Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
237 results about "Speculative execution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Speculative execution is an optimization technique where a computer system performs some task that may not be needed. Work is done before it is known whether it is actually needed, so as to prevent a delay that would have to be incurred by doing the work after it is known that it is needed. If it turns out the work was not needed after all, most changes made by the work are reverted and the results are ignored.
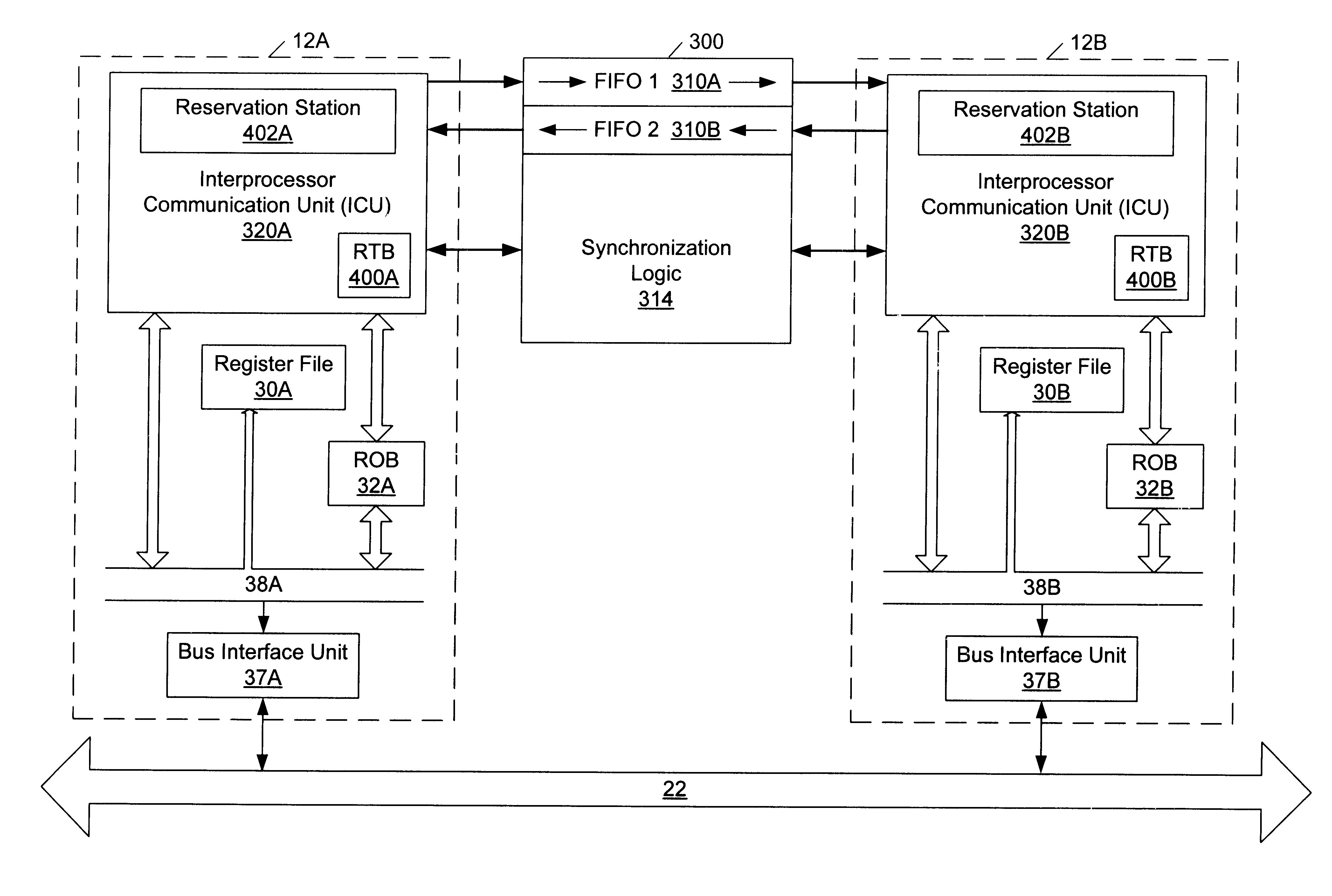
Speculative execution and rollback
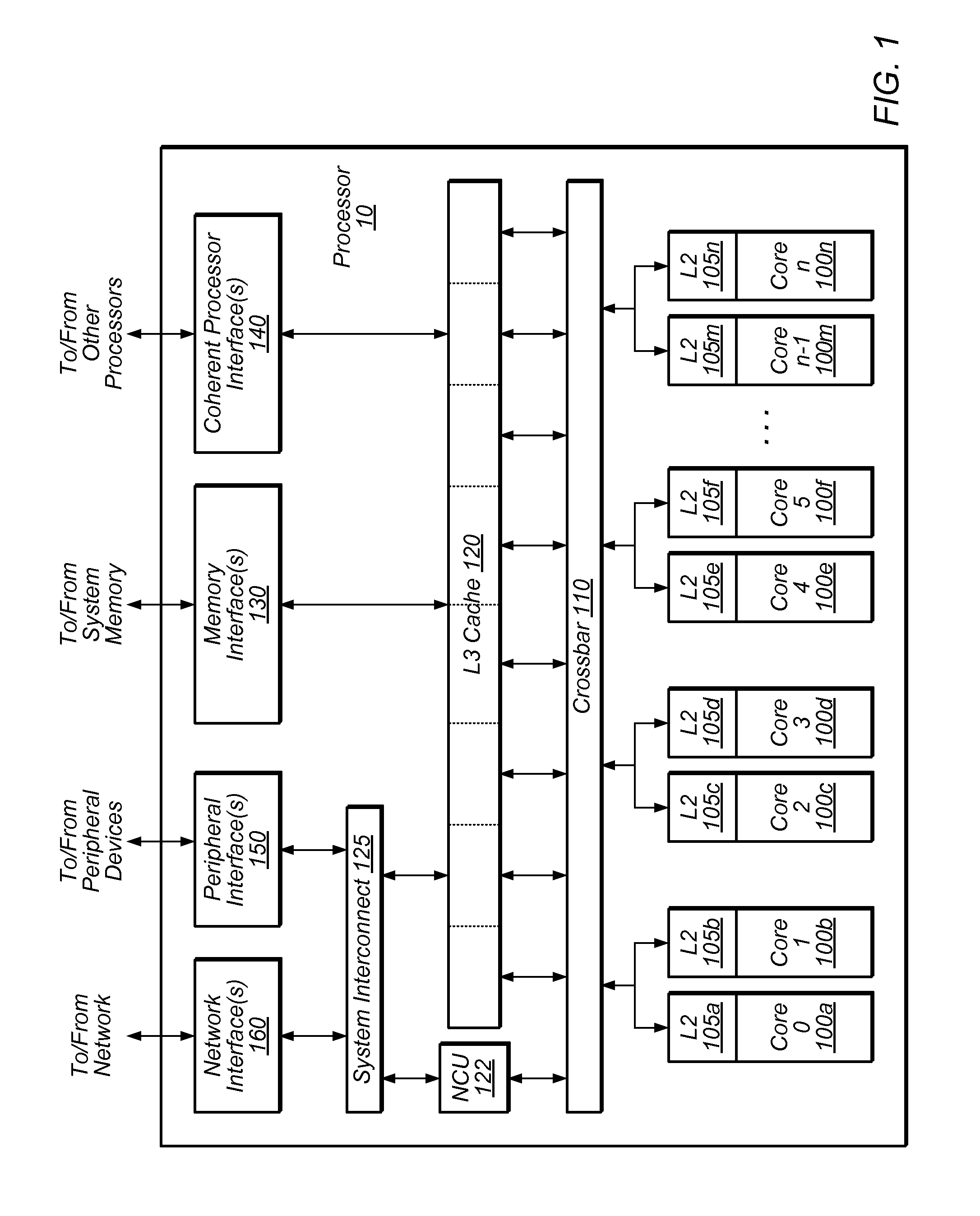
ActiveUS20130117541A1Resolve dependenciesDigital computer detailsMemory systemsSpeculative executionExecution unit
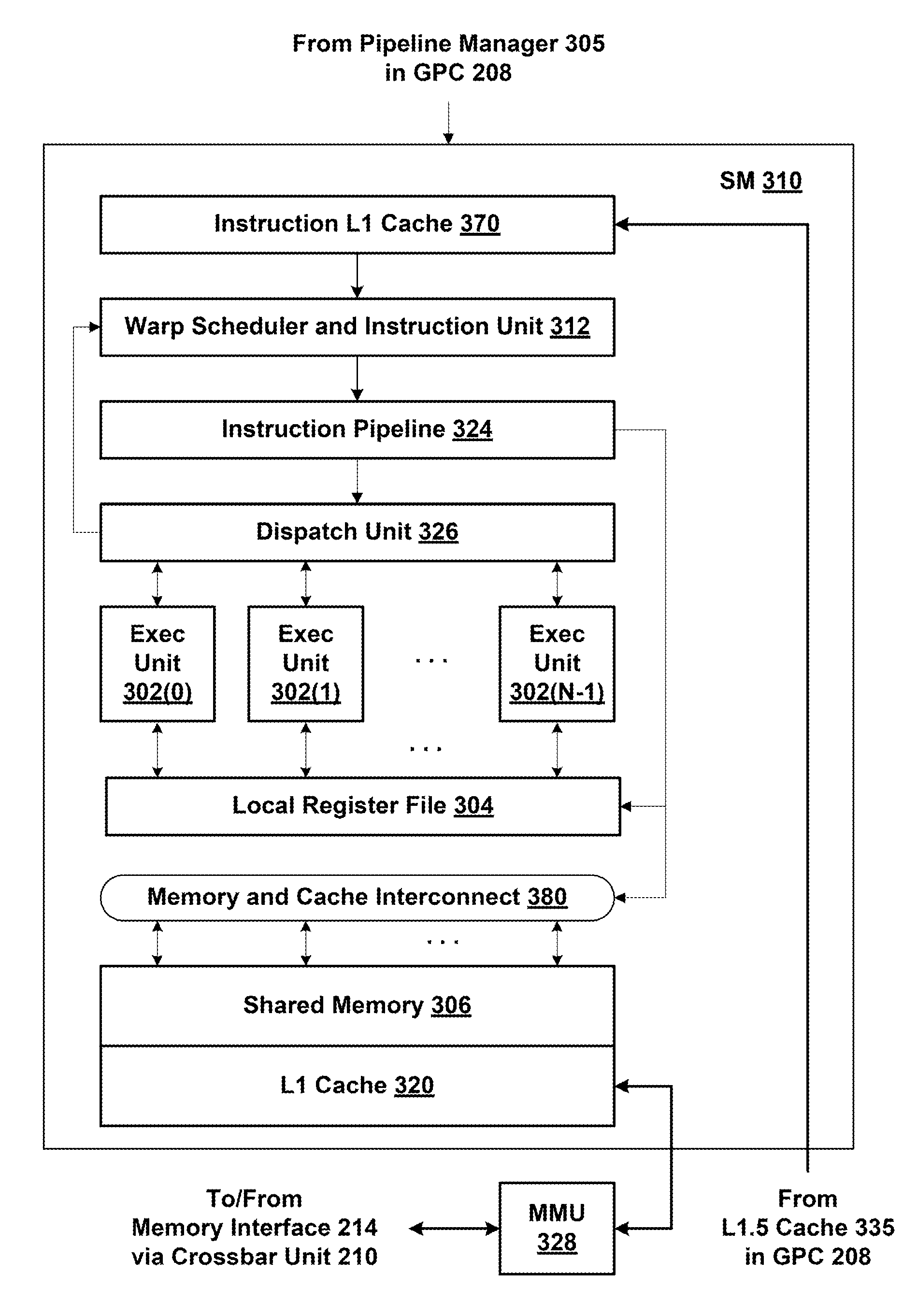
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a technique for speculatively issuing instructions to allow a processing pipeline to continue to process some instructions during rollback of other instructions. A scheduler circuit issues instructions for execution assuming that, several cycles later, when the instructions reach multithreaded execution units, that dependencies between the instructions will be resolved, resources will be available, operand data will be available, and other conditions will not prevent execution of the instructions. When a rollback condition exists at the point of execution for an instruction for a particular thread group, the instruction is not dispatched to the multithreaded execution units. However, other instructions issued by the scheduler circuit for execution by different thread groups, and for which a rollback condition does not exist, are executed by the multithreaded execution units. The instruction incurring the rollback condition is reissued after the rollback condition no longer exists.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
System and Method for Performing Incremental Register Checkpointing in Transactional Memory
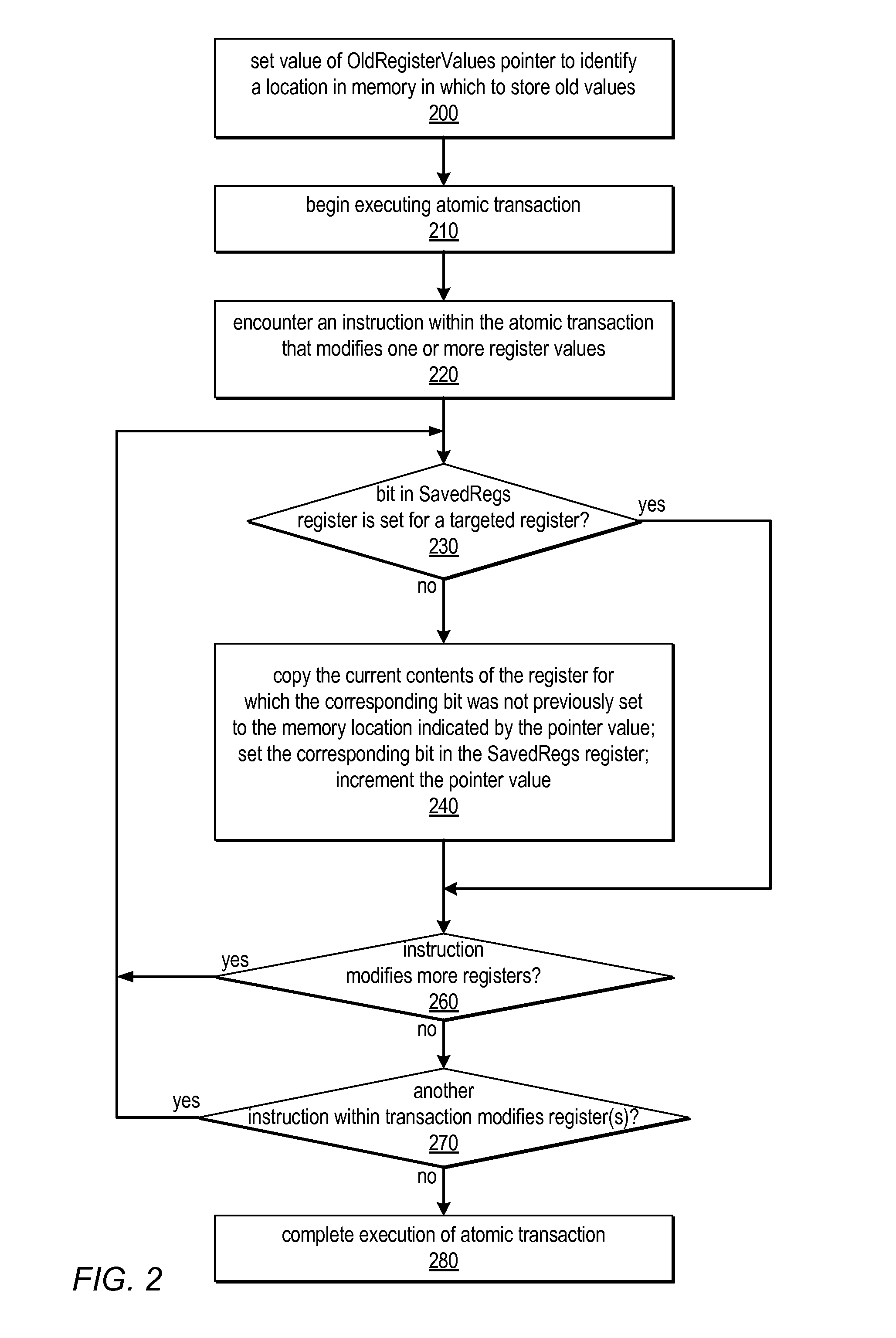
ActiveUS20120005461A1Reduce overheadSimpler and flexibleDigital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsSpeculative executionProcessor register
Systems and methods described herein for performing incremental register checkpointing may employ a special register to indicate which registers have already been checkpointed. This register may include one bit per register. These systems may also include a special pointer register whose value identifies a location in user memory or in dedicated on-chip storage at which a copy of a register's value should be saved by a checkpointing operation. Only registers modified during speculative execution or execution of a transaction may be checkpointed (e.g., when register modifying instructions are encountered) and subsequently restored (e.g., due to misspeculation or transaction abort), rather than all of the registers of the processor. Each register may be checkpointed at most once for a given speculative episode or atomic transaction. Setting a bit in the special register may prevent checkpointing of the corresponding register. Setting all of the bits in the special register may disable checkpointing.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and System for Reducing Abort Rates in Speculative Lock Elision using Contention Management Mechanisms
ActiveUS20100169623A1Reduce transactional abort rateWaste system resourceDigital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsSpeculative executionCritical section
Hardware-based transactional memory mechanisms, such as Speculative Lock Elision (SLE), may allow multiple threads to concurrently execute critical sections protected by the same lock as speculative transactions. Such transactions may abort due to contention or due to misidentification of code as a critical section. In various embodiments, speculative execution mechanisms may be augmented with software and / or hardware contention management mechanisms to reduce abort rates. Speculative execution hardware may send a hardware interrupt signal to notify software components of a speculative execution event (e.g., abort). Software components may respond by implementing concurrency-throttling mechanisms and / or by determining a mode of execution (e.g., speculative, non-speculative) for a given section and communicating that determination to the hardware speculative execution mechanisms, e.g., by writing it into a lock predictor cache. Subsequently, hardware speculative execution mechanisms may determine a preferred mode of execution for the section by reading the corresponding entry from the lock predictor cache.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Method and mechanism for speculatively executing threads of instructions
InactiveUS6574725B1Program initiation/switchingGeneral purpose stored program computerSpeculative executionOperational system
A processor architecture containing multiple closely coupled processors in a form of symmetric multiprocessing system is provided. The special coupling mechanism allows it to speculatively execute multiple threads in parallel very efficiently. Generally, the operating system is responsible for scheduling various threads of execution among the available processors in a multiprocessor system. One problem with parallel multithreading is that the overhead involved in scheduling the threads for execution by the operating system is such that shorter segments of code cannot efficiently take advantage of parallel multithreading. Consequently, potential performance gains from parallel multithreading are not attainable. Additional circuitry is included in a form of symmetrical multiprocessing system which enables the scheduling and speculative execution of multiple threads on multiple processors without the involvement and inherent overhead of the operating system. Advantageously, parallel multithreaded execution is more efficient and performance may be improved.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method, apparatus, and system for speculative execution event counter checkpointing and restoring
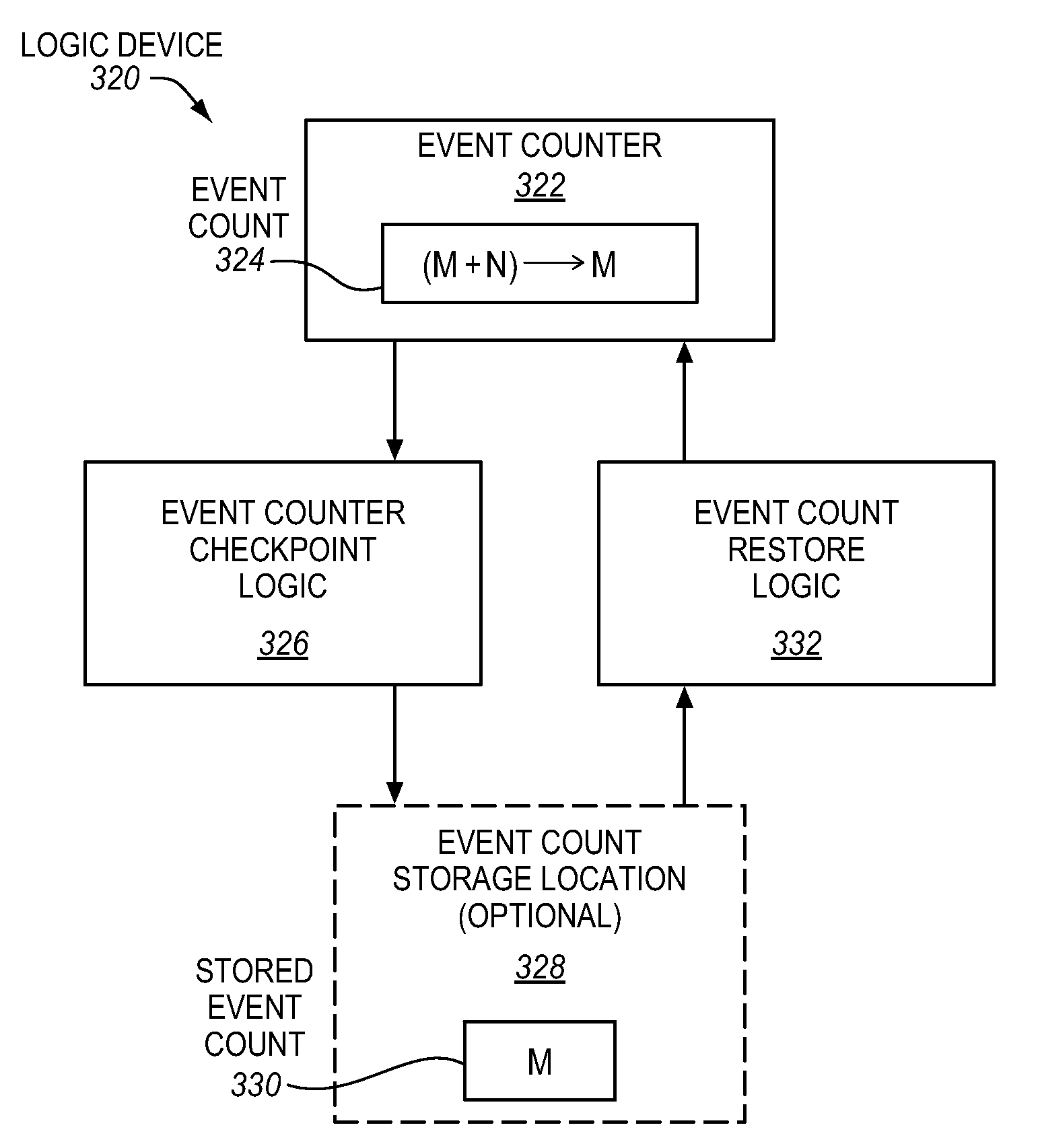
InactiveUS20120227045A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionSpeculative executionExecution cycle
An apparatus, method, and system are described herein for providing programmable control of performance / event counters. An event counter is programmable to track different events, as well as to be checkpointed when speculative code regions are encountered. So when a speculative code region is aborted, the event counter is able to be restored to it pre-speculation value. Moreover, the difference between a cumulative event count of committed and uncommitted execution and the committed execution, represents an event count / contribution for uncommitted execution. From information on the uncommitted execution, hardware / software may be tuned to enhance future execution to avoid wasted execution cycles.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Paralleling processing method, system and program
ActiveUS20100138810A1Digital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionSingle clusterParallel processing
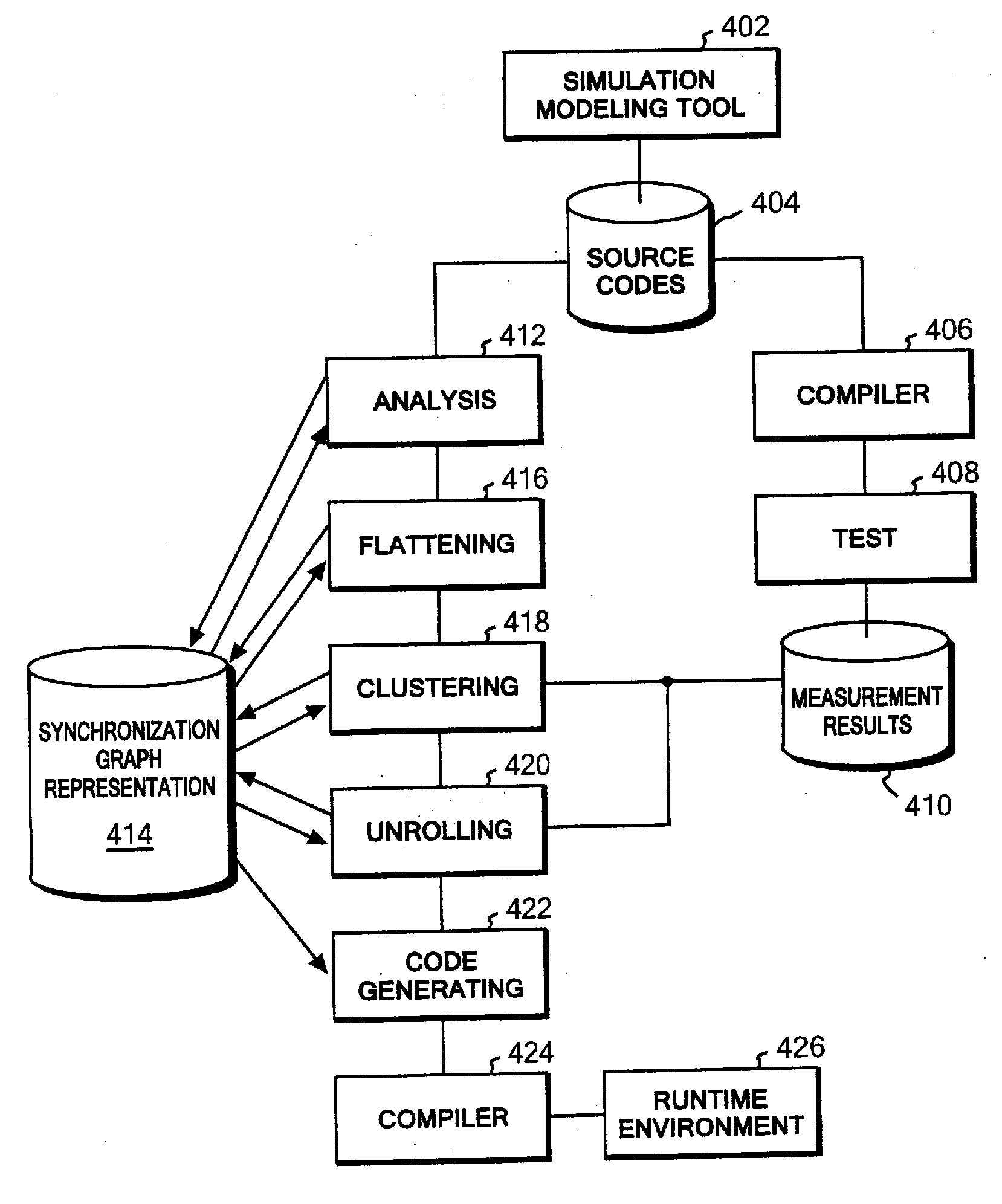
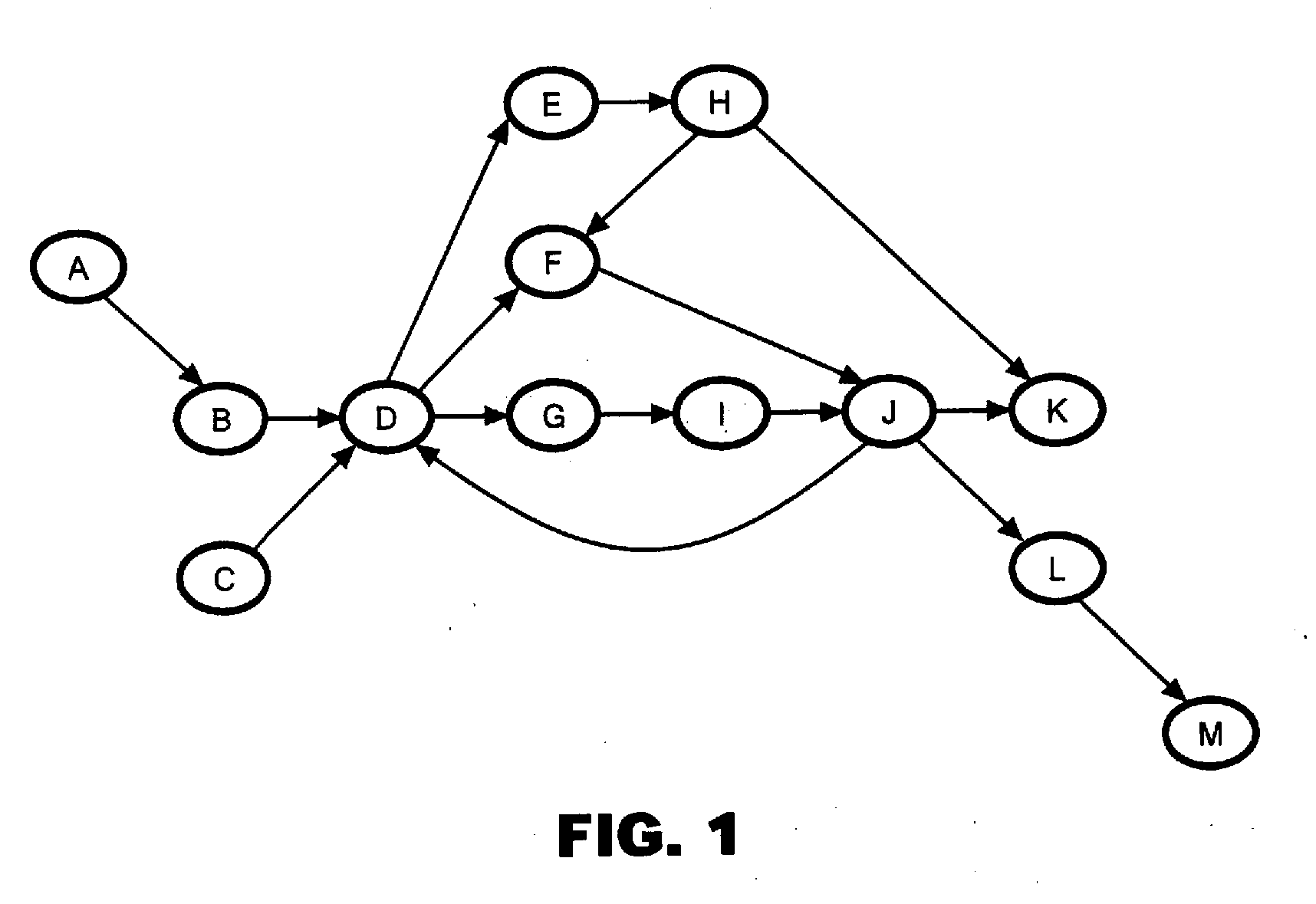
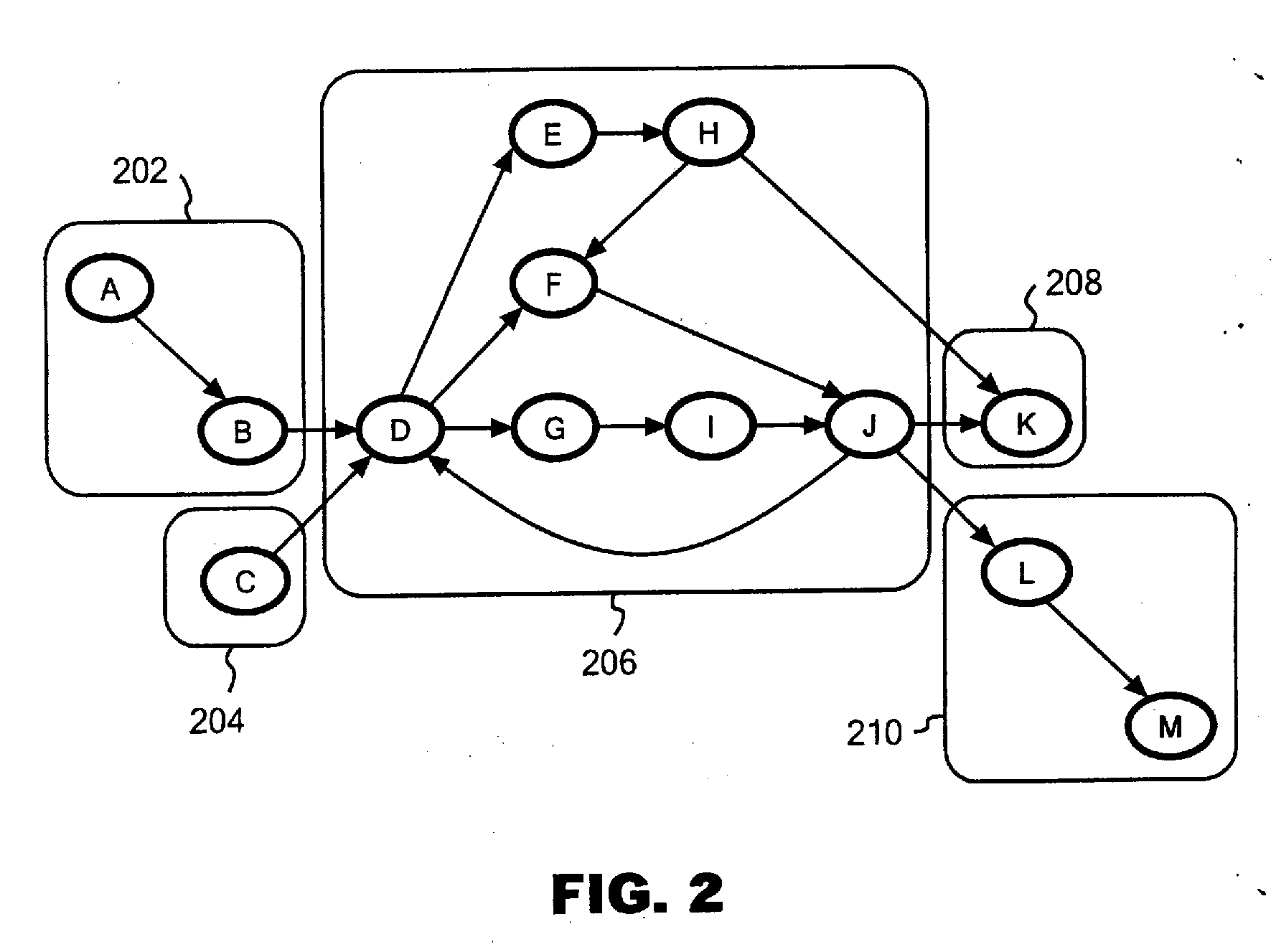
Paralleling processing system and method. When clusters are formed based on strongly connected components, a single cluster (fat cluster) having at least a predetermined number of blocks, or an expected processing time exceeding a predetermined threshold, is formed. The fat cluster is subjected to an unrolling process to make multiple copies of the processing of the fat cluster and to assign the copies to individual processors. Processing of the fat cluster is executed by the multiple processor devices in a pipelined manner. If a fat cluster to be iteratively executed cannot be executed in the pipelined manner because a processing result of an nth iteration of the fat cluster depends on a processing result of a preceding iteration of the fat cluster an input value needed for execution of the fat cluster is generated based on a certain prediction, and the fat cluster is speculatively executed.
Owner:IBM CORP
Using windowed register file to checkpoint register state
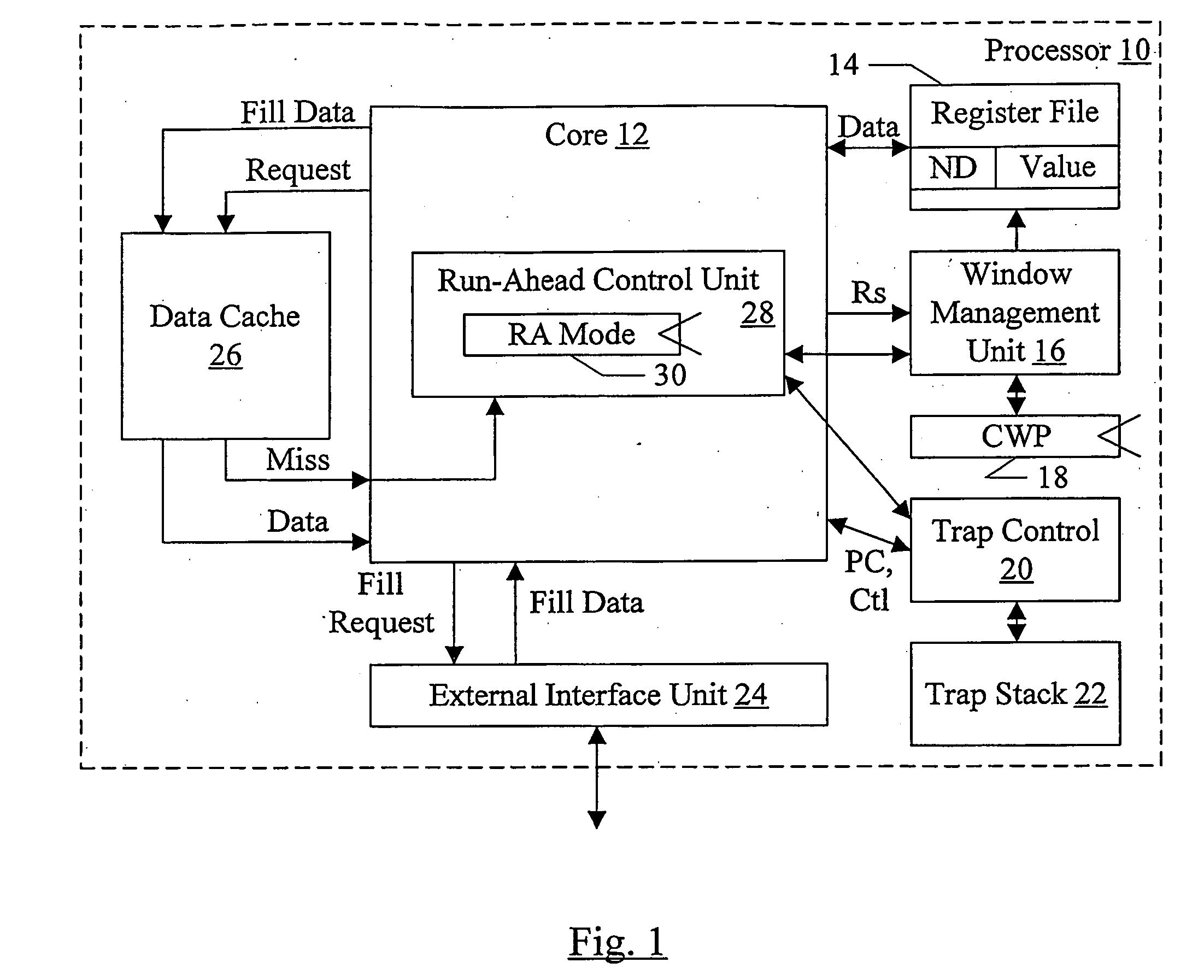
InactiveUS20080016325A1Register arrangementsDigital computer detailsSpeculative executionManagement unit
In one embodiment, a processor comprises a core configured to execute instructions; a register file comprising a plurality of storage locations; and a window management unit. The window management unit is configured to operate the plurality of storage locations as a plurality of windows, wherein register addresses encoded into the instructions identify storage locations among a subset of the plurality of storage locations that are within a current window. Additionally, the window management unit is configured to allocate a second window in response to a predetermined event. One of the current window and the second window serves as a checkpoint of register state, and the other one of the current window and the second window is updated in response to instructions processed subsequent to the checkpoint. The checkpoint may be restored if the speculative execution results are discarded.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
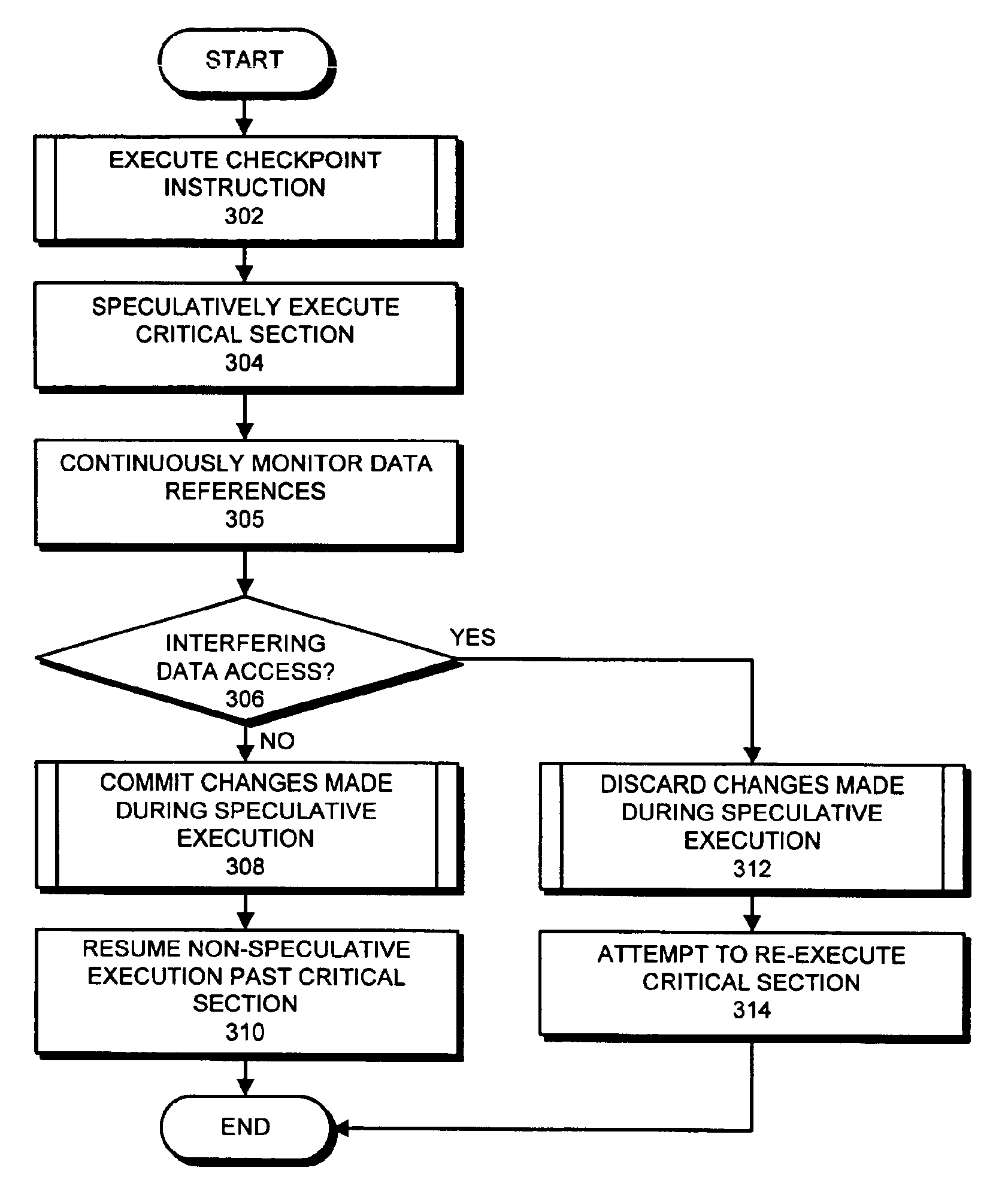
Method and apparatus for avoiding locks by speculatively executing critical sections
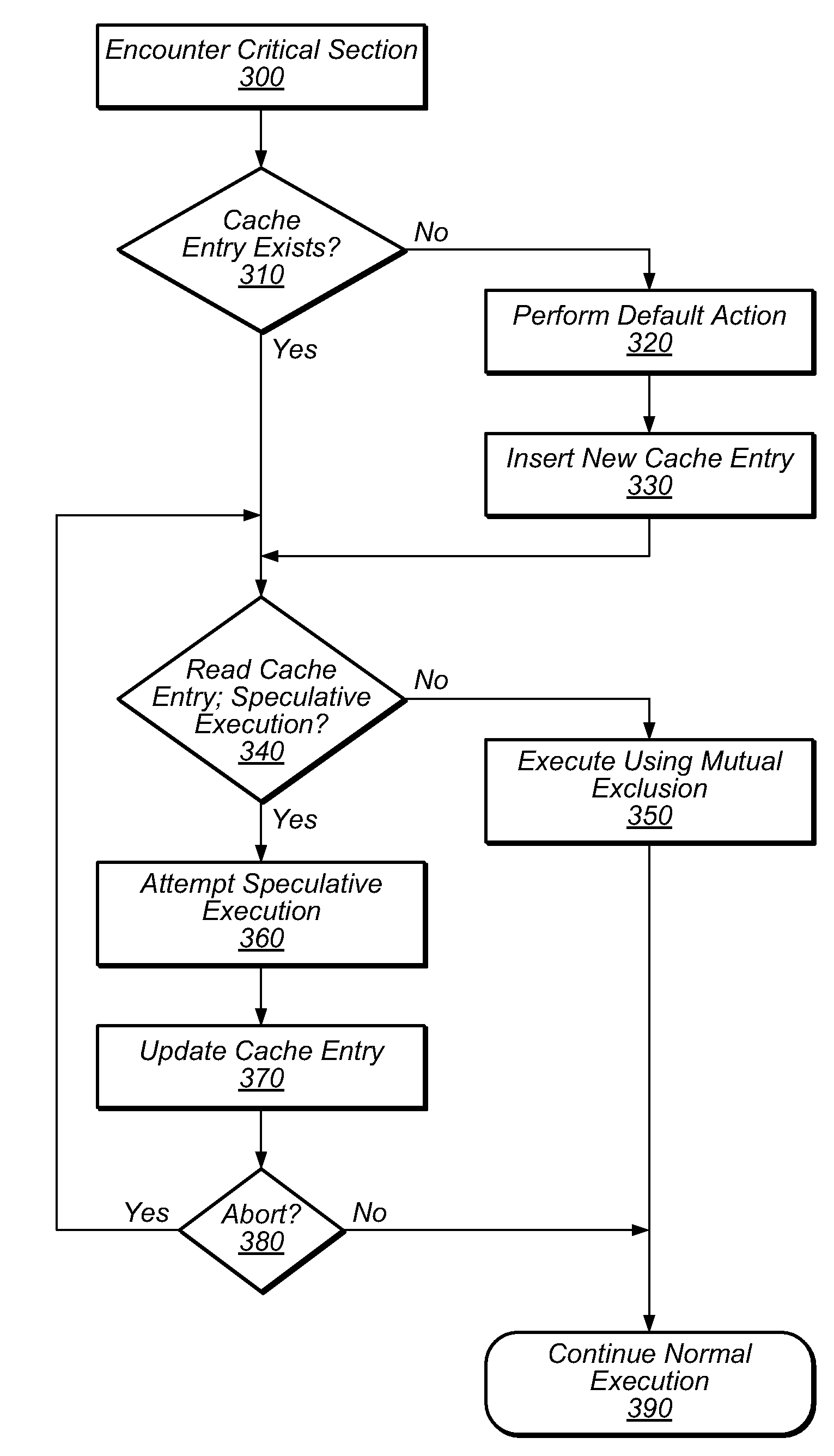
InactiveUS6862664B2Easy to solveMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMultiprogramming arrangementsSpeculative executionCritical section
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that facilitates avoiding locks by speculatively executing critical sections of code. During operation, the system allows a process to speculatively execute a critical section of code within a program without first acquiring a lock associated with the critical section. If the process subsequently completes the critical section without encountering an interfering data access from another process, the system commits changes made during the speculative execution, and resumes normal non-speculative execution of the program past the critical section. Otherwise, if an interfering data access from another process is encountered during execution of the critical section, the system discards changes made during the speculative execution, and attempts to re-execute the critical section.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
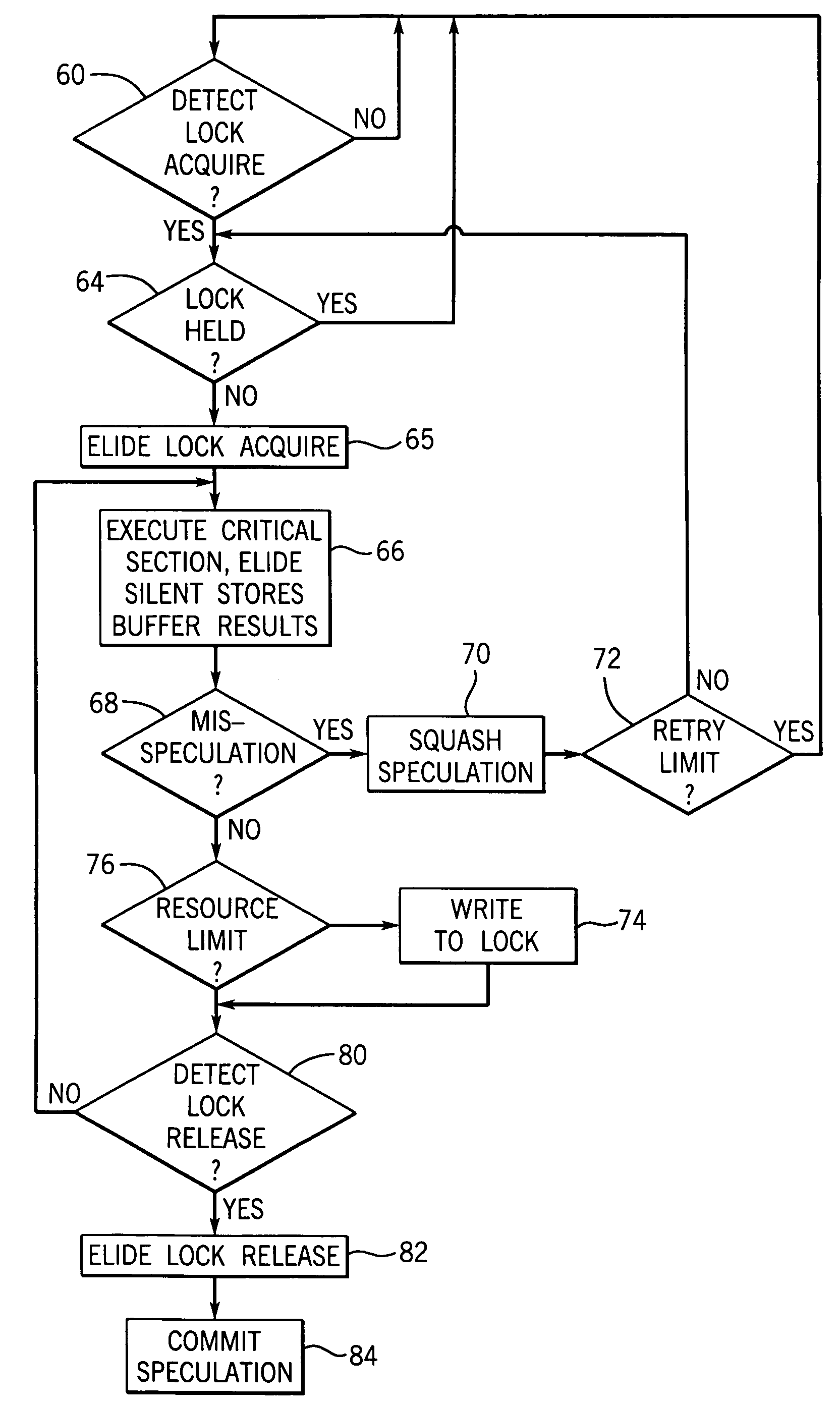
Concurrent execution of critical sections by eliding ownership of locks
ActiveUS7120762B2Ensure correct executionEfficient executionMemory architecture accessing/allocationProgram synchronisationSpeculative executionCritical section
Critical sections of multi-threaded programs, normally protected by locks providing access by only one thread, are speculatively executed concurrently by multiple threads with elision of the lock acquisition and release. Upon a completion of the speculative execution without actual conflict as may be identified using standard cache protocols, the speculative execution is committed, otherwise the speculative execution is squashed. Speculative execution with elision of the lock acquisition, allows a greater degree of parallel execution in multi-threaded programs with aggressive lock usage.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
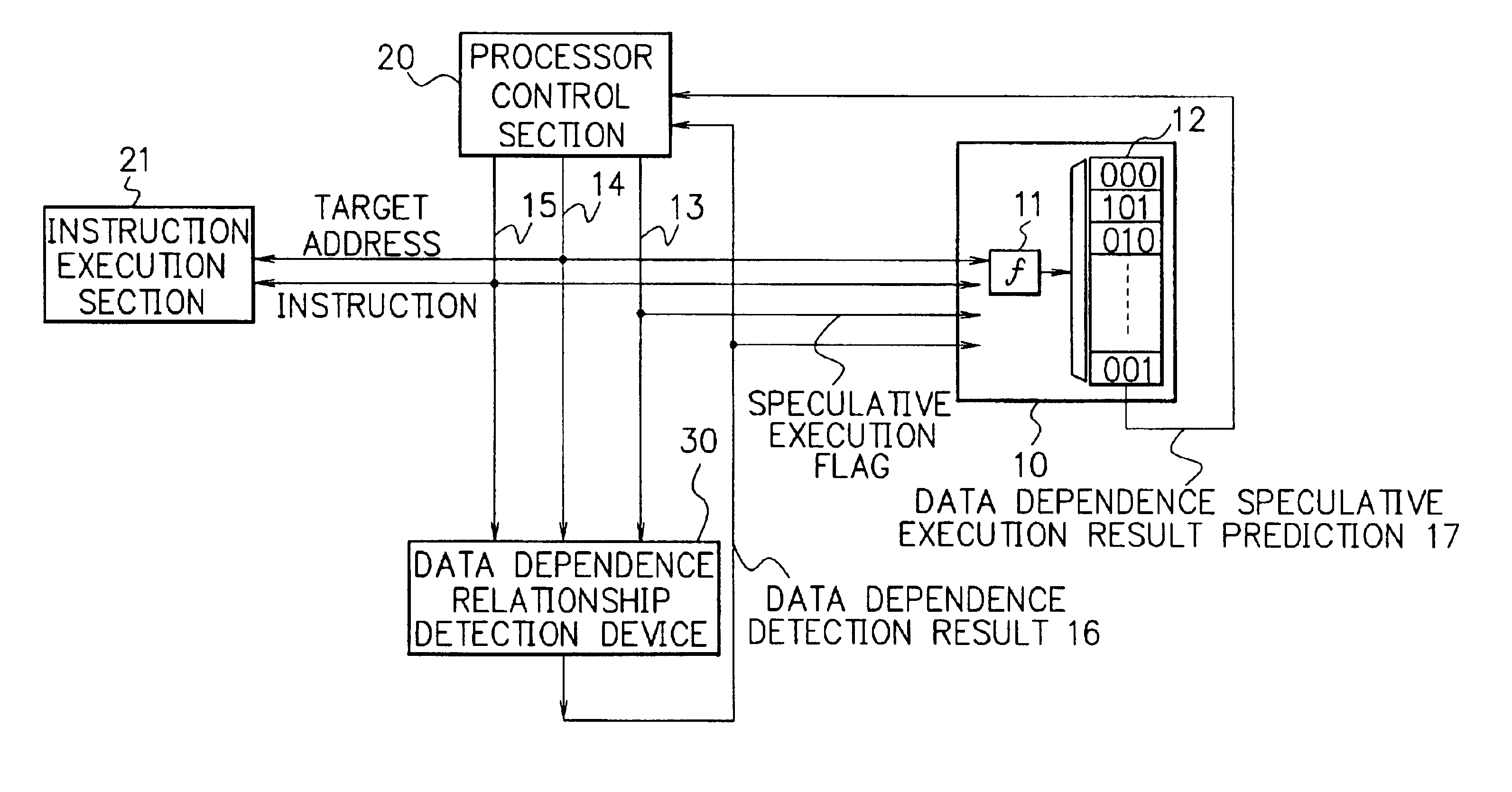
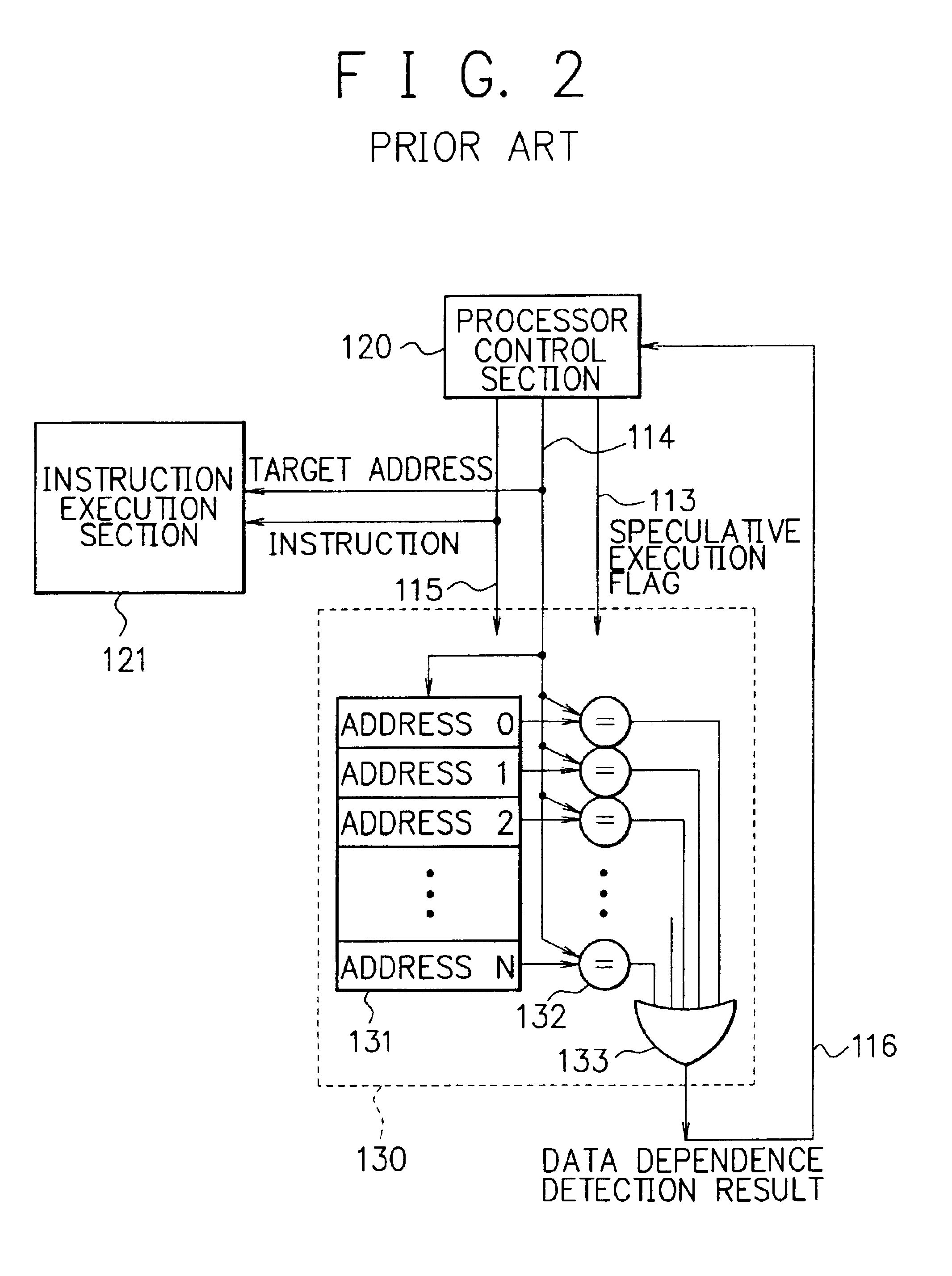
Processor, multiprocessor system and method for speculatively executing memory operations using memory target addresses of the memory operations to index into a speculative execution result history storage means to predict the outcome of the memory operation
InactiveUS6970997B2Low failure rateImprove execution performanceDigital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionMemory addressSpeculative execution
When a processor executes a memory operation instruction by means of data dependence speculative execution, a speculative execution result history table which stores history information concerning success / failure results of the speculative execution of memory operation instructions of the past is referred to and thereby whether the speculative execution will succeed or fail is predicted. In the prediction, the target address of the memory operation instruction is converted by a hash function circuit into an entry number of the speculative execution result history table (allowing the existence of aliases), and an entry of the table designated by the entry number is referred to. If the prediction is “success”, the memory operation instruction is executed in out-of-order execution speculatively (with regard to data dependence relationship between the instructions). If the prediction is “failure”, the speculative execution is canceled and the memory operation instruction is executed later in the program order non-speculatively. Whether the speculative execution of the memory operation instructions has succeeded or failed is judged by detecting the data dependence relationship between the memory operation instructions, and the speculative execution result history table is updated taking the judgment into account.
Owner:NEC CORP
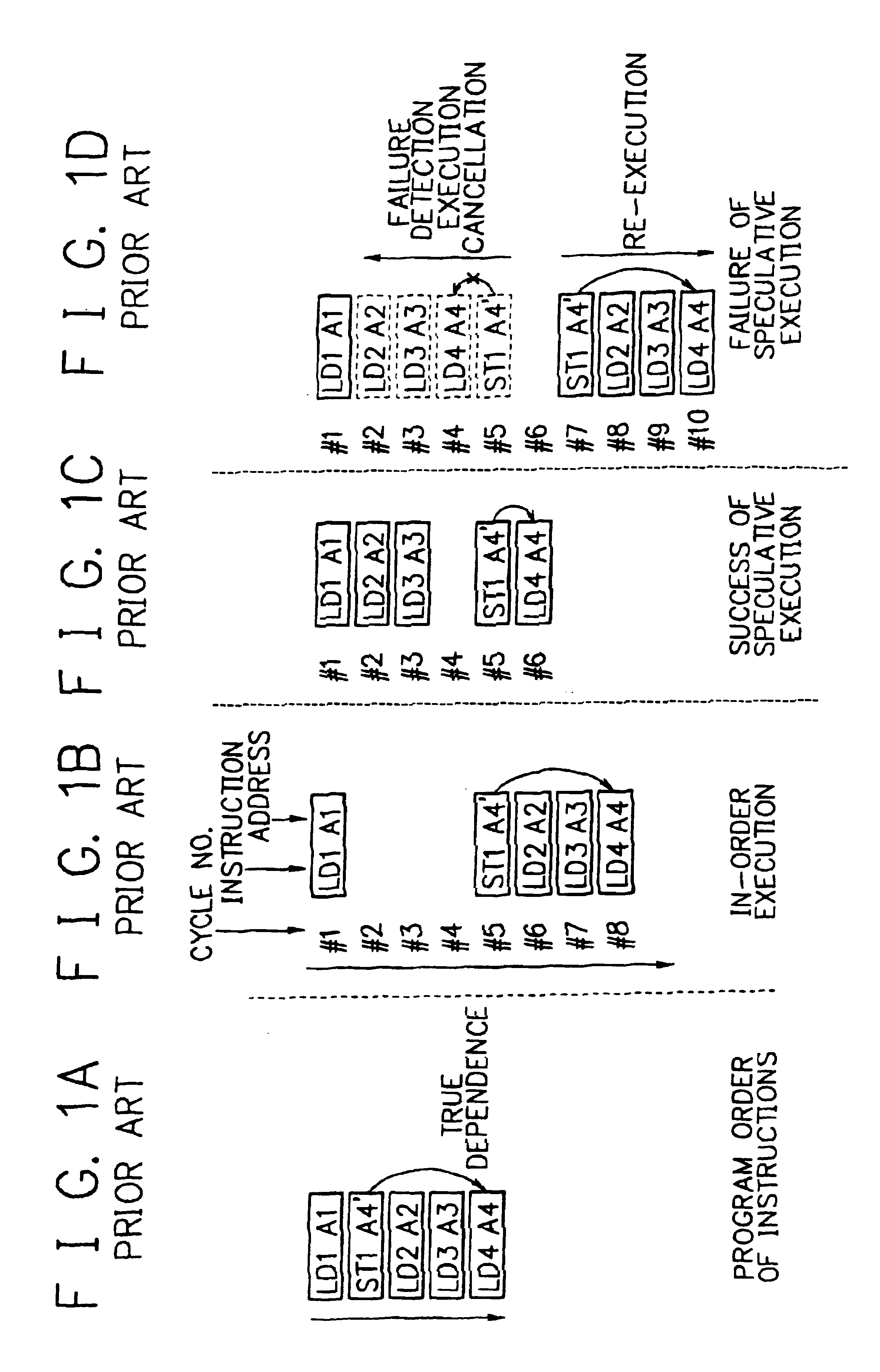
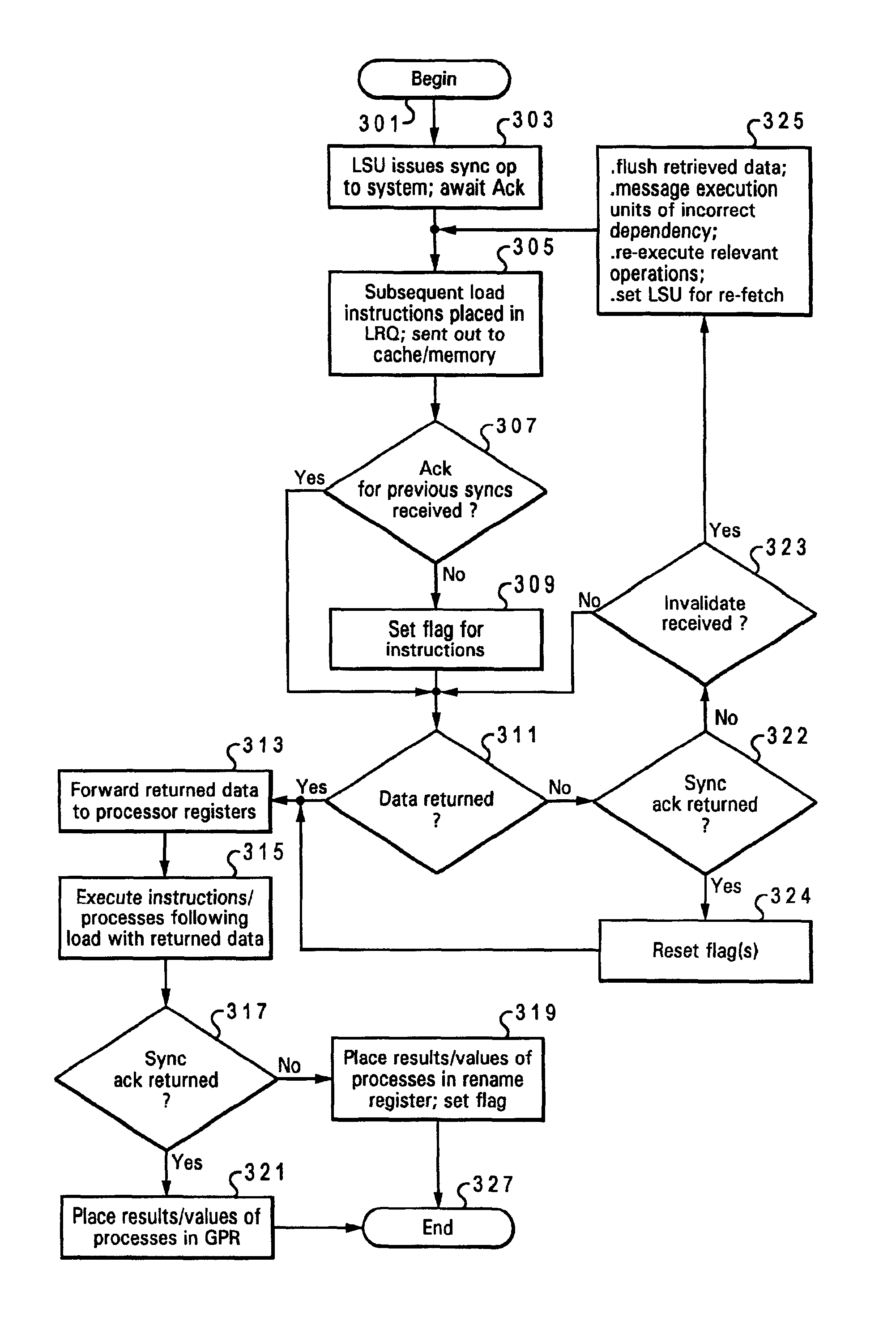
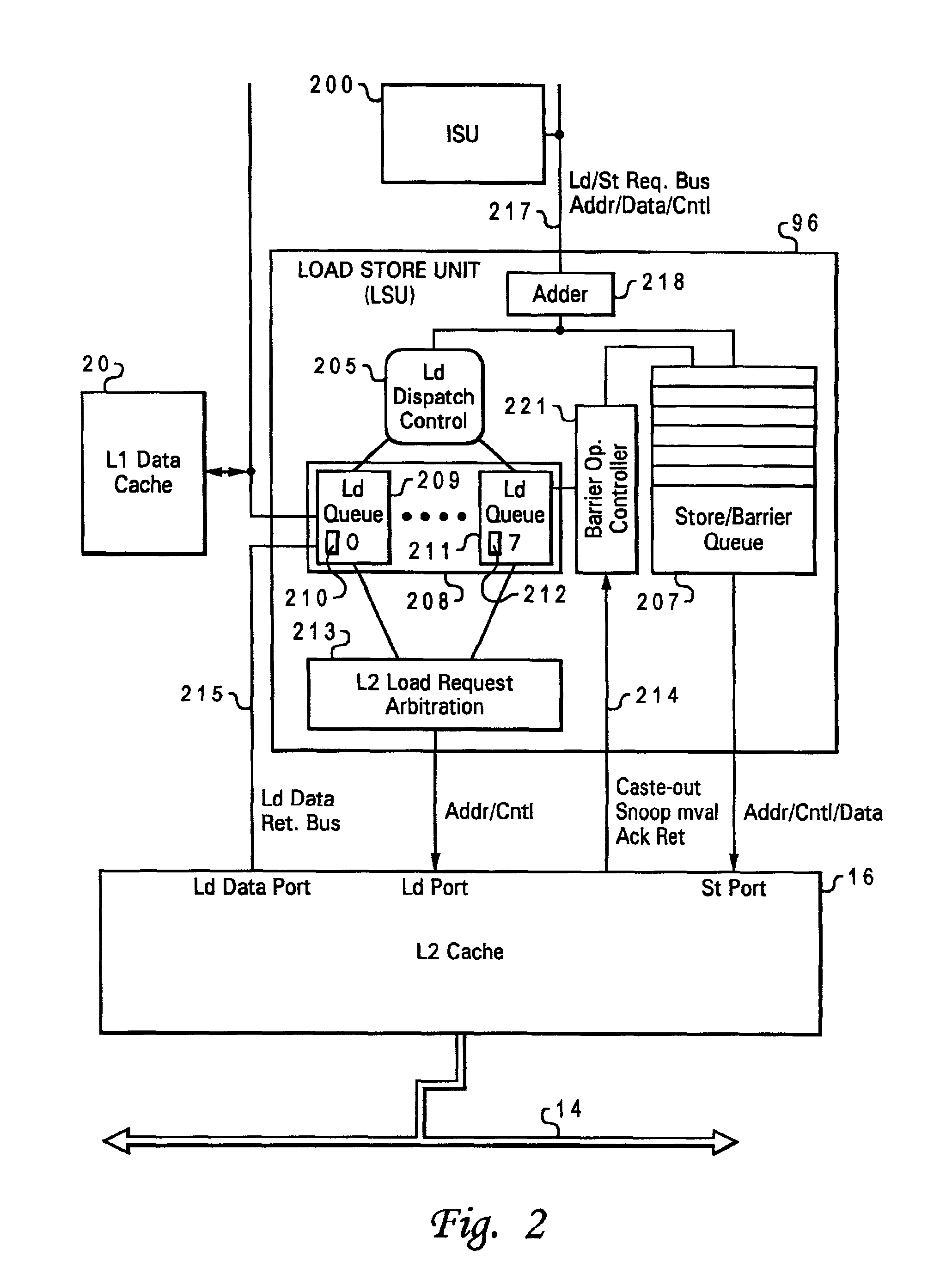
Speculative execution of instructions and processes before completion of preceding barrier operations
InactiveUS6880073B2Digital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionData processing systemSpeculative execution
Described is a data processing system and processor that provides full multiprocessor speculation by which all instructions subsequent to barrier operations in a instruction sequence are speculatively executed before the barrier operation completes on the system bus. The processor comprises a load / store unit (LSU) with a barrier operation (BOP) controller that permits load instructions subsequent to syncs in an instruction sequence to be speculatively issued prior to the return of the sync acknowledgment. Data returned is immediately forwarded to the processor's execution units. The returned data and results of subsequent operations are held temporarily in rename registers. A multiprocessor speculation flag is set in the corresponding rename registers to indicate that the value is “barrier” speculative. When a barrier acknowledge is received by the BOP controller, the flag(s) of the corresponding rename register(s) are reset.
Owner:IBM CORP
Low complexity speculative multithreading system based on unmodified microprocessor core
InactiveUS20070192545A1Efficient use ofMemory architecture accessing/allocationProgram controlMemory hierarchySpeculative execution
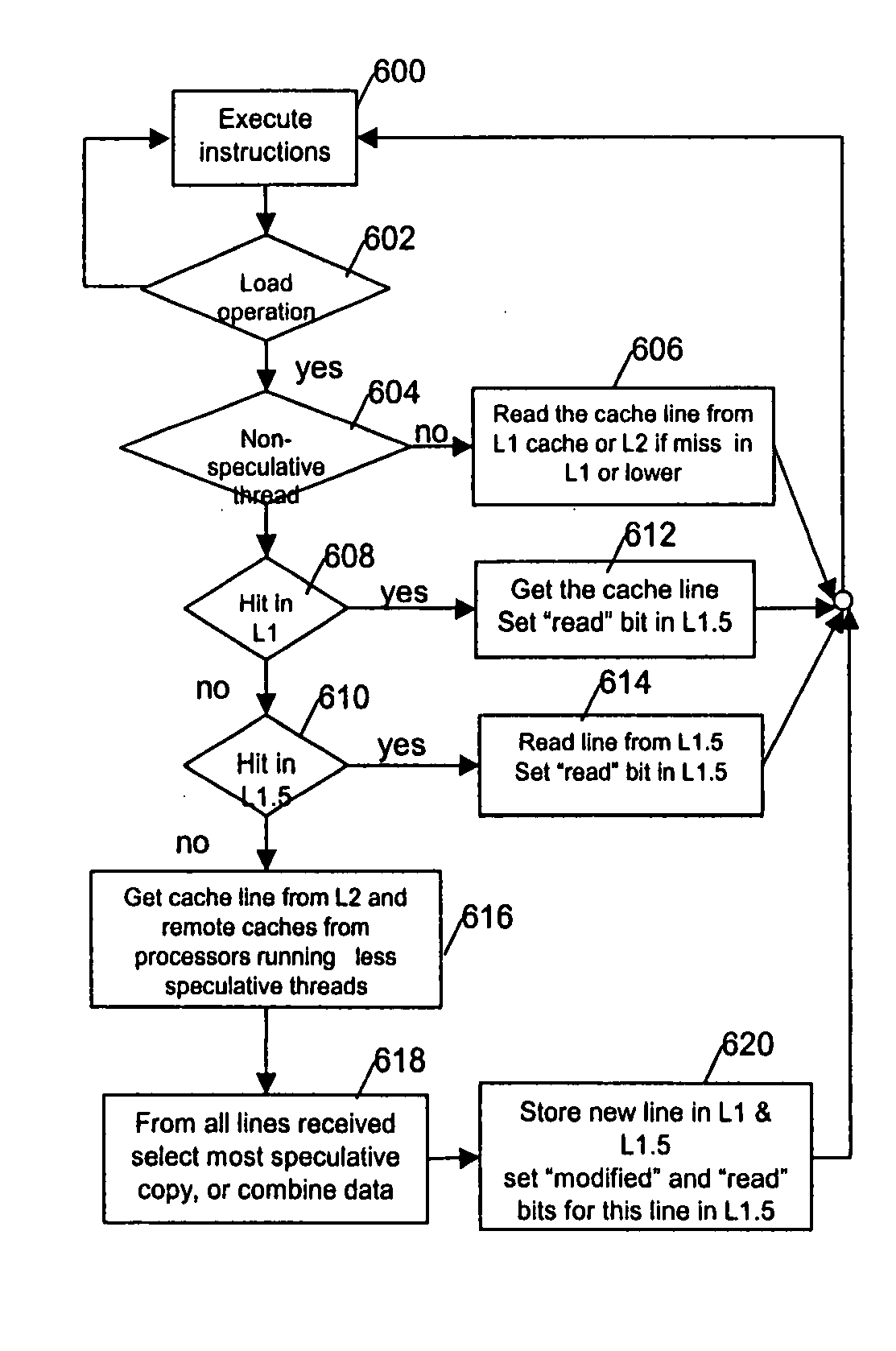
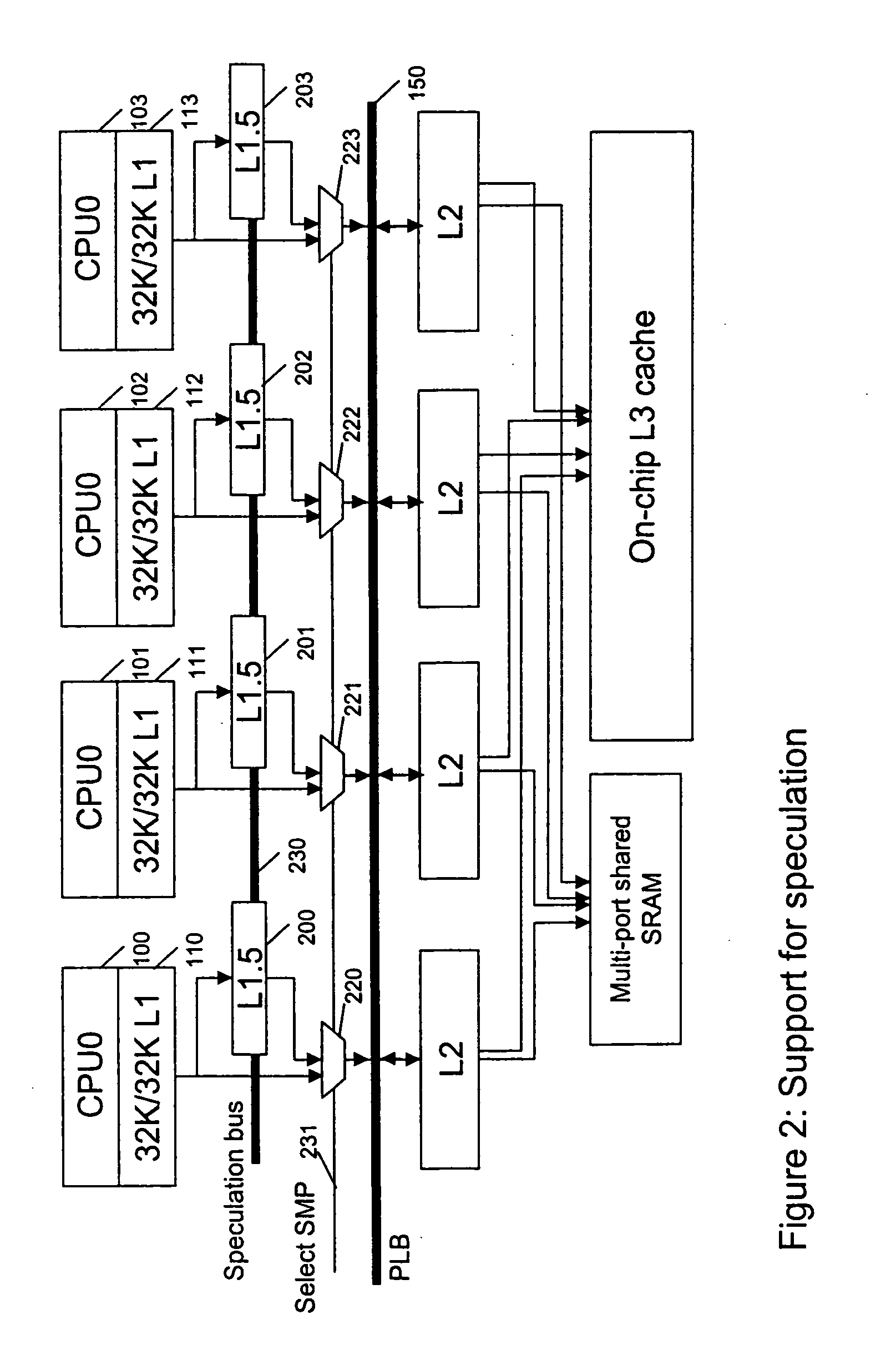
A system, method and computer program product for supporting thread level speculative execution in a computing environment having multiple processing units adapted for concurrent execution of threads in speculative and non-speculative modes. Each processing unit includes a cache memory hierarchy of caches operatively connected therewith. The apparatus includes an additional cache level local to each processing unit for use only in a thread level speculation mode, each additional cache for storing speculative results and status associated with its associated processor when handling speculative threads. The additional local cache level at each processing unit are interconnected so that speculative values and control data may be forwarded between parallel executing threads. A control implementation is provided that enables speculative coherence between speculative threads executing in the computing environment.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus, method, and system for instantaneous cache state recovery from speculative abort/commit
InactiveUS20120144126A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationProgram controlSpeculative executionTerm memory
An apparatus and method is described herein for providing instantaneous, efficient cache state recover upon an end of speculative execution. Speculatively accessed entries of a cache memory are marked as speculative, which may be on a thread specific basis. Upon an end of speculation, the speculatively marked entries are transitioned in parallel by a speculative port to their appropriate, thread specific, non-speculative coherency state; these parallel transitions allow for instantaneous commit or recovery of speculative memory state.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and logical apparatus for managing processing system resource use for speculative execution
InactiveUS20060161762A1Reduces resourceReduce energy wasteEnergy efficient ICTDigital computer detailsSpeculative executionProgram instruction
A method and logical apparatus for managing processing system resource use for speculative execution reduces the power and performance burden associated with inefficient speculative execution of program instructions. A measure of the efficiency of speculative execution is used to reduce resources allocated to a thread while the speculation efficiency is low. The resource control applied may be the number of instruction fetches allocated to the thread or the number of execution time slices. Alternatively, or in combination, the size of a prefetch instruction storage allocated to the thread may be limited. The control condition may be comparison of the number of correct or incorrect speculations to a threshold, comparison of the number of correct to incorrect speculations, or a more complex evaluator such as the size of a ratio of incorrect to total speculations.
Owner:IBM CORP
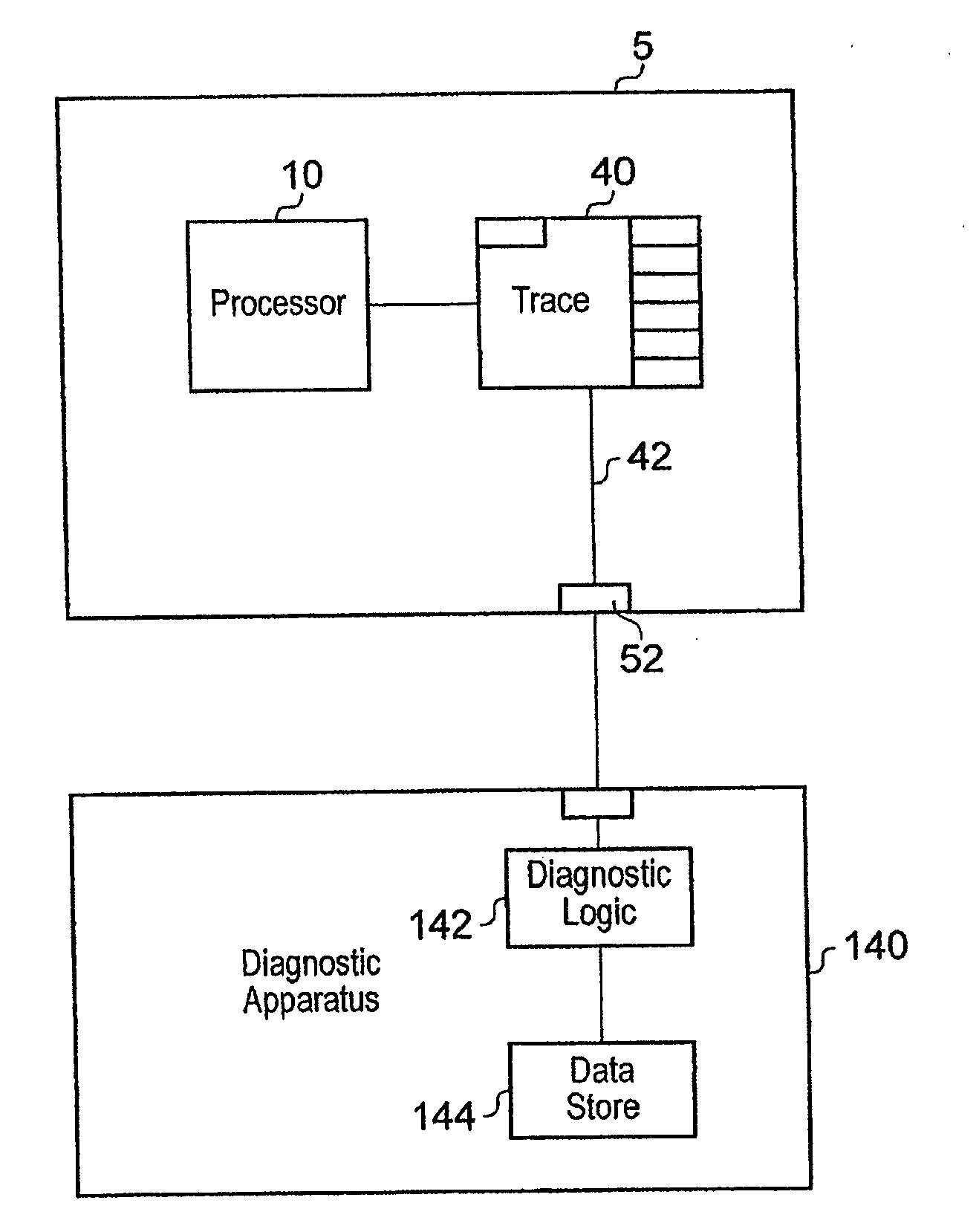
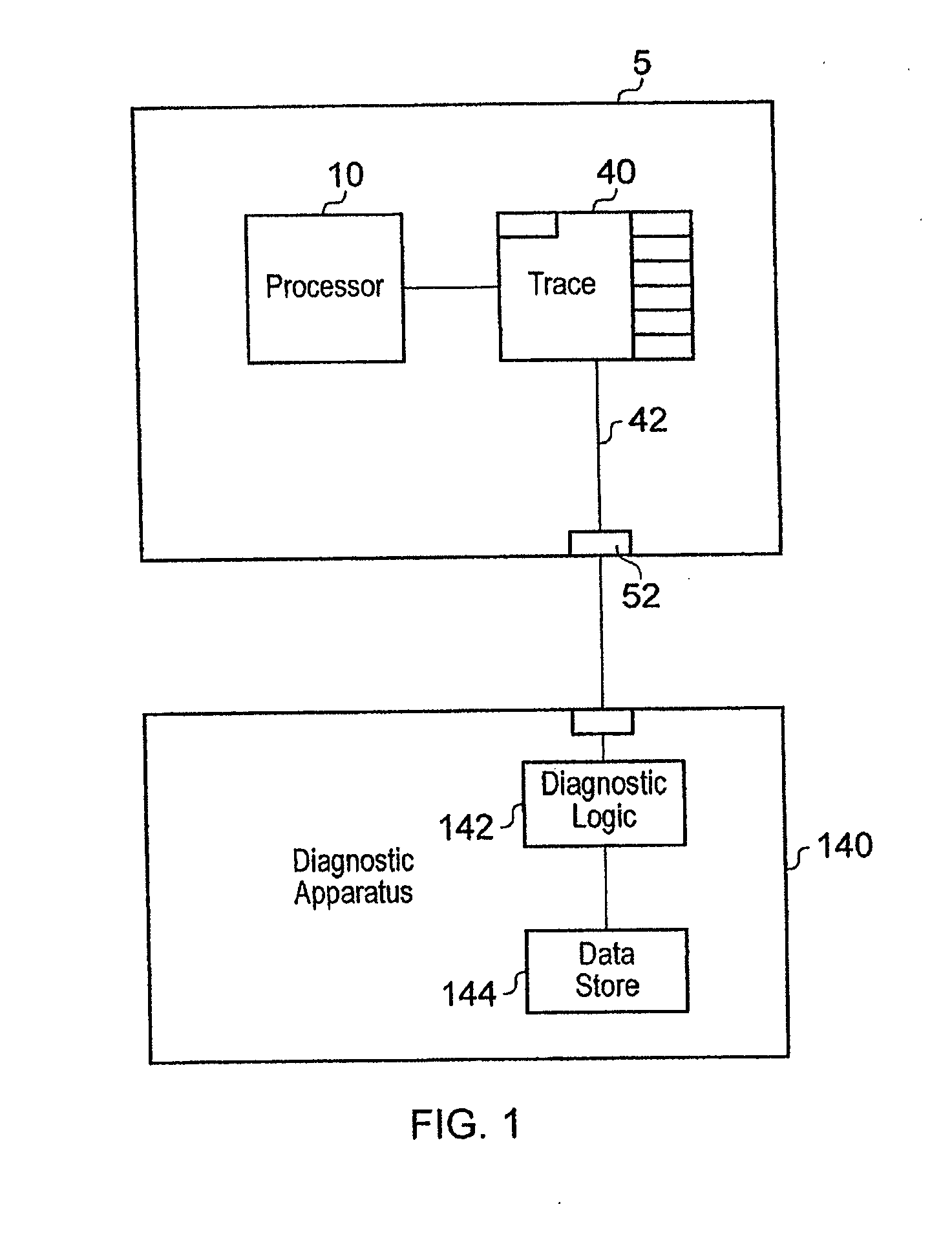
Tracing speculatively executed instructions
ActiveUS20110314342A1Easy to compressFunction providedInstruction analysisHardware monitoringSpeculative executionControl data
A trace unit for generating items of trace data indicative of processing activities of a processor executing a stream of instructions, the stream of instructions comprising a plurality of groups of instructions, the processor executing at least some of the instructions speculatively is disclosed. The trace unit comprises: trace circuitry for monitoring a behaviour of the processor; storage circuitry for storing current trace control data for controlling the trace circuitry; a data store for storing at least some of the trace control data; the trace circuitry being configured to store the trace control data in the data store in response to detection of execution of the group of instructions; the trace circuitry being responsive to detecting the at least one processor cancelling at least one group of the speculatively executed instructions to retrieve at least some of the trace control data stored in the data store for the group of instructions executed before the cancelled speculatively executed instructions and to store the retrieved trace control data in the storage circuitry.
Owner:ARM LTD
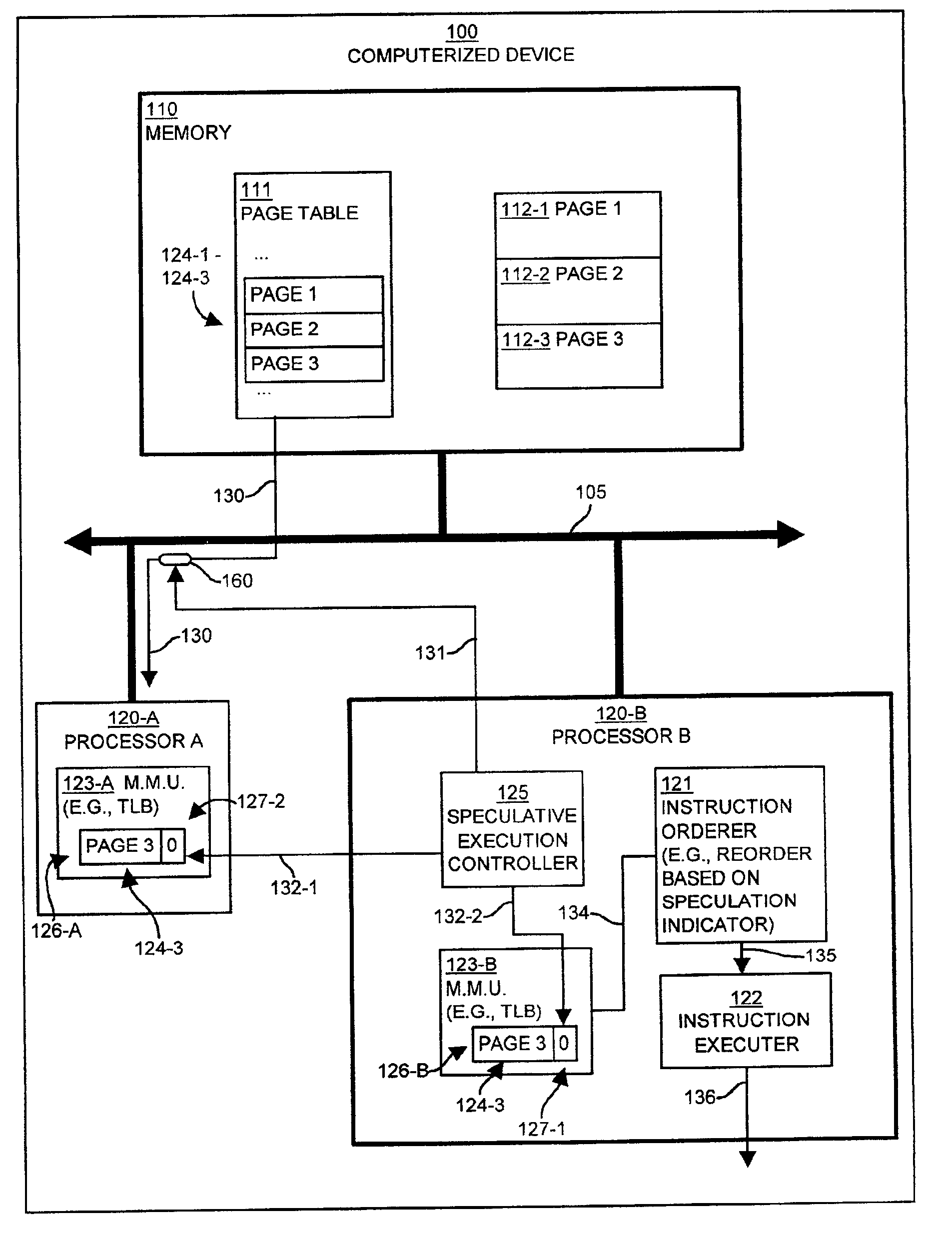
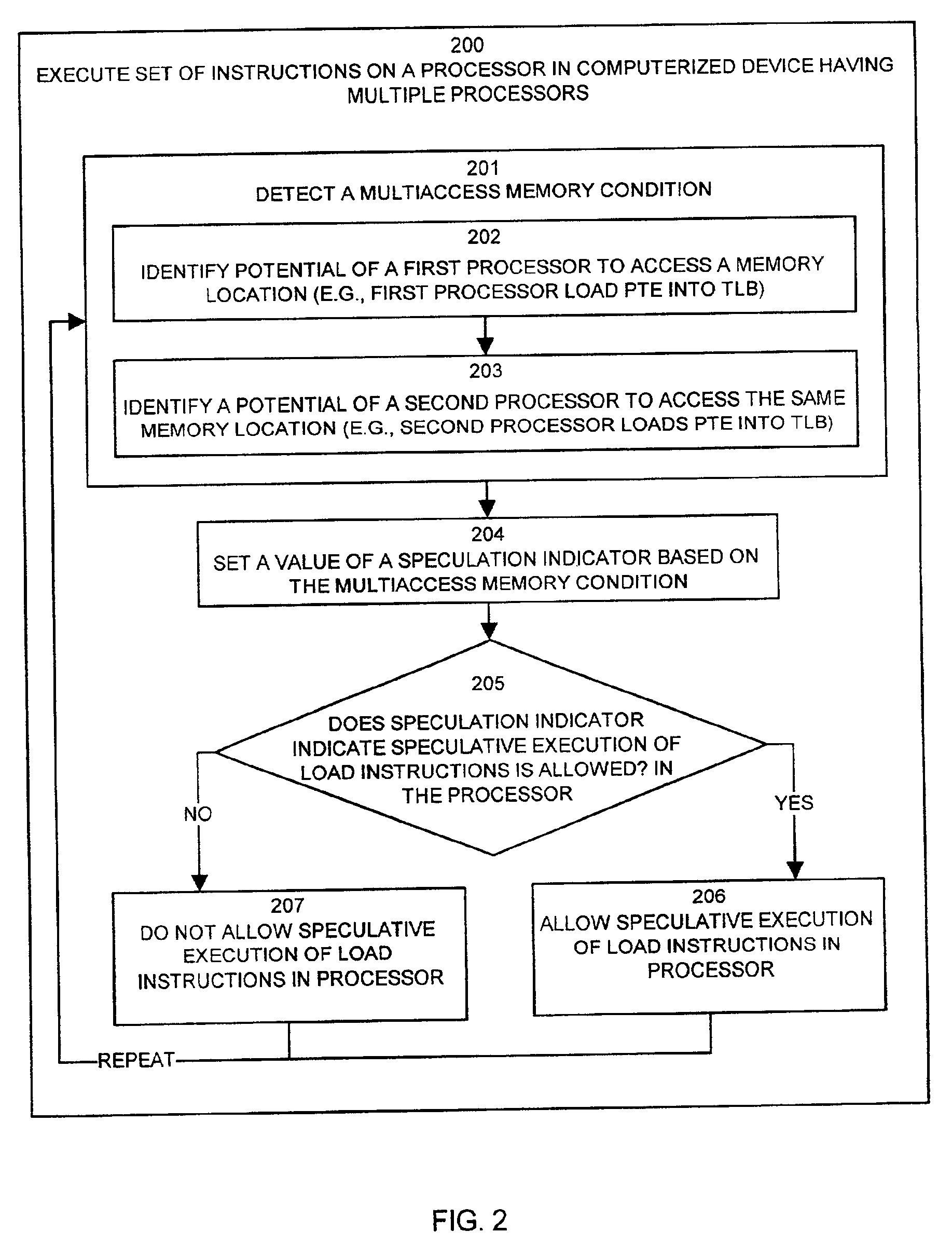
Methods and apparatus for controlling speculative execution of instructions based on a multiaccess memory condition
InactiveUS6877088B2Lower performance requirementsEnergy efficient ICTMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSpeculative executionPage table
Mechanisms and techniques operate in a computerized device to enable or disable speculative execution of instructions such as reordering of load and store instructions a multiprocessing computerized device. The mechanisms and techniques provide a speculative execution controller that can detect a multiaccess memory condition between the first and second processors, such as concurrent access to shared data pages via page table entries. This can be done by monitoring page table entry accesses by other processors. The speculative execution controller sets a value of a speculation indicator in the memory system based on the multiaccess memory condition. If the value of the speculation indicator indicates that speculative execution of instructions is allowed in the computerized device, the speculative execution controller allows speculative execution of instructions in at least one of the first and second processors in the computerized device. If the value of the speculation indicator indicates that speculative execution of instructions is not allowed in the computerized device, the speculative execution controller does not allow speculative execution of instructions.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
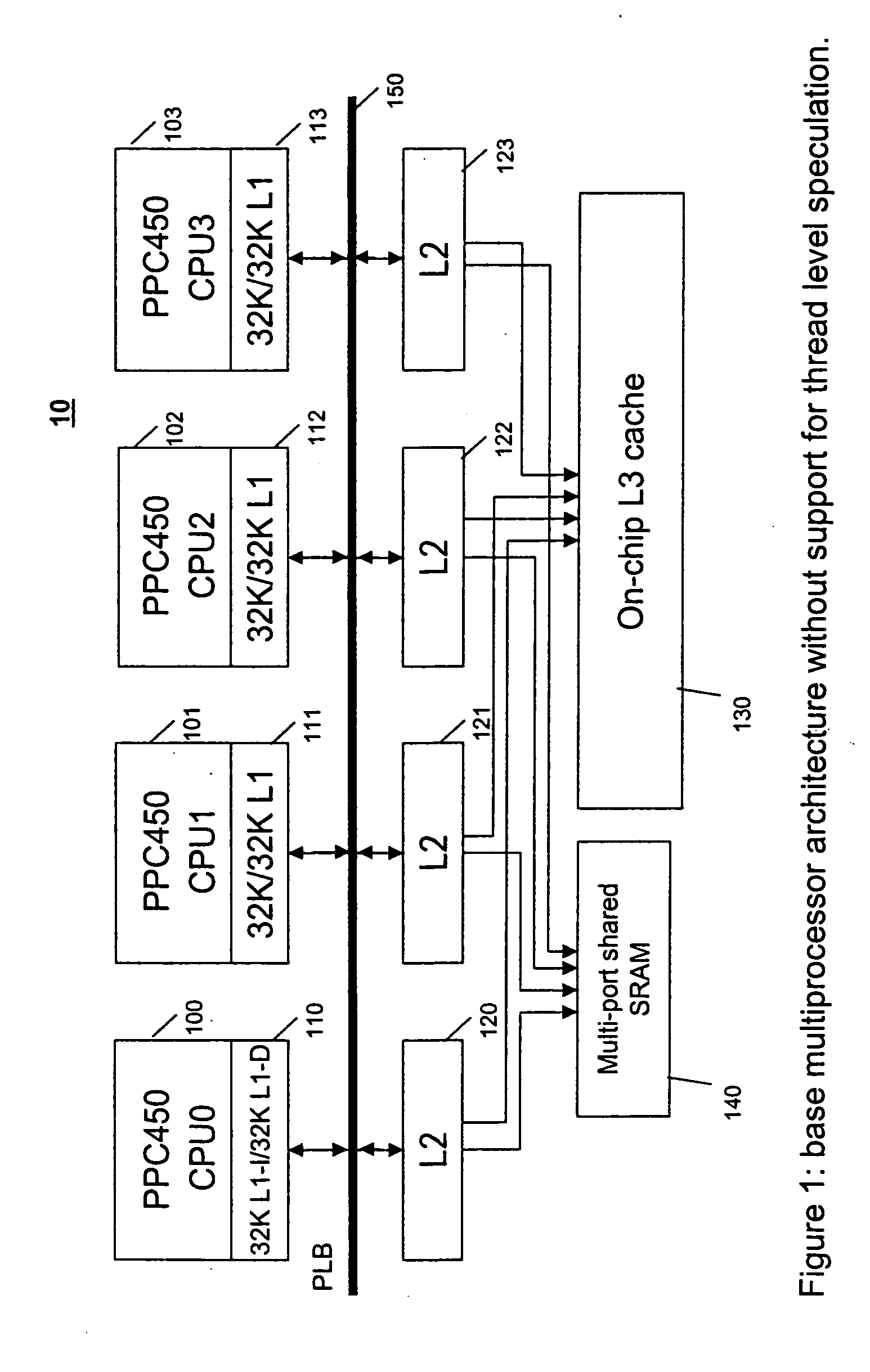
Architectural support for thread level speculative execution
A method and apparatus for hardware support of the thread level speculation for existing processor cores without having to change the existing processor core, processor core's interface, or existing caches on the L1, L2 or L3 level. Architecture support for thread speculative execution by adding a new cache level for storing speculative values and a dedicated bus for forwarding speculative values and control. The cache level is hierarchically positioned between the cache levels L1 and L2 cache levels.
Owner:IBM CORP
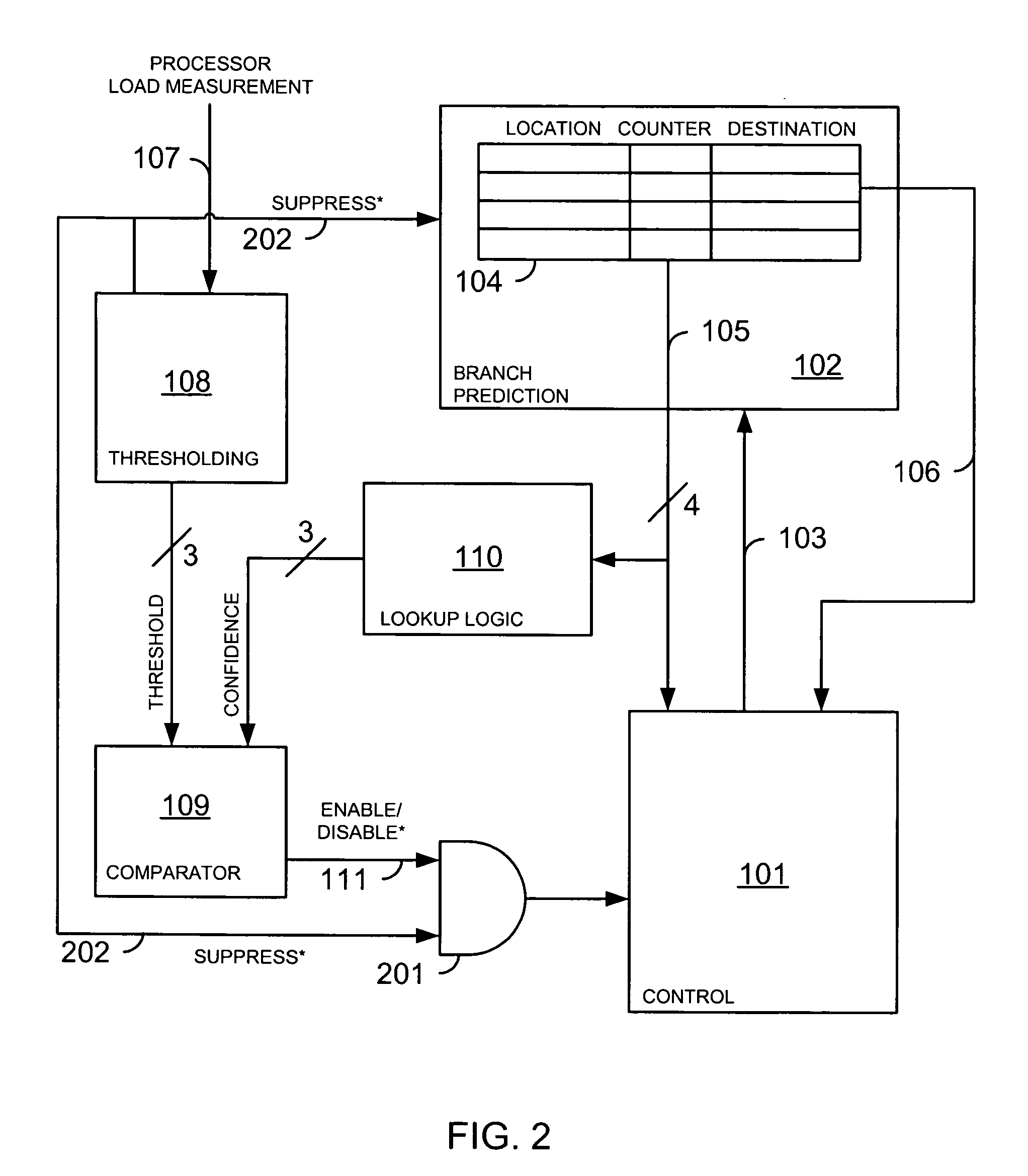
Suppression of control transfer instructions on incorrect speculative execution paths
ActiveUS20120290820A1Suppresses resultEliminates spurious flushDigital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionSpeculative executionExecution control
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
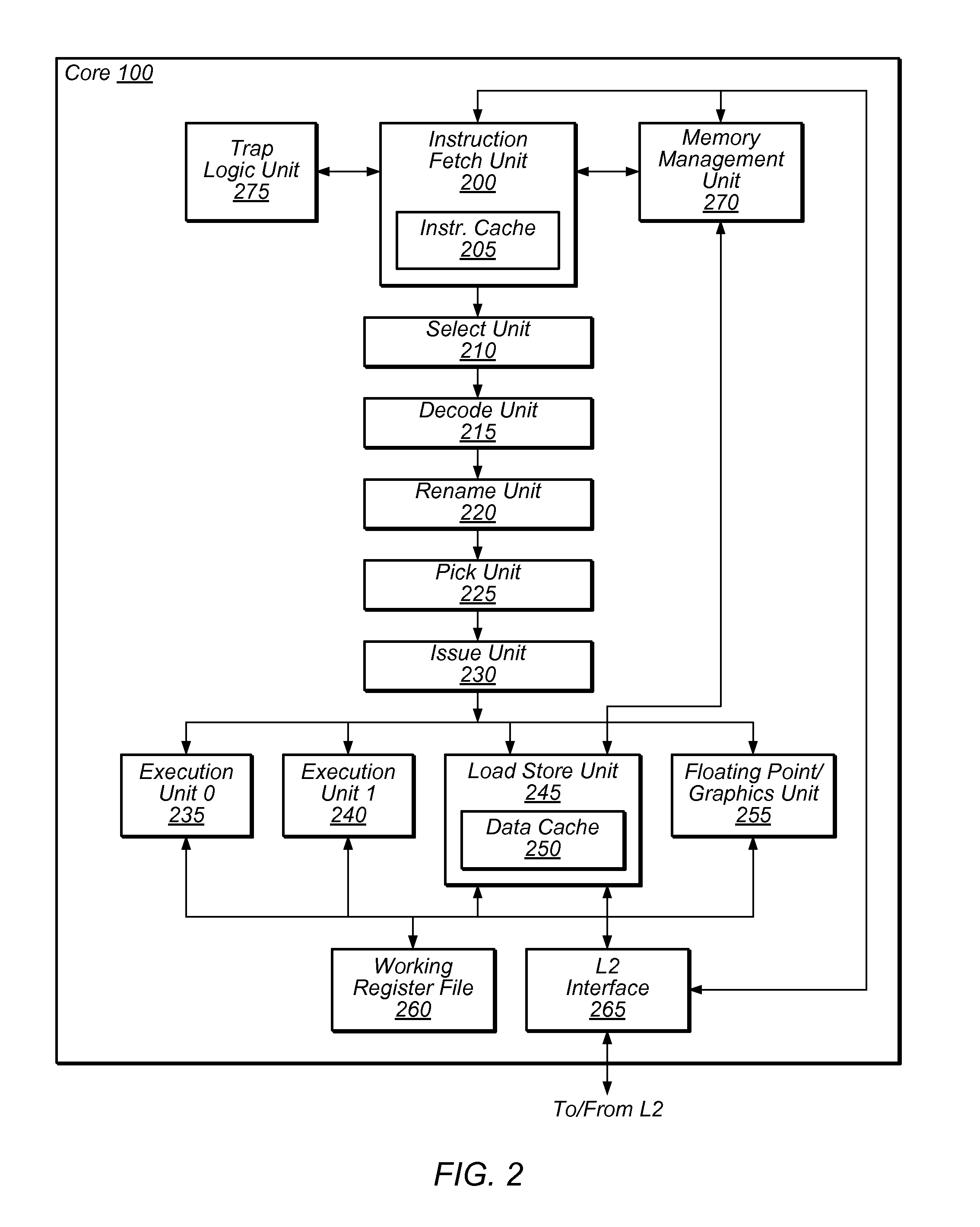
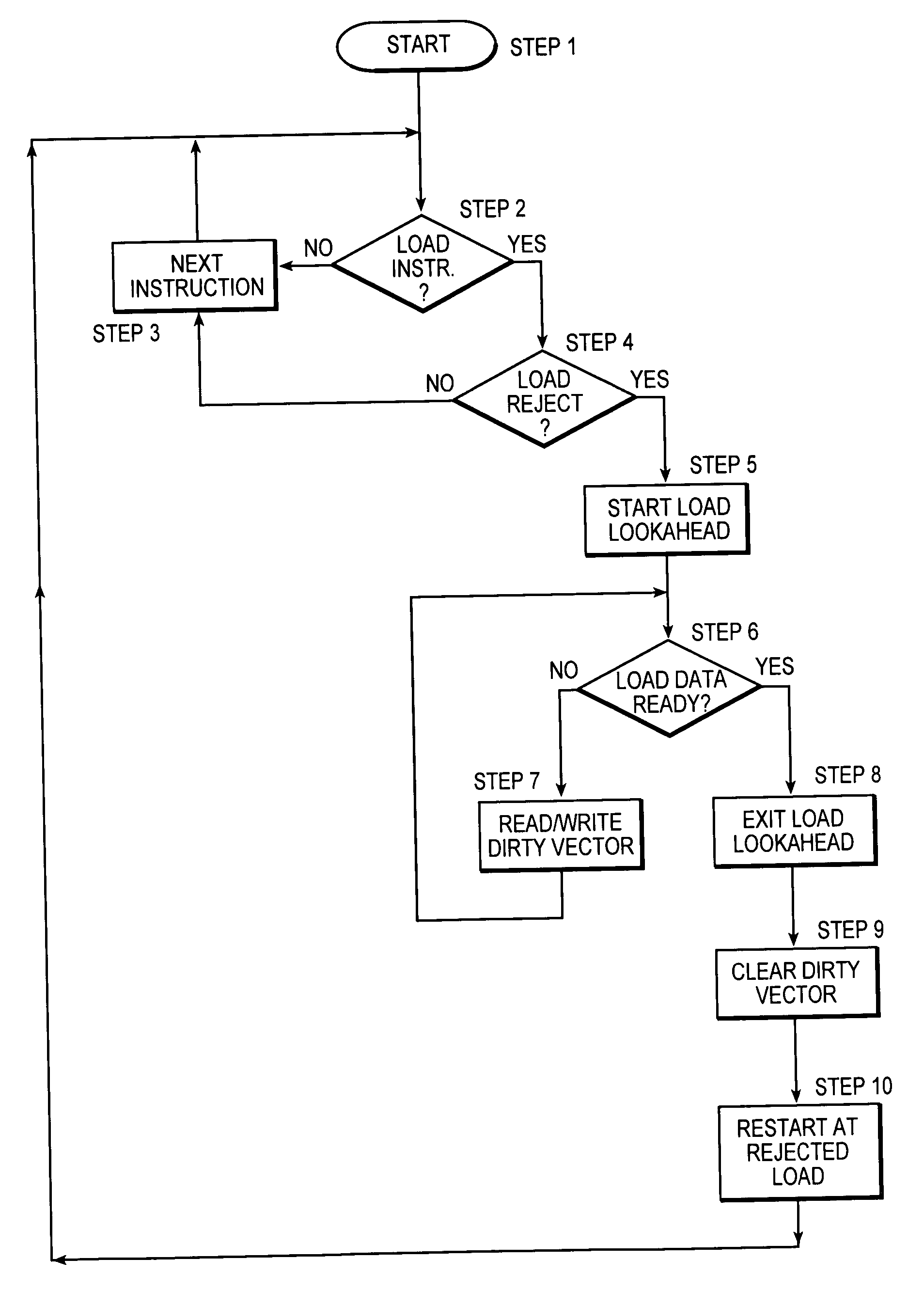
Load lookahead prefetch for microprocessors
InactiveUS20060149935A1Reduced performance impactLower latencyDigital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsSpeculative executionLoad instruction
The present invention allows a microprocessor to identify and speculatively execute future load instructions during a stall condition. This allows forward progress to be made through the instruction stream during the stall condition which would otherwise cause the microprocessor or thread of execution to be idle. The data for such future load instructions can be prefetched from a distant cache or main memory such that when the load instruction is re-executed (non speculative executed) after the stall condition expires, its data will reside either in the L1 cache, or will be enroute to the processor, resulting in a reduced execution latency. When an extended stall condition is detected, load lookahead prefetch is started allowing speculative execution of instructions that would normally have been stalled. In this speculative mode, instruction operands may be invalid due to source loads that miss the L1 cache, facilities not available in speculative execution mode, or due to speculative instruction results that are not available via forwarding and are not written to the architected registers. A set of status bits are used to dynamically keep track of the dependencies between instructions in the pipeline and a bit vector tracks invalid architected facilities with respect to the speculative instruction stream. Both sources of information are used to identify load instructions with valid operands for calculating the load address. If the operands are valid, then a load prefetch operation is started to retrieve data from the cache ahead of time such that it can be available for the load instruction when it is non-speculatively executed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
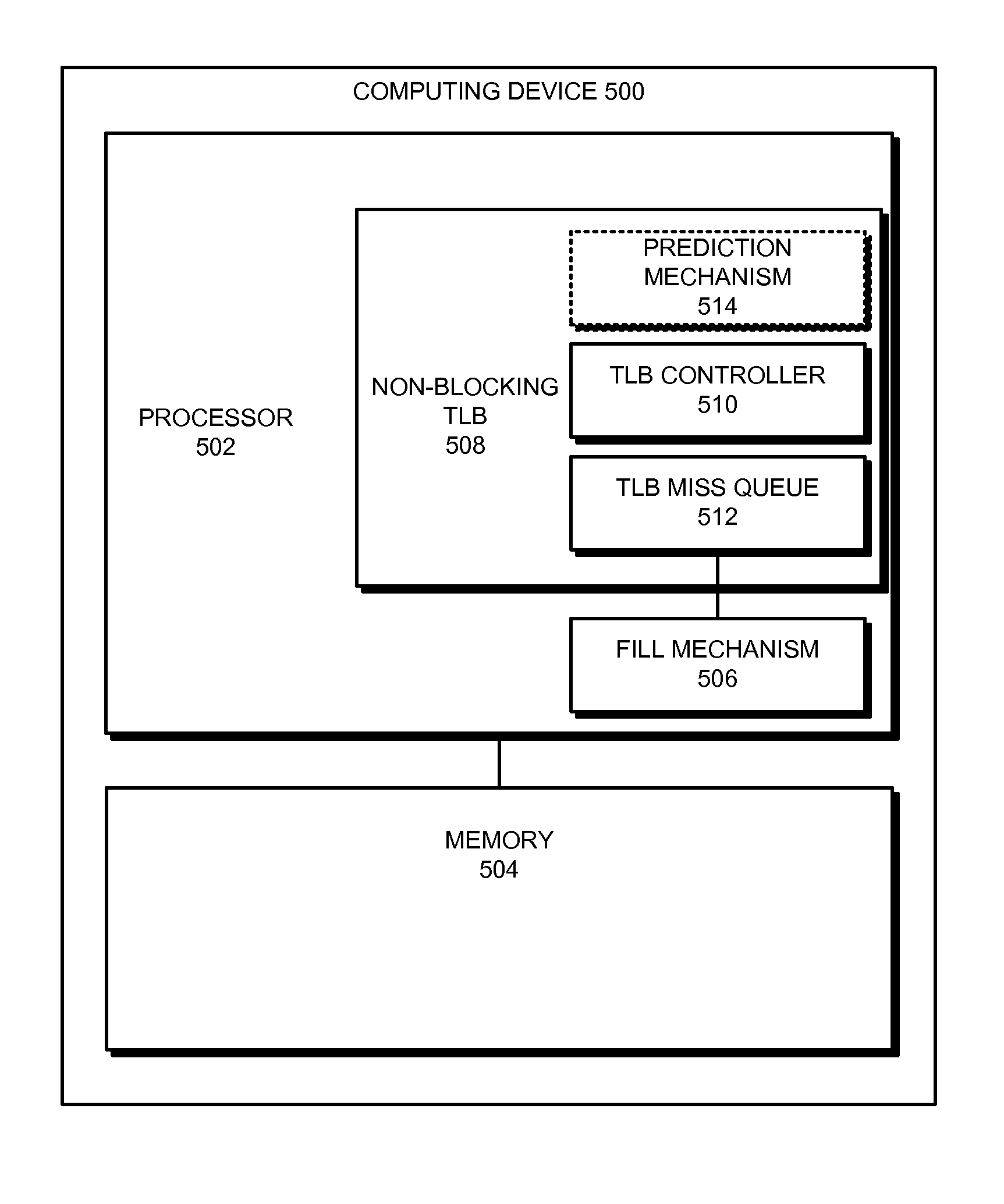
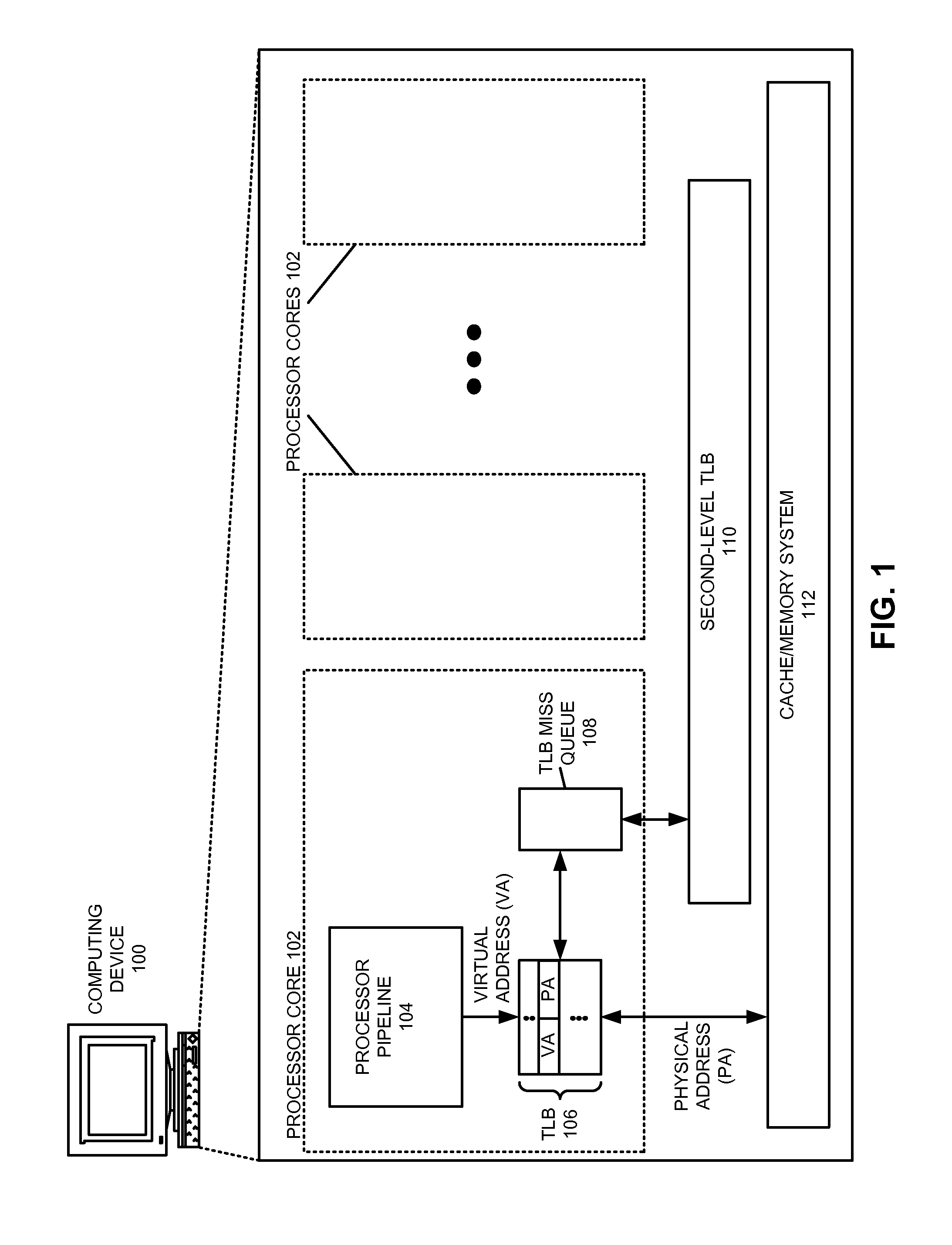
Preventing duplicate entries in a non-blocking tlb structure that supports multiple page sizes
ActiveUS20110138149A1Eliminates hardware overheadEliminates software overheadMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSpeculative executionVirtual address space
One embodiment provides a system that prevents duplicate entries in a non-blocking TLB that supports multiple page sizes and speculative execution. During operation, after a request for translation of a virtual address misses in the non-blocking TLB, the system receives a TLB fill. Next, the system determines a page size associated with the TLB fill, and uses this page size to determine a set of bits in the virtual address that identify the virtual page associated with the TLB fill. The system then compares this set of bits with the corresponding bits of other virtual addresses associated with pending translation requests. If the system detects that a second virtual address for another pending translation request is also satisfied by the TLB fill, the system invalidates the duplicate translation request associated with the second virtual address.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
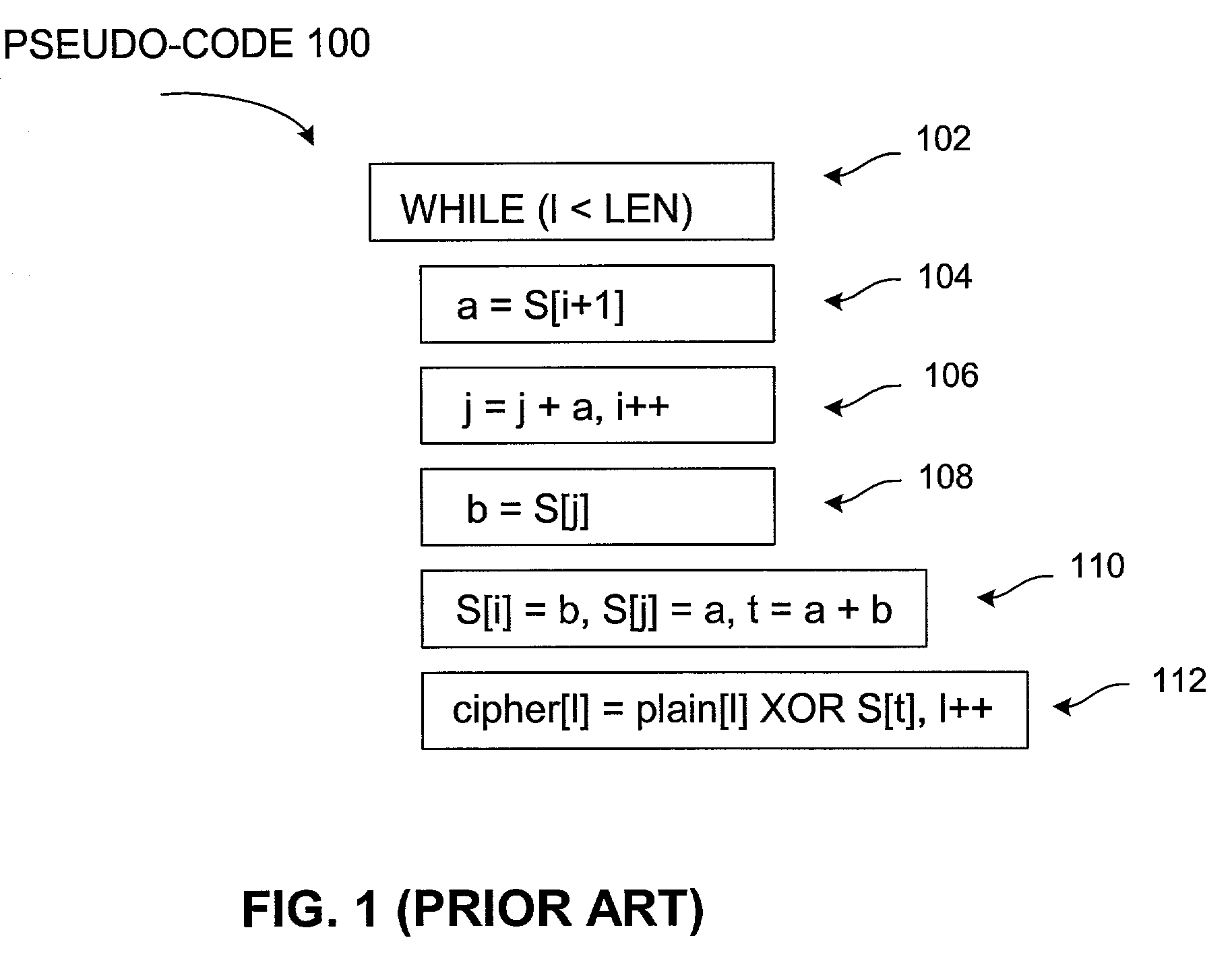
Speculative execution for data ciphering operations
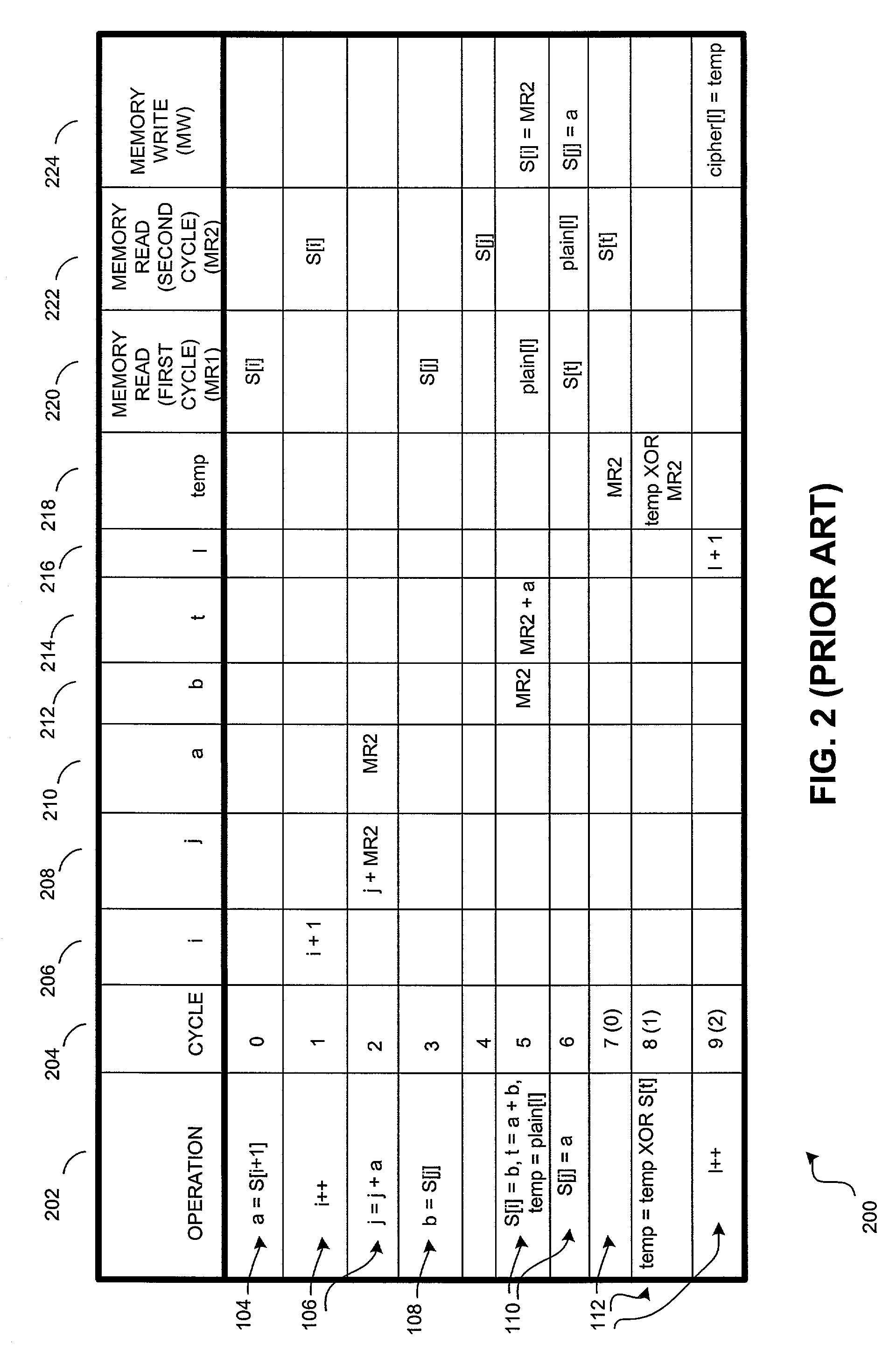
ActiveUS7260217B1Data stream serial/continuous modificationSecret communicationSpeculative executionComputer hardware
In one embodiment, a computer-implemented method comprises receiving a data cipher operation. The method also comprises processing the data cipher operation. The processing of the operation includes generating a number of portions of ciphertext from plaintext, wherein a load operation associated with the generating of at least one portion of the ciphertext executes prior to a store operation associated with the generating of a prior portion of the ciphertext.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Processor pipeline including partial replay
InactiveUS6076153AGeneral purpose stored program computerConcurrent instruction executionSpeculative executionScalar processor
The invention, in one embodiment, is a method for committing the results of at least two speculatively executed instructions to an architectural state in a superscalar processor. The method includes determining which of the speculatively executed instructions encountered a problem in execution, and replaying the instruction that encountered the problem in execution while retaining the results of executing the instruction that did not encounter the problem.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Speculative side-channel attack mitigations
ActiveUS20190114422A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationRegister arrangementsSpeculative executionTerm memory
Preventing the observation of the side effects of mispredicted speculative execution flows using restricted speculation. In an embodiment a microprocessor comprises a register file including a plurality of entries, each entry comprising a value and a flag. The microprocessor (i) sets the flag corresponding to any entry whose value results from a memory load operation that has not yet been retired or cancelled, or results from a calculation that was derived from a register file entry whose corresponding flag was set, and (ii) clears the flag corresponding to any entry when the operation that generated the entry's value is retired. The microprocessor also comprises a memory unit that is configured to hold any memory load operation that uses an address whose value is calculated based on a register file entry whose flag is set, unless all previous instructions have been retired or cancelled.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Computer power conservation apparatus and method
A computer measures a processor load and configures itself so that a lesser amount of speculative execution is enabled when the processor is lightly loaded than is enabled when the processor is heavily loaded.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Concurrent Execution of Critical Sections by Eliding Ownership of Locks
InactiveUS20070186215A1Ensure correct executionEfficient executionMemory architecture accessing/allocationProgram synchronisationSpeculative executionCritical section
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that facilitates avoiding locks by speculatively executing critical sections of code. During operation, the system allows a process to speculatively execute a critical section of code within a program without first acquiring a lock associated with the critical section. If the process subsequently completes the critical section without encountering an interfering data access from another process, the system commits changes made during the speculative execution, and resumes normal non-speculative execution of the program past the critical section. Otherwise, if an interfering data access from another process is encountered during execution of the critical section, the system discards changes made during the speculative execution, and attempts to re-execute the critical section.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
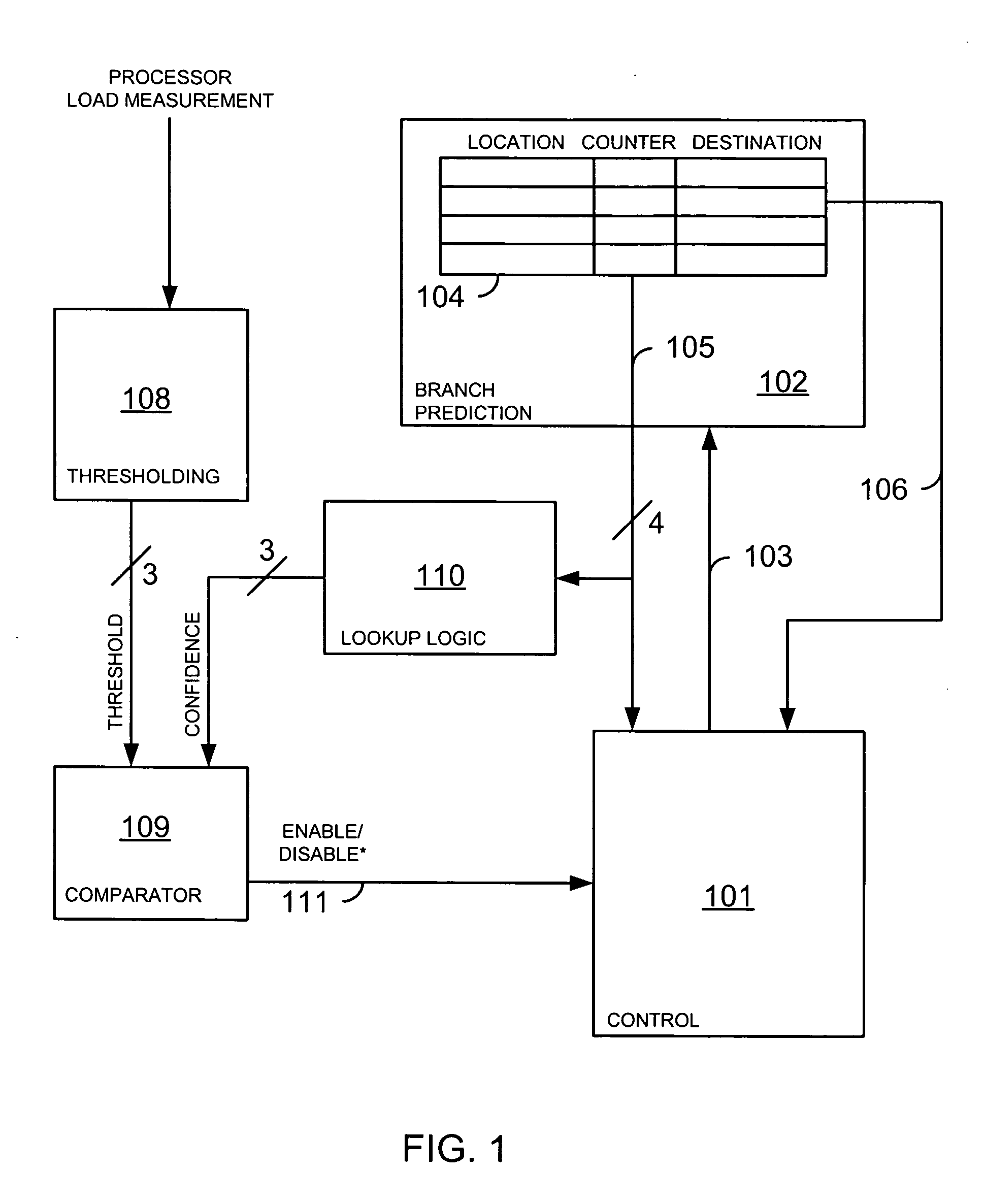
Cumulative confidence fetch throttling
ActiveUS20120124345A1Reducing prefetching operationReduce stepsDigital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionSpeculative executionConfidence measures
A method and apparatus to utilize a fetching scheme for instructions in a processor to limit the expenditure of power caused by the speculative execution of branch instructions is provided. Also provided is a computer readable storage device encoded with data for adapting a manufacturing facility to create an apparatus. The method includes calculating a cumulative confidence measure based on one or more outstanding conditional branch instructions. The method also includes reducing prefetching operations in response to detecting that the cumulative confidence measure is below a first threshold level.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
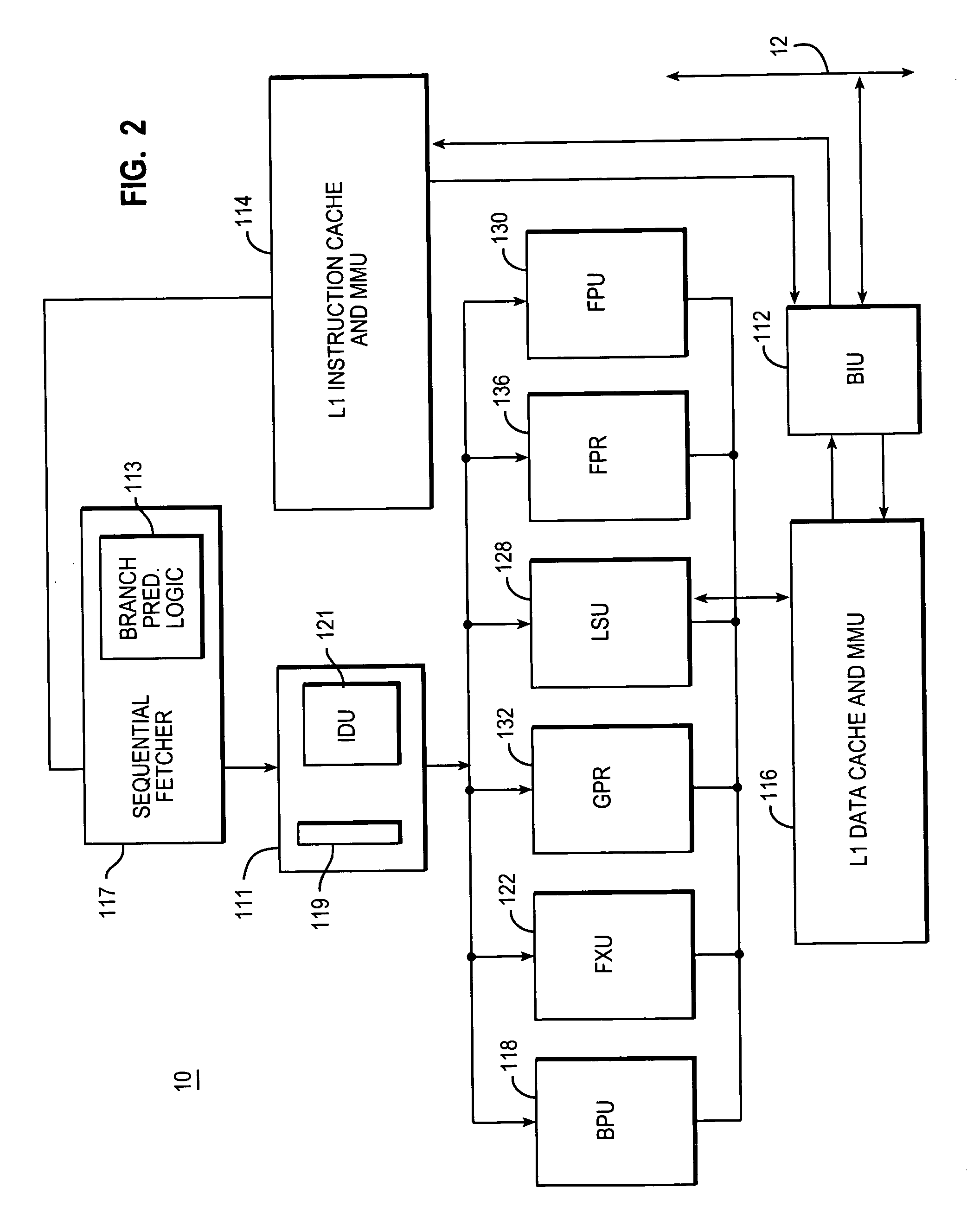
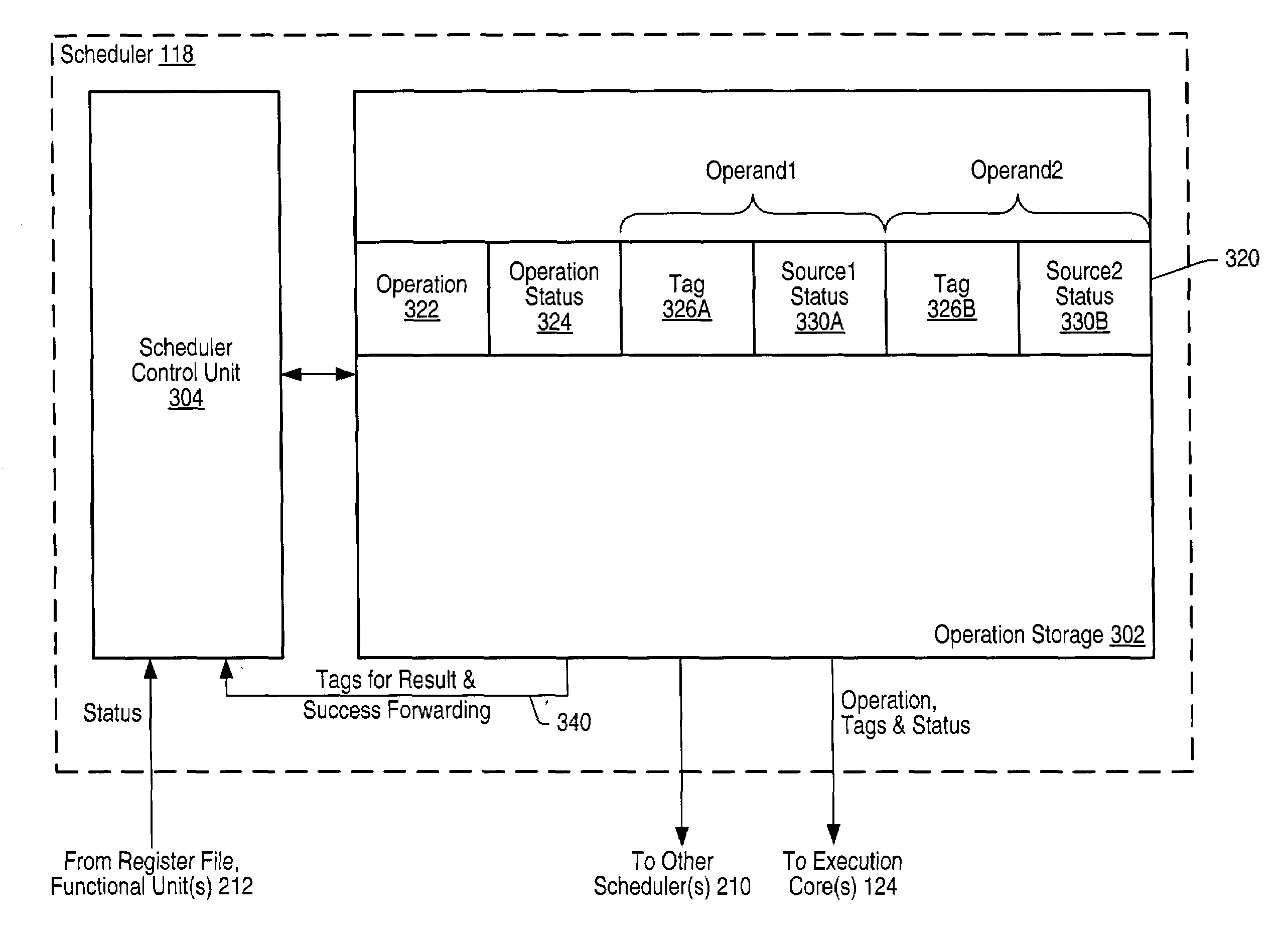
Scheduler for use in a microprocessor that supports data-speculative execution
ActiveUS6950925B1Digital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionSpeculative executionExecution unit
A microprocessor may include several execution units and a scheduler coupled to issue operations to at least one of the execution units. The scheduler may include several entries. A first entry may be allocated to a first operation. The first entry includes a source status indication for each of the first operation's operands. Each source status indication indicates whether a value of a respective one of the first operation's operands is speculative. The scheduler is configured to update one of the first entry's source status indications to indicate that a value of a respective one of the first operation's operands is non-speculative in response to receiving an indication that a value of a result of a second operation is non-speculative.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
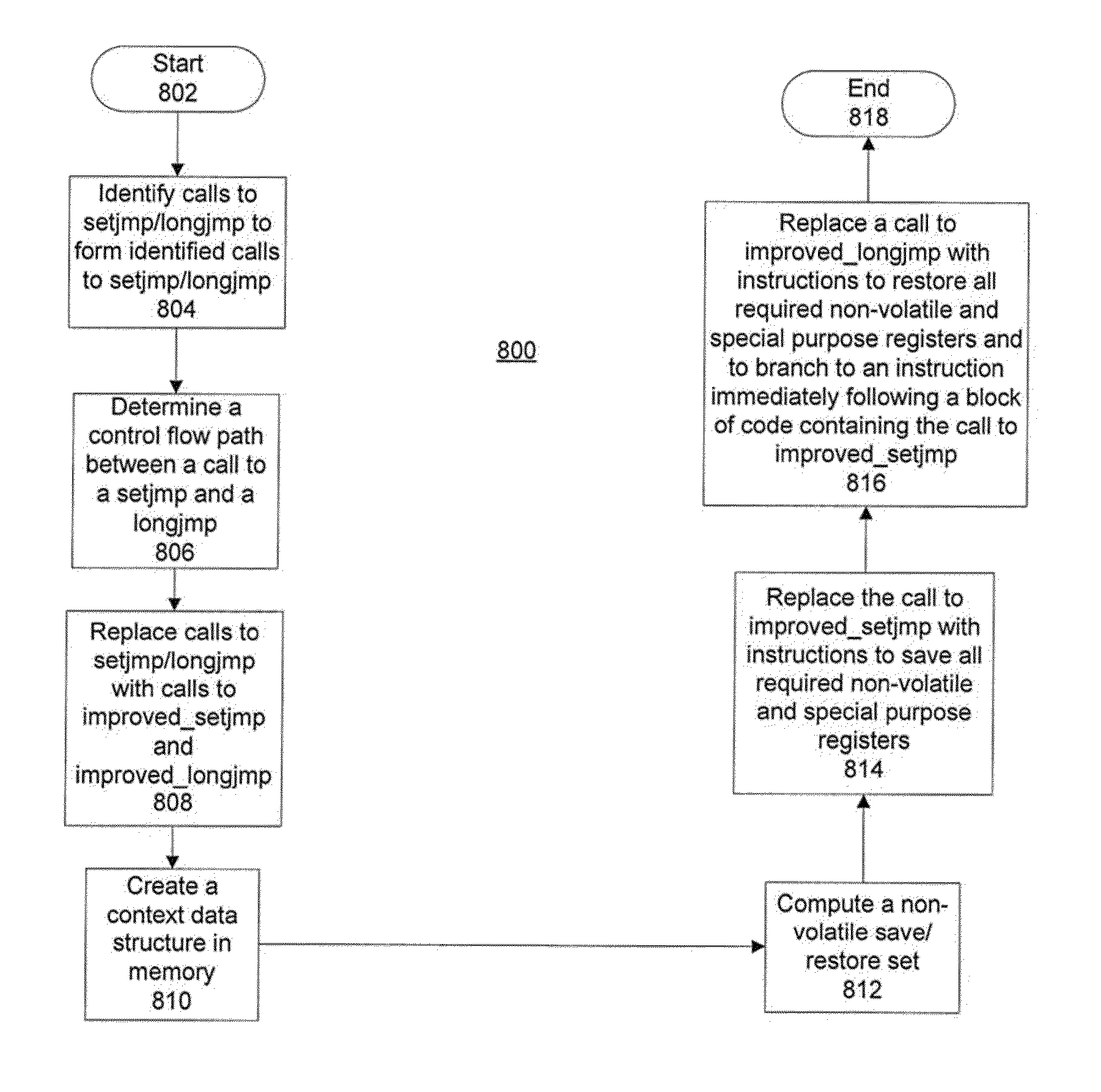
Setjmp/longjmp for speculative execution frameworks
InactiveUS20110289303A1Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsSpeculative executionControl flow
A process for check pointing in speculative execution frameworks, identifies calls to a set of setjmp / longjmp instructions to form identified calls to setjmp / longjmp, determines a control flow path between a call to a setjmp and a longjmp pair of instructions in the identified calls to setjmp / longjmp and replaces calls to the setjmp / longjmp pair of instructions with calls to an improved_setjmp and improved_longjmp instruction pair. The process creates a context data structure in memory, computes a non-volatile save / restore set and replaces the call to improved_setjmp of the setjmp / longjmp pair of instructions with instructions to save all required non-volatile and special purpose registers and replaces a call to improved_longjmp of the setjmp / longjmp pair of instructions with instructions to restore all required non-volatile and special purpose registers and to branch to an instruction immediately following a block of code containing the call to improved_setjmp.
Owner:IBM CORP
Suppression of control transfer instructions on incorrect speculative execution paths
Techniques are disclosed relating to a processor that is configured to execute control transfer instructions (CTIs). In some embodiments, the processor includes a mechanism that suppresses results of mispredicted younger CTIs on a speculative execution path. This mechanism permits the branch predictor to maintain its fidelity, and eliminates spurious flushes of the pipeline. In one embodiment, a misprediction bit is be used to indicate that a misprediction has occurred, and younger CTIs than the CTI that was mispredicted are suppressed. In some embodiments, the processor may be configured to execute instruction streams from multiple threads. Each thread may include a misprediction indication. CTIs in each thread may execute in program order with respect to other CTIs of the thread, while instructions other than CTIs may execute out of program order.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
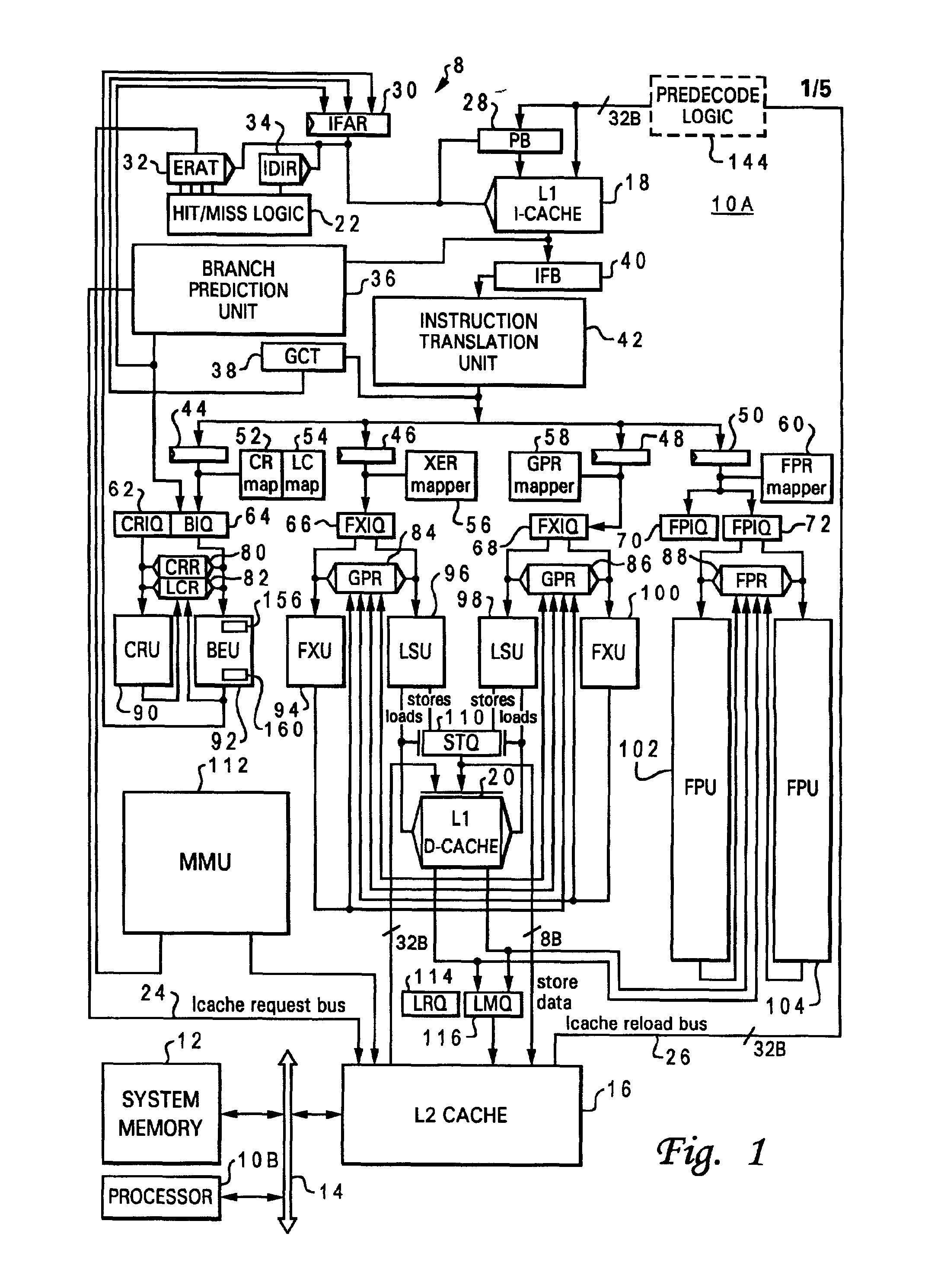
Device and processing architecture for instruction memory efficiency
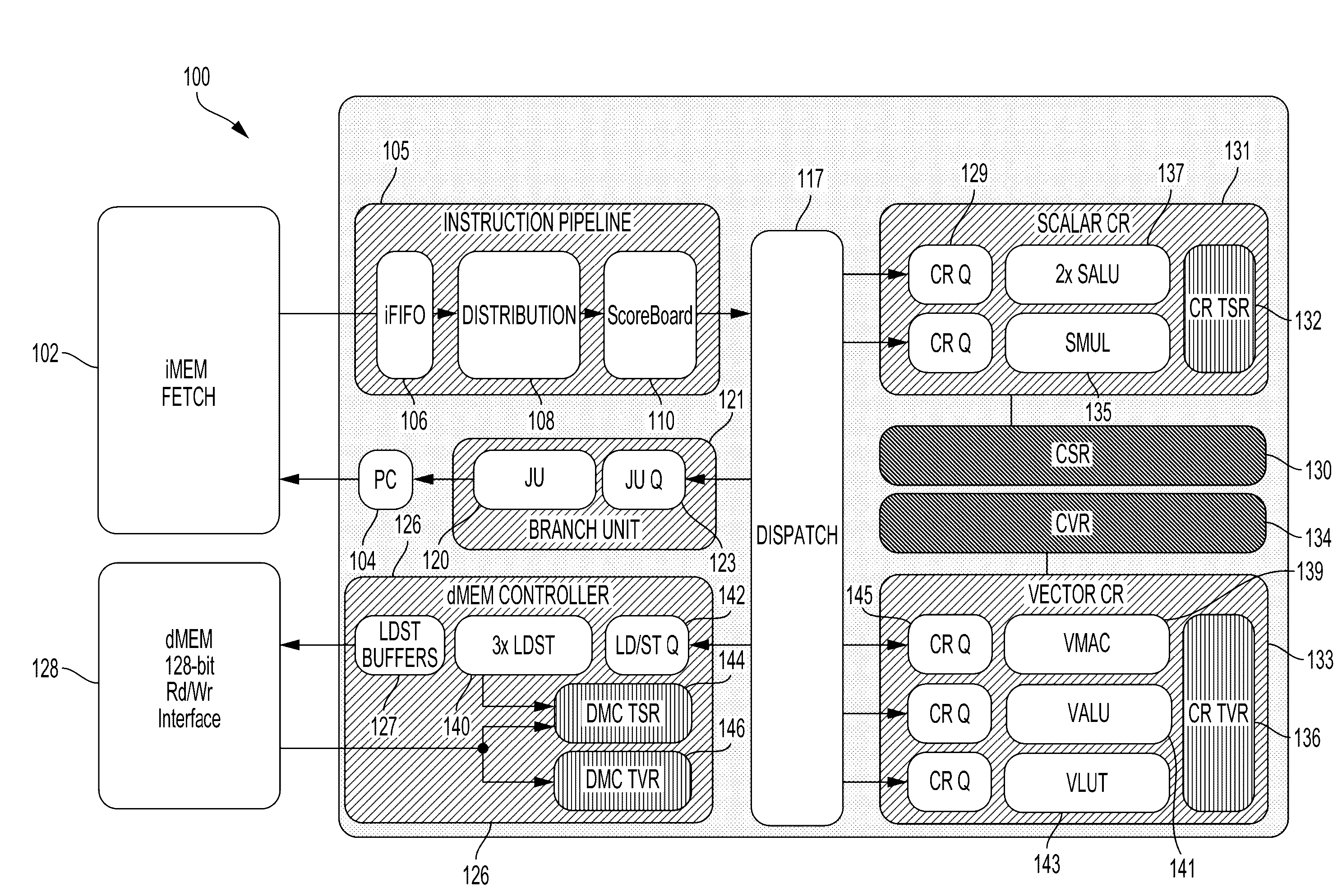
Different processor architectures are described to evaluate and track dependencies required by instructions. The processors may hold or queue instructions that require output of other instructions until required data and resources are available which may remove the requirement of NOPs in the instruction memory to resolve dependencies and pipeline hazards. The processor may divide instruction data into bundles for parallel execution and provide speculative execution. The processor may include various components to implement an evaluation unit, execution unit and termination unit.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com