Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
49 results about "Short latency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
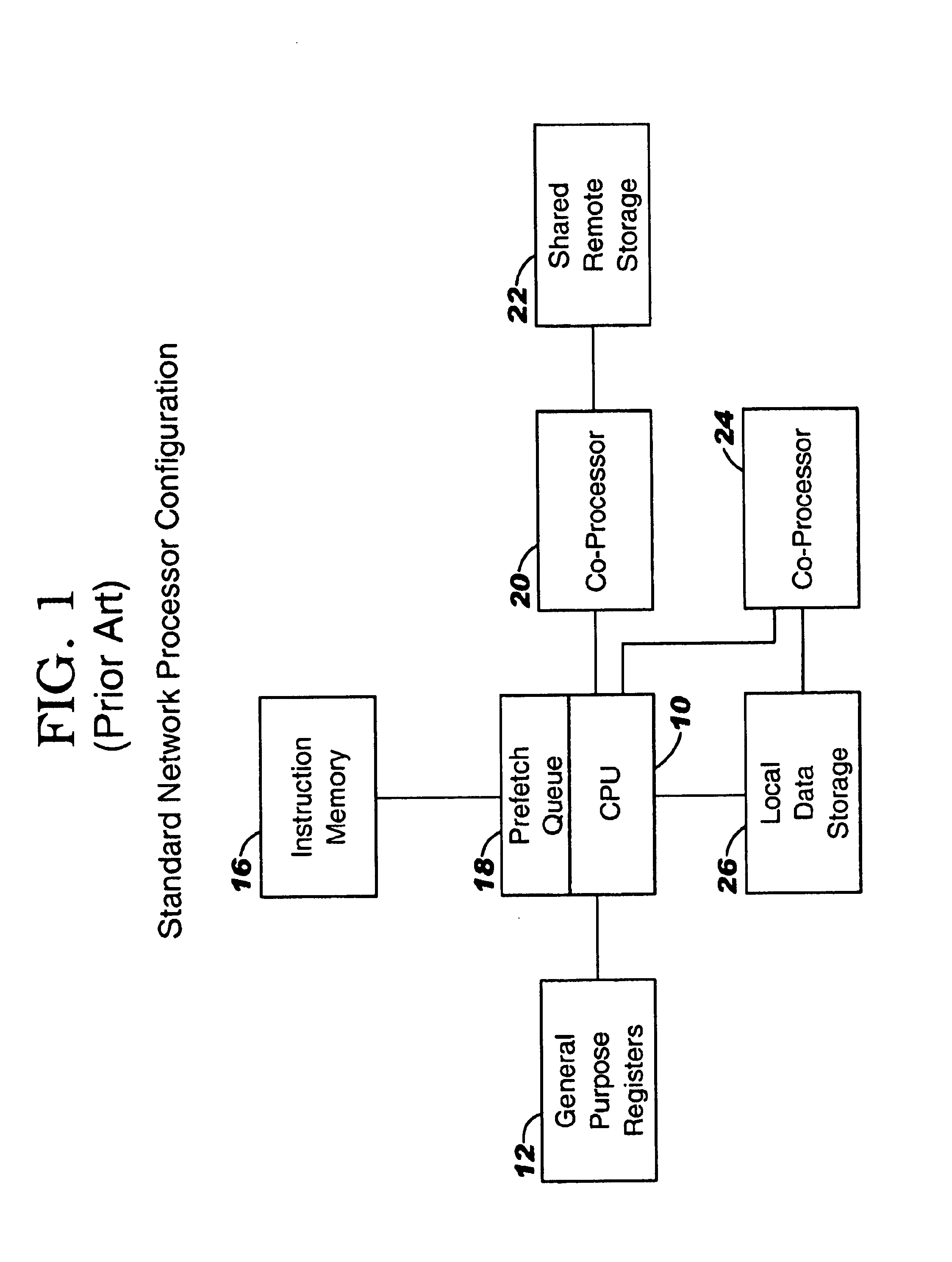
The short latency potentials are small amplitude, far field potentials; that is, they are recorded at some distance from their sources. Sophisticated techniques are needed to measure these potentials because they are buried in a background of physical and physiological noise.
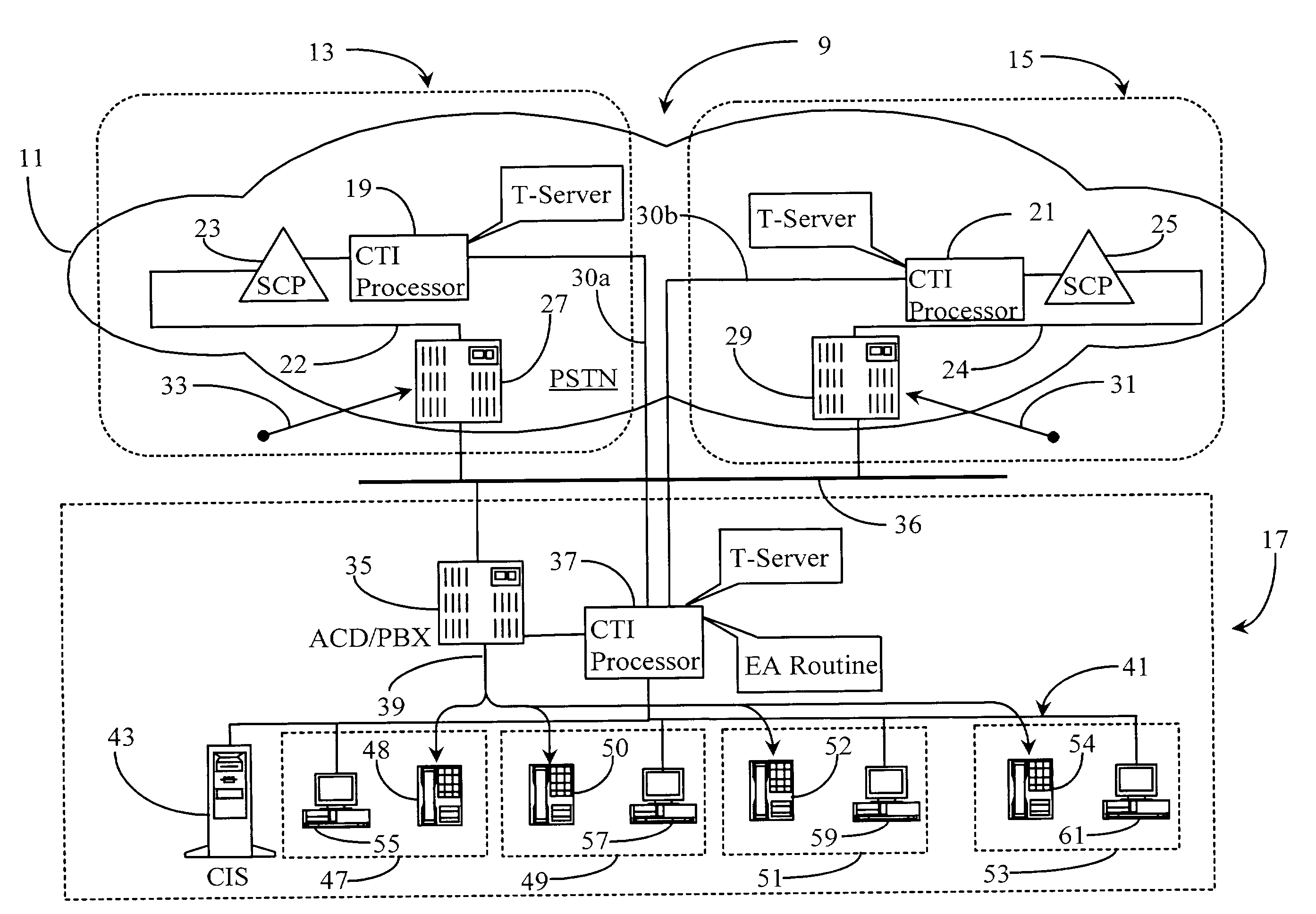
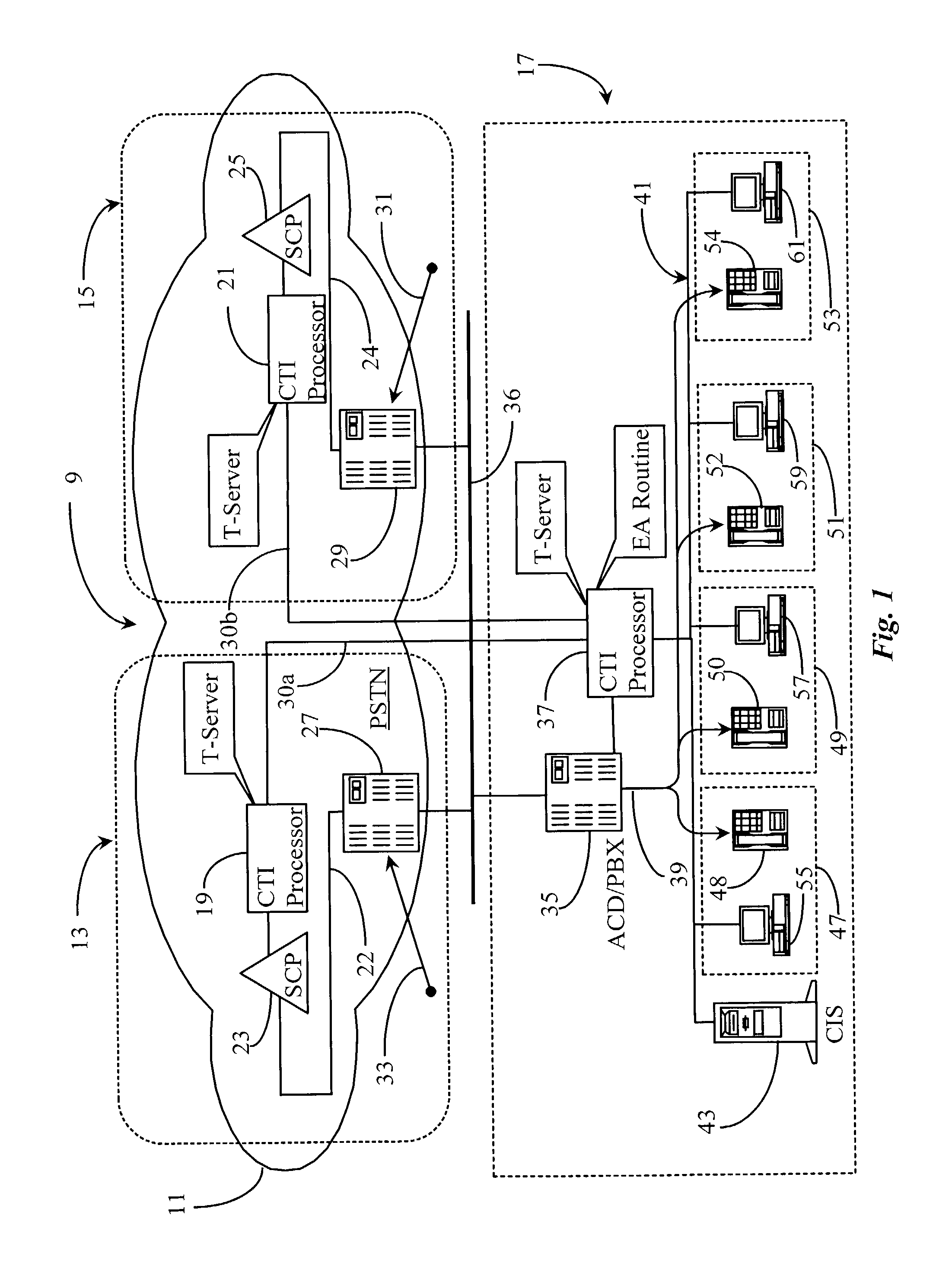
Method and apparatus for providing fair access to agents in a communication center
InactiveUS7236584B2Long latencyShort incubation periodIntelligent networksSpecial service for subscribersLong latencyTimer
A system for granting access to agents at a communication center in response to requests for connection from network-level entities starts a fairness timer having a fairness time period when a first request is received for and agent, monitors any other requests for the same agent during the fairness time, and executes an algorithm at the end of the fairness time to select the network-level entity to which the request should be granted. In a preferred embodiment the fairness time is set to be equal to or greater than twice the difference between network round-trip latency for the longest latency and shortest latency routers requesting service from the communication center. In some embodiments an agent reservation timer is set at the same point as the fairness timer to prevent calls to the same agent, and has a period longer than the fairness timer by a time sufficient for a connection to be made to the agent station once access is granted, and for notification of the connection to be made to network-level entities.
Owner:GENESYS TELECOMM LAB INC AS GRANTOR +3
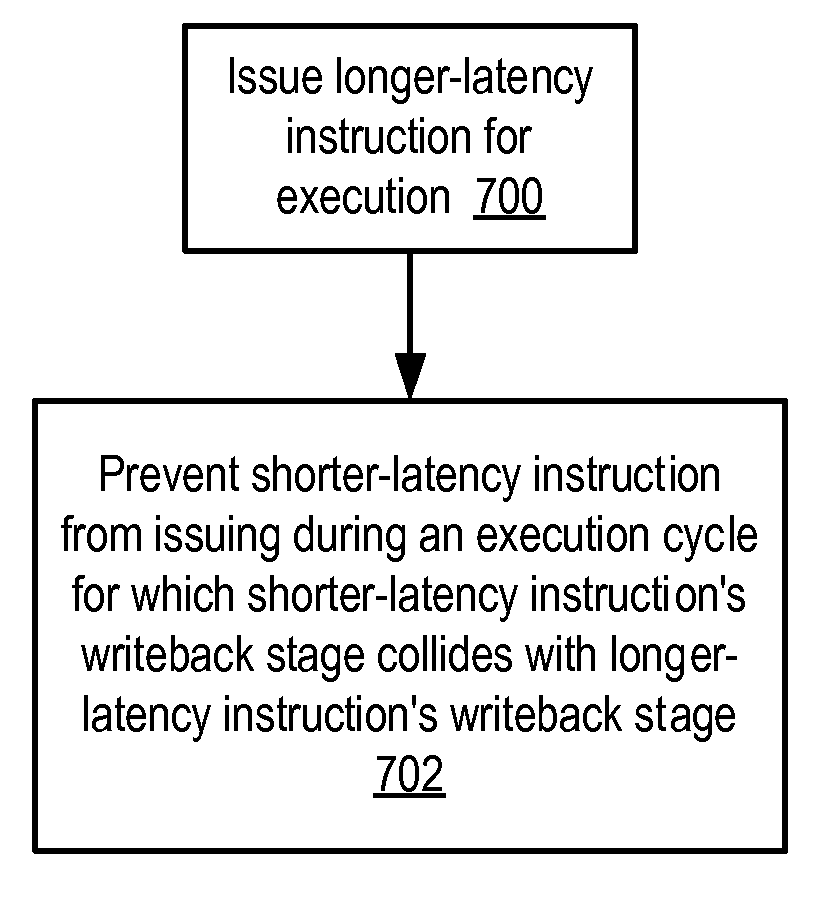
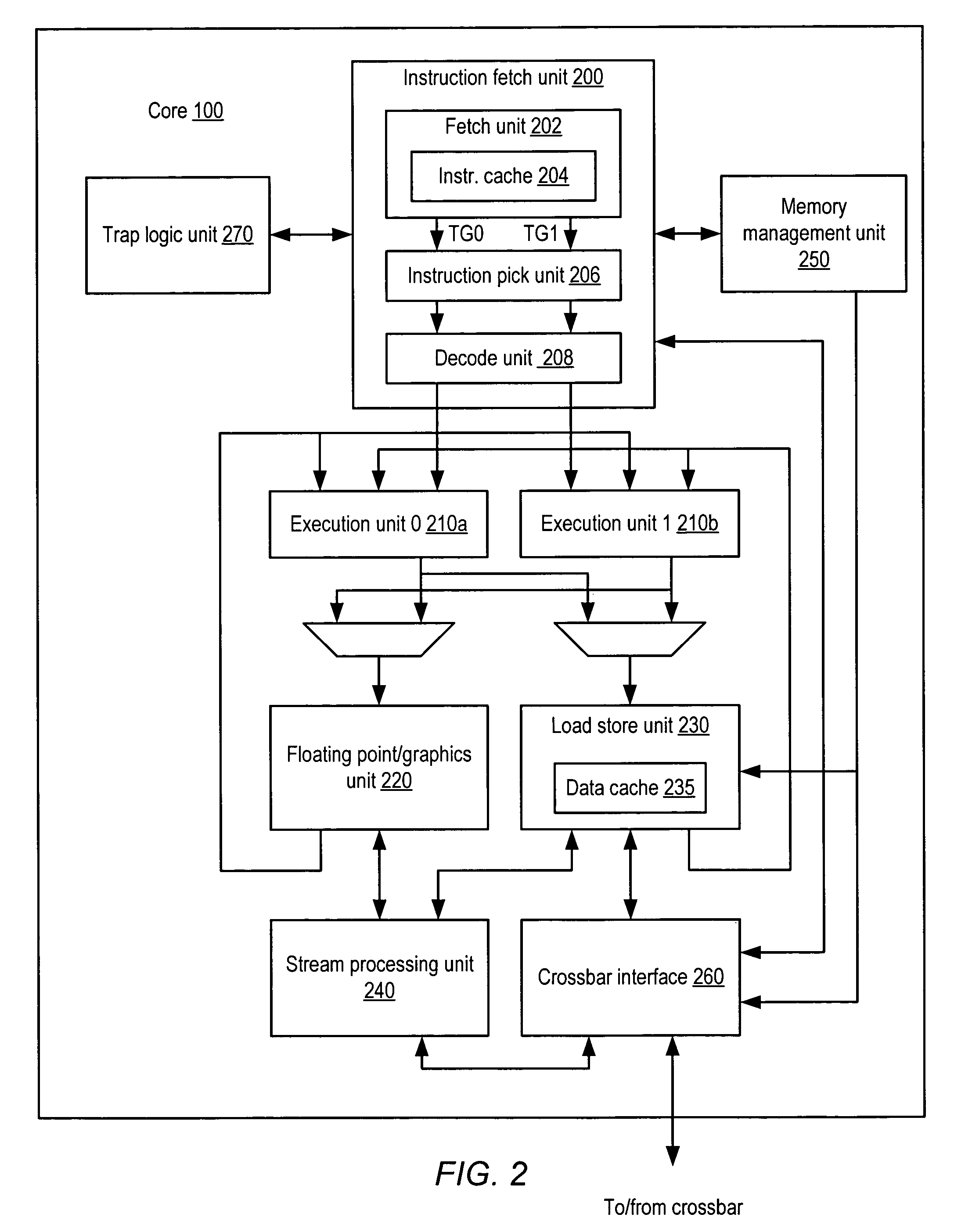
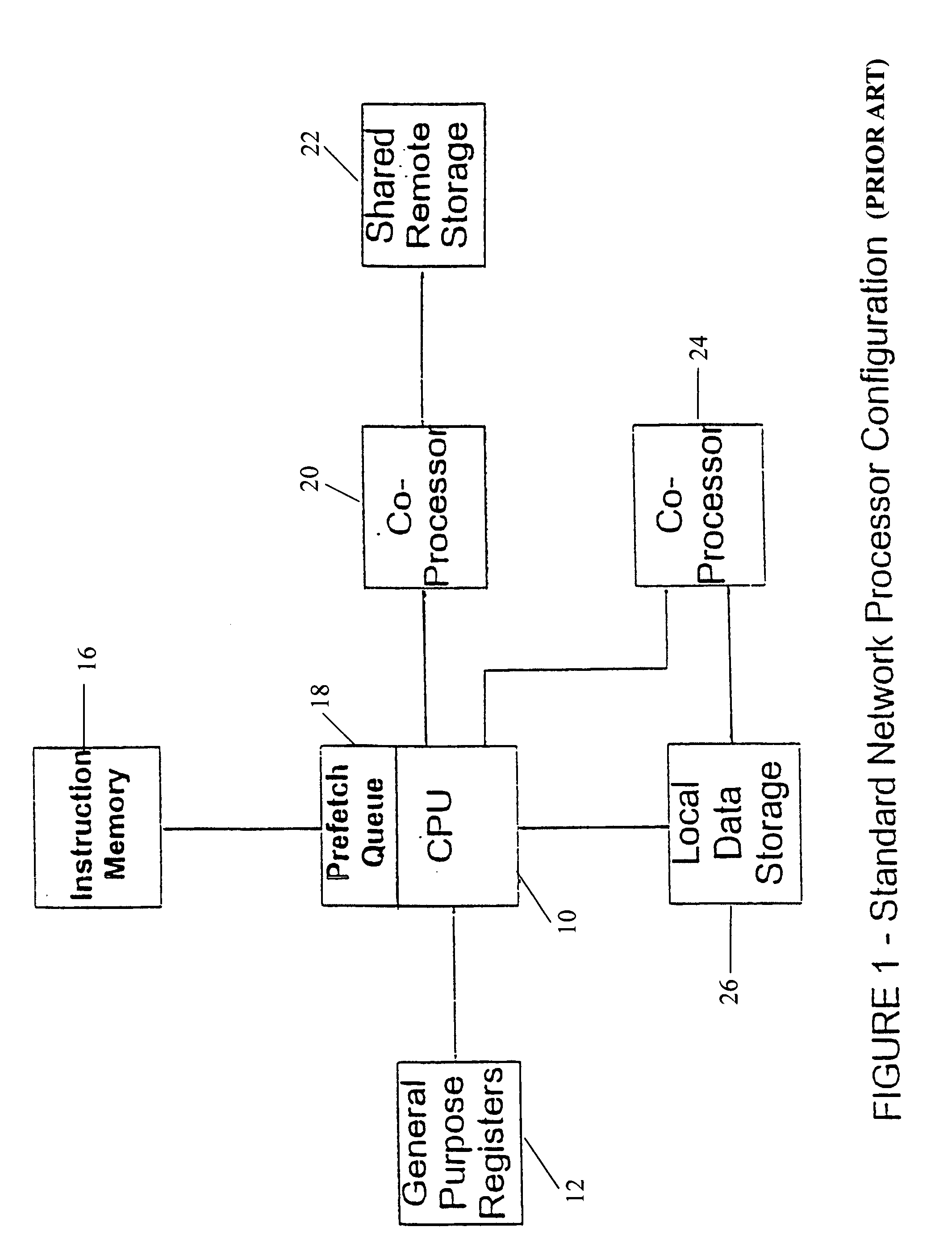
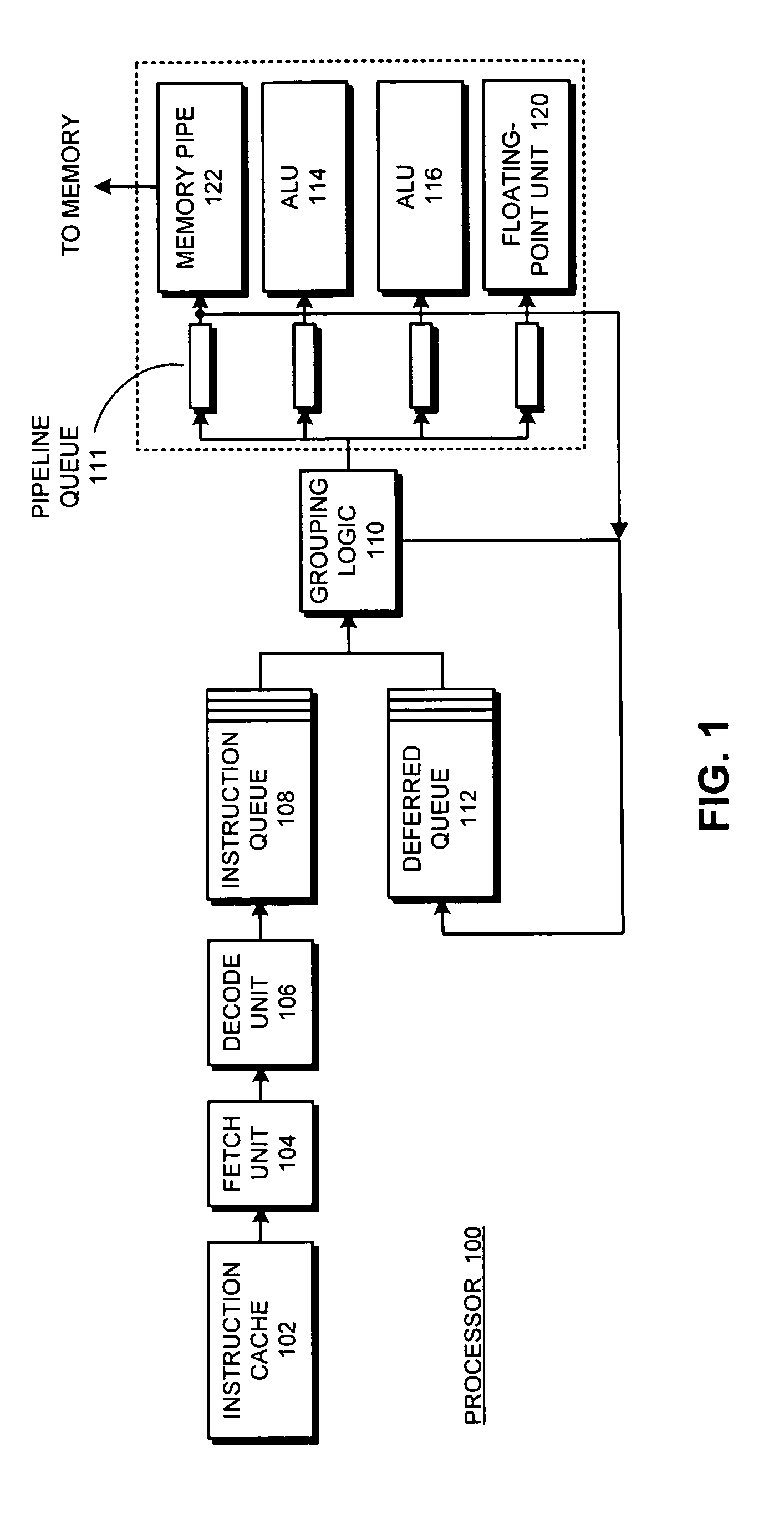
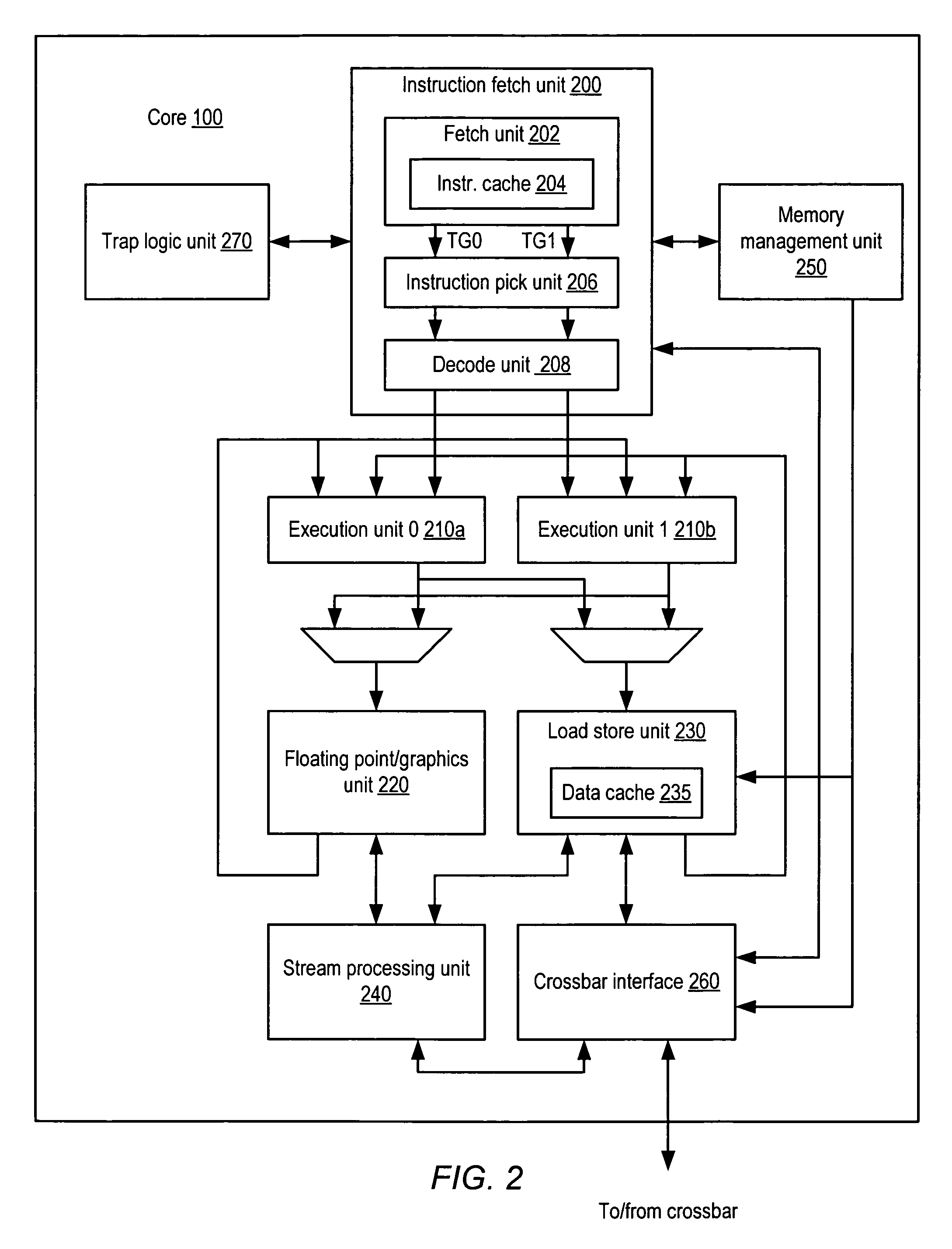
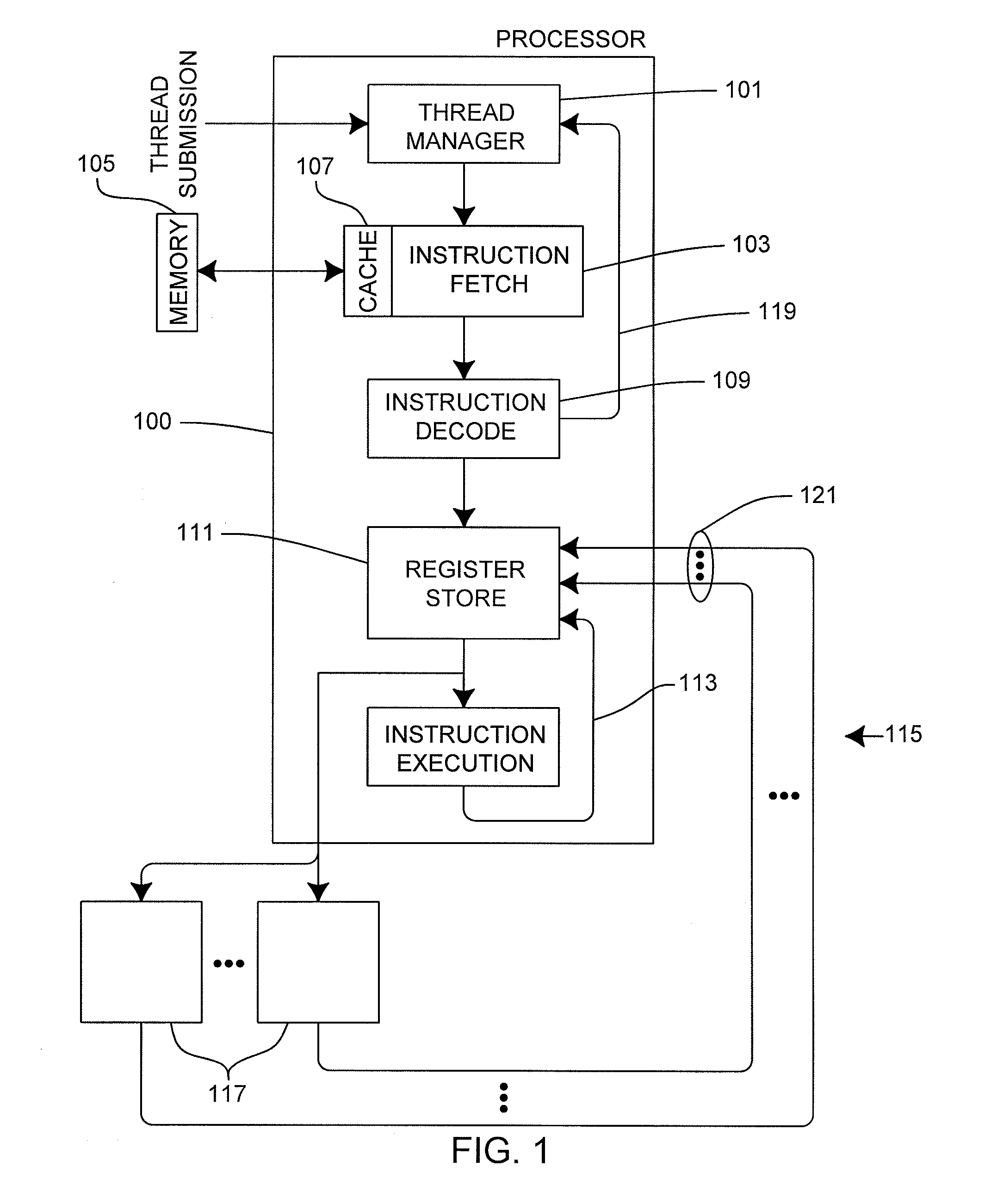
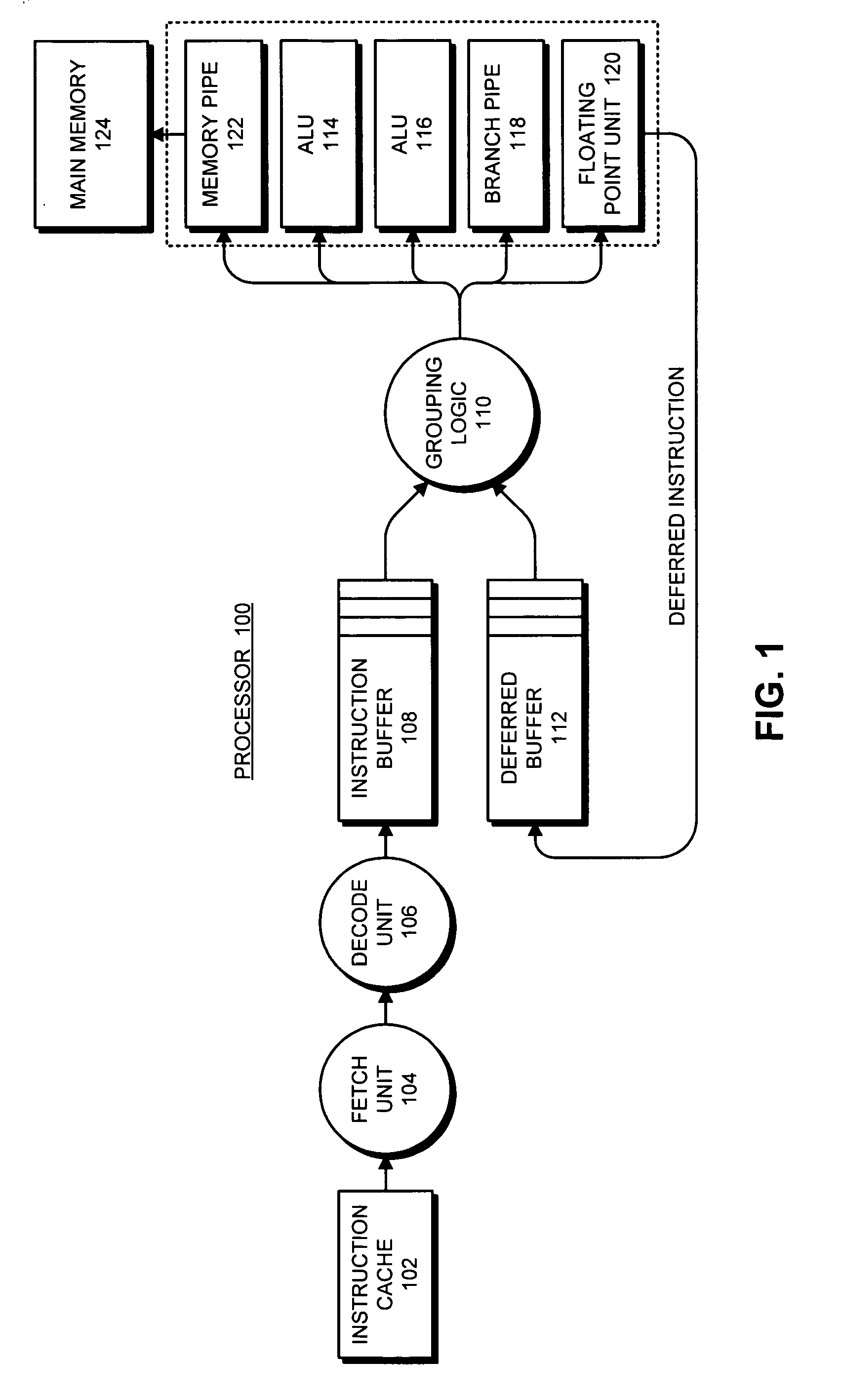
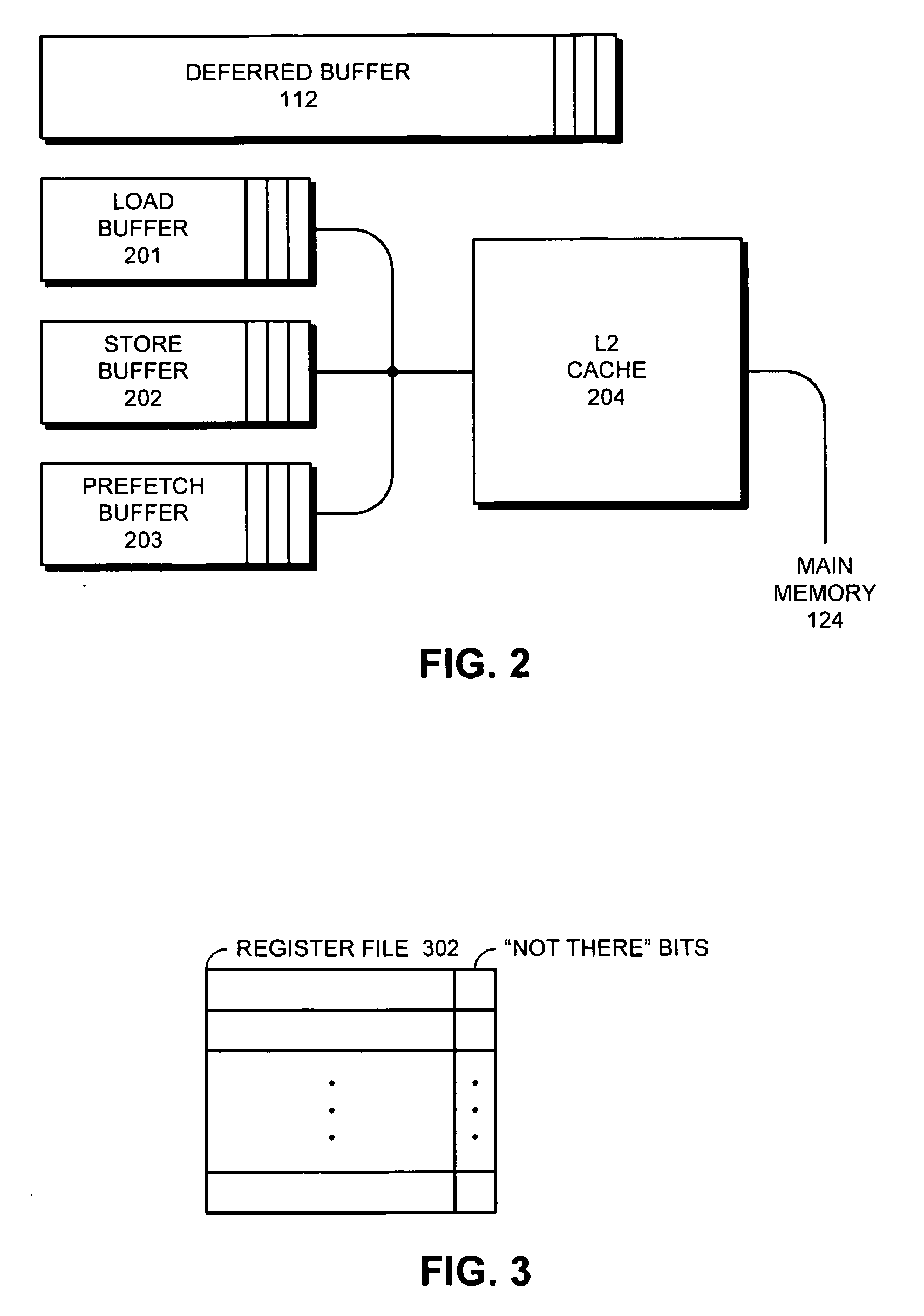
Apparatus and method to support pipelining of differing-latency instructions in a multithreaded processor
ActiveUS7478225B1Easy accessAvoid issuingDigital computer detailsMemory systemsLong latencyParallel computing
An apparatus and method to support pipelining of variable-latency instructions in a multithreaded processor. In one embodiment, a processor may include instruction fetch logic configured to issue a first and a second instruction from different ones of a plurality of threads during successive cycles. The processor may also include first and second execution units respectively configured to execute shorter-latency and longer-latency instructions and to respectively write shorter-latency or longer-latency instruction results to a result write port during a first or second writeback stage. The first writeback stage may occur a fewer number of cycles after instruction issue than the second writeback stage. The instruction fetch logic may be further configured to guarantee result write port access by the second execution unit during the second writeback stage by preventing the shorter-latency instruction from issuing during a cycle for which the first writeback stage collides with the second writeback stage.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
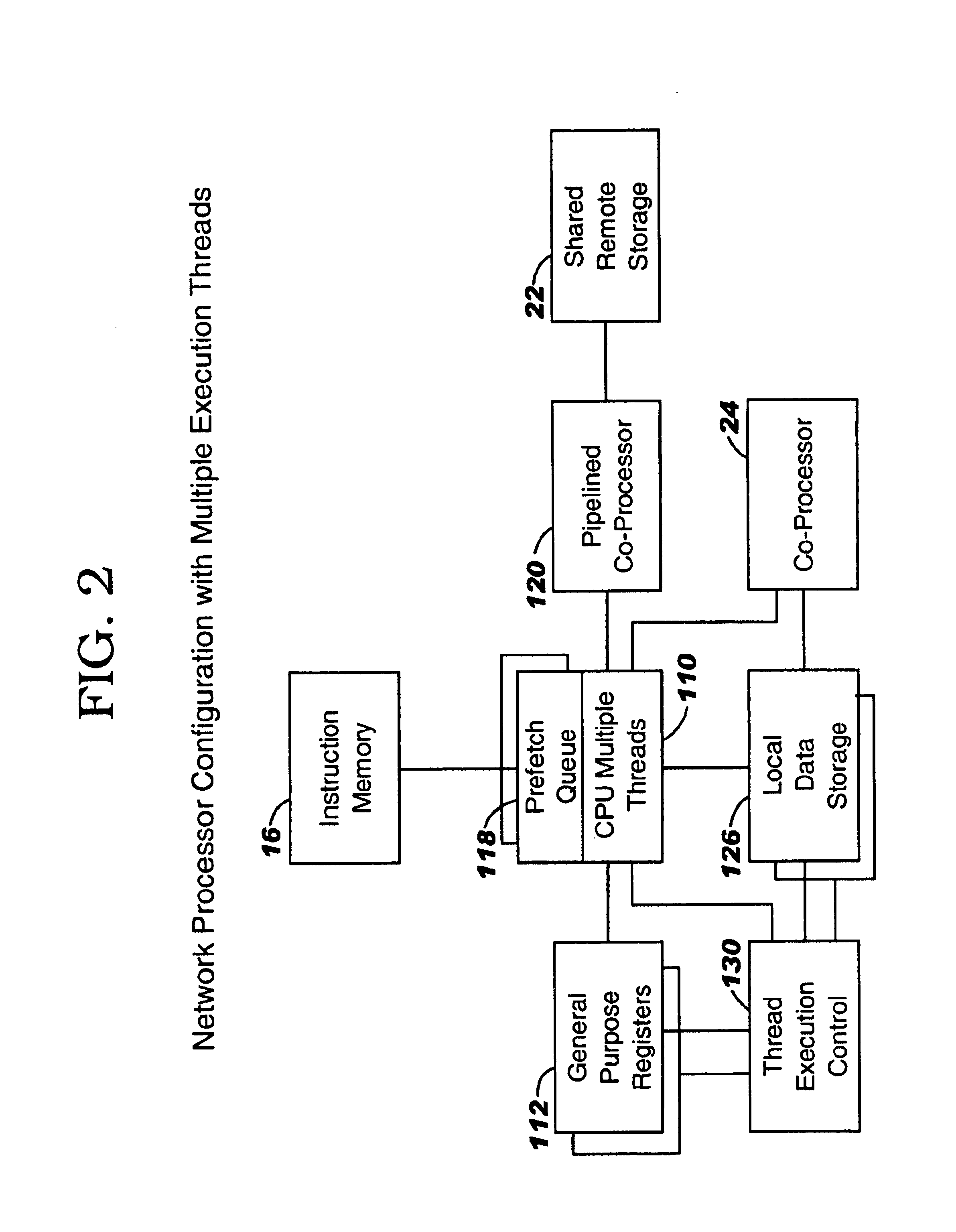
Controller for multiple instruction thread processors
InactiveUS6931641B1Efficient comprehensive utilizationProgram initiation/switchingProgram synchronisationFistLong latency
A mechanism controls a multi-thread processor so that when a fist thread encounters a latency event to a first predefined time interval temporary control is transferred to an alternate execution thread for duration of the first predefined time interval and then back to the original thread. The mechanism grants full control to the alternate execution thread when a latency event for a second predefined time interval is encountered. The first predefined time interval is termed short latency event whereas the second time interval is termed long latency event.
Owner:INTEL CORP
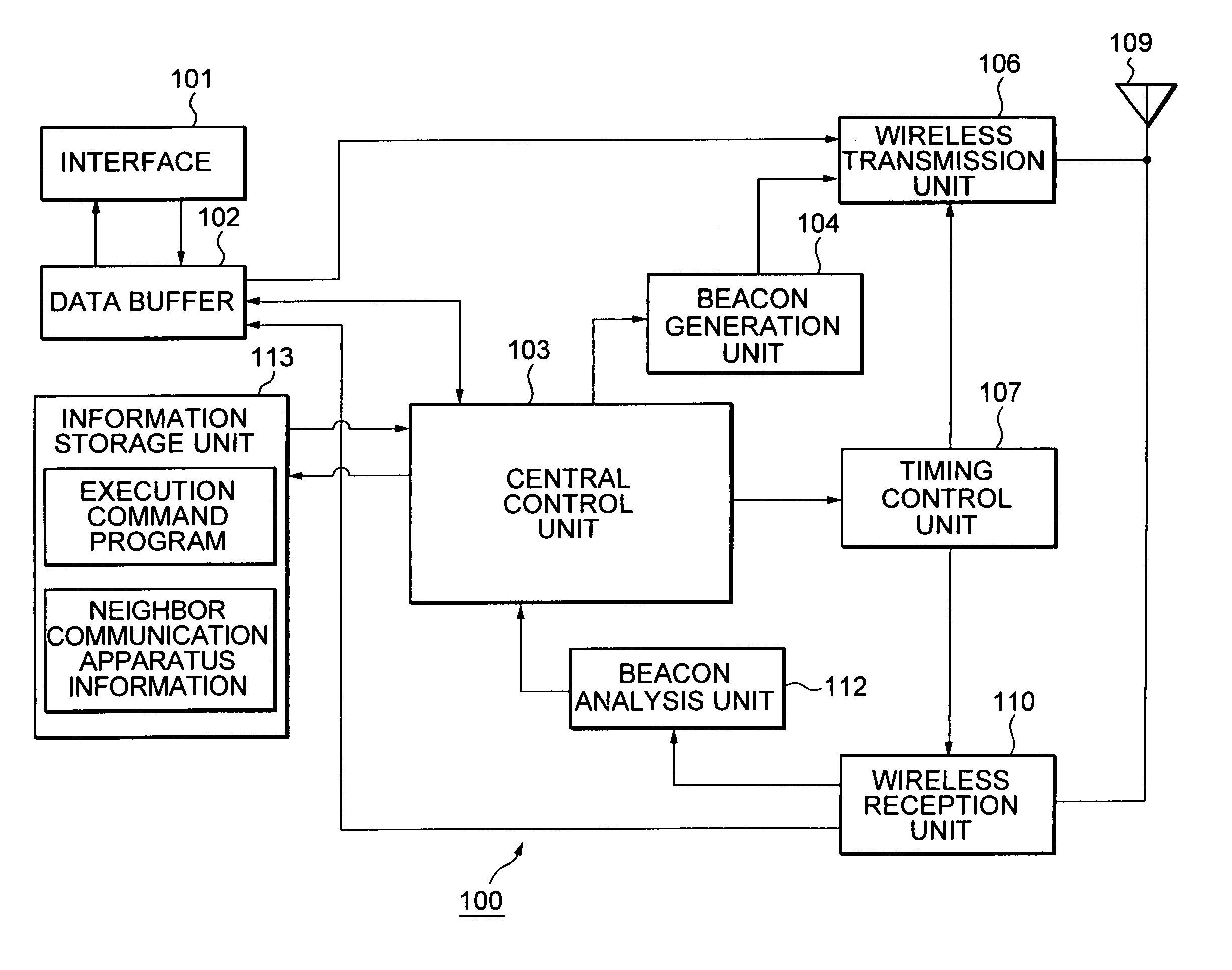
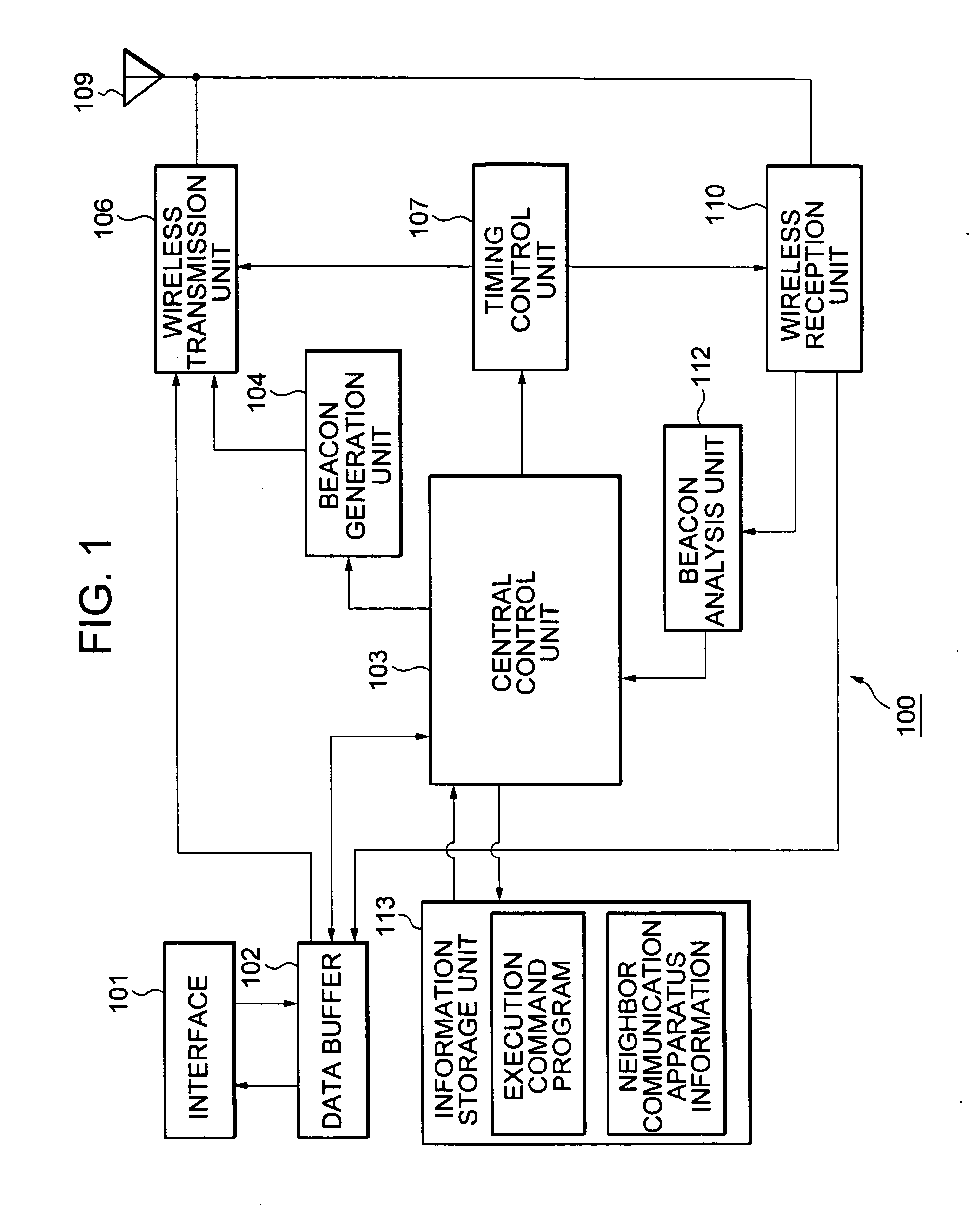
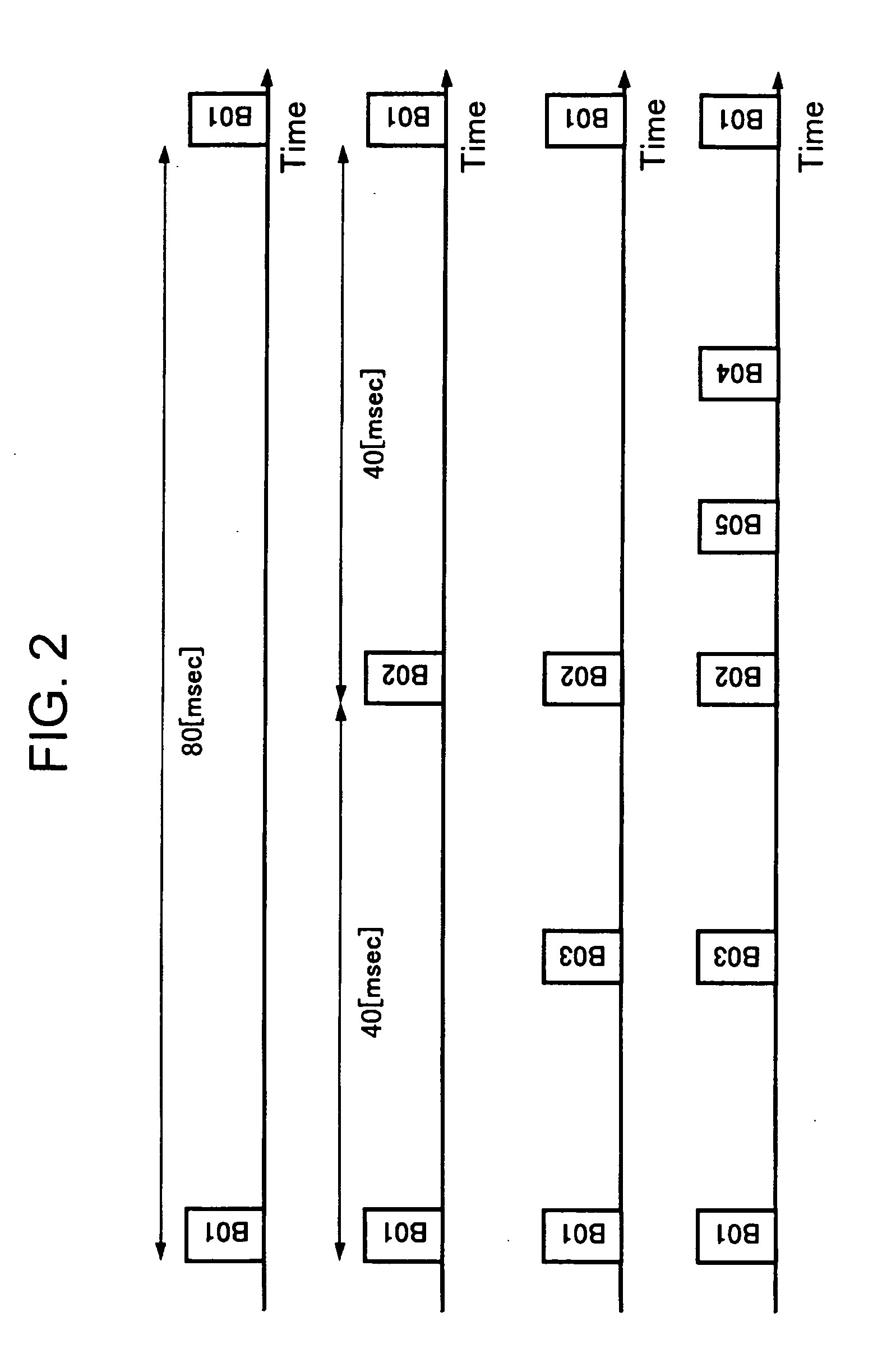
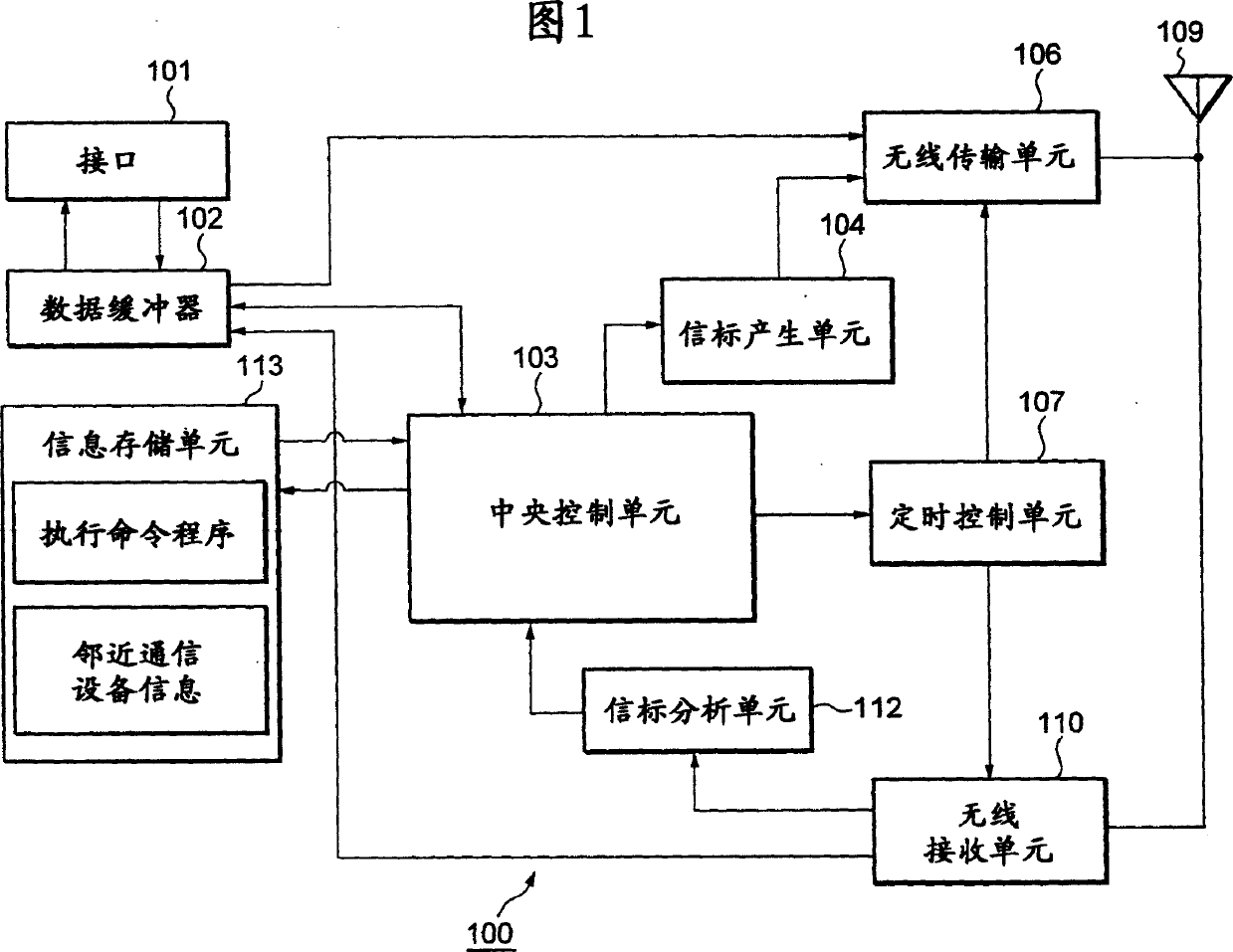
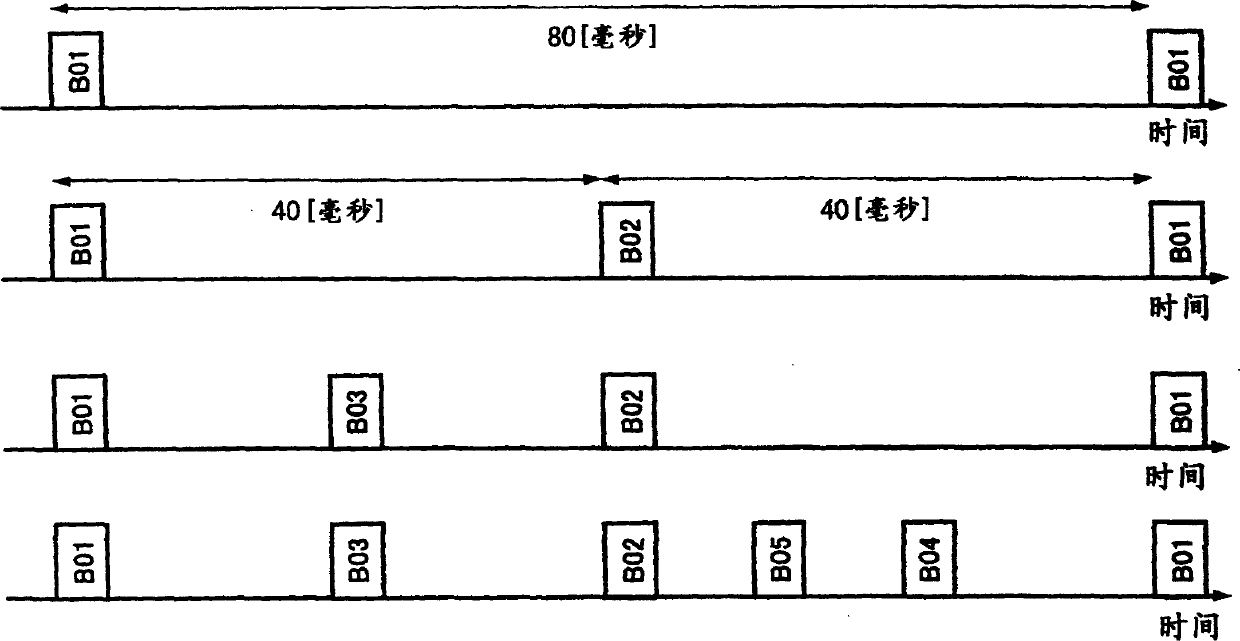
Wireless communication system, wireless communication apparatus, wireless communication method and computer program
InactiveUS20050227615A1Efficient data communicationReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTPower managementCommunications systemInformation transmission
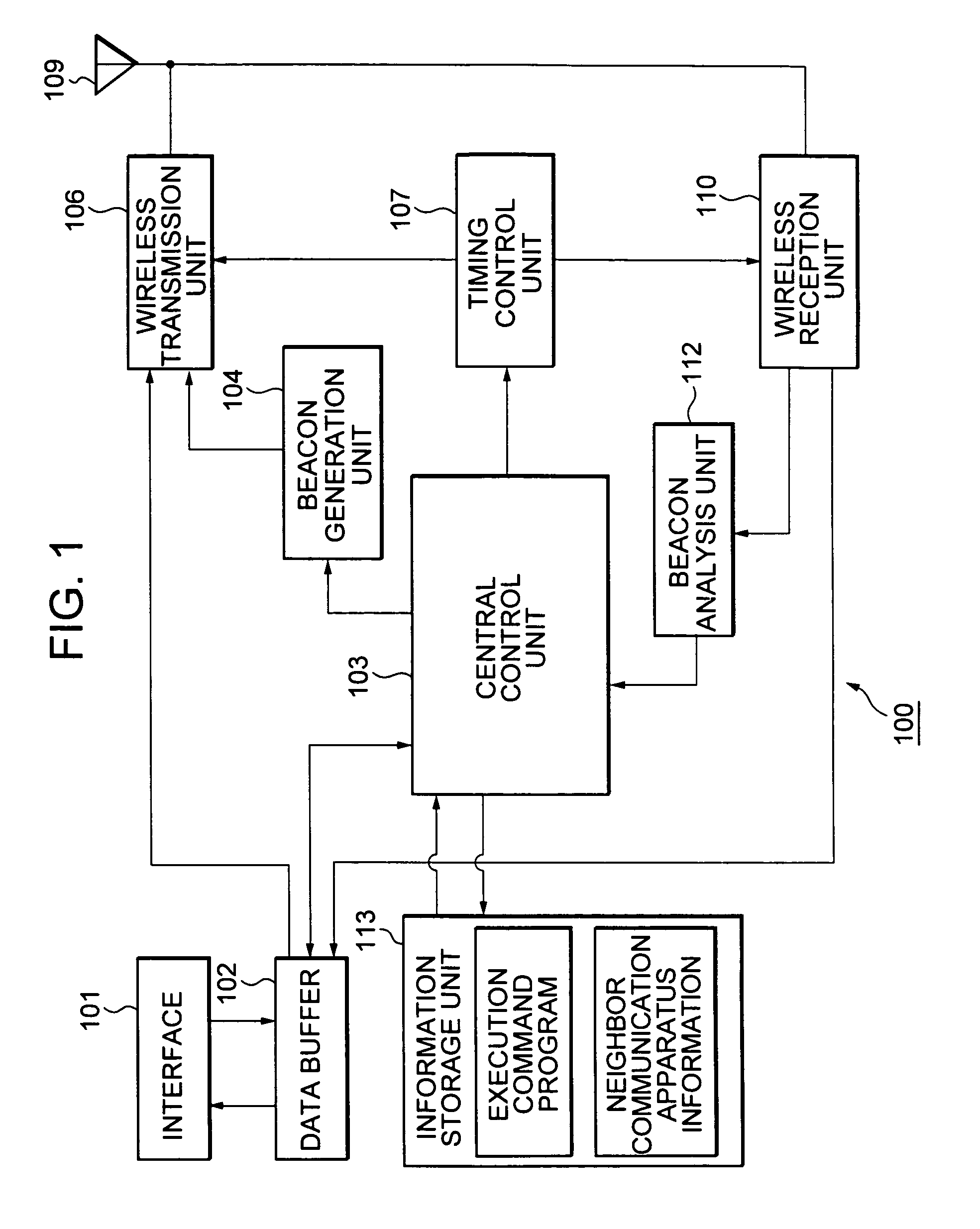
In order to realize low power consumption of a communicator and information transmission in short packets with a short latency in a network environment of a self-organized distribution type, each communication station performs a reception processing before and after a beacon transmission time of a next communication station which transmits a beacon next to a local station, and performs data transmission before and after a beacon transmission time of a communication station functioning as a data transmission destination. In a case where a certain communication station transmits information to all other communication stations, each communication station transmits information by utilizing a reception period provided after the beacon transmission time of the next communication station transmitting the beacon next to the local station to perform transmission according to a bucket-brigade system.
Owner:SONY CORP
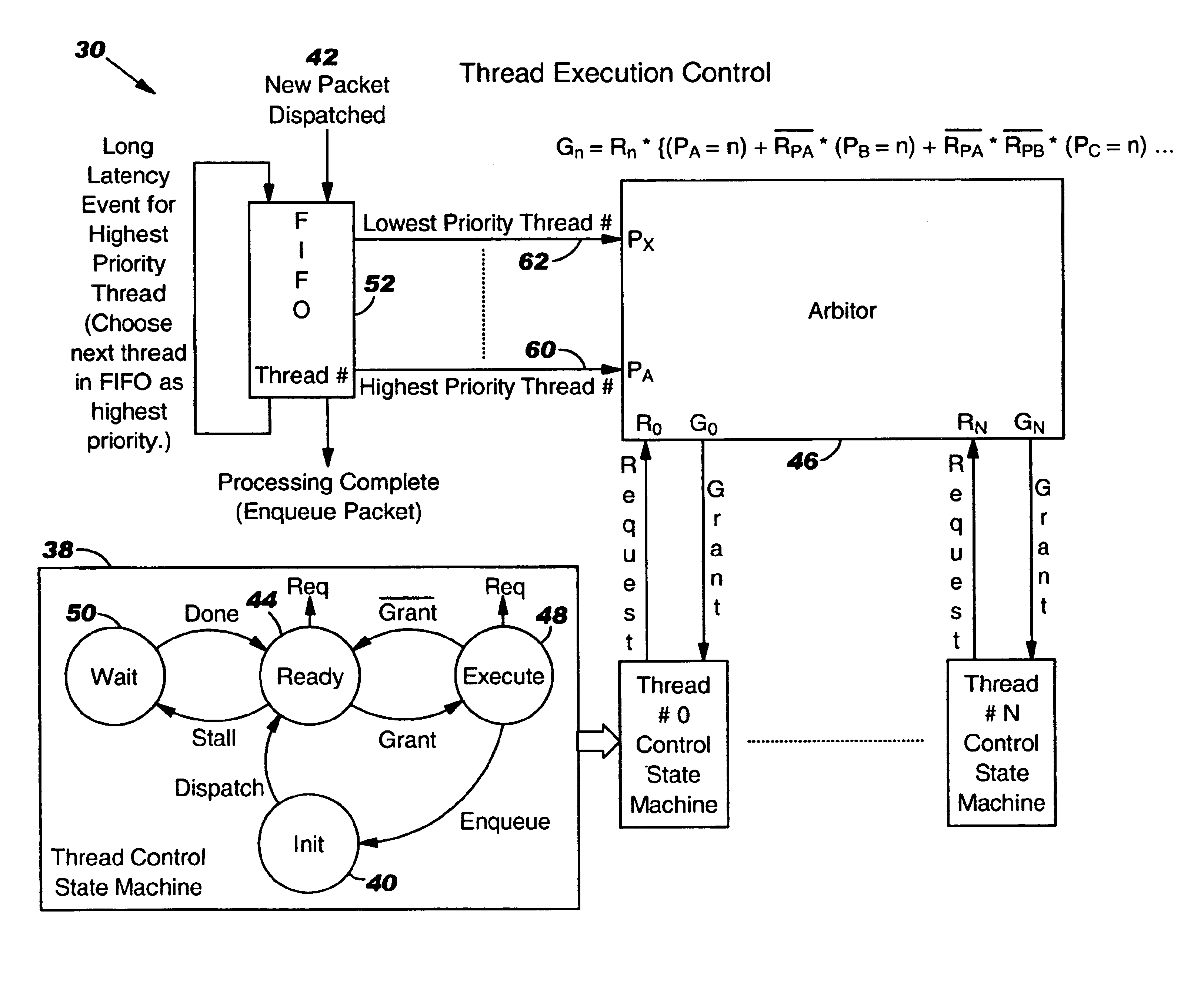
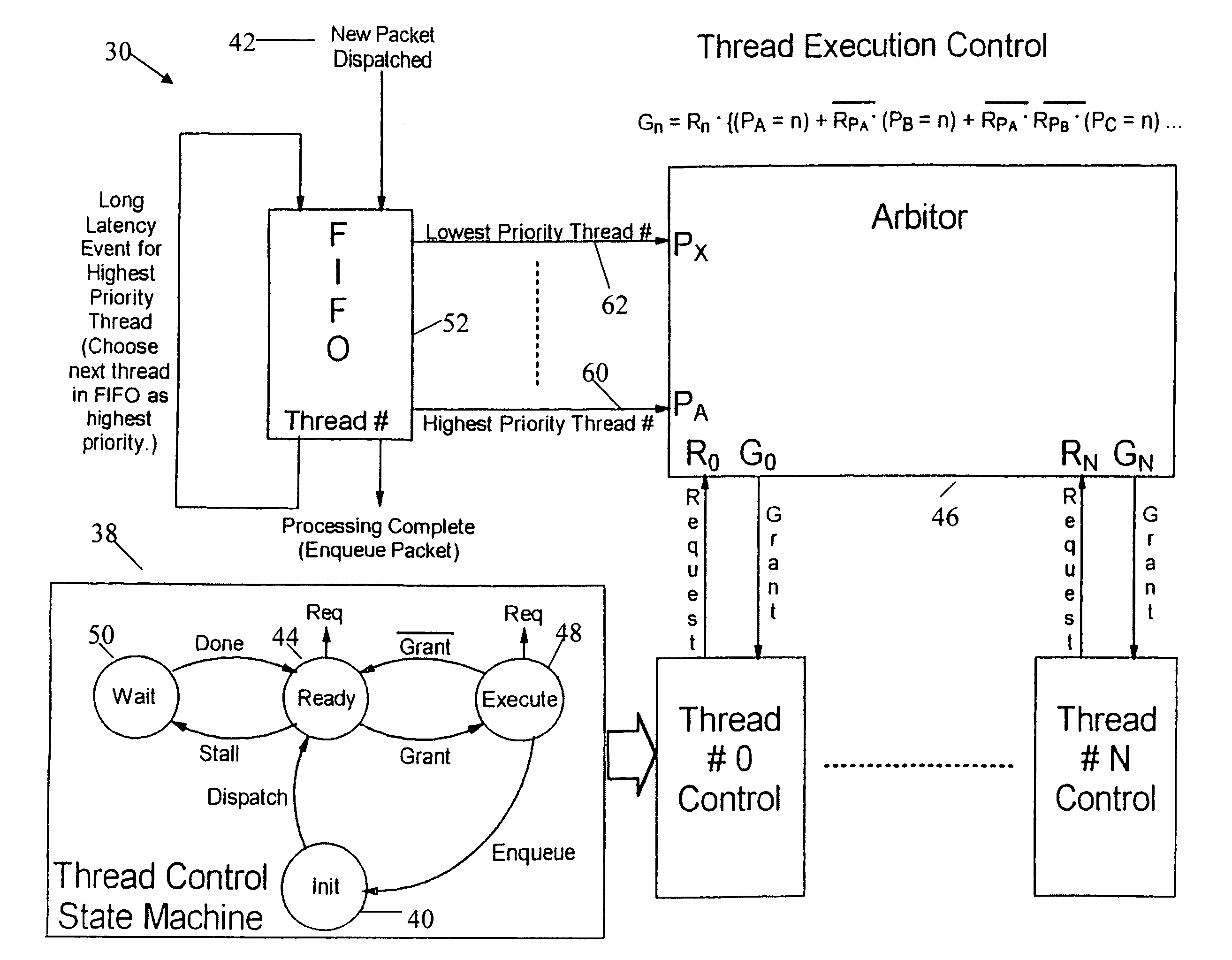
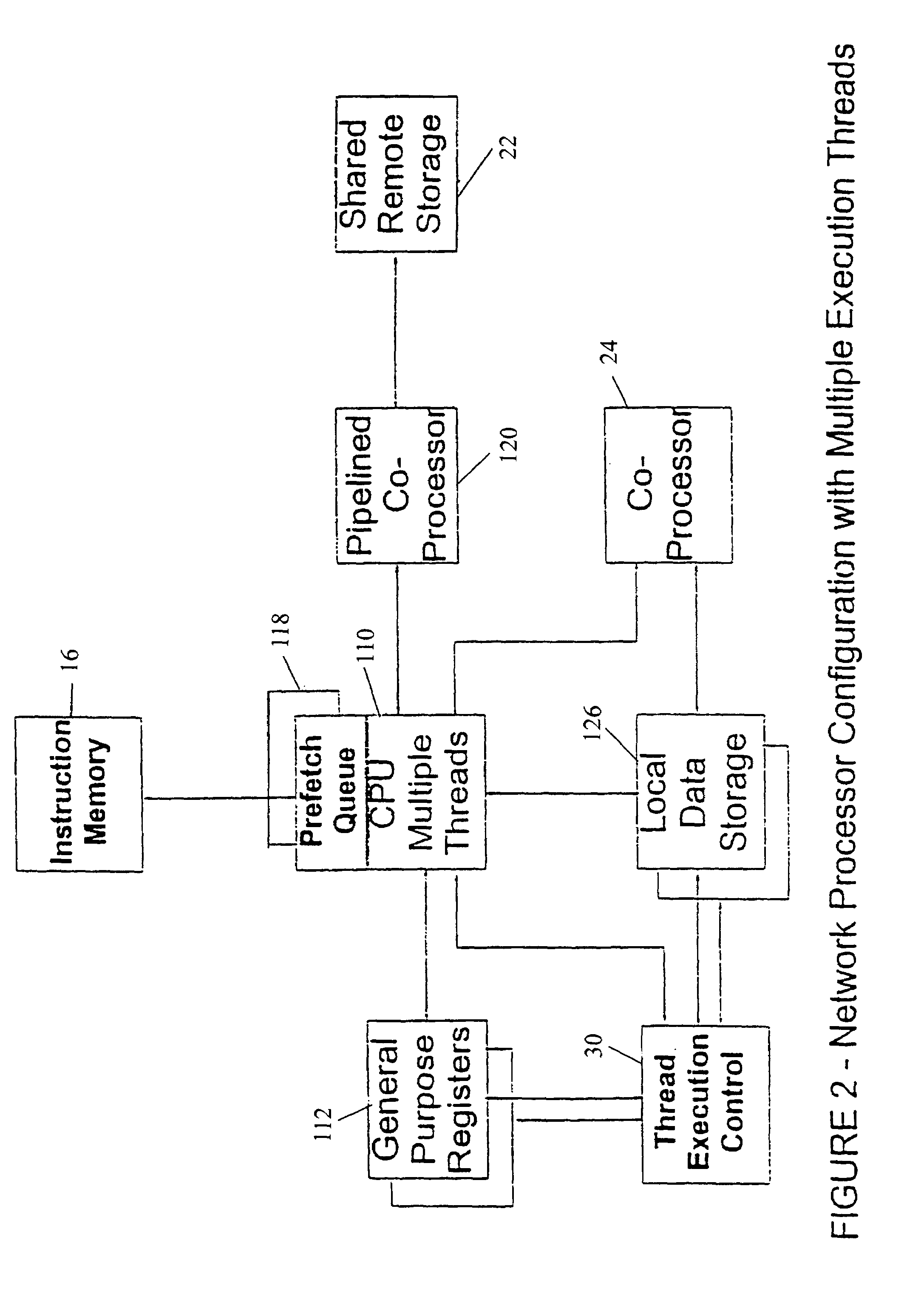
Network processor which makes thread execution control decisions based on latency event lengths
InactiveUS7093109B1Easy to useZero overheadDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsLong latencyCoprocessor
A control mechanism is established between a network processor and a tree search coprocessor to deal with latencies in accessing the data such as information formatted in a tree structure. A plurality of independent instruction execution threads are queued to enable them to have rapid access to the shared memory. If execution of a thread becomes stalled due to a latency event, full control is granted to the next thread in the queue. The grant of control is temporary when a short latency event occurs or full when a long latency event occurs. Control is returned to the original thread when a short latency event is completed. Each execution thread utilizes an instruction prefetch buffer that collects instructions for idle execution threads when the instruction bandwidth is not fully utilized by an active execution thread. The thread execution control is governed by the collective functioning of a FIFO, an arbiter and a thread control state machine.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and communication system for data exchanging data between users of a bus system
InactiveUS7260609B2Latency periodSimple initializationData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsCommunications systemNormal case
The present invention provides a method and a communications system for the exchange of data between at least two users who are in contact with one another using a bus system. The data are included in messages which are transmitted by users over the bus system. A specifiable priority is assigned to each message. In order to achieve, in the normal case, a high probability of a short latency period (t) of a message to be transmitted, and to be able to guarantee, in the worst case, a maximum latency period (tmax), it is provided that the priorities assigned to the messages be dynamically modified during the operation of bus system. Preferably, the set of all messages is subdivided into equivalence classes, and a priority is assigned to each equivalence class. During the operation of the bus system, the priorities of the messages are dynamically modified within an equivalence class, and the priorities of the equivalence classes are dynamically modified.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
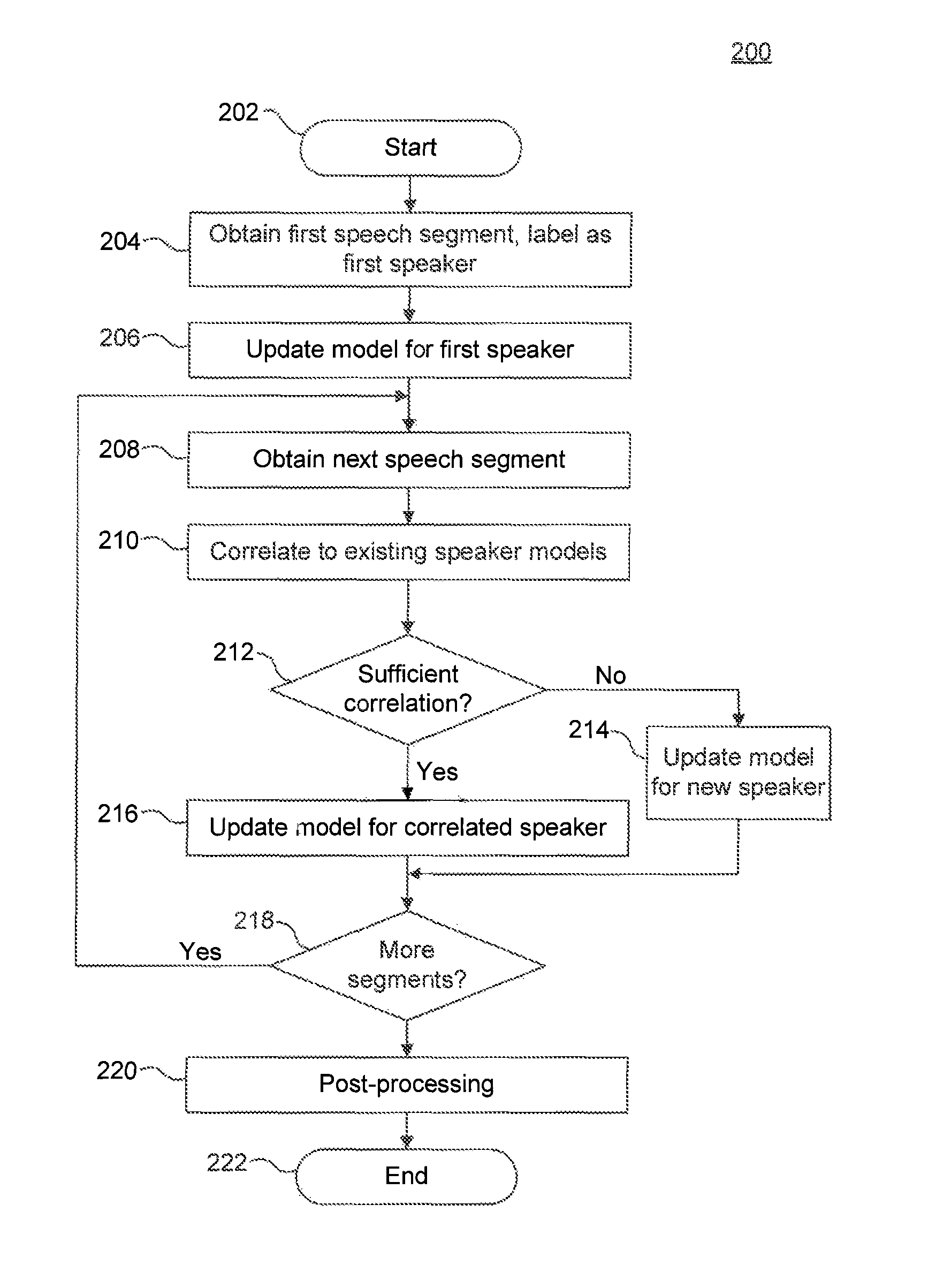
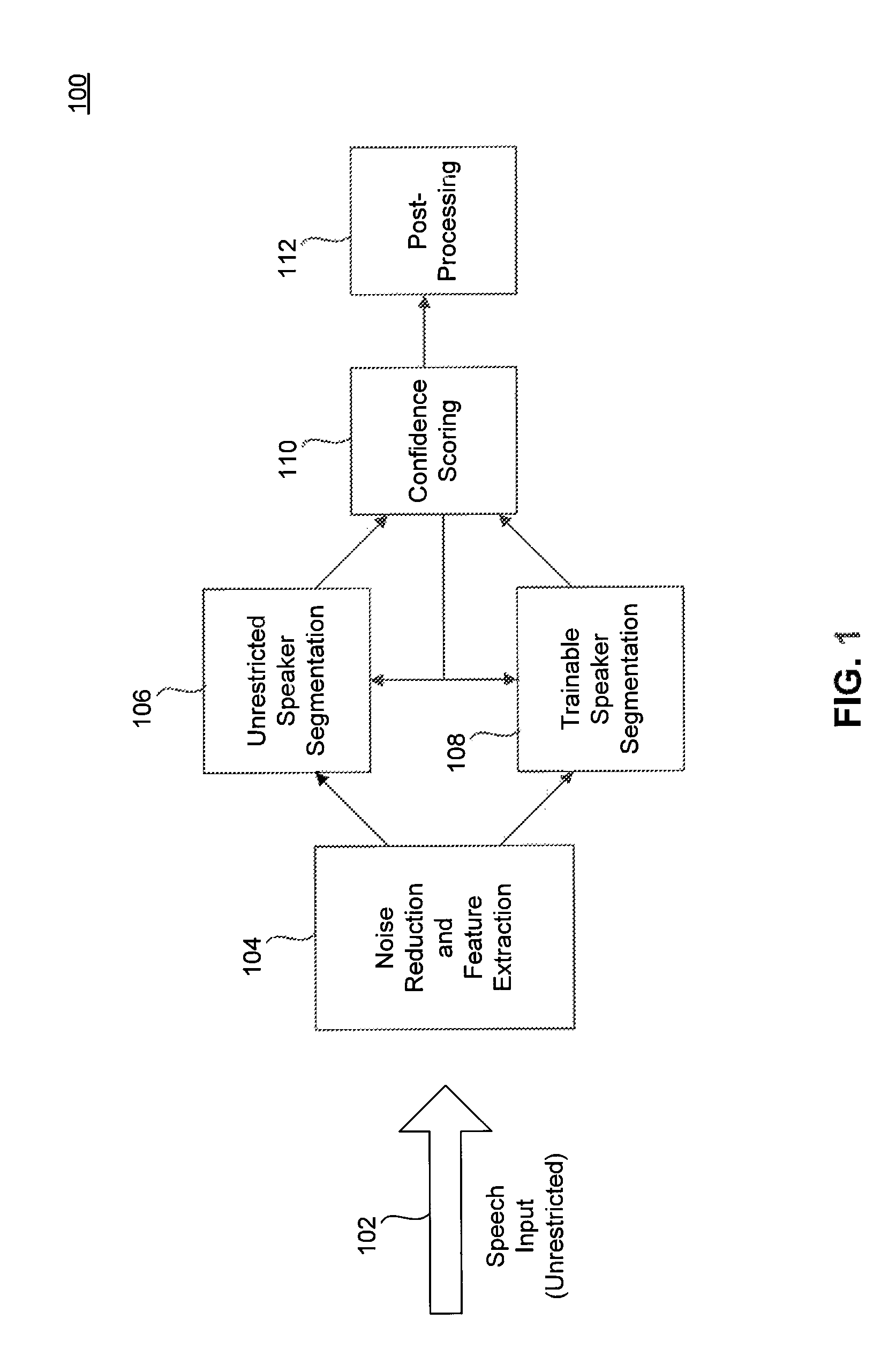
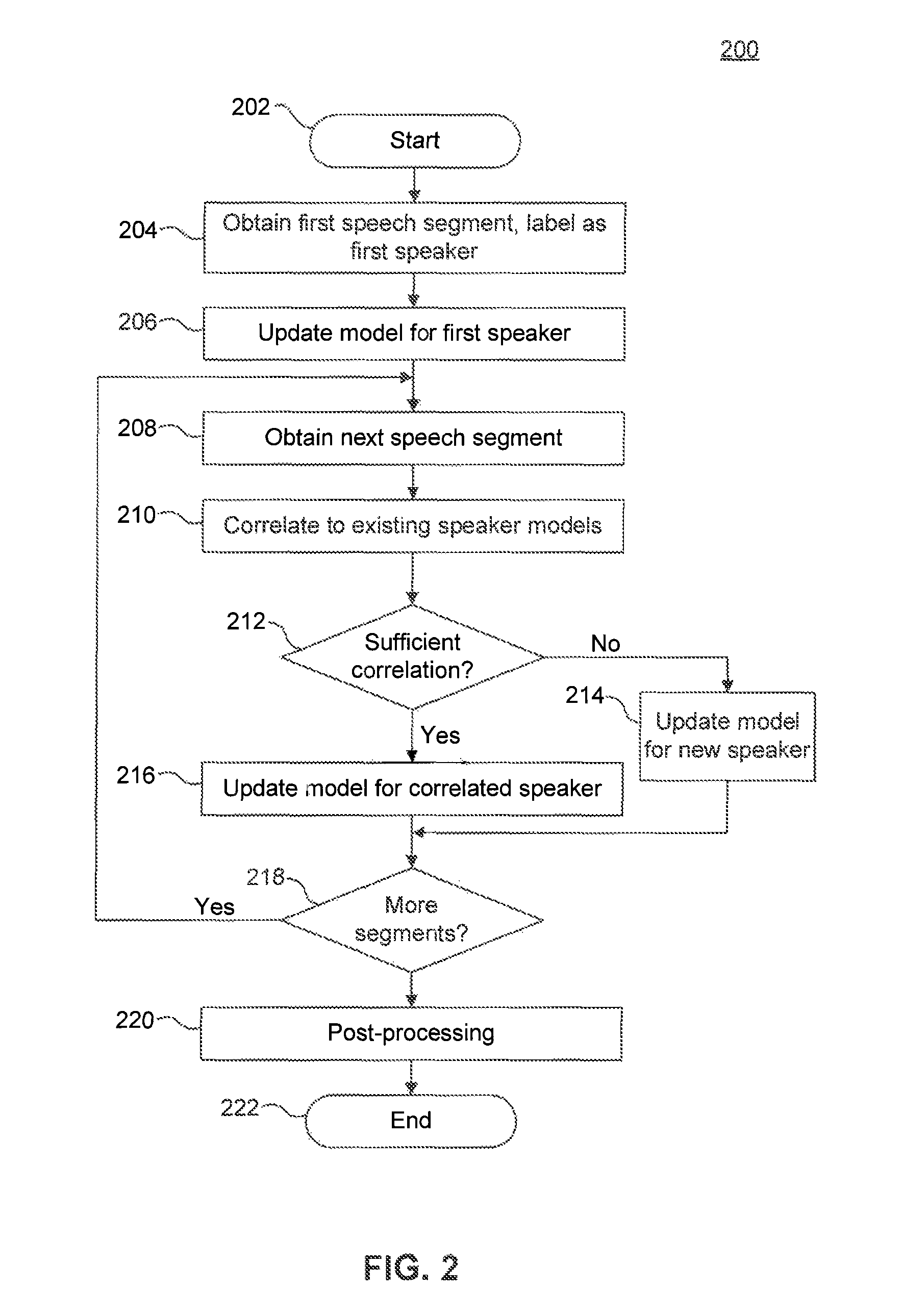
Speaker segmentation in noisy conversational speech
System and methods for robust multiple speaker segmentation in noisy conversational speech are presented. Robust voice activity detection is applied to detect temporal speech events. In order to get robust speech features and detect speech events in a noisy environment, a noise reduction algorithm is applied, using noise tracking. After noise reduction and voice activity detection, the incoming audio / speech is initially labeled as speech segments or silence segments. With no prior knowledge of the number of speakers, the system identifies one reliable speech segment near the beginning of the conversational speech and extracts speech features with a short latency, then learns a statistical model from the selected speech segment. This initial statistical model is used to identify the succeeding speech segments in a conversation. The statistical model is also continuously adapted and expanded with newly identified speech segments that match well to the model. The speech segments with low likelihoods are labeled with a second speaker ID, and a statistical model is learned from them. At the same time, these two trained speaker models are also updated / adapted once a reliable speech segment is identified. If a speech segment does not match well to the two speaker models, the speech segment is temporarily labeled as an outlier or as originating from a third speaker. This procedure is then applied recursively as needed when there are more than two speakers in a conversation.
Owner:FRIDAY HARBOR LLC
Supporting out-of-order issue in an execute-ahead processor
InactiveUS20070186081A1Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsWaiting timeProcedure sequence
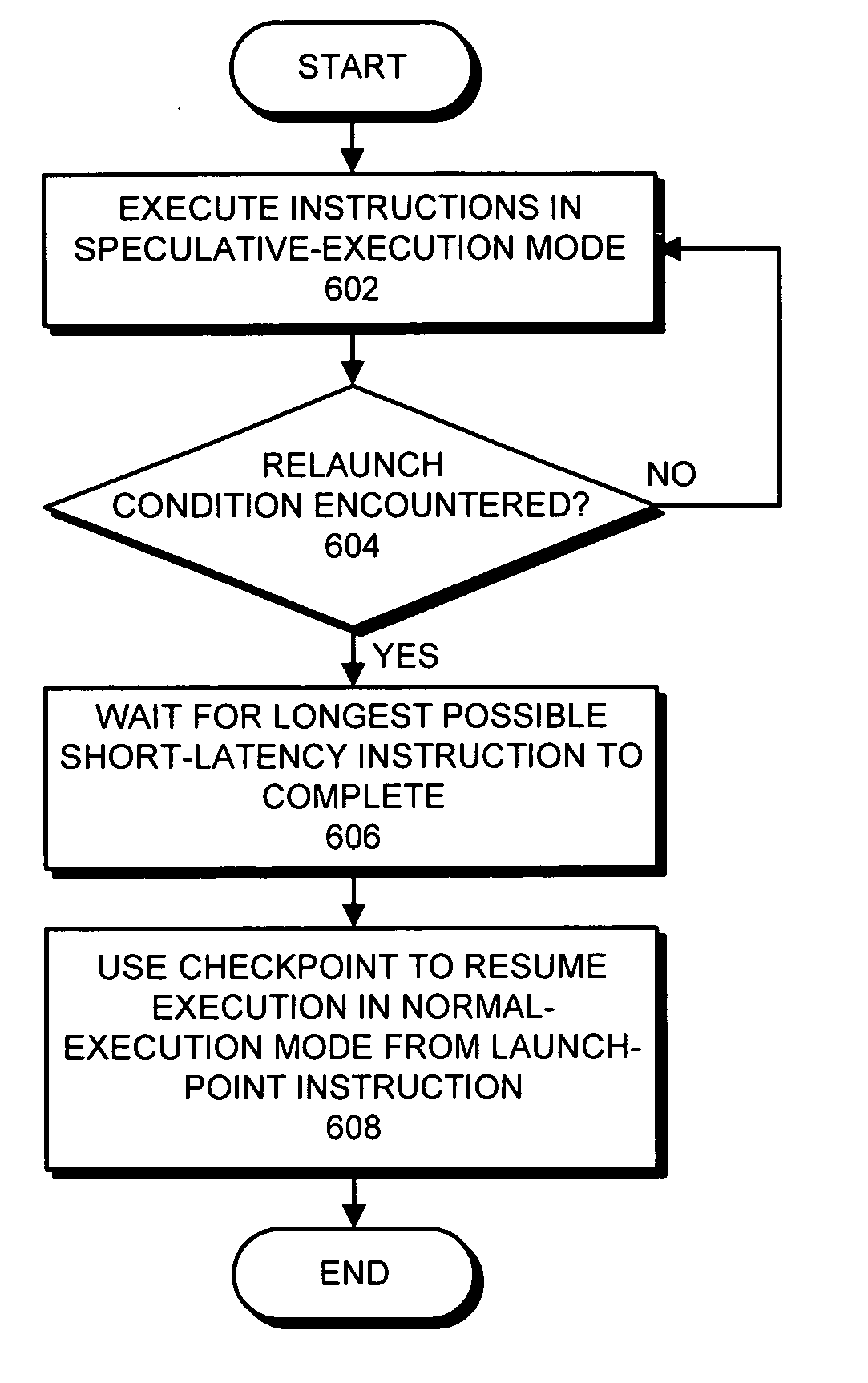
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system which supports out-of-order issue in a processor that normally executes instructions in-order. The system starts by issuing instructions from an issue queue in program order during a normal-execution mode. While issuing the instructions, the system determines if any instruction in the issue queue has an unresolved short-latency data dependency which depends on a short-latency operation. If so, the system generates a checkpoint and enters an out-of-order-issue mode, wherein instructions in the issue queue with unresolved short-latency data dependencies are held and not issued, and wherein other instructions in the issue queue without unresolved data dependencies are allowed to issue out-of-order.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Controller for multiple instruction thread processors
InactiveUS20050022196A1Efficient comprehensive utilizationProgram initiation/switchingProgram synchronisationLong latencyWaiting time
A mechanism controls a multi-thread processor so that when a first thread encounters a latency event for a first predefined time interval temporary control is transferred to an alternate execution thread for duration of the first predefined time interval and then back to the original thread. The mechanism grants full control to the alternate execution thread when a latency event for a second predefined time interval is encountered. The first predefined time interval is termed short latency event whereas the second time interval is termed long latency event.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Systolic memory arrays
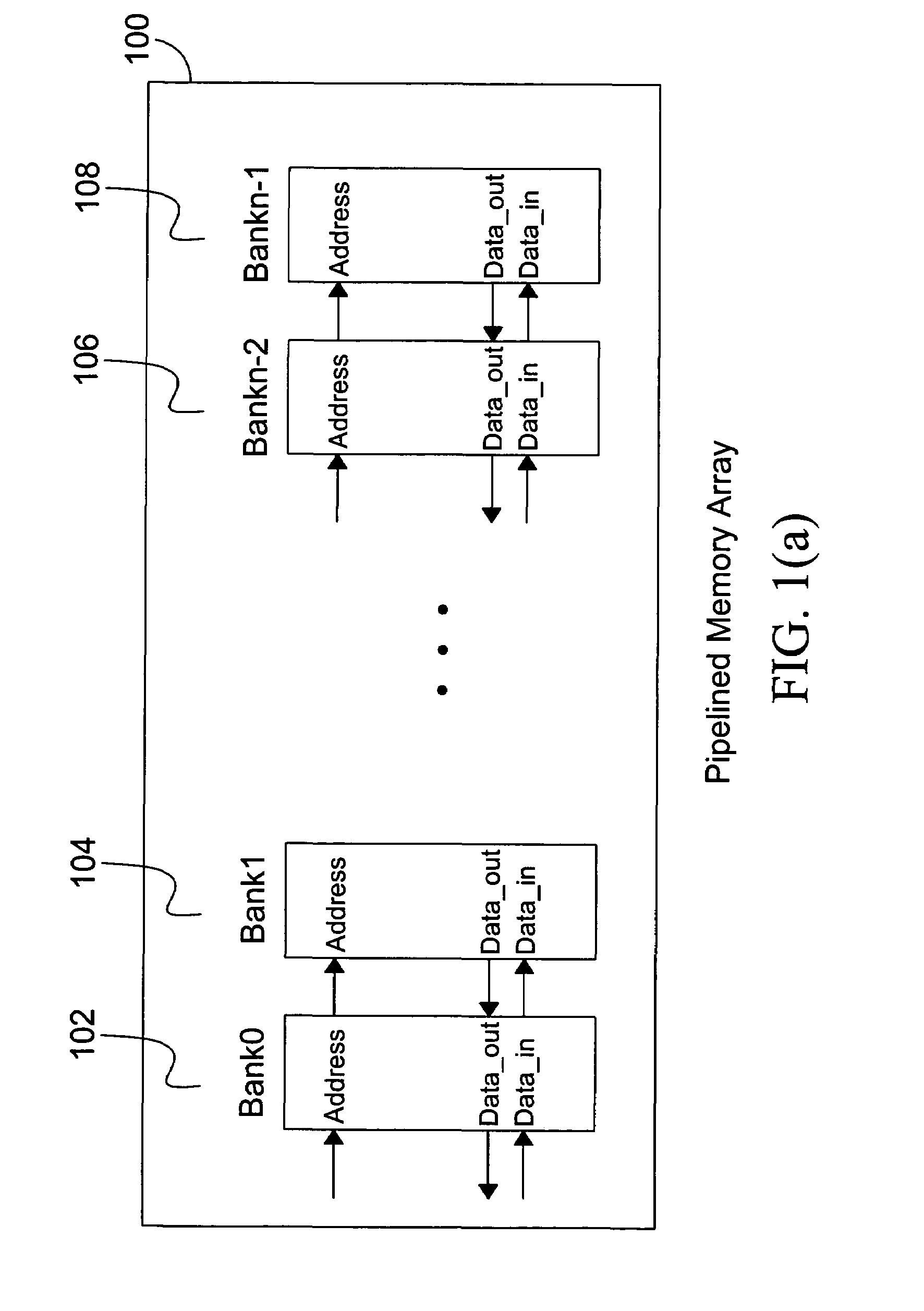
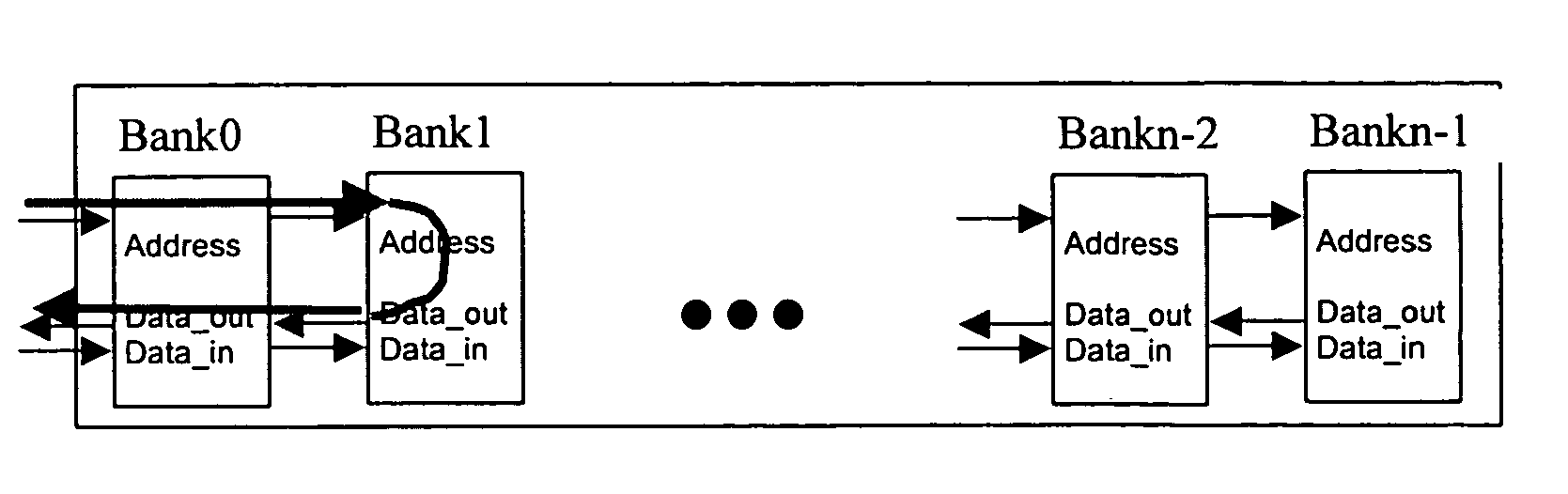
InactiveUS7246215B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationDigital storageArray data structureParallel computing
A short latency and high bandwidth memory includes a systolic memory that is sub-divided into a plurality of memory arrays, including banks and pipelines that access these banks. Shorter latency and faster performance is achieved with this memory, because each bank is smaller in size and is accessed more rapidly. A high throughput rate is accomplished because of the pipelining. Memory is accessed at the pipeline frequency with the proposed read and write mechanism. Design complexity is reduced because each bank within the memory is the same and repeated. The memory array size is re-configured and organized to fit within desired size and area parameters.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Wireless communication system, wireless communication apparatus, wireless communication method and computer program
InactiveUS7567540B2Efficient data communicationReduce power consumptionPower managementEnergy efficient ICTCommunications systemInformation transmission
In order to realize low power consumption of a communicator and information transmission in short packets with a short latency in a network environment of a self-organized distribution type, each communication station performs a reception processing before and after a beacon transmission time of a next communication station which transmits a beacon next to a local station, and performs data transmission before and after a beacon transmission time of a communication station functioning as a data transmission destination. In a case where a certain communication station transmits information to all other communication stations, each communication station transmits information by utilizing a reception period provided after the beacon transmission time of the next communication station transmitting the beacon next to the local station to perform transmission according to a bucket-brigade system.
Owner:SONY CORP
Headset distributed processing
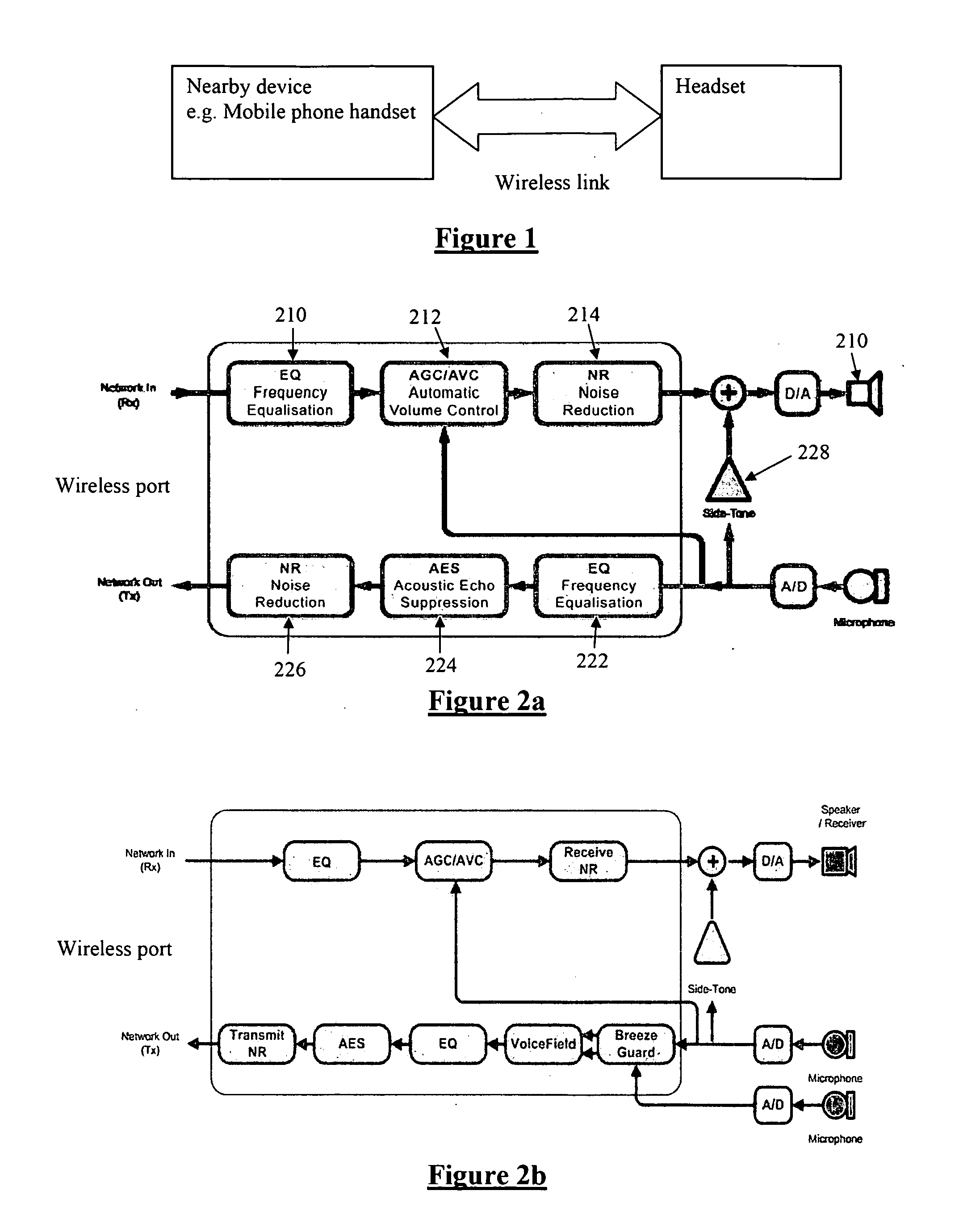
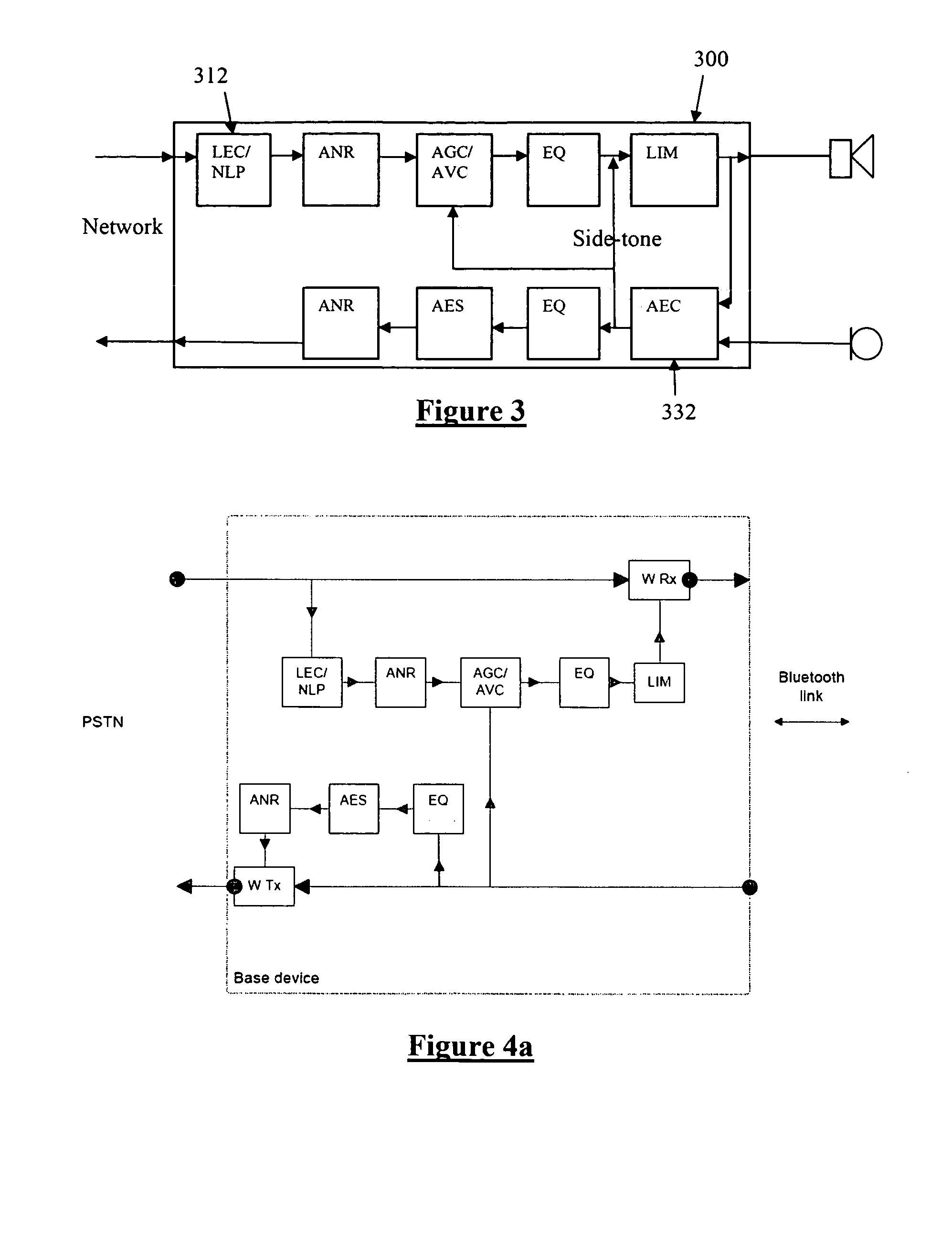
InactiveUS20100062713A1Easy to handleImprove cancellationInterconnection arrangementsDevices with bluetooth interfacesDigital signal processingTelecommunications link
Distributing signal processing for a headset. The system comprises a headset and base device. The headset has one or more microphones, and one or more speakers. The headset communicates with the base device via a bidirectional wireless communications link such as Bluetooth. The headset has an on-board digital signal processor for processing at least one of electrical signals passing to the speaker and electrical signals passing from the microphone. The base device has a processor which can carry the burden of any or all processing functions which do not require short latency. And / or the base device's processor can control at least one aspect of digital signal processing of the digital signal processor of the headset, and effect such control via the wireless communications link.
Owner:WOLFSON DYNAMIC HEARING
Systolic memory arrays
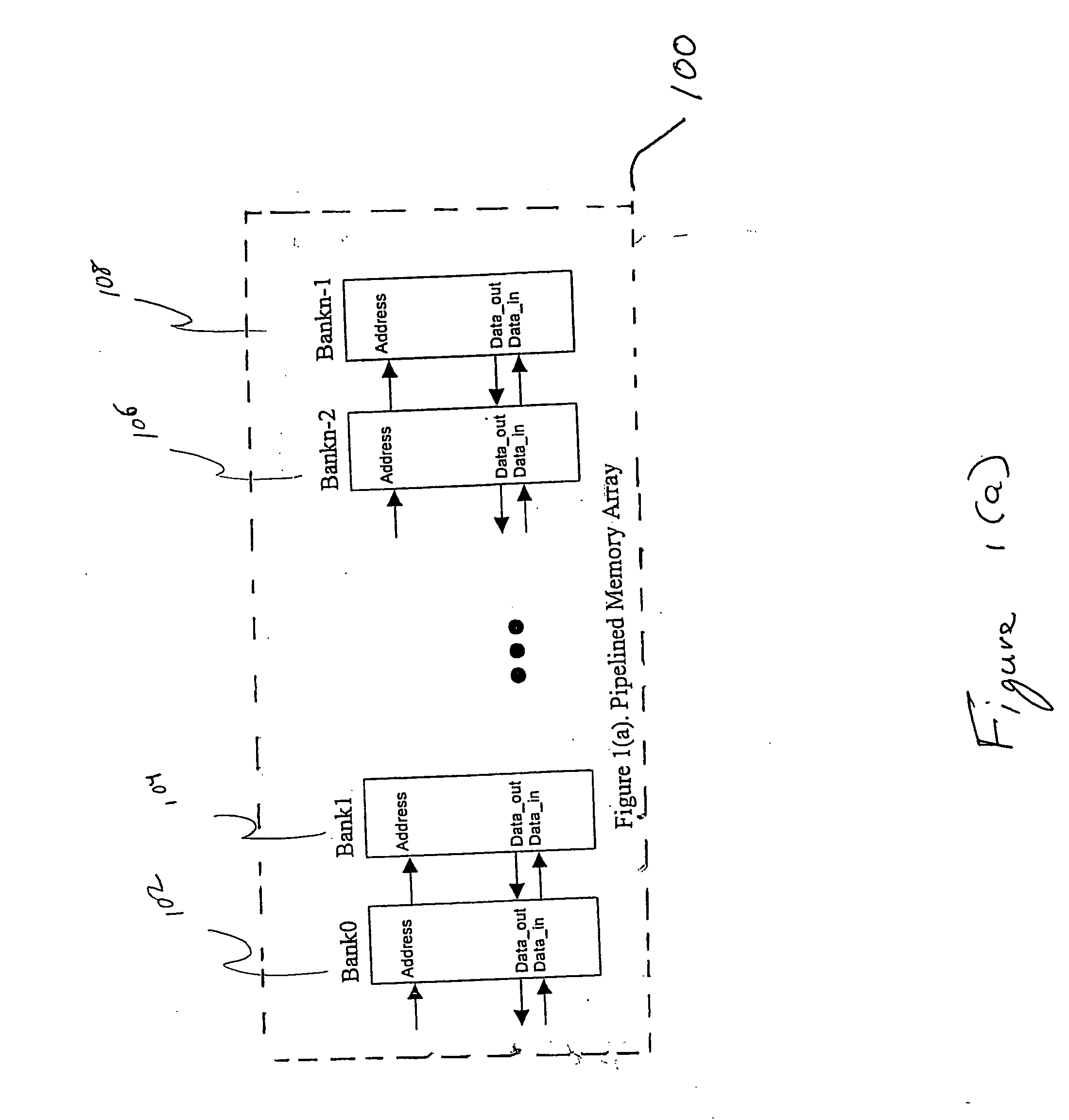
InactiveUS20050114618A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationDigital storageArray data structureParallel computing
A short latency and high bandwidth memory includes a systolic memory that is sub-divided into a plurality of memory arrays, including banks and pipelines that access these banks. Shorter latency and faster performance is achieved with this memory, because each bank is smaller in size and is accessed more rapidly. A high throughput rate is accomplished because of the pipelining. Memory is accessed at the pipeline frequency with the proposed read and write mechanism. Design complexity is reduced because each bank within the memory is the same and repeated. The memory array size is re-configured and organized to fit within desired size and area parameters.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Apparatus and method for reducing execution latency of floating point operations having special case operands
ActiveUS7437538B1Few execution cycleRegister arrangementsDigital computer detailsLong latencyFloating point
An apparatus and method for floating-point special case handling. In one embodiment, a processor may include a first execution unit configured to execute a longer-latency floating-point instruction, and a second execution unit configured to execute a shorter-latency floating-point instruction. In response to the longer-latency floating-point instruction being issued to the first execution unit, the second execution unit may be further configured to detect whether a result of the longer-latency floating-point instruction is determinable from one or more operands of the longer-latency floating-point instruction independently of the first execution unit executing the longer-latency floating-point instruction. In response to detecting that the result is determinable, the second execution unit may be further configured to flush the longer-latency floating-point instruction from the first execution unit and to determine the result.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Thread scheduling in chip multithreading processors
A thread scheduling technique for assigning multiple threads on a single integrated circuit is dependent on the CPIs of the threads. The technique attempts to balance, to the extent possible, the loads among the processing cores by assigning threads of relatively long-latency (low CPIs) with threads of relatively short-latency (high CPIs) to the same processing core.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Semiconductor memory asynchronous pipeline
An asynchronously pipelined SDRAM has separate pipeline stages that are controlled by asynchronous signals. Rather than using a clock signal to synchronize data at each stage, an asynchronous signal is used to latch data at every stage. The asynchronous control signals are generated within the chip and are optimized to the different latency stages. Longer latency stages require larger delays elements, while shorter latency states require shorter delay elements. The data is synchronized to the clock at the end of the read data path before being read out of the chip. Because the data has been latched at each pipeline stage, it suffers from less skew than would be seen in a conventional wave pipeline architecture. Furthermore, since the stages are independent of the system clock, the read data path can be run at any CAS latency as long as the re-synchronizing output is built to support it.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
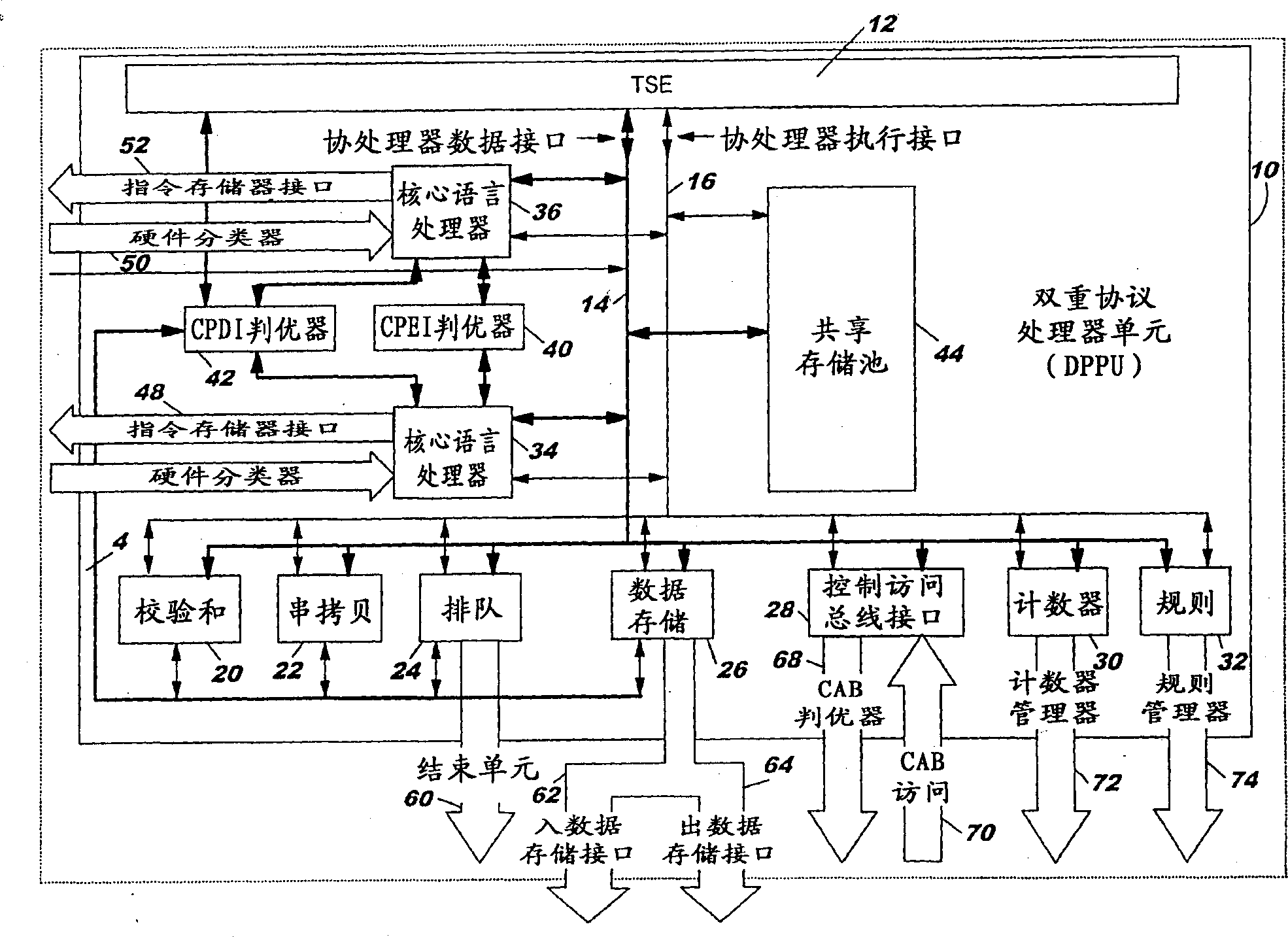
Coprocessor with multiple logic interface
InactiveCN1342940AMultiprogramming arrangementsConcurrent instruction executionOperating instructionCoprocessor
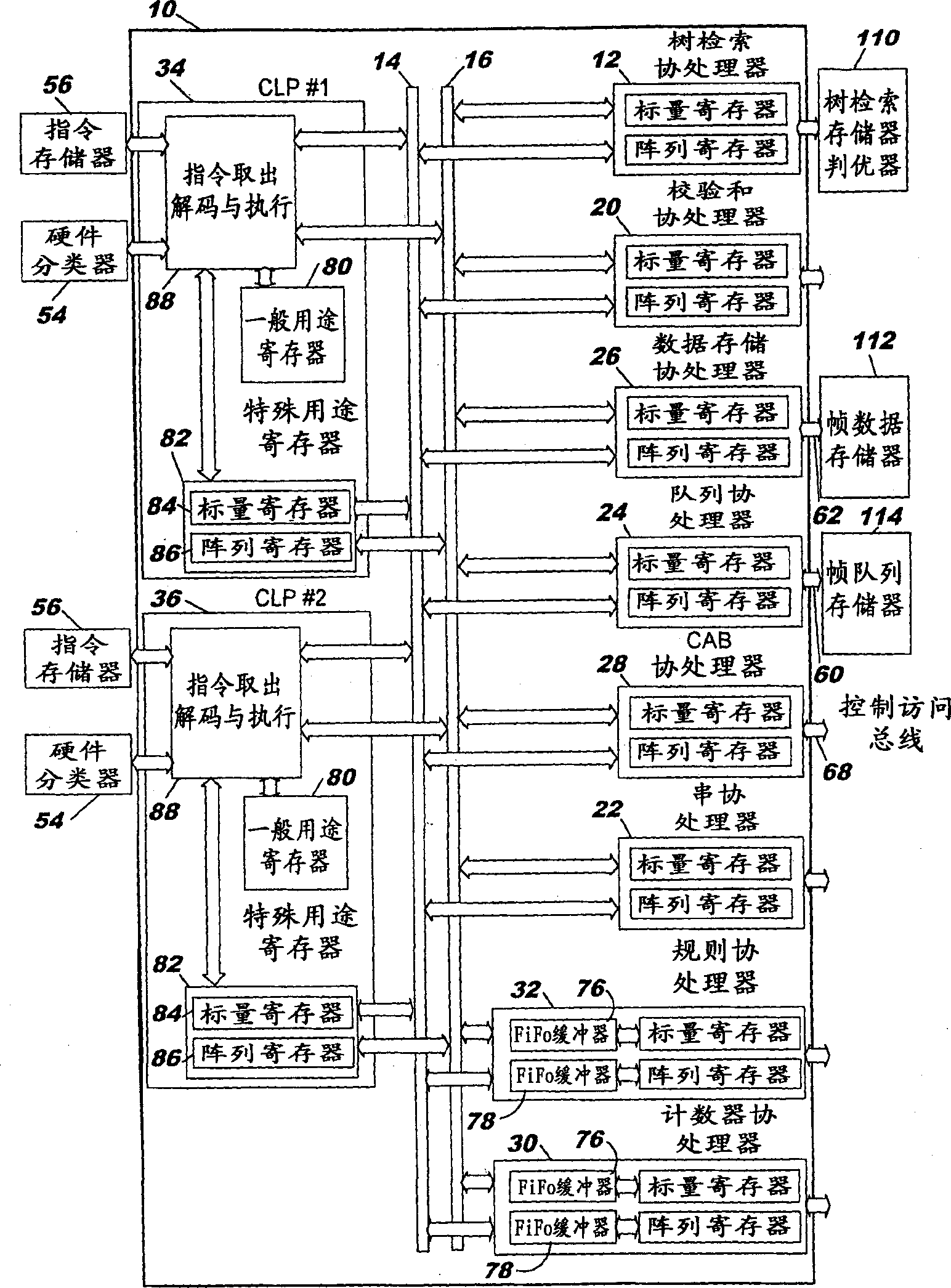
An embedded processor complex contains multiple protocol processor units (PPUs). Each unit includes at least one, and preferably two independently functioning core language processors (CLPs). Each CLP supports dual threads thread which interact through logical coprocessor execution or data interfaces with a plurality of special purpose coprocessors that serve each PPU. Operating instructions enable the PPU to identify long and short latency events and to control and shift priority for thread execution based on this identification. The instructions also enable the conditional execution of specific coprocessor operations upon the occurrence or non occurrence of certain specified events.
Owner:IBM CORP
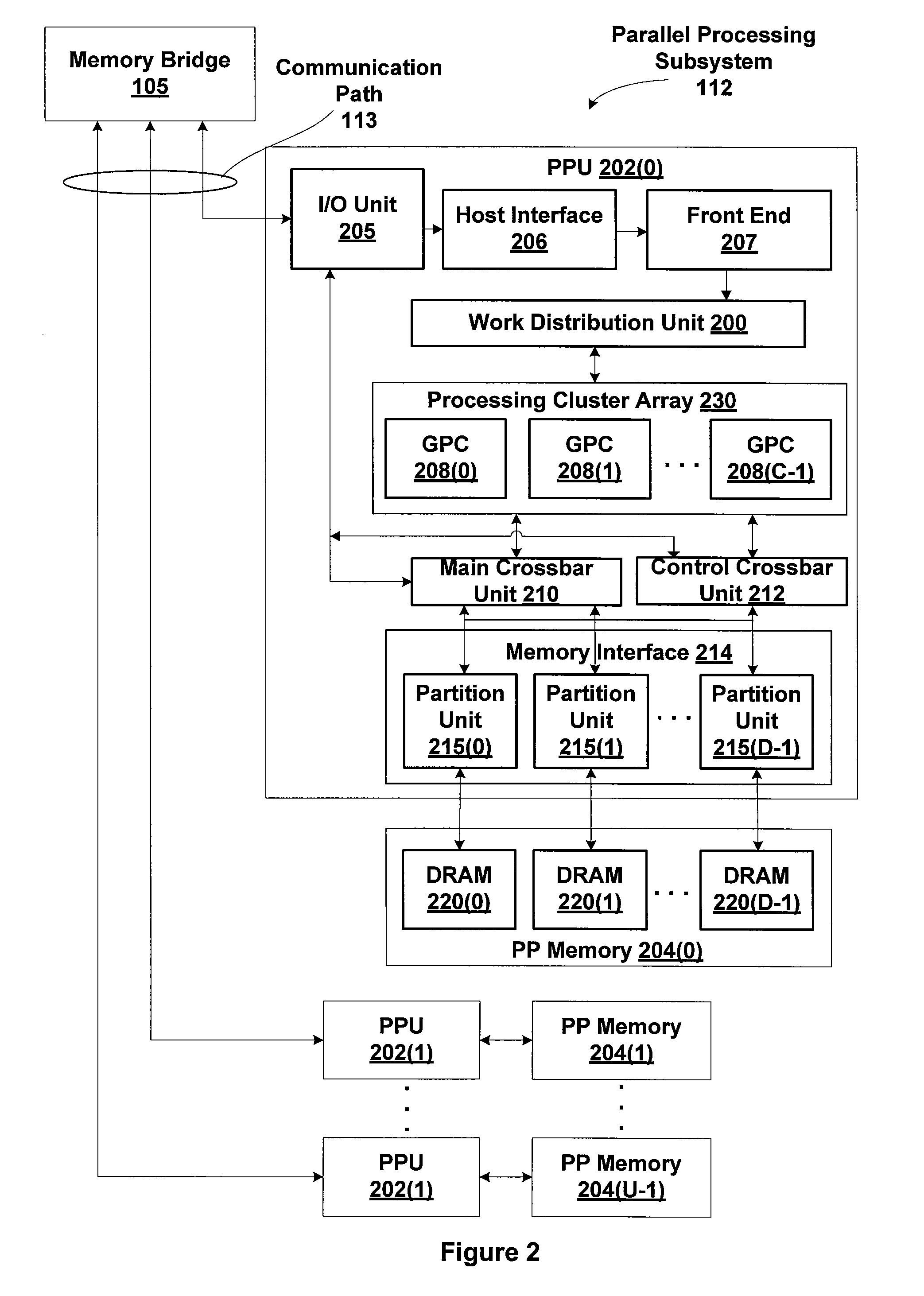
Mitigating main crossbar load using dedicated connections for certain traffic types
ActiveUS8325194B1Reduce loadWaste of bandwidthElectric digital data processingTraffic capacityComputerized system
One embodiment of the invention sets forth a control crossbar unit that is designed to transmit control information from control information generators to destination components within the computer system. The control information may belong to various traffic paradigms, such as short-latency data traffic, narrow-width data traffic or broadcast data traffic. The physical connections within the control crossbar unit are categorized based on the different types of control information being transmitted through the control crossbar unit. The physical connections belong to the following categories: one-to-one (OTO) connections, one-to-many (OTM) connections, valid-to-one (VTO) connections, valid-to-many (VTM) connections wire-to-one (WTO) connections and wire-to-many (WTM) connections.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
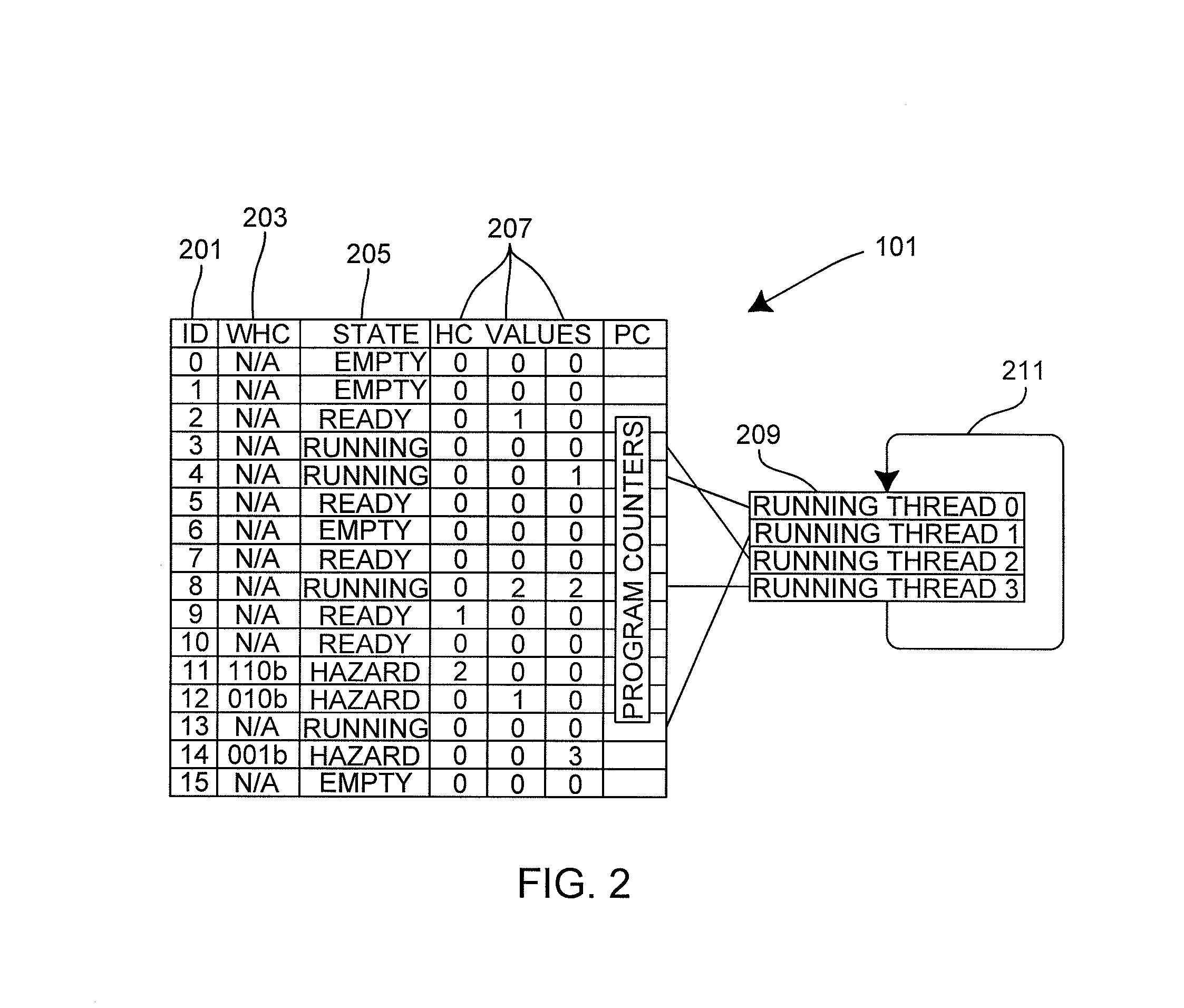
Processing long-latency instructions in a pipelined processor
ActiveUS8214624B2Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsLong latencyParallel computing
There are provided a method and a processor for processing a thread. The thread includes a plurality of sequential instructions. The plurality of sequential instructions include some short-latency instructions and some long-latency instructions and at least one hazard instruction. The hazard instruction requires one or more preceding instructions to be processed before the hazard instruction is processed. The method includes the steps of: a) before processing each long-latency instruction, incrementing by one, a counter associated with the thread; b) after each long-latency instruction has been processed, decrementing by one, the counter associated with the thread; c) before processing each hazard instruction, checking the value of the counter associated with the thread, and i) if the counter value is zero, processing the hazard instruction, or ii) if the counter value is non-zero, pausing processing of the hazard instruction until a later time. The processor includes means for performing steps a), b) and c) of the method.
Owner:IMAGINATION TECH LTD
Wireless communication system, wireless communication device, wireless communication method and computer program
InactiveCN1665208AEfficient data communicationReduce power lossEnergy efficient ICTPower managementInformation transmissionCommunications system
In order to realize low power consumption of a communicator and information transmission in short packets with a short latency in a network environment of a self-organized distribution type, each communication station performs a reception processing before and after a beacon transmission time of a next communication station which transmits a beacon next to a local station, and performs data transmission before and after a beacon transmission time of a communication station functioning as a data transmission destination. In a case where a certain communication station transmits information to all other communication stations, each communication station transmits information by utilizing a reception period provided after the beacon transmission time of the next communication station transmitting the beacon next to the local station to perform transmission according to a bucket-brigade system.
Owner:SONY GRP CORP
IoT-based wireless environment monitoring system
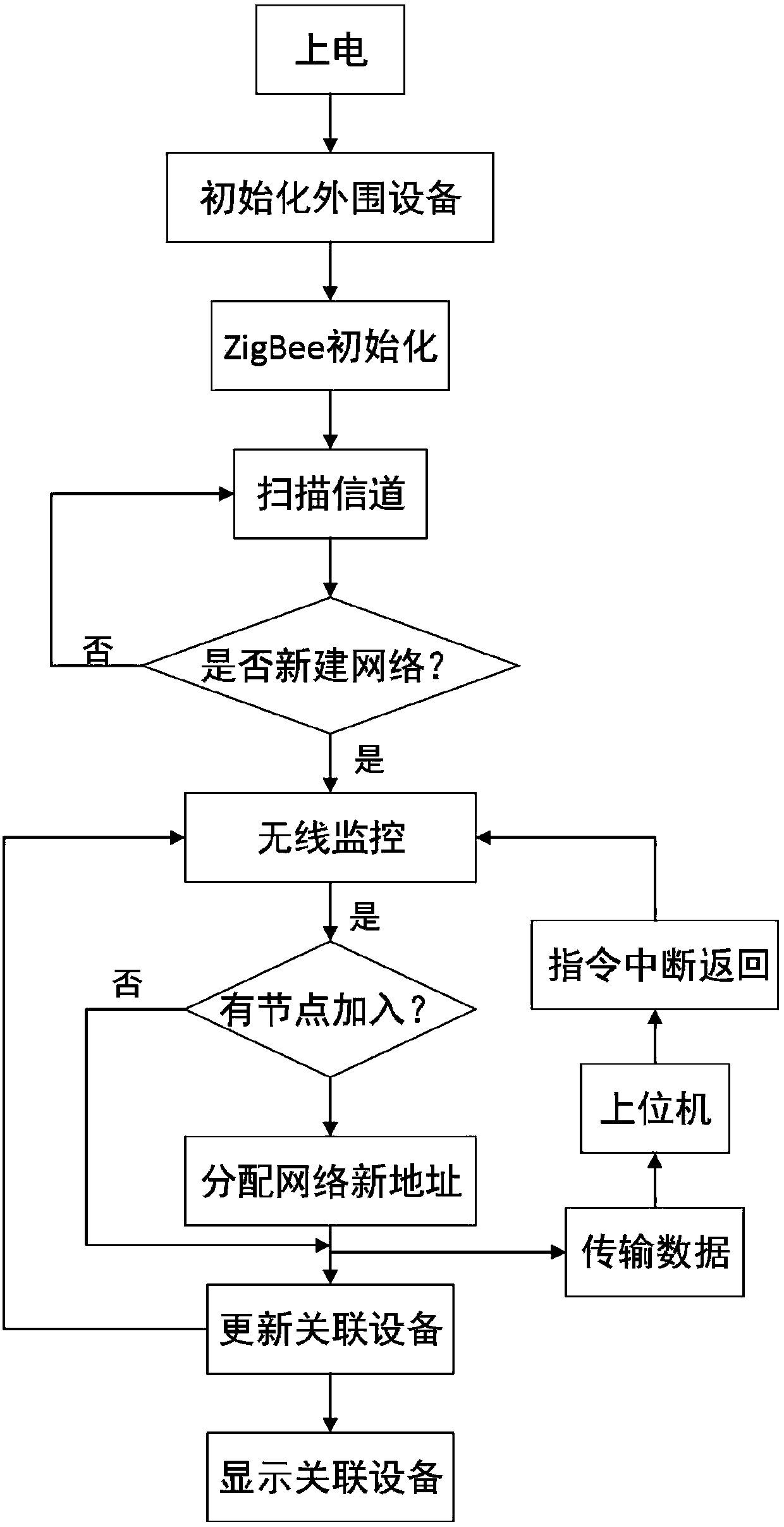
InactiveCN107767618ARealize wireless real-time monitoringRealize real-time monitoringMeasurement devicesTransmission systemsShortest distanceJoint Test Action Group
An IoT-based wireless environment monitoring system includes a ZigBee wireless communication network module and a main core control module. The ZigBee wireless communication network module includes aplurality of terminal nodes. Each terminal node is composed of a CC2530 RF module, a liquid crystal display module, a serial communication interface, a keyboard module, a power supply module, and a sensor module. The main core control module is composed of a monitoring platform, a GPRS, a WIFI module, a cell phone application client and a coordinator node. The coordinator node consists of a 8051 MCU CC2530 core, a data storage module, a power supply module, a JTAG interface module and a serial communication module. The IoT-based wireless environment monitoring system has advantages of stable performance, low speed, low power consumption, short time delay and short distance transmission, improves automation degree, realizes a purpose of monitoring indoor and outdoor regional environmental data in real time, and a monitoring effect via the cell phone and the monitoring platform.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
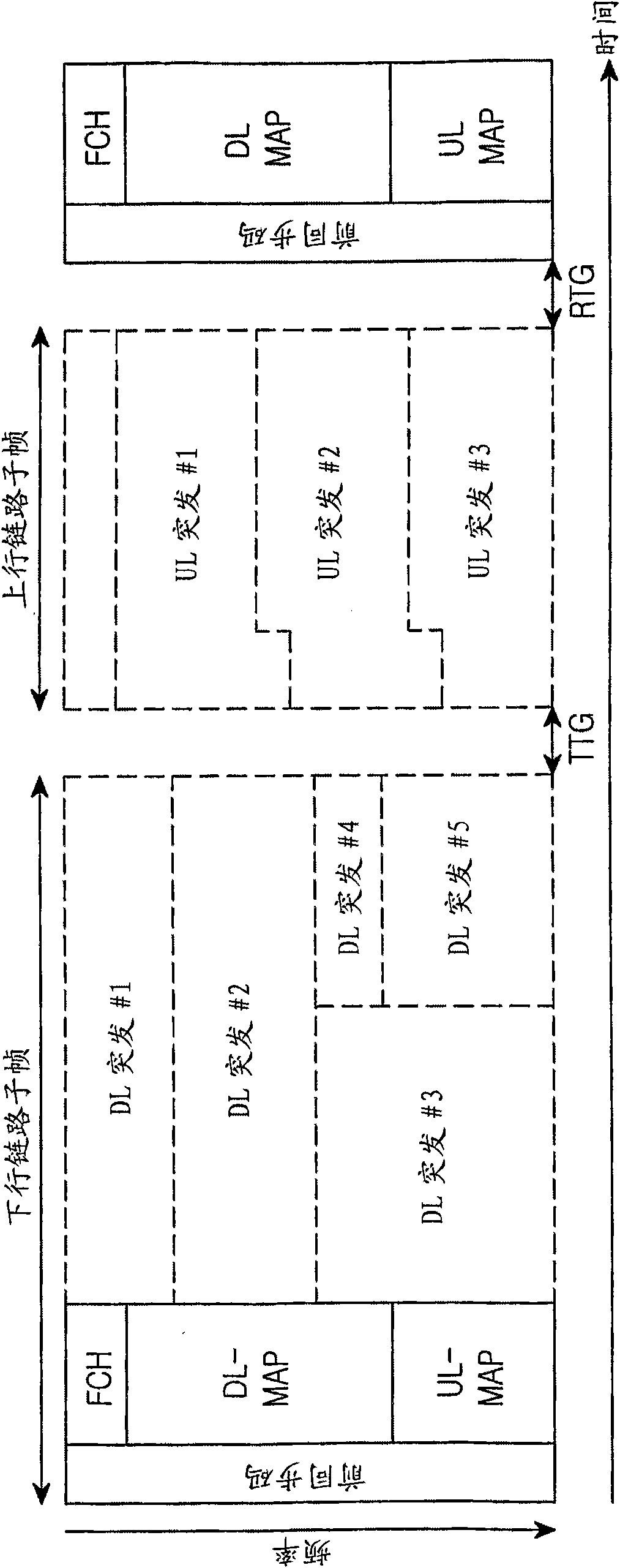
Method for supporting short latency data transmission in a mobile communication system
ActiveCN101682417AError preventionModulated-carrier systemsTelecommunicationsMobile communication systems
A method for supporting short latency data transmission in a mobile communication system is provided. A frame is divided into an uplink subframe and a downlink subframe. Each of the uplink and downlink subframes includes at least one zone for the short latency data transmission and each of the at least one zone includes a first channel for indicating data resource assignment, a second channel overwhich to transmit data, or a third channel for feedback signal reception. The method includes indicating a location and a size of the second channel using the first channel included in any one of theat least one zone by a transmitting end, transmitting data over the second channel, and receiving feedback information for the data, which has been transmitted over the second channel, over the thirdchannel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Avoiding register RAW hazards when returning from speculative execution
ActiveUS20050273580A1Promote recoveryDelay in issuanceDigital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionSpeculative executionSystem usage
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that avoids register read-after-write (RAW) hazards upon returning from a speculative-execution mode. This system operates within a processor with an in-order architecture, wherein the processor includes a short-latency scoreboard that delays issuance of instructions that depend upon uncompleted short-latency instructions. During operation, the system issues instructions for execution in program order during execution of a program in a normal-execution mode. Upon encountering a condition (a launch condition) during an instruction (a launch-point instruction), which causes the processor to enter the speculative-execution mode, the system generates a checkpoint that can subsequently be used to return execution of the program to the launch-point instruction, and commences execution in the speculative-execution mode. Upon encountering a condition that causes the processor to leave the speculative-execution mode and return to the launch-point instruction, the system uses the checkpoint to resume execution in the normal-execution mode from the launch-point instruction. In doing so, the system ensures that entries that were in the short-latency scoreboard prior to entering the speculative-execution mode, and which are not yet resolved, are accounted for in order to prevent register RAW hazard when resuming execution from the launch-point instruction.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Short latency fast retransmission triggering
ActiveUS20190149273A1Easy to operateError prevention/detection by using return channelPower managementTransmission protocolCommunications system
The invention relates to an improved transmission protocol for uplink data packet transmission in a communication system. A receiver of a user equipment receives a Fast Retransmission Indicator, referred to as FRI. The FRI indicates whether or not a base station requests a retransmission of a previously transmitted data packet. A transmitter of the user equipment retransmits the data packet using the same redundancy version as already used for the previous transmission of the data packet.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
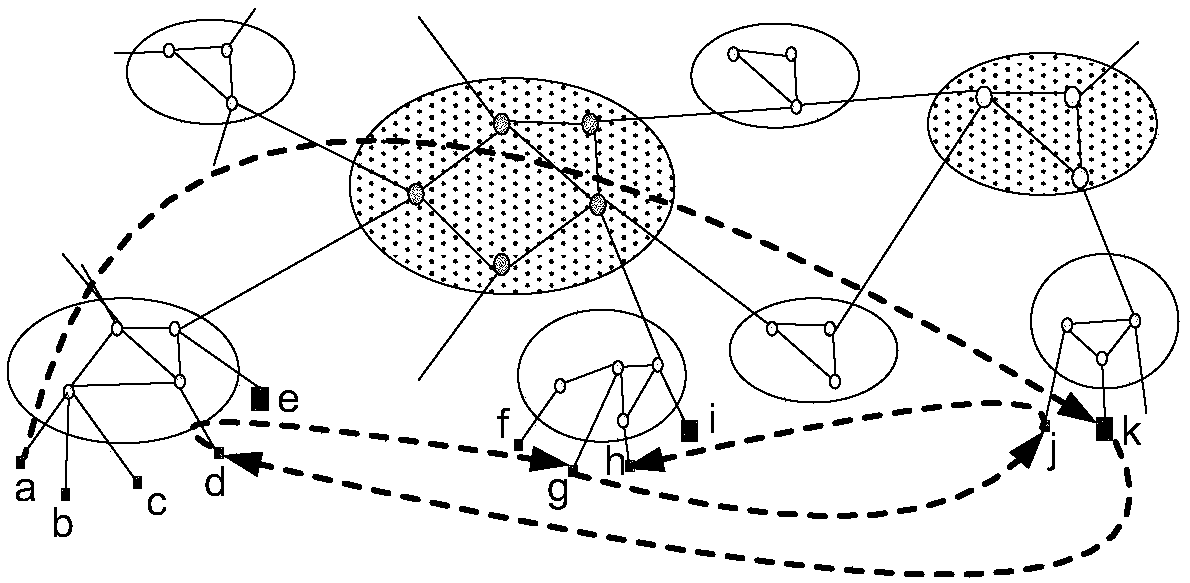
Distributed resource searching method and system
ActiveCN108337170AImprove search efficiencyShort delayData switching networksPhysical networkPeer-to-peer
The invention provides a distributed resource searching method and system and relates to the field of distributed computing; the method comprises the following steps: one or more nodes are selected assuper nodes in each local domain of a physical network; the super node aggregates routing information of each node in the local domain where the super node is located so as to obtain a local domain routing information table, wherein the routing information of each node comprises an address which can be routed by each node in a peer-to-peer network where the nodes are located and an address in thephysical network where the nodes are located; a start node is routed to a target node through the super node or the local domain routing information table; and the start node downloads resources thatneed to be lookup according to the storage address of the resources that need to be lookup, which is obtained from the target node. Compared with the prior art, according to the method or the systemdisclosed by the invention, the routing path with shorter latency can be selected, and the routing efficiency is improved.
Owner:ZHENGJIANG PUBLIC INFORMATION
Method and Programming System for Programming an Automation Component
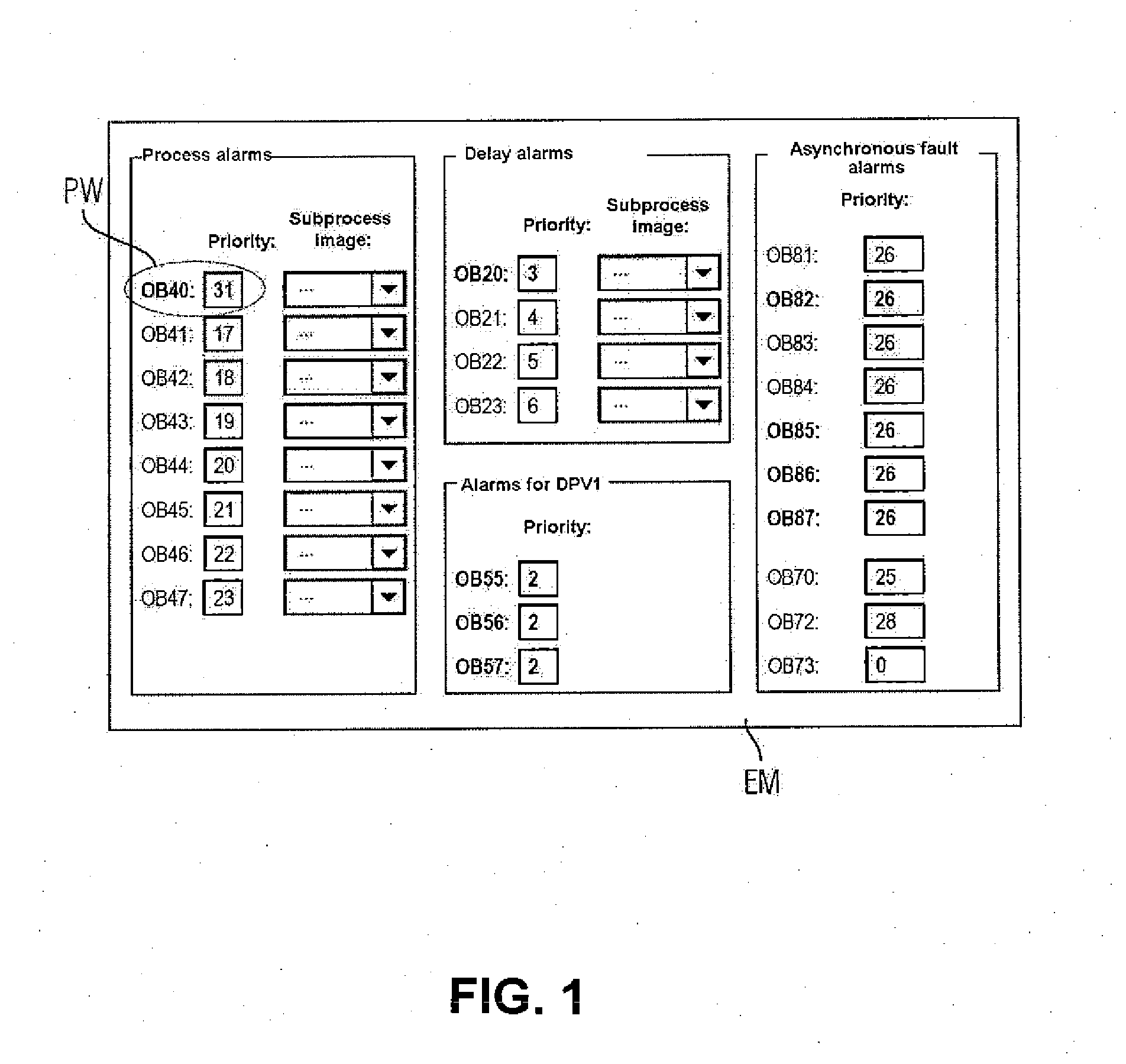
ActiveUS20130006398A1OptimallyUse speed advantageComputer controlSimulator controlEmbedded systemWaiting time
A method and programming system for programming an automation component of an industrial automation arrangement, the automation component being provided with at least one special main memory, such as a cache or a tightly coupled memory, with faster access, wherein a user is provided with an input option for assigning priority values to individual tasks of the automation program when creating the program, all of those program parts which are called when executing at least the task with the highest priority assigned by the user are automatically identified, and the identified program parts being permanently storable in the special main memory such that important program parts and routines are executable in a reproducible manner at high execution speed and with a short latency time.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Data storage device
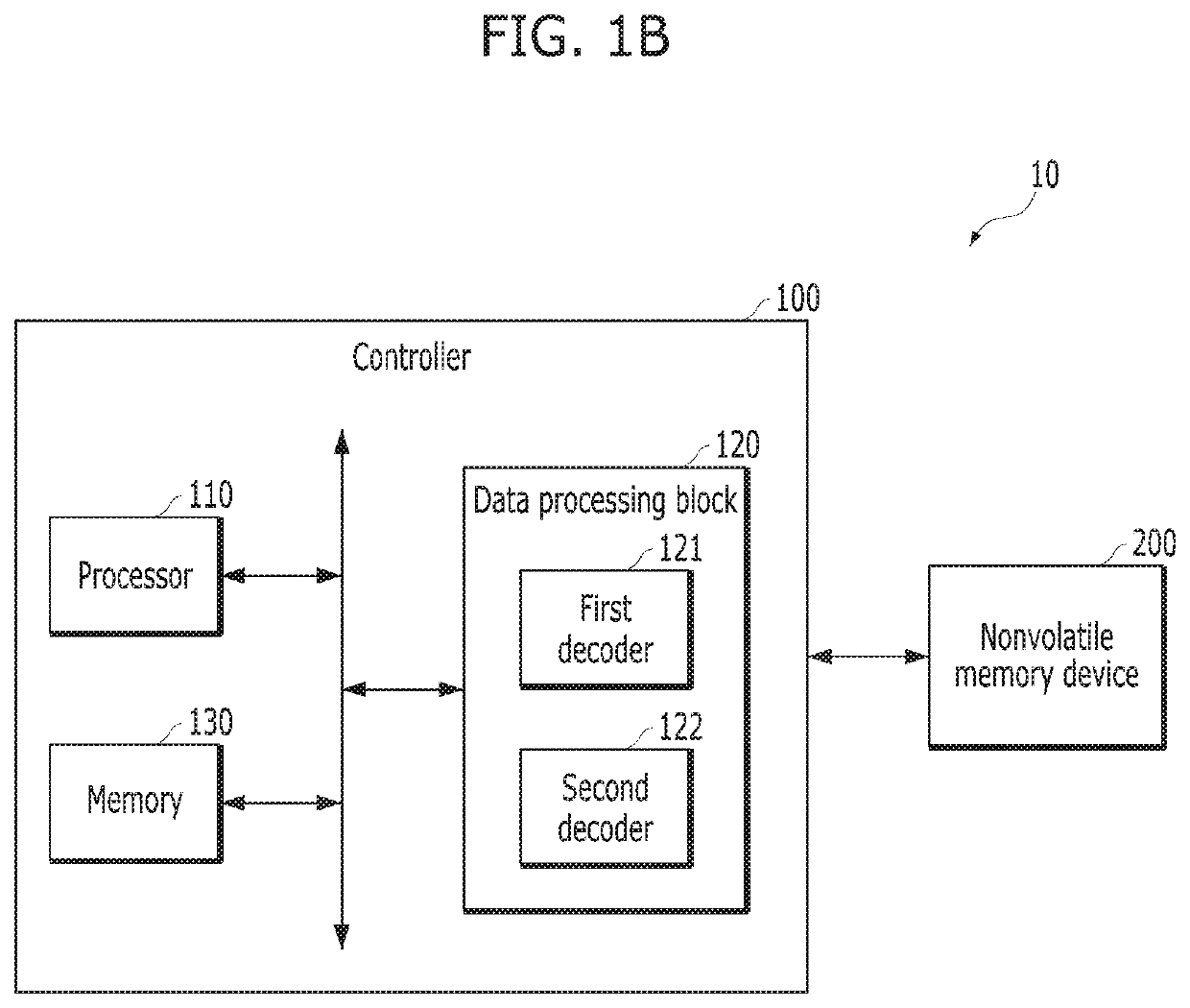
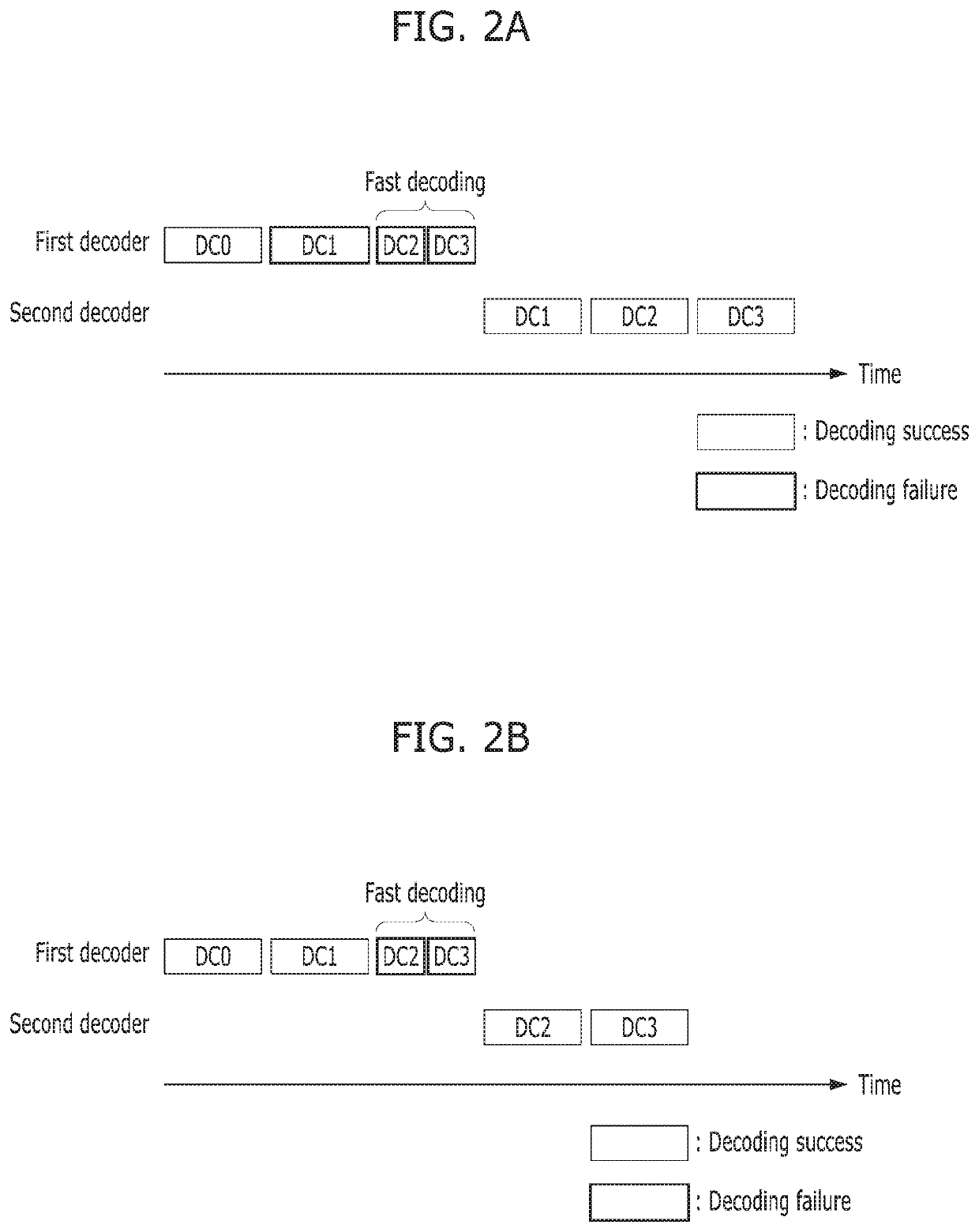
ActiveUS20190379405A1Latency of errorPerformance of errorInput/output to record carriersOther decoding techniquesData processing systemComputer module
A data processing system includes a storage medium, and a controller including a data processing block, configured to receive data from a host, transmit the received data to the storage medium, read data from the storage medium in response to a read request from the host, and decode the read data by the data processing block according to multiple decoding modes. The data processing block includes a first decoder and a second decoder, and is configured to manage the first decoder and the second decoder to run the decoding for the read data, and activate a fast decoding having shorter latency than a normal decoding after a fast decoding condition is satisfied.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
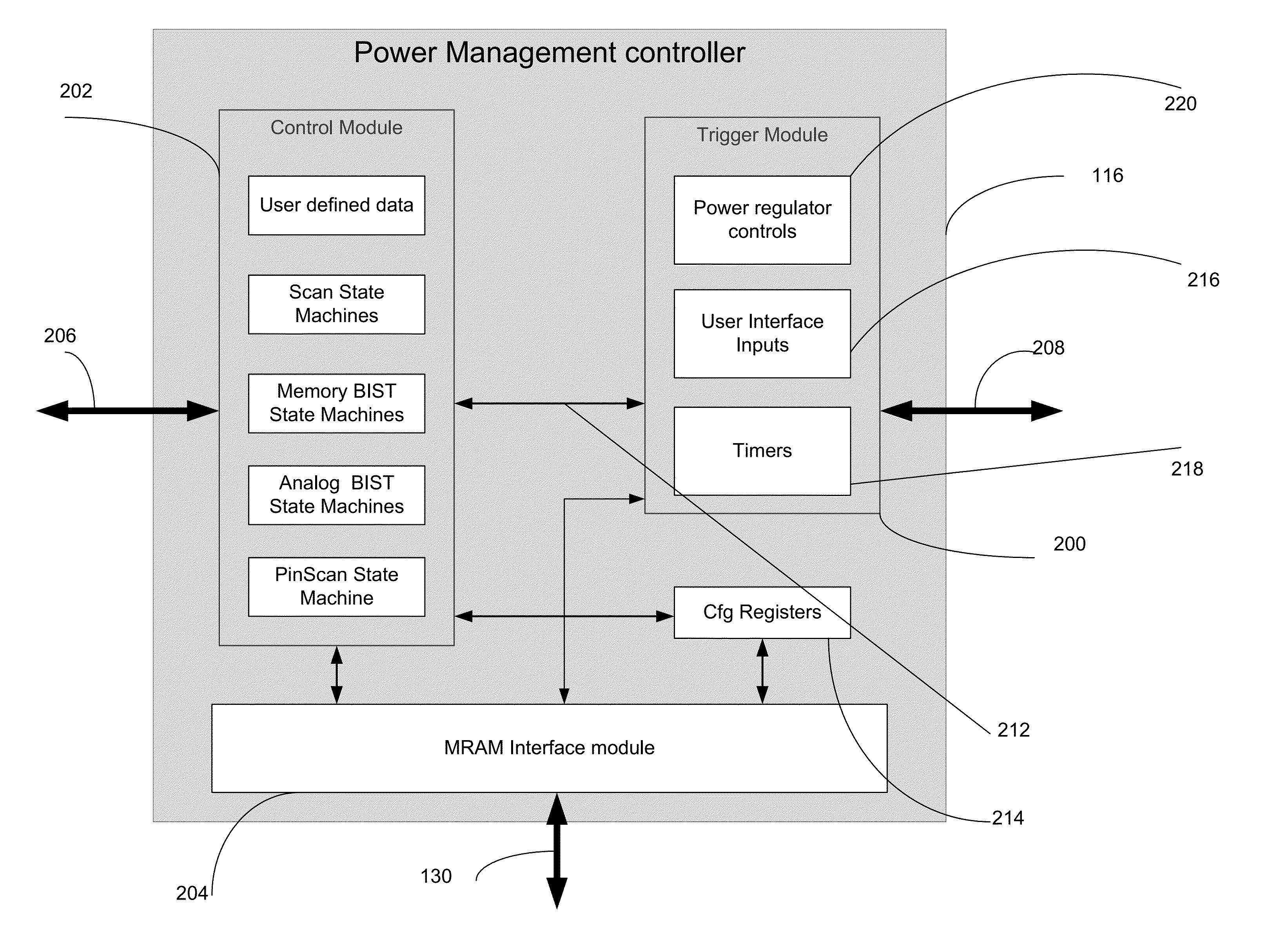
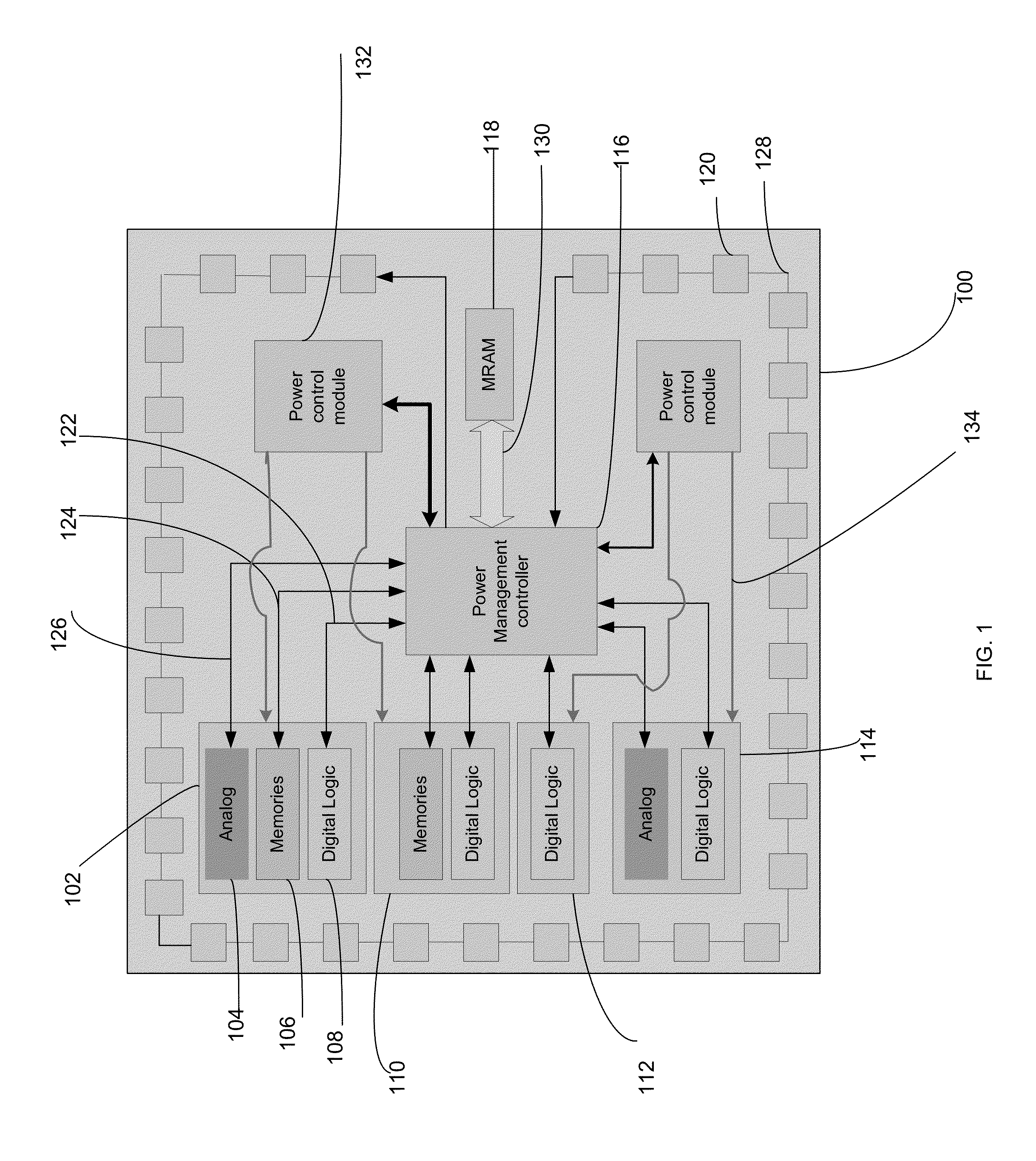
Method and apparatus to reduce power consumption of mobile and portable devices with non-volatile memories
InactiveUS20150316971A1Reduce overheadFast approachPower supply for data processingEnergy efficient computingPower gatingElectric power
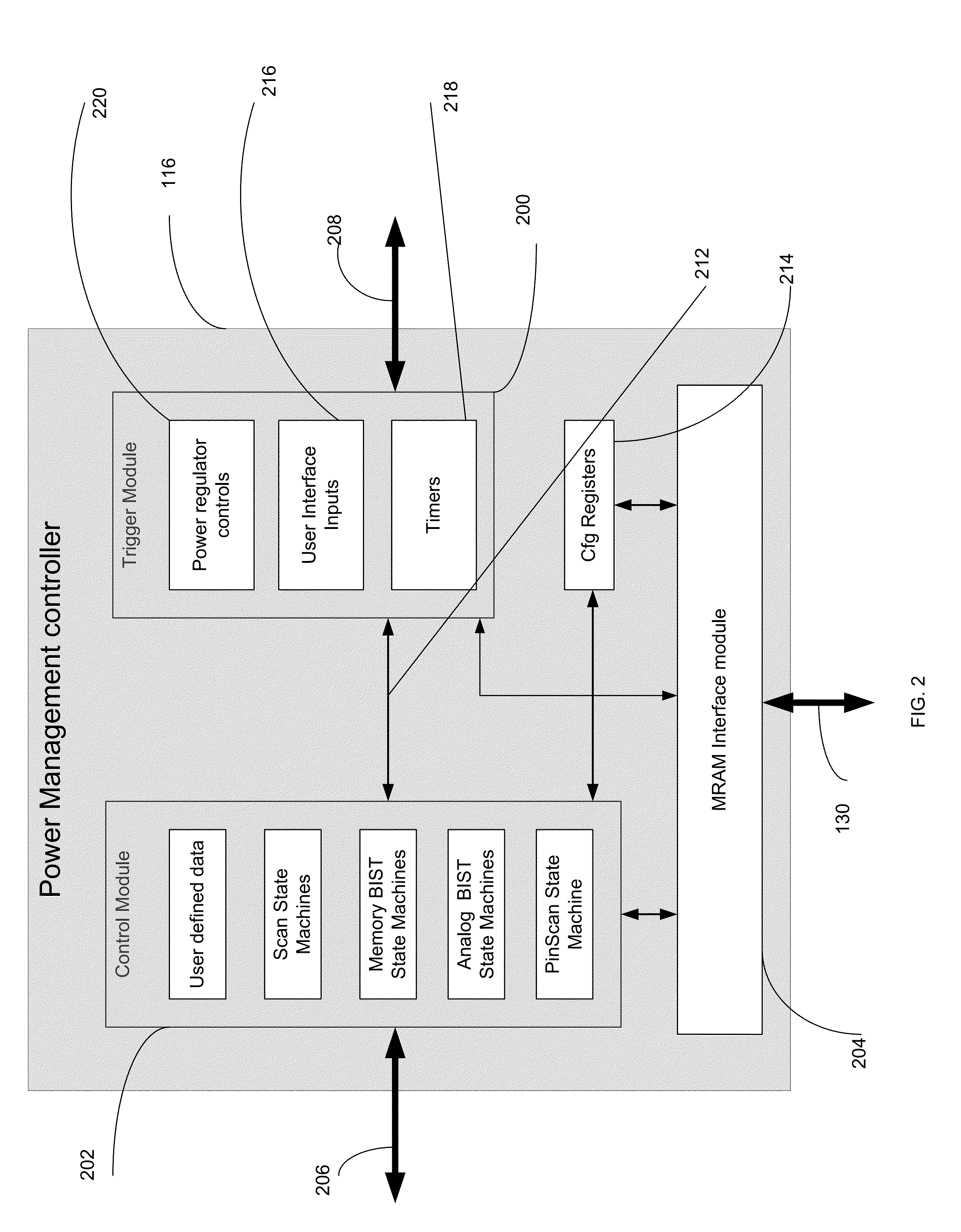
An unified power management scheme for all the idle subsystems during normal mode of operation and power save mode of operation reduces significant power and time during saving and restoring context of System on a chip (SoC). Power management schemes based on subset of manufacturing tests and high speed non-volatile memory provides transparency and shortest latency of entering and exiting power save mode and as a result providing significant power savings and extending battery life. Due to the shortest logic delays in some phases of logic scan, memory BIST and analog BIST, entry procedure and exit procedures from power save mode consume least amount of time with little overhead due to clock switching and power gating procedures. Any part of SoC that can be tested during manufacture using standard procedures of logic scan, memory BIST, analog BIST and boundary scan will be able to enter and exit power save mode and still retain the state. By enabling power to the functional units only while they are performing a function prolongs the duration of normal operation with a single charging of the battery for mobile and portable devices.
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
Mitigating main crossbar load using dedicated connections for certain traffic types
ActiveUS8065465B1Reduce loadWaste of bandwidthMultiple digital computer combinationsInput/output processes for data processingTraffic capacityComputerized system
One embodiment of the invention sets forth a control crossbar unit that is designed to transmit control information from control information generators to destination components within the computer system. The control information may belong to various traffic paradigms, such as short-latency data traffic, narrow-width data traffic or broadcast data traffic. The physical connections within the control crossbar unit are categorized based on the different types of control information being transmitted through the control crossbar unit. The physical connections belong to the following categories: one-to-one (OTO) connections, one-to-many (OTM) connections, valid-to-one (VTO) connections, valid-to-many (VTM) connections wire-to-one (WTO) connections and wire-to-many (WTM) connections.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Reliable, robust and structured duplex communication infrastructure for mobile quick service transactions
InactiveUS20170161819A1Special service provision for substationOffice automationQuality of serviceOrder fulfillment
The present invention relates to a way to provide computing and communication infrastructure to support full duplex quality of service for urgent and actionable structured communications securely transacted over a many-to-many managed network of intermittent ad hoc nodes. The invention overcomes technical challenges associated with high-volume, short-latency, semi-custom mobile order fulfillment by ensuring communications between customer and merchant are structured, robust, reliable and delivered via a duplex link. The described embodiments are advantageous in that they provide a bidirectional channel to facilitate discussion, confirmation and post-order communication. Moreover, the present invention is scalable to a many-to-many node ad-hoc network.
Owner:CARDANT HLDG LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com