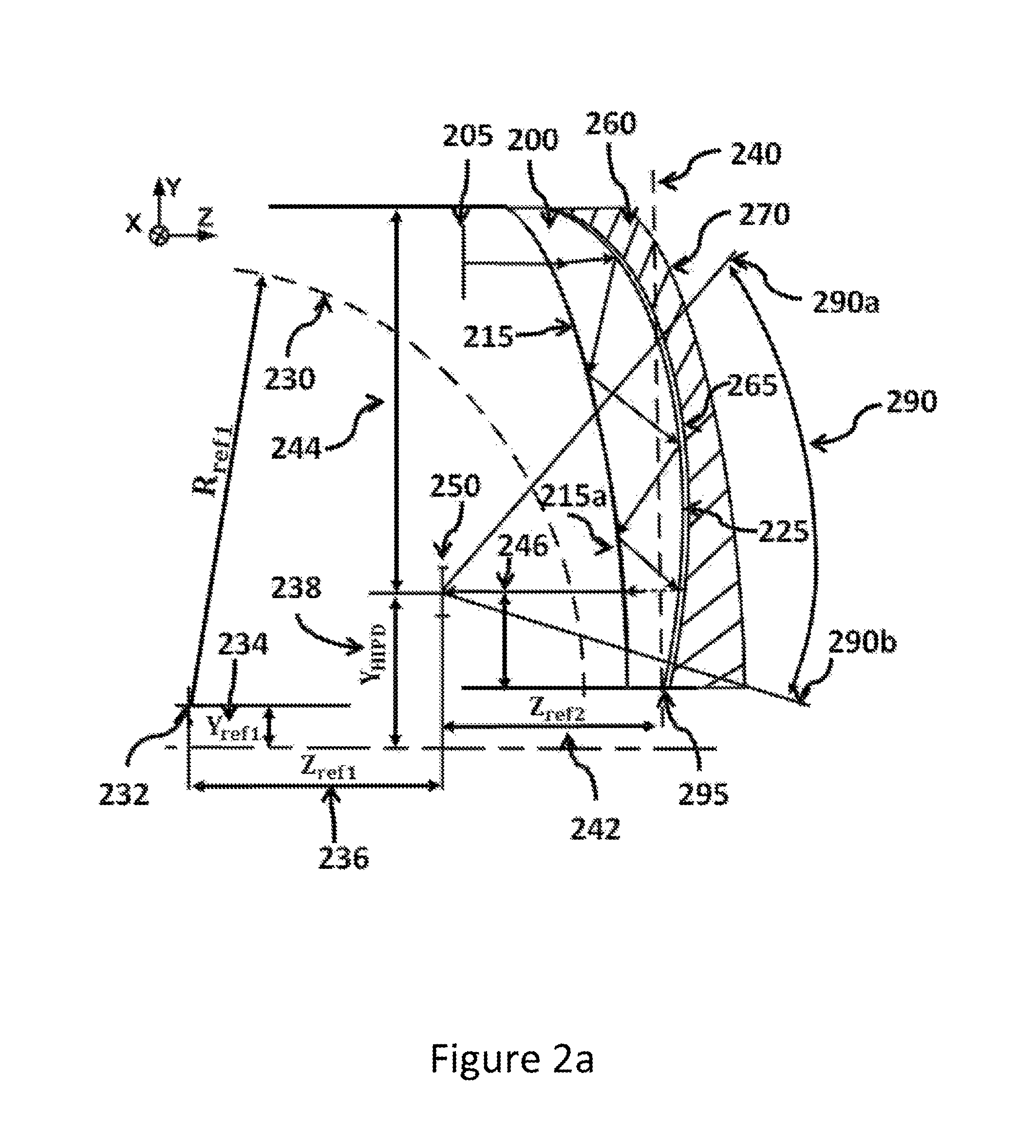
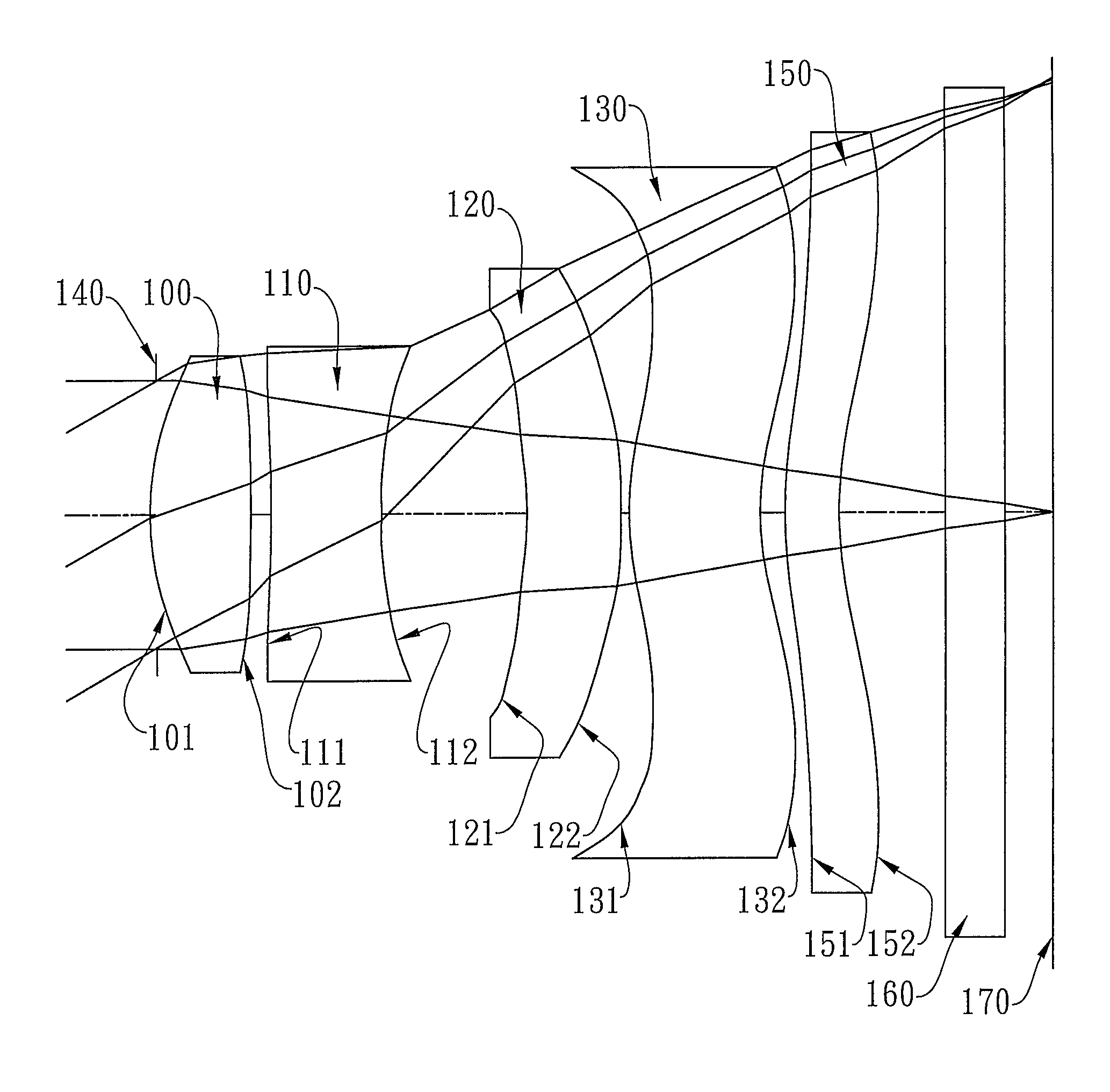
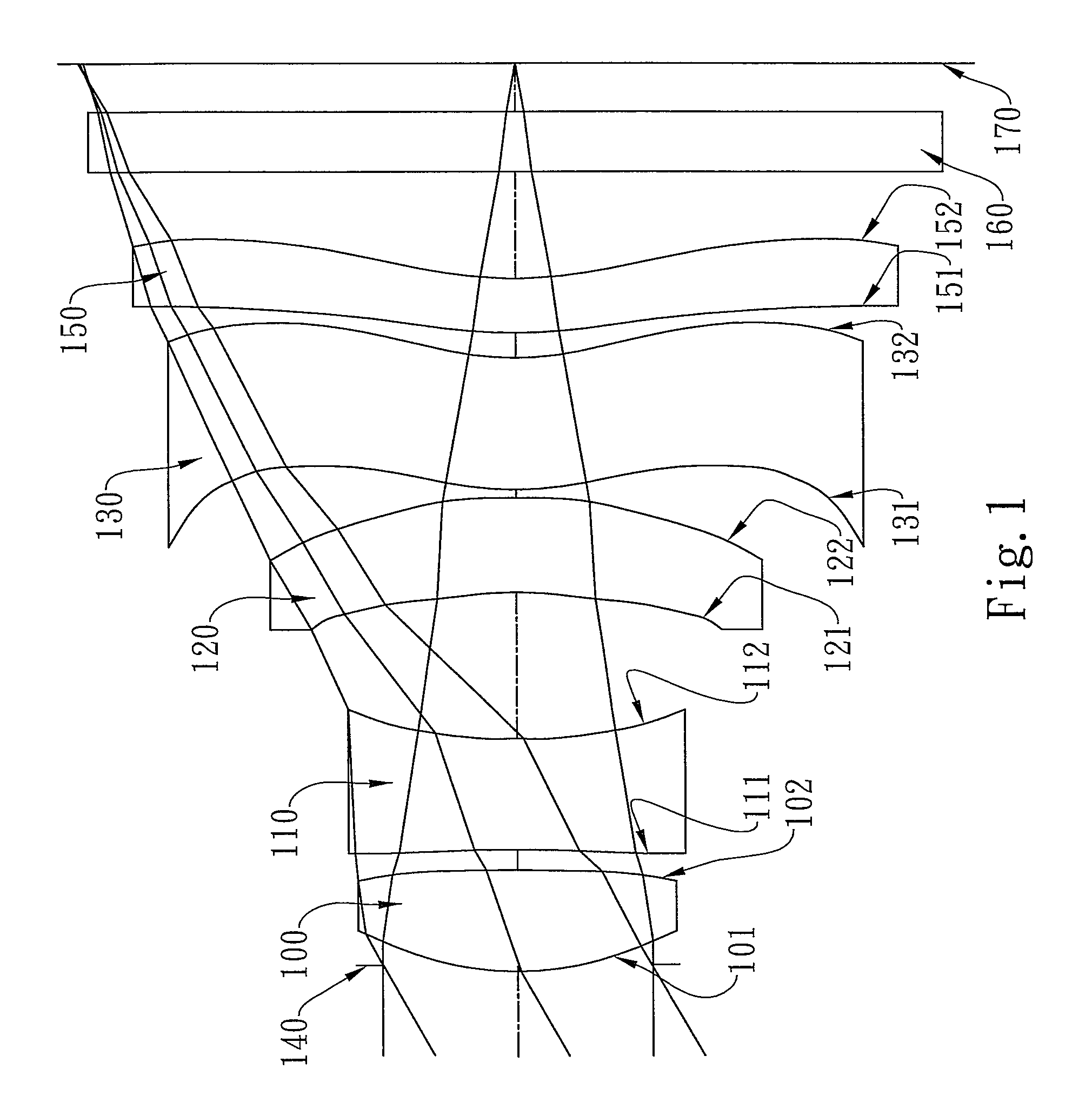
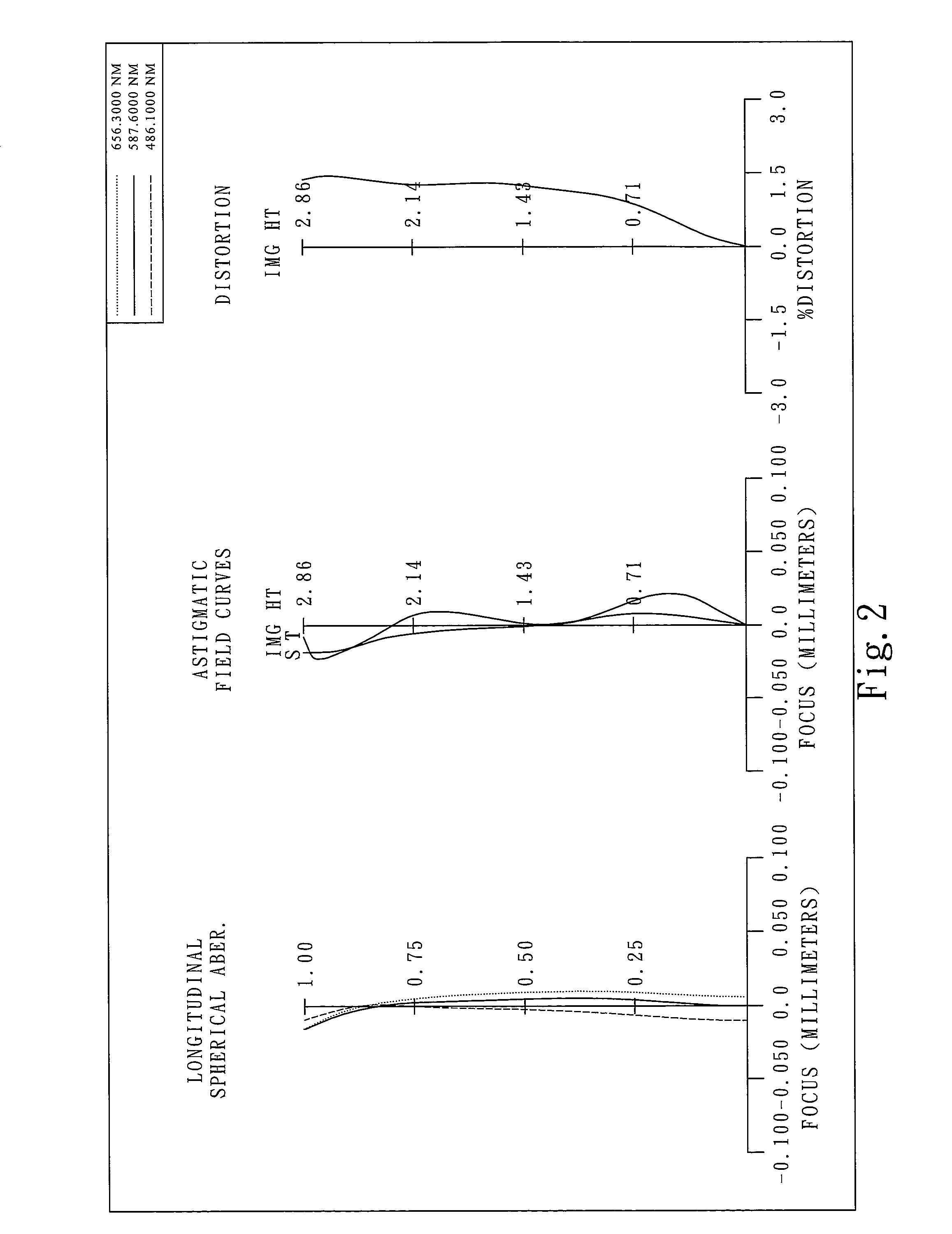
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
429results about How to "Wide field of view" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
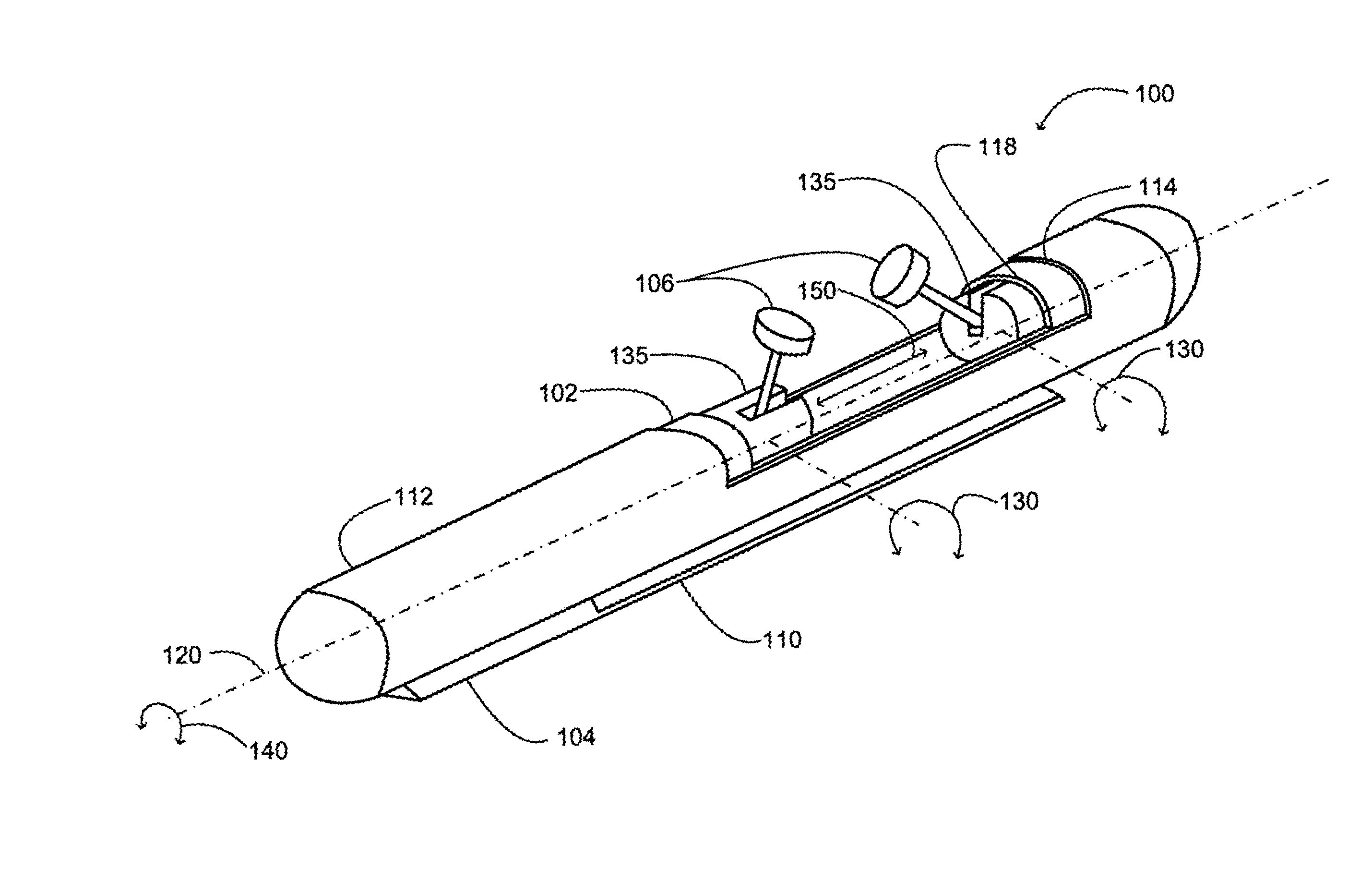
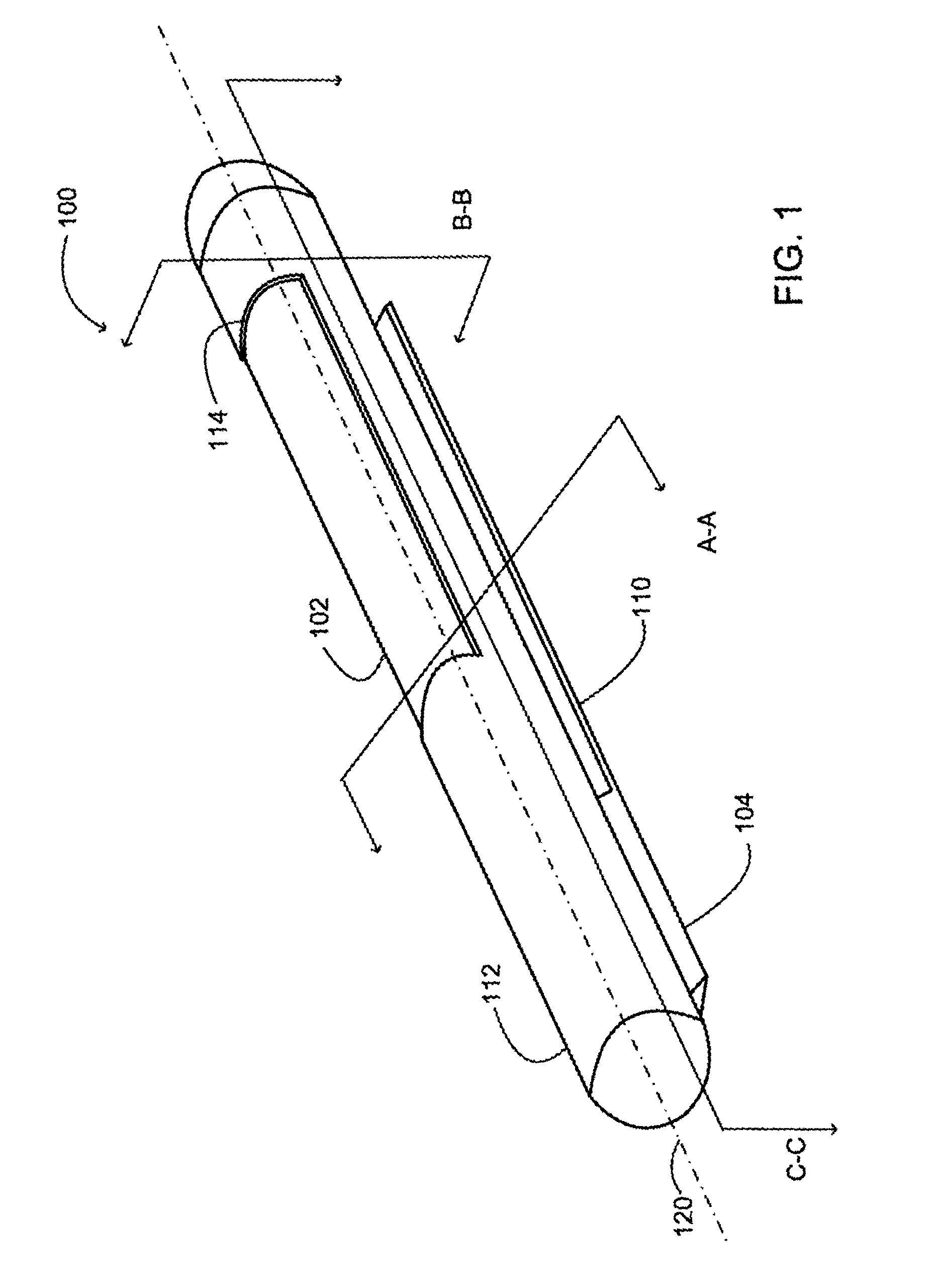
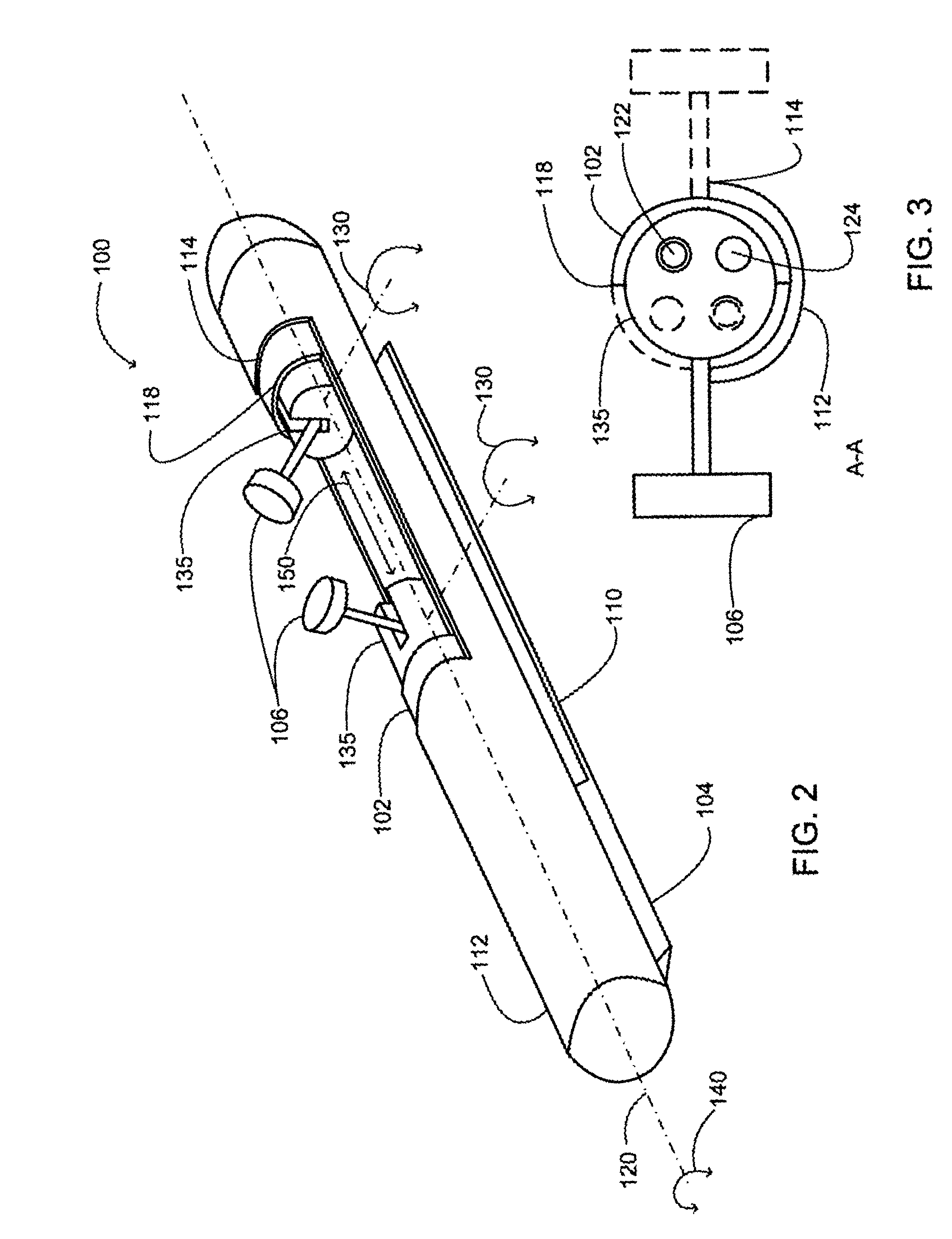
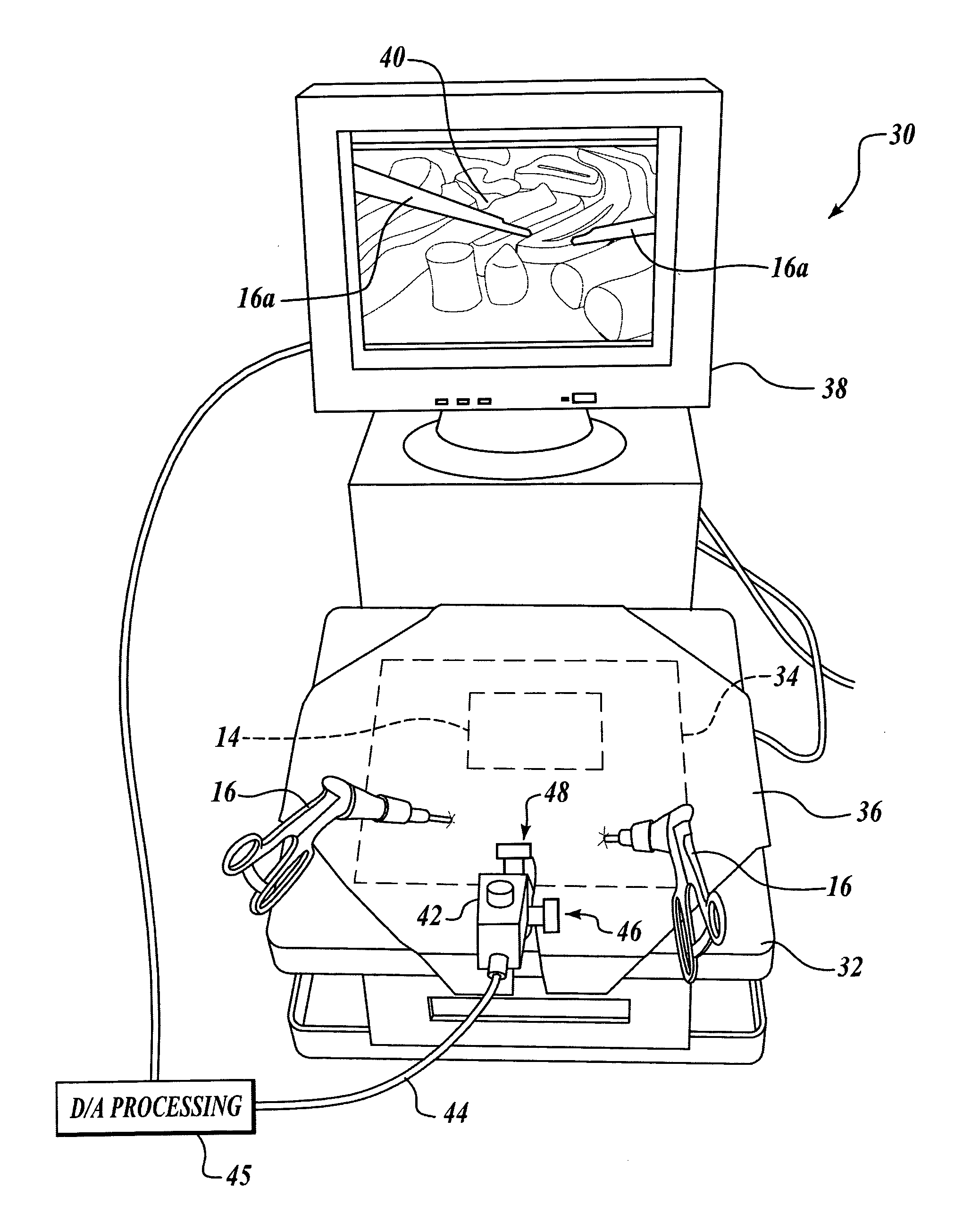
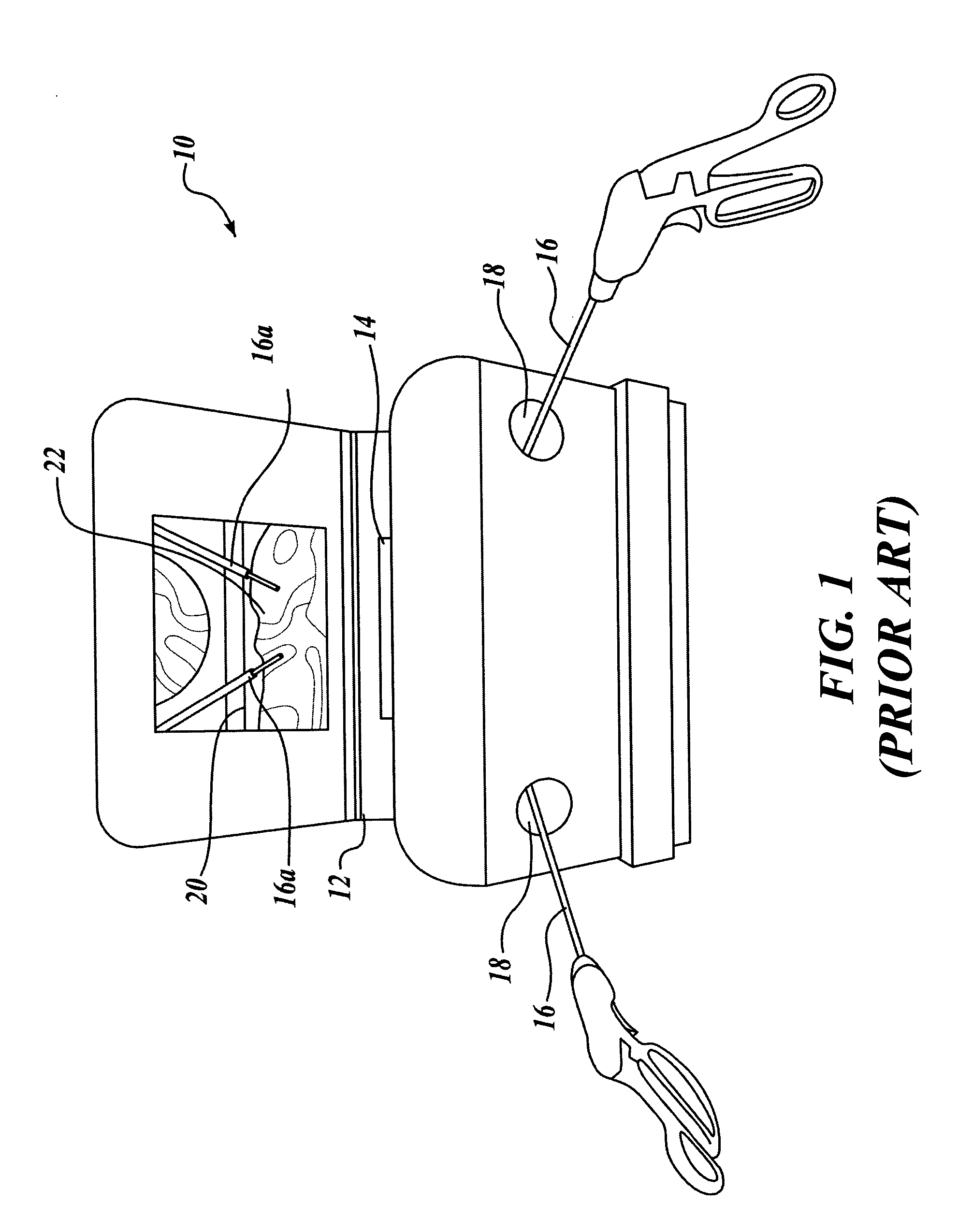
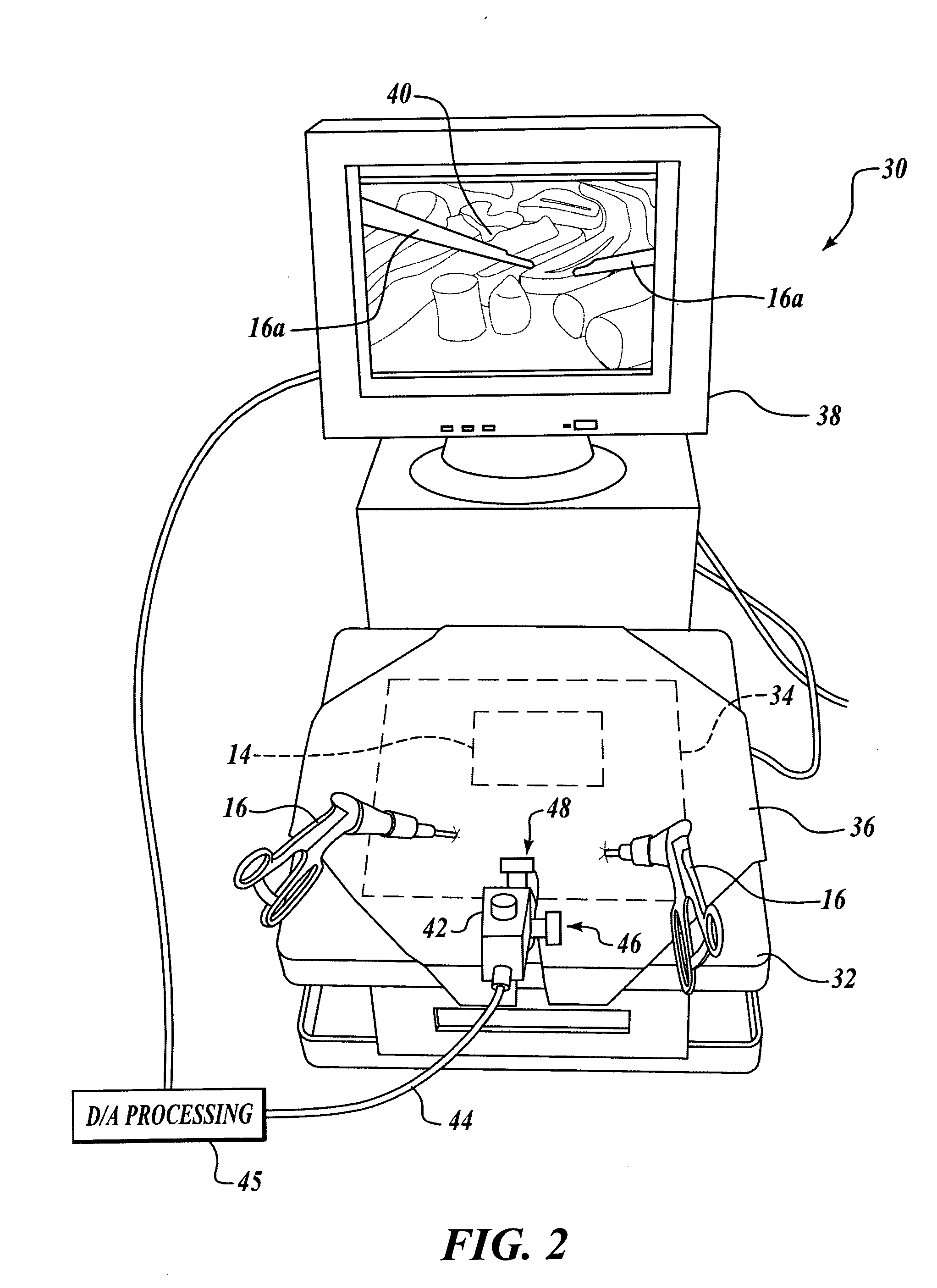
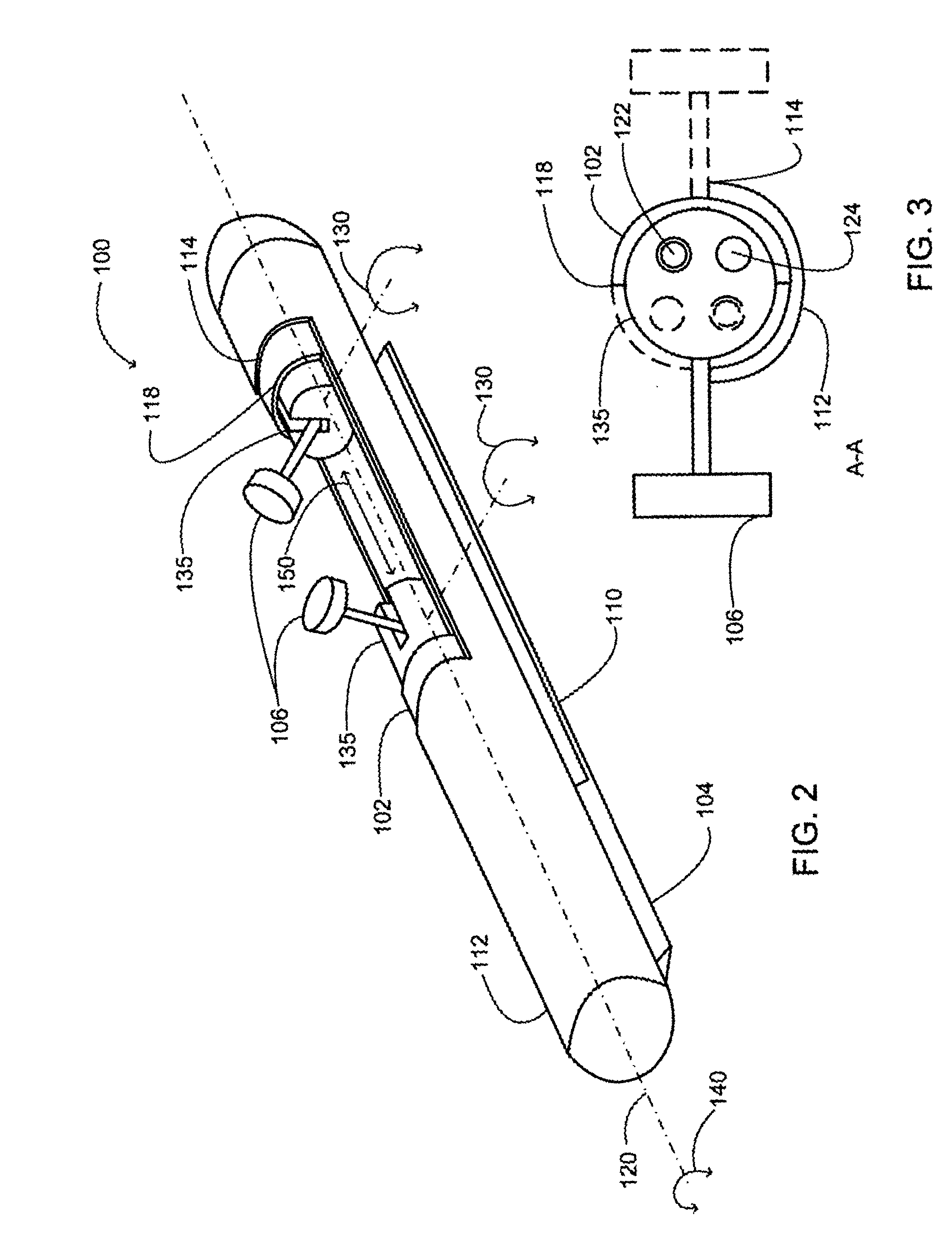
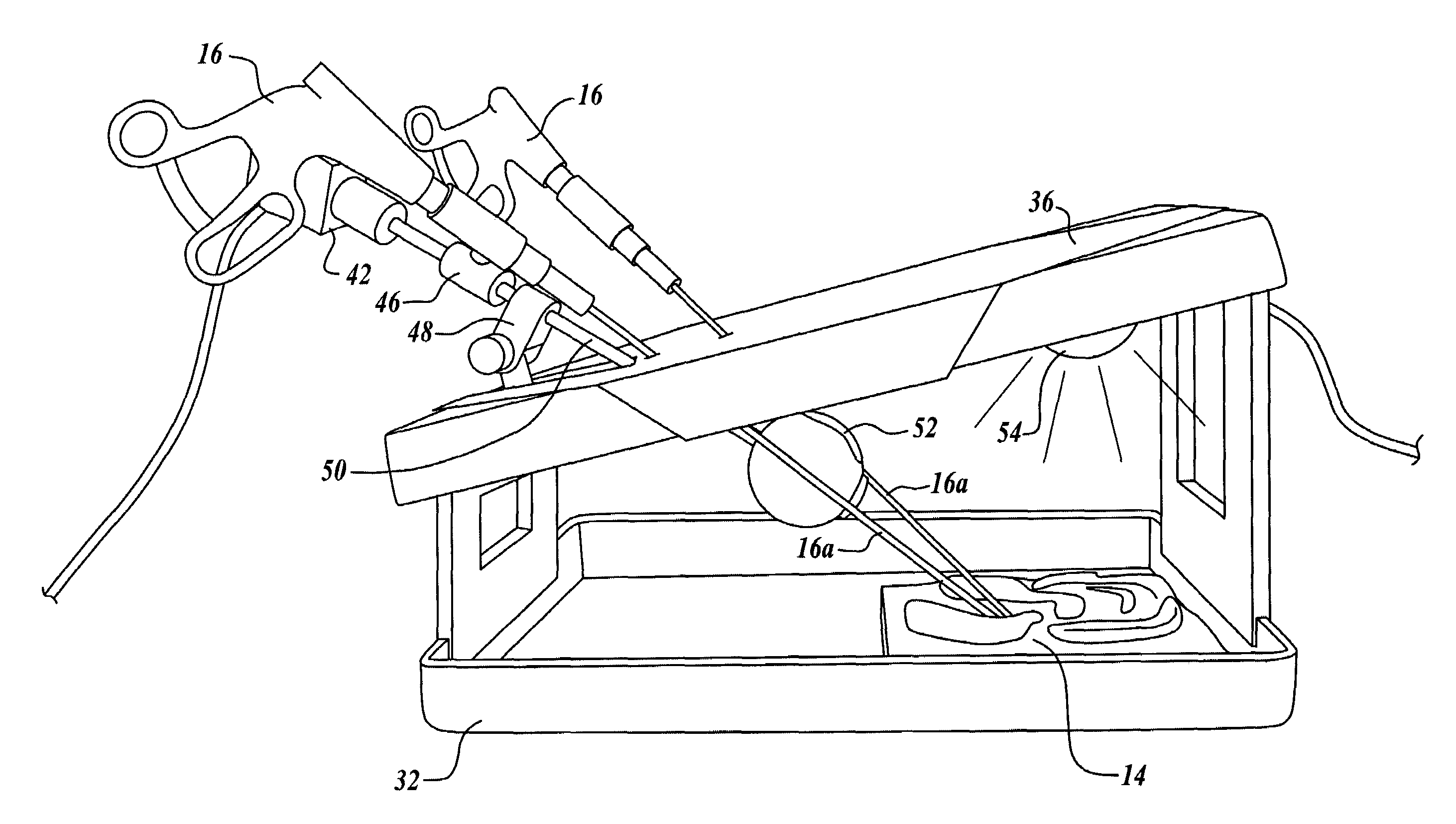
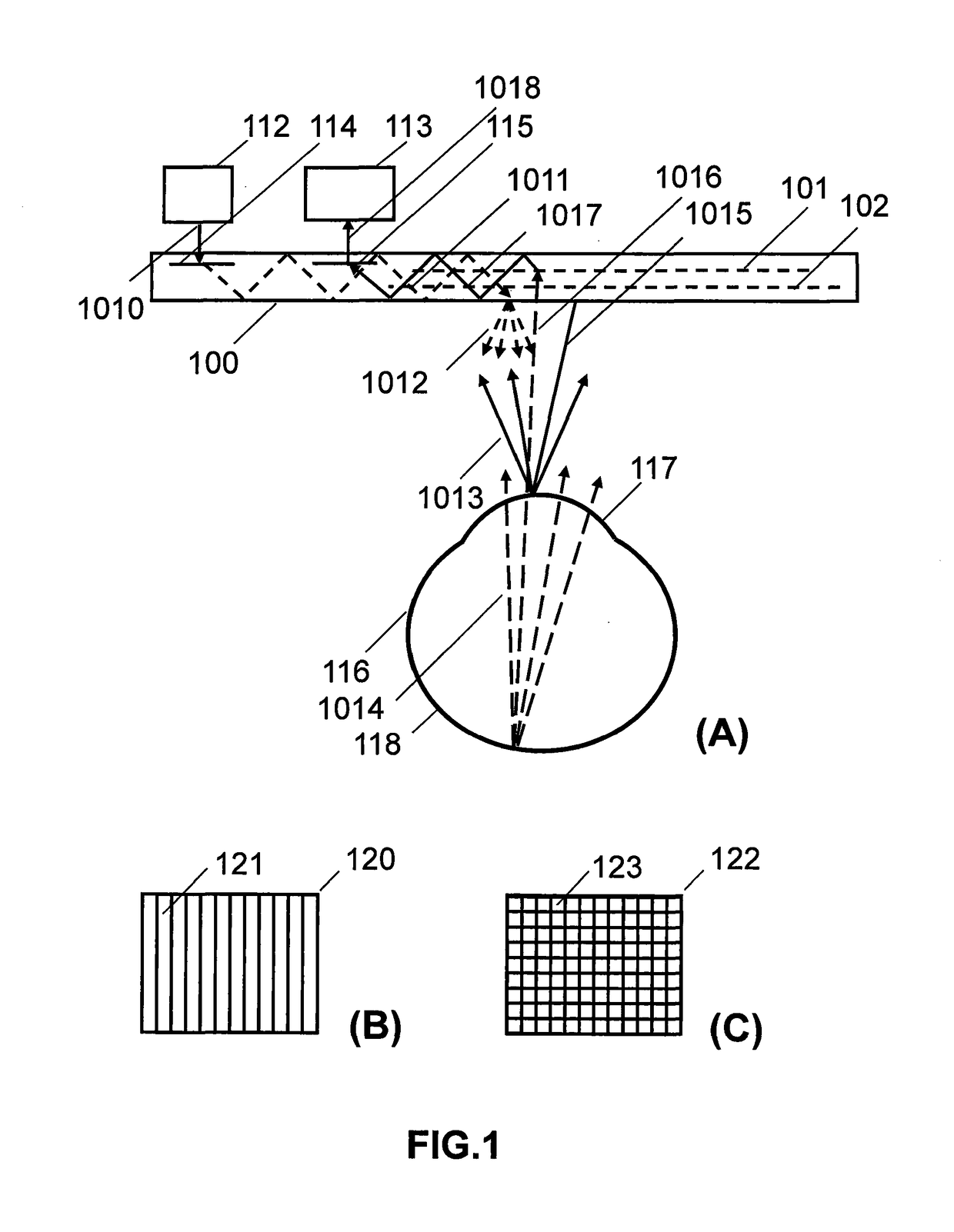
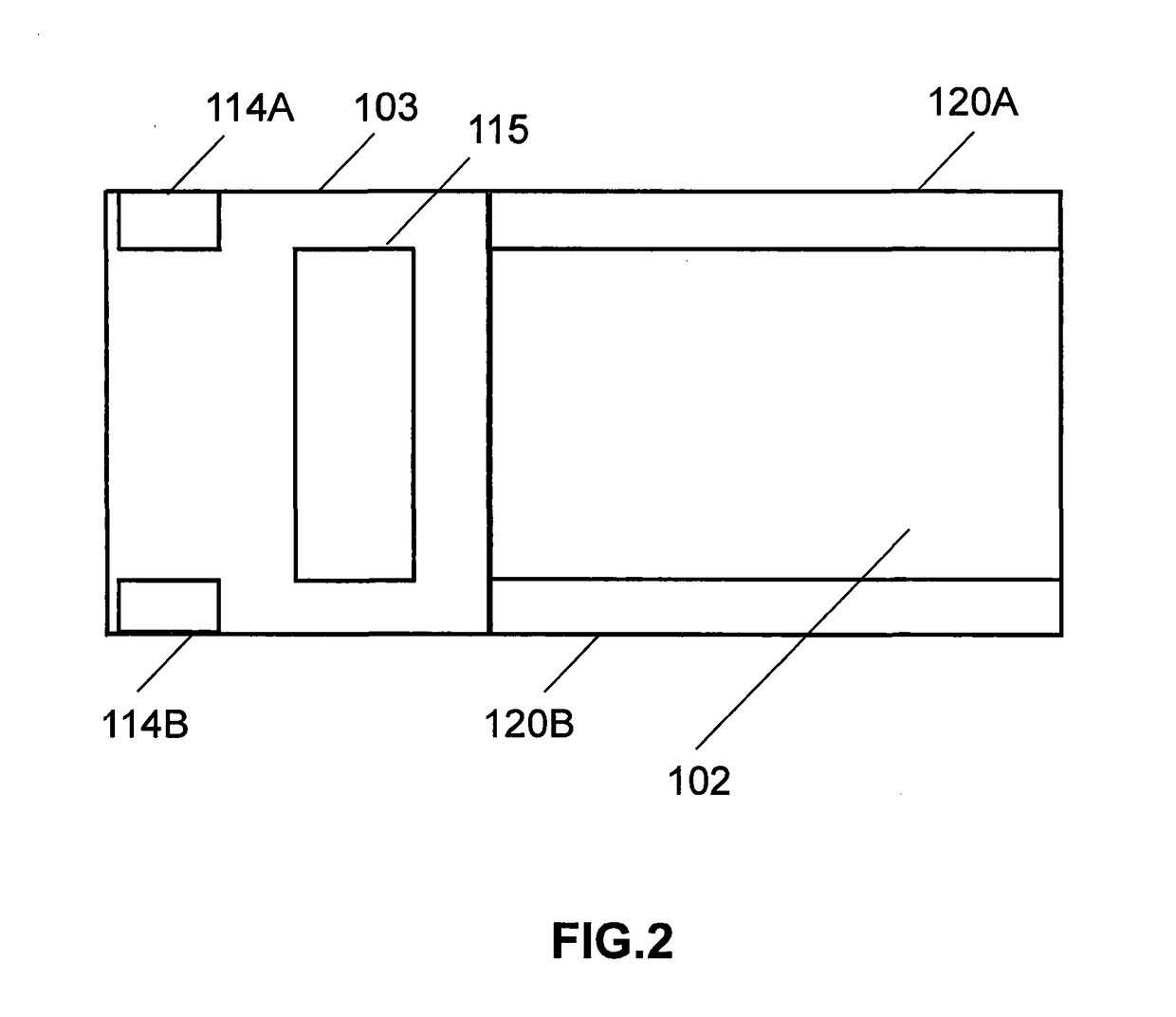
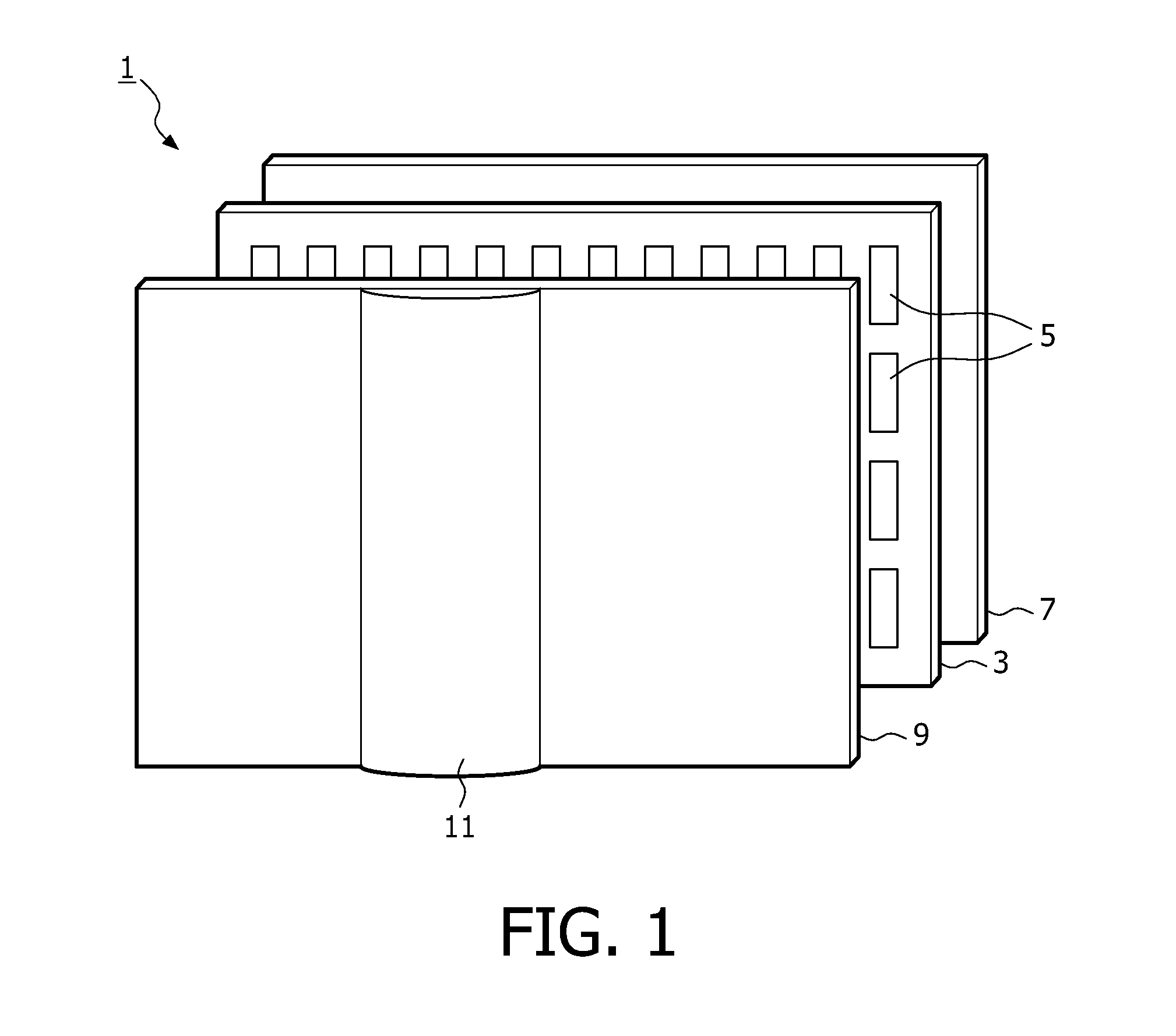
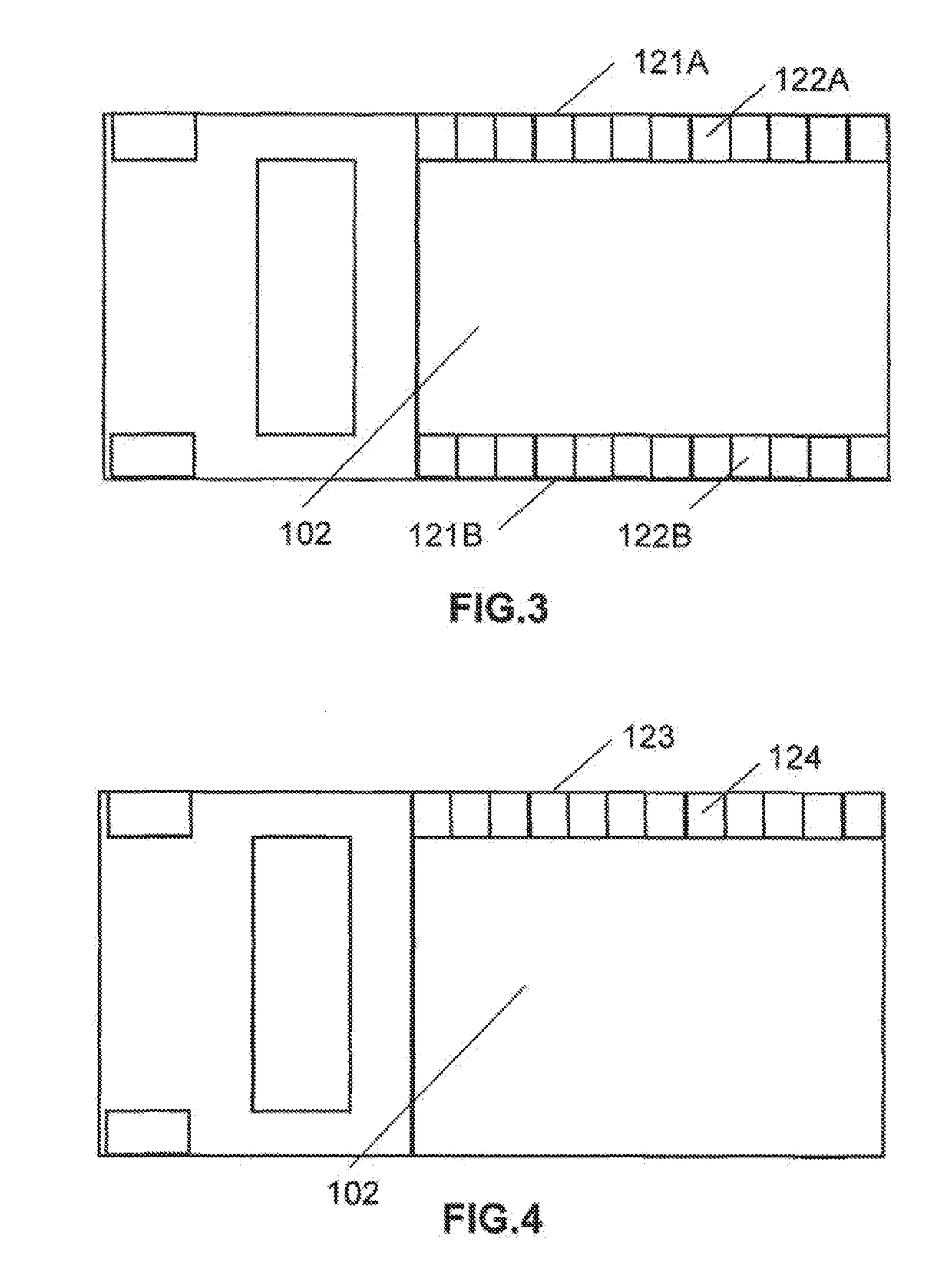
Insertable device and system for minimal access procedure
ActiveUS7066879B2Limited mobilityWide field of viewEndoscopesLaproscopesAbdominal cavityProcedure Indication
The present invention provides a system and single or multi-functional element device that can be inserted and temporarily placed or implanted into a structure having a lumen or hollow space, such as a subject's abdominal cavity to provide therewith access to the site of interest in connection with minimally invasive surgical procedures. The insertable device may be configured such that the functional elements have various degrees of freedom of movement with respect to orienting the functional elements or elements to provide access to the site from multiple and different orientations / perspectives as the procedure dictates, e.g., to provide multiple selectable views of the site, and may provide a stereoscopic view of the site of interest.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
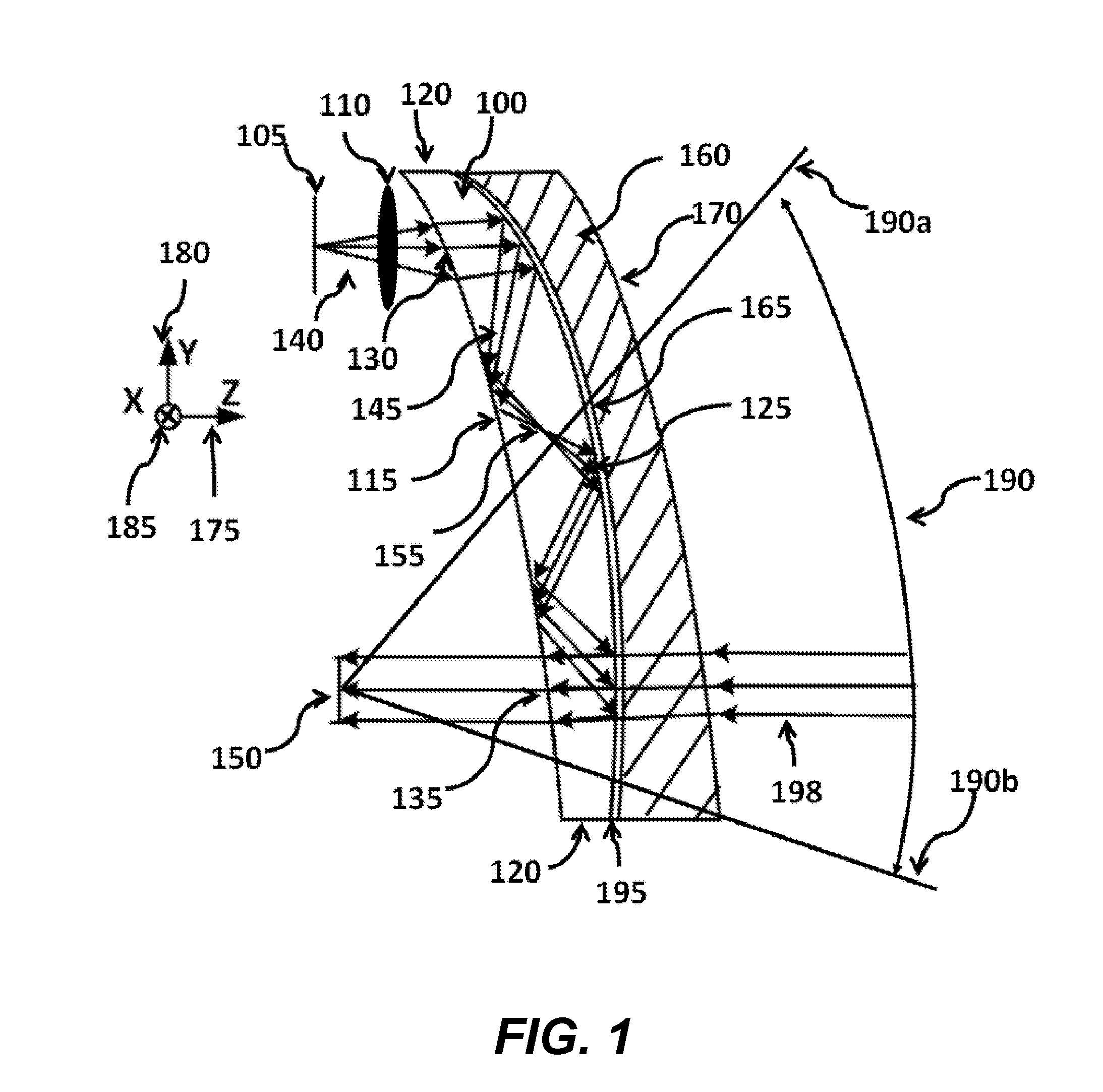
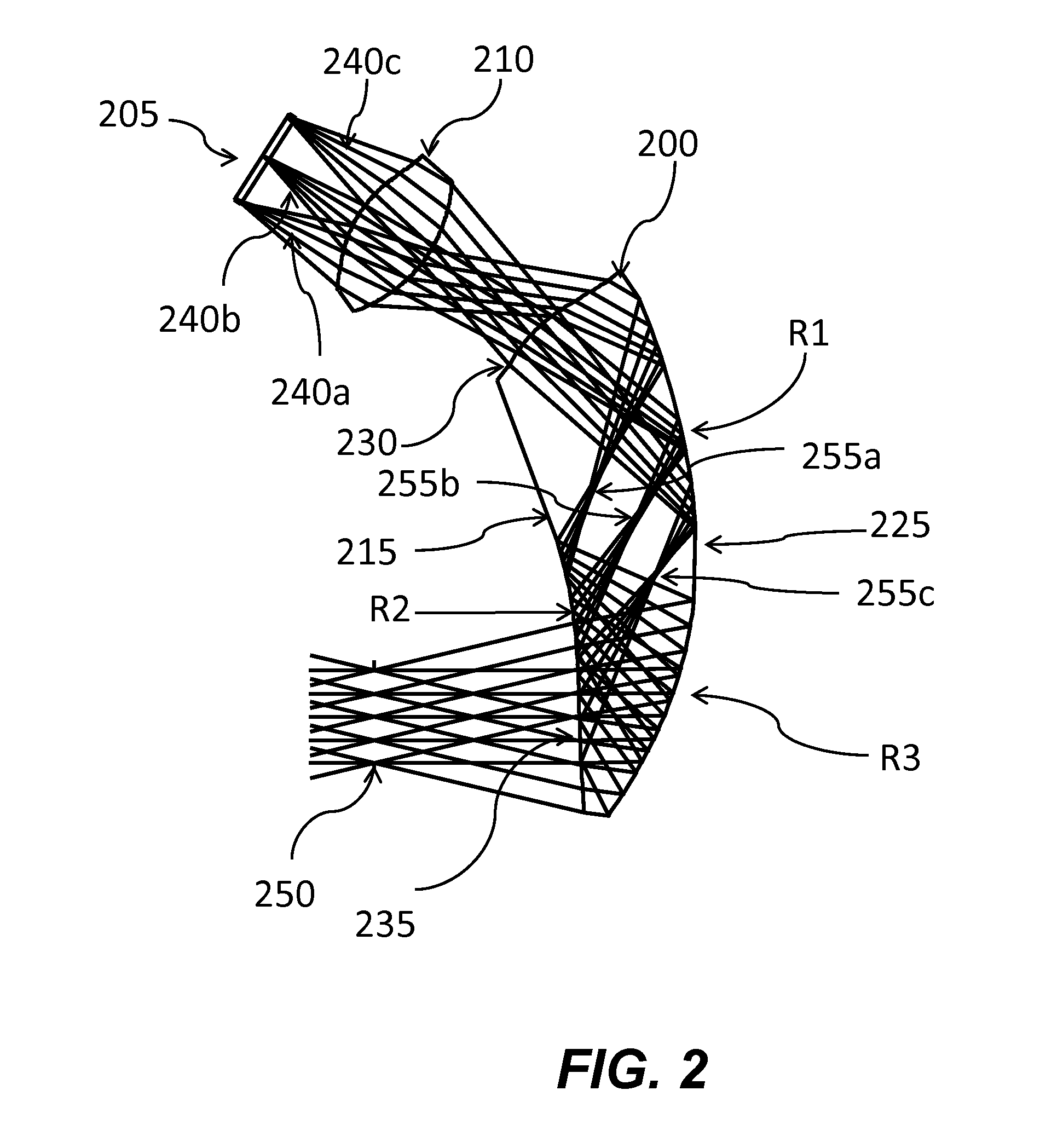
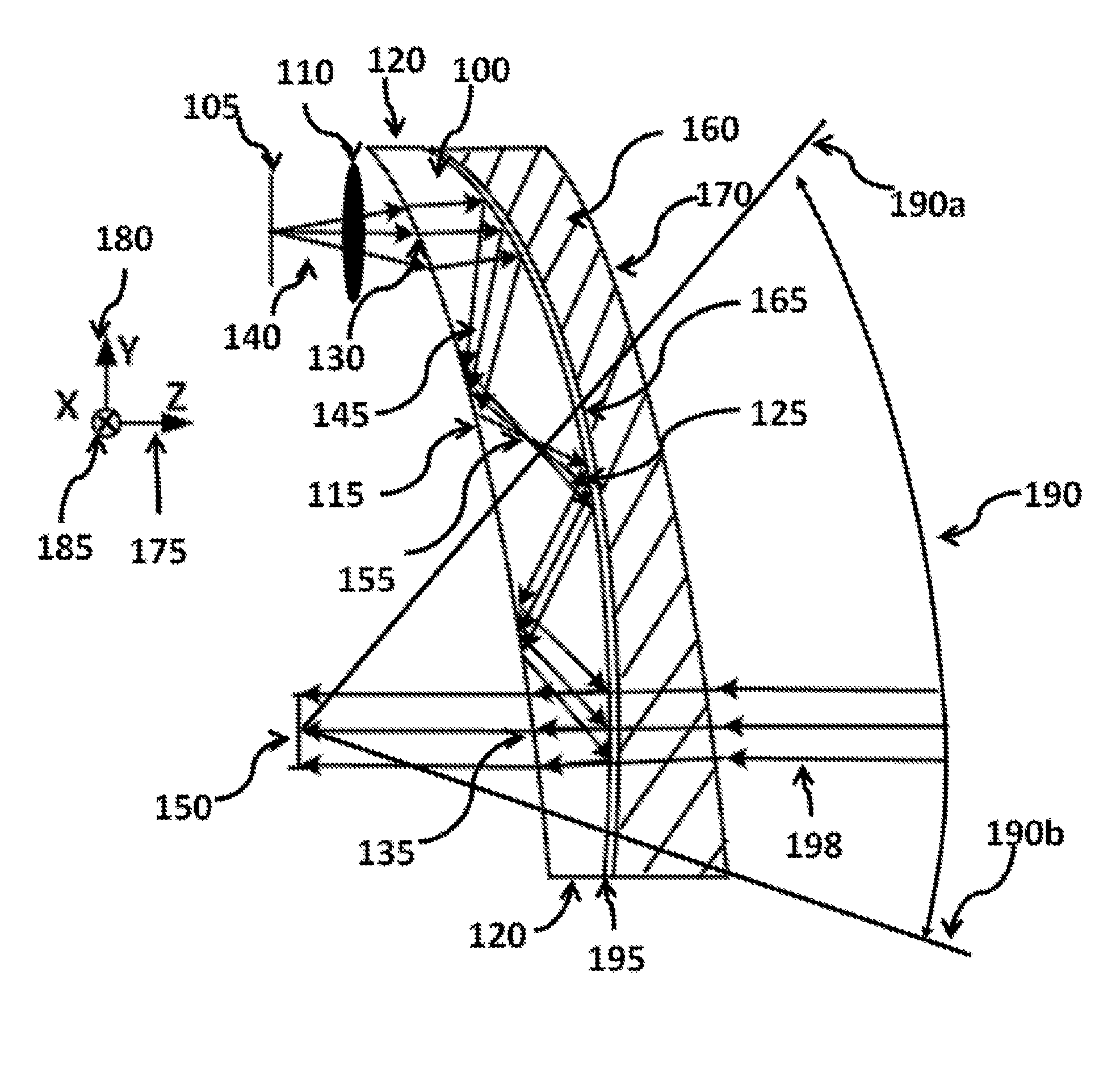
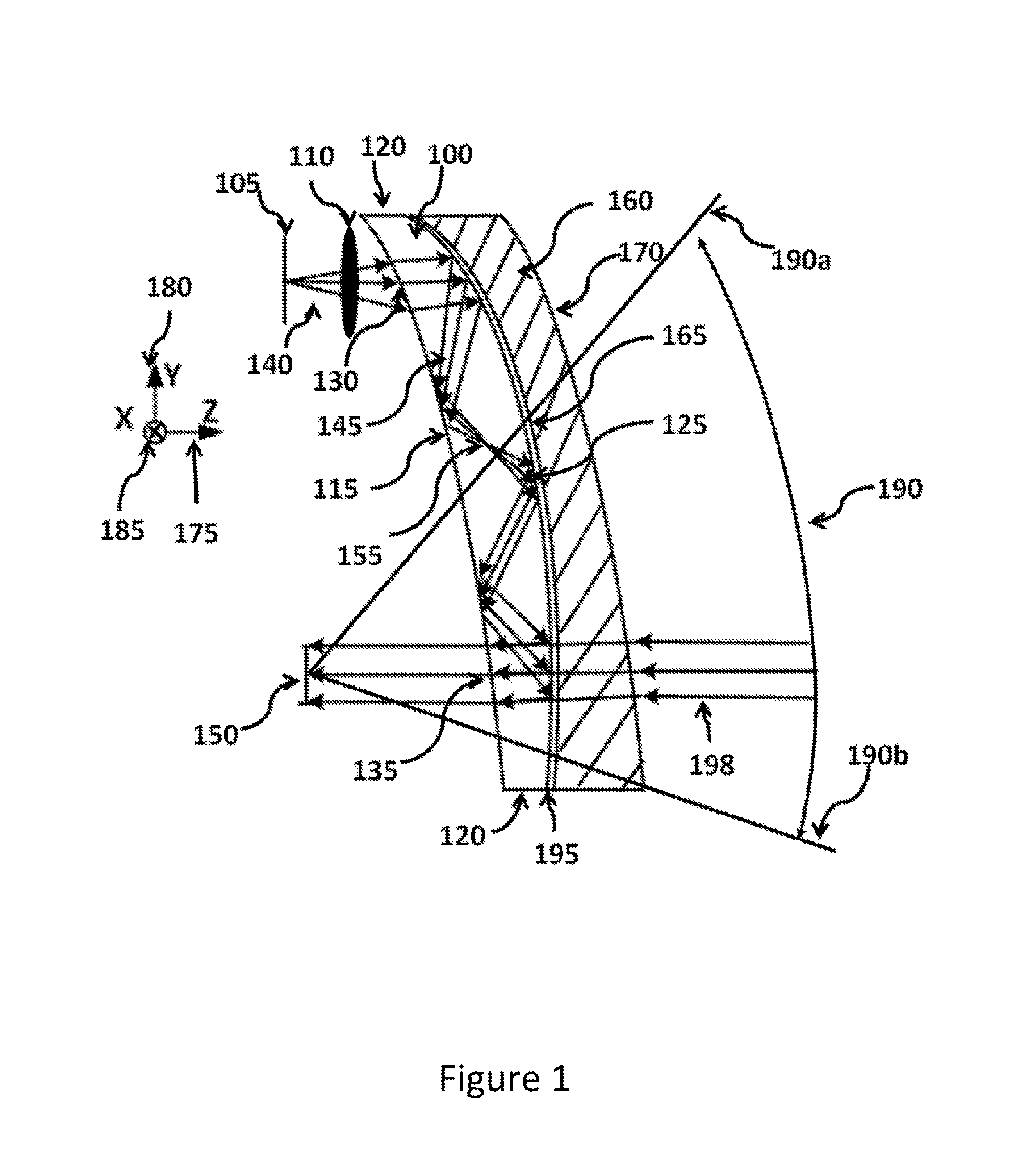
Ergonomic head mounted display device and optical system
Optical systems such as image display systems include a freeform optical waveguide prism and a freeform compensation lens spaced therefrom by a gap of air or index cement. The compensation lens corrects for aberrations which the optical waveguide prism will introduce in light or images from an ambient real-world environment. The optical waveguide prism receives actively projected images at an entry location, and emits the projected images at an exit location after internally reflecting the images along an optical path therein. The image display system may include an image source and coupling optics. The approach permits design of an optical viewing device, for example in optical see-through HMDs, achieving an eyeglass-form appearance and a wide see-through field of view (FOV).
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
Ergonomic head mounted display device and optical system
ActiveUS9348143B2Wide field of viewGood optical performancePolarising elementsPlanar/plate-like light guidesEyewearDisplay device
This invention concerns an ergonomic optical see-through head mounted display device with an eyeglass appearance. The see-through head-mounted display device consists of a transparent, freeform waveguide prism for viewing a displayed virtual image, a see-through compensation lens for enabling proper viewing of a real-world scene when combined together with the prism, and a miniature image display unit for supplying display content. The freeform waveguide prism, containing multiple freeform refractive and reflective surfaces, guides light originated from the miniature display unit toward a user's pupil and enables a user to view a magnified image of the displayed content. A see-through compensation lens, containing multiple freeform refractive surfaces, enables proper viewing of the surrounding environment, through the combined waveguide and lens. The waveguide prism and the see-through compensation lens are properly designed to ergonomically fit human heads enabling a wraparound design of a lightweight, compact, and see-through display system.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
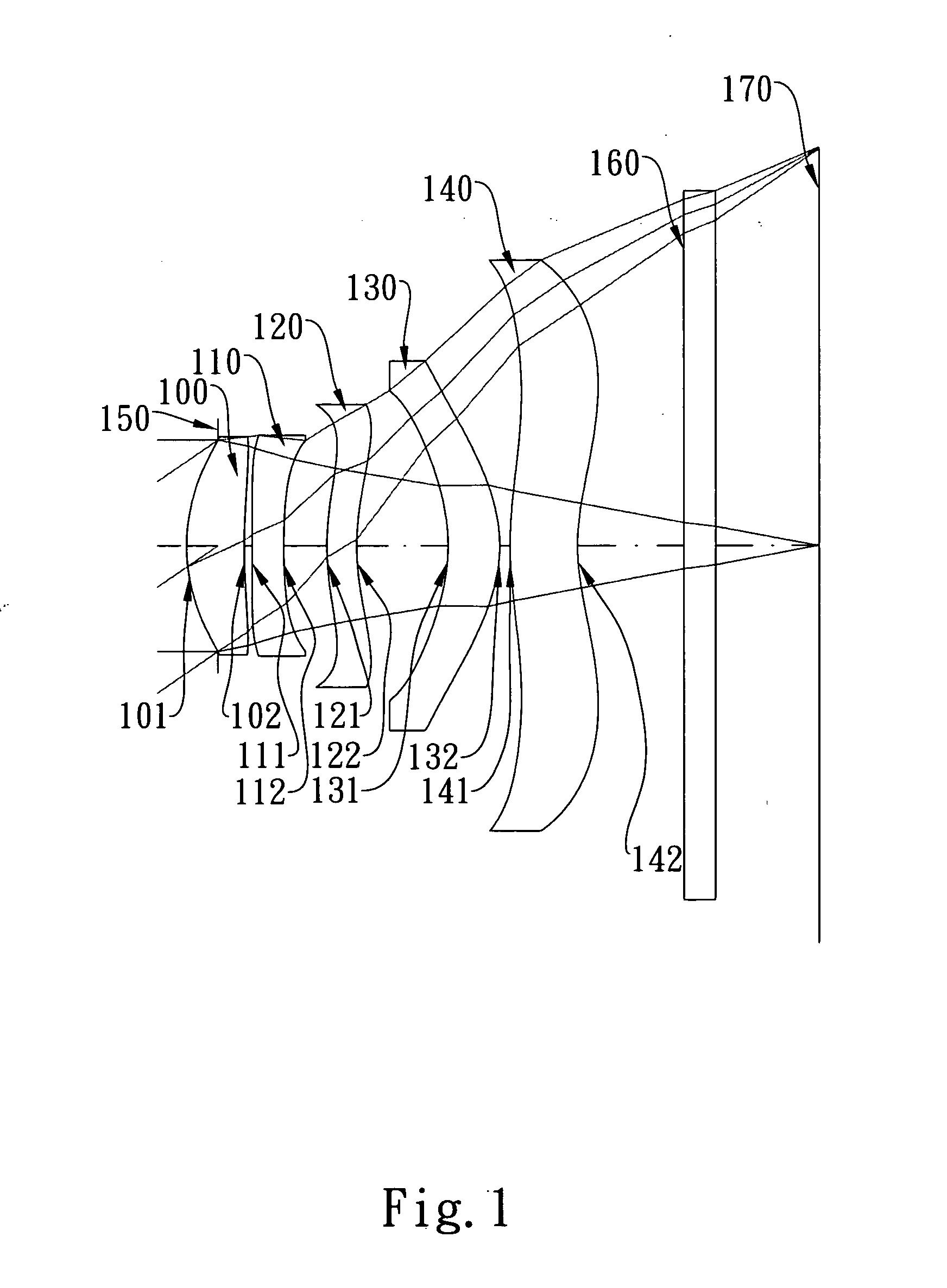
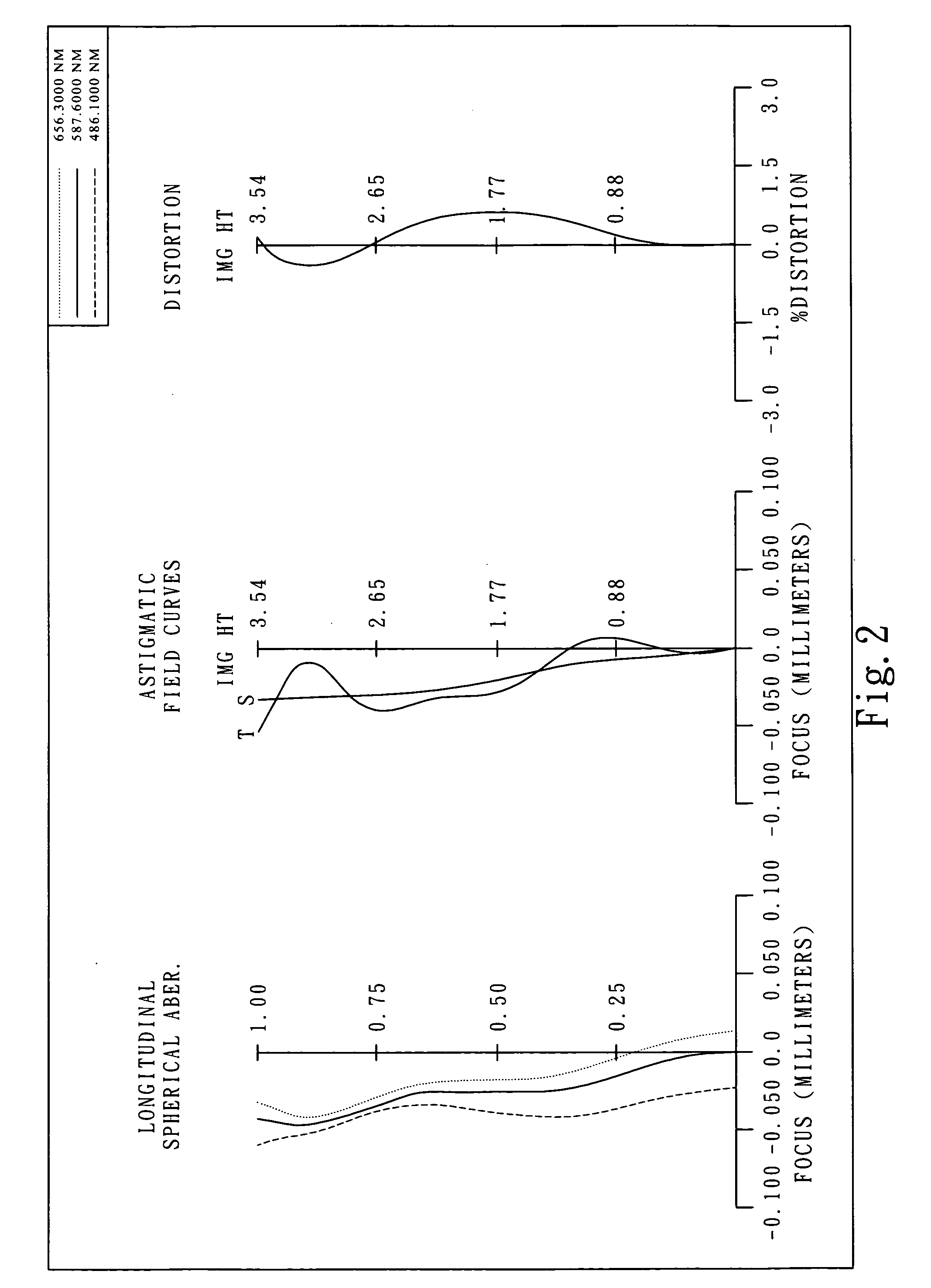
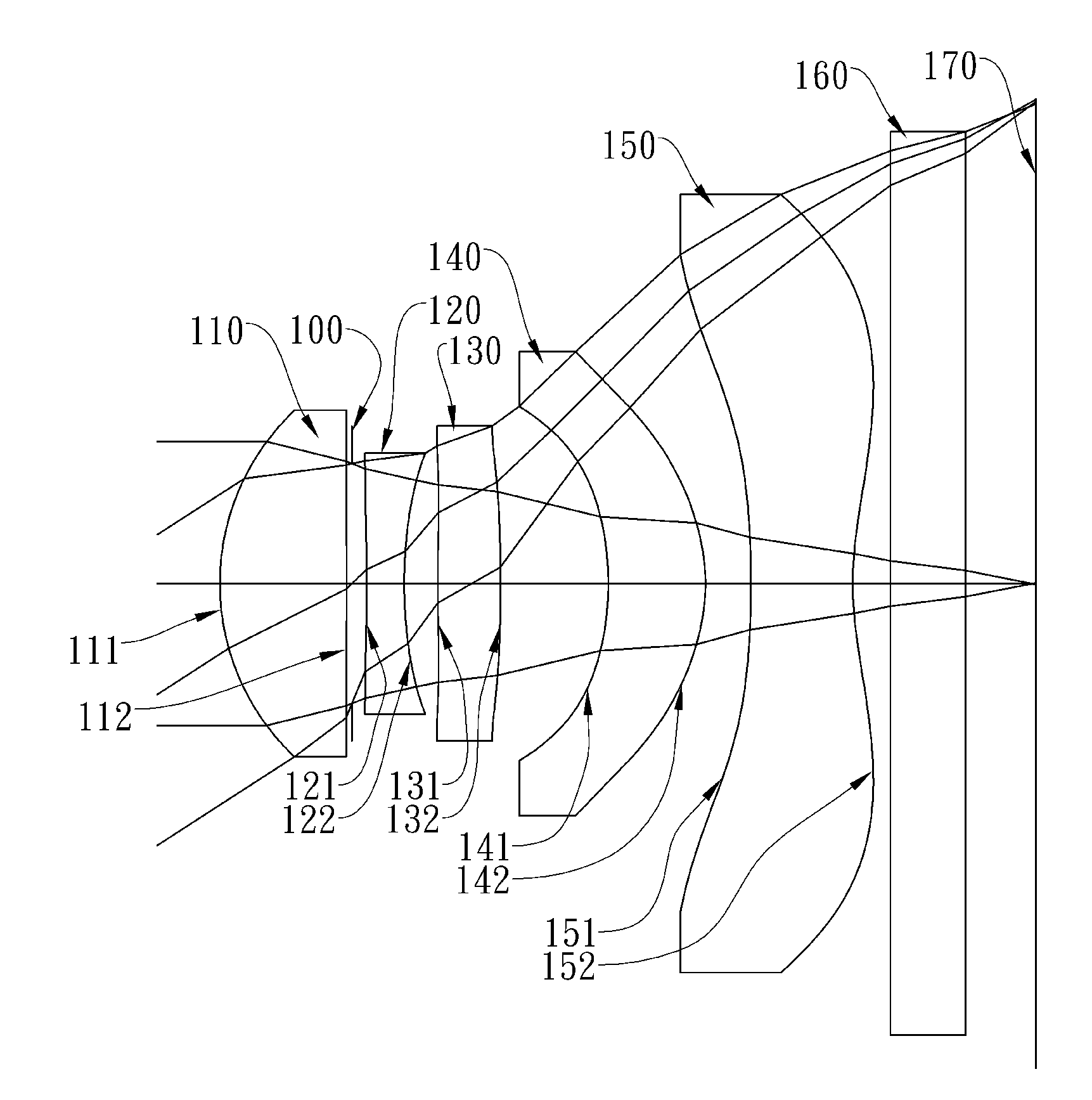
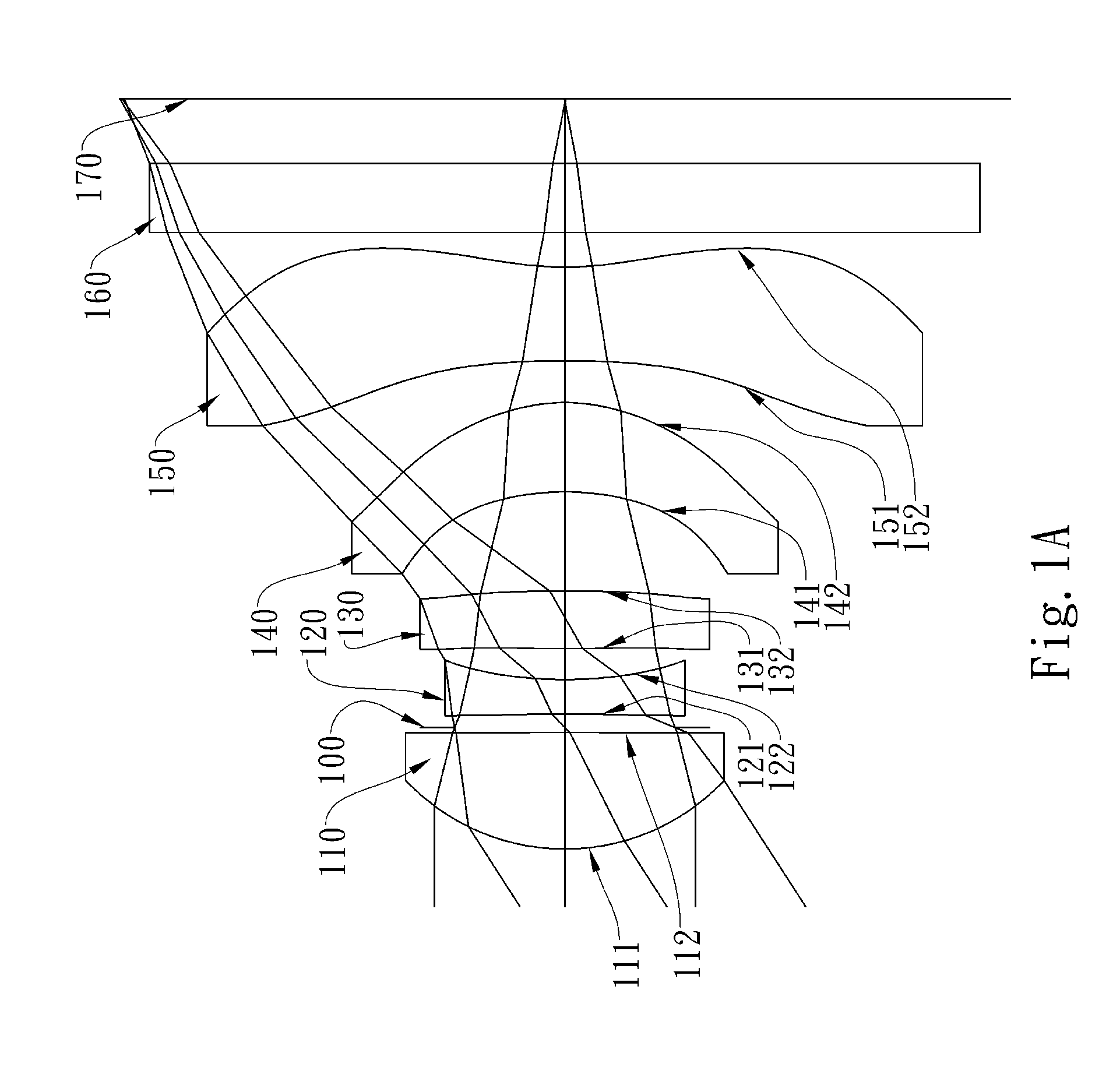
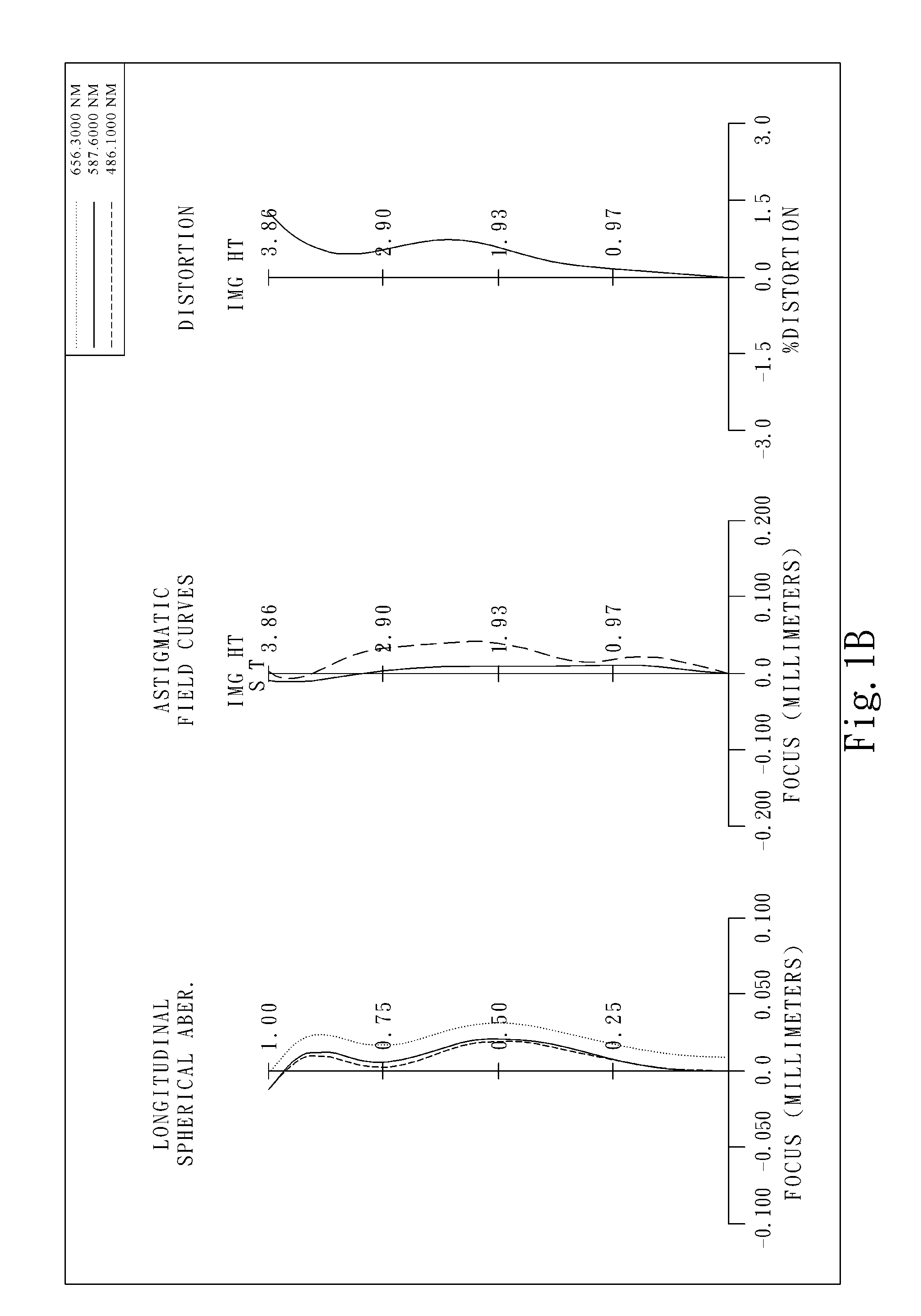
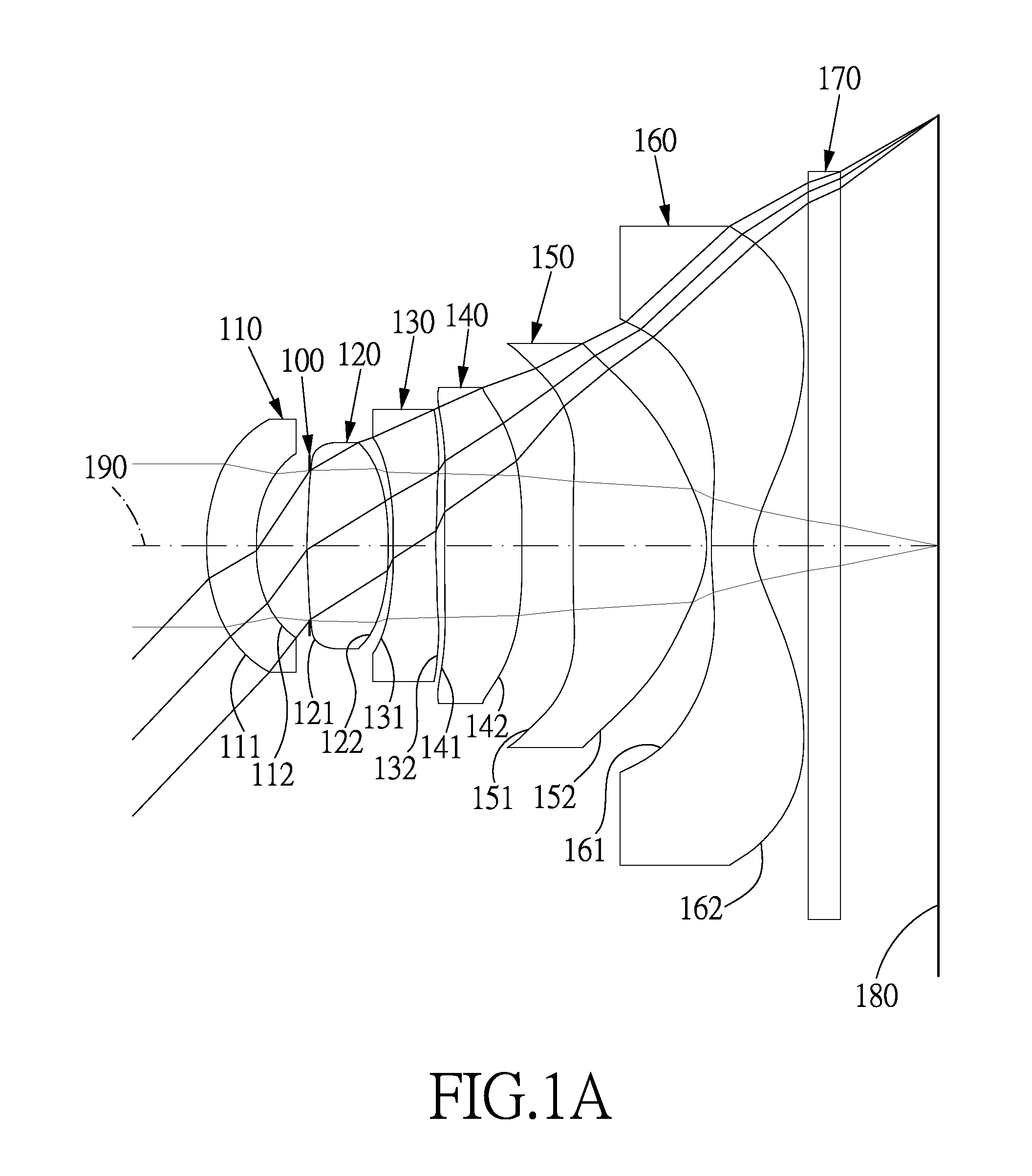
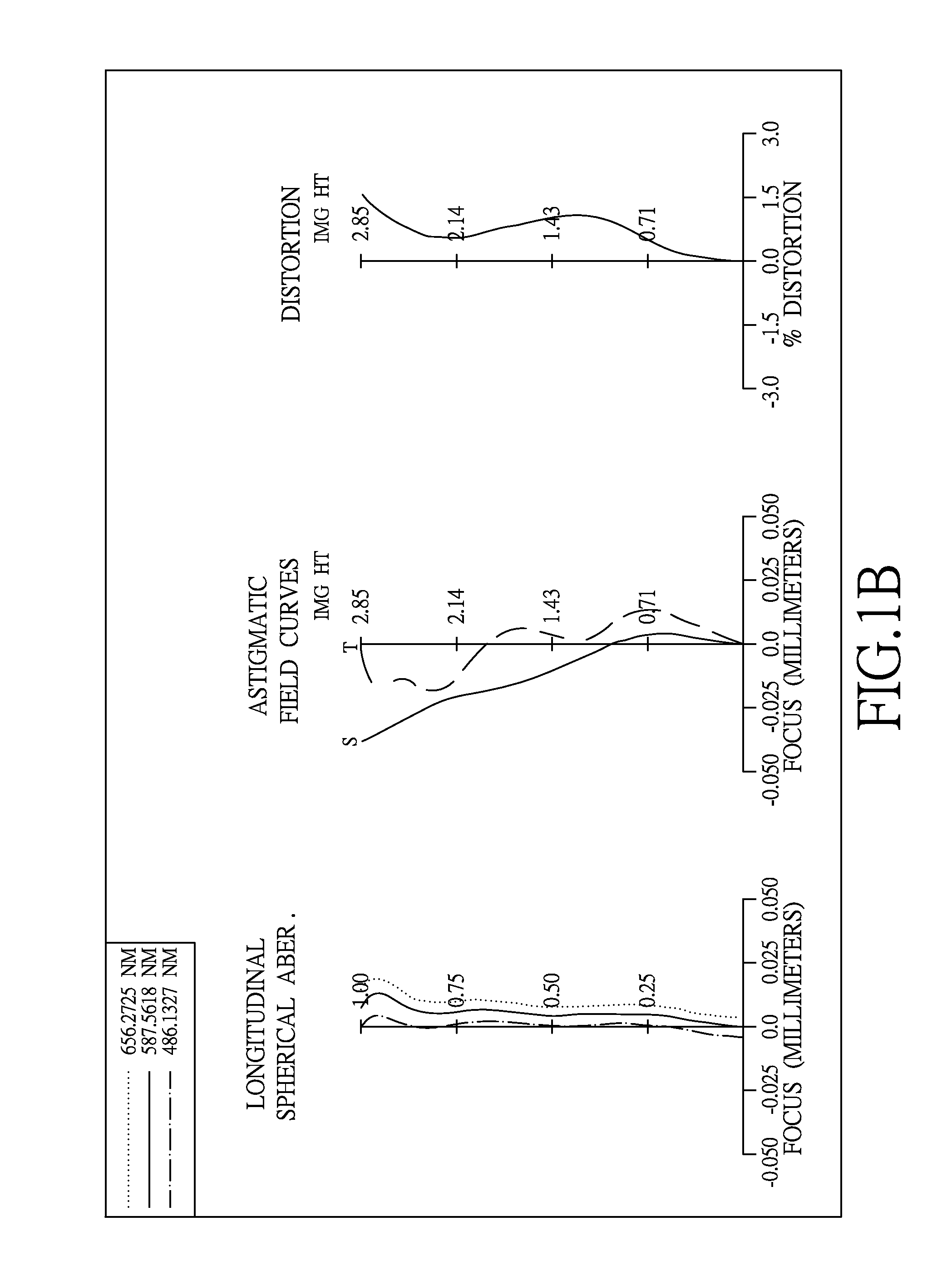
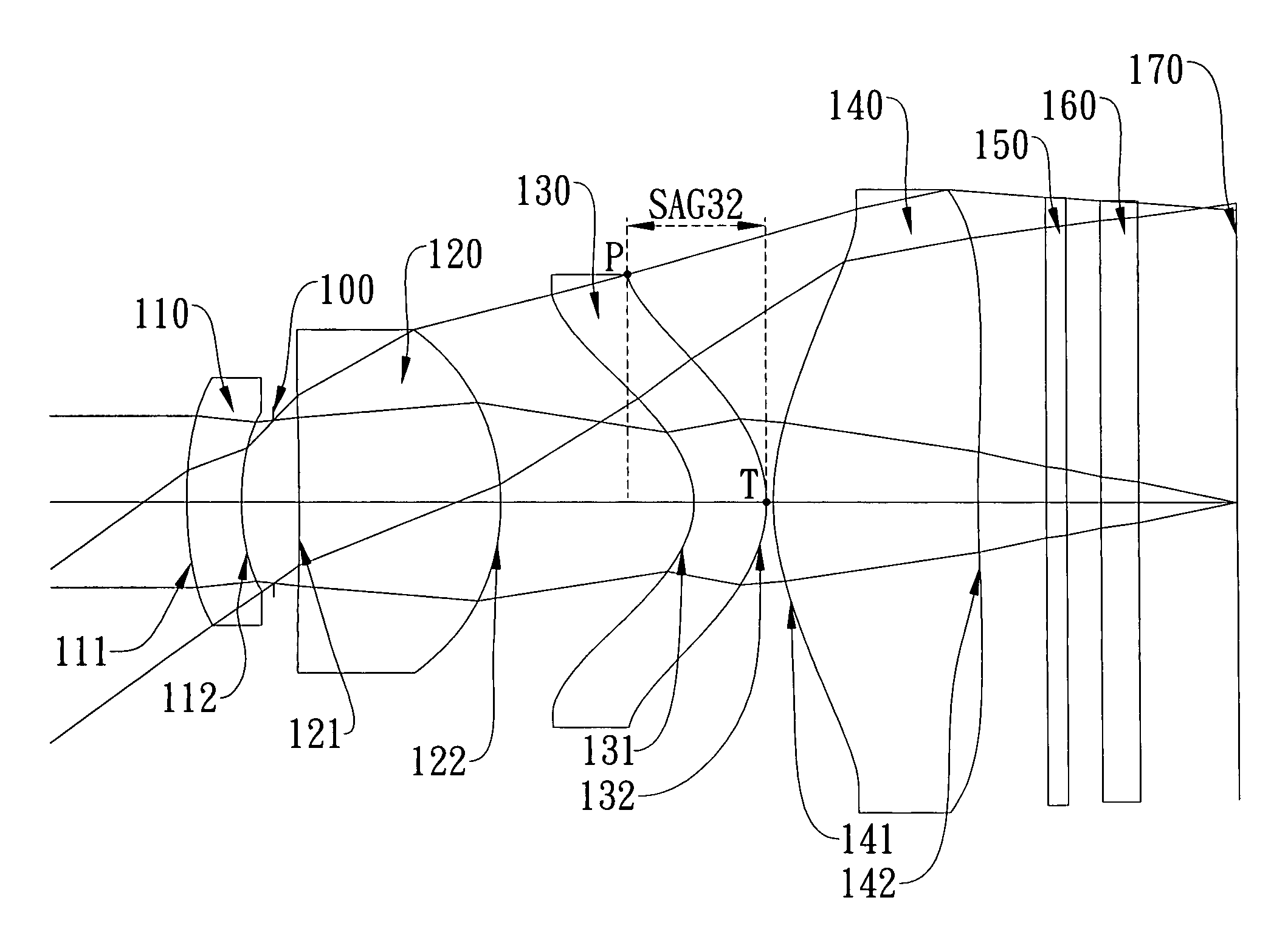
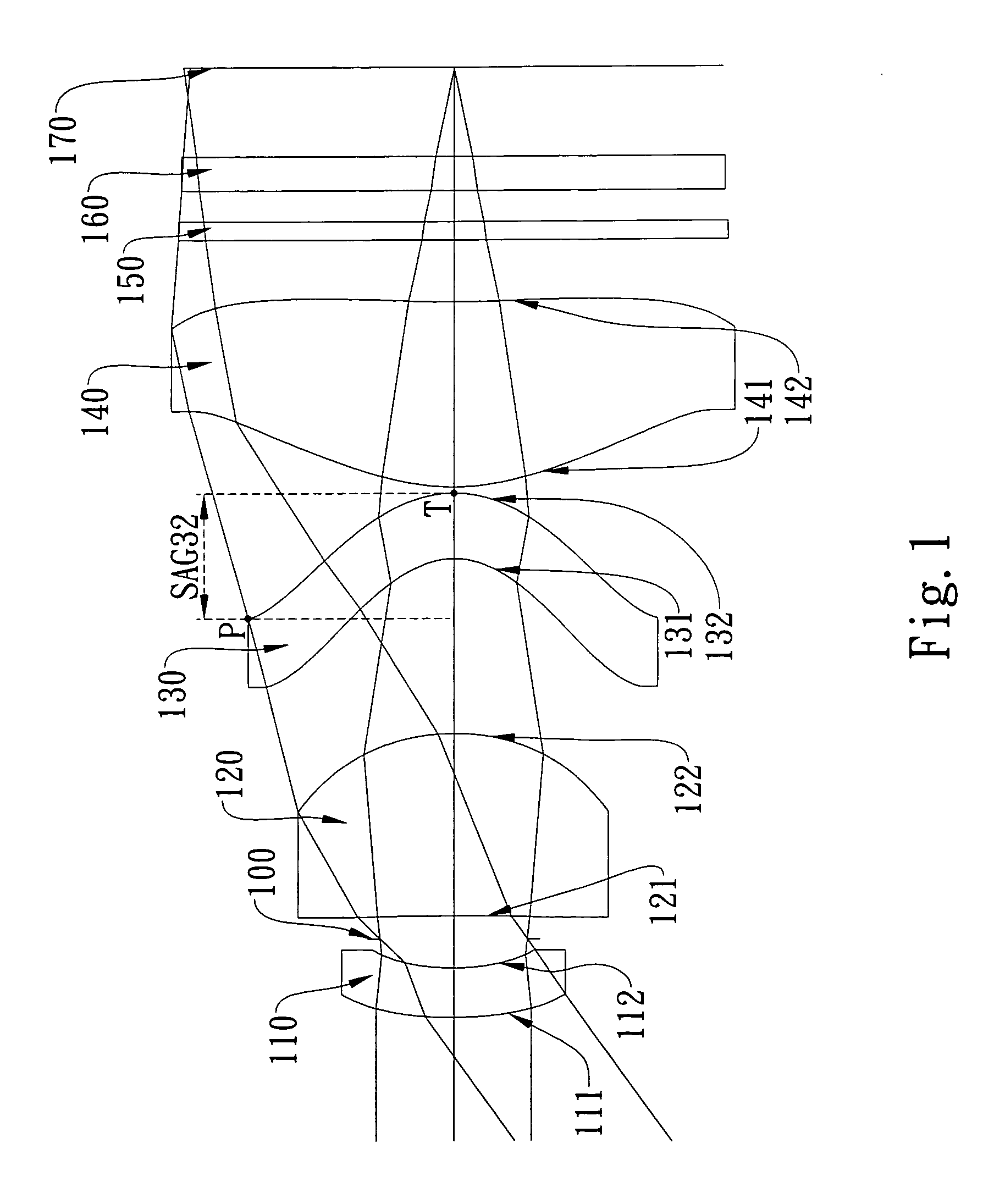
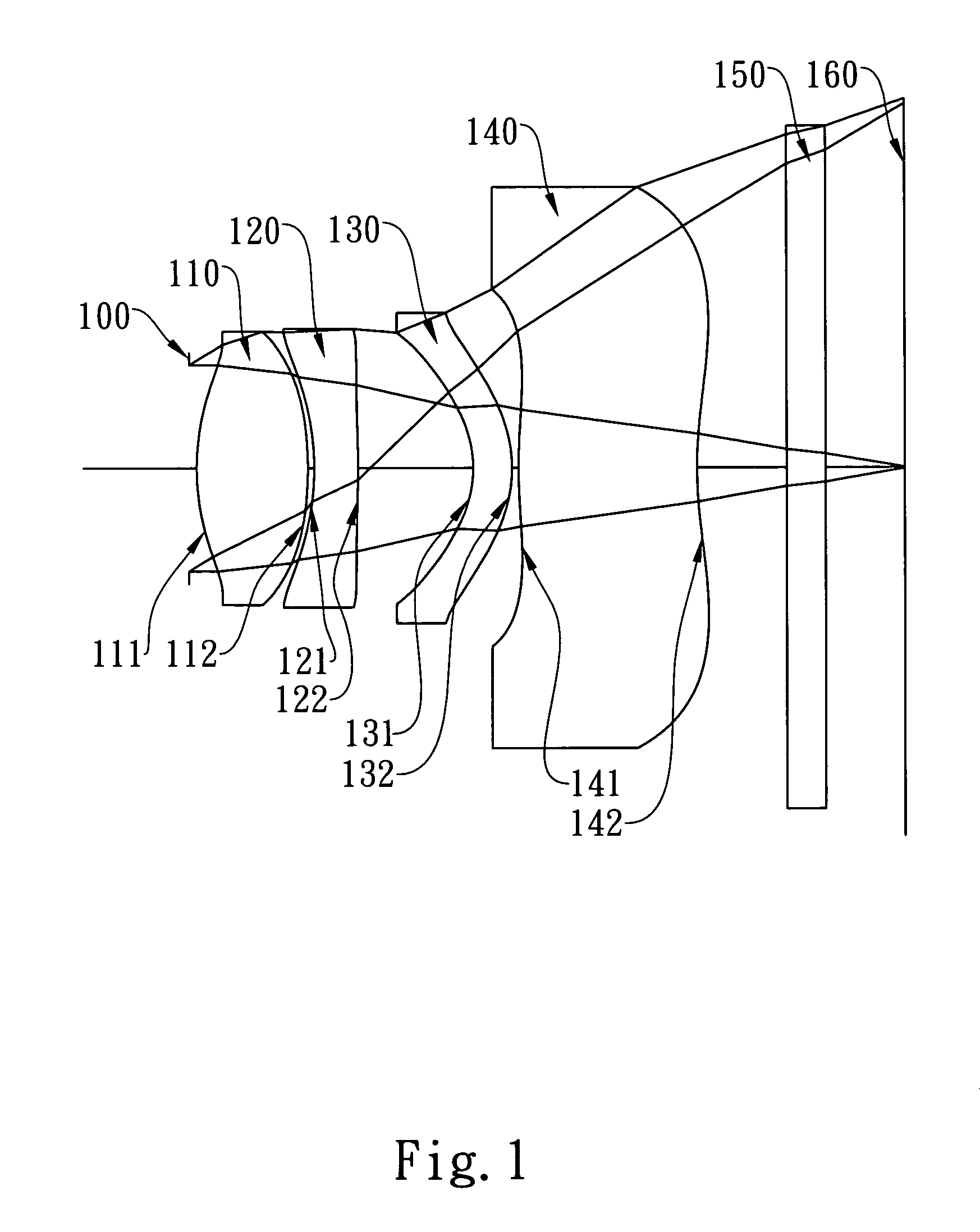
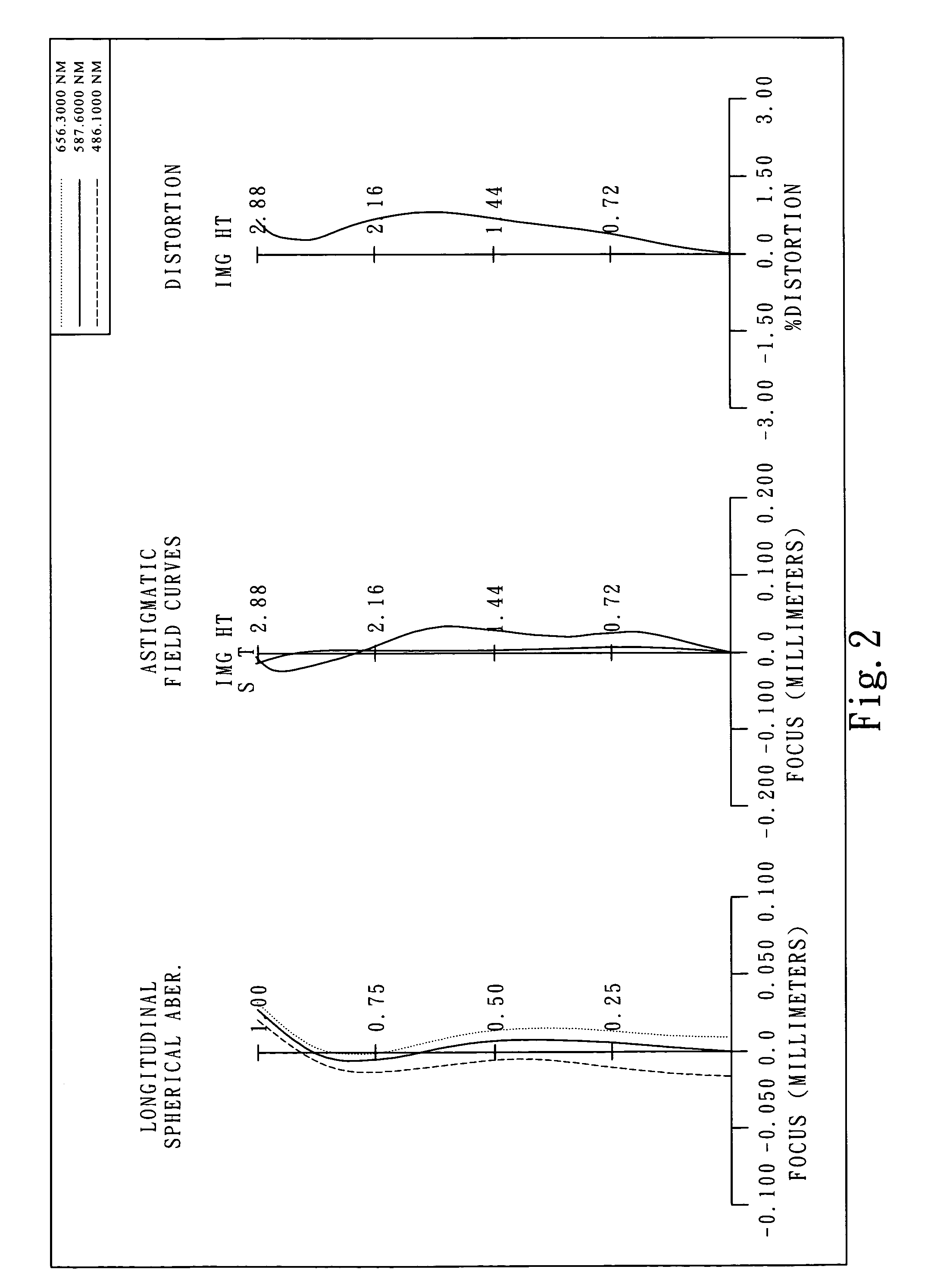
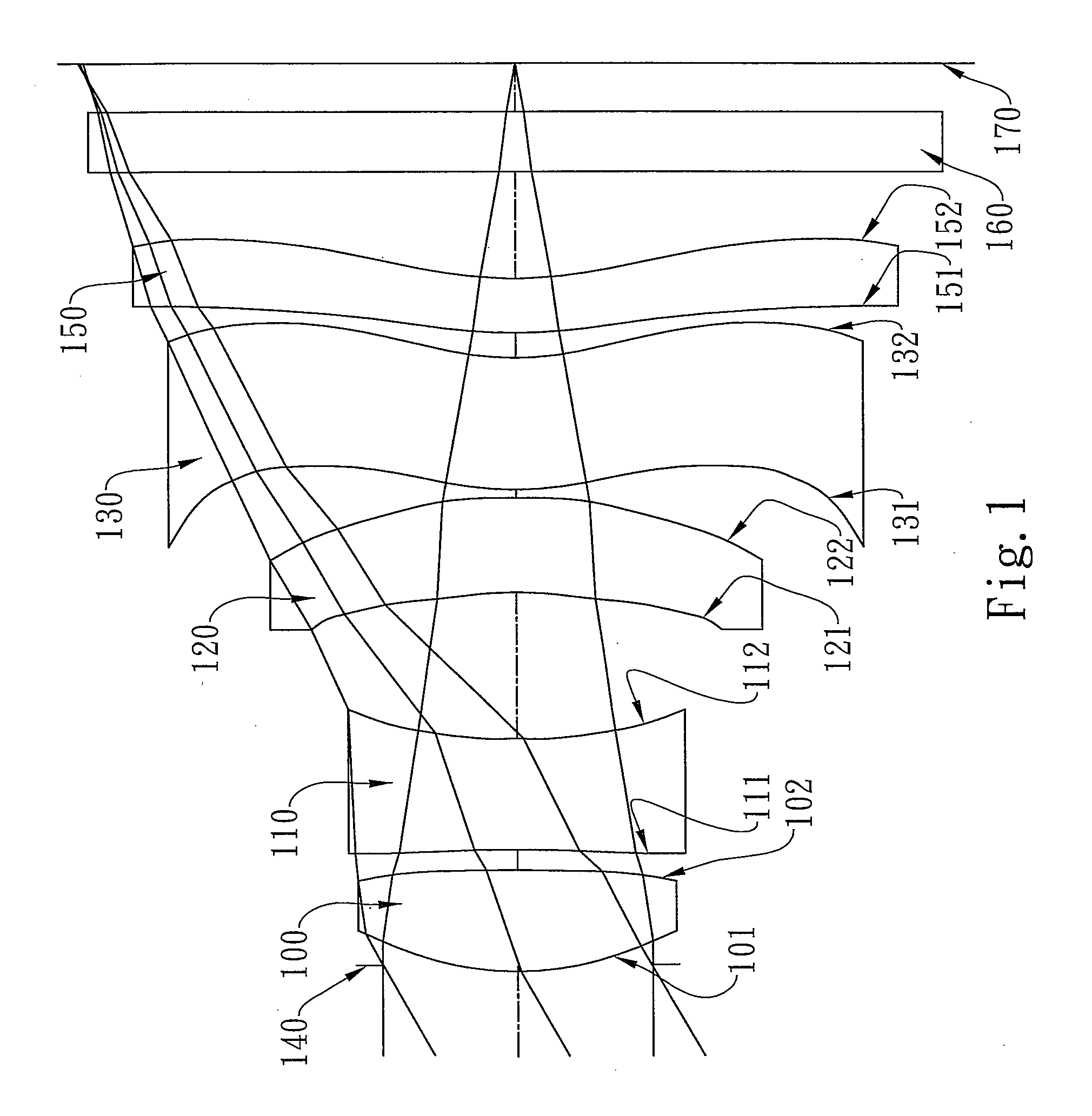
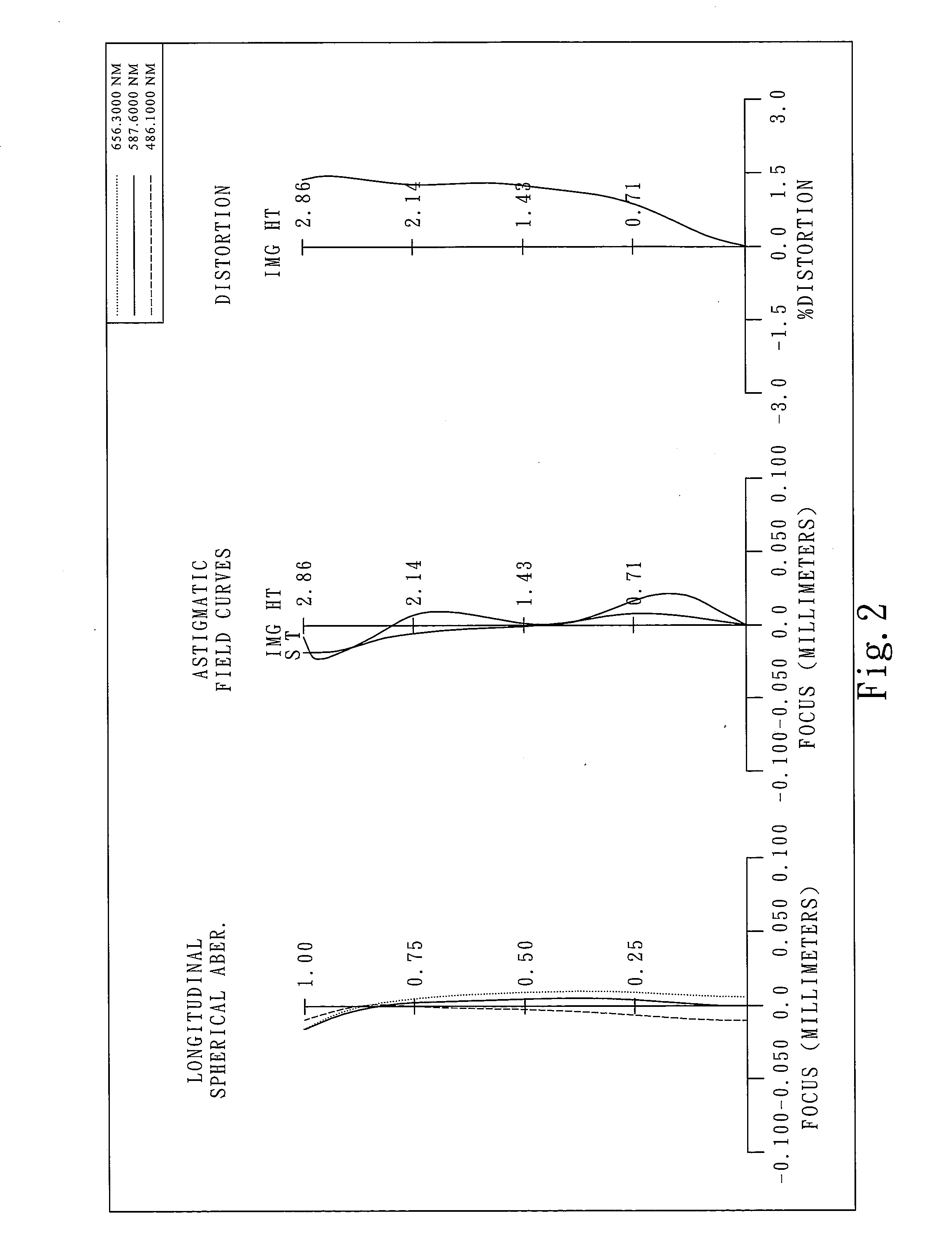
Imaging lens assembly
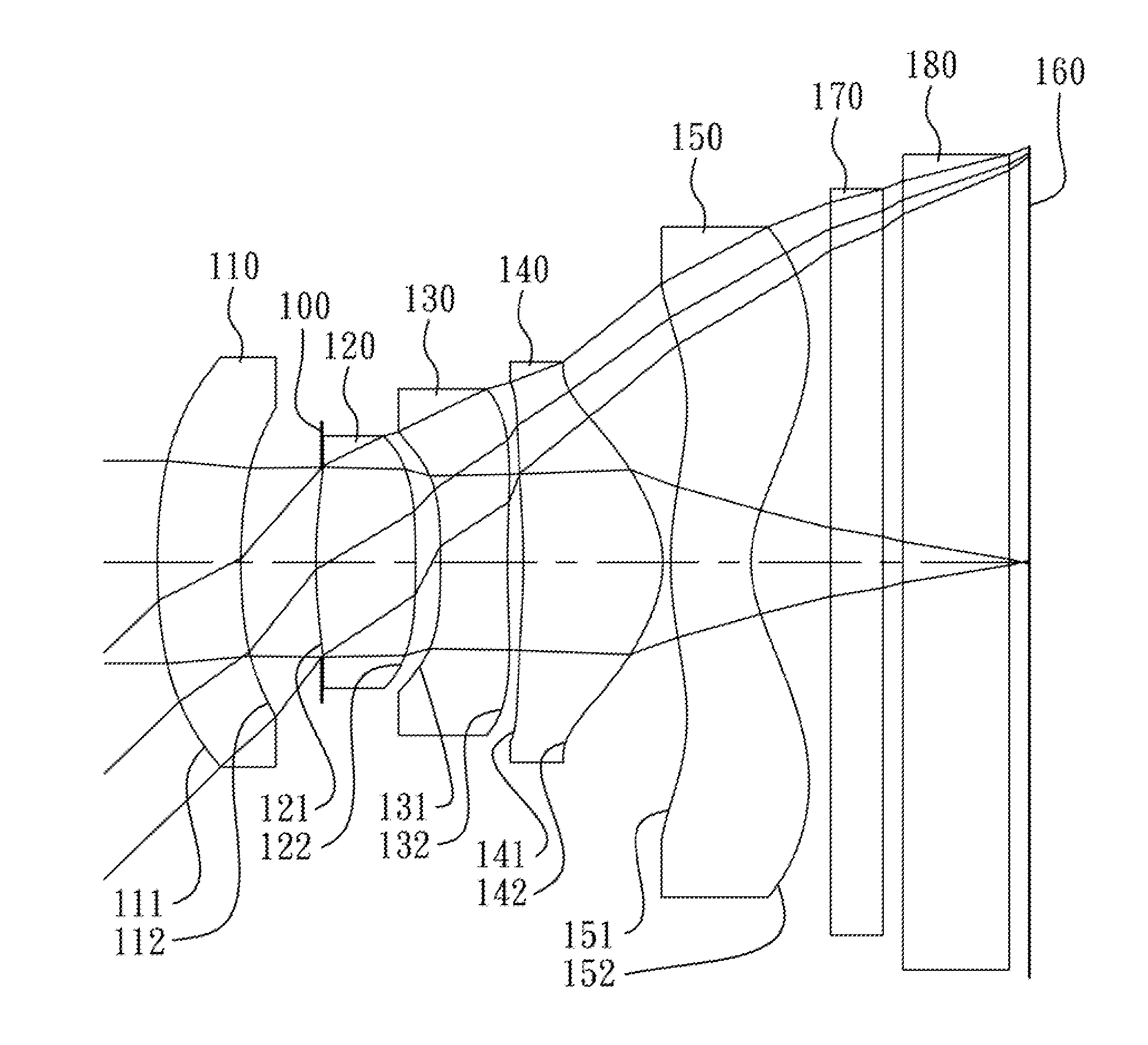
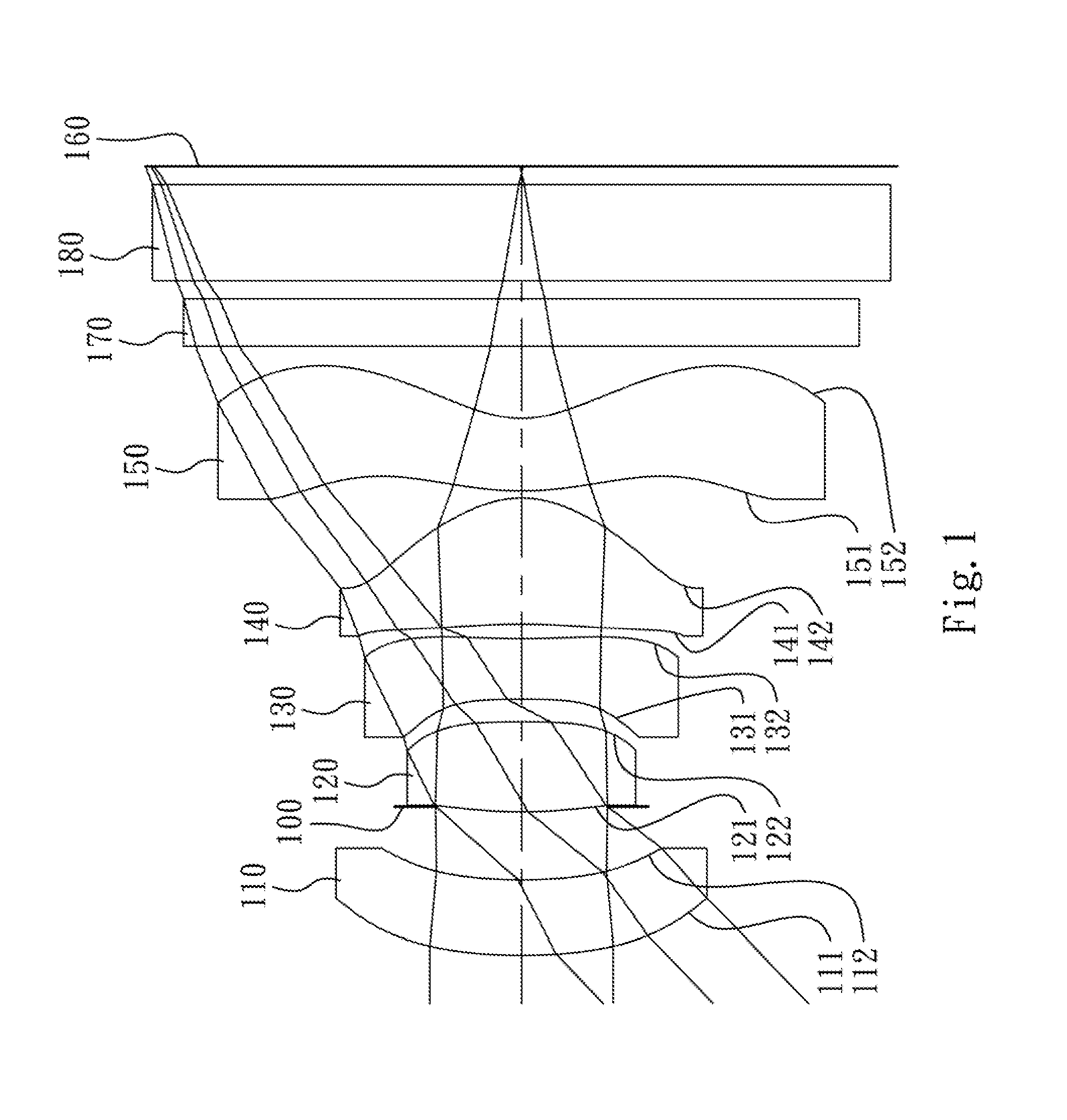
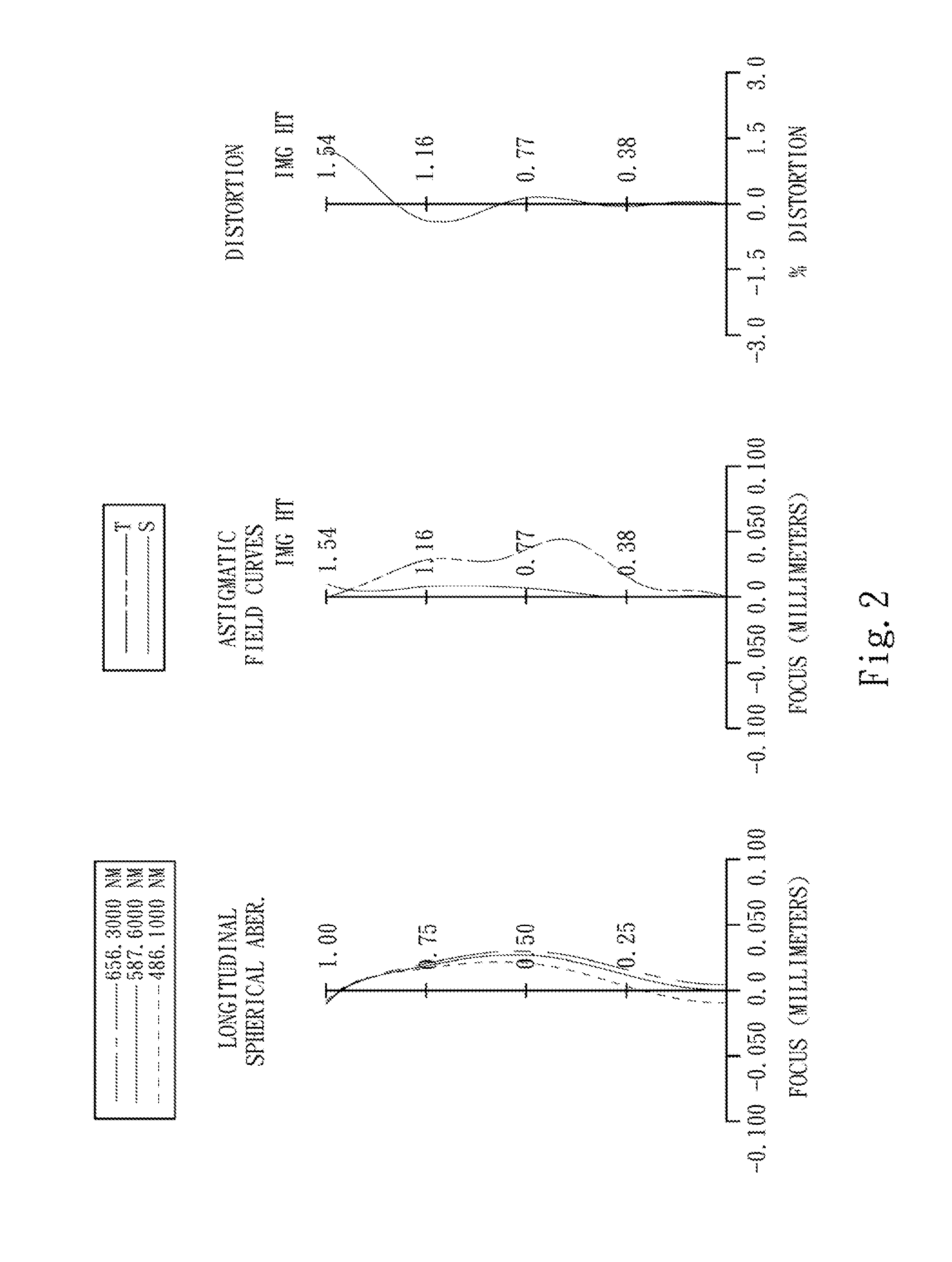
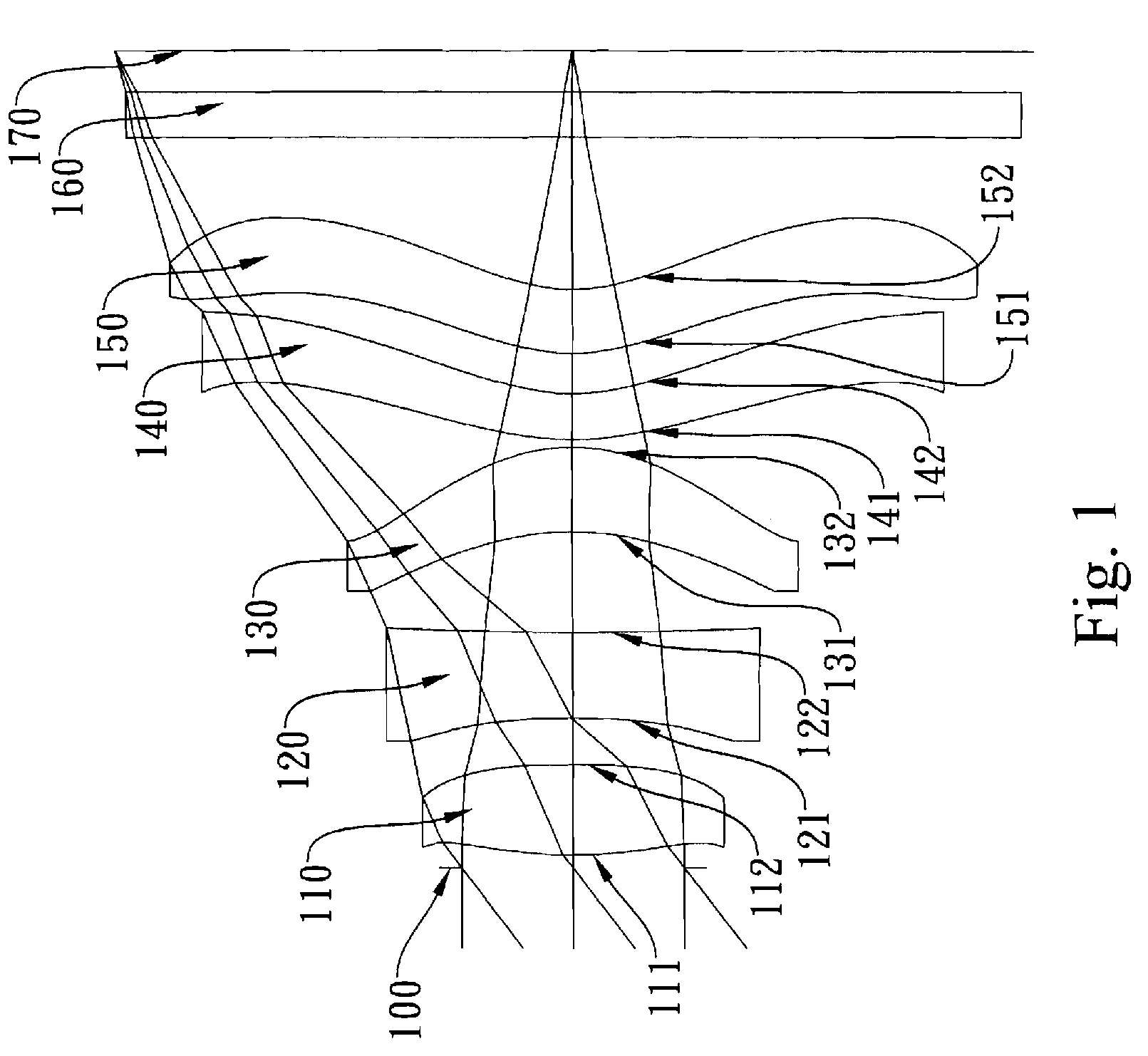
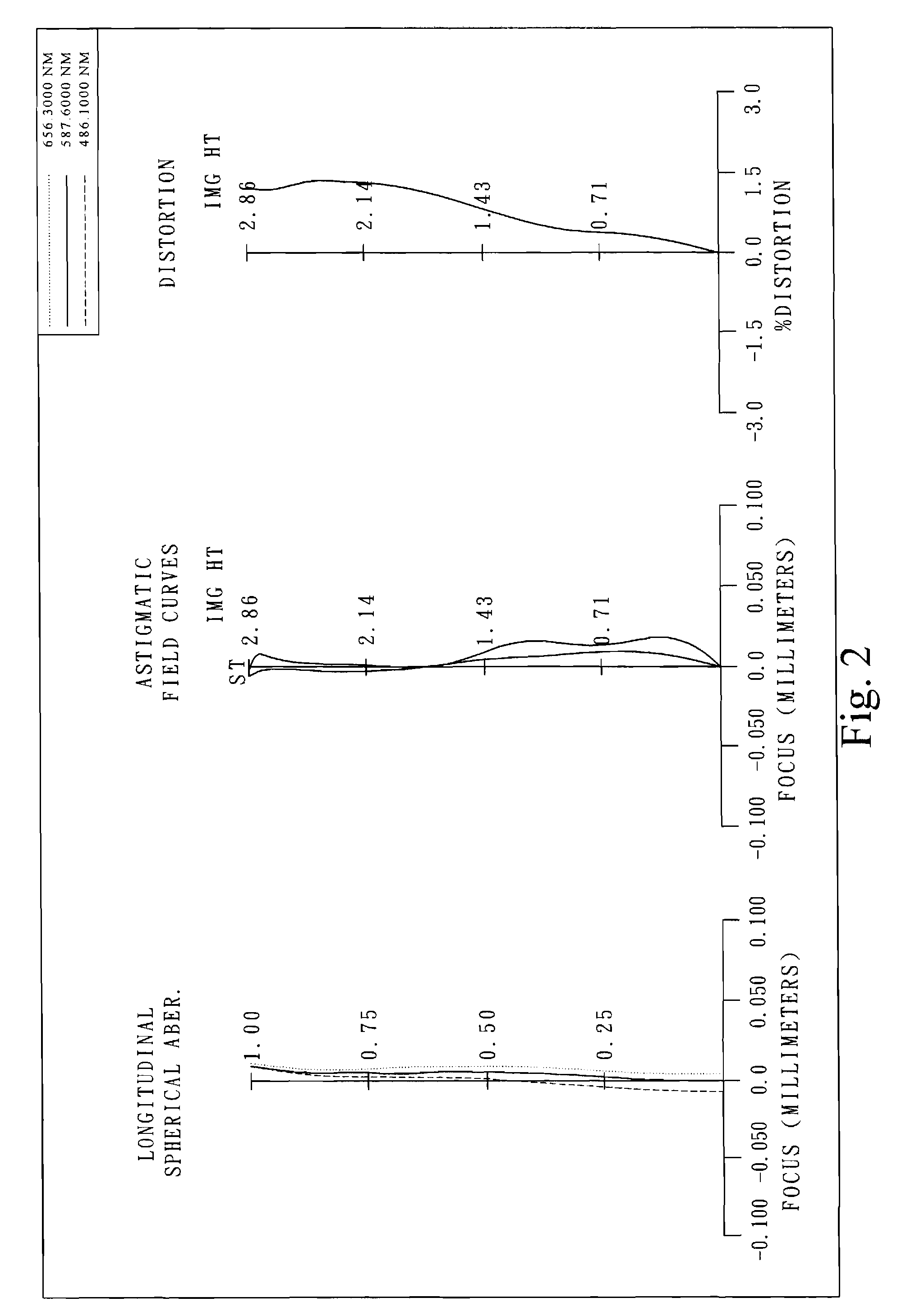
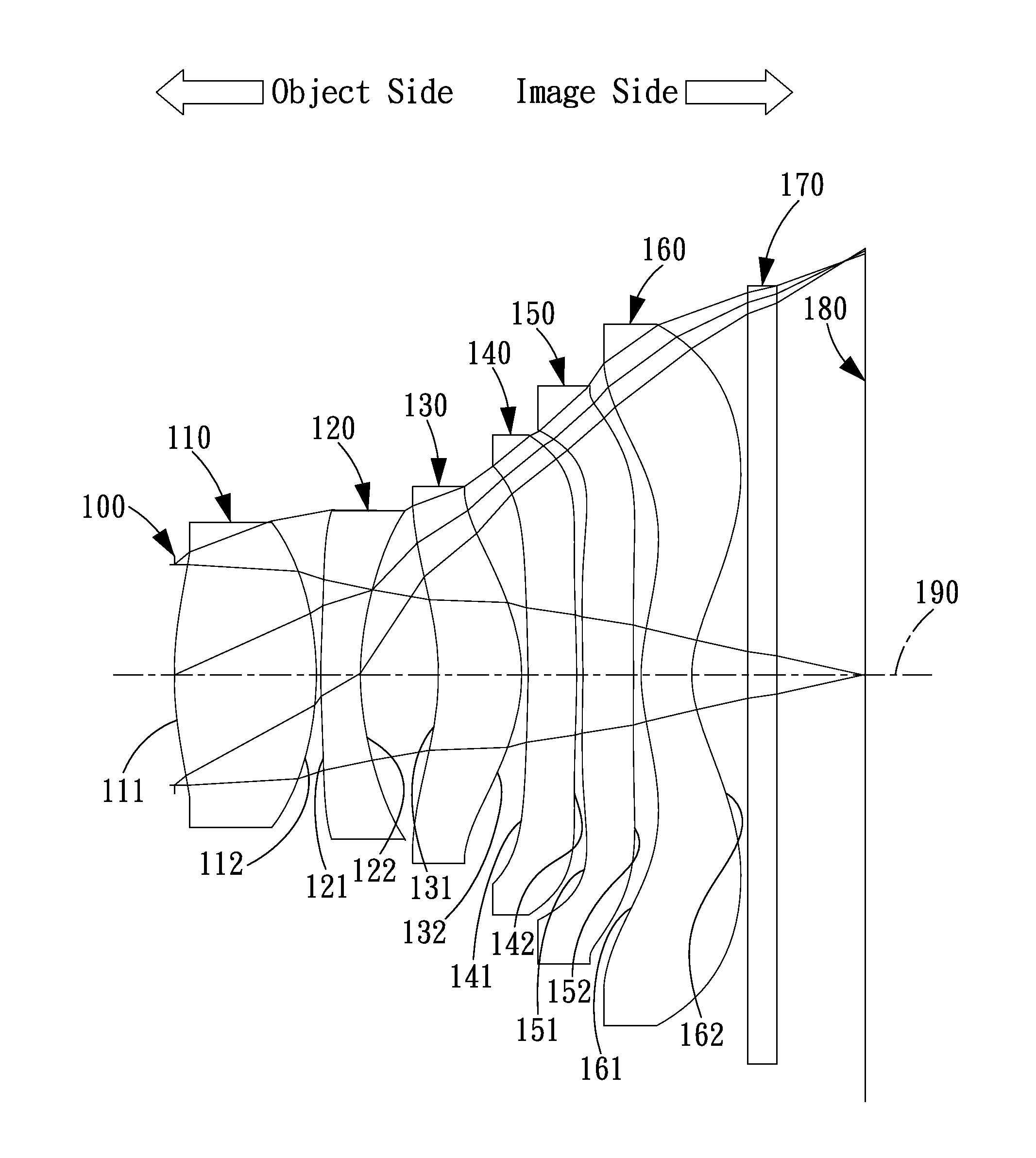
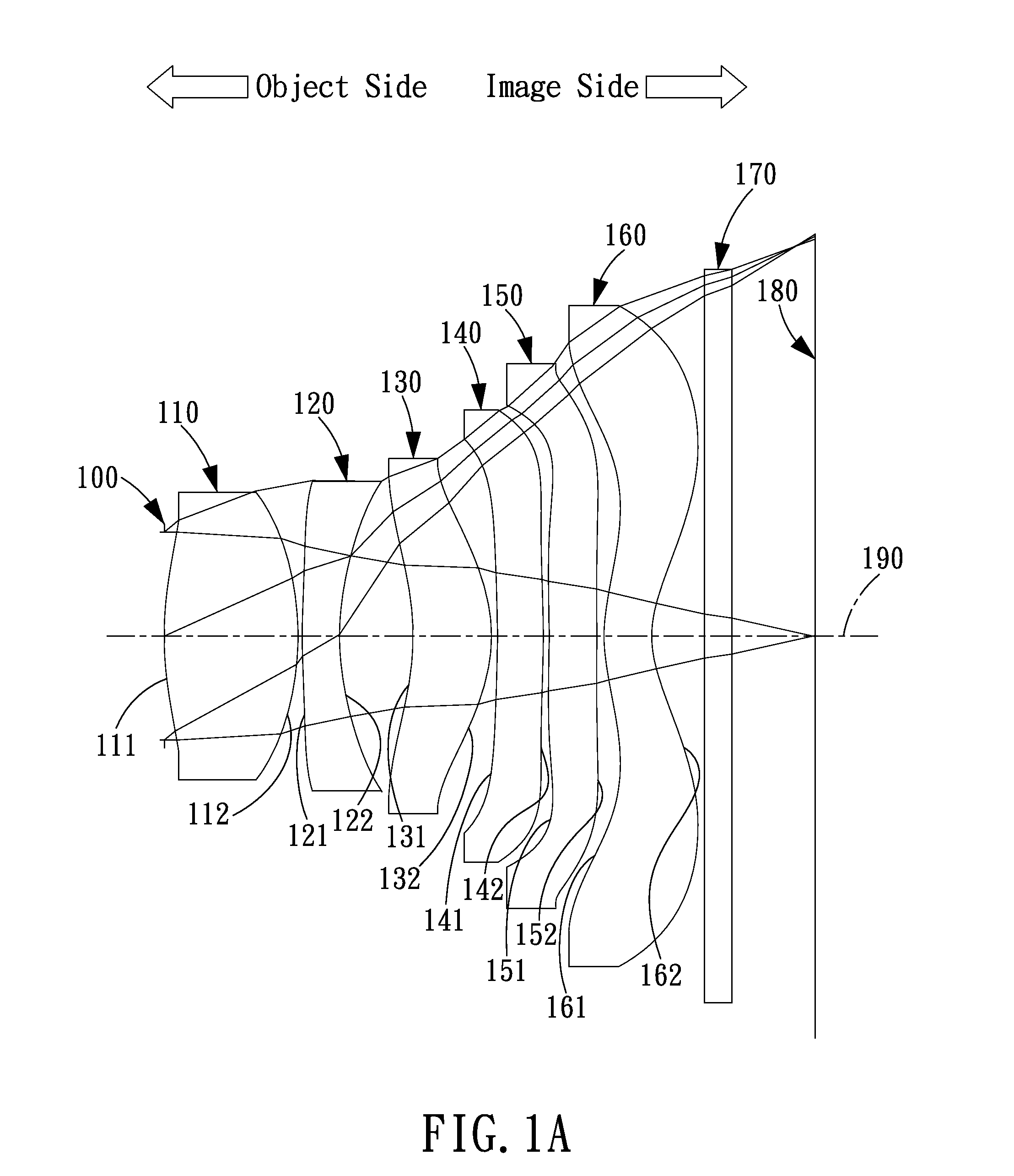
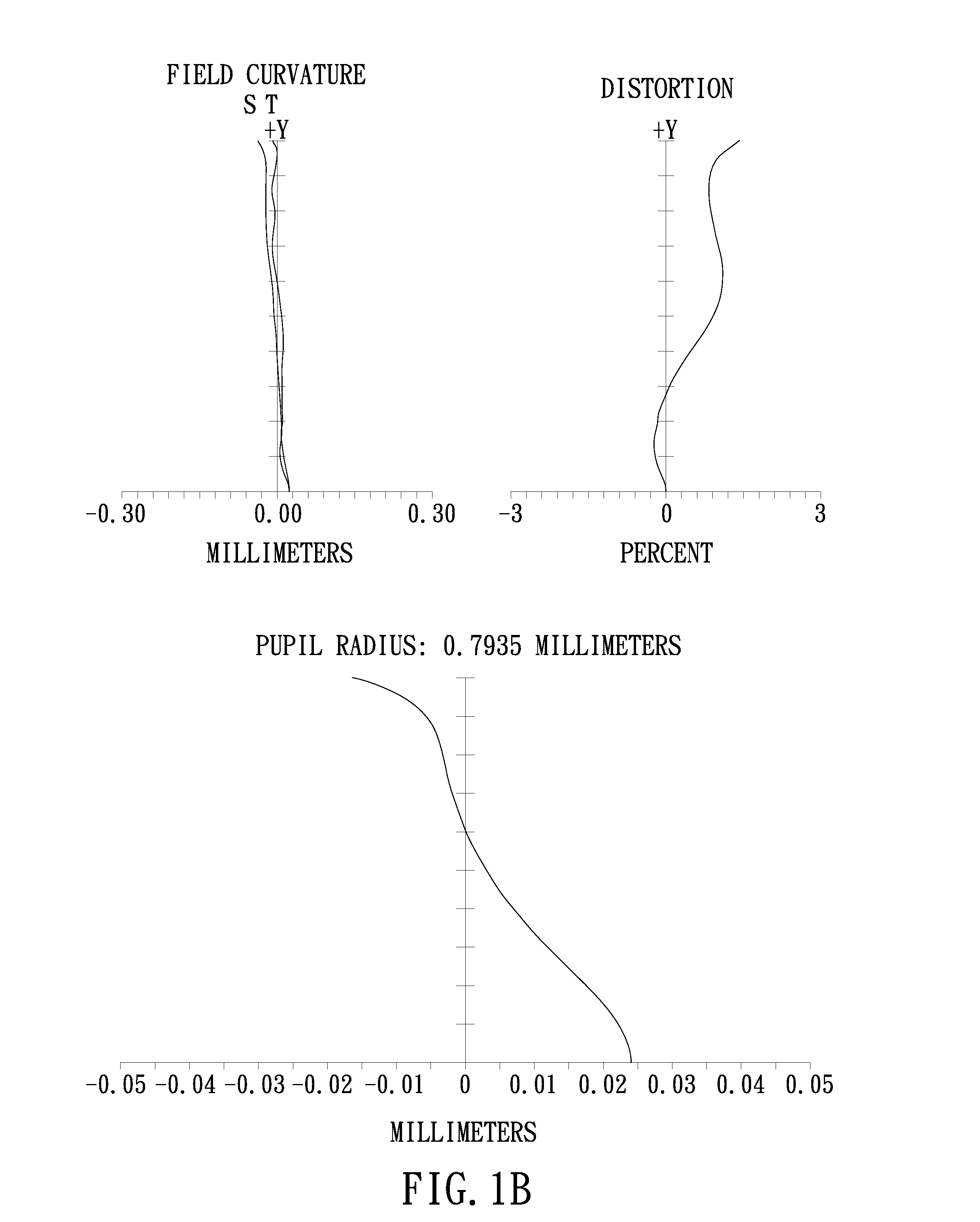
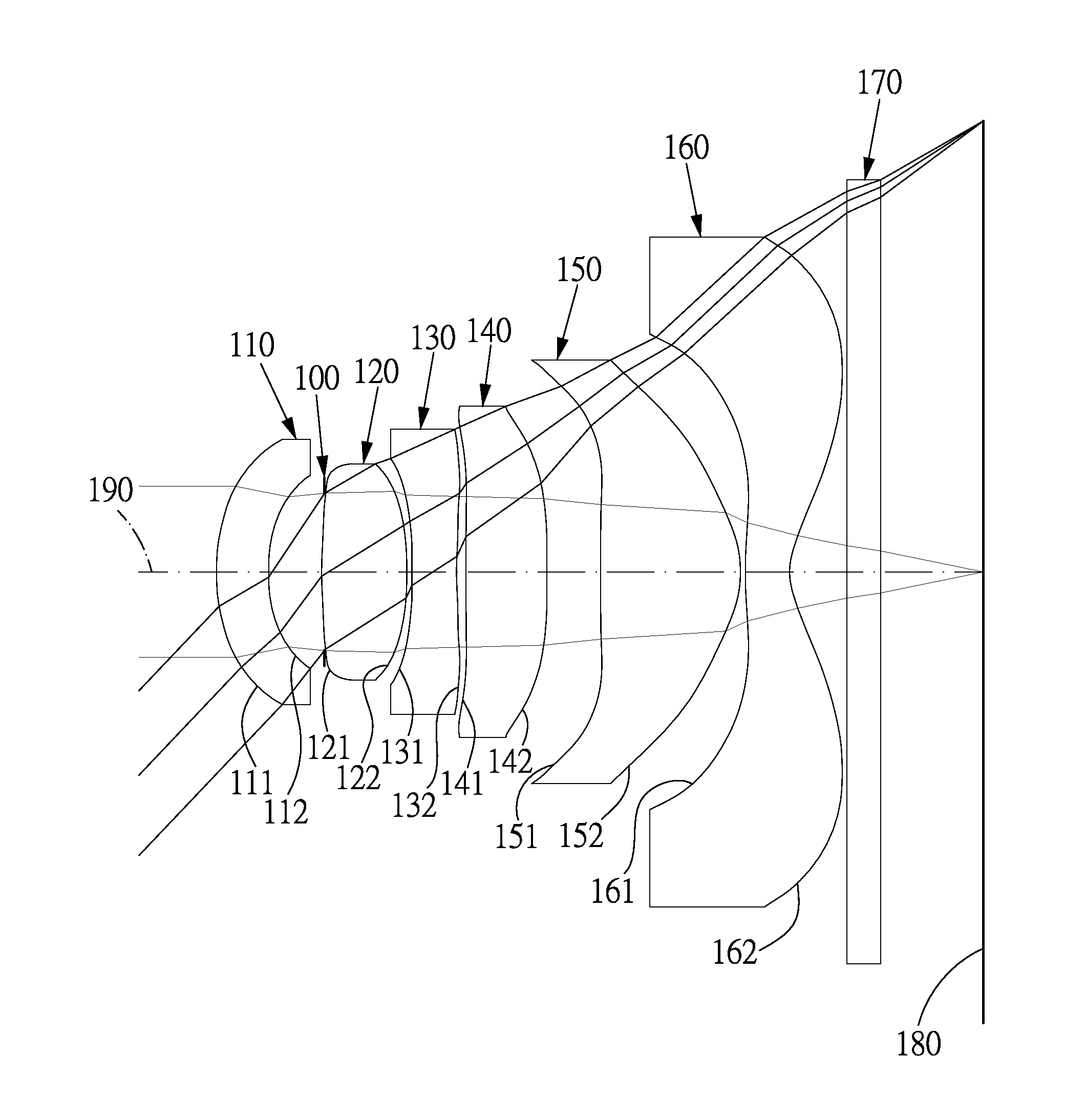
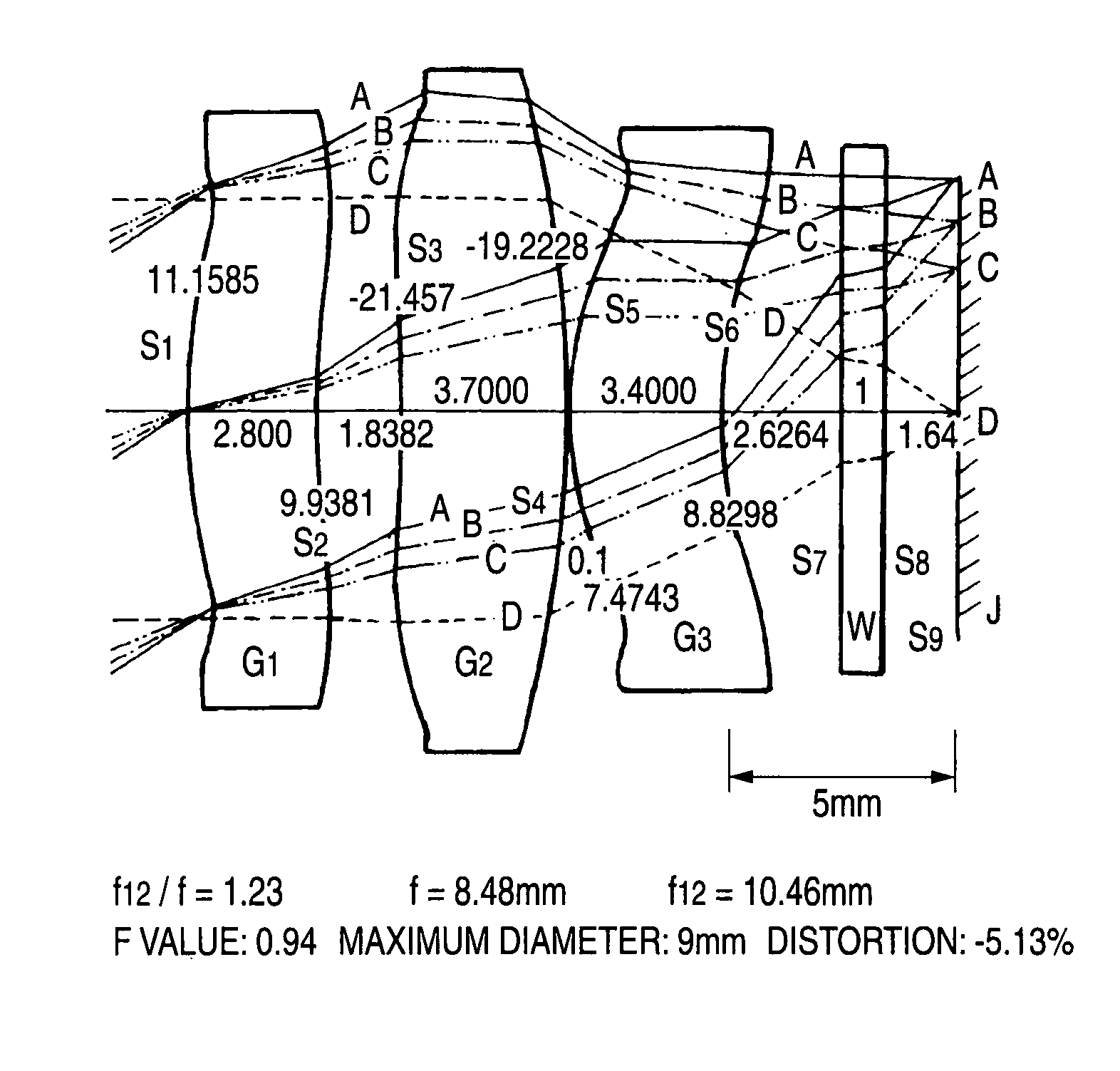
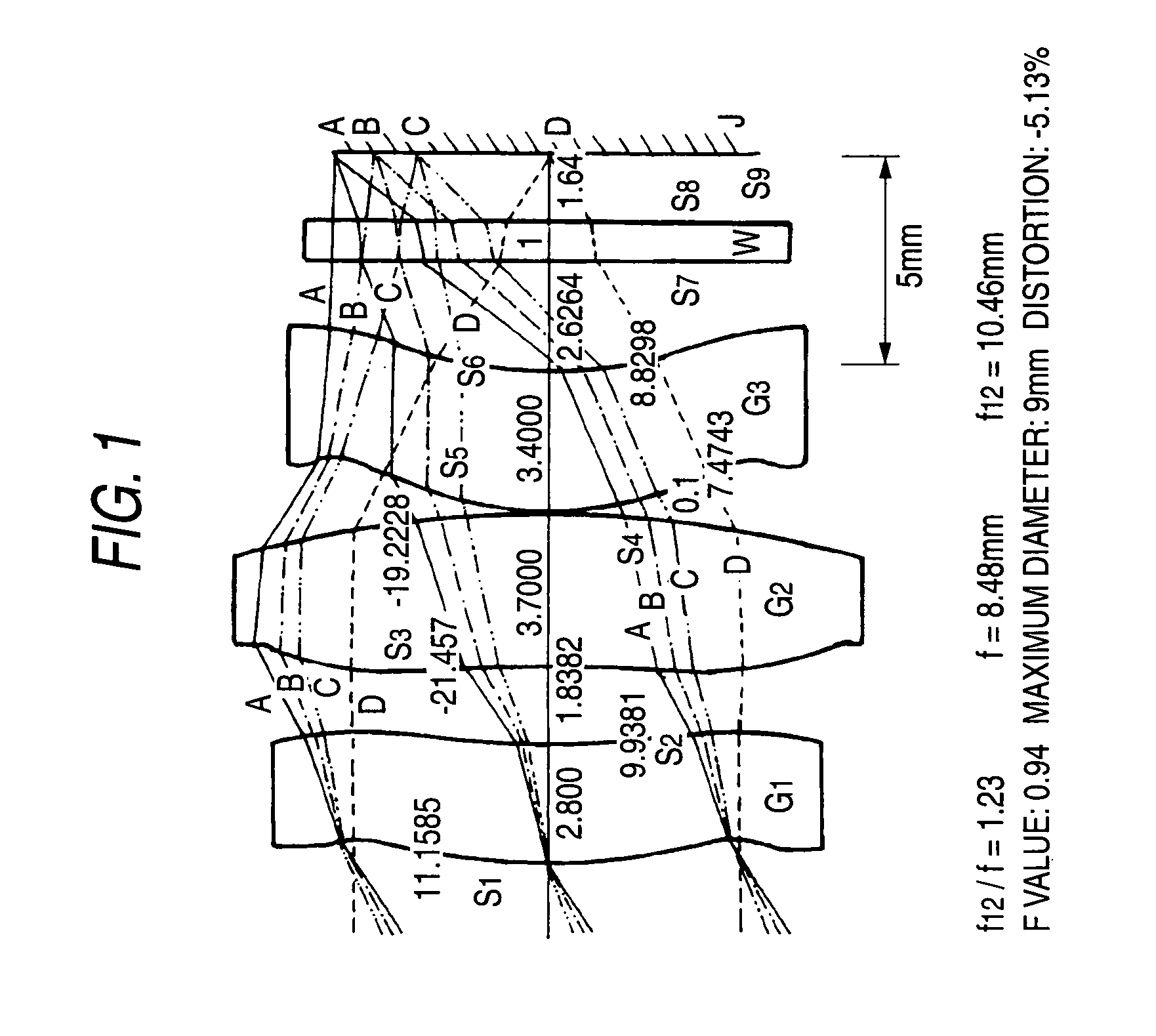
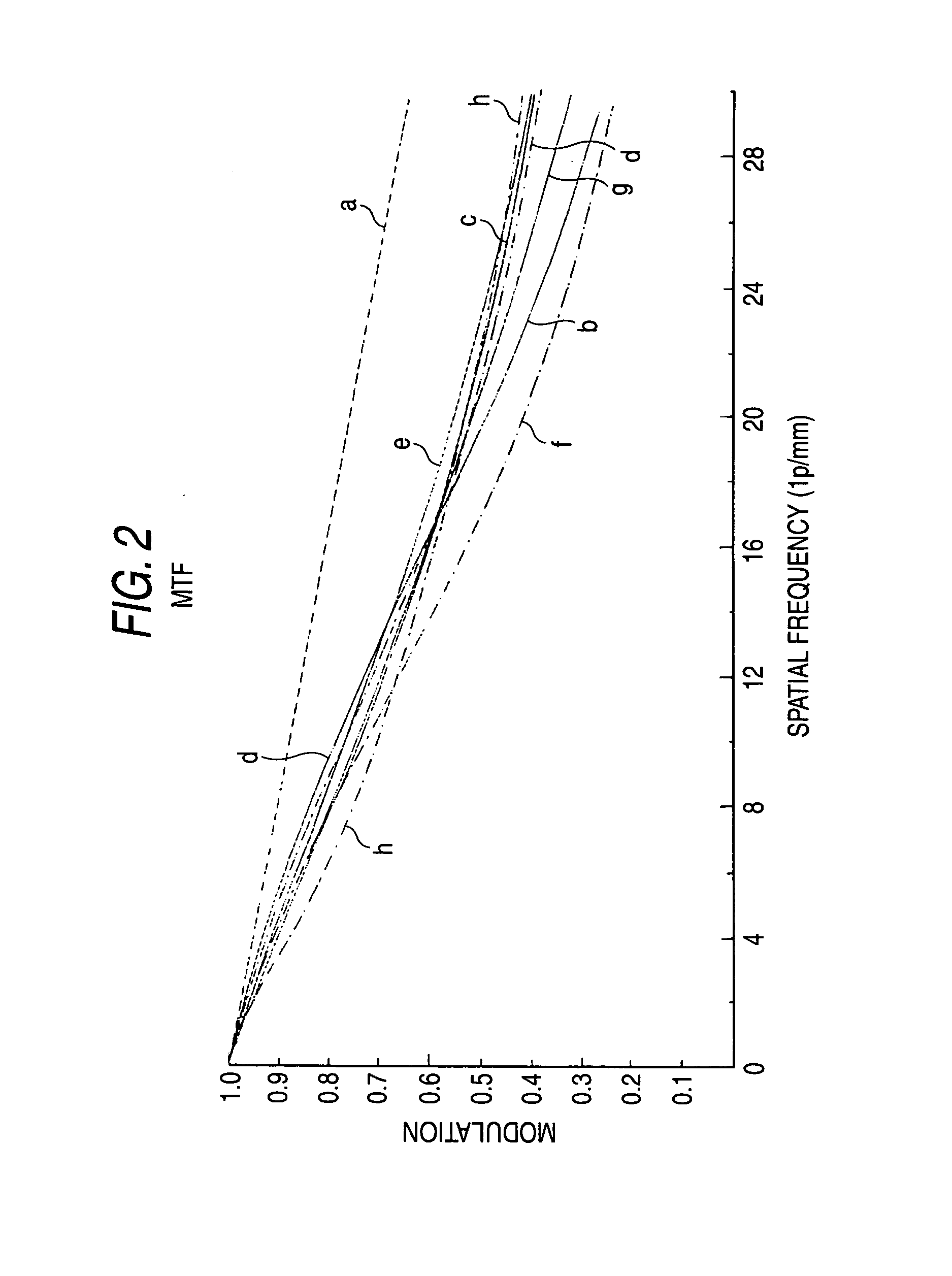
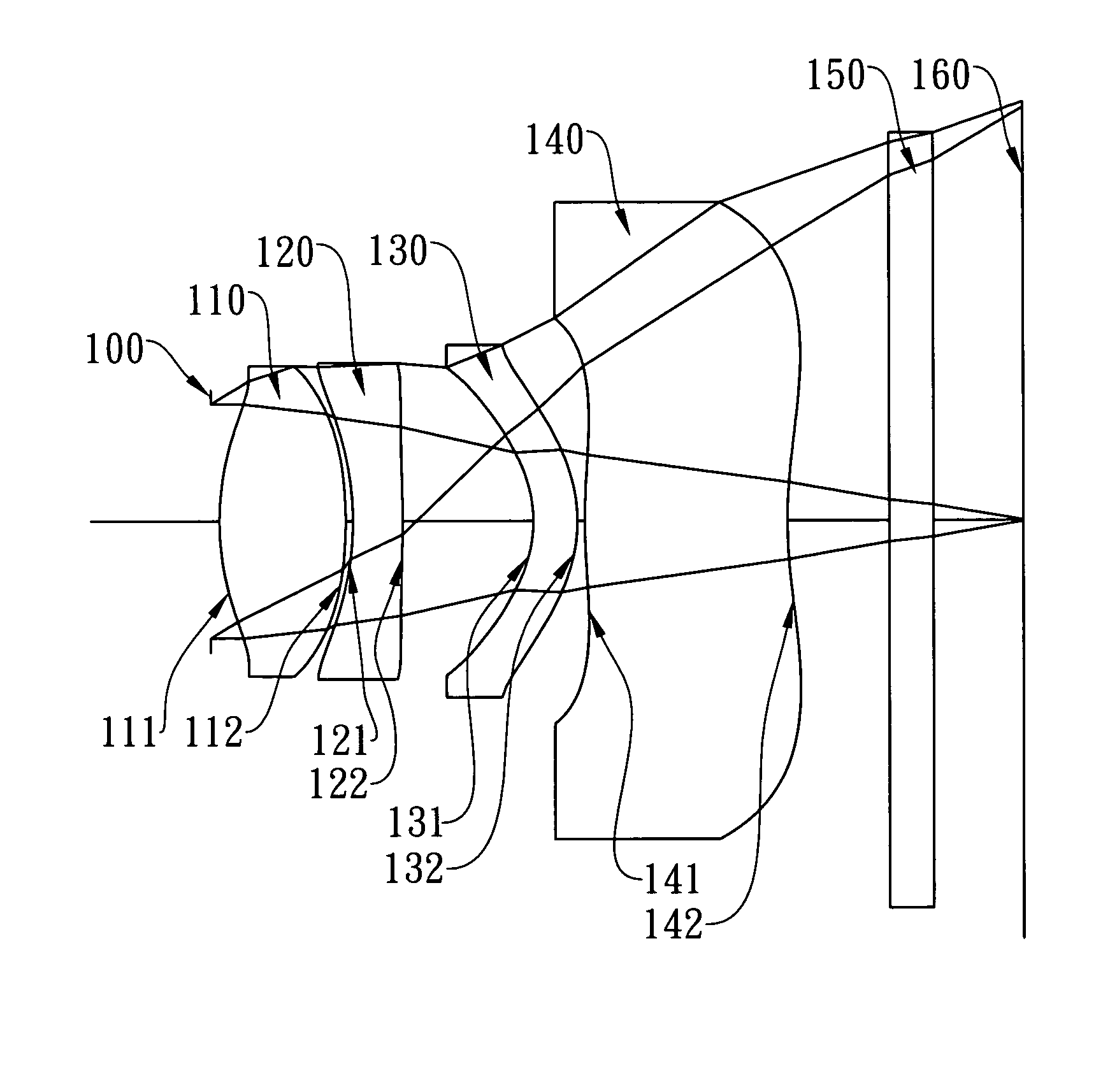
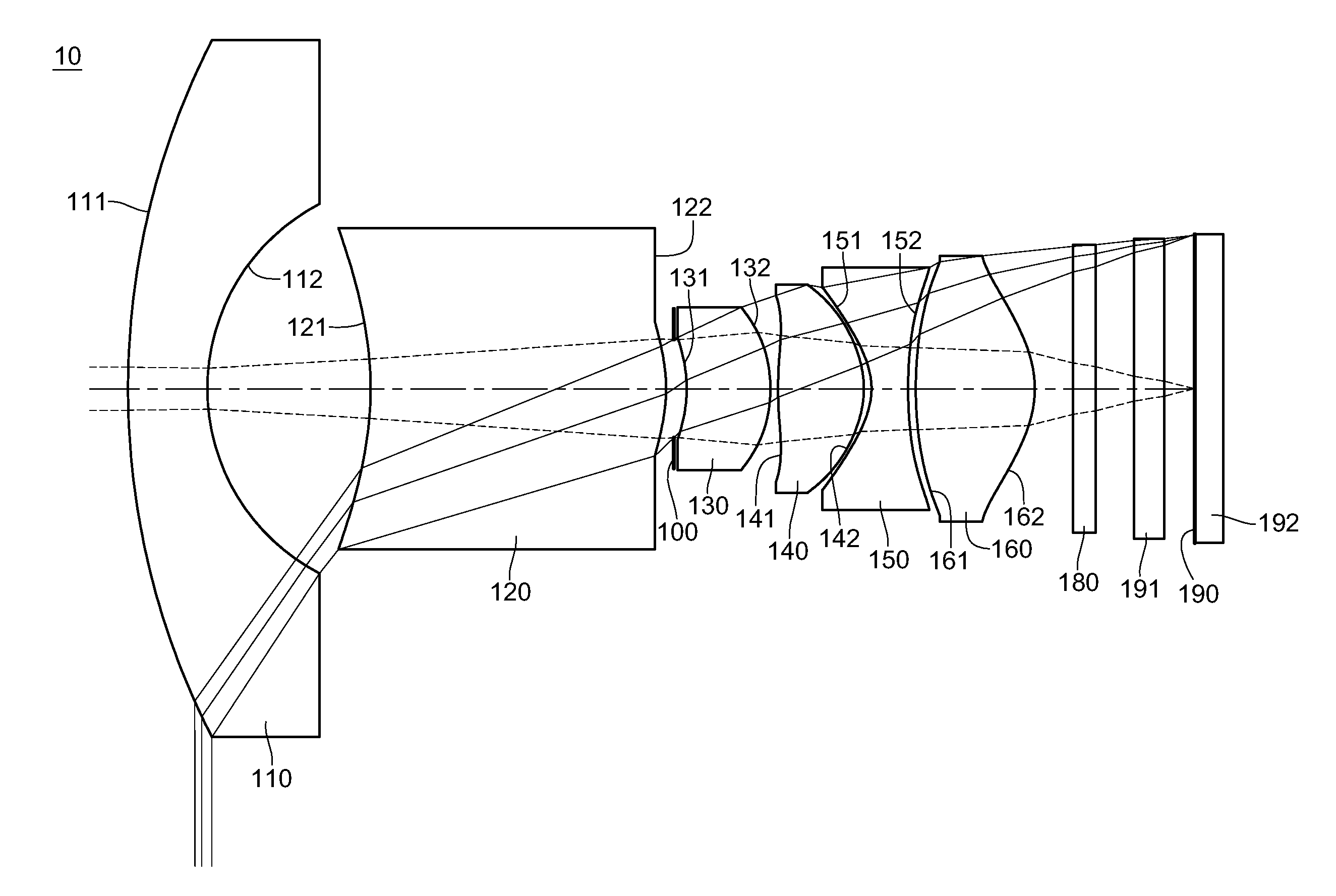
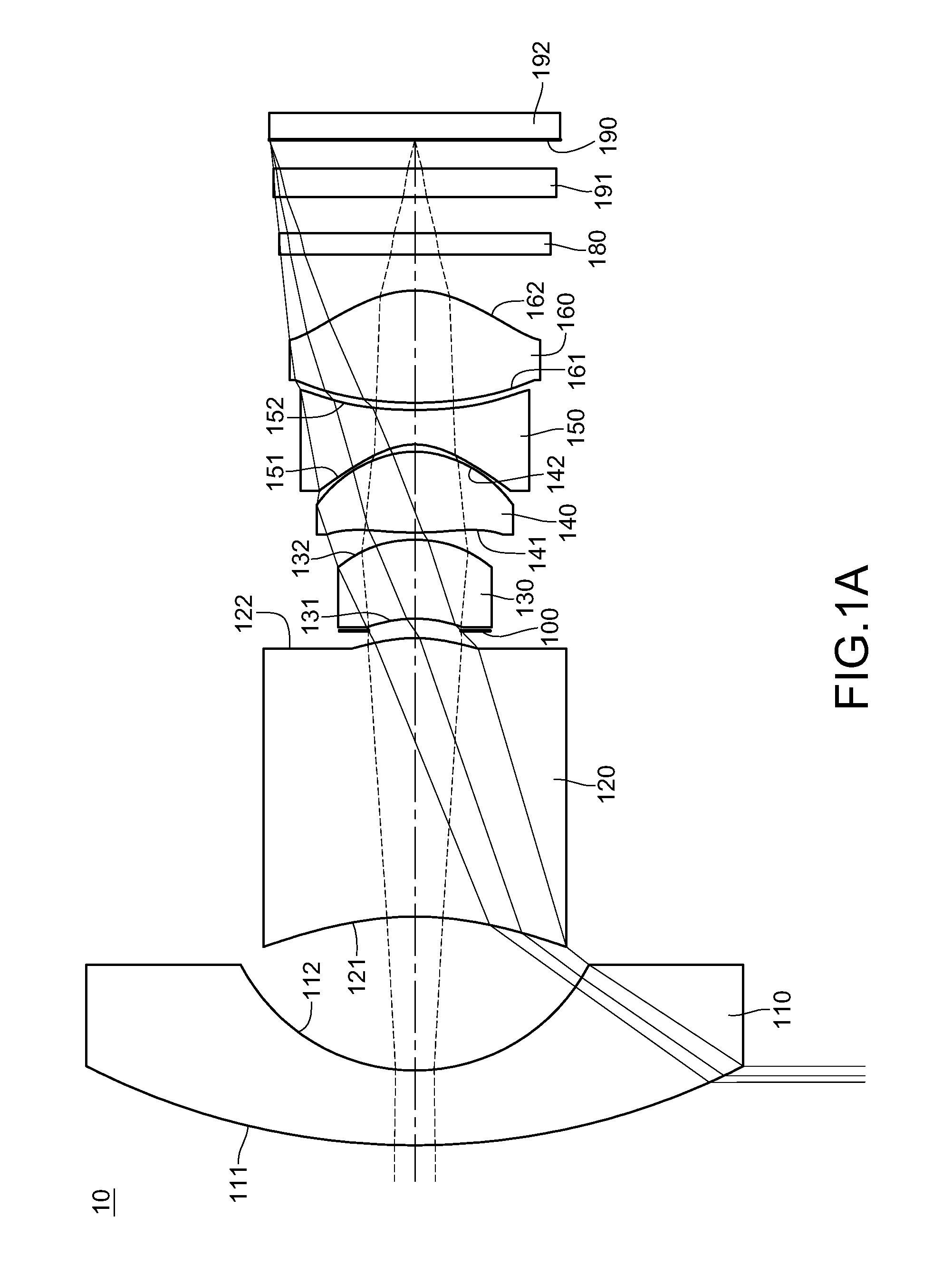
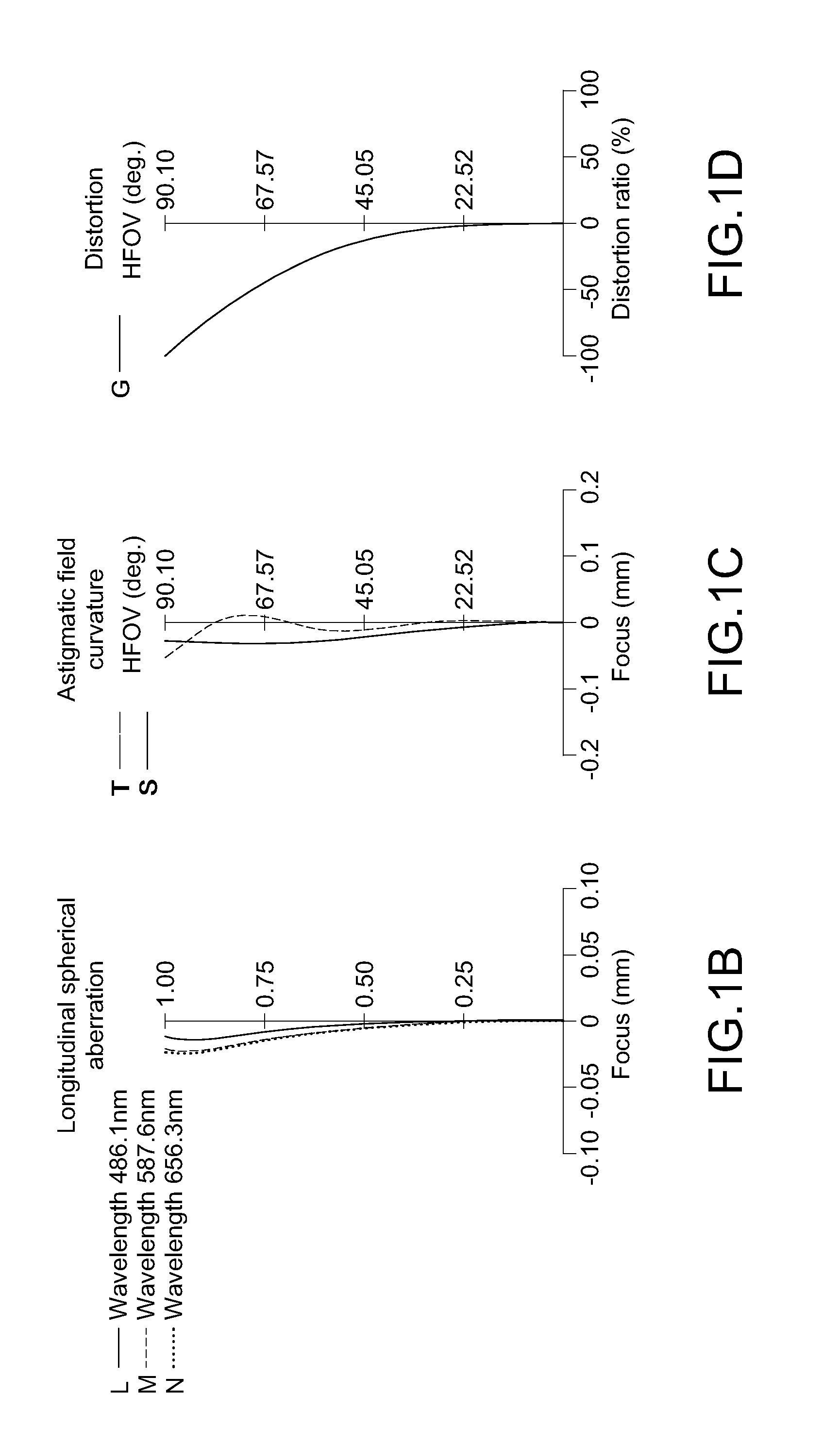
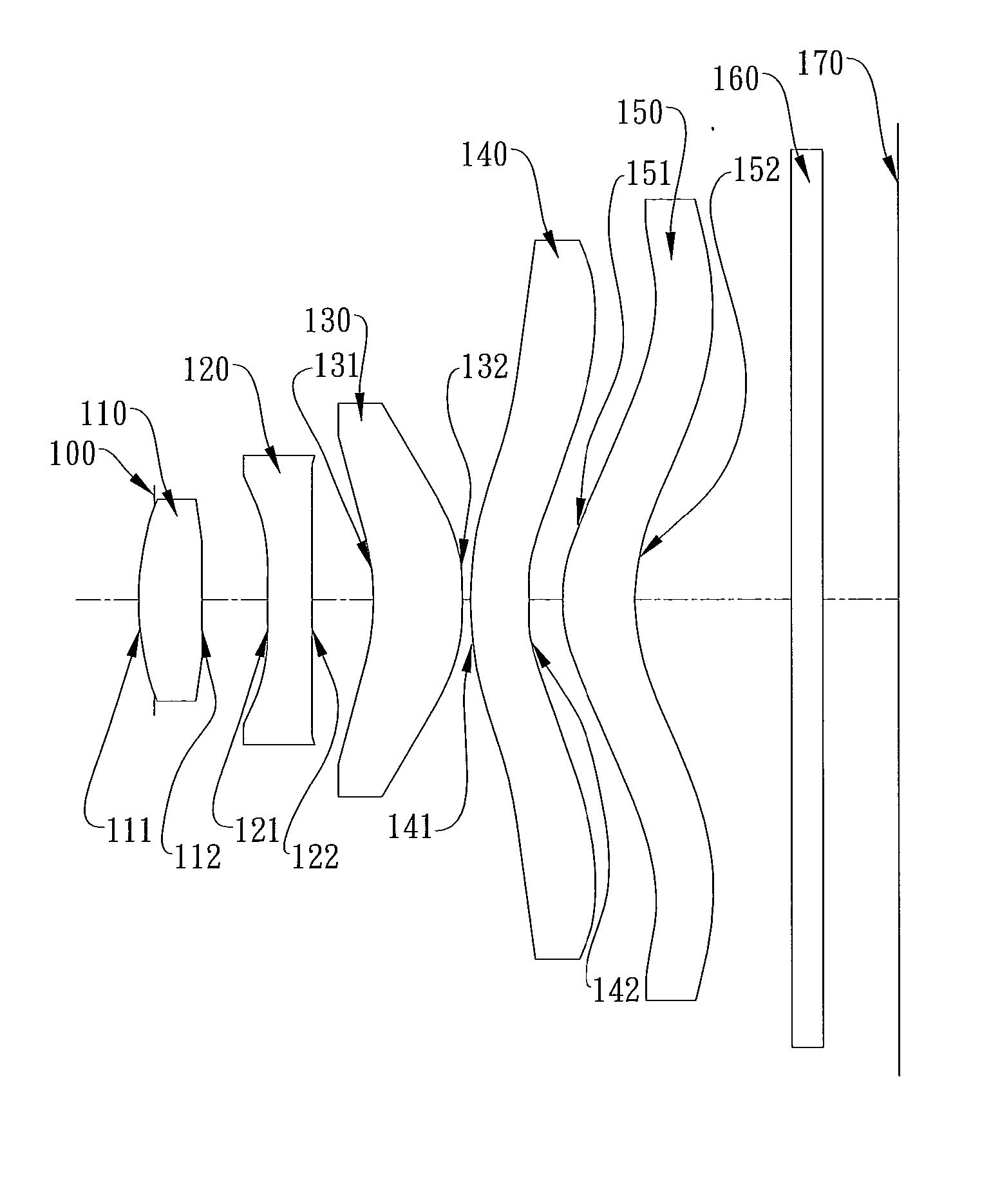
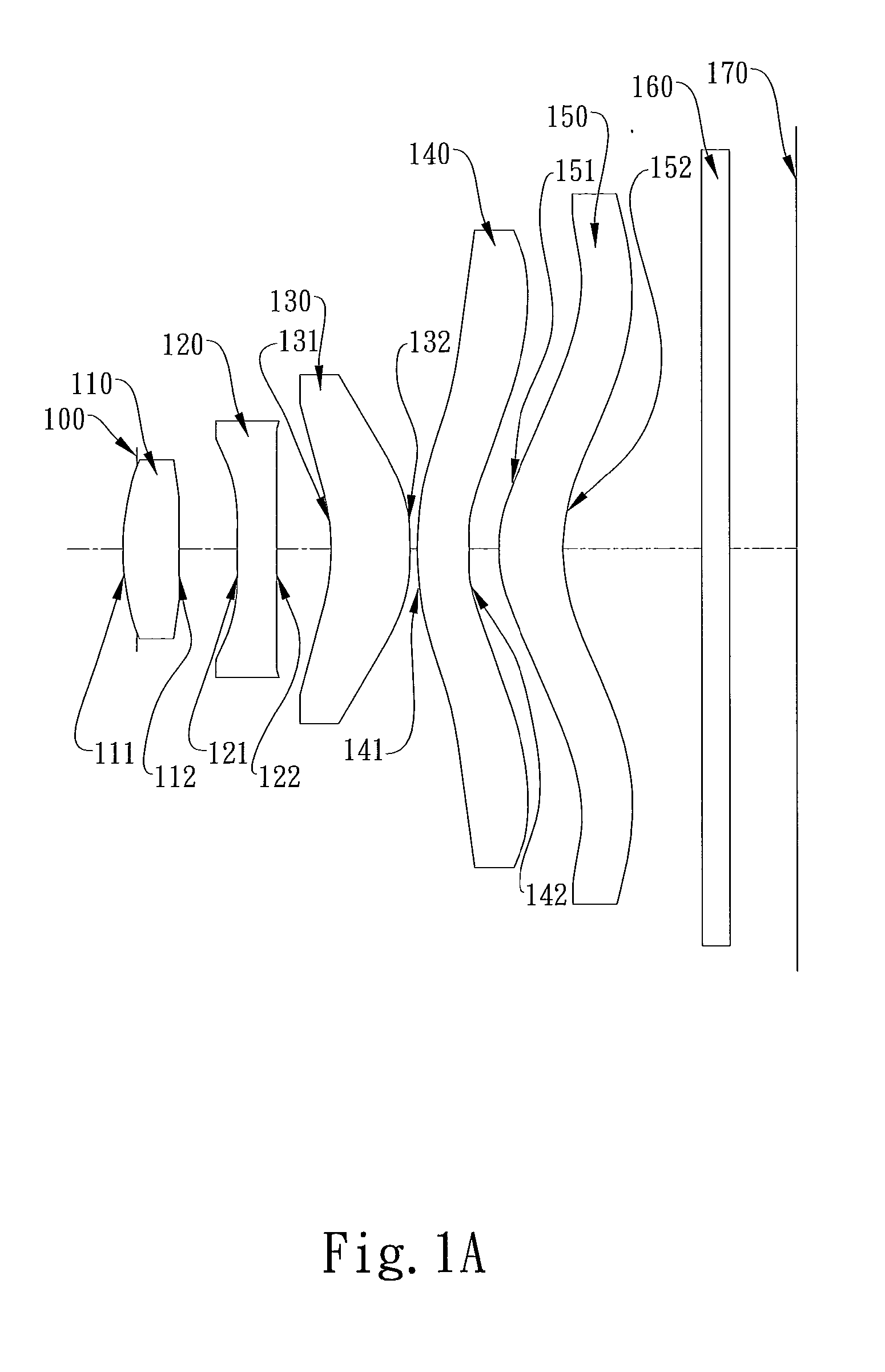
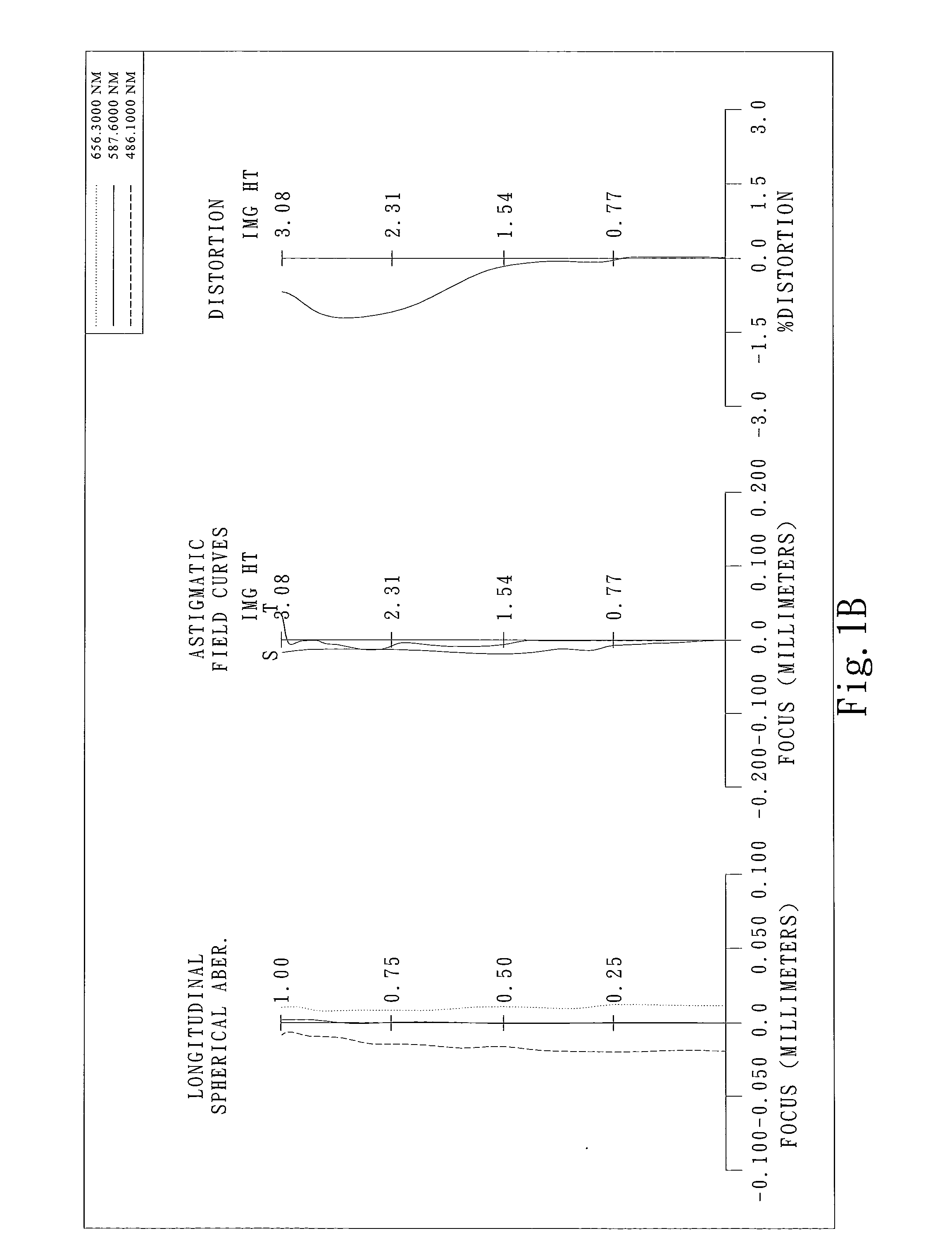
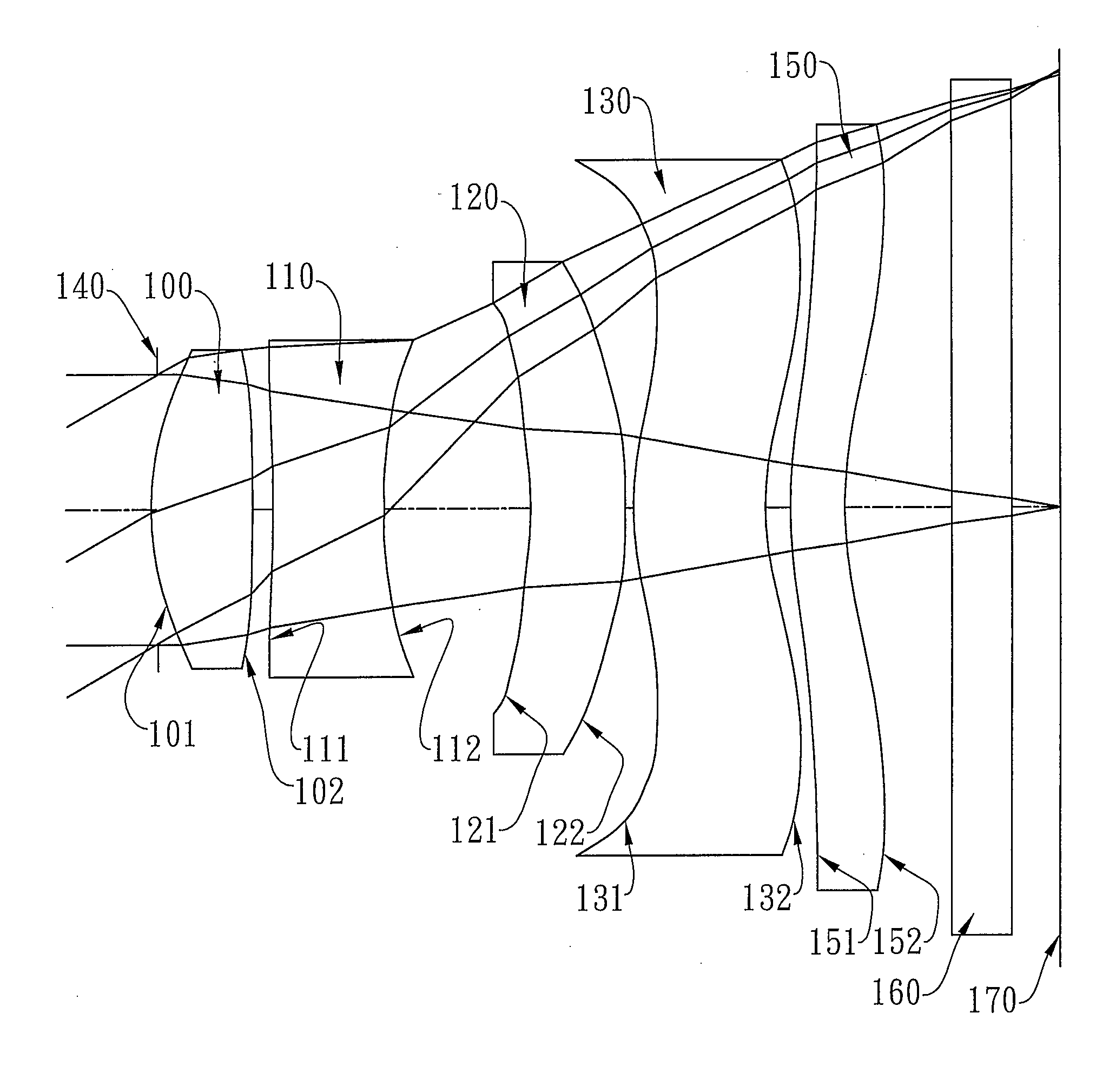
The present invention provides an imaging lens assembly including, in order from an object side to an image side: a first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface; a second lens element with negative refractive power; a third lens element with negative refractive power; a fourth lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface; a fifth lens element having a concave image-side surface, at least one inflection point being provided on the fifth lens element; and an aperture stop disposed between an imaged object and the third lens element. Such an arrangement of optical elements can effectively improve the image quality of the system and enable the imaging lens assembly to maintain a compact form. When the aperture stop is disposed near the object side, the telecentric feature is emphasized, resulting in a shorter total track length. When the aperture stop is disposed near the third lens element, the emphasis is on the wide field of view, and such an aperture stop placement helps to effectively reduce the sensitivity of the imaging lens assembly.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Image capturing optical lens assembly
An image capturing optical lens assembly includes, in order from an object side to an image side, a first lens element, a second lens element, a third lens element, a fourth lens element and a fifth lens element. The first lens element has positive refractive power. The second lens element has positive refractive power. The third lens element has negative refractive power. The fourth lens element has positive refractive power. The fifth lens element with negative refractive power is made of plastic material, and has an image-side surface being concave at a paraxial region and being convex at a peripheral region, wherein at least one of an object-side surface and the image-side surface of the fifth lens element is aspheric.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Imaging lens system
ActiveUS20110013069A1Short total track lengthImprove image qualityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPhysicsCamera lens
This invention provides an imaging lens system including, in order from an object side to an image side: a first lens with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface; a second lens with negative refractive power; a third lens having a concave image-side surface; a fourth lens with positive refractive power; a fifth lens with negative refractive power having a concave image-side surface, at least one surface thereof having at least one inflection point; and an aperture stop disposed between an imaged object and the third lens. The on-axis spacing between the first lens and second lens is T12, the focal length of the imaging lens system is f, and they satisfy the relation: 0.5<(T12 / f)×100<15.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
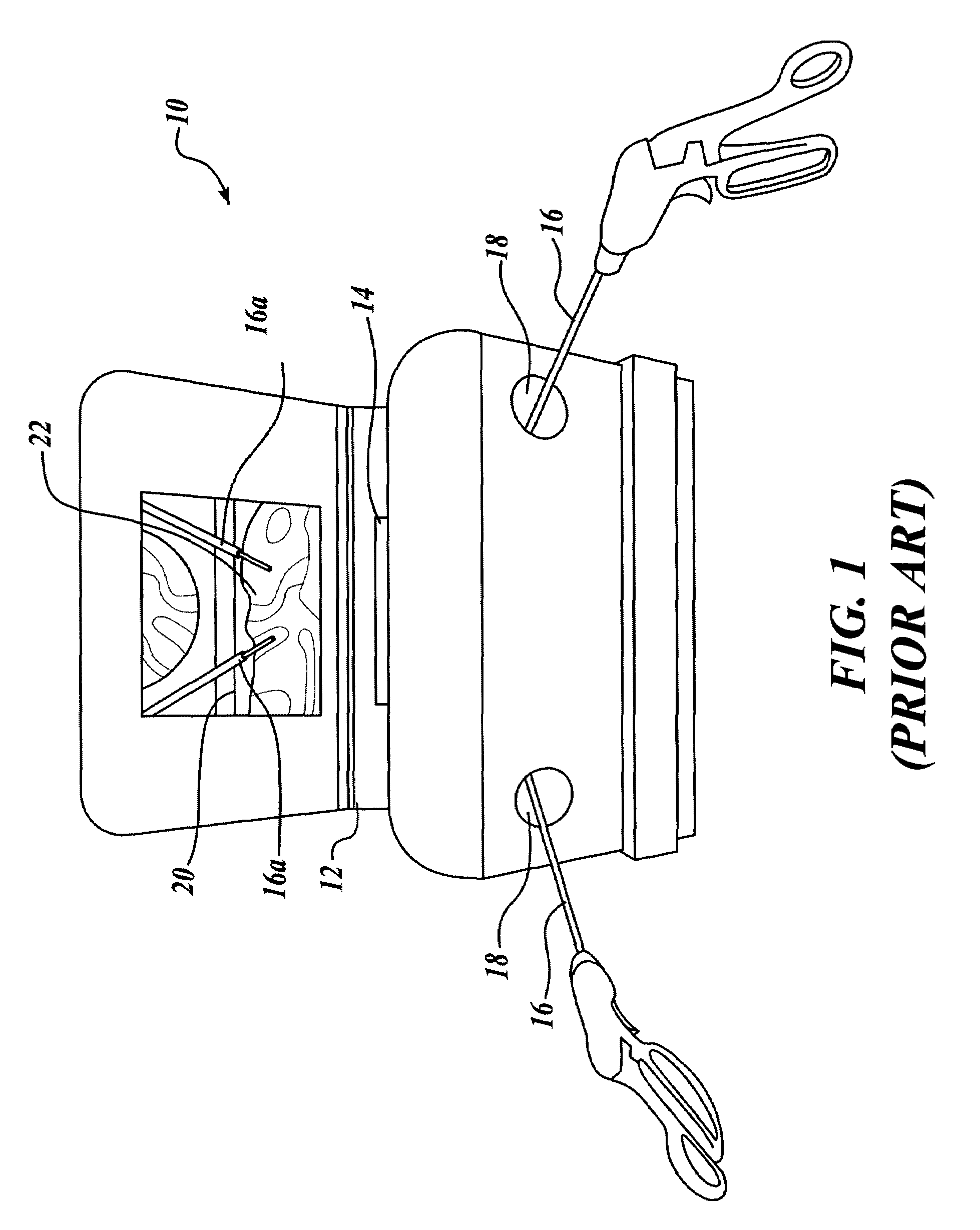
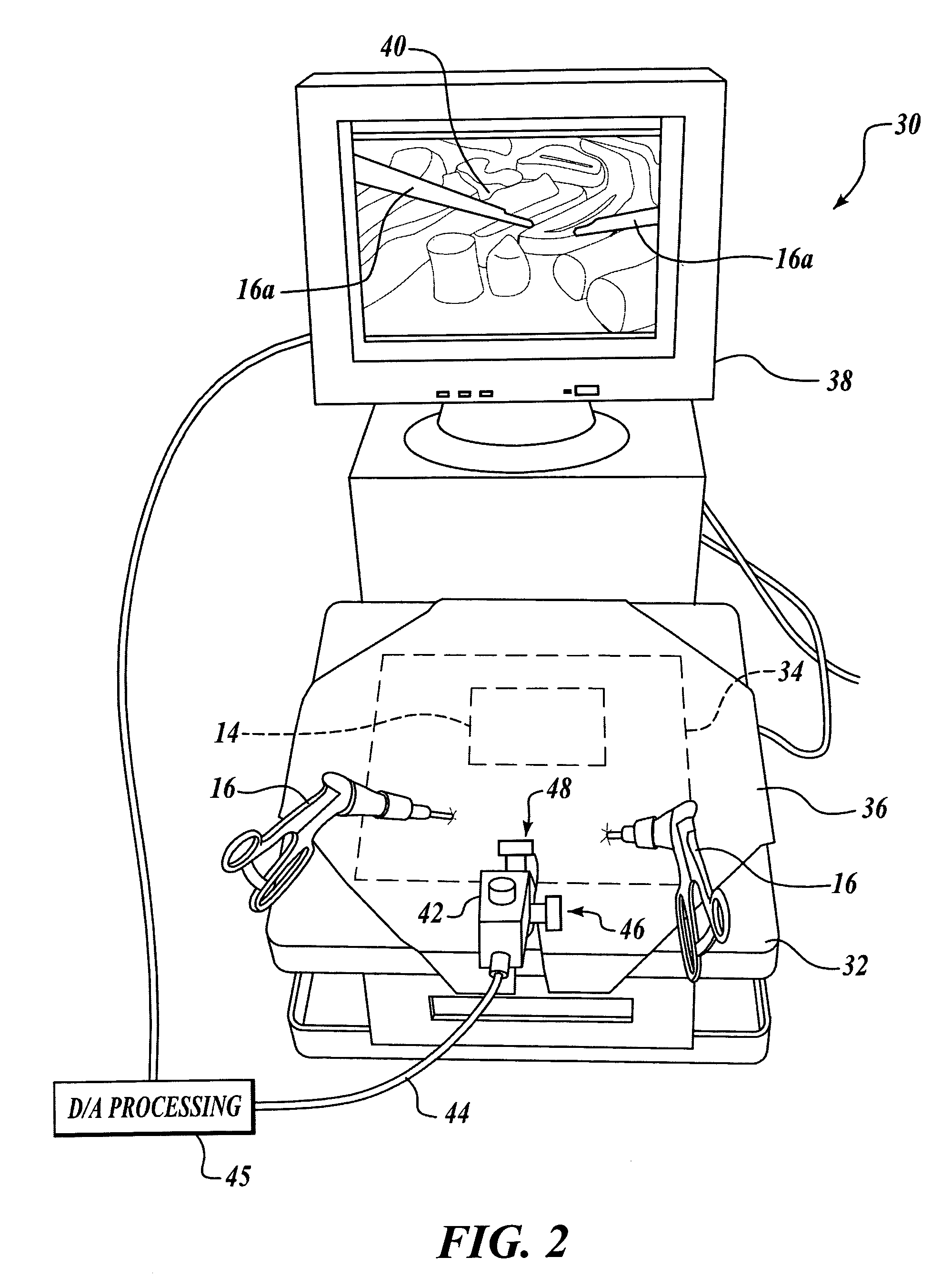
Laparoscopic and endoscopic trainer including a digital camera
ActiveUS20050064378A1Enhance endoscopic skill trainingEasy to trainSurgeryEducational modelsDigital videoAnatomical structures
A videoendoscopic surgery training system includes a housing defining a practice volume in which a simulated anatomical structure is disposed. Openings in the housing enable surgical instruments inserted into the practice volume to access the anatomical structure. A digital video camera is disposed within the housing to image the anatomical structure on a display. The position of the digital video camera can be fixed within the housing, or the digital video camera can be positionable within the housing to capture images of different portions of the practice volume. In one embodiment the digital video camera is coupled to a boom, a proximal end of which extends outside the housing to enable positioning the digital video camera. The housing preferably includes a light source configured to illuminate the anatomical structure. One or more reflectors can be used to direct an image of the anatomical structure to the digital video camera.
Owner:TOLY CHRISTOPHER C
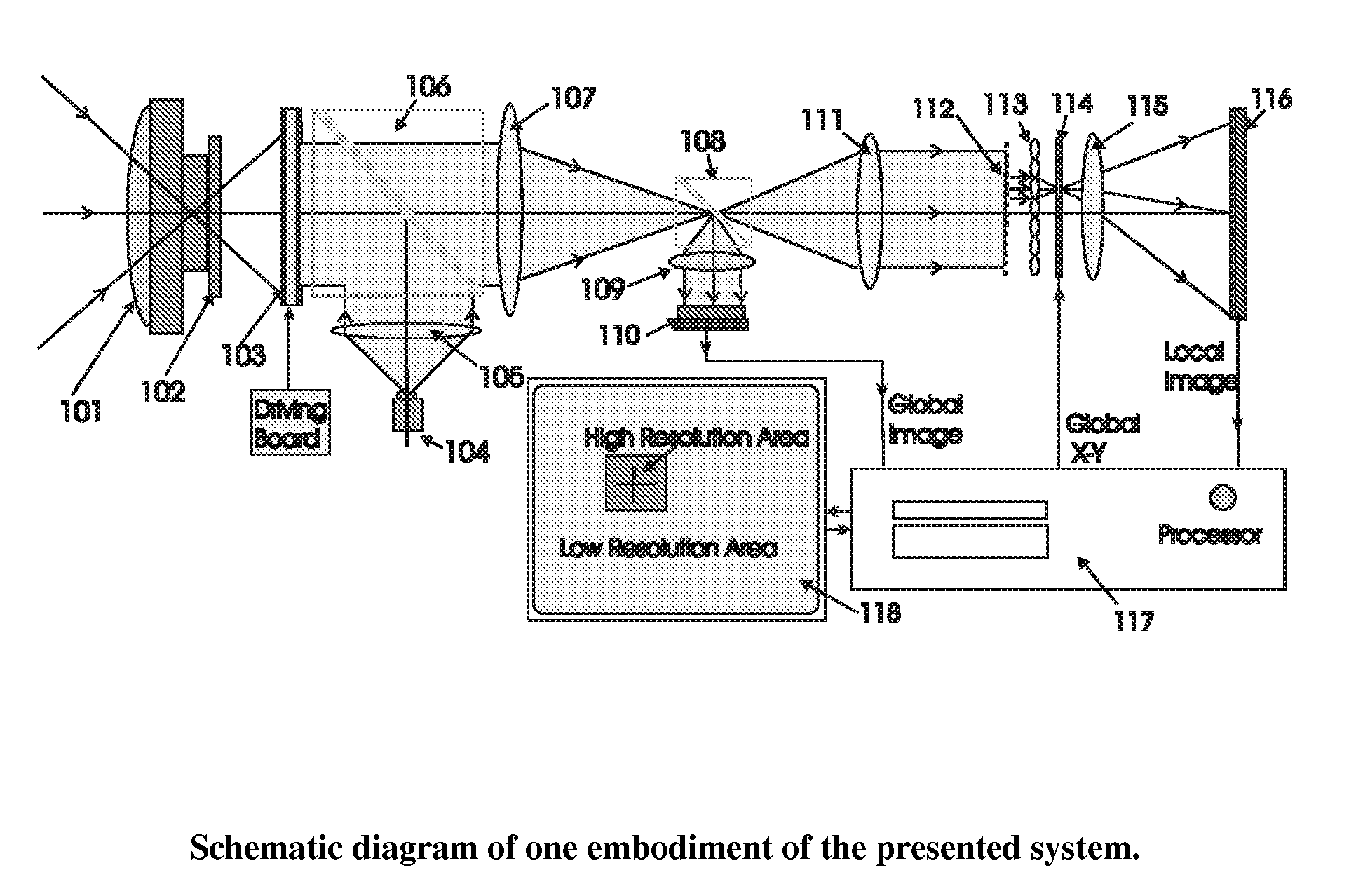
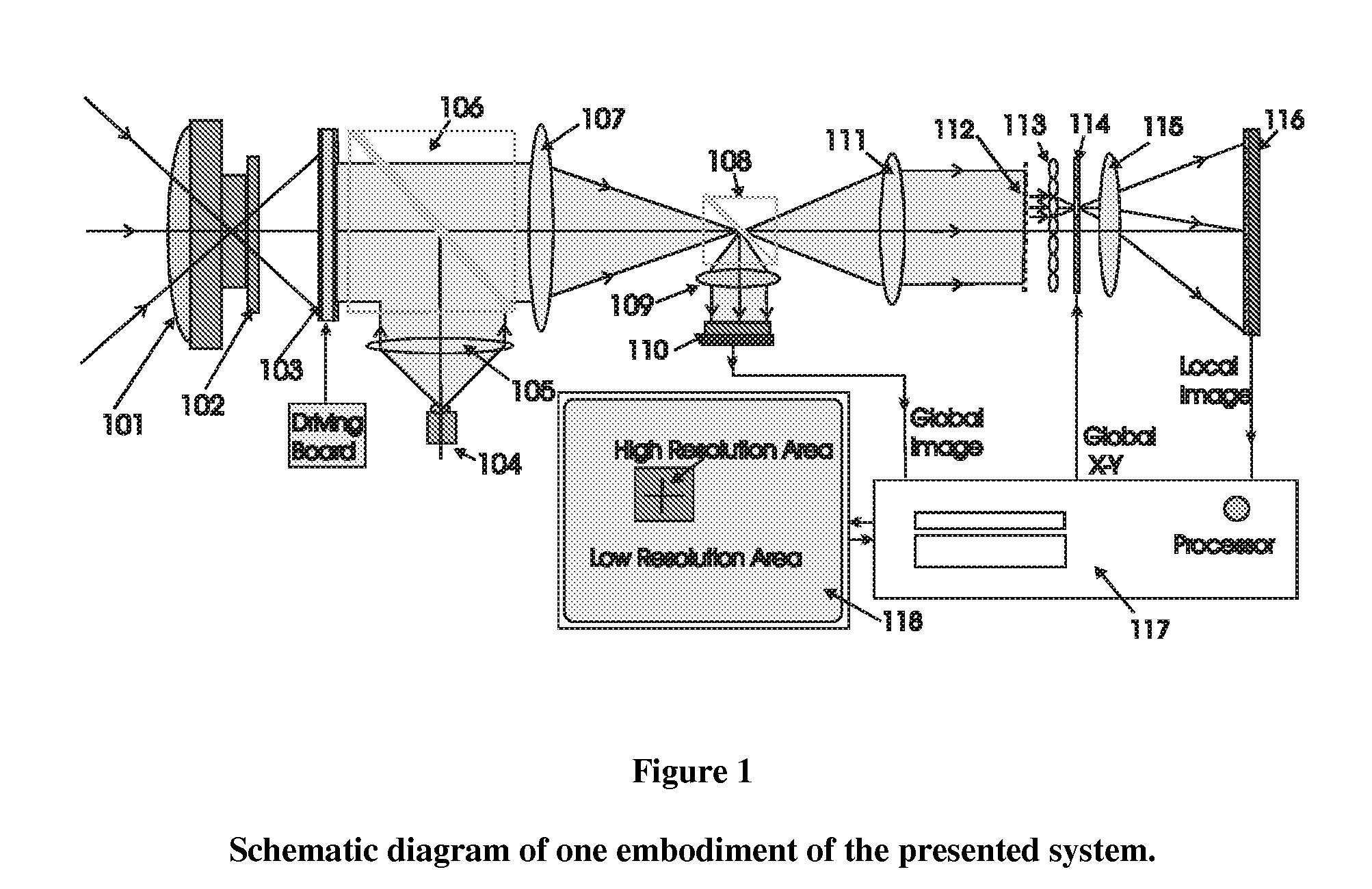
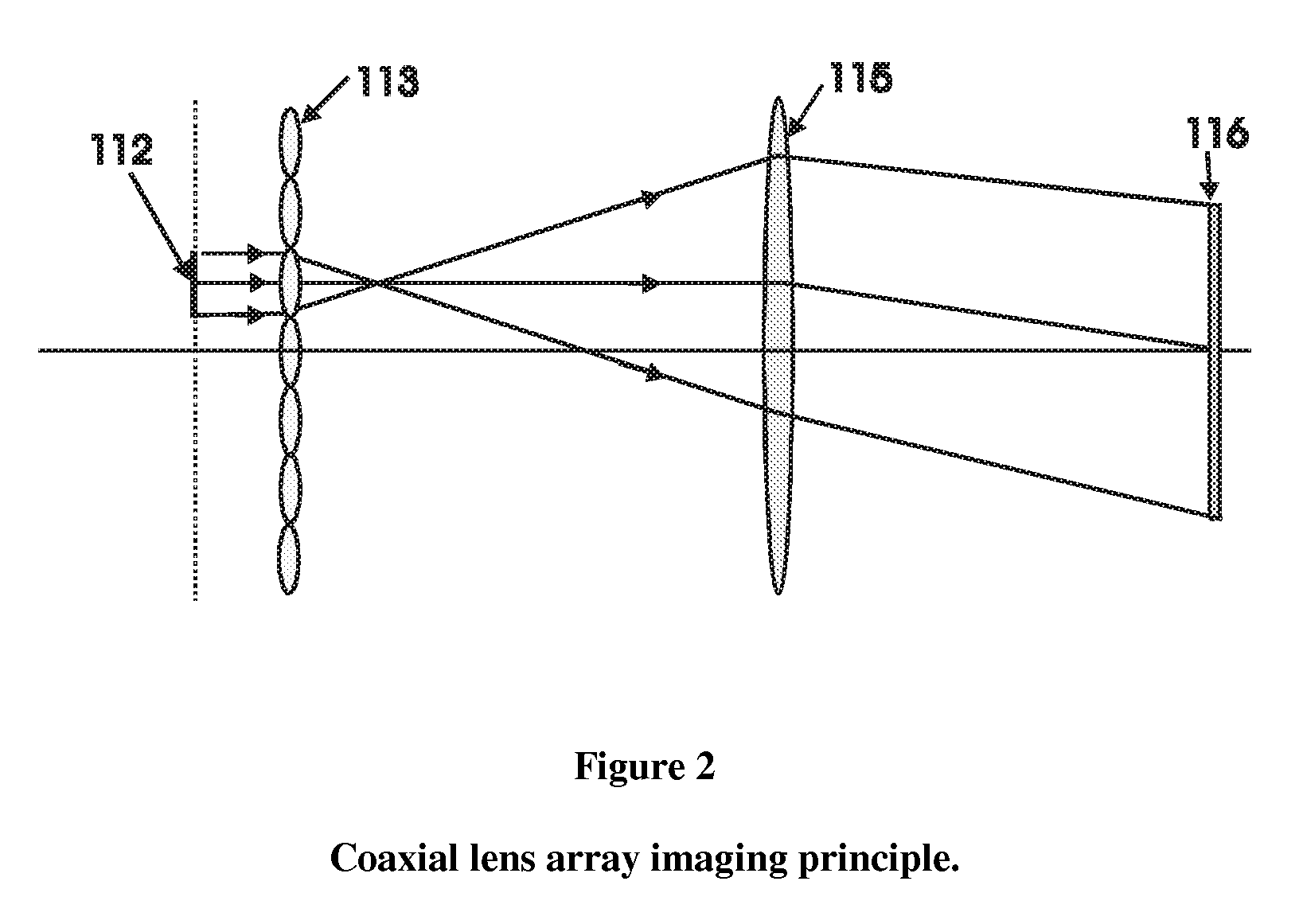
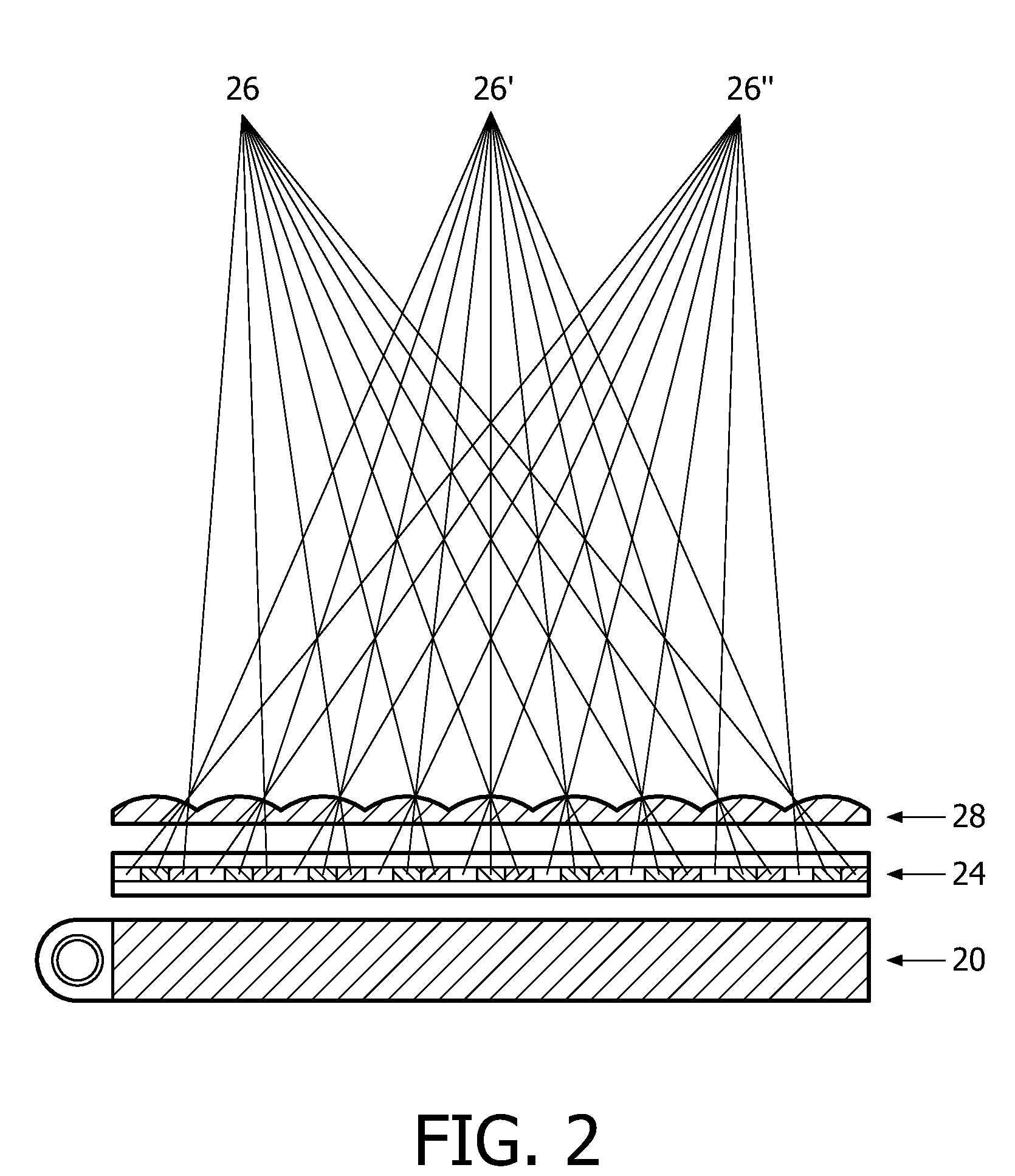
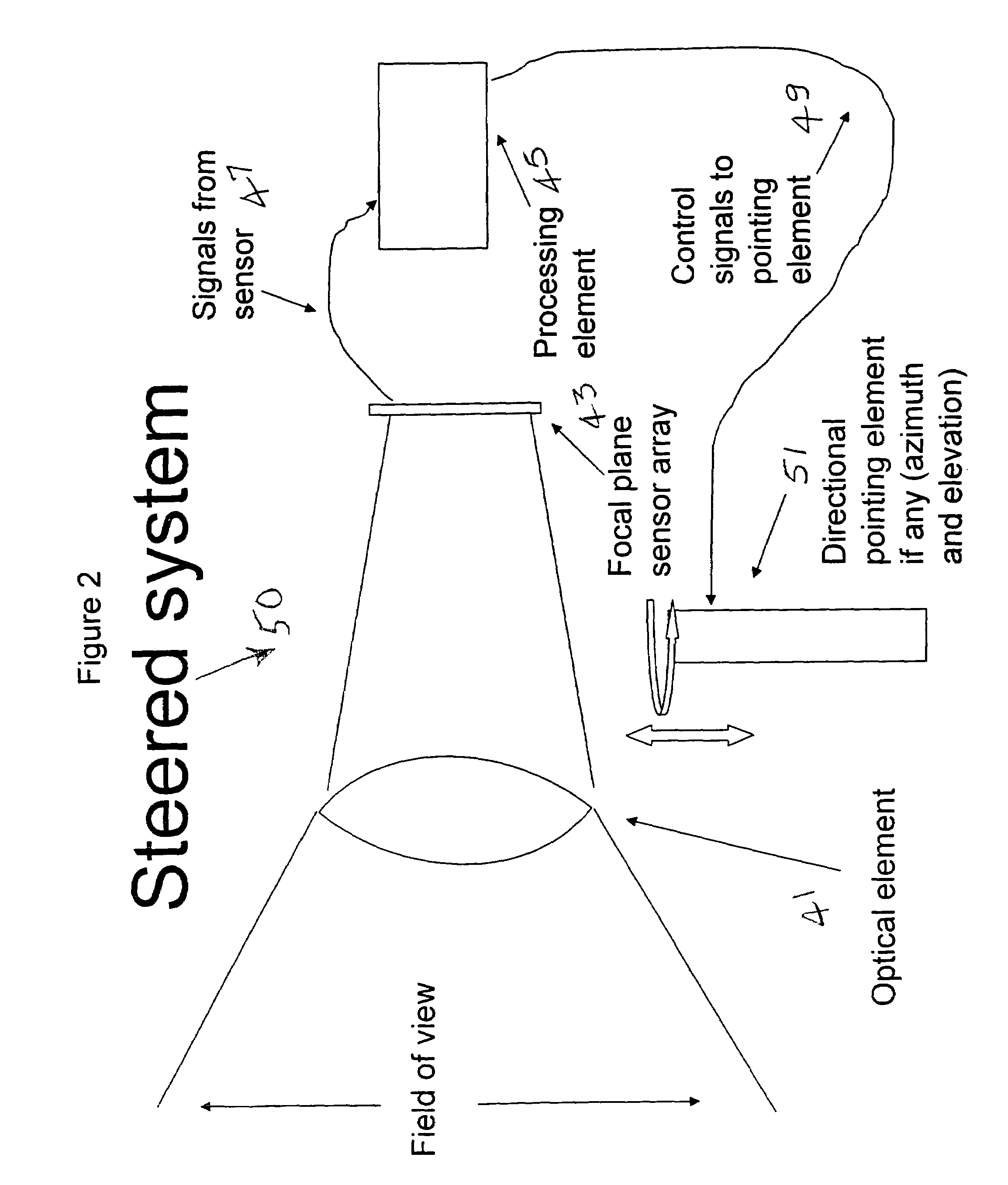
Electro-optical foveated imaging and tracking system
InactiveUS7973834B2Improve spatial resolutionWide field-of-viewTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionSensor arrayHigh resolution image
Conventional electro-optical imaging systems can not achieve wide field of view (FOV) and high spatial resolution imaging simultaneously due to format size limitations of image sensor arrays. To implement wide field of regard imaging with high resolution, mechanical scanning mechanisms are typically used. Still, sensor data processing and communication speed is constrained due to large amount of data if large format image sensor arrays are used. This invention describes an electro-optical imaging system that achieves wide FOV global imaging for suspect object detection and local high resolution for object recognition and tracking. It mimics foveated imaging property of human eyes. There is no mechanical scanning for changing the region of interest (ROI). Two relatively small format image sensor arrays are used to respectively acquire global low resolution image and local high resolution image. The ROI is detected and located by analysis of the global image. A lens array along with an electronically addressed switch array and a magnification lens is used to pick out and magnify the local image. The global image and local image are processed by the processor, and can be fused for display. Three embodiments of the invention are described.
Owner:NEW SPAN OPTO TECH
System for Extending The Observation, Surveillance, and Navigational Capabilities of a Robot
InactiveUS20110035054A1Wide field of viewComputer controlSimulator controlRobotic systemsTelecommunications link
The invention is a system that is integrated with an existing robotic system in order to extend its observation, surveillance, and navigational capabilities. The system comprises: a sensor module comprising imaging and other types of sensors that is attached to the robotic device of the robotic system and a system control station comprising a communication link to the robot control station of the existing robotic system. Both the system control station and the sensor module comprise processing units that are configured to work in complete harmony. These processing units are each supplied with software that enables using information supplied by the sensors and other components in the sensor module to provide the robotic systems with many advanced capabilities that could not be achieves prior to attachment of the sensor module to the robot.
Owner:MISTRAL DETECTION LTD
Photographing optical lens assembly
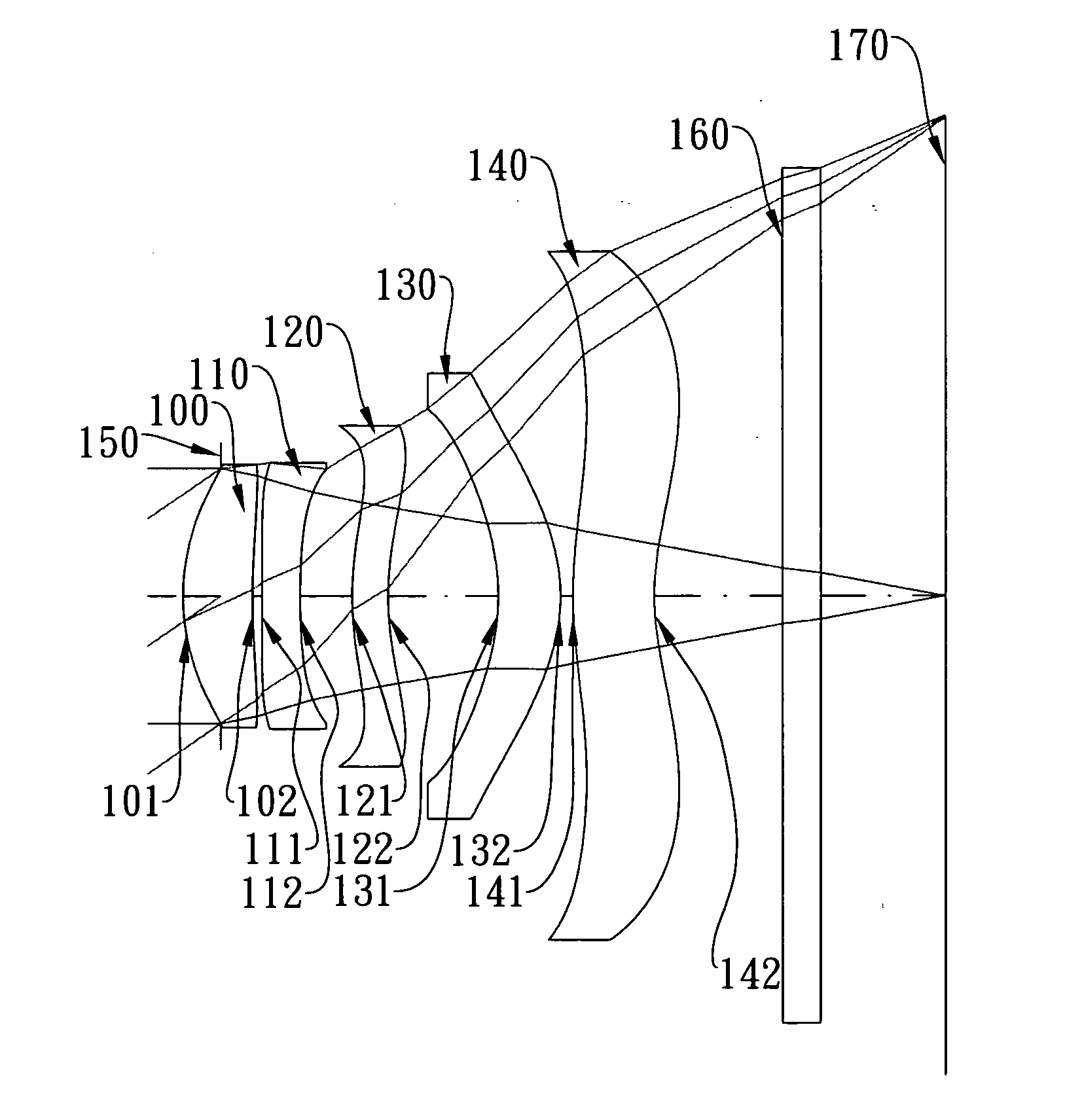
This invention provides a photographing optical lens assembly including, in order from an object side toward an image side: a first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface, a second lens element with negative refractive power having a concave object-side surface and a concave image-side surface, a third lens element with positive refractive power, a fourth lens element with negative refractive power having a convex object-side surface and a concave image-side surface, and at least one of surfaces thereof being aspheric, a plastic fifth lens element having a convex object-side surface and a concave image-side surface with at least one inflection point. An aperture stop is positioned between an imaged object and the third lens element. The photographing optical lens assembly further comprises an electronic sensor on which the object is imaged.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Insertable device and system for minimal access procedure
ActiveUS20050014994A1Expand accessMinimal incisionEndoscopesLaproscopesAbdominal cavityDegrees of freedom
The present invention provides a system and single or multi-functional element device that can be inserted and temporarily placed or implanted into a structure having a lumen or hollow space, such as a subject's abdominal cavity to provide therewith access to the site of interest in connection with minimally invasive surgical procedures. The insertable device may be configured such that the functional elements have various degrees of freedom of movement with respect to orienting the functional elements or elements to provide access to the site from multiple and different orientations / perspectives as the procedure dictates, e.g., to provide multiple selectable views of the site, and may provide a stereoscopic view of the site of interest.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Optical lens system
The present invention provides an optical lens system comprising, in order from an object side to an image side: a first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface; a second lens element with negative refractive power; a third lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface and a convex image-side surface; a fourth lens element; and a fifth lens element having a convex object-side surface and a concave image-side surface, the object-side and image-side surfaces thereof being aspheric and at least one inflection point being formed on the image-side surface. Such arrangement of optical elements can effectively minimize the size of the optical lens system, lower the sensitivity of the optical system, and obtain higher image resolution.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Laparoscopic and endoscopic trainer including a digital camera
ActiveUS7594815B2Easy to trainWide field of viewSurgeryEducational modelsAnatomical structuresDigital video
Owner:TOLY CHRISTOPHER C
Holographic waveguide optical tracker
ActiveUS20180232048A1Lower latencyWide field of viewInput/output for user-computer interactionPlanar/plate-like light guidesOptical pathLight source
There is provided an object tracker having: a first waveguide; a source of illumination light; a detector optically coupled to the waveguide; and at least one grating lamina formed within the waveguide. Illumination light propagating along a first optical path from the source to an object in relative motion to the object tracker. Image light reflected from at least one surface of an object is deflected by the grating lamina into a second optical path towards the detector.
Owner:DIGILENS
Object detection system
InactiveUS20070019181A1Wide field of viewHigh resolutionOptical rangefindersRoad vehicles traffic controlTriangulationHome robot
An object detection system utilizing one or more thin, planar structured light patterns projected into a volume of interest, along with digital processing hardware and one or more electronic imagers looking into the volume of interest. Triangulation is used to determine the intersection of the structured light pattern with objects in the volume of interest. Applications include navigation and obstacle avoidance systems for autonomous vehicles (including agricultural vehicles and domestic robots), security systems, and pet training systems.
Owner:SINCLAIR KENNETHH +2
Imaging lens
An imaging lens which uses a larger number of constituent lenses for higher performance and features a low F-value, low-profile design and a wide field of view. Designed for a solid-state image sensor, the imaging lens includes constituent lenses arranged in order from an object side to an image side: a first positive refractive power lens having a convex object-side surface; a second negative refractive power lens having a concave image-side surface; a third positive refractive power lens having a convex image-side surface; a fourth negative refractive power lens having a concave image-side surface; a fifth positive refractive power lens as a meniscus lens having a convex image-side surface; a sixth lens as a meniscus double-sided aspheric lens having a concave image-side surface near an optical axis; and a seventh negative refractive power lens as a double-sided aspheric lens having a concave image-side surface near the optical axis.
Owner:TOKYO VISIONARY OPTICS CO LTD
Agile-beam laser array transmitter
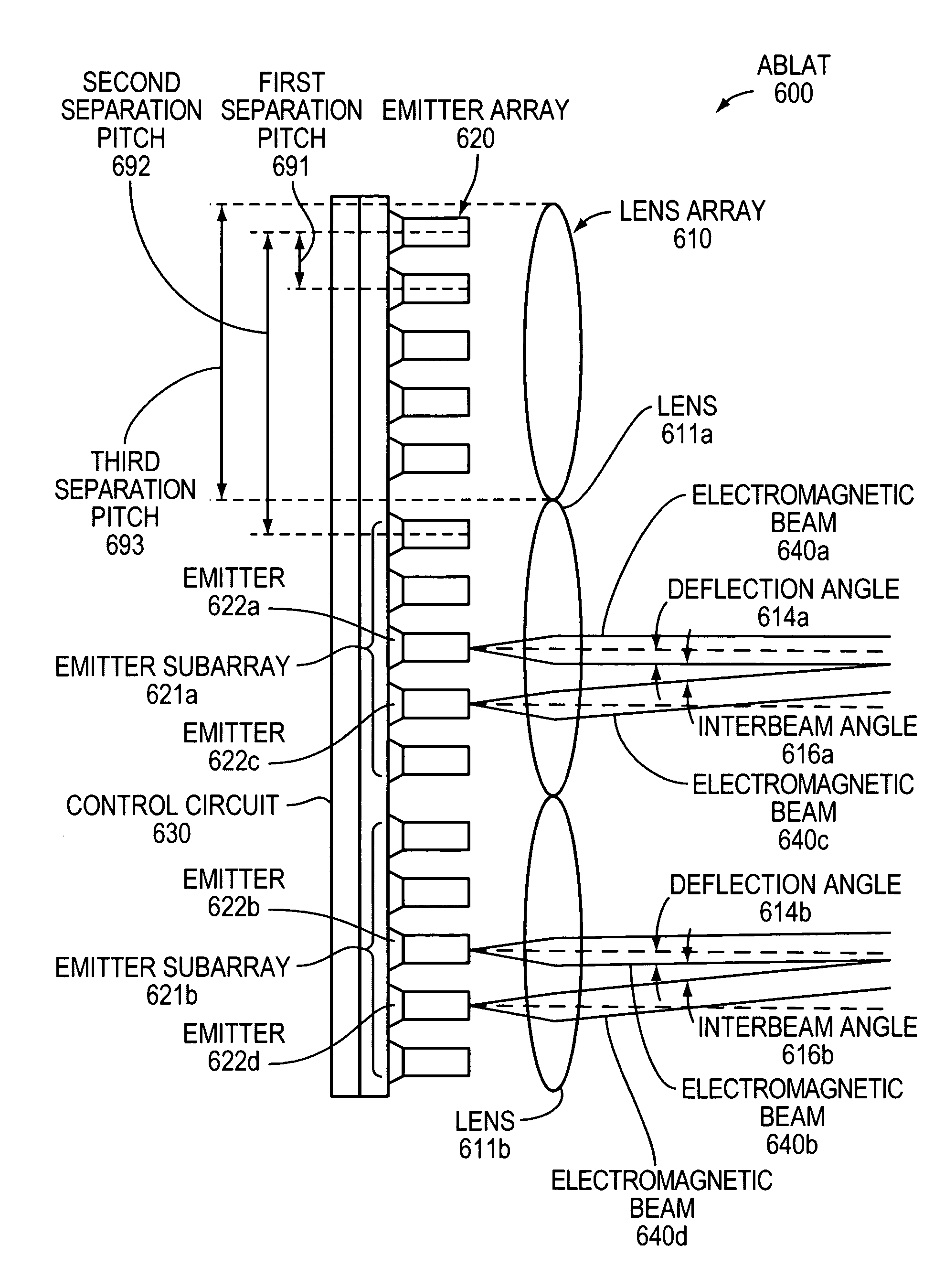
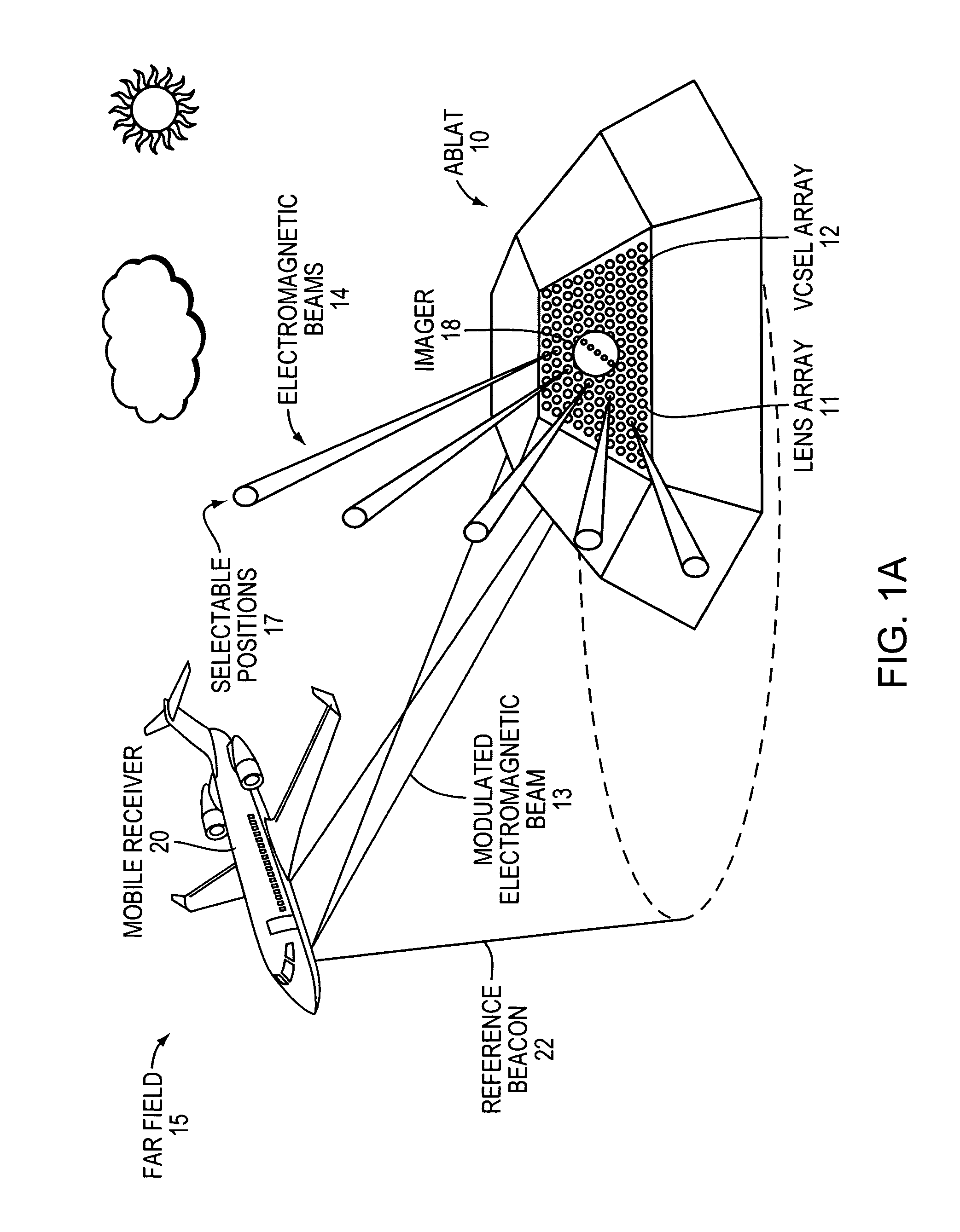
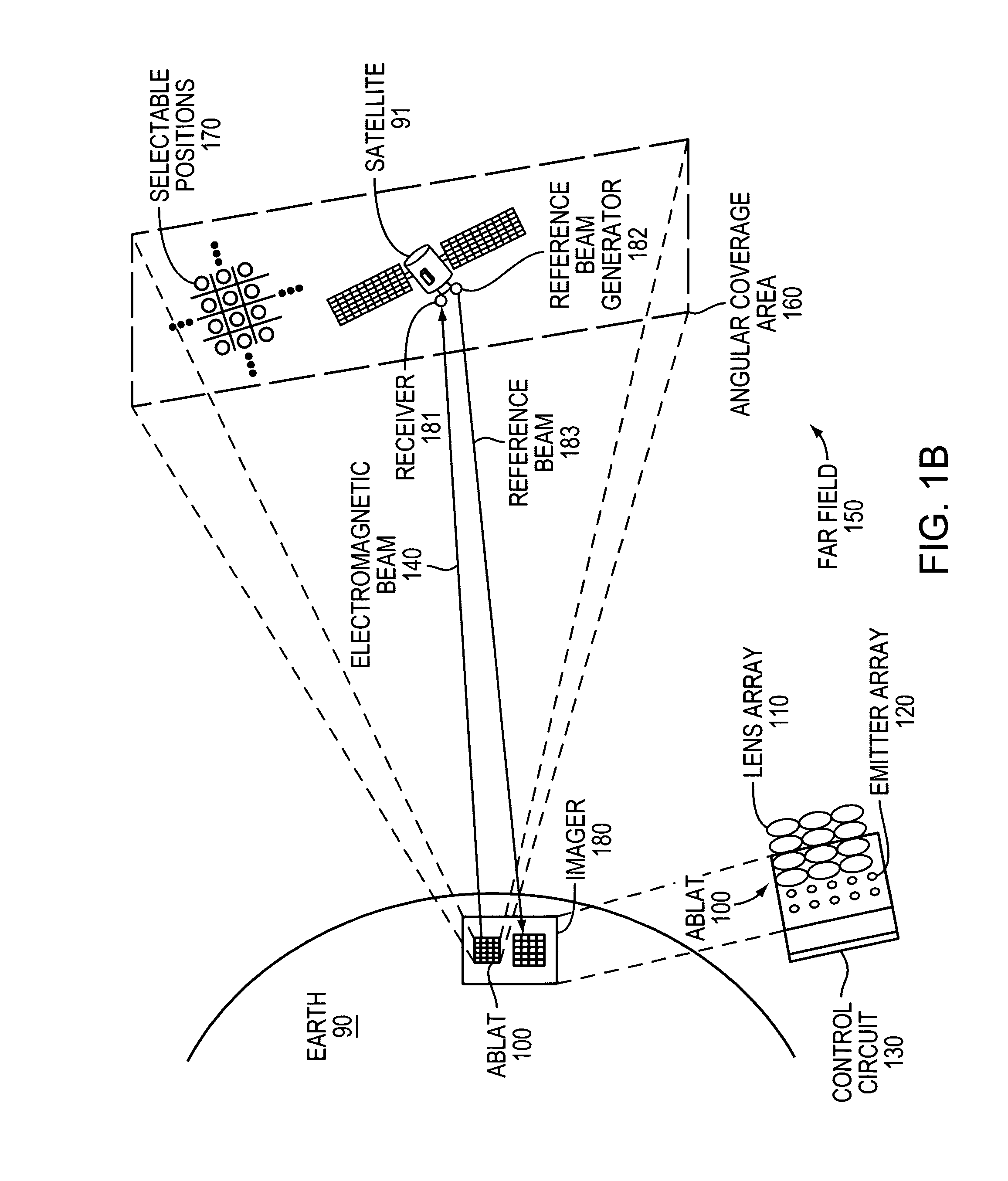
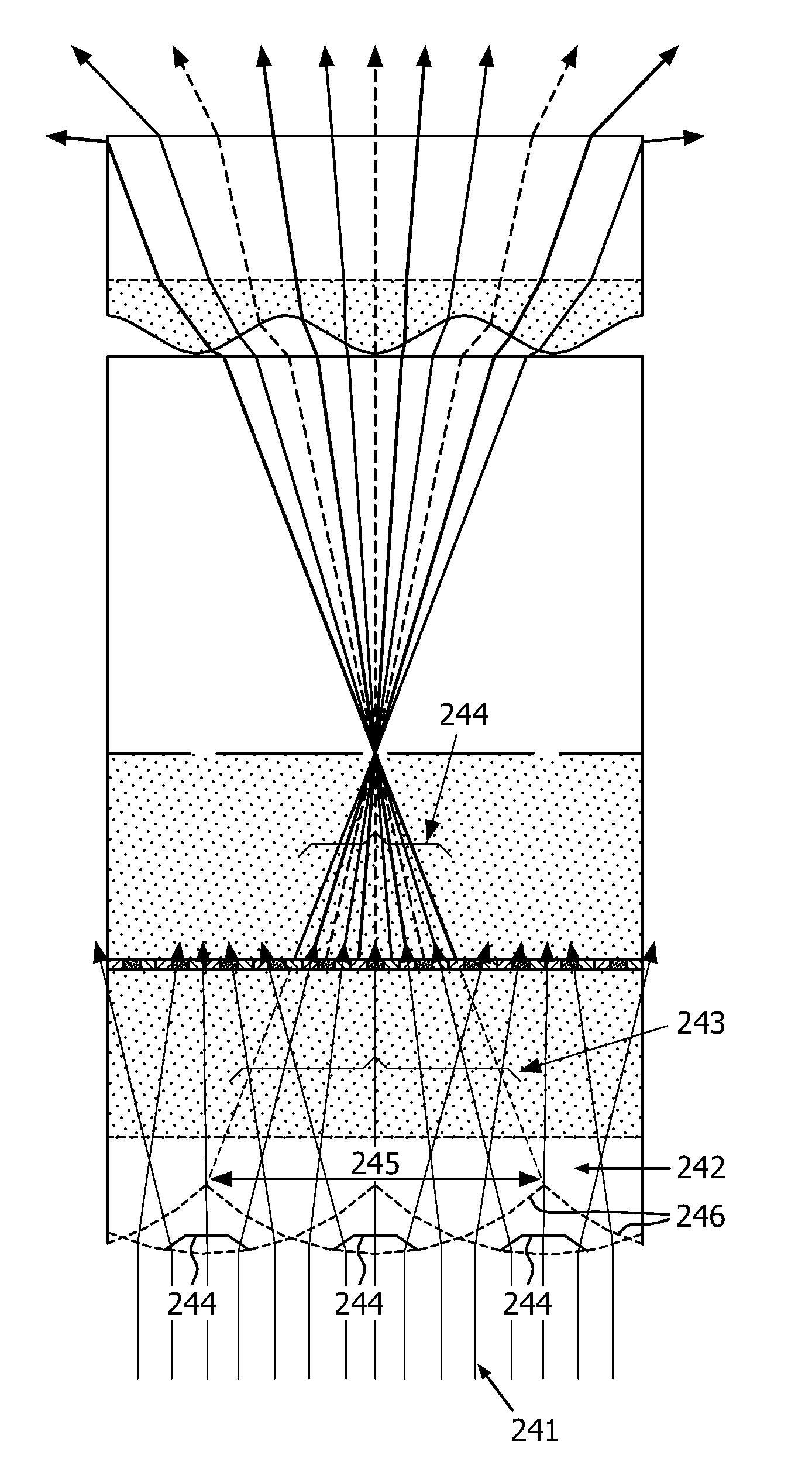
ActiveUS20100046953A1Turn fasterWide field of viewWave based measurement systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsLaser arrayColor printing
An Agile-Beam Laser Array Transmitter (ABLAT) uses an array of emitters and an array of lenses to project electromagnetic beams over a wide angular coverage area in the far field. Differences in the separation pitches of the two arrays allows the ABLAT to project beams to contiguous and / or overlapping positions, depending on the ratio of the separation pitches and the lens focal length. Compared to other beam steering technology, the ABLAT is a smaller, lighter, and more efficient means of projecting beams over wider angular coverage areas. Various embodiments can be used in any beam steering application, including, but not limited to: free-space optical communications; light detection and ranging (lidar); optical scanning (e.g., retinal or bar-code scanning); display projection; image capture; optical character recognition; scanning laser microscopy; non-destructive testing; printing; facsimiles; map making; web inspection; color print processing; phototypesetting and platemaking; laser marking; material processing; DNA analysis; and drug discovery.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Autostereoscopic display device
InactiveUS20120062991A1Reduce in quantityEliminate viewing cone boundaryIlluminated signsSteroscopic systemsComputer graphics (images)Display device
An autostereoscopic display device has both a barrier arrangement and a lens arrangement. A plurality of views are provided to different lateral viewing directions. At least a portion of the field of view has autostereoscopic output, and the portion having autostereoscopic output has no repetition of individual 2D views and comprises at least three individual 2D views. This means there is no reversal of the stereo views (“pseudo stereo views”) at viewing cone boundaries as there are no viewing cone boundaries.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Holographic Waveguide Optical Tracker
ActiveUS20190041634A1Lower latencyWide field of viewMechanical apparatusEye diagnosticsGratingWaveguide
An object tracker comprises: a source of light; at least one illumination waveguide optically coupled to said source continuing at least one grating lamina for diffracting said light towards an external object; at least one detector waveguide containing a grating lamina for in-coupling and deflecting a first polarization of light reflected from said object into a first waveguide direction and deflecting a second polarization of light reflected from said object into a second waveguide direction; at least one detector optically coupled to said detector waveguide operative to receive light propagating in said first waveguide direction; and at least one detector optically coupled to said detector waveguide operative to receive light propagating in said second waveguide direction.
Owner:DIGILENS
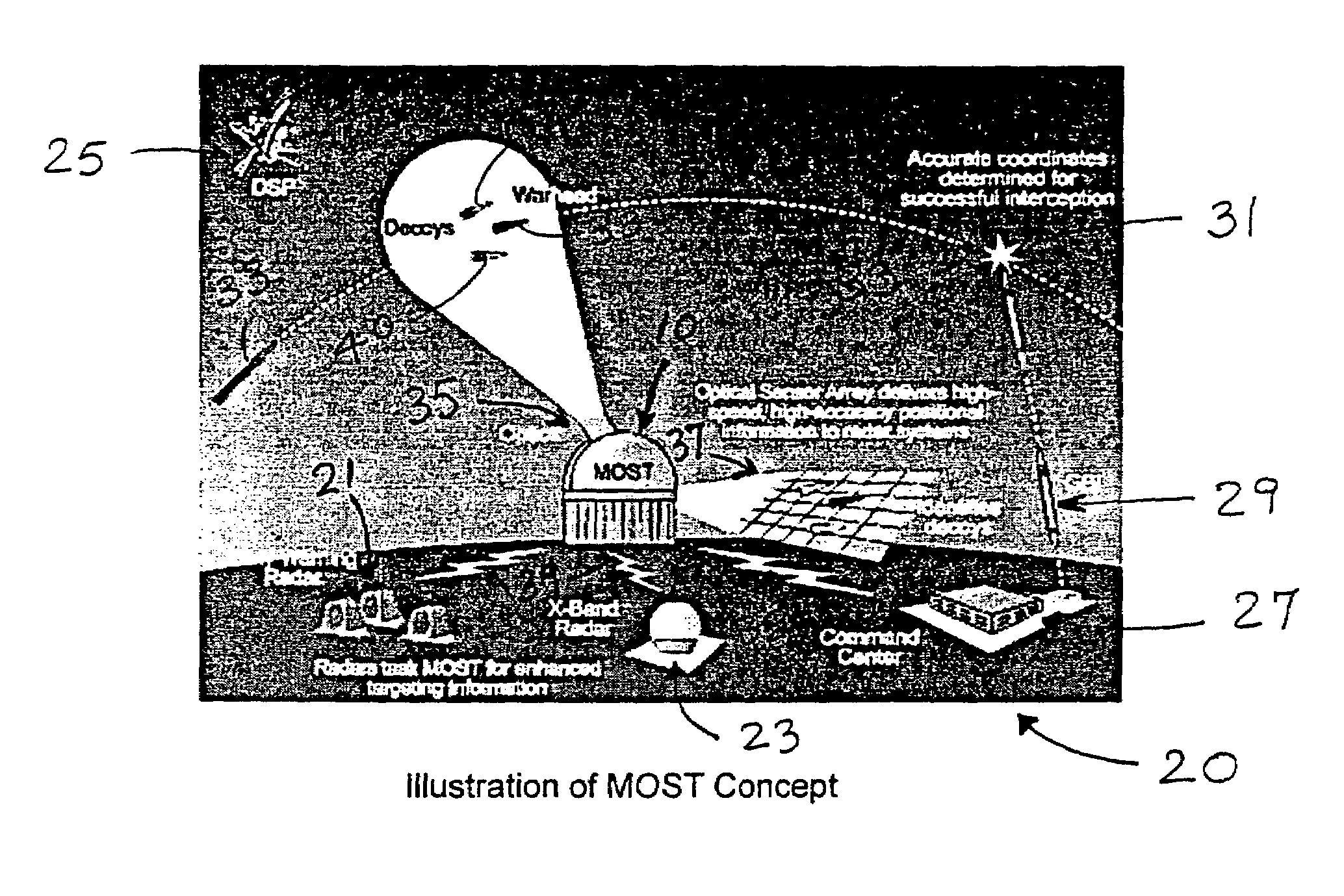
Multi-target-tracking optical sensor-array technology
ActiveUS7551121B1Highly accurate positional metricWide field-of-viewDirection controllersWeapon control systemsSensor arrayAviation
The multi-target tracking and discrimination system (MOST) fuses with and augments existing BMDS sensor systems. Integrated devices include early warning radars, X-band radars, Lidar, DSP, and MOST which coordinates all the data received from all sources through a command center and deploys the GBI for successful interception of an object detected anywhere in space, for example, warheads. The MOST system integrates the optics for rapid detection and with the optical sensor array delivers high-speed, high accuracy positional information to radar systems and also identifies decoys. MOST incorporates space situational awareness, aero-optics, adaptive optics, and Lidar technologies. The components include telescopes or other optical systems, focal plane arrays including high-speed wavefront sensors or other focal plane detector arrays, wavefront sensor technology developed to mitigate aero-optic effects, distributed network of optical sensors, high-accuracy positional metrics, data fusion, and tracking mounts. Field applications include space monitoring, battlefield artillery, battlefield management, ground defense, air defense, space protection, missile defense, gunfire detection, and the like.
Owner:OCEANIT LAB
Six-piece optical lens system
A six-piece optical lens system comprises, in order from the object side to the image side: a stop, a first lens element with a positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface and at least one aspheric surface; a second lens element with a negative refractive power having a concave image-side surface and at least one aspheric surface; a third lens element with a positive refractive power having a convex image-side surface and at least one aspheric surface; a fourth lens element with a positive refractive power having a concave object-side surface and at least one aspheric surface; a fifth lens element having a convex image-side surface and at least one aspheric surface; a sixth lens element with a negative refractive power having a concave image-side surface and at least one aspheric surface. Thereby, the total track length of the system will not be too long.
Owner:NEWMAX TECH
Wide angle optical lens system
A wide angle optical lens system includes an aperture stop and an optical assembly, the optical assembly includes, in order from the object side to the image side: a first lens element with a negative refractive power; a second lens element with a positive refractive power; a third lens element with a negative refractive power; a fourth lens element with a refractive power; a fifth lens element with a positive refractive power; a sixth lens element with a negative refractive power, wherein a focal length of the wide angle optical lens system is f, a focal length of the fifth lens element is f5, a radius of curvature of an object-side surface of the third lens element is R5, a radius of curvature of an image-side surface of the third lens element is R6, the following conditions are satisfied: 1.0<f / f5<3.8; −3.5<(R6+R5) / (R6−R5)<0.6.
Owner:GLORY SCI
Imaging lens assembly
This invention provides an imaging lens assembly comprising, in order from an object side to an image side: a first lens element with negative refractive power having a convex object-side surface and a concave image-side surface; a second lens element with positive refractive power having a convex image-side surface; a third lens element with negative refractive power having a concave object-side surface and a convex image-side surface, both being aspheric; a fourth lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface, both its two surfaces being aspheric; and a stop disposed between the first and second lenses.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Holographic waveguide optical tracker
ActiveUS10983340B2Lower latencyWide field of viewMechanical apparatusEye diagnosticsGratingWaveguide
An object tracker comprises: a source of light; at least one illumination waveguide optically coupled to said source continuing at least one grating lamina for diffracting said light towards an external object; at least one detector waveguide containing a grating lamina for in-coupling and deflecting a first polarization of light reflected from said object into a first waveguide direction and deflecting a second polarization of light reflected from said object into a second waveguide direction; at least one detector optically coupled to said detector waveguide operative to receive light propagating in said first waveguide direction; and at least one detector optically coupled to said detector waveguide operative to receive light propagating in said second waveguide direction.
Owner:DIGILENS
Far-infrared camera lens, lens unit, and imaging apparatus
Three lenses formed of ZnS are used in combination. A first lens is a meniscus lens having a middle portion which is convex on an object side. A second lens has a middle portion that is a meniscus, which is concave on an object side and has positive refractive power, and a peripheral portion, which is convex on the object side. The first and second lenses have positive refractive power in combination. A third lens is provided adjacent to the second lens with a distance therebetween 1 mm or less and has a middle portion, which is a convex meniscus on an object side, and a peripheral portion which is concave on the object side. A diffraction surface is formed in either surface of the lens.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Imaging lens assembly
ActiveUS8089704B2Improve image qualityAberration correctionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImaging lensPhysics
This invention provides an imaging lens assembly including, in order from an object side to an image side: a first lens with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface; a second lens with negative refractive power having a convex image-side surface; a third lens having a concave object-side surface and a convex image-side surface, at least one of both surfaces thereof being aspheric; a fourth lens having a concave image-side surface, at least one of both surfaces thereof having at least one inflection point; and an aperture stop disposed between an imaged object and the second lens; the on-axis spacing between the first lens and second lens is T12, the focal length of the imaging lens assembly is f, the Abbe number of the first lens and third lens is, V1 and V3, respectively, they satisfy the relations: 0.5<(T12 / f)*100<20, 23<V1−V3.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
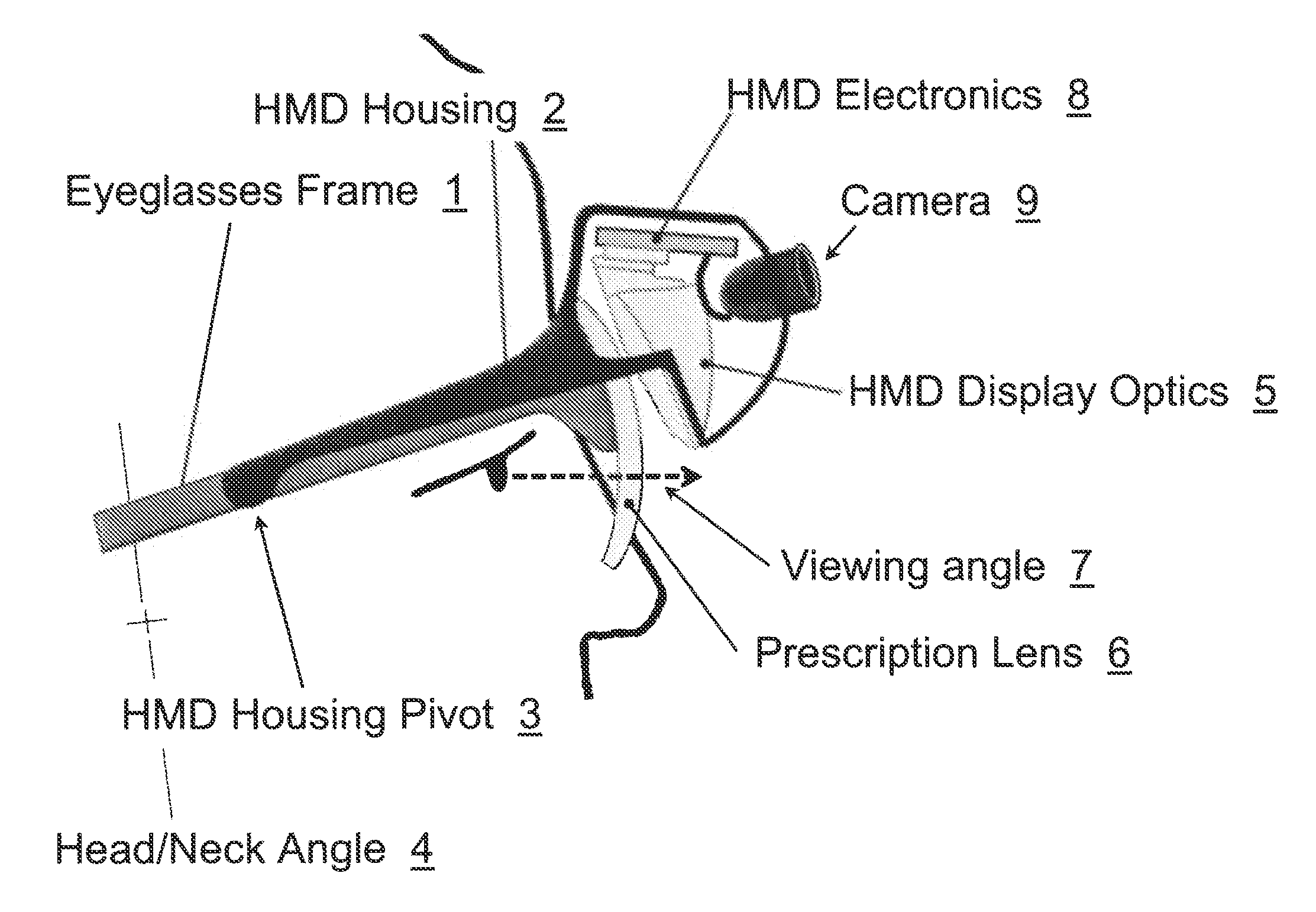
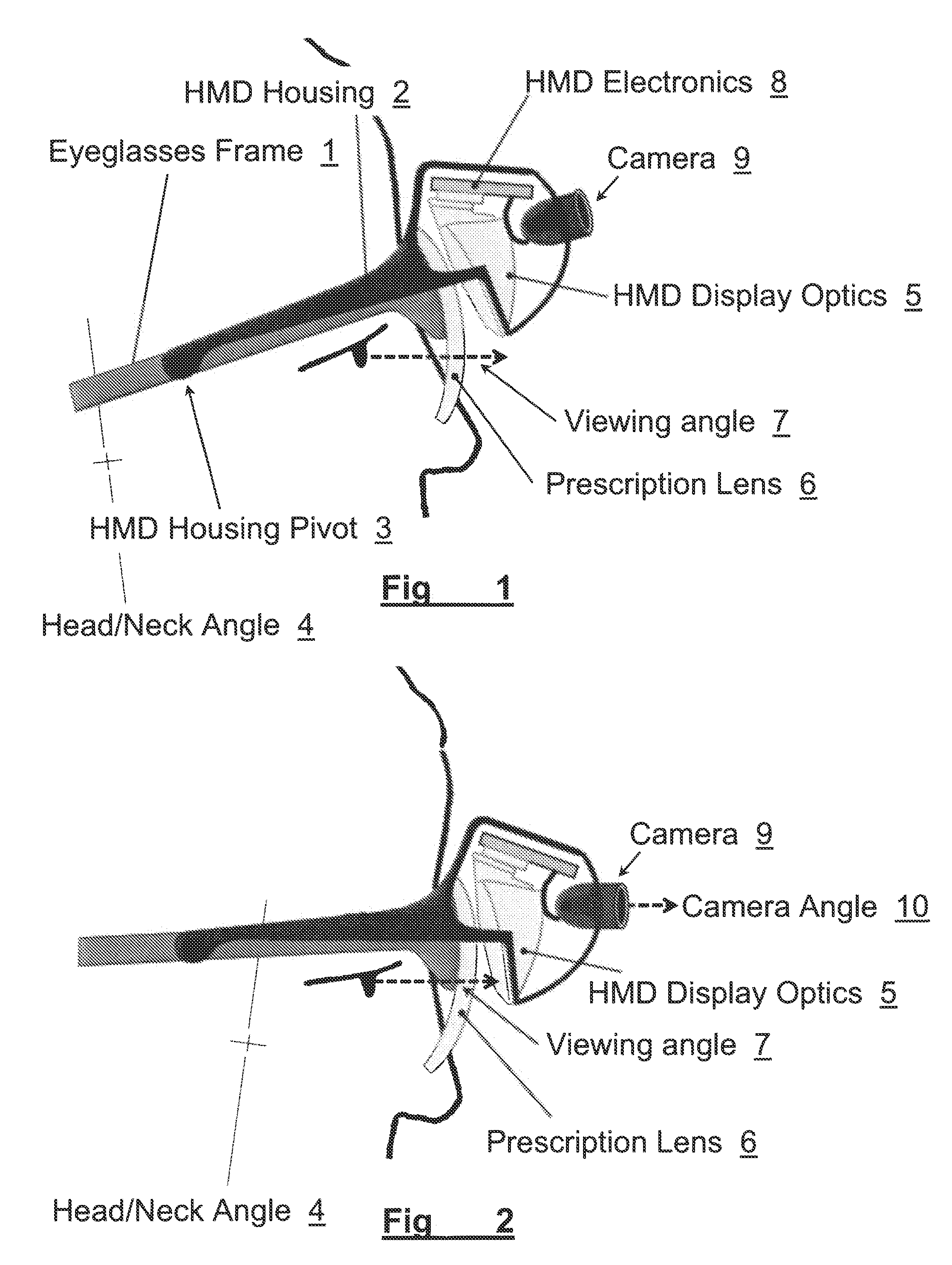
Apparatus and Method for a Bioptic Real Time Video System
ActiveUS20120306725A1Improve usabilityWide field of viewCathode-ray tube indicatorsOptical elementsComputer graphics (images)Display device
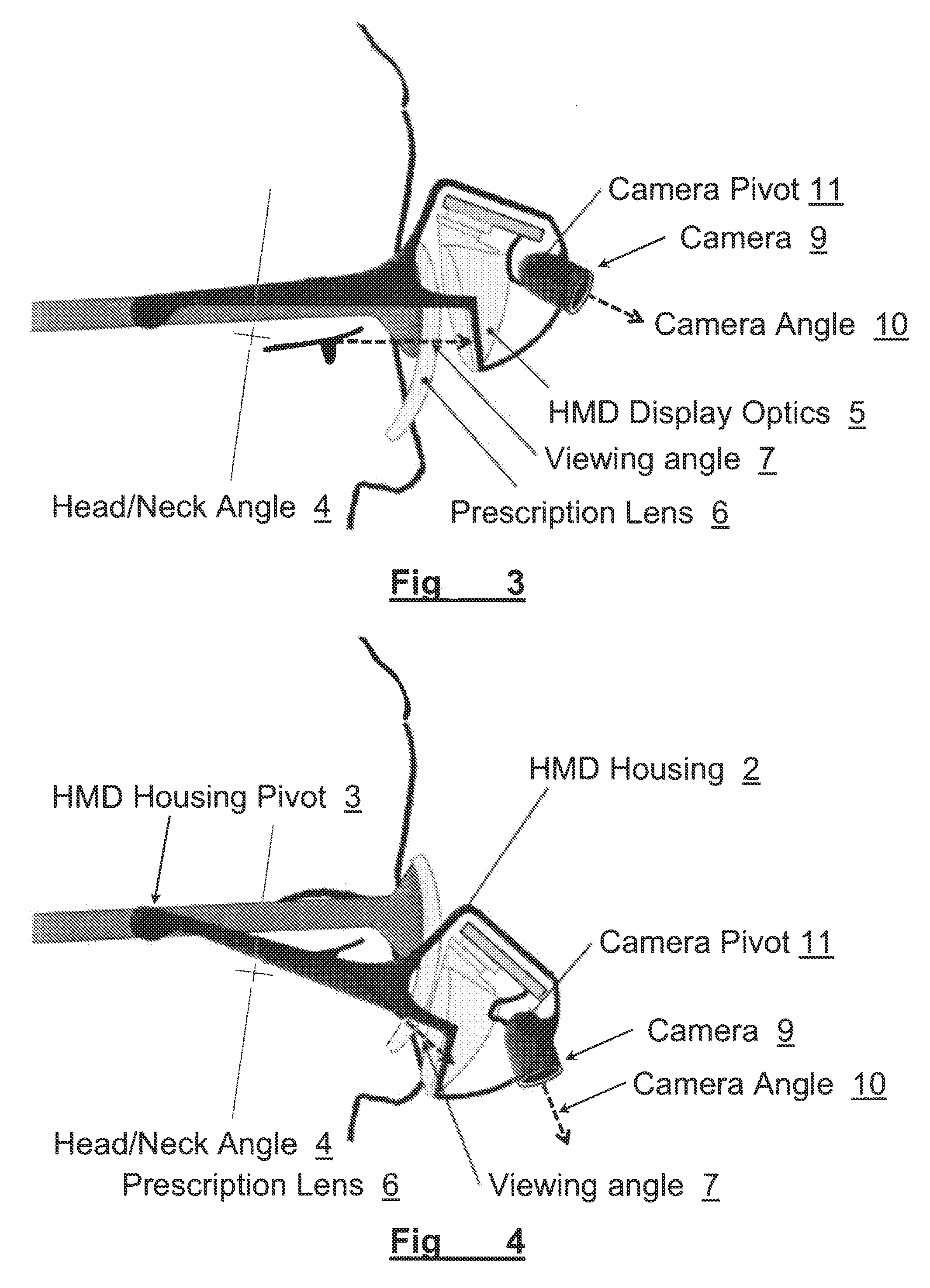
A method and apparatus of displaying an electronic video image using a head-worn near-to-eye display in a non-immersive fashion, such that the wearer can choose, through simple adjustments of their neck and eye angles, to either look at the displayed video image or their natural environment. The invention also relates to the incorporation of prescription lenses into the optical chain of the near-to-eye display. The invention also relates to the use of motion and position sensors incorporated into the head-worn device to enable automatic stabilization of the video image. The invention also relates to the use of motion and position sensors incorporated into the head-worn device to automatically adjust the vertical angle of either the camera or the electronic display or both, by sensing the vertical angular position of the user's head.
Owner:ESIGHT CORP
Wide angle photographic lens assembly
A wide angle photographic lens assembly comprises, in order from an object side to an image side, a first lens element with negative refractive power having a convex object-side surface and a concave image-side surface, a second lens element with positive refractive power having a concave object-side surface and a convex image-side surface, a third lens element, a fourth lens element with positive refractive power, a fifth lens element with negative refractive power, and a sixth lens element with positive refractive power. By adjusting the conditions among the above-mentioned lens elements, the wide angle photographic lens assembly can provide a wide-field of view and correct the aberration in order to obtain superior imaging quality.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Imaging lens assembly
The present invention provides an imaging lens assembly, comprising in order from an object side toward an image side, a first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface, a second lens element with negative refractive power having a concave object-side surface and a convex image-side surface, a third lens element with positive refractive power having a concave object-side surface and a convex image-side surface, a fourth lens element with negative refractive power, a fifth lens element with positive refractive power, and an aperture stop positioned between an imaged object and the first lens element. The above lens arrangement shortens the total track length effectively, enabling a high performance imaging lens assembly with a wide field of view.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Imaging lens assembly
The present invention provides an imaging lens assembly including, in order from an object side to an image side: a first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface; a second lens element with negative refractive power; a third lens element with negative refractive power; a fourth lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface; a fifth lens element having a concave image-side surface, at least one inflection point being provided on the fifth lens element; and an aperture stop disposed between an imaged object and the third lens element. Such an arrangement of optical elements can effectively improve the image quality of the system and enable the imaging lens assembly to maintain a compact form. When the aperture stop is disposed near the object side, the telecentric feature is emphasized, resulting in a shorter total track length. When the aperture stop is disposed near the third lens element, the emphasis is on the wide field of view, and such an aperture stop placement helps to effectively reduce the sensitivity of the imaging lens assembly.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com