Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1162 results about "Aerodynamic drag" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In aerodynamics, aerodynamic drag is the fluid drag force that acts on any moving solid body in the direction of the fluid freestream flow. From the body's perspective, the drag comes from forces due to pressure distributions over the body surface, symbolized, and forces due to skin friction, which is a result of viscosity, denoted . Alternatively, calculated from the flowfield perspective, the drag force comes from three natural phenomena: shock waves, vortex sheet, and viscosity.
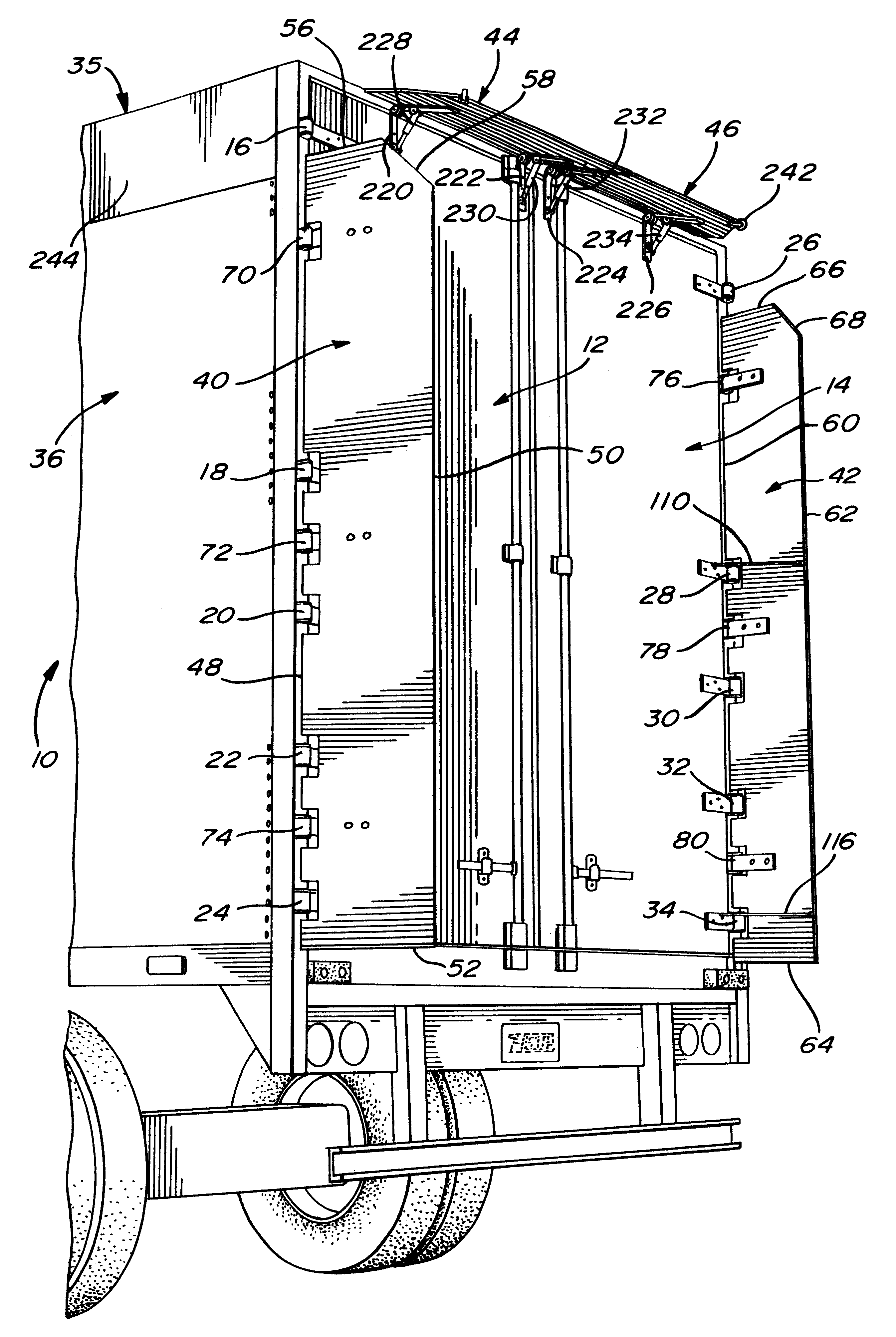
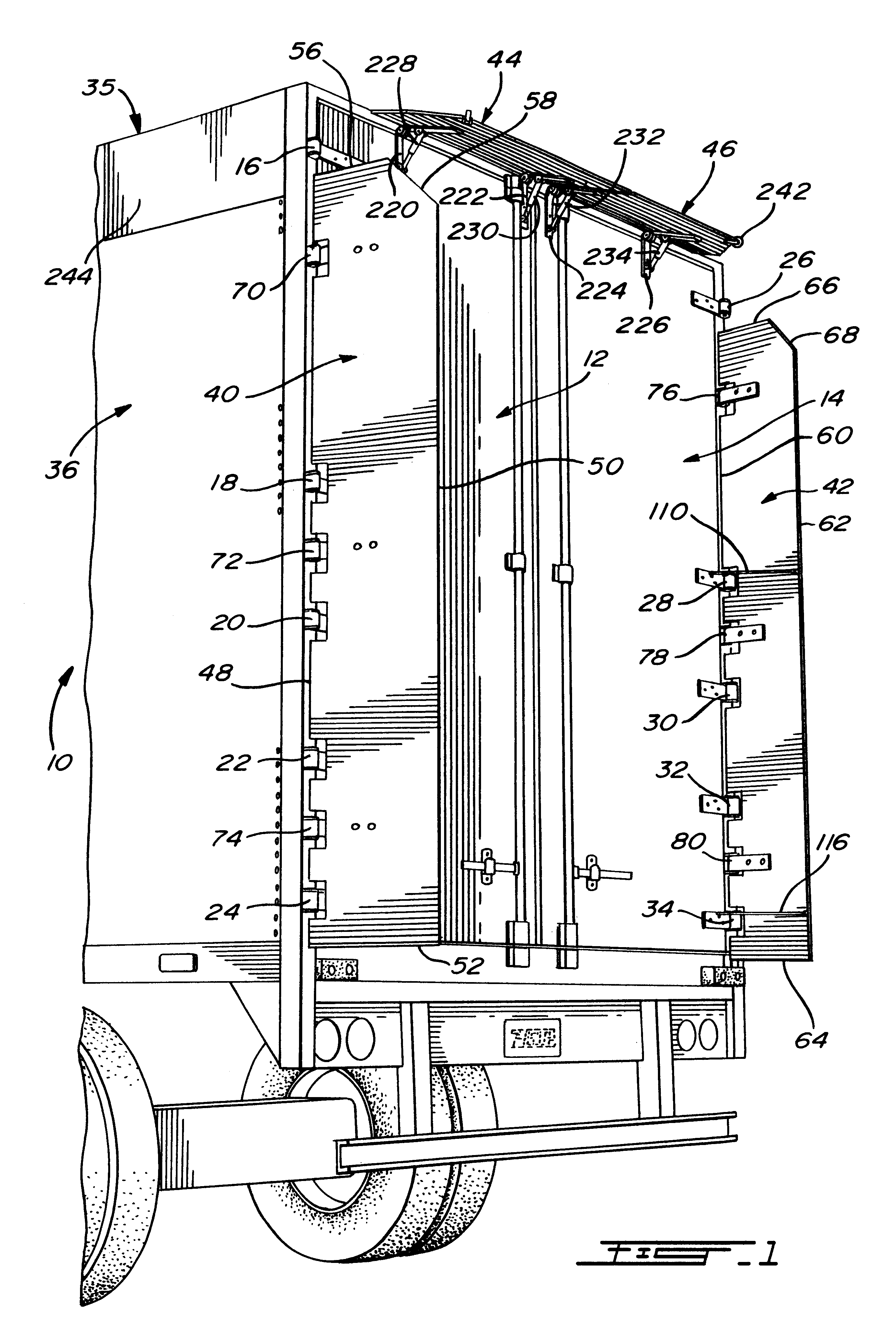
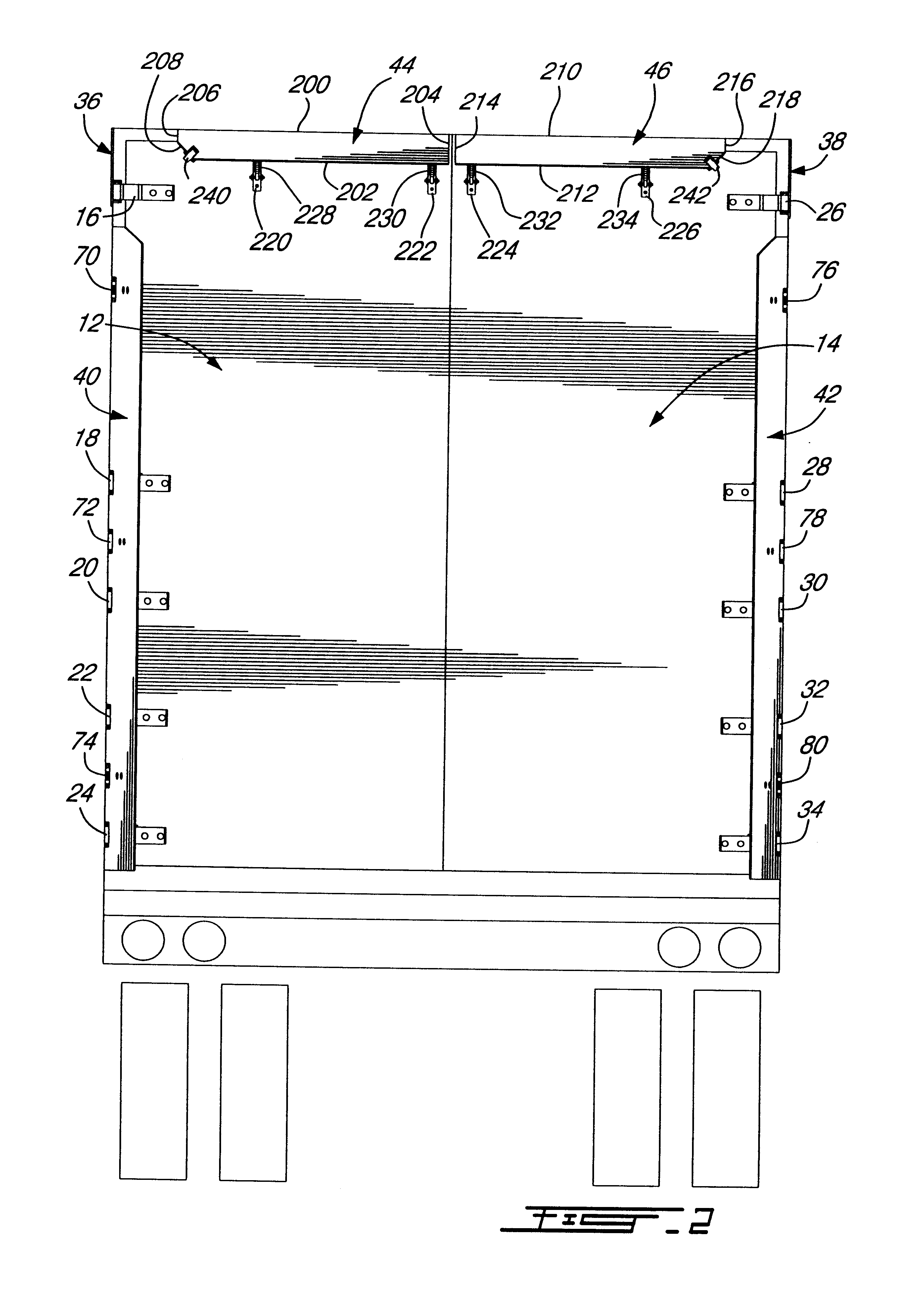
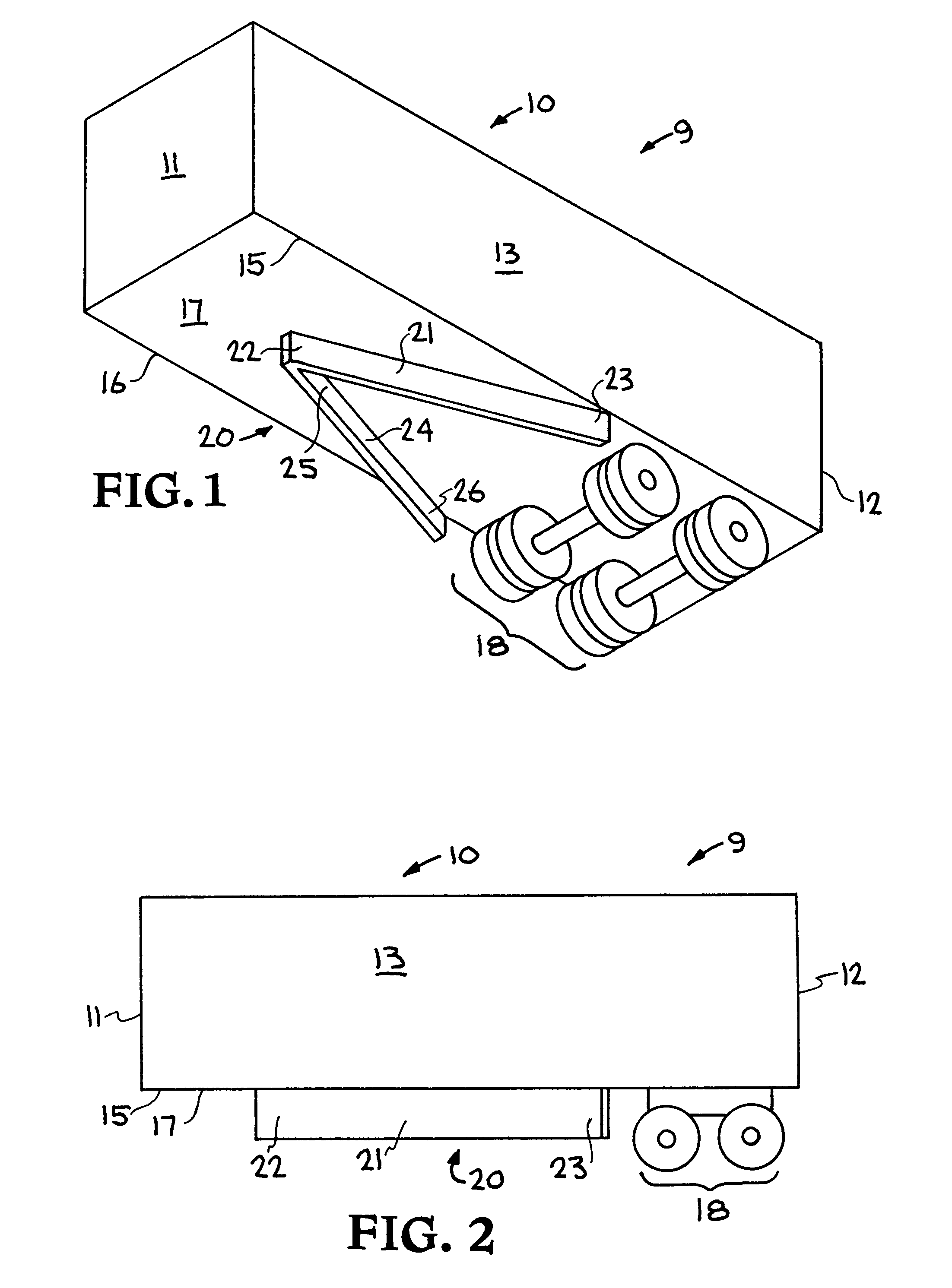
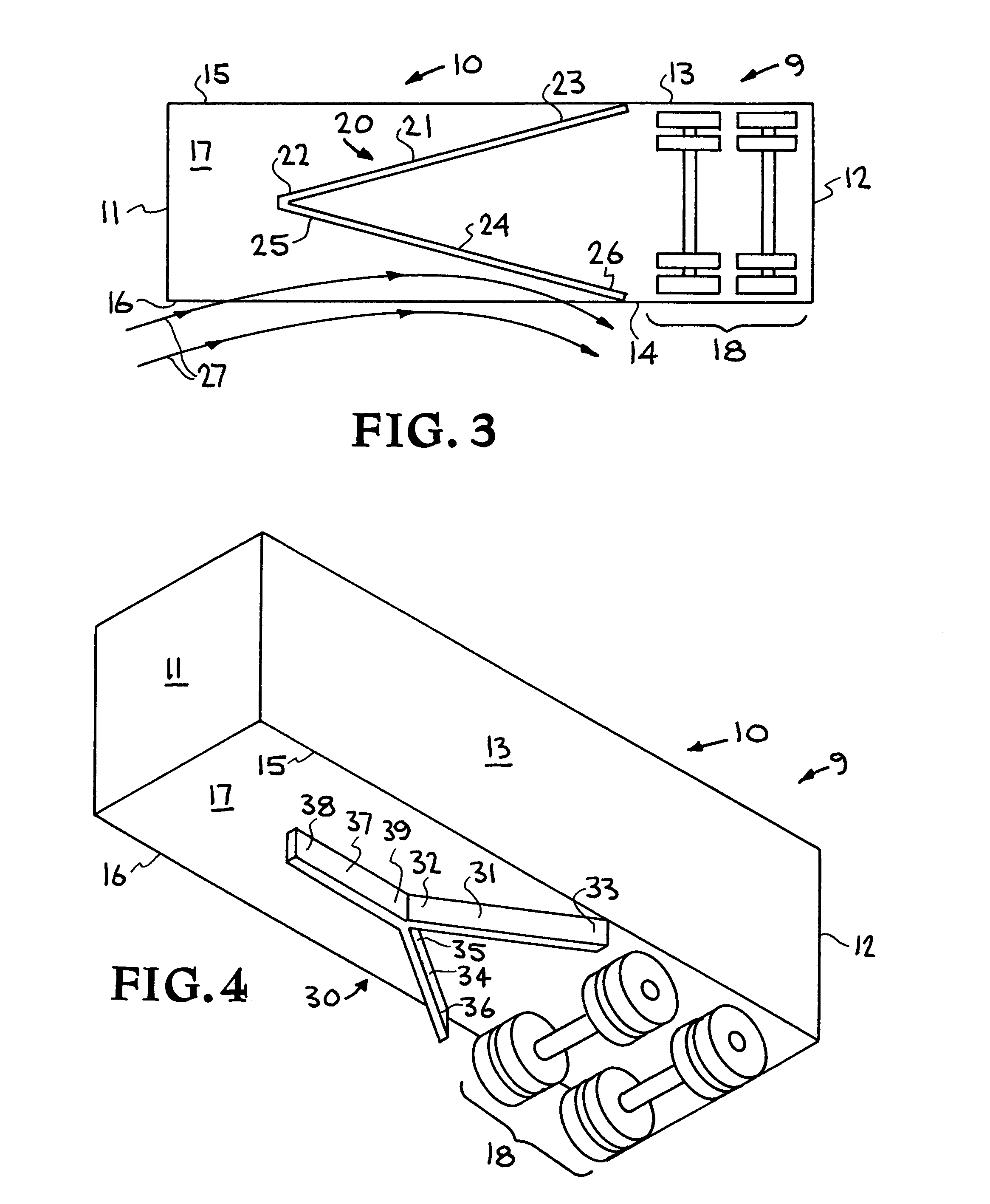
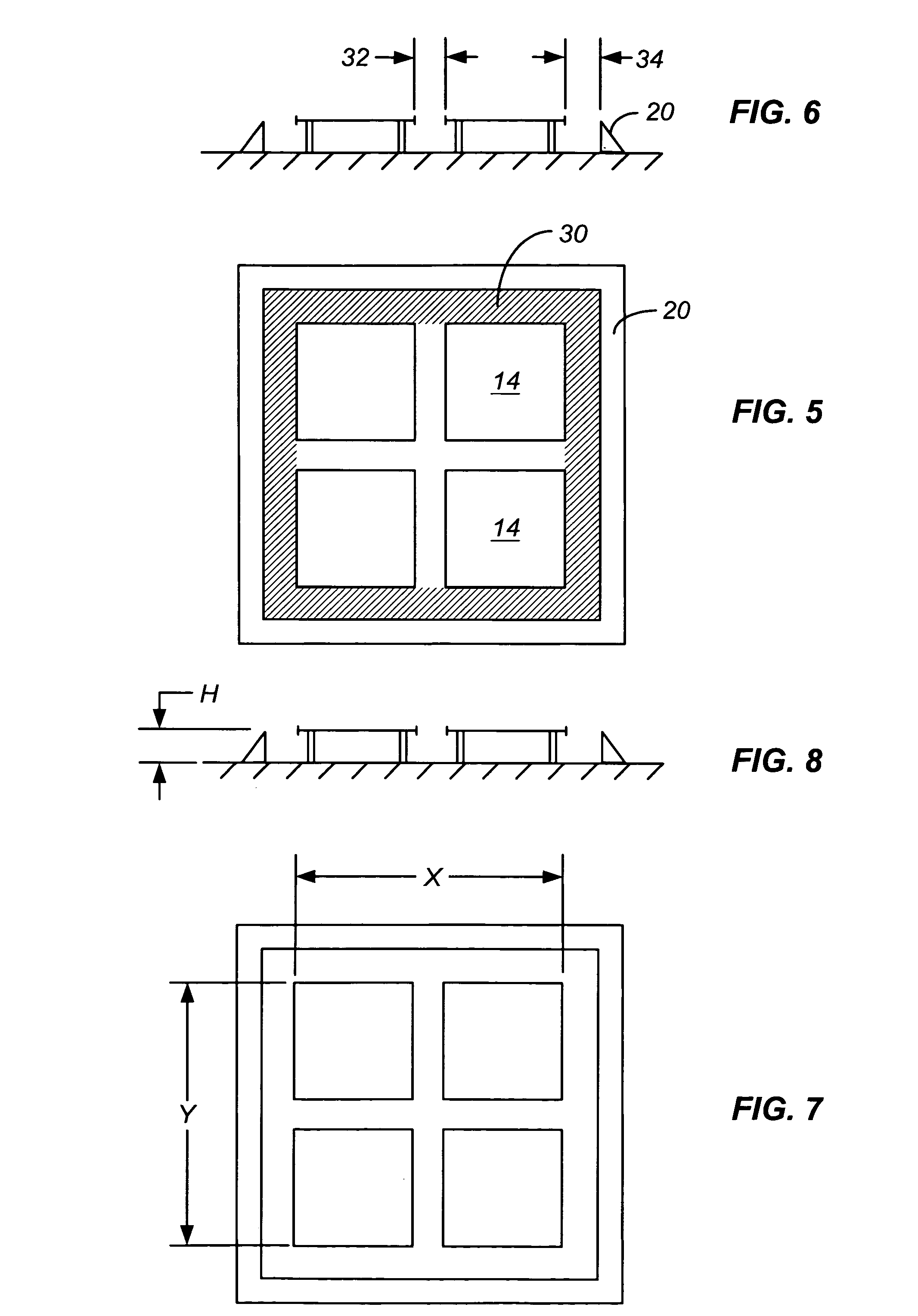
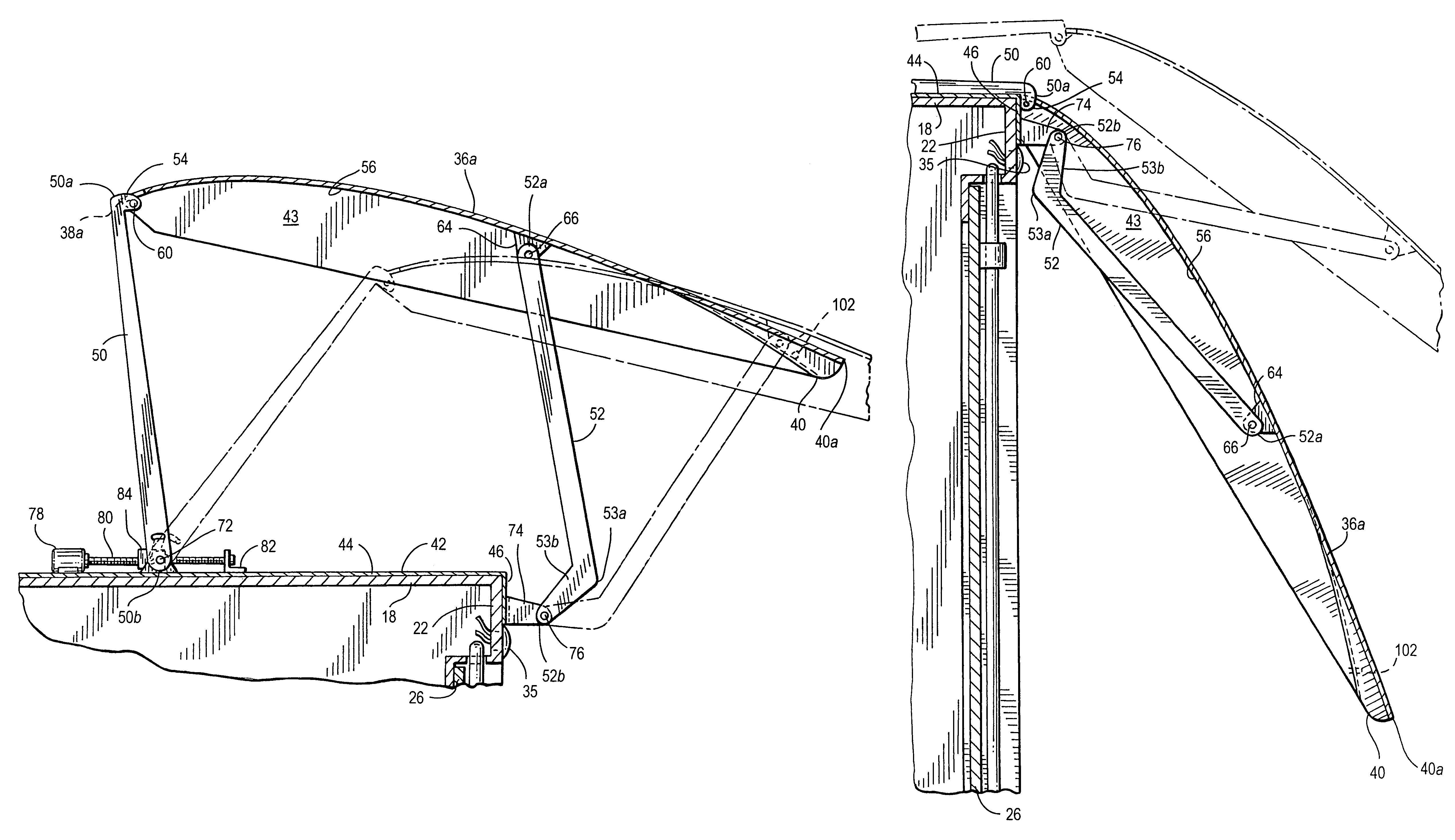
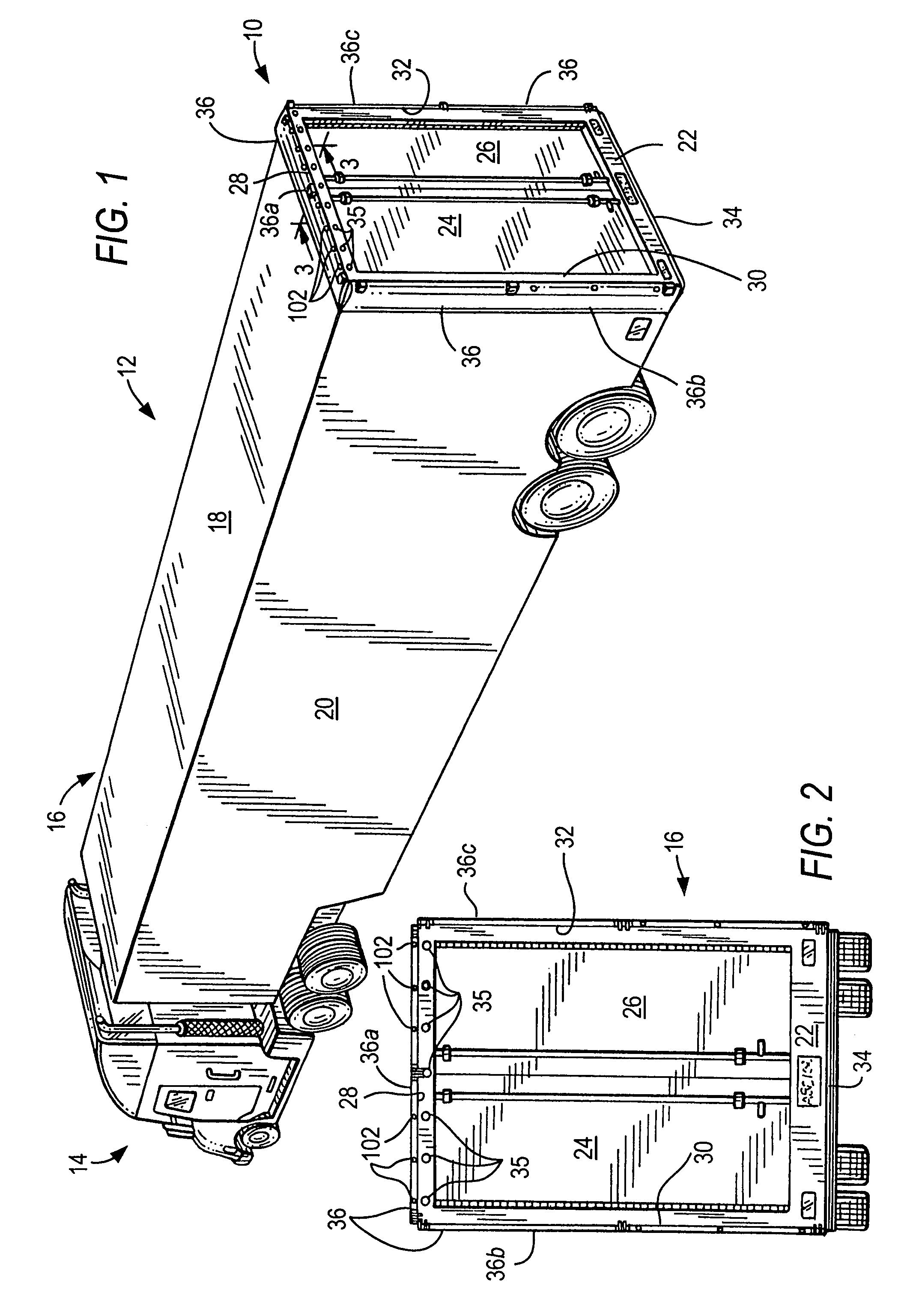
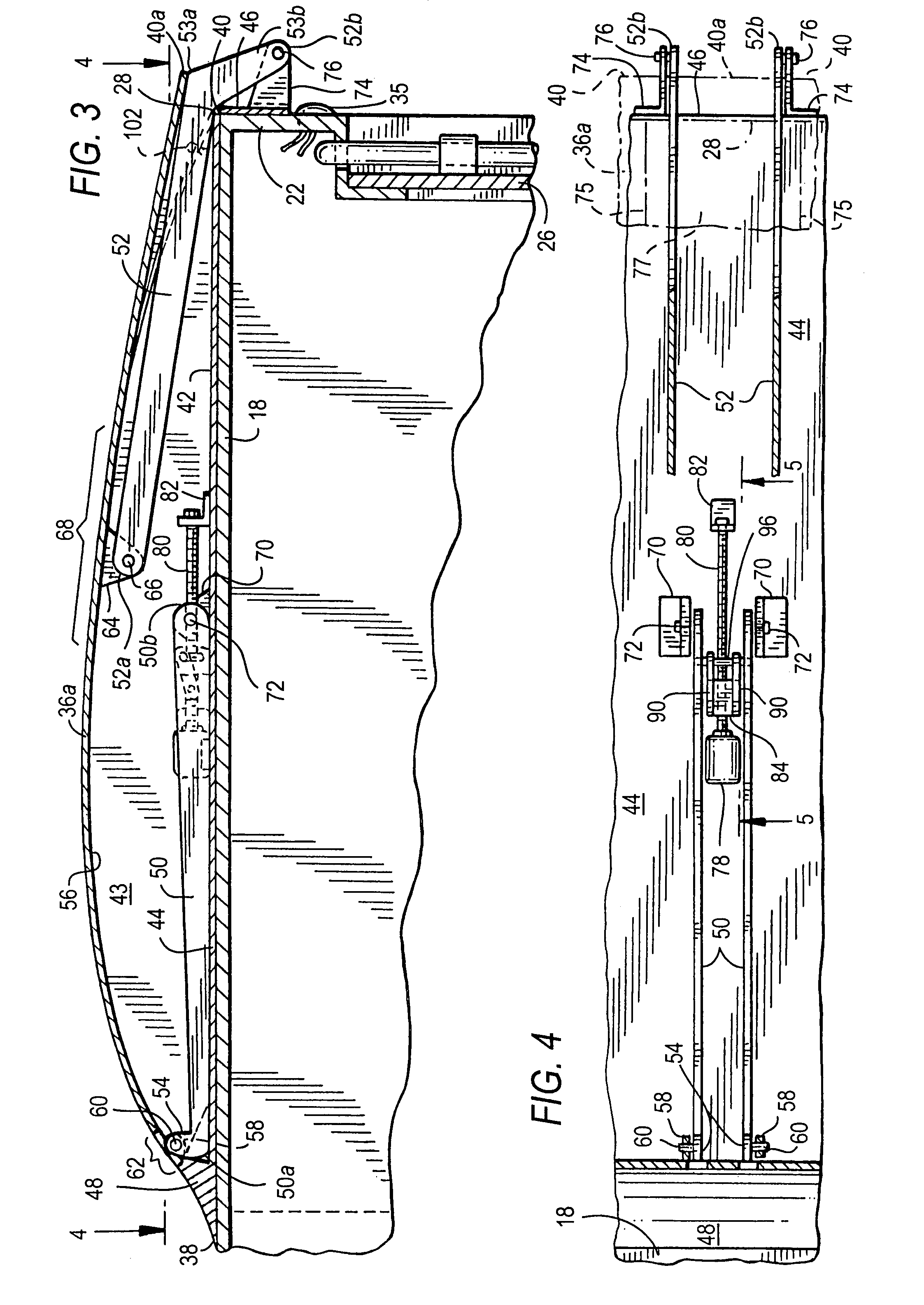
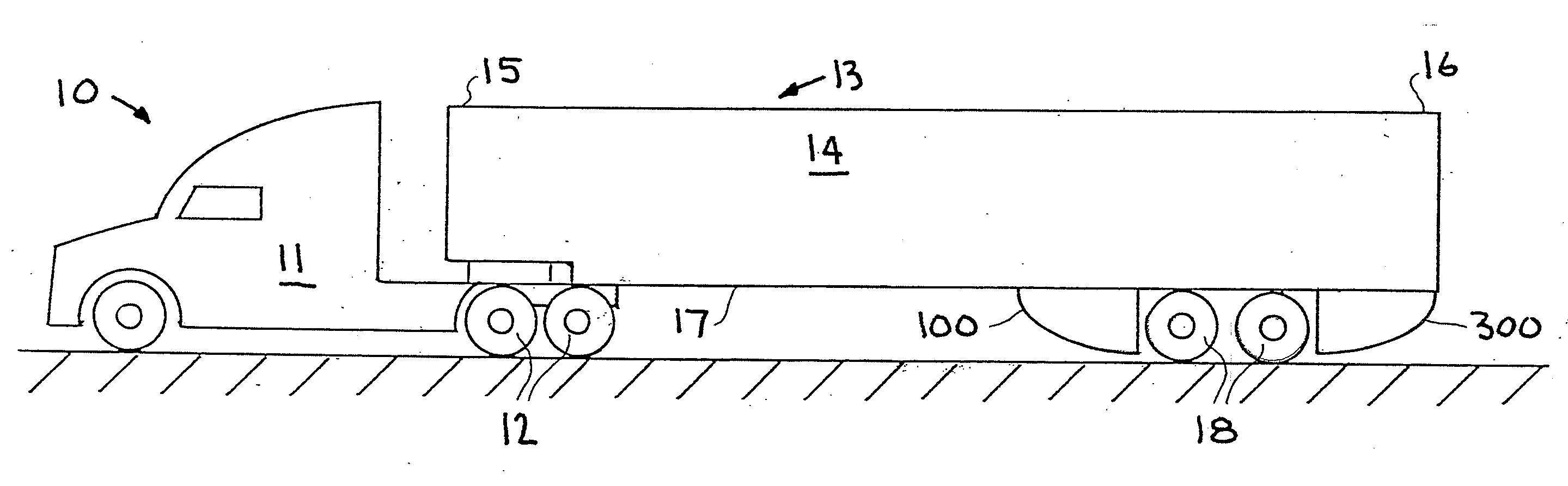
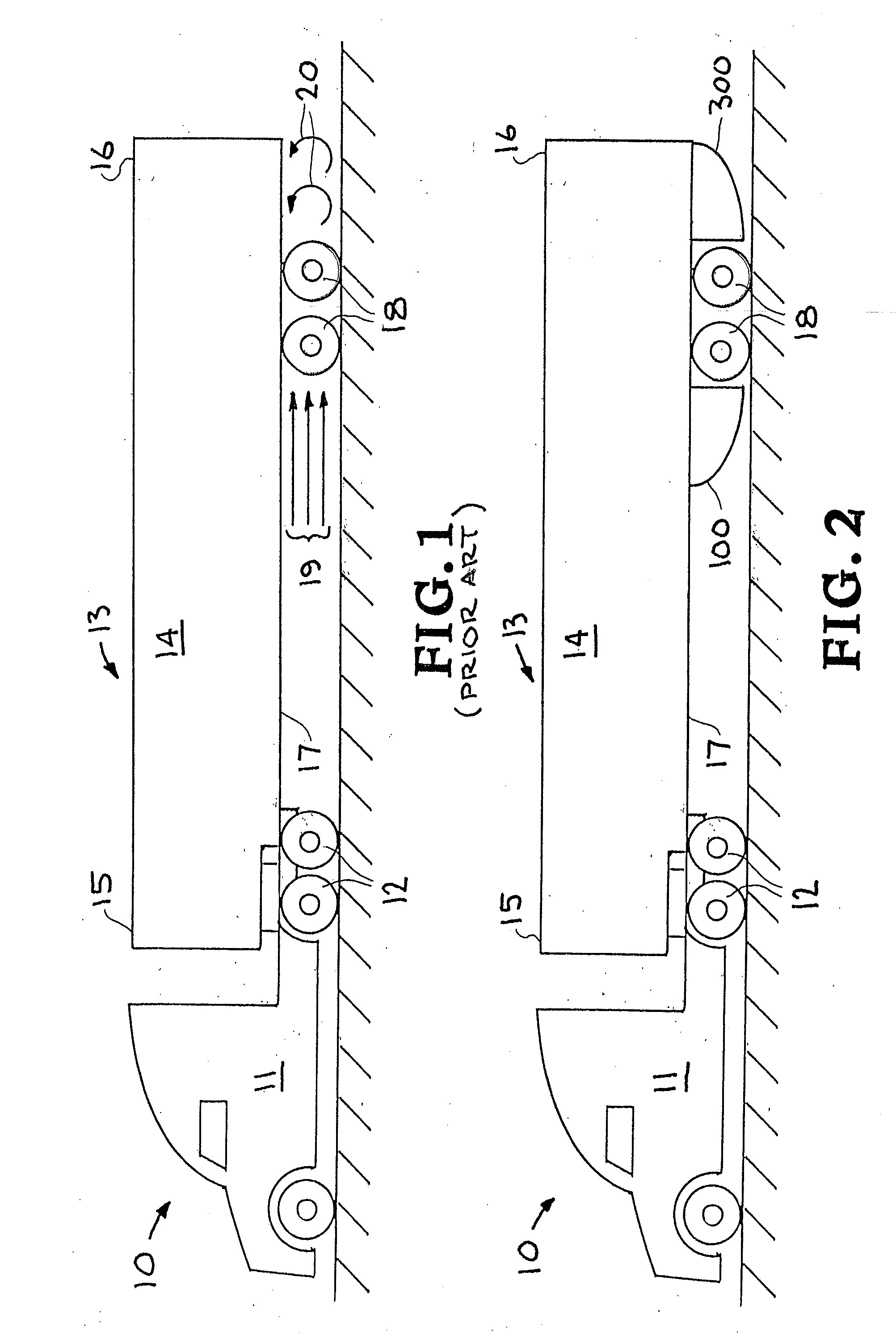
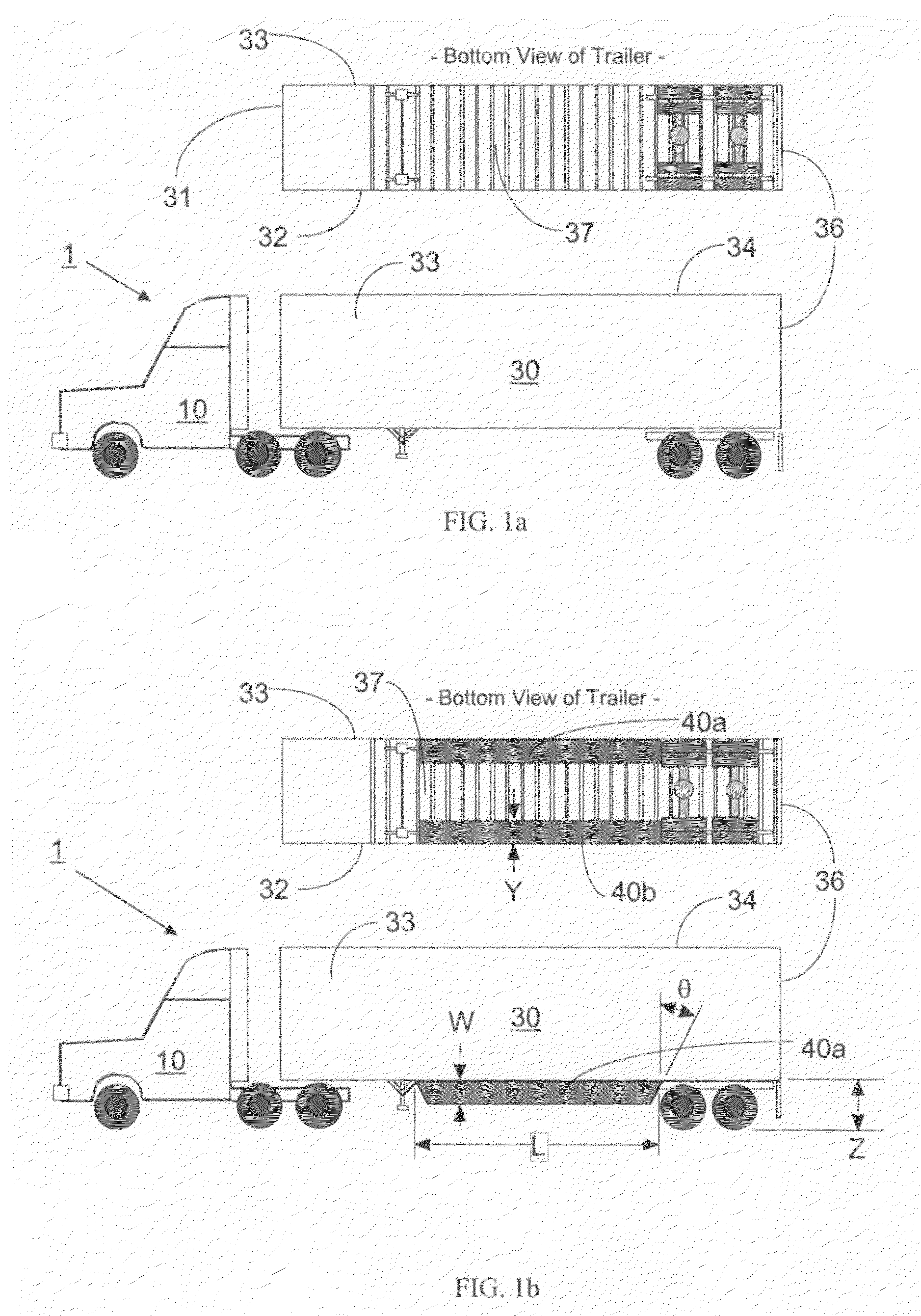
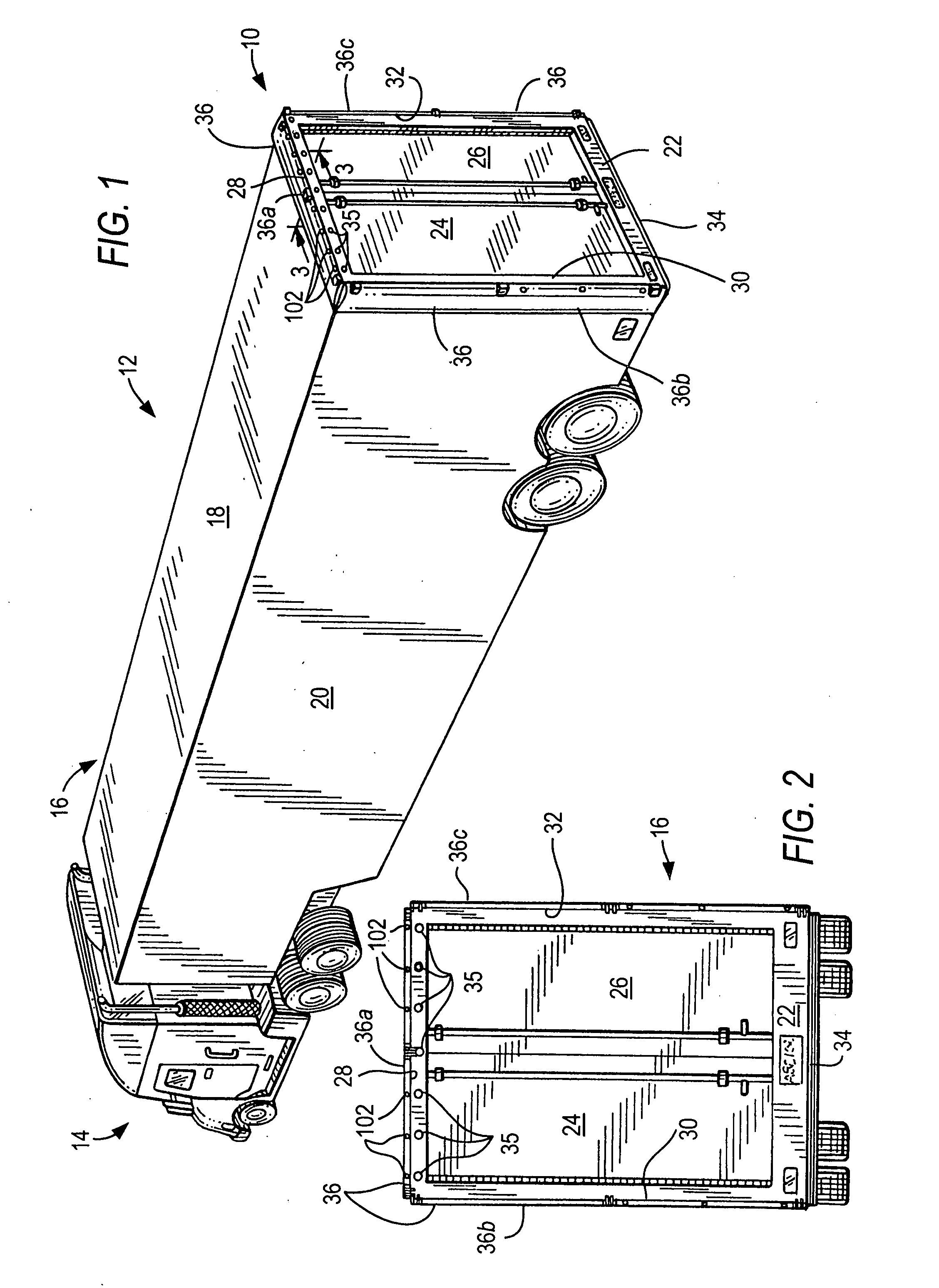
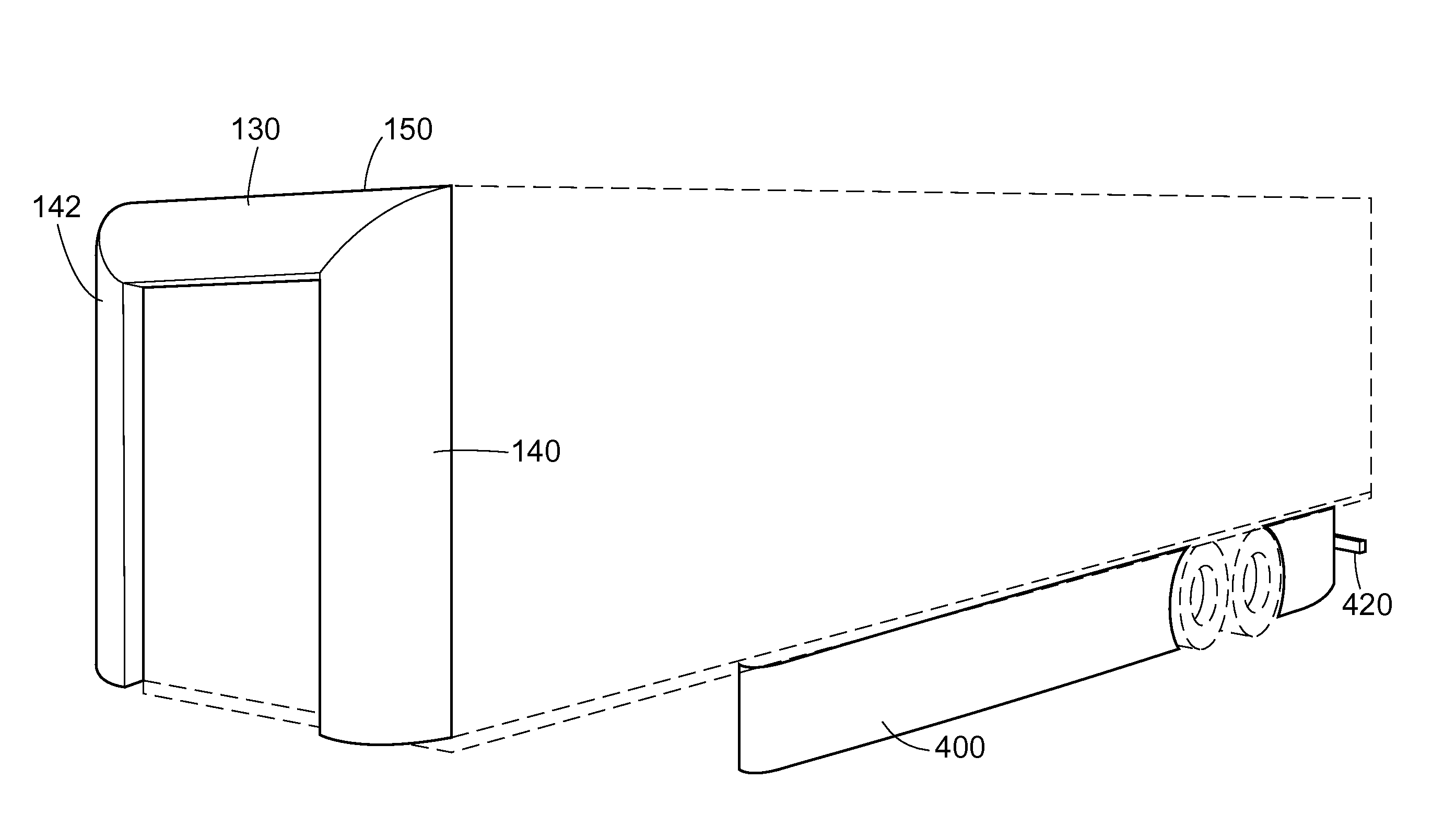
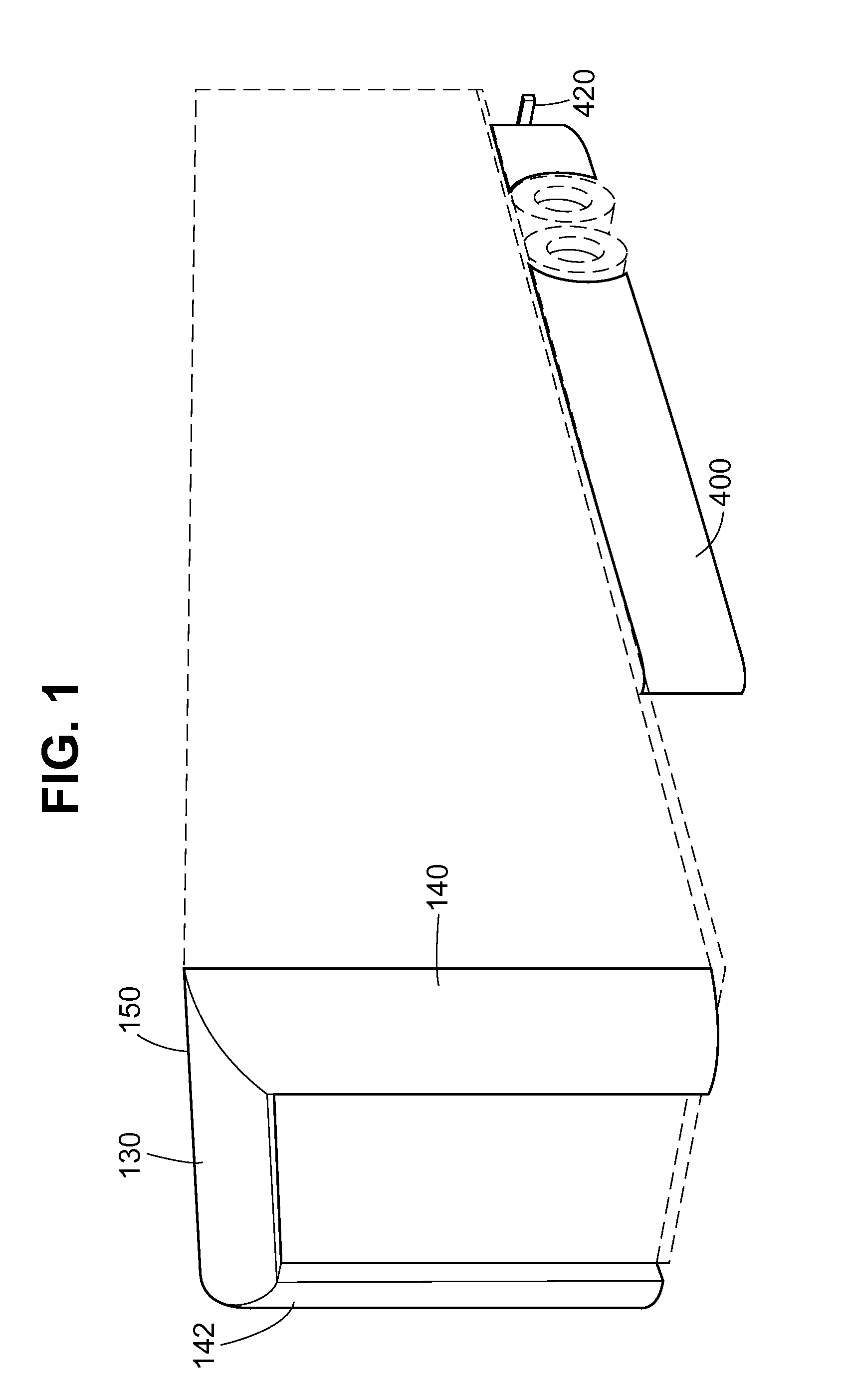
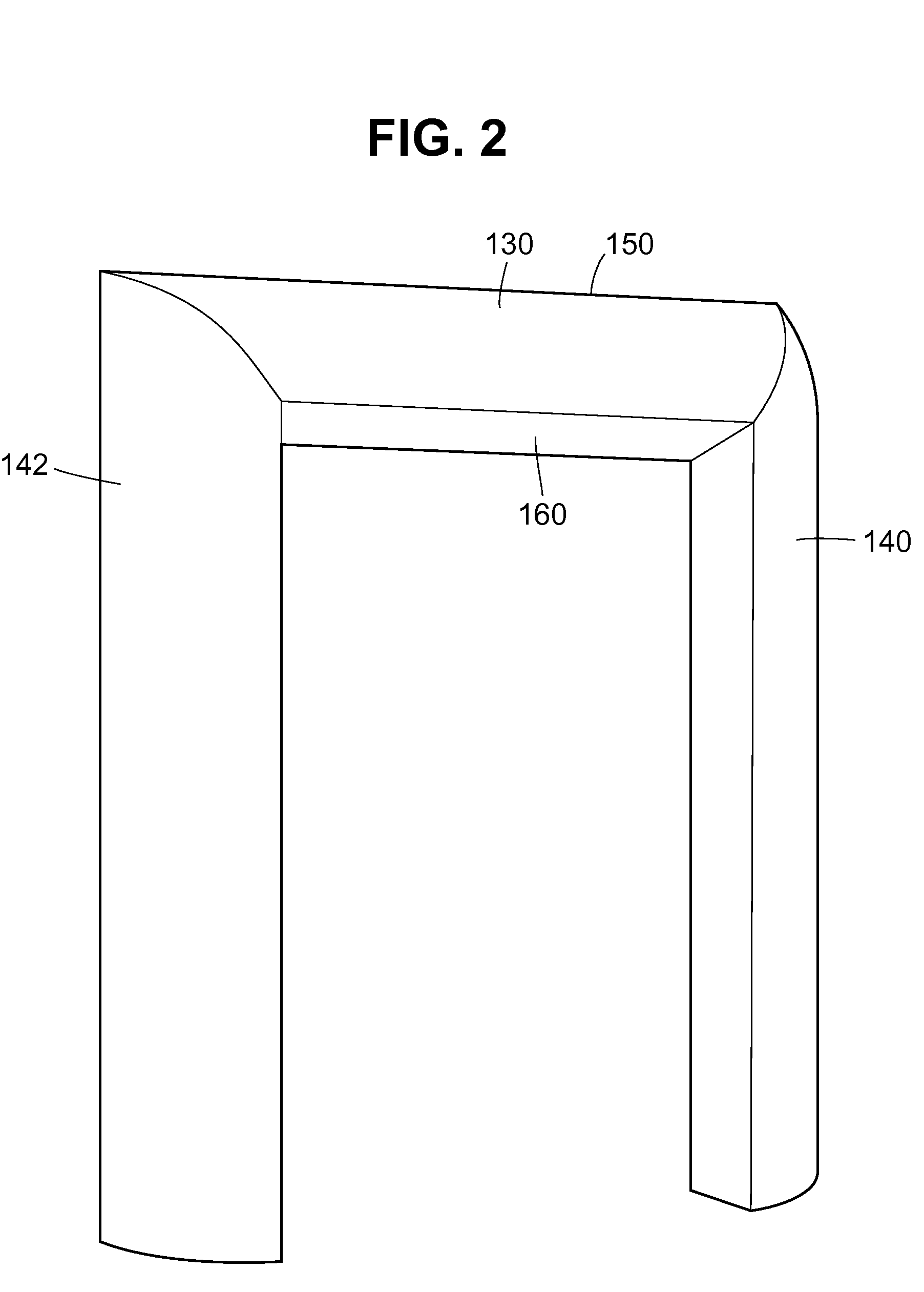
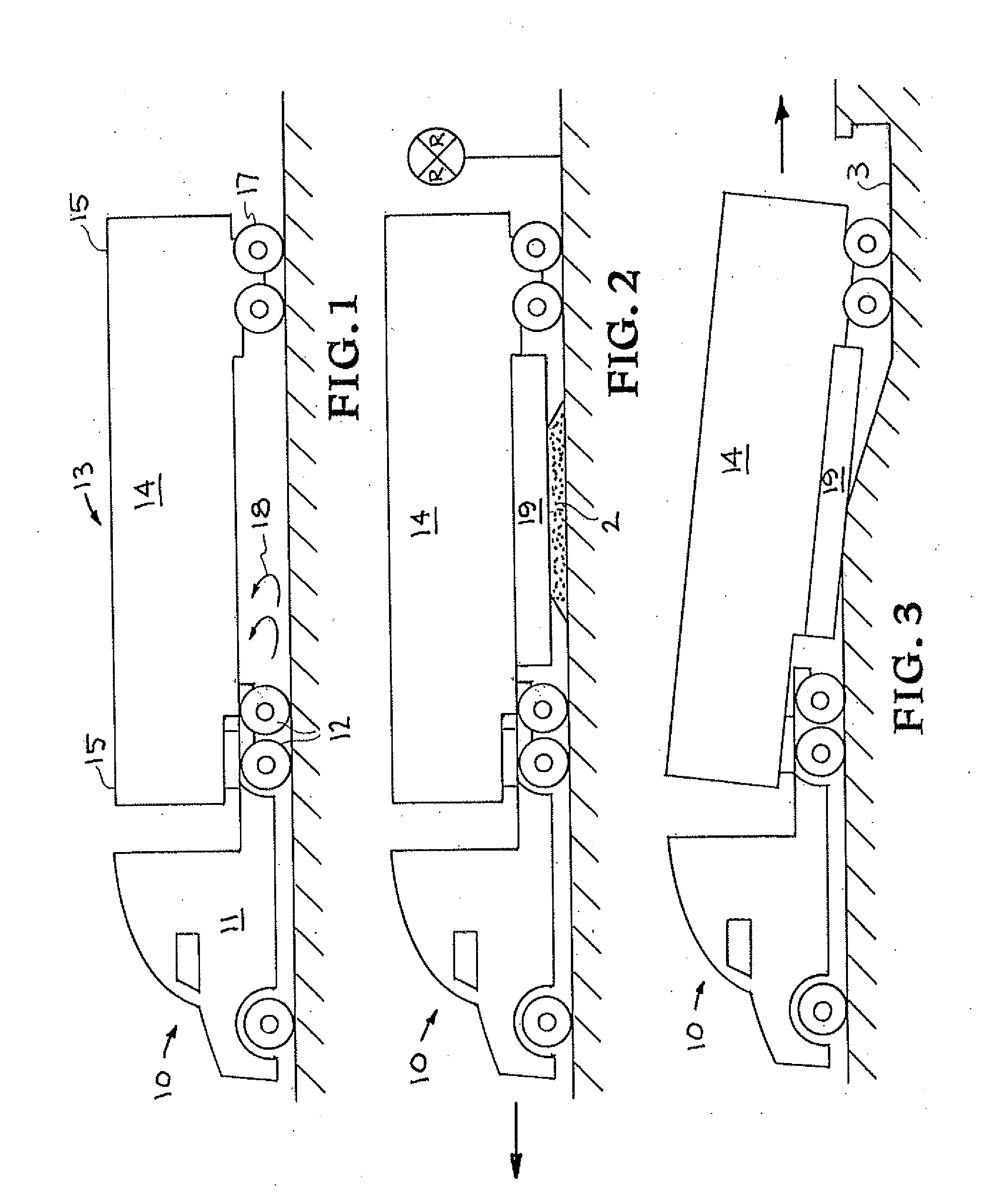
Air drag reducing apparatus
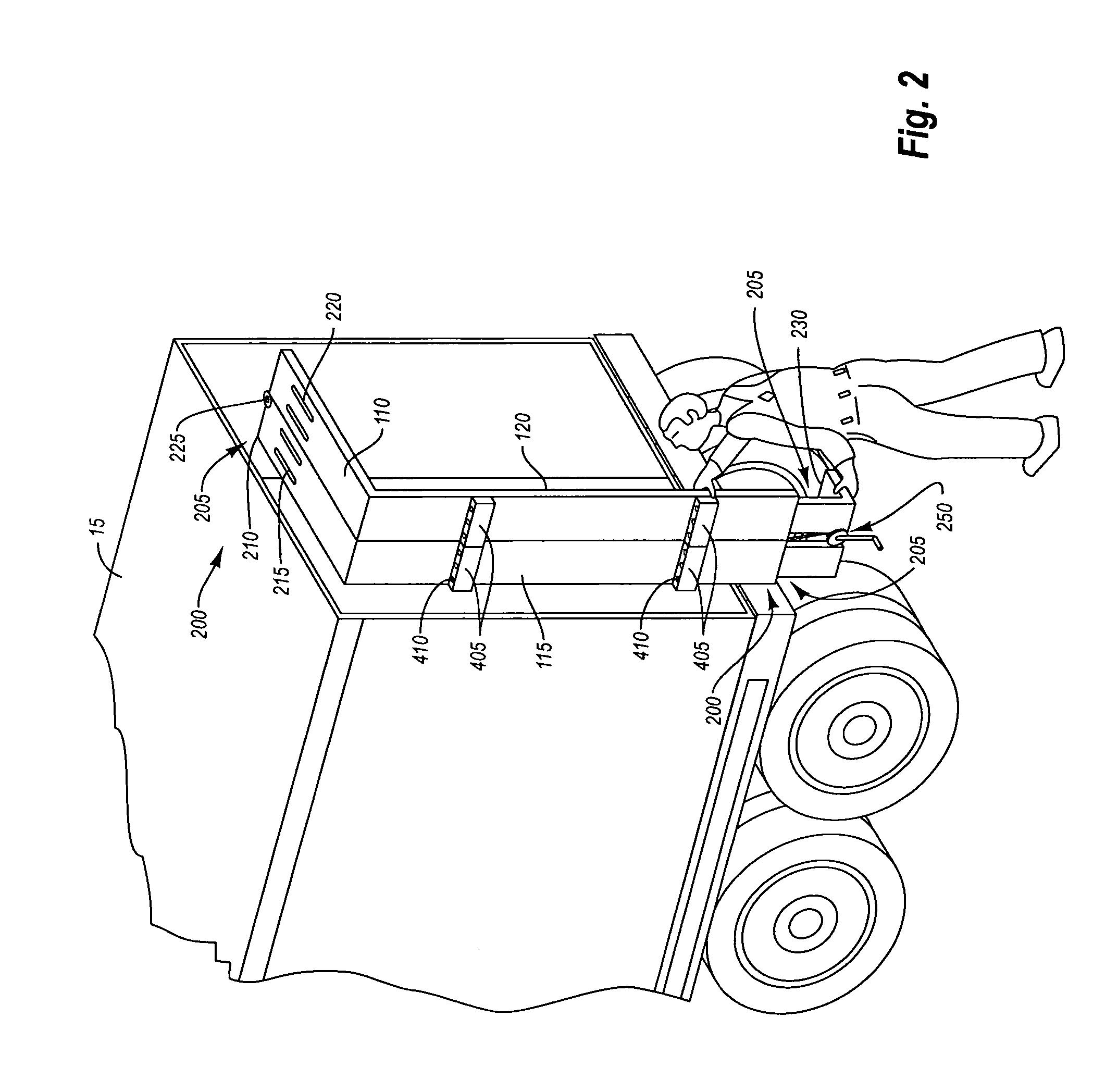
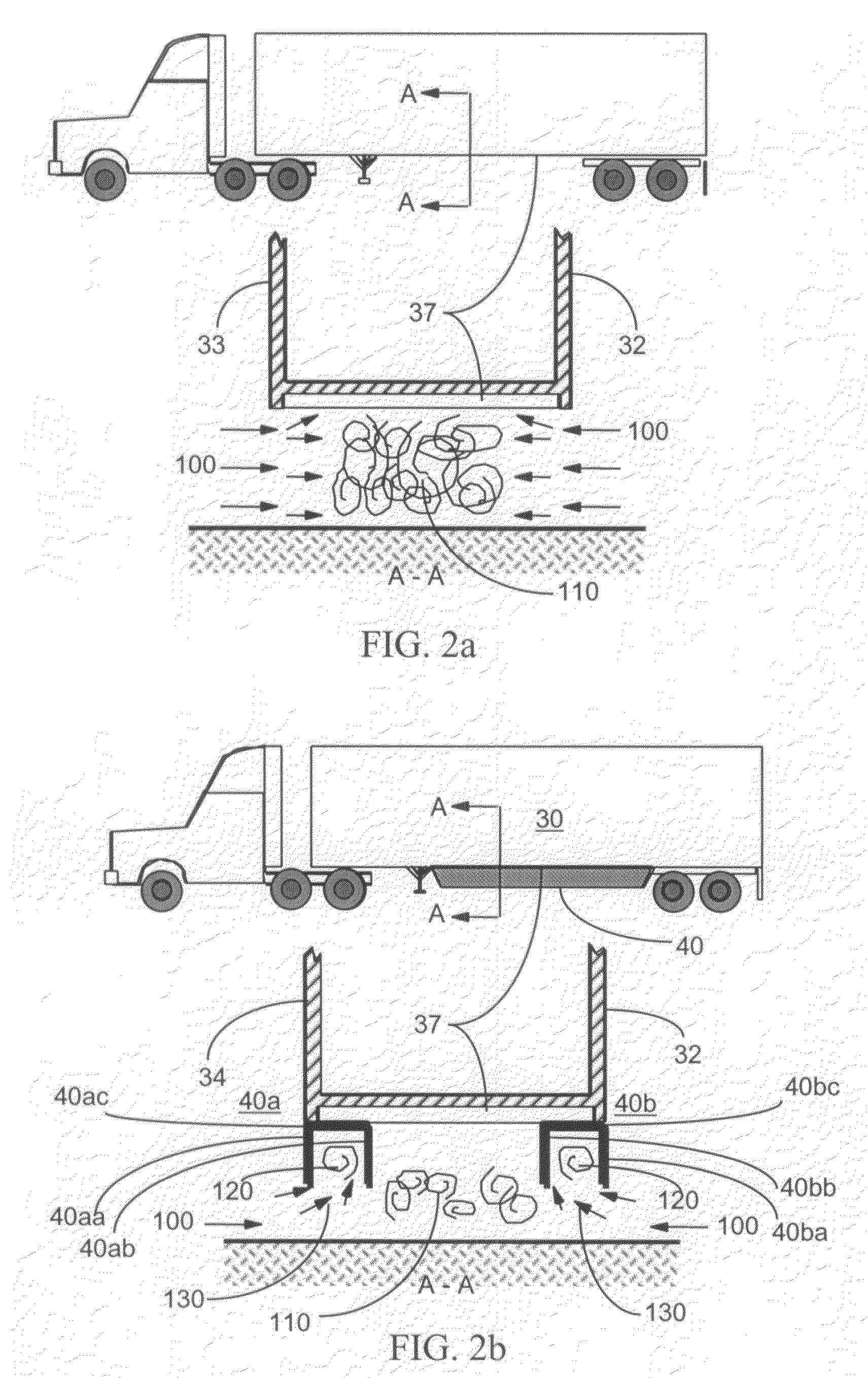
An air drag reducing apparatus for use with a vehicle having a rear end closed by a pair of doors consists of a rectangular shaped panel having a leading edge hingedly connected to the vehicle, the panel extending at about 15 degrees relative to the rearward projection of a side of the vehicle. An element positions the panel in a drag reducing position; this element is such that it allows the panel to be moved between the door and the side of the vehicle as the door is opened and moved to a position adjacent the side of the vehicle. As the door is moved back from the opened position to a closed position, the element causes the panel to return to its drag reducing position. The rear of a vehicle may include two side panels with or without two top panels.
Owner:TRANSTEX LLC
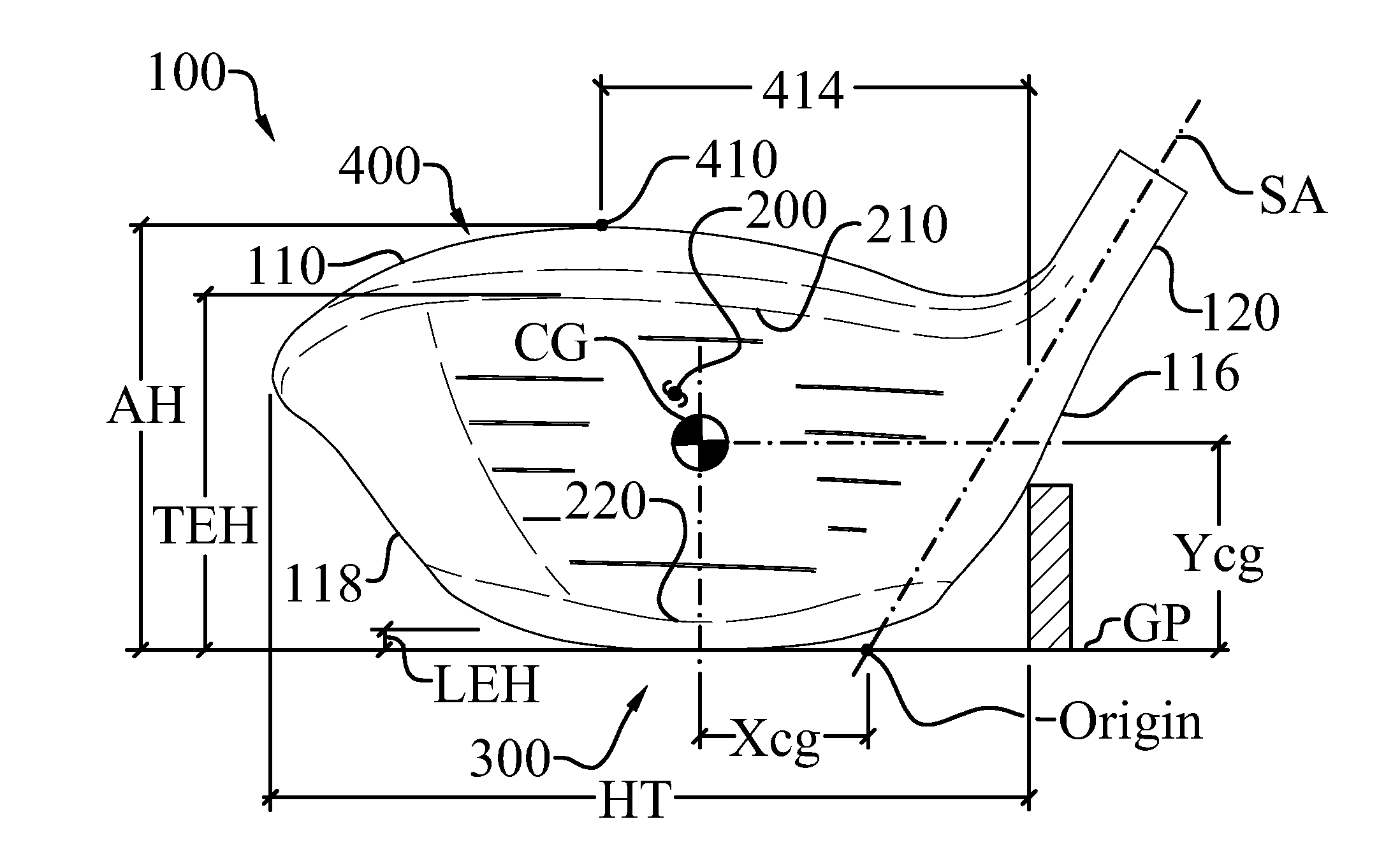
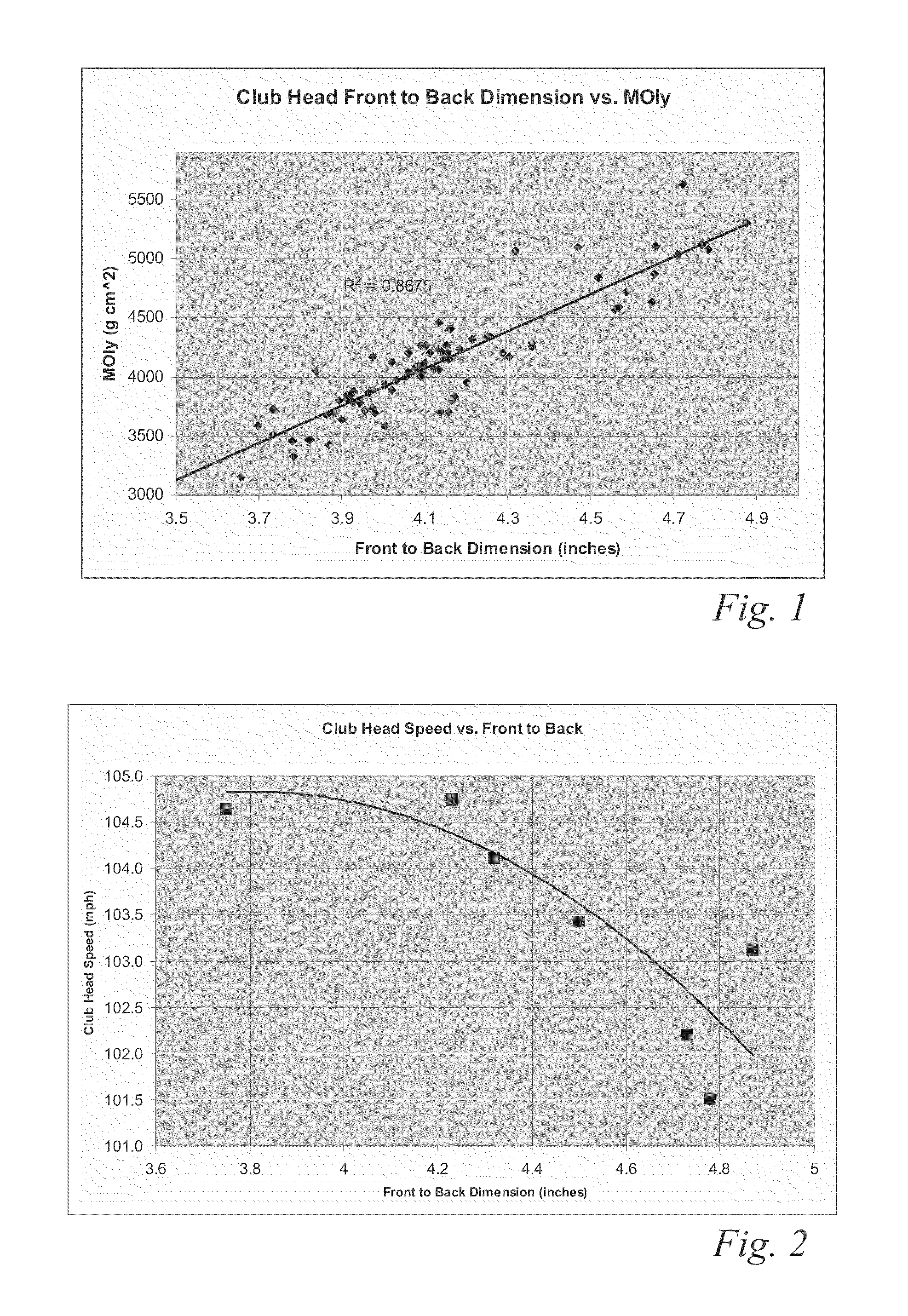
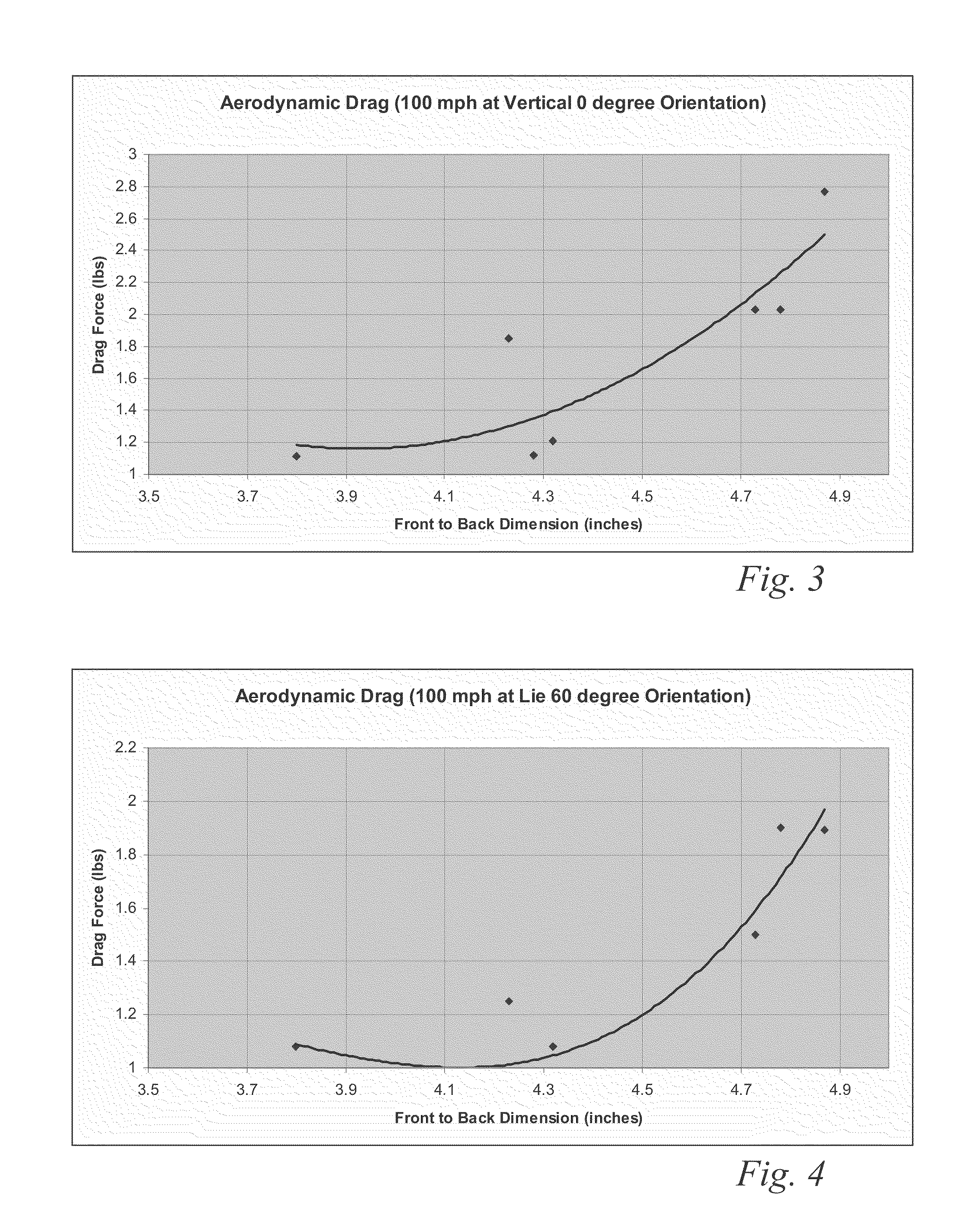
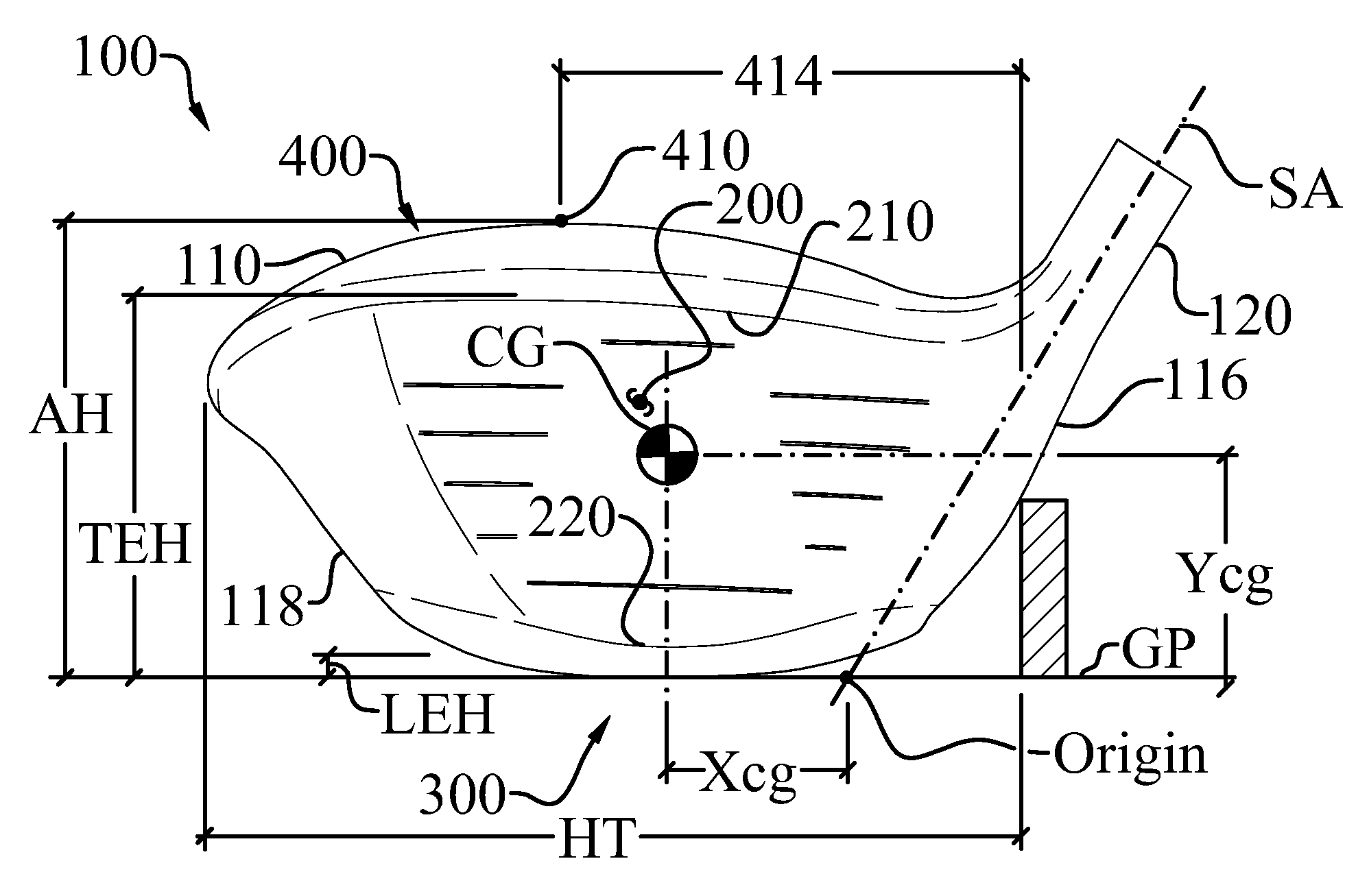
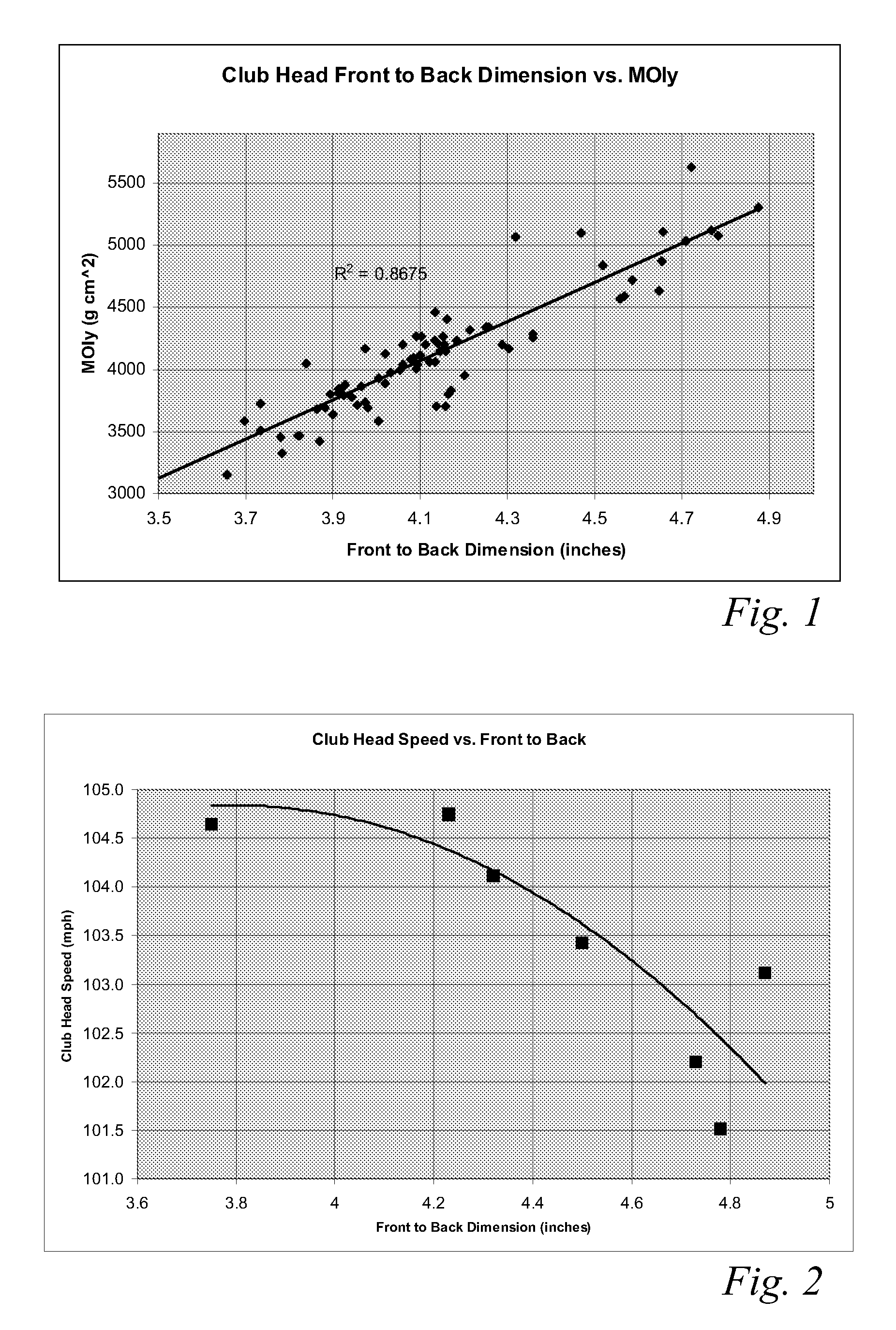
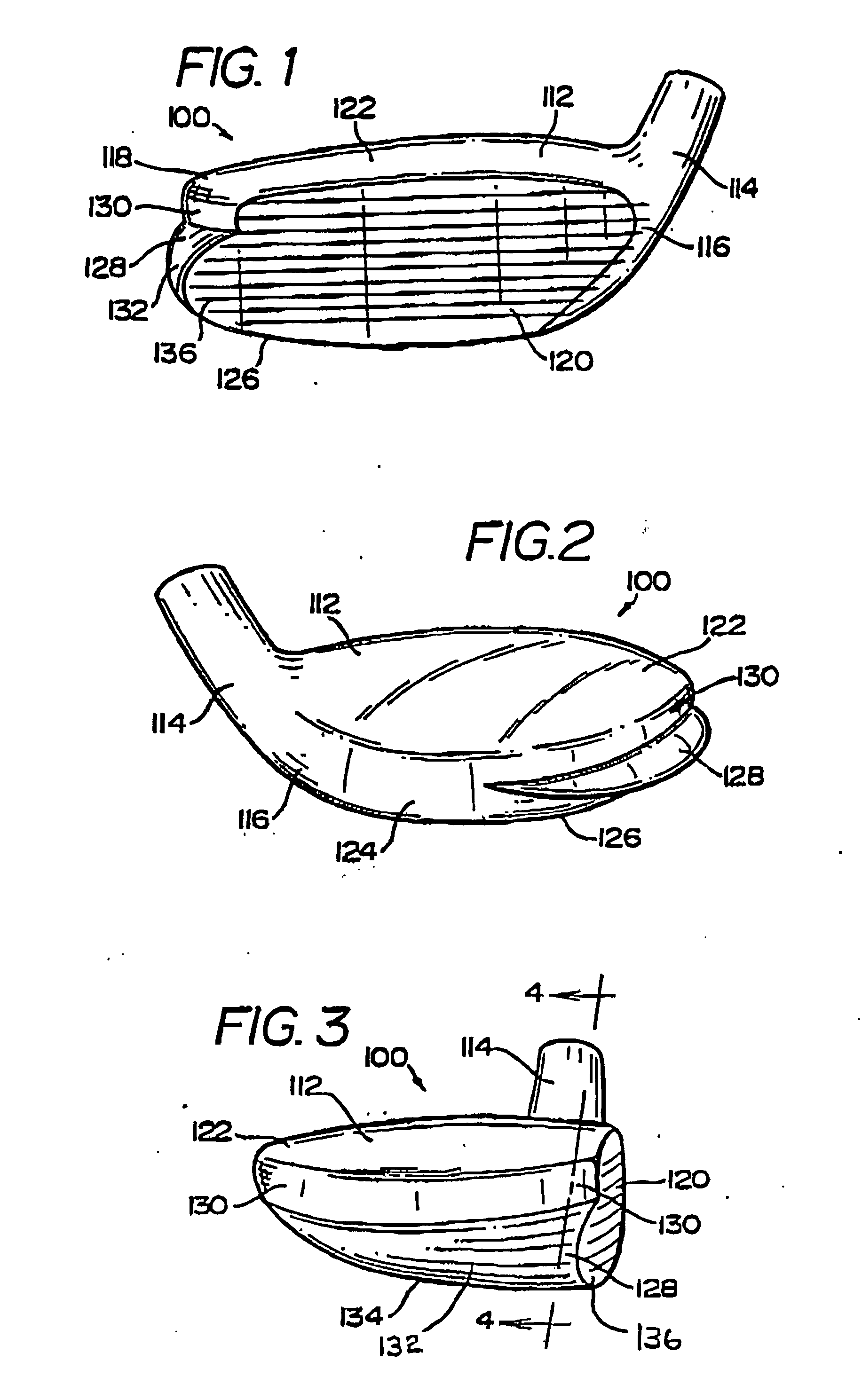
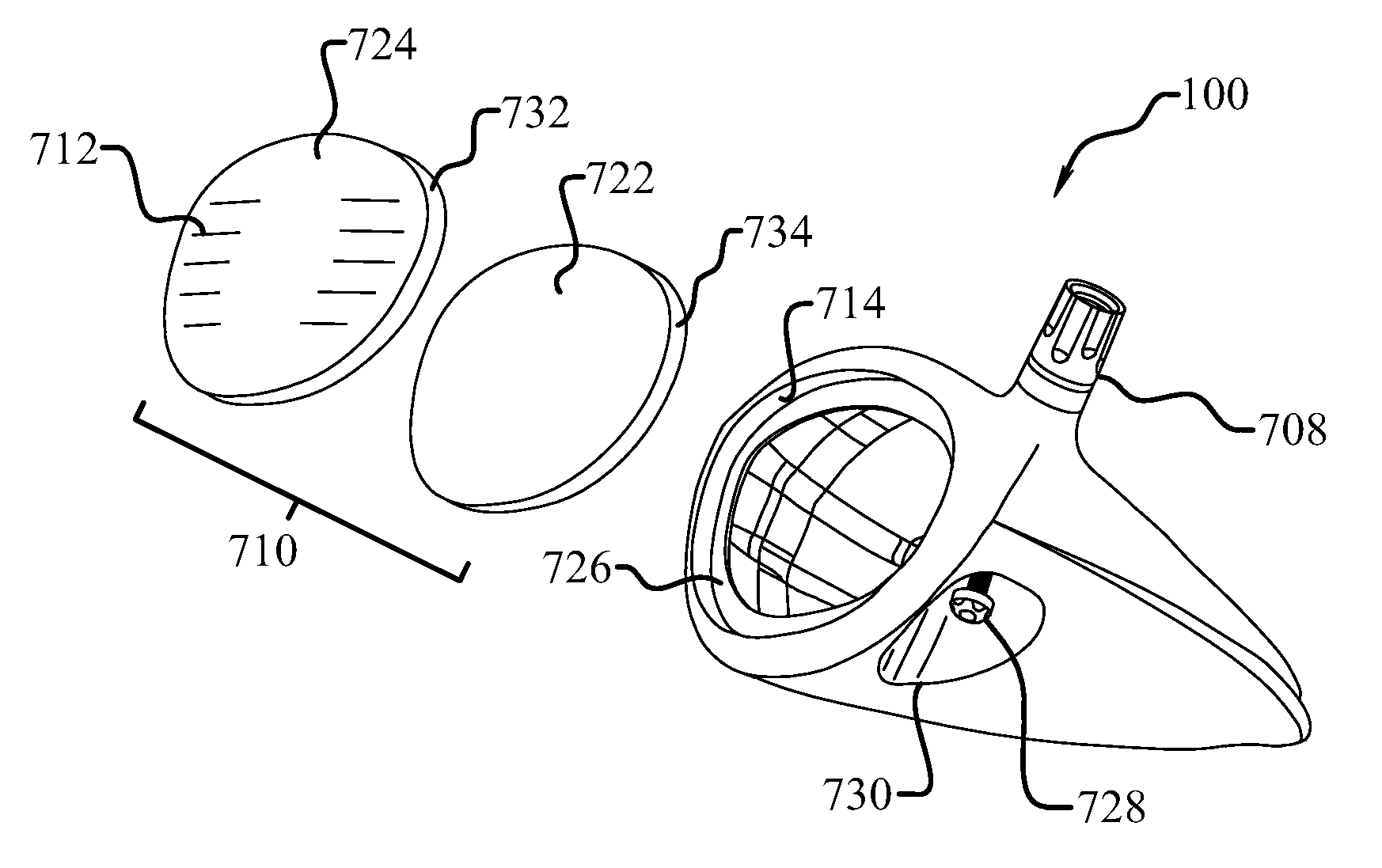
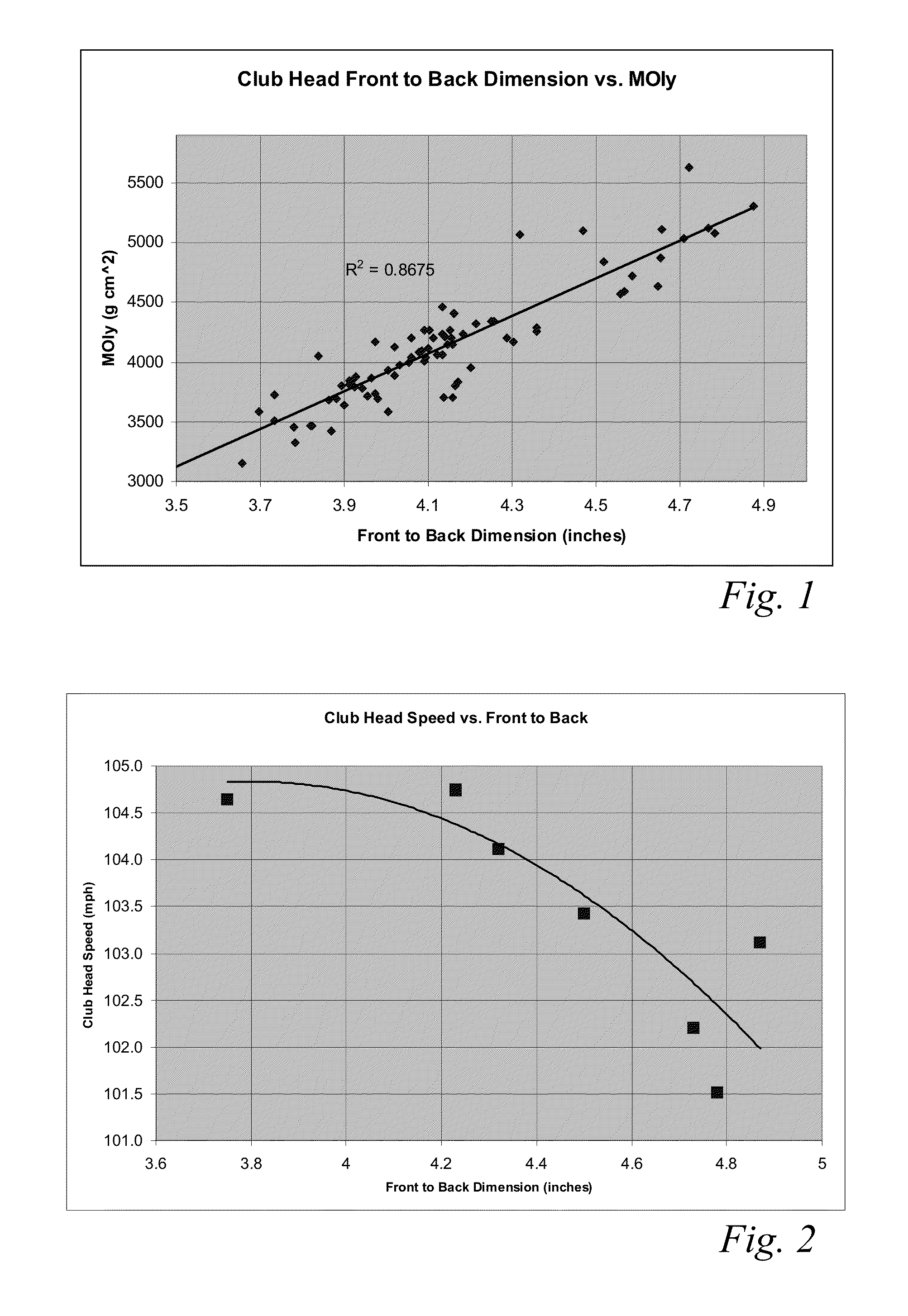
High volume aerodynamic golf club head
ActiveUS8083609B2Improve aerodynamic performanceIncrease volumeGolf clubsRacket sportsAerodynamic dragGround plane
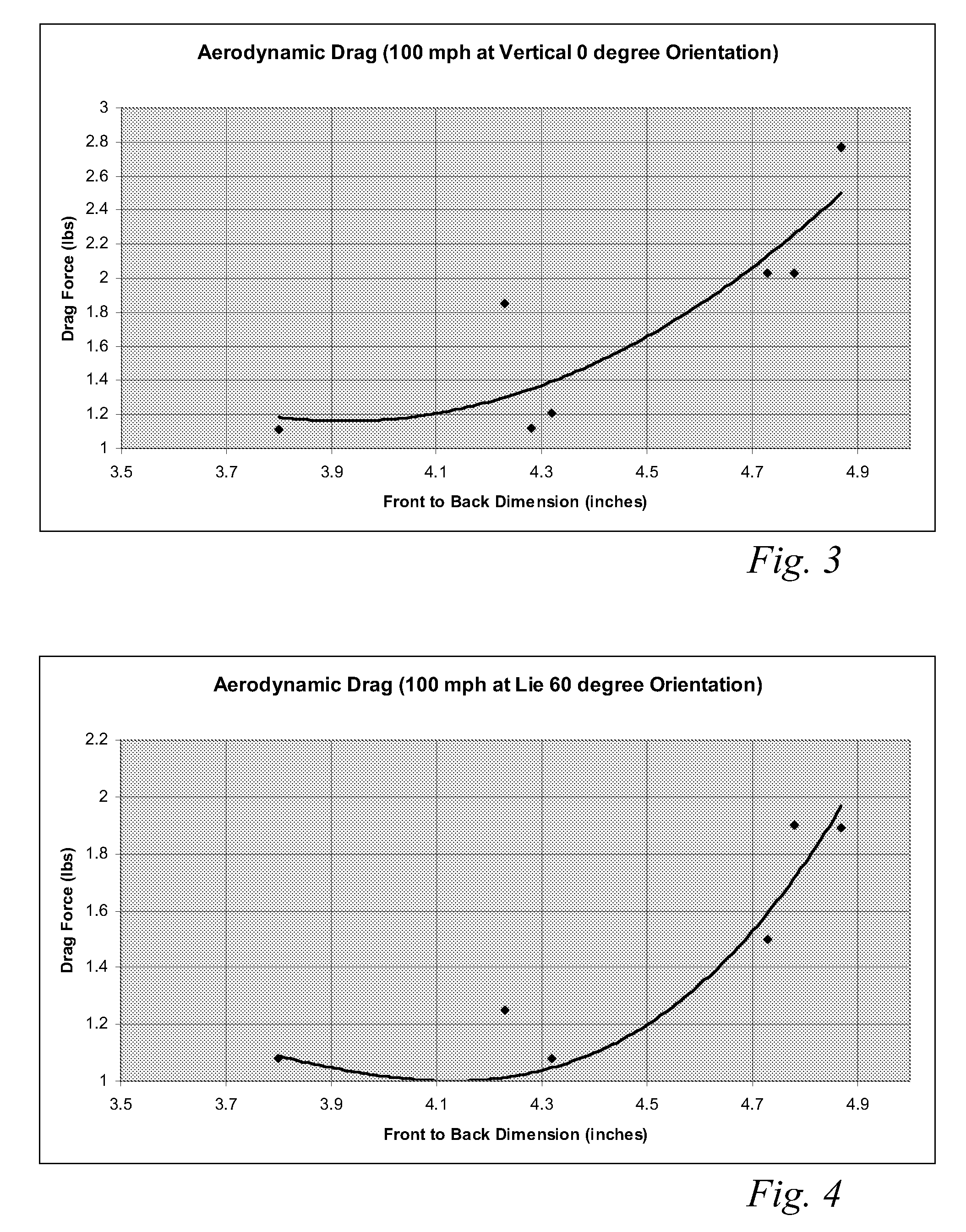
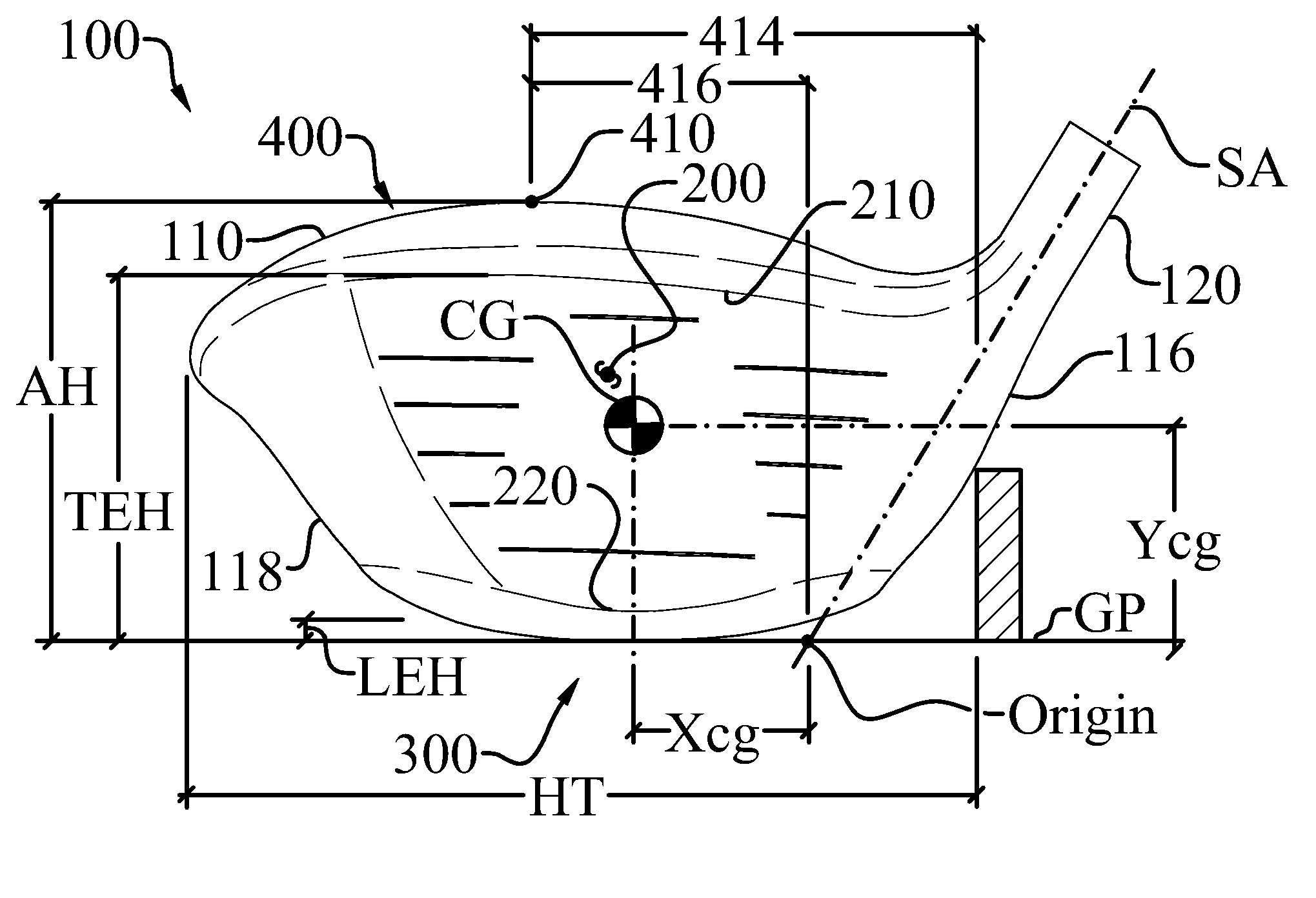
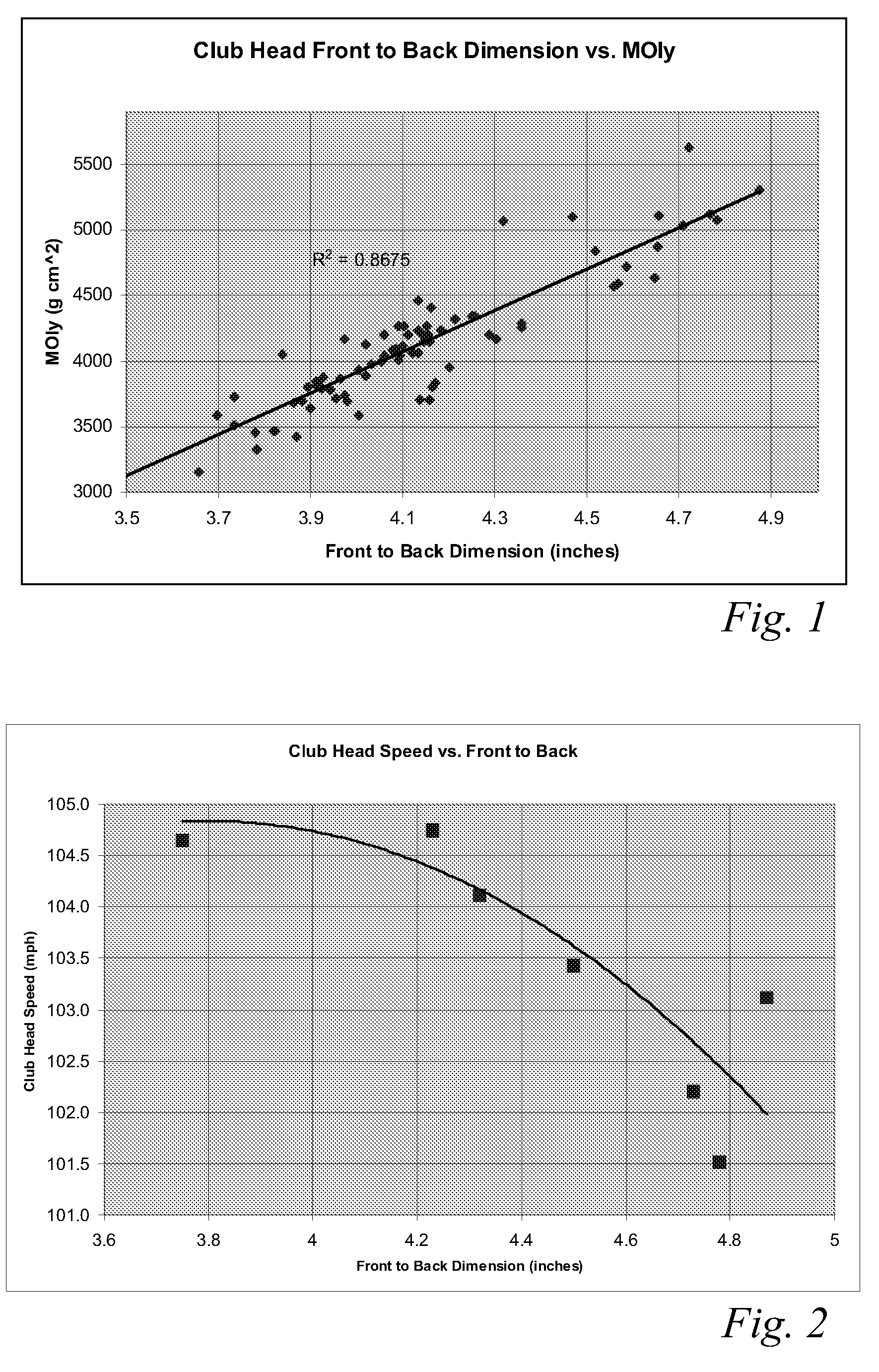
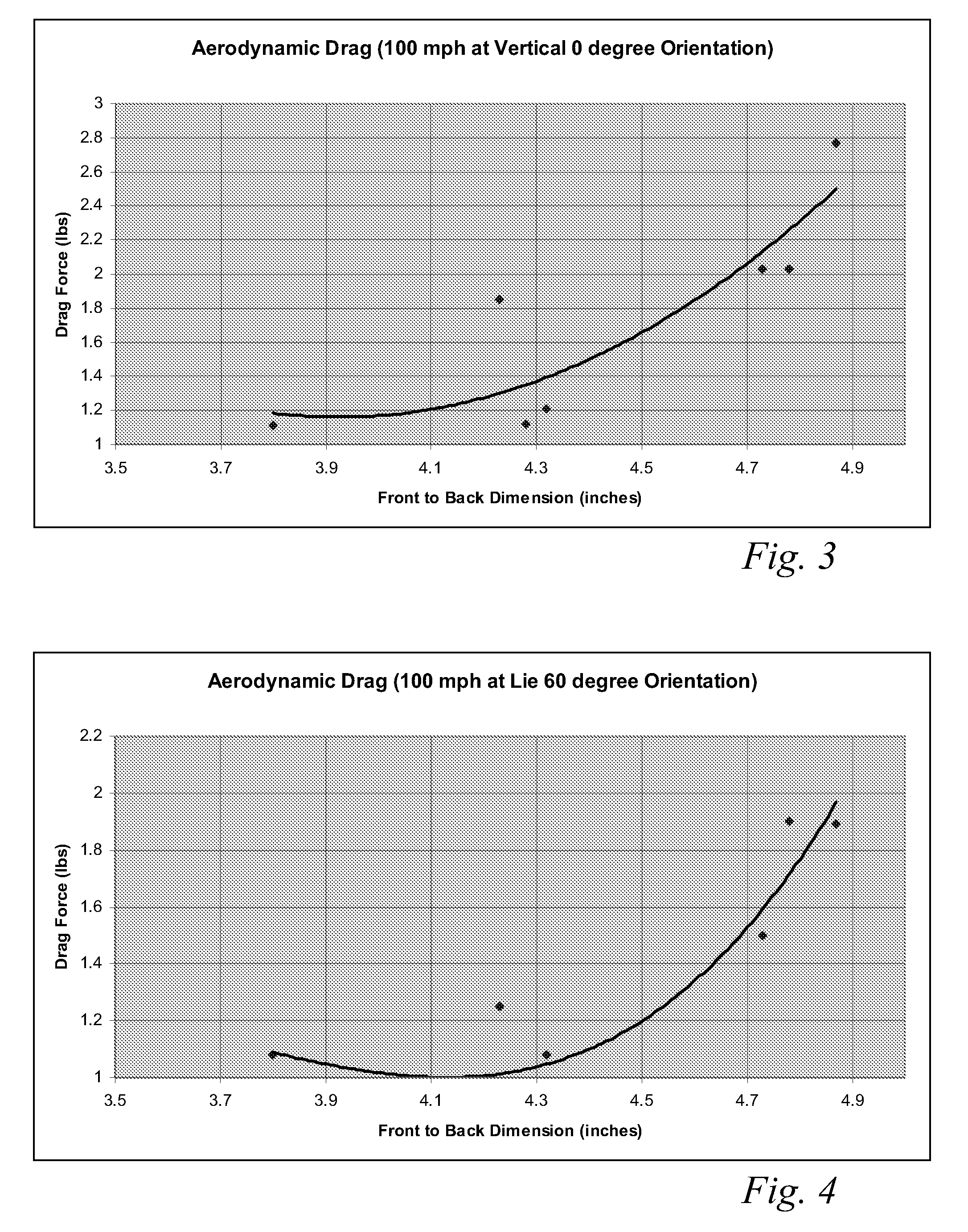
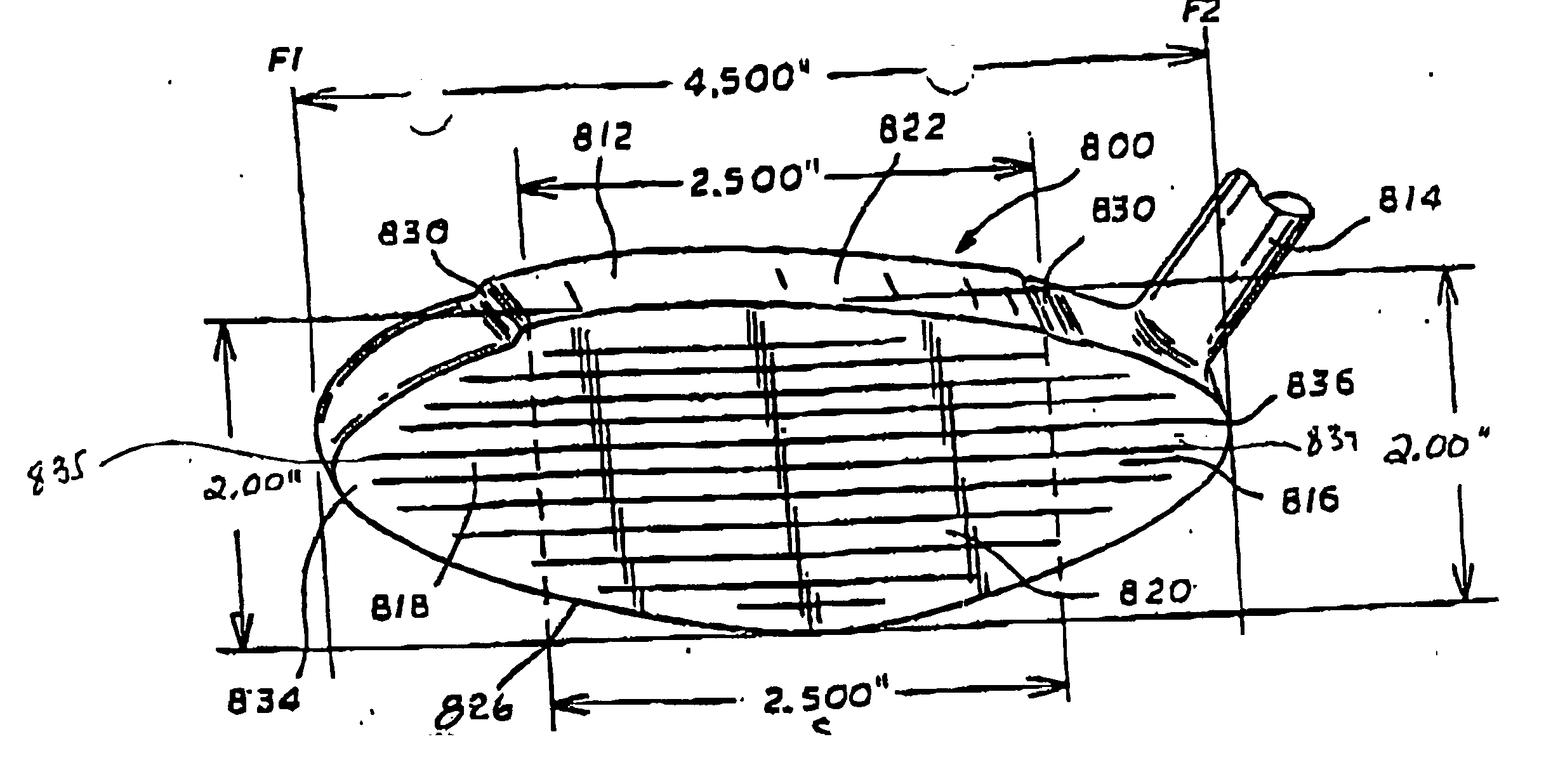
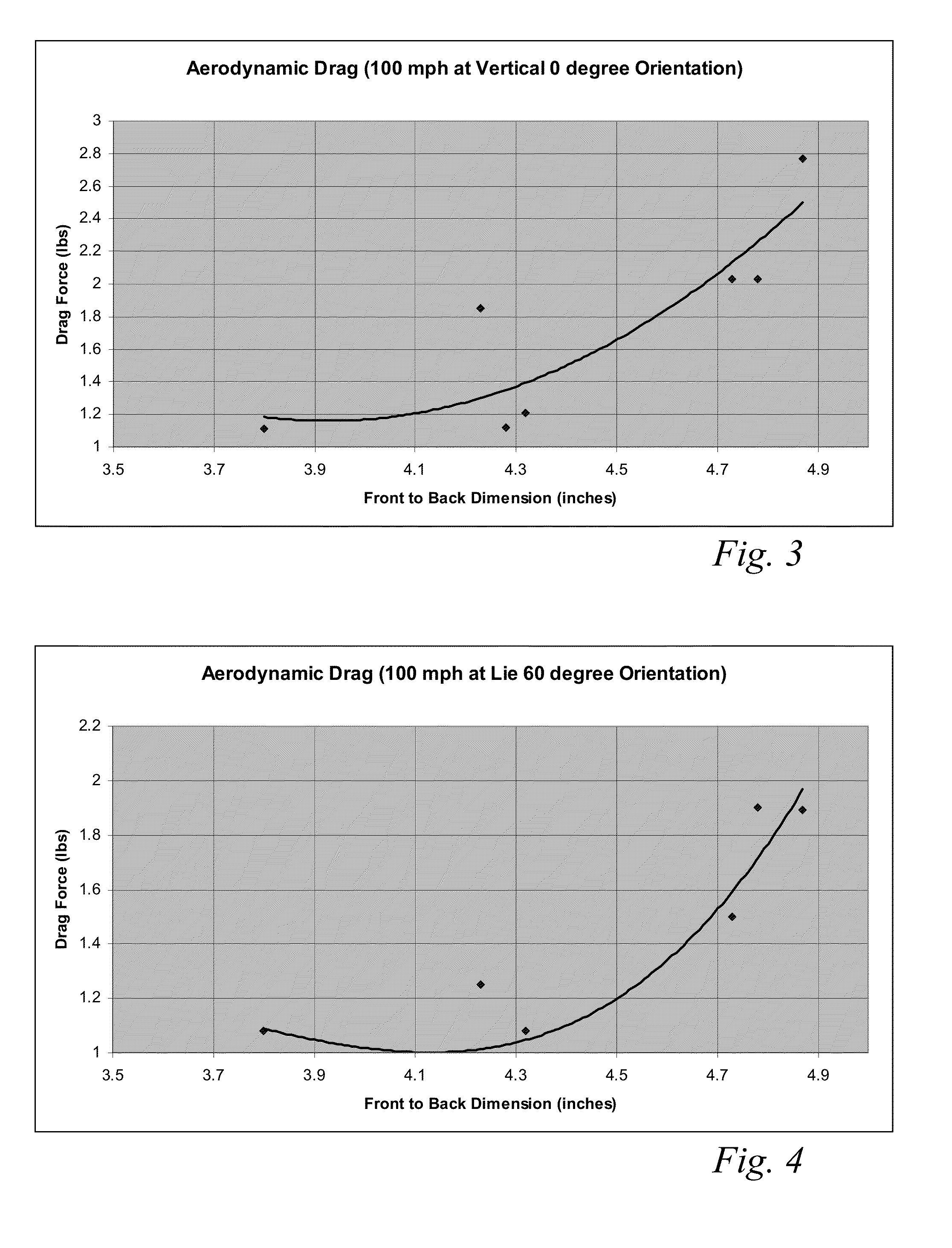
A high volume aerodynamic golf club head with a club head volume of at least 400 cc and a front-to-back dimension of at least 4.4 inches producing a face-on normalized aerodynamic drag force of less than 1.5 lbf when exposed to a 100 mph wind parallel to the ground plane and oriented at the front of the club head. The club head has a crown section having a crown apex located an apex height above a ground plane, wherein a portion of the crown section between the crown apex and the face has an apex-to-front radius of curvature that is less than 3 inches. An apex ratio of the apex height to a maximum face top edge height is at least 1.13. The apex height and location of the crown apex obtain desirable airflow reattachment close to the face and improve airflow attachment to the crown section.
Owner:TAYLOR MADE GOLF
Golf club head having trip step feature
InactiveUS20100016095A1Reduced aerodynamic drag forceLess aerodynamic dragGolf clubsRacket sportsHybrid typeAerodynamic drag
An aerodynamic golf club head incorporating a trip step feature located on the crown section. The benefits associated with the reduction in aerodynamic drag force associated with the trip step may be applied to drivers, fairway woods, and hybrid type golf club heads. The trip step is located between a crown apex and the back of the club head and may be continuous or discontinuous. The trip step enables a significant reduction in the aerodynamic drag force exerted on the golf club head by forcing the air passing over the club head from laminar flow to turbulent flow just before the natural separation point of the airstream from the crown. This selectively engineered transition from laminar to turbulent flow over the crown section slightly increases the skin friction but results in less aerodynamic drag than if the air were to detach from the crown section at the natural separation point.
Owner:TAYLOR MADE GOLF
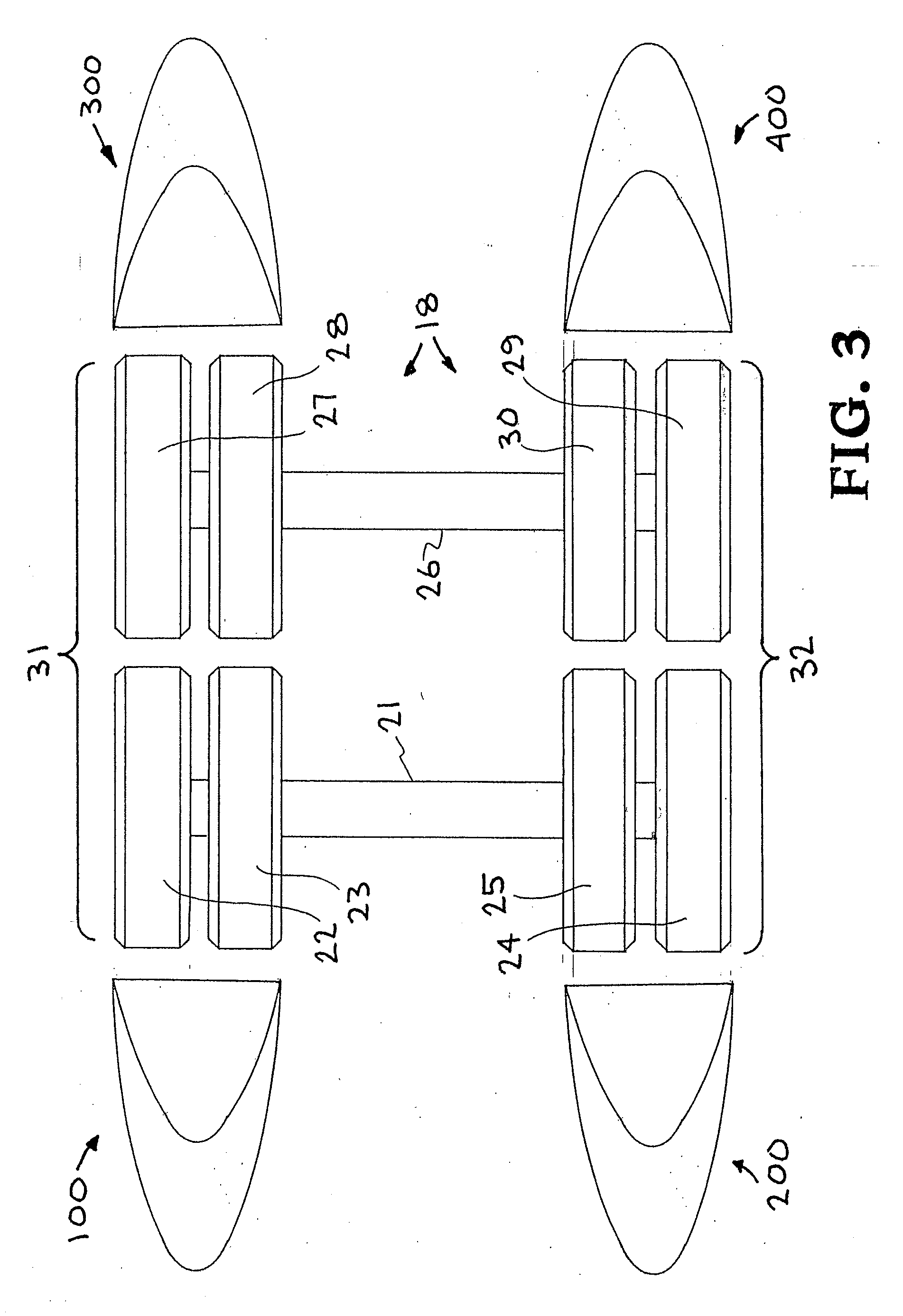
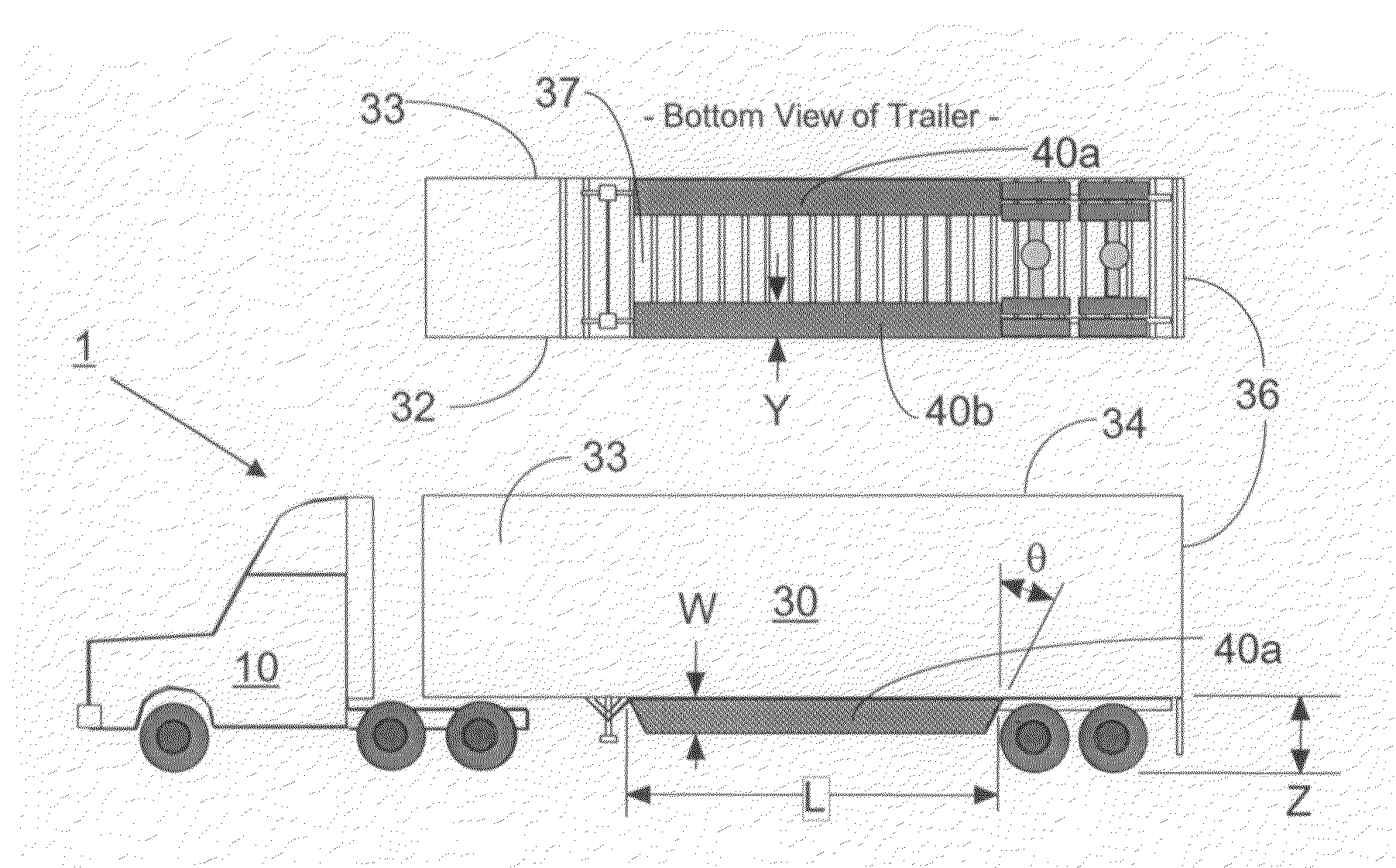
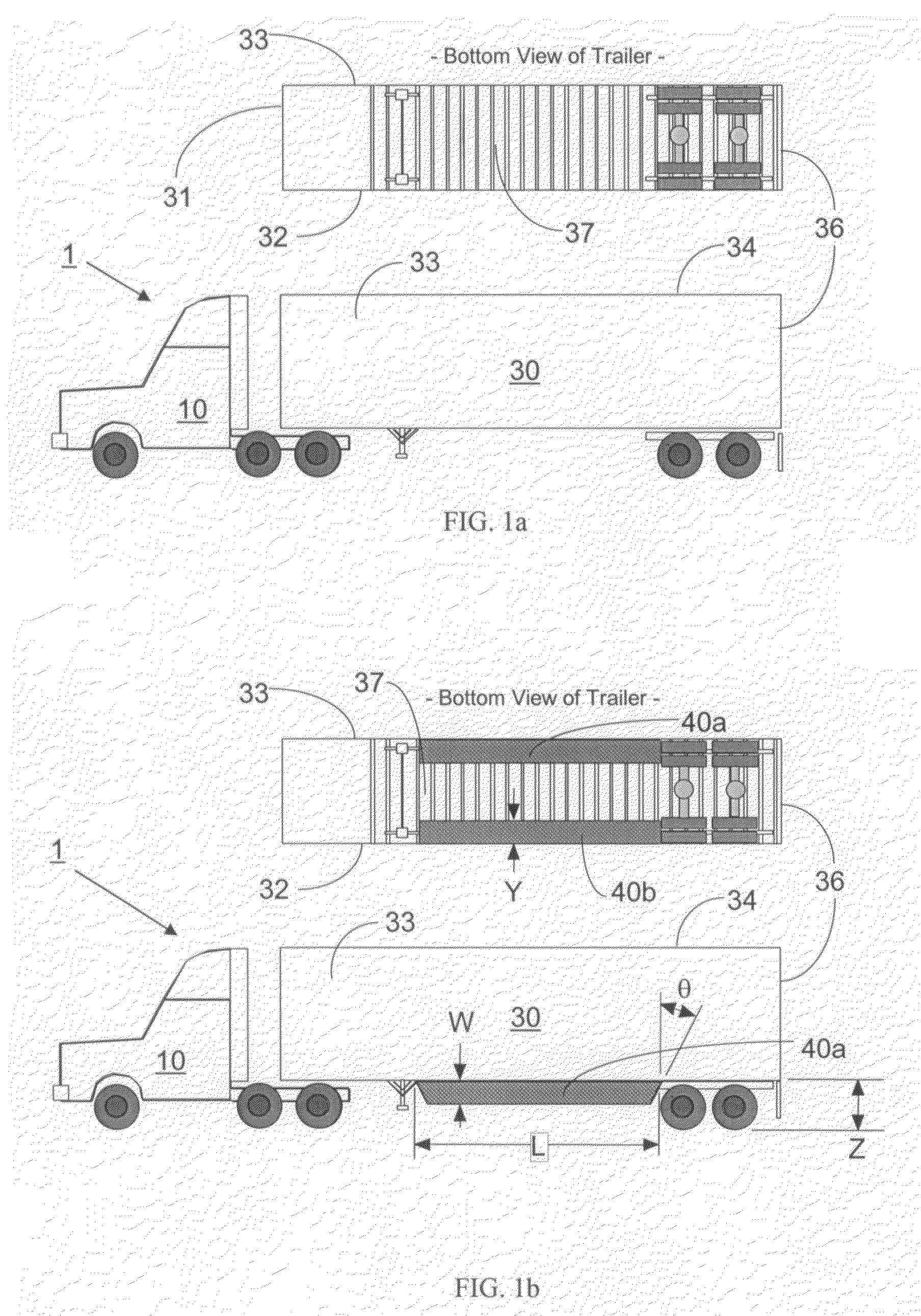
Trailer skirt panel
ActiveUS7578541B2Reducing aerodynamic drag on road vehiclesIncrease air flowVehicle seatsWindowsAerodynamic dragEngineering
A skirt panel is provided herein for interconnection to another abutted similar skirt panel for attachment beneath a lower, outer longitudinally-extending edge of a trailer including a rear wheel assembly of a tractor-trailer rig, thereby to provide a continuous fairing extending downwardly from the trailer. The skirt panel includes a monolithic, generally-rectangular composite reinforced thermoplastic structure, having vertical lateral side edges configured and arranged for connection to associated vertical lateral side edges of abutting similar skirt panels. This provides a longitudinally-extending fairing for extending contiguously on each side of the trailer, a front face of the thermoplastic structure being provided with a plurality of longitudinally-extending, vertically-spaced-apart arcuate protrusions. The outer face of the thermoplastic panel preferably also is provided with dimples. The reinforcing comprising a panel secured to an inner face of the skirt panel and is provided with laterally-extending means whereby abutting skirt panels are secured to one another; whereby, when said fairing is secured to a lower portion of said trailer, the fairing extends downwardly from the trailer to from 60% to 80% of the distance to the road, so that a portion of any impinging air is directed laterally around the wheels of the rear wheel bogeys to reduce the aerodynamic drag of the trailer and of the wheel assembly.
Owner:ZF COMPOSITES NORTH AMERICA LTD
High volume aerodynamic golf club head having a post apex attachment promoting region
ActiveUS8088021B2Improve aerodynamic performanceIncrease valueGolf clubsRacket sportsAerodynamic dragGround plane
A high volume aerodynamic golf club head having a post apex attachment promoting region with a club head volume of at least 400 cc and a front-to-back dimension of at least 4.4 inches producing a face-on normalized aerodynamic drag force of less than 1.5 lbf when exposed to a 100 mph wind parallel to the ground plane and oriented at the front of the club head. The post apex attachment promoting region is on the surface of the crown section at an elevation above a maximum face height and begins at the crown apex and extends toward the back of the club head. The post apex attachment promoting region is a relatively flat portion of the crown section that is behind the crown apex, yet above the maximum top edge plane, and aides in keeping airflow attached to the club head once it flows past the crown apex.
Owner:TAYLOR MADE GOLF
Aerodynamic drag reduction apparatus for wheeled vehicles in ground effect
InactiveUS6974178B2Reducing the aerodynamic drag of a wheeled vehicleReduce pressureVehicle seatsWindowsAerodynamic dragEngineering
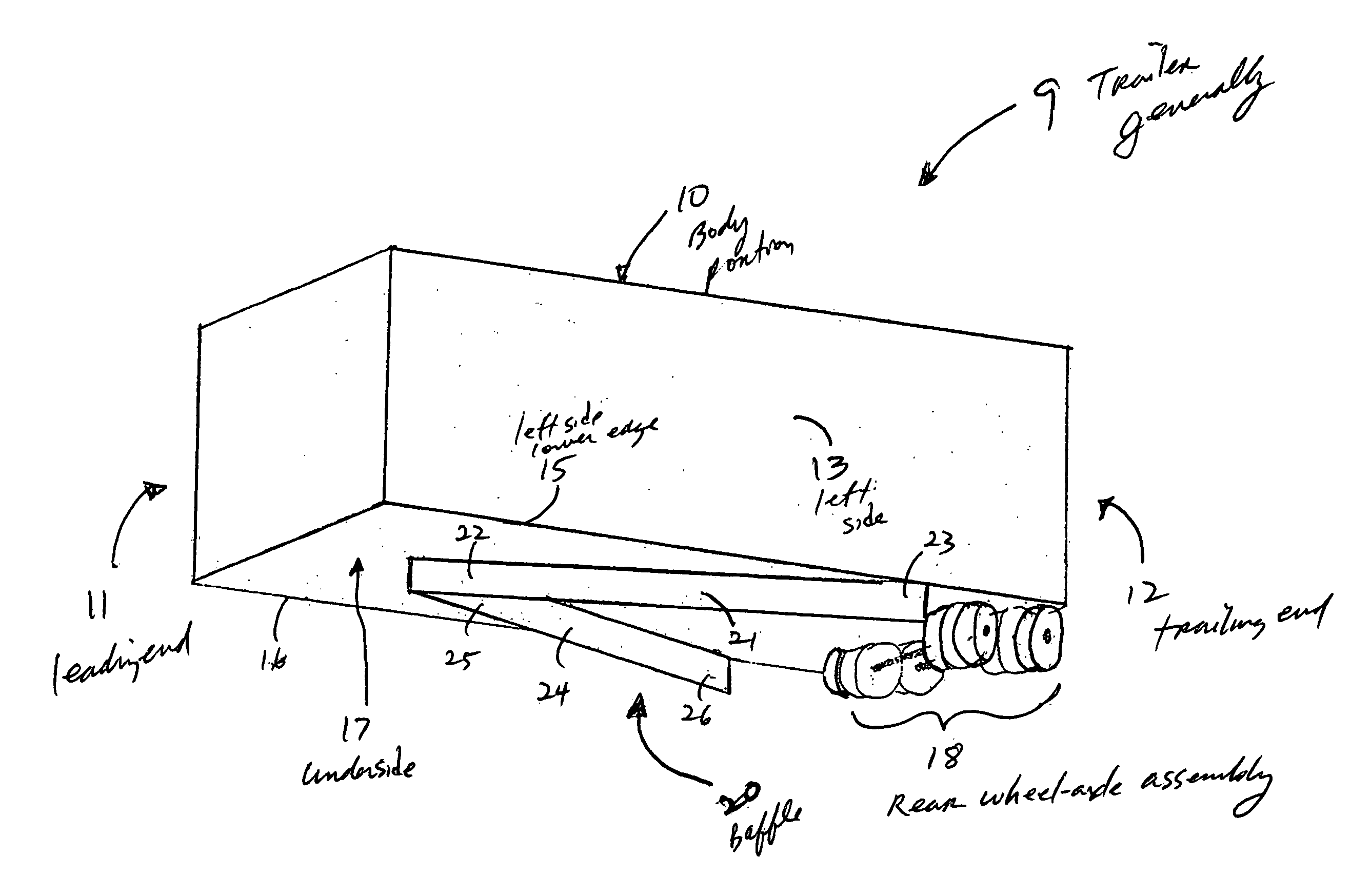
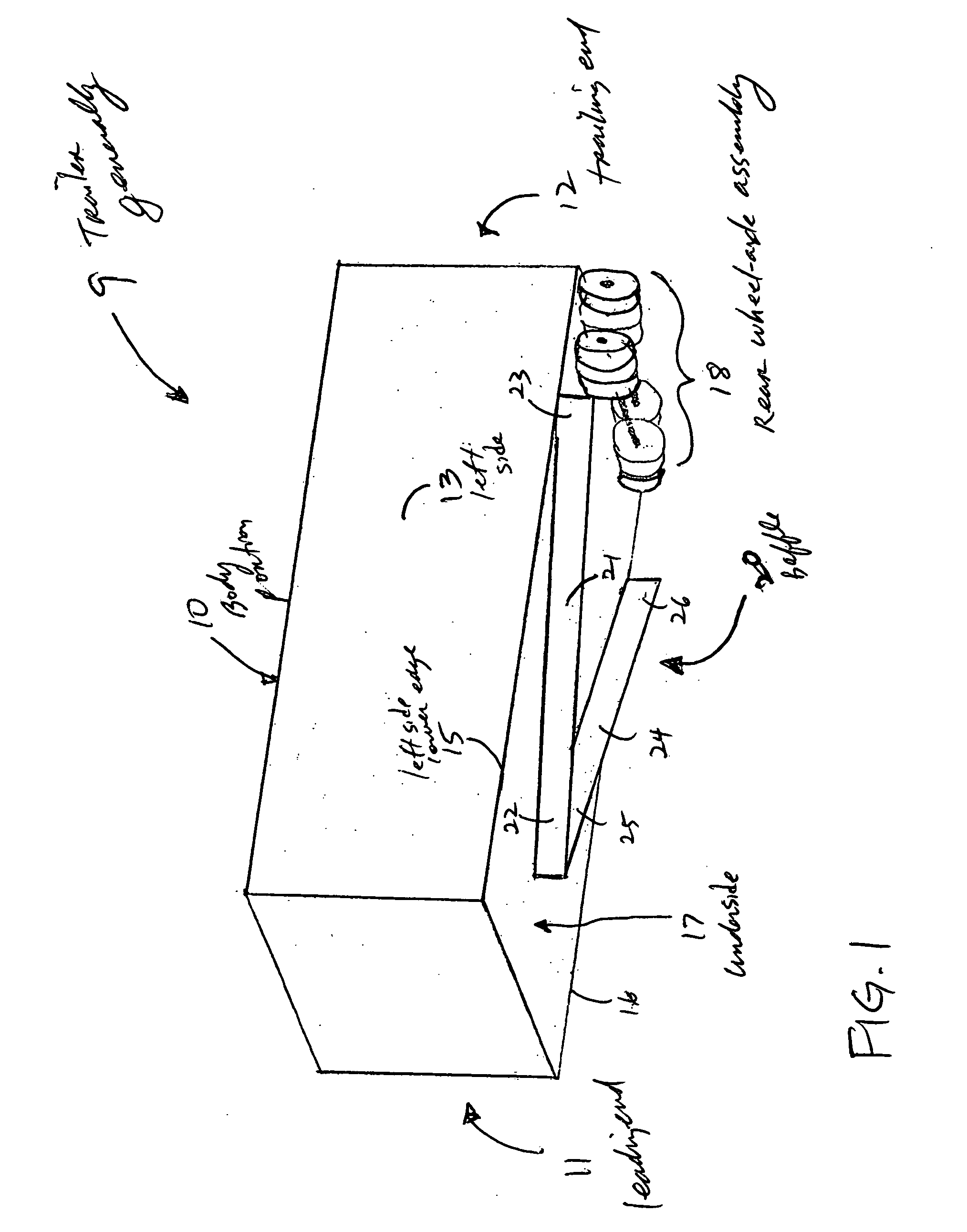
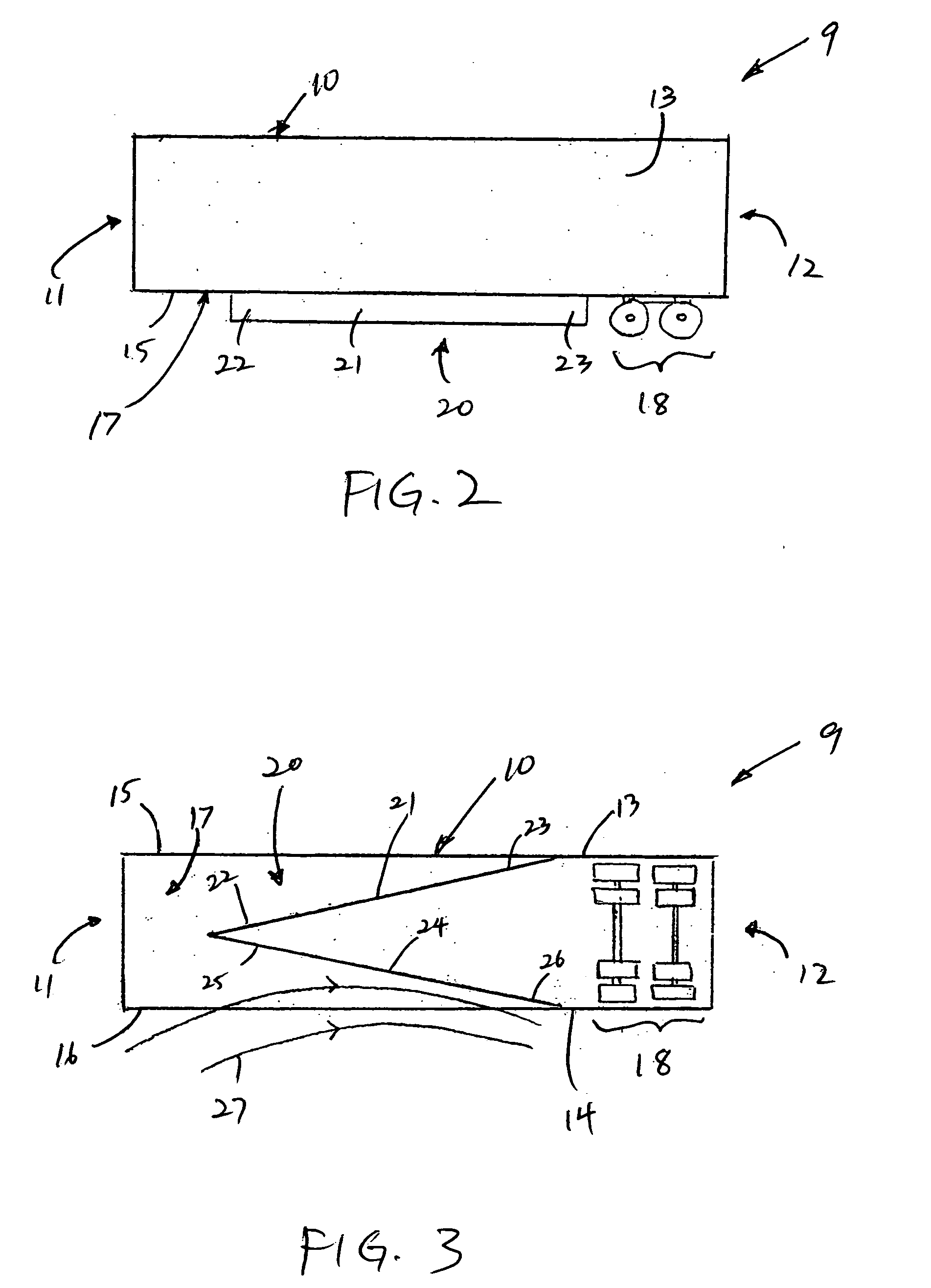
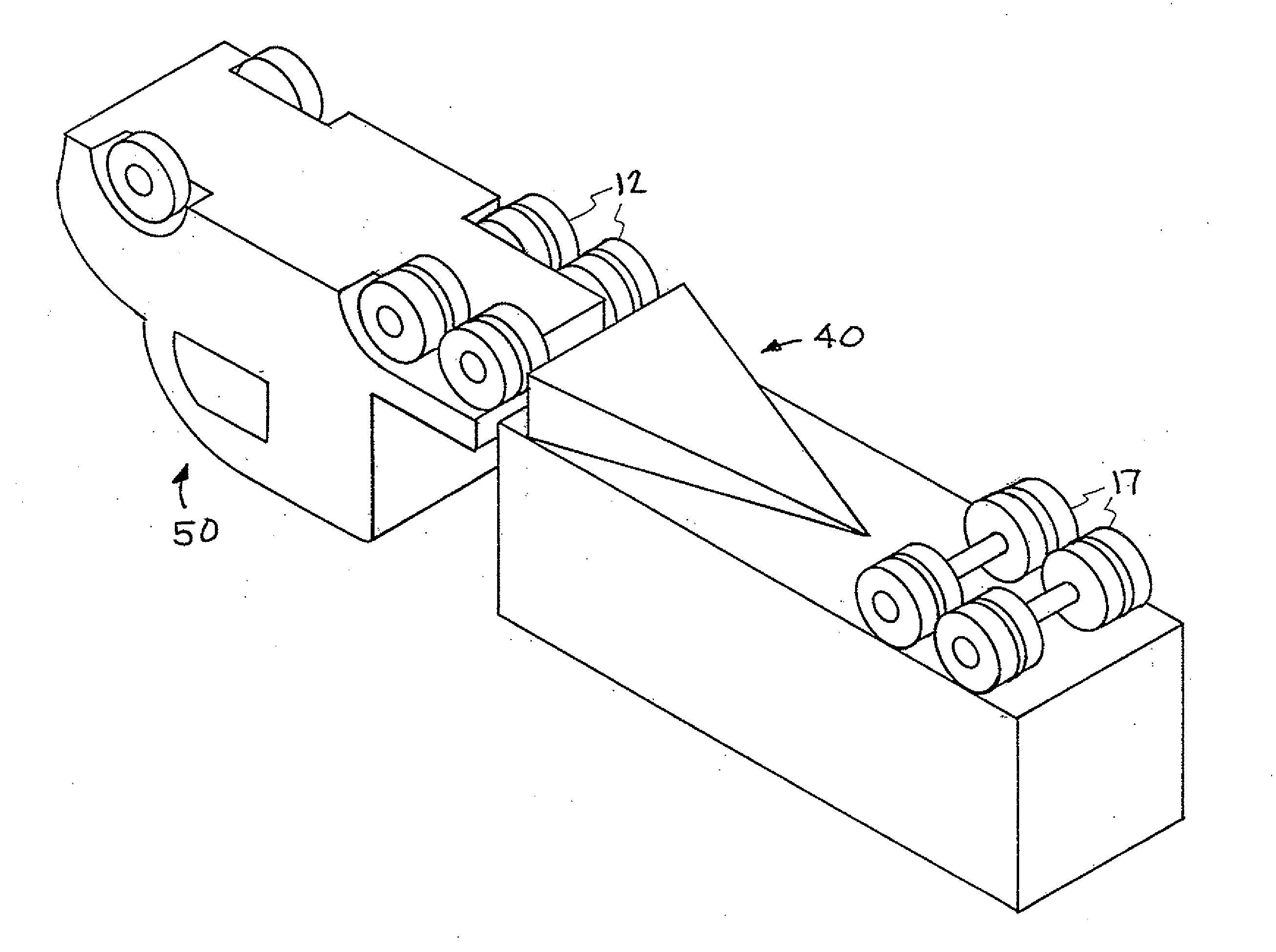
An apparatus for reducing the aerodynamic drag of a wheeled vehicle in a flowstream, the vehicle having a vehicle body and a wheel assembly supporting the vehicle body. The apparatus includes a baffle assembly adapted to be positioned upstream of the wheel assembly for deflecting airflow away from the wheel assembly so as to reduce the incident pressure on the wheel assembly.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
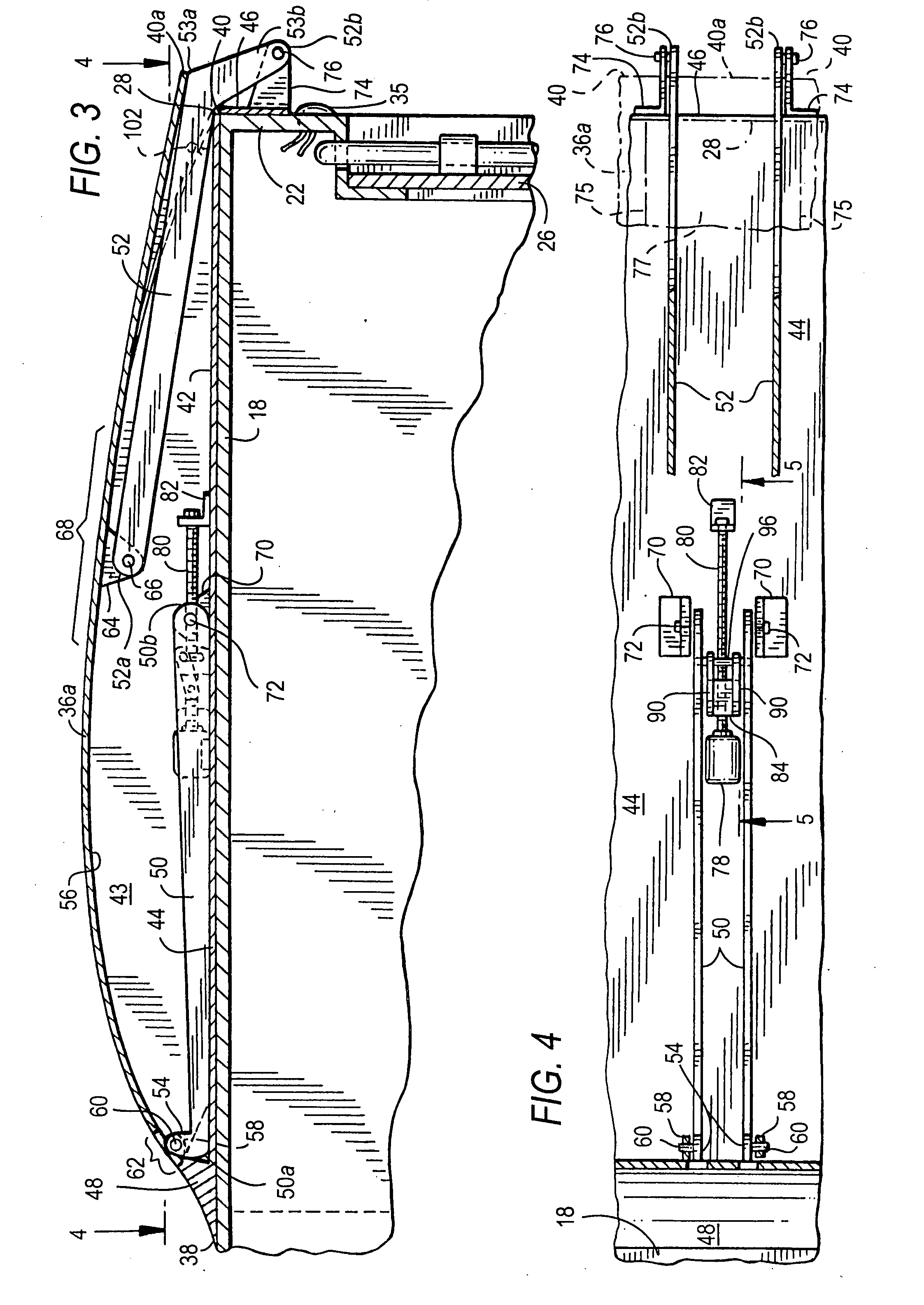
Aerodynamic drag reducing system with retrofittable, selectively removable frame
InactiveUS7207620B2The process is convenient and fastLight weightVehicle seatsWindowsAerodynamic dragTractor trailer
The present invention relates to an aerodynamic drag reducing system for land vehicles, in particular semi-tractor trailers. The drag reducing system includes a selectively removable frame and a drag reduction member. The selectively removable frame can adapt to conform to at least one of the width or height of the land vehicle, and can be secured thereto by a securement assembly. In one embodiment, the drag reducing system can be folded and collapsed for compact storage. The drag reducing system can be easily and quickly secured to the back end of a semi-tractor trailer without tools and without requiring that any permanent modifications be made to the trailer. In one embodiment, drag reducing system includes a hinge joint assembly to facilitate installation, removal, and repositioning of drag reducing system.
Owner:COSGROVE WILLIAM E +1
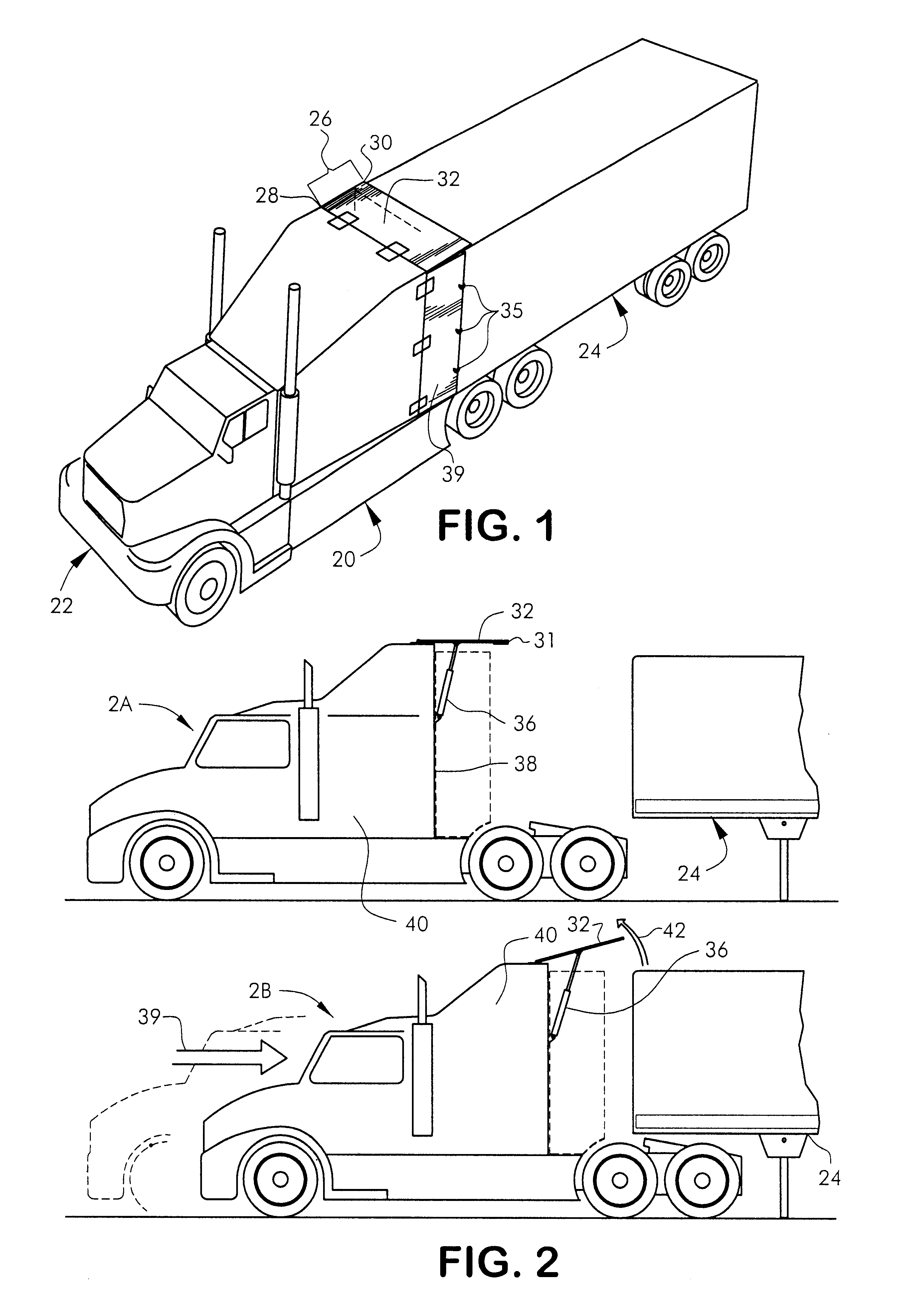
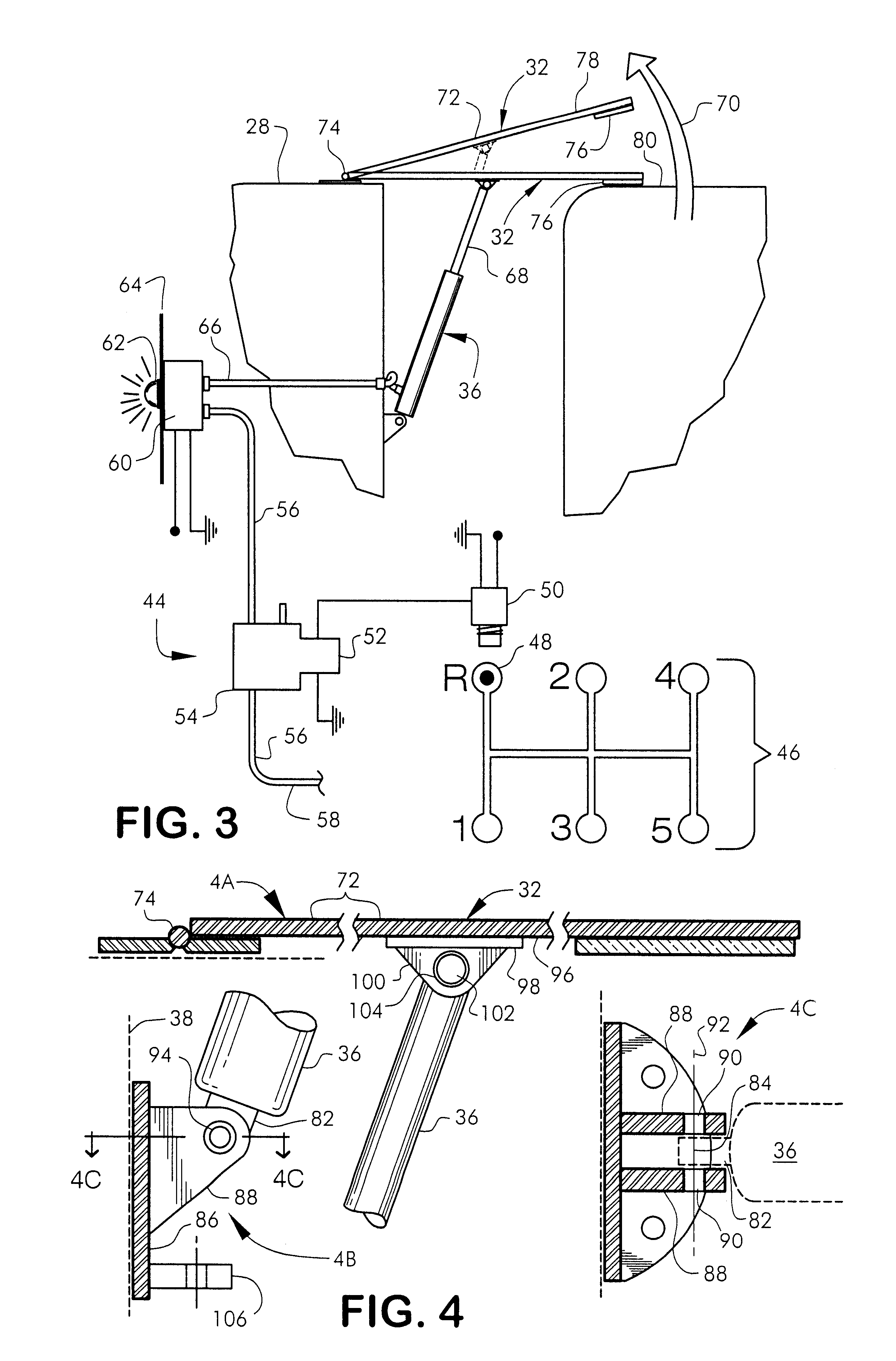
Fuel-efficient tractor-trailer system
A fuel-efficient tractor-trailer system for improving the fuel mileage of a tractor-trailer combination by improving the air resistance that occurs in the area between the rear of the tractor and the front of the semi-trailer. The fuel-efficient tractor-trailer system provides an improved roof extension, which automatically raises when the tractor is put into reverse gear and an improved wheel mechanism for assisting the side extensions to slide around the semi-trailer ends when the tractor-trailer is turning. The fuel-efficient tractor-trailer system requires only modification to the tractor and not the trailer.
Owner:GENERAL DYNAMICS C4 SYSTEMS
Hybrid electric vehicle
InactiveUS20090145674A1Improve energy efficiencyEasy to operateVehicle seatsDigital data processing detailsRolling resistanceAerodynamic drag
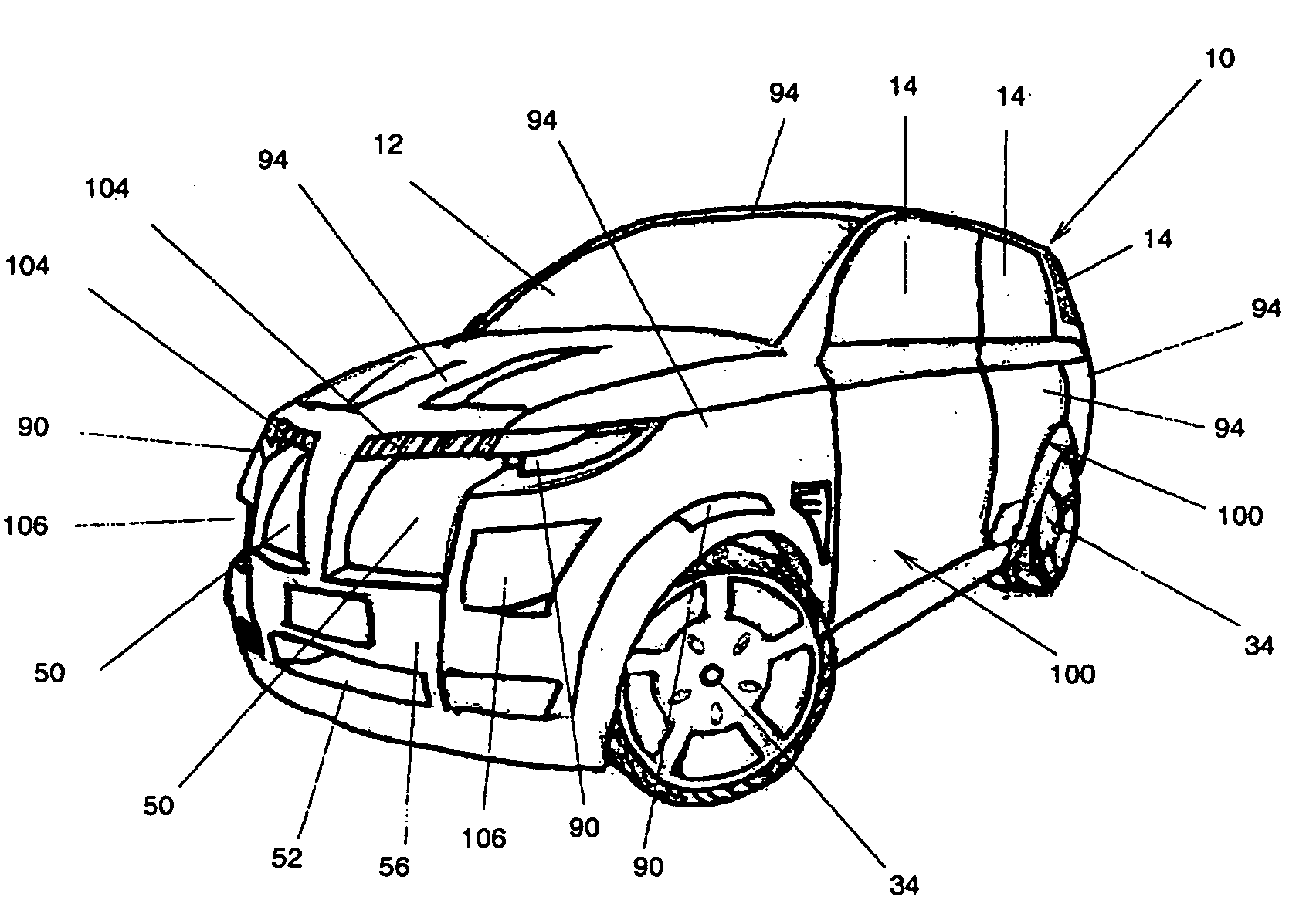
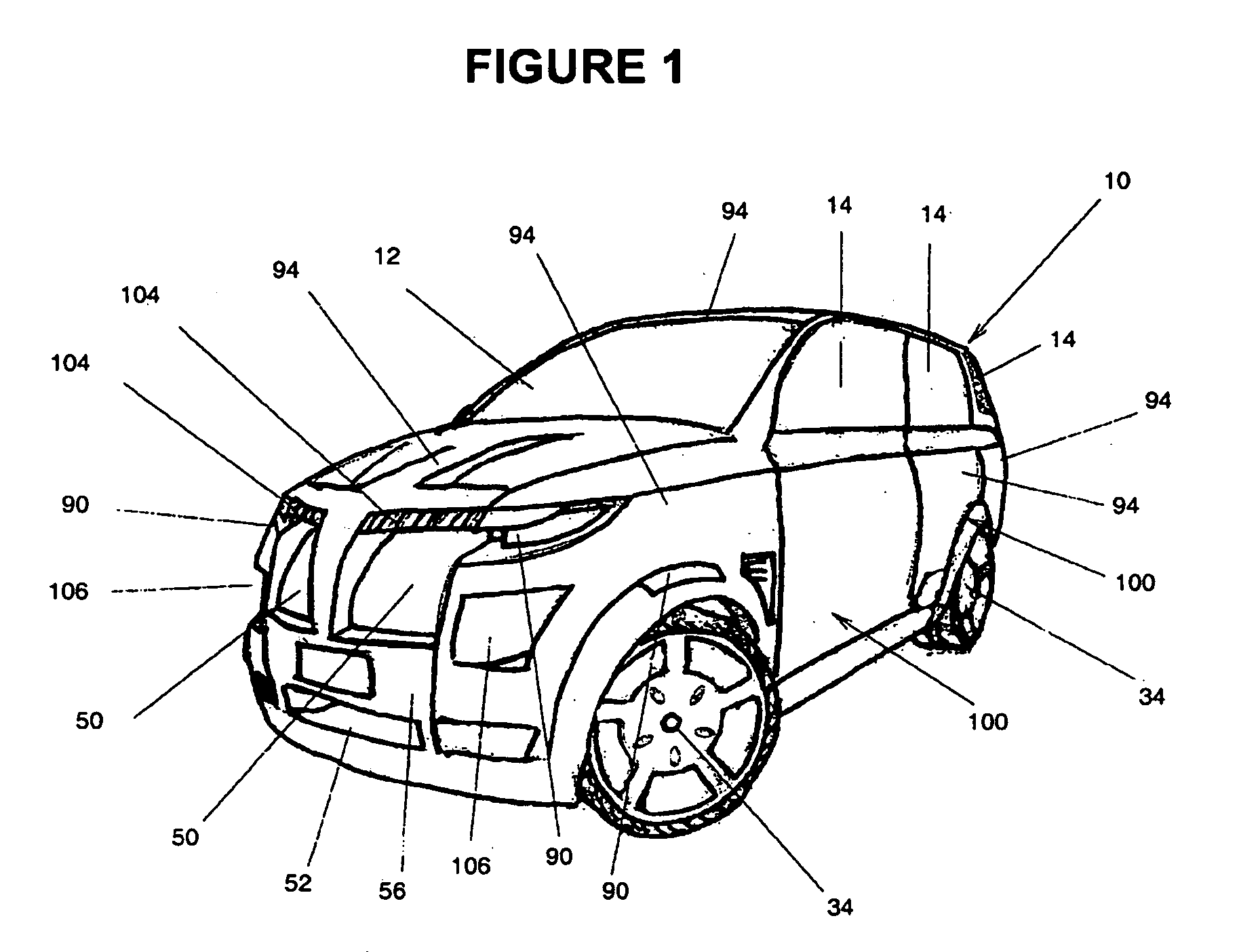
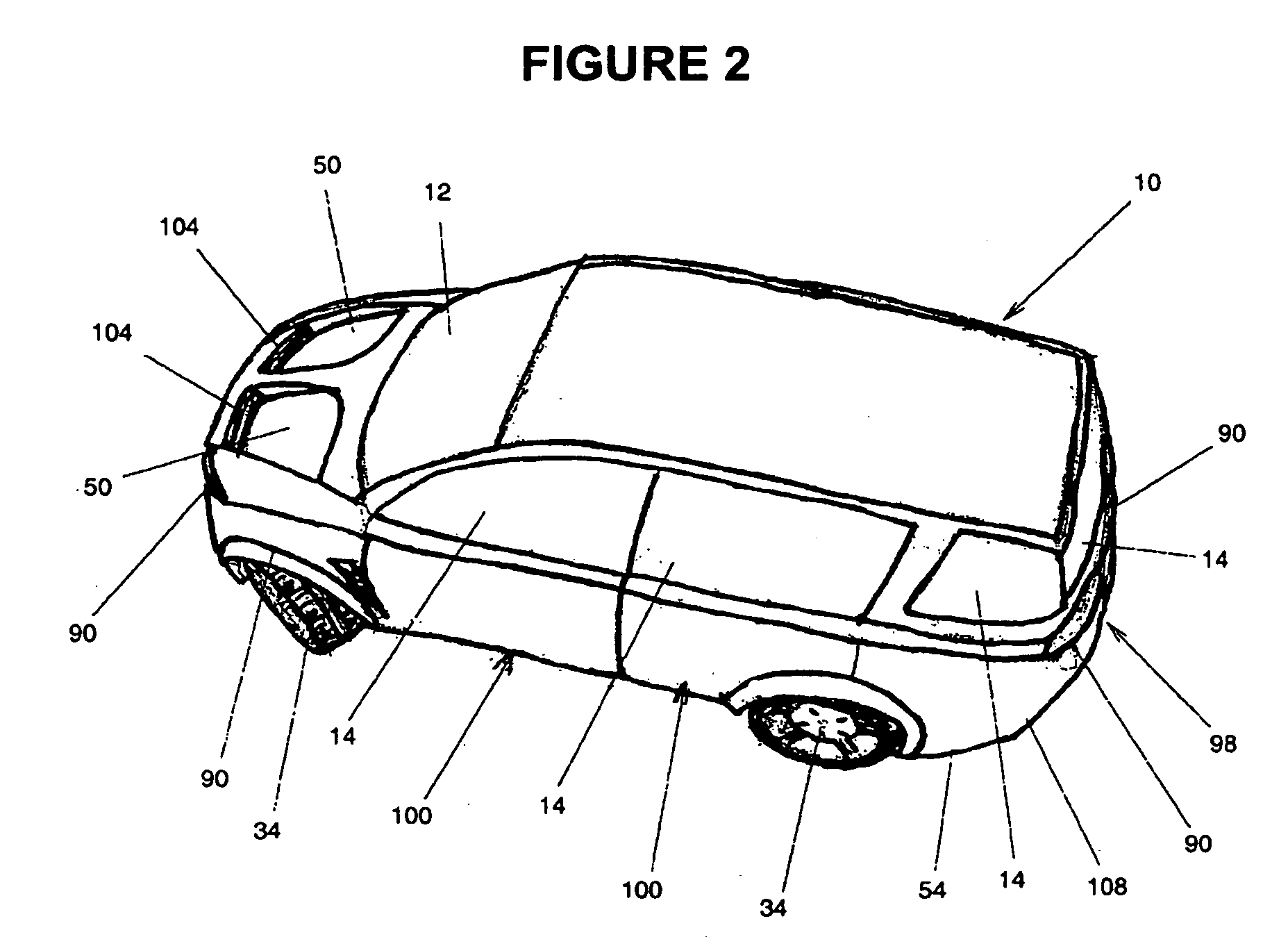
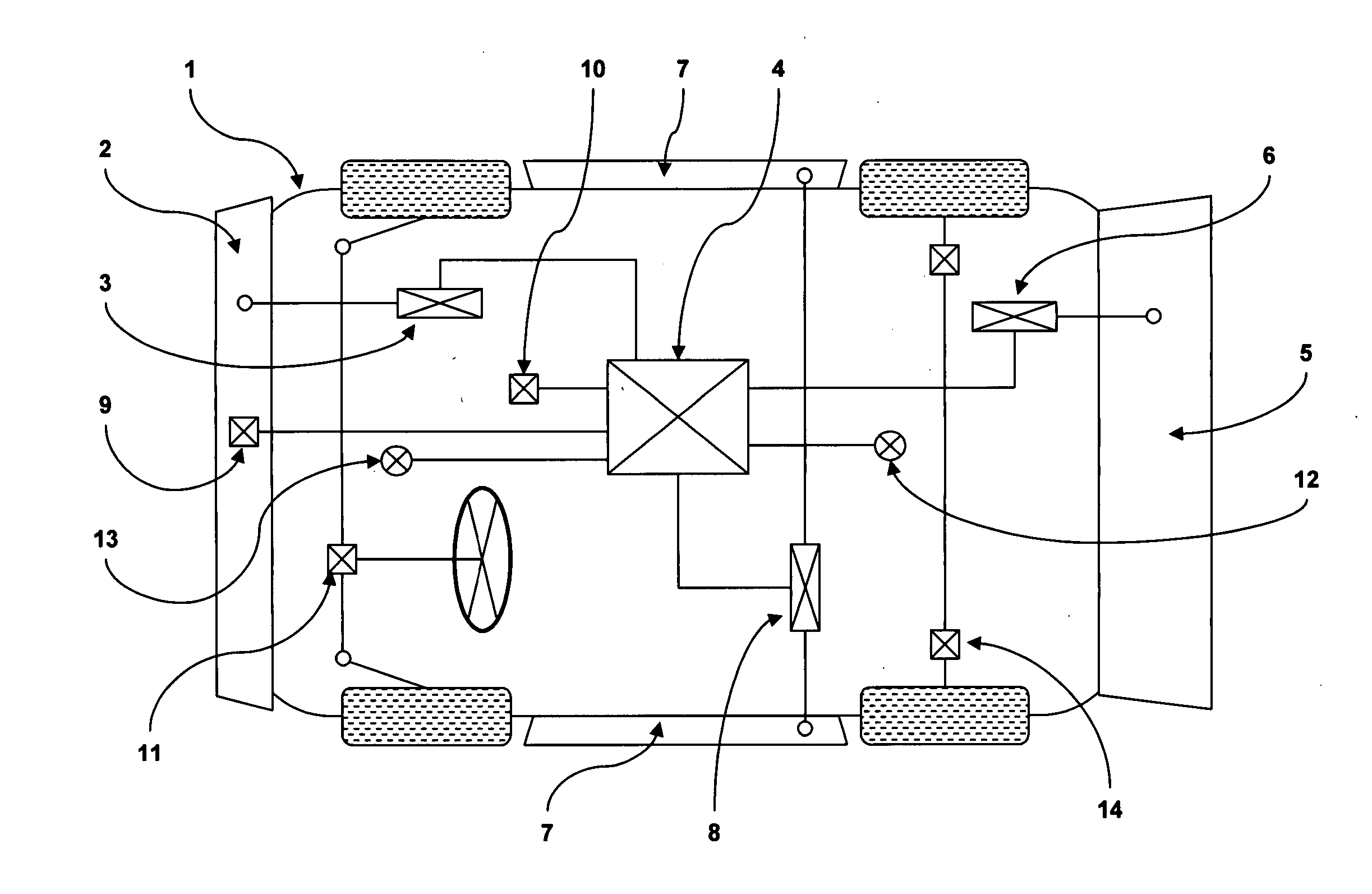
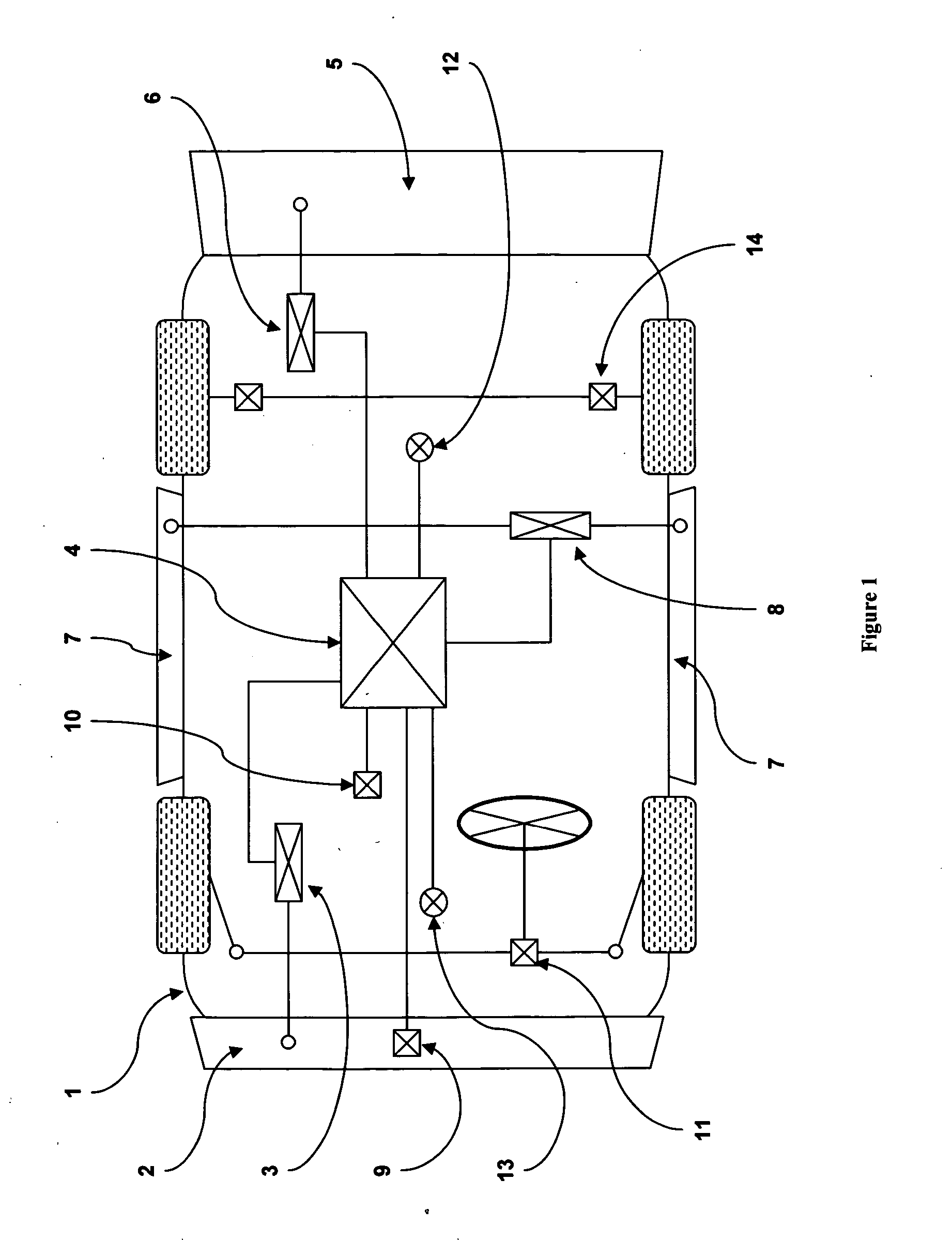
A highly energy efficient automobile that provides payload, safety and performance capacities similar to a comparable vehicle of a given vehicle class. The current invention is ideal for short to medium range urban and suburban driving. The current invention incorporates components in a unique and novel way, in which these components combine to form a system that produces an automobile that reduces overall air pollution while encouraging the commercialization of alternative energy sources. The current invention features an lightweight, low rolling resistance, digitally controlled and direct-drive electric propulsion system. A lightweight spaceframe with a suspension system provides a structure for mounting a low-aerodynamic-drag body system and other components. An intelligent power and thermal management system coupled with a removable auxiliary power module supplies the electrical energy required. While the preferred embodiment is substantially a passenger vehicle, the current invention may be scaled to other land vehicles.
Owner:INT HUMANITIES CENT
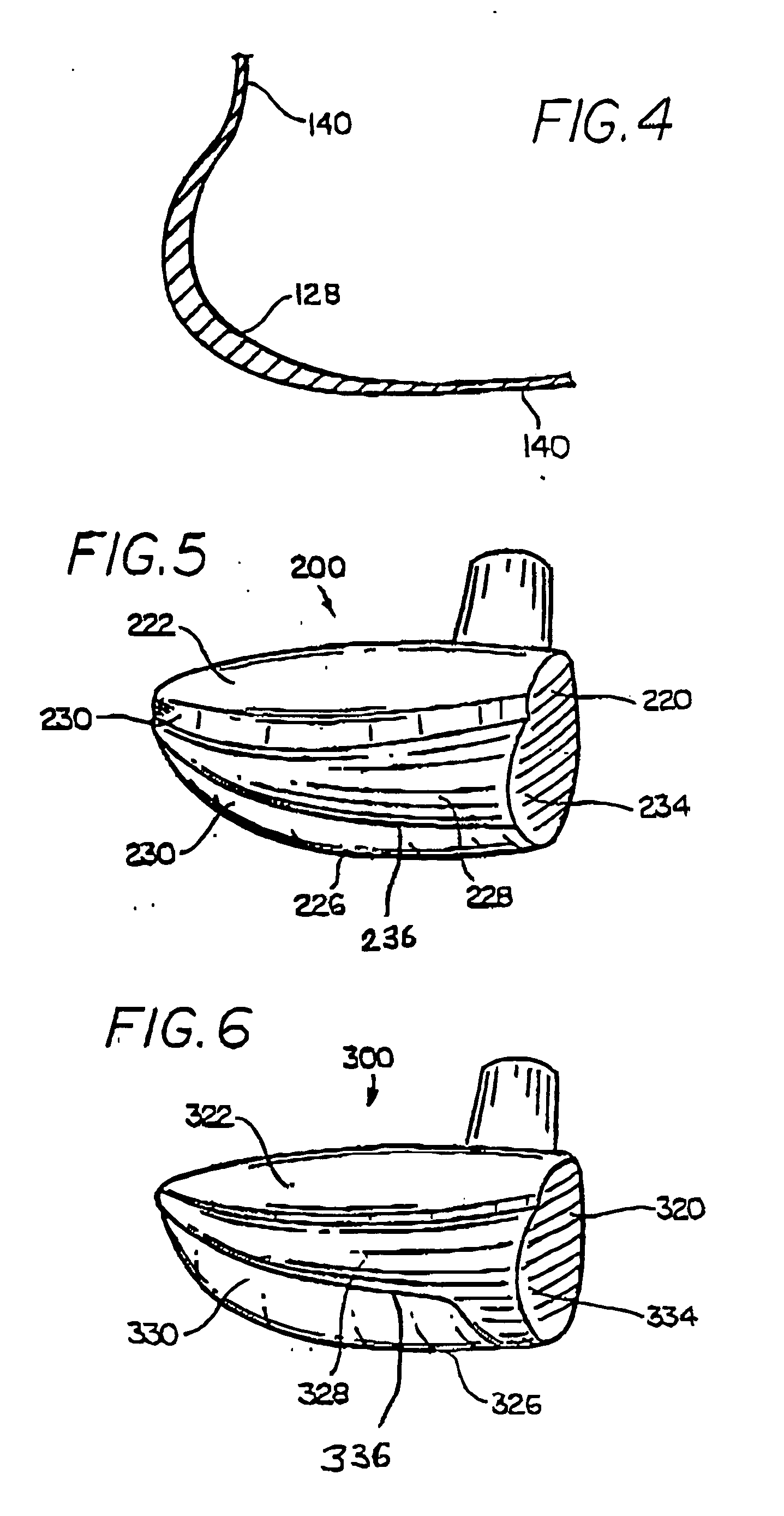
Metalwood type golf clubhead having an improved structural system for reduction of the cubic centimeter displacement and the elimination of adverse aerodynamic drag effect
InactiveUS20050009622A1Reduces cubic-centimeter displacementReduce the effect of dragGolf clubsRacket sportsAerodynamic dragEngineering
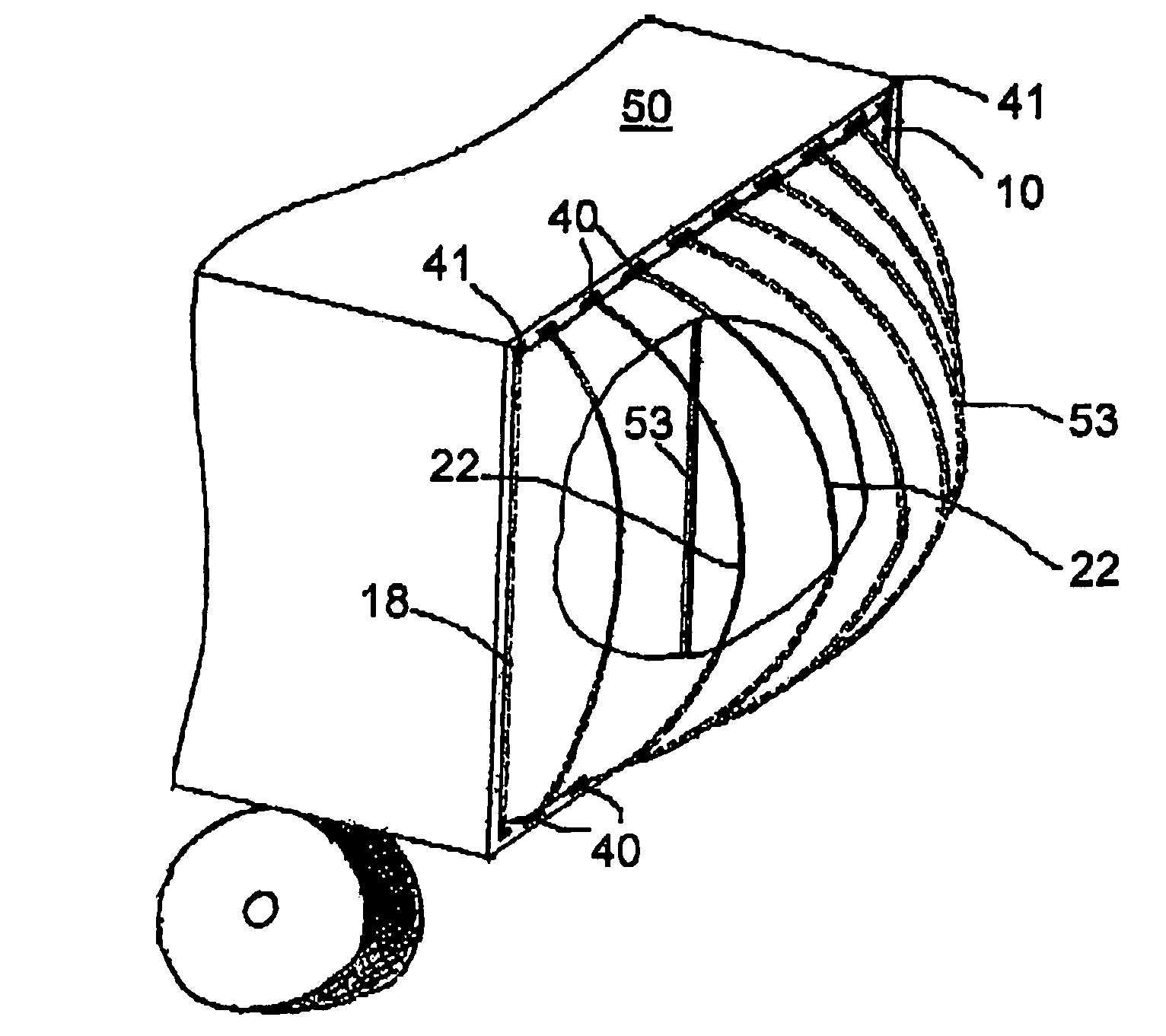
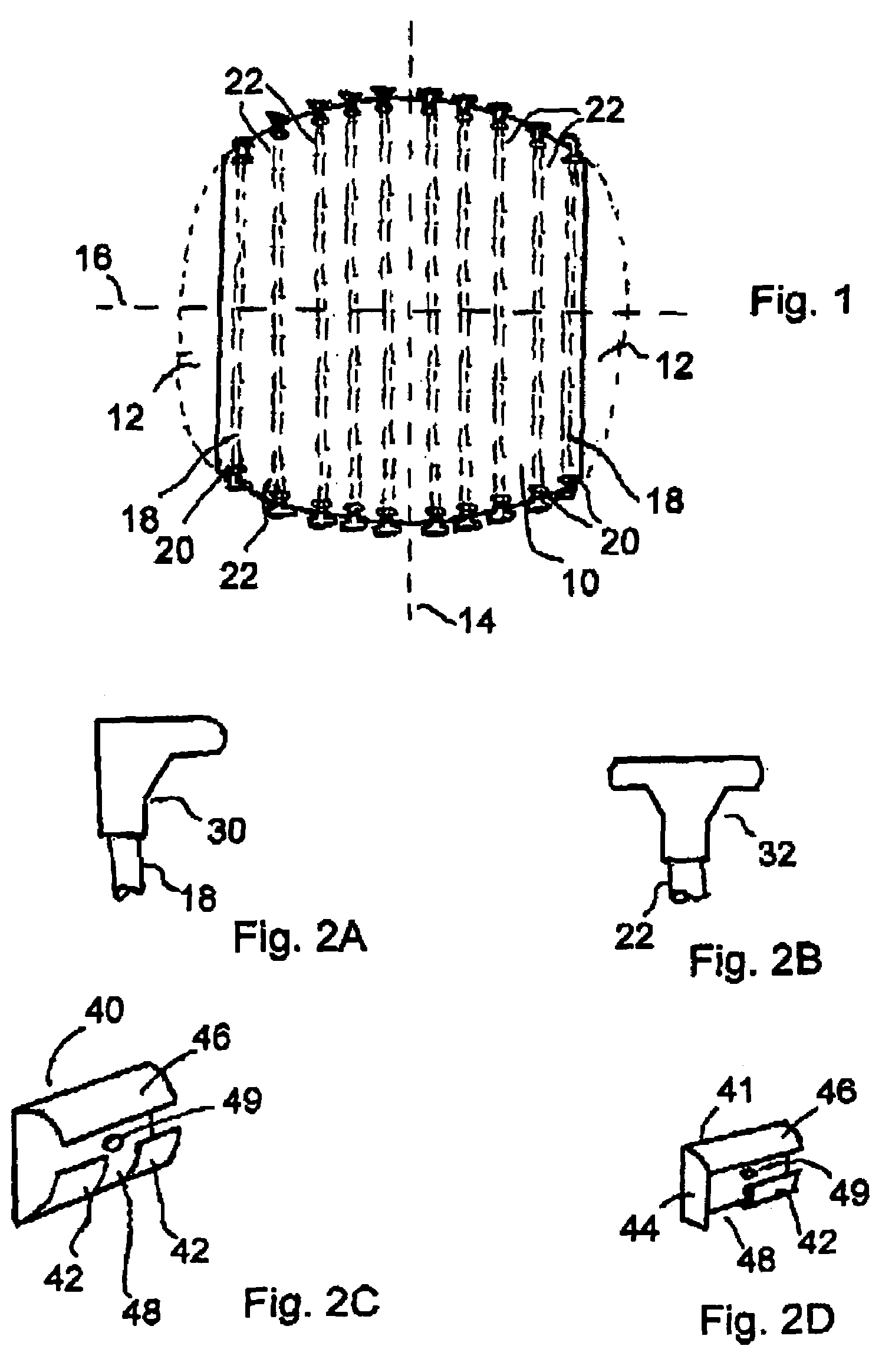
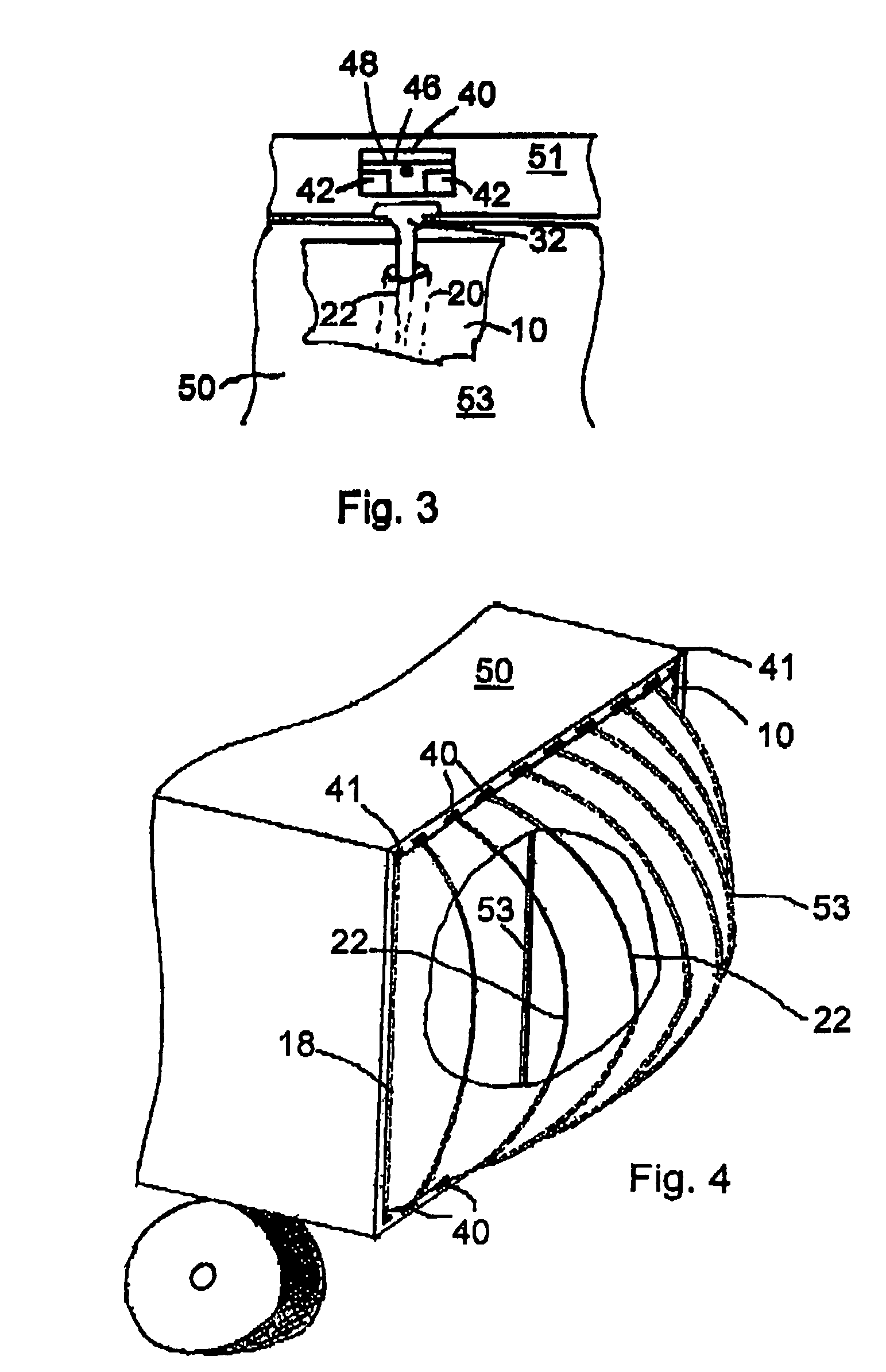
A metalwood type golf clubhead, including a clubhead body having a toe, heel, top crown surface, bottom sole surface, side surfaces, rear surface and ball-striking clubface, having an inwardly disposed lower surface located between the bottom sole surface and the top crown surface. The inwardly disposed lower structure provides improved weight distribution for better balance, additional strength and stability to clubhead and considerably decreases the overall cc displacement and overall weight / mass at the bottom of the clubhead without decreasing the size of the ball striking face and / or the upper top crown surface.
Owner:ANTONIOUS ANTHONY J
PV wind performance enhancing methods and apparatus
InactiveUS20050126621A1Uniform pressurePressure equalization can be enhancedPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyAerodynamic dragAir volume
Pressure equalization between upper and lower surfaces of PV modules of an array of PV modules can be enhanced in several ways. Air gaps opening into the air volume, defined between the PV modules and the support surface, should be provided between adjacent PV modules and along the periphery of the array. The ratio of this air volume to the total area of the air gaps should be minimized. Peripheral wind deflectors should be used to minimize aerodynamic drag forces on the PV modules. The time to equalize pressure between the upper and lower surfaces of the PV modules should be maintained below, for example, 10-20 milliseconds. The displacement created by wind gusts should be limited to, for example, 2-5 millimeters or less. For inclined PV modules, rear air deflectors are advised for each PV module and side air deflectors are advised for the periphery of the array.
Owner:SUNPOWER CORPORATION
Retractable air deflection apparatus for reduction of vehicular air drag
InactiveUS7641262B2Optimize the aerodynamic drag reductionVehicle seatsWindowsAerodynamic dragBack door
An air deflection apparatus for reduction of vehicular air drag comprises at least one air deflection element coupled to a rear portion of the vehicle but not to the rear-facing surface of the vehicle or, in other embodiments, at least one air deflection element coupled to a rear portion of the vehicle but not to any rear door which the vehicle may have. The air deflection elements are displaceable, preferably in unison, between a retracted position and at least one deployed position in which the air deflection elements intersect with the air flowing around the top and sides, and preferably also the bottom, of the vehicle, and in which they divert that airflow in a manner that enhances the aerodynamic characteristics of the vehicle and thereby improves its fuel economy, resulting in a reduction in fuel cost. The air deflection elements may be deployed and retracted manually, or remotely with powered assistance, or under microprocessor control, with the latter allowing for optimal positioning of the air deflection elements based either on pre-stored values, or on values derived, utilizing an optional feedback mechanism, from real-time vehicular speed and fuel consumption data. Vehicles equipped with the apparatus, and methods of reducing vehicular air drag using the apparatus, are also disclosed.
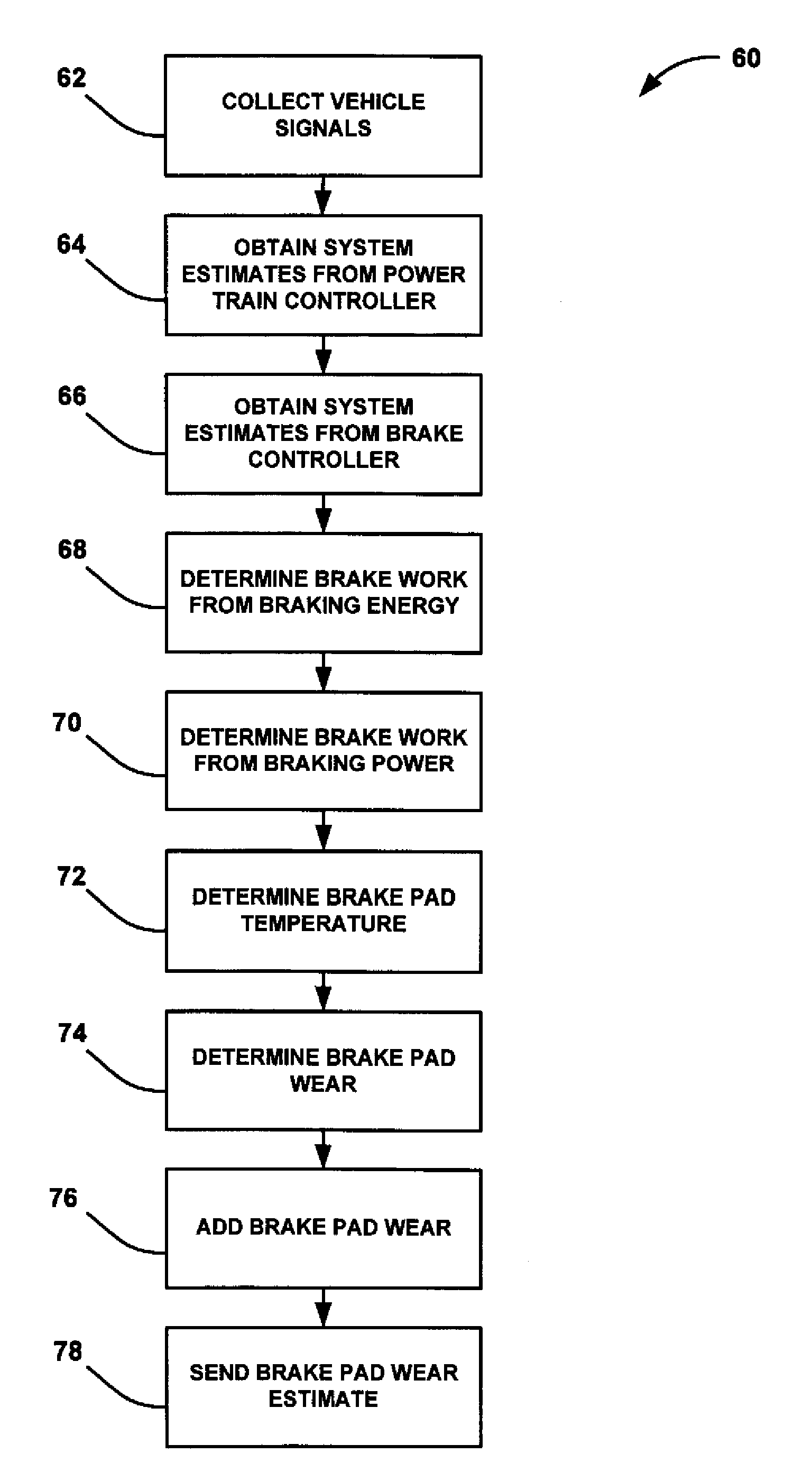
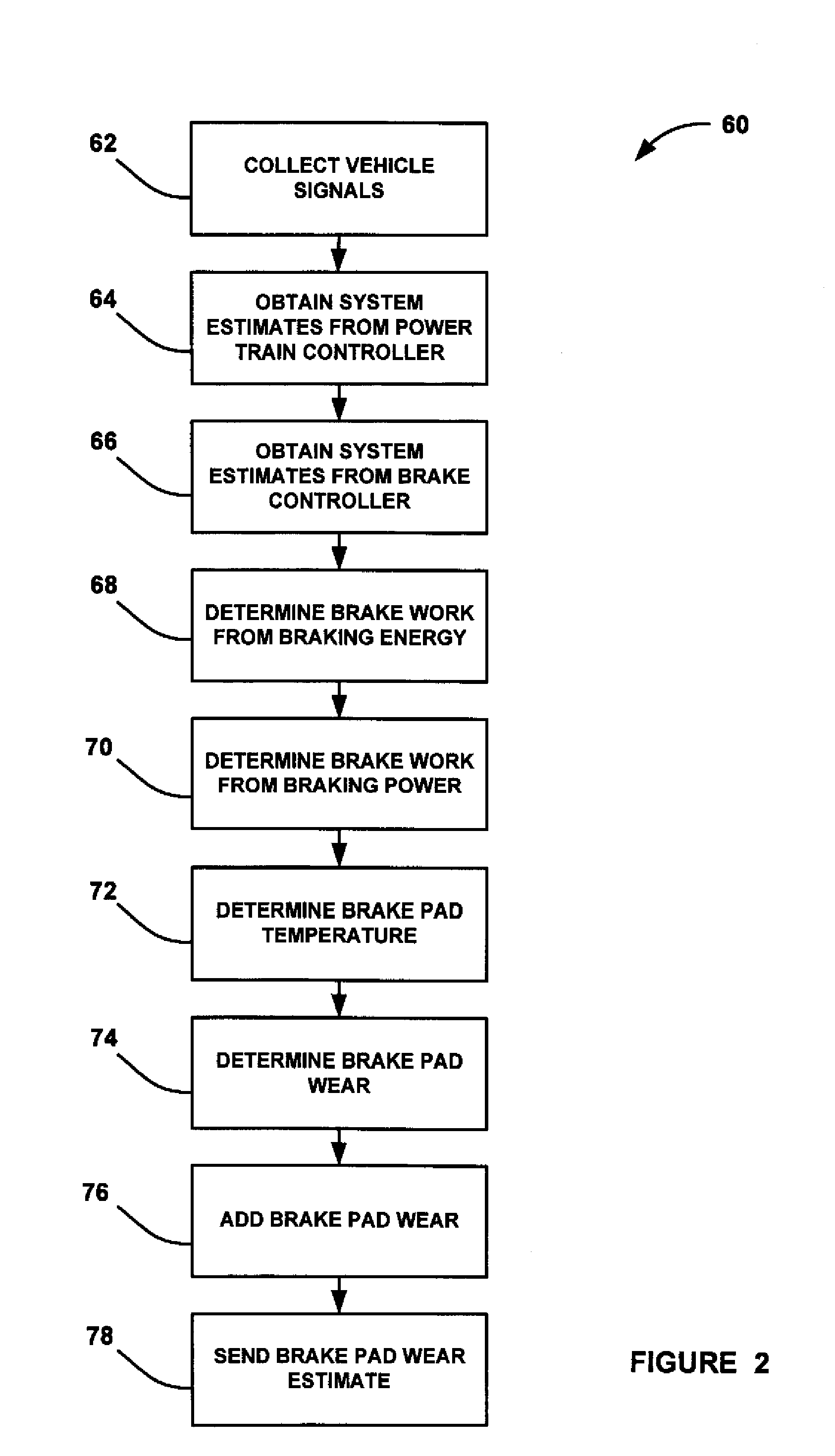
Owner:NUSBAUM HOWARD G
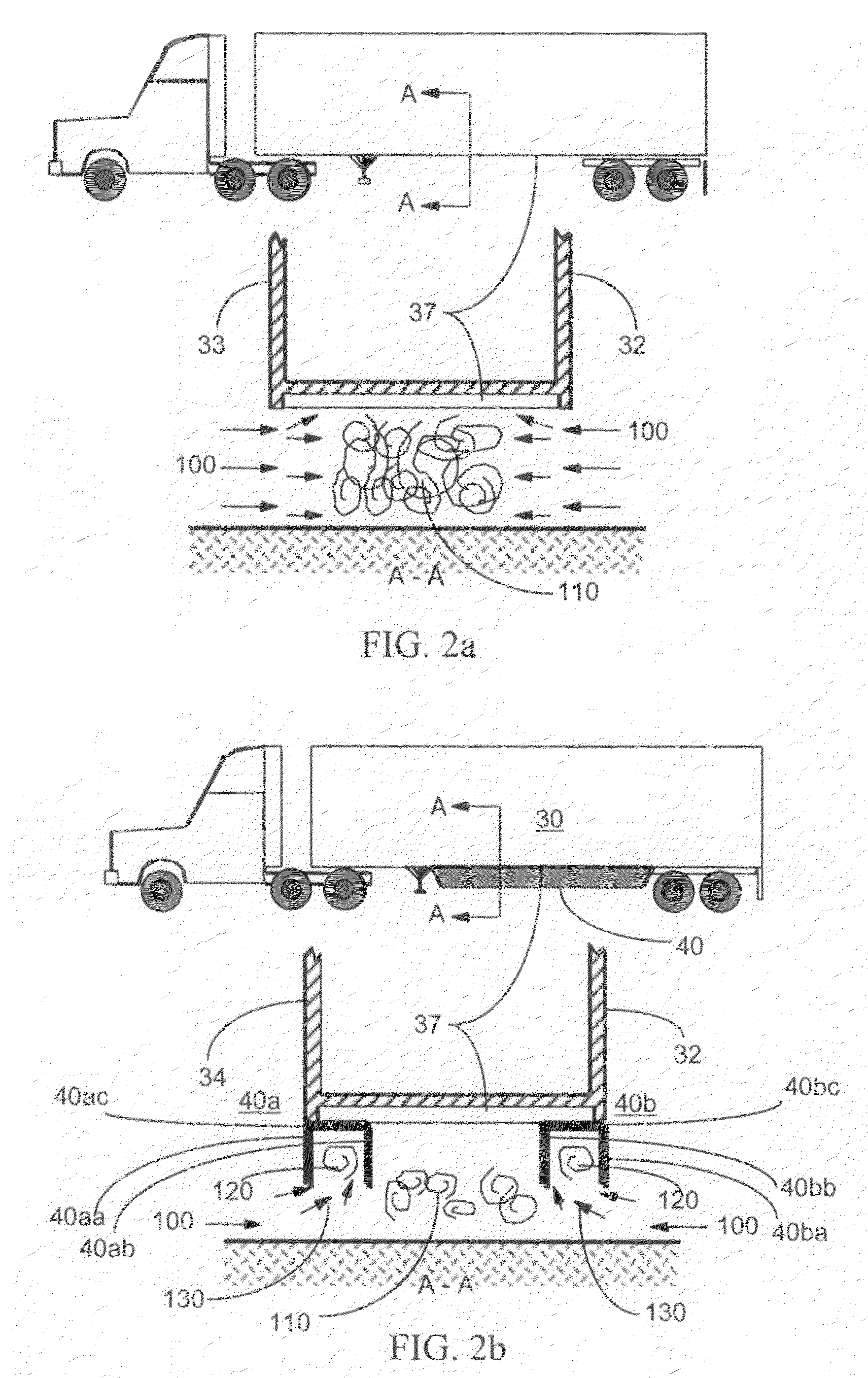
Trailer wheel fairings
InactiveUS20100066123A1Reduce air resistanceReduce pressureVehicle seatsWindowsAerodynamic dragCowling
A wheel fairing and preferably a set of wheel fairings for reducing aerodynamic drag caused by the left-side and right side wheel sets of a rear wheel assembly supporting a trailer body at its rear end. The fairing body includes a tapered aerodynamic surface with a substantially U-shaped cross-section that tapers from a second end to a first end, and a base surface at the second end with a substantially same dimensional profile as one of the left-side or right-side wheel sets. Fasteners or other mounting devices secure each fairing body to an underside of the trailer body either upstream (as a nose fairing) or downstream (as a tail fairing) of the rear wheel assembly so that the second end is adjacent to an exposed rolling surface of the left-side or right side wheel set.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
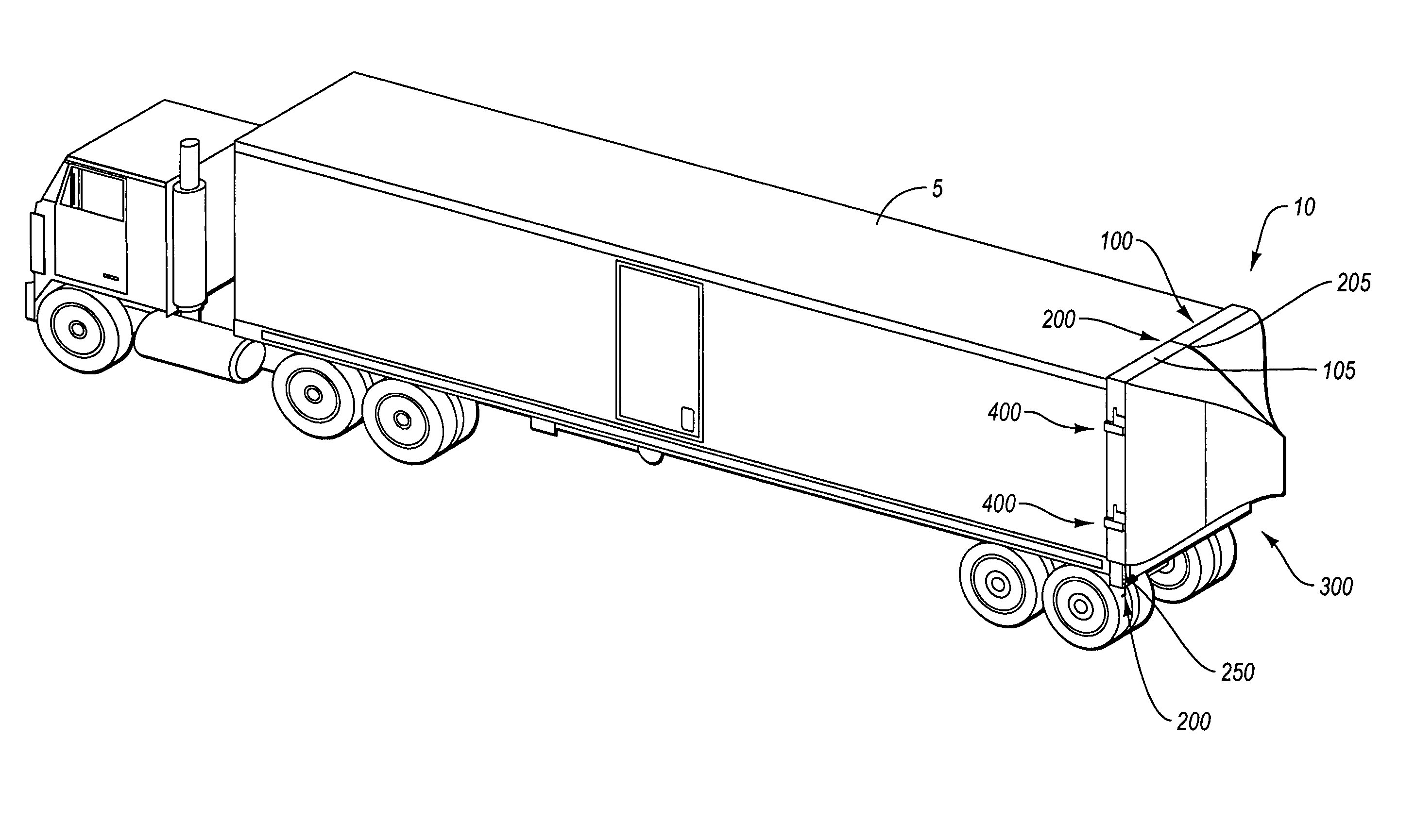
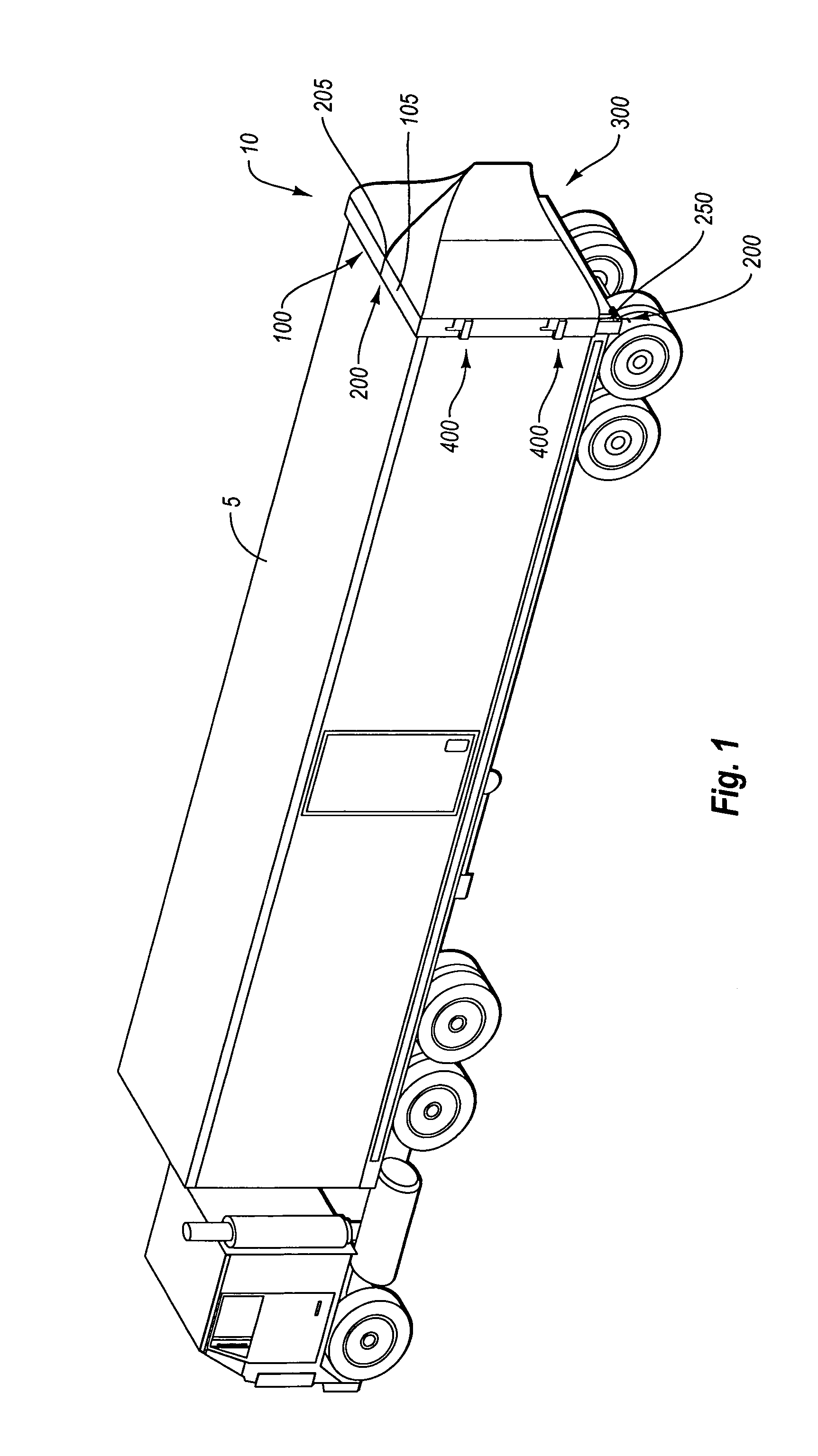
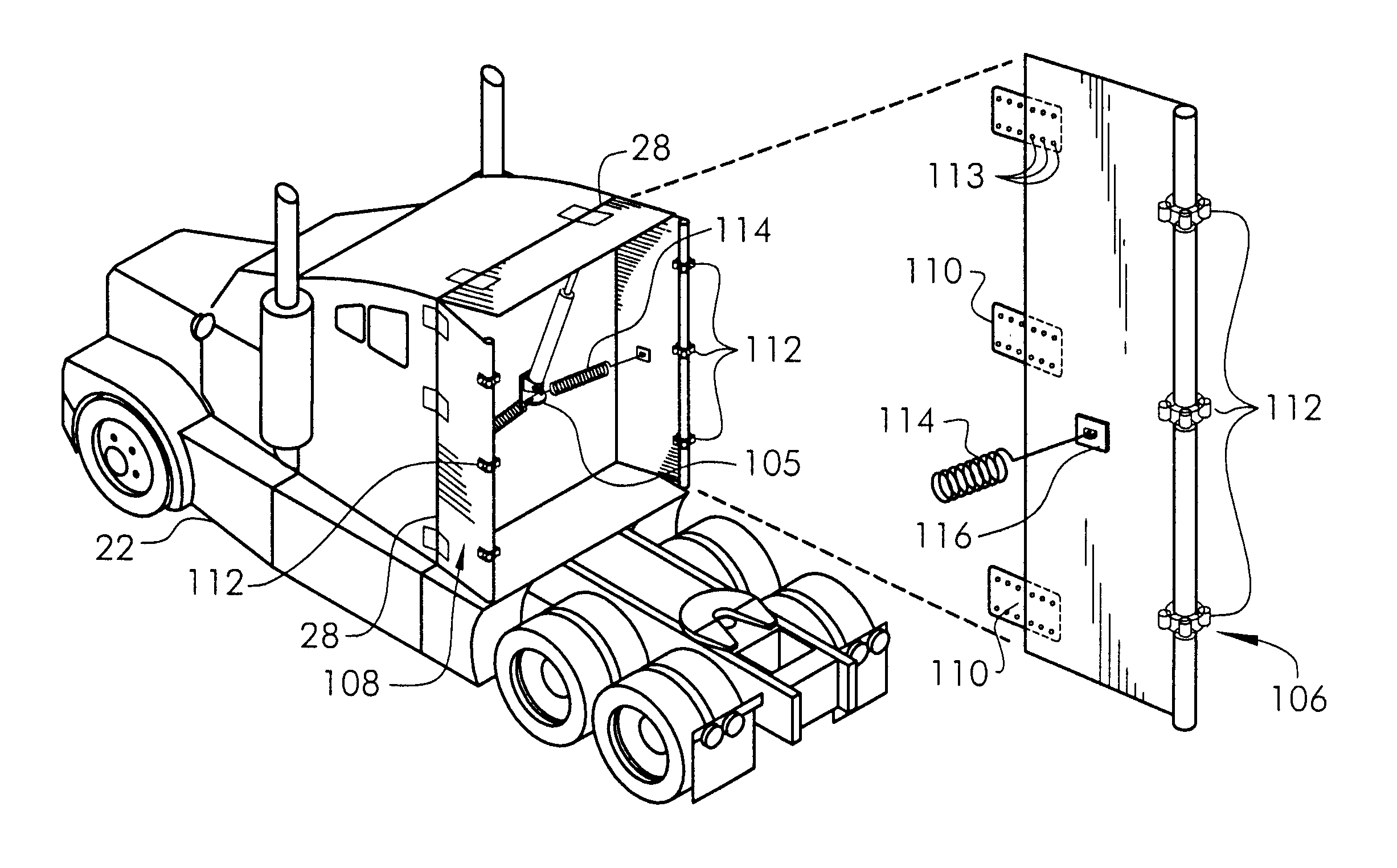
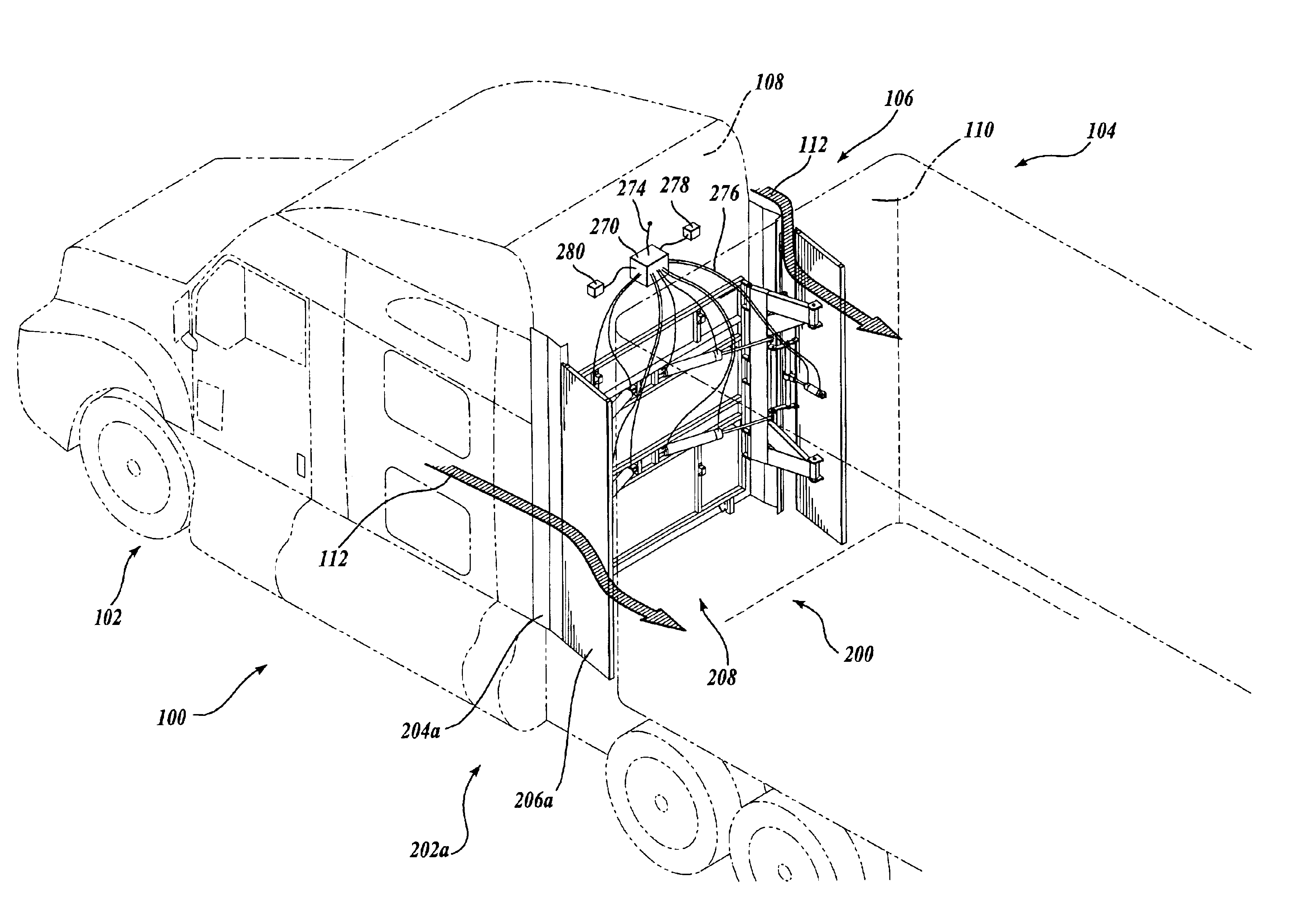
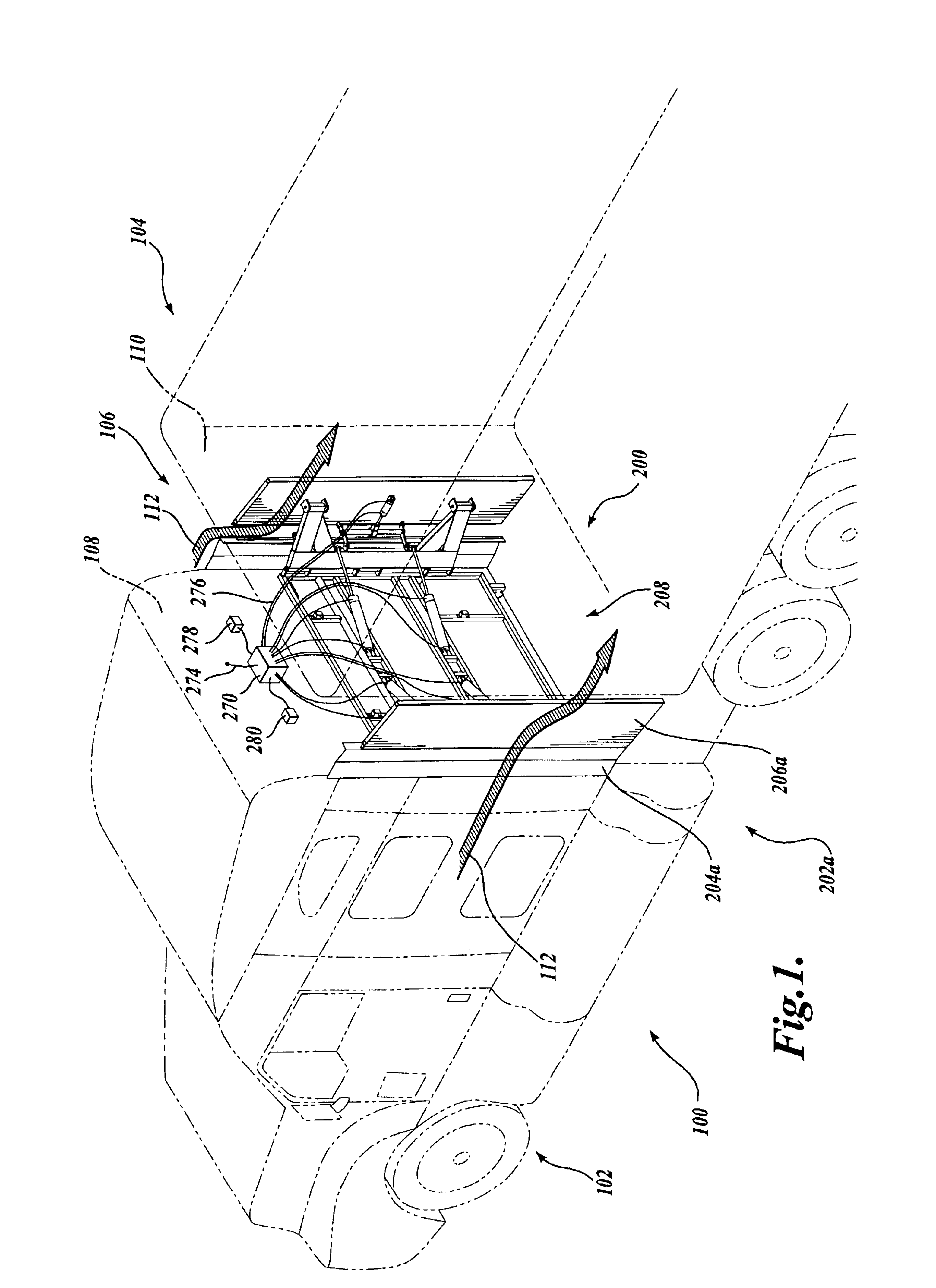
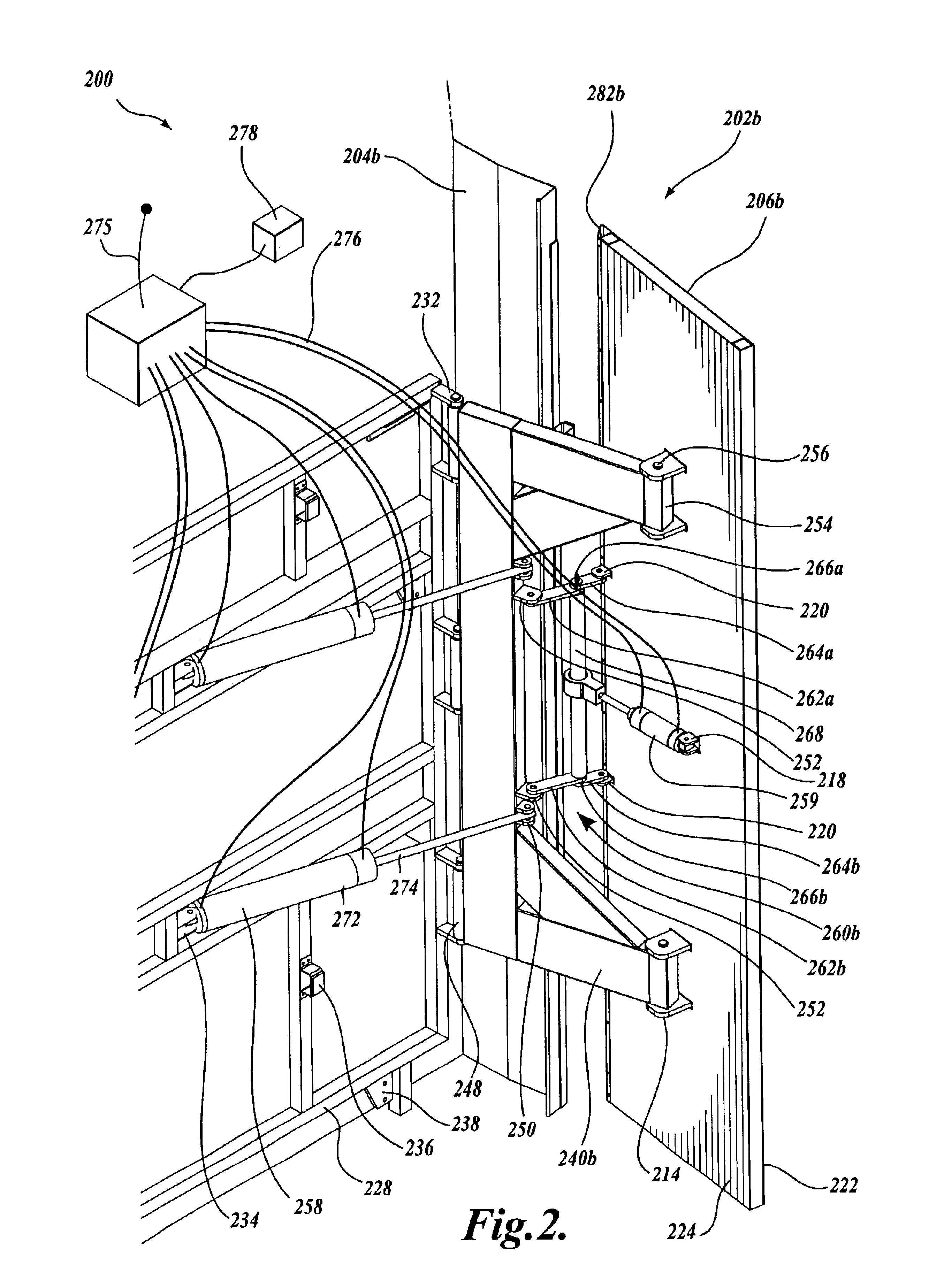
Cab extender assembly method and apparatus
InactiveUS6886882B2Improved drag coefficientSelectively manipulating an aerodynamic drag of a vehicleVehicle seatsWindowsAerodynamic dragControl system
A cab extender assembly (200) for selectively manipulating an aerodynamic drag of a vehicle (100) is provided. The cab extender assembly includes a dynamic cab extender (206a) and a control system (208) coupled to the dynamic cab extender. The control system is adapted to selectively position the dynamic cab extender between a stowed position, a deployed position in which the dynamic cab extender is substantially aligned with a side of the vehicle, and a braking position in which the dynamic cab extender is at least partially disposed into an airstream passing along the side of the vehicle to increase a drag coefficient of the vehicle. The cab extender assembly may also include a fixed cab extender (204a) substantially aligned with the dynamic cab extender when the dynamic cab extender is in the deployed position. A method of operating a cab extender assembly is also disclosed.
Owner:PACCAR INC
High volume aerodynamic golf club head
ActiveUS20130123040A1Beneficial moment of inertia valueImprove aerodynamic performanceFluid dynamicsGolf clubsAerodynamic dragEngineering
A high volume aerodynamic golf club head having a post apex attachment promoting region with a club head volume of at least 400 cc and a front-to-back dimension of at least 4.4 inches producing reduced aerodynamic drag forces. The post apex attachment promoting region is on the surface of the crown section at an elevation above a maximum face height and begins at the crown apex and extends toward the back of the club head. The post apex attachment promoting region is a relatively flat portion of the crown section that is behind the crown apex, yet above the maximum top edge plane, and aides in keeping airflow attached to the club head once it flows past the crown apex.
Owner:TAYLOR MADE GOLF
Vehicle drag reduction apparatus
A vehicle air drag reduction system is provided for mounting on the rearward facing surface of a vehicle, and in particular a truck trailer, that provides improved efficiency. The system comprises a flexible panel that will assume a cone-shape at the rearward end of the trailer, and which is held in place by a plurality of support rods fitted within the flexible panel, and which attach to brackets mounted on said trailer. An inexpensive and simple air drag reduction system is provided which is easily attached or removed from a vehicle is provided.
Owner:VALA PHILIP
Passive adaptive structures
ActiveUS20110084174A1Reduce quality problemsMinimizing weight penaltyPropellersRotary propellersMorphingAerodynamic drag
Morphing an aerodynamic body's geometry in situ can optimize its aerodynamic properties, increasing range, reducing fuel consumption, and improving many performance parameters. The aerodynamic load exerted on the body by the flow is one such parameter, typically characterized as lift or drag. It is the aim of the present disclosure to teach the use of passive adaptive morphing structures to manage these aerodynamic loads.
Owner:CORNERSTONE RES GROUP
Mini skirt aerodynamic fairing device for reducing the aerodynamic drag of ground vehicles
InactiveUS7497502B2High trafficGood blocking performanceVehicle seatsWindowsMobile vehicleAerodynamic drag
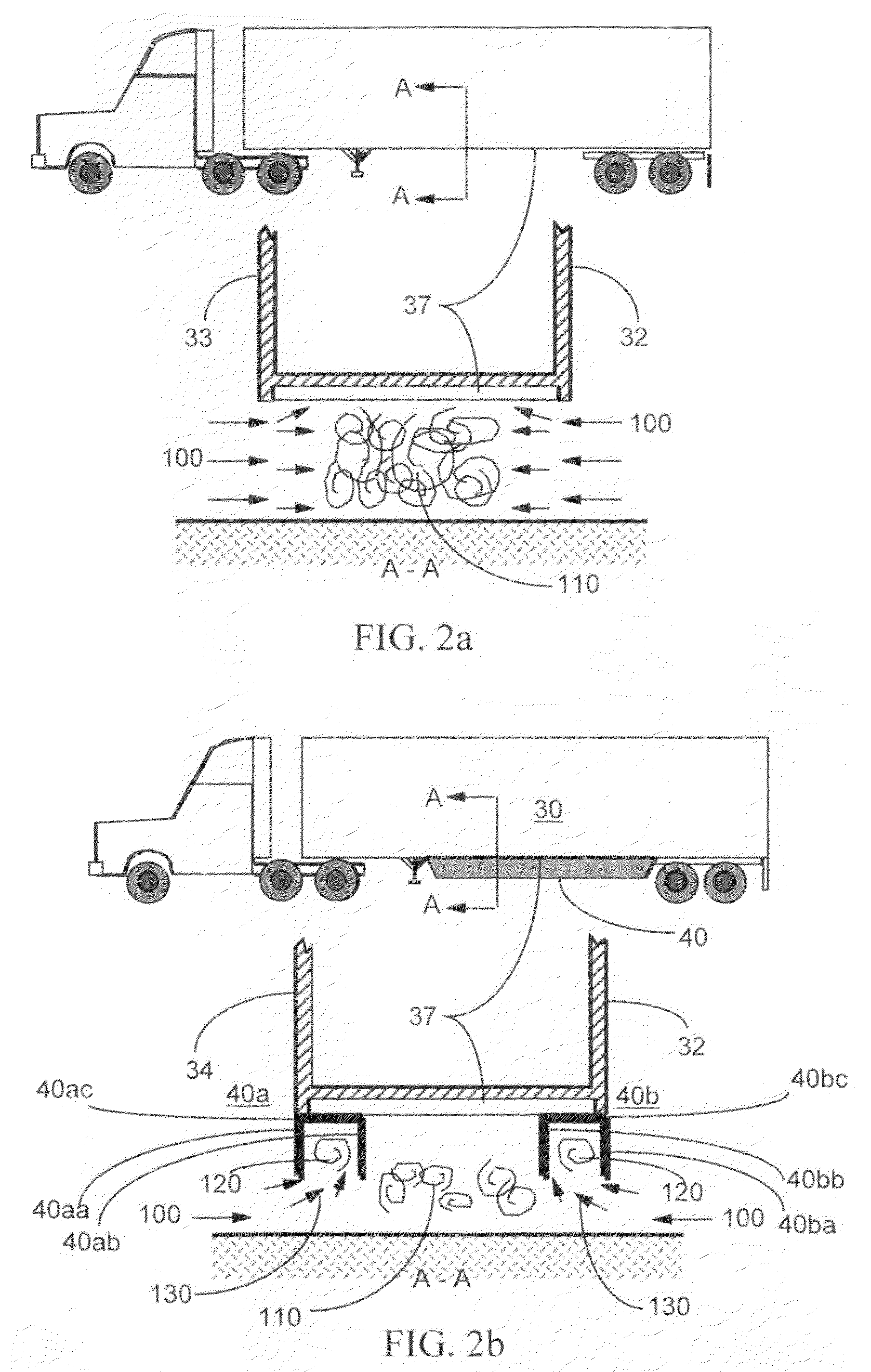
A device for the reduction of aerodynamic drag and for improved performance and stability of ground vehicles by reducing the mass and velocity of the flow passing under a vehicle is described. The device is particularly suited for a tractor-trailer truck system that includes a motorized lead vehicle pulling one or more non-motorized vehicles. The device is designed to control the flow from entering the undercarriage region from the side of a trailer of a tractor-trailer truck system.
Owner:SOLUS SOLUTIONS & TECH
Passive adaptive structures
ActiveUS20110042524A1Reduce quality problemsMinimizing weight penaltyPropellersControl initiation meansMorphingAerodynamic drag
Morphing an aerodynamic body's geometry in situ can optimize its aerodynamic properties, increasing range, reducing fuel consumption, and improving many performance parameters. The aerodynamic load exerted on the body by the flow is one such parameter, typically characterized as lift or drag. It is the aim of the present disclosure to teach the use of passive adaptive morphing structures to manage these aerodynamic loads.
Owner:CORNERSTONE RES GROUP
Brake pad prognosis system
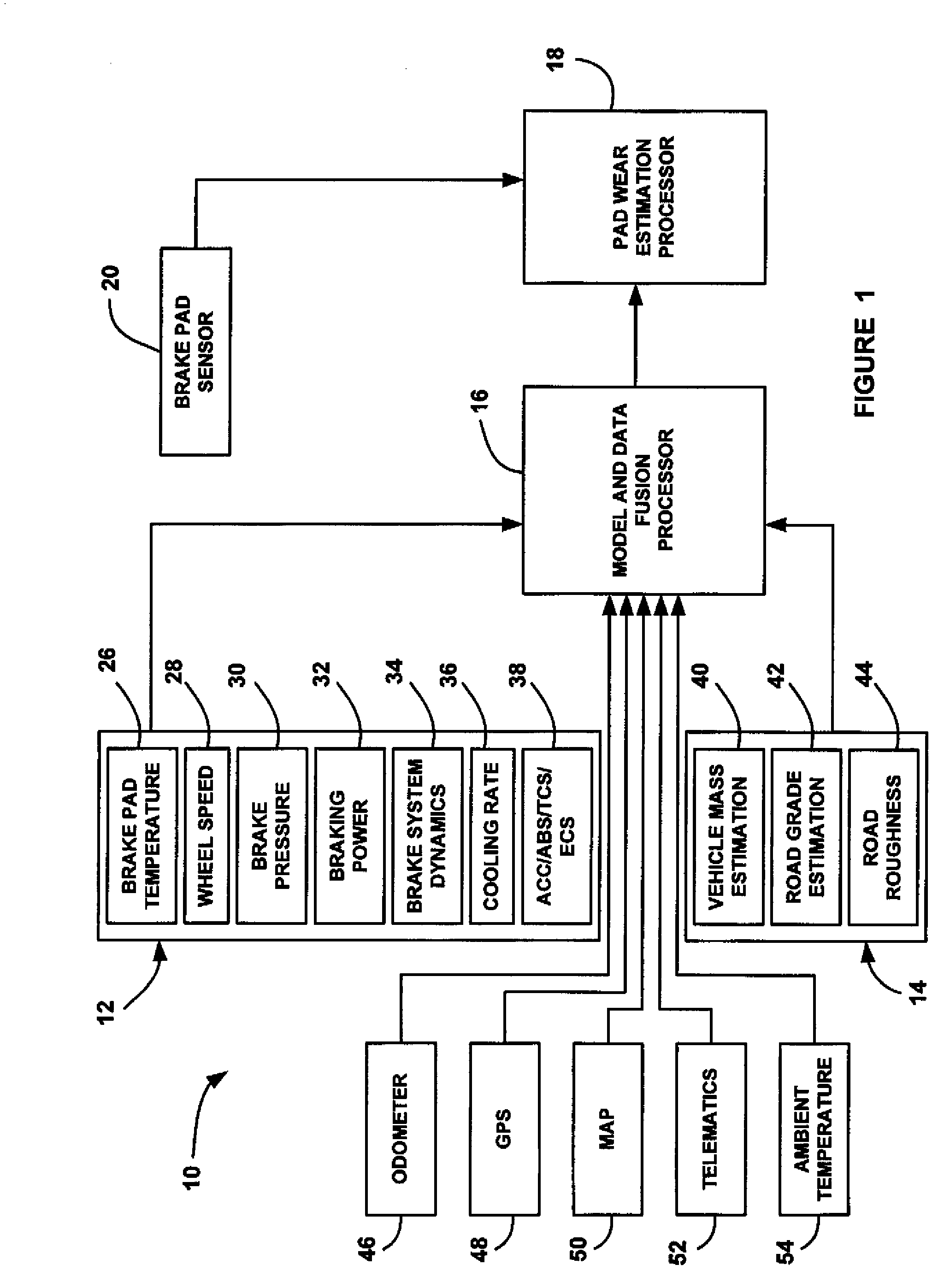
A method for providing an estimate of brake pad thickness. The method employs fusion of sensors, if used, and driver brake modeling to predict the vehicle brake pad life. An algorithm is employed that uses various inputs, such as brake pad friction material properties, brake pad cooling rate, brake temperature, vehicle mass, road grade, weight distribution, brake pressure, brake energy, braking power, etc. to provide the estimation. The method calculates brake work using total work minus losses, such as aerodynamic drag resistance, engine braking and / or braking power as braking torque times velocity divided by rolling resistance to determine the brake rotor and lining temperature. The method then uses the brake temperature to determine the brake pad wear, where the wear is accumulated for each braking event. A brake pad sensor can be included to provide one or more indications of brake pad thickness from which the estimation can be revised.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Retractable air deflection apparatus for reduction of vehicular air drag
InactiveUS20080093886A1Optimize the aerodynamic drag reductionVehicle seatsWindowsAerodynamic dragBack door
An air deflection apparatus for reduction of vehicular air drag comprises at least one air deflection element coupled to a rear portion of the vehicle but not to the rear-facing surface of the vehicle or, in other embodiments, at least one air deflection element coupled to a rear portion of the vehicle but not to any rear door which the vehicle may have. The air deflection elements are displaceable, preferably in unison, between a retracted position and at least one deployed position in which the air deflection elements intersect with the air flowing around the top and sides, and preferably also the bottom, of the vehicle, and in which they divert that airflow in a manner that enhances the aerodynamic characteristics of the vehicle and thereby improves its fuel economy, resulting in a reduction in fuel cost. The air deflection elements may be deployed and retracted manually, or remotely with powered assistance, or under microprocessor control, with the latter allowing for optimal positioning of the air deflection elements based either on pre-stored values, or on values derived, utilizing an optional feedback mechanism, from real-time vehicular speed and fuel consumption data. Vehicles equipped with the apparatus, and methods of reducing vehicular air drag using the apparatus, are also disclosed.
Owner:NUSBAUM HOWARD G
Vehicle fairing structure
A vehicle fairing structure has a top fairing surface adapted to be attached to a trailer box, and first and second side fairing surfaces adapted to be attached to the sides of the trailer box, in the gap between a tractor cab and a trailer box in a tractor-trailer combination. The fairing structure directs air flow away from the gap, and is positioned in the gap to lessen aerodynamic drag, thereby reducing fuel consumption.
Owner:ZF COMPOSITES NORTH AMERICA LTD
Mini skirt aerodynamic fairing device for reducing the aerodynamic drag of ground vehicles
InactiveUS7740303B2High trafficGood blocking performanceVehicle seatsWindowsMobile vehicleAerodynamic drag
A device for the reduction of aerodynamic drag and for improved performance and stability of ground vehicles by reducing the mass and velocity of the flow passing under a vehicle is described. The device is particularly suited for a tractor-trailer truck system that includes a motorized lead vehicle pulling one or more non-motorized vehicles. The device is designed to control the flow from entering the undercarriage region from the side of a trailer of a tractor-trailer truck system.
Owner:WOOD RICHARD
Vehicle fairing structure
ActiveUS20080061597A1Reduce air resistanceEffective closureVehicle seatsWindowsAerodynamic dragCowling
A vehicle fairing structure has a top fairing surface adapted to be attached to a trailer box, and first and second side fairing surfaces adapted to be attached to the sides of the trailer box, in the gap between a tractor cab and a trailer box in a tractor-trailer combination. The fairing structure directs air flow away from the gap, and is positioned in the gap to lessen aerodynamic drag, thereby reducing fuel consumption.
Owner:ZF COMPOSITES NORTH AMERICA LTD
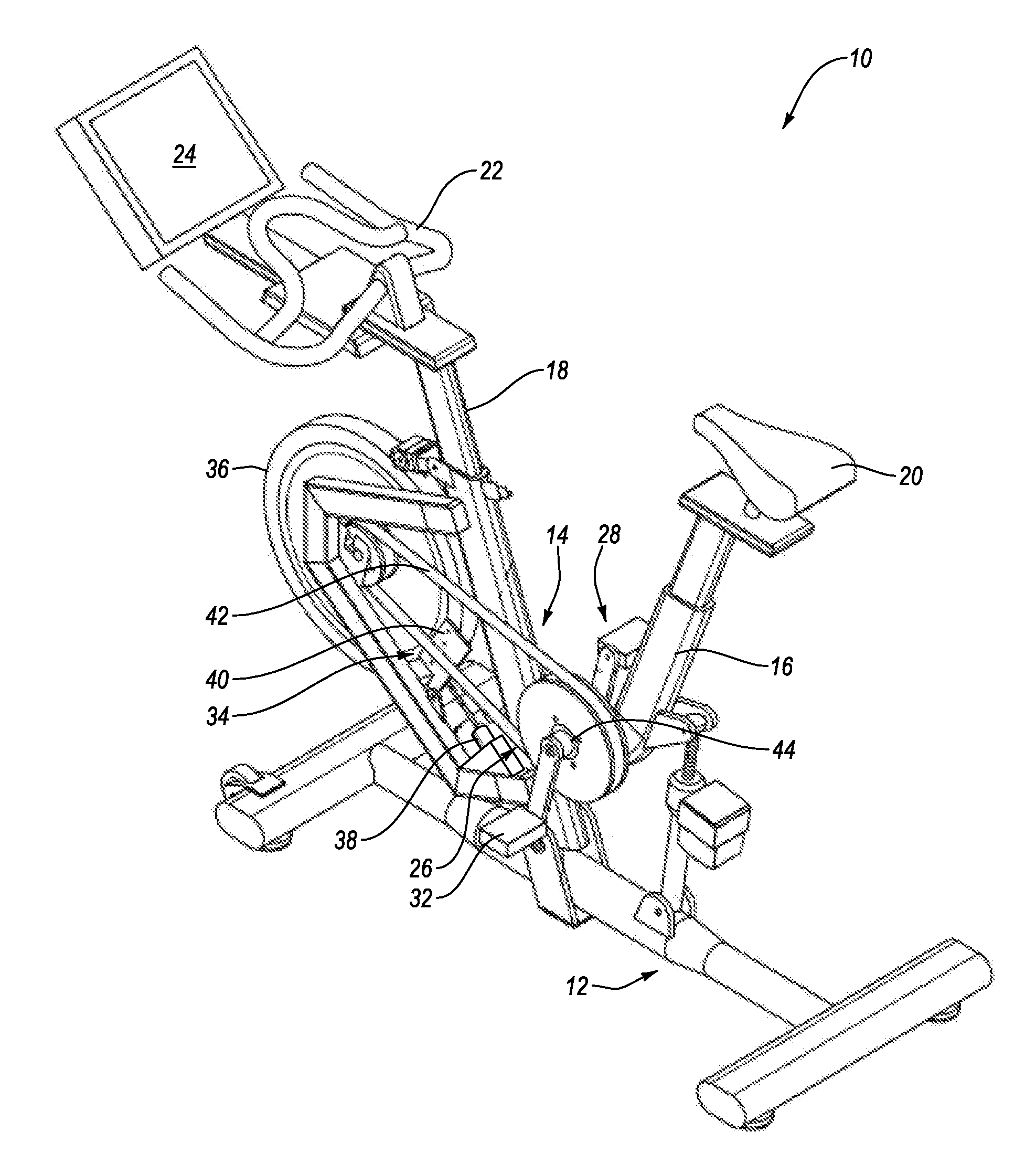
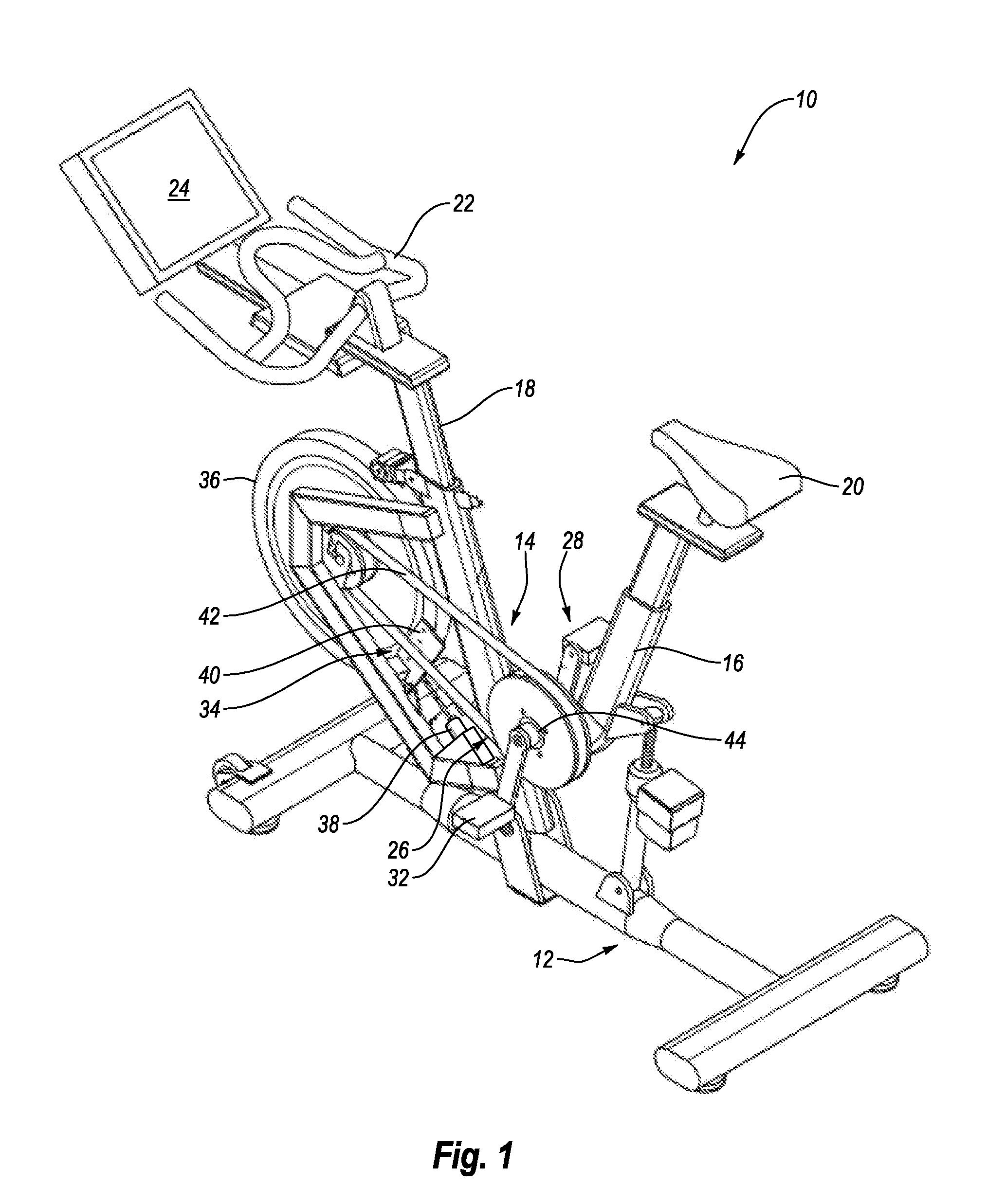
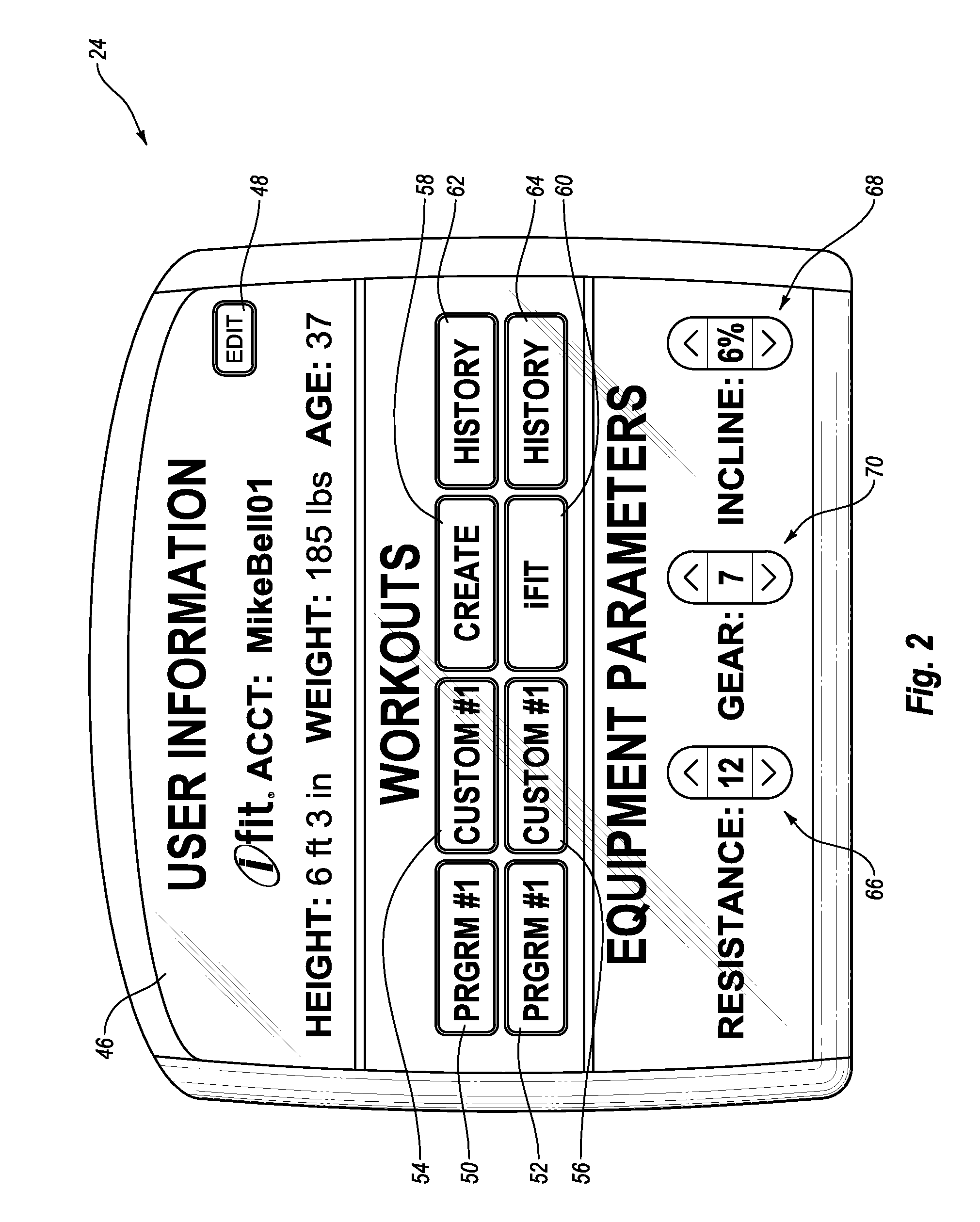
System and Method for Simulating Environmental Conditions on an Exercise Bicycle
A stationary exercise cycle includes a simulation system for simulating real-world terrain based on environmental and other real-world conditions. Using topographical or other data, an actual location can be simulated. The exercise cycle may include a resistance mechanism that is adjusted based on changes in simulated slope, and by amounts simulating actual frictional and gravitational forces. The simulated speed of the rider, as well as speed and direction of a simulated wind, are used to determine a simulated air speed. Based on the simulated air speed, the simulation system determines the simulated air resistance hindering the rider, and changes reflective of the simulated air resistance are made by the resistance mechanism. The stationary exercise cycle takes into account actual or approximate physical information of the user in determining the real-world conditions that are simulated, including the height, weight, shape, and / or rising position of the rider.
Owner:IFIT INC
Mini skirt aerodynamic fairing device for reducing the aerodynamic drag of ground vehicles
InactiveUS20080093887A1Promote upwashIncreasing effective blocking areaVehicle seatsWindowsMobile vehicleAerodynamic drag
A device for the reduction of aerodynamic drag and for improved performance and stability of ground vehicles by reducing the mass and velocity of the flow passing under a vehicle is described. The device is particularly suited for a tractor-trailer truck system that includes a motorized lead vehicle pulling one or more non-motorized vehicles. The device is designed to control the flow from entering the undercarriage region from the side of a trailer of a tractor-trailer truck system.
Owner:SOLUS SOLUTIONS & TECH
Fuel efficient dynamic air dam system
InactiveUS20070257512A1Improve fuel efficiencyMaintain securityVehicle seatsWindowsAerodynamic dragDifferential pressure
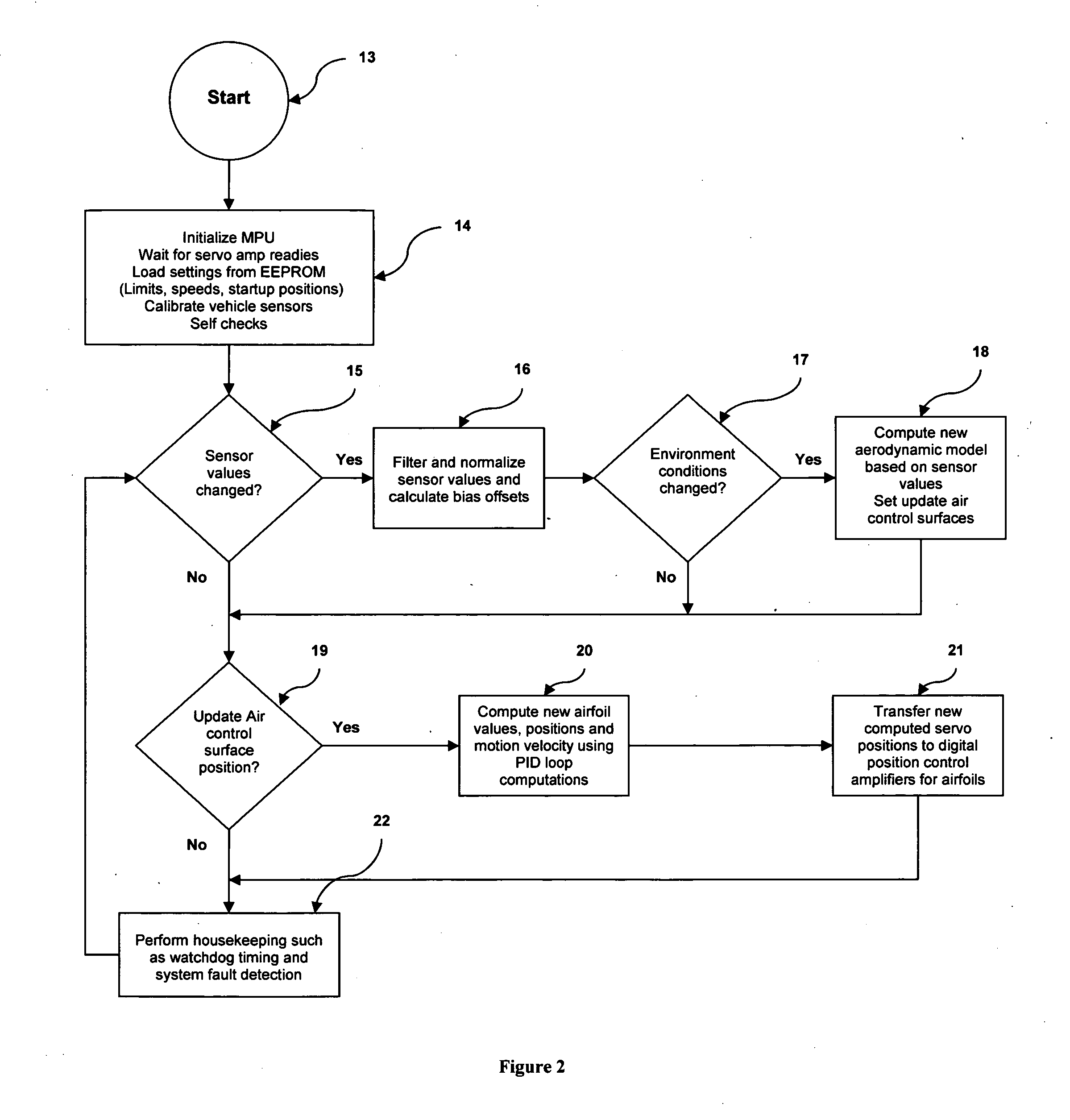
Active, aerodynamic controller that describes a method for dynamically controlling airflow using computer controlled movable air dams and airfoils on motor vehicles. It is well known that motor vehicles generally have a great deal of aerodynamic friction also known as drag. Fuel efficiency is greatly affected by a vehicle's aerodynamic drag. Aerodynamic drag is caused by both induced drag and parasitic drag. Parasite drag is somewhat fixed by the overall design and shape of a vehicle. Parasite drag is caused primarily by the laminar flow of air over the smooth surfaces of the vehicle's hood, roof, windows, side mirrors and door panels. Induced drag is much more variable and is primarily created by the differential pressure effects of air flowing over, under and around a vehicle, as well as the relative airflow caused by both ground effect and atmospheric air density and wind. This invention serves to actively minimize the effects of induced drag thus reducing the amount of fuel used by vehicles fitted with this invention.
Owner:ANDERSON SCOTT
Adjustable cab extender
A cab extender assembly for selectively changing the aerodynamic drag on a vehicle having a longitudinal axis includes a fixed cab extender and at least one track extending generally parallel to the longitudinal axis of the vehicle. An adjustable cab extender has at least one moveable member that is engaged in the track. An actuator assembly is configured for selectively reciprocating the adjustable cab extender along the track and with respect to the fixed cab extender.
Owner:INT TRUCK INTPROP LLC
Aerodynamic drag reduction apparatus for wheeled vehicles in ground effect
InactiveUS20050161976A1Reduce pressureReduce incident pressureVehicle seatsWindowsAerodynamic dragAirflow
An apparatus for reducing the aerodynamic drag of a wheeled vehicle in a flowstream, the vehicle having a vehicle body and a wheel assembly supporting the vehicle body. The apparatus includes a baffle assembly adapted to be positioned upstream of the wheel assembly for deflecting airflow away from the wheel assembly so as to reduce the incident pressure on the wheel assembly.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Vehicle Underbody Fairing
InactiveUS20090146453A1Reduce air resistanceSmall sizeVehicle seatsWindowsAerodynamic dragEngineering
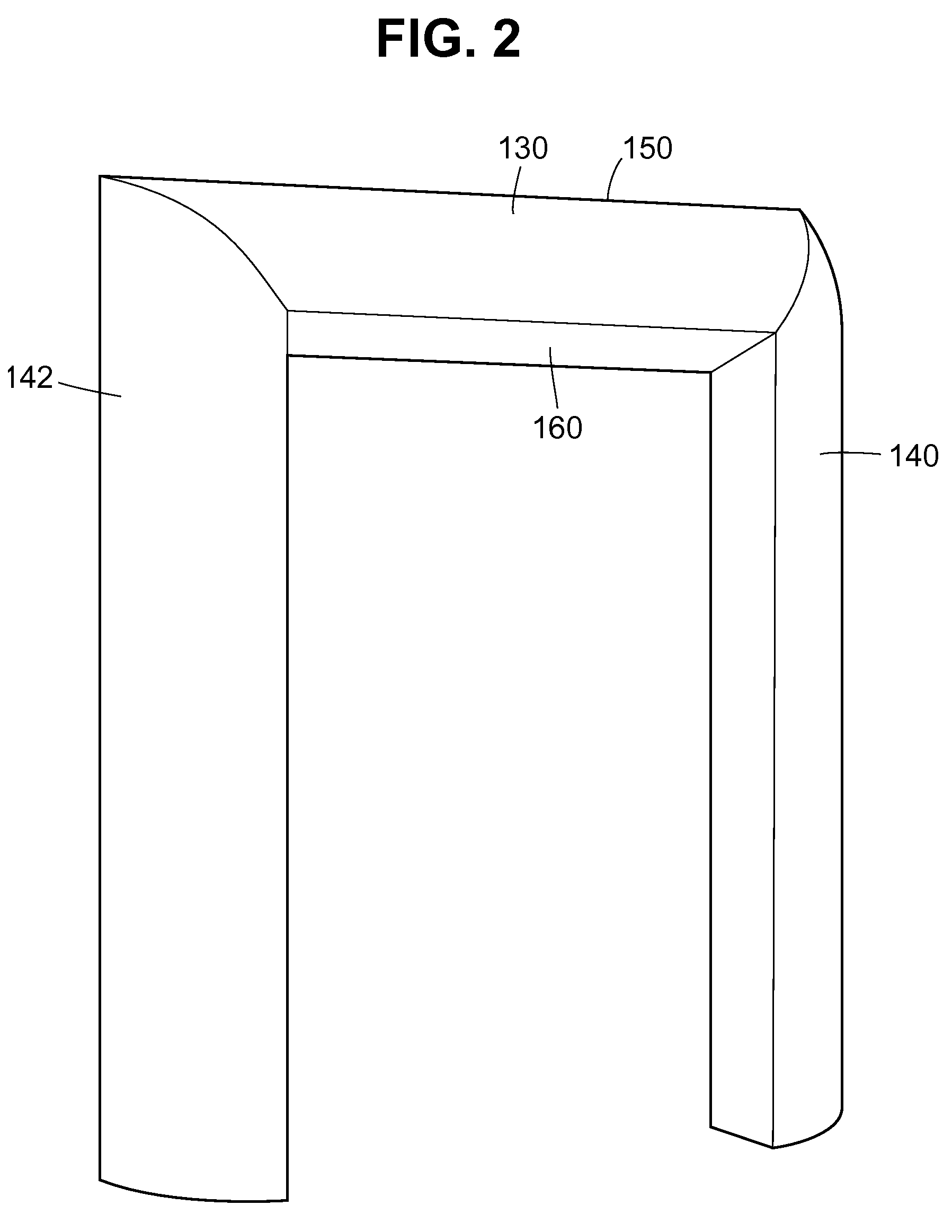
A vehicle underbody fairing apparatus for reducing aerodynamic drag caused by a vehicle wheel assembly, by reducing the size of a recirculation zone formed under the vehicle body immediately downstream of the vehicle wheel assembly. The fairing body has a tapered aerodynamic surface that extends from a front end to a rear end of the fairing body with a substantially U-shaped cross-section that tapers in both height and width. Fasteners or other mounting devices secure the fairing body to an underside surface of the vehicle body, so that the front end is immediately downstream of the vehicle wheel assembly and a bottom section of the tapered aerodynamic surface rises towards the underside surface as it extends in a downstream direction.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com