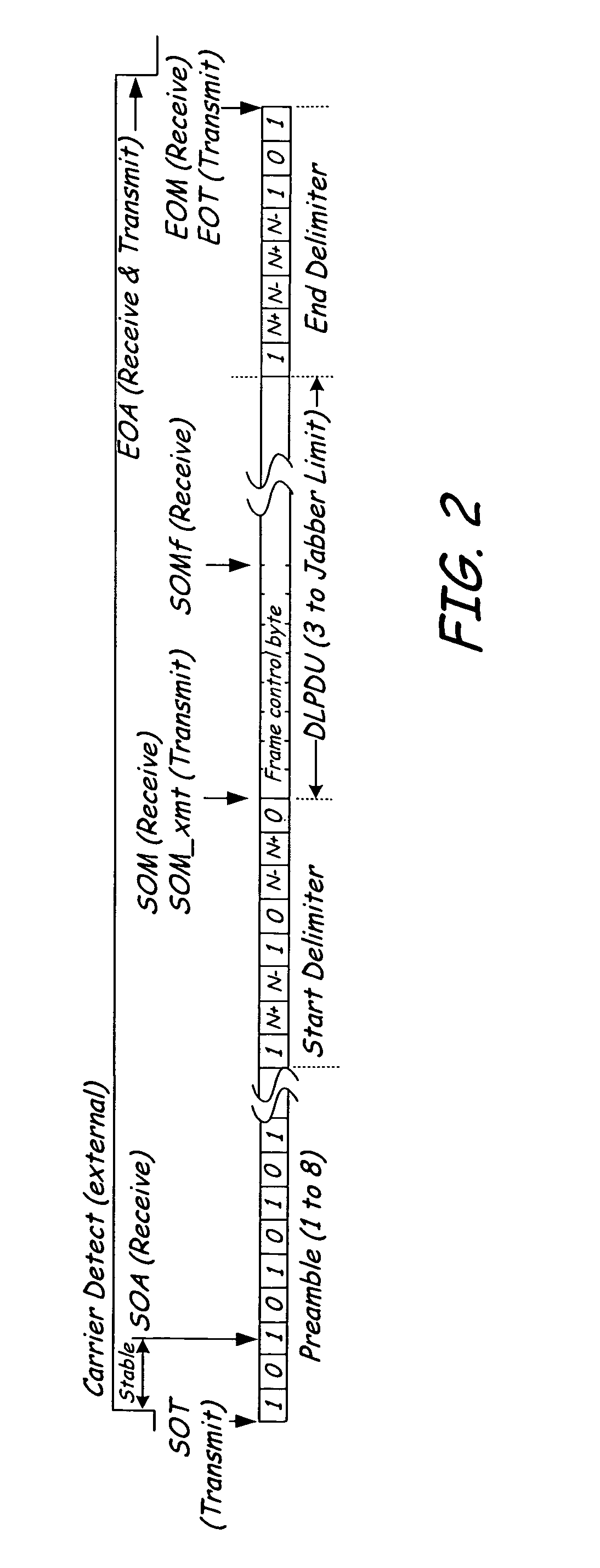
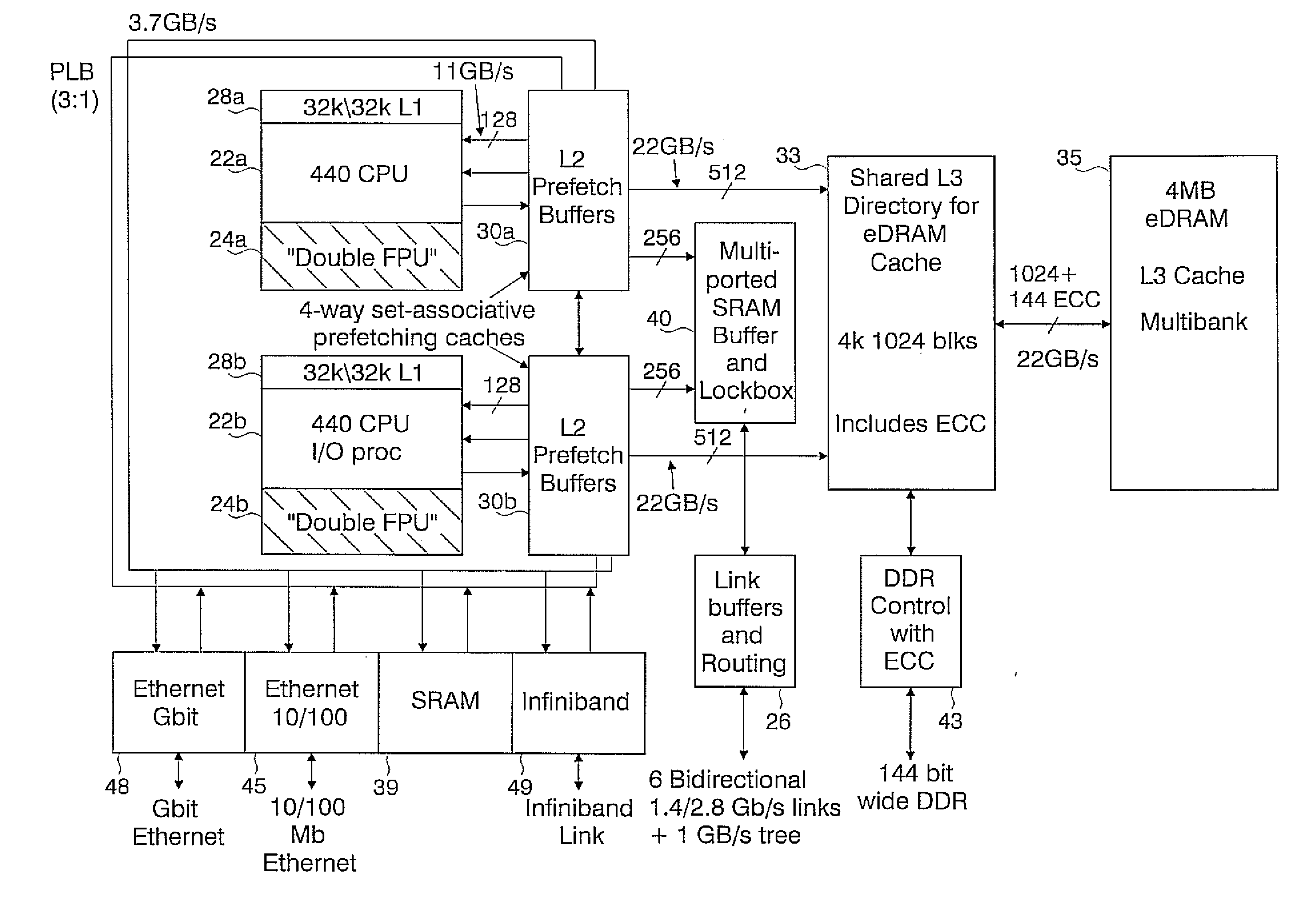
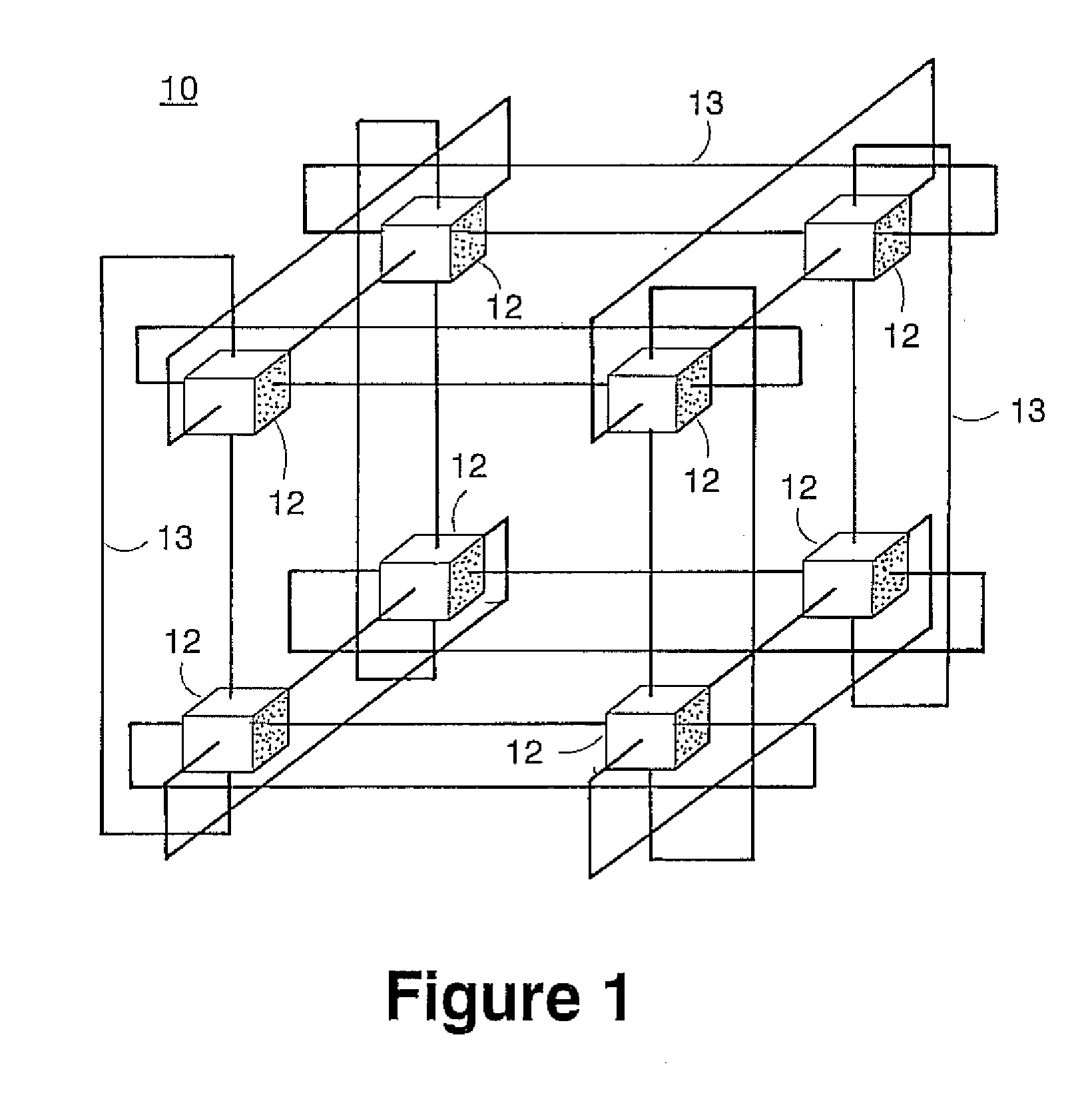
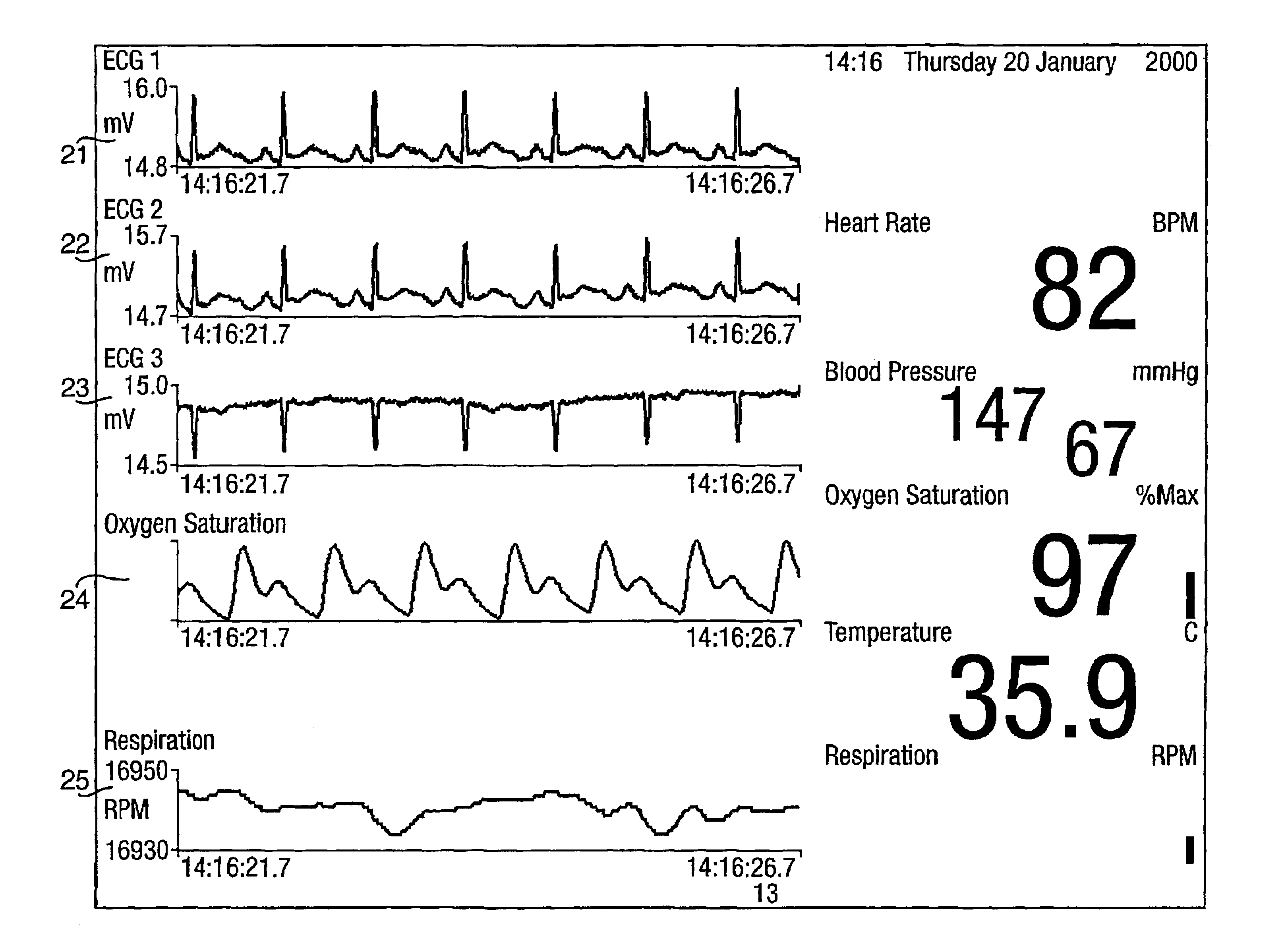
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
12879results about "Synchronising arrangement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
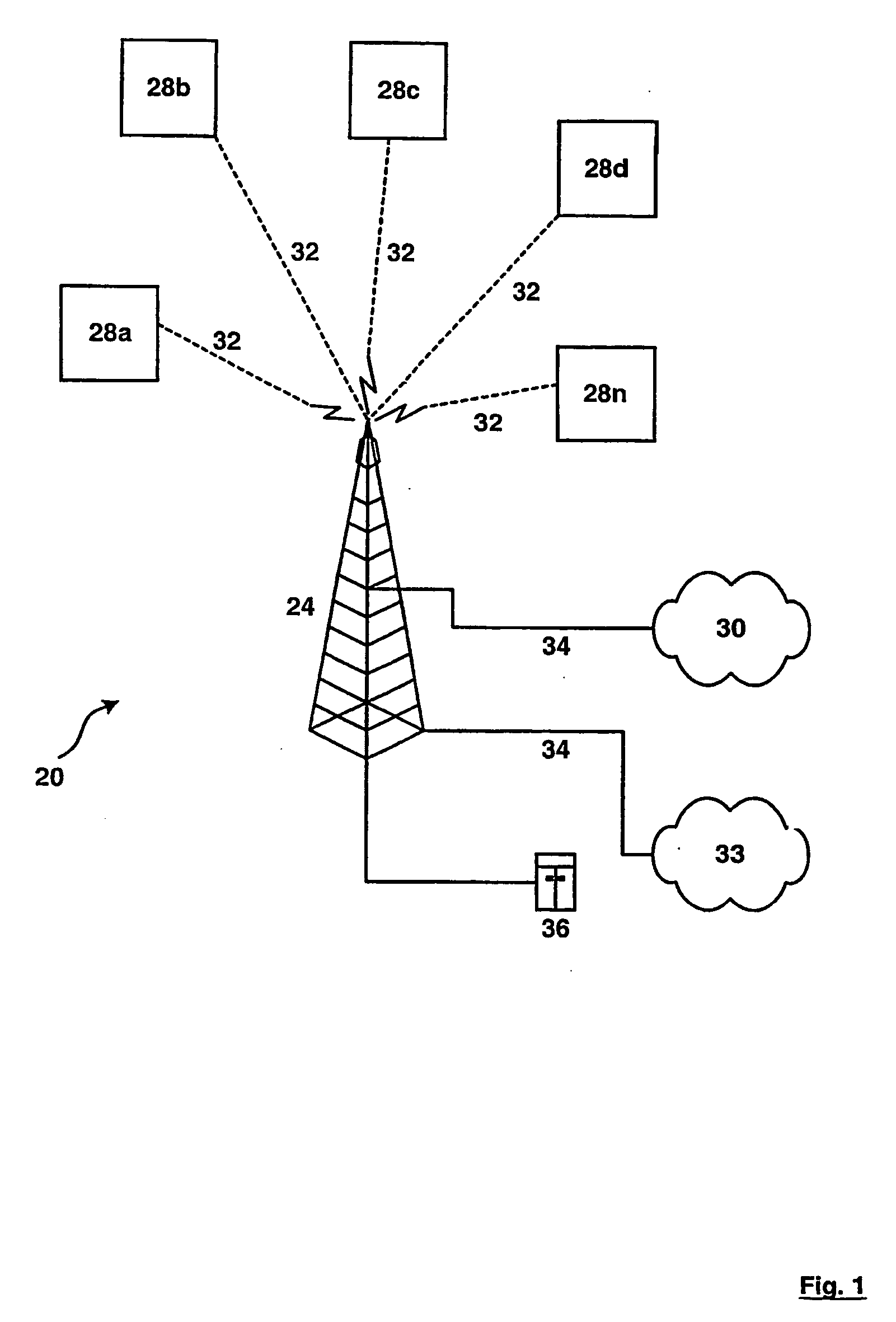
Method and system for disaggregating audio/visual components
ActiveUS7295548B2Improve user experiencePlural information simultaneous broadcastTwo-way working systemsComputer networkBrick
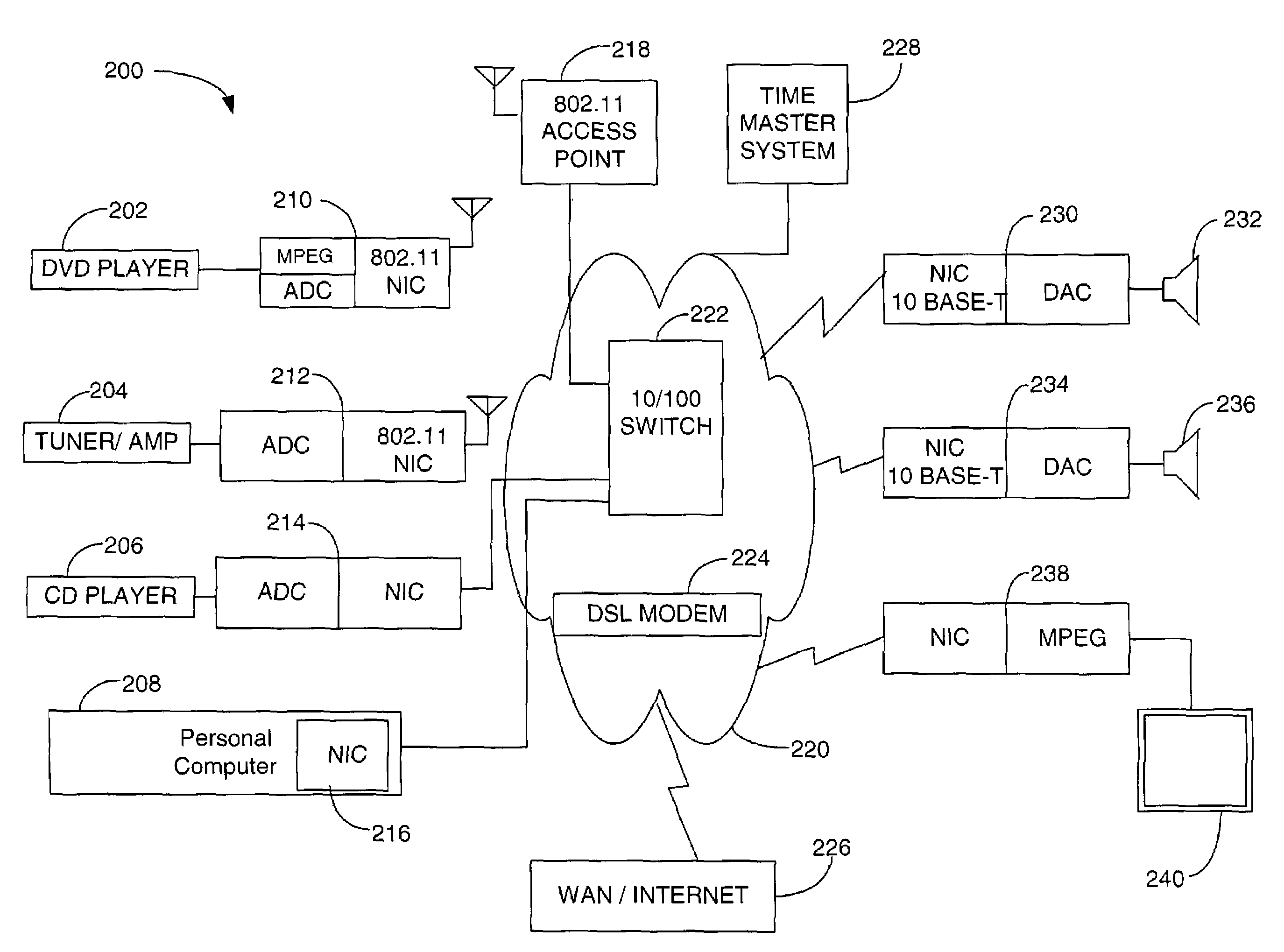
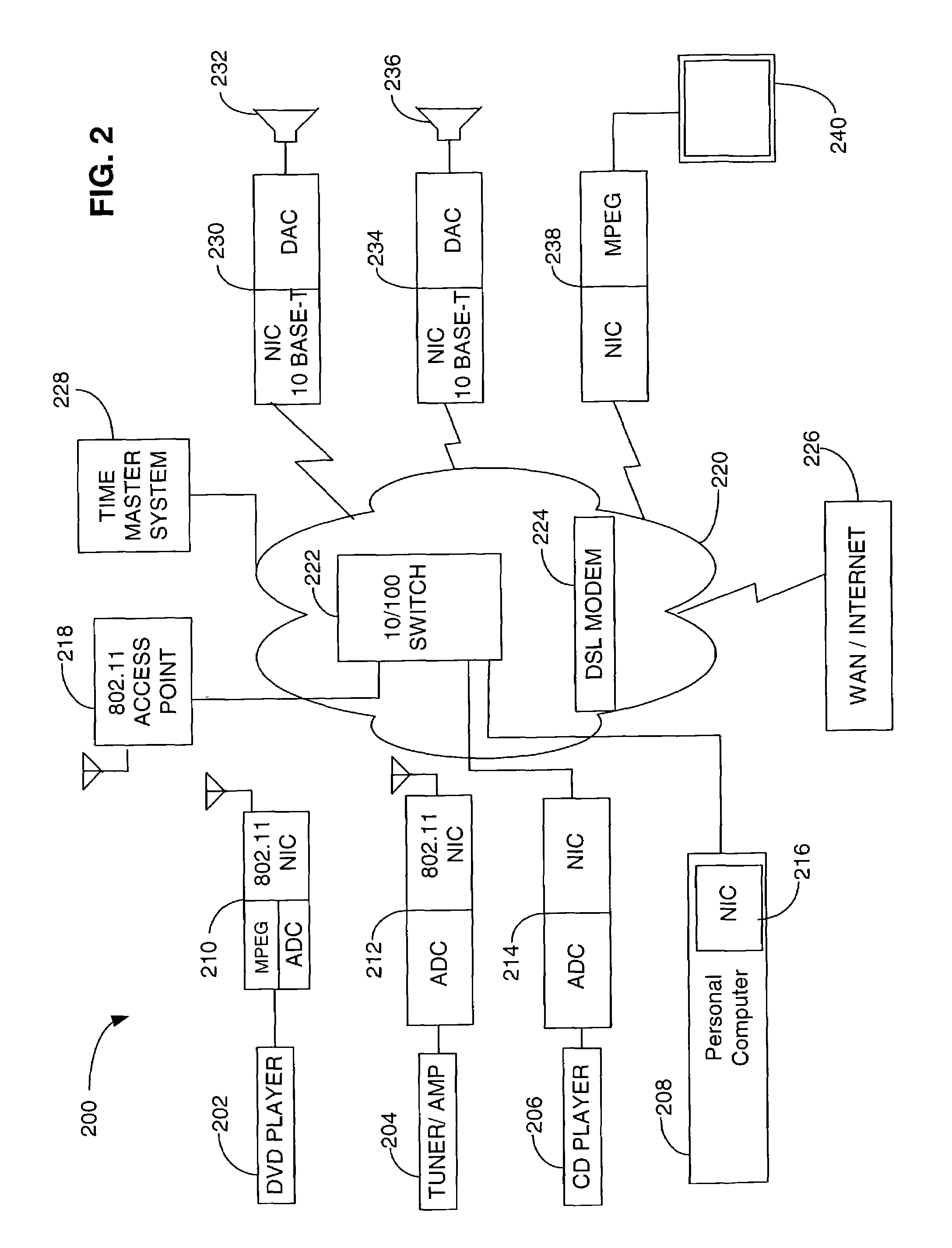
The present invention is directed to a method and system for disaggregating and connecting A / V components, and communicating A / V content stream information. An A / V stream from a source device is packaged for transmission over an IP network to one or more output devices. A brick device enables the integration of legacy A / V systems into the network supported A / V system. The brick device operates to provide analog signal and IP protocol conversion, along with the synchronization of received A / V stream data packets. The rendering and play of the A / V stream content on multiple output devices is synchronized to overcome distortions and other network idiosyncrasy and to facilitate a pleasant user experience.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Software update method, apparatus and system
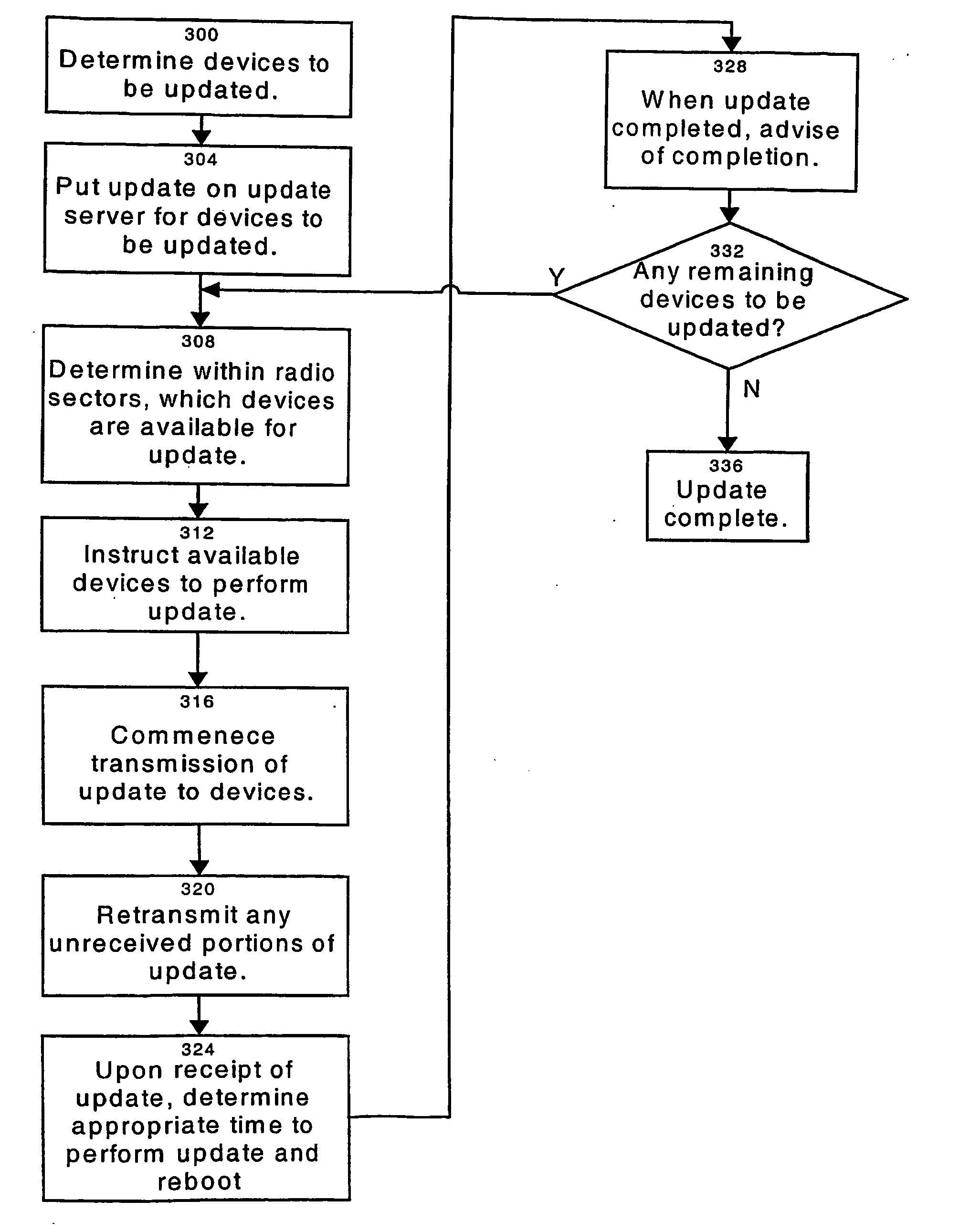
A system for remotely updating software on at least one electronic device connected to a network. The electronic devices have a non-volatile rewritable storage unit divided into at least two partitions, one of which will contain core firmware and the other of which will contain auxiliary software. When an update is received at the device, the updated core firmware is written to overwrite the partition in the rewritable storage unit that contained the auxiliary software. When this is completed and verified, the previous version of the core firmware stored in the storage unit is disabled from execution by the device. Next, the updated auxiliary software is written to overwrite the old version of the core firmware. When this write is complete, the device determines a suitable time for it to be rebooted to execute the updated software. In another embodiment, the present core firmware in the device is copied from the partition it is in to the other partition, overwriting the auxiliary software stored there. The new core firmware received to update the device is overwritten into the first partition, the old copied core firmware being present in case of an upgrade failure, and upon a successful update of the first partition, the auxiliary software is written to the second partition, overwriting the copied old core firmware. In this manner, the position of the core firmware and auxiliary software within the partitions is preserved during normal operation of the device.
Owner:WI LAN INC
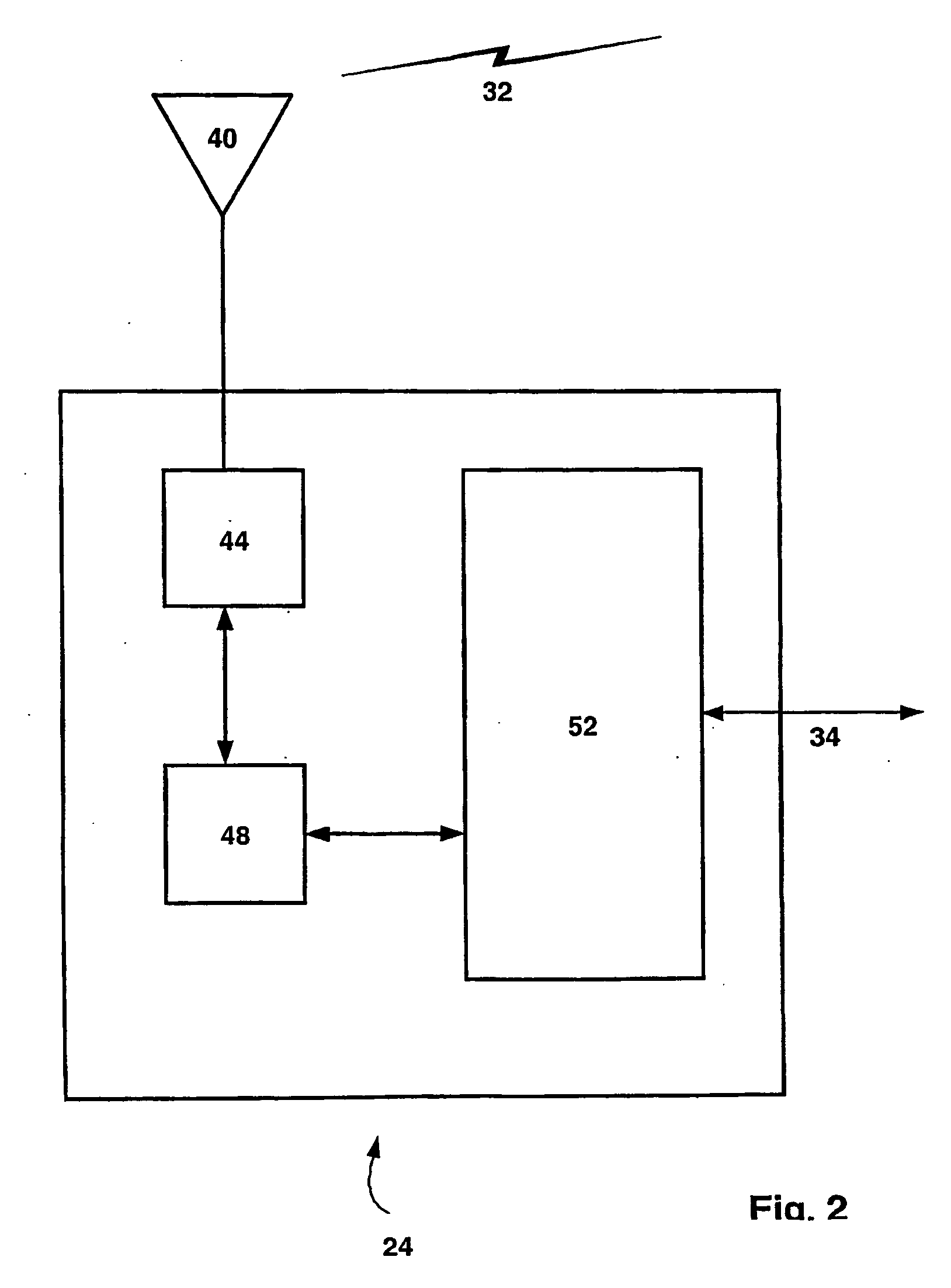
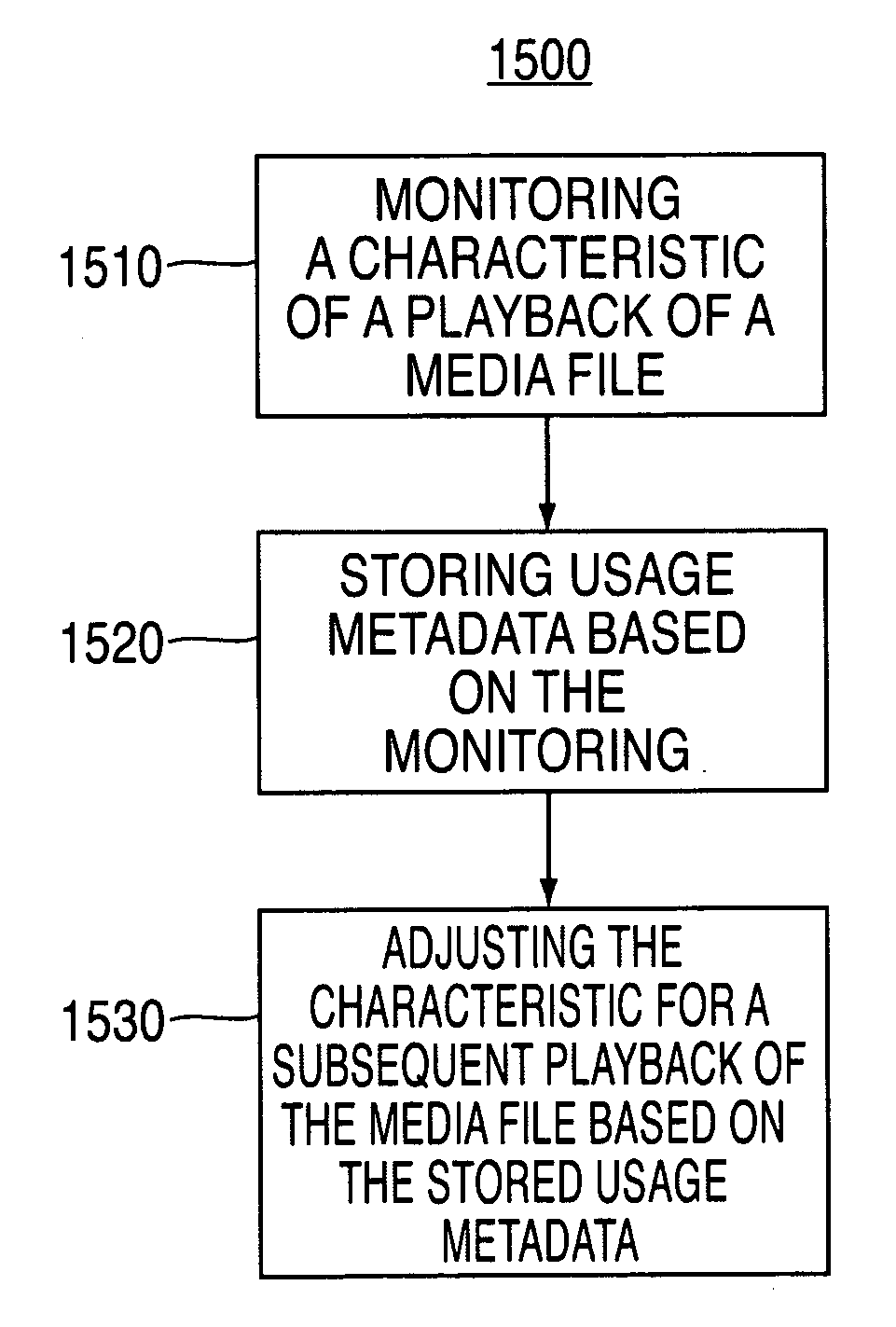
System and methods for adjusting graphical representations of media files based on previous usage
Systems and methods for adjusting playback and graphical representations of media files are provided. The systems and methods can monitor playback and access of media files to create usage metadata. The usage metadata can then be used to adjust the playback of the media file. For example, the usage metadata may indicate that a user skips, on average, the first 22 seconds of a particular song so the next time that song is played, the first 22 seconds will automatically be skipped. The usage metadata can additionally or alternatively be used to adjust a graphical representation of the media file. For example, the usage metadata may indicate that a user rarely accesses a particular song so the graphical representation of that song will be small and faded. This change in graphical representation can help a user find more commonly used media files.
Owner:APPLE INC
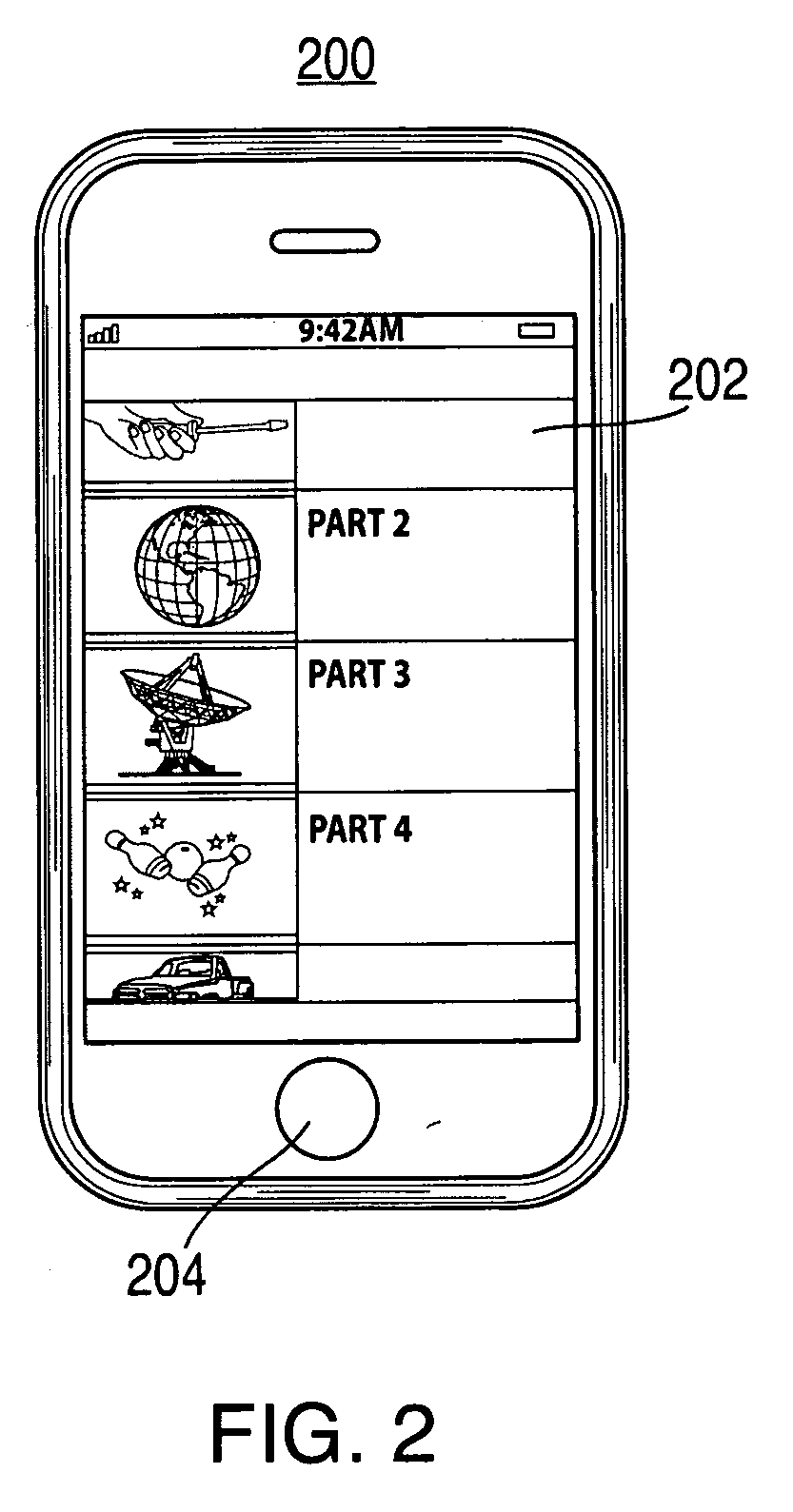
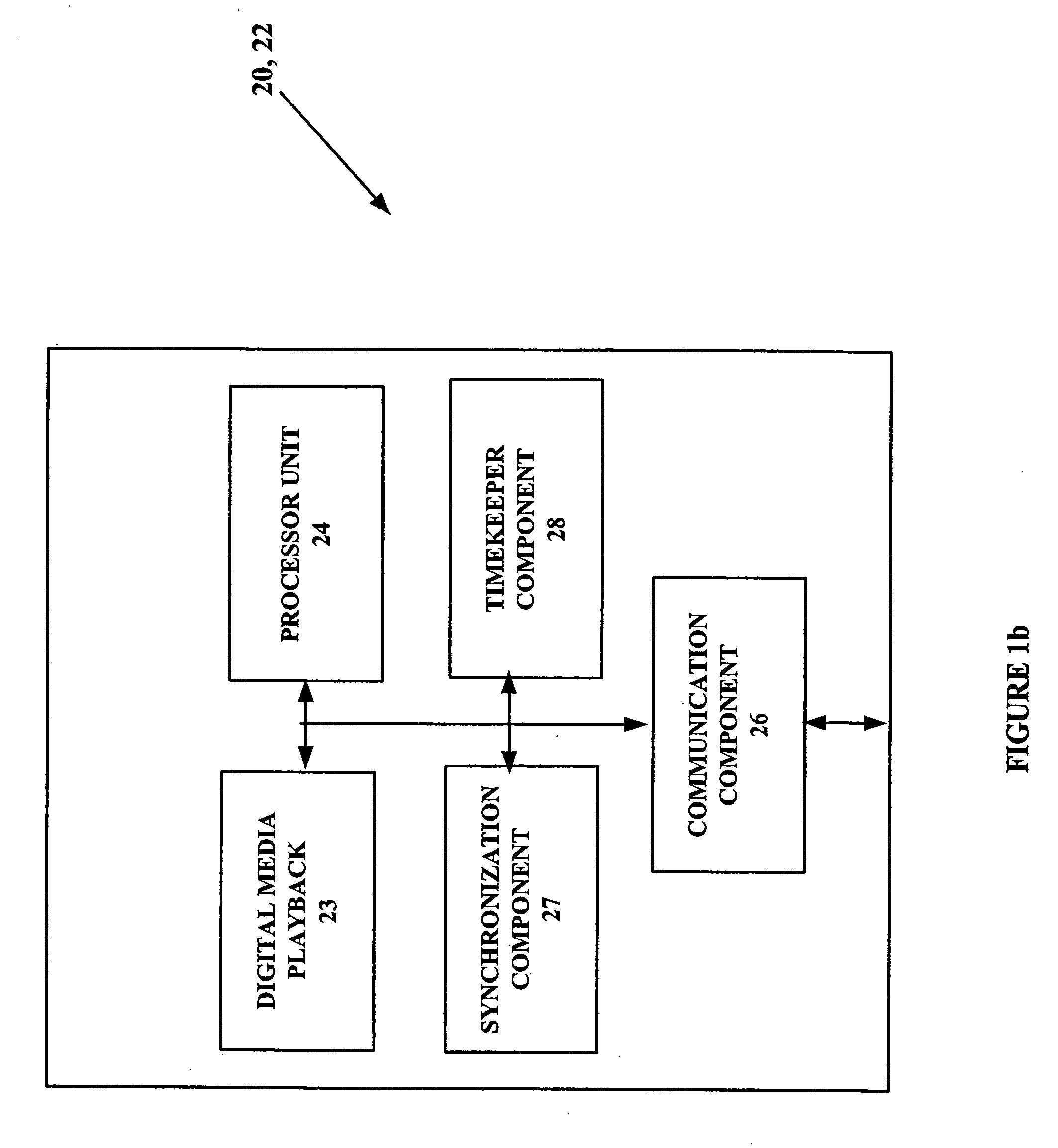
Method and system for synchronization of digital media playback
A system and method for synchronizing digital media playback at multiple digital media playback devices interconnected on a network is provided. A digital media playback device comprising a processor, a synchronization component, a timekeeper component and a digital media source performs synchronization processes to arrange for other players to begin playback at a predetermined position and time in the digital media signal. Synchronization is accomplished by processes which approximate the arrival time of a packet containing audio and / or video digital content across the network and instruct the playback devices as to when playback is to begin, and at what point in the streaming media content signal to begin playback. One method uses a time-stamp packet on the network to synchronize all players. Other methods utilize reiterative processes to narrow approximations of packet arrival time at each playback device.
Owner:ARLO TECH INC
Unified digital architecture
InactiveUS20060029177A1Pulse automatic controlModulated-carrier systemsFinite impulse responseComputer science
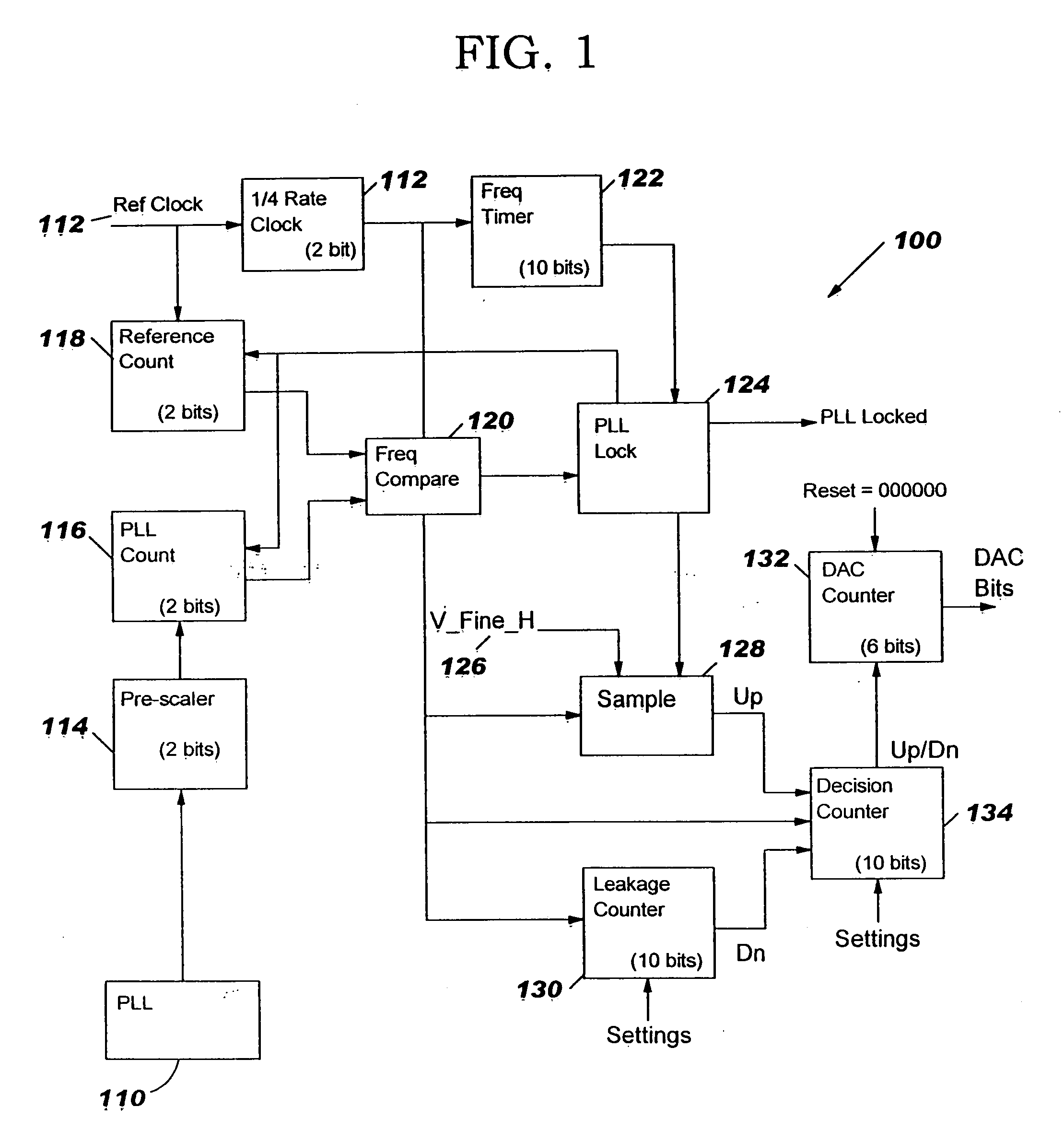
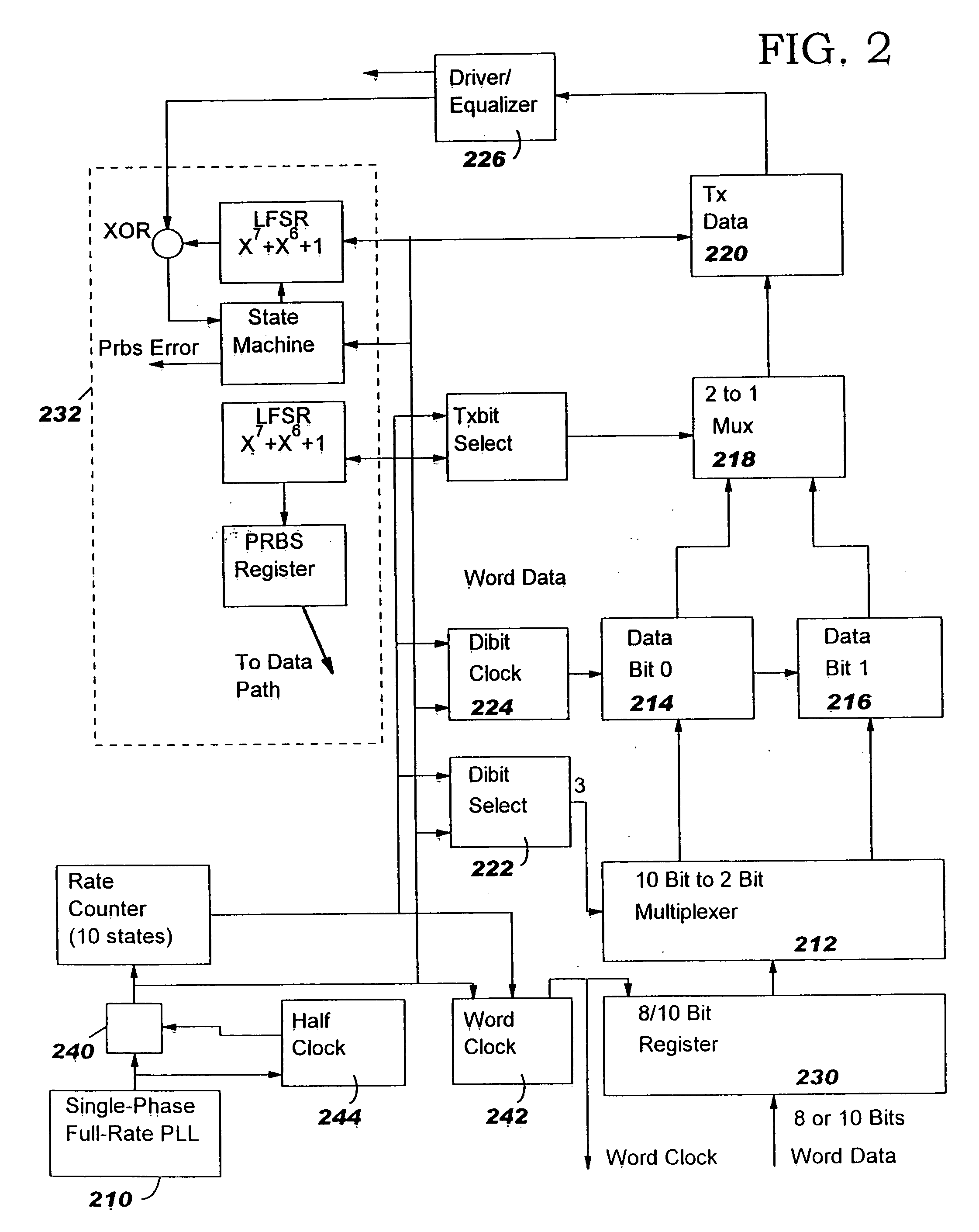
A unified, unidirectional serial link is described for providing data across wired media, such as a chip-to chip or a card-to-card interconnect. It consists of a transmit section and a receive section that are operated as pairs to allow the serial data communication. The serial link is implemented as part of a VLSI ASIC module and derives its power, data and clocking requirements from the host modules. The logic transmitter portion contains a phase locked loop (PLL), a dibit data register, a finite impulse response (FIR) filter and a transmit data register. The phase locked loop comprises both a digital coarse loop and an analog fine loop. The digital receiver portion contains a PLL, an FIR phase rotator, a phase rotator control state machine, and a clock buffer. The transmitter and the receiver each preferably utilize a pseudo-random bit stream (PRBS) generator and checker.
Owner:IBM CORP
Communication controller with automatic time stamping
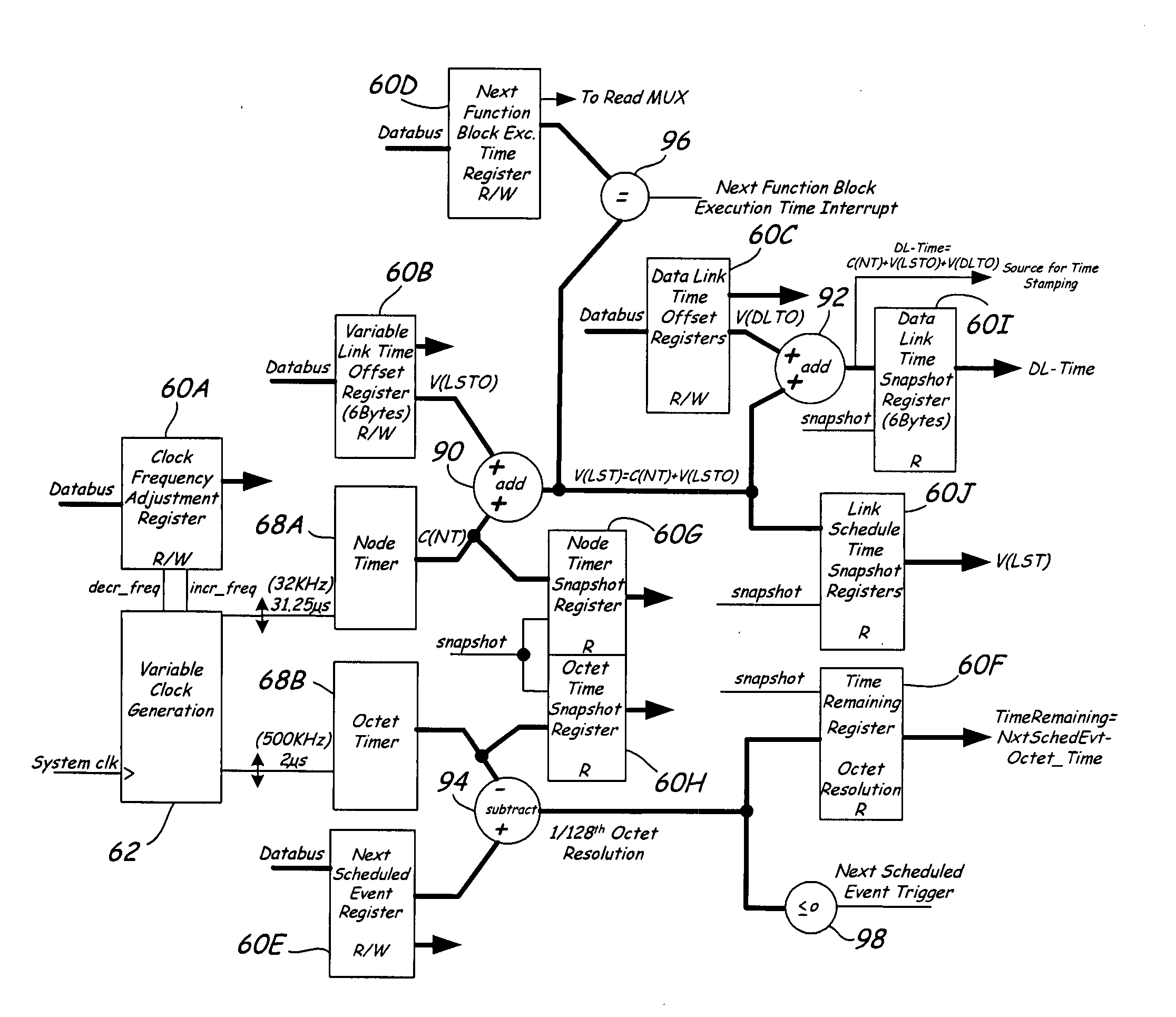
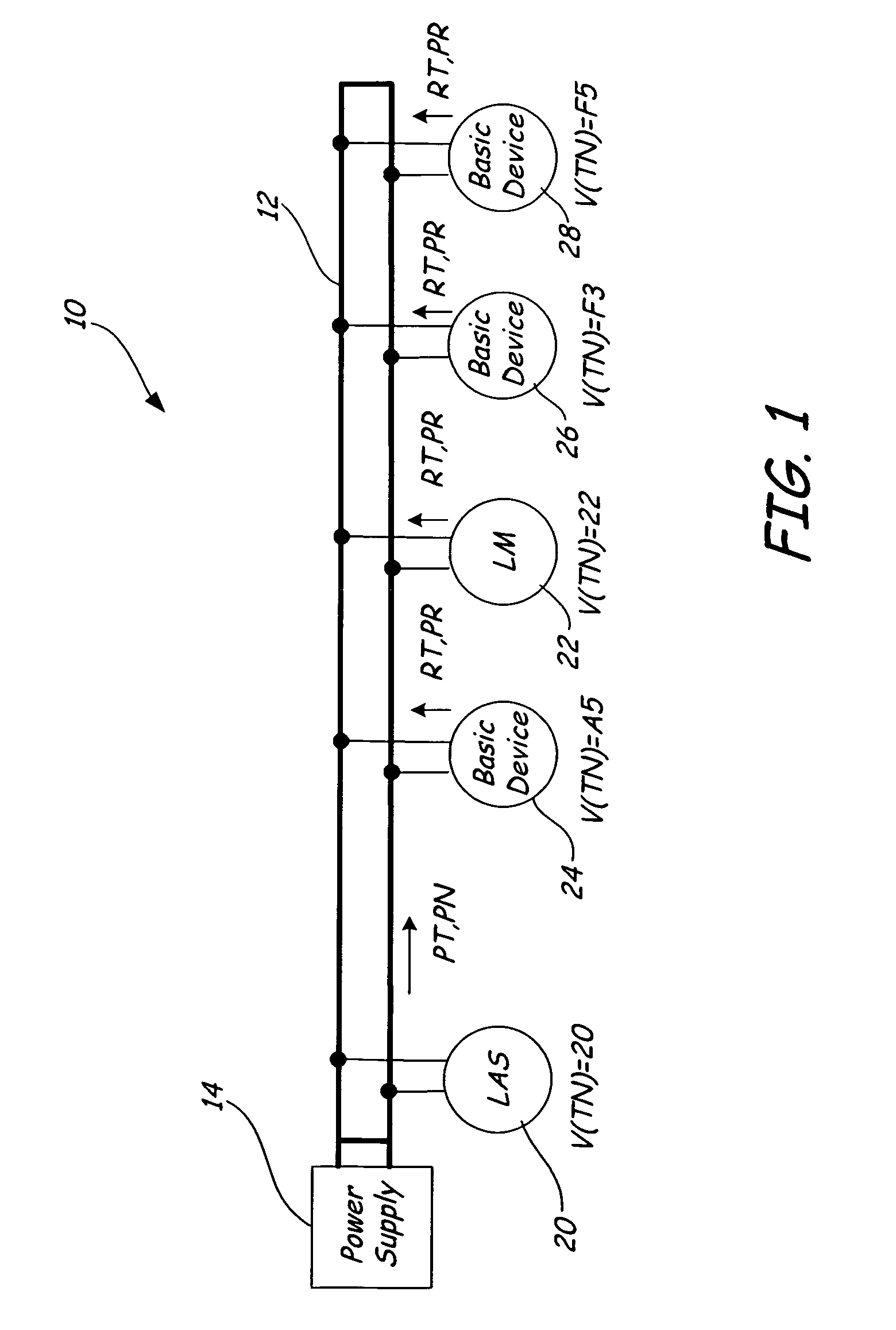
ActiveUS20060026314A1Programme controlInput/output to record carriersControl systemCommunication control
Devices in a process control system communicate by data messages over a communication medium segment. Each device includes a communication controller that automatically time stamps events associated with received and transmitted messages.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
Novel massively parallel supercomputer
InactiveUS20090259713A1Low costReduced footprintError preventionProgram synchronisationSupercomputerPacket communication
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
System and method for acquiring data
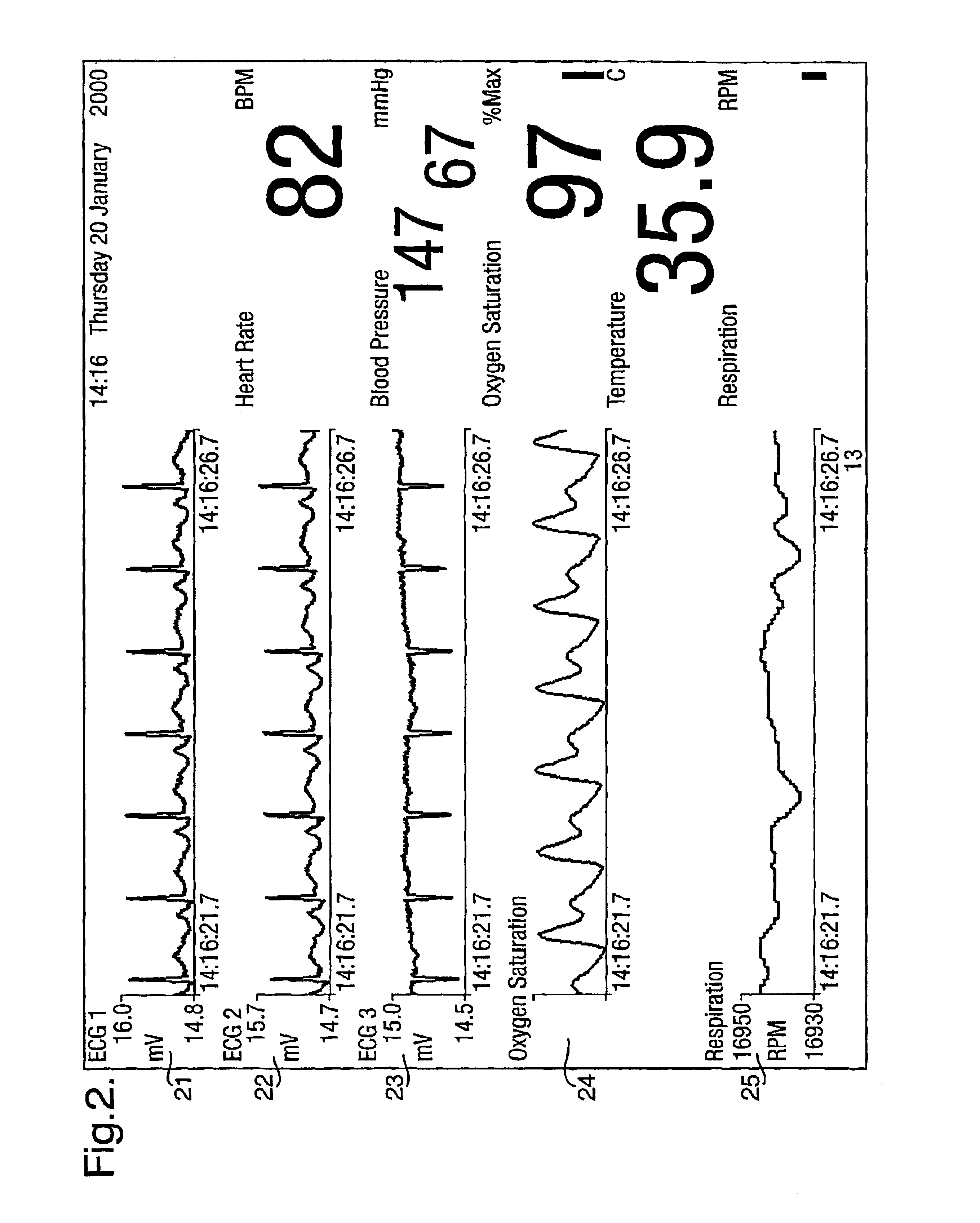
InactiveUS6839659B2Easy to carryImprove clarityAngiographyData acquisition and loggingData connectionHigh rate
A system for acquiring, and displaying, data such as physiological data, from a plurality of data connection devices, each of which monitor one or more different parameters and output data at different sampling frequencies based on their own system clocks. The system receives the data signals at different sampling frequencies and associates each sample of each signal with a time stamp derived from a single master clock. Low rate and high rate data are treated differently. Low rate data is associated with the current value of the master clock, where as high rate data is time stamped by giving the first sample a time stamp equal to the current value of the current master clock, subsequent samples being given an estimated time stamp based on the expected interval between samples derived from the sampling frequency of the data collection device, and the timescale given to the first example. The estimated time stamp may be periodically corrected, and the estimation calculation can be improved by correcting the value used for the interval between samples. The different signals can be displayed together on a display aligned with respect to a time axis. The system can display, the data in two different timescales, one showing a few seconds of data and one showing a few hours of data. The data traces are scrolled across the time axis, new data being added to one end of the trace.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
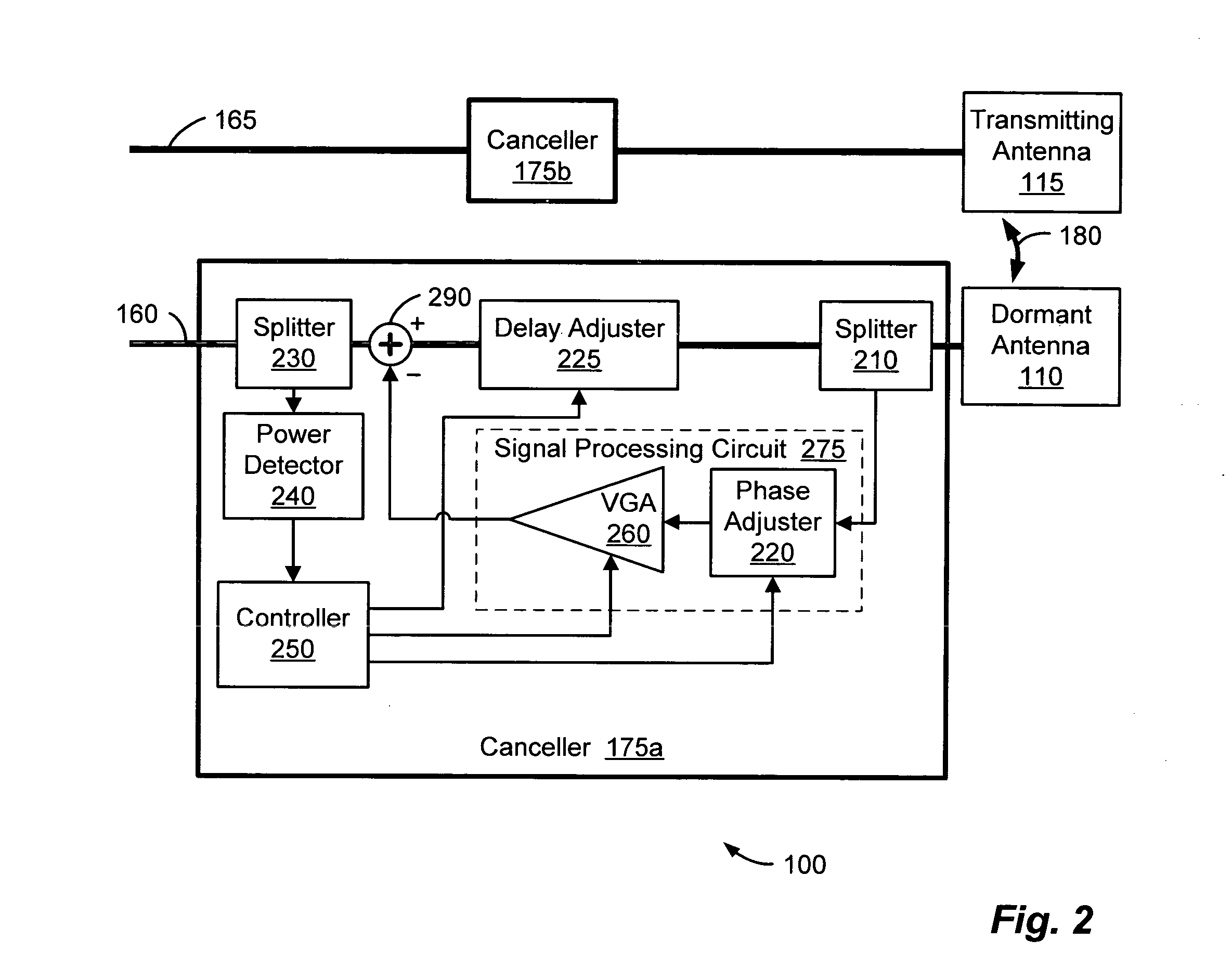
Method and system for antenna interference cancellation
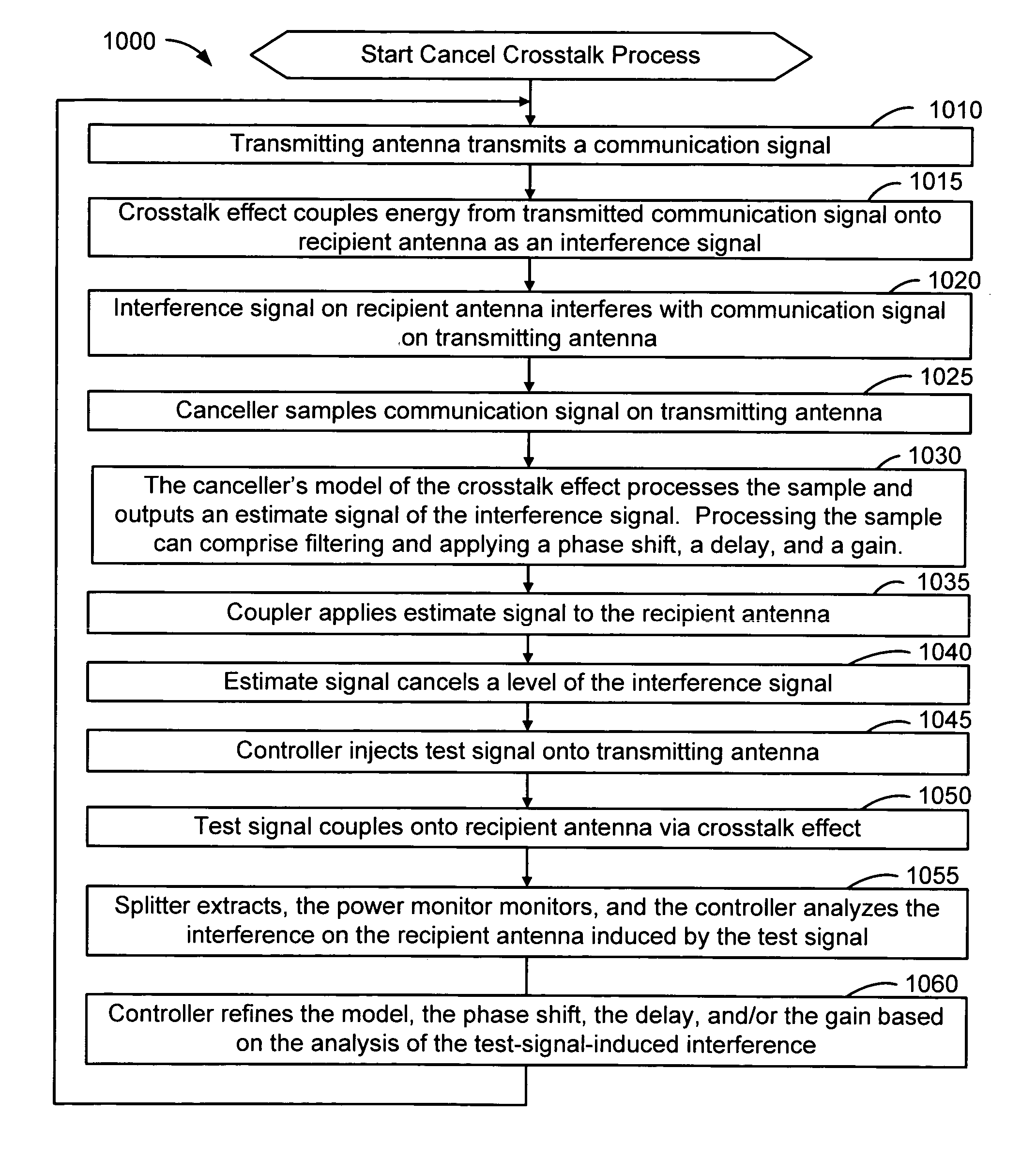
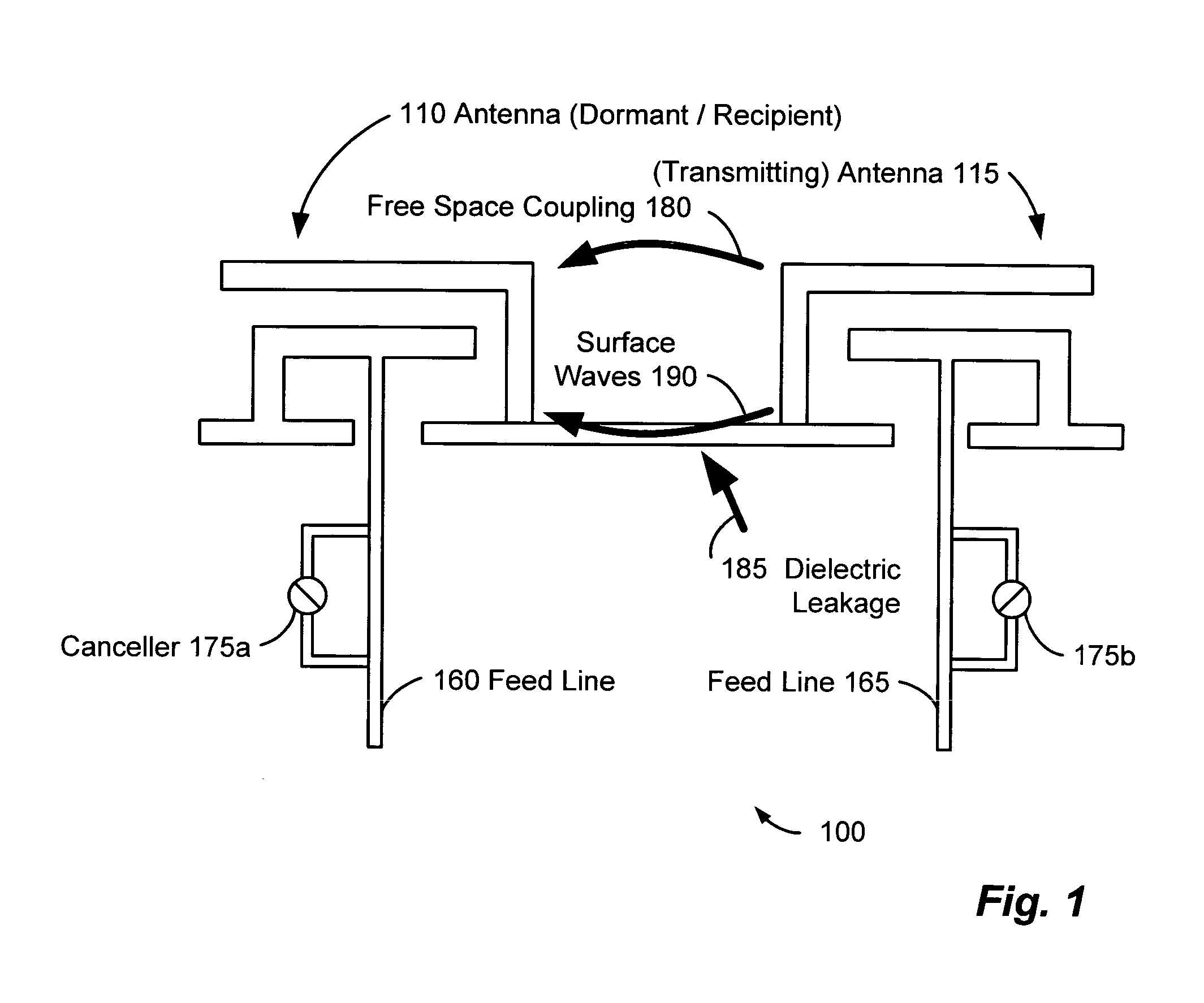
InactiveUS20050226353A1Improve signal qualityHigh bandwidthCorrect operation testingLine-faulsts/interference reductionCommunications systemSignal on
A wireless communication system can comprise two or more antennas that interfere with one another via free space coupling, surface wave crosstalk, dielectric leakage, or other interference effect. The interference effect can produce an interference signal on one of the antennas. A cancellation device can suppress antenna interference by generating an estimate of the interference signal and subtracting the estimate from the interference signal. The cancellation device can generate the estimate based on sampling signals on an antenna that generates the interference or on an antenna that receives the interference. The cancellation device can comprise a model of the crosstalk effect. Transmitting test signals on the communication system can define or refine the model.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
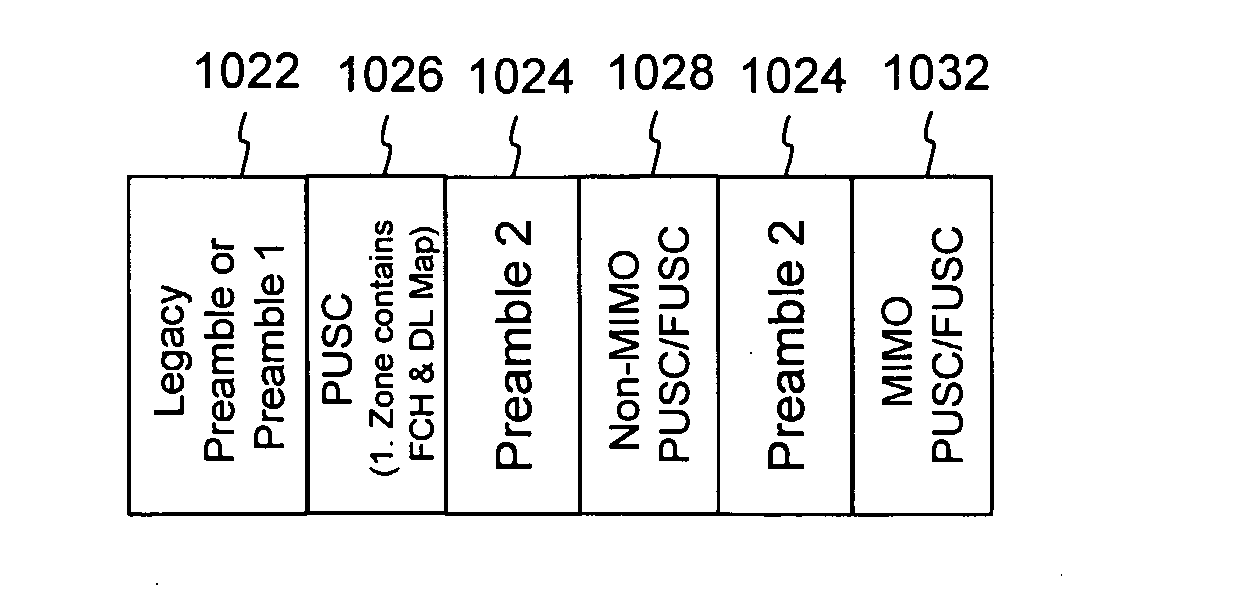
Preambles in Ofdma System
ActiveUS20080039107A1Reducing a search windowModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionMulti inputCell search
The present invention provides a preamble that is inserted into an OFDMA frame and has a common sequence for all the base stations participating in a transmission. The subscriber station performs fine synchronization using the common sequence on the common preamble, and the resulting peaks will provide the locations of candidate base stations. The base station specific search is then performed in the vicinities of those peaks by using base station specific pseudo-noise sequences. With this two stage cell search, the searching window is drastically reduced. The preamble is matched to known values by a respective receiver to decode the signals and permit multiple signals to be transferred from the transmitter to the receiver. The preamble may comprise two parts, Preamble-1 and Preamble-2, which may be used in different systems, including multioutput, multi-input (MIMO) systems.
Owner:APPLE INC
Apparatus and method for controlling a master/slave system via master device synchronization
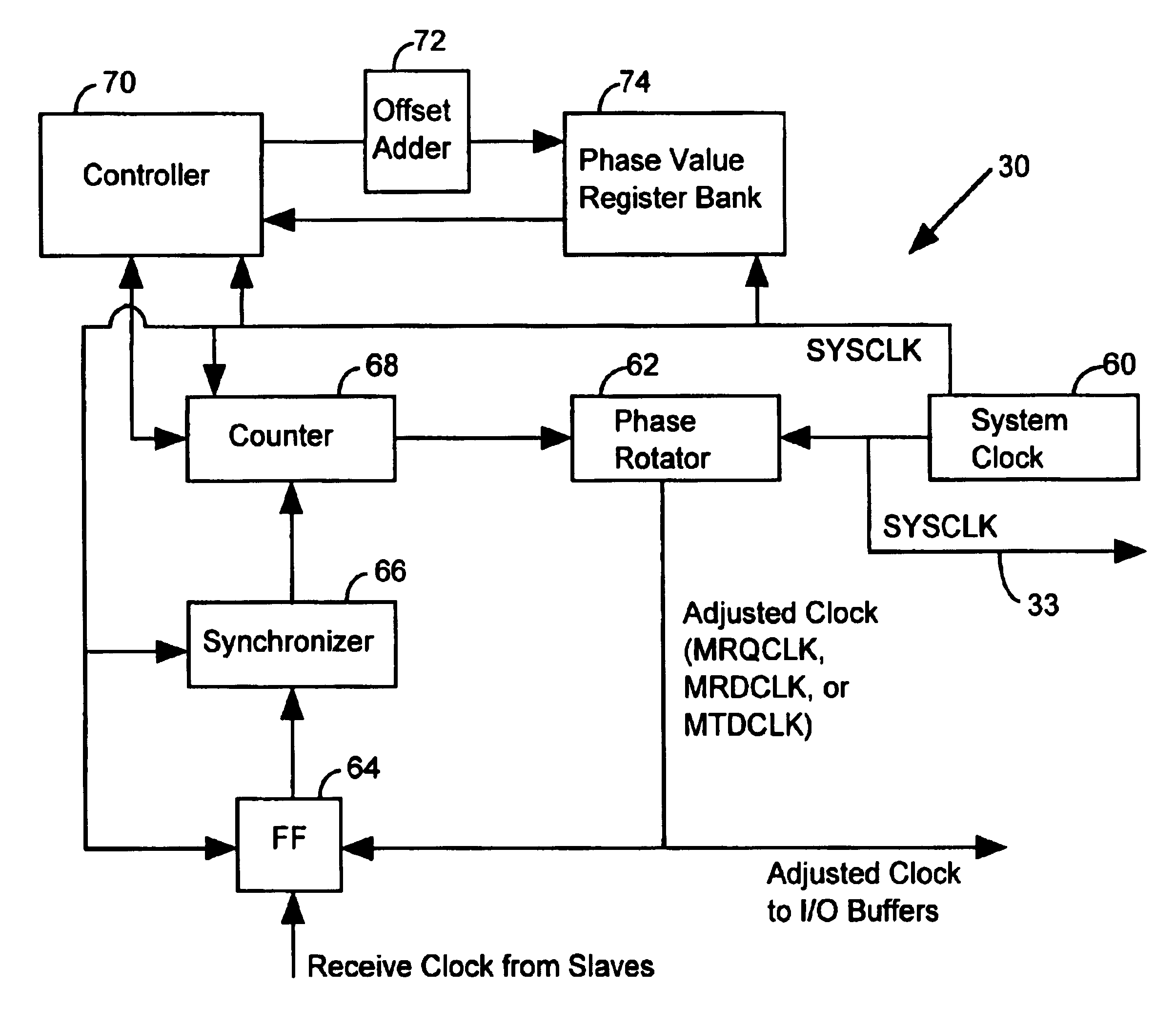
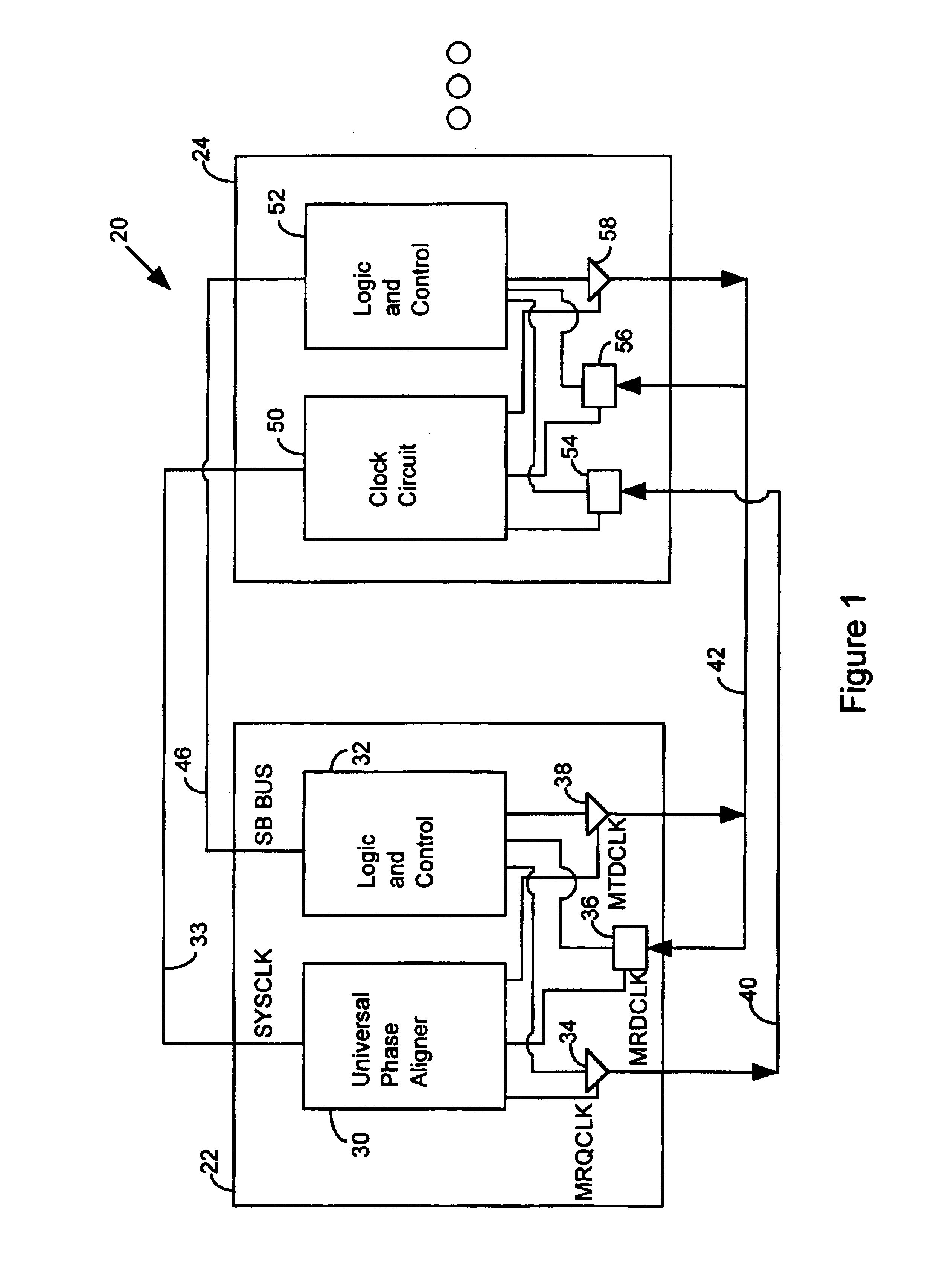
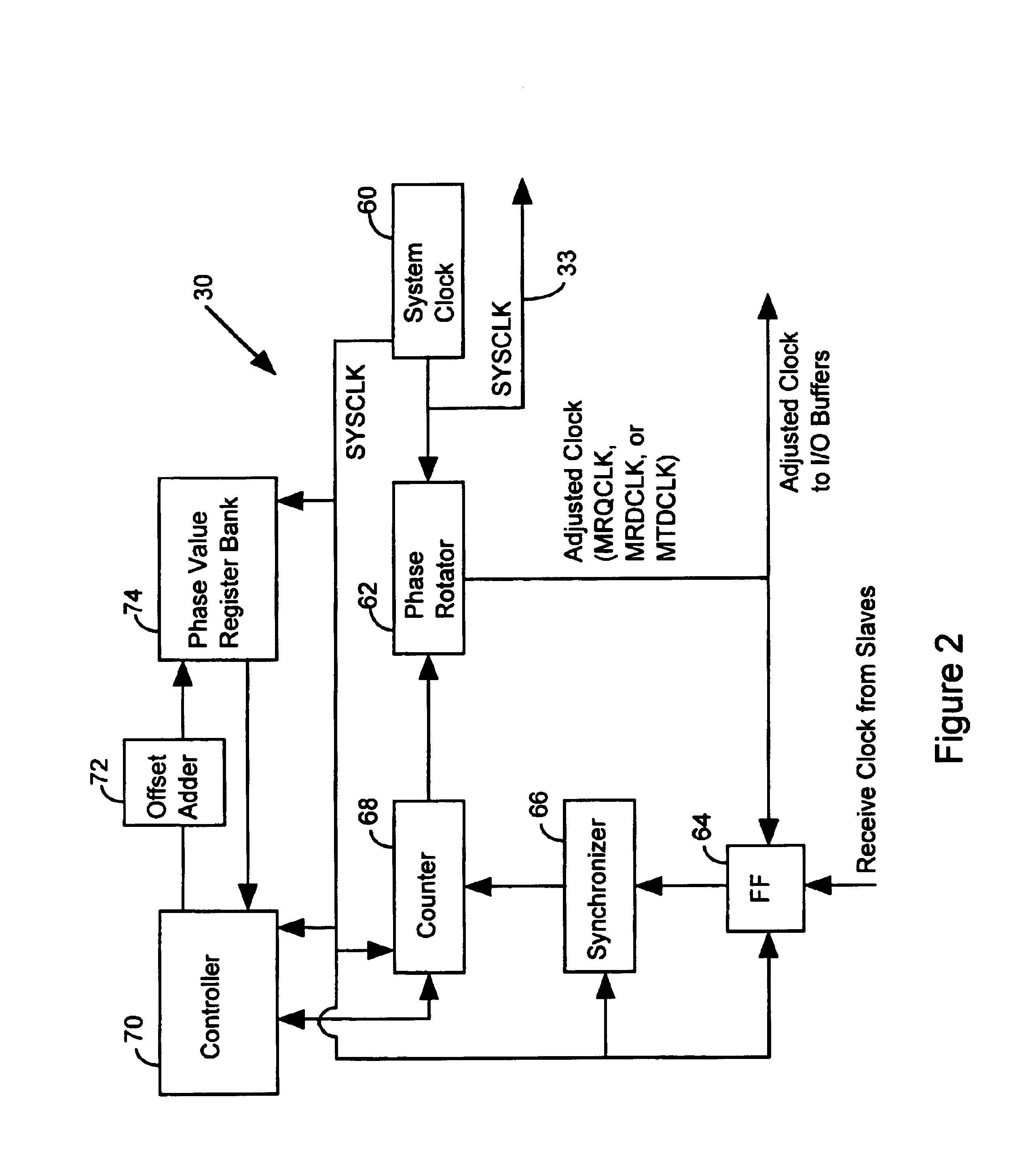
InactiveUS6839393B1Reduce power consumptionImprove throughputEnergy efficient ICTPulse automatic controlComputer hardwareData shipping
A method of operating a master / slave system includes the step of identifying a master receive data phase value to coordinate the transfer of data from a slave device without phase alignment circuitry to a master device with a universal phase aligner. Data is transferred from the slave device to the master device in accordance with the master receive data phase value. The master device characterizes a master transmit data phase value to coordinate the transfer of data from the master device to the slave device. Subsequently, the master device routes data to the slave device in accordance with the master transmit data phase value.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
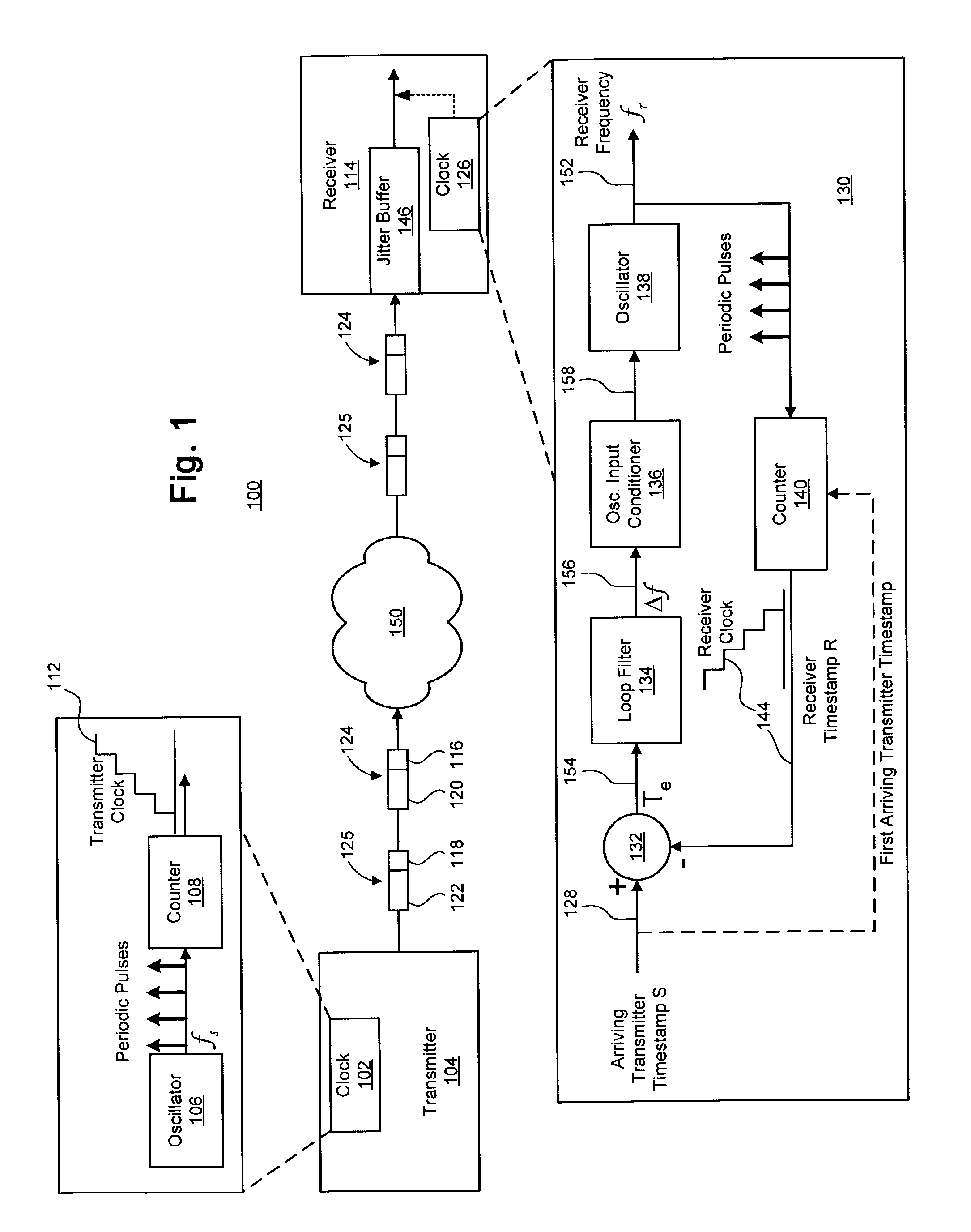
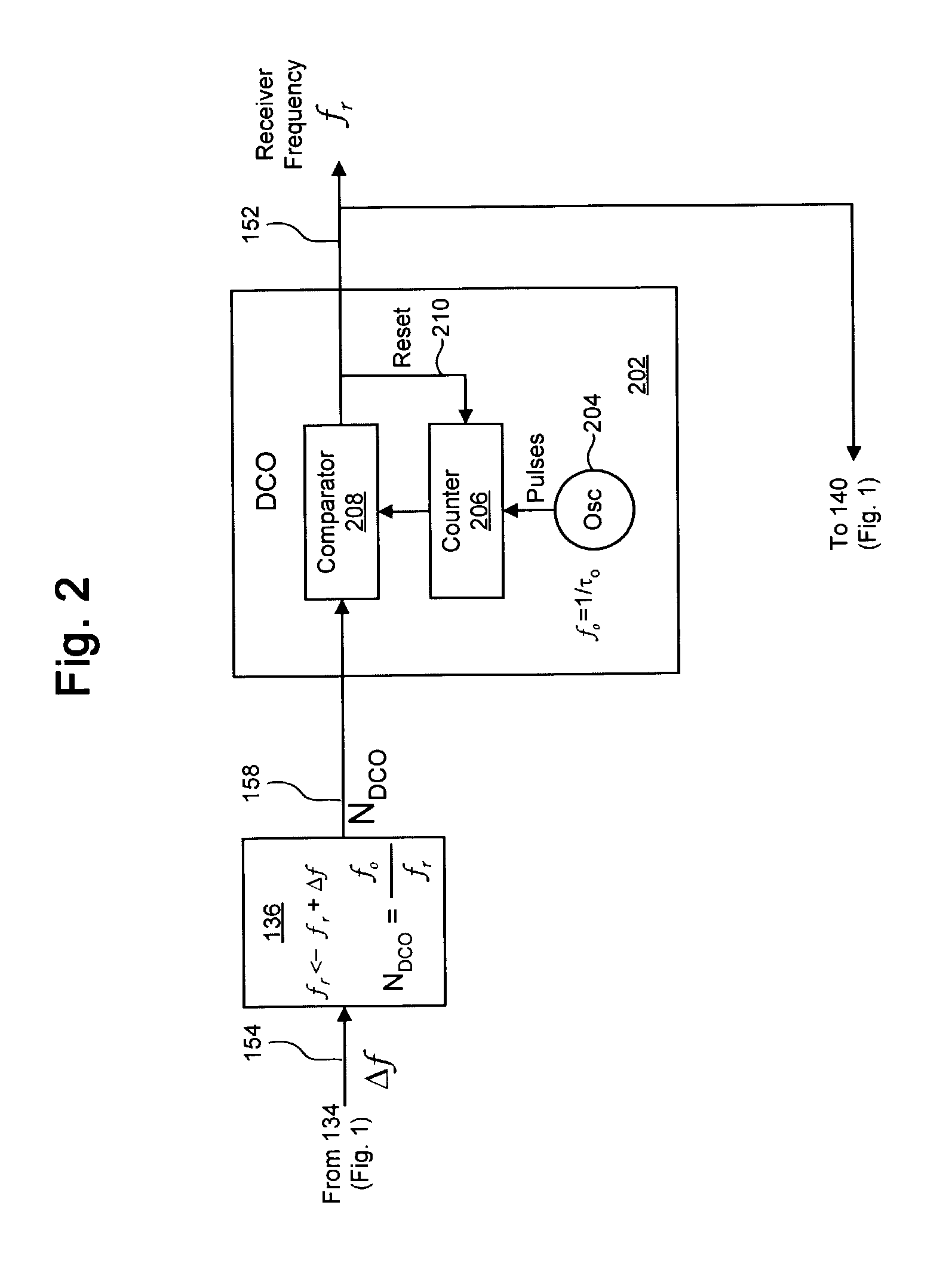
Clock recovery using a double-exponential smoothing process
A system and method for synchronizing a local clock to a reference clock using a linear model of the clock error between the local clock and the reference clock is disclosed. In one embodiment, a double-exponential smoothing process is used in conjunction with the linear model to estimate a frequency offset by which the frequency of an oscillator of the local clock is adjusted. Also disclosed herein is a phased-lock loop (PLL) adapted to synchronize a local clock with a reference clock using the double-exponential smoothing process, as well as a system implementing the PLL for timing the playout of data received from a transmitter.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
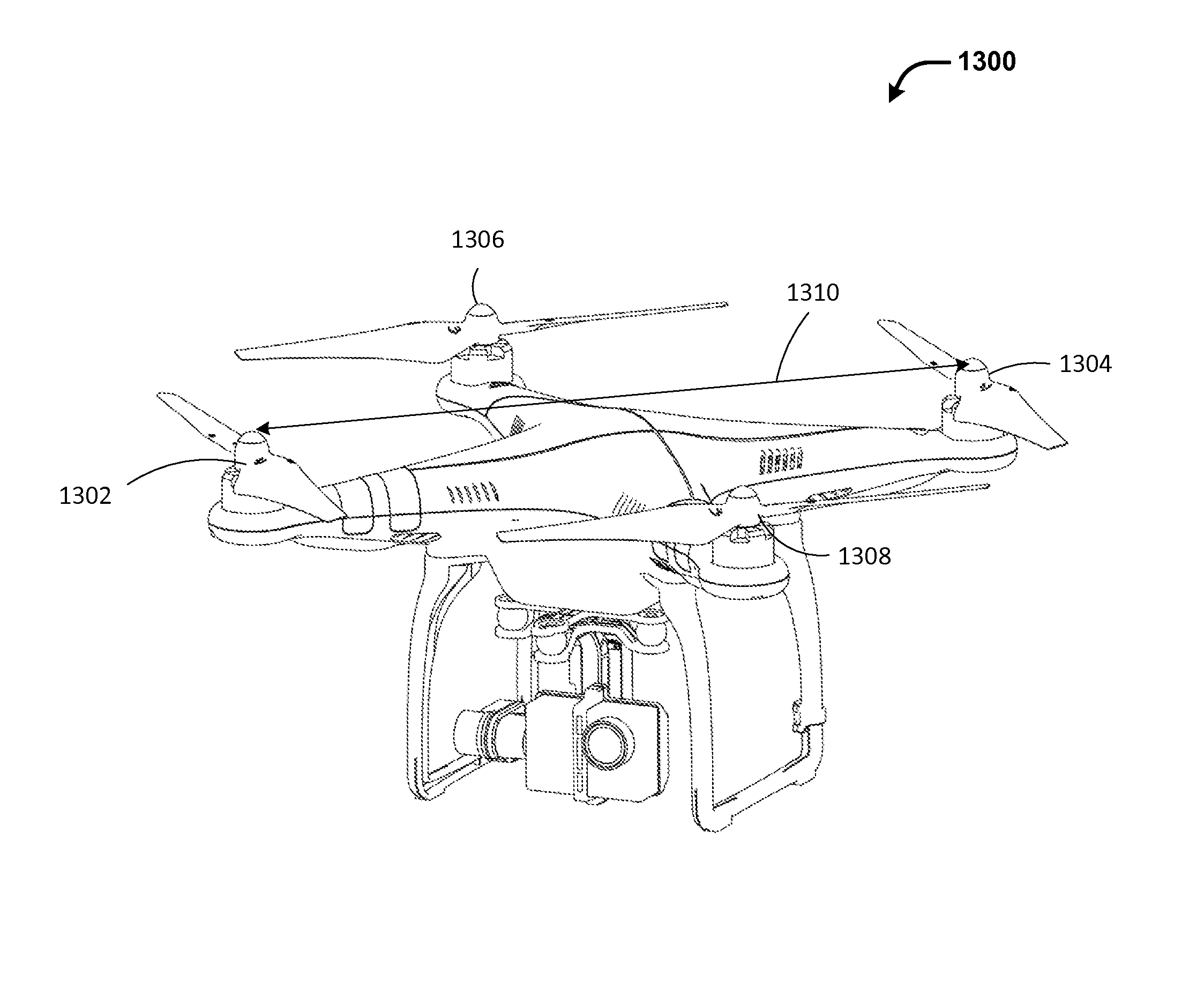
Data communication systems and methods
ActiveUS8908573B1Facilitate data communicationAvoid interferenceError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorCriteria allocationCommunications systemBroadband transmission
The present invention provides systems and methods for improved data communication between communication terminals such as a base station and an unmanned aerial vehicle. In some instances, the systems and methods described herein provide robust transmission uplink data such as control data and wideband transmission of downlink data such as image data or other sensor data, while avoiding interference between the uplink data transmission and the downlink transmission.
Owner:SZ DJI TECH CO LTD
Clock recovery using a direct smoothing process
ActiveUS7130368B1Guaranteed maximum utilizationPulse automatic controlModulated-carrier systemsClock recoveryLinear model
A system and method for synchronizing a local clock to a reference clock using a linear model of the error between the local clock and the reference clock is disclosed. In one embodiment, a direct smoothing process is used in conjunction with the linear model to estimate a frequency offset by which the frequency of an oscillator of the local clock is adjusted. Also disclosed herein is a phased-lock loop (PLL) adapted to synchronize a local clock with a reference clock using the direct smoothing process, as well as a system implementing the PLL for timing the playout of data received from a transmitter.
Owner:CIENA
Method for software driven generation of multiple simultaneous high speed pulse width modulated signals
InactiveUS7113541B1Electroluminescent light sourcesVoltage-current phase angleTime segmentControl signal
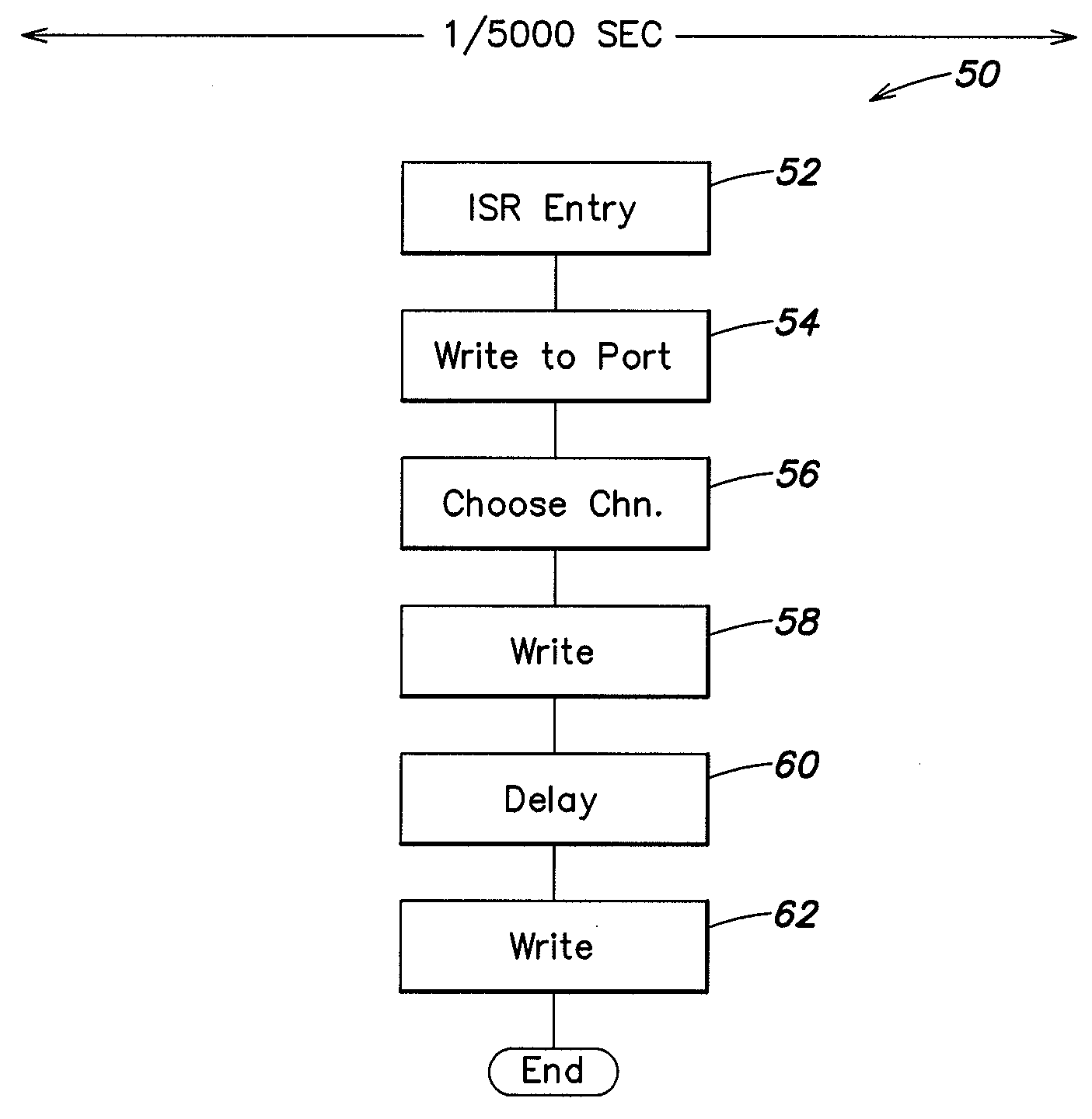
Systems and methods can provide, in one aspect, a method for modulating the pulse width of control signals generated on a plurality of separate channels. In one practice, the methods described herein are suitable for execution on a microprocessor or micro controller platform that includes a timer interrupt mechanism which will generate an interrupt in response to a timer counting down a selected time interval or time period. In one practice, the timer is set to count down a period of time that is representative of a portion, or sub period, of the PWM cycle. Upon expiration of that time period, the timer executes an interrupt that causes the micro controller to enter an interrupt service routine (ISR) that can further modulate the PWM cycle of one or more signals.
Owner:PHILIPS SOLID STATE LIGHTING SOLUTIONS
Dynamic bandwidth allocation
InactiveUS7069577B2Prevents untoward spectral effectMore balancedError preventionModulated-carrier systemsFiberModem device
The communication system includes a hybride fiber / coax distribution network. A head end provides for downstream transmission of telephony and control data in a first frequency bandwidth over the hybrid fiber / coax distribution network and reception of upstream telephony and control data in a second frequency bandwidth over the hybrid fiber / coax distribution network. The head end includes head end multicarrier modem for modulating at least downstream telephony information on a plurality of orthogonal carriers in the first frequency bandwidth and demodulating at least upstream telephony information modulated on a plurality of orthogonal carriers in the second frequency bandwidth. The head end further includes a controller operatively connected to the head end multicarrier modem for controlling transmission of the downstream telephony information and downstream control data and for controlling receipt of the upstream control data and upstream telephony information. The system further includes service units, each service unit operatively connected to the hybrid fiber / coax distribution network for upstream transmission of telephony and control data in the second frequency bandwidth and for receipt of the downstream control data and telephony in the first frequency bandwidth. Each service unit includes a service unit multicarrier modem for modulating at least the upstream telephony information on at least one carrier orthogonal at the head end terminal to another carrier in the second frequency bandwidth and for demodulating at least downstream telephony information modulated on at least a band of a plurality of orthogonal carriers in the first frequency bandwidth. Each service unit also includes a controller operatively connected to the service unit multicarrier modem for controlling the modulation of and demodulation performed by the service unit multicarrier modem. A method of monitoring communication channels, a distributed loop method for adjusting transmission characteristics to allow for transmission of data in a multi-point to point communication system, a polyphase filter technique for providing ingress protection and a scanning method for identifying frequency bands to be used for transmission by service units are also included. Also provided is a method and apparatus for performing a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). In one embodiment, a scalable FFT system is built using a novel dual-radix butterfly core.
Owner:HTC CORP
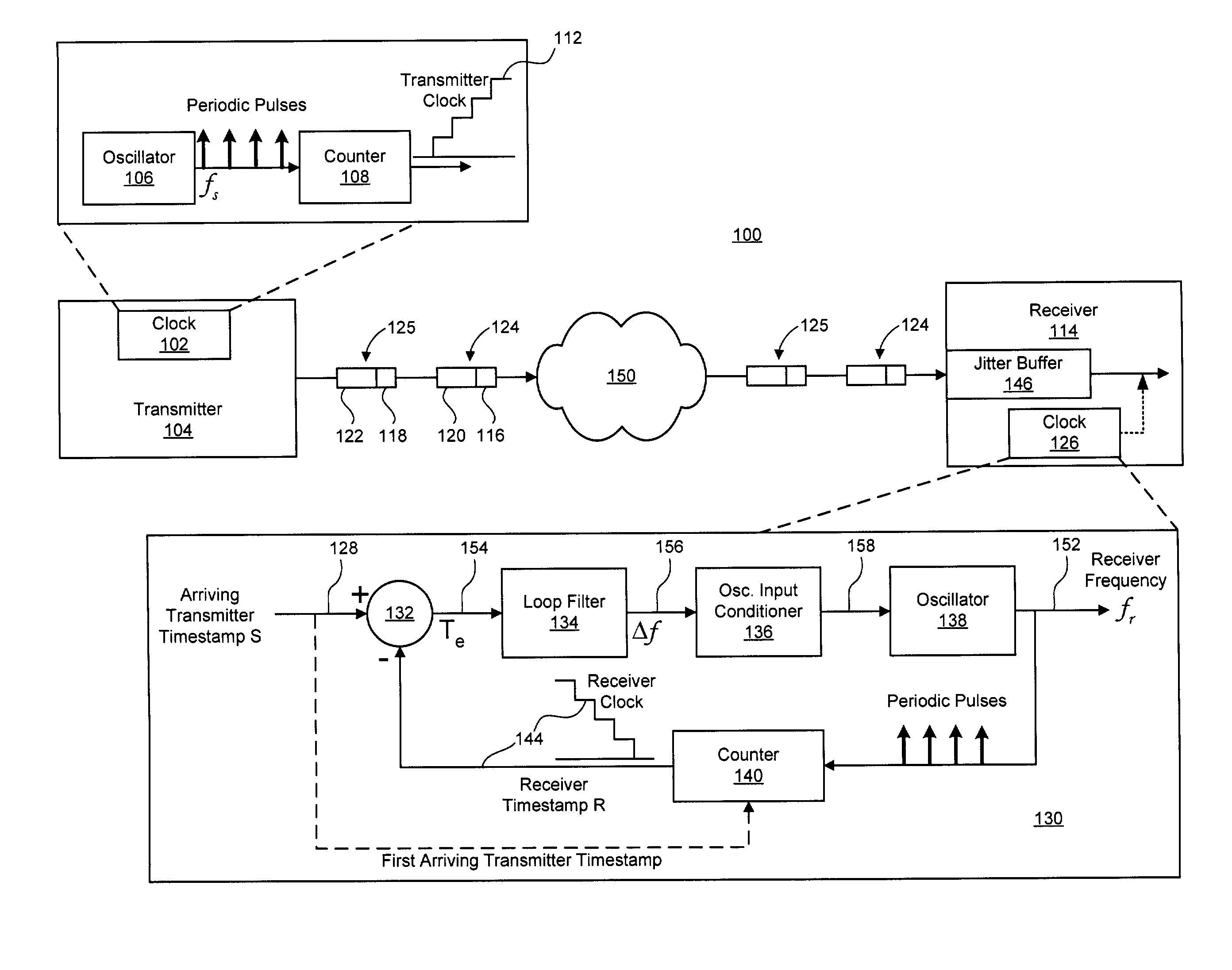
Technique for synchronizing clocks in a network
A technique for synchronizing clocks in a network is disclosed. In one exemplary embodiment, the technique may be realized as a method for synchronizing clocks in a network. The method comprises receiving a first timestamp and a second timestamp, each indicating a respective time instance as determined by a first clock signal within the network. The method also comprises measuring a first time interval between the first timestamp and the second timestamp. The method further comprises generating a difference signal representing a difference between the first time interval and a second time interval, and generating a second clock signal based upon the difference signal such that the second clock signal is synchronized with the first clock signal.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
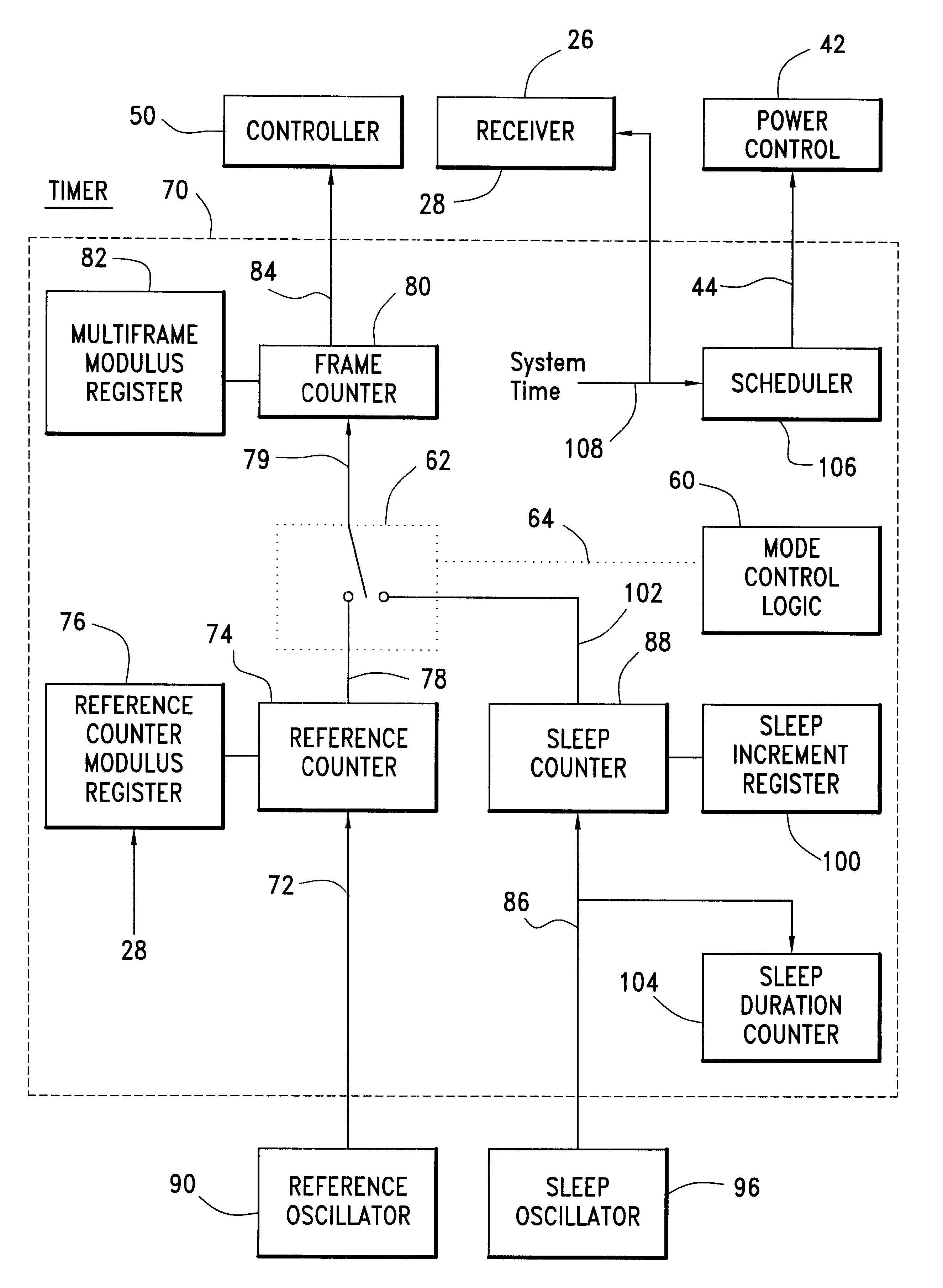
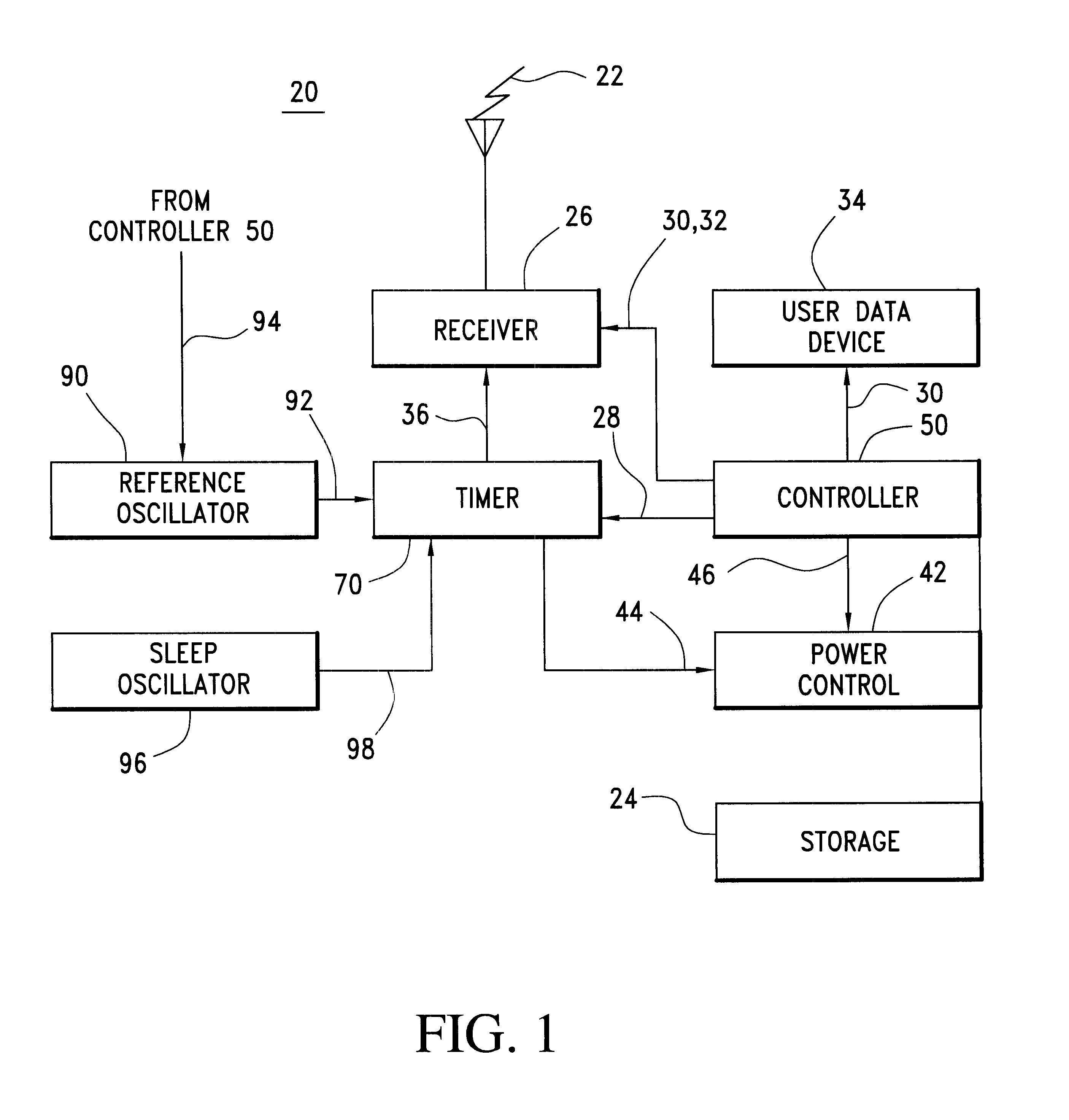
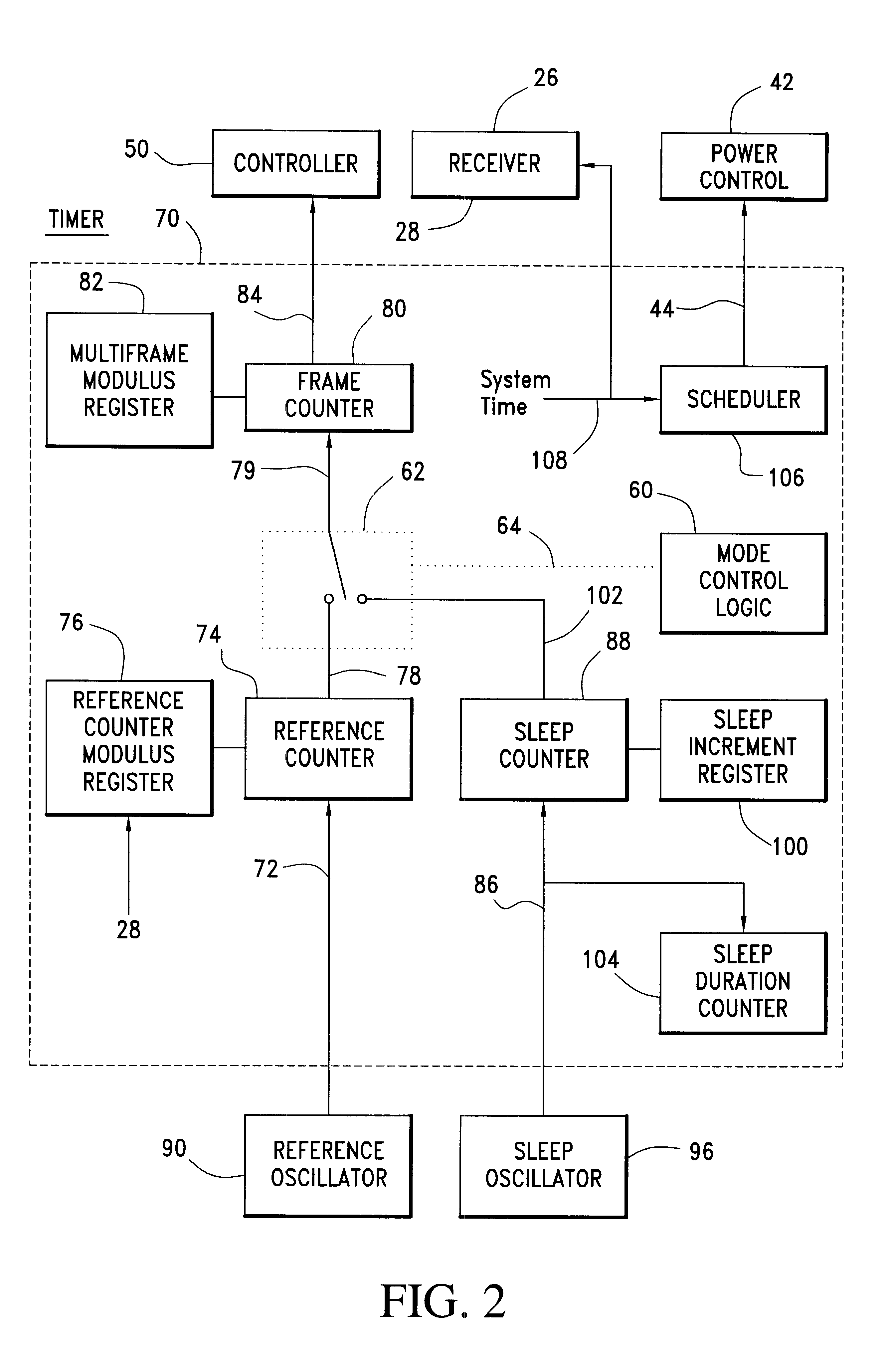
Communication device with a self-calibrating sleep timer
The present invention provides for a system for operating a communication device (20) for reception of scheduled intermittent information messages (22) with a dual mode timer (70) that extends battery life. A controller (50) schedules the timer (70) to power down all idle components of the device (20) between message receptions in a power saving sleep mode to conserve battery power. During active mode when the device is fully active in reception of messages, the timer (70) uses a reference oscillator (90) with a relatively high frequency to support digital processing by the receiver (26). During sleep mode when only the timer is powered on, a much lower frequency sleep oscillator (96) is used to maintain the lowest possible level of power consumption within the timer itself. The timer (70) has provision for automatic temperature calibration to compensate for timing inaccuracies inherent to the low-power low-frequency crystal oscillator (96) used for the sleep mode. The resultant improvement in timer accuracy during sleep mode eliminates the need for an initial reacquisition period following wake up in active mode, thereby reducing battery drain in active mode as well.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
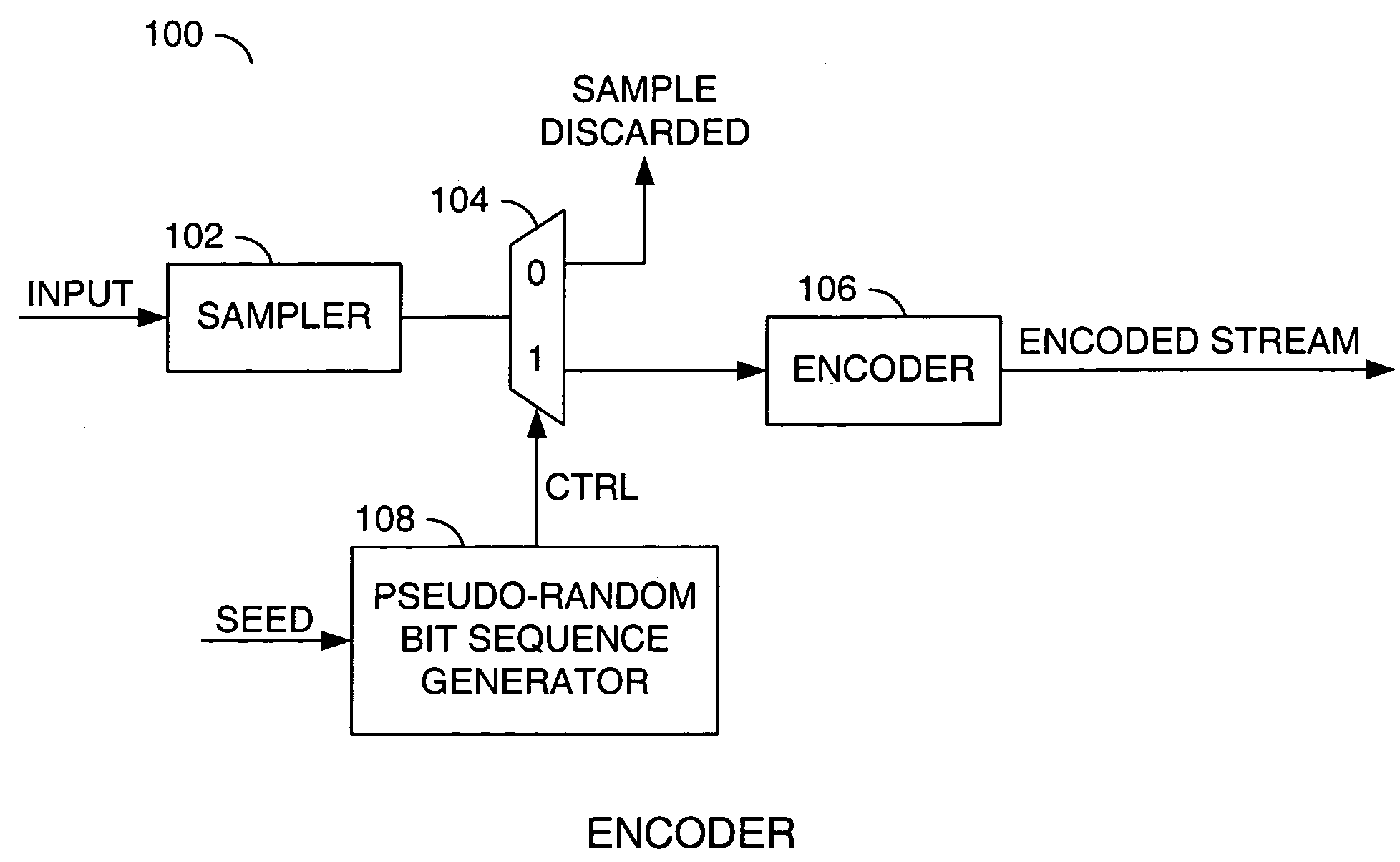
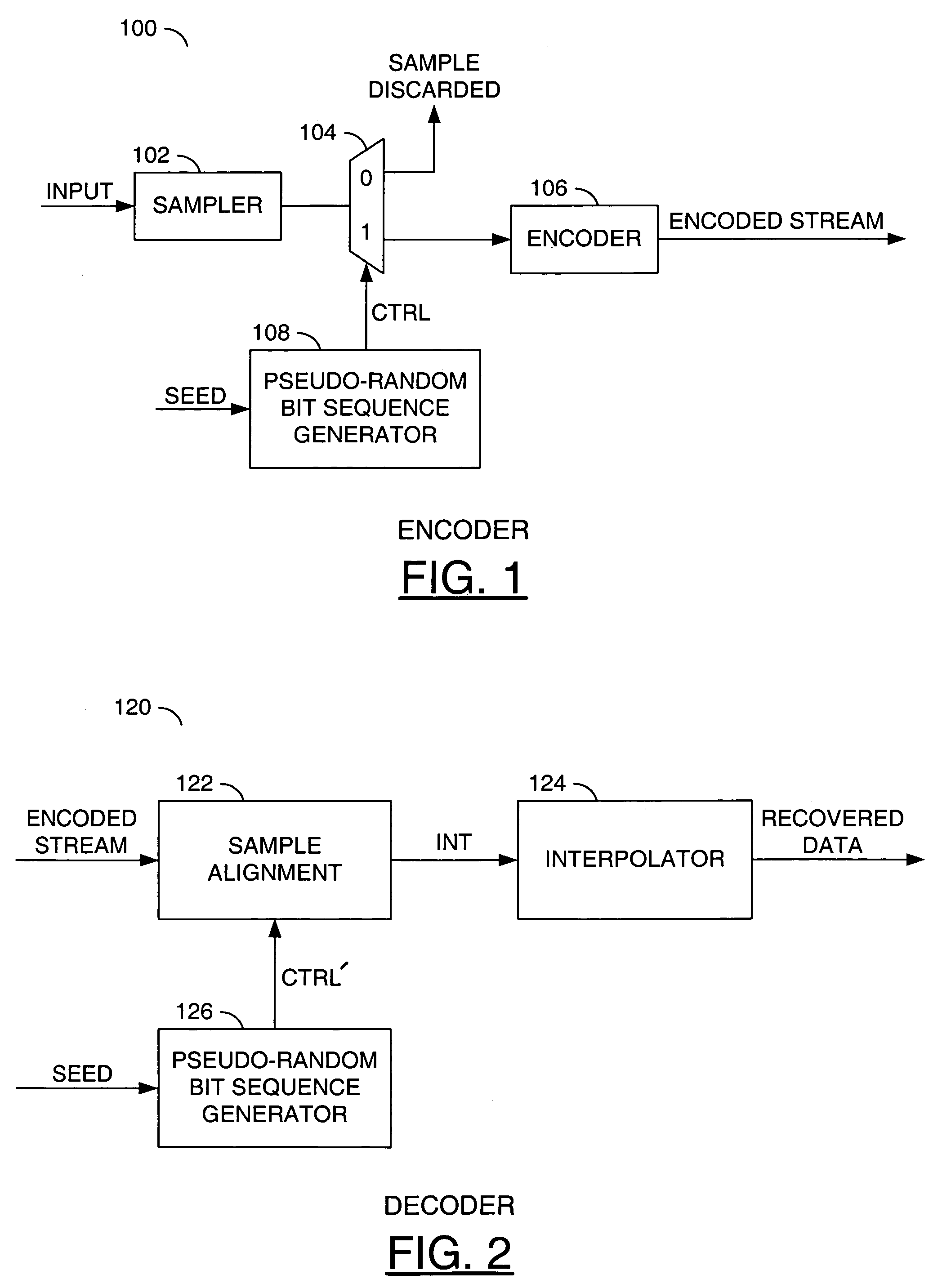
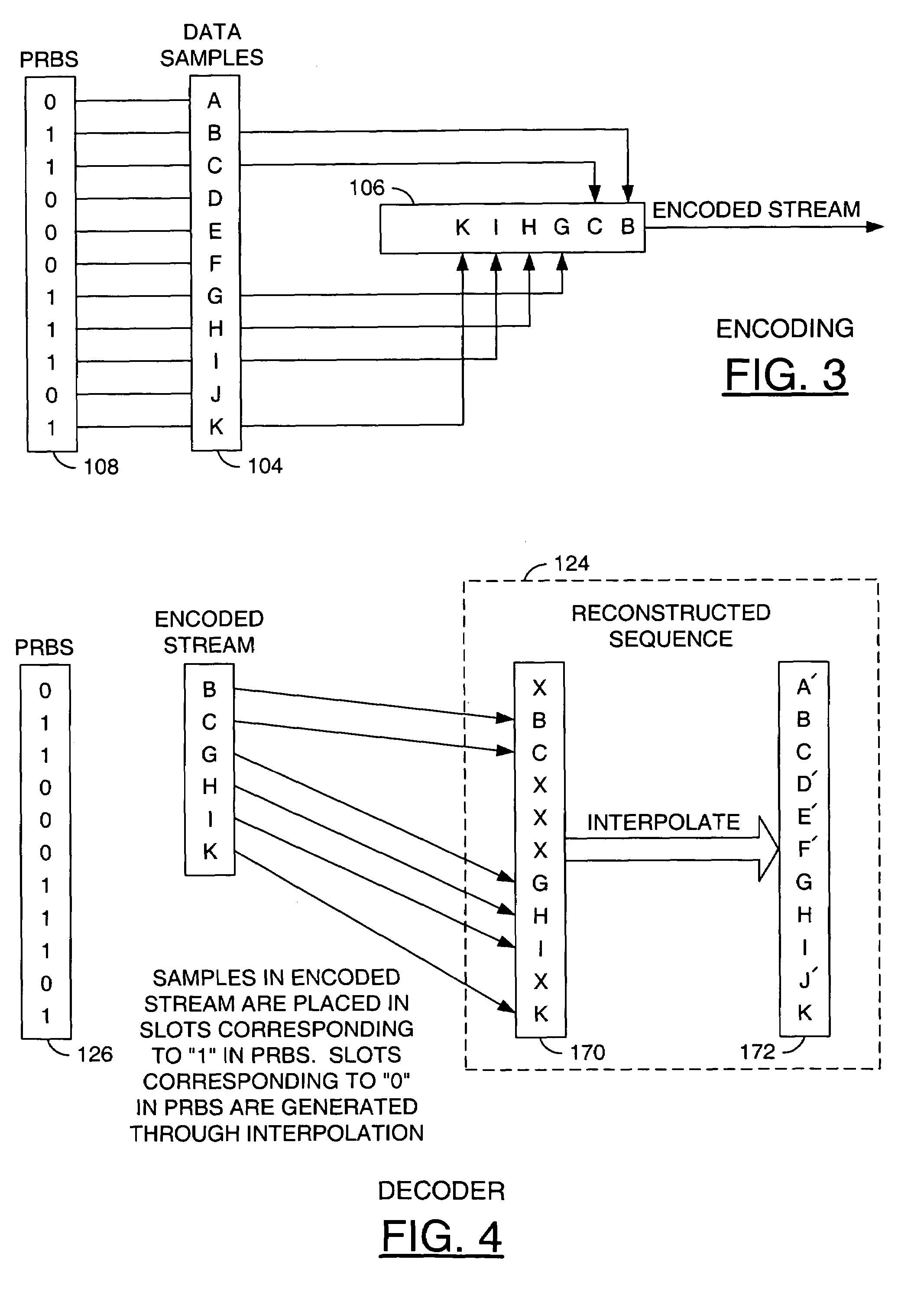
Flexible sampling-rate encoder
A method for implementing a flexible sampling-rate encoder, comprising the steps of (A) sampling an input signal at a regular time-interval to produce sampled data, (B) generating a pseudo-random bit sequence having a plurality of bits, wherein each bit corresponds to a different sampling time, (C) encoding a first set of the sampled data to generate an encoded stream when any bit in the pseudo-random bit sequence is equal to a first value, wherein each bit in the encoded stream corresponds to one of the sampling times defined in step (B), and (D) determining the different sampling time for each sample in the encoded stream.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Three phase and polarity encoded serial interface
ActiveUS8064535B2Shorten the timeImprove efficiencyIndividual digits conversionPhase-modulated carrier systemsSerial digital interfaceElectrical conductor
A high speed serial interface is provided. In one aspect, the high speed serial interface uses three phase modulation for jointly encoding data and clock information. Accordingly, the need for de-skewing circuitry at the receiving end of the interface is eliminated, resulting in reduced link start-up time and improved link efficiency and power consumption. In one embodiment, the high speed serial interface uses fewer signal conductors than conventional systems having separate conductors for data and clock information. In another embodiment, the serial interface allows for data to be transmitted at any speed without the receiving end having prior knowledge of the transmission data rate. In another aspect, the high speed serial interface uses polarity encoded three phase modulation for jointly encoding data and clock information. This further increases the link capacity of the serial interface by allowing for more than one bit to be transmitted in any single baud interval.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
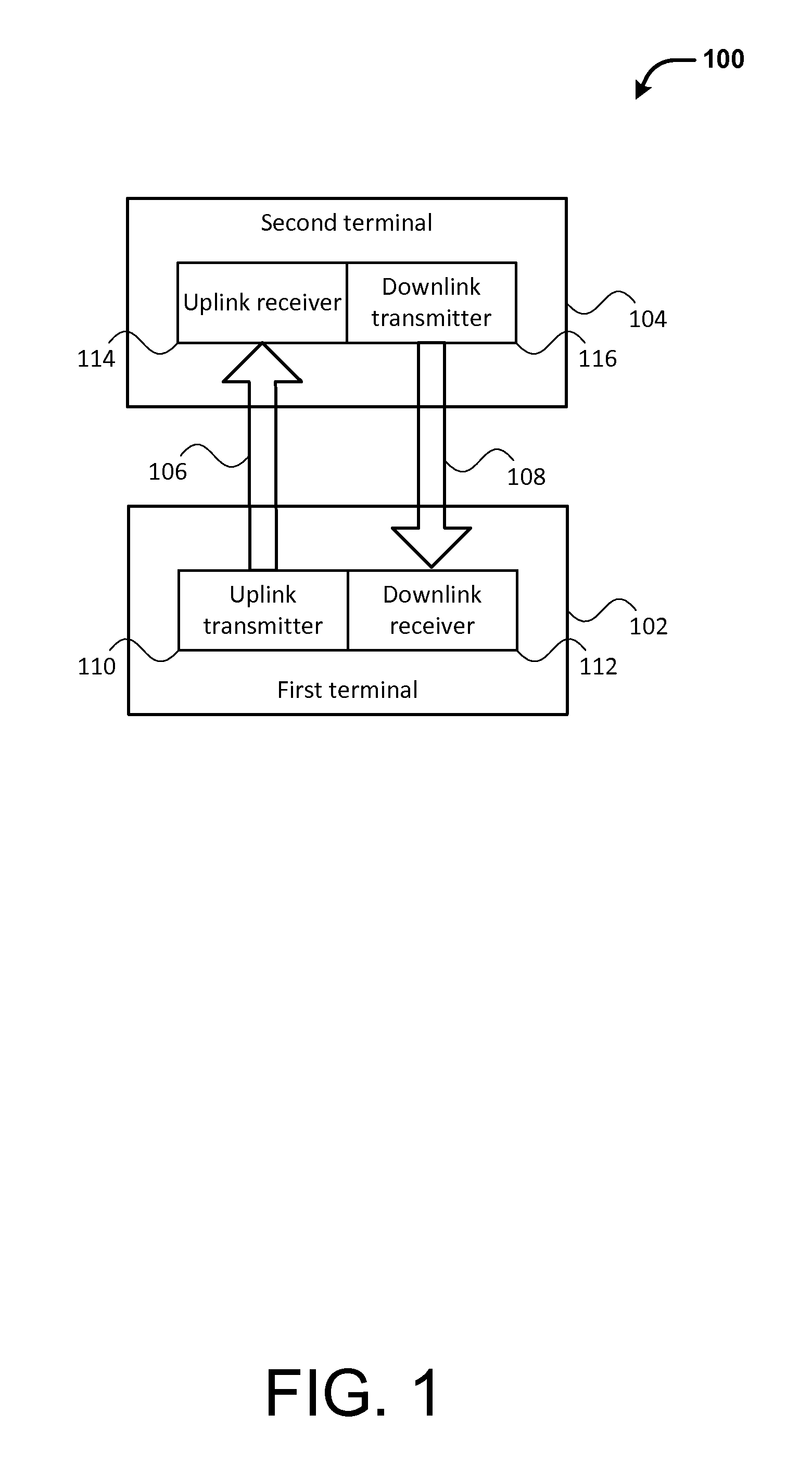
Synchronization of timestamps to compensate for communication latency between devices
InactiveUS20050010691A1To overcome the large delayTime-division multiplexMultiple digital computer combinationsTimestampControl signal
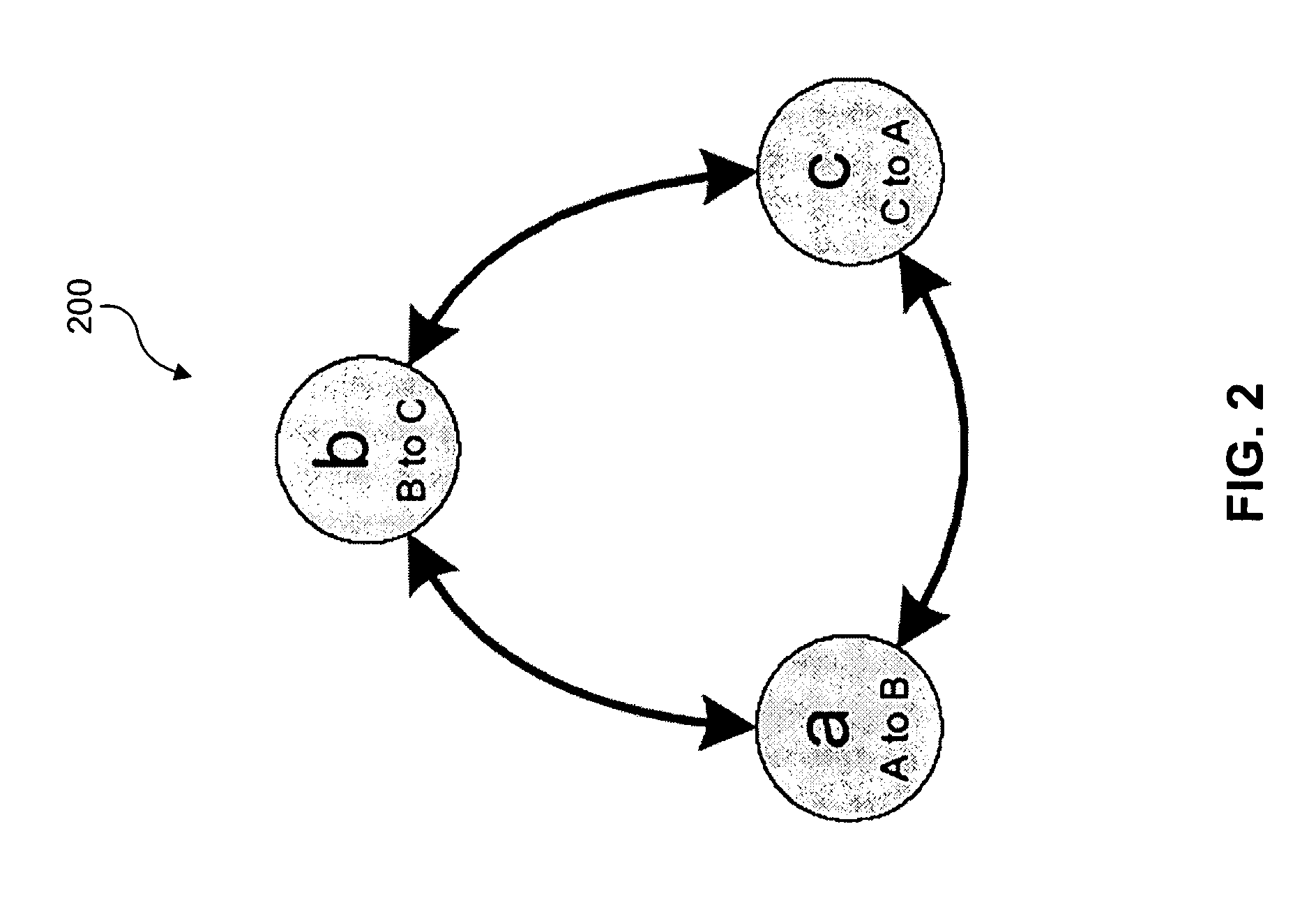
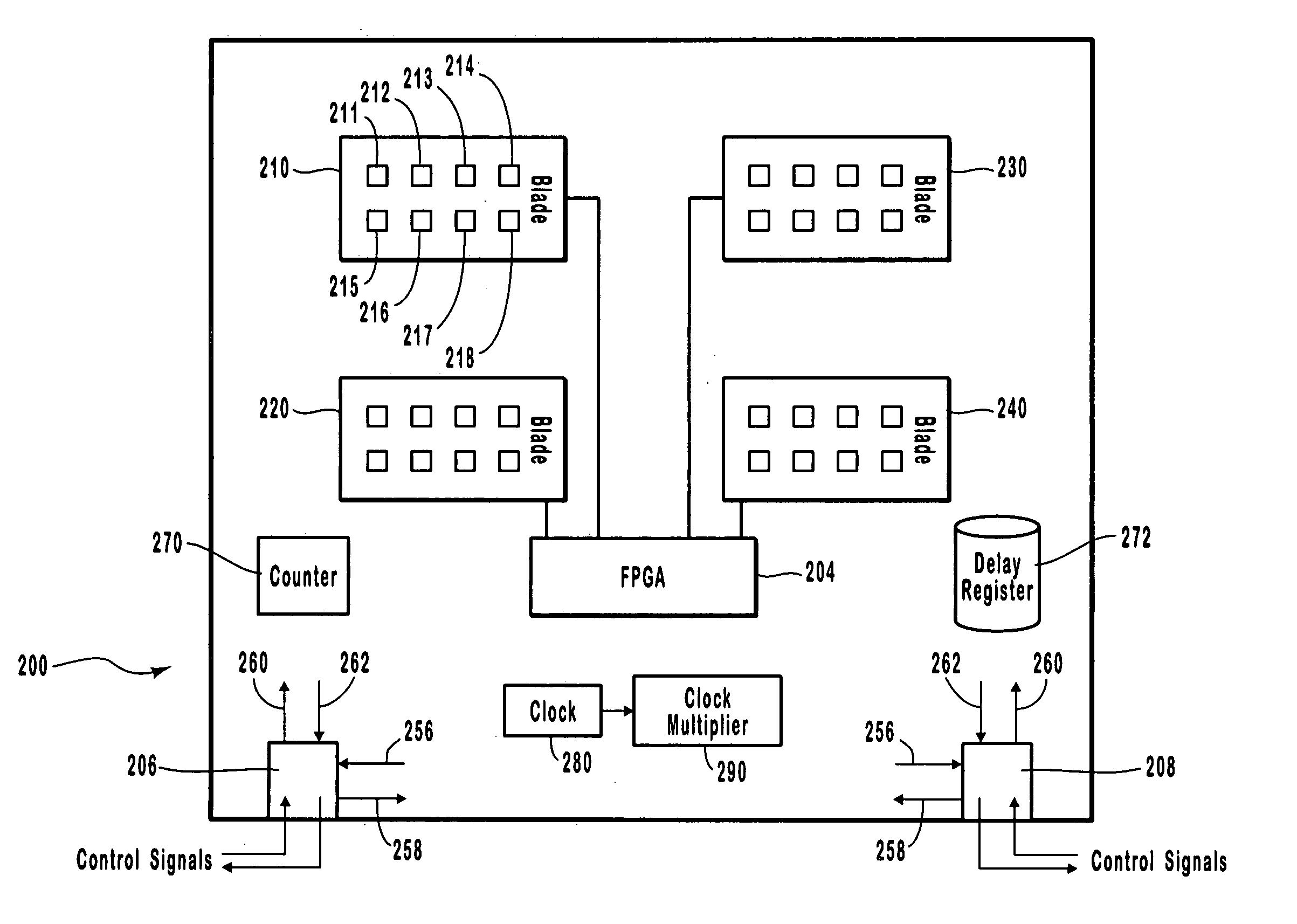
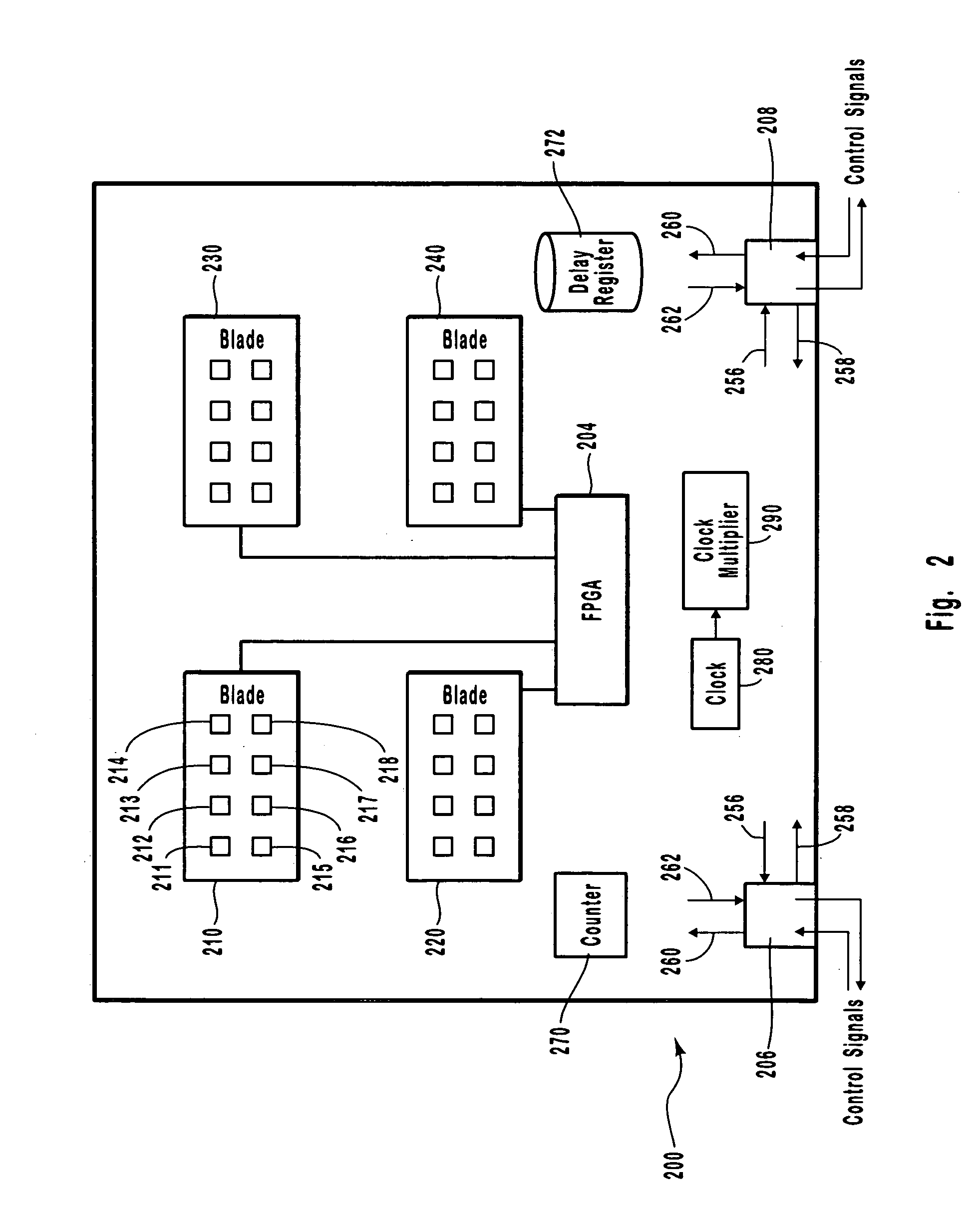
Protocol analyzer systems enable synchronization of timestamps and the capture of data across serially chained boxes that are used together to monitor and capture network data. Through experiment, it can be determined how long it takes to propagate a signal to each box in the chain. These values are then recorded in each box in a delay register so that each box has a recorded delay value corresponding to the time required to propagate a signal to or receive a signal from every other box. Each box applies a control signal, such as a run signal or a trigger signal, to the ports in the box only after the expiration of the delay value indicated in the delay register. The box initiating the signal has the largest delay since the other boxes need to get the signal before the boxes can begin to operate with a common counter, with successive boxes having smaller delays.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Method of band multiplexing to improve system capacity for a multi-band communication system
ActiveUS20070054680A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMulti bandCommunications system
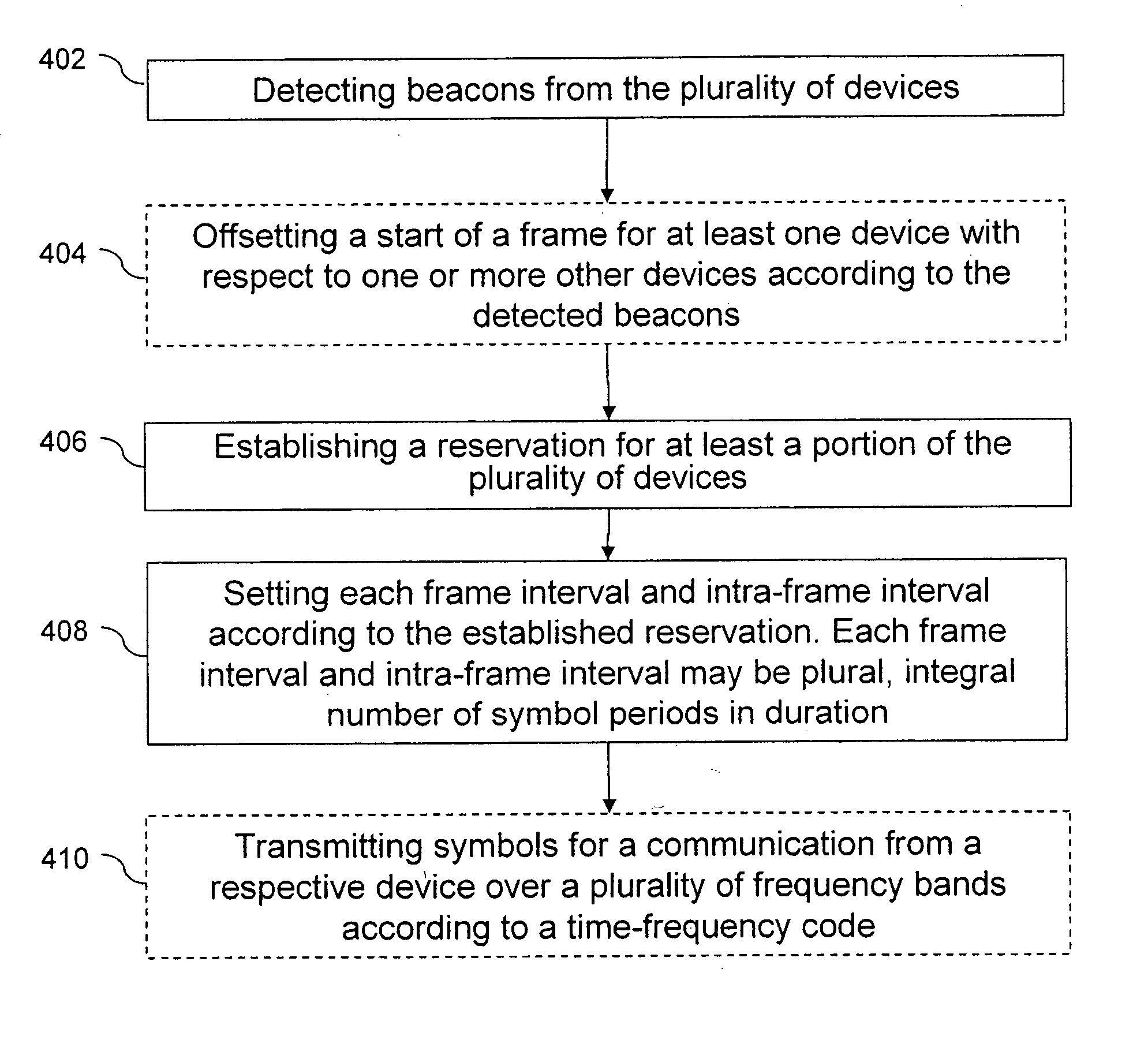
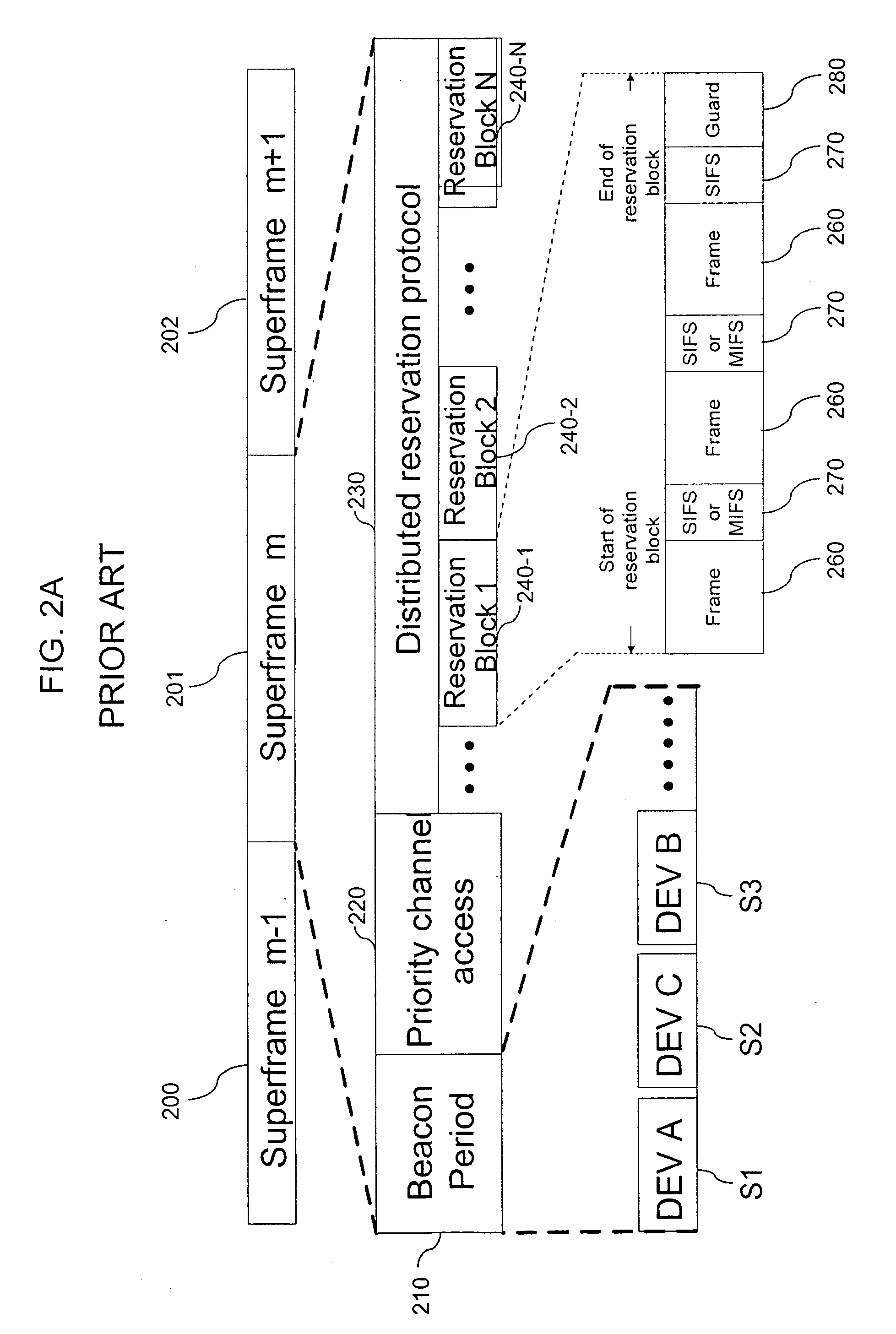
A control method of synchronizing communications between or among a plurality of devices in a communication system includes detecting beacons from the plurality of devices in the communication system, and establishing a reservation for at least a portion of the plurality of devices in the communication system. Each reservation is a frame interval in which to transmit symbols from one device to one or more of the other devices in the communications system. Each frame interval and intra-frame interval is set according to the established reservation. Each frame interval and intra-frame interval is a plural, integral number of symbol periods in duration.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
Method for self-synchronizing time between communicating networked systems using timestamps
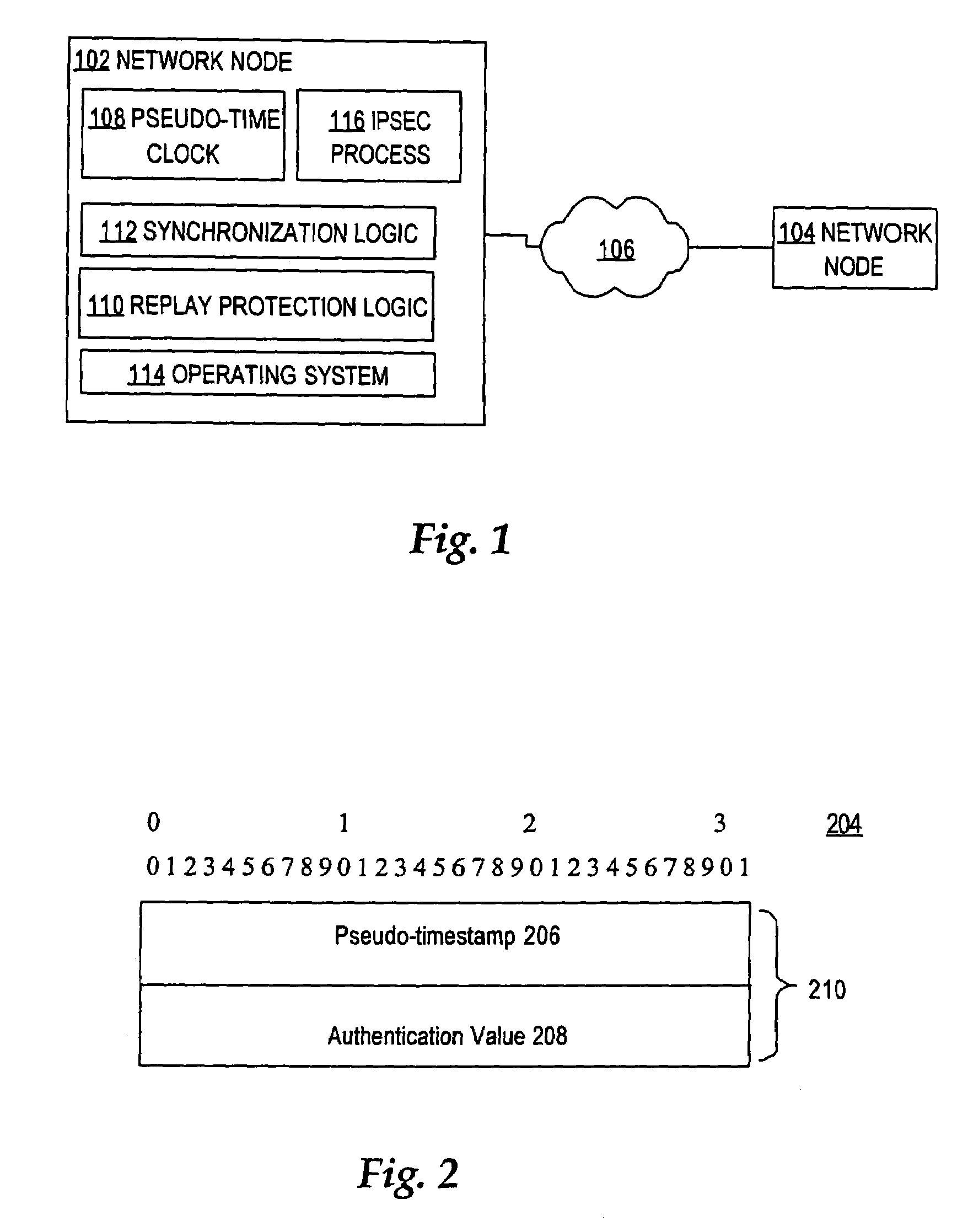
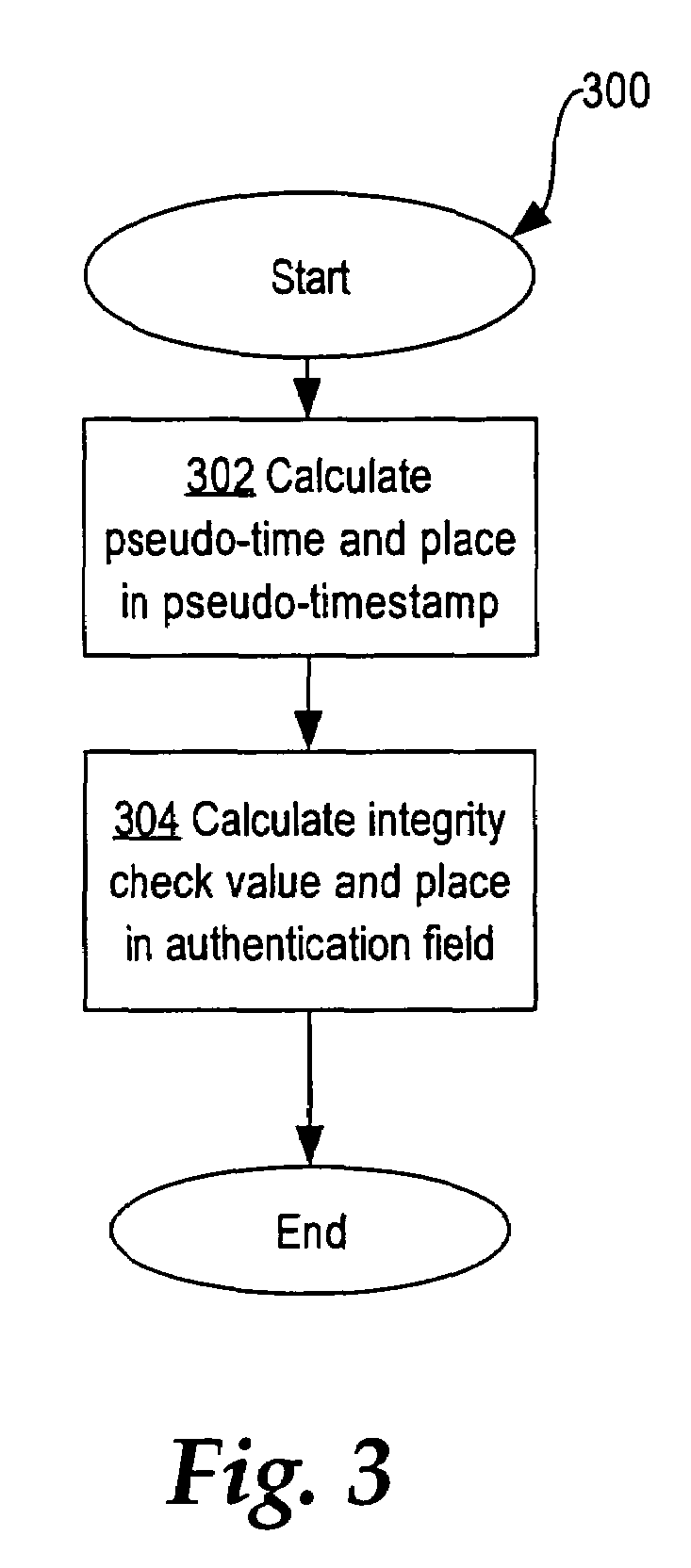
ActiveUS7676679B2Synchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesError detection/correctionTimestampNetworked system
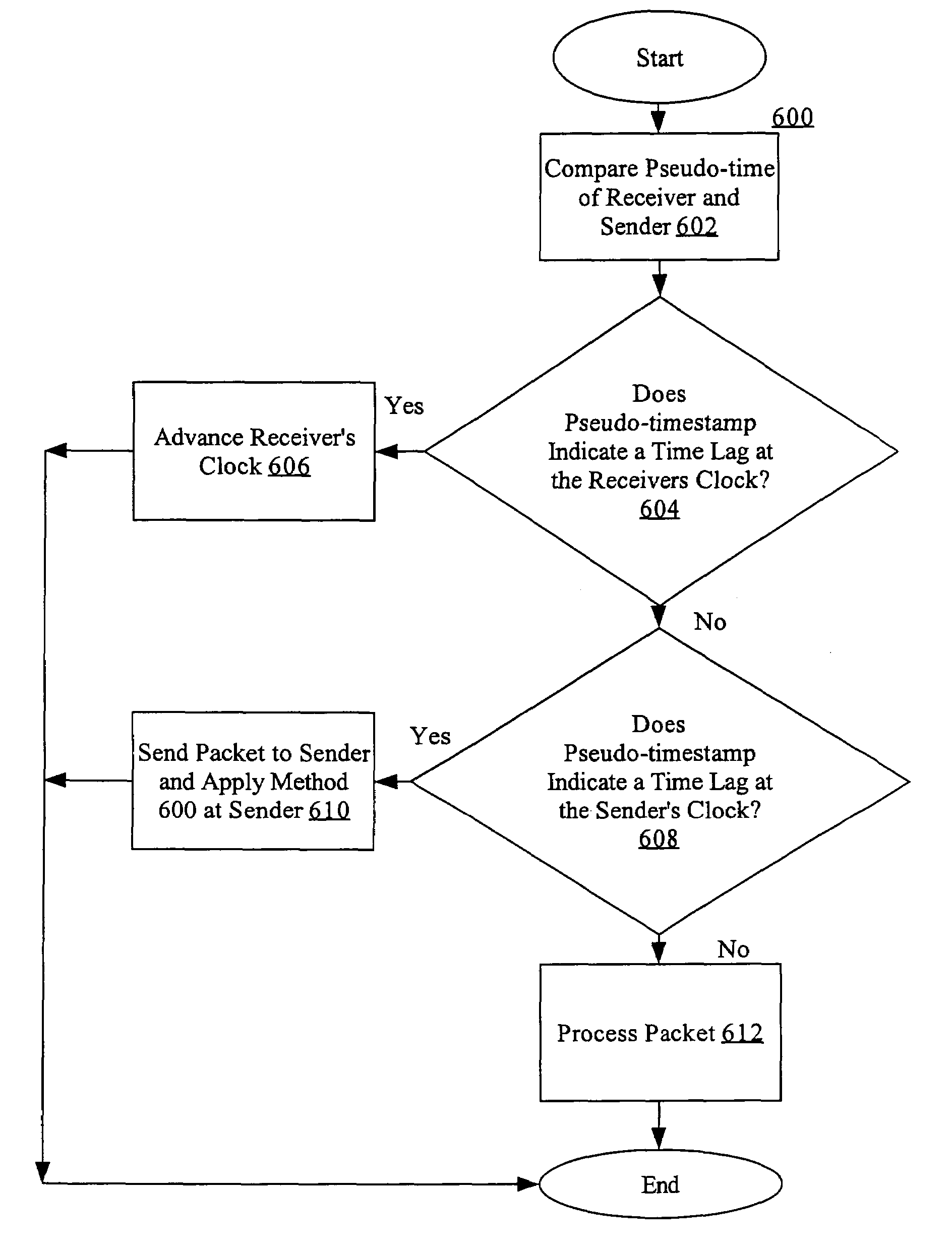
Nodes in a network include a pseudo-timestamp in messages or packets, derived from local pseudo-time clocks. When a packet is received, a first time is determined representing when the packet was sent and a second time is determined representing when the packet was received. If the difference between the second time and the first time is greater than a predetermined amount, the packet is considered to be stale and is rejected, thereby deterring replay. Because each node maintains its own clock and time, to keep the clocks relatively synchronized, if a time associated with a timestamp of a received packet is later than a certain amount with respect to the time at the receiver, the receiver's clock is set ahead by an amount that expected to synchronize the receiver's and the sender's clocks. However, a receiver never sets its clock back, to deter attacks.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
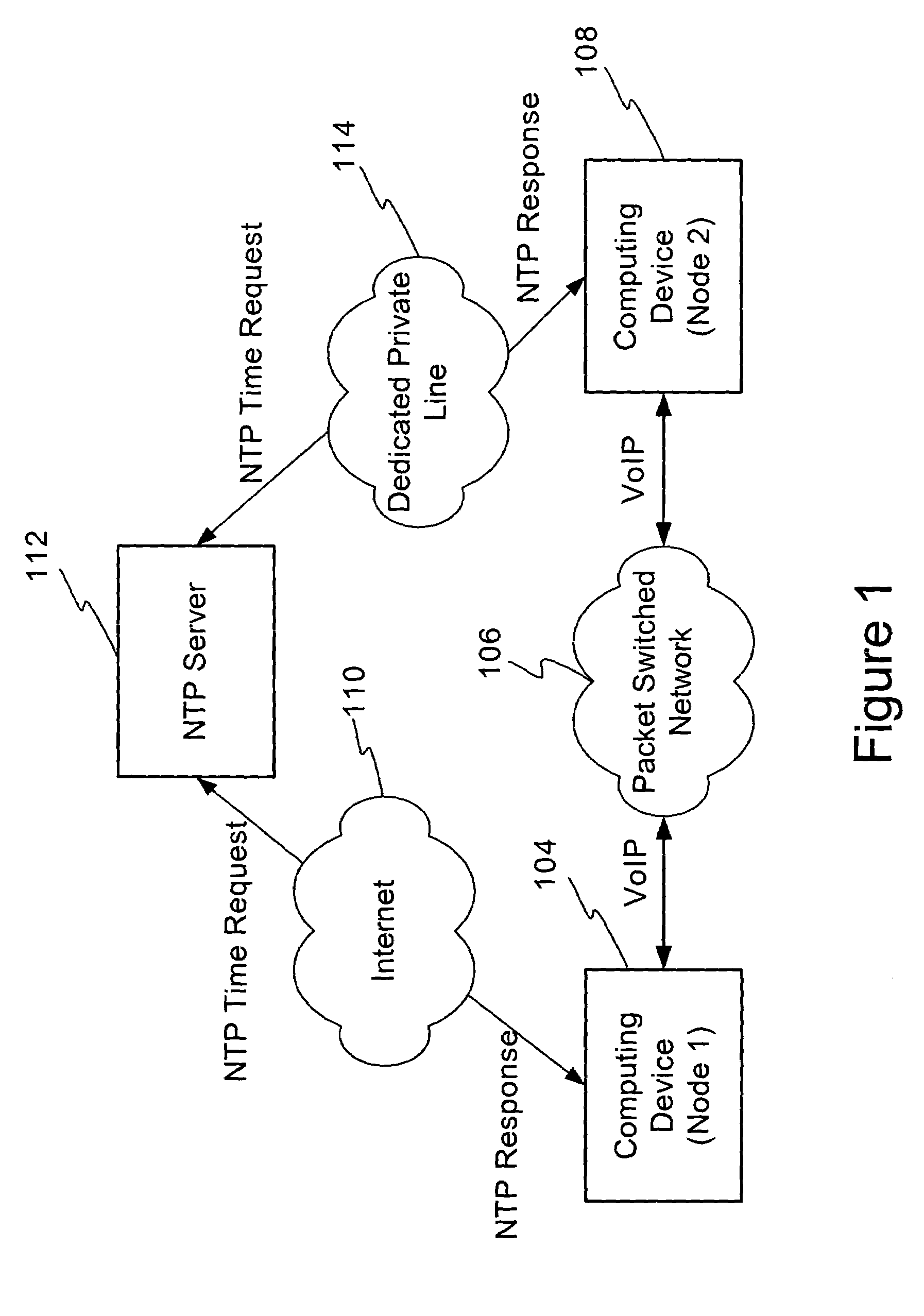
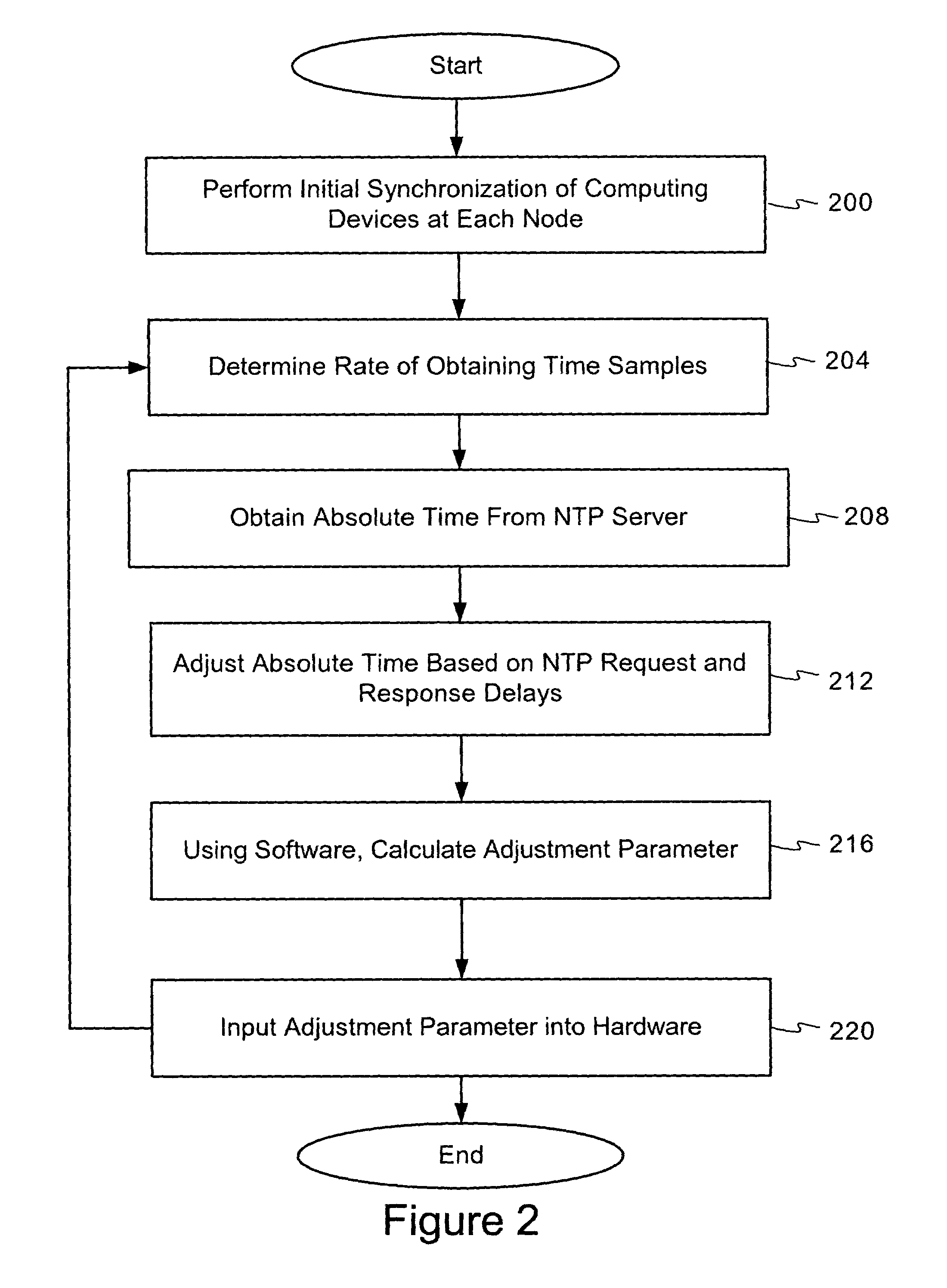
Using network time protocol in voice over packet transmission
ActiveUS7602815B2Guaranteed normal transmissionEffective maintenanceTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationTTEthernetVoice over packet
One or more methods and systems of effectively transmitting voice and voice band data from one node to another are presented. In one embodiment, the system comprises an NTP time server generating absolute times to computing devices such as residential voice over internet protocol (VoIP) gateways. The NTP time server generates absolute times in response to NTP time requests made by one or more computing devices such as residential VoIP gateways. In one embodiment, the method comprises determining an adequate rate for requesting absolute times from an NTP server, making periodic requests to the NTP server, obtaining the absolute times from the NTP server, and generating an adjustment parameter for use by a computing device such as a residential VoIP gateway.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
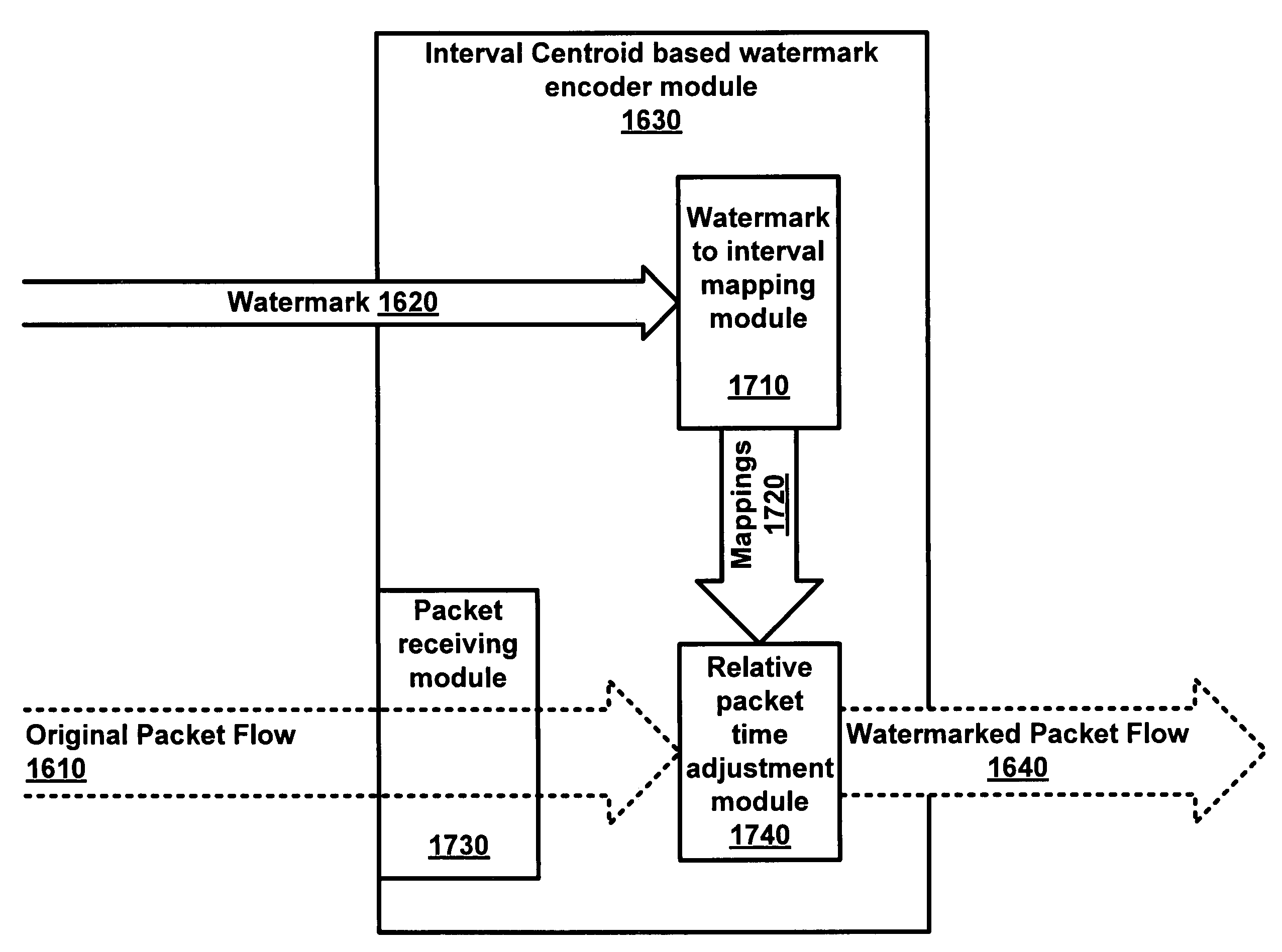
Interval centroid based watermark
An interval centroid-based watermark encoder encodes a watermark into a packet flow. Intervals are defined for the packet flow. Some of the intervals are selected as group A intervals while other intervals are selected as group B intervals. Group A and group B intervals are paired and assigned to watermark bits. A first or second value may be encoded by increasing the relative packet time between packets in either the group A (for the first bit value) or group B (for the second bit value) interval(s) of the interval pair(s) assigned to the watermark bits that are to represent the first or second bit value and the beginning of the same group interval(s). The relative packet times may be measured by a decoder and used to calculate a centroid difference for each interval pair. The centroid differences may be used to reconstruct the watermark.
Owner:GEORGE MASON INTPROP INC
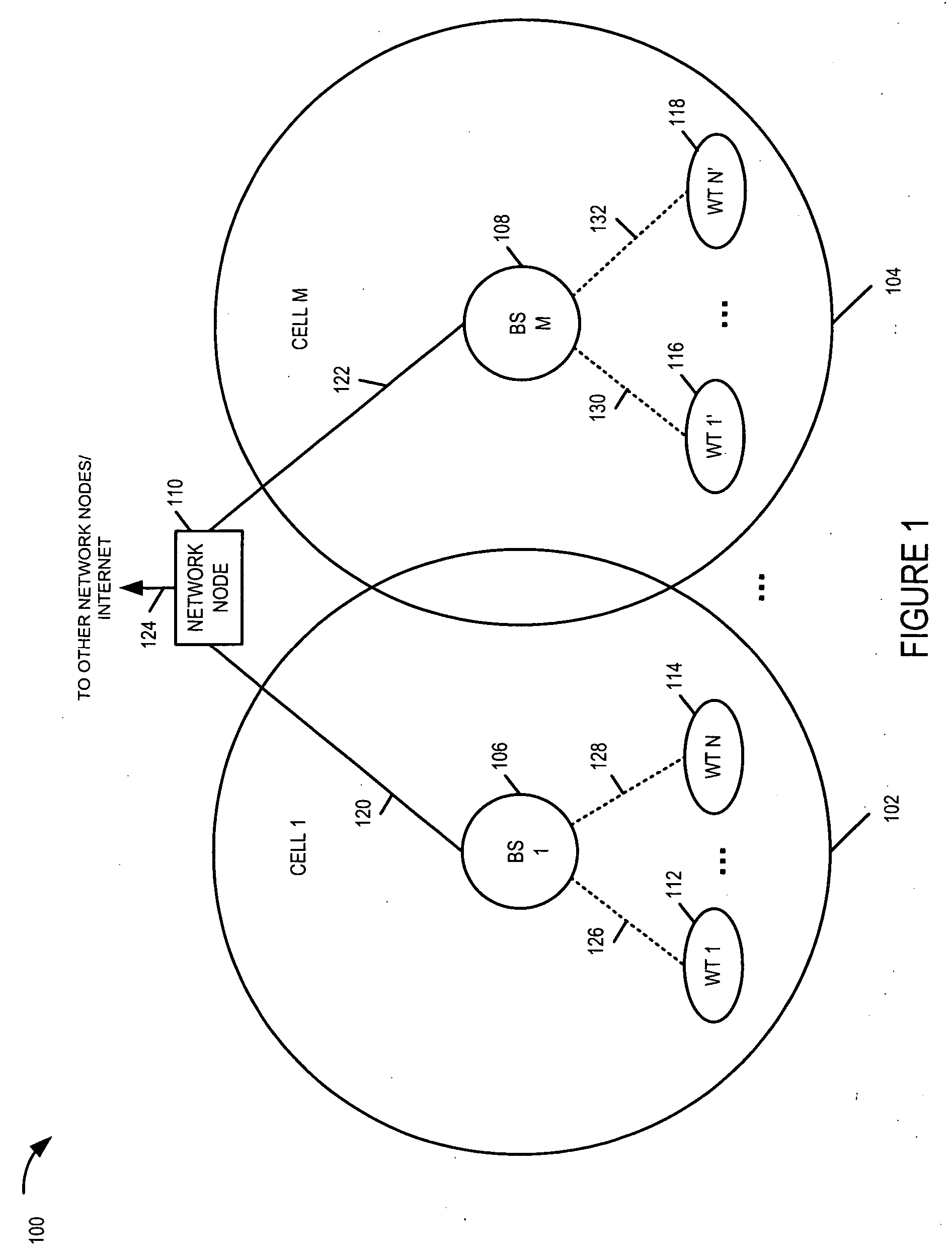
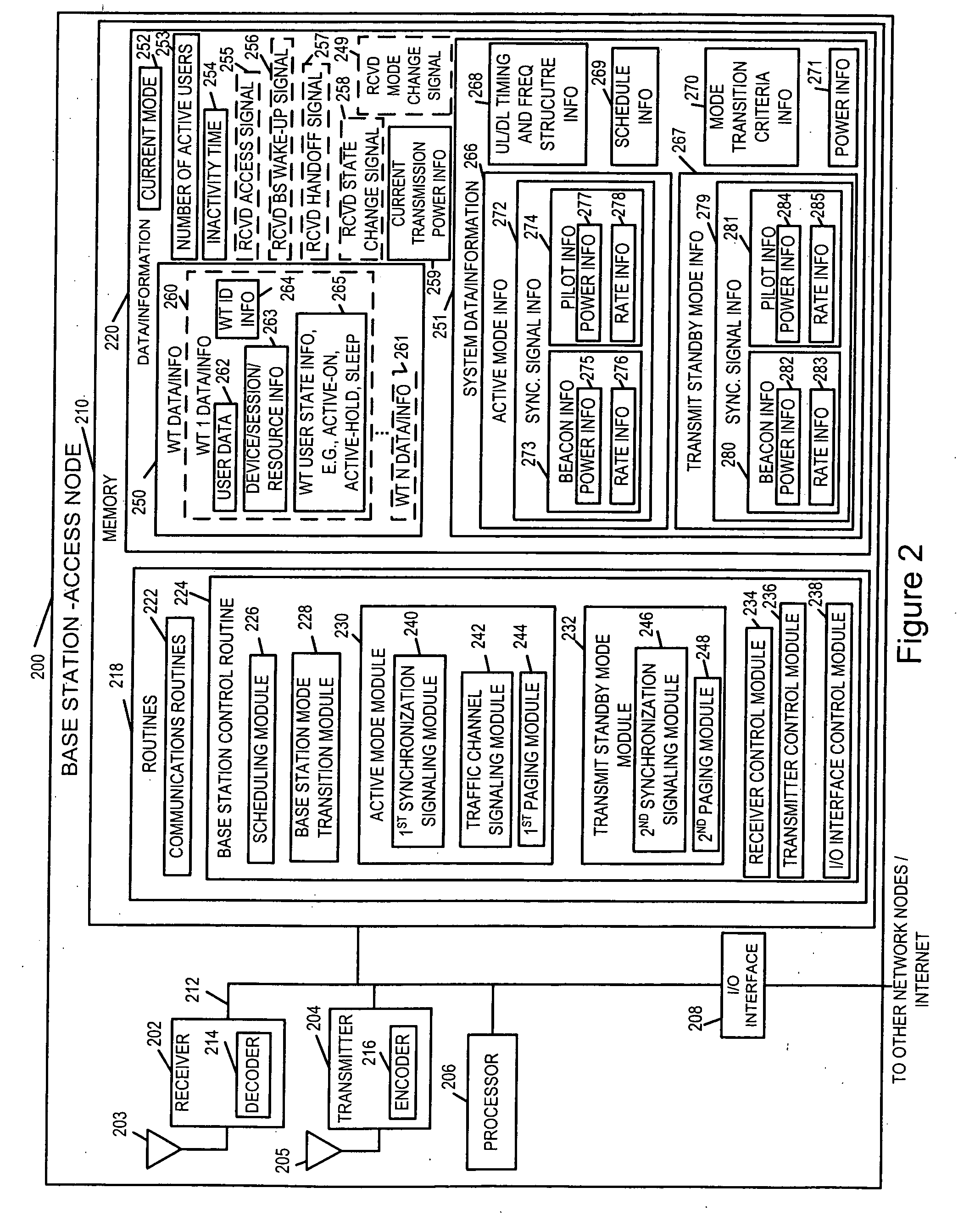
Wireless terminal methods and apparatus for use in a wireless communications system that uses a multi-mode base station
ActiveUS20070066273A1Improve throughputReducing base stationPower managementEnergy efficient ICTCommunications systemSleep state
Wireless terminal for use with a multi-mode base station that supports a transmit standby mode and an active mode is described. Transmit standby mode of base station operation is a low power / low interference level of operation as compared to active mode. In transmit standby mode at least some of the synchronization signaling such as pilot tone signaling is reduced in power level and / or rate with respect to the active mode. In transmit standby mode, the base station has no active state registered wireless terminals being serviced but may have some sleep state registered wireless terminals being serviced. Mode transitions from active to transmit standby may be in response to: a detected period of inactivity, scheduling information, base station mode change signals, and / or detected wireless terminal state transition. Mode transitions from transmit standby to active may be in response to: scheduling information, access signals, wake-up signals from the wireless terminal, hand-off signals, etc.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
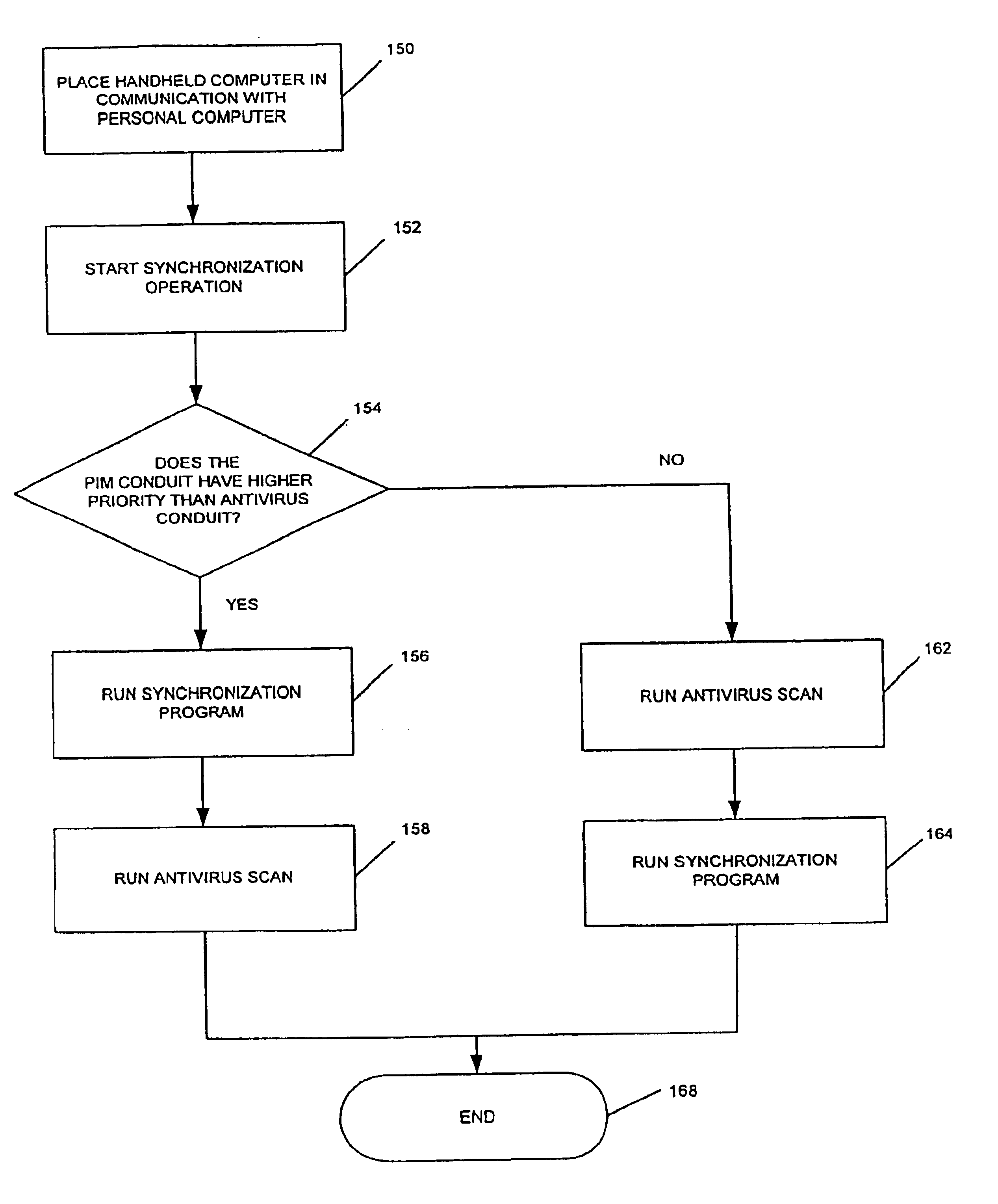
Method and system for detecting viruses on handheld computers
InactiveUS6842861B1Memory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionComputerized systemHand Held Computer
A method and system for detecting viruses on handheld computers. The handheld computer is in communication with a computer system having a virus detection program. The method includes reading data from the handheld computer and writing the data at least temporarily to a database on the computer system. The data is scanned for viruses with the virus detection program. The method further includes updating data on the handheld computer based on results of the scanning.
Owner:MCAFEE INC
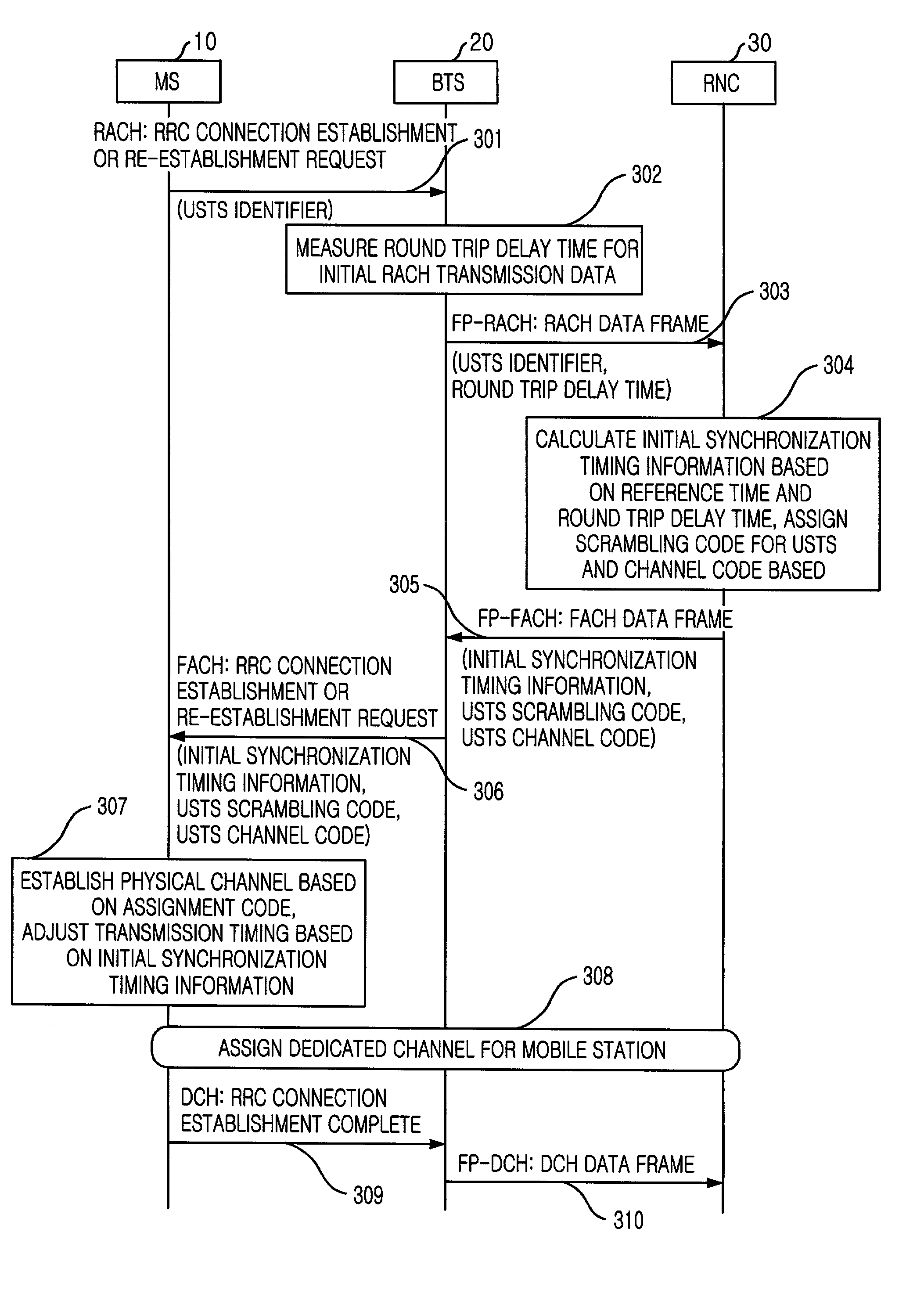
Handover method in wireless telecommunication system supporting USTS
InactiveUS20020045448A1Provide mobilitySynchronisation arrangementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMobile stationHandover
A handover method in wireless telecommunication system supporting USTS is disclosed. The method for performing a handover of a mobile station in an asynchronous wireless telecommunication system supporting an uplink synchronous transmission scheme (USTS) mode, includes the steps of: a) performing a mode conversion of the mobile station from the USTS mode to a non-USTS mode based on a first signal measurement result from the mobile station; and b) performing a handover for the mobile station. In another embodiment of the present invention, the method further includes the step of: c) performing a mode conversion from the non-USTS mode to the USTS mode based on a second signal measurement result from the mobile station.
Owner:SK TELECOM CO LTD
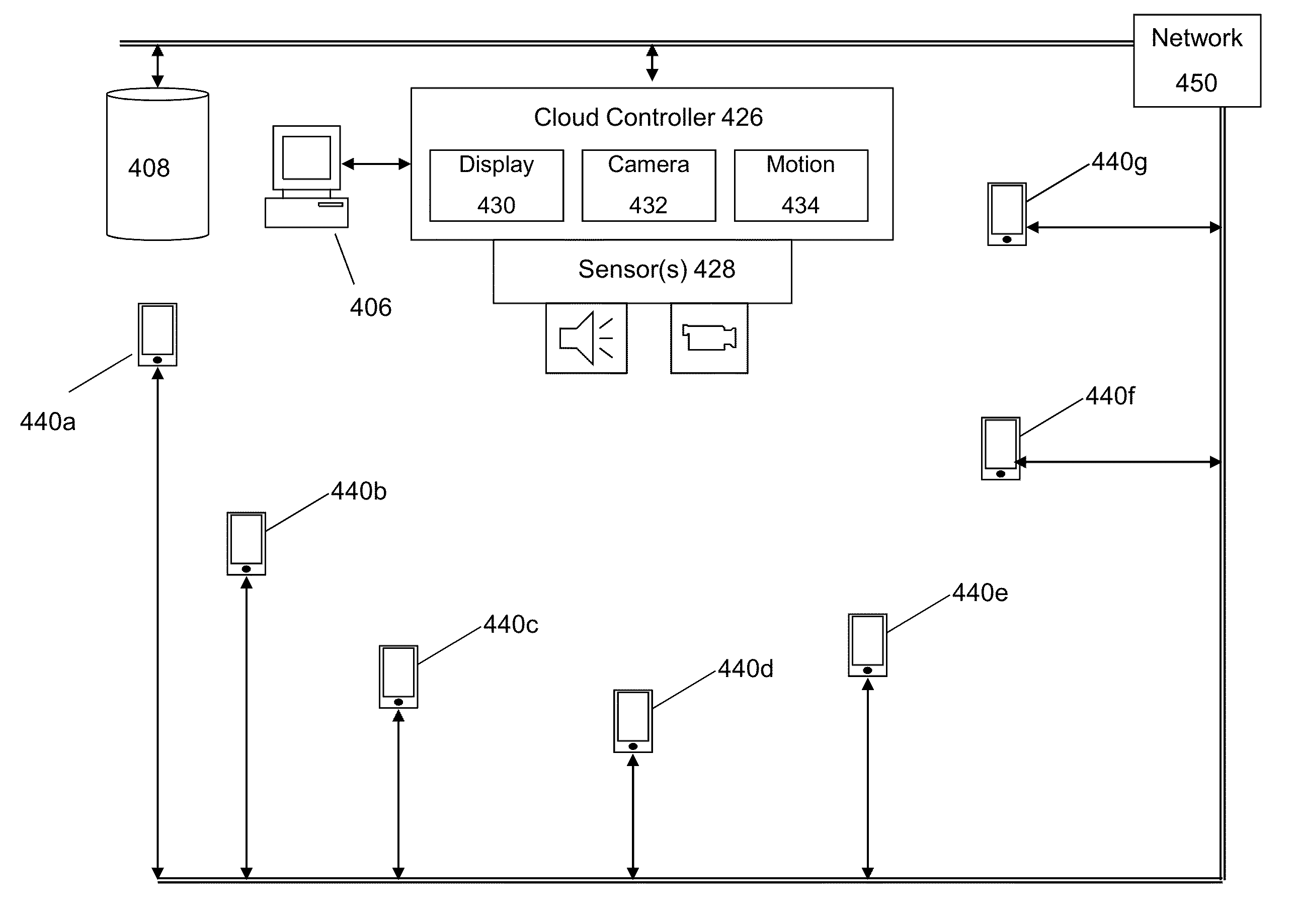
Method and mechanism for performing cloud image display and capture with mobile devices
ActiveUS8499038B1Television system detailsServices signallingHuman–computer interactionMobile device
Disclosed is an improved approach for implementing participatory interaction at events using mobile devices. One approach is to utilize distributed display screens for the mobile devices in an audience to display a much larger collective image. Another approach is to utilize the distributed cameras of mobile devices in an audience to form a massive capture device from the different locations and perspectives of the audience members. Yet another approach is directed to the use of mobile devices in the audience to capture motion events among the audience, which are then used to synthesize new media items and types for the event.
Owner:ENCONCERT
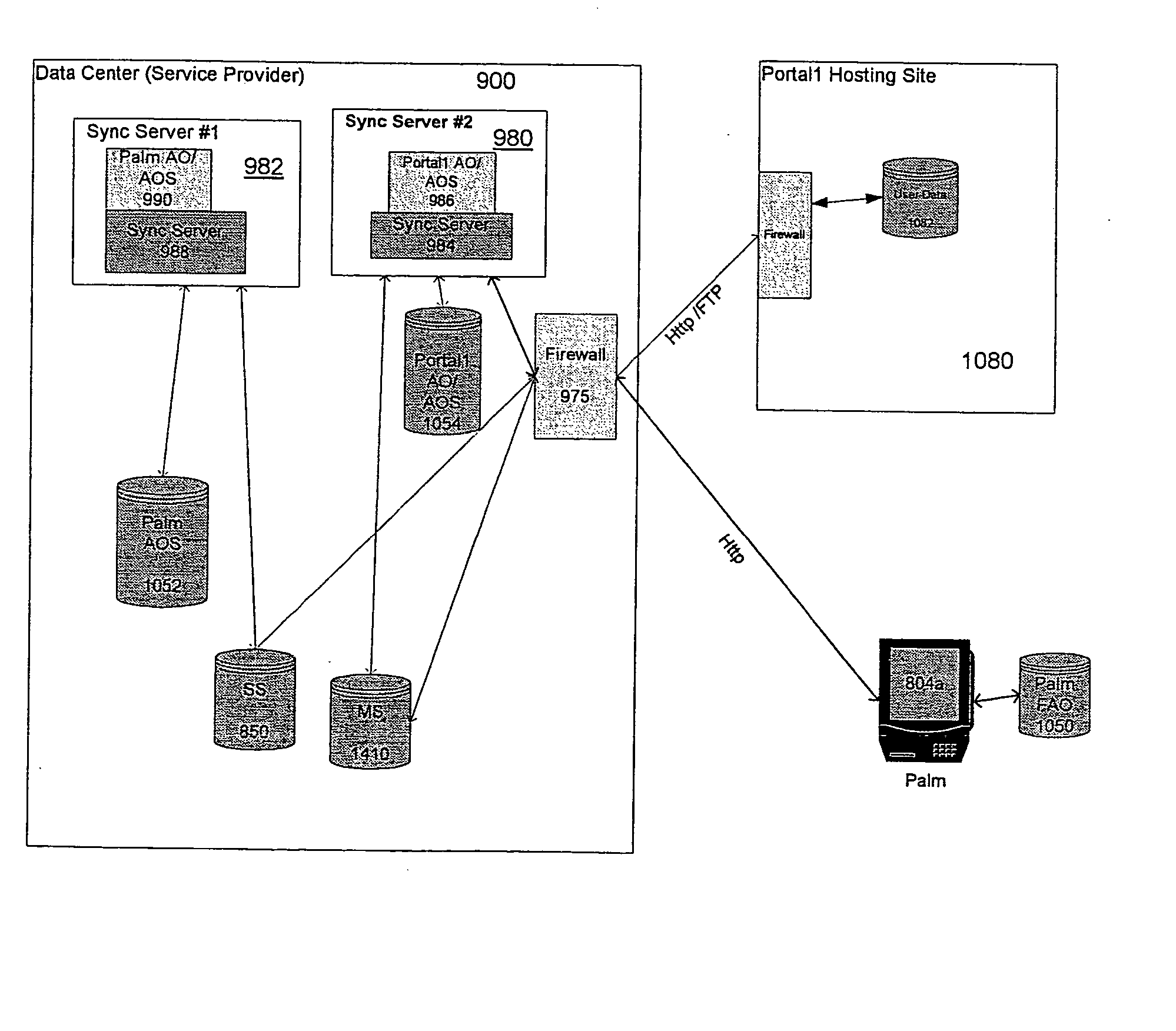
Data transfer and synchronization system
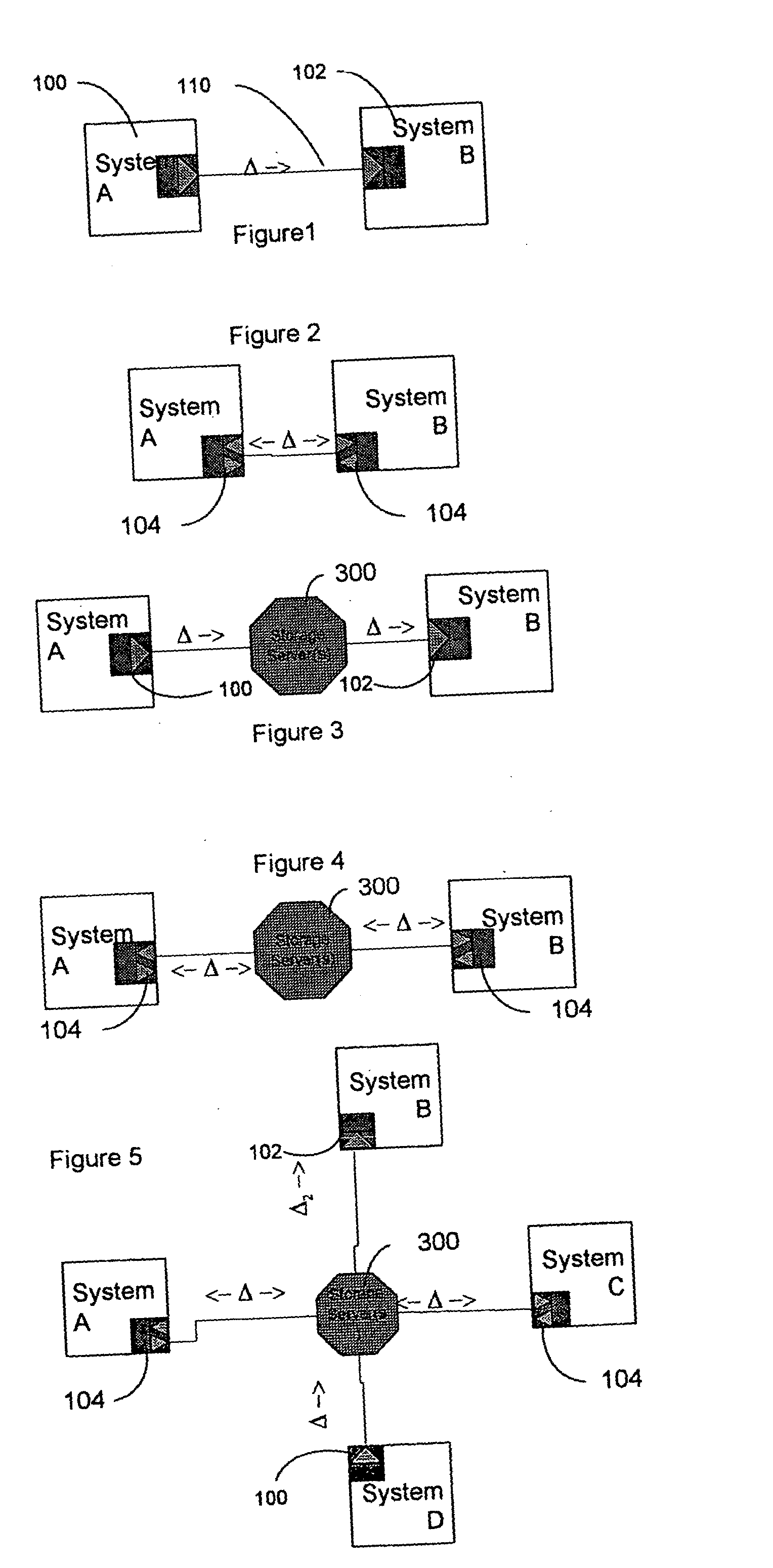
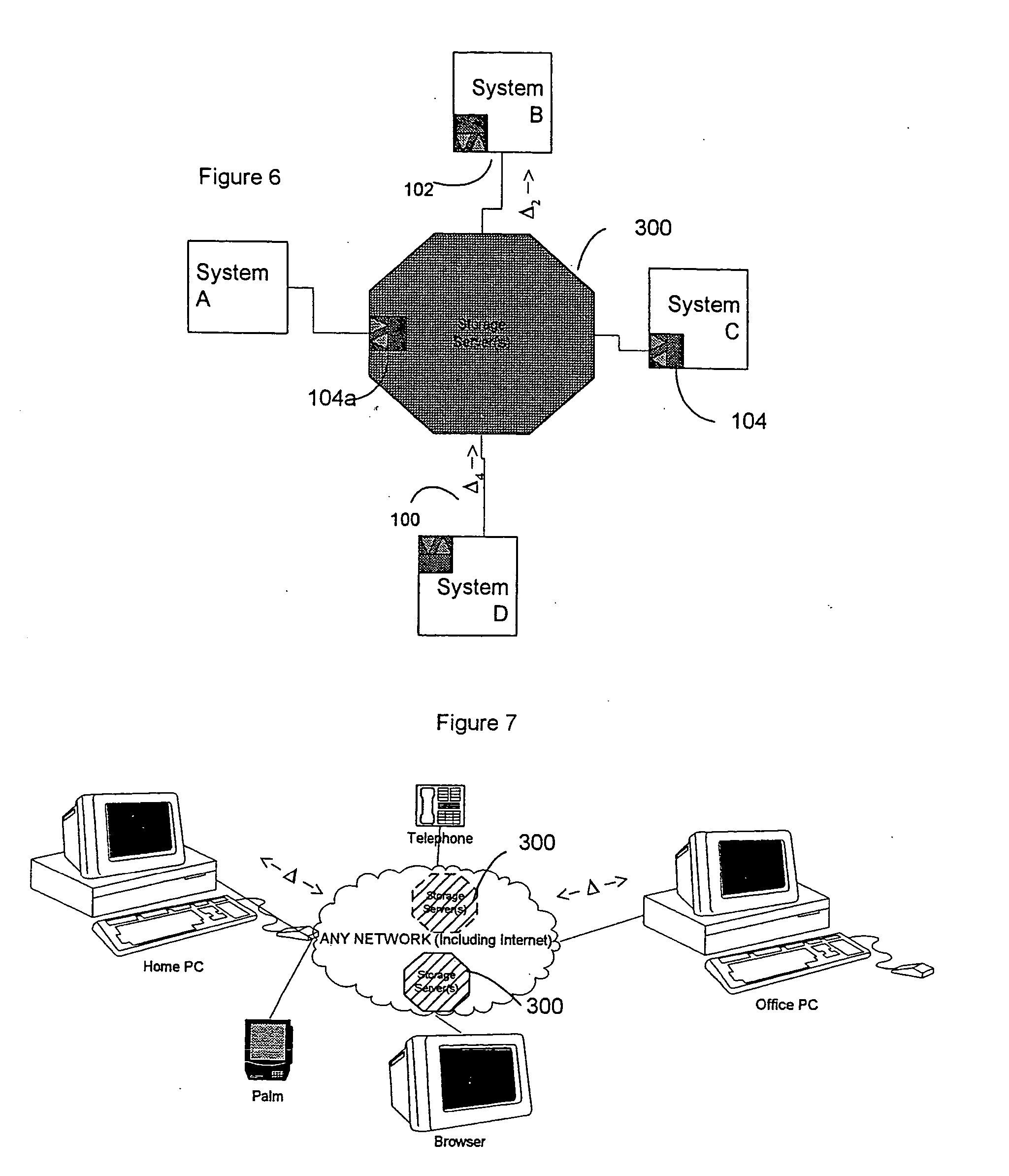
InactiveUS20040054711A1Data processing applicationsMultiple digital computer combinationsFile synchronizationData information
A system and method for synchronizing devices which can couple to the Internet, or any network. In one aspect a system for synchronizing data between a first system and a second system is provided. The system includes a first sync engine on the first system interfacing with data on the first system to provide difference information. A data store is coupled to network and in communication with the first and second systems. A second sync engine is provided on the second system coupled to receive the difference information from the data store via the network, and interfacing with data on the second system to update said data on the second system with said difference information. Difference information is transmitted to the data store by the first sync engine and received from the data store from the second sync engine. The system may include a management server coupled to the network and in communication with the first sync engine, the second sync engine and the data store. The system may include a plurality of sync engines on a respective plurality of systems, each of said plurality of engines being coupled to receive difference information from each of said first, second and plurality of sync engines from the data store via the network. Each said engine interfaces with data on the system on which it resides to update said data on said system on which it resides with said difference information, and interfaces with data on said system on which it resides to provide difference data information from the system on which it resides to the data store. In a further embodiment, the invention comprises a method for synchronizing at least a first file and a second file resident on a first and a second systems, respectively, coupled to the Internet, respectively. The method includes the steps of: determining difference data resulting from changes to the first file on the first system; transmitting the difference data to a server via the Internet; querying the server from a second system to determine whether difference data exists for files on the second system; retrieving the difference data to the second system; and updating the second file on the second system with the difference data.
Owner:SYNCHRONOSS TECH
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com