Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
842results about How to "Sufficient flexibility" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
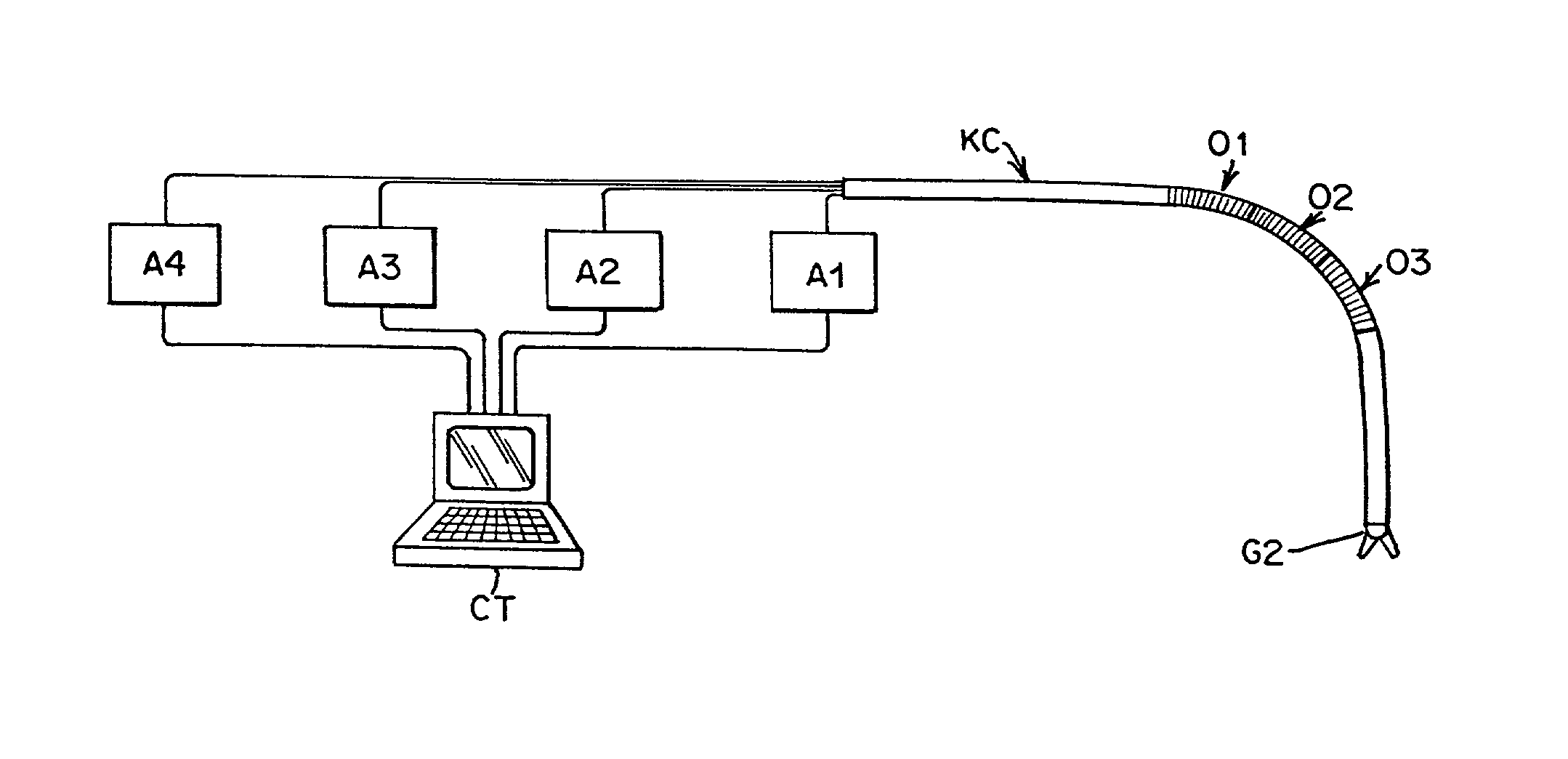
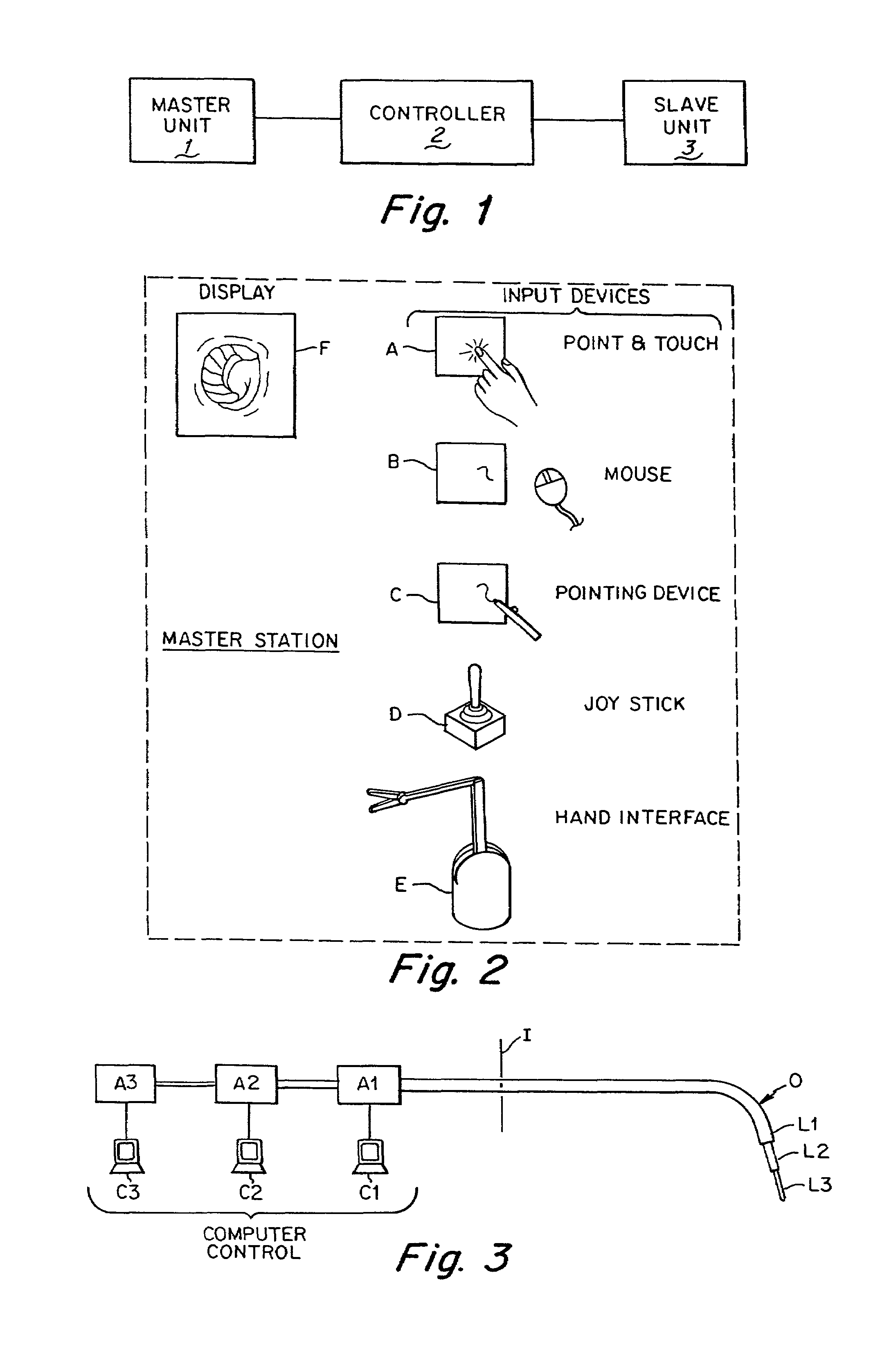
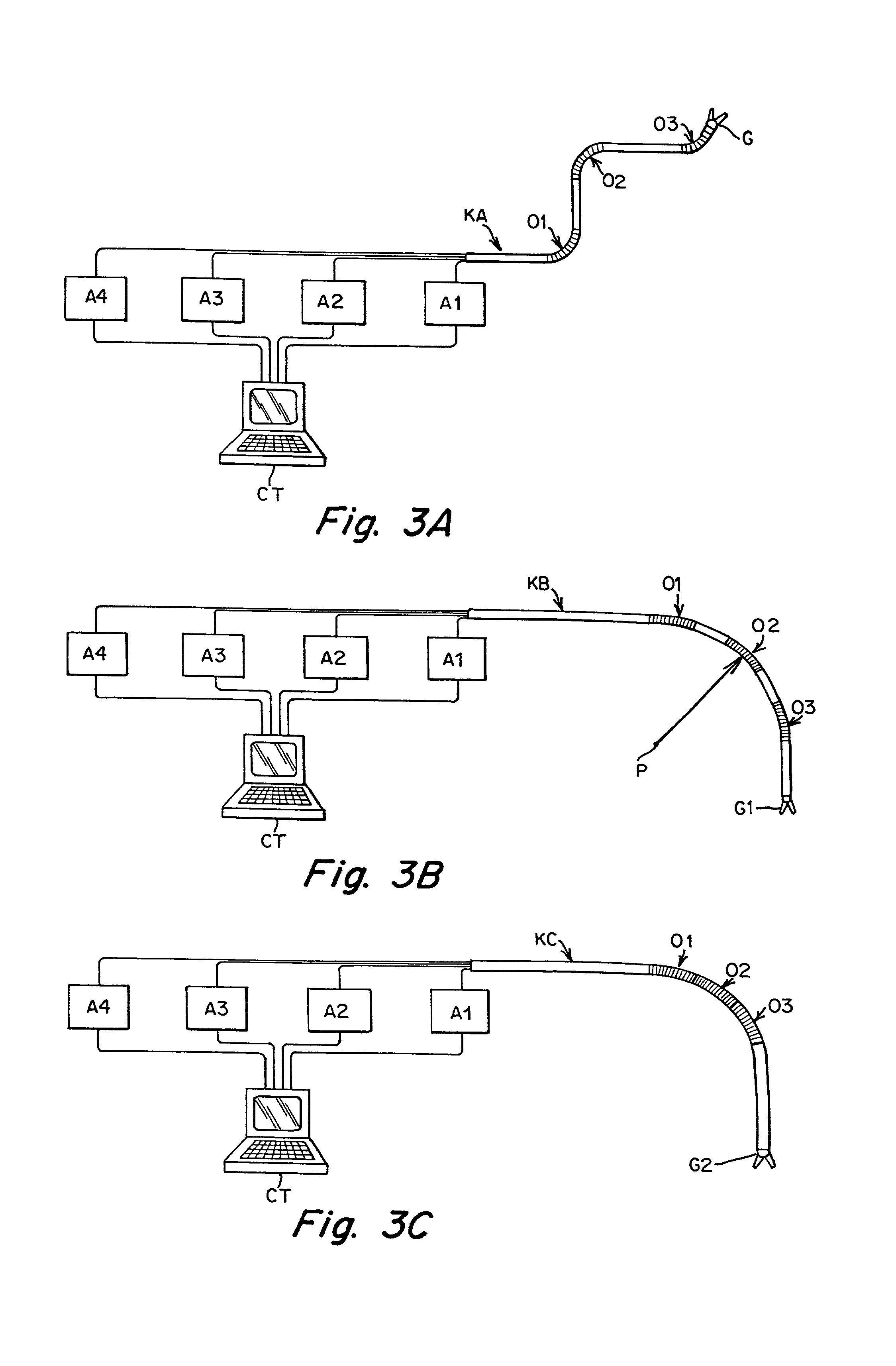
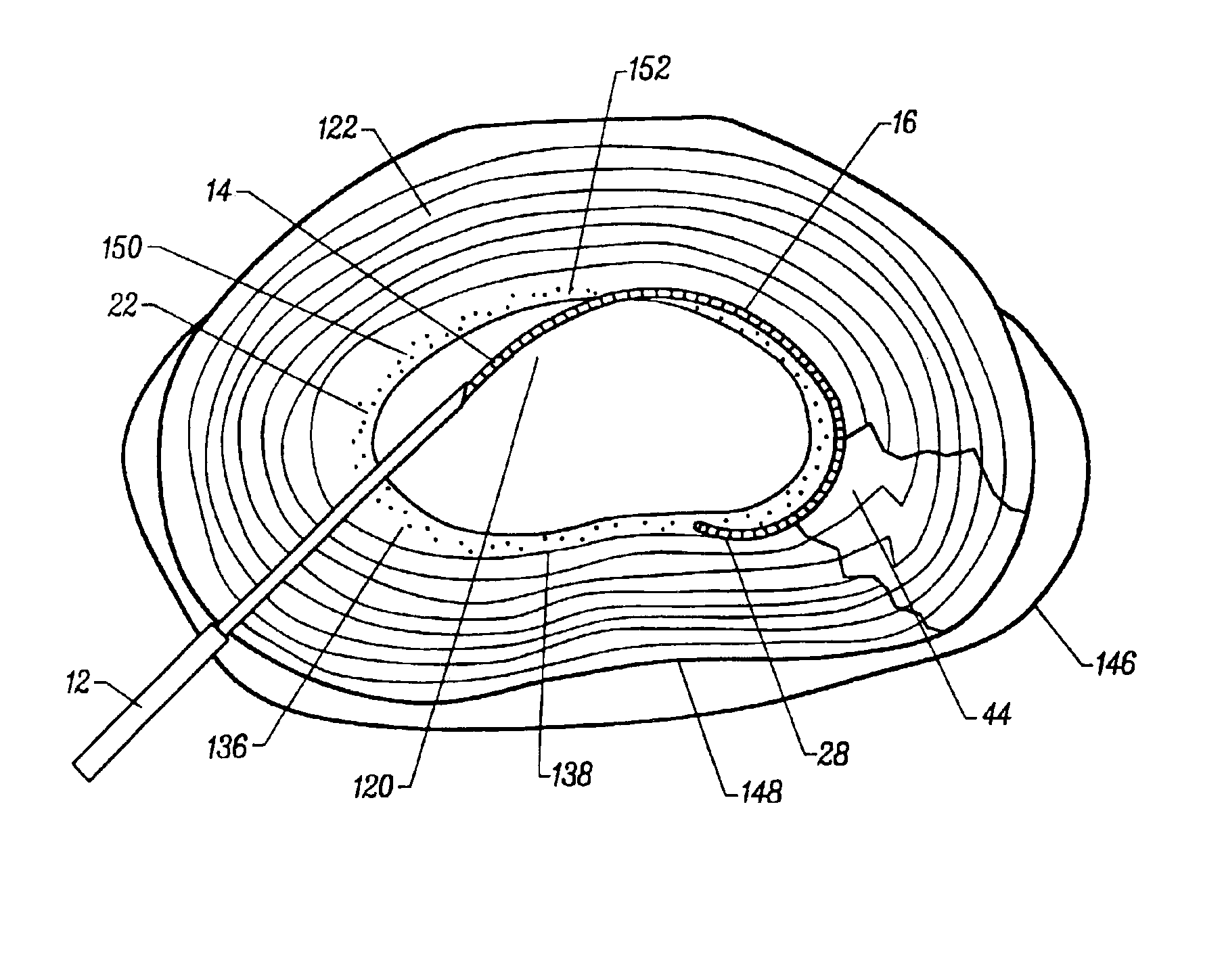
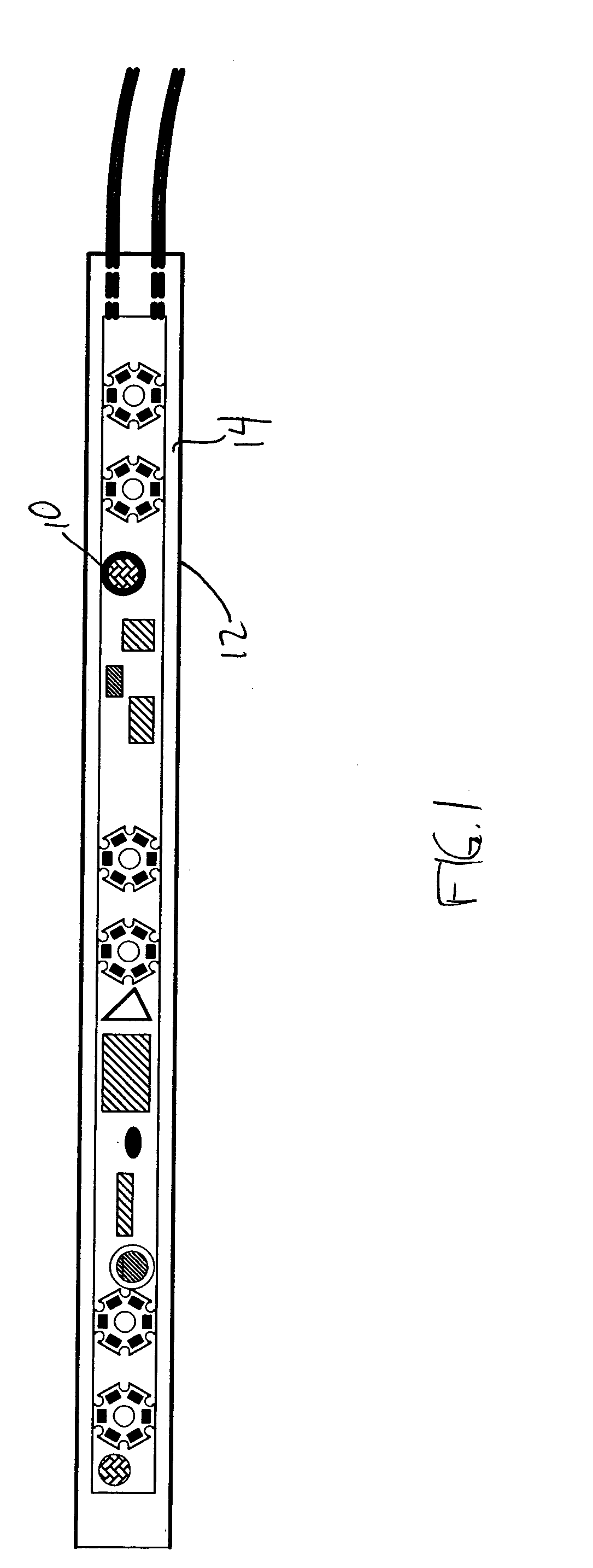
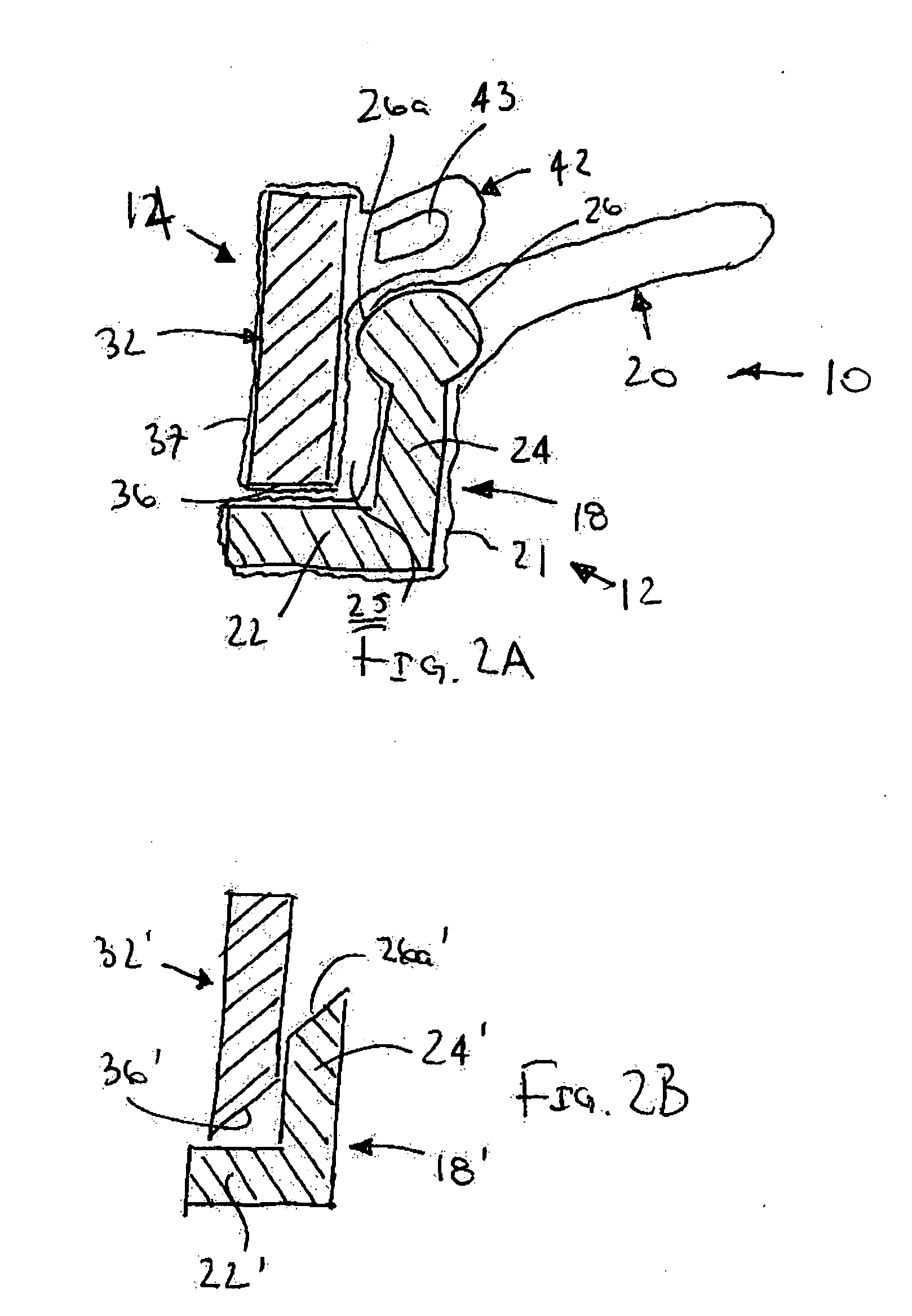
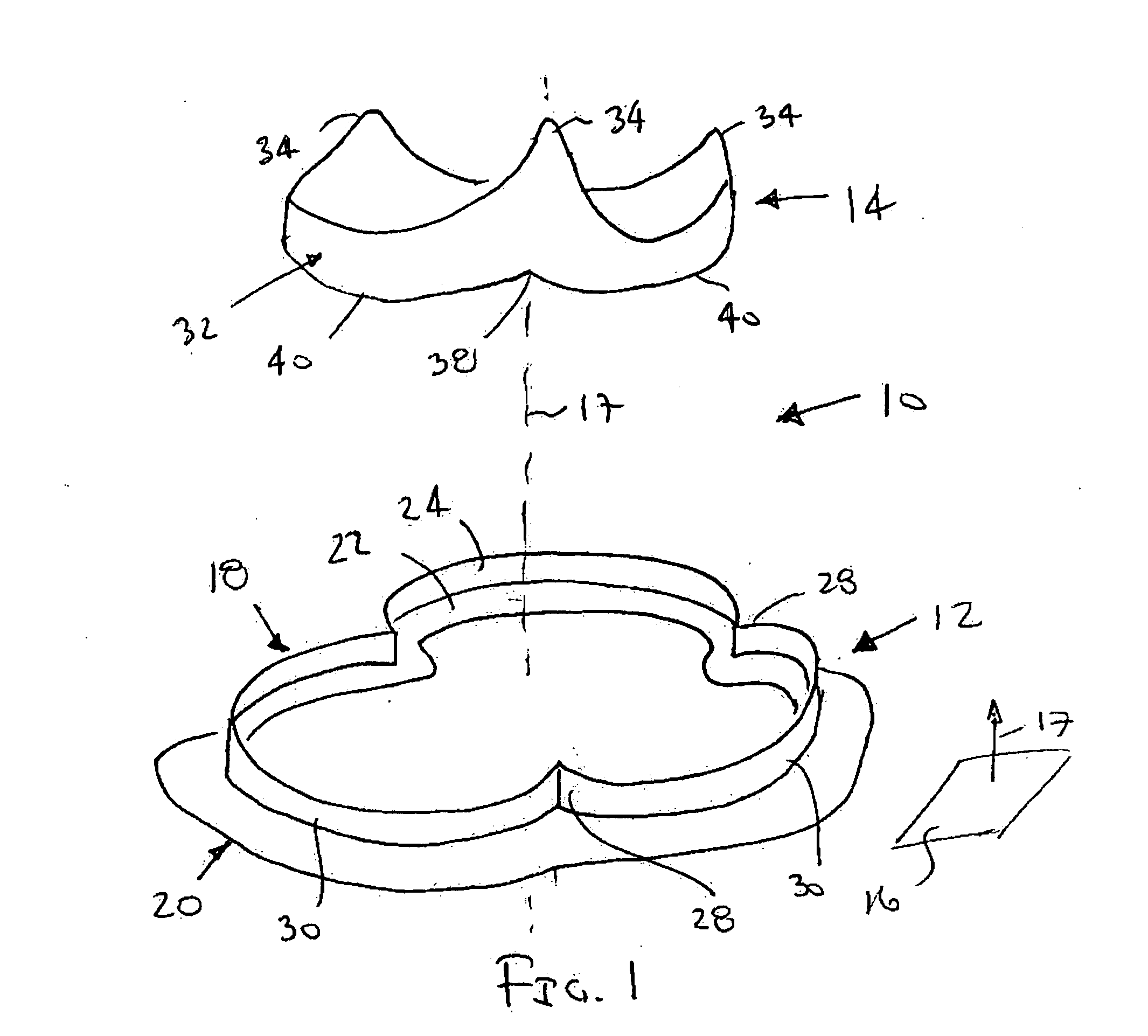
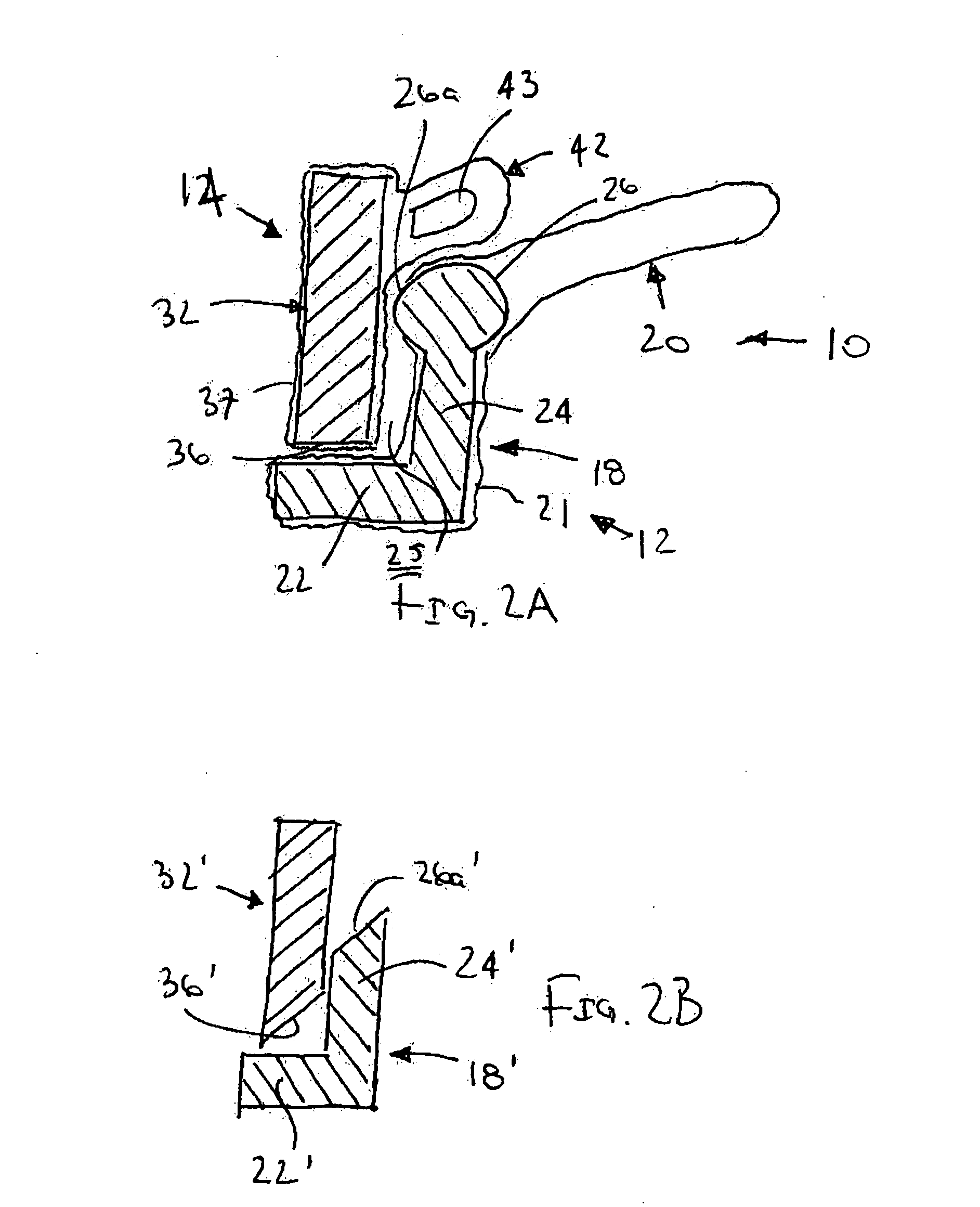
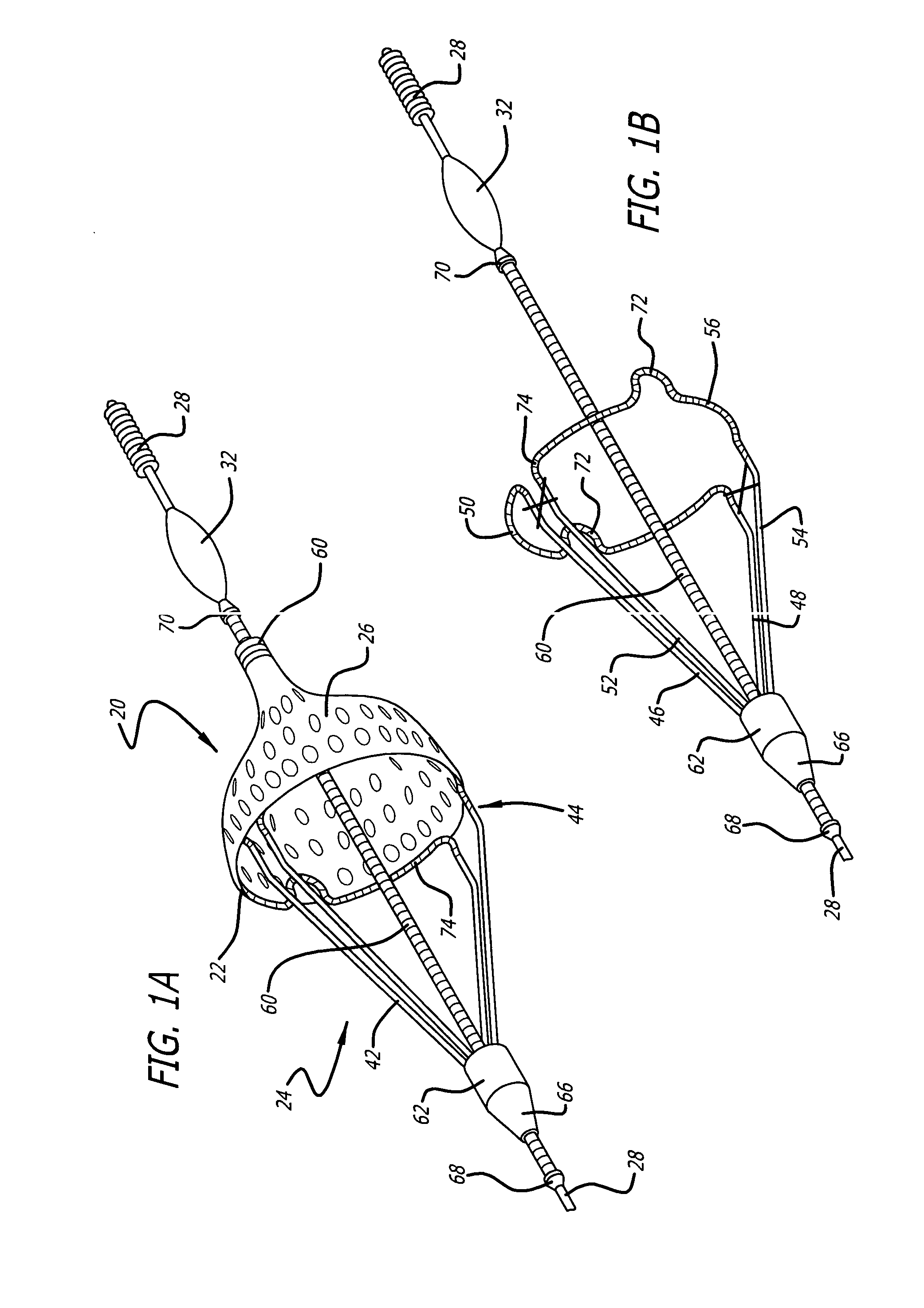
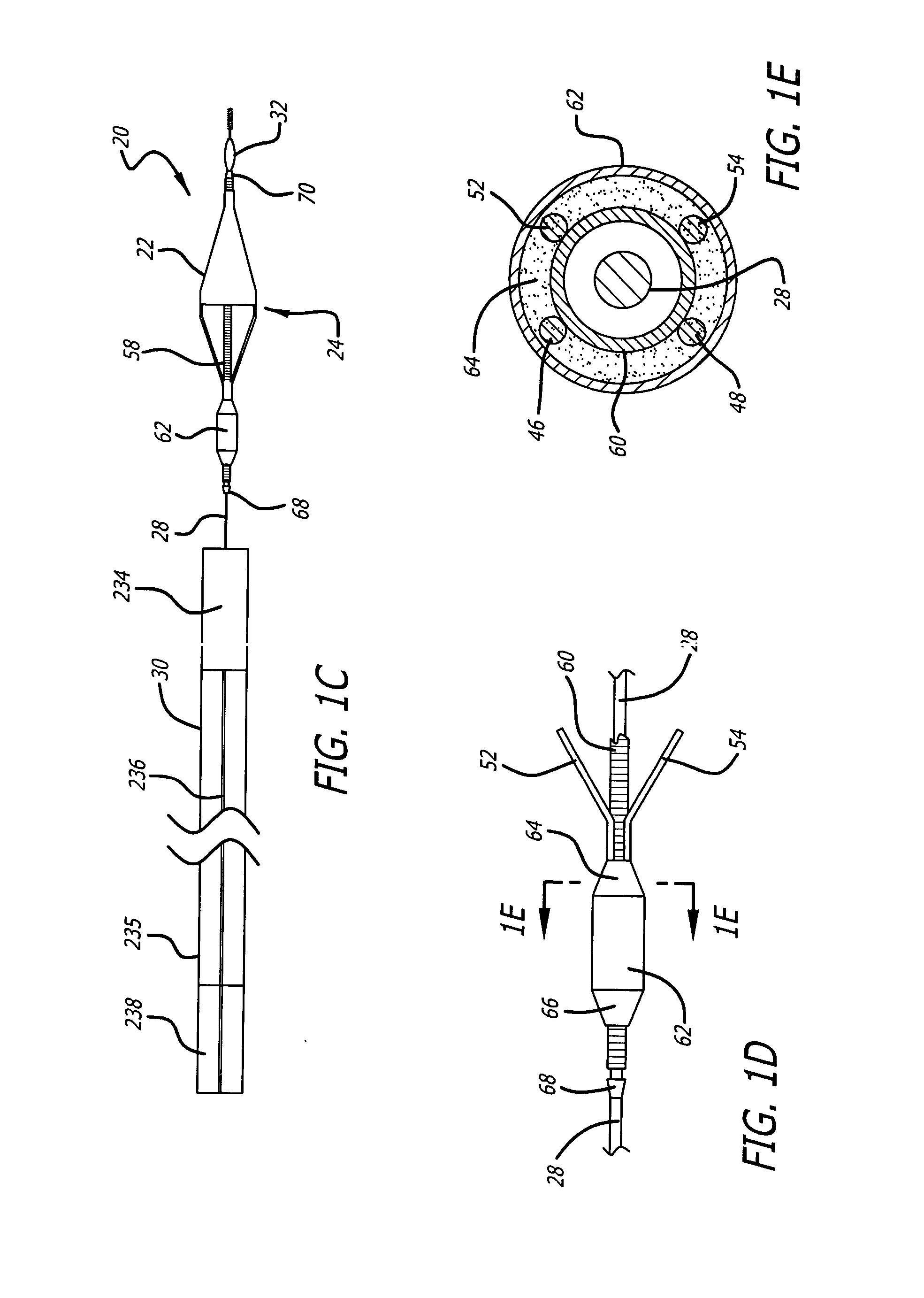
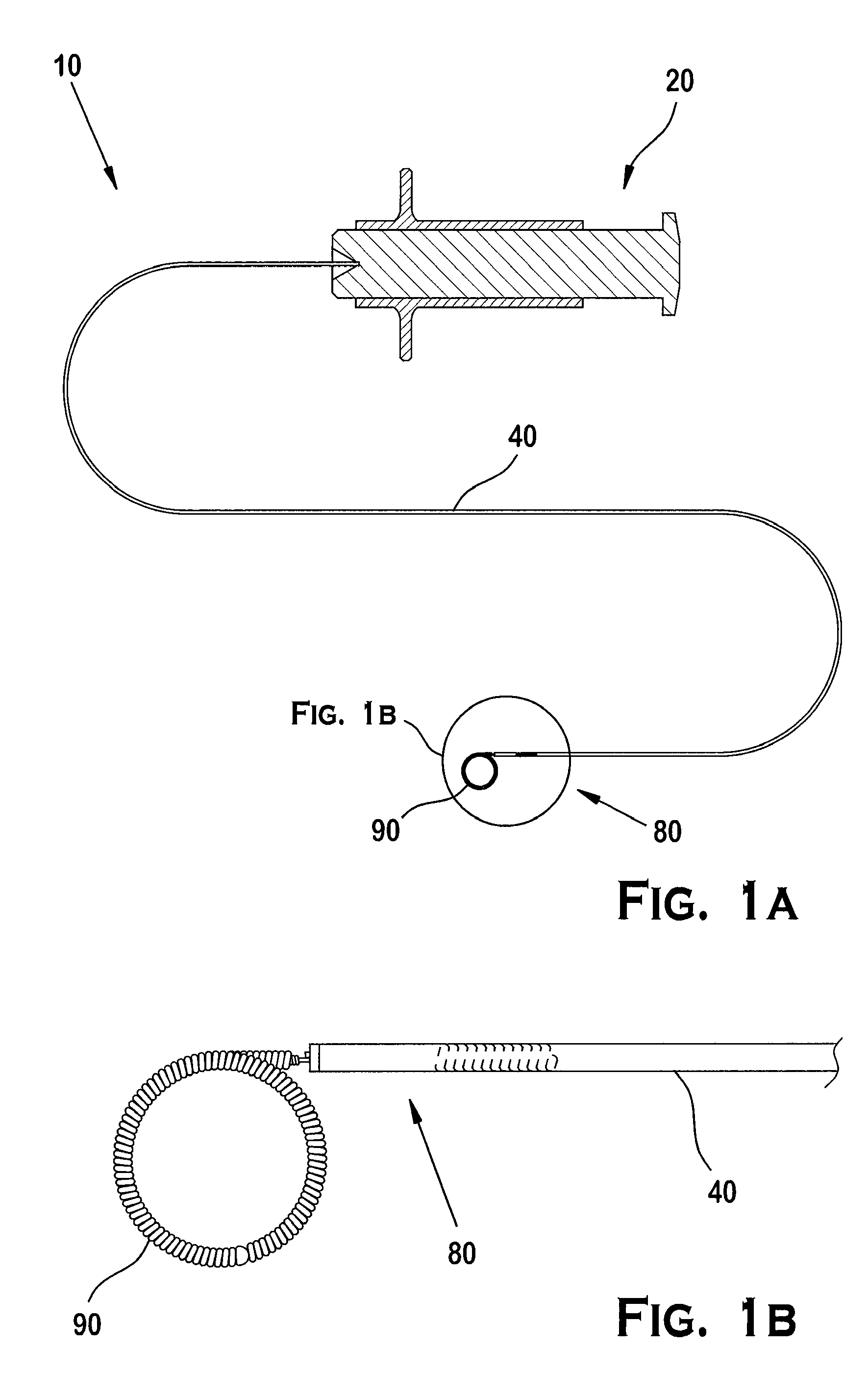
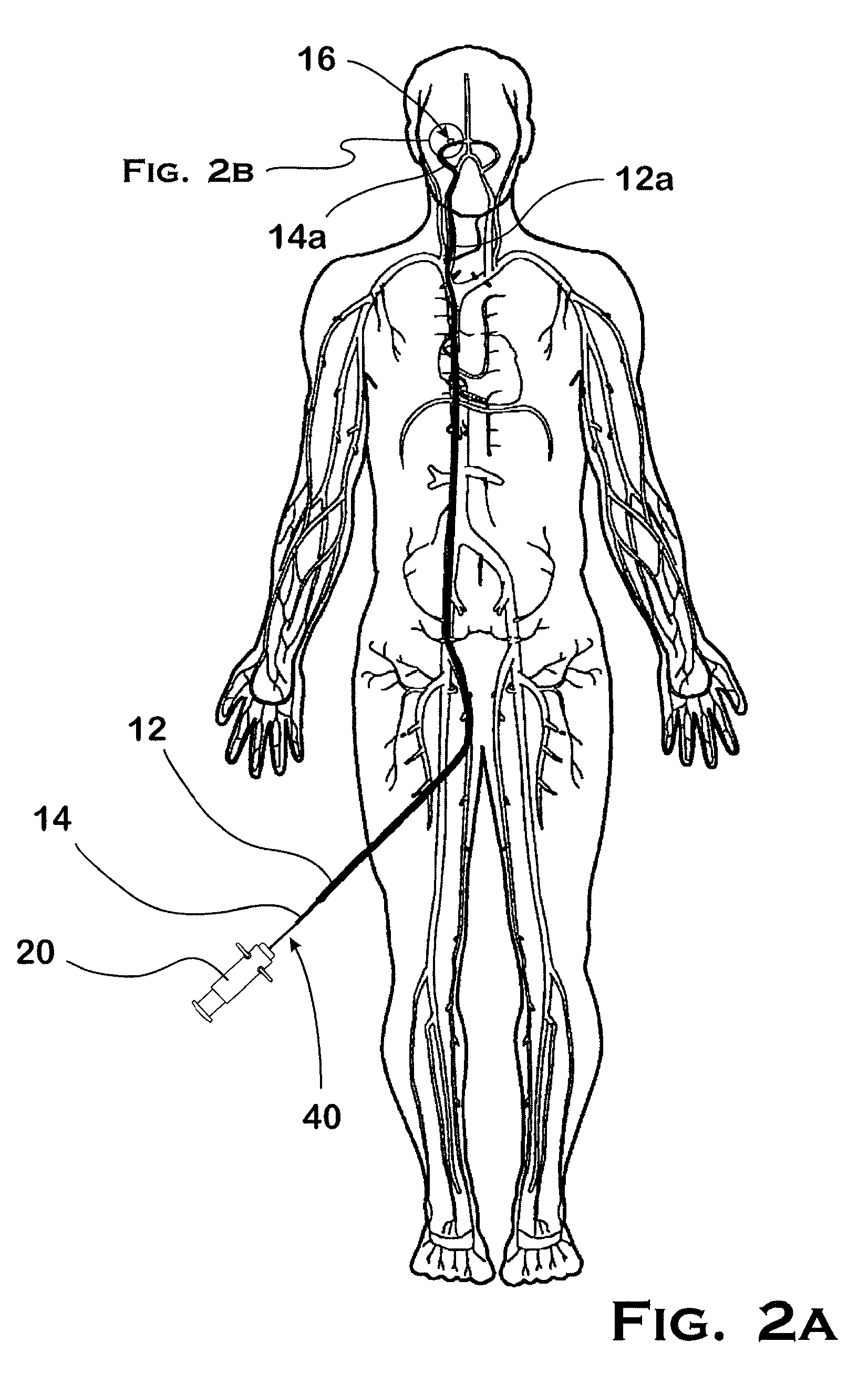
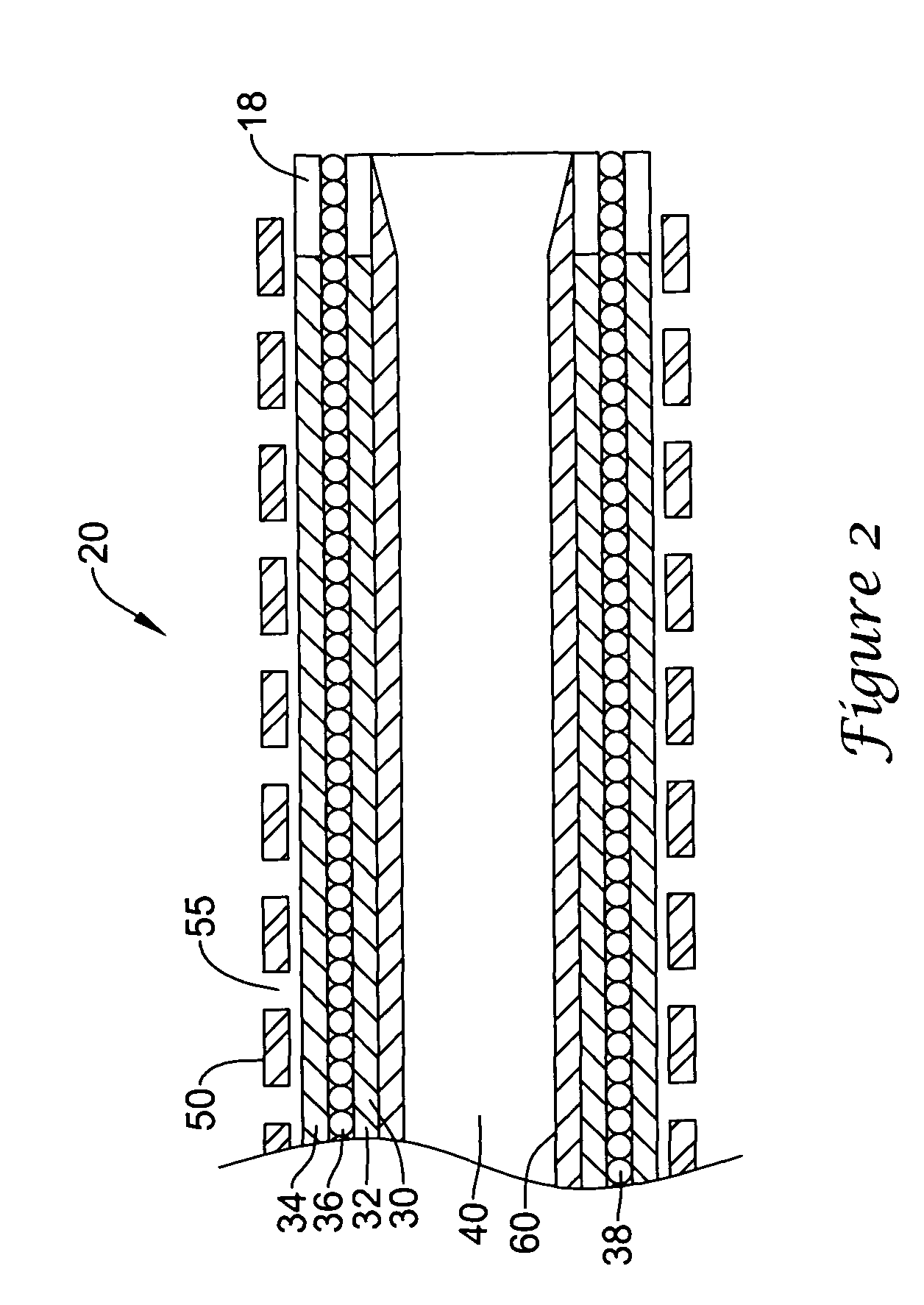
Flexible instrument
InactiveUS7090683B2Small diameterSufficient flexibilitySuture equipmentsProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringComputer algorithm
A remote control flexible instrument system, employing a shaft which supports a tool, is described in which the has proximal and distal ends with at least a portion thereof extending through a lumen of the human body so as to locate the shaft at an internal target site. A master station including an input device provides control of the instrument situated at a slave station. The master station can control at least one degree-of-freedom of the flexible instrument. A controller intercouples the master and slave stations and is operated in accordance with a computer algorithm that receives a command from the input device for controlling at least one degree-of-freedom of the catheter so as to respond in accordance with action at the input device. The flexible instrument further comprises a controlled flexible segment along the shaft, for controlled bending at the flexible segment to guide the shaft and to dispose the tool at an operative site.
Owner:HANSEN MEDICAL INC
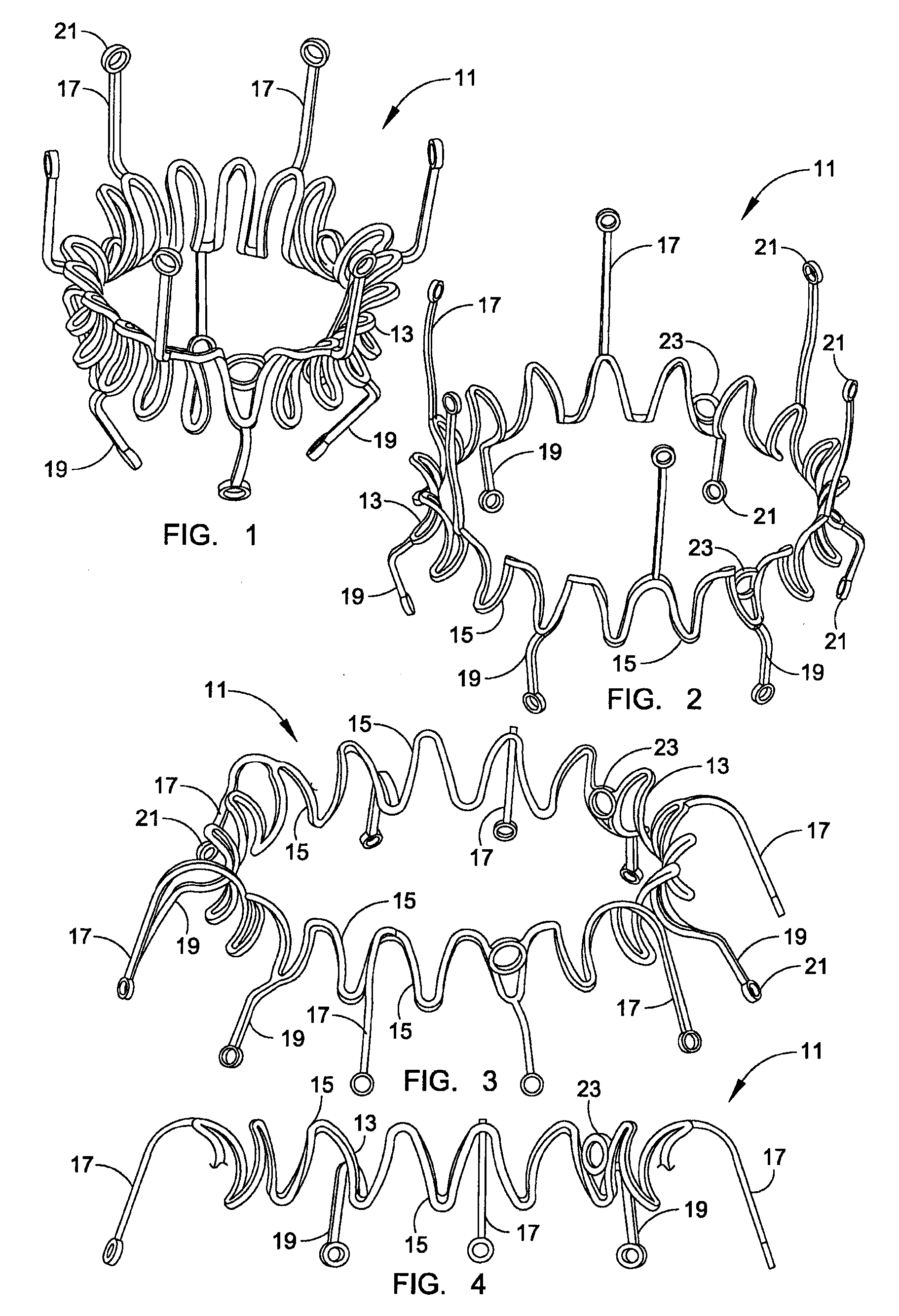
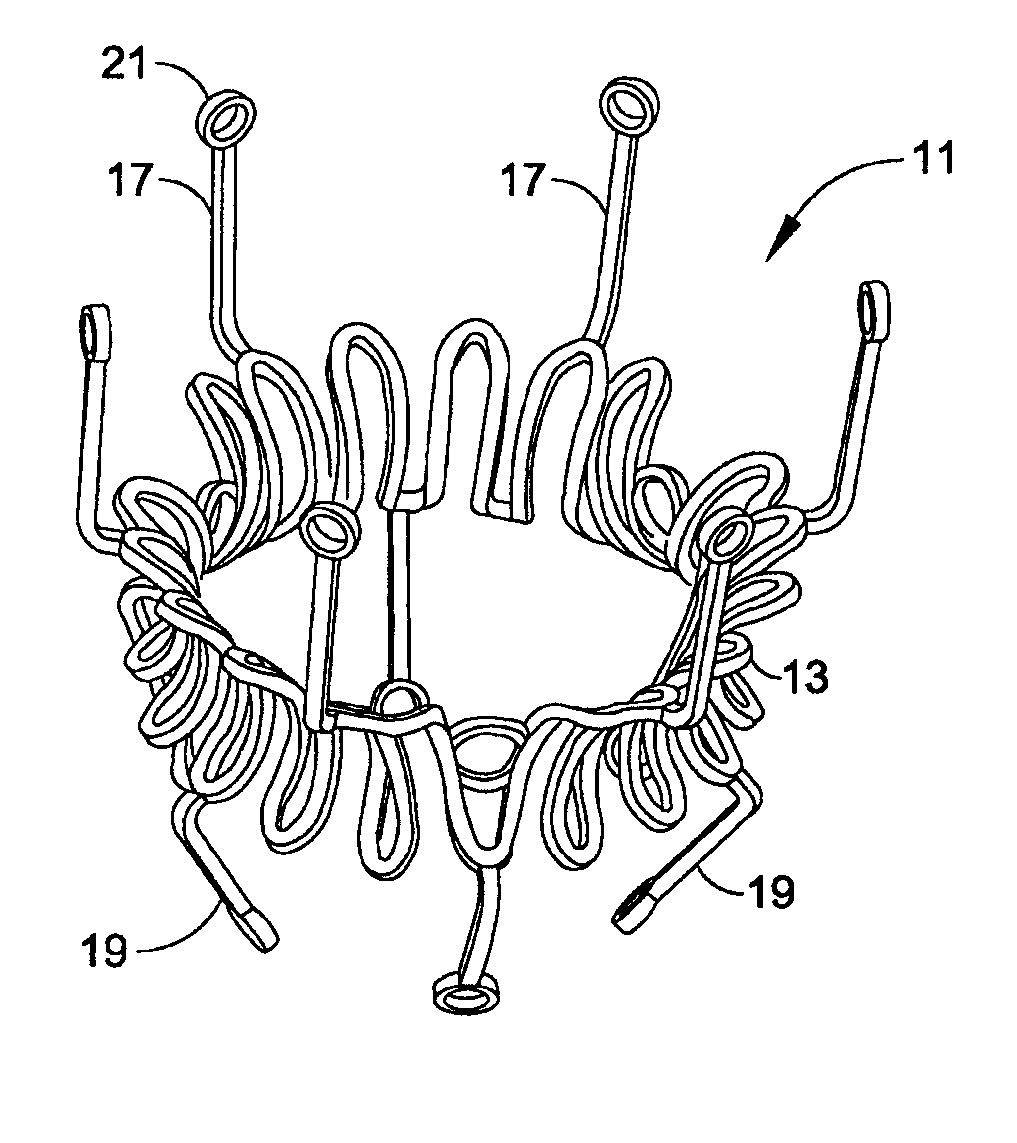
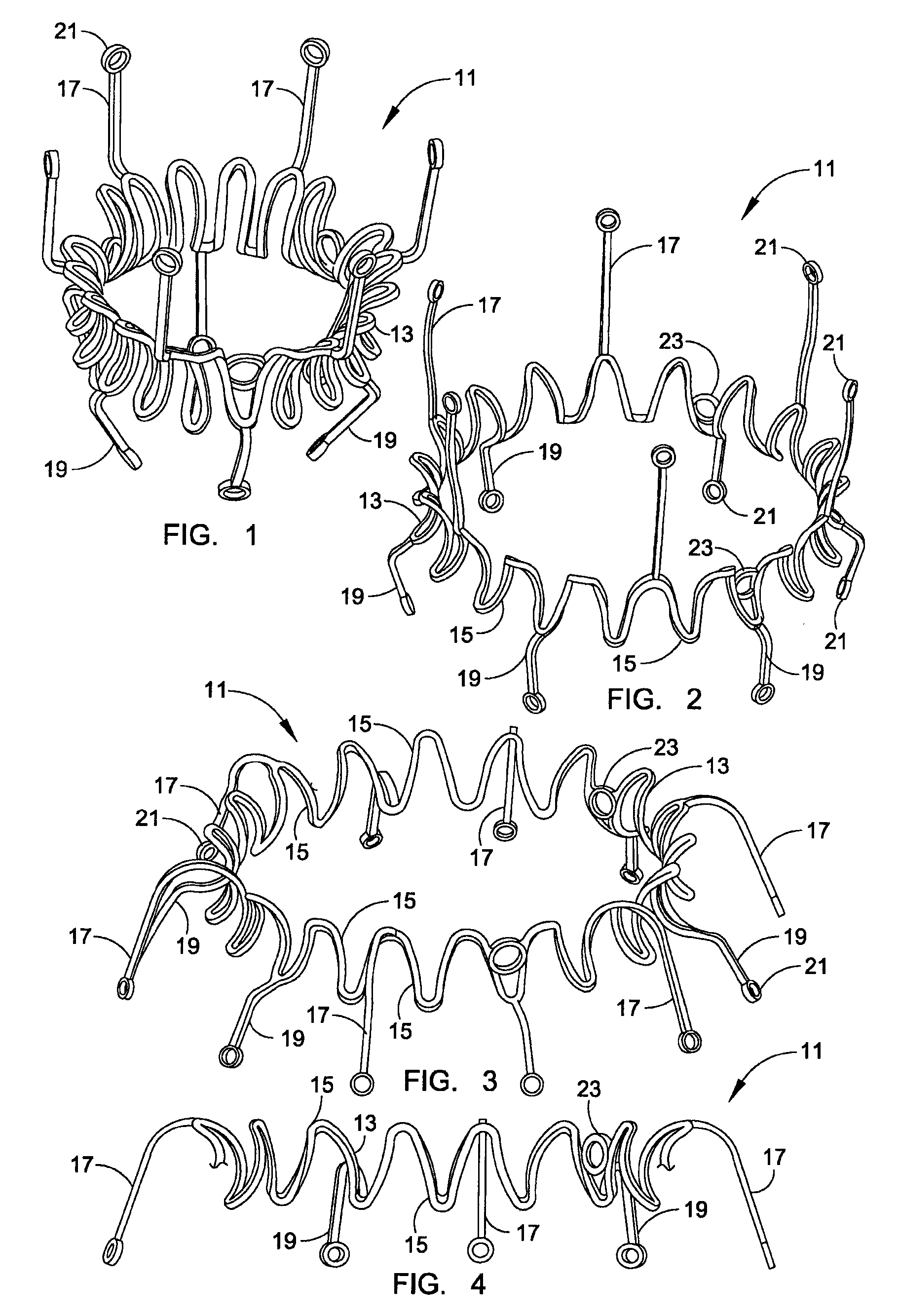
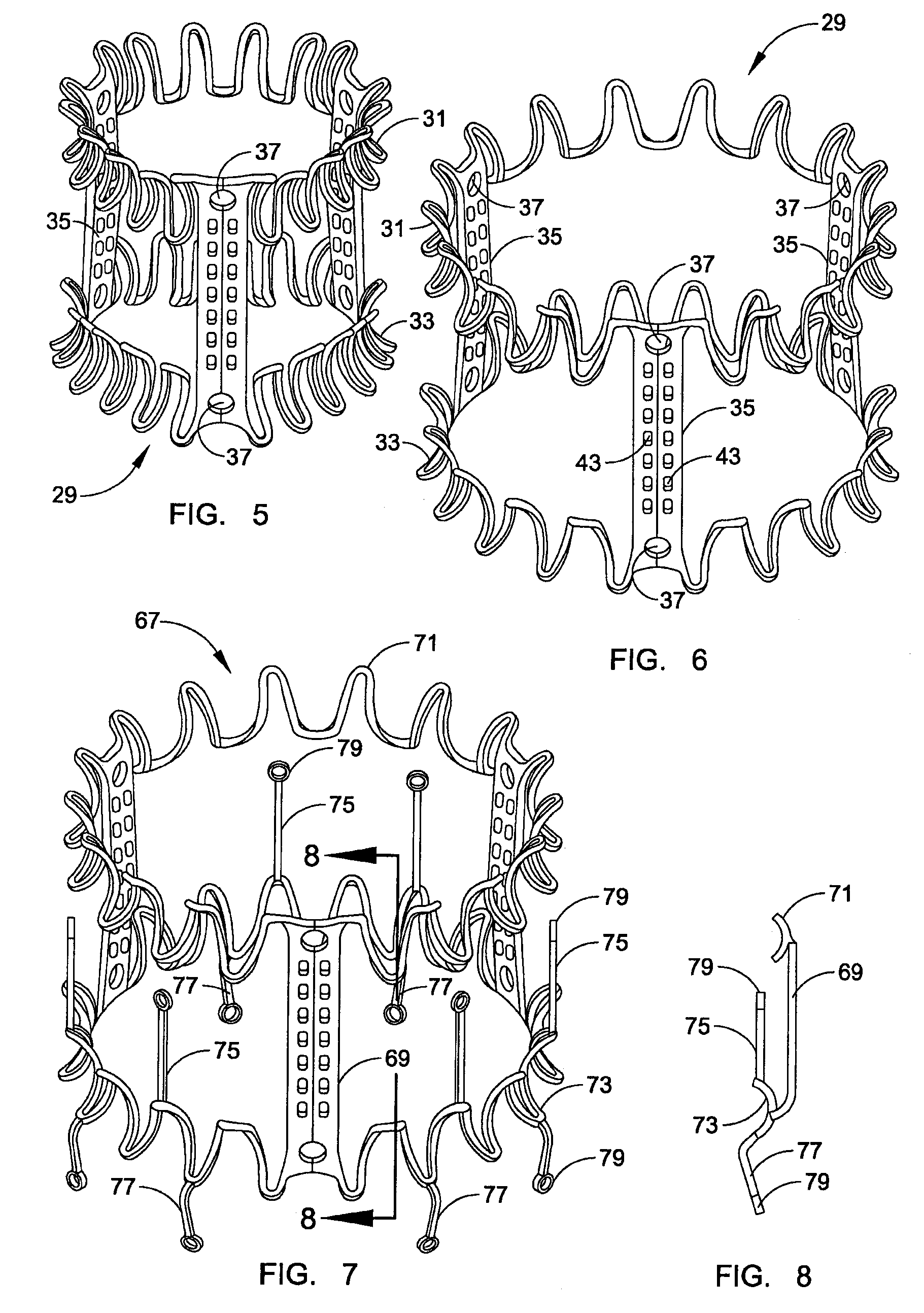
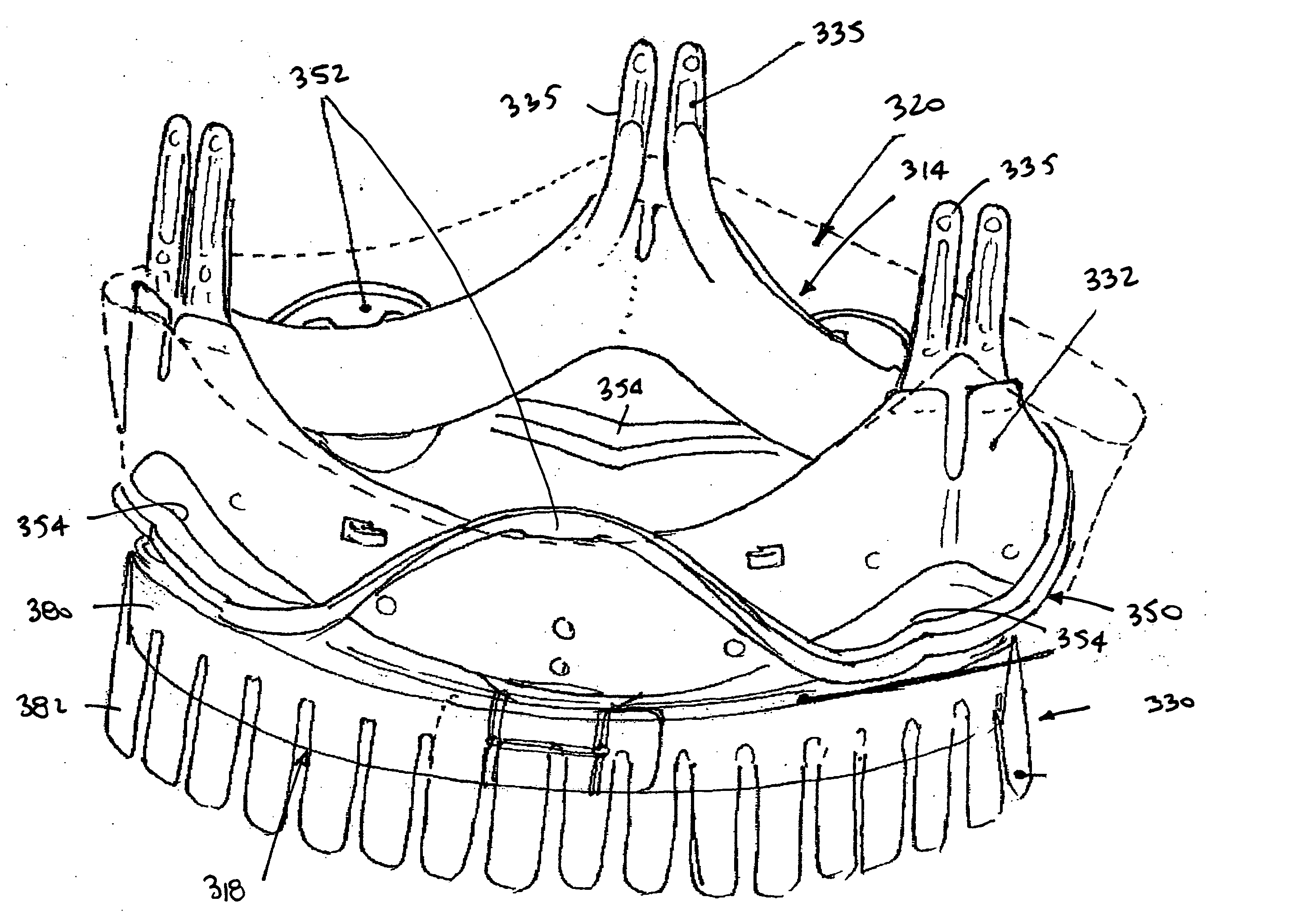
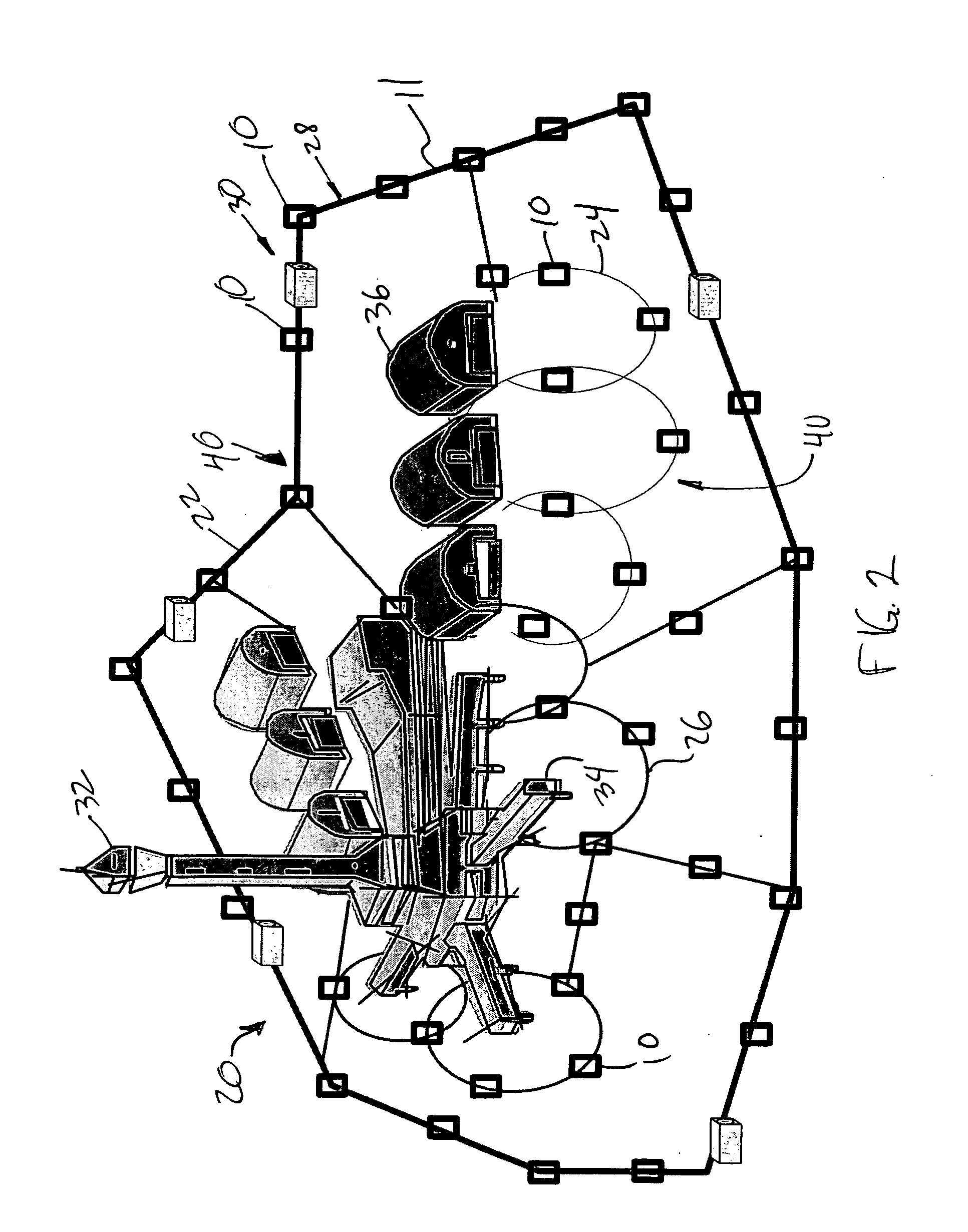
Minimally invasive heart valve replacement
ActiveUS20090005863A1Minimally invasiveSufficient flexibilityHeart valvesBlood vesselsHeart valve replacementThoracic cavity
A replacement valve for implantation centrally within the orifice of a malfunctioning native heart valve. The valve is designed for minimally invasive entry through an intercostal opening in the chest of a patient and an opening in the apex of the human heart. The replacement valve includes either a separate anchor (11, 87, 111) or a combined anchor (67) that folds around the malfunctioning native valve leaflets, sandwiching them in a manner so as to securely anchor the replacement valve in a precise, desired location.
Owner:VENUS MEDTECH (HANGZHOU) INC
Minimally invasive heart valve replacement
ActiveUS7837727B2Sufficient flexibilitySevere size constraintHeart valvesBlood vesselsHeart valve replacementThoracic cavity
A replacement valve for implantation centrally within the orifice of a malfunctioning native heart valve. The valve is designed for minimally invasive entry through an intercostal opening in the chest of a patient and an opening in the apex of the human heart. The replacement valve includes either a separate anchor (11, 87, 111) or a combined anchor (67) that folds around the malfunctioning native valve leaflets, sandwiching them in a manner so as to securely anchor the replacement valve in a precise, desired location.
Owner:VENUS MEDTECH (HANGZHOU) INC
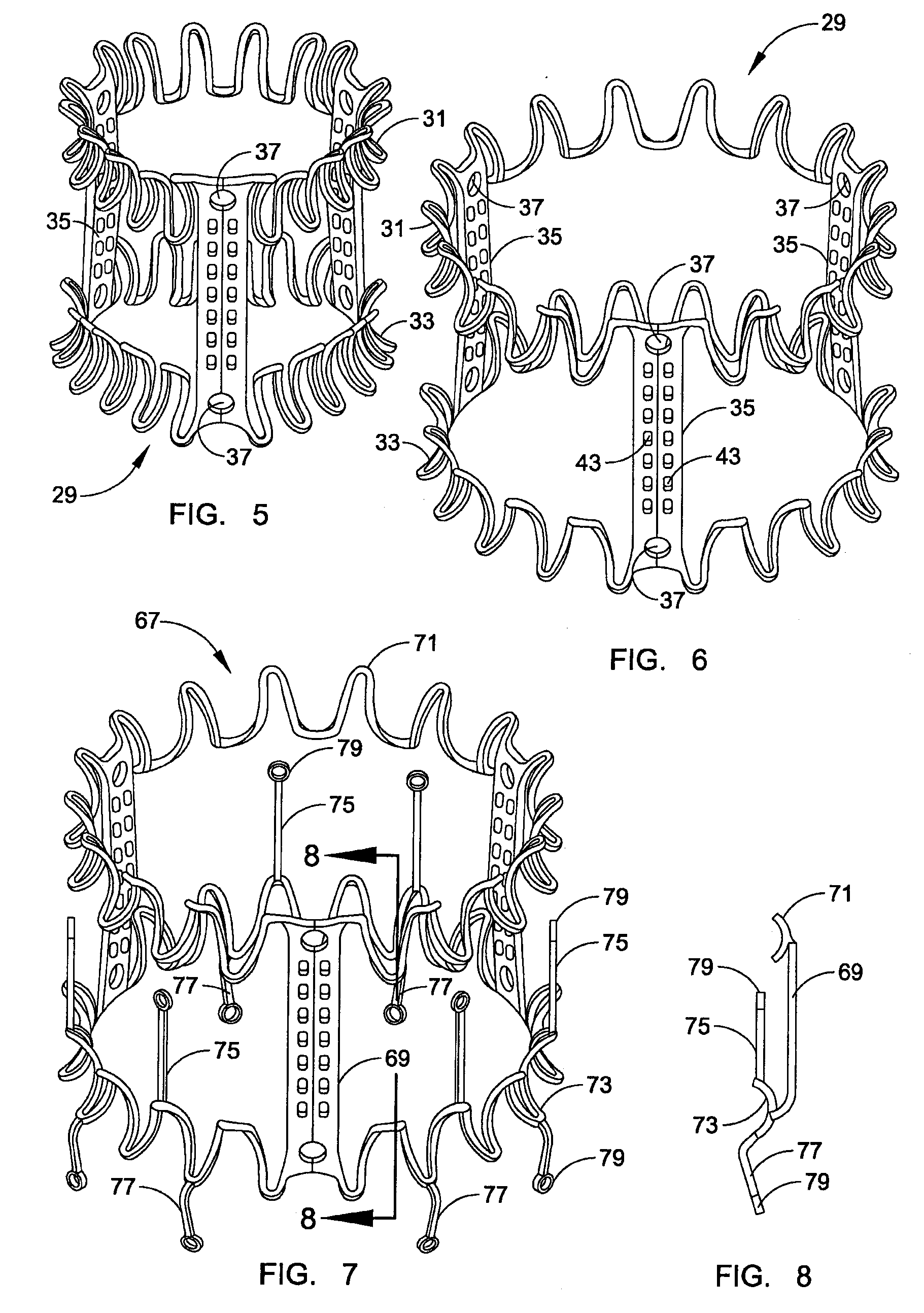
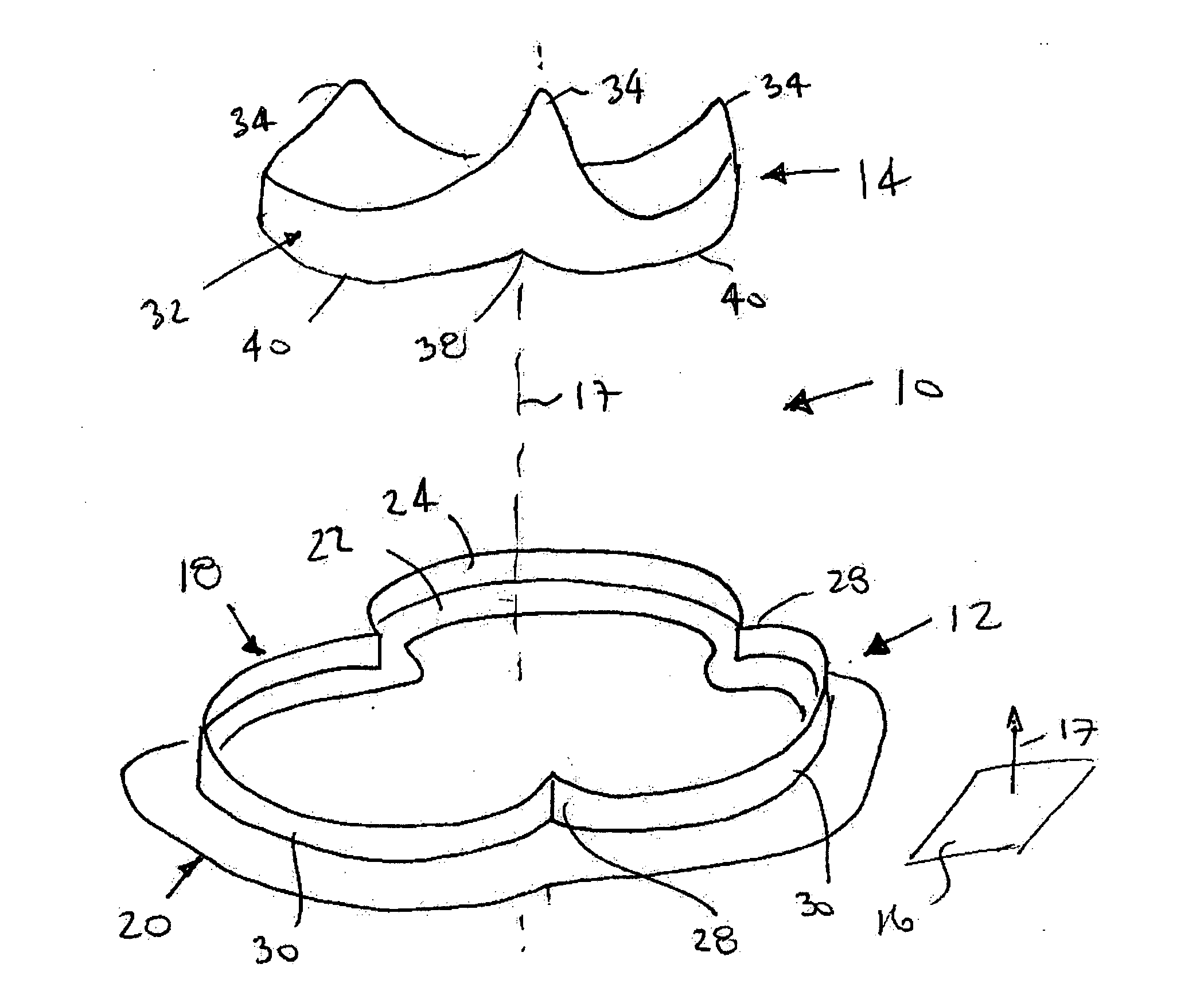
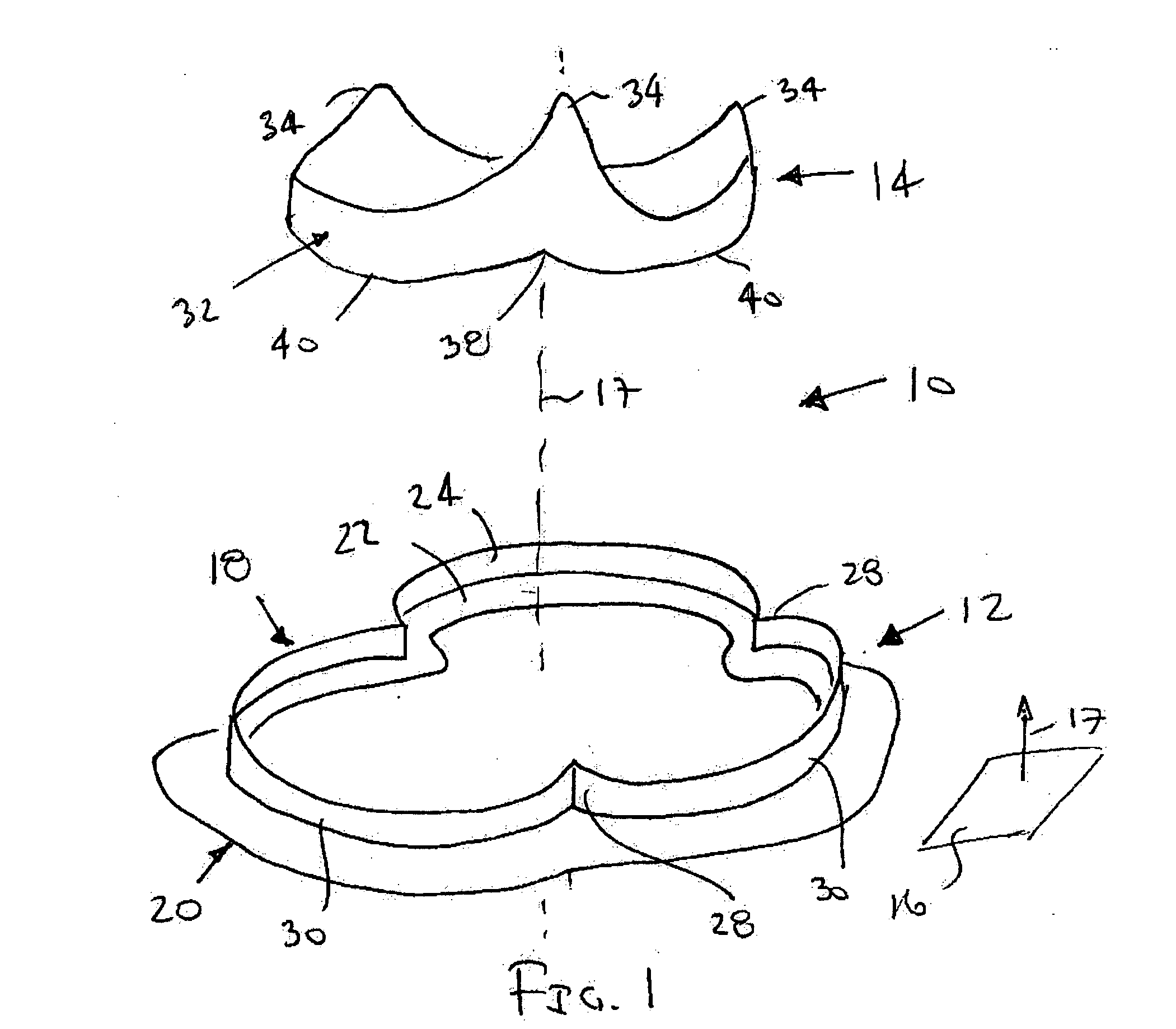
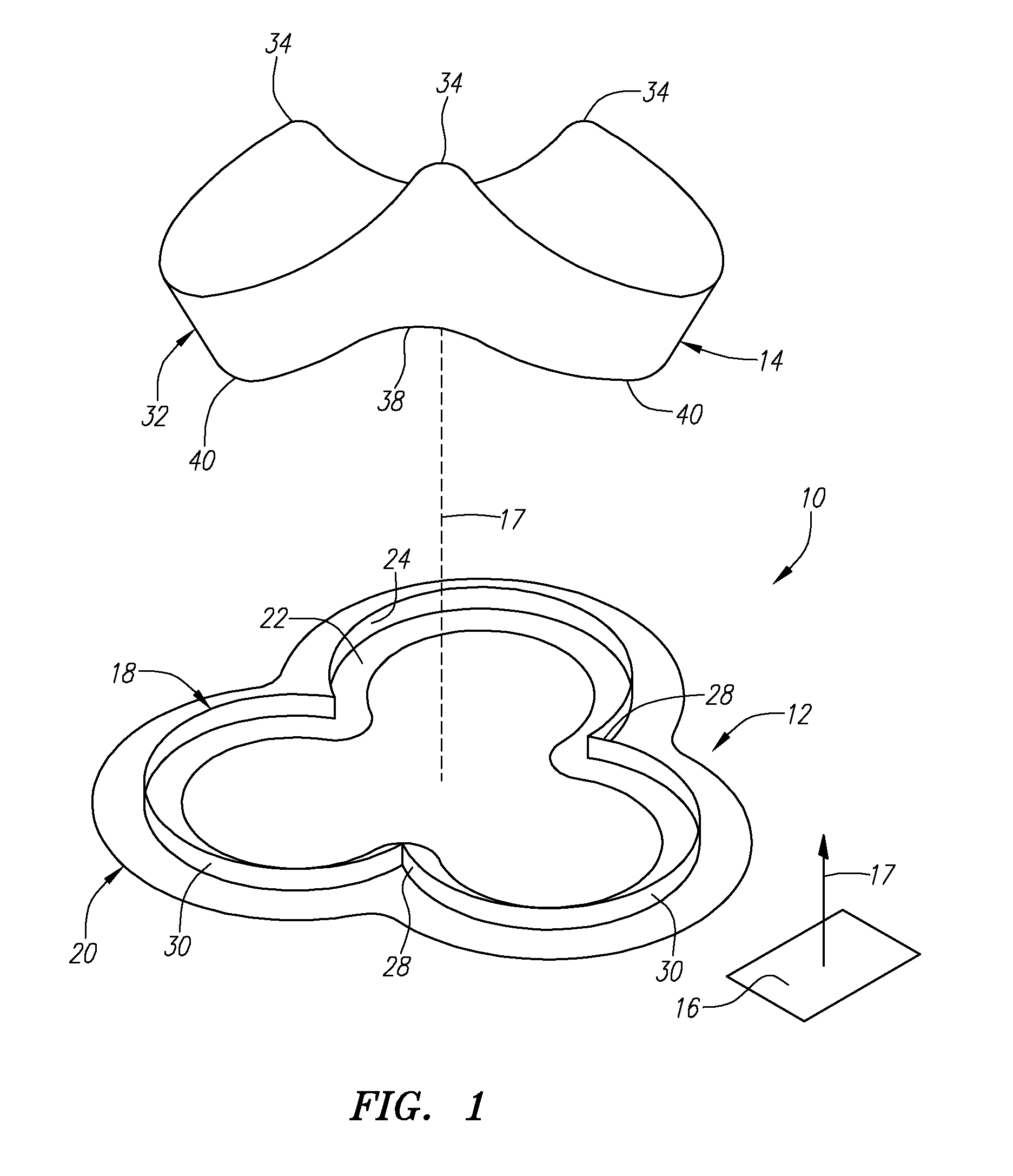
Conformable prosthesis for implanting two-piece heart valves and methods for using them
A heart valve assembly includes an annular prosthesis and a valve prosthesis. The annular prosthesis includes an annular ring for dilating tissue within a biological annulus and a conformable sewing cuff extending radially from the annular member. The valve prosthesis includes a frame and a valve component. The annular ring is introduced into the biological annulus to dilate tissue surrounding the biological annulus and the sewing cuff conforms to tissue above the biological annulus. Fasteners are directed through the sewing cuff to secure the annular prosthesis to the biological annulus. The annular prosthesis may include a baleen element for biasing fabric on the annular ring outwardly to enhance sealing against the biological annulus. A valve prosthesis is then advanced into the sinus cavity, and secured relative to the annular prosthesis. The sewing cuff may enhance a seal between the valve prosthesis and annular prosthesis.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
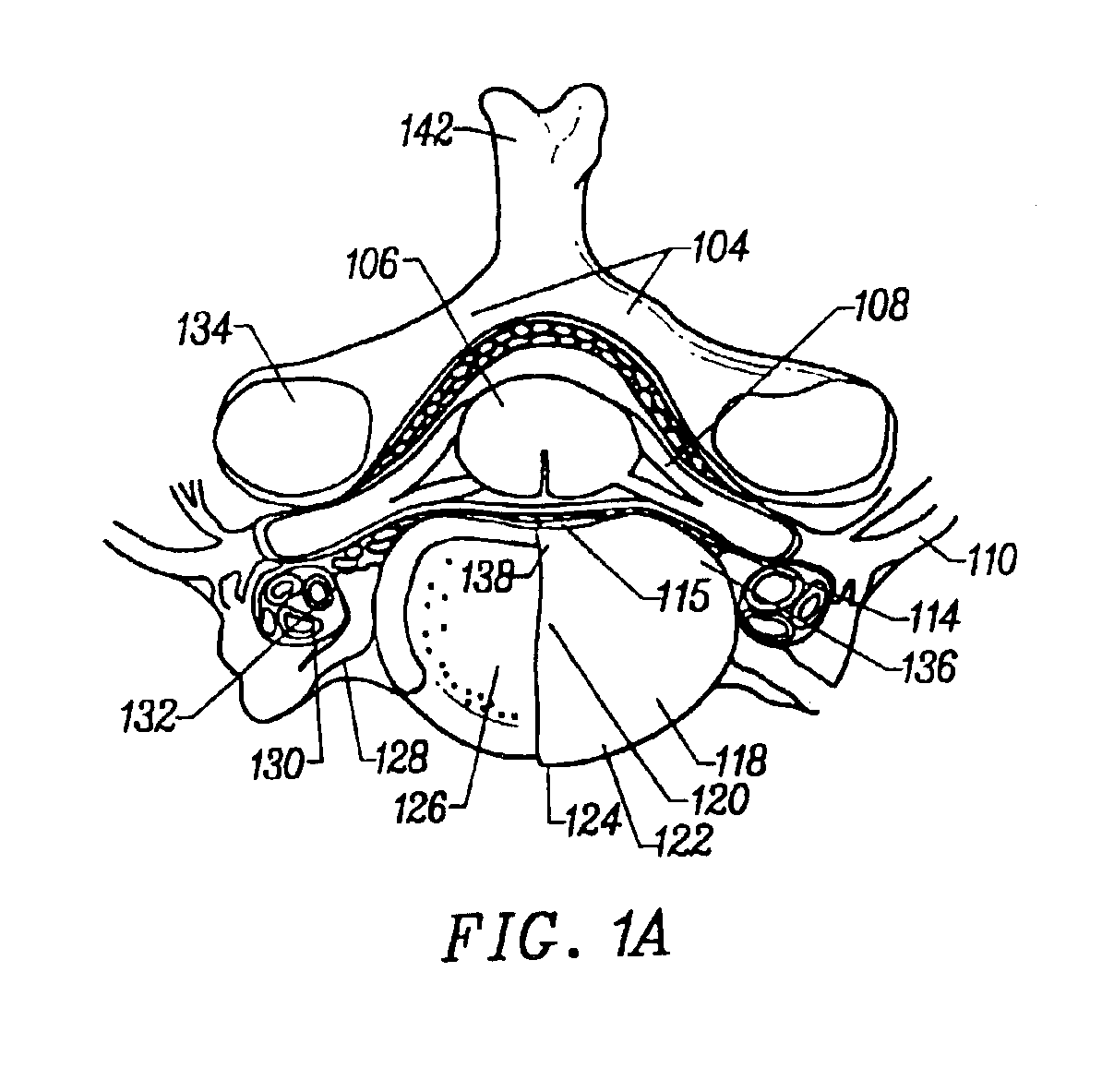
Method and apparatus for treating annular fissures in intervertebral discs
InactiveUS6997941B2Sufficient energyReduce pressureElectrotherapyInternal osteosythesisSufficient timeMedicine
A device is described that may be positioned at a location in an intervertebral disc for diagnosis or treatment of the disc. Treatment may include, for example, applying energy or removing material, and may decrease intradiscal pressure. Radiofrequency energy may be applied. A percutaneous method of repairing a fissure in the annulus pulposus comprises placing an energy source adjacent to the fissure and providing sufficient energy to the fissure to raise the temperature to at least about 45-70° C. and for a sufficient time to cause the collagen to weld. An intervertebral fissure also can be treated by placing a catheter with a lumen adjacent to the fissure and injecting sealant into the fissure via the catheter, thereby sealing the fissure. An intervertebral fissure additionally can be treated by providing a catheter having a distal end, a proximal end, a longitudinal axis, and an intradiscal section at the catheter's distal end on which there is at least one functional element. The next step is applying a force longitudinally to the proximal of the catheter which is sufficient to advance the intradiscal section through the nucleus pulposus and around an inner wall of an annulus fibrosus, but which force is insufficient to puncture the annulus fibrosus. Next the functional element is positioned at a selected location of the disc by advancing or retracting the catheter and optionally twisting the proximal end of the catheter. Then the functional unit treats the annular fissure. Optionally, there is an additional step of adding a substance to seal the fissure. An externally guidable intervertebral disc apparatus also is disclosed.
Owner:NEUROTHERM
Facilities management system
InactiveUS20050078006A1Improve securityEffective time managementIndividual entry/exit registersBurglar alarm electric actuationActive monitoringSystems management
A system is described for management of an operations area. The management system includes a central processing component with one or more central processors. An active monitoring system component is connected to the central processor. The active monitoring system includes tags and readers for individual identification of one or more tagged entities. The active monitoring system component is arrayed to create a management zone. The tags and readers are linked to the central processing component such that information from the tags and readers is received and analyzed by the central processing component. A passive monitoring system component is connected to the central processor. The passive monitoring system identifies non-tagged entities entering the management zone and additional information is communicated to the central processing component for analysis.
Owner:HUTCHINS J MARC +1
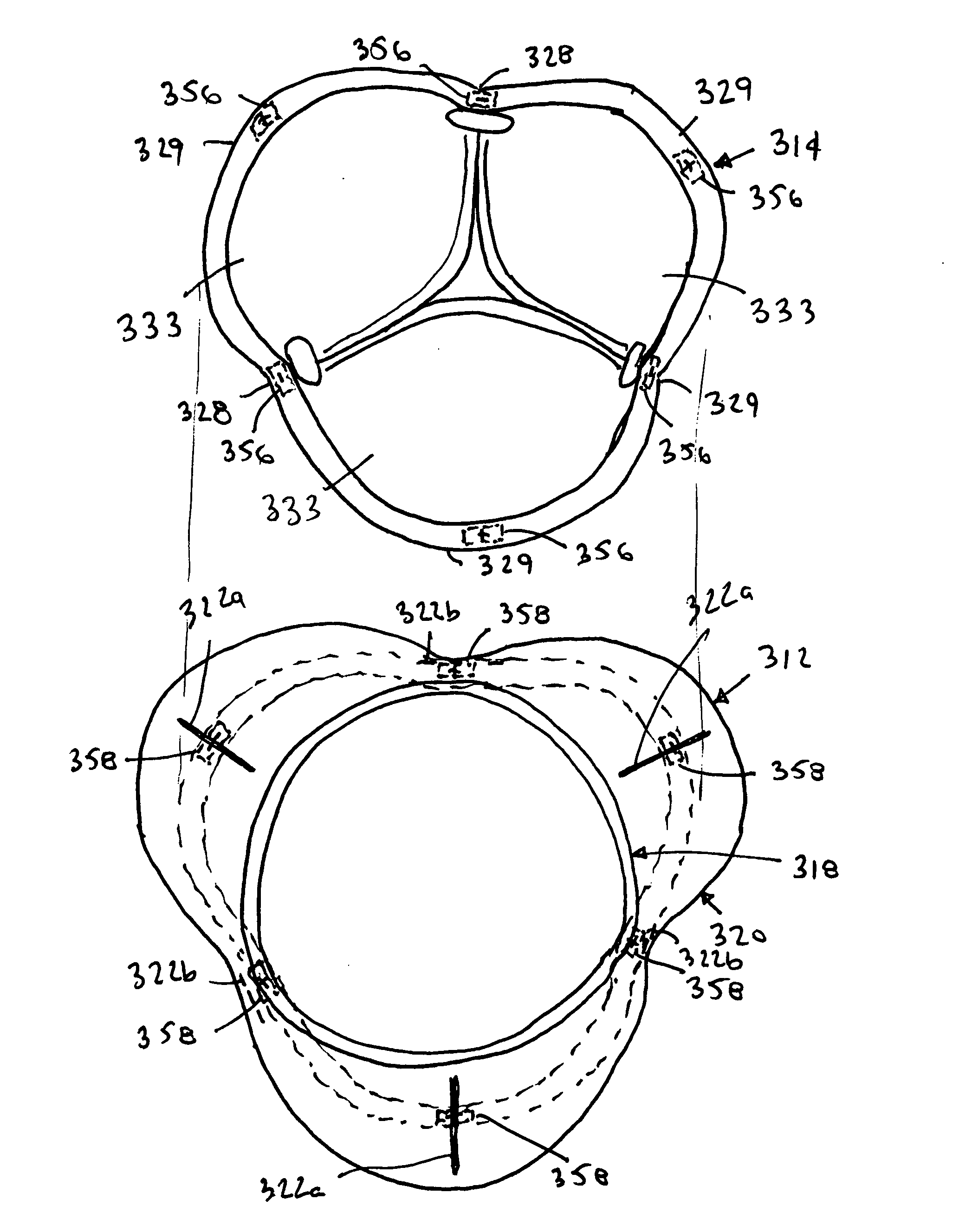
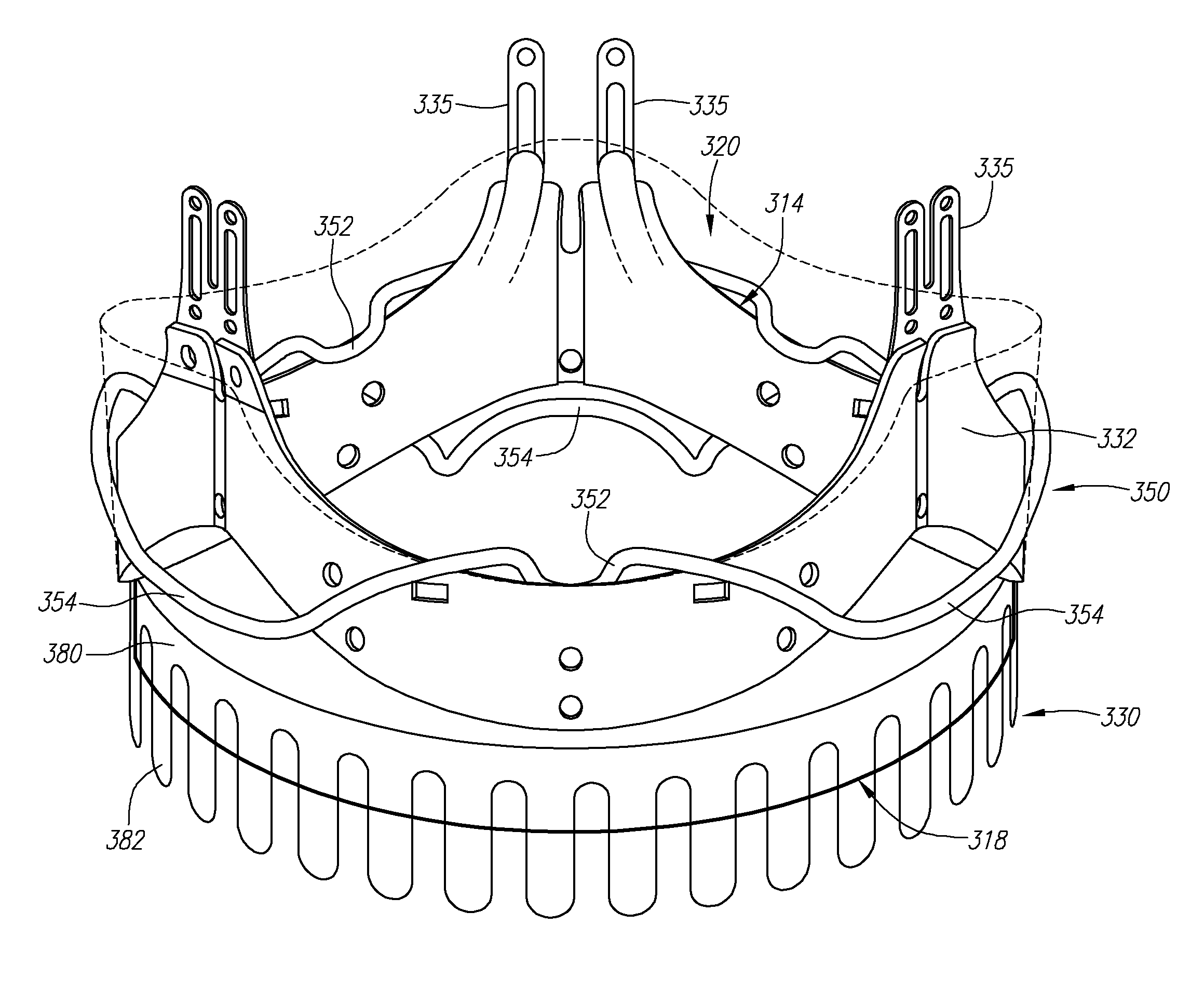
Two piece heart valves including multiple lobe valves and methods for implanting them
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
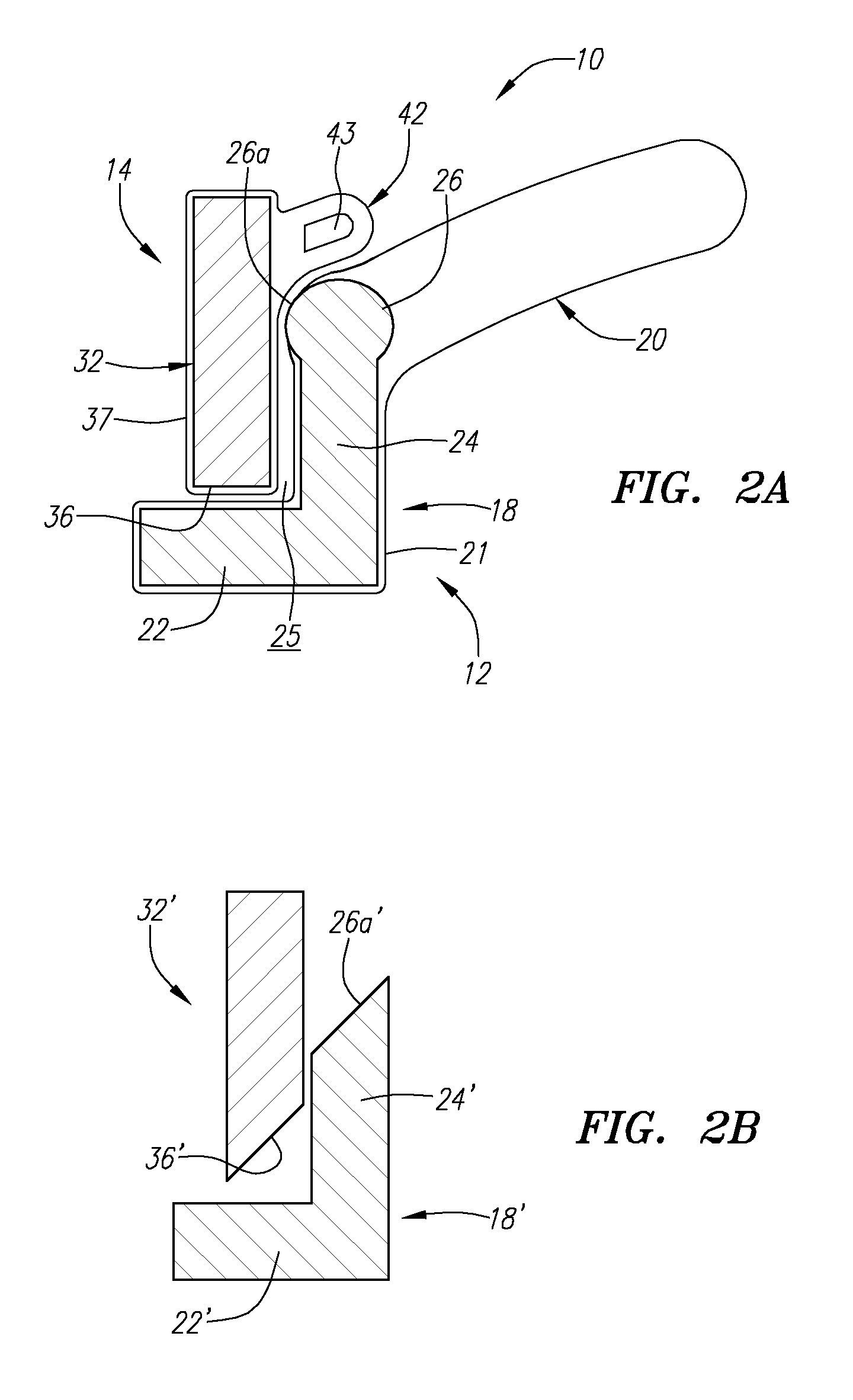
Connectors for two piece heart valves and methods for implanting such heart valves
InactiveUS20060195186A1Enhance interference fitImprove sealingHeart valvesInterference fitProsthesis
A heart valve assembly includes an annular prosthesis including an annular member and a sewing cuff extending radially from the annular member, and a valve member including a frame and a plurality of leaflets carried by struts. The annular prosthesis includes a plurality of pockets extending upwardly from the annular prosthesis for receiving a portion of the frame for securing the valve member to the annular prosthesis. Each pocket may include a flexible rim extending upwardly the sewing cuff and a cover at least partially defining a recess. The rim may be deflectable radially outwardly to accommodate a portion of the frame being received in the recess, and may be resiliently biased to return inwardly when released to cover the portion of the frame with the respective cover. The valve member may be further secured to the annular prosthesis by an interference fit between the rim and the frame.
Owner:ARBOR SURGICAL TECH
Conformable prosthesis for implanting two-piece heart valves and methods for using them
A heart valve assembly includes an annular prosthesis and a valve prosthesis. The annular prosthesis includes an annular ring for dilating tissue within a biological annulus and a conformable sewing cuff extending radially from the annular member. The valve prosthesis includes a frame and a valve component. The annular ring is introduced into the biological annulus to dilate tissue surrounding the biological annulus and the sewing cuff conforms to tissue above the biological annulus. Fasteners are directed through the sewing cuff to secure the annular prosthesis to the biological annulus. The annular prosthesis may include a baleen element for biasing fabric on the annular ring outwardly to enhance sealing against the biological annulus. A valve prosthesis is then advanced into the sinus cavity, and secured relative to the annular prosthesis. The sewing cuff may enhance a seal between the valve prosthesis and annular prosthesis.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
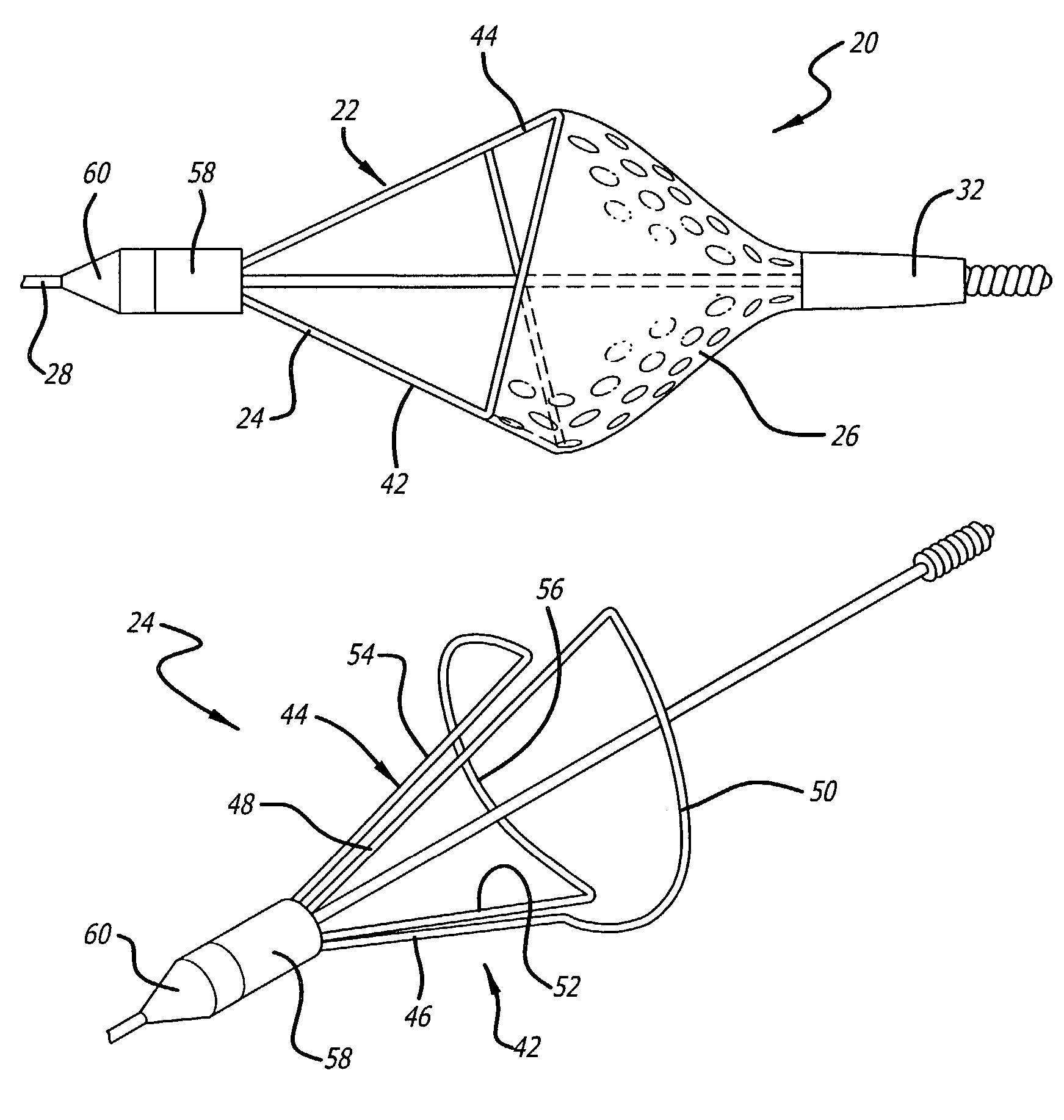
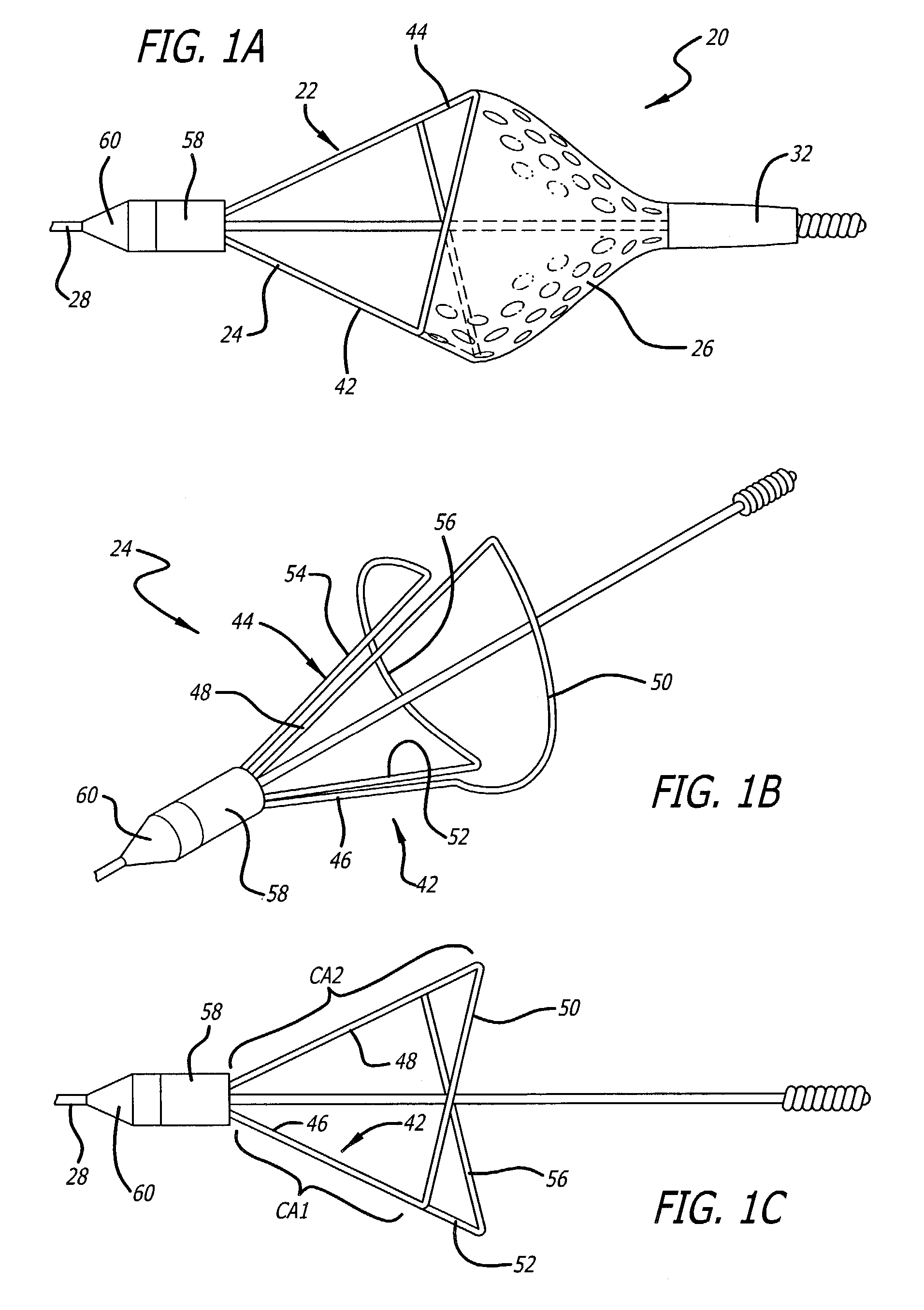
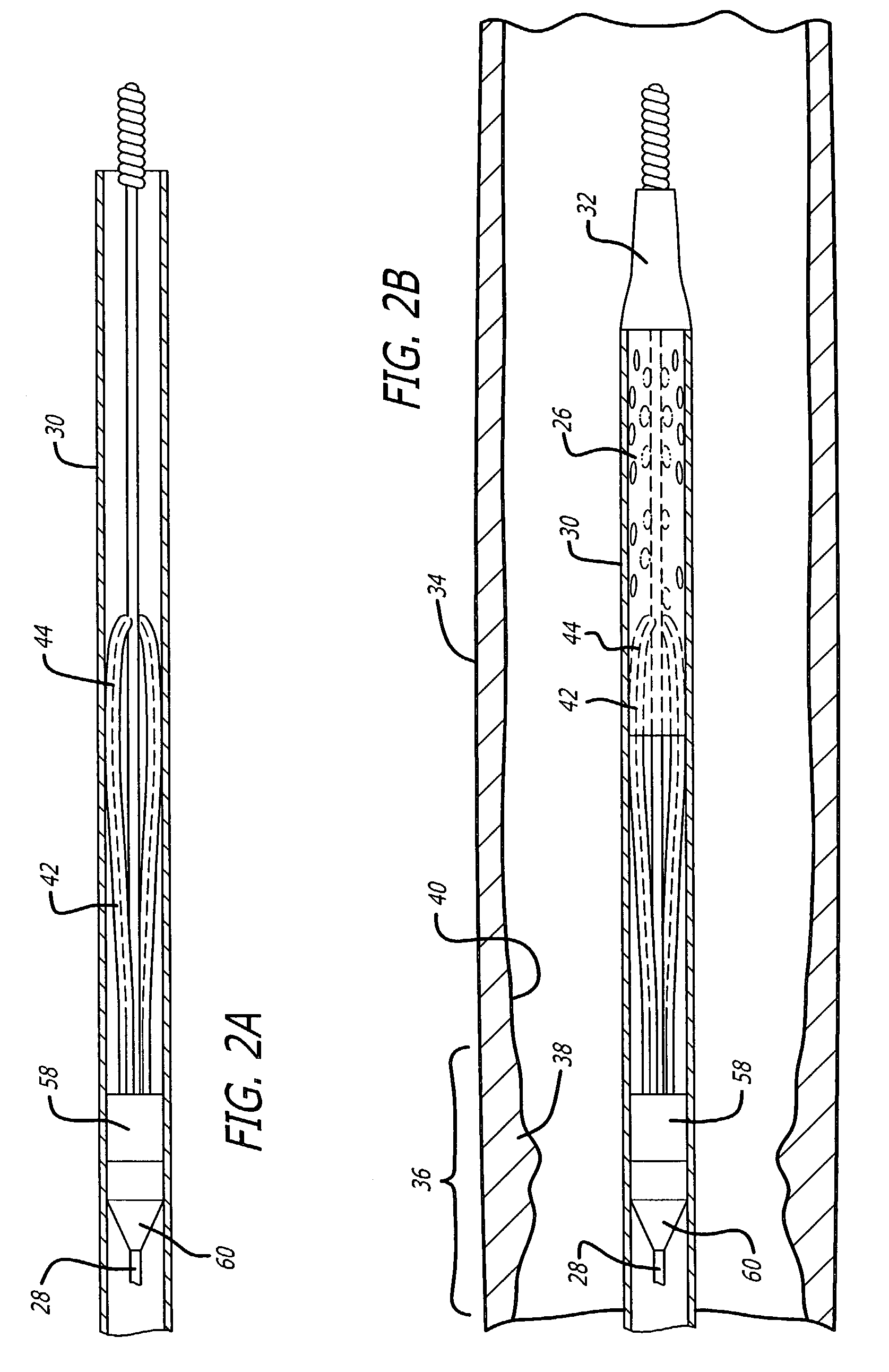
Embolic filtering devices
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
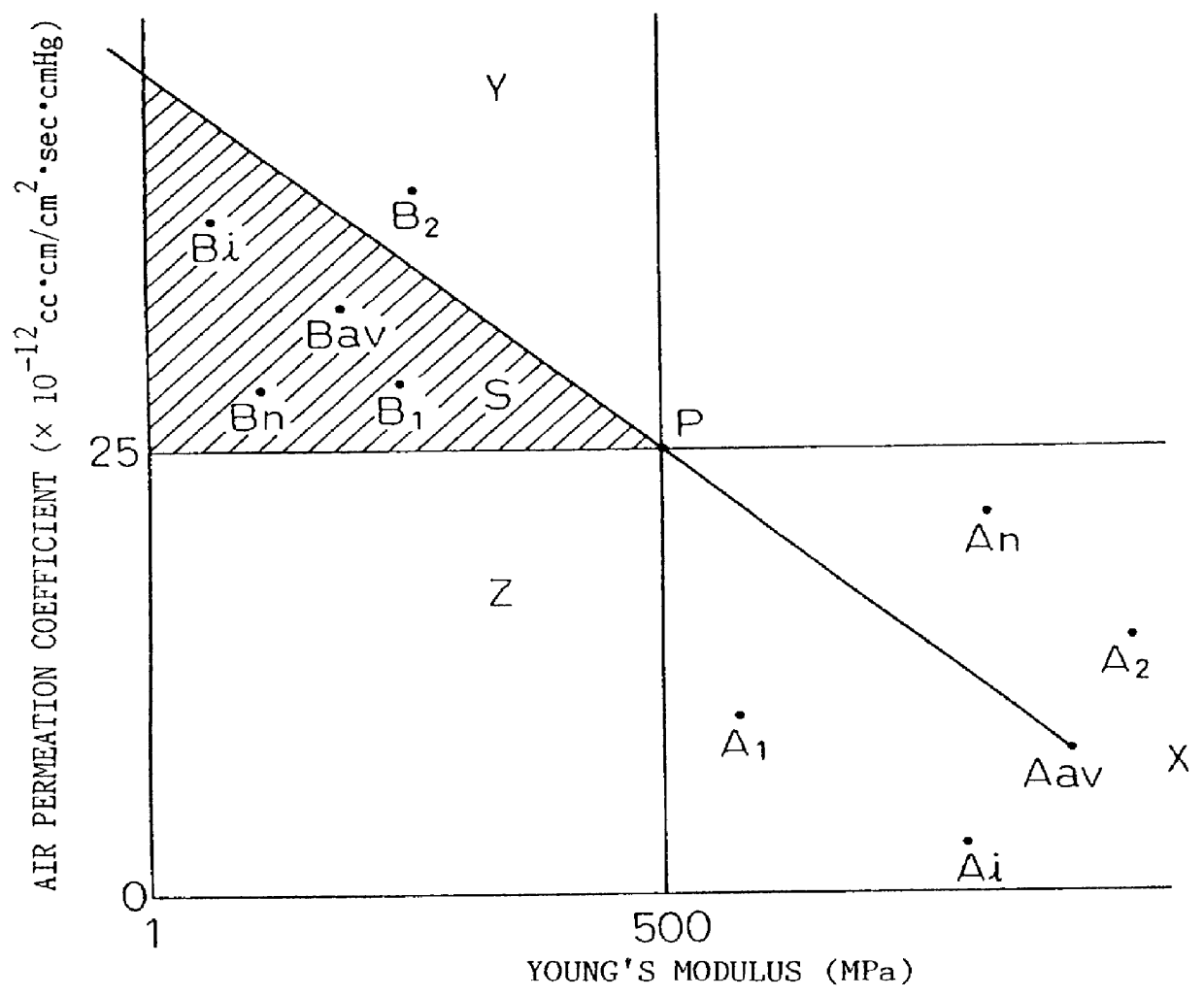
Pneumatic tire made by using lowly permeable thermoplastic elastomer composition in gas-barrier layer and thermoplastic elastomer composition for use therein
InactiveUS6062283AHigh elastomer ratioAbundant flexibilityWithout separate inflatable insertsWith separate inflatable insertsElastomerThermoplastic elastomer
PCT No. PCT / JP97 / 01514 Sec. 371 Date Jan. 28, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jan. 28, 1998 PCT Filed May 2, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 45489 PCT Pub. Date Dec. 4, 1997A pneumatic tire having an air permeation preventive layer comprising a low permeability thermoplastic elastomer composition comprising a thermoplastic elastomer having a thermoplastic resin composition as a continuous phase and a rubber composition as a dispersed phase, in which a barrier resin composition is contained, which low permeability thermoplastic elastomer composition has a phase structure in which the barrier resin composition is dispersed in the form of a flat state in the thermoplastic elastomer, is abundant in flexibility, is superior in gas permeation preventive property, and enables the tire to be reduced in weight.
Owner:YOKOHAMA RUBBER CO LTD
Two piece heart valves including multiple lobe valves and methods for implanting them
ActiveUS8083793B2Improve sealingSufficient flexibilityHeart valvesAnatomical structuresProsthetic valve
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and apparatus for indirect bonding of orthodontic appliances
ActiveUS7020963B2Broaden applicationEasy to disengageBracketsAdditive manufacturing apparatusEngineeringAnodic bonding
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
System and method for mechanically positioning intravascular implants
ActiveUS20100030200A1Avoids and minimizes developmentDevelopment is minimized and avoidedStentsMedical devicesBlood vesselDelivery system
An intravascular implant delivery system carries an implant by retaining an engagement member engaging the implant in a position proximal of an aperture at a distal end of the delivery system. The engagement member is retained proximal to the aperture by a cord that obstructs the movement of the engagement member through the aperture. The engagement member is free to rotate and move within an area defined by the delivery system, allowing the implant to react to forces imparted to the implant by the movement of the delivery system and implant through a delivery catheter. Once the implant is in a desired implant position, the cord is moved away from an aperture and the engagement member is allowed to move away from the delivery system.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
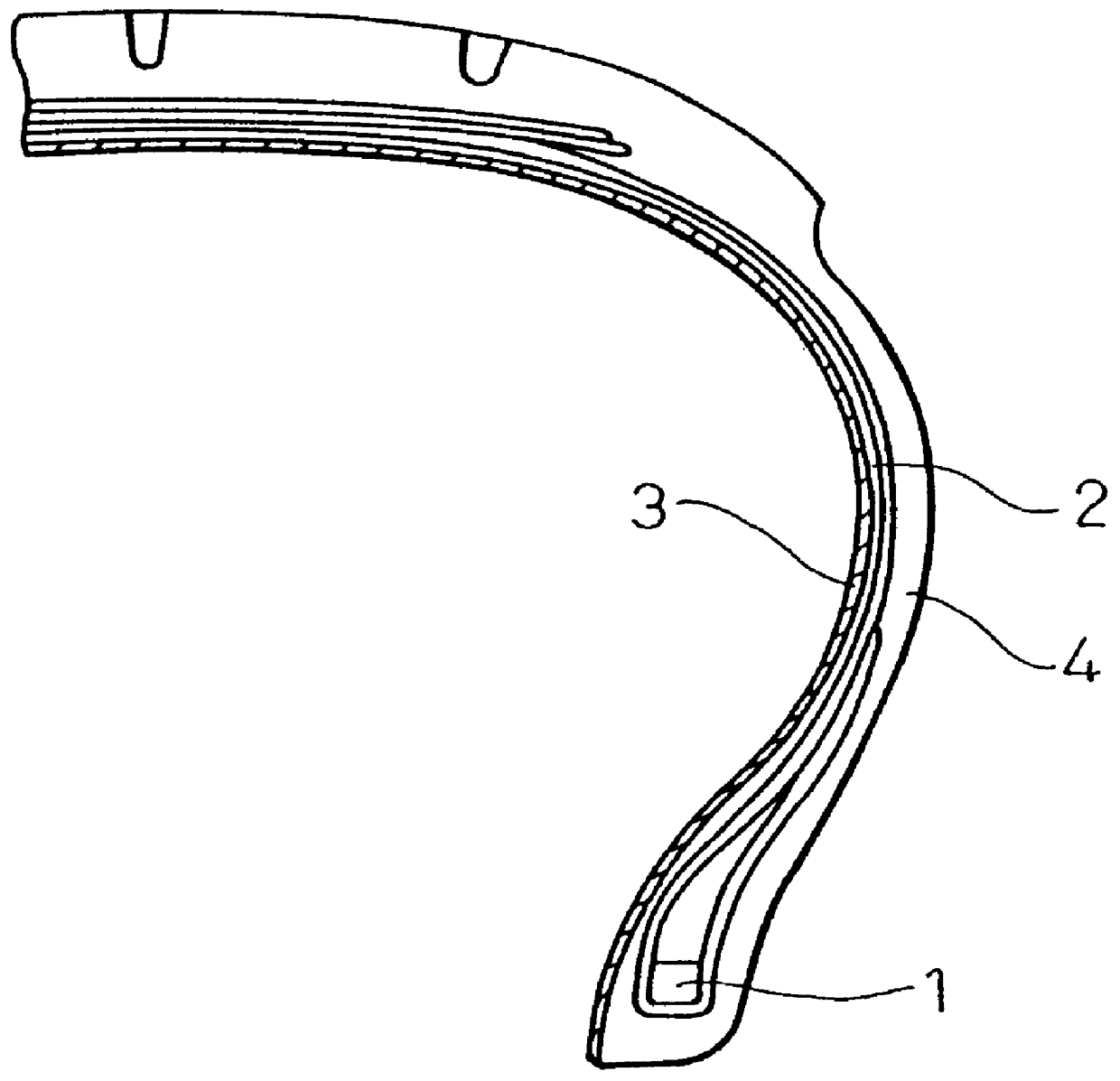
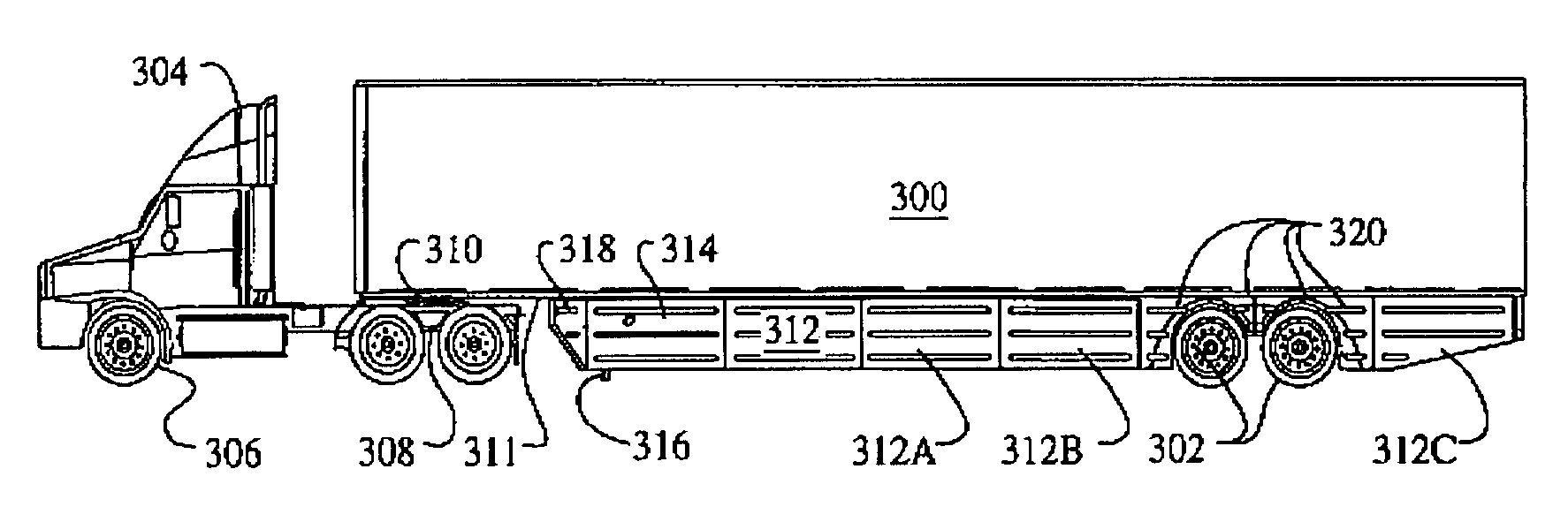
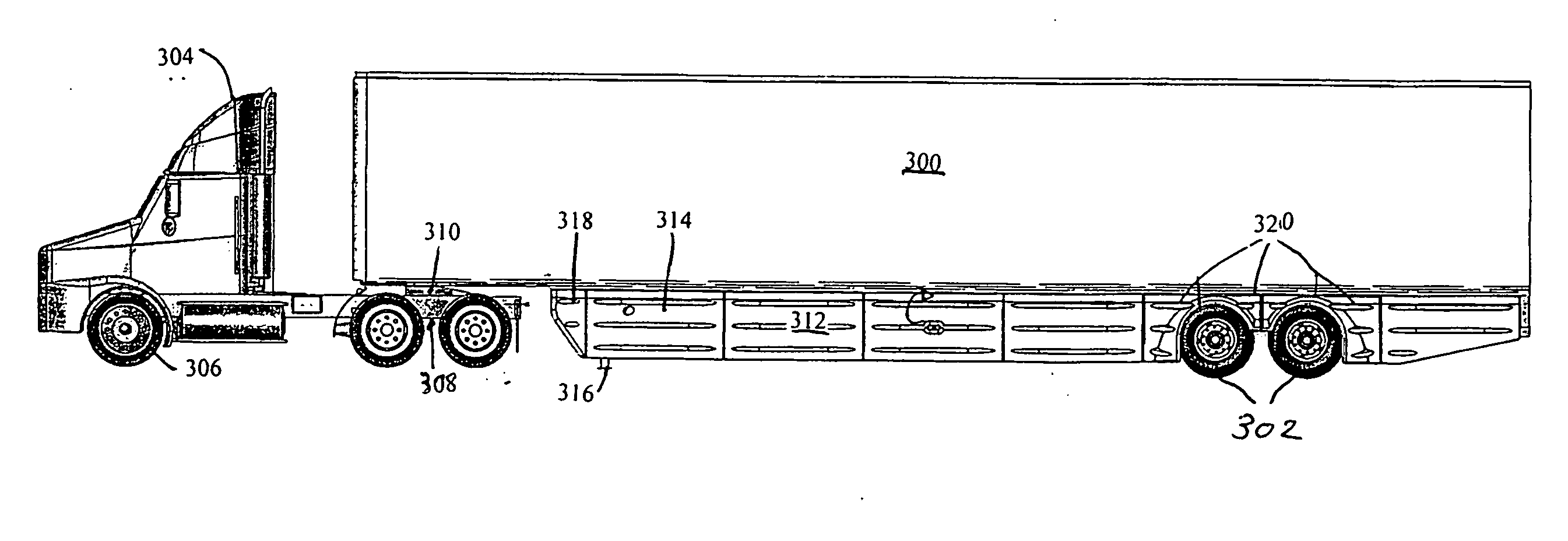
Trailer skirt panel
ActiveUS7578541B2Reducing aerodynamic drag on road vehiclesIncrease air flowVehicle seatsWindowsAerodynamic dragEngineering
A skirt panel is provided herein for interconnection to another abutted similar skirt panel for attachment beneath a lower, outer longitudinally-extending edge of a trailer including a rear wheel assembly of a tractor-trailer rig, thereby to provide a continuous fairing extending downwardly from the trailer. The skirt panel includes a monolithic, generally-rectangular composite reinforced thermoplastic structure, having vertical lateral side edges configured and arranged for connection to associated vertical lateral side edges of abutting similar skirt panels. This provides a longitudinally-extending fairing for extending contiguously on each side of the trailer, a front face of the thermoplastic structure being provided with a plurality of longitudinally-extending, vertically-spaced-apart arcuate protrusions. The outer face of the thermoplastic panel preferably also is provided with dimples. The reinforcing comprising a panel secured to an inner face of the skirt panel and is provided with laterally-extending means whereby abutting skirt panels are secured to one another; whereby, when said fairing is secured to a lower portion of said trailer, the fairing extends downwardly from the trailer to from 60% to 80% of the distance to the road, so that a portion of any impinging air is directed laterally around the wheels of the rear wheel bogeys to reduce the aerodynamic drag of the trailer and of the wheel assembly.
Owner:ZF COMPOSITES NORTH AMERICA LTD
Live graphics on absorbent articles using electrochromic displays
An absorbent article is provided that includes an electroactive display. The electroactive display may include an electrochromic composition positioned between two electrodes. The electroactive display is configured to create and exhibit an image that contains active features such as moving graphics or color-changing objects. For instance, the electroactive display may display an animated cartoon character or a moving vehicle. The electroactive display may also create symbols or words. When combined with sensors, a power source, and the proper circuitry, the electroactive display may be used, for instance, as a wetness indicator or to indicate the presence of a particular substance. In other embodiments, the electroactive display may be used solely for aesthetic purposes.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Trailer skirt panel
ActiveUS20070120397A1Reducing aerodynamic drag on road vehiclesIncrease air flowVehicle seatsWindowsCHEEK DIMPLESEngineering
A skirt panel is provided herein for interconnection to another abutted similar skirt panel for attachment beneath a lower, outer longitudinally-extending edge of a trailer including a rear wheel assembly of a tractor-trailer rig, thereby to provide a continuous fairing extending downwardly from the trailer. The skirt panel includes a monolithic, generally-rectangular composite reinforced thermoplastic structure, having vertical lateral side edges configured and arranged for connection to associated vertical lateral side edges of abutting similar skirt panels. This provides a longitudinally-extending fairing for extending contiguously on each side of the trailer, a front face of the thermoplastic structure being provided with a plurality of longitudinally-extending, vertically-spaced-apart arcuate protrusions. The outer face of the thermoplastic panel preferably also is provided with dimples. The reinforcing comprising a panel secured to an inner face of the skirt panel and is provided with laterally-extending means whereby abutting skirt panels are secured to one another; whereby, when said fairing is secured to a lower portion of said trailer, the fairing extends downwardly from the trailer to from 60% to 80% of the distance to the road, so that a portion of any impinging air is directed laterally around the wheels of the rear wheel bogeys to reduce the aerodynamic drag of the trailer and of the wheel assembly.
Owner:ZF COMPOSITES NORTH AMERICA LTD
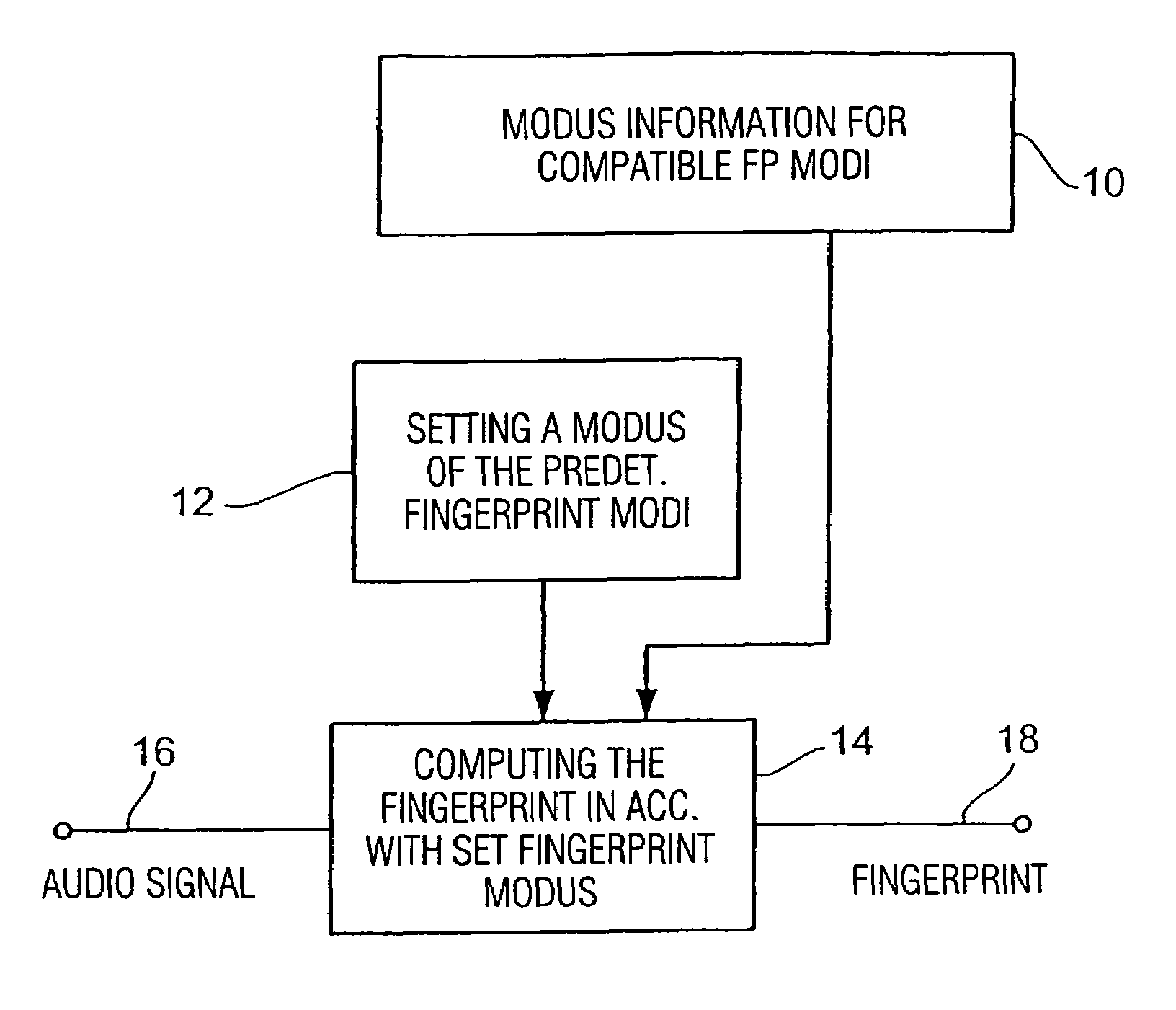
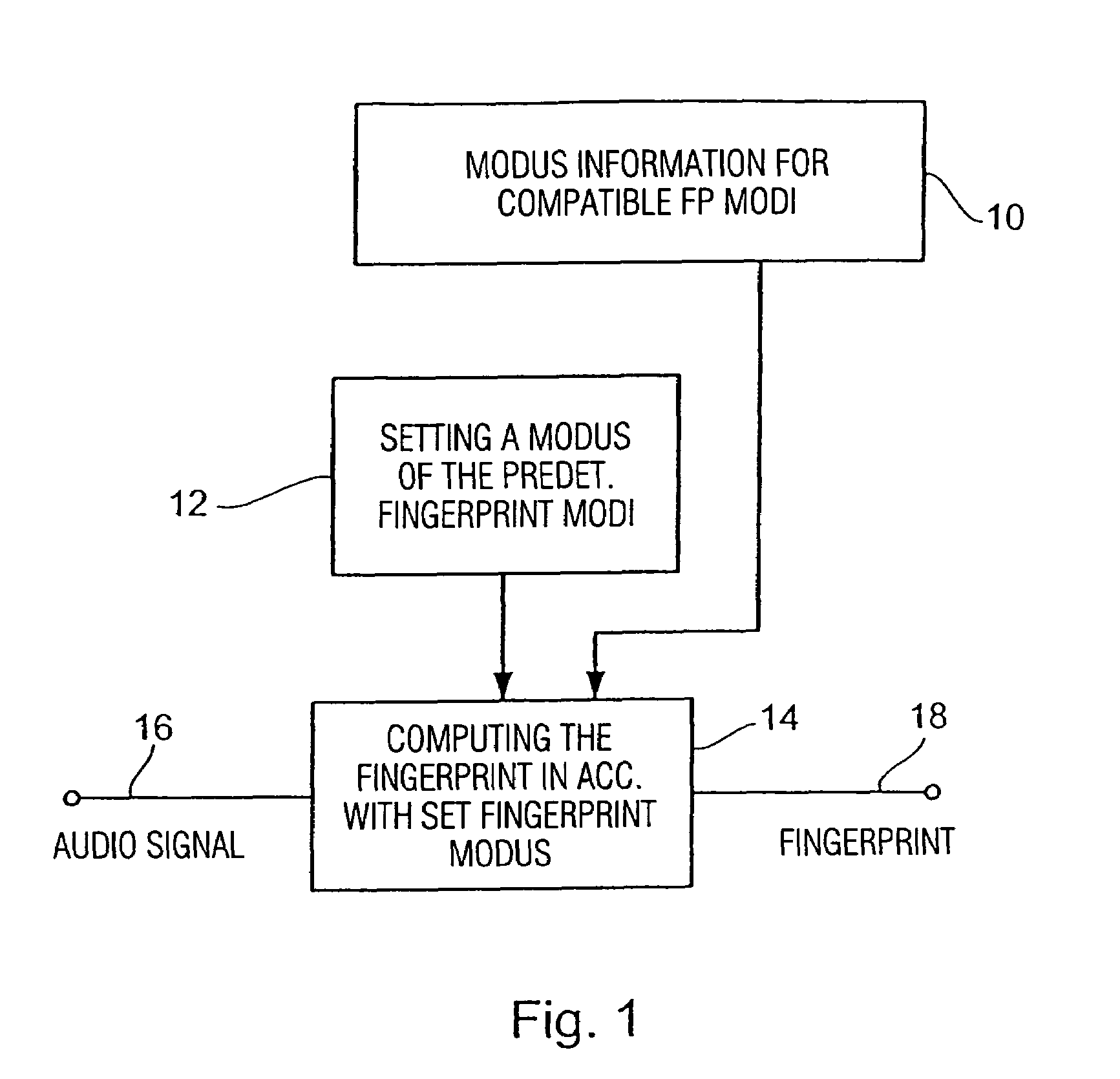
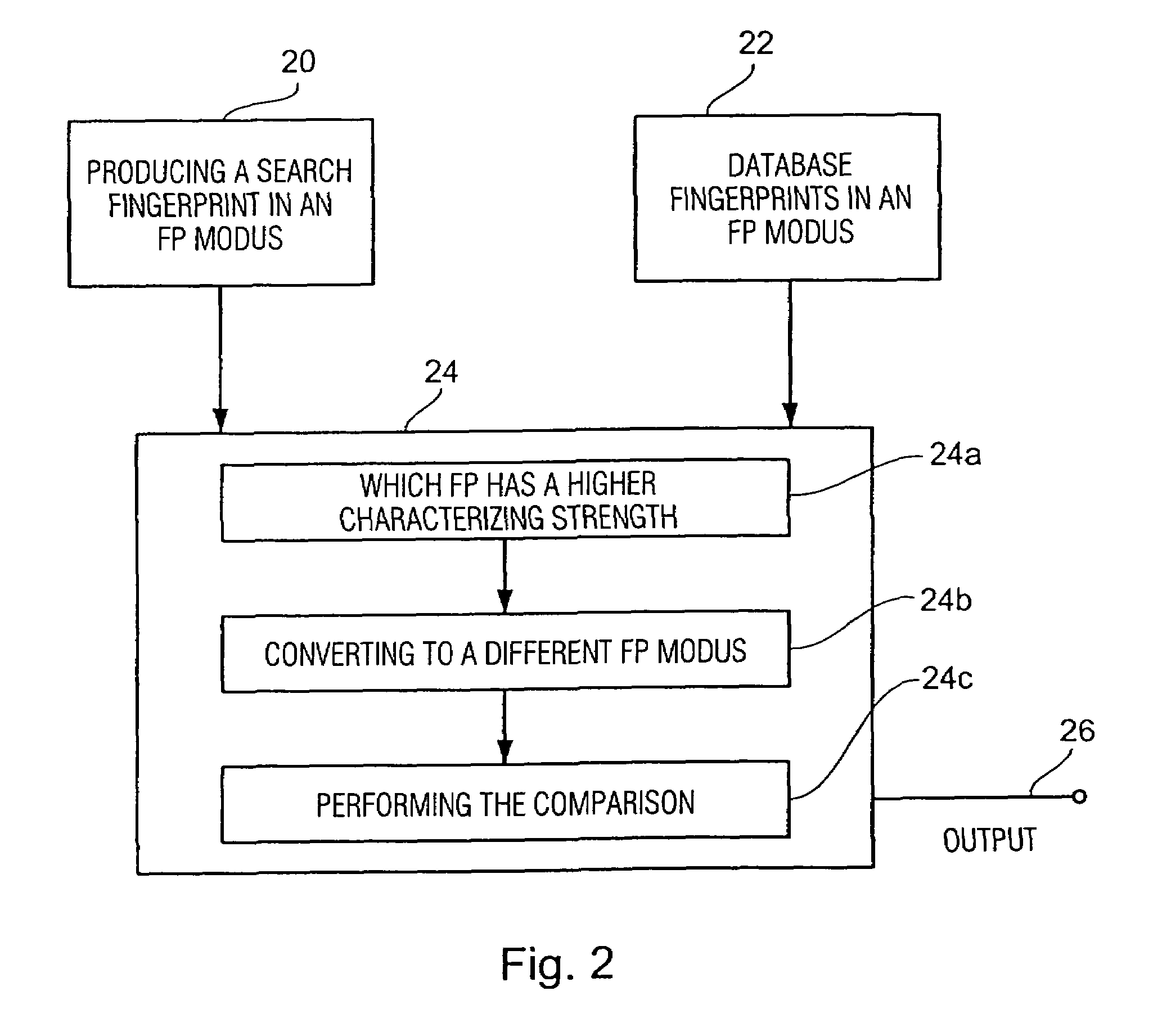
Method and apparatus for producing a fingerprint, and method and apparatus for identifying an audio signal
InactiveUS7460994B2Meet different requirementsHigh strengthDigital data information retrievalUsing non-detectable carrier informationPattern recognitionUltimate tensile strength
Owner:M2ANY
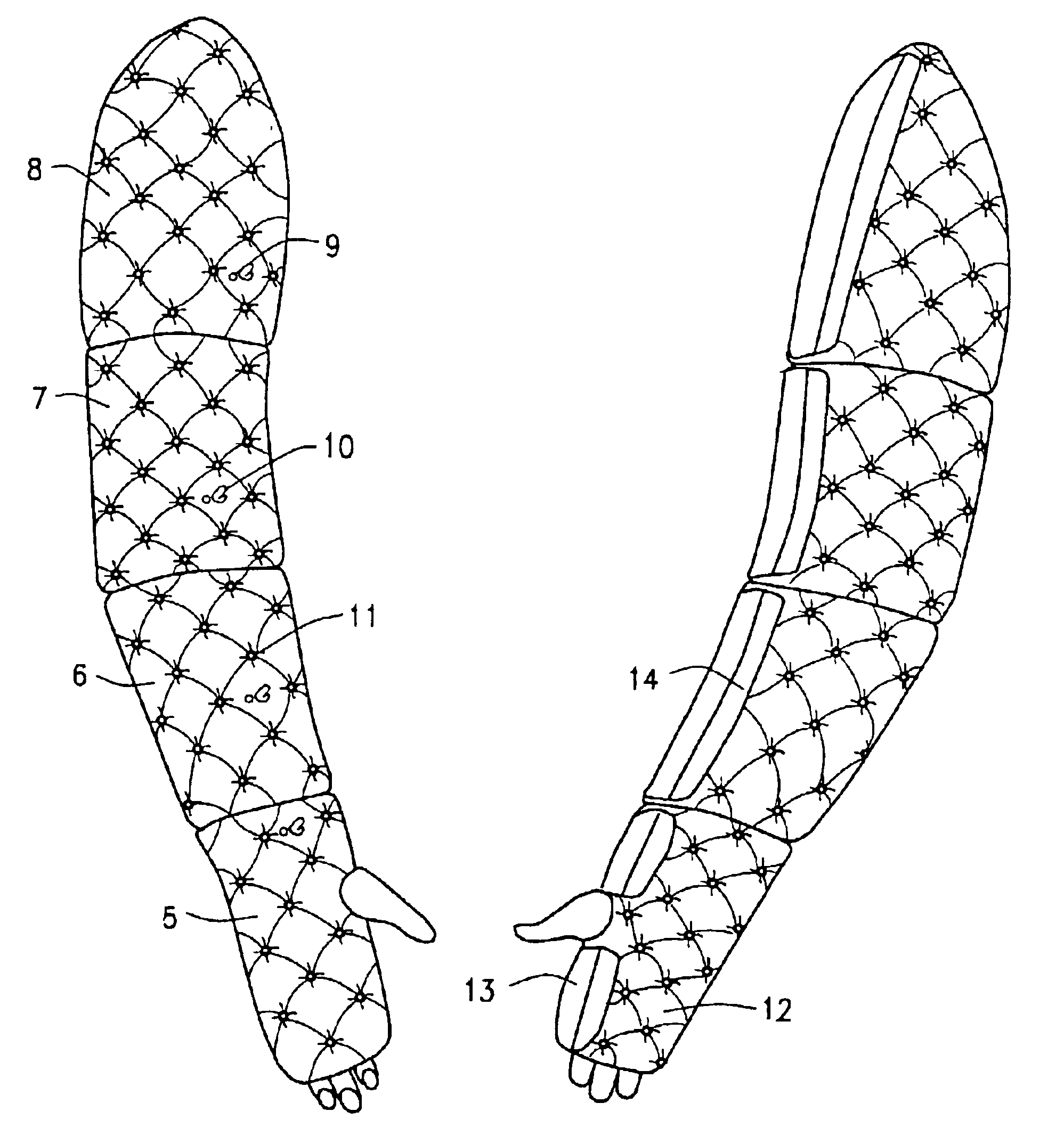
Compression garment for selective application for treatment of lymphedema and related illnesses manifested at various locations of the body
InactiveUS6852089B2Sufficient flexibilityLimit the amount of flexion of a limbPneumatic massageRestraining devicesDiseaseAfter treatment
A compression garment for selective application for treatment of lymphedema and related illnesses manifested at various locations of the body. The garment includes a pair or series of layers of hermetically sealed material, that can capture pressurized air, when applied therein, and is formed through the patterned sealing of the layers of the garment together, at select locations, to form air pockets that can selectively apply isolated points of pressure to the patient's affected area, without disrupting normal vascular and lymphatic functioning. The garment is design cut, for application to various segments of the body, and applies encompassing pressure over the entire affected area, and includes valves that can allow for the injection of measurable air, to the desired pressure points, or its deflation, after treatment.
Owner:INNOVATIVE MEDICAL CORP
Bisphenol a and aromatic glycidyl ether-free coatings
ActiveUS20070036903A1Good metal substrateGood inter-coat adhesionLiquid surface applicatorsSynthetic resin layered productsPolyesterMeth-
Disclosed are Bisphenol A (BPA), Bisphenol F, Bisphenol A diglycidyl ether (BADGE), and Bisphenol F diglycidyl ether (BFDGE)-free coating compositions for metal substrates including an under-coat composition containing a polyester (co)polymer, and an under-coat cross-linker; and an over-coat composition containing a poly(vinyl chloride) (co)polymer dispersed in a substantially nonaqueous carrier liquid, an over-coat cross-linker, and a functional (meth)acrylic (co)polymer. Also provided is a method of coating a metal substrate using the BPA, BPF, BADGE and BFDGE-free coating system to produce a hardened protective coating useful in fabricating metal storage containers. The coated substrate is particularly useful in fabricating multi-part foodstuffs storage containers with “easy-open” end closures.
Owner:SWIMC LLC
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS7840188B2Reduce the amount requiredReduce total powerEnergy efficient ICTNear-field transmissionThread schedulingControl circuit
In a multi-core semiconductor device, a data bus between CPUs or the like consumes a larger amount of power. By provision of a plurality of CPUs which transmit data by a backscattering method of a wireless signal, a router circuit which mediates data transmission and reception between the CPUs or the like, and a thread control circuit which has a thread scheduling function, a semiconductor device which consumes less power and has high arithmetic performance can be provided at low cost.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Micromirror systems with concealed multi-piece hinge structures
InactiveUS6906848B2Sufficient flexibilityPromotes relative motionNon-linear opticsOptical elementsOut of planeHinge angle
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
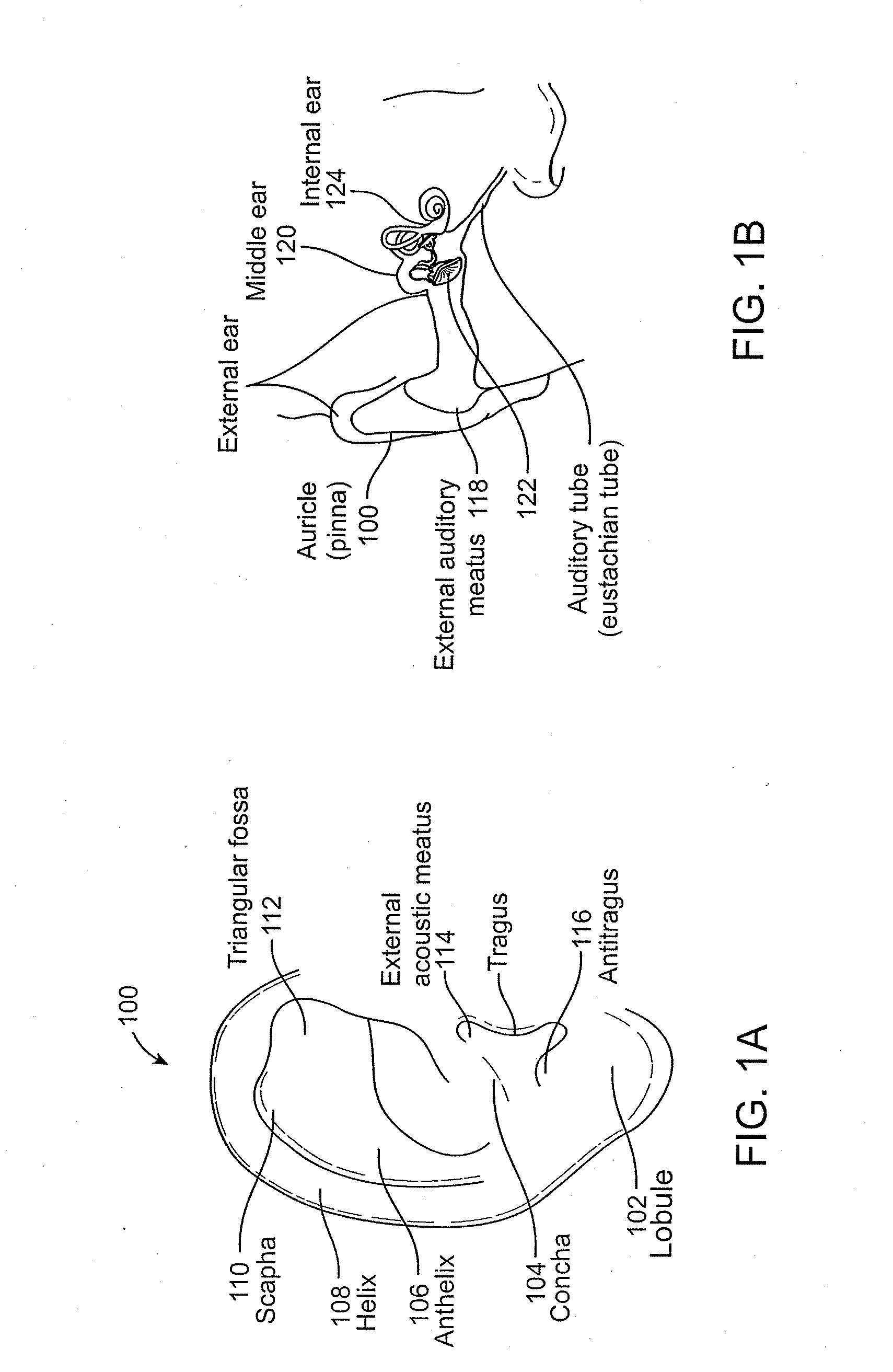
Systems and methods for anesthetizing ear tissue
A system and method for use in iontophoretic anesthesia of a tympanic membrane are disclosed. The system generally includes an earplug and an electrode device. The earplug includes at least one sealing member for sealing the earplug in an ear canal. The sealing member includes microholes which vent fluid above a certain pressure threshold. A headset may connect the earplug to a second earplug. The method involves using the system on a human or animal subject.
Owner:TUSKER MEDICAL
Selectively flexible catheter and method of use
ActiveUS7828790B2Sufficient flexibilityEnhanced retention and back-out supportMedical devicesCatheterVitrificationGlass transition
Catheter assembly including an elongate shaft comprising a thermoplastic polymer such as a thermoplastic shape memory polymer having a pre-selected glass transition temperature (Tg) and a means for heating the thermoplastic polymer, wherein the thermoplastic polymer is in a rubbery state at temperatures above the glass transition temperature and is in a glassy state at temperatures below the glass transition temperature. The elongate shaft may be selectively heated and cooled to provide sufficient flexibility and retention during a medical procedure.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC +1
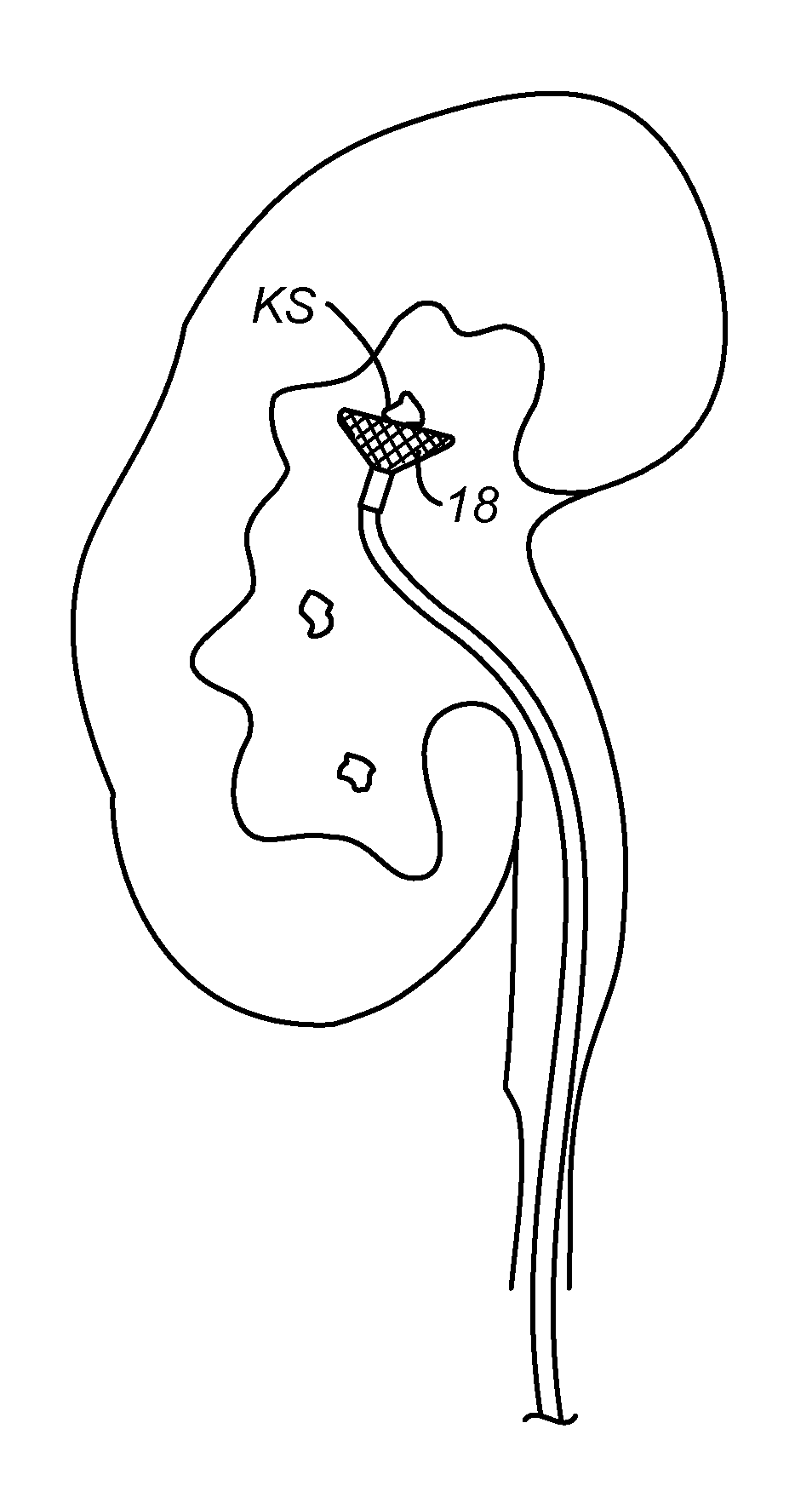
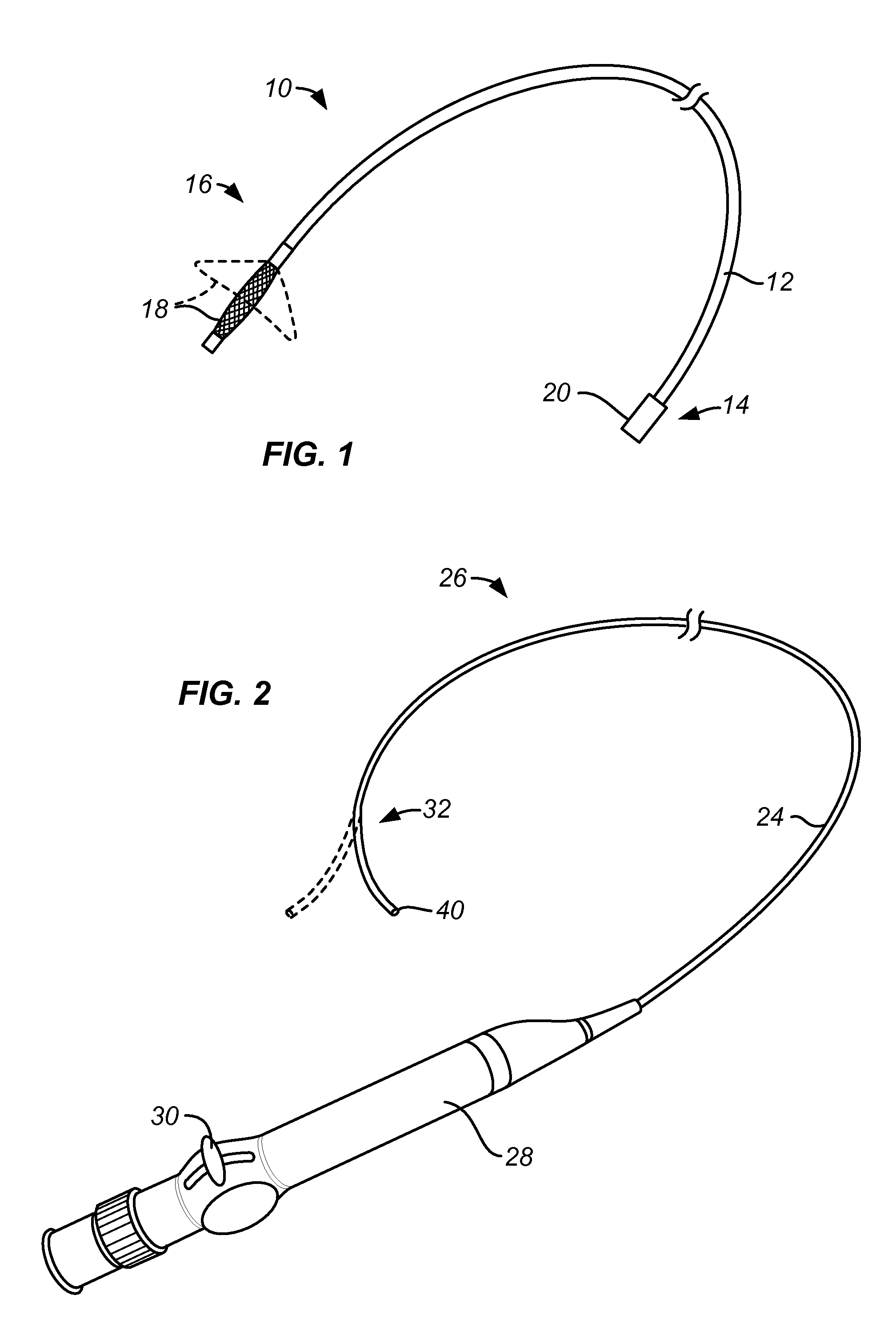
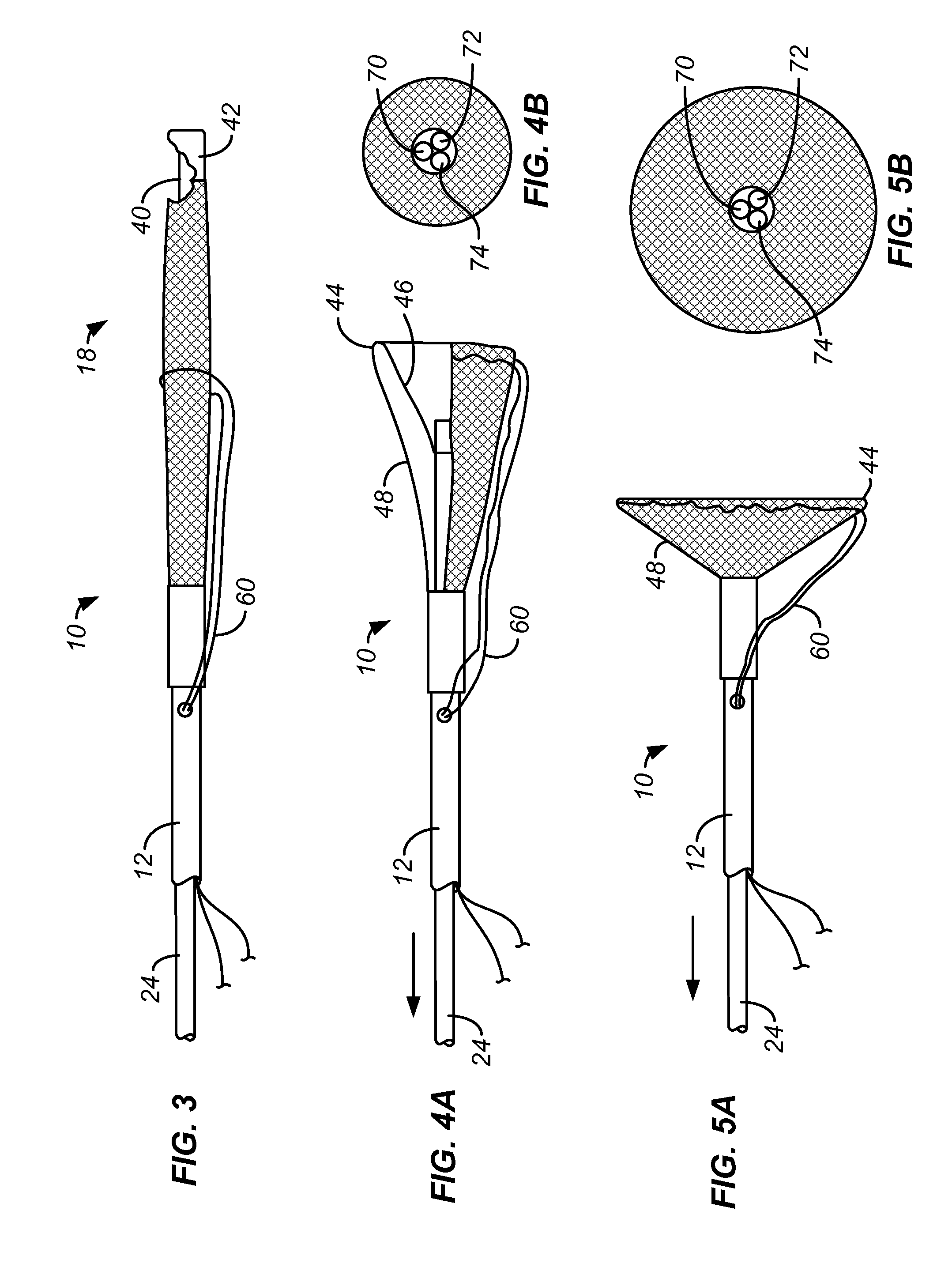
Methods and systems for capturing and removing urinary stones from body cavities
A stone capture device comprises a shaft with a deployable sweeping structure at its distal end. The shaft is adapted to be removably placed over and connected to a conventional ureteroscope. The combination of the stone capture device and ureteroscope can be introduced into the urinary tract to capture, fragment, and remove stones from the bladder and kidney.
Owner:PERCUTANEOUS SYST
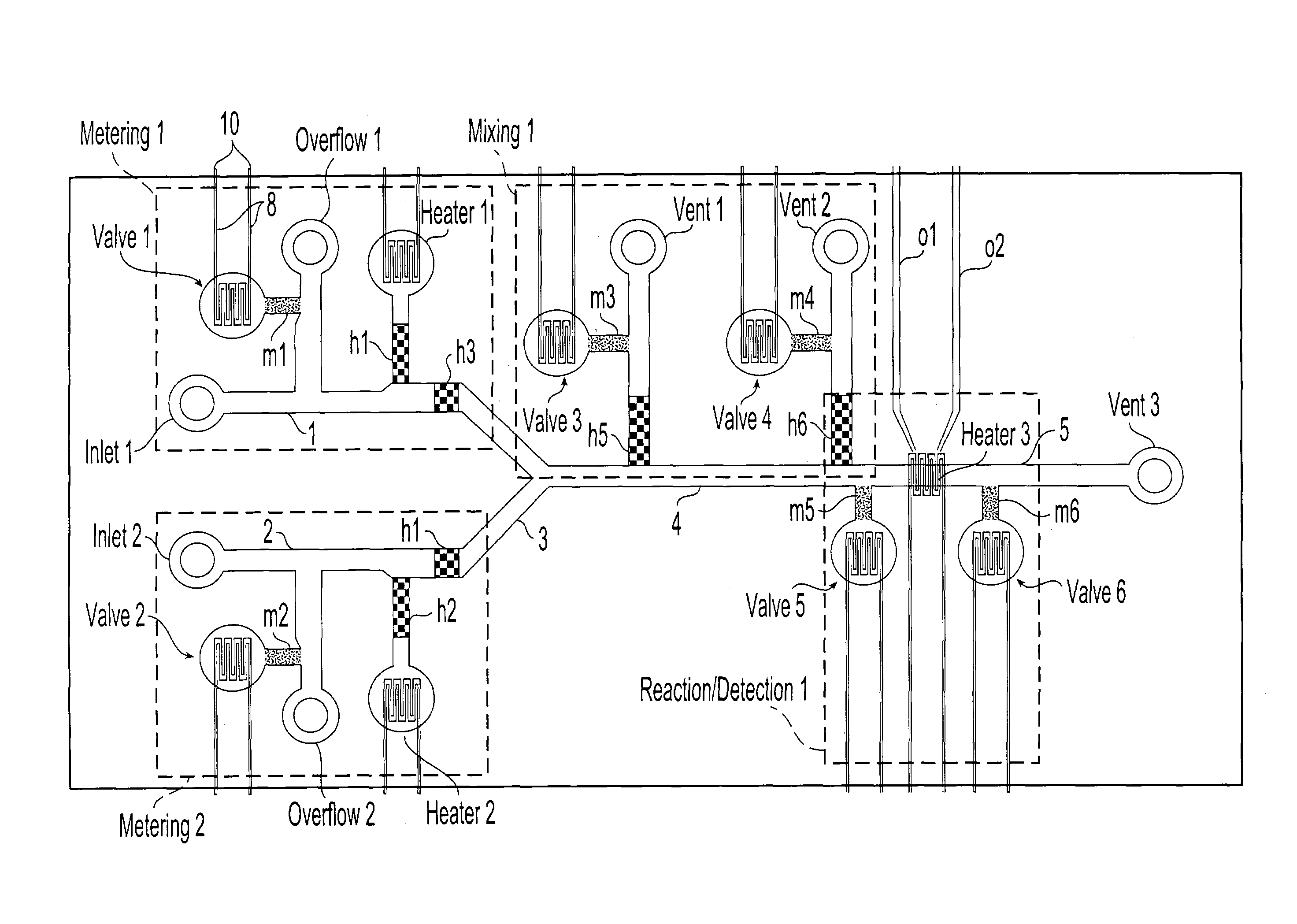
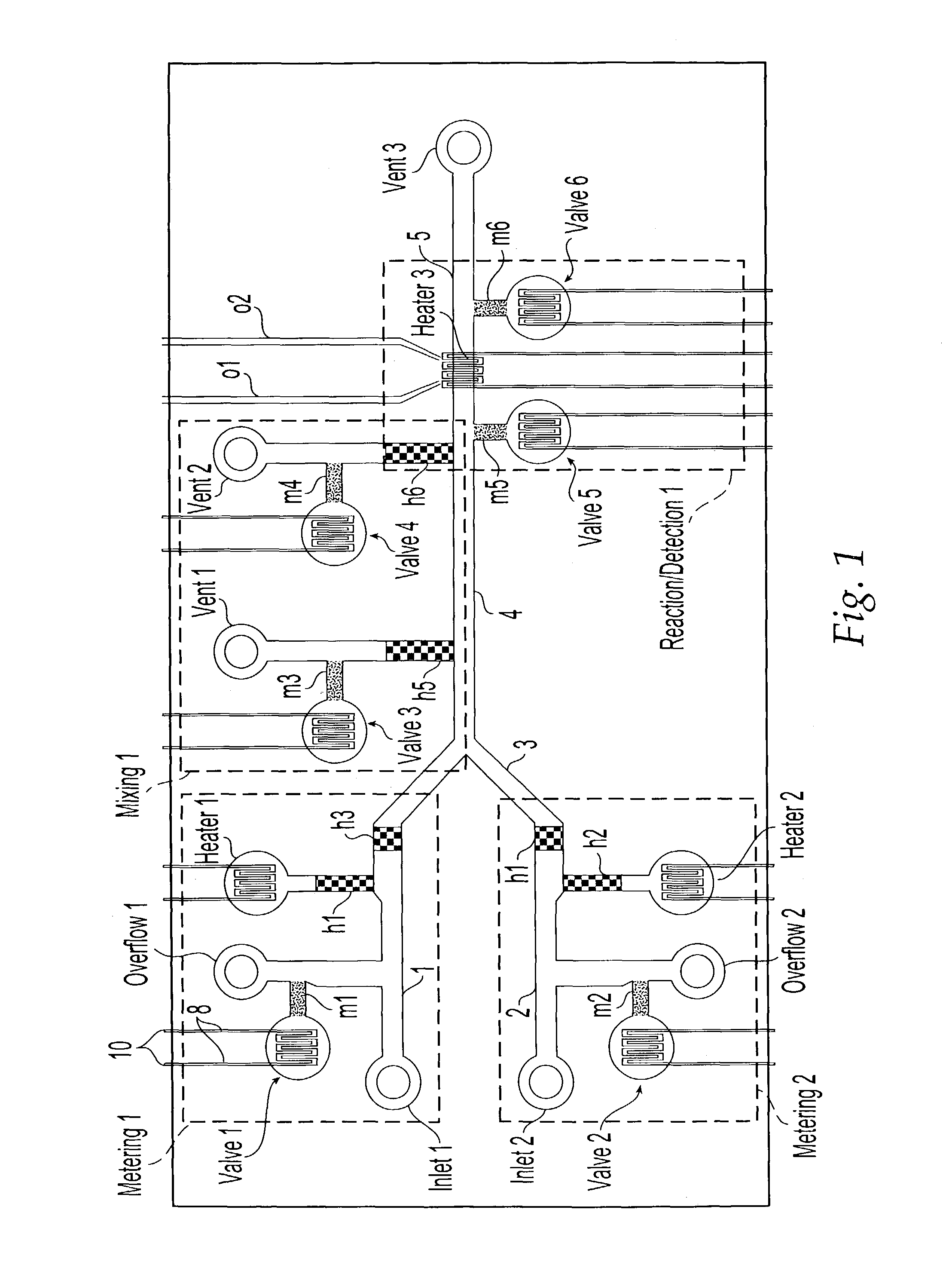
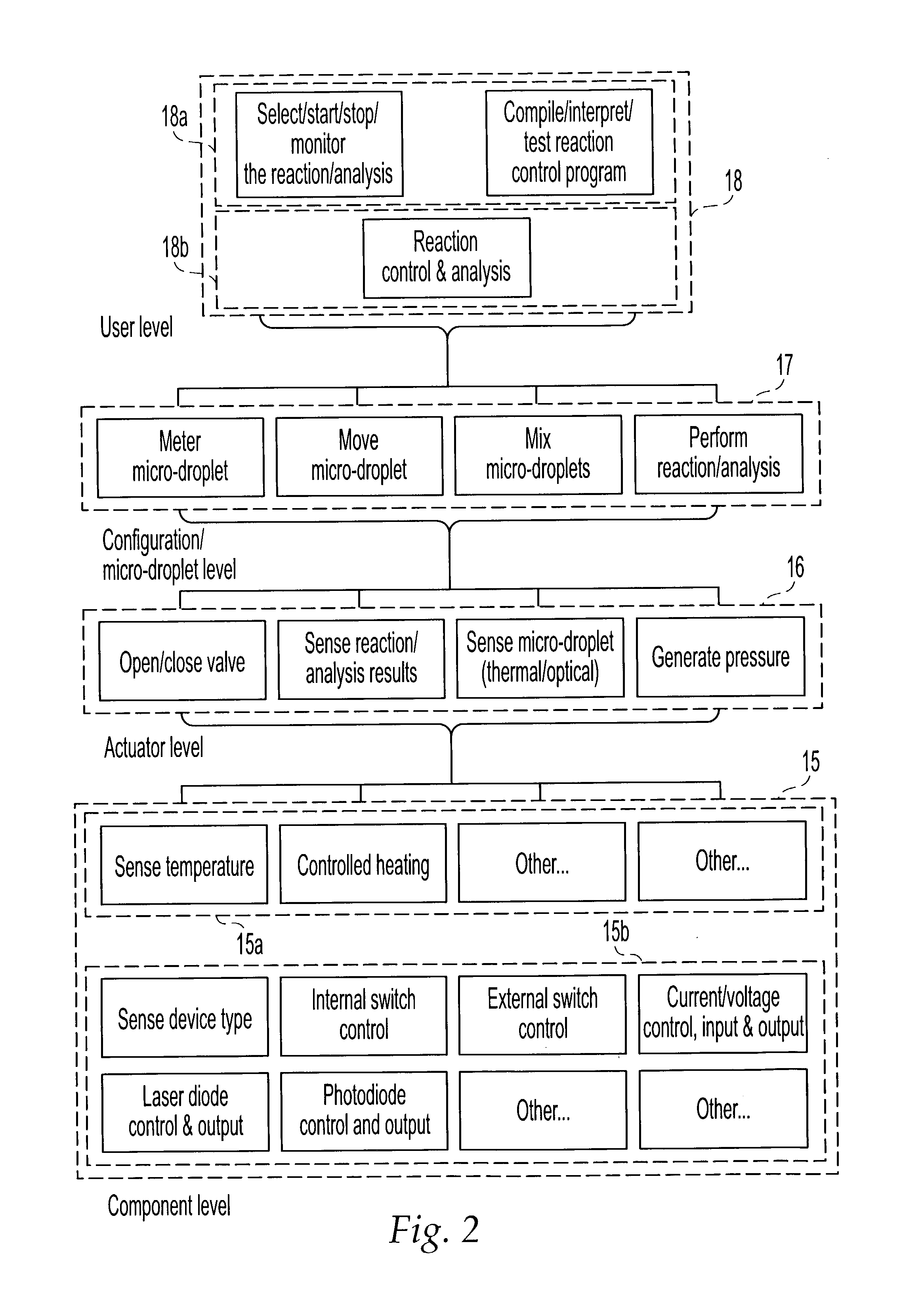
Methods and systems for control of general purpose microfluidic devices
ActiveUS8895311B1Overcome deficienciesEasy programmingHeating or cooling apparatusSamplingGeneral purposeLow voltage
The present invention provides control methods, control systems, and control software for microfluidic devices that operate by moving discrete micro-droplets through a sequence of determined configurations. Such microfluidic devices are preferably constructed in a hierarchical and modular fashion which is reflected in the preferred structure of the provided methods and systems. In particular, the methods are structured into low-level device component control functions, middle-level actuator control functions, and high-level micro-droplet control functions. Advantageously, a microfluidic device may thereby be instructed to perform an intended reaction or analysis by invoking micro-droplet control function that perform intuitive tasks like measuring, mixing, heating, and so forth. The systems are preferably programmable and capable of accommodating microfluidic devices controlled by low voltages and constructed in standardized configurations. Advantageously, a single control system can thereby control numerous different reactions in numerous different microfluidic devices simply by loading different easily understood micro-droplet programs.
Owner:HANDYLAB
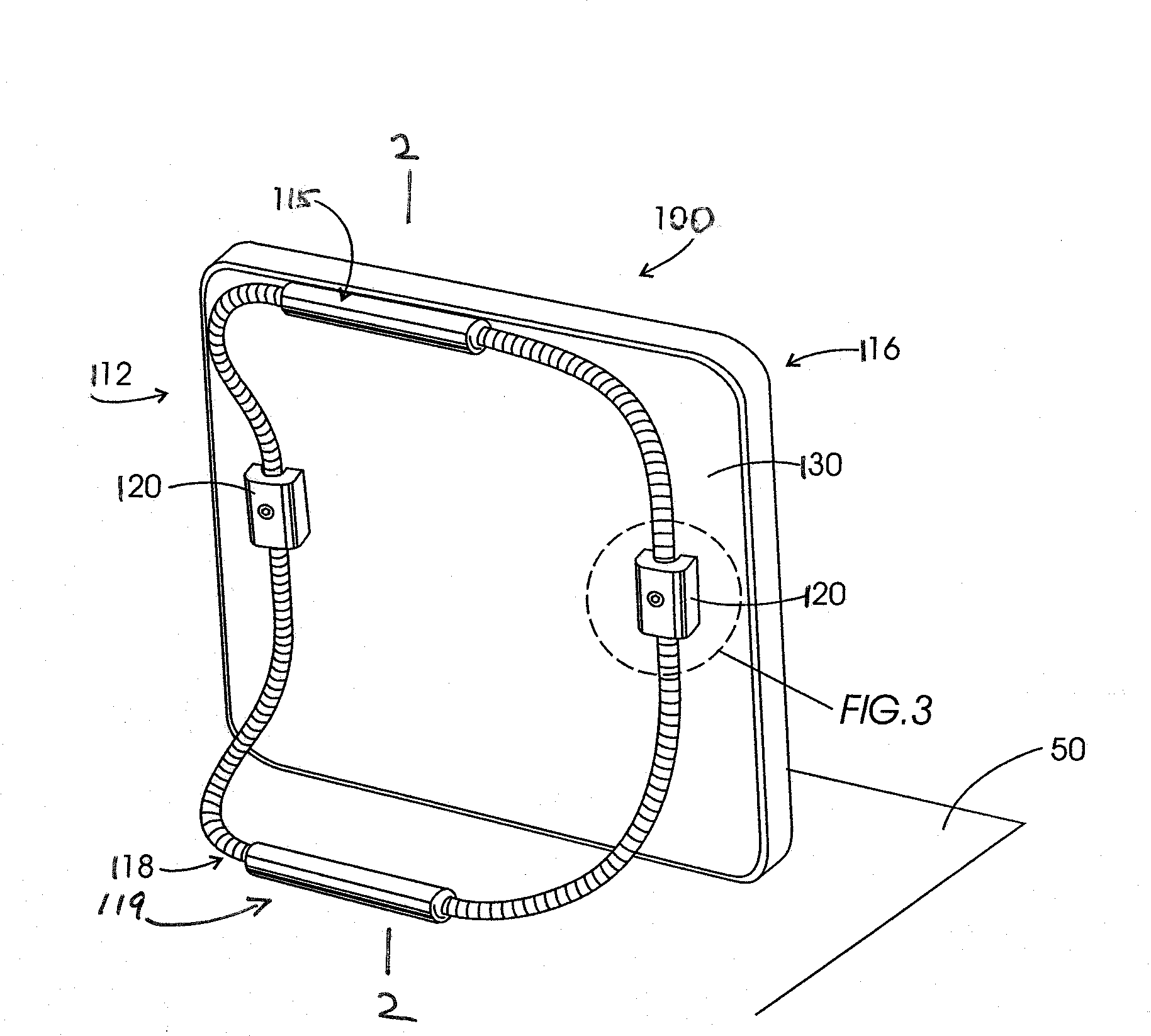
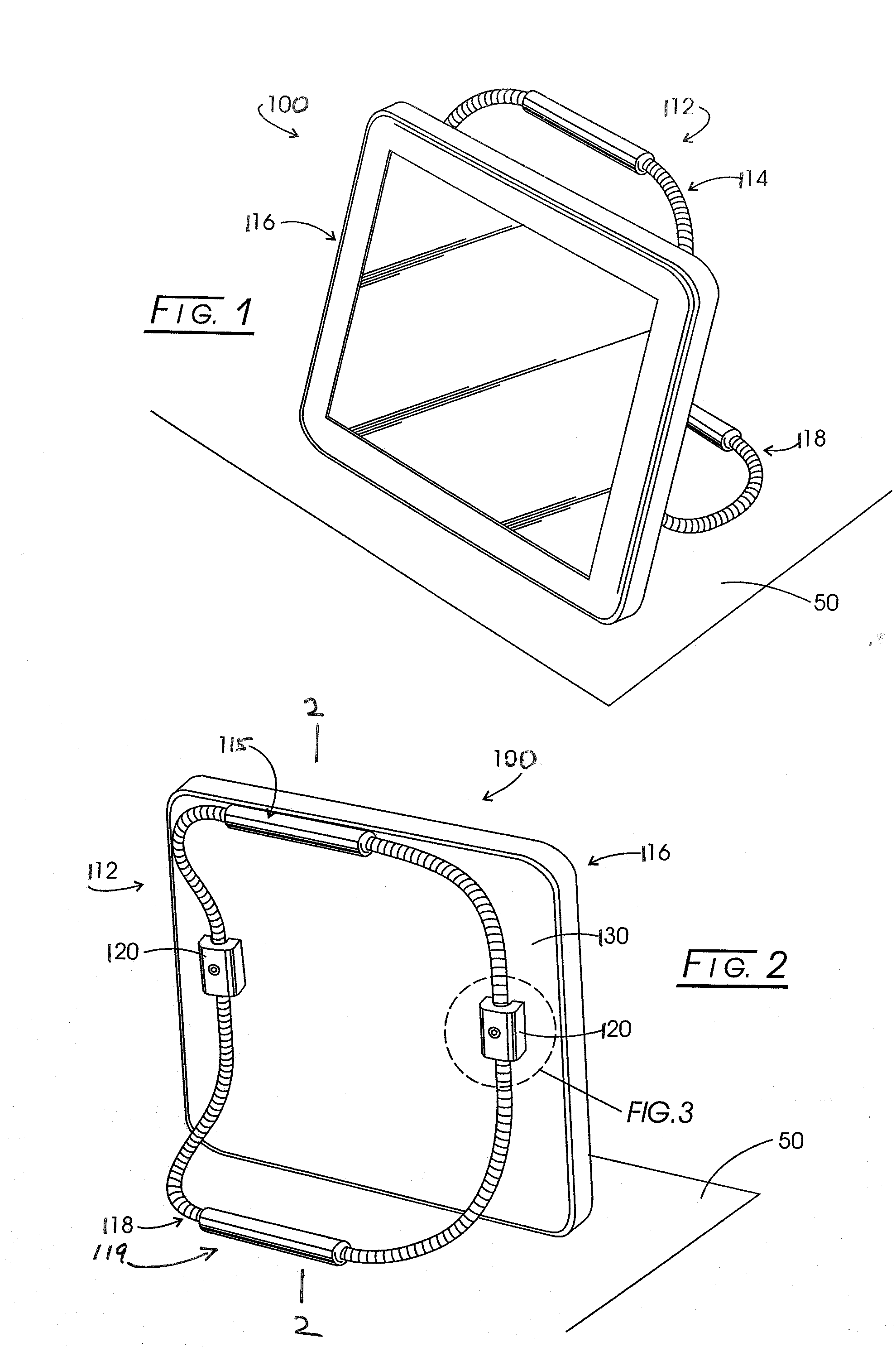
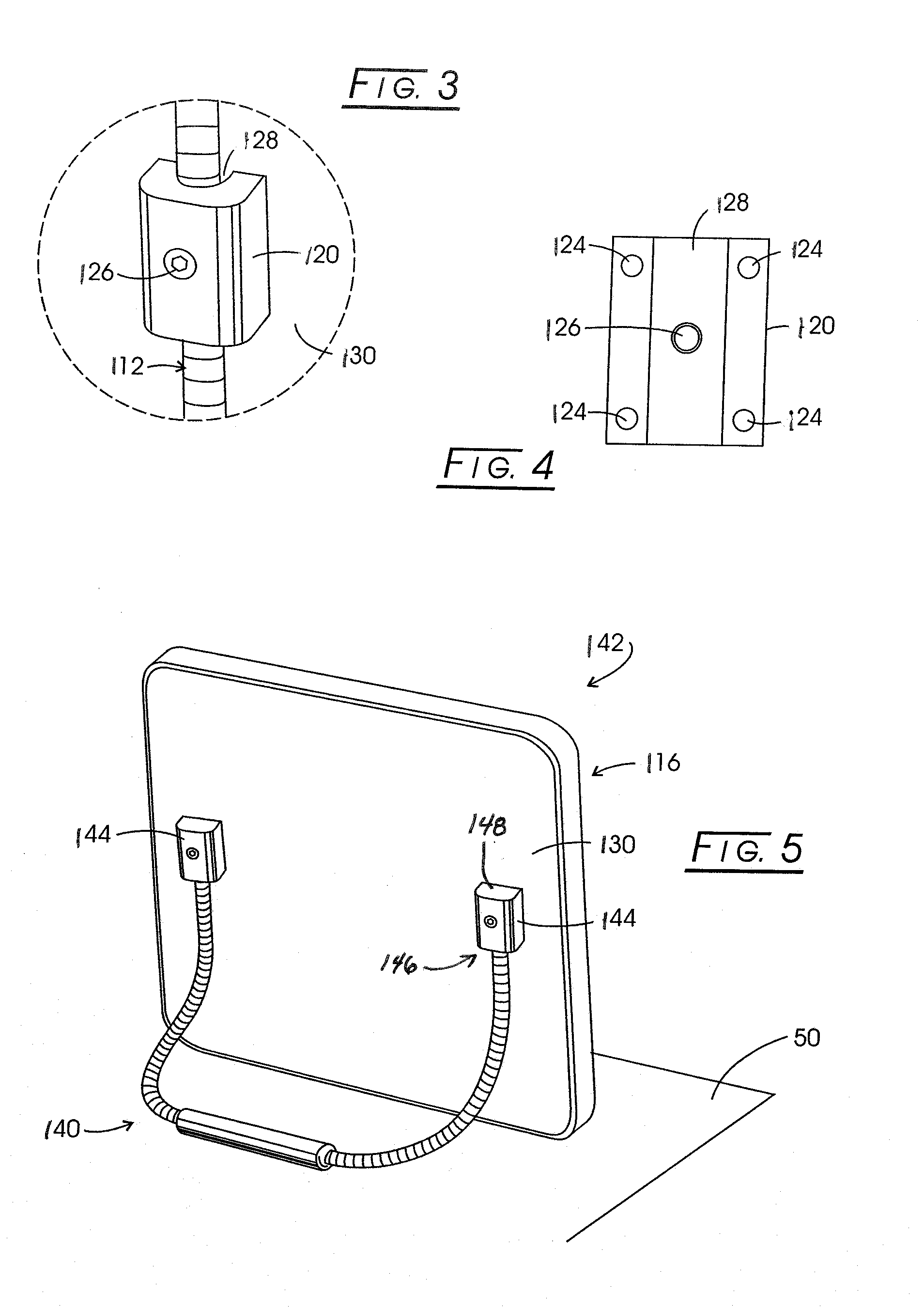
Formable Stand System
InactiveUS20090095854A1Reduce slippageHigh strengthPicture framesDomestic mirrorsSupporting systemTablet computer
A formable support stand system for portable electronic devices that provides a manner to support a device such as a tablet computer in a variety of orientations from a supporting surface such as a tray or table. The embodiments comprise a flex-rod prop, and a fastener for attaching the prop to an electronic device, such that the flex rod resists deformation, but can be adjusted into a wide variety of positions. The stand system is adapted for use with devices used by those with limited or erratic motor control, in order to allow positioning of the screen face of a tablet computer in a chosen orientation relative to a support tray on a wheelchair, for instance. The stand system comprises a flexible, positionable flex-rod, an anti-skid sleeve and is removeably attached to the electronic device by means of rod clamp system. The formable support system is also provided as a kit for retrofitting existing devices.
Owner:FORBES REHAB SERVICES
Shape-morphing space frame apparatus using unit cell bistable elements
ActiveUS9783977B2Facilitate behaviorSufficient flexibilityElongated constructional elementsExtraordinary structuresMorphingCompliant mechanism
Unit cell bistable elements, and particular arrangements thereof, that can transform or morph a structure from one shape to another. In certain embodiments, the current invention includes unit cell bistable elements, and particular arrangements and uses thereof, that can transform or morph a structure from one shape to another. In an embodiment, the current invention provides a method / ability to transform any four-bar compliant mechanism into a bistable compliant mechanism. It is an object of the current invention to facilitate structures morphing from one specific shape to another specific shape using unit cell bistable elements.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Fluid seal for endoscope
An endoscope seal that effectively inhibits the egress of fluids from the working channel of an endoscope when an elongate device having a non-circular shaft is disposed therein. The endoscope seal includes a body portion having a proximal end adapted for insertion of an elongate device such as a rapid exchange biliary catheter, a distal end adapted for connection to the proximal end of an endoscope, a lumen extending therethrough which is adapted to receive the elongate device and to provide access to the working channel of the endoscope, and a means for conforming to the non-circular shaft of the elongate device to inhibit the flow of fluid from the working channel of the endoscope. The conforming means may, for example, comprise one or more protrusions extending radially inward in the lumen of the body portion, a sealing material such as a surgical foam that is disposed in the lumen of the body portion, or a sealing mandrel. Whether a single protrusion, a plurality of protrusions, a sealing material or a sealing mandrel is utilized, the present invention provides endoscope seals that readily seal about elongate devices having either circular or non-circular profiles.
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST
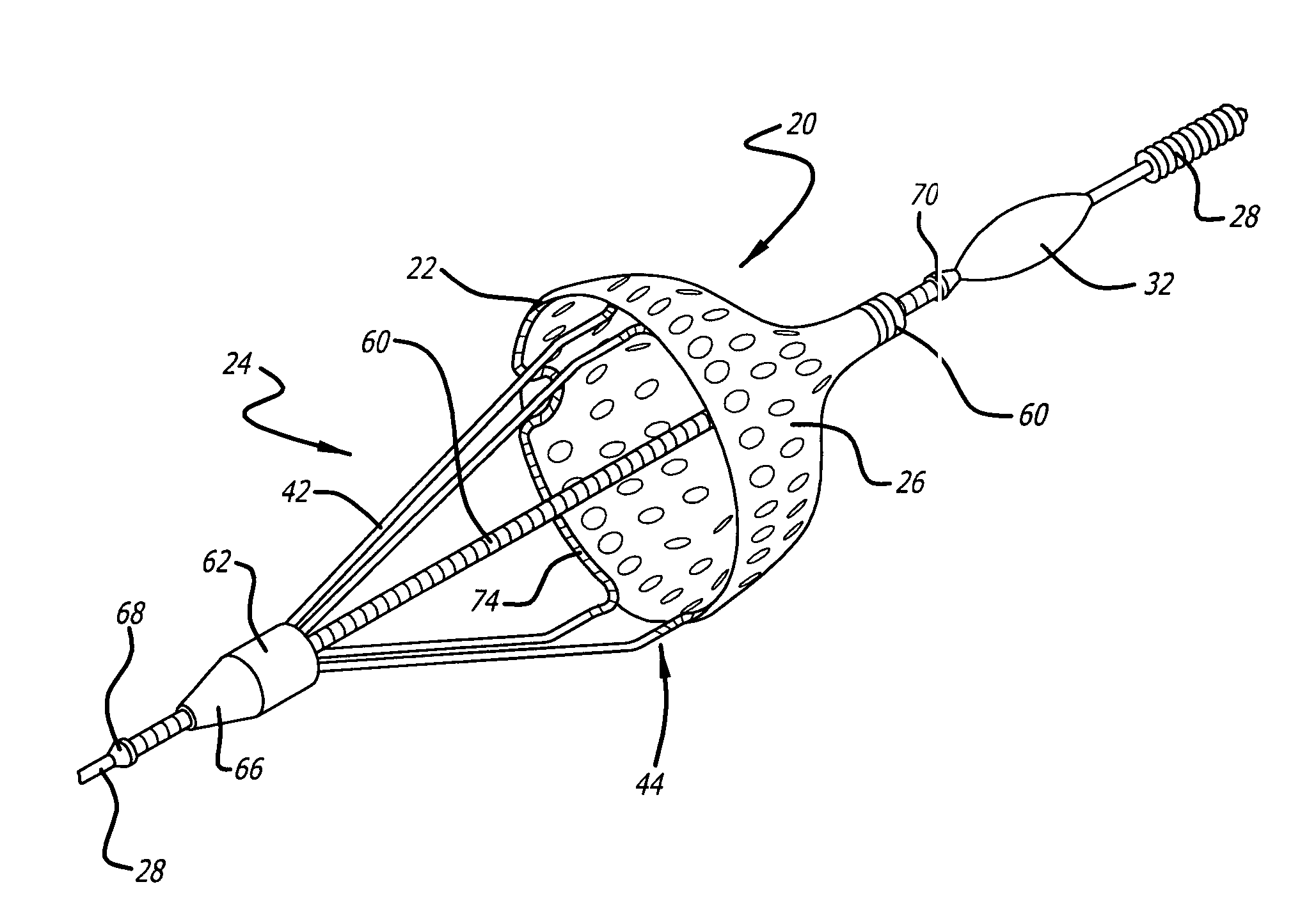
Embolic filtering devices
An expandable frame for an embolic filtering device used to capture embolic debris in a body vessel includes a first half frame having a first control arm connected to a second control arm by a partial loop and a second half frame having a first control arm connected to a second control arm by a partial loop. The partial loops cooperatively form a composite loop for attachment of a filtering element which will expand in the body vessel to capture embolic debris entrained in the fluid of the vessel. The lengths and positioning of the first and second control arms of each half frame can be varied to create an expandable frame which conforms to the size and shape of the body vessel in which the filtering device is deployed. Additionally, the radius of the partial loops, along with the length of the arc of the partial loops, can be varied on each of the frames to create a composite filtering assembly that can easily adapt to the size and shape of the body vessel. Additionally, the control arms of the half frames can be disposed either proximally or distally of the composite loop to create a distinct filtering structure.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com