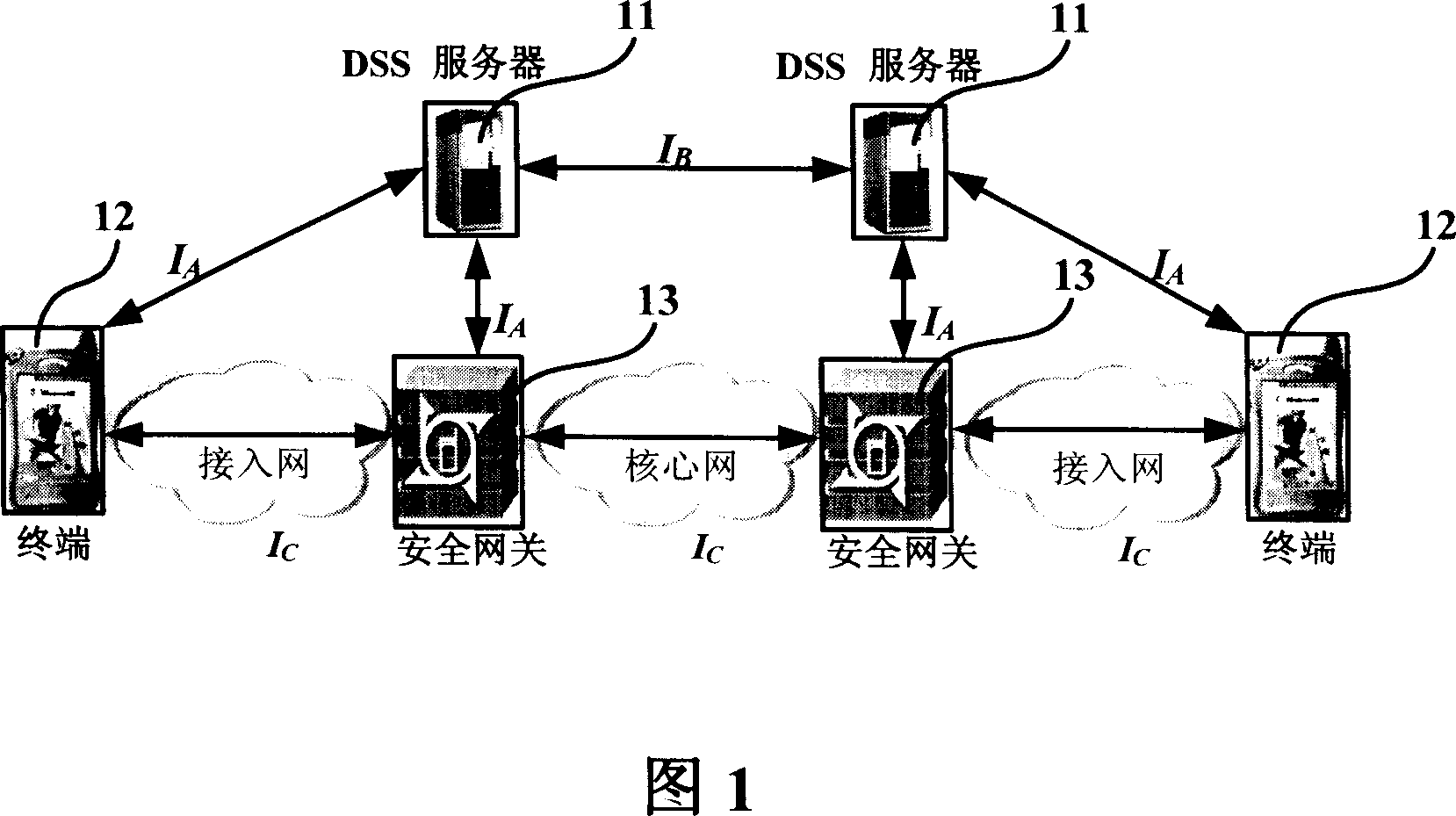
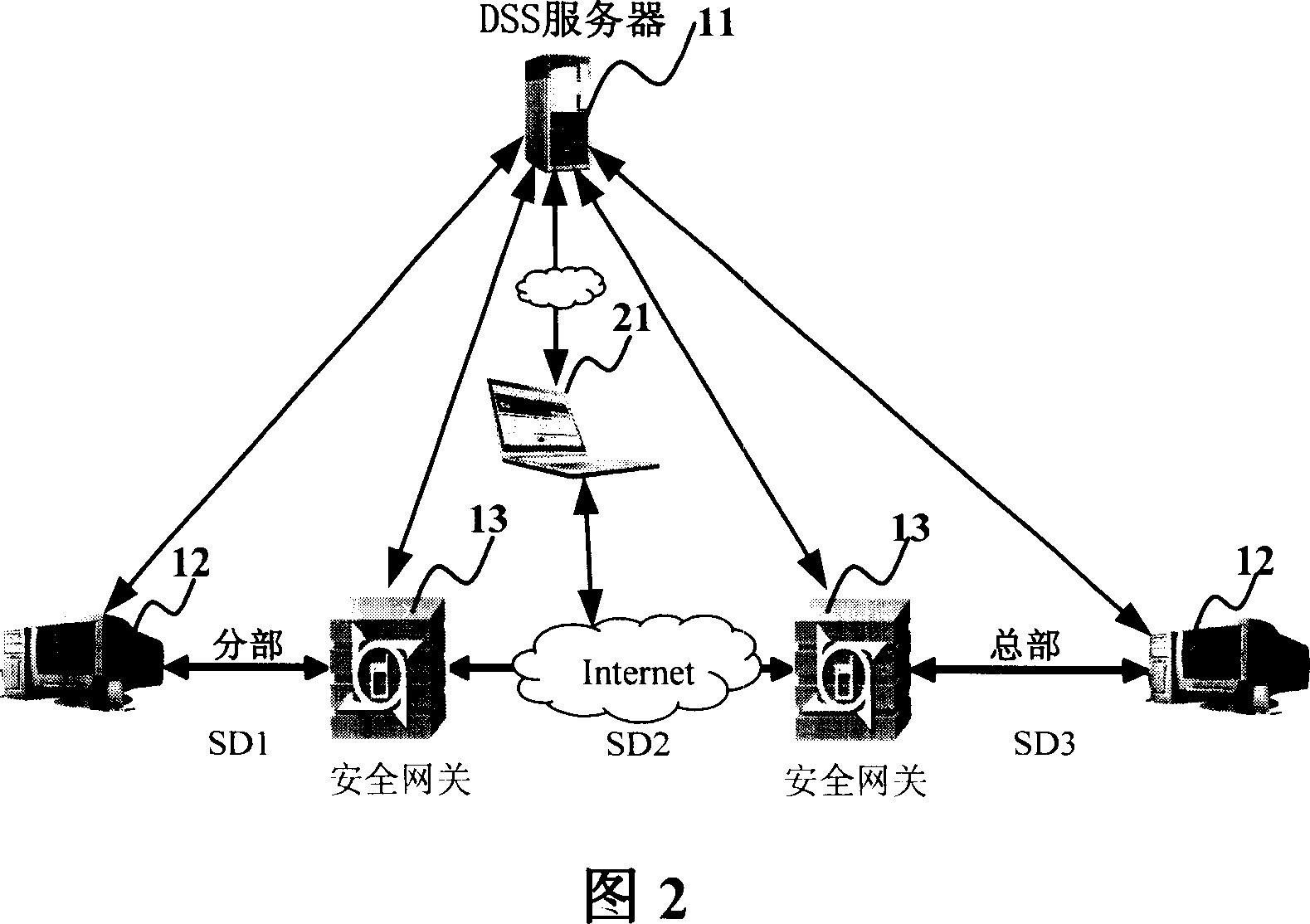
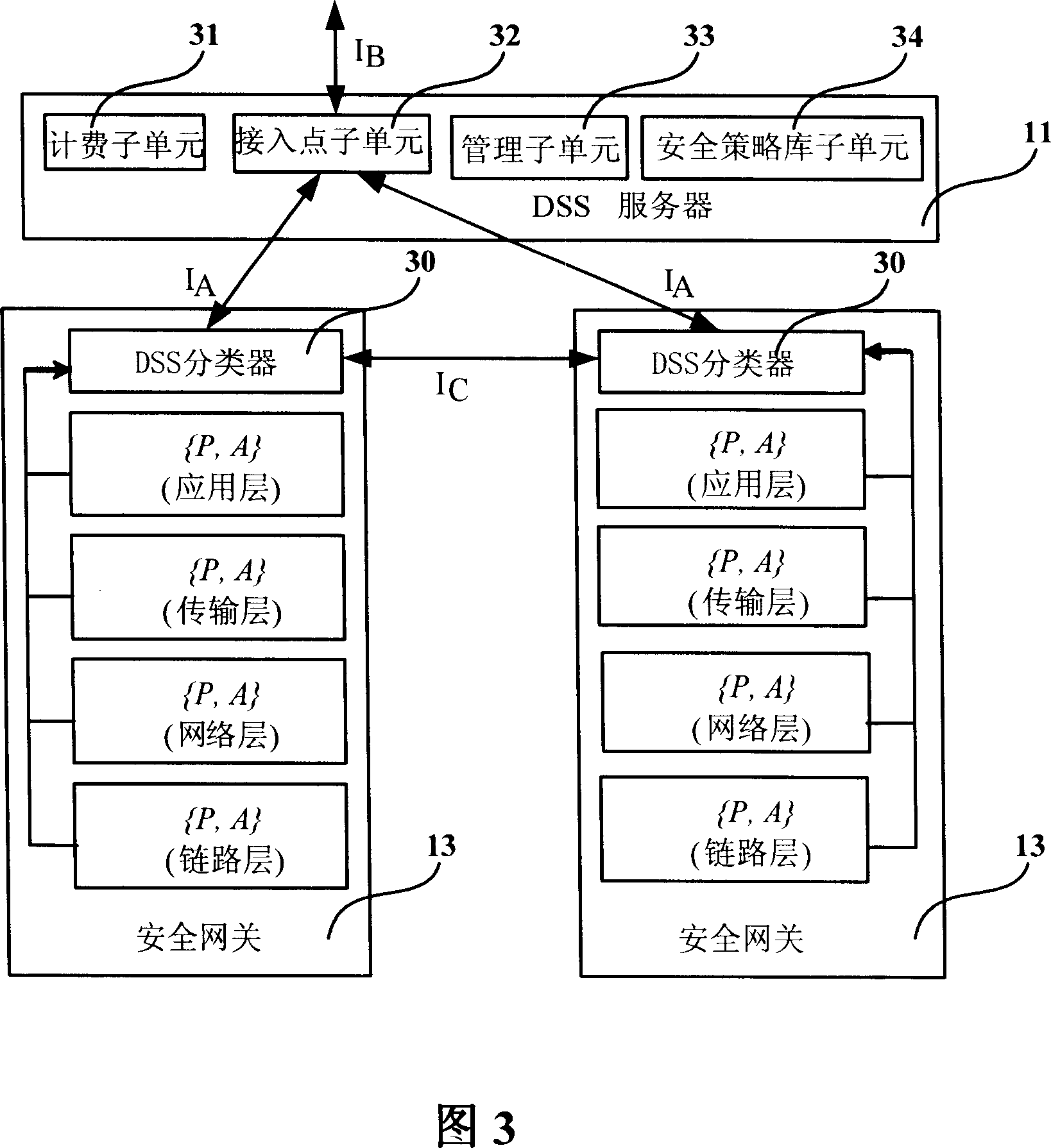
ActiveCN101094225AGood service safety and qualityMeet security needsTransmissionDifferentiated serviceSecurity level
The system thereof comprises: at least one DSS server, at least two DSS classifiers and at least two security gateways. Said DSS server is used for storing the differential security service policy base, and according to the security policy for triggering the DSS classifier, determines the security level information, and managing and controlling the DSS classifier. Said DSS classifier is used for making security service negotiation according to different security level information, and according to the negotiation result, triggering the relevant security service in security gateway. Said security gateway is used for receiving the negotiation result of DSS classifier and triggering and executing relevant security service.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Systems and methods for multi-level quality of service classification in an intermediary device
ActiveUS20120039332A1Improve network performanceNetwork performance can be enhanced and optimizedData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityCode point
The present invention is directed towards systems and methods for providing multi-level classification of a network packet. In some embodiments, network performance may be enhanced and optimized by providing QoS and acceleration engines with packet- or data-specific information. In addition to source and destination IP addresses and port numbers, packet- or data-specific information can include direction of traffic (client to host or server; server or host to client; or both), Virtual LAN (VLAN) ID, source or destination application or associated application, service class, ICA priority, type of service, differentiated service code point (DSCP), or other information. Some or all of this information may be used to classify the network packet at a plurality of layers of a network stack, allowing for deep inspection of the packet and multiple levels of granularity of classification.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
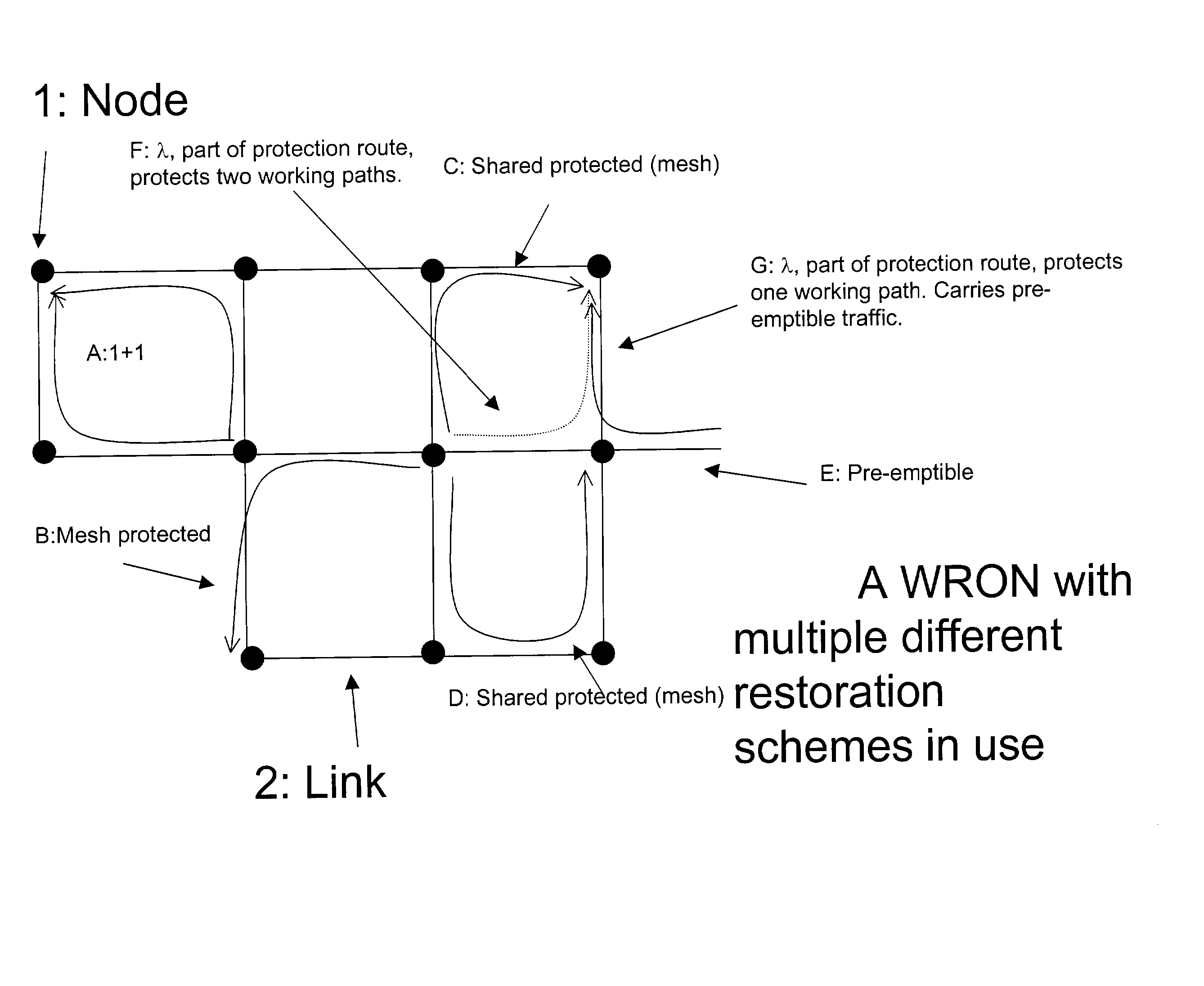
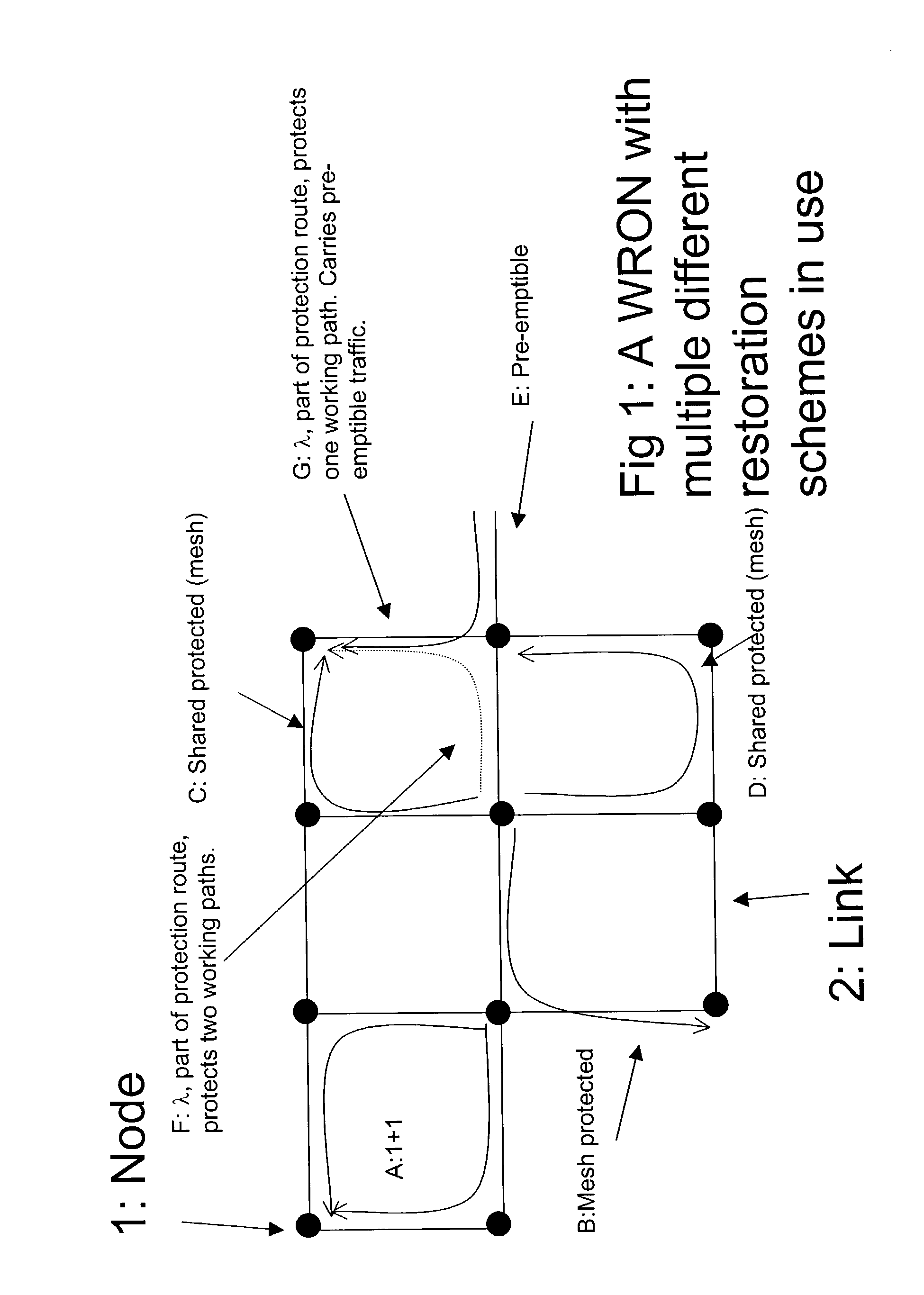
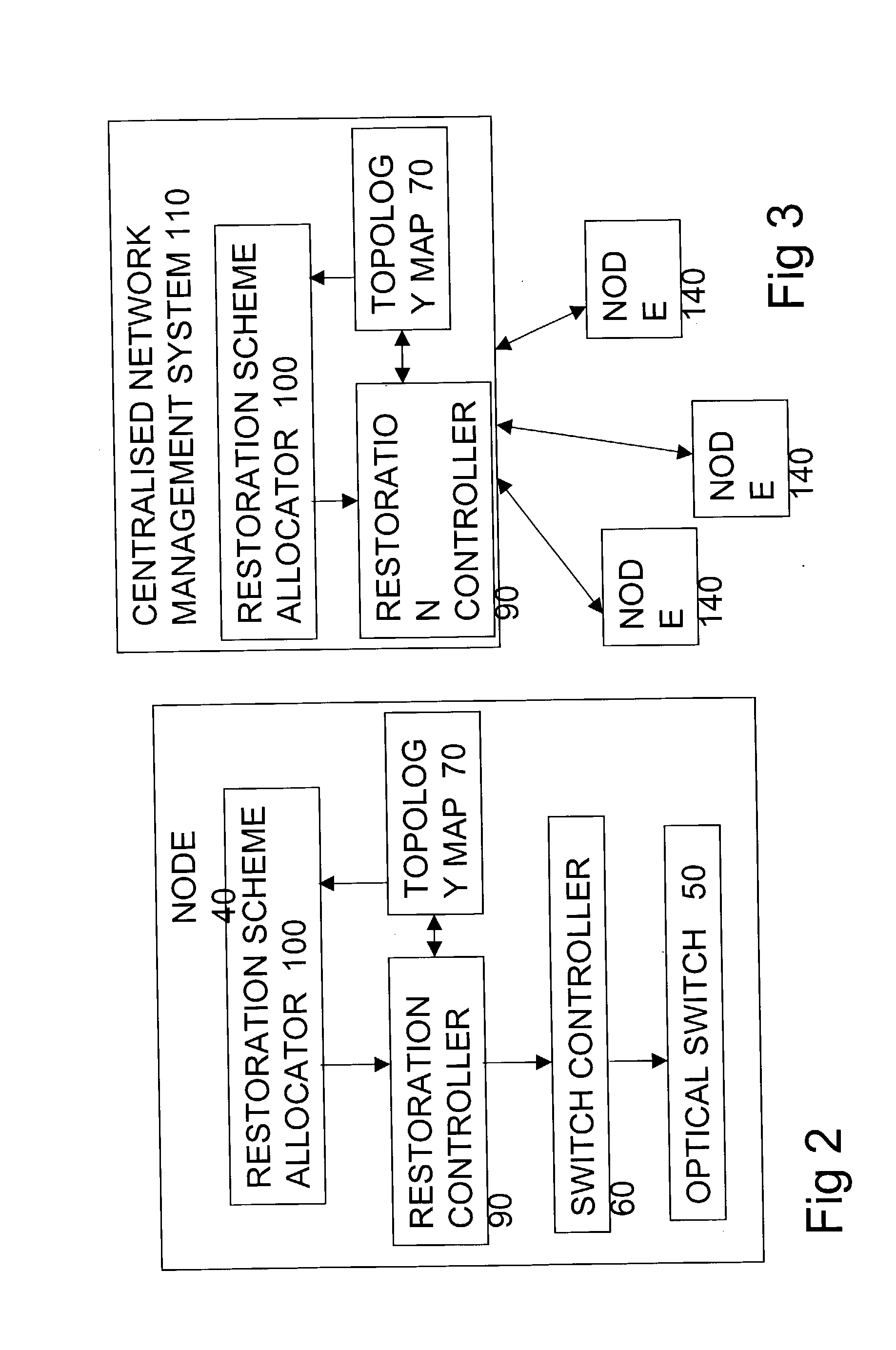
Differentiated resilience in optical networks
InactiveUS20040120705A1Easy to useSame capacityLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsTraffic capacityDifferentiated service
A transparent wavelength routed optical network has two or more different optical layer restoration schemes to provide different levels of resilience, and a restoration allocator arranged to allocate the optical layer restoration schemes, to different parts of the traffic. This can enable similar capacity for high resilience traffic as a single resilience level network, and provide additional capacity for lower resilience level traffic, which can reflect the value of the traffic. The allocator can be located centrally in a network manager, or in distributed fashion at each node, and can depend on a translation of a parameter requested by the customer. Nodes have message processors for receiving a message for reserving a path, determining if the path has become unavailable, and if so, sending a second message to collect information about any other paths still available on the same route.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
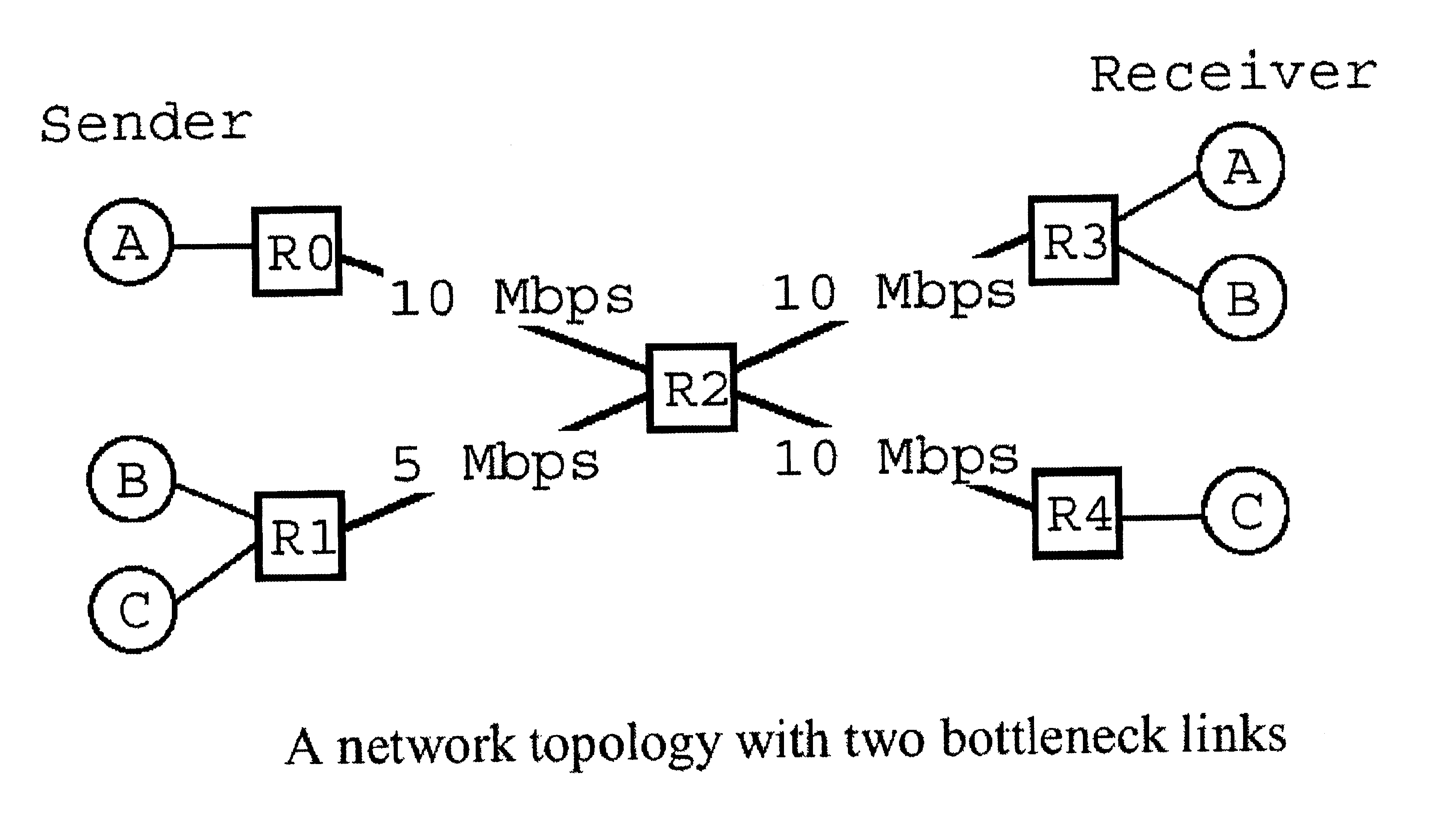
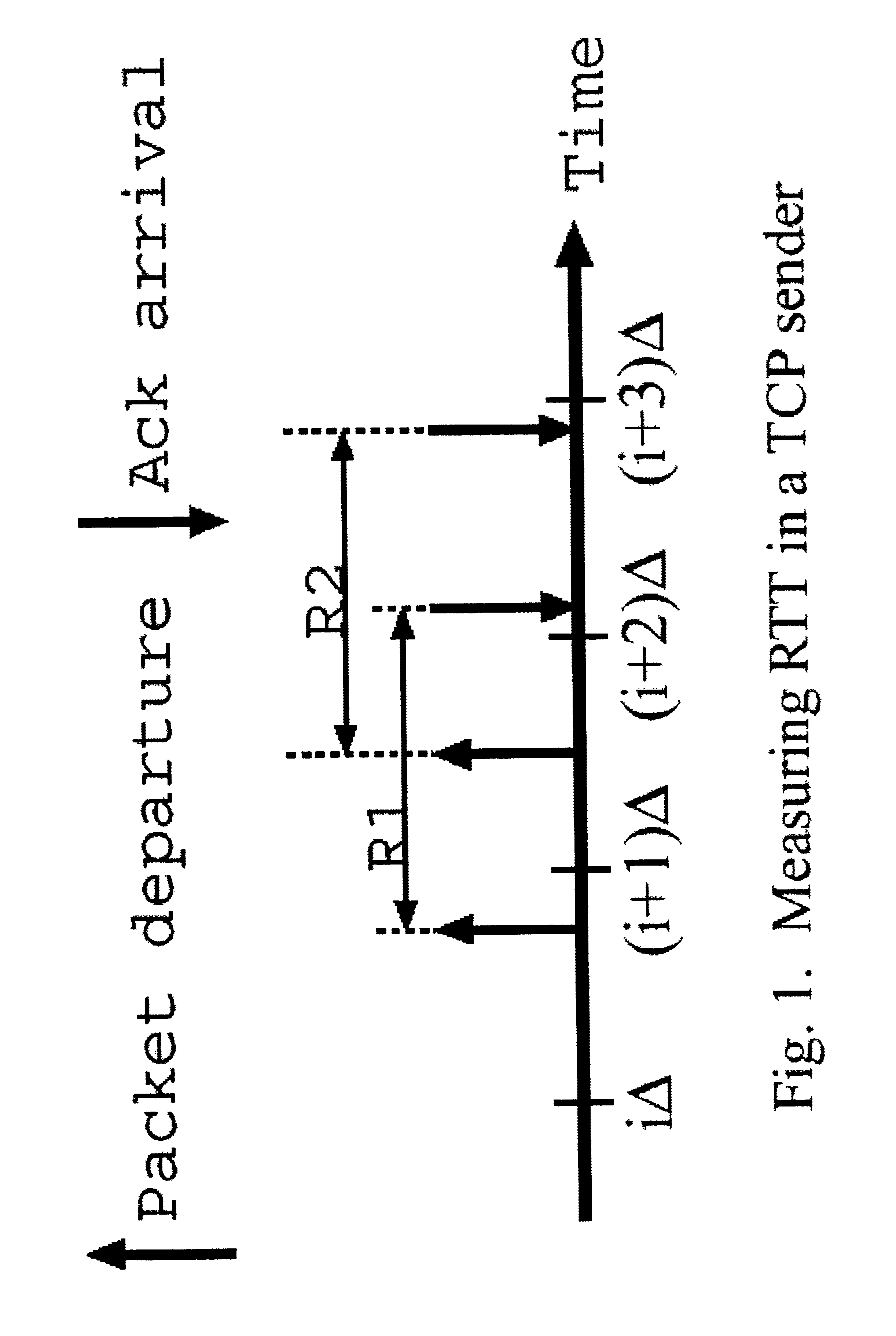
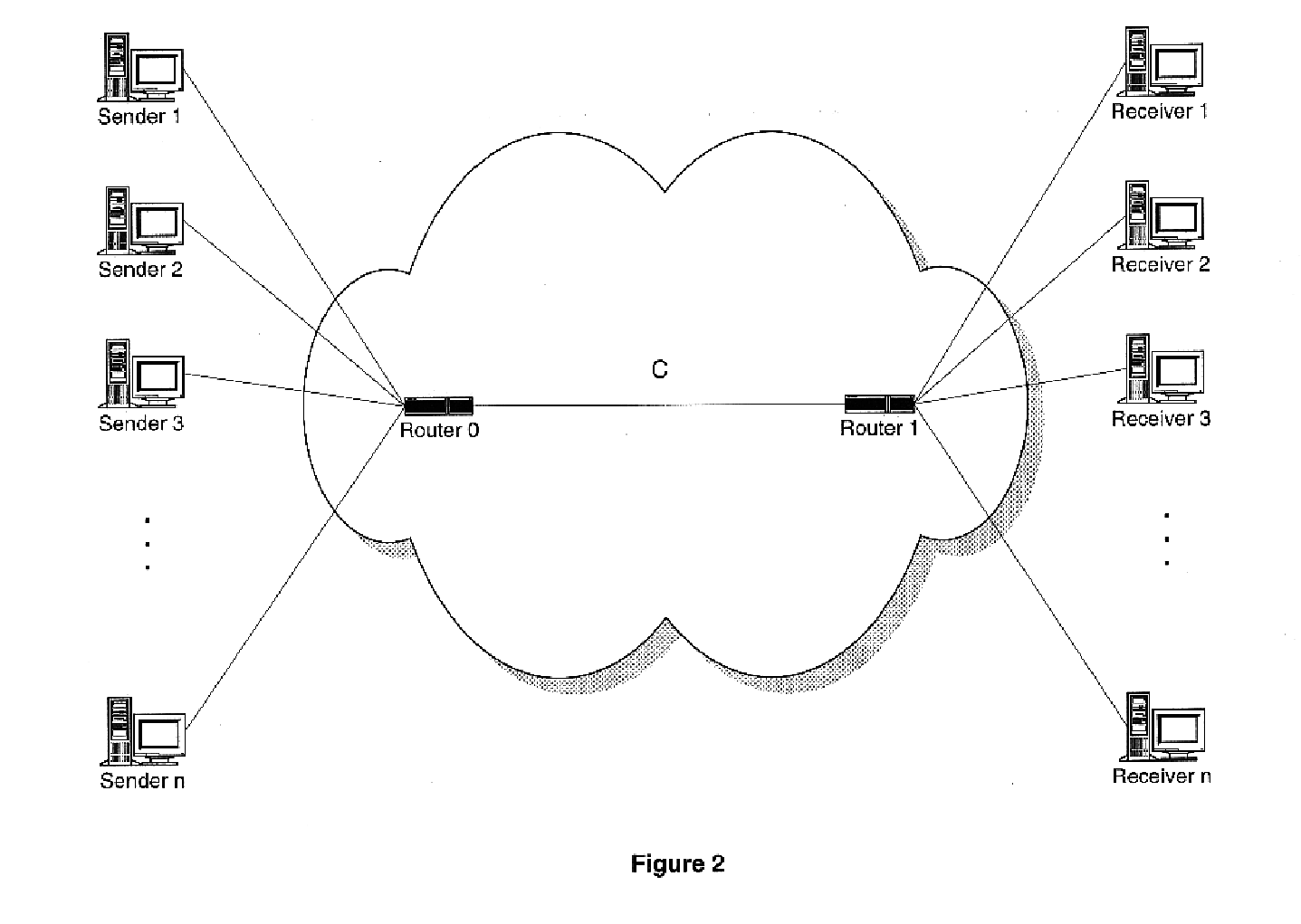
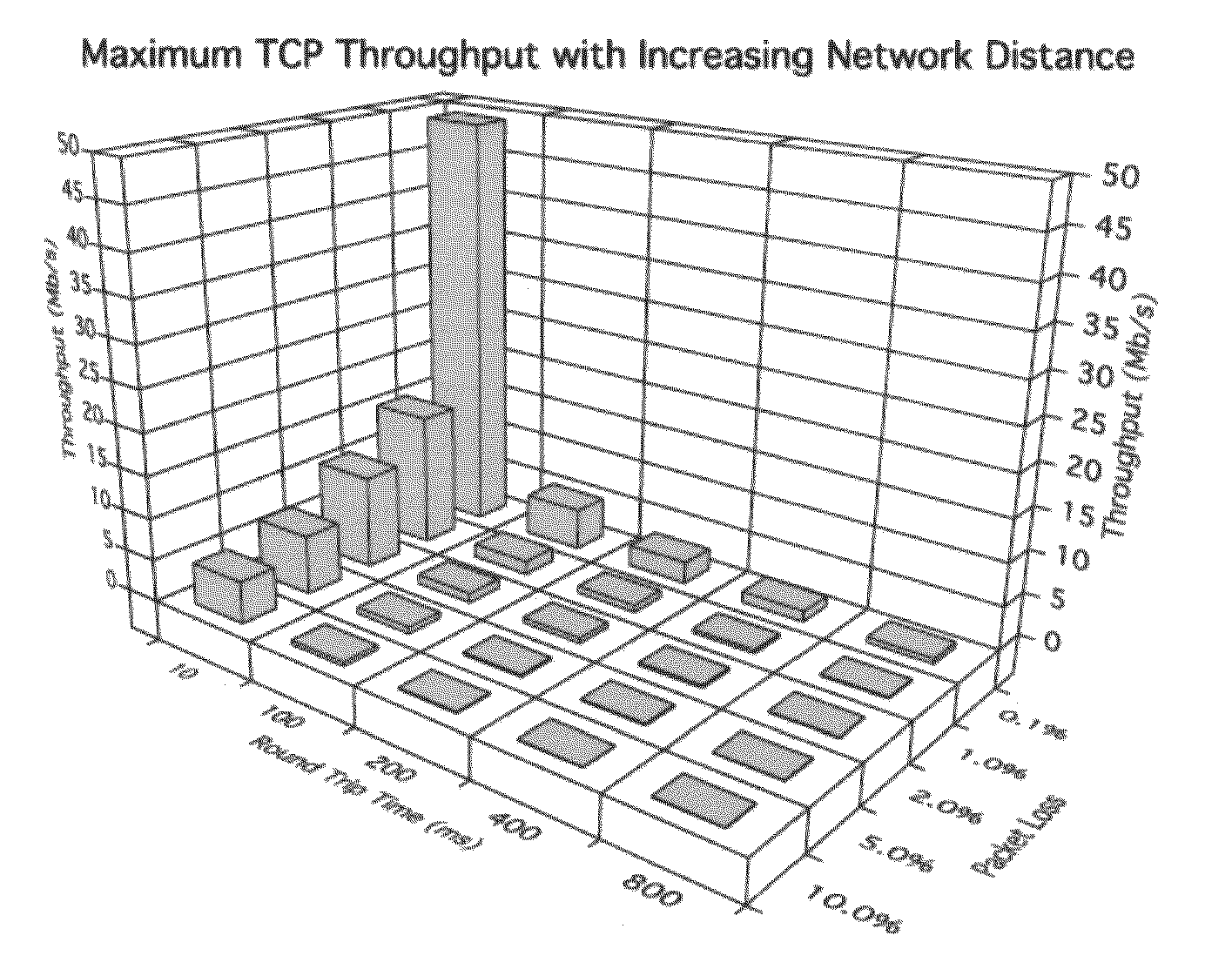
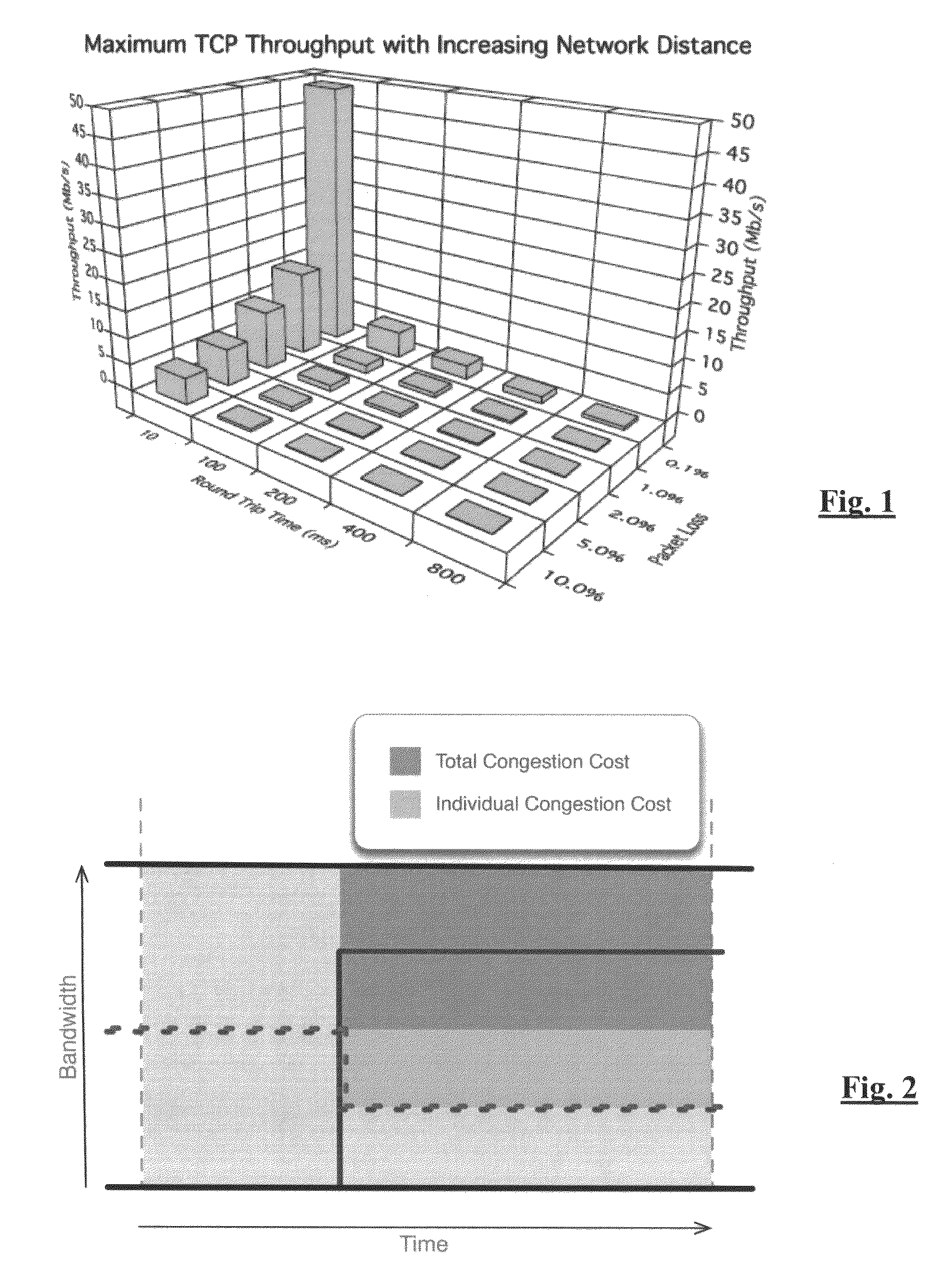
Modeling link throughput in IP networks
A model is given for performance evaluation of IP computer networks that are dominated by congestion-controlled traffic. The model includes heterogeneous TCP flows, UDP flows, short-lived TCP flows, and TCP flows in a differentiated services network. The performance of large-scale networks is estimated where flows may encounter multiple congested links.
Owner:AVAYA INC
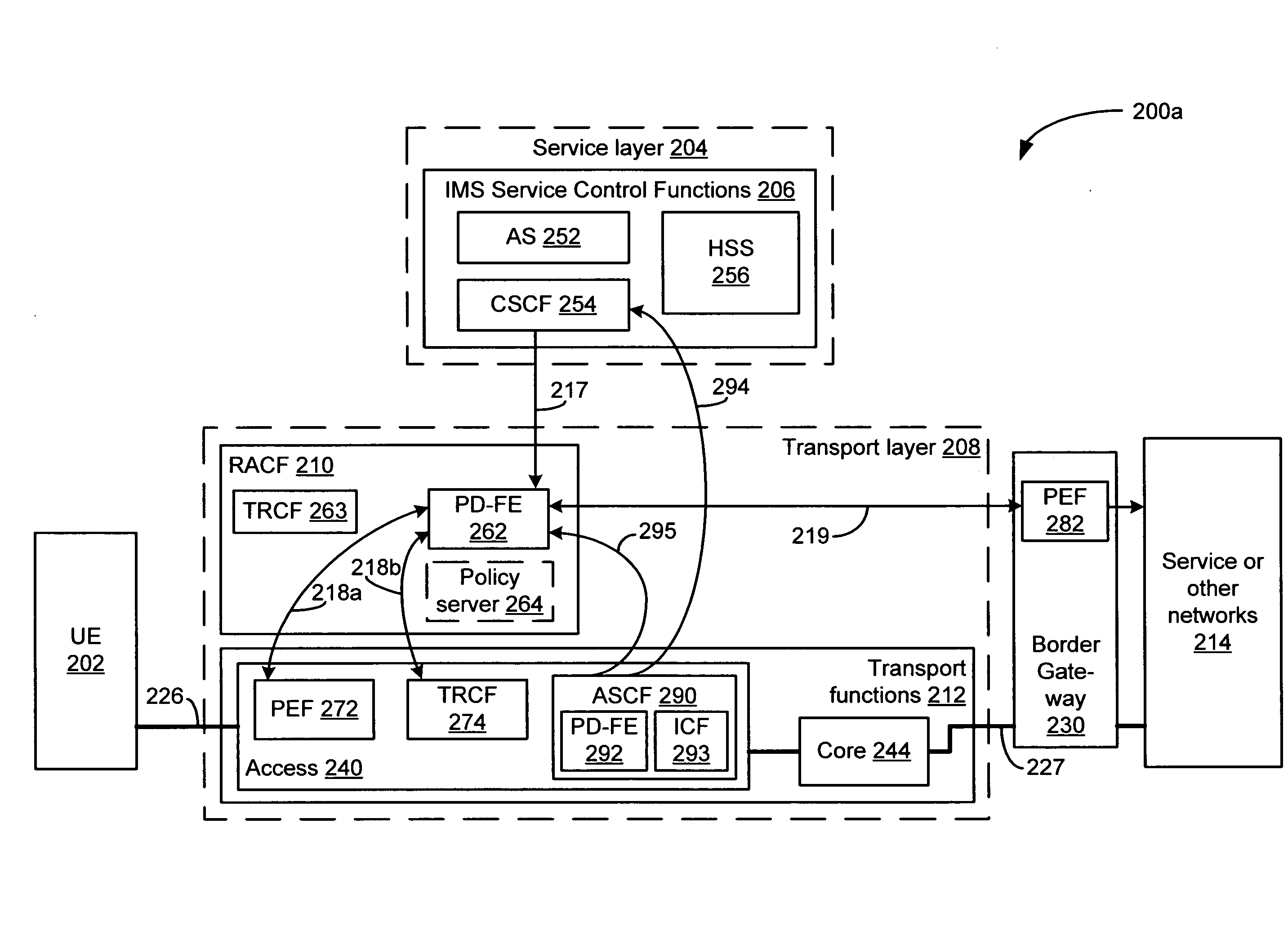
System and method for controlling non-compliant applications in an IP multimedia subsystem
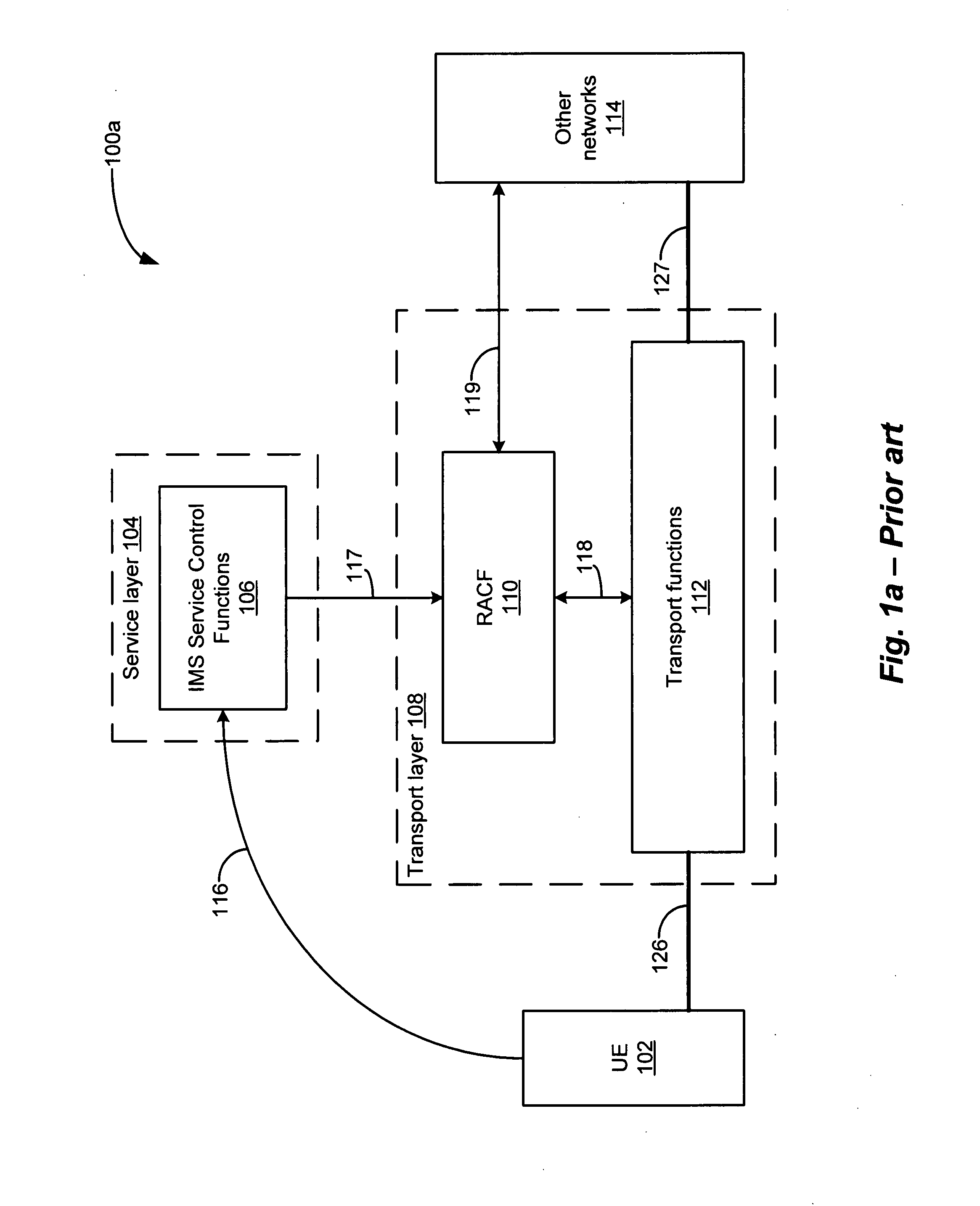
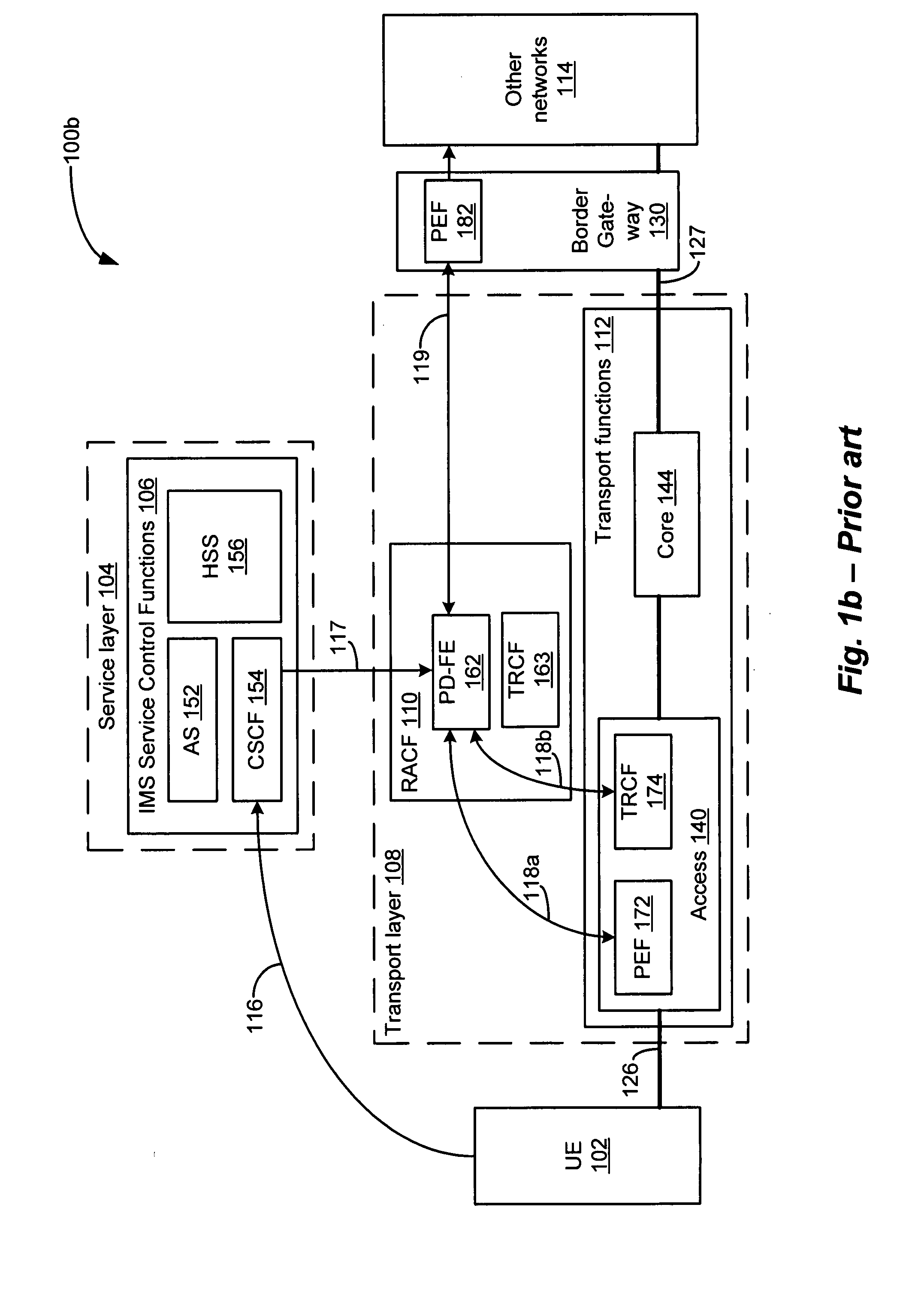
A system and method that enables session-based and non-session-based application services to be controlled and managed within the IMS / NGN architecture. The IMS / NGN architecture includes a service layer and a transport layer. IMS service control functions are implemented within the service layer, and RACF and transport functions are implemented within the transport layer. The transport functions include access and core network functions, which have corresponding QoS resources. The access or core network function includes an application service control function (ASCF), which includes a PD-FE and a functional element for inspecting packet data flows, and identifying and classifying application services associated with the flows. The ASCF is employed to signal the IMS service control functions on behalf of non-session-based application services, and to reserve and allocate the QoS resources needed to support packet data flows associated with the non-session-based services. As a result, service providers can provide users or subscribers of such non-session-based services with guaranteed or differentiated QoS and / or differentiated service plans, thereby allowing charges to be calculated for the non-session-based services and service plans that are commensurate with the value of the respective service or plan.
Owner:ELLACOYA NETWORKS LLC
Practical model for high speed file delivery services supporting guaranteed delivery times and differentiated service levels
InactiveUS8051017B2Energy efficient ICTError preventionDifferentiated servicesDifferentiated service
A practical economic and technical model for building commercial-grade electronic file delivery services that provide the same scale, predictability, and differentiated service levels as physical courier services traditionally used to move electronic data on physical media. Systems and methods for providing such services using a charge-back scheme based on congestion pricing are described.
Owner:IBM CORP
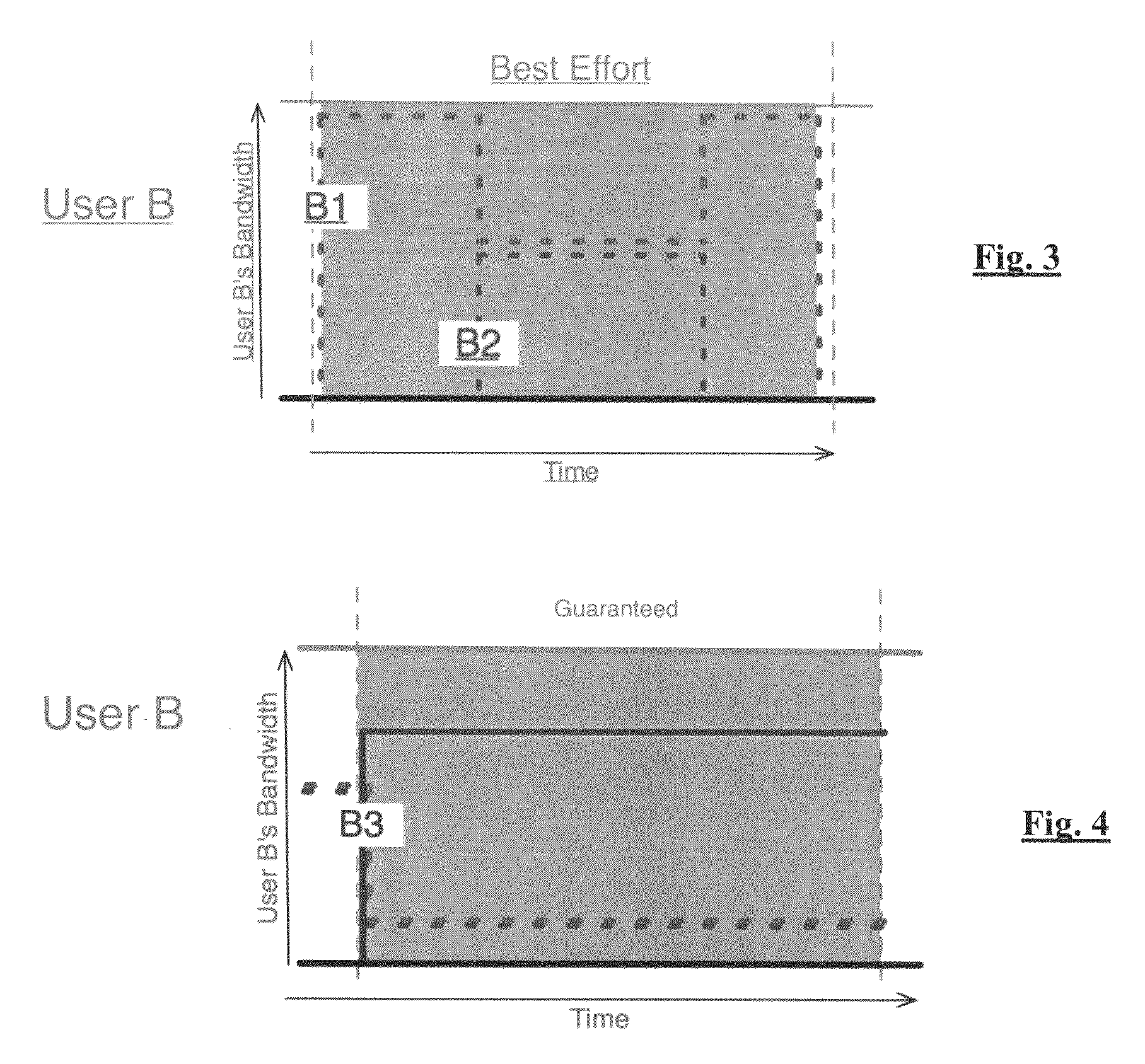
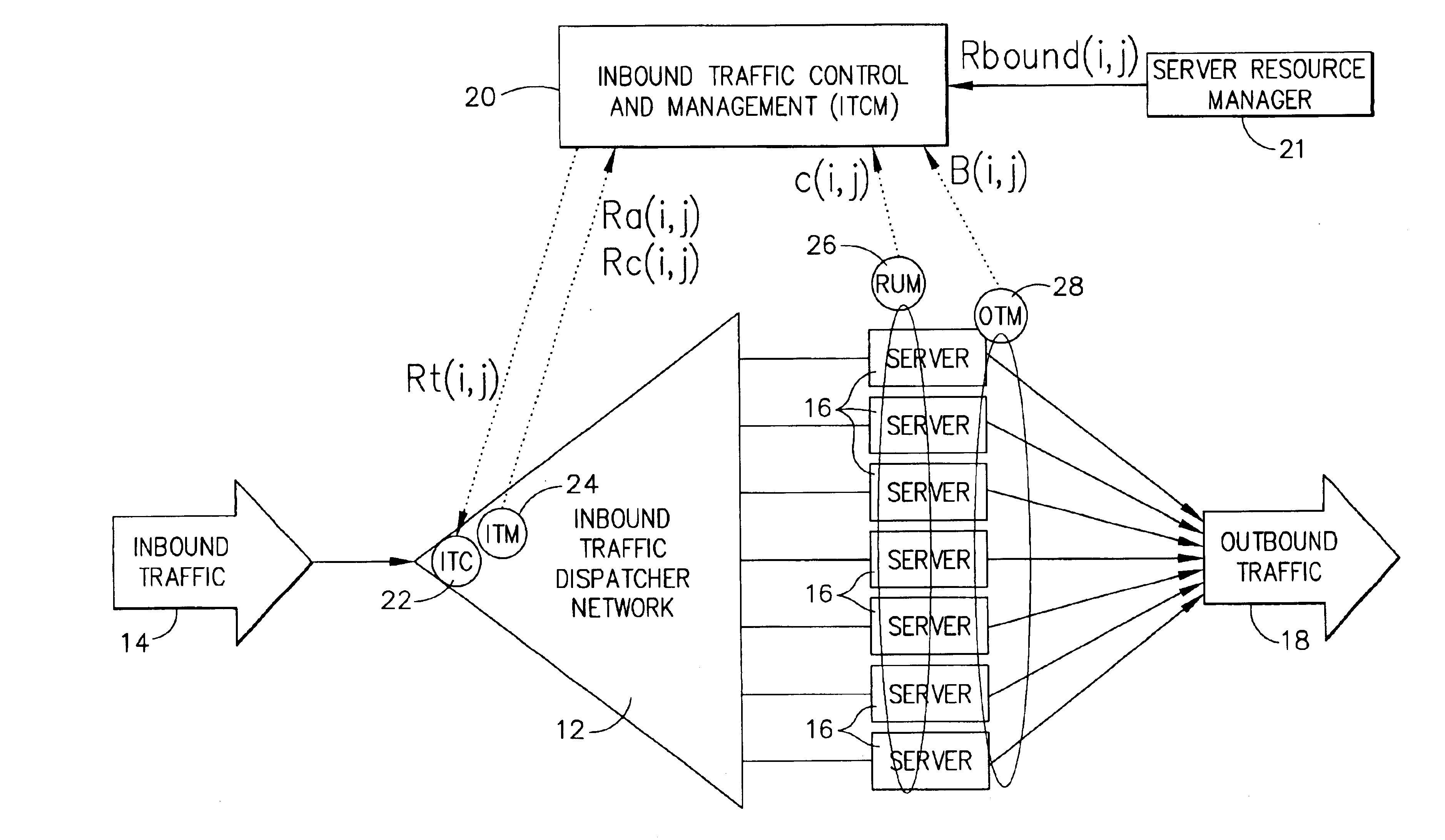
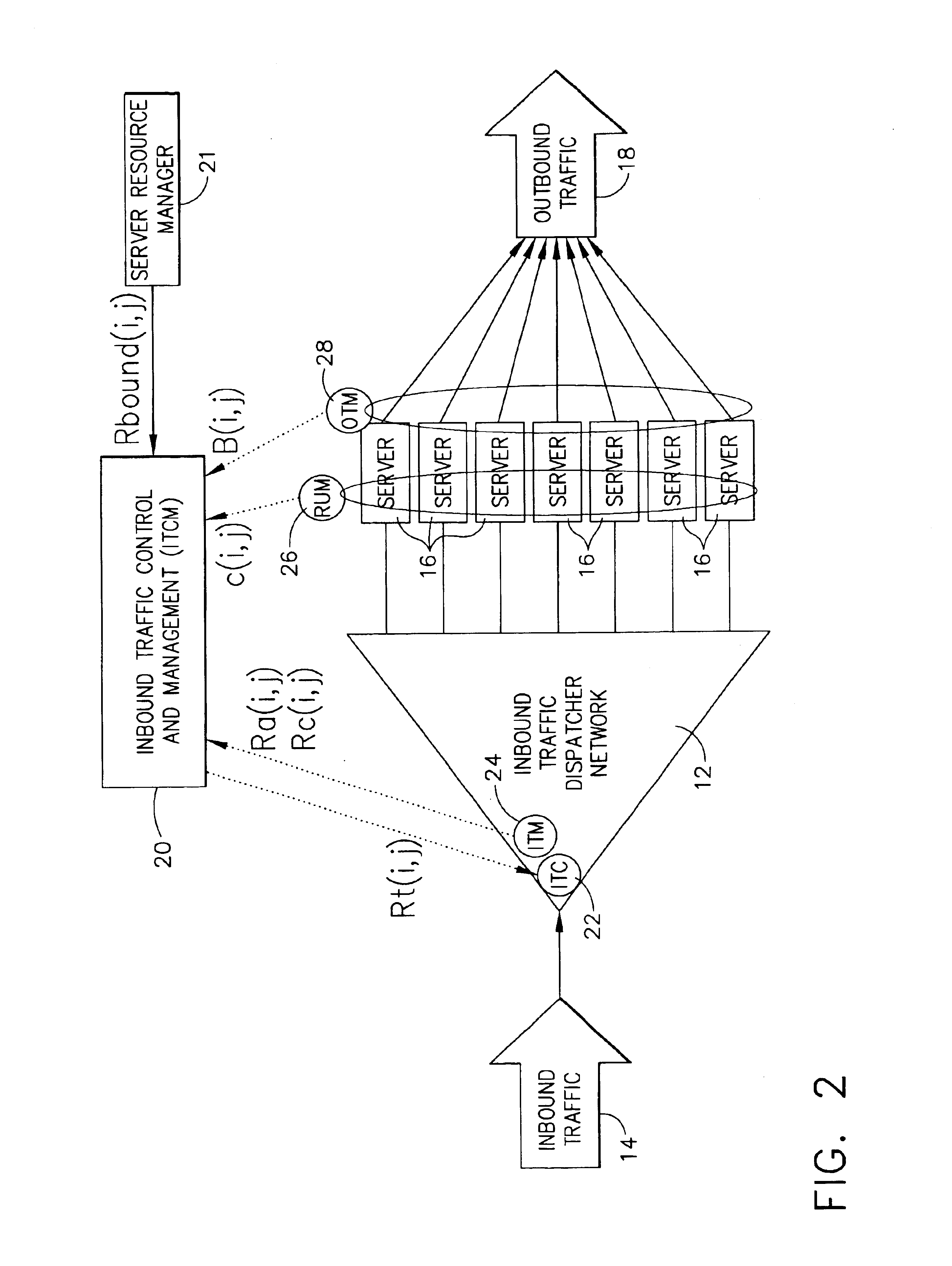
Highly scalable system and method of regulating internet traffic to server farm to support (min,max) bandwidth usage-based service level agreements
InactiveUS6857025B1Improve scalabilityInhibit outputMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksScalable systemService-level agreement
A highly scalable system and method for supporting (mim,max) based Service Level Agreements (SLA) on outbound bandwidth usage for a plurality of customers whose applications (e.g.,Web sites) are hosted by a server farm that consists of a very large number of servers. The system employs a feedback system that enforces the outbound link bandwidth SLAs by regulating the inbound traffic to a server or server farm. Inbound traffic is admitted to servers using a rate denoted as Rt(i,j), which is the amount of the ith customer's jth type of traffic that can be admitted within a service cycle time to servers which support the ith customer. A centralized device computes Rt(i,j) based on the history of admitted inbound traffic to servers, the history of generated outbound traffic from servers, and the SLAs of various customers. The Rt(i,j) value is then relayed to one or more inbound traffic limiters that regulate the inbound traffic using the rates Rt(i,j) in a given service cycle time. The process of computing and deploying Rt(i,j) values is repeated periodically. In this manner, the system provides a method by which differentiated services can be provided to various types of traffic, the generation of output from a server or a server farm is avoided if that output cannot be delivered to end users, and revenue can be maximized when allocating bandwidth beyond the minimums.
Owner:IBM CORP
Multiple transmission bandwidth streams with differentiated quality of service
ActiveUS20040208120A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsQuality of serviceDifferentiated service
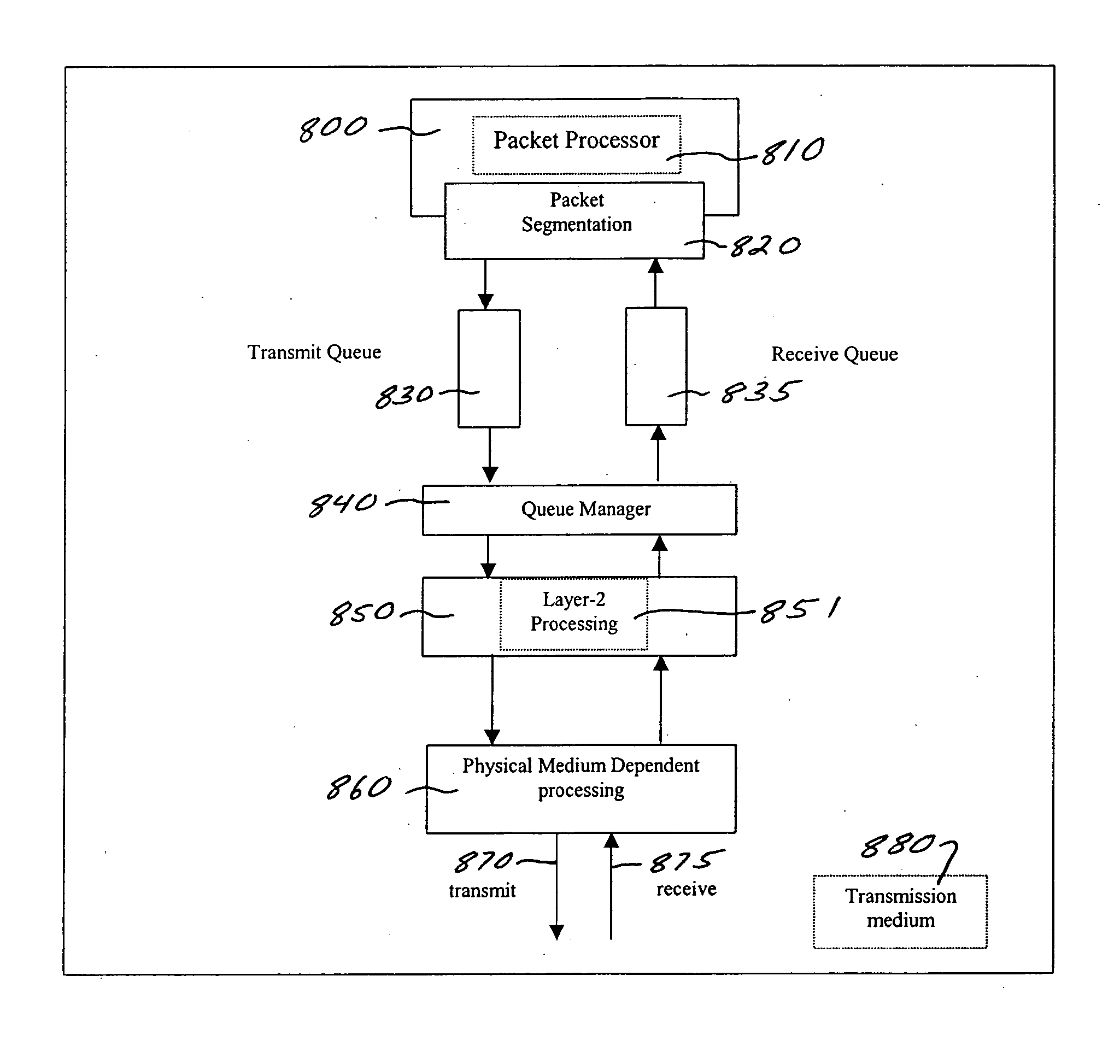
Methods and apparatus are described for providing multiple transmission bandwidth streams with differentiated quality of service on a inter-machine trunk. One approach includes time-division multiplexing. Another approach includes statistical multiplexing. Another approach includes packet segmentation. The approaches are commercially important because they significantly reduce time-delay variation.
Owner:IP GEM GRP LLC
Differential serving method for virtual system competition resources
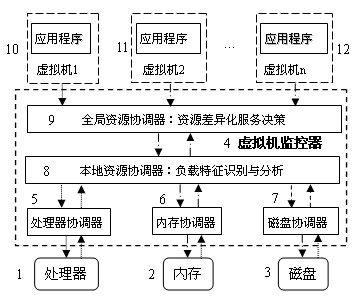
InactiveCN102156665AImprove performance qualityImprove service qualityResource allocationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationVirtualizationDifferentiated service
The invention relates to a differential serving method for virtual system competition resources. Resource application features of a specific virtual machine application program are not differentiated in the conventional virtual machine monitor software and operating system, so that service quality of an important application program and a client operating system cannot be guaranteed. The method comprises three parts of contents: a Markov model used by the virtual system resources, a response time based service quality evaluation model of a multi-virtual machine system and a competition resource differential serving method based on the two models. Through the differential serving method for the virtual system competition resources, provided by the invention, competition degree of the system resources can be effectively relieved under the condition of high competition of the system, so that performance and service quality of the entire virtual system are obviously improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com