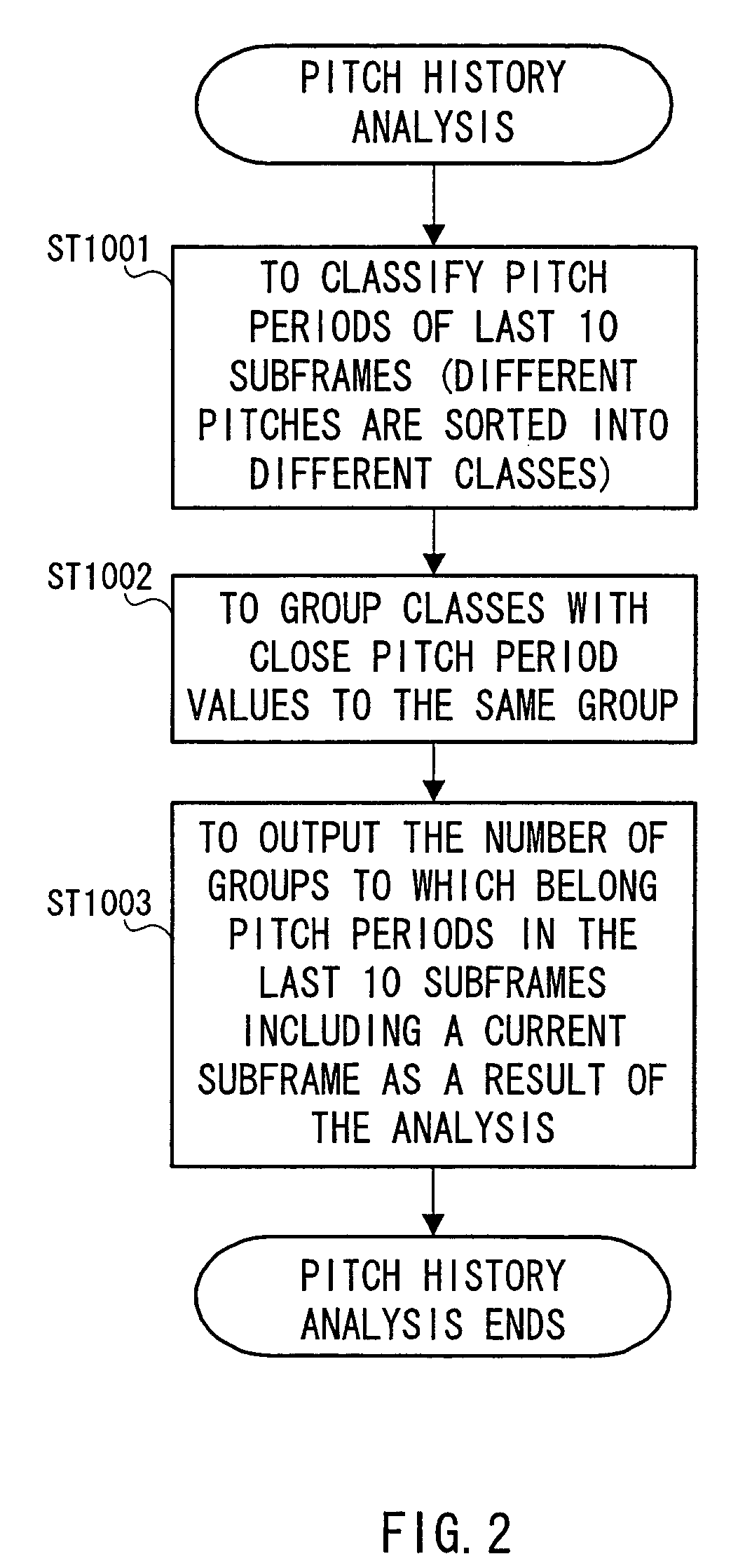
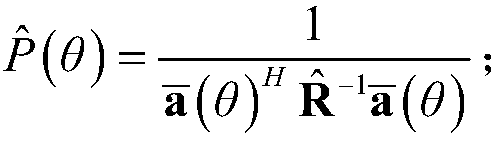Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
103 results about "Stationary noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Stationary noise. A random noise for which the probability that the noise voltage lies within any given interval does not change with time.
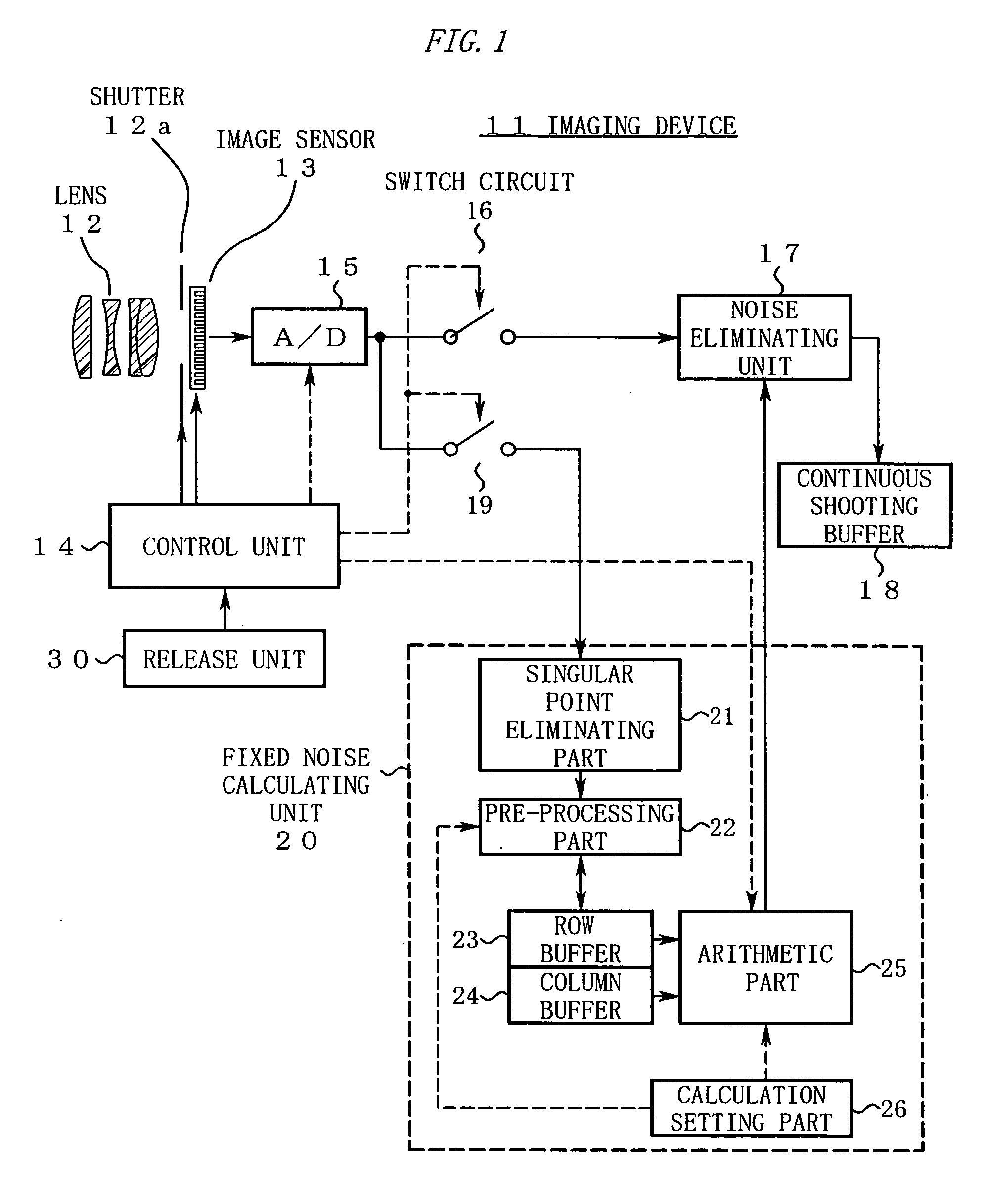
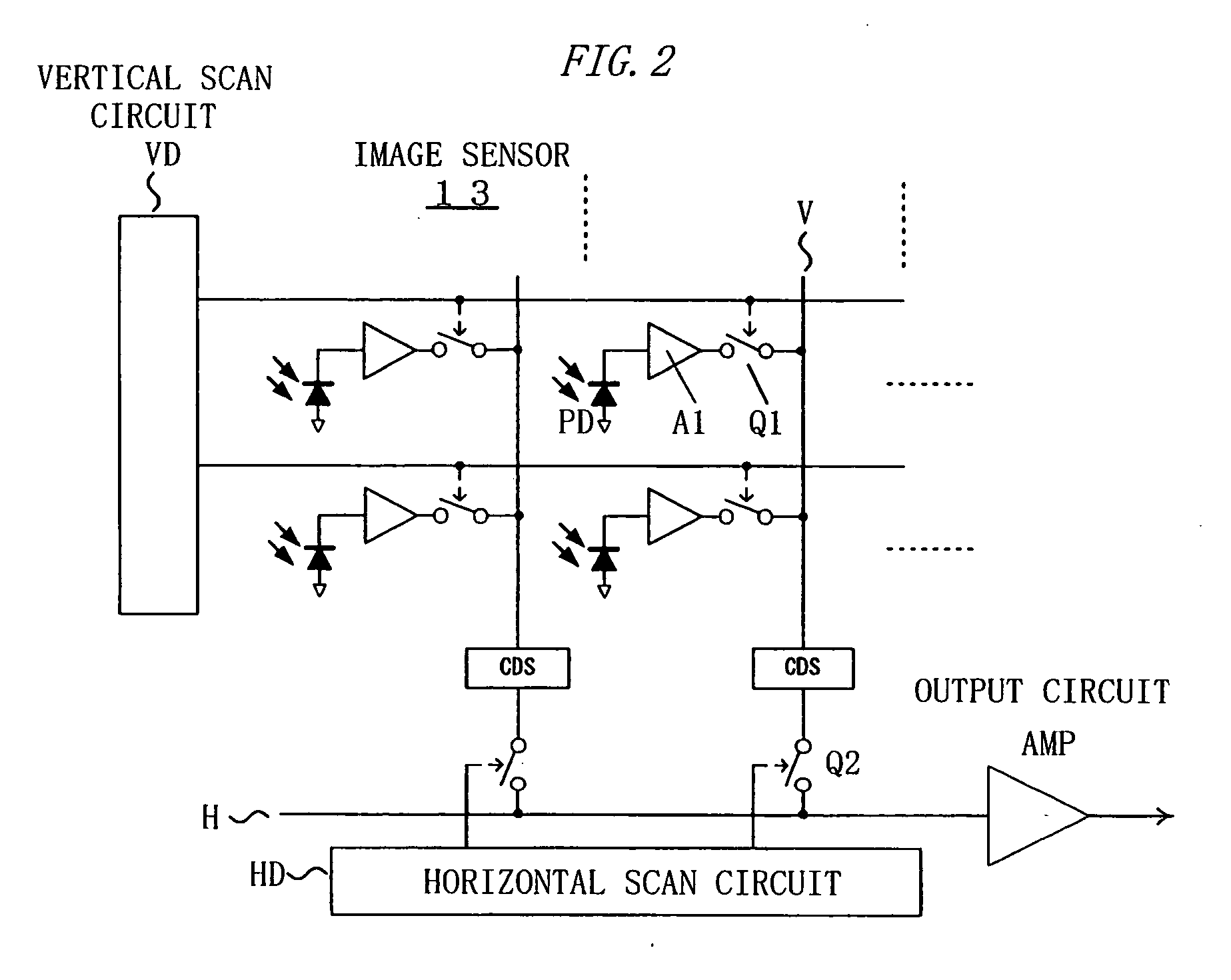
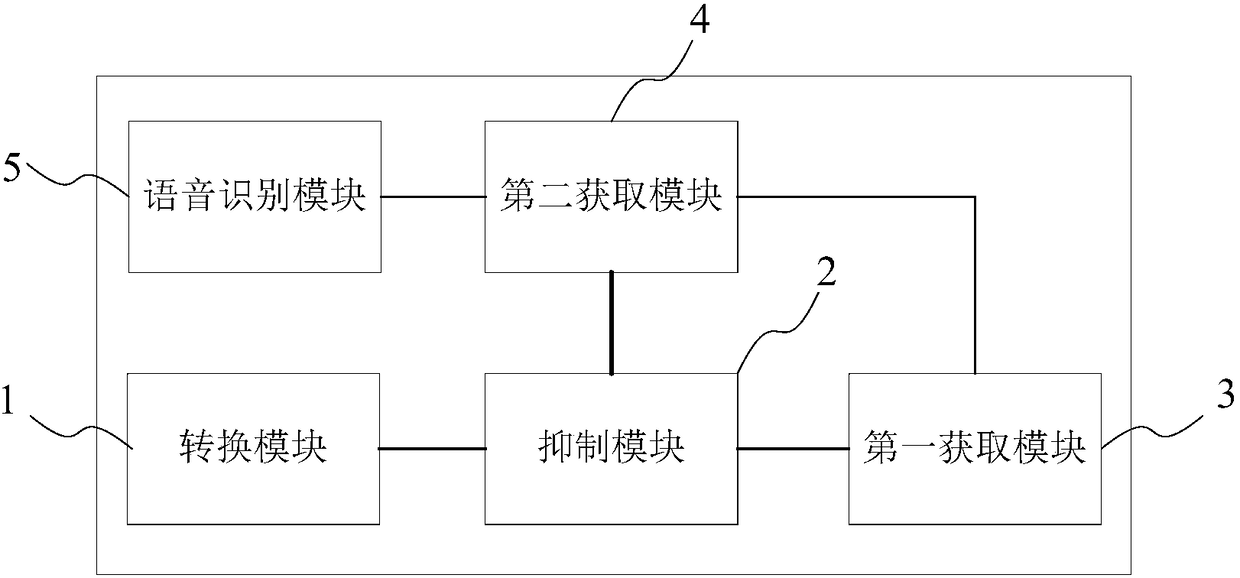
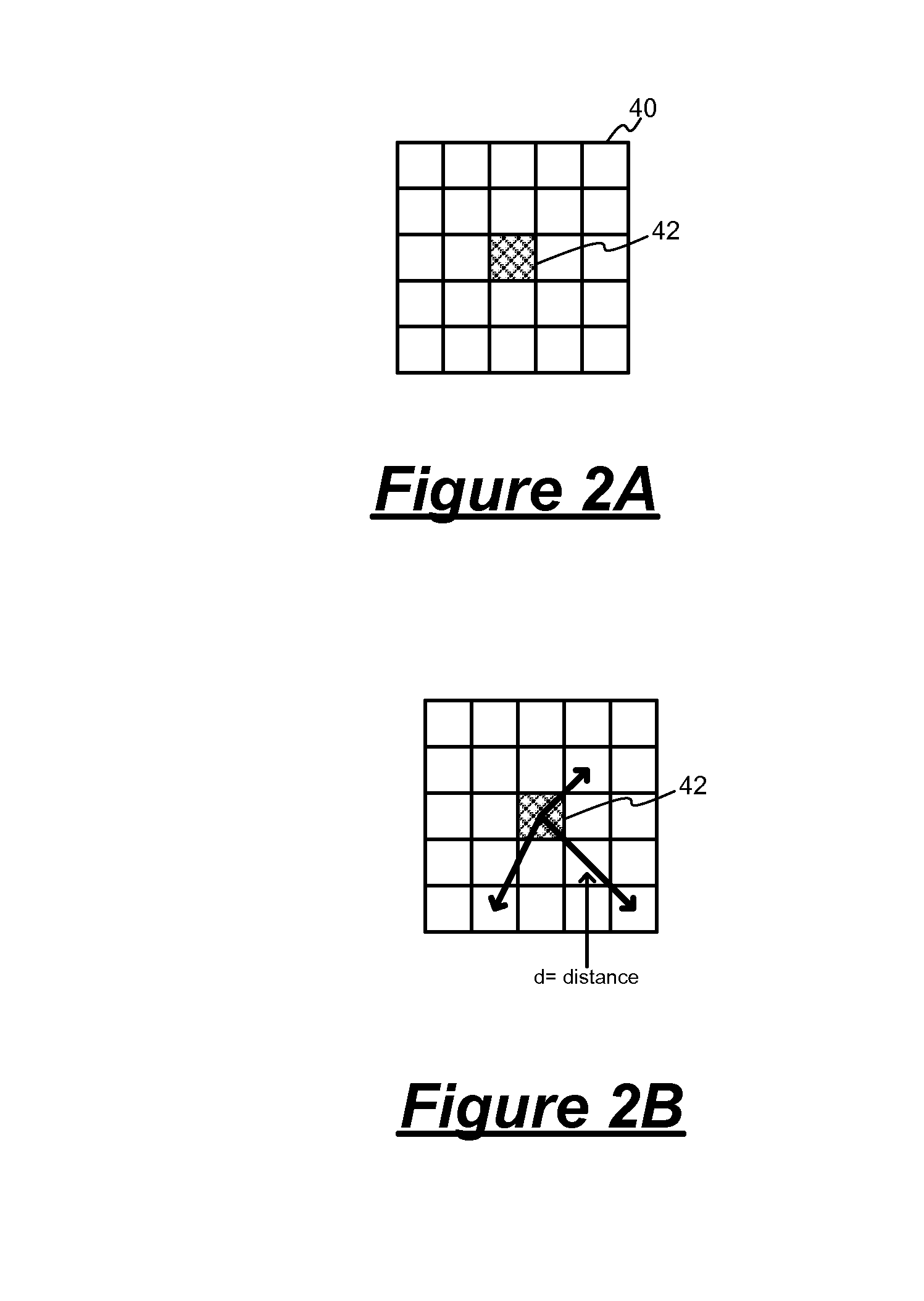
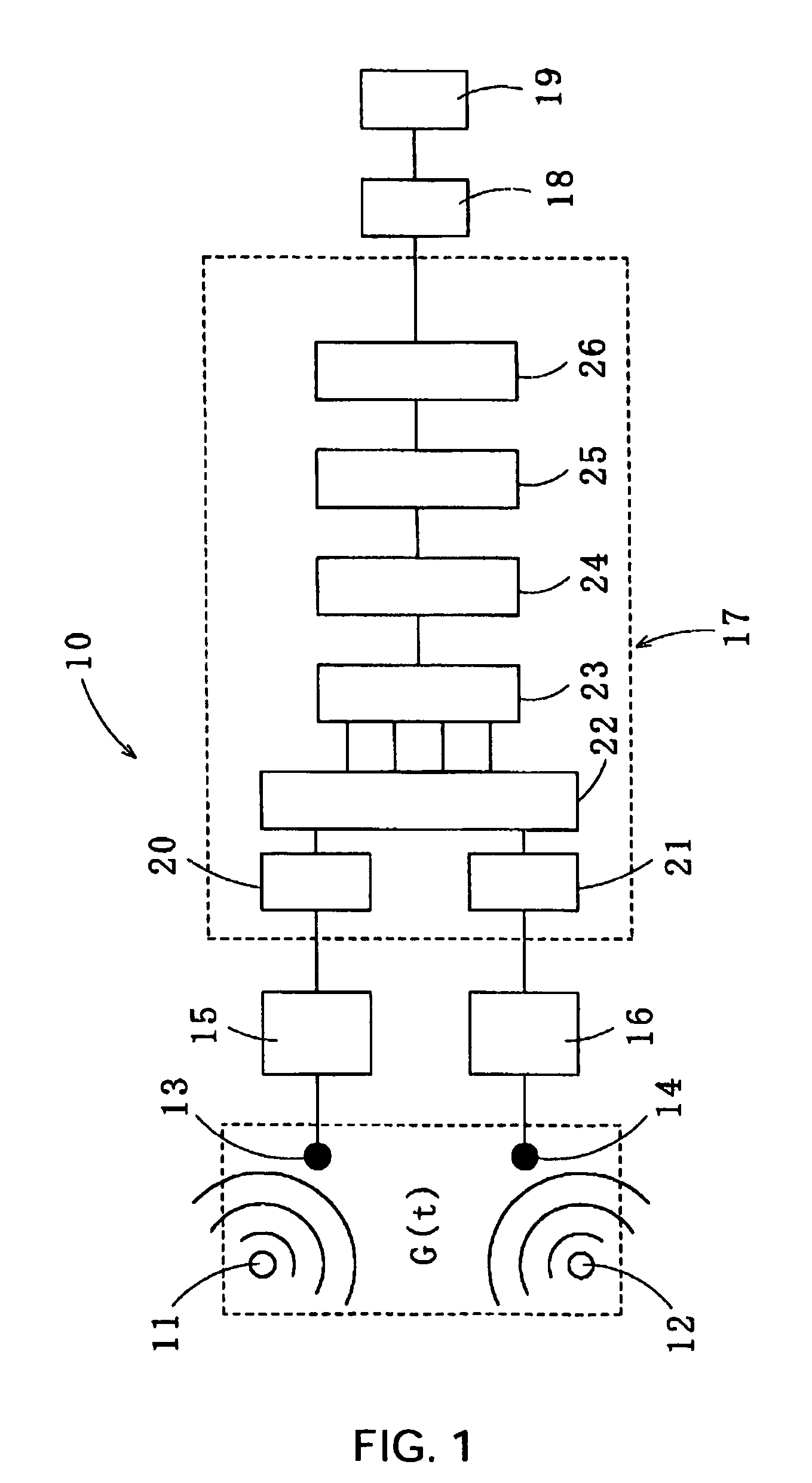
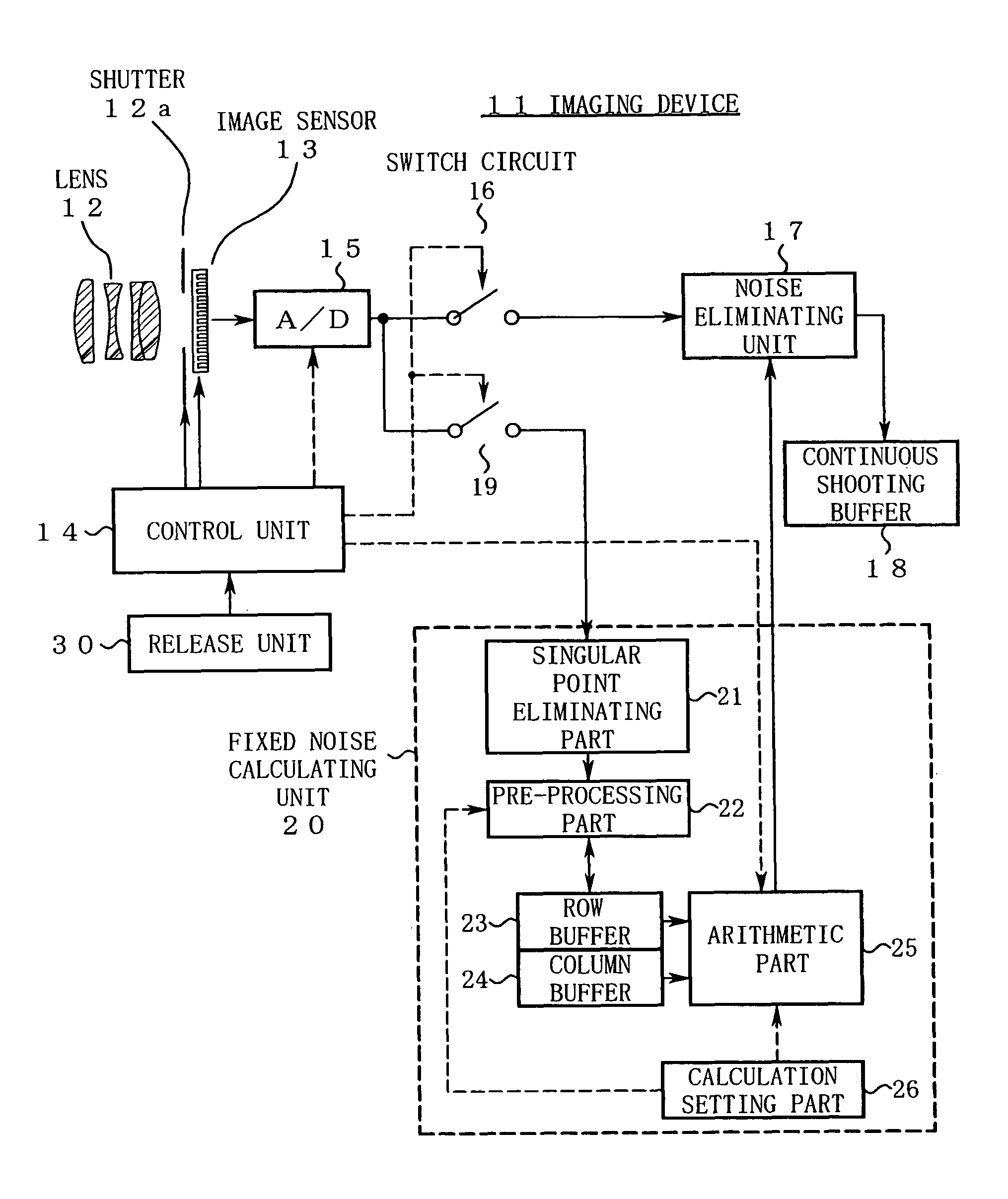
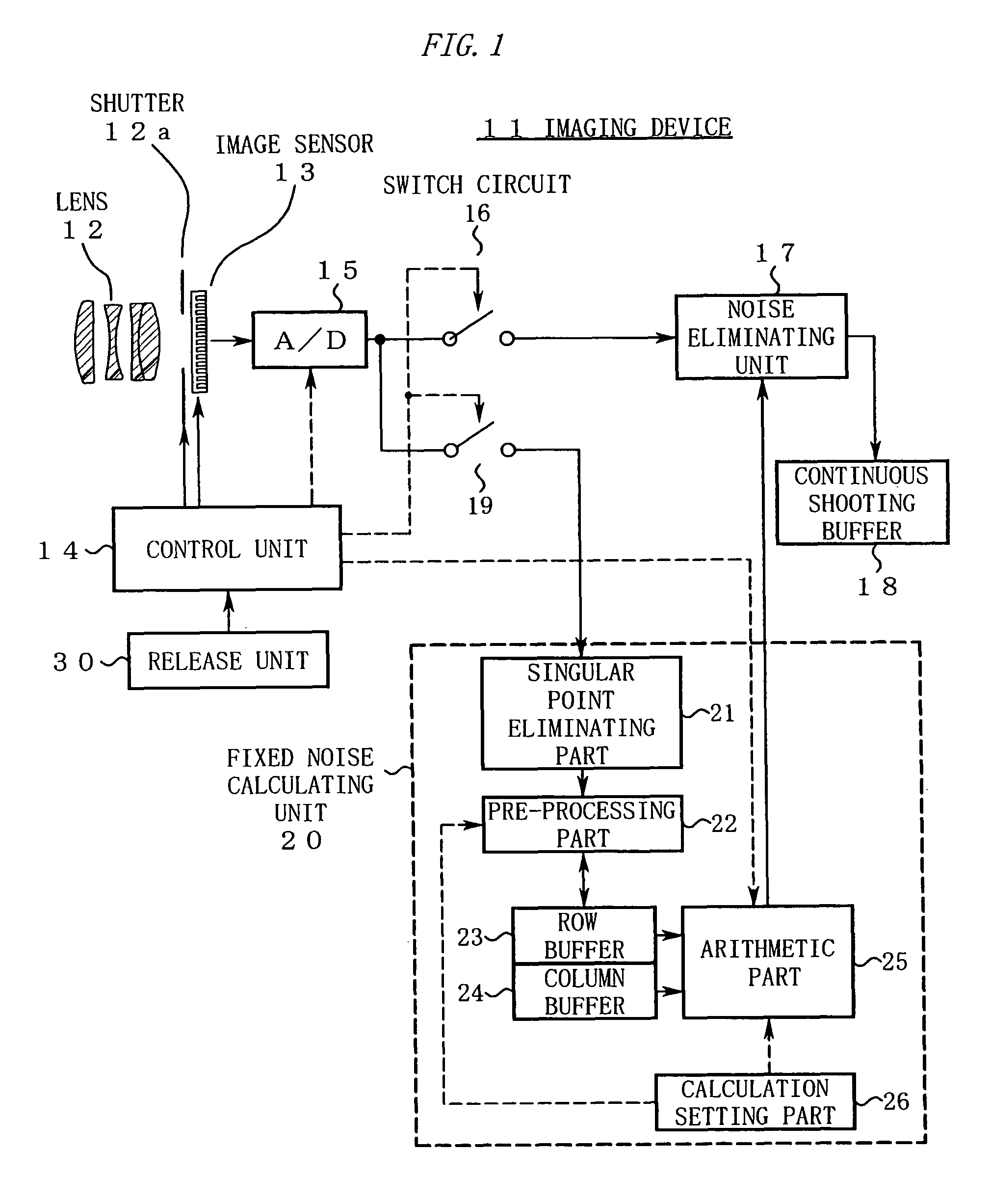
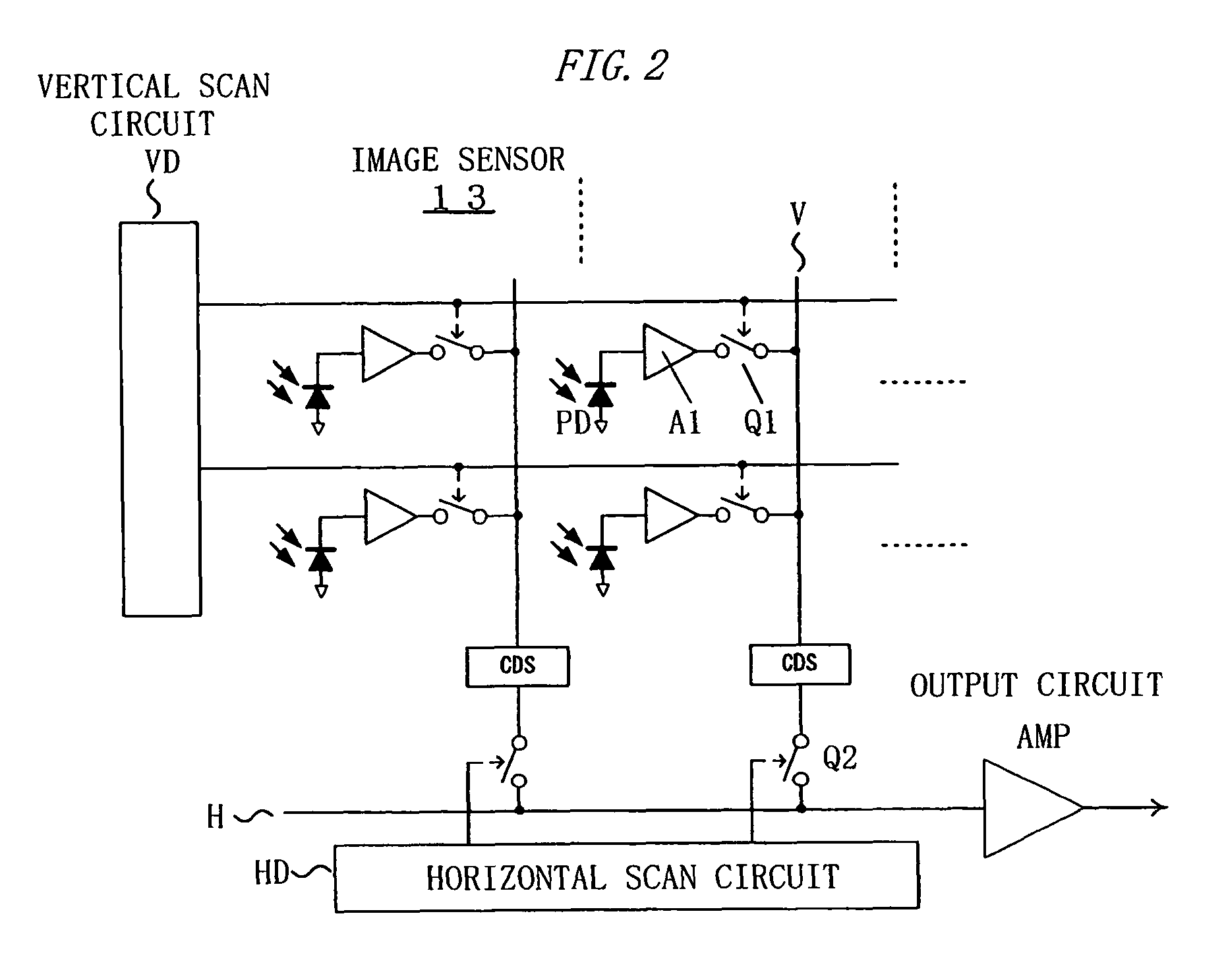
Imaging device and image processing program for estimating fixed pattern noise from partial noise output of available pixel area
ActiveUS20060098888A1Shorten the timeTelevision system detailsDigitally marking record carriersPattern recognitionImaging processing
An imaging device of the present invention includes an image capturing unit, a noise obtaining unit, a fixed noise calculating unit, and a noise eliminating unit. The image capturing unit generates image data by photoelectrically converting, pixel by pixel, a subject image formed on an available pixel area of a light-receiving surface. The noise obtaining unit reads a noise output from a partial area of the available pixel area. The fixed noise calculating unit calculates an estimation of fixed pattern noise of the available pixel area based on the noise output read from the partial area. The noise eliminating unit subtracts the fixed pattern noise from the image data.
Owner:NIKON CORP
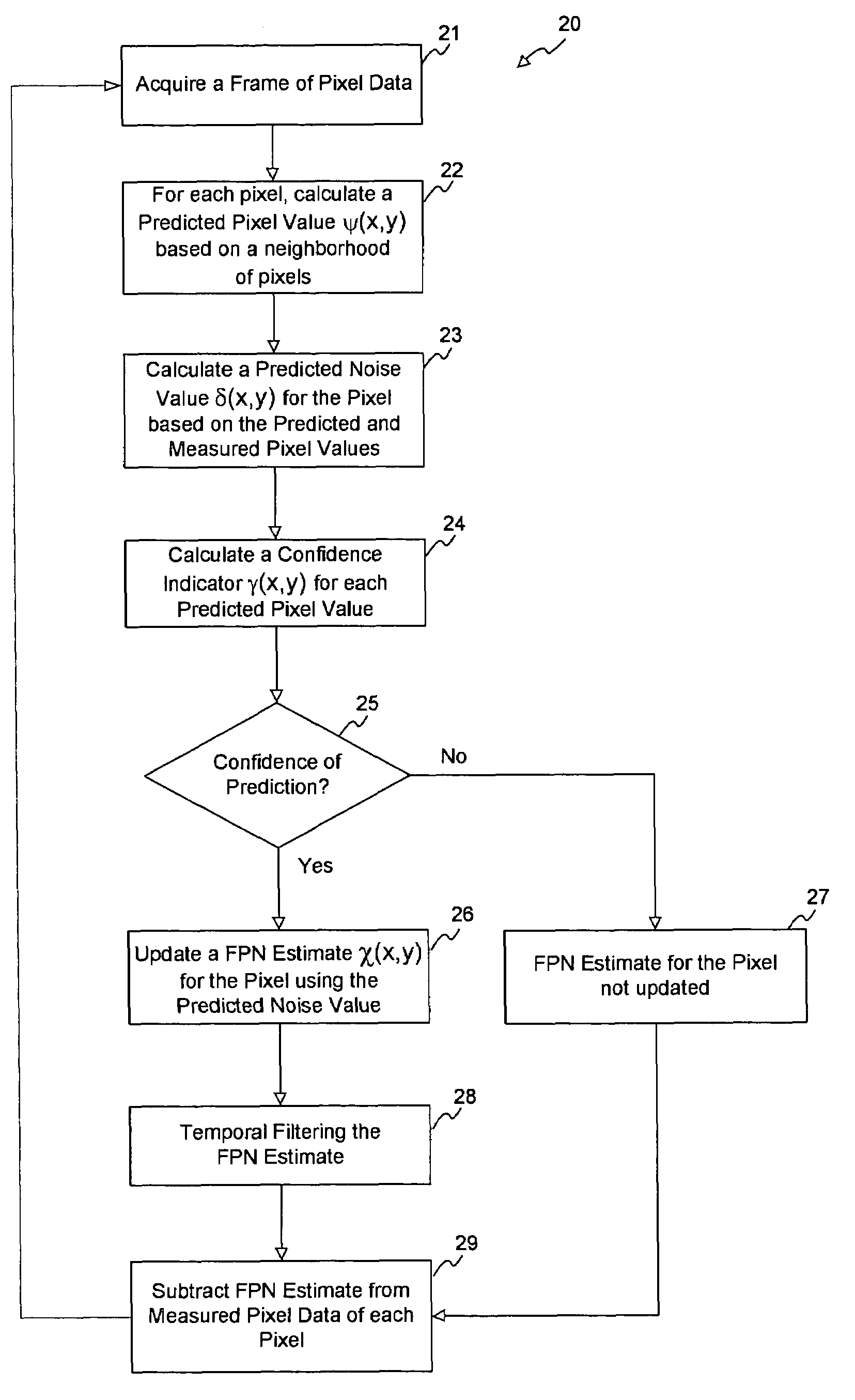
Removal of stationary noise pattern from digital images
A method for removing a stationary noise pattern from digital images uses an adaptive noise estimation algorithm to calculate a prediction of the fixed pattern noise and a confidence estimate for the prediction. In one embodiment, a predicted noise value is obtained from the captured image and a predicted image derived from spatial and temporal pixel value prediction techniques. The predicted noise value is used to update a fixed pattern noise estimate only when the confidence estimate for the predicted image is high. In another embodiment, the confidence estimate is used as a weight factor for blending the noise prediction into the noise estimate. In yet another embodiment, the adaptive noise estimation algorithm is applied to a prediction area in the image for calculating scaling parameters which scaling parameters are used to calculate a noise estimate for the entire image based on a reference noise image.
Owner:PIXIM
Two microphone noise reduction system
A two microphone noise reduction system is described. In an embodiment, input signals from each of the microphones are divided into subbands and each subband is then filtered independently to separate noise and desired signals and to suppress non-stationary and stationary noise. Filtering methods used include adaptive decorrelation filtering. A post-processing module using adaptive noise cancellation like filtering algorithms may be used to further suppress stationary and non-stationary noise in the output signals from the adaptive decorrelation filtering and a single microphone noise reduction algorithm may be used to further provide optimal stationary noise reduction performance of the system.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE SILICON RADIO PLC +1
Noise reduction device, program and method
InactiveUS20060136203A1Improve Noise RobustnessMaintain compatibilitySpeech analysisStationary noiseAdaptive learning
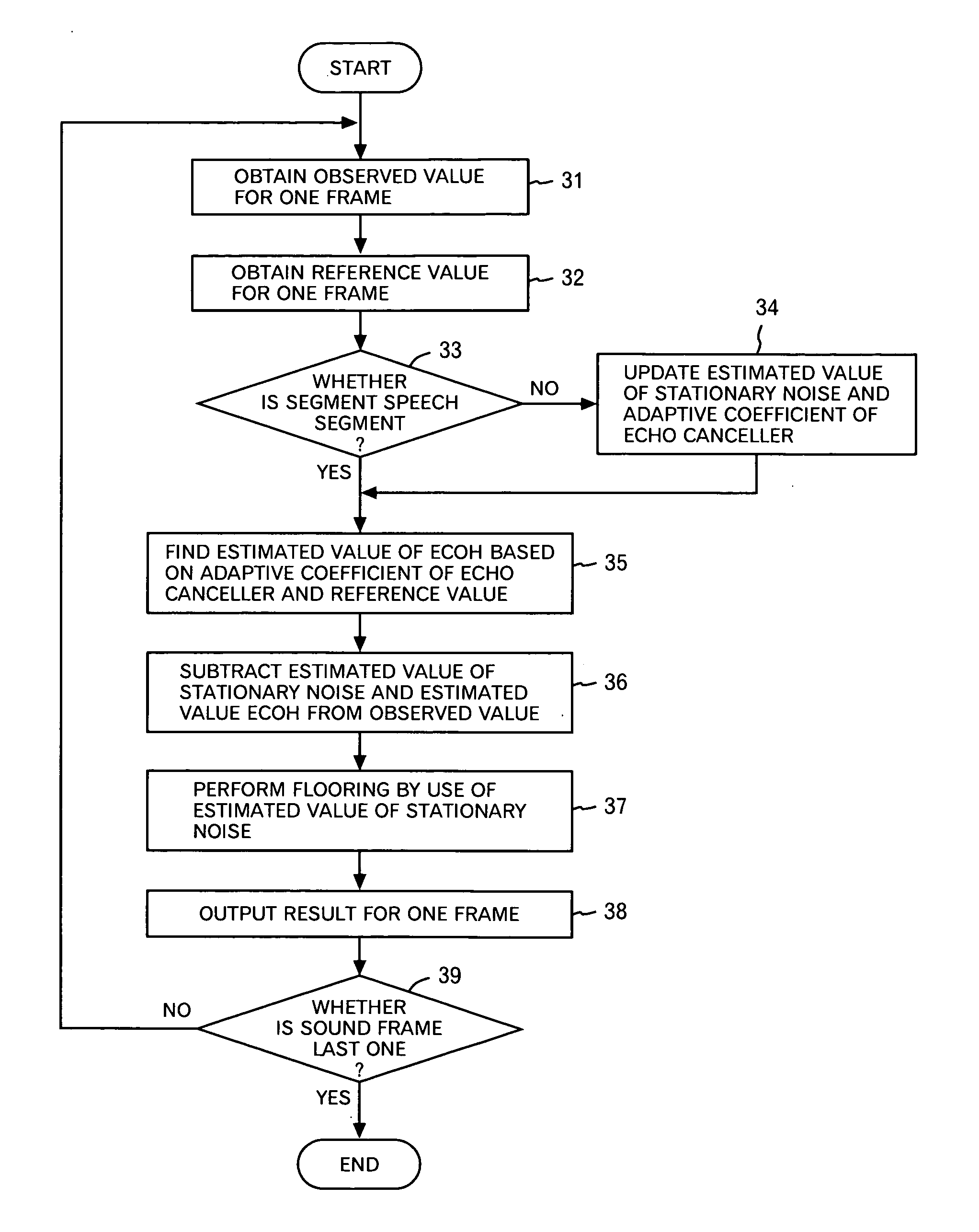
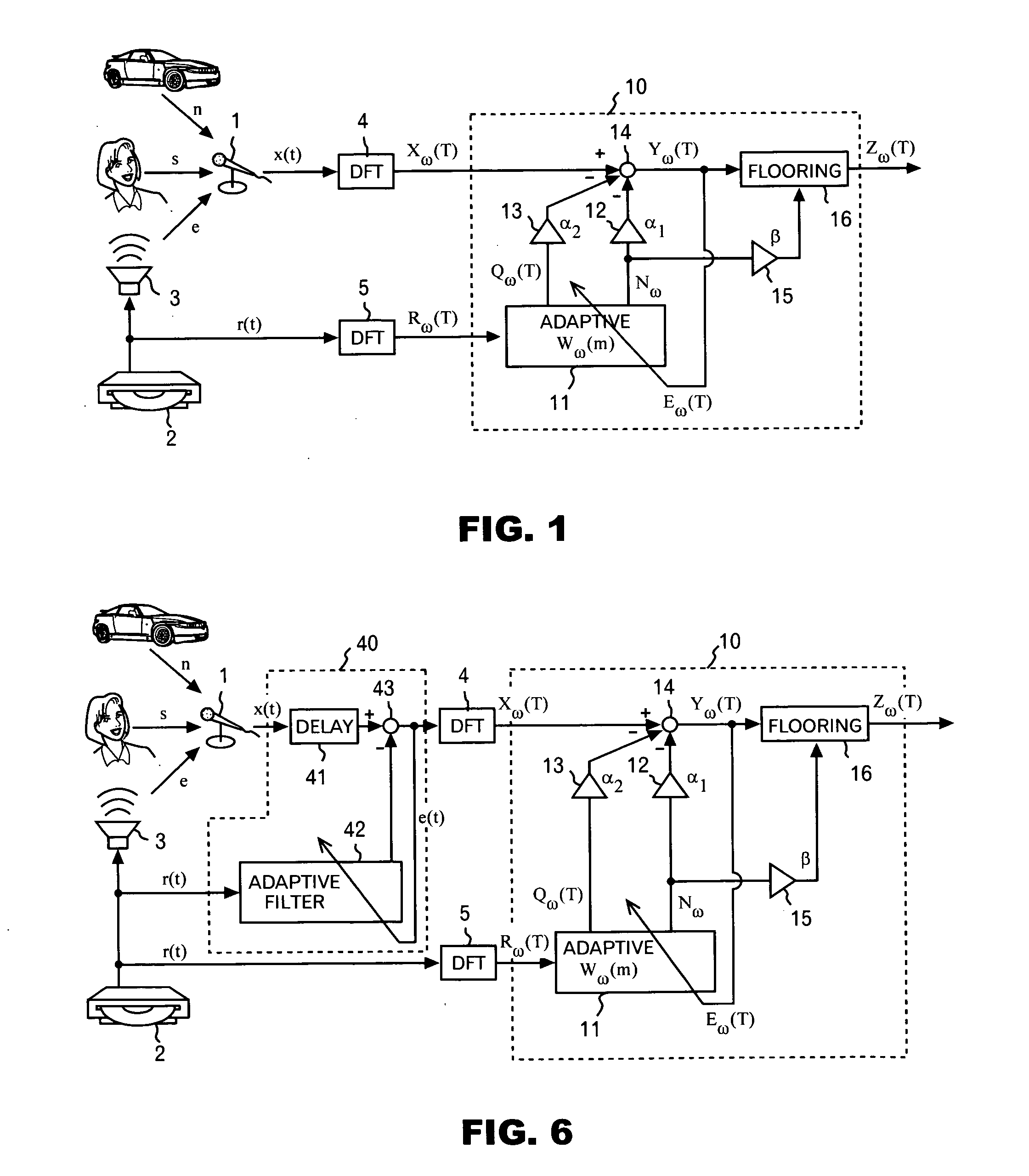
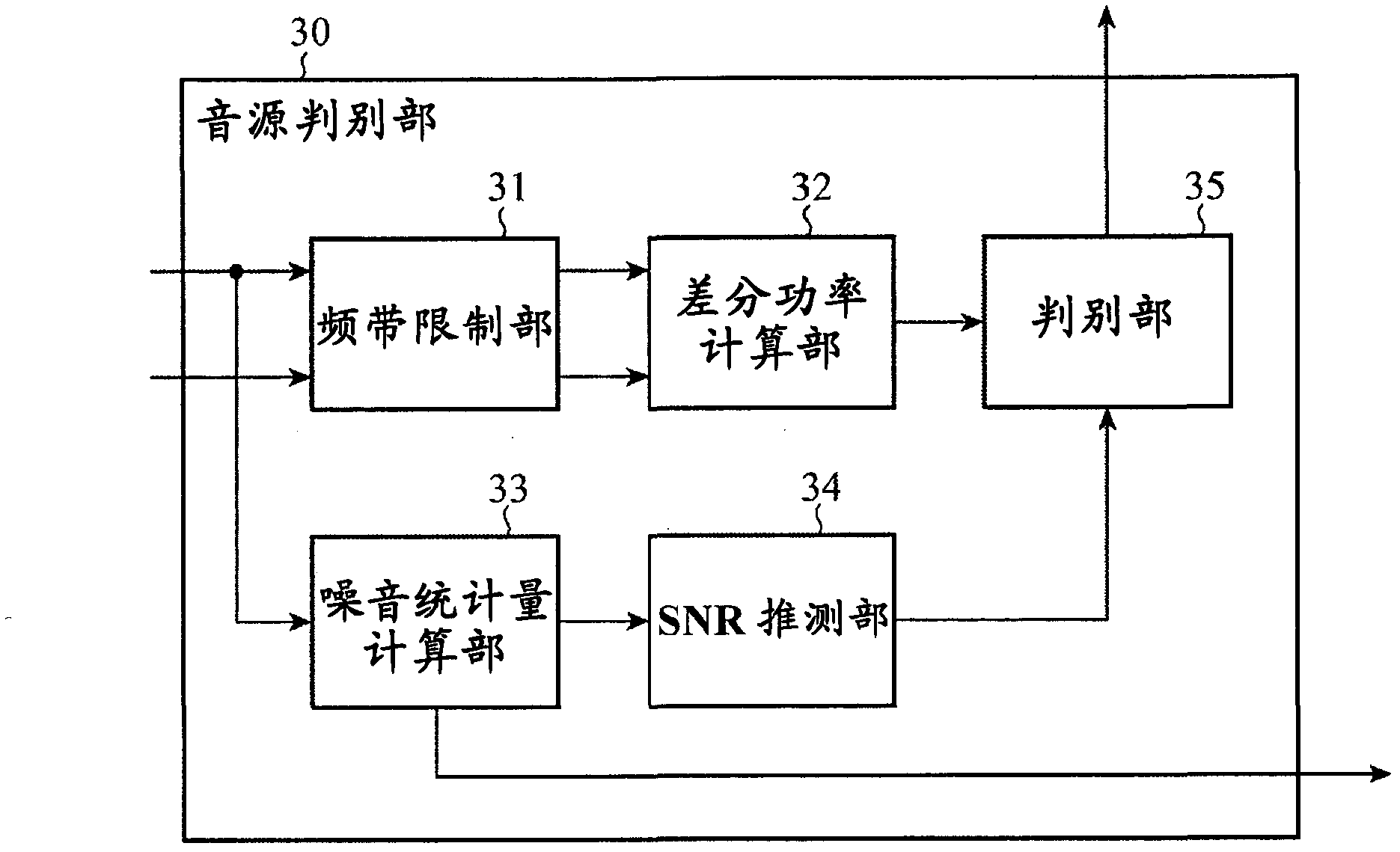
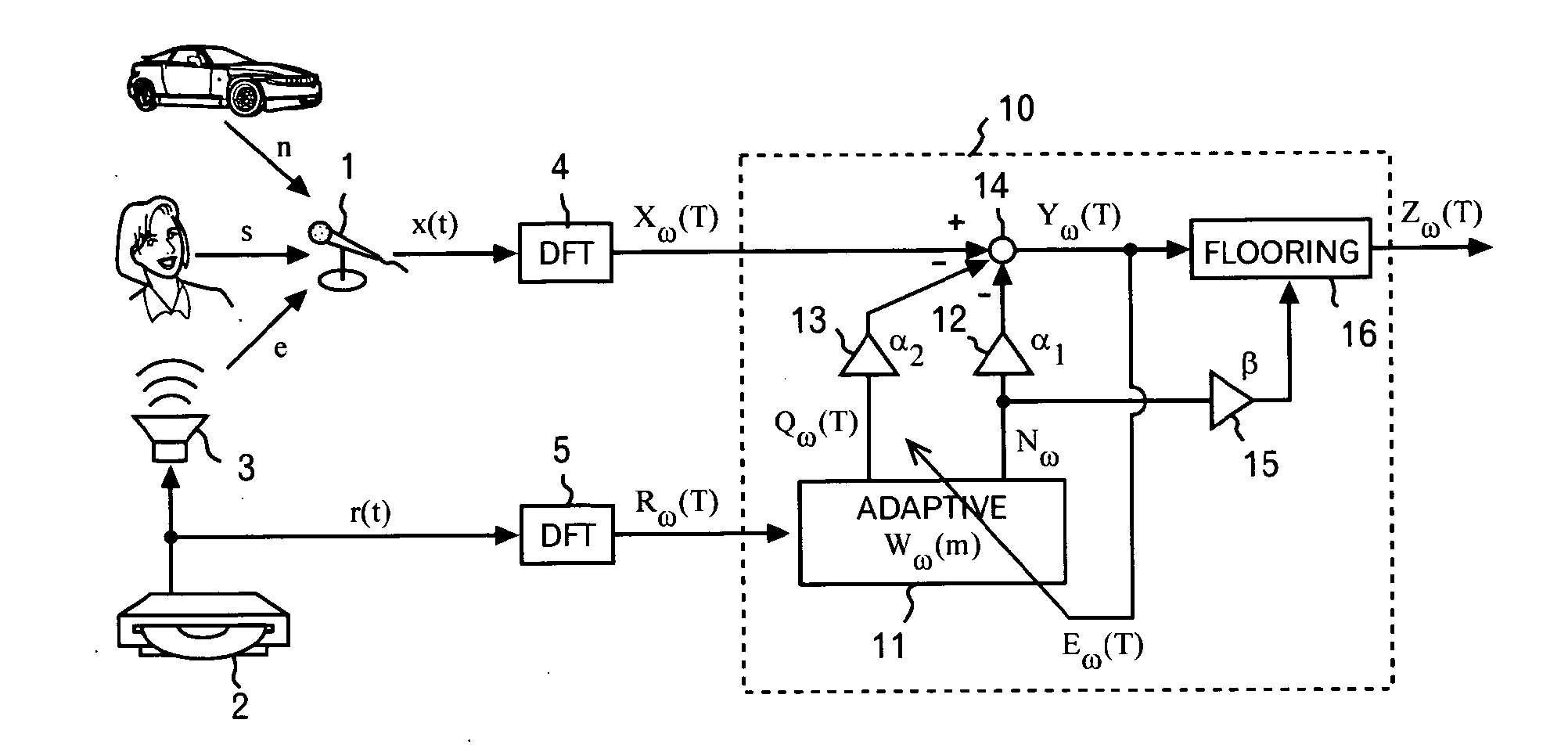
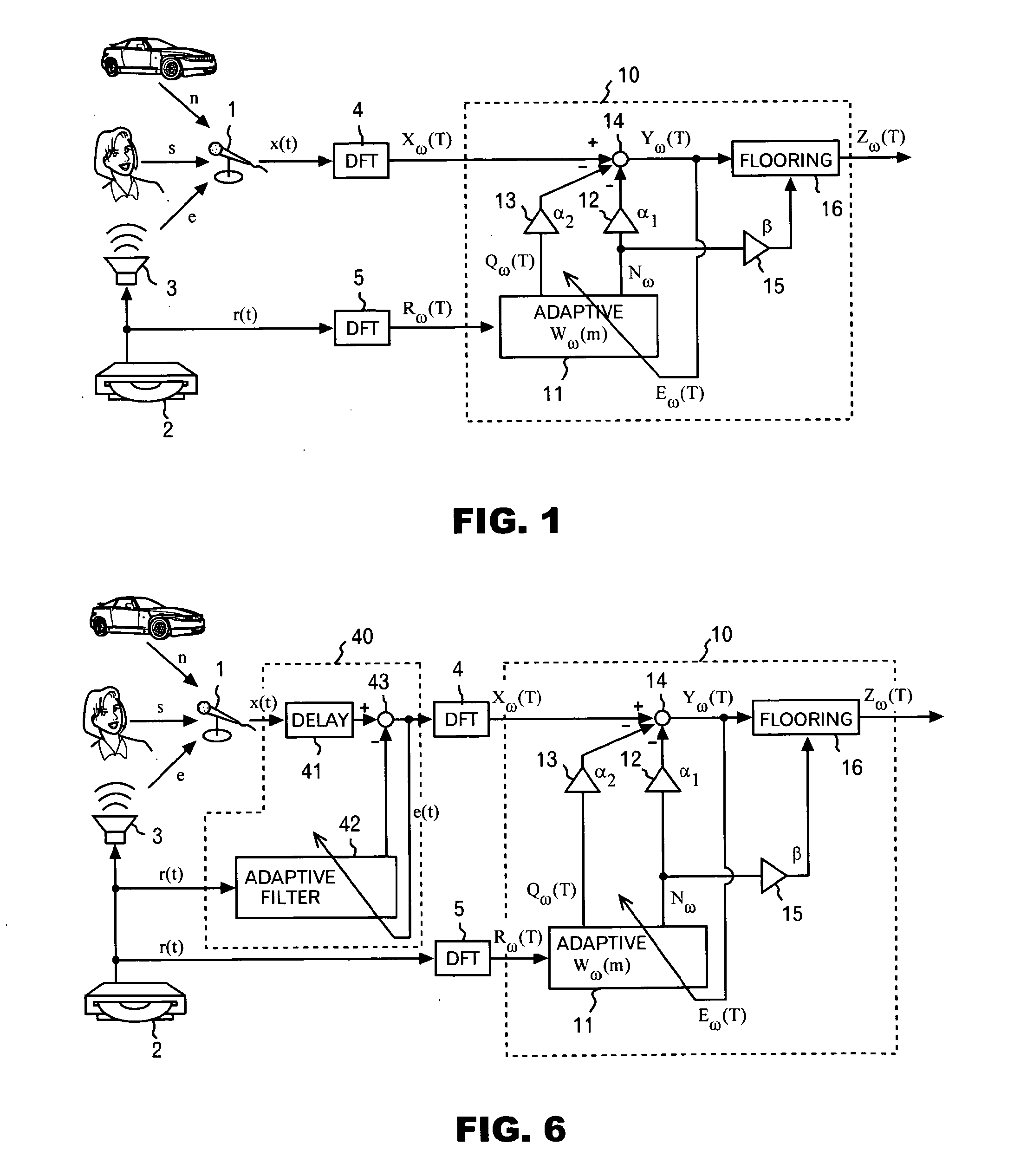
A noise reduction device is configured by use of: means for calculating a predetermined constant, and a predetermined reference signal Rω(T) in the frequency domain, respectively by use of adaptive coefficients Wω(m), and for thereby obtaining estimated values Nω and Qω(T) respectively of stationary noise components, and non-stationary noise components corresponding to the reference signal, which are included in a predetermined observed signal Xω(T) in the frequency domain; means and for applying a noise reduction process to the observed signal on the basis of each of the estimated values, and for updating each of the adaptive coefficients on the basis of a result of the process; and an adaptive learning means and for repeating the obtaining of the estimated values and the updating of the adaptive coefficients, and for thereby learning each of the adaptive coefficients.
Owner:IBM CORP
Noise evaluation method for automobile generator under finished automobile state
ActiveCN102393246AEasy to operateEasy to handleSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementStationary noiseEngineering
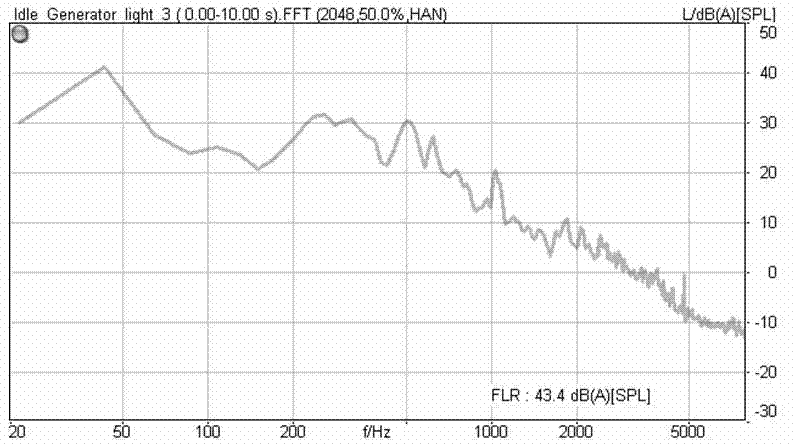
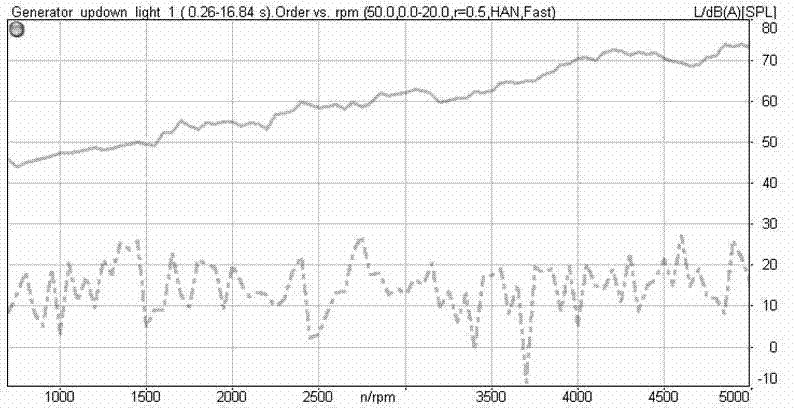
The invention discloses a noise evaluation method for an automobile generator under a finished automobile state. The noise evaluation method comprises the following steps: first, preparing test conditions; second, testing idle noise; third, testing fast acceleration / deceleration noise; fourth, testing stationary noise under fixed rotational speed; fifth, processing tested noise data; and finally,evaluating noise of the automobile generator. The invention has the characteristics of simplicity in operation, convenience in processing, accuracy in judgment, high relevance between subjective evaluation and objective evaluation, and the like, and is suitable for noise evaluation of the automobile generator under the finished automobile state.
Owner:CHONGQING CHANGAN AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
Suppressing noise in an audio signal
InactiveCN102549659ASignal processing for reducing noiseSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
An electronic device for suppressing noise in an audio signal is described. The electronic device includes a processor and instructions stored in memory. The electronic device receives an input audio signal and computes an overall noise estimate based on a stationary noise estimate, a non-stationary noise estimate and an excess noise estimate. The electronic device also computes an adaptive factor based on an input Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) and one or more SNR limits. A set of gains is also computed using a spectral expansion gain function. The spectral expansion gain function is based on the overall noise estimate and the adaptive factor. The electronic device also applies the set of gains to the input audio signal to produce a noise-suppressed audio signal and provides the noise-suppressed audio signal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Noise suppression apparatus and program
InactiveUS20100296665A1Suppressing musical noiseInhibition is effectiveEar treatmentSpeech analysisStationary noiseFrequency spectrum
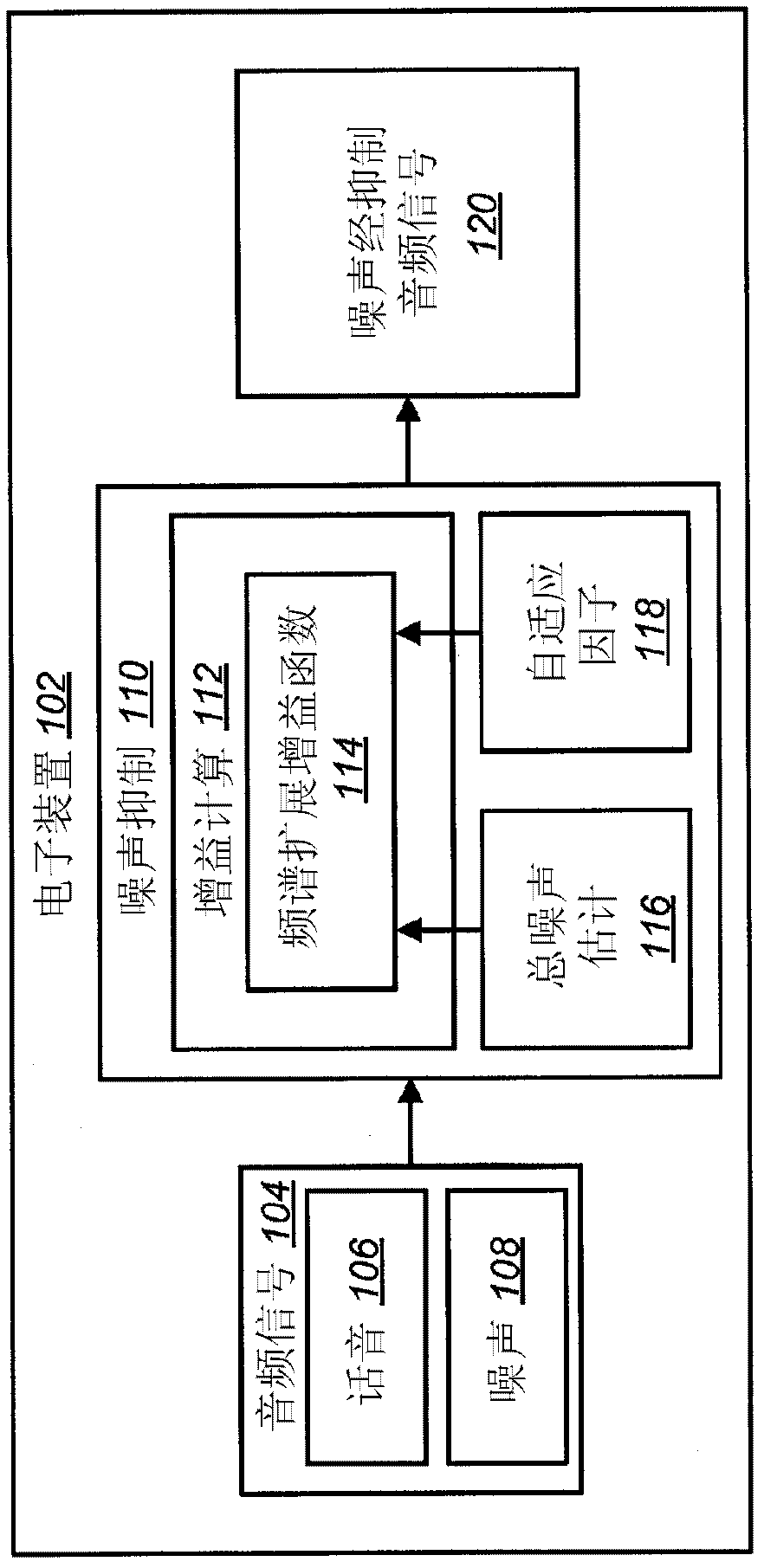
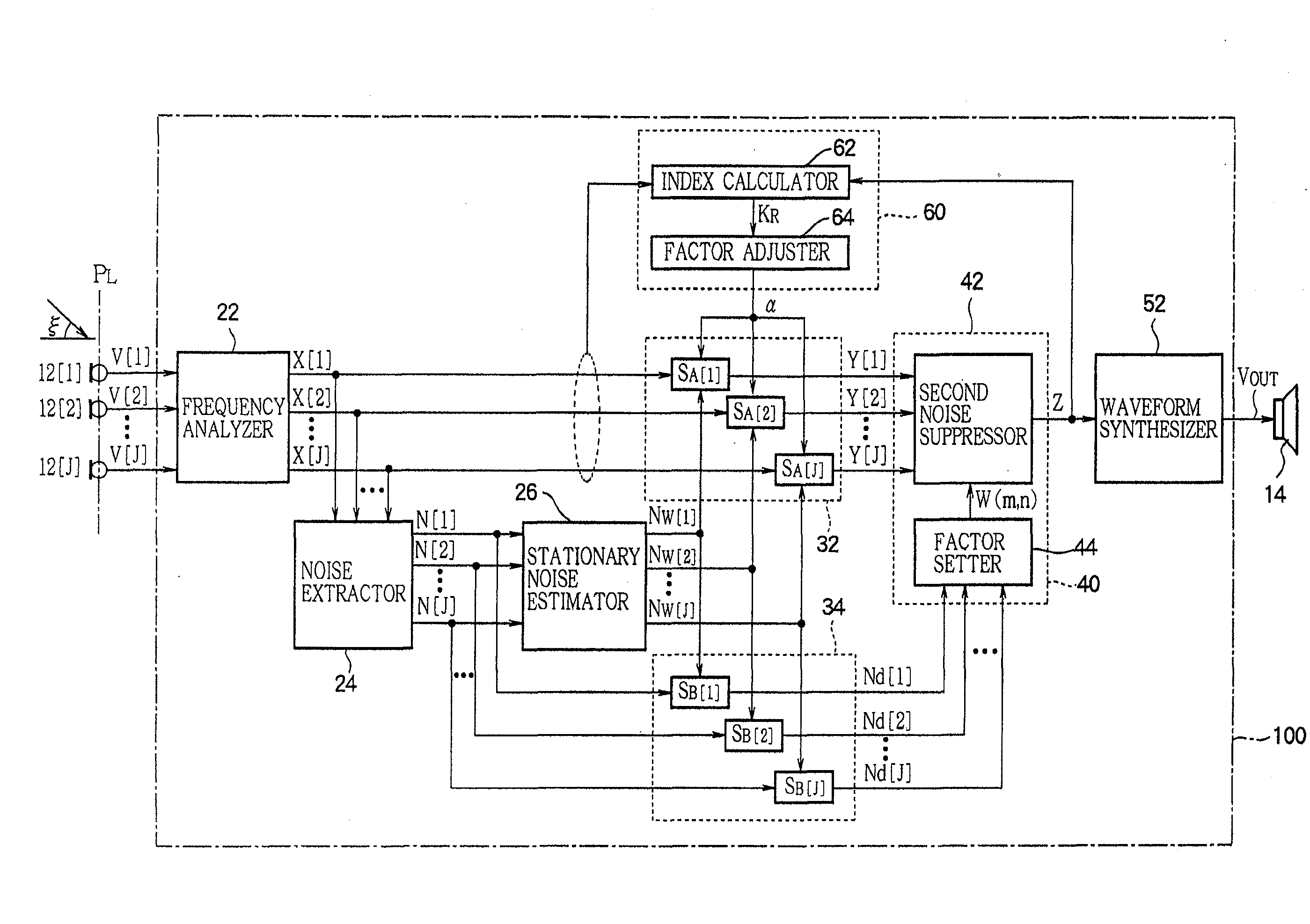
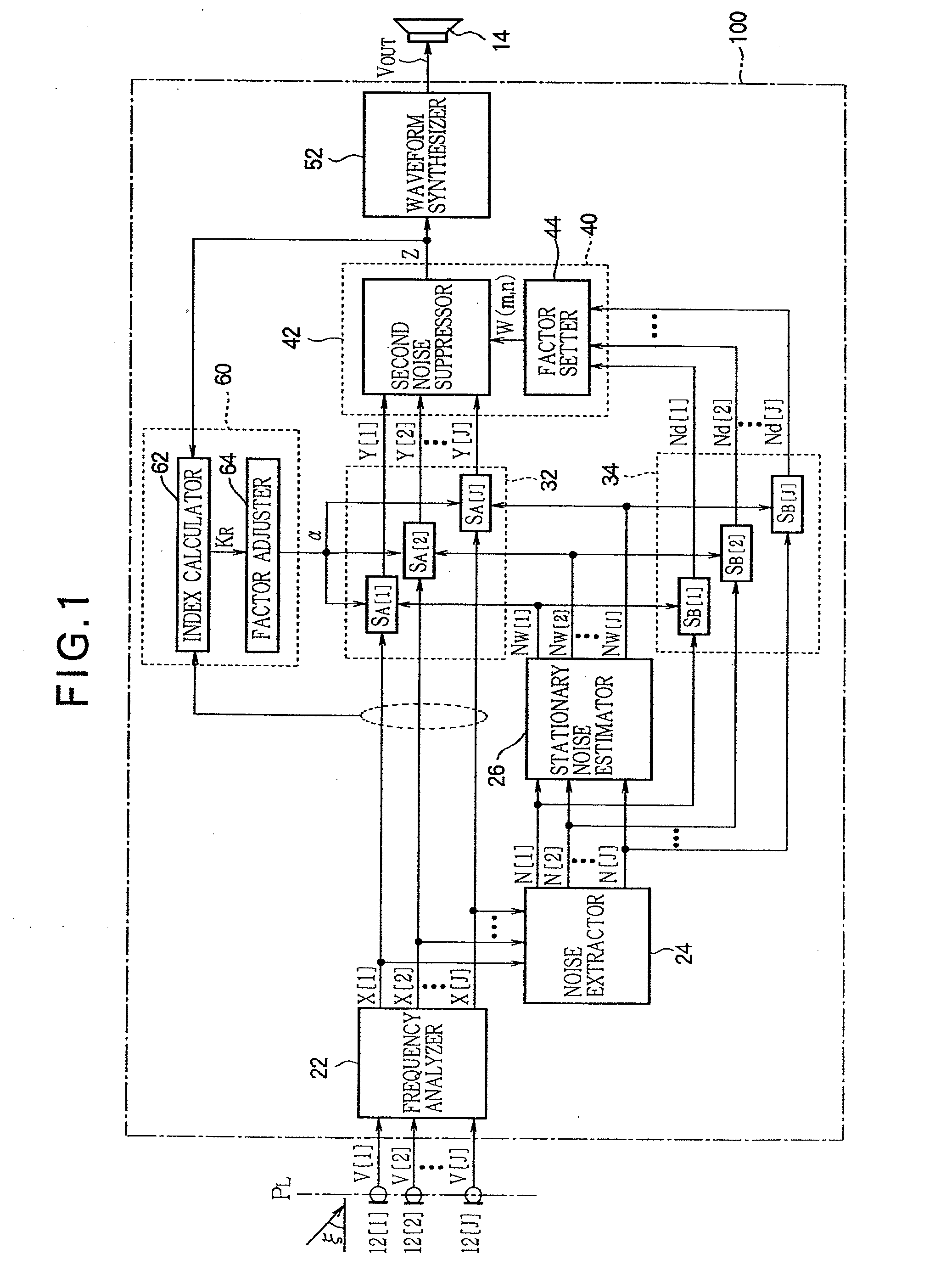
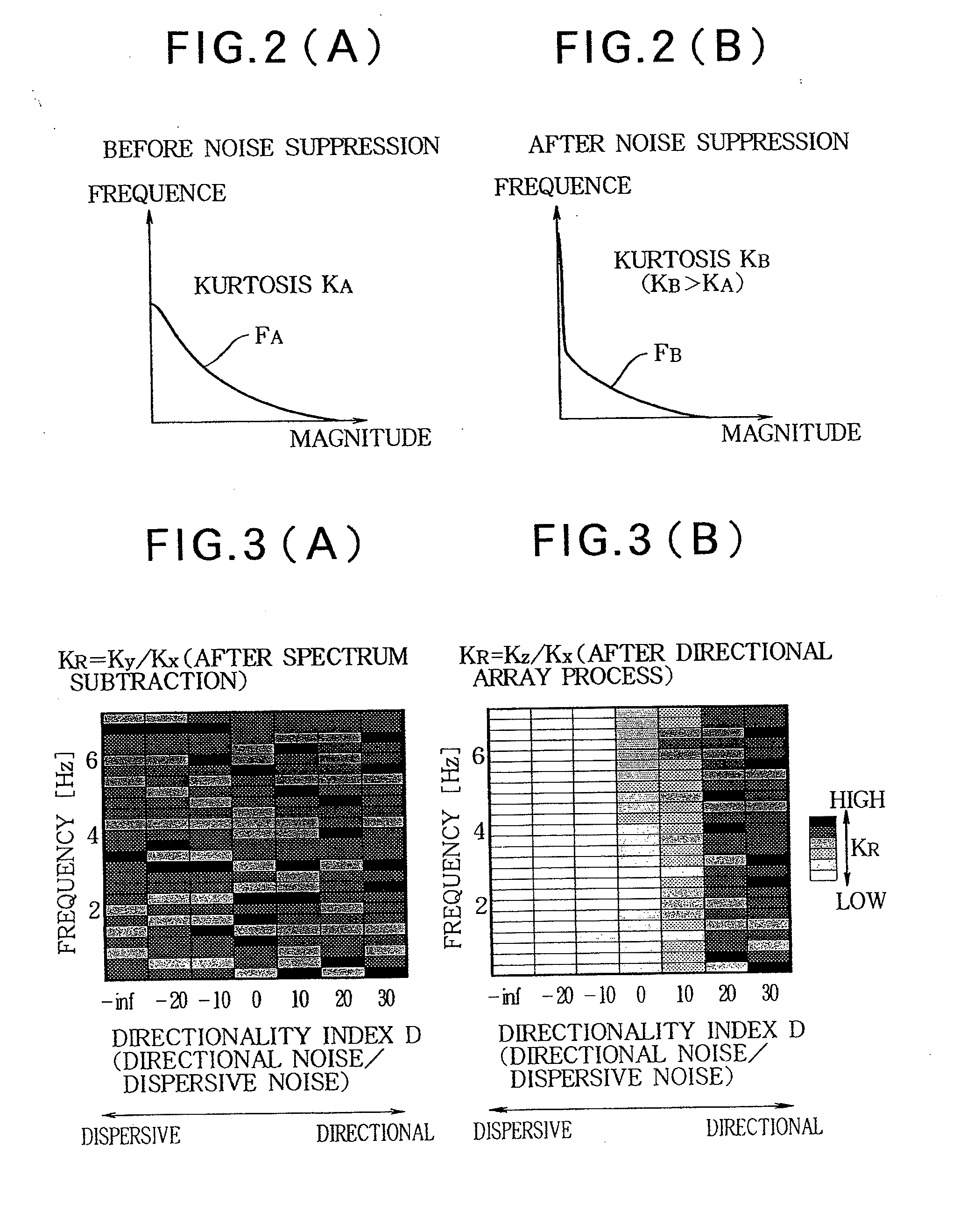
A In a noise suppression apparatus, an extractor extracts a noise component from an audio signal. A stationary noise estimator estimates stationary noise included in the noise component. A first noise suppressor removes a spectrum of the stationary noise from a spectrum of the audio signal to an extent determined by a subtraction factor. A non-stationary noise estimator estimates a spectrum of non-stationary noise by subtracting the spectrum of the stationary noise from the spectrum of the noise component. A factor setter generates a filtering factor for emphasizing a target sound component contained in the audio signal from the spectrum of the non-stationary noise. A second noise suppressor performs a filtering process using the filtering factor on the audio signal after processing of the first noise suppressor. An index calculator calculates a kurtosis change index representing an extent of change of kurtosis in a frequence distribution of magnitude of the audio signal between the kurtosis observed when processing of the first noise suppression part is performed and the kurtosis observed when processing of the second noise suppression part is performed. A factor adjuster variably controls the subtraction factor according to the kurtosis change index.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
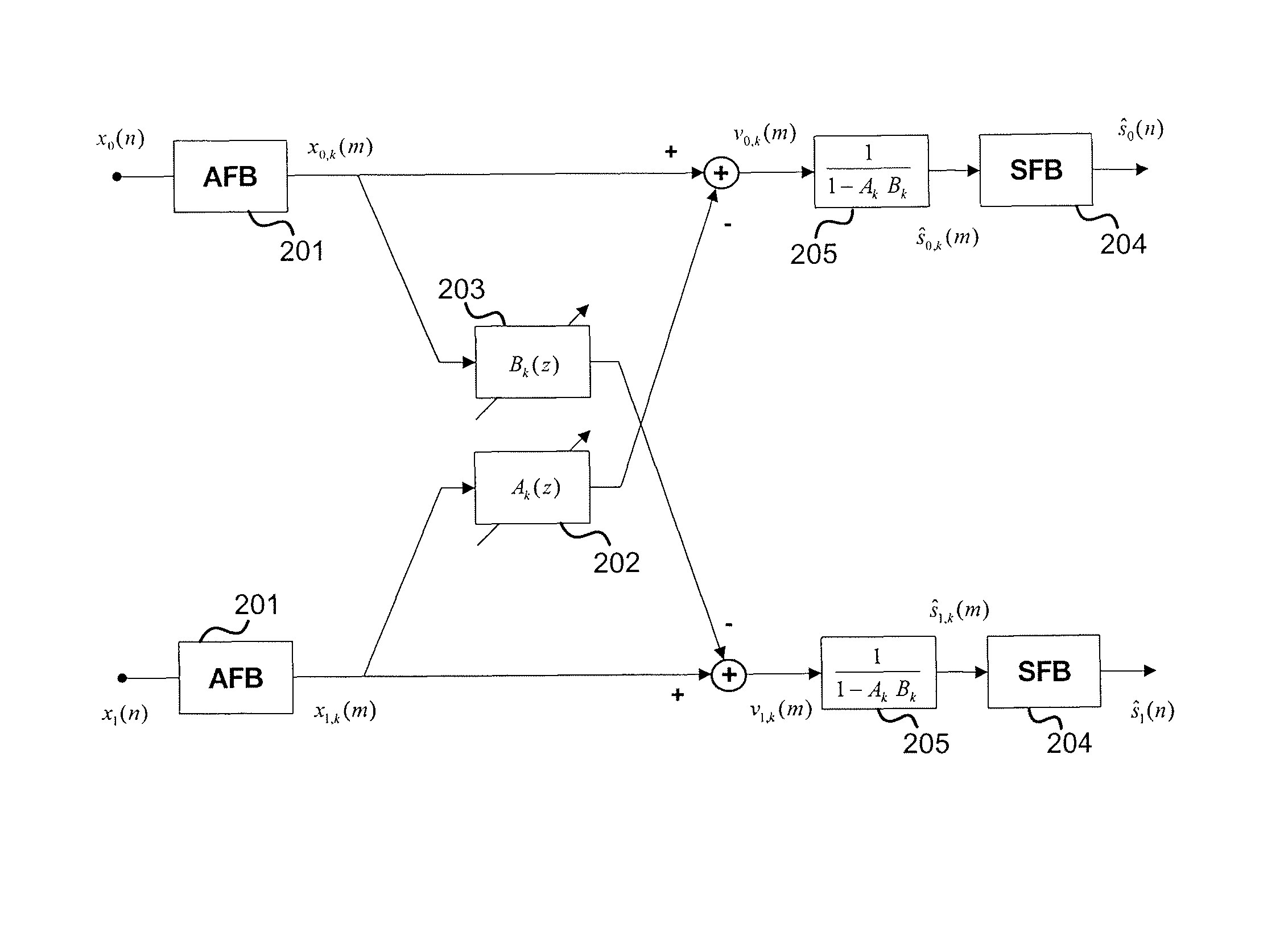
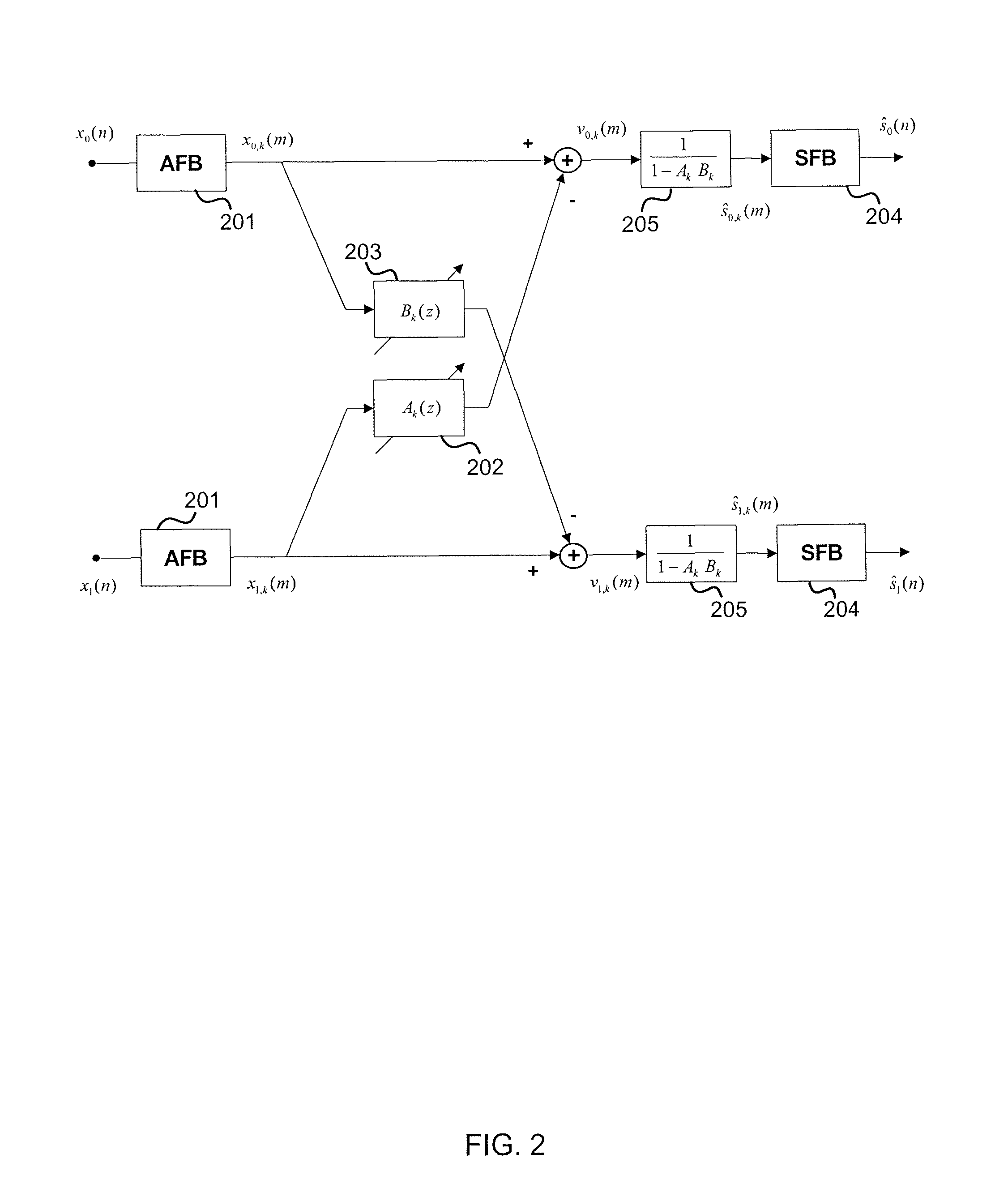
Audio decoding device and audio decoding method
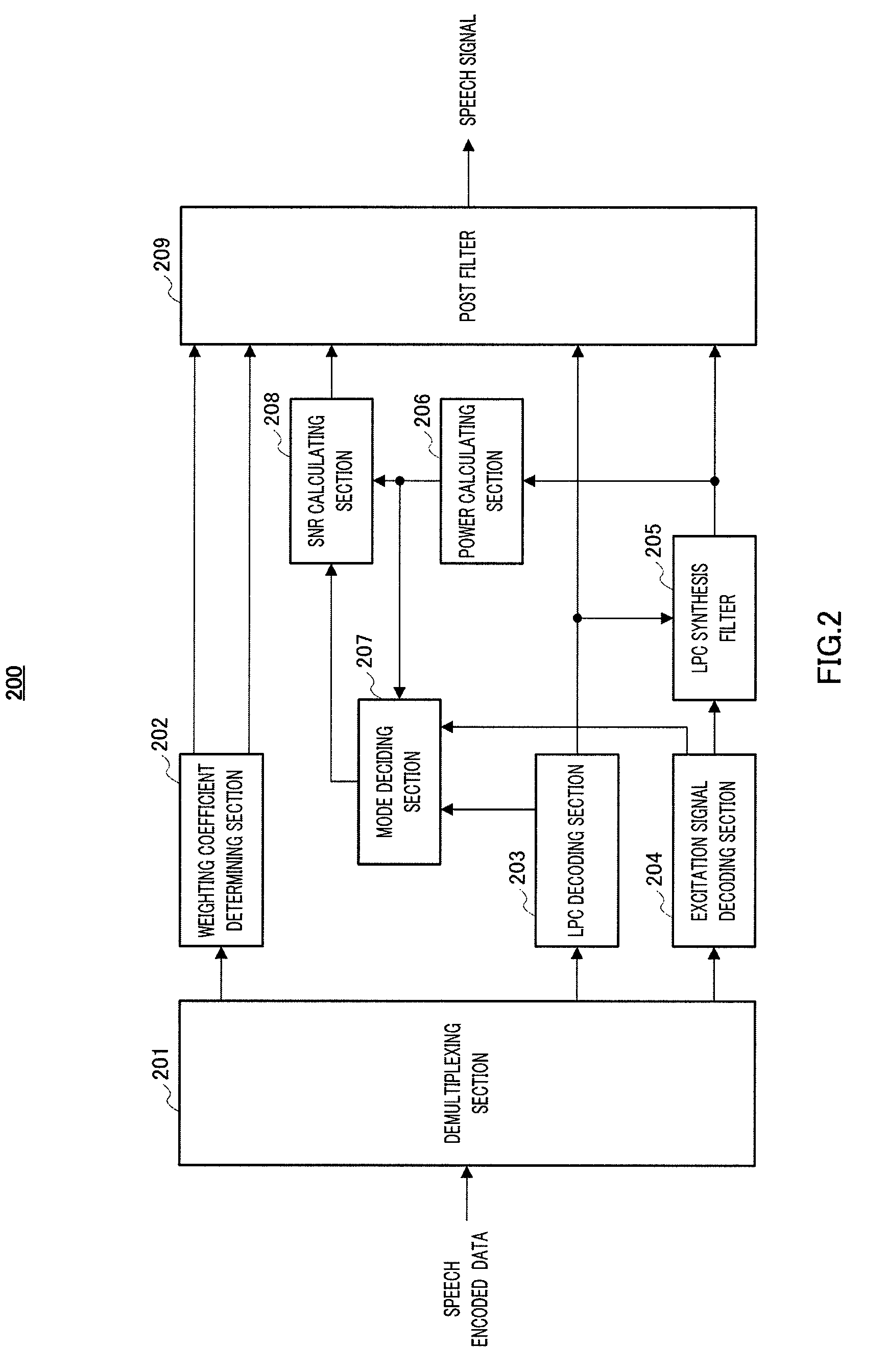
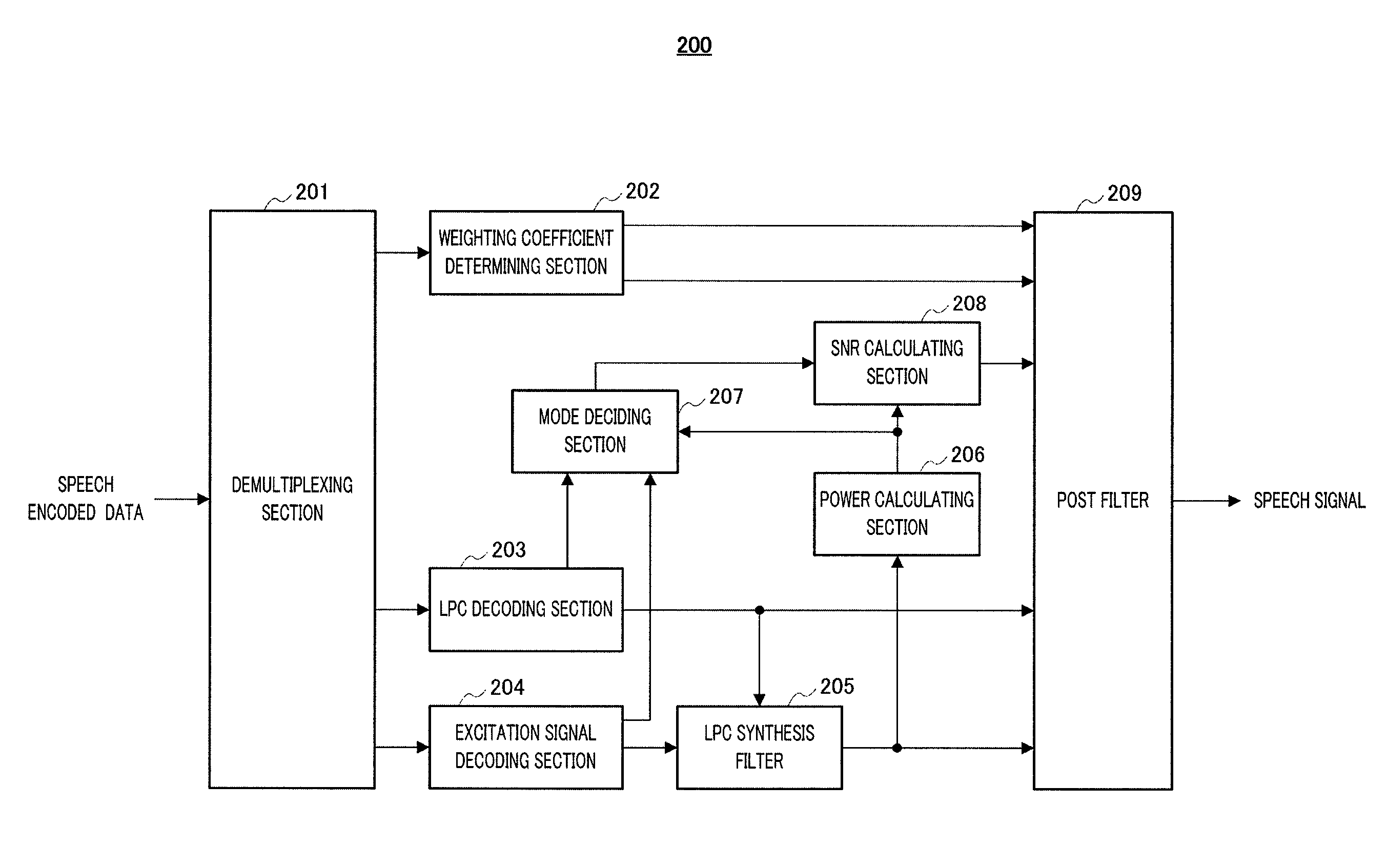
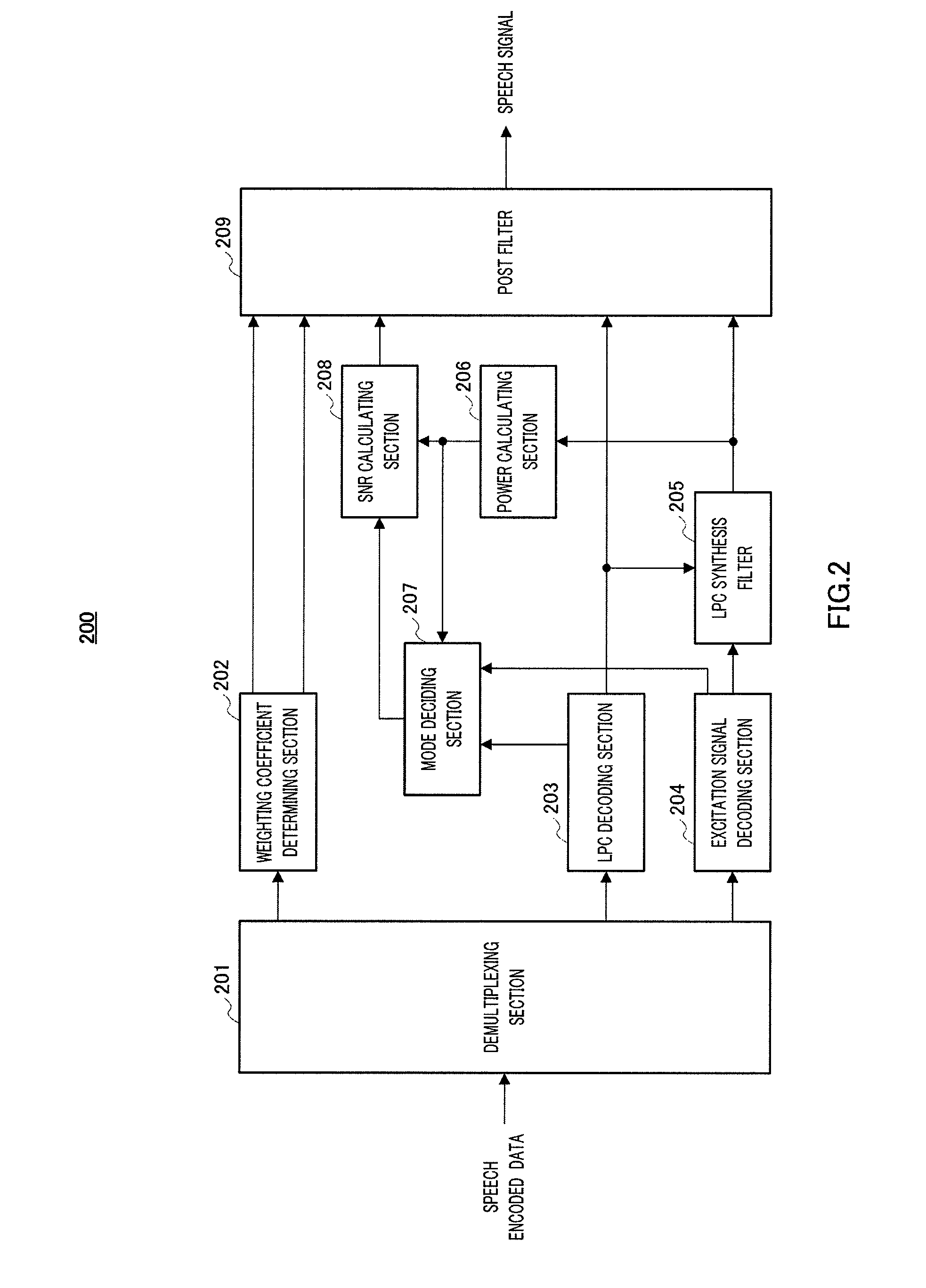
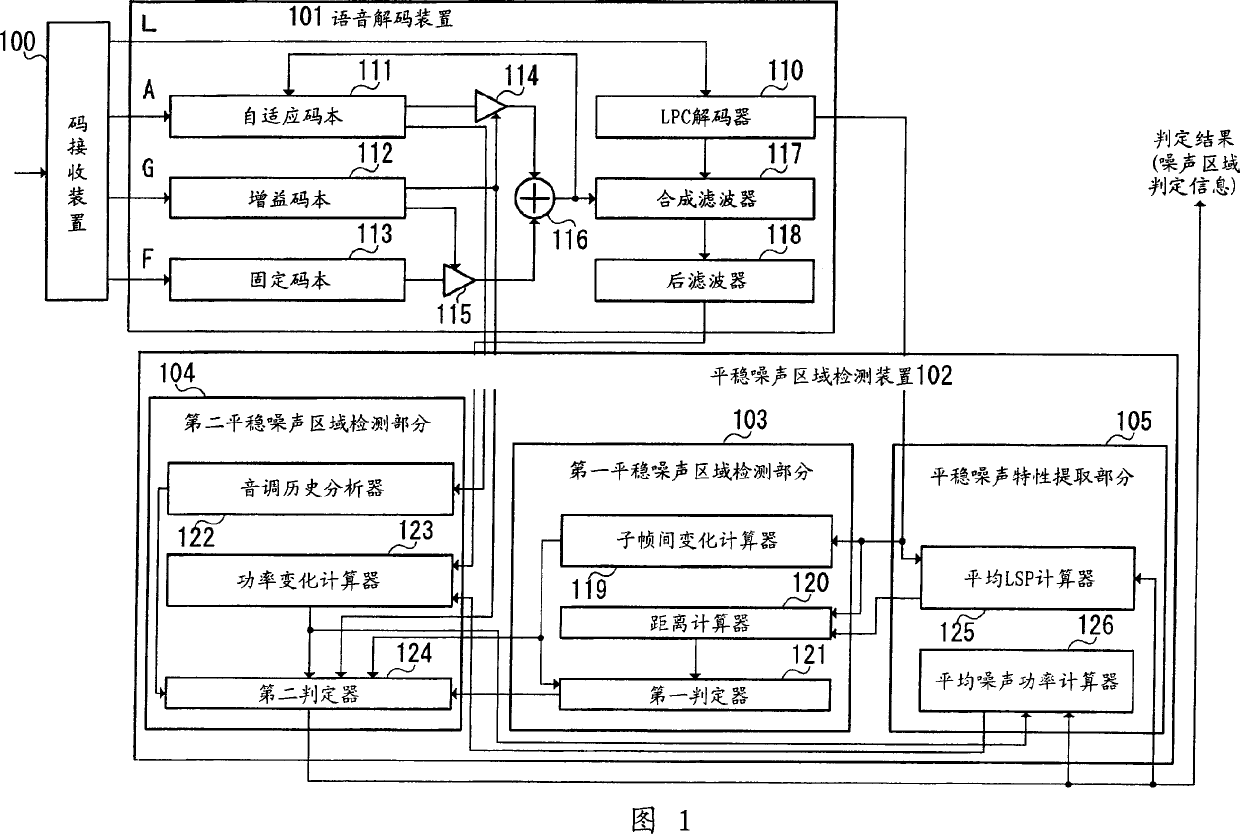
ActiveUS20100100373A1Improve subjective qualitySpeech analysisTransmissionSound sourcesStationary noise
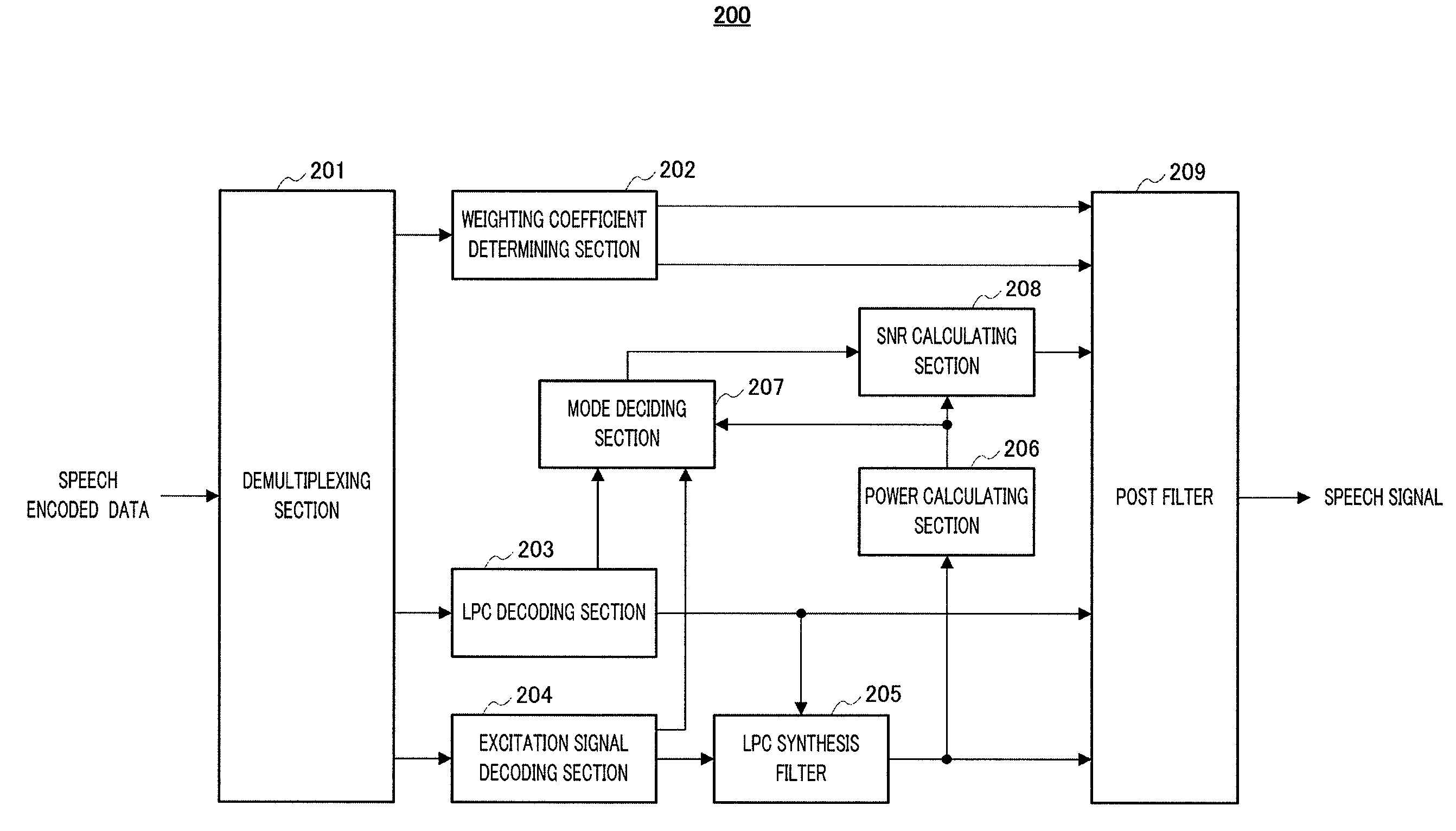
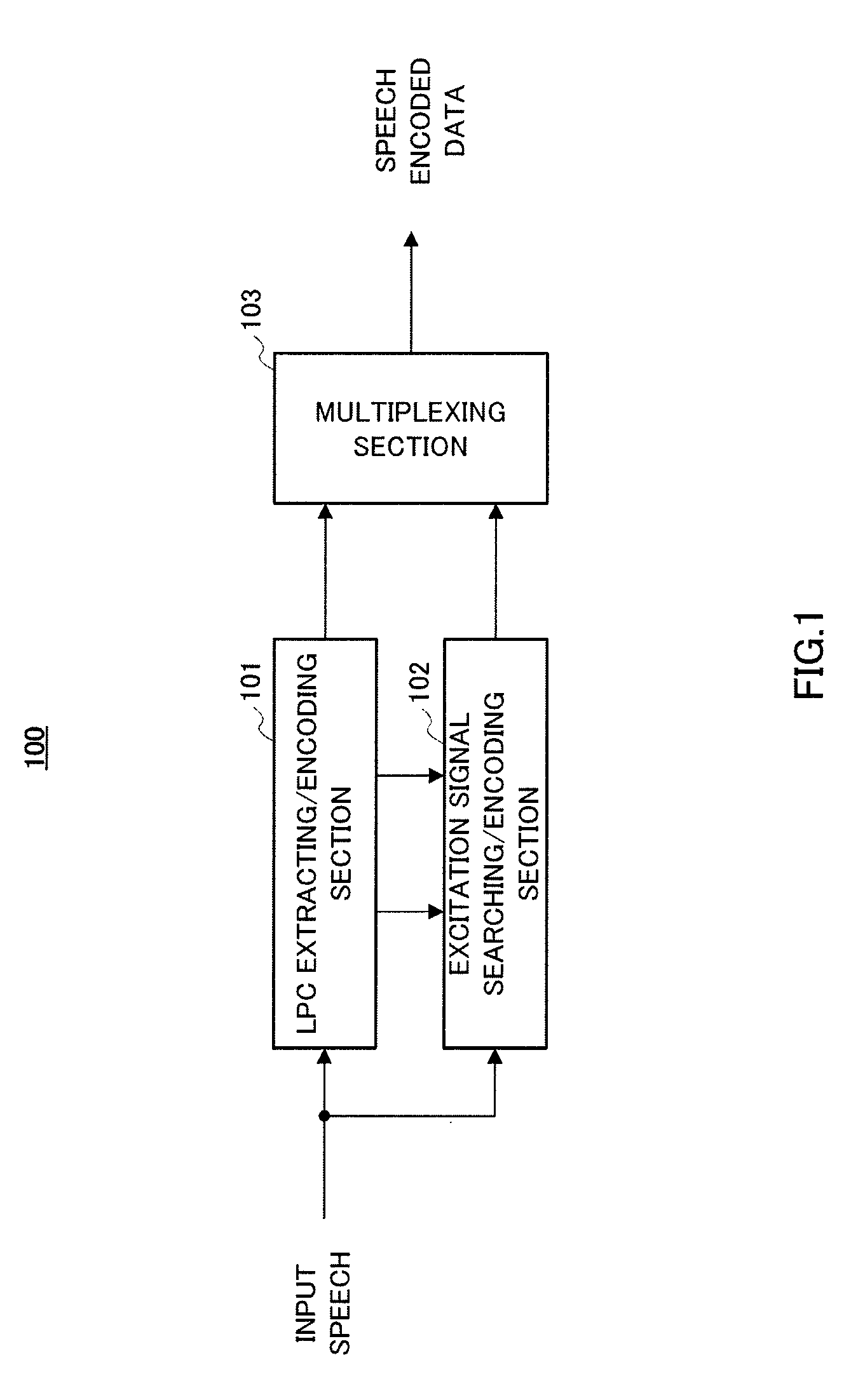
Provided is an audio decoding device which can adjust the high-range emphasis degree in accordance with a background noise level. The audio decoding device includes: a sound source signal decoding unit (204) which performs a decoding process by using sound source encoding data separated by a separation unit (201) so as to obtain a sound source signal; an LPC synthesis filter (205) which performs an LPC synthesis filtering process by using a sound source signal and an LPC generated by an LPC decoding unit (203) so as to obtain a decoded sound signal; a mode judging unit (207) which determines whether a decoded sound signal is a stationary noise section by using a decoded LSP inputted from the LPC decoding unit (203); a power calculation unit (206) which calculates the power of the decoded audio signal; an SNR calculation unit (208) which calculates an SNR of the decoded audio signal by using the power of the decoded audio signal and a mode judgment result in the mode judgment unit (207); and a post filter (209) which performs a post filtering process by using the SNR of the decoded audio signal.
Owner:III HLDG 12 LLC
Programmable electronic stethoscope devices, algorithms, systems, and methods
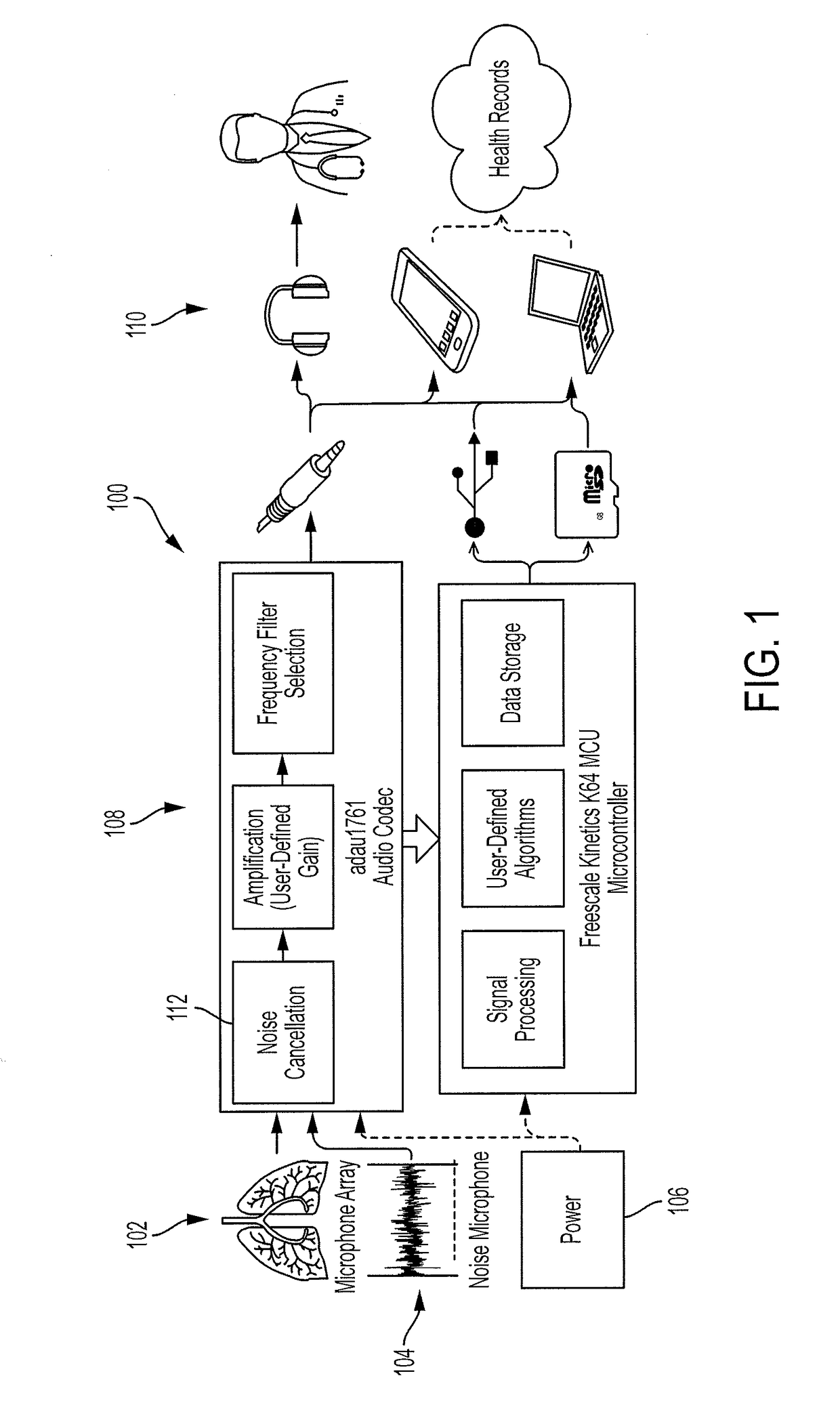
ActiveUS20180317876A1Clean auscultation signalDistortion freeStethoscopeSpeech analysisEnvironmental noiseStationary noise
A digital electronic stethoscope includes an acoustic sensor assembly that includes a body sensor portion and an ambient sensor portion, the body sensor portion being configured to make acoustically coupled contact with a subject while the ambient sensor portion is configured to face away from the body sensor portion so as to capture environmental noise proximate the body sensor portion; a signal processor and data storage system configured to communicate with the acoustic sensor assembly so as to receive detection signals therefrom, the detection signals including an auscultation signal comprising body target sound and a noise signal; and an output device configured to communicate with the signal processor and data storage system to provide at least one of an output signal or information derived from the output signal. The signal processor and data storage system includes a noise reduction system that removes both stationary noise and non-stationary noise from the detection signal to provide a clean auscultation signal substantially free of distortions. The signal processor and data storage system further includes an auscultation sound classification system configured to receive the clean auscultation signal and provide a classification thereof as at least one of a normal breath sound or an abnormal breath sound.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
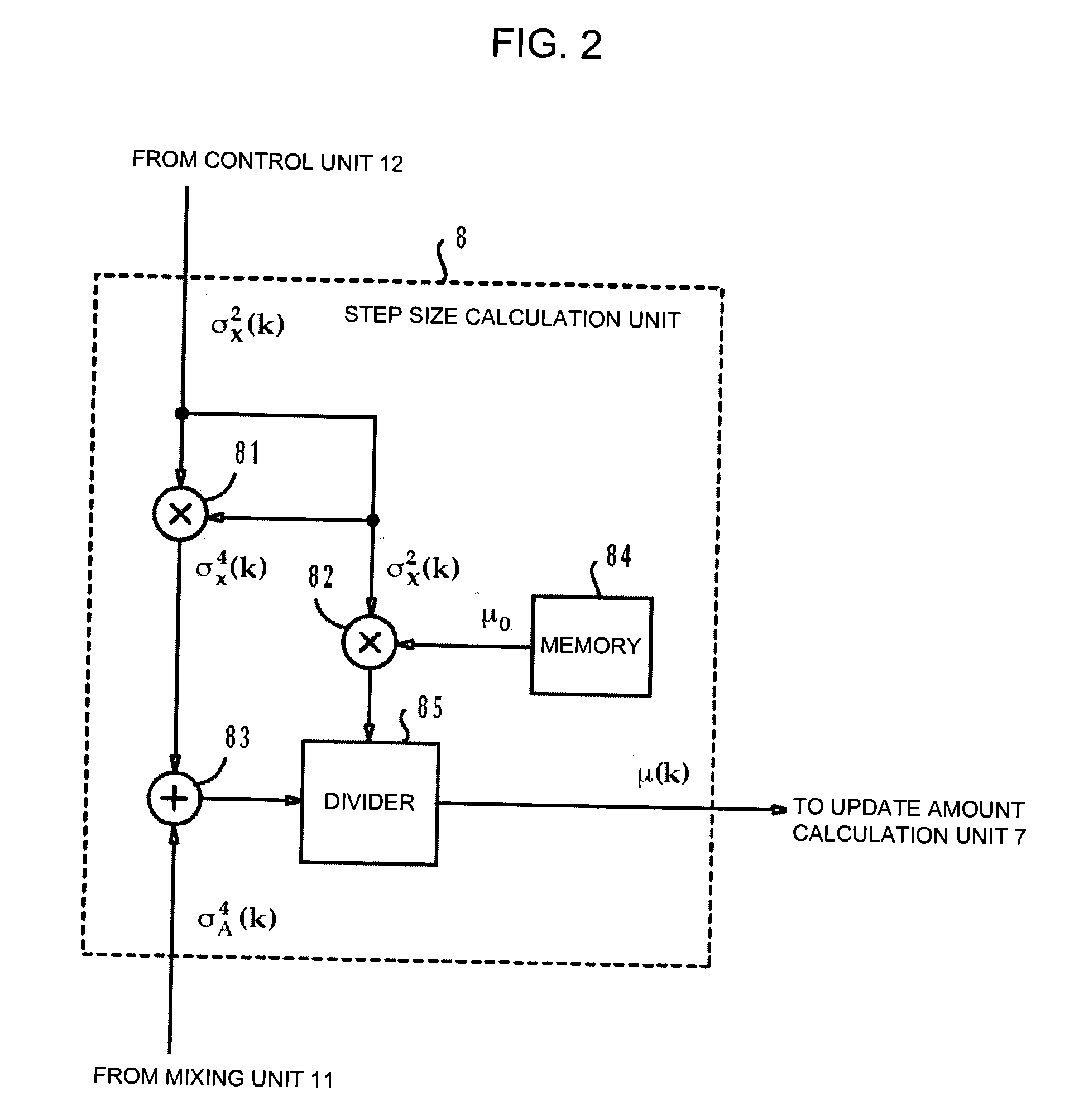
Particular signal cancel method, particular signal cancel device, adaptive filter coefficient update method, adaptive filter coefficient update device, and computer program
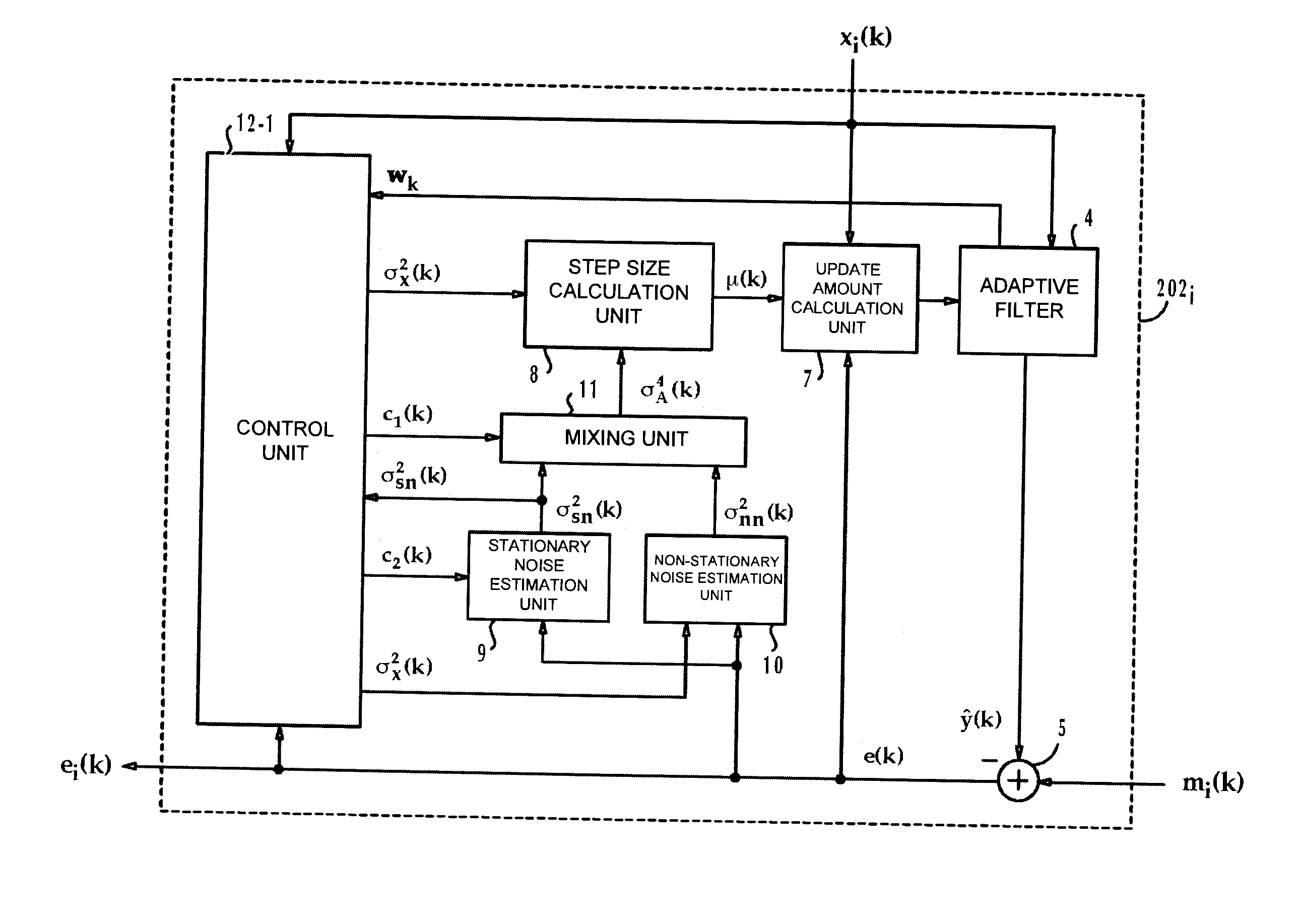
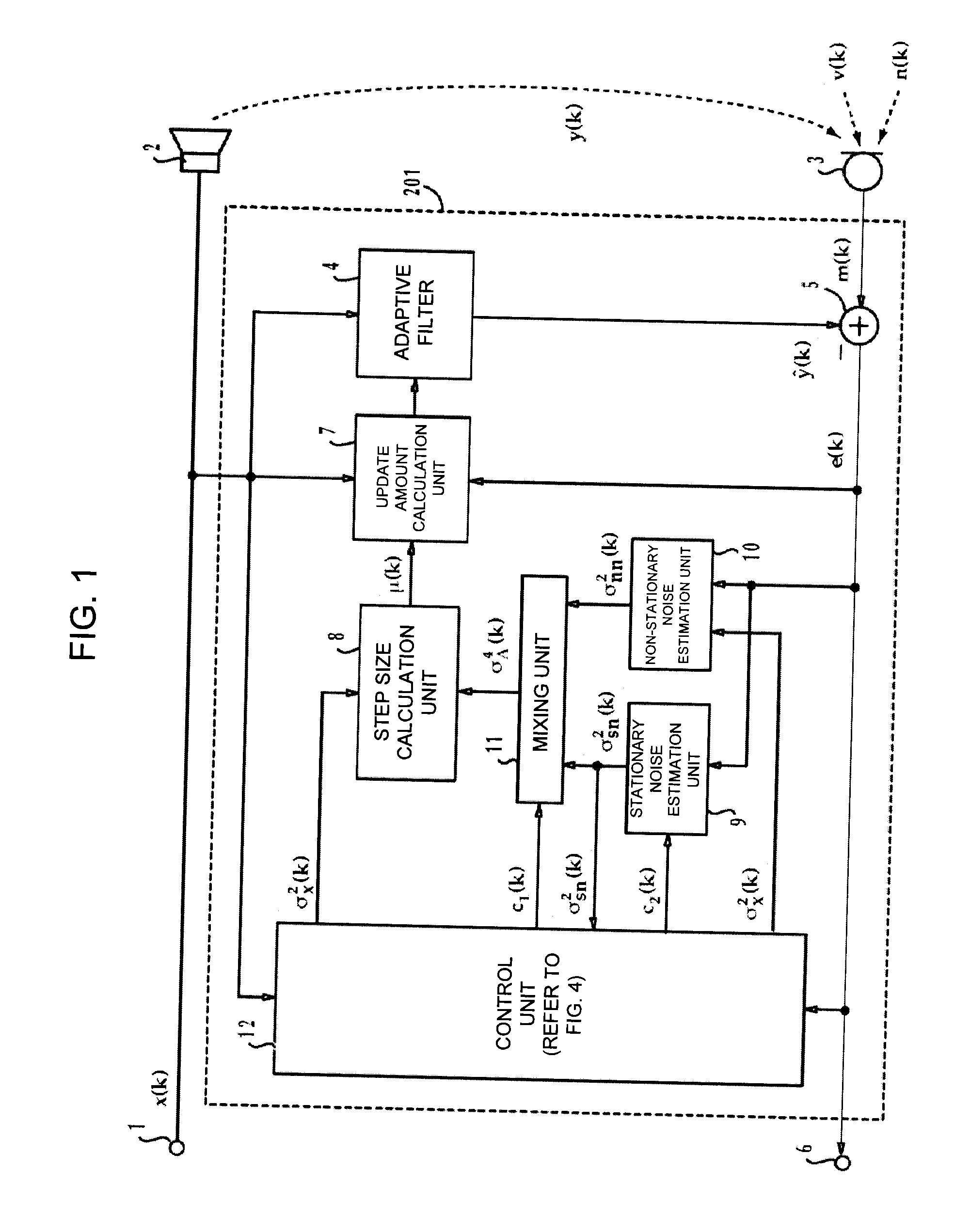
InactiveUS20100223311A1Improve accuracyInterconnection arrangementsAdaptive networkStationary noiseMixed noise
By using the adaptive filter, the reference input signal is processed so as to identify a pseudo-signal of a particular signal to be deleted. The pseudo-signal is subtracted from the mixture containing a target signal inputted from a microphone, the particular signal to be deleted, and a noise so as to obtain an error signal. A stationary noise is estimated to obtain a stationary noise estimated value. A non-stationary noise is estimated to obtain a non-stationary noise estimated value. The stationary noise estimated value is mixed with the non-stationary estimated value to obtain a mixed noise estimated value. An update amount is calculated according to a correlation value between the error signal and the reference input signal, and the mixed noise estimated value. According to the update amount, a coefficient of the adaptive filter is updated.
Owner:NEC CORP
Two microphone noise reduction system
A two microphone noise reduction system is described. In an embodiment, input signals from each of the microphones are divided into subbands and each subband is then filtered independently to separate noise and desired signals and to suppress non-stationary and stationary noise. Filtering methods used include adaptive decorrelation filtering. A post-processing module using adaptive noise cancellation like filtering algorithms may be used to further suppress stationary and non-stationary noise in the output signals from the adaptive decorrelation filtering and a single microphone noise reduction algorithm may be used to further provide optimal stationary noise reduction performance of the system.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE SILICON RADIO PLC +1
Robust adaptive beam formation method
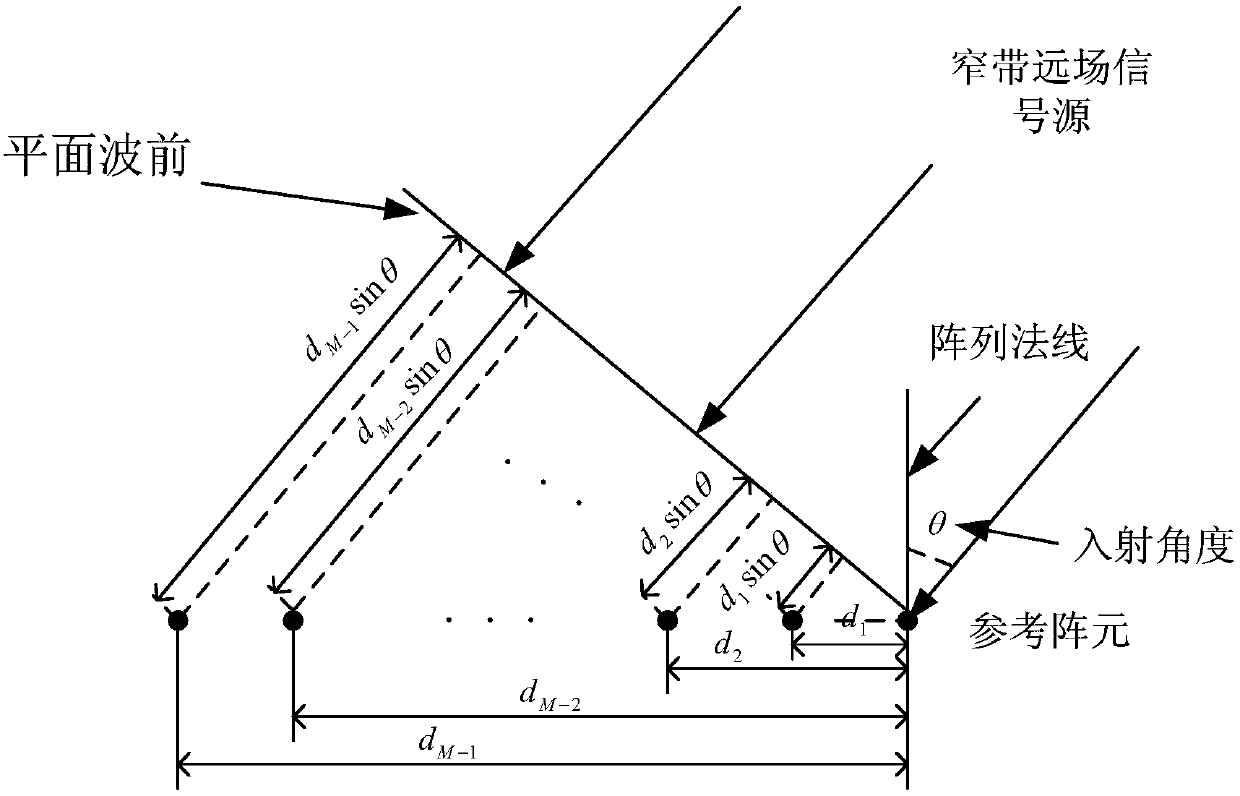
ActiveCN108181507AImprove robustnessImprove performanceSpectral/fourier analysisStationary noiseSpace power
A robust adaptive beam formation method disclosed by the present invention comprises a step 1 of utilizing a Capon space power spectrum to estimate the average noise power in an angle area only containing the stationary noise, and obtaining a corresponding noise covariance matrix; a step 2 of adopting the Capon space power spectrum to collect all interference information located in an interferencesignal angle area, rejecting a noise component, and reconstructing an interference covariance matrix; then reconstructing an interference and noise covariance matrix according to the noise covariancematrix and the interference covariance matrix; a step 3 of correcting a steering vector of a desired signal of a beam former according to the reconstructed interference and noise covariance matrix, calculating an optimal weight vector, and forming a robust adaptive beam. The method can obtain the more accurate interference and noise covariance matrix and the steering vector of the desired signal,so that the robustness of the adaptive beam formation method on various array error conditions is improved further.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Speech decoding apparatus and speech decoding method including high band emphasis processing
ActiveUS8554548B2Improve subjective qualitySpeech analysisTransmissionDecoding methodsStationary noise
An audio decoding device can adjust the high-range emphasis degree in accordance with a background noise level. The audio decoding device includes: a sound source signal decoder which performs a decoding process by using sound source encoding data separated by a separator so as to obtain a sound source signal; an LPC synthesis filter which performs an LPC synthesis filtering process by using a sound source signal and an LPC generated by an LPC decoder so as to obtain a decoded sound signal; a mode judger which determines whether a decoded sound signal is a stationary noise period by using a decoded LSP inputted from the LPC decoder a power calculator which calculates the power of the decoded audio signal; an SNR calculator which calculates an SNR of the decoded audio signal by using the power of the decoded audio signal and a mode judgment result in the mode judger and a post filter which performs a post filtering process by using the SNR of the decoded audio signal.
Owner:III HLDG 12 LLC
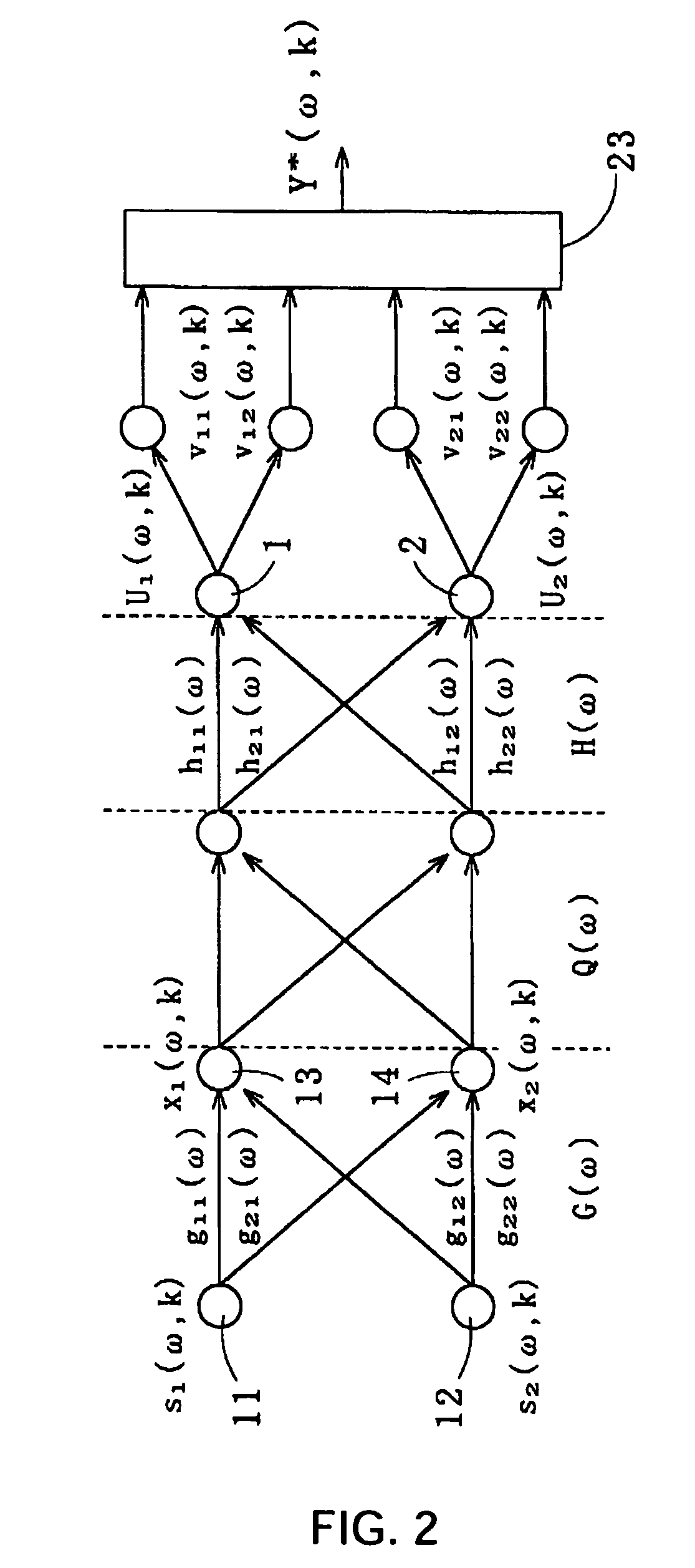
Method for recovering target speech based on speech segment detection under a stationary noise
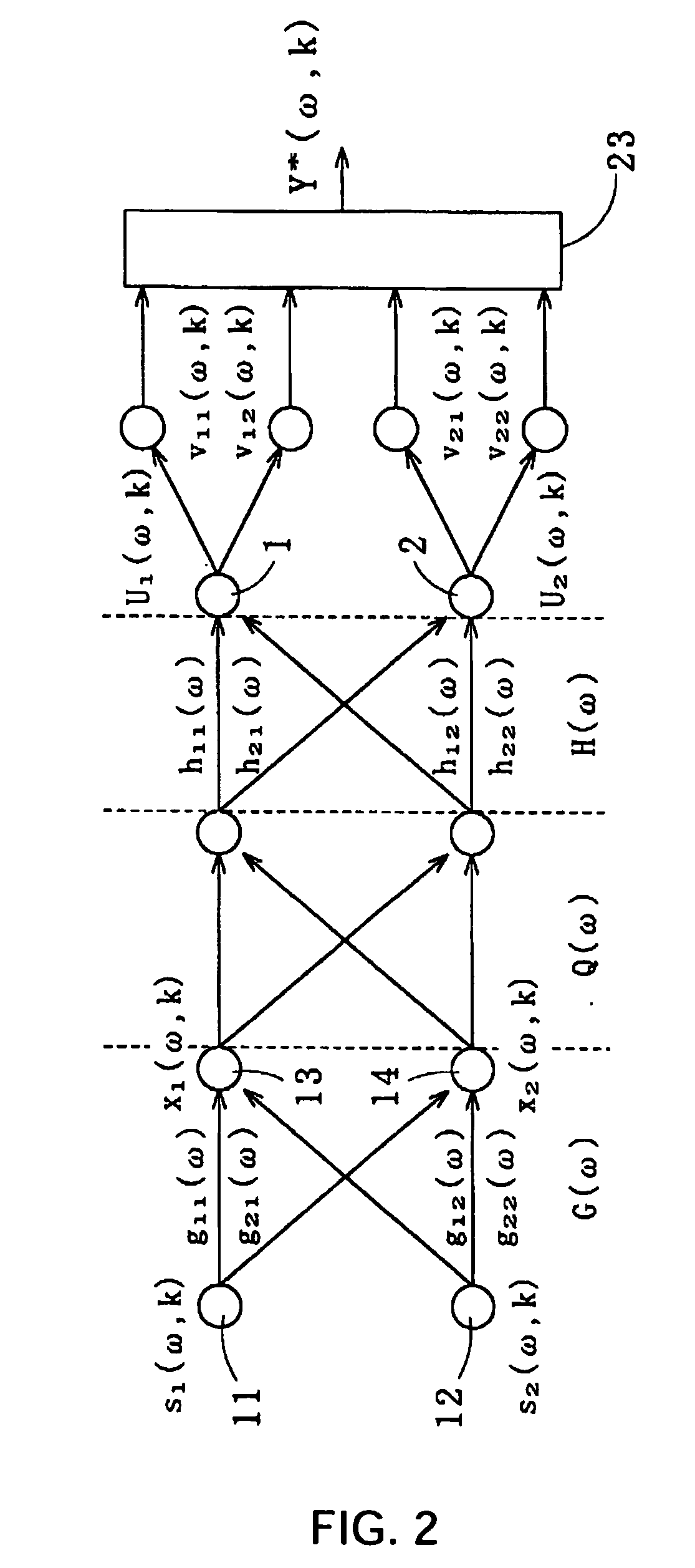
InactiveUS20070055511A1Minimizing residual noiseNoise minimizationSpeech recognitionFrequency spectrumPresent method
Method for recovering target speech by extracting signal components falling in a speech segment, which is determined based on separated signals obtained through the Independent Component Analysis, thereby minimizing the residual noise in the recovered target speech. The present method comprises: the first step of receiving target speech emitted from a sound source and a noise emitted from another sound source and extracting estimated spectra Y* corresponding to the target speech by use of the Independent Component Analysis; the second step of separating from the estimated spectra Y* an estimated spectrum series group y* in which the noise is removed by applying separation judgment criteria based on the kurtosis of the amplitude distribution of each of estimated spectrum series in Y*; the third step of detecting a speech segment and a noise segment of the total sum F of all the estimated spectrum series in y* by applying detection judgment criteria based on a predetermined threshold value T that is determined by the maximum value of F; and the fourth step of extracting components falling in the speech segment from the estimated spectra Y* to generate a recovered spectrum group of the target speech for recovering the target speech.
Owner:KITAKYUSHU FOUND FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF IND SCI & TECH +1
Speech enhanced interaction method, system, storage medium and electronic device
ActiveCN108877827AAvoid interferenceImprove stabilitySpeech recognitionInteraction systemsSound sources
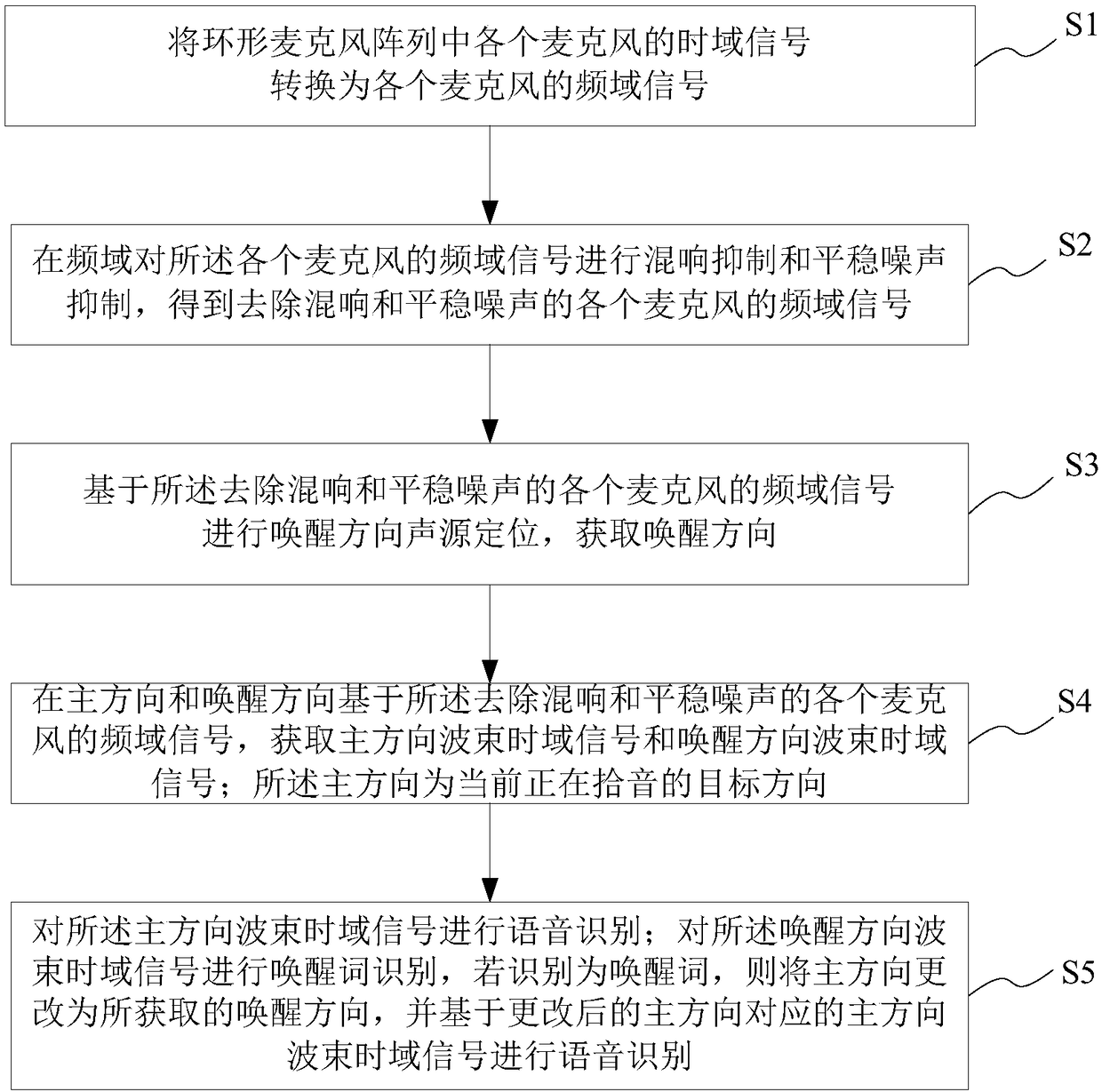
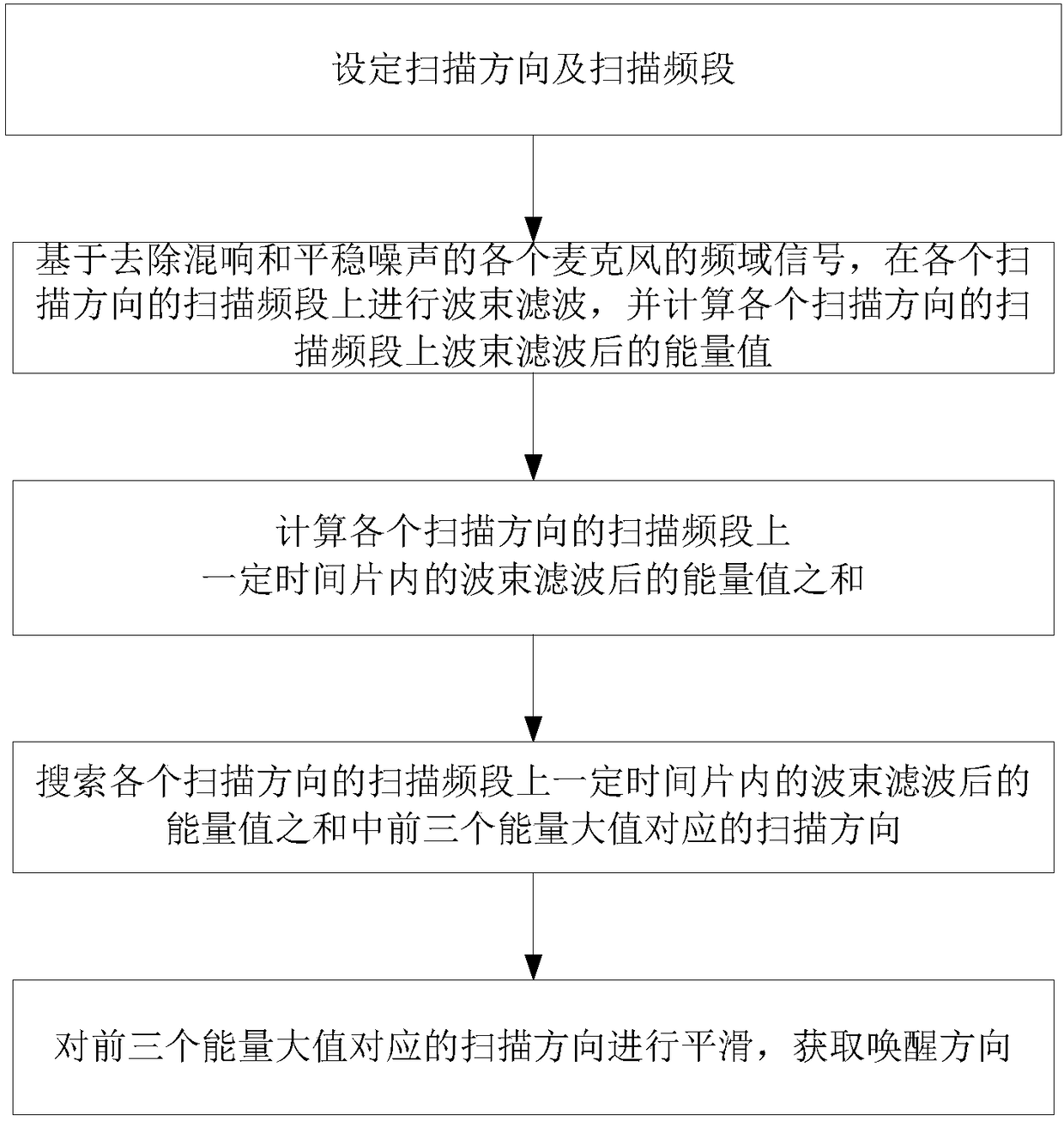
The invention provides a speech enhanced interaction method, a speech enhanced interaction system, a storage medium and an electronic device. The method includes the following steps that: the time-domain signals of microphones in an annular microphone array are converted into the frequency-domain signals of the microphones, and reverberation suppression and stationary noise suppression are performed on the frequency-domain signals of the microphones; wake-up direction sound source positioning is performed based on the reverberation and stationary noise-removed frequency-domain signals of the microphones, so that a wake-up direction is obtained; main direction beam time-domain signals and wake-up direction beam time-domain signals are obtained in a main direction and the wake-up direction on the basis of the reverberation and stationary noise-removed frequency-domain signals of the microphones; speech recognition is performed on the main direction beam time-domain signals; and wake-up word recognition is performed on the wake-up direction beam time-domain signals, and if the signals are identified as wake-up words, the main direction is changed to the obtained wake-up direction. With the speech enhanced interaction method, the speech enhanced interaction system, the storage medium and the electronic device of the invention adopted, the stability and reliability of speech interaction can be improved effectively.
Owner:FUZHOU ROCKCHIP SEMICON
Removal of Stationary Noise Pattern From Digital Images
InactiveUS20080151081A1Image enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionStationary noise
A method for removing a stationary noise pattern from digital images uses an adaptive noise estimation algorithm to calculate a prediction of the fixed pattern noise and a confidence estimate for the prediction. In one embodiment, a predicted noise value is obtained from the captured image and a predicted image derived from spatial and temporal pixel value prediction techniques. The predicted noise value is used to update a fixed pattern noise estimate only when the confidence estimate for the predicted image is high. In another embodiment, the confidence estimate is used as a weight factor for blending the noise prediction into the noise estimate. In yet another embodiment, the adaptive noise estimation algorithm is applied to a prediction area in the image for calculating scaling parameters which scaling parameters are used to calculate a noise estimate for the entire image based on a reference noise image.
Owner:PIXIM
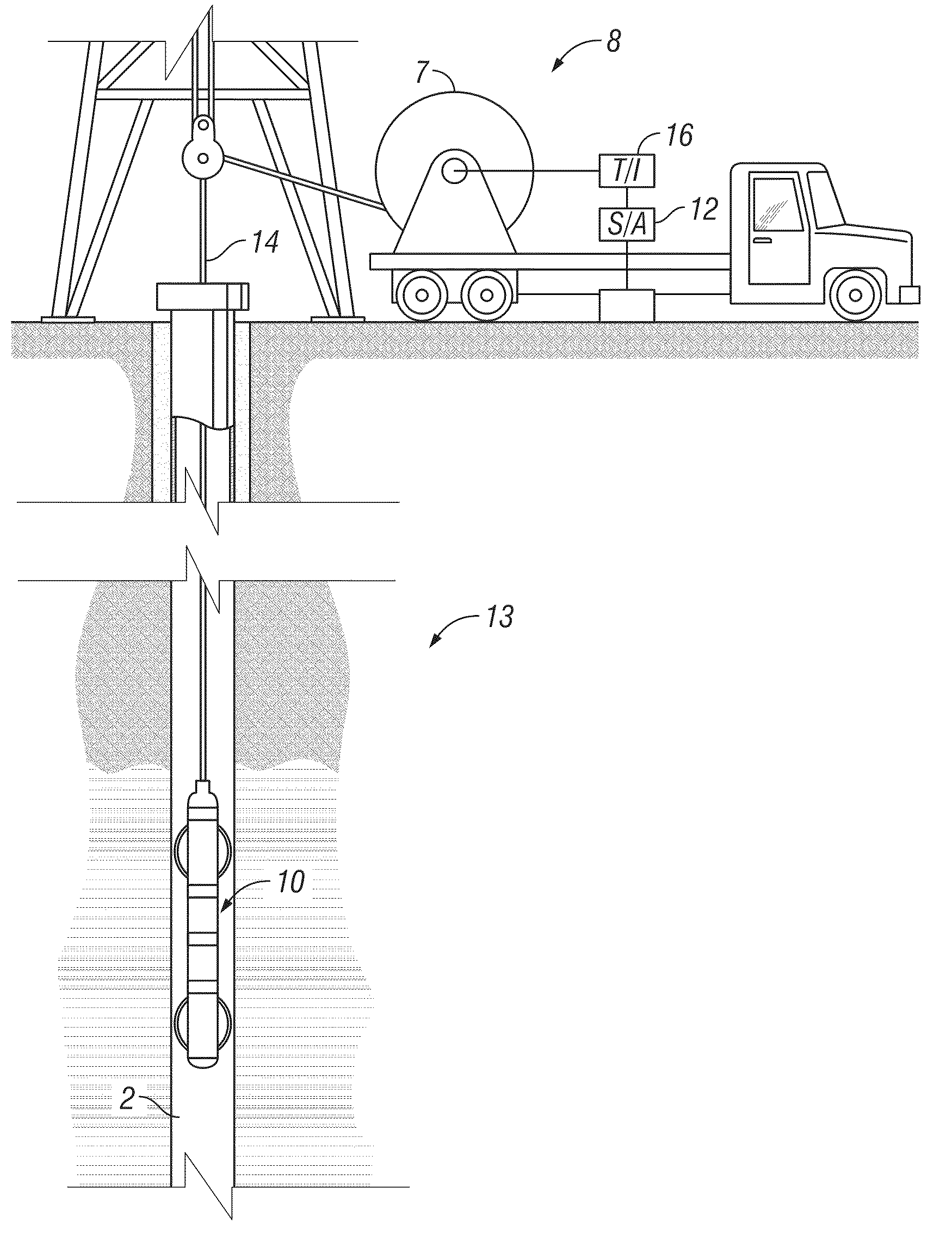
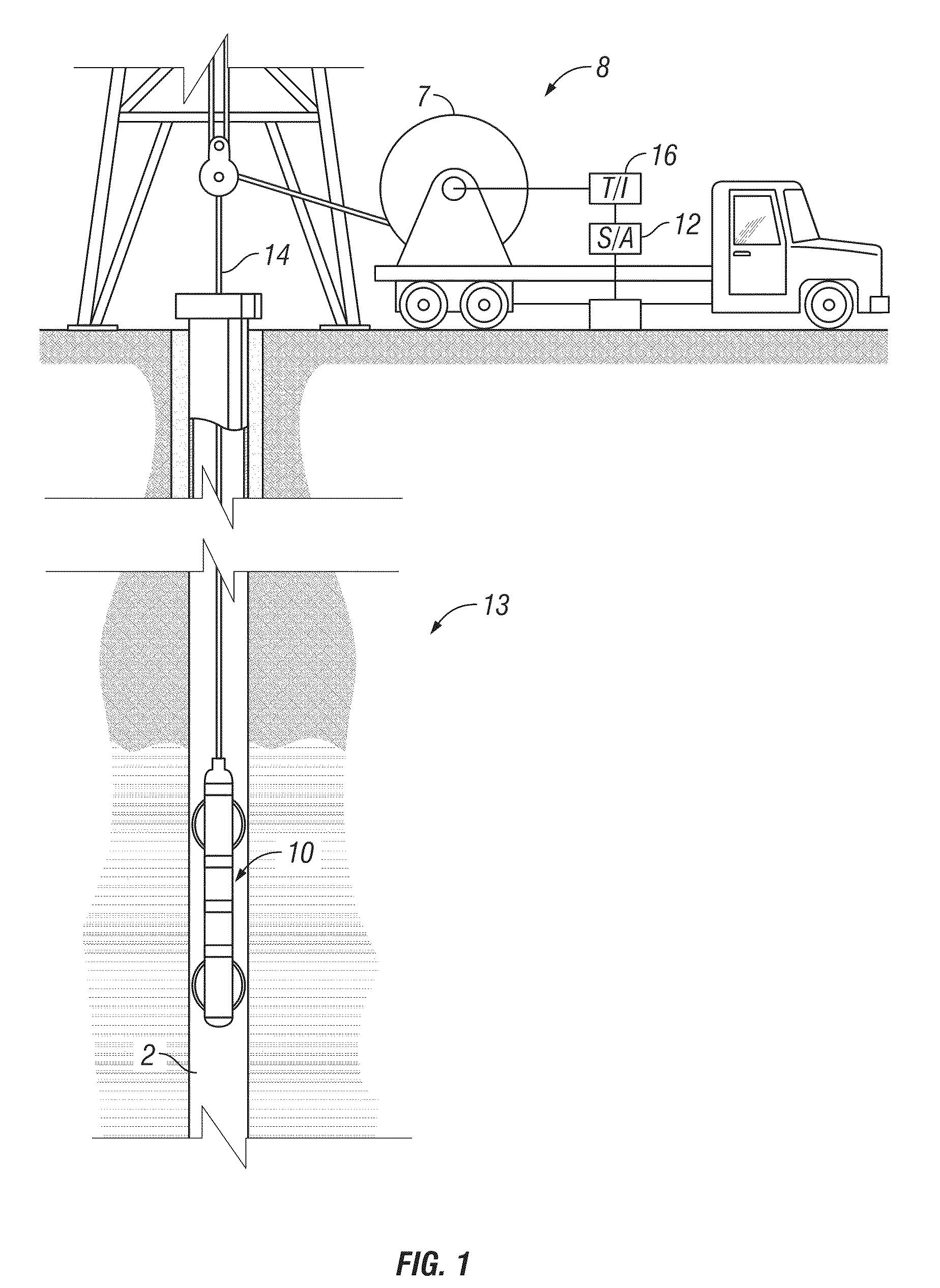
Televiewer Image Wood-Grain Reduction Techniques
ActiveUS20100265796A1Mechanical vibrations separationSeismology for water-loggingStationary noiseSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Measurements made by a transducer assembly for downhole imaging are affected by reverberations between the transducer and the window on the outside of the assembly. The reverberations result in a stationary noise on the image. Hardware solutions to improve signal-to-noise ratio includes using a composite transducer, adjusting the distance between the transducer and the window. SNR can also be improved by processing techniques that include stacking, fitting a sinusoid to the reverberation, by envelope peak detection, and by applying a notch filter.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
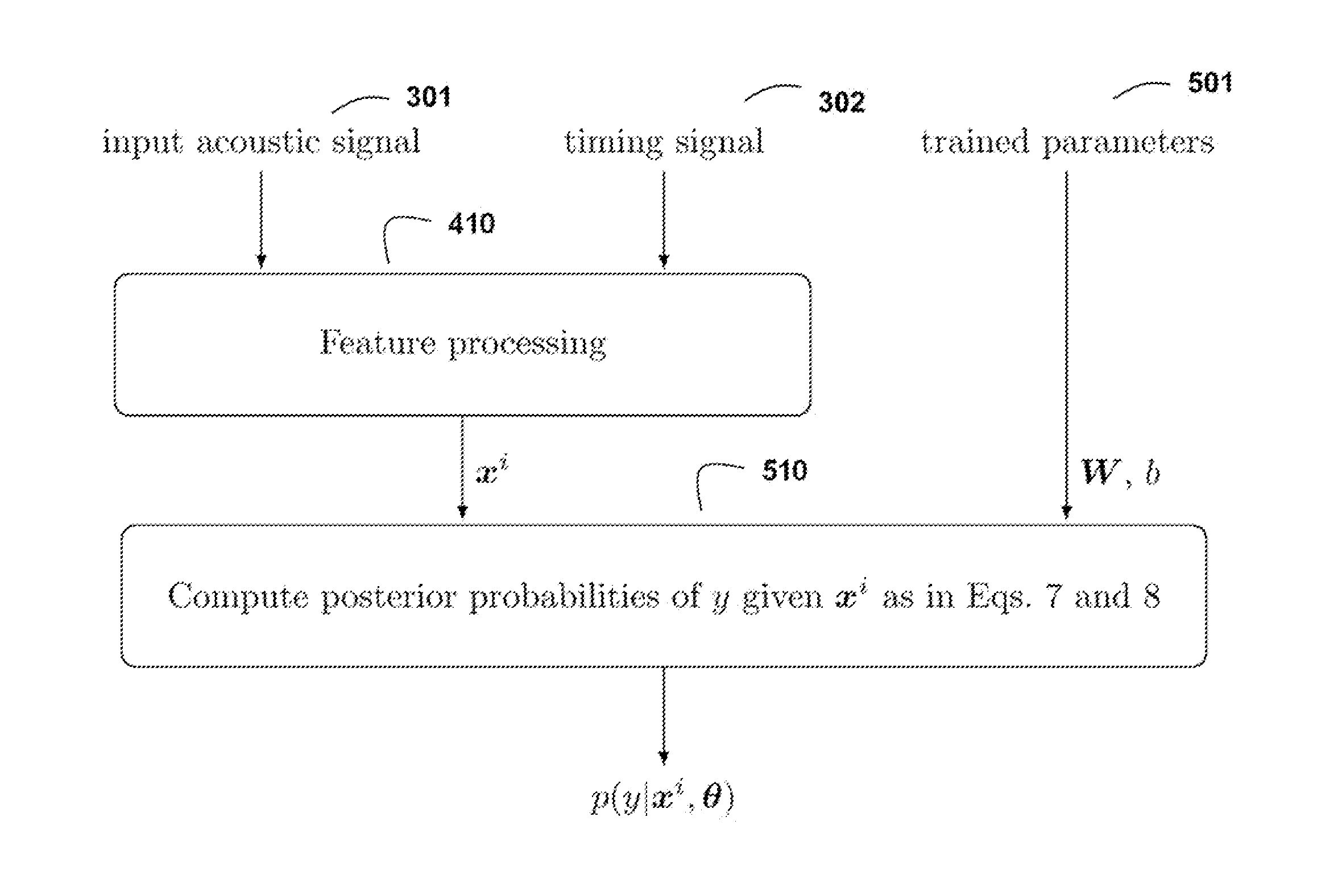
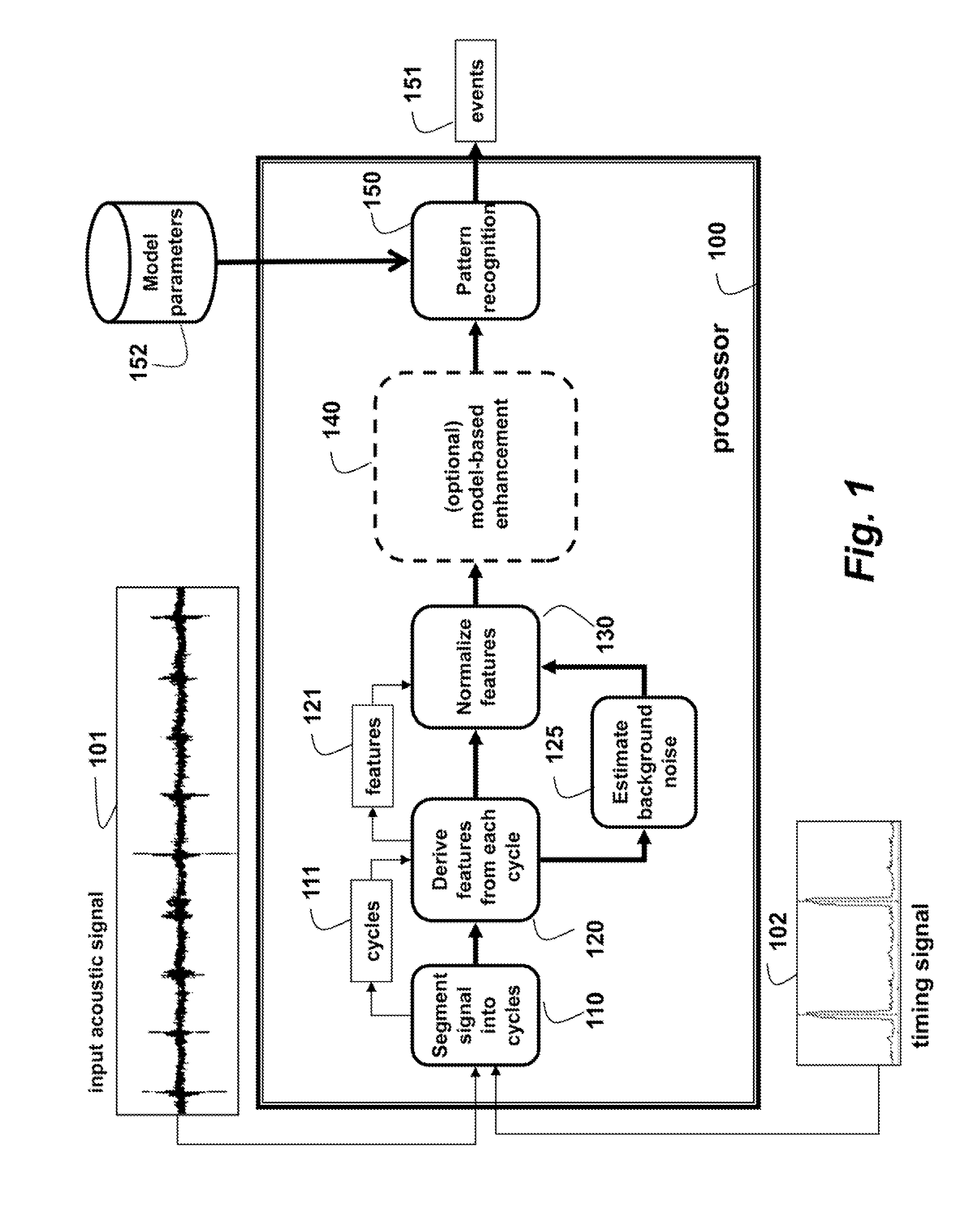
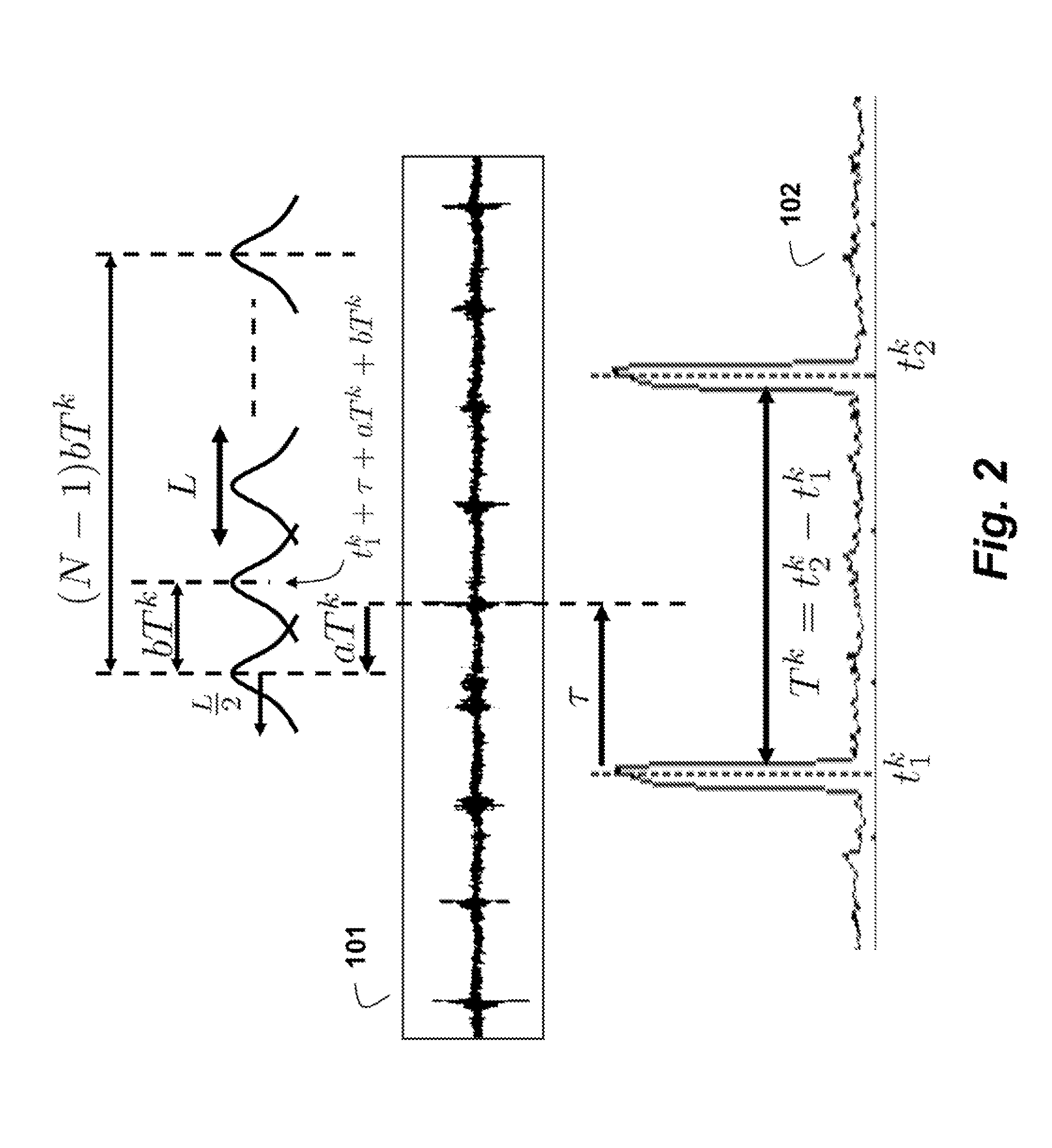
Method and System for Detecting Events in an Acoustic Signal Subject to Cyclo-Stationary Noise
A method detects events in an accoustic signal subject to cyclostationary background noise by first segmenting the signal into cycles. Features with a fixed dimension are derived from the cycles, such that the timing of the features is relative to a cycle time. The features are normalized using an estimate of the cyclostationary background noise. Then, after the normalizing, a classifier is applied to the features to detect the events.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Noise cancellation device and noise cancellation program
InactiveCN102227768AClear power differenceImproved Noise Removal CapabilityMicrophones signal combinationSpeech recognitionSound sourcesStationary noise
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Noise reduction device, program and method
InactiveUS20080294430A1Improve Noise RobustnessMaintain compatibilitySpeech analysisAdaptive learningStationary noise
A noise reduction device is configured by use of: means for calculating a predetermined constant, and a predetermined reference signal Rω(T) in the frequency domain, respectively by use of adaptive coefficients Wω(m), and for thereby obtaining estimated values Nω and Qω(T) respectively of stationary noise components, and non-stationary noise components corresponding to the reference signal, which are included in a predetermined observed signal Xω(T) in the frequency domain; means and for applying a noise reduction process to the observed signal on the basis of each of the estimated values, and for updating each of the adaptive coefficients on the basis of a result of the process; and an adaptive learning means and for repeating the obtaining of the estimated values and the updating of the adaptive coefficients, and for thereby learning each of the adaptive coefficients.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Audio decoder and audio decoding method
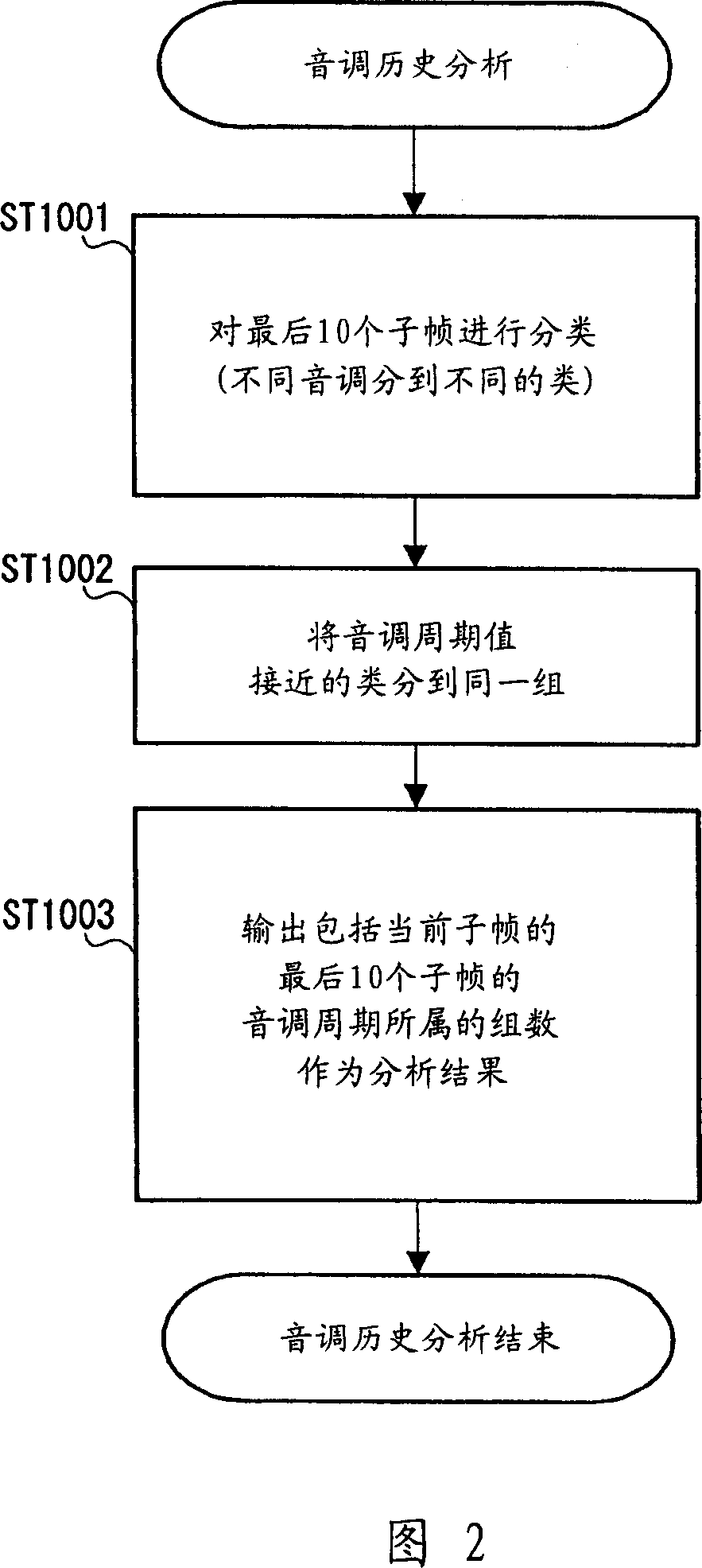
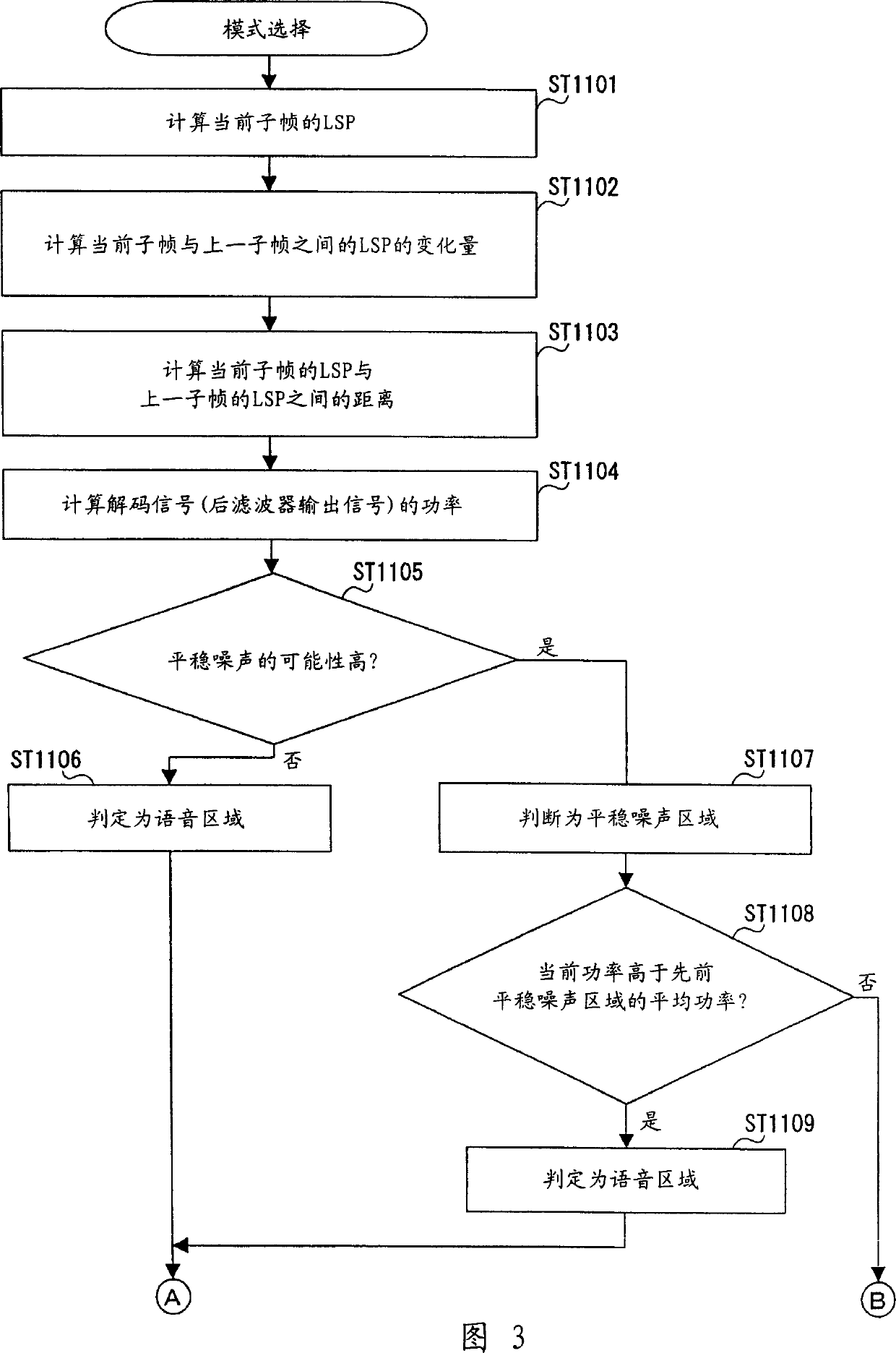
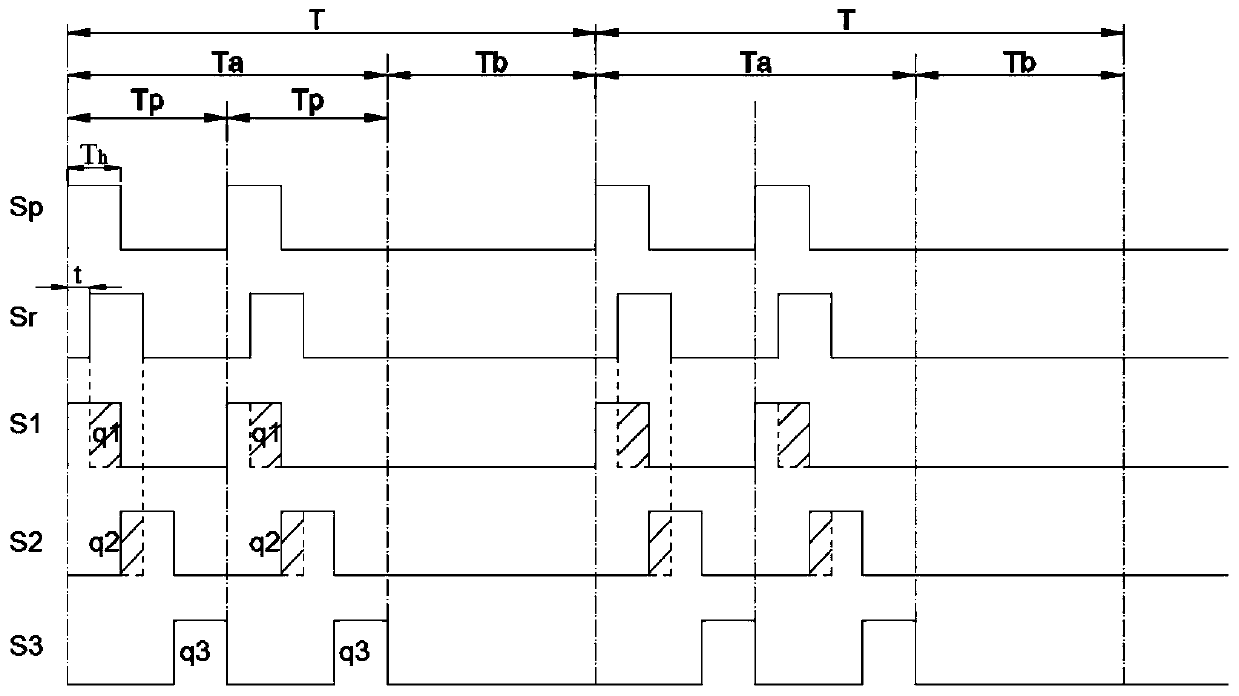
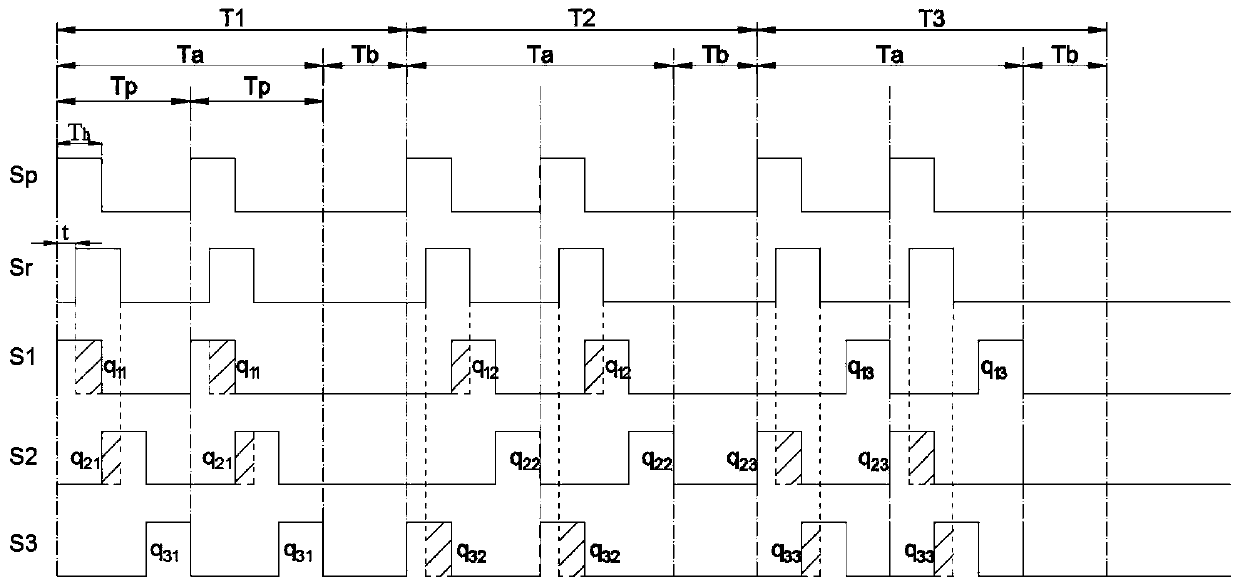
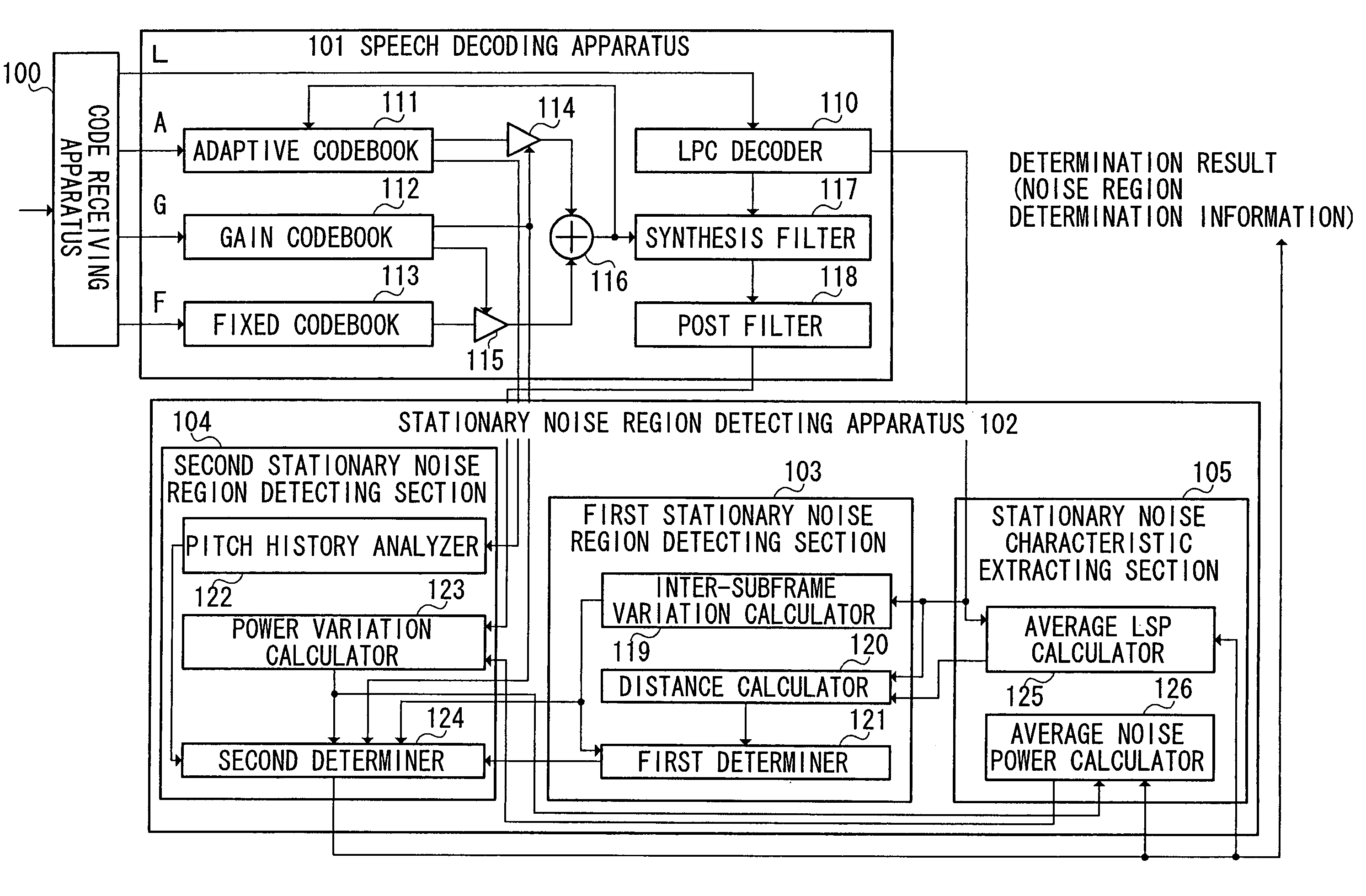
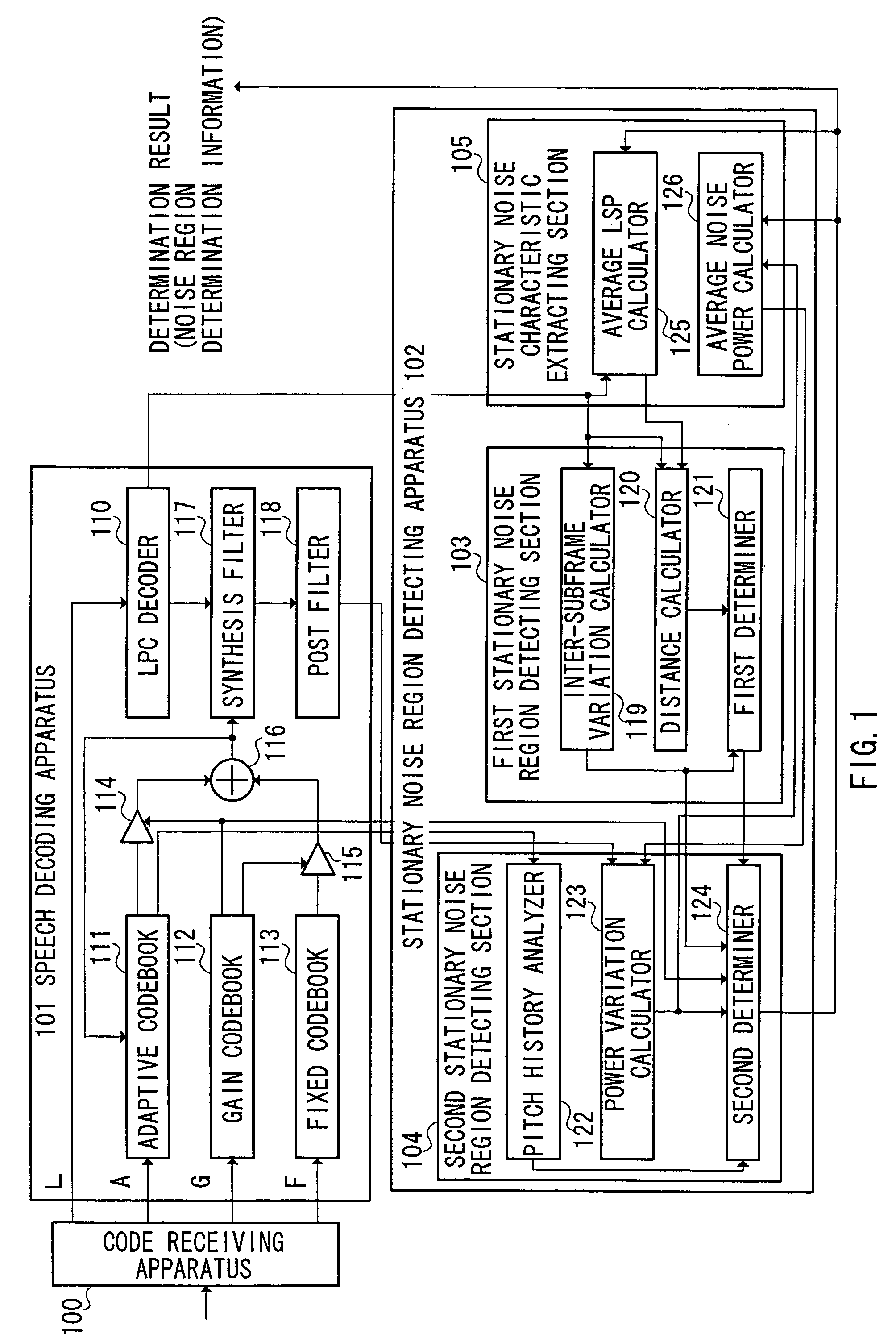
First determiner 121 provisionally determines whether a current processing unit is a stationary noise region based on a determination result on stationary characteristics of a decoded signal. Based on the provisional determination result and a determination result on periodicity of the decoded signal, second determiner 124 further determines whether the current processing unit is a stationary noise region, whereby a decoded signal including a stationary speech signal such as a stationary vowel is distinguished from a stationary noise, and thus the stationary noise region is detected accurately.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
Method for recovering target speech based on speech segment detection under a stationary noise
Method for recovering target speech by extracting signal components falling in a speech segment, which is determined based on separated signals obtained through the Independent Component Analysis, thereby minimizing the residual noise in the recovered target speech. The present method comprises: the first step of receiving target speech emitted from a sound source and a noise emitted from another sound source and extracting estimated spectra Y* corresponding to the target speech by use of the Independent Component Analysis; the second step of separating from the estimated spectra Y* an estimated spectrum series group y* in which the noise is removed by applying separation judgment criteria based on the kurtosis of the amplitude distribution of each of estimated spectrum series in Y*; the third step of detecting a speech segment and a noise segment of the total sum F of all the estimated spectrum series in y* by applying detection judgment criteria based on a predetermined threshold value T that is determined by the maximum value of F; and the fourth step of extracting components falling in the speech segment from the estimated spectra Y* to generate a recovered spectrum group of the target speech for recovering the target speech.
Owner:KITAKYUSHU FOUND FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF IND SCI & TECH +1
Automatic Selection of Reduction or Enhancement of Transient Sounds
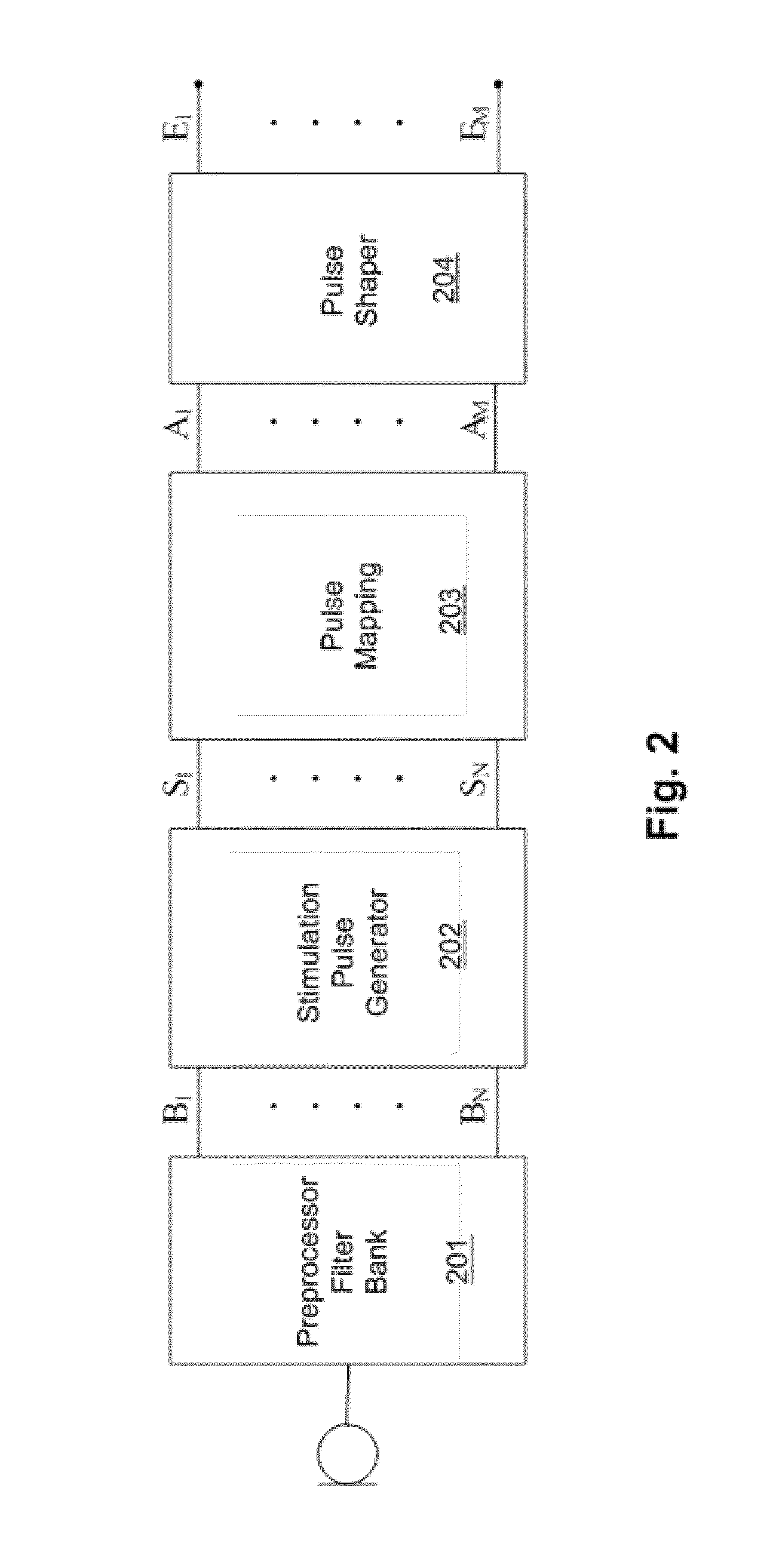
ActiveUS20150163604A1Reduce noiseReduce distortion problemsHead electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsStationary noiseEngineering
A system and method of generating electrode stimulation signals for electrode contacts in an electrode array associated with a hearing implant is presented. An input audio signal is processed to generate a plurality of band pass channel signals each representing an associated band of audio frequencies. A stationary noise reduction is applied so as to provide a stationary noise reduced channel envelope from each channel signal. A transient in one or more of the channel envelopes is detected. The channel envelopes are modified as a function of whether the transient is transient noise or transient speech, so as to form transient modified envelope. The transient modified envelopes are used to generate electrode stimulation signals to the electrode contacts.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Speech enhancement method and system
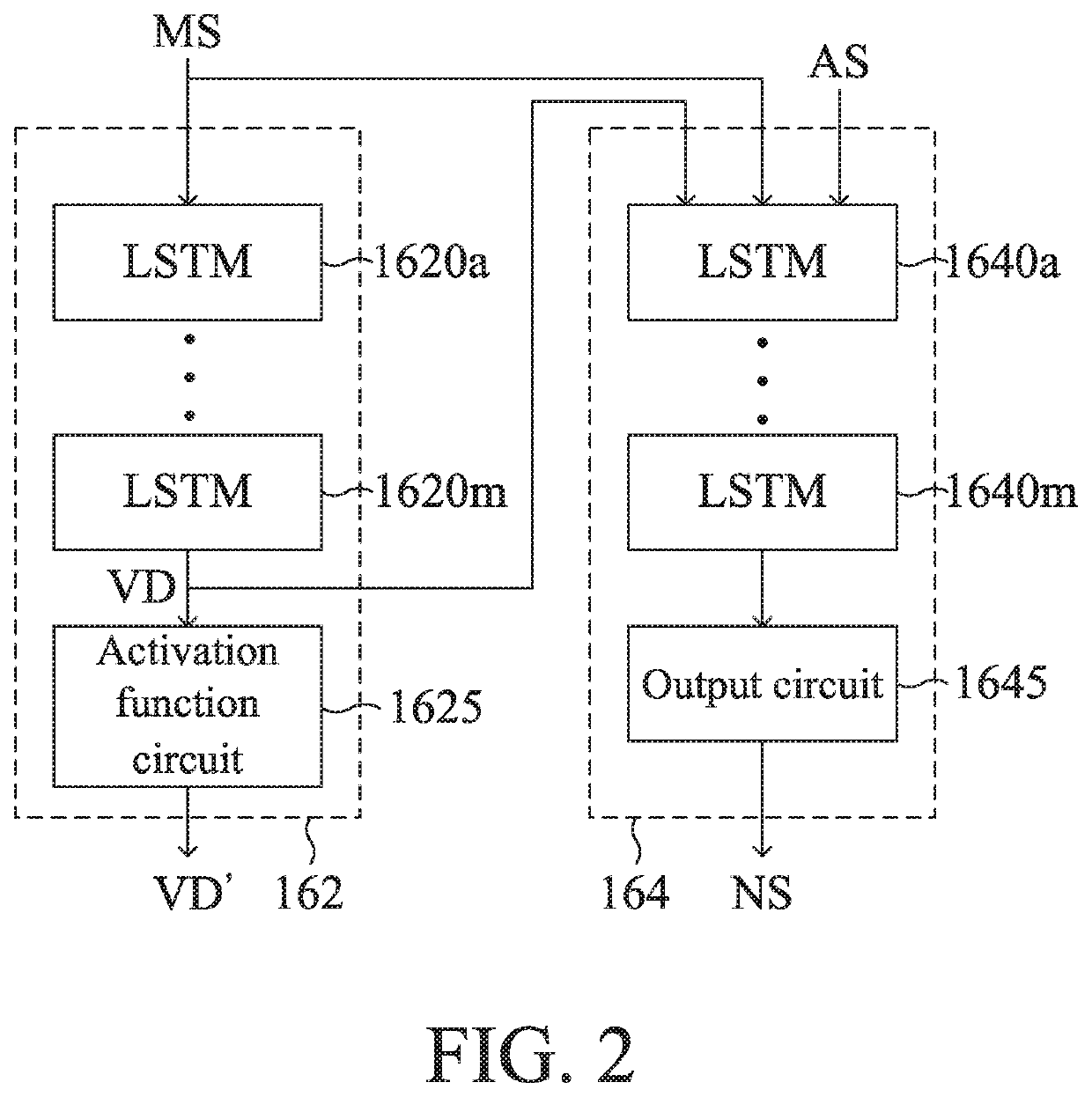
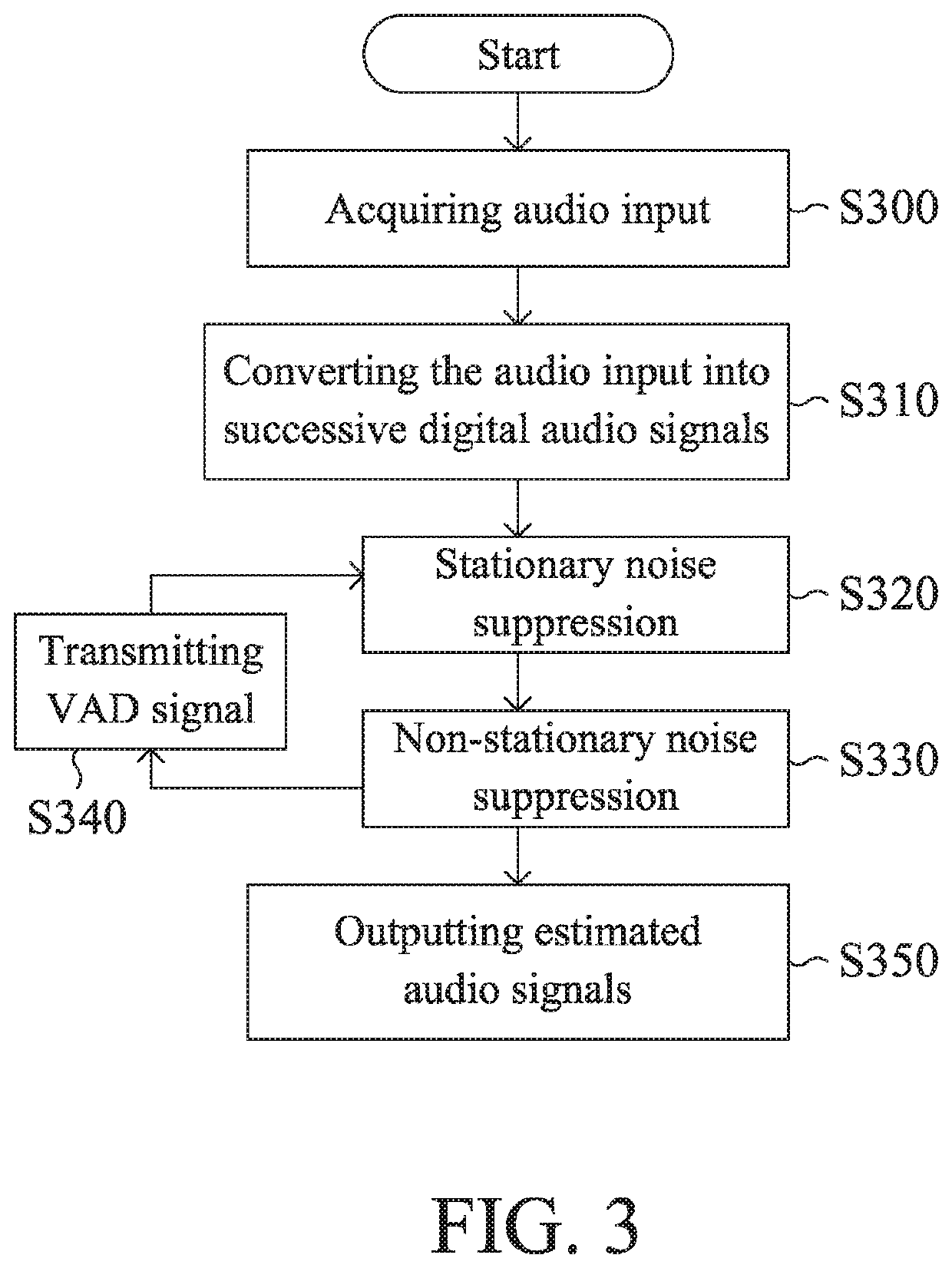
ActiveUS20200312343A1Reduce stationary noiseReduce noiseEnsemble learningSpeech analysisDigital signal processingStationary noise
A speech enhancement method and a speech enhancement system are provided. The speech enhancement method performs two-stage noise suppression by using digital signal processing and neural network approach. The first-stage noise suppression generates artifact signals by reducing stationary noise in the digital audio signals. The second-stage noise suppression performs voice activity detection and further reduces non-stationary noise in the artifact signals. The result of the voice activity detection is fed back to establish or update a noise model used in the first-stage noise suppression.
Owner:QNAP SYST INC
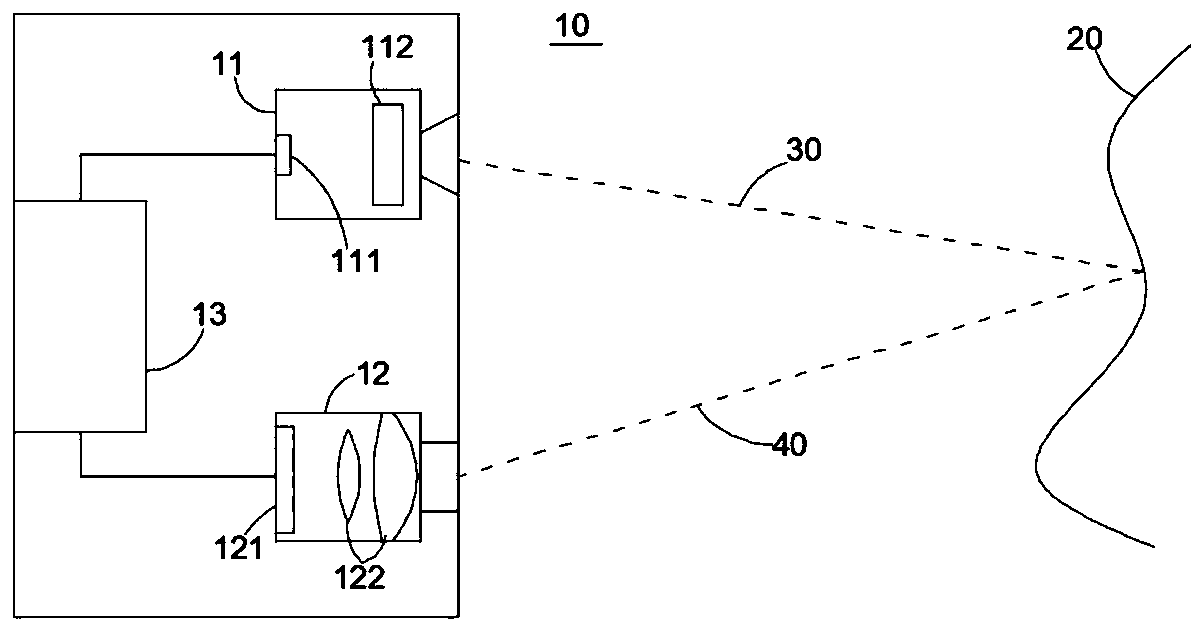
Time-of-flight depth camera and single-frequency modulation-demodulation noise-reducing distance measuring method
ActiveCN110361751AReduce or eliminate stationary noiseShort pulse widthElectromagnetic wave reradiationPulse beamStationary noise
The invention provides a time-of-flight depth camera and a single-frequency modulation-demodulation noise-reducing distance measuring method. The time-of-flight depth camera comprises a transmitting module, an acquisition module and a processing circuit, wherein the transmitting module comprises a light source which is used for transmitting a pulse beam to an object to be measured; the acquisitionmodule comprises an image sensor composed of at least one pixel, each pixel comprises at least three taps, and the taps are sued for acquiring a charge signal generated by a reflected pulse beam which is reflected by means of the object to be measured and / or a charge signal of background light; and the processing circuit is used for controlling the at least three taps to acquire the charge signals alternatively between at least three frame periods of a macro period, and receiving data of the charge signals to calculate a time of flight of the pulse beam and / or a distance of the object to be measured. The expansion of the measurement distance is no longer limited by the pulse width, and the fixed-pattern noise caused by mismatch between the taps or read-out circuits due to process manufacturing errors and the like is reduced or eliminated by adopting a tap alternative acquisition method.
Owner:SHENZHEN ORBBEC CO LTD
Speech decoder that detects stationary noise signal regions
A first determiner 121 tentatively determines whether the current processing unit represents a stationary noise period, based on stationary properties of a decoded signal. Based on the tentative determination result and a determination result of the periodicity of the decoded signal, a second determiner 124 determines whether the current processing unit represents a stationary noise period, thereby distinguishing a decoded signal including a stationary speech signal such as a stationary vowel from stationary noise and correctly identifying the stationary noise period.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
Method for enhancing voice based on signal to noise ratio soft masking
The invention discloses a method for enhancing voice based on signal to noise ratio soft masking. The method comprises: establishing noise power spectrum updates of a sub-band time varying coefficient, using different threshold update smooth spectrums for different frequency points, enhancing voice and restraining noise; determining a posterior signal to noise ratio from a noise power spectrum, performing iterative computation to obtain a prior signal to noise ratio of a present frame according to the posterior signal to noise ratio and the prior signal to noise ratio of a previous frame, and obtaining that each frequency point is in a masking region or in a target signal region according to values of the prior signal to noise ratio. A masking value is calculated by probability distribution obtained by hypothesis testing. The method uses correlation of adjacent frames to extract information to realize enhancement of voice spectrum smooth iteration estimation. For non-stationary noise and strong background noise, a voice enhancement algorithm based on signal to noise ratio soft masking is provided. A rapid tracking noise algorithm performs smooth update on the non-stationary noise frame by frame, preferably estimating a noise spectrum. The algorithm can effectively restrain background noise and improve voice quality and speech intelligibility after denoising.
Owner:HUNAN INT ECONOMICS UNIV
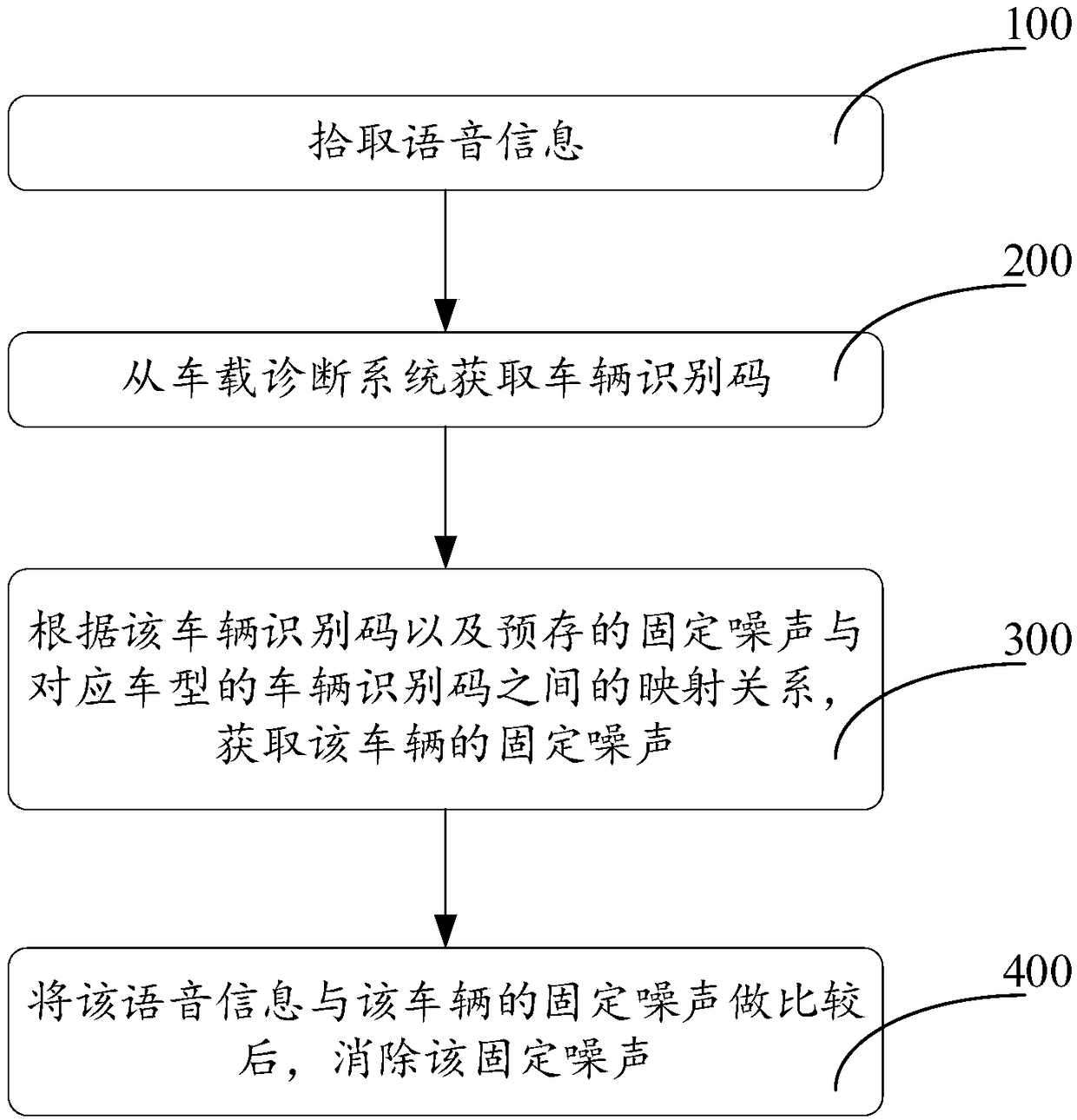
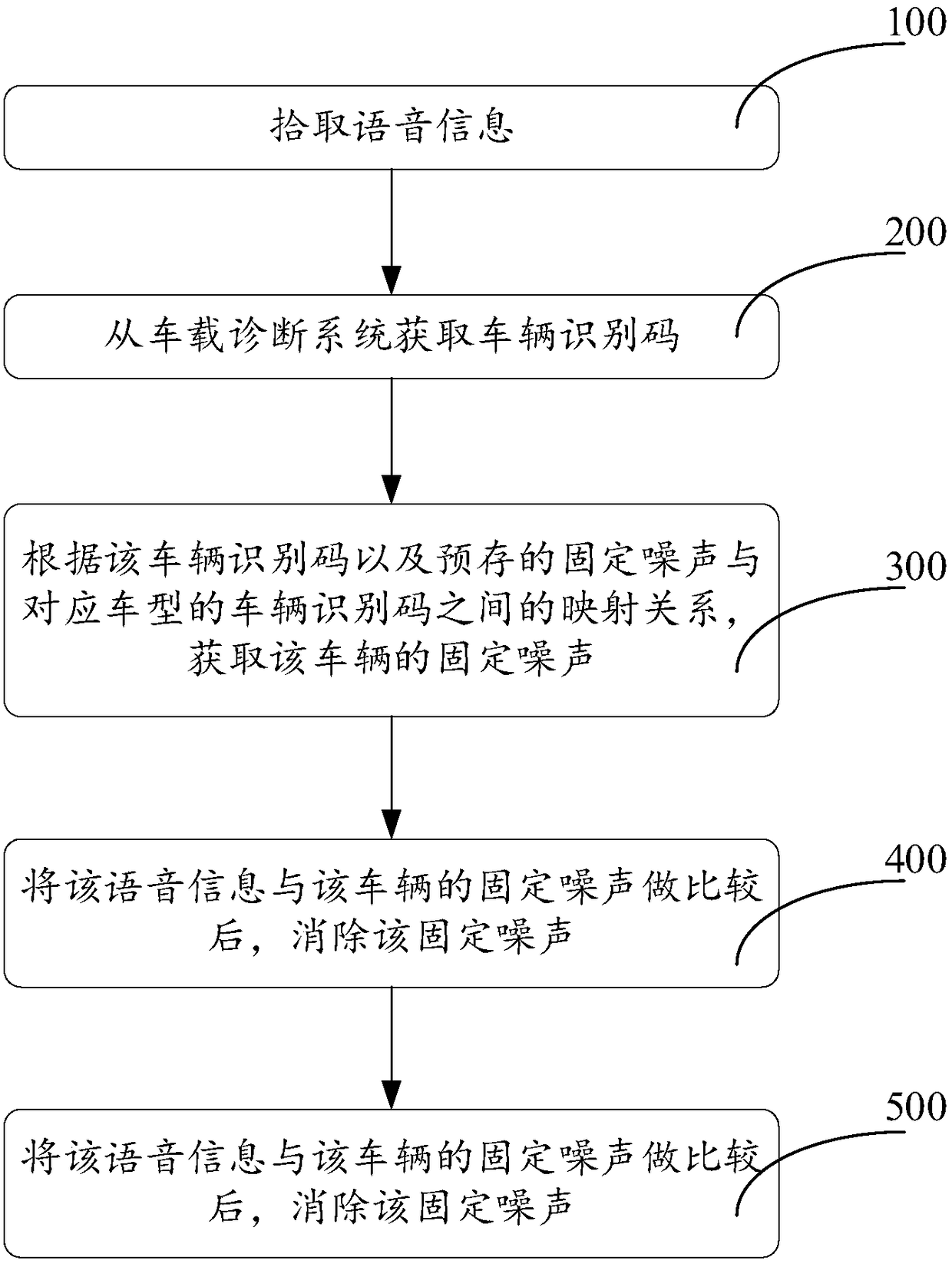
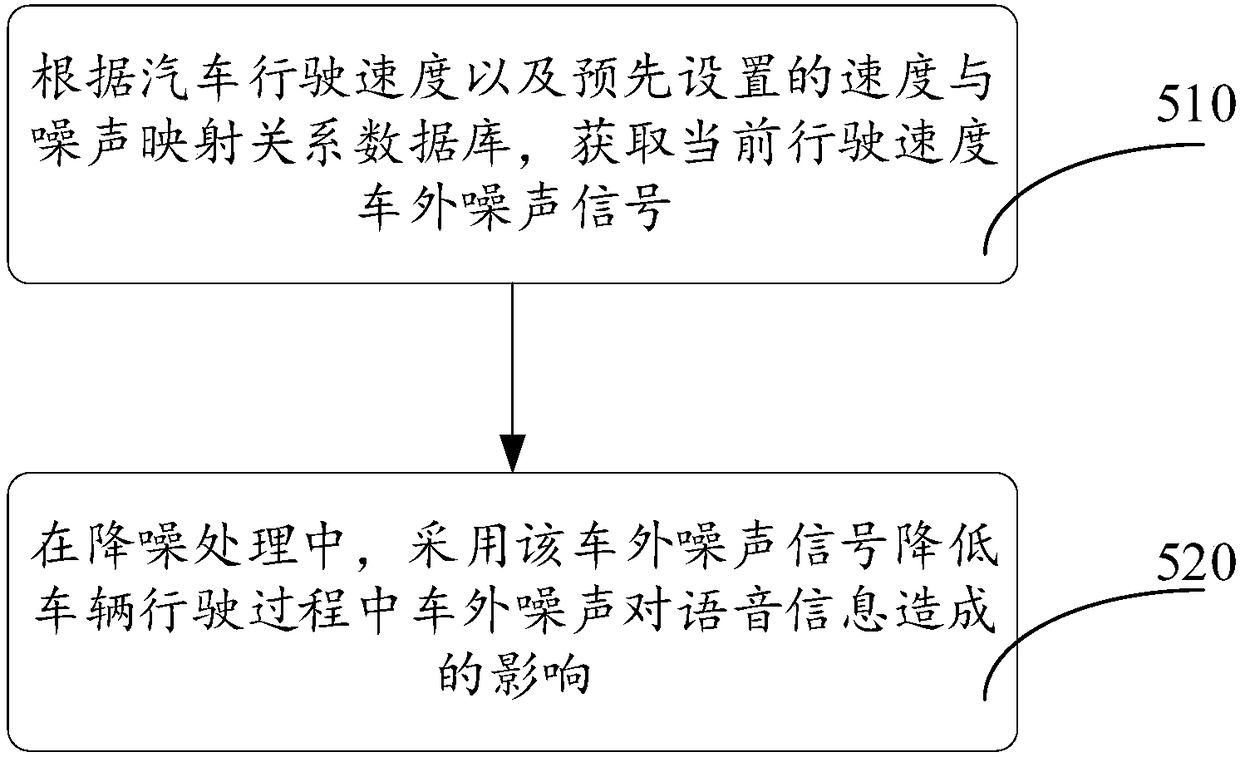
Speech signal processing method and vehicle-mounted electronic device
The invention relates to a speech signal processing method and a vehicle-mounted electronic device. The method includes the following steps that: speech information is picked up; a vehicle identification code is acquired from a vehicle-mounted diagnostic system; the constant noises of a vehicle are acquired according to the vehicle identification code and mapping relations between pre-stored constant noises and vehicle identification codes of corresponding vehicle models, wherein the mapping relations between the pre-stored constant noises and vehicle identification codes of the correspondingvehicle models include the constant noises of different vehicle models and mapping relations between the constant noises of the different vehicle models and the vehicle identification codes of the corresponding vehicle models; and after the speech information is compared with the constant noises of the vehicle, the constant noises are eliminated. Since the constant noises introduced by the vehicleare obtained in advance, the constant noises can be directly eliminated during sound processing.
Owner:ANKER INNOVATIONS TECH CO LTD
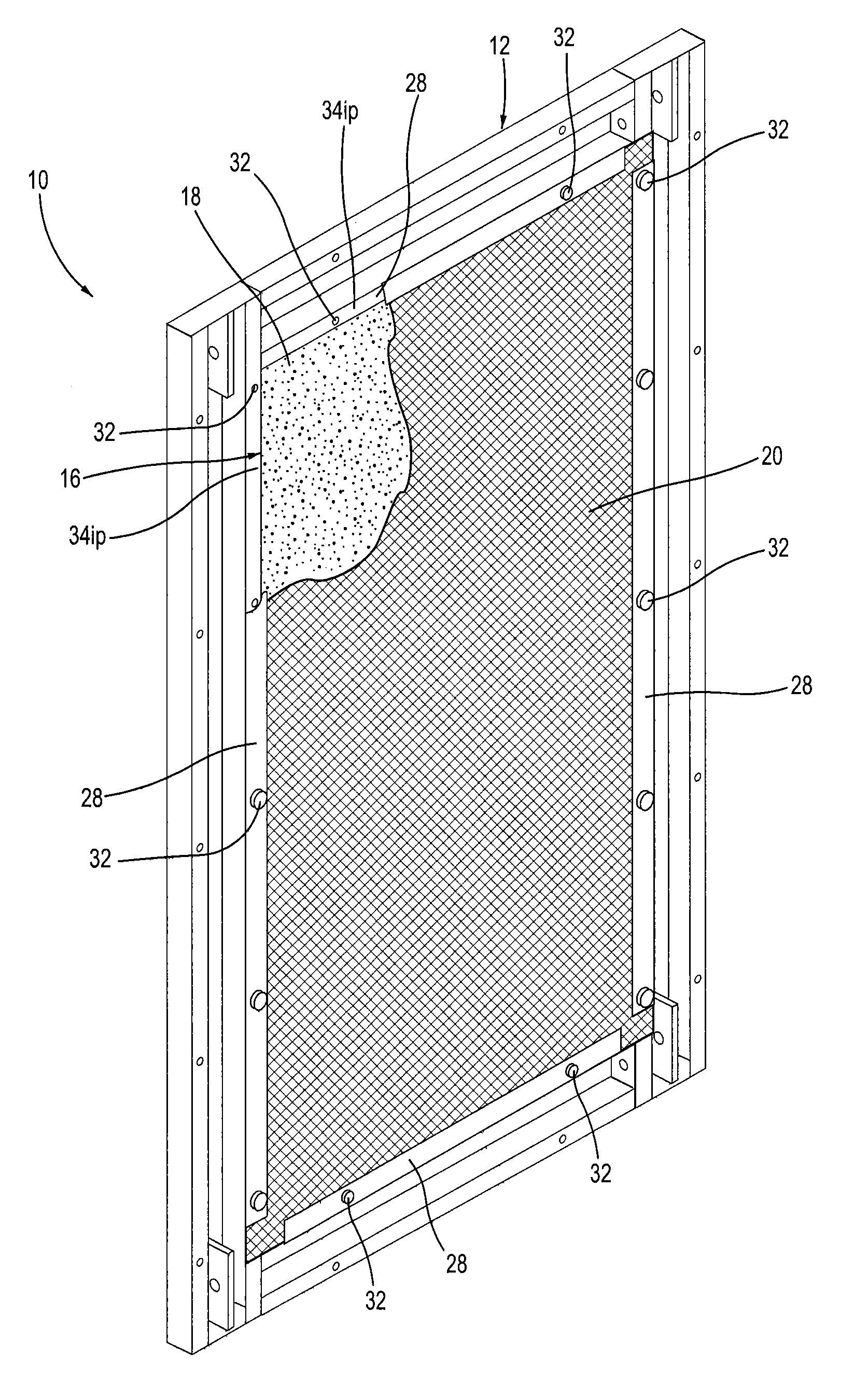
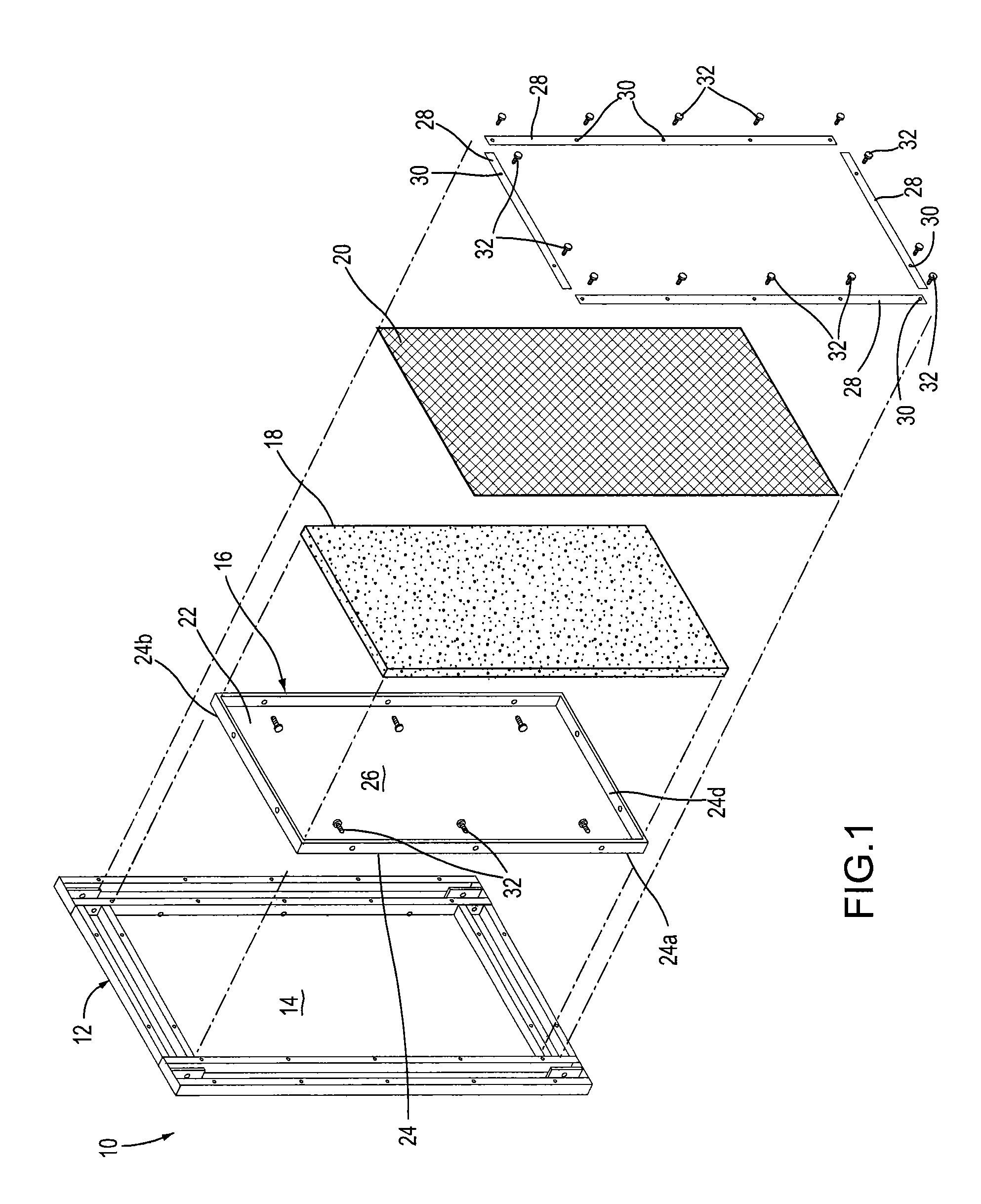
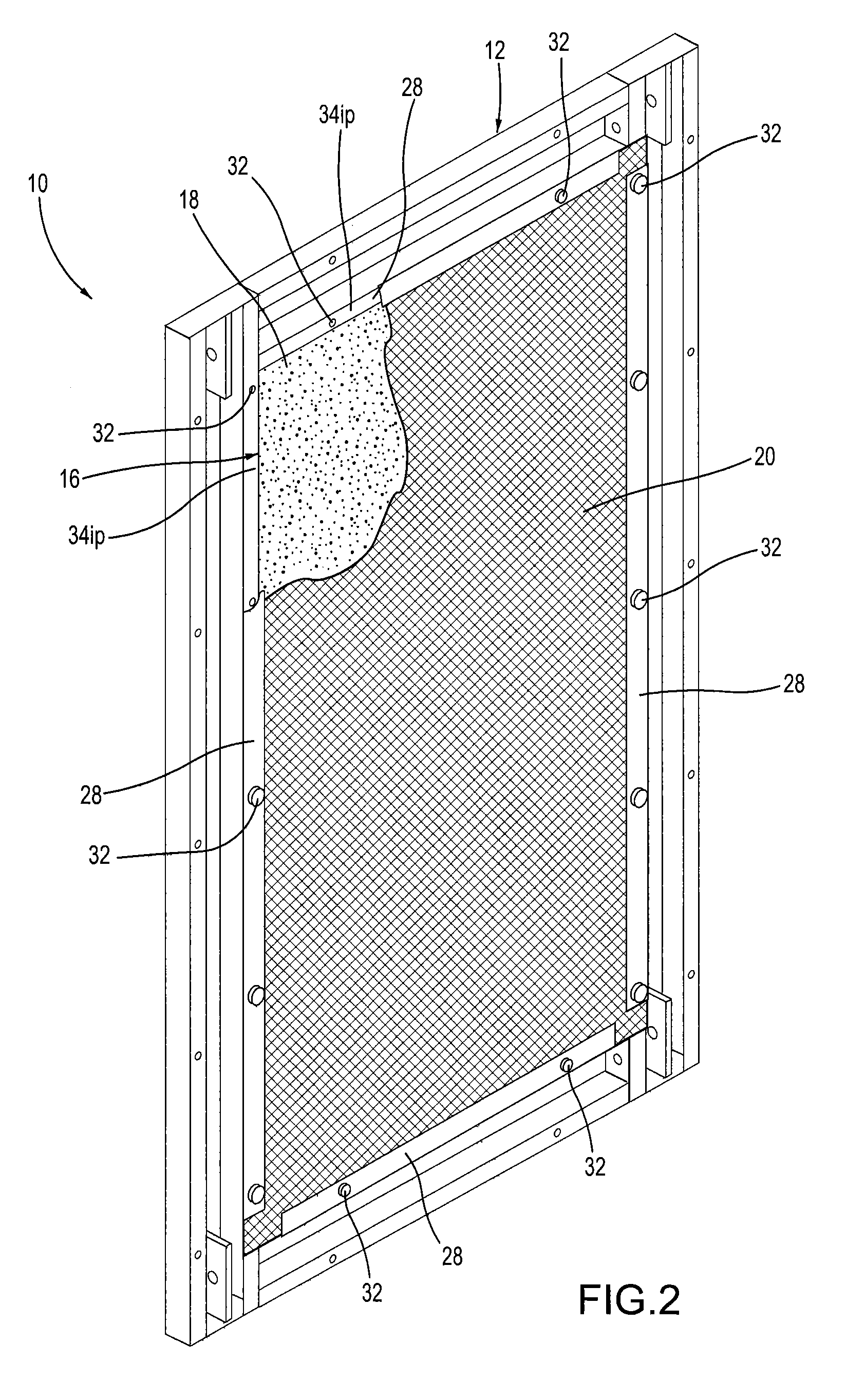
Noise abatement wall and a noise abatement wall system
A noise abatement wall includes a frame defining a window, at least one shell, at least one sheet of sound-insulating material and a sheet of screen material. The at least one shell has a base panel portion and a peripheral panel portion integrally formed with and extending perpendicularly from the base panel portion to surround the base panel portion thereby forming a shell cavity. The at least one shell is sized and configured to be received by the window in a close-fitting relationship therewith and is connected to the frame. The at least one sheet of sound-insulating material is disposed in and occupies the shell cavity. The sheet of screen material covers the at least one sheet of sound-insulating material and is connected to the frame. A plurality of noise abatement walls are connected together to form a noise abatement wall system for abating noise generated from stationary noise-generating equipment.
Owner:EVAPCO
Imaging device and image processing program for estimating fixed pattern noise from partial noise output of available pixel area
ActiveUS8300977B2Television system detailsDigitally marking record carriersPattern recognitionImaging processing
An imaging device of the present invention includes an image capturing unit, a noise obtaining unit, a fixed noise calculating unit, and a noise eliminating unit. The image capturing unit generates image data by photoelectrically converting, pixel by pixel, a subject image formed on an available pixel area of a light-receiving surface. The noise obtaining unit reads a noise output from a partial area of the available pixel area. The fixed noise calculating unit calculates an estimation of fixed pattern noise of the available pixel area based on the noise output read from the partial area. The noise eliminating unit subtracts the fixed pattern noise from the image data.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com