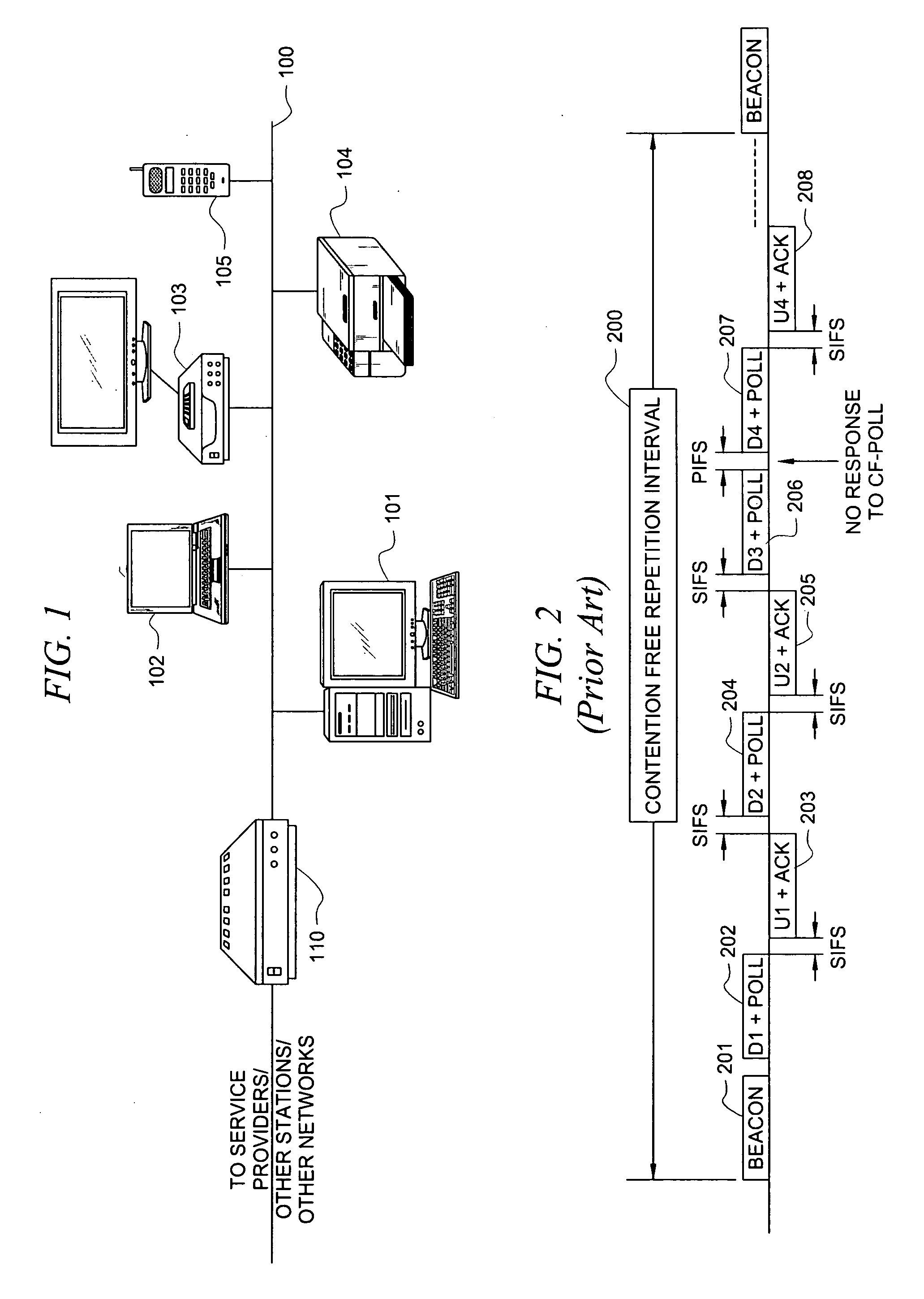
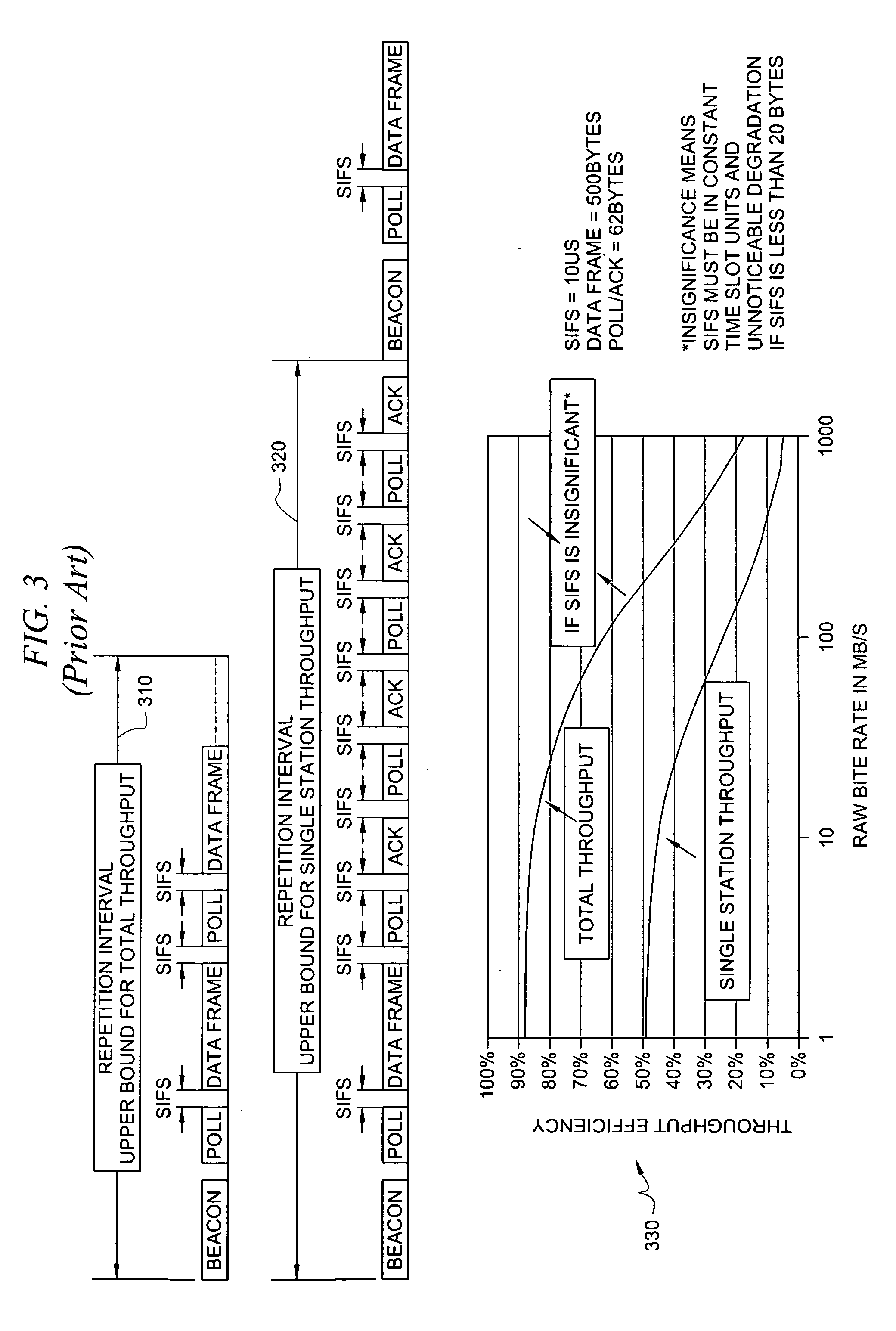
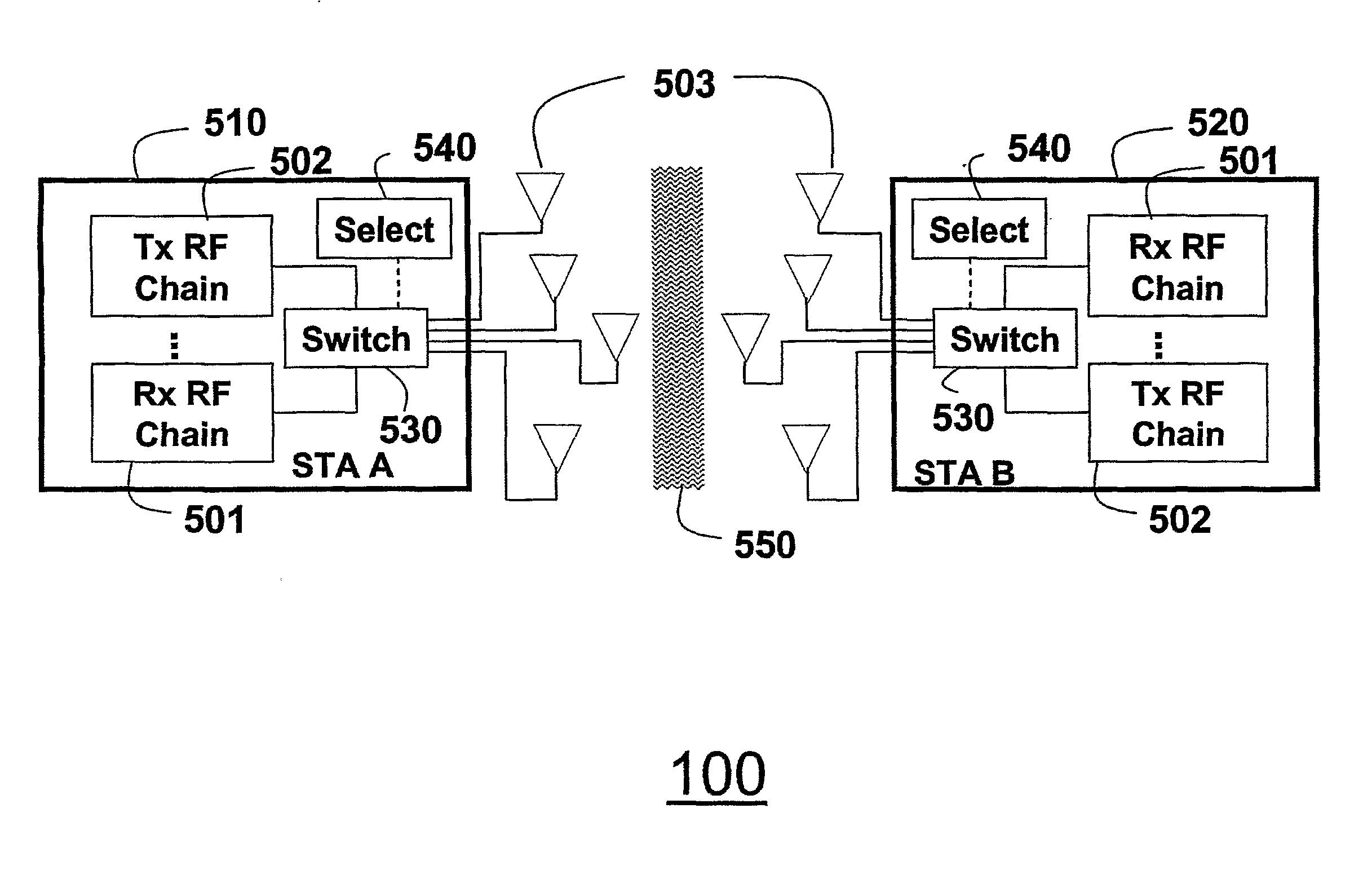
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1864 results about "Goodput" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
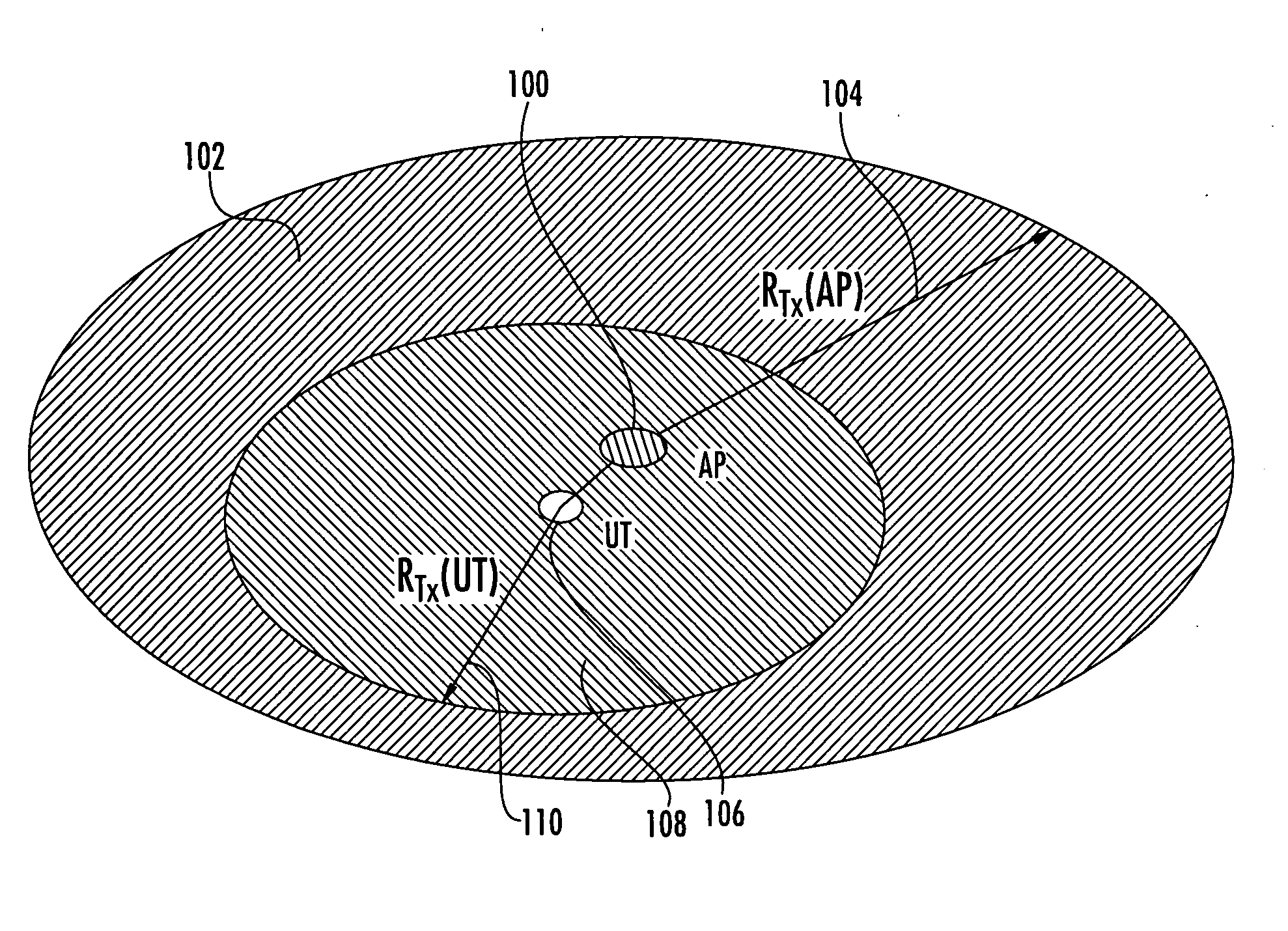
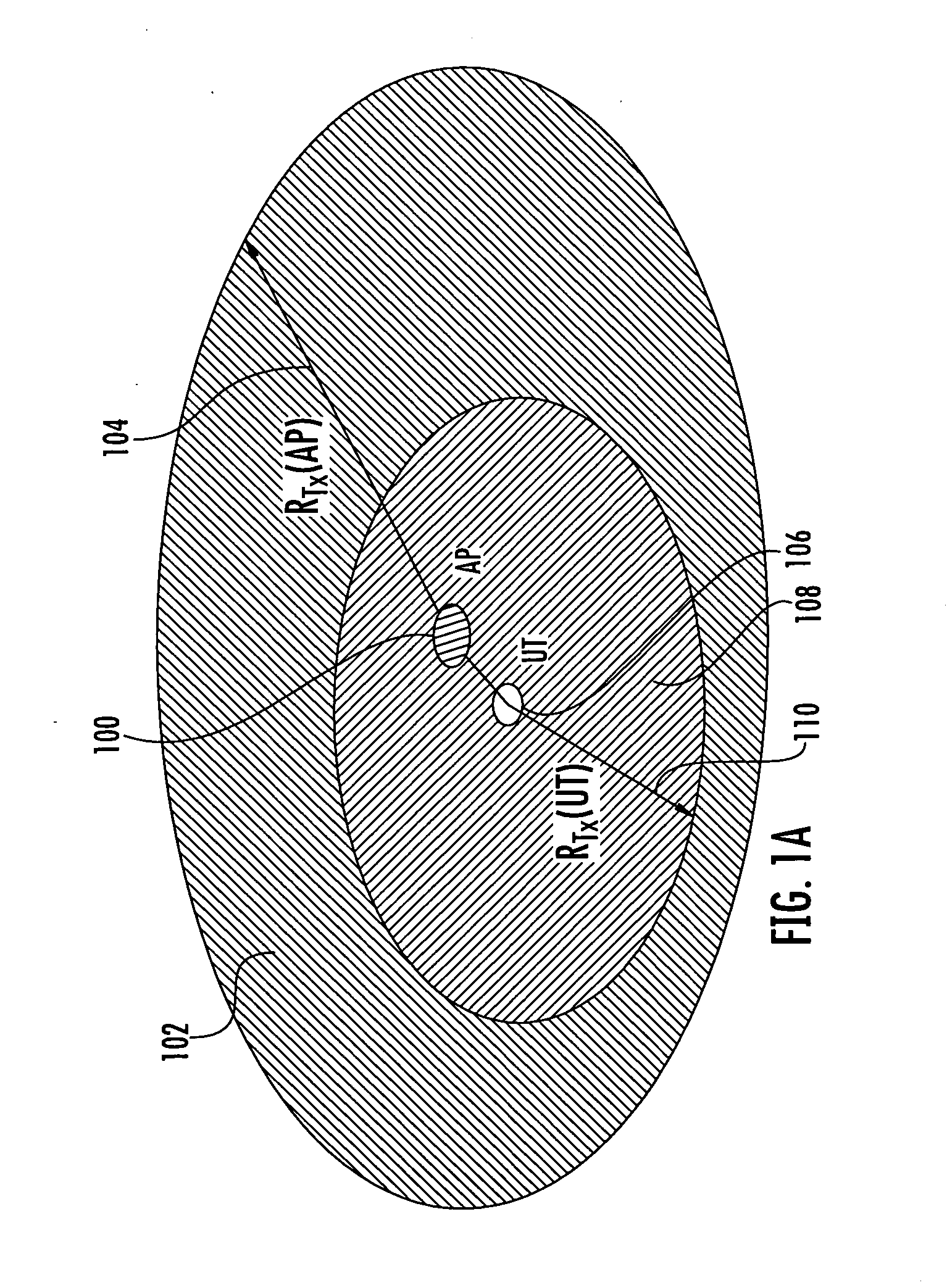
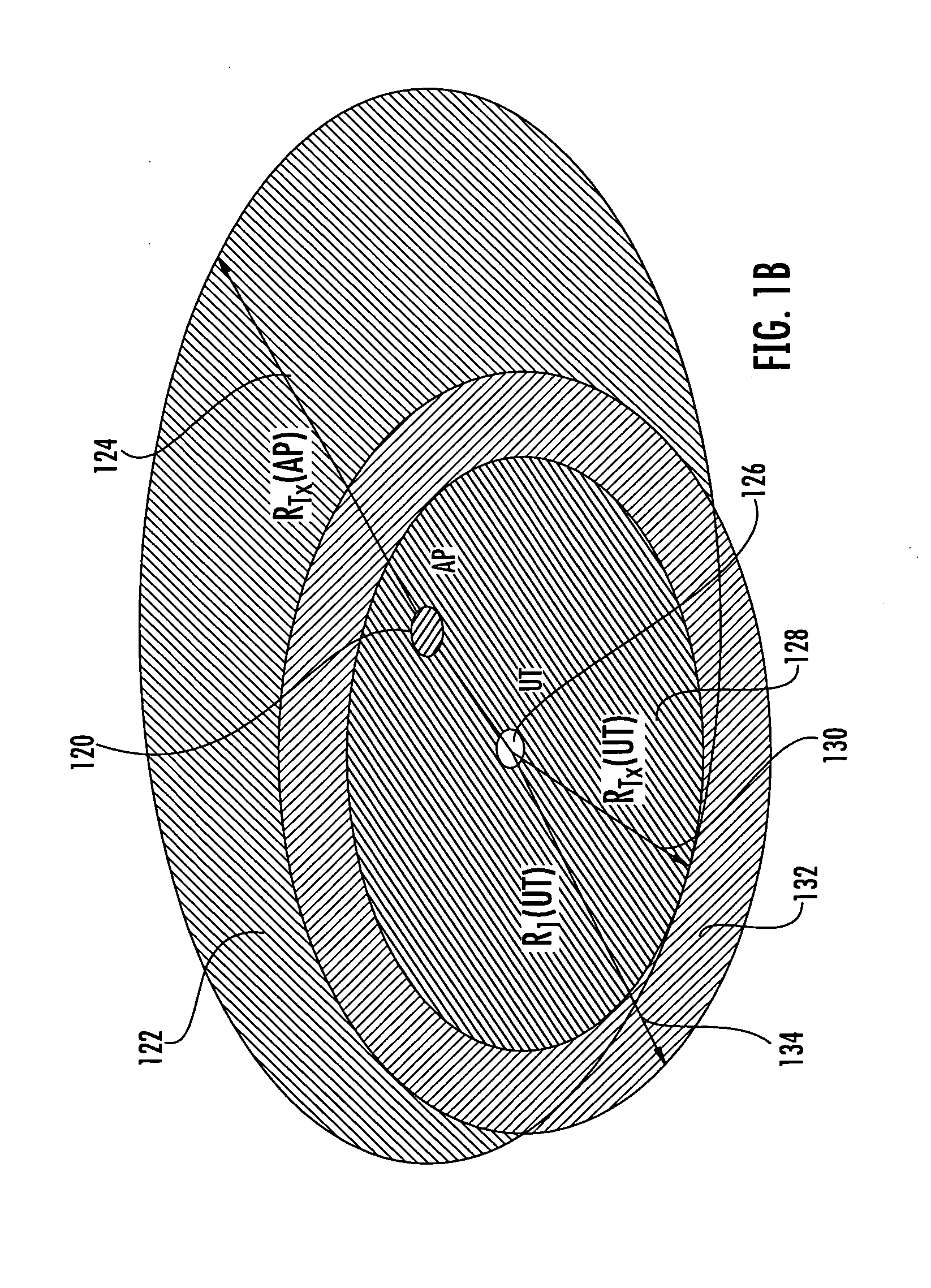
In computer networks, goodput (a portmanteau of good and throughput) is the application-level throughput of a communication; i.e. the number of useful information bits delivered by the network to a certain destination per unit of time. The amount of data considered excludes protocol overhead bits as well as retransmitted data packets. This is related to the amount of time from the first bit of the first packet sent (or delivered) until the last bit of the last packet is delivered.
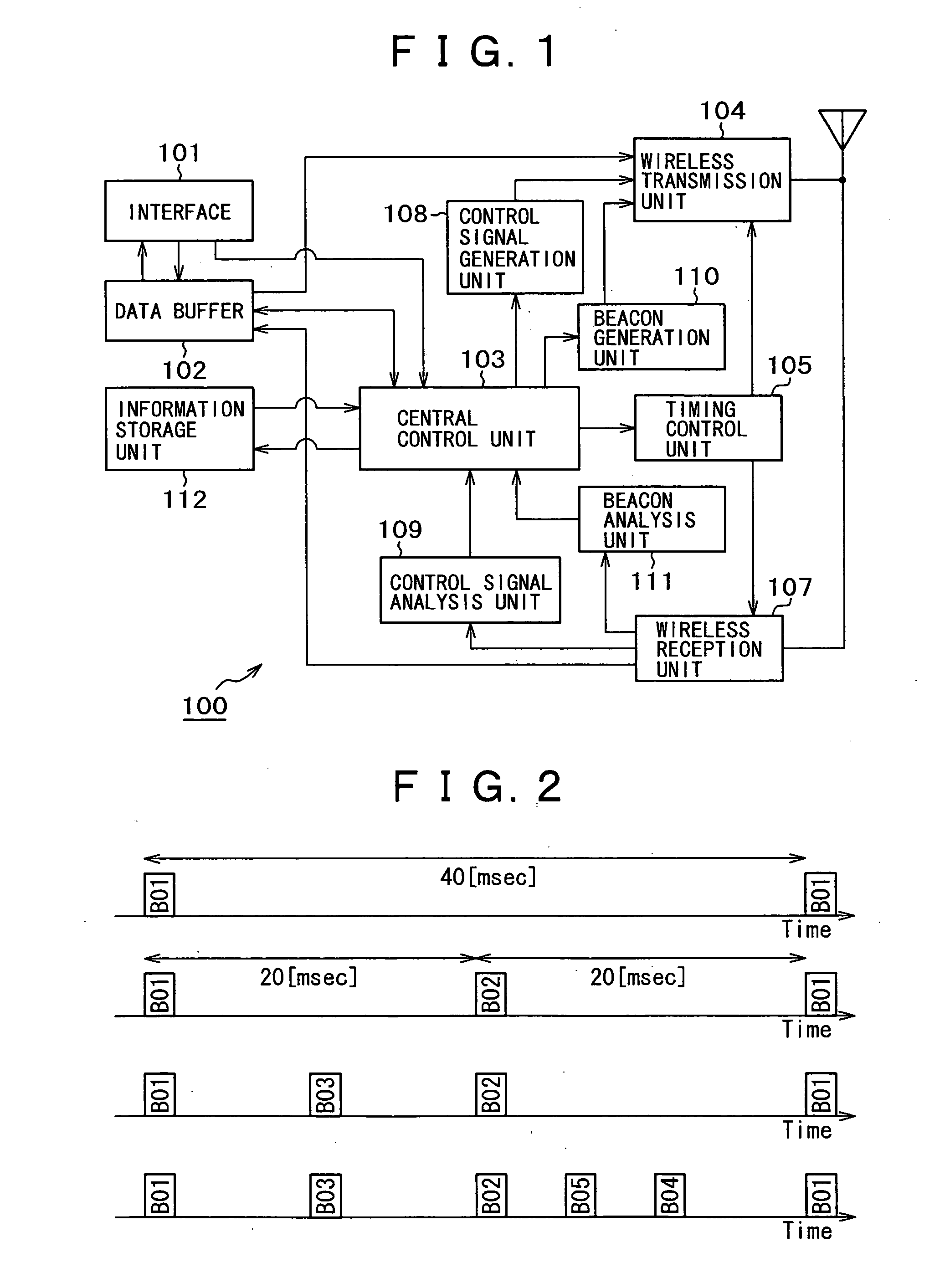
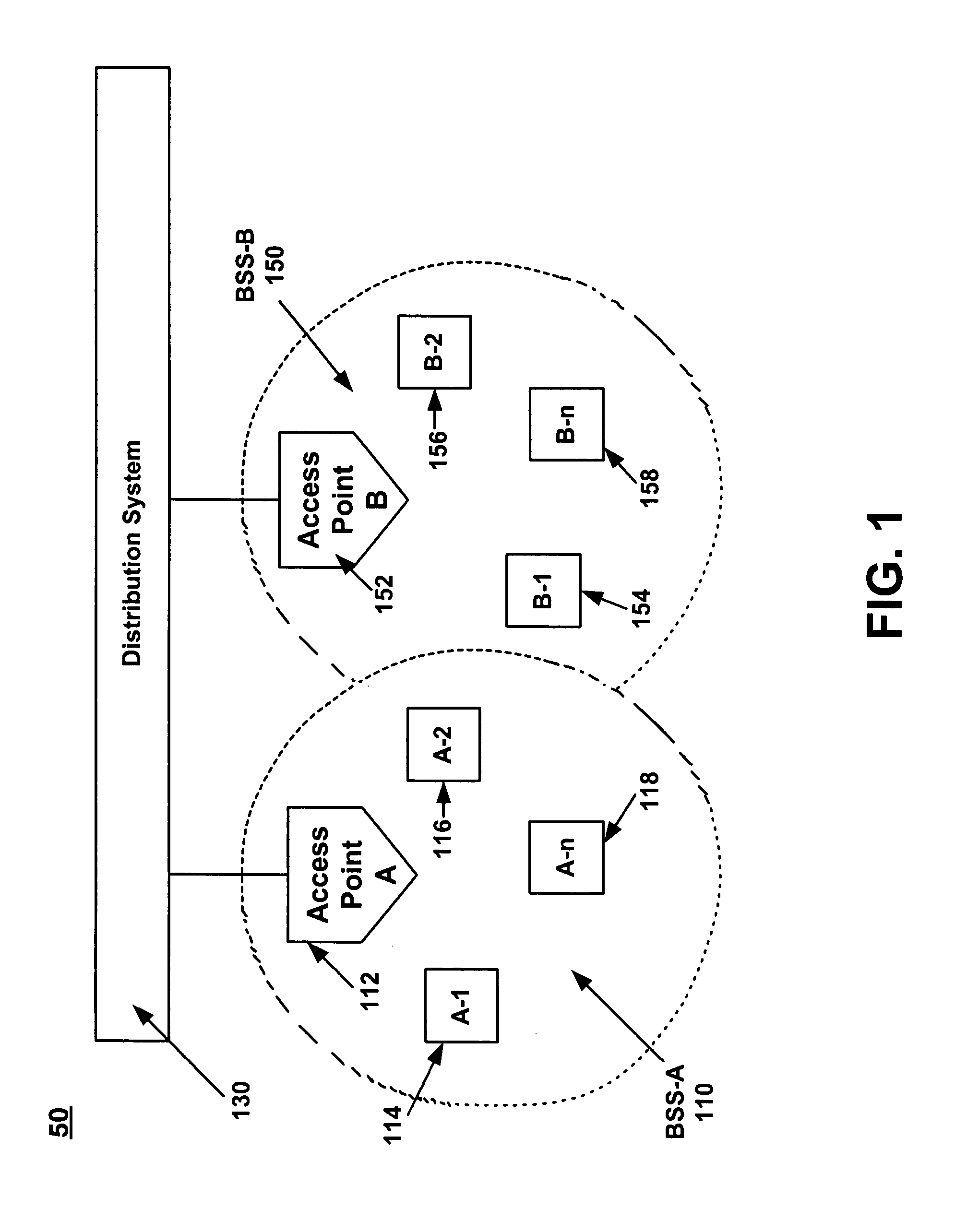
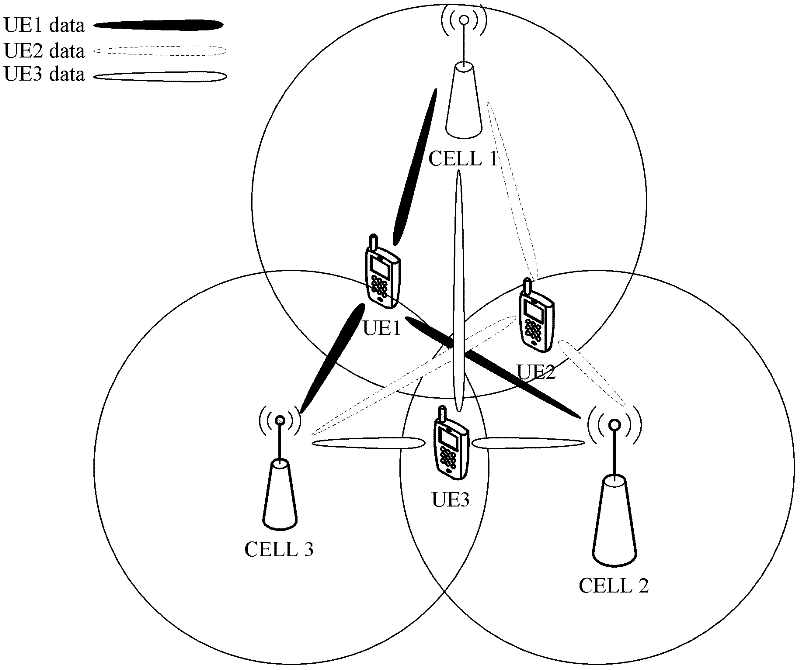
Method of interference management for interference/collision avoidance and spatial reuse enhancement
InactiveUS20050058151A1Improve rendering capabilitiesImprove channel utilizationEnergy efficient ICTPower managementDifferentiated servicesDifferentiated service
A method called the evolvable interference management (EIM) method is disclosed in this patent for avoiding interference and collision and increasing network throughput and energy efficiency in wireless networks. EIM employs sensitive CSMA / CA, patching approaches, interference engineering, differentiated multichannel, detached dialogues, and / or spread spectrum techniques to solve the interference and QoS problems. EIM-based protocols can considerably increase network throughput and QoS differentiation capability as compared to IEEE 802.11e in multihop networking environments. Due to the improvements achievable by EIM, the techniques and mechanisms presented in this application may be applied to obtain an extension to IEEE 802.11 to better support differentiated service and power control in ad hoc networks and multihop wireless LANs. New protocols may also be designed based on EIM.
Owner:YEH CHIHSIANG
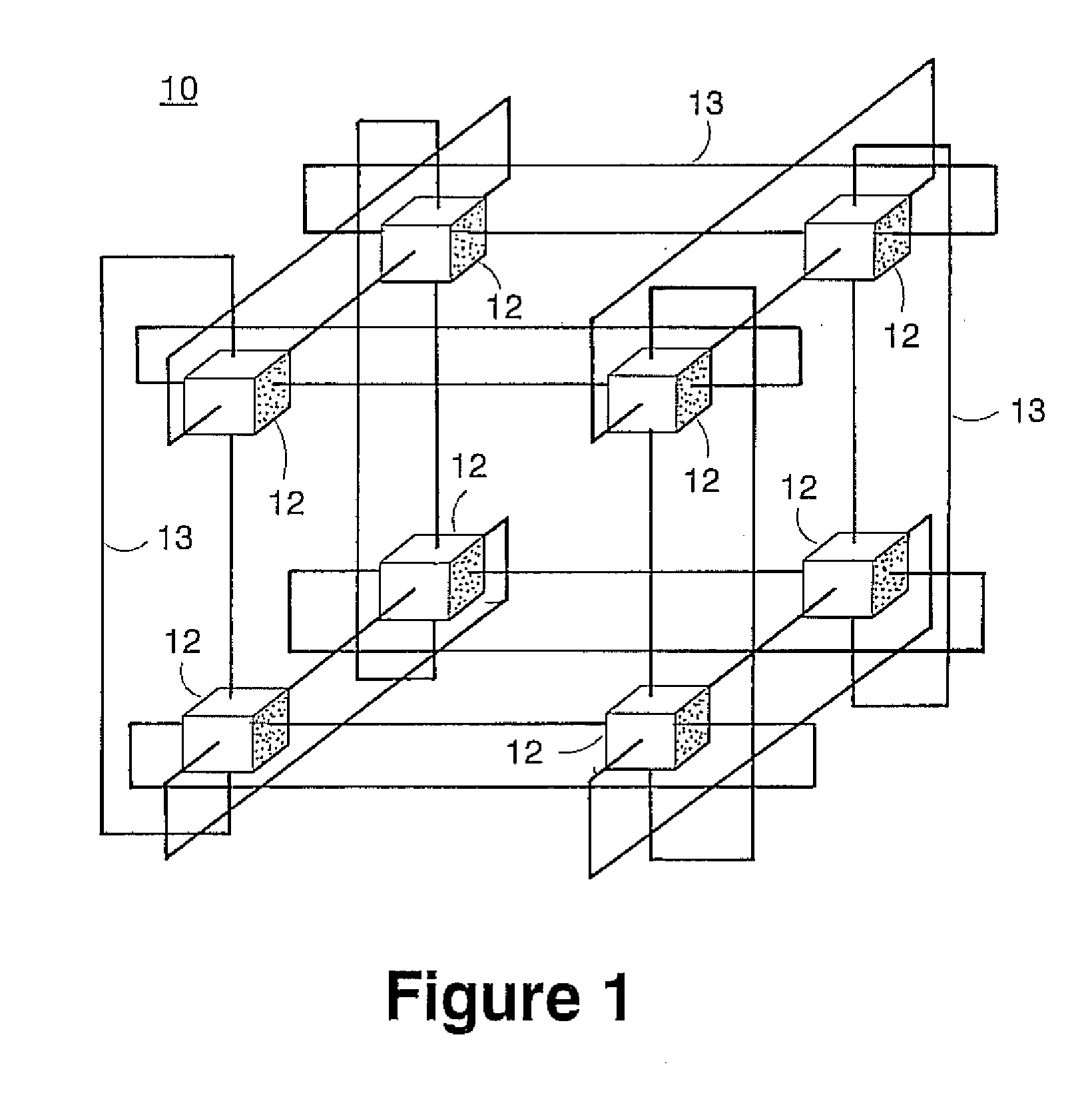
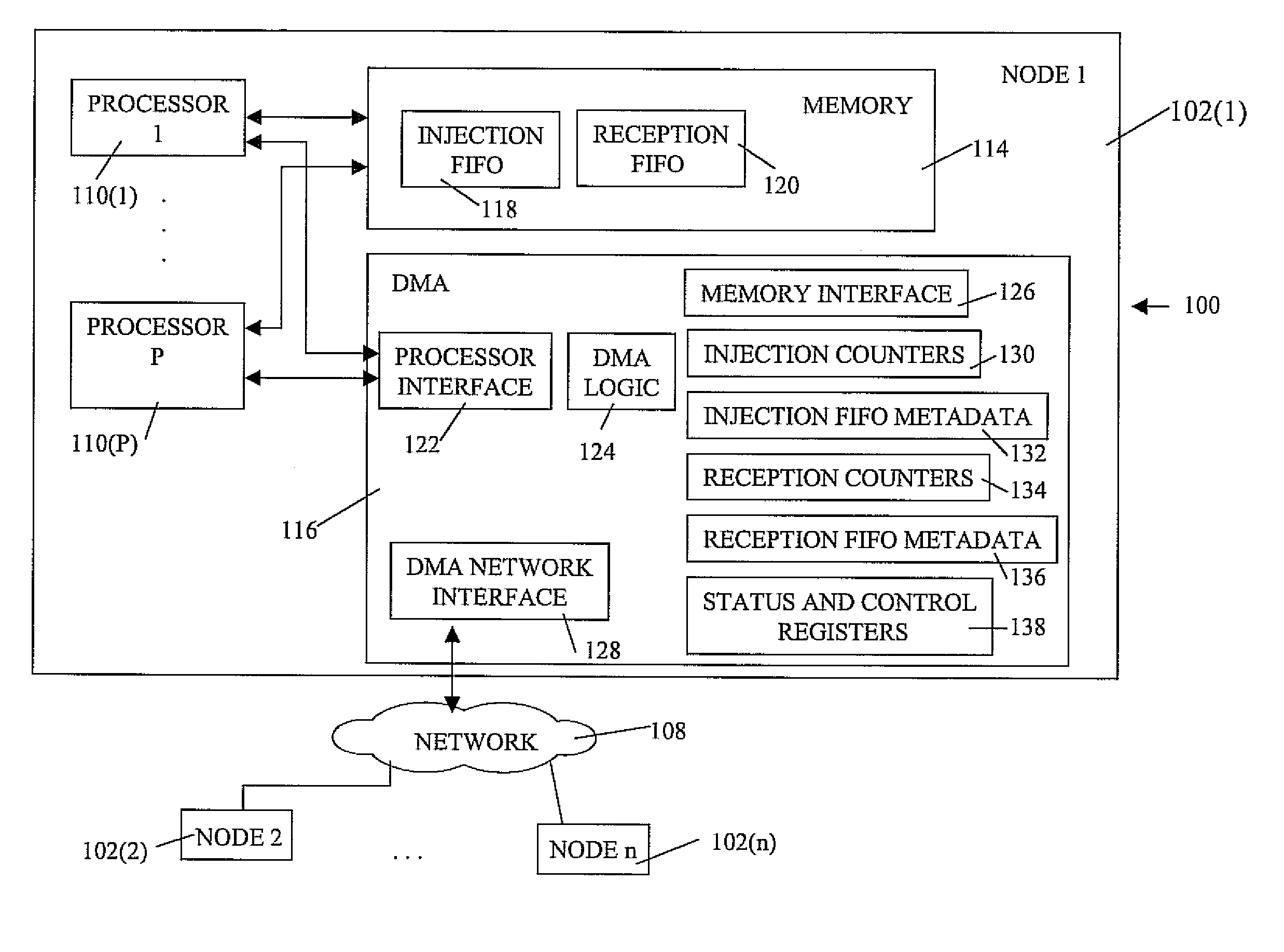
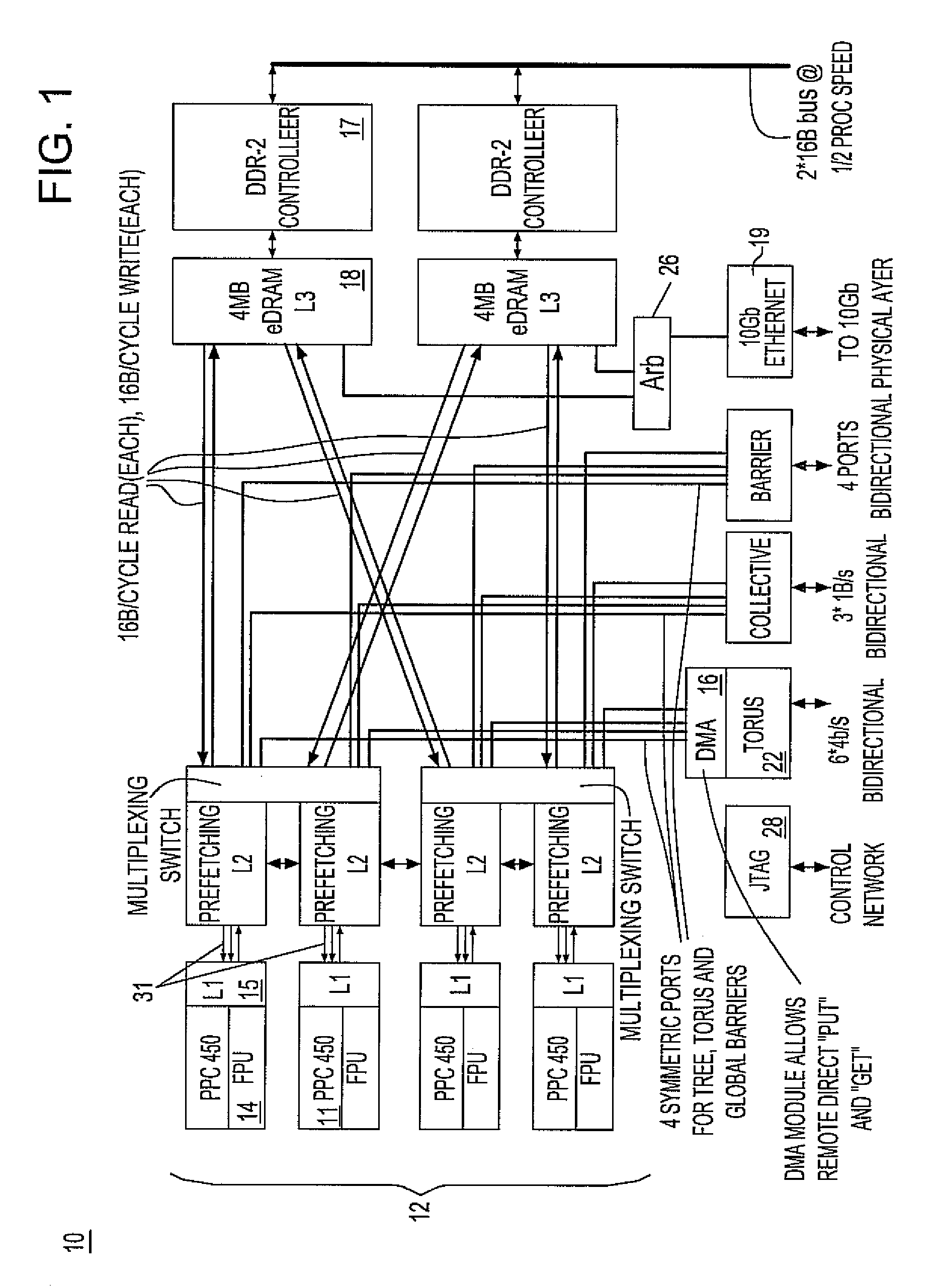
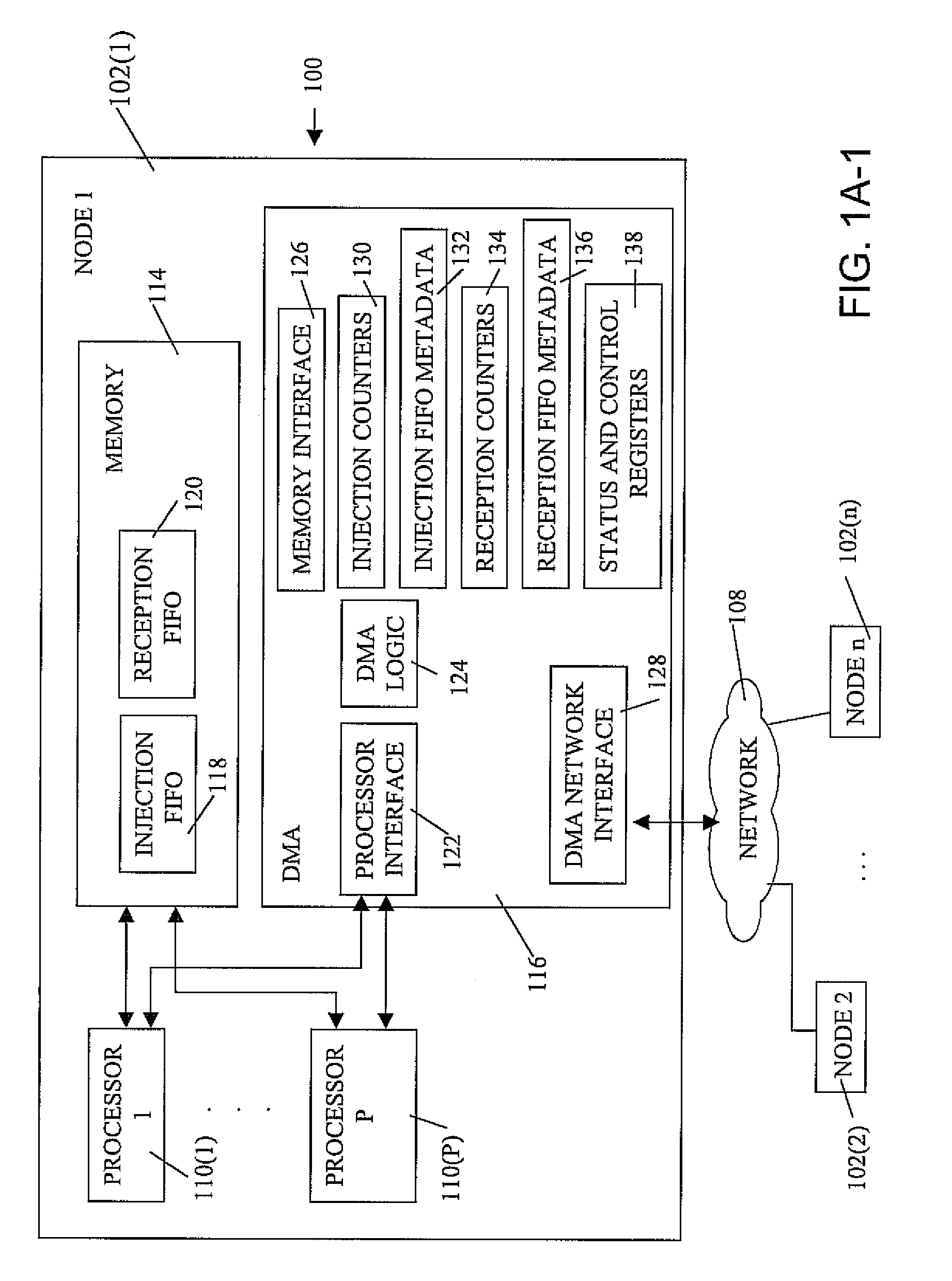
Novel massively parallel supercomputer
InactiveUS20090259713A1Low costReduced footprintError preventionProgram synchronisationSupercomputerPacket communication
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
High-throughput, low-latency next generation internet networks using optical tag switching
InactiveUS6111673AEfficient comprehensive utilizationSignificant overheadMultiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsSignal routingInternet network
An optical signaling header technique applicable to optical networks wherein packet routing information is embedded in the same channel or wavelength as the data payload so that both the header and data payload propagate through network elements with the same path and the associated delays. The header routing information has sufficiently different characteristics from the data payload so that the signaling header can be detected without being affected by the data payload, and that the signaling header can also be removed without affecting the data payload. The signal routing technique can be overlaid onto the conventional network elements in a modular manner using two types of applique modules. The first type effects header encoding and decoding at the entry and exit points of the data payload into and out of the network; the second type effects header detection at each of the network elements.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
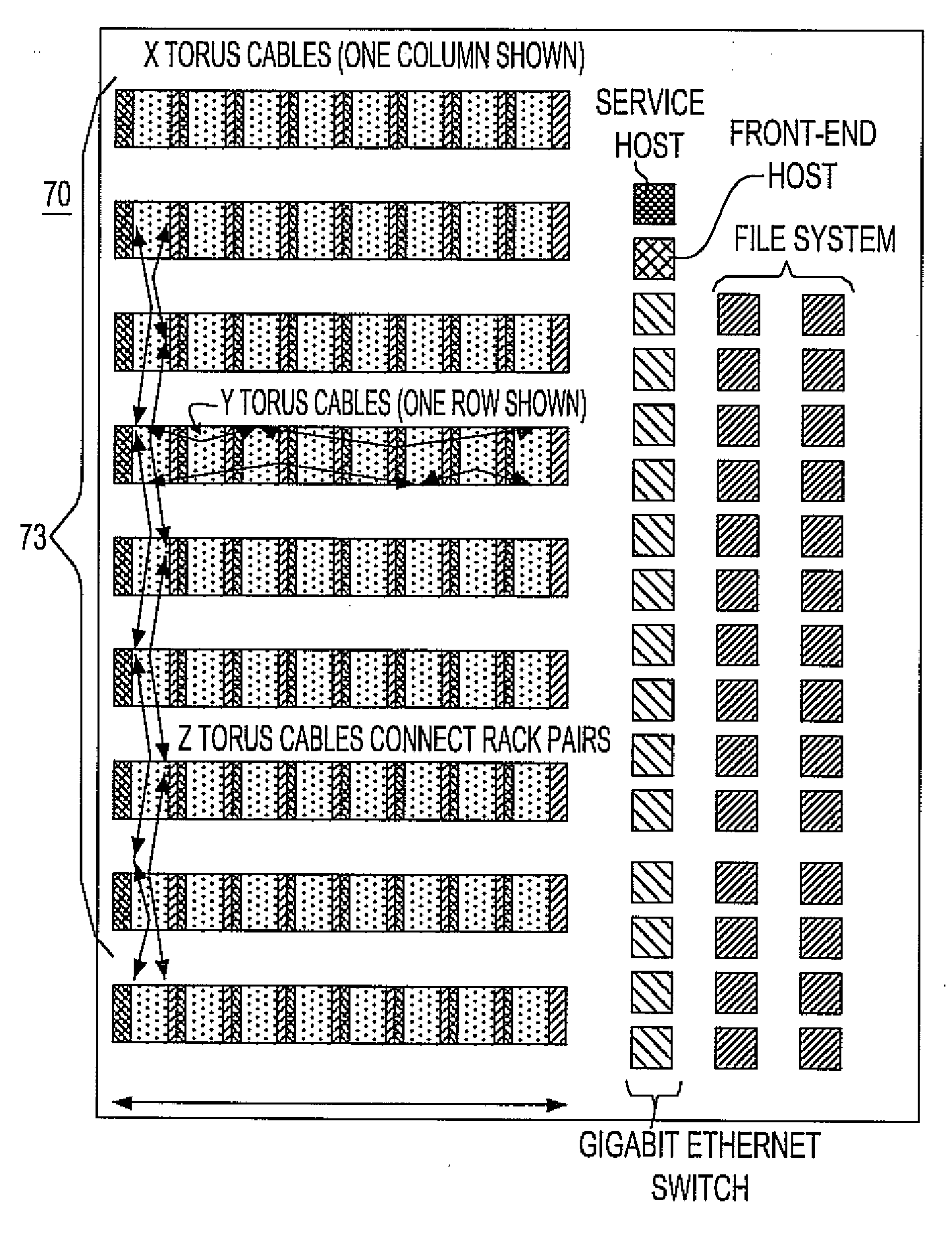
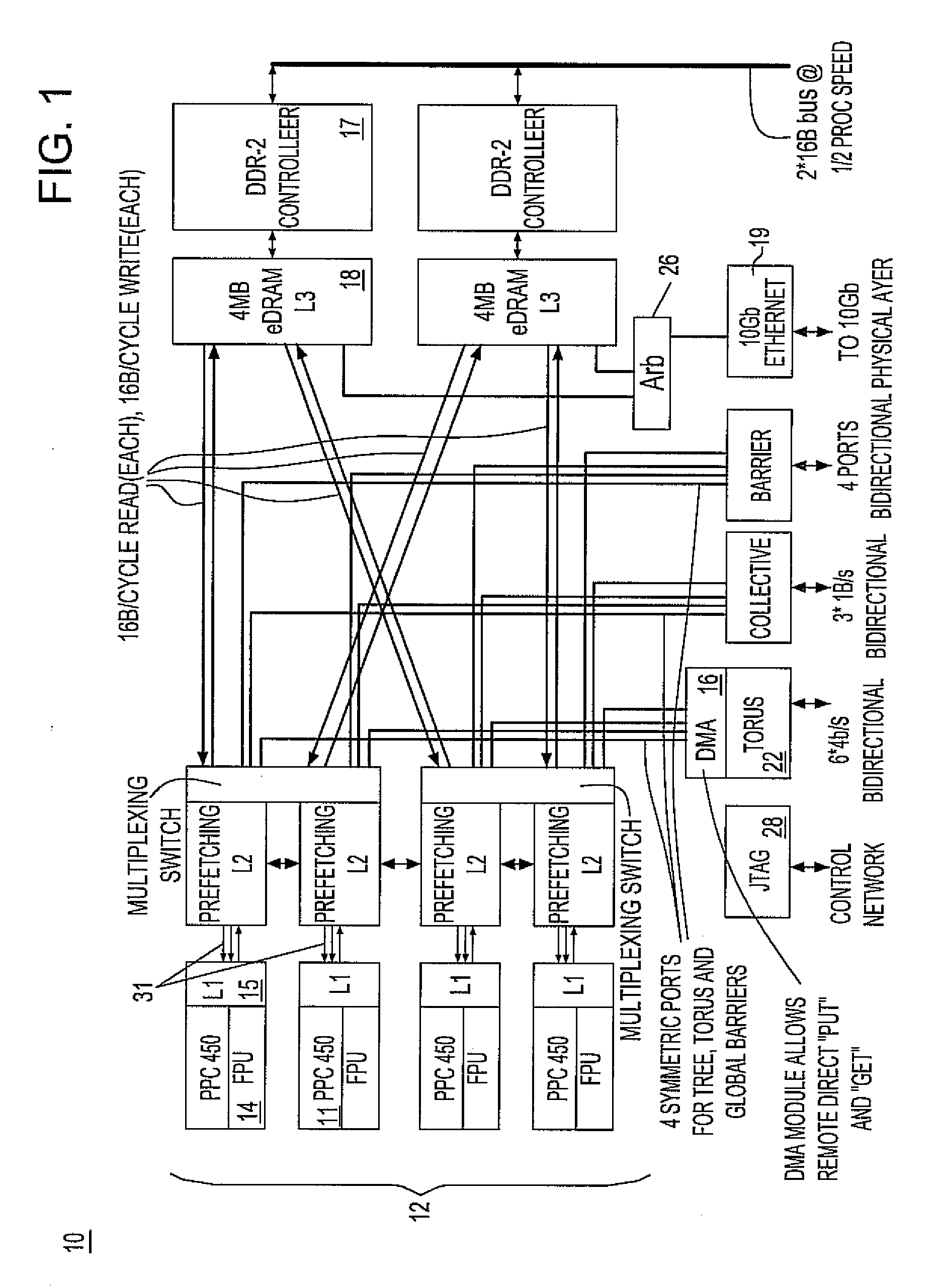
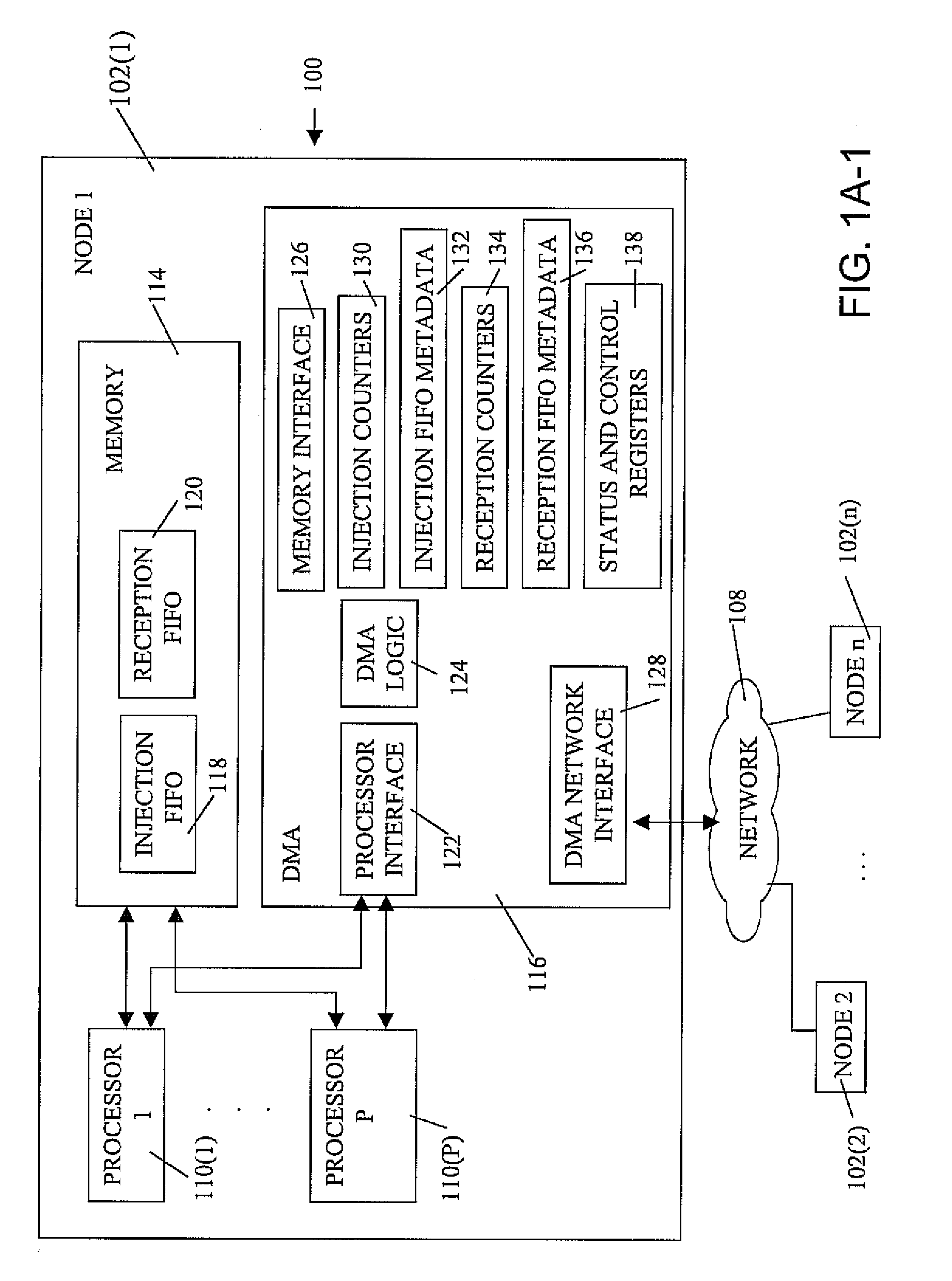
Ultrascalable petaflop parallel supercomputer
InactiveUS20090006808A1Massive level of scalabilityUnprecedented level of scalabilityProgram control using stored programsArchitecture with multiple processing unitsMessage passingPacket communication
A novel massively parallel supercomputer of petaOPS-scale includes node architectures based upon System-On-a-Chip technology, where each processing node comprises a single Application Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC) having up to four processing elements. The ASIC nodes are interconnected by multiple independent networks that optimally maximize the throughput of packet communications between nodes with minimal latency. The multiple networks may include three high-speed networks for parallel algorithm message passing including a Torus, collective network, and a Global Asynchronous network that provides global barrier and notification functions. These multiple independent networks may be collaboratively or independently utilized according to the needs or phases of an algorithm for optimizing algorithm processing performance. Novel use of a DMA engine is provided to facilitate message passing among the nodes without the expenditure of processing resources at the node.
Owner:IBM CORP
Transparent, look-up-free packet forwarding method for optimizing global network throughput based on real-time route status
ActiveUS20040032856A1Fast protection re-routingEfficient multicastingData switching by path configurationPrivate networkOSI model
A packet forwarding method for optimizing packet traffic flow across communications networks and simplifying network management. The invention provides look-up-free and packet-layer-protocol transparent forwarding of multi-protocol packet traffic among Layer-N (N=2 or upper in the ISO OSI model) nodes. The invention enables flexible and efficient packet multicast and anycast capabilities along with real-time dynamic load balancing and fast packet-level traffic protection rerouting. Applications include fast and efficient packet traffic forwarding across administrative domains of Internet, such as an ISP's backbone or an enterprise virtual private network, as well as passing packet traffic over a neutral Internet exchange facility between different administrative domains.
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
Method and apparatus for monitoring latency, jitter, packet throughput and packet loss ratio between two points on a network
InactiveUS7961637B2Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorCorrect operation testingPacket lossWaiting time
Owner:SPIRENT COMM
Media access control architecture
InactiveUS20070058661A1Data switching by path configurationWireless commuication servicesTraffic flow managementStation
Owner:OPTIMAL INNOVATIONS INC
Antenna/Beam Selection Training in MIMO Wireless LANs with Different Sounding Frames
ActiveUS20090290563A1Novel methodFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission systemsWireless lanMultiple input
A method selects antennas in a multiple-input, multiple-output (MIMO) wireless local area network (WLAN) that includes a plurality of stations, and each station includes a set of antennas. Plural consecutive packets, received at a station, include plural consecutive sounding packets. Each sounding packet corresponds to a different subset of the set of antennas, and at least one of the plural consecutive packets includes a high throughput (HT) control field including a signal to initiate antenna selection and a number N indicative of a number of sounding packets which follow the at least one packet including the HT control field and which are to be used for antenna selection. A channel matrix is estimated based on a characteristic of the channel as indicated by the received N sounding packets, and a subset of antennas is selected according to the channel matrix. Station and computer program product embodiments include similar features.
Owner:FREEDOM PATENTS LLC
System and method of base station performance enhancement using coordinated antenna array
ActiveUS20100054196A1High system throughputReduce interferenceError preventionTransmission systemsSmart antennaNetwork management
In wireless system, a group of Basestations (BTSs) can be managed by a centralized network management identity or can be self-organized by communicating with each other via wireless air-interfaces or wired interfaces. One such example are Femtocell systems. When the BTSs are using the same frequency for transmitting and receiving with relatively large transmitting power and when they are closer to each other, performance of such a system and user throughput or QoS (Quality of Service) gets degraded due to the interference between the BTSs and among the users. Smart antenna technique can be used in a coordinated way among a group of BTSs, such as Femtocells, to avoid or reduce interference or manage how interference happens to achieve performance enhancement such as higher system throughput or better QoS to individual applications.
Owner:AIRHOP COMMUNICATIONS
Ultrascalable petaflop parallel supercomputer
InactiveUS7761687B2Maximize throughputDelay minimizationGeneral purpose stored program computerElectric digital data processingSupercomputerPacket communication
A massively parallel supercomputer of petaOPS-scale includes node architectures based upon System-On-a-Chip technology, where each processing node comprises a single Application Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC) having up to four processing elements. The ASIC nodes are interconnected by multiple independent networks that optimally maximize the throughput of packet communications between nodes with minimal latency. The multiple networks may include three high-speed networks for parallel algorithm message passing including a Torus, collective network, and a Global Asynchronous network that provides global barrier and notification functions. These multiple independent networks may be collaboratively or independently utilized according to the needs or phases of an algorithm for optimizing algorithm processing performance. The use of a DMA engine is provided to facilitate message passing among the nodes without the expenditure of processing resources at the node.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Wireless communication apparatus, wireless communication method, and computer program
InactiveUS20050036475A1Data transmissionEfficient executionNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesData transmissionCommunication device
Communication bands are effectively allocated to each communication station under a communication environment of an autonomous distributed type system such as an ad-hoc communication. Each communication station acquires a priority slot with which each communication station itself performs data transmission preferentially at predetermined time intervals, and releases or allocates its own priority slot to other communication station in response to a permission form upper layer of a communication protocol based on a fact that the transmission data is not in a buffer. Thereby, it is able to effectively utilize the communication bands, and to improve a throughput of the whole system.
Owner:SONY CORP
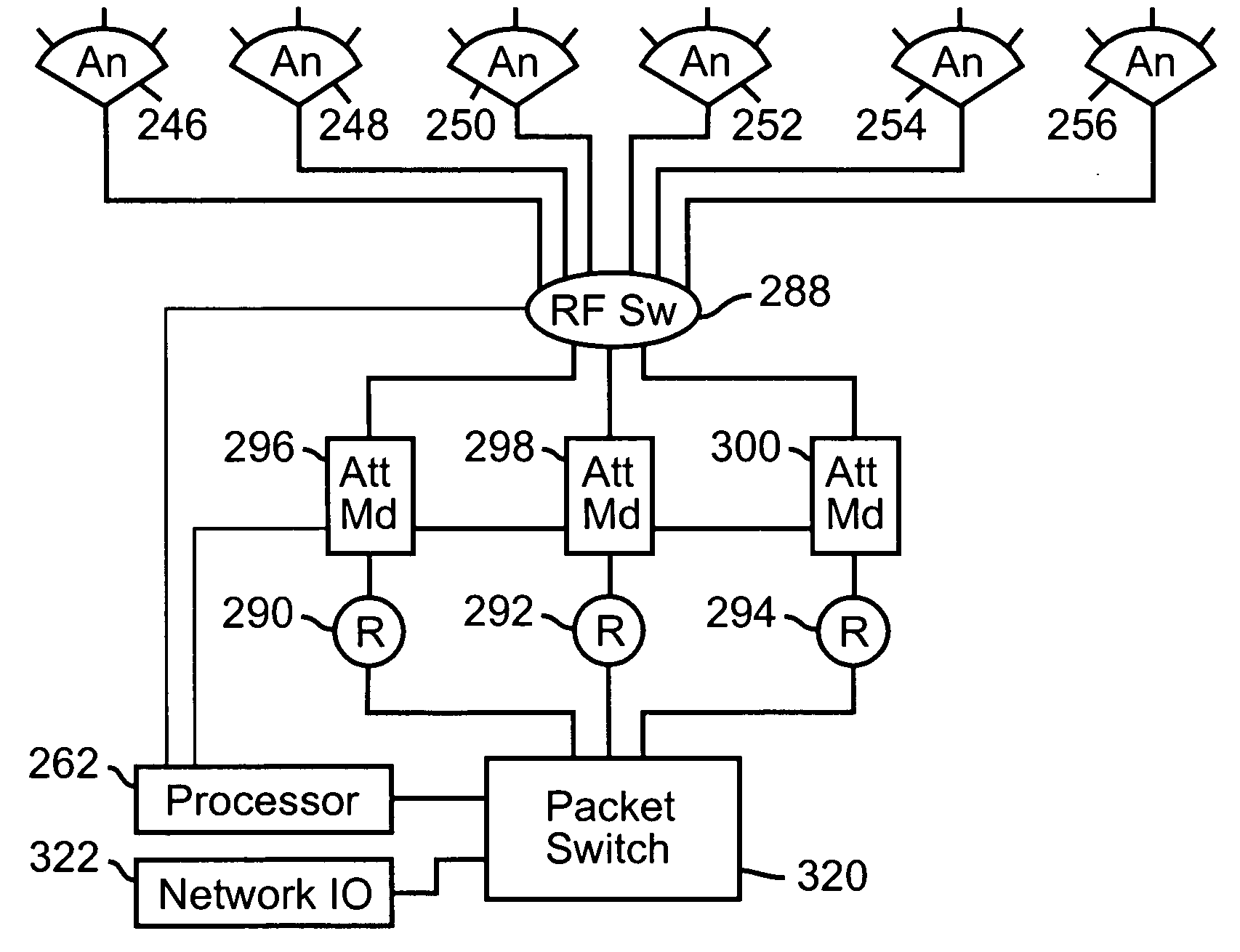
Methods and apparatus for high throughput multiple radio wireless cells and networks
InactiveUS20050003763A1Minimize interferenceImprove data throughputSite diversitySpatial transmit diversityUltrasound attenuationWireless
Methods and apparatus for high throughput wireless cells and networks are described. The wireless cells may be equipped with multiple radios. Antennas may be arranged into overlapping and non-overlapping patterns. Channels may be assigned to foster servicing clients, and inter-cell communication. Attenuation may be used to decrease interference. Networks may be formed using a variety of methods and apparatus.
Owner:ROTANI
United scheduling method for ascending multi-point collaboration in LTE-A
InactiveCN101442808AReduce distractionsImprove throughputNetwork traffic/resource managementComputer networkComputation complexity
The invention relates to a combined dispatching method for uplink multi-point cooperation in LTE-A. The method comprises following steps: 1) determining cooperative and non-operative dispatching user; 2) dispatching of cooperative user in cell; 3) combined resource dispatching for cooperative user of cell; 4) dispatching for non-cooperative user of cell. The invention adopts stepping optimizing method in cell or intercell, and simultaneously considers user dispatching priority and channel relation in combined dispatching in cell, reduces interference between users of shared frequency cooperation, promotes throughout of whole system while guaranteeing user fairness and possesses low computation complexity.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Centralized cross-layer enhanced method and apparatus for interference mitigation in a wireless network
InactiveUS20110021153A1Improve throughputIncrease capacityReceivers monitoringRadio transmissionTelecommunicationsInterference (communication)
Apparatus and methods for improving the throughput and capacity of a wireless communications network. In one embodiment, this improvement is accomplished by focusing upon reduction of the co-channel interference, including the interferences that are unpredictable or undetectable to a traditional network. Various implementations detect the receiver interference (i.e. the interference affecting the receiver performance) at the transmitting node in order to avoid or reduce its effect at the receiving node. This detection can be as simple as e.g., spectral sensing constituting power measurement, and / or can be more sophisticated such as measurements including bandwidth, duty cycle and statistical behavior of the unwanted signal.
Owner:SAFAVI SAEID
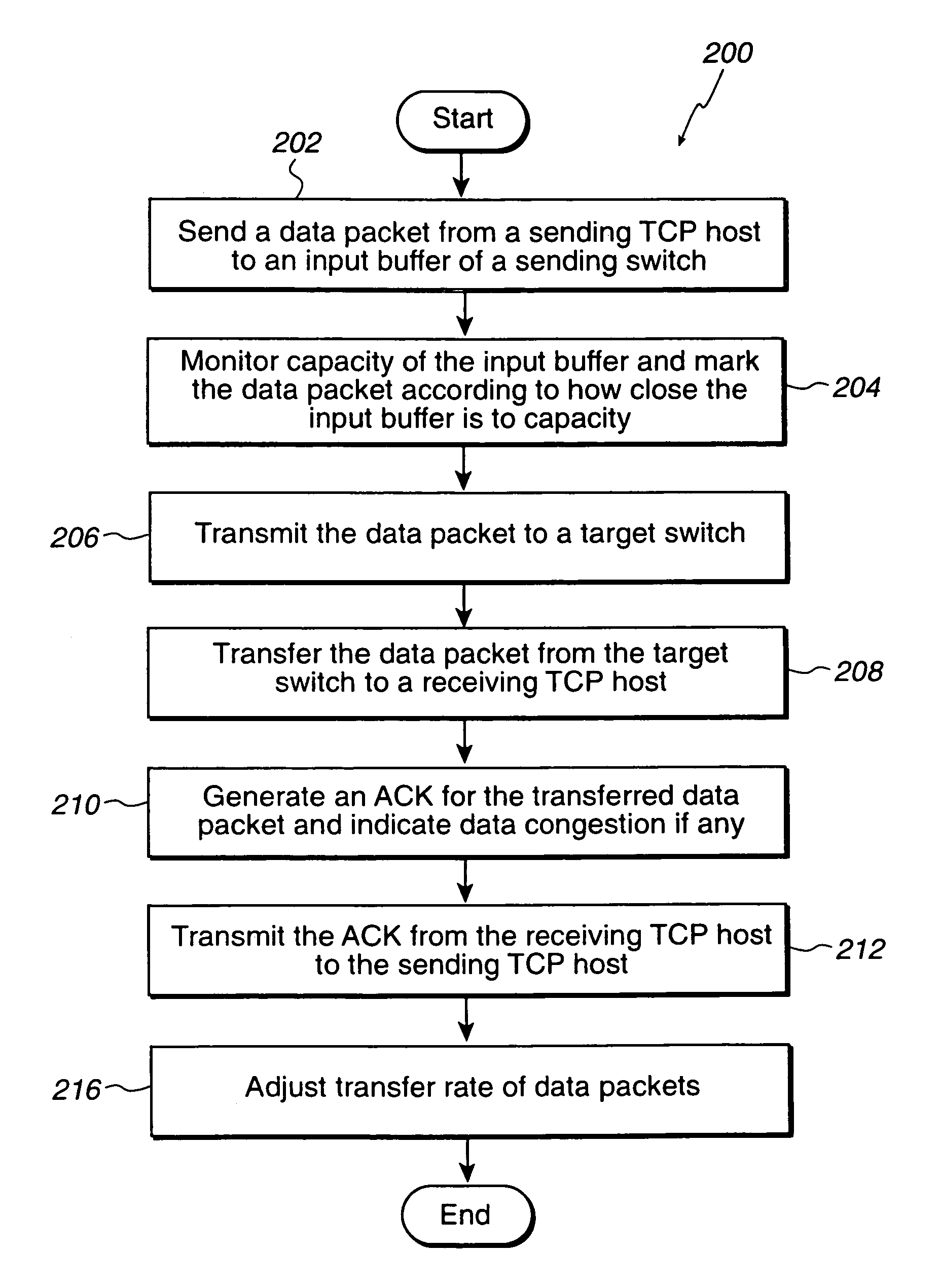
Congestion control for internet protocol storage
InactiveUS7058723B2Reduce congestionEasy data transferEnergy efficient ICTInput/output to record carriersTraffic capacityNetworking protocol
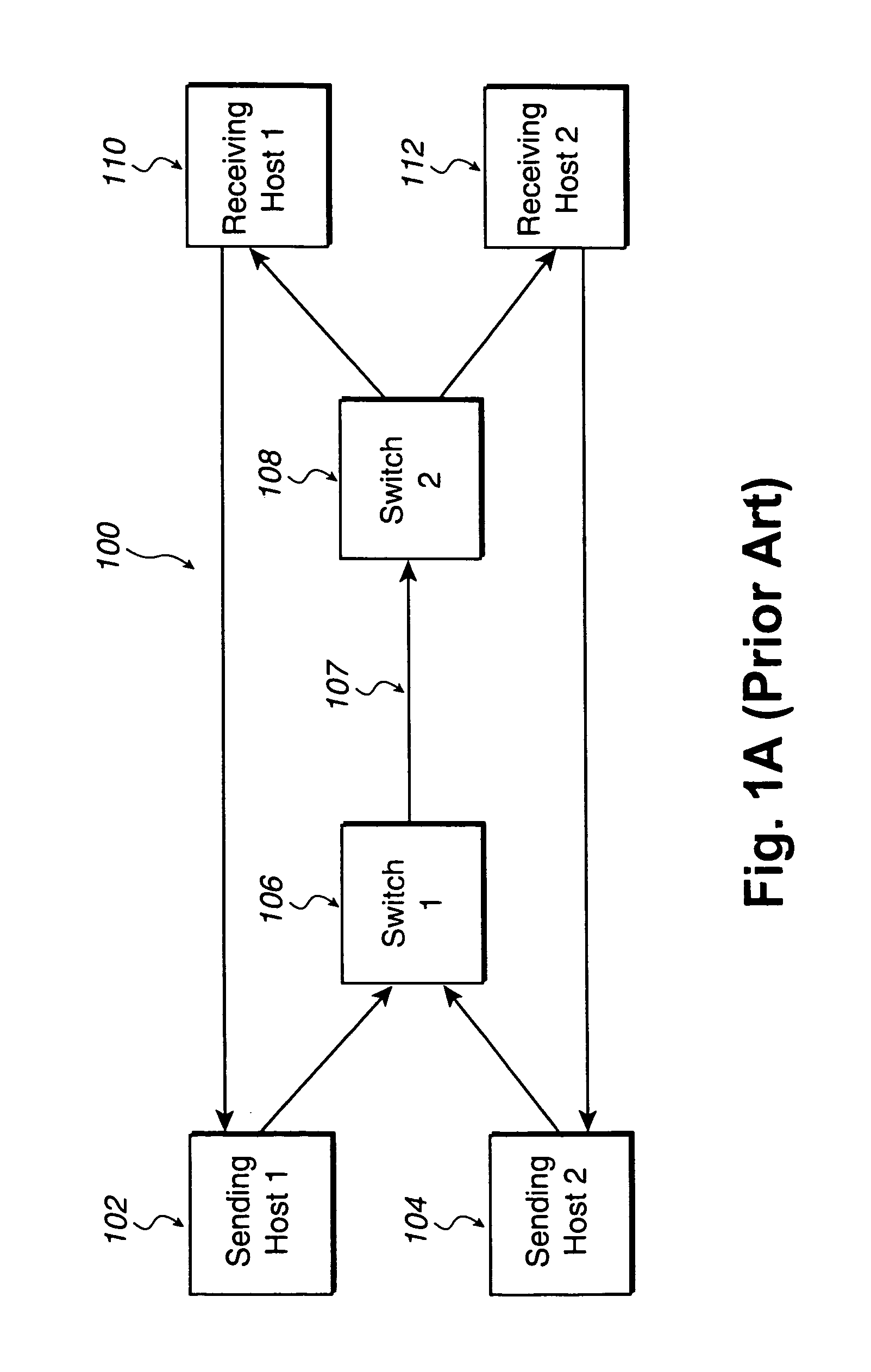
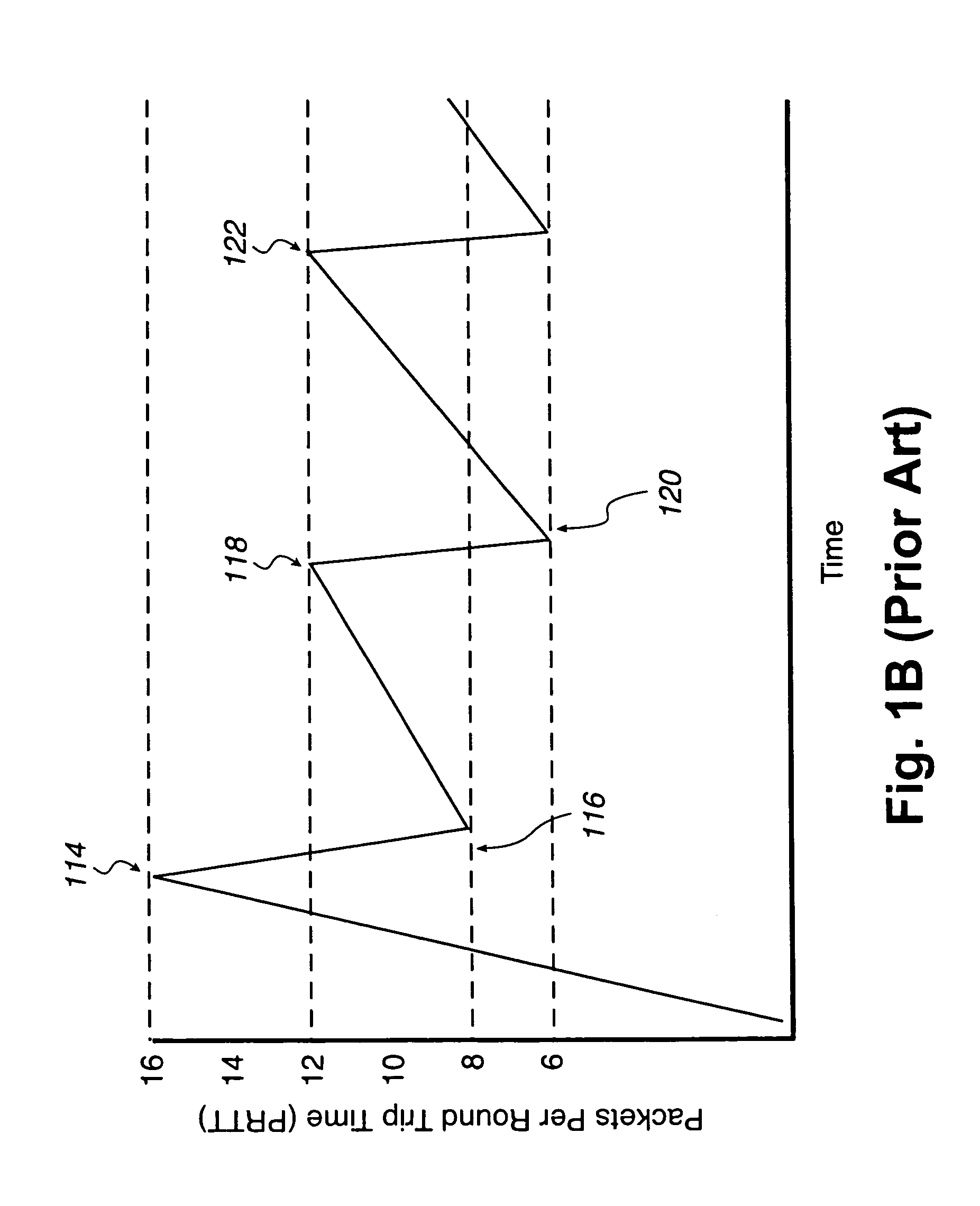
A network system for actively controlling congestion to optimize throughput is provided. The network system includes a sending host which is configured to send packet traffic at a set rate. The network system also includes a sending switch for receiving the packet traffic. The sending switch includes an input buffer for receiving the packet traffic at the set rate where the input buffer is actively monitored to ascertain a capacity level. The sending switch also includes code for setting a probability factor that is correlated to the capacity level where the probability factor increases as the capacity level increases and decreases as the capacity level decreases. The sending switch also has code for randomly generating a value where the value is indicative of whether packets being sent by the sending switch are to be marked with a congestion indicator. The sending switch also includes transmit code that forwards the packet traffic out of the sending switch where the packet traffic includes one of marked packets and unmarked packets. The network system also has a receiving end which is the recipient of the packet traffic and also generates acknowledgment packets back to the sending host where the acknowledgment packets are marked with the congestion indicator when receiving marked packets and are not marked with the congestion indicator when receiving unmarked packets. In another example, the sending host is configured to monitor the acknowledgment packets and to adjust the set rate based on whether the acknowledgment packets are marked with the congestion indicator. In a further example, the set rate is decreased every time one of the marked packets is detected and increased when no marked packets are detected per round trip time (PRTT).
Owner:ADAPTEC +1
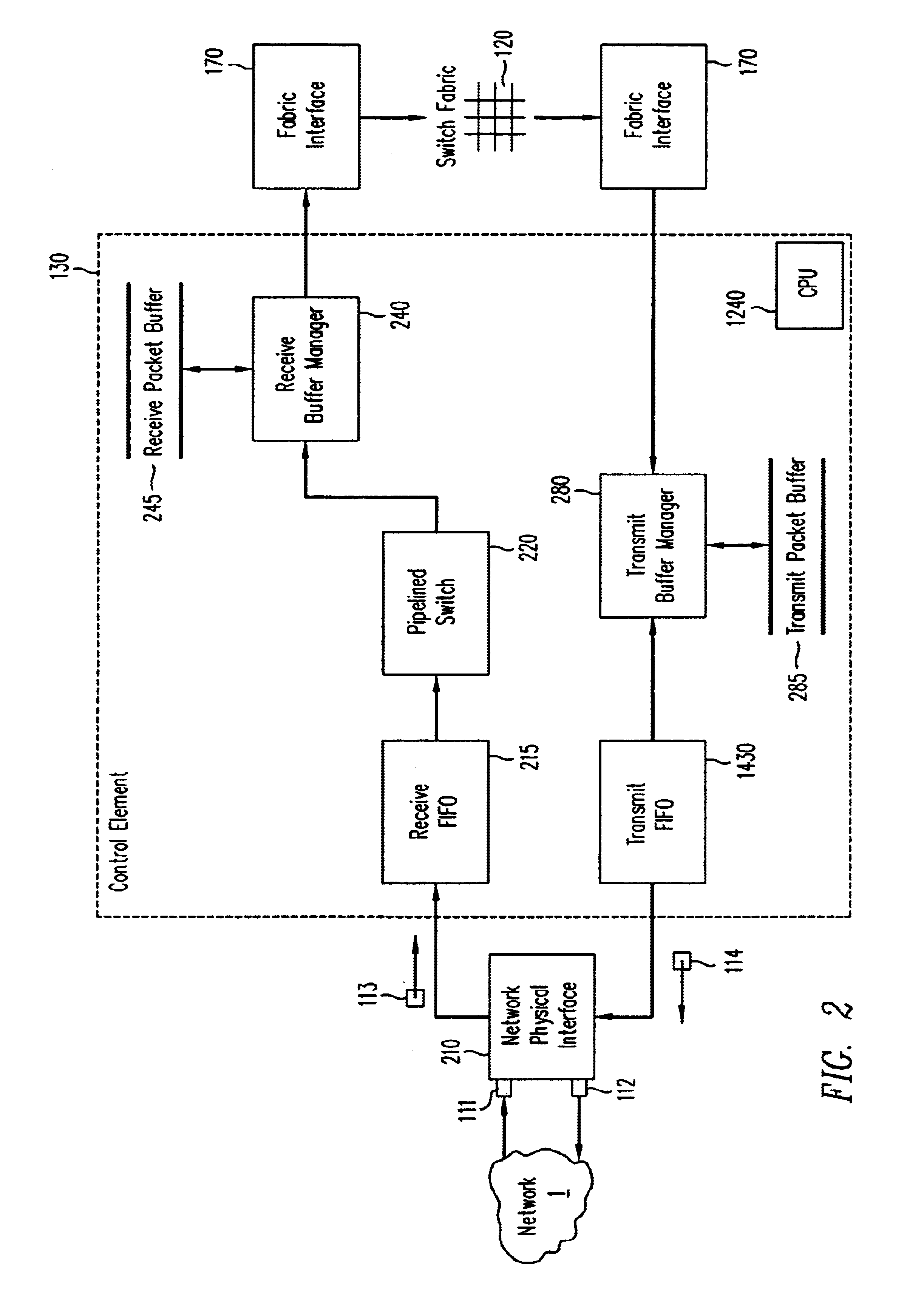
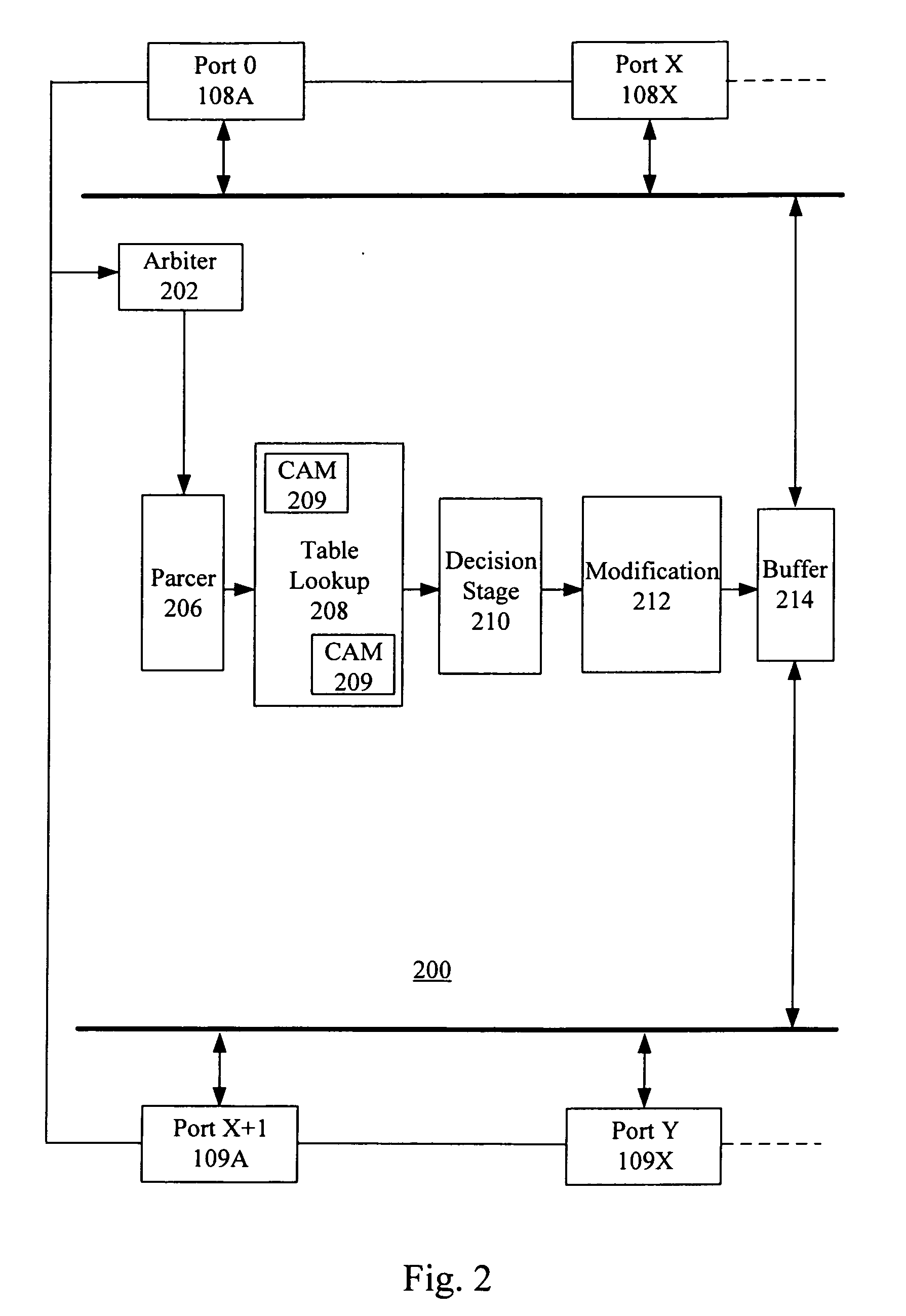
Flexible DMA engine for packet header modification
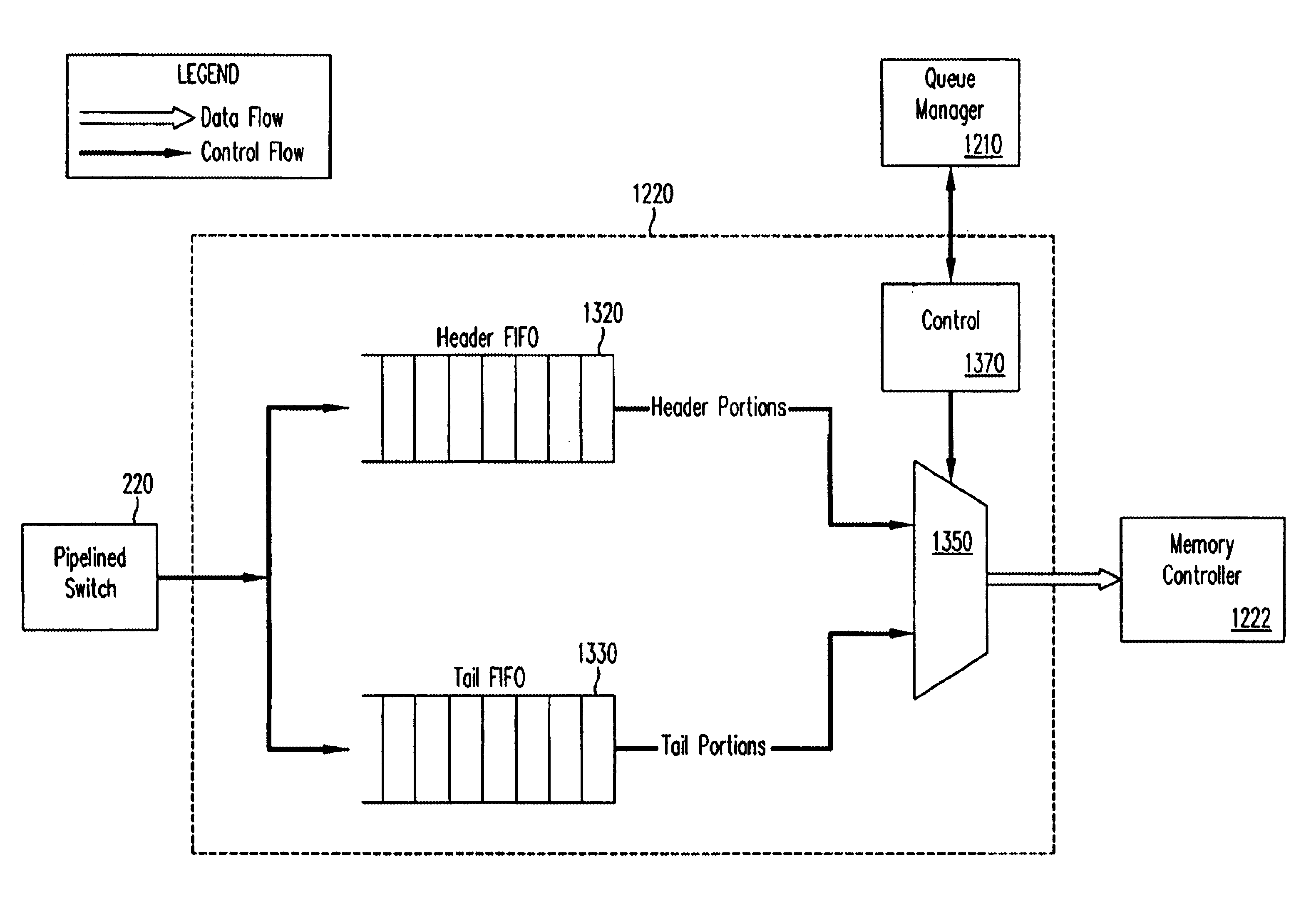
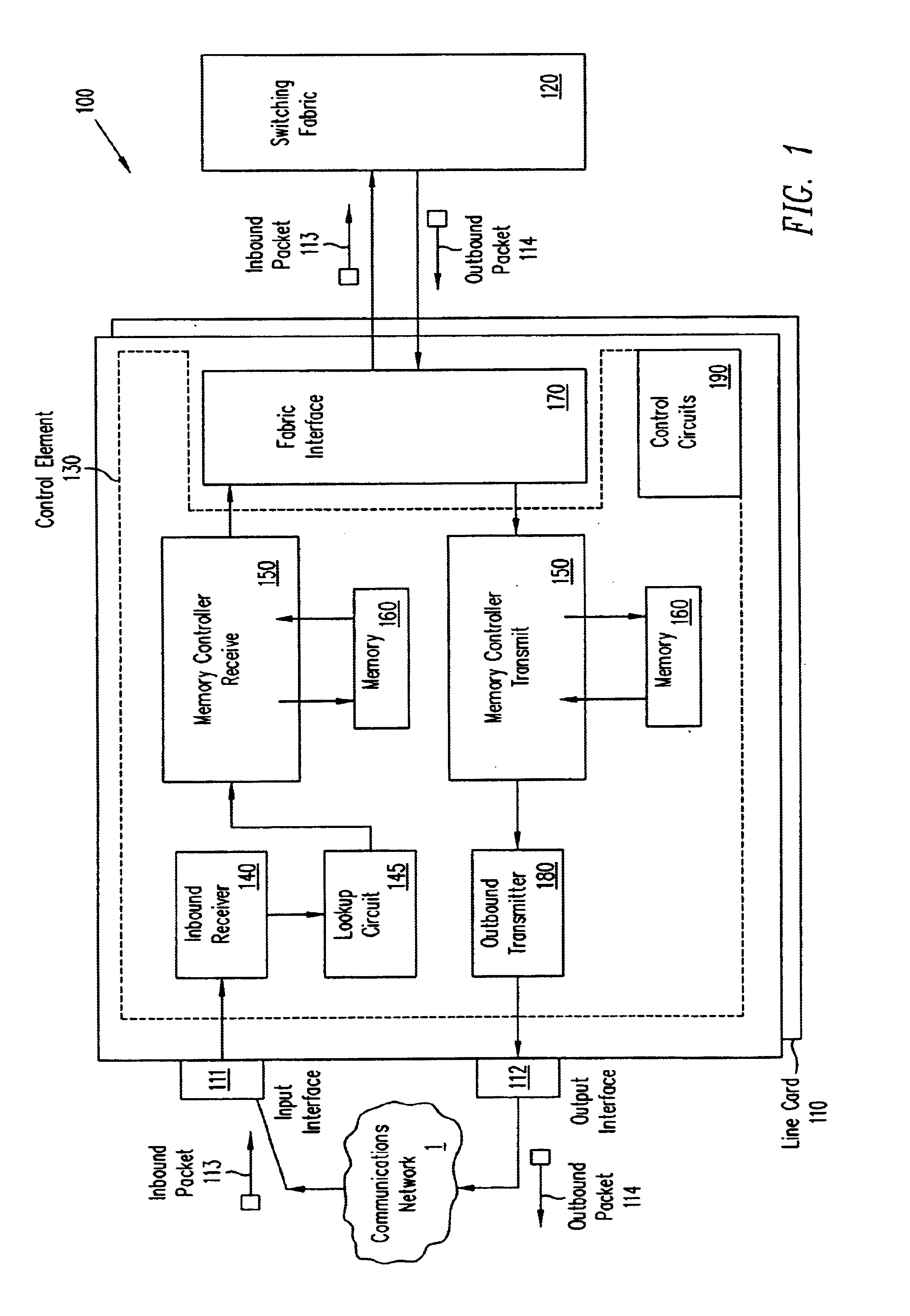
A pipelined linecard architecture for receiving, modifying, switching, buffering, queuing and dequeuing packets for transmission in a communications network. The linecard has two paths: the receive path, which carries packets into the switch device from the network, and the transmit path, which carries packets from the switch to the network. In the receive path, received packets are processed and switched in an asynchronous, multi-stage pipeline utilizing programmable data structures for fast table lookup and linked list traversal. The pipelined switch operates on several packets in parallel while determining each packet's routing destination. Once that determination is made, each packet is modified to contain new routing information as well as additional header data to help speed it through the switch. Each packet is then buffered and enqueued for transmission over the switching fabric to the linecard attached to the proper destination port. The destination linecard may be the same physical linecard as that receiving the inbound packet or a different physical linecard. The transmit path consists of a buffer / queuing circuit similar to that used in the receive path. Both enqueuing and dequeuing of packets is accomplished using CoS-based decision making apparatus and congestion avoidance and dequeue management hardware. The architecture of the present invention has the advantages of high throughput and the ability to rapidly implement new features and capabilities.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for coverage and throughput enhancement in a wireless communication system
InactiveUS7136655B2Spatial transmit diversitySimultaneous aerial operationsCommunications systemInterference (communication)
A multiple access wireless communications architecture provides selective, simultaneous communications with wireless devices located in different sections of a spatial area around a communications apparatus referred to as “sectors”. In one embodiment, channel allocation techniques for increasing one or more of throughput and coverage in a wireless communications environment. In one embodiment, a mode of operation is selected from a plurality of modes of operation, enabling a wireless communications transmitter to be dynamically configured to reach a wireless communications devices at a greater distance from the transmitter without increased interference between communications channels (“range mode”) or to provide wireless communications to a greater number of wireless communications devices within a relatively closer distance to the wireless transmitter (“capacity mode”) or to provide wireless communications using a single channel to provide wireless communications at a relatively greatest distance from the transmitter (“super range mode”).
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
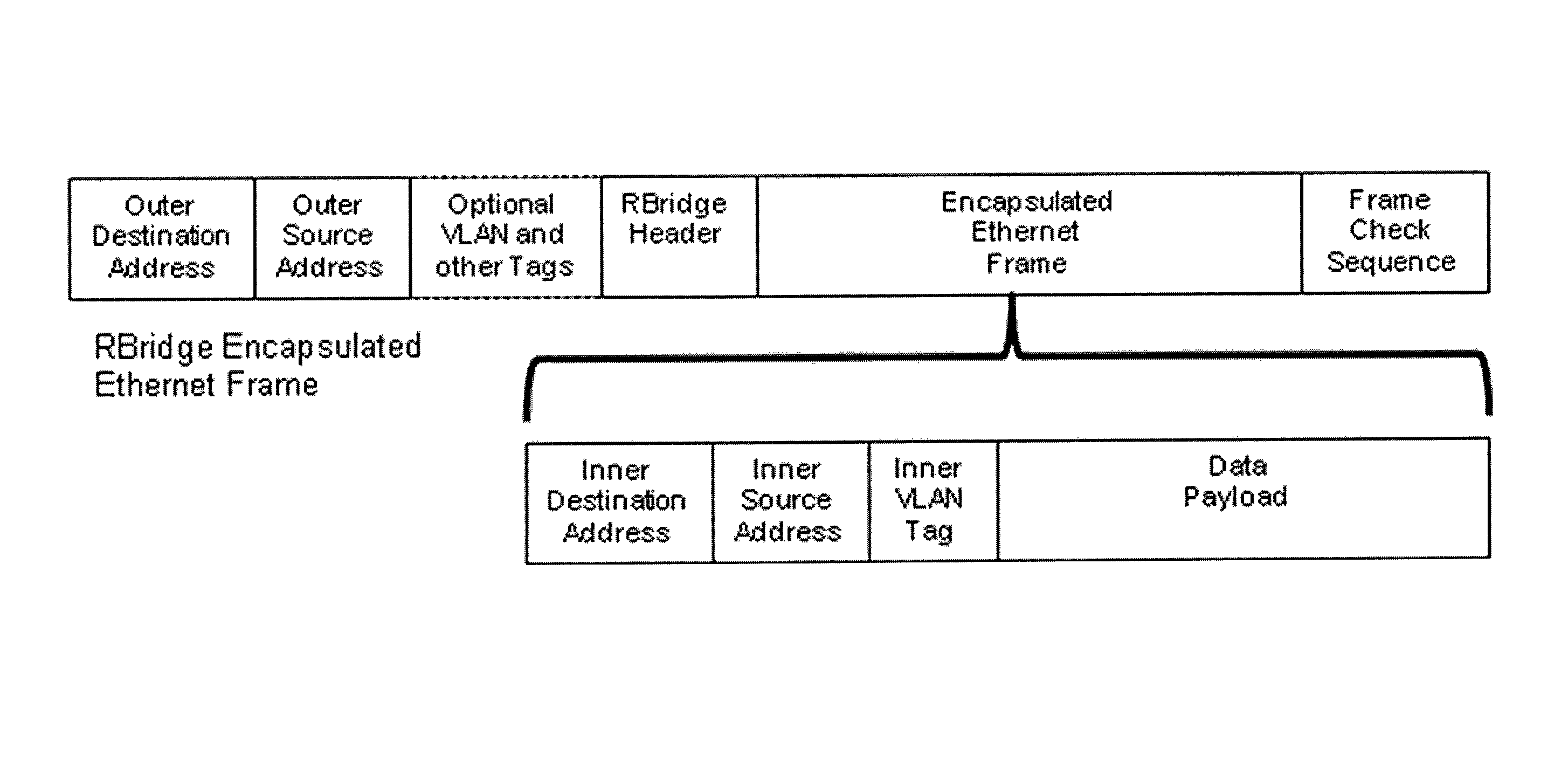
Methods and apparatus for RBridge hop-by-hop compression and frame aggregation
InactiveUS8351352B1Digital computer detailsData switching by path configurationData compressionRobust Header Compression
Some embodiments relate to a network comprising two RBridges connected by a link where the two RBridges are not the ingress and egress RBridge for said frames, wherein said RBridges automatically exchange information as to their support of hop-by-hop reversible frame aggregation, reversible header compression, and reversible data compression, and wherein if both RBridges support any or all of these features in the same fashion, one or more of said features are automatically applied to appropriate frames at the transmitting RBridge and removed at the receiving RBridge, increasing the throughput of the link.
Owner:EASTLAKE III DONALD E
Method and system for improving throughput over wireless local area networks with mode switching
InactiveUS6990116B1Improve throughputNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexDistributed coordination functionStation
A method and system for increasing the overall network throughput over a wireless local area network (WLAN). Specifically, in one embodiment of the present invention, the dynamic switching between the Distributed Coordination Function (DCF) and Point Coordination Function IEEE 802.11 access modes is determined according to the load conditions over the WLAN in a method and system. Stations and access points within a WLAN monitor conditions within the network to determine which access mechanism is most optimum for the current load conditions. Some factors to consider in determining the load conditions include but are not limited to the number of transmissions, number of receptions, and number of collisions.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD
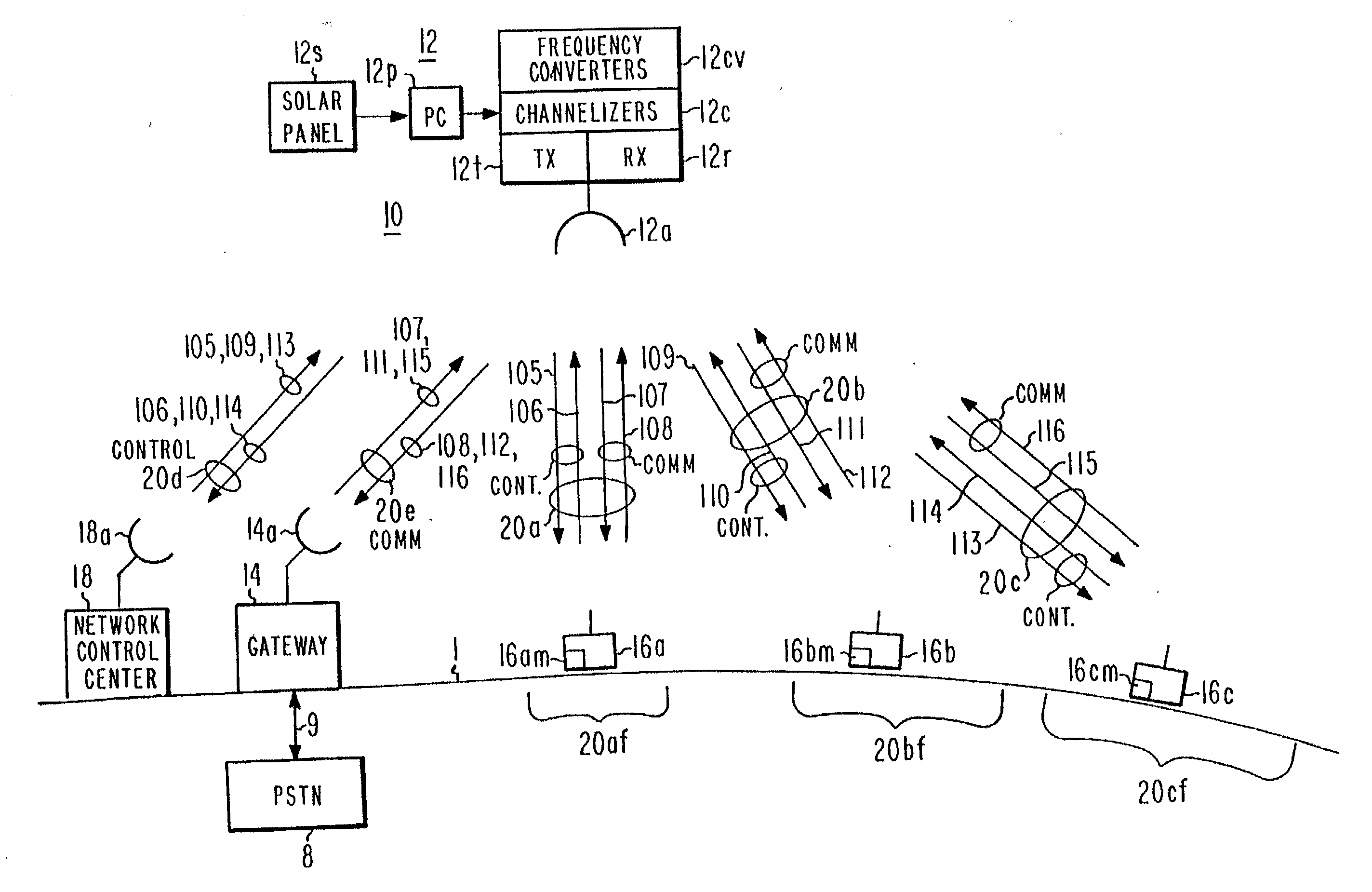
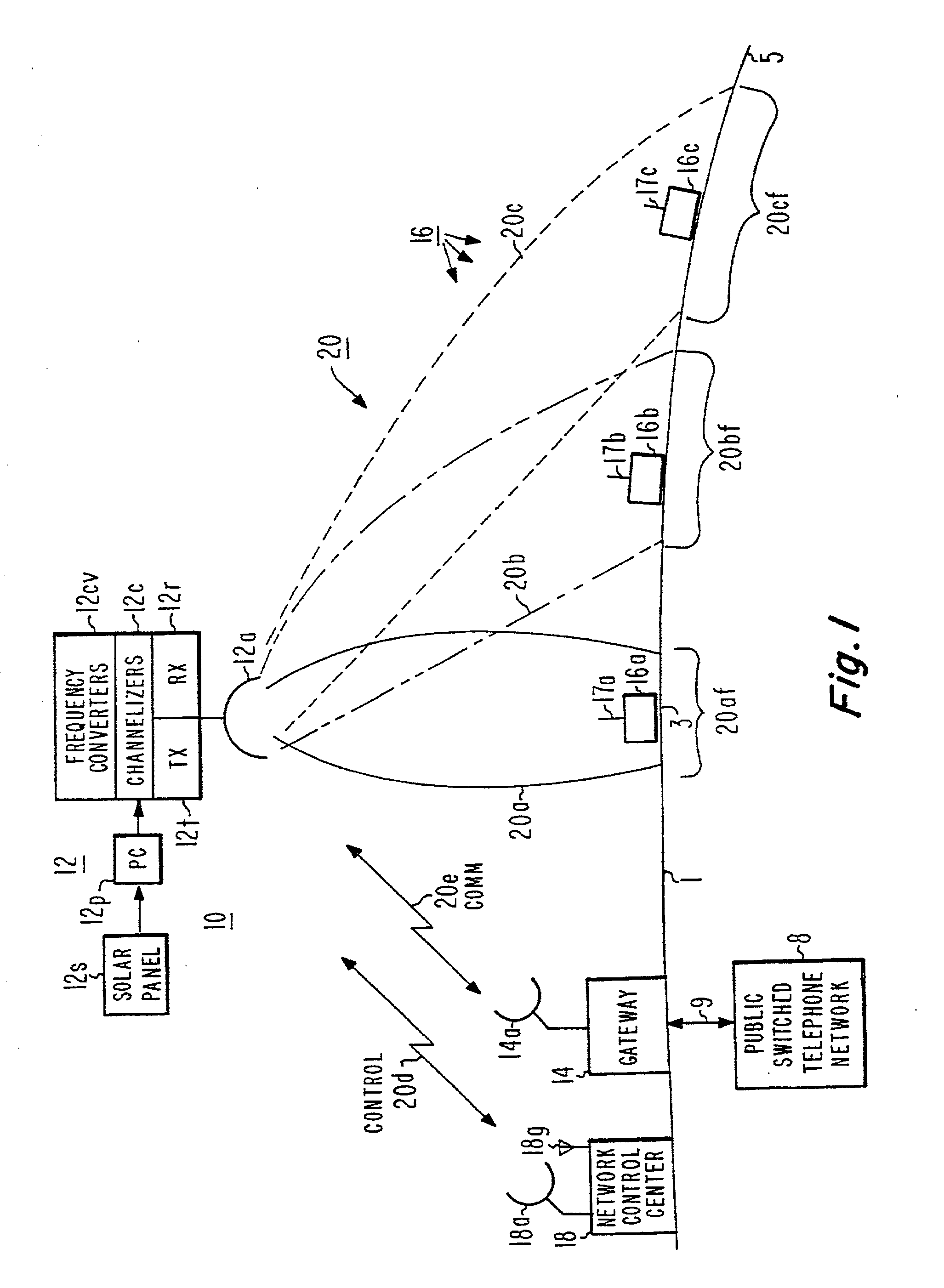
Time synchronized standby state to the GPRS medium access control protocol with applications to mobile satellite systems
InactiveUS20060072520A1Time-division multiplexRadio transmissionCommunications systemCellular communication systems
Improved throughput is provided in a spacecraft TDMA cellular communications system by introducing a standby state, in addition to the idle and transfer states, of the medium access control (MAC) protocol, which controls the transfer of data over the radio interface between the network and the user terminals. The terrestrial locations include mobile user terminals and gateways which provide connections to the land line telephone system and / or the land packet data network i.e. Internet service provider. Each of the terrestrial terminals and gateways include a MAC to control the transmitting and receiving of data between the gateway and user terminals. Since packet data is bursty, multiple transitions occur between the idle and transfer states during data transfers. The new standby state maintains synchronization, reducing the transition time to the data transfer state by comparison with the transition time from an idle state where the network does not maintain user synchronization.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
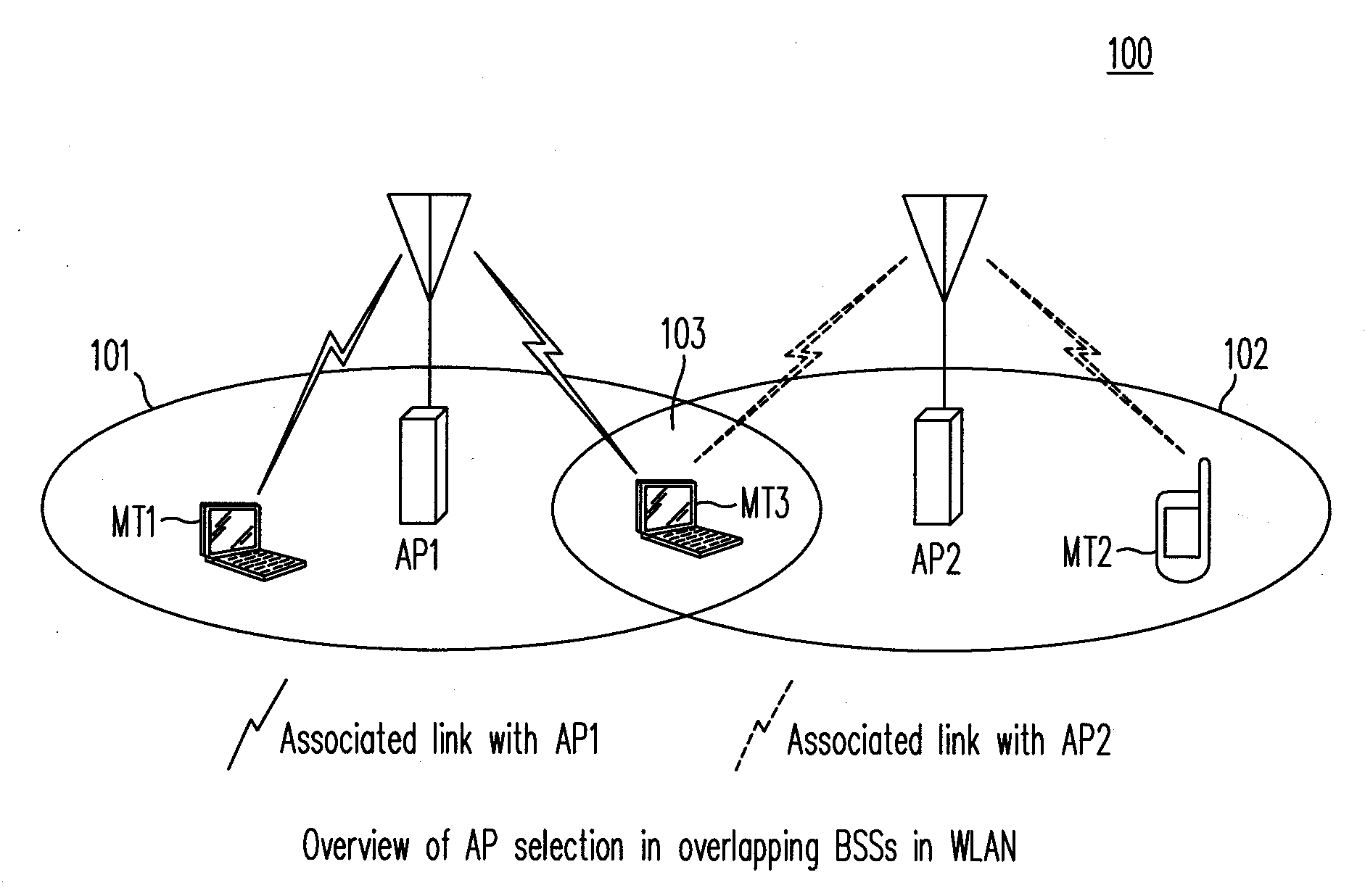
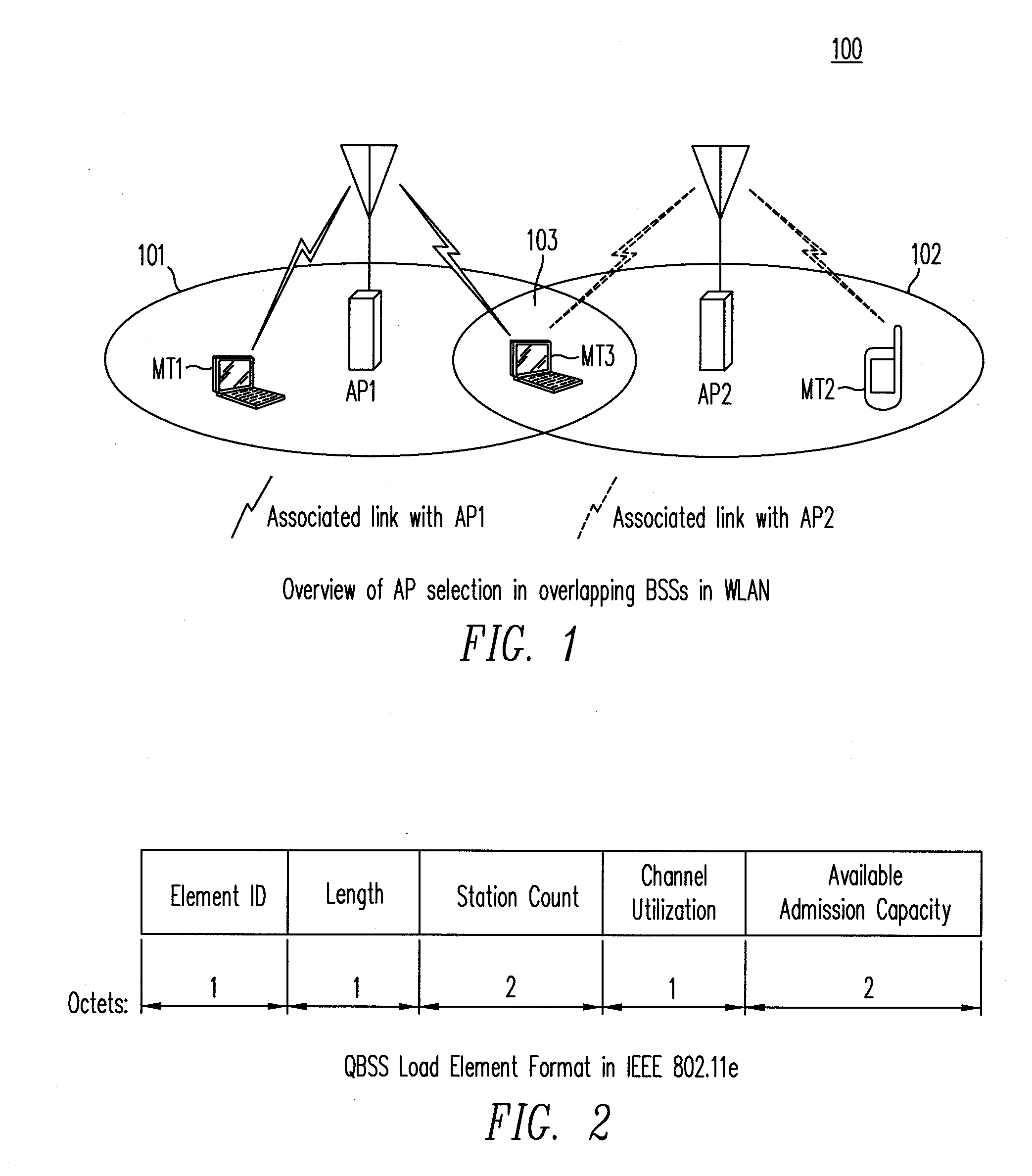
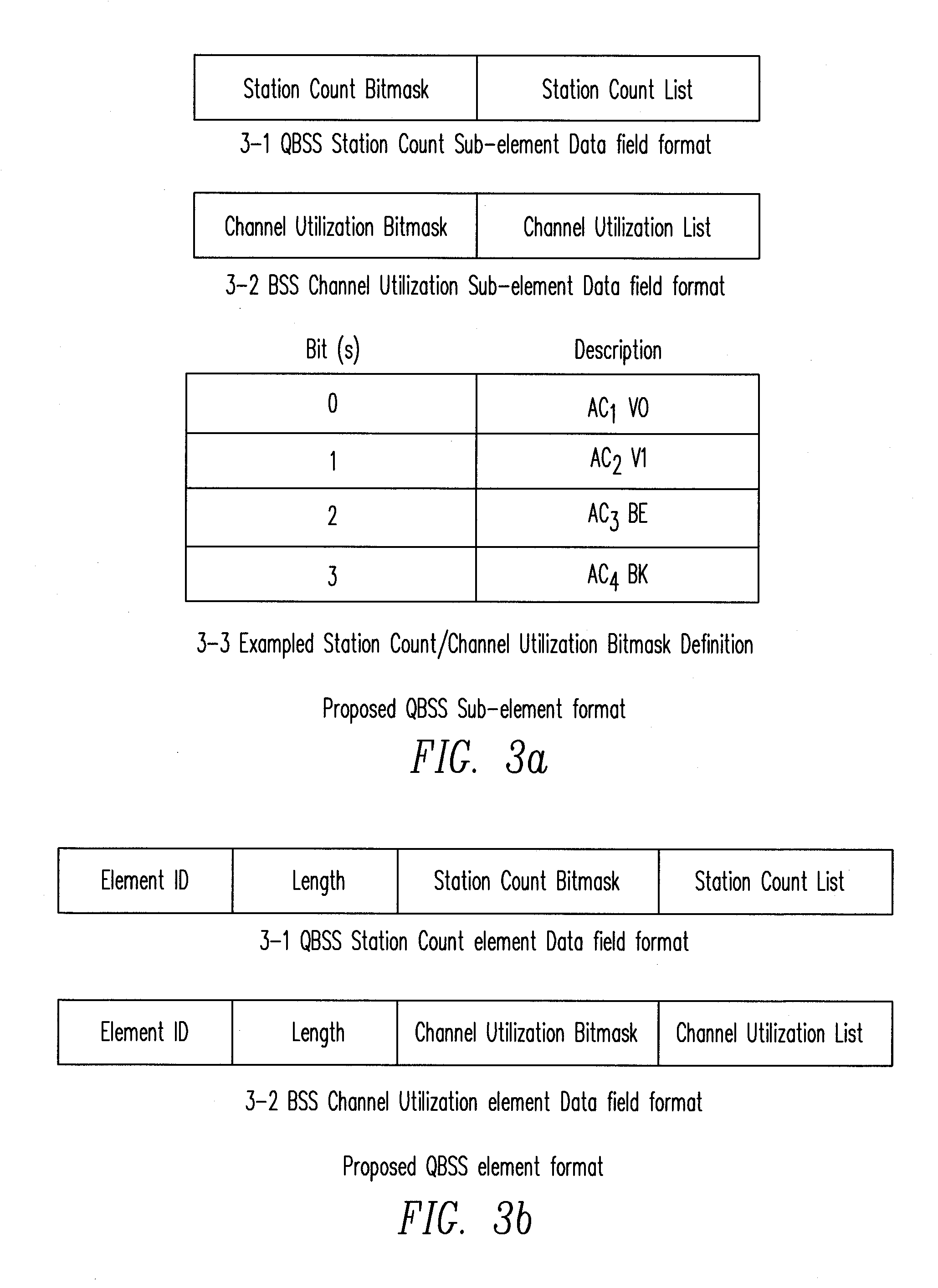
Method and Apparatus for Access Point Selection in Wireless LAN
ActiveUS20080102852A1Improve performanceSensitive to delay characteristicError preventionTransmission systemsTransmission throughputQos quality of service
A method and an apparatus select an access point (AP) in a wireless LAN to associate or reassociate, based on considerations that take into account the quality-of-service (QoS) status of the stations (STAs) and the potential hidden terminal effect. The method utilizes advertised or requested information obtained from an AP which includes the QoS status in each basic service set (BSS) and estimates the potential hidden terminal (HT) effect based on local channel sensing by the STA. The method selects the AP in a manner that reduces the possibility of collision from equal and higher priority HTs, thus providing greater transmission throughput and improving performance.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Apparatus and method for cooperative transmission in multi-antenna relay wireless communication system
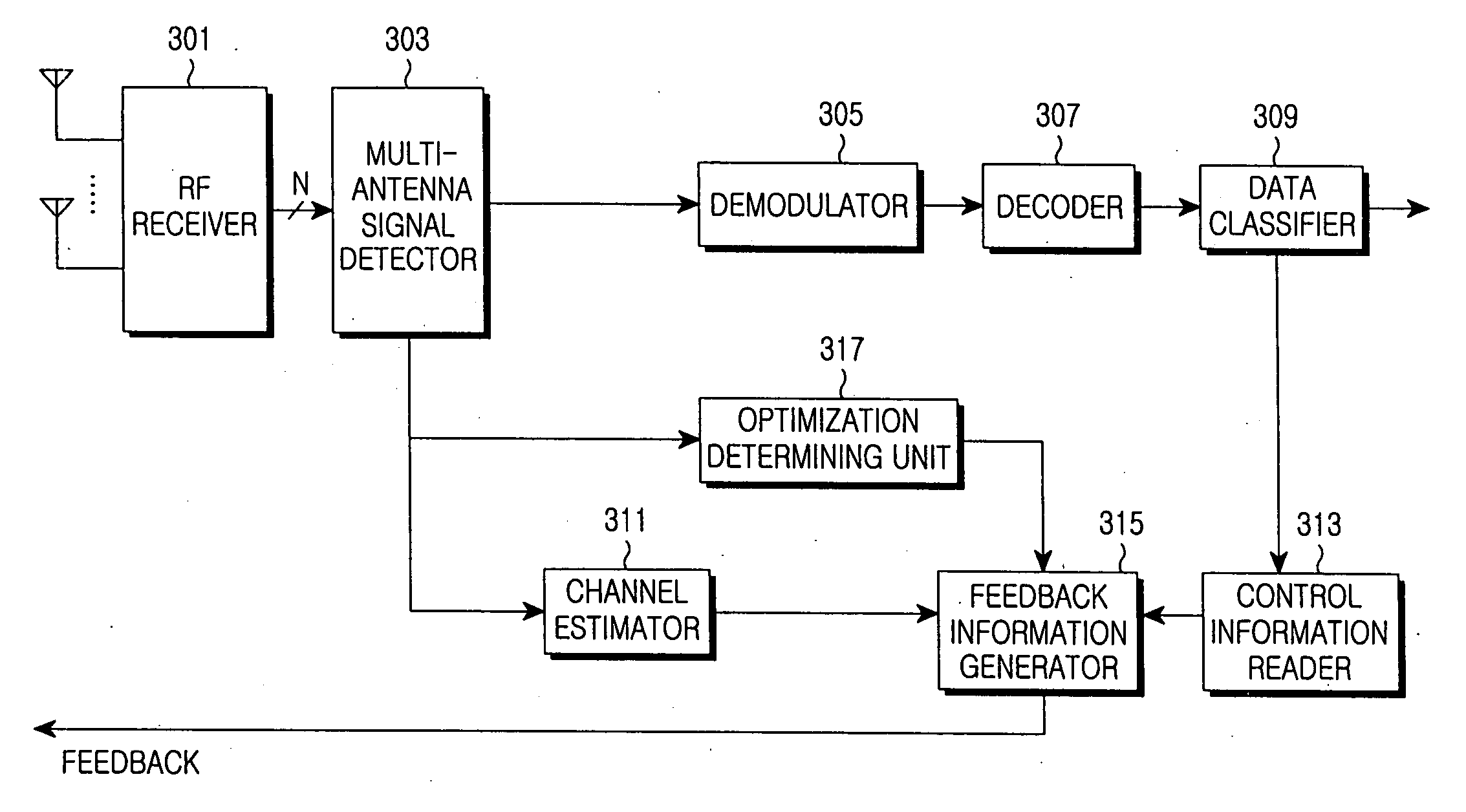
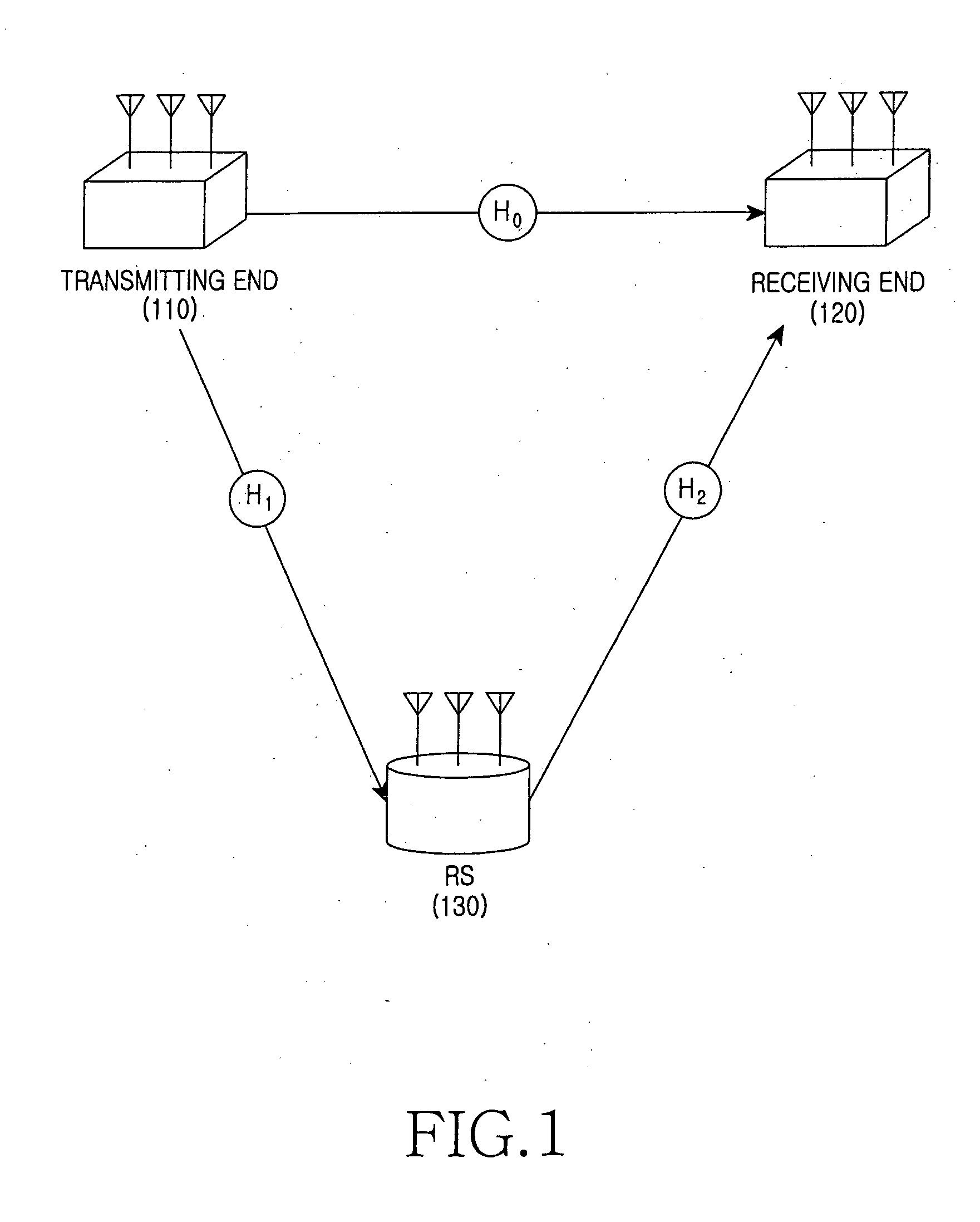
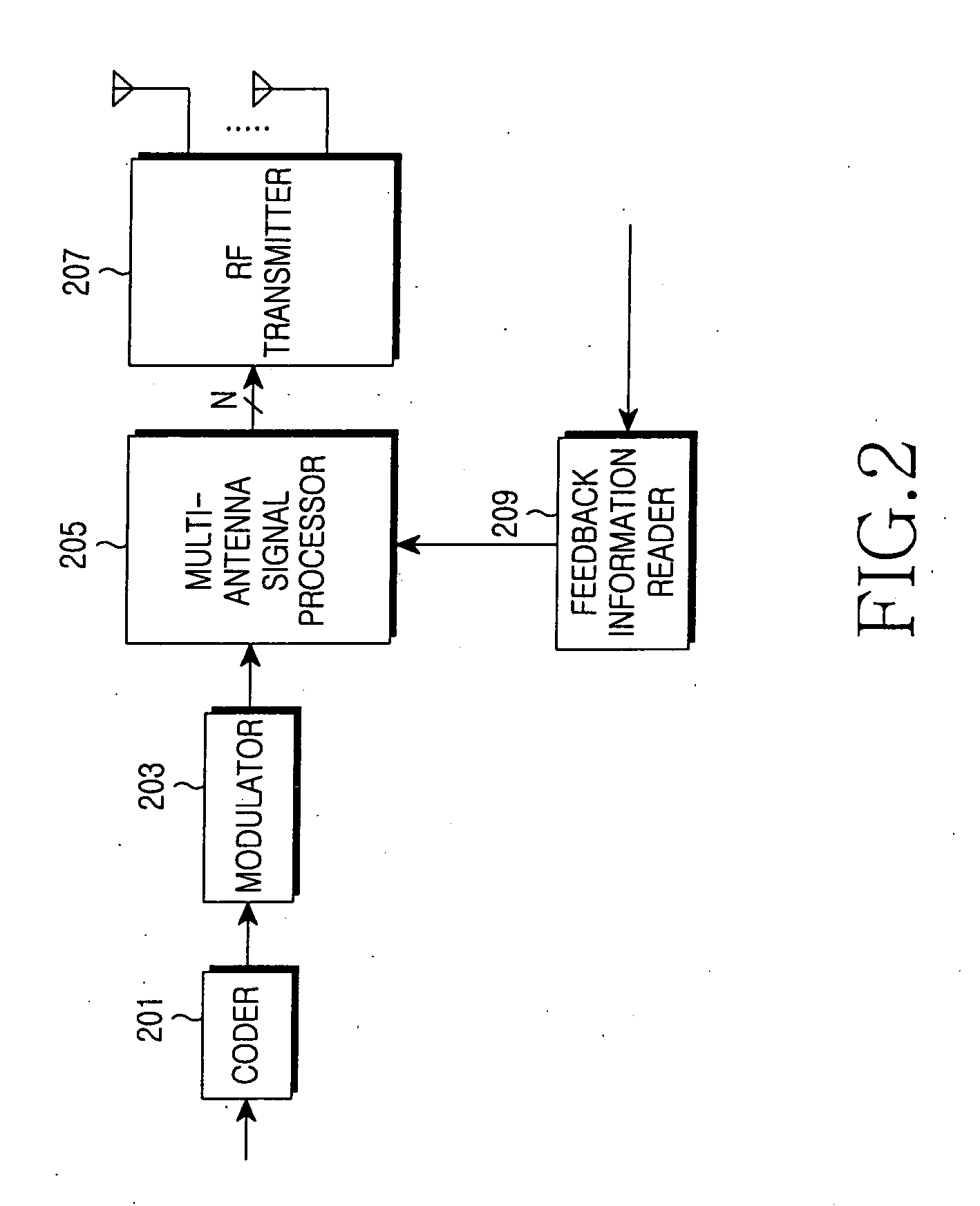
An apparatus and method for cooperative transmission in a multi-antenna relay wireless communication system are provided. A receiving end includes an estimator, a reader, a feedback unit and a detector. According to the present invention, the receiving end receives the signal from both the transmitting end and the relay station. Therefore, a reception gain is obtained and a high throughput can be ensured.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Tool for measuring available bandwidth in computer networks
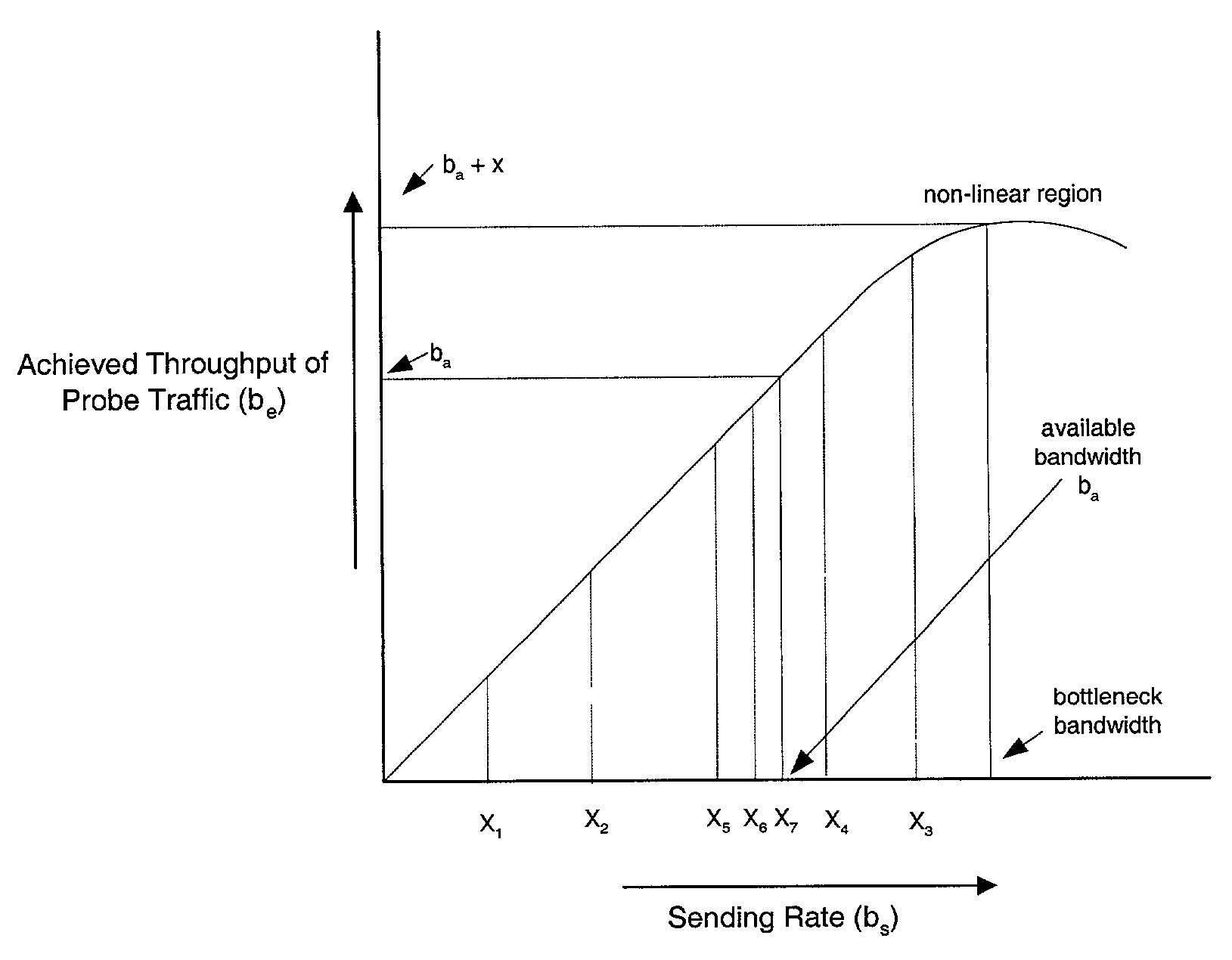
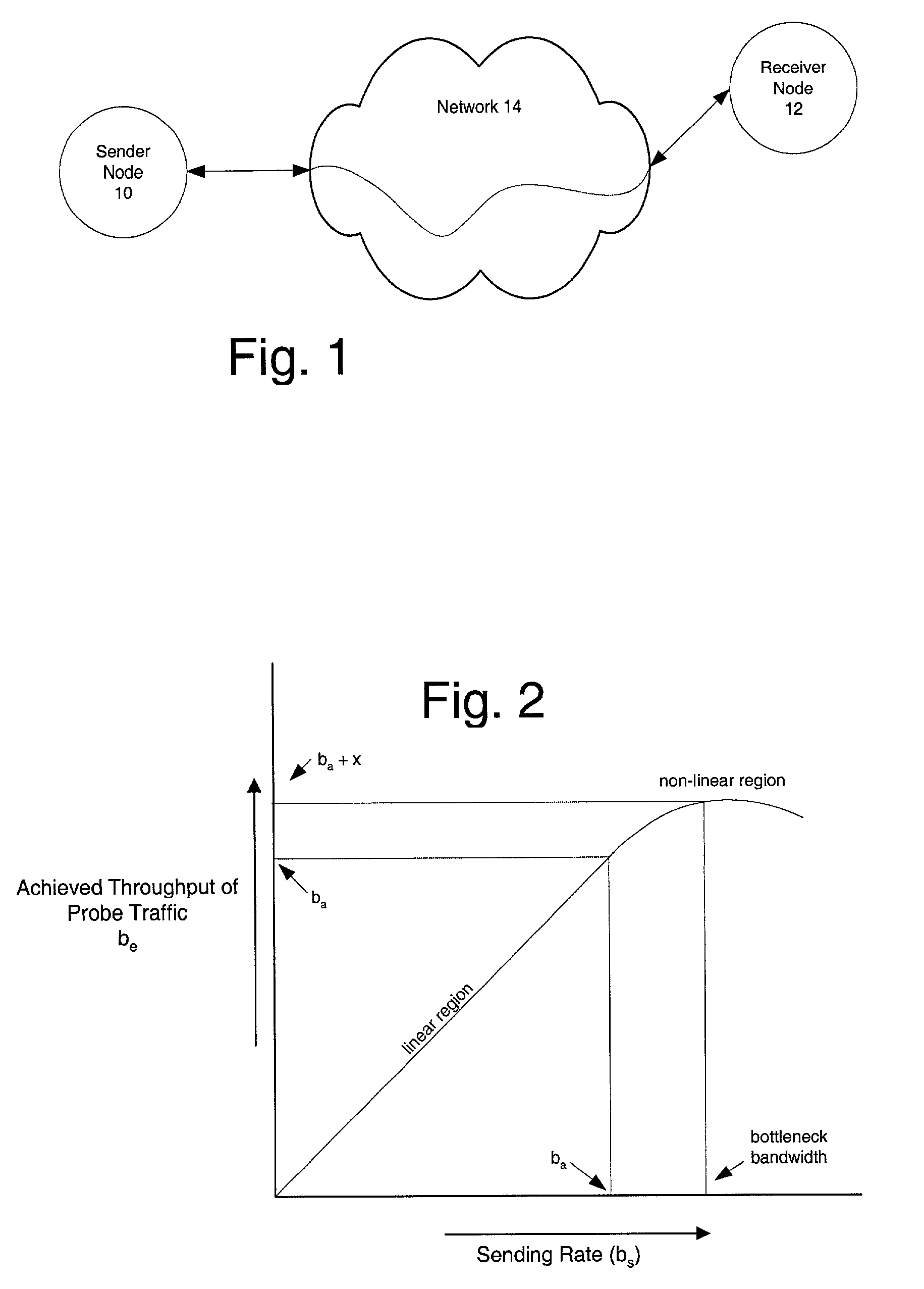
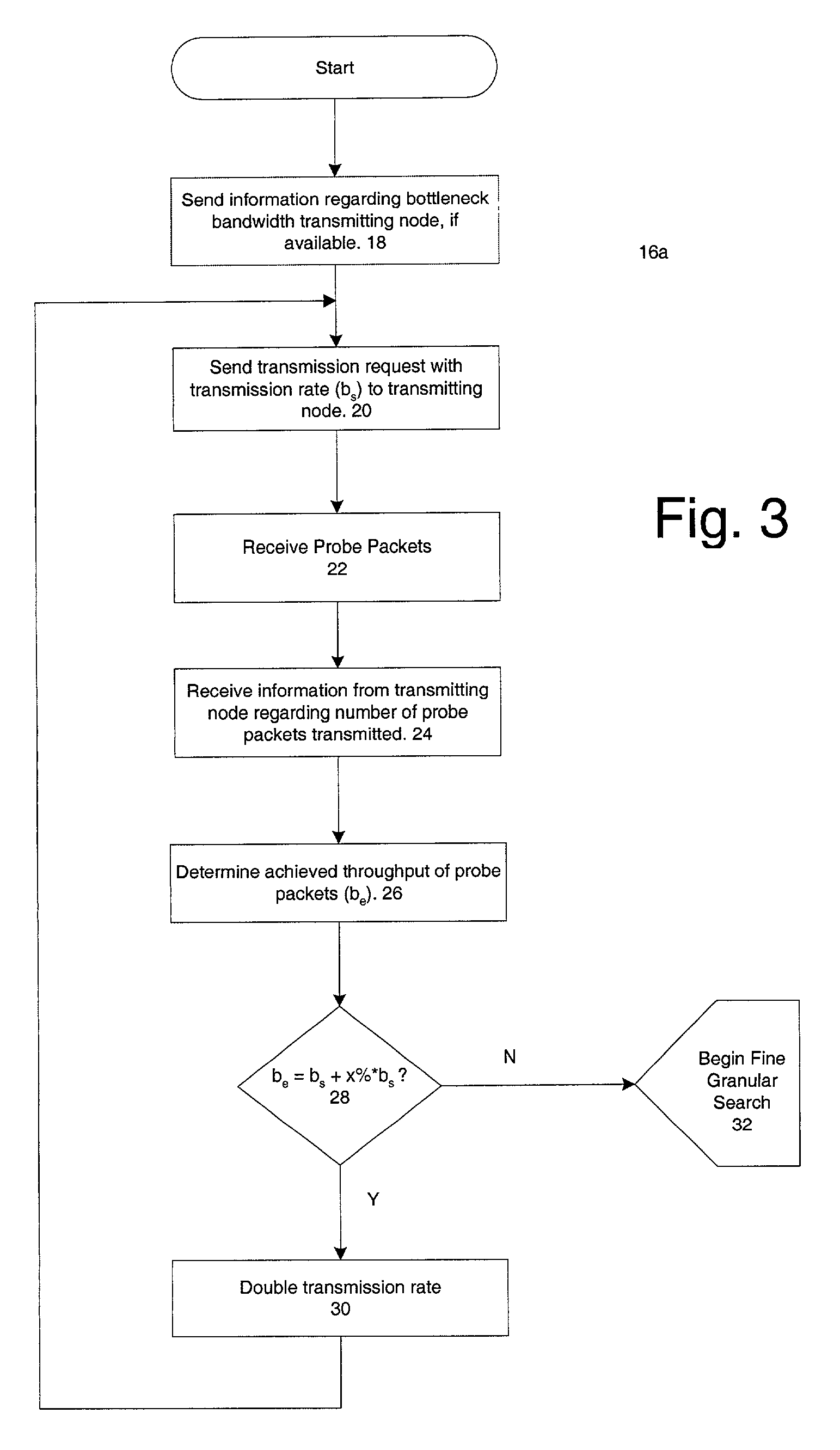
The available bandwidth of a communication path between two nodes of a computer network is determined using probe packages that are transmitted between a sender one of the nodes and a receiver one of the nodes at varying transmission rates. Each successive transmission rate of the probe packages is selected according to: (i) an achieved throughput for a transmission of a preceding one of the probe packages, and (ii) a deviation between the achieved throughput for the transmission of the preceding one of the probe packages and a corresponding transmission rate of the preceding one of the probe packages.
Owner:ADARA NETWORKS
Method and apparatus for adaptive transmission control in a high data rate communication system
InactiveUS7088701B1Improve throughputIncrease chanceError prevention/detection by using return channelTime-division multiplexCommunications systemSelf adaptive
In a high data rate communication system, a method and apparatus for improved throughput while transmitting data packets within multiple time slots. In order to avoid unnecessary retransmissions of a packet, a subscriber station sends a Stop-Repeat signal to a base station, causing the base station to cease further transmissions of the packet. In order to enable successful decoding of a packet, a subscriber station sends a Continue-Repeat signal to a base station, causing the base station to send retransmissions of the packet during time slots beyond a predetermined default number of time slots.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
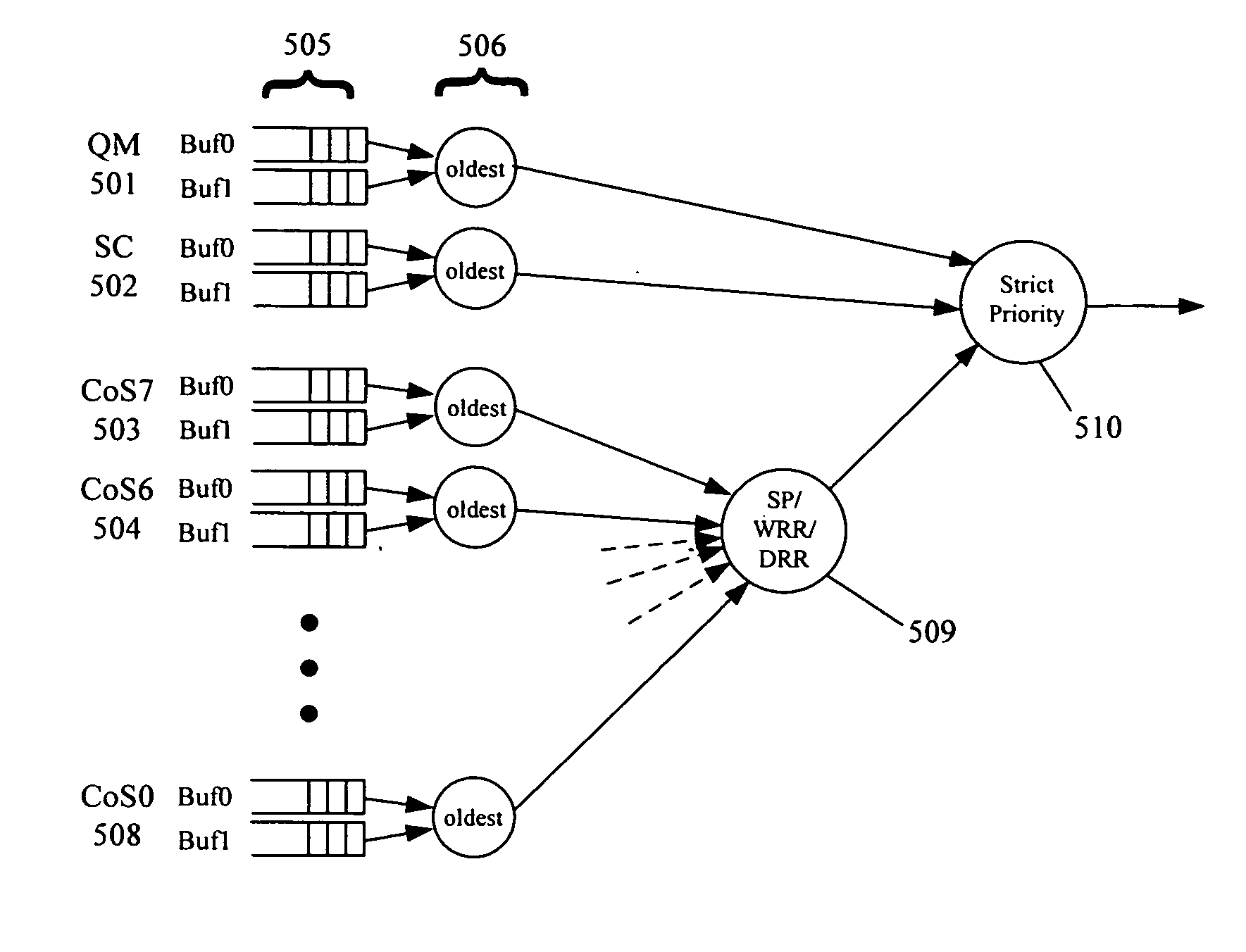
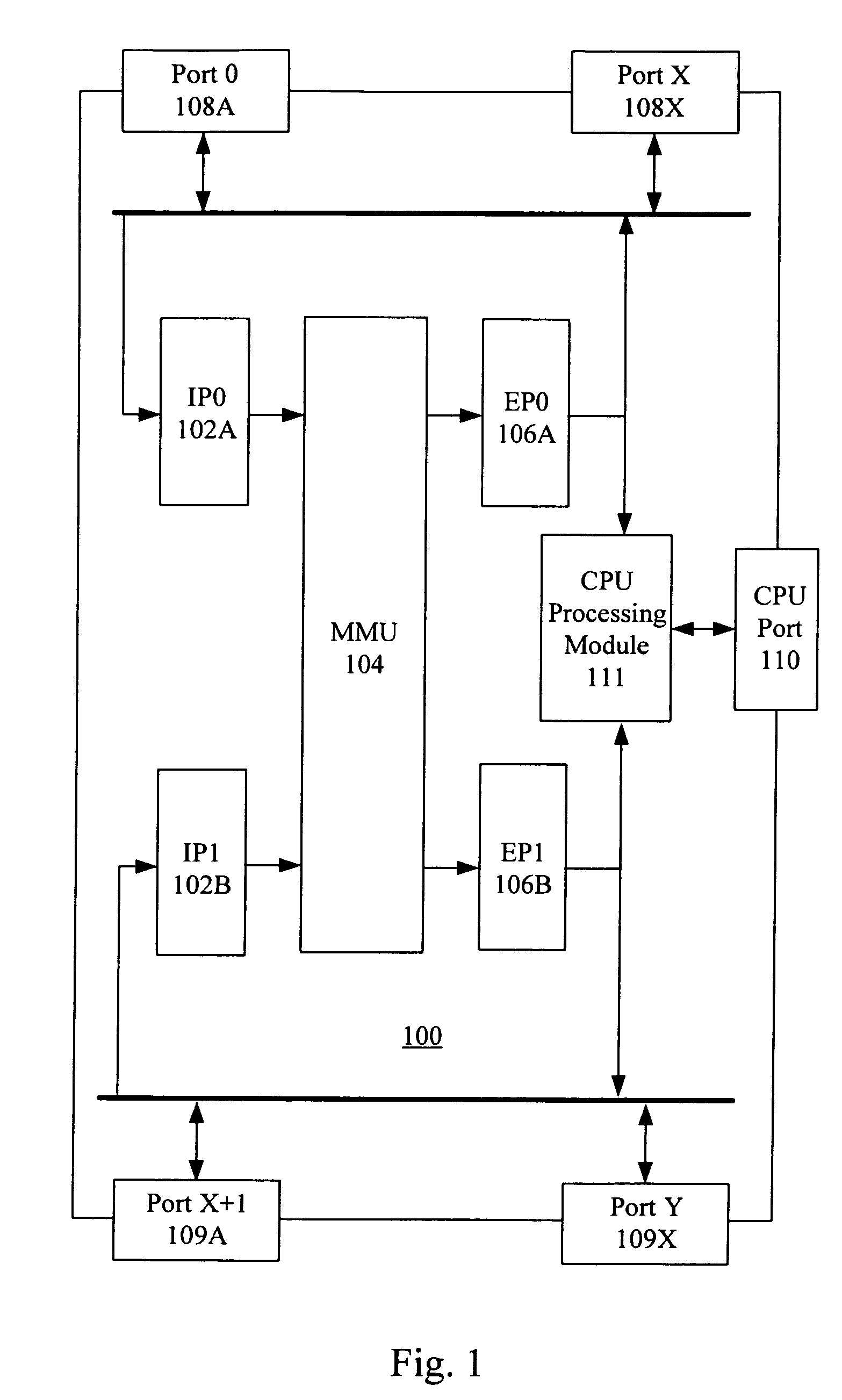
Buffer management and flow control mechanism including packet-based dynamic thresholding
A network device for processing data includes at least one ingress module for performing switching functions on incoming data, a memory management unit for storing the incoming data and at least one egress module for transmitting the incoming data to at least one egress port. The at least one ingress module is configured to determine a priority for the incoming data, where that priority is mapped to a discrete number of priority groups and where the priority groups are determined on a per-port basis and provide guaranteed delivery or best throughput, and flow of data through the network device is controlled on a basis of at least one of the priority groups and assigned priorities.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
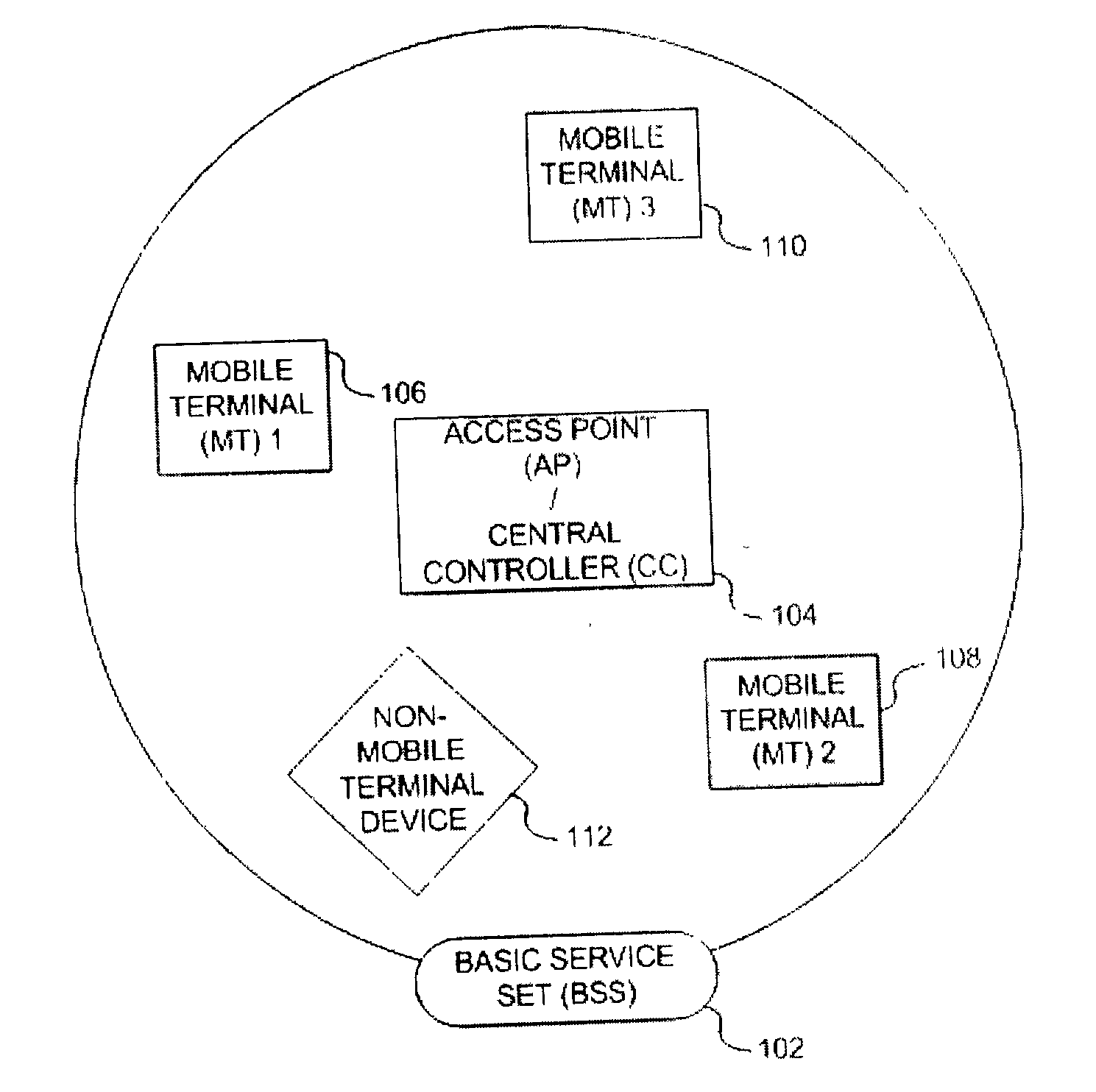
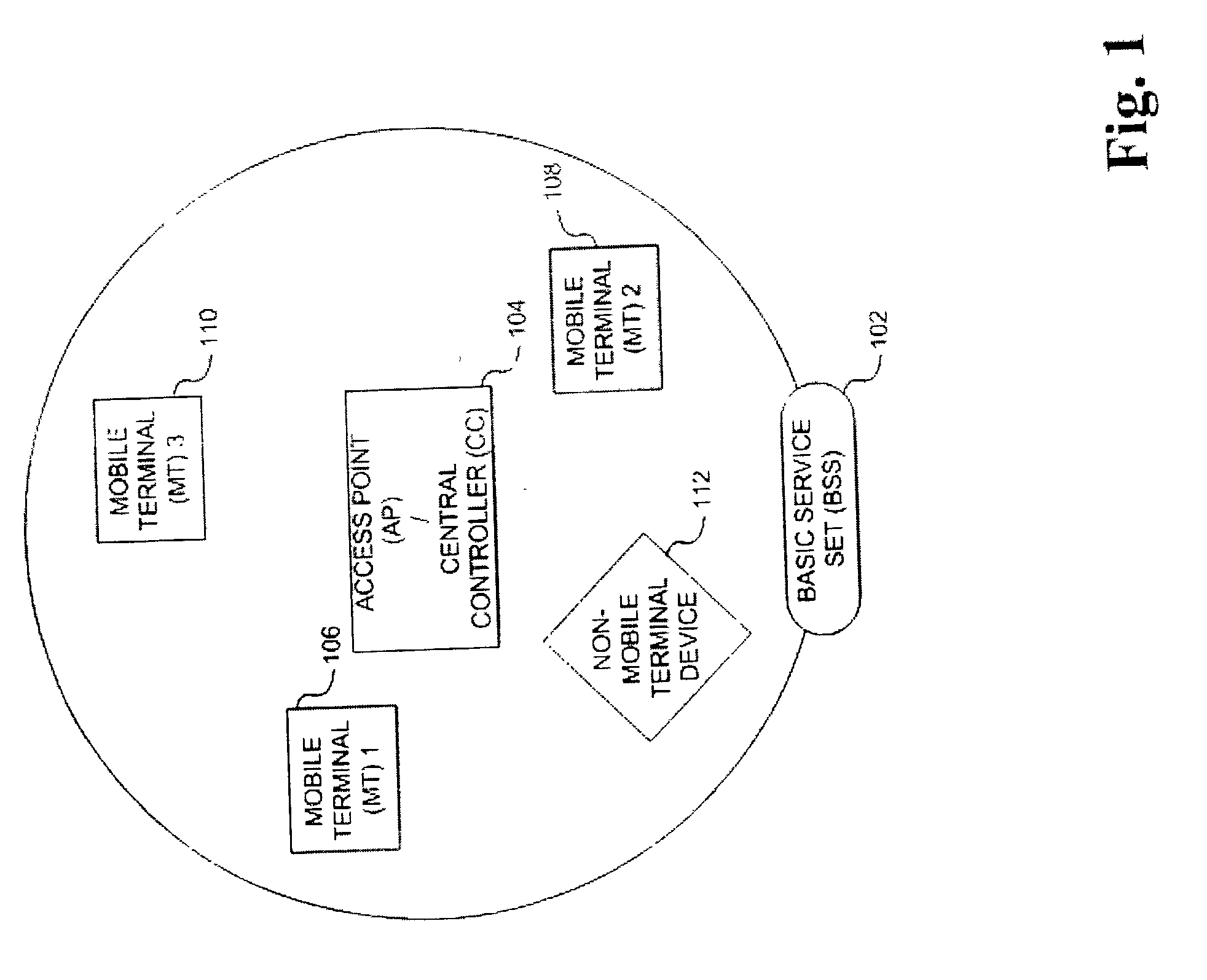
Method and apparatus for assuring quality of service in wireless local area networks
InactiveUS20040037257A1Network traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesQuality of serviceReliable transmission
A method and apparatus is described for maintaining quality of service (QoS) between a central controller and a set of mobile terminals (MTs) located within the coverage area of a basic service set (BSS) in a wireless local area network (WLAN). Upon a detection of a connection request by an MT and determining if adequate resources are available, establishing a connection with the MT using the most robust physical layer (PHY) mode with a sufficiently large set of packets to fulfill throughput requirements, if adequate resources are available and additional resources can be allocated. If adequate resources are not available, then attempting to allocate additional resources. In addition, a method is described for providing reliable transmission for a critical packet in a connection, including the steps of transmitting the critical packet at a first PHY mode; determining if adequate resources in the connection are available; and, transmitting a duplicate packet on a second PHY mode if adequate resources are available.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
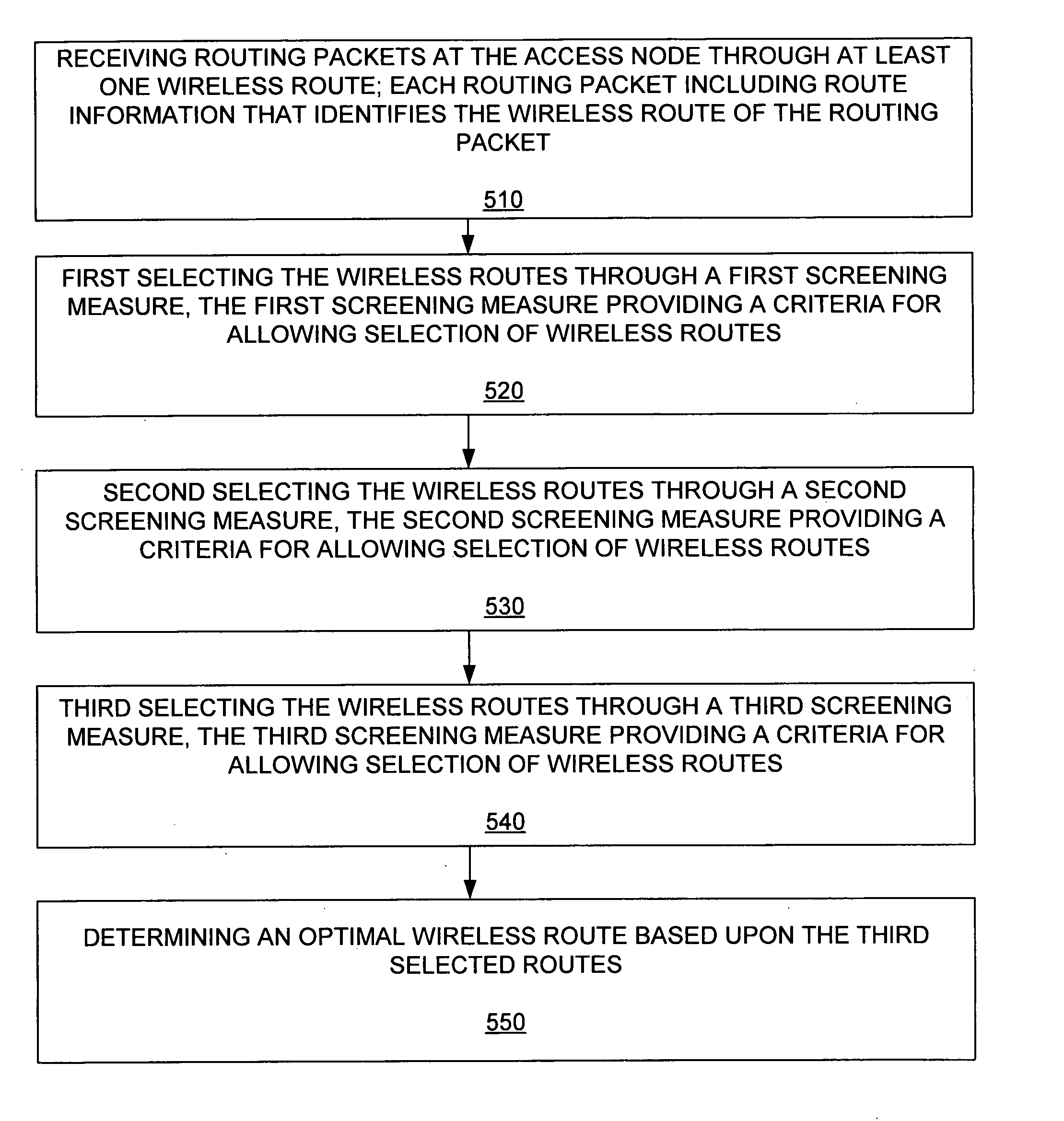
Selection of routing paths based upon path qualities of a wireless routes within a wireless mesh network
InactiveUS20050129005A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsNetwork connectionsWireless mesh networkOptimal route
The invention includes an apparatus and method for determining an optimal route based upon path quality of routes to an access node of a wireless mesh network. The method includes receiving routing packets at the access node through at least one wireless route. Each routing packet including route information that identifies the wireless route of the routing packet. A success ratio of a number of successfully received routing packets versus a number of transmitted routing packets is determined over a period of time T1, for each wireless route. The wireless route having a greatest success ratio is first selected, as are other wireless routes that have success ratios within a predetermined amount of the greatest success ratio. Of the first selected routes, routing packets are at the access node through the first selected routes. Again, each routing packet including route information that identifies the wireless route of the routing packet. A success long ratio of a number of successfully received routing packets versus a number of transmitted routing packets is determined over a period of time T2, wherein T2 is substantially greater than T1, for each first selected route. The wireless route having a greatest success long ratio are second selected, as are other wireless routes that have success long ratios within a second predetermined amount of the greatest success long ratio. The second selected routes having a greatest throughput are third selected. An optimal wireless route based upon the third selected routes is determined.
Owner:ABB POWER GRIDS SWITZERLAND AG
Unified channel access for supporting quality of service (QoS) in a local area network
ActiveUS7058074B2Free communicationEasy to useMultiplex system selection arrangementsCircuit switching systemsFree accessQuality of service
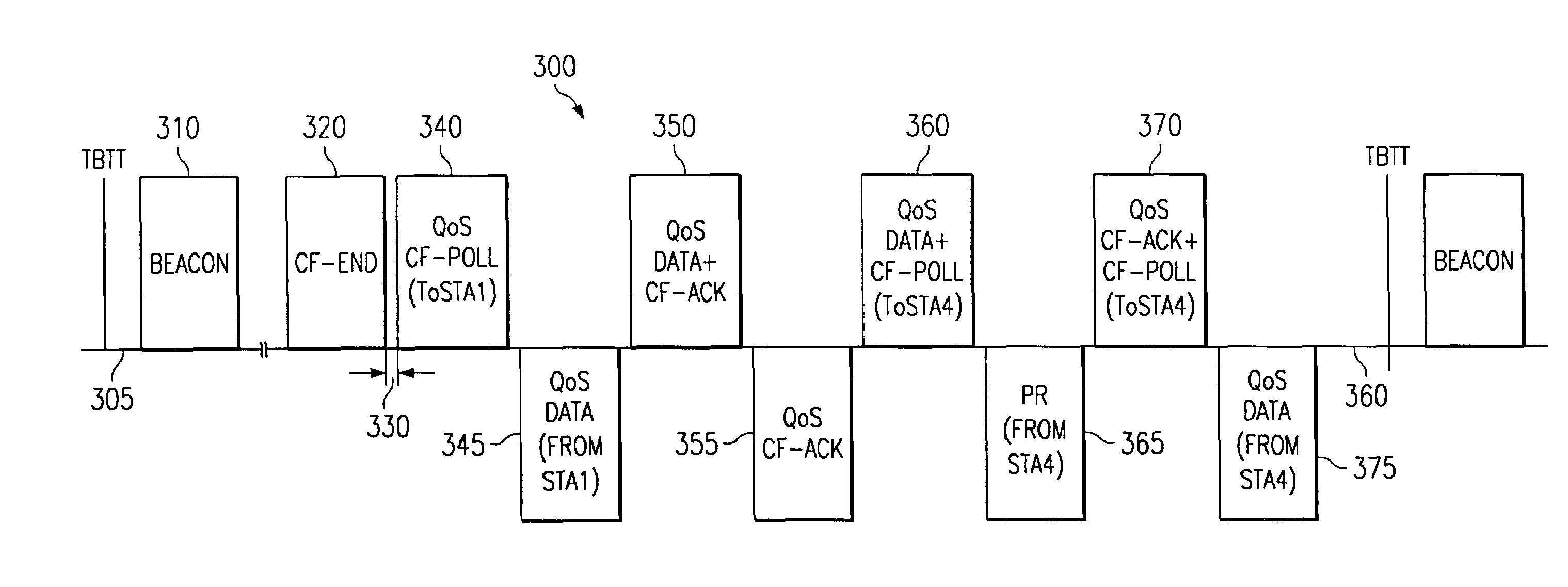
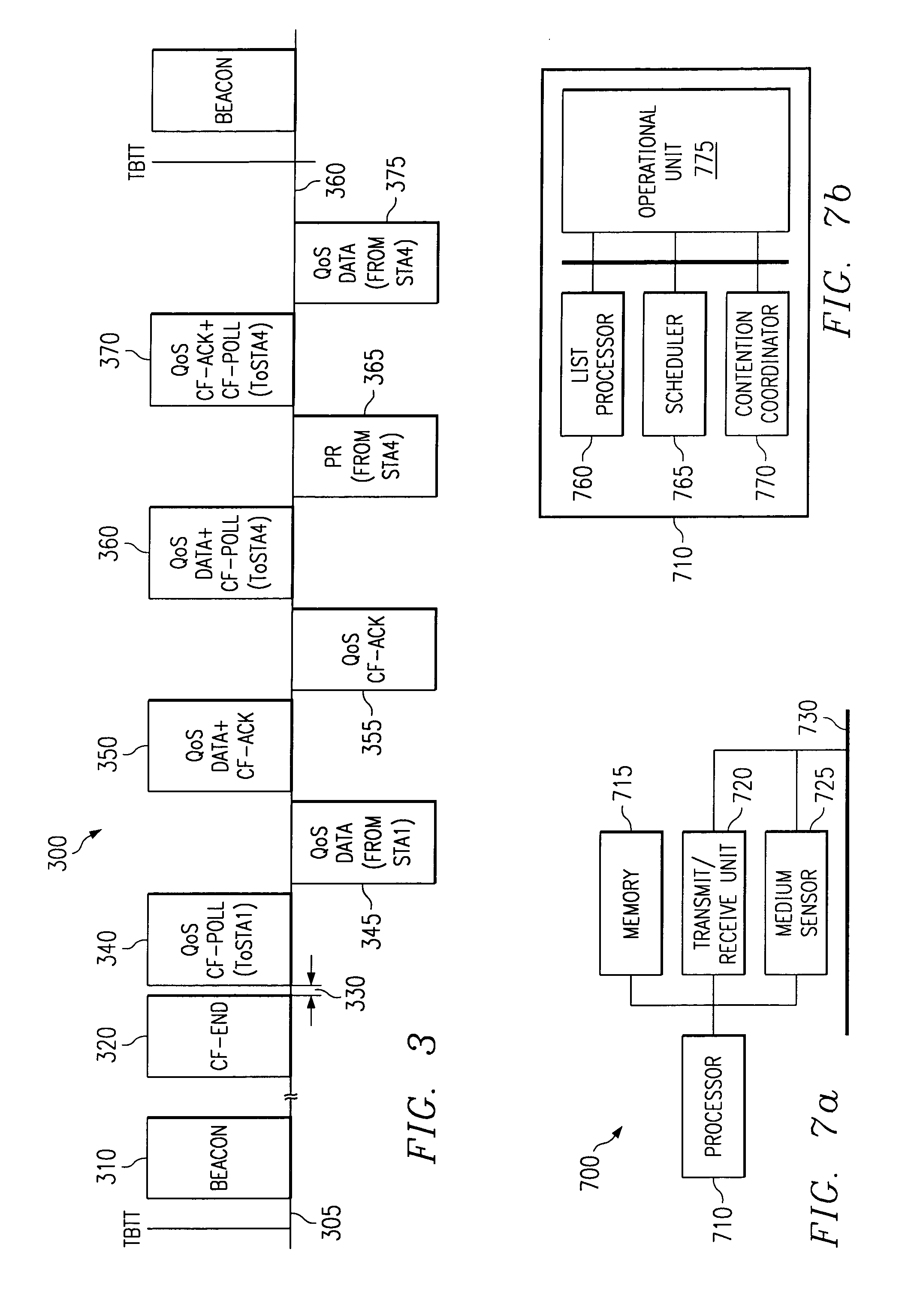
Contention communications often requires a station to wait an inordinate amount of time before the station is able to transmit its data successfully. In many applications, an extended delay is not acceptable. Contention-free communications in a contention period allows a hybrid coordinator (HC) to schedule contention-free access to a communications medium so that extended delays may be eliminated, and to coordinate contention access to the medium so that better throughput and delay performance is achieved. A method for creating contention-free communications within a contention communications period is presented, along with adaptive algorithms for contention access during the same contention period.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and device for configuring DMRS (demodulation reference signal) scrambling code sequence
InactiveCN102340382AGuaranteed signal demodulation performanceReduce signal demodulation performanceWireless communicationError prevention/detection by diversity receptionMultiplexingMimo transmission
The invention relates to the field of communication, and discloses a method and device for configuring a DMRS (demodulation reference signal) scrambling code sequence so as to reduce signal interference between UE (user equipment) adopting DMRS multiplexing and guarantee the signal demodulation performance of UE. In the method, a base station refers to the current application scene, and indicates the initial value configuration of the downlink DMRS scrambling code sequence used by single UE or UE group in current transmission through a signaling so as to ensure that the inter-cell or in-cell UE can flexibly perform MU (multiple -user)-MIMO (multiple input multiple output) multiplexing, thereby reducing the mutual interference between the multiplexing UE and guaranteeing the signal demodulation performance of the UE; and meanwhile, the overhead of a PDCCH (physical downlink control channel) is reduced through joint coding, the configuration of the same DMRS scrambling code sequence for the UE of different cells can be flexibly supported, and the configuration of different DMRS scrambling code sequences for the UE of the same cell can be flexibly supported, thereby supporting high-rank MU-MIMO transmission and effectively increasing the system throughput.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF TELECOMM TECH
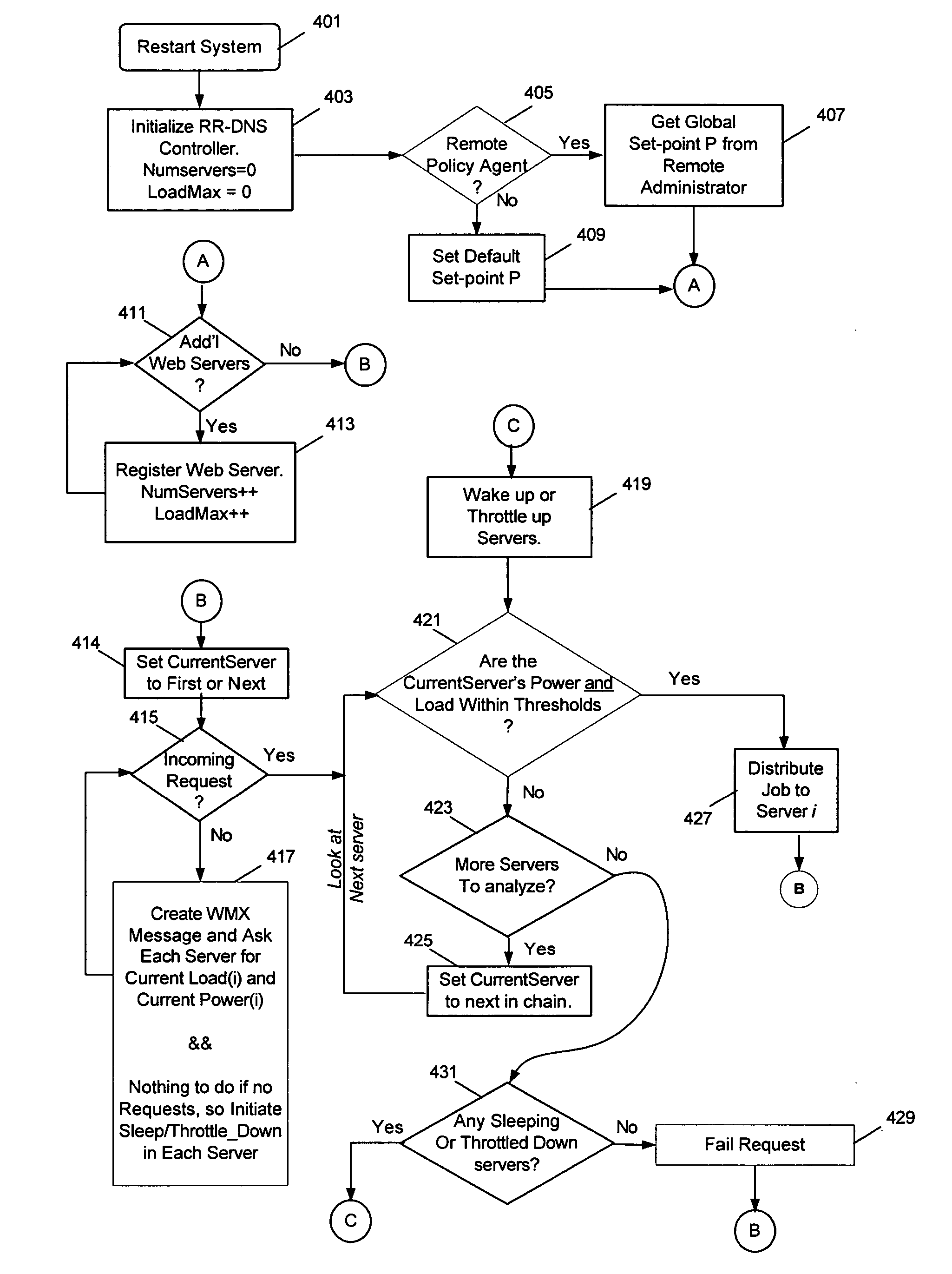
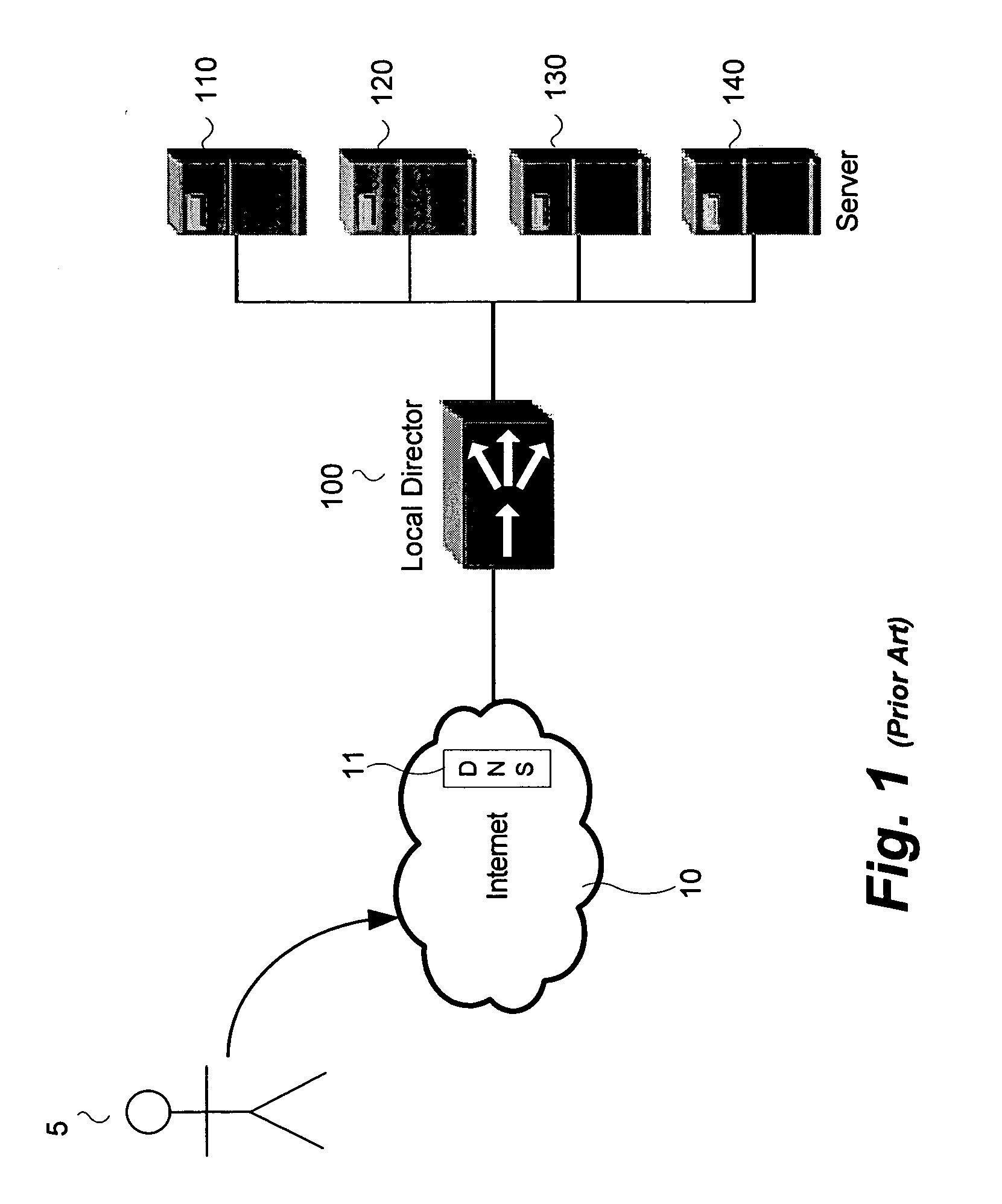
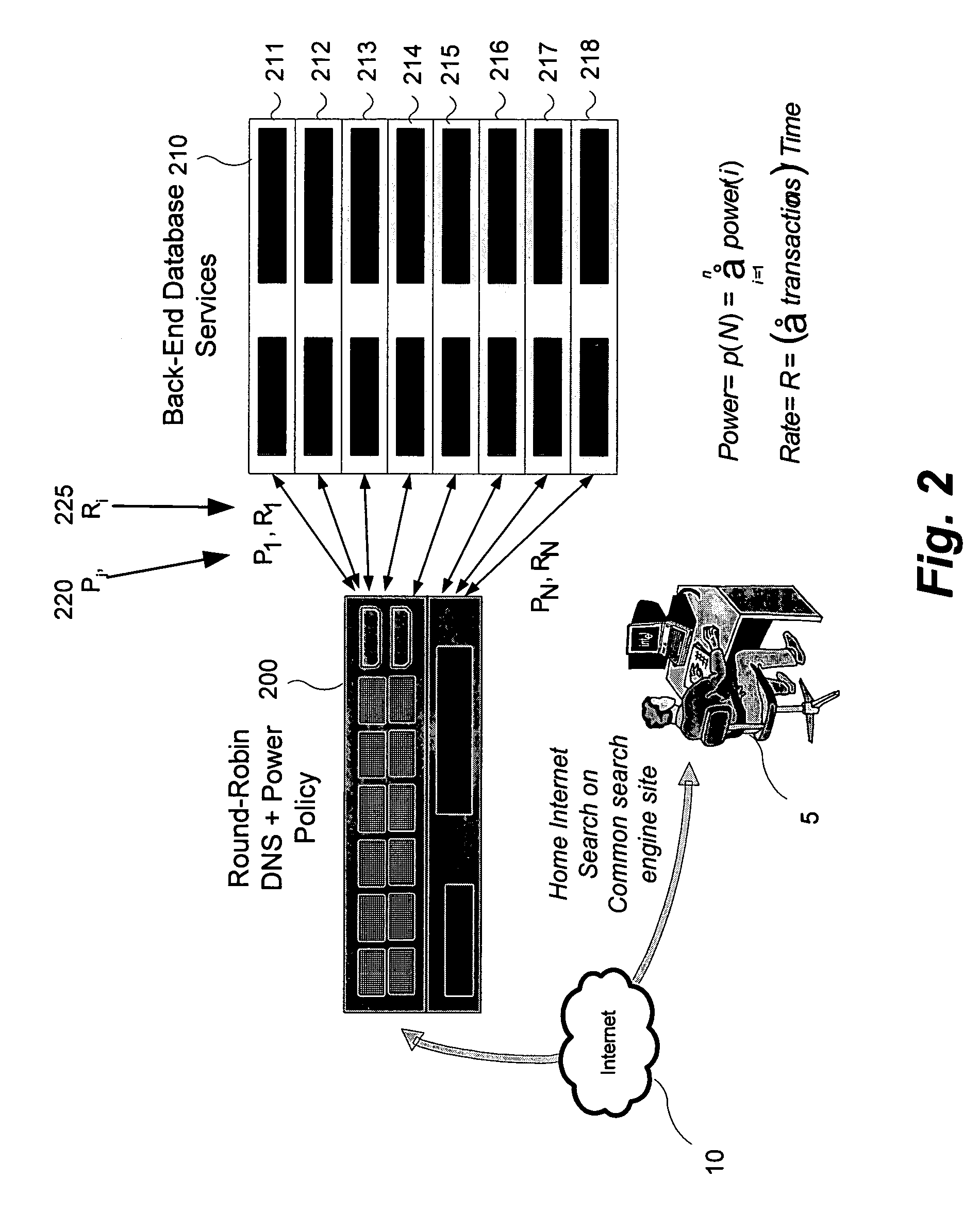
System and method to reduce platform power utilization
InactiveUS20060129675A1Digital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsBalancing networkEngineering
In some embodiments, the invention involves utilizing an enhanced round robin DNS (eRR-DNS) scheme to maximize throughput while minimizing power consumption in a network of computers. In at least one embodiment, the present invention is intended to balance the work load of network platforms in order to minimize or optimize power utilization. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com