Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
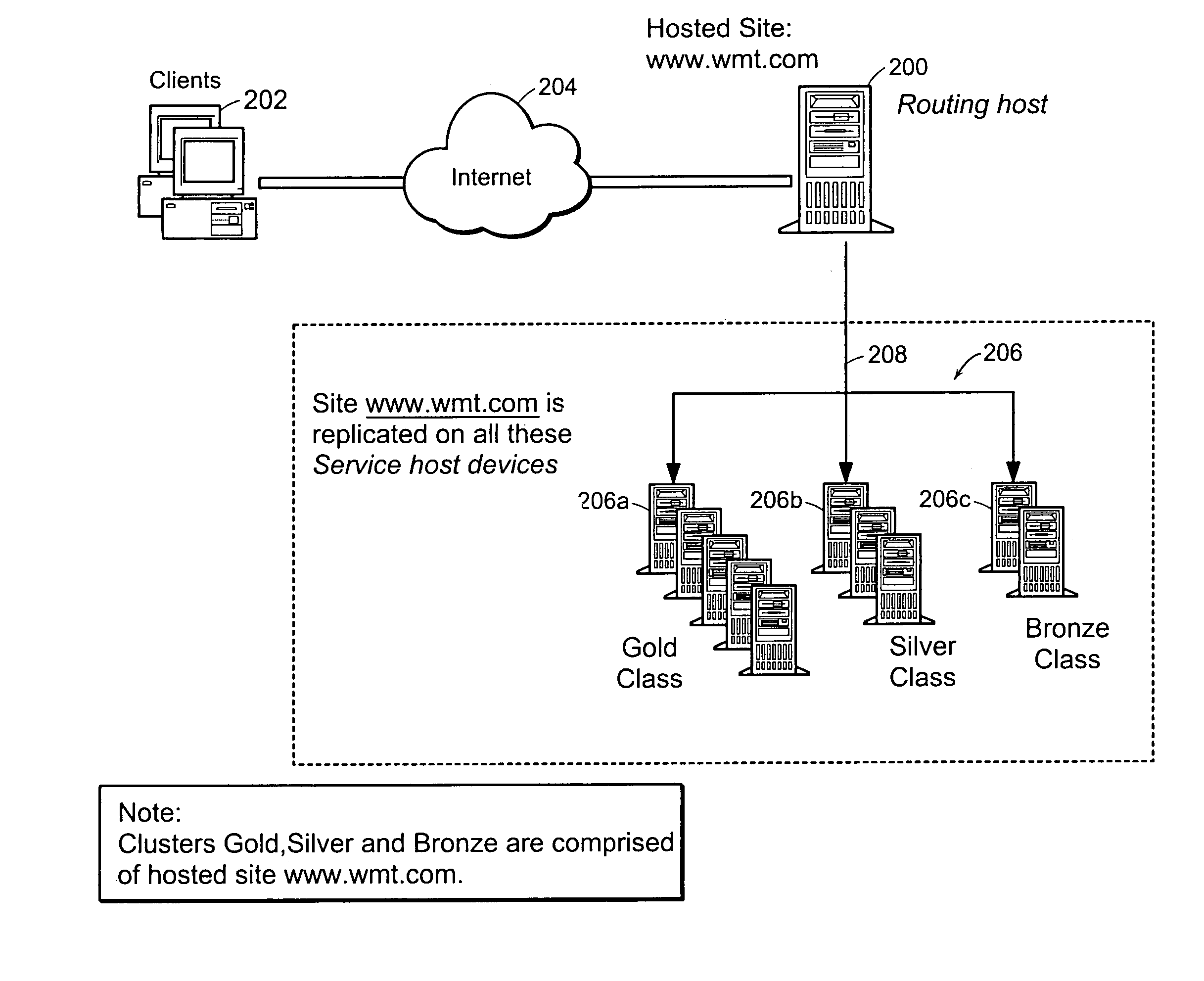
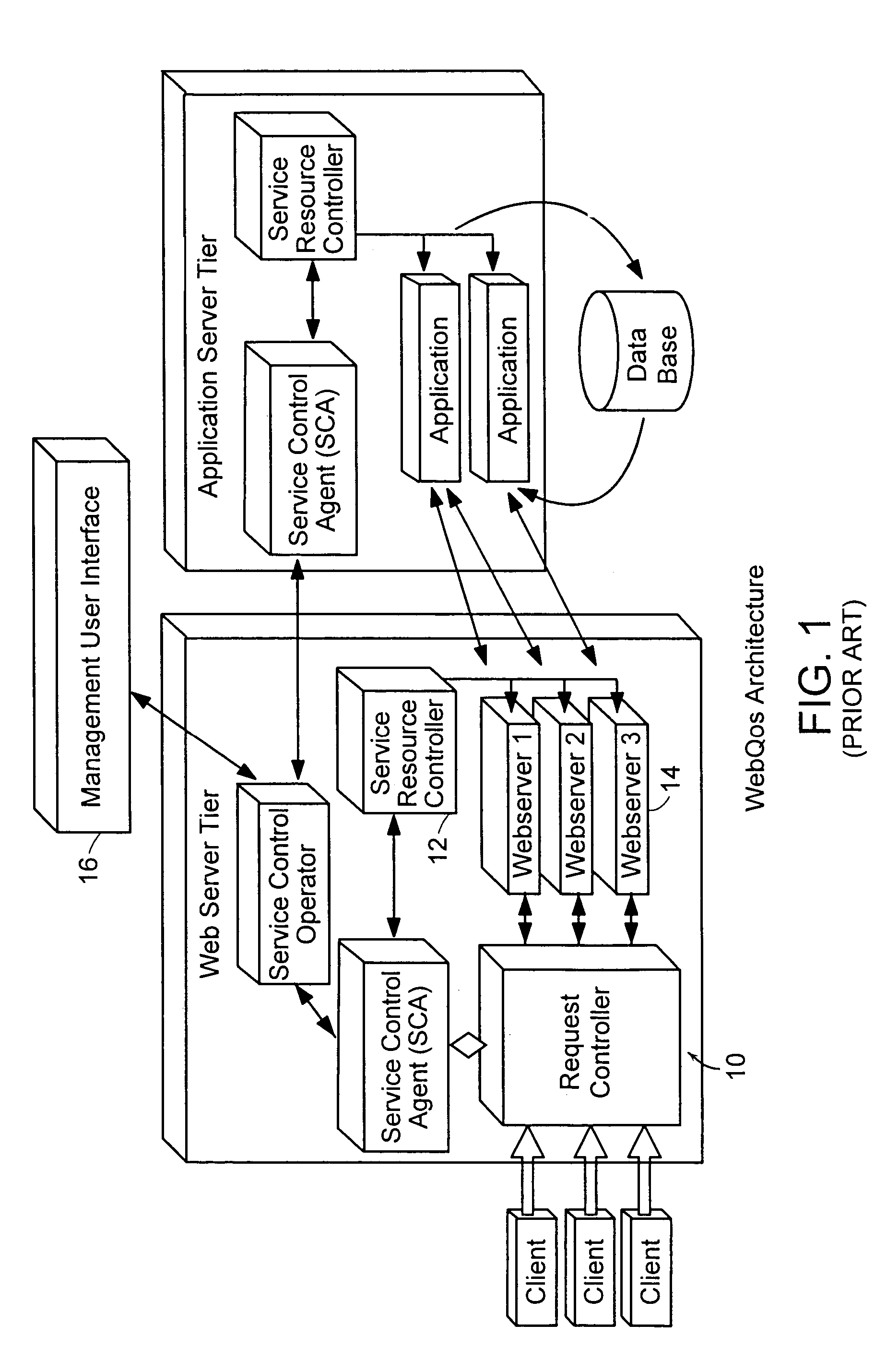
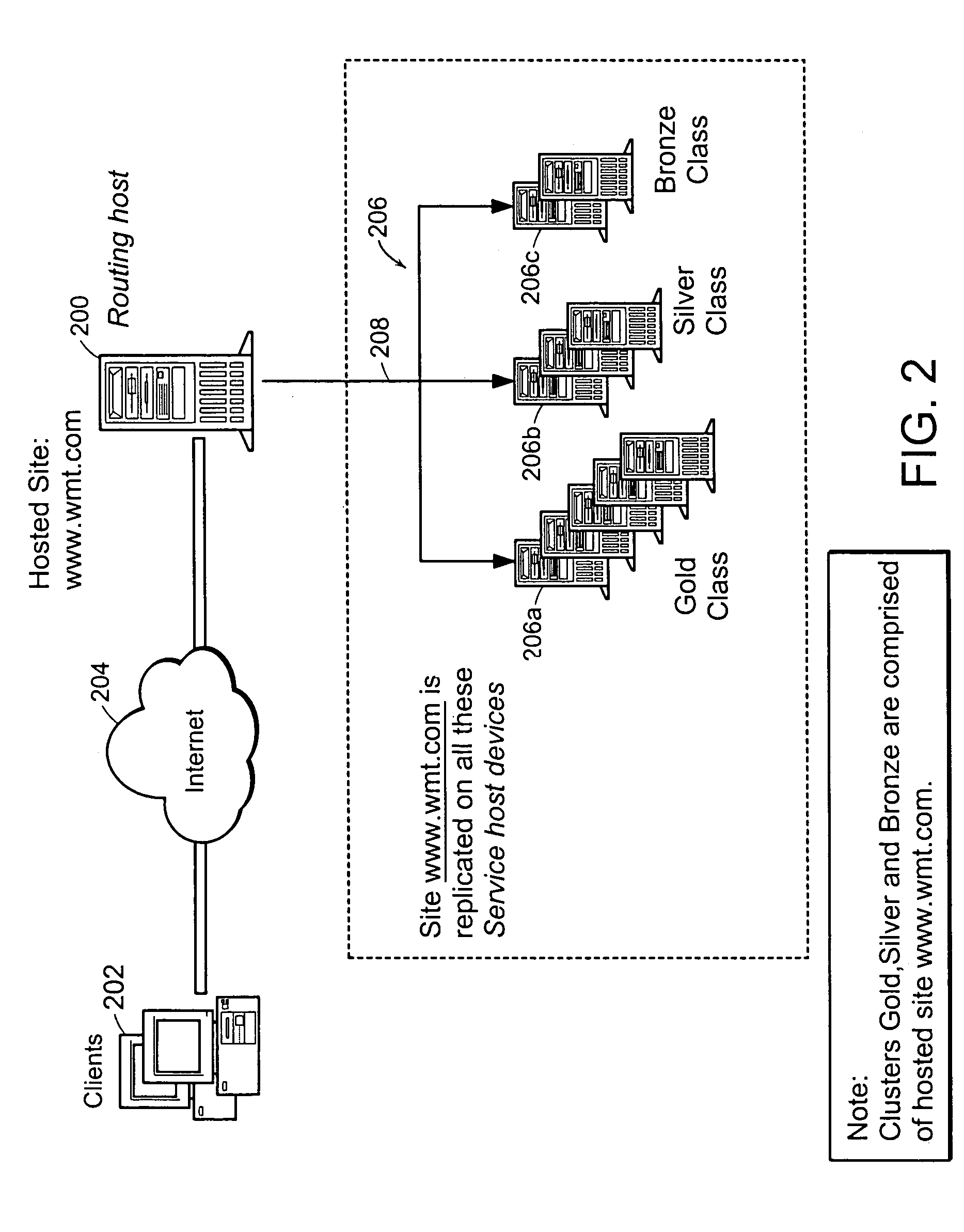
636 results about "Class of service" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
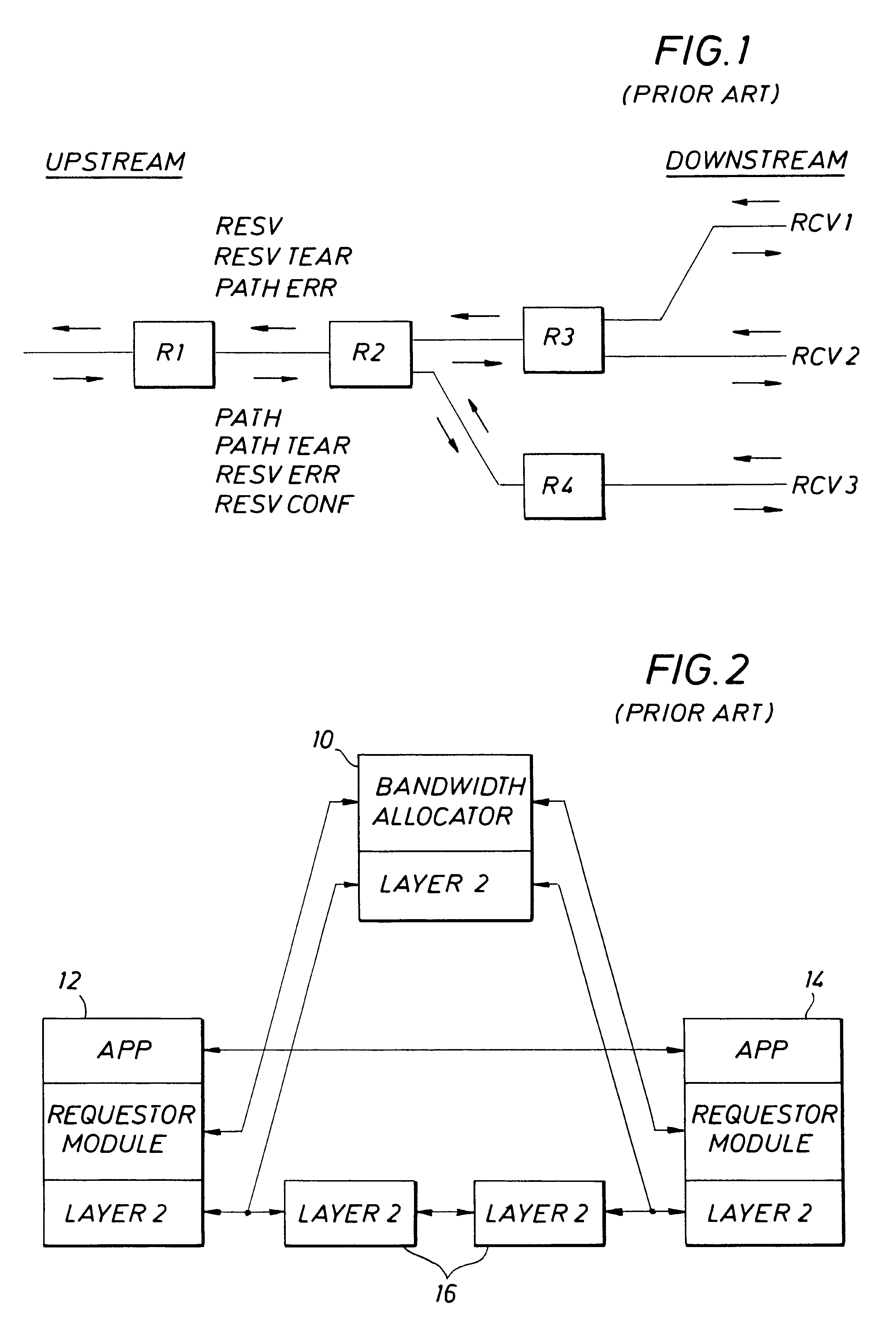
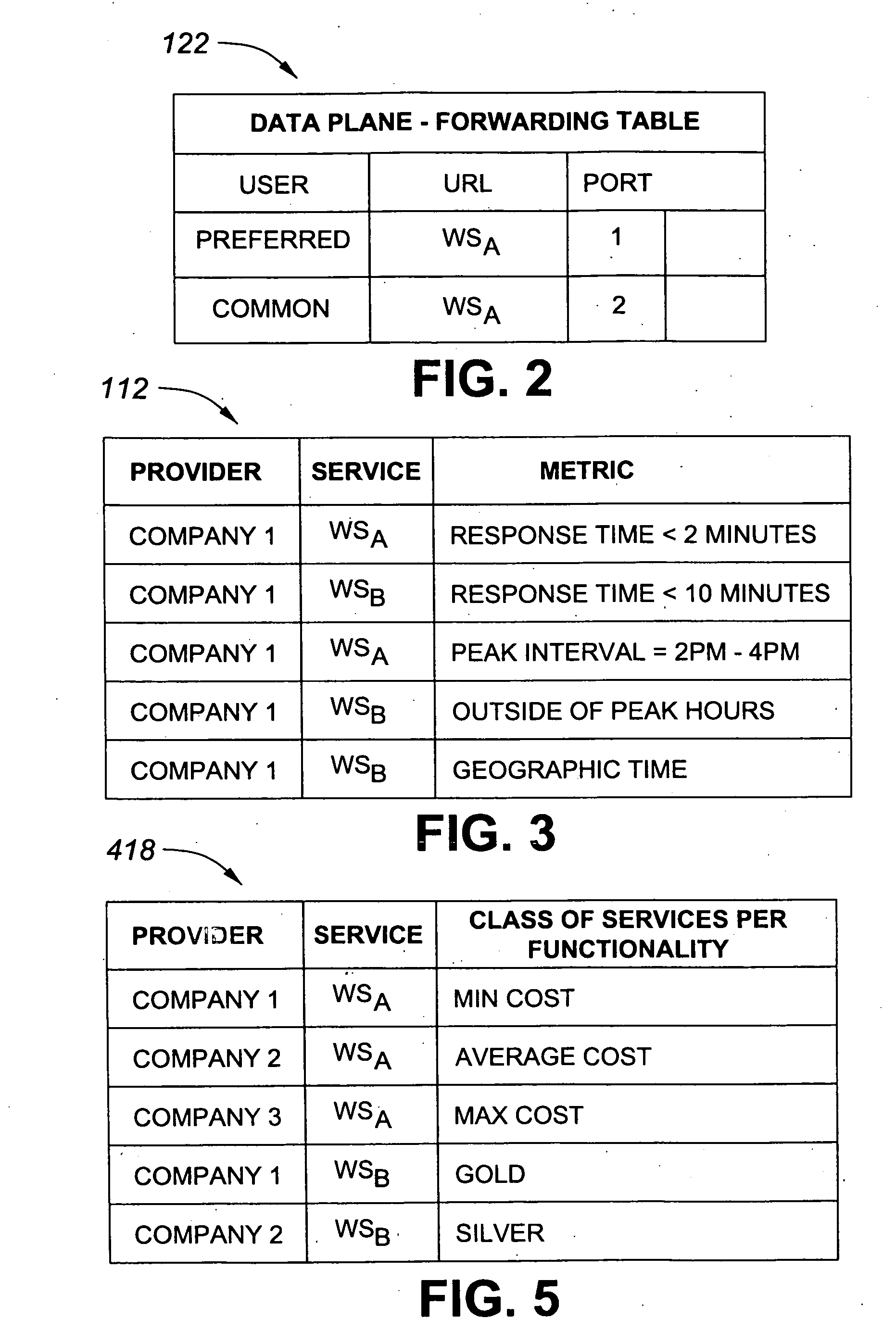
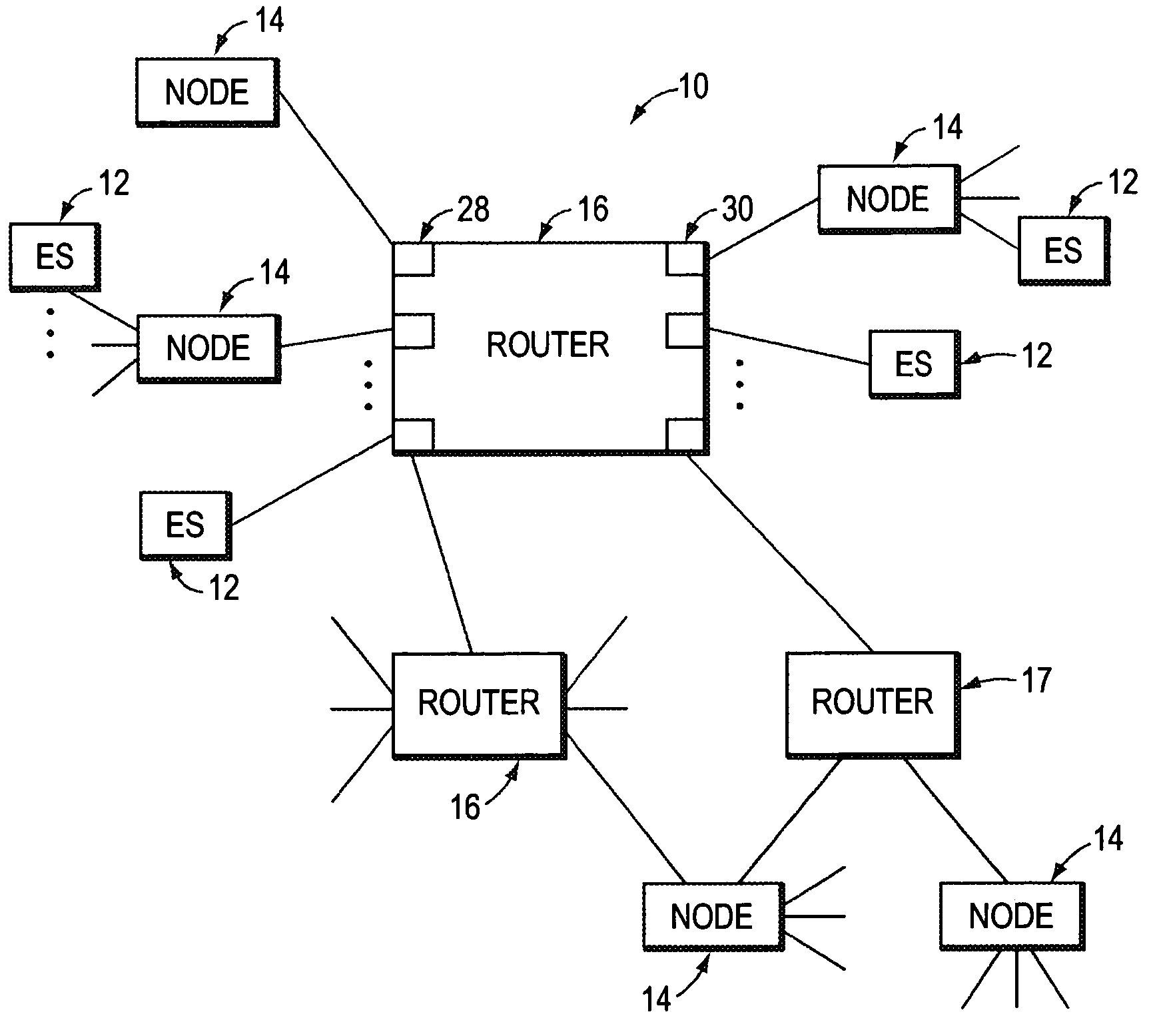
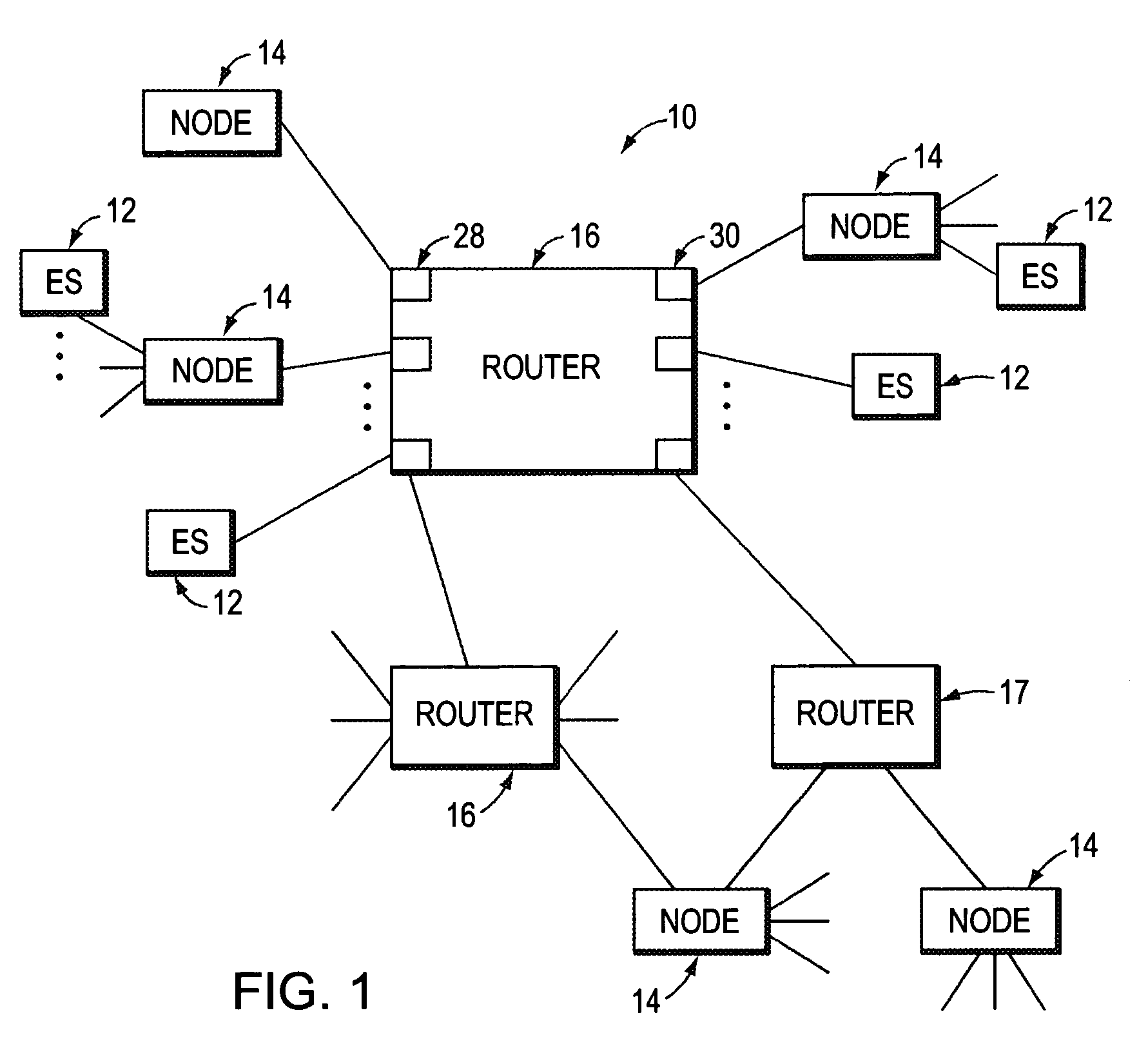
Class of service is a parameter used in data and voice protocols to differentiate the types of payloads contained in the packet being transmitted. The objective of such differentiation is generally associated with assigning priorities to the data payload or access levels to the telephone call.
Systems and methods for allocation of classes of service to network connections corresponding to virtual channels
ActiveUS20110276699A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionInternet trafficClass of service
A system for allocating a different class of service to each network connection in a plurality of network connections, where each network connection corresponds to one or more virtual channels. The system can include a plurality of virtual channels that connect a first computer and a second computer. Each virtual channel can service at least a portion of the network traffic generated using a remote-display protocol. The system can also include a plurality of network connections, where each network connection corresponds to at least one of the virtual channels. Each network connection of the system can have an assigned port number and an assigned class of service that corresponds to a transmission priority level. The class of service assigned to each network connection can be unique from the classes of service assigned to other network connections.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Method and apparatus for providing guaranteed quality/class of service within and across networks using existing reservation protocols and frame formats
InactiveUS6563793B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsAssurance qualityClass of service
A method and apparatus provide reserved bandwidth and QOS / COS virtual circuit connections in a network using both conventional and novel reservation protocols and frame formats. An apparatus according to the invention includes an enterprise control point that communicates with switches via a reserved signaling channel. The switches have been upgraded or replaced to include enhanced functionality. The enhanced switches detect packets that include requests for reserved connections according to existing reservation protocols such as RSVP and IEEE 802.1P / Q. Such detected packets are forwarded to the enterprise control point for processing via a reserved signaling channel. The enterprise control point identifies a path within the network that can satisfy the requested QOS / COS and reserves the requested resources all along the path from beginning to end. A method according to the invention includes detecting packets that include requests for reserved connections according to existing reservation protocols such as RSVP and IEEE 802.1P / Q, forwarding detected packets to an enterprise control point for processing via a reserved signaling channel, identifying a path within the network that can satisfy the requested QOS / COS and reserving the requested resources all along the path from beginning to end.
Owner:WARPSPEED COMM
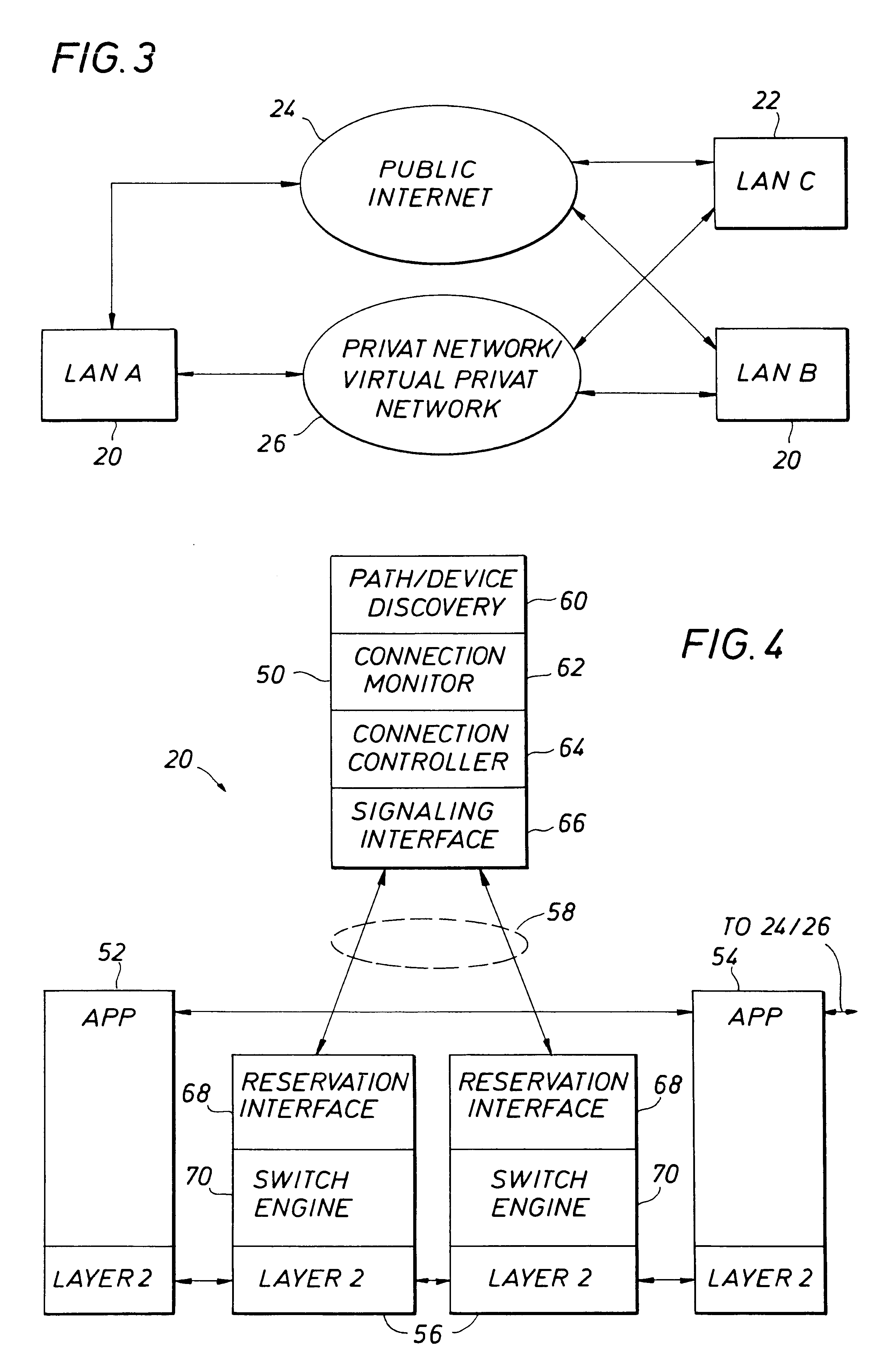
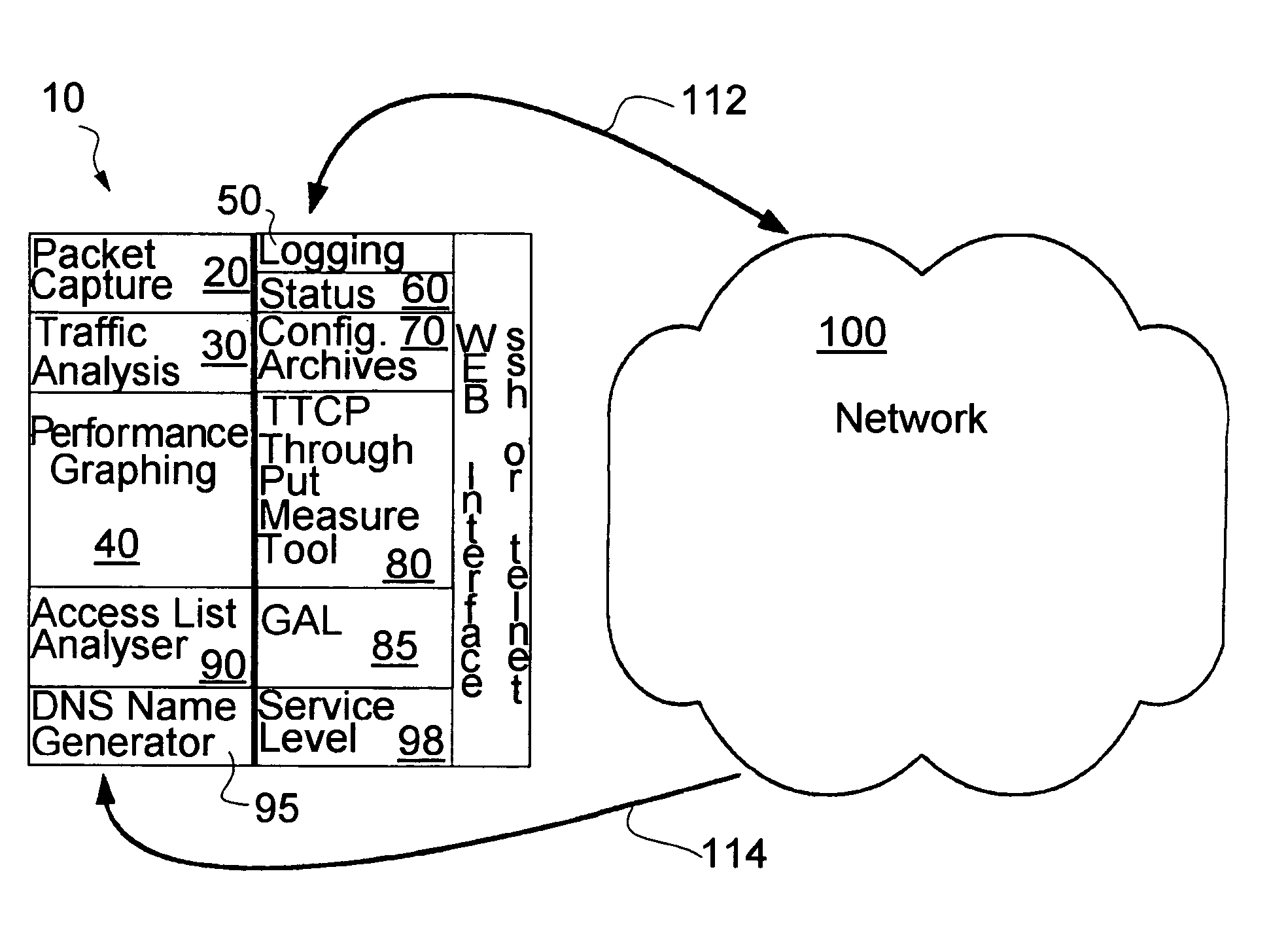
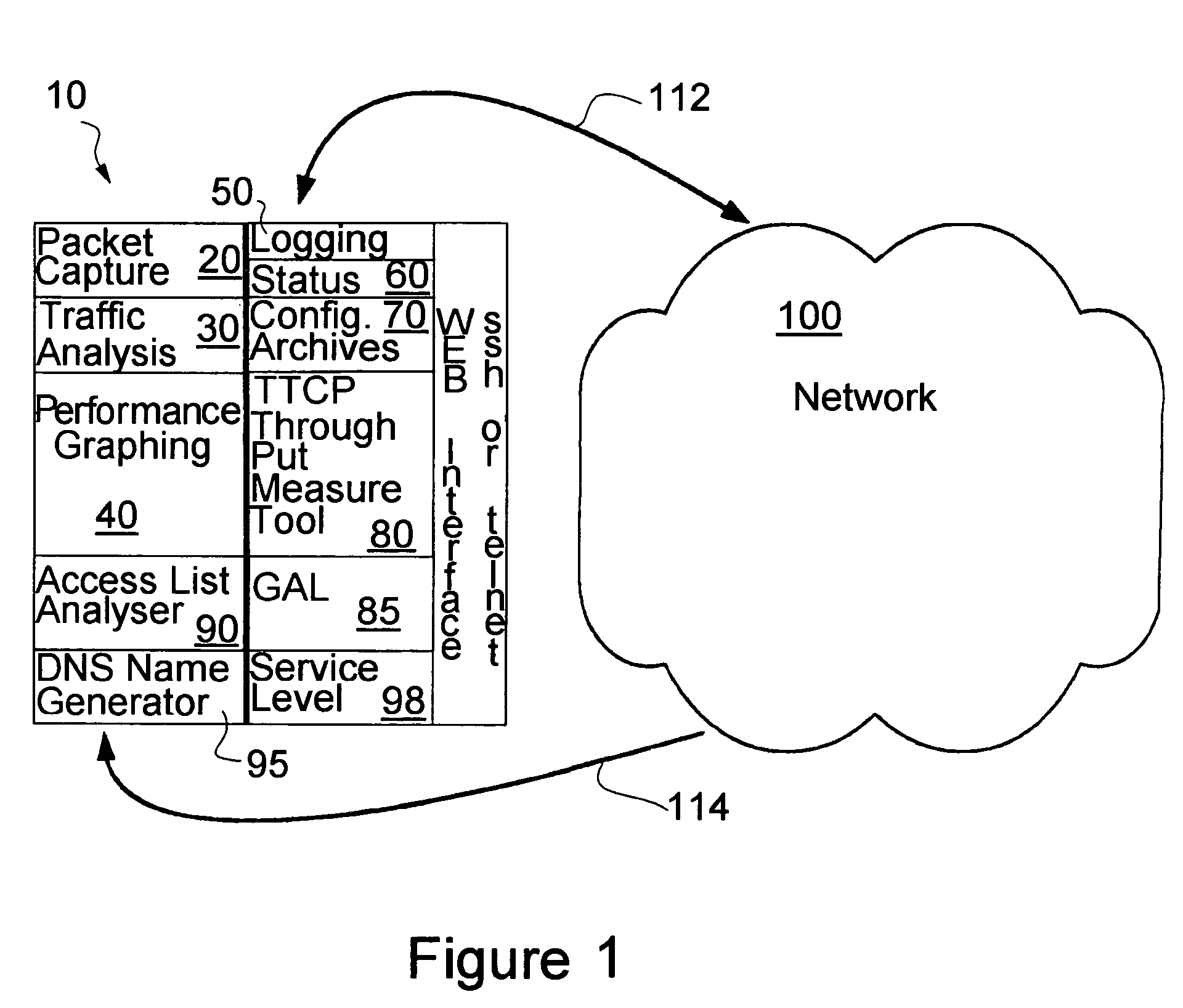
Proactive network analysis system
A proactive network analysis system is a single unit for diagnosing network problems, measuring network performance, and monitoring network status in a comprehensive manner. The system is a compilation of individual tools including a distributed network packet capture data stream collector; a traffic analyzer; a performance graphing unit; a syslog recorder analyzer and archiving unit; a system availability monitor; a device configuration archiving unit; and a throughput measurement tool. The system can further provide an access list generator, an access list analyzer, a router DNS name generator and a service level agreement measurement device.
Owner:SOLUTIONS4NETWORKS
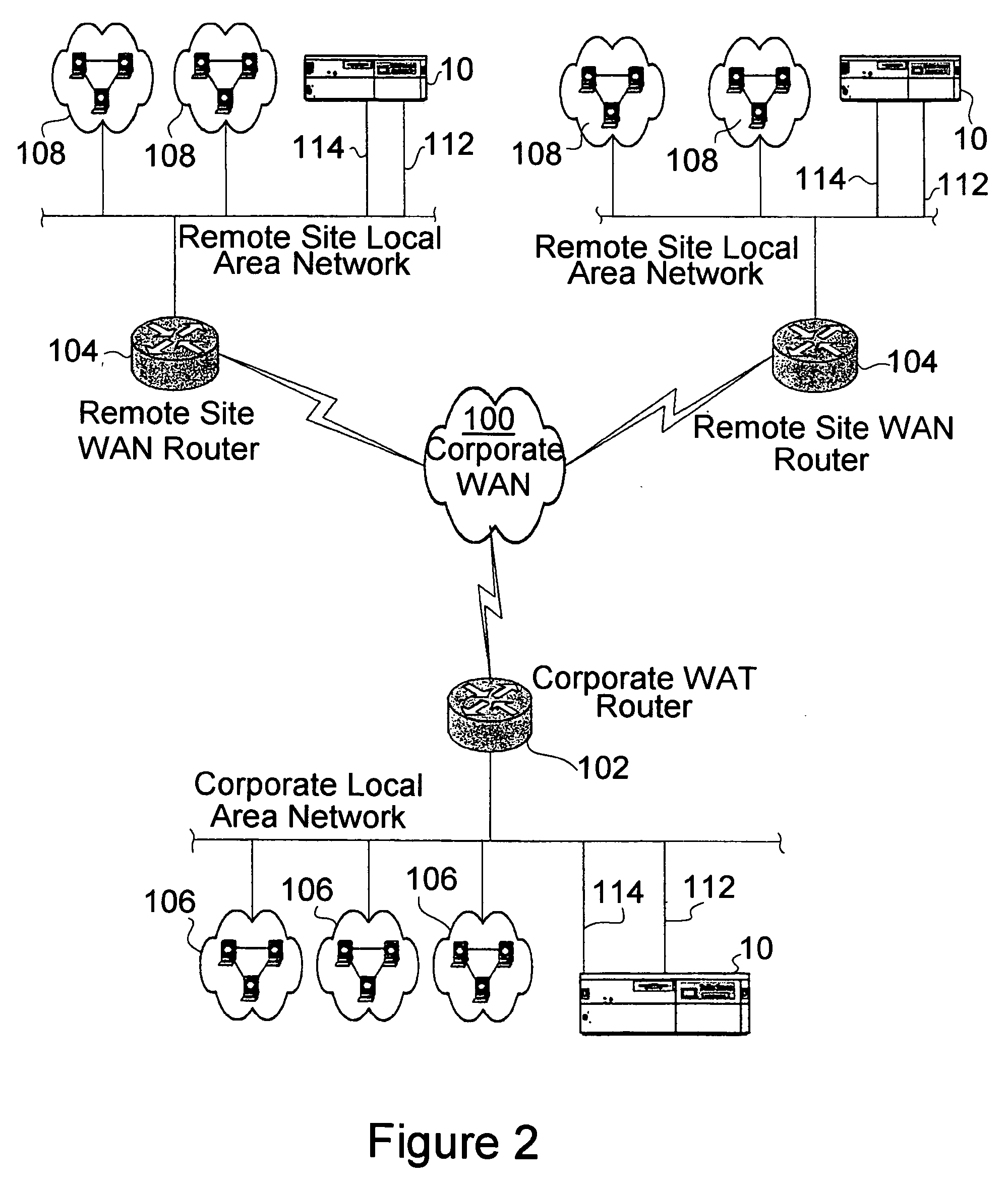
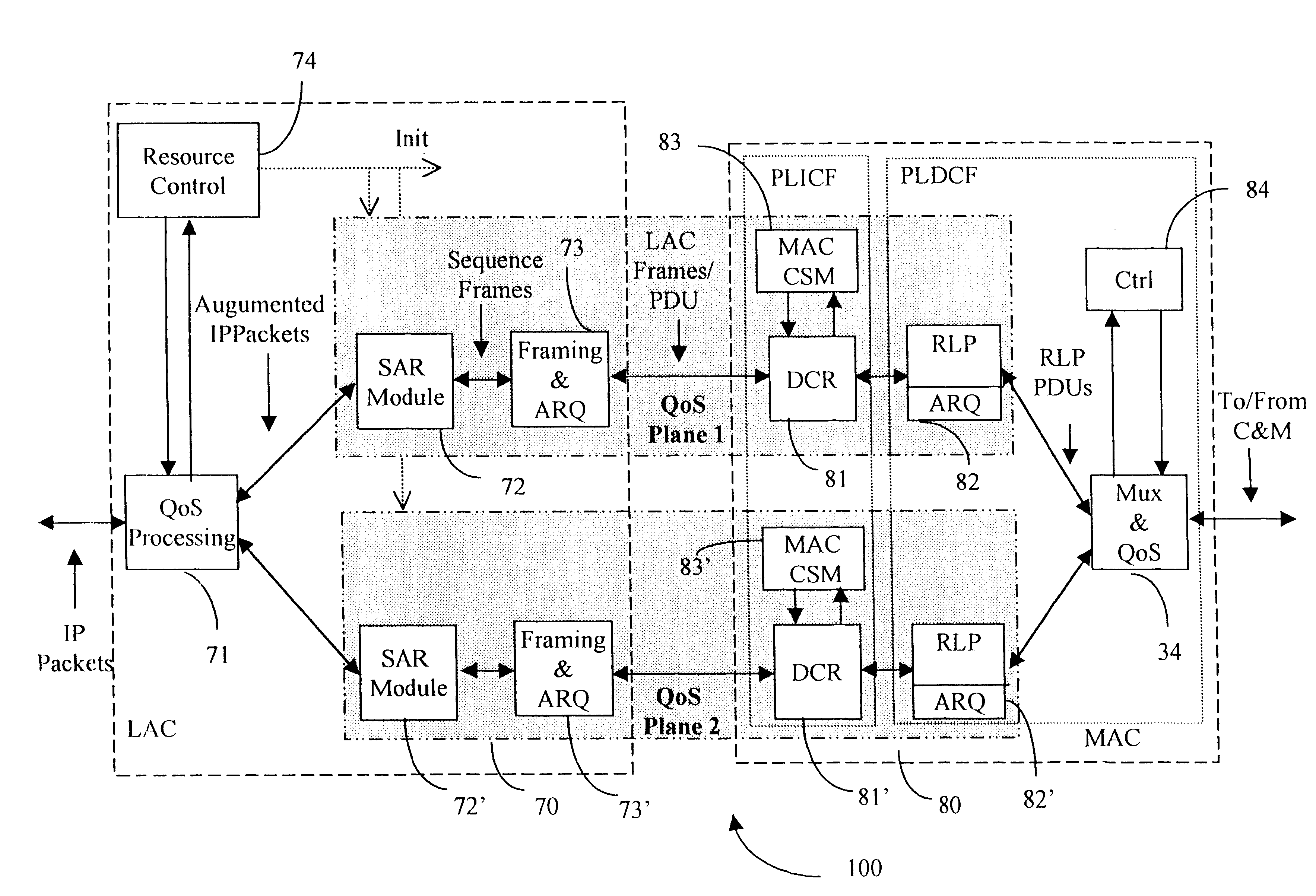
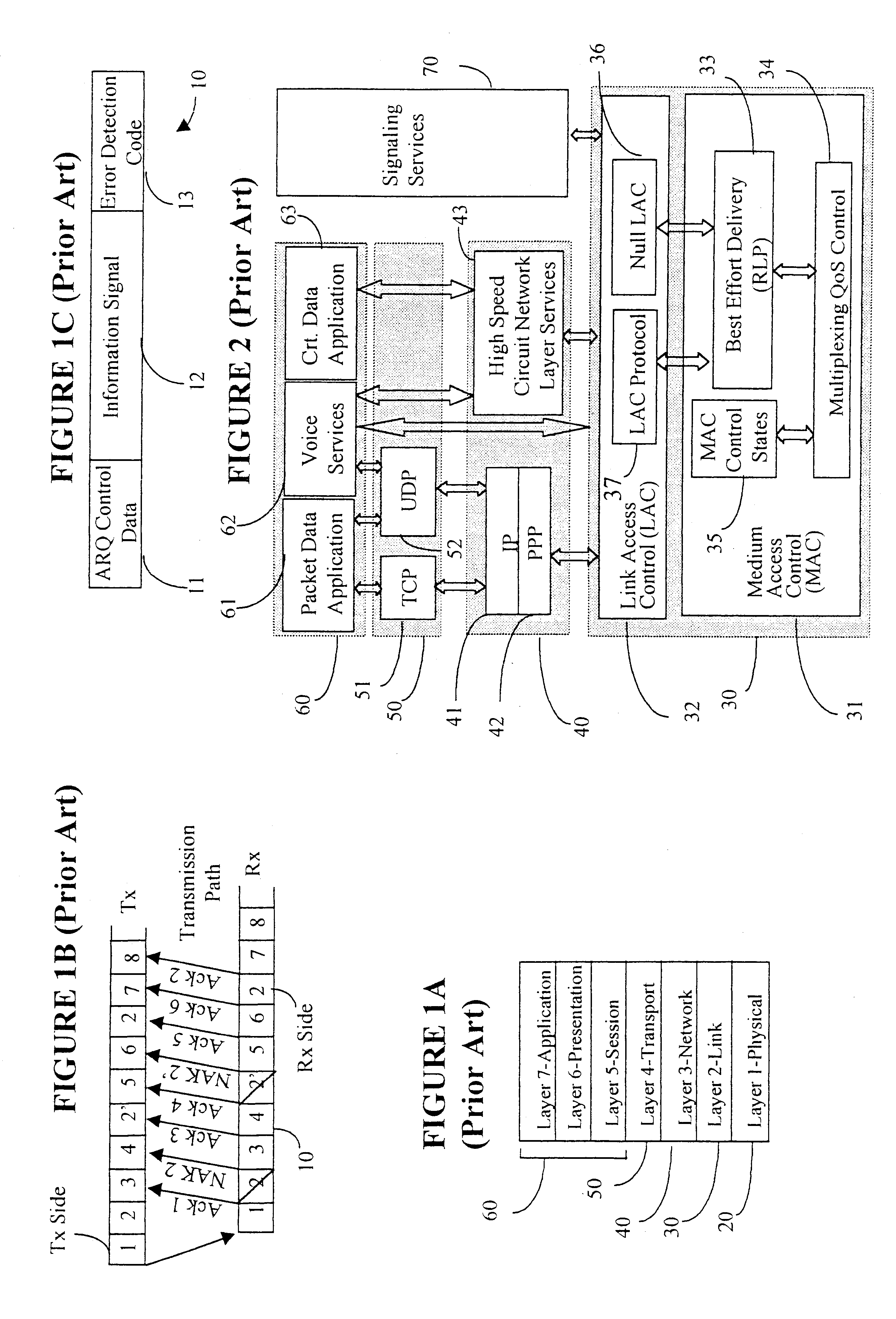
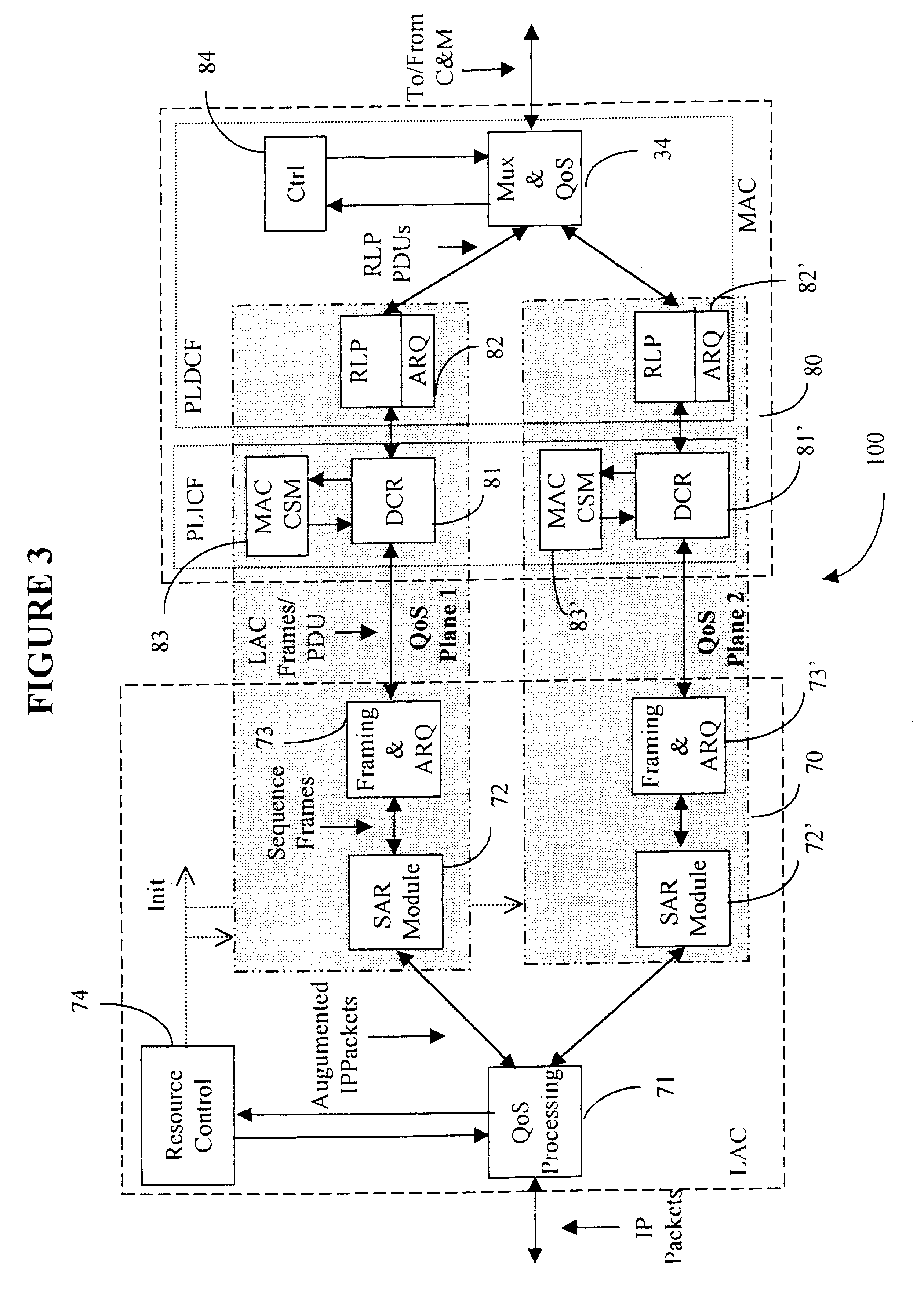
Data link control proctocol for 3G wireless system
InactiveUS6542490B1Error prevention/detection by using return channelElectronic circuit testingTelecommunications linkDual mode
A Data Link Control protocol for 3G wireless communication system for direct support for network layer protocols, e.g. the Internet Protocol (IP), is provided. The Link Layer disclosed comprises a Link Access Control (LAC) sublayer and a Medium Access Control (MAC) sublayer. At a transmit end of the wireless system, a plurality of Quality of Service (QoS) data planes are created to directly support the IP QoS. Each QoS data plane is optimized to handle QoS requirements for a corresponding Class of Service (CoS). Data packets received at the LAC sublayer are directed to a QoS data plane according to the particular QoS information they contain and processed according to the particular QoS requirement to generate variable size LAC frames. The variable size LAC frames are transmitted to the MAC sublayer for generating radio link protocol data units (RLP PDUs) to be transmitted to a receiving end. A new level of error correction is provided at the LAC sublayer as the size of the LAC PDUs can be dynamically adjusted in response to the conditions of the communication link. A dual mode ARQ is provided at the MAC sublayer to improve the quality of the air transmission for bursty as well as non-bursty traffic conditions.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
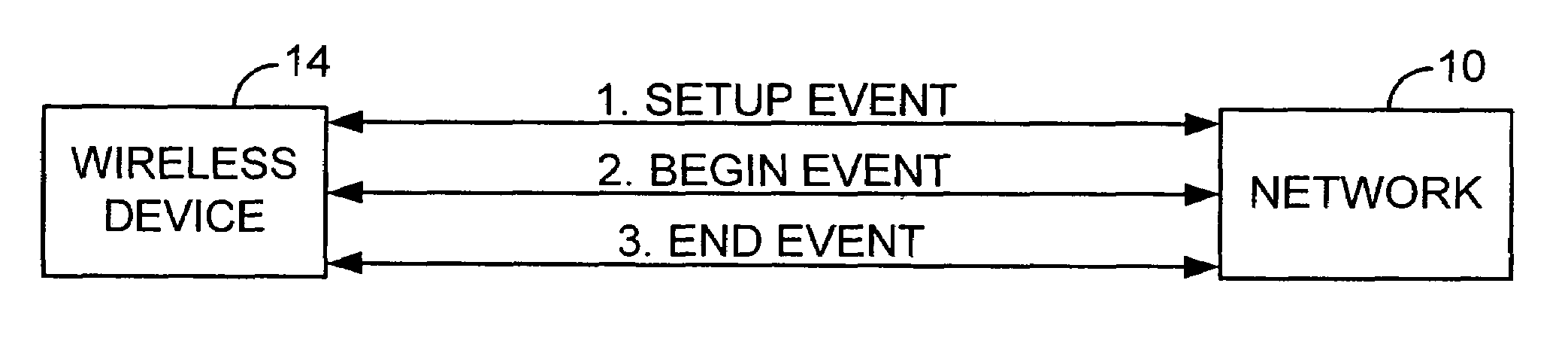
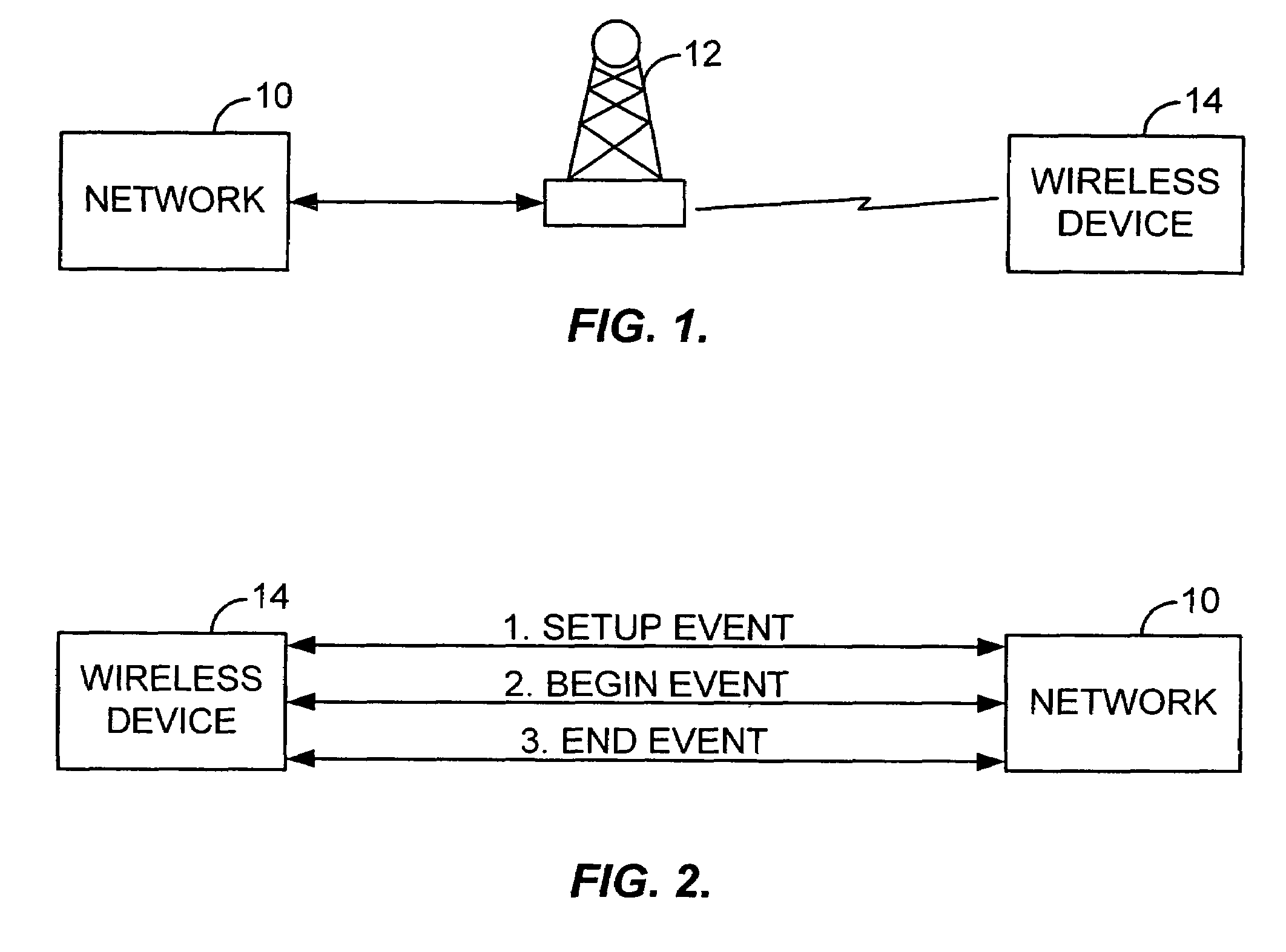
Method and system for data rating for wireless devices
InactiveUS7373136B2Avoiding complication and capacity burdenMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsAccounting/billing servicesClass of serviceReal-time computing
A method and system for rating a data communication session between a network and a wireless device is disclosed. In an exemplary embodiment, the method monitors a series of events, namely, a setup event, a begin event and an end event, which take place during a communication session. The monitoring of such events is accomplished by a data rating application which resides on the wireless device. By monitoring such events, the data rating application is then able to rate the communication session using a number of rating options. The rating option selected includes both how to meter the data transmitted during a data communication session and determine the rate to be applied to each metered increment. Examples of methods used to meter the data include time and volume. Different rating options which can be used to rate the communication session include, for example, application, data utilization, source of data, class of service, quality of service and transmission efficiency.
Owner:TRACFONE WIRELESS
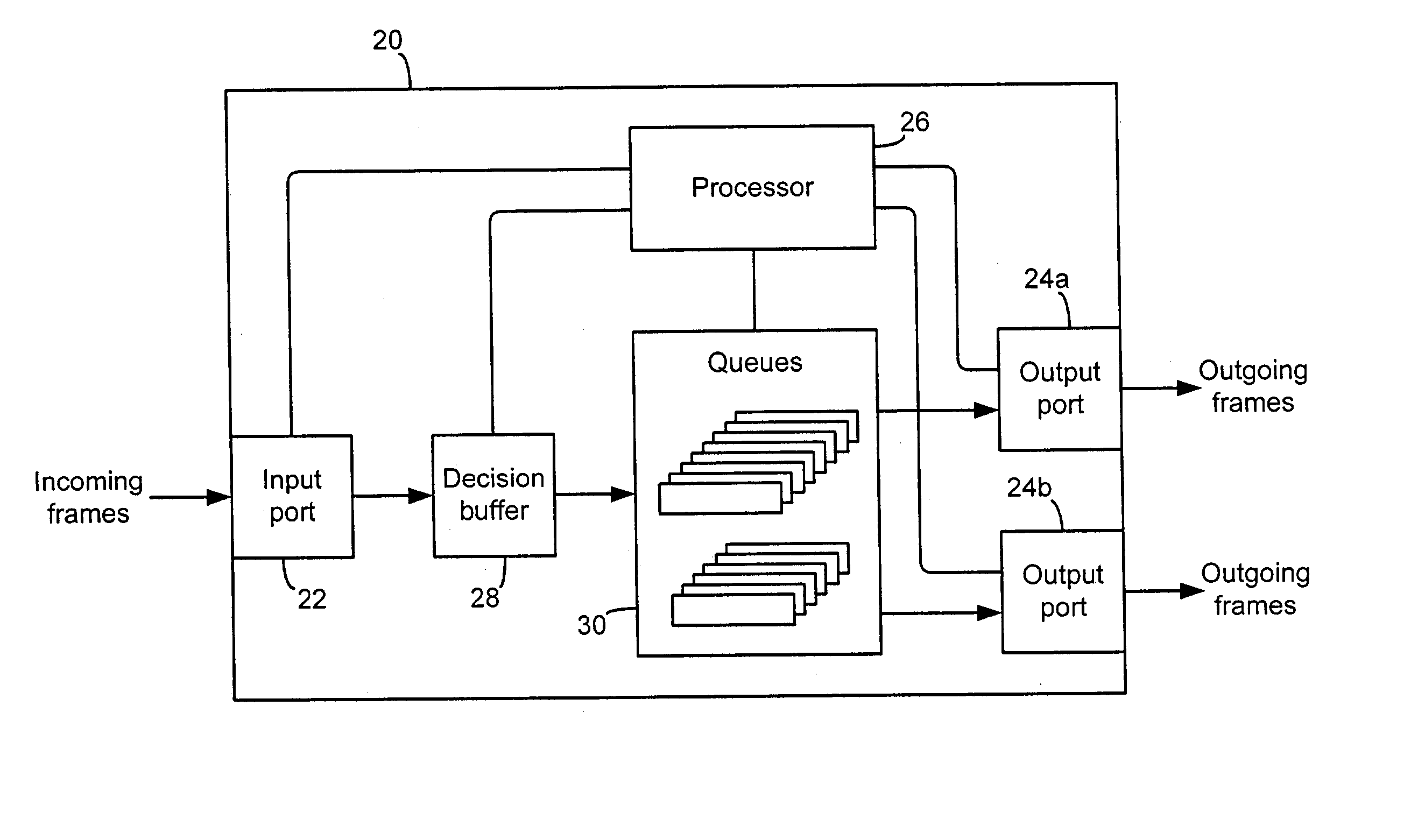
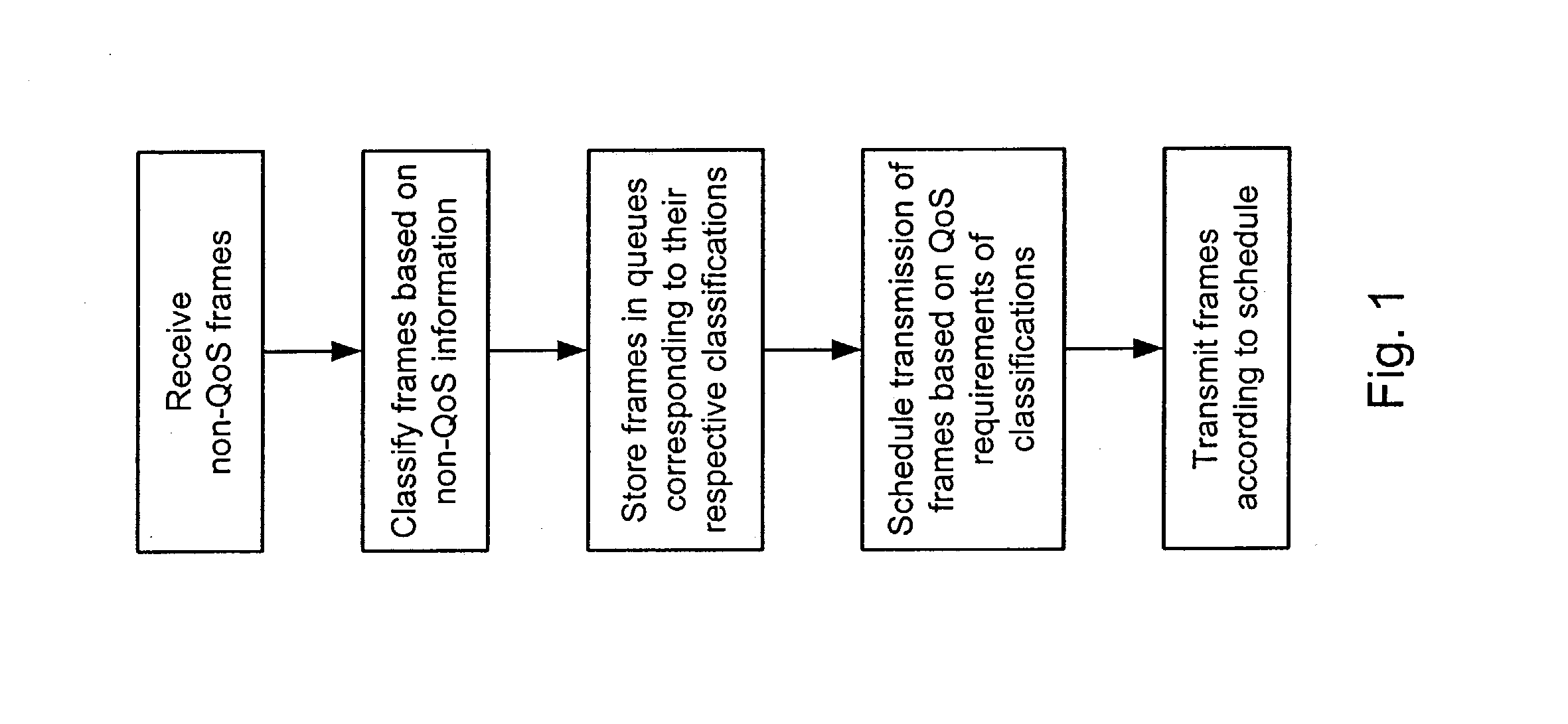
Systems and methods for providing quality of service (QoS) in an environment that does not normally support QoS features
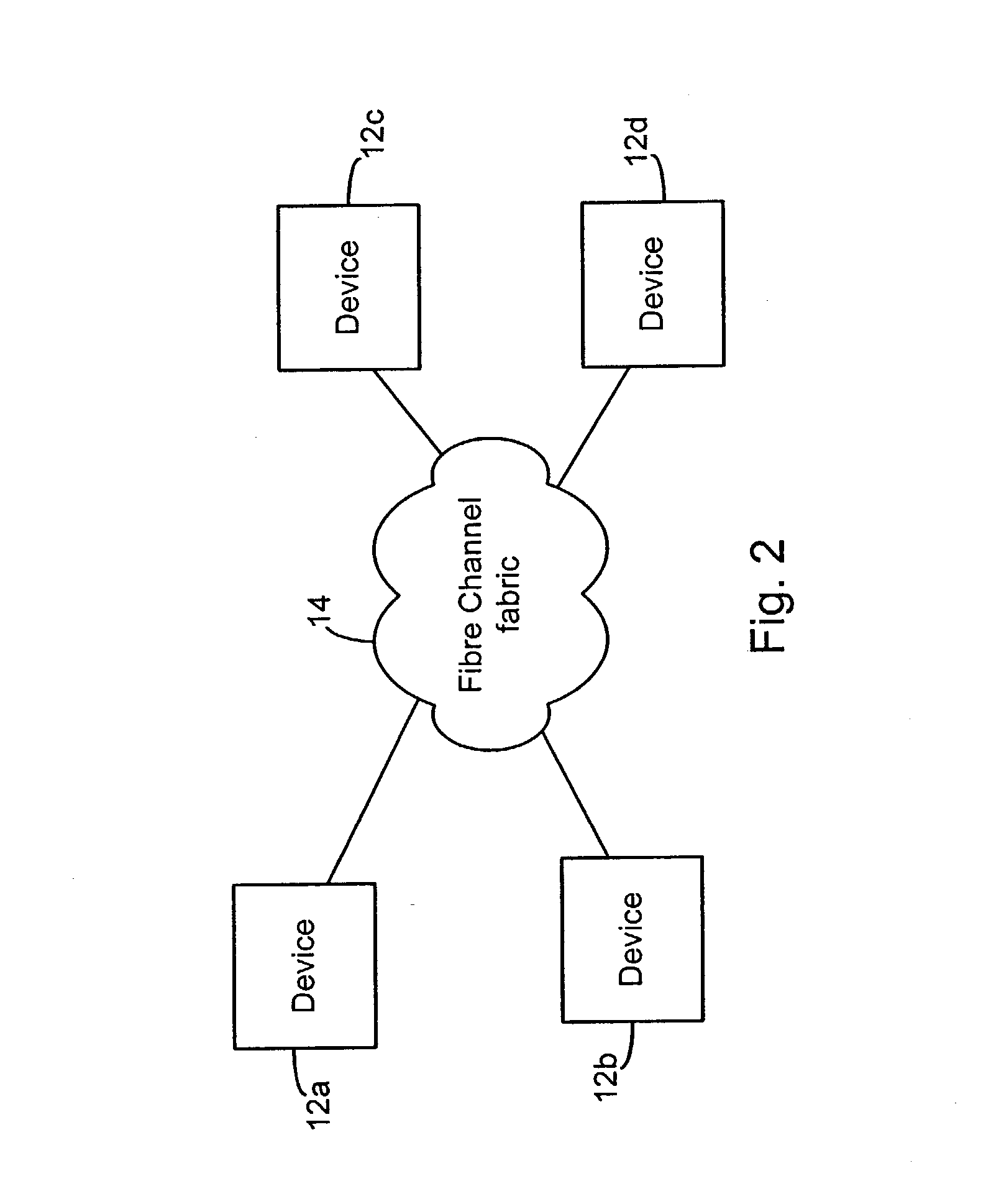
Systems and methods for providing fractional bandwidth communication channels in classes of service that do not normally support these types of channels. In one embodiment, a method comprises receiving one or more frames, wherein each frame contains non-QoS header information, classifying the one or more frames based on the corresponding non-QoS header information and scheduling delivery of the one or more frames based upon corresponding frame classifications, wherein frames in classifications corresponding to QoS circuits are scheduled in a manner that meets QoS requirements associated with the QoS circuits. When the frames are classified, they are forwarded to dynamically allocated queues corresponding to the respective classifications. Frames are scheduled for delivery from the queues according to a modified bin-filling algorithm that is designed to meet the QoS requirements of the respective circuits. This method may be implemented, for example, in a Fibre Channel Class 2 or Class 3 fabric.
Owner:QOS IP
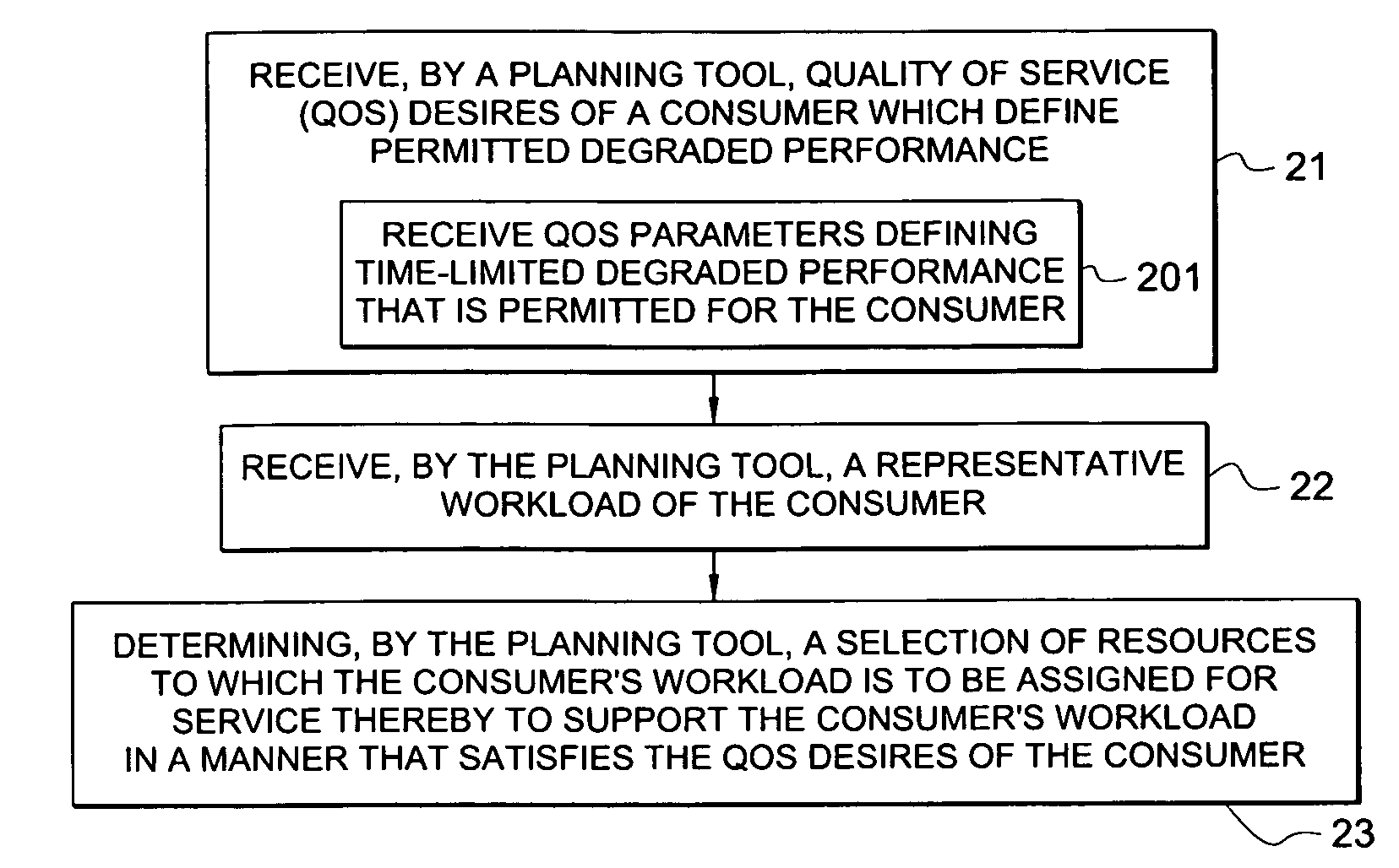
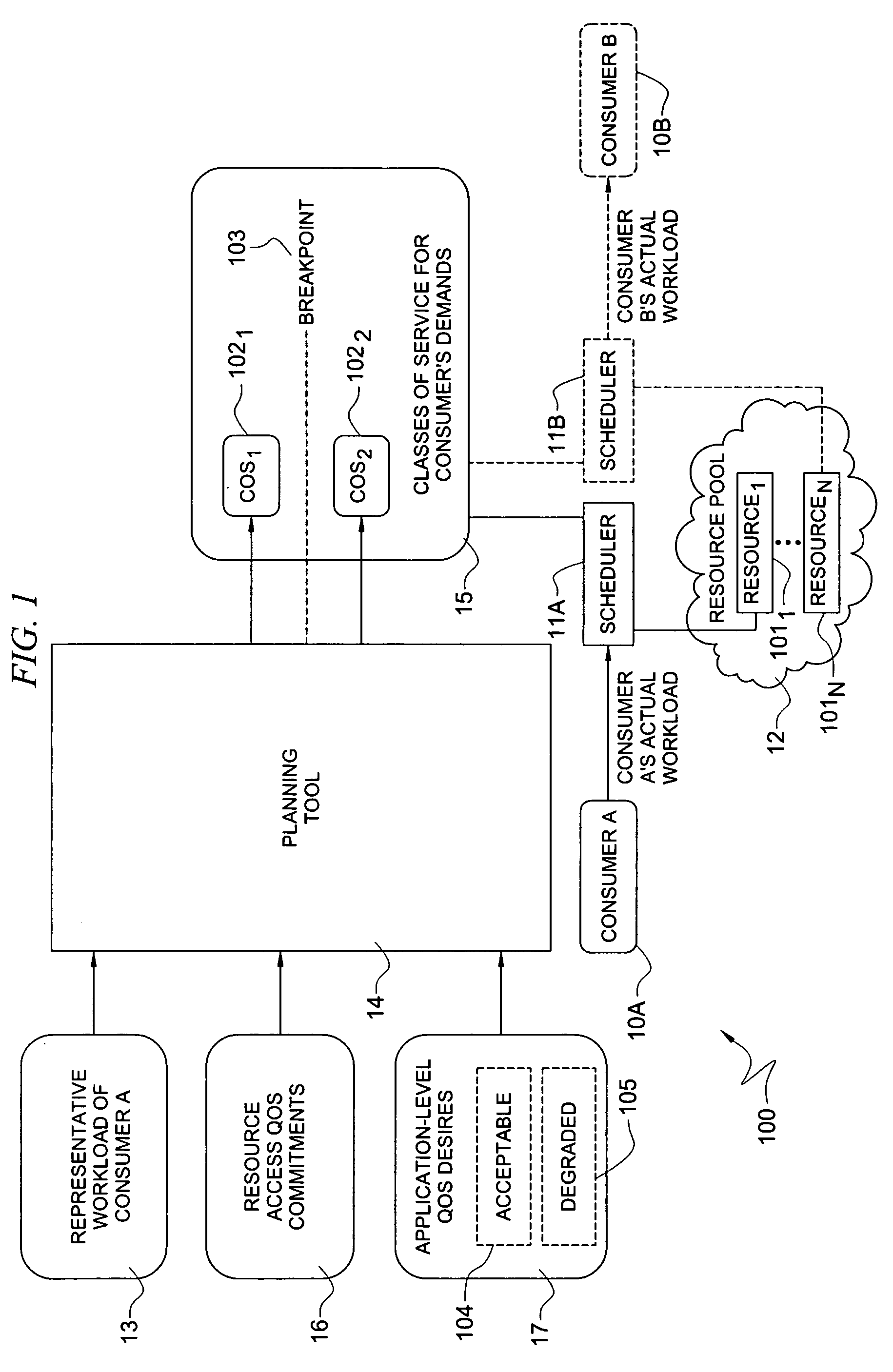
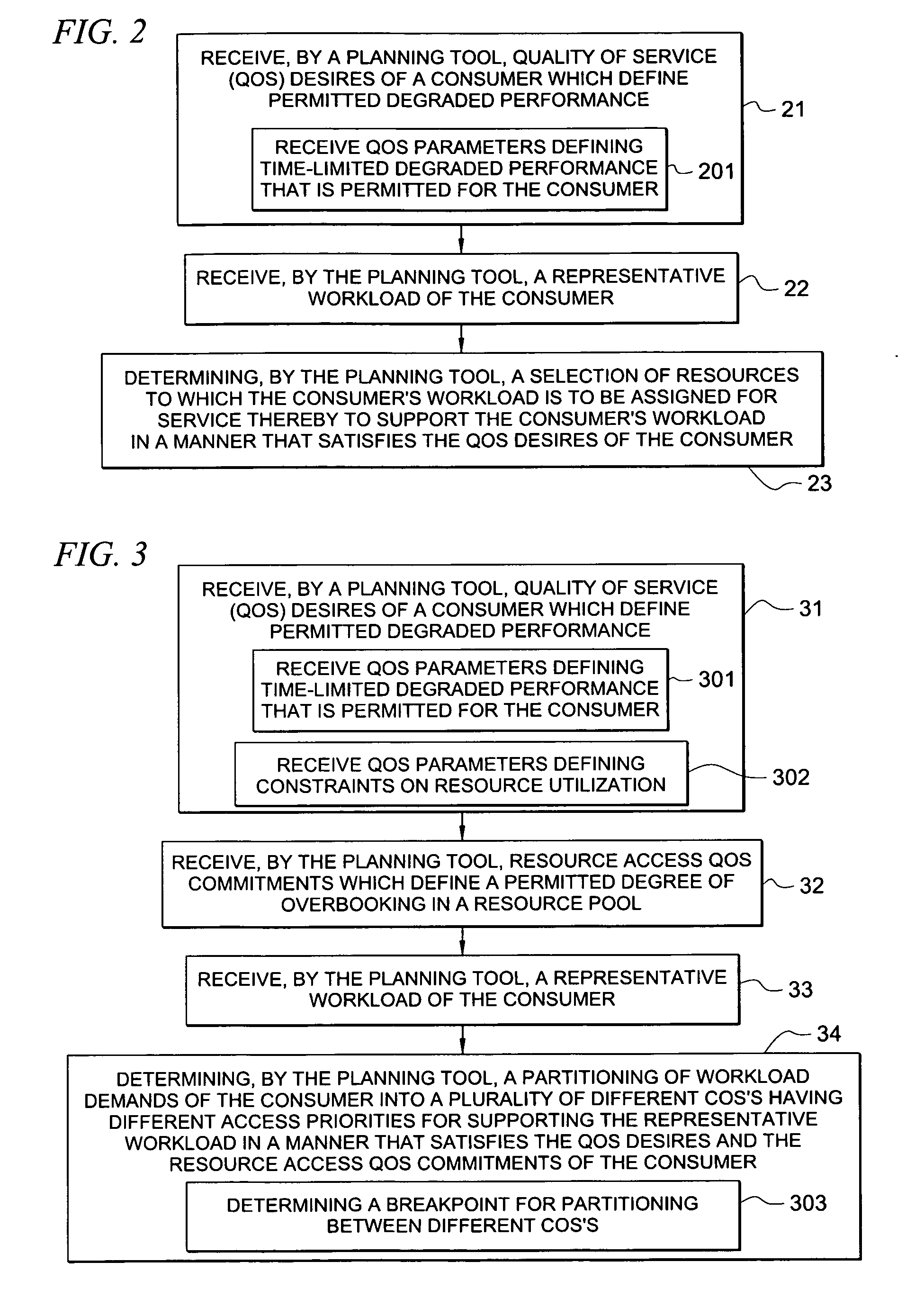
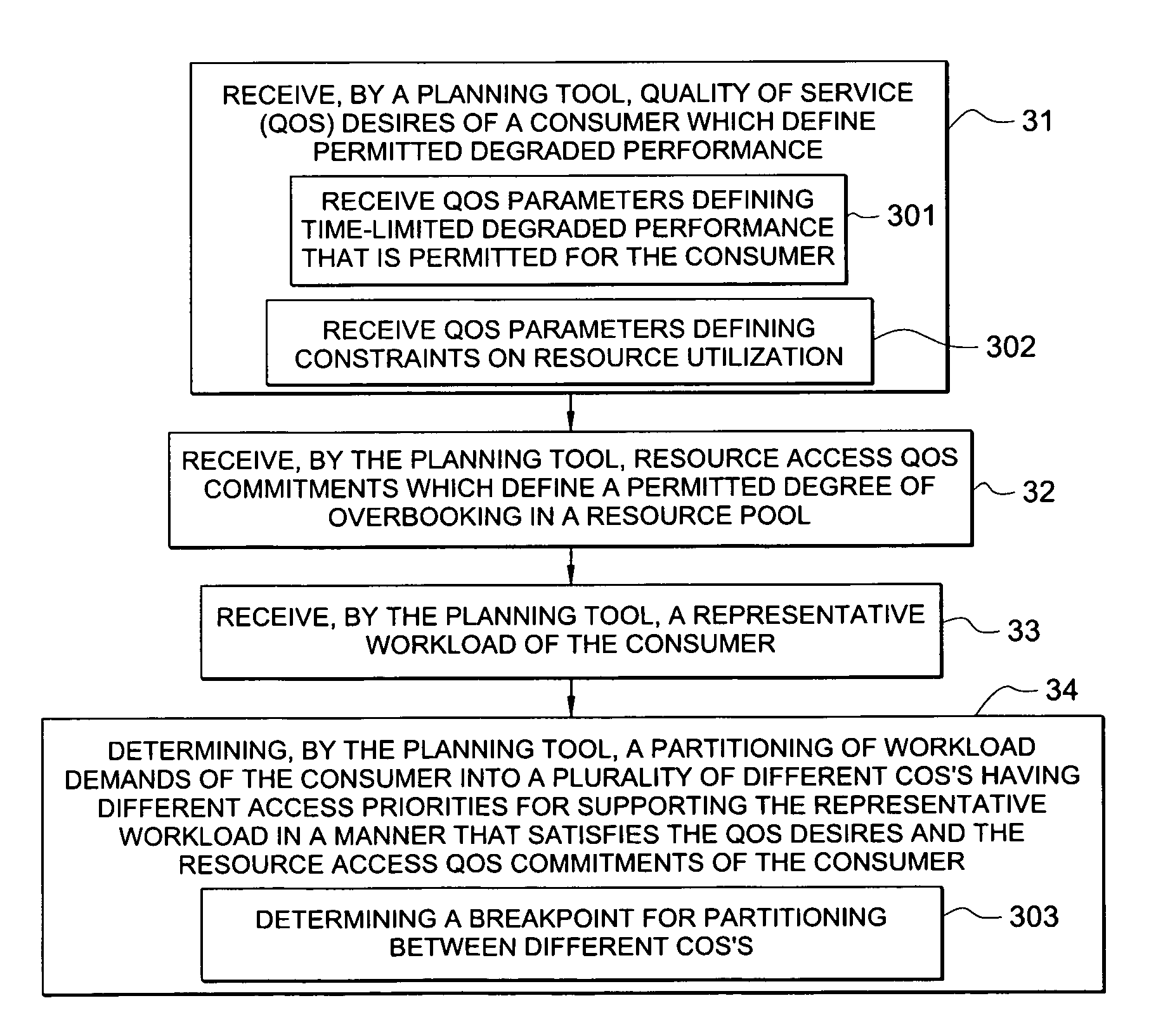
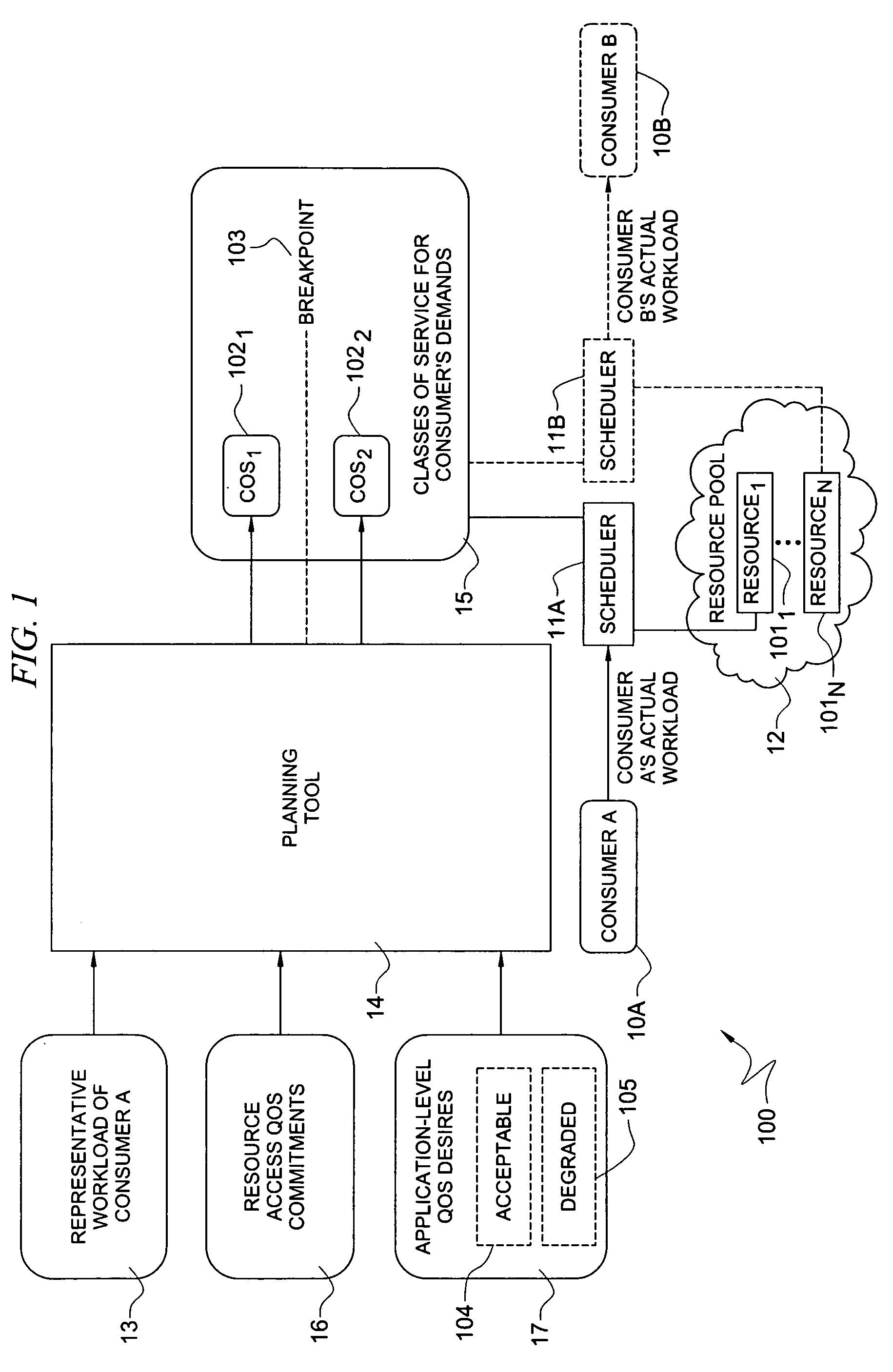
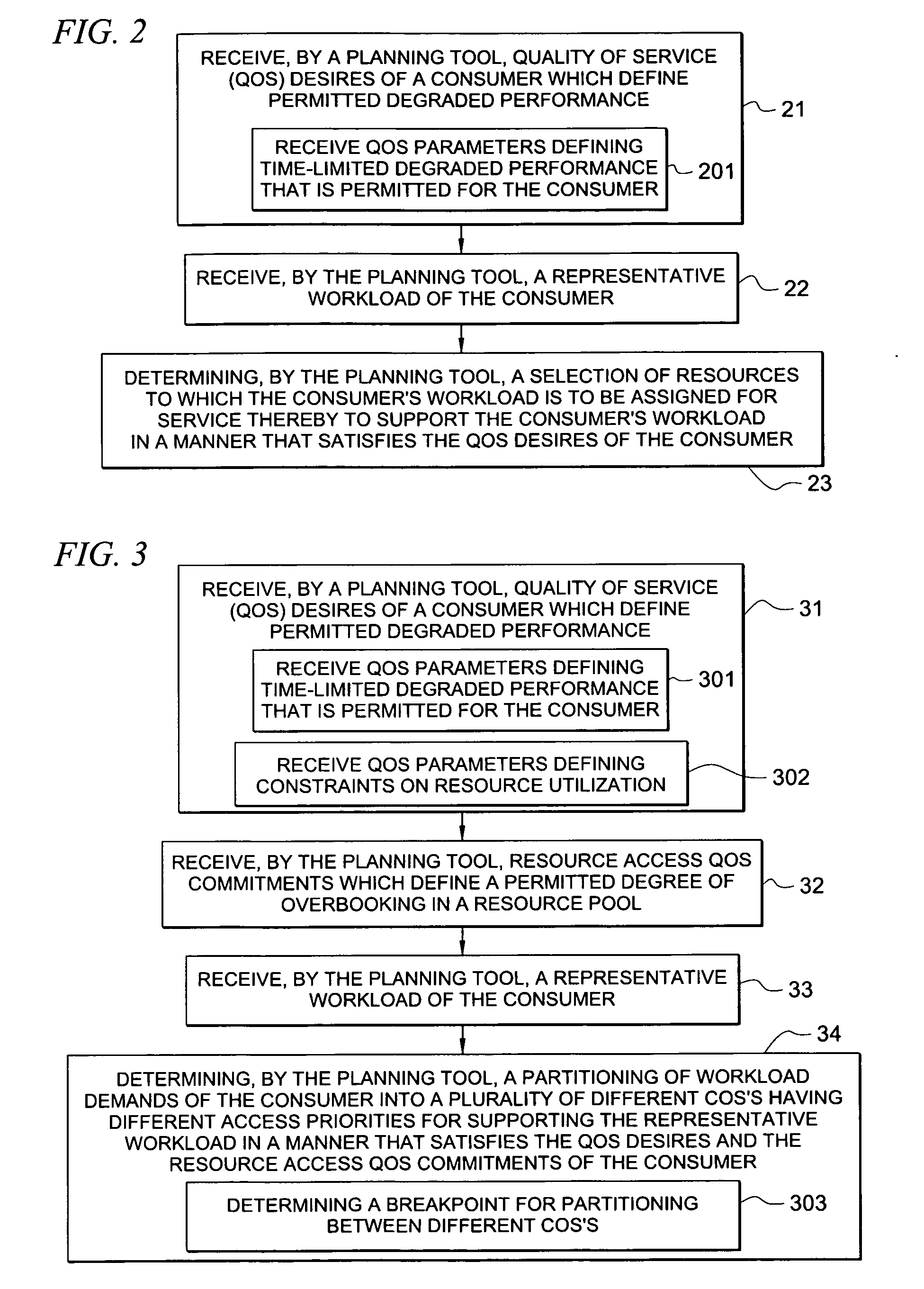
System and method for determining allocation of resource access demands to different classes of service based at least in part on permitted degraded performance
A method comprises receiving into a planning tool a representative workload for a consumer. The method further comprises receiving into the planning tool quality of service desires of the consumer which define permitted degraded performance. In certain embodiments, the permitted degraded performance is time-limited wherein demands of the representative workload may exceed a pre-defined utilization constraint for at least one resource servicing the demands for no more than a pre-defined amount of contiguous time. The planning tool determines an allocation of demand of the consumer for each of a plurality of different classes of service (COSs). In certain embodiments, a first COS provides guaranteed resource access for servicing demand allocated thereto, and a second COS provides non-guaranteed resource access for servicing demand allocated thereto. In certain embodiments, the allocation of demand to the different COSs may be determined for both a normal mode and a failure mode of operation.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
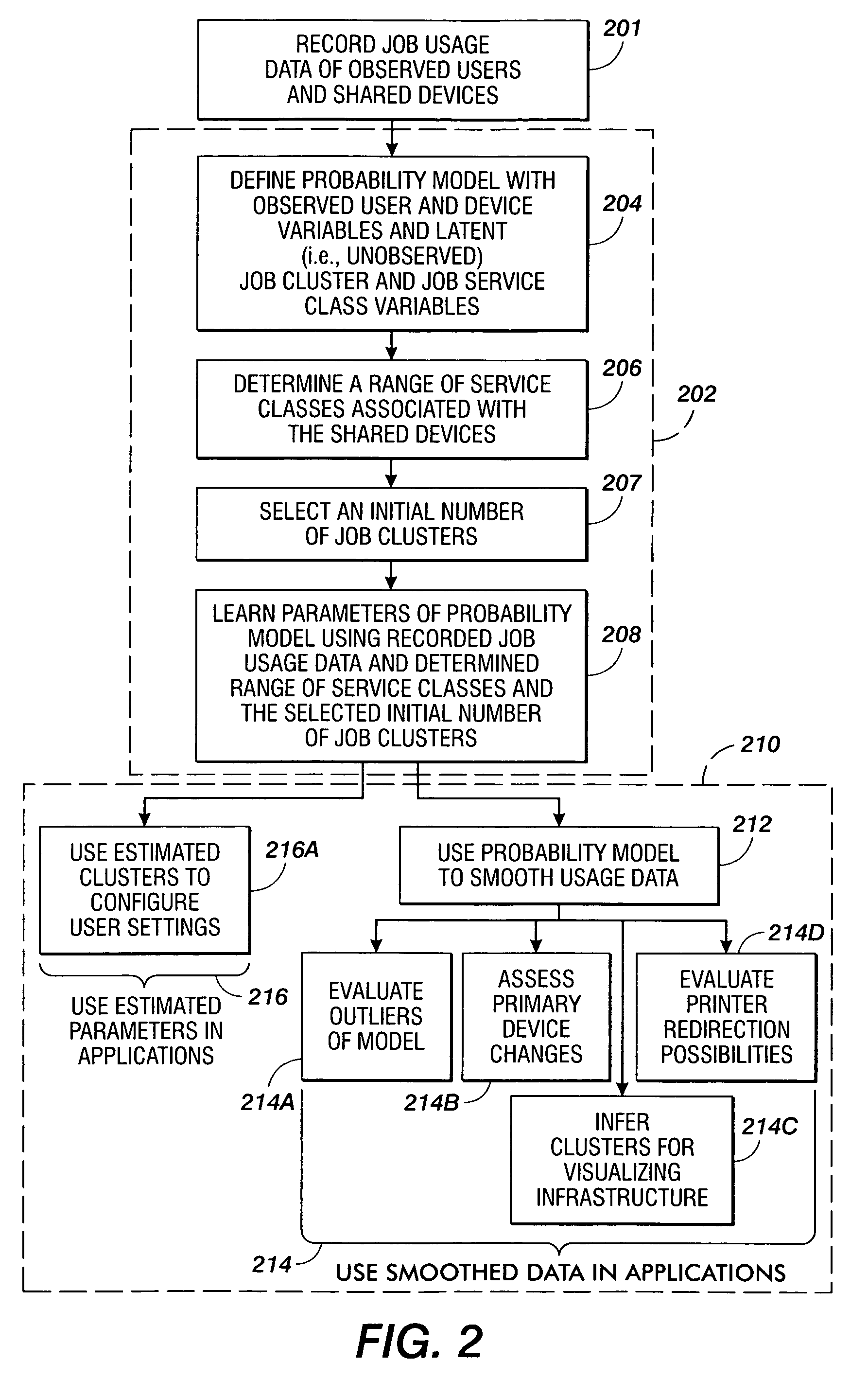
Probabilistic modeling of shared device usage
ActiveUS20060206445A1Wide rangeDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionClass of serviceModel parameters
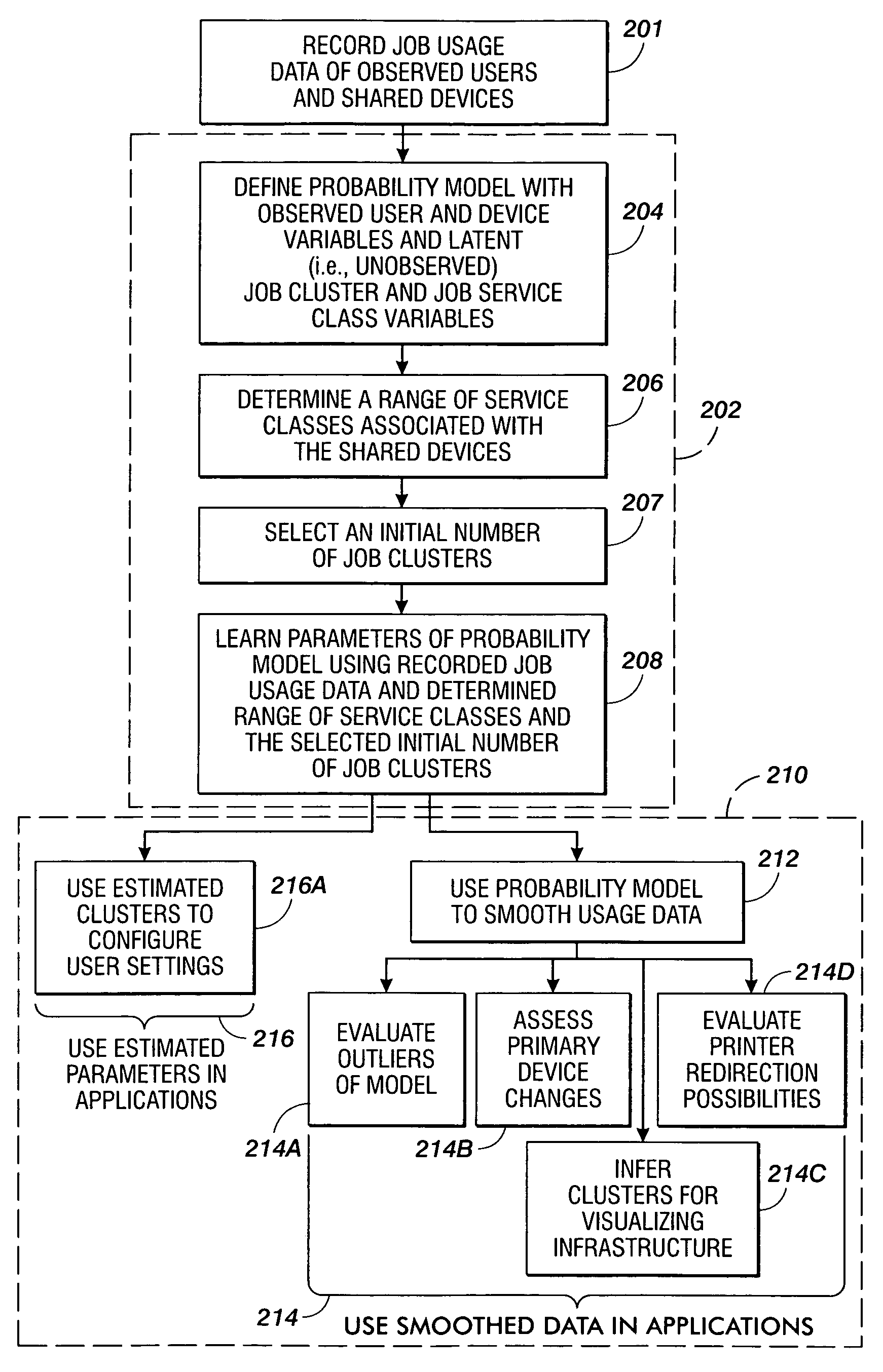
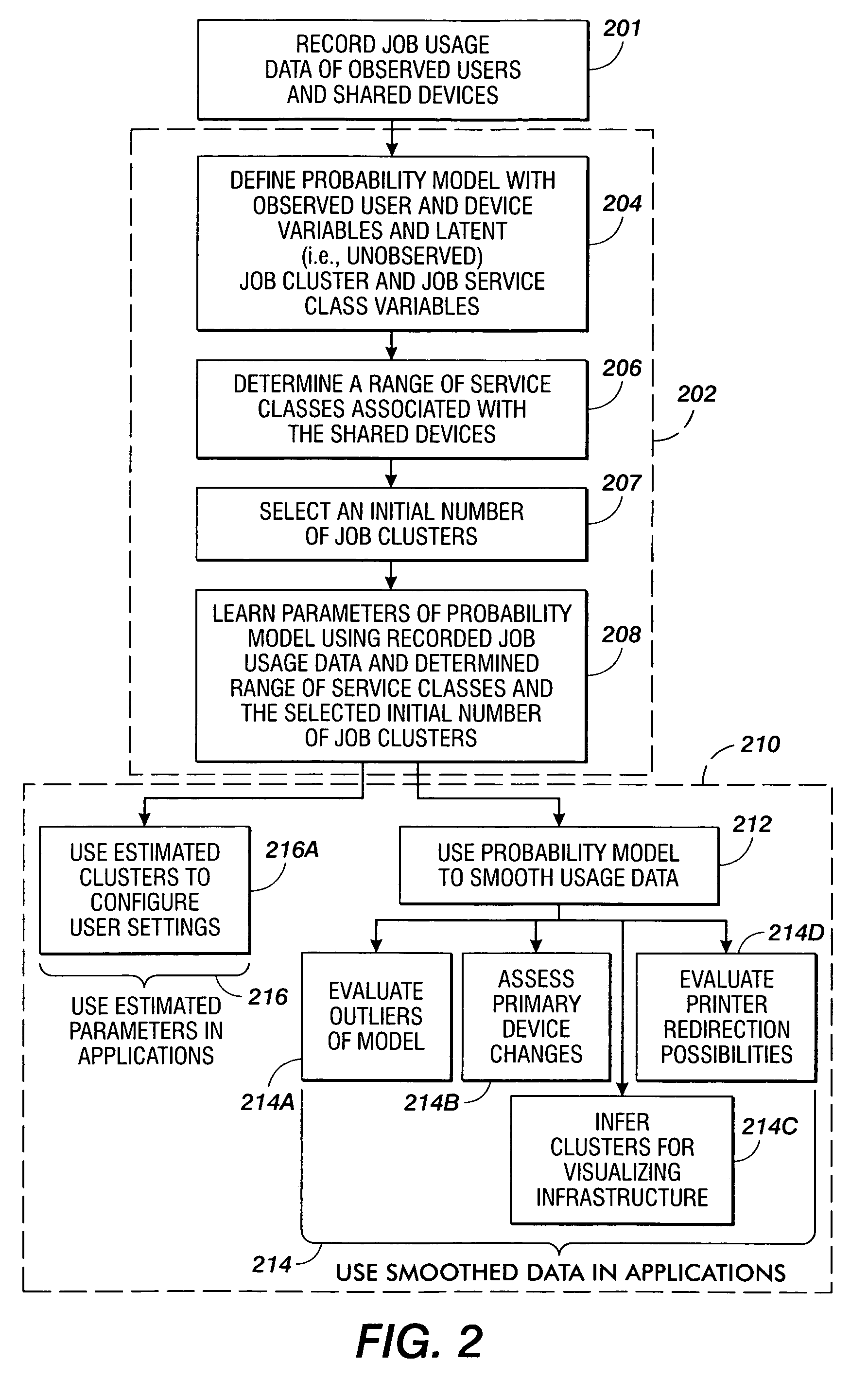
Methods are disclosed for estimating parameters of a probability model that models user behavior of shared devices offering different classes of service for carrying out jobs. In operation, usage job data of observed users and devices carrying out the jobs is recorded. A probability model is defined with an observed user variable, an observed device variable, a latent job cluster variable, and a latent job service class variable. A range of job service classes associated with the shared devices is determined, and an initial number of job clusters is selected. Parameters of the probability model are learned using the recorded job usage data, the determined range of service classes, and the selected initial number of job clusters. The learned parameters of the probability model are applied to evaluate one or more of: configuration of the shared devices, use of the shared devices, and job redirection between the shared devices.
Owner:XEROX CORP
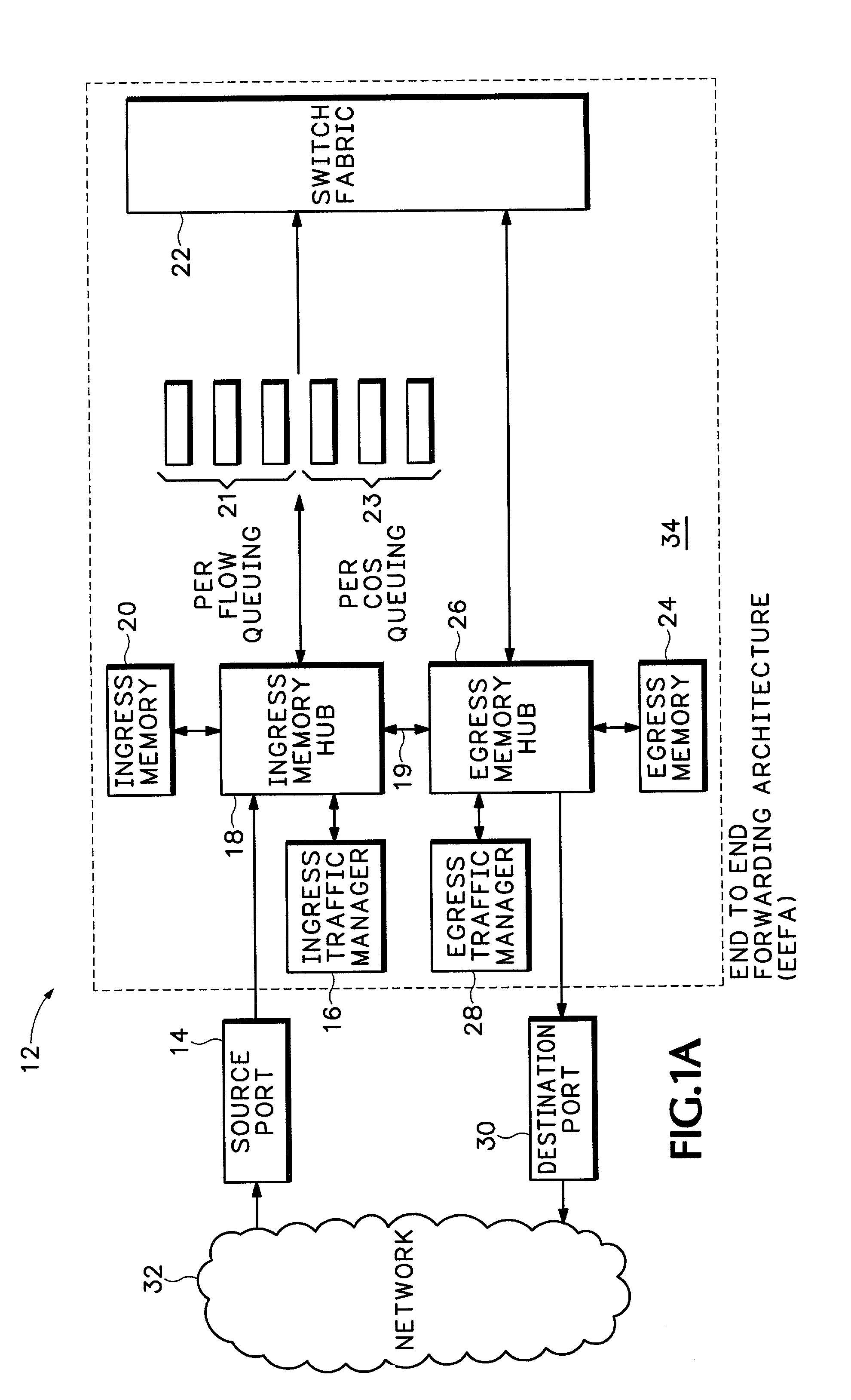
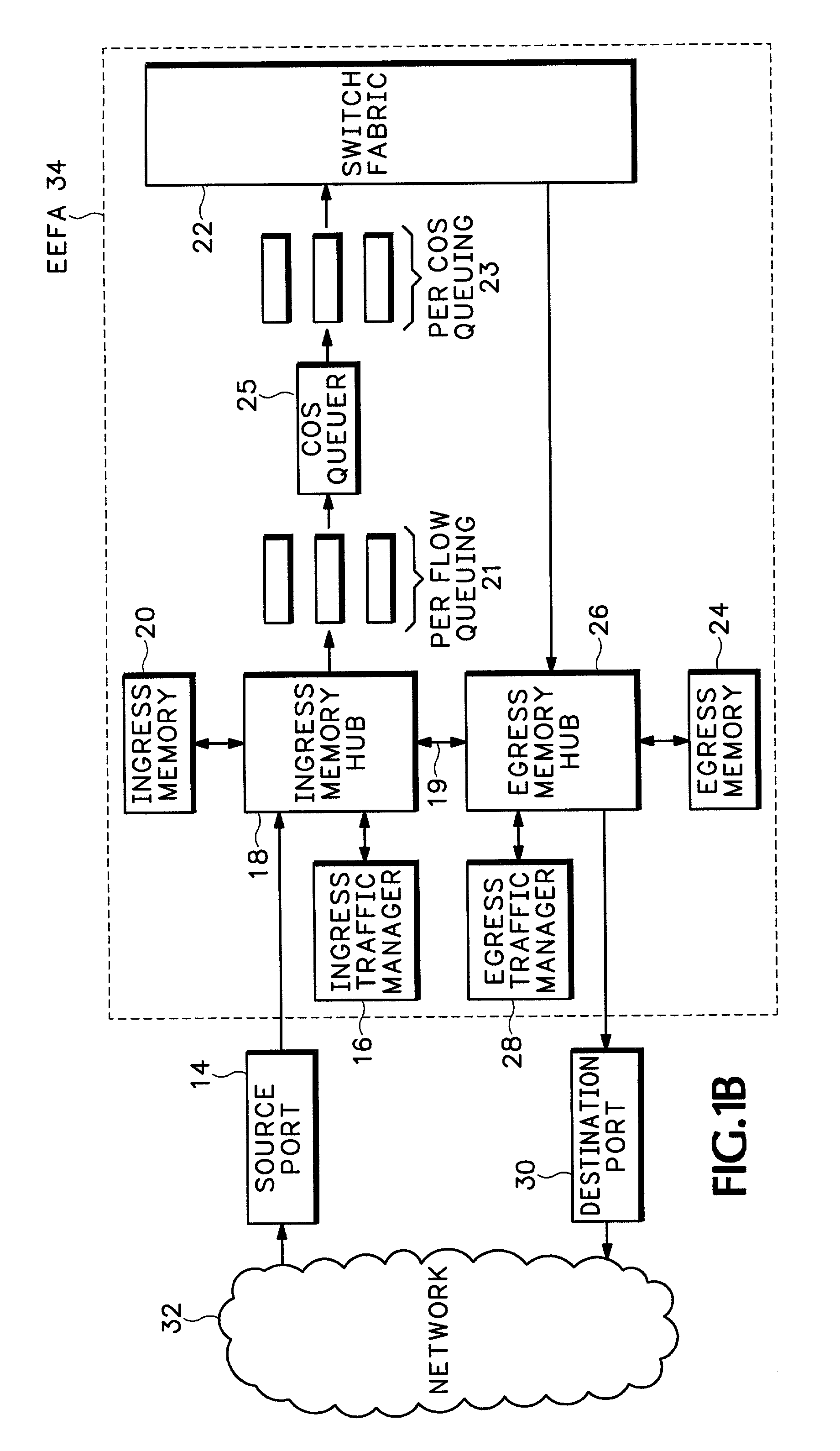
Method and apparatus for end to end forwarding architecture
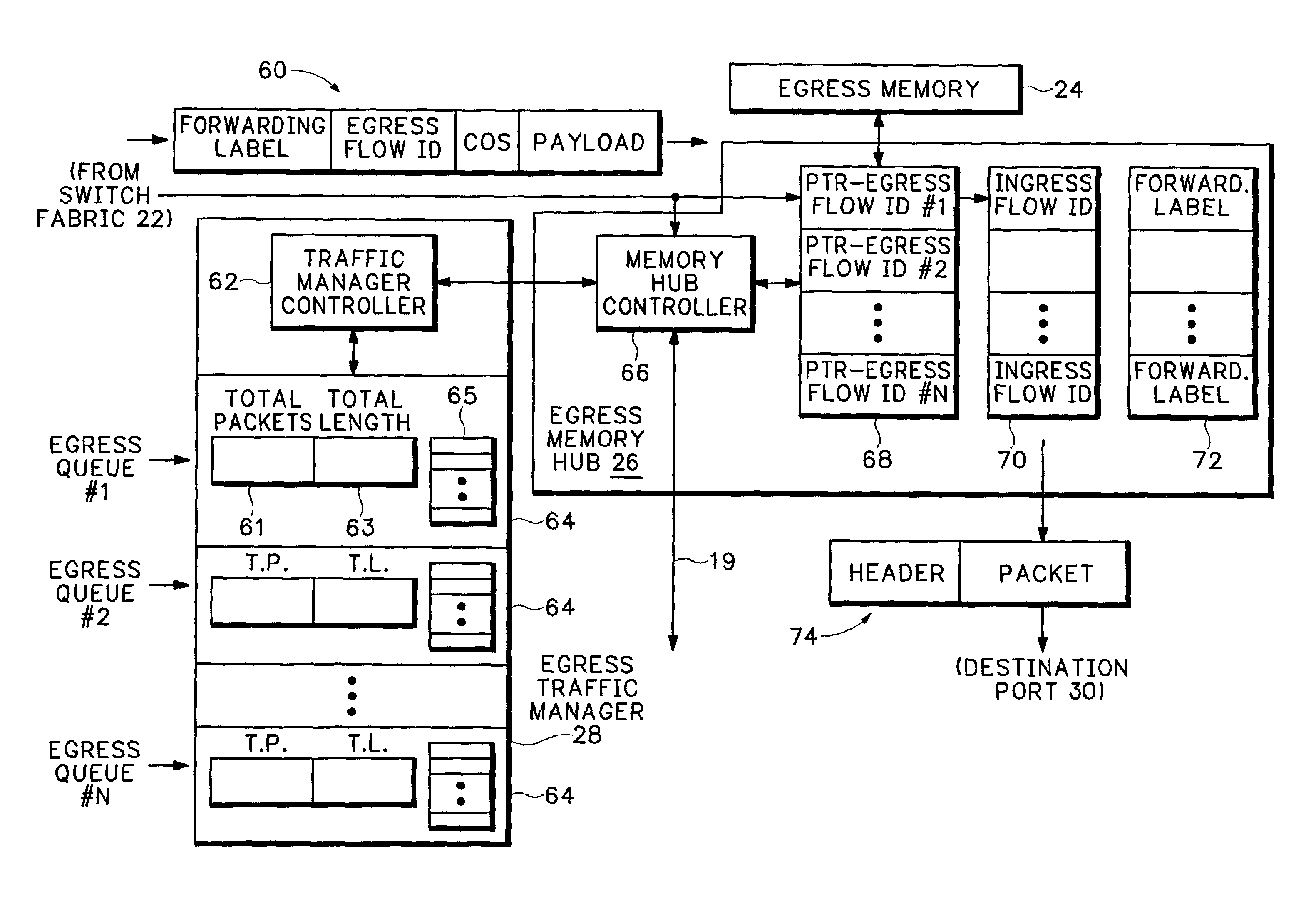
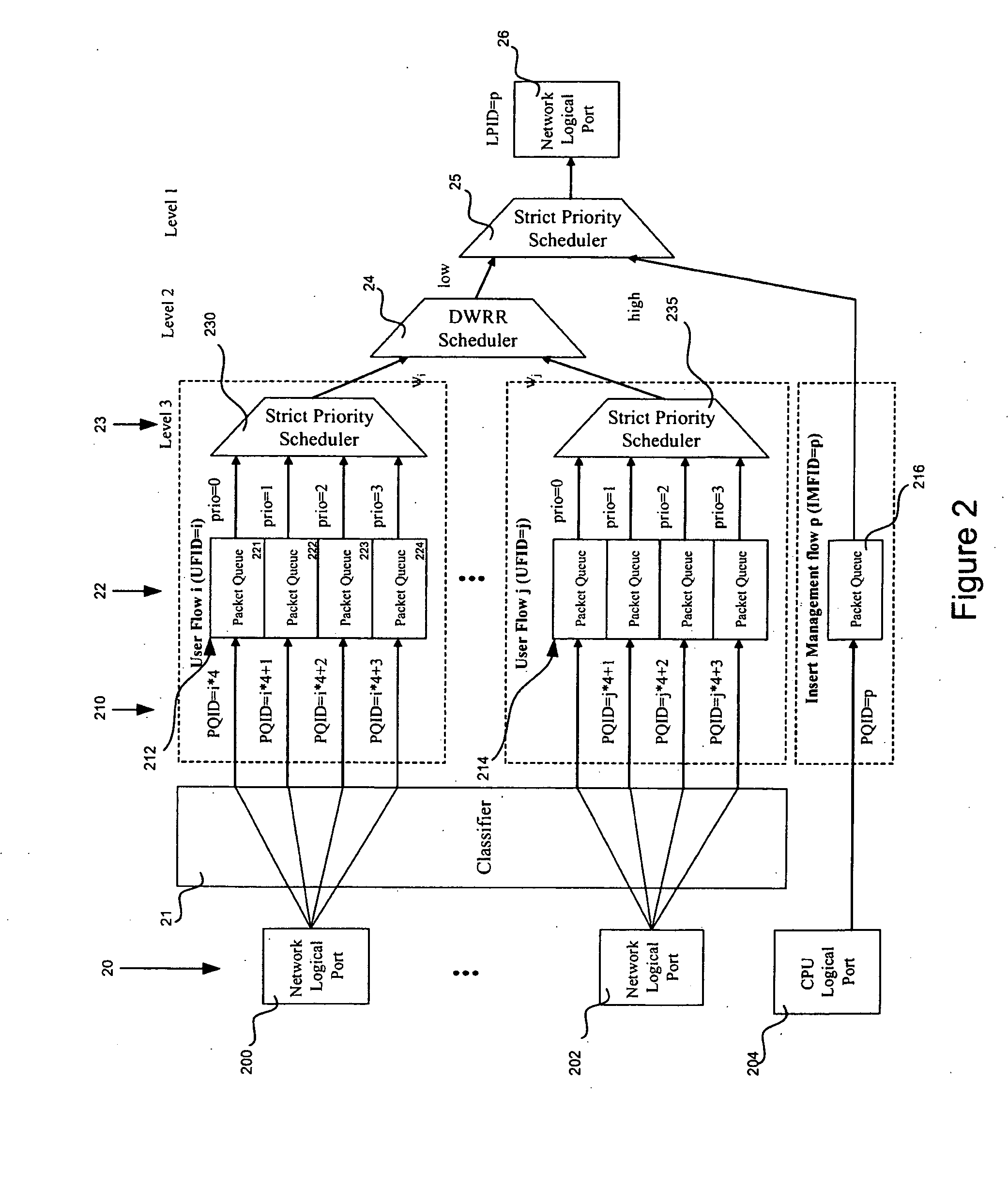
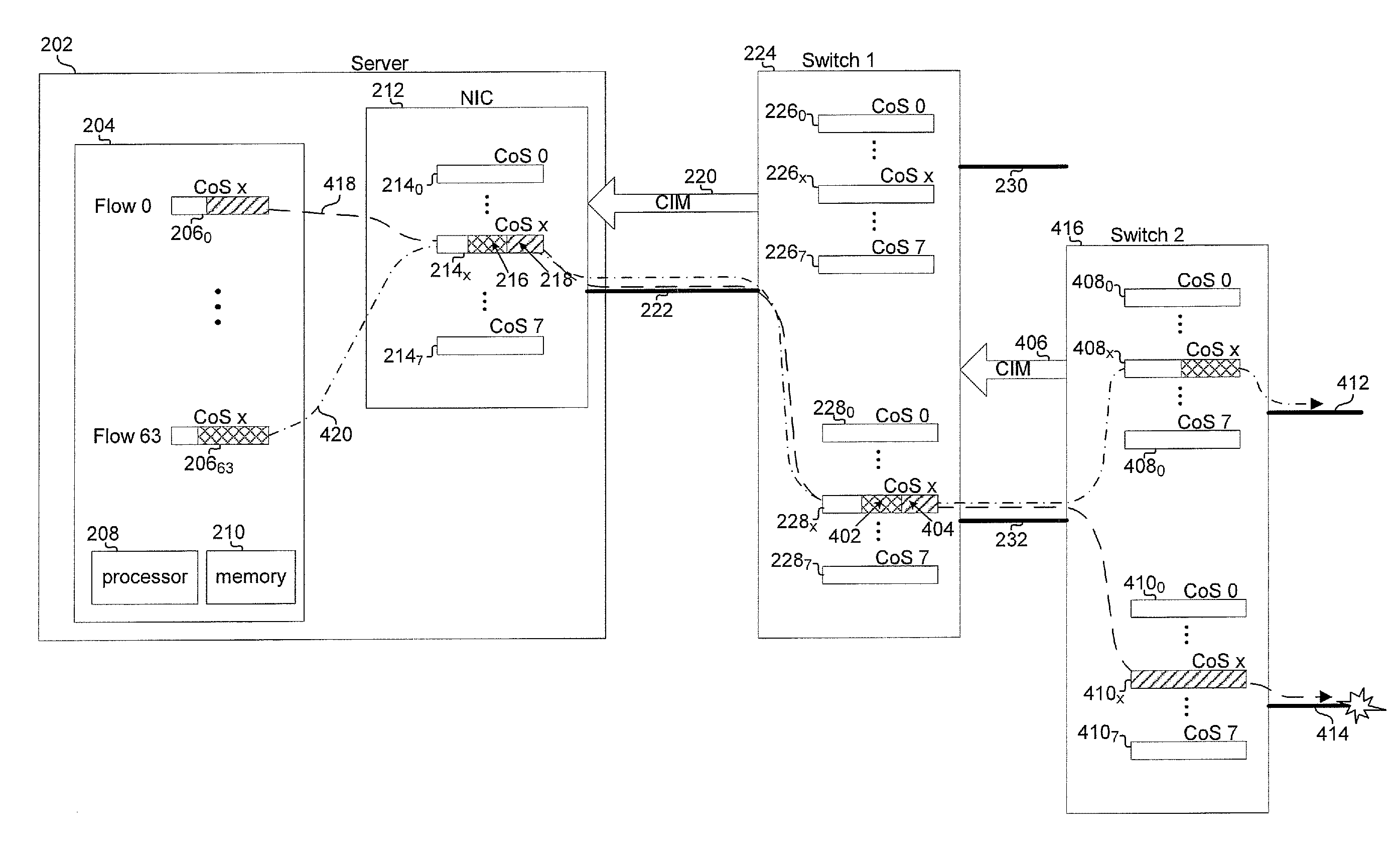
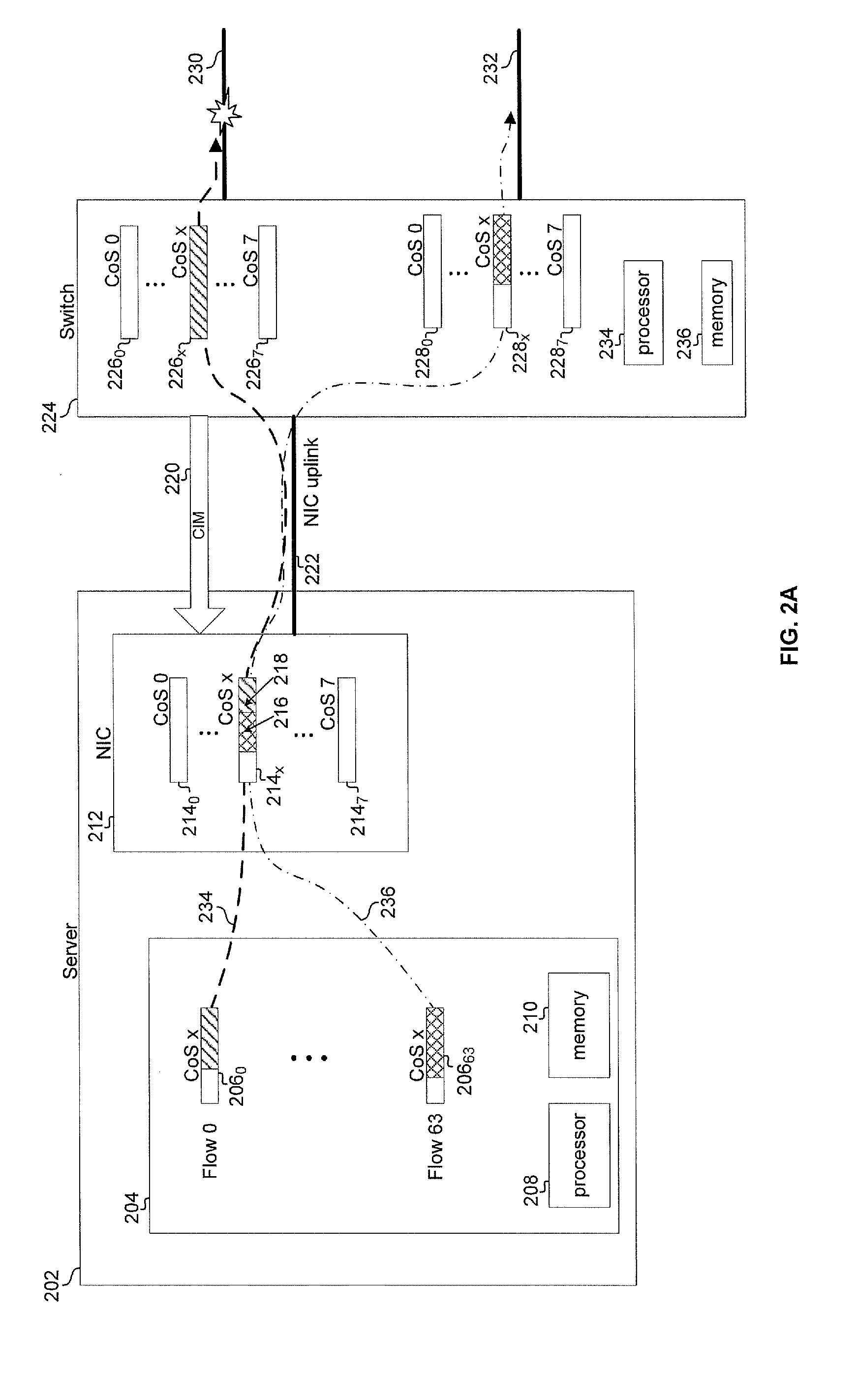
An end to end forwarding architecture includes a memory hub having a first ingress interface for receiving packets from a source port. The packets have associated ingress flow identifiers. A second ingress interface outputs the packets to a switch fabric. An ingress controller manages how the packets are queued and output to the switch fabric. The same memory hub can be used for both per flow queuing and per Class of Service (CoS) queuing. A similar structure is used on the egress side of the switch fabric. The end to end forwarding architecture separates per flow traffic scheduling operations performed in a traffic manager from the per flow packet storage operations performed by the memory hub.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
Method, apparatus, and article of manufacture for estimating parameters of a probability model on shared device usage probabilistic semantic analysis
ActiveUS7567946B2Digital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionProbabilistic semanticsAlgorithm
Methods are disclosed for estimating parameters of a probability model that models user behavior of shared devices offering different classes of service for carrying out jobs. In operation, usage job data of observed users and devices carrying out the jobs is recorded. A probability model is defined with an observed user variable, an observed device variable, a latent job cluster variable, and a latent job service class variable. A range of job service classes associated with the shared devices is determined, and an initial number of job clusters is selected. Parameters of the probability model are learned using the recorded job usage data, the determined range of service classes, and the selected initial number of job clusters. The learned parameters of the probability model are applied to evaluate one or more of: configuration of the shared devices, use of the shared devices, and job redirection between the shared devices.
Owner:XEROX CORP
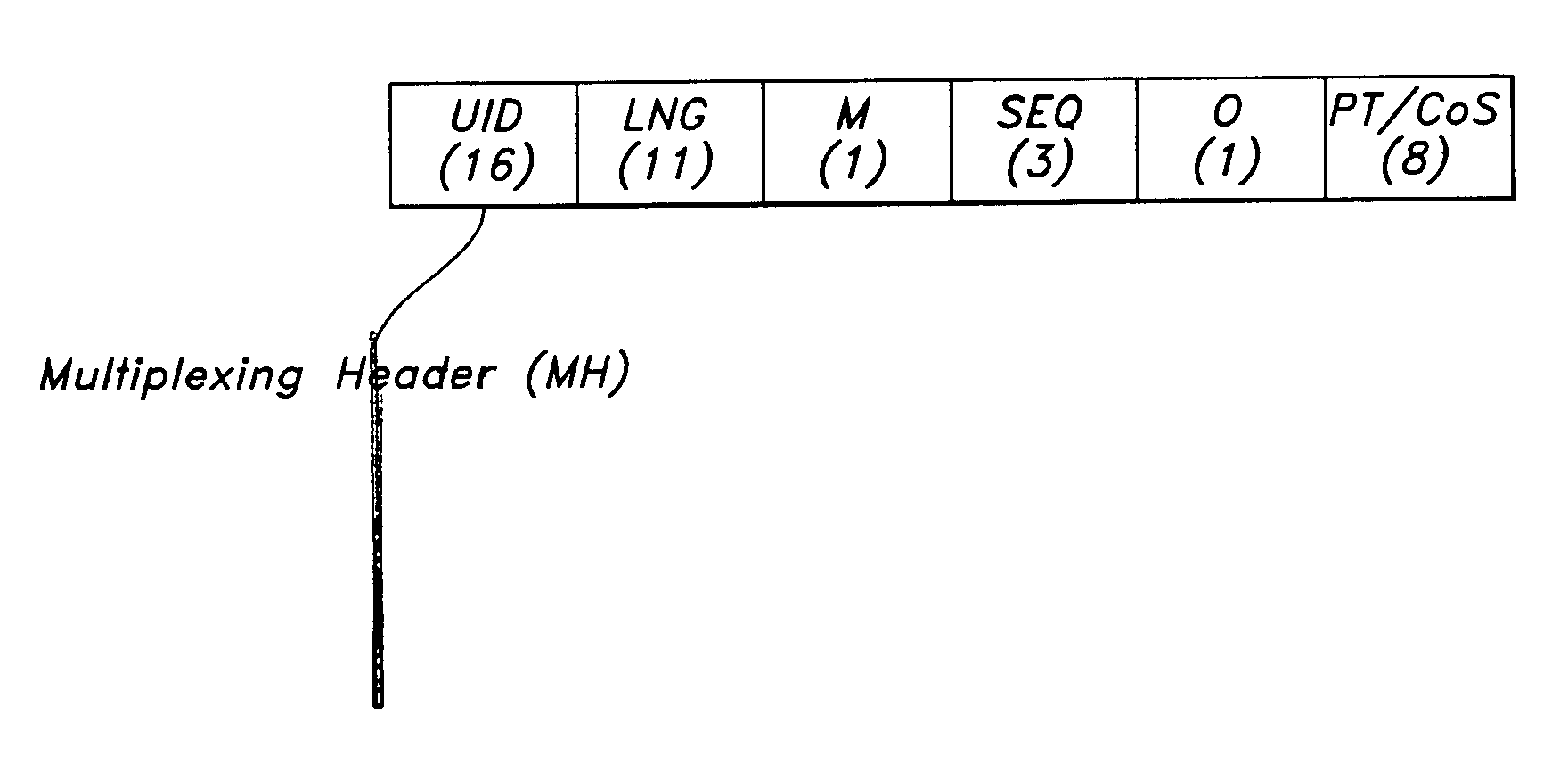
Lightweight internet protocol encapsulation (LIPE) scheme for multimedia traffic transport
InactiveUS6993021B1Increase in sizeTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityClass of service
A packet encapsulation scheme for multiplexing application sessions—Lightweight IP Encapsulation (LIPE)—is described. An LIPE packet comprises at least one multiplexing header (NH) and associated multimedia data packet (MDP). The LIPE packet uses UDP / IP as transport. An MH field further comprises a 16-bit a user identifier (UID) field, an 11 bit length indicator (LNG) field, a 1 bit “more” (M) field and an optional payload type / class of service (PT / CoS) field comprising 8 bits.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
Scaleable channel scheduler system and method
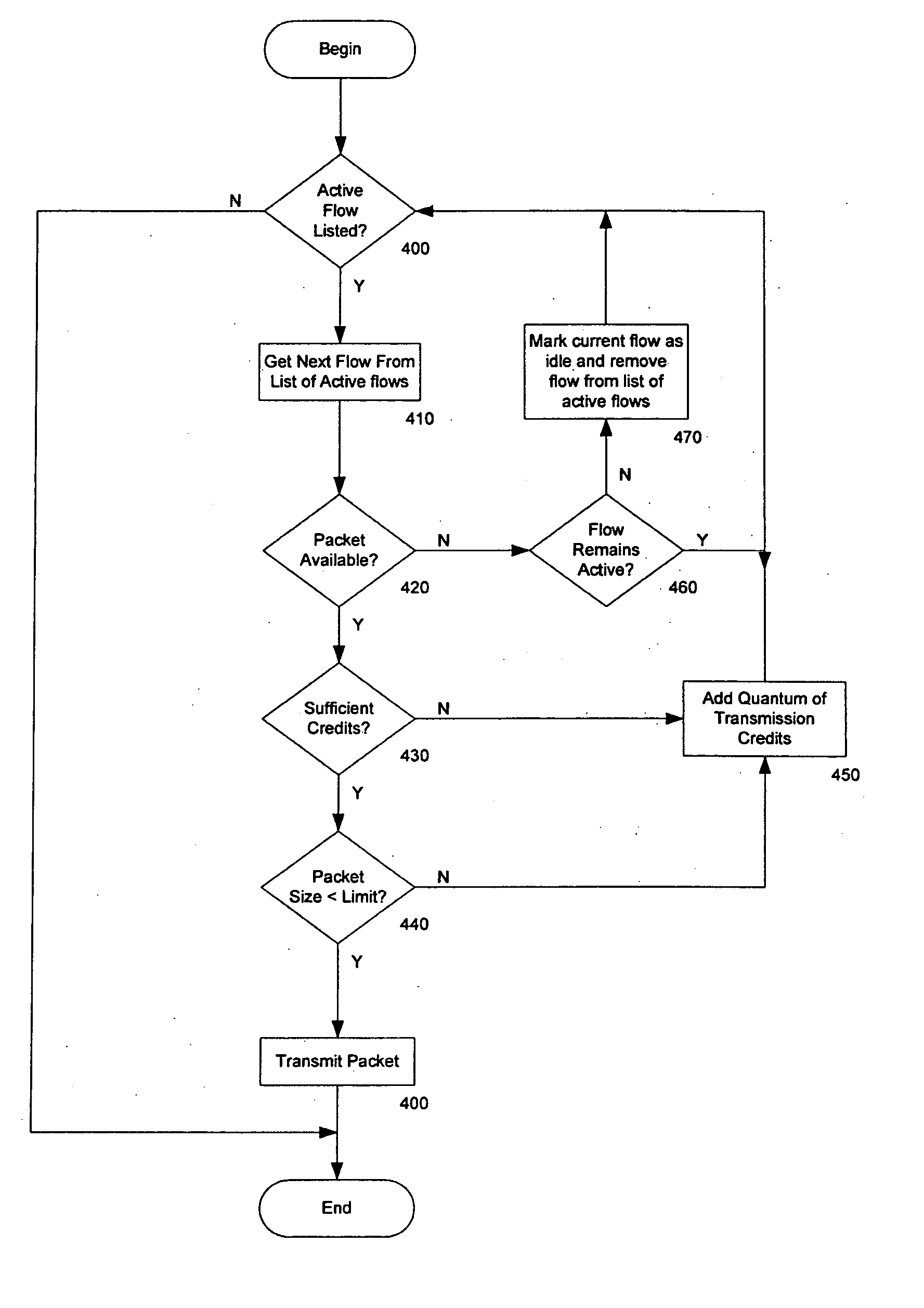
InactiveUS20070070895A1Reduce hardware complexityError preventionTransmission systemsThree levelData stream
A data flow egress scheduler and shaper provides multiple levels of scheduling for data packets exiting communications devices. A classifier separates data from multiple sources by data flow and by priority within a data flow. An output controller requests a data packet for transmission and the scheduler selects a next available highest priority packet from a next in sequence data flow or from a management data queue. The shaper can control the rates of classes of service to be scheduled by the device. The scheduler typically comprises three levels of scheduling. Large numbers of output ports can be implemented in a single device by a virtual scheduler that services each data flow, output port and data source as a shared component, maintain context for groups of schedulers and data flows.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
System and method for determining allocation of resource access demands to different classes of service based at least in part on permitted degraded performance
A method comprises receiving into a planning tool a representative workload for a consumer. The method further comprises receiving into the planning tool quality of service desires of the consumer which define permitted degraded performance. In certain embodiments, the permitted degraded performance is time-limited wherein demands of the representative workload may exceed a pre-defined utilization constraint for at least one resource servicing the demands for no more than a pre-defined amount of contiguous time. The planning tool determines an allocation of demand of the consumer for each of a plurality of different classes of service (COSs). In certain embodiments, a first COS provides guaranteed resource access for servicing demand allocated thereto, and a second COS provides non-guaranteed resource access for servicing demand allocated thereto. In certain embodiments, the allocation of demand to the different COSs may be determined for both a normal mode and a failure mode of operation.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
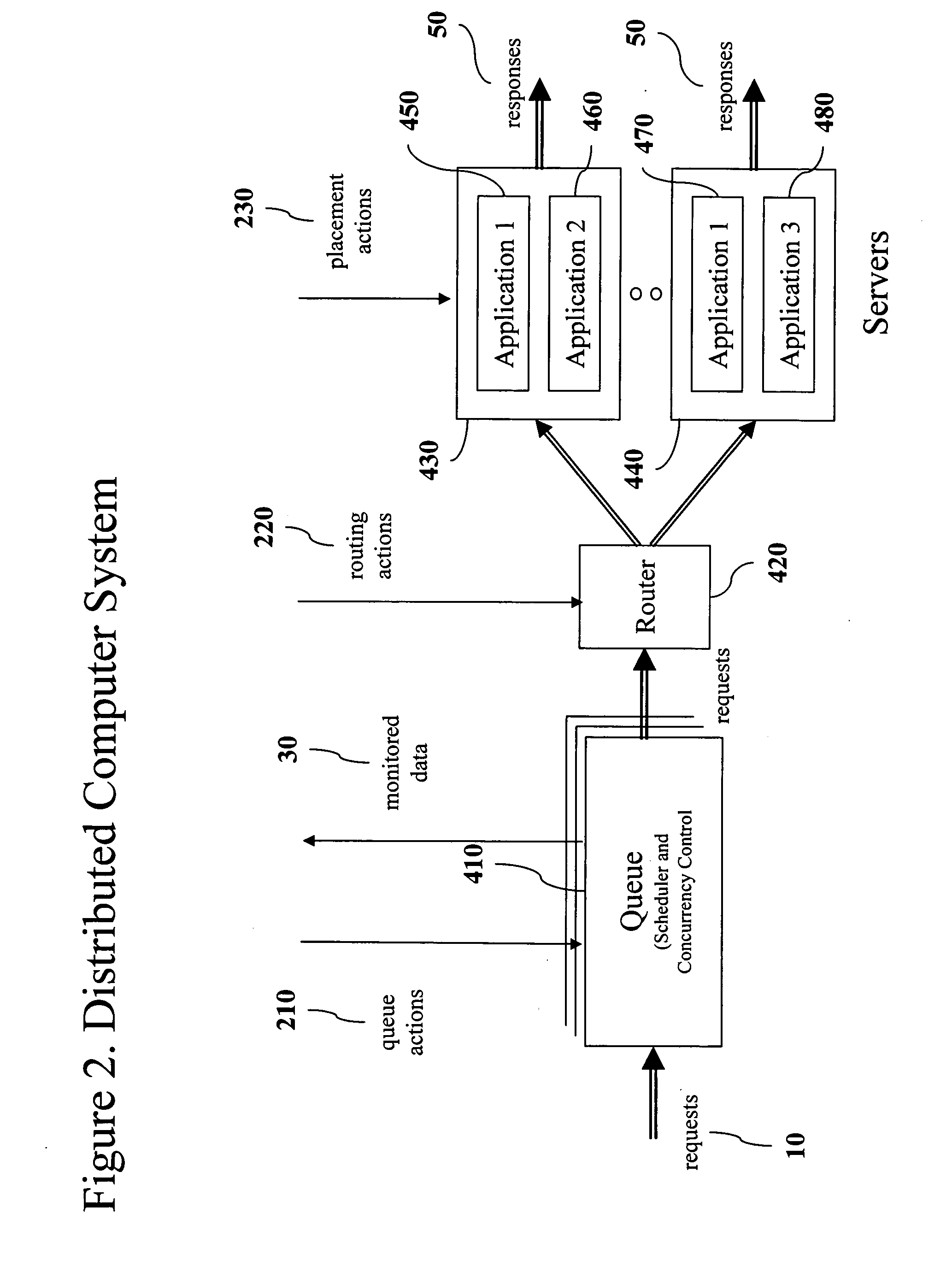
Coordinating service performance and application placement management
InactiveUS20060070060A1Reducing manual administration costReduce human errorProgram loading/initiatingMemory systemsClass of serviceHuman error
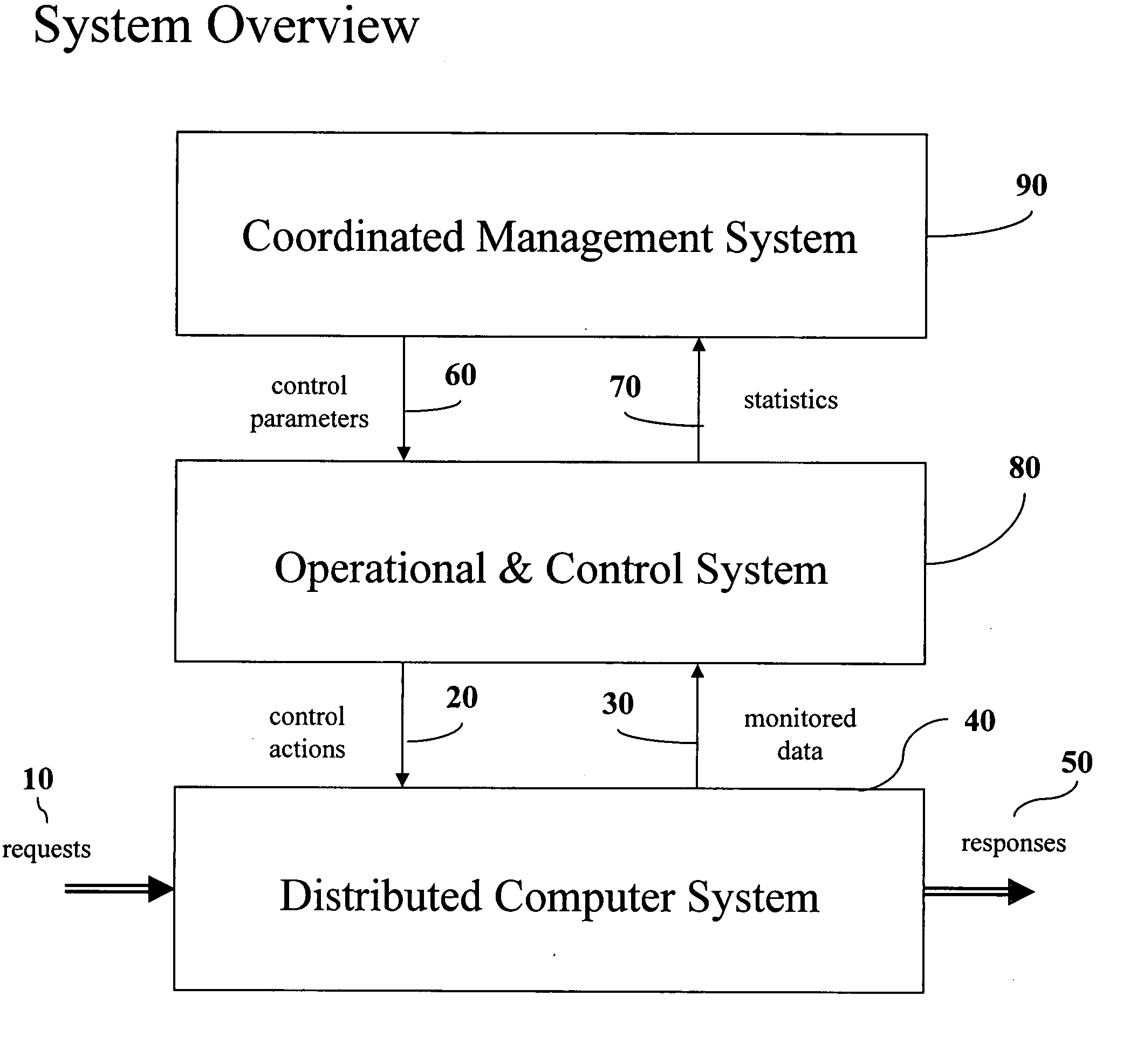
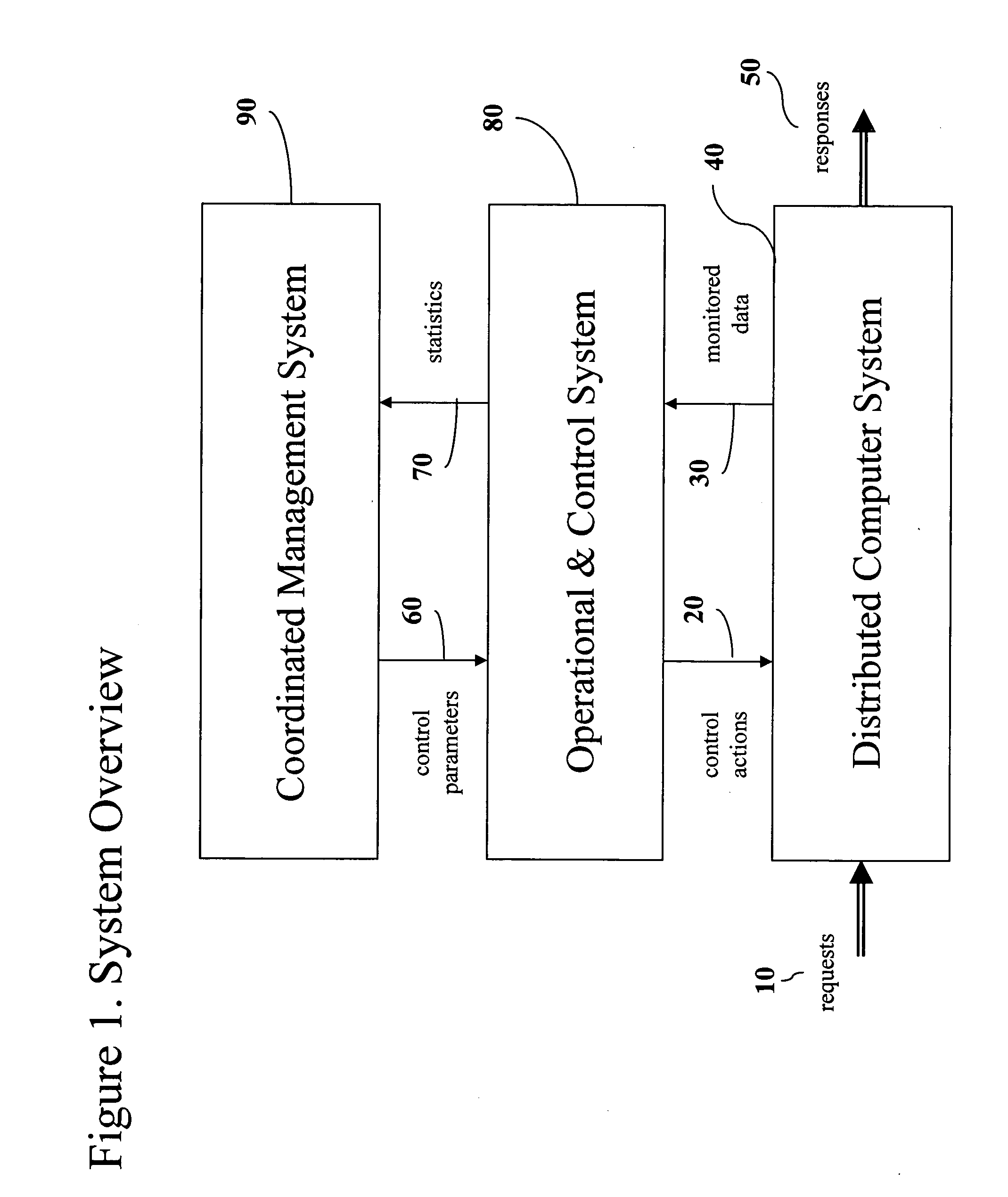
Apparatus, systems and methods for service and / or business for coordinating tasks of performance management and application placement management in a dynamic fashion. An example process is dynamic in the face of fluctuations in the request load to the distributed computer system and the periodic adjustments to the placement of applications onto servers in said distributed computer system. There are two opposite functional flows in said process: a demand estimation function and a capacity adjustment function. The coordination system involves two subsystems: a demand estimator and a capacity adjuster, along with appropriate interfaces to of the performance manager and the application placement manager. This results in application placement process reacting quicker to demand fluctuations, performance guarantees are better met by rearranging the resources to be allocated to the various classes of service, and the management system works in an unsupervised mode, thus reducing manual administration costs and human errors.
Owner:IBM CORP
Methods, systems, and computer program products for marking data packets based on content thereof
ActiveUS20080019371A1Improve the level ofData switching by path configurationClass of serviceDistributed computing
Owner:BELLSOUTH INTPROP COR
Method and system for path based network congestion management
InactiveUS20090300209A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionForward algorithmData stream
Aspects of a method and system for path based network congestion management are provided. In this regard, an indication of conditions, such as congestion, in a network may be utilized to determine which data flows may be affected by congestion in a network. A path table may be maintained to associate conditions in the network with flows affected by the conditions. Flows which are determined as being affected by a condition may be paused or flagged and transmission of data belonging to those flows may be deferred. Flows affected by a condition such as congestion may be identified based on a class of service with which they are associated. Transmission of one or more of the plurality of flows may be scheduled based on the determination. The determination may be based on one or both of a forwarding table and a forwarding algorithm of the downstream network device.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Voice call alternative routing through PSTN and internet networks
InactiveUS6870827B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsInterconnection arrangementsQuality levelAutomatic control
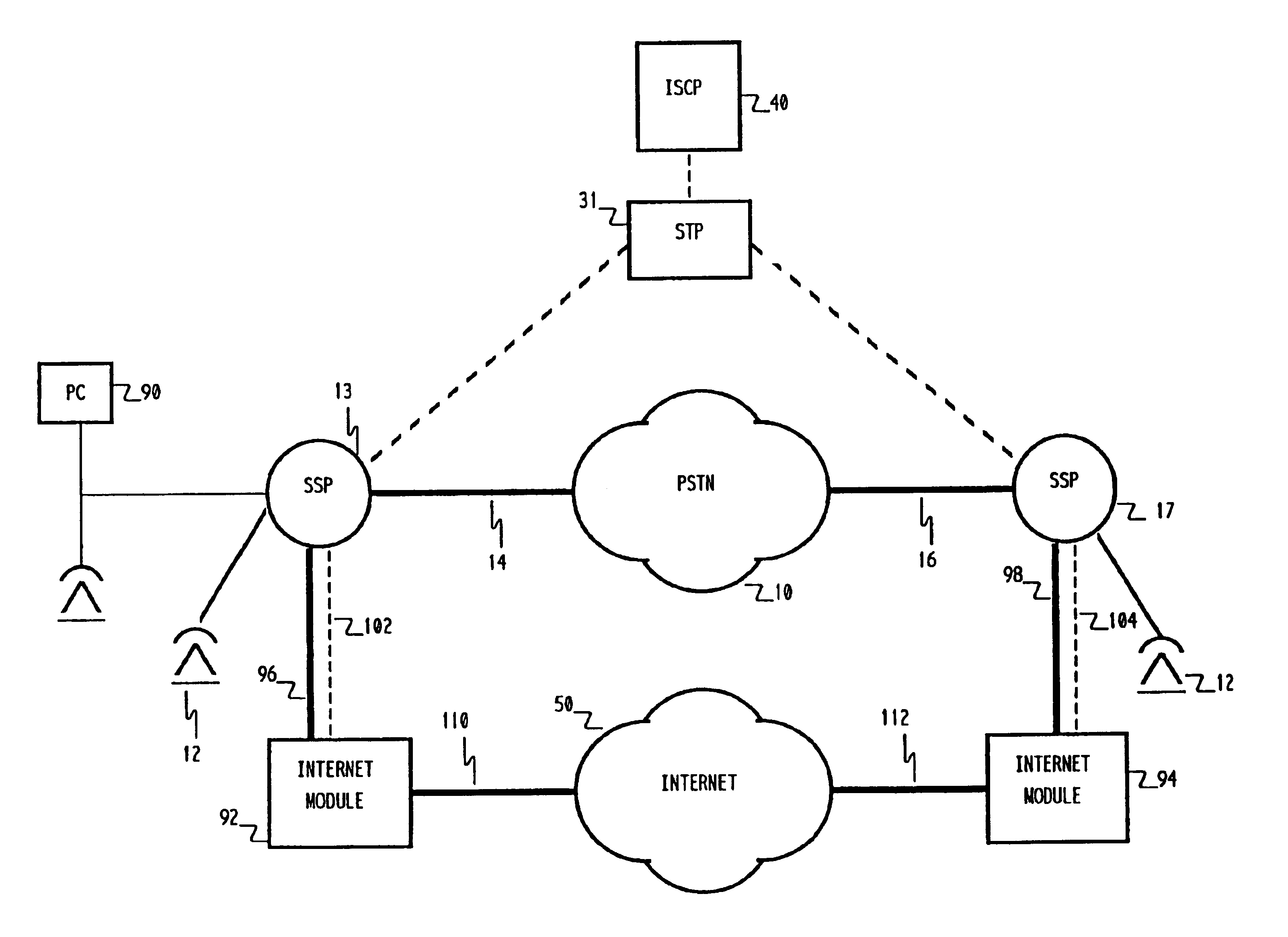
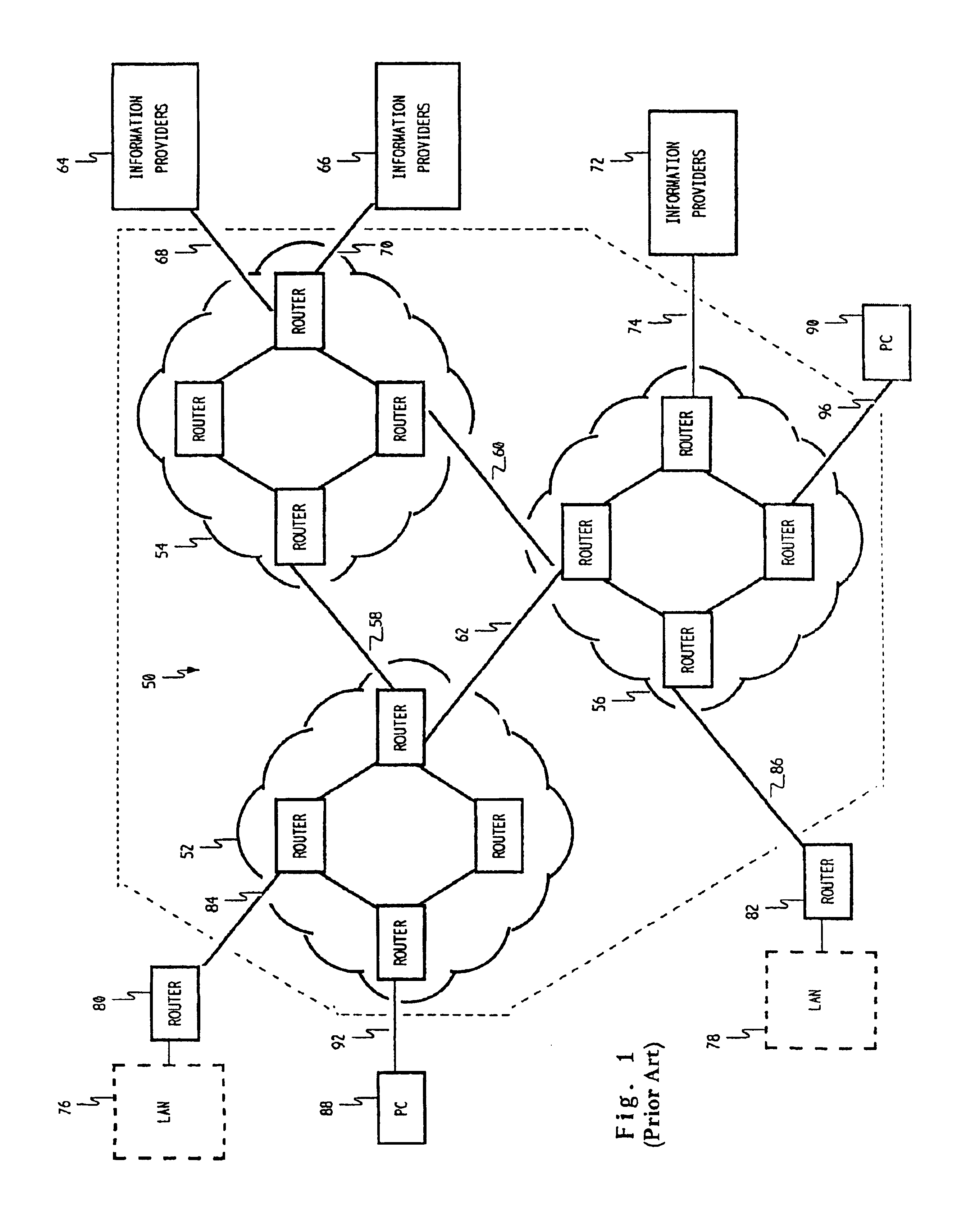
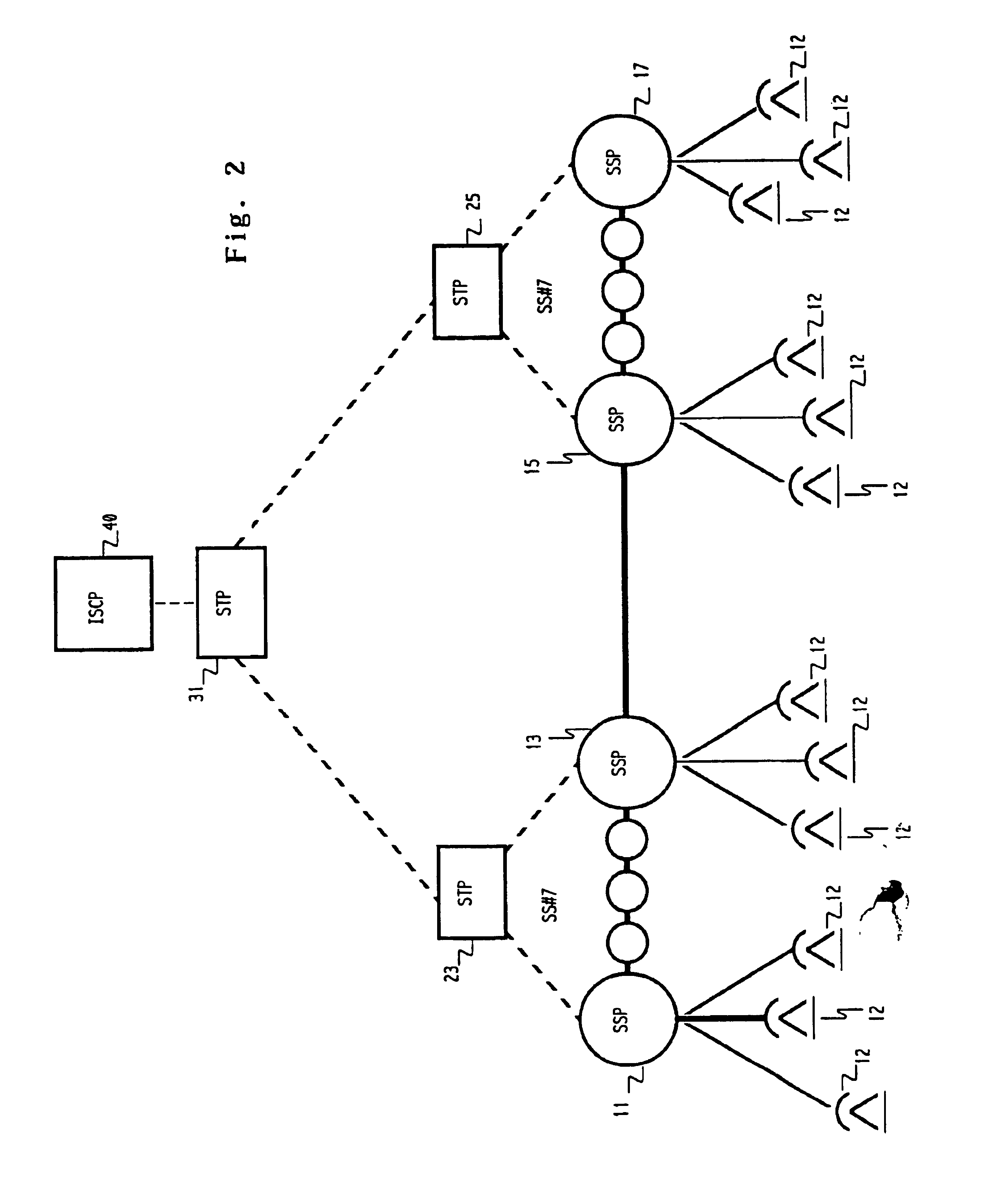
The advanced intelligent network (AIN) to determine routing of voice calls alternatively between the public switched telephone network (PSTN) and a data packet network, such as the Internet, in accordance with the quality of service existing in the data packet network at the times of call origination. The user's acceptable level of service may be predefined with a threshold quality level stored in the user's Call Processing Record (CPR) in the AIN Integrated Services Control Point (ISCP). On a per call basis, the caller linked to a first public switched network may indicate a preference to route through the Internet. This indication is recognized by the AIN system, in response to which the quality of service currently present on the Internet for completion of the call is measured. If the result exceeds the stored threshold, the call is setup and routed through the Internet to the switched network link to the destination party. If the quality of service on the Internet is not satisfactory, the call is alternatively routed through the PSTN, which may include an Interexchange Carrier link. The AIN system automatically controls the alternative routing of such calls.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
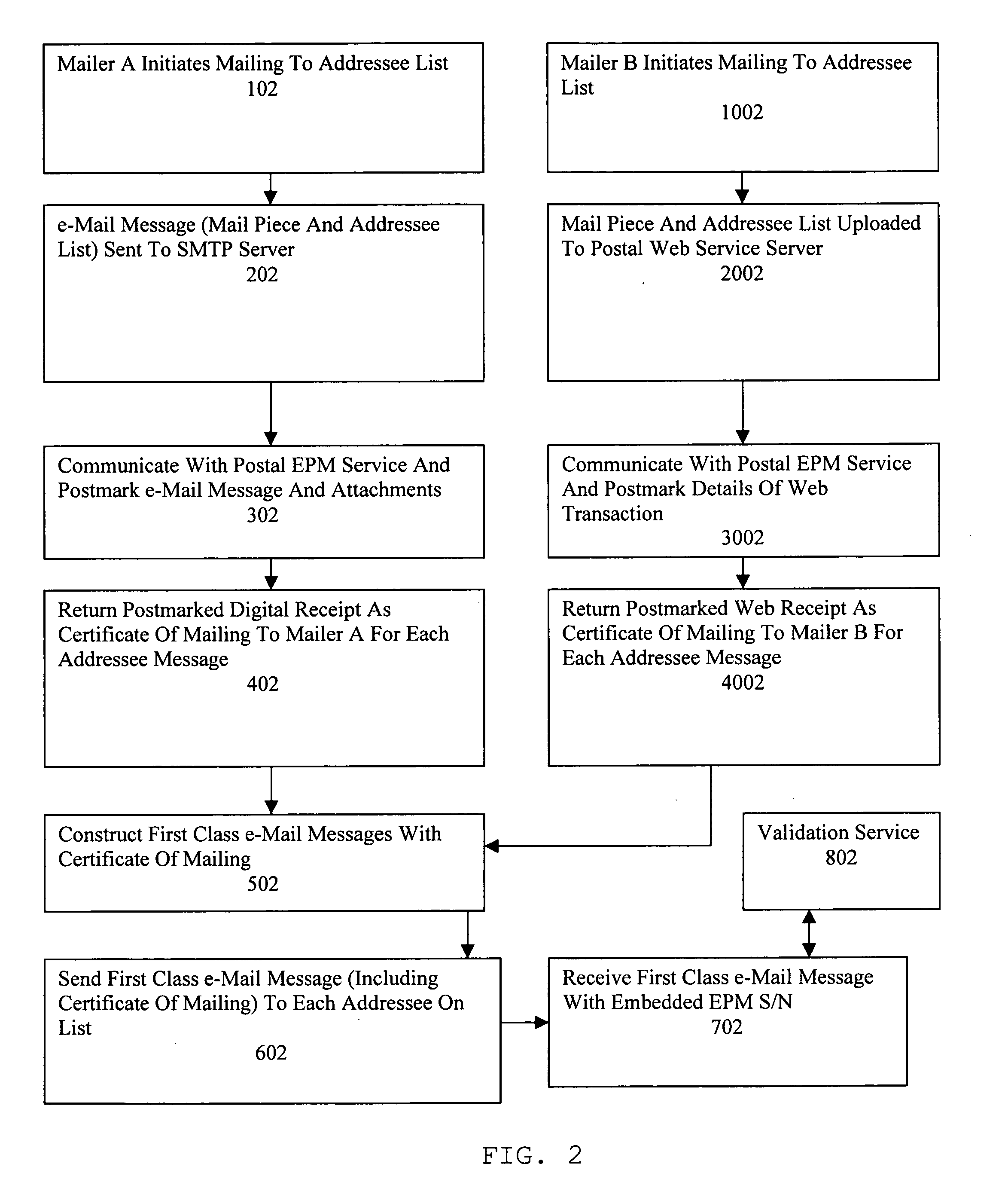
Method, apparatus and system for regulating electronic mail
ActiveUS20050193075A1Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionClass of serviceUnique identifier
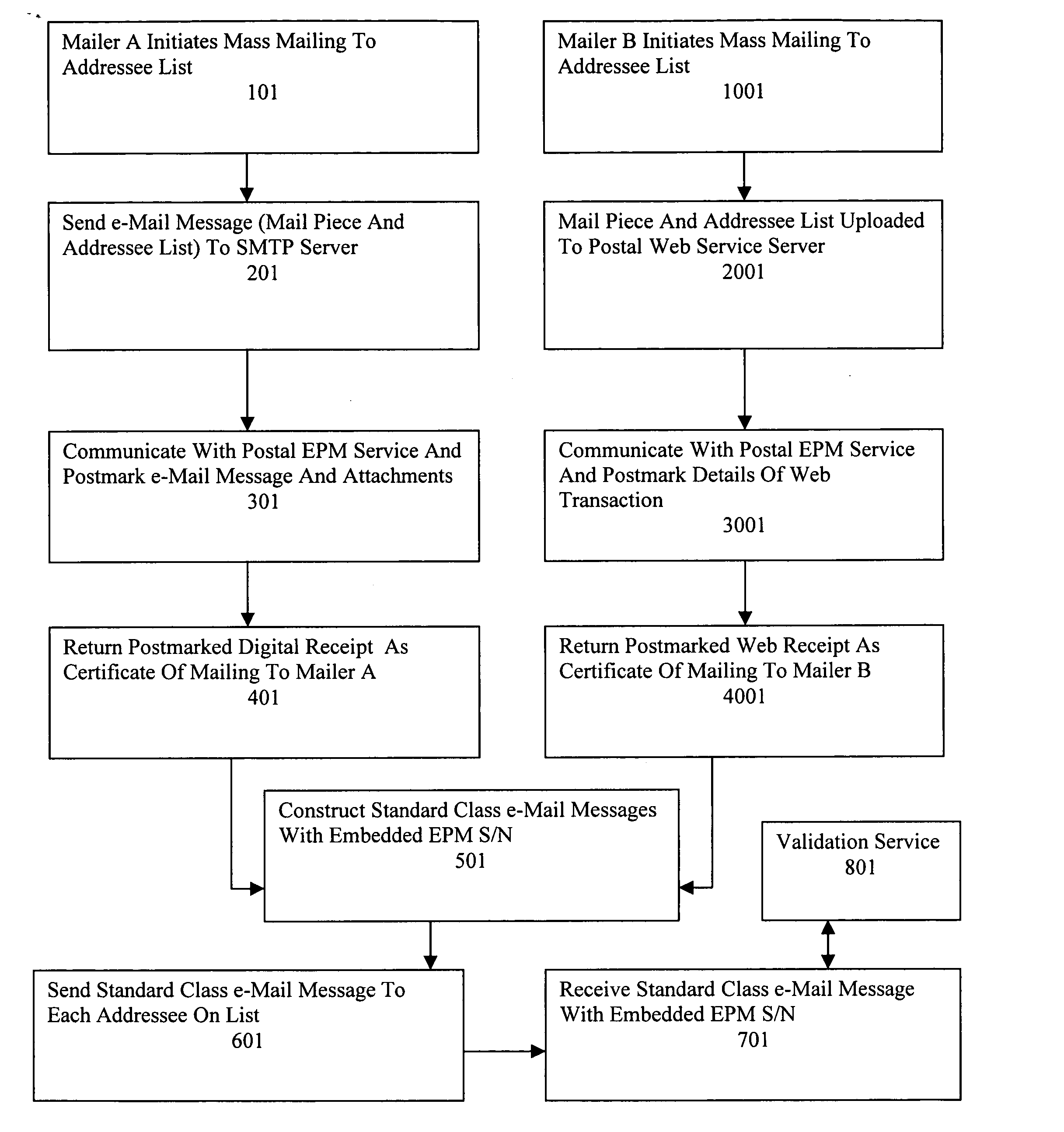
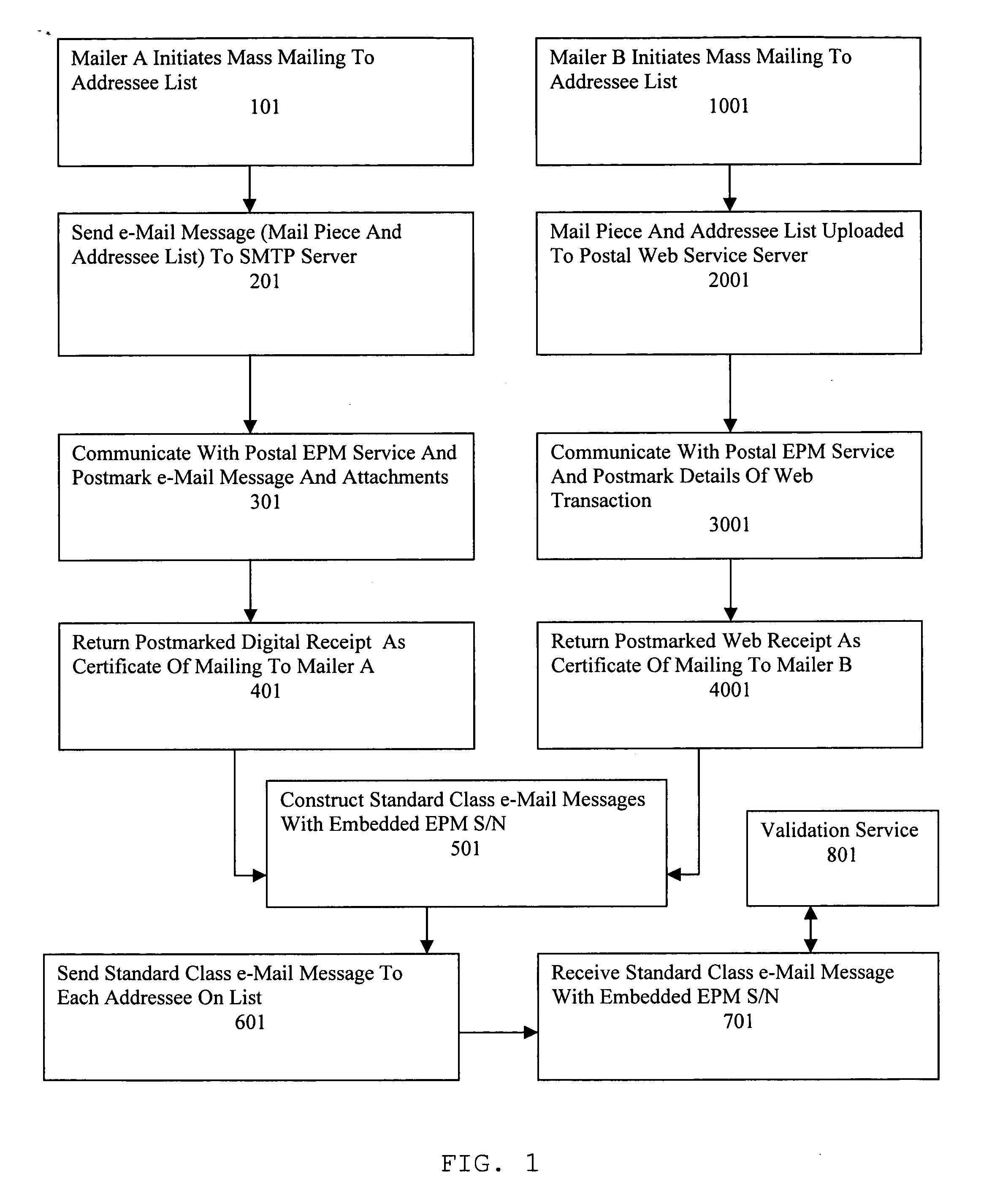
A Postal Authority regulated e-Mail messaging application is provided over a public network to a plurality of mailers and addressees using authenticated transaction records. The application transmits at least one e-Mail message through at least one e-Mail account configured for a specific class of service. The application creates transaction records relevant to the specific class of service based upon details of completed transactions. Electronic postmarks are obtained to authenticate transaction records. Authenticated transaction records are sent to the mailer. A unique identifier of an electronic postmark is embedded in the e-Mail message. The e-Mail message incorporating the unique identifier is sent to at least one addressee. Authenticated e-Mail messages and transaction records are created and protected from undetectable modification.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
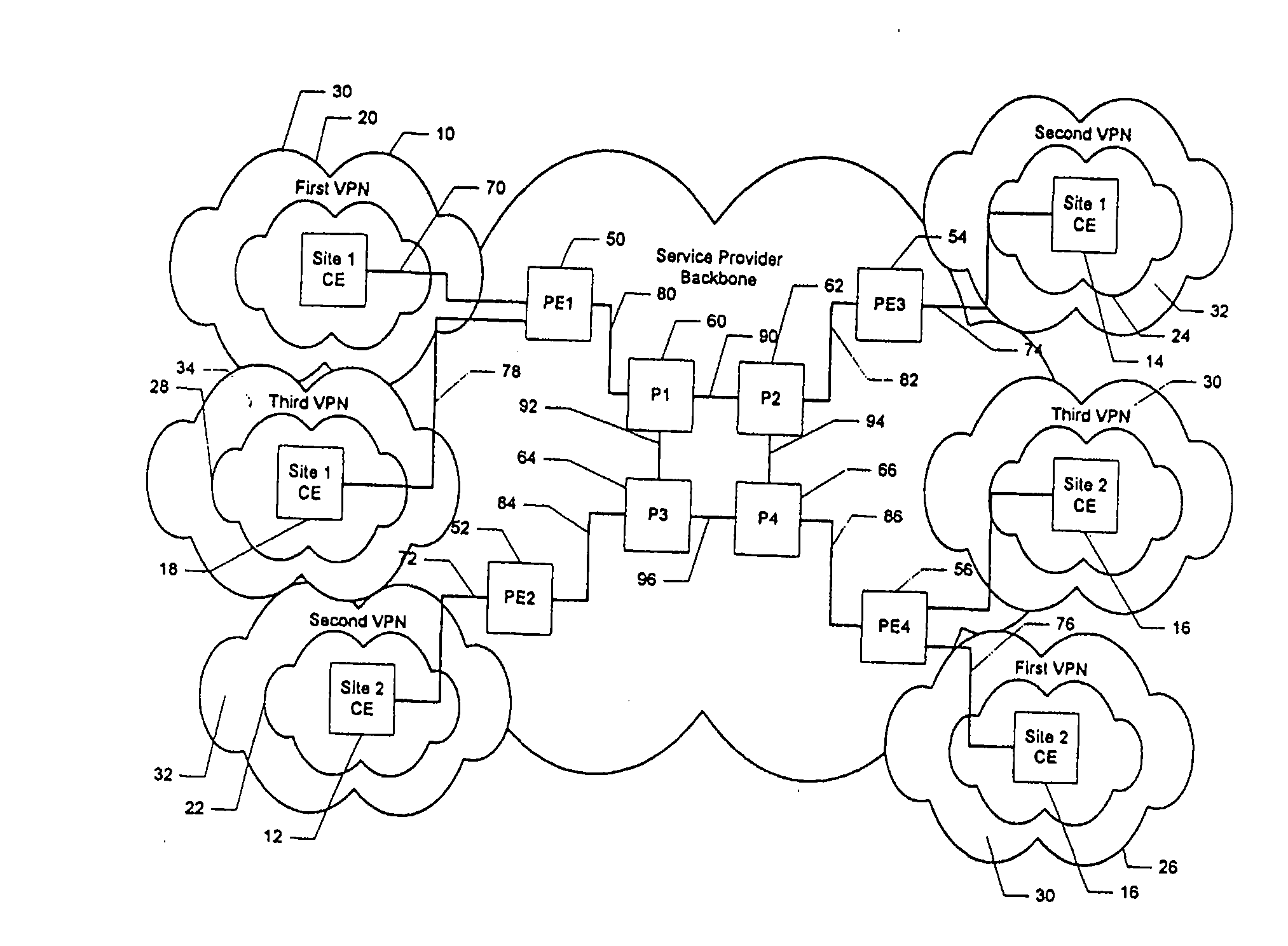
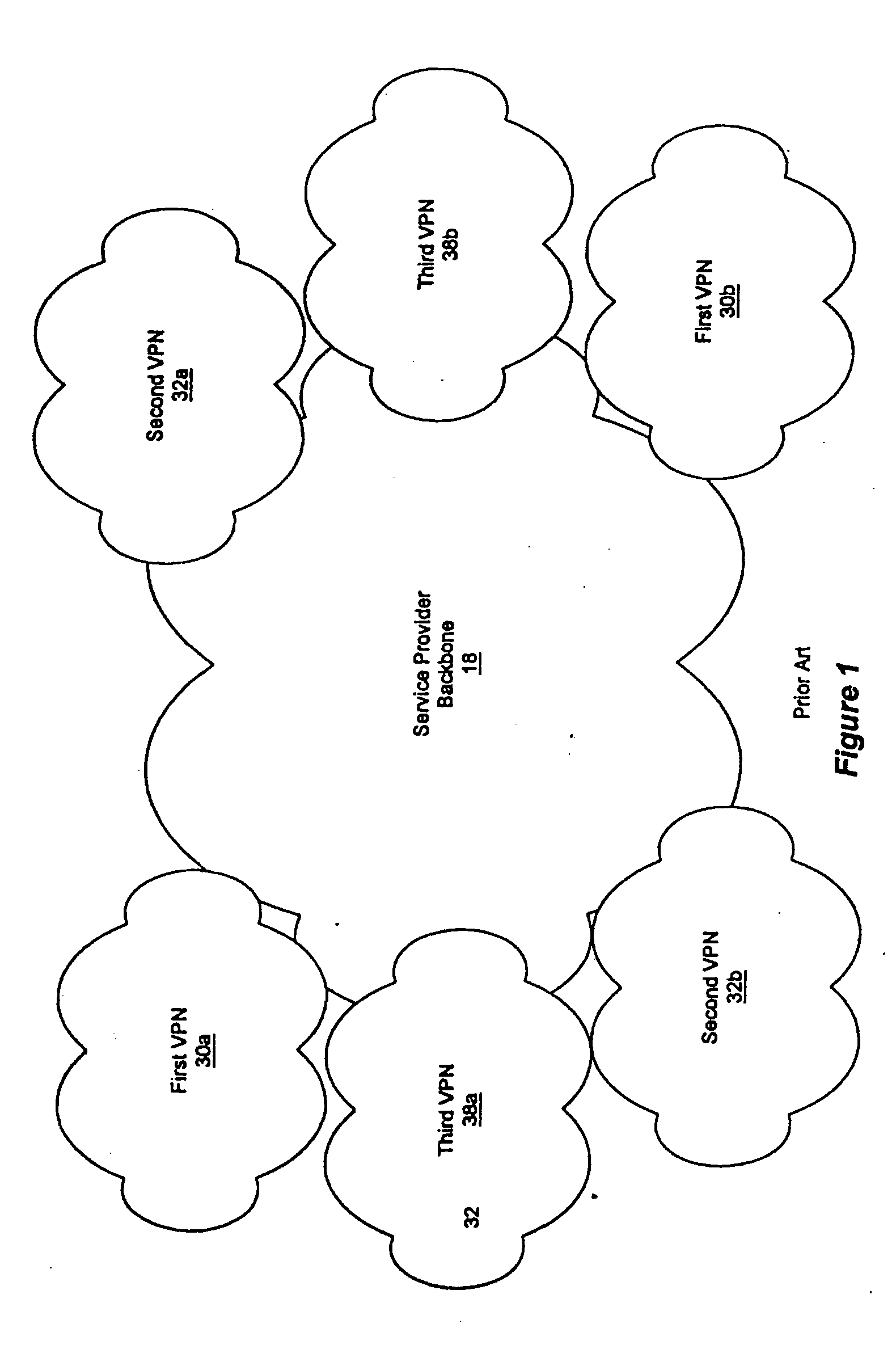
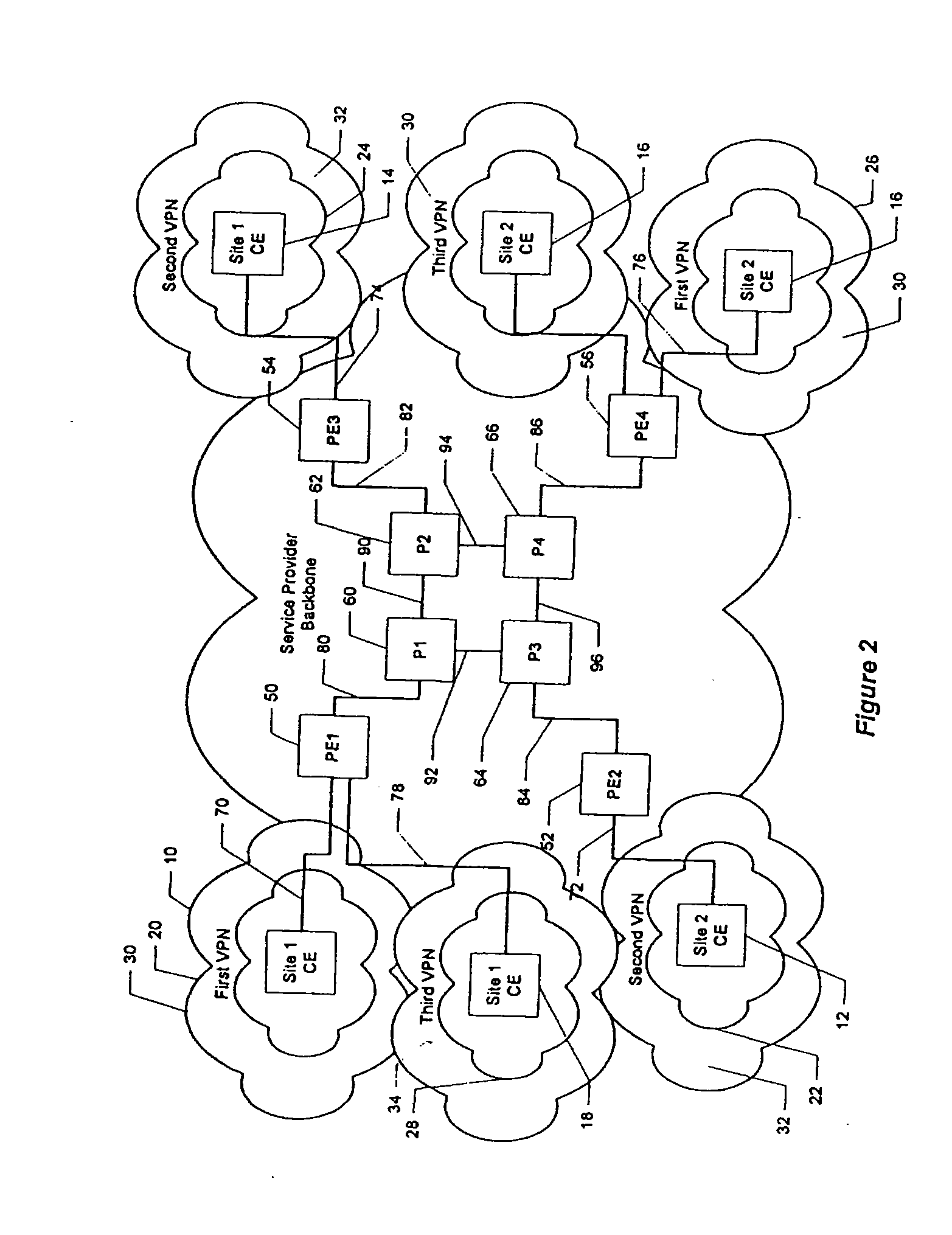
Fairness of capacity allocation for an mpls-based VPN
Owner:AT & T INTPROP II LP
Method and apparatus for policy based class service and adaptive service level management within the context of an internet and intranet
InactiveUS7124188B2Meet expectationsStable deliveryDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsAdaptive servicesTraffic capacity
A method and apparatus for robustly enhanced Class of Service (COS) at the application layer permits highly flexible privilege based access and enables implementation of complex policies and rules for classification and differentiation of services. Differentiation facilitates categorization of traffic to permit flexible design and implementation of multiple Class of Service levels.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Method and apparatus for signaling VoIP call based on class of service in VoIP service system
InactiveUS20060104264A1Improve efficiencyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDifferentiated servicesTelecommunications
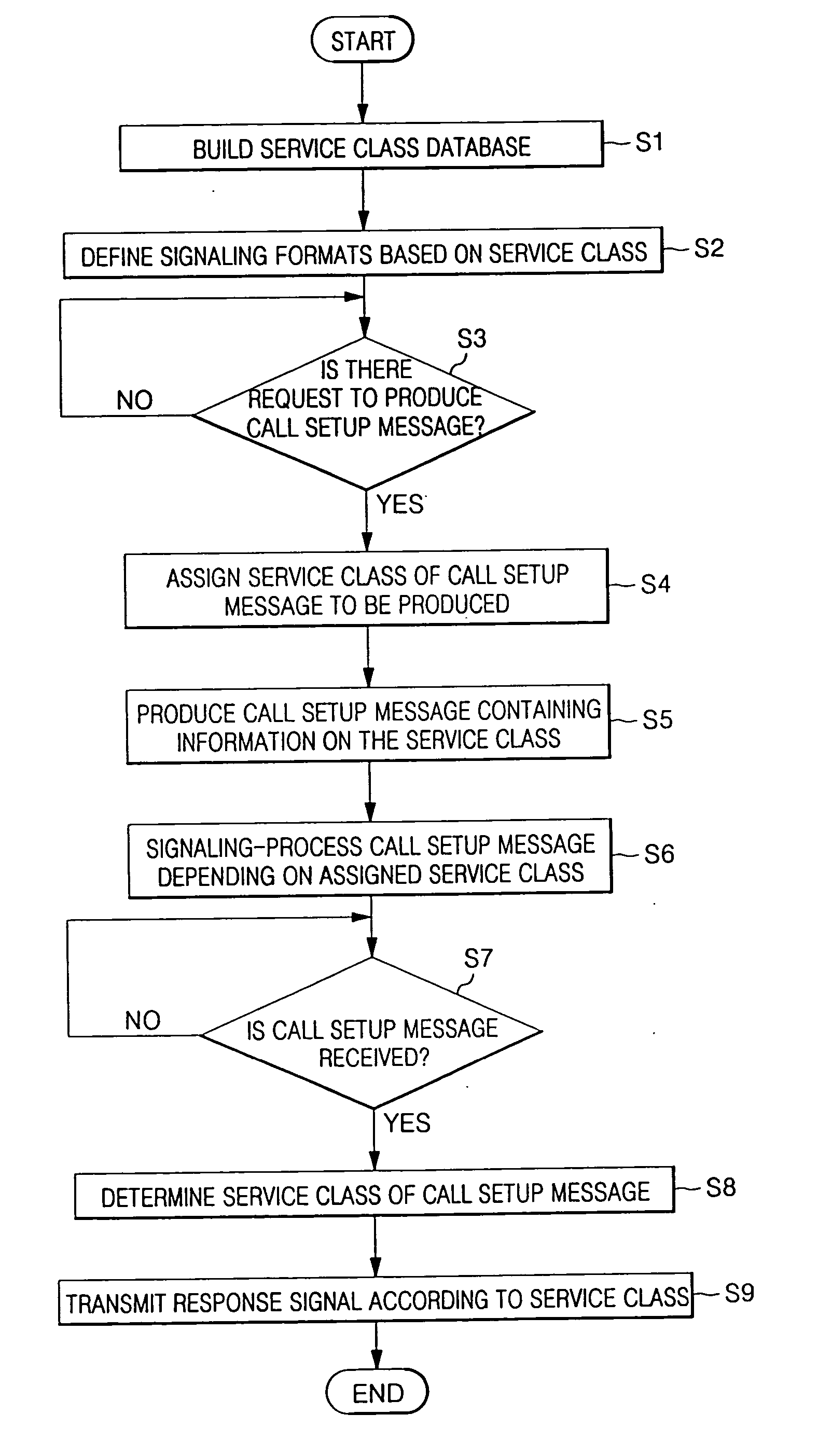
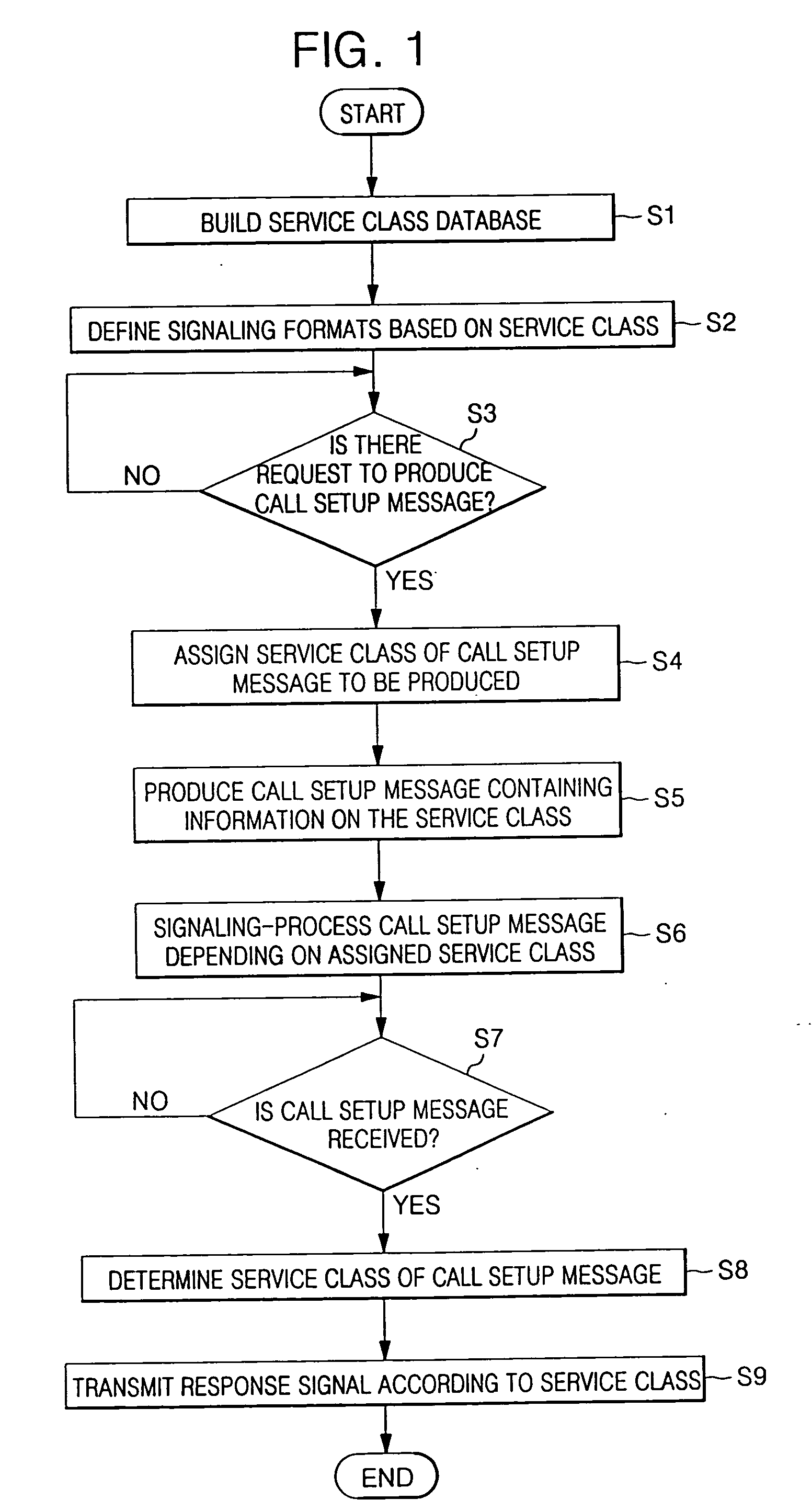
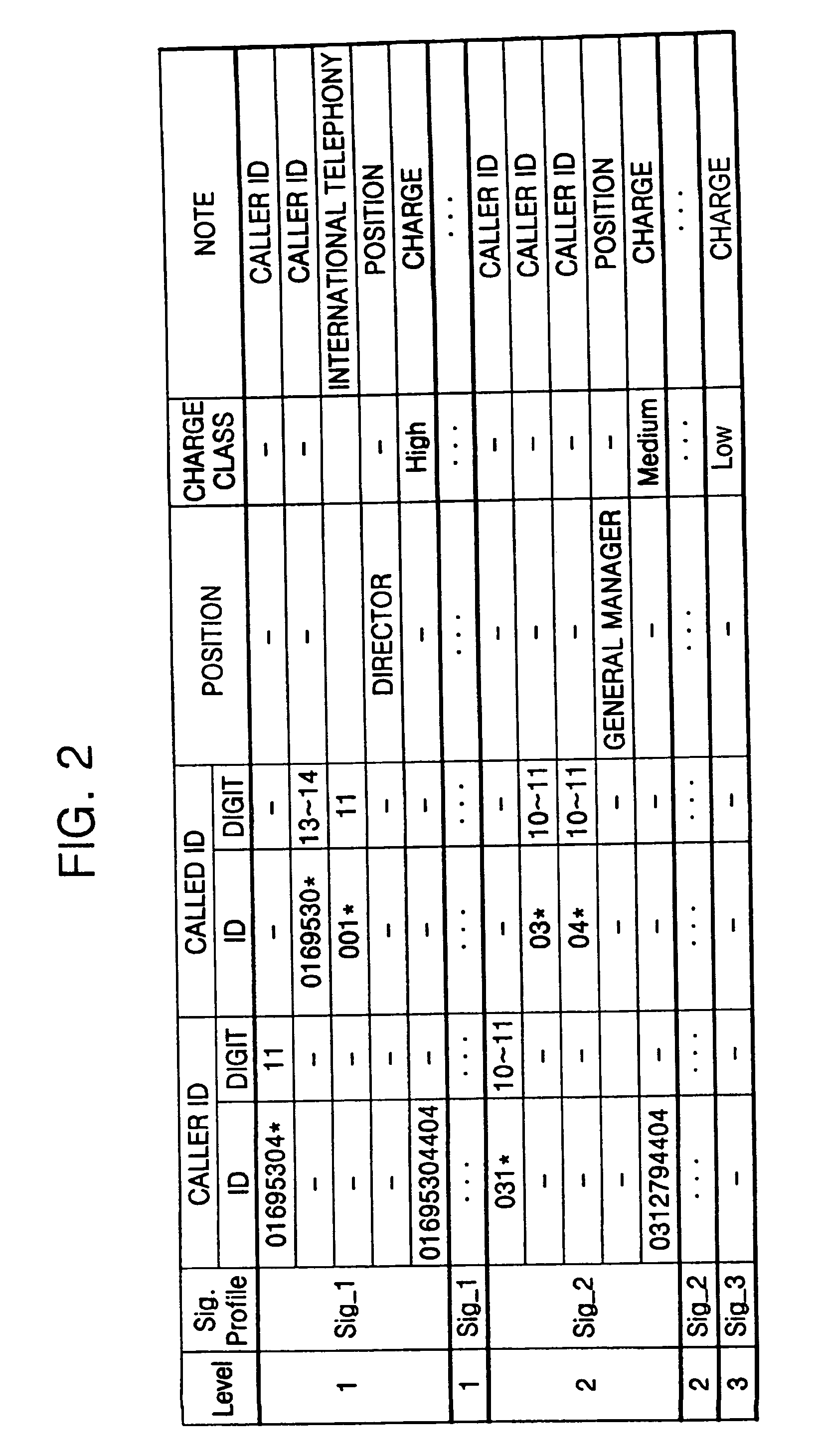
In a method and apparatus for signaling a voice over Internet protocol (VoIP) call based on a class of service in a VoIP service system, a database which includes VoIP signaling information differentiated by the class of VoIP service is built, and the database is retrieved by a service class assignment condition to produce a call setup message. The call setup message includes information related to the service class. Accordingly, it is possible to perform dynamic VoIP signaling by setting a differentiated service class based on each user or a primary factor of each class of the VoIP service.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for establishing class of service configuration in a network device of a broadband cable network using dynamic host configuration protocol
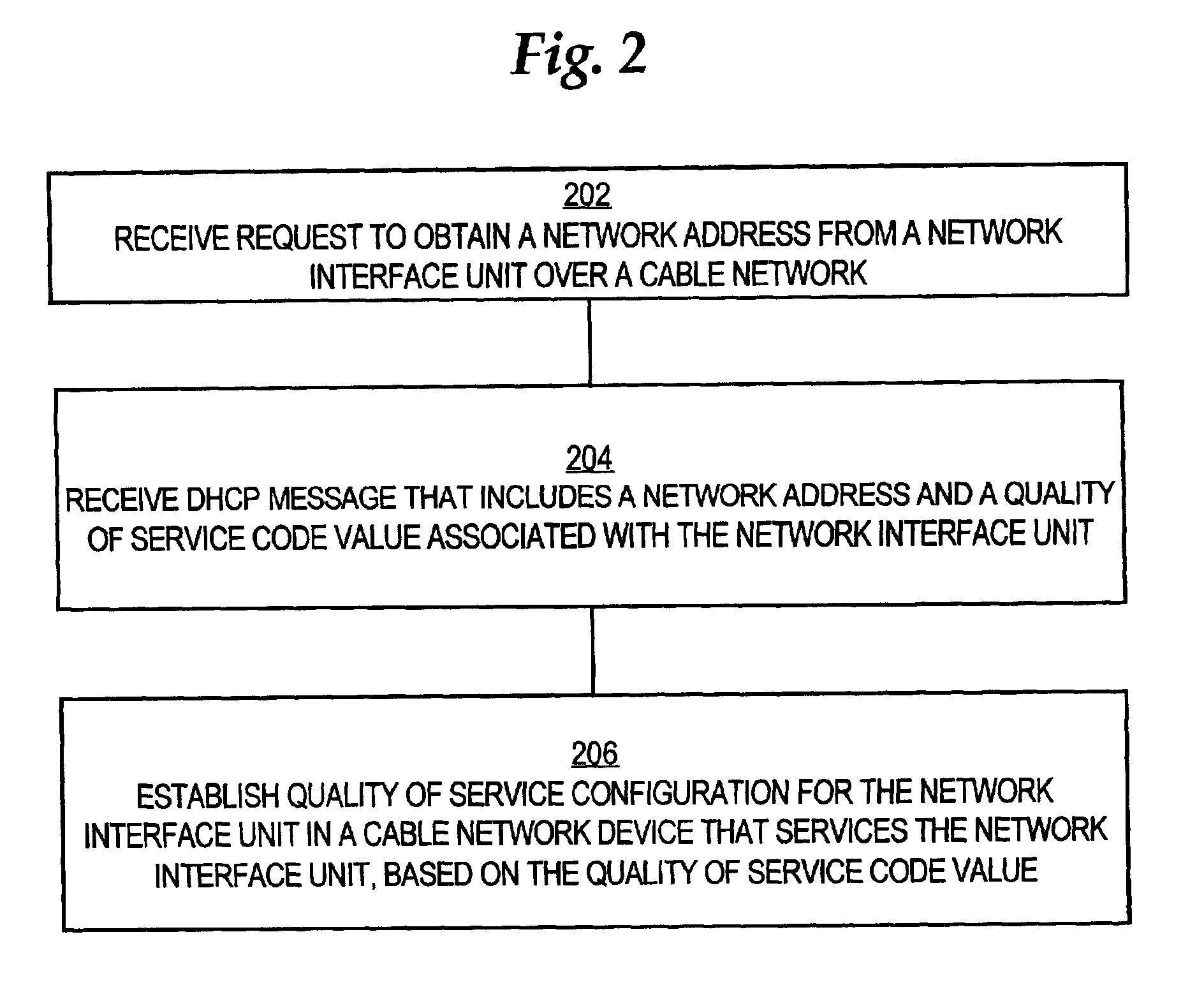
InactiveUS6876667B1Quick configurationBroadband local area networksTime-division multiplexClass of serviceNetwork addressing
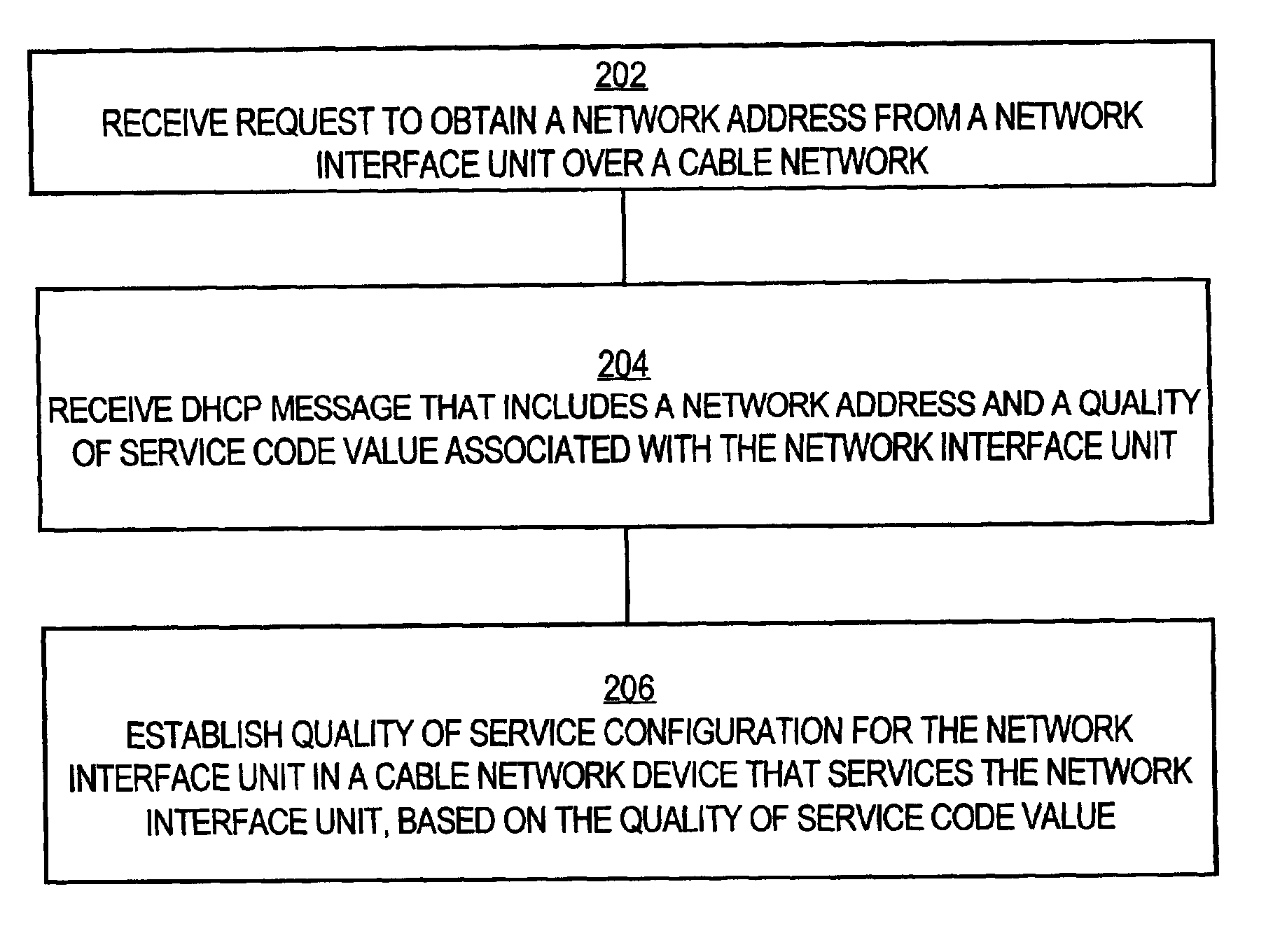
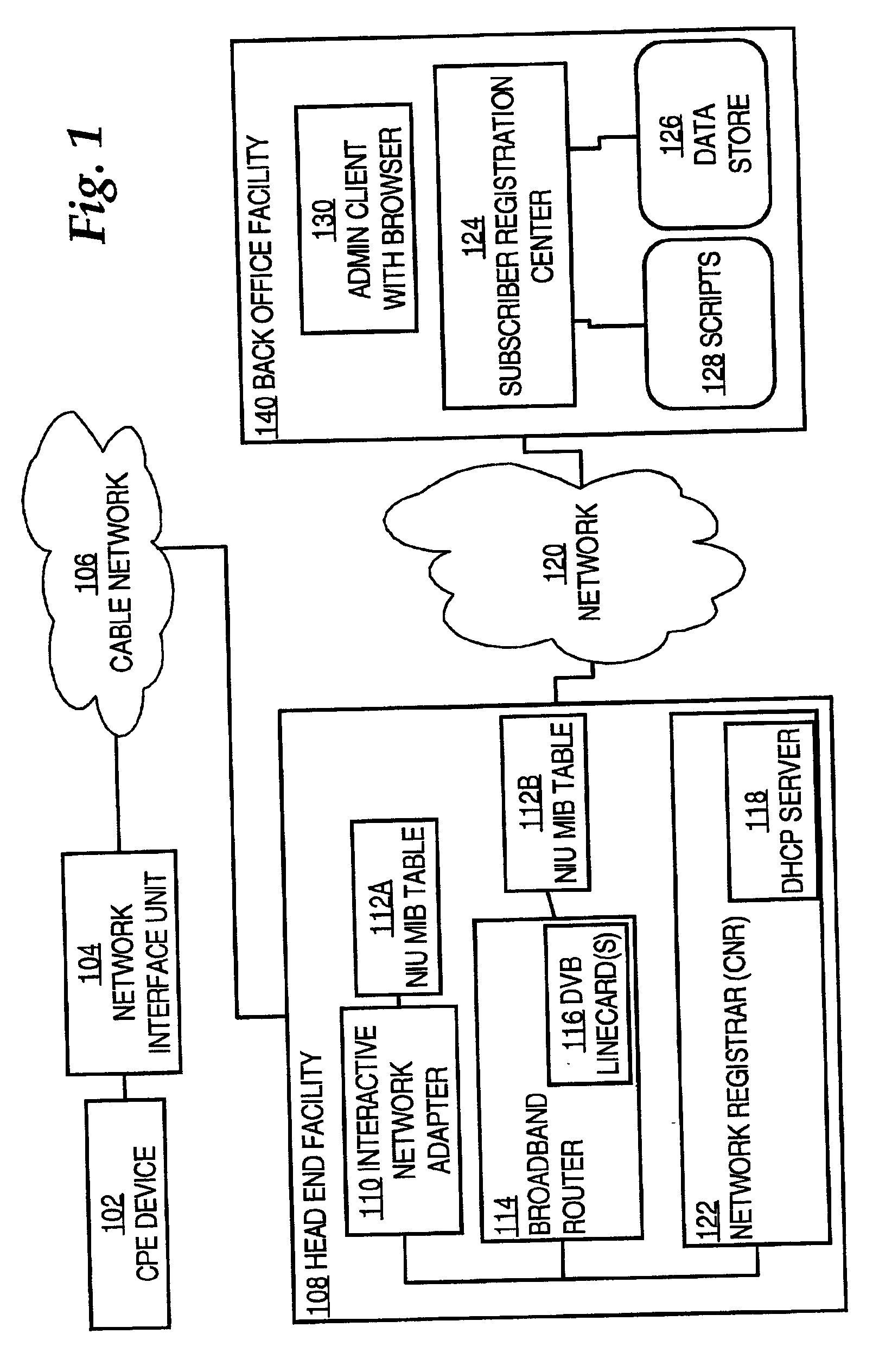
A method for establishing class of service configuration in a network device of a broadband cable network using Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is disclosed. A request to obtain a network address presented using DHCP is received from a network interface unit over the cable network, generally upon boot up of the network interface unit. A DHCP message is received from a registration center, and the message includes a network address and a quality of service code value associated with the network interface unit. Based on the quality of service code value, a quality of service configuration is established in the cable network for the network interface unit. As a result, quality of service information is obtained for each network interface unit in the network, specifically when the network interface unit is activated, and as part of its boot-up sequence. Carrying the quality of service information in a DHCP message enables configuration of the network rapidly and without introducing an additional protocol.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Algorithm for time based queuing in network traffic engineering
The present invention provides a method for prioritizing packet flows within a switching network. The method includes the steps of receiving packets at an input port, stamping the packets with an arrival time, and classifying the packet into a flow, wherein the flow is determined based upon at least a class of service of the packet, assigning the packet to a queuing ring according to the flow of the packet, and maintaining a flow ratio pending within the switch based upon the classification of the packet.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Admission control for services
ActiveUS20100246393A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionTopology informationClass of service
An admission control system is disclosed in combination with a network and a computing system in communication with the network. The computing system is configured to determine a class of service requirement from a service request. The computing system is furnished with topology information about the network, a portion of the topology being based on a protocol (e.g., Multiple Spanning Tree protocol) whereby multiple paths are created for provisioning a connection for the service request. A mechanism is configured to determine if at least one path is available that satisfies the class of service requirement and to admit the service request into the network when the path is available for provisioning the connection. Bandwidth usage may be tracked and used in provisioning decisions. Requests may be made to the network to add bandwidth (e.g., through additional optical wavelengths) to accommodate service requests.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
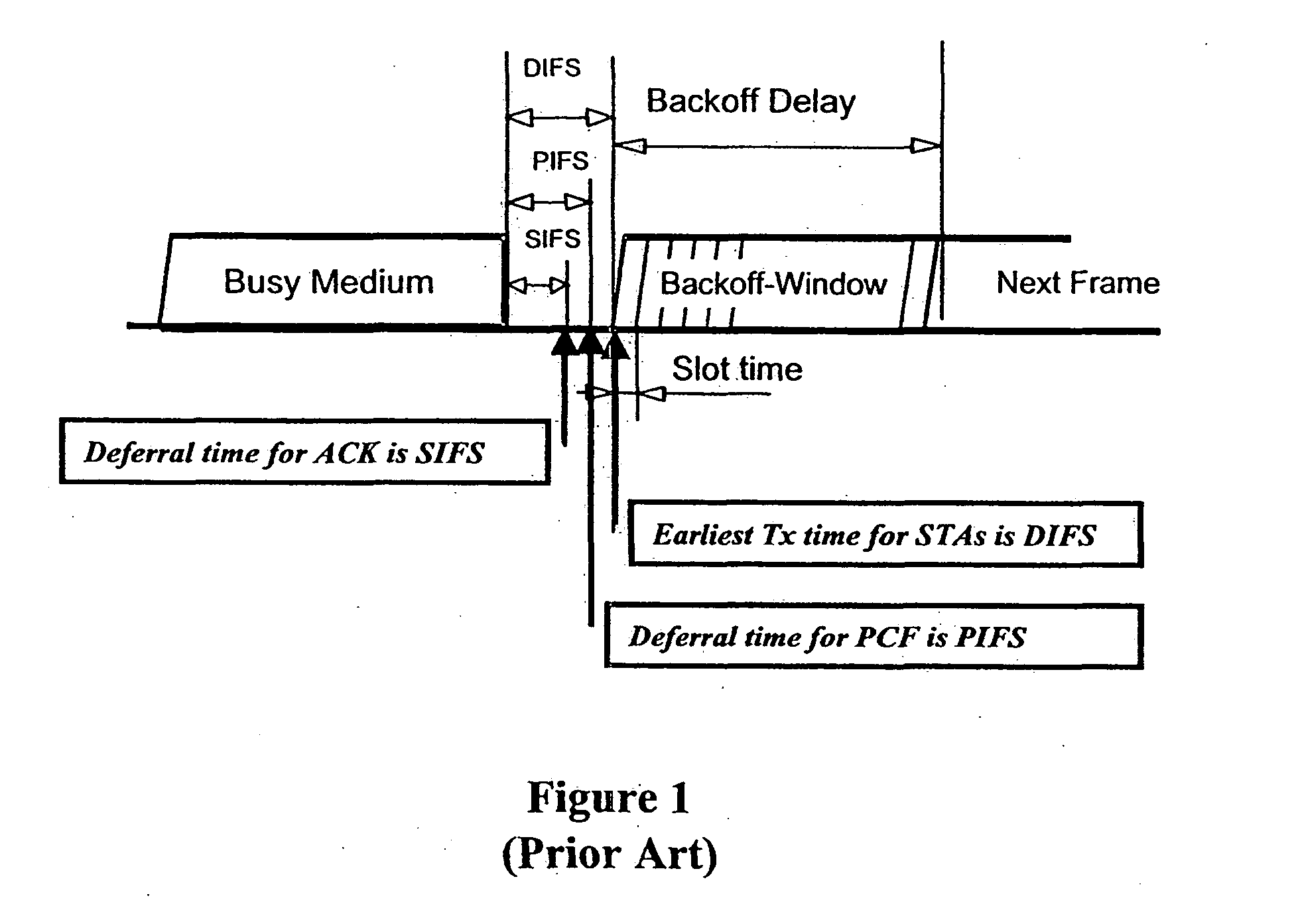
Tiered contention multiple access (TCMA): a method for priority-based shared channel access
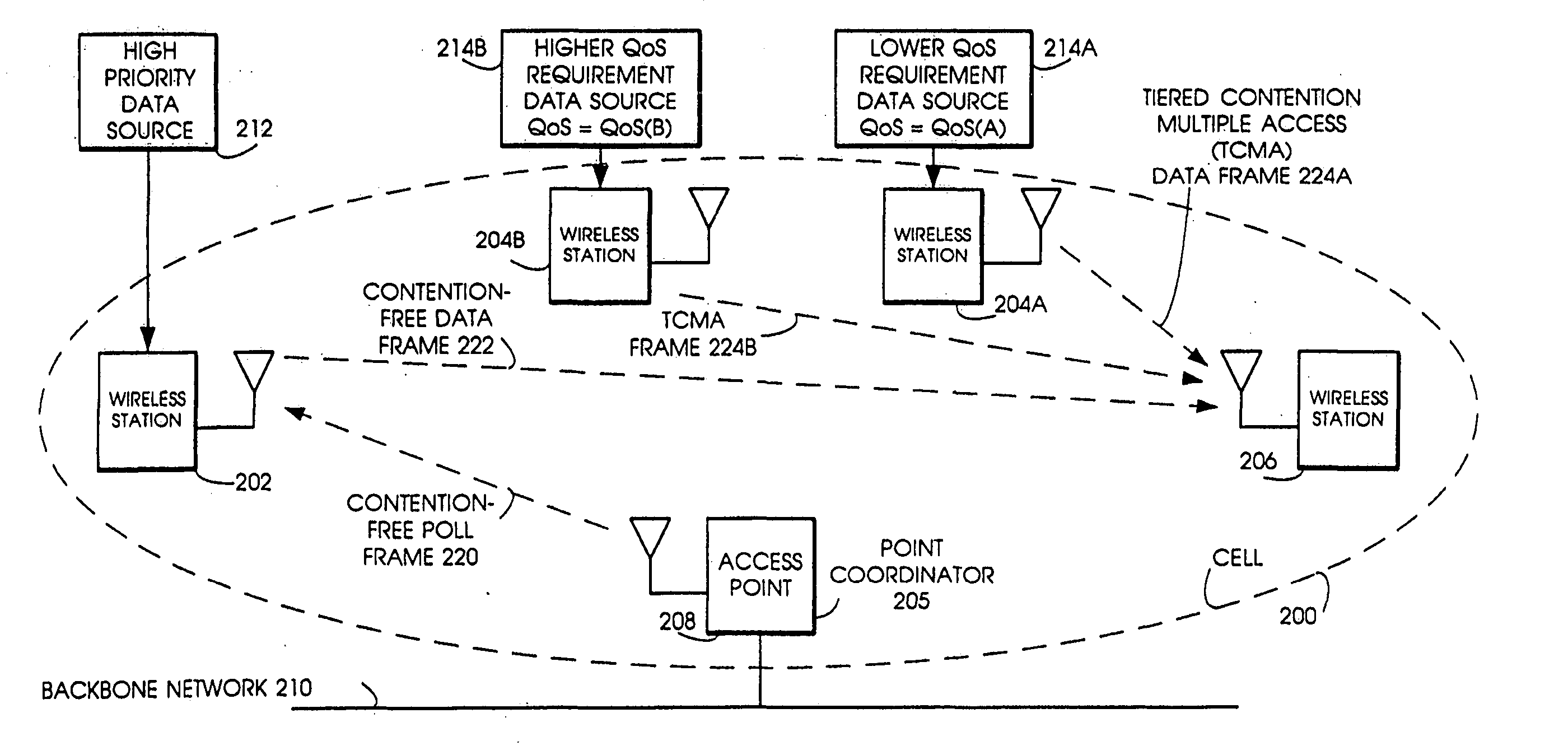
InactiveUS20070019664A1Minimizing chanceLower latencySynchronisation arrangementError preventionService-level agreementClass of service
Quality of Service (QoS) support is provided by means of a Tiered Contention Multiple Access (TCMA) distributed medium access protocol that schedules transmission of different types of traffic based on their service quality specifications. In one embodiment, a wireless station is supplied with data from a source having a lower QoS priority QoS(A), such as file transfer data. Another wireless station is supplied with data from a source having a higher QoS priority QoS(B), such as voice and video data. Each wireless station can determine the urgency class of its pending packets according to a scheduling algorithm. For example file transfer data is assigned lower urgency class and voice and video data is assigned higher urgency class. There are several urgency classes which indicate the desired ordering. Pending packets in a given urgency class are transmitted before transmitting packets of a lower urgency class by relying on class-differentiated urgency arbitration times (UATs), which are the idle time intervals required before the random backoff counter is decreased. In another embodiment packets are reclassified in real time with a scheduling algorithm that adjusts the class assigned to packets based on observed performance parameters and according to negotiated QoS-based requirements. Further, for packets assigned the same arbitration time, additional differentiation into more urgency classes is achieved in terms of the contention resolution mechanism employed, thus yielding hybrid packet prioritization methods. An Enhanced DCF Parameter Set is contained in a control packet sent by the AP to the associated stations, which contains class differentiated parameter values necessary to support the TCMA. These parameters can be changed based on different algorithms to support call admission and flow control functions and to meet the requirements of service level agreements.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
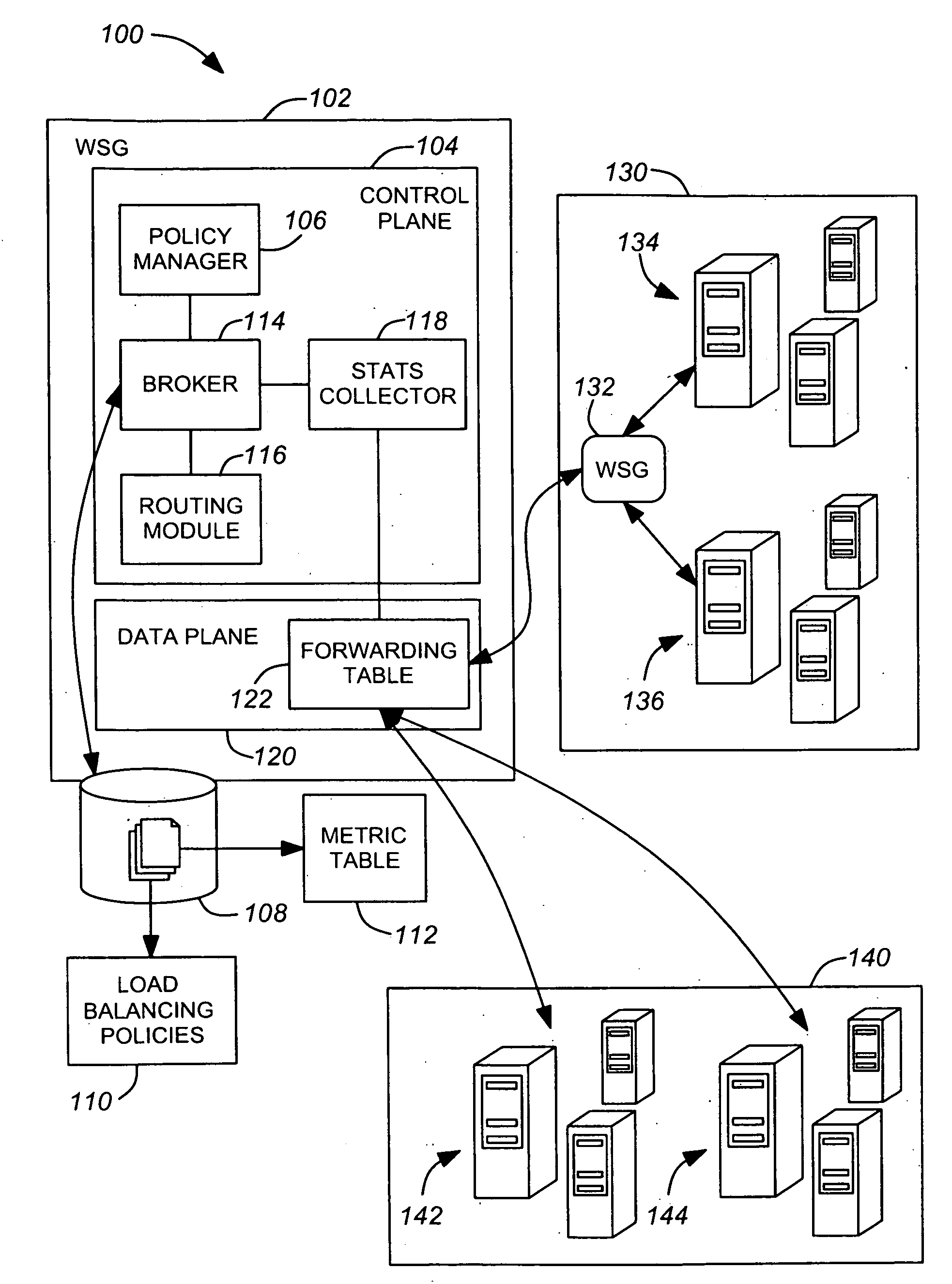
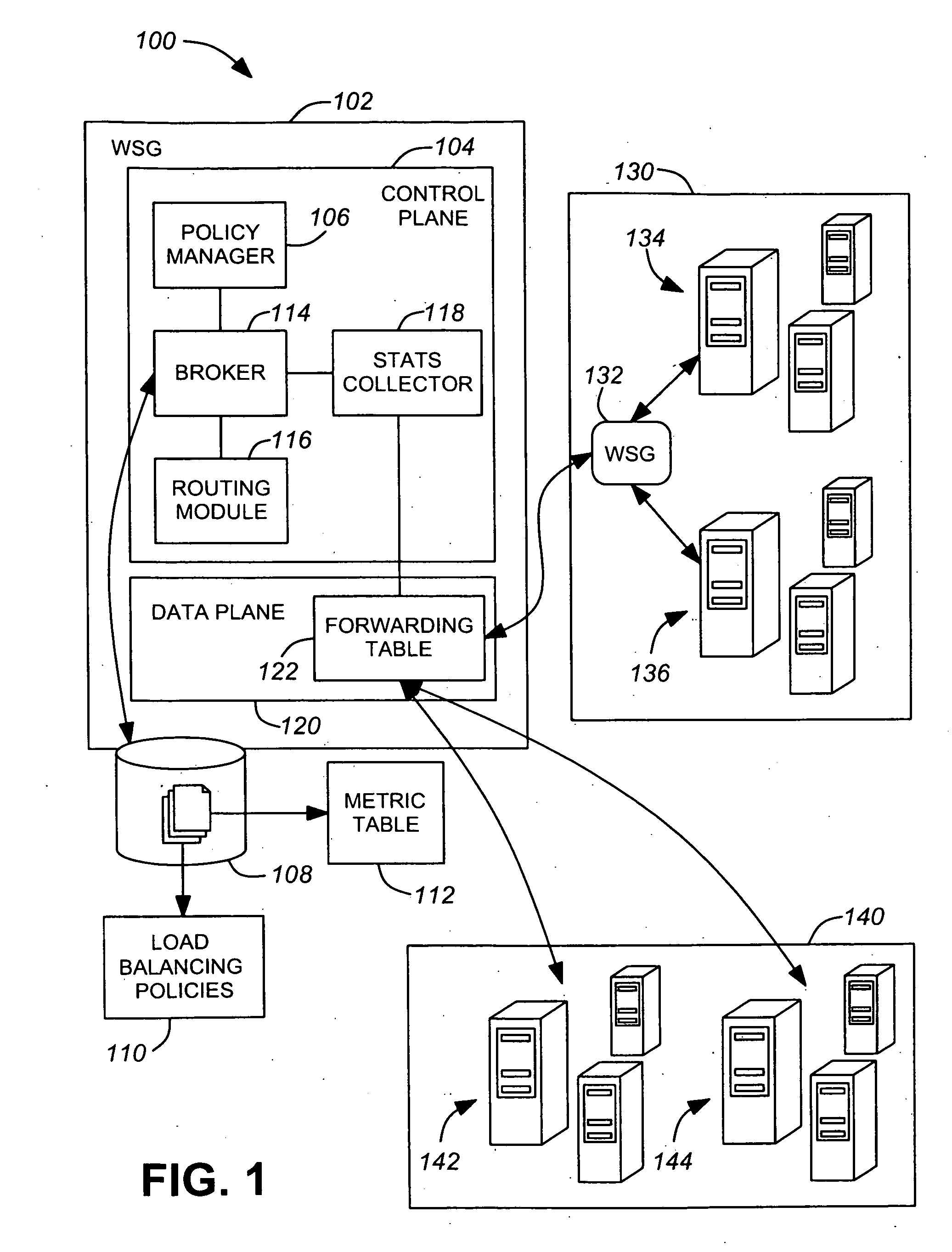
SOA infrastructure for application sensitive routing of web services
InactiveUS20090150565A1Conducive to loadLow costSpecific access rightsMultiple digital computer combinationsWeb serviceClass of service
Various exemplary embodiments are a system and related method for application sensitive forwarding of a request for a web service including a broker that manages the forwarding of the request, a metric table that stores statistics for the web service, and a database storing the metric table and least one load balancing policy. Various exemplary embodiments include an optimization policy manager that manages forwarding of the request, a class of services table that stores information, and a database storing the class of services table and at least one optimization policy. Various exemplary embodiments include a database storing a security-based policy and a location-based policy defining trust environments, a request processor that receives the request from the client and determines a current environment of the client based on the at least one location-based policy, and a quarantining subsystem that drops the request when the request violates the security-based policy.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
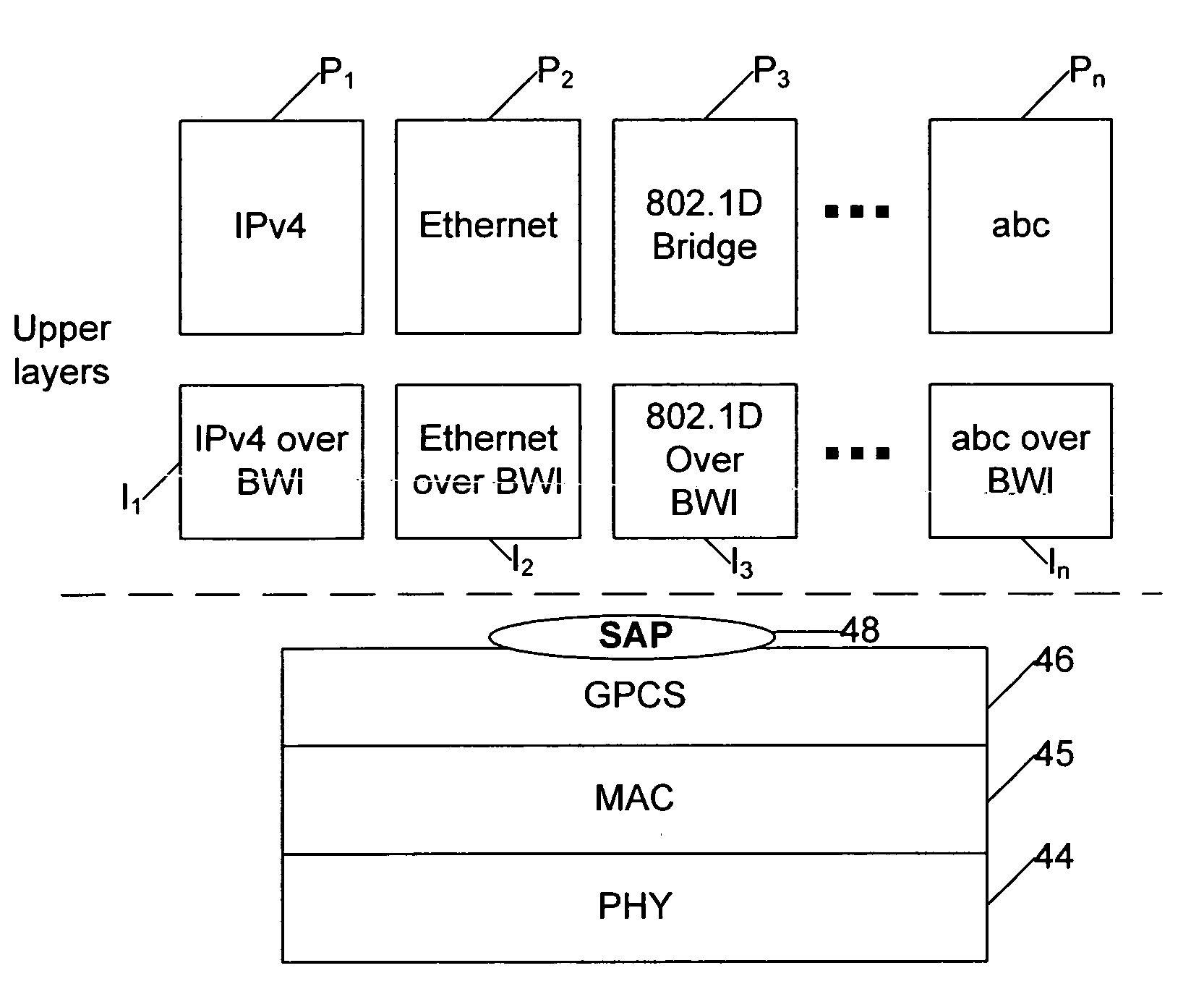
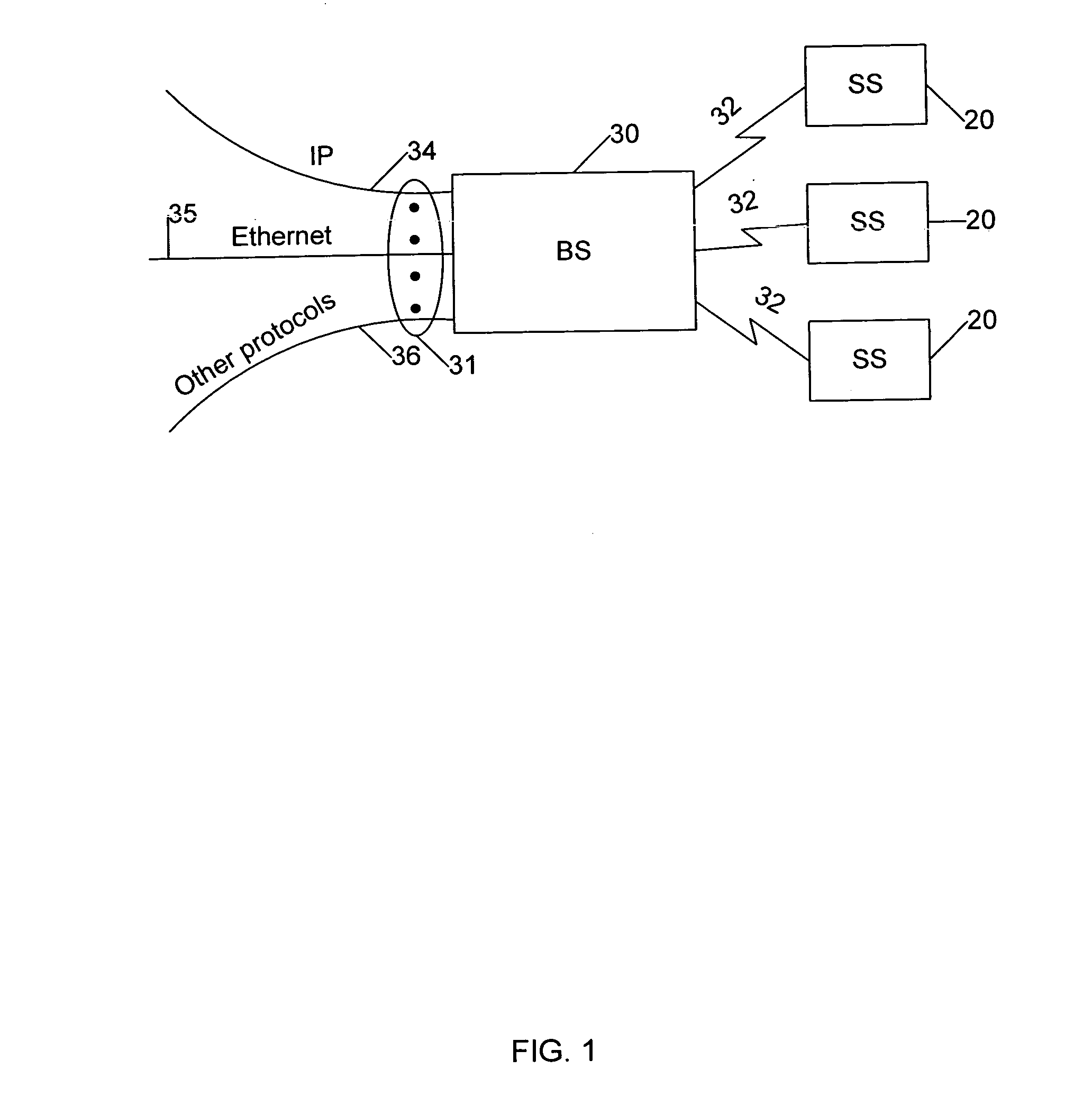
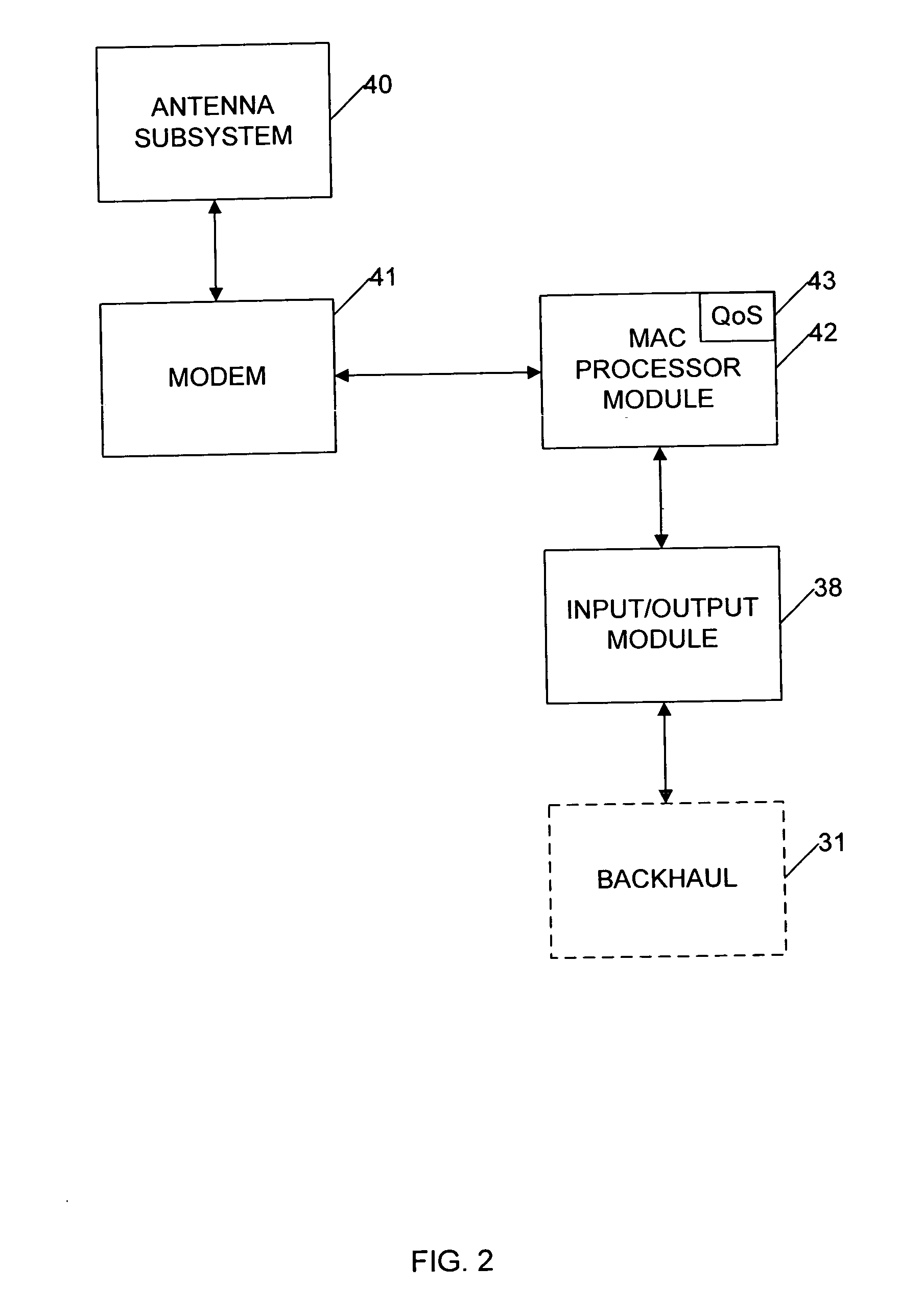
Method and system for generic multiprotocol convergence over wireless air interface
InactiveUS20080008159A1Network traffic/resource managementInformation formatComputer networkAir interface
Data packets of multiple different protocols are transmitted over a broadband wireless air interface between network stations subscribing to the broadband wireless access service. A first network station receives data packets of different network protocols in an upper layer for transmission to a second station over the wireless air interface. The different protocol data packets are processed in the upper layer to look up a destination address and class of service, and are transmitted to a single generic packet convergence sublayer along with an identification tag indicating the destination address and class of service. The generic packet convergence sublayer maps the identification tag to a single connection ID (CID) of a second station of the broadband wireless access service, without having to carry out any packet inspection.
Owner:MONUMENT BANK OF INTPROP LLC
Router with class of service mapping
A router classifies packets assigned to X*Y classes of service into X classes of service supported by the router, each of the X classes of service having Y loss-priority levels. The router maintains a free queue that links available entries of a buffer in which packets are stored. A weighted average depth of the free queue is used to determine whether to retain a given packet. If the weighted average is above a maximum threshold, the packet is retained. If the weighted average is below a minimum threshold, the packet is discarded. If the weighted average is between the two thresholds, a probability of discard that is based on the X*Y classes of service is calculated and compared to a random value to determine whether the packet should be retained.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
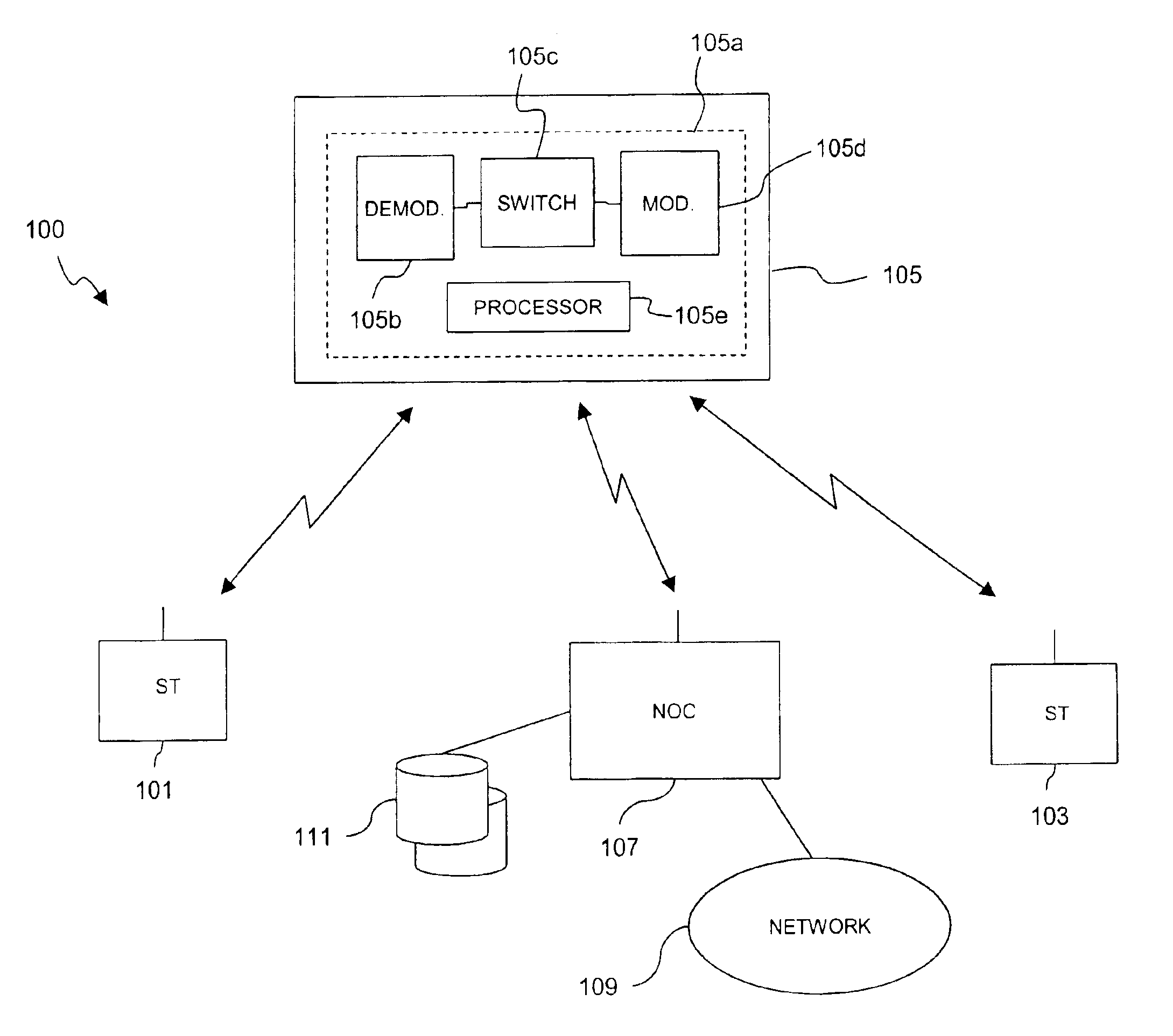
Capacity management in a broadband satellite communications system
InactiveUS6904265B1Partly effectiveMeet efficiency requirementsRadio transmissionWireless commuication servicesCommunications systemSystem capacity
An approach for managing system capacity of a satellite communications system is disclosed. A satellite communications system provides communication services to a region. A terminal (101, 103) is located within the region and is configured to transmit and receive signals over a satellite (105) having a payload that processes the signals. The terminal (101, 103) has a predetermined profile that includes service class information and rate information. A hub (107) is configured to receive system capacity resource configuration data that reflect capacity requirements of a service provider and to determine partitioning of system capacity over the region based upon the system capacity resource configuration data. The hub (107) transmits configuration information to the payload of the satellite (105) according to the determined partitions. The terminal (101, 103) is configured to transmit a bandwidth request message to the payload. The payload selectively allocates bandwidth in response to the request message based upon the configuration information.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
Traffic shaping of cellular service consumption through delaying of service completion according to geographical-based pricing advantages
InactiveUS20060040641A1Low costMaximum convenienceAccounting/billing servicesFinanceProgram planningClass of service
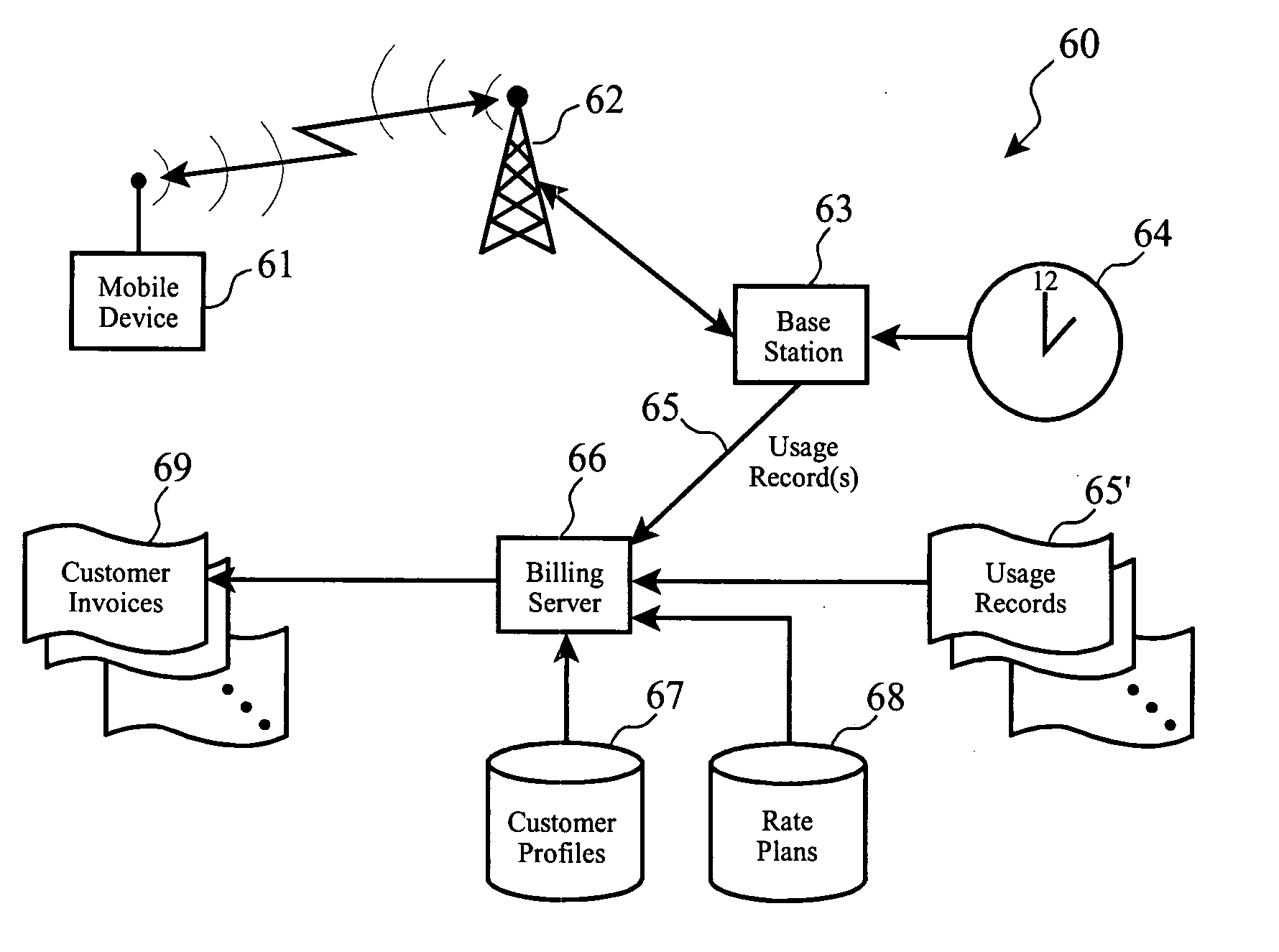
Changes in user behavior of usage of wireless services from a mobile device are encouraged in order to effect shaping of traffic and utilization patterns among a plurality of cells within a rate plan region, wherein a discount indicator disposed in said mobile device is provided to notify a user of a discount available for consuming wireless service from a given cell. A geo-cost policy is established for that user or mobile device in which rules and conditions according to the available discounts and class of service are defined. A service completer queues services and automatically completes queued services upon present conditions meeting said geo-cost policy rules, such as delaying and later delivering messages when the mobile device is relocated to a cell where discounts are being offered.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com