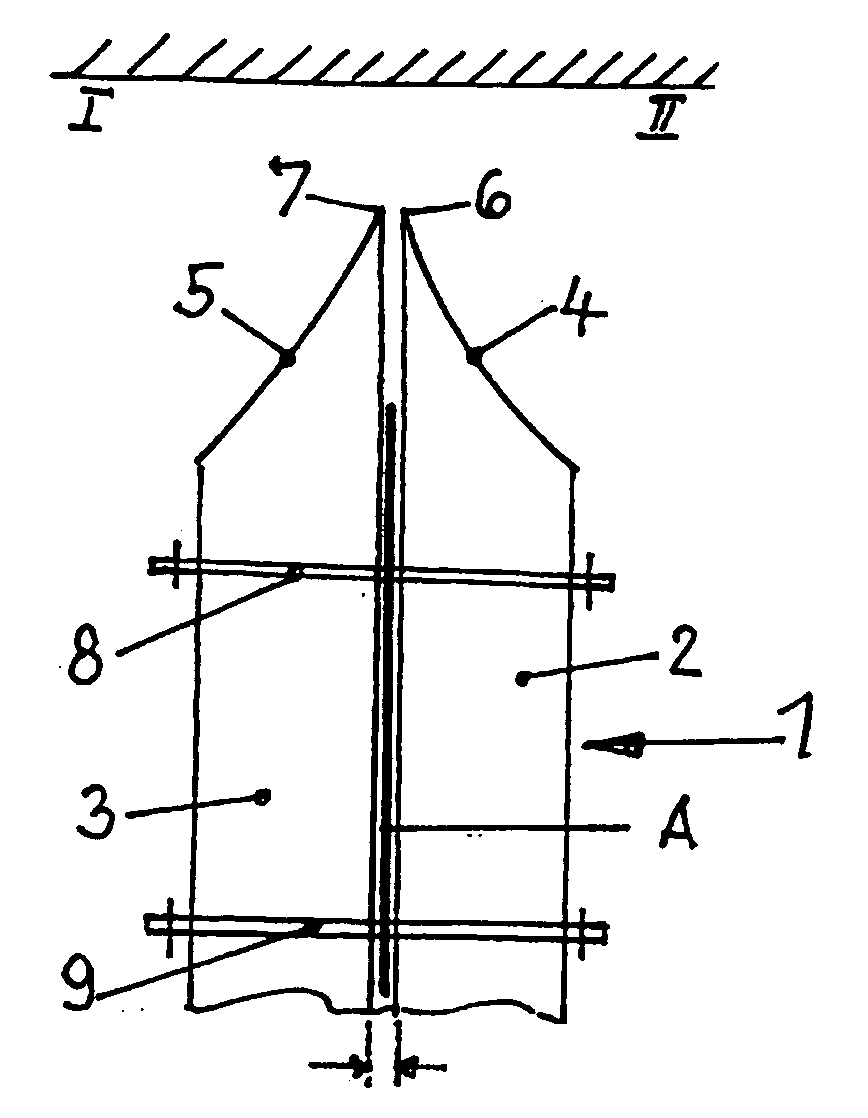
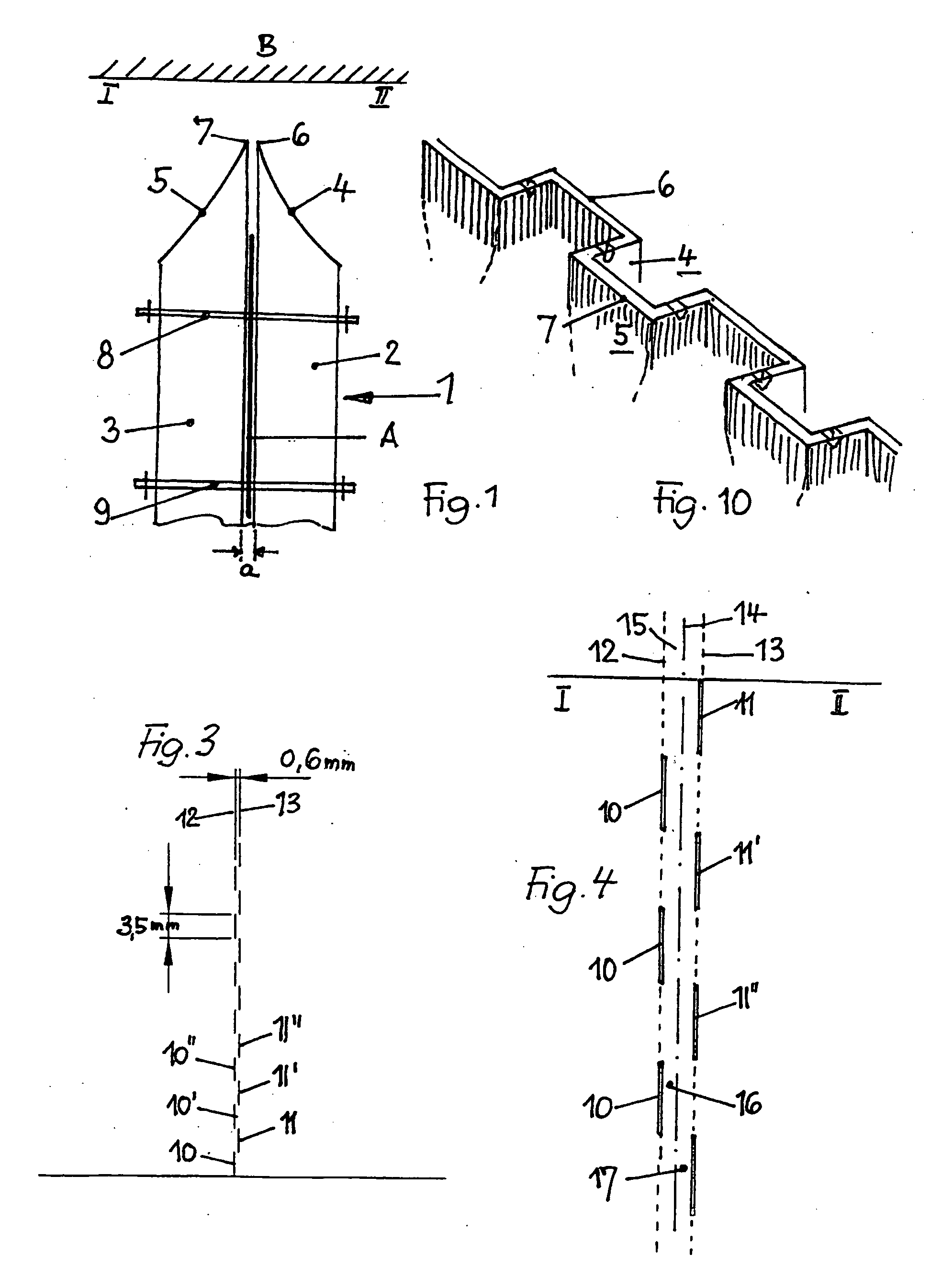
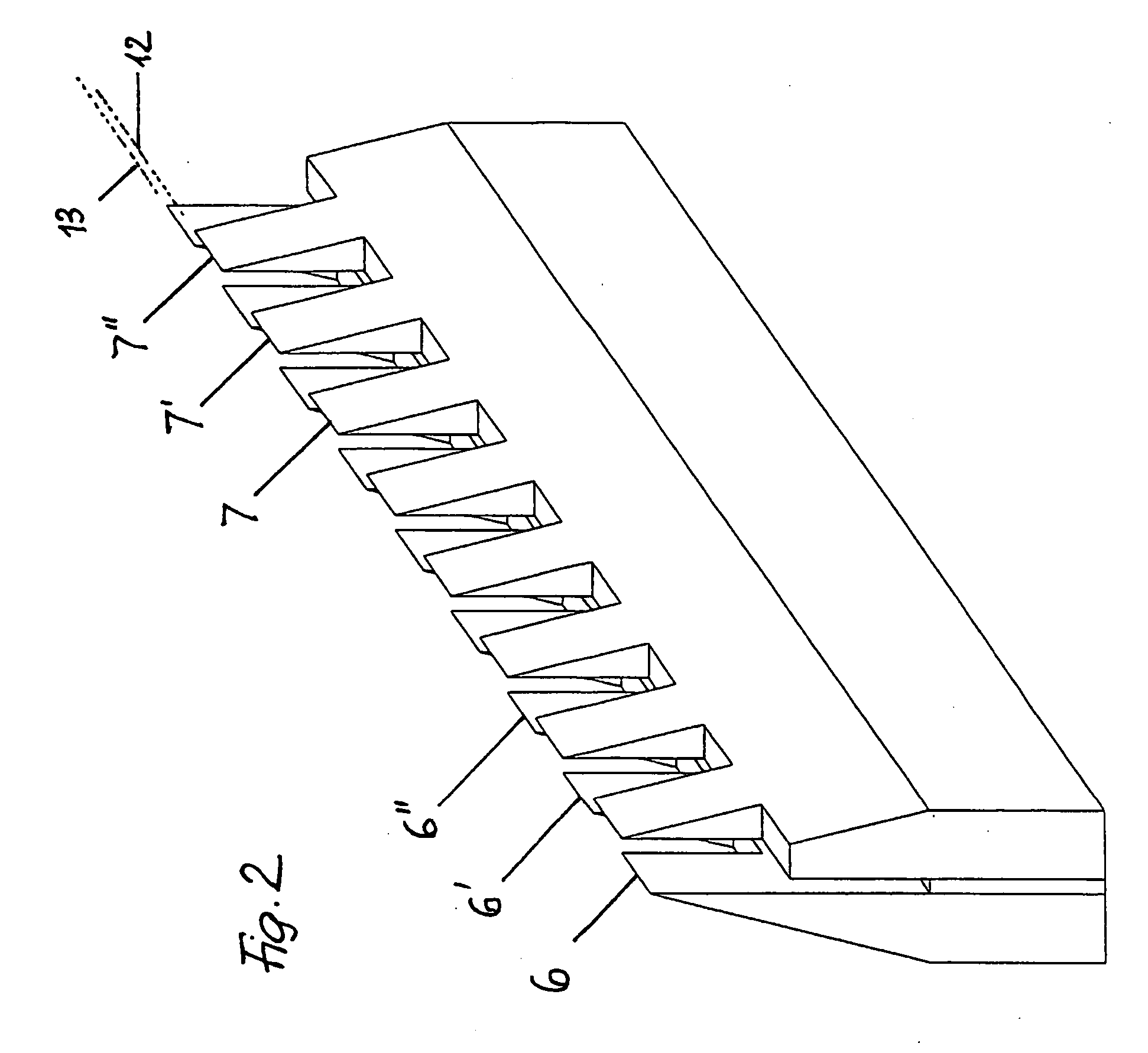
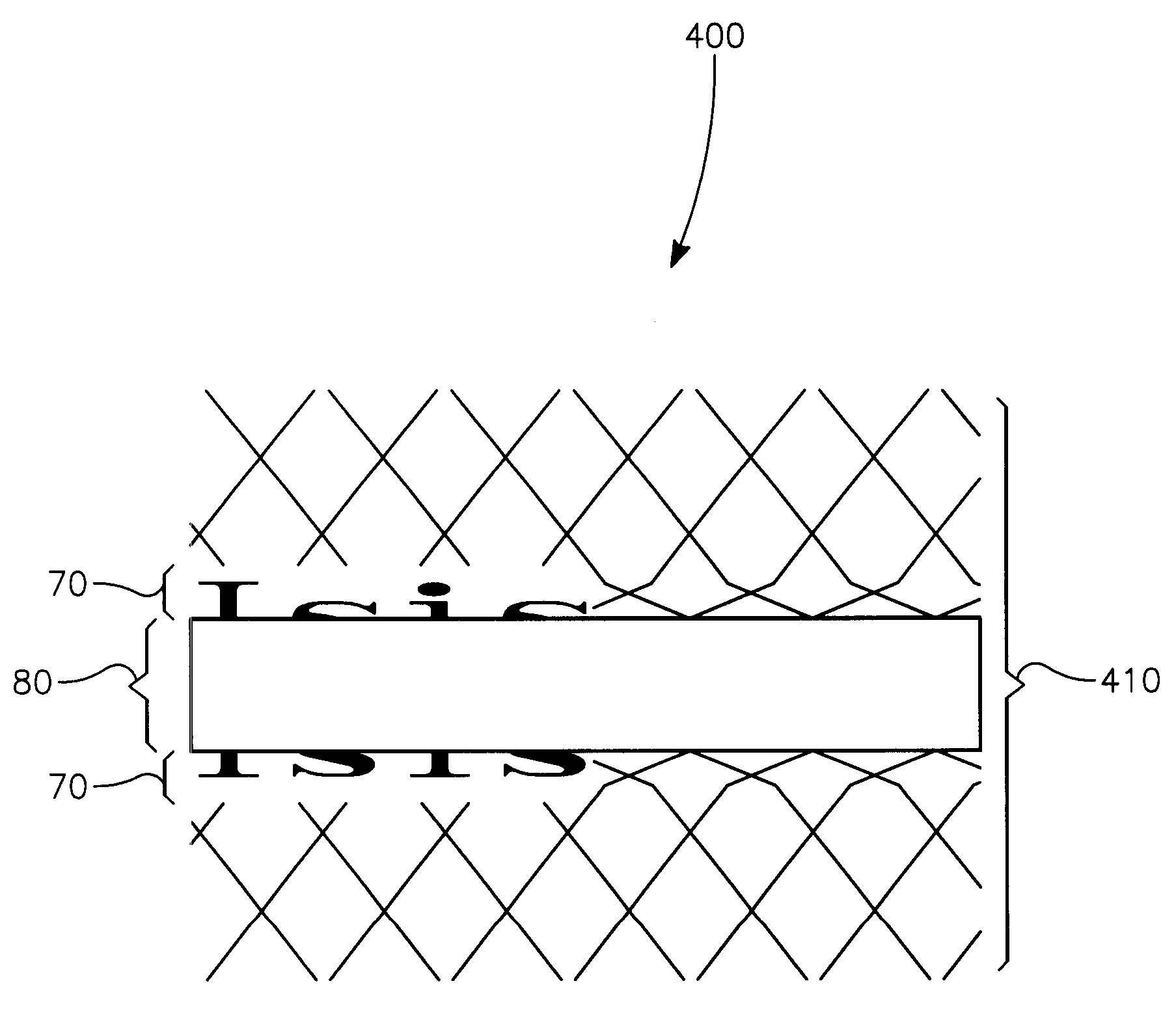
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
43results about How to "Distortion free" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
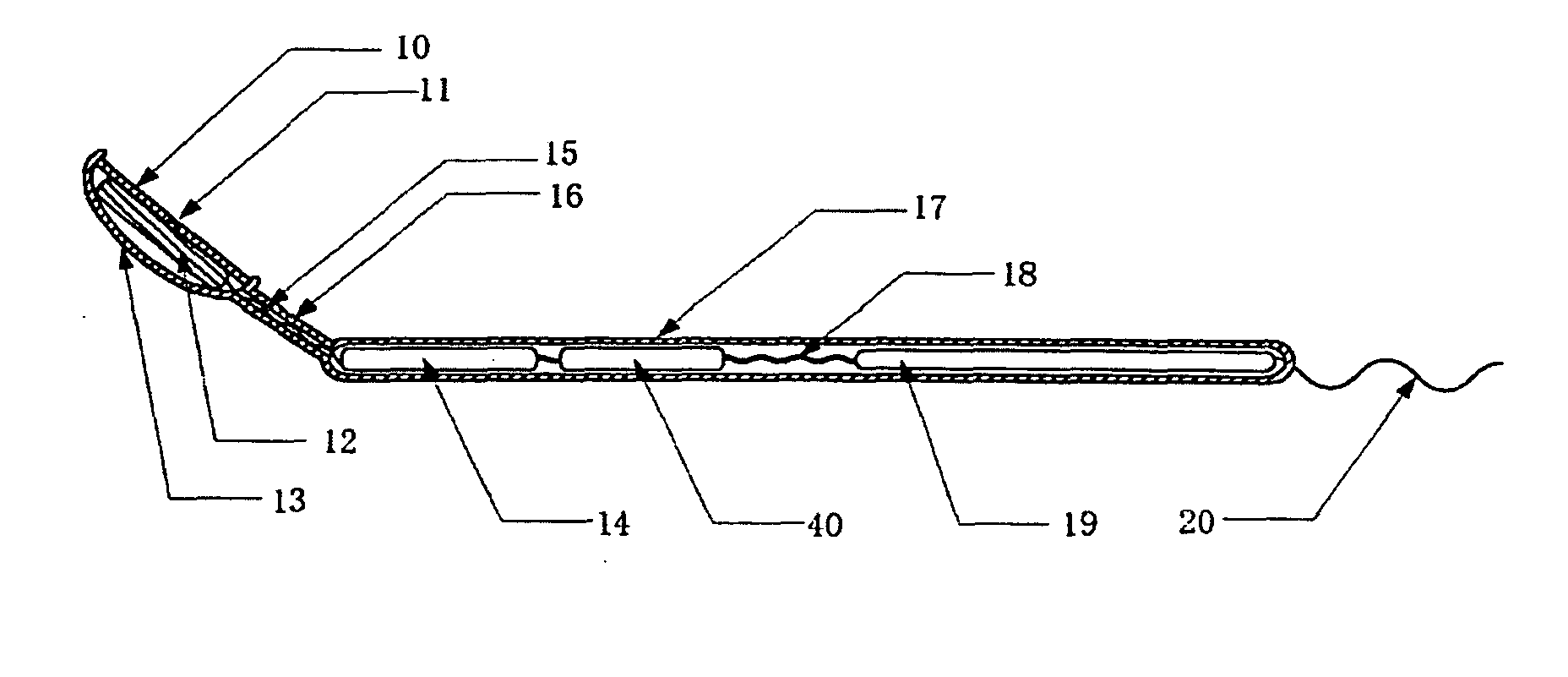
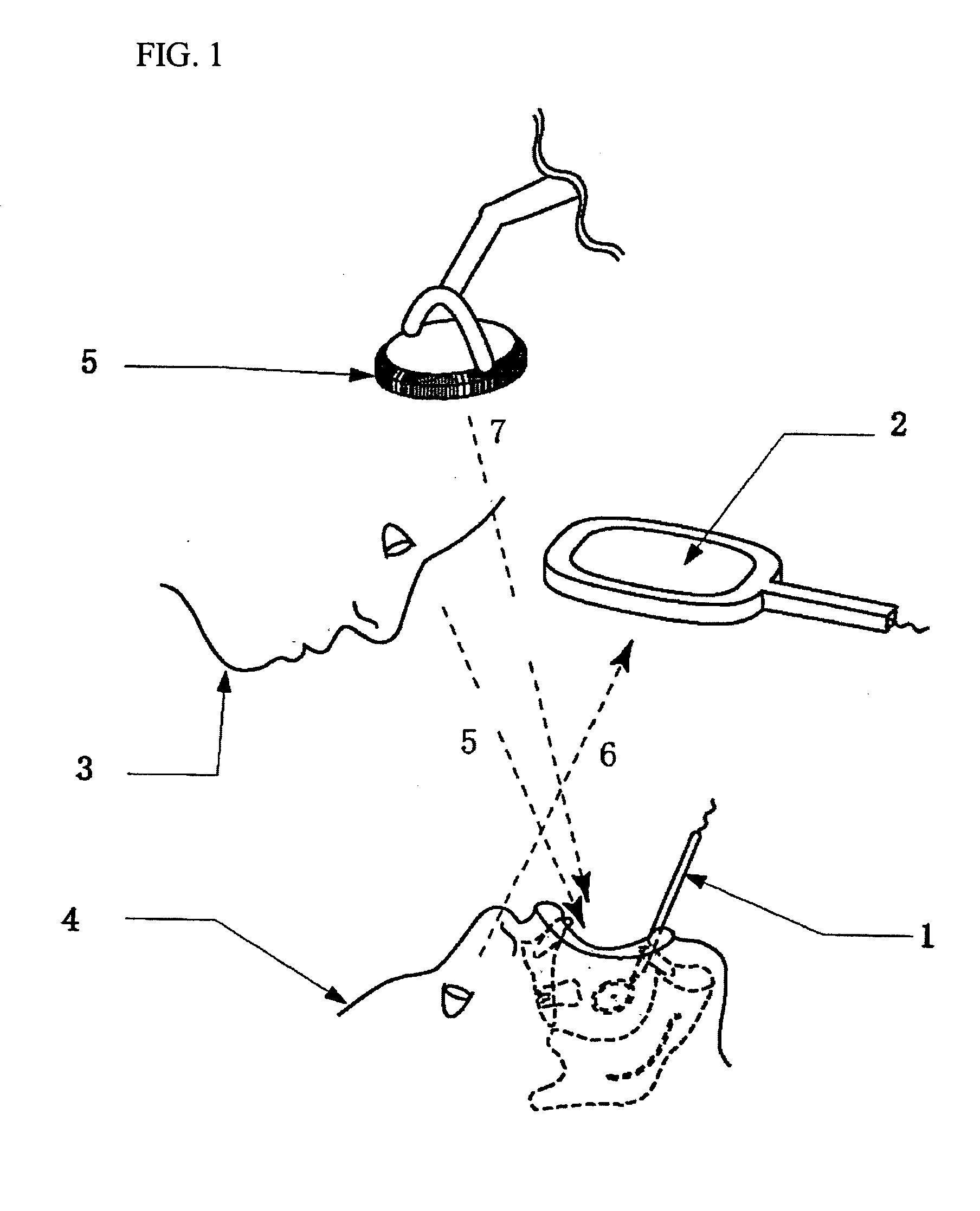
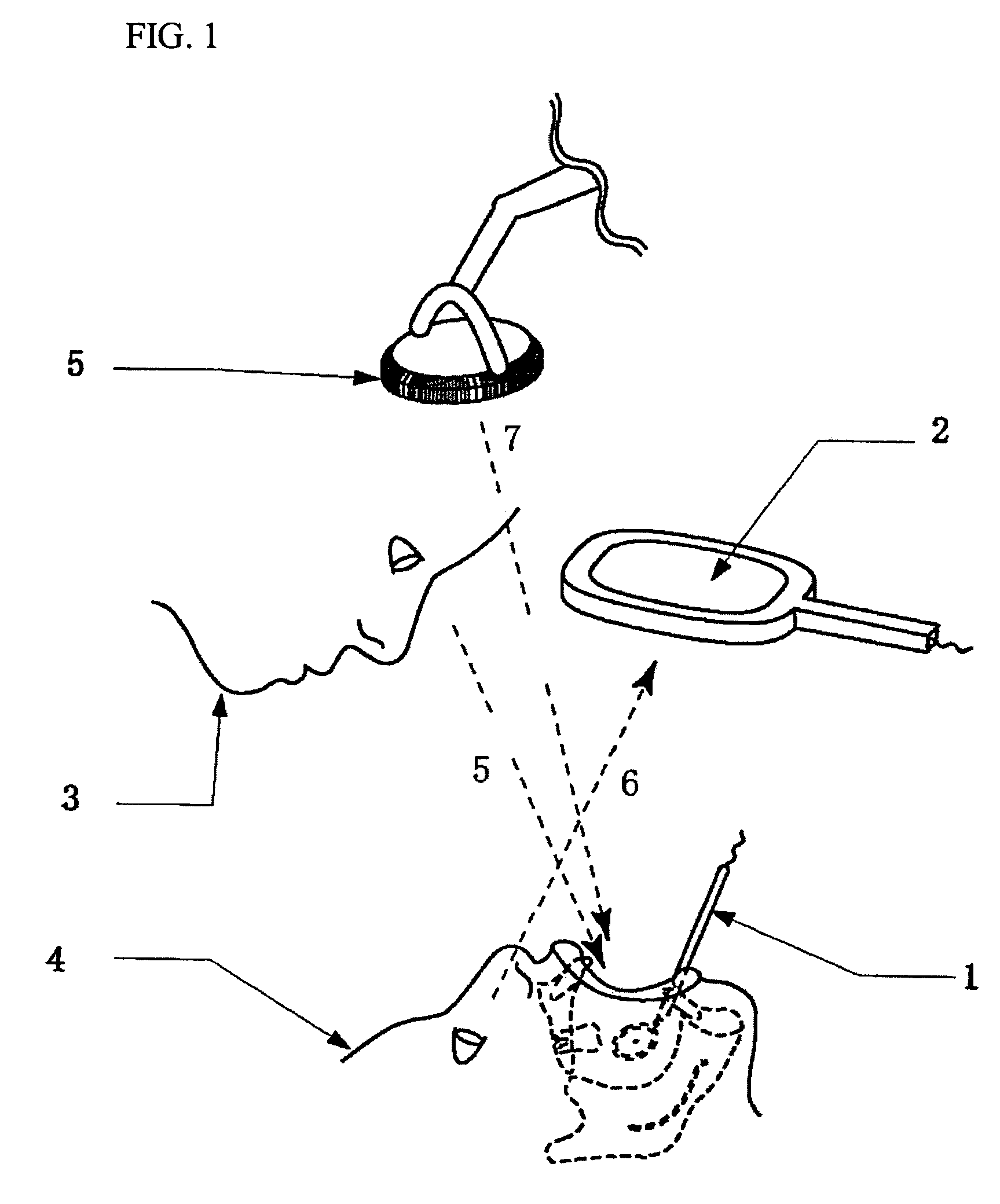
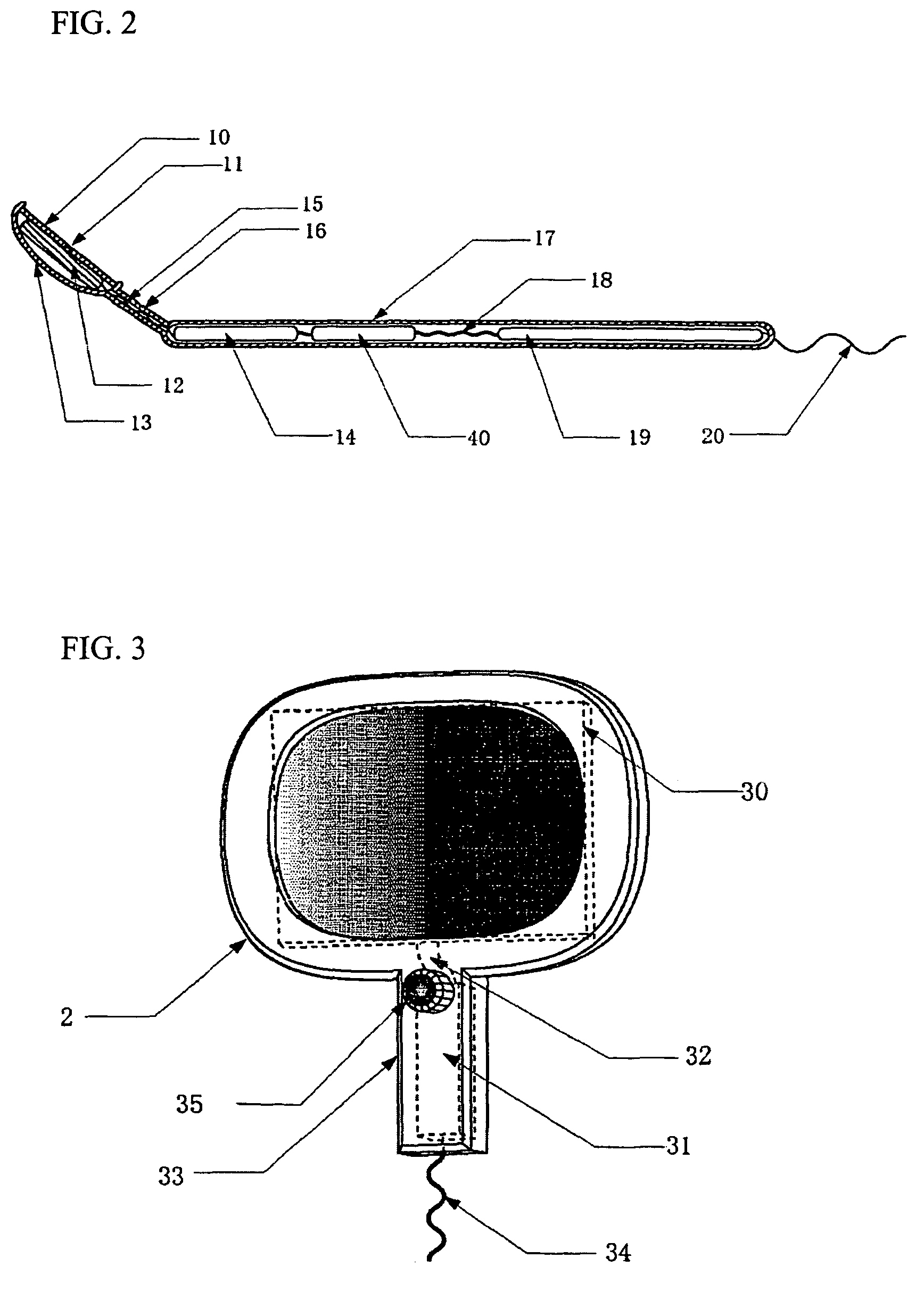
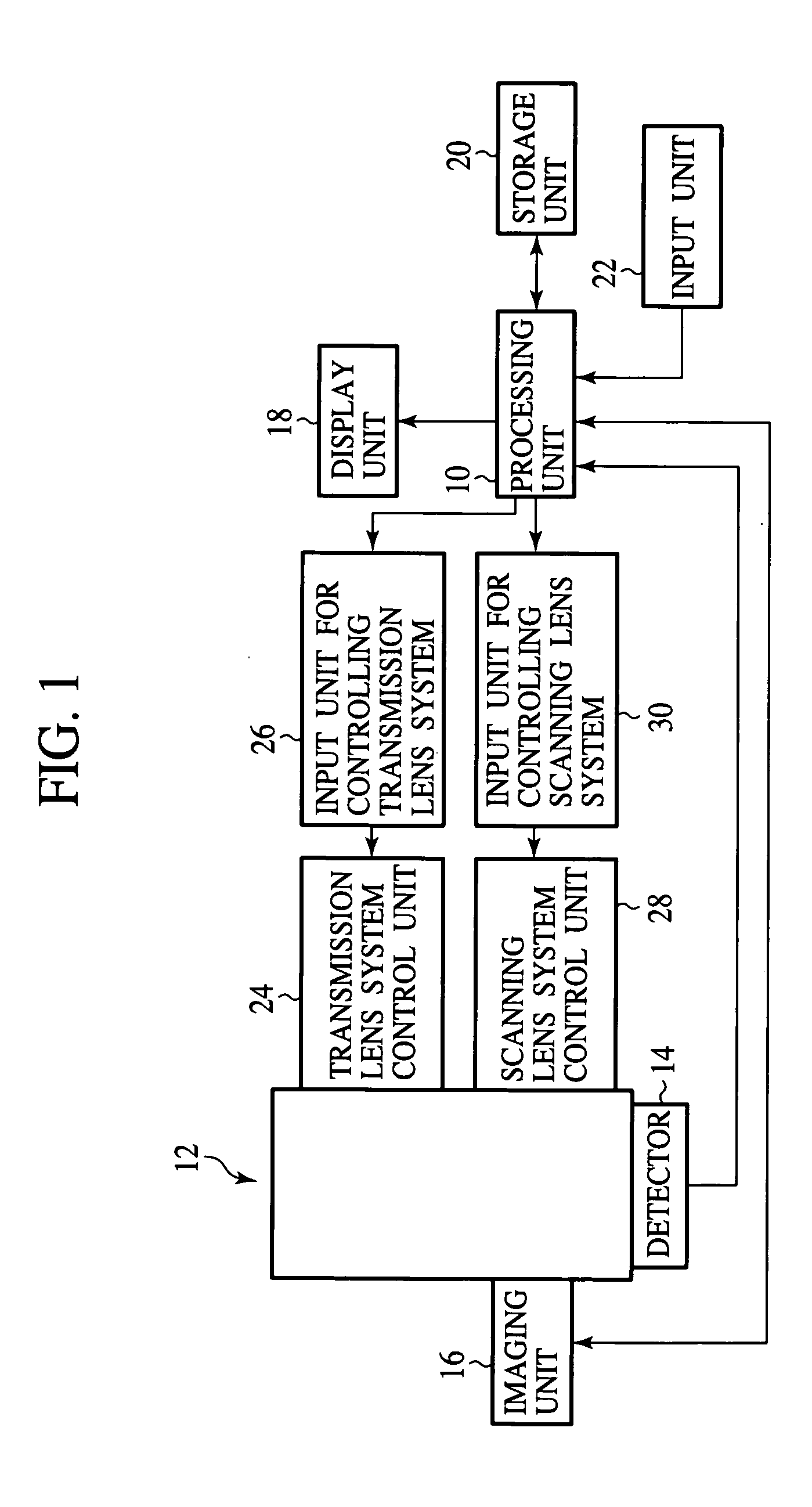
Dental mirror, and an intraoral camera system using the same
An intraoral camera system is disclosed, which includes a dental mirror having a aperture for transmitting light therethrough, the aperture being provided in the center or any other part of the mirror by removing a reflective material therefrom. A CCD camera is secured on a back surface of the dental mirror in such a manner that the aperture coincides with its incident portion coincides with aperture in the dental mirror. A hand mirror shaped monitor is also provided for displaying image data received from the CCD camera via cable or radio, and a server is also provided that is capable of storing and outputting the image data any time onto the monitor, wherein even though a patient is laid down on a chair in a horizontal position, the patient or a third party can utilize the hand mirror shaped monitor to view an image which is very close to the image that a dentist views through reflection from the dental mirror having said CCD camera built therein.
Owner:TAKAHASHI ATSUSHI
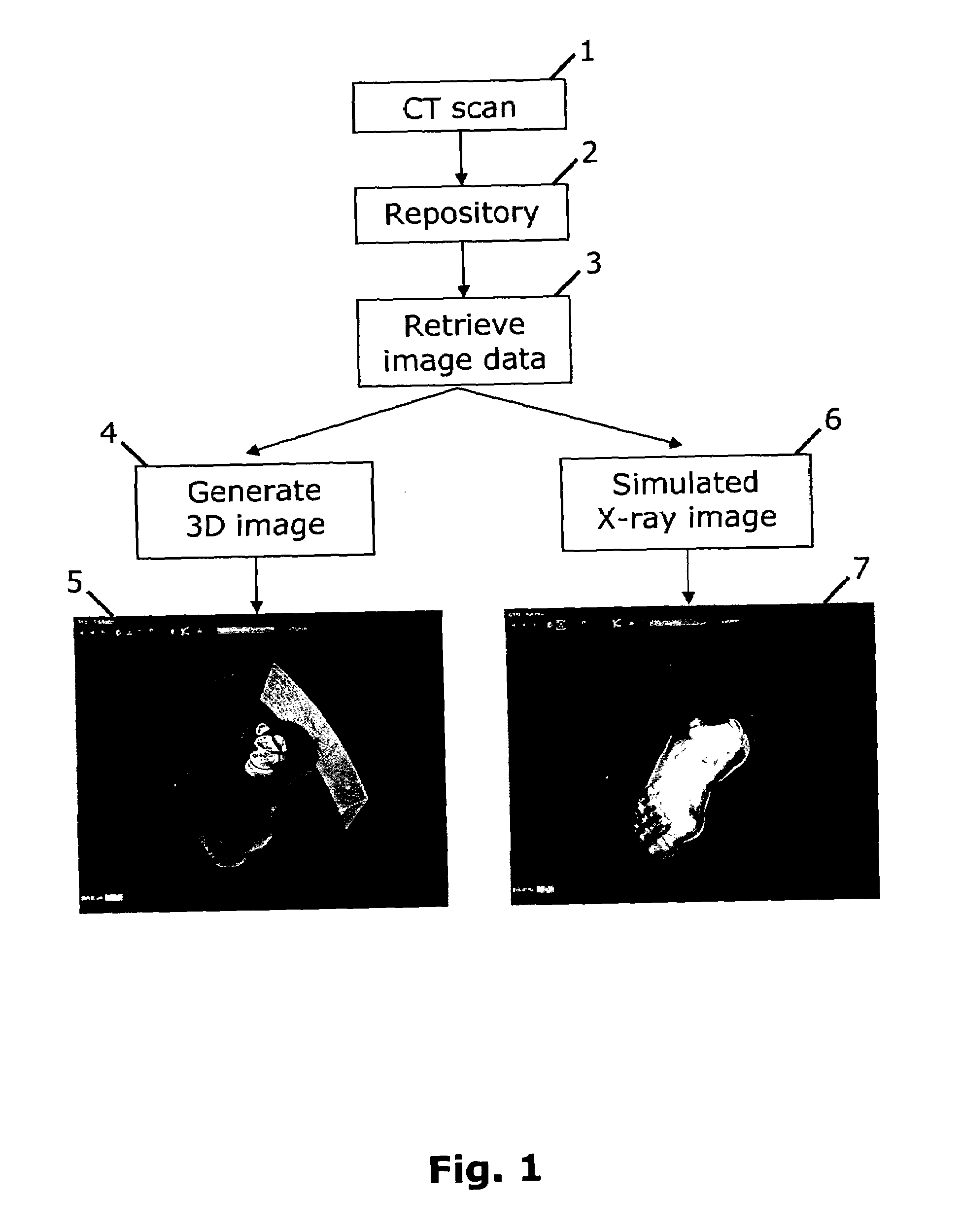
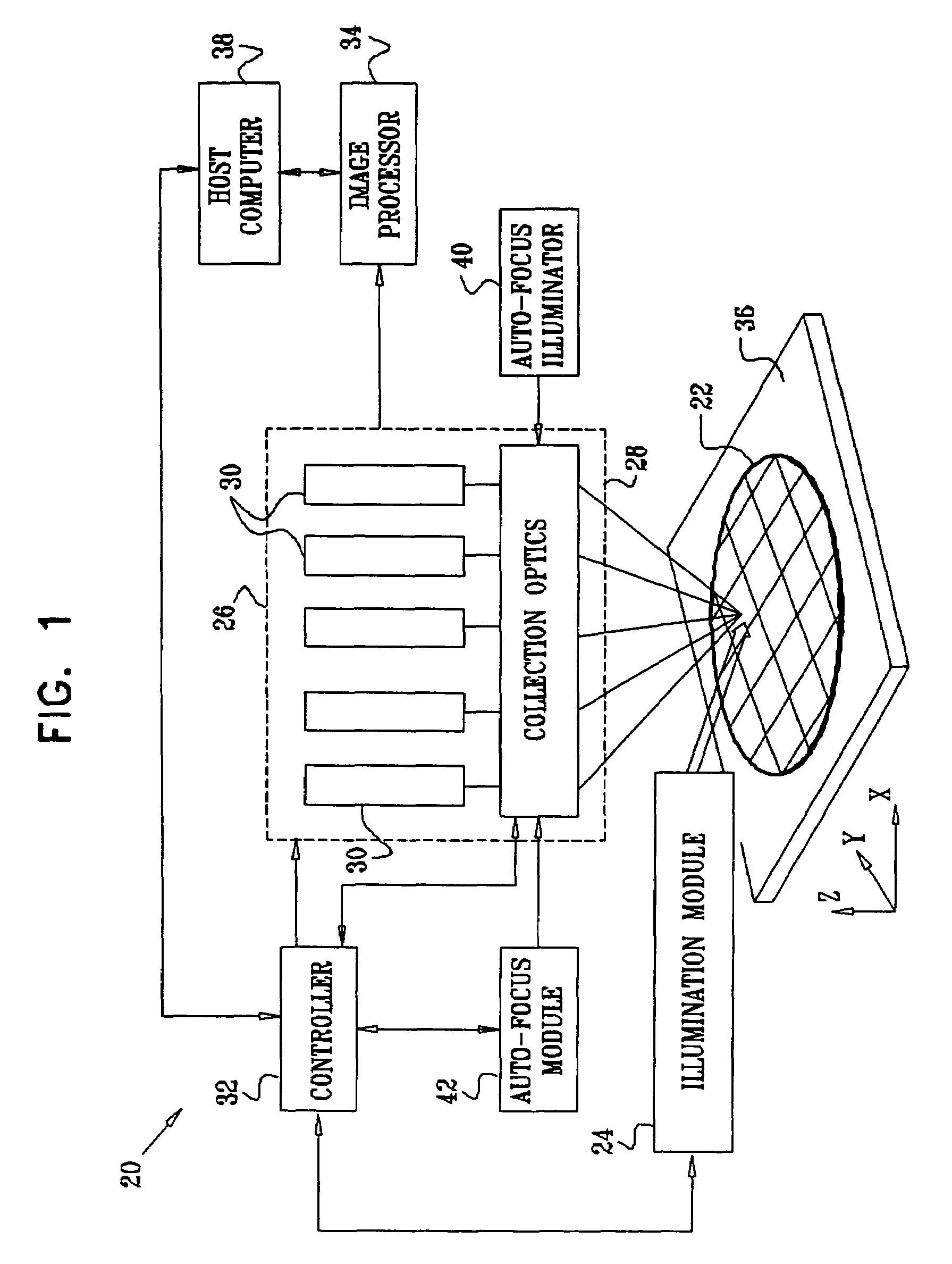
Method and system for simulating X-ray images
ActiveUS7154985B2Distortion freeReconstruction from projectionRadiation/particle handlingViewpointsComputed tomography
The invention relates to simulating 2D X-ray images from 3D CT data. A user can access a repository of CT data of a patient's anatomy 2 by using a computer network system. The CT data has been obtained by a CT scanning of the patient 1. Firstly, the user retrieves the CT image data 3 and a 3D image is generated 4. Secondly, the user may orient the CT image in any orientation desirable with respect to a virtual X-ray source and a virtual image plane. And thirdly, a 2D X-ray image is simulated 6 from the chosen viewpoint and shown to the user.
Owner:MEDICAL INSIGHT
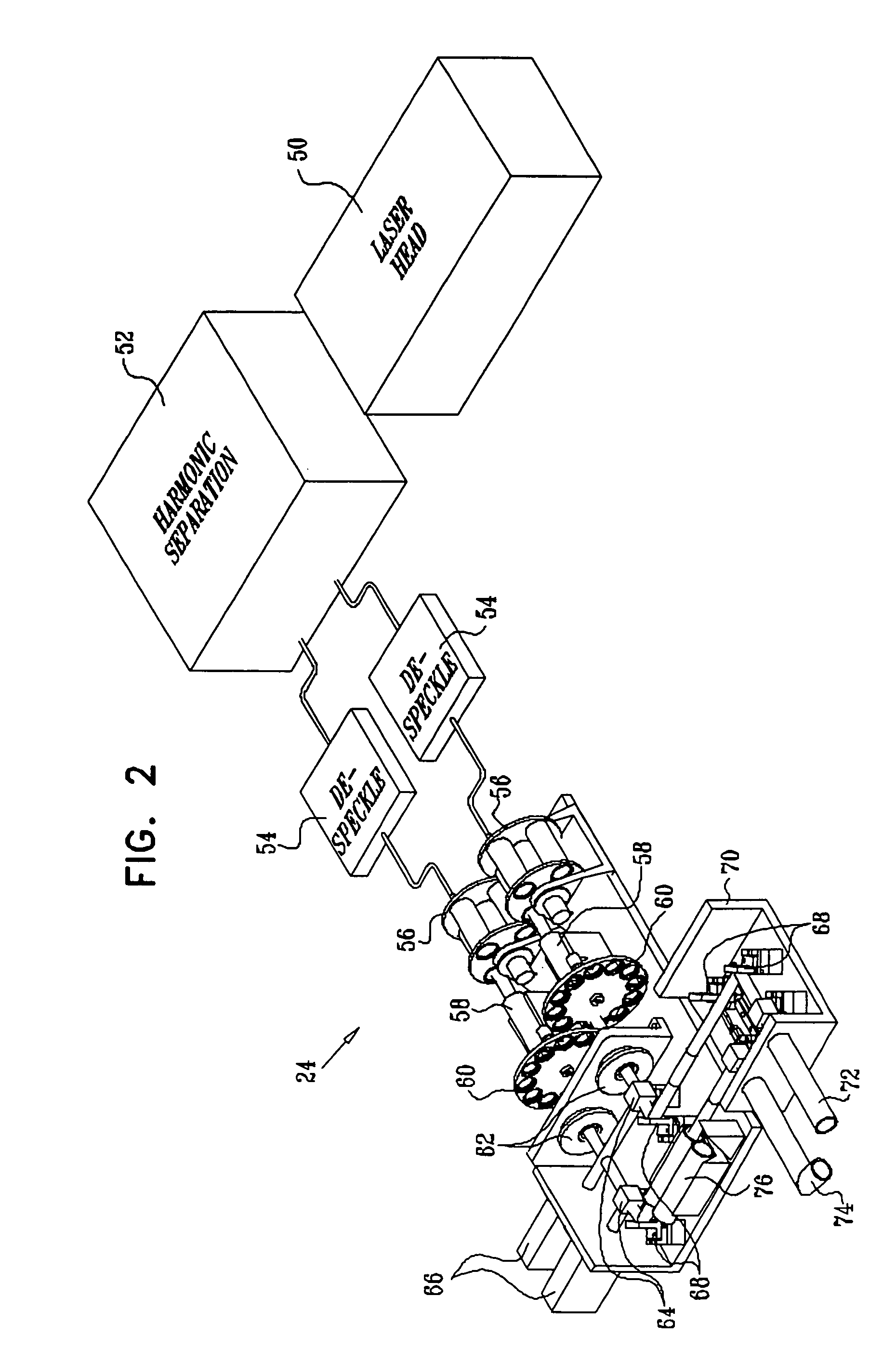
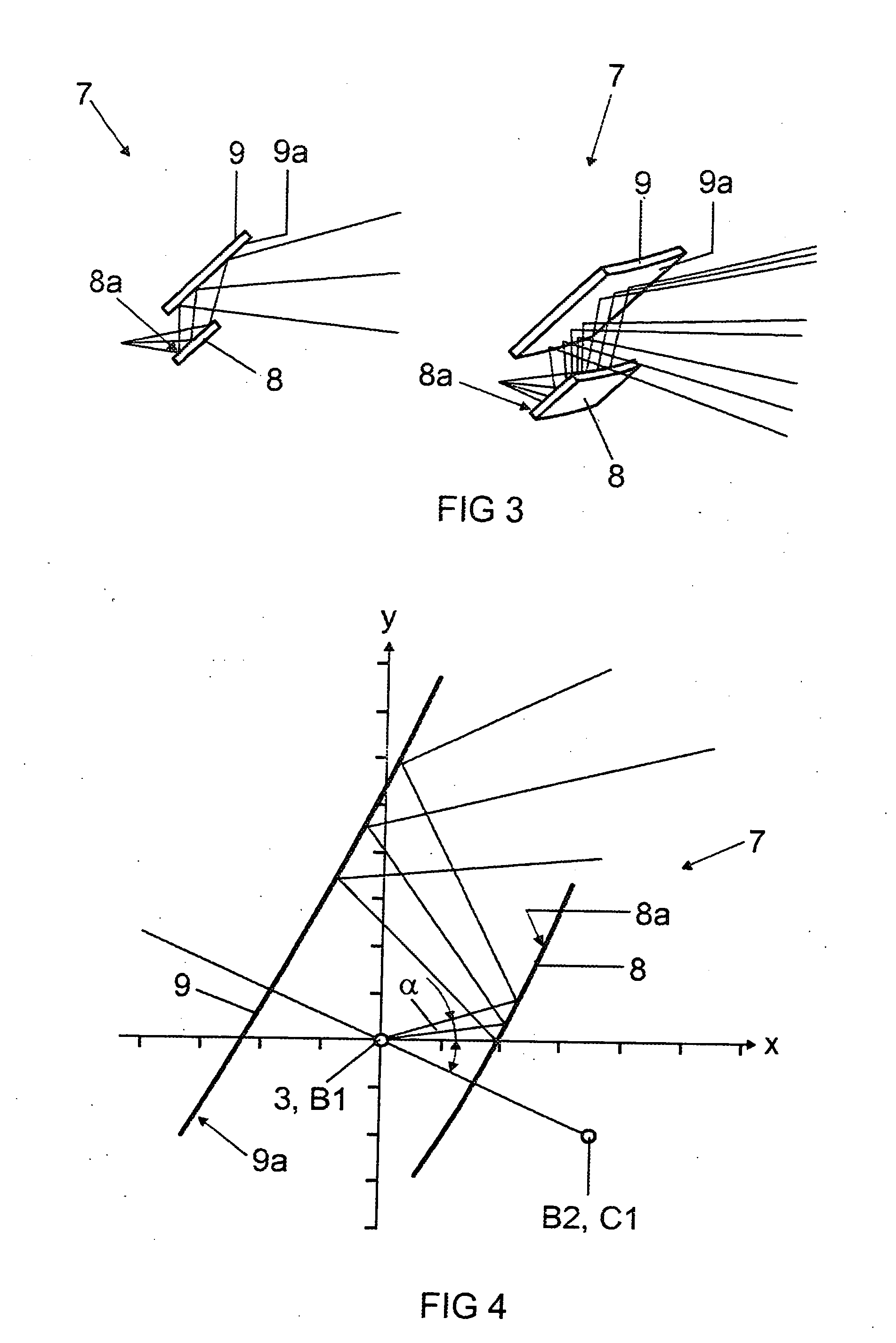
Mathematically optimized family of ultra low distortion bellow fold patterns
An improved mathematically modeled family of bellow fold patterns, useful for making bellows from stiff but foldable materials, which forms a corner of a bellow consisting of a series of several single inversion fold patterns, each having a characteristic design angle which is mathematically computed to provide a desired initial wall angle for the bellow and to minimize wall tilting over a predetermined extension angle range, thereby allowing low cost bellows to be made which can extend long distances while using a minimal amount of stiff but foldable material. In addition, each characteristic design angle can be computed to provide exactly zero tilting of the bellow walls at one or more non-zero extension lengths specified by a designer, thus allowing, unlike all other prior art folds, a structurally stiff, long extending bellow to be formed in an extended state using fast production techniques such as vacuum forming, blow molding or injection molding, while also allowing the bellow to be free of distortion in the compressed state.
Owner:KANE NATHAN R
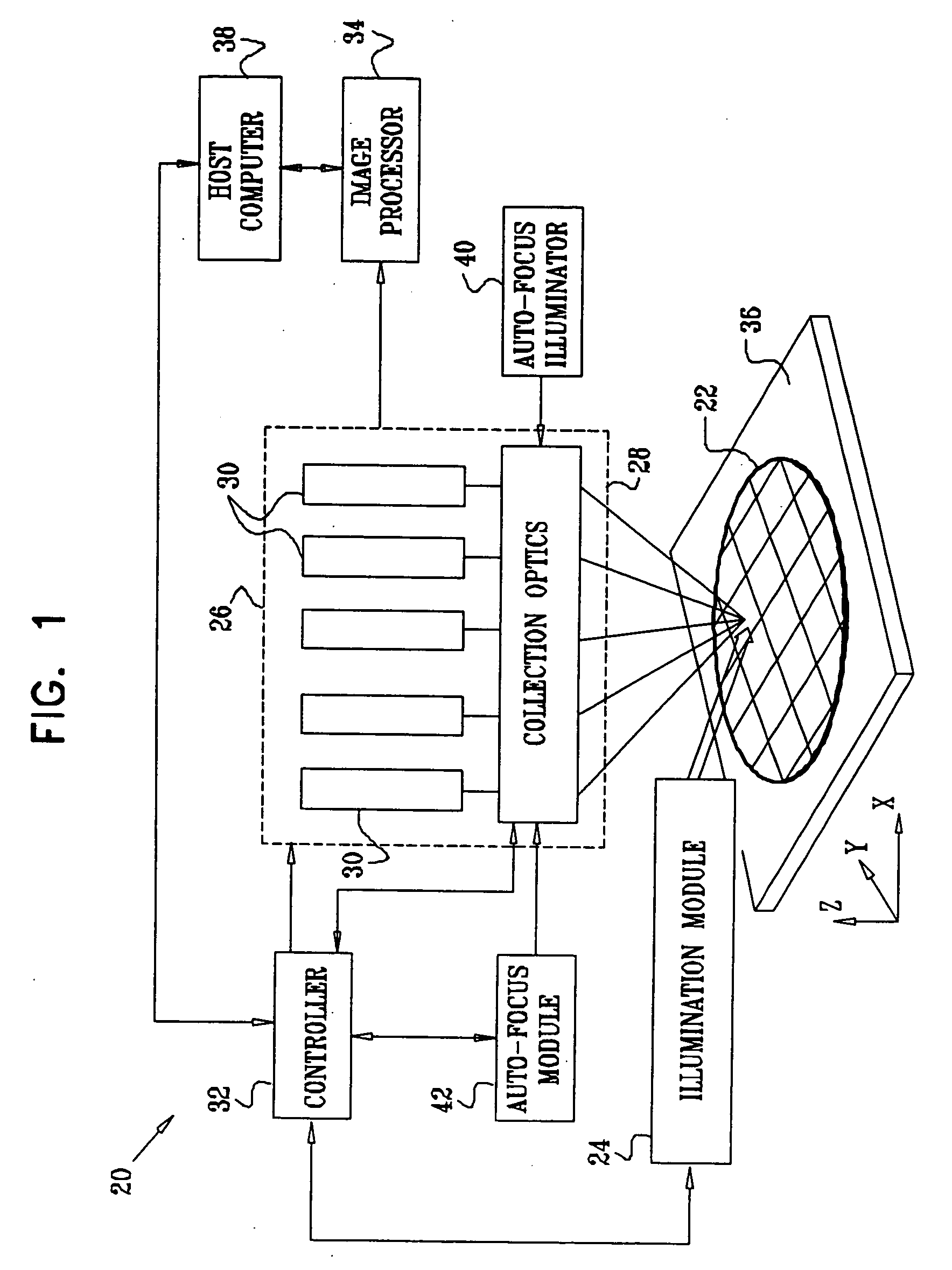
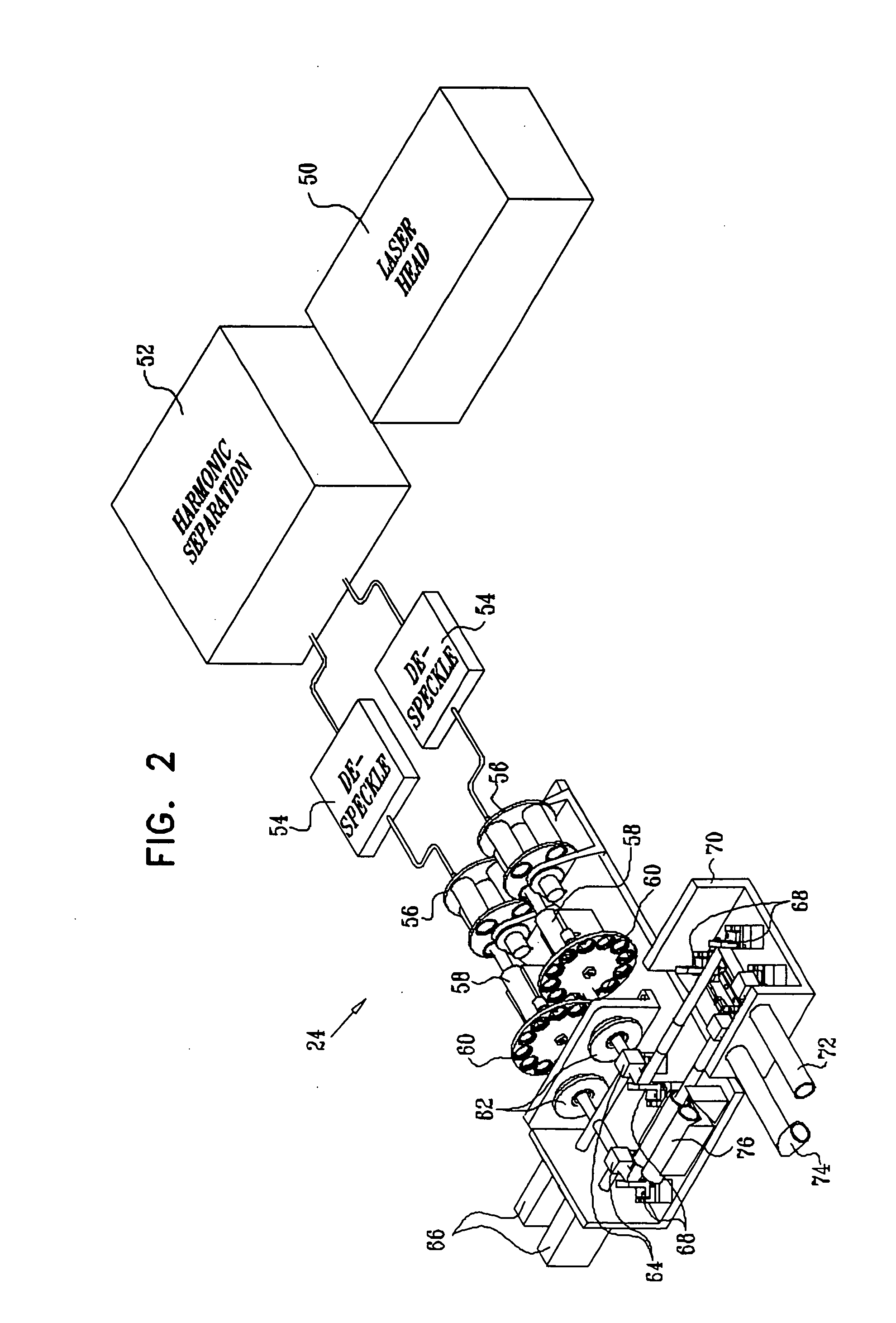
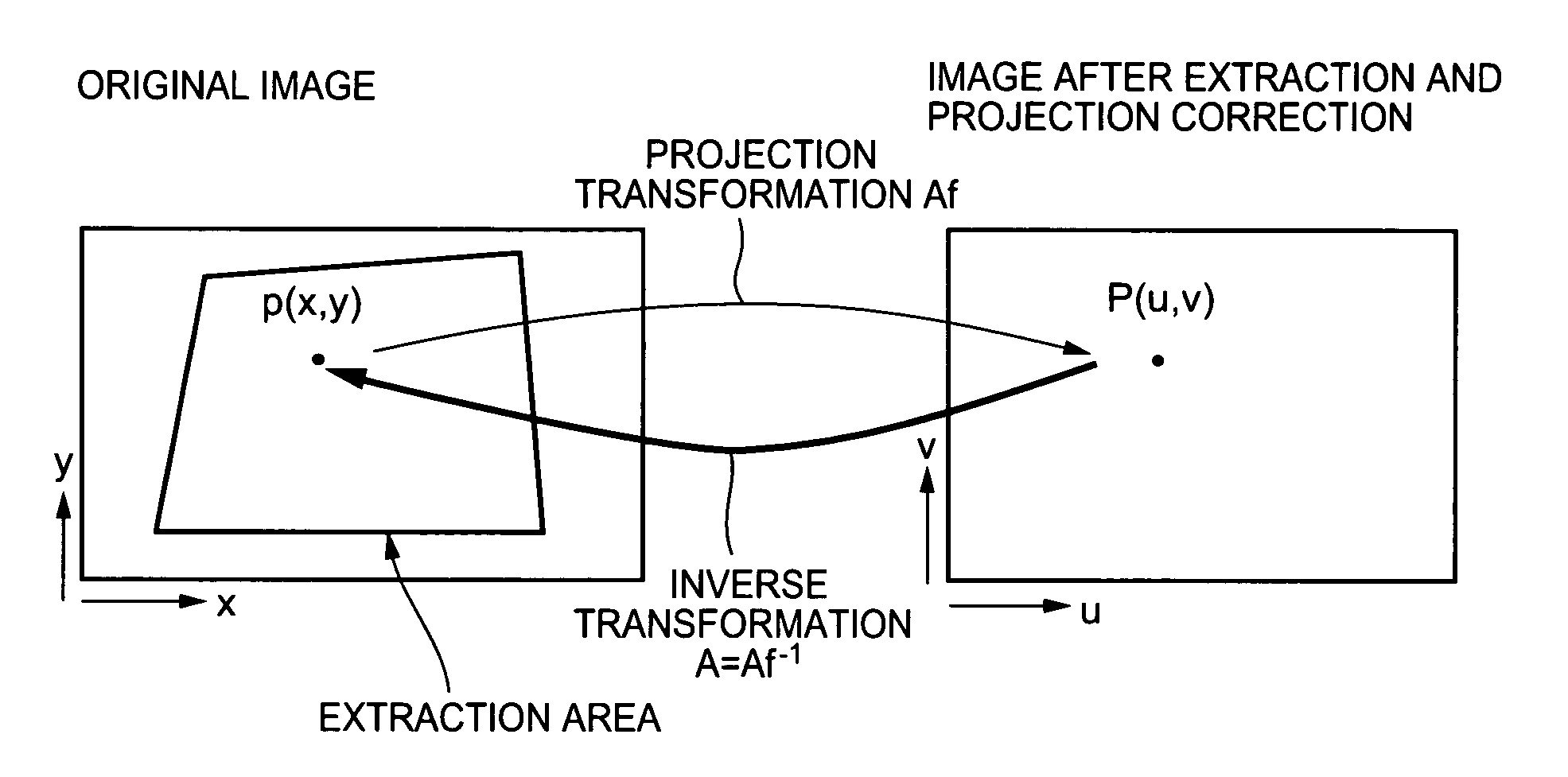
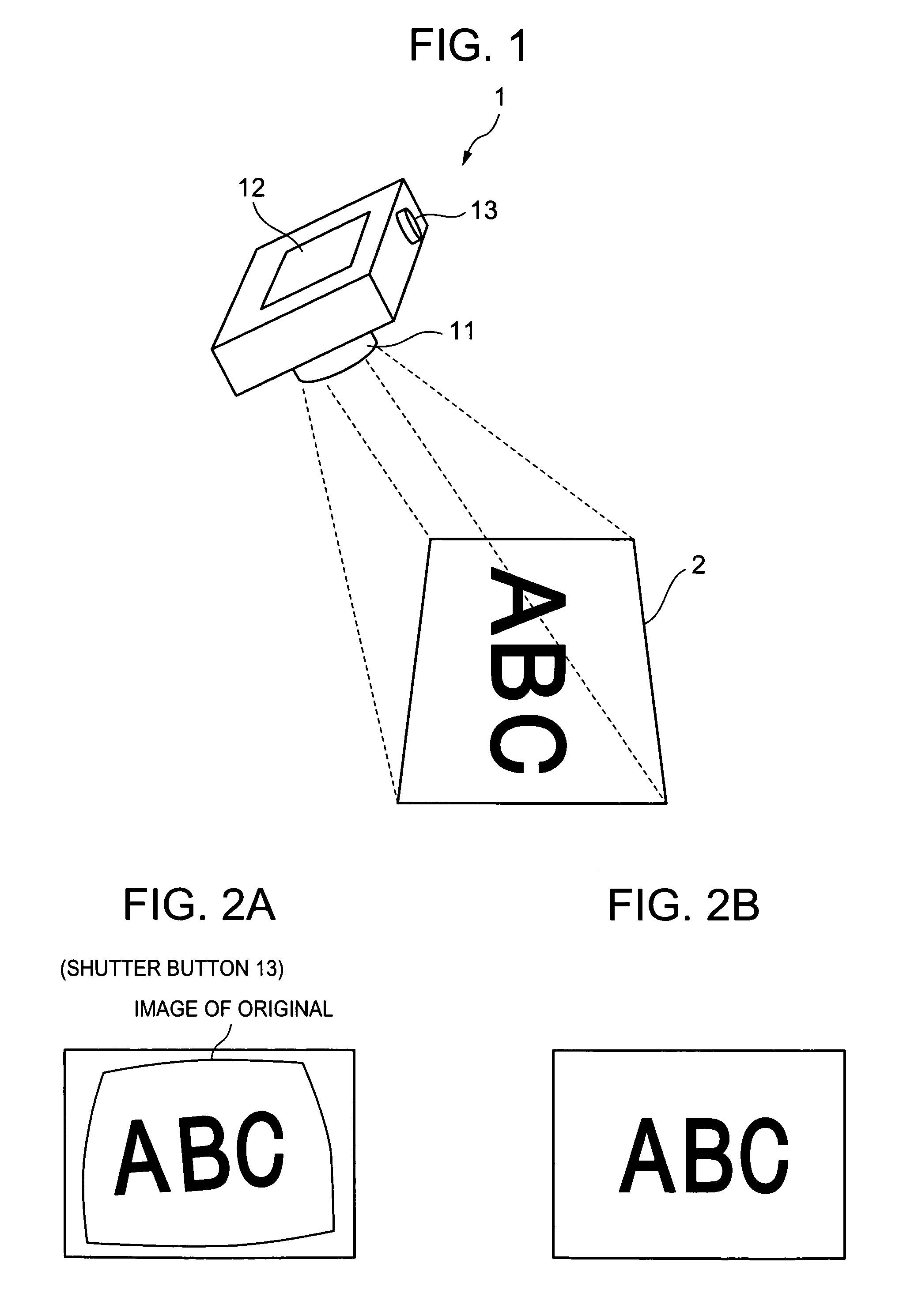
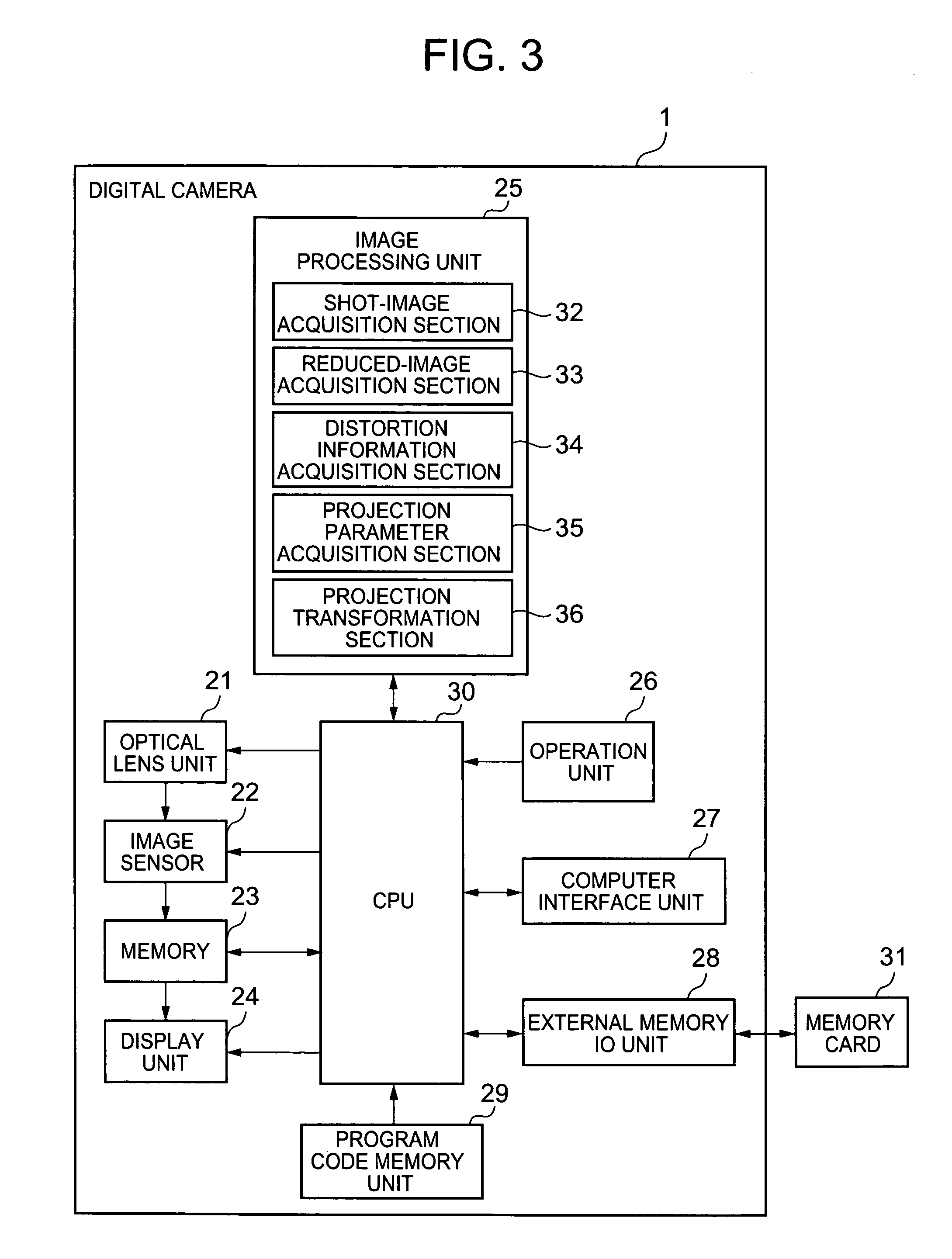
Image processing apparatus for correcting distortion of image and image shooting apparatus for correcting distortion of shot image
ActiveUS20050206753A1Correct distortionDistortion freeImage enhancementTelevision system detailsDistortion correctionDigital camera
A digital camera acquires the image of an original including an original from a shot image acquired by shooting. The digital camera reduces the image of the original and corrects distortion of the reduced image which is originated from the characteristic of a lens. As the digital camera performs distortion correction on the reduced image, the number of arithmetic operations in distortion correction is reduced, making distortion correction simpler. The digital camera acquires a rectangle defined by the contour of the original, extracts the image of the original to acquire an original image before reduction, and acquires an associated projection-transformed image by affine transformation. The digital camera acquires pixel positions of the original image using an affine parameter, and acquires pixel positions of the image before distortion correction using a relational expression of distortion correction performed on the reduced image.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
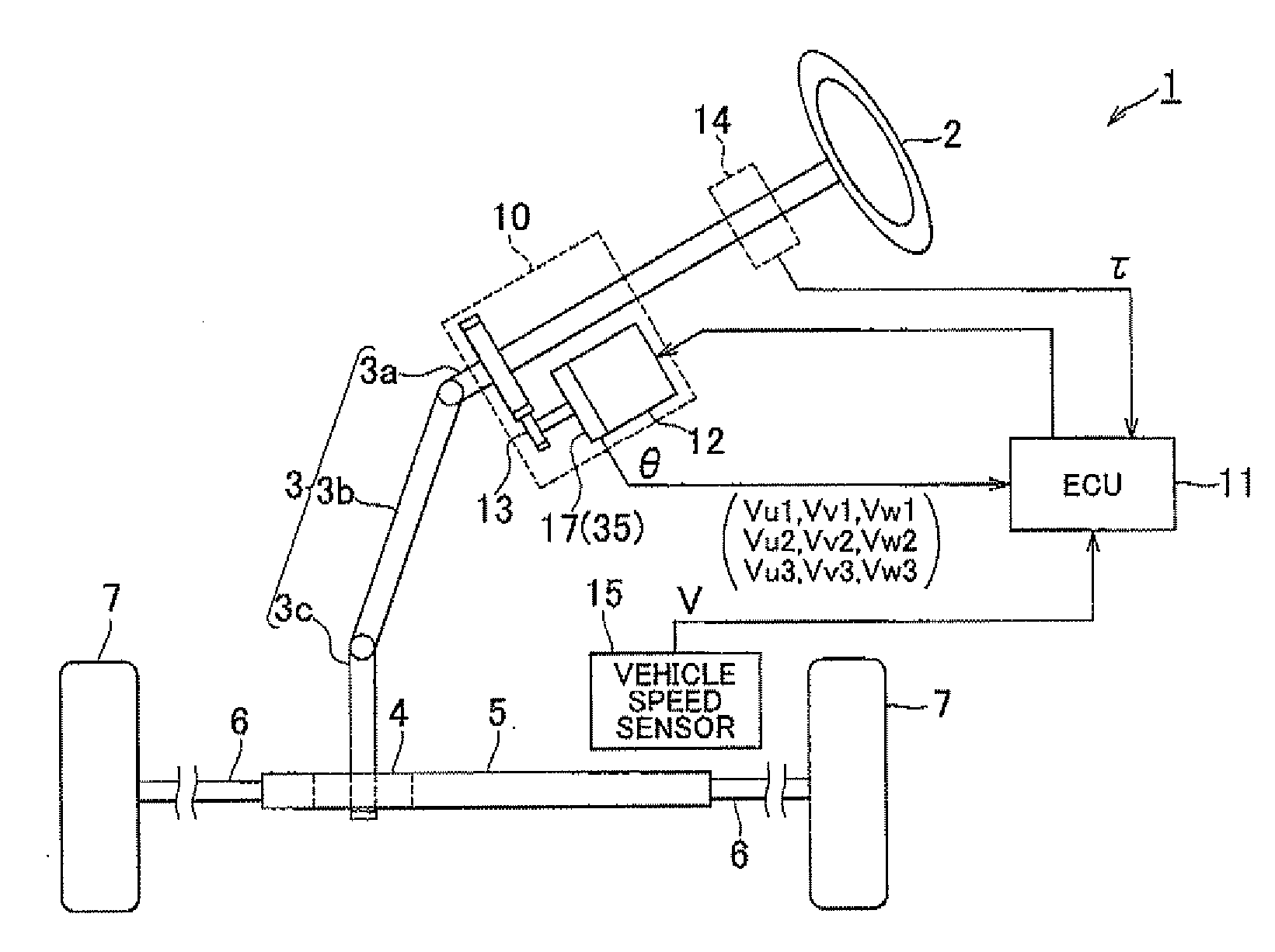
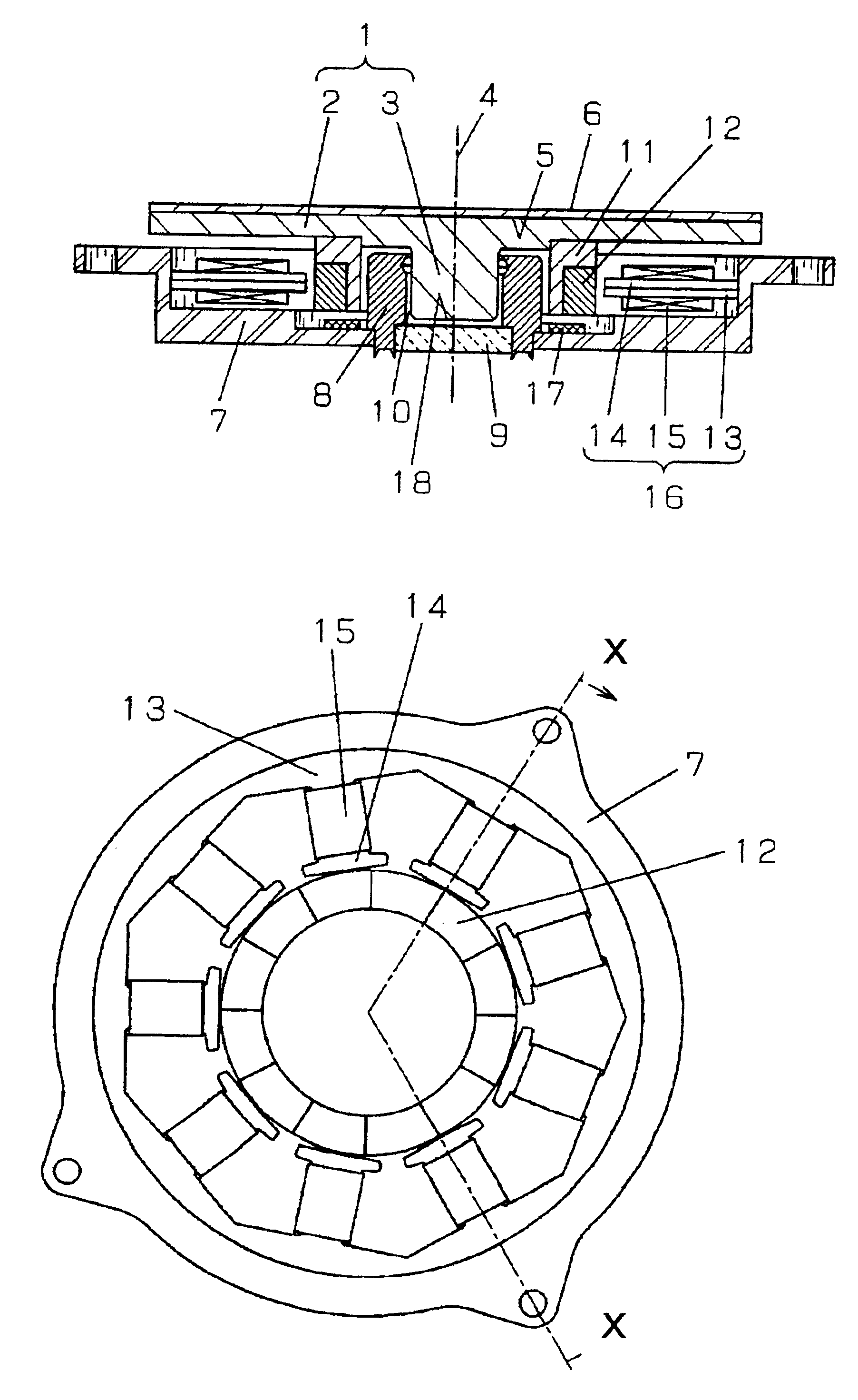
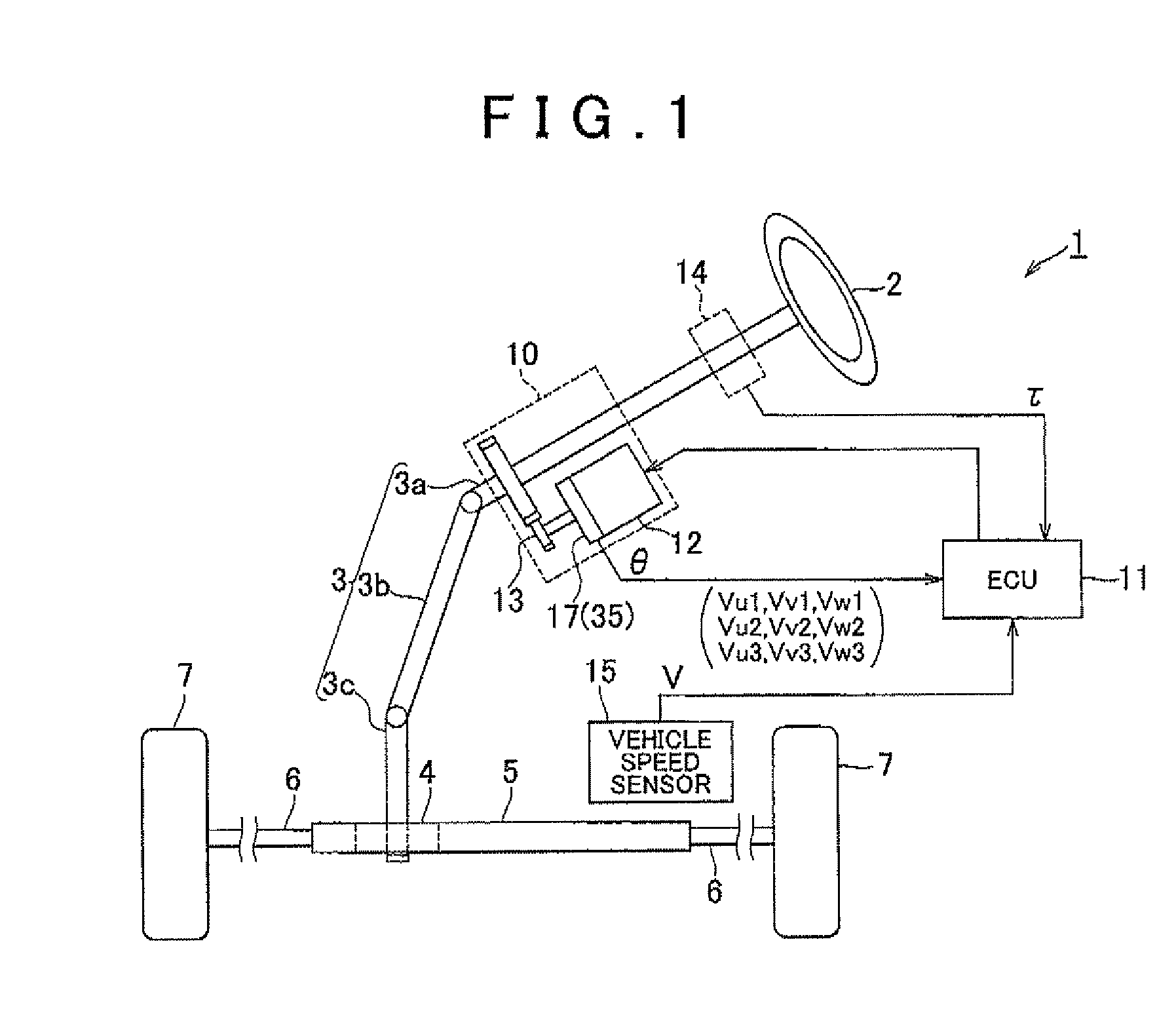
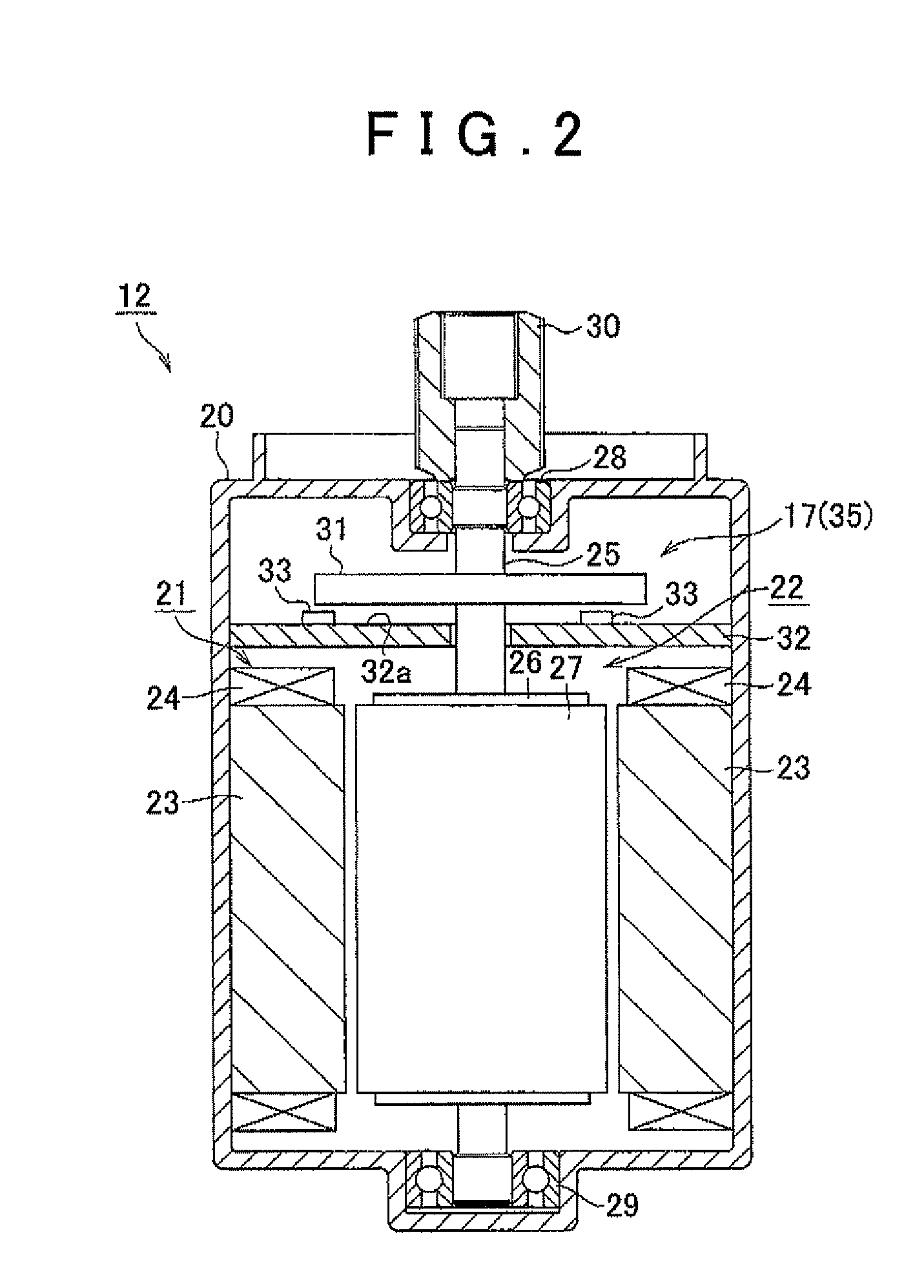
Rotational angle sensor, motor, rotational angle detector, and electric power steering system
ActiveUS20110068780A1Simple configurationHigh precisionMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesElectric power steeringElectric power system
A rotational angle sensor includes: a magnet rotor in which multiple magnetic poles are formed along the circumferential direction of the magnet rotor; and three sensor devices that are arranged on a circle concentric with the magnet rotor at regular angle intervals. Each of the sensor devices includes three half-bridge circuits each of which has a pair of spin valve magnetic resistances that are connected in series in such a manner that the magnetization directions of spin fixed layers of the spin valve magnetic resistances are opposite to each other. Each of the sensor devices is formed in such a manner that phases of the sensor signals output from the respective half-bridge circuits based on a change in magnetic flux caused by the rotation of the magnet rotor are offset from each other by an electrical angle of 120°.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
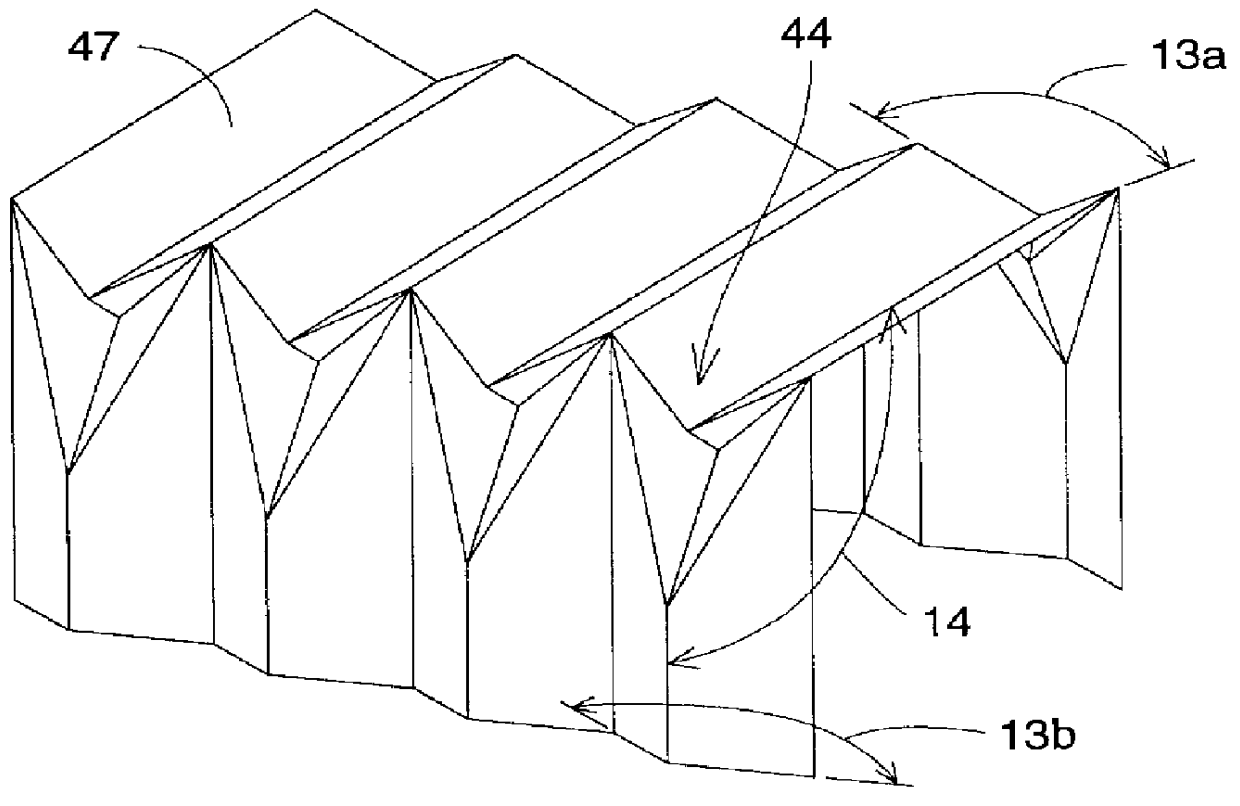
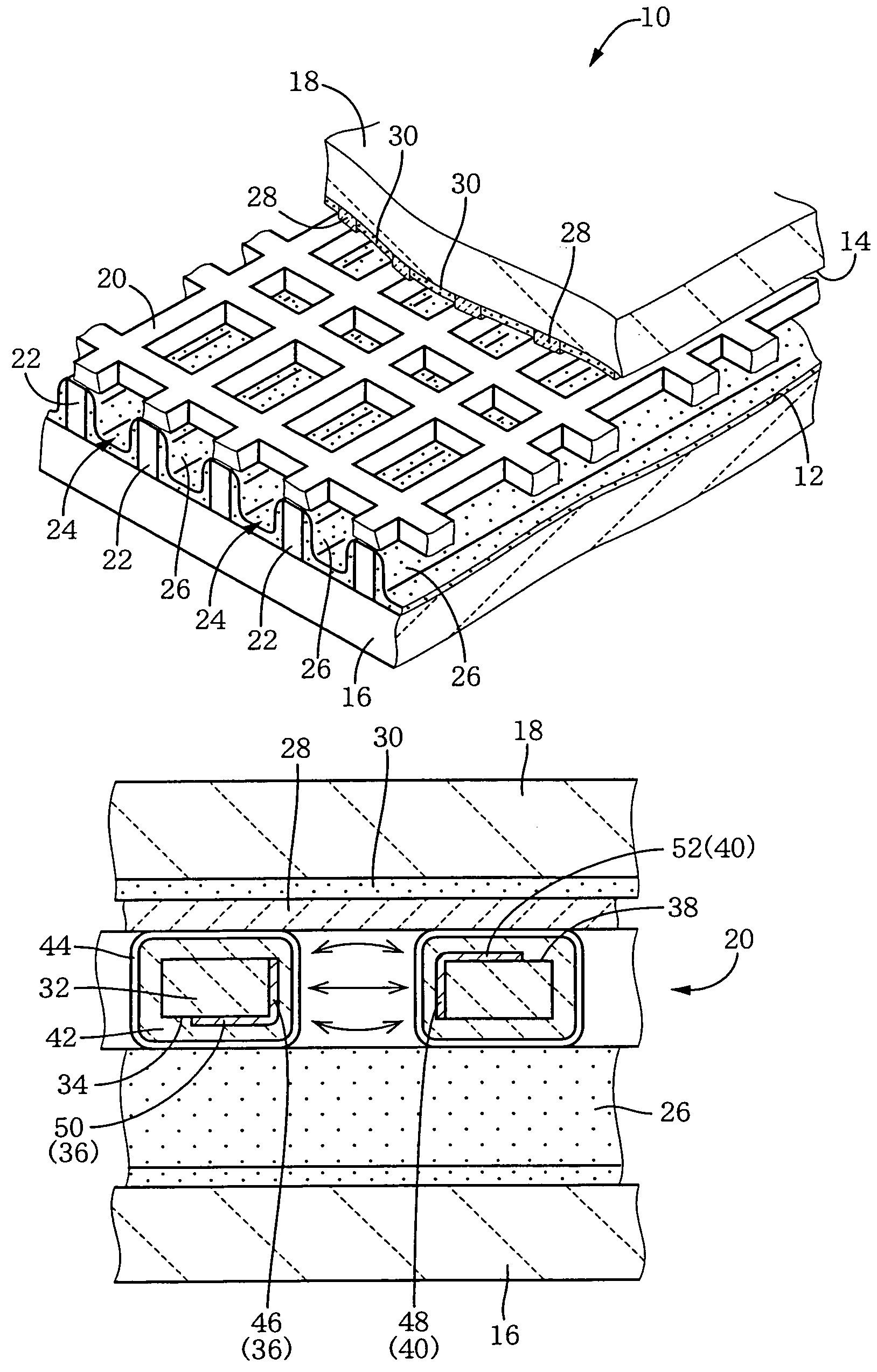
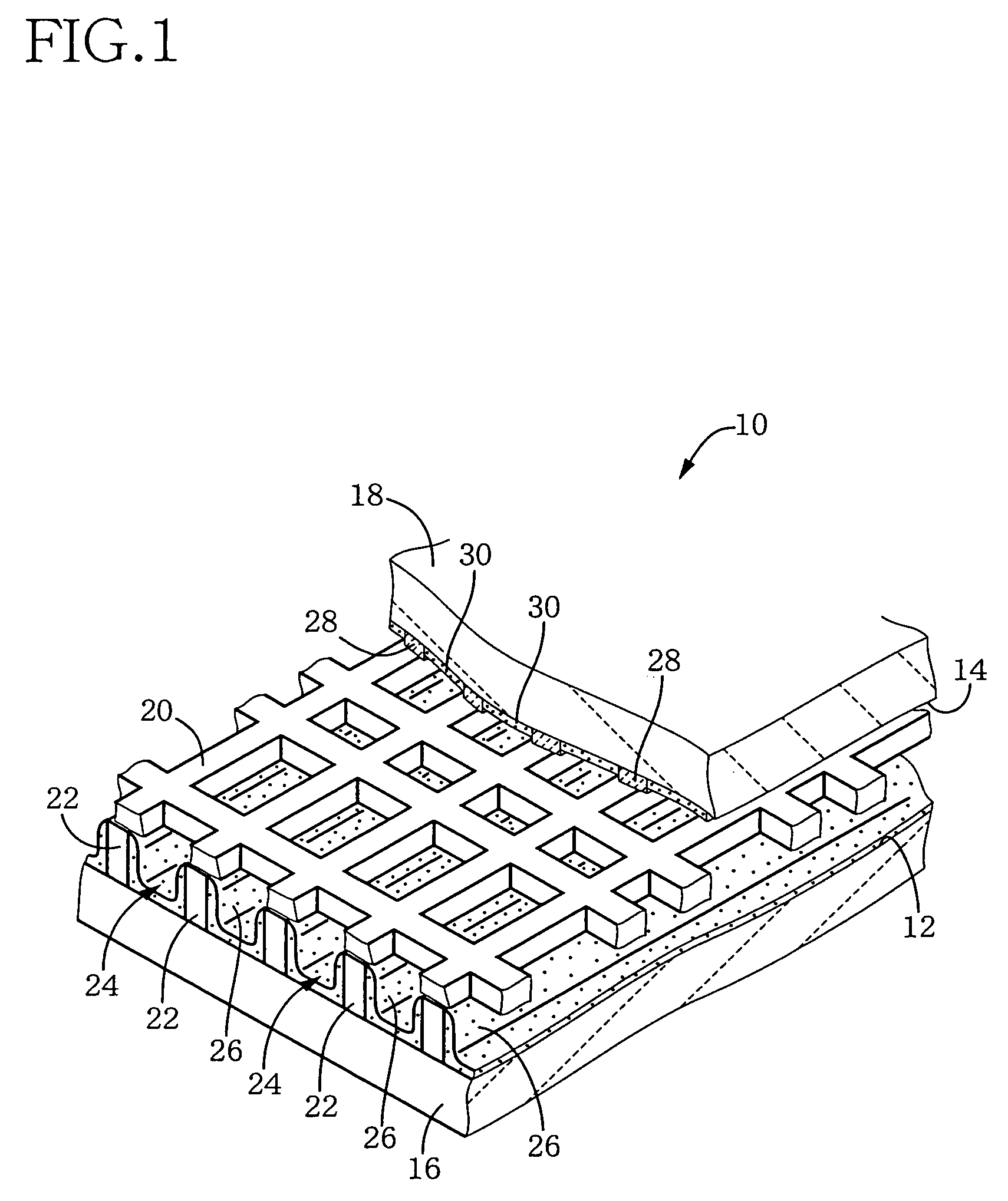
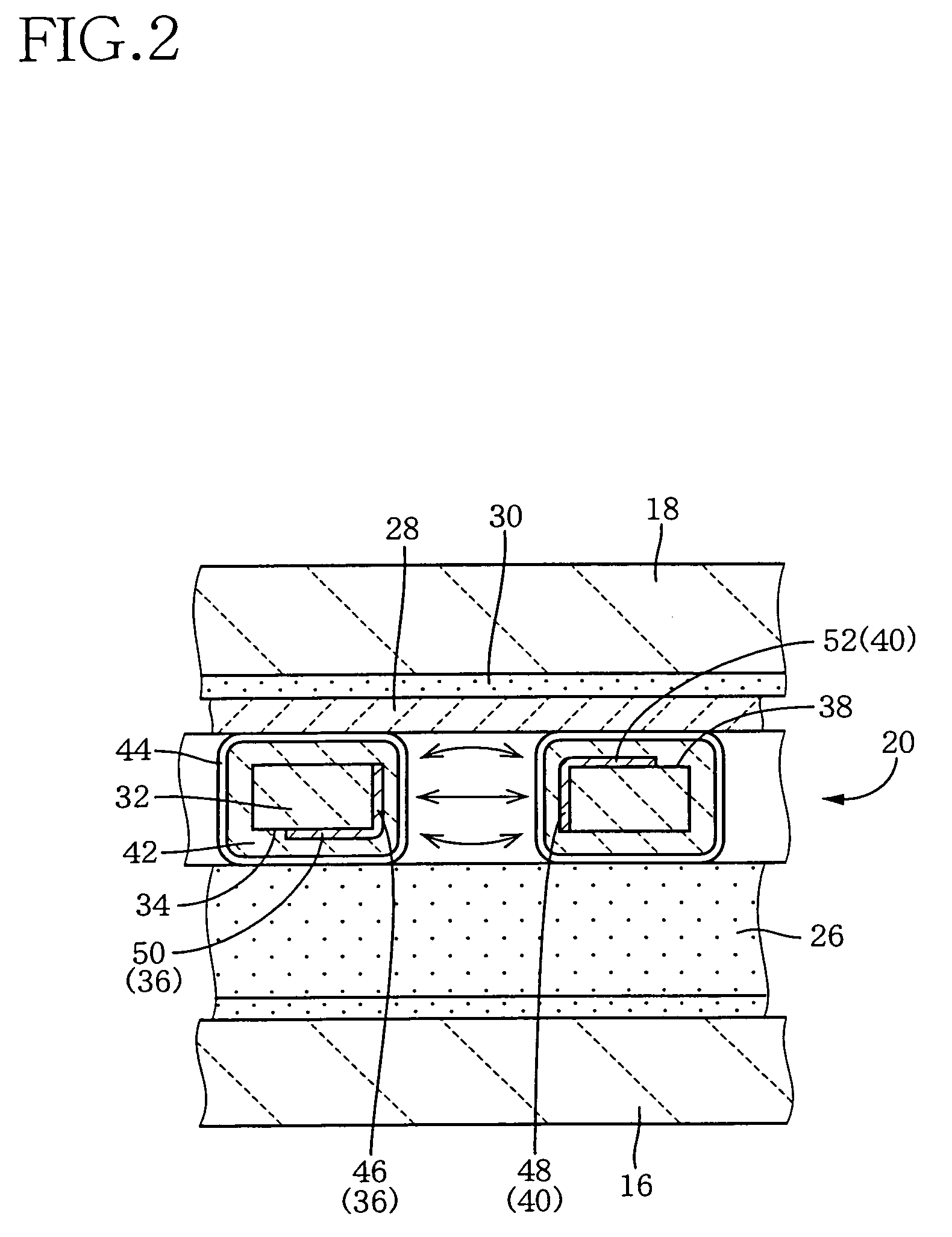
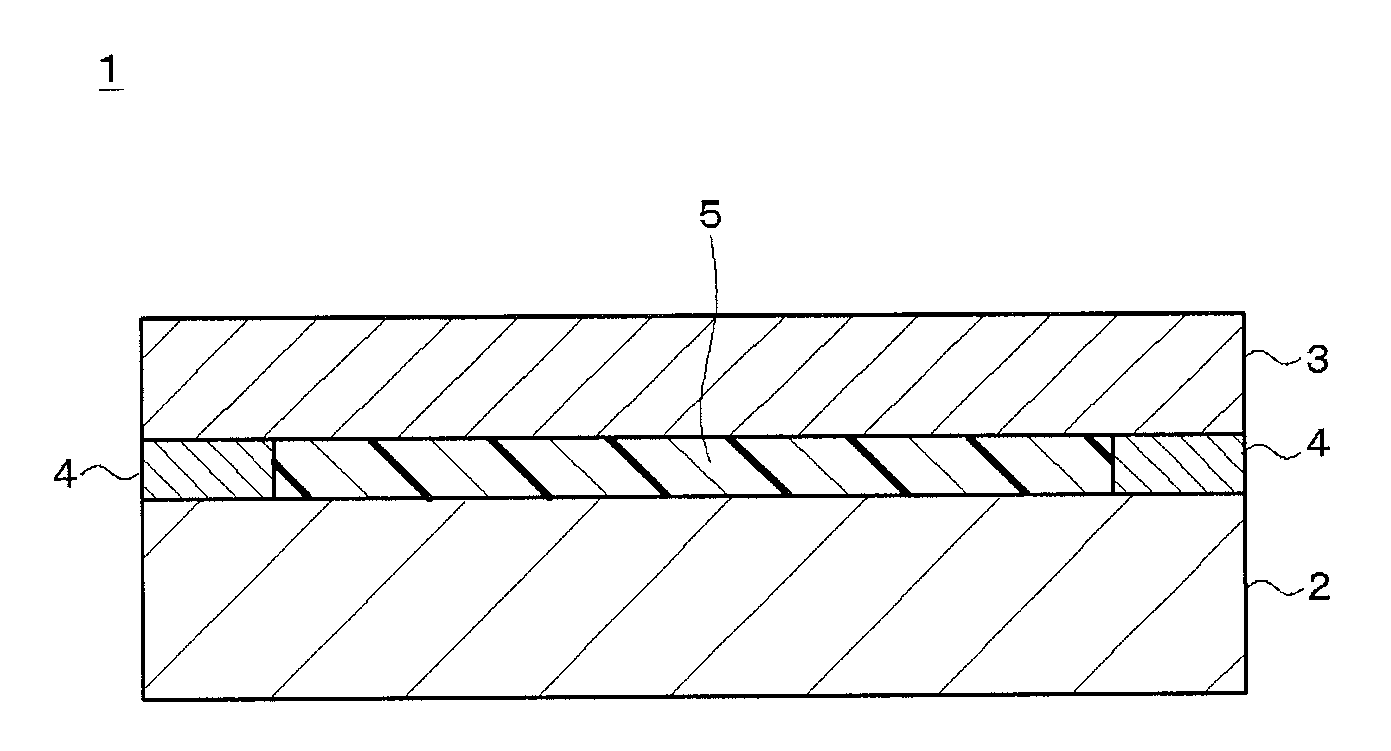
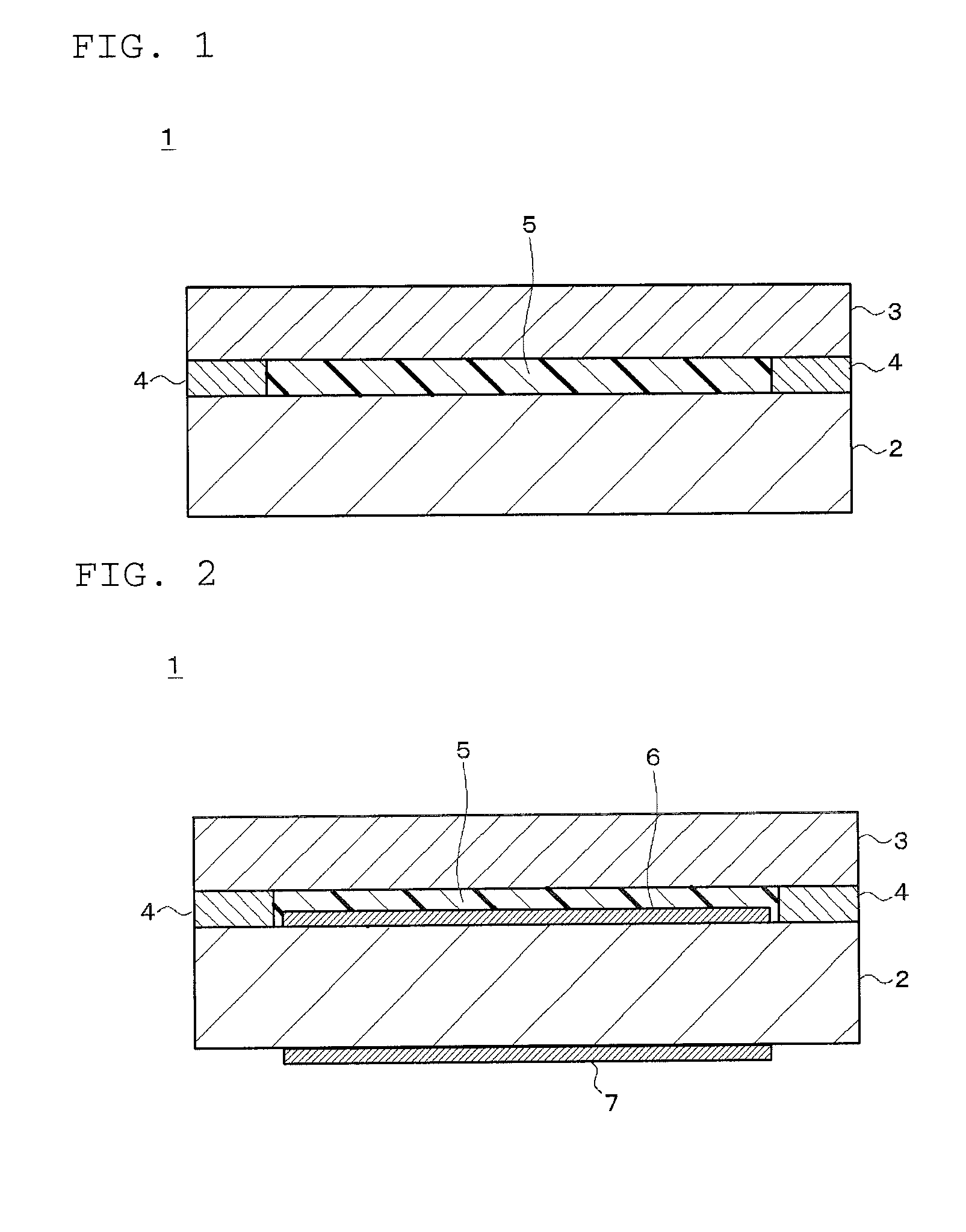
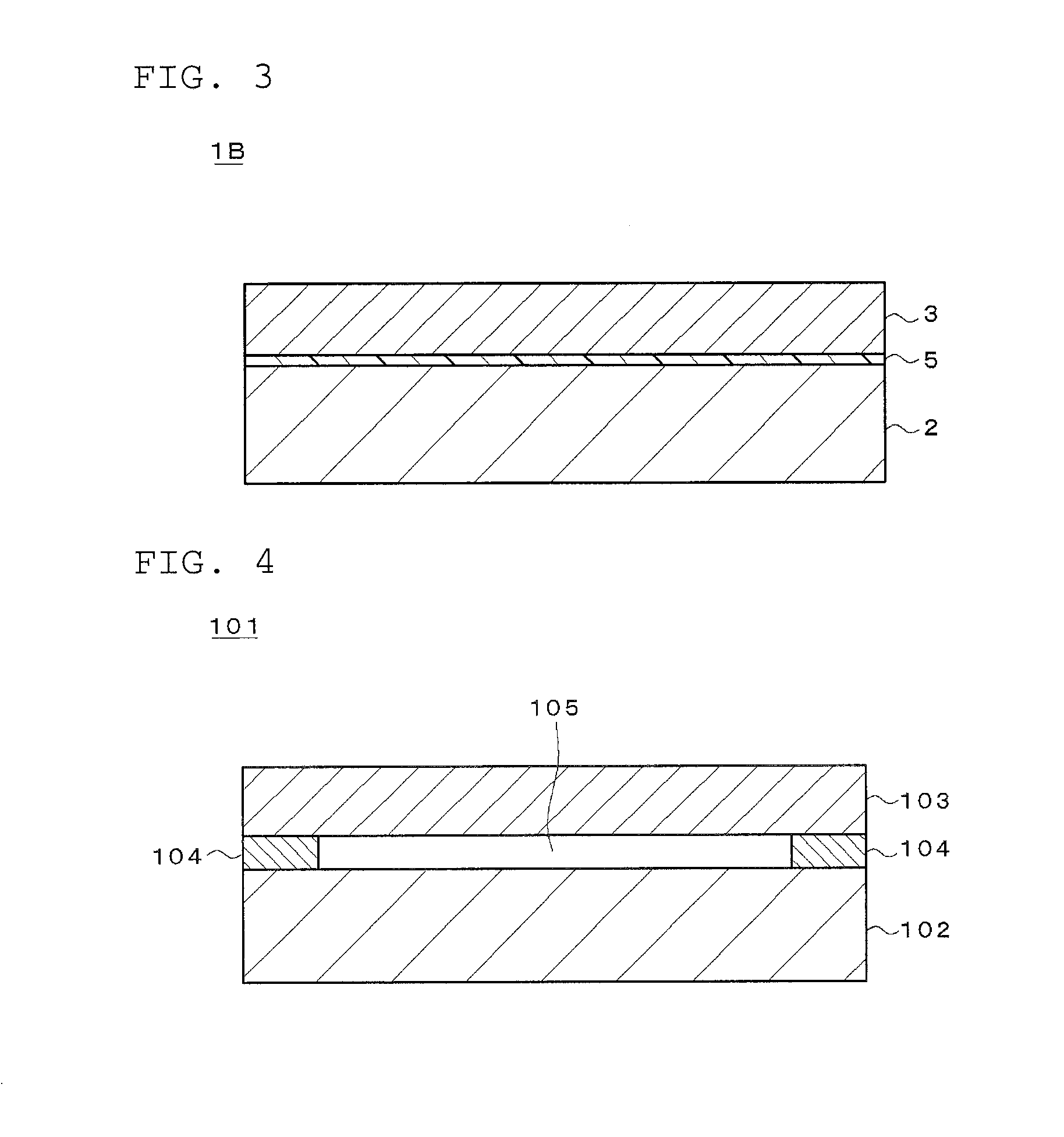
Gas-discharge display device and its manufacturing method
InactiveUS7067979B2Distortion freeSustain/scan electrodesAlternating current plasma display panelsDisplay deviceEngineering
When a PDP 10 is produced by superposing, and fixing, a front plate 16 and a rear plate 18 on, and to, each other, a sheet member 20 including an X wiring layer 36 and a Y wiring layer 40 is fixed to the front plate 16 or the rear plate 18, so that X electrodes 46 and Y electrodes 48 are provided in respective discharge spaces 24. Thus, the X electrodes 46 and the Y electrodes 48 can be assembled with the front and rear plates 16, 18, by just placing the sheet member 20 between the two plates 16, 18. Therefore, in the PDP 10, the front plate 16, the rear plate 18, and the discharge electrodes 46, 48 are free of distortions resulting from a heat treatment that would otherwise be carried out to form the electrodes.
Owner:NORITAKE CO LTD
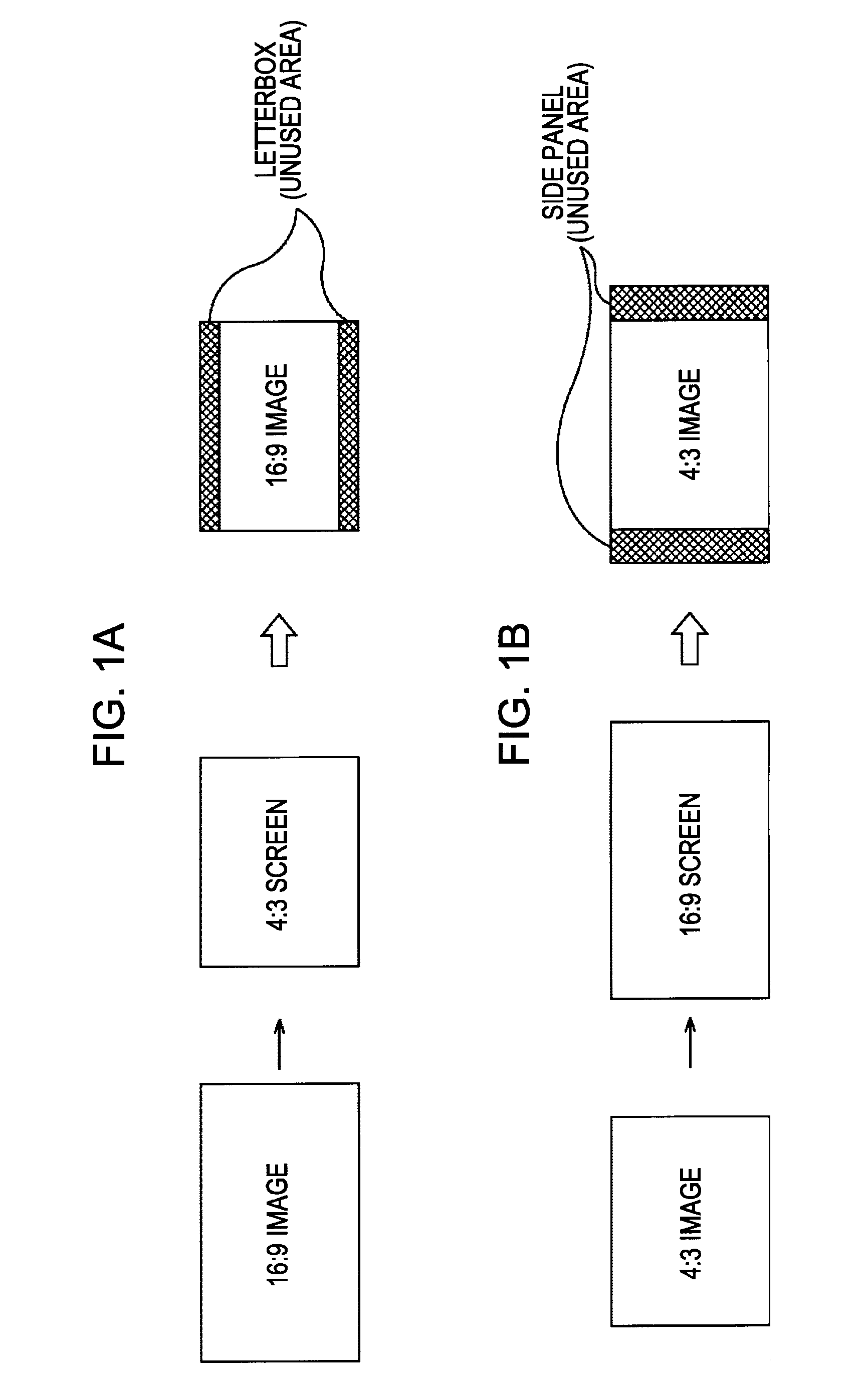
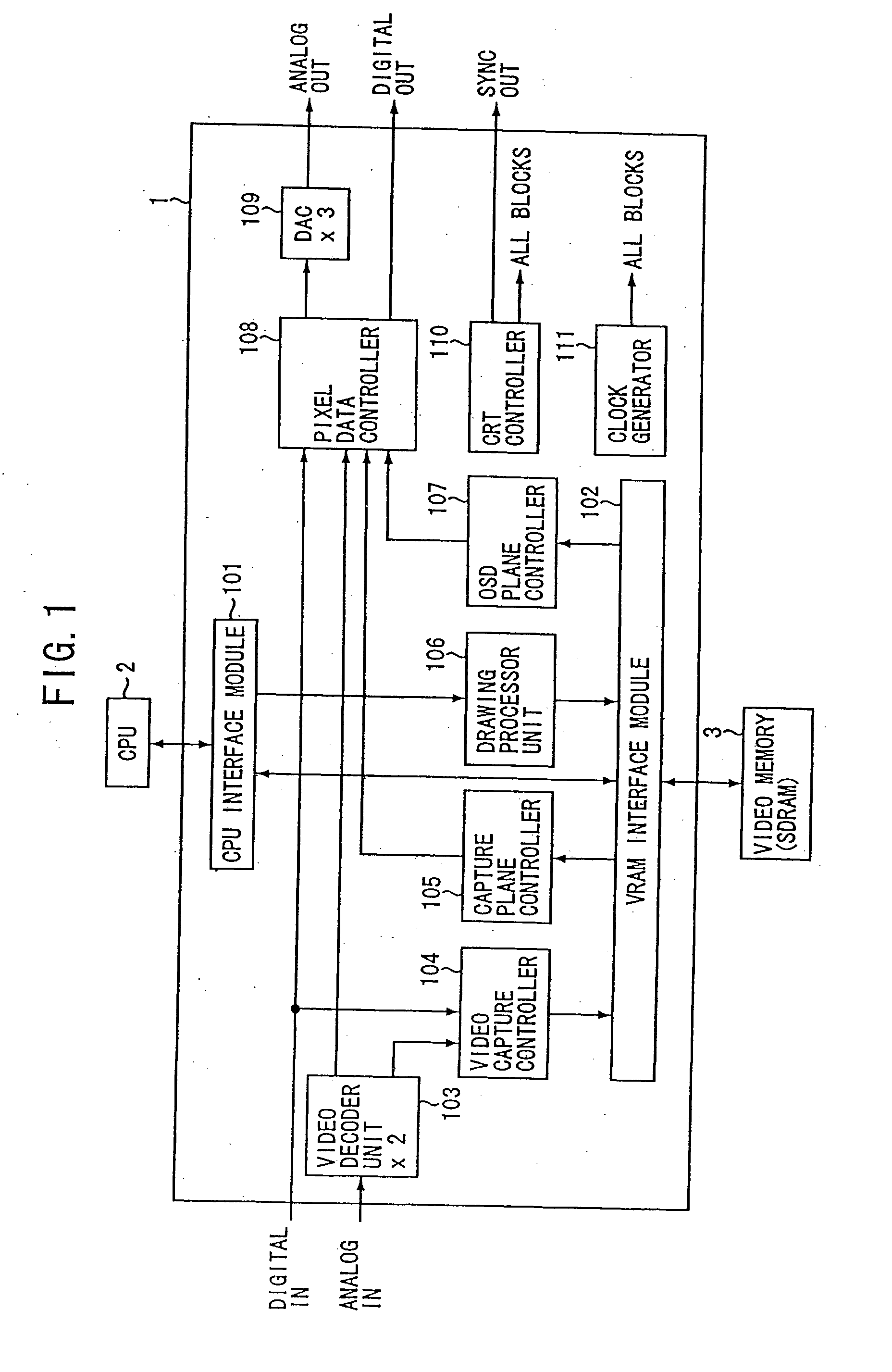
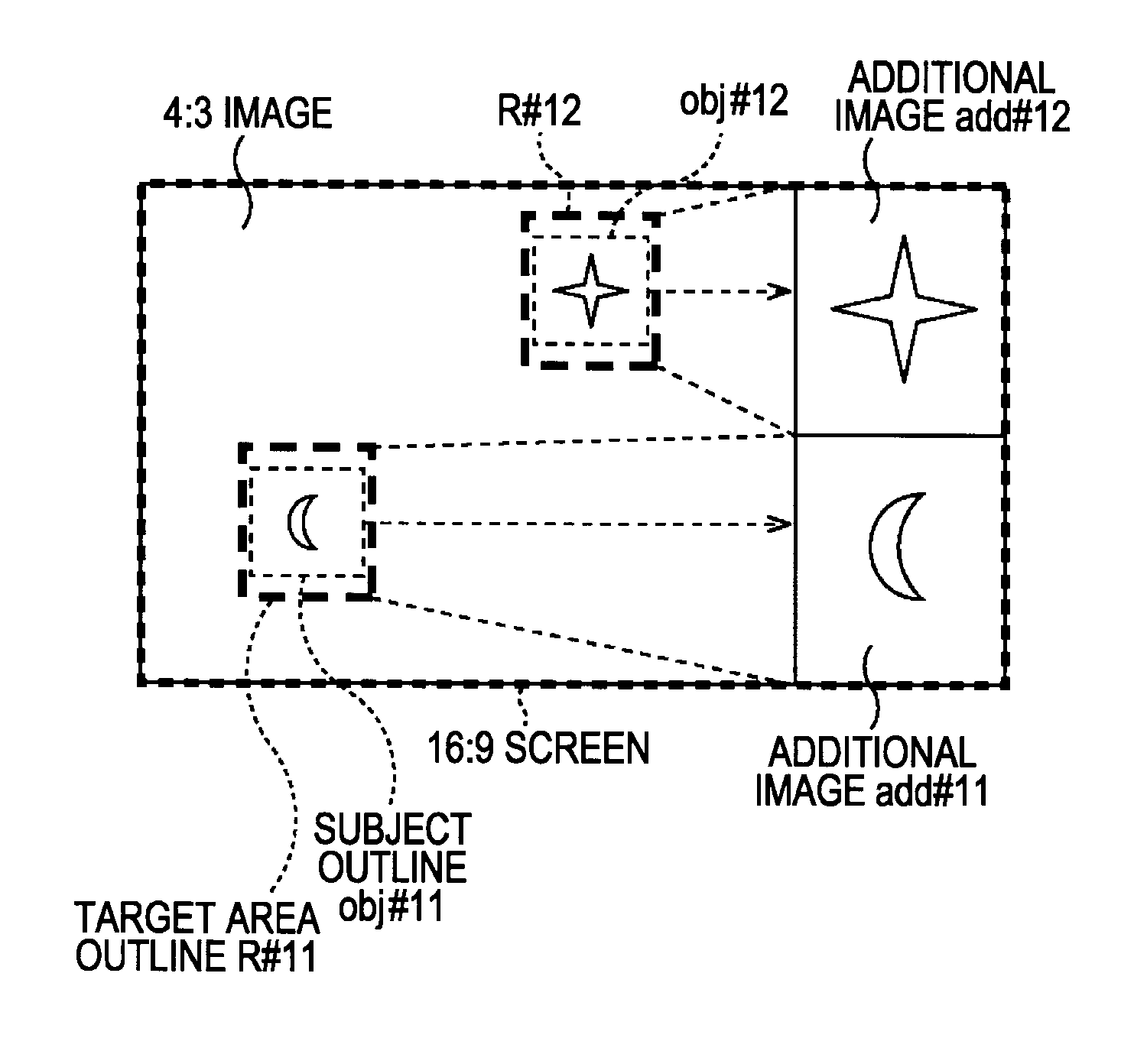
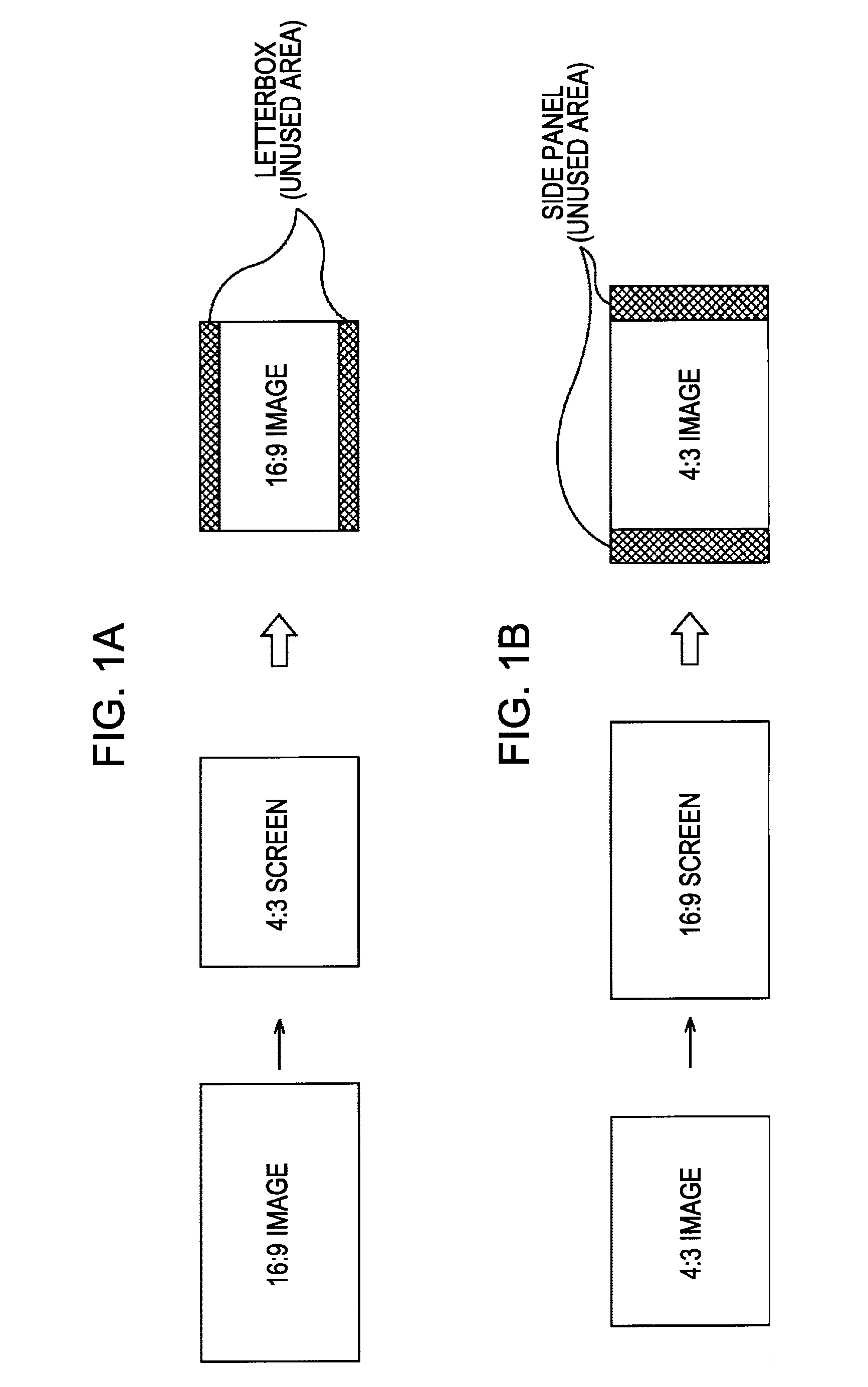
Information processing apparatus, information processing method, and computer program
InactiveUS20080088740A1Easy to useDistortion freeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsInformation processingImaging processing
An image processing apparatus for displaying an input image on a display, includes an image converting unit for converting the input image into an equiaspect ratio image, the equiaspect ratio image having the same aspect ratio as the input image, having one of a horizontal size and a vertical size thereof equal to one of a horizontal size and a vertical size of a display screen of the display, and having an image size thereof being equal to or smaller than the size of the display screen, an additional image generating unit for generating an additional image from the input image, a combination image generating unit for generating a combination image into which the equiaspect ratio image and the additional image are combined, and a display control unit for causing the display to display the combination image.
Owner:SONY CORP
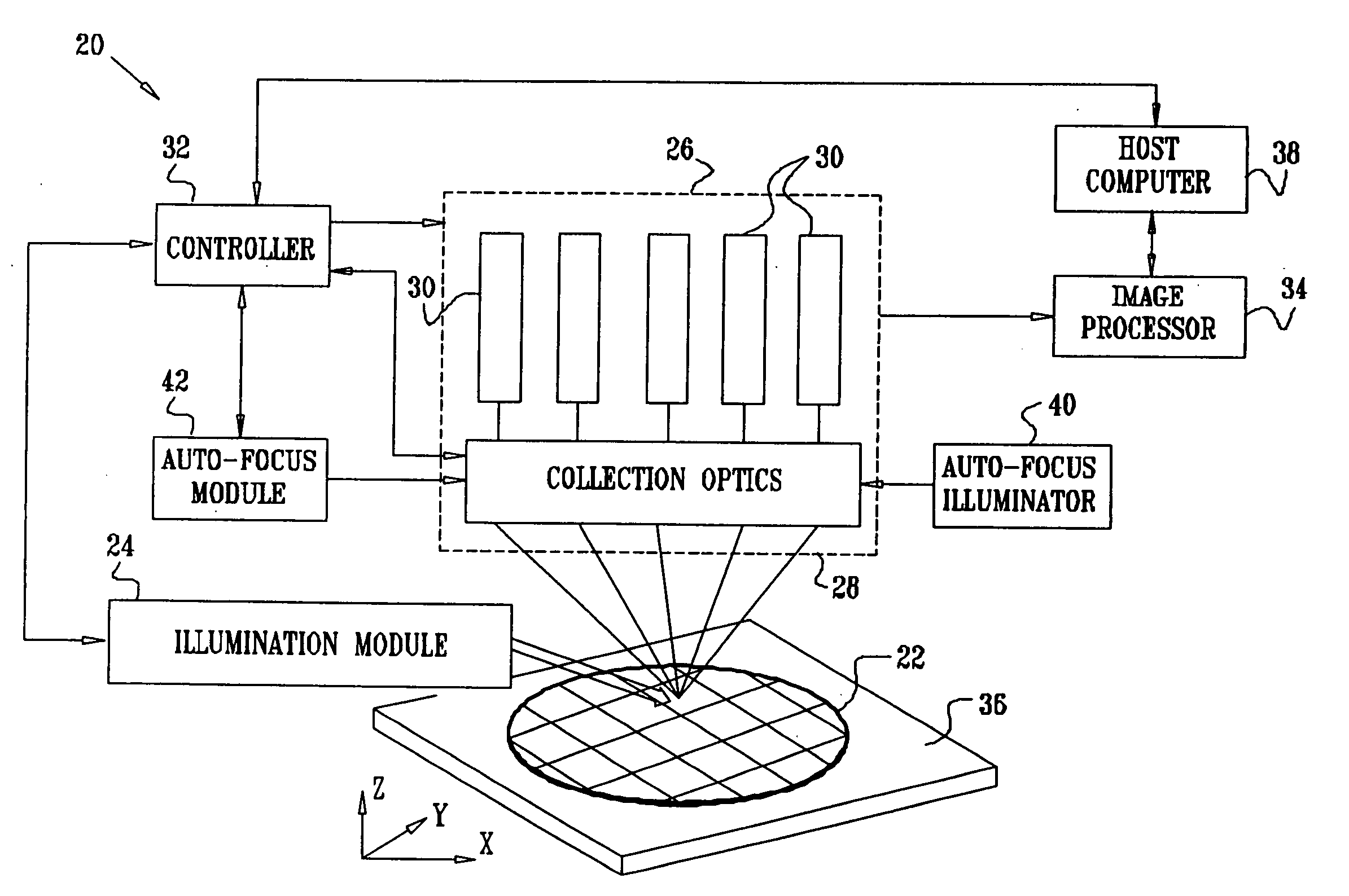
Inspection system with oblique viewing angle
ActiveUS20060007531A1High resolutionPrecise positioningOptically investigating flaws/contaminationMicroscopesImage detectorPhysics
Apparatus for imaging an area of a surface along a viewing angle that is oblique to the surface includes an afocal optical relay, which is adapted to form a tilted initial image of the area by collecting optical radiation from the area along an optical axis oriented at the viewing angle. A tilt correction unit is coupled to correct a tilt of the initial image so as to form a substantially undistorted intermediate image. A magnification module is coupled to focus the intermediate image onto an image detector.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC +1
Image processing apparatus for correcting distortion of image and image shooting apparatus for correcting distortion of shot image
ActiveUS7619663B2Correct distortionDistortion freeImage enhancementTelevision system detailsCamera lensImaging processing
A digital camera acquires the image of an original including an original from a shot image acquired by shooting. The digital camera reduces the image of the original and corrects distortion of the reduced image which is originated from the characteristic of a lens. As the digital camera performs distortion correction on the reduced image, the number of arithmetic operations in distortion correction is reduced, making distortion correction simpler. The digital camera acquires a rectangle defined by the contour of the original, extracts the image of the original to acquire an original image before reduction, and acquires an associated projection-transformed image by affine transformation. The digital camera acquires pixel positions of the original image using an affine parameter, and acquires pixel positions of the image before distortion correction using a relational expression of distortion correction performed on the reduced image.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
Dental mirror, and an intraoral camera system using the same
Owner:TAKAHASHI ATSUSHI
Rotor assembly, information-recording/-reproducing device using the rotor assembly and method of assembling the rotor assembly
InactiveUS6965492B2Distortion freeReduce thicknessShaftsRecord information storageCentre of rotationStator
An information-recording / -reproducing device comprises a rotor assembly formed of a disc portion having information recording layer provided on the main surface and an axle portion, the disc portion being connected at the center of a surface opposite to the main surface with the rotating axle so that the rotating axis crosses at right angle with the main surface of disc portion at the center of rotation, a bearing for supporting the axle of disc portion freely rotatable, a rotating magnet fixed to a rotor yoke, a stator disposed opposing to the rotating magnet, and a motor for rotating the disc portion with the rotating axis of the axle as the center of rotation. Preferably, the disc portion with the rotating axle portion having a round column shape or a cylindrical shape, further may have a shallow hollow in the central part of the main surface which being a surface opposite to the surface having the rotating axle.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
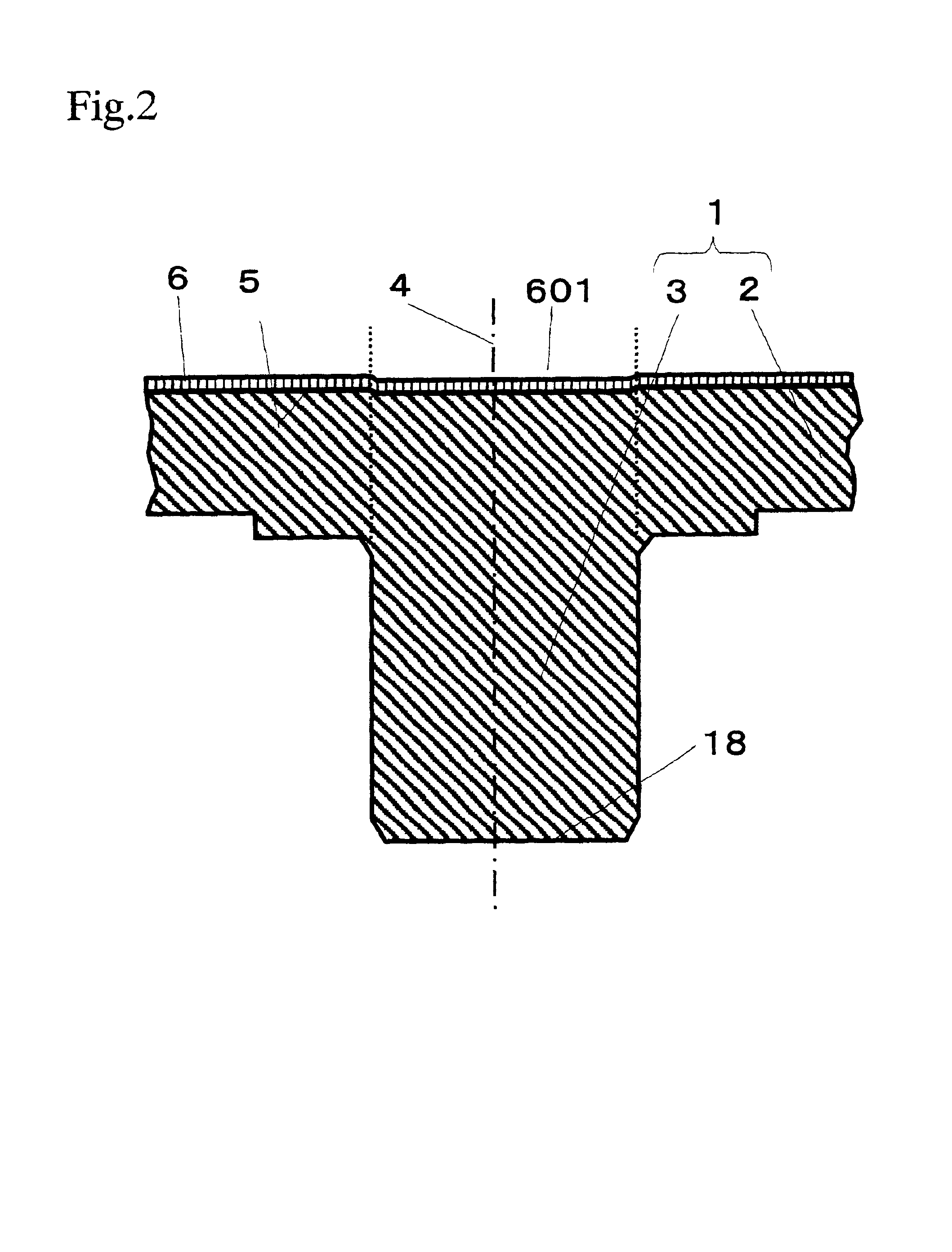
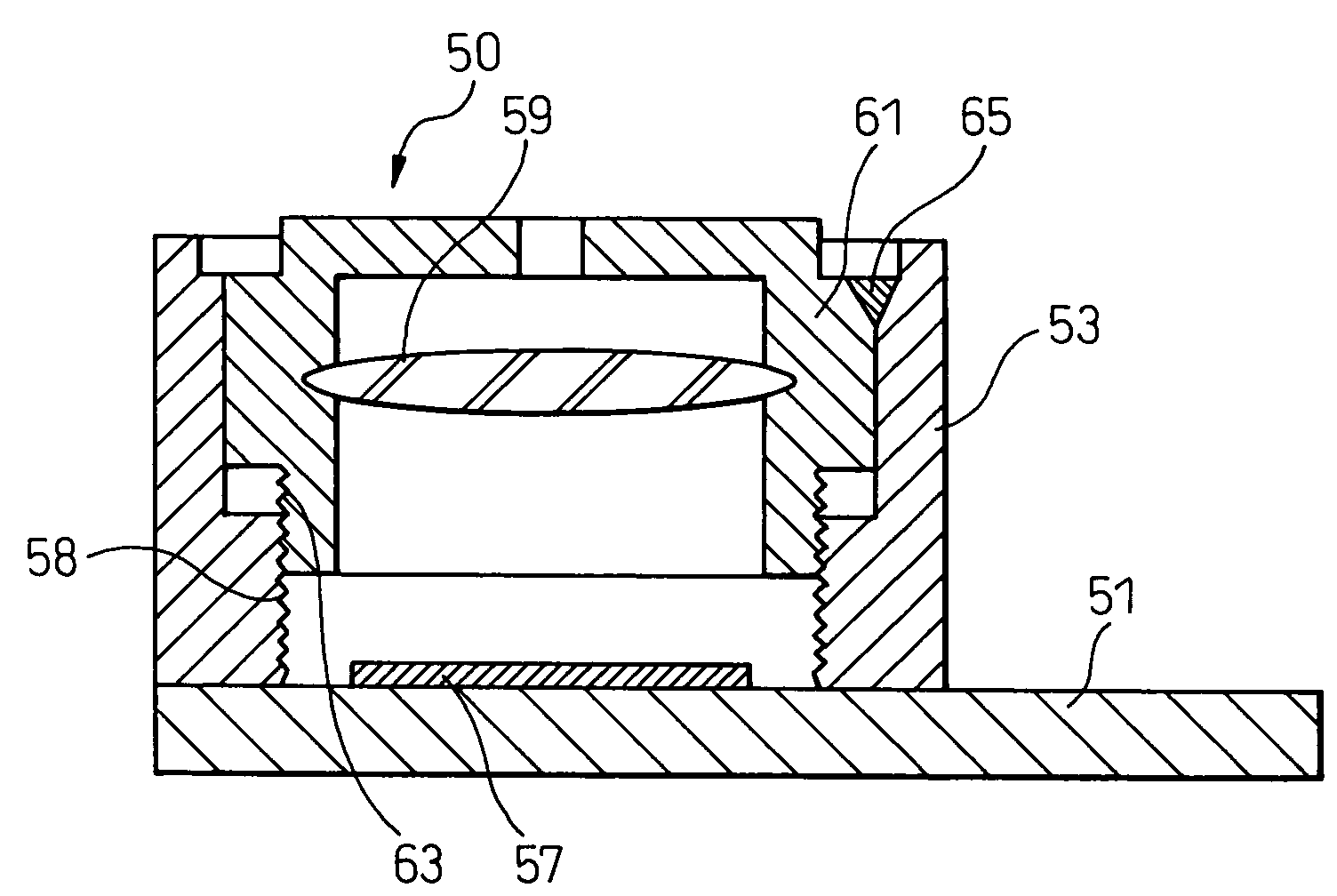
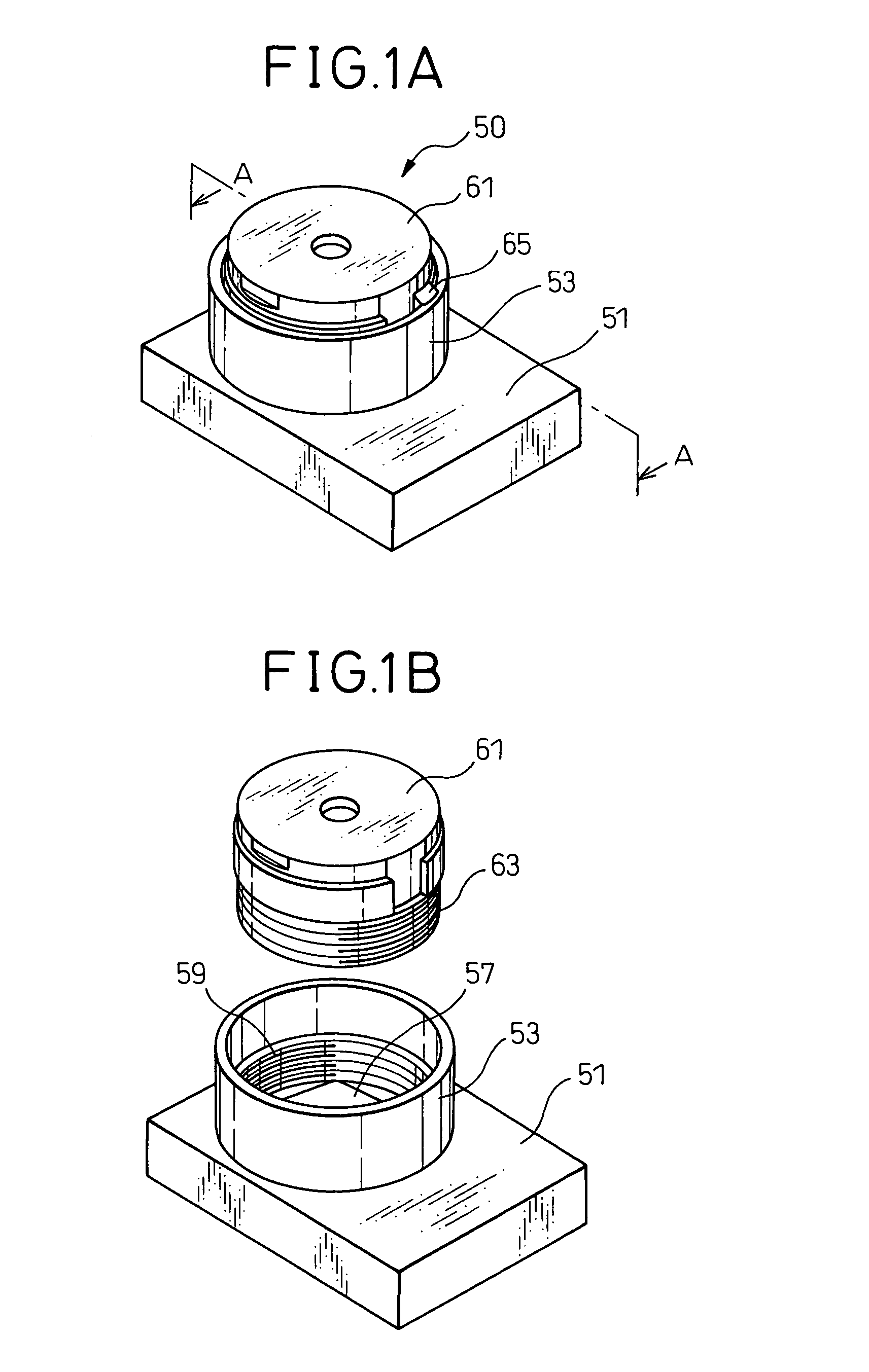
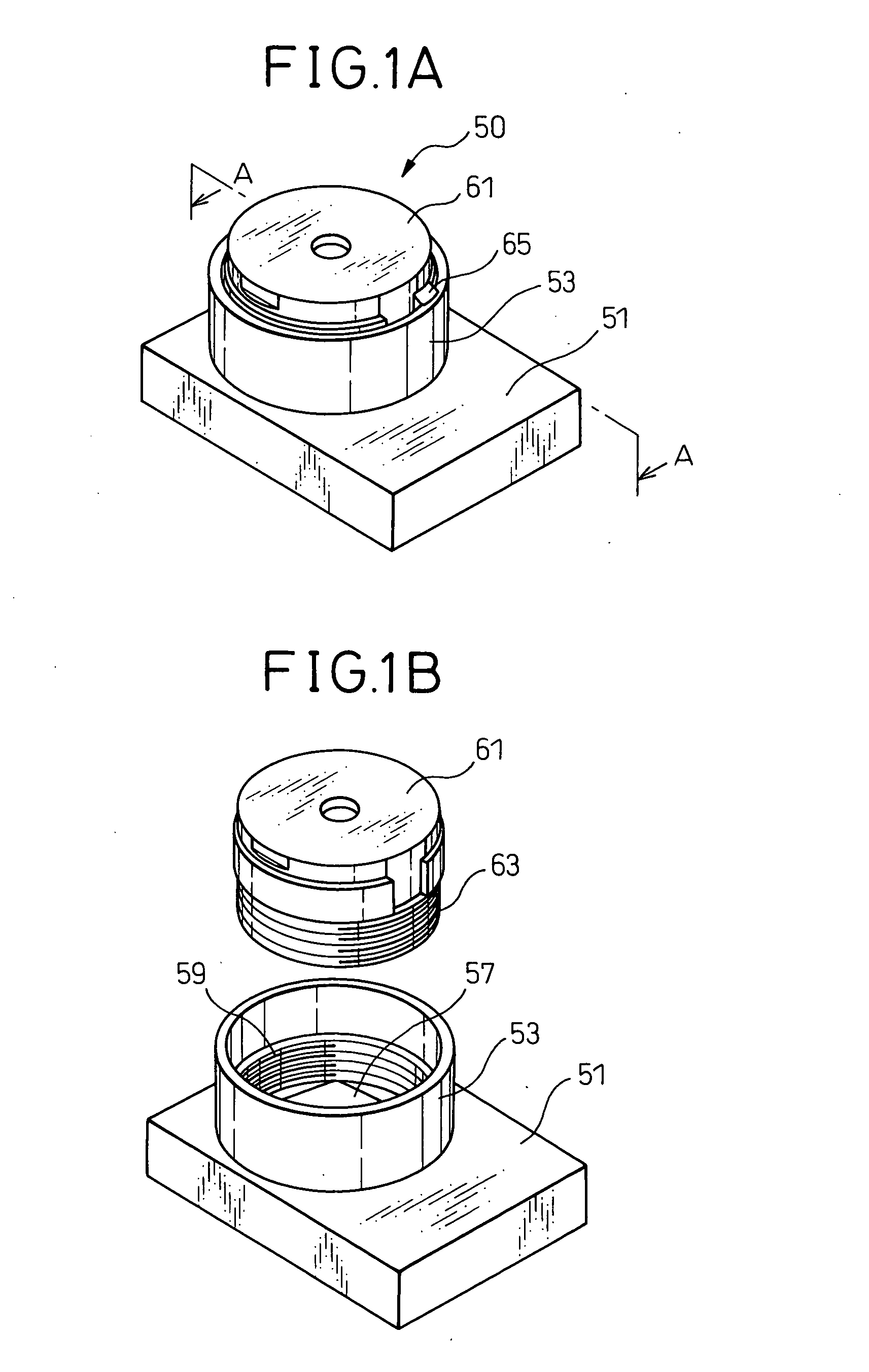
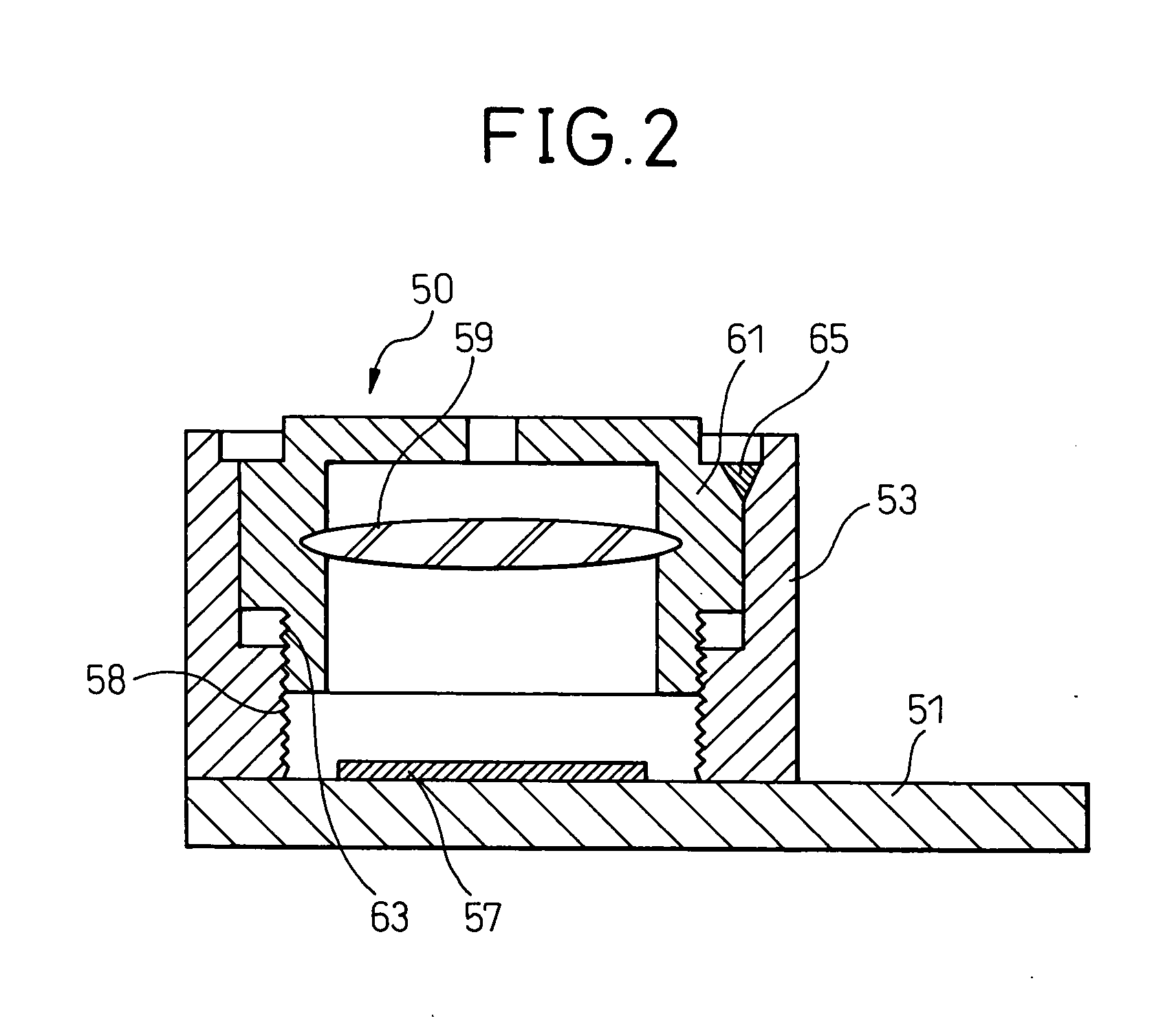
Imaging device, method of production of same, and holding mechanism of same
InactiveUS7367724B2Short timeFirmly assembledTelevision system detailsOptical articlesCamera lensMethods of production
An imaging device including a base on which an imaging element is provided, a cylindrically shaped plastic lens member holding a condensing lens at the inside, and a plastic barrel member in which the lens member can move in the axial direction and provided above the imaging element, wherein the barrel member and the lens member are affixed by laser welding, a method of production of the same, and an imaging device holding mechanism used for that production.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Inspection system with oblique viewing angle
ActiveUS7265900B2High resolutionPrecise positioningOptically investigating flaws/contaminationMicroscopesOptical radiationIntermediate image
Apparatus for imaging an area of a surface along a viewing angle that is oblique to the surface includes an afocal optical relay, which is adapted to form a tilted initial image of the area by collecting optical radiation from the area along an optical axis oriented at the viewing angle. A tilt correction unit is coupled to correct a tilt of the initial image so as to form a substantially undistorted intermediate image. A magnification module is coupled to focus the intermediate image onto an image detector.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC +1
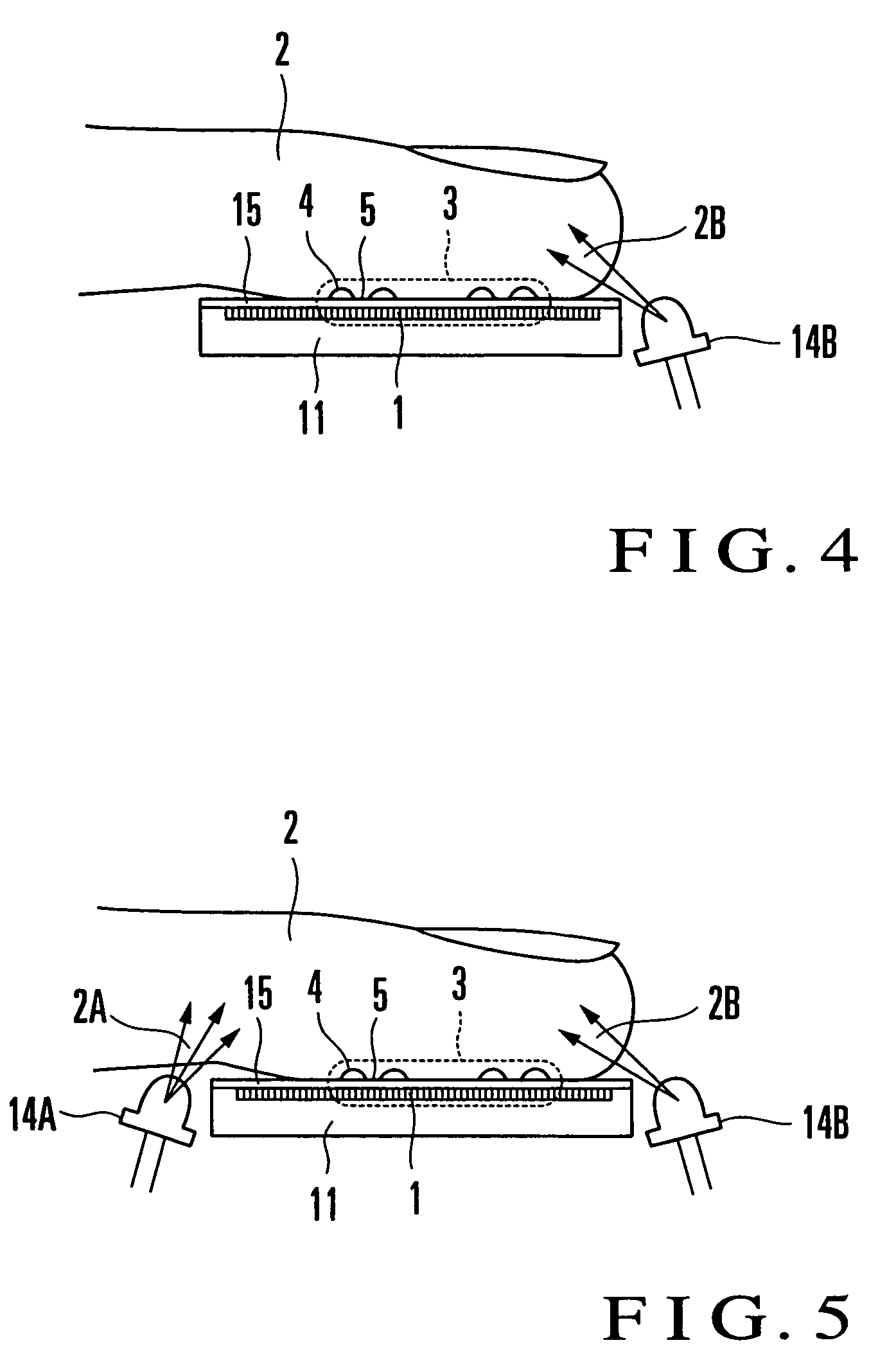
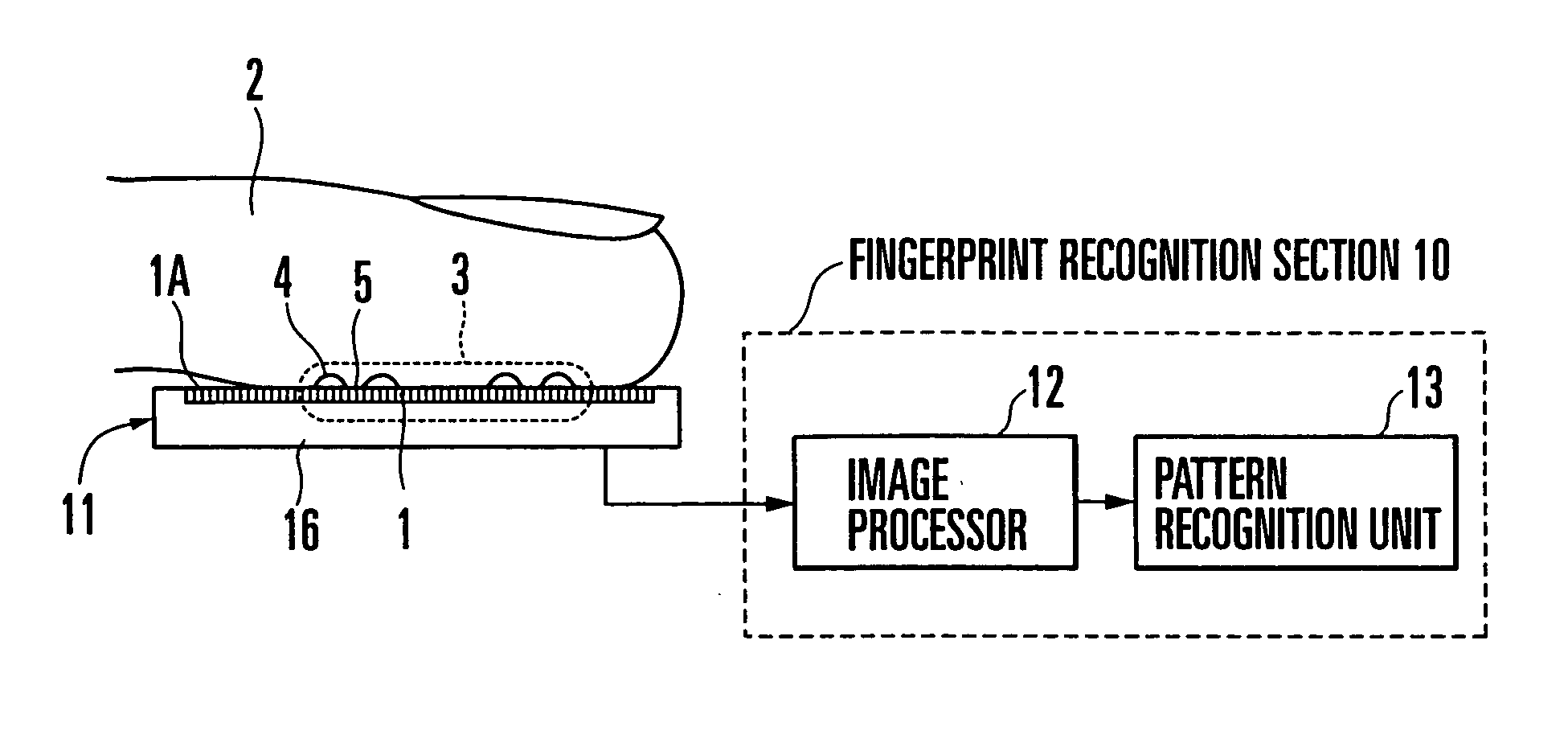
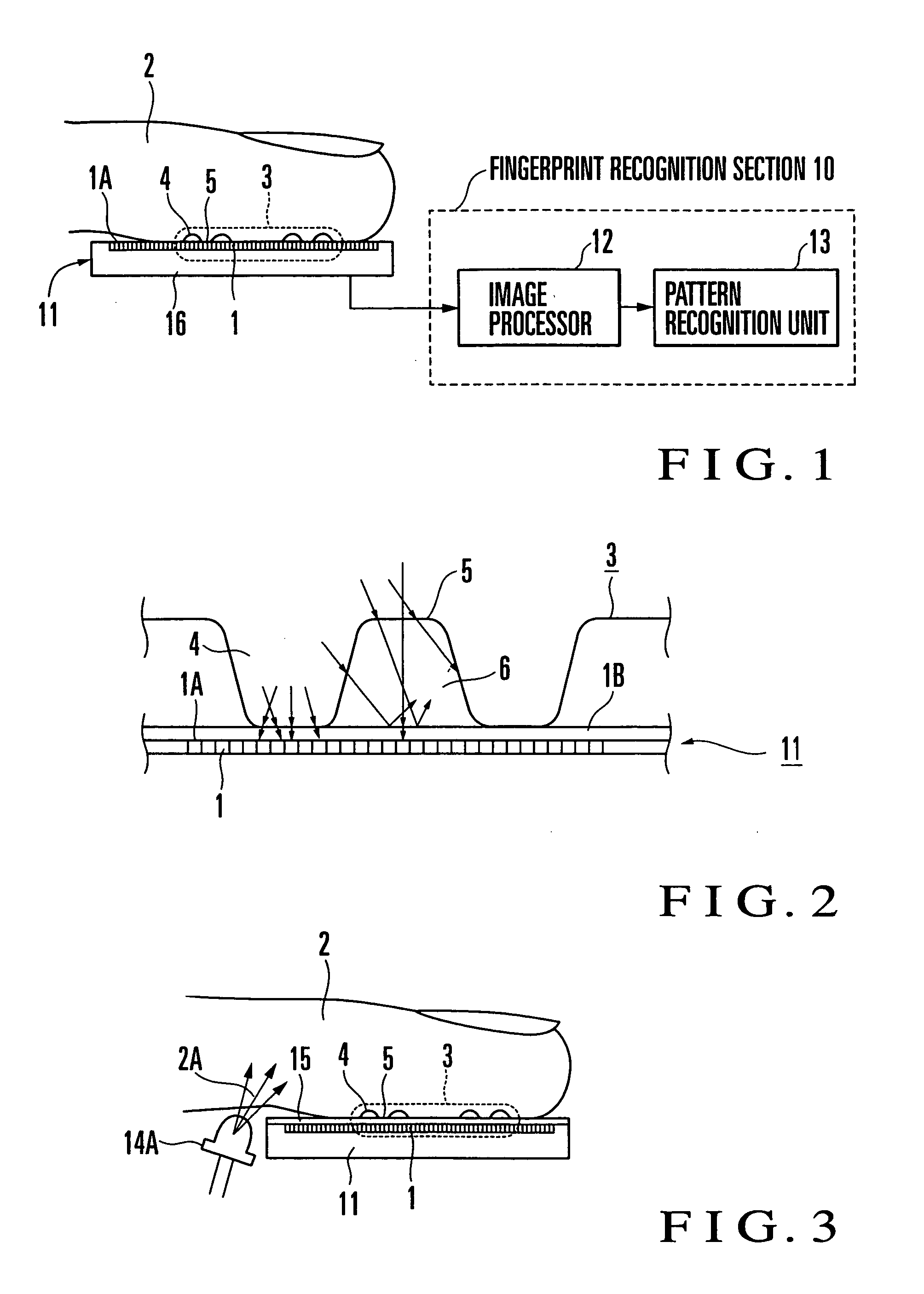
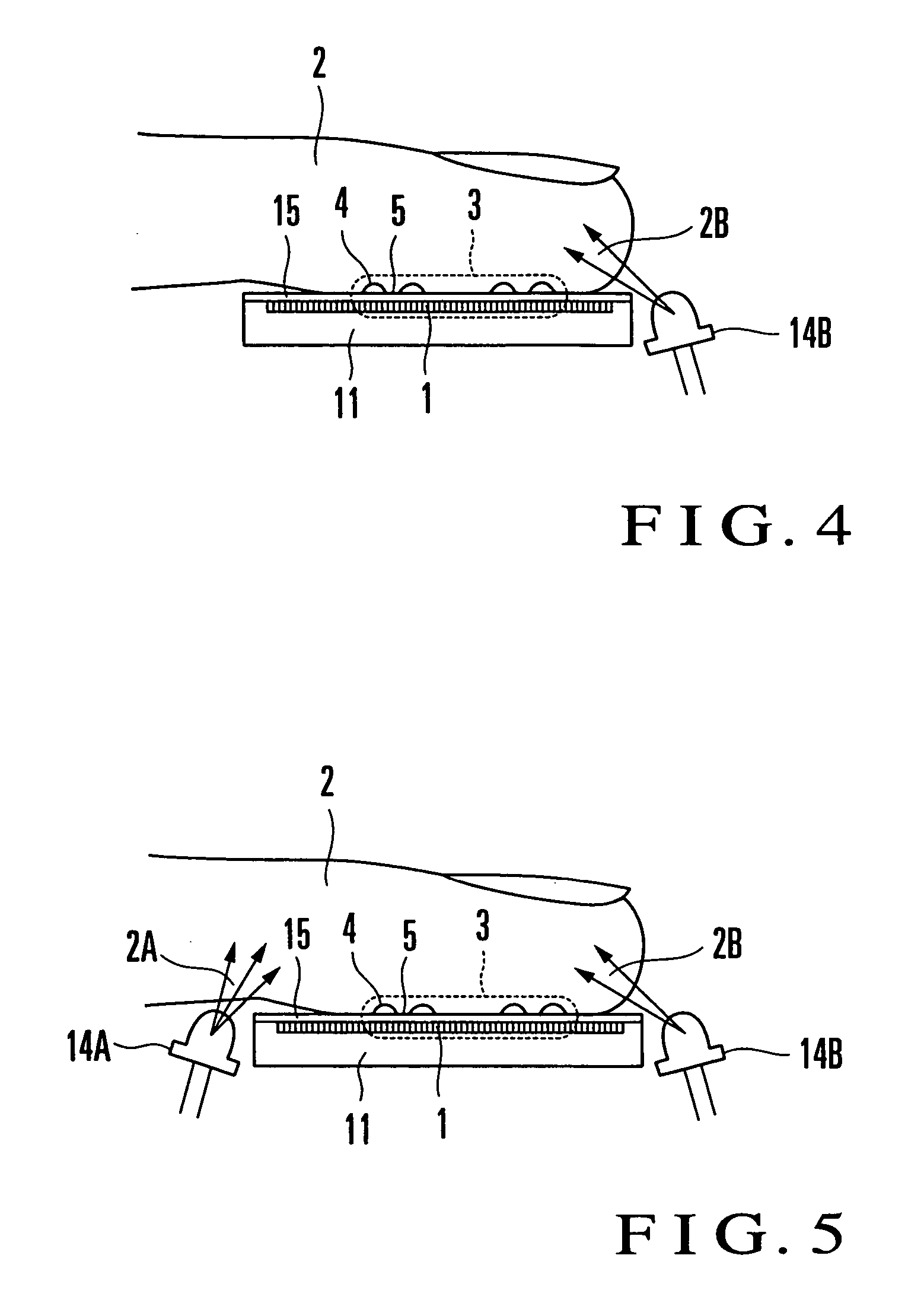
Fingerprint input apparatus
InactiveUS7177451B2Distortion freeImage analysisPerson identificationHigh intensityUltimate tensile strength
A fingerprint input apparatus includes scattered light and a two-dimensional image sensor. The scattered light is generated inside a finger having a fingerprint pattern in accordance with external light. The fingerprint pattern is made up of a ridge portion and a valley portion. The two-dimensional image sensor is made of a large number of light-receiving elements arranged in a two-dimensional array. The image of the fingerprint pattern is input to a light-receiving surface of the light-receiving element. The light-receiving element whose light-receiving surface is in substantially contact with the ridge portion detects as the ridge portion a bright portion where the scattered light emerging from the finger reaches at a high intensity. The light-receiving element whose light-receiving surface corresponds to the valley portion via a space detects as the valley portion a dark portion where the scattering light emerging from the finger reaches at a low intensity.
Owner:NEC CORP
Image processing apparatus
InactiveUS20070252905A1Distortion freeTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationVideo memoryVideo storage
An image processing apparatus is designed for displaying an image written in a video memory, on a display device in the form of an array of dots, by performing distortion correction of the image based on a distortion rate, and by performing tilt correction of the image based on a tilt angle. In the image processing apparatus, a first computing part computes a position before the tilt correction based on the tilt angle, for each dot of the image displayed in the display device. A second computing part computes a position before the distortion correction based on the distortion rate, for each position computed by the first computing part. A color data computing part computes color data of the position computed by the second computing part, based on color data of dots around the position in the video memory.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Adhesive binding method and device for carrying out this method
InactiveUS20070031211A1Distortion freeMechanical working/deformationLamination ancillary operationsShortest distanceEngineering
In order to produce an adhesive binding for bookbinding, in which the sheets, in letter paper format, are perforated on the folding edge, folded, provided with adhesive on the folding edge and assembled to form a book block, the perforating process is carried out on the folding edge in such a manner that two interrupted perforation lines are punched, these perforation lines being parallel at a short distance from one another, offset in a longitudinal direction and forming a widened folding edge. The punch locations of both perforation lines are, along the folding edge, offset by the length of one perforating tooth. The sheets, which are folded on the folding edge and which are assembled and squeezed to form a book block, are provided with the application of adhesive on surfaces, which are formed by the double perforating and which are assigned to one another, between full locations of one perforation line and full locations of the other perforation line.
Owner:SCHMIDKONZ PETER
Real time desktop image warping system
ActiveUS20090102862A1Distortion freeReduce distortion problemsImage enhancementCathode-ray tube indicatorsOperational systemComputer graphics (images)
The present invention relates to an image warping software algorithm for a real time alteration of a display scene running under the Microsoft Windows Operating System. The image warping software algorithm alters the display scene and allows an observer to view the display scene as a single unbroken image when the display scene is distributed across multiple display screens. The purpose of the image warping software algorithm is to significantly reduce the distortion observed at the abutting edges of the joined display screens.
Owner:U S OF A AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY
Imaging device, method of production of same, and holding mechanism of same
InactiveUS20050117048A1Short timeFirmly assembledTelevision system detailsOptical articlesEngineeringMethods of production
An imaging device including a base on which an imaging element is provided, a cylindrically shaped plastic lens member holding a condensing lens at the inside, and a plastic barrel member in which the lens member can move in the axial direction and provided above the imaging element, wherein the barrel member and the lens member are affixed by laser welding, a method of production of the same, and an imaging device holding mechanism used for that production.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
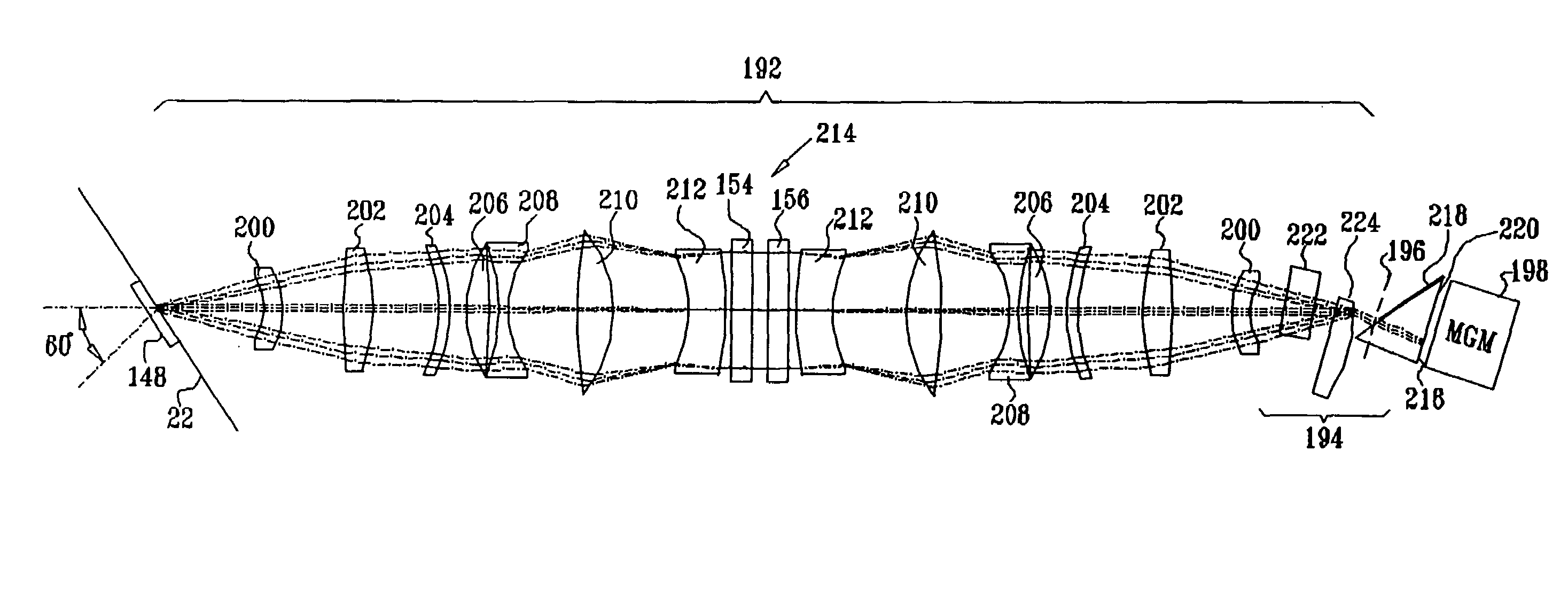
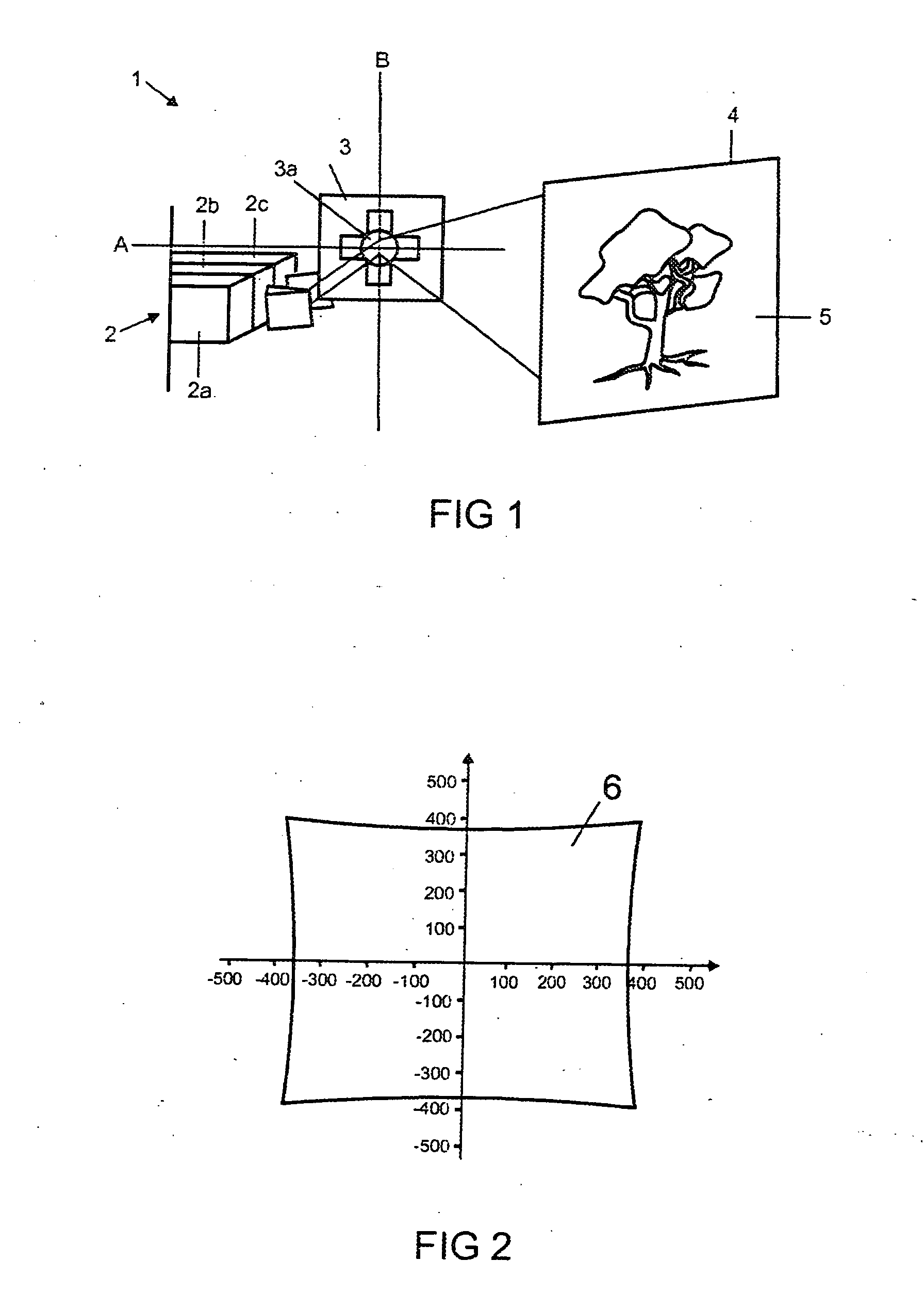
Projector for projecting an image and corresponding method
ActiveUS20100302516A1Small distortionRealized cost-effectively and compactlyProjectorsMicroscopesProjection imageLight beam
The invention relates to a projector (1) for projecting an image (6), comprising: a light source (2) for generating a light bundle (12); a pivotable deflection unit (3) designed for deflecting the light bundle (12) generated by the light source (2) onto a projection surface (5); and an imaging device (7, 8, 9) for imaging an aperture of the deflection unit (3) onto the projection surface (5); wherein the imaging device (7, 8, 9) comprises a mirror objective (7) having at least two mirror elements (8, 9). The invention further relates to a corresponding method.
Owner:OSRAM GMBH
Semiconductor device and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20160027830A1Good light collection characteristicMaintain pressure balanceTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPower semiconductor deviceEngineering
Provided is a semiconductor device including: a multilayer substrate including an optical element; a light-transmitting plate provided on the substrate to cover the optical element; and a lens of an inorganic material provided between the substrate and the light-transmitting plate. A structure having a same strength as a strength per unit area of the lens is provided at a portion outside an effective photosensitive region where the optical element is formed, when the substrate is viewed in plan.
Owner:SONY CORP
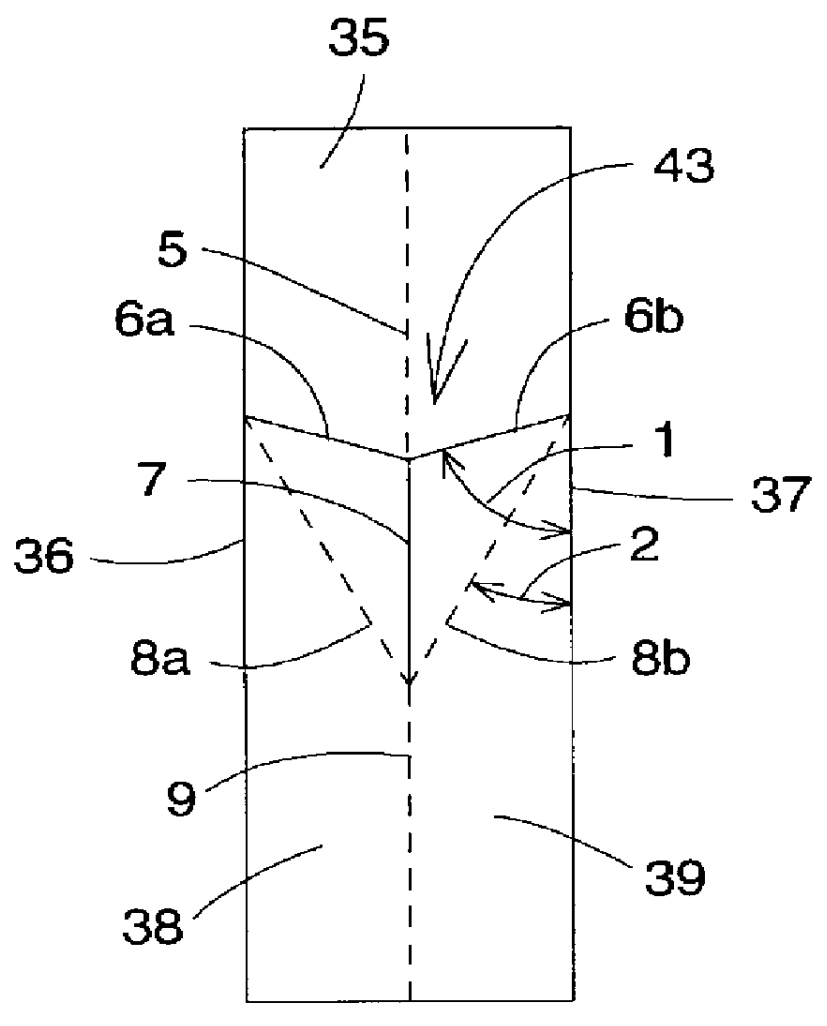
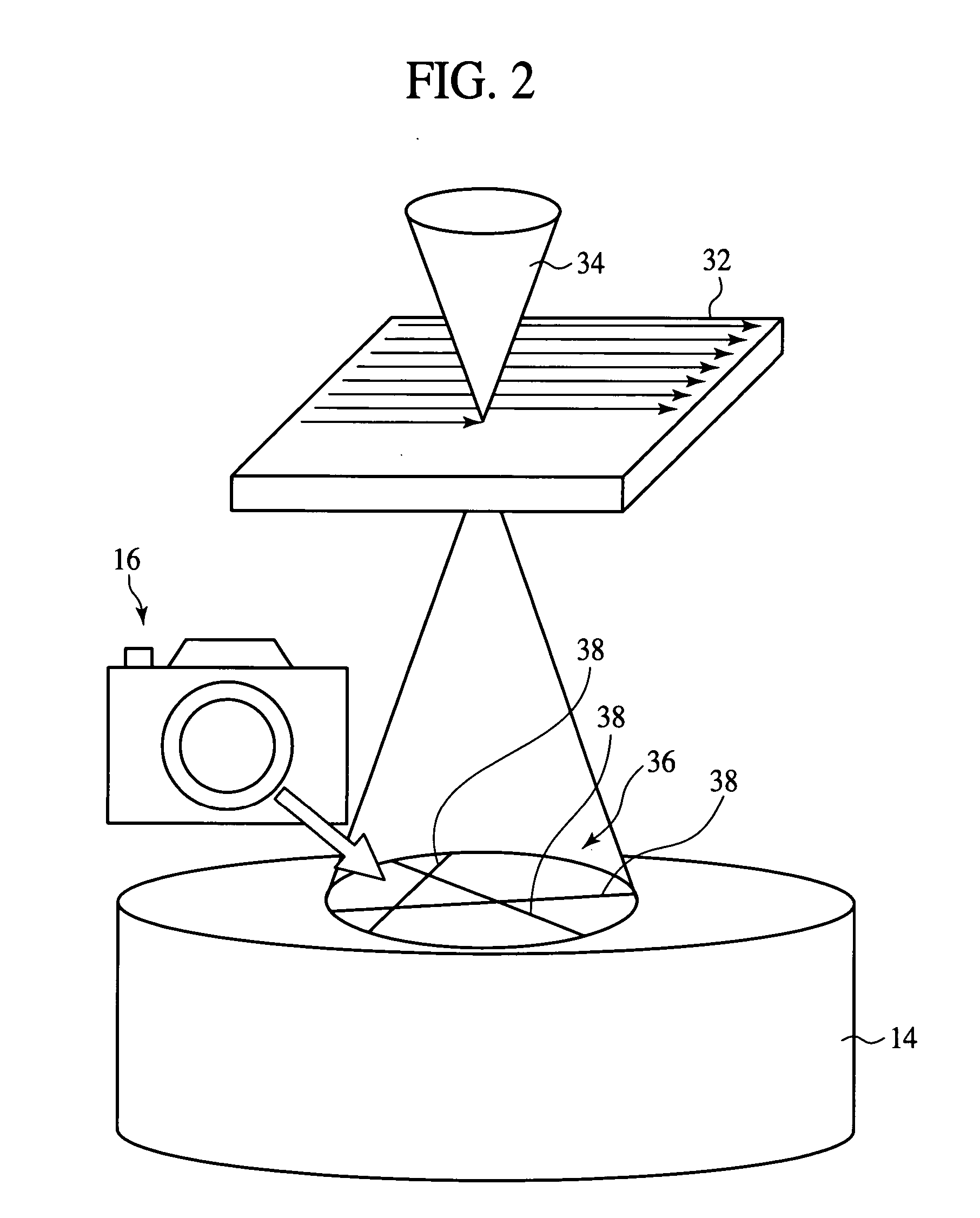
Lattice strain measuring system and method
ActiveUS20050082477A1High resolve powerHigh accuracyElectric discharge tubesForce measurementDistortionTransmission electron microscopy
A lattice strain measuring method comprising the steps of: using a scanning transmission electron microscope 12 to apply convergent electron beams 34 to a sample 32 and obtain a convergent-beam electron diffraction image 36 of the sample 32; computing a lattice strain magnitude of the sample 32, based on the obtained convergent-beam electron diffraction image; and displaying the computed lattice strain magnitude, associated with an electron microscope image of the sample 32. A scanning transmission electron microscope 12 is used, whereby electron beams 34 are caused to scan to thereby suitably set an incidence position. Accordingly, the incidence position of the electron beams can be displaced at a nanometer-order pitch accurately in a short period of time. The use of a scanning transmission electron microscope 12 requires no image forming lens below the sample 32, and the convergent-beam electron diffraction image is free from the distortion due to the influence of an image forming lens. Thus, a distribution of lattice strains in an electronic device having, e.g., a micronized structure can be displayed in an image with high resolving power and with high accuracy and furthermore in a short period of time.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Lattice strain measuring system and method
ActiveUS7084400B2High resolutionImprove accuracyElectric discharge tubesForce measurementLight beamElectron microscope
A lattice strain measuring method including the steps of: using a scanning transmission electron microscope 12 to apply convergent electron beams 34 to a sample 32 and obtain a convergent-beam electron diffraction image 36 of the sample 32; computing a lattice strain magnitude of the sample 32, based on the obtained convergent-beam electron diffraction image; and displaying the computed lattice strain magnitude, associated with an electron microscope image of the sample 32. A scanning transmission electron microscope 12 is used, whereby electron beams 34 are caused to scan to thereby suitably set an incidence position. Accordingly, the incidence position of the electron beams can be displaced at a nanometer-order pitch accurately in a short period of time. The use of a scanning transmission electron microscope 12 requires no image forming lens below the sample 32, and the convergent-beam electron diffraction image is free from the distortion due to the influence of an image forming lens. Thus, a distribution of lattice strains in an electronic device having, e.g., a micronized structure can be displayed in an image with high resolving power and with high accuracy and furthermore in a short period of time.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
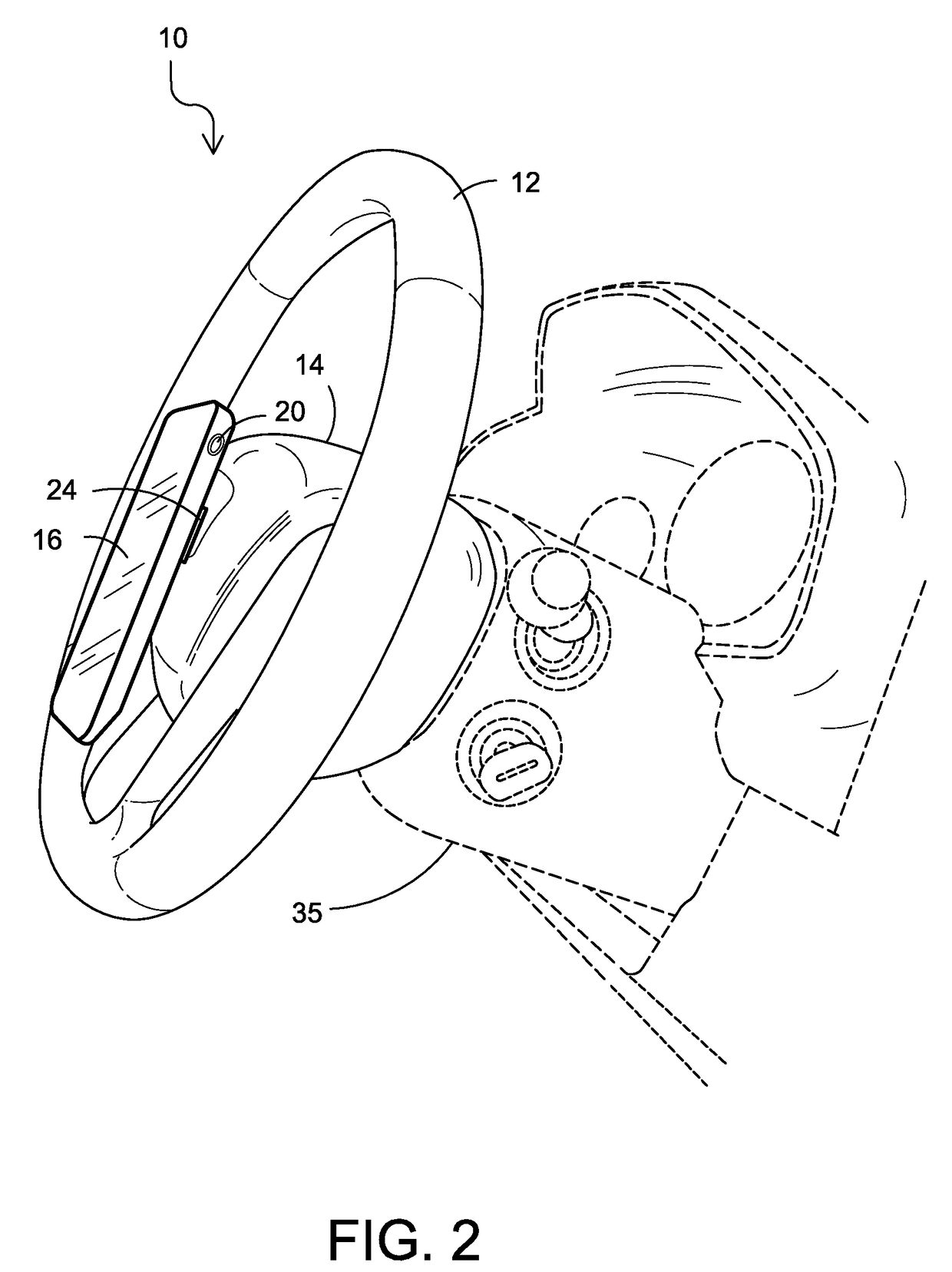
Self Leveling Steering Wheel Mount Assembly for Electronic Cell Phone Device Having Side Camera
InactiveUS20180022292A1Avoid insufficient thicknessSimple designDigital data processing detailsVehicle componentsSteering wheelEngineering
A combination of a vehicle including a steering wheel assembly and an electronic cell phone device having a side positioned camera and a mounting system that enables said cell phone device to be mounted on said steering wheel assembly. The camera faces at least one front seat side window of the vehicle allowing handsfree recording and uploading to cloud storage of events inside and outside the vehicle without the necessity of the driver positioning the camera at the area being recorded.
Owner:LOWELL THOMAS A
Rotational angle sensor, motor, rotational angle detector, and electric power steering system
ActiveUS8278916B2Simple configurationHigh precisionMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesElectric power steeringElectric power system
A rotational angle sensor includes: a magnet rotor in which multiple magnetic poles are formed along the circumferential direction of the magnet rotor; and three sensor devices that are arranged on a circle concentric with the magnet rotor at regular angle intervals. Each of the sensor devices includes three half-bridge circuits each of which has a pair of spin valve magnetic resistances that are connected in series in such a manner that the magnetization directions of spin fixed layers of the spin valve magnetic resistances are opposite to each other. Each of the sensor devices is formed in such a manner that phases of the sensor signals output from the respective half-bridge circuits based on a change in magnetic flux caused by the rotation of the magnet rotor are offset from each other by an electrical angle of 120°.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
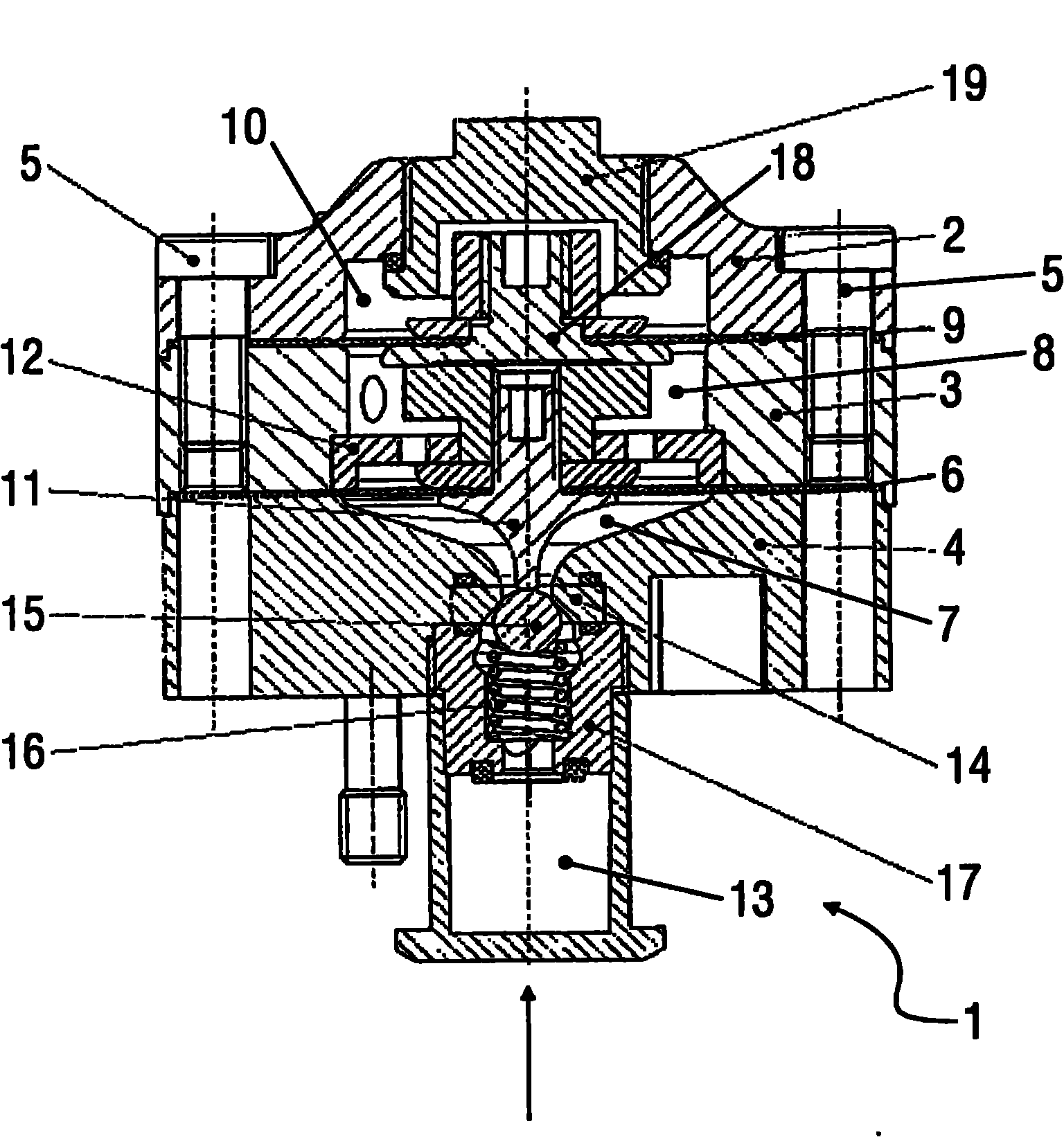
Pressure-actuated member, in particular paint pressure controller or coating agent valve
ActiveCN101978333ANo frequent replacementExtended use timeSpraying apparatusFluid pressure control with auxillary non-electric powerEngineeringBiomedical engineering
The invention relates to a pressure-actuated member (1), in particular a paint pressure controller or a coating agent valve, for influencing a mean coating agent pressure of a coating agent to be applied in a painting system, comprising a component (6, 14), which is subjected directly to the coating agent during operation and is mobile and / or can be deformed to influence the pressure. It is proposed that the component (6, 14) subjected to the coating agent at least partially comprises a ceramic material in order to achieve a longer service life.
Owner:DUERR SYST GMBH
Fingerprint input apparatus
InactiveUS20050025346A1Low profileDistortion freeImage analysisPerson identificationHigh intensityUltimate tensile strength
A fingerprint input apparatus includes scattered light and a two-dimensional image sensor. The scattered light is generated inside a finger having a fingerprint pattern in accordance with external light. The fingerprint pattern is made up of a ridge portion and a valley portion. The two-dimensional image sensor is made of a large number of light-receiving elements arranged in a two-dimensional array. The image of the fingerprint pattern is input to a light-receiving surface of the light-receiving element. The light-receiving element whose light-receiving surface is in substantially contact with the ridge portion detects as the ridge portion a bright portion where the scattered light emerging from the finger reaches at a high intensity. The light-receiving element whose light-receiving surface corresponds to the valley portion via a space detects as the valley portion a dark portion where the scattering light emerging from the finger reaches at a low intensity.
Owner:NEC CORP
Apparatus and Method for Correcting for Aberrations in a Lens System
InactiveUS20080225227A1Obtain goodEnhance the imageOptical measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionOptical aberrationDistortion
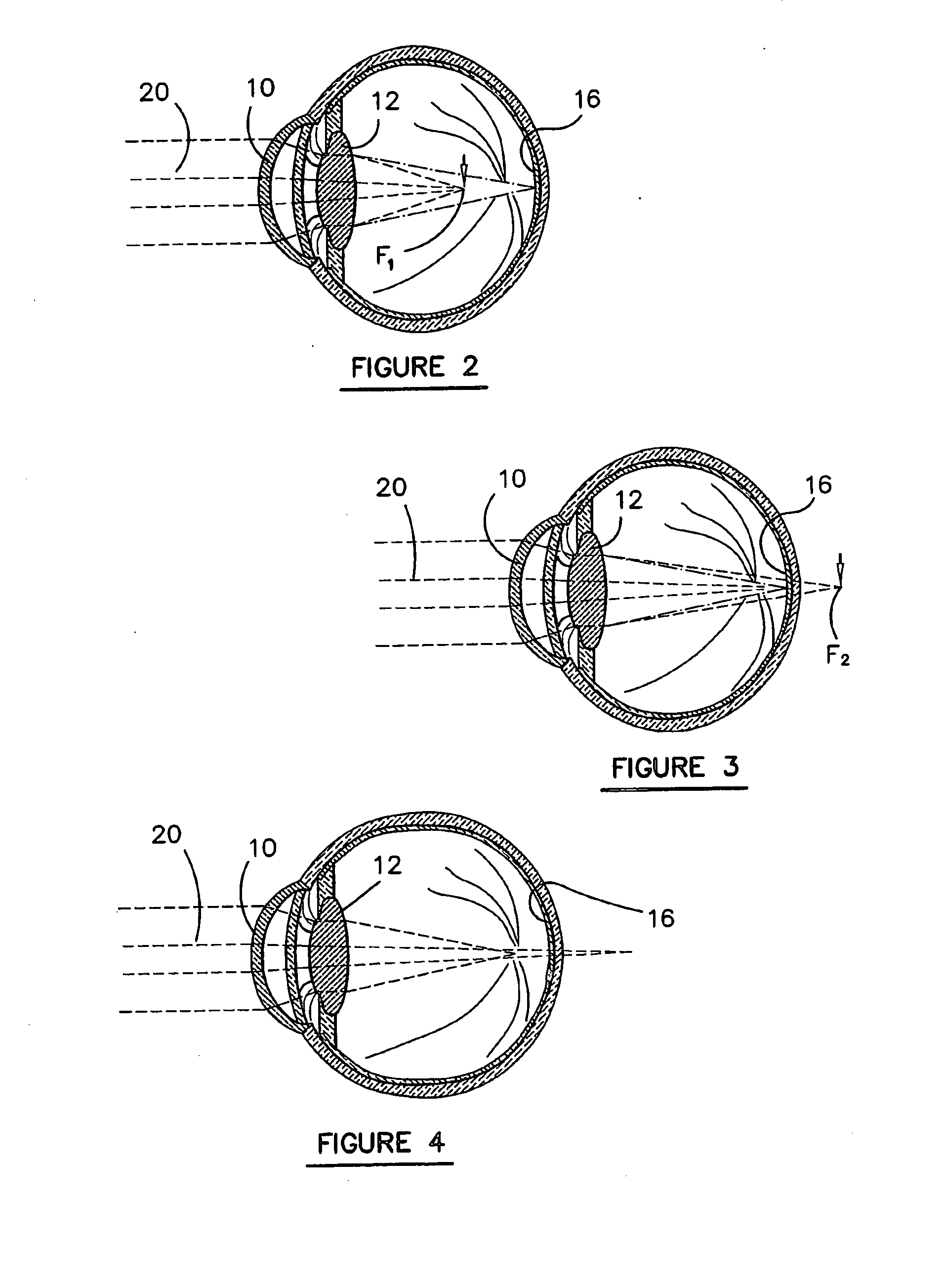
A method and apparatus for compensating for aberrations or distortions of an optical system such as an eye of a patient which is to be imaged by a camera is disclosed. Light passing through the optical system is detected by a charge coupled device (62) via an imaging system (60). Phase data relating to the light passing through the system is determined and a processor (64) processes the data so that a transformation is determined which transforms the data relating to the wavefront of the light so that the phase data is transformed to remove aberrations or distortions introduced by the optical system. Thus, clearer images of the fundus of an eye generated by light passing through the optical system of the eye and for determining distortions or aberrations introduced by the optical system of the eye are provided.
Owner:IATIA IMAGING
Resin composition and display unit
ActiveUS20140329431A1Minimum shrinkage stressEffects can be minimizedVessels or leading-in conductors manufactureThin material handlingContraction rateTransmittance
A display unit that includes an image display part and a light-transmitting protective part arranged on the image display part. A cured resin layer is arranged between the display part and the protective part. The cured resin layer has a transmittance of 90% or higher in the visible range and a storage modulus at 25° C. of 1×107 Pa or less. The cured resin layer is formed from a resin composition that has a cure shrinkage of 5% or less.
Owner:DEXERIALS CORP
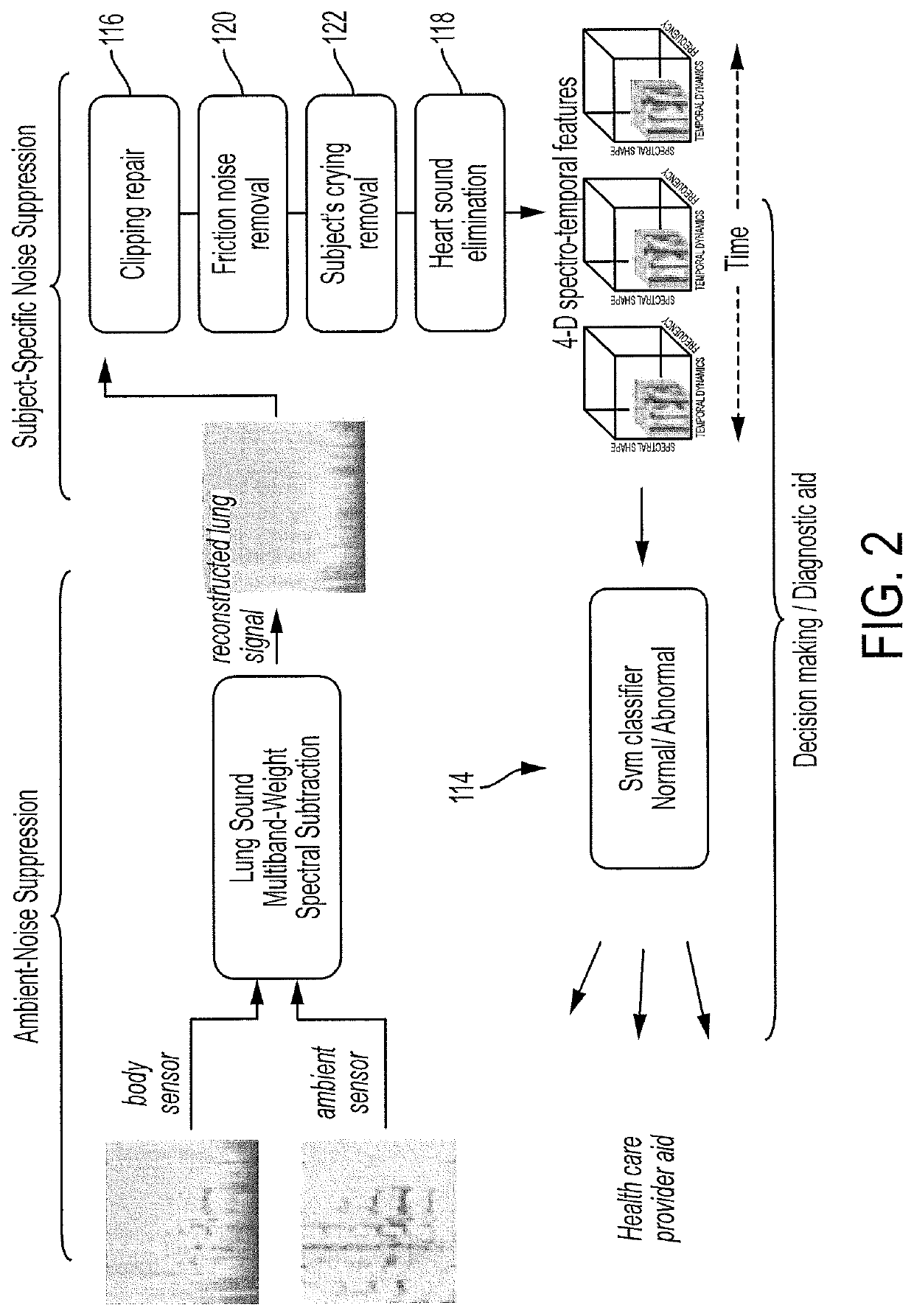
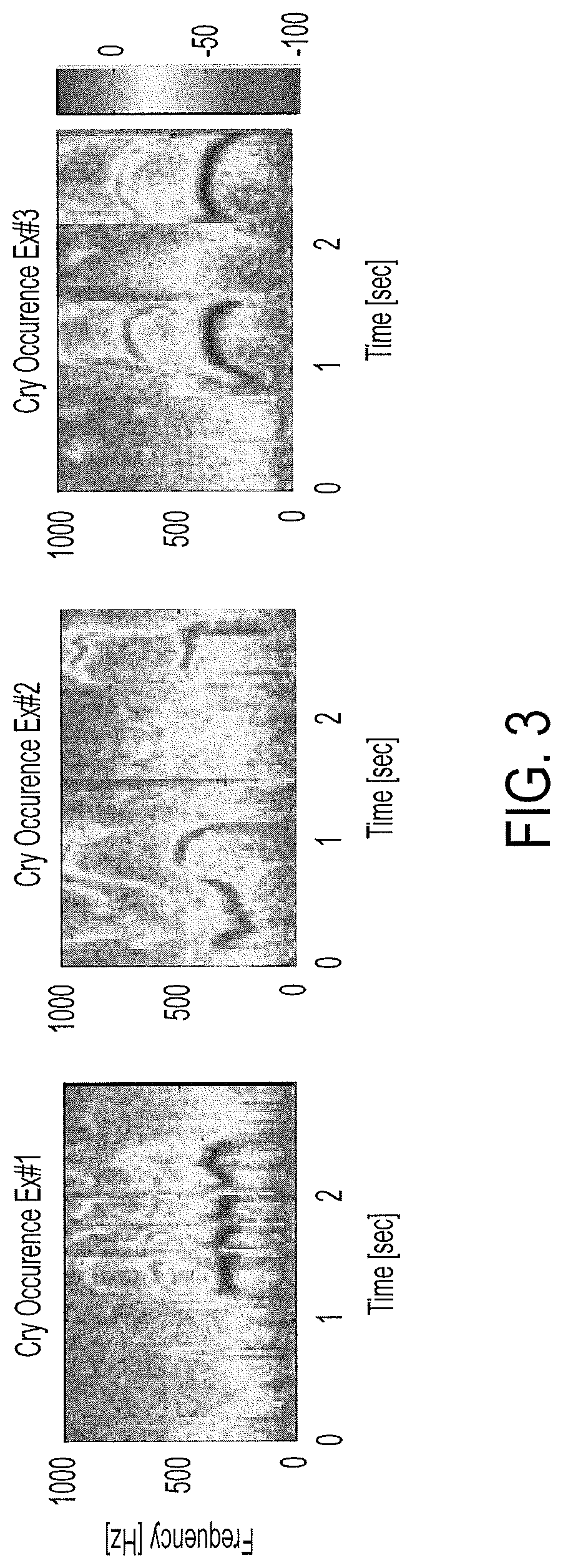
Programmable electronic stethoscope devices, algorithms, systems, and methods
ActiveUS10765399B2Distortion freeClean auscultation signalStethoscopeSpeech analysisEnvironmental noiseStationary noise
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Information processing apparatus, information processing method, and computer program
InactiveUS8305491B2Distortion freeTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsInformation processingImaging processing
An image processing apparatus for displaying an input image on a display, includes an image converting unit for converting the input image into an equiaspect ratio image, the equiaspect ratio image having the same aspect ratio as the input image, having one of a horizontal size and a vertical size thereof equal to one of a horizontal size and a vertical size of a display screen of the display, and having an image size thereof being equal to or smaller than the size of the display screen, an additional image generating unit for generating an additional image from the input image, a combination image generating unit for generating a combination image into which the equiaspect ratio image and the additional image are combined, and a display control unit for causing the display to display the combination image.
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com