Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
47results about How to "Light loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Light source
ActiveUS20130250546A1Simplify Optical DesignEasy to manufacturePoint-like light sourceProjectorsLight sourceLaser
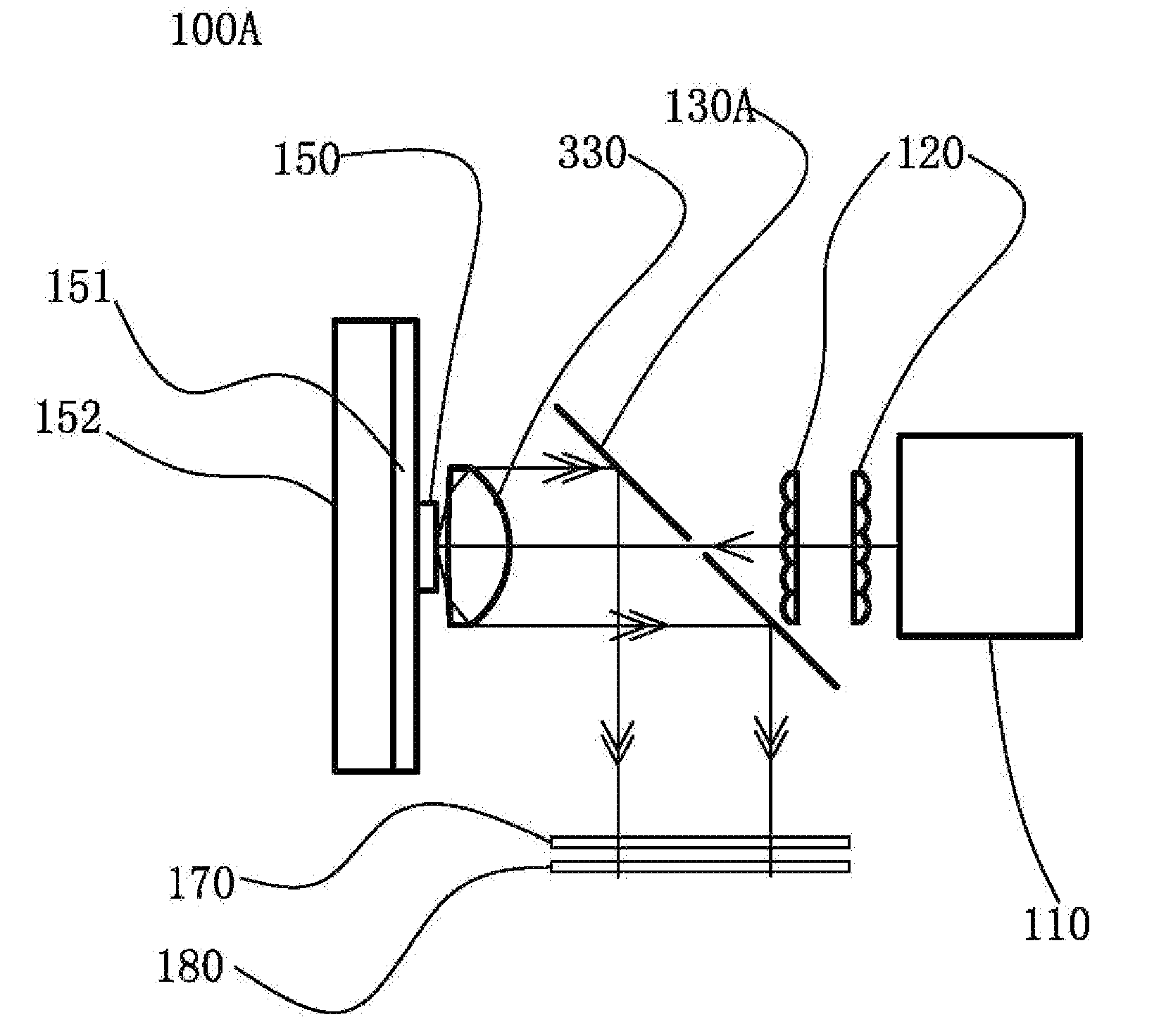
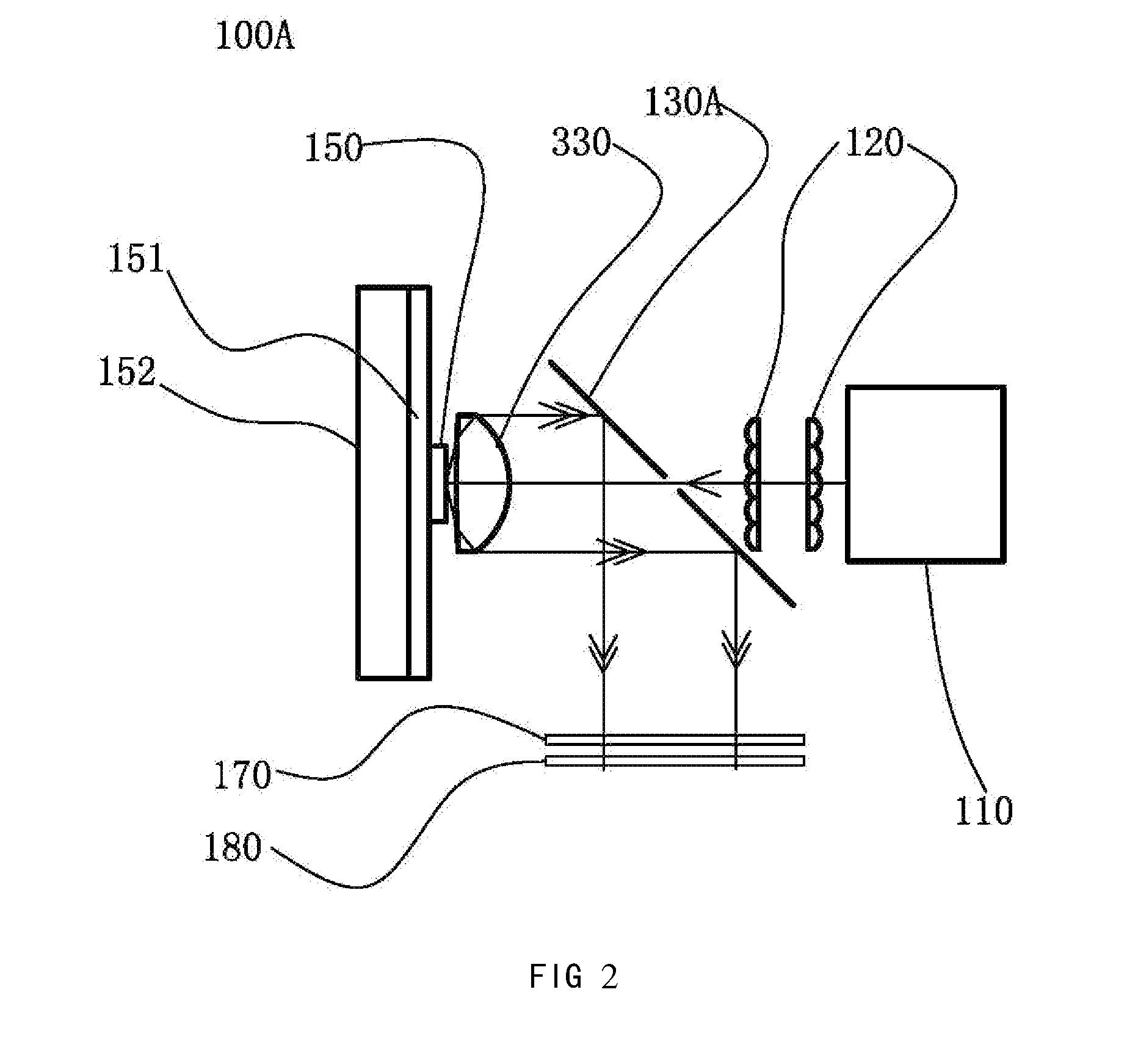
A light source comprising an excitation light source (110) for providing excitation light, and an optical wavelength conversion member disposed at a distance from the excitation light source. The optical wavelength conversion member comprises an optical wavelength conversion material (150) for converting the excitation light into stimulated light. The light source also comprises an optical-guiding member that allows the excitation light to be incident on the optical wavelength conversion material, and an optical-collecting member (130A) for collecting stimulated light originating from the optical wavelength conversion material. To separate the paths of the stimulated light and the excitation light, the etendue of the optical-guiding member is less than or equal to ¼ of the etendue of the optical-collecting member. This allows the optical-guiding member to draw in the excitation light while preventing the excessive escape of the stimulated light through the optical-guiding member. The advantages of the light source are that it can separate the paths of the excitation light and the stimulated light, the light path is simple, and the optical members are easy to manufacture.
Owner:APPOTRONICS CORP LTD
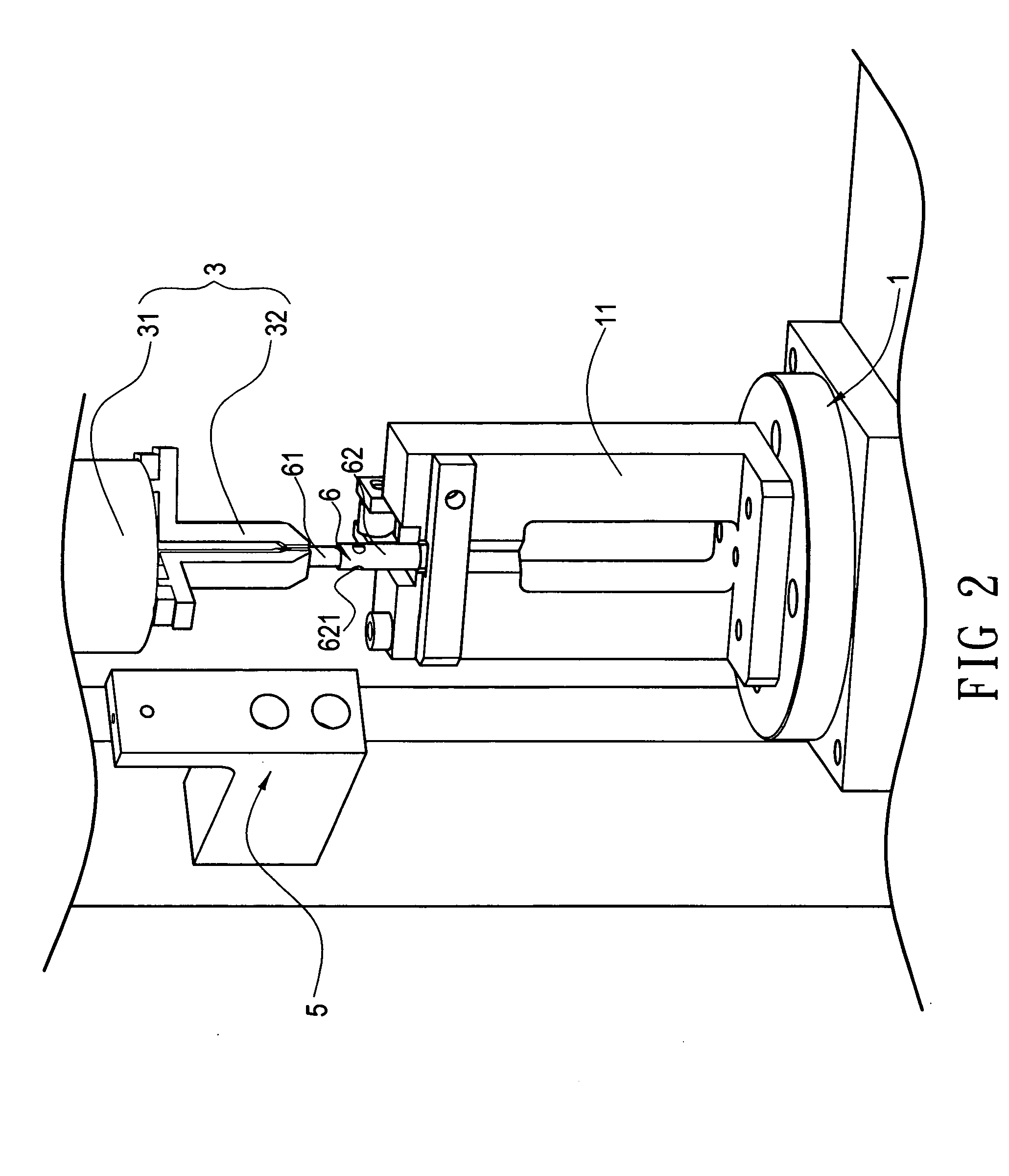
Endoscope
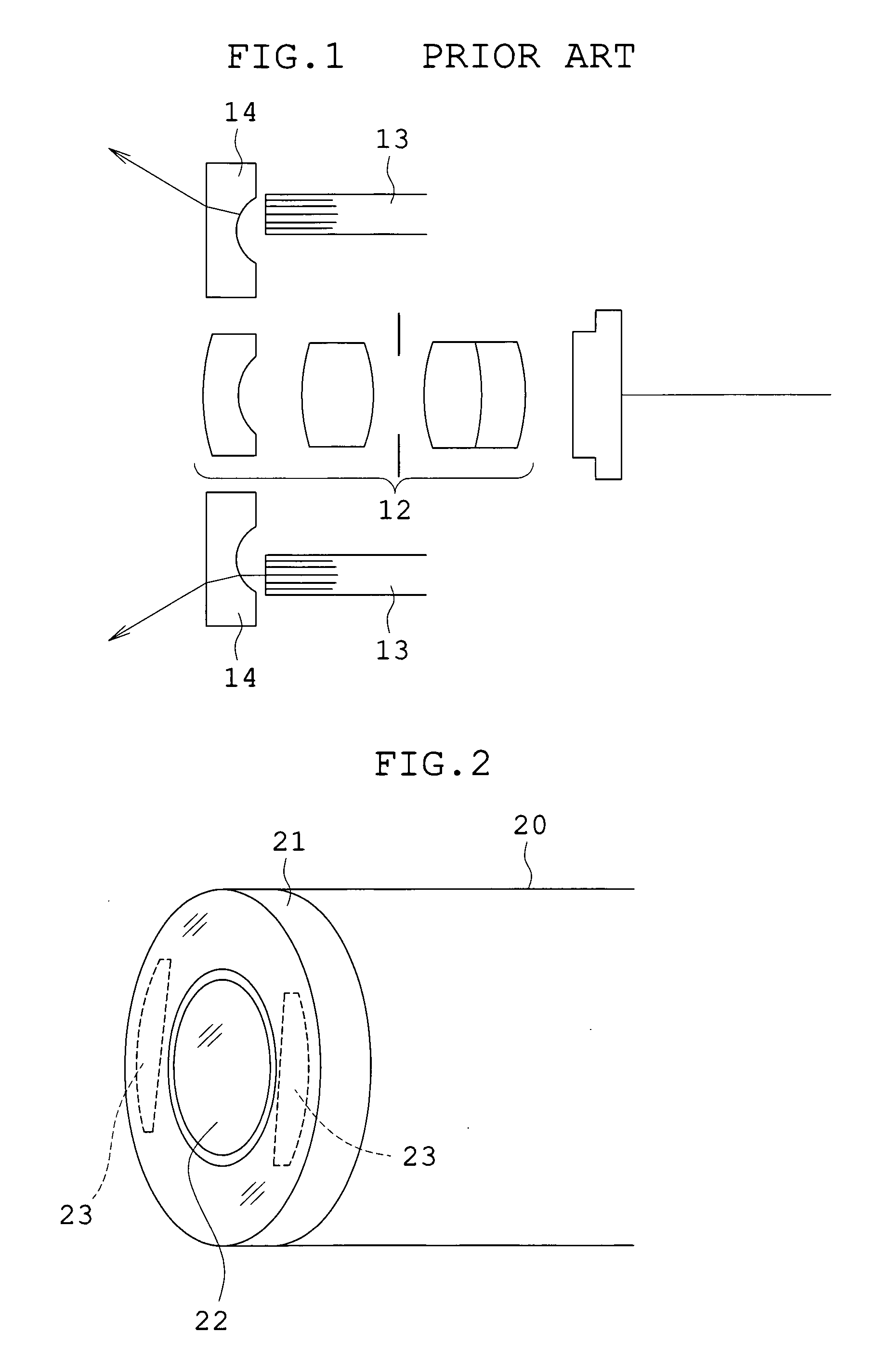
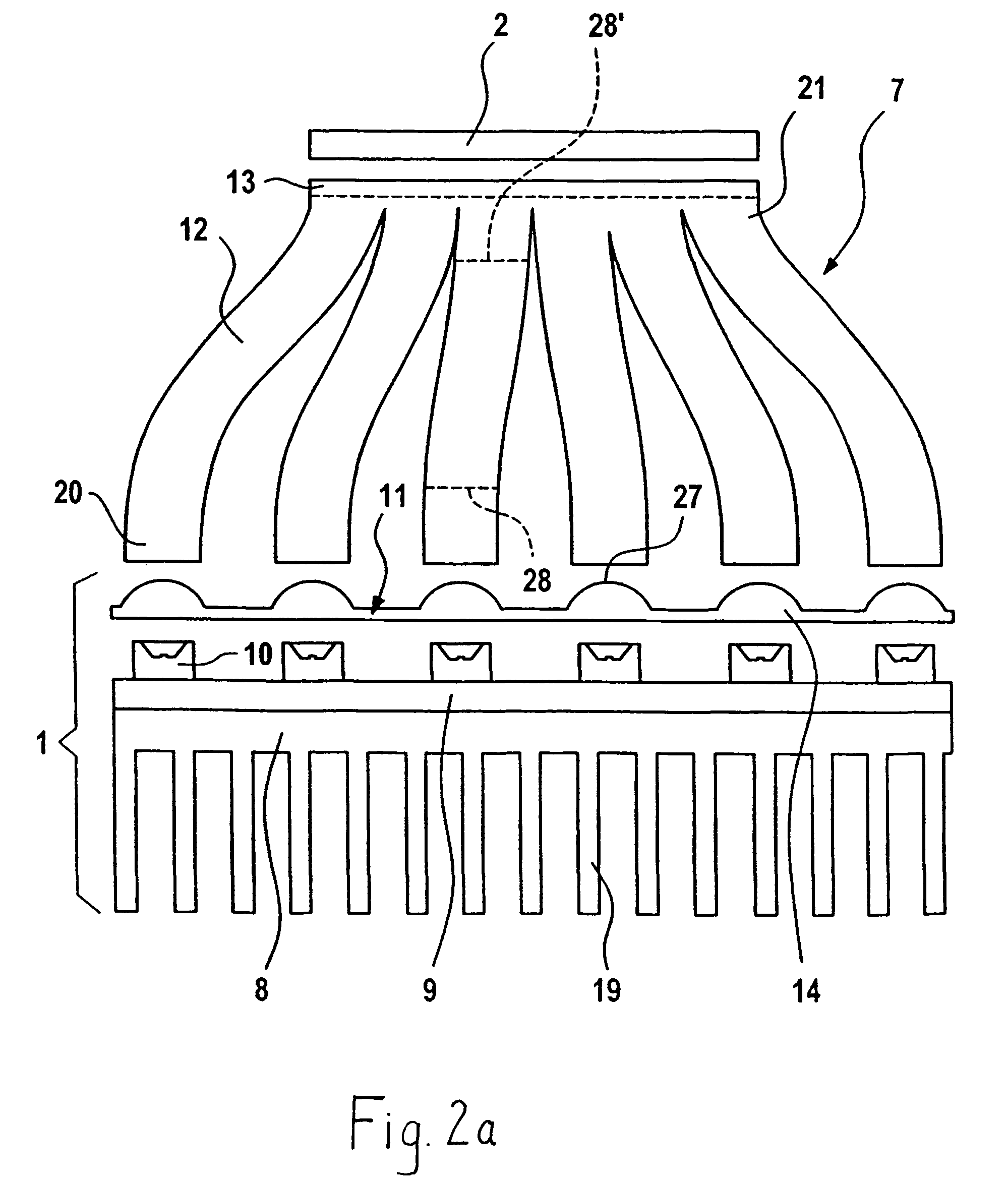
An endoscope incorporates an objective optical system and an image sensor at its distal end and has light guides around the objective optical system. In this case, when a direction parallel to the major side of an imaging region of the image sensor is taken as a lateral direction, exit end faces of the light guides are arranged only in the lateral direction of the objective optical system, a top cover is placed opposite to the exit end faces, and an illumination light diffusing portion is provided at the position of the top cover opposite to the exit end faces. Whereby, the endoscope in which the small-diameter design of the distal end is attained and the loss of emergent light is minimized can be provided.
Owner:OLYMPUS MEDICAL SYST CORP
Display device
InactiveUS7128431B2Small space requirementLight lossPoint-like light sourceMeasurement apparatus componentsLight guideDisplay device
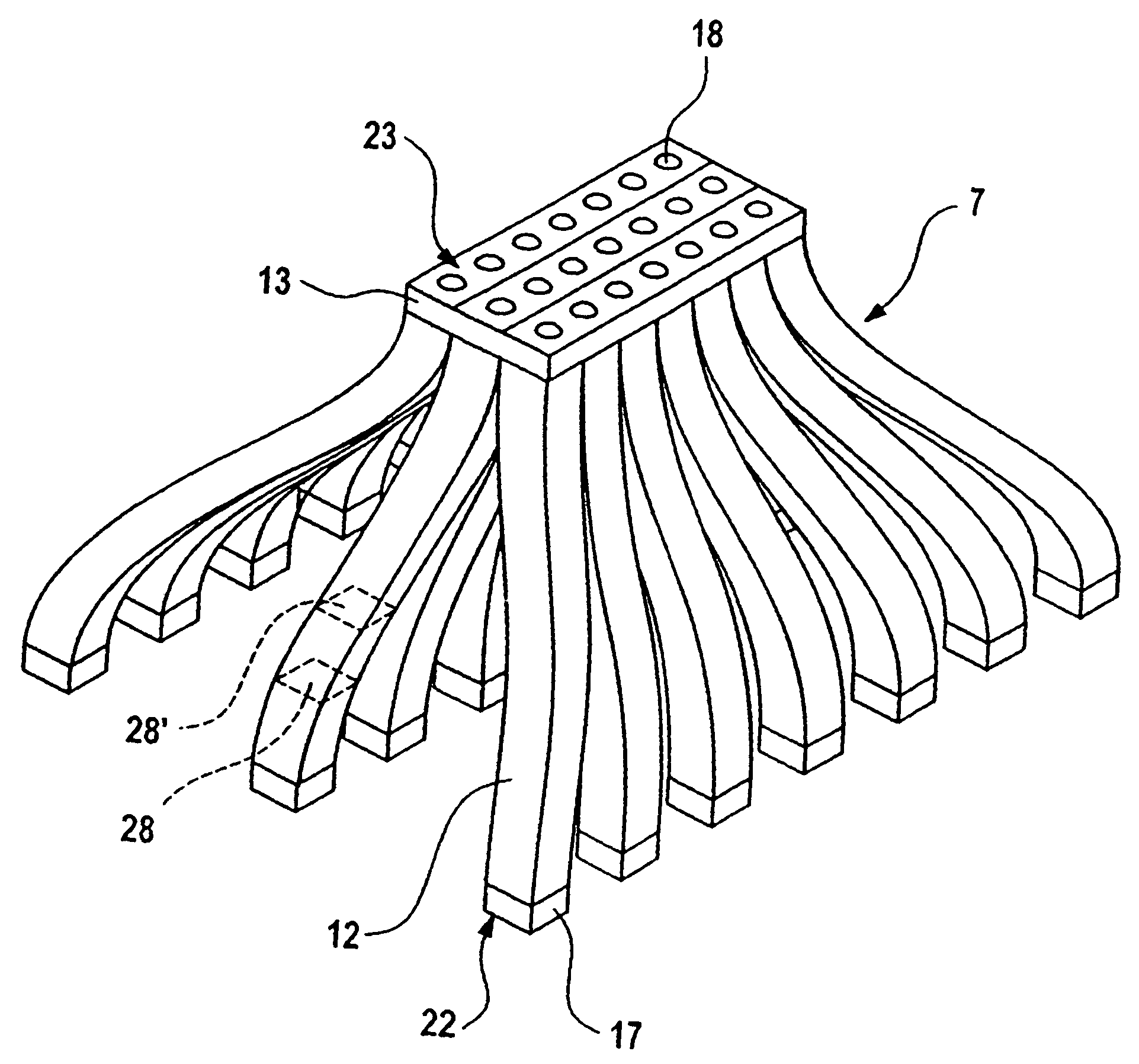
The invention relates to a display device, especially in a motor vehicle, comprising a display (2) which can be illuminated by a light source (1), and a light guide (7) which is arranged between the light source (1) and the display (2). Said light source (1) comprises a plurality of individual light sources (10), the entire light-radiating surface of said light sources being larger than the surface of the display (2). In order to increase the light efficiency, the light guide (7) comprises, on the light source side, individual light guiding sections (12) which are associated with the individual light sources (10), said sections forming a common light guiding section (13) on the display side.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
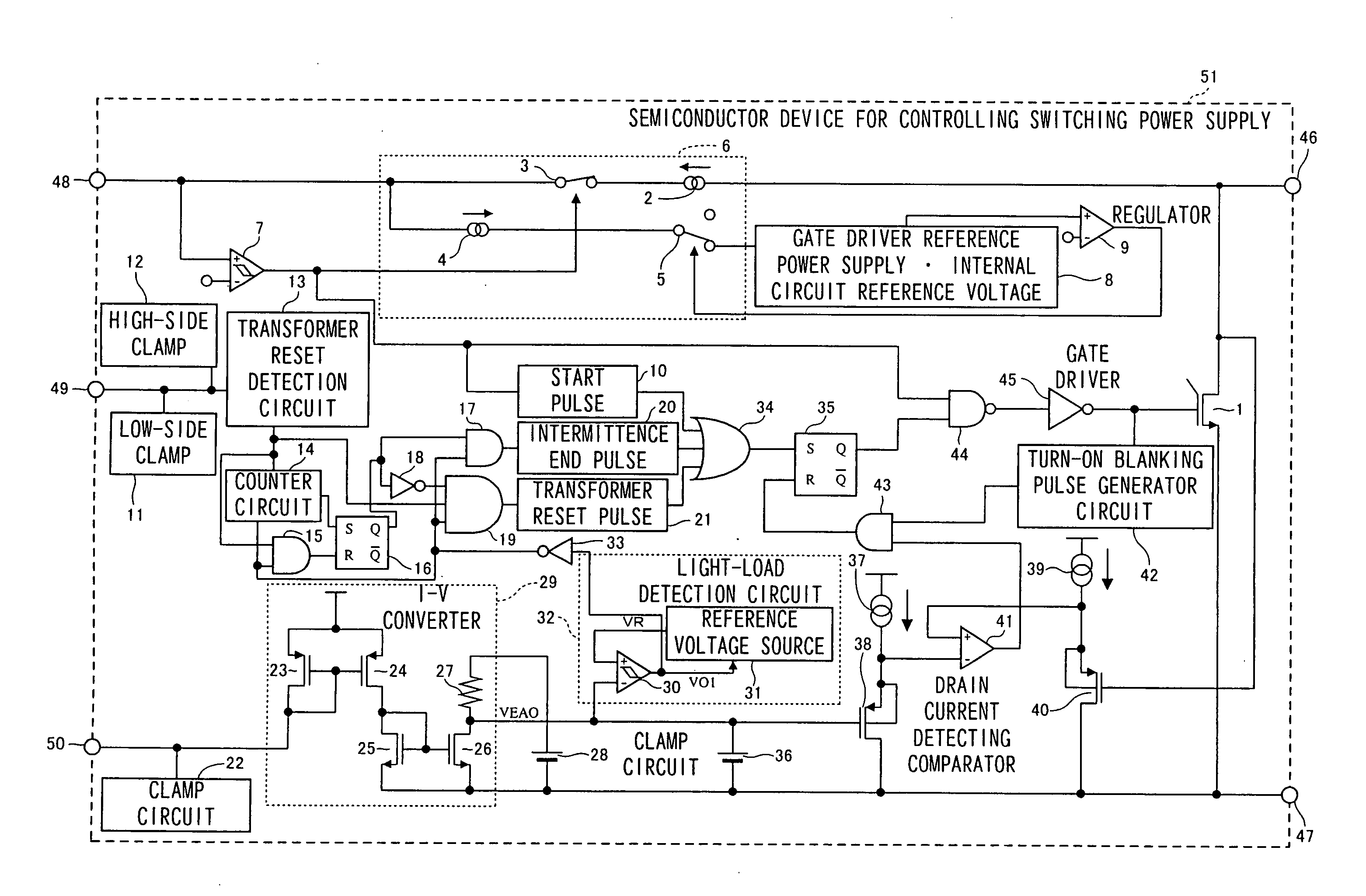
Semiconductor device for controlling switching power supply
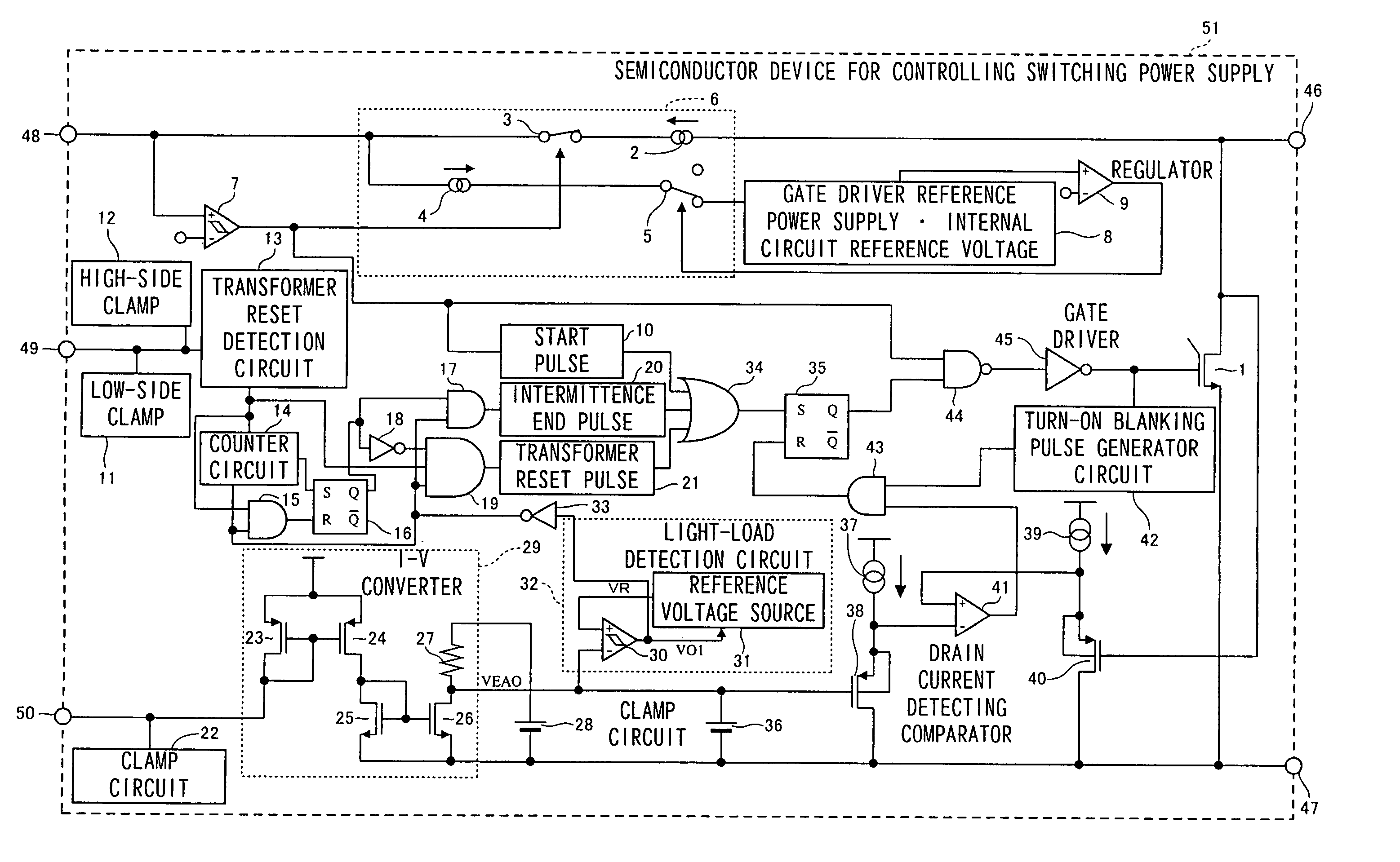
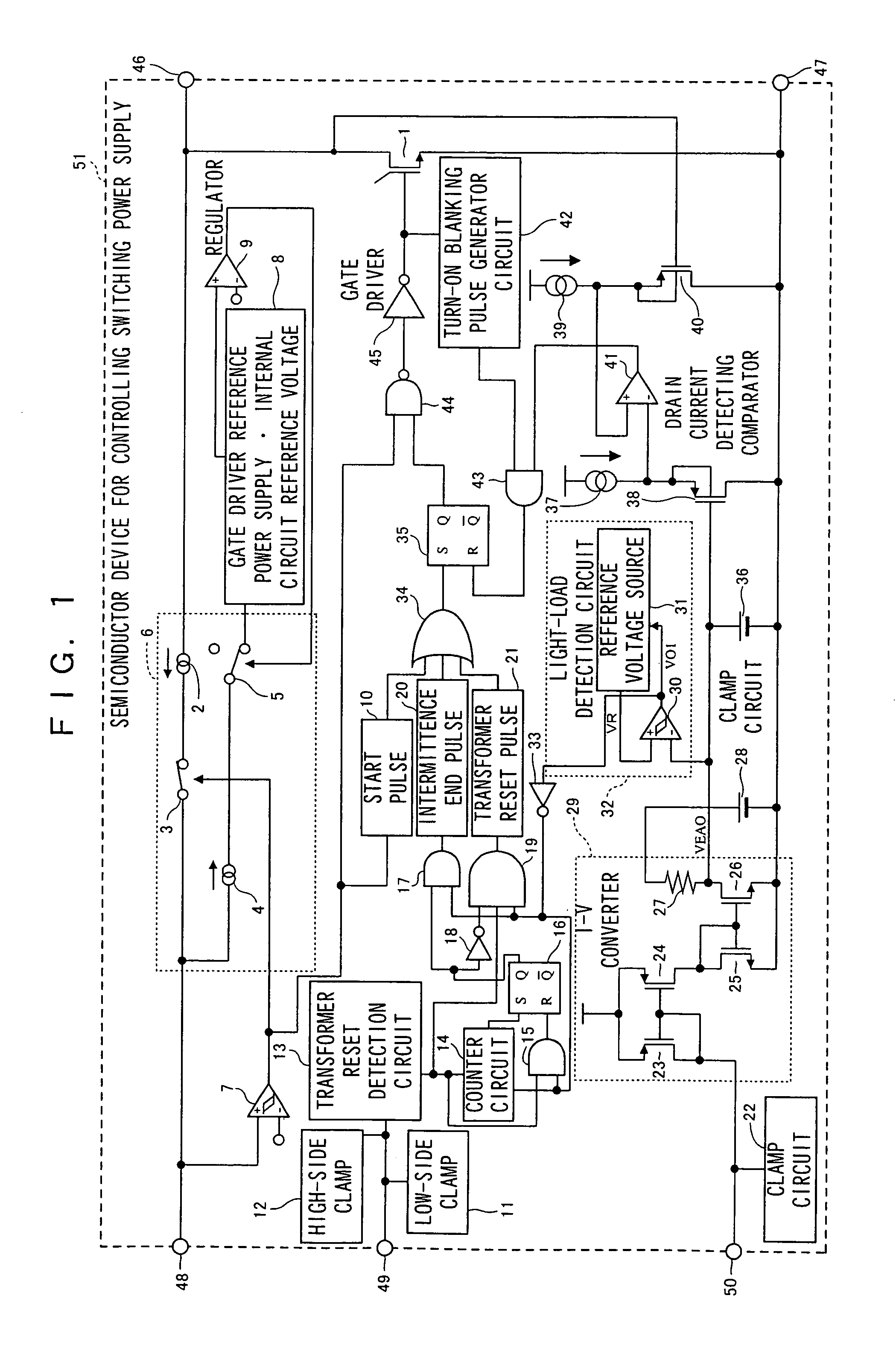
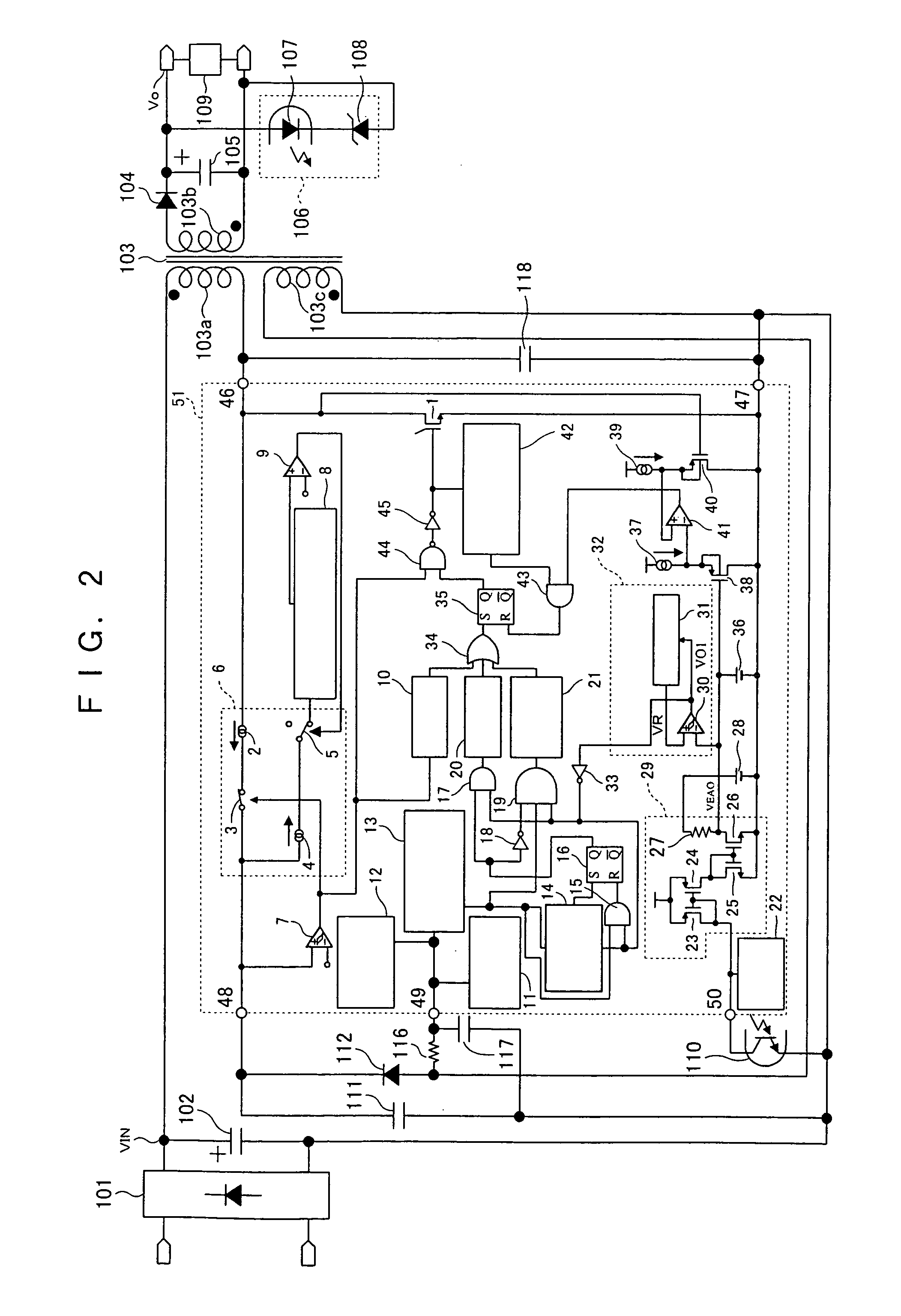
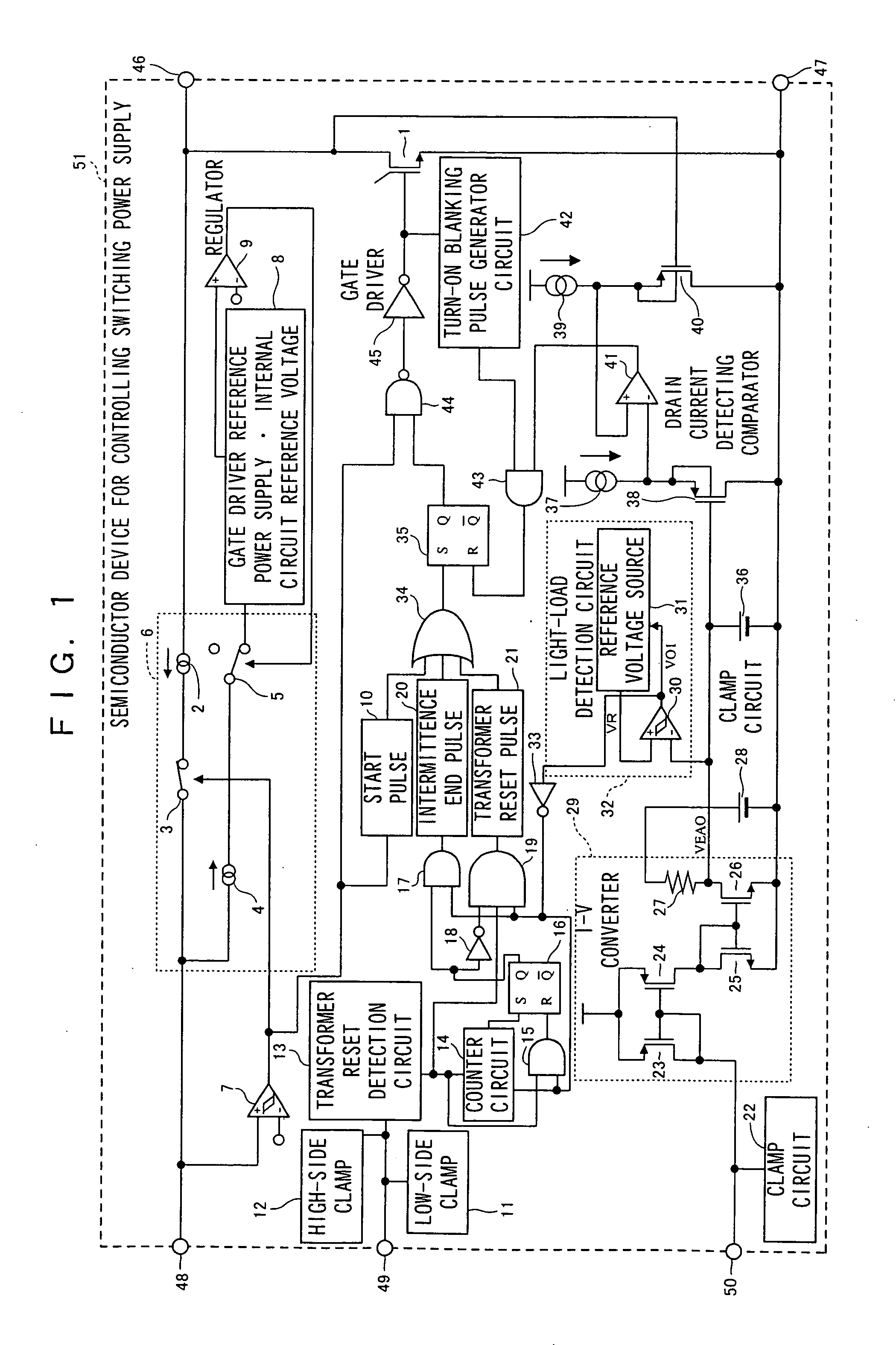
InactiveUS7075802B2Light lossReduce power consumptionEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionTransformerEngineering
A semiconductor device (51) for controlling a switching power supply, includes a switching element (1) and a switching control circuit. During an intermittent switching operation of the switching element (1), when a return signal is outputted from a light load detection circuit (32) before the counting of a counter circuit (14), the switching operation of the switching element (1) is restarted at the timing of a transformer reset signal from a transformer reset detection circuit (13) after the return signal is outputted. When the return signal is outputted from the light load detection circuit (32) after the counting of the counter circuit (14), the switching operation of the switching element (1) is restarted, regardless of the transformer reset signal, only when the return signal is outputted.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
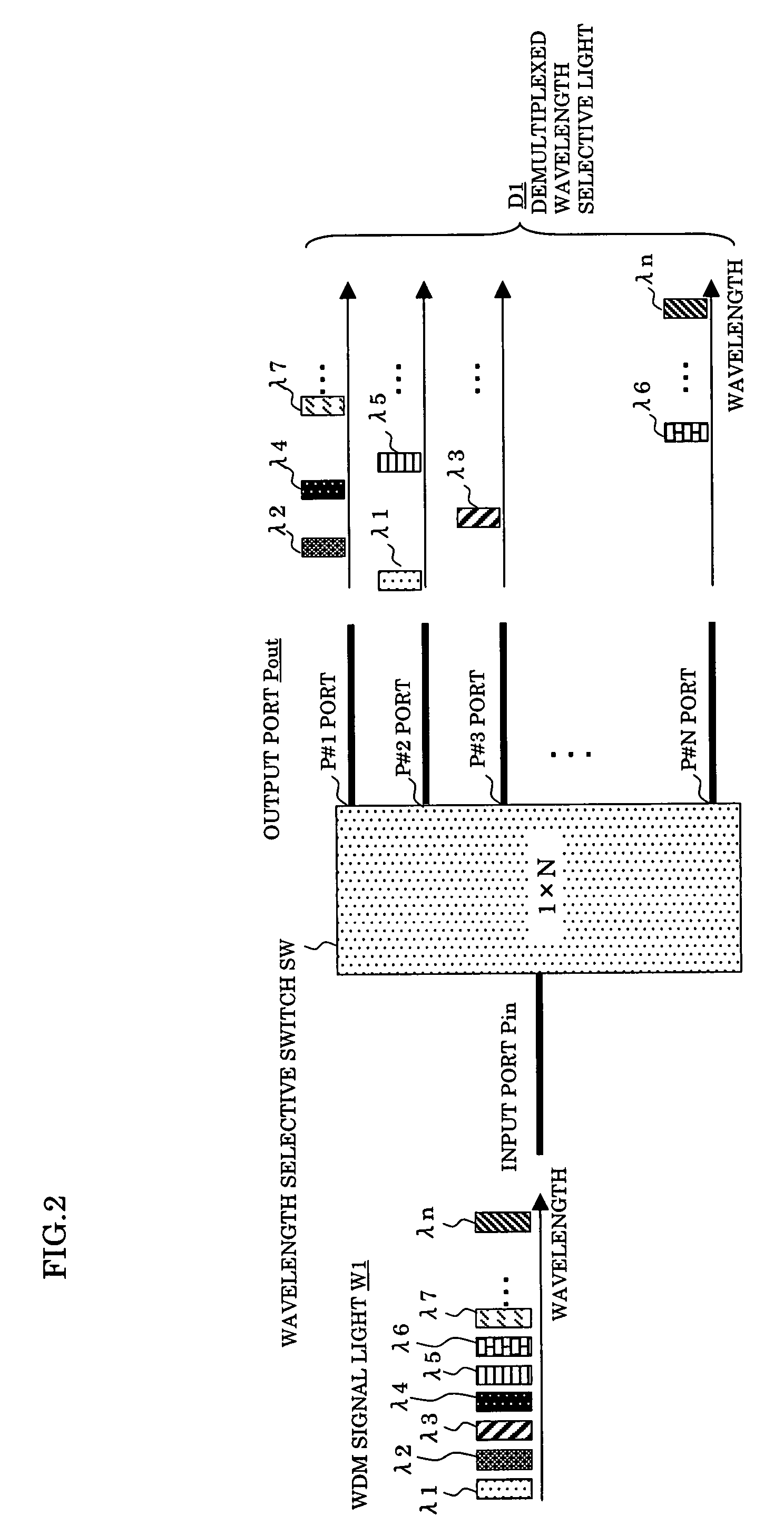
Optical add/drop multiplexer and optical network system
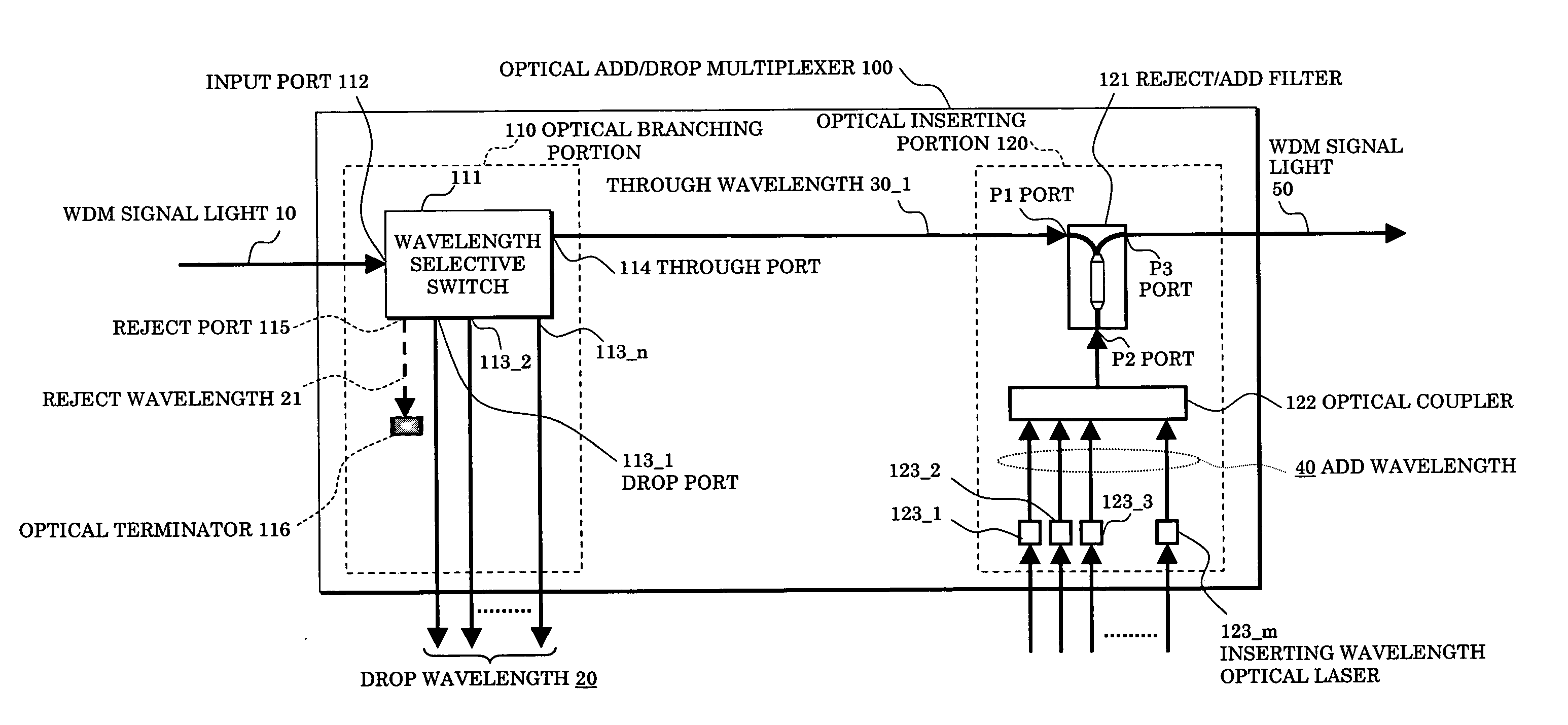
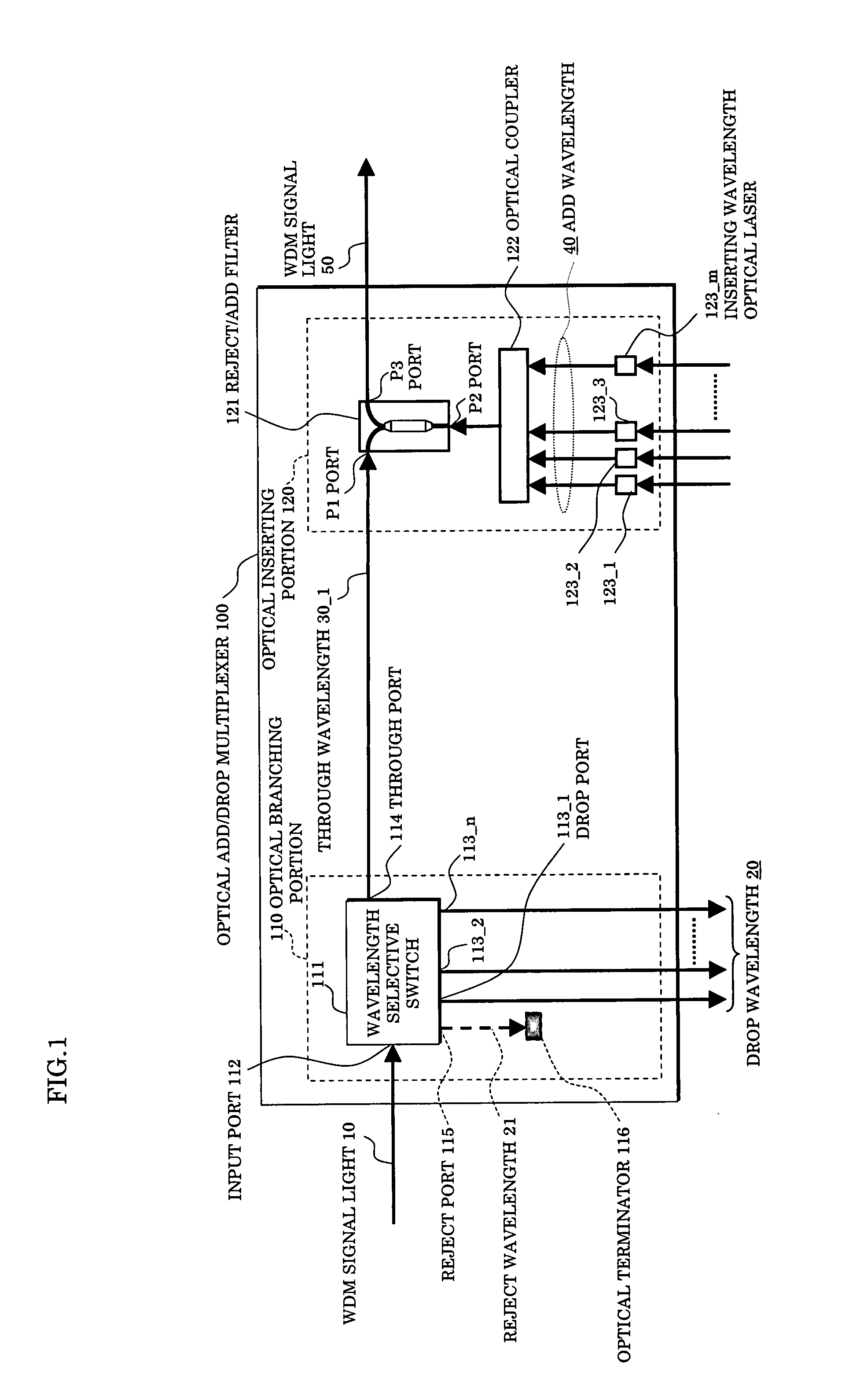
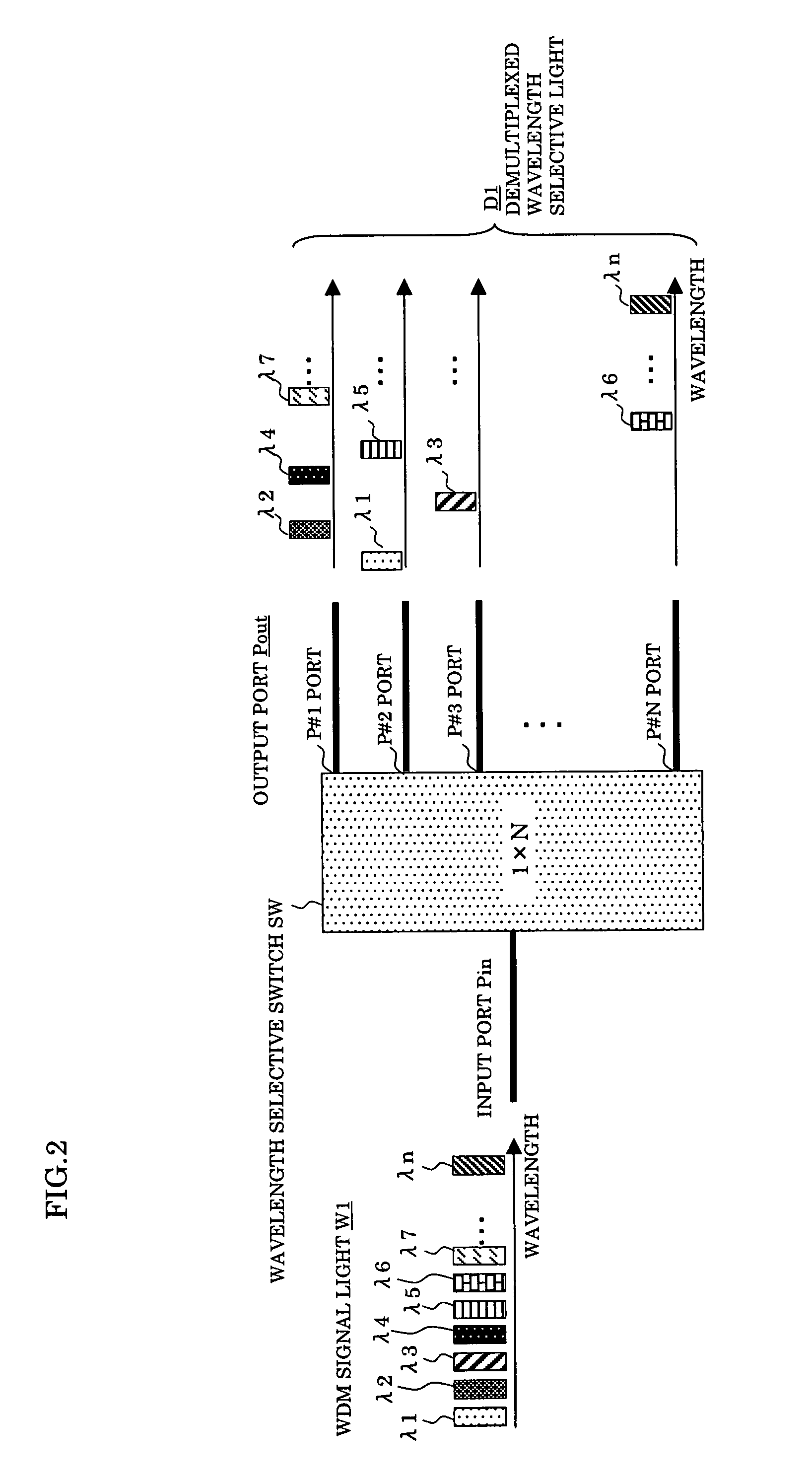
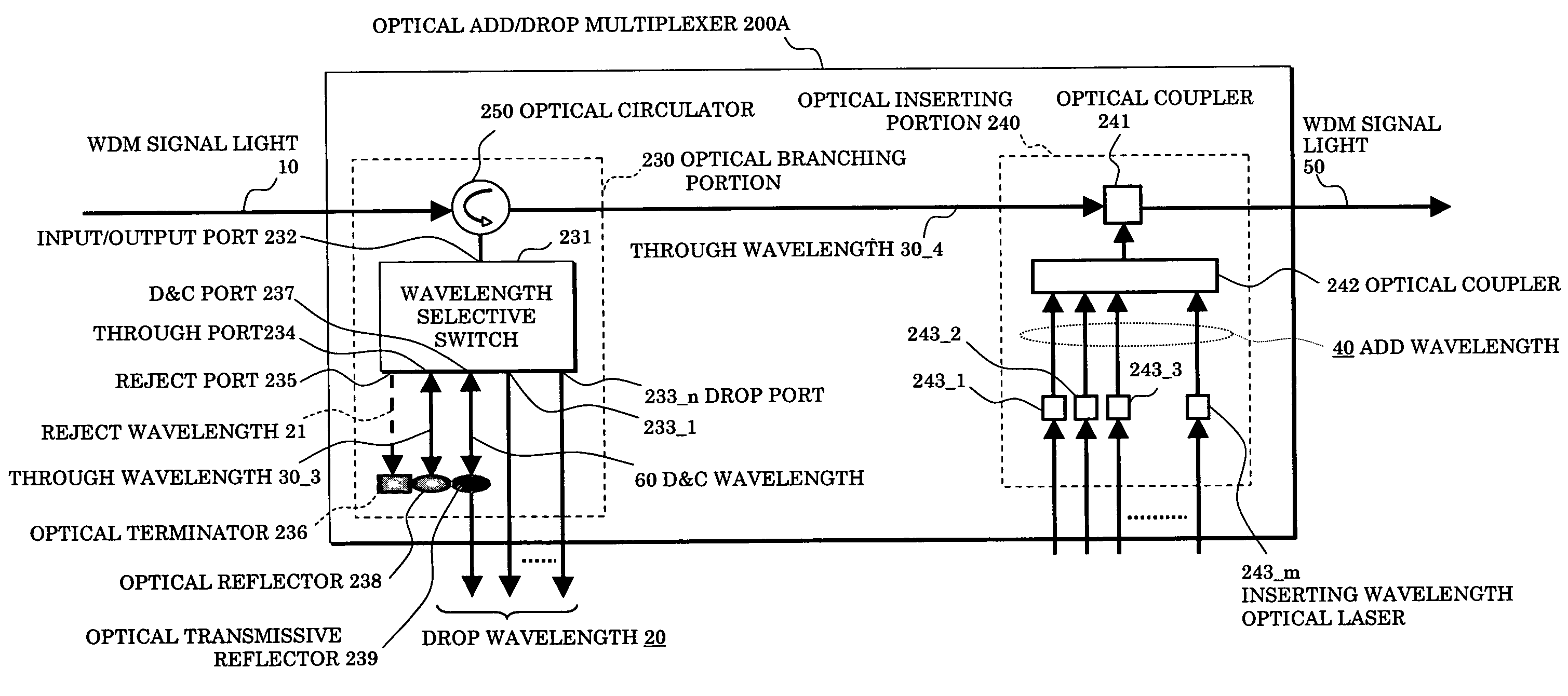
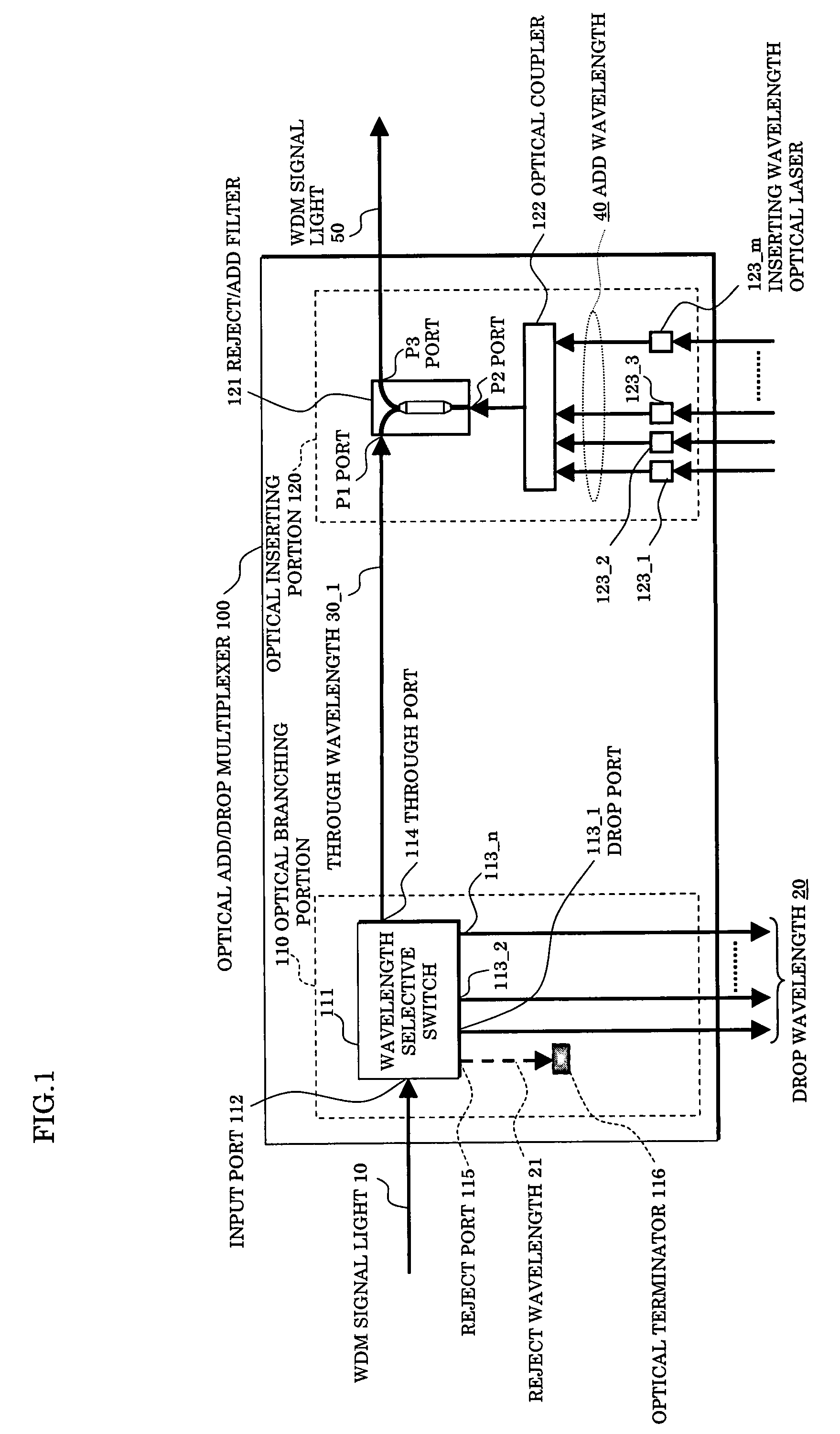
InactiveUS20070172240A1Increase in size and costAvoid increase of cost and sizeRing-type electromagnetic networksWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexerSignal light
In an optical add / drop multiplexer dropping and inserting a light of a specific wavelength for a WDM signal light and an optical network system utilizing the same, a wavelength selective switch selects a part of WDM signal lights inputted as lights of drop wavelengths and outputting other lights, and a reject / add filter terminates lights of same wavelengths as add wavelengths among output lights from the wavelength selective switch and multiplexes other lights than the terminated lights and lights of the add wavelengths to be outputted. At this time, the drop wavelengths are made to include all of the add wavelengths.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Daylight illumination apparatus
InactiveUS20130155643A1Improve imitation abilityAdjustable intensityLighting applicationsPoint-like light sourcePhotoluminescenceLight guide
The invention relates to a daylight illumination apparatus. A daylight collector (3) collects daylight (4), which is guided to an illumination location to be illuminated along an optical path by a light guide (5), wherein the daylight is absorbed by the light guide. A photoluminescent material (6, 8) is arranged within the optical path and emits photoluminescent light that compensates for the absorption of the daylight by the light guide. Absorption losses of the daylight can therefore effectively be compensated, without necessarily needing, for example, an active compensation light source. This allows providing compensated day-light illumination in a technically relatively simple way.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Method of heat-treating semiconductor
InactiveUS20090253273A1Stable heat-treatingReduce energy consumptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsLaser light
The present invention relates to a method of heat-treating a semiconductor, and the object is to enable heat-treating to a semiconductor or semiconductor device in a short period time and to obtain a stable and high reforming effect. The present invention is a method in which carbon or a layer including carbon is provided as a light absorbing layer, and a semiconductor material as a heat-treating target layer or semiconductor device contacting the heat absorbing layer directly or through a heat transfer layer of 5 nm-100 μm in thickness is heat-treated, and the light source to be used is a semiconductor laser light of wavelength of 600 nm-2 μm, and this semiconductor laser light is caused to continuously irradiate and sweep the surface of the heat-treating target material. The light source can be easily made to output high power, and heat-treating at a high speed and with low energy consumption is realized.
Owner:HIGHTEC SYST CORP
Vehicle lighting device
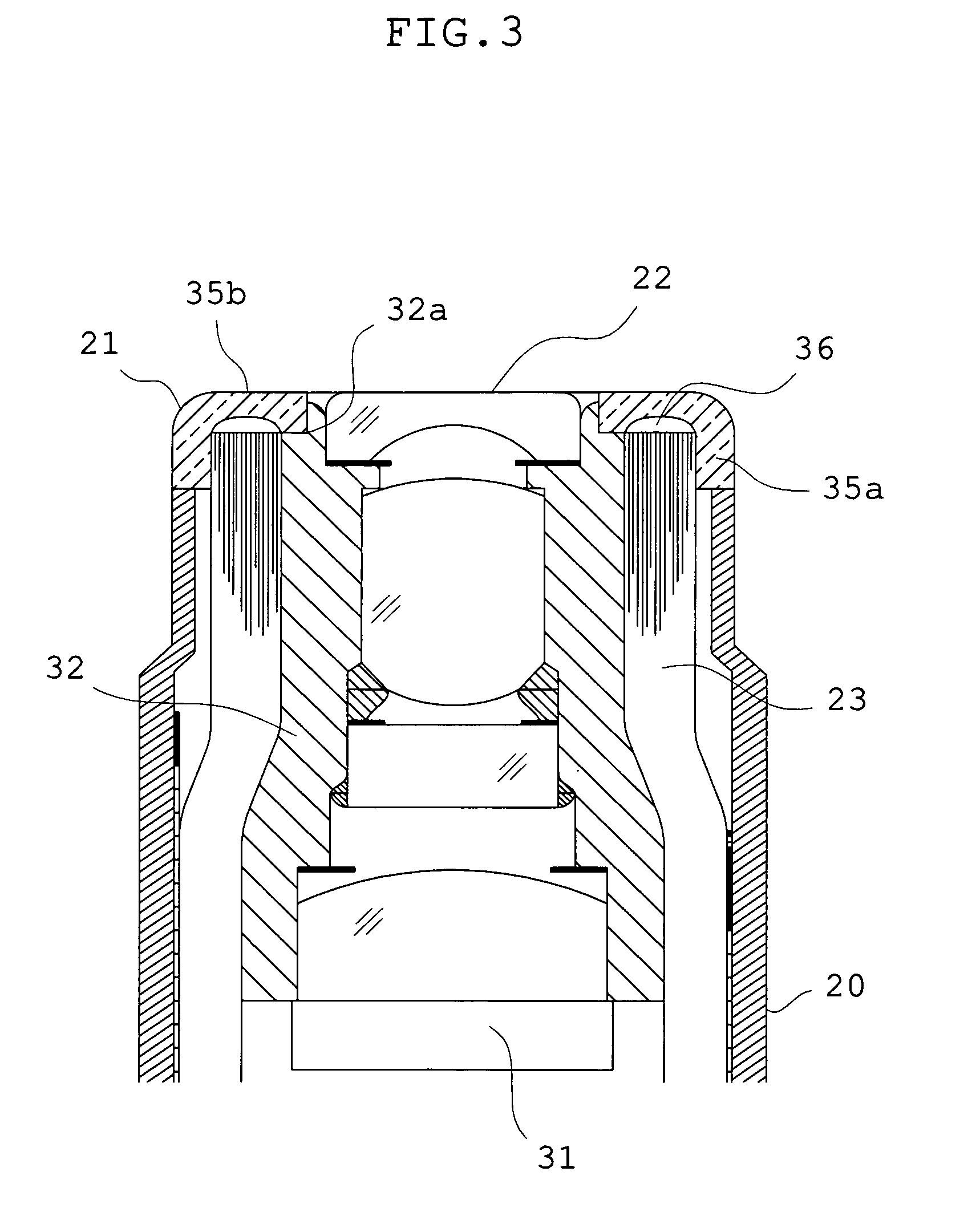
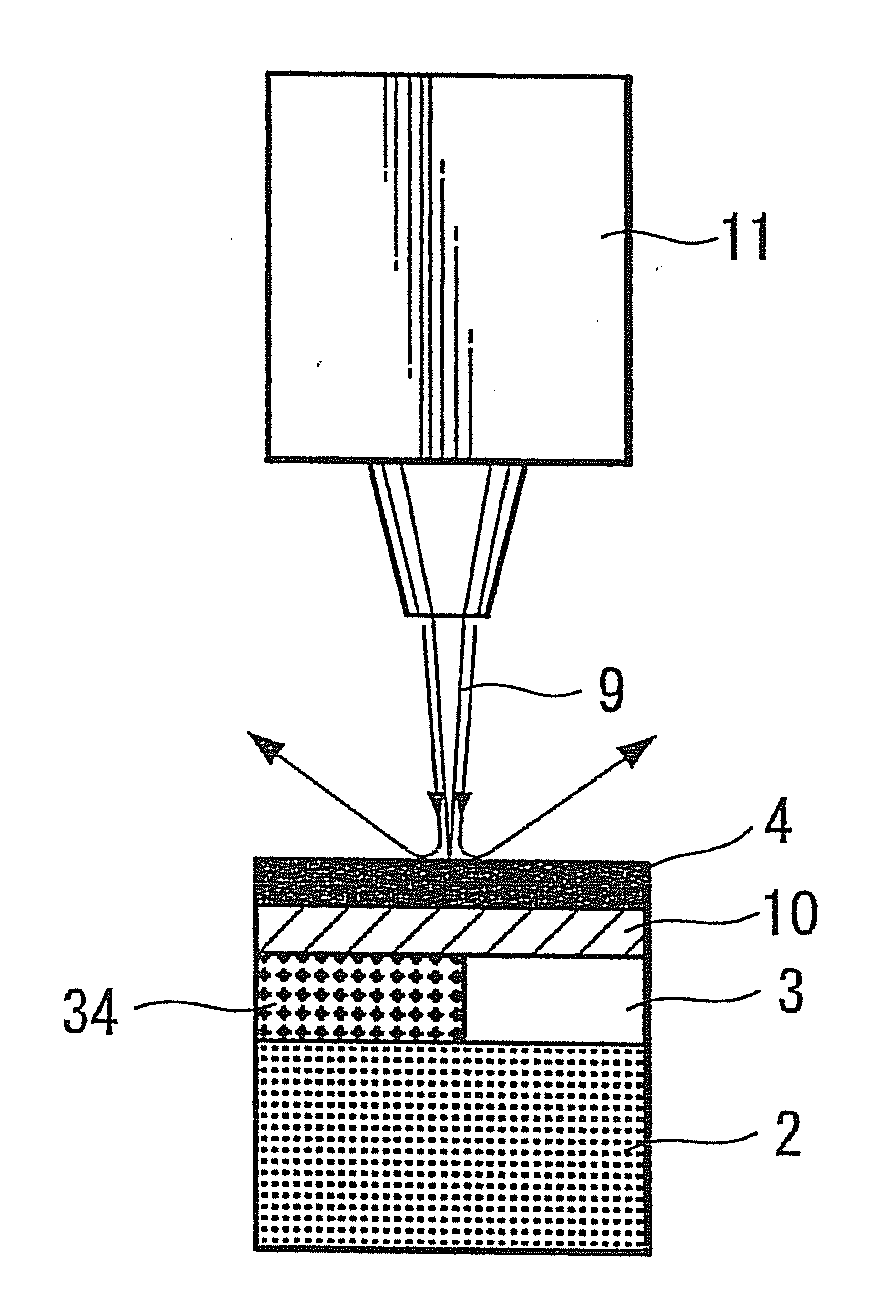
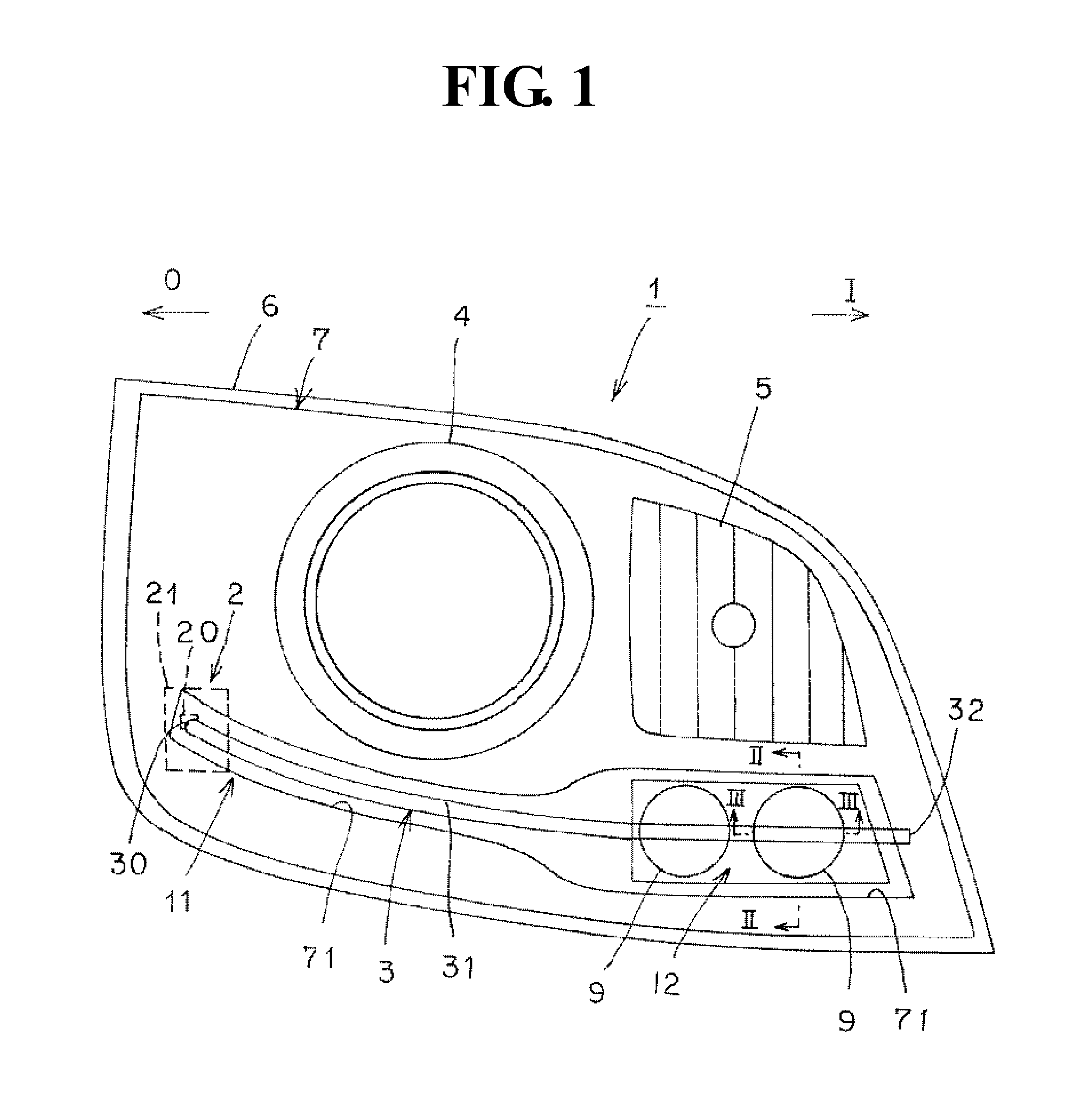
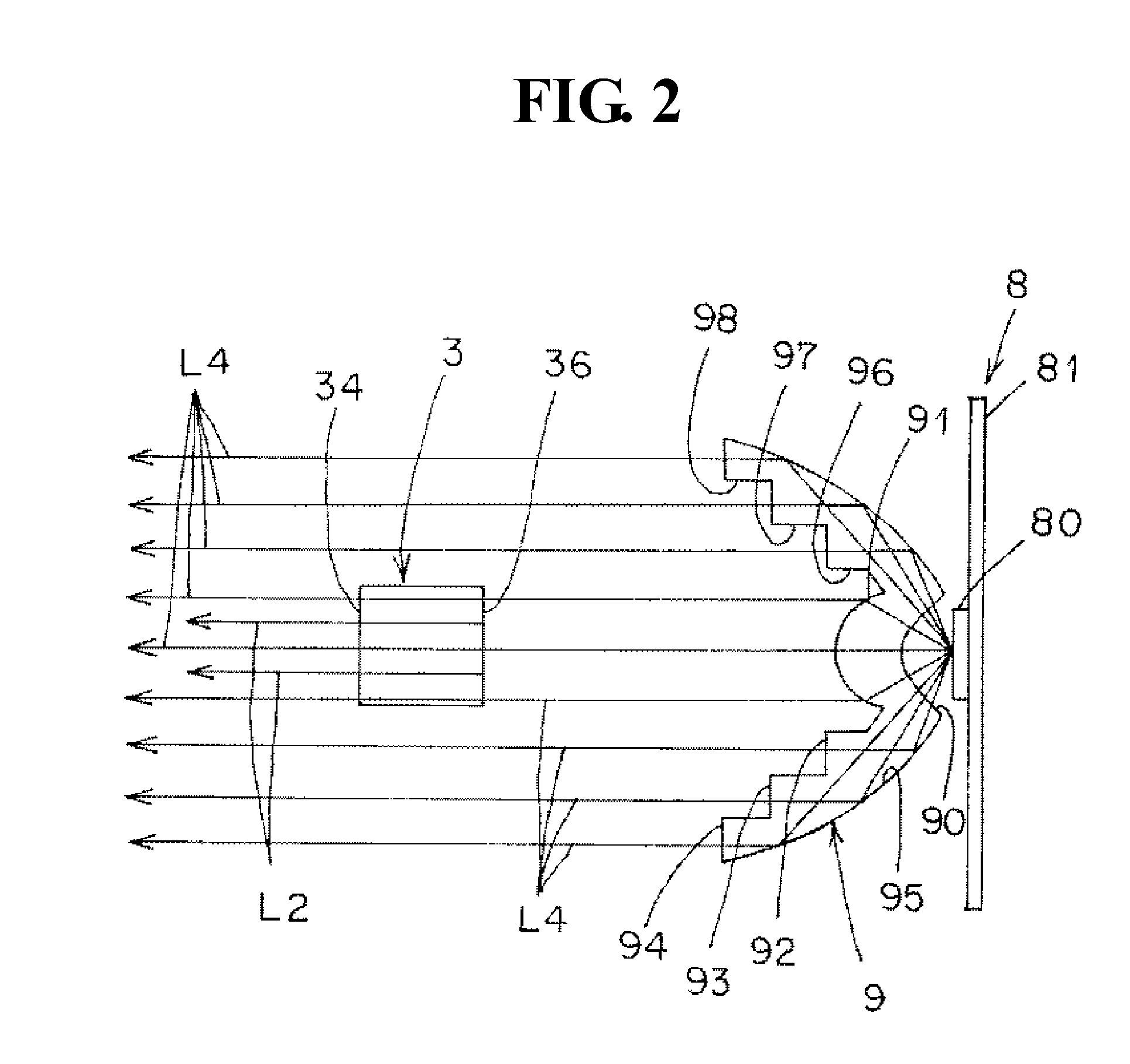
ActiveUS20150292704A1Light loss is minimizedLight lossOptical signallingVehicle lighting systemsLight guideEngineering
A present invention includes a lamp housing, a lamp lens, a first lamp unit, and a second lamp unit. The first lamp unit includes a semiconductor-type light source, and a light guide member. The light guide member has an exit surface, and a reflection surface. A plane exit surface is provided in a part of the exit surface for blocking a part of a radiated light L4 from the second lamp unit, and a plane incident surface is provided in a part of the reflection surface for blocking a part of the radiated light L4 from the second lamp unit. As a result, the present invention is able to minimize an optical loss of the radiated light L4, even when the light guide member is located at a position for blocking a part of the radiated light L4 from the second lamp unit.
Owner:ICHIKOH IND LTD
Automated packaging apparatus and method of optical elements
InactiveUS20050139638A1Efficient solutionMinimize thermal strainWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesEngineering
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
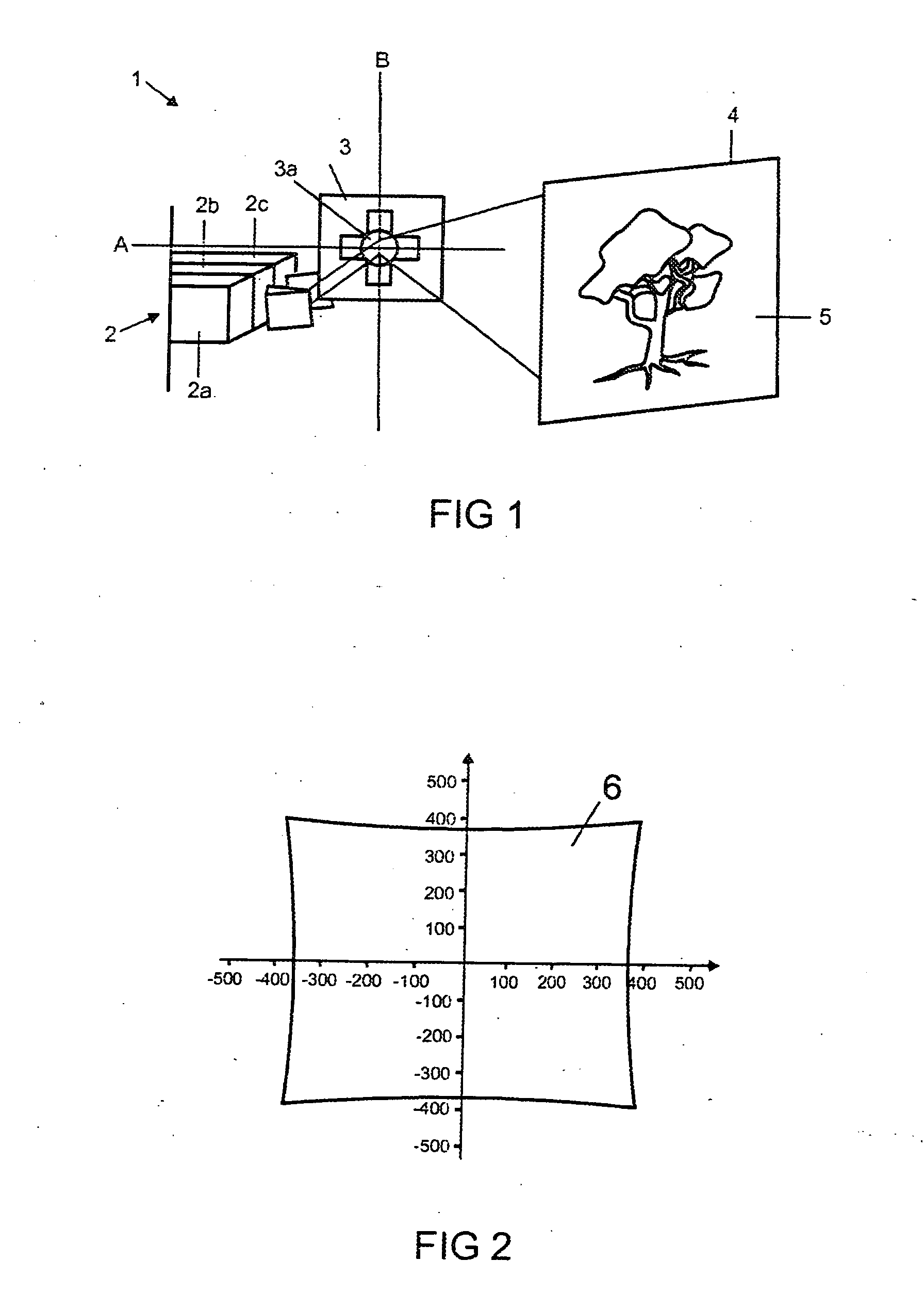
Projector for projecting an image and corresponding method
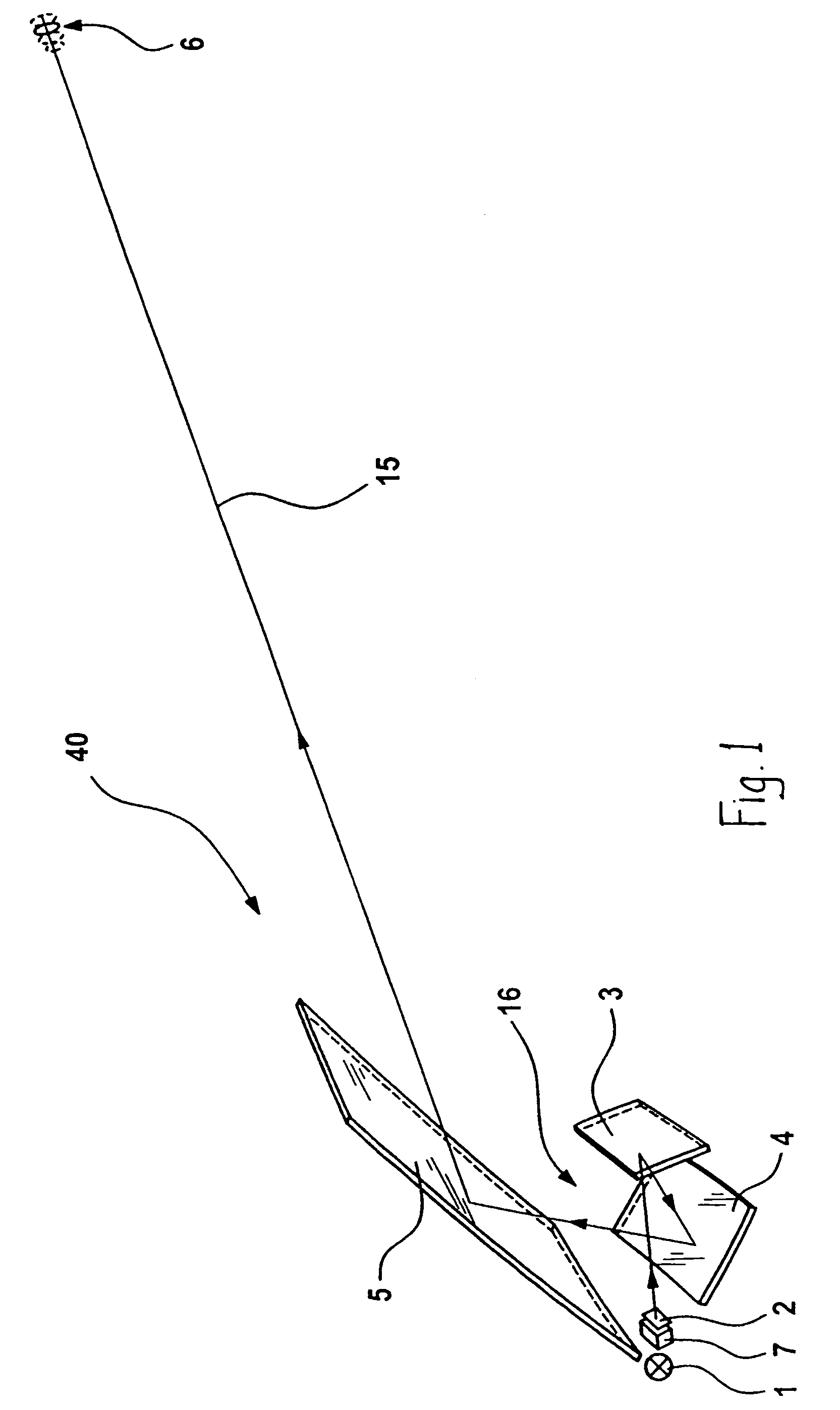
ActiveUS20100302516A1Small distortionRealized cost-effectively and compactlyProjectorsMicroscopesProjection imageLight beam
The invention relates to a projector (1) for projecting an image (6), comprising: a light source (2) for generating a light bundle (12); a pivotable deflection unit (3) designed for deflecting the light bundle (12) generated by the light source (2) onto a projection surface (5); and an imaging device (7, 8, 9) for imaging an aperture of the deflection unit (3) onto the projection surface (5); wherein the imaging device (7, 8, 9) comprises a mirror objective (7) having at least two mirror elements (8, 9). The invention further relates to a corresponding method.
Owner:OSRAM GMBH
Semiconductor device for controlling switching power supply
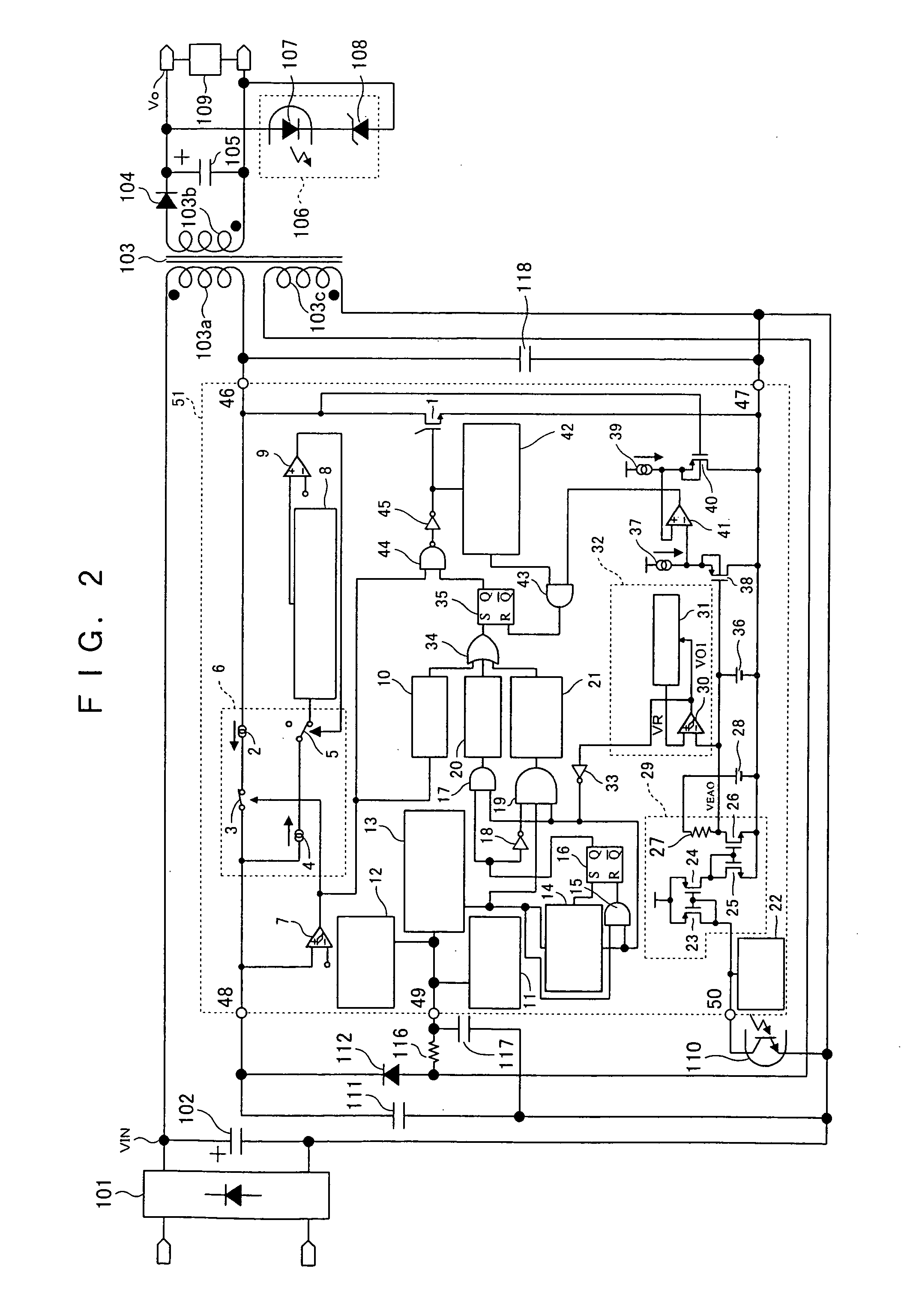
InactiveUS20050219776A1Light lossReduce power consumptionEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionTransformerDevice material
A semiconductor device (51) for controlling a switching power supply, includes a switching element (1) and a switching control circuit. During an intermittent switching operation of the switching element (1), when a return signal is outputted from a light load detection circuit (32) before the counting of a counter circuit (14), the switching operation of the switching element (1) is restarted at the timing of a transformer reset signal from a transformer reset detection circuit (13) after the return signal is outputted. When the return signal is outputted from the light load detection circuit (32) after the counting of the counter circuit (14), the switching operation of the switching element (1) is restarted, regardless of the transformer reset signal, only when the return signal is outputted.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Light-emitting sign device
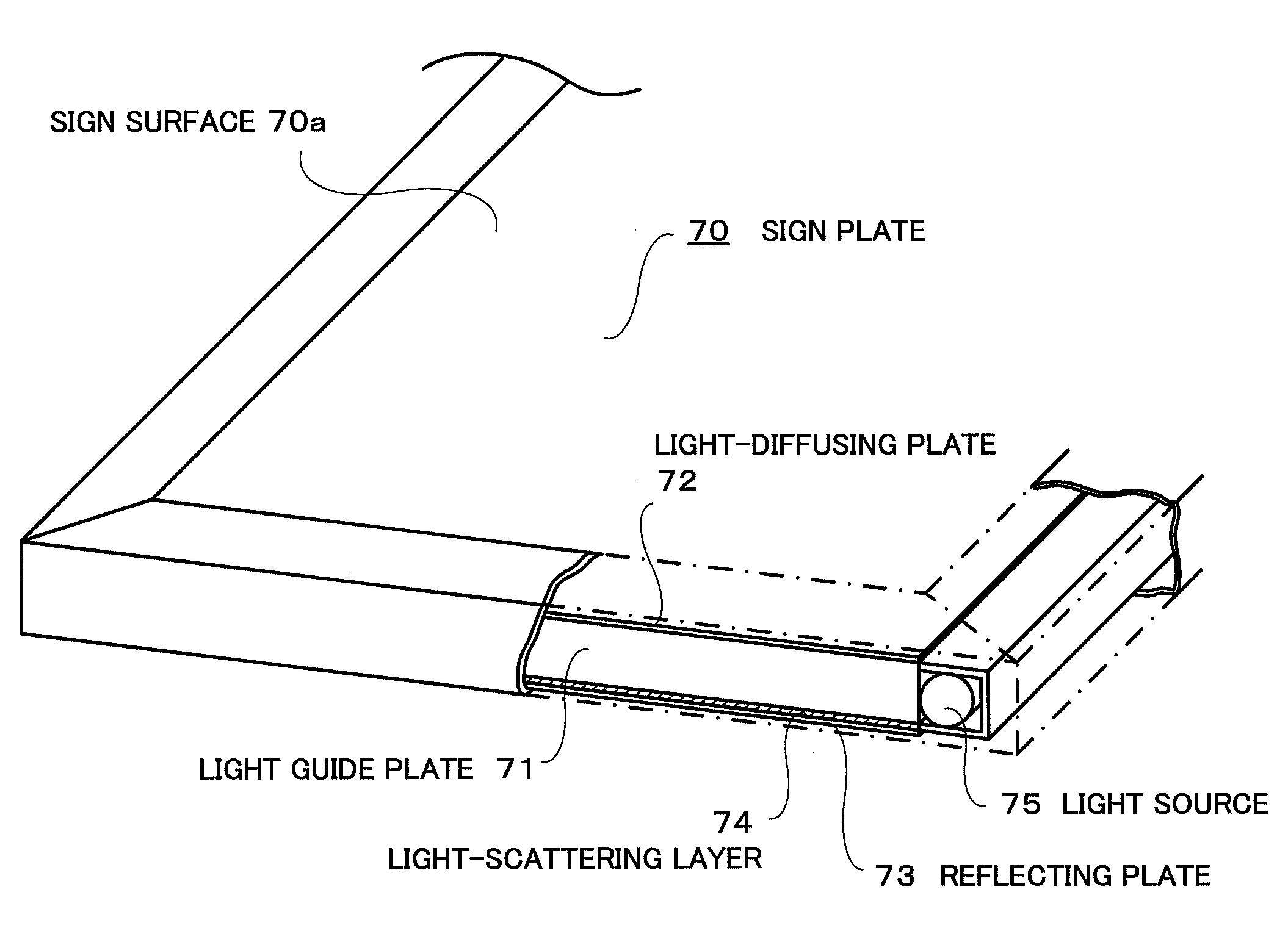
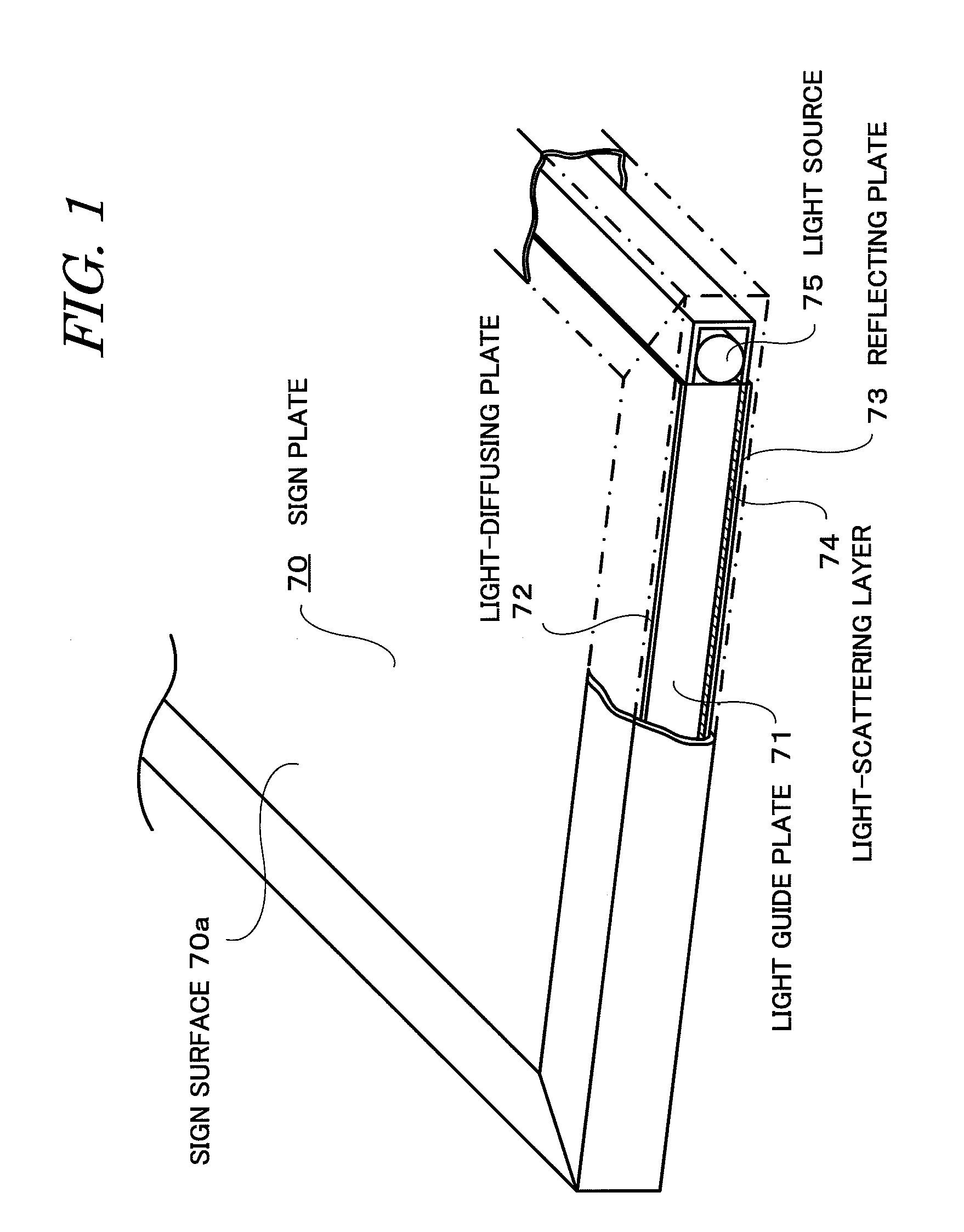
InactiveUS20090025264A1Reduce intensityEfficient illuminationIlluminated signsOptical light guidesVisibilityLight guide
A light-emitting sign device is provided, in which optimum scattering of light from a light source is ensured, light loss can be reduced to a minimum, uniform and bright emission is made possible, and visibility and cost efficiency are improved. A sign plate having a sign surface is provided, and a light-diffusing plate, light guide plate, and white reflecting plate are arranged in this order on the rear surface of the sign plate. A light-scattering layer that scatters the light from the light source is coated on the rear surface of the light guide plate. The light-scattering layer has a binder layer composed of a coating composition using a transparent resin as a binder. A filler in the form of transparent and substantially spherical fine particles of silica is uniformly dispersed in the binder layer.
Owner:TAMURA KK +1
Optical system with optical waveguides
InactiveUS20070110363A1Increase production costSmall sizeCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideEngineeringOptic system
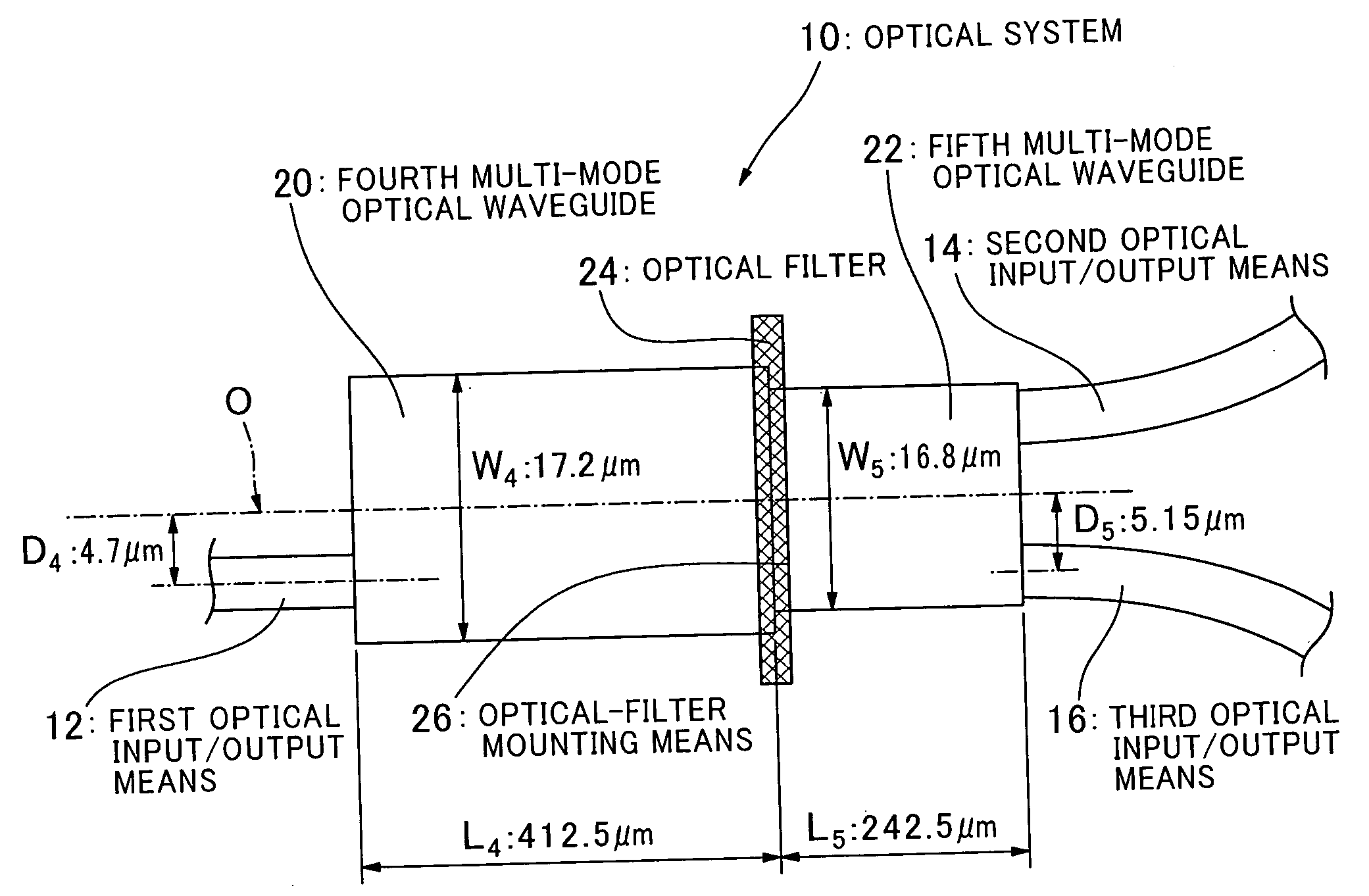
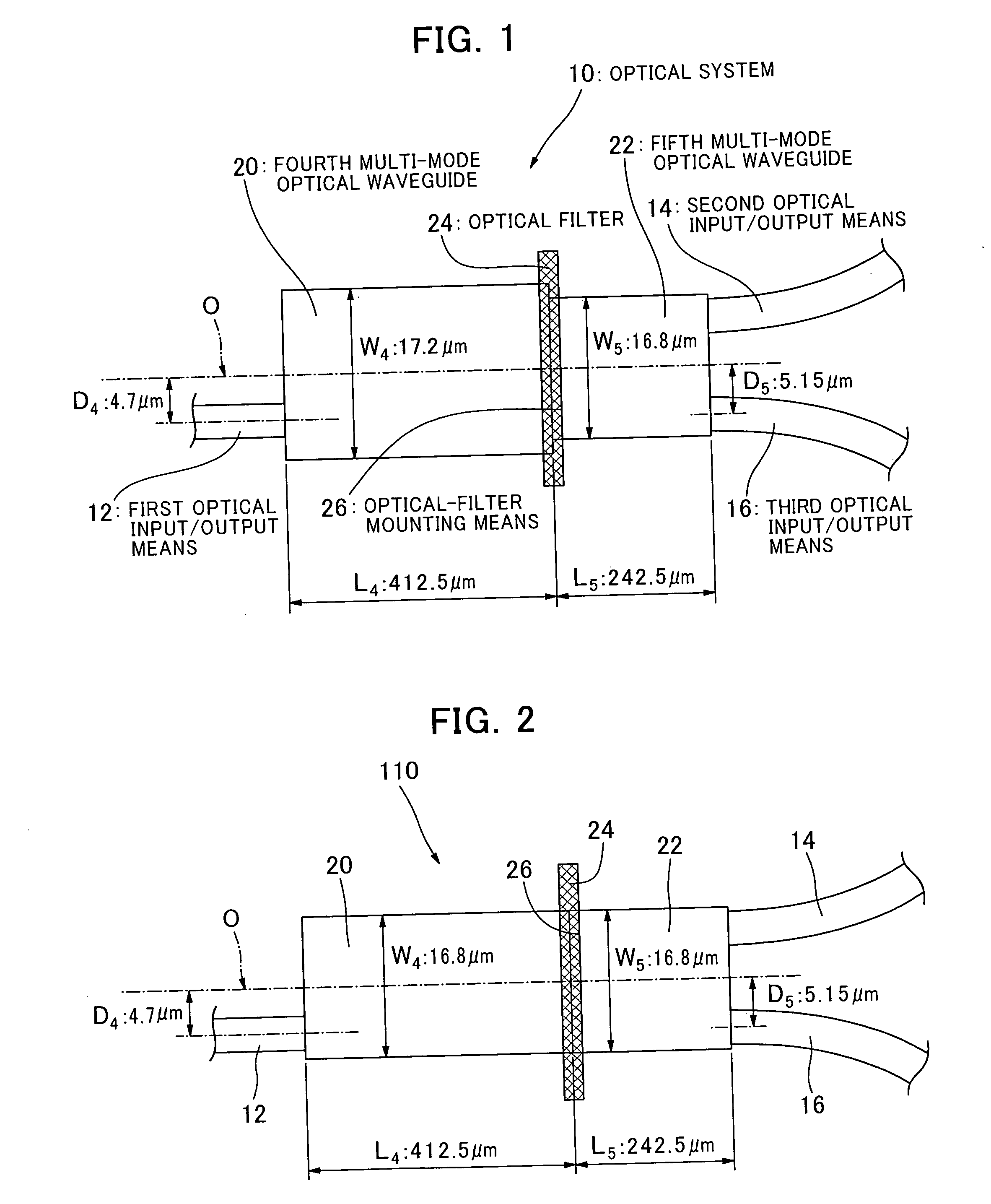
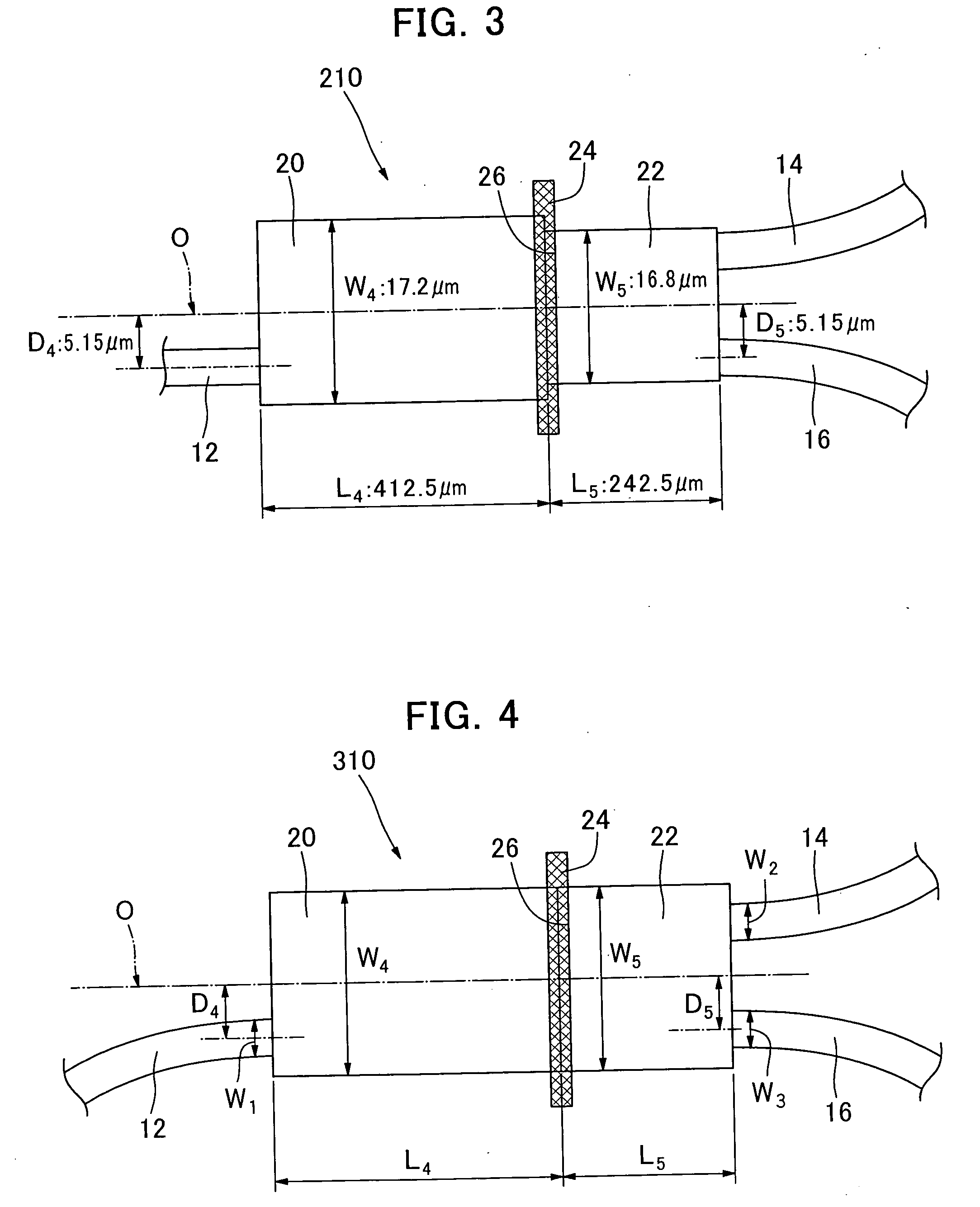
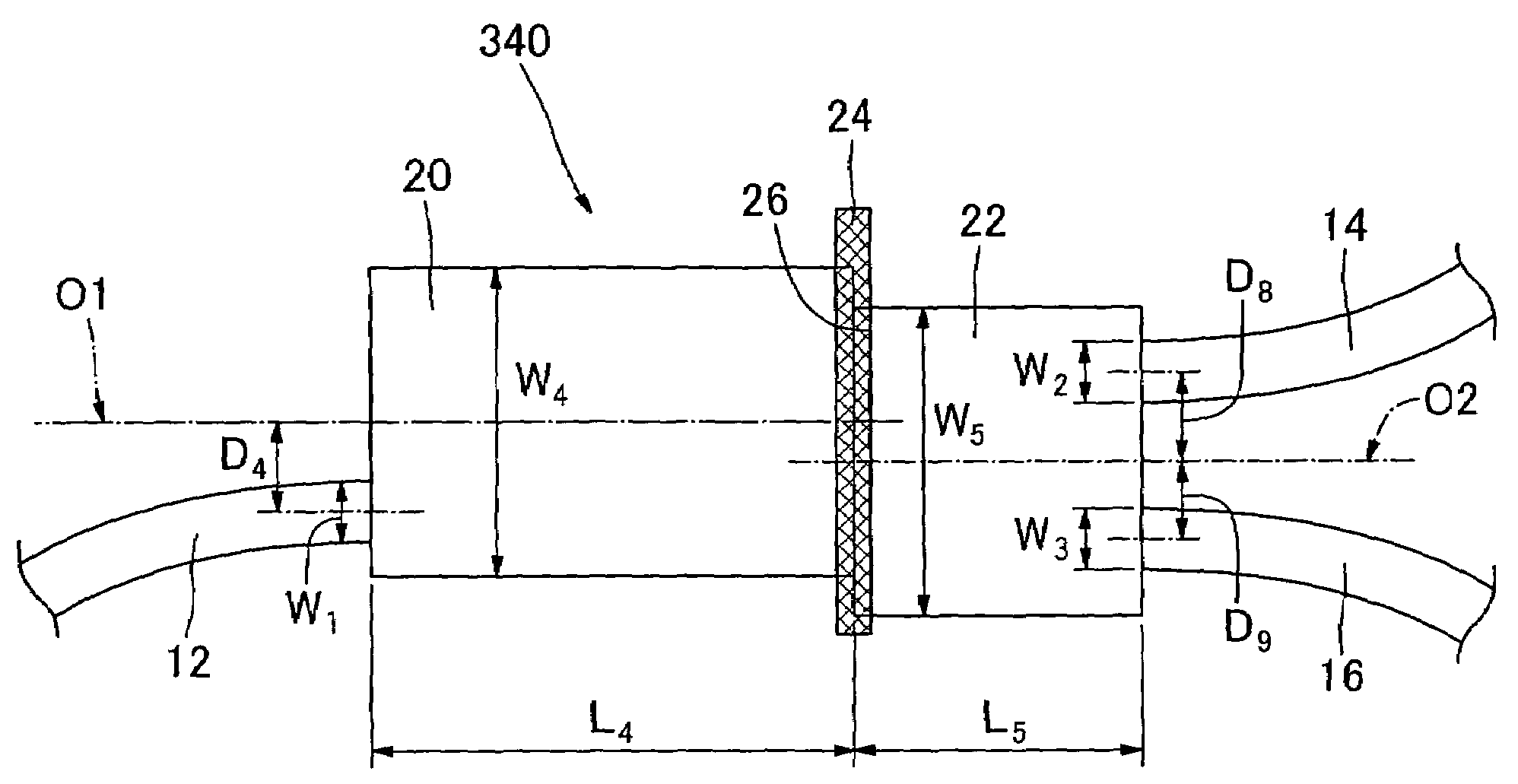
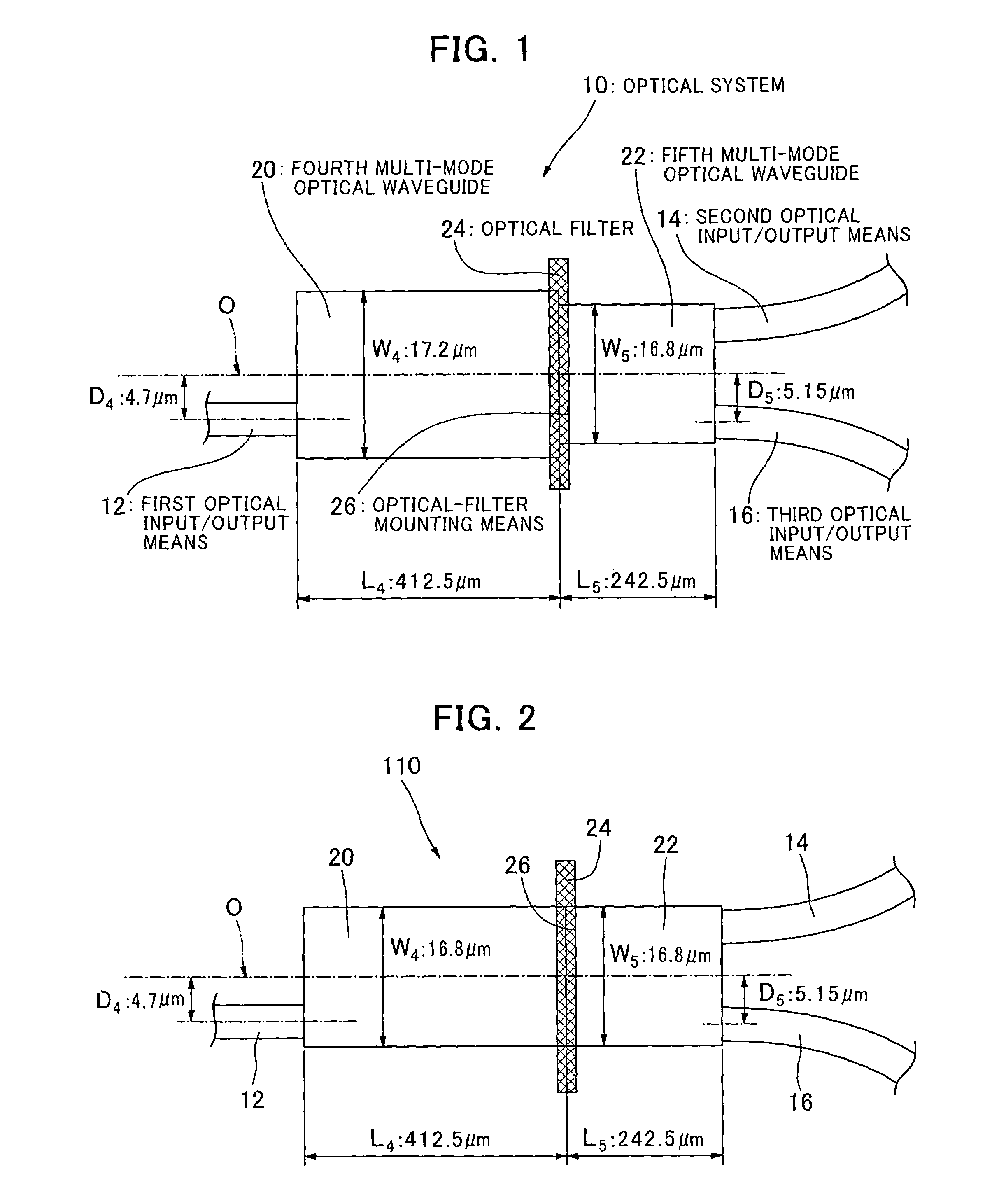
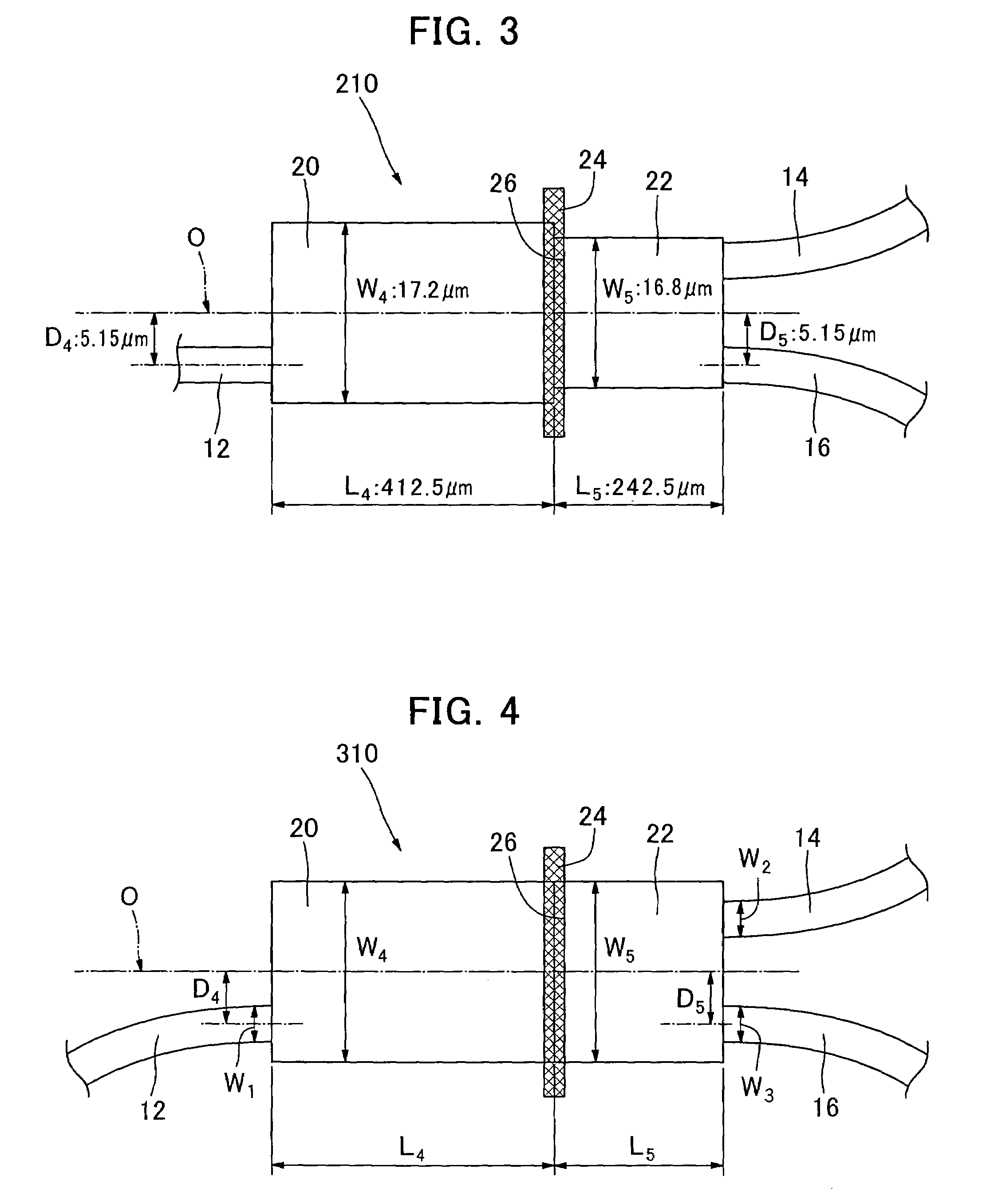
The present invention provides an optical system with waveguides, which comprises first, second and third optical input / output means (12, 14, 16), fourth and fifth multi-mode optical waveguides (20, 22) each capable of propagating light with plural propagation modes, and optical-filter mounting means (26) for mounting an optical filter (24) between the fourth and fifth multi-mode optical waveguides (20, 22) across a traveling direction of light in the fourth and fifth multi-mode optical waveguides (20, 22). The first optical input / output means (12) is connected to an end face of the fourth multi-mode optical waveguide (20) on a side thereof opposite to the optical-filter mounting means (26). Each of the second and third optical input / output means (14, 16) is connected to an end face of the fifth multi-mode optical waveguide (22) on a side opposite to the optical-filter mounting means (26). Respective widths in a direction orthogonal to the light-traveling direction of the fourth and fifth multi-mode optical waveguides (20, 22) are different from each other.
Owner:HITACHI CHEM CO LTD
Optical head apparatus and optical information recording or reproducing apparatus
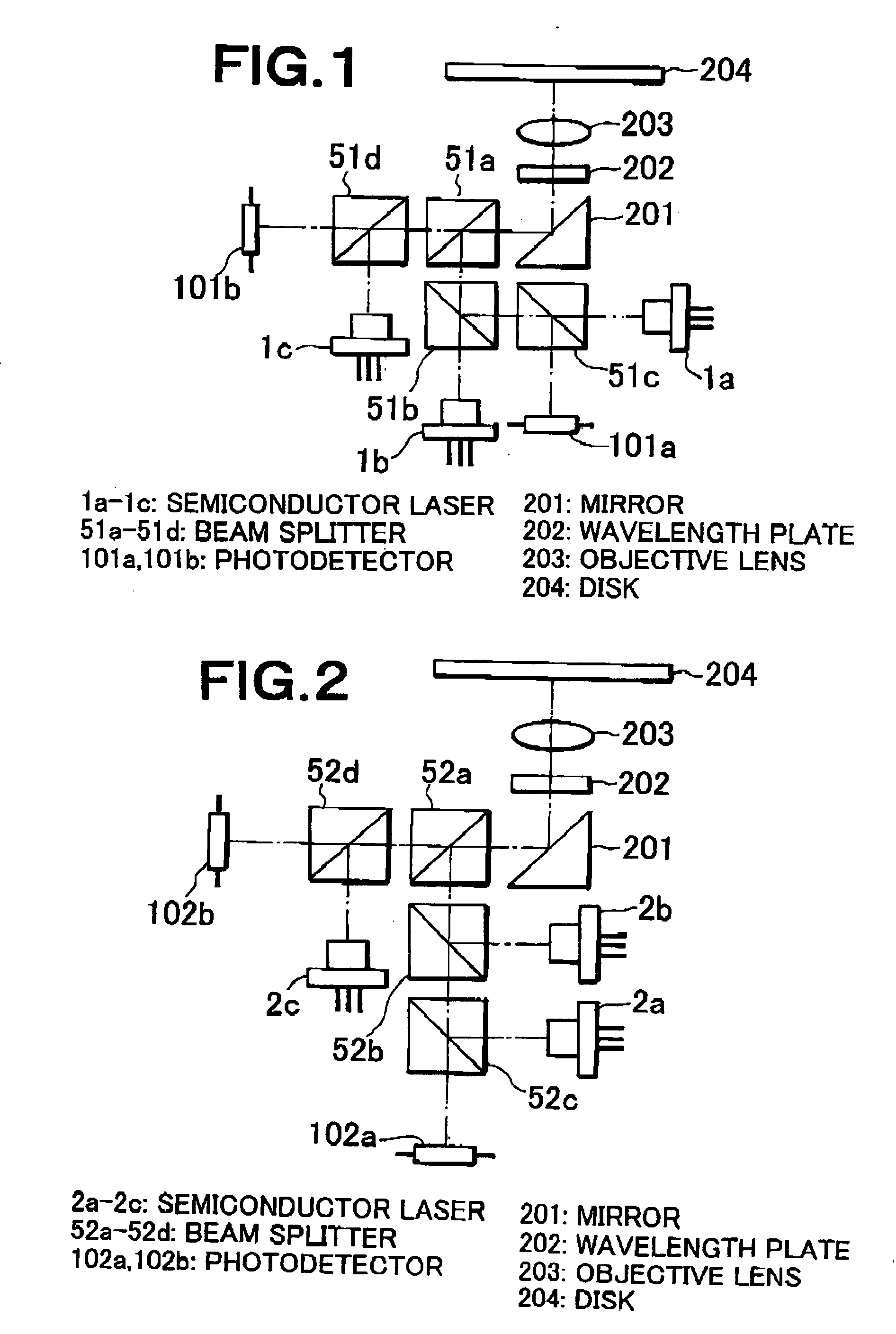
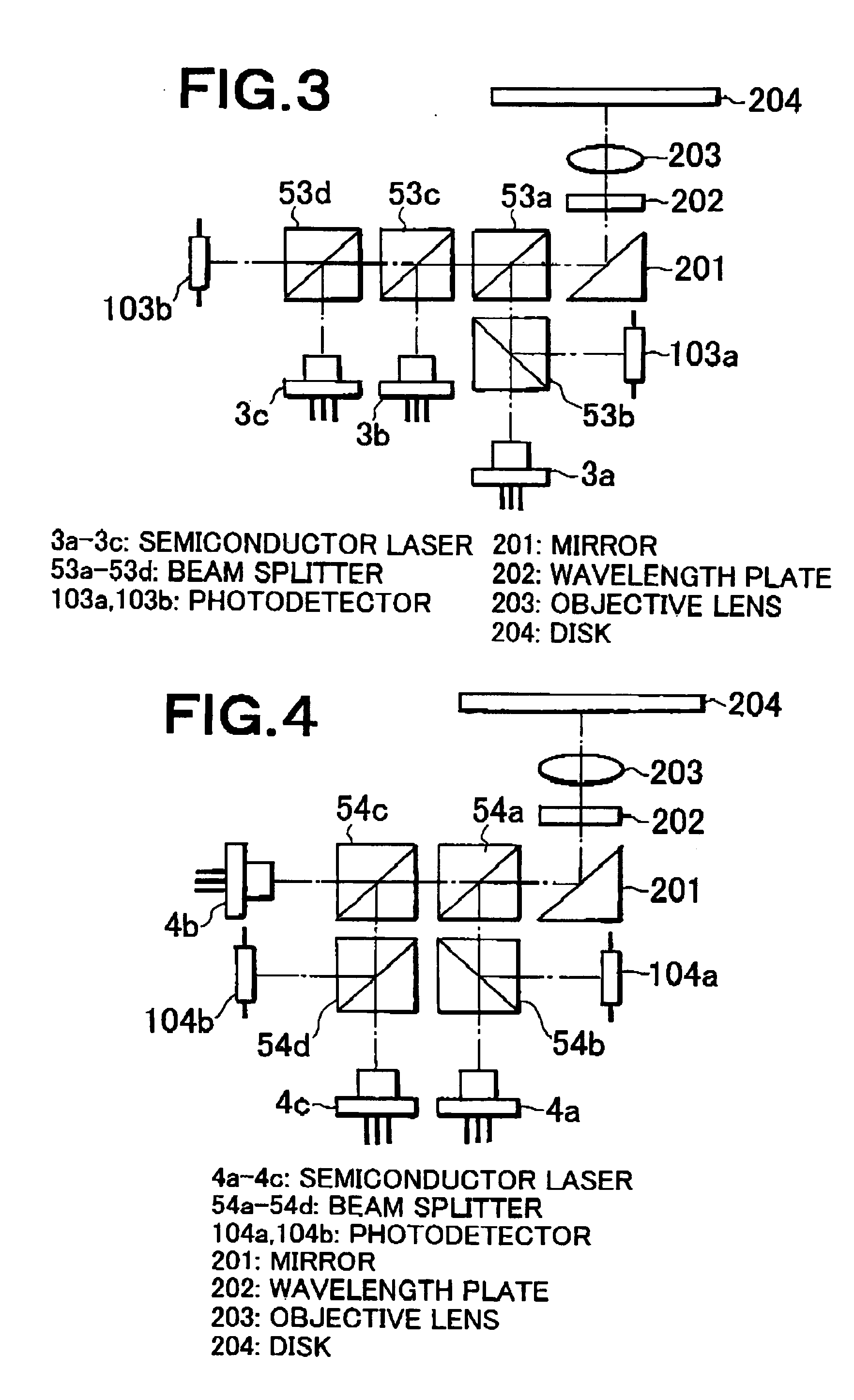
InactiveUS20050087678A1High S/N ratioLight lossIntegrated optical head arrangementsOptical beam sourcesPhotodetectorPhotovoltaic detectors
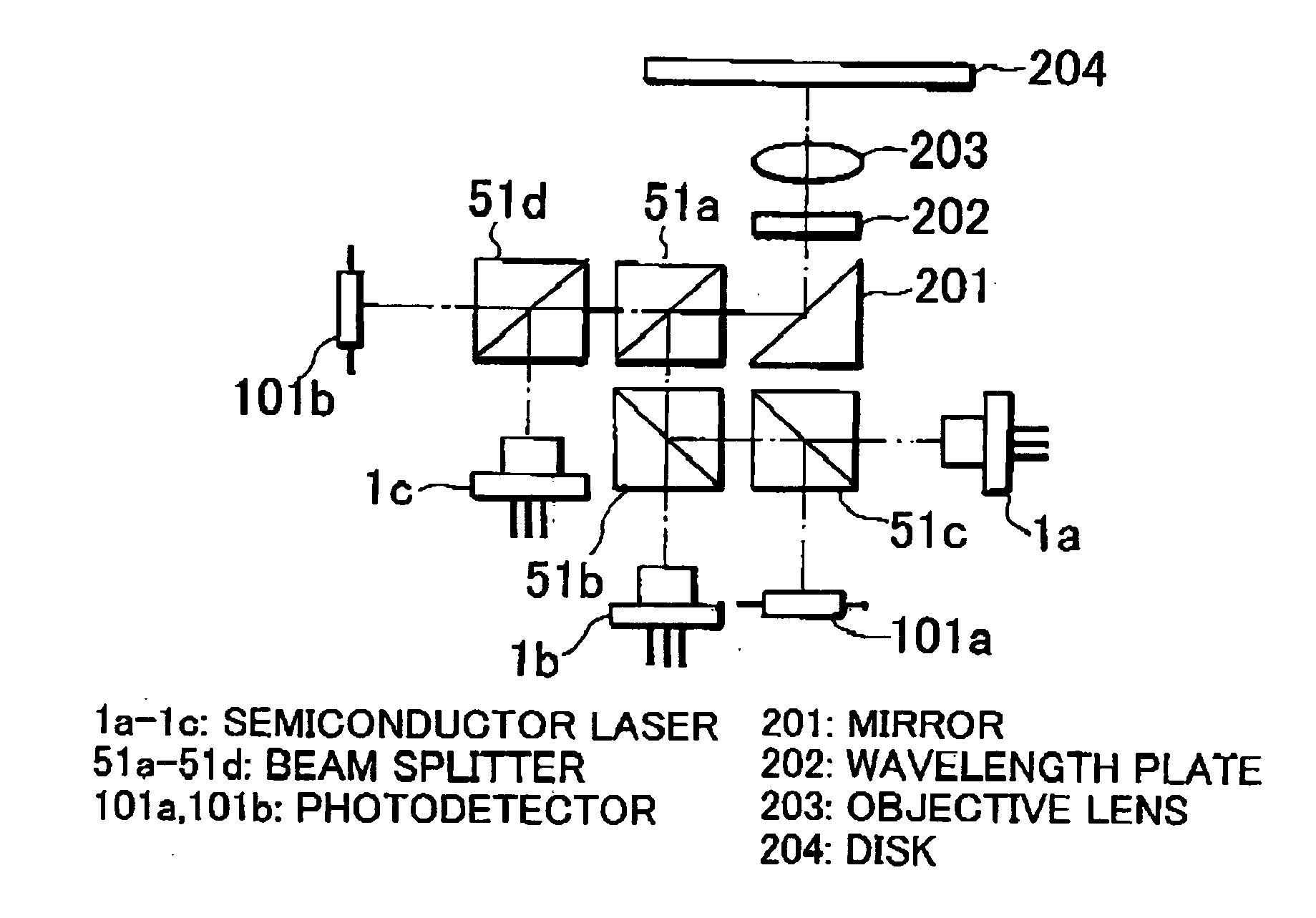
Light emitted from a light source and having a wavelength of 400 nm is reflected by a beam splitter (BS), and converged on a disk according to a next-generation standard. Reflection light therefrom passes through the BS and is received by a photodetector. Light emitted from a light source and having a wavelength of 660 nm is reflected by the BS and passes through the BS, and converged on a disk according to a DVD standard. Reflection light therefrom passes through the BS and is received by the photodetector. About 50% of light emitted from a light source and having a wavelength of 780 nm is reflected by the BS. The light passes through the BS and is then converged on a disk according to a CD standard. Reflection light therefrom passes through the BS. About 50% of the light passes through the BS and is received by the photodetector. Thus, recording and reproduction can be performed on any of disks according to a next-generation standard, DVD standard, and CD standard. With respect to disks according to the next-generation standard, a high optical output is obtained during recording and a high S / N ratio is obtained during reproduction. With respect to disks according to the CD standard, the amount of light received by the photodetector does not substantially vary even when birefringence of a disk varies.
Owner:NEC CORP
Optical add/drop multiplexer and optical network system
InactiveUS7657181B2Light lossLow costRing-type electromagnetic networksWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexingOptical add-drop multiplexer
In an optical add / drop multiplexer dropping and inserting a light of a specific wavelength for a WDM signal light and an optical network system utilizing the same, a wavelength selective switch selects a part of WDM signal lights inputted as lights of drop wavelengths and outputting other lights, and a reject / add filter terminates lights of same wavelengths as add wavelengths among output lights from the wavelength selective switch and multiplexes other lights than the terminated lights and lights of the add wavelengths to be outputted. At this time, the drop wavelengths are made to include all of the add wavelengths.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Source Module and Optical System For Line-Field Imaging
ActiveUS20200201058A1Improve illuminationGreat powerMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesTomographyCollimated light
A source module suitable for an optical coherence tomography system. The source module comprises a source operable to emit a divergent, source output beam either of circular cross-section (e.g. as output by a vertical cavity surface emitting laser) or of elliptical cross-section (e.g. as output by an edge-emitting semiconductor laser or diode). Collimation optics are provided to convert the source output beam into a non-divergent, collimated beam of elliptical cross-section having a major axis and a minor axis. A cylindrical lens is arranged with its plano axis aligned with the major axis of the elliptical collimated beam and its power axis aligned with the minor axis of the elliptical collimated beam so as to form a line focus extending along the major axis of the elliptical collimated beam.
Owner:EXALOS
Optical system with optical waveguides
InactiveUS7574081B2Loss of signal lightLight lossCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideEngineeringWaveguide
The present invention provides an optical system with waveguides, which comprises first, second and third optical input / output means (12, 14, 16), fourth and fifth multi-mode optical waveguides (20, 22) each capable of propagating light with plural propagation modes, and optical-filter mounting means (26) for mounting an optical filter (24) between the fourth and fifth multi-mode optical waveguides (20, 22) across a traveling direction of light in the fourth and fifth multi-mode optical waveguides (20, 22). The first optical input / output means (12) is connected to an end face of the fourth multi-mode optical waveguide (20) on a side thereof opposite to the optical-filter mounting means (26). Each of the second and third optical input / output means (14, 16) is connected to an end face of the fifth multi-mode optical waveguide (22) on a side opposite to the optical-filter mounting means (26). Respective widths in a direction orthogonal to the light-traveling direction of the fourth and fifth multi-mode optical waveguides (20, 22) are different from each other.
Owner:RESONAC CORPORATION
Diffusion sheet
InactiveUS20070053065A1Improve utilization efficiencyEffective reflectionPrismsDiffusing elementsLight guideLight reflection
A diffusion sheet interposed between a light guide plate and a prism sheet includes: a light reflection unit reflecting a feedback light toward the prism sheet again, the feedback light being returned by the prism sheet.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Light source system and projection system
ActiveUS20180129123A1Light lossEffective lightingProjectorsColor photographyFluorescenceScattering loss
A light source system and a projection system. The light source system comprises: an excitation light source (101) for emitting excitation light in at least a first time sequence and a second time sequence; a compensation light source (102) for emitting compensation light in at least a third time sequence, the compensation light emitted by the compensation light source (102) comprising laser of at least one color; and a rotating color wheel (103), comprising at least a first region (201) and a second region (202), wherein the first region (201) generates light of at least two different colors in time sequence under the irradiation of the excitation light in the first time sequence and the second time sequence, and the second region (202) is used for transmitting the compensation light in at least the third time sequence. The light of the at least two different colors comprises at least one type of wide-spectrum fluorescence, and the laser of the at least one color is used for compensating for the fluorescence or light split from the fluorescence. In this way, the compensation light is directly transmitted without being irradiated upon fluorescent powder, scattering loss of the compensation light is reduced, and utilization rate of the compensation light is increased.
Owner:APPOTRONICS CORP LTD
System and method for therapy and diagnosis comprising translatory distributor for distribution of radiation
ActiveUS7988715B2Small sizeReduce impactDiagnostics using spectroscopyDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionOptical radiationElectrical conductor
Owner:SPECTRACURE
Photovoltaic cell
InactiveUS20120055542A1Enhance absorptionLight lossFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationLattice mismatchEngineering
A structure of photovoltaic cell for improving conversion efficiency has been disclosed, including a first bandgap layer, a second bandgap layer, a third bandgap layer, a back electrode and a finger electrode, wherein the first bandgap layer is a wafer while the second bandgap layer is a semiconductor film with a thickness of 1˜100 Å and a greater bandgap than one of the first bandgap layer, and the third bandgap layer comprises wide bandgap materials and a greater bandgap than one of the second bandgap layer. Thereby, the lattice mismatch of heterostructures between the first bandgap layer and the third bandgap layer may be solved by the second bandgap layer. Also, the carrier recombination within devices may be decreased and the output photocurrent may thus be enhanced to improve energy conversion efficiency.
Owner:TATUNG UNIVERSITY +1
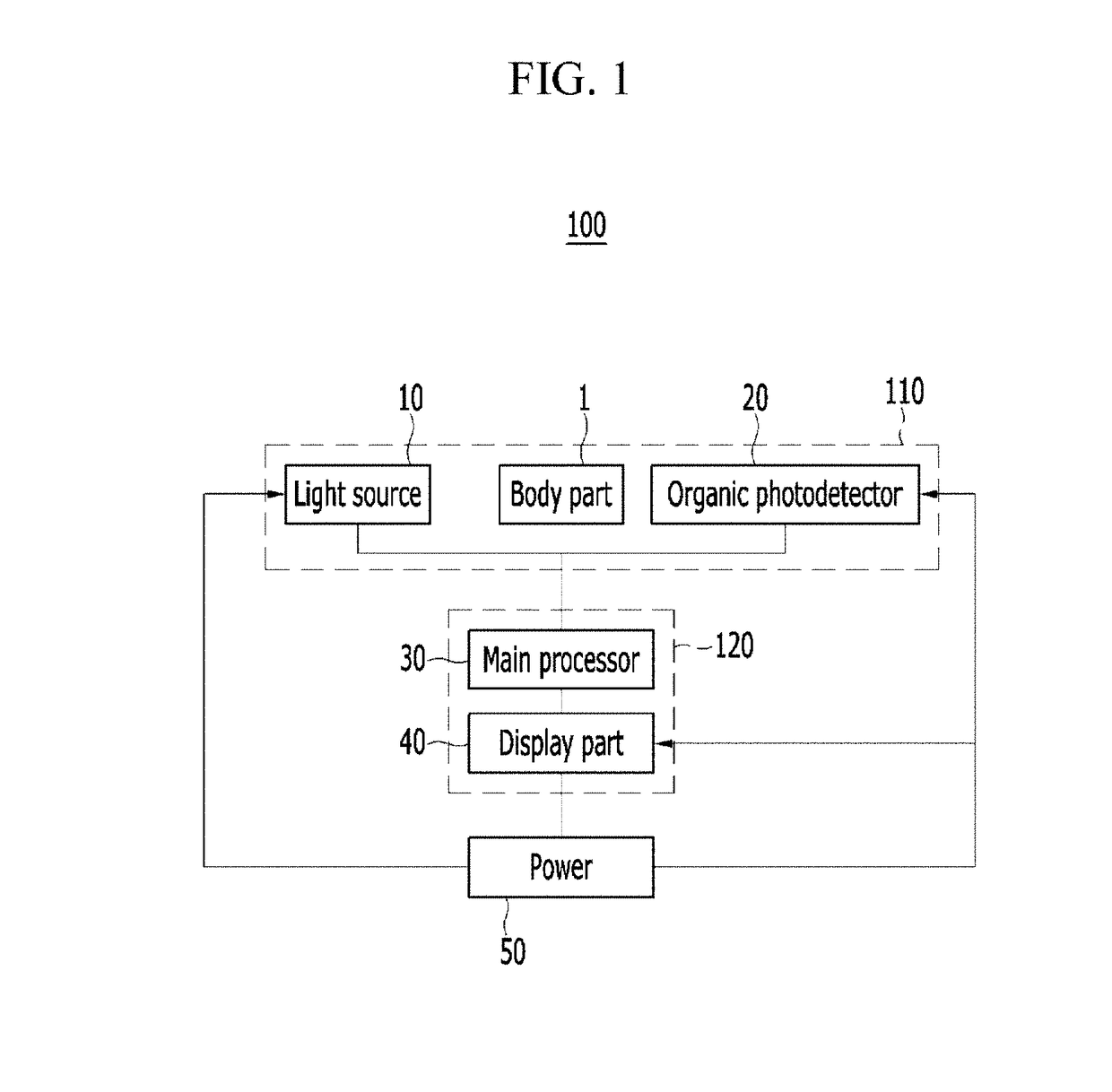
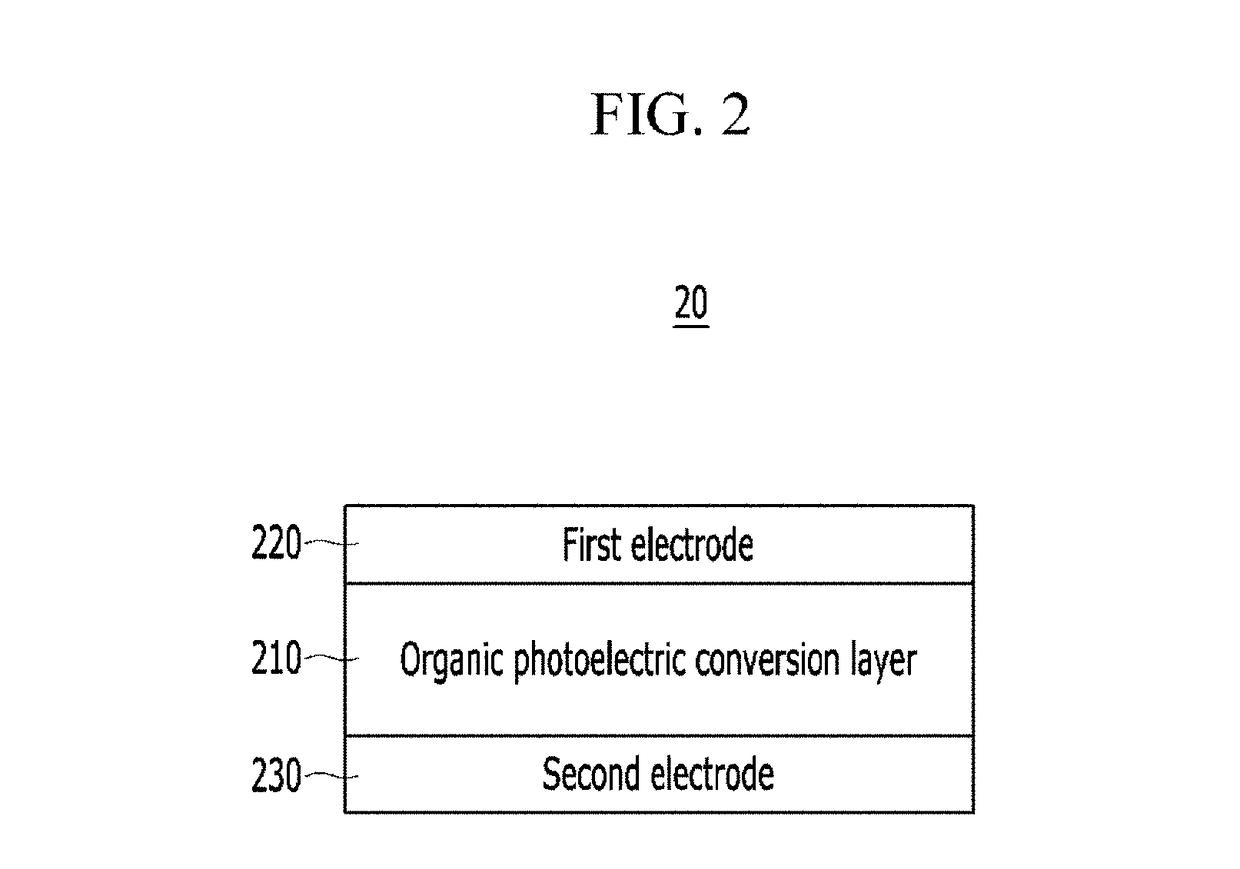
Non-invasive biometric sensor based on organic photodetector
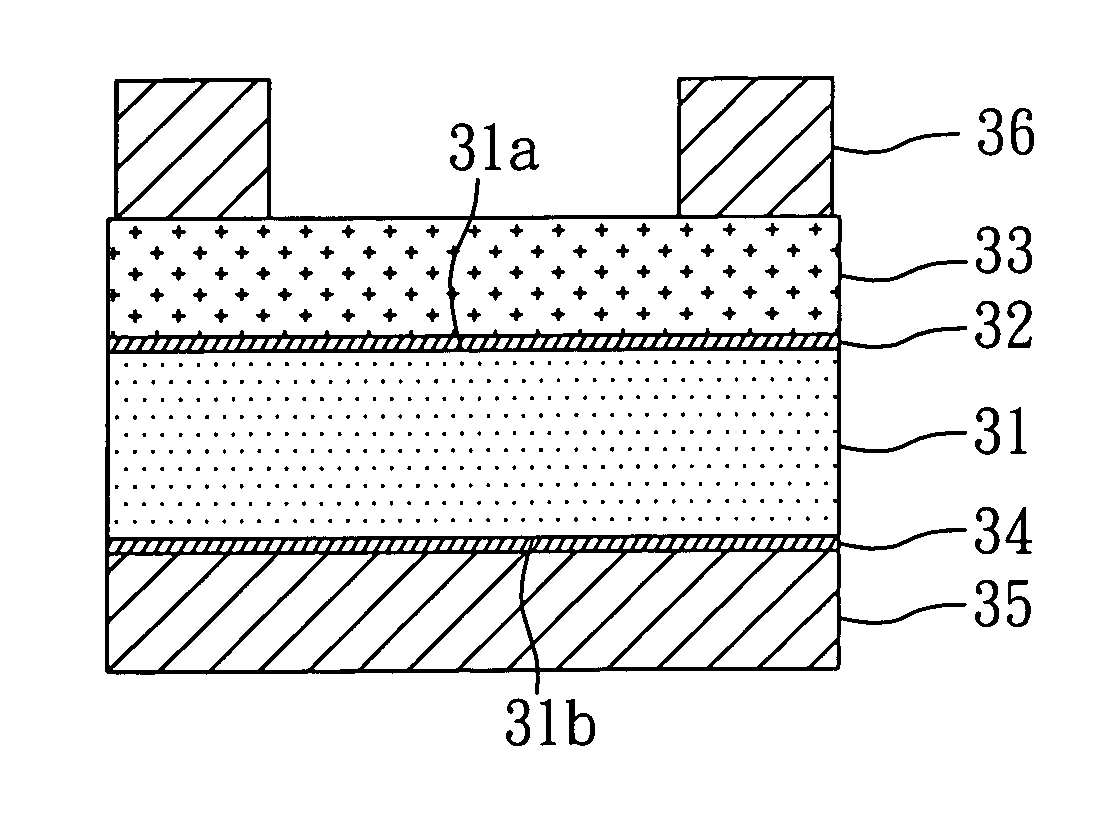
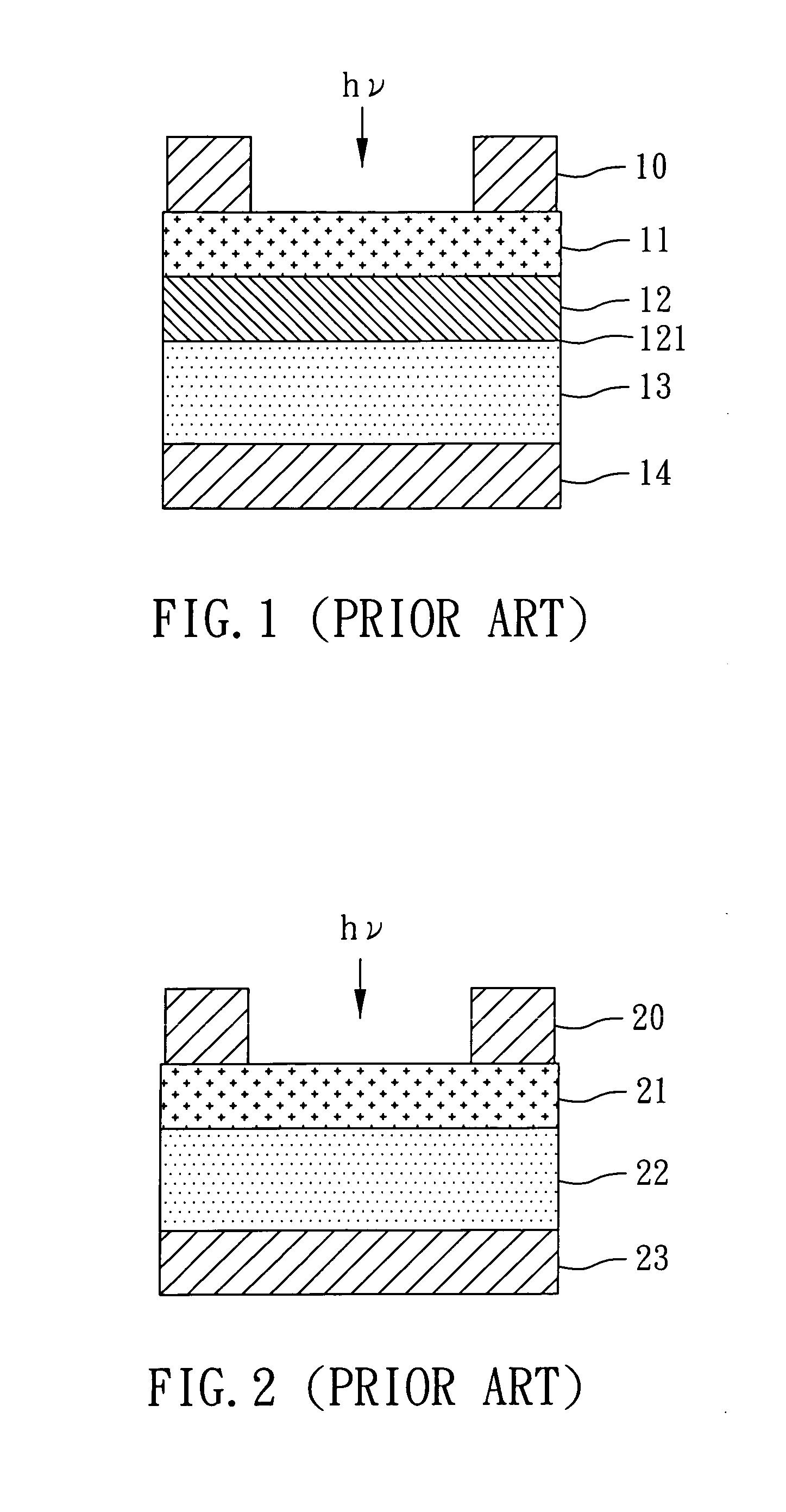
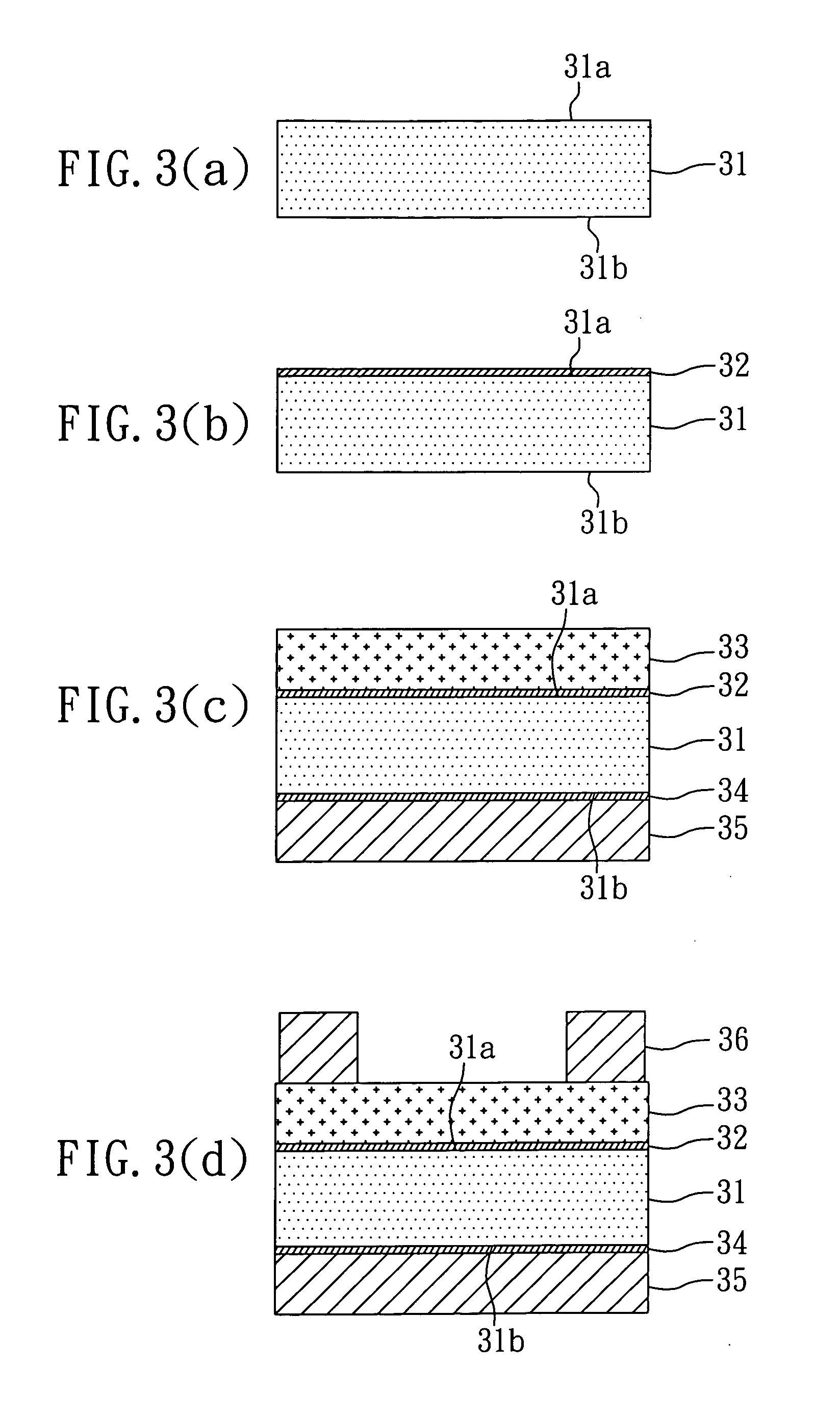
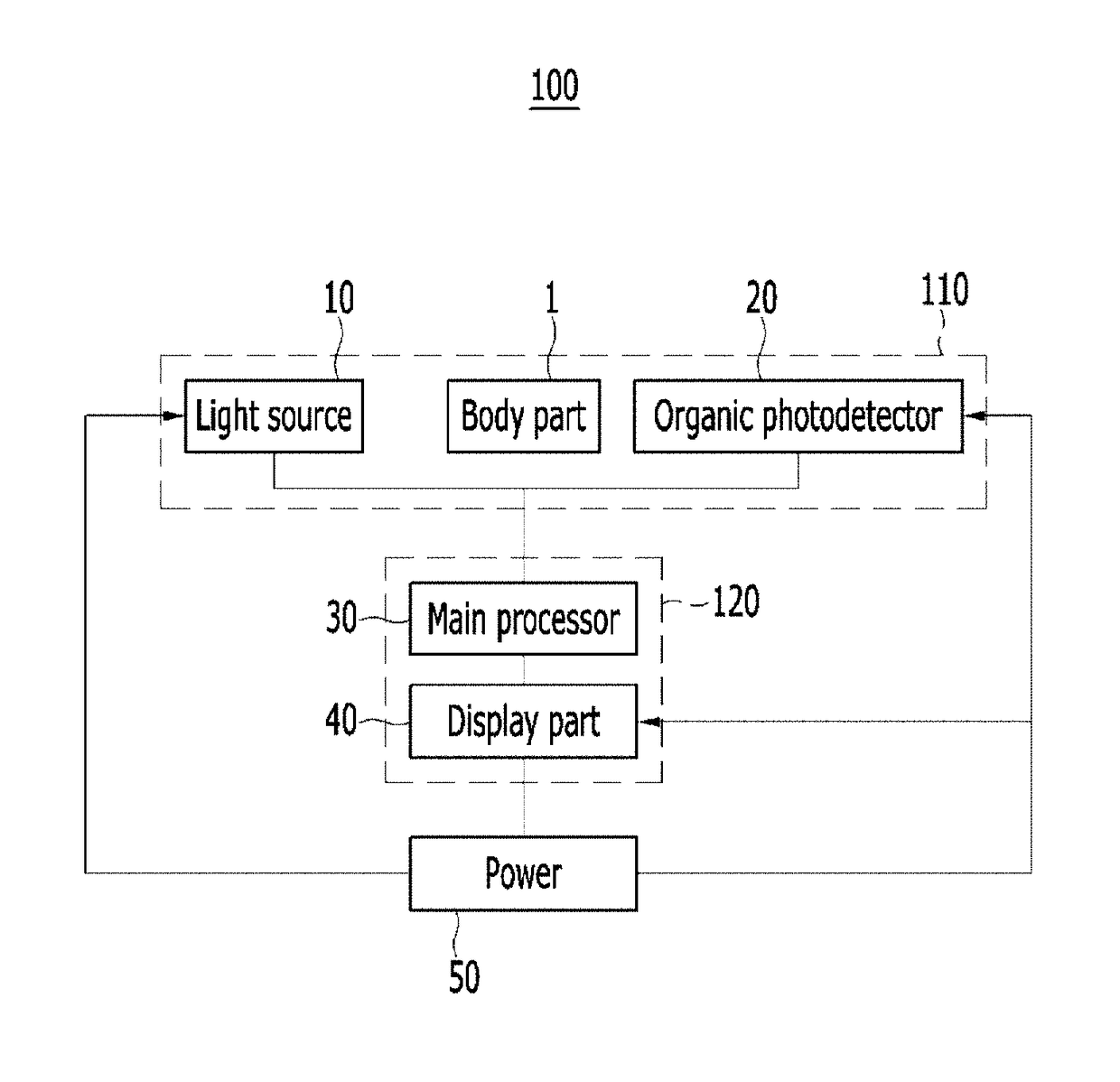
ActiveUS20180000387A1Less-light lossHigh Photoelectric Conversion EfficiencyMaterial analysis by optical meansSensorsLight sensingPhotovoltaic detectors
Disclosed is a non-invasive biometric sensor including a light source, an organic photodetector, and a detector. The light source is configured to irradiate light in a desired (and / or alternatively predetermined) wavelength range to a body part. The organic photodetector is configured to sense the light in the desired (and / or alternatively predetermined) wavelength range in response to the light in the desired (and / or alternatively predetermined) range being transmitted through the body part. The detector is configured to determine biomedical information of the body part based on an amount of the light sensed by the organic photodetector.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Light deflection element, light deflection device and image display device
InactiveUS7057700B2Efficiently deflectedIncrease the light areaLiquid crystal compositionsTelevision system detailsDisplay deviceLarge size
A light deflection element has a pair of transparent substrates 2, 3; a chiral smectic C phase liquid crystal 5 with a homeotropic alignment filled between the pair of transparent substrates 2, 3; and at least an electric field applying device 6 for activating an electric field in the liquid crystal 5. Because a chiral smectic C phase liquid crystal is used, the problems of the conventional light deflection element, such as high cost, light loss, large size, and optical noise etc. due to its complicated structure, can be greatly improved. The conventional low response time due to the smectic A phase or the nematic liquid crystal is improved, thereby the high-speed response is possible.
Owner:RICOH KK
Wavelength conversion element, light source device, and projector
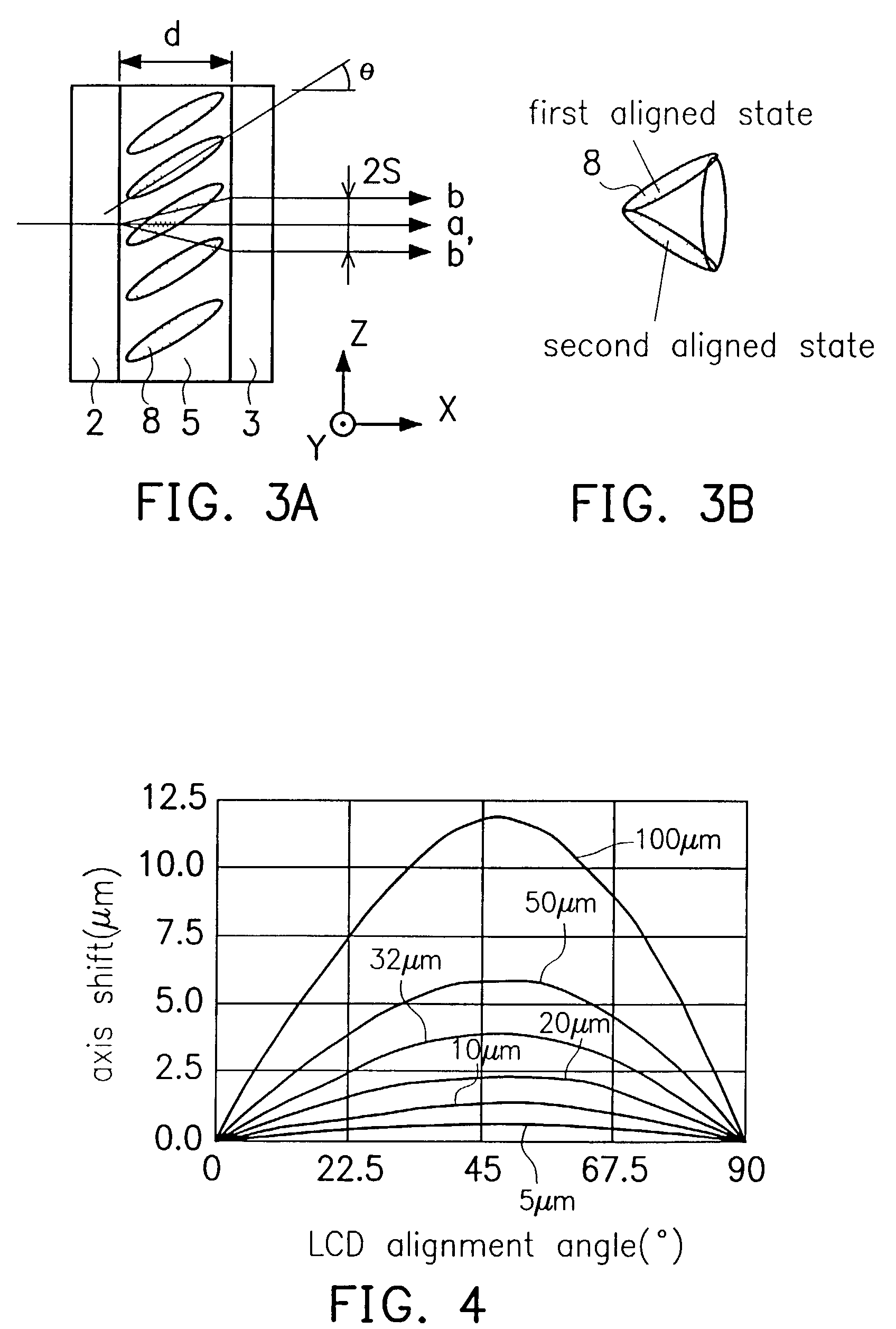
ActiveUS20190079376A1High fluorescence intensityRaise the ratioProjectorsOptical elementsFluorescenceReflective layer
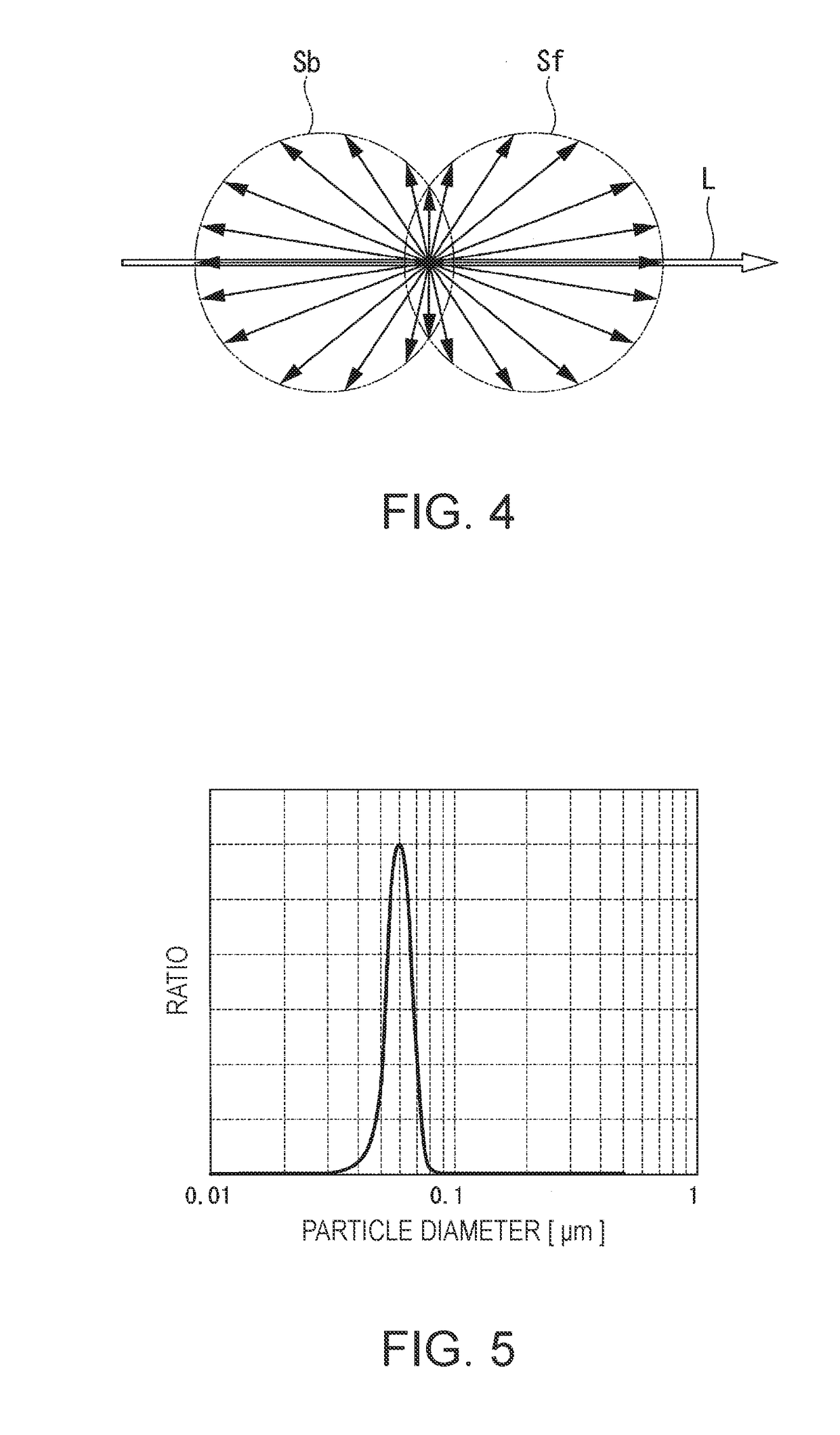
A wavelength conversion element includes: a wavelength conversion layer including a first surface on which excitation light is incident, and a second surface opposed to the first surface; a scattering layer provided to face the second surface, containing a plurality of particles, and at least scattering fluorescence obtained by wavelength-converting the excitation light by the wavelength conversion layer; and a reflective layer provided to face the scattering layer and reflecting the excitation light or the fluorescence. The particle diameter of the particle is smaller than the wavelength of the fluorescence.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Flip chip type light emitting diode chip
ActiveUS20200127167A1Reduce light lossImprove luminous efficiencyLaser detailsSolid-state devicesDistributed Bragg reflectorEngineering
A flip chip type light emitting diode chip is disclosed. The light emitting diode chip includes a substrate; a first conductivity type semiconductor layer disposed on the substrate; a mesa disposed on a partial region of the first conductivity type semiconductor layer, and including an active layer and a second conductivity type semiconductor layer; a transparent electrode; a contact electrode laterally spaced apart from the mesa; a current spreader electrically connected to the transparent electrode; a first insulating reflection layer covering the substrate; and a second insulating reflection layer disposed under the substrate, and including the distributed Bragg reflector.
Owner:SEOUL VIOSYS CO LTD
Rare-earth doped optical fiber, method of producing the same, and fiber laser
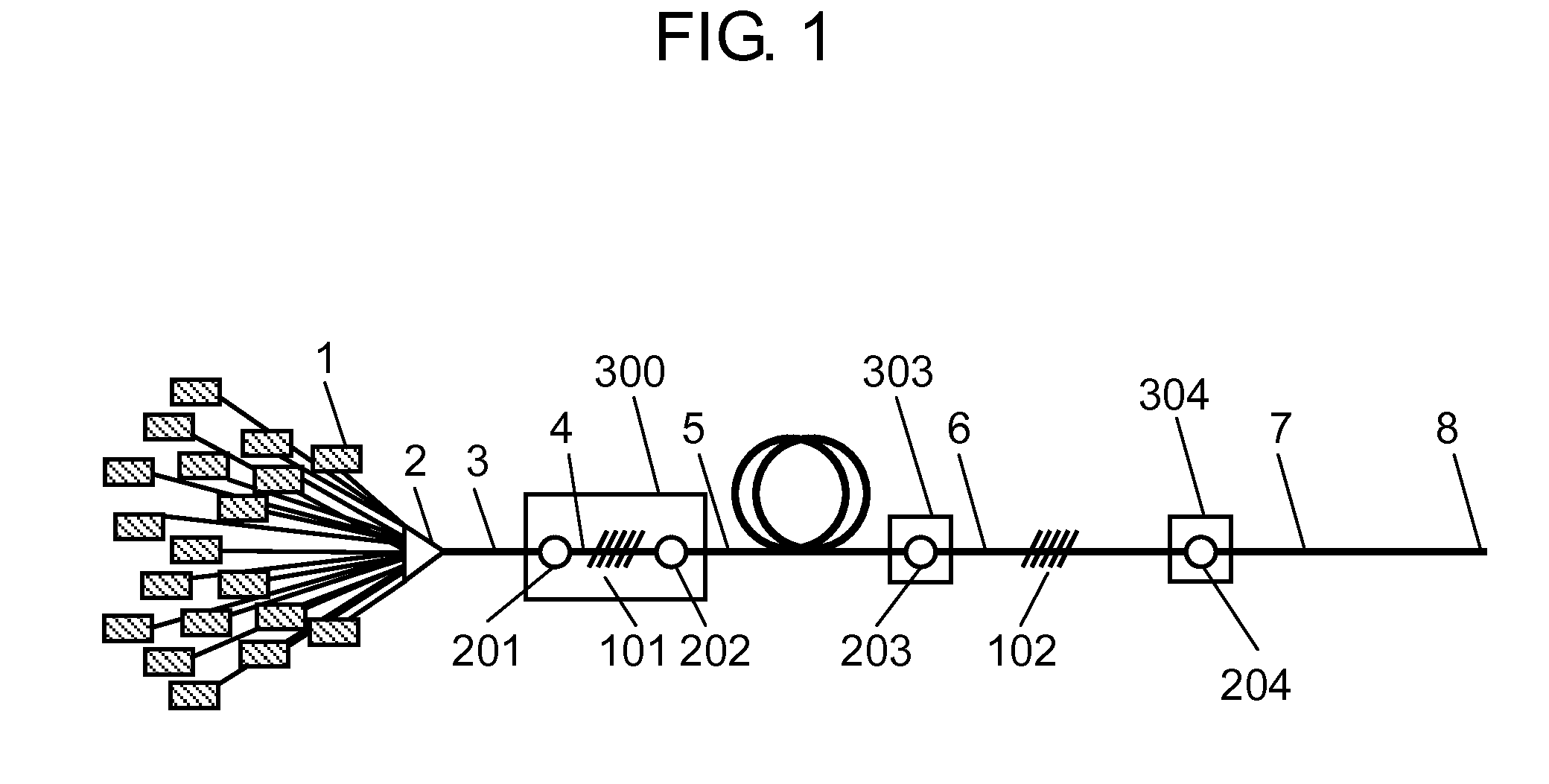
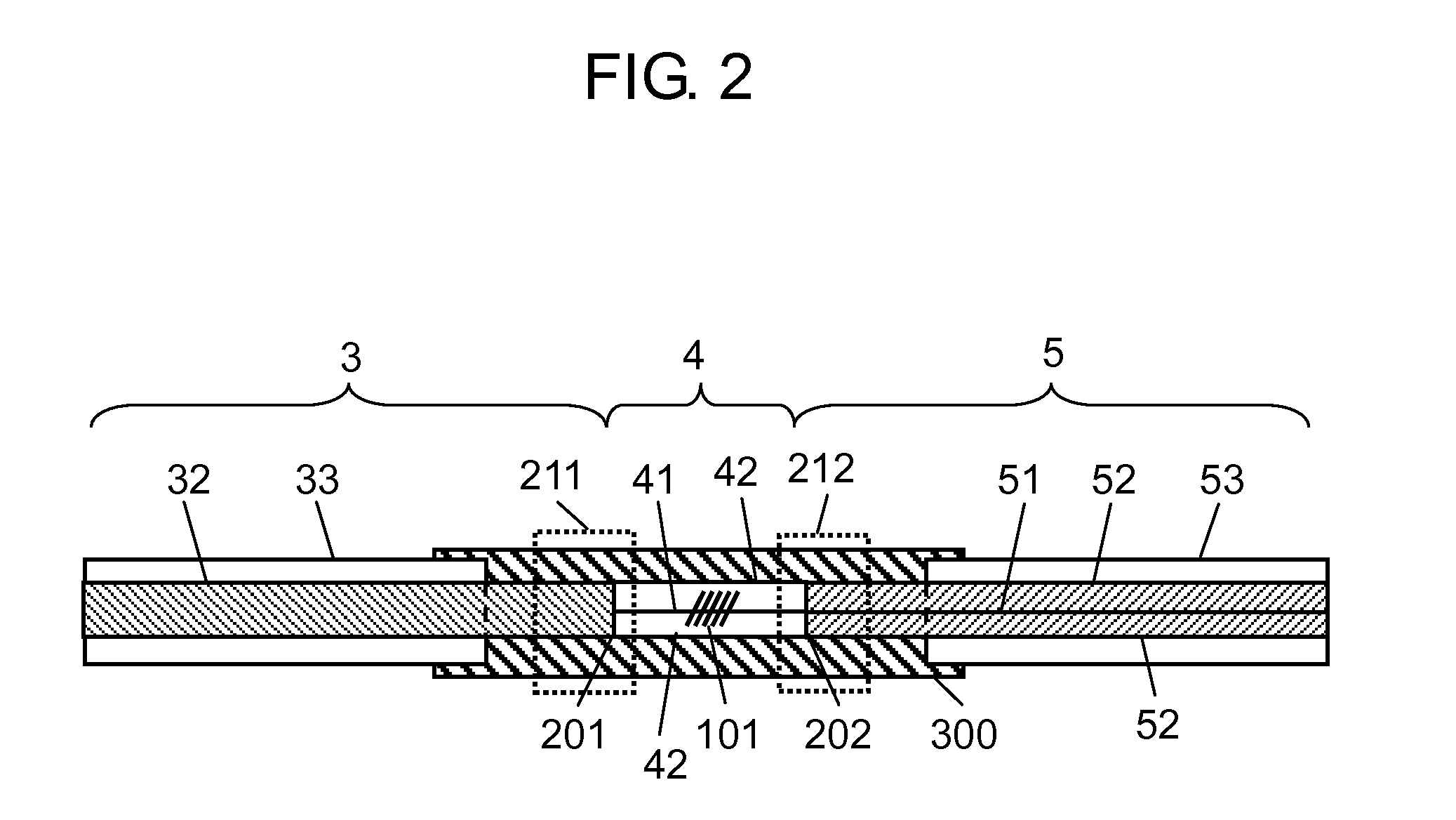
ActiveUS20090238216A1Increasing optical loss of the optical fiberLight lossLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingDopantRare earth
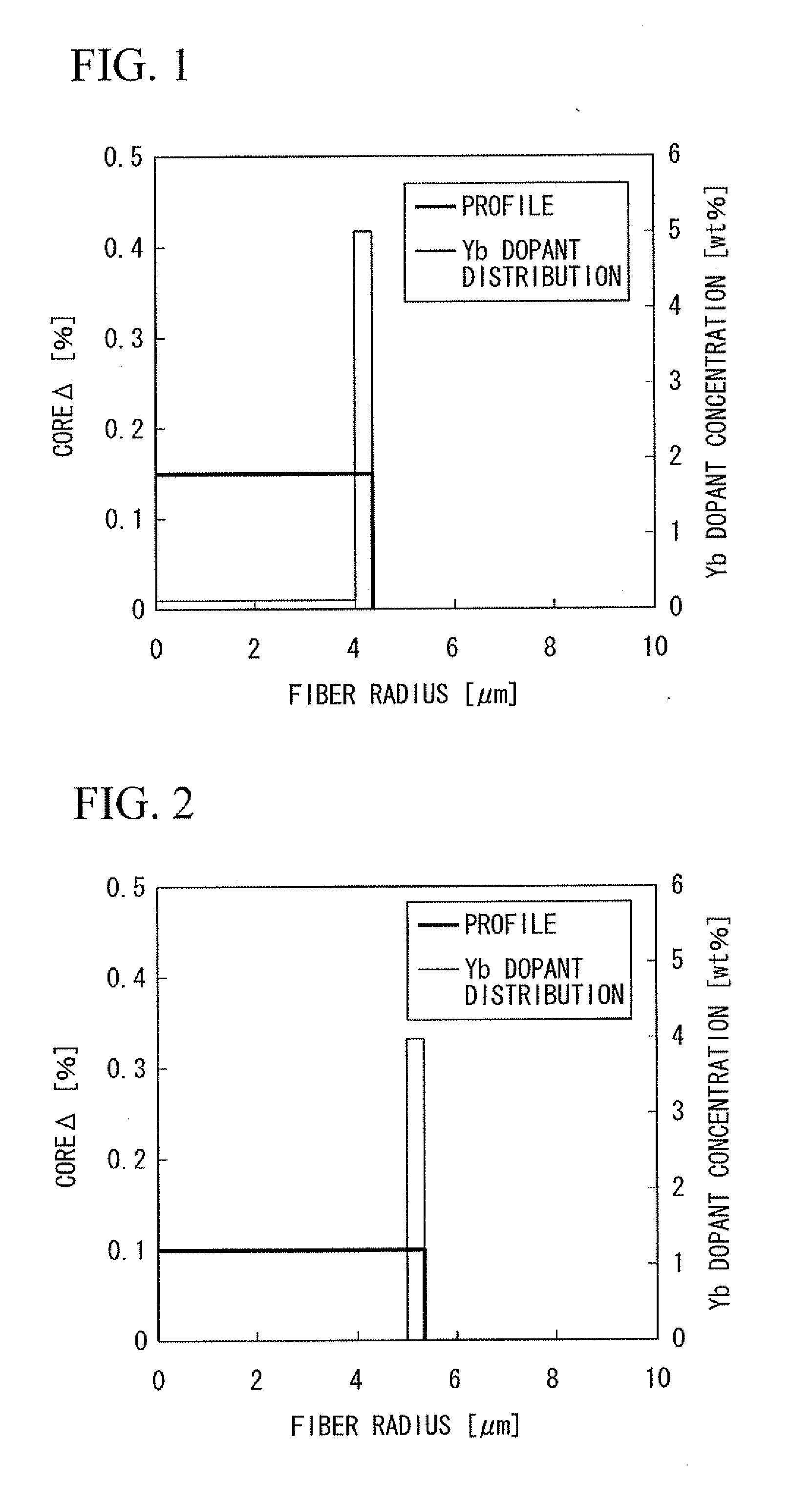
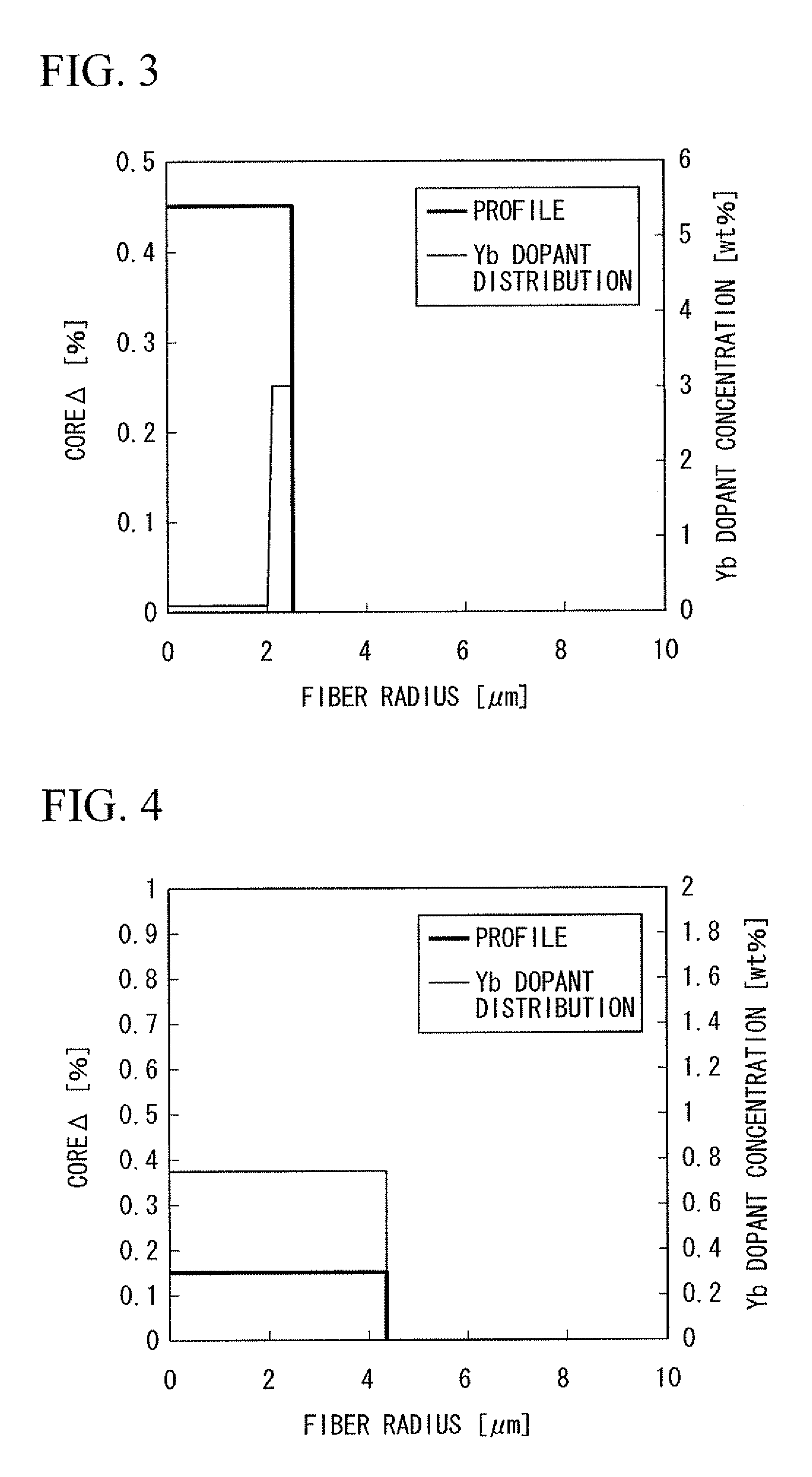
A rare-earth doped optical fiber that includes a core and one or more clad layers surrounding the core, in which the core has a rare earth dopant, and a relationship of Equation (1) is satisfied:0<∫r0rcD(r)·Pp2(r)·Ps2(r)rr∫r0rcD(r)·Pp2(r)rr≤0.35(1)where Pp(r) represents an electric field distribution in an exciting wavelength, Ps(r) represents an electric field distribution in wavelengths of spontaneous emission and / or stimulated emission carried in the core, D(r) (mass %) represents a rare-earth dopant distribution, ro represents a core center, and rc represents a core diameter.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Light-emitting element package and lighting device
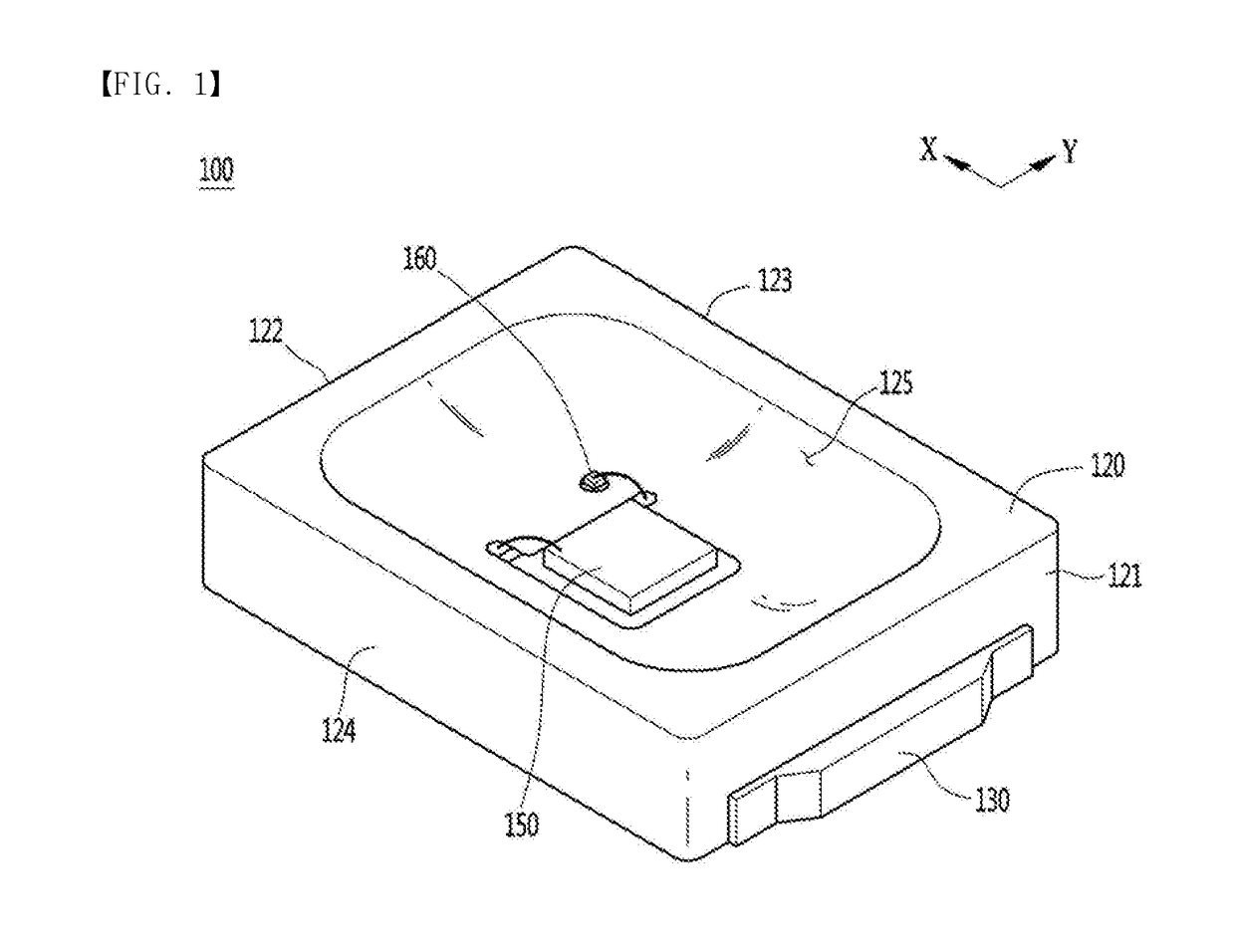
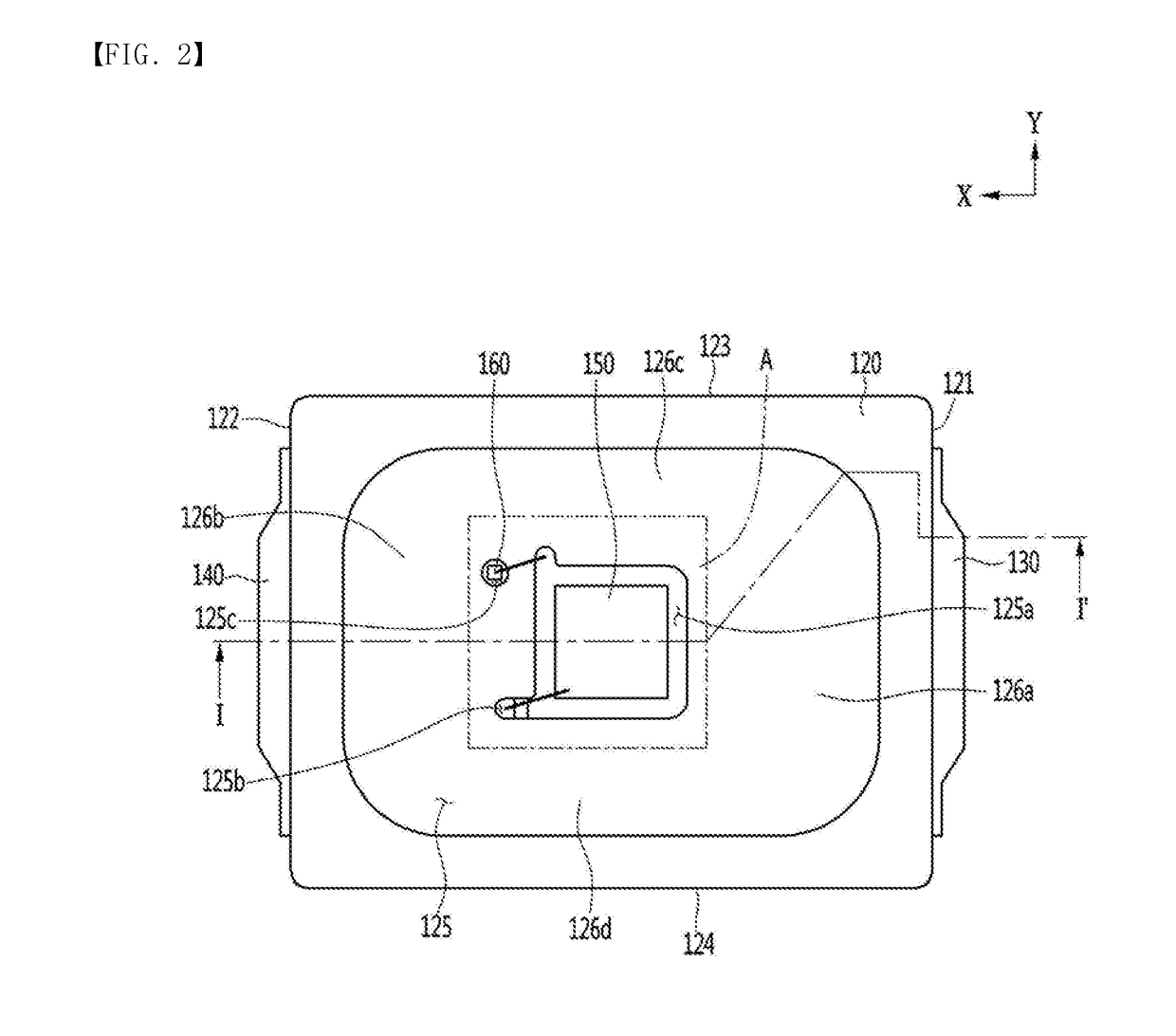
ActiveUS20180358523A1Improve productivityEasy injectionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesProduction rateEngineering
Embodiments relate to a light emitting device package and a lighting device. The light emitting device package of an embodiment includes: a first lead frame; a light emitting device mounted on the first lead frame; a second lead frame spaced apart from the first lead frame in a first direction; a protective device mounted on the second lead frame; and a body coupled to the first and second lead frames, wherein the first lead frame includes a first stepped portion disposed along an edge of a lower surface thereof, and the second lead frame includes a third stepped portion disposed along an edge of a lower surface thereof, a mounting region of the protective device which is not overlapped in a vertical direction and spaced apart from the third stepped portion, and a second wire recess portion which is partially overlapped with the third stepped portion in the vertical direction, wherein the first and third stepped portions may be disposed in the body to improve injection molding into a spaced space between the first lead frame and second lead frame. That is, in an embodiment, an edge portion or a curved surface portion may be disposed around a spaced space of the first and second lead frames to improve injection molding defects, thereby improving productivity.
Owner:SUZHOU LEKIN SEMICON CO LTD
4Pi microscope
InactiveUS7453578B2Enhance excitationSolve the low detection efficiencyMicroscopesUsing optical meansLight beam4Pi microscope
A 4Pi microscope provided with an interferometer wherein two lenses (31, 33) are arranged in such a way that they are opposite to each other on different sides of a sample plane (35); also comprising an optical element (19) which is used to inject illuminating light (3) into the interferometer and / or used to discharge detection light (41) from the interferometer and to deflect a detection beam path, containing a reflecting means (51) which reflects illuminating light discharged by the optical element back into the interferometer and / or which allows detection light which is deflected onto the deflection beam to pass, also reflecting other discharged detection light which is not deflected onto the detection beam path into the interferometer.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Optical fiber, fiber laser, and optical fiber manufacturing method
InactiveUS20150247972A1Efficiently outputs lightAmount of loss can be minimizedGlass making apparatusLaser using scattering effectsLaser fiberRefractive index
An optical fiber of the present invention includes an uncoated FBG fiber in which an FBG mirror is written in a core glass, a first optical fiber that is spliced to one end of the FBG fiber with a first spliced point interposed therebetween, and a second optical fiber that is spliced to the other end of the FBG fiber with a second spliced point interposed therebetween. The optical fiber of the present invention also includes a collectively recoated portion in which at least the FBG fiber, the first spliced point, and the second spliced point are collectively recoated with a recoat resin having a refractive index less than that of silica, the FBG fiber being sandwiched between the first spliced point and the second spliced point.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com