Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
536results about How to "Efficient comprehensive utilization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
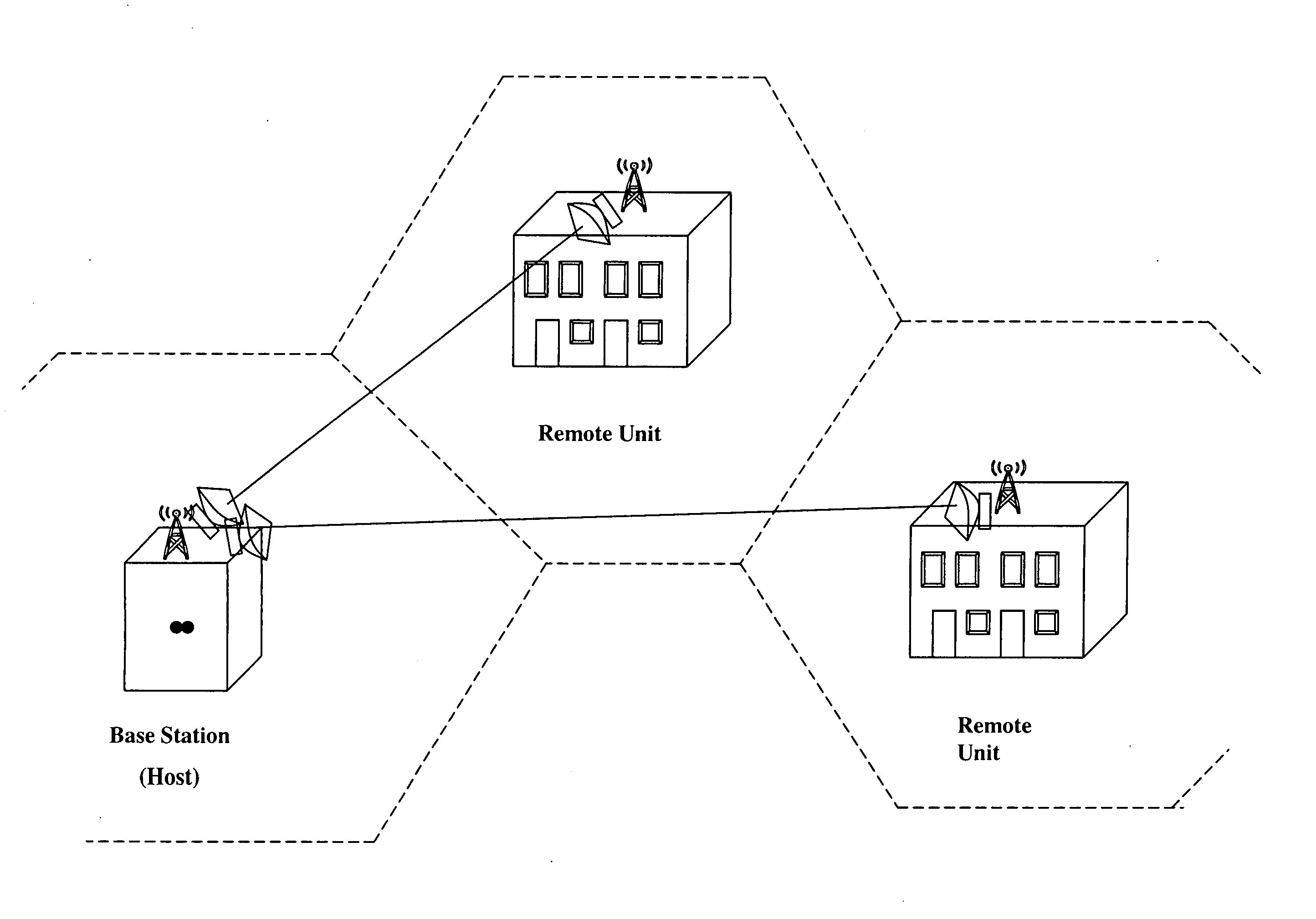
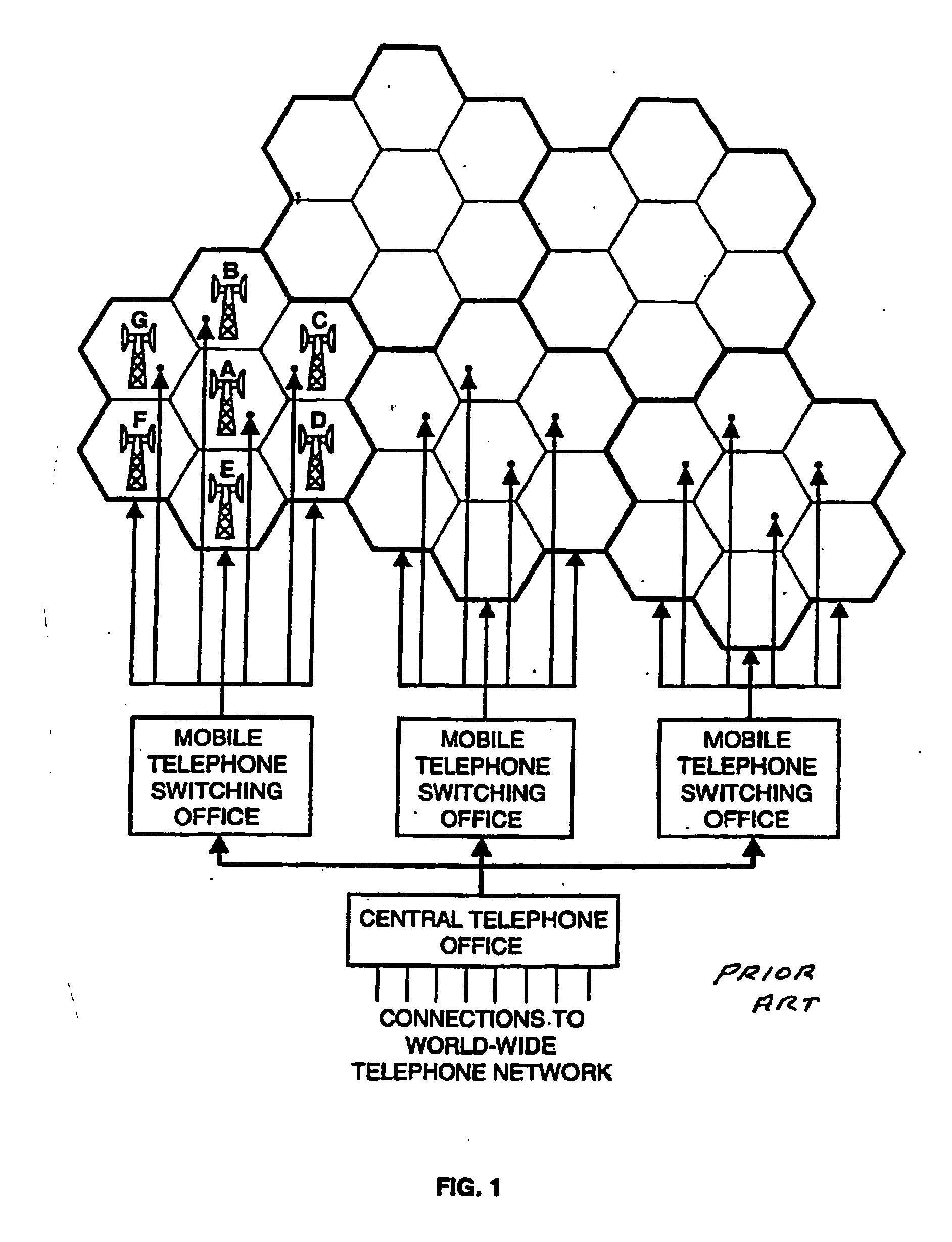
Cellular systems with distributed antennas
InactiveUS20090258652A1Efficient use ofIncrease data rateNetwork topologiesInformation formatWireless transceiverTransceiver
A communication system providing wireless communication among wireless users through a number of cellular base stations, each including at least transport management equipment and broadband equipment, at least one of which supports at least remote cellular station including RF equipment for communication with users of cellular devices. The system includes at lease one wireless narrow beam communication link operating at millimeter wave frequencies in excess of 60 GHz connecting a remote cellular station with a cellular base station equipped with broad band conversion electronic equipment and transport management equipment. In preferred embodiment the communication system includes a large number of remote cellular stations with each remote cellular station serving a separate communication cell. Each remote cellular station is equipped with a low frequency wireless transceiver for communicating with the wireless users within the cell at a radio frequency lower than 6 GHz and a narrow beam millimeter wave wireless transceiver operating at a millimeter wave frequency higher than 60 GHz for communicating with another millimeter wave transceiver at another remote cellular station or a millimeter wave transceiver at a base station.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
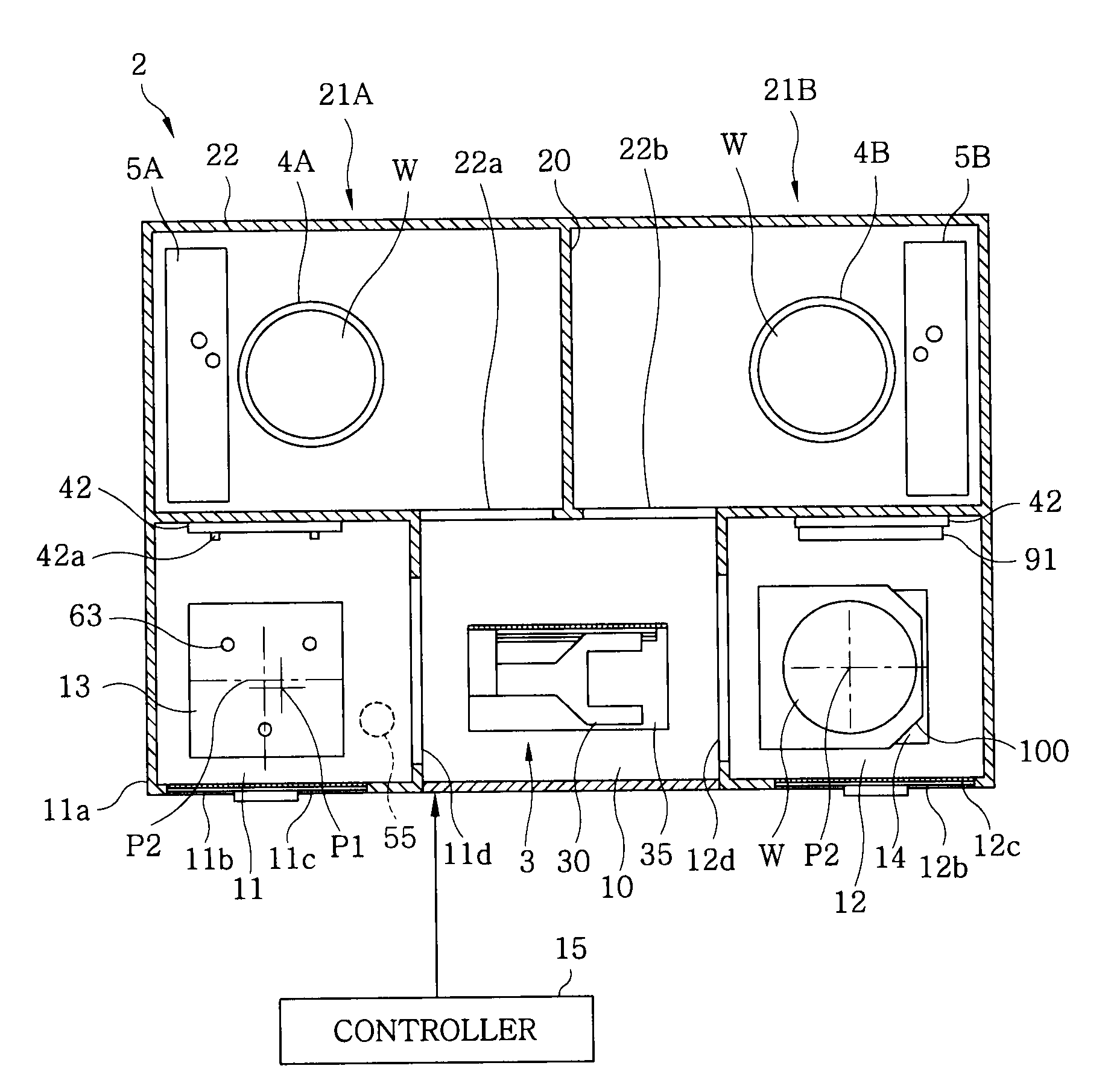
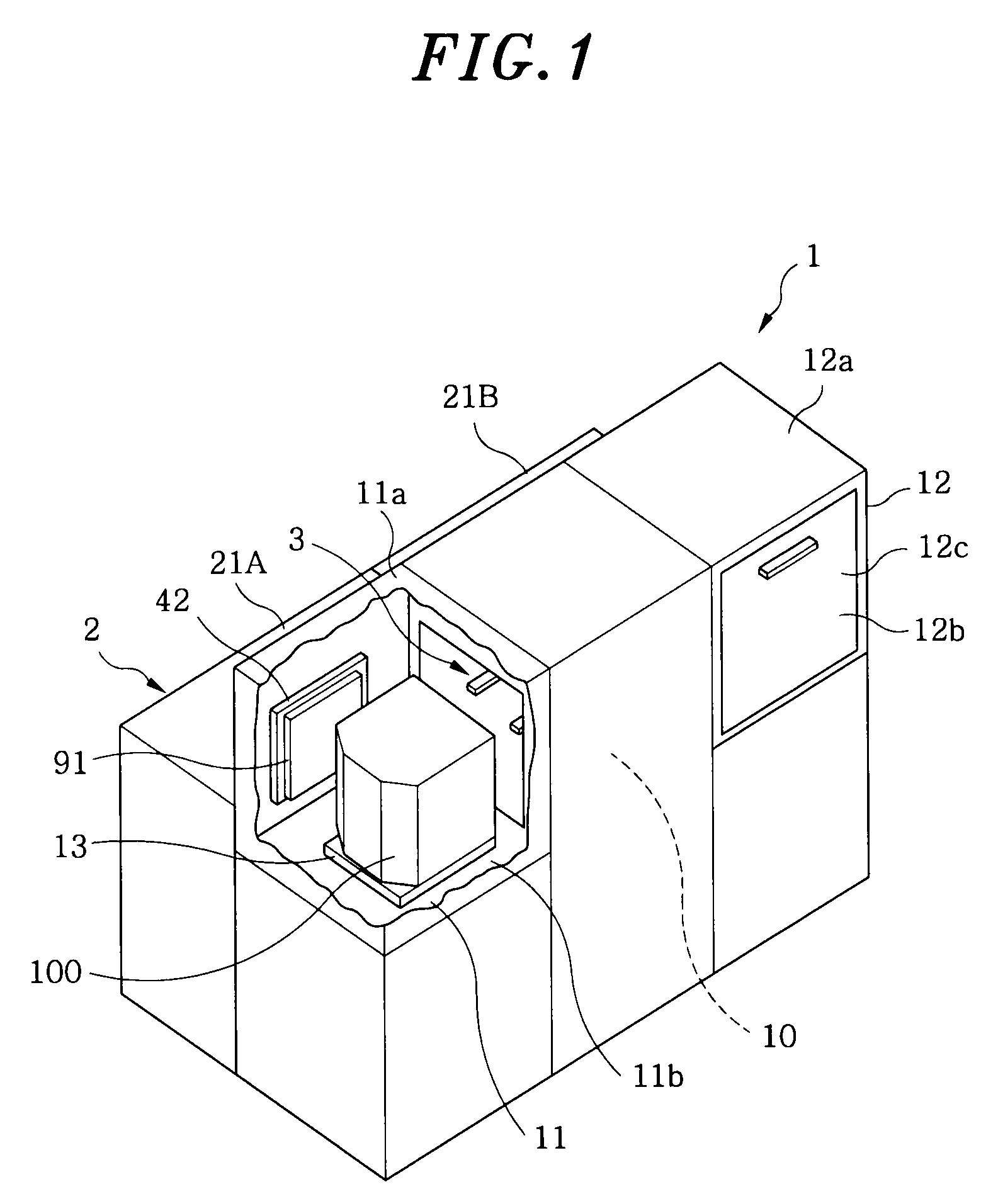
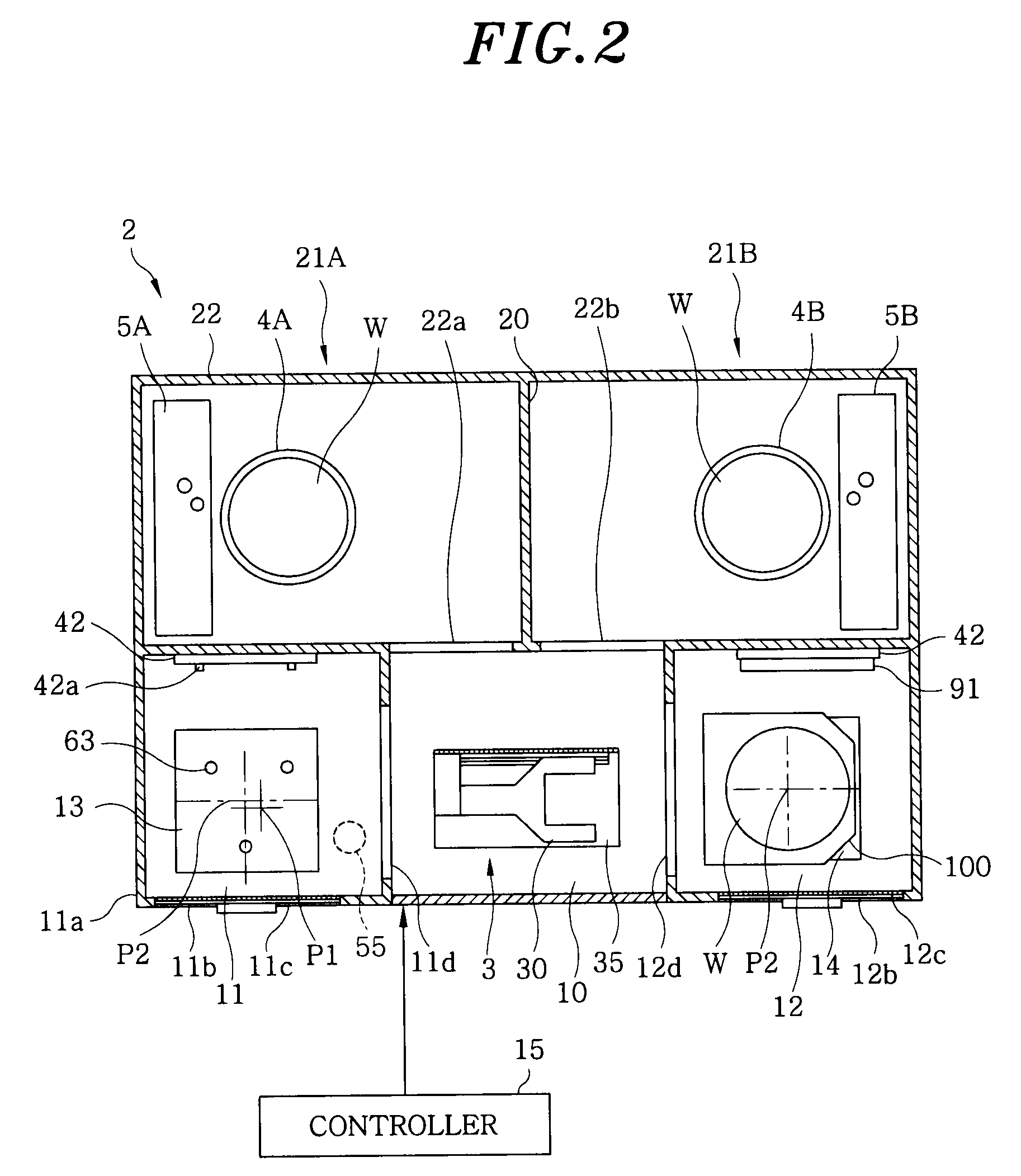
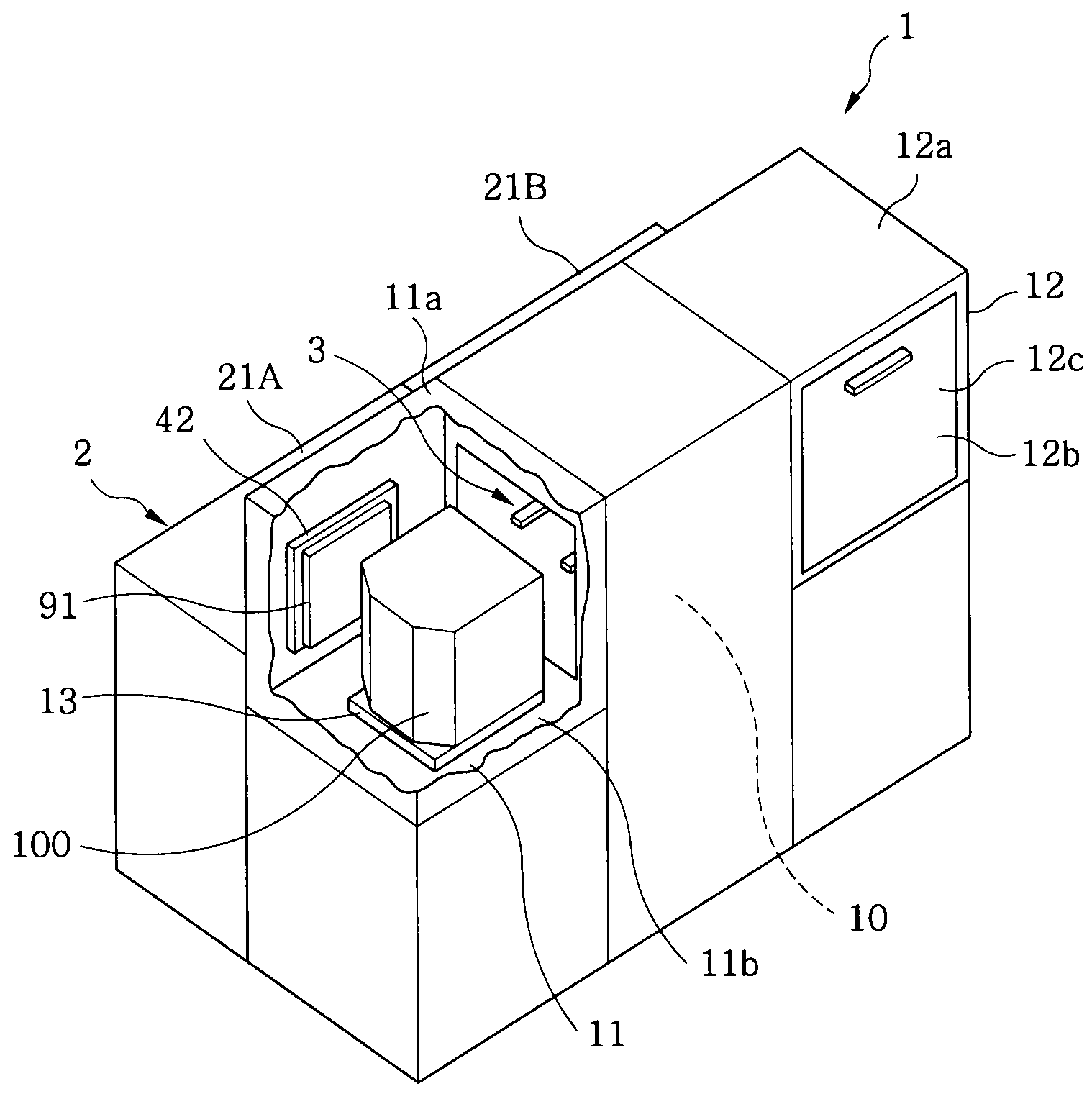
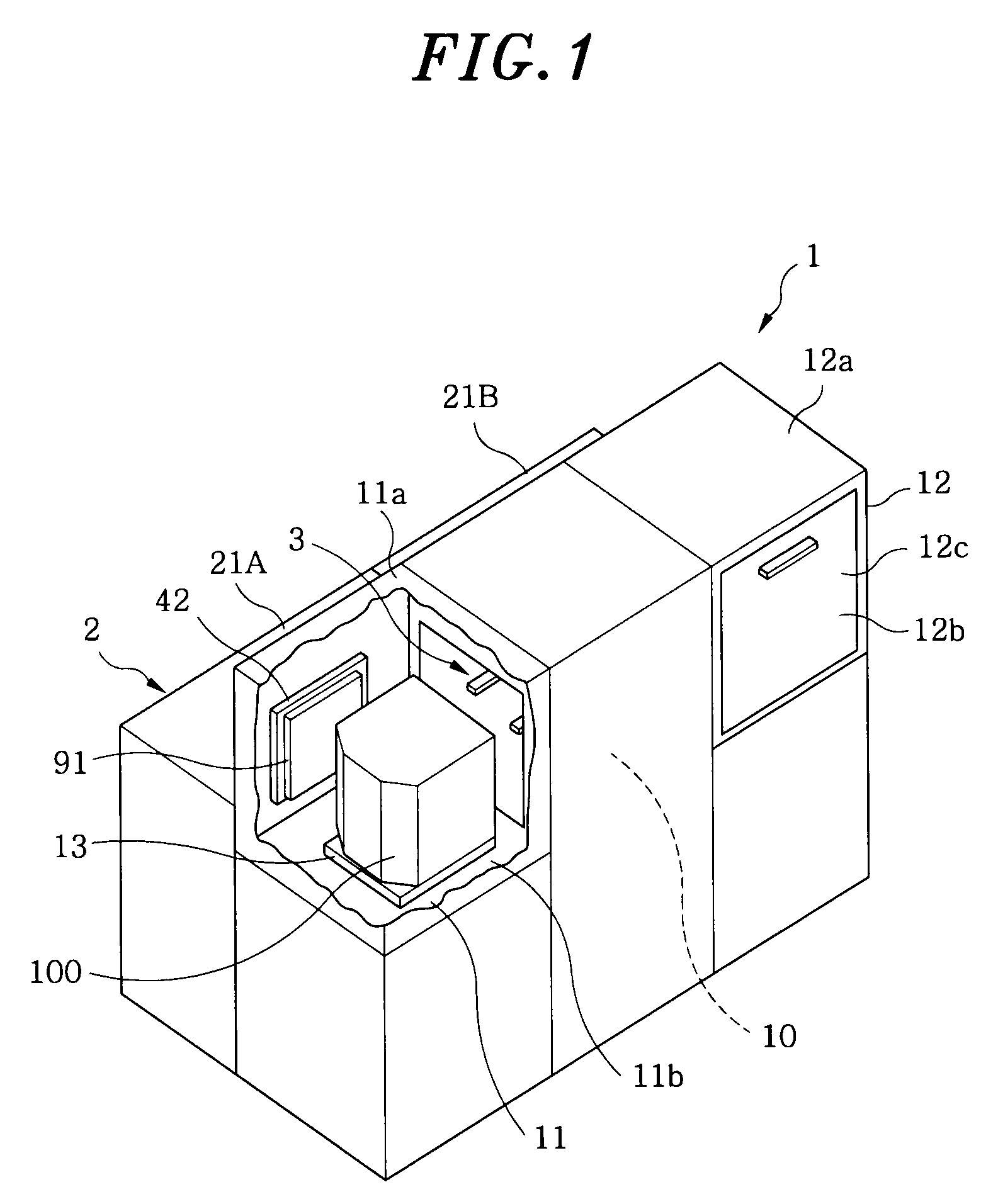
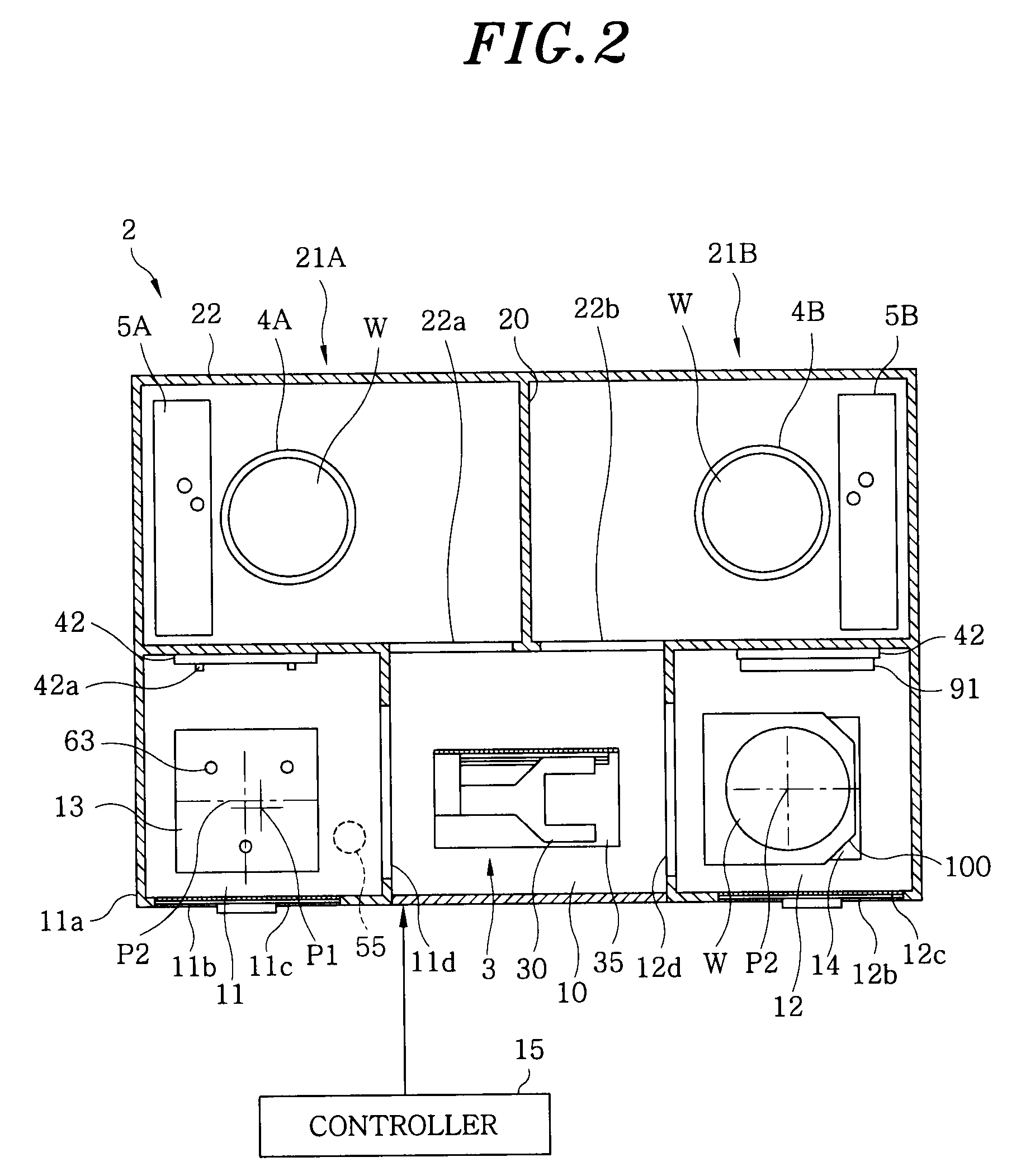
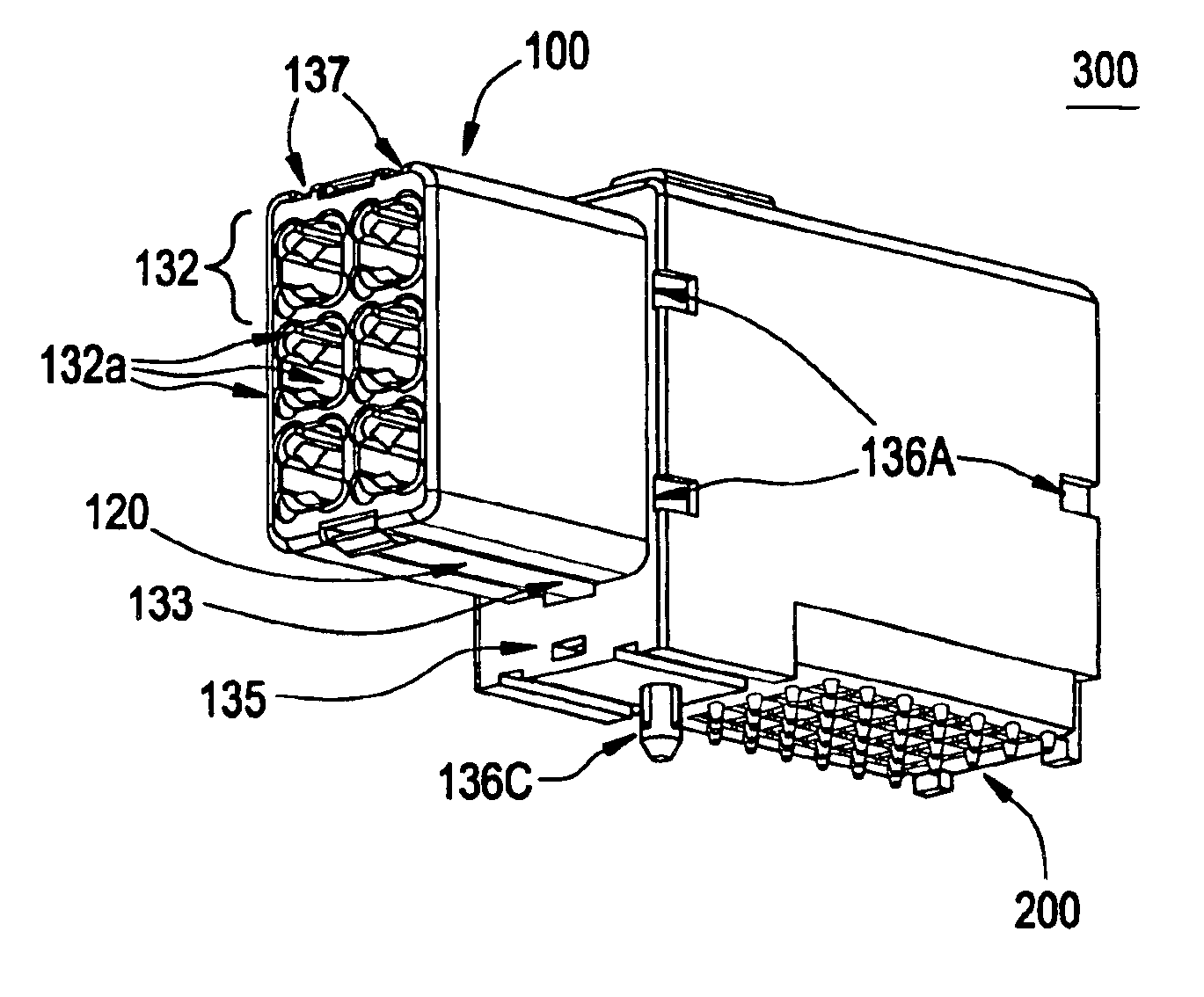
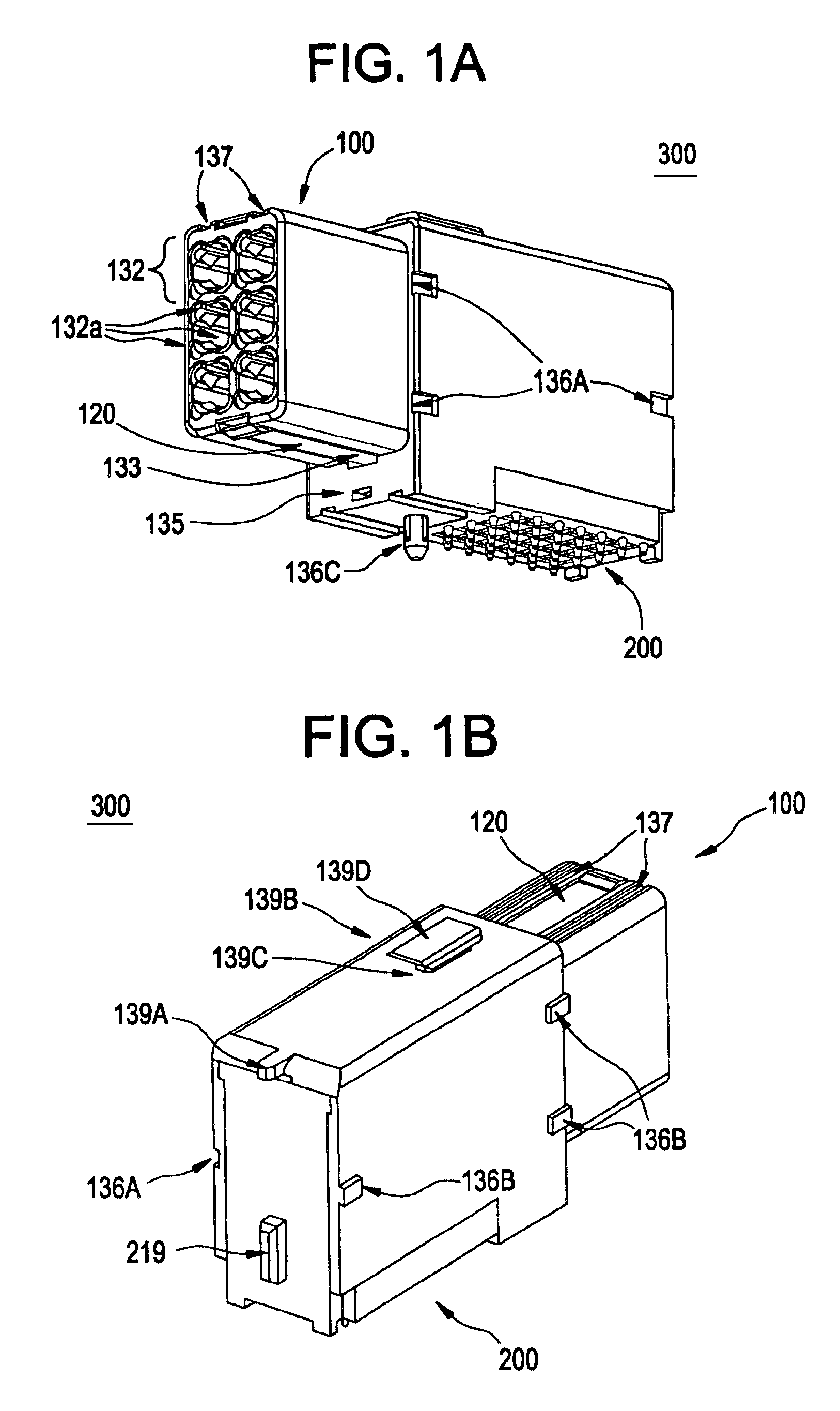
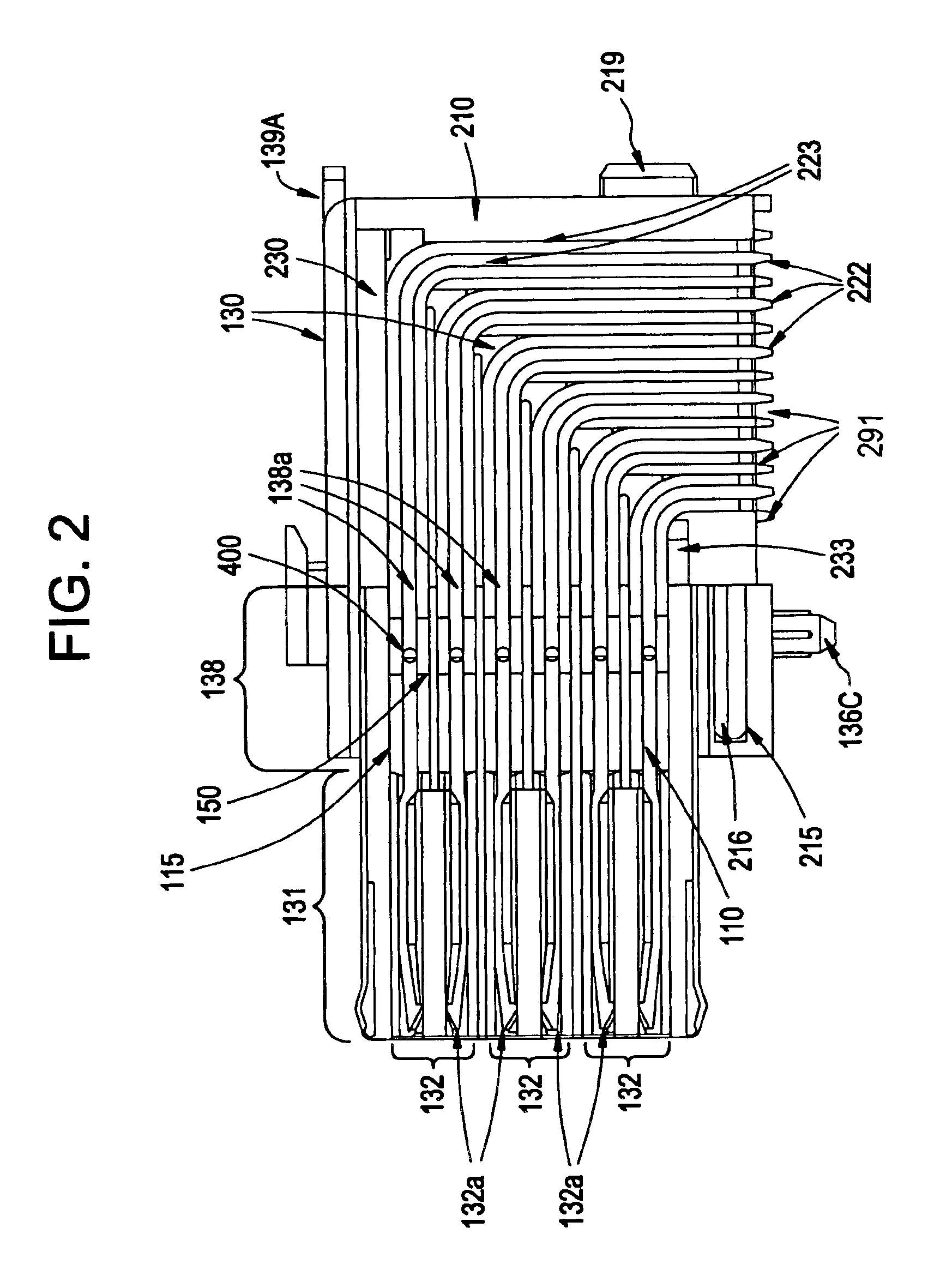
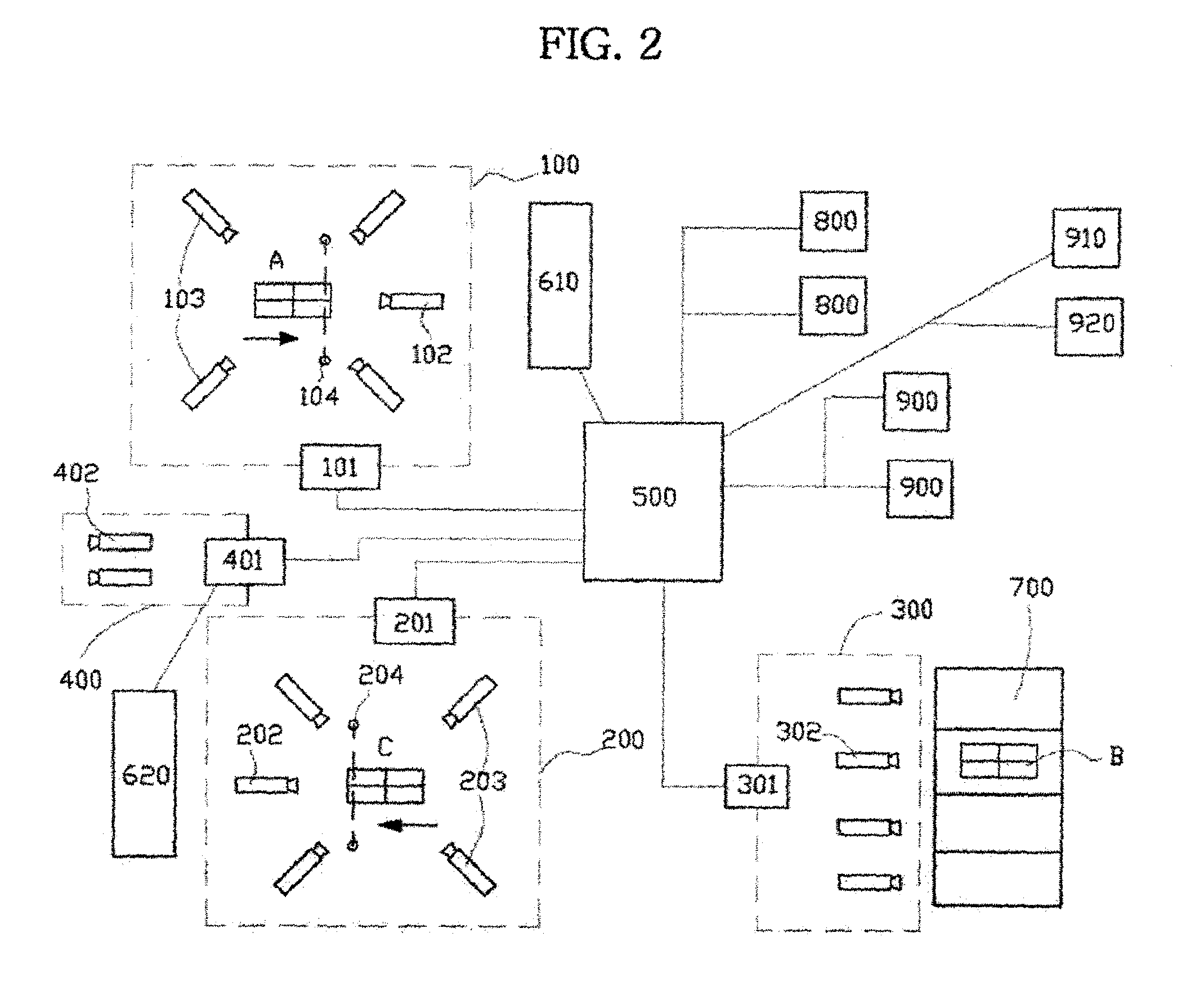
FOUP opening/closing device and probe apparatus
ActiveUS8267633B2Assure great degree of freedomEfficient comprehensive utilizationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingControl signalFOUP
A FOUP opening / closing device includes a housing containing a mounting table for mounting the FOUP thereon, an FOUP loading opening, and a delivery opening. The device further includes a rotator for rotating the mounting table, a door opening / closing unit to open or close the door of the FOUP and keep the door open, a mover for moving the FOUP and the door opening / closing unit in a reciprocating manner, to allow the FOUP and the door opening / closing unit to be connected to or separated from each other, and a controller to output control signals for moving the FOUP and the door opening / closing unit via operation of the mover to mount the door of the FOUP to the door opening / closing unit, separating the door from the FOUP, moving the FOUP and the door opening / closing unit away from each other, and rotating the mounting table to make the FOUP face the delivery opening.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Foup opening/closing device and probe apparatus
ActiveUS20100040441A1Efficient space utilizationThe degree of freedom becomes largerSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingControl signalEngineering
A FOUP opening / closing device includes a housing containing a mounting table for mounting the FOUP thereon, an FOUP loading opening, and a delivery opening. The device further includes a rotator for rotating the mounting table, a door opening / closing unit to open or close the door of the FOUP and keep the door open, a mover for moving the FOUP and the door opening / closing unit in a reciprocating manner, to allow the FOUP and the door opening / closing unit to be connected to or separated from each other, and a controller to output control signals for moving the FOUP and the door opening / closing unit via operation of the mover to mount the door of the FOUP to the door opening / closing unit, separating the door from the FOUP, moving the FOUP and the door opening / closing unit away from each other, and rotating the mounting table to make the FOUP face the delivery opening.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
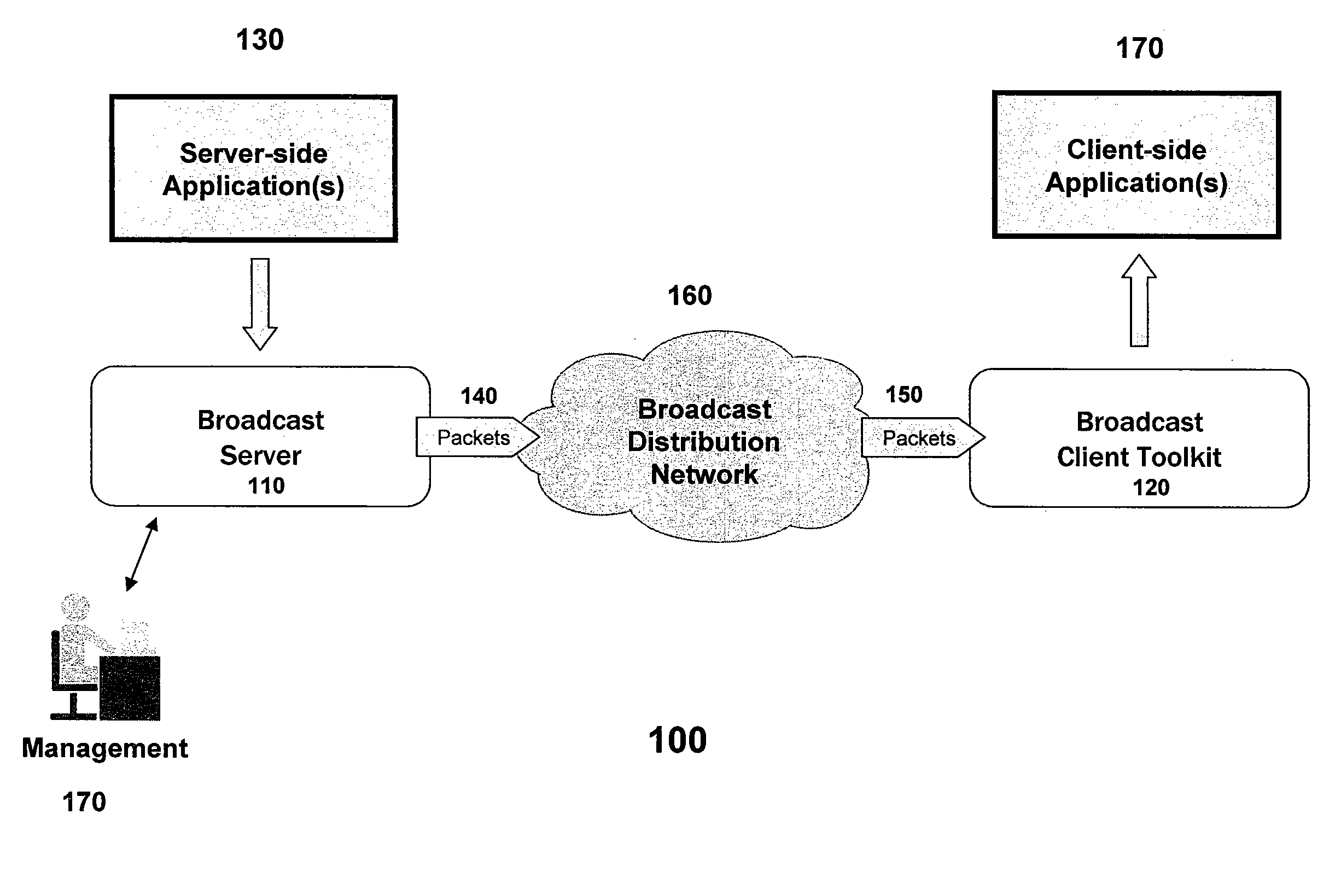
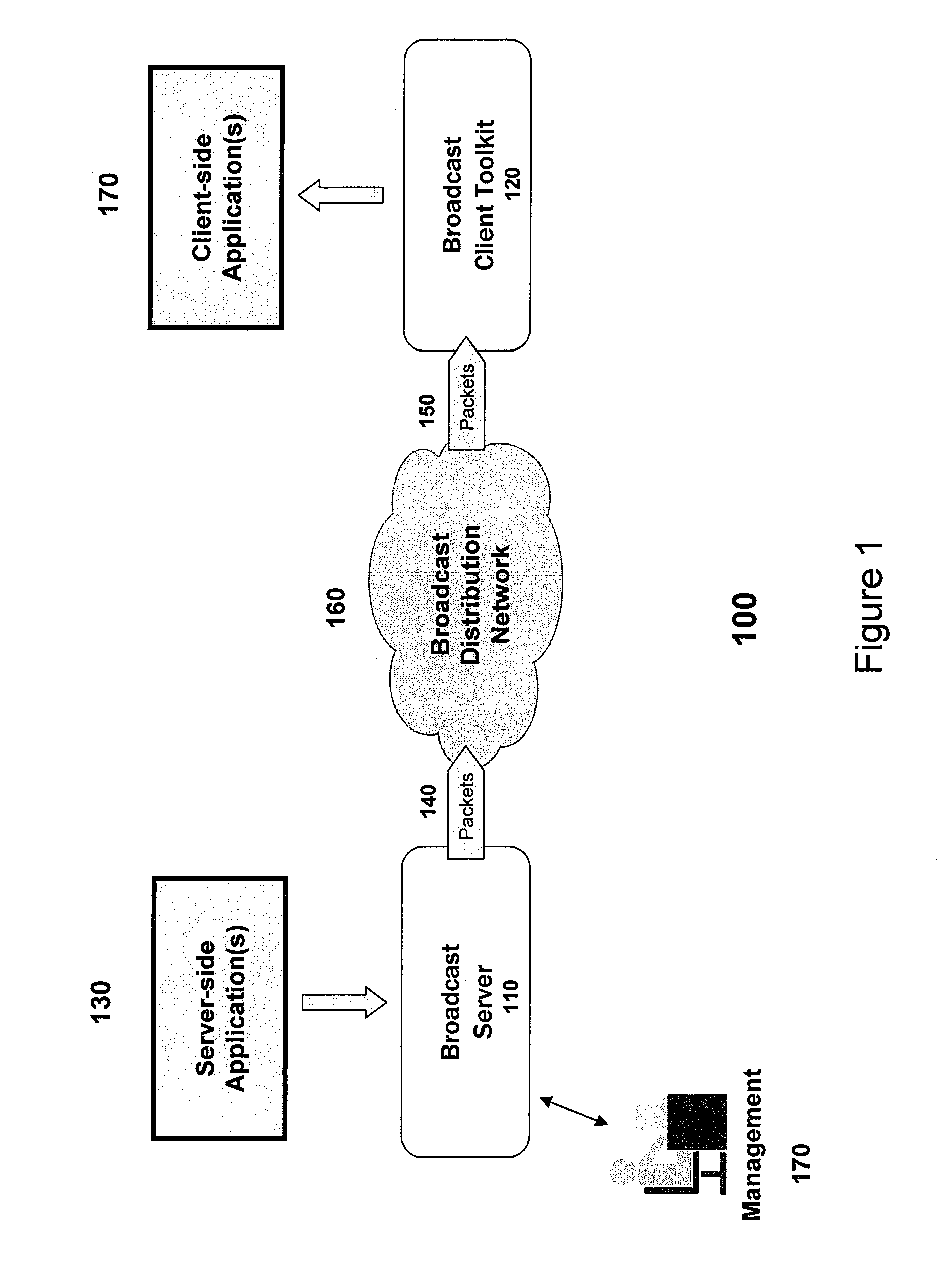
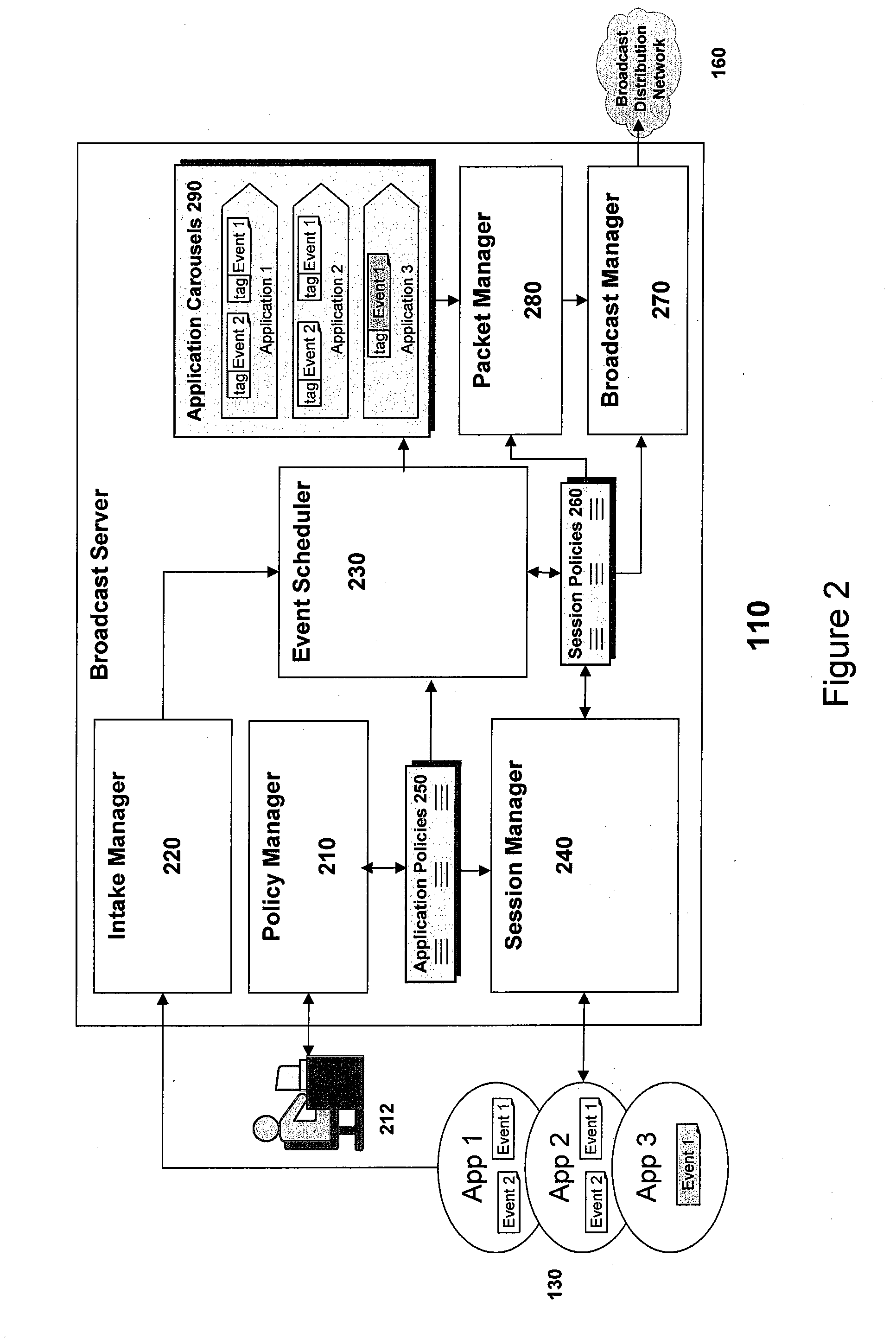
Reliable event broadcaster with multiplexing and bandwidth control functions
ActiveUS20070180119A1Desired level of qualityEfficient use ofError preventionTransmission systemsControl functionMultiple device
A system, apparatus, and method for transmitting data in a broadcast mode to multiple devices operating in a network. The invention enables the efficient utilization of bandwidth while providing a desired level of quality of service for the applications executing on the devices that utilize the broadcasted data. The invention utilizes a set of bandwidth constraints in combination with a set of heuristics and rules for the allocation and re-allocation of bandwidth among multiple applications in a manner that minimizes the impact on the quality of service metrics of importance to the affected applications when contention exists for the network resources. The present invention implements processes to cause the quality of service provided to each application to degrade smoothly, with certain priorities and guarantees being maintained. The present invention also provides event segmentation and reassembly functions for applications, and includes reliability mechanisms to increase the ability to provide data to client devices that have not been actively receiving for significant periods of time.
Owner:DIRECTV LLC
High-throughput, low-latency next generation internet networks using optical tag switching
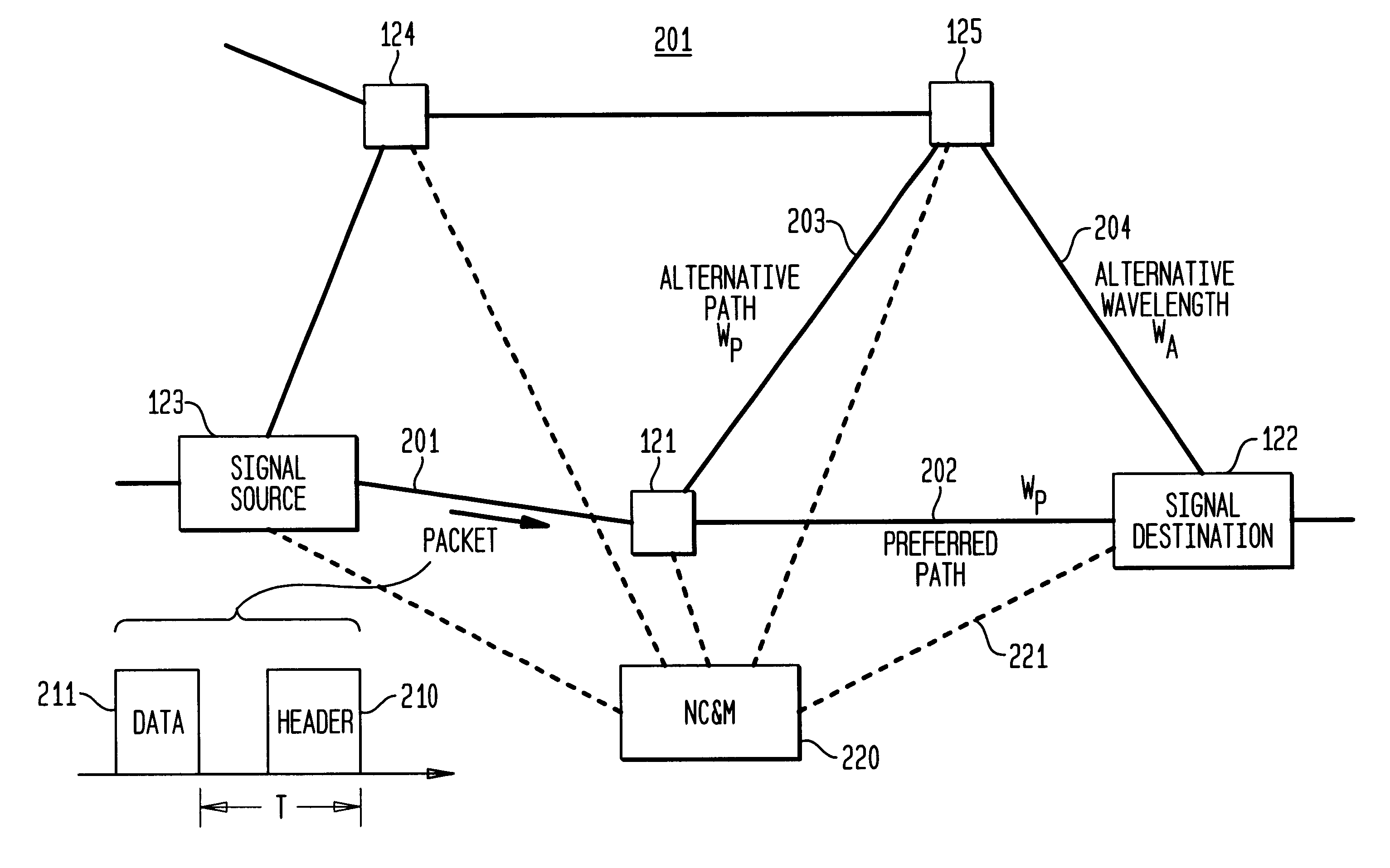
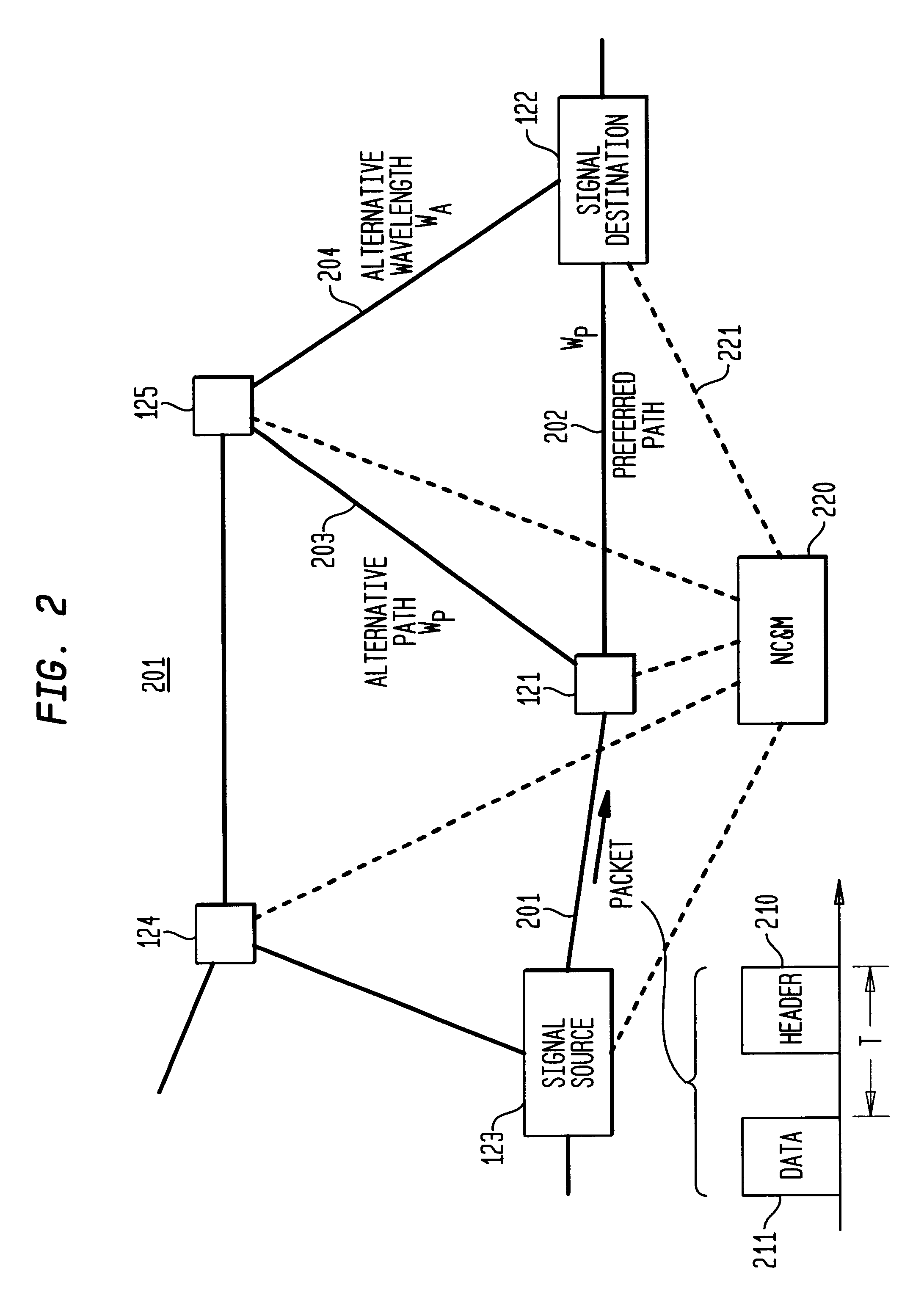
InactiveUS6111673AEfficient comprehensive utilizationSignificant overheadMultiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsSignal routingInternet network
An optical signaling header technique applicable to optical networks wherein packet routing information is embedded in the same channel or wavelength as the data payload so that both the header and data payload propagate through network elements with the same path and the associated delays. The header routing information has sufficiently different characteristics from the data payload so that the signaling header can be detected without being affected by the data payload, and that the signaling header can also be removed without affecting the data payload. The signal routing technique can be overlaid onto the conventional network elements in a modular manner using two types of applique modules. The first type effects header encoding and decoding at the entry and exit points of the data payload into and out of the network; the second type effects header detection at each of the network elements.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Biomass Char Compositions for Catalytic Gasification
InactiveUS20090217575A1Efficient utilization of carbonEfficient comprehensive utilizationProductsReagentsParticulatesHydrogen
Particulate compositions are described comprising an intimate mixture of a biomass char producedfrom the combustion of a biomass, such as switchgrass or hybrid poplar, with at least a second carbonaceous material, such as petroleum coke or coal, and, optionally a gasification catalyst, for gasification in the presence of steam to yield a plurality of gases including methane and at least one or more of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and other higher hydrocarbons are formed. Processes are also provided for the preparation of the particulate compositions and converting the particulate composition into a plurality of gaseous products.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
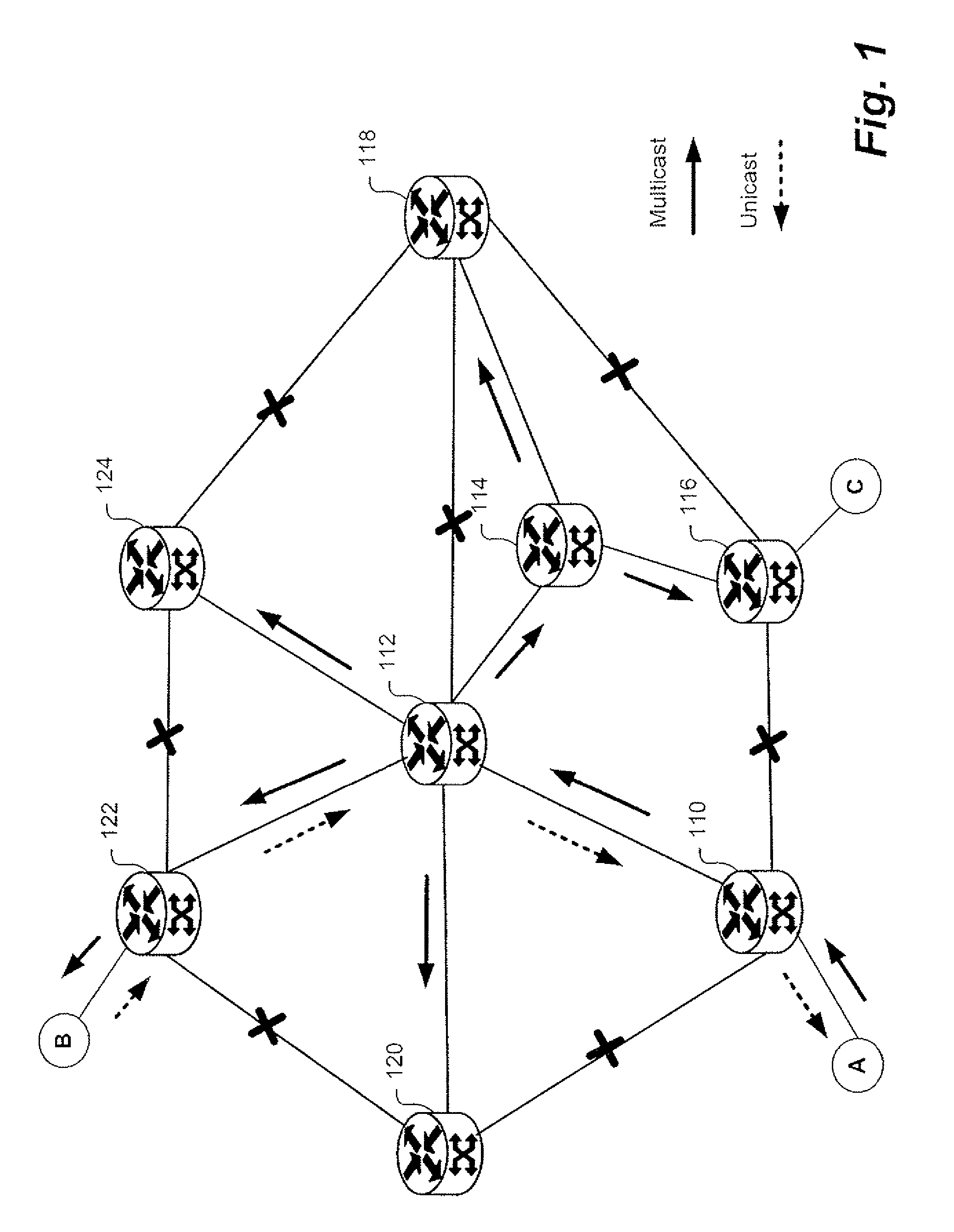
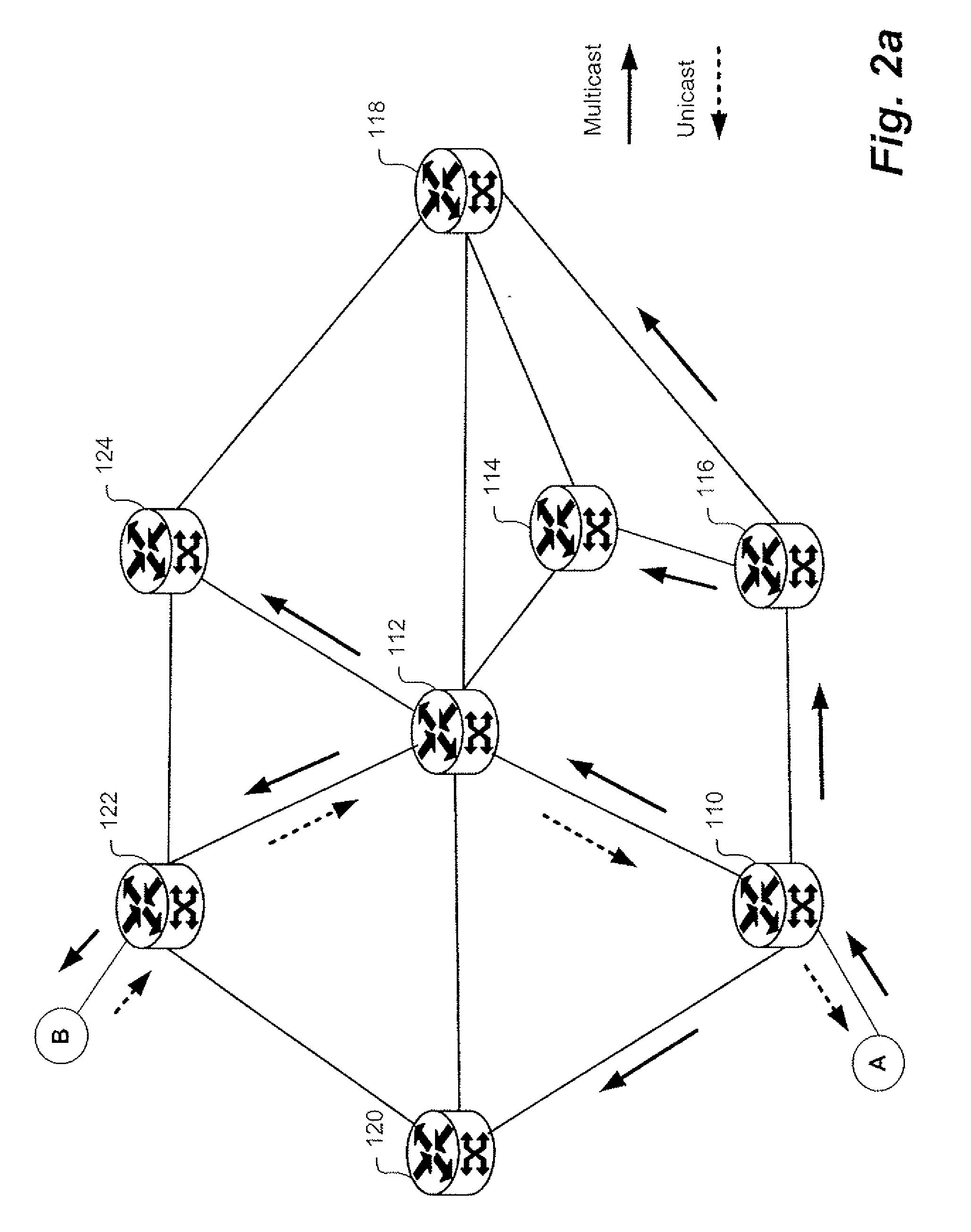
Provider link state bridging
InactiveUS20070086361A1Effective link utilizationMinimize impactSpecial service provision for substationData switching by path configurationMedia access controlInstability
Provider Link State Bridging (PLSB) expands static configuration of Ethernet MAC forwarding tables by the control plane and utilizes direct manipulation of Ethernet forwarding by a link state routing system. At least one media-access-control (MAC) address for unicast forwarding to the bridge and at least one MAC address for multicast forwarding from the bridge are assigned. Bridges exchange state information by a link state bridging protocol so that a synchronized configured view of the network is shared between nodes. Each node can calculate shortest path connective between peer bridging nodes and populated the appropriate forwarding tables. A reverse path forwarding check is performed on incoming packets to provide loop suppression. During times of network instability the loop suppression can be disabled for unicast packets as identified by the destination MAC address to buffer packets and minimize the impact on traffic flow.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
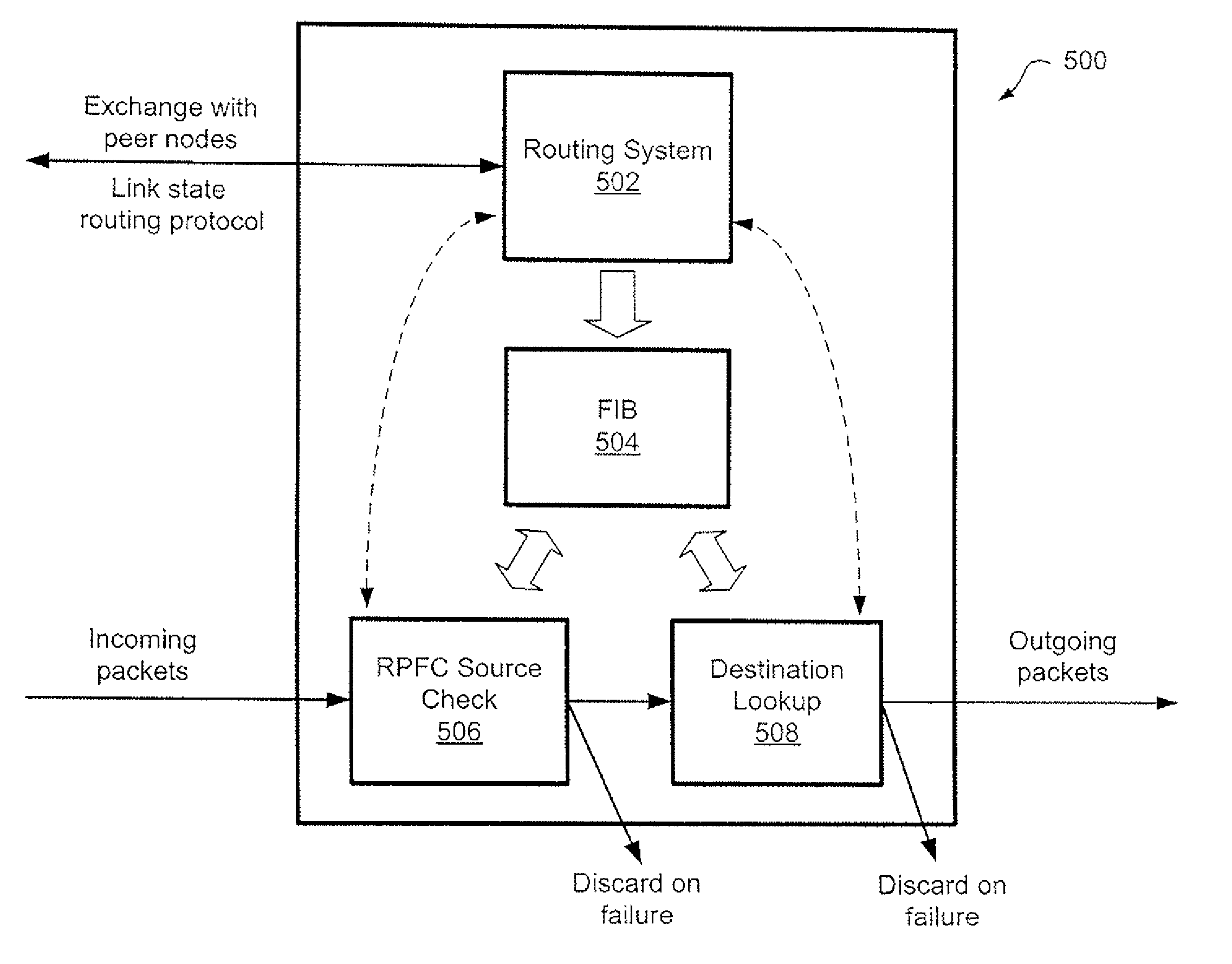
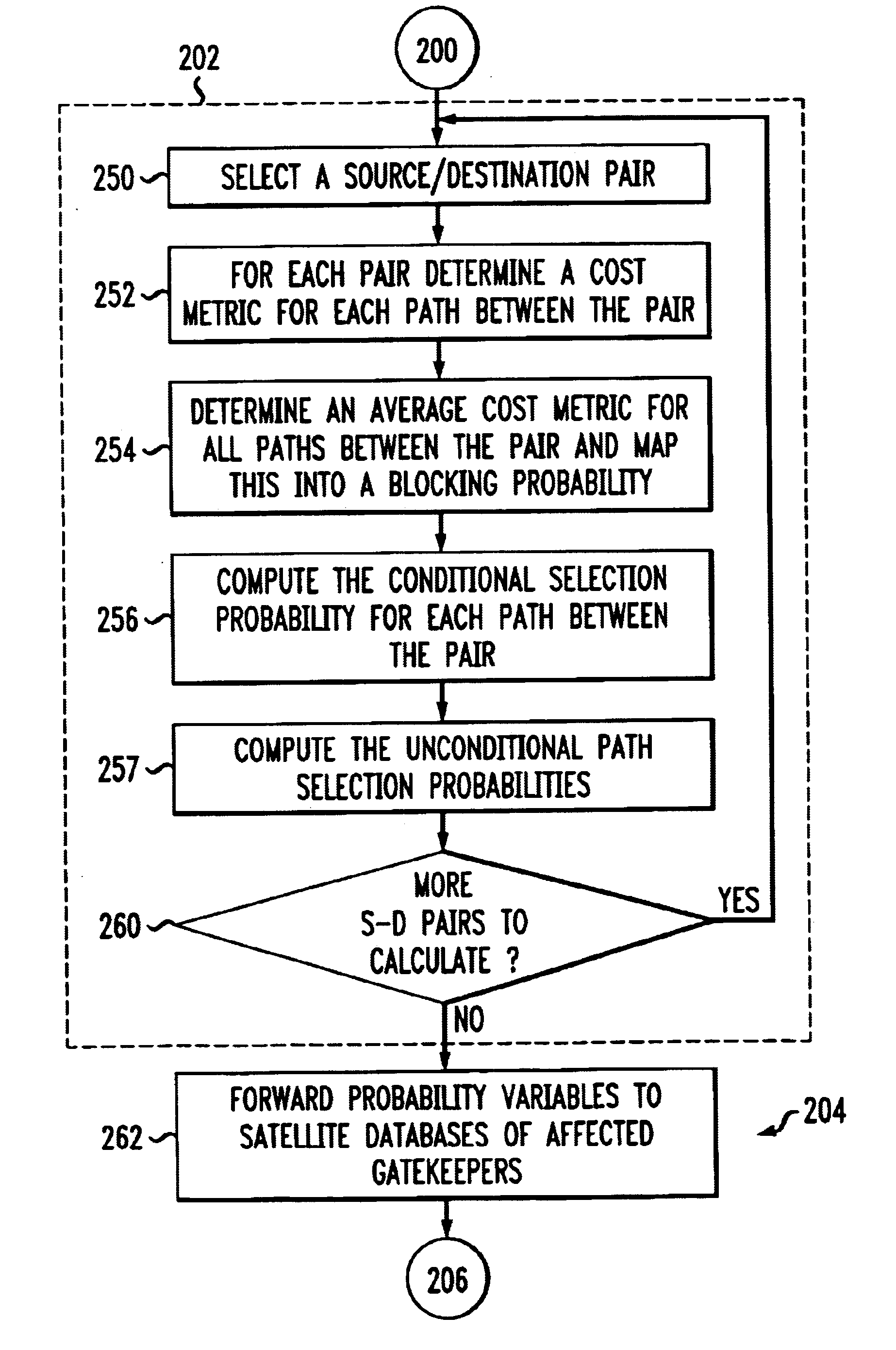
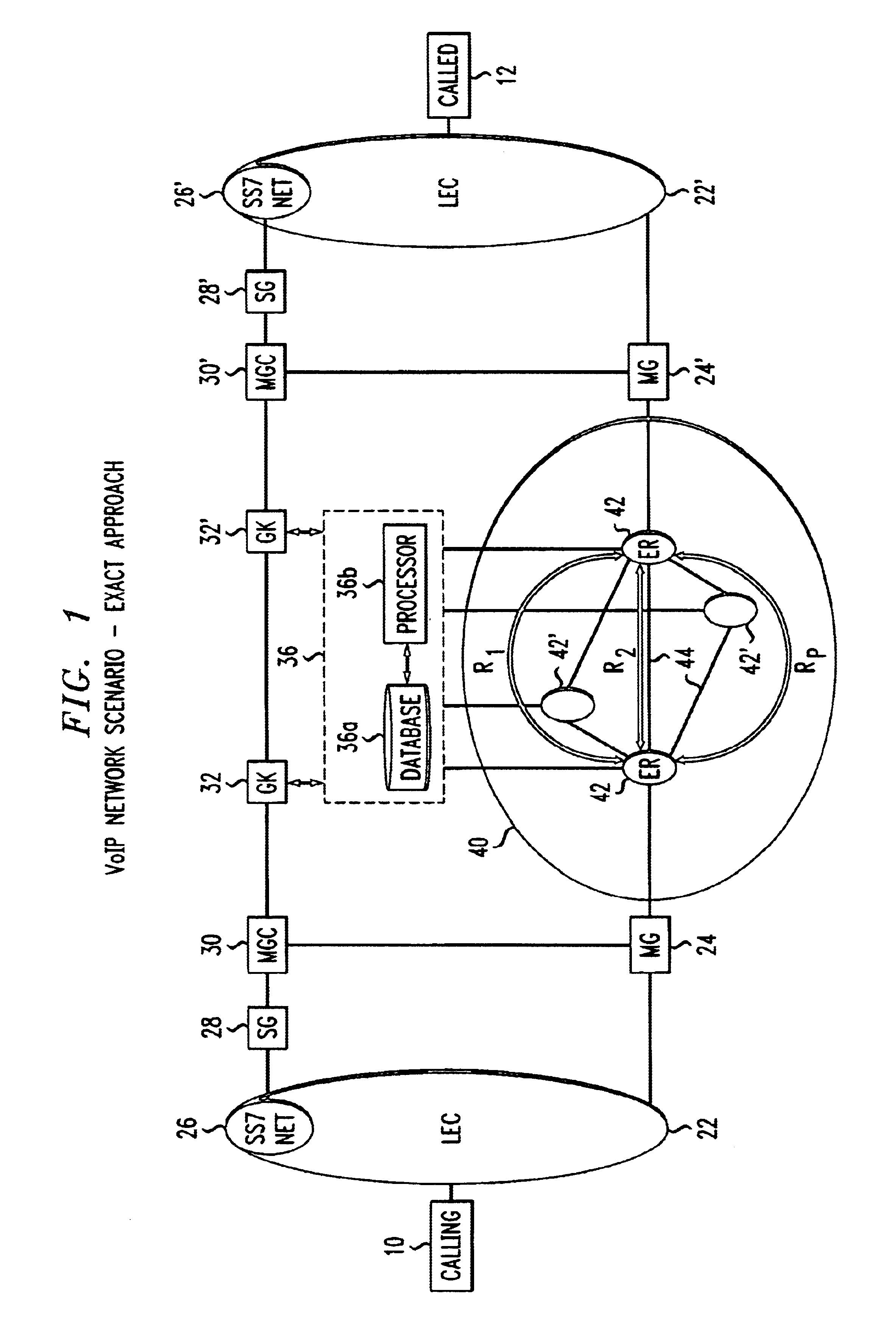
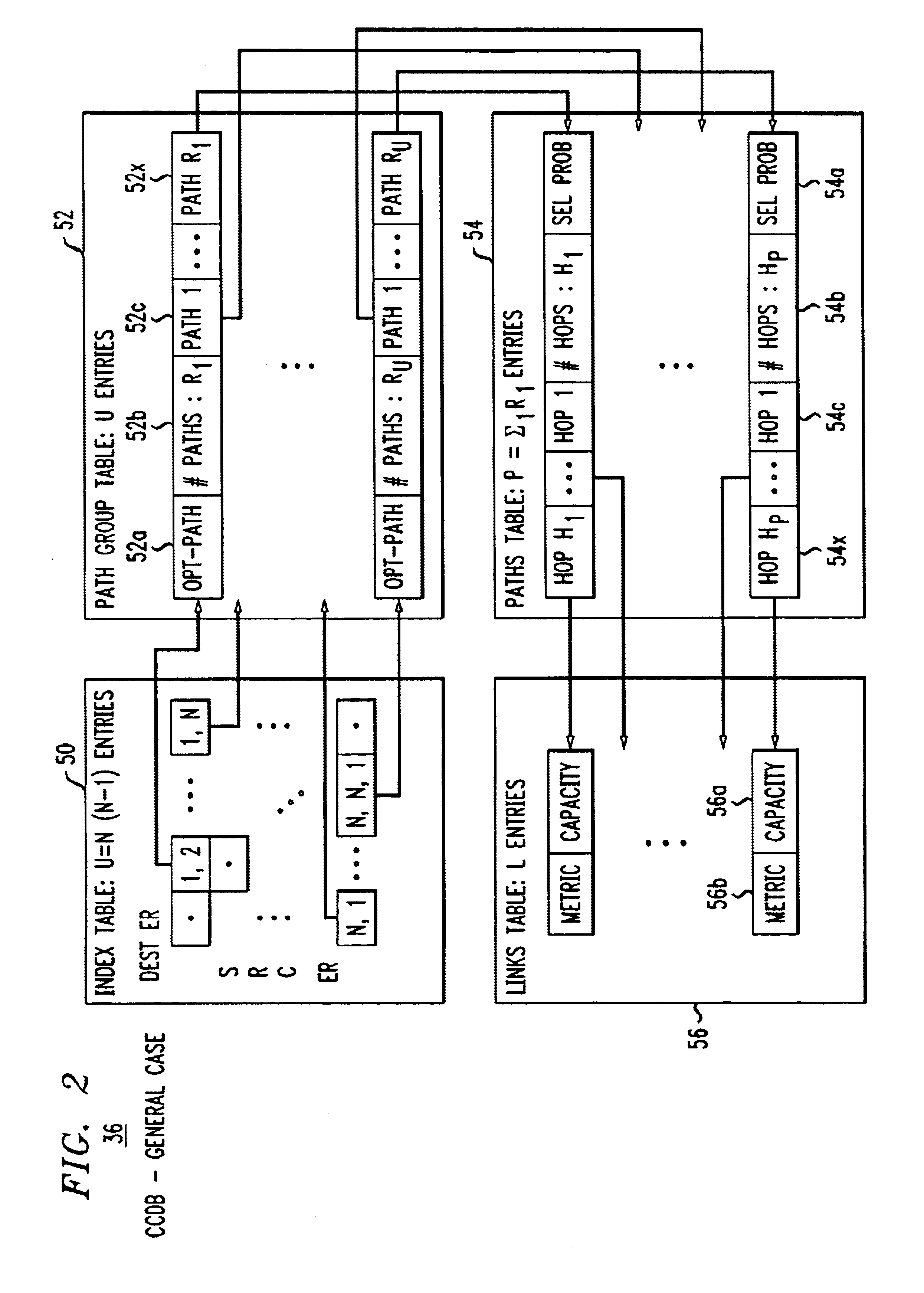
Method and apparatus to provide centralized call admission control and load balancing for a voice-over-IP network
InactiveUS6904017B1Improve service qualityBandwidth sharingInterconnection arrangementsError preventionExtensibilityBalancing network
An admission control and load balancing system controls admission of packet streams or calls to a network and balances the packet traffic across the network, improving quality of service. The system includes a central database which stores information including cost data associated with individual paths and links across the network. A processor, in communication with the database, coordinates the admission control and load balancing decisions, and updates of the database cost data to reflect the dynamic network conditions, based on input from appropriate data sources. In one embodiment, referred to as the exact algorithm, the database is consulted by the admission control points or gatekeepers prior to admitting each arriving packet stream, and the database contents are updated call-by-call to reflect the allocation of resources to each admitted stream. In another embodiment, referred to as the inexact algorithm, control decision as well as database updates occur on a periodic rather than on a call-by-call basis to promote better scalability. In this embodiment, the processor periodically calculates admission decisions based on cost data in the central database. These admission decisions are then periodically forwarded to a satellite database associated with each gatekeeper, for storage and use in admission decisions until the next update epoch.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
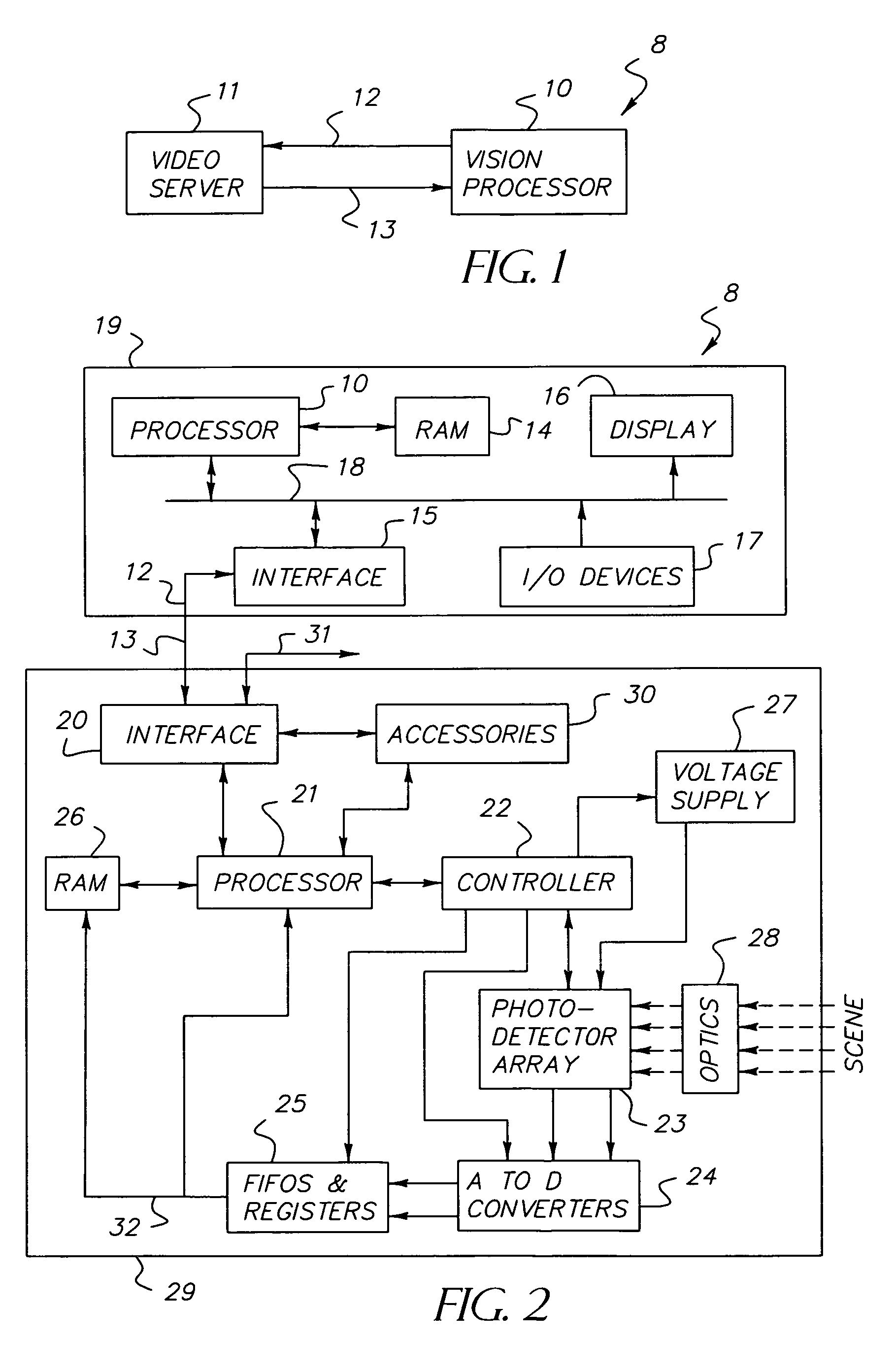
Dynamically reconfigurable vision system
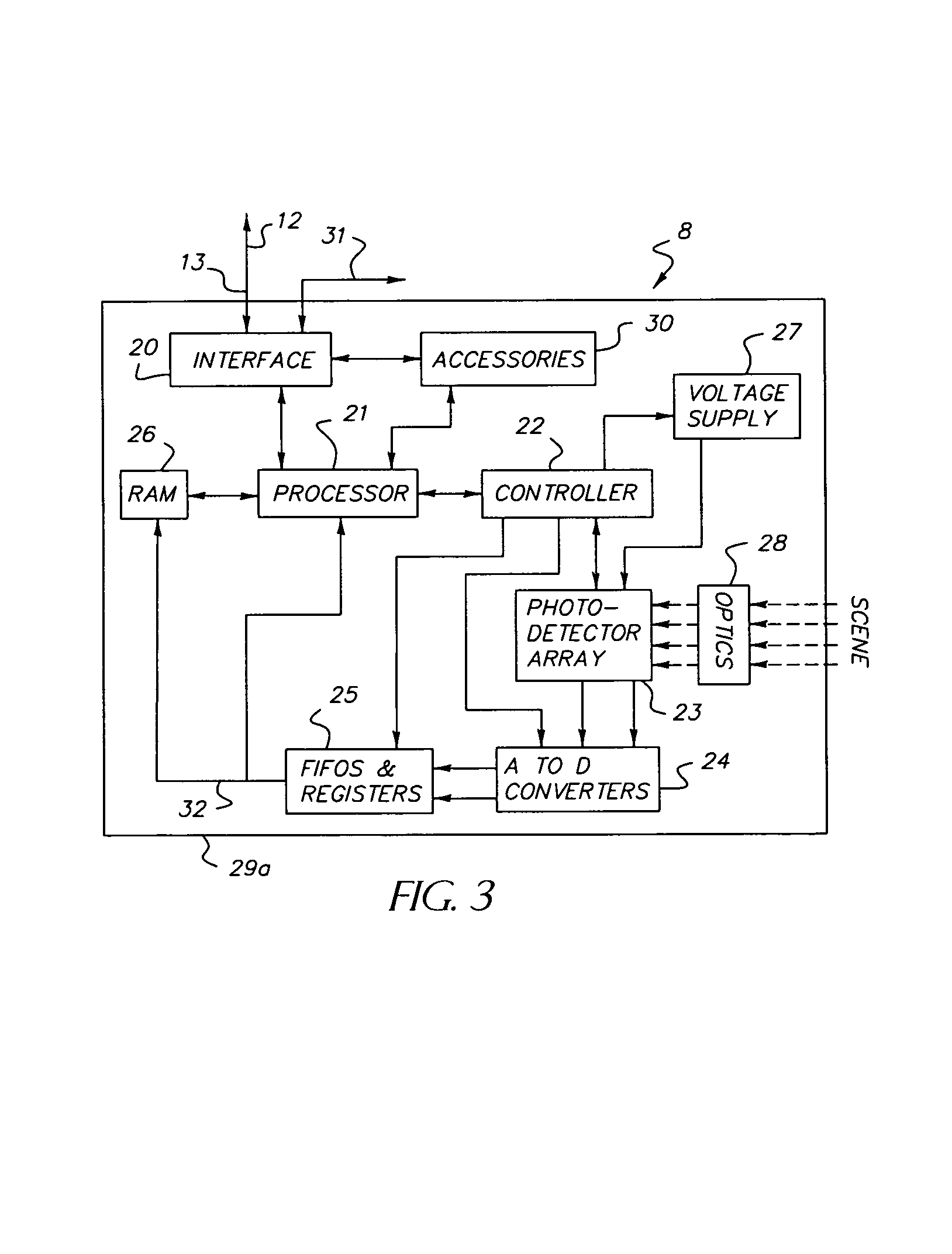
InactiveUS7106374B1Efficiently usEffective resourcesTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsVision processingPhotodetector
A closed-loop vision system is disclosed that utilizes a concept known as Dynamically Reconfigurable Vision (DRV), which is adaptive image sensing driven by a computer or human operator's response to changing scenery. The system reduces the amount of irrelevant video information sensed and thus achieves more effective bandwidth and computational resource utilization, as compared to traditional vision systems. One or more reconfigurable photodetector arrays sensitive to either visible, infrared or ultraviolet radiation are present in the DRV system. These photodetector arrays feature on-chip means for spatial and temporal data reduction implemented through multiple independently controllable, time-correlated, frequently overlapping windows on the photodetector array that may be programmed according to their size, location, resolution, integration time, and frame rate. All photodetector array windows are dynamically reconfigurable in real time on a frame-by-frame basis. Furthermore, a DRV system is constructed in a client-server architecture in which a vision processor client passes window request command messages to the reconfigurable photodetector array server, which in turn delivers the requested video back to the client processor. The ability to simultaneously reconfigure, integrate, process, and readout multiple photodetector array video windows is an important characteristic of the DRV system.
Owner:COMPTEK AMHERST SYST INC
Remote office duplication
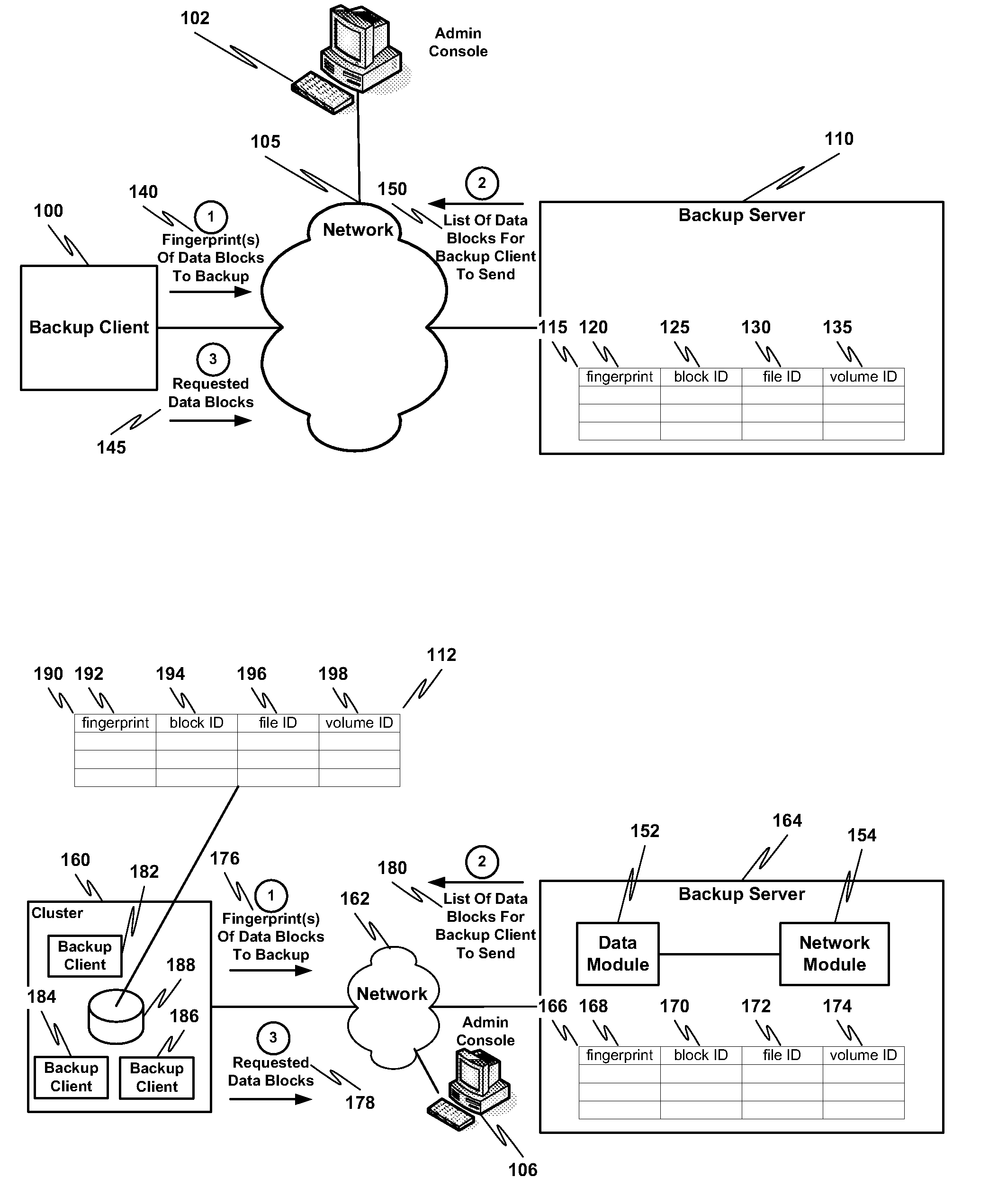
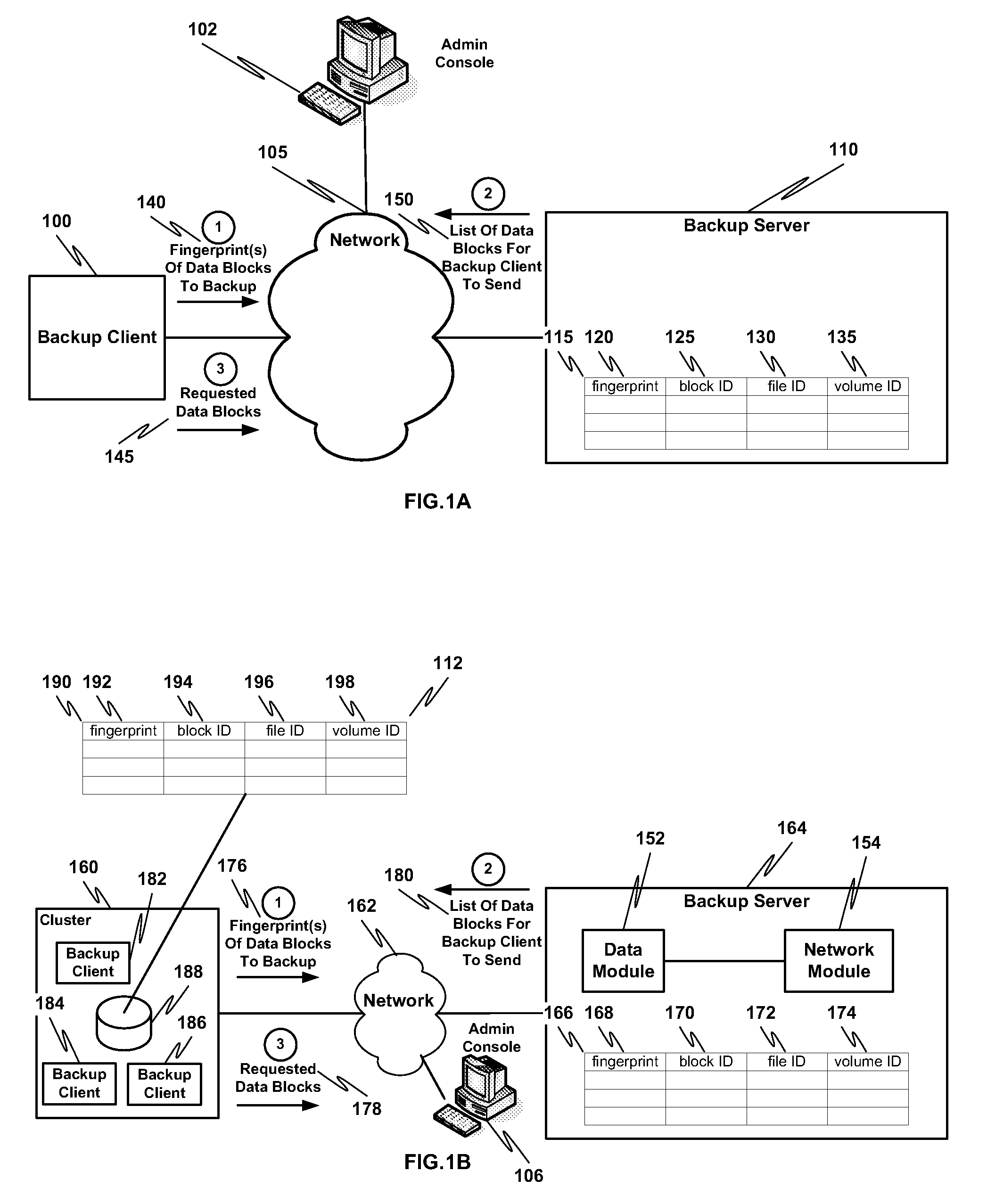
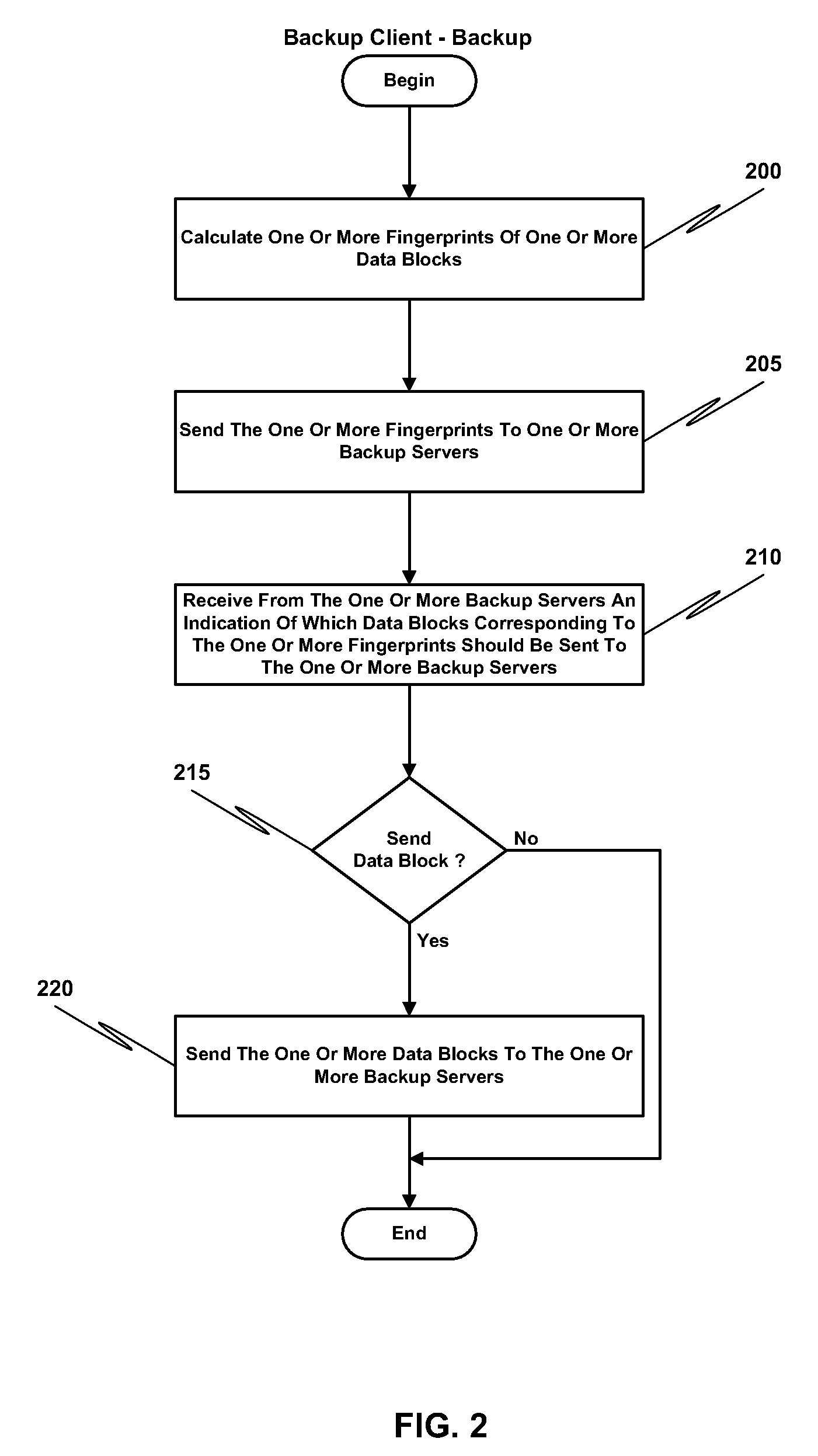
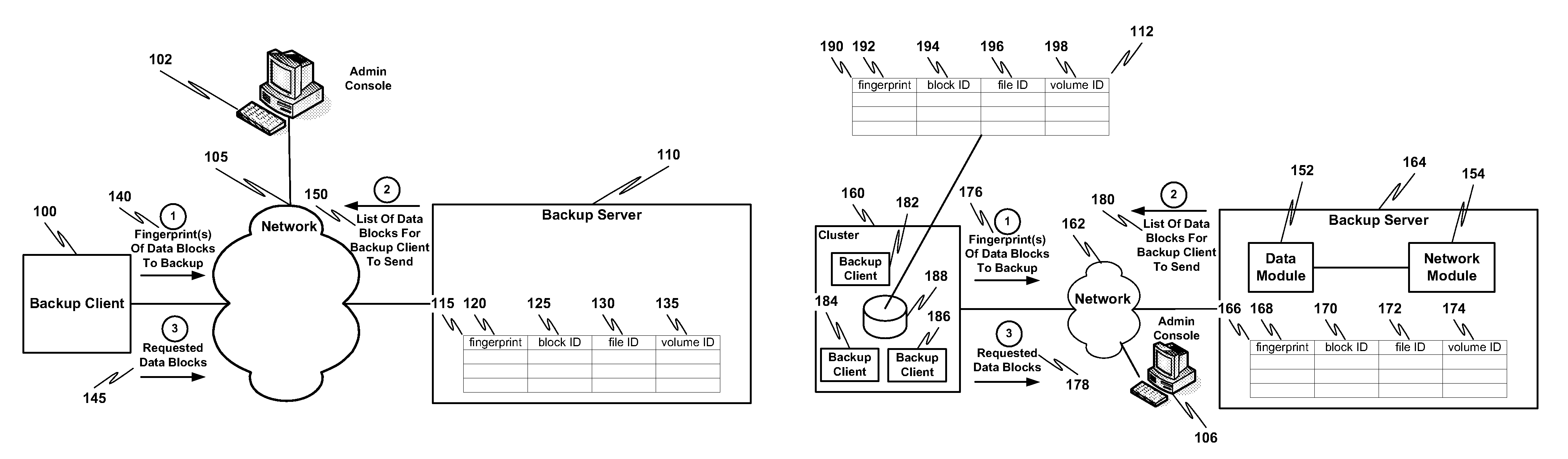
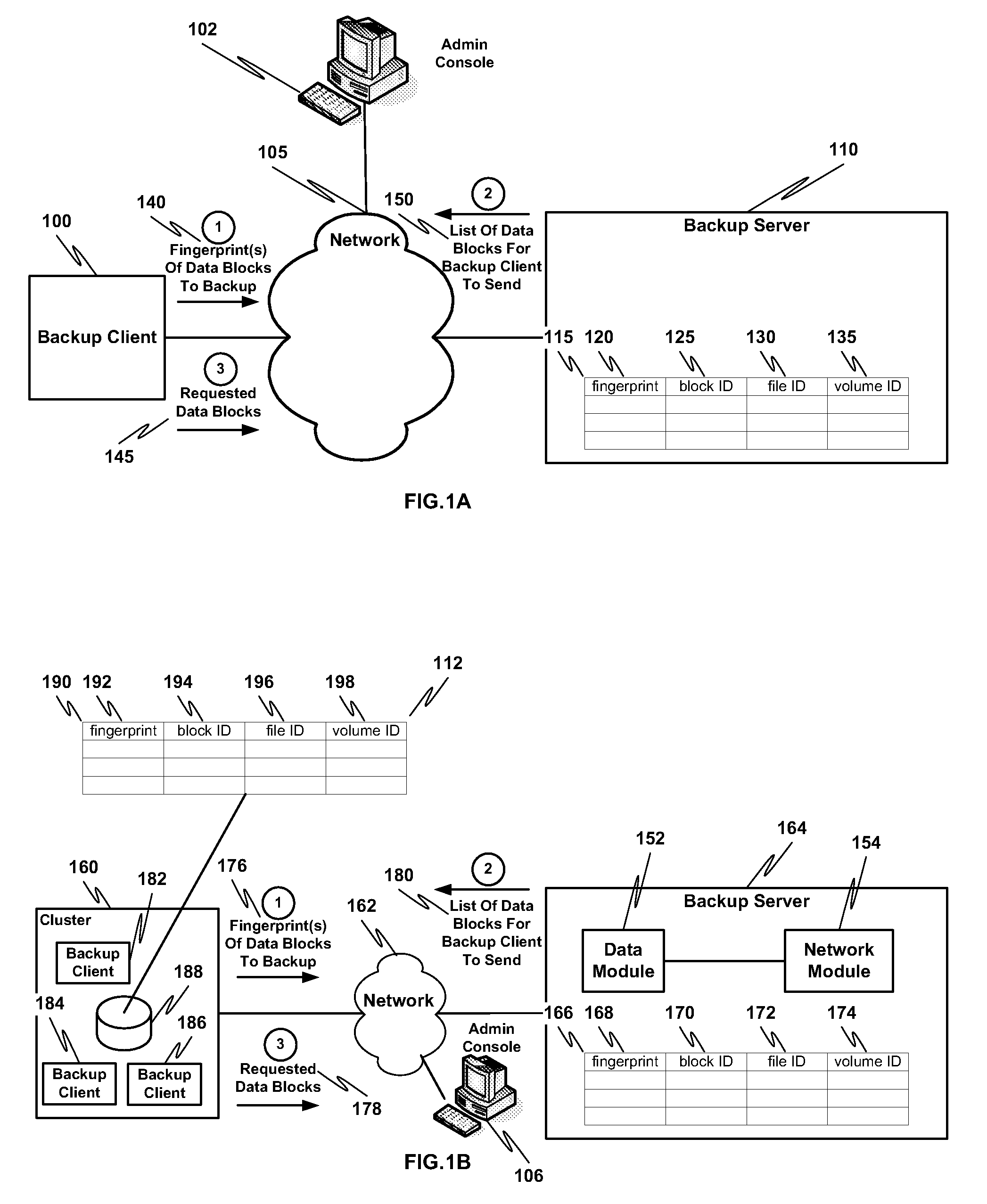
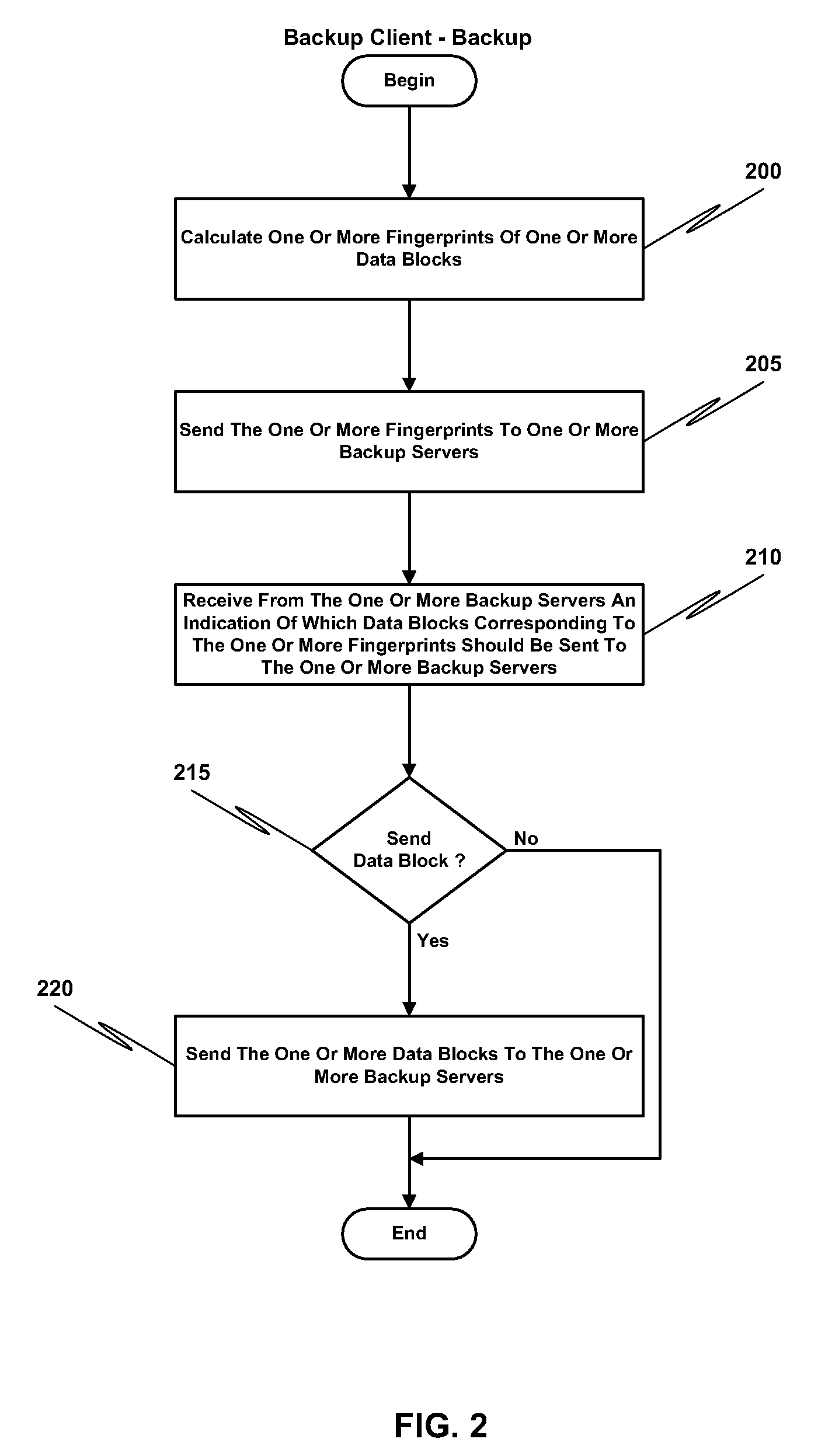
ActiveUS20100114833A1Efficient network utilizationShorten the timeMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsFingerprintData deduplication
Remote office deduplication comprises calculating one or more fingerprints of one or more data blocks, sending the one or more fingerprints to one or more backup servers via a network interface, receiving from the one or more backup servers an indication of which one or more data blocks corresponding to the one or more fingerprints should be sent to the one or more backup servers, and if the indication indicates one or more data blocks to be sent to the one or more backup servers, sending the one or more data blocks to the one or more backup servers via the network interface.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Automated process for isolating and amplifying a target nucleic acid sequence
InactiveUS6890742B2Efficient and high through-put operationEfficient space utilizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsRotating receptacle mixersIsolation proceduresTemperature control
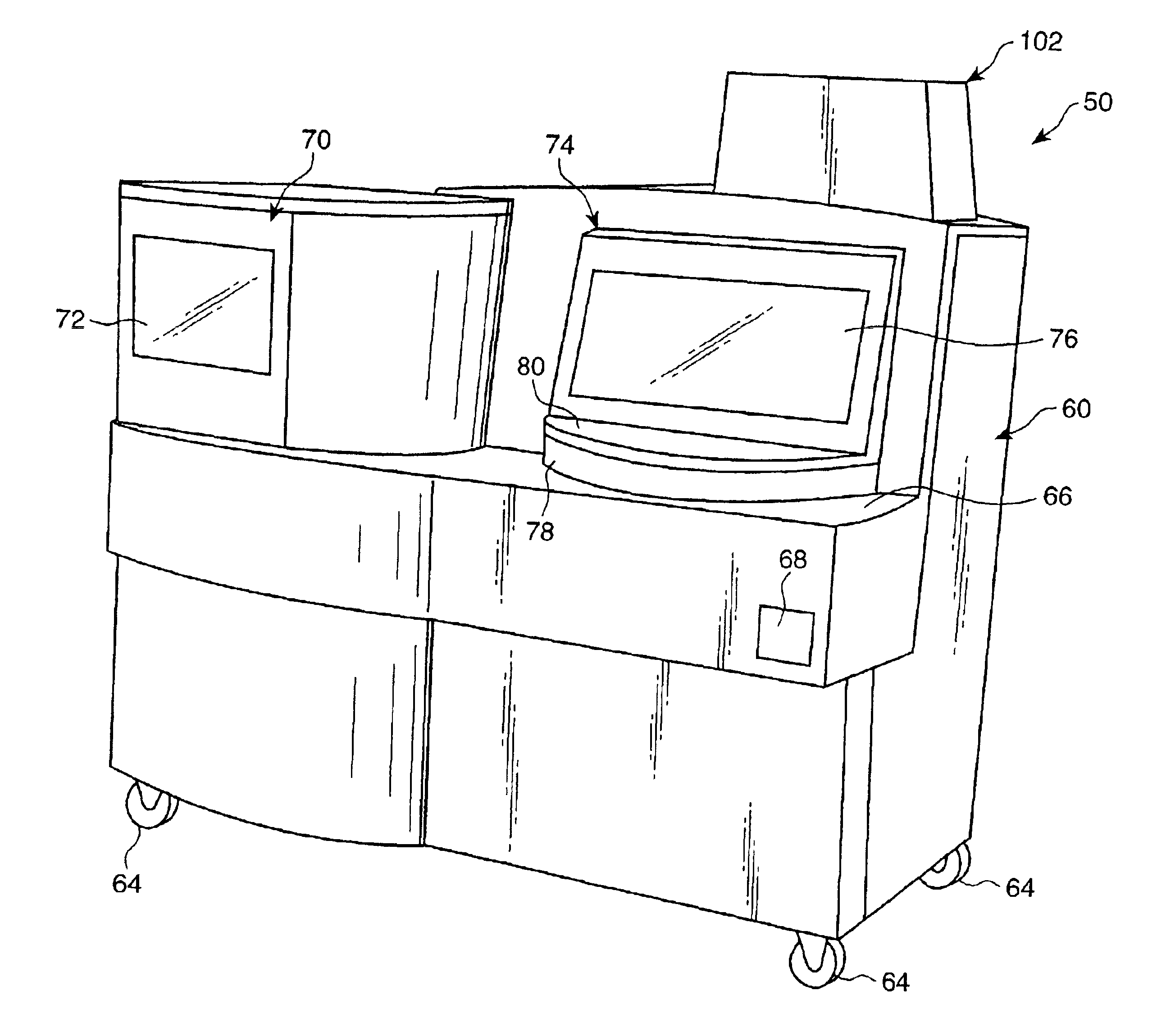
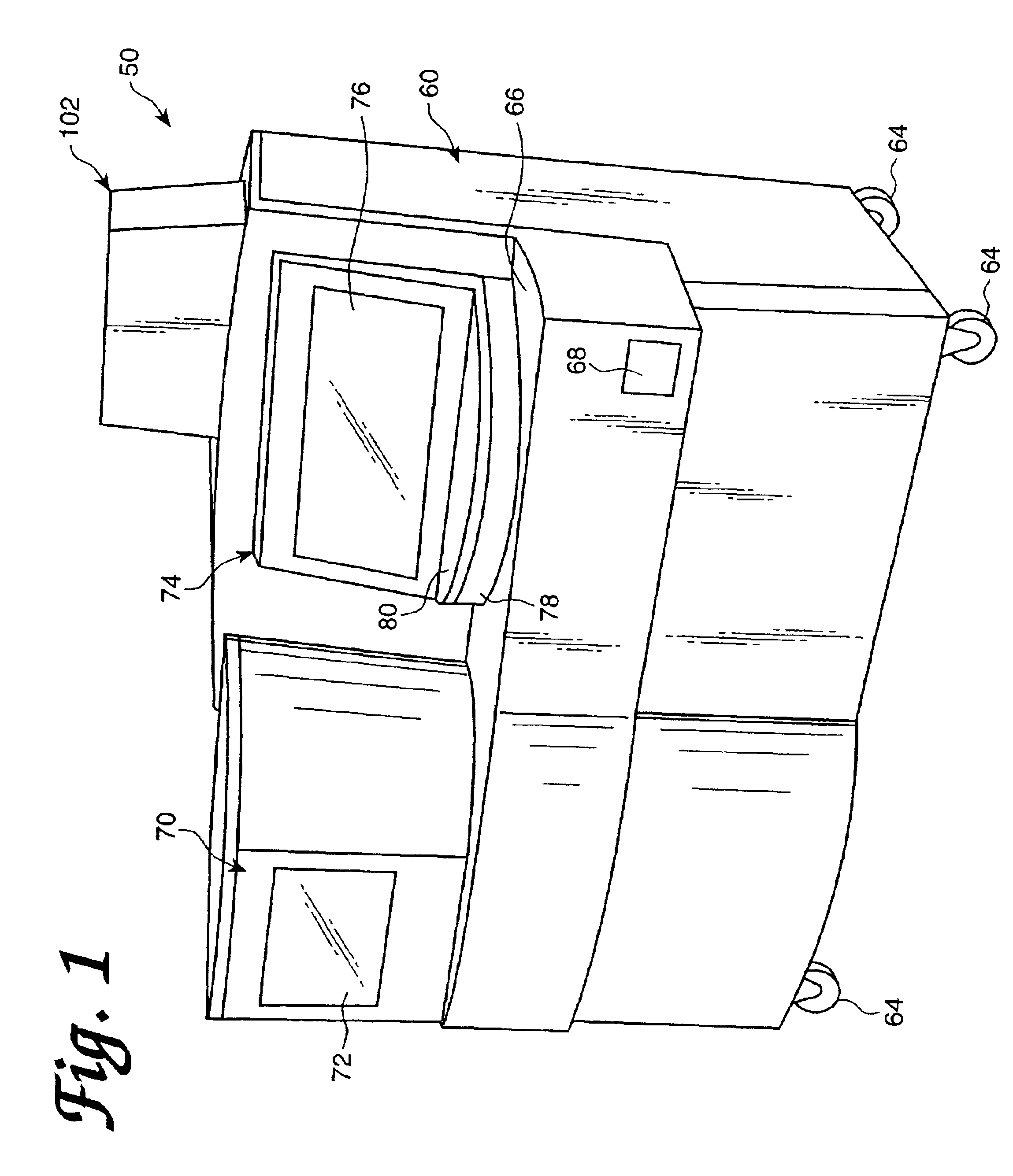
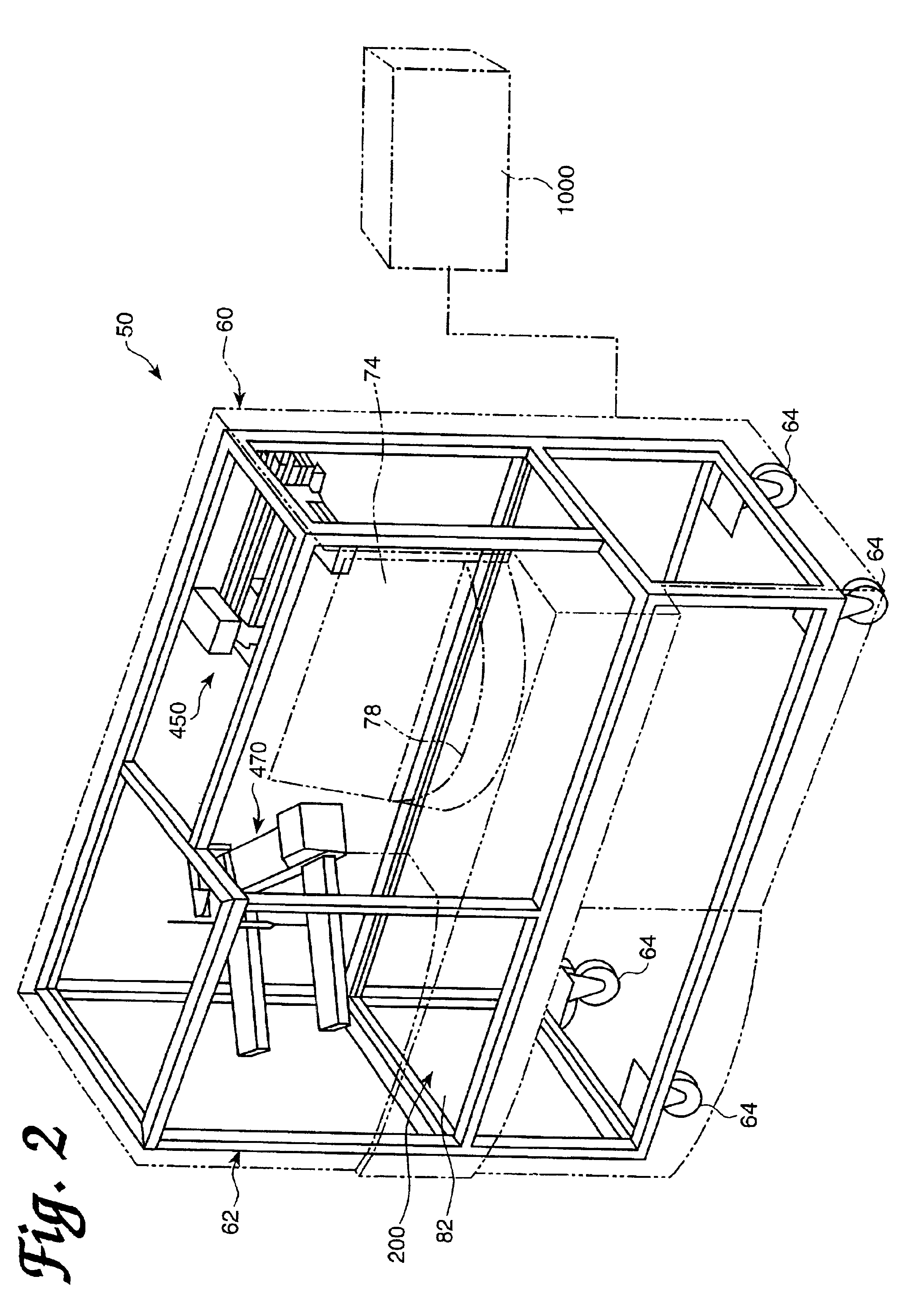
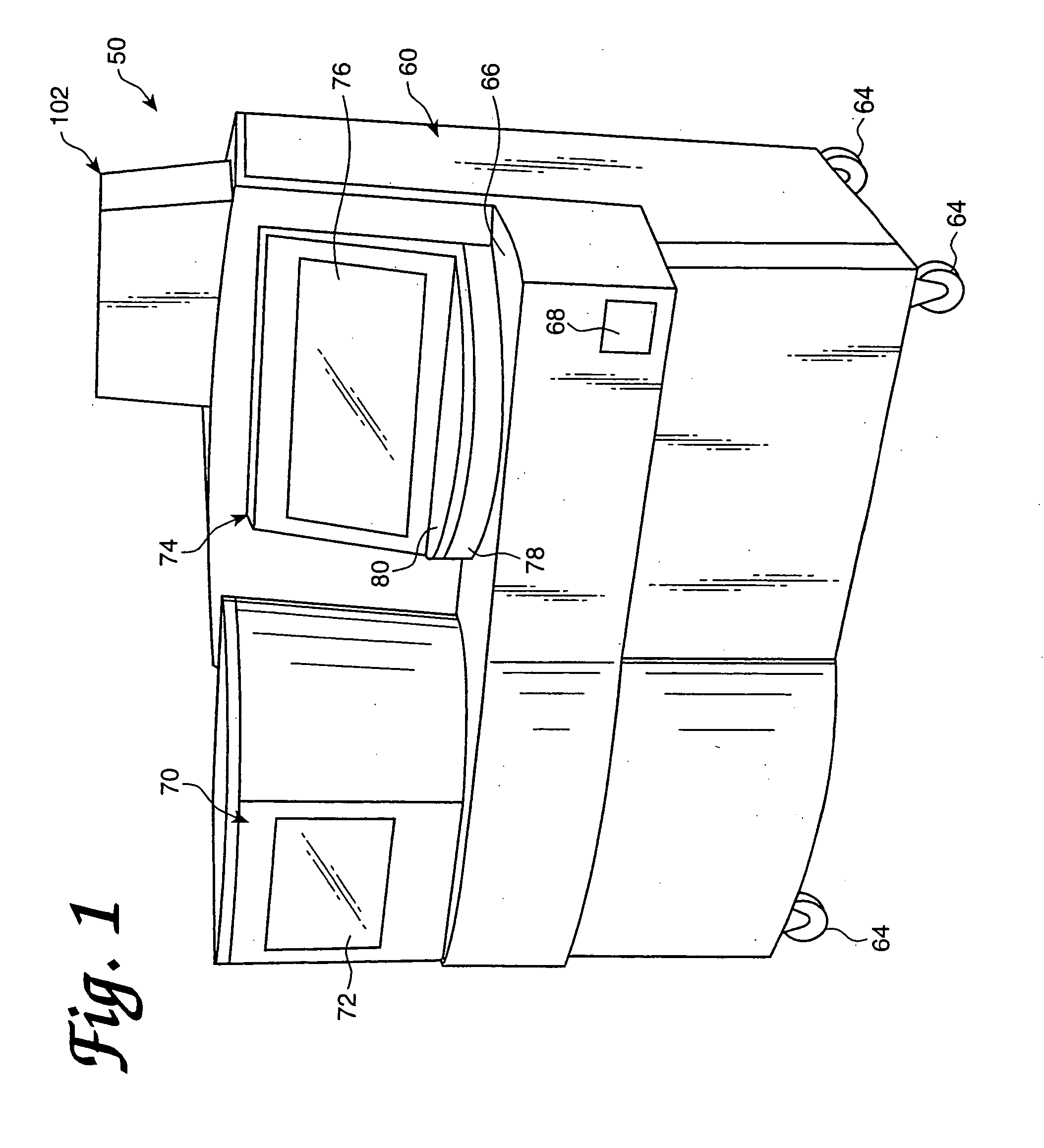
An automated analyzer for performing multiple diagnostic assays simultaneously includes multiple stations, or modules, in which discrete aspects of the assay are performed on fluid samples contained in reaction receptacles. The analyzer includes stations for automatically preparing a specimen sample, incubating the sample at prescribed temperatures for prescribed periods, preforming an analyte isolation procedure, and ascertaining the presence of a target analyte. An automated receptacle transporting system moves the reaction receptacles from one station to the next. The analyzer further includes devices for carrying a plurality of specimen tubes and disposable pipette tips in a machine-accessible manner, a device for agitating containers of target capture reagents comprising suspensions of solid support material and for presenting the containers for machine access thereto, and a device for holding containers of reagents in a temperature controlled environment and presenting the containers for machine access thereto. A method for performing an automated diagnostic assay includes an automated process for isolating and amplifying a target analyte. The process is performed by automatically moving each of a plurality of reaction receptacles containing a solid support material and a fluid sample between stations for incubating the contents of the reaction receptacle and for separating the target analyte bound to the solid support from the fluid sample. An amplification reagent is added to the separated analyte after the analyte separation step and before a final incubation step.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Automated process for isolating and amplifying a target nucleic acid sequence
InactiveUS20050130198A1Efficient and high through-put operationEfficient comprehensive utilizationRotating receptacle mixersBioreactor/fermenter combinationsIsolation proceduresTemperature control
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Continuously Variable Transmission with Mutliple Outputs
ActiveUS20080081728A1Efficient power utilizationSaving of weightFriction gearingsManual control with multiple controlling membersEngineeringProsthetic hand
A transmission or actuator offering multiple rotational outputs proportionate in speed to that of a common rotational input, each output according to its own ratio. The ratios are continuously variable between positive and negative values, including zero, and may be varied by electromechanical actuators under computer control. The transmission relates the output speeds one to another under computer control, and thus makes possible the establishment of virtual surfaces and other haptic effects in a multidimensional workspace to which the transmission outputs are kinematically linked. An example of such a workspace is that of a robotic or prosthetic hand.
Owner:HDT EXPEDITIONARY SYST
Control and sensor systems for an environmentally controlled vertical farming system
ActiveUS20180014486A1High yieldCost per square footSelf-acting watering devicesLayeringControl systemSensor system
A computer implemented system for a vertical farming system comprising at least a first crop growth module and operating in an environmentally-controlled growing chamber, the control system comprising sensors for measuring environmental growing conditions in the environmentally-controlled growing chamber over time to generate environmental condition data, a device configured for measuring a crop characteristic of a crop grown in the crop growth module of the environmentally-controlled growing chamber to generate crop growth data and a processing device comprising software modules for receiving the environmental condition data and the crop growth data; applying an algorithm to the environmental condition data and the crop growth data to generate an improved environmental growing condition and generating instructions for adjustment of the environmental growing conditions in or around the growth module in the environmentally-controlled growing chamber to the improved environmental growing condition.
Owner:MJNN LLC
Modular coaxial electrical interconnect system having a modular frame and electrically shielded signal paths and a method of making the same
InactiveUS6905367B2Increasing signal speedEfficient space utilizationCoupling protective earth/shielding arrangementsModular connectorSurface projection
A modular connector assembly includes a modular frame having a first holes, second holes, and third holes formed at evenly spaced intervals. A plurality of modular interconnect components, fixable within the modular frame, have a back surface projection formed thereon. Each modular interconnect includes a contact housing made of electrically insulating material, an exterior of the contact housing comprising first and second side surfaces, a back surface, and a top surface. Contact signal pins are fixed within and electrically insulated from the contact housing.
Owner:SILICON BANDWIDTH
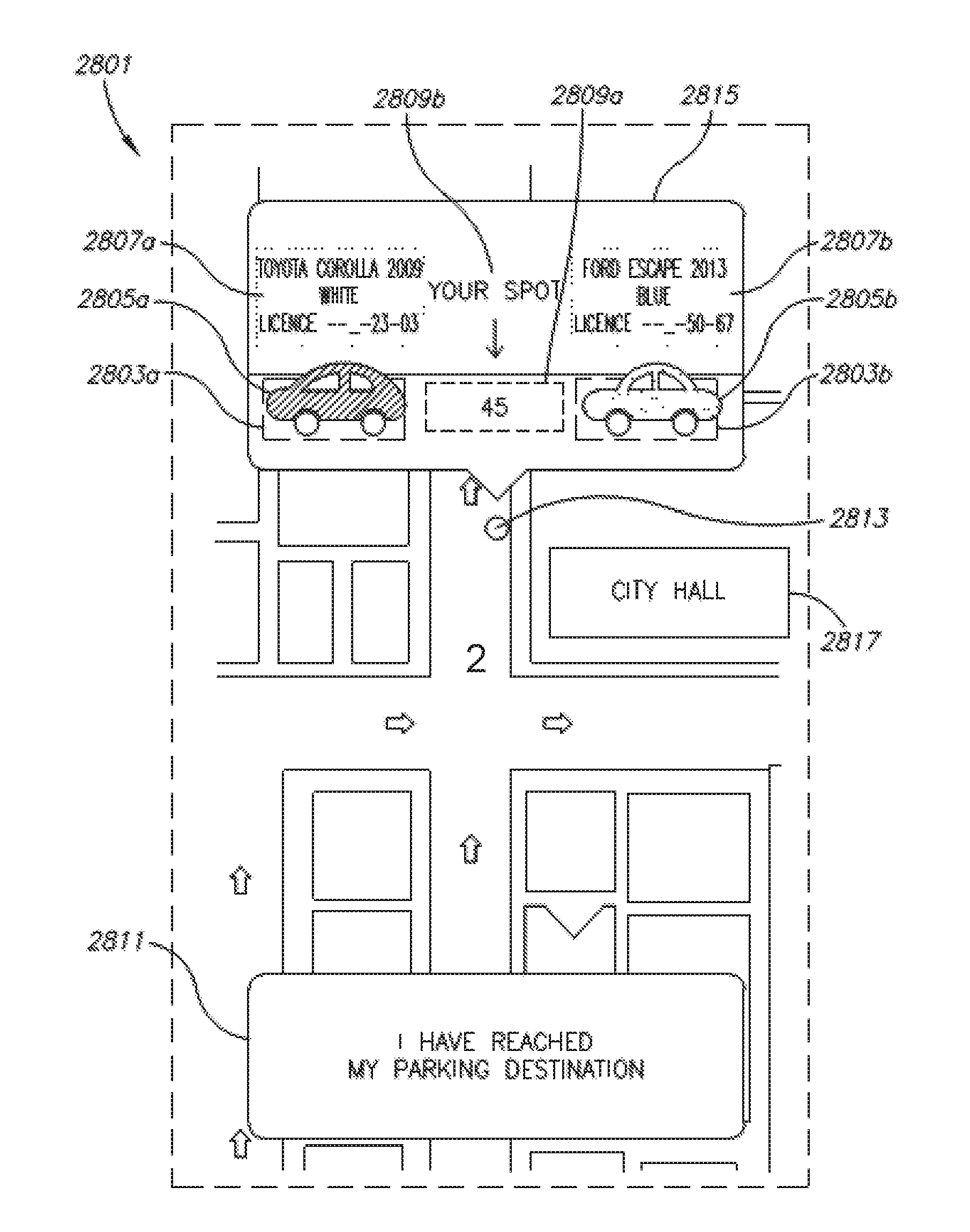
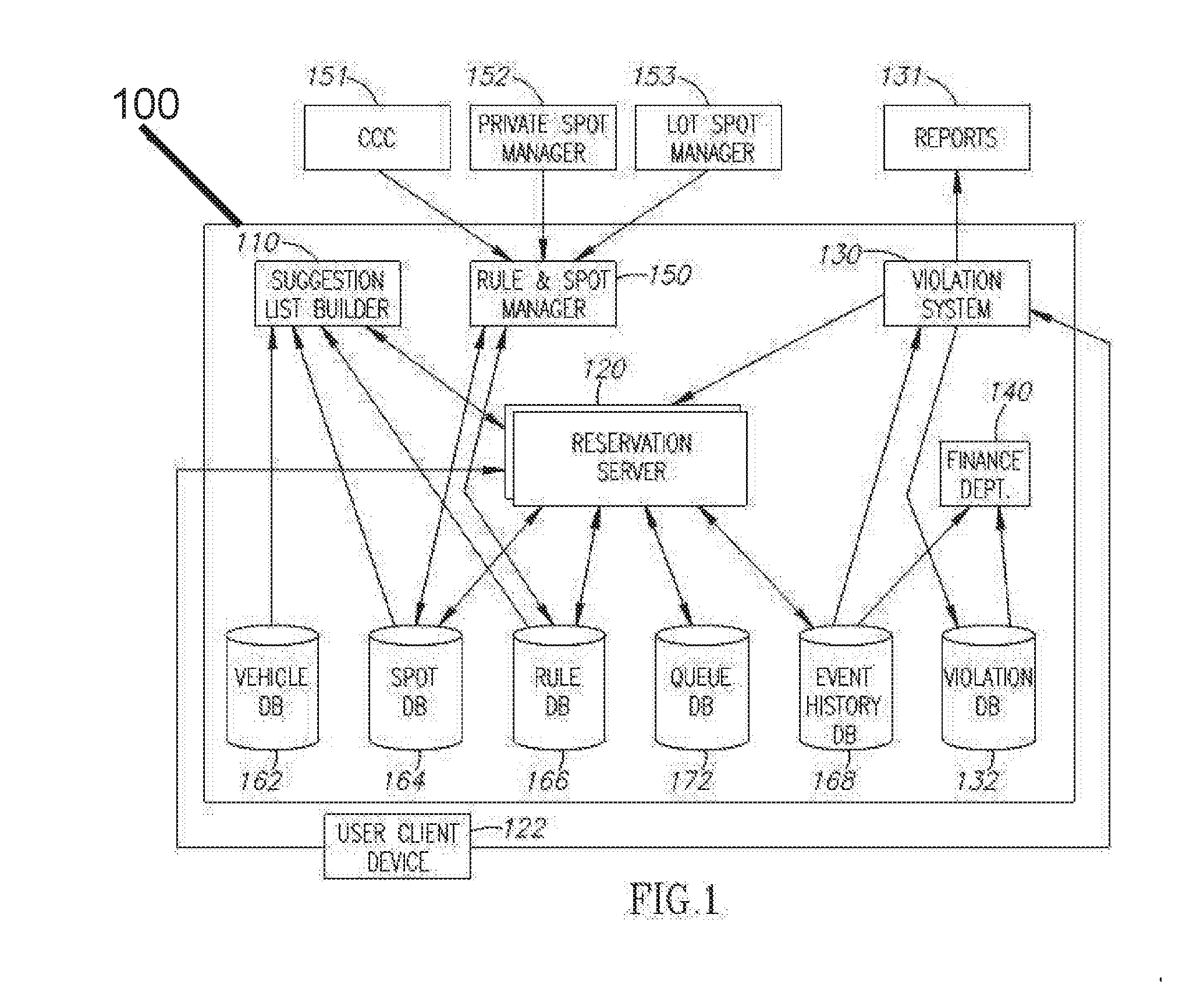
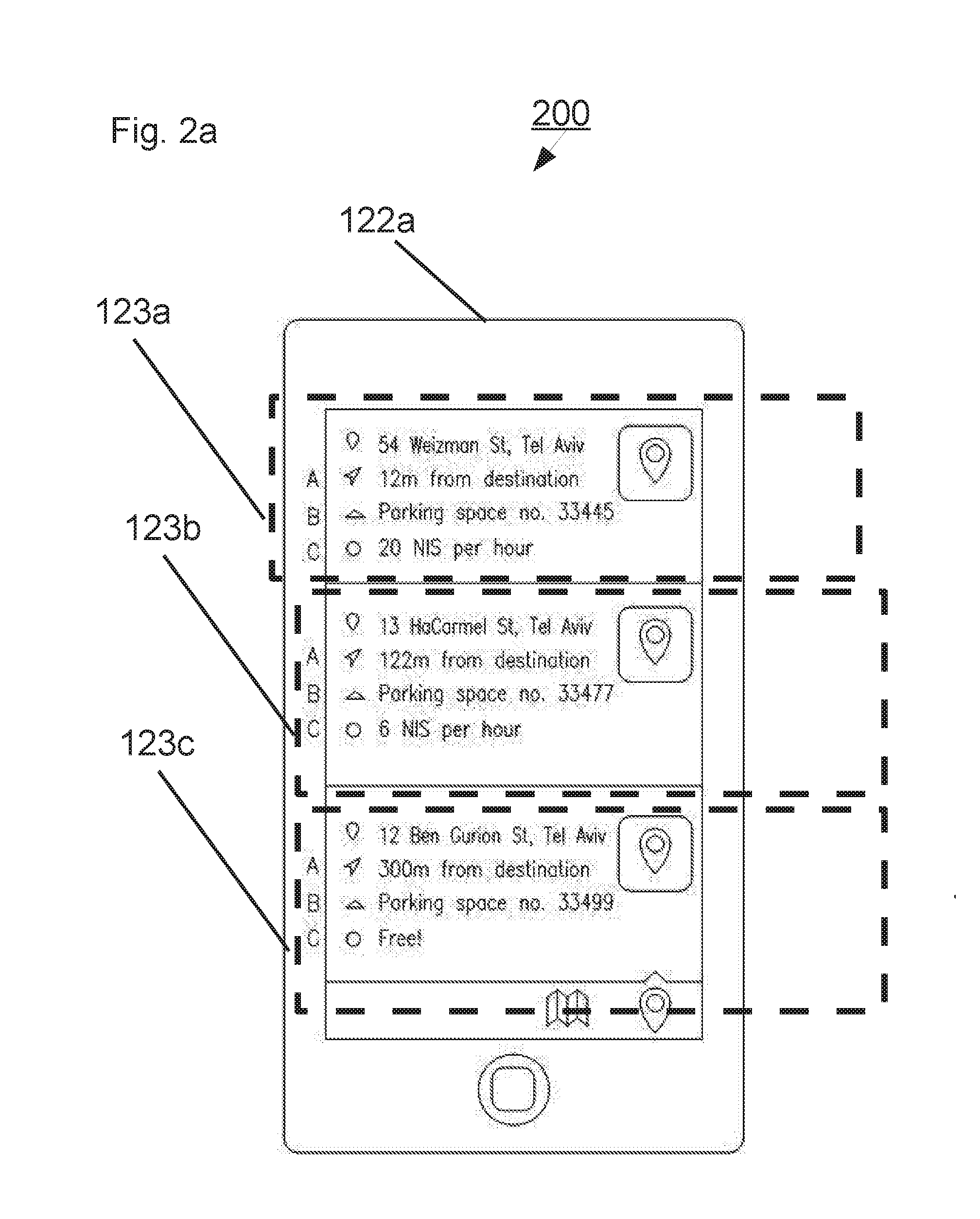
Citywide parking system and method
InactiveUS20160371607A1Improve parking efficiencyDecreasing parking effortInstruments for road network navigationTransportation facility accessComputer moduleParking space
A system including: (a) a database of individual on-street parking spots, and individual off-street parking spots, each of the individual parking spots associated with a unique identifier (UID) and location coordinates; and (b) an off street spot management module in communication one or more external client devices, adapted to receive parking rules from an external client device operated by an owner of each of the individual off-street parking spots.
Owner:SPARKCITY COM
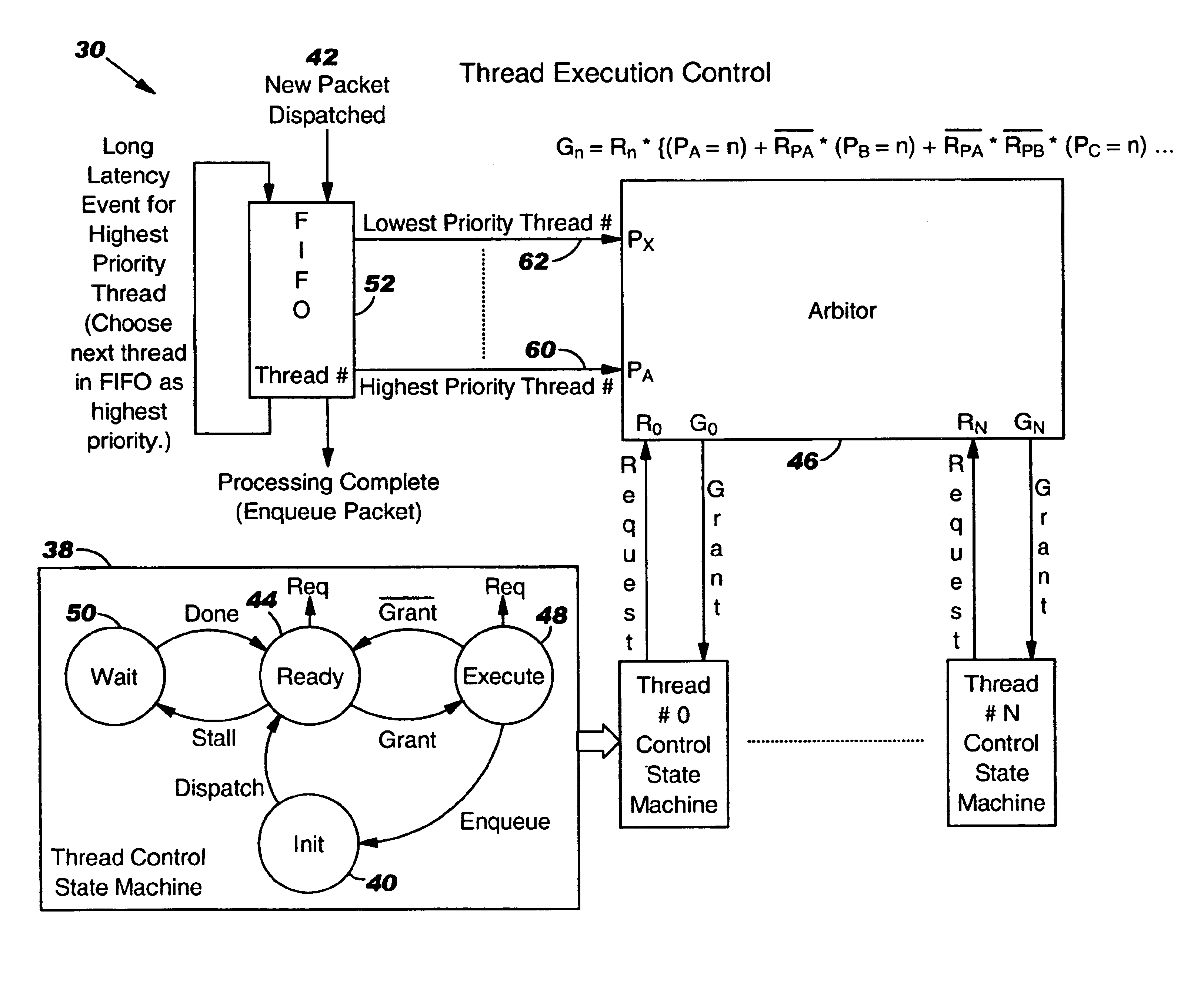
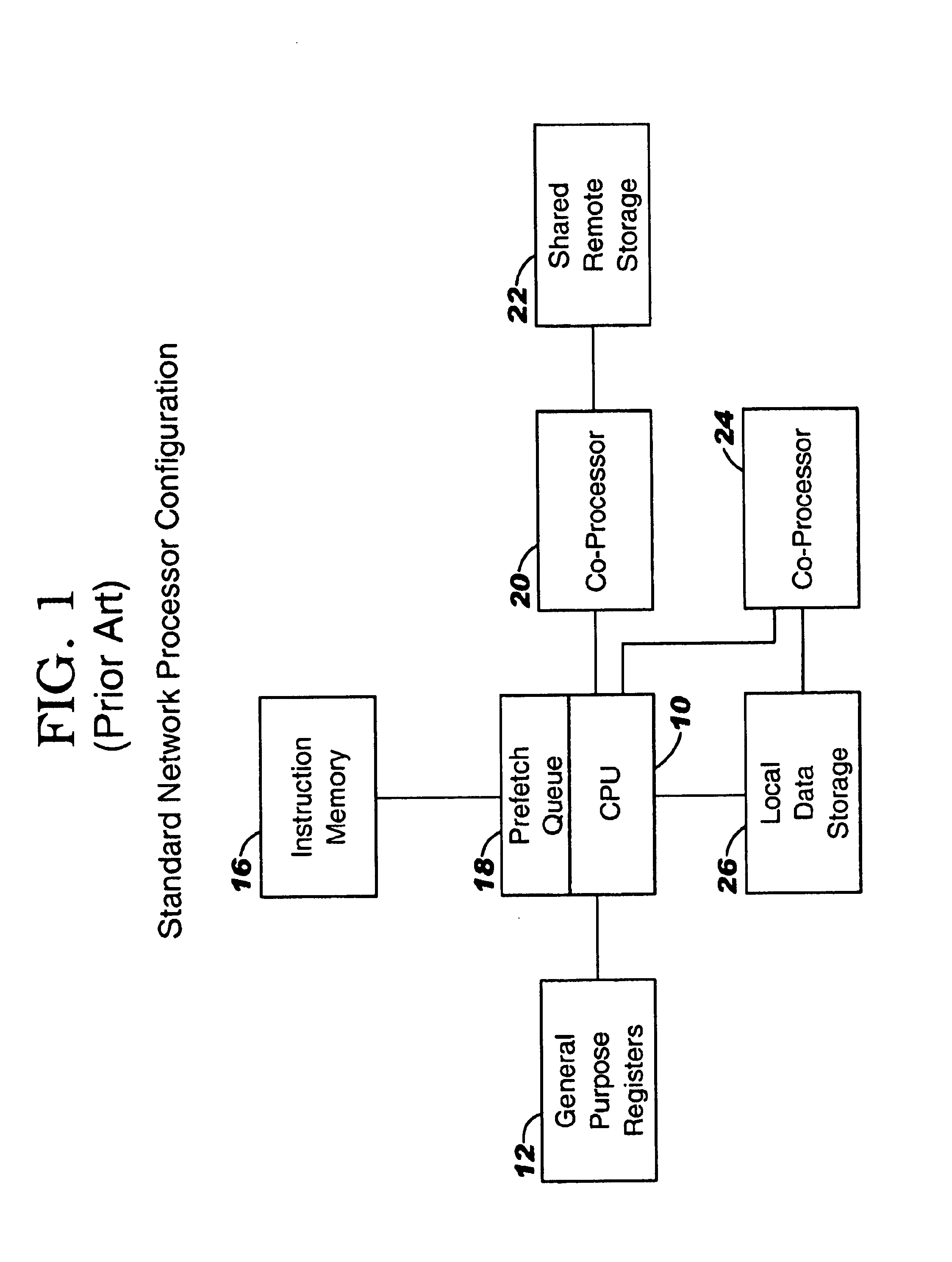
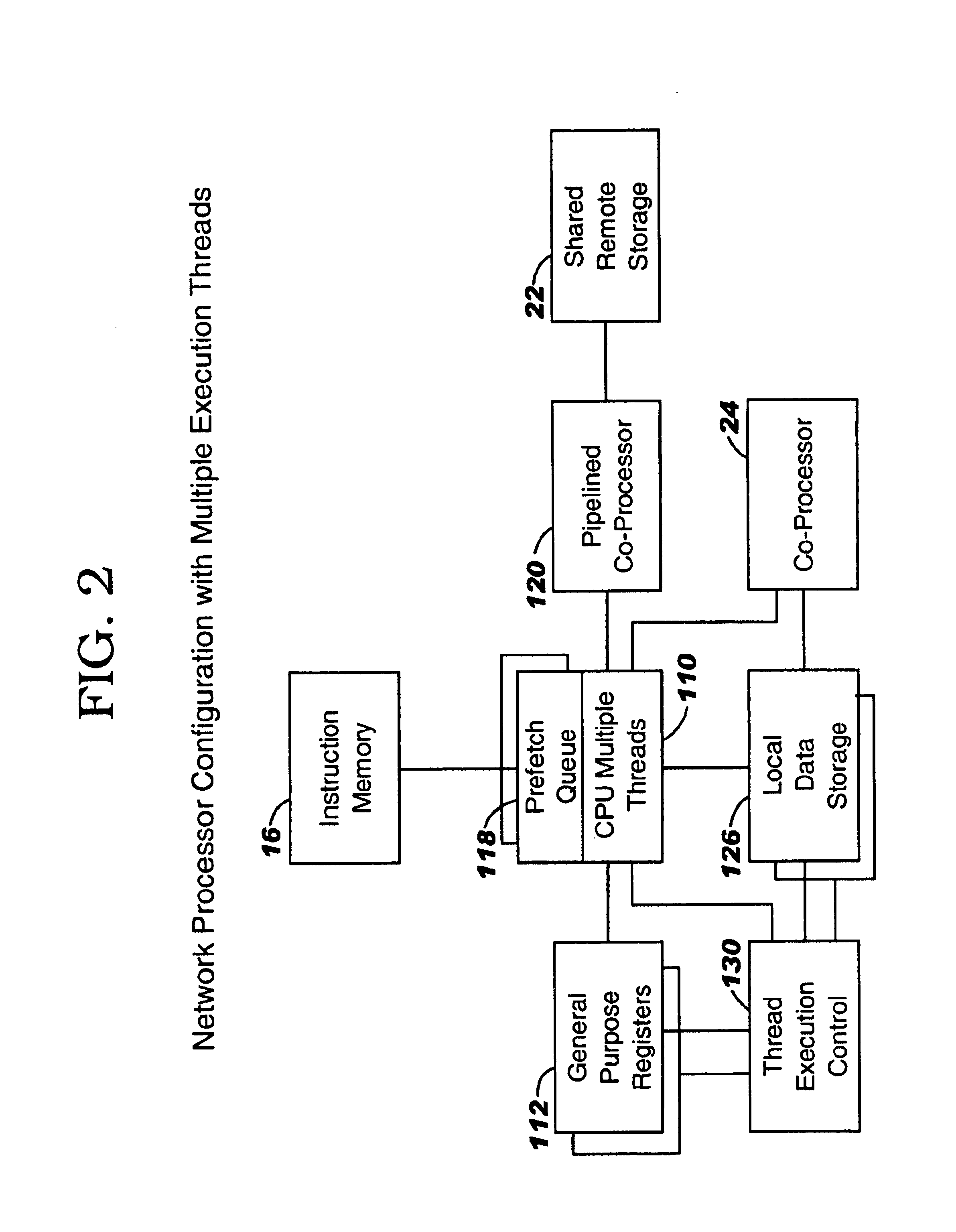
Controller for multiple instruction thread processors
InactiveUS6931641B1Efficient comprehensive utilizationProgram initiation/switchingProgram synchronisationFistLong latency
A mechanism controls a multi-thread processor so that when a fist thread encounters a latency event to a first predefined time interval temporary control is transferred to an alternate execution thread for duration of the first predefined time interval and then back to the original thread. The mechanism grants full control to the alternate execution thread when a latency event for a second predefined time interval is encountered. The first predefined time interval is termed short latency event whereas the second time interval is termed long latency event.
Owner:INTEL CORP
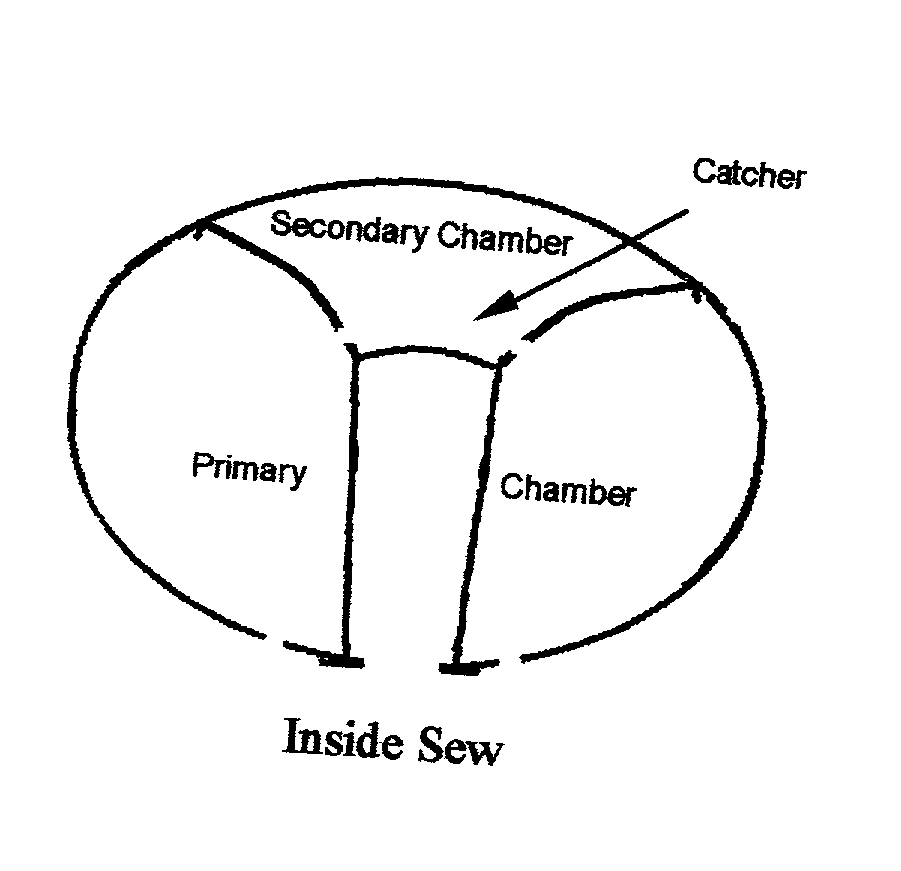
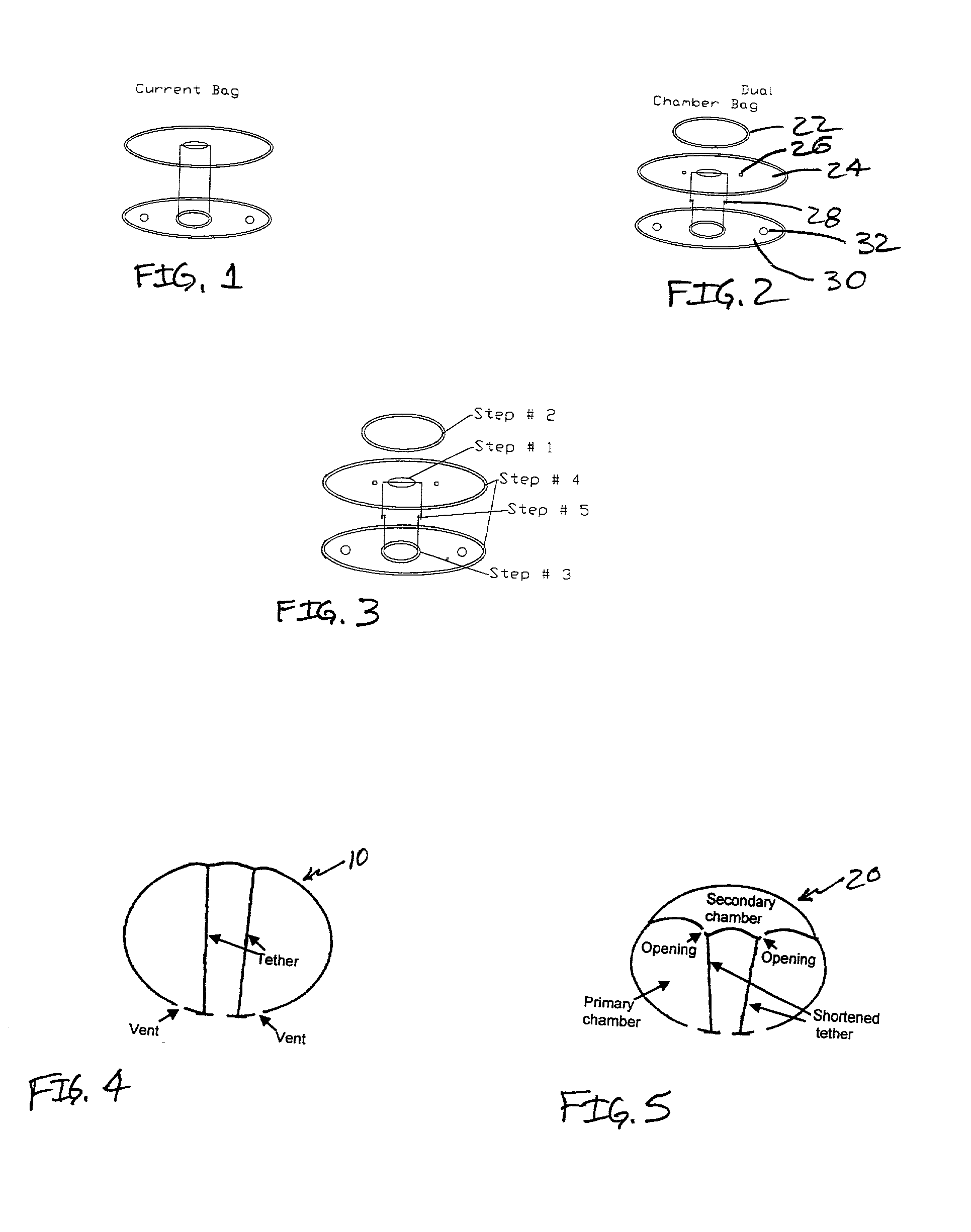
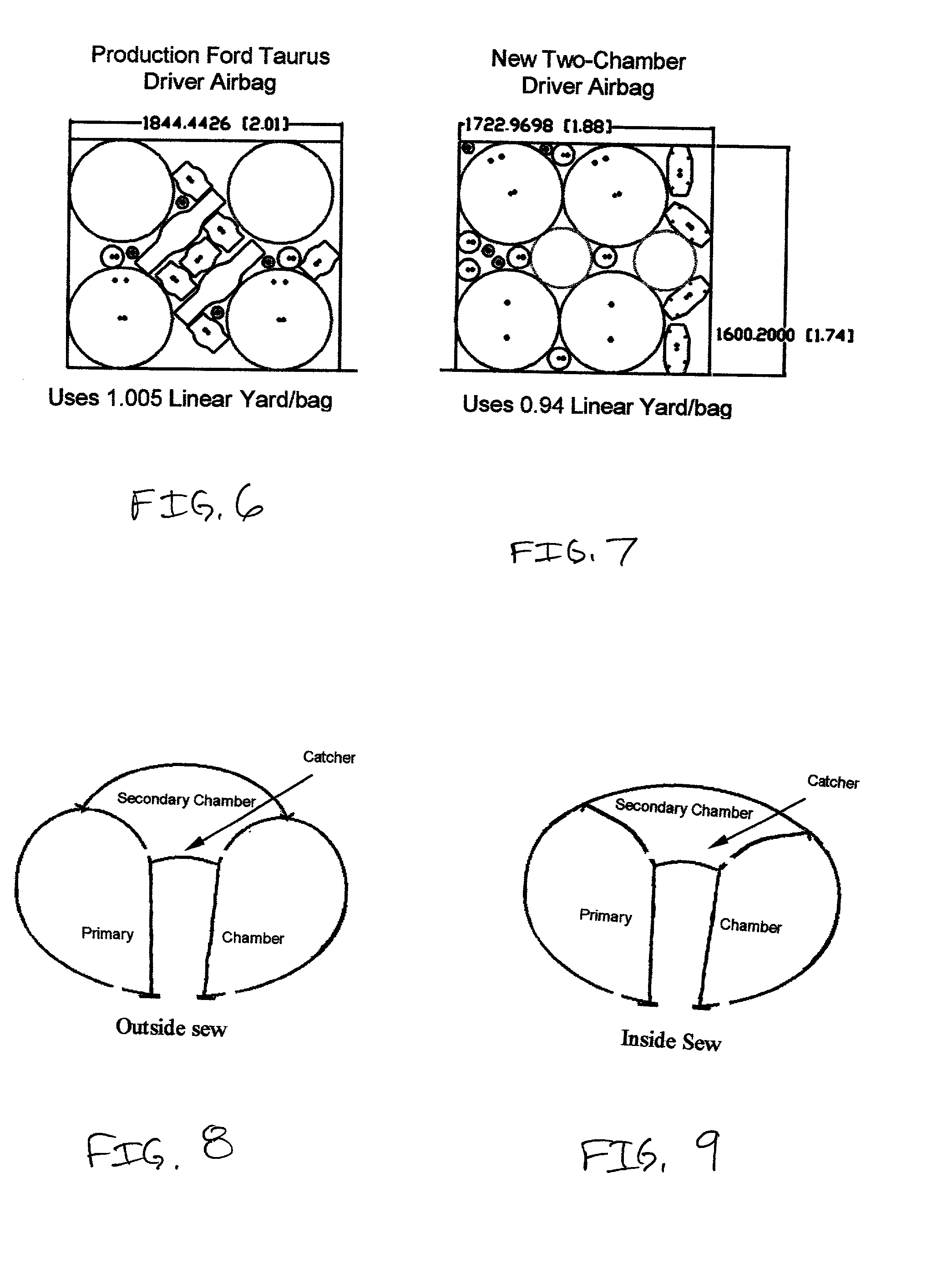
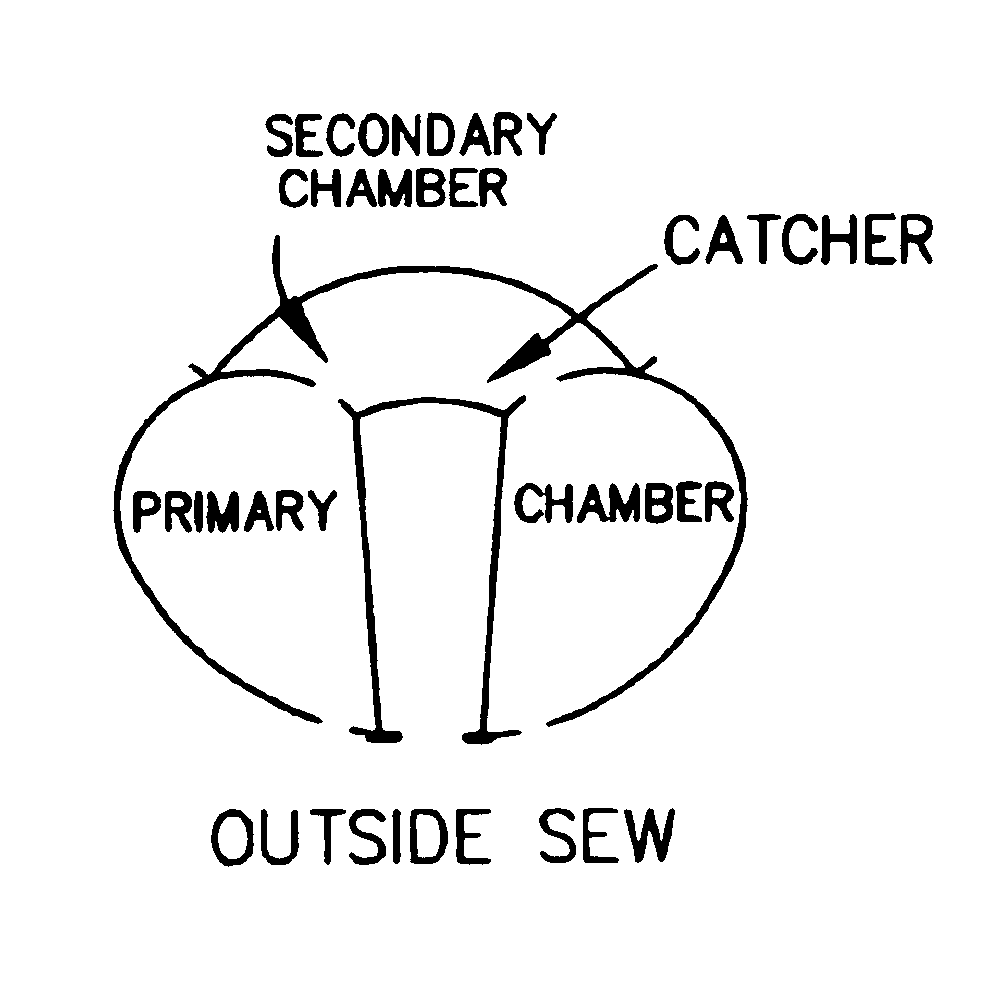
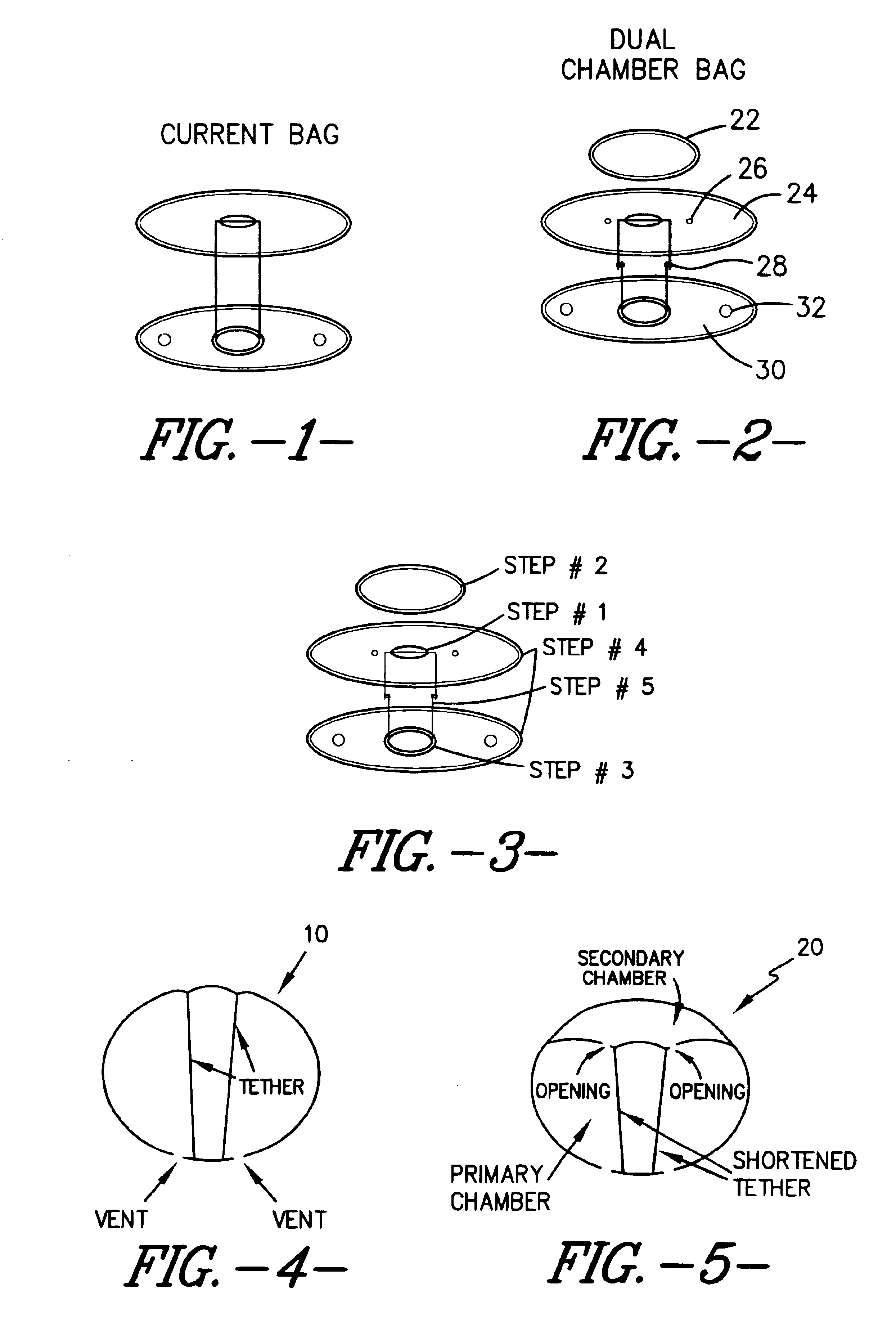
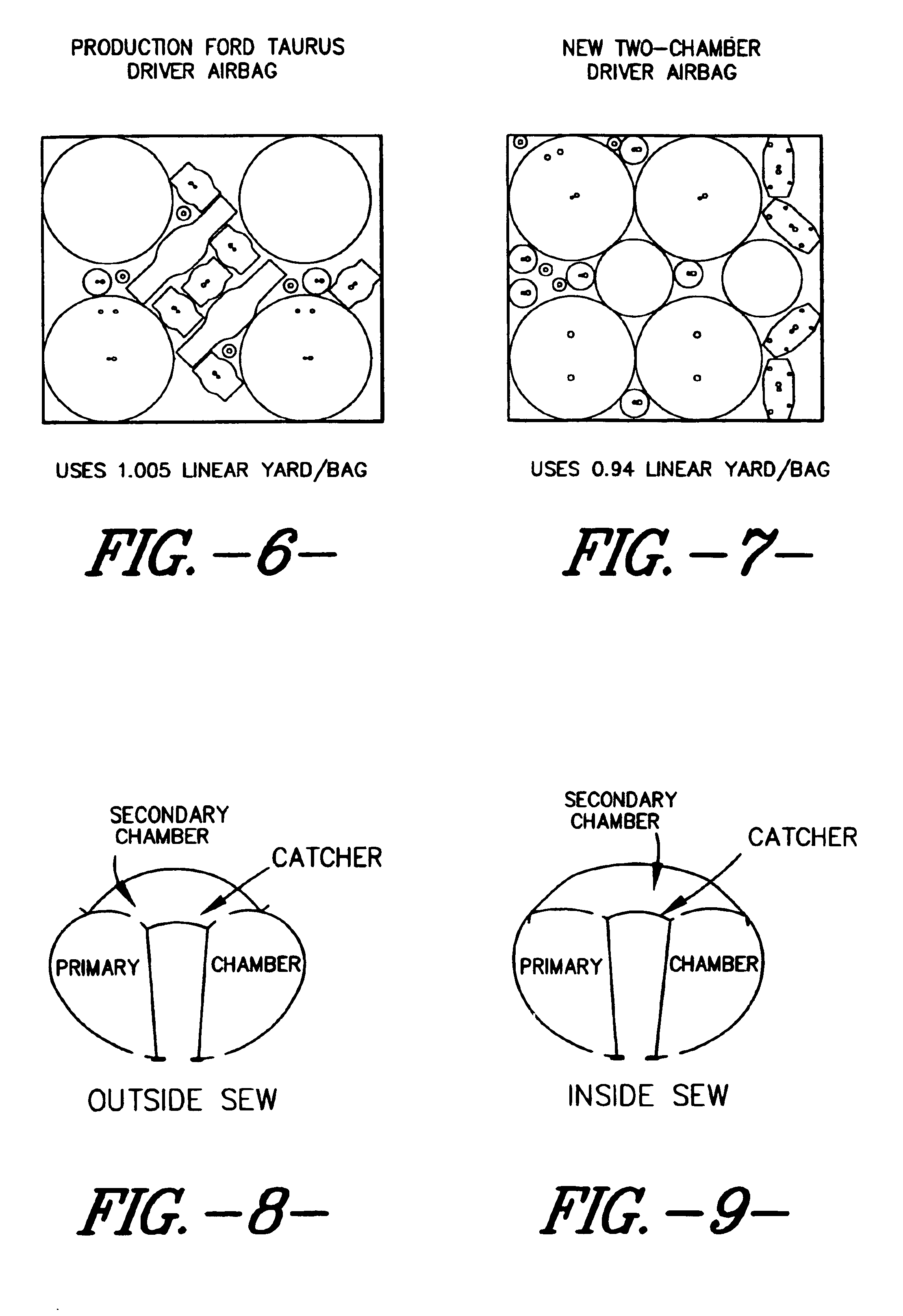
Multiple chamber airbags and methods
InactiveUS20030034637A1Efficient use ofEfficient comprehensive utilizationPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementEngineeringSingle chamber
A two or more chambered airbag provides much improved safety and / or performance. A modified single chamber airbag can be used as the primary chamber of the two-chamber airbag. A piece of fabric of appropriate size is sewn to the inside or outside surface of the front panel of the primary chamber to create the secondary chamber. One or more apertures are opened between the primary and secondary chambers. In order for the secondary chamber to inflate properly, the tethers of the primary chamber are shortened to 50% to 80% of their original length. The size or location of the tether sewing to the inner surface of the front panel of the primary chamber is also adjusted to create a desired shape of the secondary chamber when deployed.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
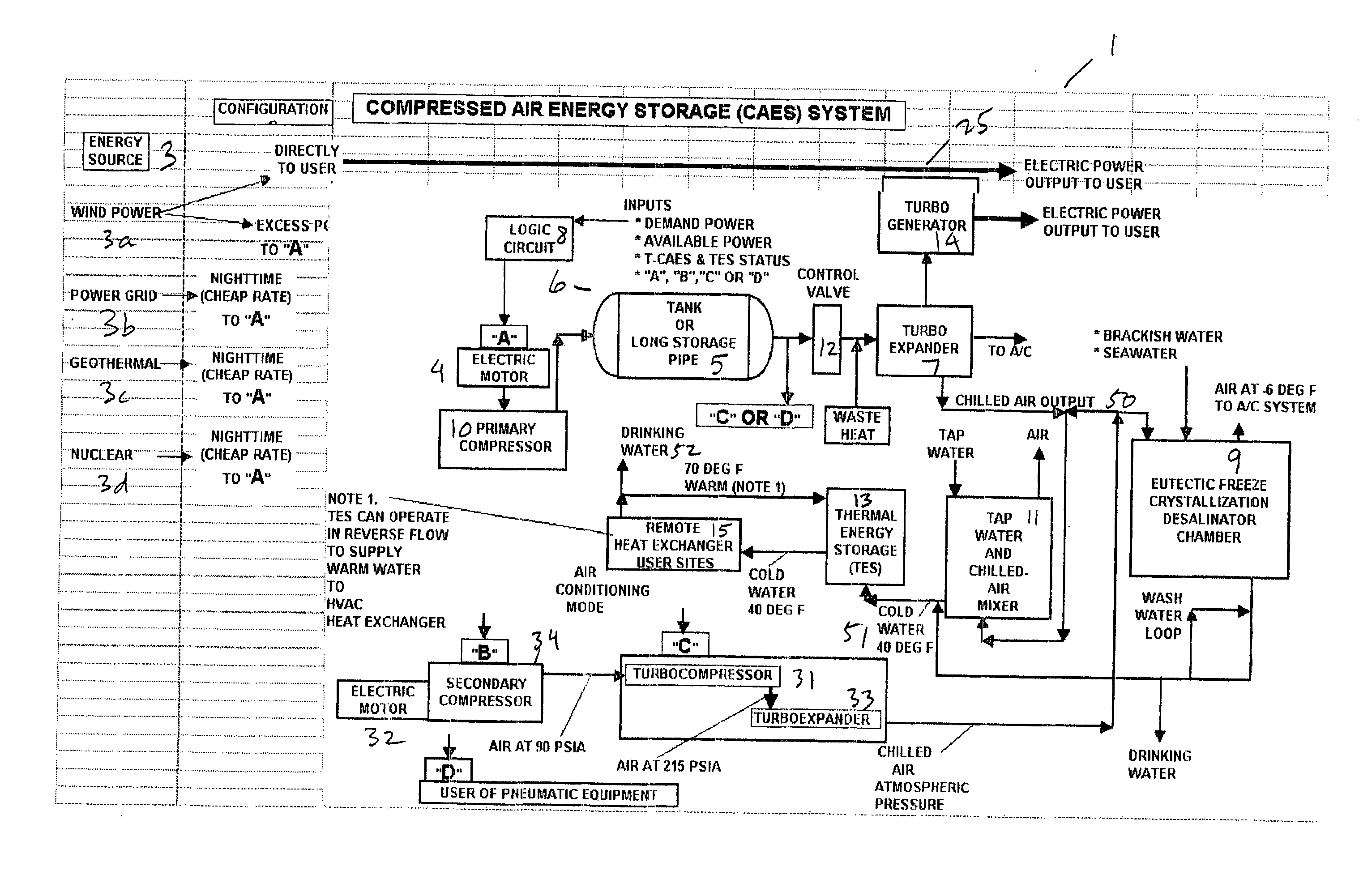
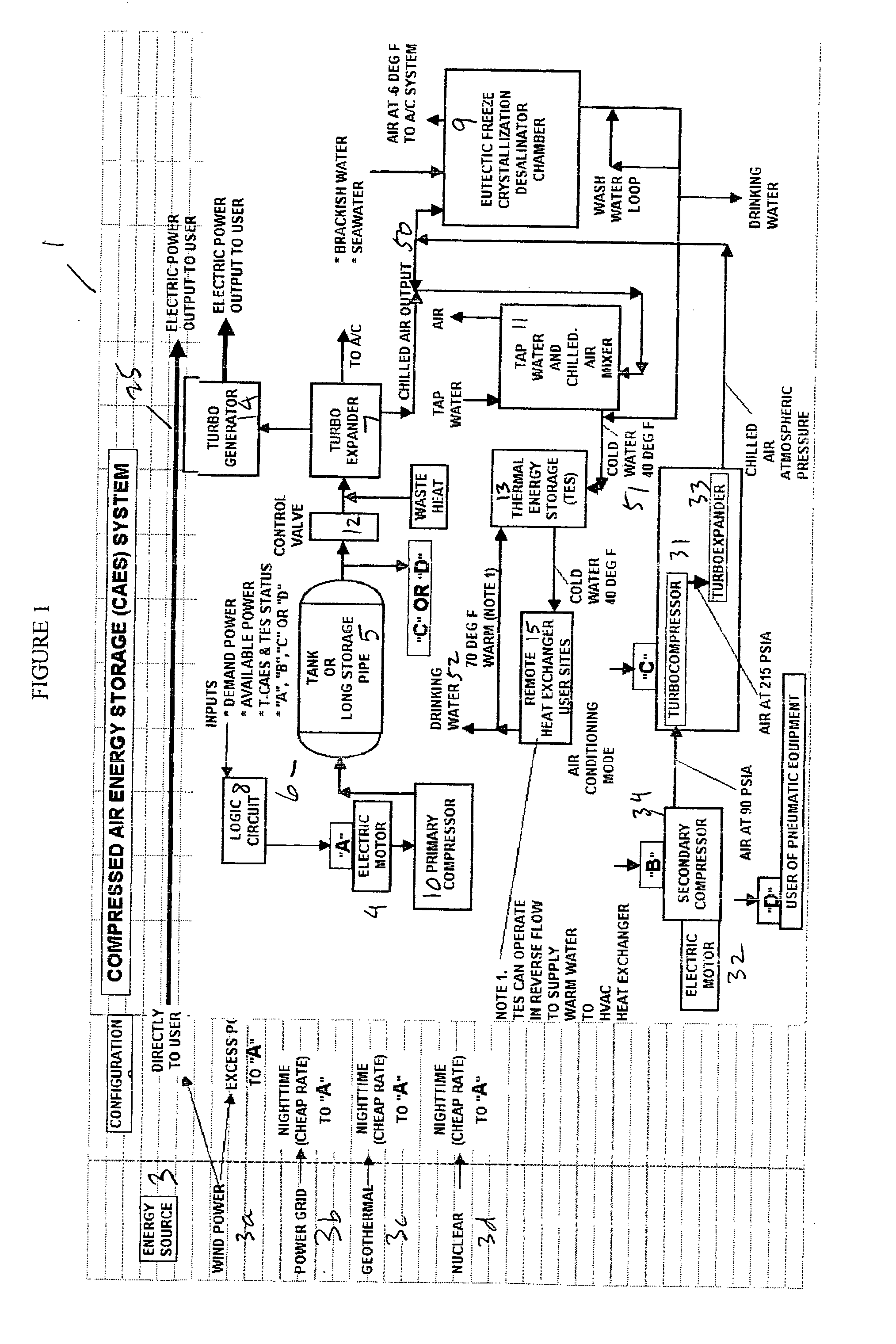
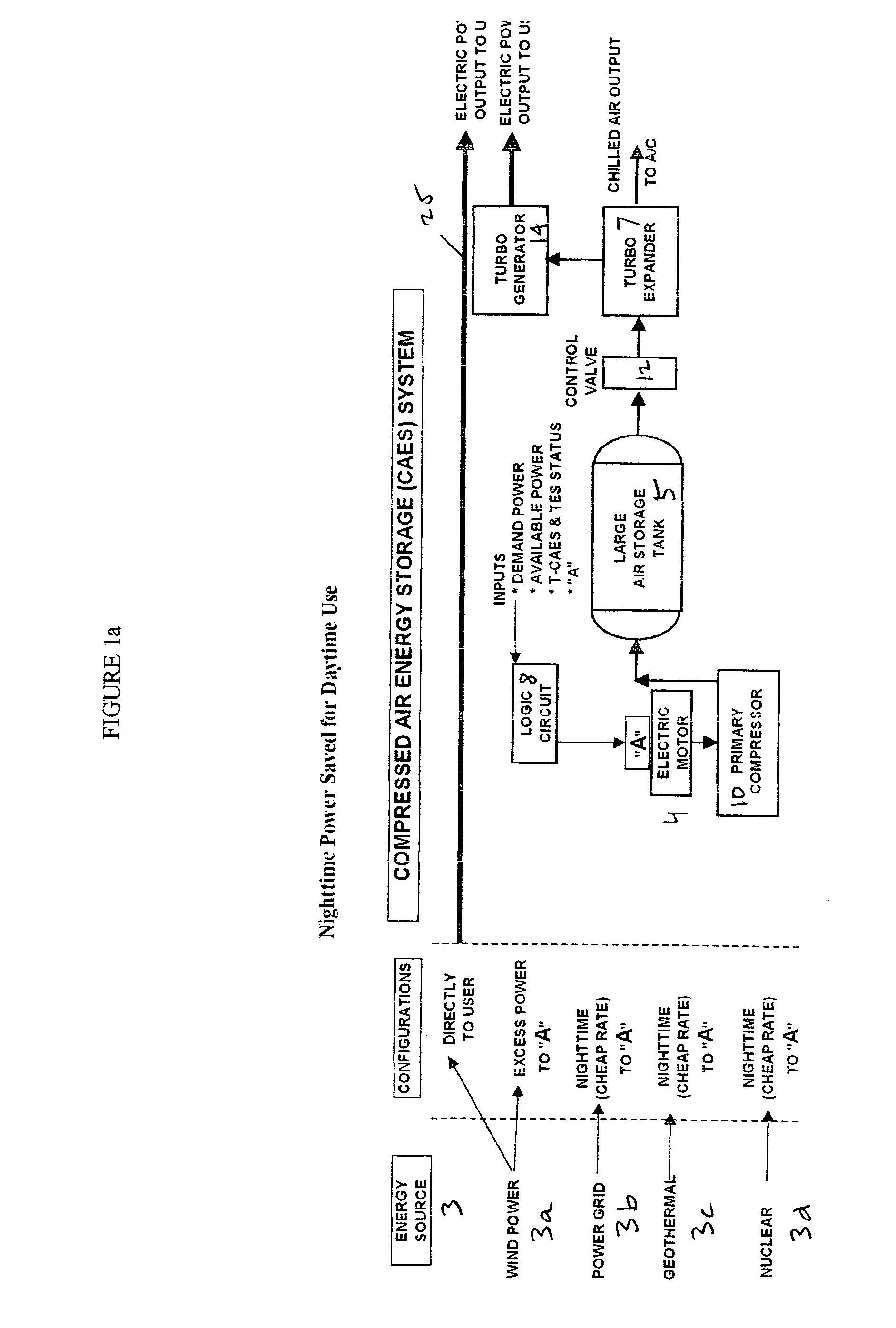
Thermal energy storage system using compressed air energy and/or chilled water from desalination processes
InactiveUS20070234749A1Reducing end-user cost of energyEnergy efficiencyWater treatment parameter controlGeneral water supply conservationThermal energyThermal energy storage system
The invention relates to a universal system for producing cost effective energy particularly for cooling purposes. In one embodiment, wind turbines are used to generate electricity and compressed air energy, wherein the compressed air energy is used to co-generate electricity and chilled air. The chilled air is then used to chill water in either a mixing chamber, or a desalination system, wherein the chilled water is stored in a separation tank, wherein it can later be used to provide cooling for an air conditioning system for a facility. When desalination is used, the system produces chilled fresh drinking water which can be used for air conditioning, and then used as fresh drinking water. Any exhaust chilled air can be used directly for air conditioning.
Owner:ENIS BEN M +1
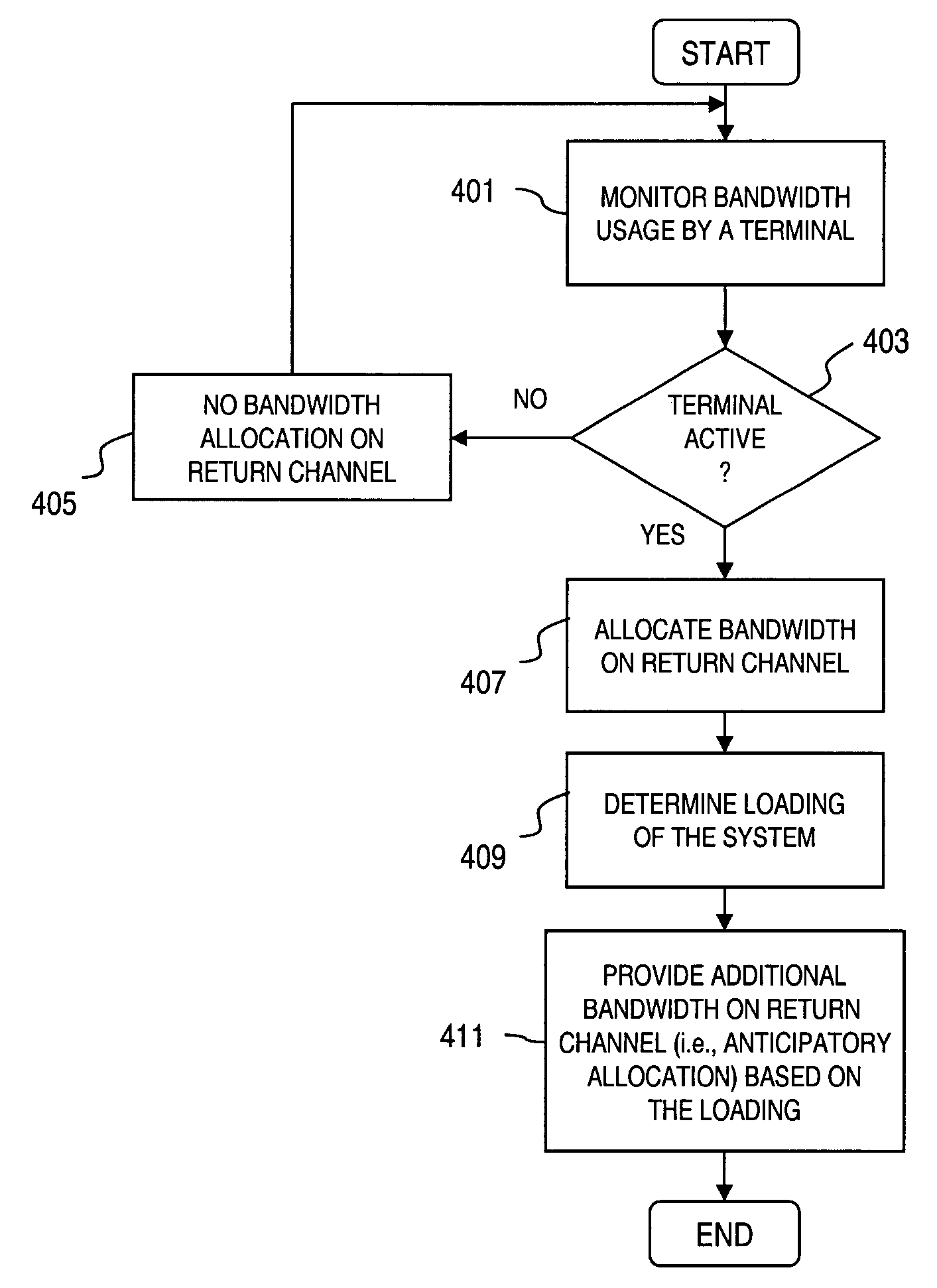
Method and system for providing load-sensitive bandwidth allocation
ActiveUS7336967B2Size be alterEfficient bandwidth utilizationTime-division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsBandwidth allocationNetwork management
An approach is provided for managing bandwidth in a data network. Capacity is allocated on a communication channel, which can be utilized for transporting data traffic or support network administrative functions (e.g., ranging), for a terminal to transmit data over the communication channel. In anticipation of the terminal having to transmit additional data, additional capacity is allocated on the communication channel for the terminal prior to receiving a request for bandwidth by the terminal. The anticipatory allocation is determined according to loading of the data network. This approach as particular applicability to shared capacity systems, such as a satellite communication system.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
Multiple chamber airbags and methods
InactiveUS6962363B2Low amount and weightMinimally labor-intensive to manufacturePedestrian/occupant safety arrangementEngineeringSingle chamber
A two or more chambered airbag provides much improved safety and / or performance. A modified single chamber airbag can be used as the primary chamber of the two-chamber airbag. A piece of fabric of appropriate size is sewn to the inside or outside surface of the front panel of the primary chamber to create the secondary chamber. One or more apertures are opened between the primary and secondary chambers. In order for the secondary chamber to inflate properly, the tethers of the primary chamber are shortened to 50% to 80% of their original length. The size or location of the tether sewing to the inner surface of the front panel of the primary chamber is also adjusted to create a desired shape of the secondary chamber when deployed.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Environmentally controlled vertical farming system
ActiveUS20180014485A1Efficient comprehensive utilizationEasy to understandSelf-acting watering devicesLayeringGrowth plantAgricultural engineering
A plant growing system configured for high density crop growth and yield, including an environmentally-controlled growing chamber and a vertical growth column within, the column configured to support a hydroponic plant growth module which is configured for containing and supporting plant growth media for containing and supporting a root structure of at least one gravitropic crop plant growing therein and for detachably mounting to the vertical growth column, the hydroponic plant growth module including a lateral growth opening to allow the plant to grow laterally through toward a light emitting source, a nutrient supply system to direct aqueous crop nutrient solution through an upper opening of the hydroponic plant growth module, an airflow source to direct airflow away from the growth opening and through an under-canopy of the plant, so as to disturb the boundary layer, and a control system for regulating, at least one growing condition in an area in or adjacent to the under-canopy.
Owner:MJNN LLC
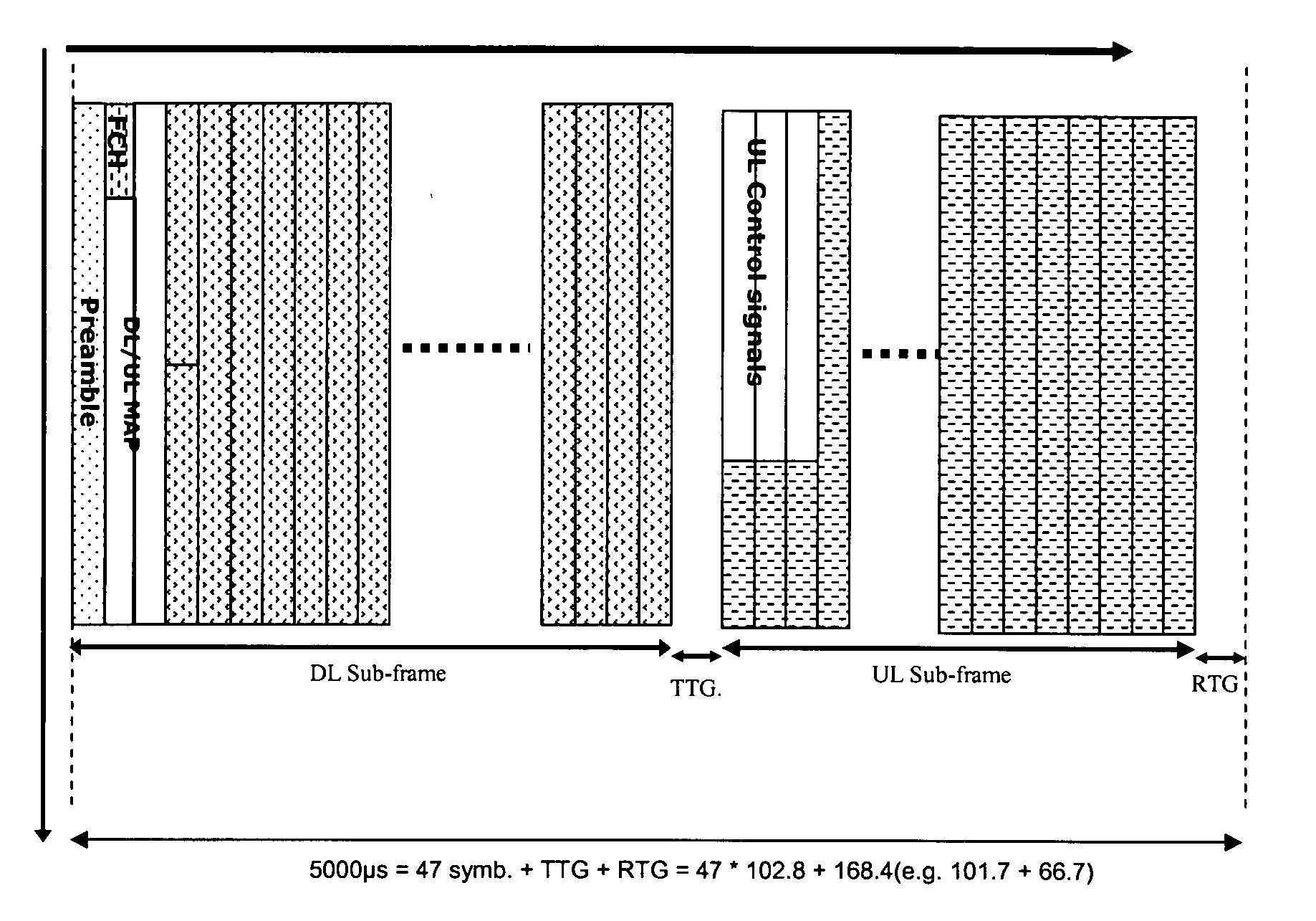
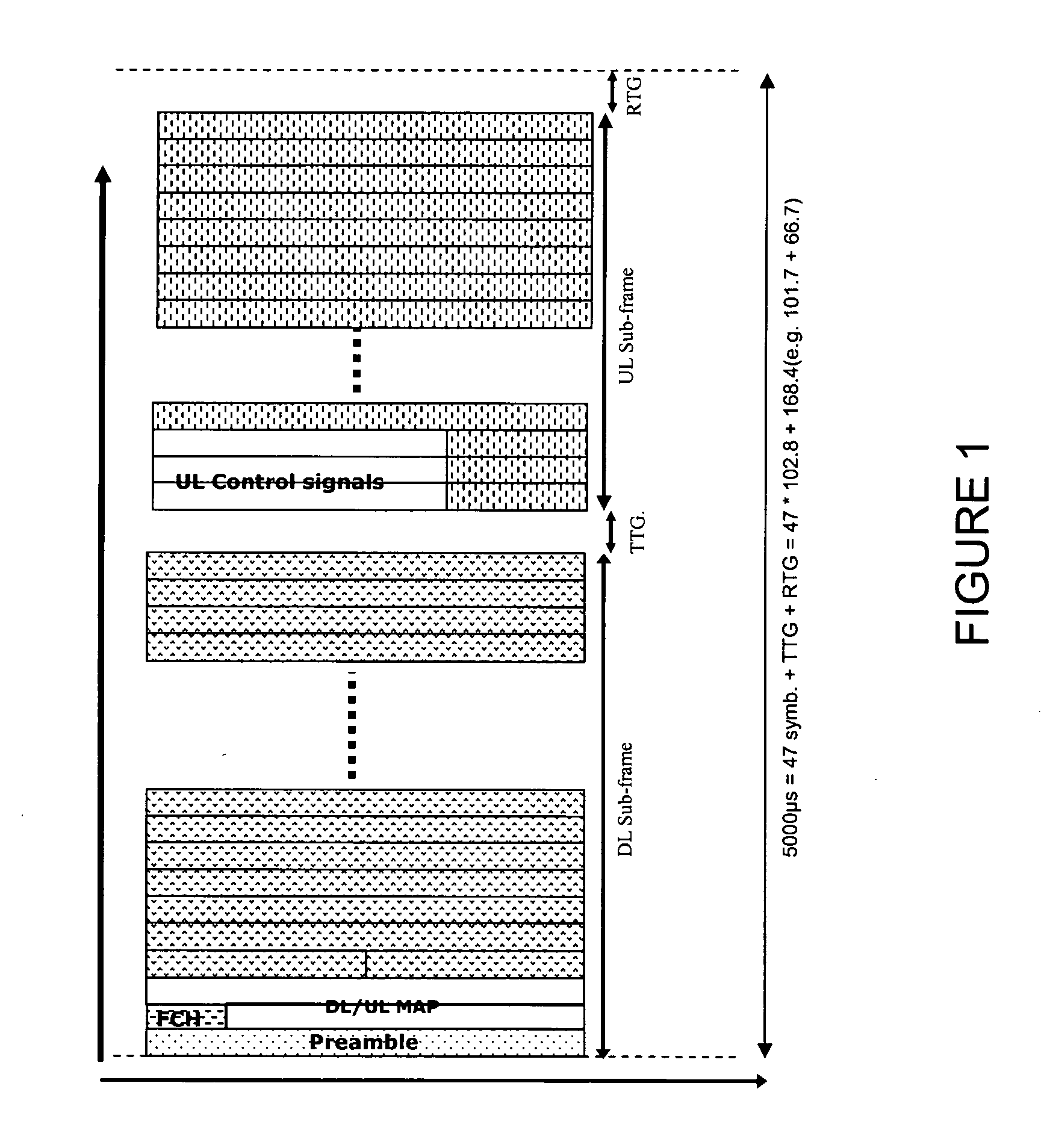
Systems and methods of supporting multiple wireless communication technologies
ActiveUS20080107047A1Preserve efficiencyEfficient comprehensive utilizationTime-division multiplexLoop networksBase stationMethod of support
Systems and methods for supporting multiple wireless communications technologies are provided. When a first and second base station operate according to different wireless communication technologies on the same carrier frequency in different cells or on different carrier frequencies in the same cell the frame structure of each base station is controlled in such a way that idle periods of transmissions from one base station are aligned with idle periods of the other base station. When the first and second base stations are located in the same cell and operate on the same carrier frequency the frames of the first and second base stations are time-interlaced.
Owner:CLEARWIRE IP HLDG
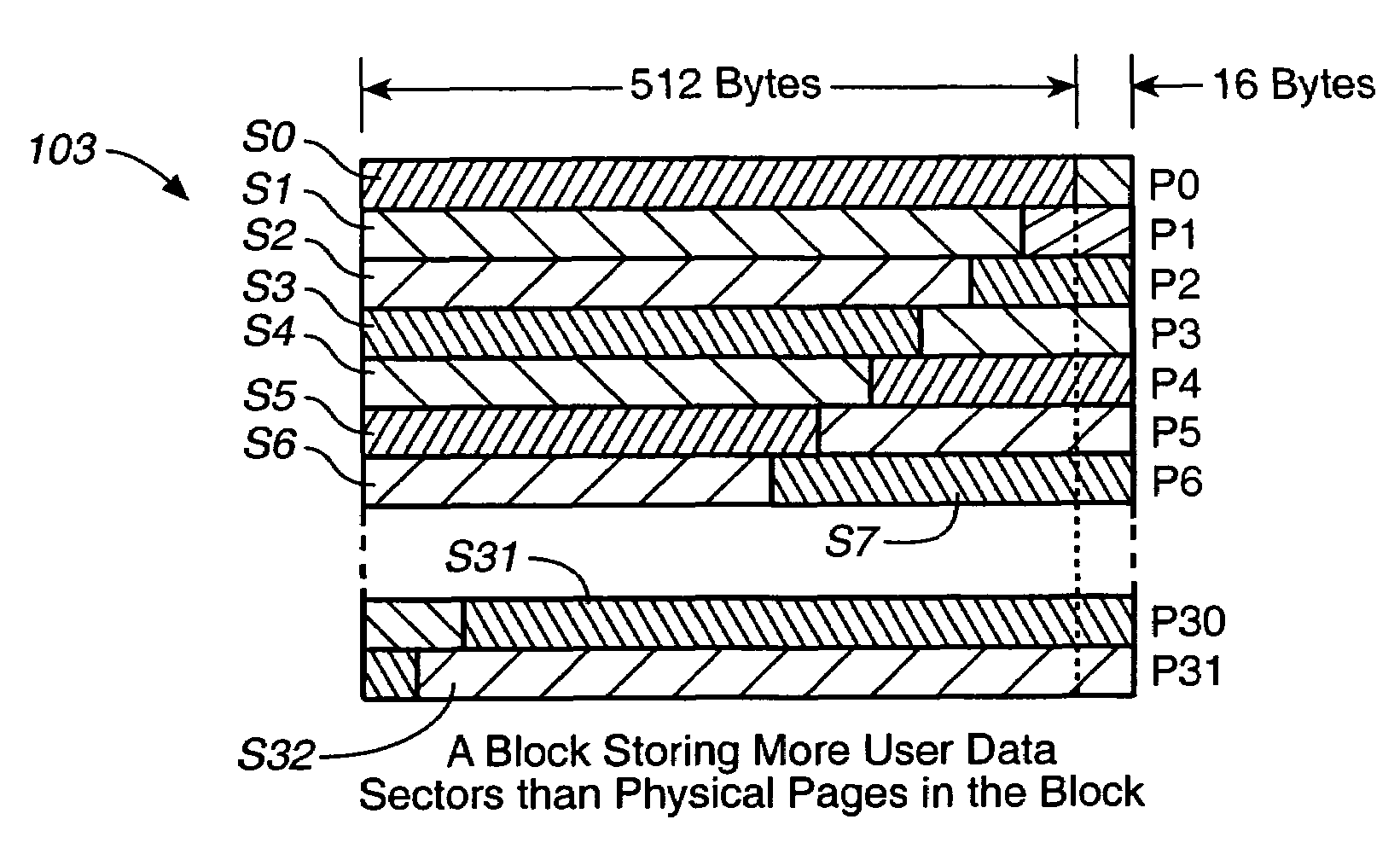
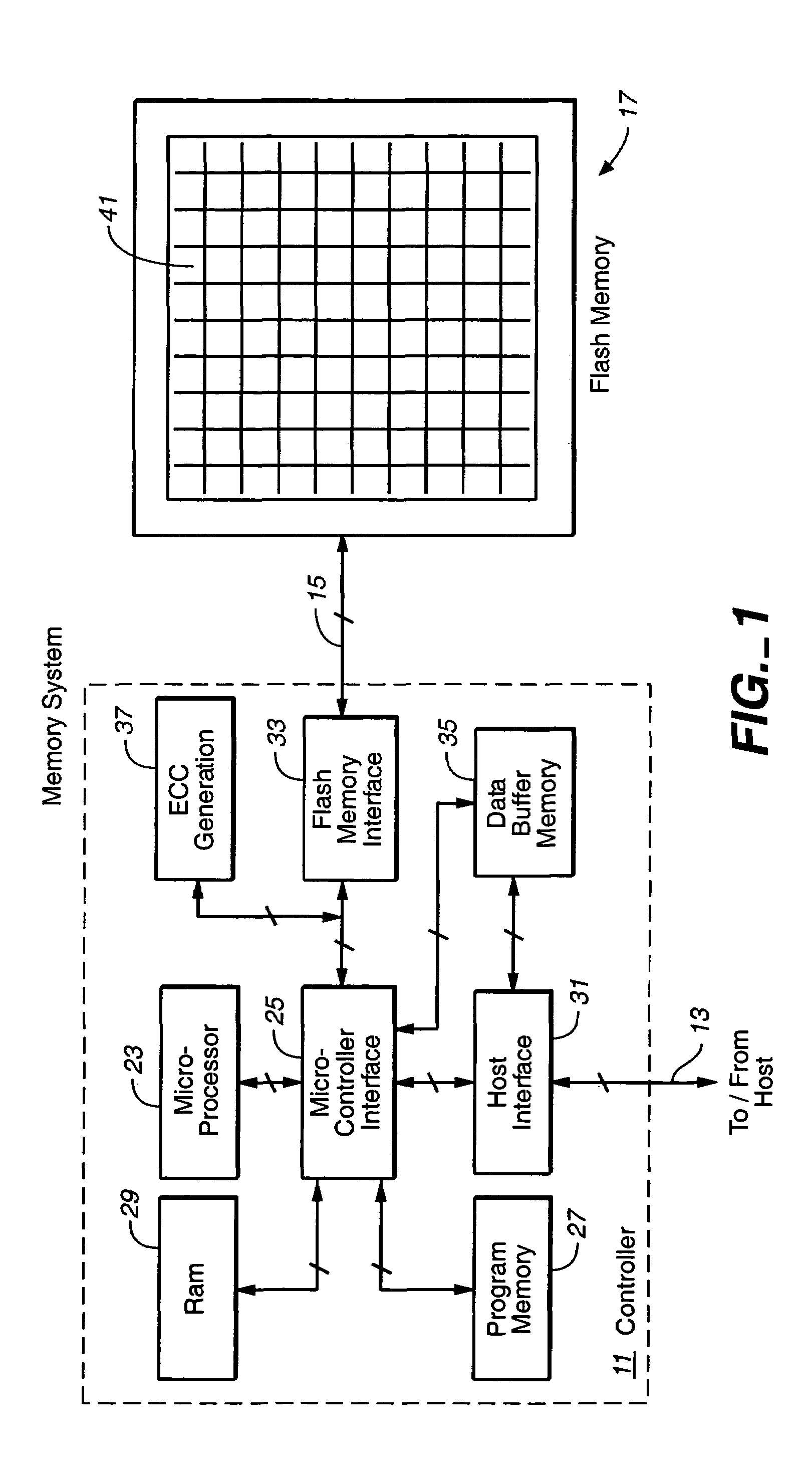
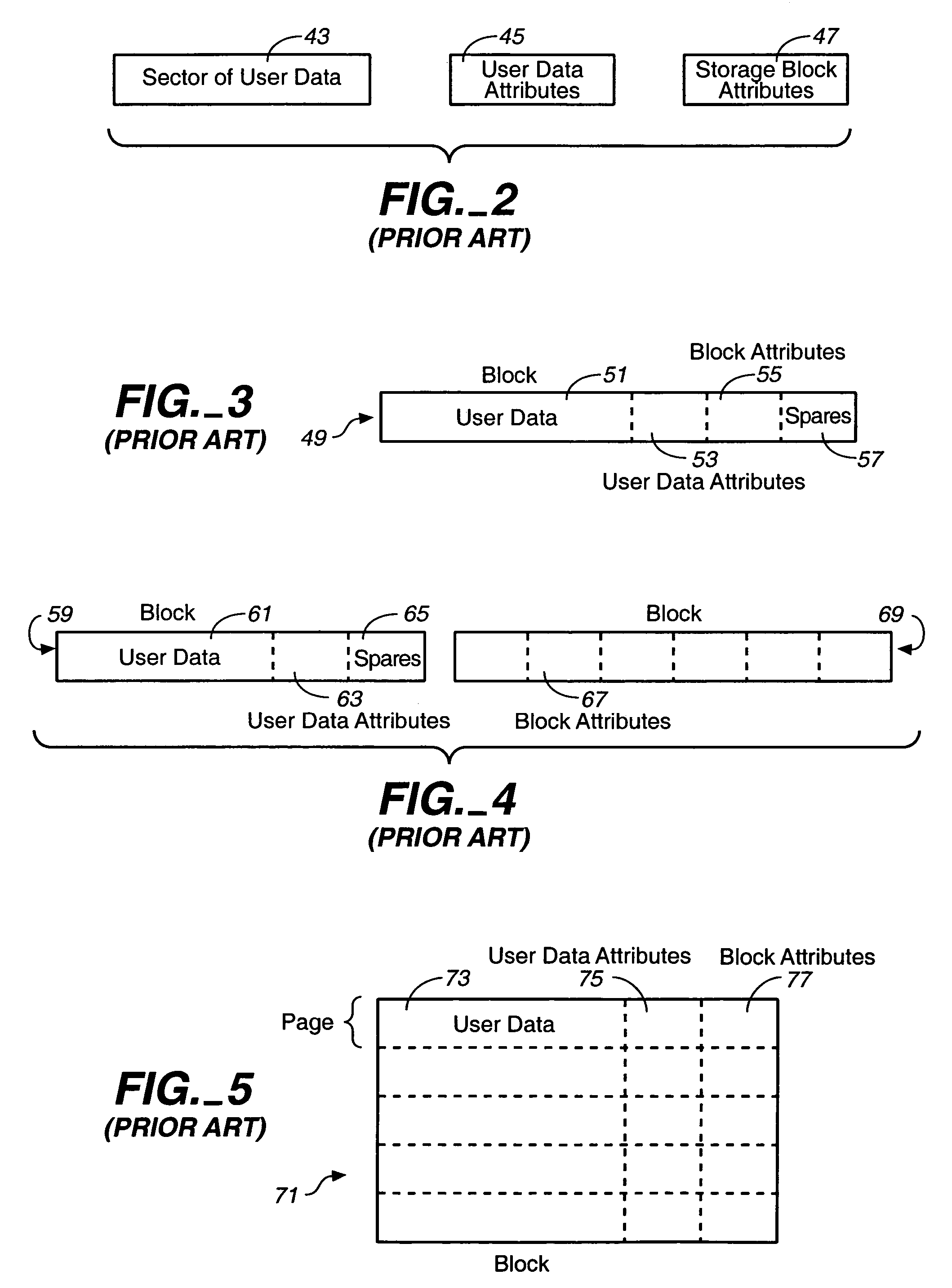
Techniques for operating non-volatile memory systems with data sectors having different sizes than the sizes of the pages and/or blocks of the memory
InactiveUS7032065B2Efficient use ofImprove performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationEEPROMNon-volatile memory
A non-volatile memory system, such as a flash EEPROM system, is disclosed to be divided into a plurality of blocks and each of the blocks into one or more pages, with sectors of data being stored therein that are of a different size than either the pages or blocks. One specific technique packs more sectors into a block than pages provided for that block. Error correction codes and other attribute data for a number of user data sectors are preferably stored together in different pages and blocks than the user data.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
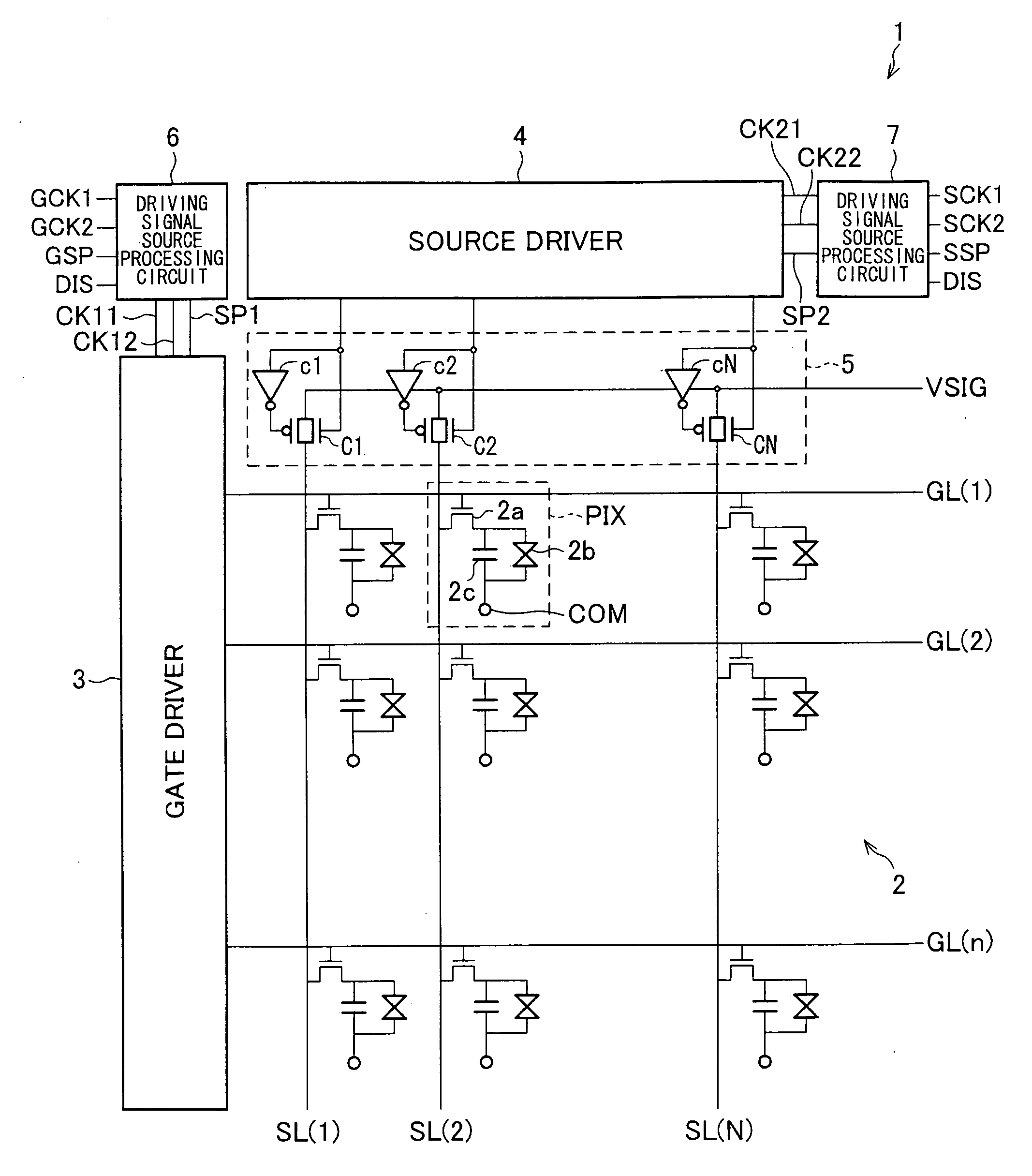
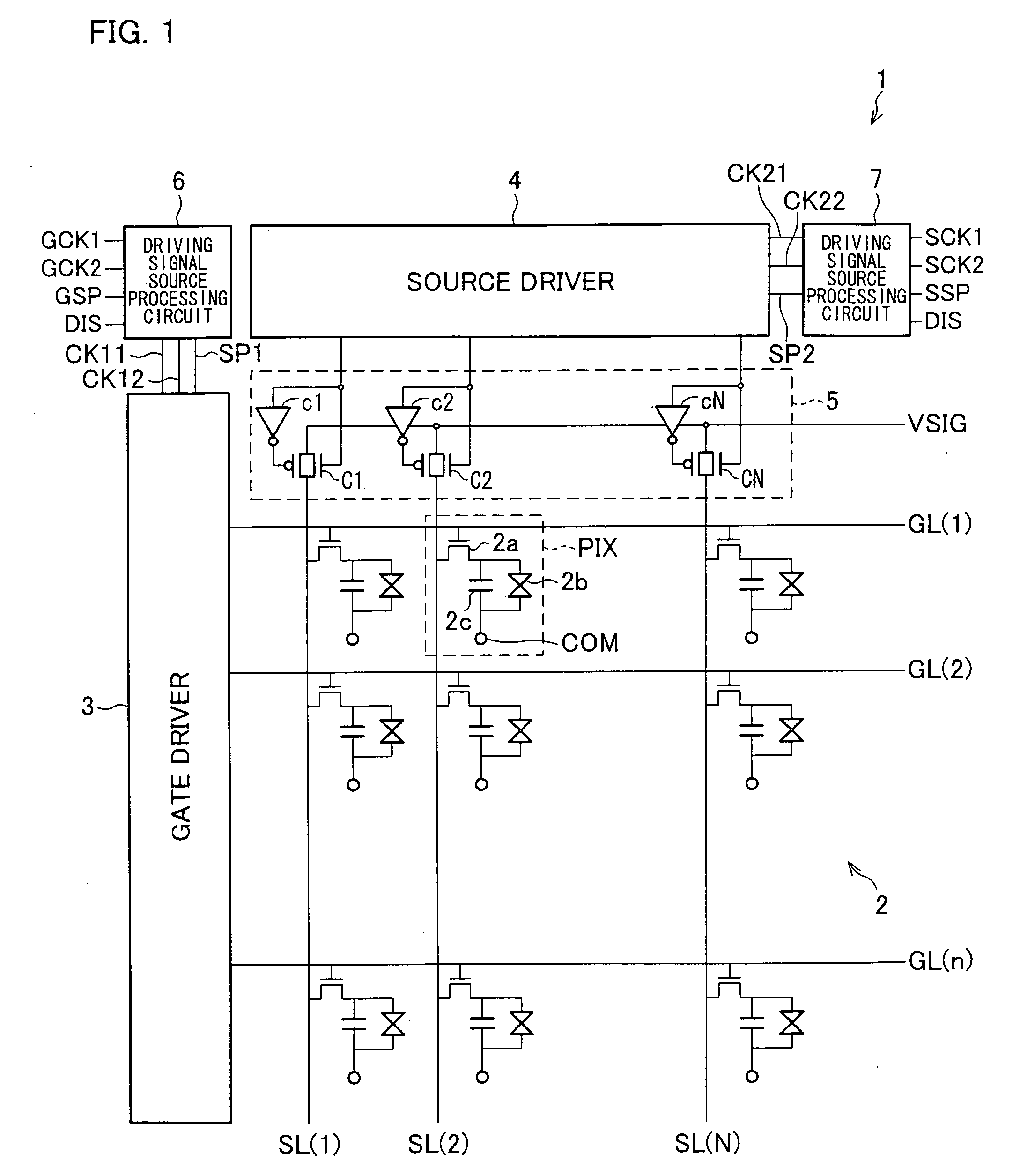
Display Apparatus and Method For Driving The Same
ActiveUS20090121998A1Prevent degradationReduce displayStatic indicating devicesDigital storageShift registerLiquid-crystal display
A liquid crystal display apparatus (1) wherein the shift registers of a source driver (4) are configured by use of asynchronous RS flip-flops in which an active input to a set input terminal has a higher priority than an active input to a reset terminal. In a second mode of operation, first and second clock signals and a start pulse are fixed at high levels, thereby performing discharges from all the pixels (PIX) of a liquid crystal panel (2).
Owner:SHARP KK
Efficiently storing transport streams
ActiveUS20100189122A1Efficient storageEasy to transportData switching by path configurationNetwork packetPage header
Described are computer-based methods and apparatuses, including computer program products, for efficiently storing transport streams. A first sequence of one or more packets associated with the first transport stream is received, the first sequence comprising one or more data packets. A storage packet is generated by selecting one or more packets from the first sequence, the storage packet comprising a packet header and the one or more data packets. One or more null packet insertion locations are identified in a second sequence of one or more packets associated with a second transport stream. Null packet insertion information is generated based on the one or more null packet insertion locations, the information including data indicative of a reconstruction parameter related to reconstructing the second sequence from the storage packet by inserting one or more null packets that are not stored in the storage packet, wherein the packet header includes the null packet insertion information. The storage packet is stored.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
High-throughput, low-latency next generation internet networks using optical label switching and high-speed optical header generation, detection and reinsertion
InactiveUS6545781B1Efficient comprehensive utilizationSignificant overheadMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsComputer hardwareOptical IP Switching
An optical signaling header technique applicable to optical networks wherein packet routing information is embedded in the same channel or wavelength as the data payload so that both the header and data payload propagate through network elements with the same path and the associated delays. The header routing information has sufficiently different characteristics from the data payload so that the signaling header can be detected without being affected by the data payload, and that the signaling header can also be removed without affecting the data payload. The signal routing technique can overlaid onto the conventional network elements in a modular manner using two types of applique modules. The first type effects header encoding and decoding at the entry and exit points of the data payload into and out of the network; the second type effects header detection at each of the network elements.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Remote office duplication
ActiveUS8082228B2Shorten the timeLess storageMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsFingerprintData deduplication
Remote office deduplication comprises calculating one or more fingerprints of one or more data blocks, sending the one or more fingerprints to one or more backup servers via a network interface, receiving from the one or more backup servers an indication of which one or more data blocks corresponding to the one or more fingerprints should be sent to the one or more backup servers, and if the indication indicates one or more data blocks to be sent to the one or more backup servers, sending the one or more data blocks to the one or more backup servers via the network interface.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Parking Control System and Method
InactiveUS20080258935A1More convenienceSimple processTicket-issuing apparatusDetection of traffic movementParking areaRelevant information
Provided are a parking control system and method. In particularly, the present invention provides a total parking control system and method which are capable of automatically managing and controlling a whole process from a time when a vehicle enters a parking lot to a time when it goes out of there by using a server incorporating therein a program for a very high speed image recognition technique and parking management. For this, the present invention provides a parking location search unit which manages a parking location of an individual vehicle by recognizing vehicle numbers by photographing vehicles entering a parking space and going out of there as well as parked vehicles, and provides related information upon search. The present invention further provides a parking guiding unit guiding a driver of a vehicle entering the parking lot to an empty place for parking.
Owner:SEEVIDER
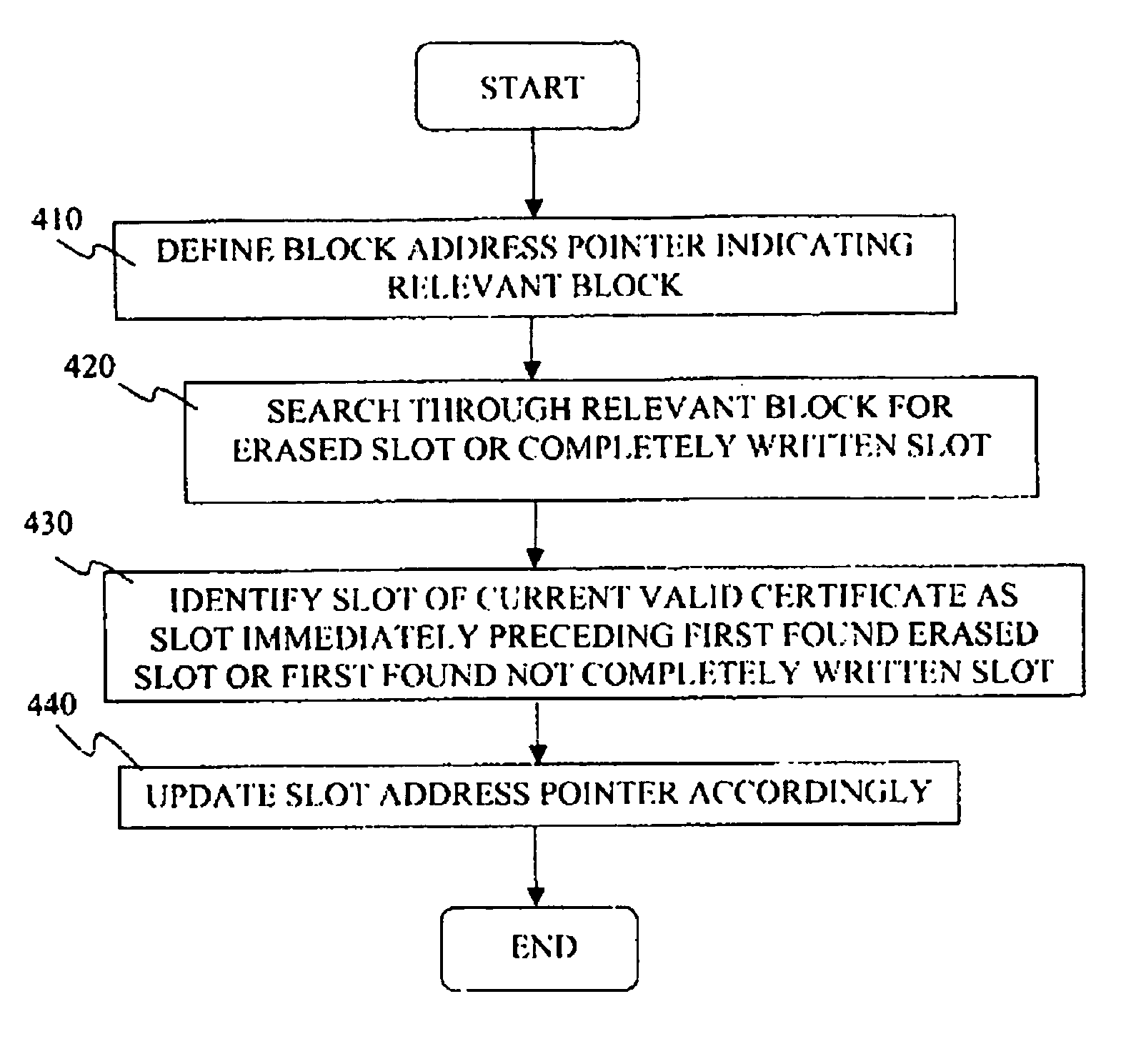
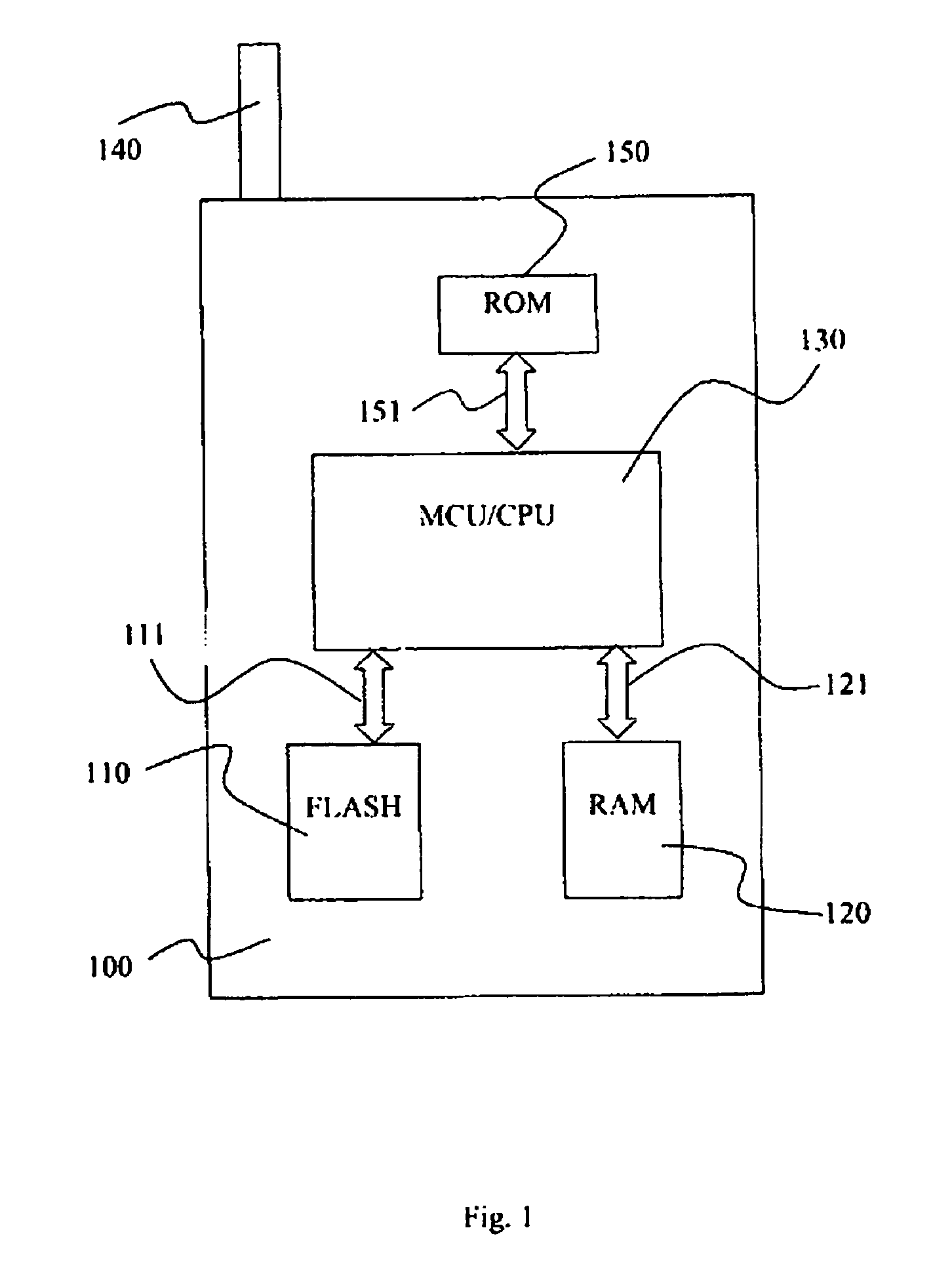
Secure digital certificate storing scheme for flash memory and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20070130439A1Improve featuresImprove data securityUser identity/authority verificationRead-only memoriesData memoryVerified procedure
The invention relates generally to data security and to data memory technologies, and more specifically provides a method for storing and updating digital certificates in a flash memory, and provides further a flash memory and an electronic apparatus exploiting said method. The method according to the invention is applicable for a flash memory (110) having predefined erase-write blocks and write-read blocks, for enhancing the tampering proof characteristics of said flash memory (110), said certificates authenticating a computer program and being verified by a verification program associated with the computer program, said method comprising the steps of: (230) defining a plurality of memory slots within said at least one erased erase-write block wherein each memory slot have a commencing address comprising a binary “0”- or a binary “1” bit pattern, (240) writing a first and second digital certificate in a first and second one of said memory slots, (250) defining a certificate slot address pointer, (260) updating said certificate slot address pointer by replacing said “0”- or “1”-bit pattern of said pointer with a “1”-or a “0” bit pattern, respectively.
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com