Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
619 results about "Sensor fusion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sensor fusion is combining of sensory data or data derived from disparate sources such that the resulting information has less uncertainty than would be possible when these sources were used individually. The term uncertainty reduction in this case can mean more accurate, more complete, or more dependable, or refer to the result of an emerging view, such as stereoscopic vision (calculation of depth information by combining two-dimensional images from two cameras at slightly different viewpoints).
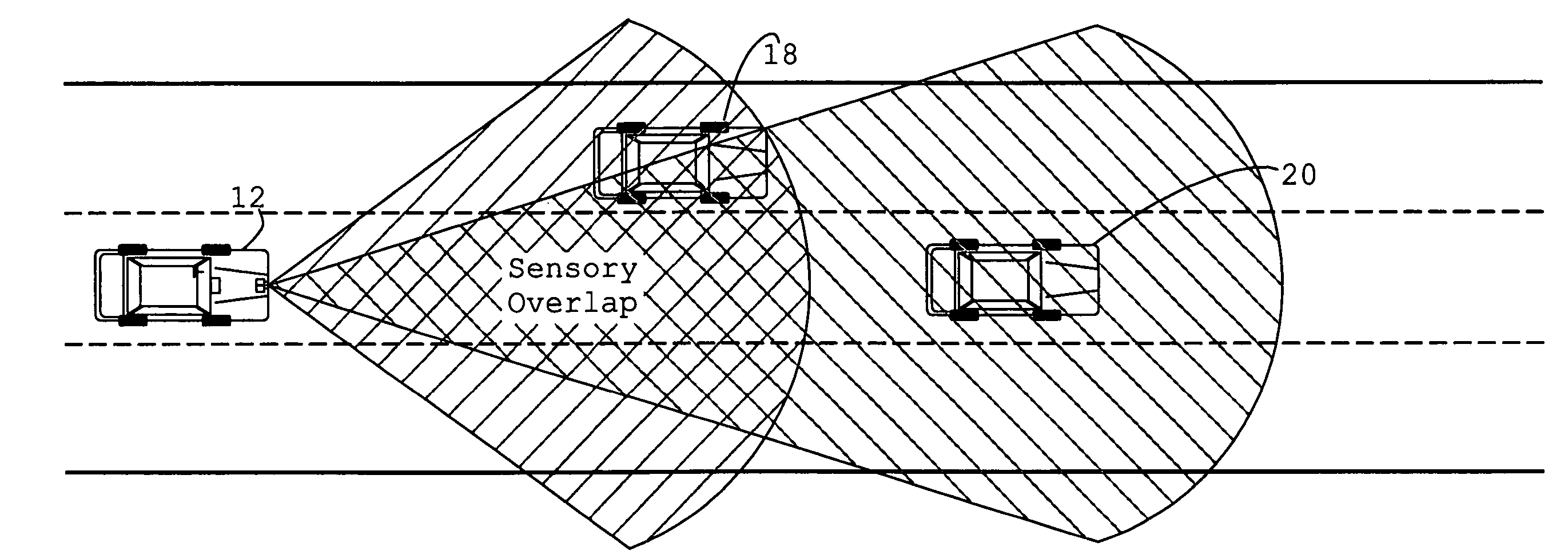
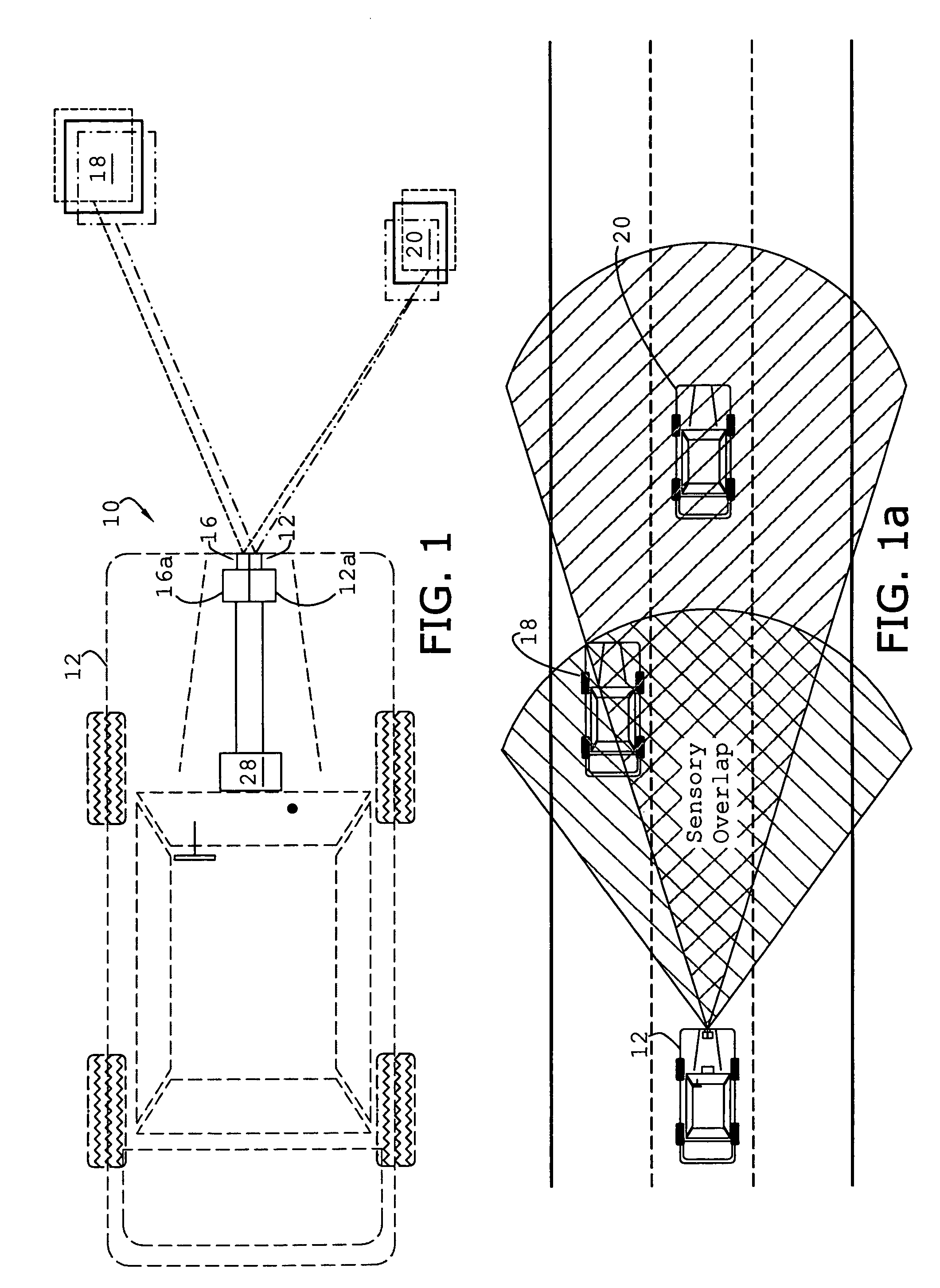
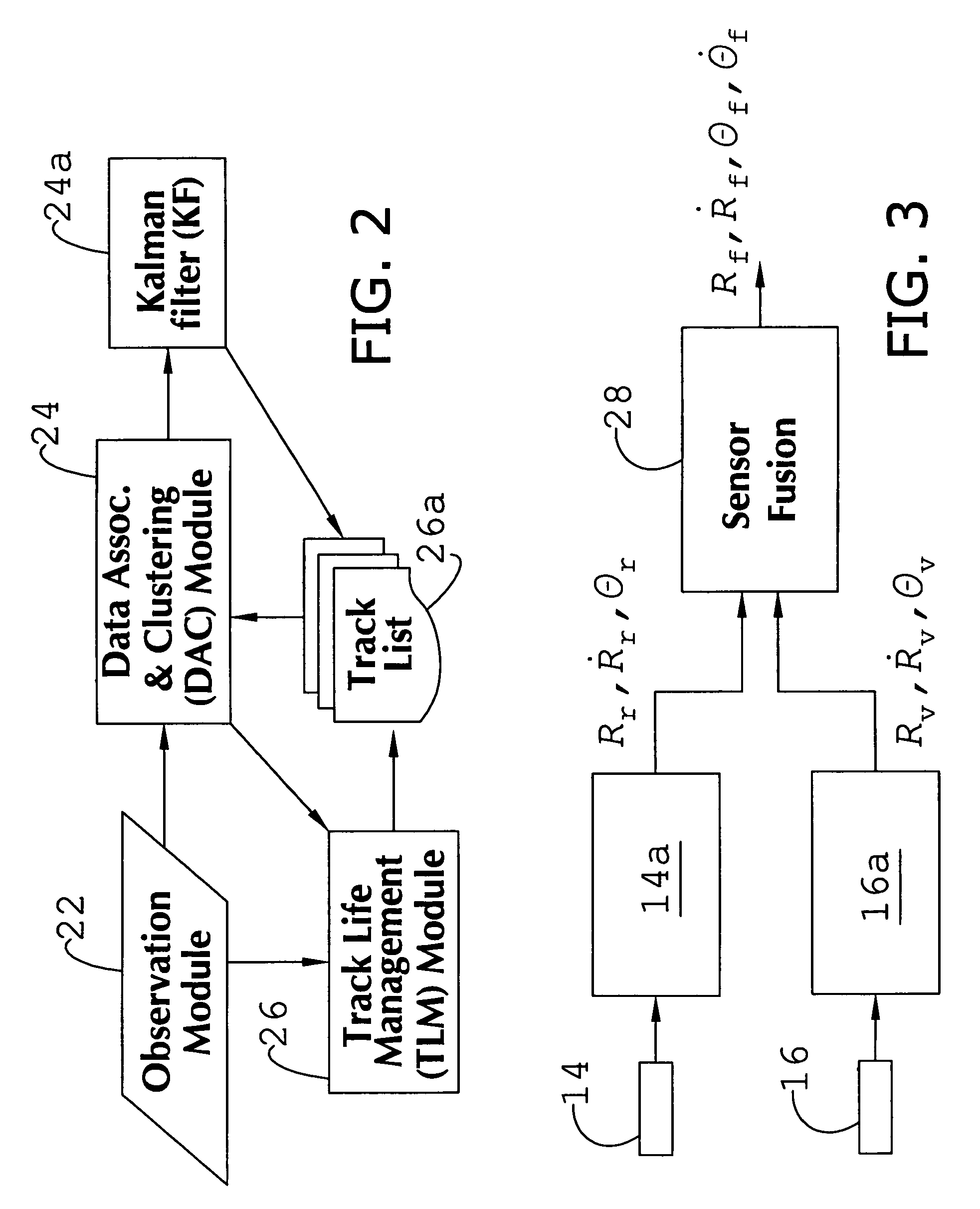
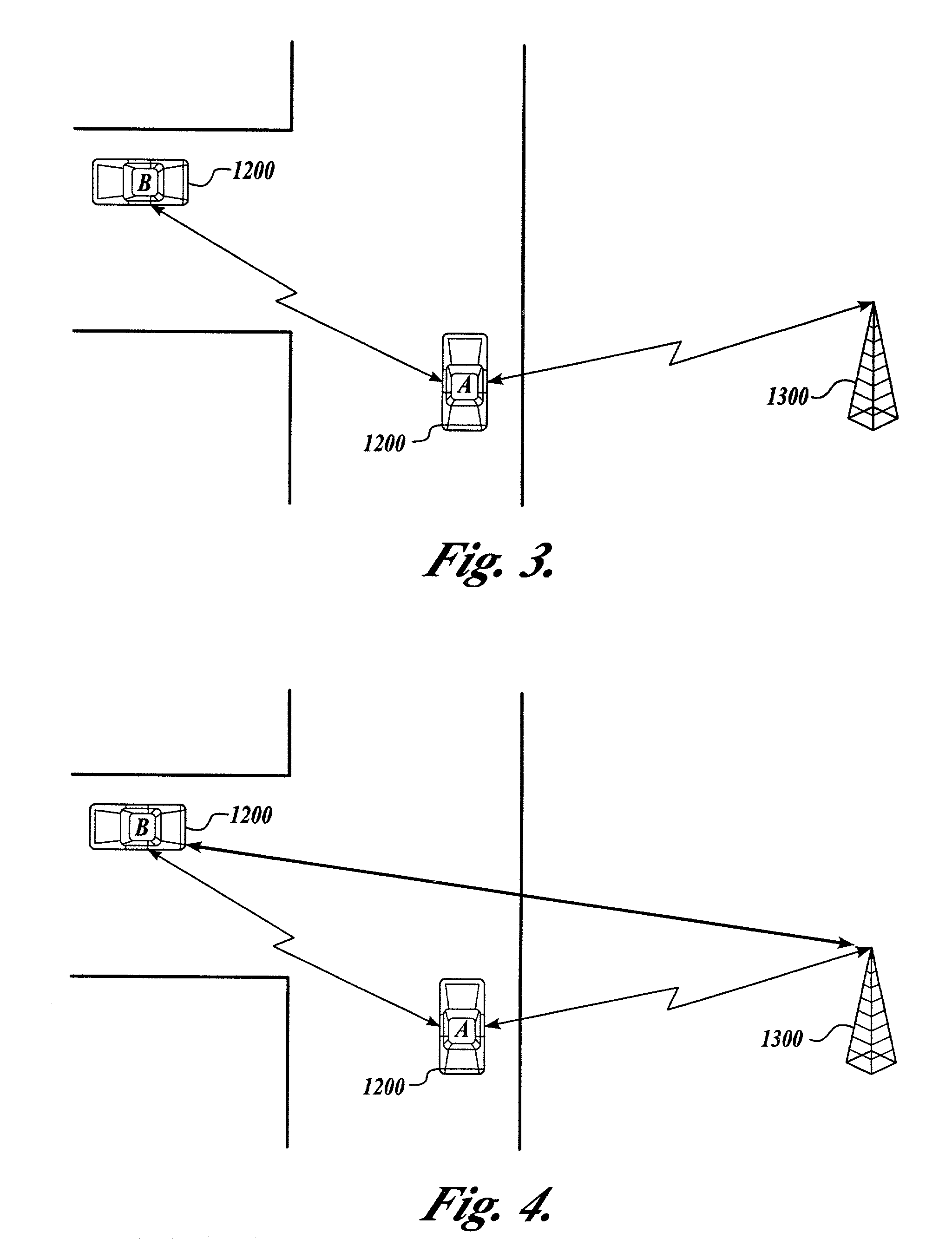
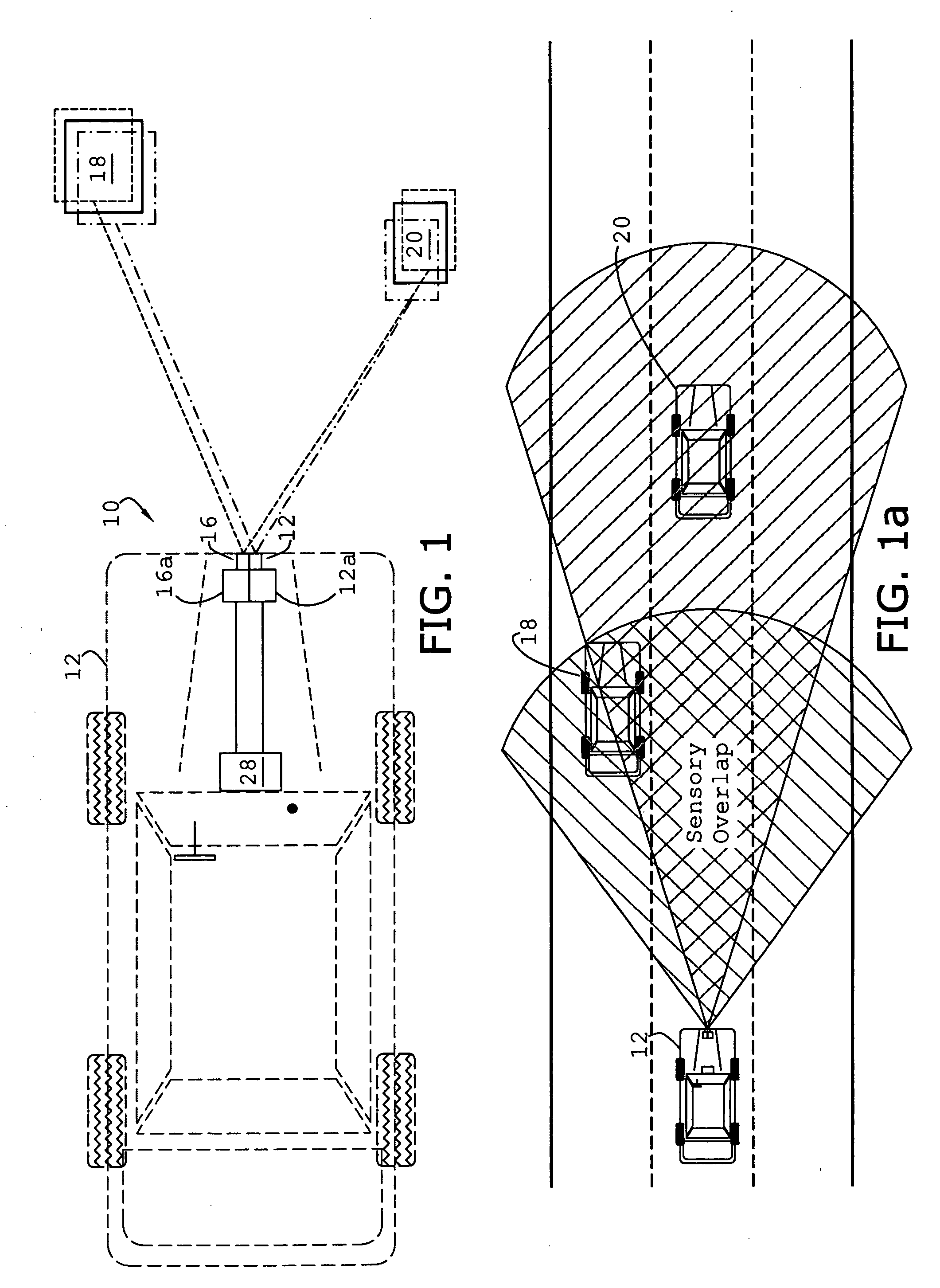
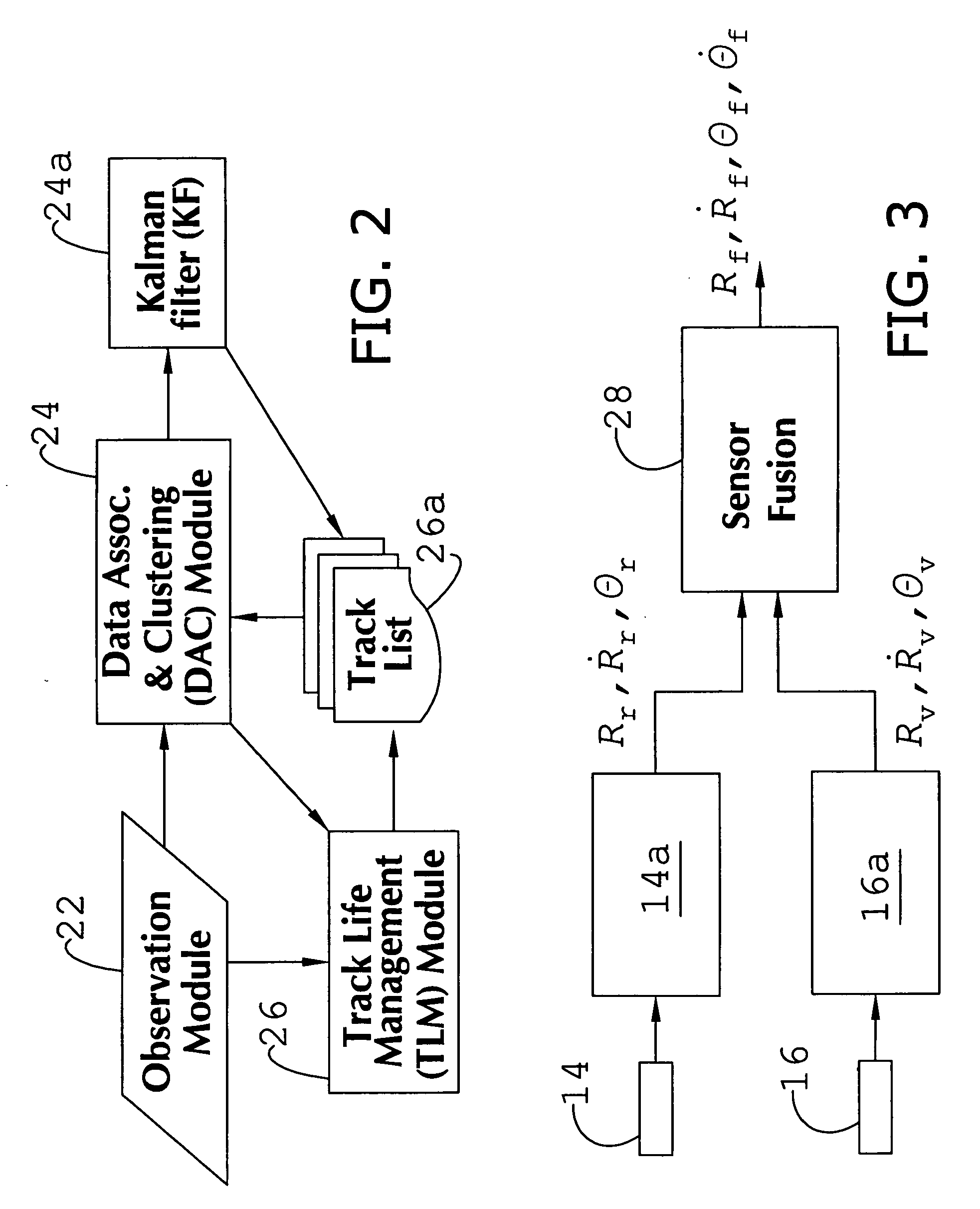
System and method of target tracking using sensor fusion
ActiveUS7460951B2Increasing precision and certaintyShorten the timeInstruments for road network navigationAnti-collision systemsSensor fusionEngineering
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
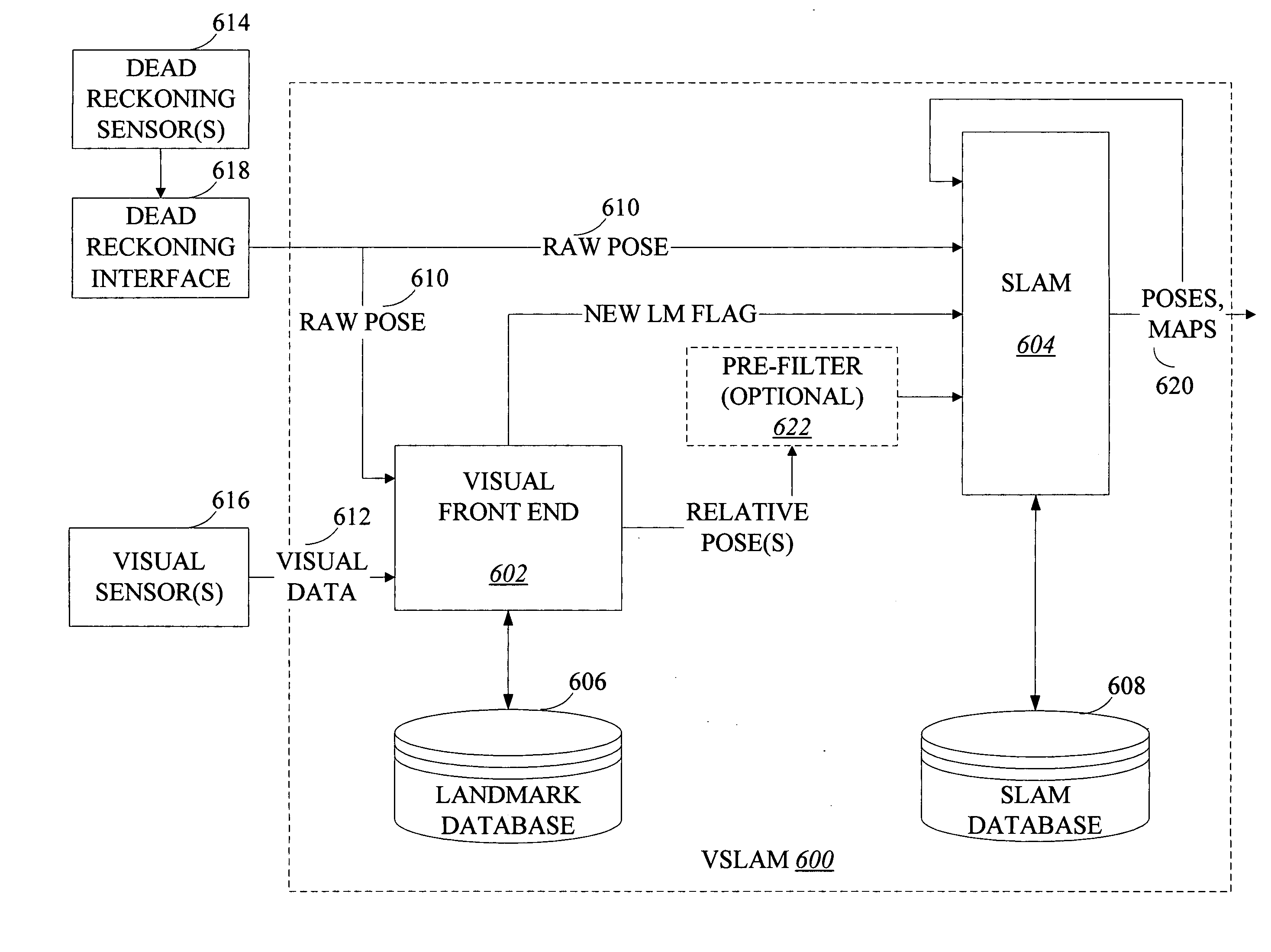
Robust sensor fusion for mapping and localization in a simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) system
This invention is generally related to methods and apparatus that permit the measurements from a plurality of sensors to be combined or fused in a robust manner. For example, the sensors can correspond to sensors used by a mobile, device, such as a robot, for localization and / or mapping. The measurements can be fused for estimation of a measurement, such as an estimation of a pose of a robot.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
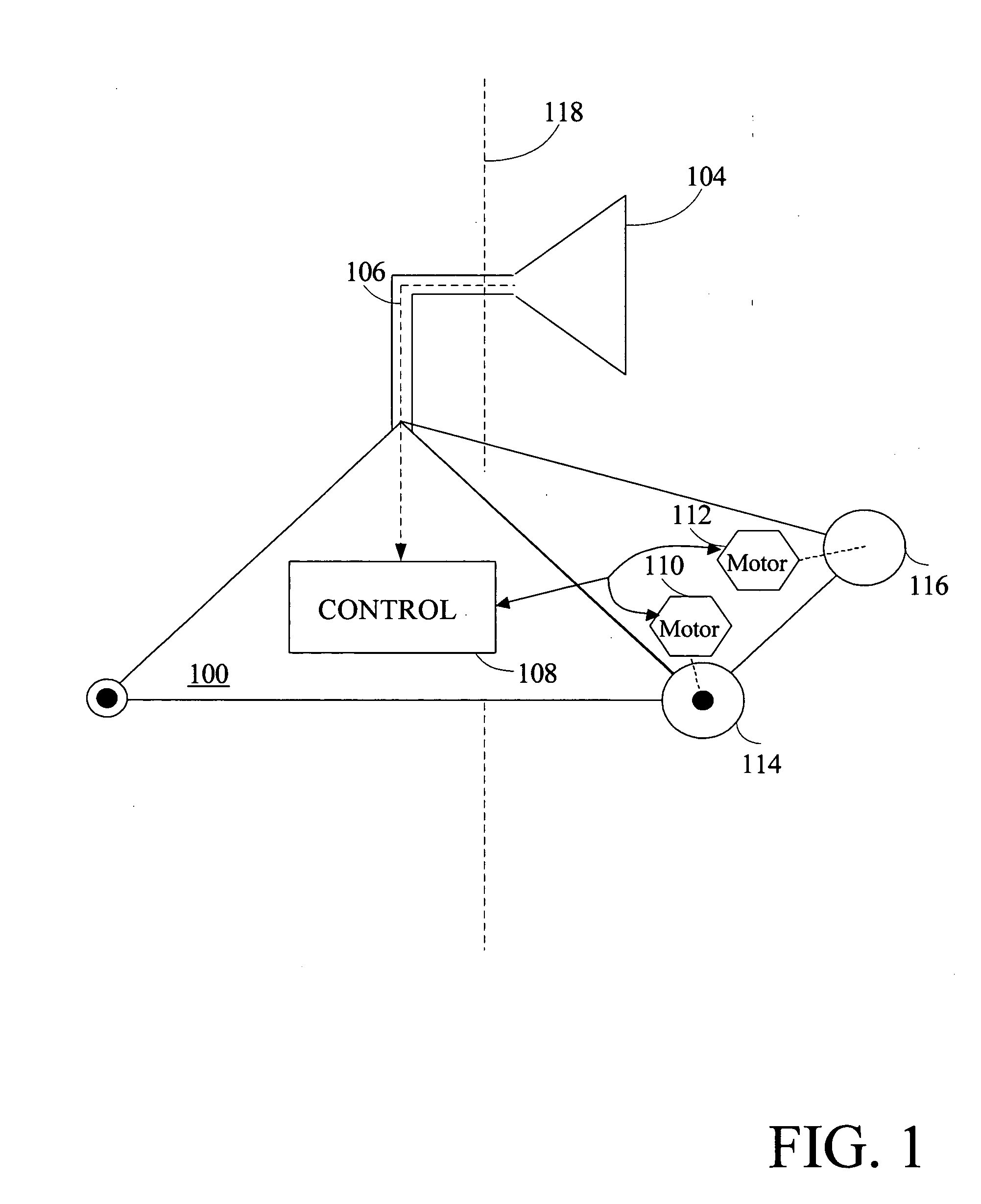
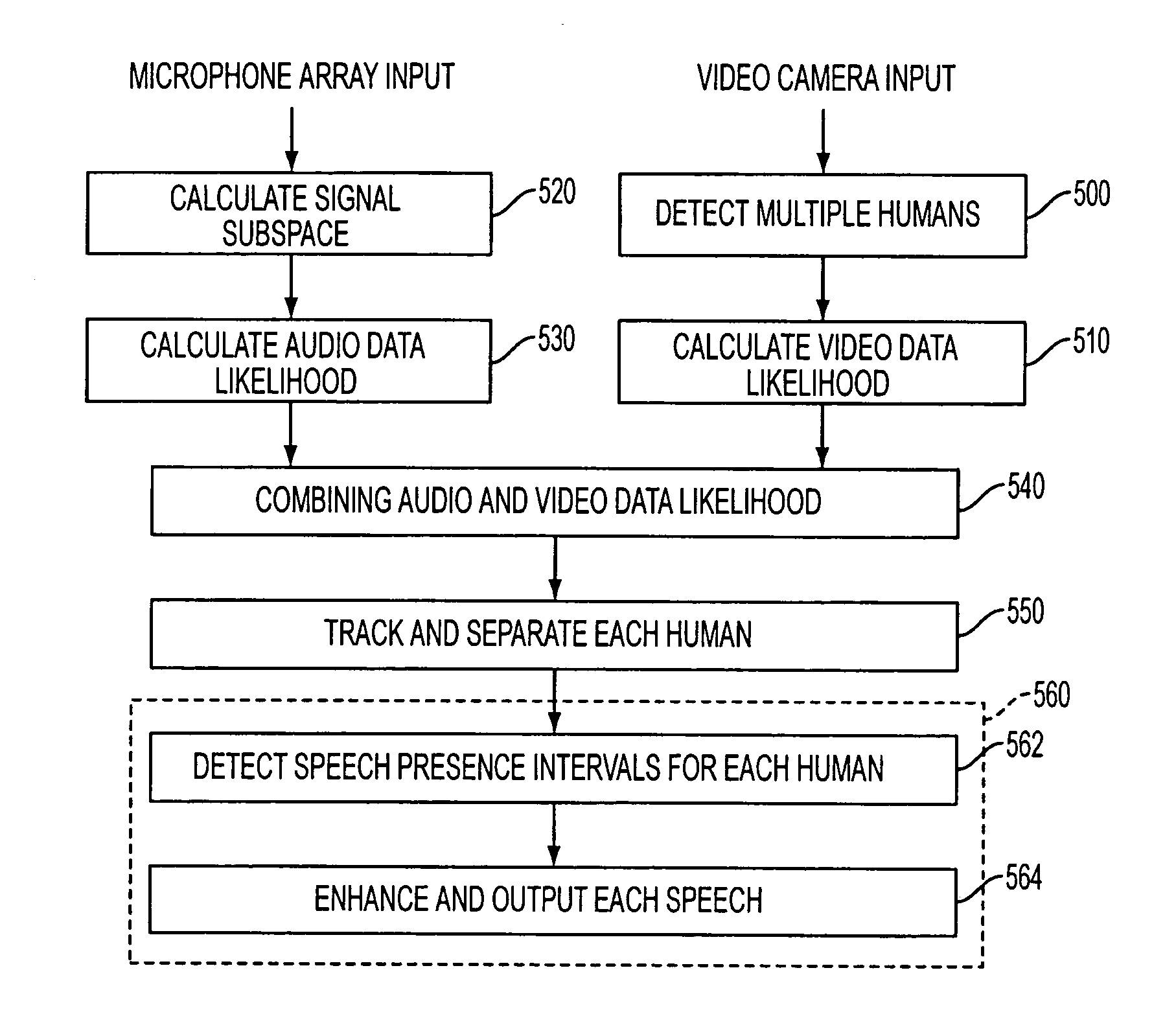
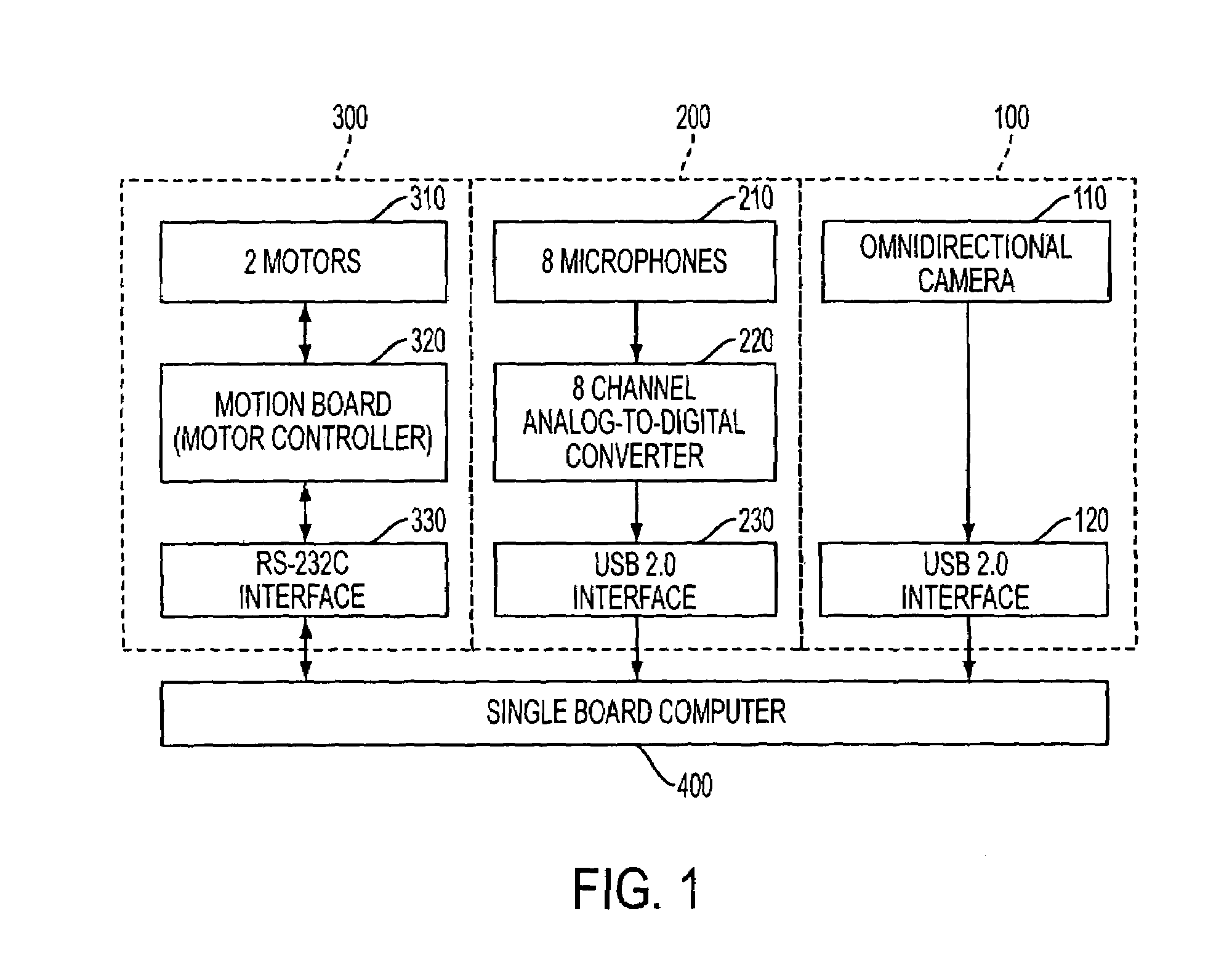
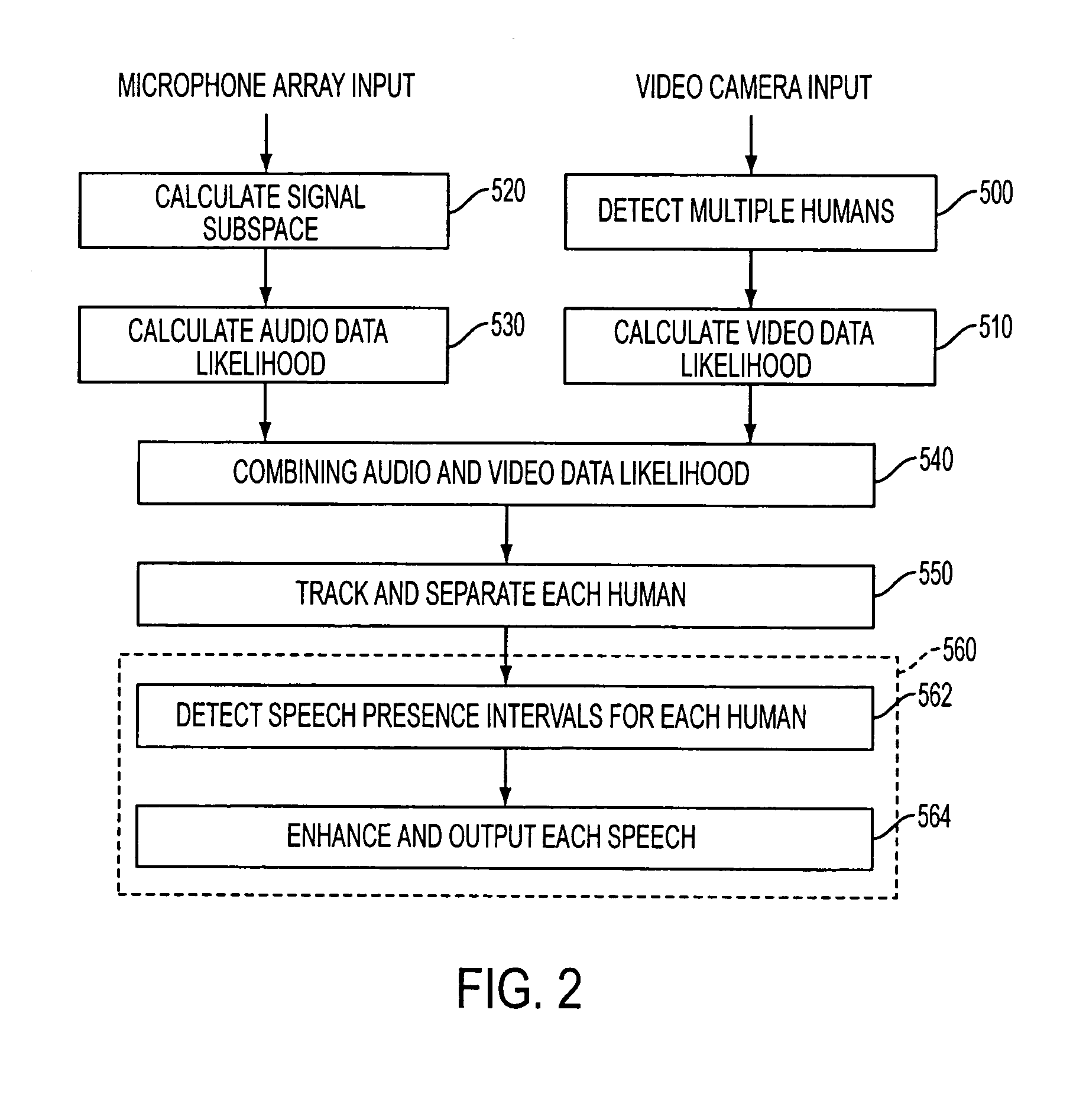
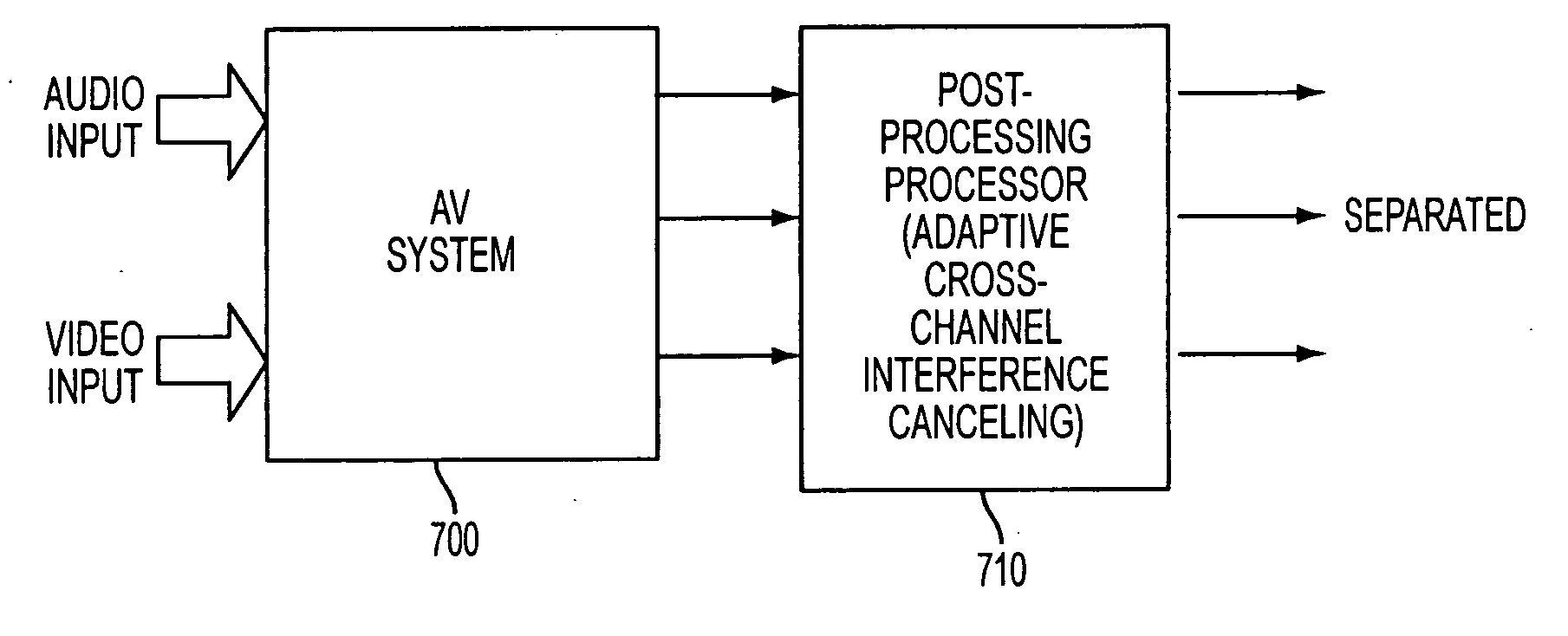
Apparatus and method performing audio-video sensor fusion for object localization, tracking, and separation
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
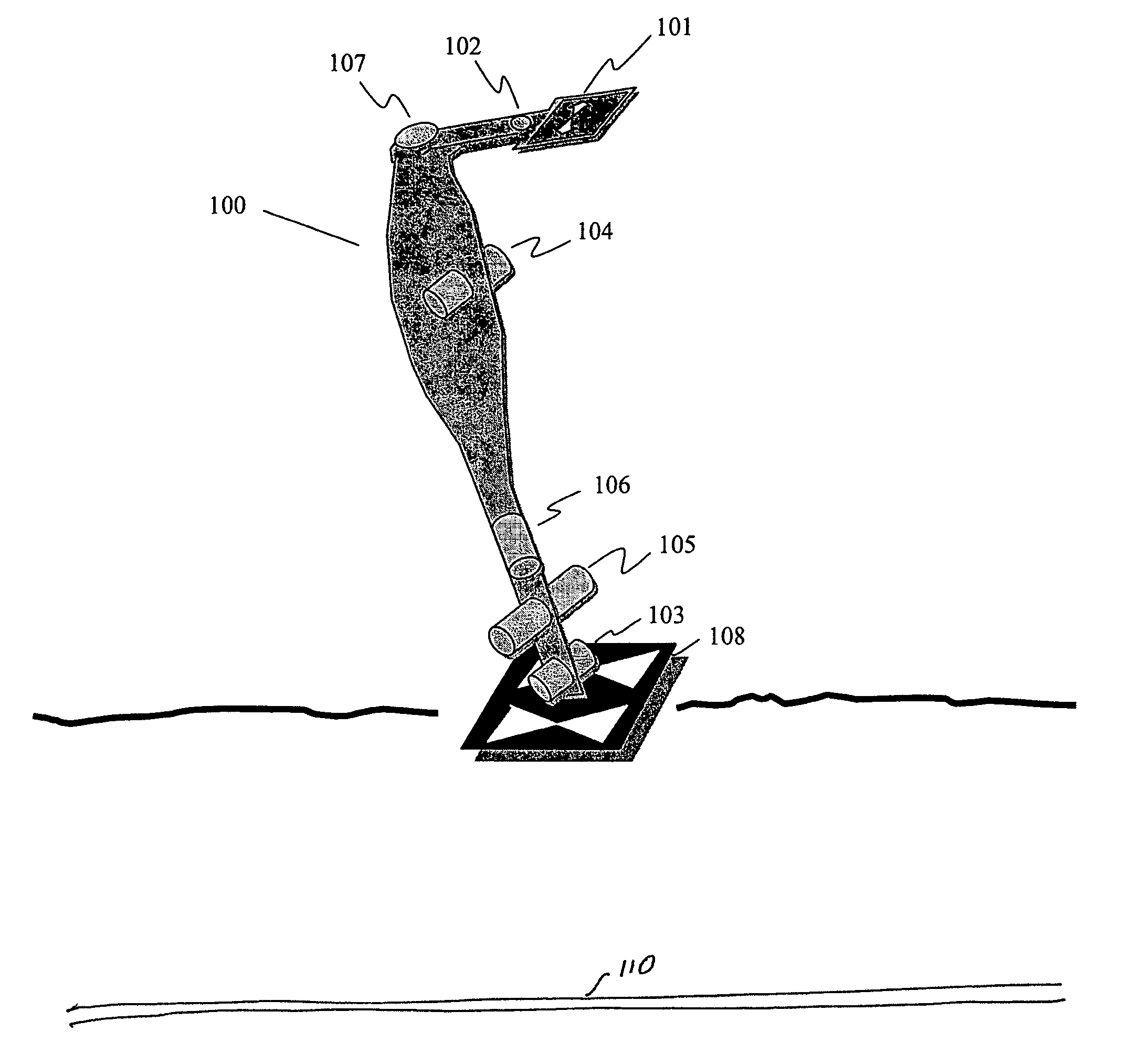
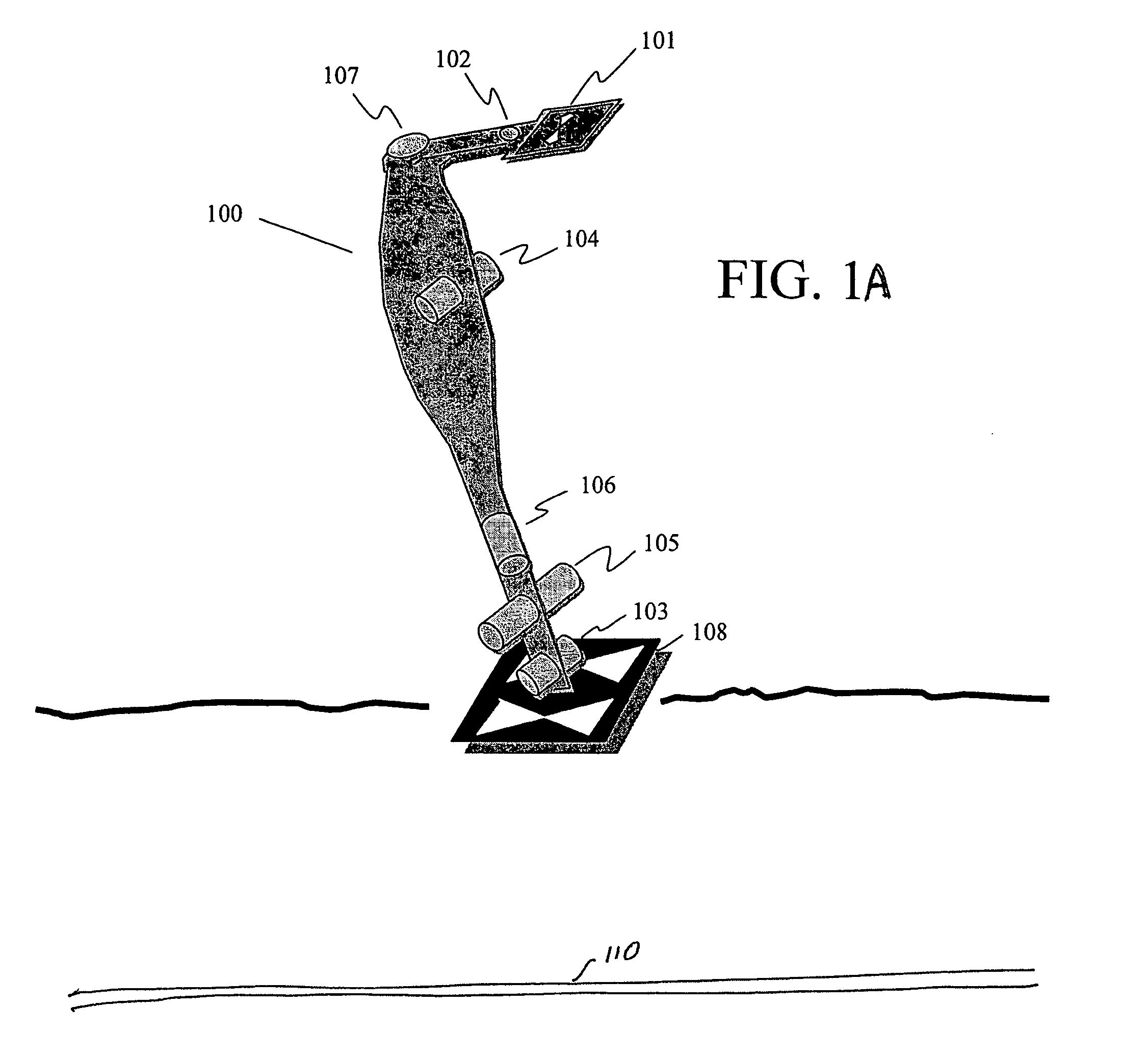
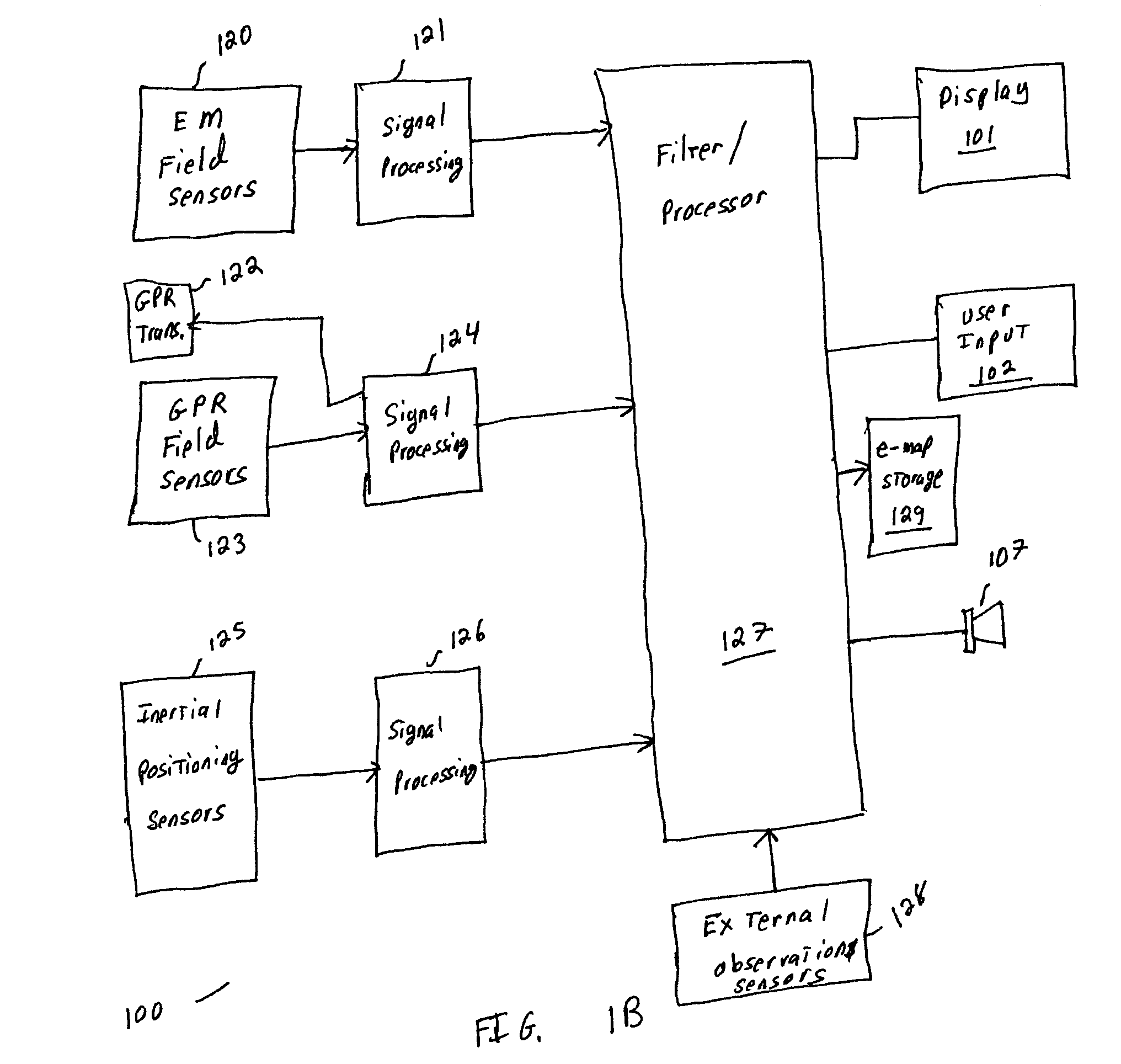
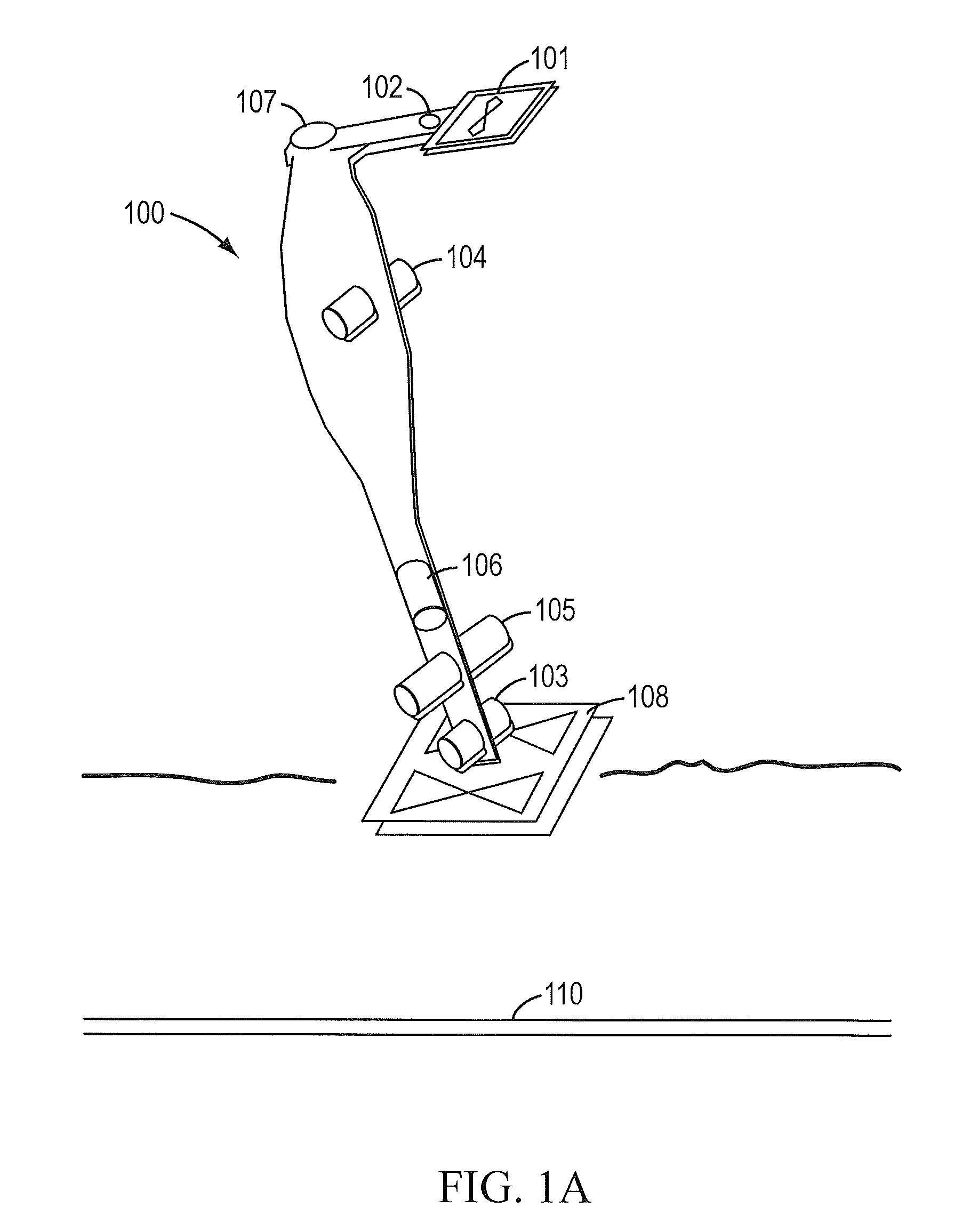
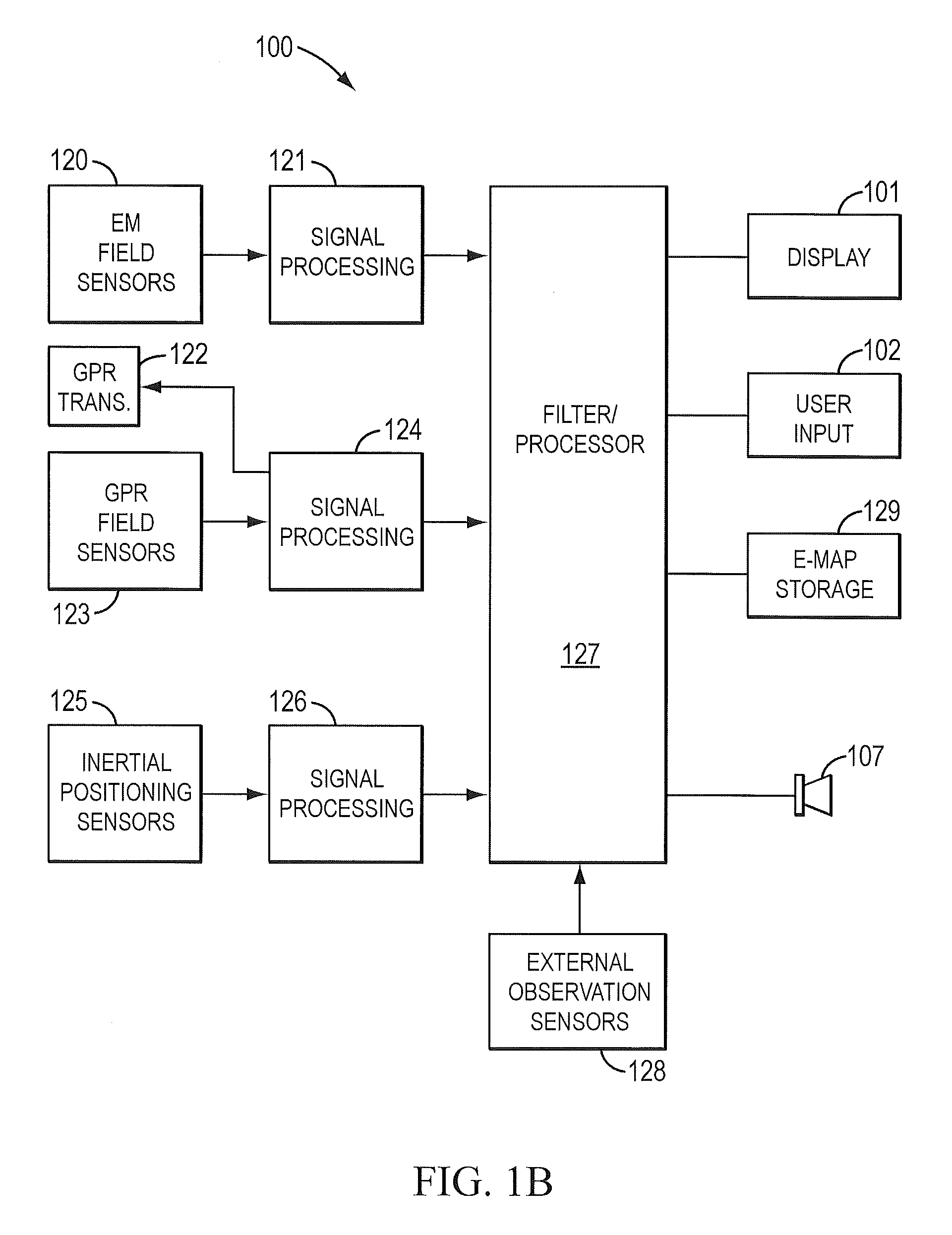
Sensor fusion for model-based detection in pipe and cable locator systems
ActiveUS20060055584A1Improve positionSatellite radio beaconingDetection using electromagnetic wavesAccelerometerGyroscope
Line locator systems that fuse traditional sensors used in a combined pipe and cable locator (electromagnetic coils, magnetometers, and ground penetrating radar antennas) with low cost inertial sensors (accelerometers, gyroscopes) in a model-based approach are presented. Such systems can utilize inexpensive MEMS sensors for inertial navigation. A pseudo-inertial frame is defined that uses the centerline of the tracked utility, or an aboveground fixed object as the navigational reference. An inertial sensor correction mechanism that limits the tracking errors over time when the model is implemented in state-space form using, for example, the Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) is disclosed.
Owner:BUSAN TRANSPORTATION CORPORATION
Collision avoidance method and system using stereo vision and radar sensor fusion
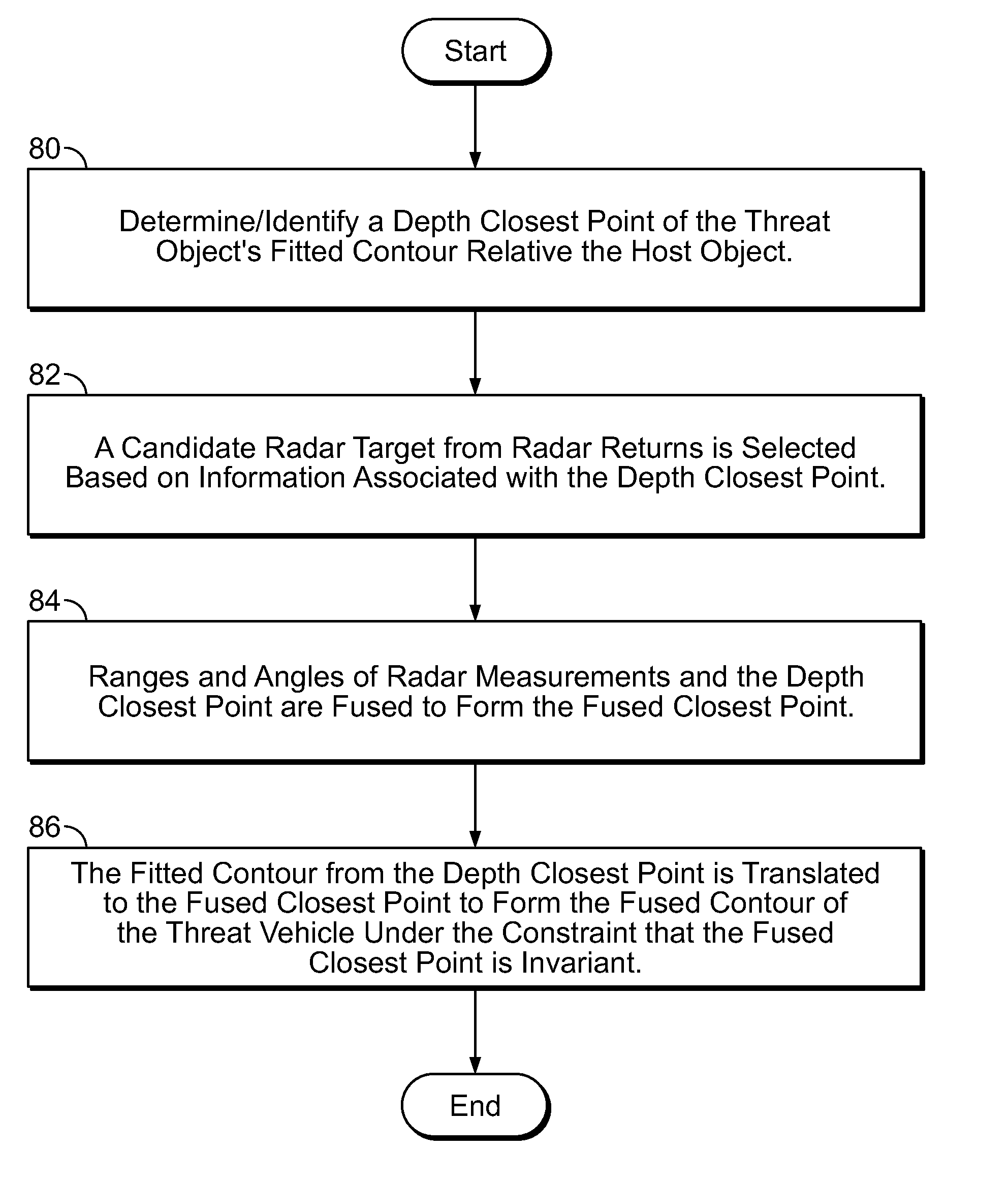
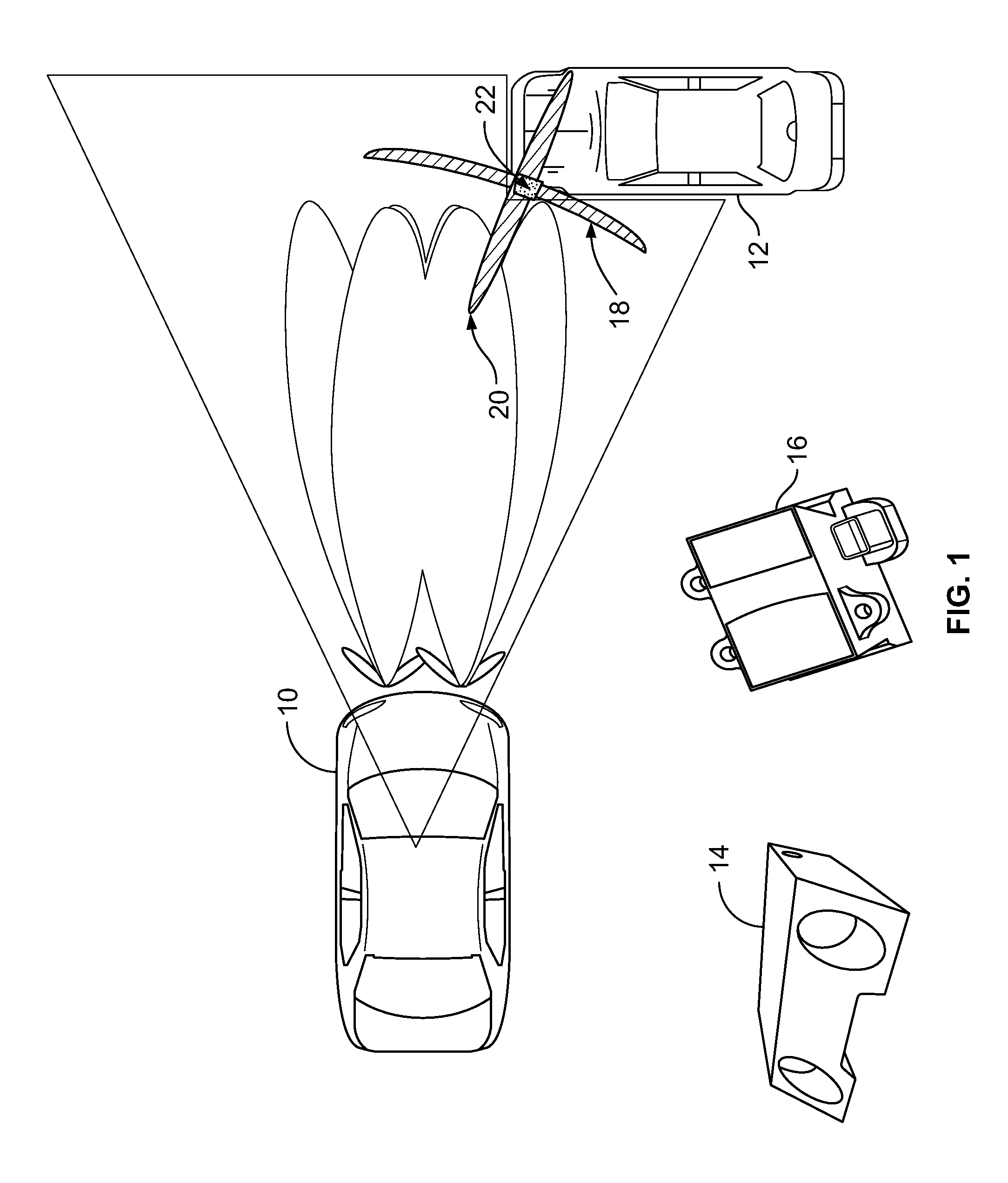
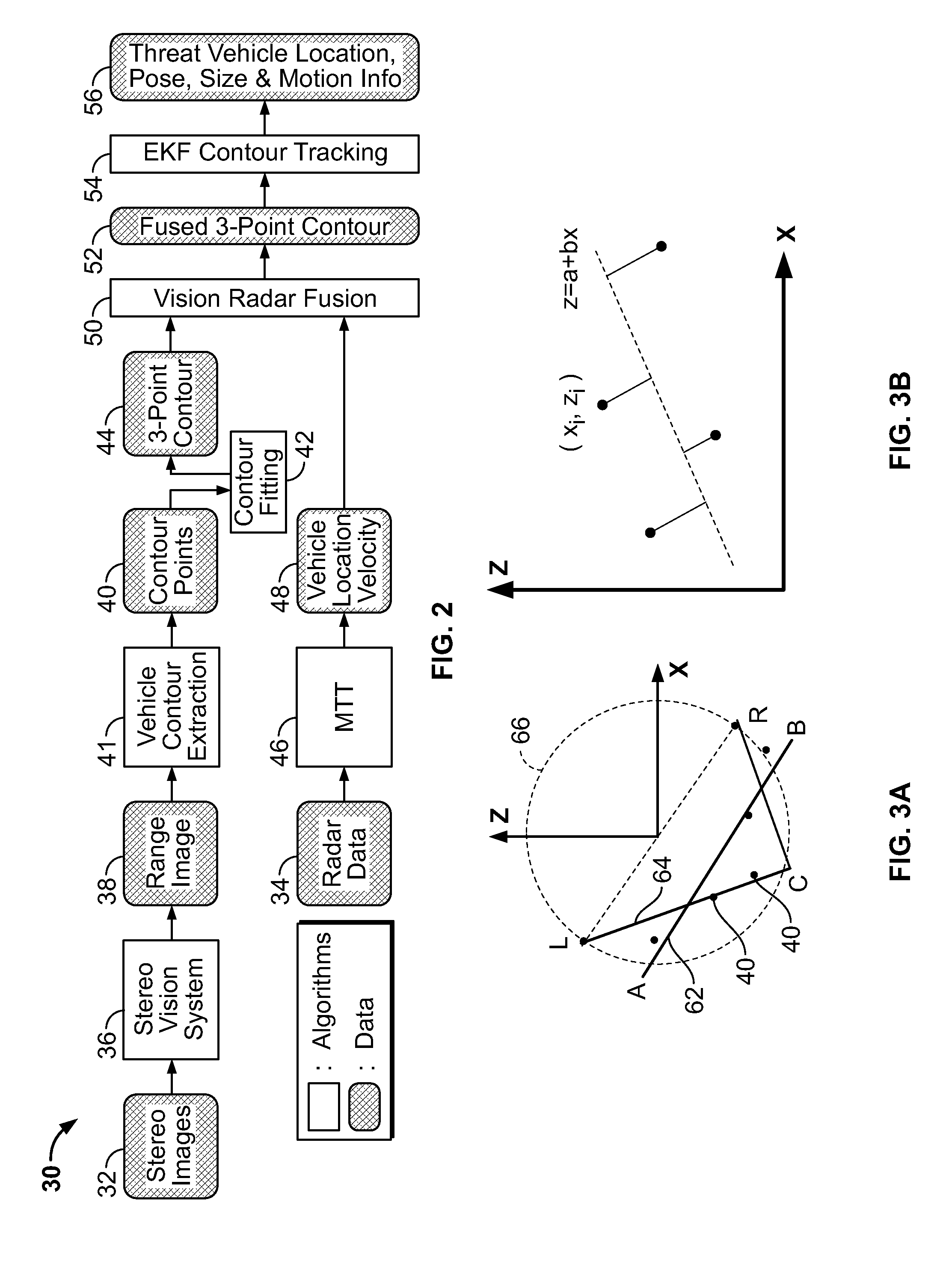
A system and method for fusing depth and radar data to estimate at least a position of a threat object relative to a host object is disclosed. At least one contour is fitted to a plurality of contour points corresponding to the plurality of depth values corresponding to a threat object. A depth closest point is identified on the at least one contour relative to the host object. A radar target is selected based on information associated with the depth closest point on the at least one contour. The at least one contour is fused with radar data associated with the selected radar target based on the depth closest point to produce a fused contour. Advantageously, the position of the threat object relative to the host object is estimated based on the fused contour. More generally, a method is provided for aligns two possibly disparate sets of 3D points.
Owner:SARNOFF CORP
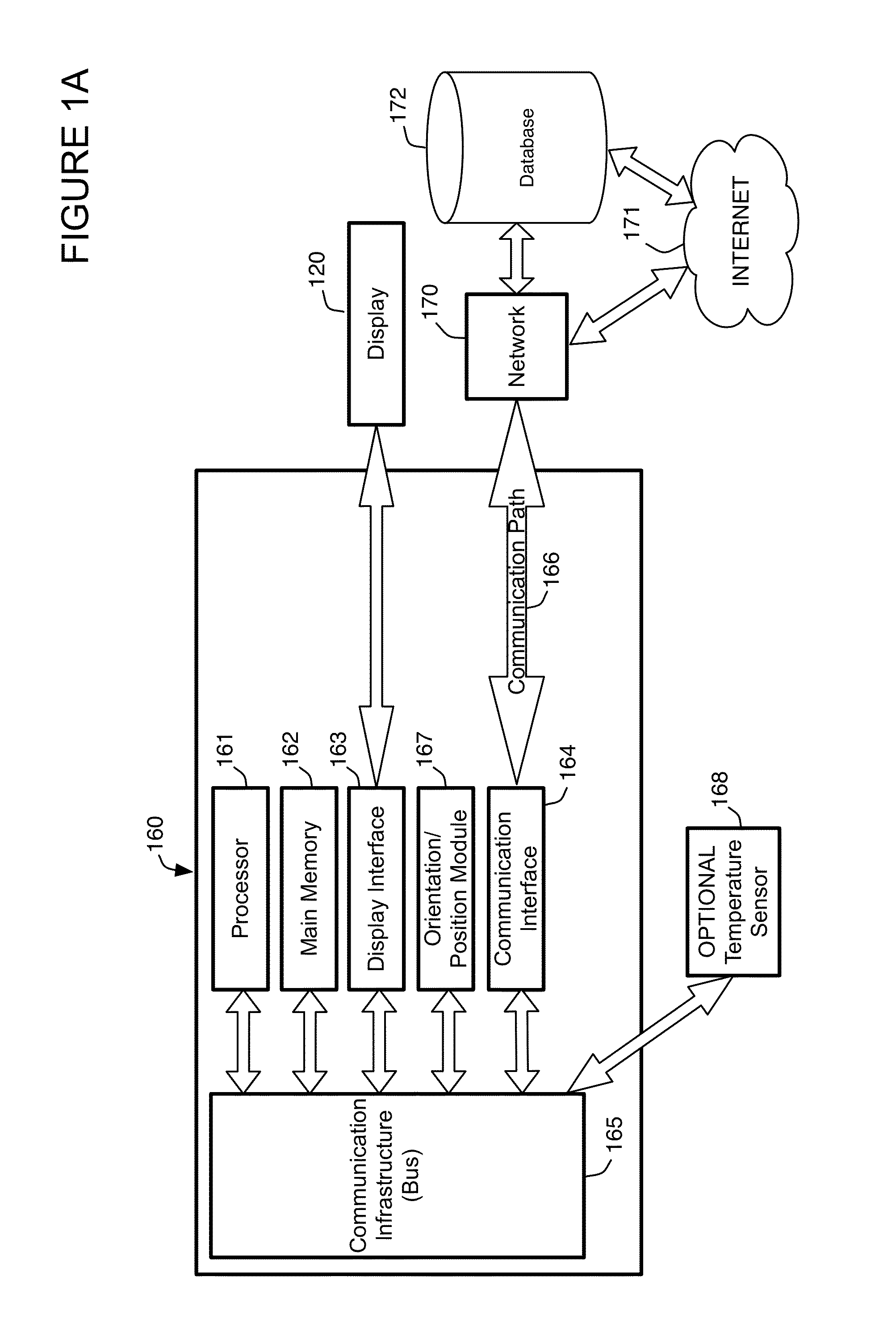
Optical see-through augmented reality modified-scale display
InactiveUS7002551B2Improve accuracyAccurate currentInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsDisplay device
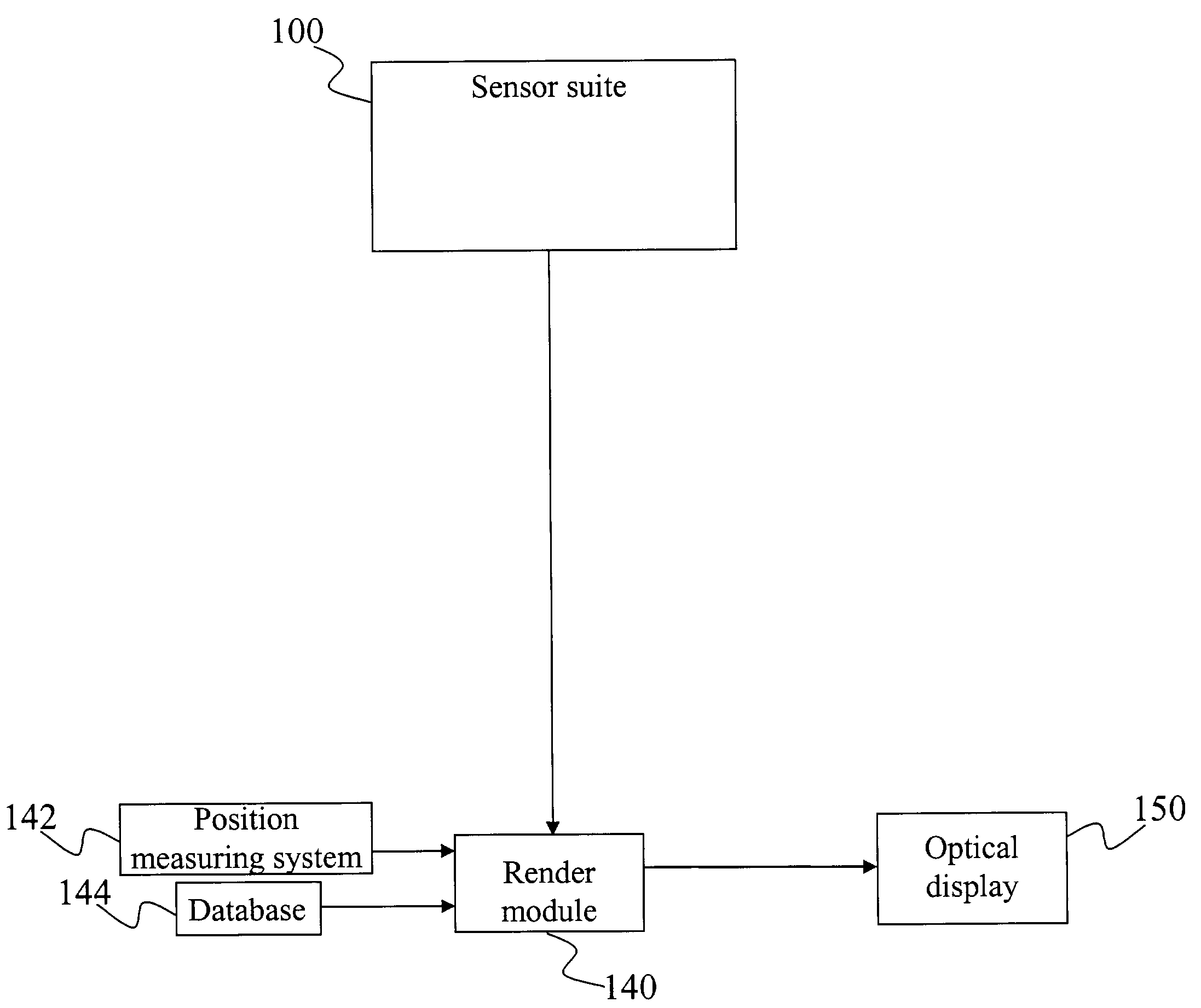
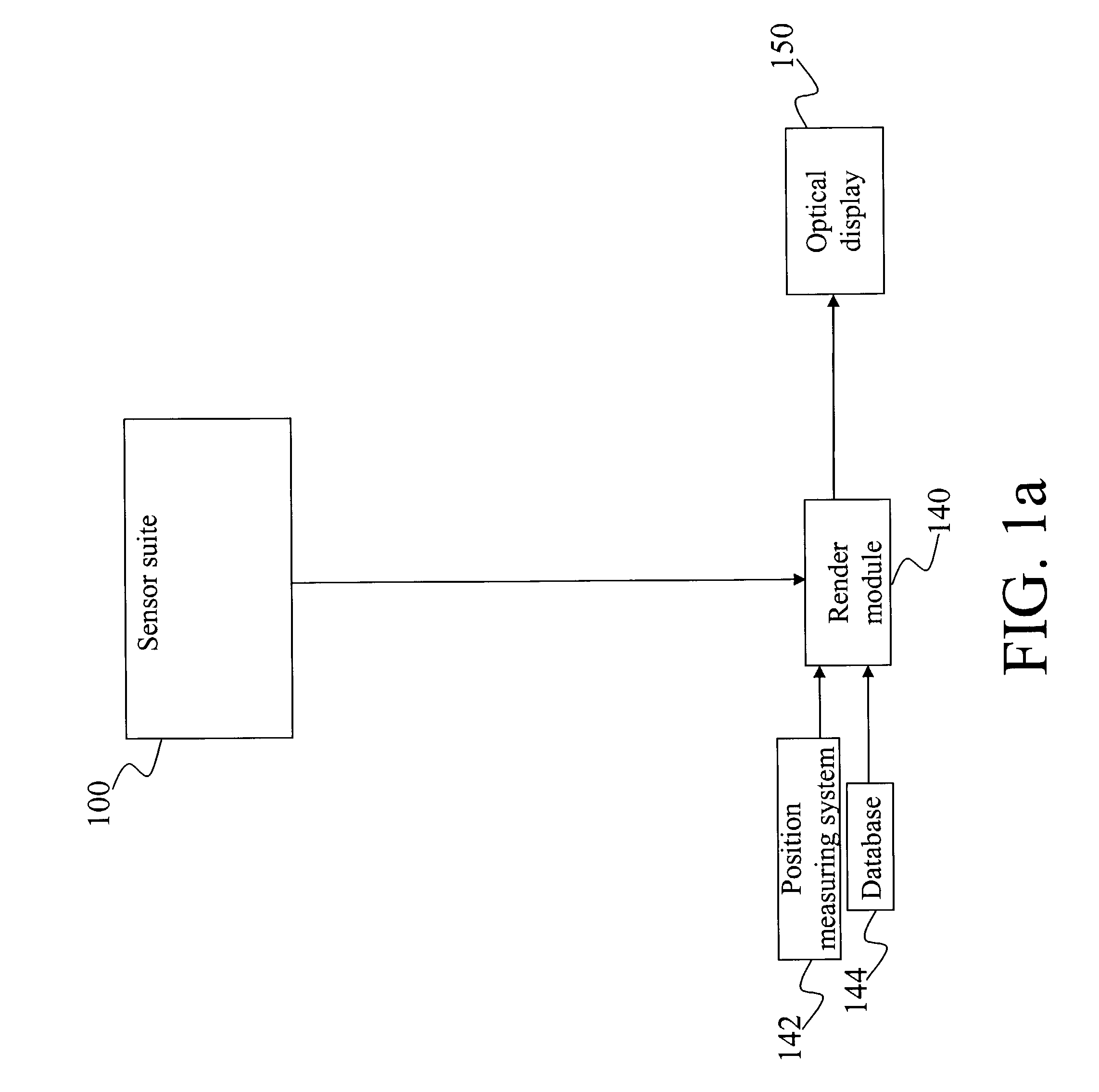
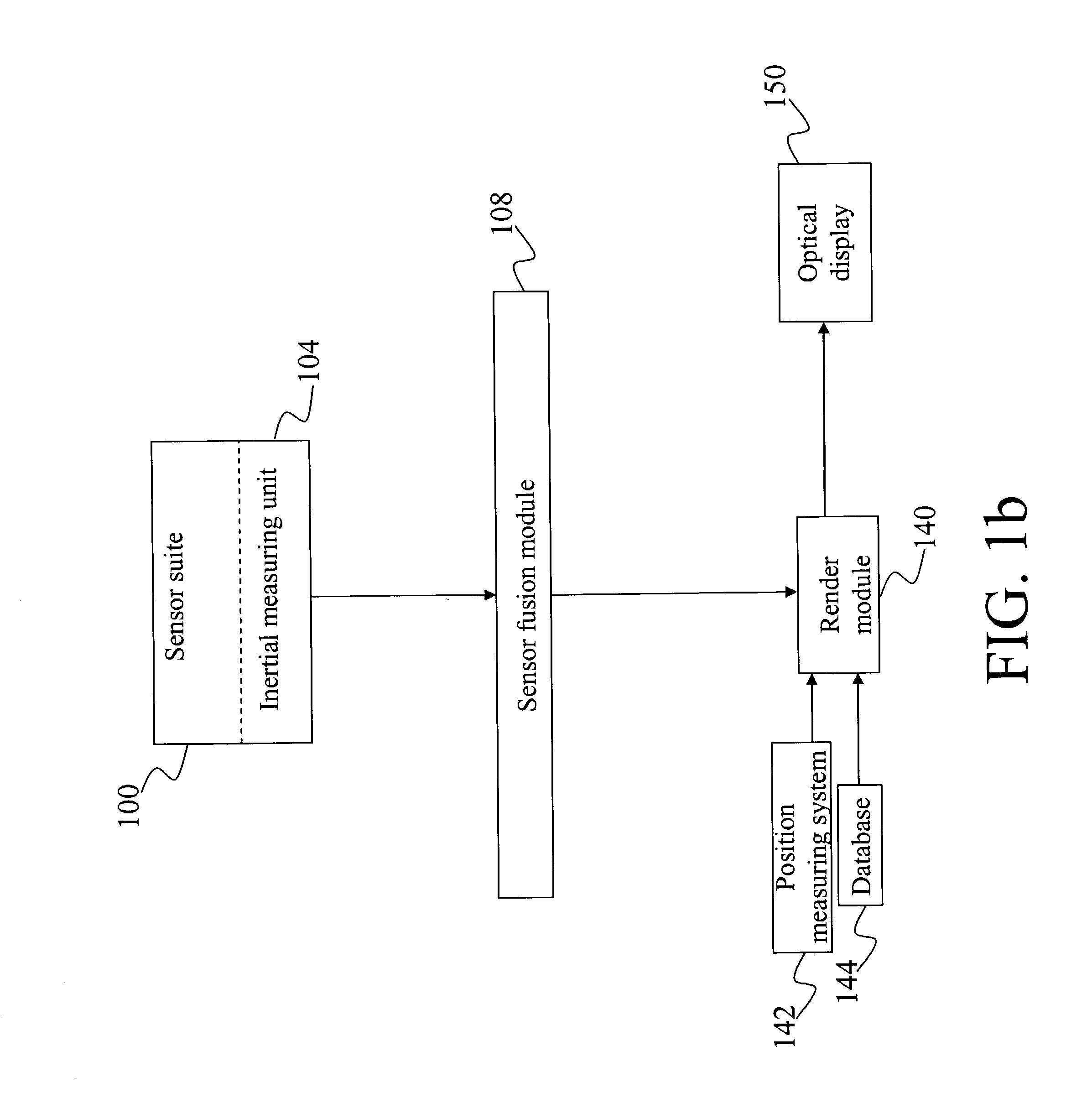
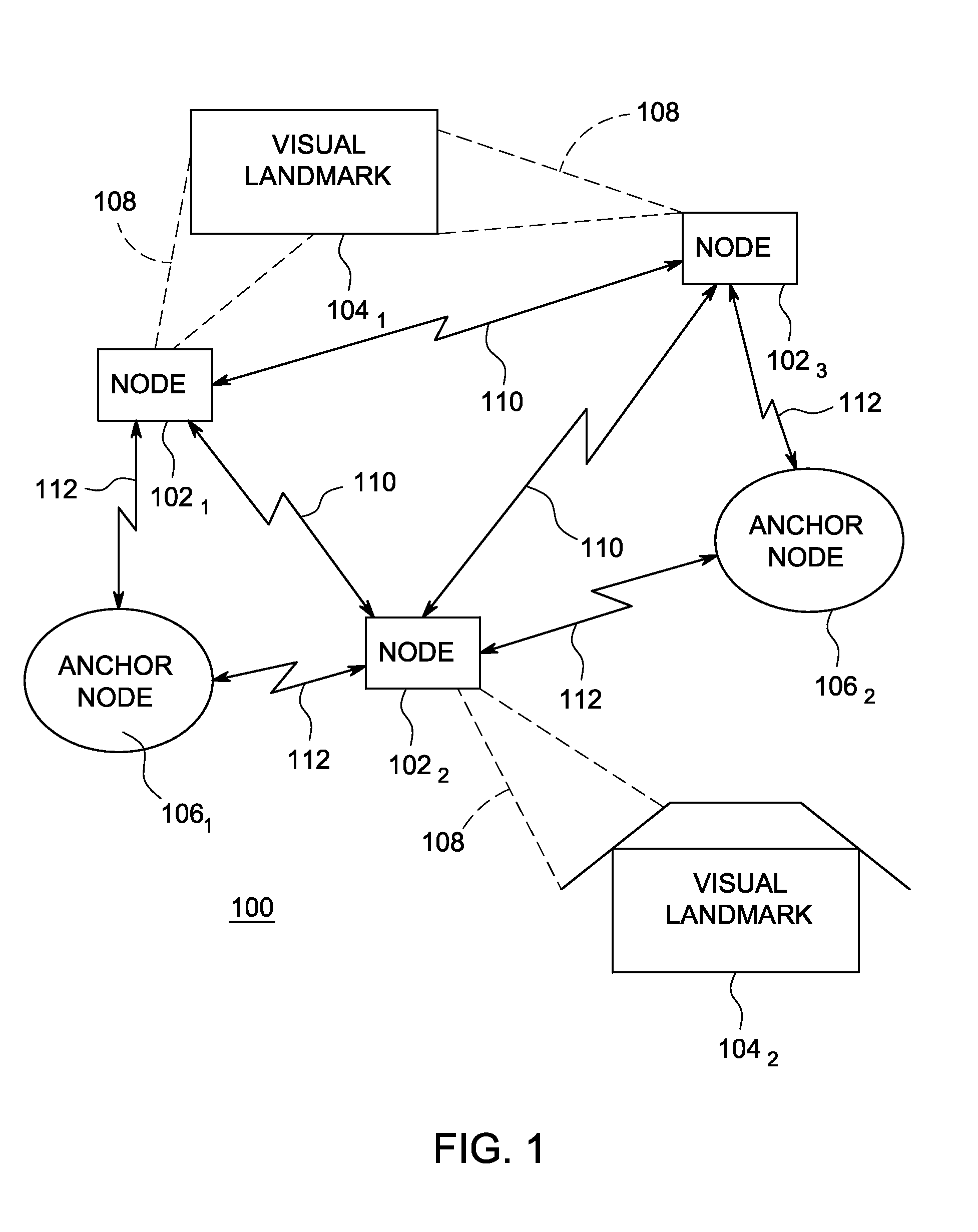
A method and system for providing an optical see-through Augmented Reality modified-scale display. This aspect includes a sensor suite 100 which includes a compass 102, an inertial measuring unit 104, and a video camera 106 for precise measurement of a user's current orientation and angular rotation rate. A sensor fusion module 108 may be included to produce a unified estimate of the user's angular rotation rate and current orientation to be provided to an orientation and rate estimate module 120. The orientation and rate estimate module 120 operates in a static or dynamic (prediction) mode. A render module 140 receives an orientation; and the render module 140 uses the orientation, a position from a position measuring system 142, and data from a database 144 to render graphic images of an object in their correct orientations and positions in an optical display 150.
Owner:HRL LAB
System and method for locating, tracking, and/or monitoring the status of personnel and/or assets both indoors and outdoors
ActiveUS20120130632A1Improving location estimatesImprove the accuracy of both outdoorInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlSensor fusionOrbit
Owner:TRX SYST
Automotive occupant sensor system and method of operation by sensor fusion
InactiveUS6026340AReliable detectionImprove reliabilityVehicle seatsDigital data processing detailsUltrasonic sensorTyping Classification
A system for sensing the presence, position and type classification of an occupant in a passenger seat of a vehicle, as well as for sensing the presence of a rear-facing child seat therein, for use in controlling a related air bag activator control system to enable, disable or control inflation rate or amount of inflation of an air bag. The sensor system employs sensor fusion, a process of combining information provided by two or more sensors (24, 26), each of which "sees" the world in a unique sense. In a preferred embodiment, infrared sensor inputs (78) and ultrasonic sensor inputs (79) are combined in a microprocessor by a sensor fusion algorithm (80) to produce an occupancy state output signal (85) to the air bag controller.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH CORP
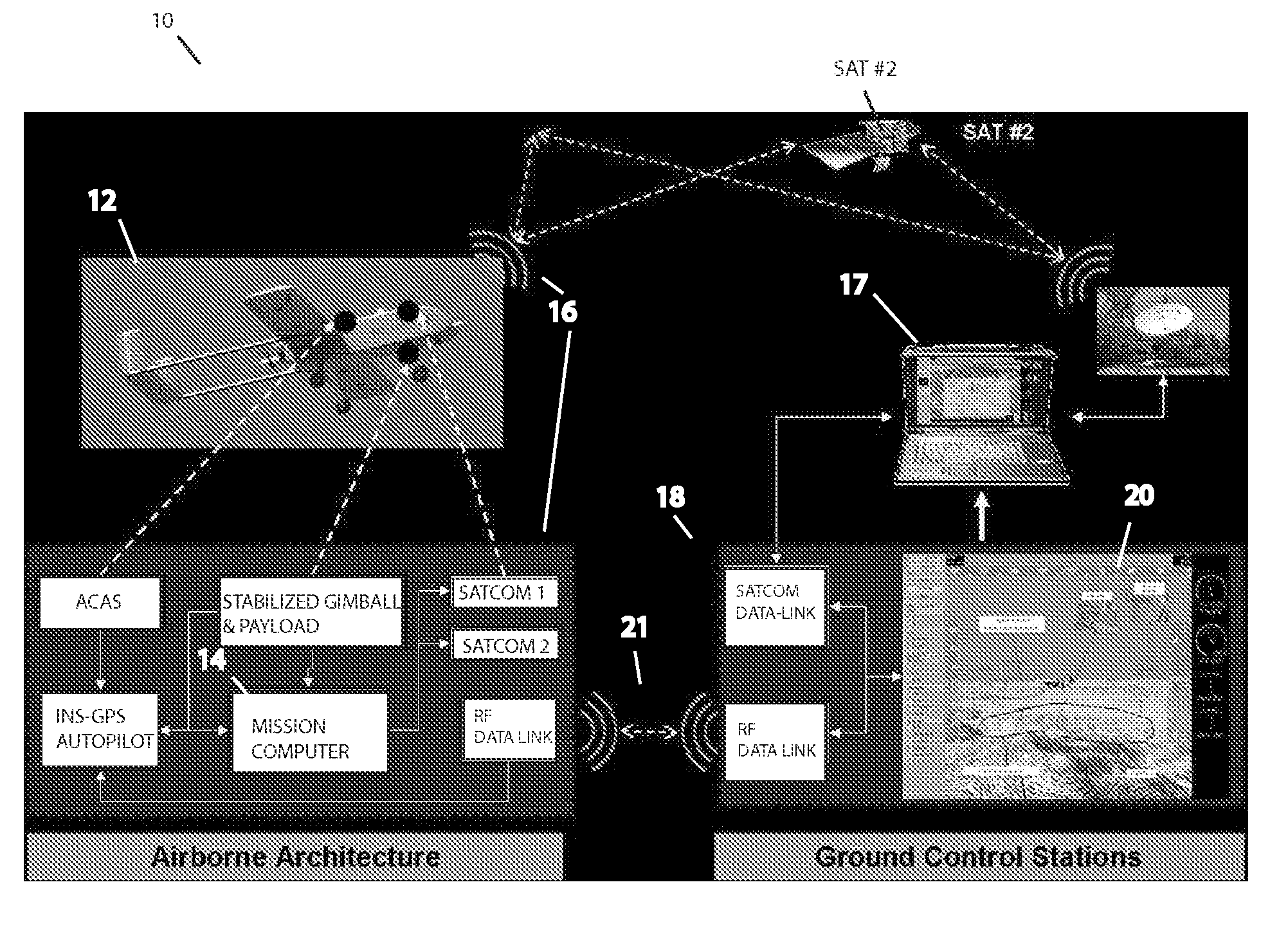
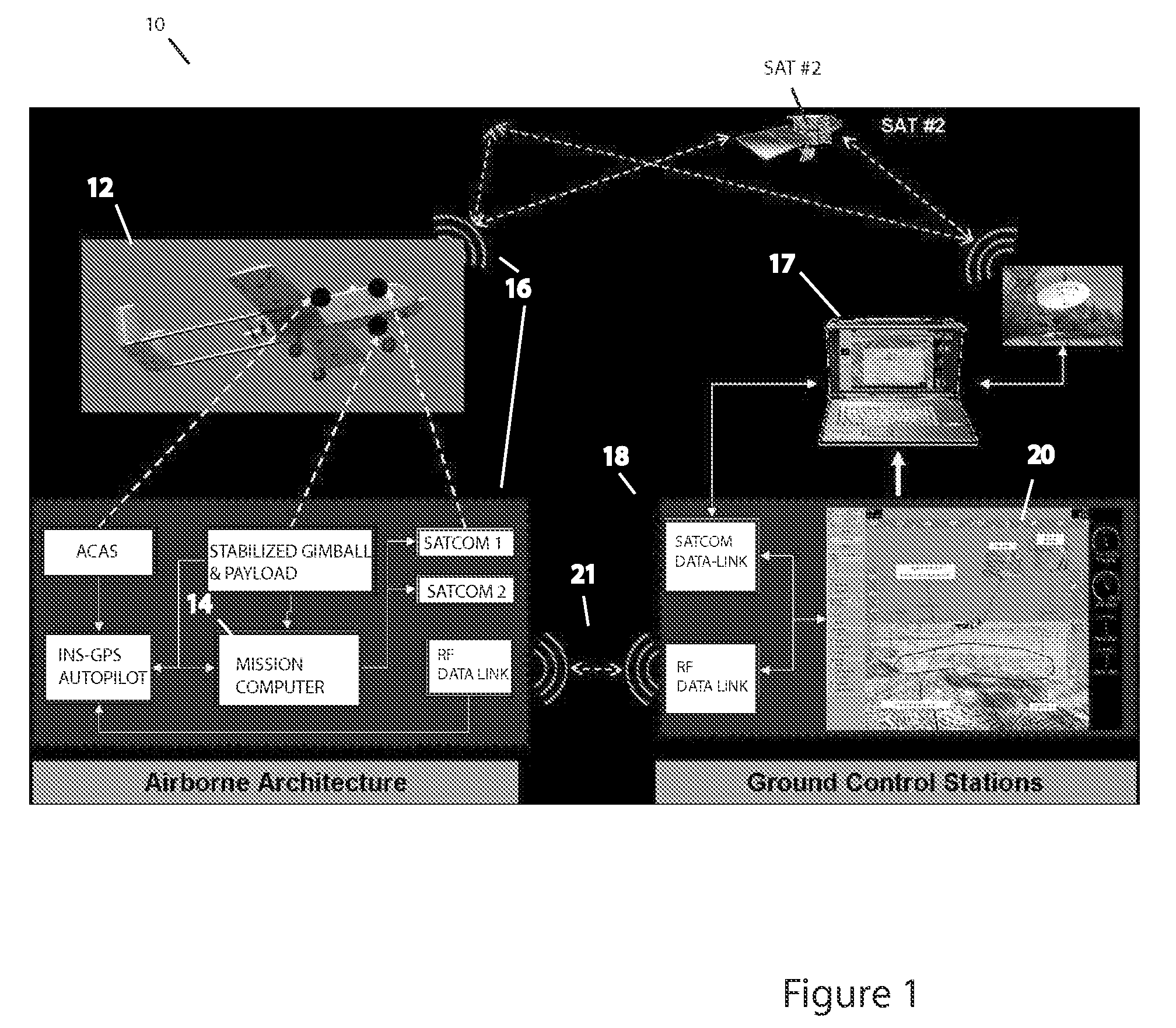
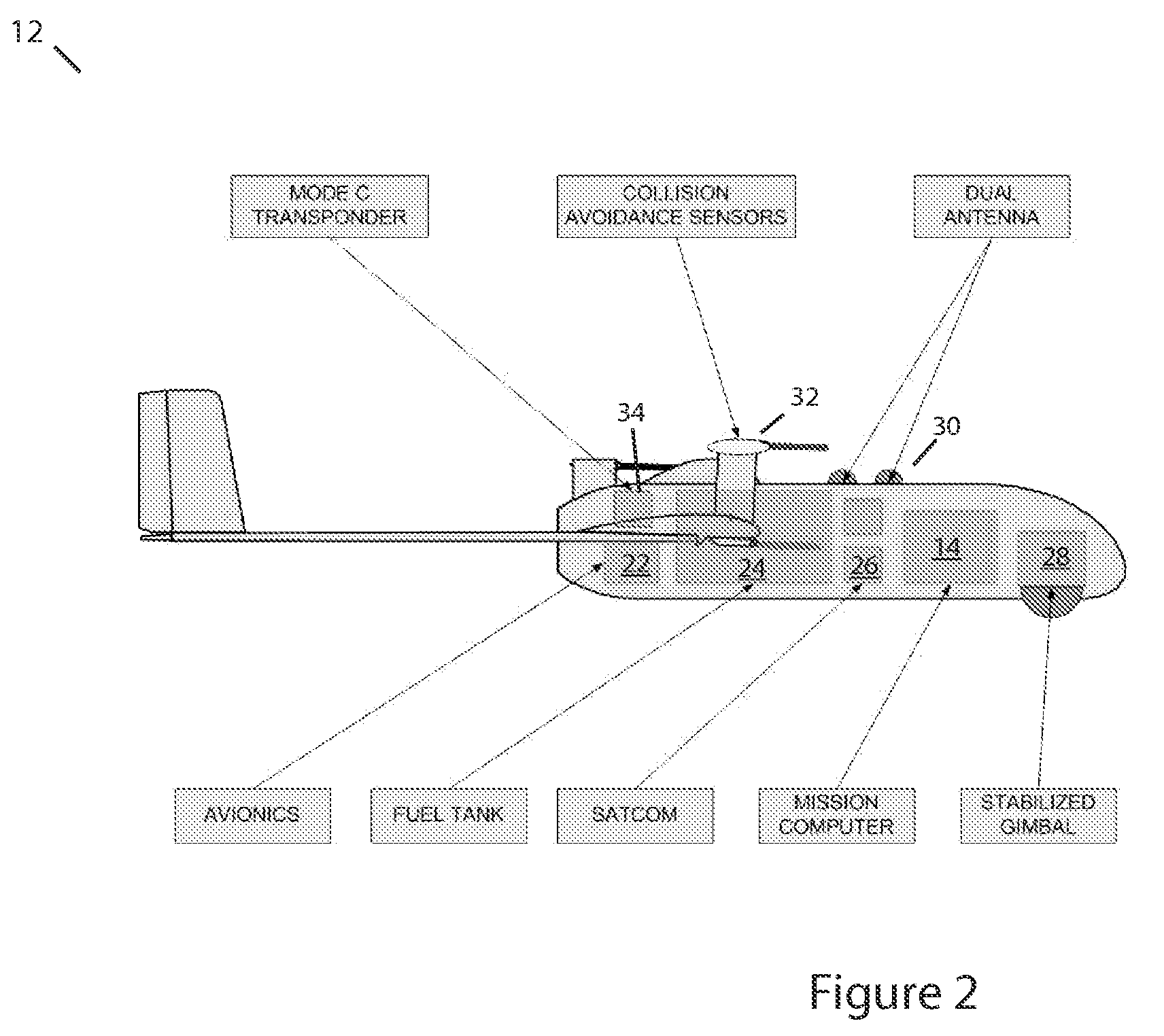
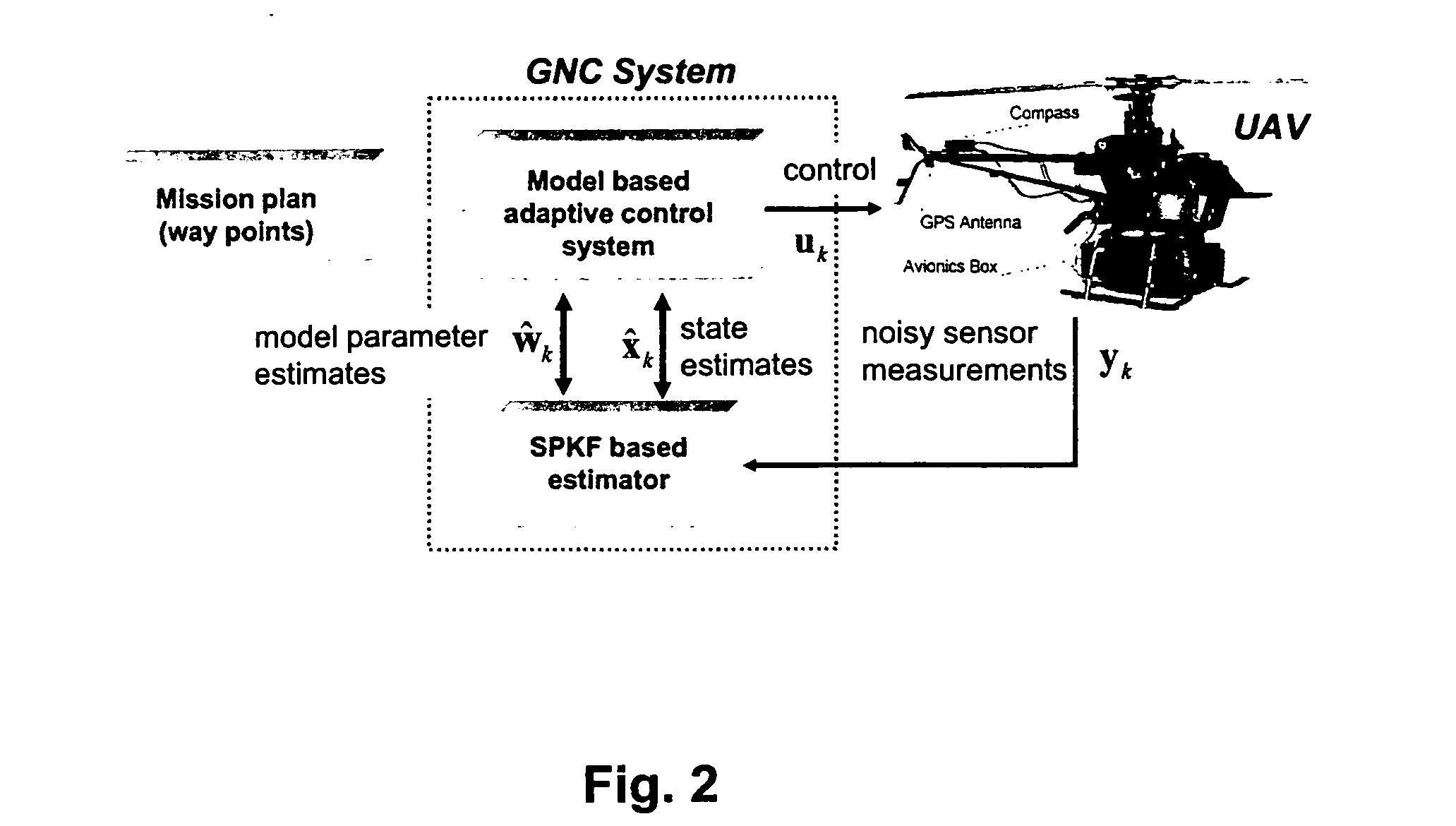
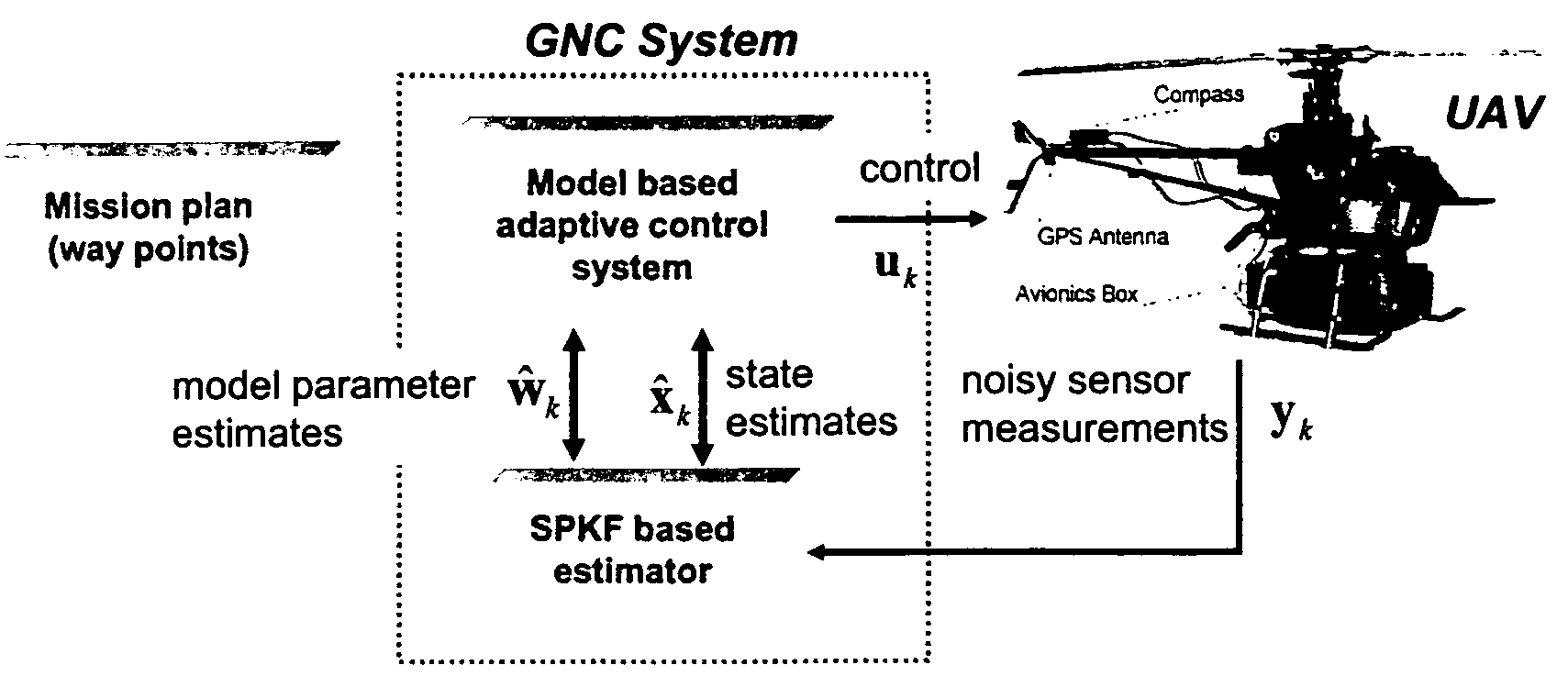
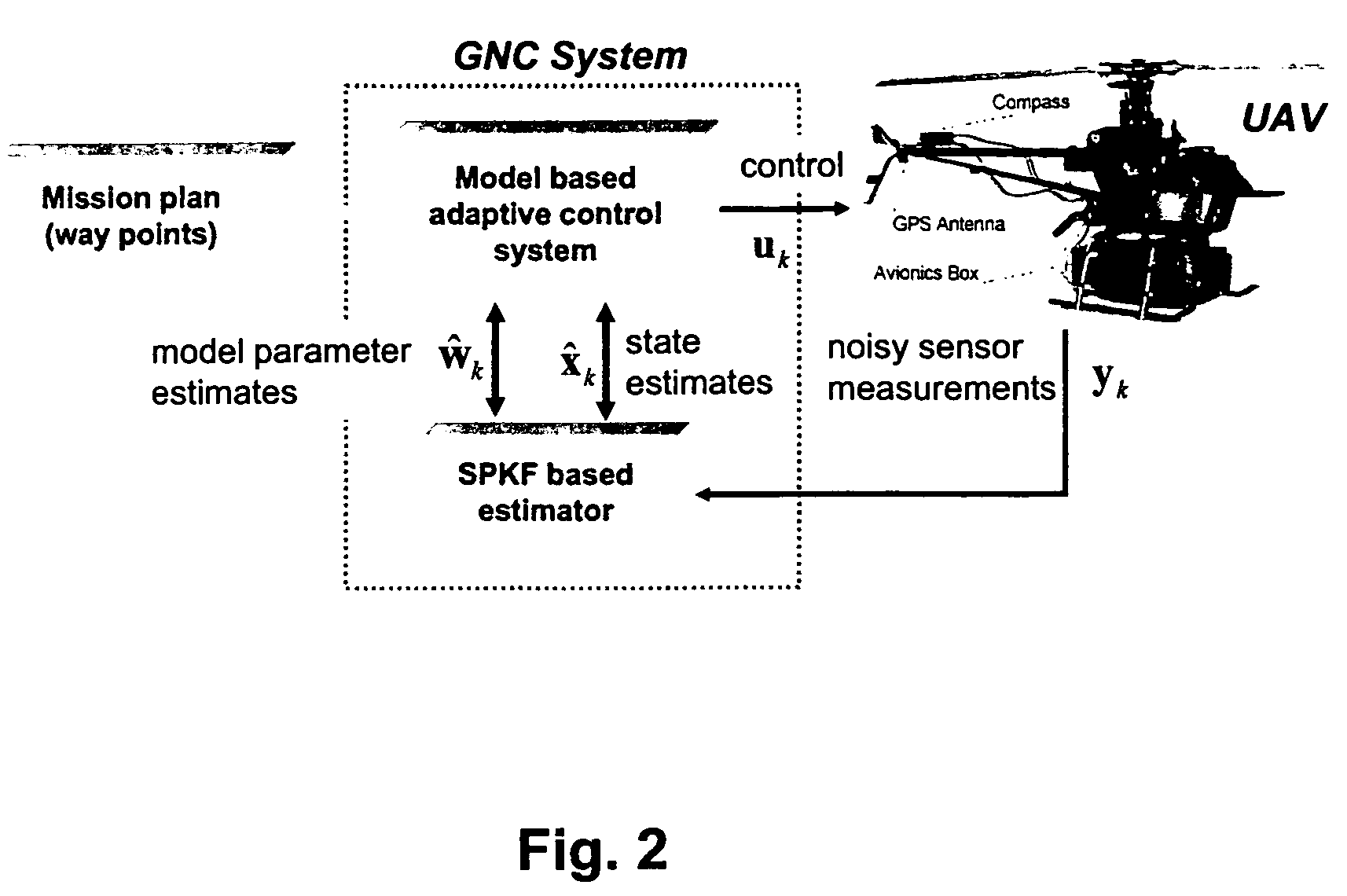
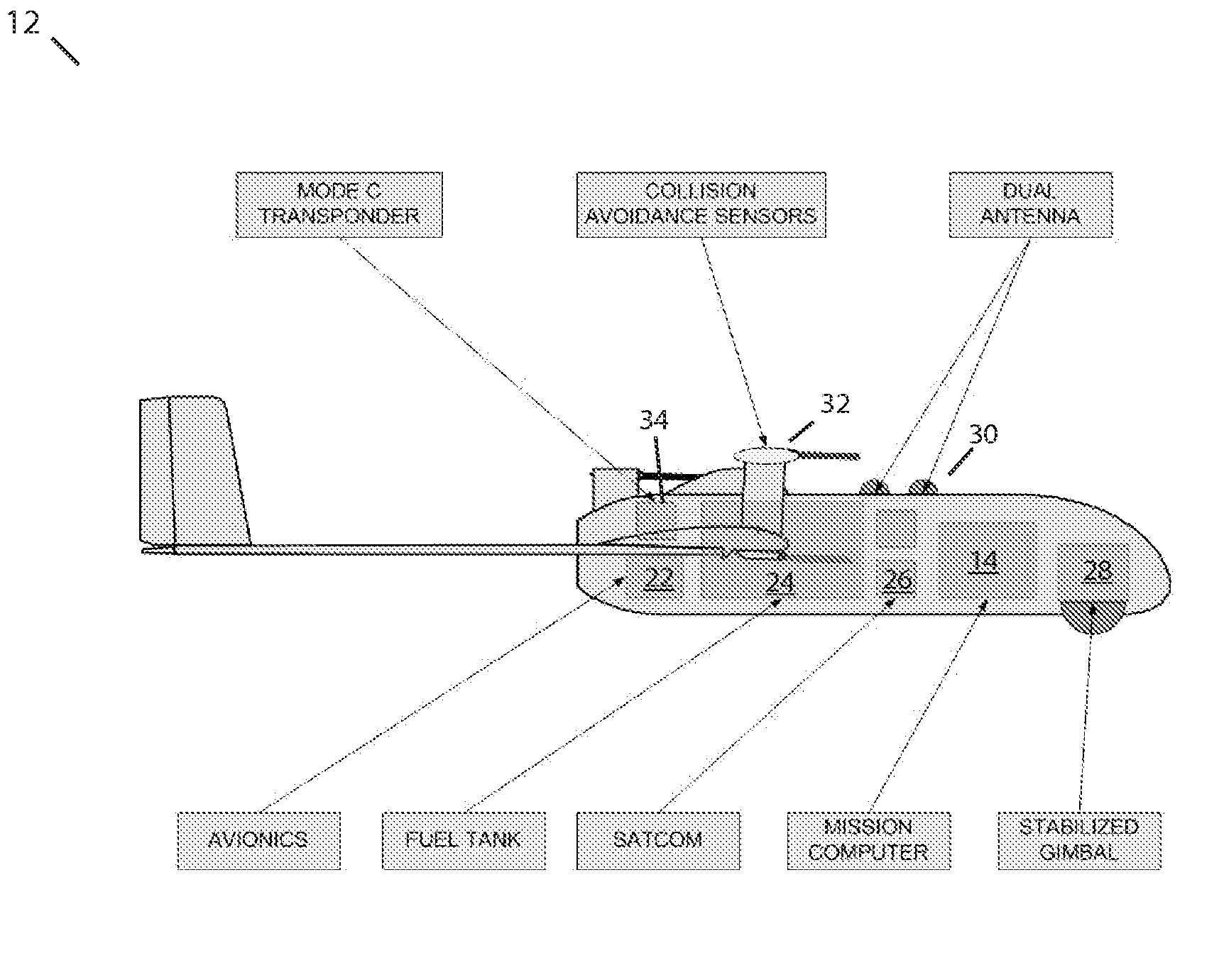
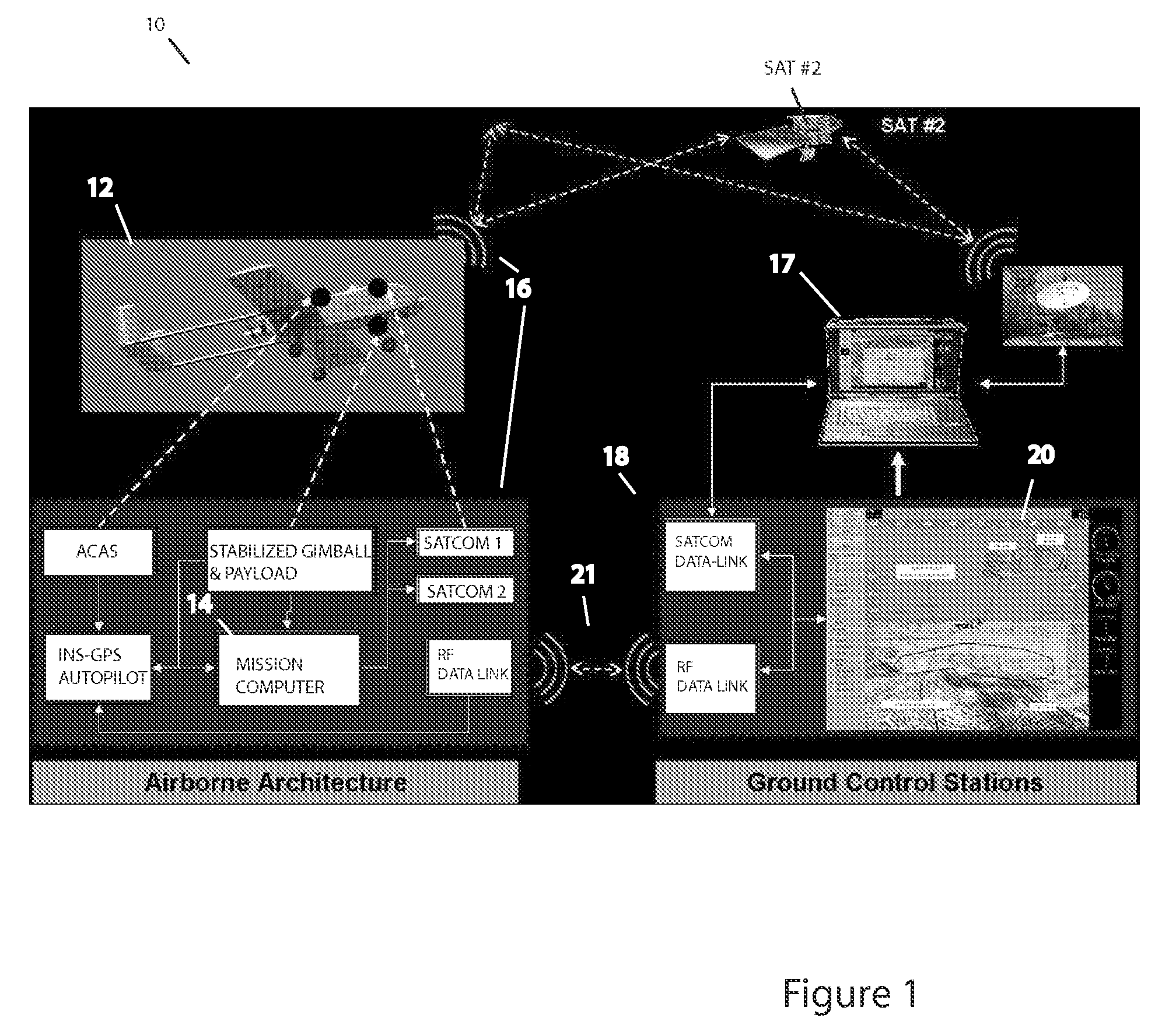
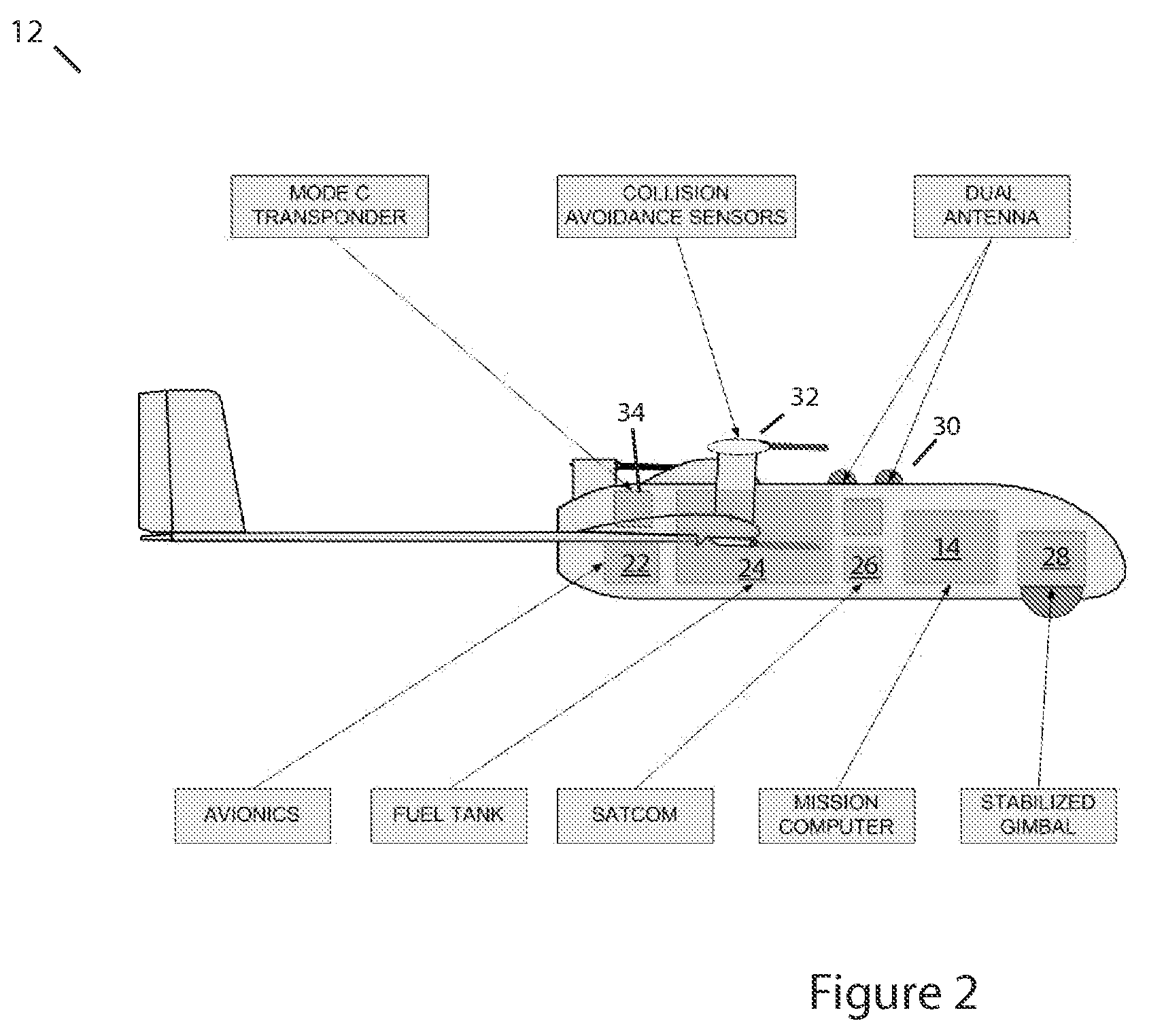
Methods, apparatus and systems for enhanced synthetic vision and multi-sensor data fusion to improve operational capabilities of unmanned aerial vehicles
ActiveUS20080215204A1Increase capacityImprove the display effectVehicle testingCosmonautic vehiclesSatelliteSensor fusion
The invention provides, in some aspects, improved methods, apparatus and systems for unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) operation that utilize multiple data links between a UAV and a control station in order to transmit control and actionable intelligence data. Such methods, apparatus and systems can be used, for example, to monitor a selected environment (e.g., an oil field or other terrain / environment of interest). In a related aspect, such data links comprise satellite communication channels.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
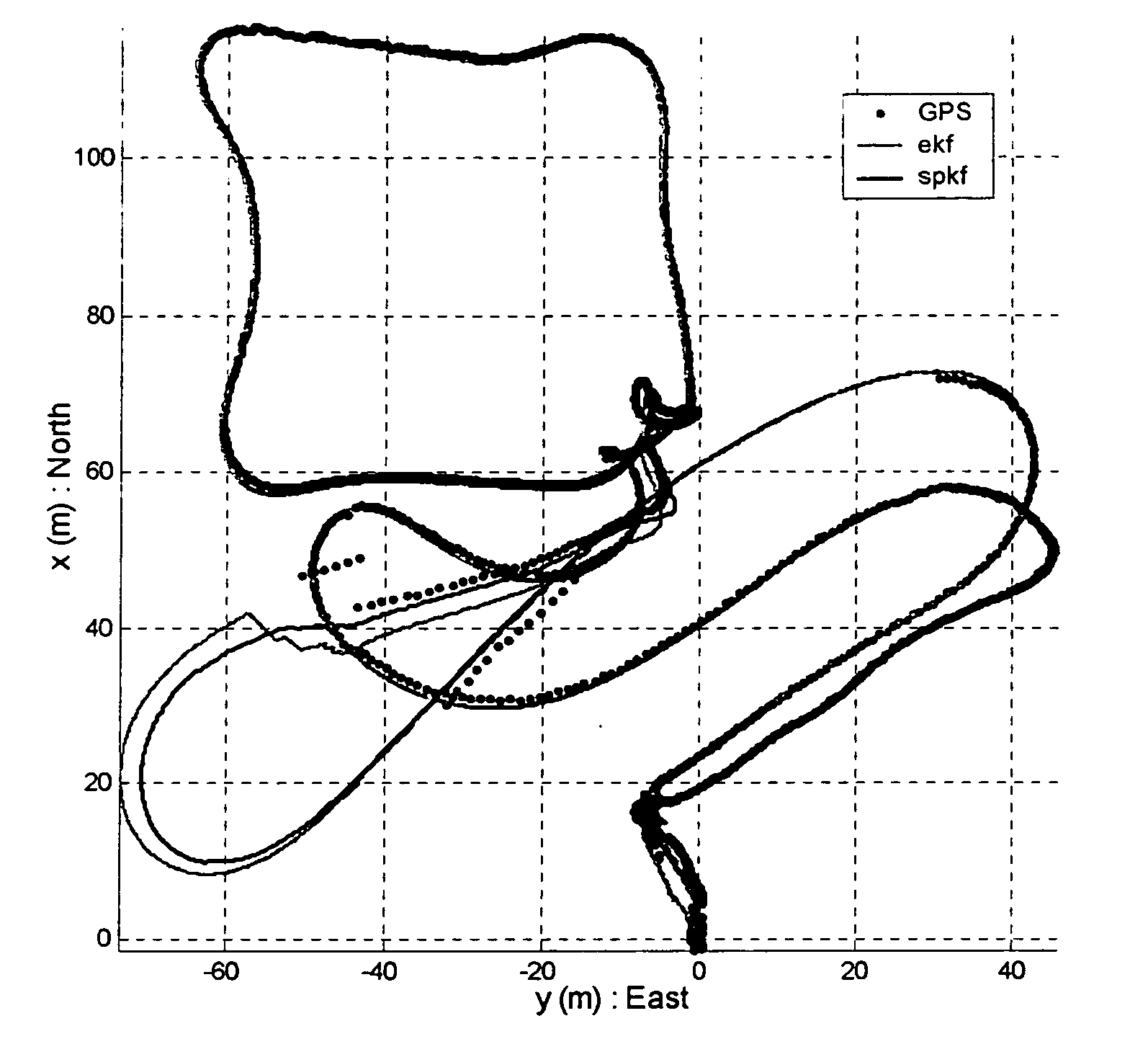
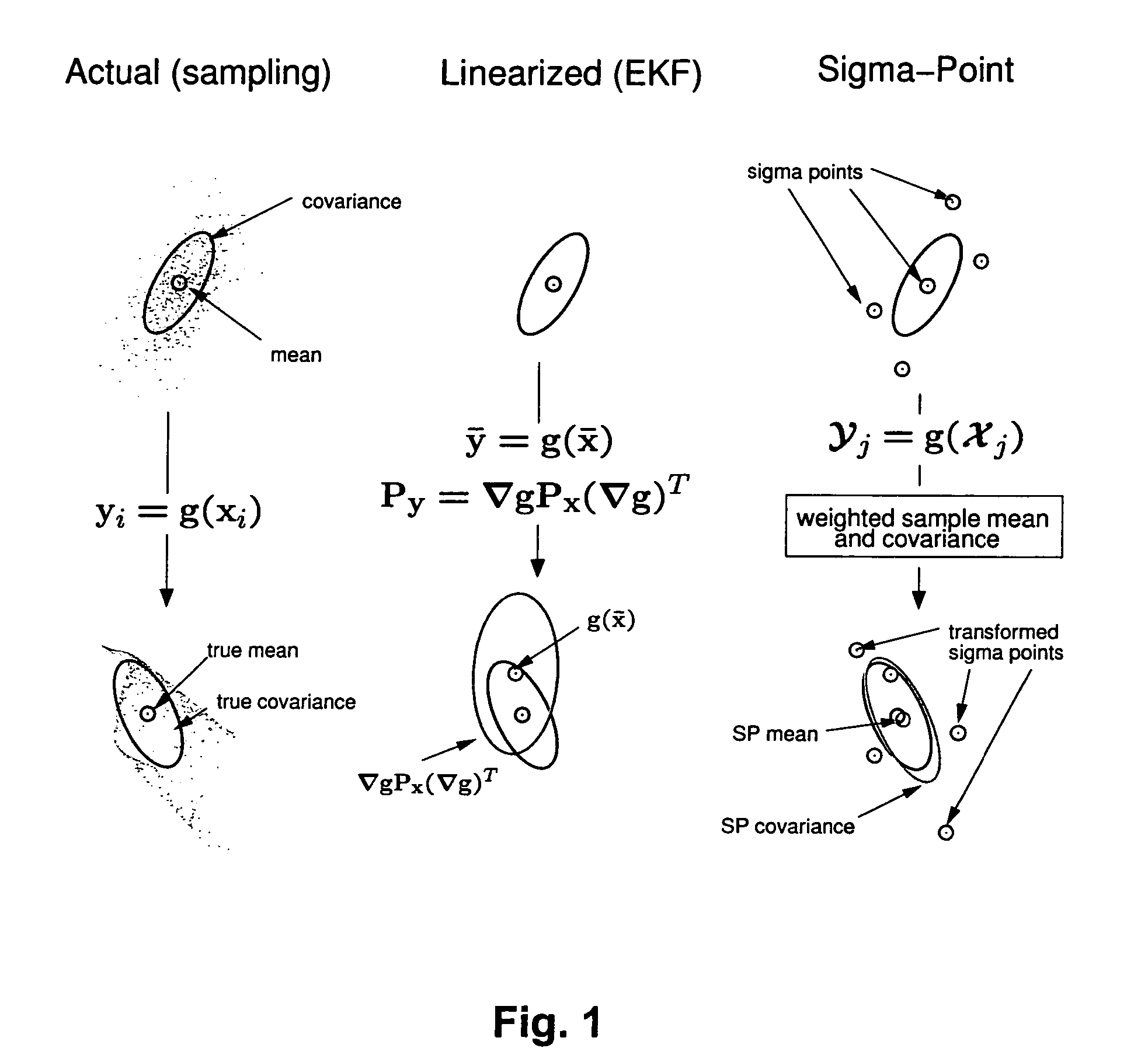
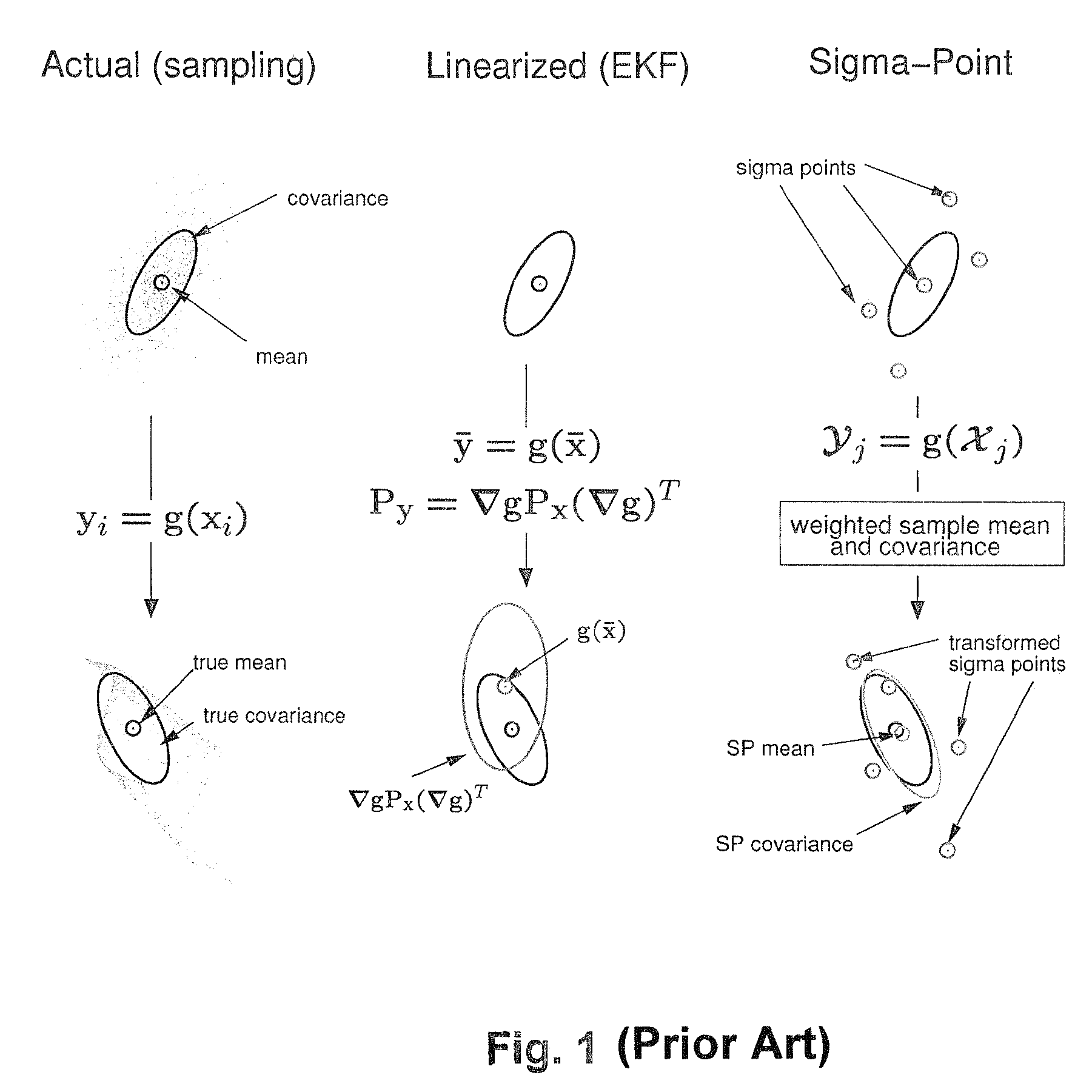
Navigation system applications of sigma-point Kalman filters for nonlinear estimation and sensor fusion
ActiveUS20050251328A1Improve estimation accuracyInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationKaiman filterAlgorithm
A method of estimating the navigational state of a system entails acquiring observation data produced by noisy measurement sensors and providing a probabilistic inference system to combine the observation data with prediction values of the system state space model to estimate the navigational state of the system. The probabilistic inference system is implemented to include a realization of a Gaussian approximate random variable propagation technique performing deterministic sampling without analytic derivative calculations. This technique achieves for the navigational state of the system an estimation accuracy that is greater than that achievable with an extended Kalman filter-based probabilistic inference system.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
Multi-sensor fusion
ActiveUS7283904B2Increase the difficultyFacilitates selection allocationAnalogue computers for vehiclesNear-field transmissionDriver/operatorThe Internet
Systems and methods are disclosed for establishing a mobile network in which each mobile unit, such as a car, becomes a node able to receive and transmit a wide variety of information, including for example, traffic conditions, vehicle mechanical / electrical status, interactive game playing information, streaming audio and video, email, and voice mail. In one aspect, multi-sensor fusion technology is used to determine the best value of a monitored variable, for example, the real time locations of each mobile unit, that may be communicated to others via the network. In addition, a new method of traffic control using real time traffic positioning and density data is disclosed. Further, methods and systems for enhancing driver safety are disclosed. In another aspect, the system may use a unique secure dynamic link allocation system to improve the information transfer from one node (mobile unit) to another and to other networks, such as the Internet.
Owner:AIRBIQUITY INC
Sensor fusion
ActiveUS20120072167A1Snap fastenersDigital data processing detailsSensor fusionIntensive care medicine
Owner:APPLE INC
Apparatus and method performing audio-video sensor fusion for object localization, tracking, and separation
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
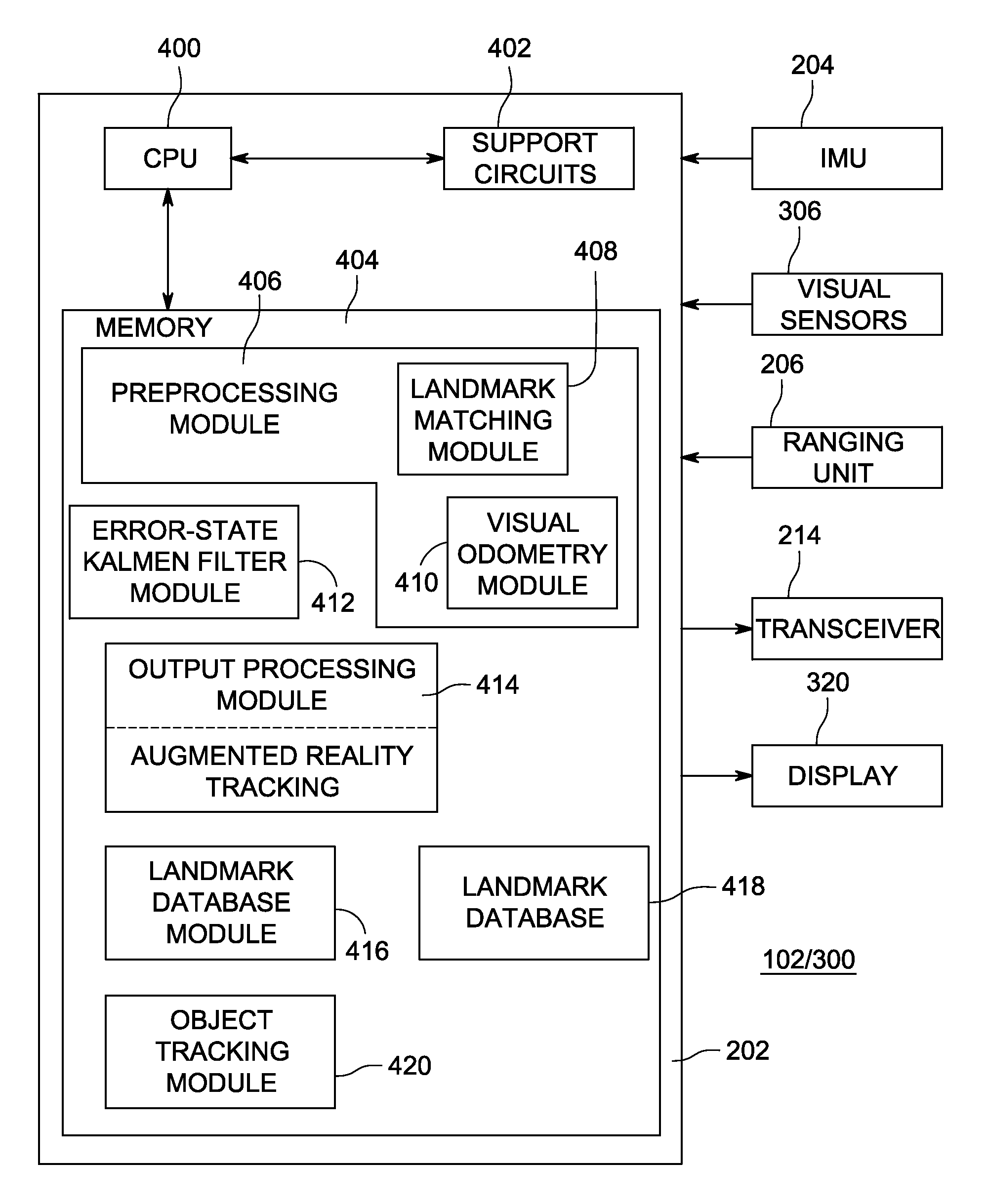
Method and apparatus for generating three-dimensional pose using multi-modal sensor fusion
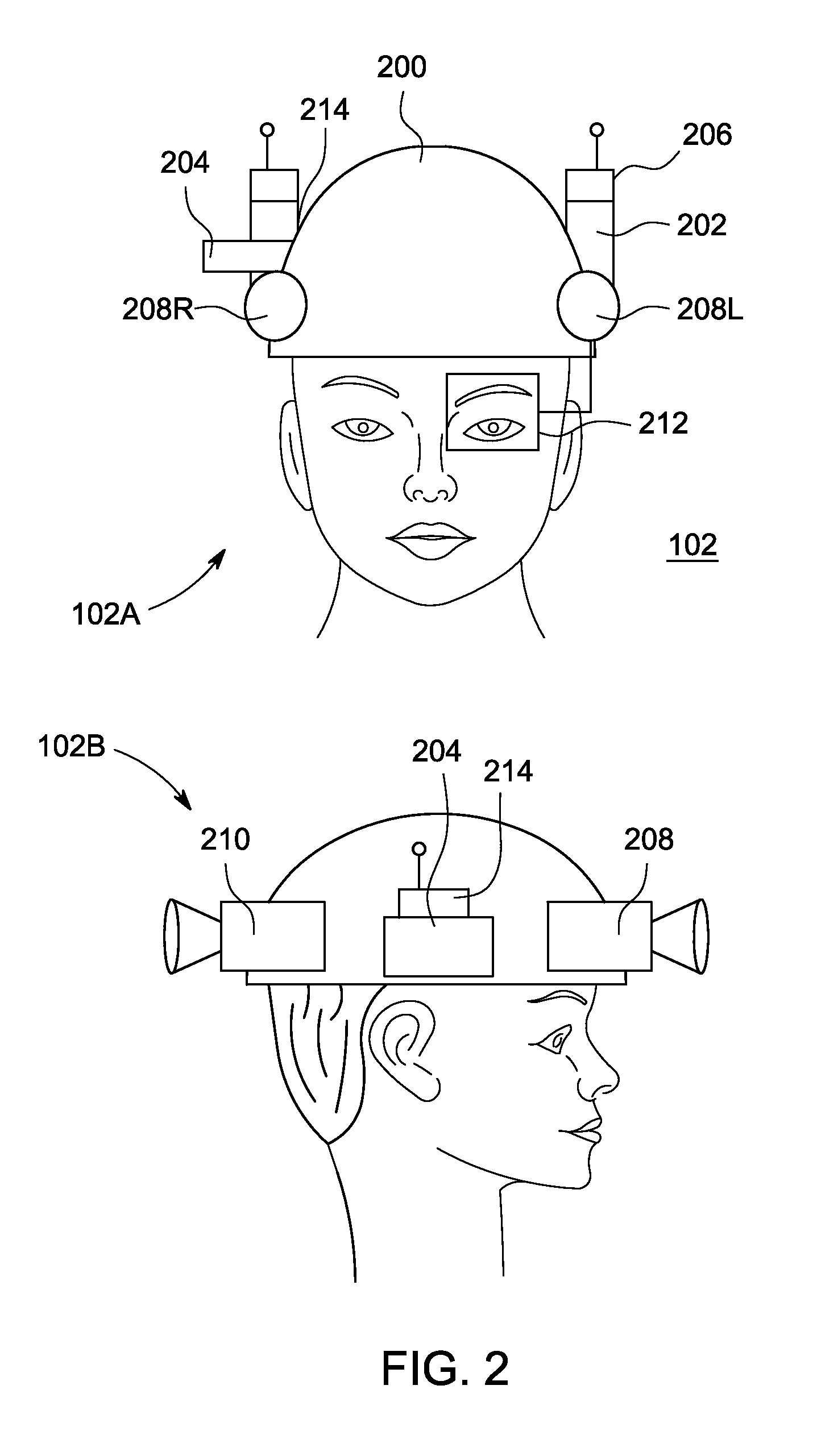
A method and apparatus for providing three-dimensional navigation for a node comprising an inertial measurement unit for providing gyroscope, acceleration and velocity information (collectively IMU information); a ranging unit for providing distance information relative to at least one reference node; at least one visual sensor for providing images of an environment surrounding the node; a preprocessor, coupled to the inertial measurement unit, the ranging unit and the plurality of visual sensors, for generating error states for the IMU information, the distance information and the images; and an error-state predictive filter, coupled to the preprocessor, for processing the error states to produce a three-dimensional pose of the node.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
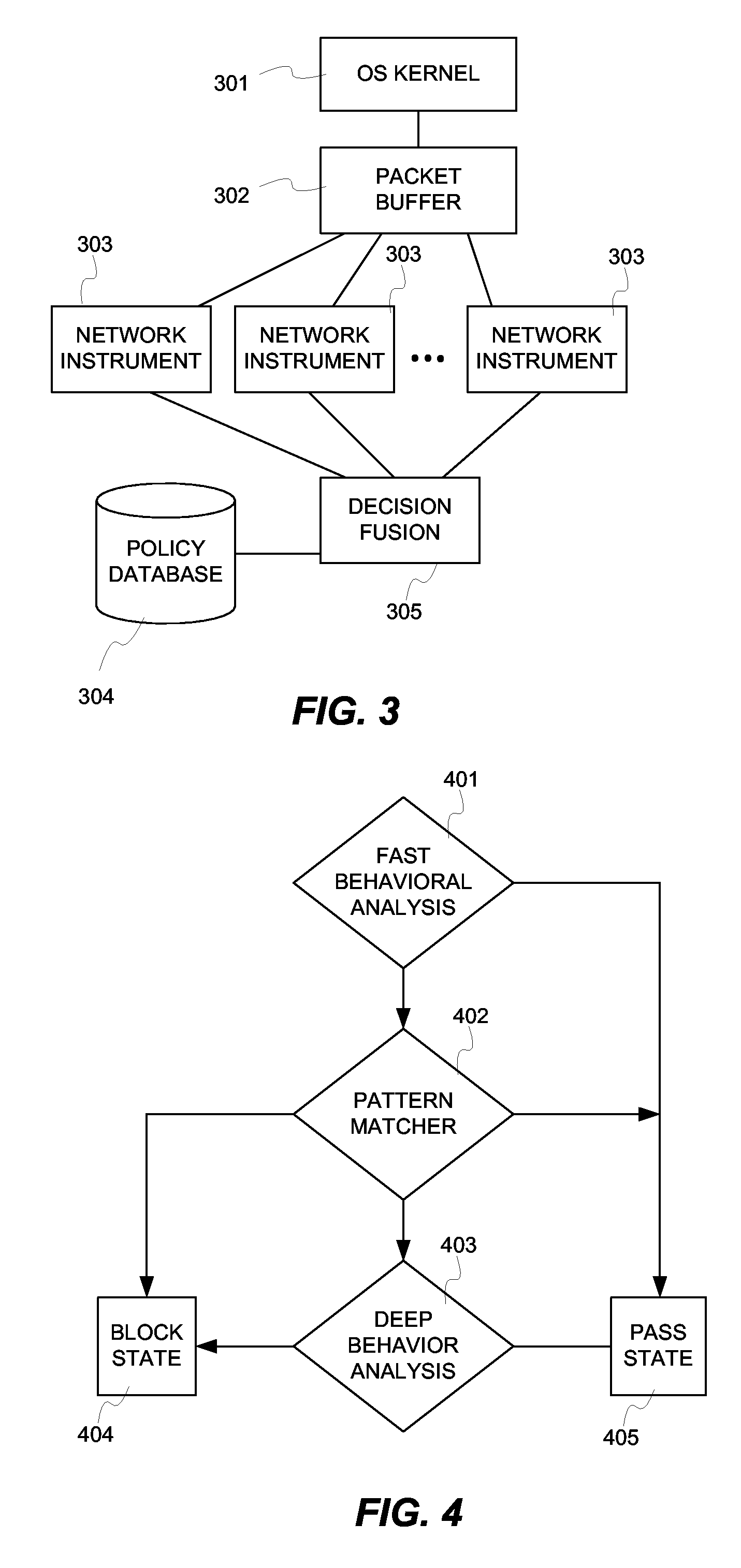
Fusion instrusion protection system
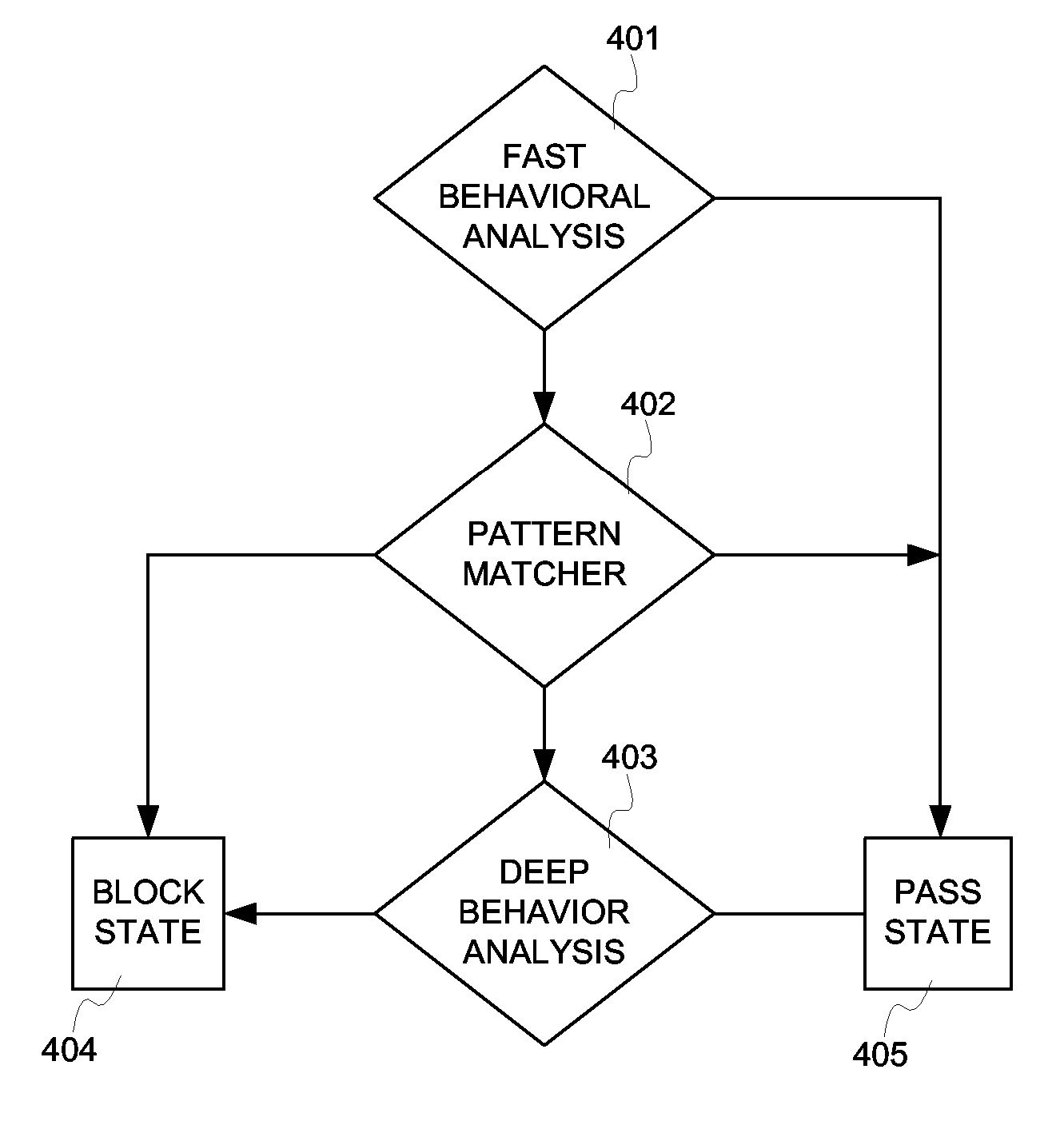
InactiveUS20070056038A1Solve the high false positive rateEfficient Anomaly DetectionMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionAnomaly detectionSensor fusion
An intrusion protection system that fuses a network instrumentation classification with a packet payload signature matching system. Each of these kinds of systems is independently capable of being effectively deployed as an anomaly detection system. By employing sensor fusion techniques to combine the instrumentation classification approach with the signature matching approach, the present invention provides an intrusion protection system that is uniquely capable of detecting both well known and newly developed threats while having an extremely low false positive rate.
Owner:LOK TECH
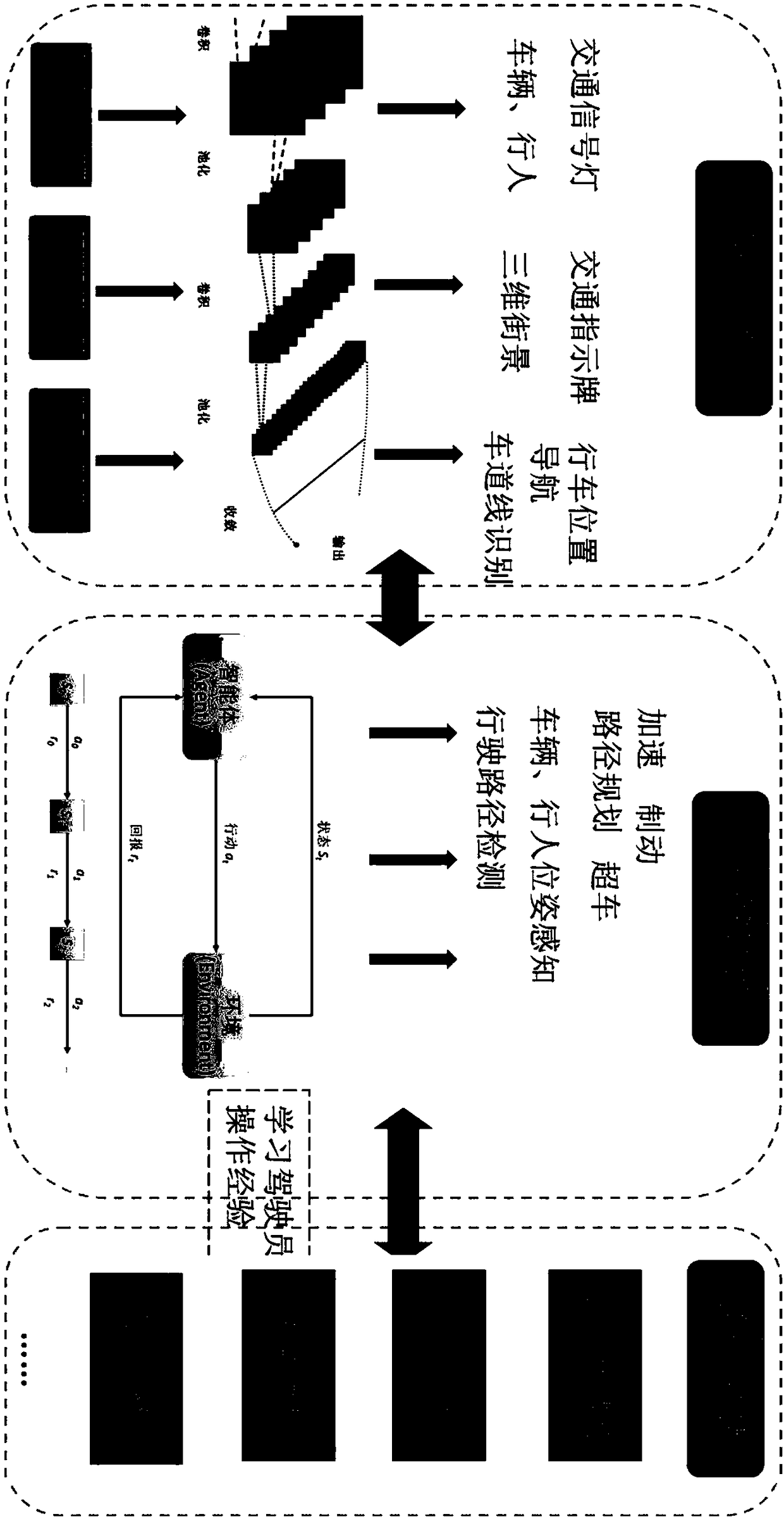
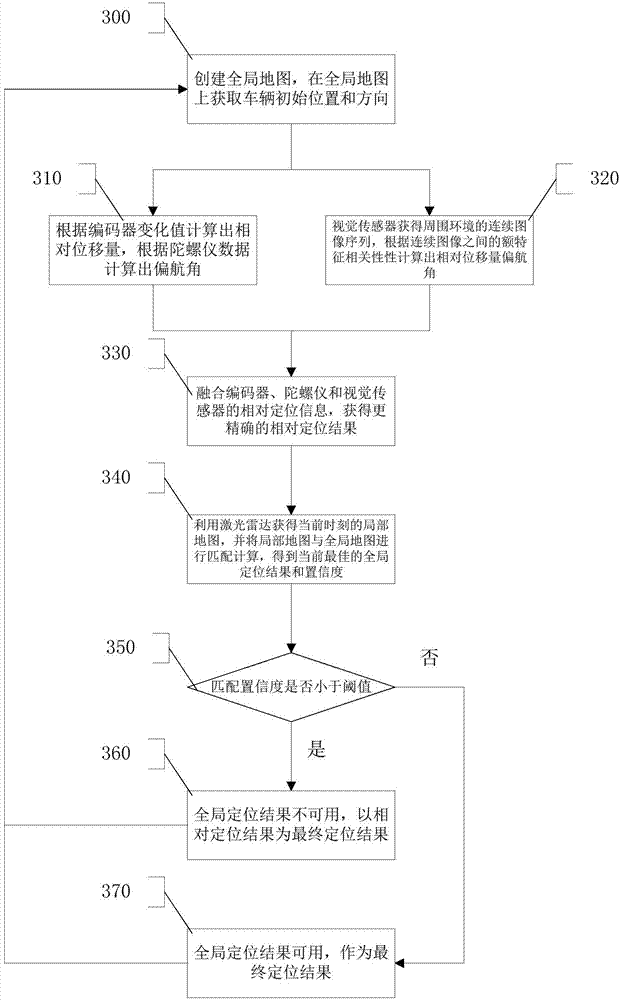
Automatic driving system based on enhanced learning and multi-sensor fusion
ActiveCN108196535APrecise positioningAccurate understandingPosition/course control in two dimensionsLearning networkProcess information
The invention discloses an automatic driving system based on enhanced learning and multi-sensor fusion. The system comprises a perception system, a control system and an execution system. The perception system high-efficiently processes a laser radar, a camera and a GPS navigator through a deep learning network so as to realize real time identification and understanding of vehicles, pedestrians, lane lines, traffic signs and signal lamps surrounding a running vehicle. Through an enhanced learning technology, the laser radar and a panorama image are matched and fused so as to form a real-time three-dimensional streetscape map and determination of a driving area. The GPS navigator is combined to realize real-time navigation. The control system adopts an enhanced learning network to process information collected by the perception system, and the people, vehicles and objects of the surrounding vehicles are predicted. According to vehicle body state data, the records of driver actions are paired, a current optimal action selection is made, and the execution system is used to complete execution motion. In the invention, laser radar data and a video are fused, and driving area identification and destination path optimal programming are performed.
Owner:清华大学苏州汽车研究院(吴江)
Integrated sensor and video motion analysis method
ActiveUS20150324636A1Conserve camera powerConserve video memoryTelevision system detailsImage enhancementObject motionSensor fusion
A method that integrates sensor data and video analysis to analyze object motion. Motion capture elements generate motion sensor data for objects of interest, and cameras generate video of these objects. Sensor data and video data are synchronized in time and aligned in space on a common coordinate system. Sensor fusion is used to generate motion metrics from the combined and integrated sensor data and video data. Integration of sensor data and video data supports robust detection of events, generation of video highlight reels or epic fail reels augmented with metrics that show interesting activity, and calculation of metrics that exceed the individual capabilities of either sensors or video analysis alone.
Owner:NEWLIGHT CAPITAL LLC
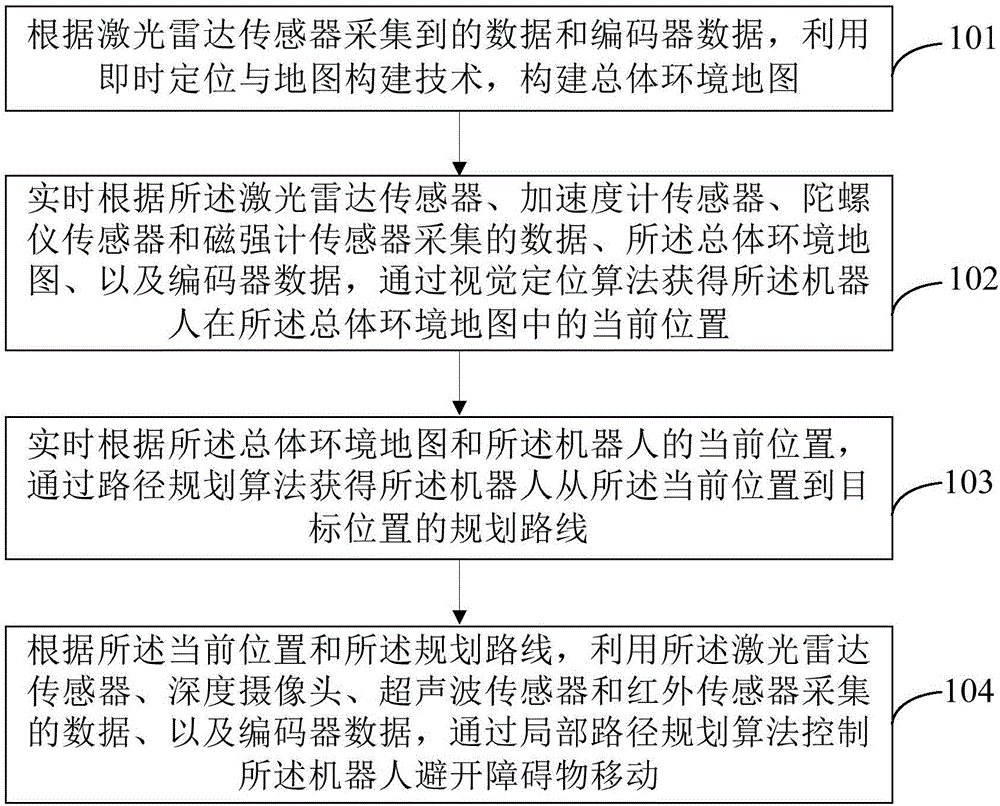
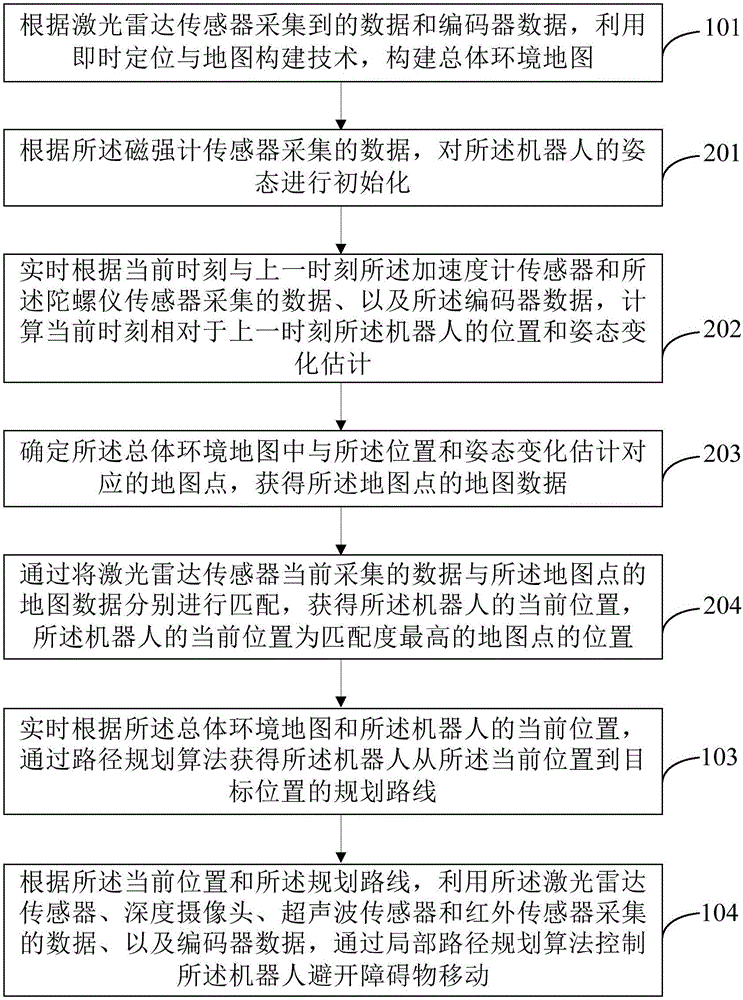
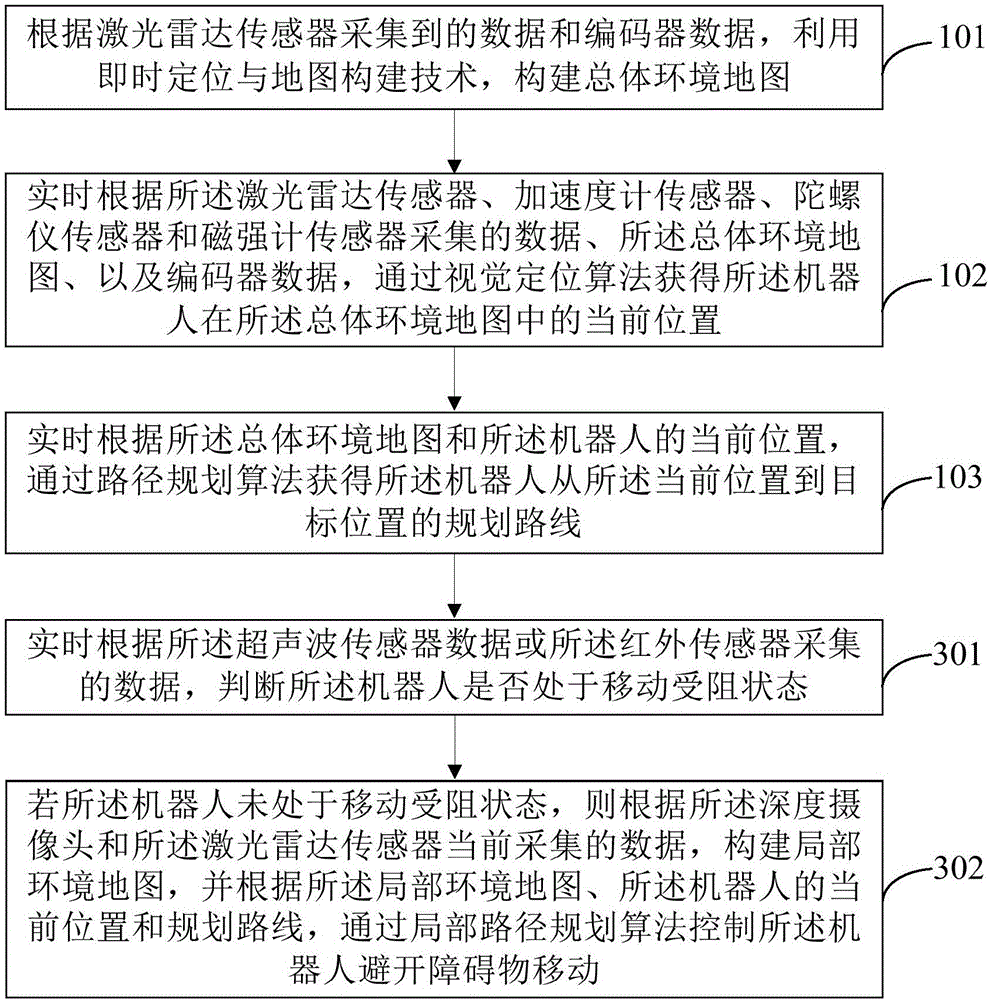
Robot navigation method and device based on multi-sensor data fusion
InactiveCN106681330ARealize autonomous navigationTaking into account the costPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesUltrasonic sensorGyroscope
The invention provides a robot navigation method and device based on multi-sensor data fusion. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a map of a total environment according to data acquired by a laser radar sensor and data of an encoder; acquiring the current position of a robot in the map of the total environment in real time according to data acquired by a laser radar sensor, an accelerometer sensor, a gyroscope sensor and a magnetometer sensor, the map of the total environment and the data of the encoder; acquiring a planned route of the robot from the current position to a targeted position in real time according to the map of the total environment and the current position of the robot; and controlling the robot to keep away from barriers during movement by the data which are acquired by the laser radar sensor, a deep camera, an ultrasonic sensor and an infrared sensor and the data of the encoder. On the basis of reasonable utilization of the sensors to realize navigation of the robot, the method is flexibly applied to various scenes, costs are considered, and the autonomous navigation effect can be achieved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Sensor fusion for model-based detection in pipe and cable locator systems
ActiveUS7834801B2Improve positionSatellite radio beaconingElectric/magnetic detectionGyroscopeAccelerometer
Line locator systems that fuse traditional sensors used in a combined pipe and cable locator (electromagnetic coils, magnetometers, and ground penetrating radar antennas) with low cost inertial sensors (accelerometers, gyroscopes) in a model-based approach are presented. Such systems can utilize inexpensive MEMS sensors for inertial navigation. A pseudo-inertial frame is defined that uses the centerline of the tracked utility, or an aboveground fixed object as the navigational reference. An inertial sensor correction mechanism that limits the tracking errors over time when the model is implemented in state-space form using, for example, the Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) is disclosed.
Owner:BUSAN TRANSPORTATION CORPORATION
Sensor fusion
Owner:APPLE INC
Navigation system applications of sigma-point Kalman filters for nonlinear estimation and sensor fusion
ActiveUS7289906B2Instruments for road network navigationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsKaiman filterAlgorithm
A method of estimating the navigational state of a system entails acquiring observation data produced by noisy measurement sensors and providing a probabilistic inference system to combine the observation data with prediction values of the system state space model to estimate the navigational state of the system. The probabilistic inference system is implemented to include a realization of a Gaussian approximate random variable propagation technique performing deterministic sampling without analytic derivative calculations. This technique achieves for the navigational state of the system an estimation accuracy that is greater than that achievable with an extended Kalman filter-based probabilistic inference system.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
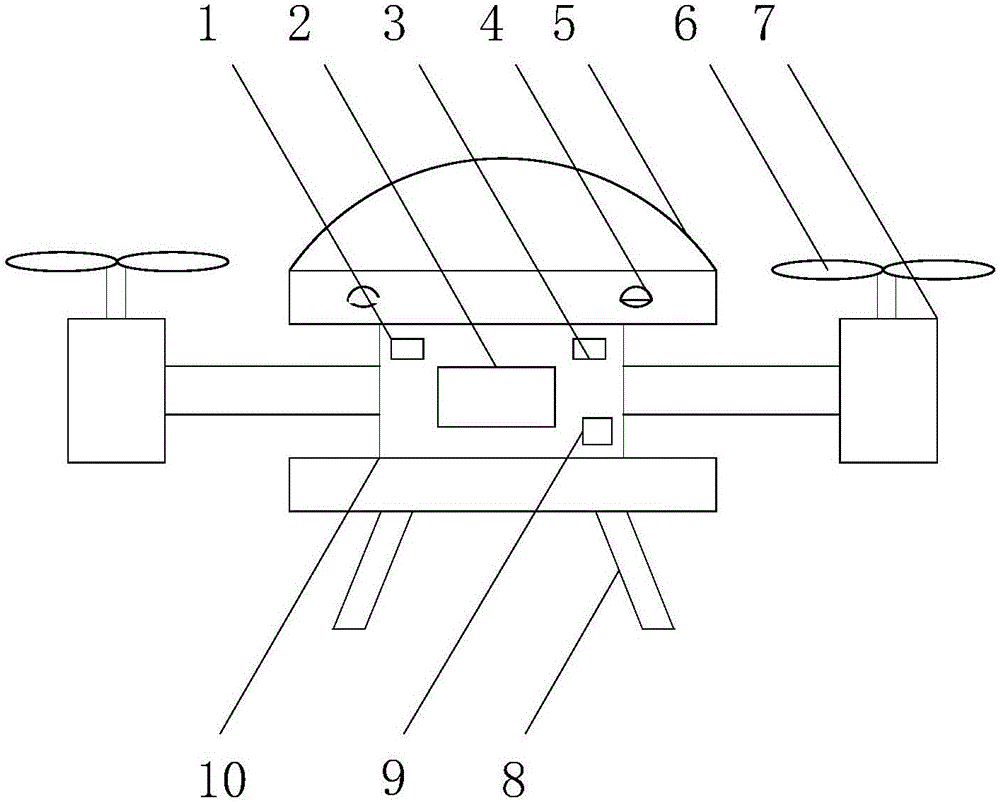
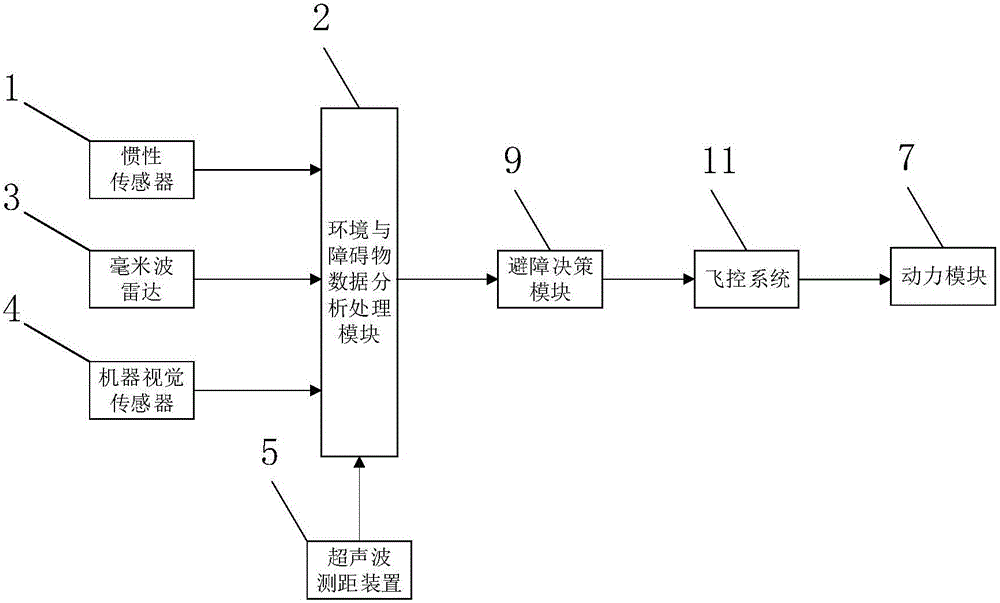
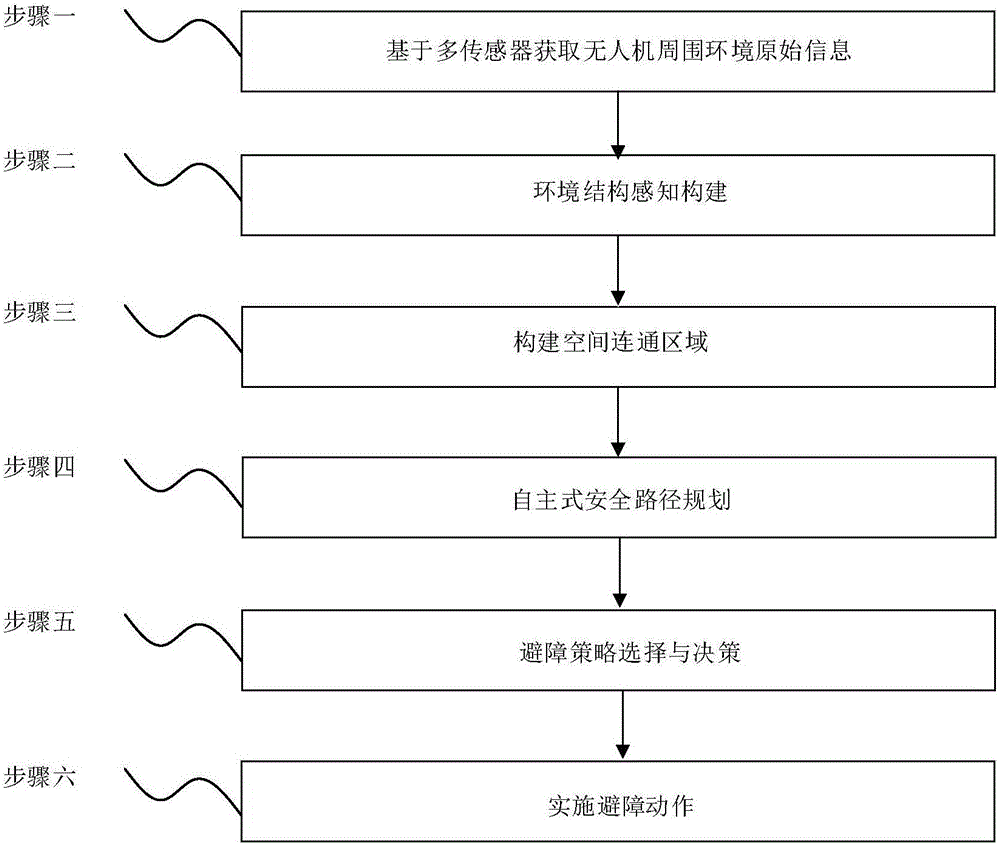
Multi-sensor fusion-based autonomous obstacle avoidance unmanned aerial vehicle system and control method
ActiveCN105892489AAvoid collisionImprove real-time detectionPosition/course control in three dimensionsMulti sensorBinocular distance
The invention discloses a multi-sensor fusion-based autonomous obstacle avoidance unmanned aerial vehicle system and a control method. The system includes an environment information real-time detection module which carries out real-time detection on surrounding environment through adopting a multi-sensor fusion technology and transmits detected information to an obstacle data analysis processing module, the obstacle data analysis processing module which carries out environment structure sensing construction on the received information of the surrounding environment so as to determine an obstacle, and an obstacle avoidance decision-making module which determines an obstacle avoidance decision according to the output result of the obstacle data analysis processing module, so as to achieve obstacle avoidance of an unmanned aerial vehicle through the driving of power modules which is performed by a flight control system. According to the multi-sensor fusion-based autonomous obstacle avoidance unmanned aerial vehicle system and the control method of the invention, binocular machine vision systems are arranged around the body of the unmanned aerial vehicle, so that 3D space reconstruction can be realized; and an ultrasonic device and a millimeter wave radar in an advancing direction are used in cooperation, so that an obstacle avoidance method is more comprehensive. The system has the advantages of high real-time performance of obstacle detection, long visual detection distance and high resolution.
Owner:STATE GRID INTELLIGENCE TECH CO LTD
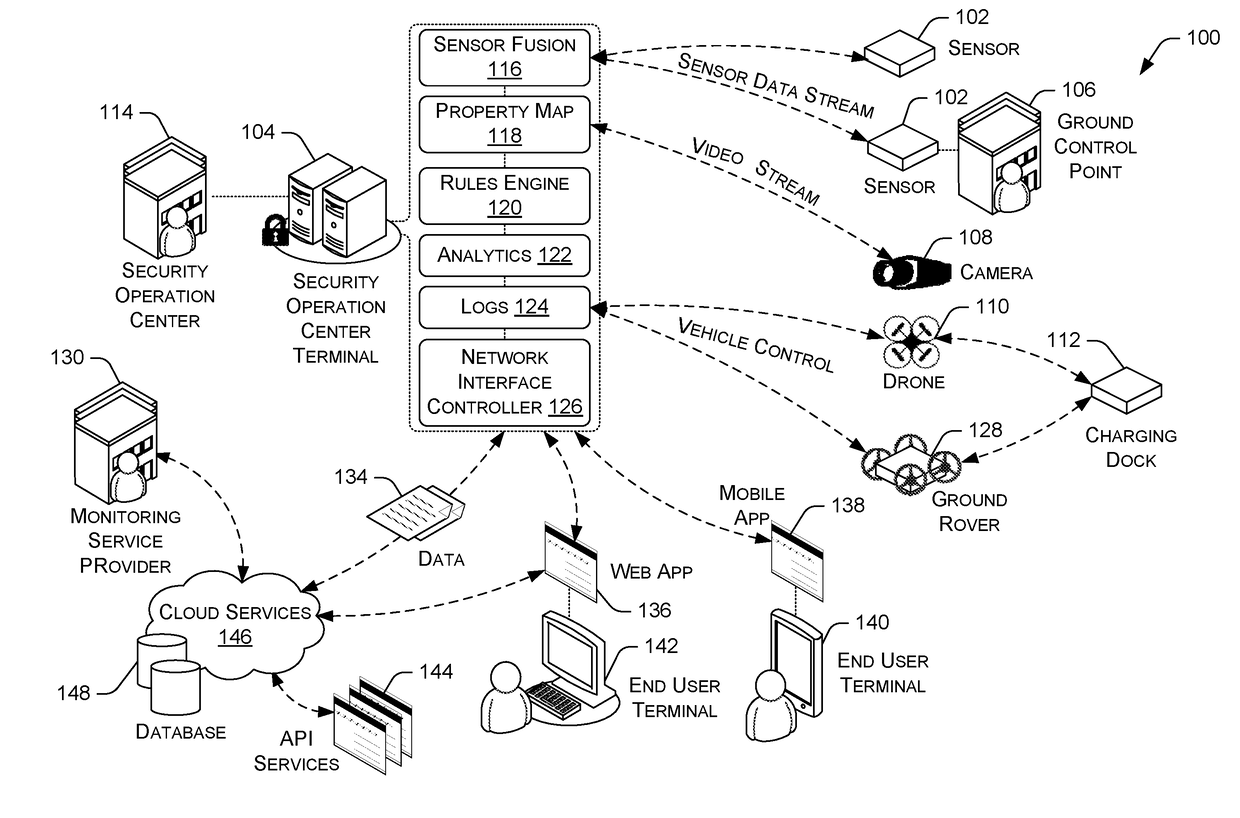
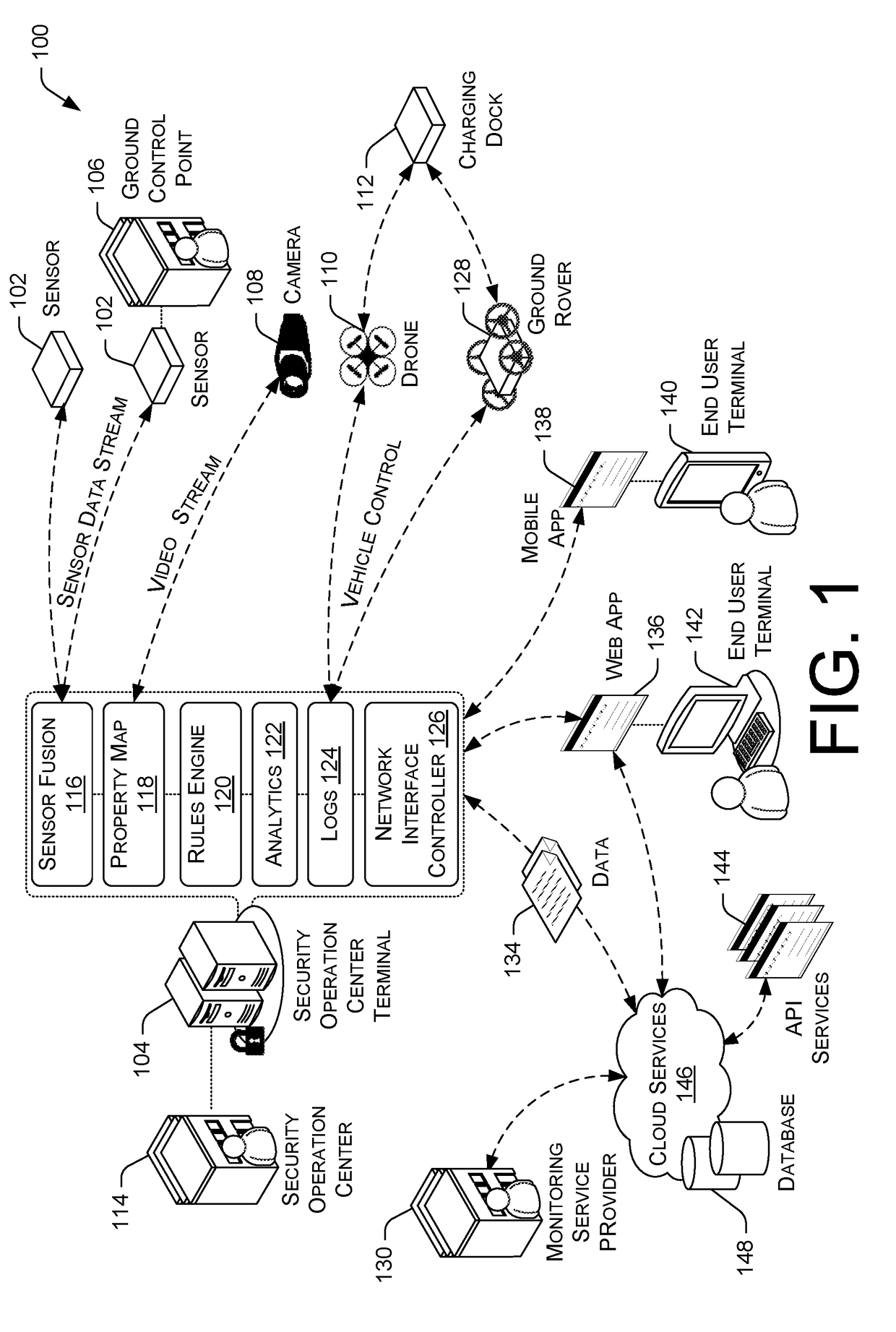
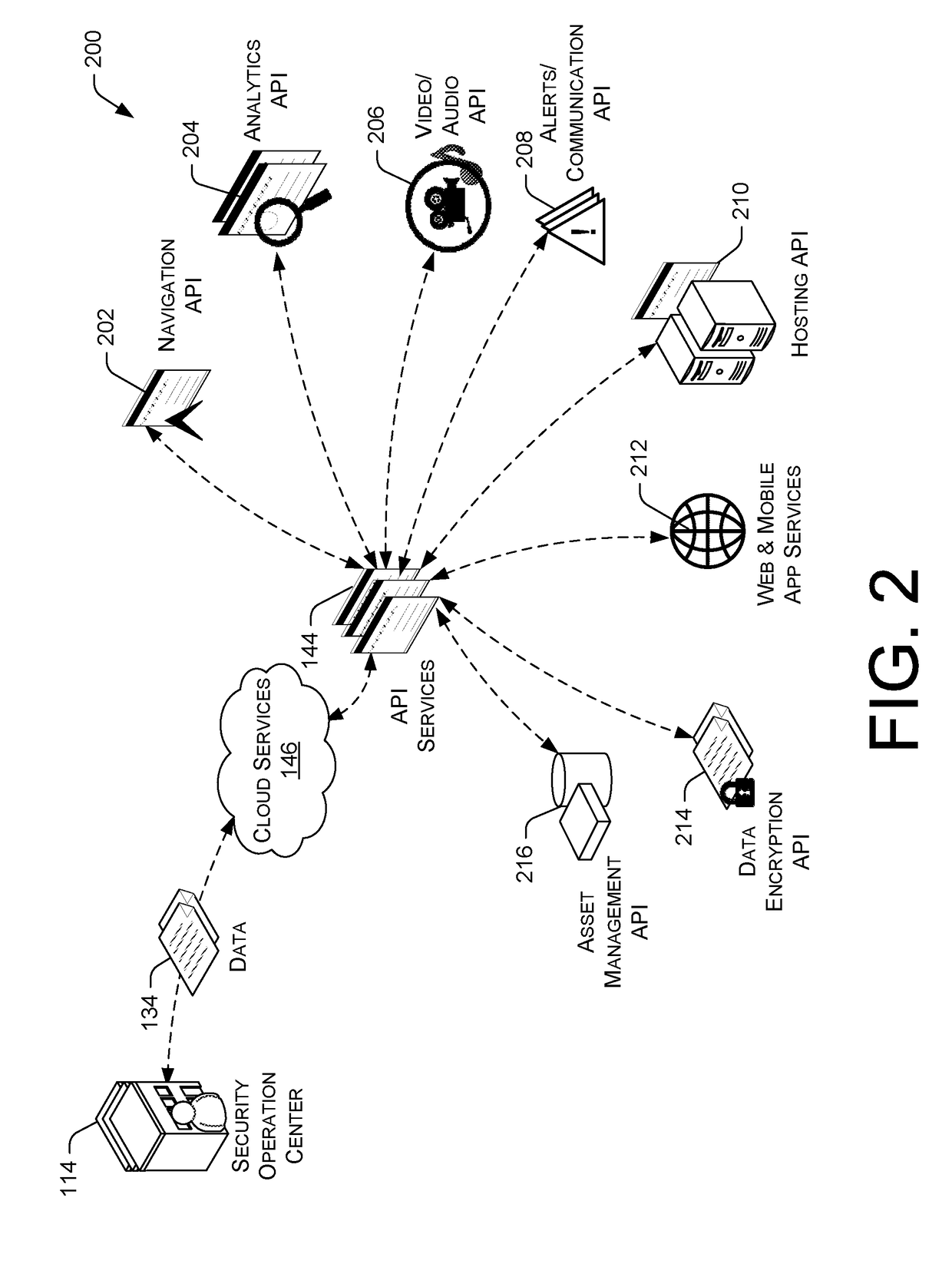
Total Property Intelligence System
ActiveUS20180211115A1Multiple keys/algorithms usagePublic key for secure communicationPhysical securityApplication software
A total property security system may be implemented to conduct security and surveillance operations. The system includes security operations centers that are connected to one or more sensors and vehicles for collecting and transmitting surveillance data to a database hosted on cloud services. The collected surveillance data is analyzed in order to automatically deploy security measures and / or recommend courses of action using a rules engine that can be configured to client-specific or user-specific security needs. The cloud services can provide a set of application program interface services that can act on the surveillance operations center. Sensor fusion data and other surveillance data can be also transmitted to vetted monitoring service providers on a subscription basis to provide physical security services to the area within the property perimeter. During the subscription period, the selected monitoring service providers can obtain time-based encryption token for accessing surveillance data.
Owner:KLEIN MATIAS
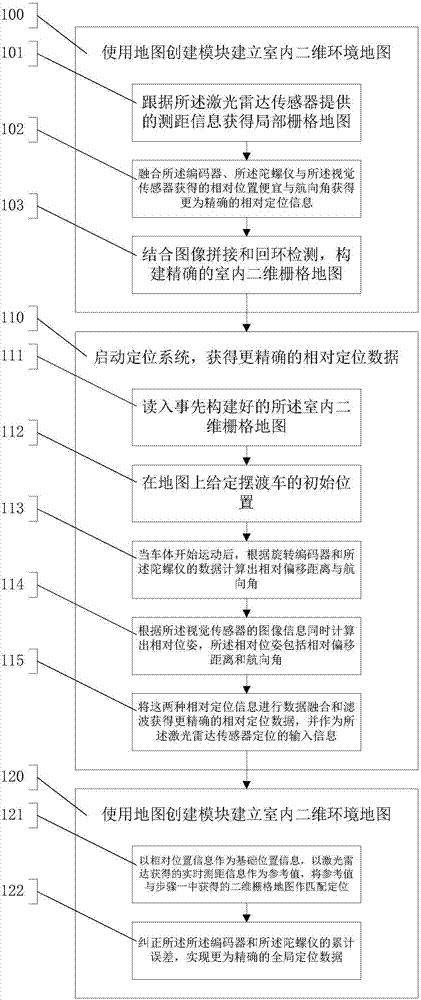
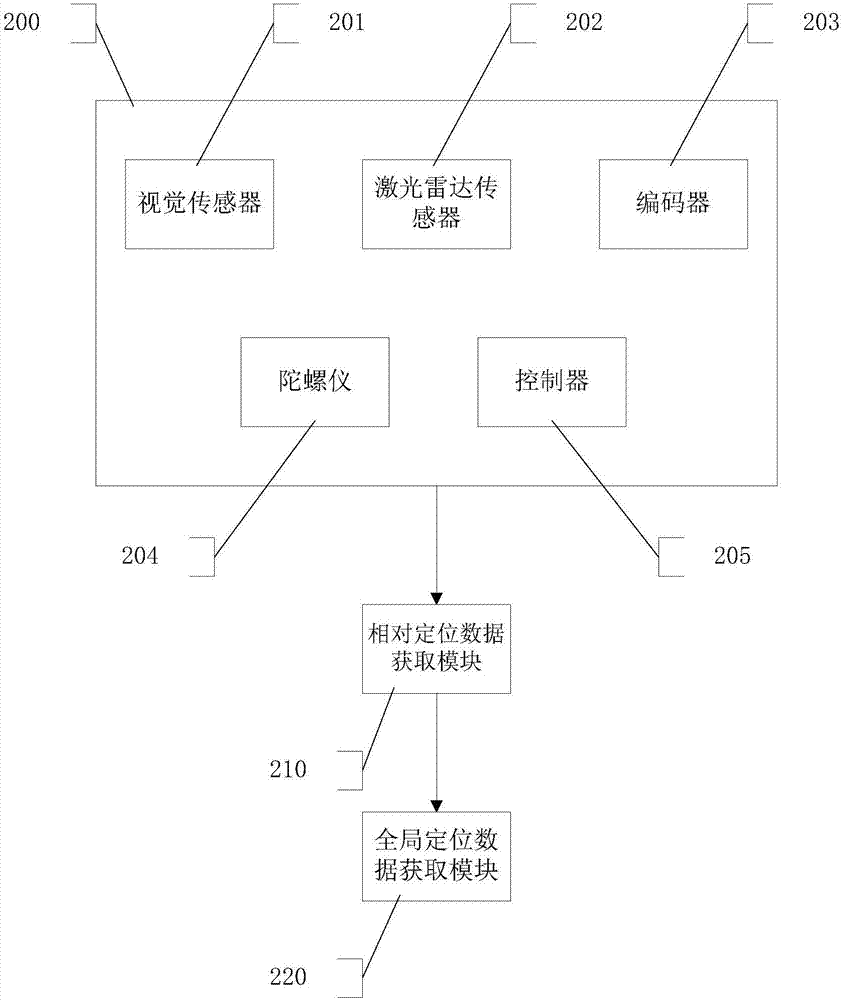
Multi-sensor fusion-based indoor positioning method and system thereof
InactiveCN107478214AAvoid interferenceRapid deploymentNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsElectromagnetic wave reradiationRobot controlSensor fusion
The invention provides a multi-sensor fusion-based indoor positioning method and a system thereof. The method comprises the following steps: using a map creating module to establish an indoor two-dimensional environment map; starting a positioning system to obtain accurate relative positioning data; and starting the positioning system to obtain global positioning data. The purpose of the invention is to rapidly construct indoor two-dimensional environment information by means of indoor two-dimensional modeling, indoor positioning, robot control and visual positioning in order to generate an indoor two-dimensional grid map, the relative offset positioning information and the direction information of a vehicle body are acquired by using an encoder, a gyroscope and a visual sensor, and a laser radar sensor is used to calibrate an accumulated error in order to obtain accurate global positioning information.
Owner:杨华军
System and method of target tracking using sensor fusion
ActiveUS20070073473A1Improve precisionImprove certaintyInstruments for road network navigationAnti-collision systemsSensor fusionEngineering
A target tracking and sensory fusion system is adapted for use with a vehicle, and configured to observe a condition of at least one object during a cycle. The system includes a plurality of sensors, and a novel controller communicatively coupled to the sensors and configured to more accurately estimate the condition based on sensory fusion. In a preferred embodiment, Kalman filtering is utilized to produce a fused estimate of the object location. The preferred controller is further configured to match each new sensory observation with a track in a track list, and remove the track from the track list, when a matching observation is not determined, during a subsequent cycle.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
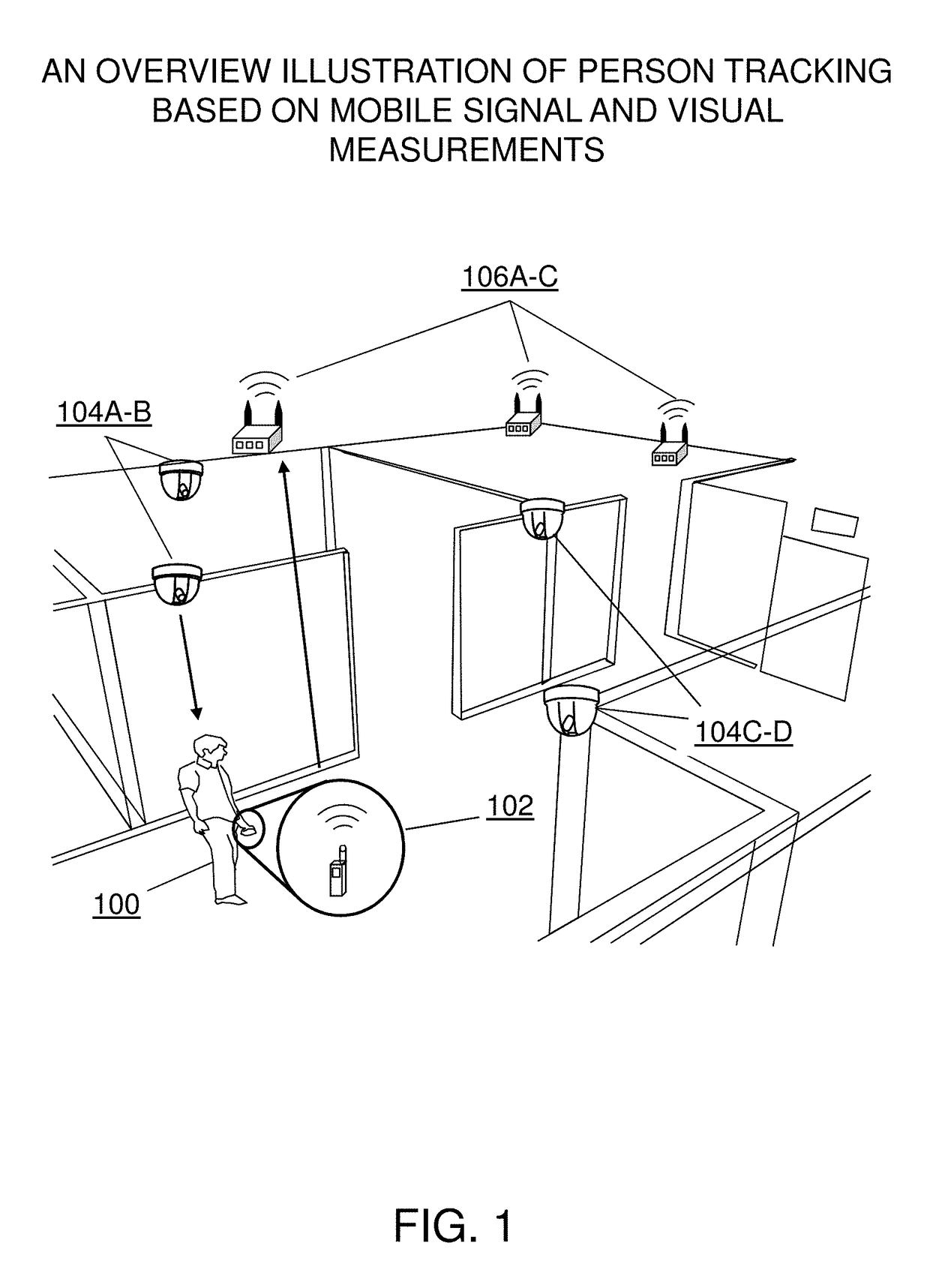
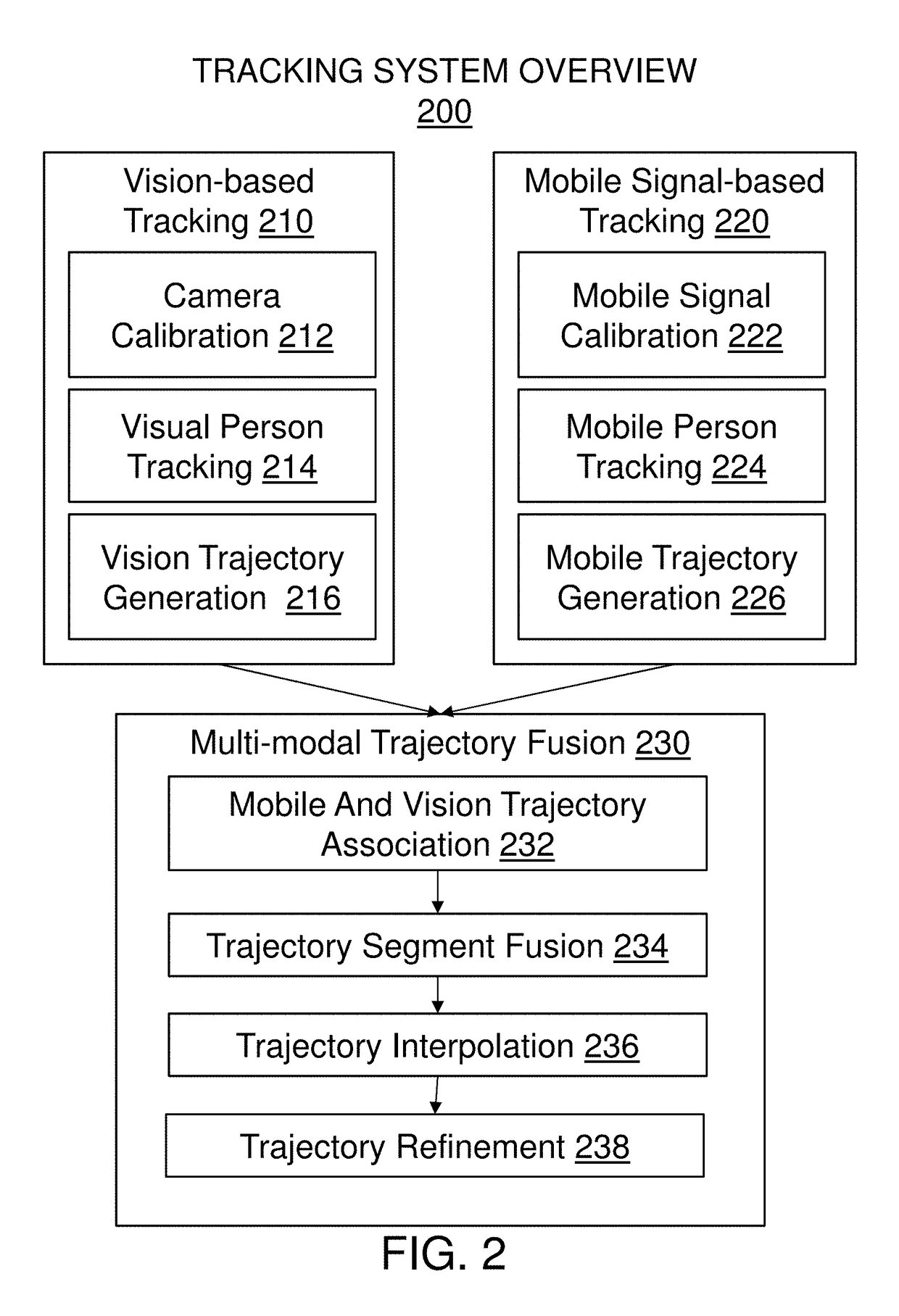
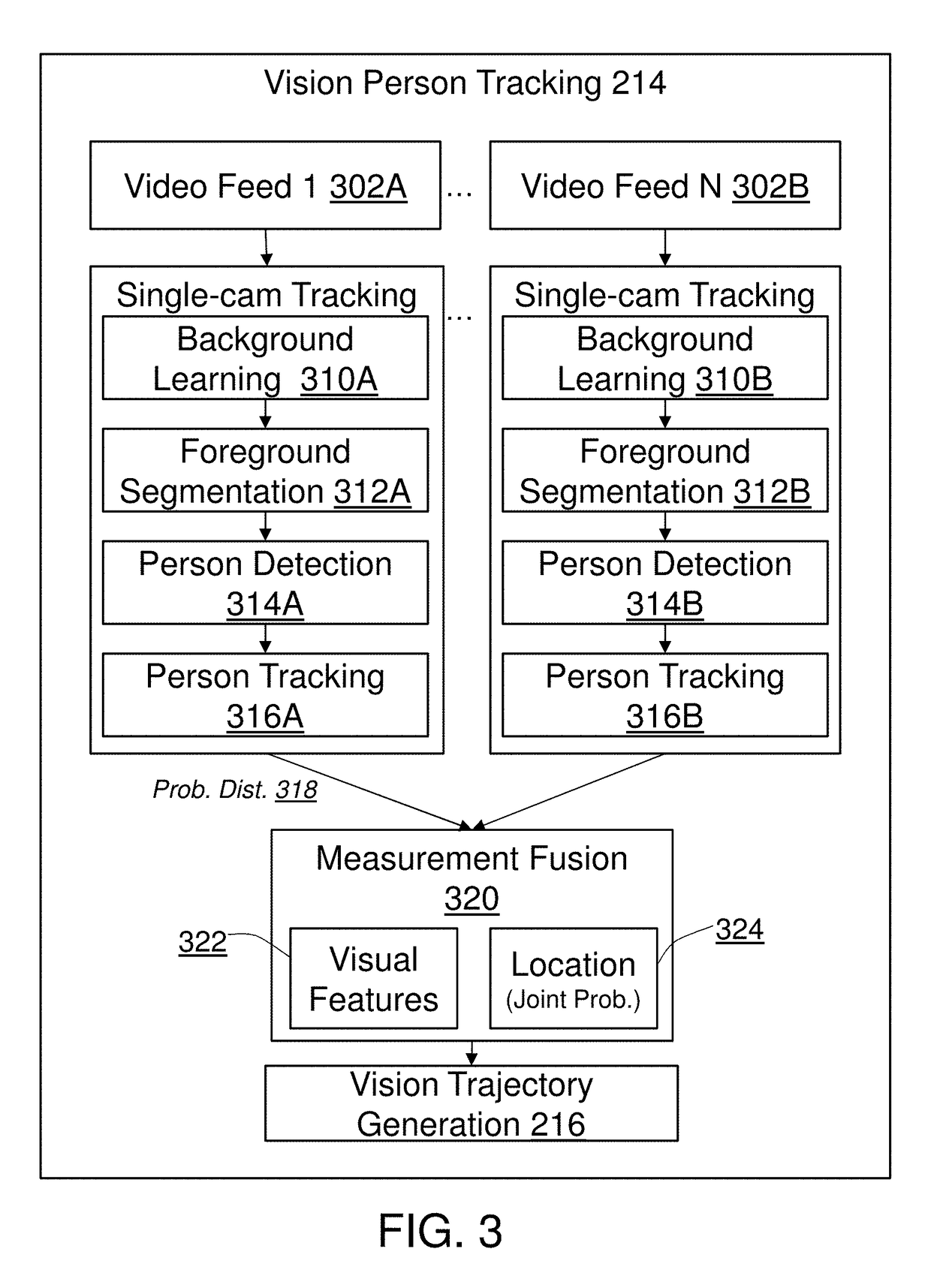
Method and system for in-store shopper behavior analysis with multi-modal sensor fusion
ActiveUS10217120B1Improve reliabilityImprove balanceTelevision system detailsPosition fixationWi-FiPhysical space
The present invention provides a comprehensive method for automatically and unobtrusively analyzing the in-store behavior of people visiting a physical space using a multi-modal fusion based on multiple types of sensors. The types of sensors employed may include cameras for capturing a plurality of images and mobile signal sensors for capturing a plurality of Wi-Fi signals. The present invention integrates the plurality of input sensor measurements to reliably and persistently track the people's physical attributes and detect the people's interactions with retail elements. The physical and contextual attributes collected from the processed shopper tracks includes the motion dynamics changes triggered by an implicit and explicit interaction to a retail element, comprising the behavior information for the trip of the people. The present invention integrates point-of-sale transaction data with the shopper behavior by finding and associating the transaction data that corresponds to a shopper trajectory and fusing them to generate a complete an intermediate representation of a shopper trip data, called a TripVector. The shopper behavior analyses are carried out based on the extracted TripVector. The analyzed behavior information for the shopper trips yields exemplary behavior analysis comprising map generation as visualization of the behavior, quantitative shopper metric derivation in multiple scales (e.g., store-wide and category-level) including path-to-purchase shopper metrics (e.g., traffic distribution, shopping action distribution, buying action distribution, conversion funnel), category dynamics (e.g., dominant path, category correlation, category sequence). The present invention includes a set of derived methods for different sensor configurations.
Owner:VIDEOMINING CORP
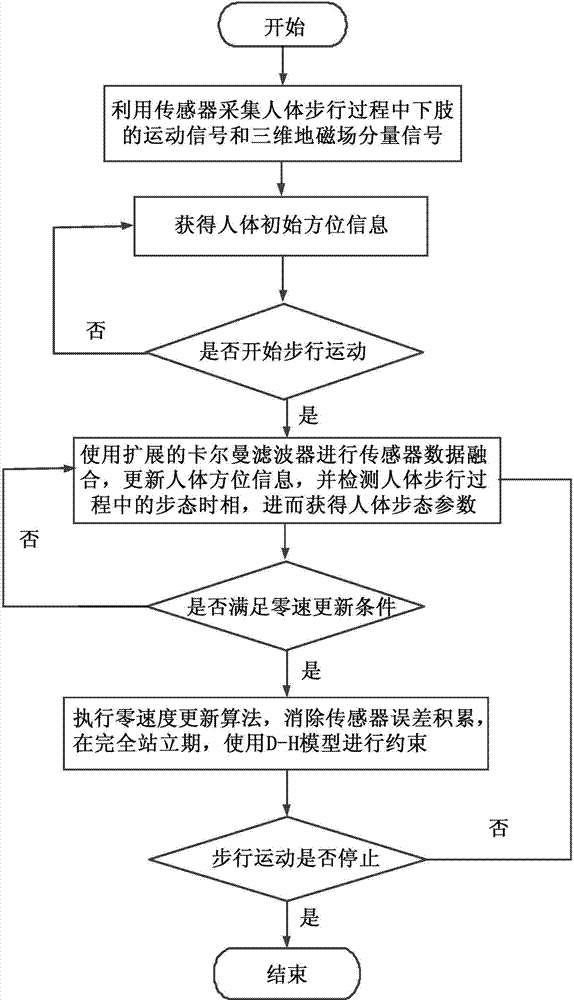
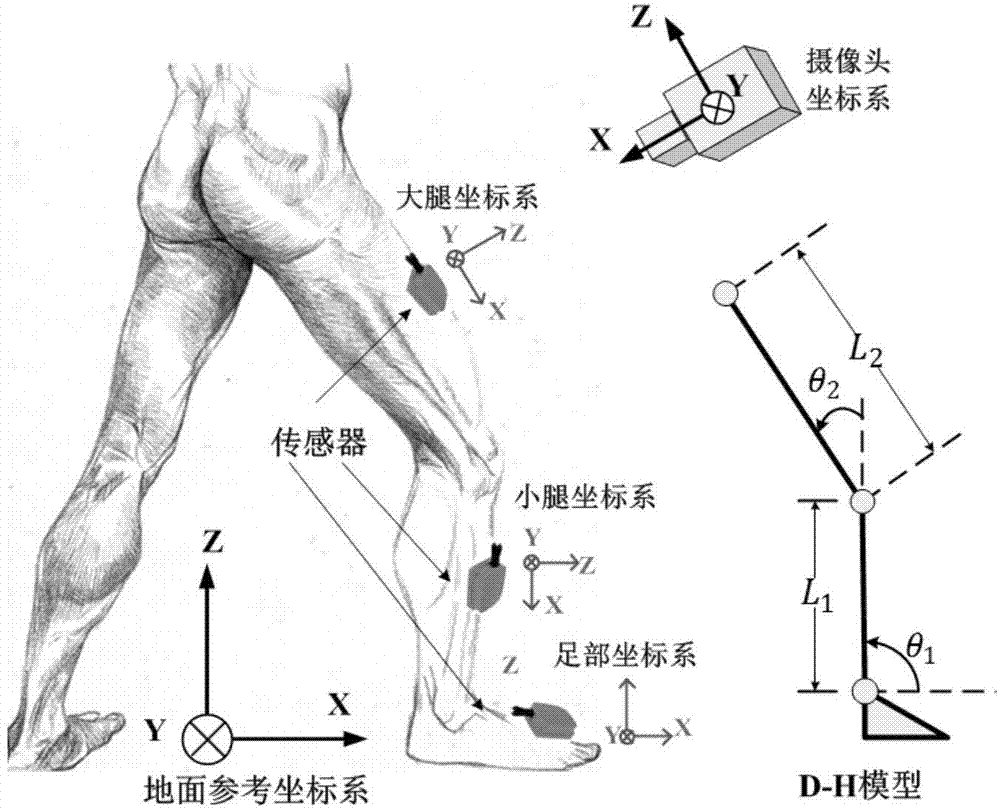
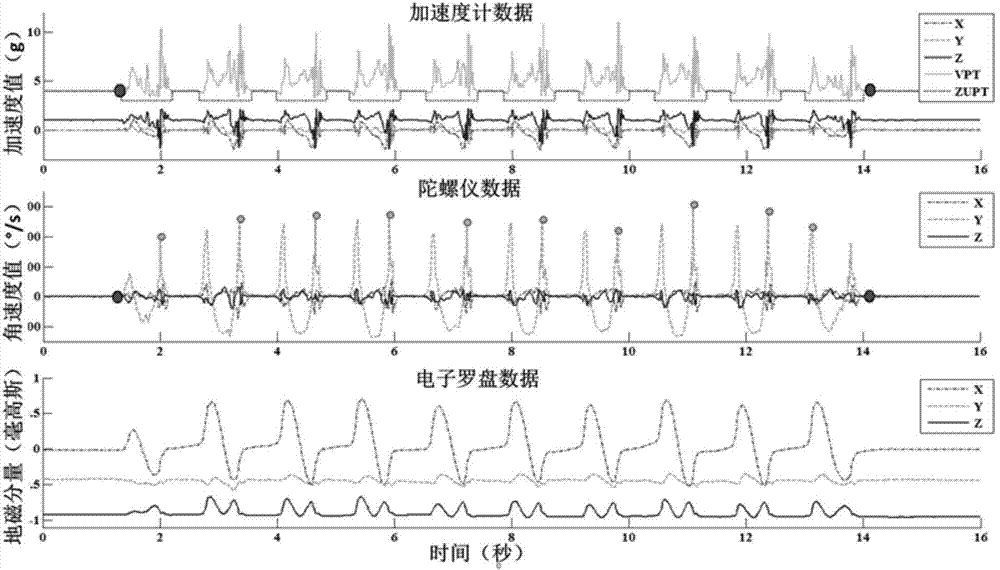
Human gait analyzing method and system based on multi-sensor fusion
ActiveCN104757976AImprove effectivenessImprove calculation accuracyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsQuantile regressionGait database
The invention relates to the technical field of gait analysis in biomedical engineering and provides a human gait analyzing method and system based on multi-sensor fusion. The method comprises the steps of filtering sensor signals to eliminate the signal noise error according to human motion features, and eliminating the integral error by means of the improved zero velocity updating algorithm, so that the method and system can be adapted to different walking scenes; fusing multiple sensor data with the Denavit-Hartenberg method, and reducing the leg position calculation error; calculating the step speed, step length, step frequency, walking period and walking track of a tested person accurately during walking after error correction is conducted; establishing a gait database, and conducting statistic analysis on gait data of different tested persons with the quantile regression analysis method. By the adoption of the method and system, gait parameter measurement precision can be improved, and gait parameters of different tested persons are comparable through standardization.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
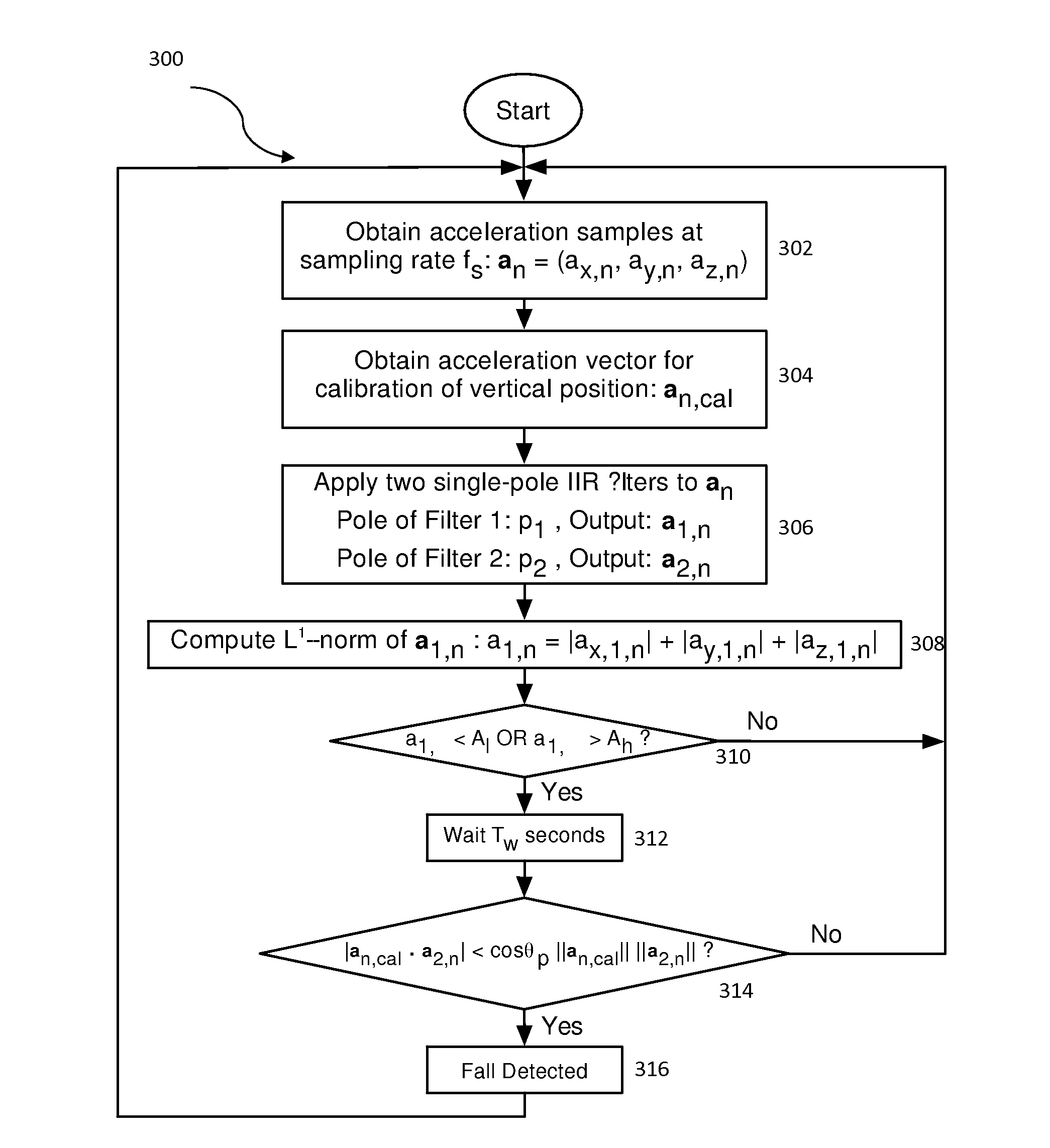
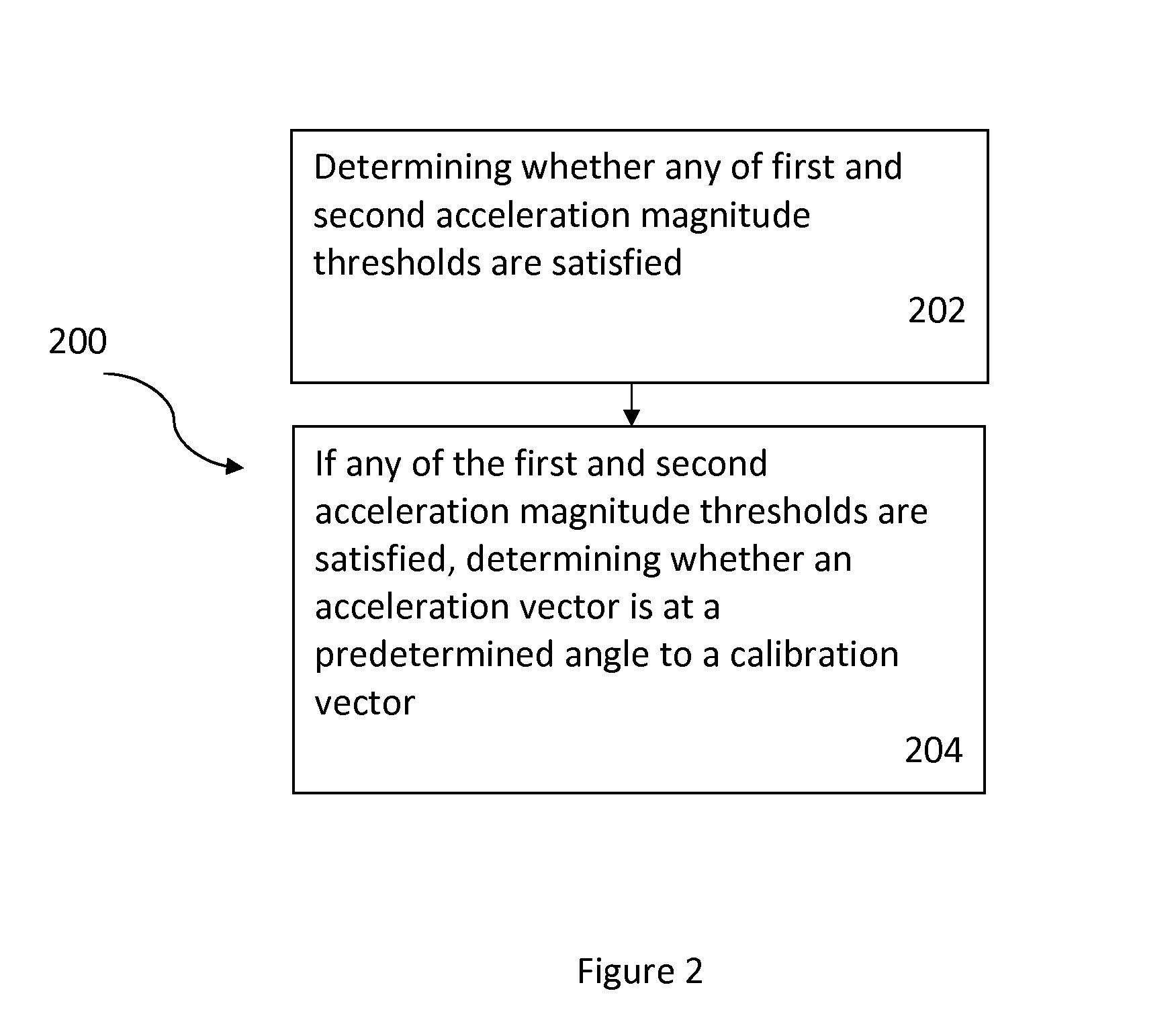
Fall detection using sensor fusion
A method and system for fall detection using sensor fusion are disclosed. In a first aspect, the method comprises in response to any of first and second acceleration magnitude thresholds being satisfied, determining whether a height difference before and after impact of a fall satisfies a threshold and whether an angle threshold between an acceleration vector and a calibration vector is satisfied. In a second aspect, the system comprises a processing system and an application coupled to the processing system, wherein the application carries out the steps of the method.
Owner:VITAL CONNECT
Methods, apparatus and systems for enhanced synthetic vision and multi-sensor data fusion to improve operational capabilities of unmanned aerial vehicles
ActiveUS7747364B2Improve the display effectStation can be limitedVehicle testingCosmonautic vehiclesSynthetic vision systemSensor fusion
The invention provides, in some aspects, improved methods, apparatus and systems for unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) operation that utilize multiple data links between a UAV and a control station in order to transmit control and actionable intelligence data. Such methods, apparatus and systems can be used, for example, to monitor a selected environment (e.g., an oil field or other terrain / environment of interest). In a related aspect, such data links comprise satellite communication channels.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Robot locating method adopting multi-sensor data fusion
InactiveCN106123890AReduce the impactRemove Inherent ConstraintsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsElectromagnetic wave reradiationPattern recognitionLaser scanning
The invention discloses a robot locating method adopting multi-sensor data fusion. On the basis of laser scanning, combination of odometer displacement and a yaw angle of an inertial measurement unit is taken as initial estimation of pose change, then the current pose of a robot is calculated with a scan matching method, and Kalman filtering is performed finally on the basis of two pose calculation results of an odometer and scan matching. The robot locating method adopting multi-sensor data fusion has the advantages that inherent constraints of conventional odometer system location can be eliminated effectively, and influence of accumulated errors on a locating result is reduced; and mismatching results in a matching process can be reduced effectively; displacement change data of the odometer in a short time interval and the robot yaw angle provided by the inertial measurement unit are taken as initial estimation of a laser scan matching process, so that the speed and the accuracy rate of the scan matching process can be increased greatly, and a better matching result can be obtained finally.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com