Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
74 results about "Synthetic vision system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
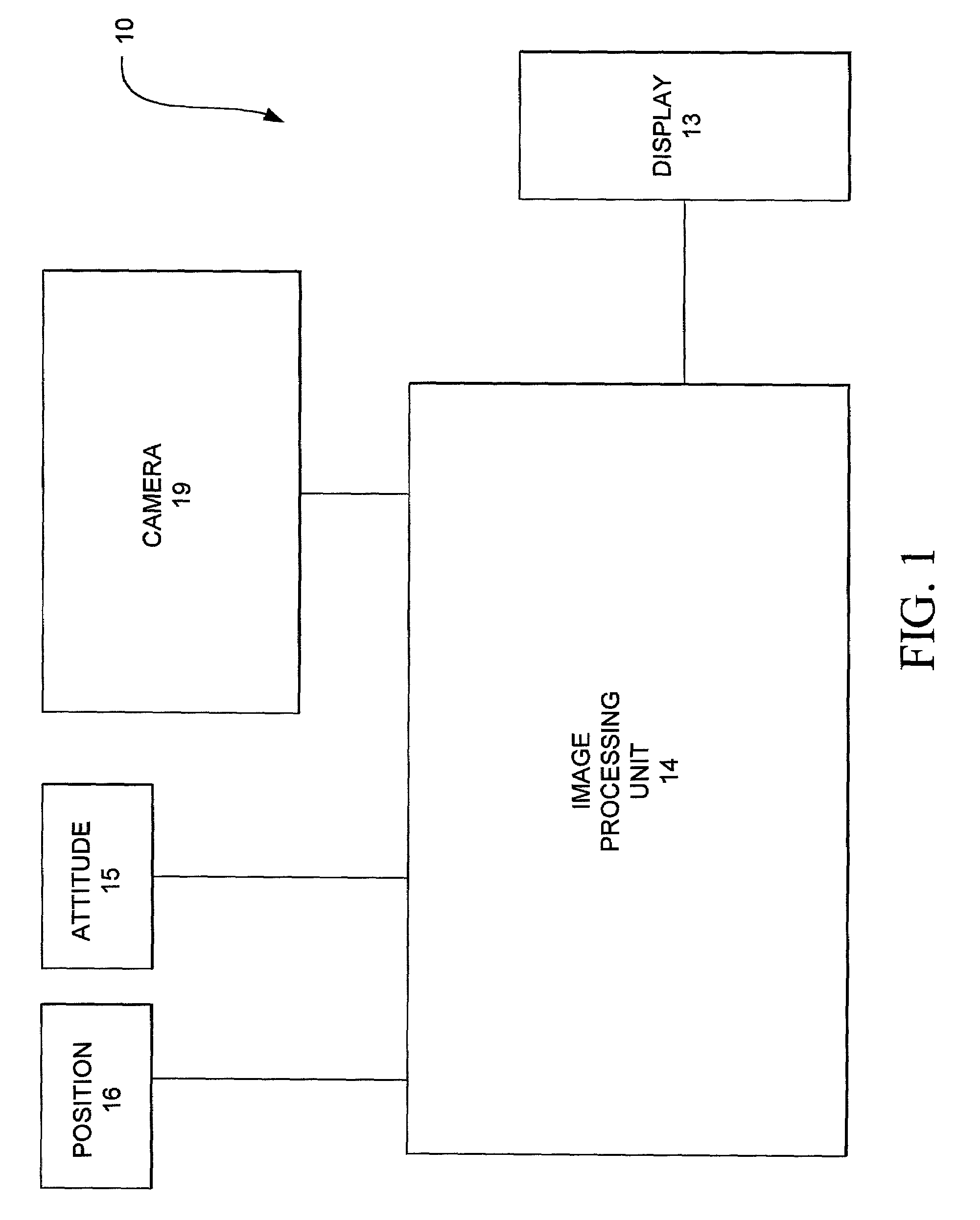
A synthetic vision system (SVS) is a computer-mediated reality system for aerial vehicles, that uses 3D to provide pilots with clear and intuitive means of understanding their flying environment. Synthetic vision is also a generic term, which may pertain to computer vision systems using artificial intelligence methods for visual learning, see "Synthetic Vision using Volume Learning and Visual DNA".
Electro-optic vision systems
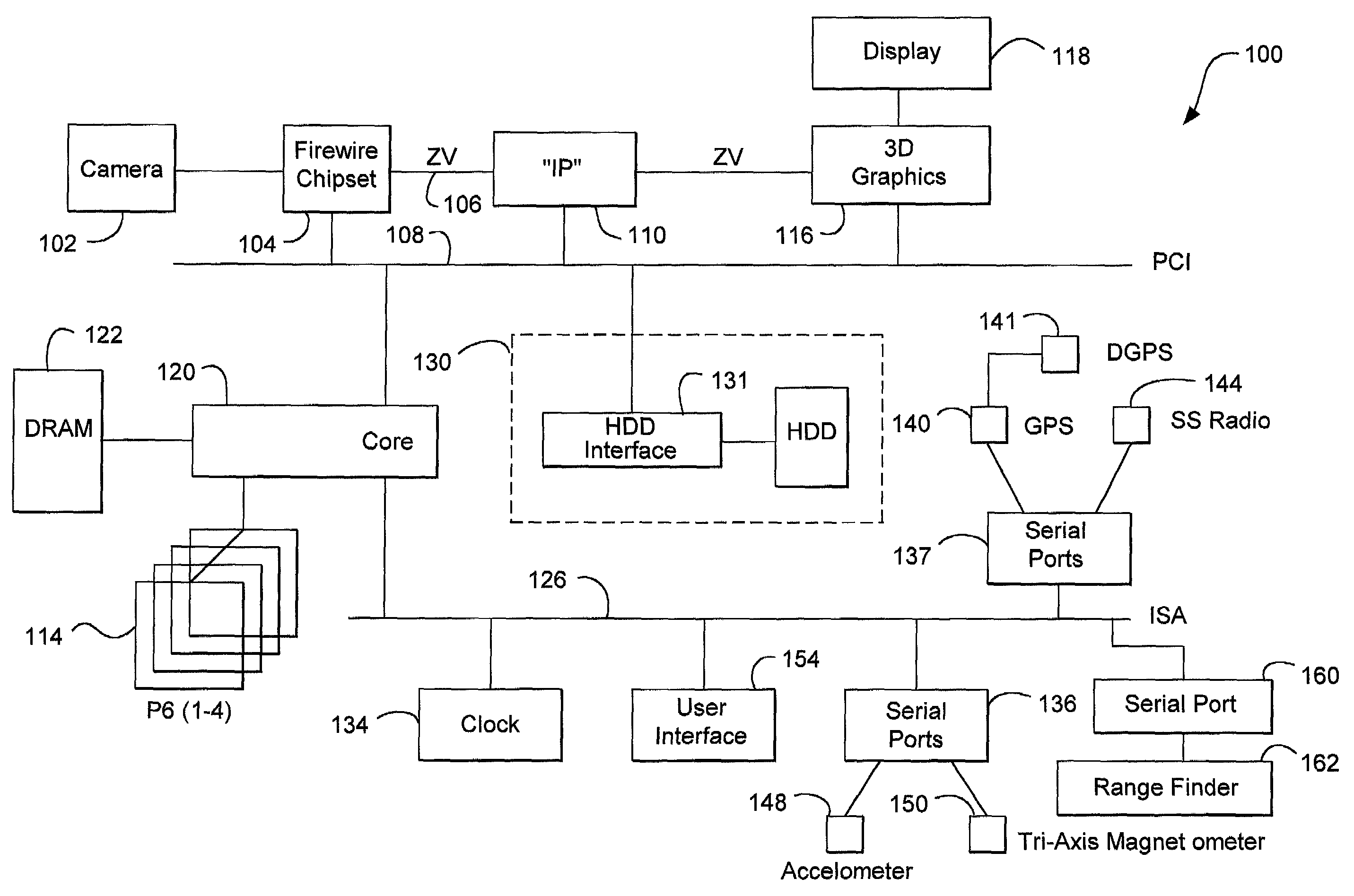
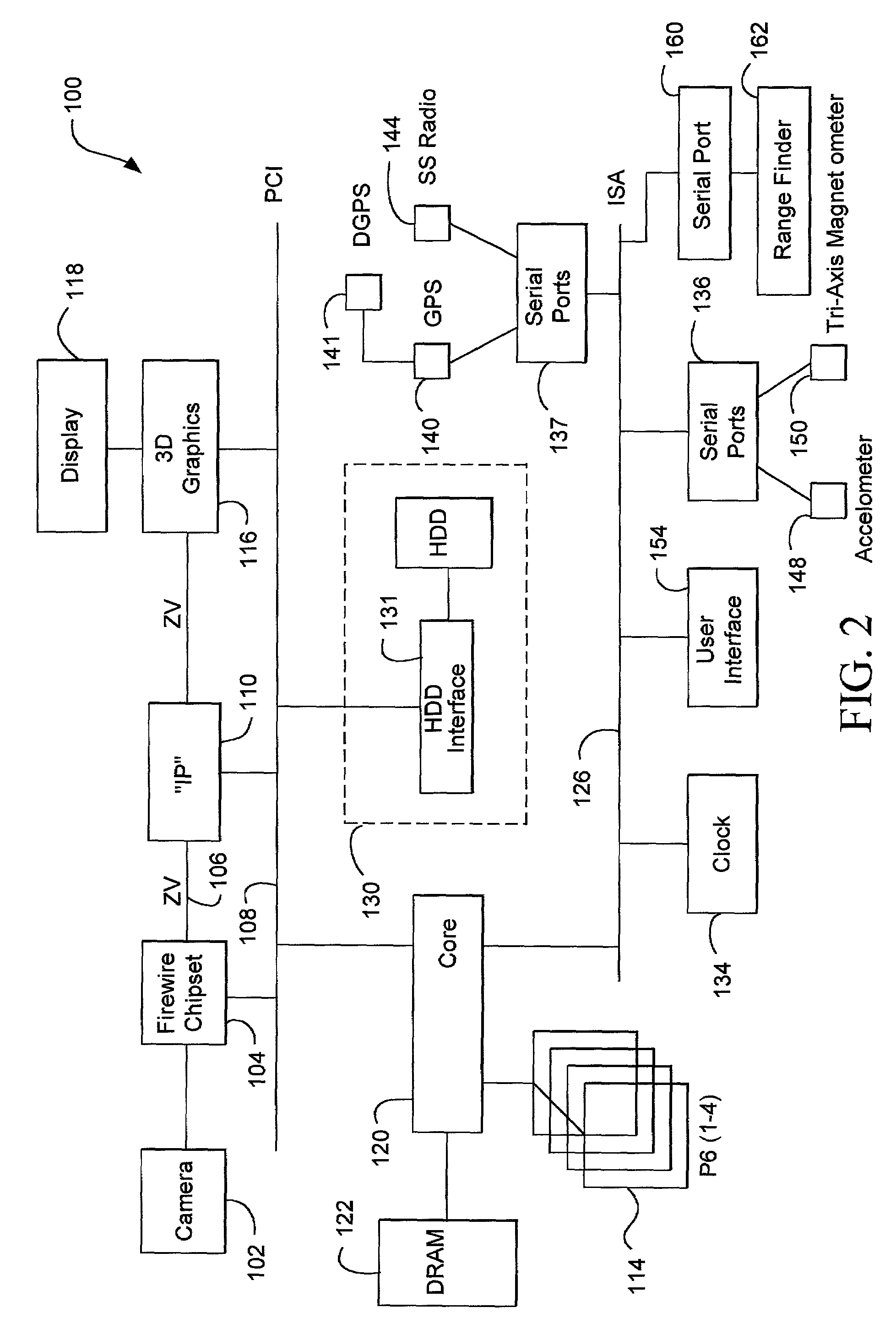
InactiveUS7301536B2Programme controlNavigational calculation instrumentsGraphicsSynthetic vision system
An image processing system for delivering real scene information to a data processor. The system includes the data processor, an image-delivery mechanism, an information delivery mechanism, and a graphic processor.
Owner:GEOVECTOR
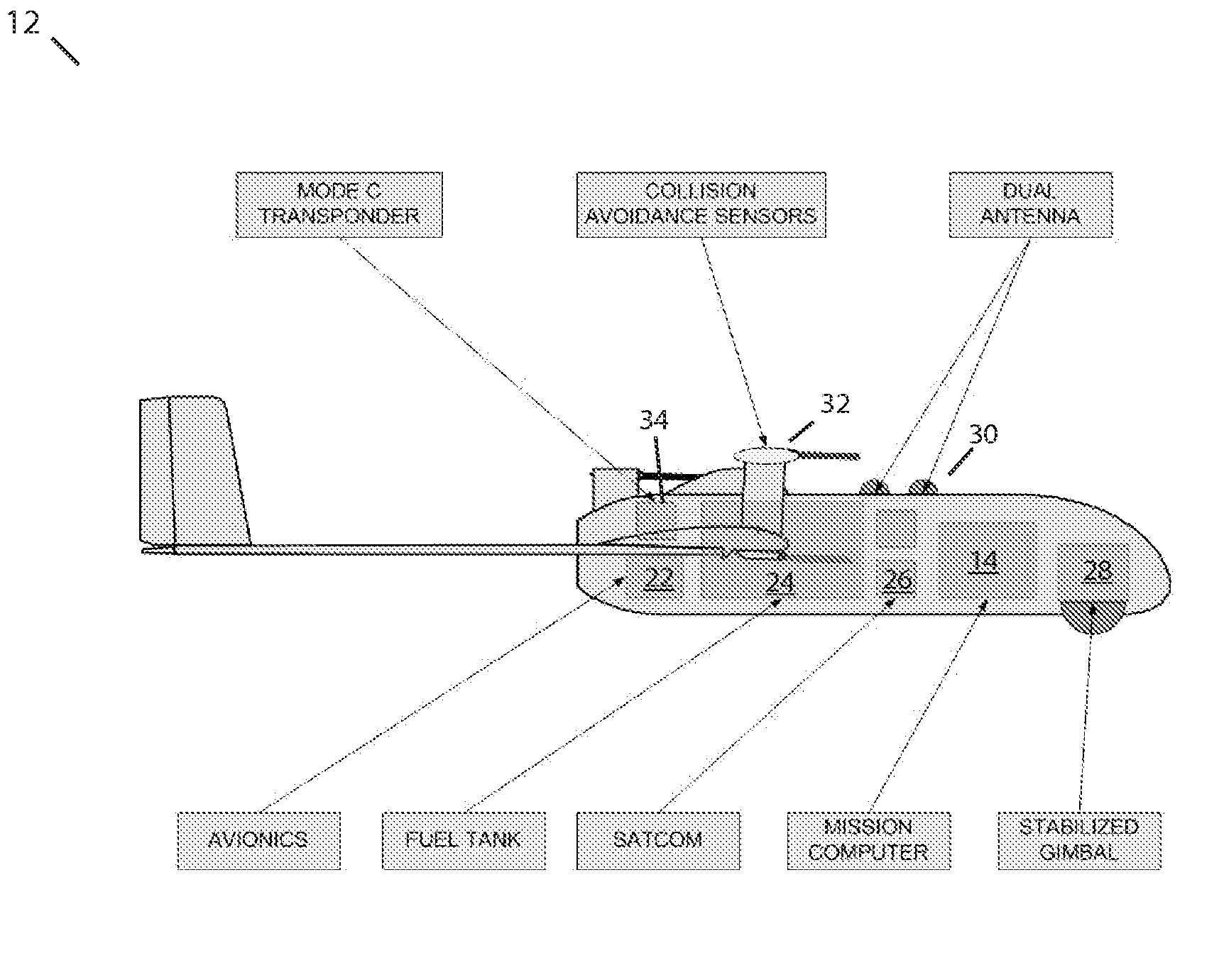
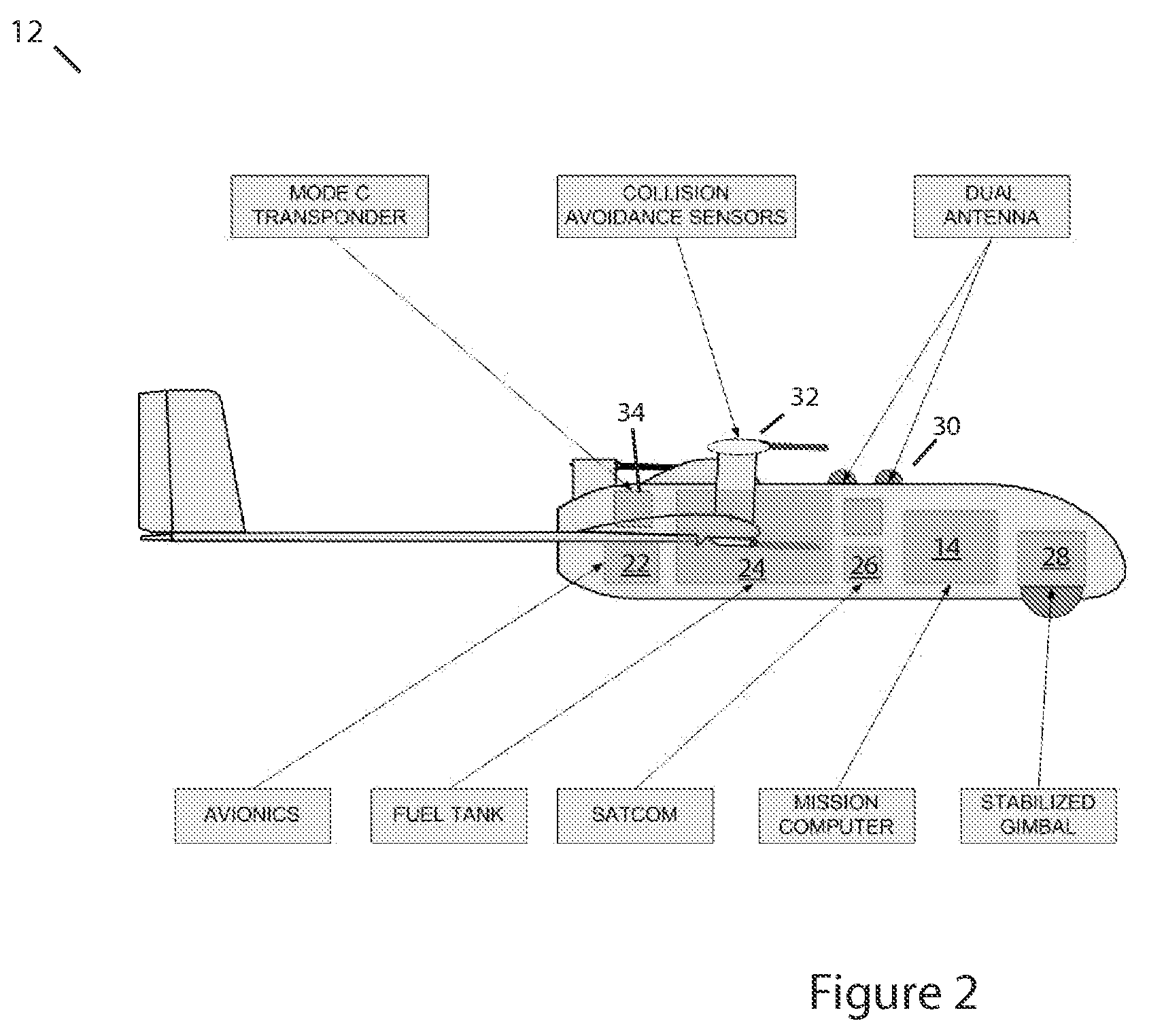
System and Method For Safely Flying Unmanned Aerial Vehicles in Civilian Airspace
InactiveUS20080033604A1Improve eyesightSafely share airspace with other usersDigital data processing detailsActuated automaticallySynthetic vision systemFlight vehicle
A system and method for safely flying an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), unmanned combat aerial vehicle (UCAV), or remotely piloted vehicle (RPV) in civilian airspace uses a remotely located pilot to control the aircraft using a synthetic vision system during at least selected phases of the flight such as during take-offs and landings.
Owner:MARGOLIN JED
Enhancing the performance of near-to-eye vision systems
ActiveUS20190179409A1Wide field of viewHigh image resolutionInput/output for user-computer interactionPrismsEyepieceDisplay device
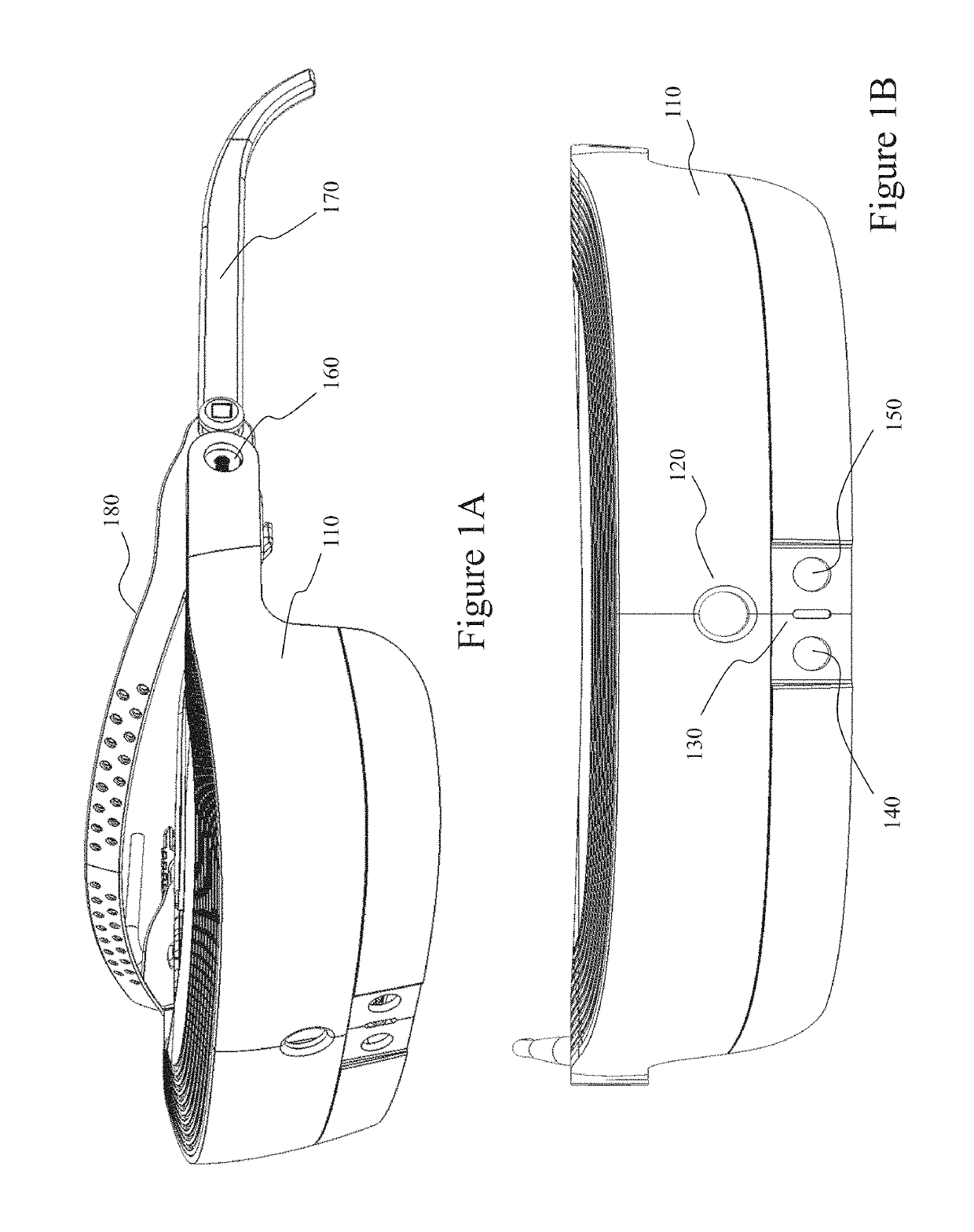
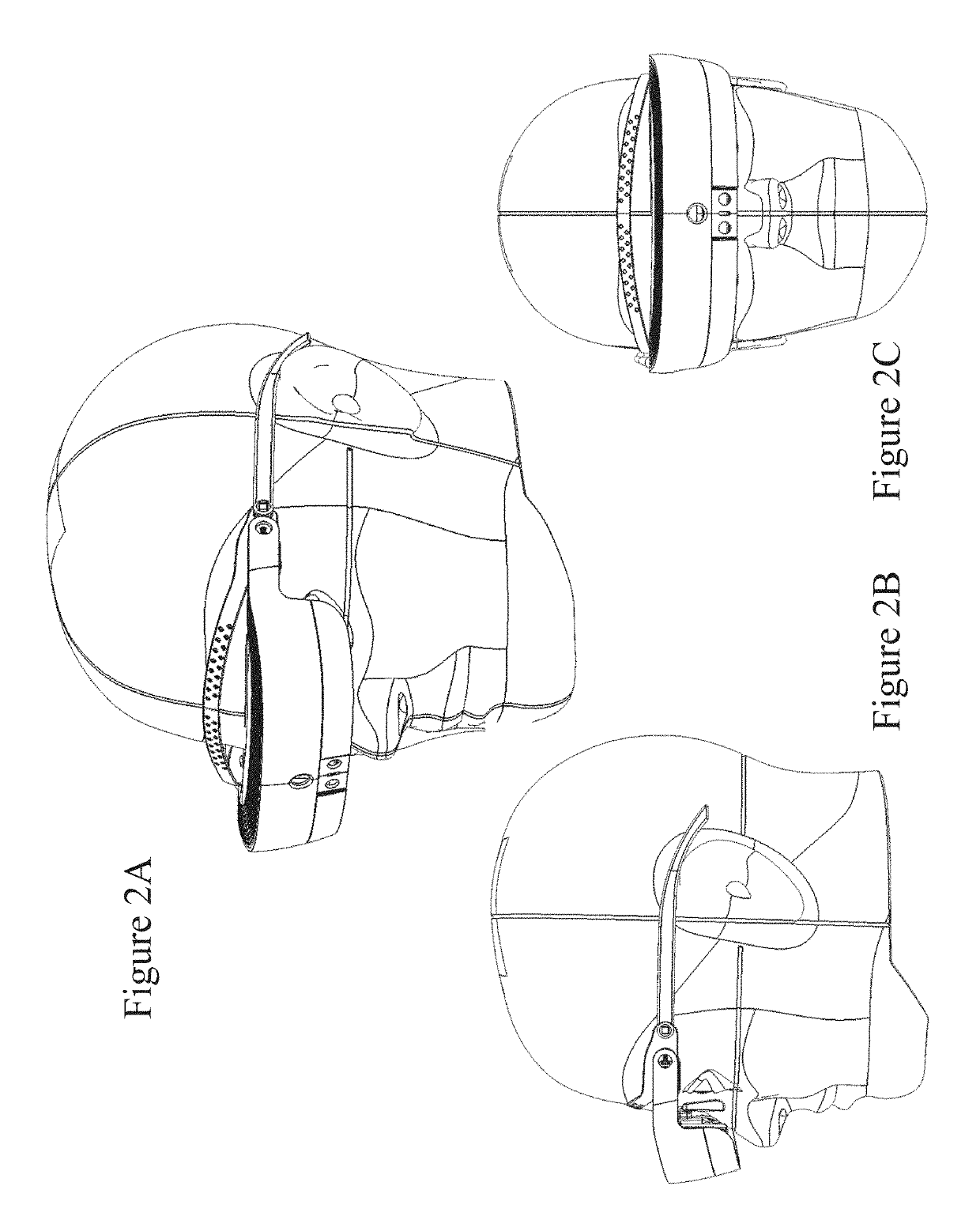
The majority of applications for head mounted display (HMD) users, irrespective of whether they are for short-term, long-term, low vision, augmented reality, etc. yield a conflicting set of tradeoffs between user comfort and minimal fatigue and strain during use, ease of attachment, minimizing intrusiveness and aesthetics which must be concurrently balanced with and are often in conflict with providing an optical vision system that provides the user with a wide field of view and high image resolution whilst also offering a large exit pupil for eye placement with sufficient eye clearance. Further, individual users' needs vary as do their needs with the general task at-hand, visual focus, and various regions-of-interest within their field of view. To address these issues, it is necessary to provide a high performance optical system, eyepiece design, and system features which overcome these limitations.
Owner:ESIGHT CORP
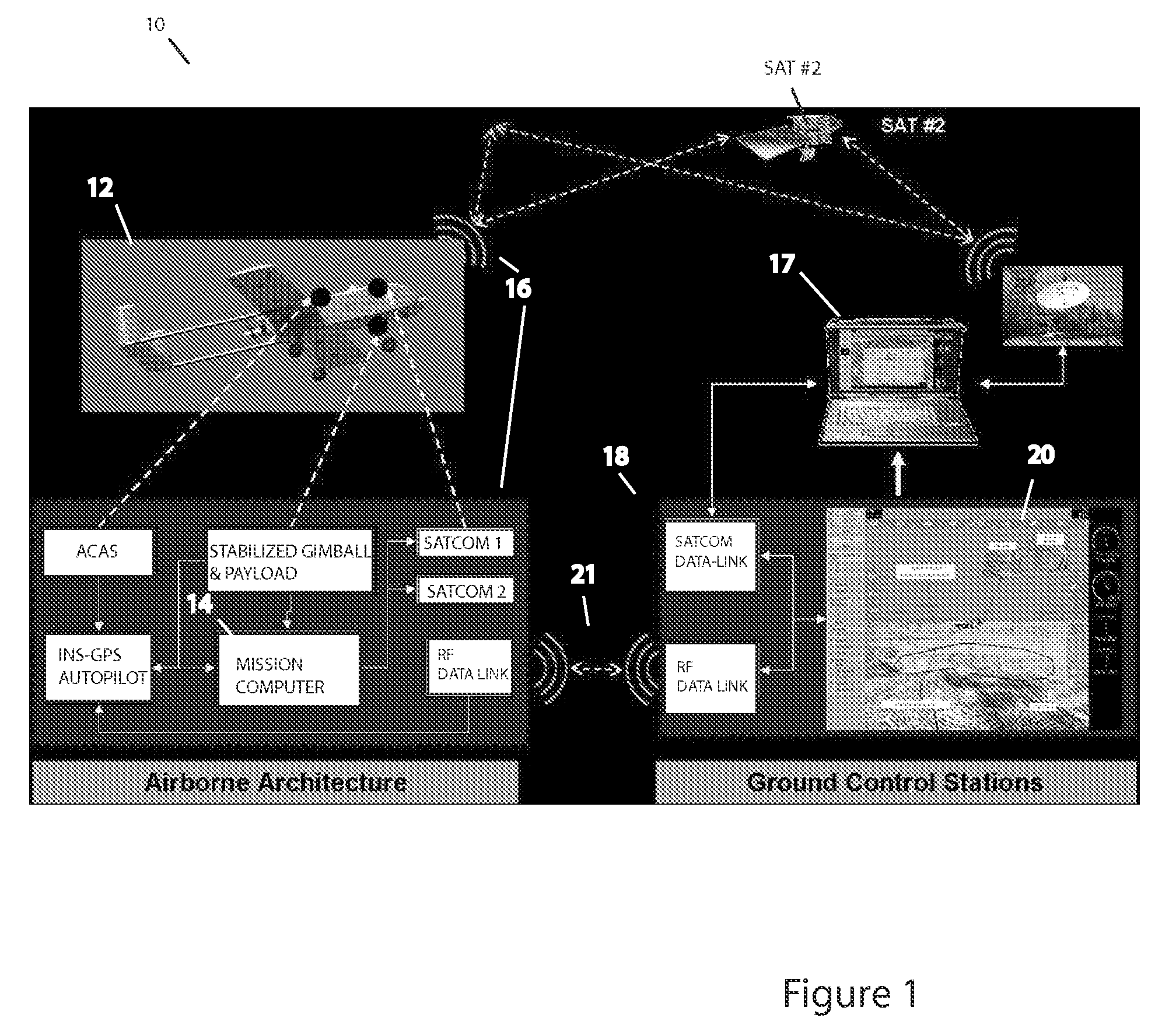
Methods, apparatus and systems for enhanced synthetic vision and multi-sensor data fusion to improve operational capabilities of unmanned aerial vehicles
ActiveUS7747364B2Improve the display effectStation can be limitedVehicle testingCosmonautic vehiclesSynthetic vision systemSensor fusion
The invention provides, in some aspects, improved methods, apparatus and systems for unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) operation that utilize multiple data links between a UAV and a control station in order to transmit control and actionable intelligence data. Such methods, apparatus and systems can be used, for example, to monitor a selected environment (e.g., an oil field or other terrain / environment of interest). In a related aspect, such data links comprise satellite communication channels.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Synthetic vision system and methods
InactiveUS20080262664A1Solve the real problemEasily search for informationDigital data processing detailsNavigation instrumentsMulti-function displaySynthetic vision system
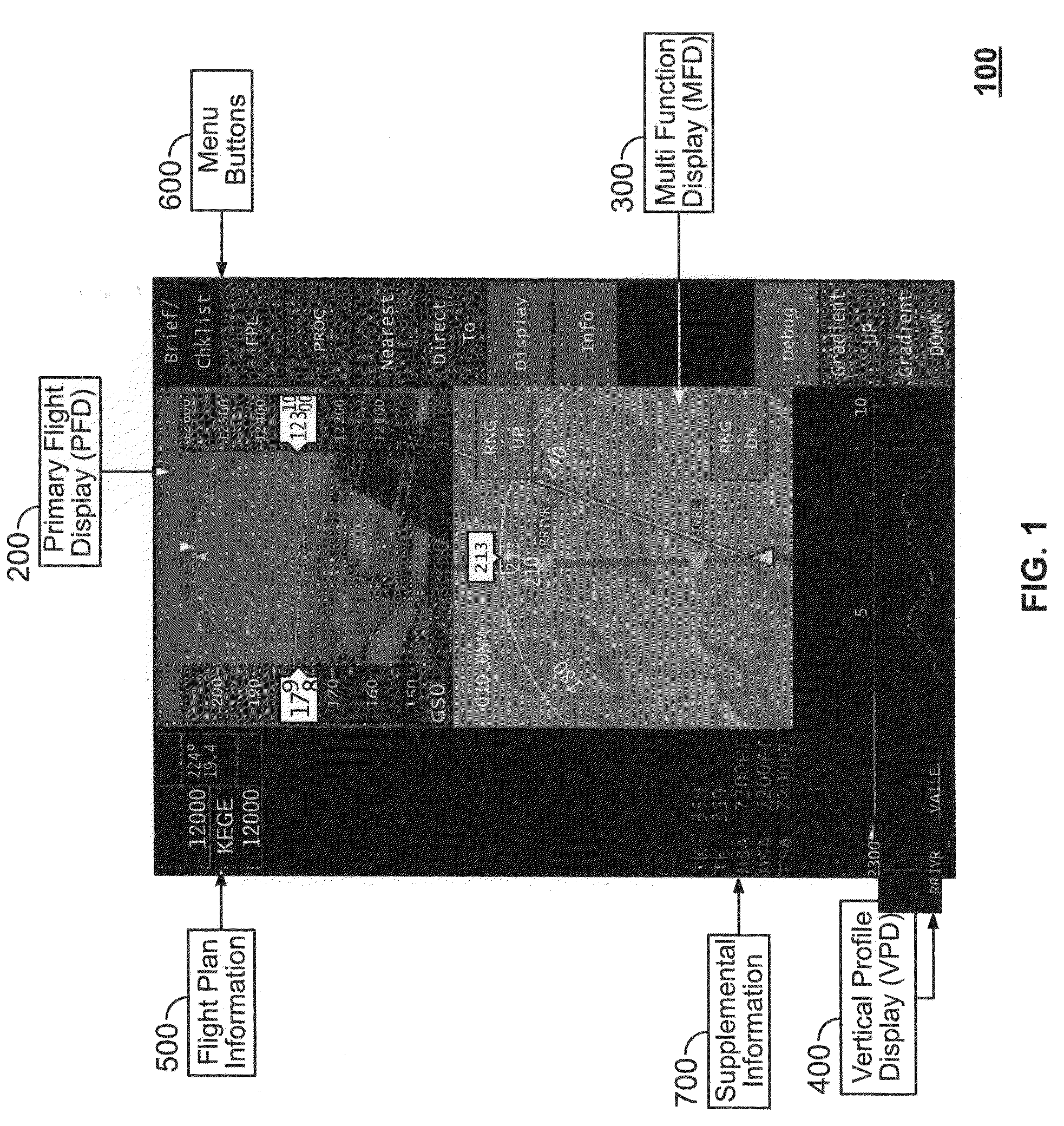
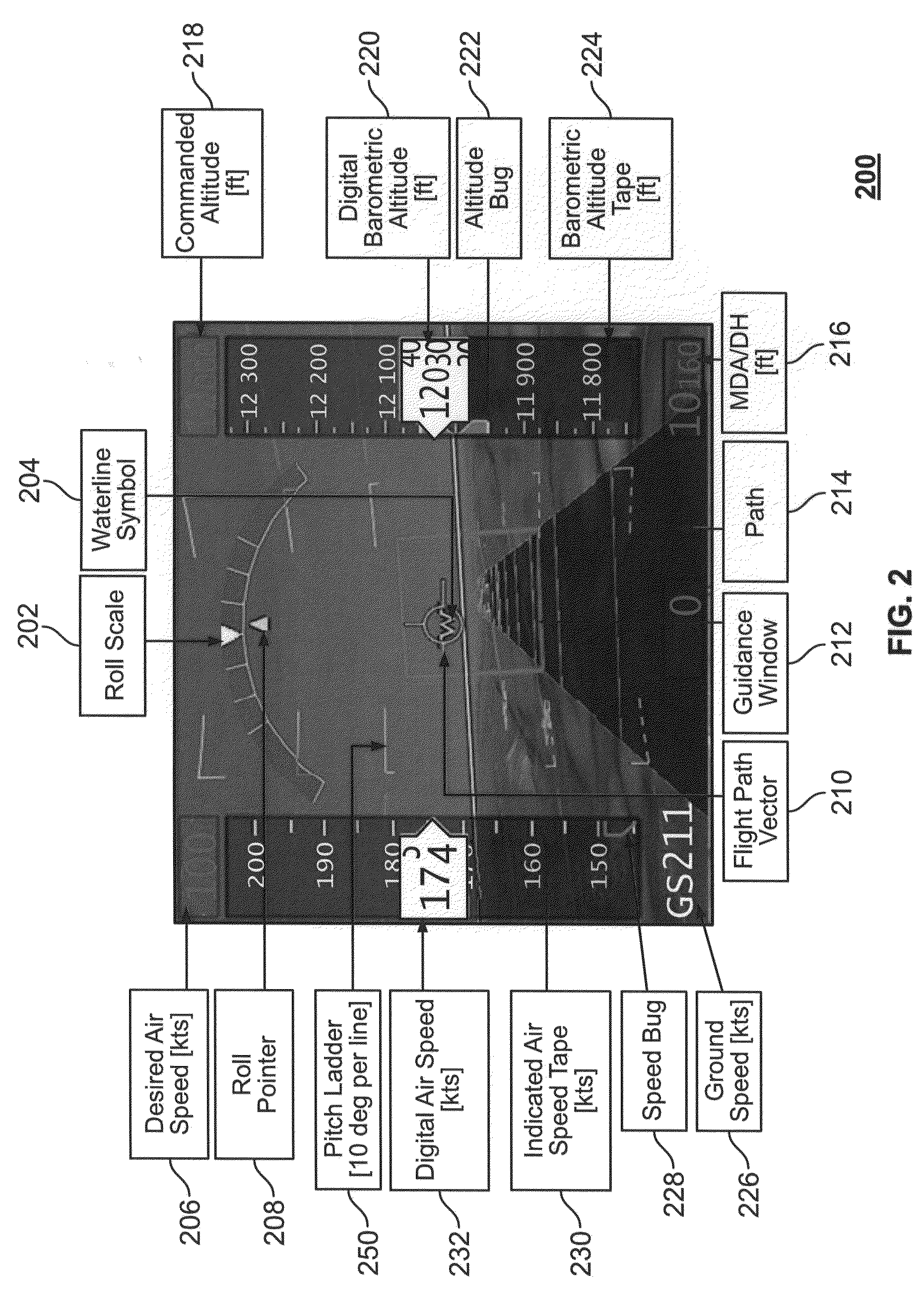
The present invention is directed to a system and methods, embodiments of which provide increased situation awareness information in an improved Synthetic Vision System (SVS). According to the present invention, a Primary Flight Display (PFD), a top-down view Multi-Function Display (MFD), and side-view Vertical Profile Display (VPD) are presented on one user interface with an input device, such as a transparent touch screen for quick and easy data entry. The present invention also provides color shading, such as red, to communicate areas where the aircraft may be in conflict with terrain or obstacles at a point in time in the future.
Owner:STC UNM +1
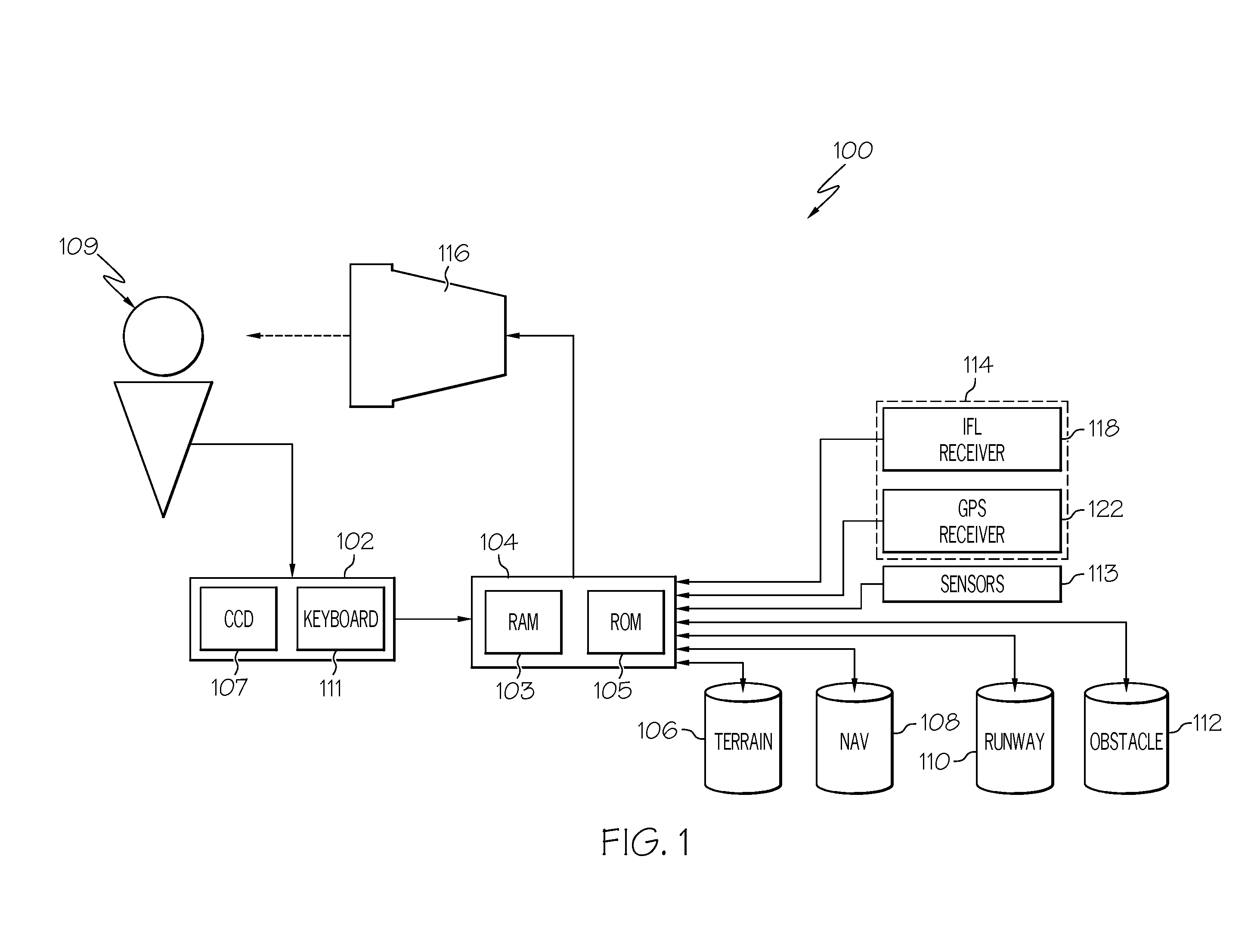
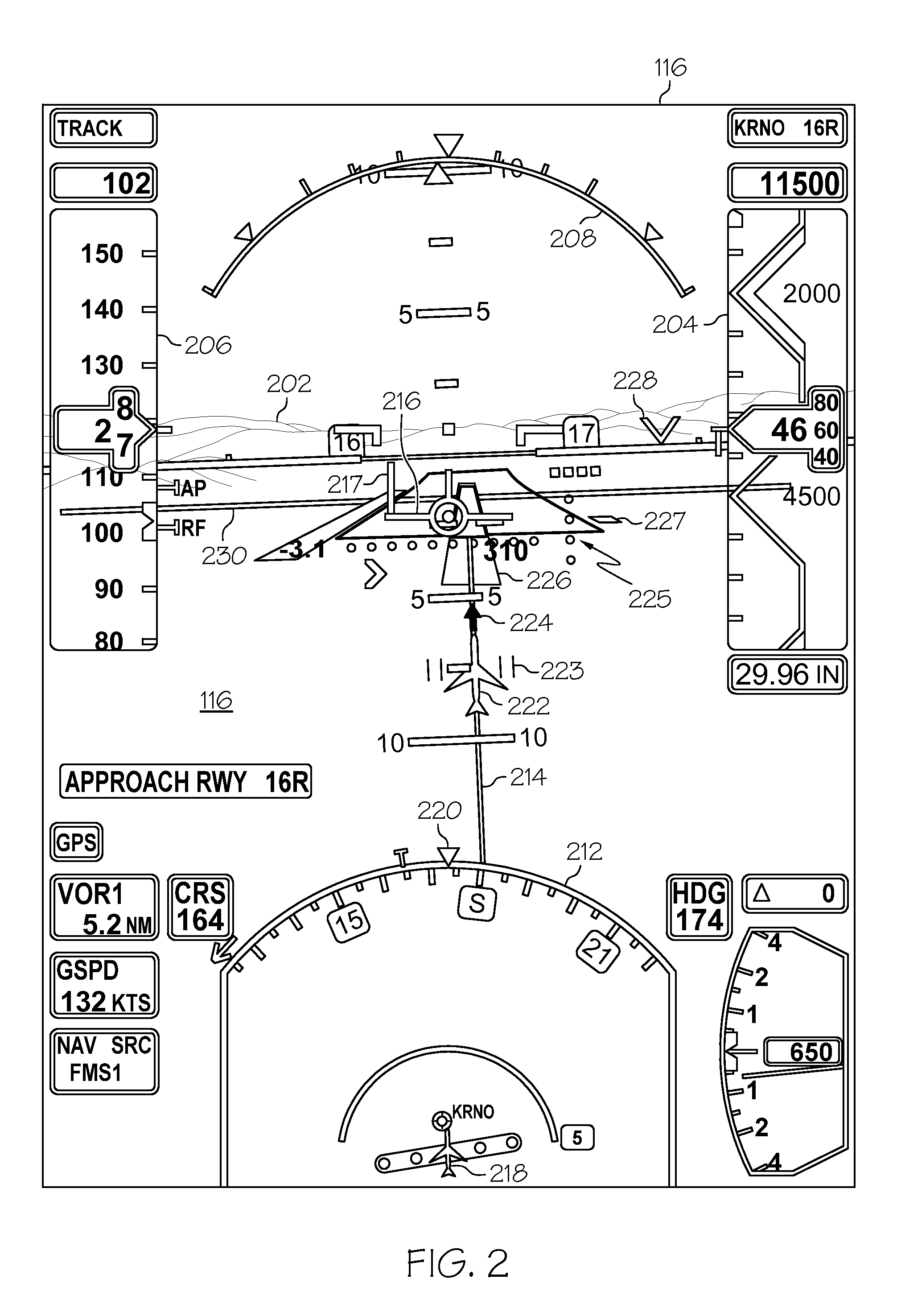
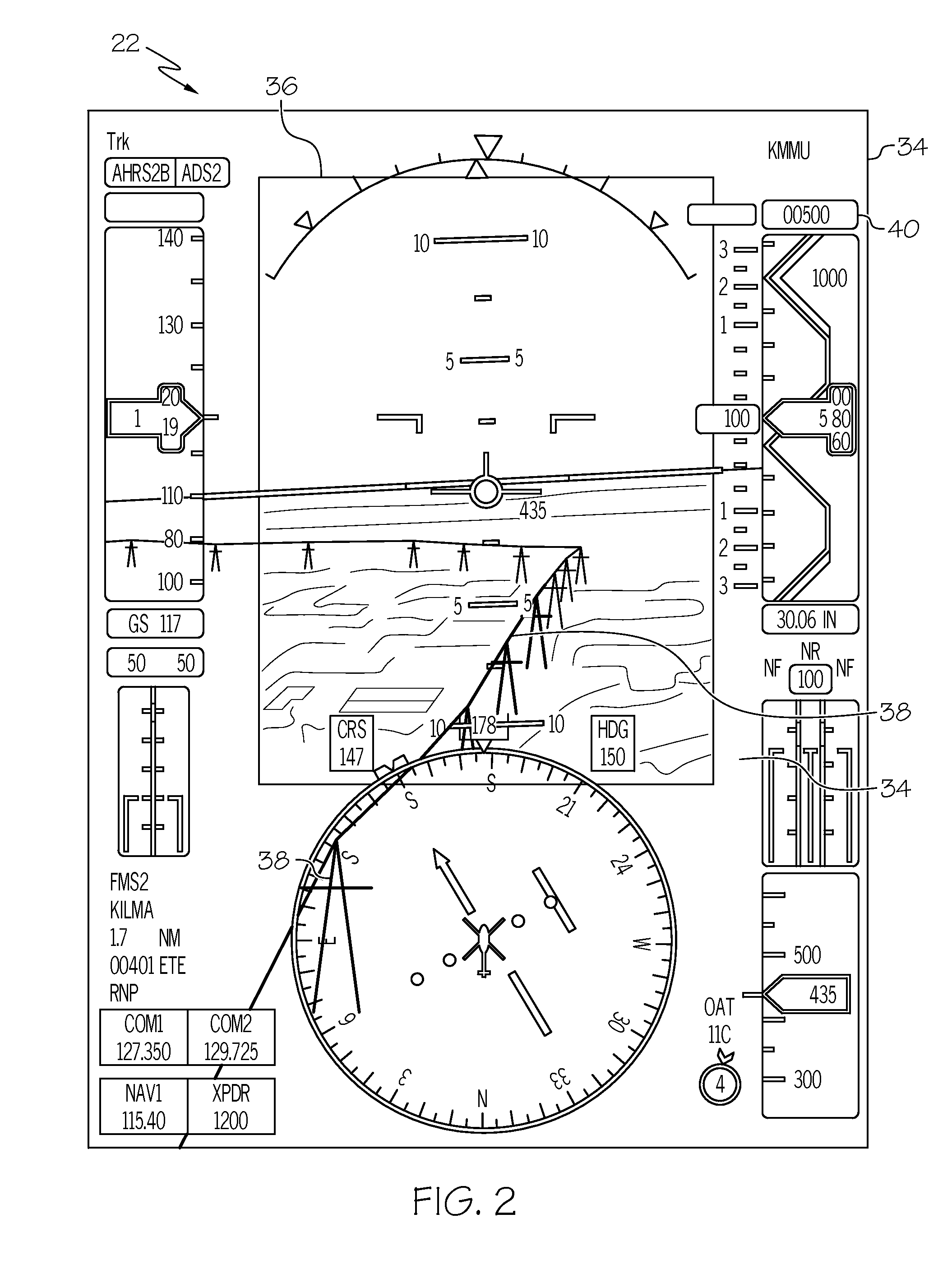
Aircraft synthetic vision system for approach and landing
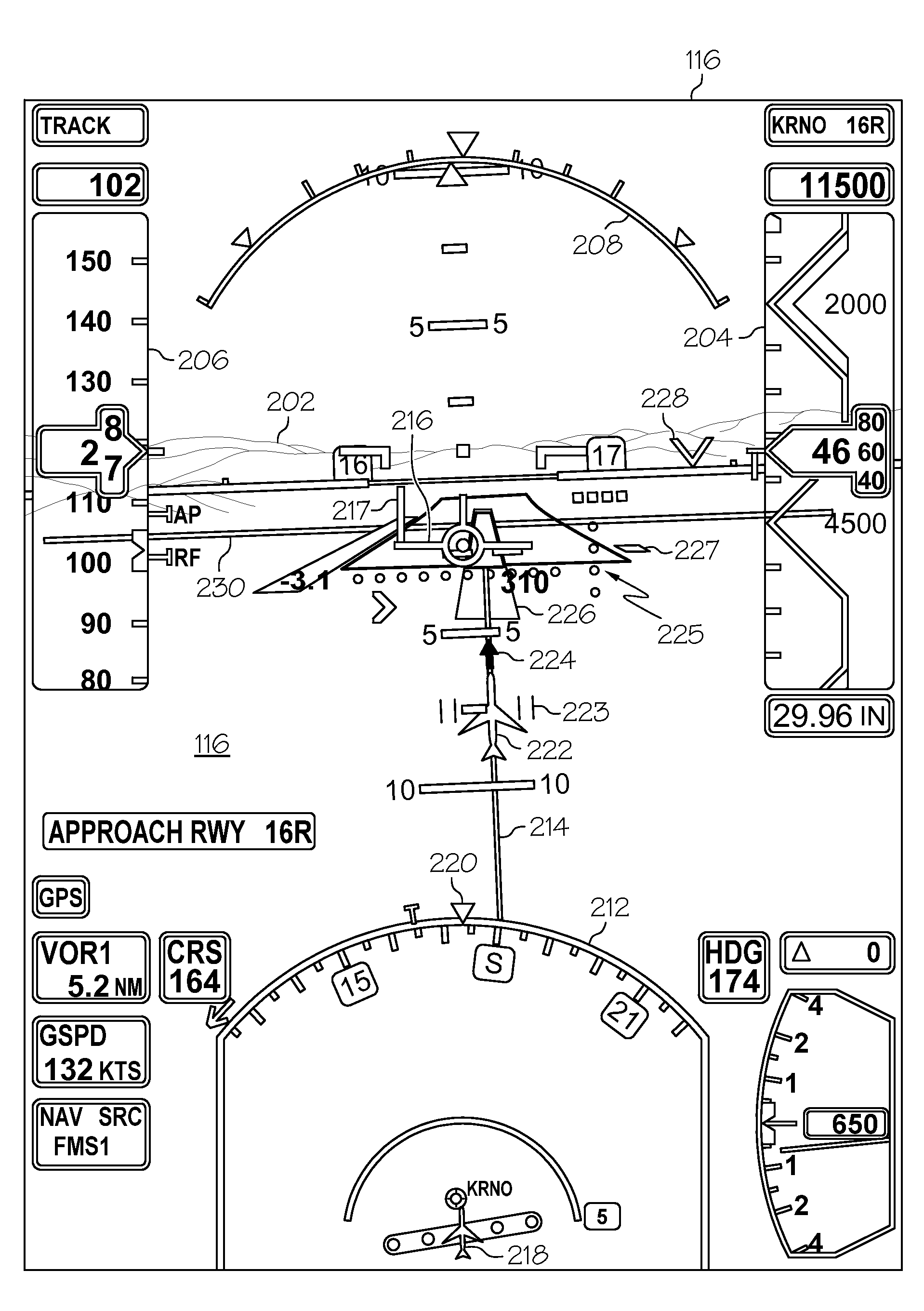
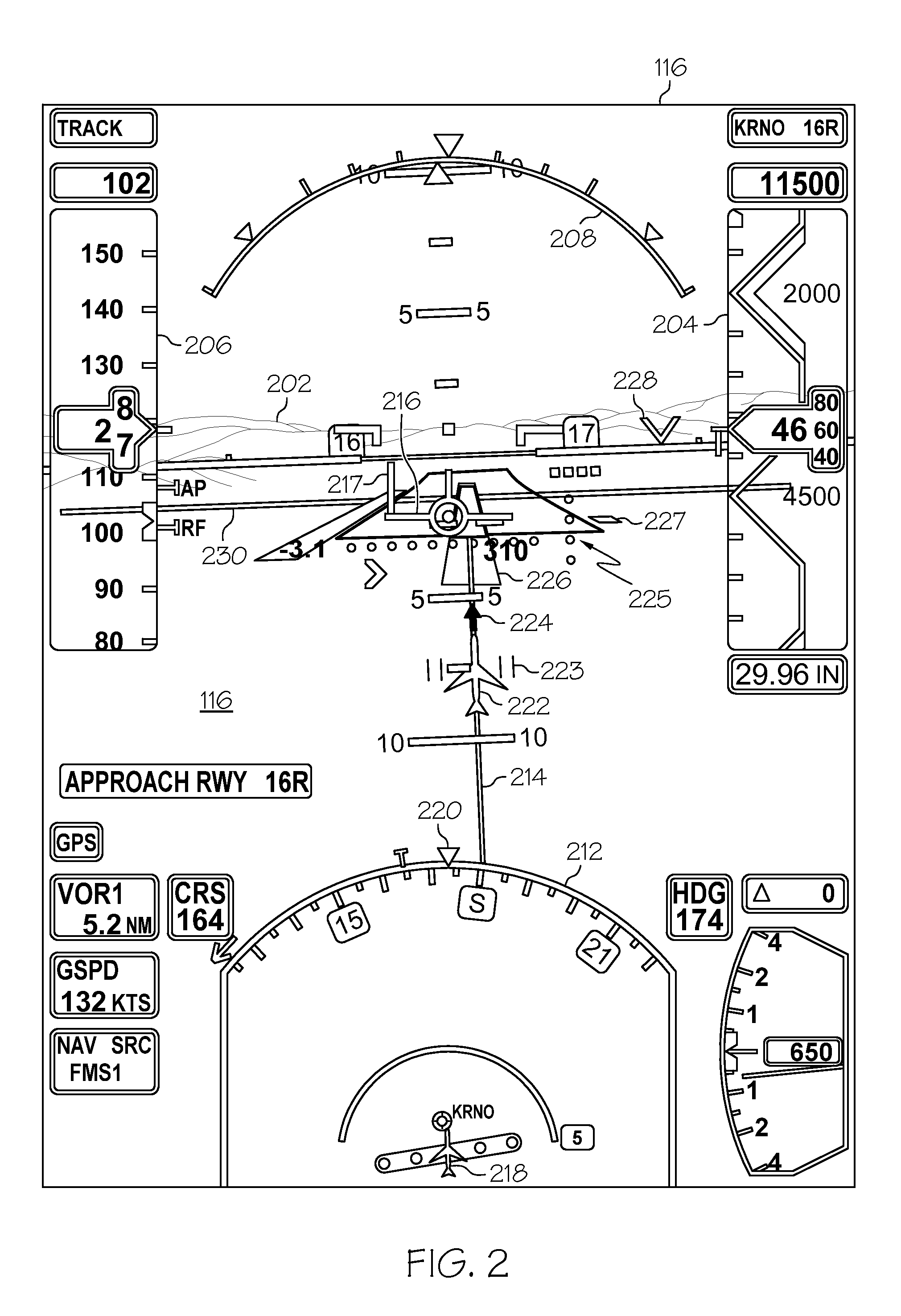
ActiveUS20100026525A1Analogue computers for vehiclesDigital data processing detailsData displaySynthetic vision system
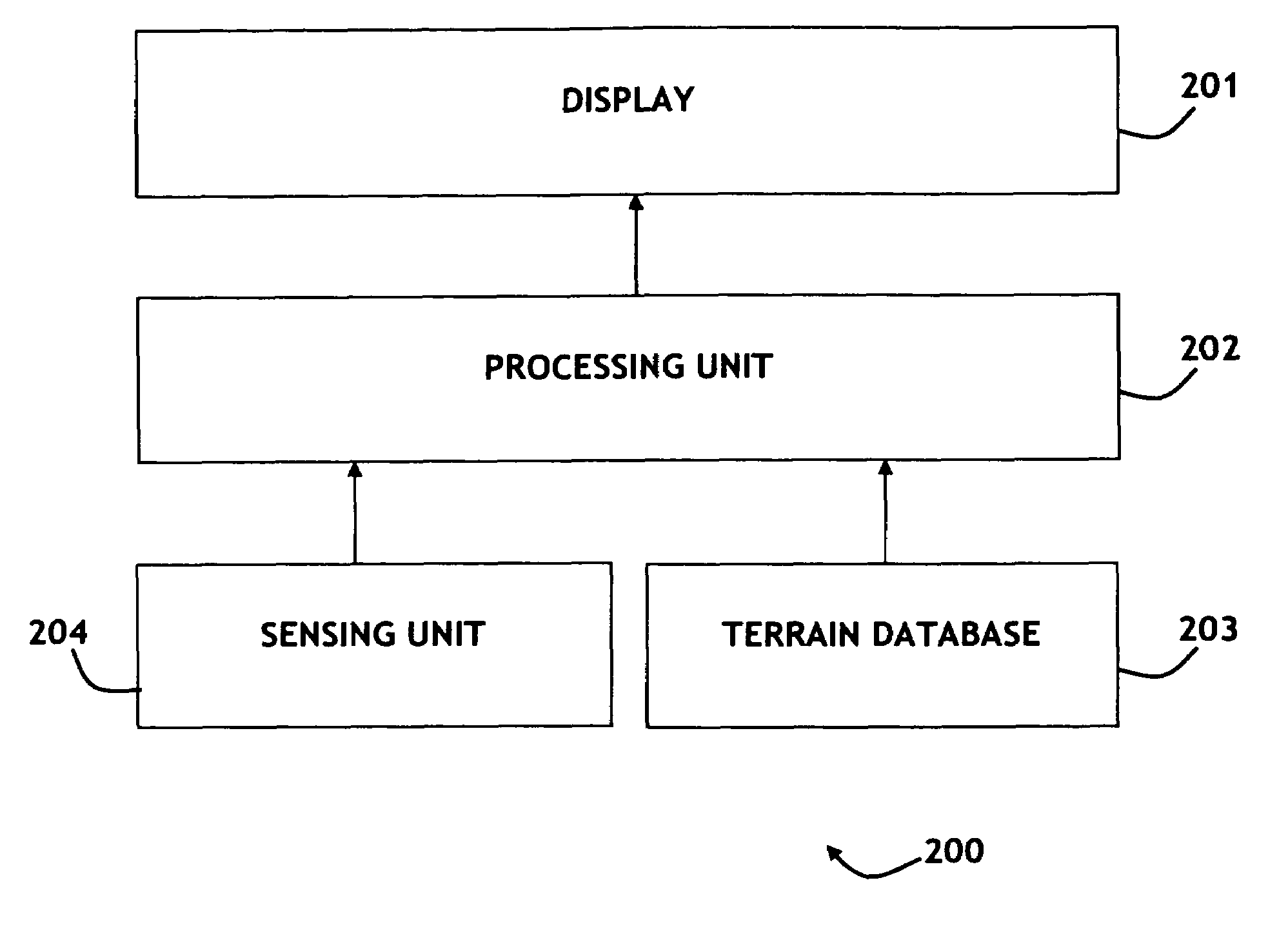
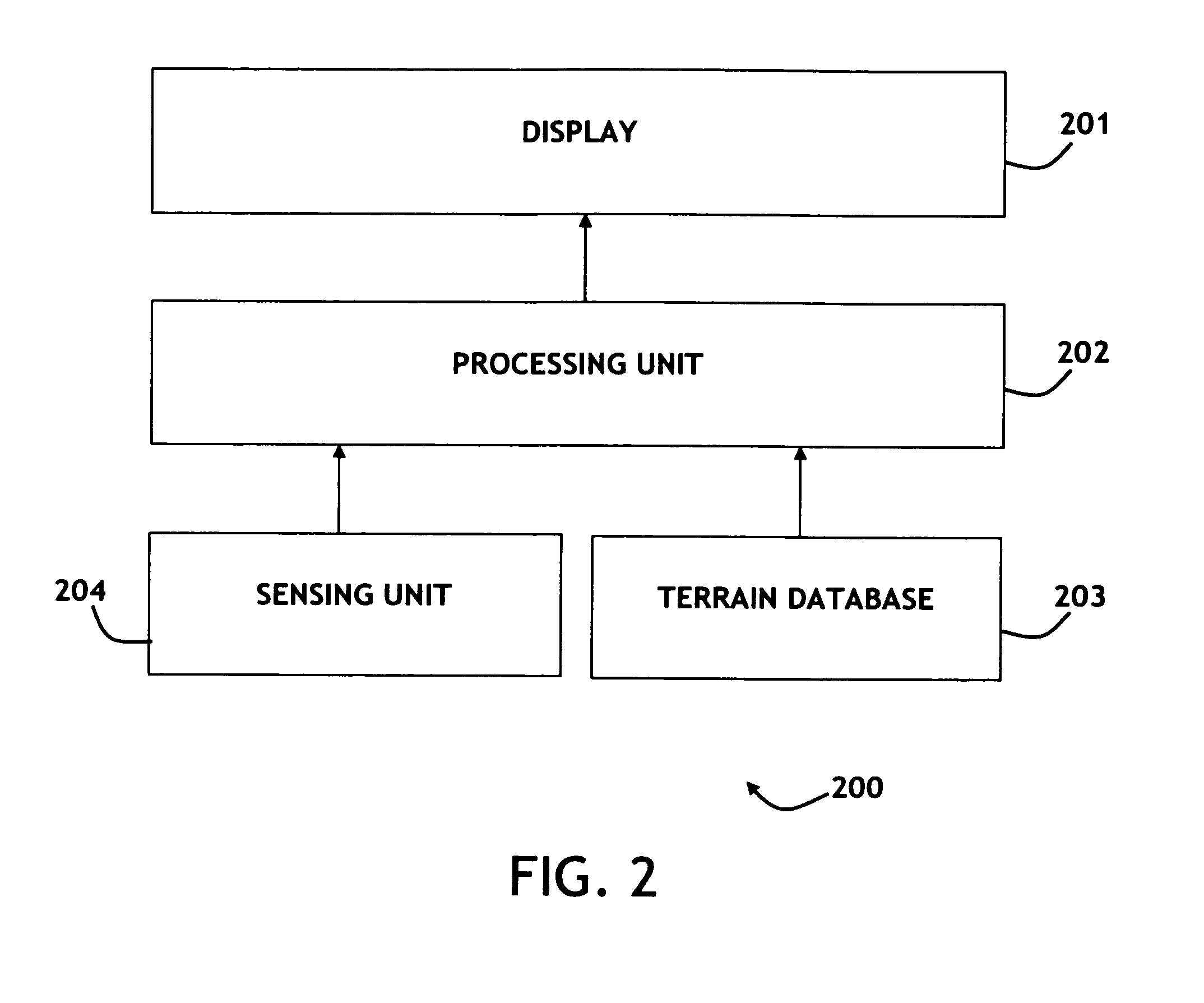
An aircraft synthetic vision system (100) is provided for increasing data input to a pilot (109) during approach and landing flight operations, and includes a runway assistance landing system (114) and a plurality of databases (106, 108, 110, 112) which may include, for example, a terrain database (106), an obstacle database (112); and a validated runway database (110). The processor (104) detects the likelihood of an error in determining the altitude from at least one of the runway assistance landing system (114), the plurality of databases (106, 108, 110, 112), and identifies the error. The processor (104) further determines augmented coordinates, and a processor (104) generates symbology commands to a first display (116) for displaying a runway environment in response to data provided to the processor (104) from each of the runway assistance landing system (114), the plurality of databases (106, 108, 110, 112), and the processor (104).
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
System and method for safely flying unmanned aerial vehicles in civilian airspace
InactiveUS8838289B2Safely share airspace with other usersMinimize changesCosmonautic vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficSynthetic vision systemUnmanned air vehicle
A system and method for safely flying an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), unmanned combat aerial vehicle (UCAV), or remotely piloted vehicle (RPV) in civilian airspace uses a remotely located pilot to control the aircraft using a synthetic vision system during at least selected phases of the flight such as during take-offs and landings.
Owner:MARGOLIN JED
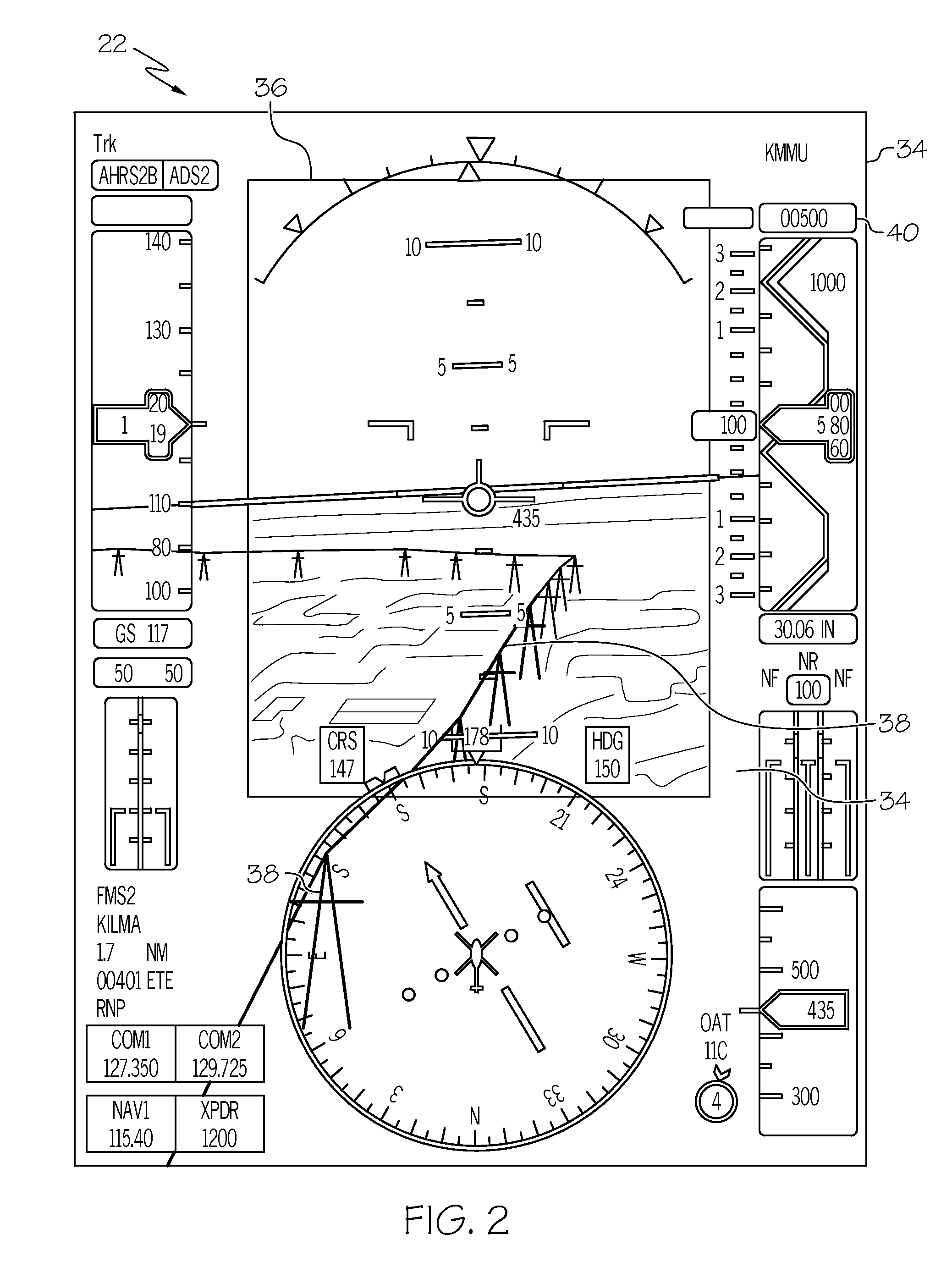
Vehicle display system and method with enhanced vision system and synthetic vision system image display
ActiveUS20080180351A1Improve eyesightCathode-ray tube indicatorsNavigation instrumentsSynthetic vision systemDisplay device
A vehicle display system displays enhanced vision (EV) and synthetic vision (SV) images to an operator of a vehicle. The display system includes: an EV vision image sensor for generating EV images; an SV database containing information regarding terrain and objects of interest for a travel path of a vehicle; an SV image generating unit for generating SV images based on travel of the vehicle and information from the SV database; an EV image sensor control unit for controlling a field of view of the EV image sensor as a function of object of interest information from the SV database; and a display for displaying images generated by said EV image sensor and the SV image generating unit.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
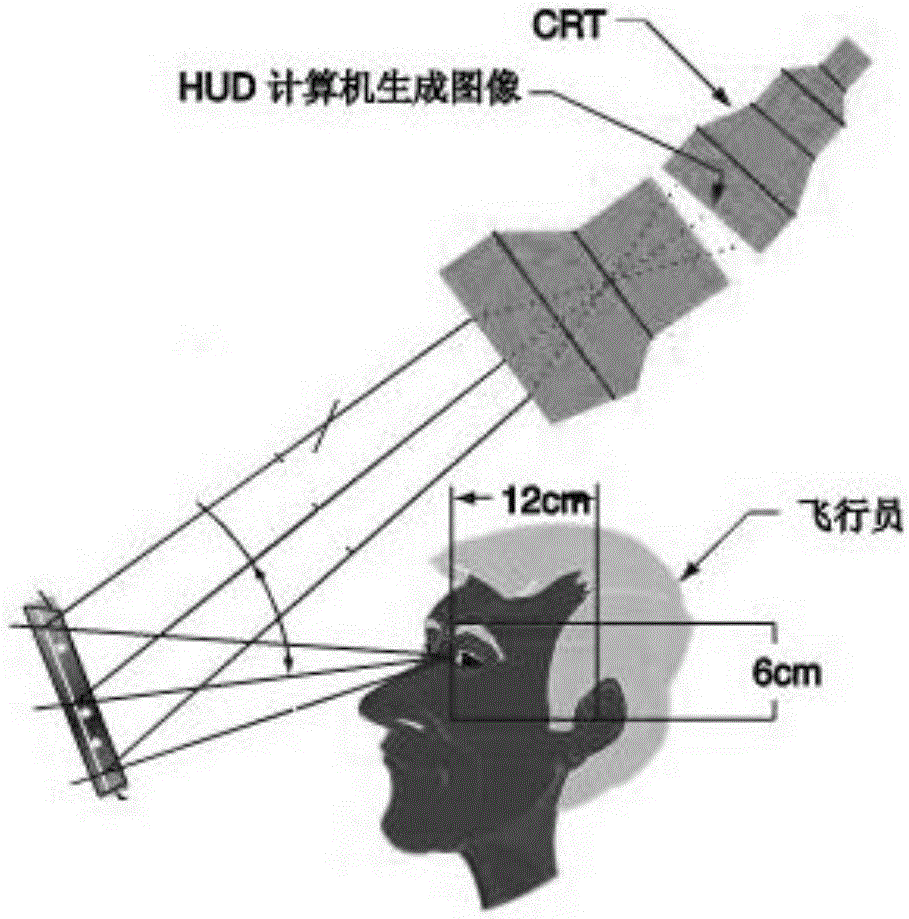
HUD (head-up display) based synthetic vision guiding display system
ActiveCN105139451ASave money on upgradesClosed circuit television systemsICT adaptationGuidance systemHead-up display
The invention belongs to the field of aviation electronic systems and particularly relates to an HUD based synthetic vision guiding display system. At present, an SVS (synthetic vision system) only can be displayed in a head-down display, and during high-speed taxiing, even the fastest scanning of a lower traditional instrument can lead to vision interruption with the outside world. An HGS (head-up guidance system) is not endowed with ability of displaying a three-dimensional terrain synthetic vision, and when inclement weather is encountered, it is difficult to provide better vision awareness for a pilot. With the adoption of the HUD based synthetic vision guiding display system provided by the invention, fused display of a synthetic image of the SVS and a flight guiding image is realized on an HUD system, and a civil aircraft cockpit display system capable of strengthening situation sensing ability especially combines a three-dimensional image display technology with a flight guiding information calculation display technology to simulate an outer aircraft environment and display flight guiding data in a cockpit head-up display.
Owner:BEIJING AERONAUTIC SCI & TECH RES INST OF COMAC +1
Aircraft synthetic vision system for approach and landing
ActiveUS7852236B2Analogue computers for vehiclesDigital data processing detailsSymbolic SystemsSynthetic vision system
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Dual simultaneous image presentation for a three-dimensional aviation display
ActiveUS9762895B1Satisfies needEnhanced Situational AwarenessTelevision system detailsInstruments for road network navigationHead-up displayAviation
A system is disclosed which utilizes a three-dimensional (3D) display system, in combination with an avionics Synthetic Vision System (SVIS), to provide 3D synthetic images of scenes around an aircraft where the systems are dynamically modified to meet particular needs of a flight crew, depending upon variable characteristics of the aircraft and environment including: phase of flight of the aircraft; attitude of the aircraft; proximity of the aircraft to Degraded Visual Environment (DVE) conditions; whether the 3D display system is an head-down display (HDD) or an immersive head-mounted display (HMD); and whether the 3D display system is an head-up display (HUD) or an HMD with a transparent visor.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
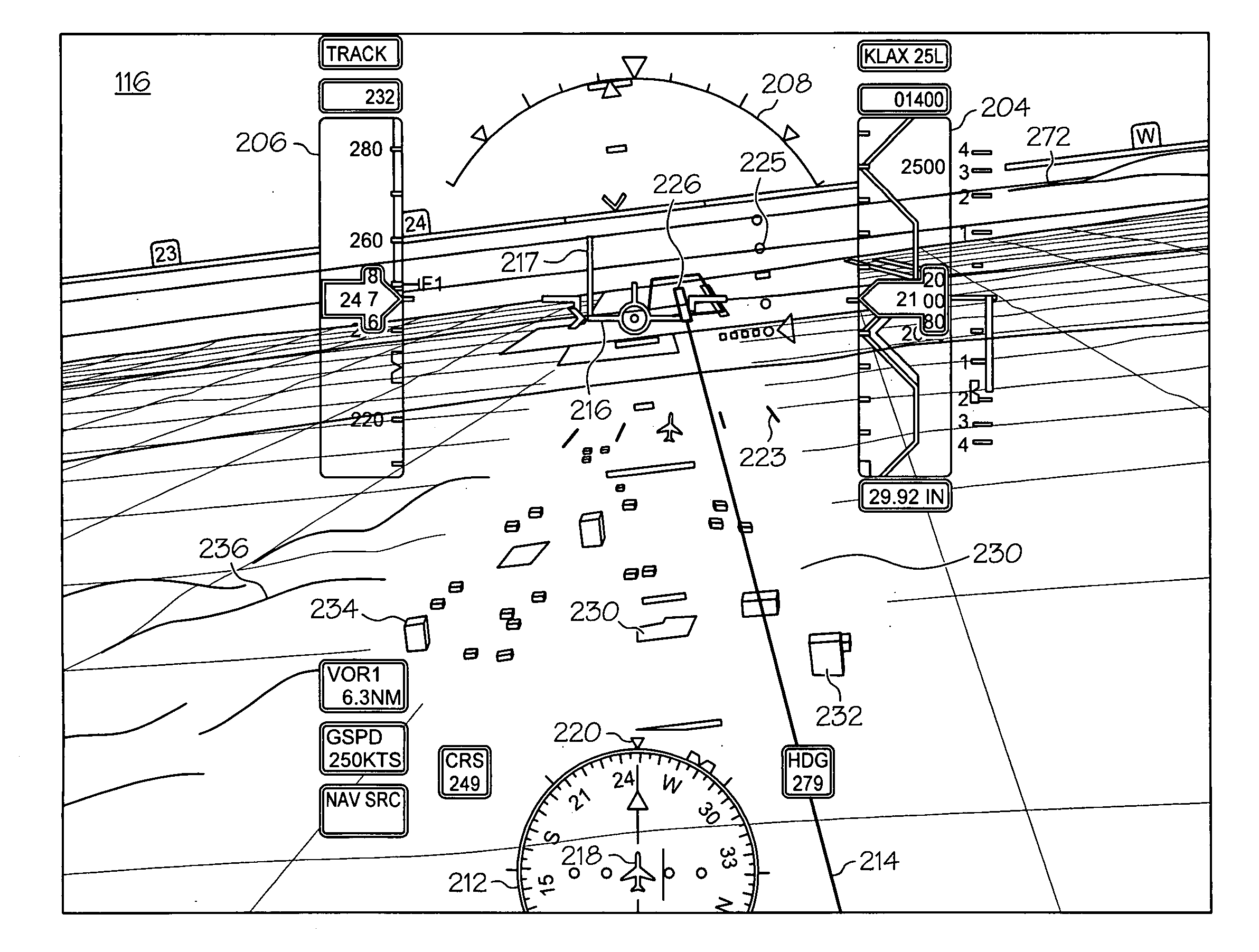
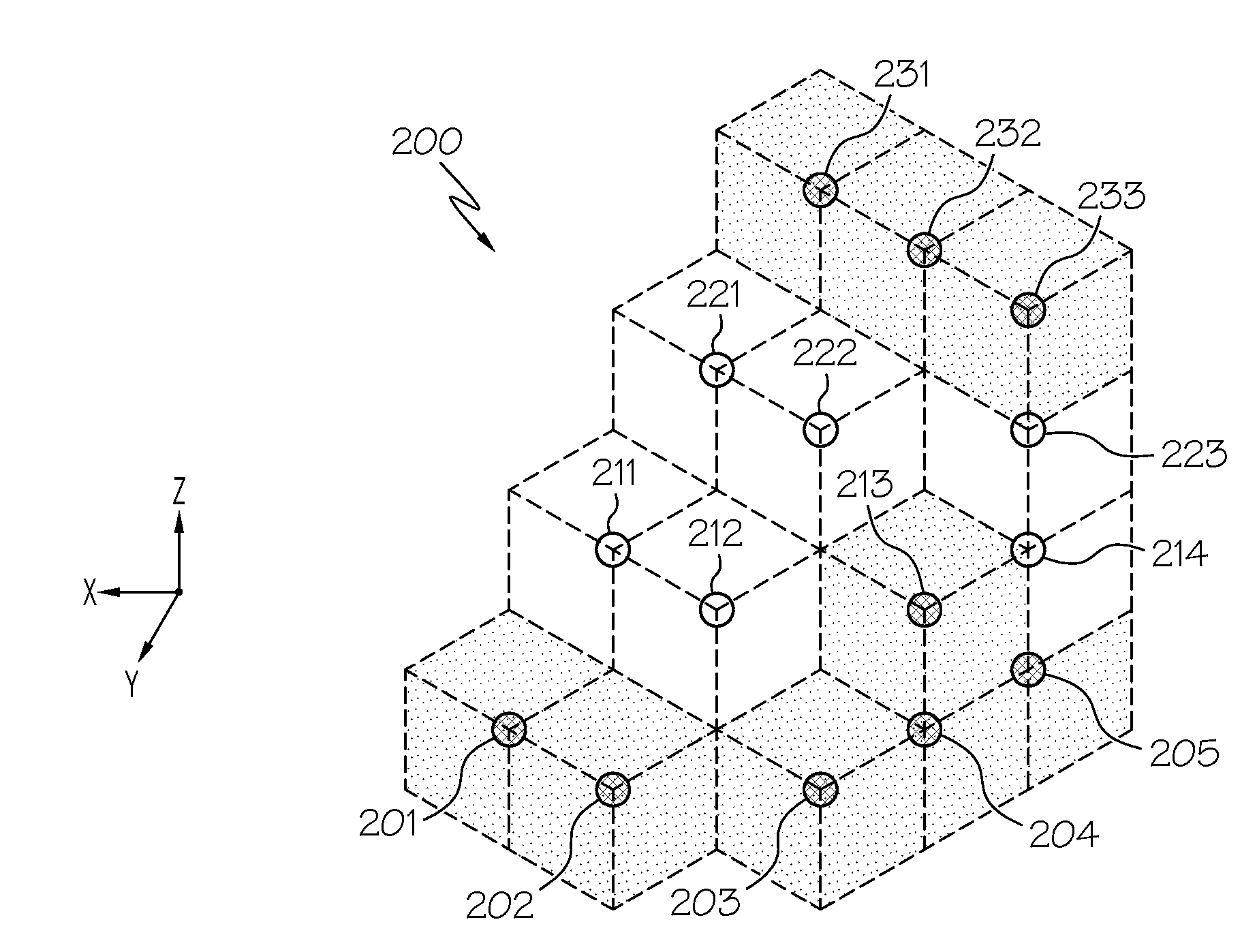
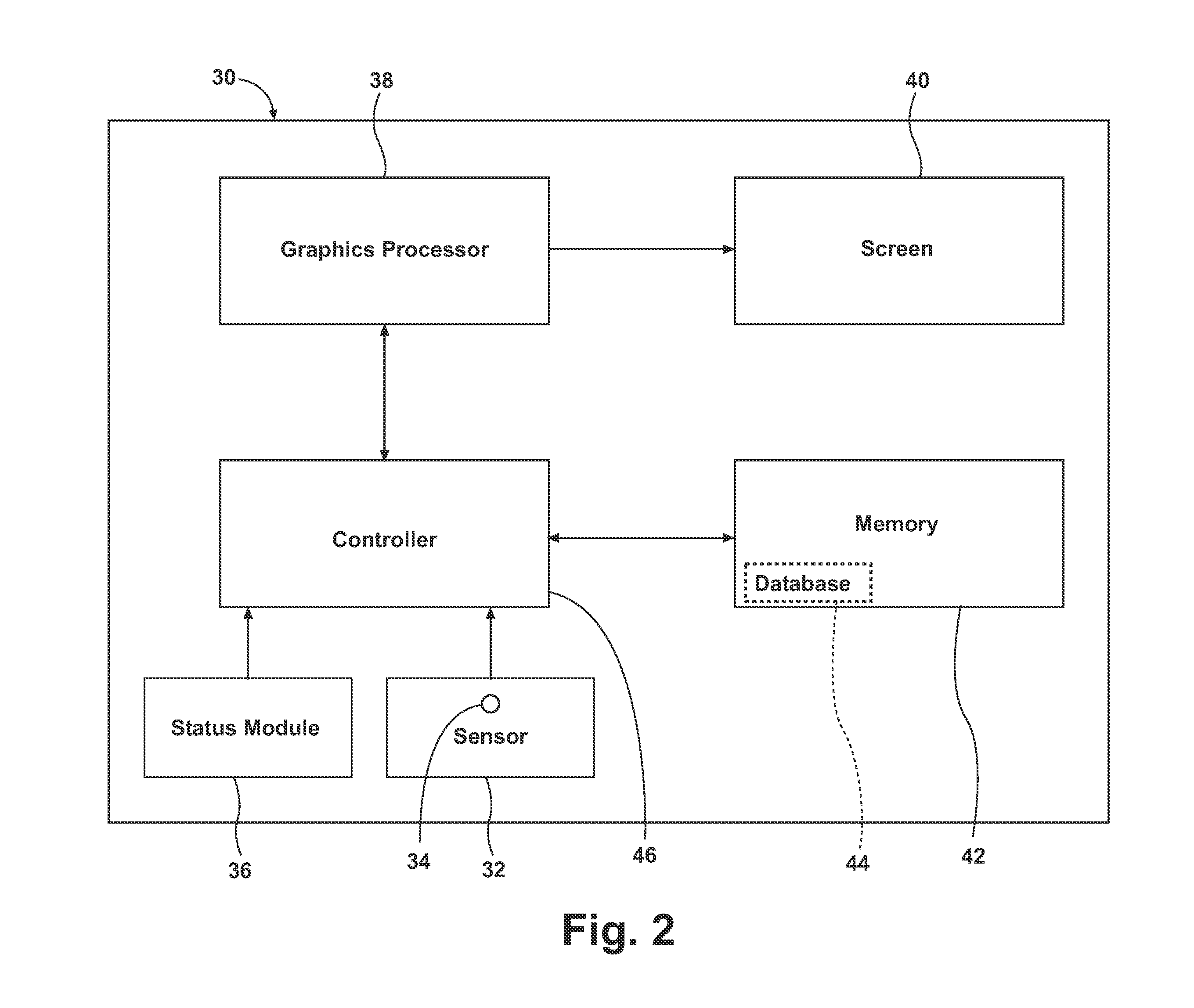
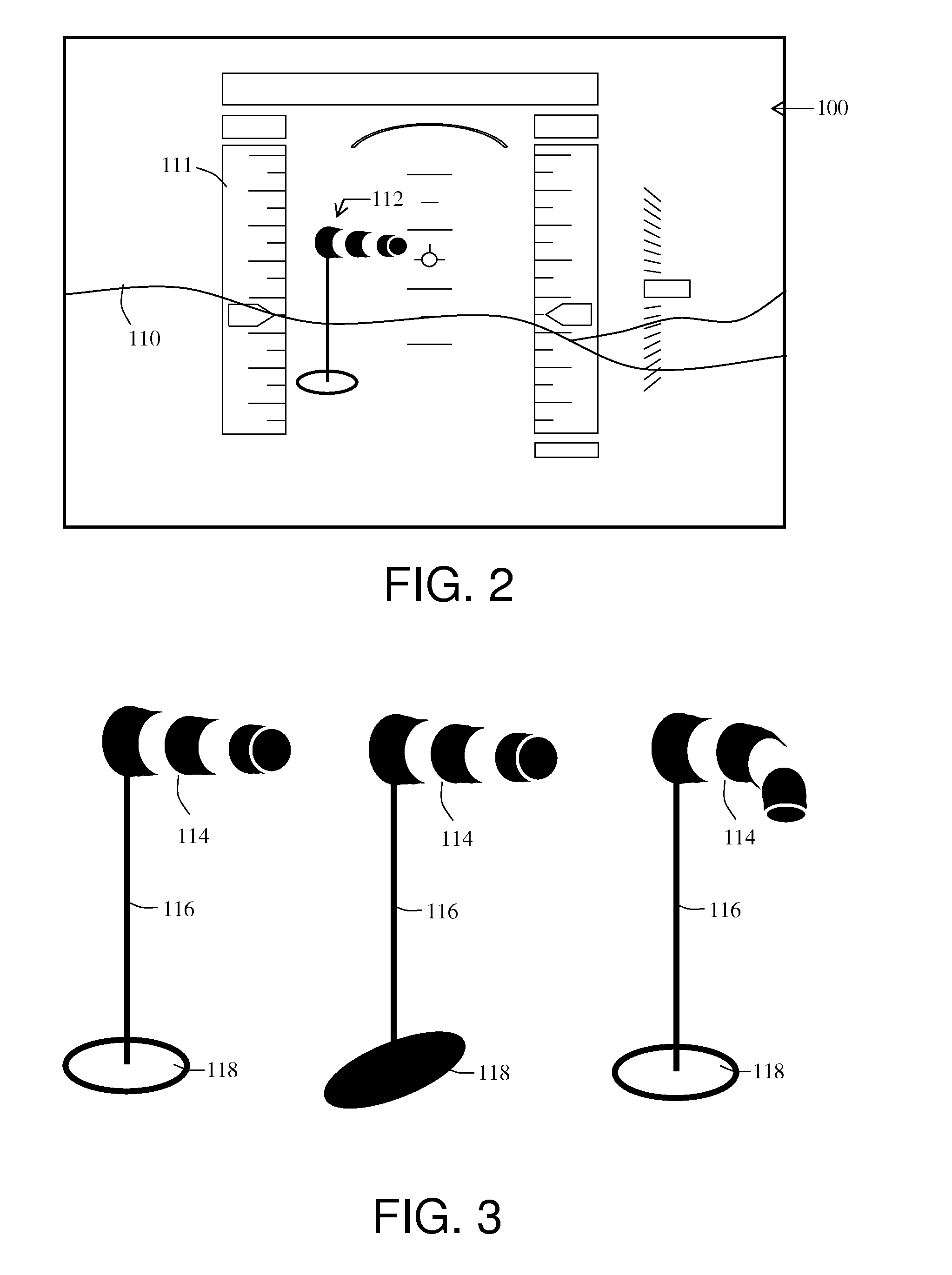
Method and apparatus for displaying prioritized photo realistic features on a synthetic vision system
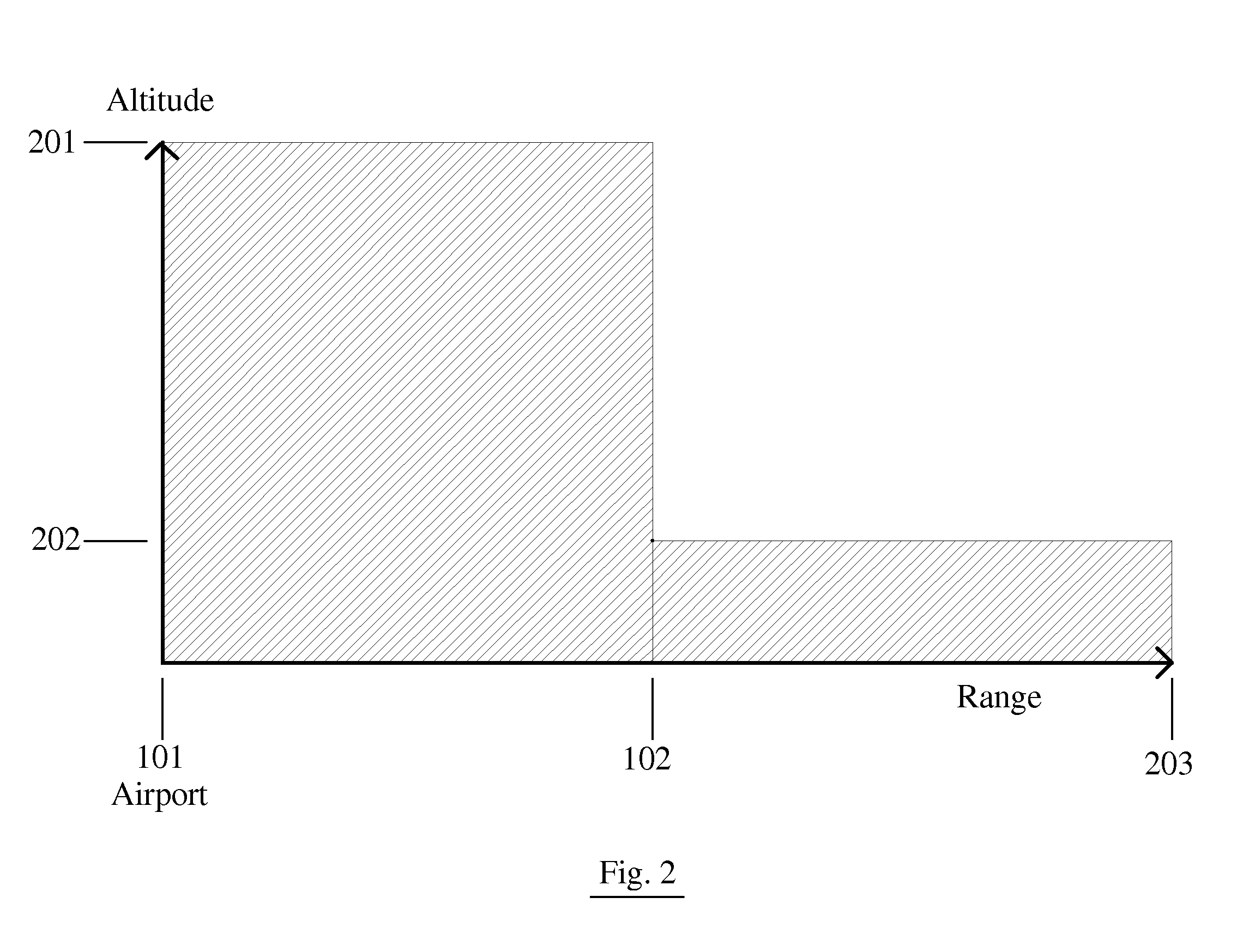
An apparatus and method for displaying photo realistic features (230, 232, 234) on a display (116) of an aircraft (218) include storing (302) a plurality of photo realistic features (230, 232, 234), the photo realistic features including at least one of terrain (230) and obstacle (232) features. A priority factor is determined (304) that is based on one of, for example, aircraft type, speed, and altitude, and a plurality of display state is prioritized (304) for each of the plurality of photo realistic features (230. 232, 234) in accordance with the priority factor. One of the first and second display states is displayed (308) for each of the plurality of photo realistic features (230, 232, 234) as determined by the prioritizing step (306).
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
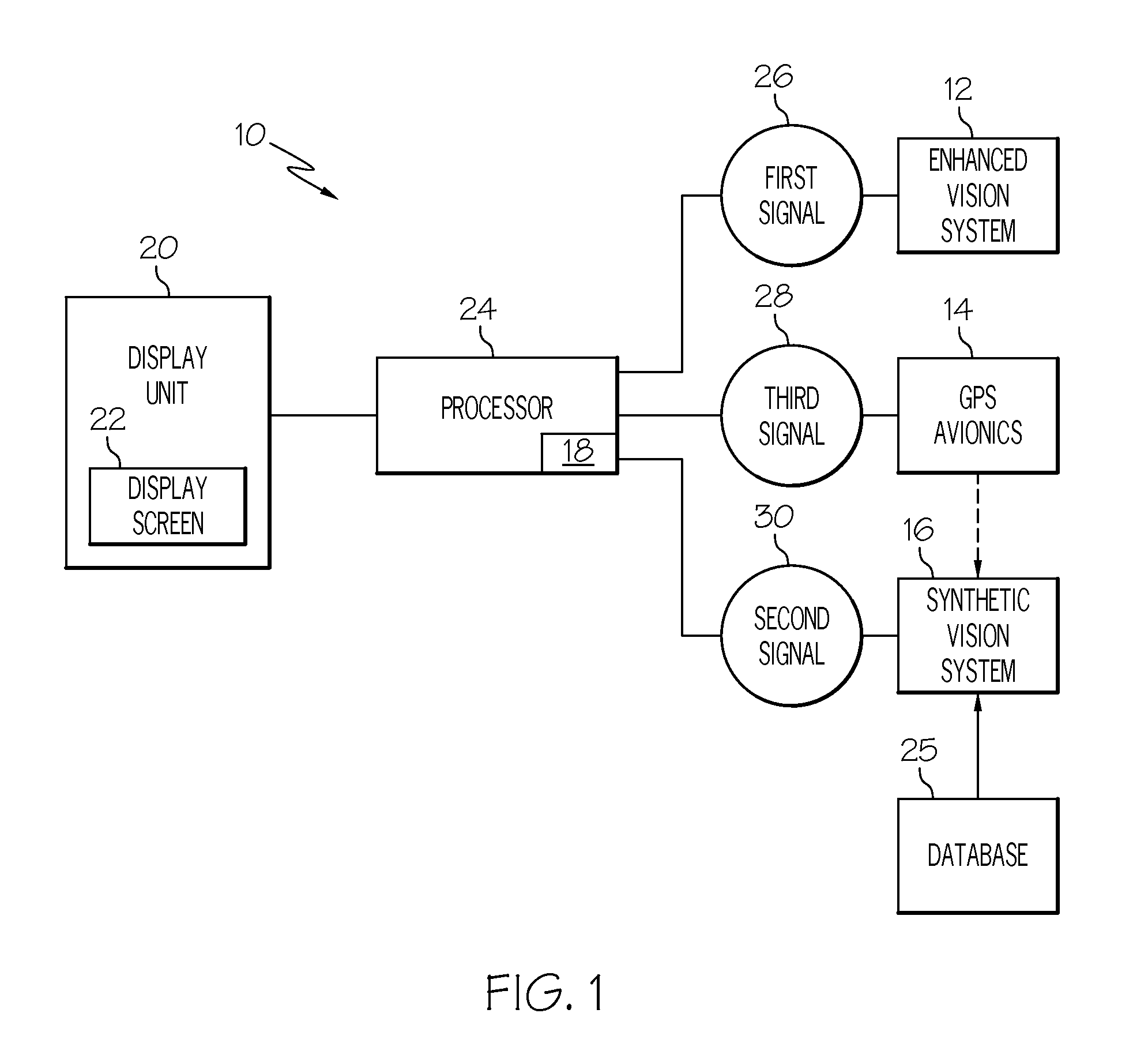
Aircraft flight deck displays and systems and methods for enhanced display of obstacles in a combined vision display
ActiveUS20140267422A1Improve the display effectRaise the potentialCathode-ray tube indicatorsNavigation instrumentsSynthetic vision systemDisplay device
Systems and methods for enhanced display of obstacles in a combined vision display are provided. The system comprises a display unit and an enhanced vision system configured to generate first signals representative of enhanced vision images. Data storage device contains obstacle data representative of obstacles. Synthetic vision system is configured to selectively retrieve obstacle data from data storage device and generate second signals representative of synthetic vision images of one or more obstacles. Processor is in operable communication with display unit and coupled to receive first and second signals and configured, in response thereto, to: overlay the synthetic vision images of the one or more obstacles over the enhanced vision images and command display unit to display the synthetic vision images of the one or more obstacles overlaid over the enhanced vision images. The overlaid synthetic vision images of the one or more obstacles may be visually highlighted.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
System, apparatus, and method for generating location information on an aircraft display unit using location markers
ActiveUS8099234B1Enhance the imageImprove abilitiesInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlAviationHead-up display
A present novel and non-trivial system, apparatus, and method for presenting information to the pilot on an aircraft display unit employed in a synthetic vision system (“SVS”), an enhanced vision system (“EVS”), or combined system. Information regarding the locations of visible and invisible objects related to aviation such as airports, navigation aids and facilities, and airspace are provided by location markers. Data representative of the terrain and location of objects depicted in a scene outside the aircraft are retrieved from one or more data sources. An image generating processor generates an image data set representative of a three-dimensional perspective view of a scene outside the aircraft, wherein the image data set is determined as a function of the terrain data and location marker data associated with the location data. The image data set may be provided to a Head-Down Display unit, a Head-Up Display unit, or both.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
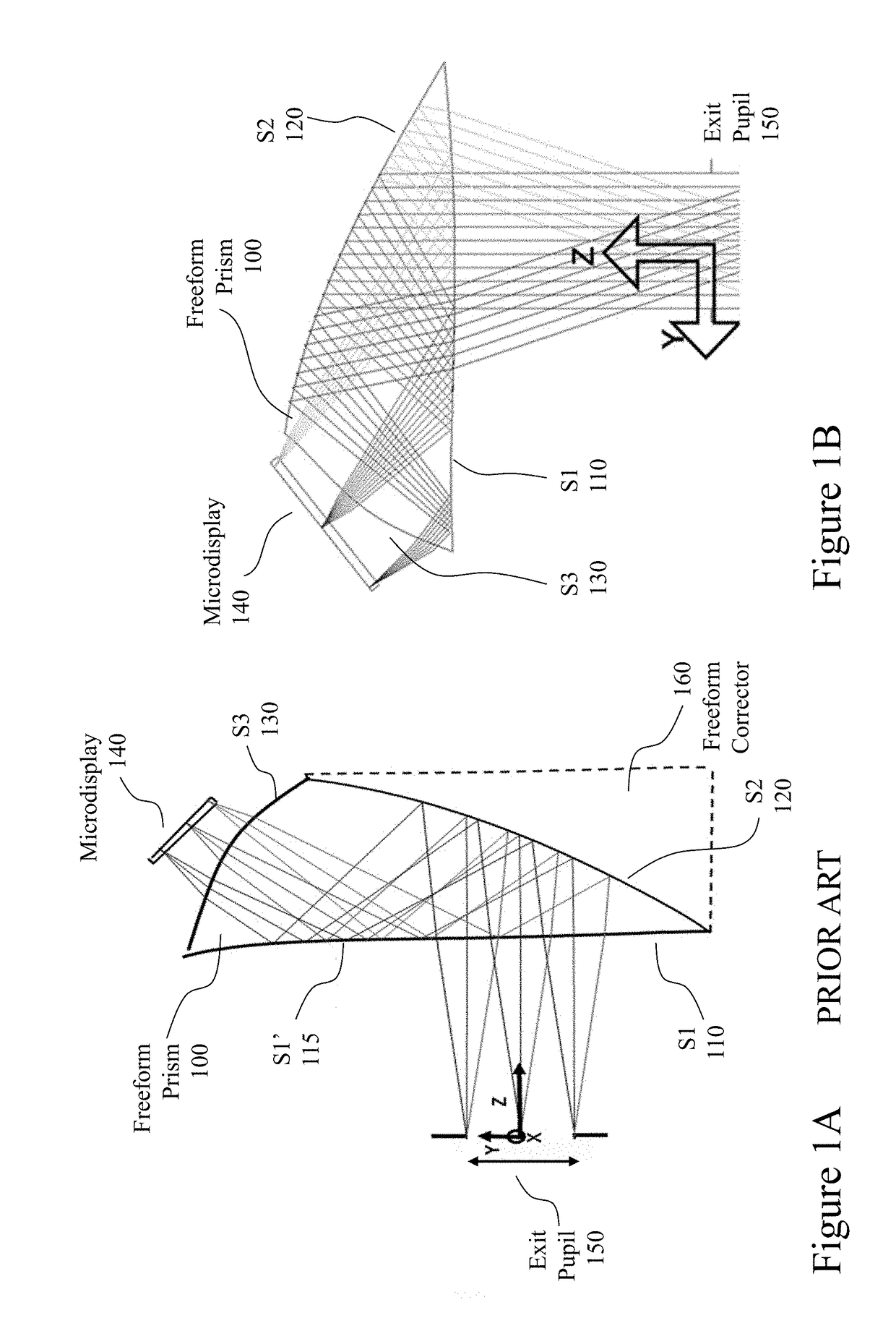
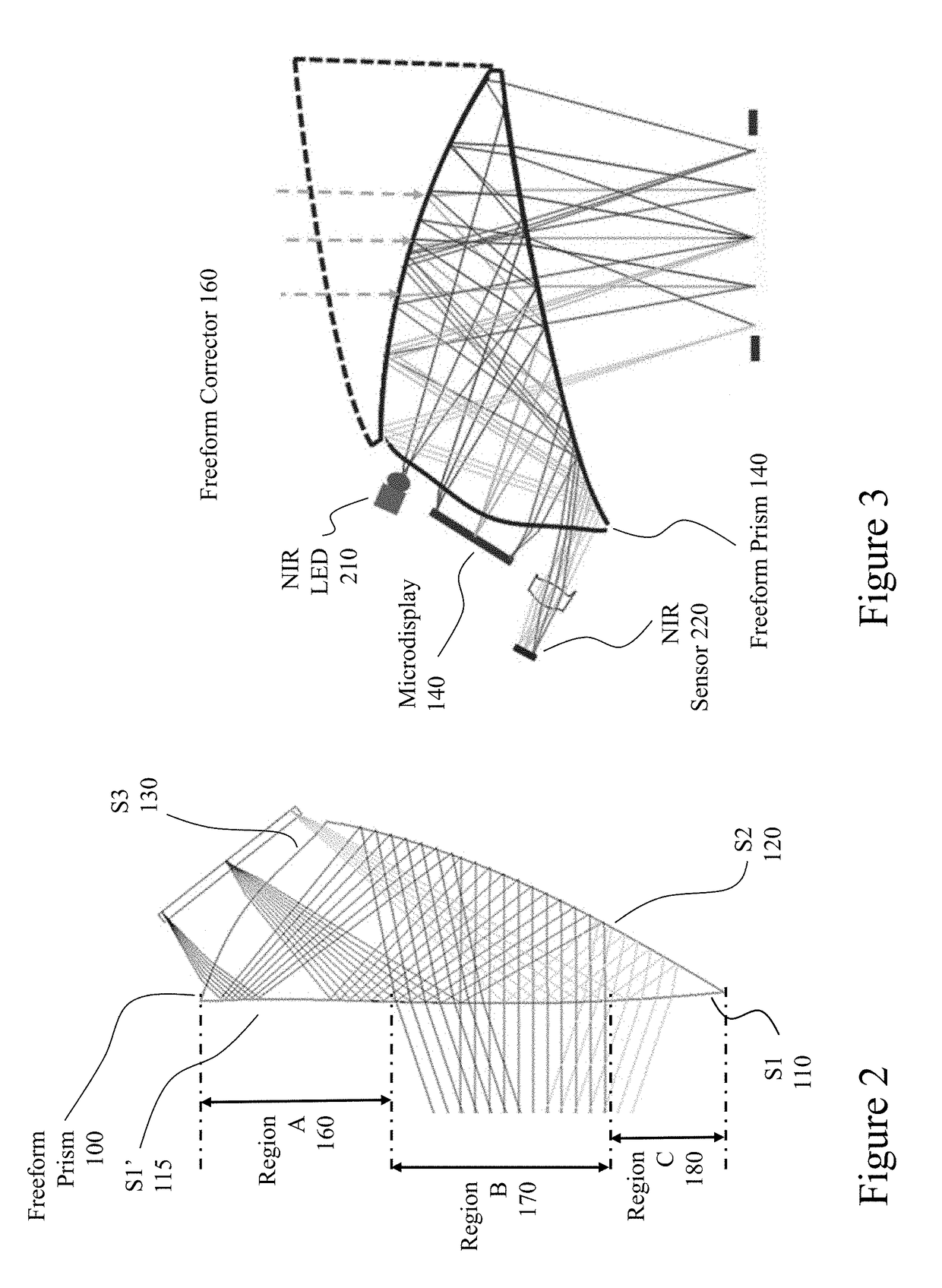
Large exit pupil wearable near-to-eye vision systems exploiting freeform eyepieces
InactiveUS20180045964A1Wide field of viewHigh image resolutionDetails for portable computersOptical elementsEyepieceDisplay device
Within applications for Near-to-Eye (NR2I) displays, irrespective of whether they are for short-term, long-term, low vision, augmented reality, etc., there is a conflicting tradeoff between user comfort, ease of attachment, minimizing intrusiveness and aesthetics which must be concurrently balanced with and are often in conflict with providing an optical vision system within the NR2I display that provides the user with a wide field of view and high image resolution whilst also offering a large exit pupil for eye placement with sufficient eye clearance. Embodiments of the invention address these issues and provide a high performance optical system through the design of the optical eyepiece design to overcome these limitations within a bioptic configuration with laterally disposed displays.
Owner:ESIGHT CORP
Aircraft flight deck displays and systems and methods for enhanced display of obstacles in a combined vision display
ActiveUS9390559B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsNavigation instrumentsSynthetic vision systemDisplay device
Systems and methods for enhanced display of obstacles in a combined vision display are provided. The system comprises a display unit and an enhanced vision system configured to generate first signals representative of enhanced vision images. Data storage device contains obstacle data representative of obstacles. Synthetic vision system is configured to selectively retrieve obstacle data from data storage device and generate second signals representative of synthetic vision images of one or more obstacles. Processor is in operable communication with display unit and coupled to receive first and second signals and configured, in response thereto, to: overlay the synthetic vision images of the one or more obstacles over the enhanced vision images and command display unit to display the synthetic vision images of the one or more obstacles overlaid over the enhanced vision images. The overlaid synthetic vision images of the one or more obstacles may be visually highlighted.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
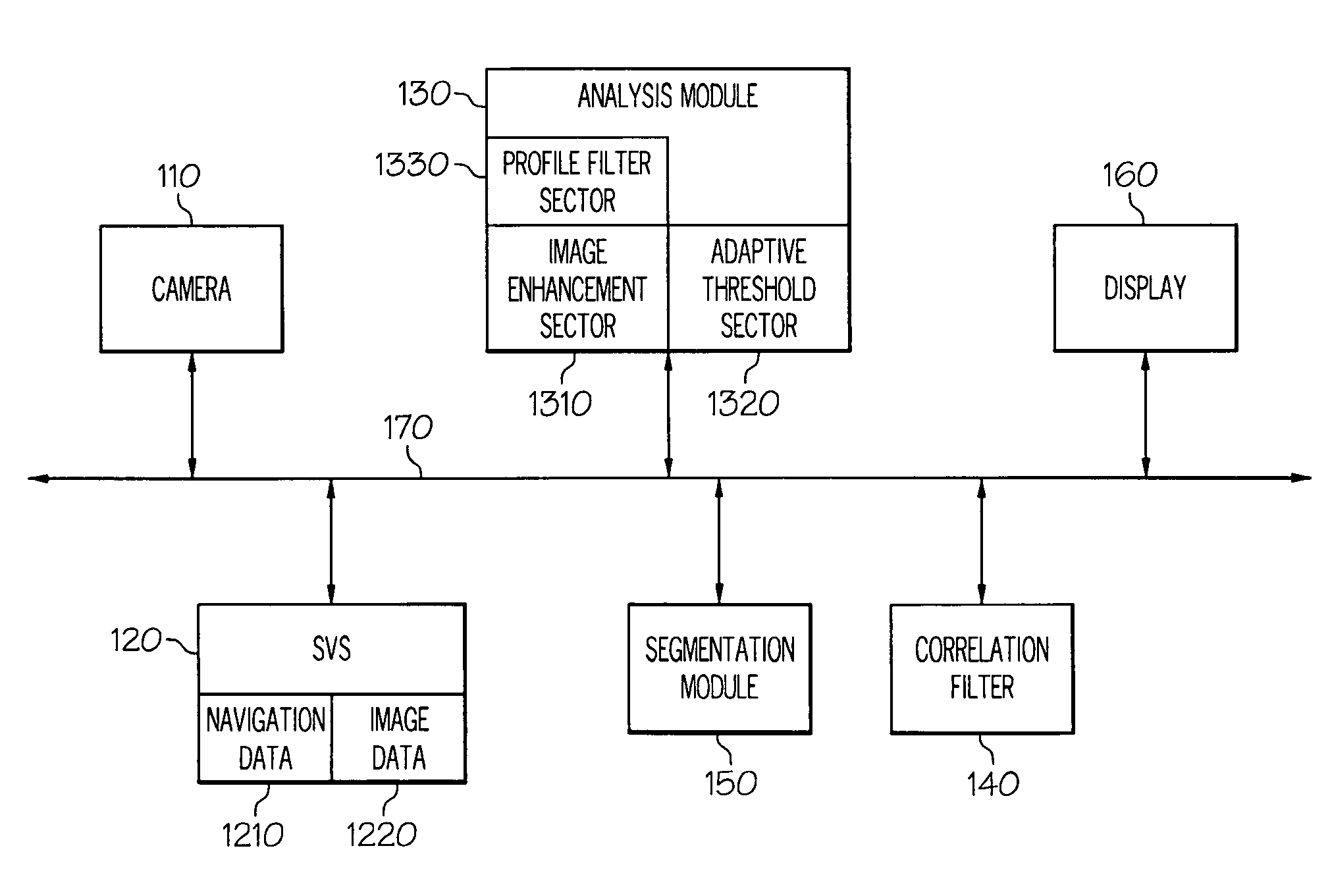
Methods and apparatus for runway segmentation using sensor analysis
ActiveUS7826666B2Image enhancementAnalogue computers for vehiclesSynthetic vision systemTemplate based
Systems and methods for determining whether a region of interest (ROI) includes a runway are provided. One system includes a camera for capturing an image of the ROI, an analysis module for generating a binary large object (BLOB) of at least a portion of the ROI, and a synthetic vision system including a template of the runway. The system further includes a segmentation module for determining if the ROI includes the runway based on a comparison of the template and the BLOB. One method includes the steps of identifying a position for each corner on the BLOB and forming a polygon on the BLOB based on the position of each corner. The method further includes the step of determining that the BLOB represents the runway based on a comparison of the polygon and a template of the runway. Also provided are computer-readable mediums storing instructions for performing the above method.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Synthetic vision systems and methods for displaying detached objects
ActiveUS20130257852A1Navigation instrumentsElectromagnetic wave reradiationGraphicsSynthetic vision system
A display system is provided for a vehicle. The display system includes a data source configured to provide terrain data with detached objects that are detached from ground terrain and attached objects that are attached to ground terrain; a processing unit coupled to the data source configured to receive the terrain data and to distinguish the detached objects from the attached objects to generate display commands for a three-dimensional view that comprises graphical elements representing both the detached objects and the attached objects; and a display device coupled to the processing unit and configured to receive the display commands and operable to render the common three-dimensional view to thereby allow viewing of the detached objects and the attached objects.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
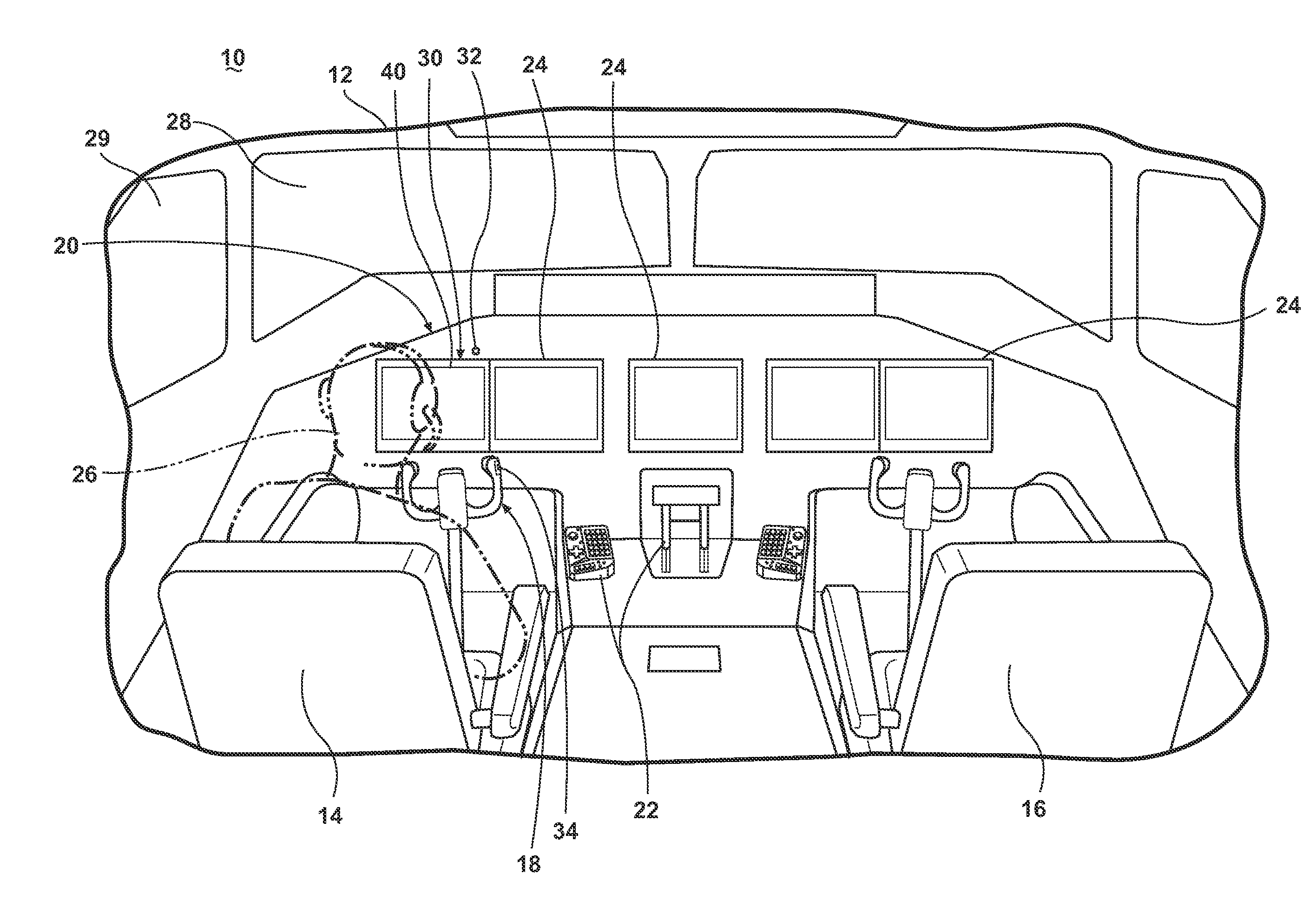
Method of operating a synthetic vision system in an aircraft
A method of operating an aircraft comprising a cockpit with a flight deck having at least one flight display, a pilot's seat facing the flight deck, and a synthetic vision system producing a synthetic image for displaying on the at least one flight display.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Converting aircraft enhanced vision system video to simulated real time video
ActiveUS20110142281A1High resolutionRoad vehicles traffic controlCharacter and pattern recognitionSynthetic vision systemImage resolution
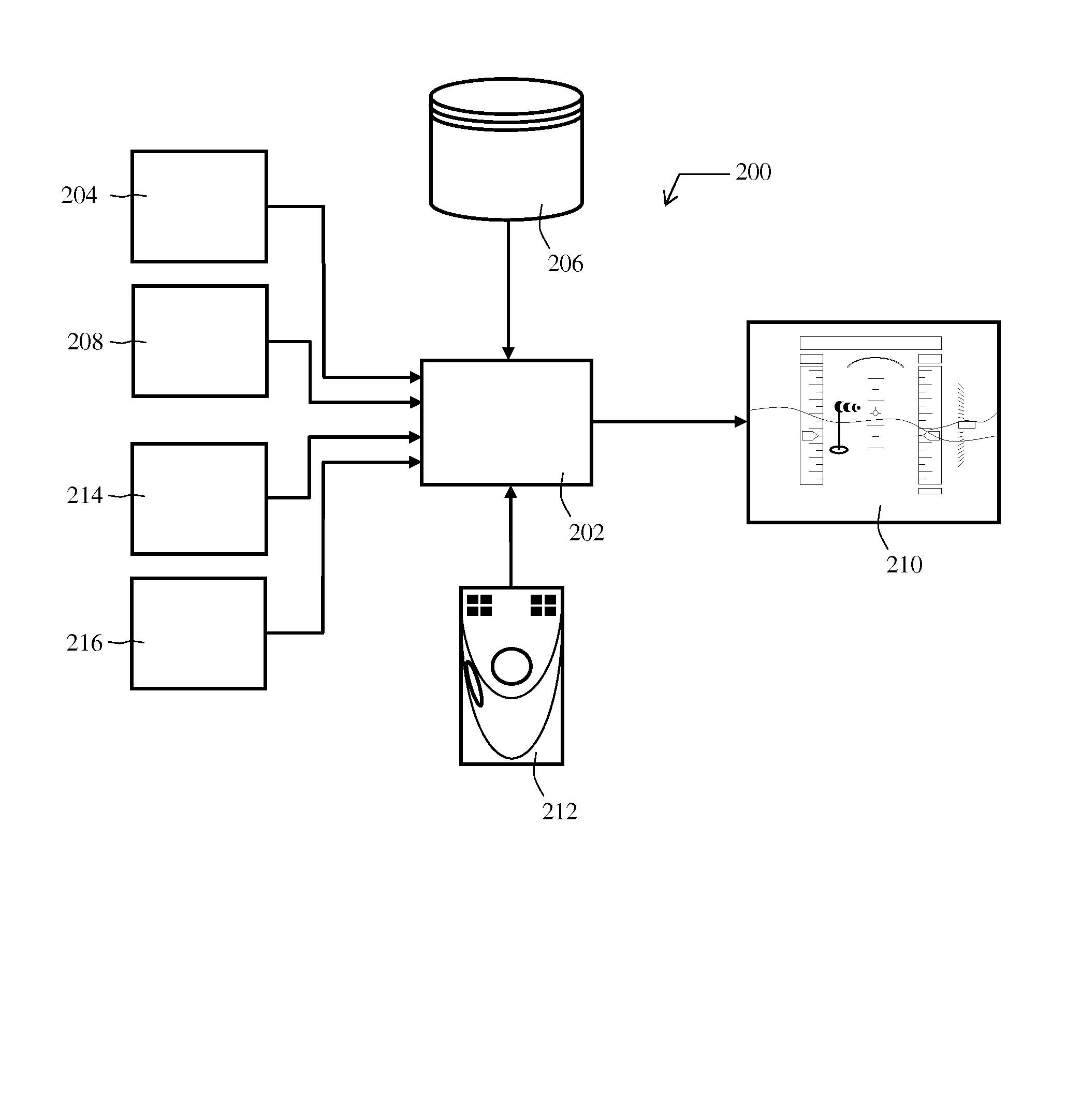
A method for overcoming image latency issues of a synthetic vision system include generating (602, 704) a video comprising a plurality of images (300, 400, 500) of a target (208, 212) viewed from a moving platform (202), enhancing (604, 704) the resolution of the video, processing (606, 706) a parameter of the moving platform (202) related to the relative position of the platform to the target (208, 212), adjusting each of the plurality of images based on the processed parameter to simulate a real time video, and displaying (610, 710) the simulated real time video.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Viewing device for aircraft comprising means of displaying the final destination and associated display method
ActiveUS8224508B2Analogue computers for vehiclesNavigation instrumentsHuman–machine interfaceDisplay device
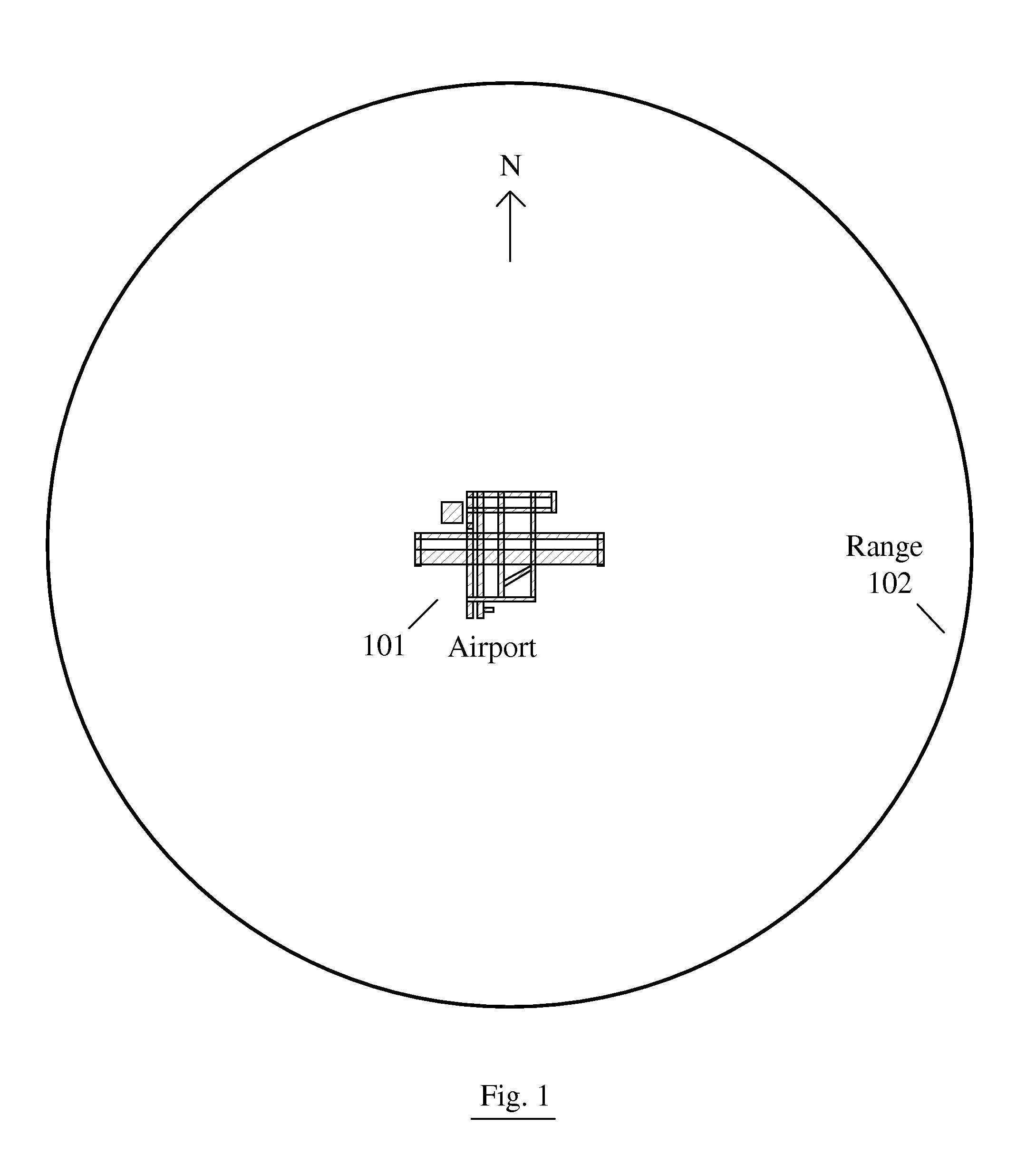
The general field of the invention is that of synthetic vision system SVS type viewing systems, for aircraft, said system comprising at least one navigation database, a cartographic database of a terrain, position sensors, anemometric sensors, sensors for measuring the gradient of said terrain, an electronic computer, a man-machine interface means and a display screen, the computer comprising means of processing the various information obtained from the databases, from the sensors and from the interface means, said processing means arranged so as to provide on the display screen a synthetic image of the terrain comprising a representation of the final destination in the form of an air sock of aeronautical type.
Owner:THALES SA
Method of positioning perspective terrain on SVS primary flight displays using terrain database and radio altitude
ActiveUS7715978B1Instruments for road network navigationDigital data processing detailsSynthetic vision systemDisplay device
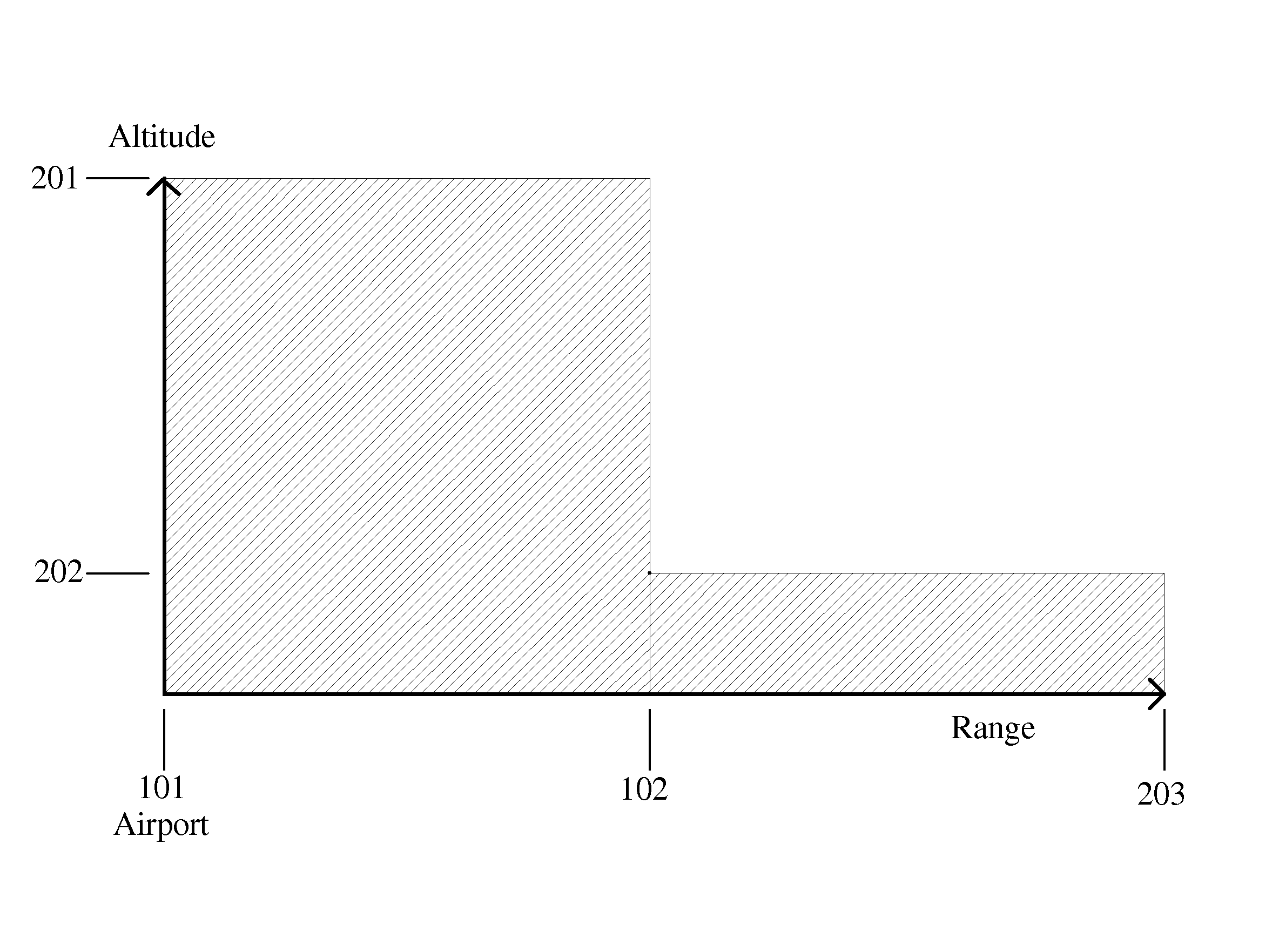
The present invention is directed to a method of positioning perspective terrain on a SVS (Synthetic Vision System) based on a navigation solution, the vertical component of which is calculated utilizing a terrain database and sensing unit (which provides height above terrain). The terrain database provides elevation of terrain above MSL. A sensor, such as a GNSS sensor, may be utilized to calculate the navigation solution. In alternative embodiments, the navigation solution is calculated differently based upon the phase of flight. In one, the vertical component calculation utilizes the sensing unit at or below the sensing unit's rated altitude. In another, vertical component calculation blends the sensing unit with the sensor. The blending may be based upon percentages based upon altitude or utilize filtering such as Kalman filtering. The present invention is particularly advantageous for close to ground operations, insuring perspective terrain will stay consistent with the real world.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Synthetic vision system calibration method based on airborne instrument landing device
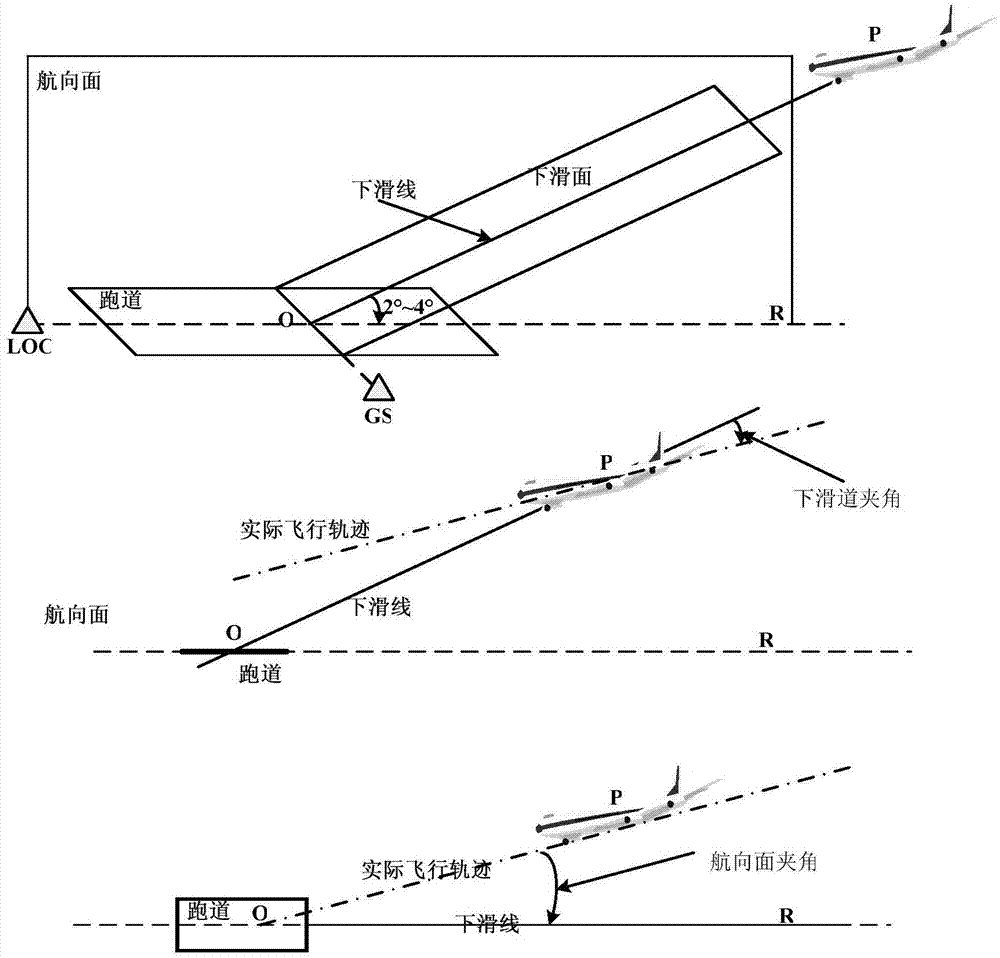
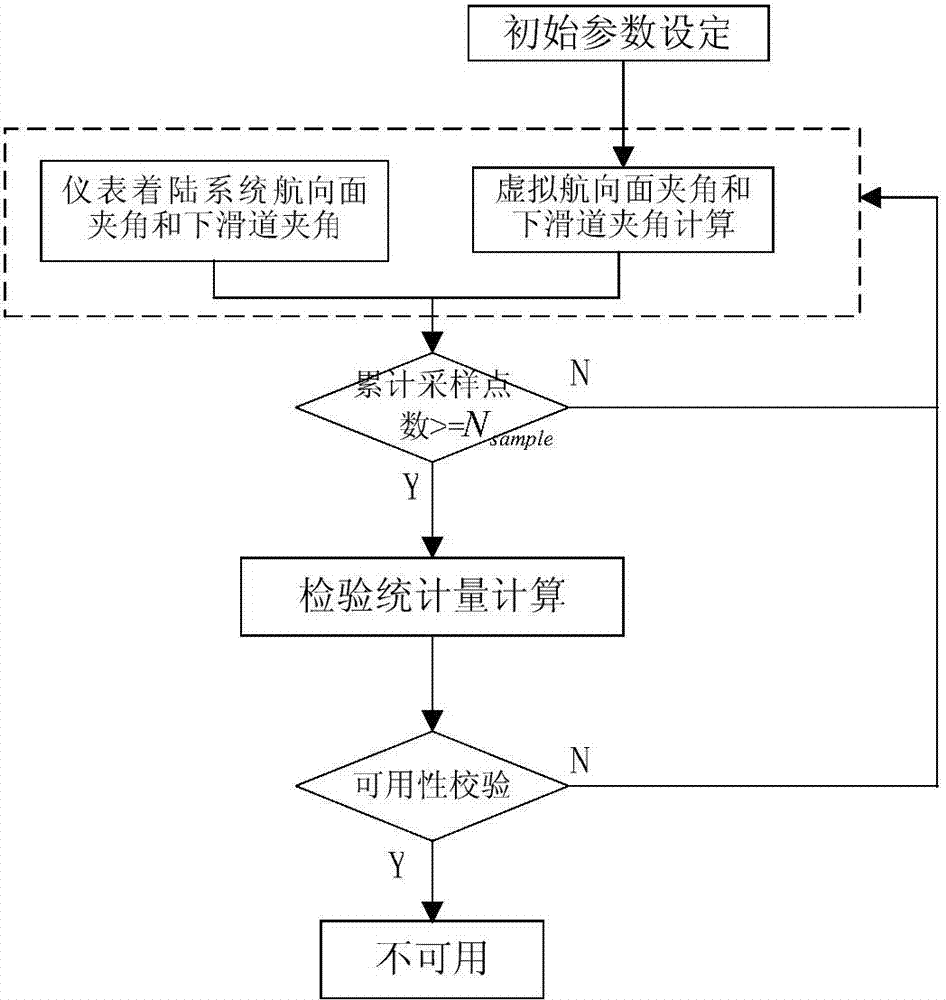
InactiveCN104501834AImprove verification efficiencyImprove practicalityMeasurement devicesSynthetic vision systemWeakness
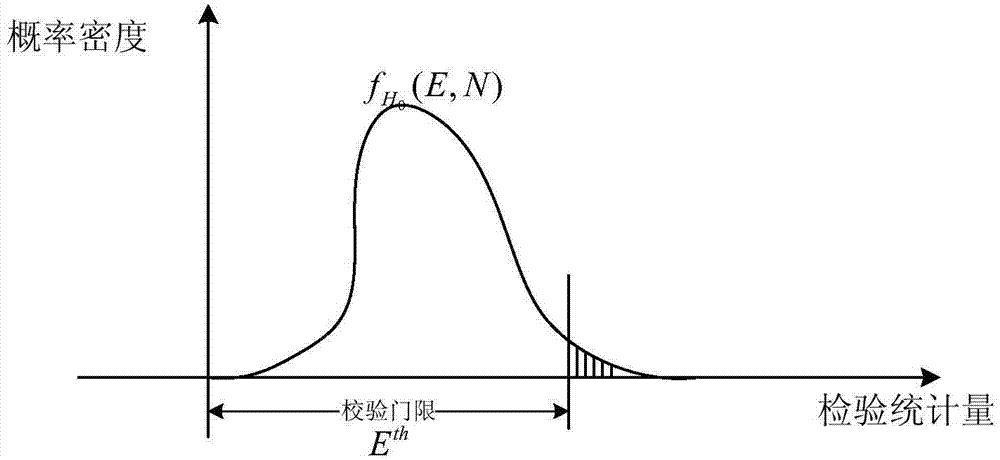
The invention discloses a synthetic vision system calibration method based on an airborne instrument landing device. The method comprises the following steps: calibrating a synthetic vision system at an approach stage by adopting spatial angle information given by an instrument landing system as a reference system; determining a calibration sampling time, calibrating a single-time sampling number, and calibrating the threshold; acquiring a course surface included angle and a lower slide-way angle obtained by the synthetic vision and instrument landing system in real time in the approach process; calculating calibration statistics by adopting the acquired included angle data; carrying out the availability calibration for the synthetic vision system by utilizing the calculated calibration statistics. By adopting the method, the weakness of the traditional method for calibrating the airport characteristic synthetic vision display availability can be overcome, the capacity for calibrating the altitude or angle information situation of the synthetic vision system can be improved, and the calibration efficiency for the updating of the synthetic vision caused by little change of the altitude of an airplane in the calibration process can be improved; the practicability of the synthetic vision system at the approach stage can be effectively improved, and the security of the low altitude flight can be improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Obstacle alarm implementing method of synthetic vision system
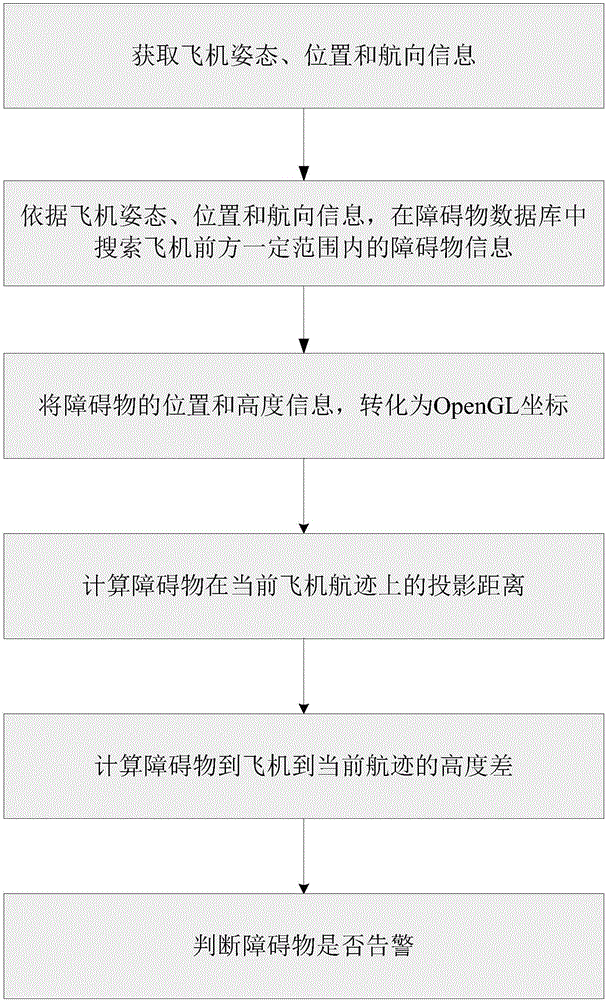
ActiveCN106741985AClear perceptionPerceive as early as possibleAircraft componentsSynthetic vision systemHeight difference
The invention provides an obstacle alarm implementing method of a synthetic vision system. The flying attitude, position and speed of an airplane are acquired through sensors on the airplane, obstacle information within the set range of the airplane is searched for, the sought obstacle information is converted into three-dimensional scene coordinates, and the three-dimensional scene coordinates are transmitted to a three-dimensional scene display system on the airplane. The distance between an obstacle and the current airplane is calculated according to the position, speed and attitude of the airplane, the height difference between the obstacle and the current airplane track position is calculated, whether it is needed to give an alarm about the obstacle is judged according to the defined alarm range value, the obstacle is drawn at the corresponding position according to the alarm information, and therefore a pilot can clearly perceive obstacle alarm information on a visual scene display system. The pilot can accurately and clearly perceive the obstacle alarm information on the visual scene display system as soon as possible to avoid the obstacle as soon as possible, the workload of the pilot is reduced, and the flying quality and safety are improved.
Owner:LUOYANG INST OF ELECTRO OPTICAL EQUIP OF AVIC
Aircraft synthetic vision systems utilizing data from local area augmentation systems, and methods for operating such aircraft synthetic vision systems
ActiveUS20160282120A1Navigational calculation instrumentsSatellite radio beaconingGeographic siteSynthetic vision system
An aircraft synthetic vision display system (SVS) includes a topographical database including topographical information relating to an airport, a global positioning system receiver that receives a satellite signal from a global positioning satellite to determine a geographical position of the aircraft, and a ground-based augmentation system receiver that receives a ground-based signal from a ground-based transmitter associated with the airport, wherein the ground-based signal includes geographical information associated with the airport. The SVS further includes a computer processor that retrieves the topographical information from the topographical database based on the geographical position of the aircraft, that retrieves the geographical information associated with the airport, and that corrects the topographical information using the geographical information associated with the airport to generate corrected topographical information. Still further, the SVS includes a display device that renders three-dimensional synthetic imagery of environs of the aircraft based on the corrected topographical information.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method for producing sensor-supported, synthetic vision for landing support of helicopters under brown-out or white-out conditions
ActiveUS8803727B2Electromagnetic wave reradiationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionElectricitySynthetic vision system
Owner:HENSOLDT SENSORS GMBH
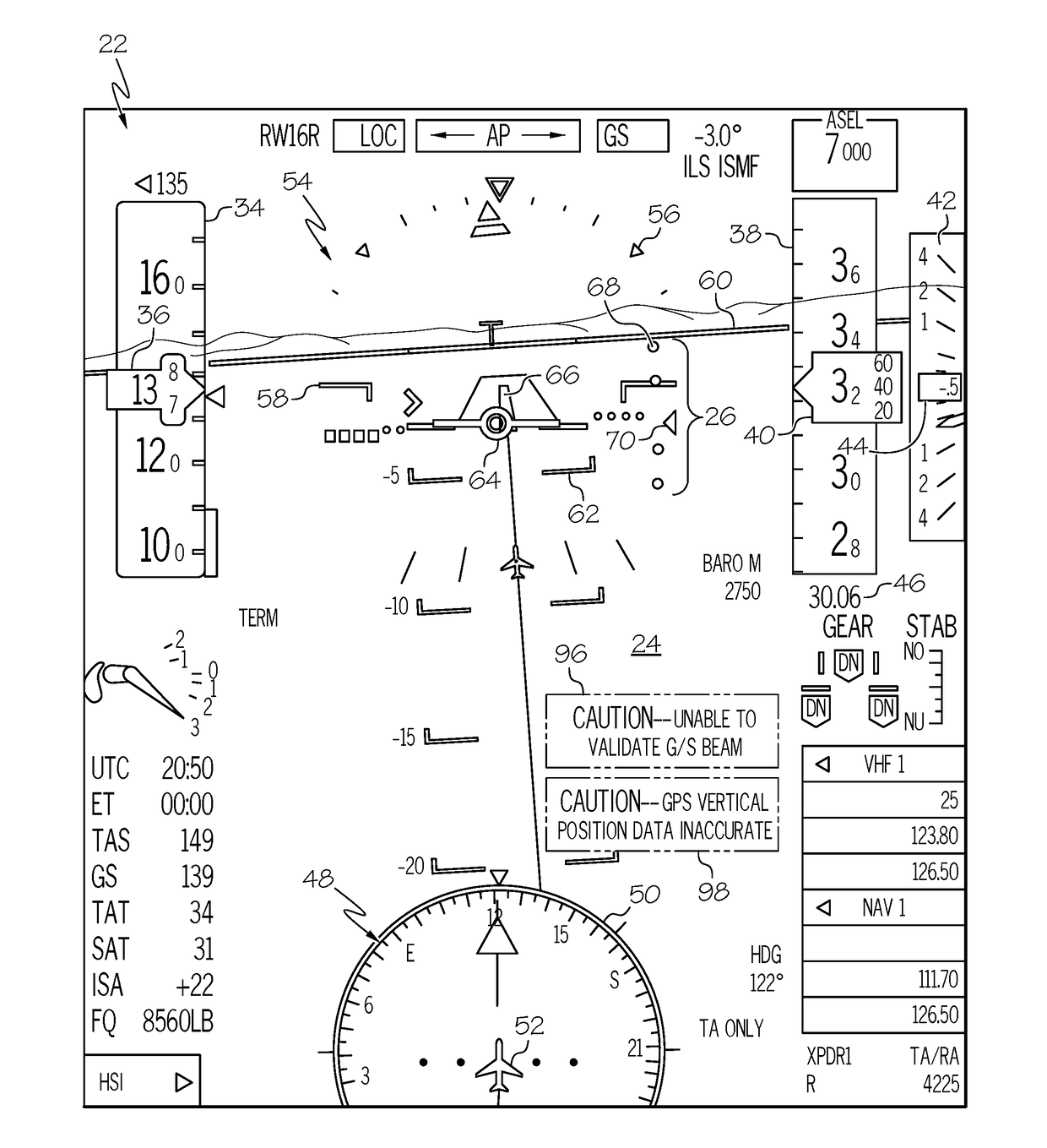
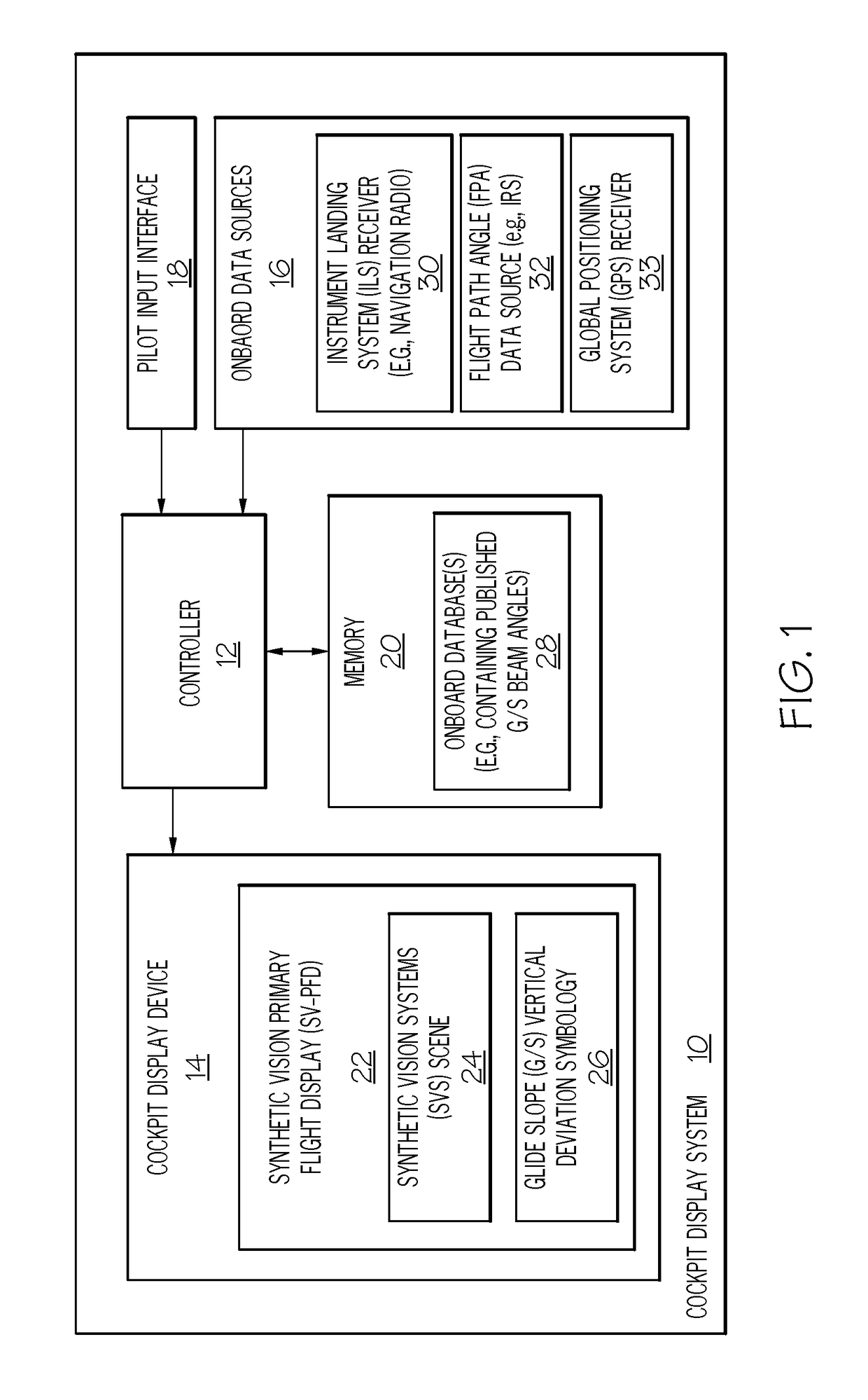
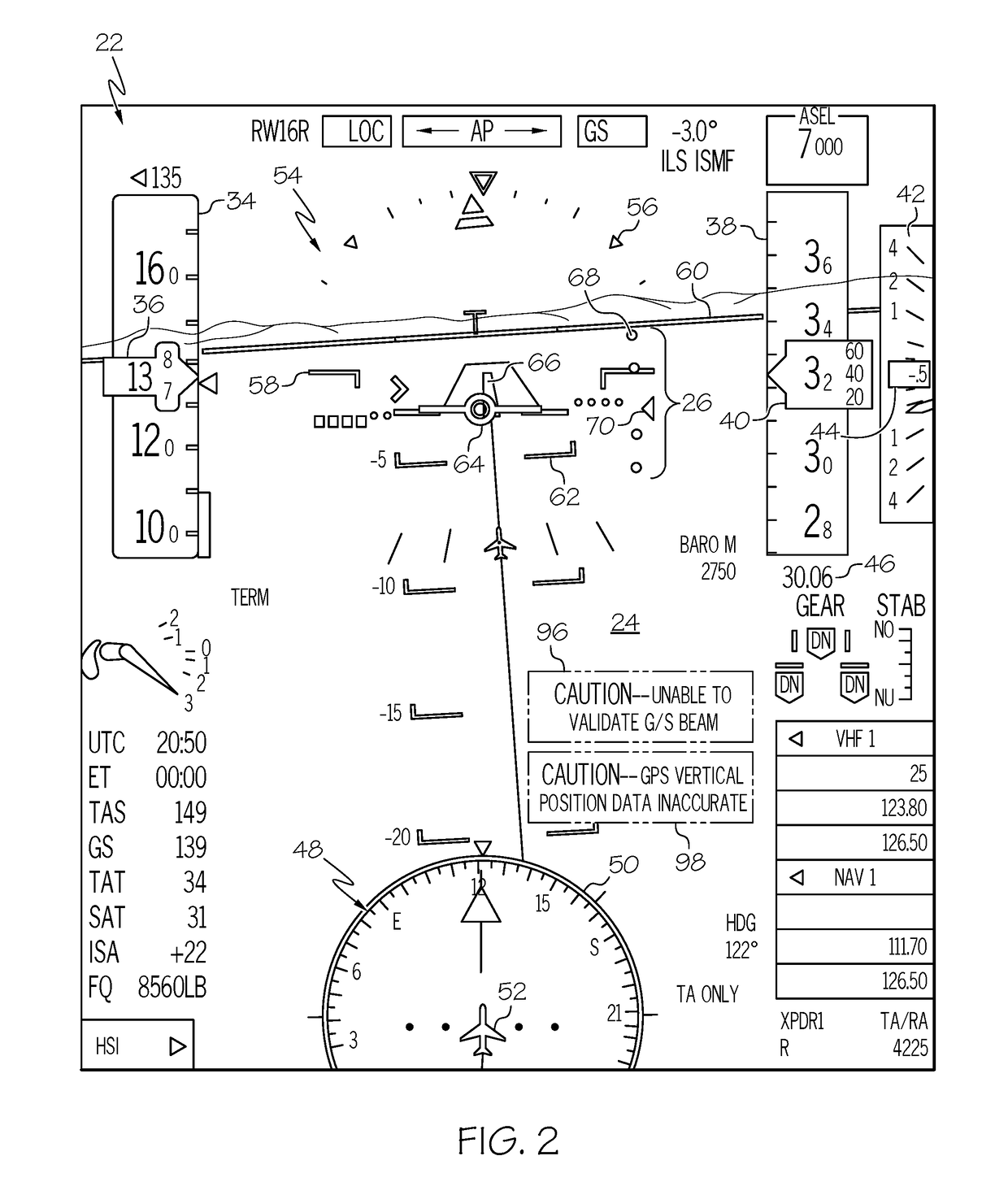
Cockpit display systems and methods for performing glide slope validation processes during instrument landing system approaches
ActiveUS20180238708A1Reduce gapProgramme controlAircraft landing aidsViewpointsSynthetic vision system
Cockpit display systems and methods are provided for performing Glide Slope (G / S) validation processes during Instrument Landing System (ILS) approaches. In one embodiment, the cockpit display system utilizes validated G / S signals to selectively correct the viewpoint of a Synthetic Vision System (SVS) scene generated on a Synthetic Vision Primary Flight Display (SV-FPD). In such an embodiment, the cockpit display system may include an ILS receiver, a cockpit display device on which the SV-PFD is generated, and a controller operably coupled to the cockpit display device and to the ILS receiver. During an ILS approach, the controller selectively performs a G / S validation algorithm to determine the validity of the G / S signals received during the ILS approach. If determining that the G / S signals are valid, the controller then repeatedly updates the SVS viewpoint during the ILS approach based, at least in part, on the validated G / S signals.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
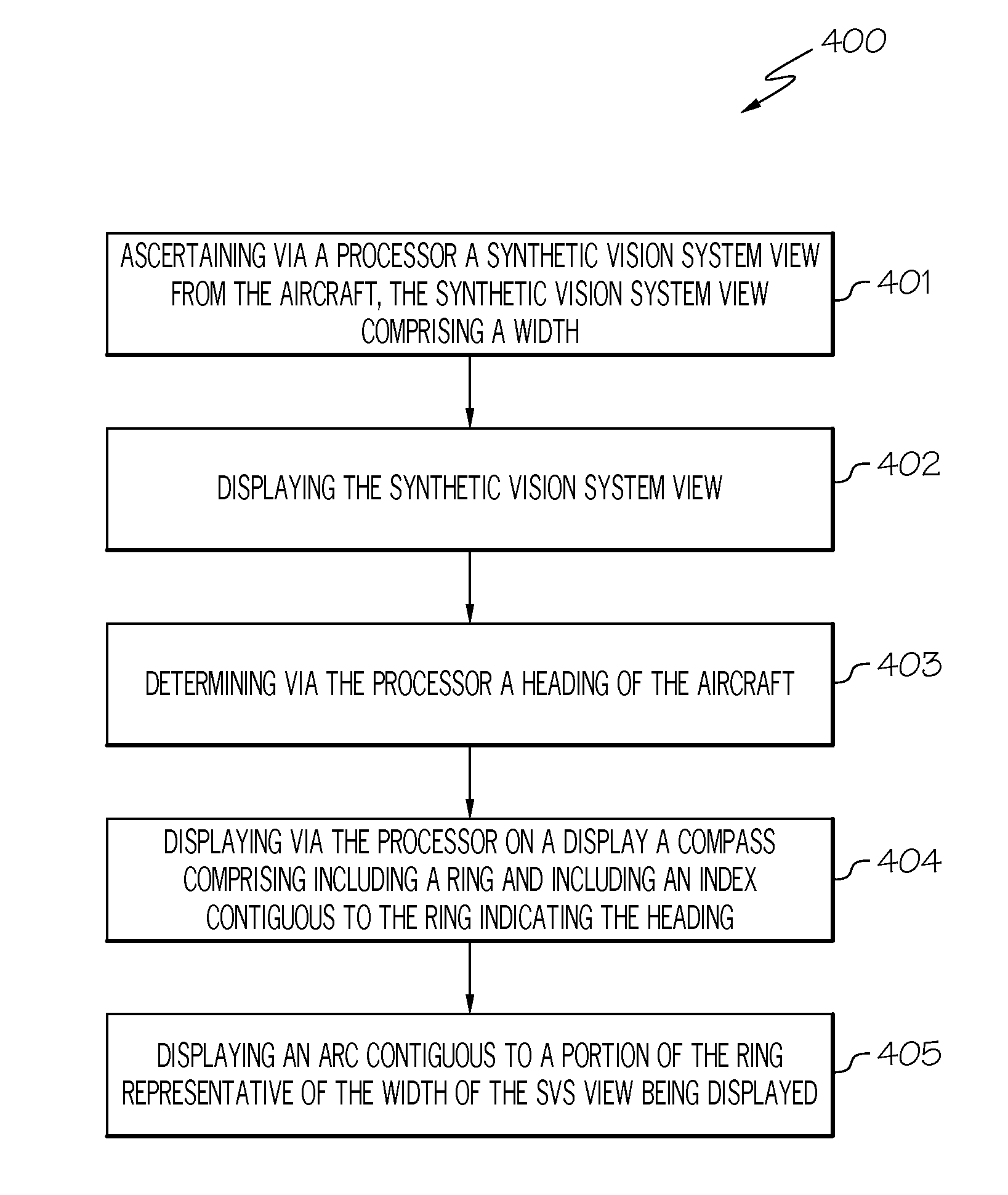
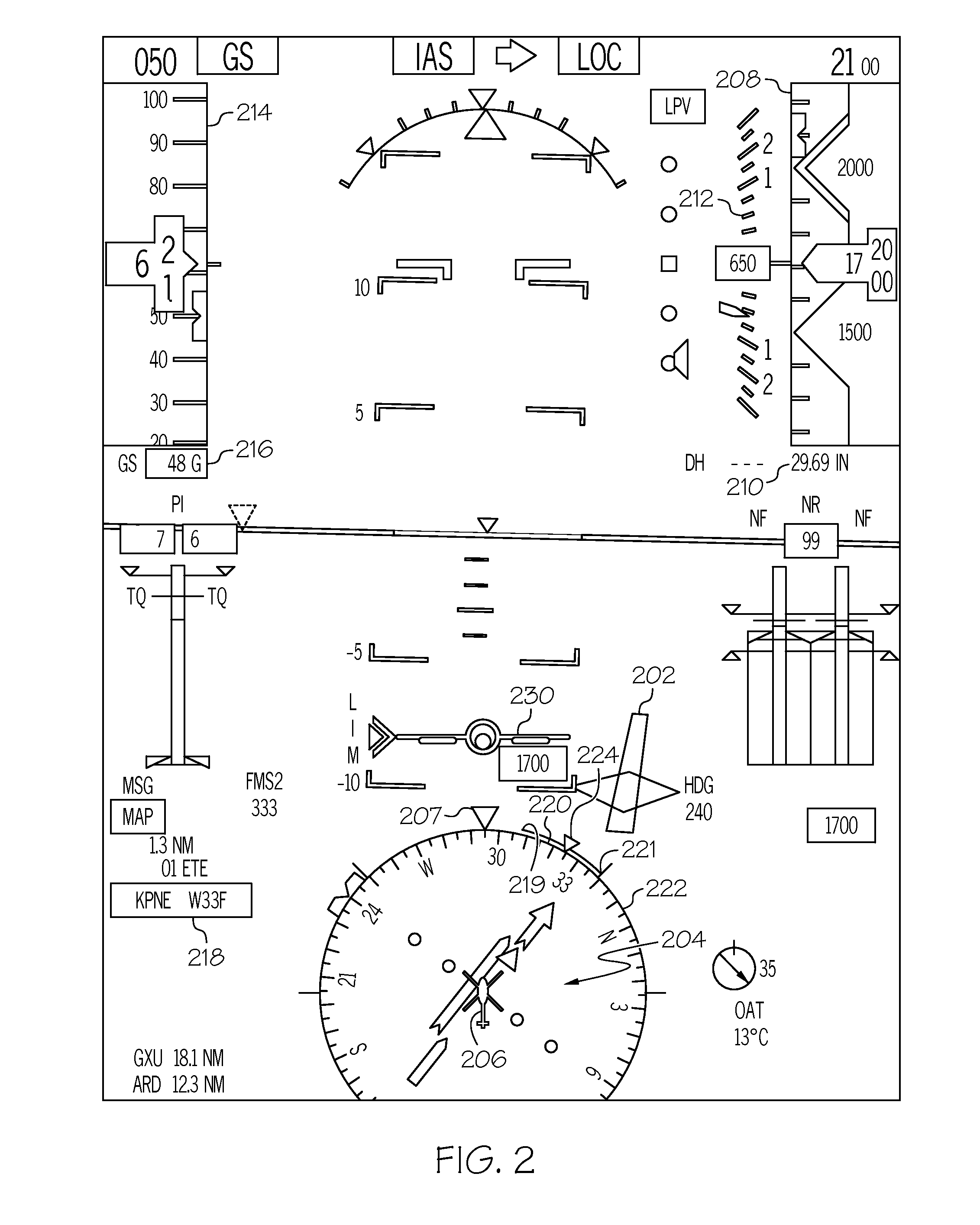
Apparatus and method for displaying a synthetic vision system view direction
ActiveUS20160209233A1Navigation instrumentsPosition/course control in three dimensionsSynthetic vision systemViewing frustum
A system and method displays a synthetic vision system (SVS) image combined with a primary flight display (PFD) including a compass indicating the aircraft heading. An arc on or near the outer edge of the compass indicates the viewing frustum of the SVS view.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
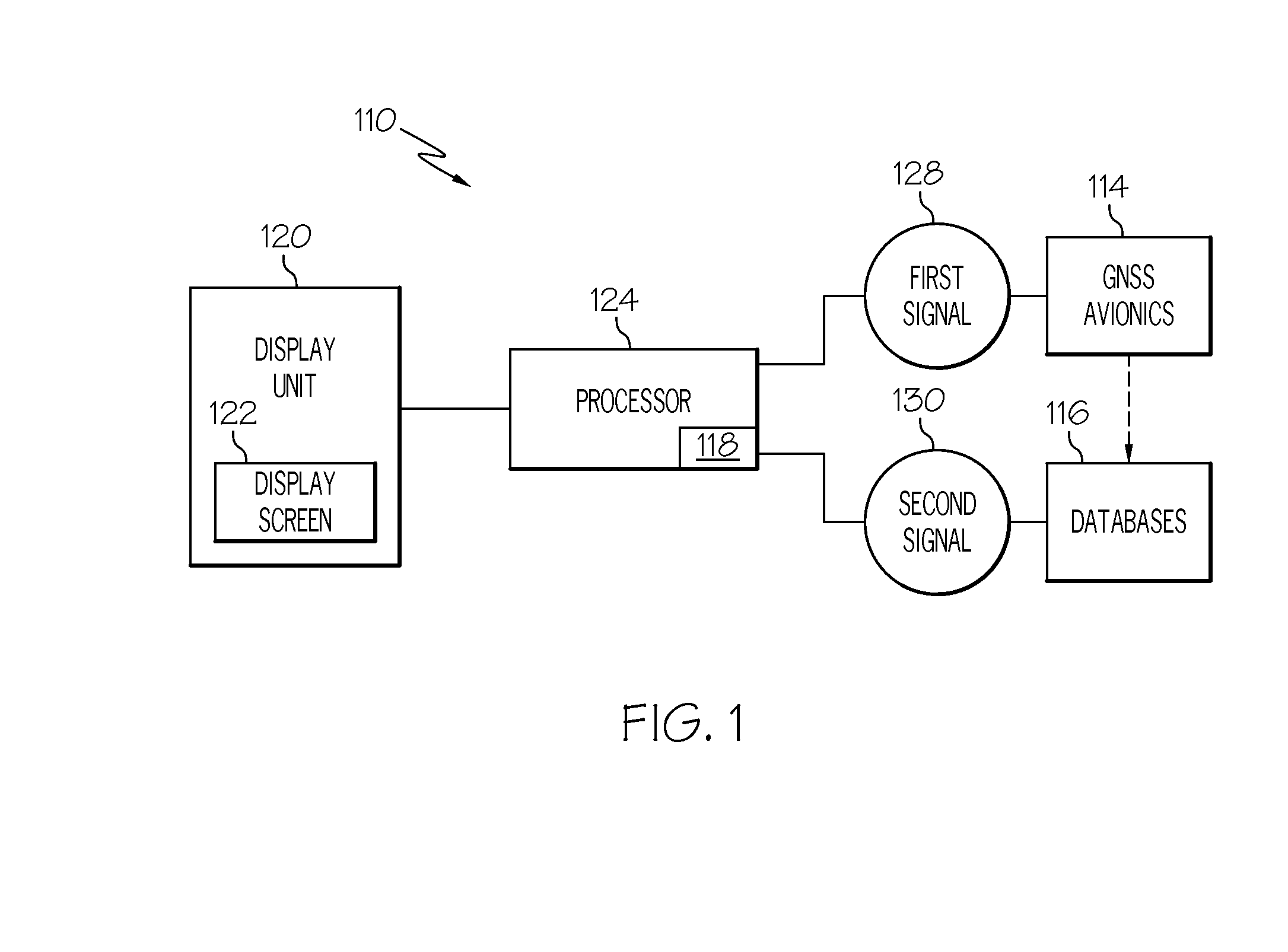
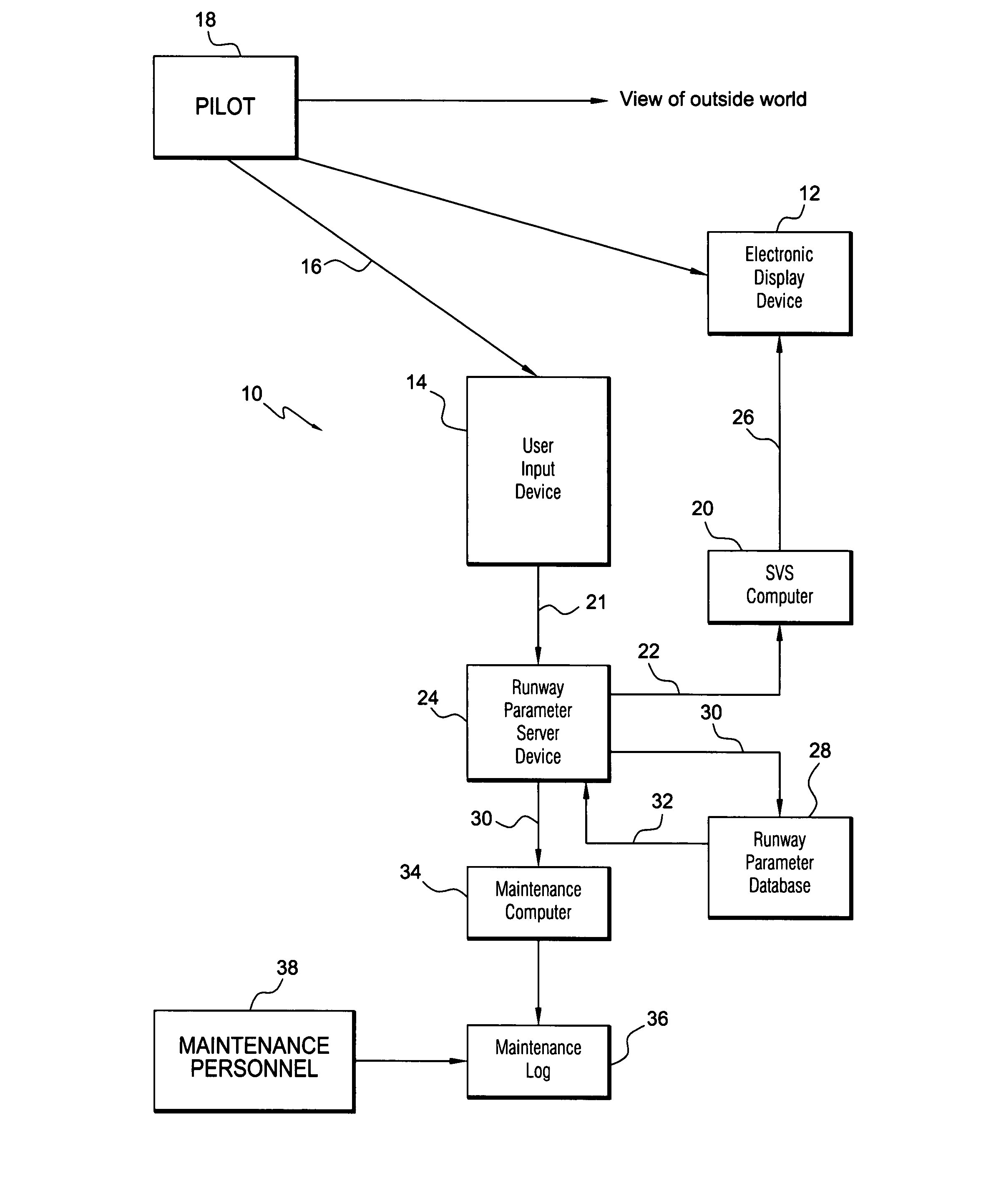
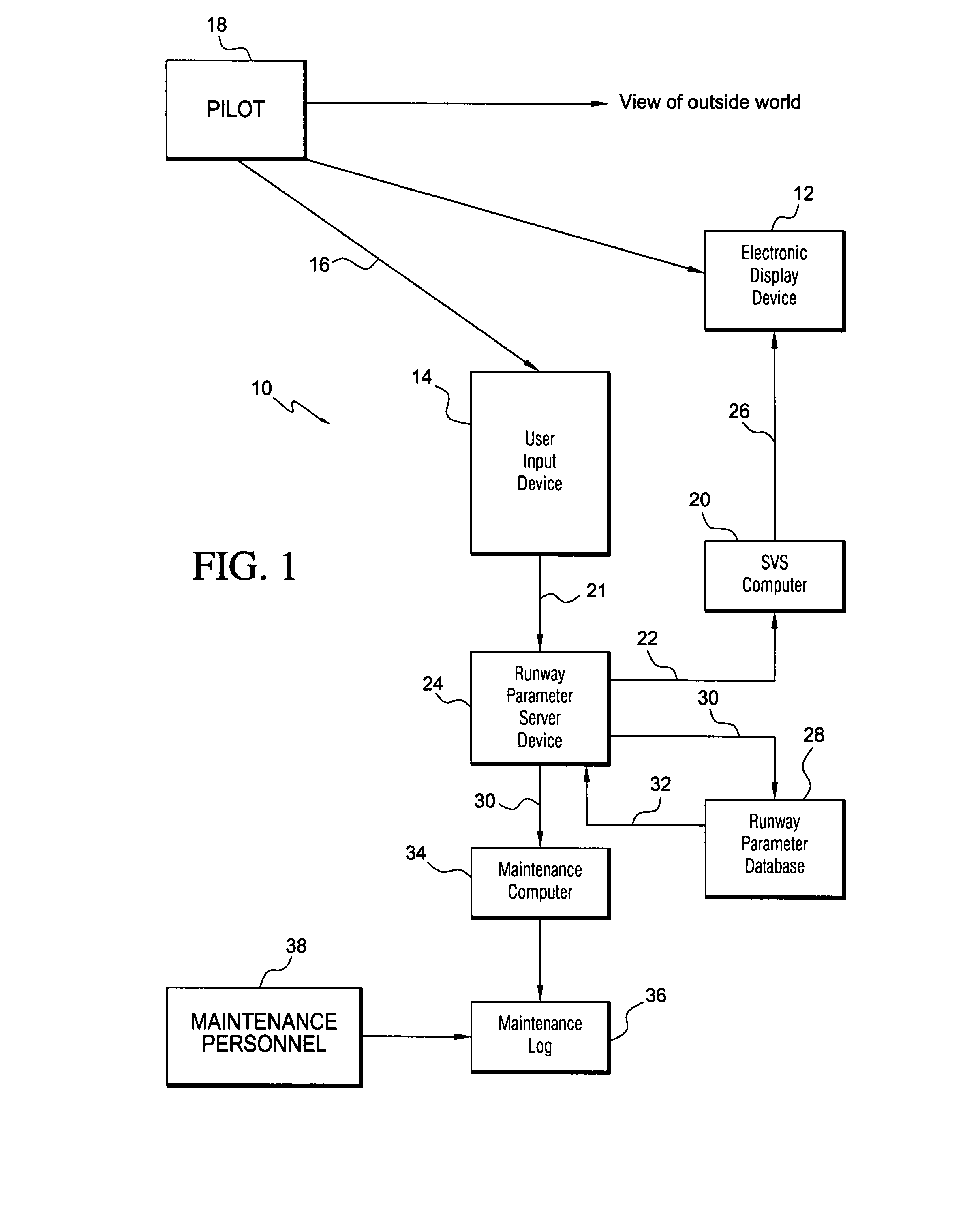
Synthetic vision runway corrective update system
ActiveUS7924172B1Enhanced runway environment informationNavigation instrumentsAlarmsSynthetic vision systemUser input
A synthetic vision system (SVS) for an aircraft, including a user input device for receiving runway correction commands from a user. The runway correction commands are in response to discrepancies observed by the user between an observed runway position in the real world and a synthetic vision runway position depicted on an electronic display device. The user input device provides runway corrections. An SVS computer is operatively connected to the electronic display device for providing SVS image data to the electronic display device in response to received runway parameter data. A runway parameter server device (RPSD) is operatively connected to the user input device and to the SVS computer for receiving the runway corrections from the user input device and providing the runway parameter data, including any corrected data provided by the user, to the SVS computer. A runway parameter database is operatively connected to the RPSD for receiving correction data from the RPSD and providing corrected data to the RPSD. The user input device provides the capability of stewing the synthetic vision runway position to the observed real-world runway position when the synthetic vision runway position is observed to be misaligned, the corrected data being subsequently used to provide enhanced runway environment information for taxi operations.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Synthetic vision systems and methods for displaying detached objects
ActiveUS9347793B2Instruments for road network navigationElectromagnetic wave reradiationGraphicsSynthetic vision system
A display system is provided for a vehicle. The display system includes a data source configured to provide terrain data with detached objects that are detached from ground terrain and attached objects that are attached to ground terrain; a processing unit coupled to the data source configured to receive the terrain data and to distinguish the detached objects from the attached objects to generate display commands for a three-dimensional view that comprises graphical elements representing both the detached objects and the attached objects; and a display device coupled to the processing unit and configured to receive the display commands and operable to render the common three-dimensional view to thereby allow viewing of the detached objects and the attached objects.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com