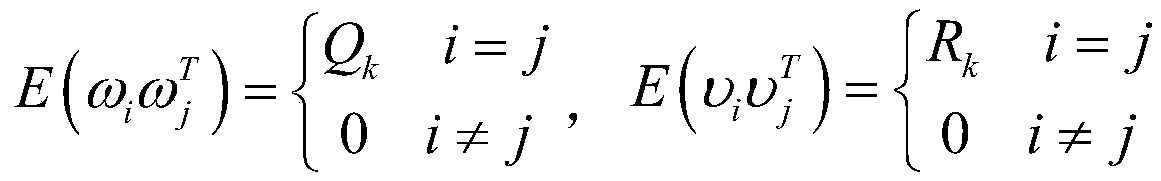Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32results about How to "Simple initialization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and communication system for data exchanging data between users of a bus system
InactiveUS7260609B2Latency periodSimple initializationData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsCommunications systemNormal case
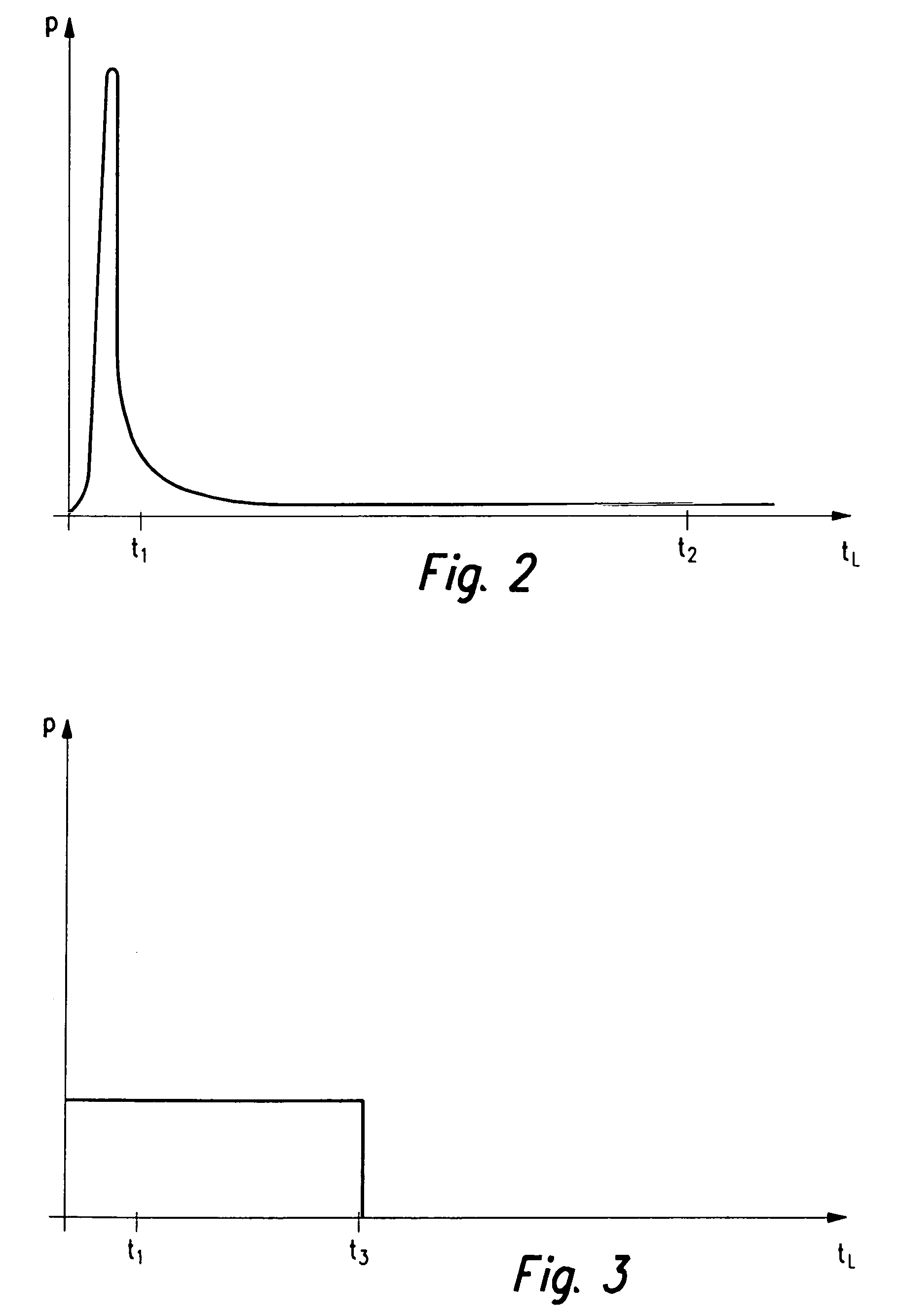
The present invention provides a method and a communications system for the exchange of data between at least two users who are in contact with one another using a bus system. The data are included in messages which are transmitted by users over the bus system. A specifiable priority is assigned to each message. In order to achieve, in the normal case, a high probability of a short latency period (t) of a message to be transmitted, and to be able to guarantee, in the worst case, a maximum latency period (tmax), it is provided that the priorities assigned to the messages be dynamically modified during the operation of bus system. Preferably, the set of all messages is subdivided into equivalence classes, and a priority is assigned to each equivalence class. During the operation of the bus system, the priorities of the messages are dynamically modified within an equivalence class, and the priorities of the equivalence classes are dynamically modified.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Method & apparatus for an auxiliary train control system
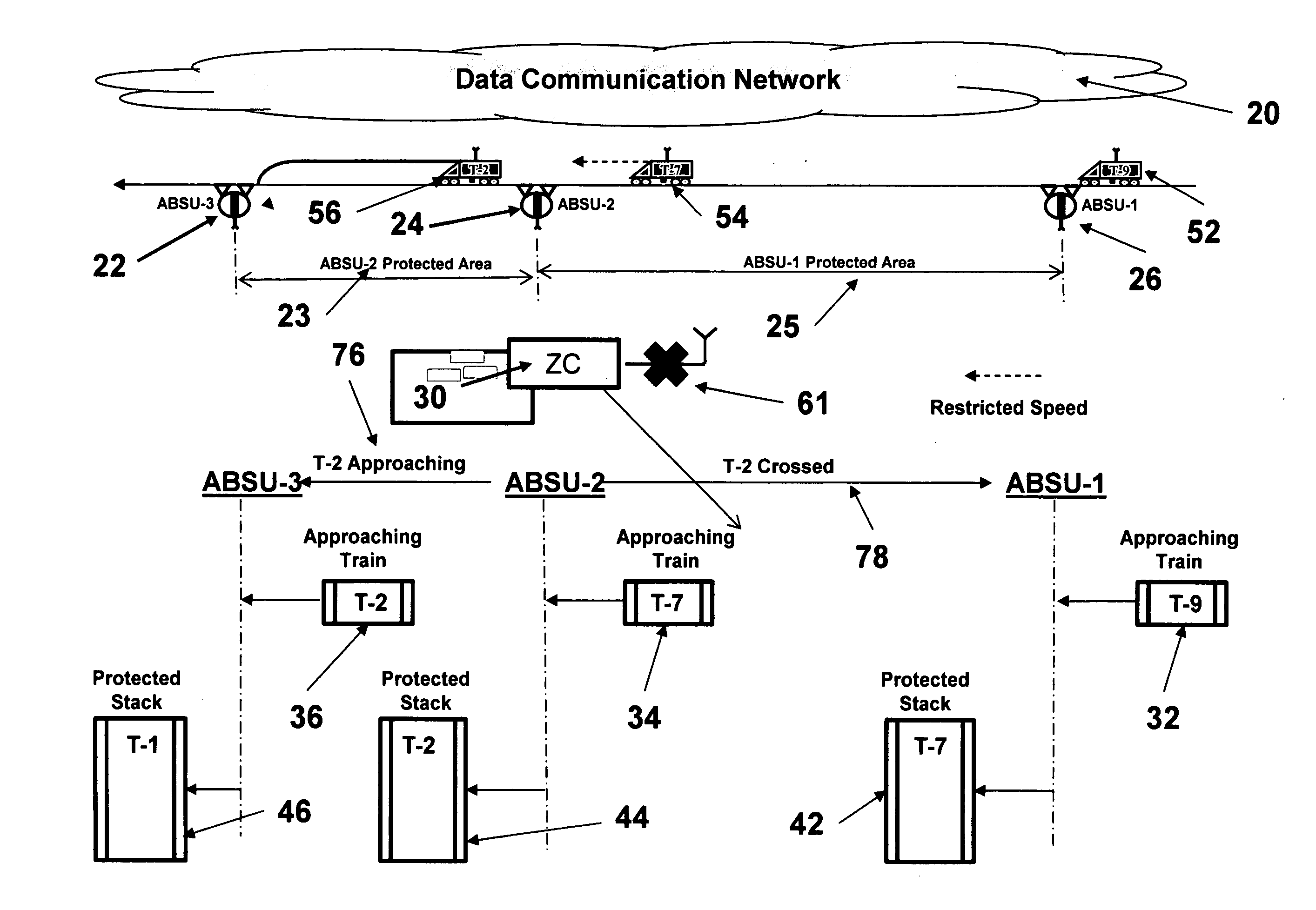
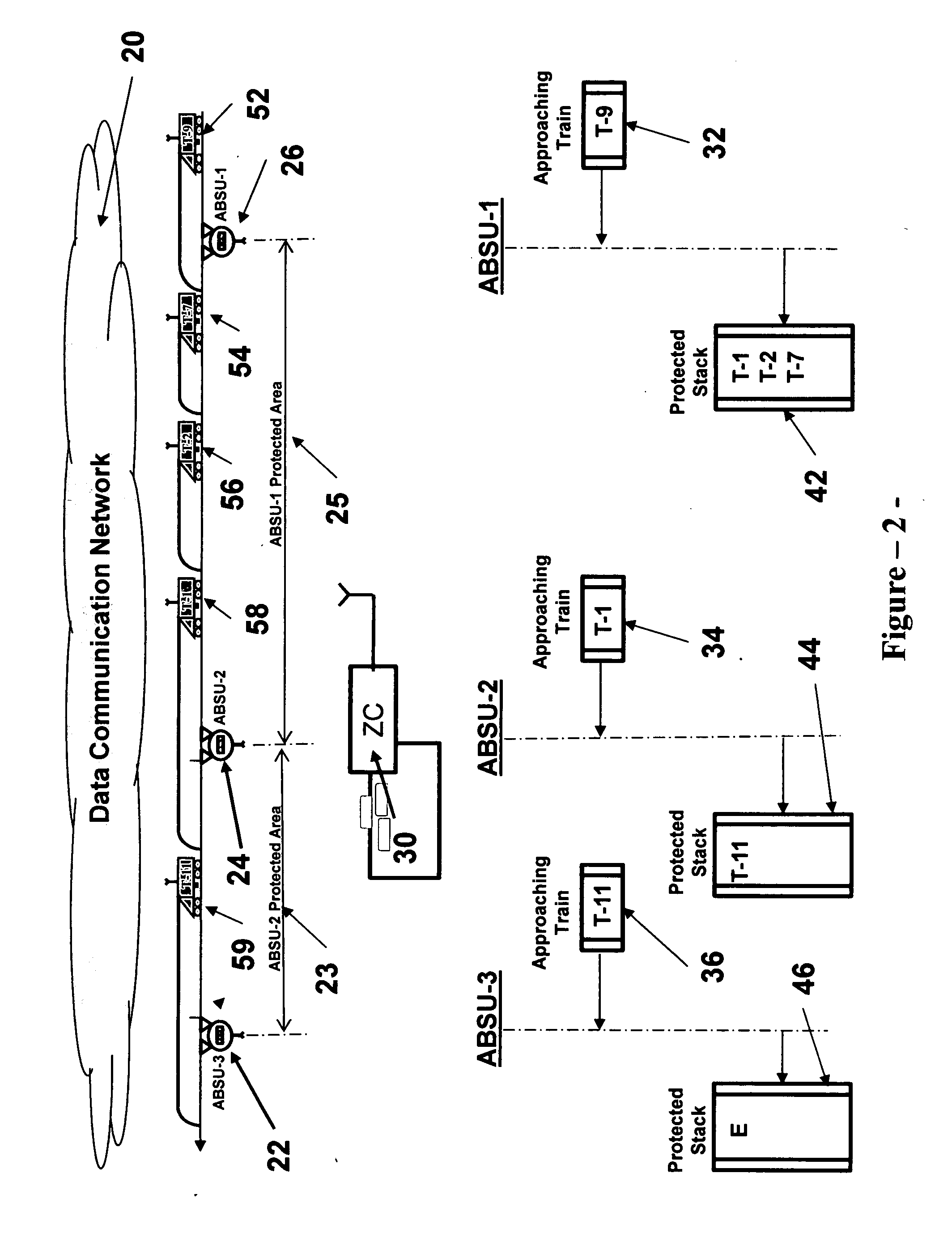
PendingUS20150307119A1Minimize application engineering effortEasy to initializeRailway traffic control systemsVehicle route interaction devicesSelf-healingEngineering
A method and an apparatus for a train control installation are disclosed, and are based on the absolute permissive block concept. The train control installation employs a plurality of generic absolute block signal units (ABSU), wherein each signal unit includes means for detecting the crossing of a train passed a discrete point, means for exchanging data with adjacent ABSUs, means for generating and communicating a movement authority limit to a train, means for generating and displaying a signal indication, and means for enforcing a stop aspect. The train control installation can be used in conjunction with a communication based train control (CBTC) system to provide a degraded mode of operation without impacting the availability and the reliability of the CBTC system. Further, the train control installation has a self-healing feature to maintain train service during an ABSU failure.
Owner:GHALY NABIL N
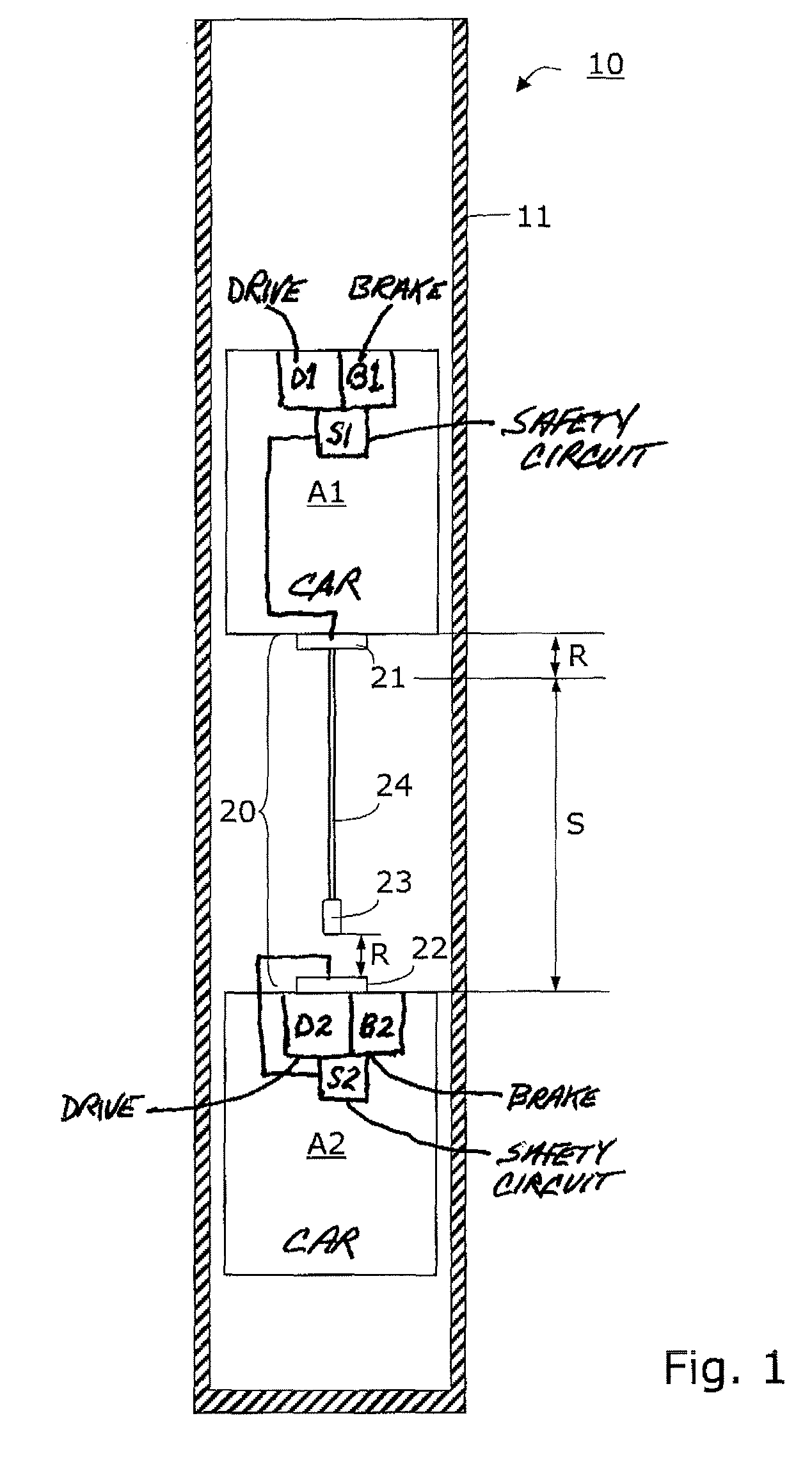
Method of operating an elevator installation, an elevator installation operable by this method and safety equipment for this elevator installation
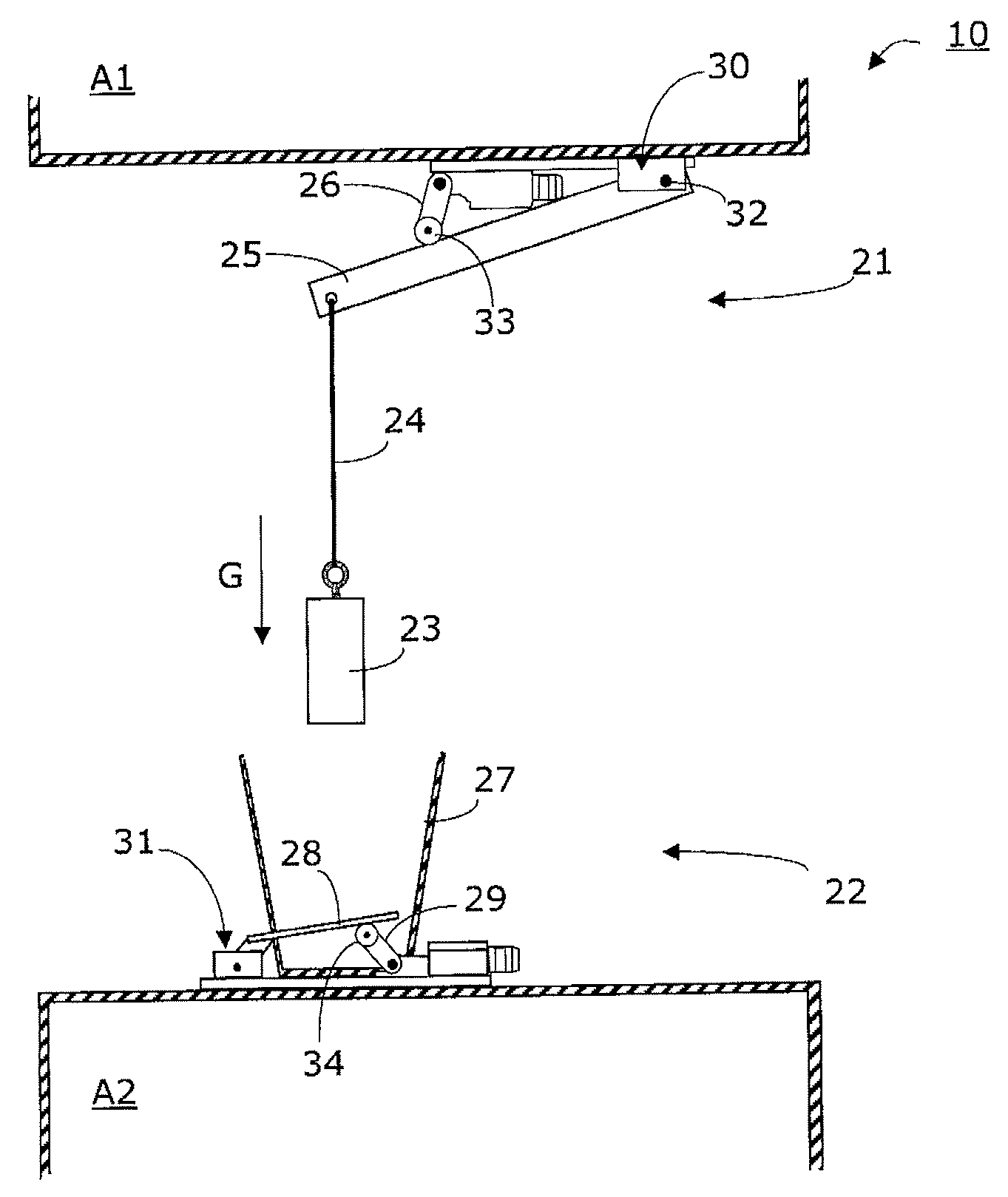
InactiveUS7779967B2Advantageously producedSimple initializationElevatorsBuilding liftsHeavy loadTest equipment
An elevator installation with at least one upper elevator car and at least one lower elevator car includes a first electromechanical switching mechanism mounted on the upper car and having a weight fastened at a downwardly extending elongate run, the run being held in a travel setting by the weight force, and a second electromechanical switching mechanism mounted on the lower car vertically below the weight. In the case of undesired approach of the two elevator cars, the weight impinges on the second electromechanical switching mechanism and thereby opens a safety circuit of the lower elevator car. The safety circuit of the upper elevator car is also opened by a diminishing of the weight force.
Owner:INVENTIO AG
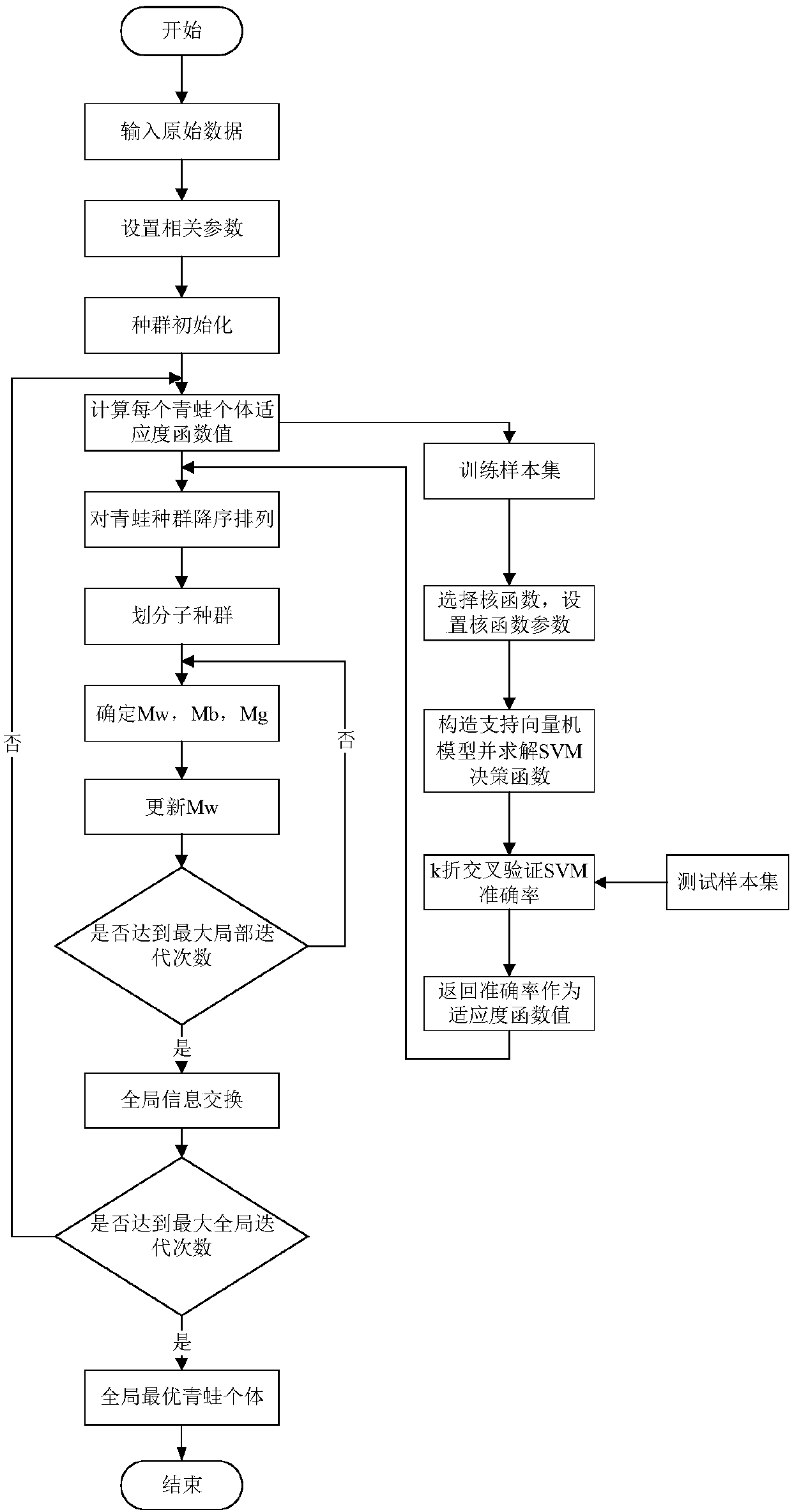
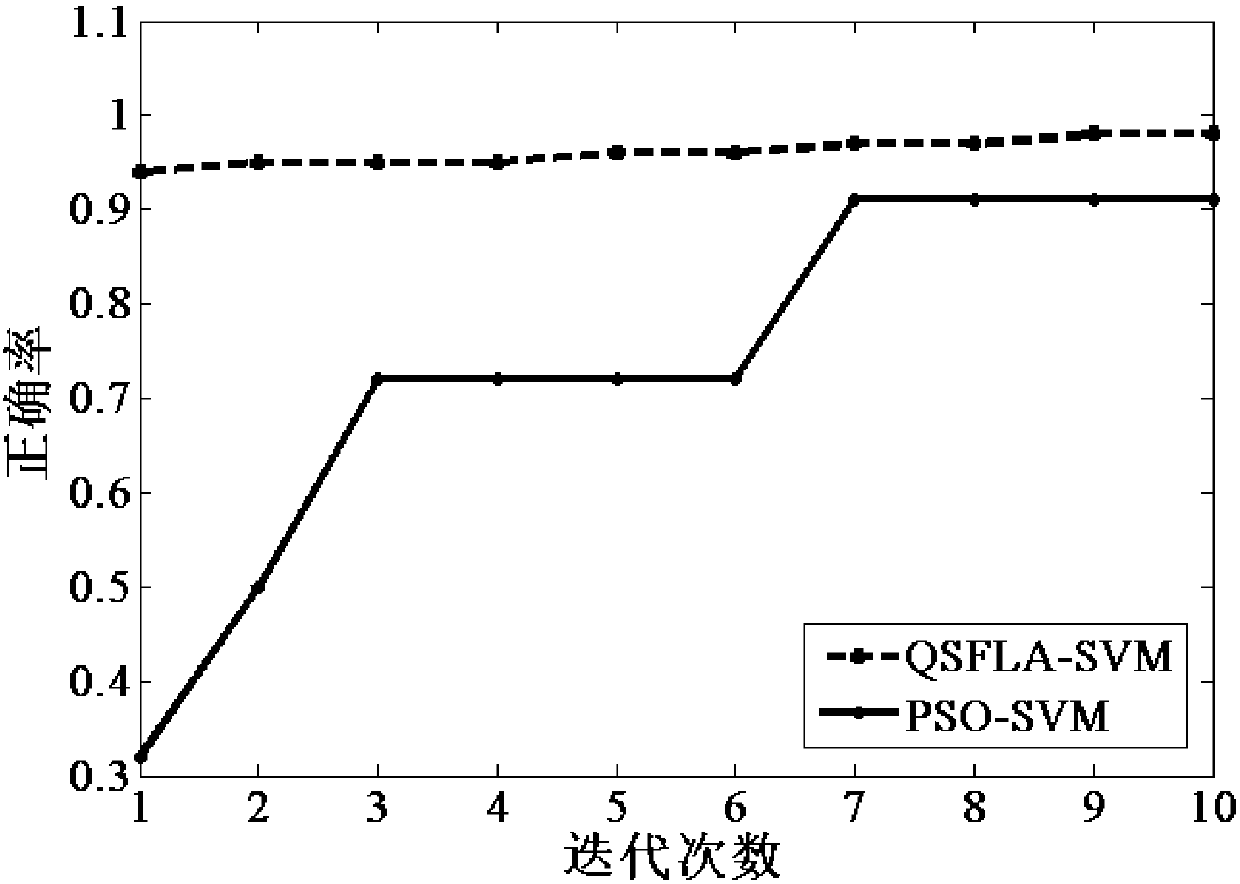
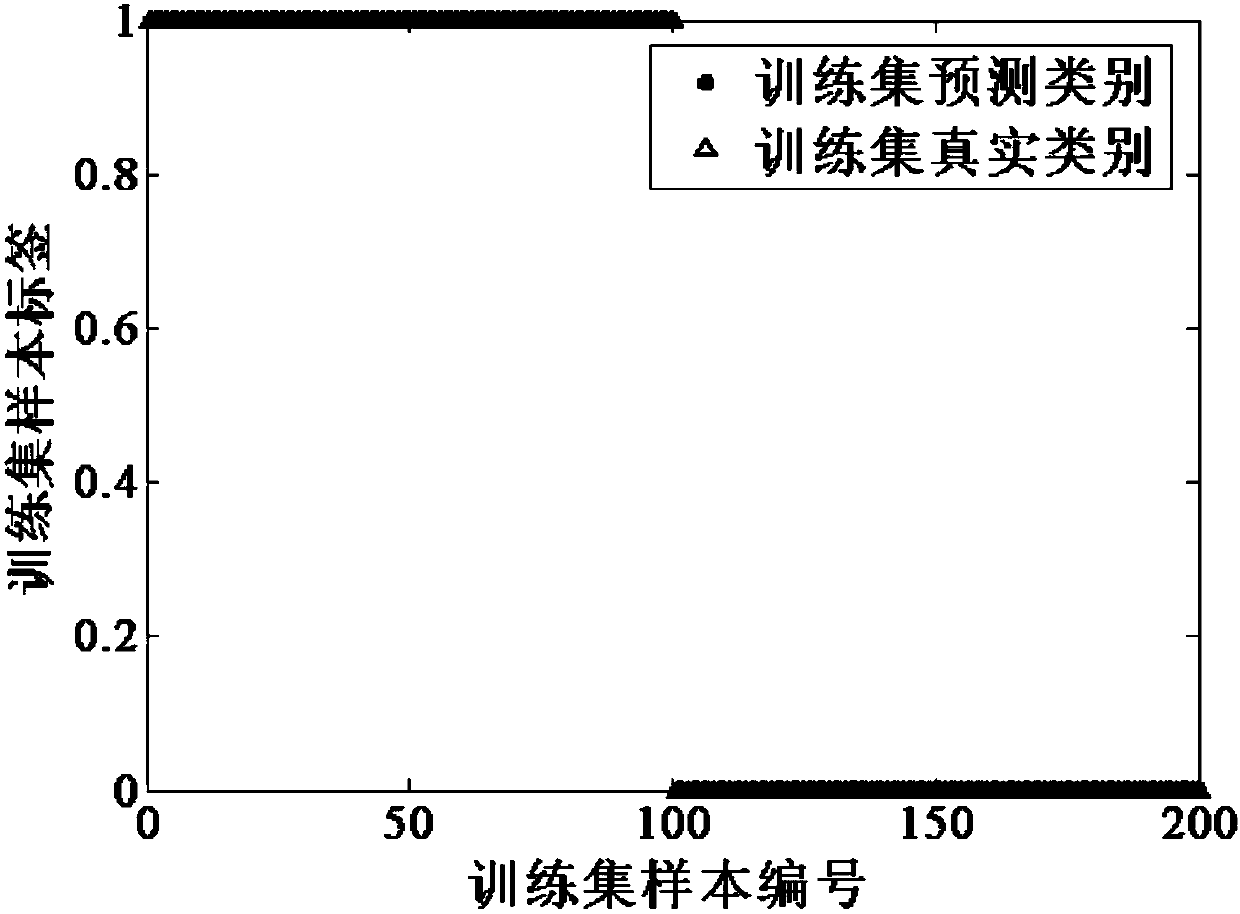
QSFLA-SVM-based perceptive intrusion detection method
ActiveCN108052968ASimple initializationAccurate evaluationCharacter and pattern recognitionArtificial lifeFitness functionMechanism based
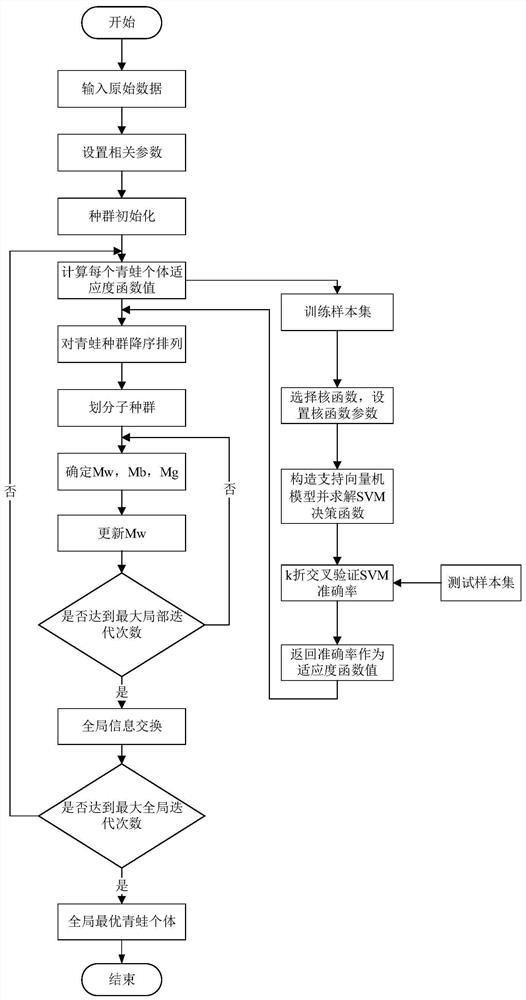
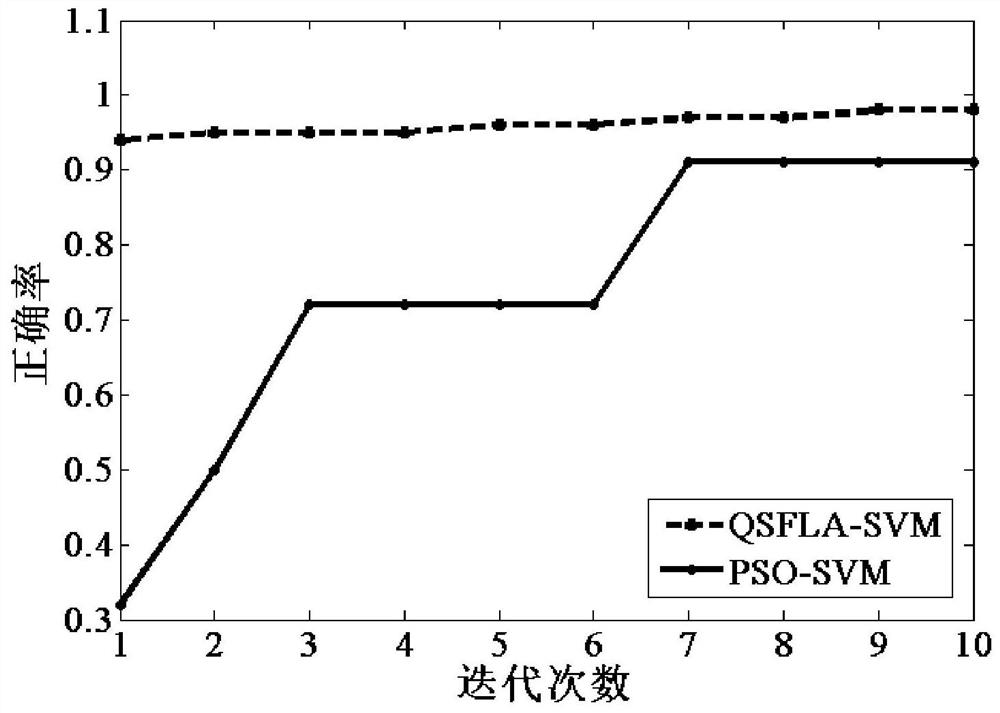
The invention provides a QSFLA-SVM-based perceptive intrusion detection method. The method comprises the steps of setting related parameters; initializing the position of a frog population; transmitting position information of each frog individual to an SVM abnormal sequence detection model, taking a calculated correct rate of test set classification as a fitness function value of each frog individual, performing descending order arrangement on the frog population and performing sub-population division on the arranged population; updating worst individuals of each frog sub-population by utilizing a quantum particle swarm update mechanism, until a local maximum iterative frequency is reached; and performing global information exchange, and if a global maximum iterative frequency is reached,returning a global optimal frog individual, and outputting an optimal test set classification result, wherein at the moment, position information of the global optimal frog individual is an optimal parameter value when the SVM abnormal sequence detection model obtains the maximum correct rate of the test set classification. According to the method, intrusion detection is performed in combinationwith a quantum particle swarm search mechanism-based QSFLA and an SVM.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method and system for a communication session initialization in a telecommunication network
InactiveUS20100146063A1Effective and simple user interfaceImprove communicationInterconnection arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network AccessClient-side
A first terminal residing telecommunication network is arranged for initializing media sessions of at least two media types such as voice and messaging to a second terminal. The first terminal is known by a message server as a message client. The first terminal submits a request for a media session set up by means of a message protocol for a media session of a different media type. The request is sent to the message server which forwards the message to a network node. The network node is also known message server as well as to the terminal as a message client. After receiving the media session set up request the network node either sets up the requested media session to both the terminals and bridges the connections for a media session or instructs the first terminal to setup the media session.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
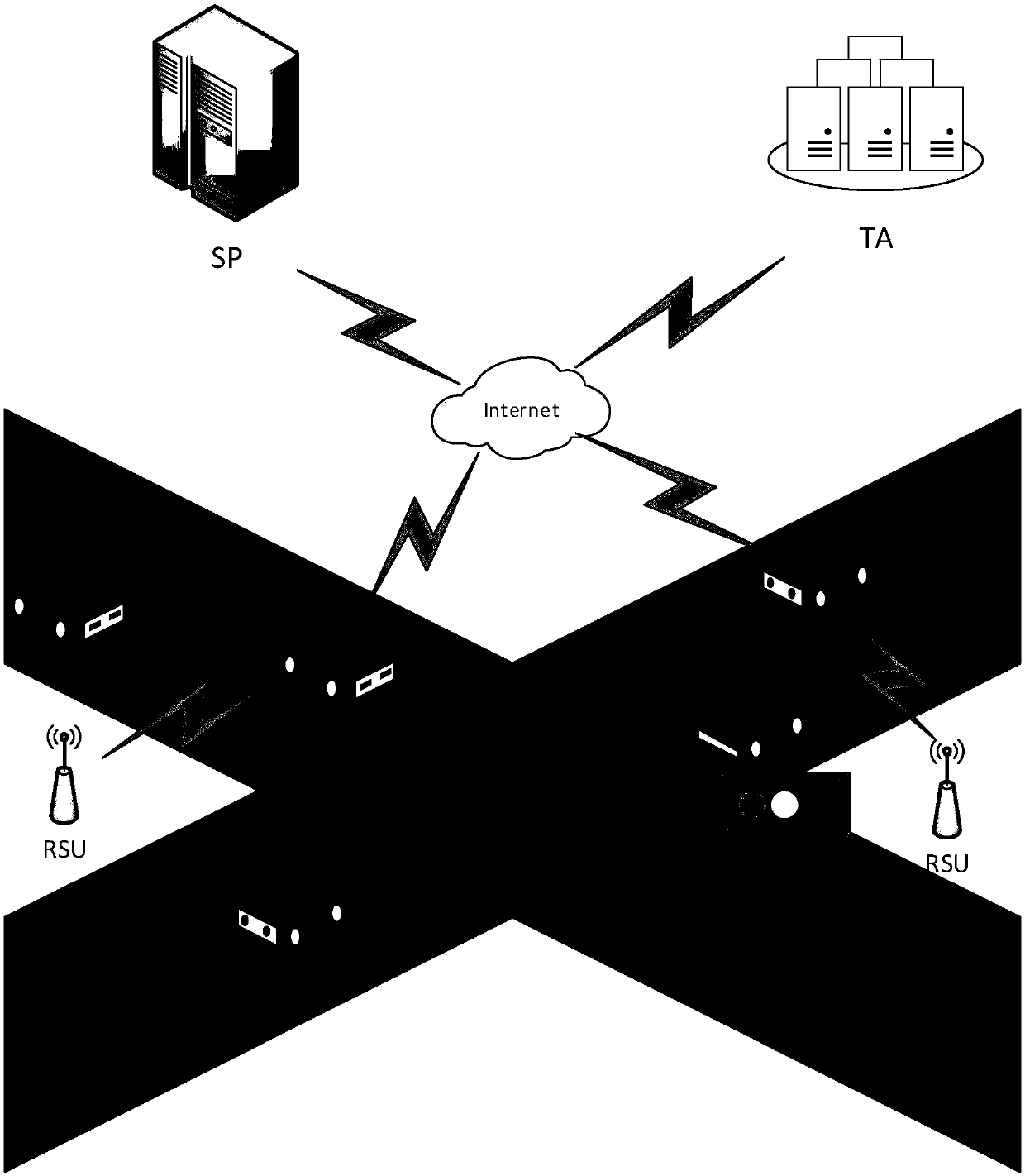
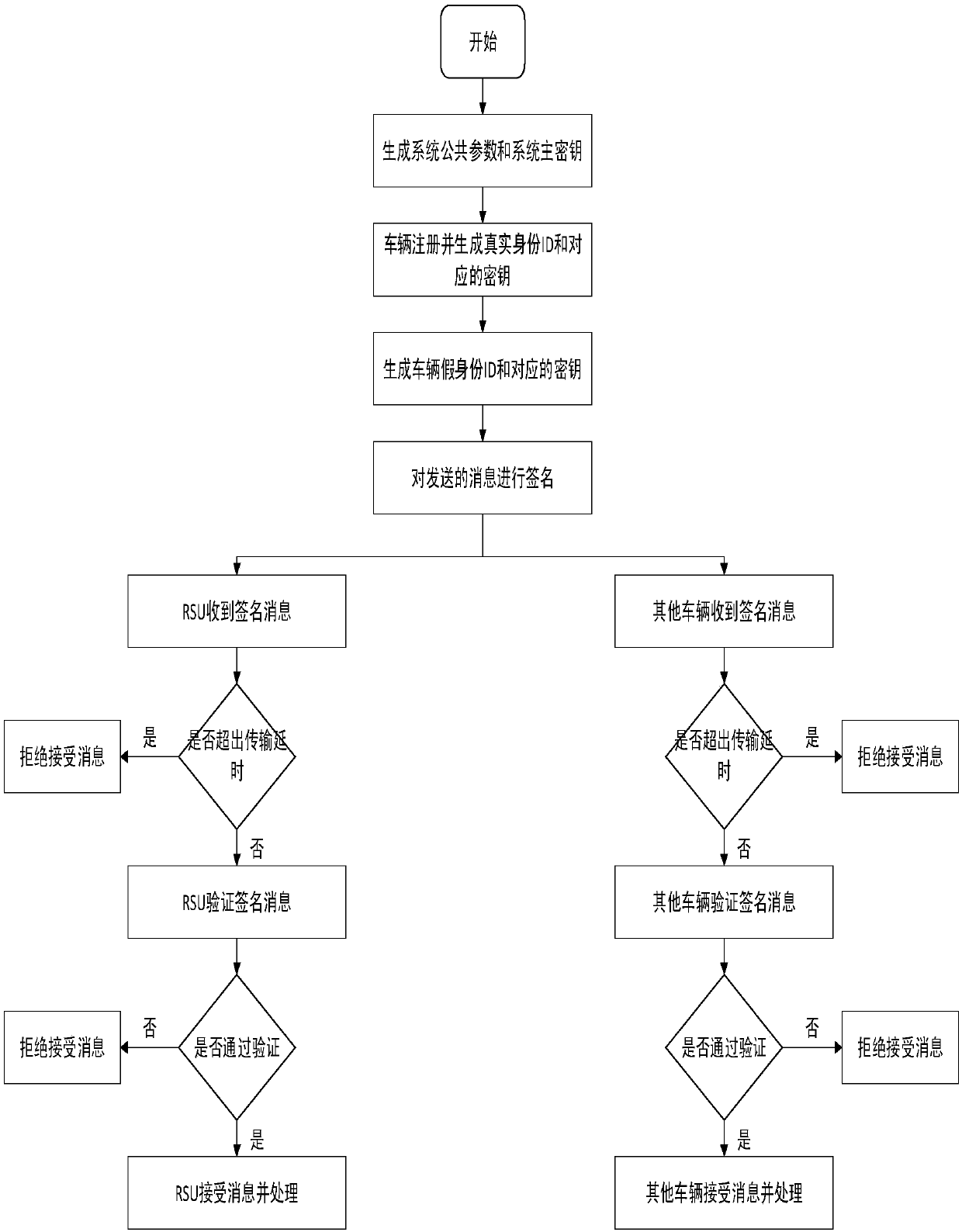
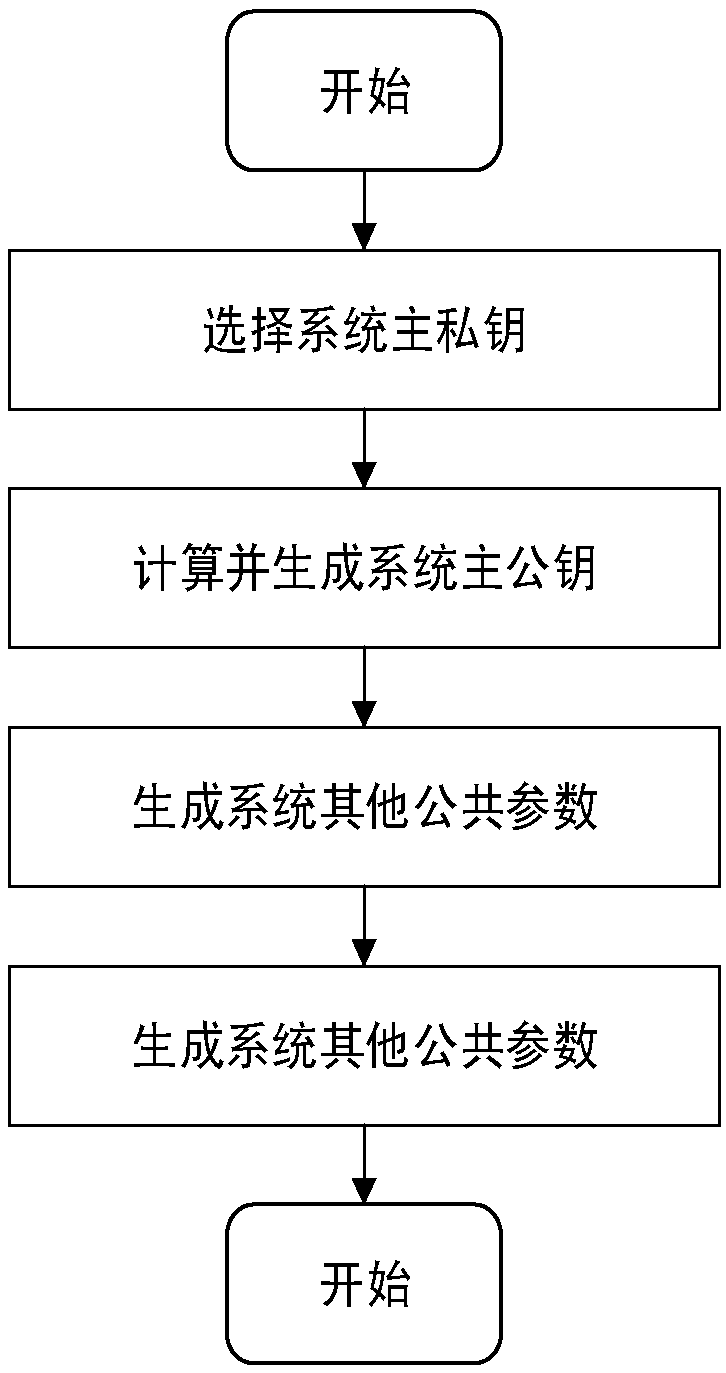
Efficient message transmission and authentication method based on mobile vehicle ad hoc network
InactiveCN107896369AReduce overheadSimple initializationParticular environment based servicesVehicle-to-vehicle communicationMobile vehicleThe Internet
The invention provides an efficient message transmission and authentication method based on a mobile vehicle ad hoc network. The invention provides an efficient low-bandwidth message transmission andauthentication mechanism, the mechanism is a scheme based on identity encryption and anonymous authentication, can protect user privacy information in a message transmission and authentication process, and meanwhile if the transmitted message is not legitimate, the unique authority TA (trusted center) can track vehicle identity through a main private key; the mechanism also supports message batchtransmission and batch authentication. In the method, the authority TA (trusted center) is responsible for the generation of system security parameters in the environment of the Internet of Vehicles and is responsible for calculating and storing related data; and a RSU (road test unit) transits the information through a wireless channel and TA and OBU, and is responsible for calculating and transmitting related data.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method and device for operating an audio and/or videoconference with at least two participants
InactiveUS20100269159A1Avoid difficult choicesSimple initializationDigital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsHuman–computer interactionVideoconferencing
The embodiments relate to a method for operating an audio and / or videoconference having at least two participants. A central computer, which controls the audio and / or videoconference, ascertains an identification datum of the participant initiating the conference. The central computer ascertains, on the basis of the identification datum from at least one database, which is coupled to the central computer, contact data of potential participants of the conference, the contact data being associated with the user. The contact data ascertained by the central computer are provided to the user initiating the conference as further conference participants for selection.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
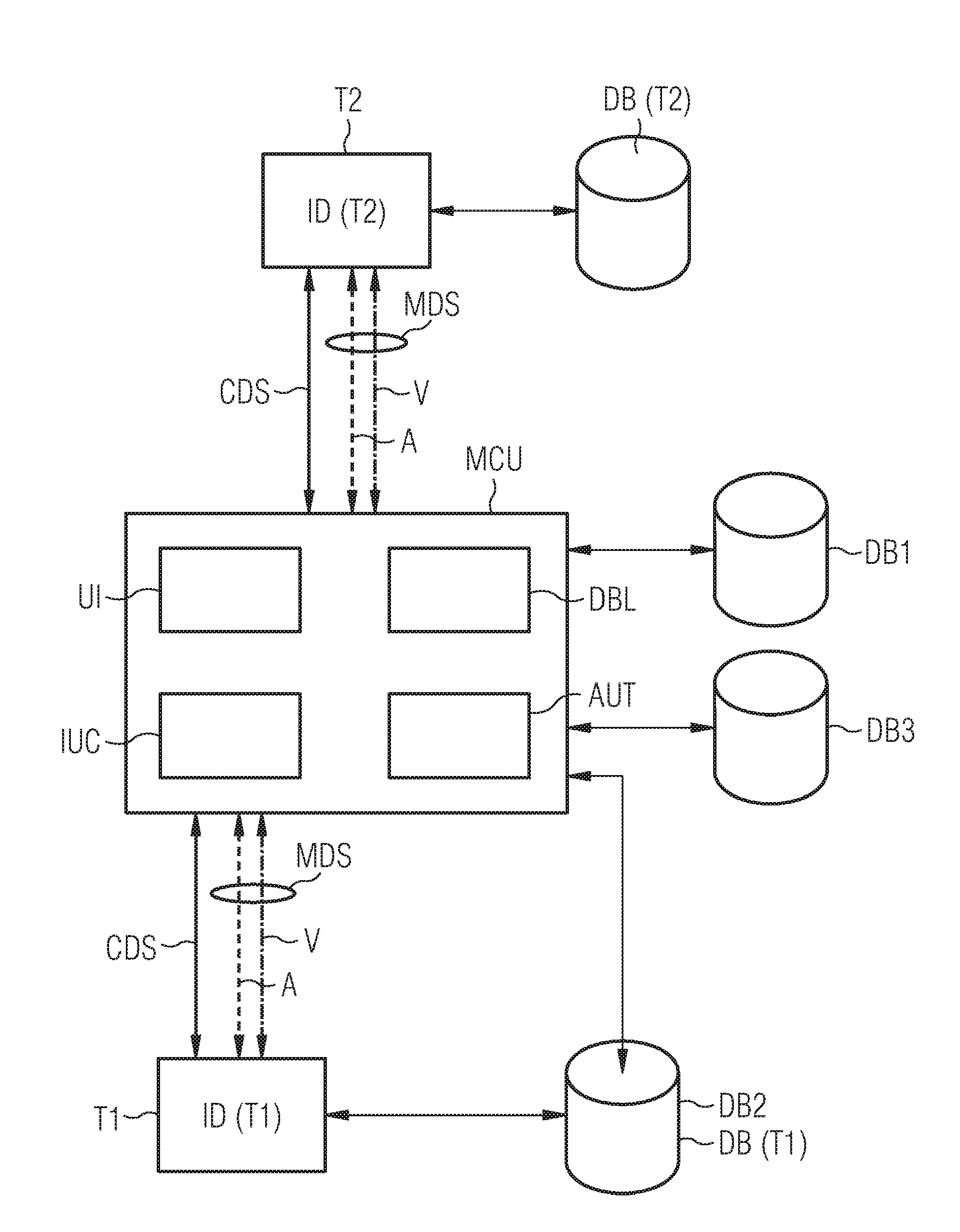
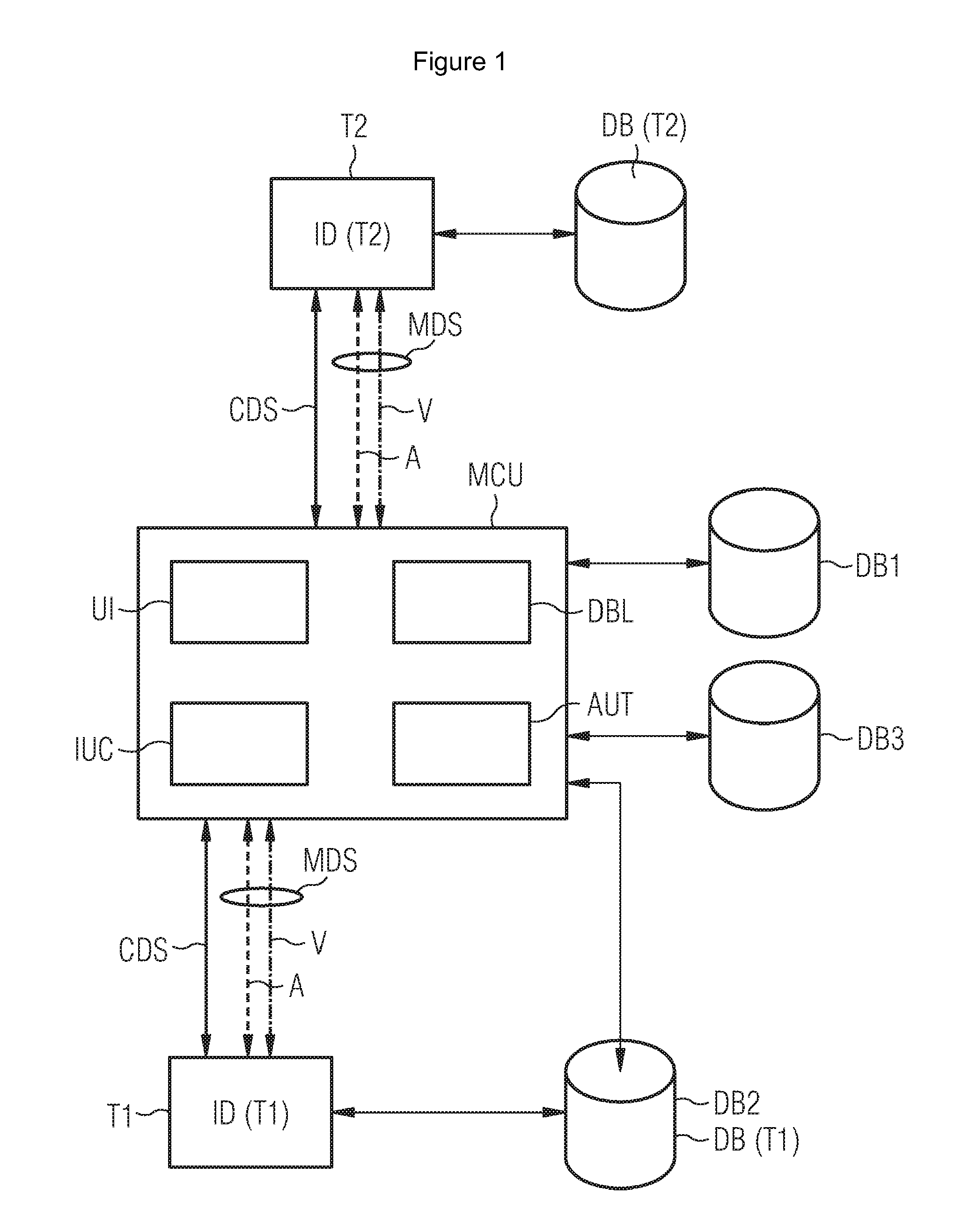
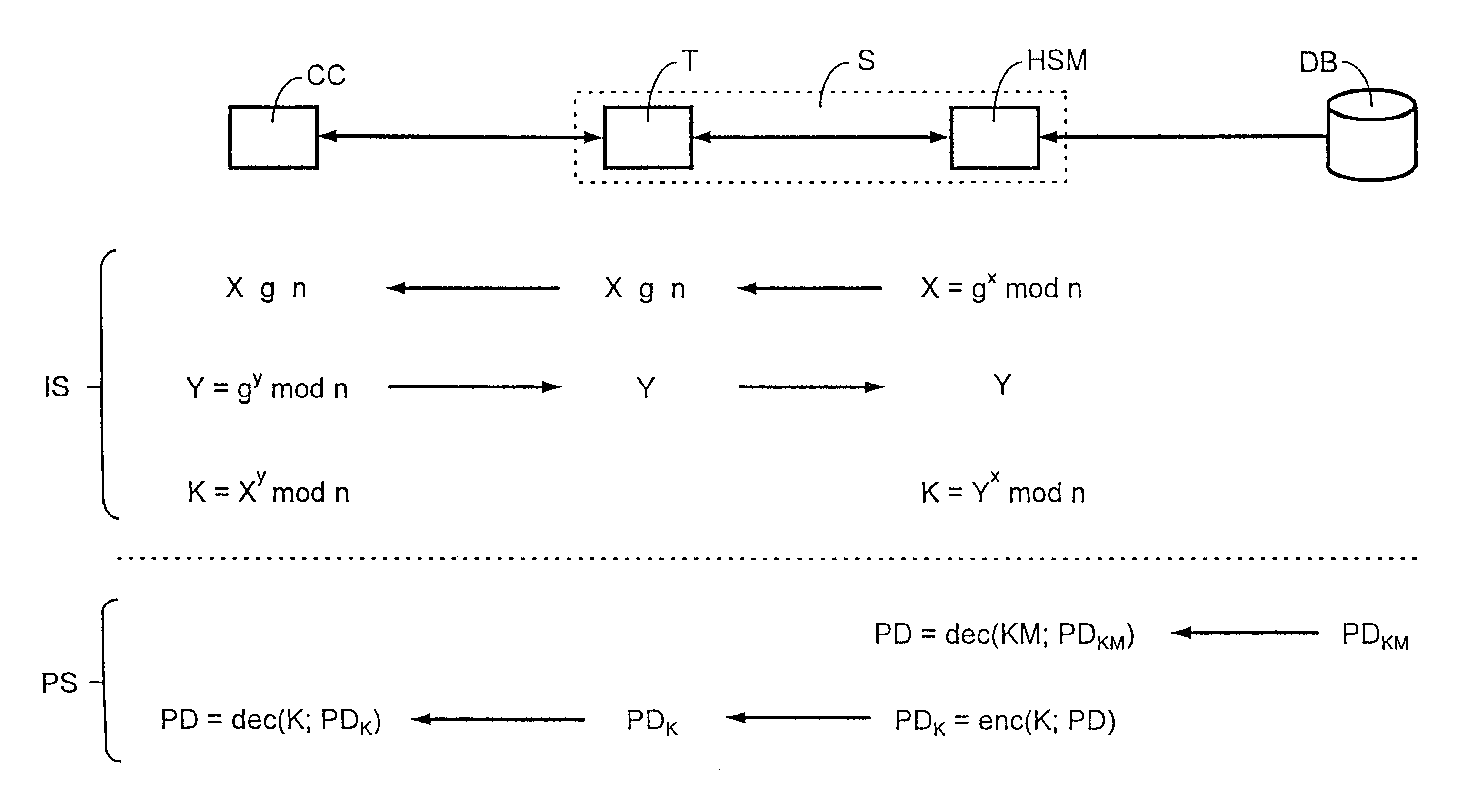
Method for exchanging at least one secret initial value between a processing station and a chip card
InactiveUS7181602B1Improve securitySimple initializationKey distribution for secure communicationRandom number generatorsComputer hardwarePlaintext
The invention relates to a method for exchanging at least one secret initial value between a processing station and a chip card, in an initializing step for the chip card.In the initialization of chip cards in known methods an initial value, e.g. a key, is transmitted from a processing station to the chip card and stored therein. Since this key is transmitted in plaintext this involves security problems.In the present invention the described security problems are solved by only parts of the key being exchanged between processing station and chip card and the key being generated in the chip card and the processing station from the parts.
Owner:GIESECKE & DEVRIENT MOBILE SECURITY GMBH
Magnetic revolution counter and method for determining numbers of revolutions that can be determined by means of said revolution counter
ActiveCN108369110AAchieve one-to-one determinationSimple initializationMagnetic measurementsLinear/angular speed measurementElectrical resistance and conductanceLoop closing
The invention relates to a magnetic revolution counter and to a method for determining a specifiable quantity n of revolutions of an external magnetic field that are to be determined, said external magnetic field produced by a rotating element (4), or a quantity n of magnetic poles of a rotating pole wheel, which quantity of magnetic poles can be moved past, or a linear magnetic scale that can bemoved past, containing a revolution sensor (2), which contains magnetic domain-wall conducting tracks, which consist of open spirals or multiply wound loops closed in themselves, which are formed by aGMR layer stack or a soft magnetic layer having locally present TMR layer stacks and into which magnetic 180 degrees domain walls can be introduced and - by measurement of the electrical resistance of specifiable spiral sections or loop sections - can be located, wherein a single domain wall is introduced into the domain-wall conducting tracks or at least two magnetic domain walls are introducedinto the domain-wall conducting tracks in such a way that the at least two domain walls are brought into a defined distance of greater than 360 degrees from each other, with respect to the location change thereof from a first to a second position in the event of rotation of the external magnetic field by the angle of greater than 360 degrees, and are lastingly thus spaced apart from each other andwherein electrical contacts arranged in a defined manner are provided on the domain-wall conducting tracks, which electrical contacts, together with associated domain-wall conducting track sections covered thereby, are interconnected to form separate but jointly readable Wheatstone half-bridges, wherein the resistance ratios determined by the Wheatstone half-bridges are stored as a signal level completely in a memory (9) as a table, which memory can be continuously compared with table-like target value patterns stored in a further memory (10) for each permissible revolution i (0 < i < n) in order to determine the number of revolutions and, for the number of revolutions i to be determined, the number of revolutions for which the measured resistance ratios match the target value pattern inthe memory (10) is output, determined by a corresponding processing unit (11).
Owner:LEIBNIZ INST FUR PHOTONISCHE TECHNOLOGIEN EV +1
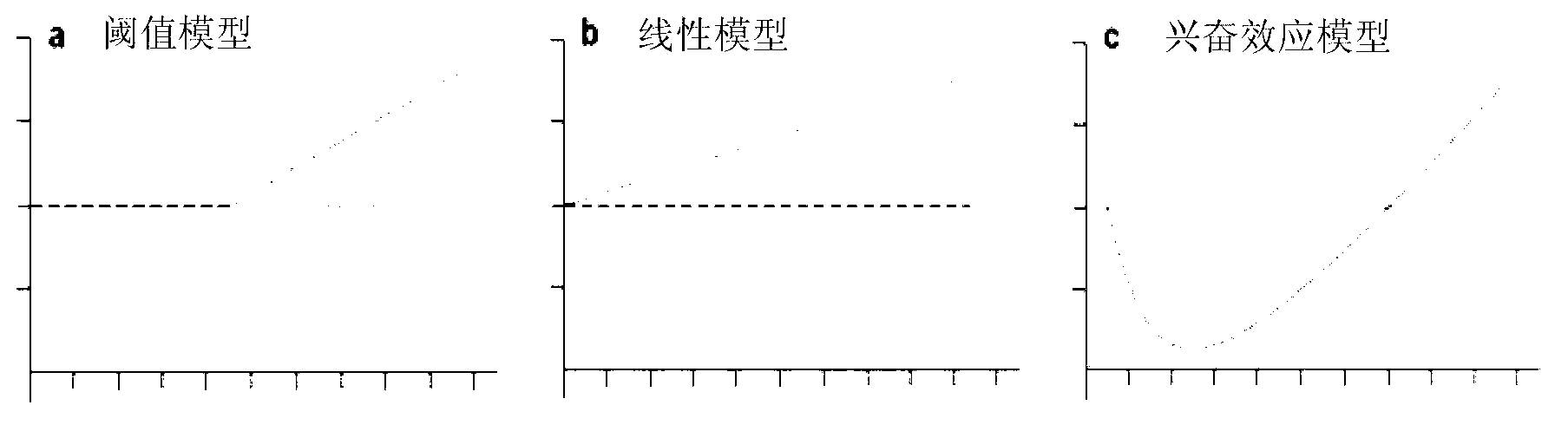
Method of establishing Hormesis dose-effect fitting model
InactiveCN103014116ASimple initializationEasy to initializeMicrobiological testing/measurementAcute toxicity testingHypothesis
The invention belongs to the field of environment pollution detection technology and relates to a method of establishing a Hormesis dose-effect fitting model, namely a Bilogistic model. The method comprises the following steps: (1) analyzing the stability of a compound; (2) recovering and culturing strains; (3) conducting toxicity test including acute toxicity test and chronic toxicity test; (4) calculating the inhibition ratio of the compound analyzed in the step (1) to the strains recovered and cultured in the step (2) by applying the experiment result obtained in the step (3), and conducting toxicity representation by taking inhibition ratio as an index; and (5) fitting the toxicity data to obtain the Bilogistic model. The data fitting is more convenient through the model; parameters in the model are initialized simply; the model is established based on a receptor mechanism hypothesis, thereby having great biological significance; good fitting can be conducted under the condition of high stimulatory effect; the Hormesis effect can be effectively guided to the application in the drug design.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
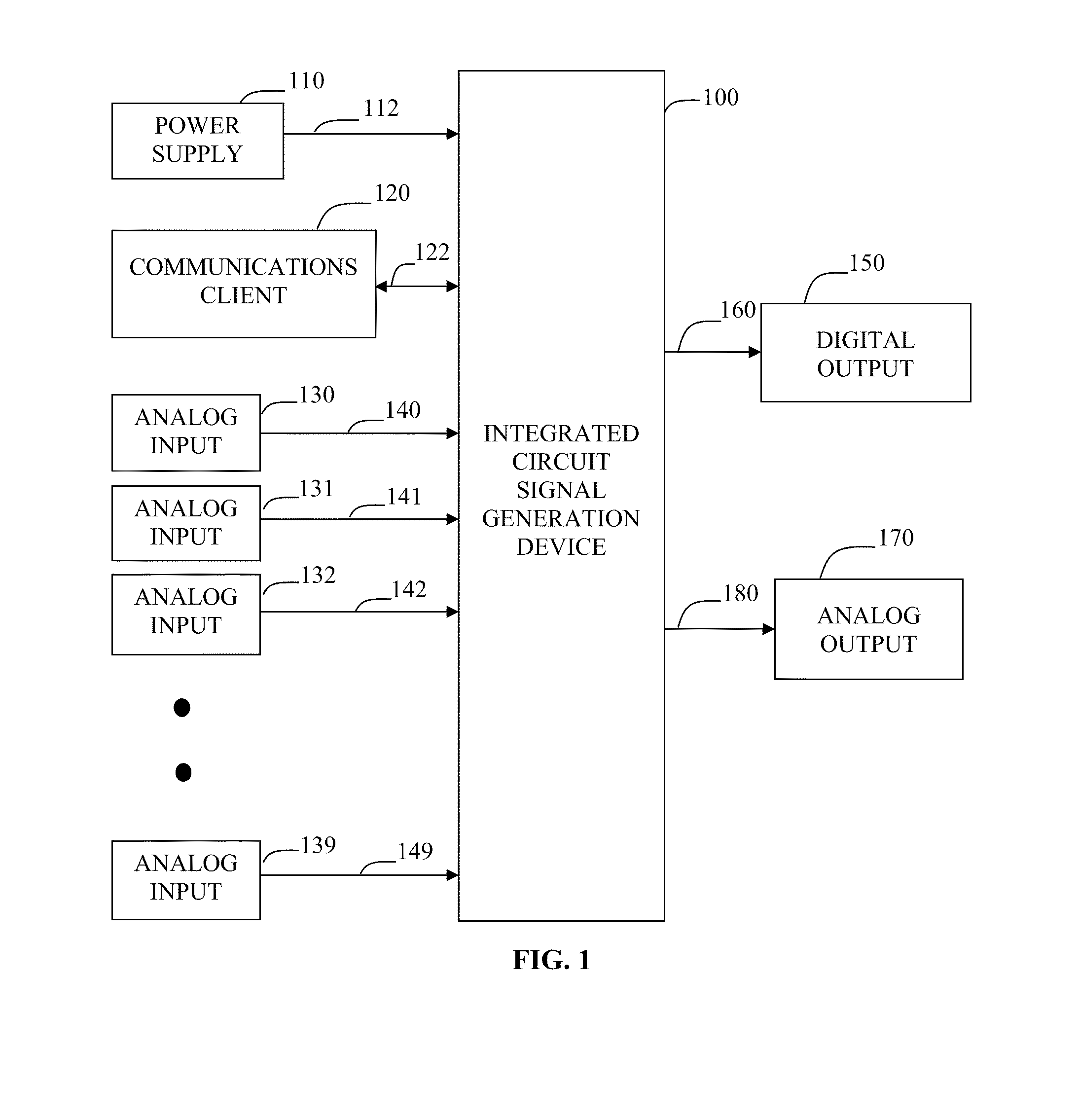
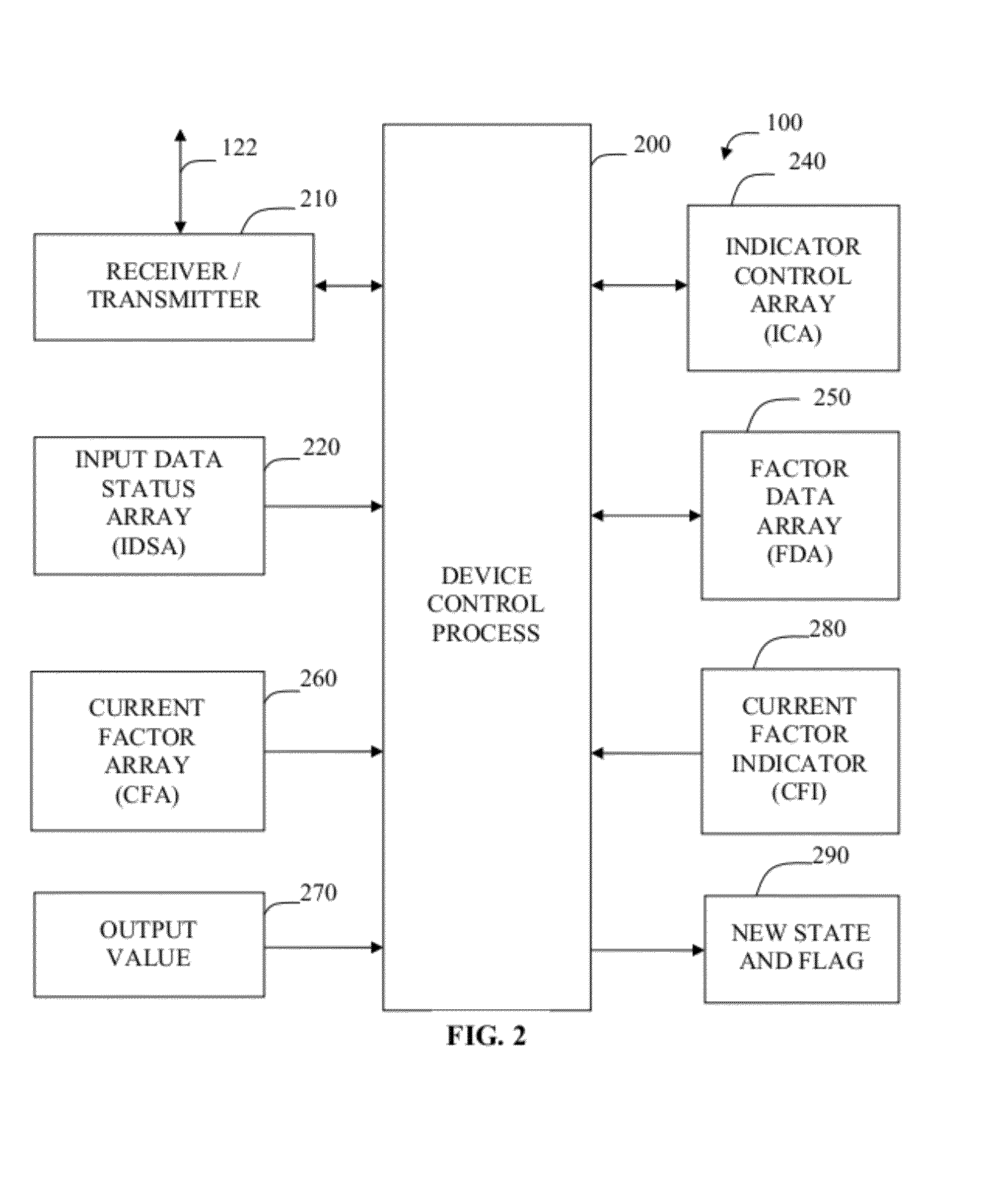
Integrated Circuit Signal Generation Device
InactiveUS20120019286A1Error minimizationSimple initializationSolid-state devicesPulse shapingMicrocontrollerAudio power amplifier
An electronic integrated-circuit device is described in which mode control commands are stored. Mode parameters are also stored in the device. One or more inputs are used according to a predetermined process as determined by the stored parameters according to the stored commands and current mode. One or more output signals are produced. In various applications an output signal may be input to a sound amplifier, a lamp, a motor, a servo, etc. One application is a variety of sensor fusion. Procedural programming is avoided. The device operates with more speed and flexibility than other available configurations. Higher level supervisory management and control is useful for setup and initialization and is optional during operation. Selected platforms include microcontrollers; field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) and application specific integrated circuits (ASICs).
Owner:SALHANY WAYNE F
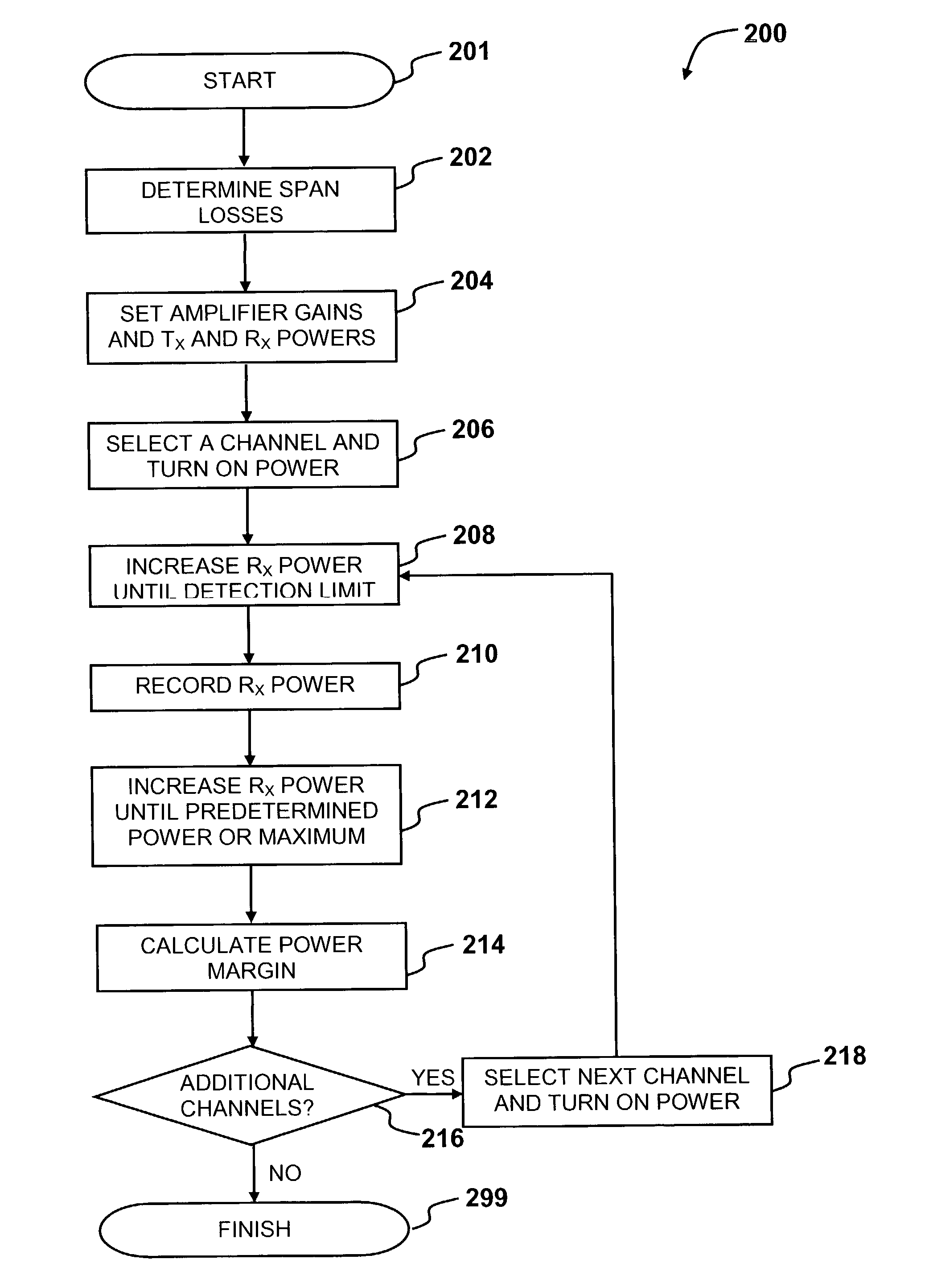
Method and system for automatic initialization of an optical network
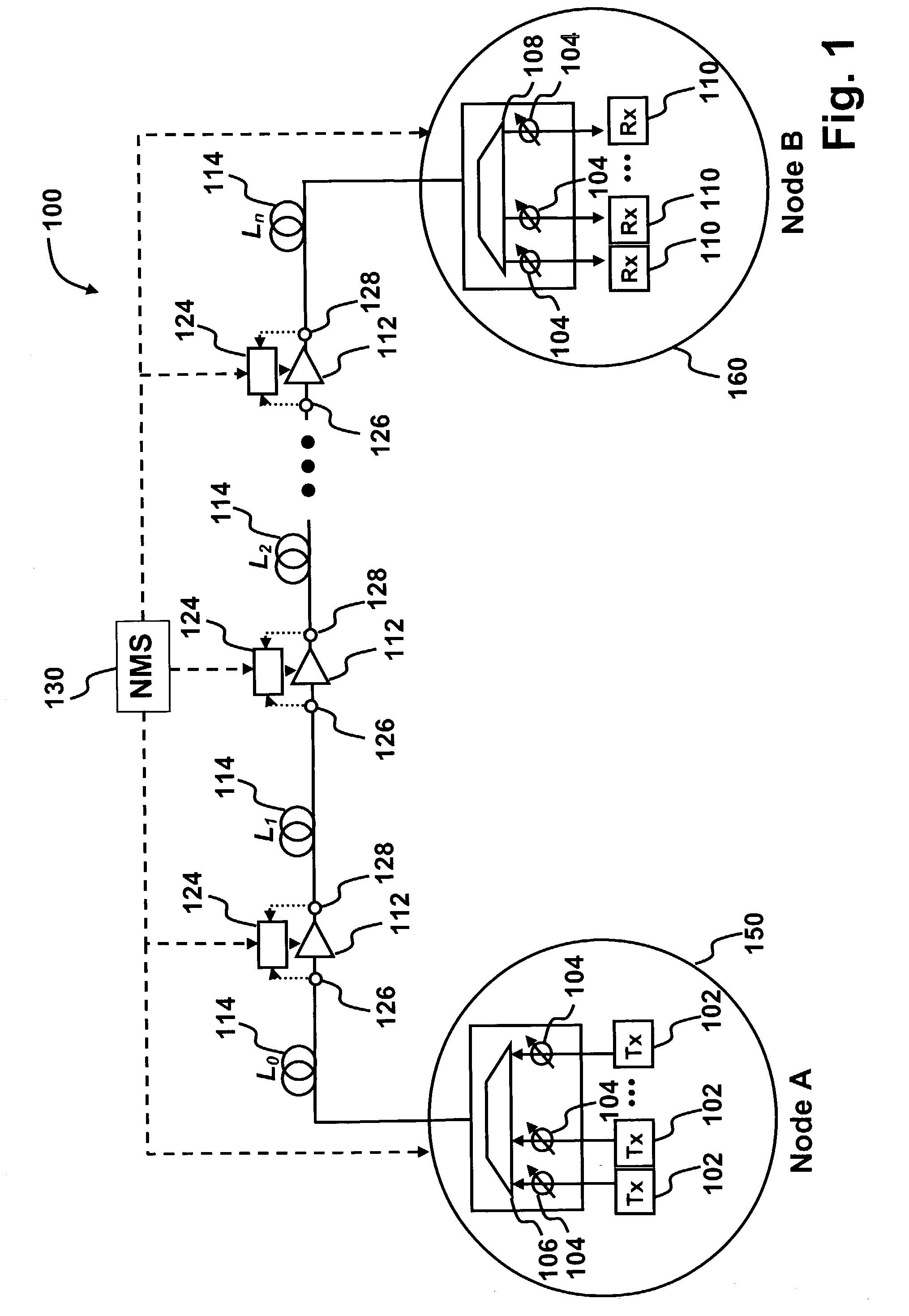
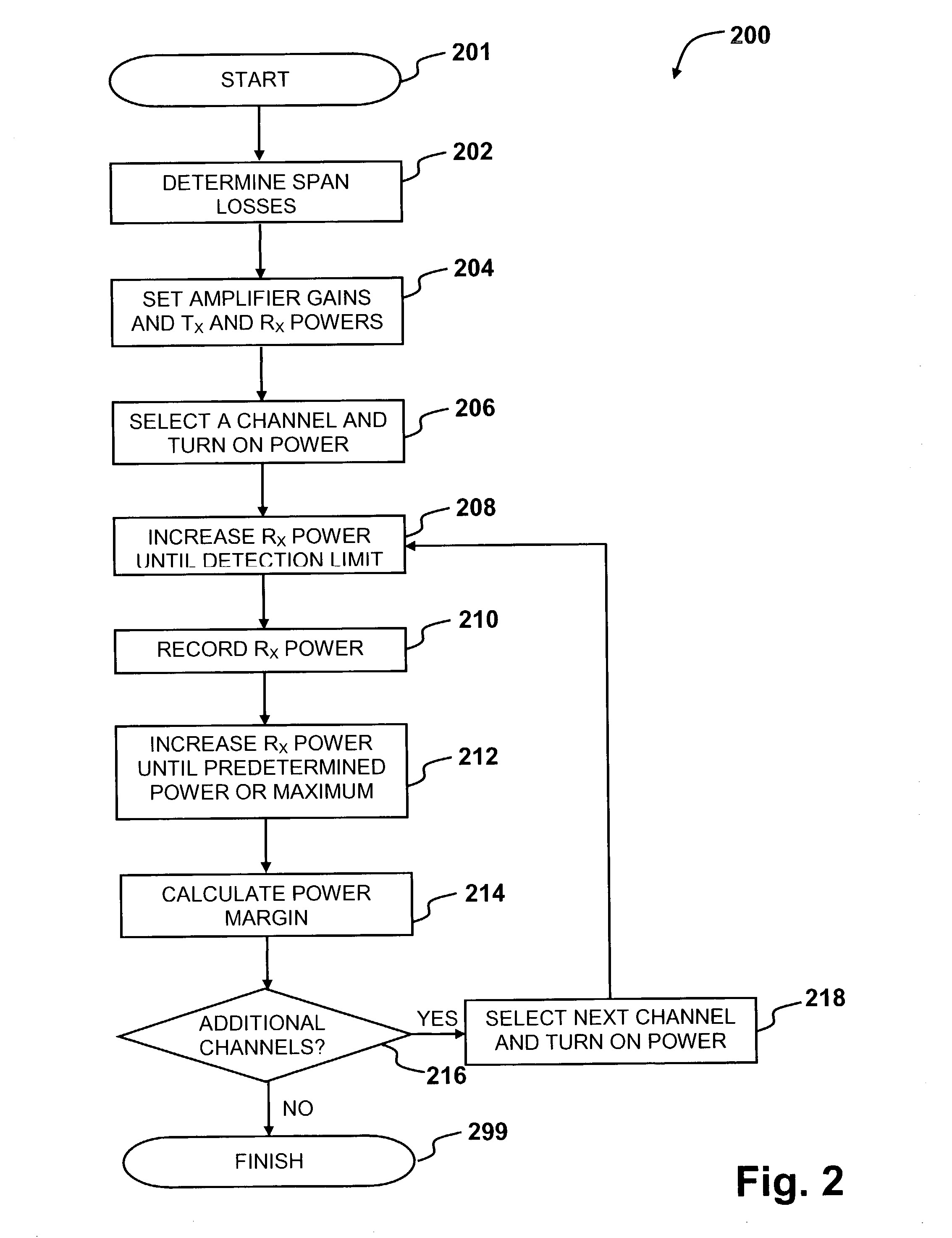
ActiveUS7068932B2Avoid and minimize drawbackSimple initializationTransmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsChannel powerOperating point
A method for automatic initialization of an optical network is provided. A network management system (NMS) performs remote determination of span losses and sets the operating points of network components. The initialization method comprises remotely and automatically setting target gains of optical amplifiers and signal power levels at transmitters and receivers to required operating values. The methods for initialization of the optical network of the embodiments include gain excursion minimization (GEM) for individual channels passing through amplifiers and / or pre-emphasis of the optical link, where channel powers at the transmitters are biased to compensate for the effects of optical amplifiers gain ripple.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +2
Image forming apparatus, optical writing device, and controlling method thereof
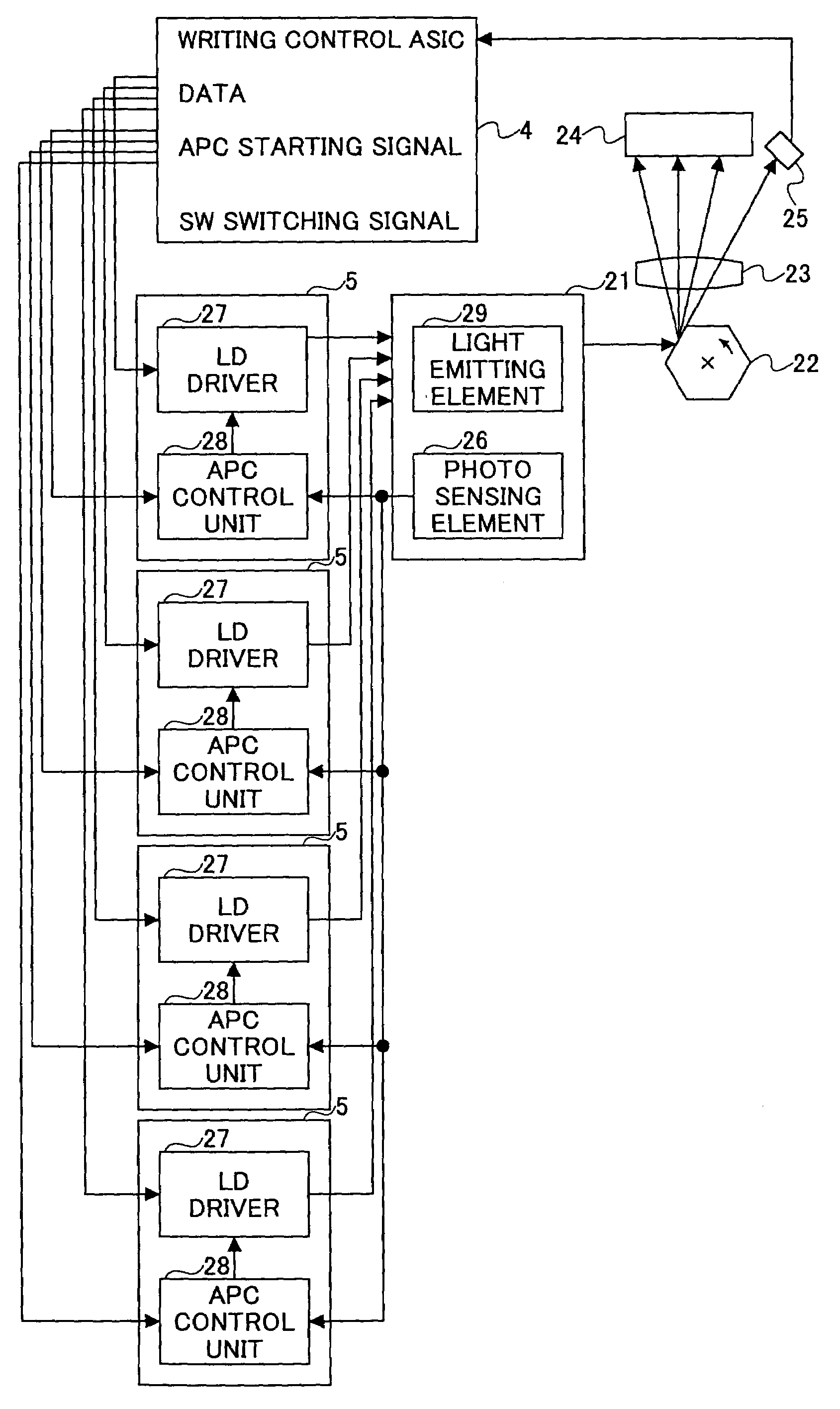
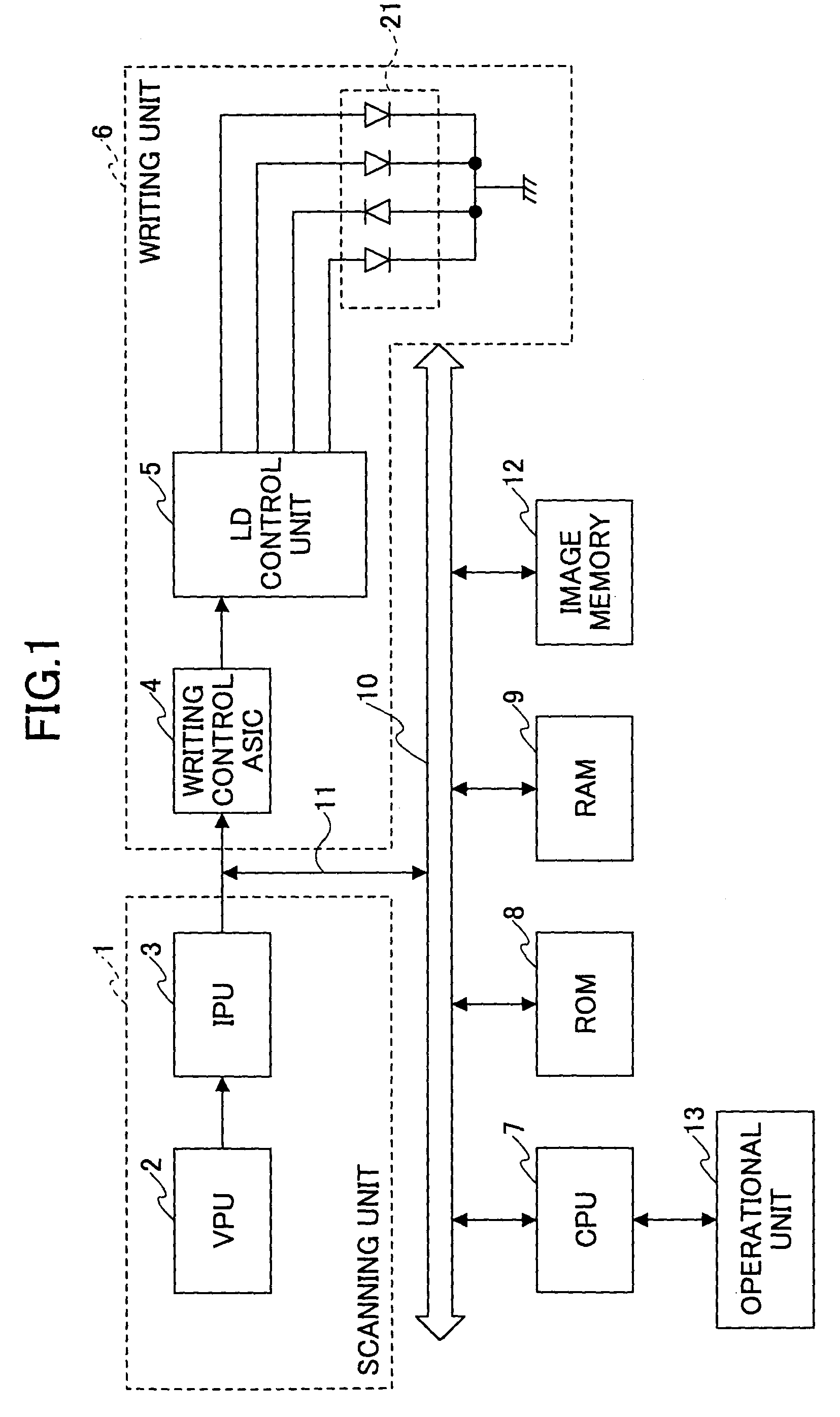
InactiveUS6998603B2Reliable adjustmentEasy to monitorPhotometry using reference valueBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsEngineeringLaser beams
An image forming apparatus is disclosed that is capable of making it simple to initialize a laser system thereof. The image forming apparatus includes a first photo detector that detects a part of a laser beam from each of the lasers and generates respective power adjustment signals for the lasers, a second photo detector that detects another part of the scanning laser beam of each of the lasers and generates a synchronization signal corresponding to each laser, and a power adjustment control unit that changes the output power of each of the lasers to a predetermined value. During the adjustment of output powers of the lasers, the power of a laser is monitored by using the synchronization signal. The power adjustment control unit turns on a laser for power adjustment, and turns off the laser when the scanning synchronization signal is detected twice to complete the power adjustment of the laser, and then starts power adjustment of the next laser.
Owner:RICOH KK
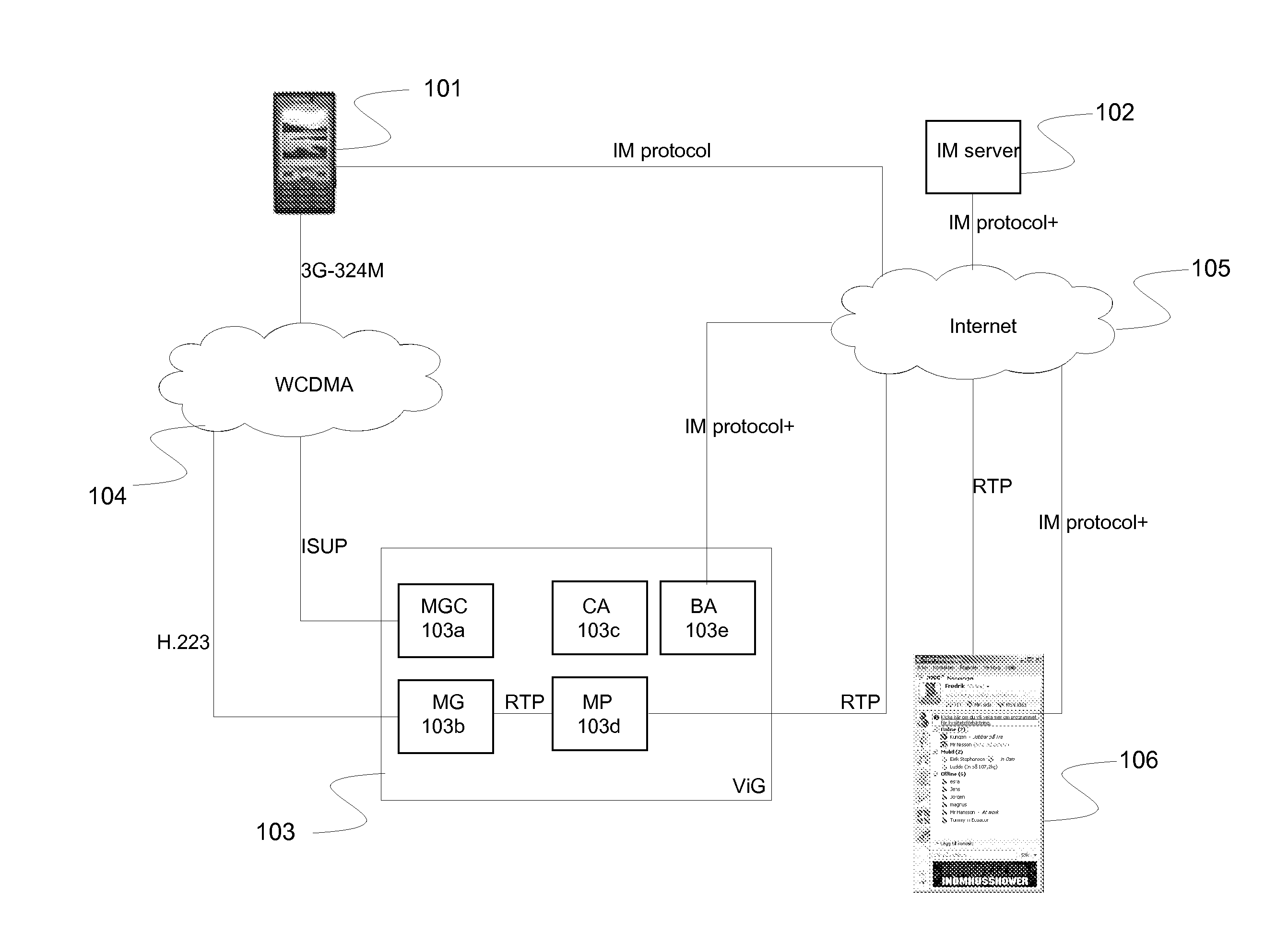
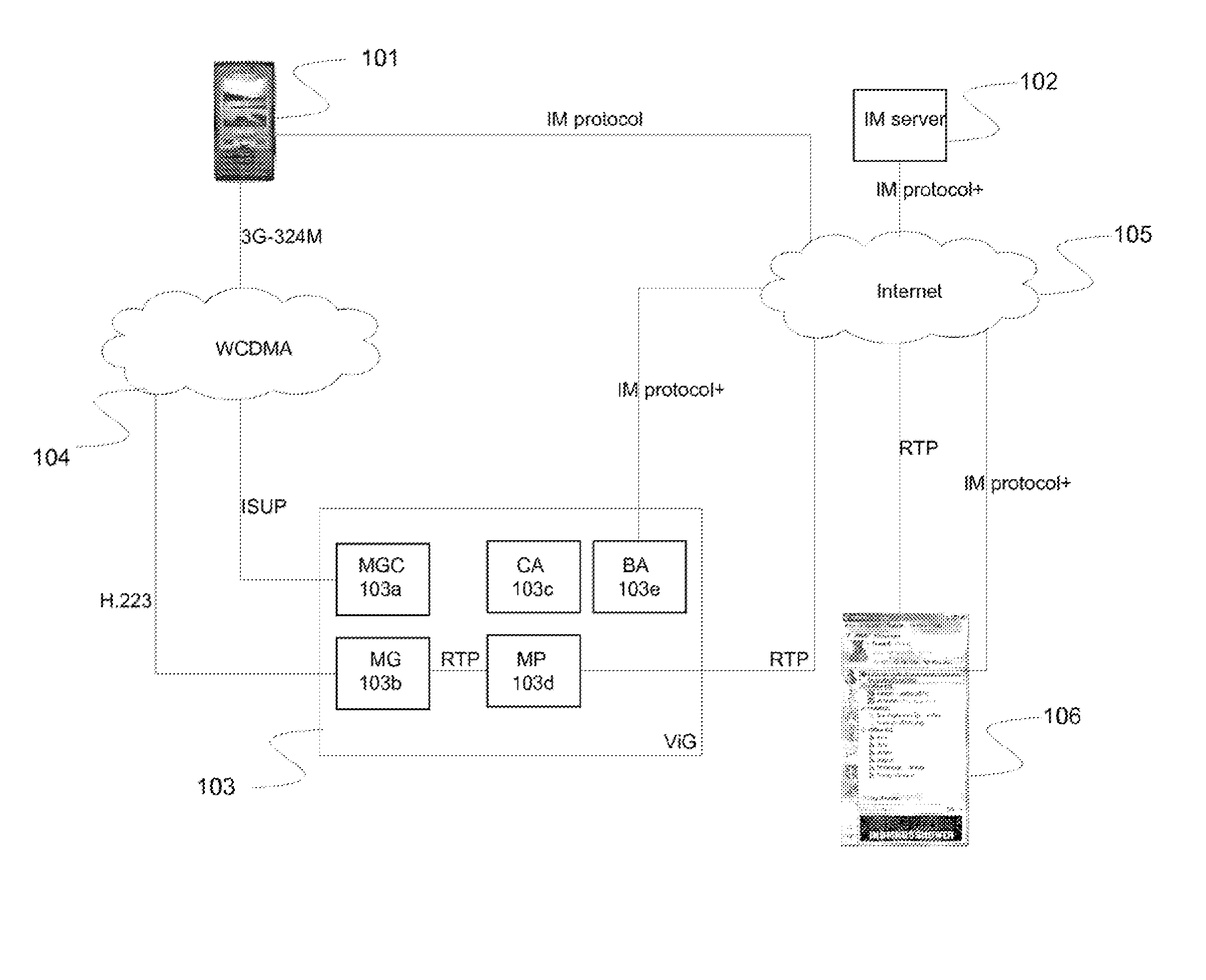
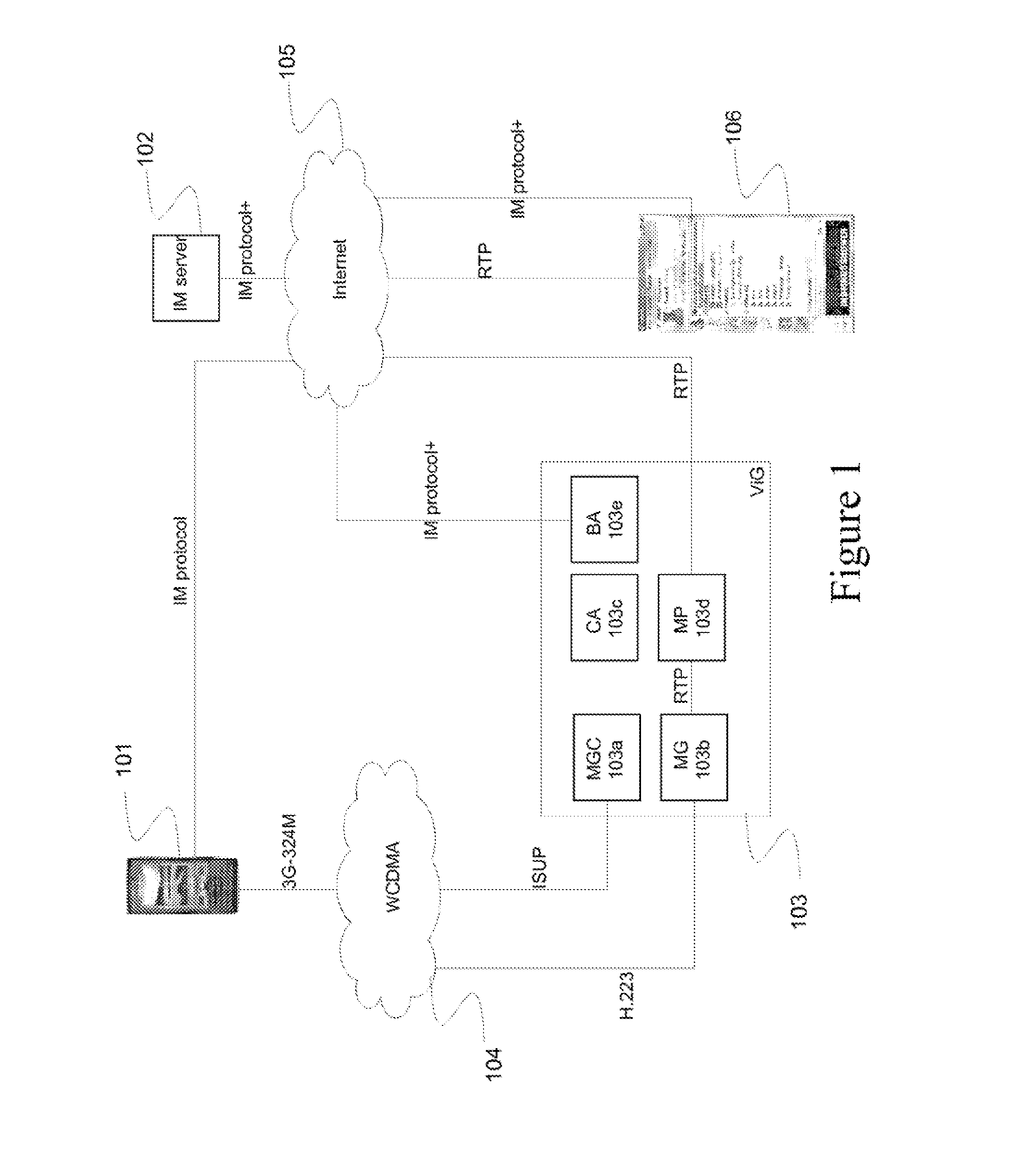
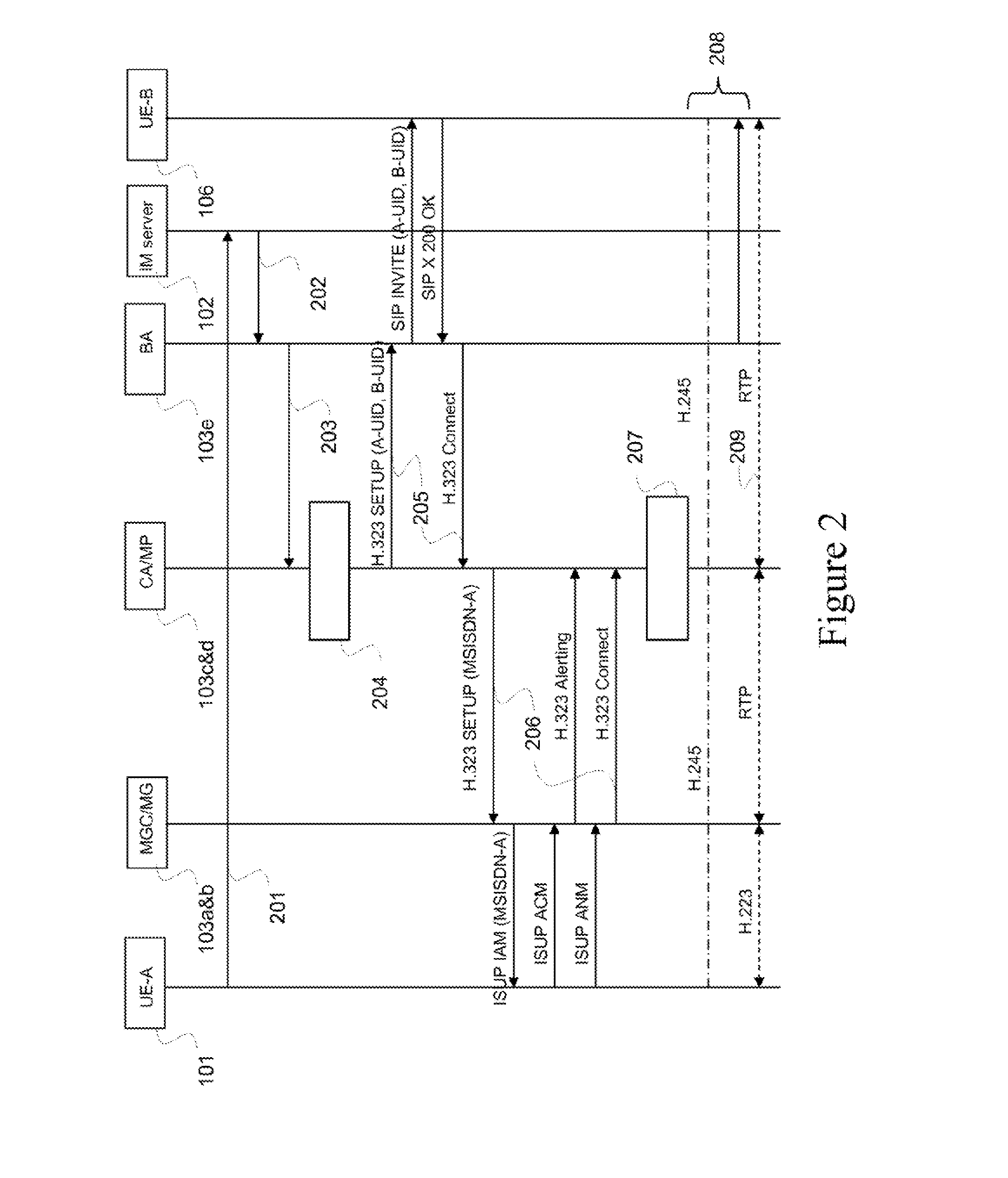
Method and system for a communication session initialization in a telecommunication network
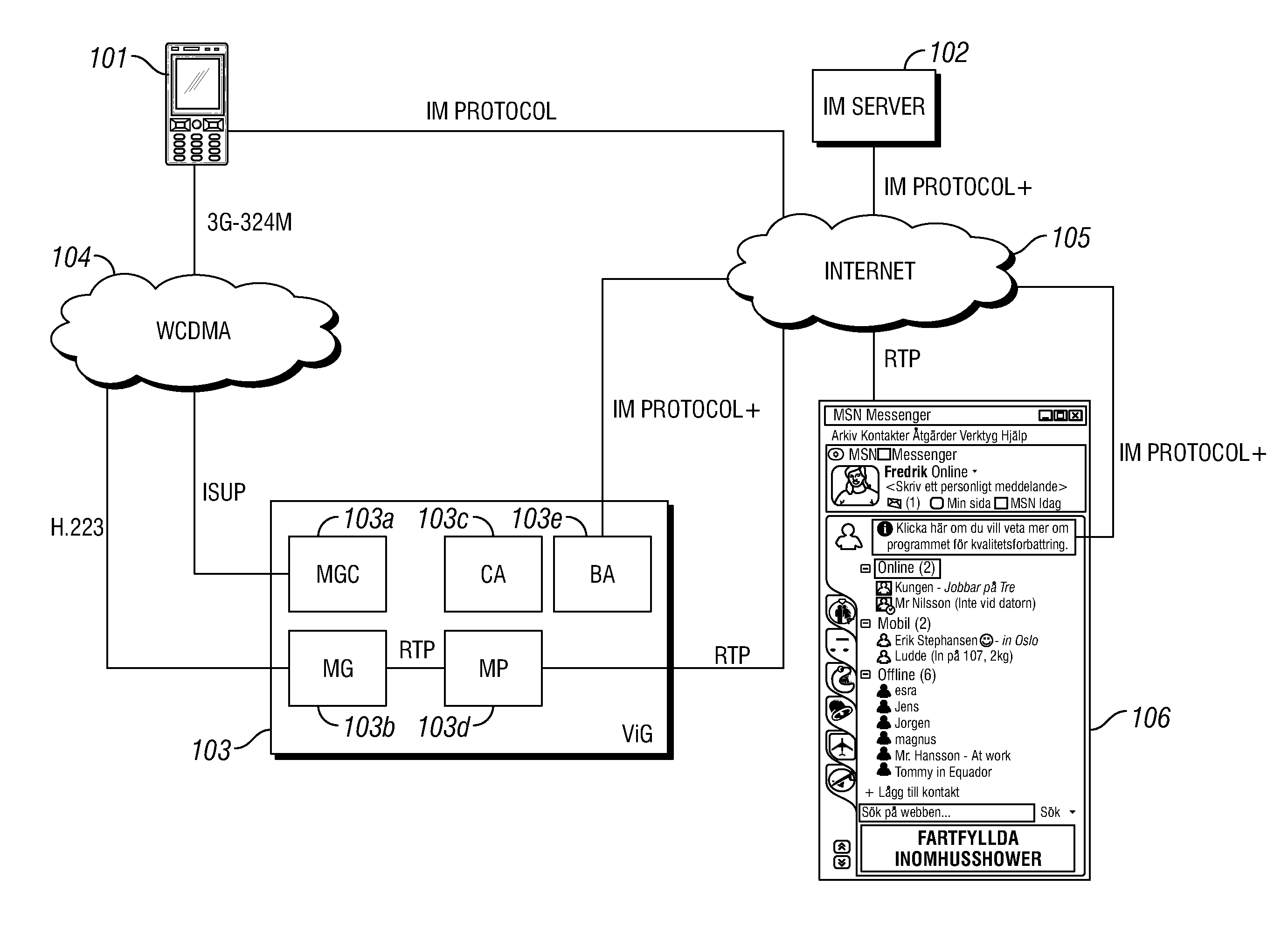
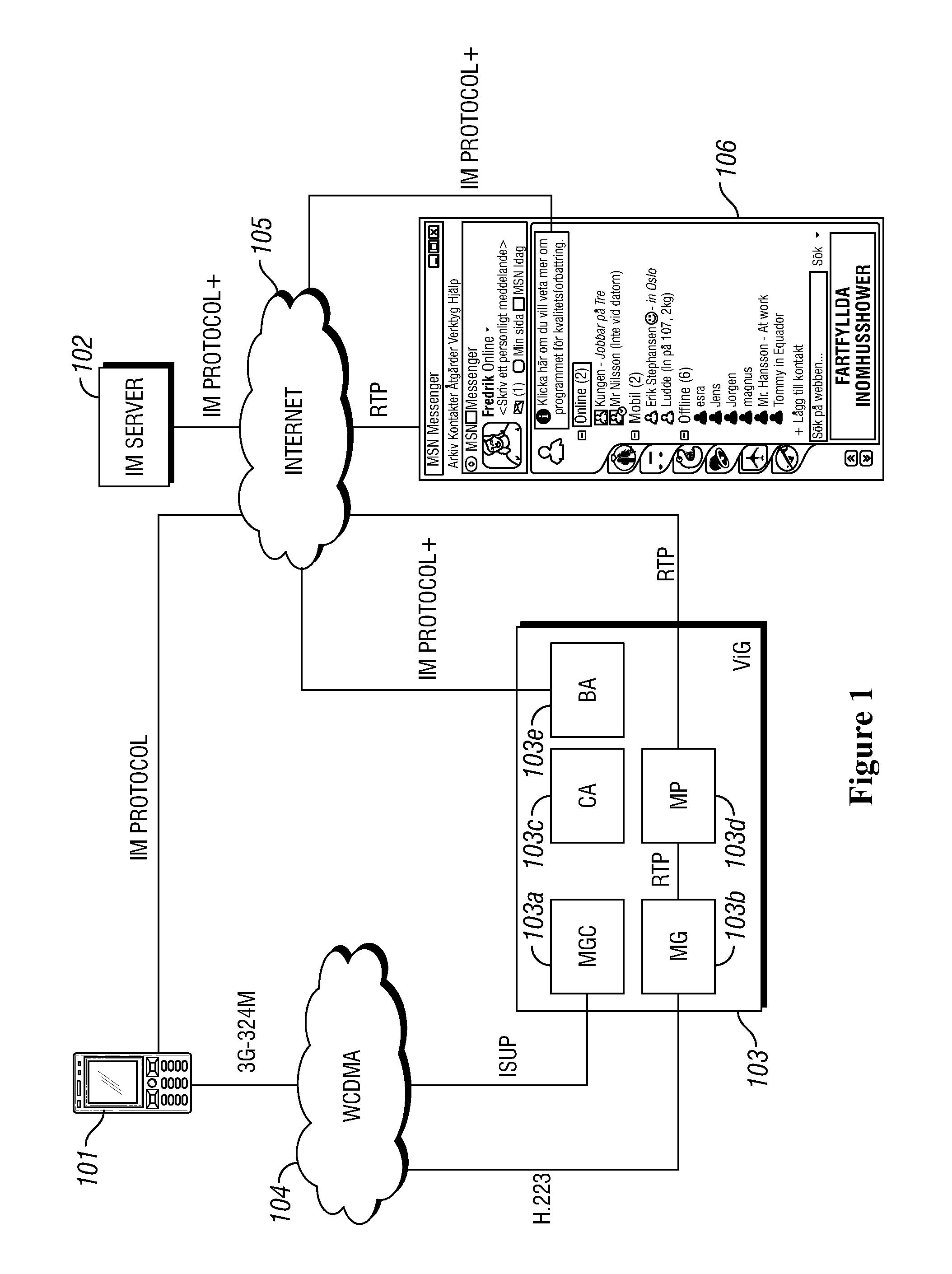
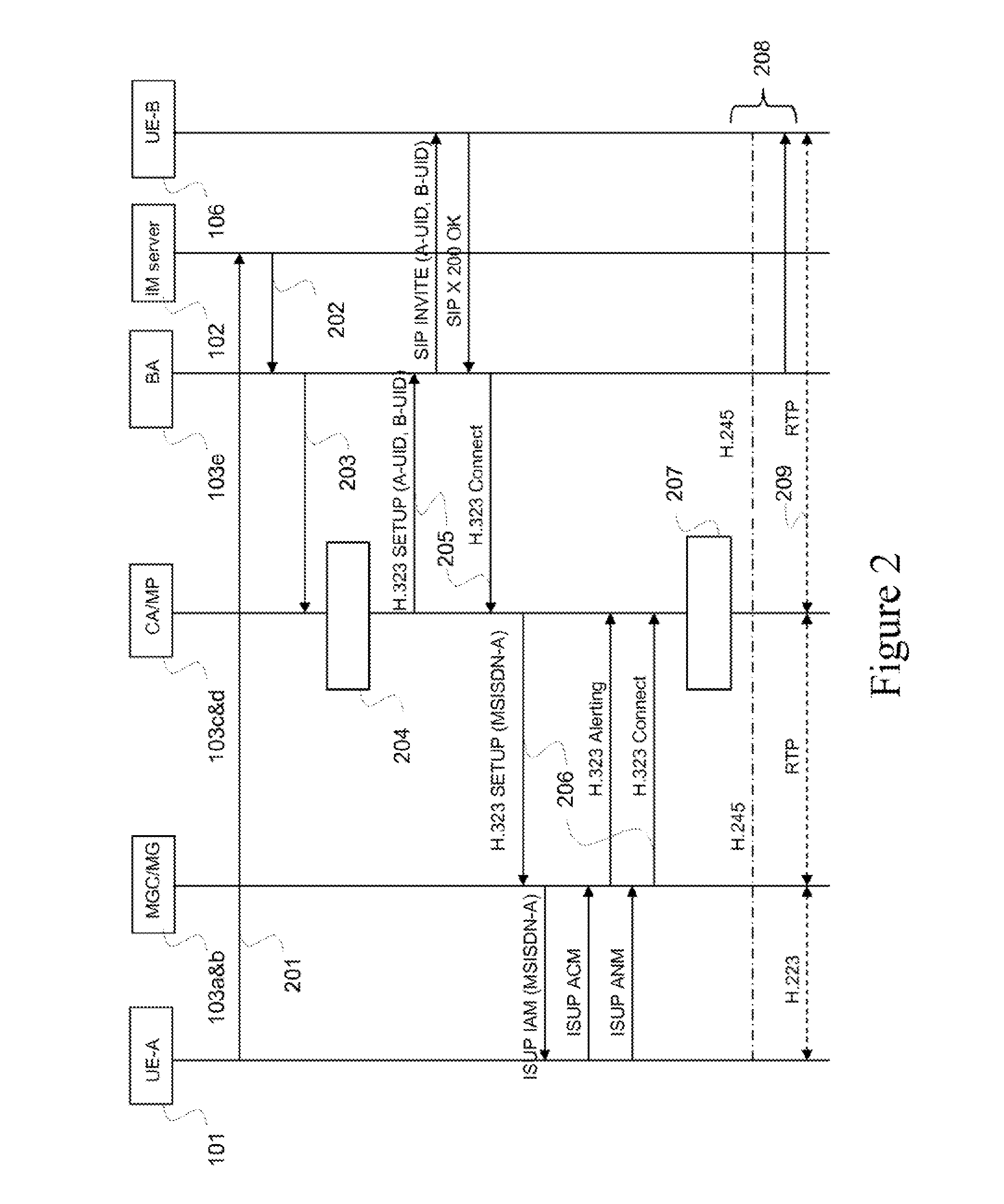
ActiveUS20130107875A1The process is simple and effectiveImprove usabilityNetwork connectionsTelecommunications networkComputer terminal
A method, Call Agent (CA), and circuit-switched terminal for setting up a multimedia session from the circuit-switched terminal toward a packet-switched terminal in a telecommunication network. An Instant Messaging (IM) server receives an IM message from the circuit-switched terminal and forwards the contents of the IM message to the CA. The CA generates or retrieves a unique call token that identifies the terminals, and sends the call token to the IM server, which forwards the token to the circuit-switched terminal. In response, the circuit-switched terminal initiates setup of a circuit-switched call to an identified Media Gateway Controller (MGC). The MGC then sets up a packet-switched session with the packet-switched terminal to complete the setup of the multimedia session.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
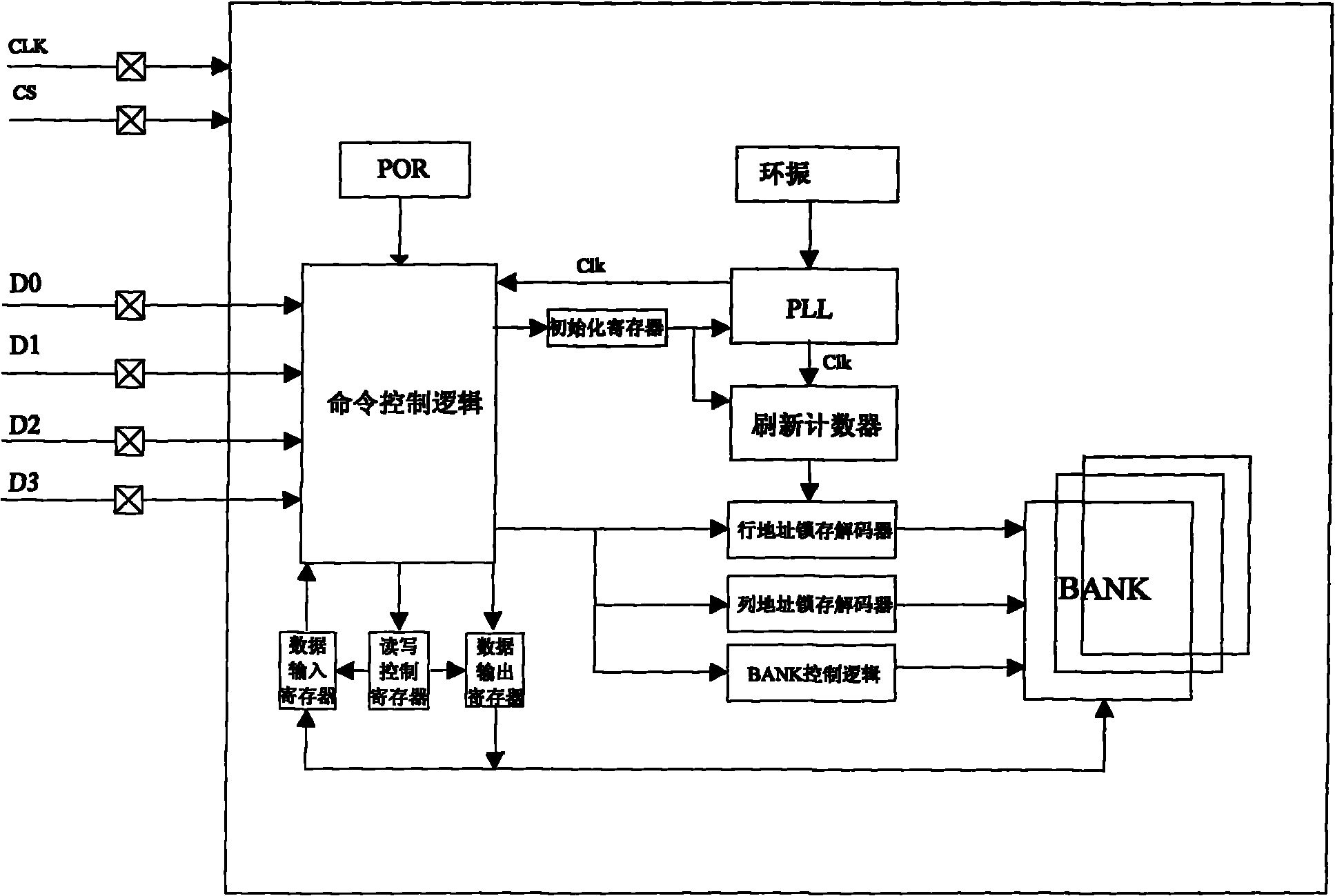
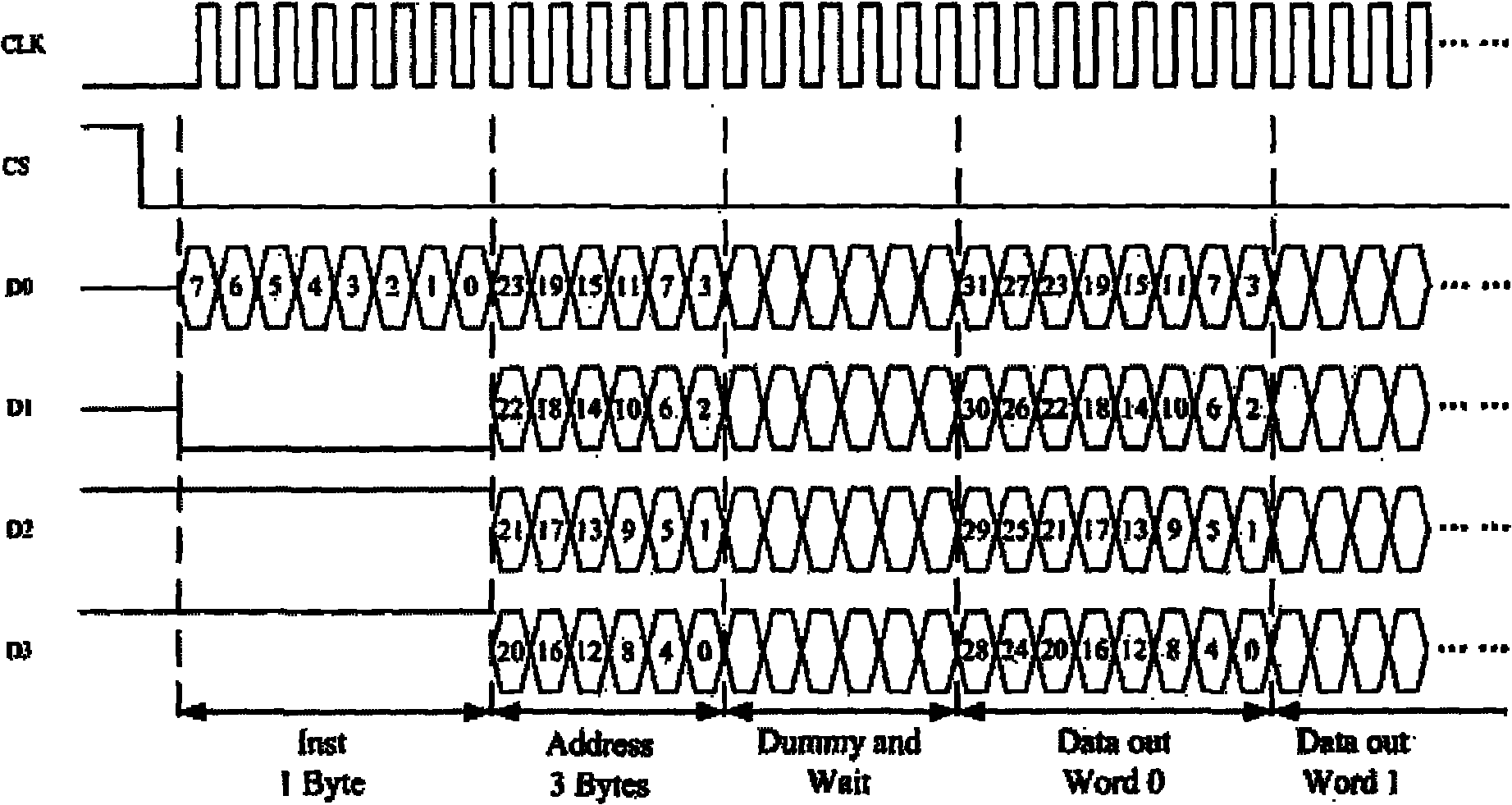
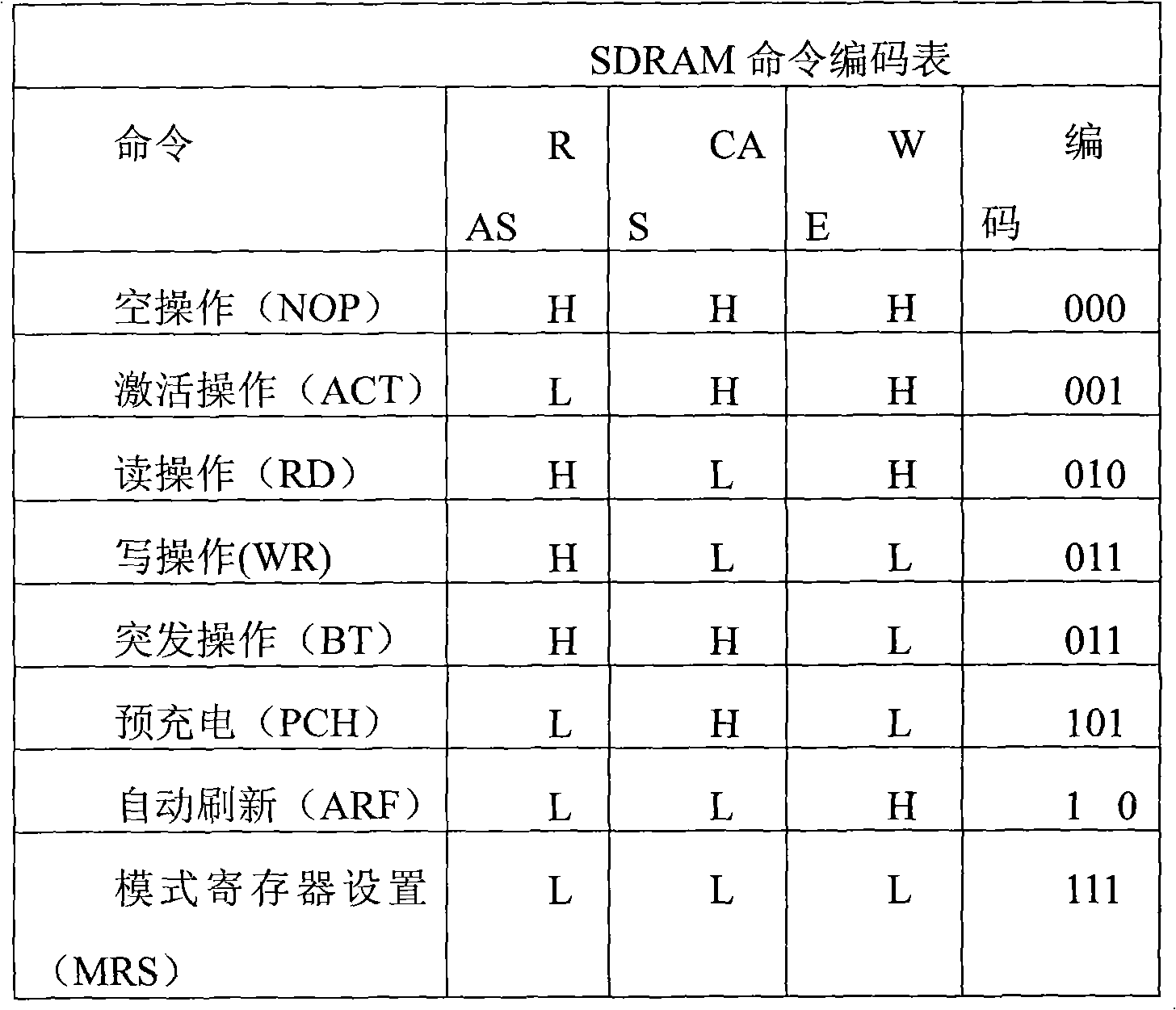
Method for realizing four-channel serial communication of SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory)
ActiveCN102063392AReduce the number of instructionsReduce the number of portsElectric digital data processingProcessor registerSynchronous dynamic random-access memory
The invention relates to a method for realizing four-channel serial communication of an SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory). The method comprises the steps of: transmitting command signals through one channel, and decoding command signals received from a serial channel D0 through a command control logic unit and recognizing the commands, wherein commands for serial four-channel SDRAM include a read operation command, a write operation command and an initialized configuration command; after the command control logic unit recognizes the initialized command, outputting a signal for configuring a PLL (Phase Locked Loop) and refreshing a counter, executing the configuring operations of configuring the PLL and refreshing the counter; after the command control logic unit recognizes the read and write commands, analyzing a received address signal to generate a column address, a row address and a BANK signal and sending the column address, the row address and the BANK signal to a column address latch decoder, a row address latch decoder and a BANK control logic; and then transmitting data signals, wherein the transmission of the data signals is controlled by a read-write register. The method changes the parallel communication mode of the SDRAM to the serial communication and realizes the four-channel serial communication function of the SDRAM.
Owner:HANGZHOU SYNOCHIP DATA SECURITY TECH CO LTD
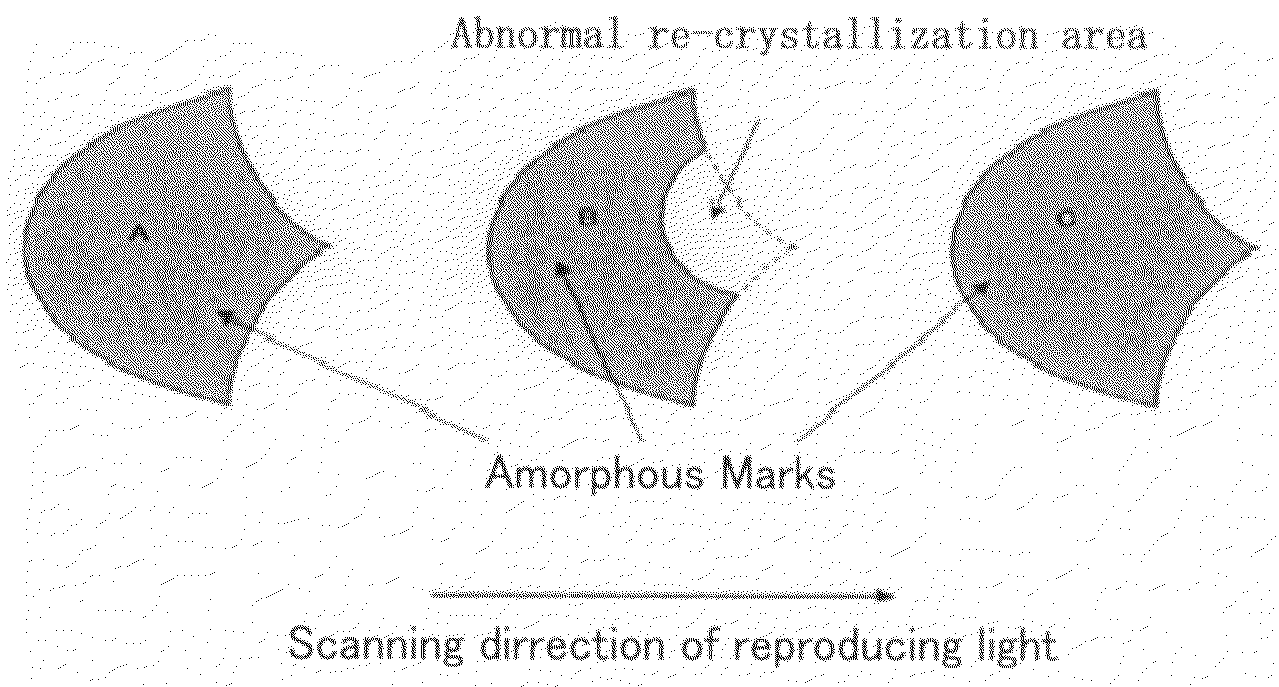
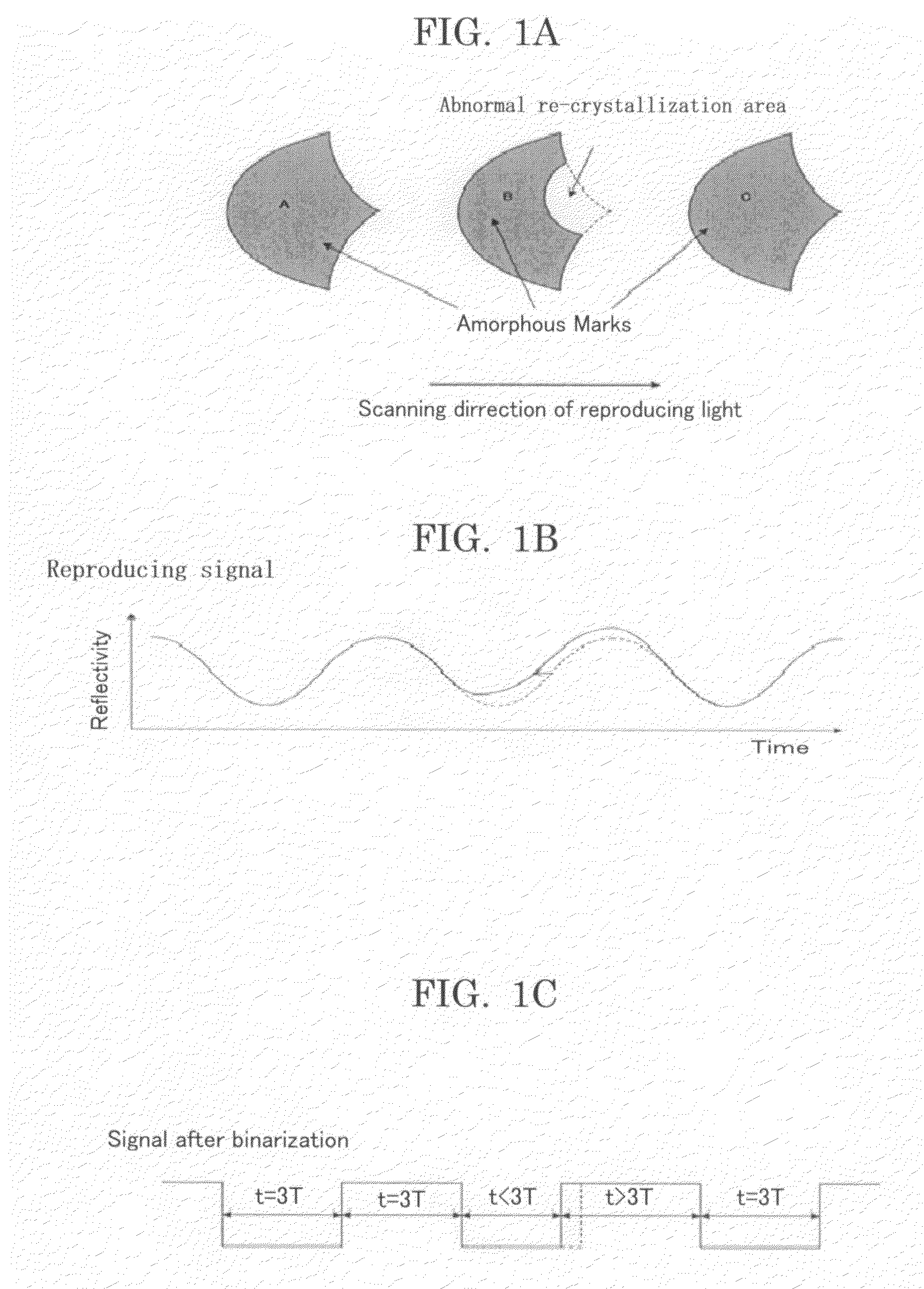
Optical Recording Medium and Optical Recording Method
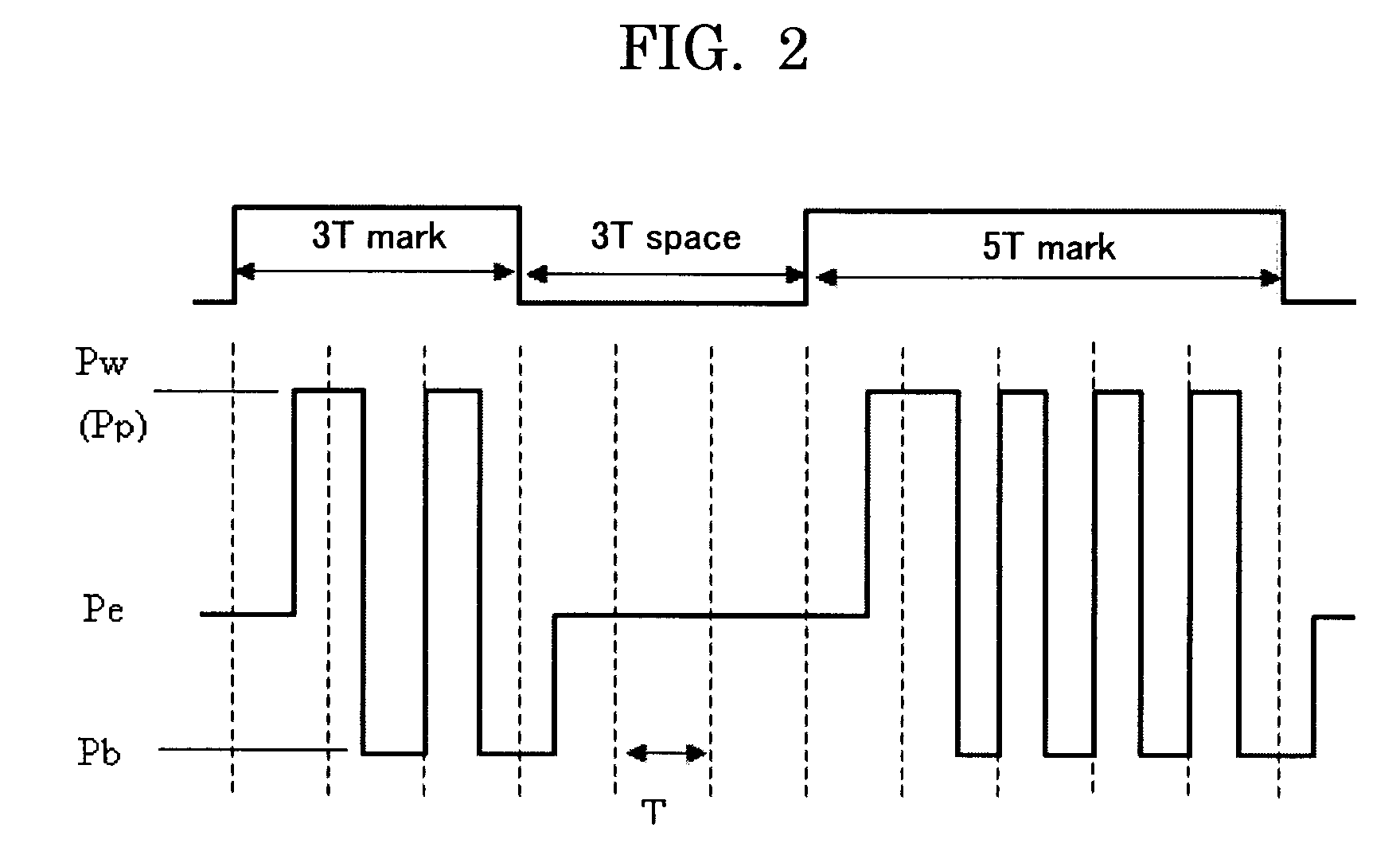
InactiveUS20090116365A1Superior in re-writing performanceStable amorphous and crystal phaseOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageOptical recordingComputer science
An optical recording method to record information with a mark length recording method, where an amorphous mark and a crystal space are recorded only in the groove of a substrate having a guide groove, with the temporal length of the mark and the space of nT (T denotes a reference clock period; n denotes a natural number). The space is formed at least by an erase pulse of power Pe; all the marks of 4T or longer are formed by a multi pulse alternatively irradiating a heating pulse of power Pw and a cooling pulse of power Pb while Pw>Pb; and the Pe and the Pw satisfy the following relations:0.15≦Pe / Pw≦0.4, and0.4≦τw / (τw+τb)≦0.8,where τw denotes the sum of the length of the heating pulses, and τb denotes the sum of the length of the cooling pulses.
Owner:RICOH KK
Control system for several separately arranged consumers, especially lamp operating devices, and start-up method
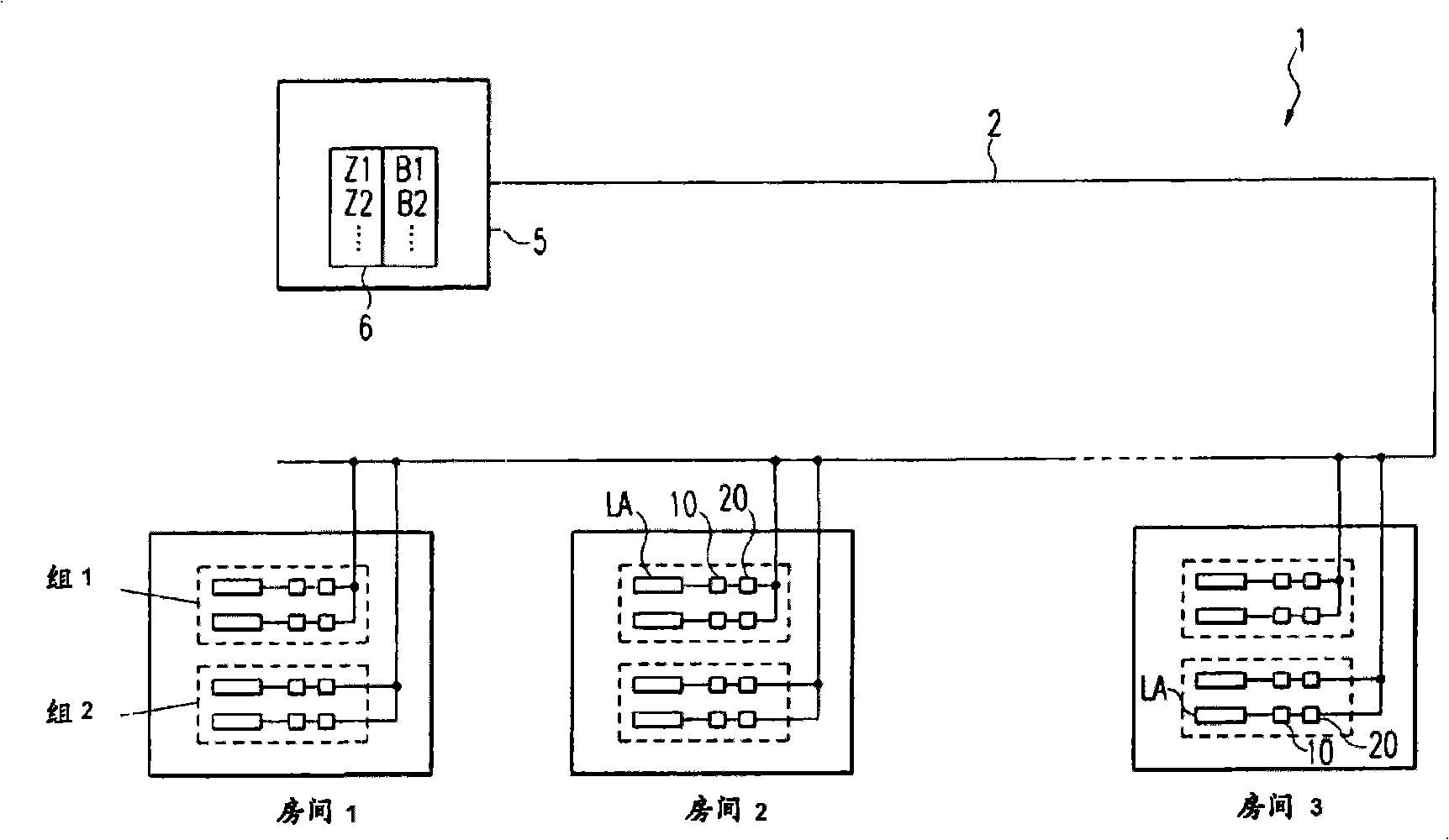
InactiveCN101322442ASimplify workReduce consumptionElectric light circuit arrangementTransmissionTransceiverControl system
Disclosed is a control system (1) for several separately arranged consumers (10), especially lamp operating devices. Said control system comprises at least one control station (5), a control line (2) that connects the control station (5) to each consumer (10), and a transceiver unit (11) which is allocated to each consumer (10) and is used for communicating with the control station (5). A serviceaddress via which the consumer (10) can be contacted by the control station (5) is assigned to each consumer (10). According to the invention, a memory part (20) that is separated from the consumer (10) is associated with each consumer (10) in order to store the service address, said memory part (20) being connected to the associated consumer (10) via the control line (2).
Owner:ZUMTOBEL LIGHTING INC
Wireless transmission device
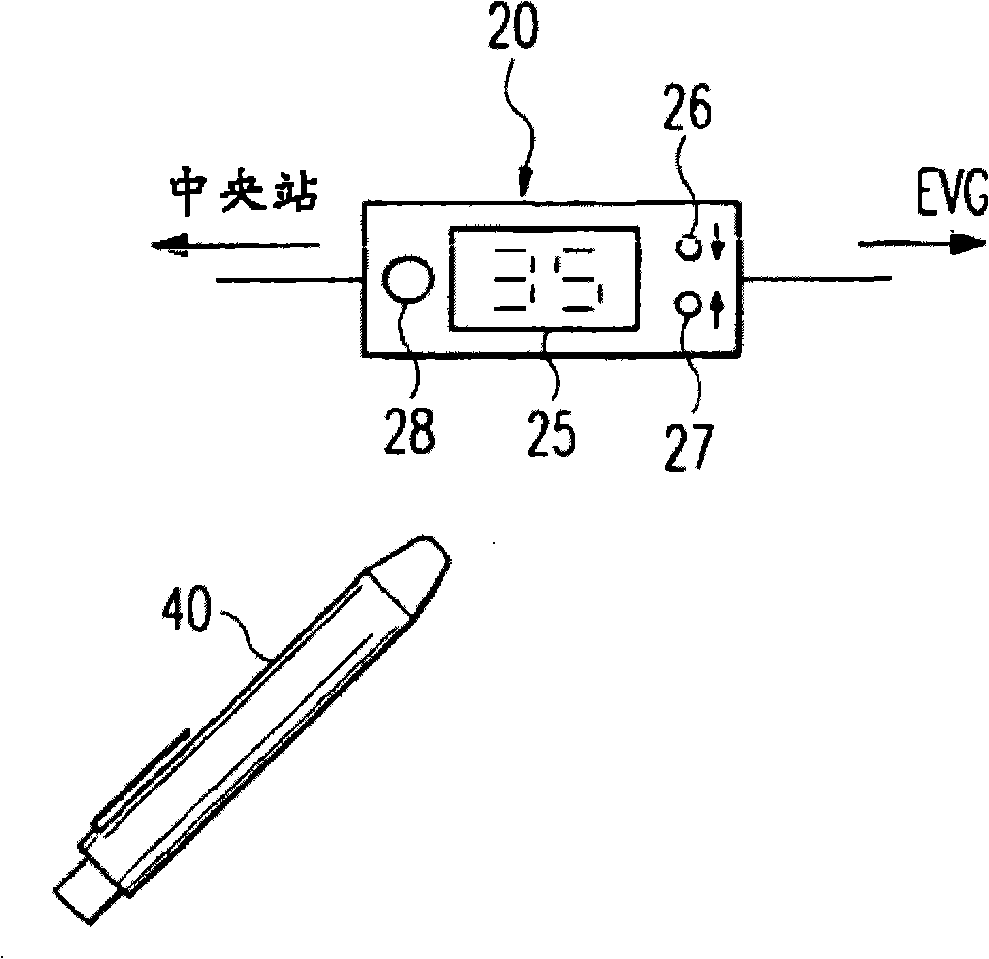
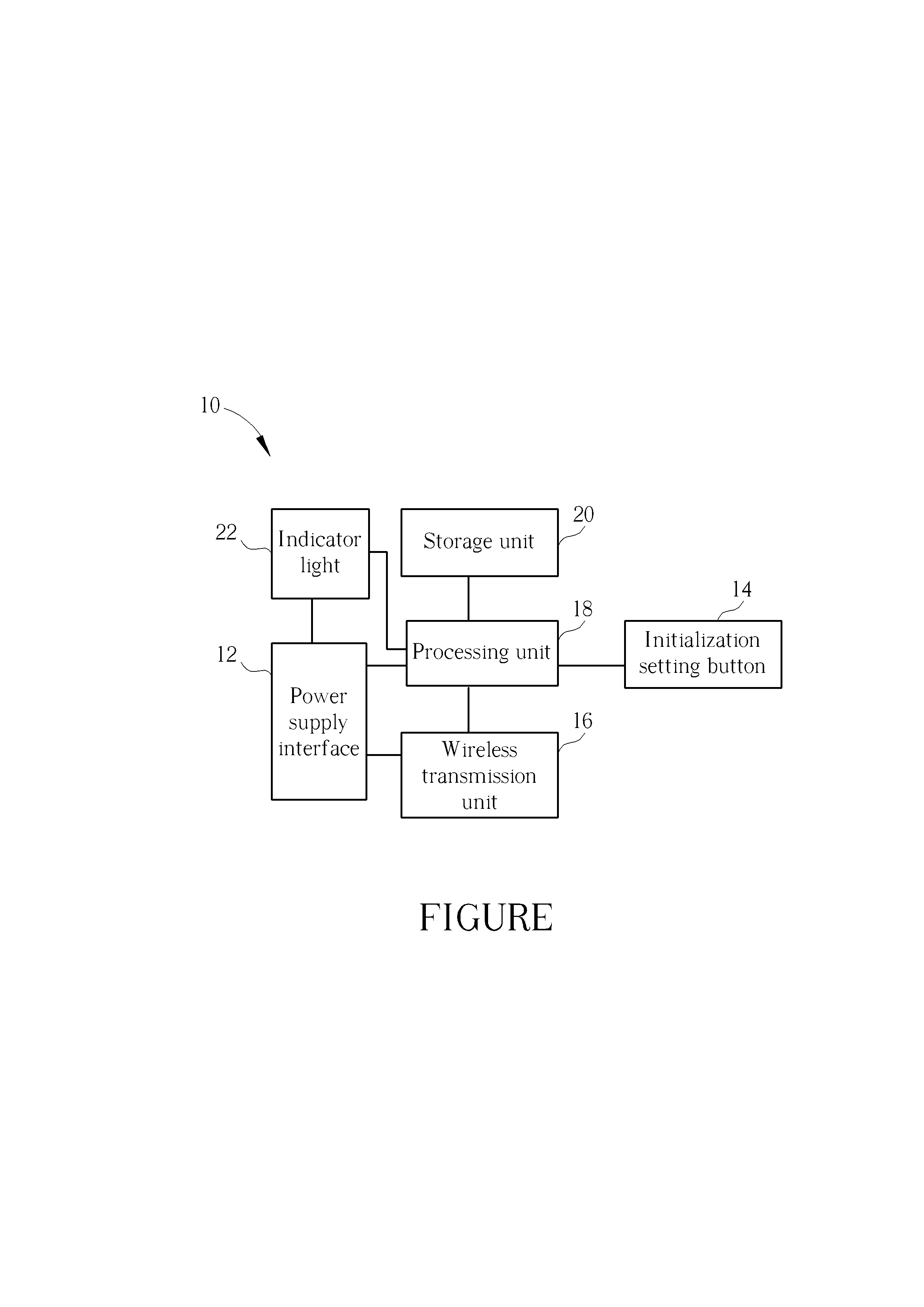
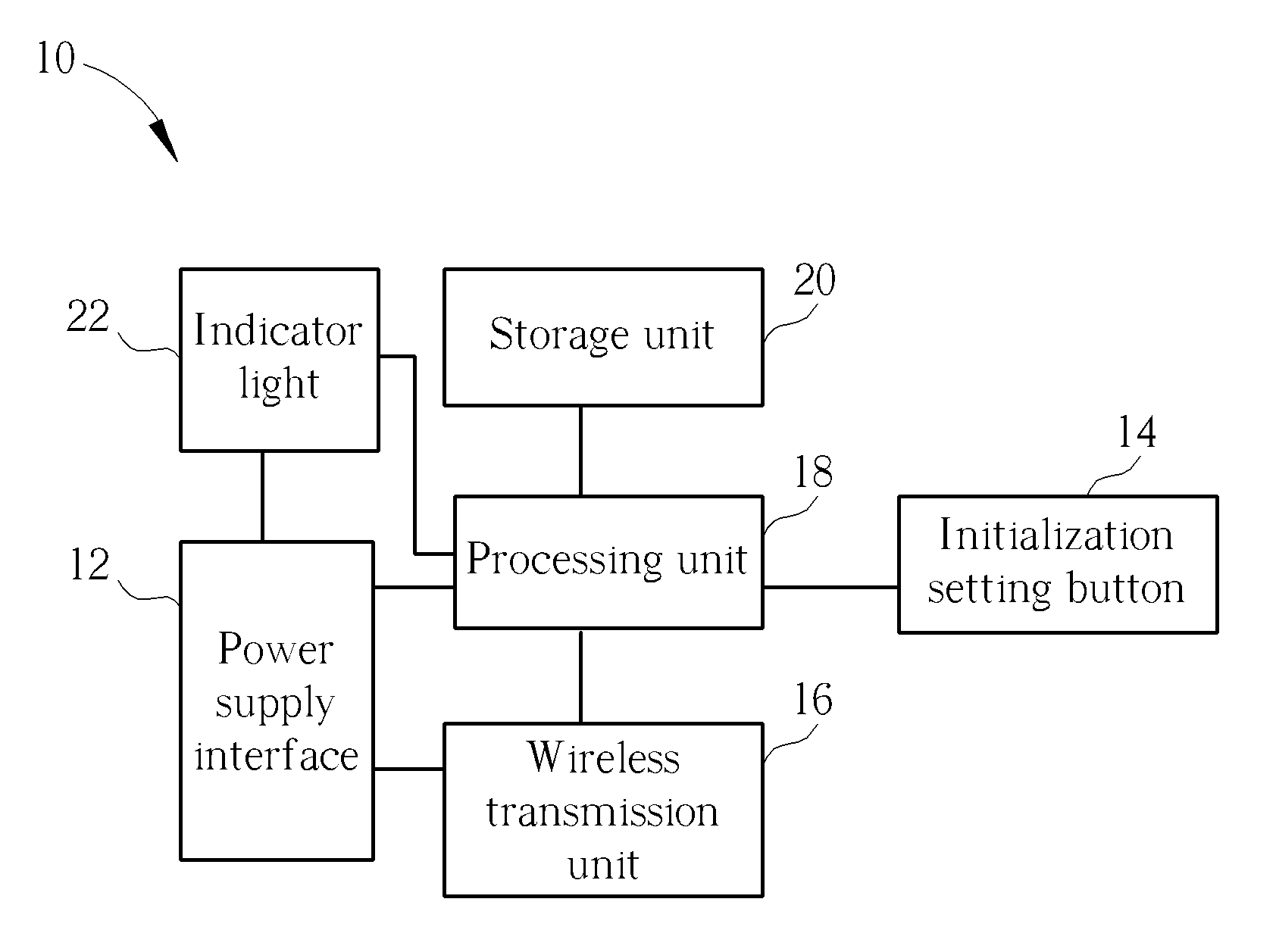
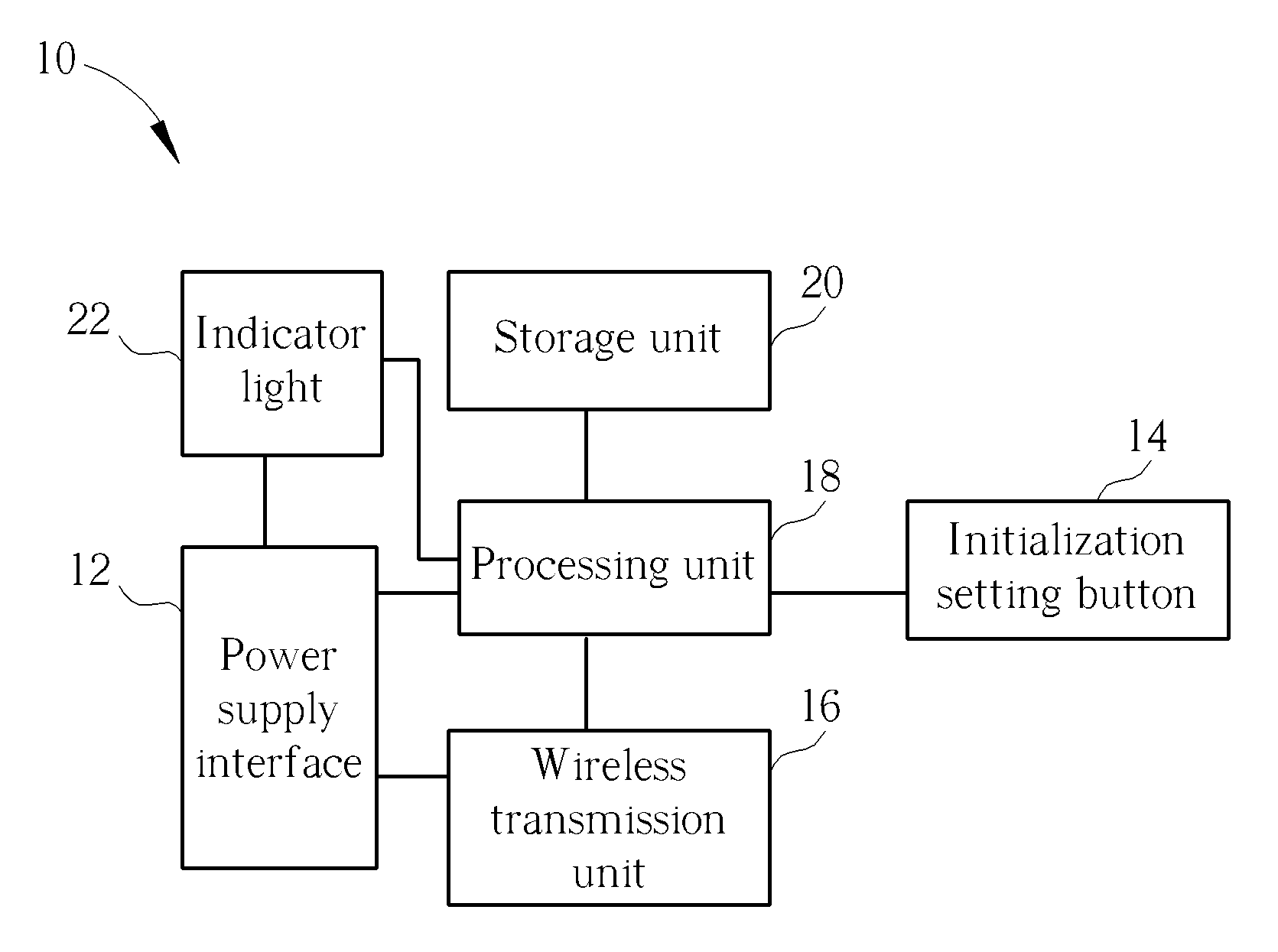
ActiveUS20130322098A1Low investment costPrecise positioningElectrical apparatusLighting support devicesWireless transmissionEmbedded system
A wireless transmission device, arranged inside a display object or connected with the display object, includes a power supply interface, an initialization setting button, a wireless transmission unit, a processing unit, and a storage unit. The input end of the power supply interface is connected with the power supply end of the display object, the output end of the power supply interface is connected with the wireless transmission unit and the processing unit respectively, and the initialization setting button and the storage unit are connected with the processing unit respectively. A unique identification assigned to the display object is stored in the storage unit. Initialization setting of the wireless transmission device is implemented by pressing the initialization setting button, and the processing unit transmits out the identification, orientation, and / or predetermined viewable angle of the display object constantly or regularly via the wireless transmission unit.
Owner:LEE TING YAN +1
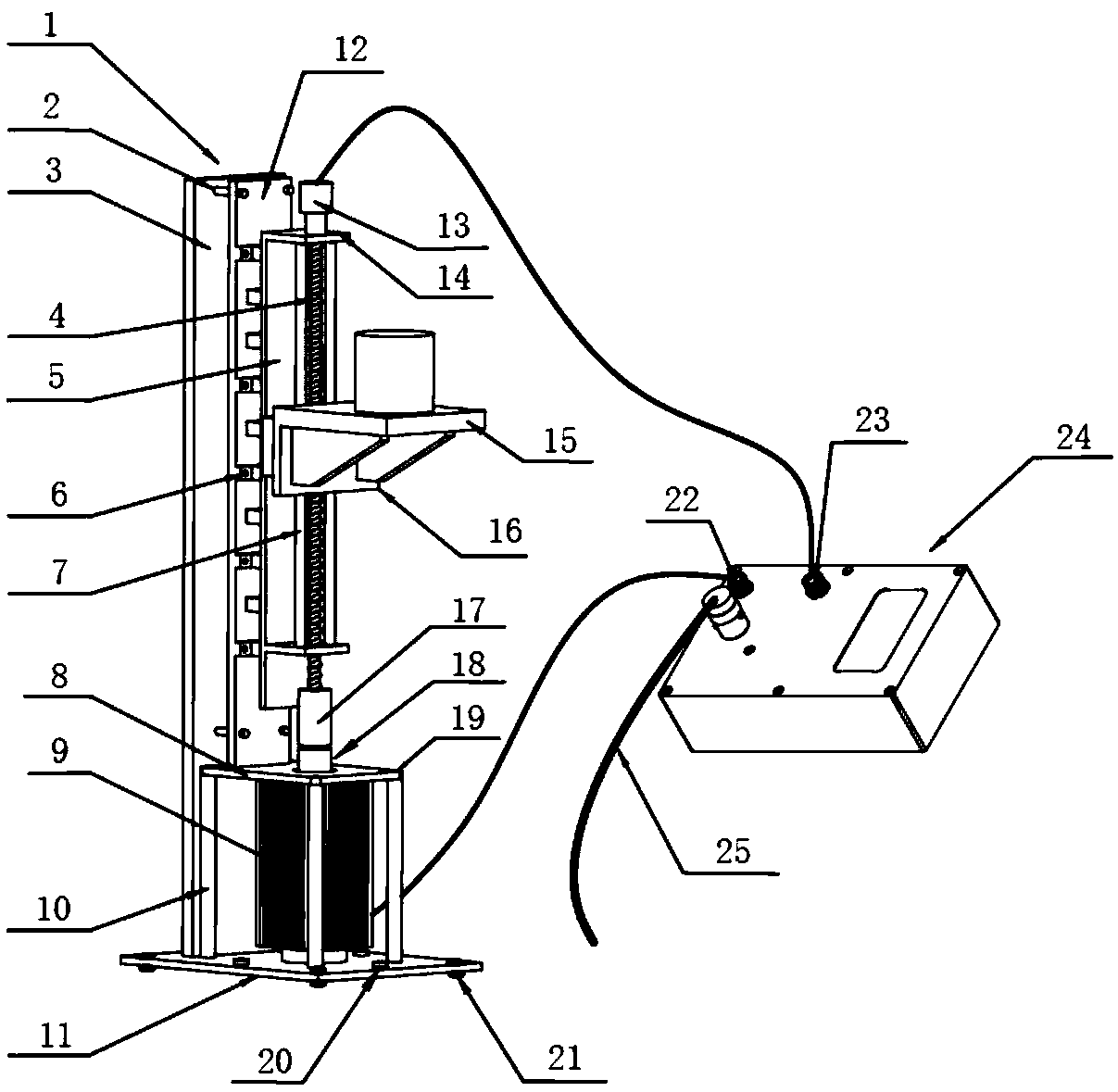
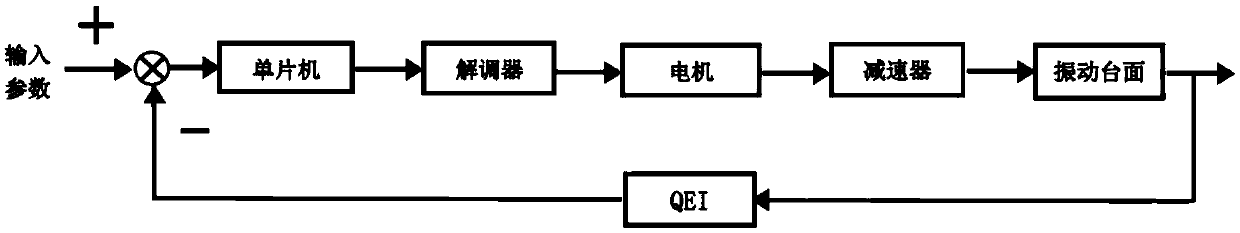
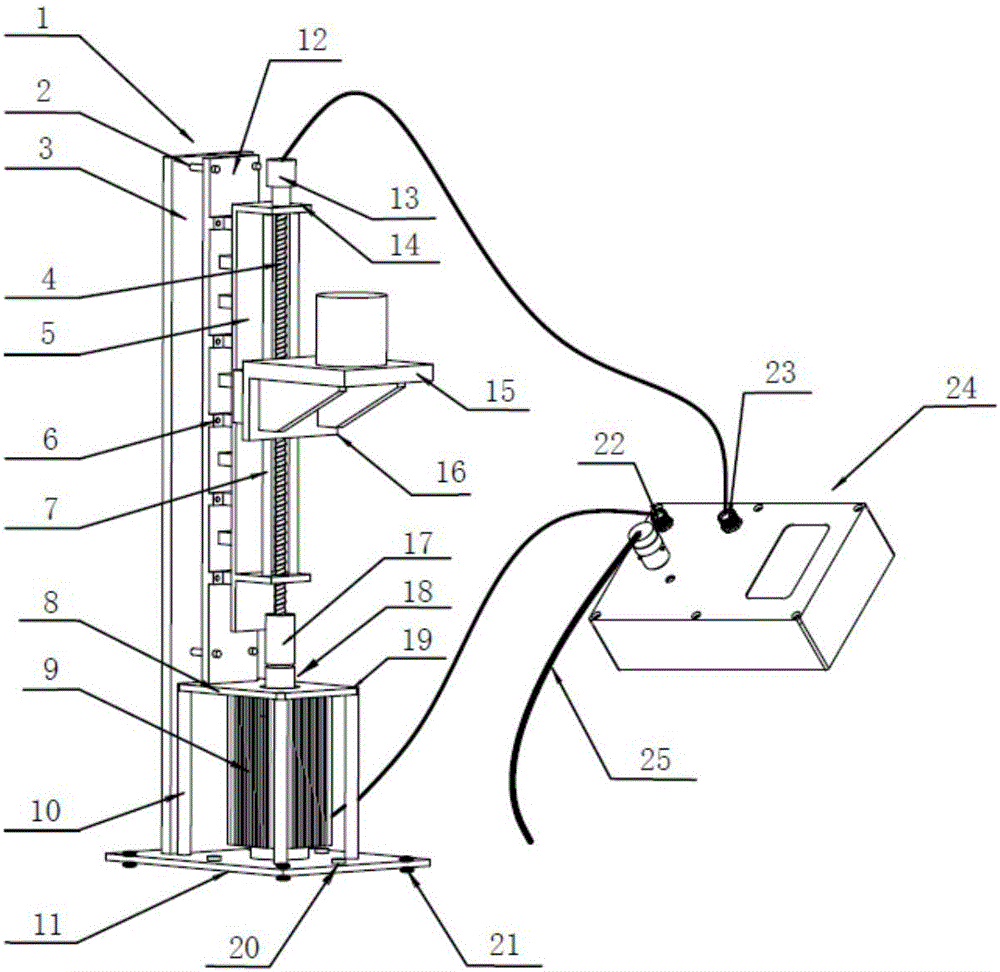
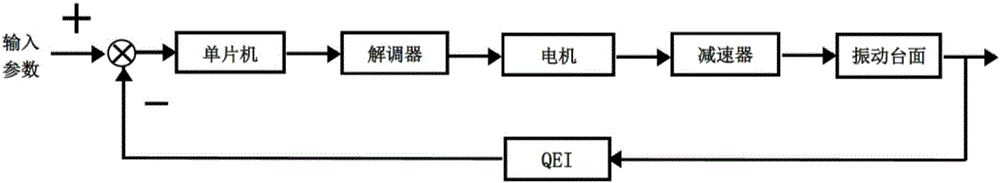
A Feedback Control Vibration Table Based on Stepping Motor
InactiveCN106768769BIncrease the itineraryWide range of measurement applicationsVibration testingMicrocomputerMicrocontroller
The invention discloses a stepper motor based feedback-control vibrating table. The vibrating table comprises a vibrating table body and a controller, wherein the vibrating table body consists of a stepper motor, a shaft coupling, a fixed guide rail, a vibrating table top, an orthogonal decoder and a base, and a control system consists of a single-chip microcomputer and a demodulator. According to the vibrating table, the stepper motor is adopted to carry out driving, and the control system adopts feedback-control regulation, so that the problems of the existing vibrating tables that the size is large, the initialized calibration is complicated, the upgrading cost is high, and the like are overcome.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Stepper motor based feedback-control vibrating table
InactiveCN106768769AIncrease the itineraryWide range of measurement applicationsVibration testingMicrocomputerMicrocontroller
The invention discloses a stepper motor based feedback-control vibrating table. The vibrating table comprises a vibrating table body and a controller, wherein the vibrating table body consists of a stepper motor, a shaft coupling, a fixed guide rail, a vibrating table top, an orthogonal decoder and a base, and a control system consists of a single-chip microcomputer and a demodulator. According to the vibrating table, the stepper motor is adopted to carry out driving, and the control system adopts feedback-control regulation, so that the problems of the existing vibrating tables that the size is large, the initialized calibration is complicated, the upgrading cost is high, and the like are overcome.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
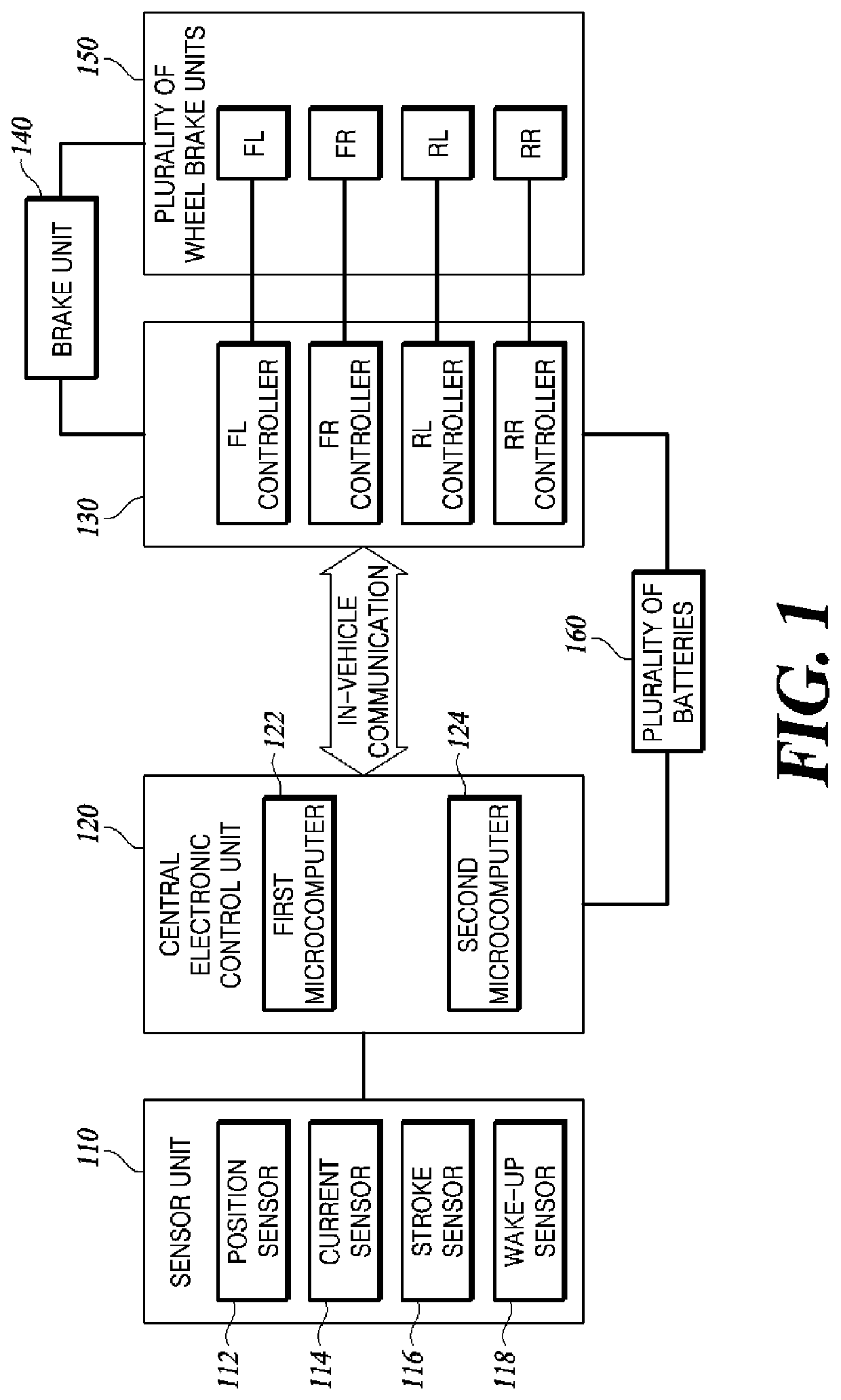
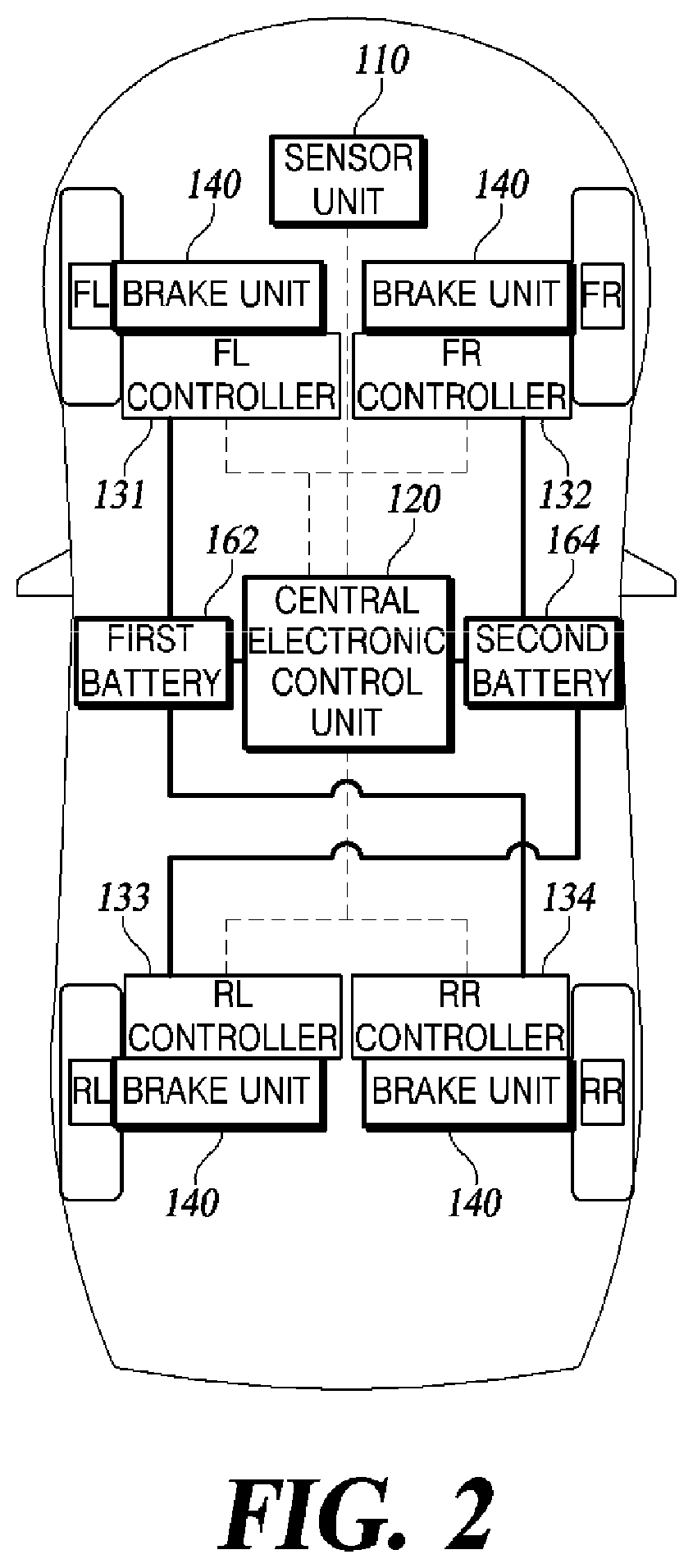
Electro-mechanical brake device and method of controlling the same
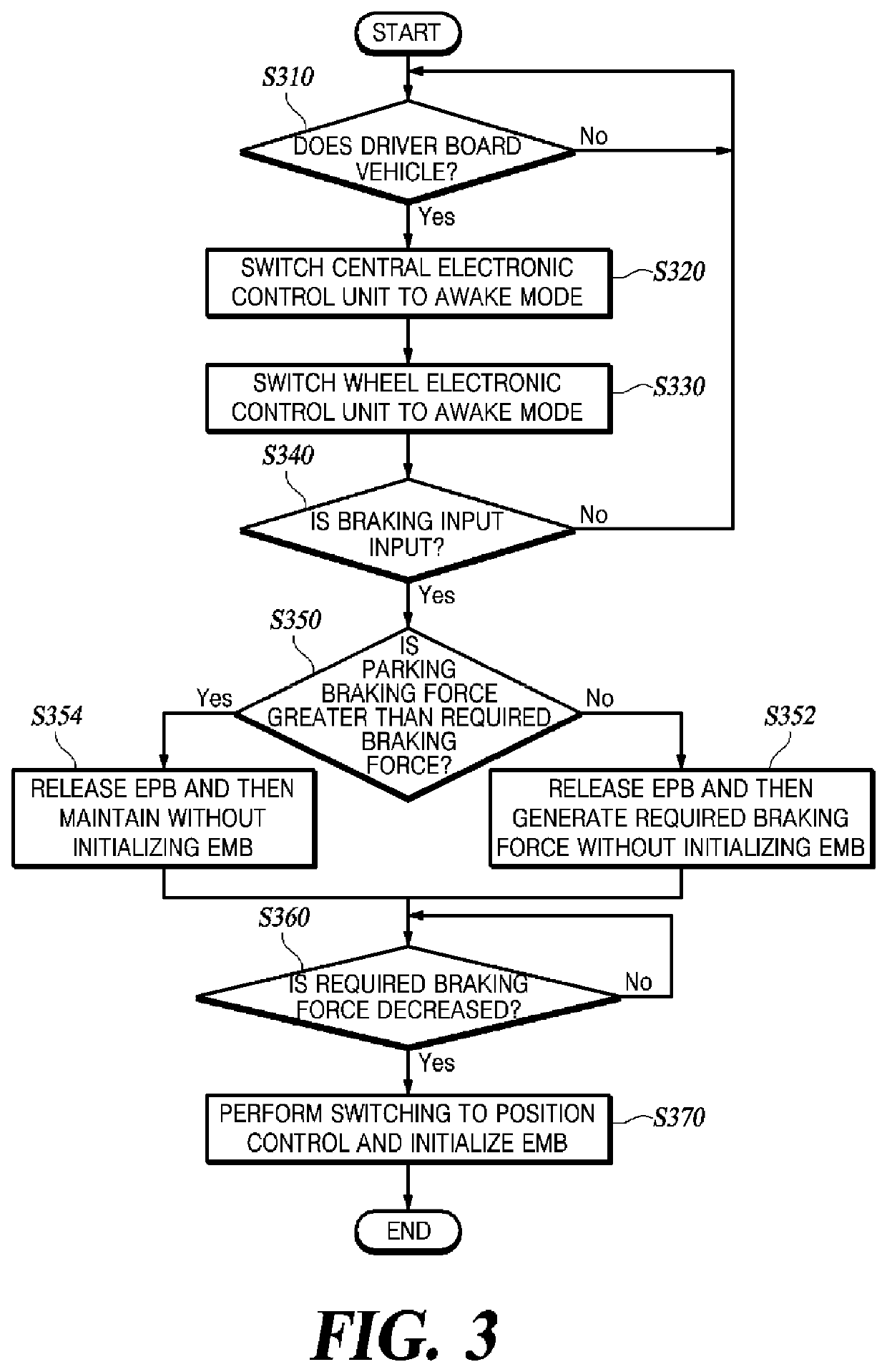
PendingUS20220111824A1Reduce in quantitySimple connection structureBraking action transmissionVehicle sub-unit featuresElectric machineryControl cell
A method of controlling an electro-mechanical brake device, includes: switching a central electronic control unit (ECU) to an awake mode based on a wake-up signal; transmitting a signal such that a wheel ECU is switched from a sleep mode to the awake mode; when a braking input is detected, supplying a current to a motor mounted on an electro-mechanical brake (EMB) using current control to generate a braking force; when a parking braking force is less than a required braking force, controlling the wheel ECU to release the parking braking force and generate the required braking force, and when the parking braking force is greater than or equal to the required braking force, releasing the parking braking force and maintaining the braking force generated in a wheel; when the braking force reaches the required braking force or the braking force is maintained, switching the current control to position control.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOBIS CO LTD
Method and system for a communication session initialization in a telecommunication network
ActiveUS9065702B2Simple initializationChoose simpleNetwork connectionsTelecommunications networkCircuit switching
A method, Call Agent (CA), and circuit-switched terminal for setting up a multimedia session from the circuit-switched terminal toward a packet-switched terminal in a telecommunication network. An Instant Messaging (IM) server receives an IM message from the circuit-switched terminal and forwards the contents of the IM message to the CA. The CA generates or retrieves a unique call token that identifies the terminals, and sends the call token to the IM server, which forwards the token to the circuit-switched terminal. In response, the circuit-switched terminal initiates setup of a circuit-switched call to an identified Media Gateway Controller (MGC). The MGC then sets up a packet-switched session with the packet-switched terminal to complete the setup of the multimedia session.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
A perceptual intrusion detection method based on qsfla-svm
ActiveCN108052968BSimple initializationAccurate evaluationCharacter and pattern recognitionArtificial lifeOptimal testQuantum particle
The invention provides a perceptual intrusion detection method of QSFLA-SVM, which sets relevant parameters; initializes the position of the frog population; transfers the position information of each frog individual into a support vector machine abnormal sequence detection model, and uses the calculated test set The classification accuracy is used as the fitness function value of each frog individual, and the frog population is sorted in descending order and the sub-population is divided into sub-populations; the worst individual of each frog sub-population is updated by using the quantum particle swarm update mechanism until reaching Local maximum number of iterations; global information exchange is performed. If the global maximum number of iterations is reached, the global optimal frog individual will be returned. At this time, the location information of the individual is the optimal value of the parameter when the SVM anomaly sequence detection model obtains the maximum accuracy rate for the classification of the test set. , and output the optimal test set classification result. The invention combines a quantum-derived hybrid leapfrog intrusion detection algorithm based on a quantum particle swarm search mechanism and a support vector machine to perform intrusion detection.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
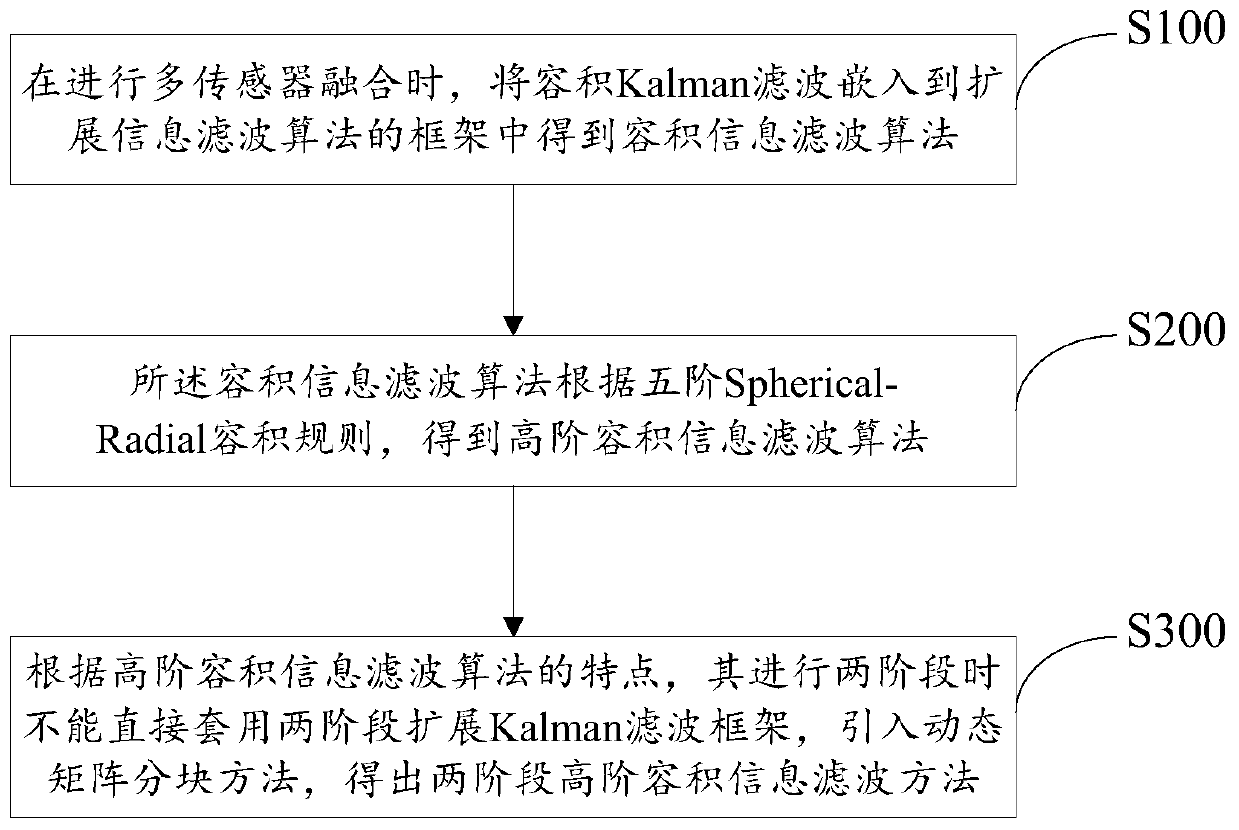
Two-stage high-order volumetric information filtering method
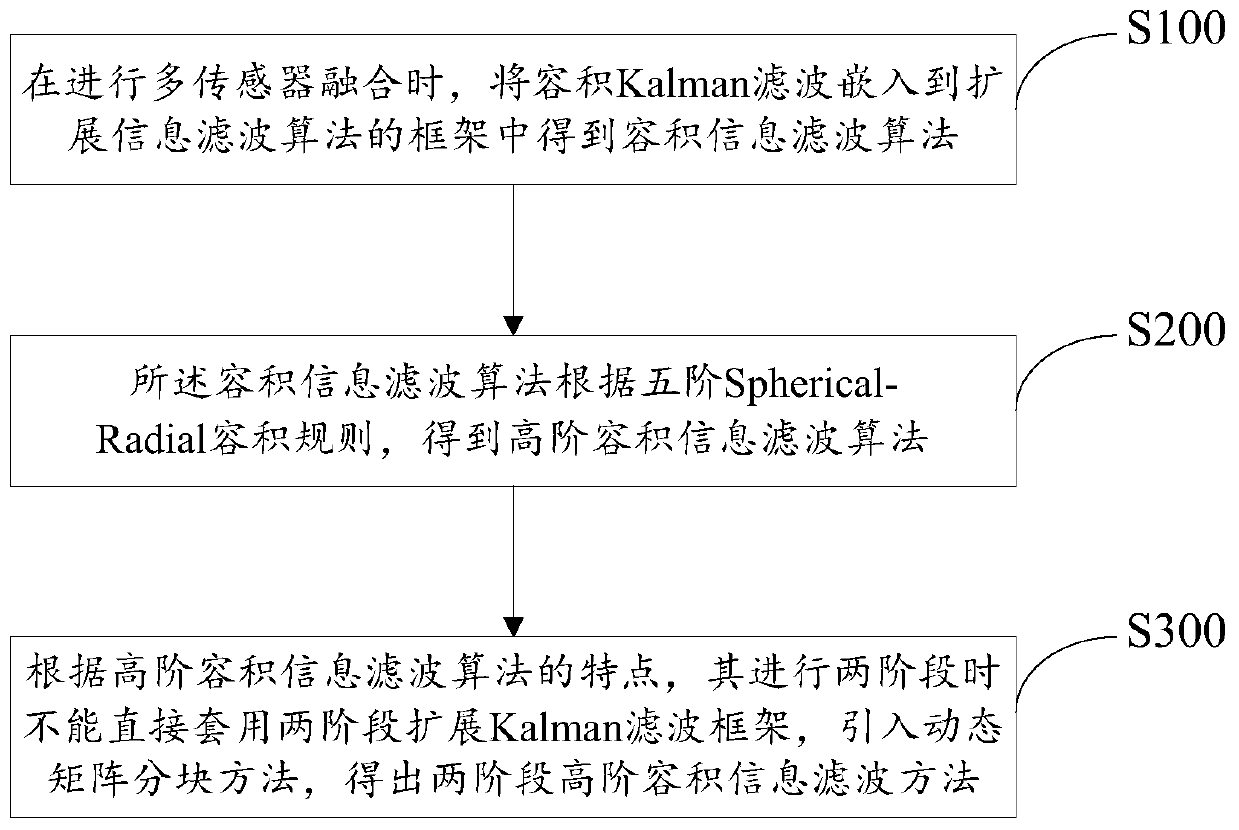
InactiveCN107992877BVerify availabilitySimple initializationCharacter and pattern recognitionFilter gainMultiple sensor
The invention discloses a two-stage high-order volume information filtering method, which includes: when performing multi-sensor fusion, the volume Kalman filter is embedded into the framework of the extended information filtering algorithm to obtain the volume information filtering algorithm; the volume information filtering algorithm is based on The fifth-order Spherical-Radial volume rule is used to obtain the high-order volume information filtering algorithm; according to the characteristics of the high-order volume information filtering algorithm, the two-stage extended Kalman filter framework cannot be directly applied when it is carried out in two stages, and the dynamic matrix block method is introduced to obtain Two-stage high-order volumetric information filtering method; the present invention proposes a two-stage high-order volumetric information filtering method, the algorithm is easy to initialize, the amount of calculation is small, and the equivalent relationship between the inverse of the covariance matrix and the information matrix is directly used Participating in the process of filter recursion reduces the calculation of the filter gain matrix.
Owner:QUZHOU UNIV
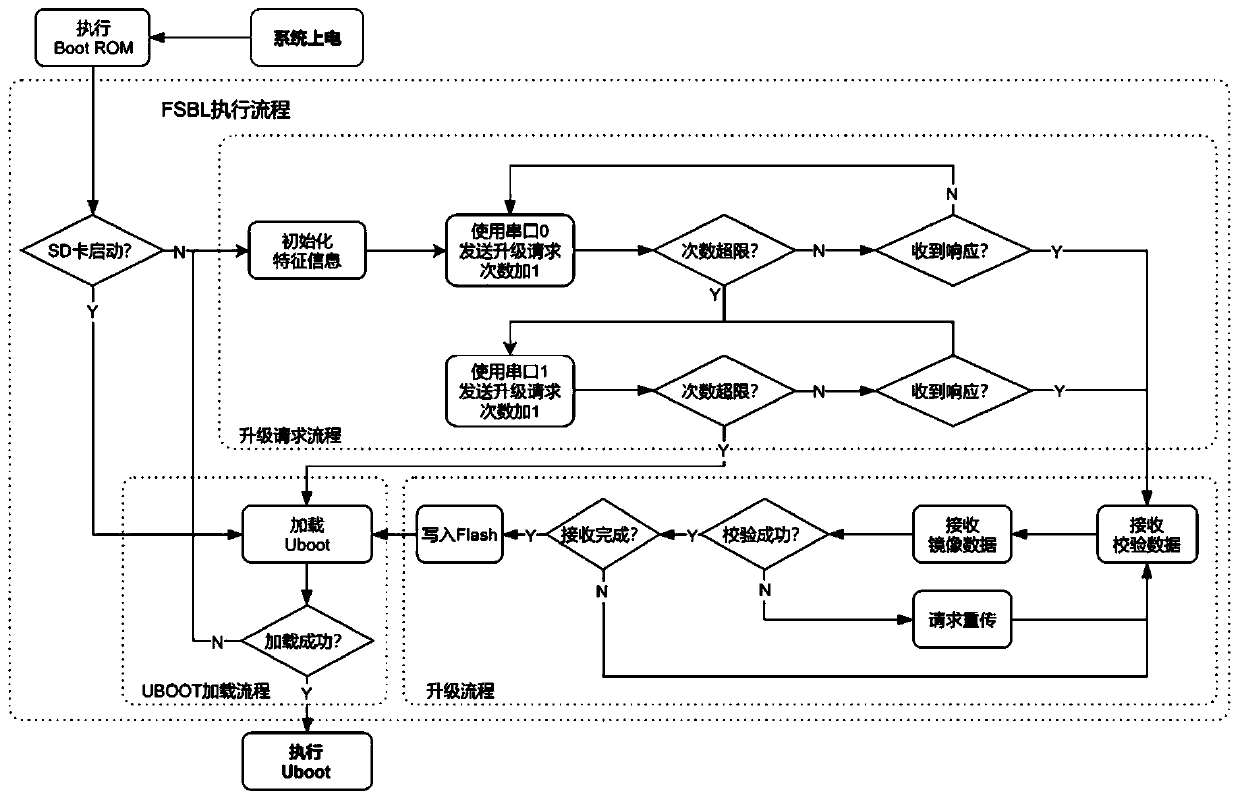
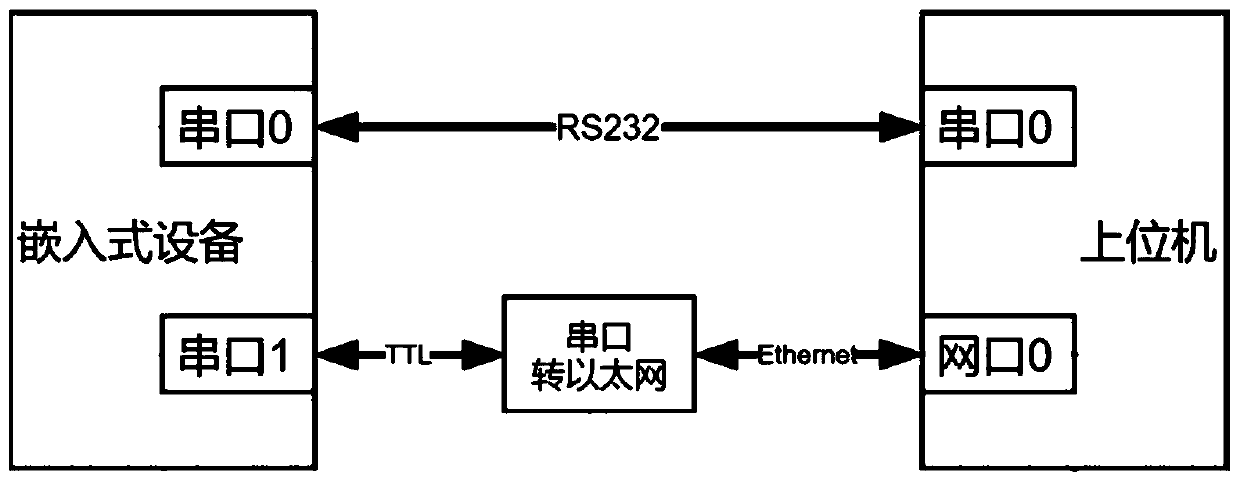
Zynq platform remote upgrading method
ActiveCN110837390AReduce dependenceGuaranteed accuracySoftware engineeringEnergy efficient computingData transmissionSerial port
The invention discloses a Zynq platform remote upgrading method, which comprises the following steps that: 1) a Zynq platform enters an FSBL execution process and executes steps 2) and 3); 2) the Zynqplatform sends an upgrade request data packet to an upper computer; after receiving the upgrading request data packet, the upper computer matches a corresponding upgrading mirror image file and sendsthe upgrading mirror image file to a Zynq platform; (3) the Zynq platform receives the check code and the upgrading mirror image file, verifies the upgrading mirror image file, and writes the received upgrading mirror image file into FLASH; (4) the Zynq platform continues to execute the subsequent starting process, and the Uboot mirror image is loaded from the FLASH; if the loading succeeds, skipping to the DDR to execute the Uboot code; if the loading is unsuccessful, skipping to the step 2); and the Zynq platform resends the upgrading request data packet. According to the method, mirror image receiving and storing of the upgrading data are completed in the FSBL execution process, the dependence of the upgrading process on the running state of the Zynq platform is greatly reduced, and stable transmission of the data is ensured by using a data transmission mode of a main serial port and a standby serial port.
Owner:易思维(杭州)科技有限公司
A method and device for generating m-sequences in parallel
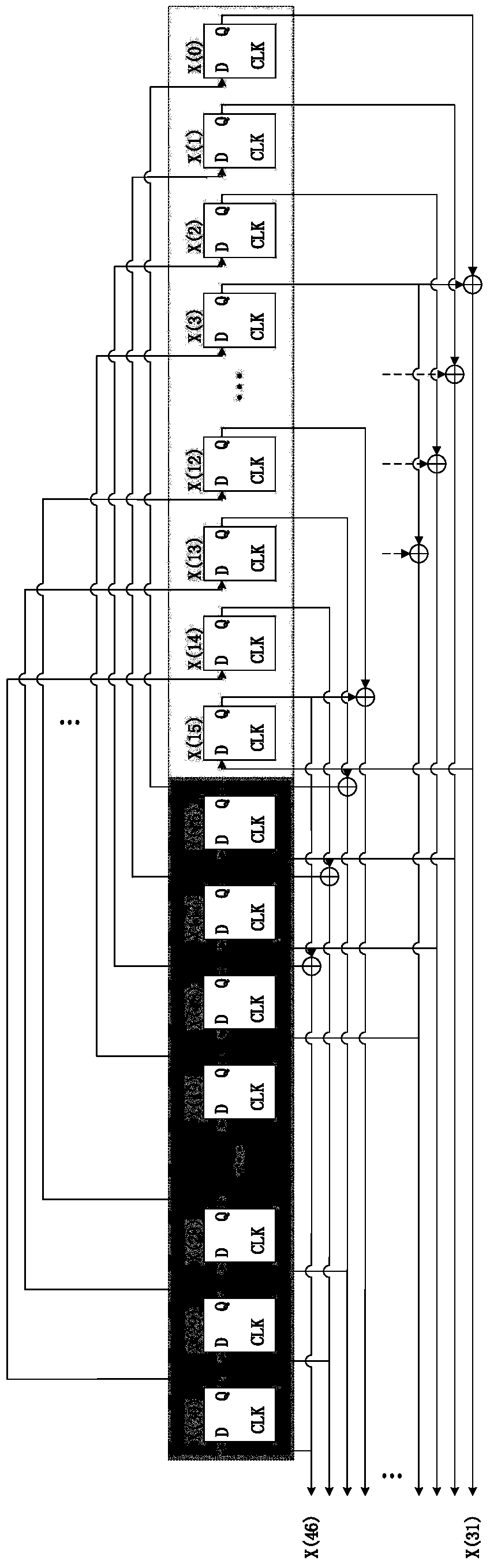
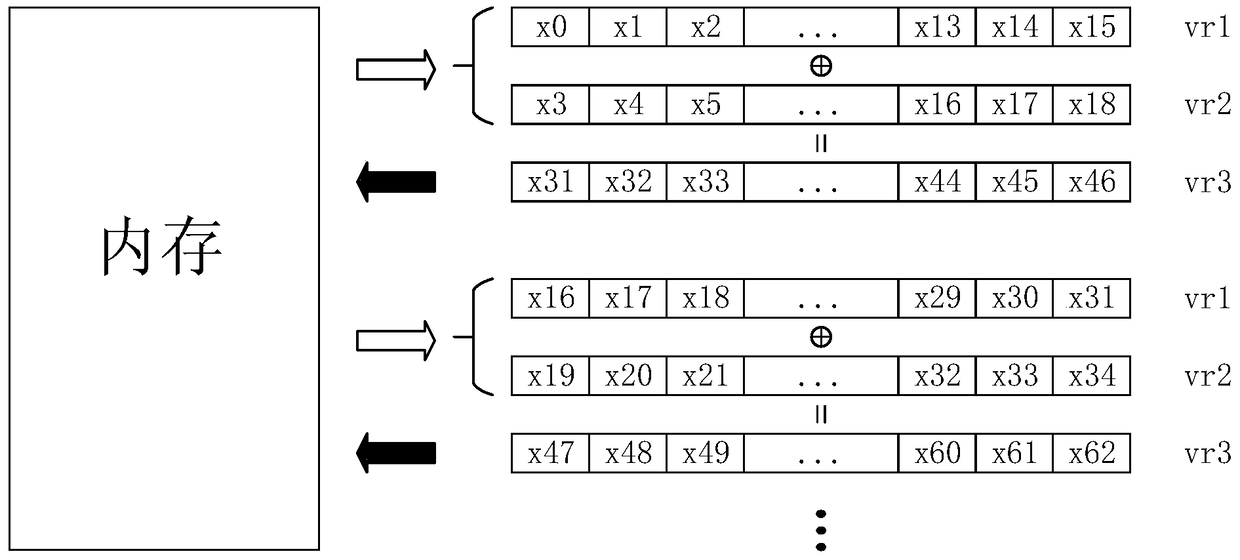
ActiveCN105227259BImprove parallelismSimple feedbackMultiplex code generationEngineeringHardware implementations
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Wireless transmission device
ActiveUS9273854B2Low investment costPrecise positioningLighting support devicesElectrical apparatusWireless transmissionEmbedded system
A wireless transmission device, arranged inside a display object or connected with the display object, includes a power supply interface, an initialization setting button, a wireless transmission unit, a processing unit, and a storage unit. The input end of the power supply interface is connected with the power supply end of the display object, the output end of the power supply interface is connected with the wireless transmission unit and the processing unit respectively, and the initialization setting button and the storage unit are connected with the processing unit respectively. A unique identification assigned to the display object is stored in the storage unit. Initialization setting of the wireless transmission device is implemented by pressing the initialization setting button, and the processing unit transmits out the identification, orientation, and / or predetermined viewable angle of the display object constantly or regularly via the wireless transmission unit.
Owner:LEE TING YAN +1
Method for automatically generating stock ground belt flow control program
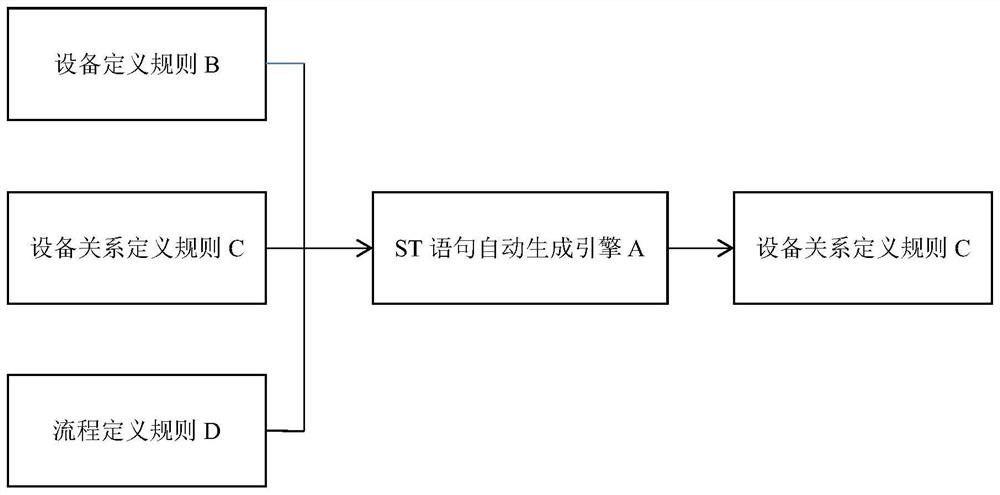
PendingCN113485182AEasy to modifySimple initializationProgramme controlComputer controlProgramming languageSimulation
The invention discloses a method for automatically generating a stock ground belt flow control program. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) compiling an engine according to a generated ST statement; (2) reading each equipment definition rule, each equipment relation definition rule and each process definition rule in sequence by the engine to obtain a relation between a turning plate and a belt conveyor; and (3) processing by the engine according to a preset rule to generate an ST text. According to the method, ST statements are generated by the engine through the agreed compiling rules and meanings of codes, it is guaranteed that the ST statements can be continuously produced only by developing an engine program once and adjusting the rules later, modification is convenient, initialization is simple, and time and labor are saved.
Owner:HUATIAN ENG & TECH CORP MCC +2
Integrated circuit signal generation device
InactiveUS8384442B2Error minimizationSimple initializationSolid-state devicesPulse shapingMicrocontrollerAudio power amplifier
Owner:SALHANY WAYNE F
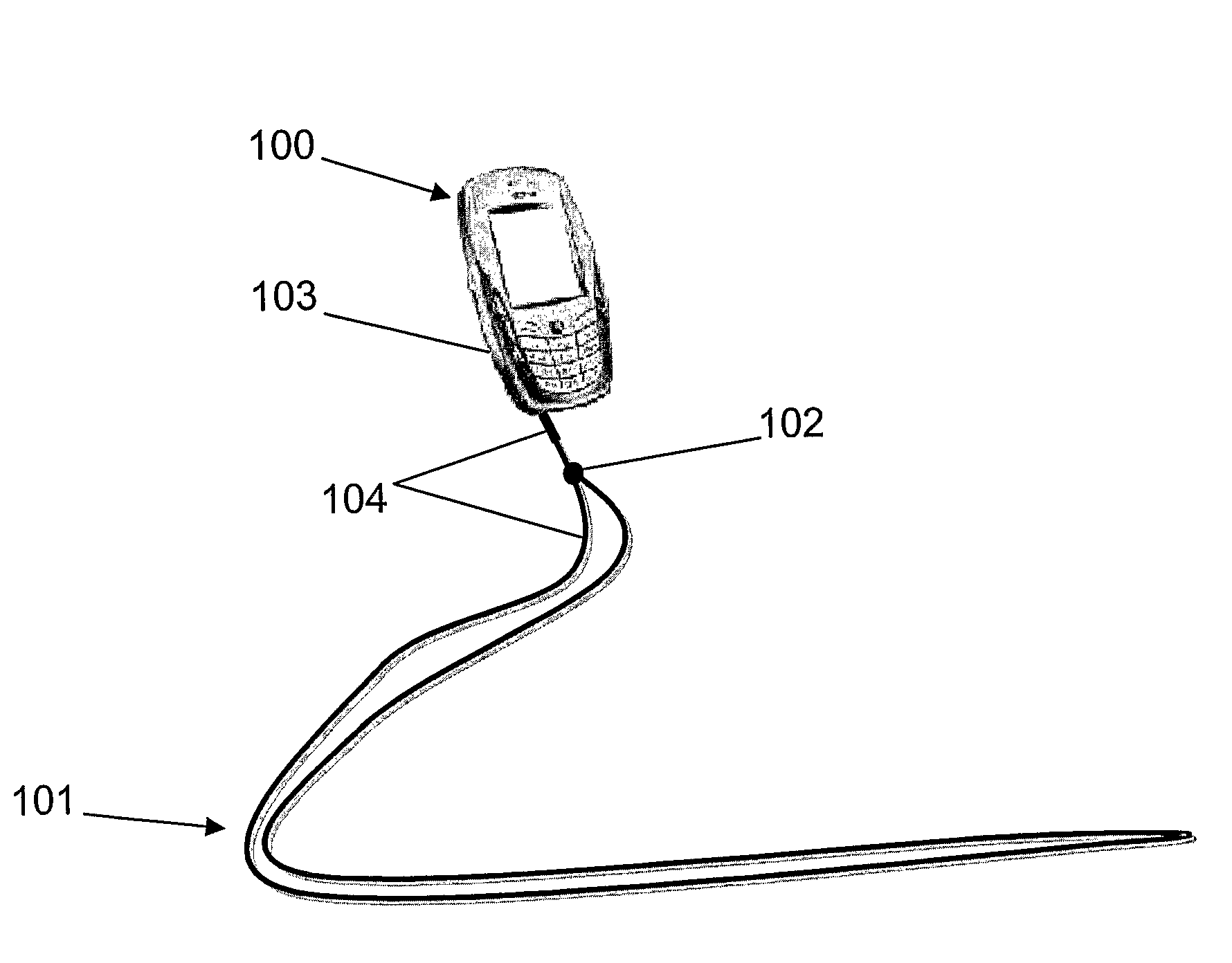
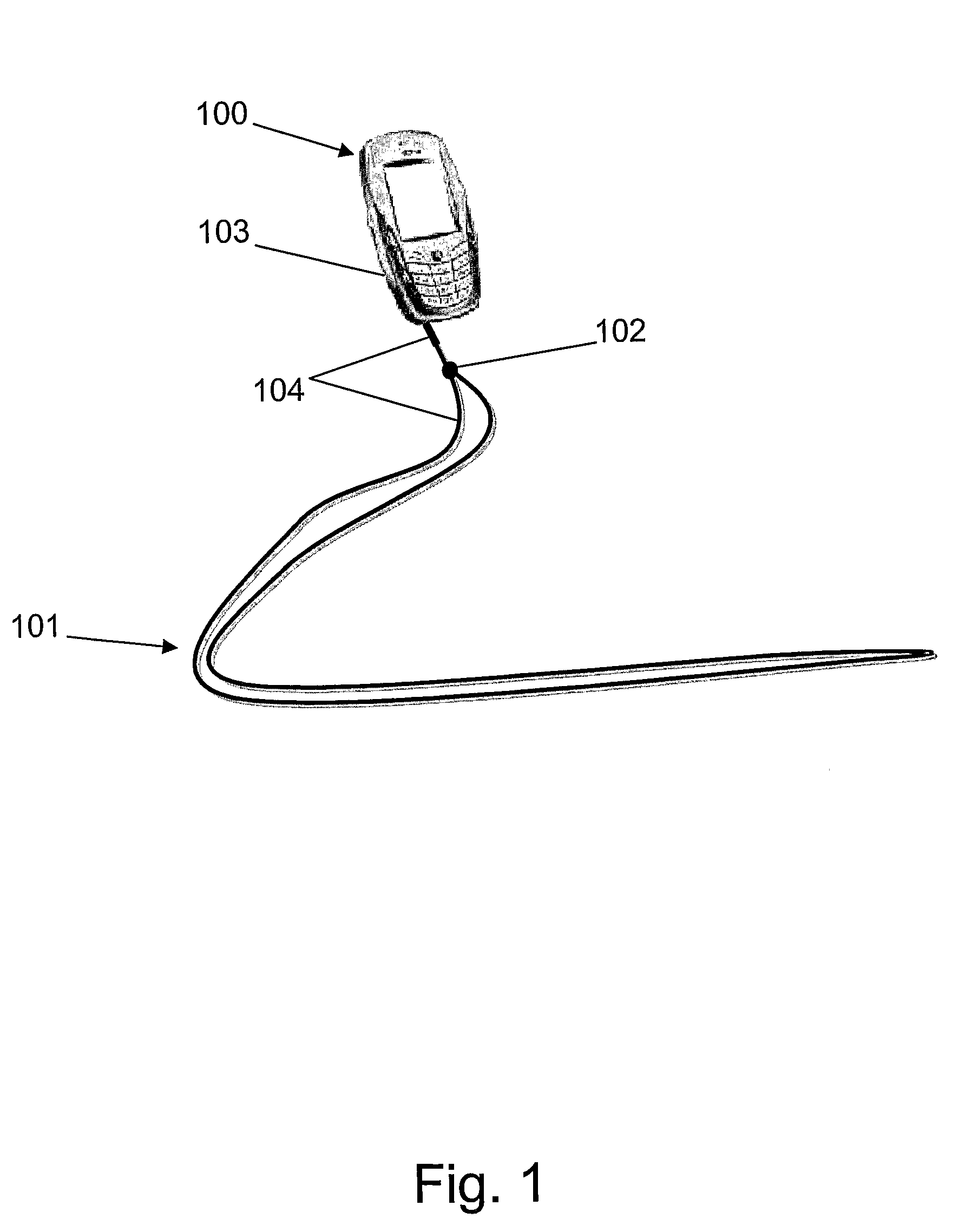
Subscription antenna strap
InactiveUS20090072027A1Easy accessSimple initializationBroadcast systems controlFlexible aerialsWireless broadcastMobile device
An antenna strap for the mobile device is being provided with an antenna extension (means) for receiving wireless broadcast in the mobile device. The antenna extension of the antenna strap extends beyond the traditional antenna of the mobile device so that the mobile broadcast is more feasible and that the antenna strap comprises parameters for initializing an access to the subscribed service delivered by the wireless broadcast. The parameters set the initializing phase for accessing and eventually obtaining at least one subscribed broadcast service.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com