Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
548results about "Integrated optical head arrangements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
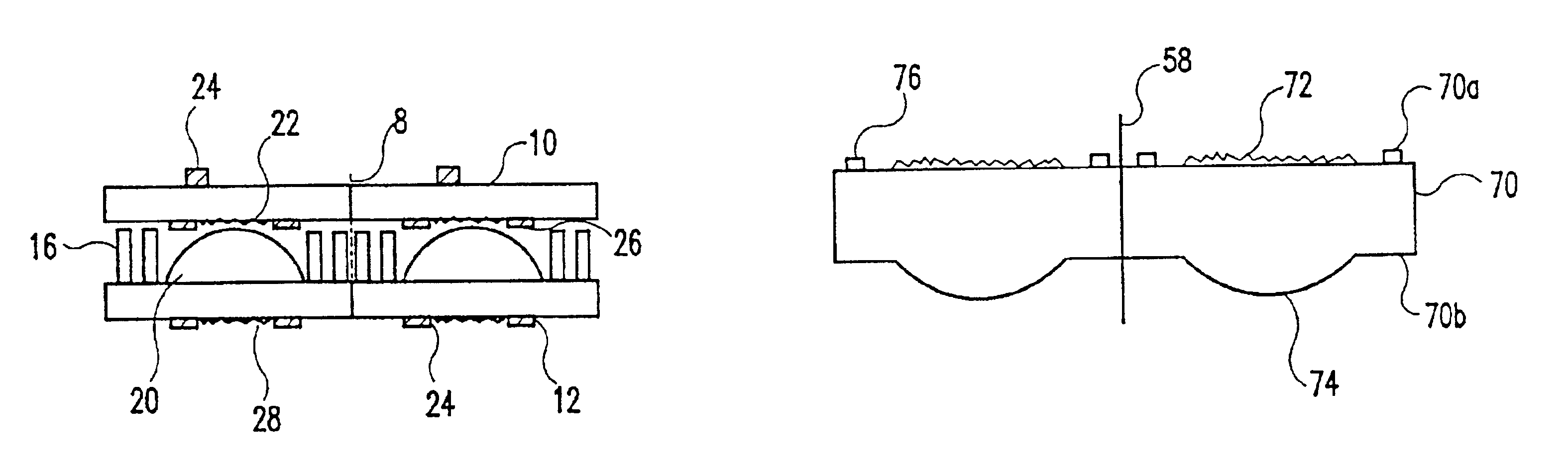
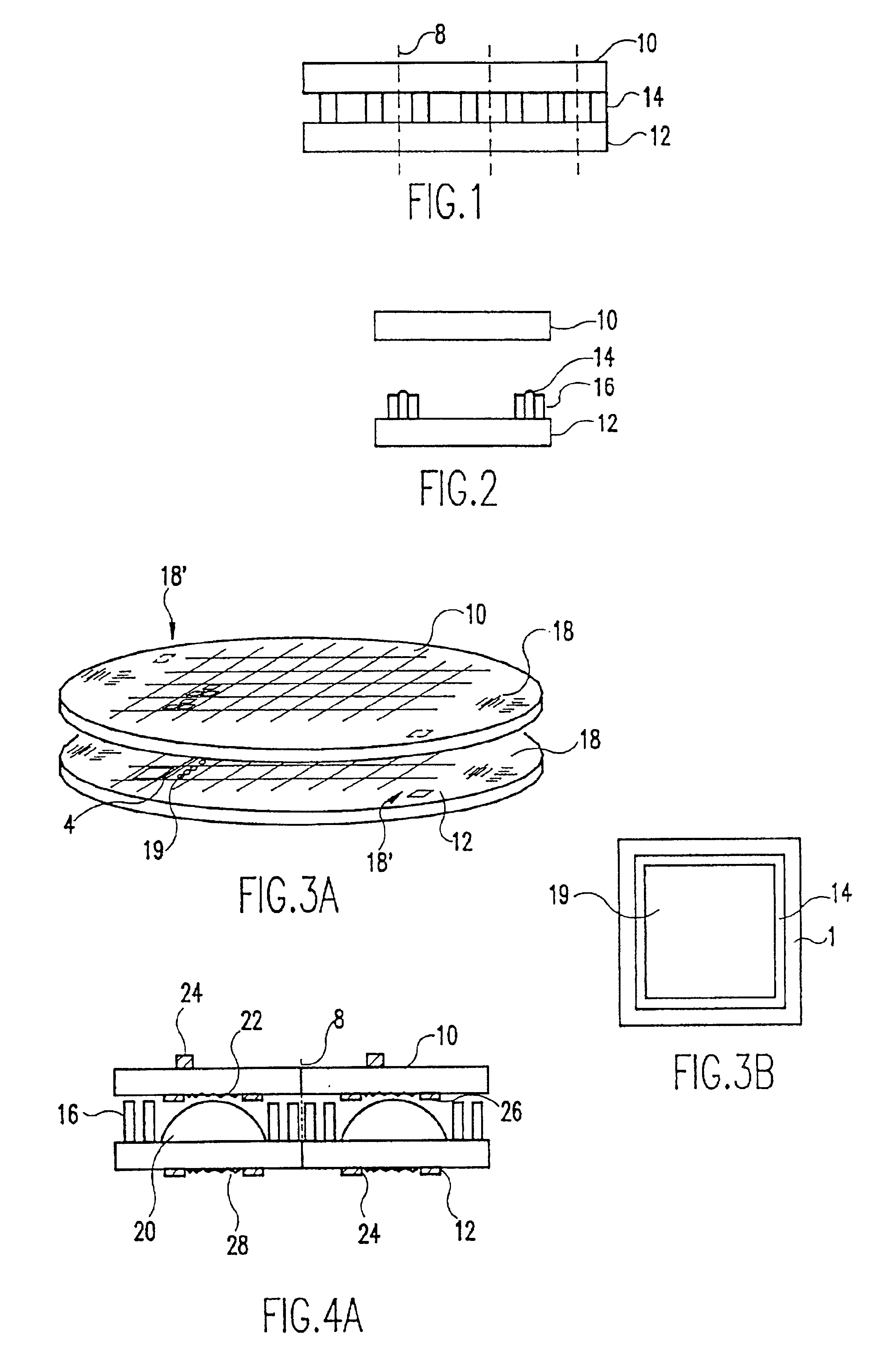
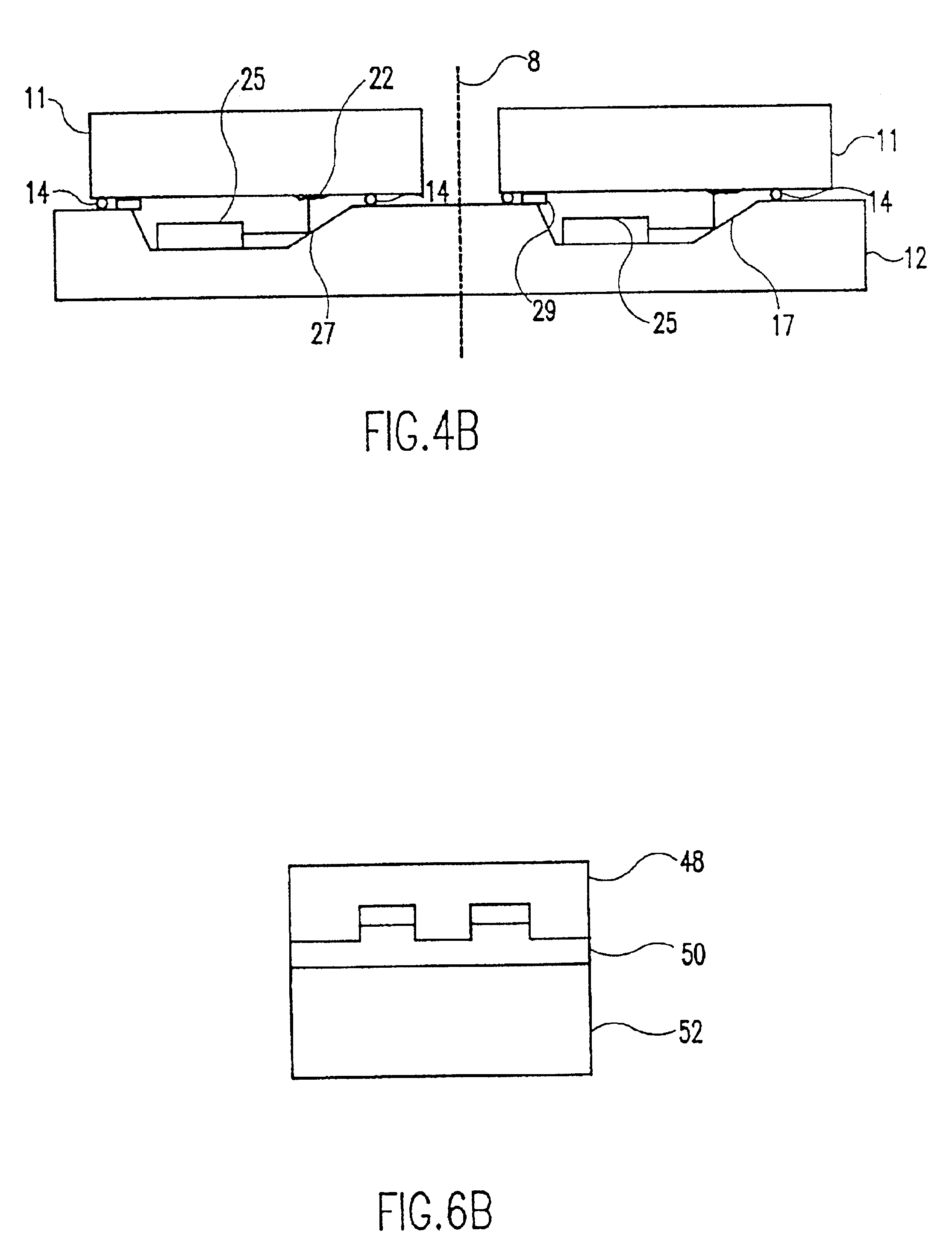
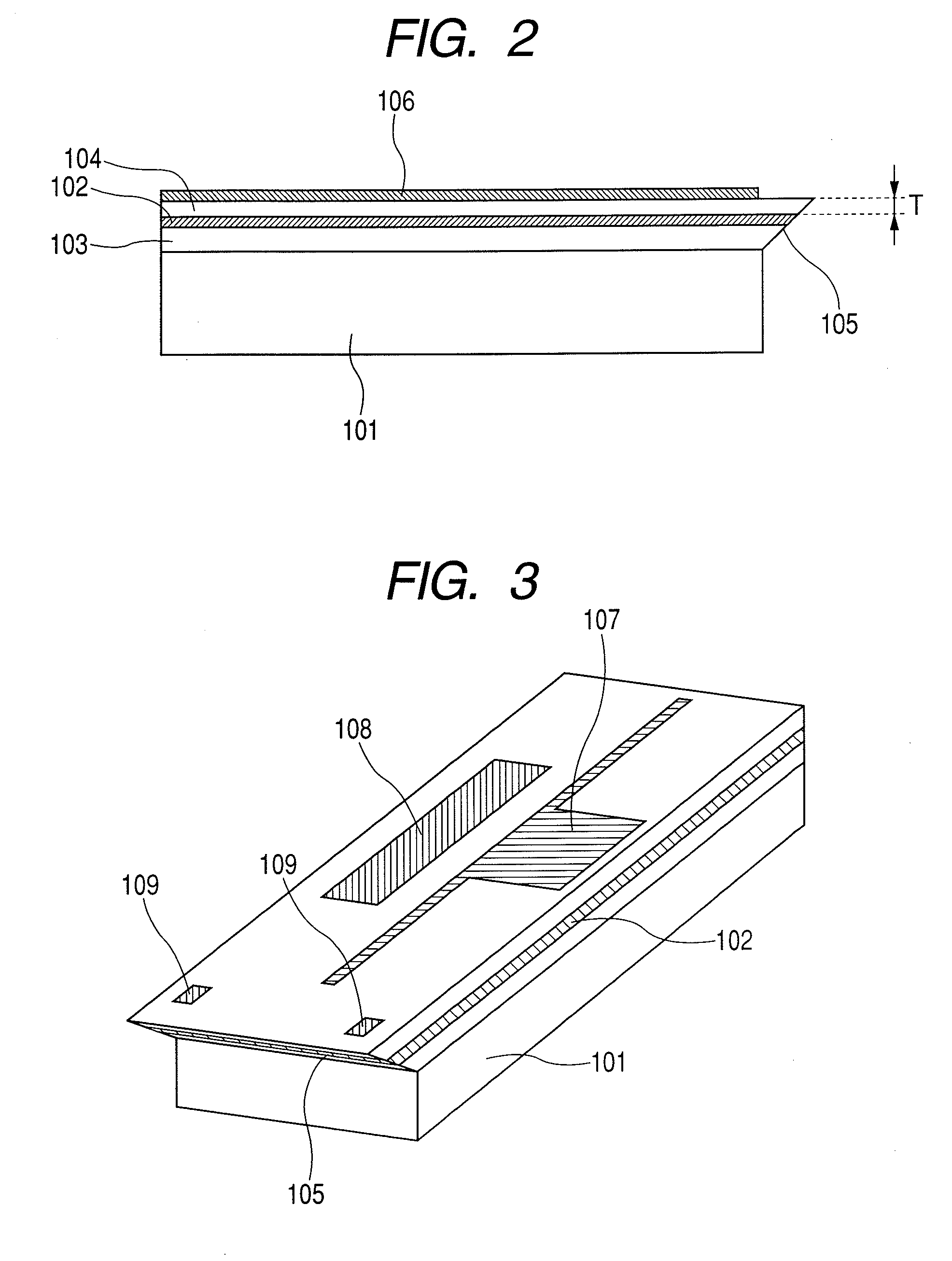
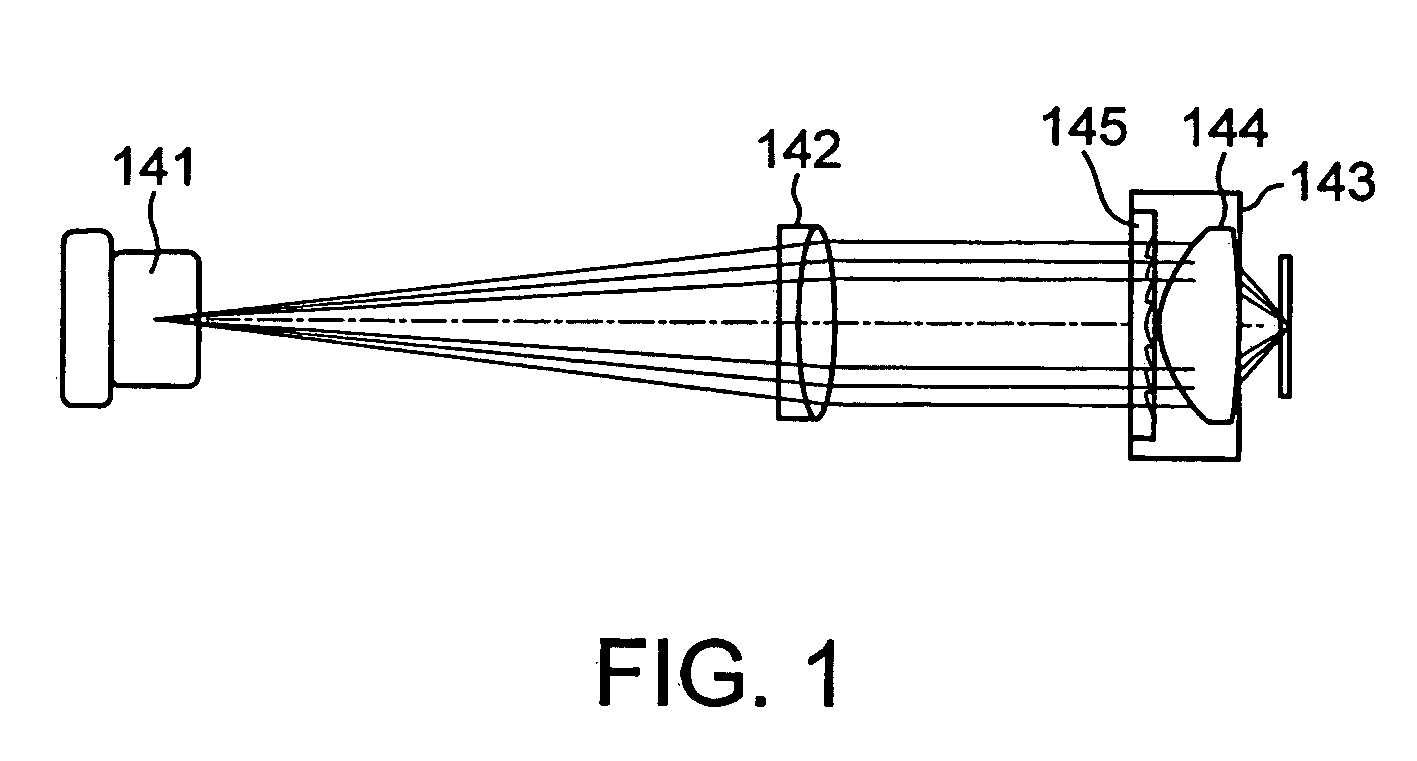
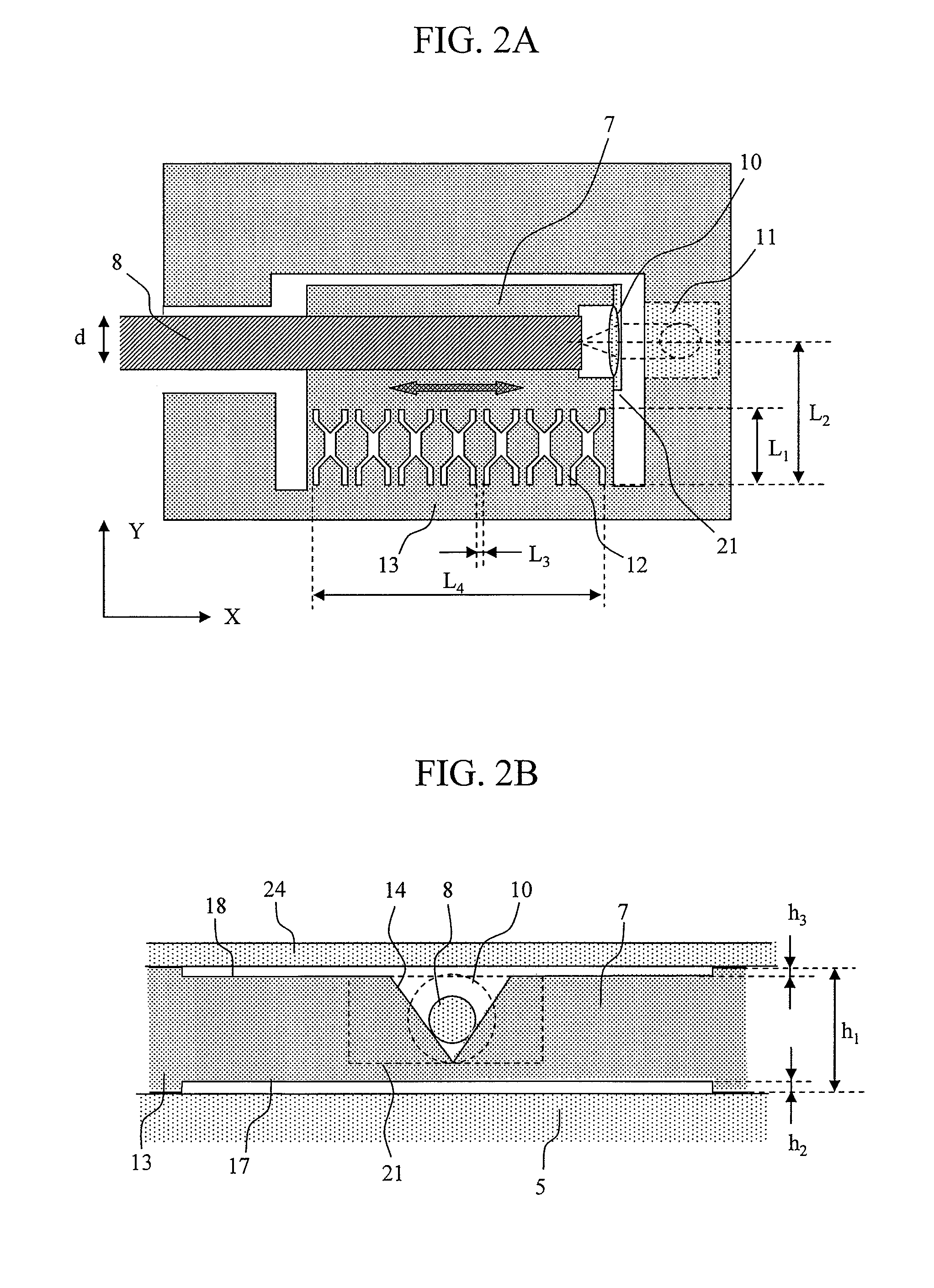
Wafer level creation of multiple optical elements
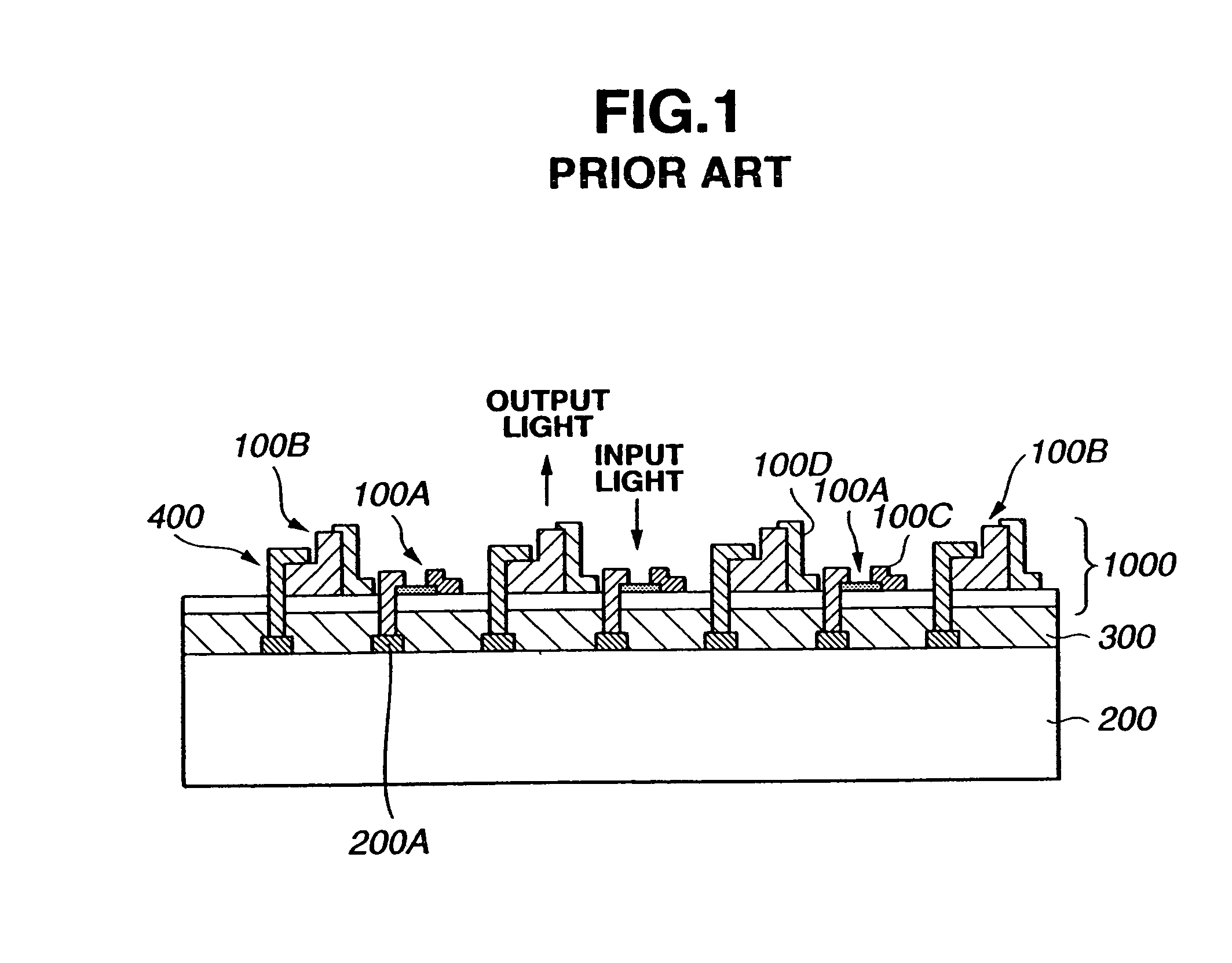
InactiveUS6844978B2Efficiently produceEfficient productionSolid-state devicesOptical articlesEngineering
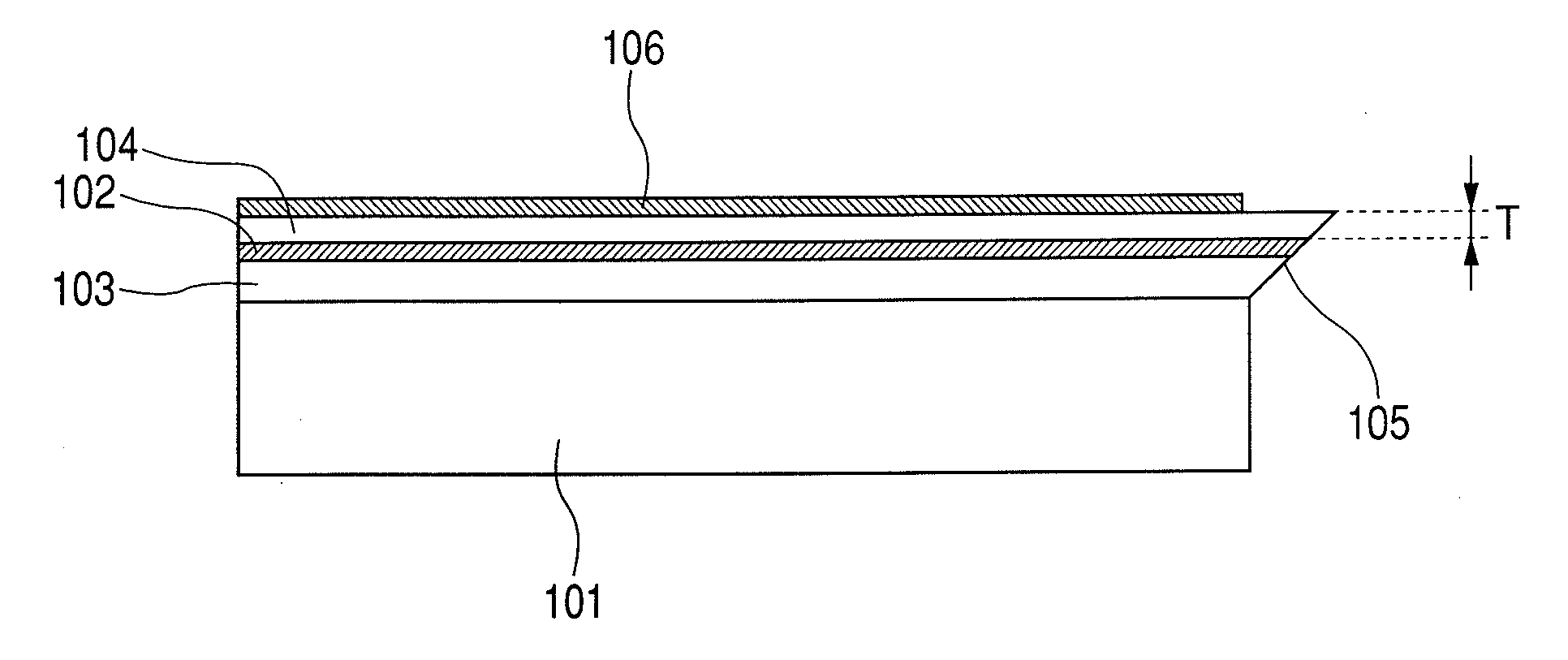
Integrated multiple optical elements may be formed by bonding substrates containing such optical elements together or by providing optical elements on either side of the wafer substrate. The wafer is subsequently diced to obtain the individual units themselves. The optical elements may be formed lithographically, directly, or using a lithographically generated master to emboss the elements. Alignment features facilitate the efficient production of such integrated multiple optical elements, as well as post creation processing thereof on the wafer level.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
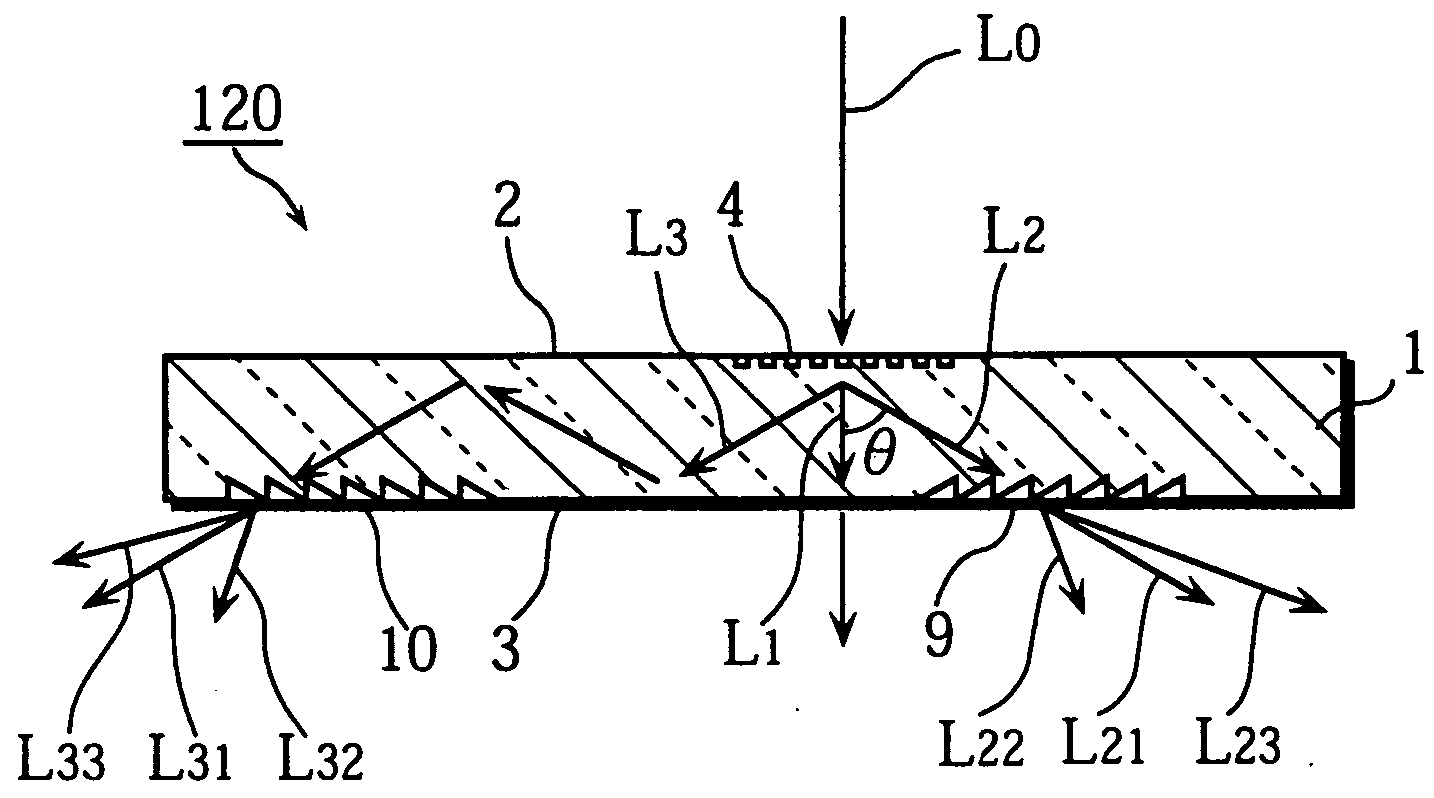
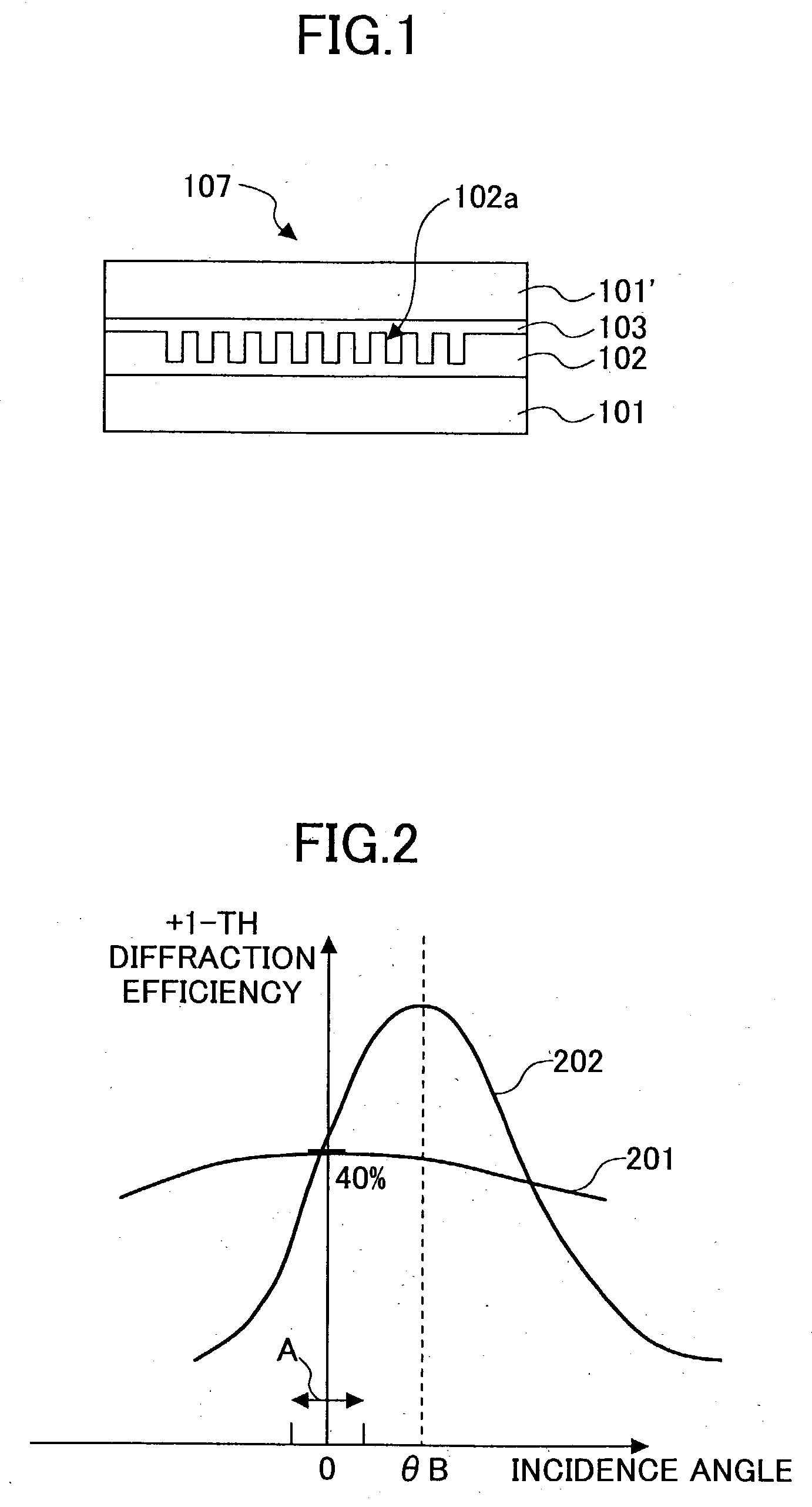
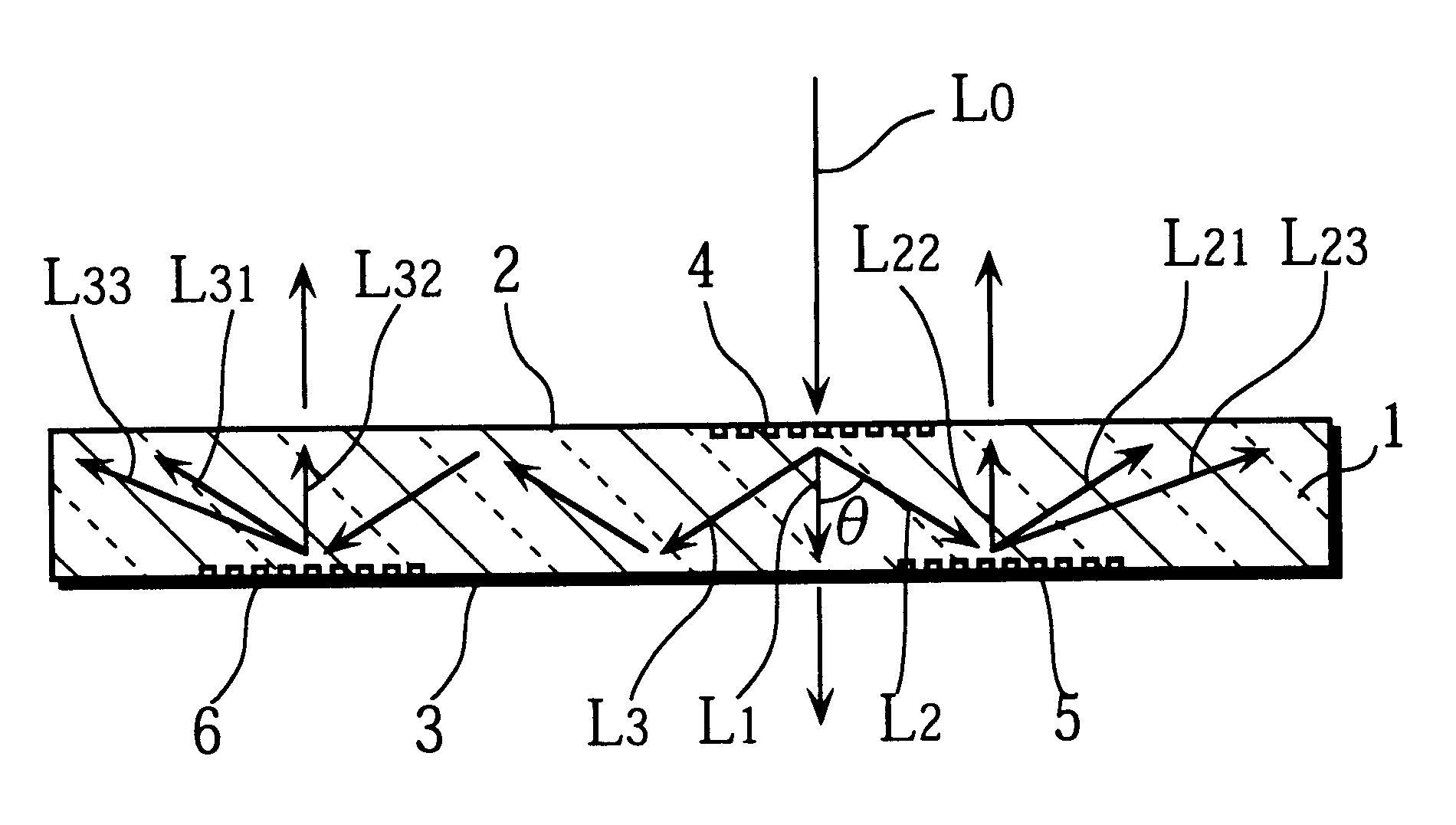
Diffractive optical element that polarizes light and an optical pickup using the same
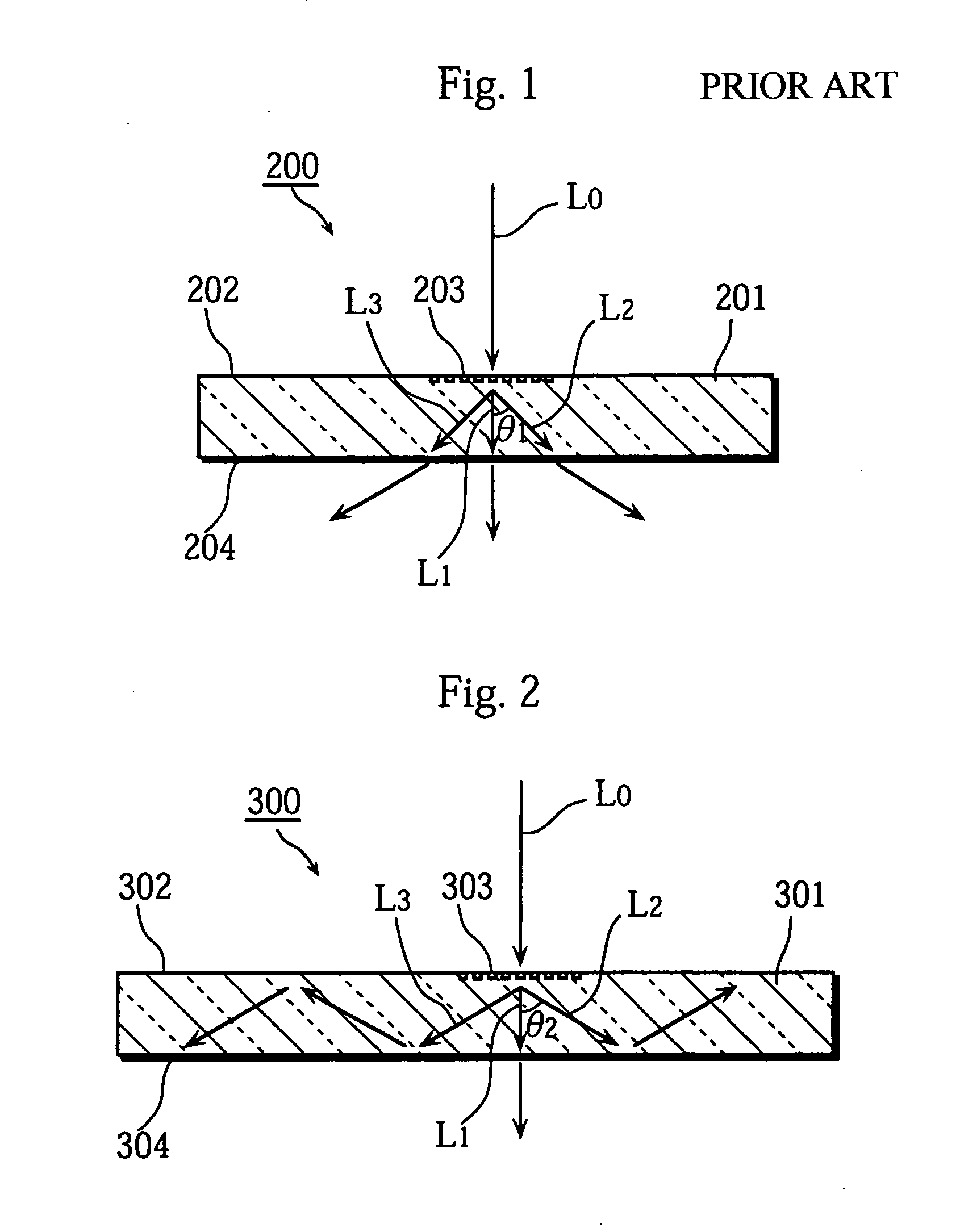
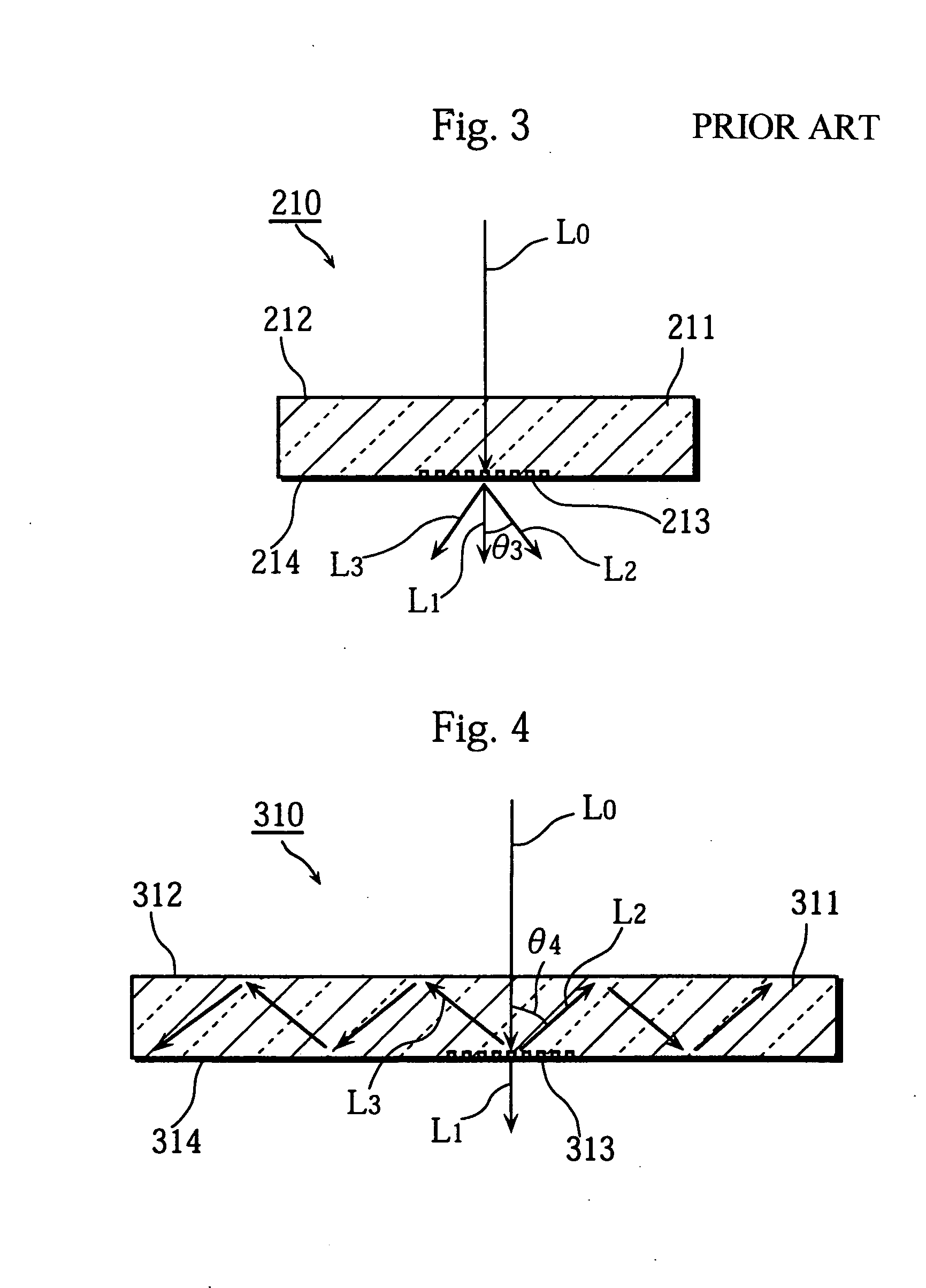
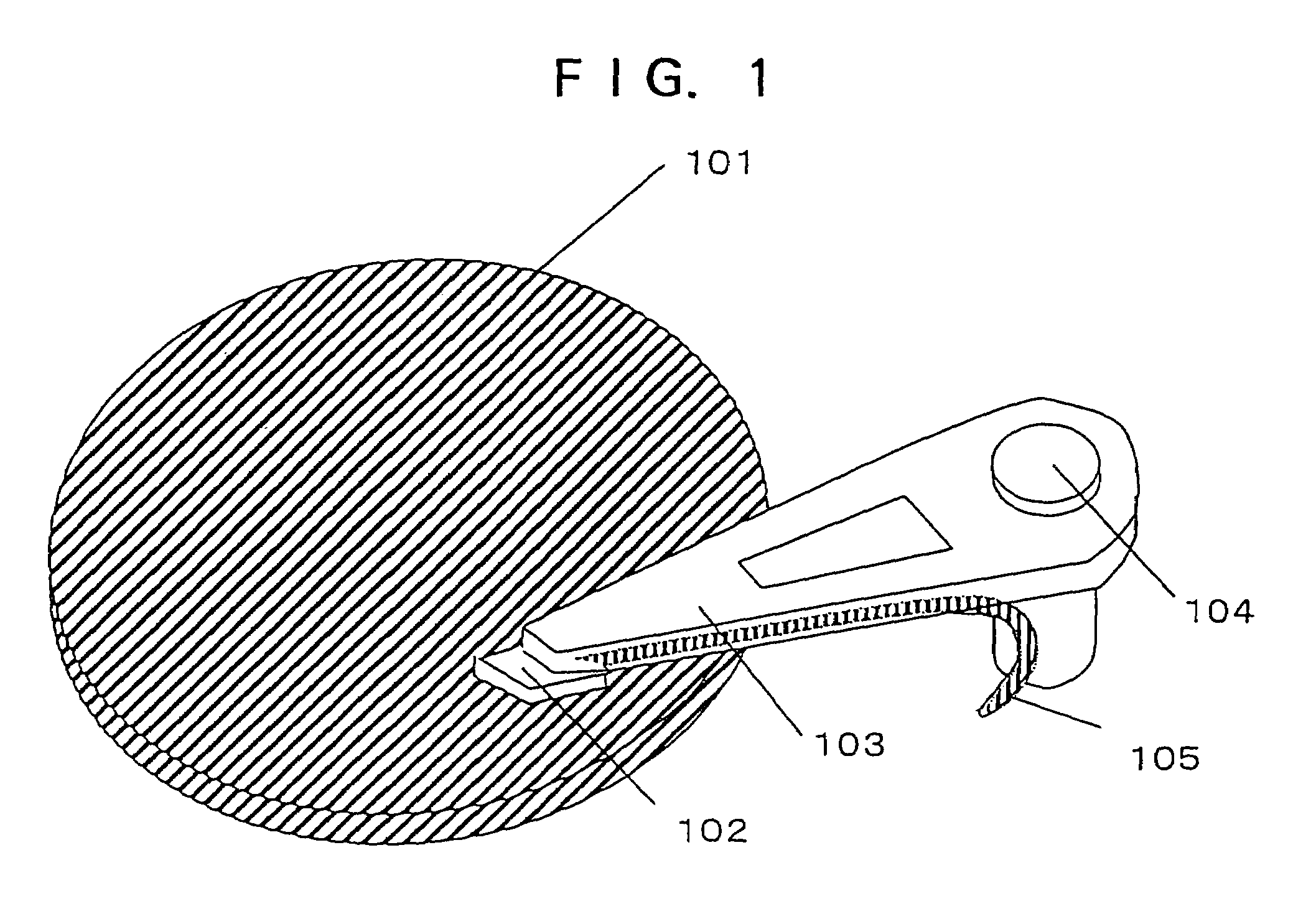
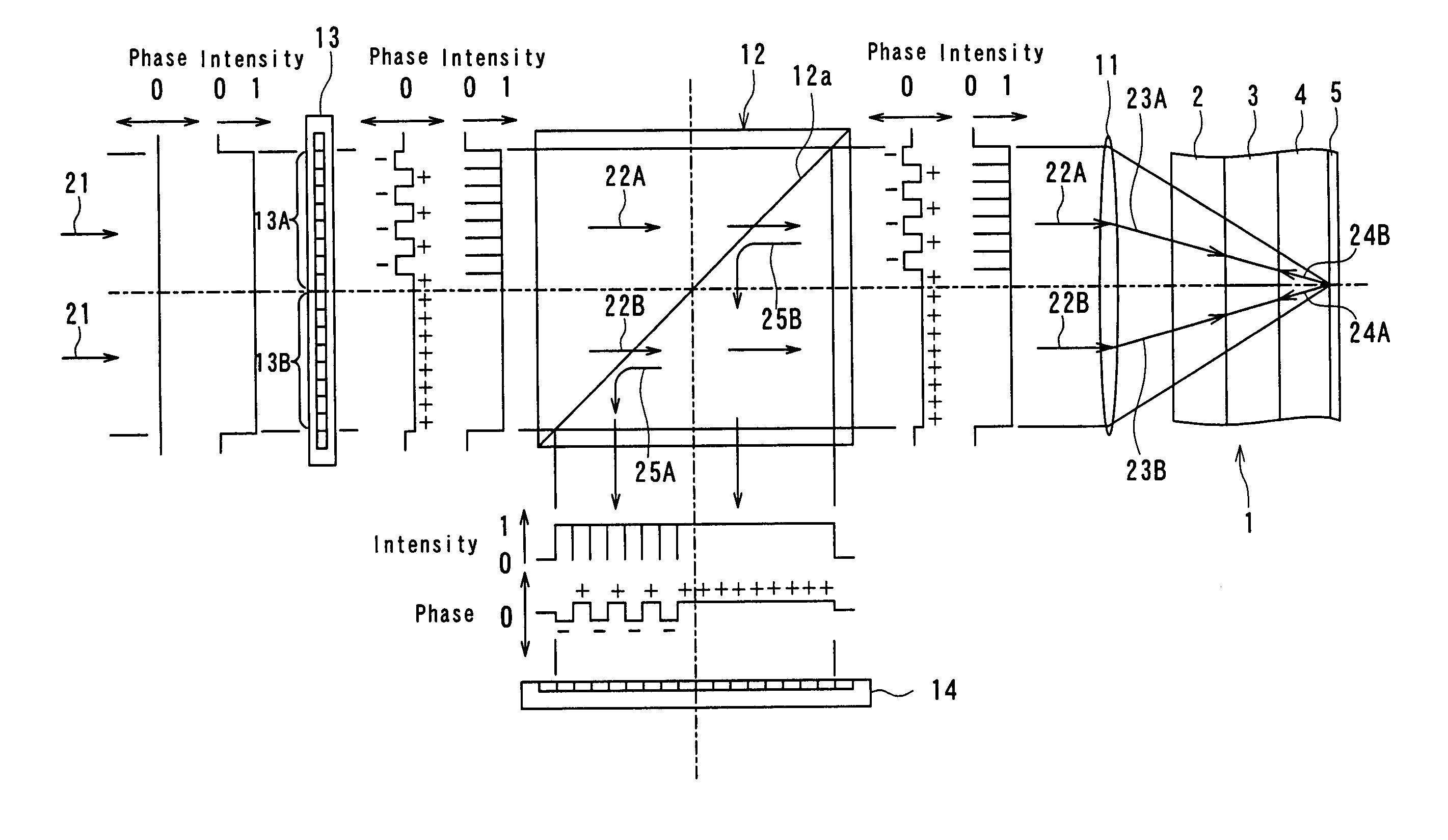
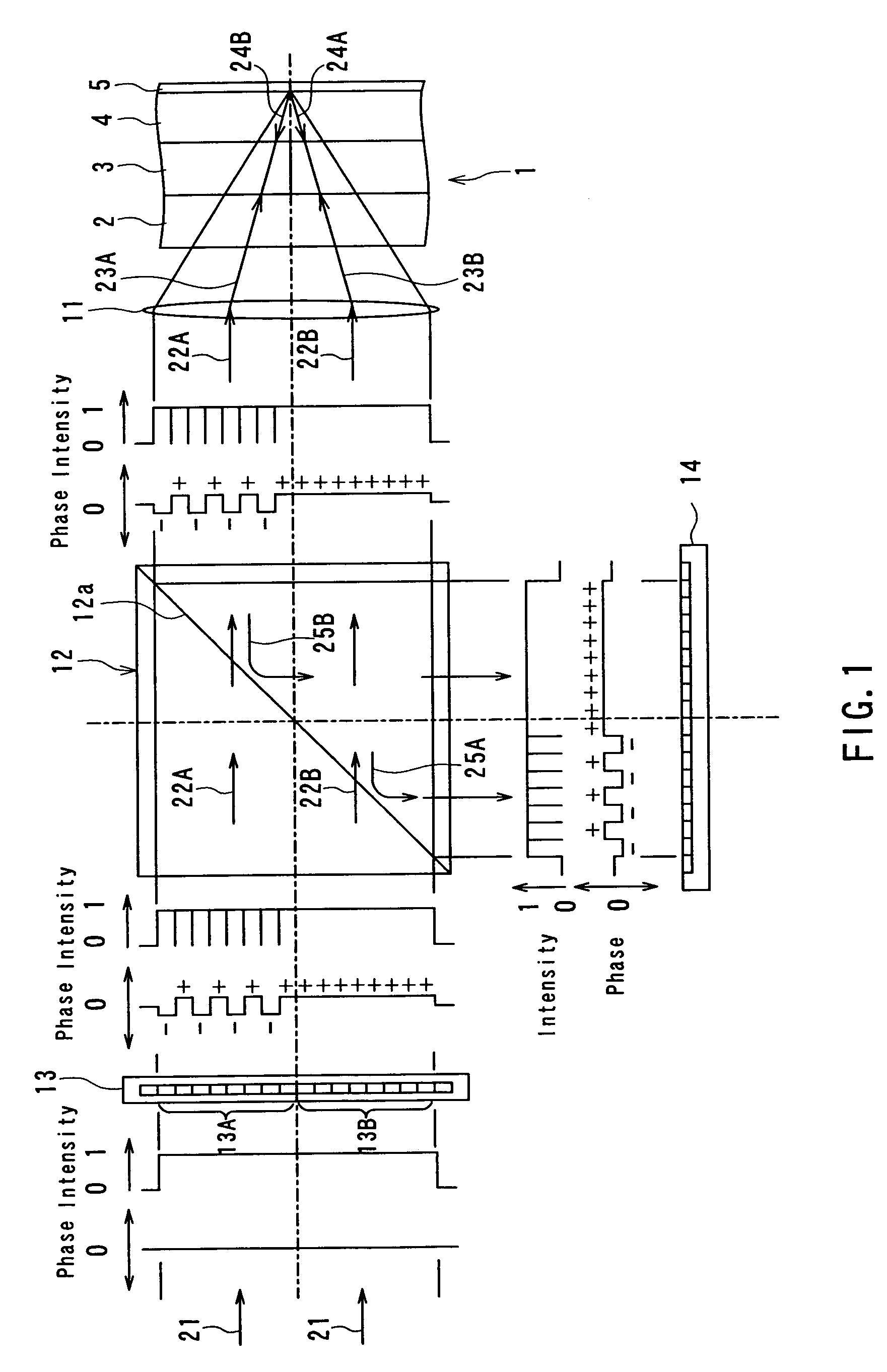
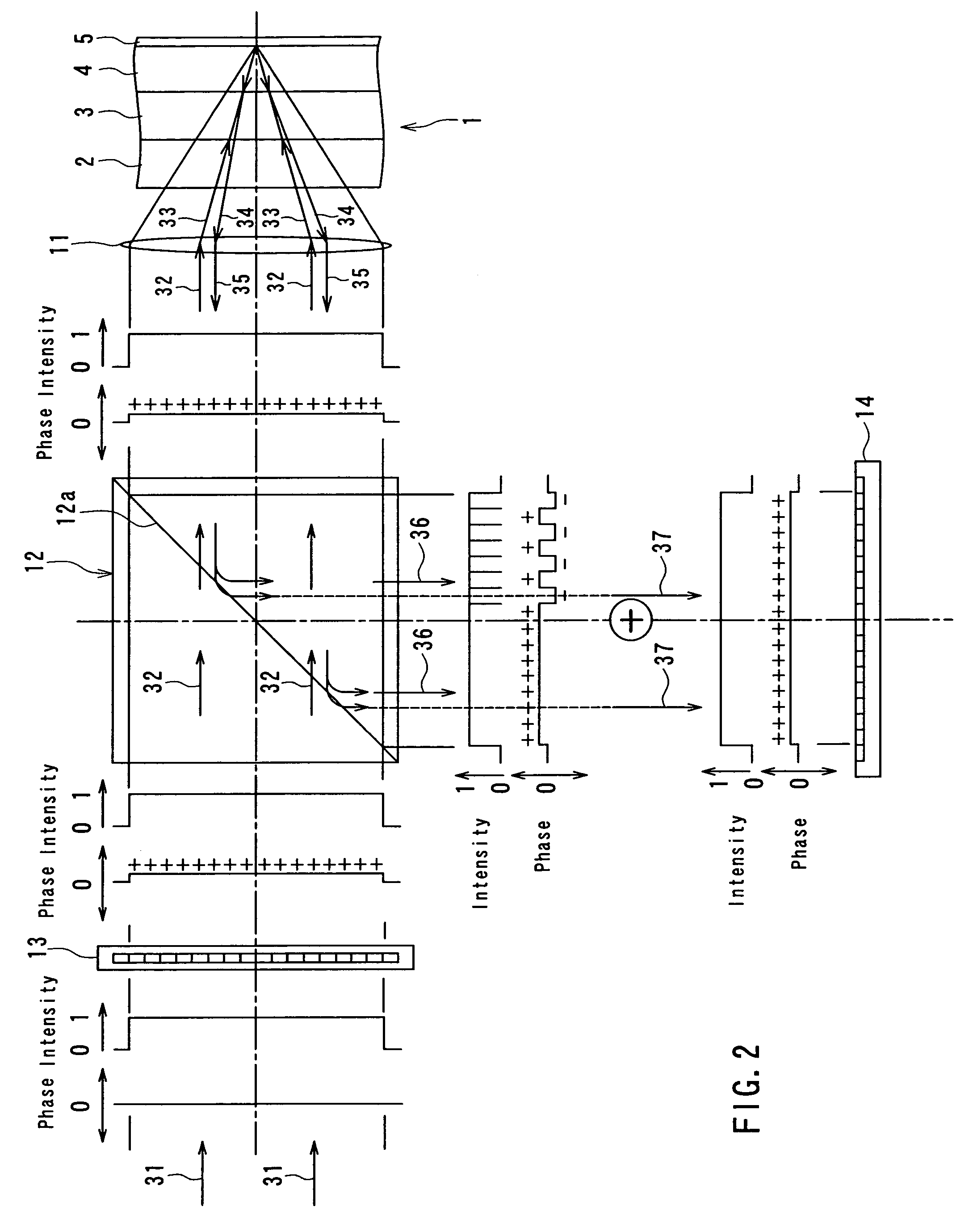
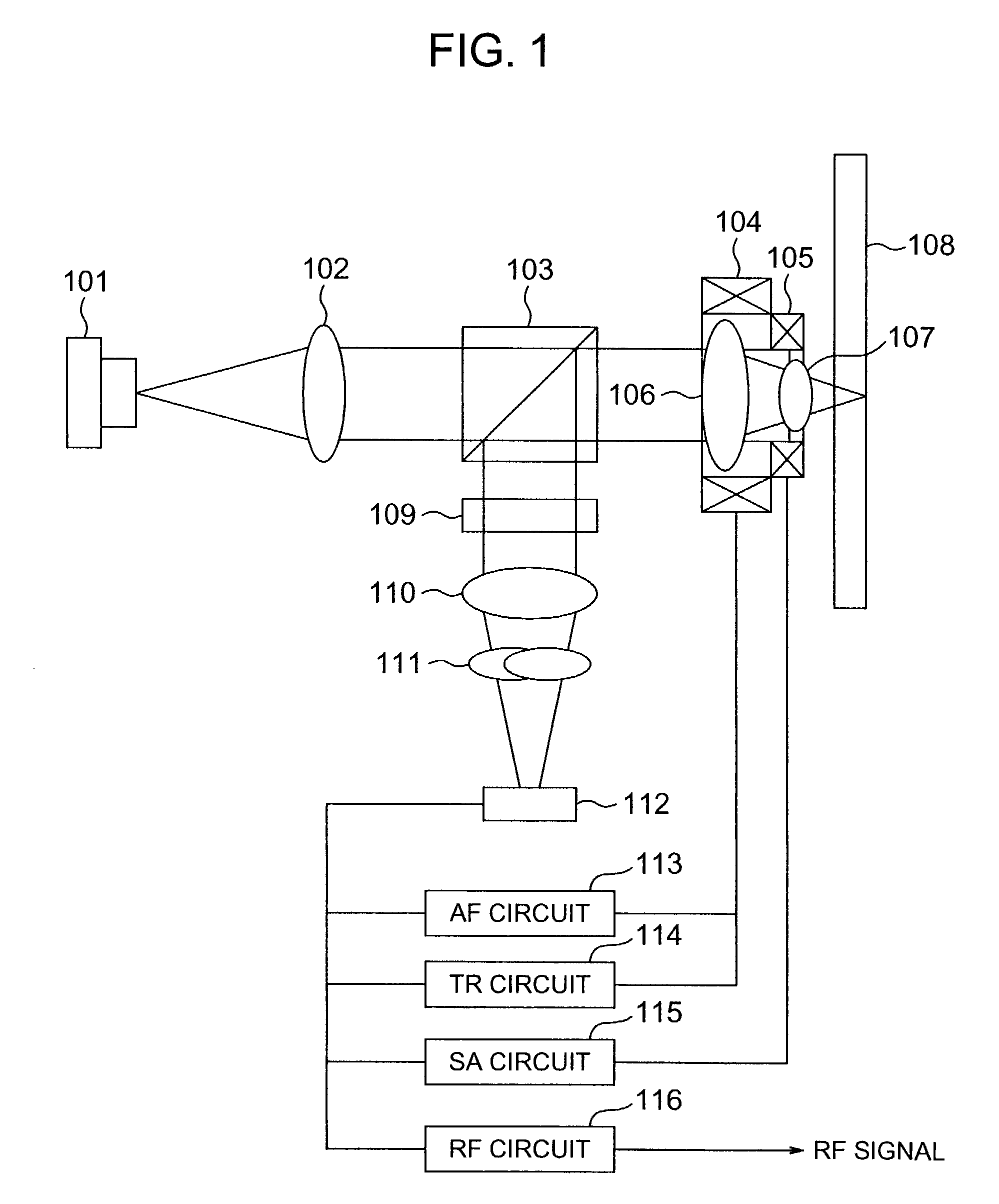
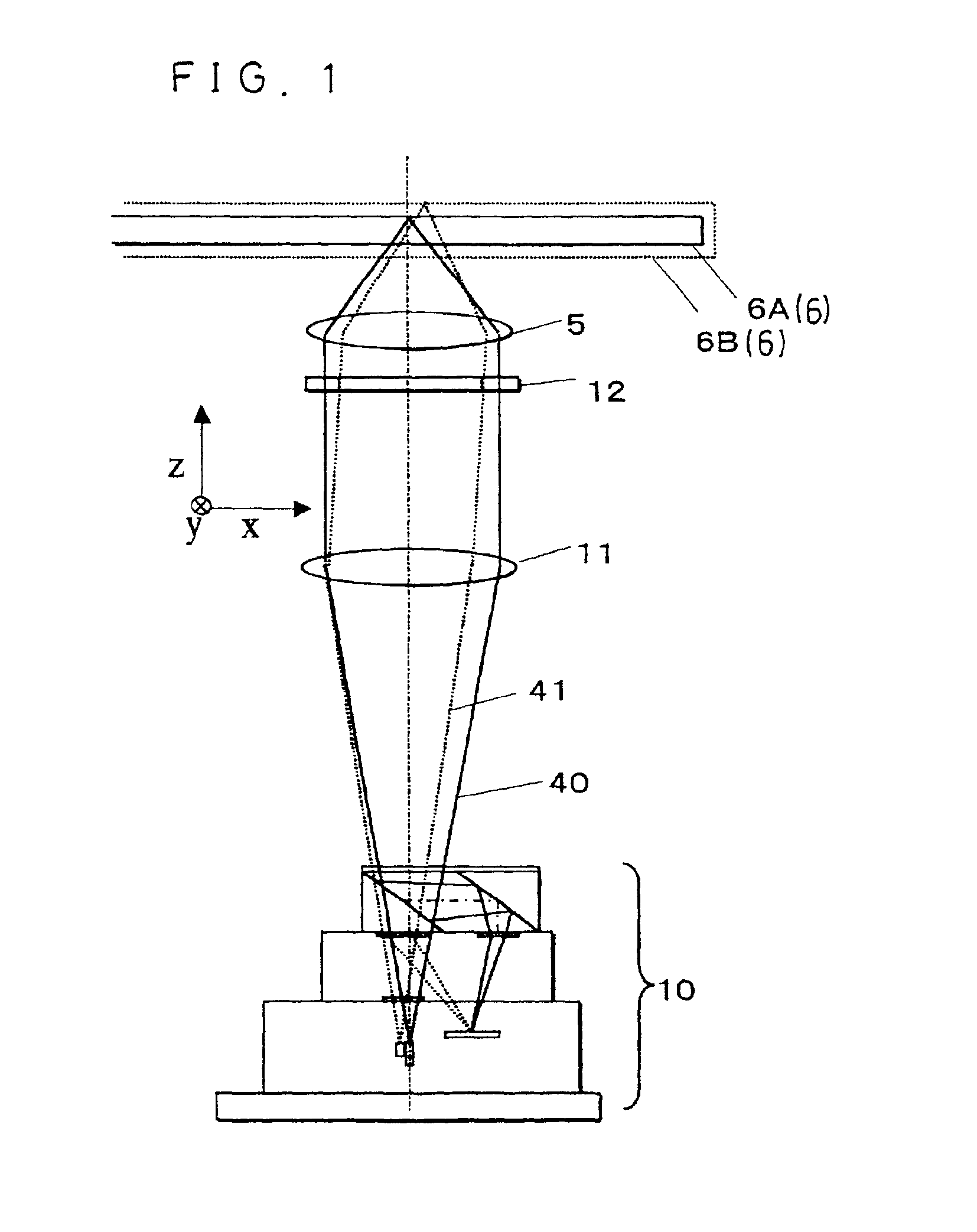
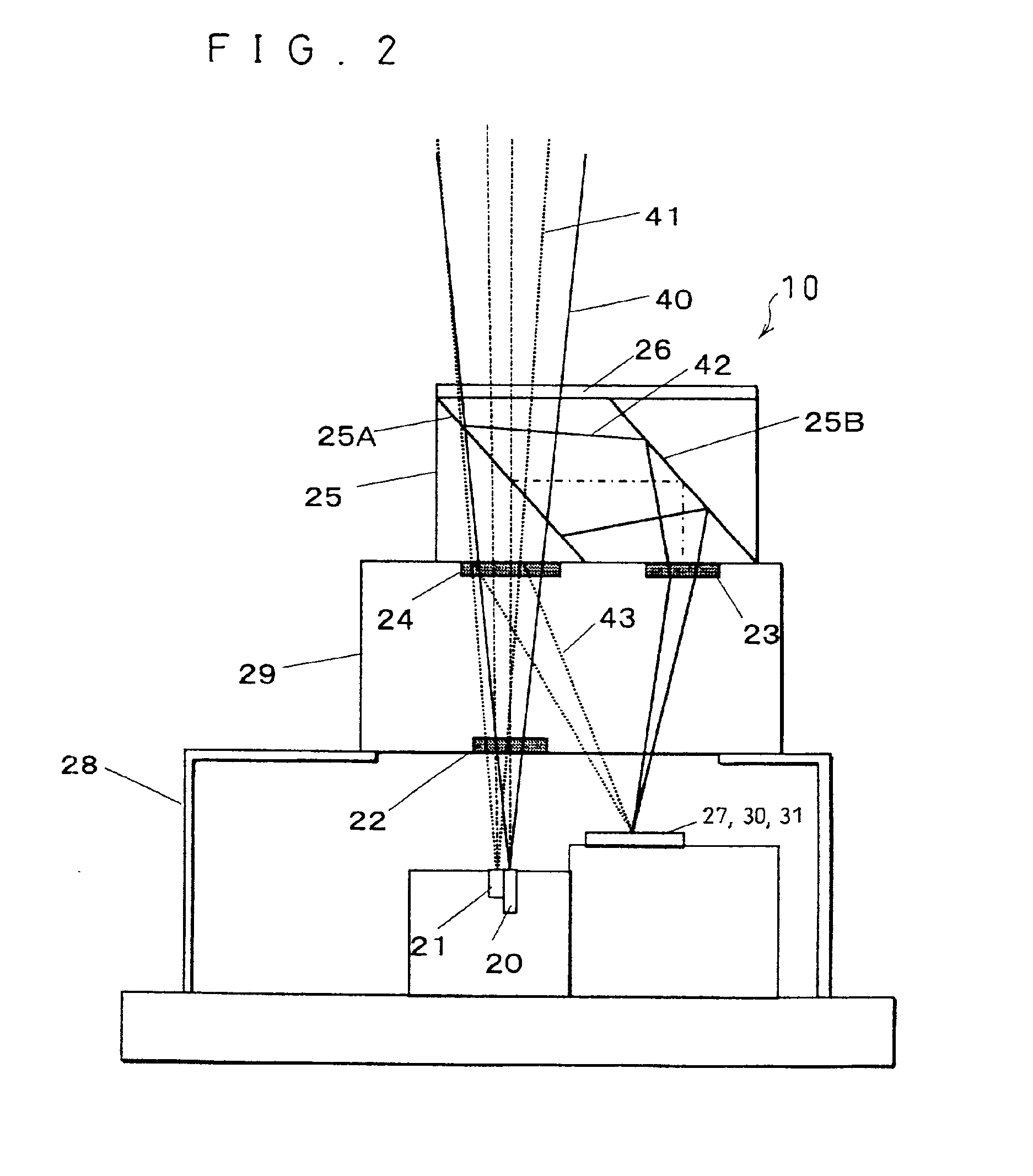
InactiveUS20040233534A1Integrated optical head arrangementsPolarising elementsOptical pickupLength wave
A first diffractive optical element pattern with a pattern pitch that is no greater than a wavelength of incident light is formed on a first main surface of substrate such as a glass plate. Second diffractive optical element patterns are formed at positions that are respectively incident to positive first-order diffracted light and negative first-order diffracted light produced by the first diffractive optical element pattern. Negative first-order diffracted light produced by each second diffractive optical element pattern is incident upon a boundary face of the substrate at an angle that is smaller than the critical angle, and so exits the substrate.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Recording head
InactiveUS20080056073A1Reduce lossesEffective guidanceCombination recordingIntegrated optical head arrangementsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingLight beam
It is an objective that the optical loss and the number of optical components are reduced in an optical recording head using a near-field where a laser beam is guided from a light source to the tip of the head and a thermally assisted magnetic recording head. A structure where the traveling direction of emitted beam is rotated in the direction of the cavity of the laser diode element and a reflector for guiding the beam to the surface of the surface of the laser diode element is monolithically integrated in the laser diode element is mounted over the slider so that the direction of the cavity of the laser diode element is parallel to the surface of the recording medium, and the substrate side of the laser diode element is mounted to be in the direction opposite the face adjacent to the upper face of the slider.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Objective lens, optical pick-up device, and optical disk device
InactiveUS20050007906A1Reduce thicknessSmall sizeOptical head protectionIntegrated optical head arrangementsOptical pickupMiniaturization
To provide an optical pickup device and optical disk device capable of realizing at least one of thickness reduction, size reduction and suppression against characteristic deterioration even where coping with various wavelengths of laser including a blue laser. An optical pickup device comprising light sources for respectively emitting a plurality of different wavelengths of light, unit structured for causing at least a part of the light emitted from the light sources to pass a same optical path; and focusing unit for focusing the light. The focusing unit includes at least first and second focusing parts, the first focusing part being to focus mainly a wavelength of light different from a wavelength of light to be mainly focused by the second focusing part.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Optical pickup device, optical disk apparatus, and light-receiving unit
InactiveUS20060028935A1Improve configurationSpherical aberration in the short wavelength light can be reducedIntegrated optical head arrangementsRecord information storageOptical pickupLength wave
An optical pickup device, comprises a first light source emitting light with a short wavelength; a second light source emitting s light with a wavelength longer than that of the first light source; an optical member guiding the light from the first light source and the light from the second light source on almost the same optical path; a focusing member focusing the light from the optical member; a movable lens provided between the optical member and the focusing lens; and a drive member driving the movable lens, wherein a position of the lens when at least one of recording and reproducing of information is carried out on a medium using the light from the first light source is made different from a position of the lens when at least one of the recording and reproducing of information is carried out on the medium using the light from the second light source.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
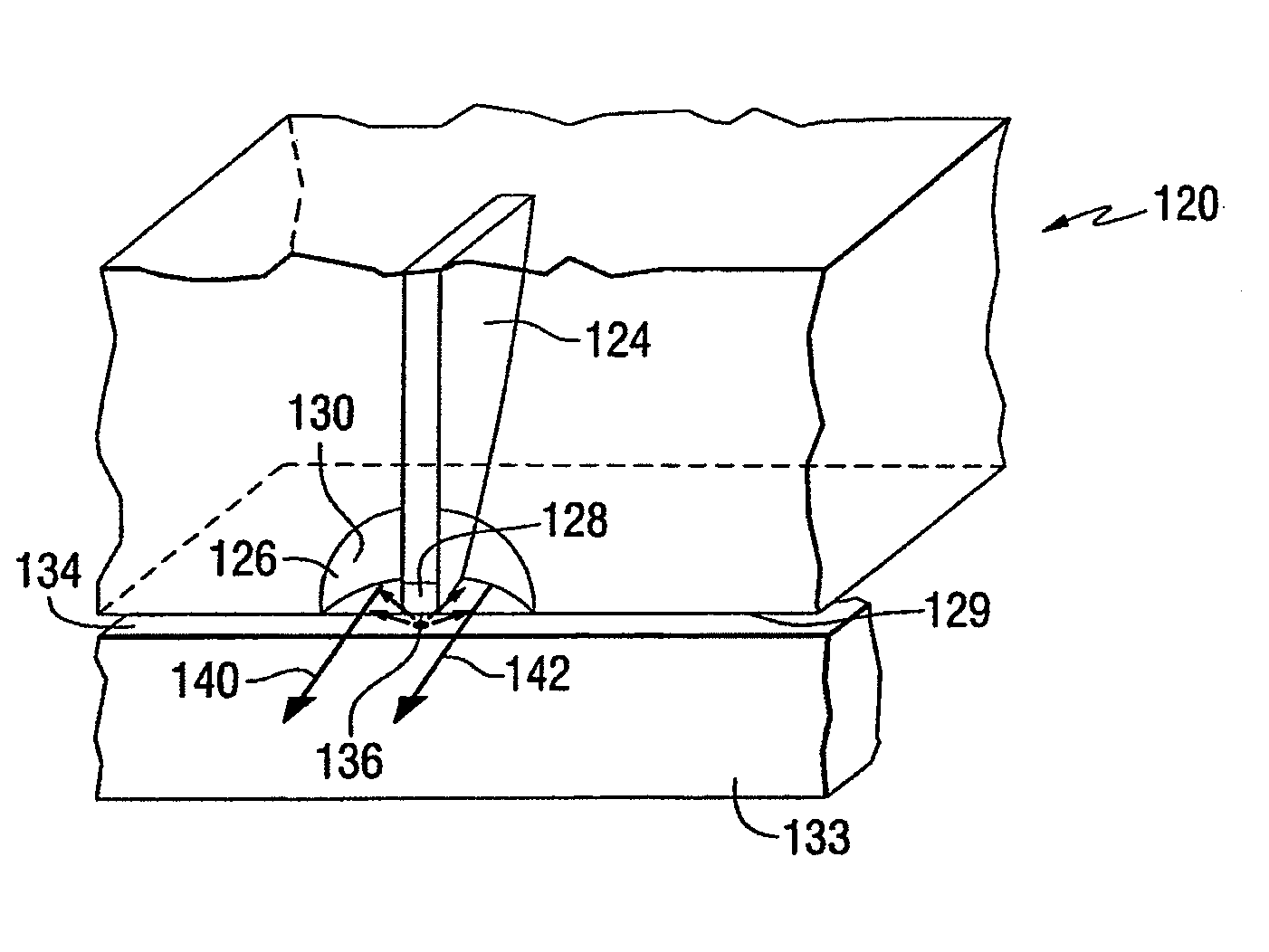
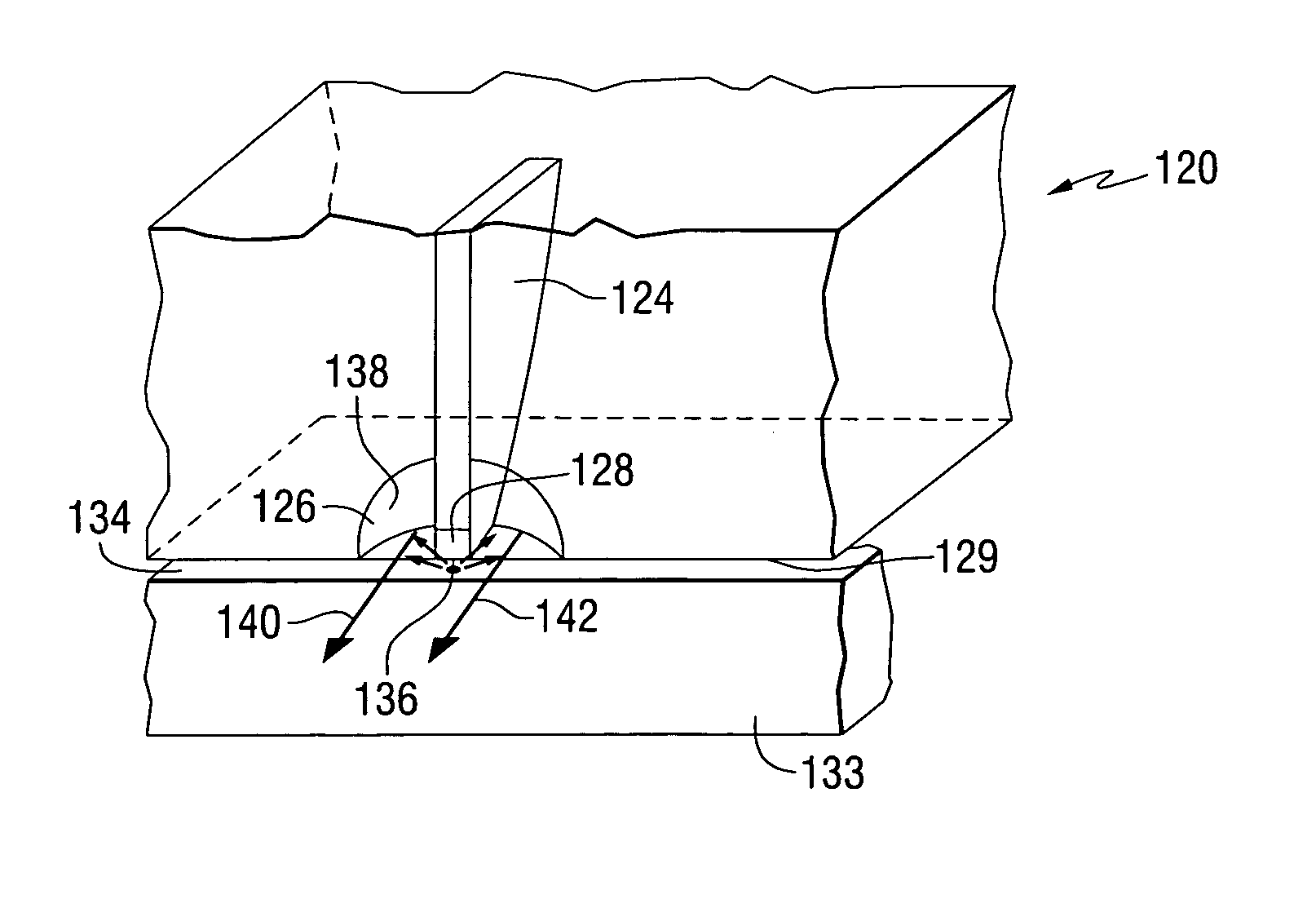
Near-field optical head having tapered hole for guiding light beam
InactiveUS7599277B1High strengthHigh mechanical strengthOptical flying-type headsIntegrated optical head arrangementsPlanar substrateLight reflection
A near-field optical head has a planar substrate having a first surface, a second surface disposed opposite to the first surface, and an inverted conical or pyramidal hole extending through the first and second surfaces. The conical or pyramidal hole has at least one fine aperture formed at an apex thereof and is disposed on the first surface of the planar substrate. An optical waveguide is disposed on the second surface of the planar substrate for propagating light. A light reflection film is disposed in the optical waveguide for reflecting in the direction of the fine aperture light propagated through the optical waveguide.
Owner:SEIKO INSTR INC
Optical device, method of producing the same, optical pickup, and optical information processing device
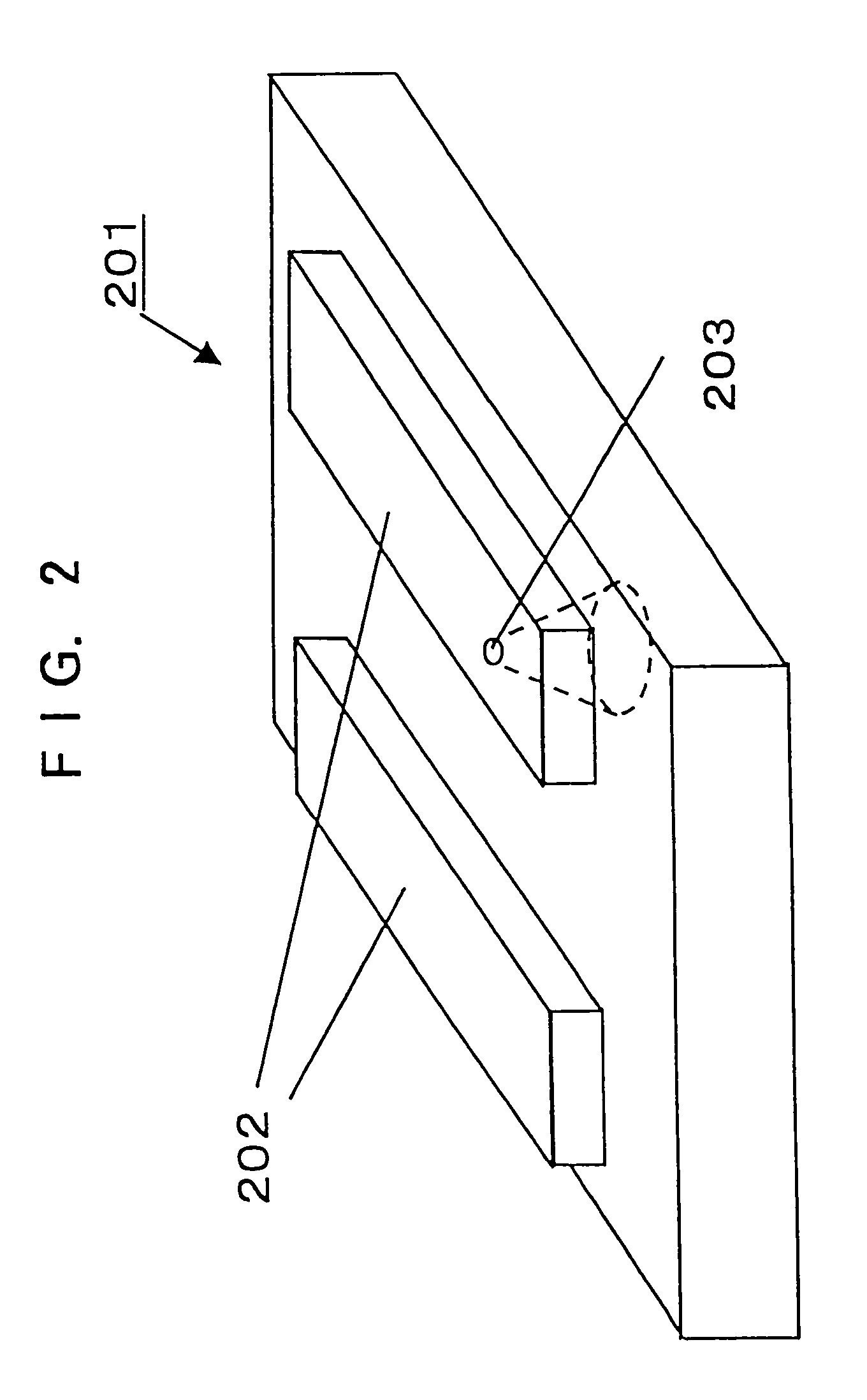
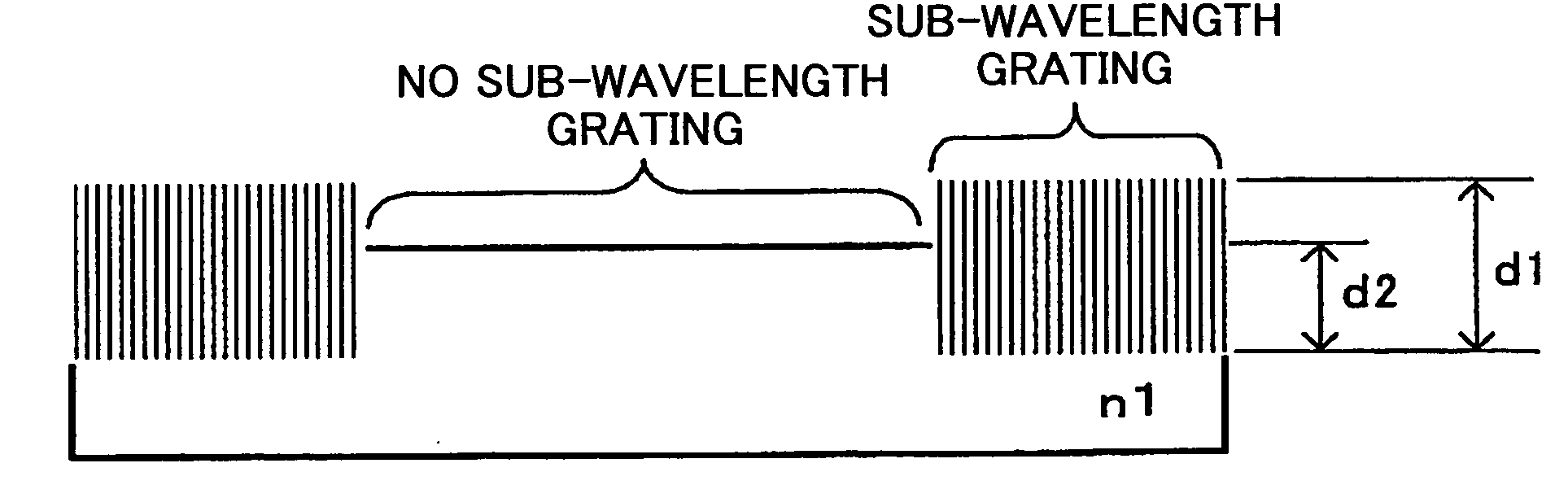
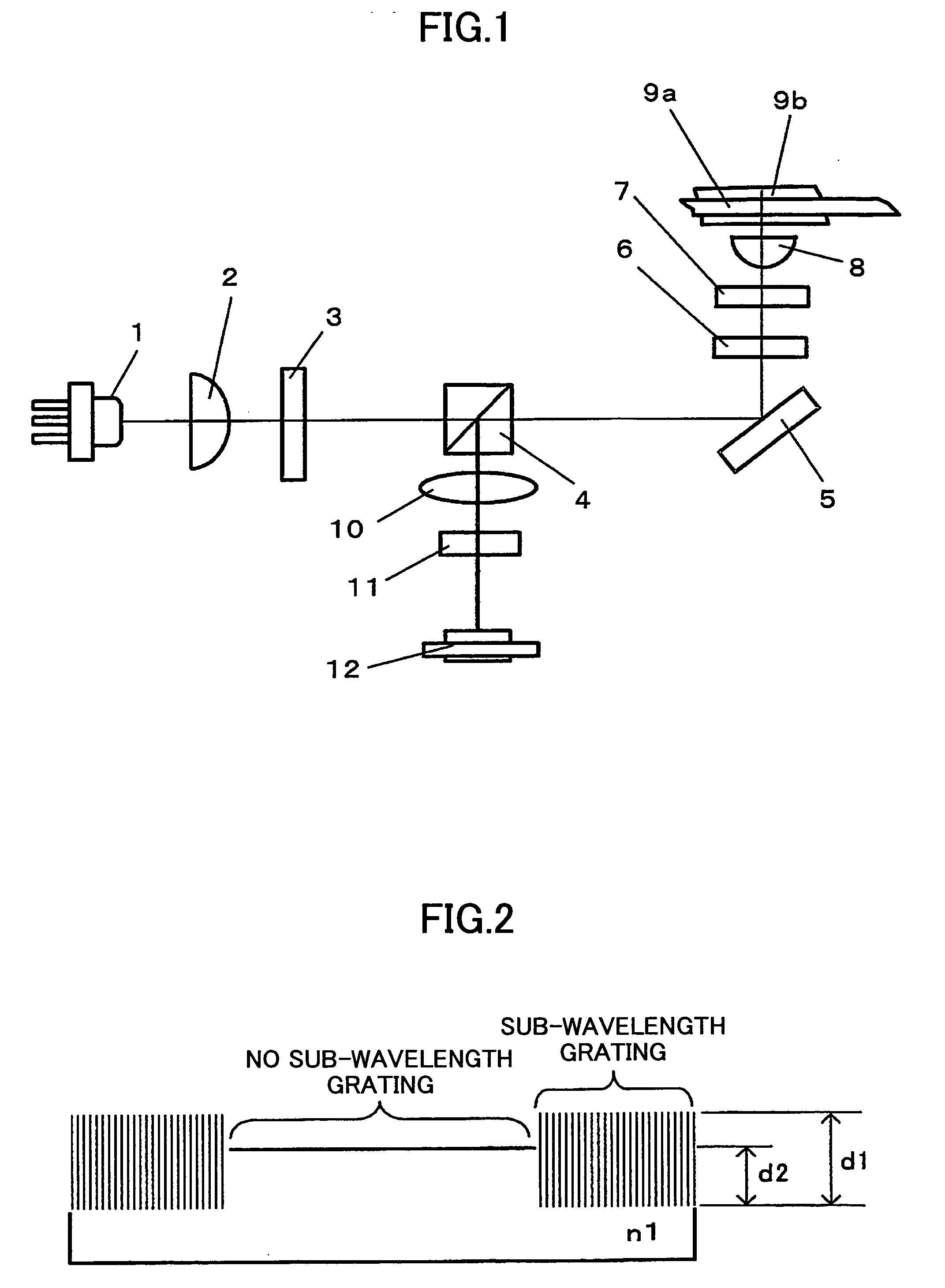
InactiveUS20050195485A1Improve compatibilitySmall sizeIntegrated optical head arrangementsOptical articlesInformation processingOptical pickup
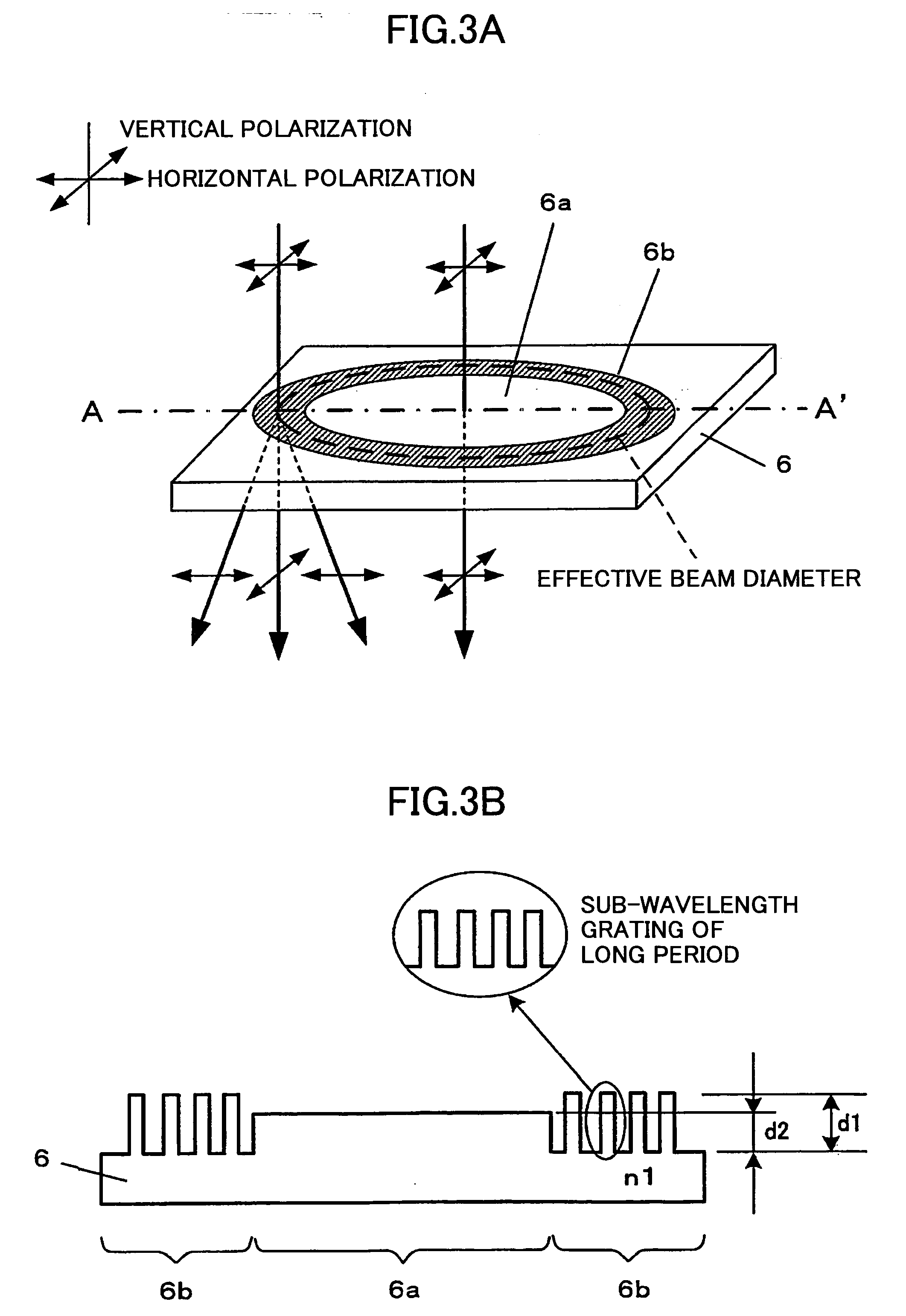
An optical device having a sub-wavelength grating formed in a specified region is disclosed that is able to prevent wave front degradation accompanying a phase difference of a polarized light beam passing through the optical device. The optical device includes a circular-belt-like region where the sub-wavelength diffraction grating is formed, and a center portion where the sub-wavelength diffraction grating is not formed. A vertically polarized light beam used for operations on a blue-light optical recording medium A has a phase difference in the sub-wavelength diffraction grating to be an integral multiple of 2π and hence is transmitted through the sub-wavelength diffraction grating. A horizontally polarized light beam used for operations on a blue-light optical recording medium is diffracted by the sub-wavelength diffraction grating. The light path length L1 of the light beam passing through the circular-belt-like region is the same as that of the light beam passing through the center portion without the sub-wavelength grating.
Owner:RICOH KK
Integrated camera and associated methods
InactiveUS20080136955A1Reduce thicknessTelevision system detailsIntegrated optical head arrangementsEngineeringIntegrated optics
Owner:FLIR SYSTEMS TRADING BELGIUM BVBA
Apparatus and method for recording/reproducing optical information
InactiveUS7065032B2Small configurationImprove signal-to-noise ratioIntegrated optical head arrangementsOptical beam sourcesSpatial light modulatorPhotovoltaic detectors
Apparatus and method for recording and reproducing optical information using holography is designed to provide a small configuration and to improve the S / N ratio of reproduced information. During recording, a phase spatial light modulator generates information light spatially modulated in phase based on information to be recorded, and recording-specific reference light, that irradiate an information recording layer of an optical recording medium to record the information in the form of an interference pattern, resulting from interference between the information light and the recording-specific reference light. During reproduction, reproduction-specific reference light irradiates the information recording layer to generate reproduction light which is superimposed on the reproduction-specific reference light to generate composite light. The composite light is detected by a photodetector to reproduce the information.
Owner:OPTWARE
Optical tape media, marking, systems, and apparatus and process for producing thereof
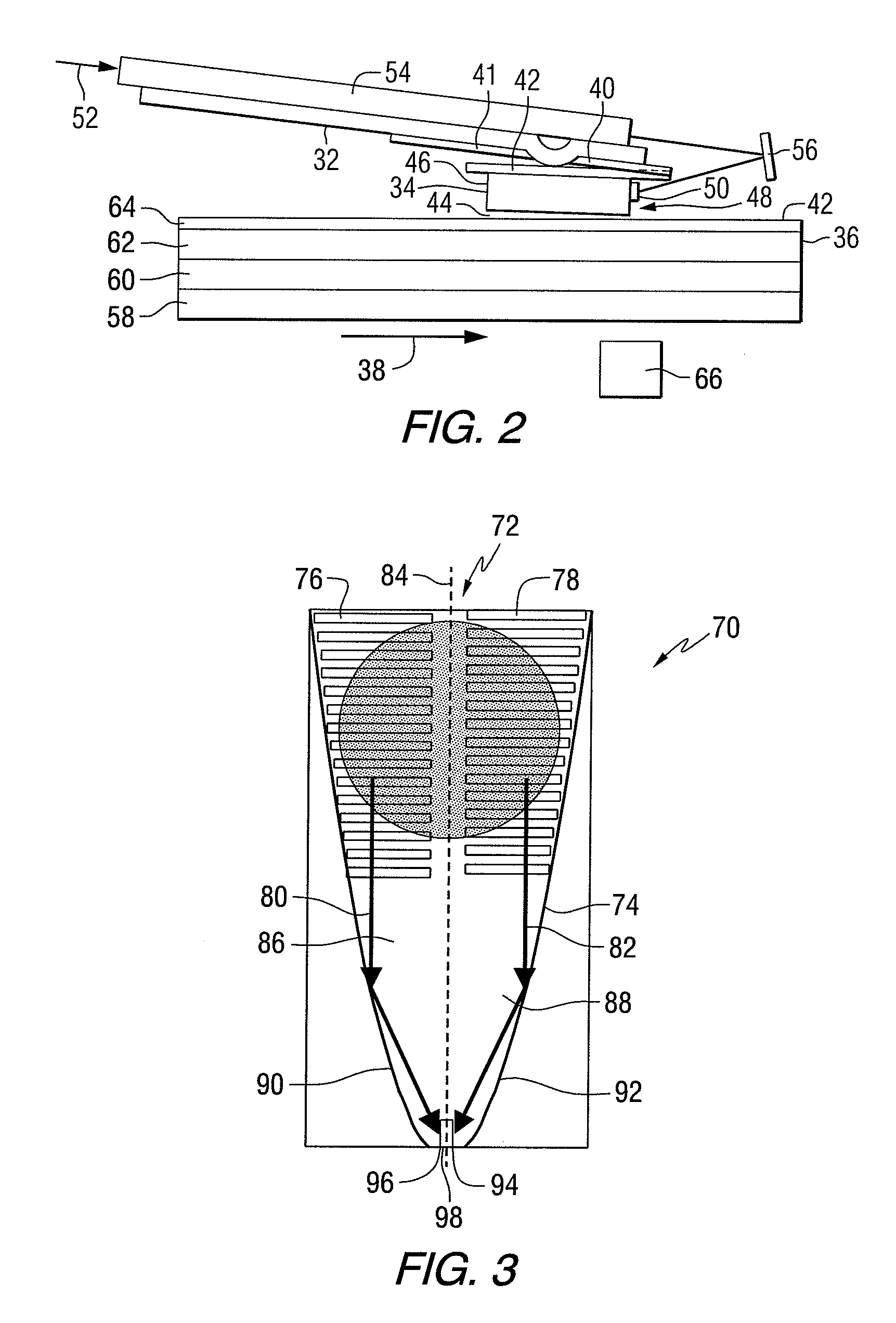
ActiveUS20070206477A1Facilitate spoolingRecording verificationIntegrated optical head arrangementsMagnetic tapeEngineering
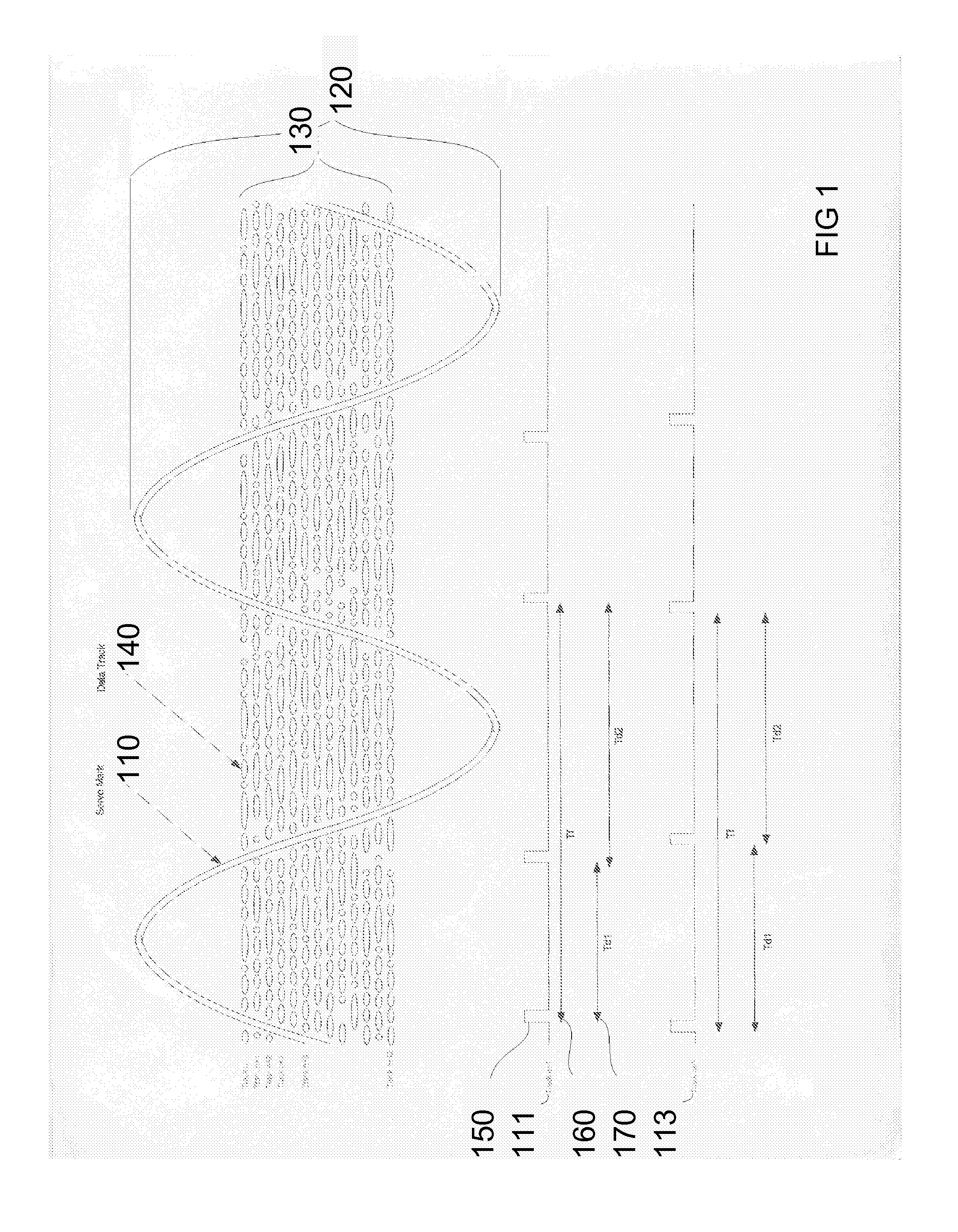
Disclosed herein are aspects of optical tape technology, tape manufacturing, and tape usage. Methods and systems of tape technology disclose optical tape media including: configurations, formulations, markings, and structure; optical tape manufacturing methods, systems, and apparatus methods and systems including: curing processes, coating methods, embossing, drums, testing, tracking alignment stamper strip; optical tape methods and systems including: pick up head adapted for the disclosed optical tape; and optical tape uses including optical storage media devices for multimedia applications
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Variable mirror and information apparatus comprising variable mirror
A deformable mirror according to the invention comprises a substrate, a reflector which is supported by said substrate and the shape of whose reflecting areas is variable, and a plurality of drive units for independently driving a plurality of regions of the reflector and thereby controlling the distances between said plurality of regions and said substrate. Each of the plurality of drive units comprises a plurality of electrodes disposed over said substrate, a tilt member which is rotated round the axis of tilt by being attracted by the selected one of the plurality of electrodes, and an action member for varying the distance between a specific region of the reflector and said substrate following the motion of the tilt member.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Optical Near-Field Generator and Near-Field Optical Recording and Reproduction Apparatus
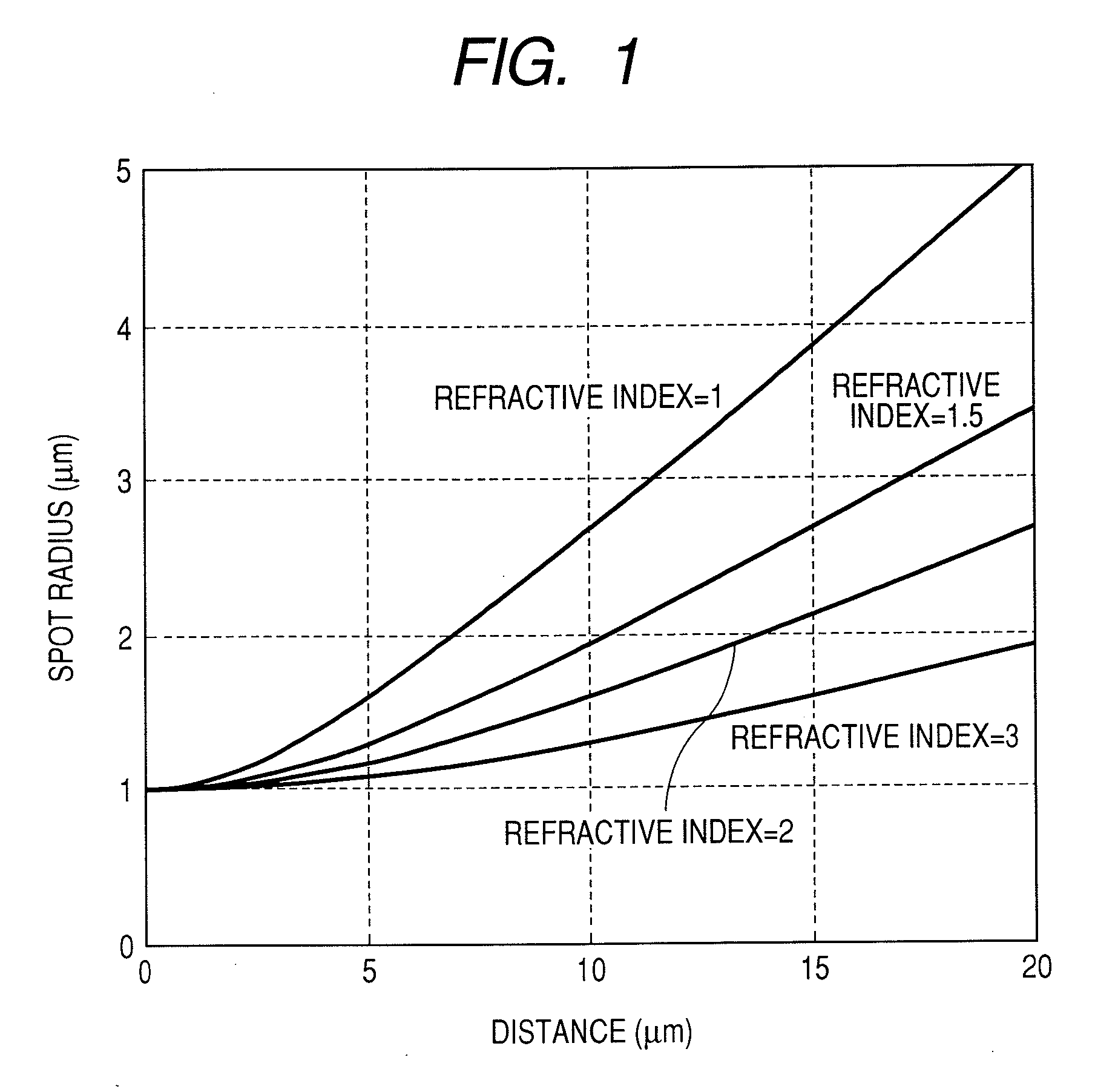
InactiveUS20070242921A1Decrease in optical near-field intensity can be preventedImprove efficiencyIntegrated optical head arrangementsNanoinformaticsRefractive indexOptical recording
Decrease in optical near-field intensity is prevented when an light propagating medium made of a high refractive index material, such as a waveguide or a lens, is combined with a scatterer for producing optical near-field. Near the optical near-field generating element, a second light propagating medium is disposed in contact with a first light propagating medium of a high refractive index material, such as a waveguide or a lens. The refractive index of the second light propagating medium is made smaller than the refractive index of the first light propagating medium.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
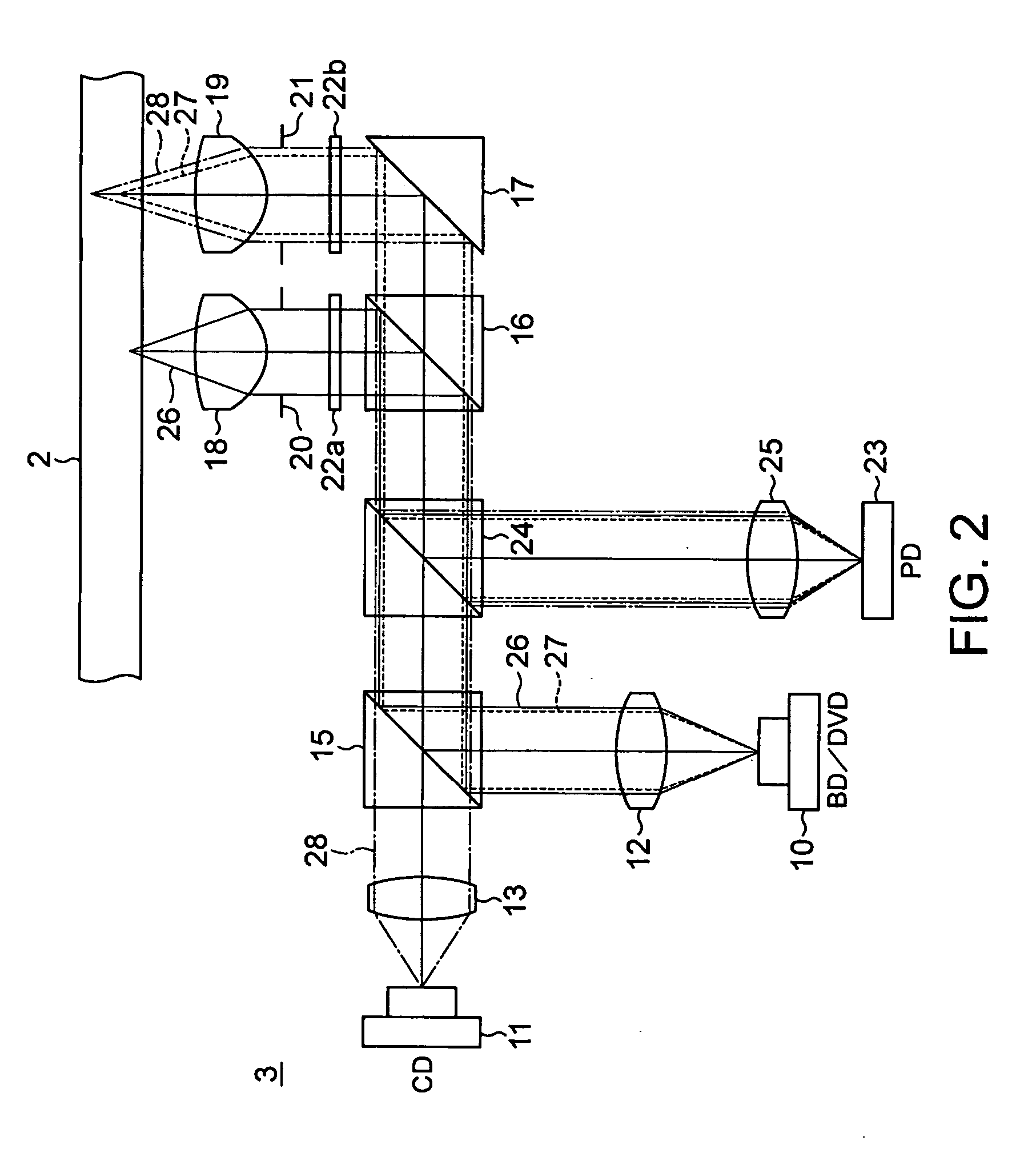
Optical pick-up, optical disk apparatus and information processing apparatus
InactiveUS6928035B2Reduce areaReduce in quantityIntegrated optical head arrangementsOptical beam sourcesInformation processingPhotovoltaic detectors
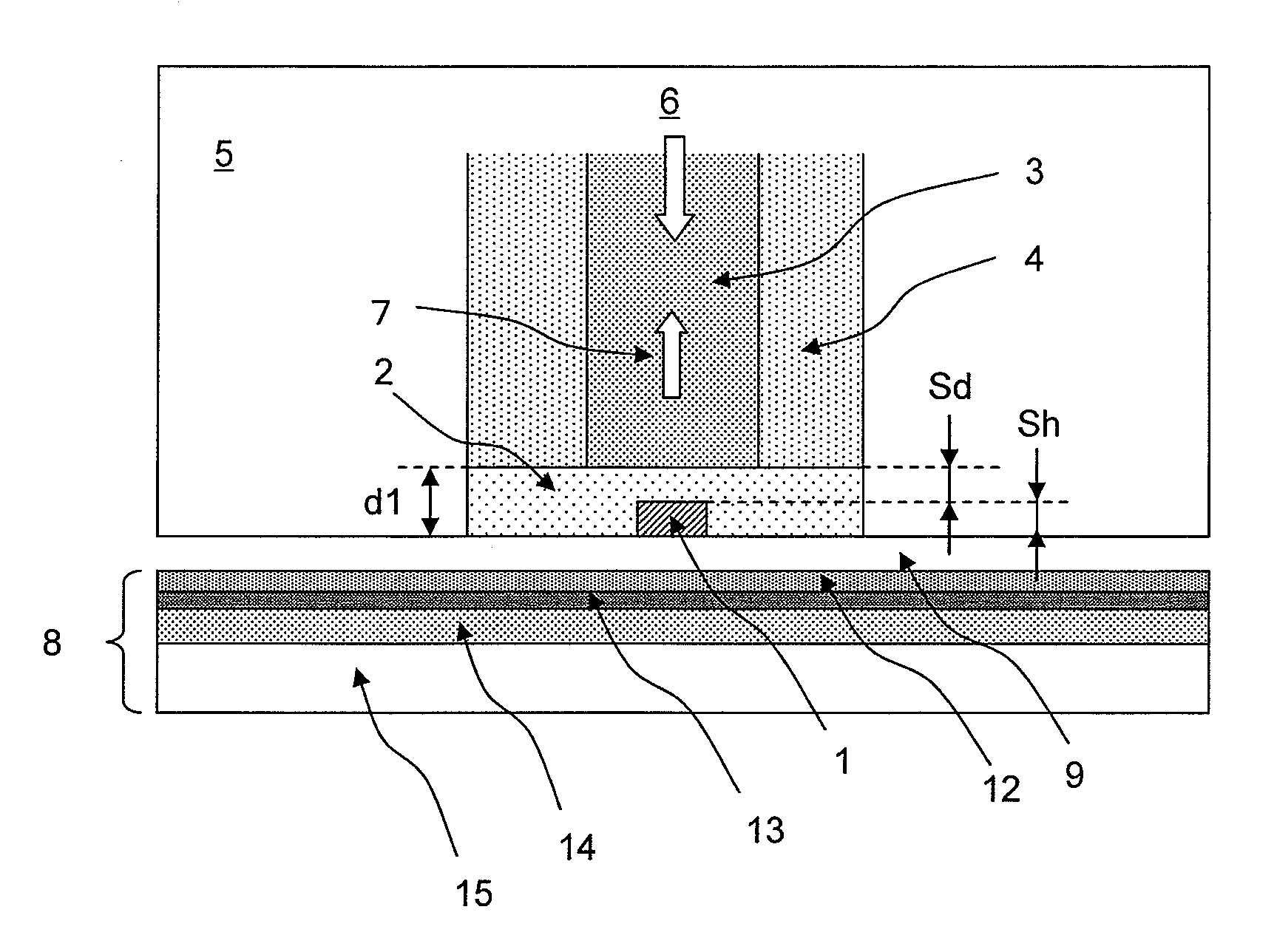
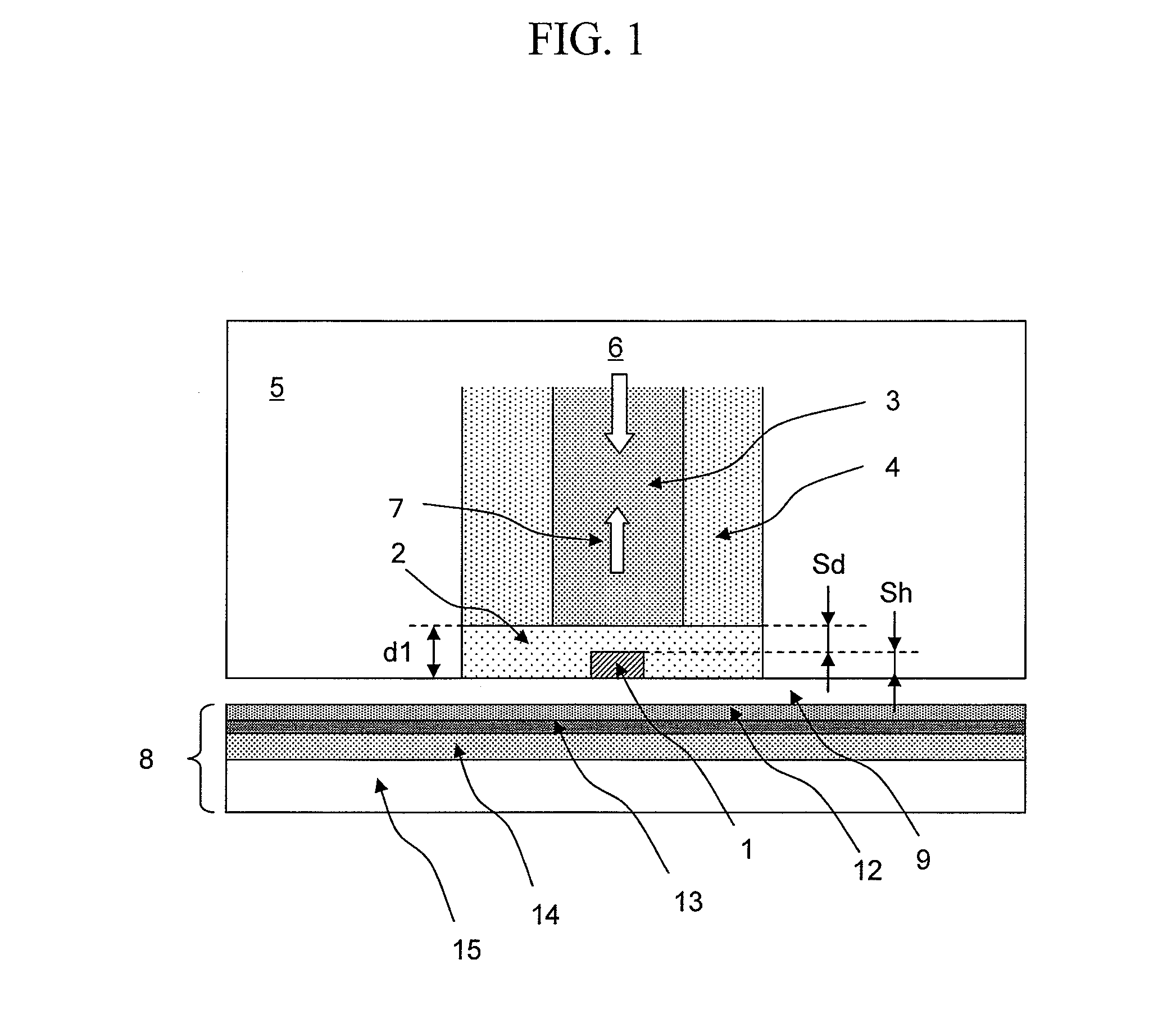
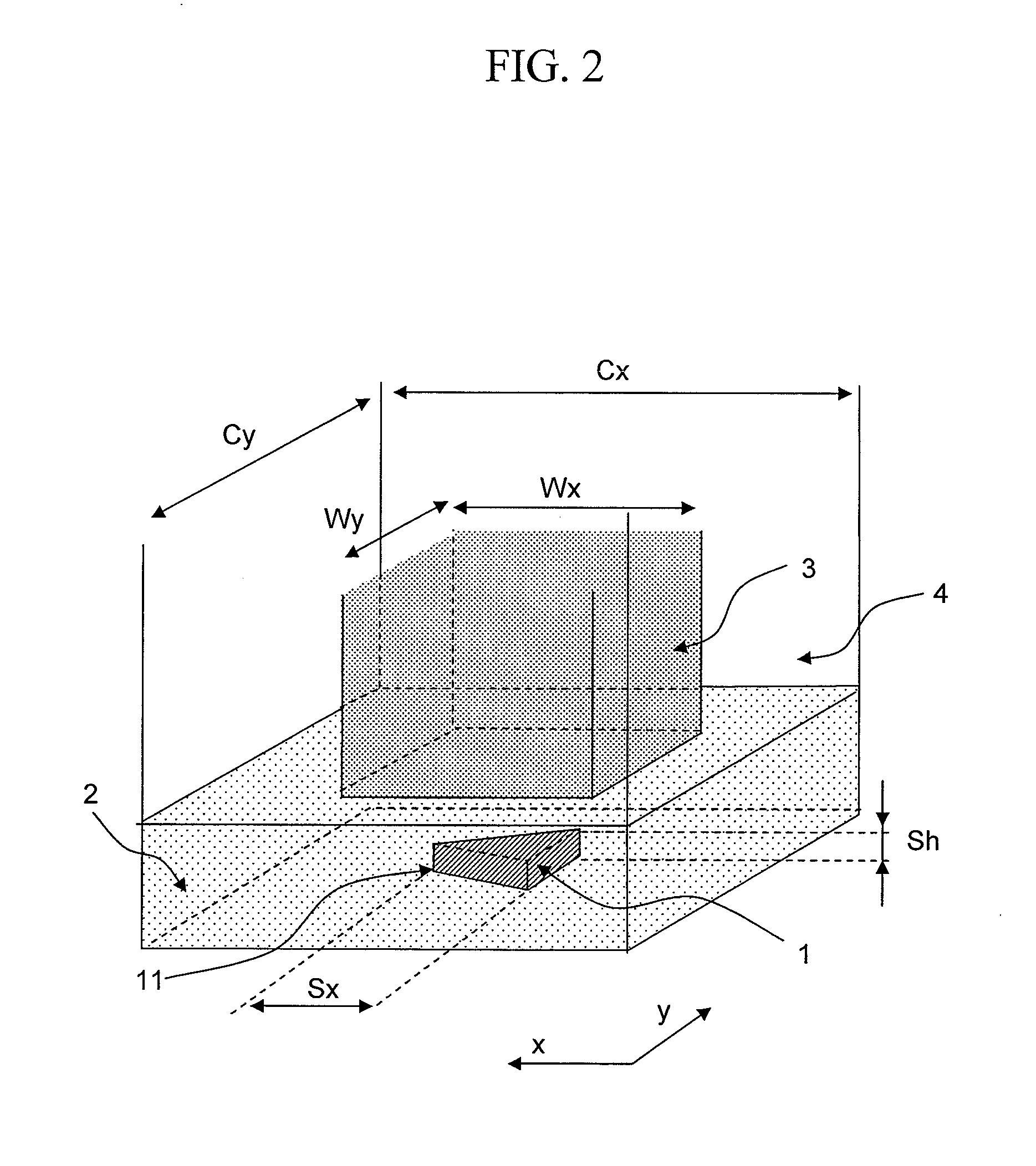
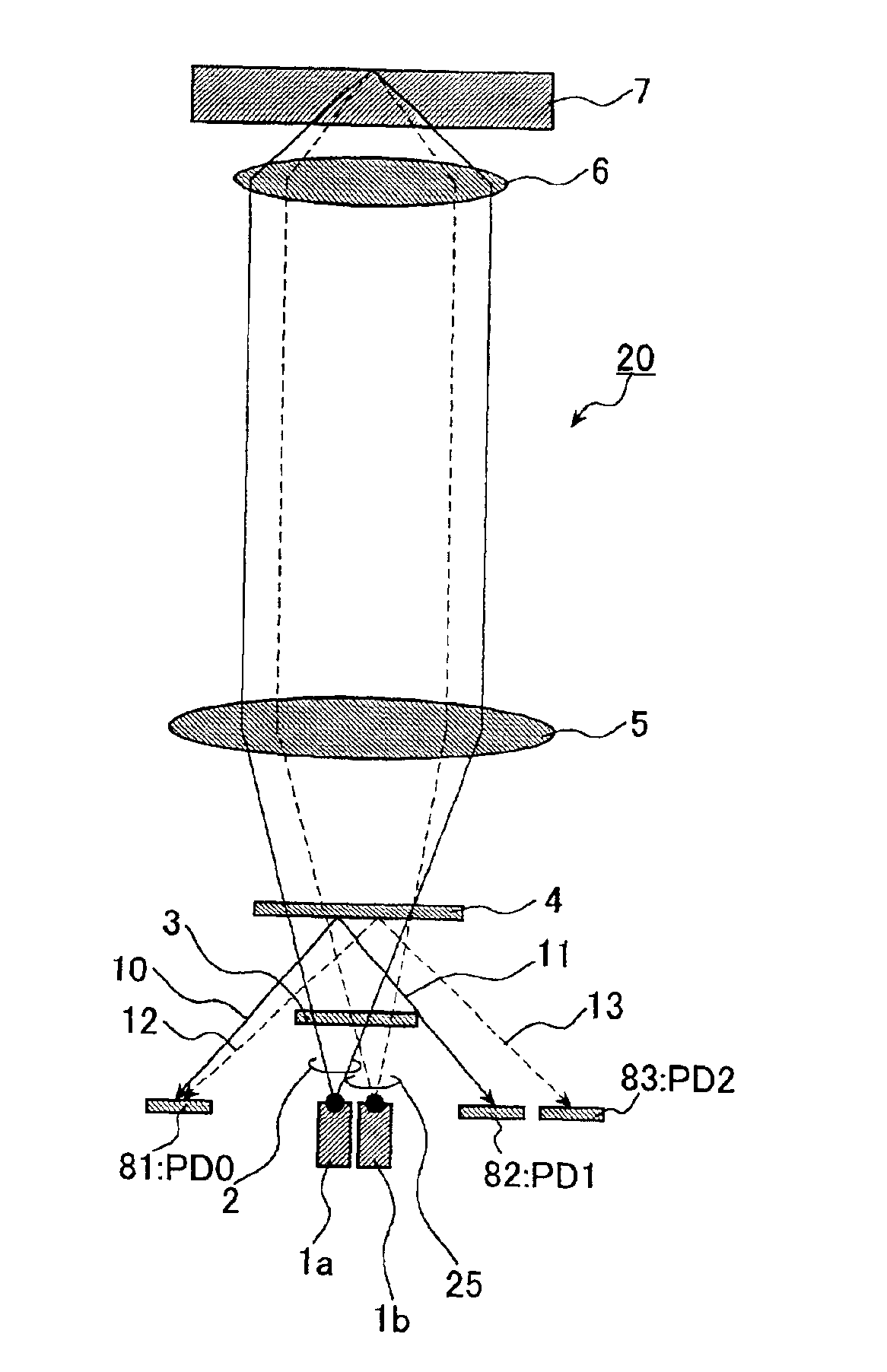
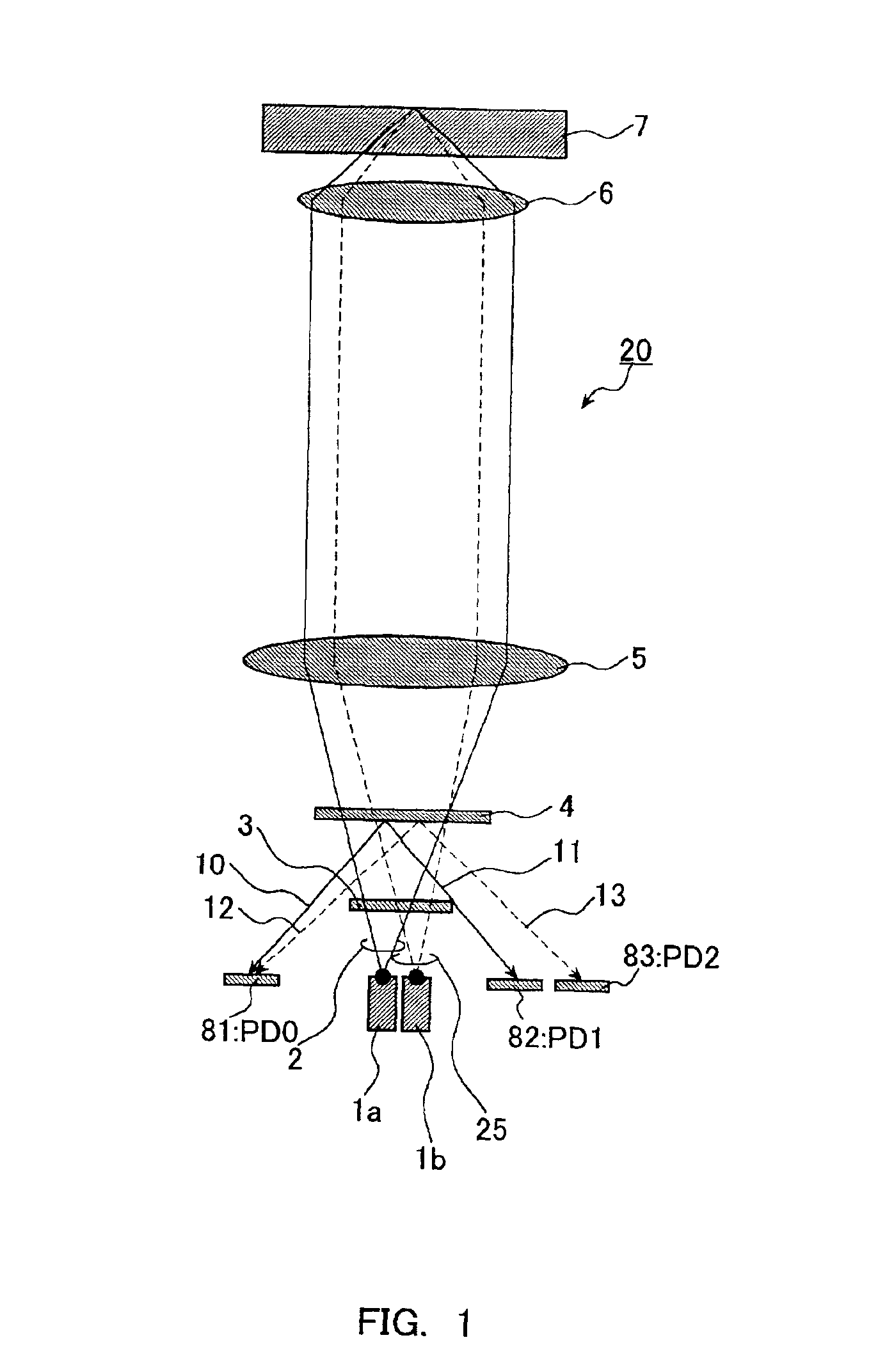
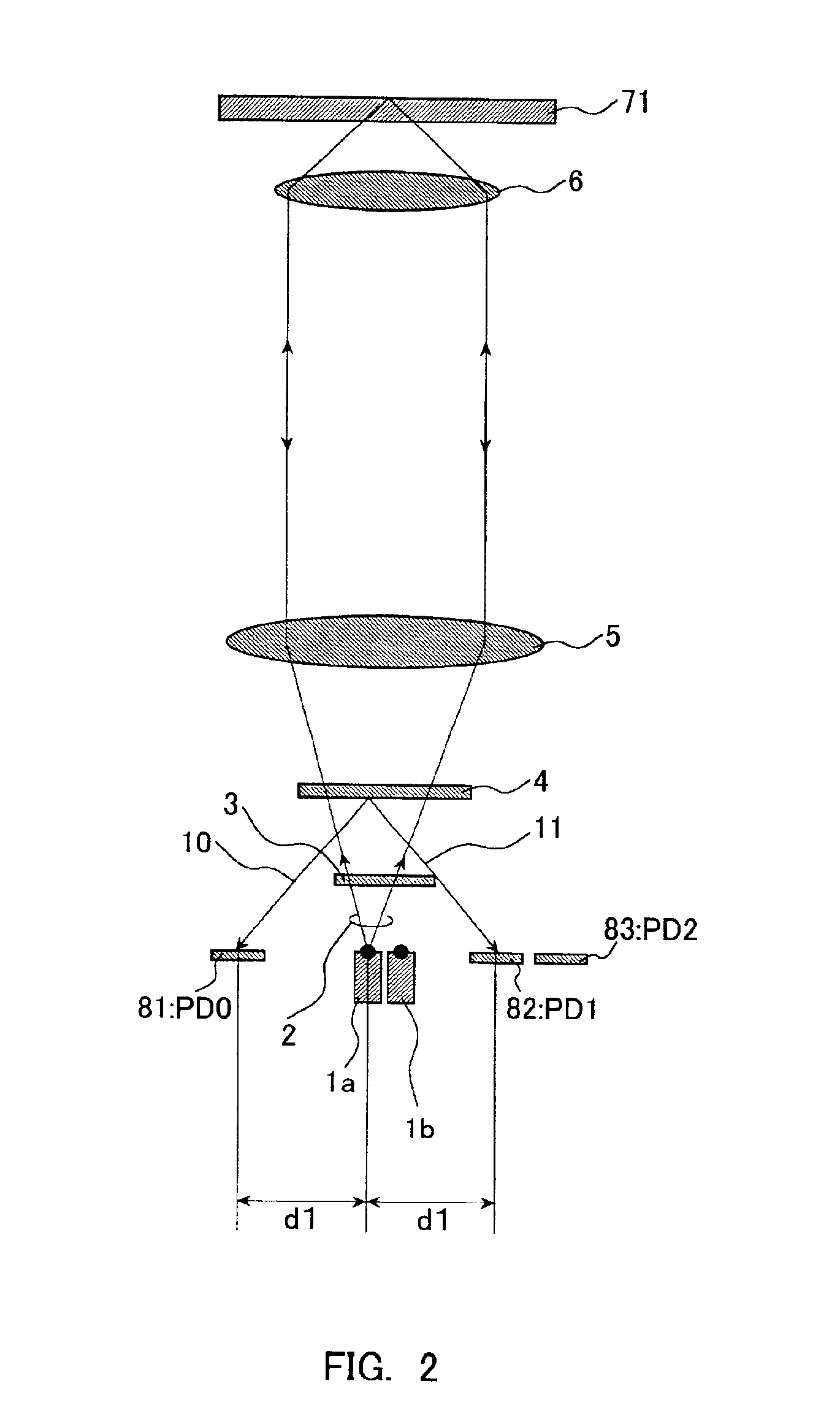
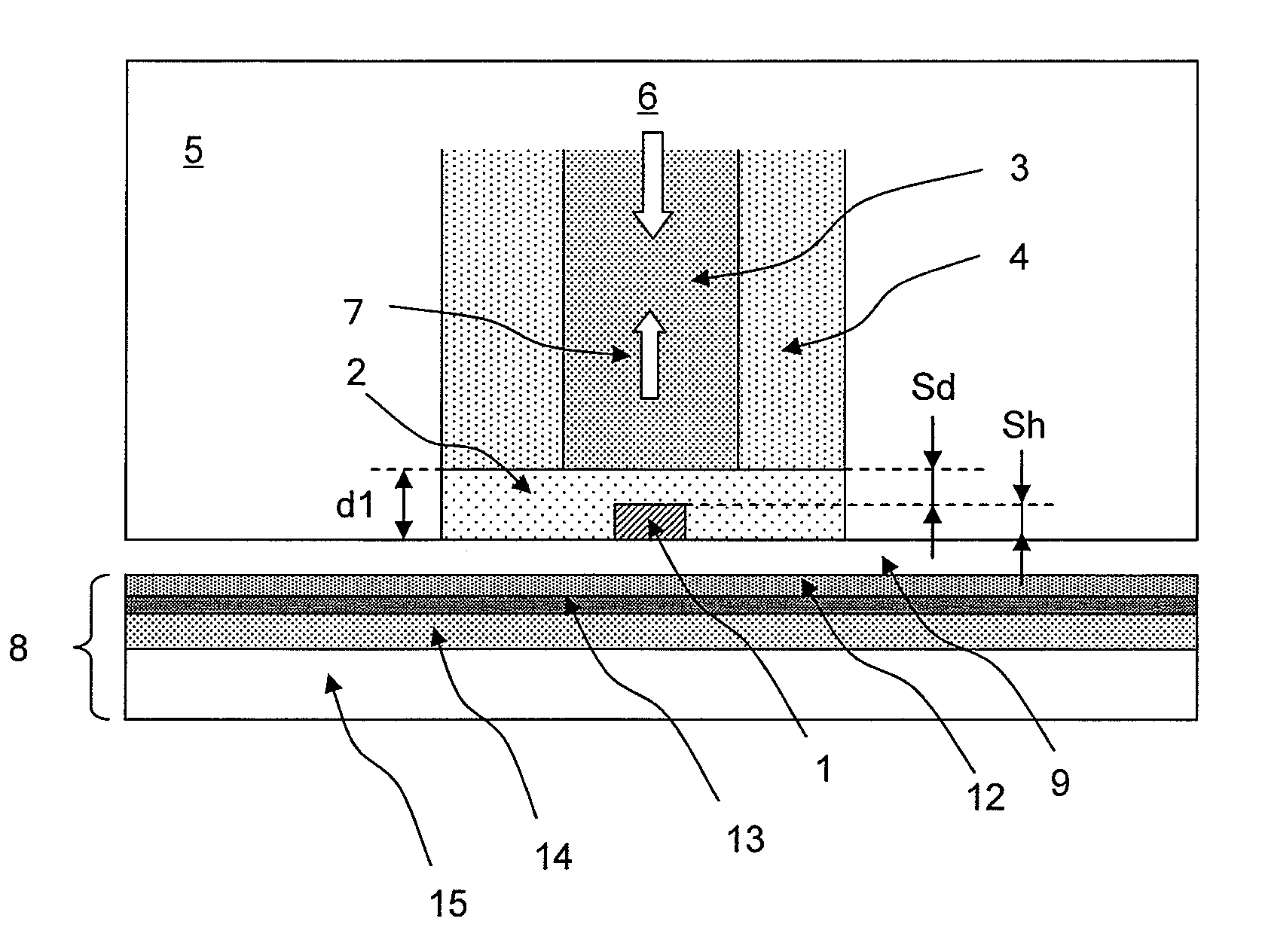
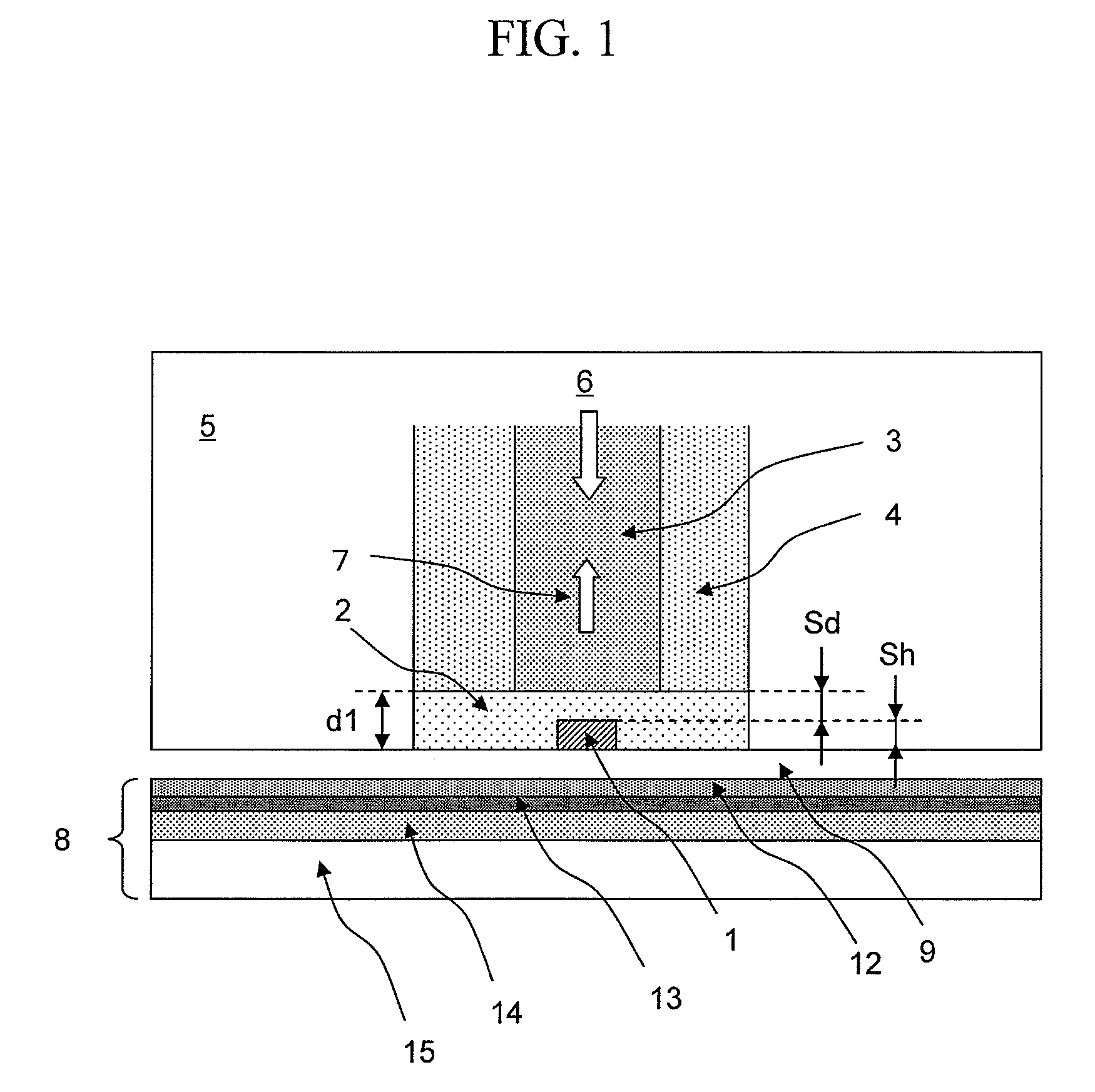
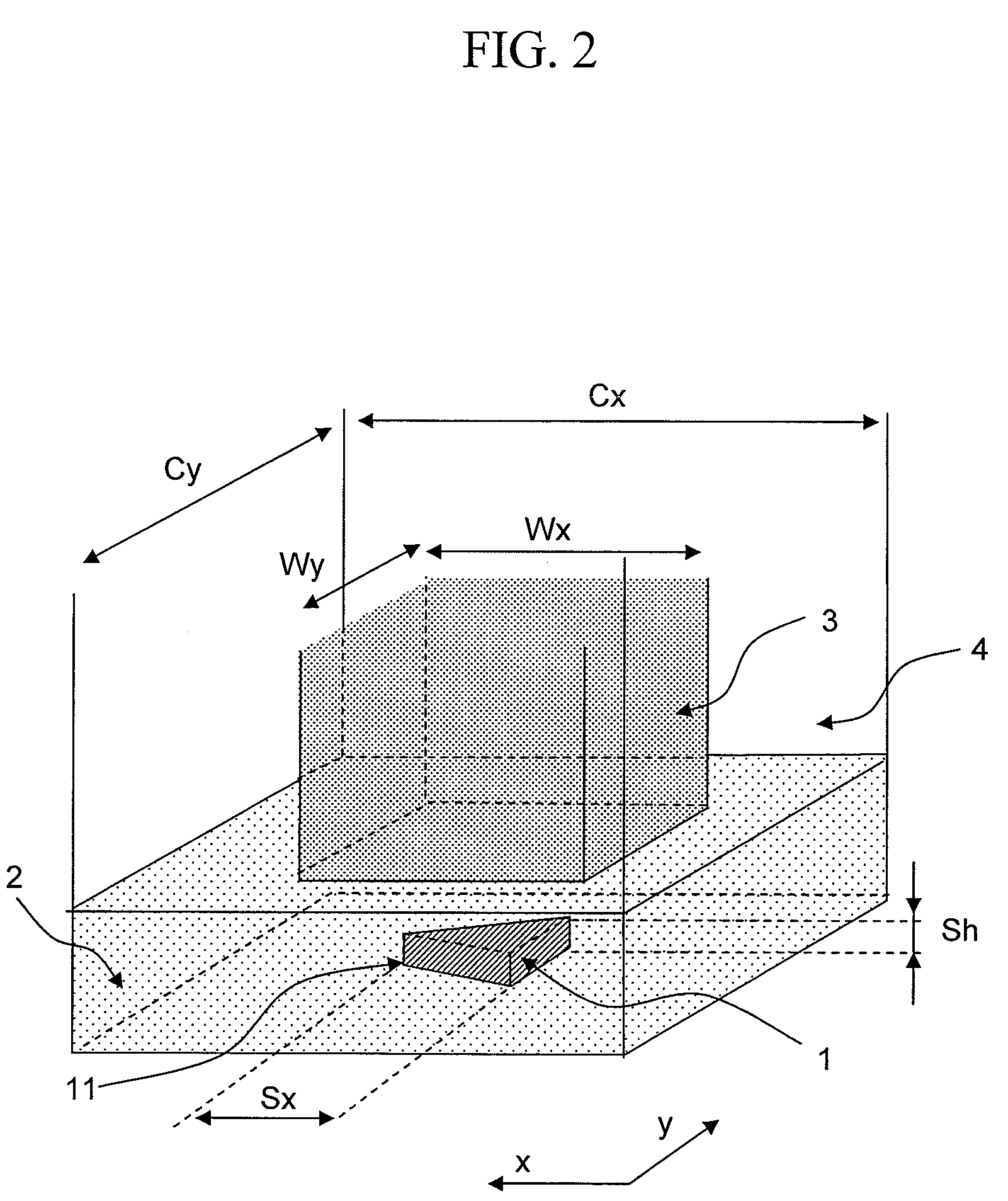
An optical pick-up capable of reproducing information excellently on both CD and DVD, which are significantly different in terms of three kinds of factors, a base material thickness, a wavelength of a light source, and NA, and detecting TE signals by three kinds of methods, that is, the phase difference method, the PP method, and the 3-beam method, which are necessary to record and reproduce information. The optical pick-up is formed by integrating laser light sources having two kinds of wavelengths (λ1, λ2) for detecting TE signals; photodetectors, and hologram for generating the diffracted light for detecting signals. The distance d1 between the center of the photo detecting portion PD0 and the light emitting spot of the first semiconductor laser light source and a distance d2 between the center of the photo detecting portion PD0 and the light emitting spot of the second semiconductor laser light source substantially satisfy the following relationship:λ1 / λ2=d1 / d2.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
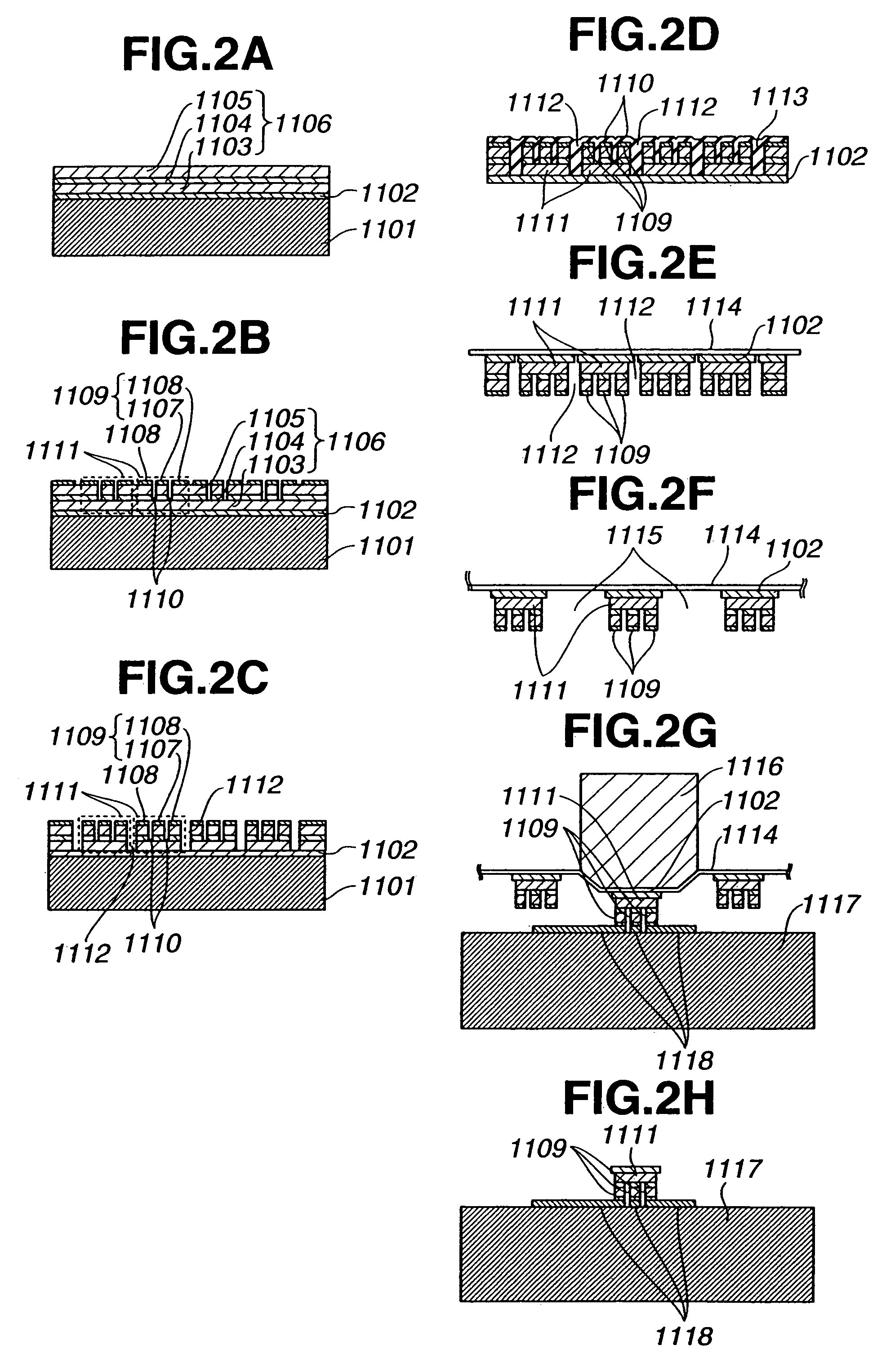
Surface optical device apparatus, method of fabricating the same, and apparatus using the same
InactiveUS6970612B2High alignment precisionEasy to handleIntegrated optical head arrangementsSolid-state devicesLight emissionElectrical contacts
A surface optical device apparatus includes a surface optical device and a second substrate. The surface optical device includes a functional layer grown on a first substrate, which acts as a supporting substrate for fabricating the functional layer thereon. The first substrate is later thinned or removed, and a first electrode is formed on at least one of surfaces of the functional layer. The surface optical device performs light emission or light reception along a direction approximately perpendicular to the first substrate, and the first electrode has functionality for electrically controlling the light emission or reception. The second substrate includes a second electrode formed thereon, and the surface optical device is bonded to the second substrate with the first electrode and the second electrode in electrical contact with each other.
Owner:CANON KK
Optical recording using a waveguide structure and a phase change medium
InactiveUS7596072B2Optical flying-type headsVariable resistance carrier recordingPhase changeElectromagnetic radiation
An apparatus comprises a slider having an air bearing surface, a first waveguide for directing electromagnetic radiation to a focal point adjacent to the air bearing surface, a storage medium position adjacent to the air bearing surface, a detector for detecting electromagnetic radiation reflected from the storage medium, and a structure positioned adjacent to the focal point for collecting the reflected electromagnetic radiation and for transmitted the reflected electromagnetic radiation toward the detector.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
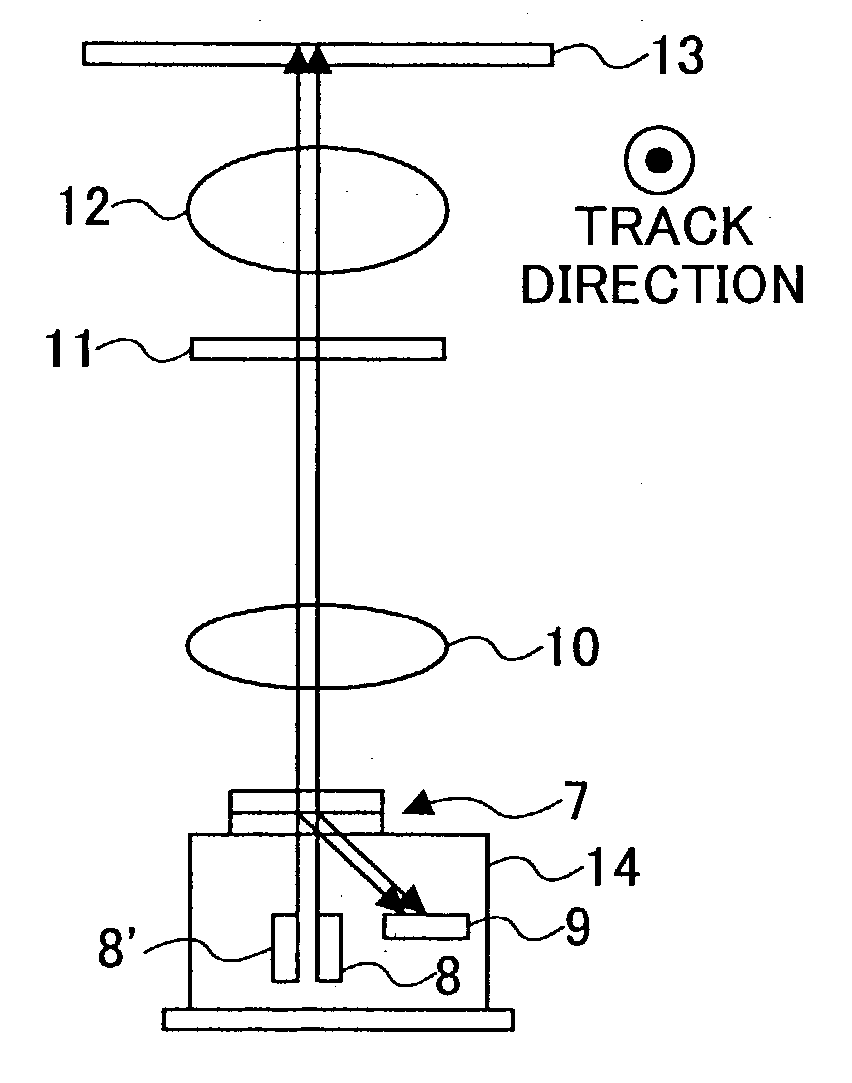
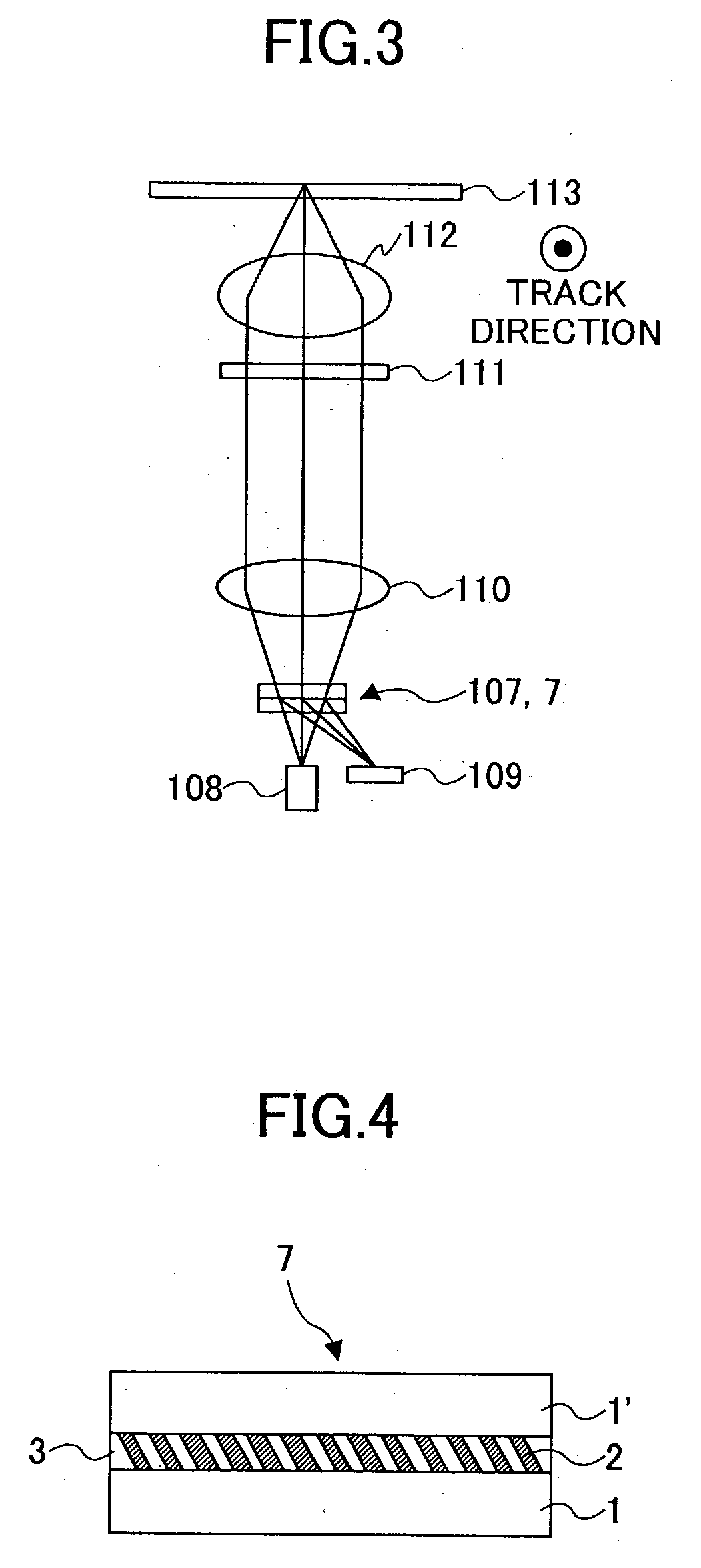
Diffraction grating, light source unit applying the same therein, and optical head device employing the same
InactiveUS20040013076A1Integrated optical head arrangementsOptical beam sourcesOptical polarizationLight source
A polarization diffraction grating includes two media having different orientation states arranged alternately and cyclically, wherein each boundary between the media forms an oblique rectangular shape.
Owner:RICOH KK
Diffractive optical element that polarizes light and an optical pickup using the same
A first diffractive optical element pattern with a pattern pitch that is no greater than a wavelength of incident light is formed on a first main surface of substrate such as a glass plate. Second diffractive optical element patterns are formed at positions that are respectively incident to positive first-order diffracted light and negative first-order diffracted light produced by the first diffractive optical element pattern. Negative first-order diffracted light produced by each second diffractive optical element pattern is incident upon a boundary face of the substrate at an angle that is smaller than the critical angle, and so exits the substrate.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Optical pickup device, recorder and/or reproducer
InactiveUS20060007812A1Maximizing of optical pathGood magnificationIntegrated optical head arrangementsRecord information storageOptical pickupMagnification
The present invention provides an optical pickup device which realizes an optical system having an optical magnification suitable for each disc format between three optical discs and a light emitting means for emitting a laser beam having a wavelength corresponding to each disc in the optical system of the optical pickup for recording and / or reproducing an information signal to the optical discs and which prevents the number of components from being increased to simplify the composition of the optical system, thereby preventing the length of an optical path from being lengthened, the optical pickup from being increased in size. The optical pickup device has a first light emitting unit for emitting a laser beam having a first wavelength and a laser beam having a second wavelength, a second light emitting unit for emitting a laser beam having a third wavelength, a first collimator lens for transmitting the laser beam having the first wavelength and the laser beam having the second wavelength, a second collimator lens for transmitting the laser beam having the third wavelength, a first objective lens for transmitting the laser beam having the first wavelength transmitted through the first collimating lens or the laser beam having the third wavelength transmitted through the second collimator lens, and a second objective lens for transmitting the laser beam having the second wavelength transmitted through the first collimator lens.
Owner:SONY CORP
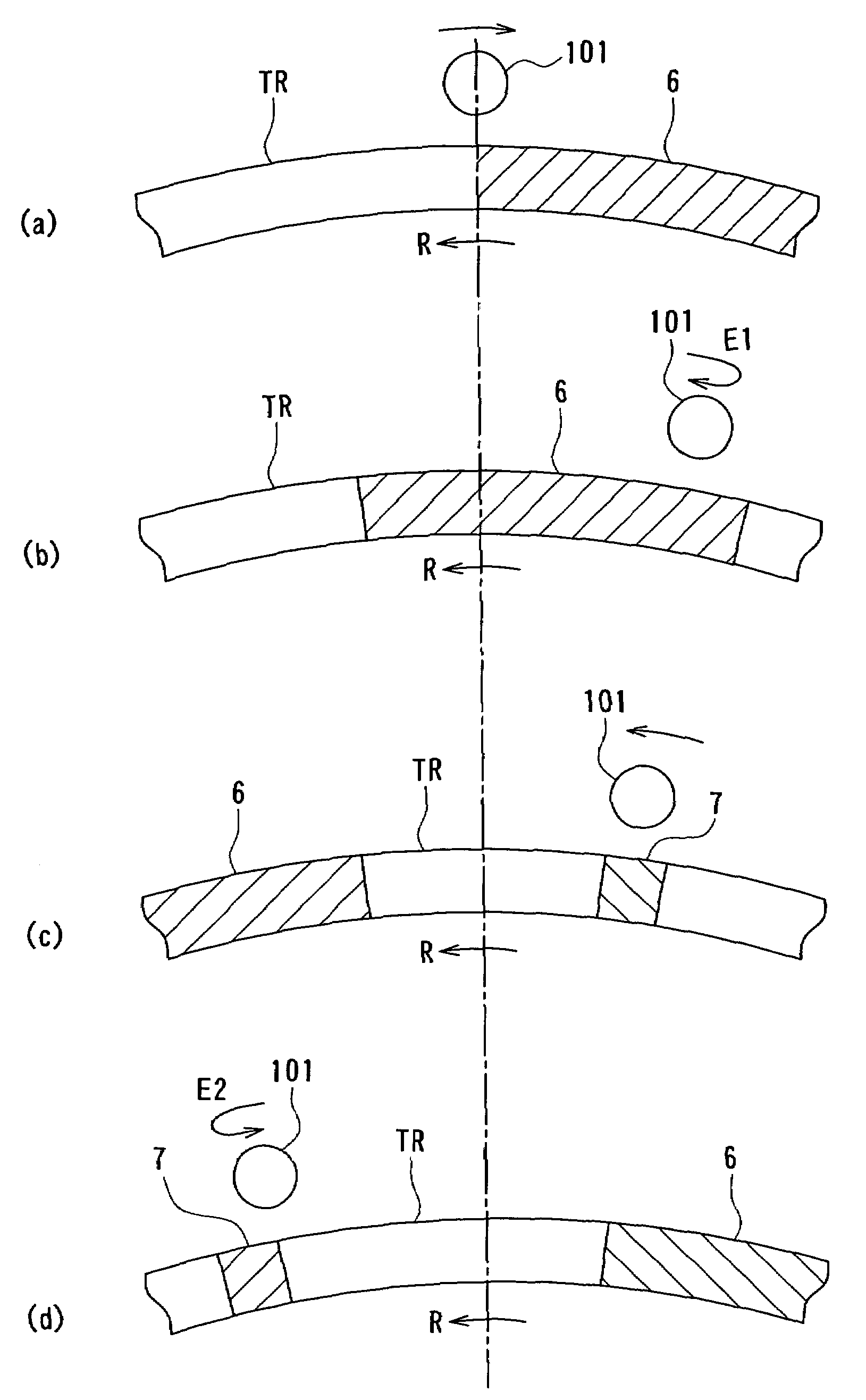
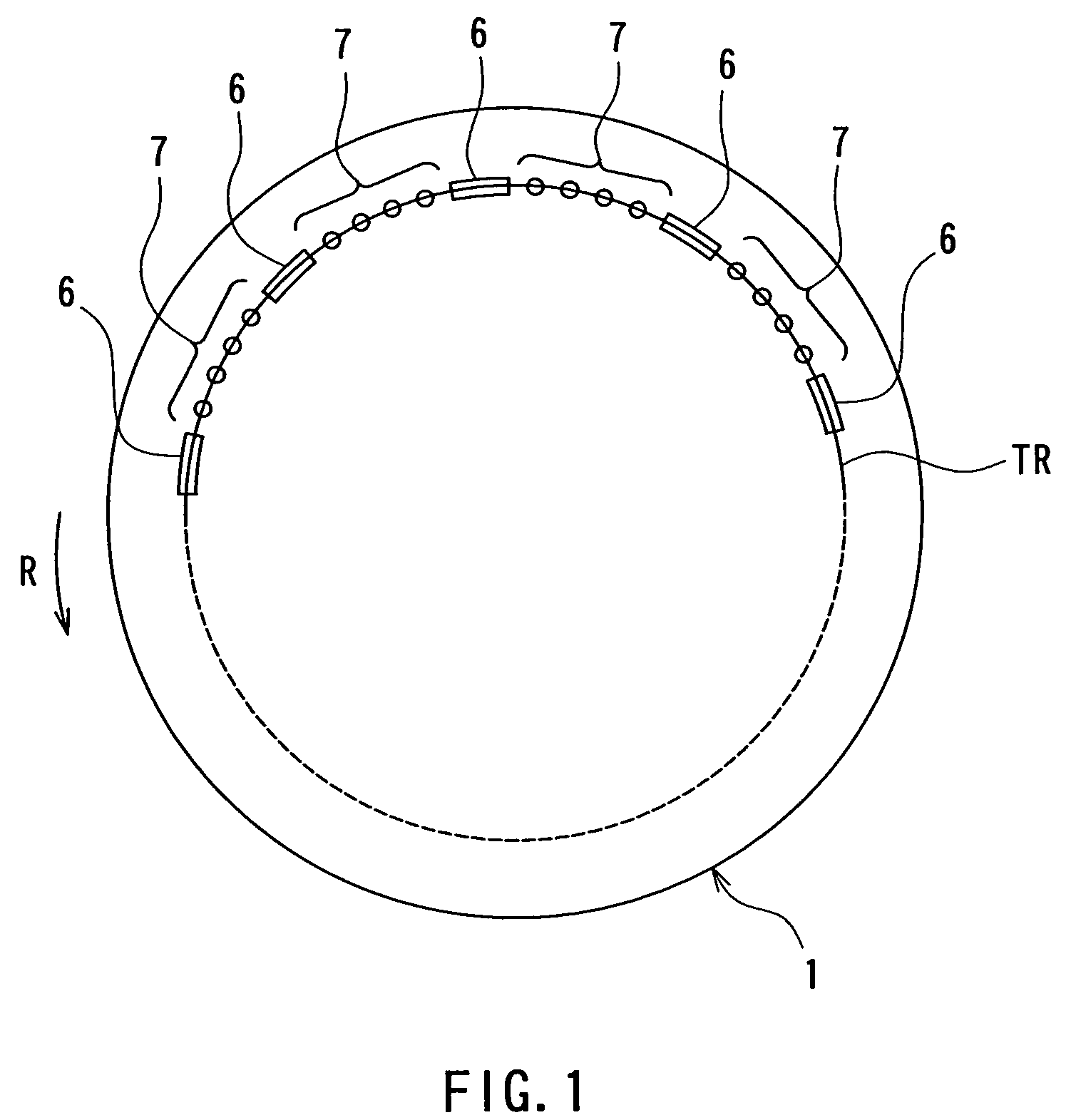
Optical information recording apparatus and method using holography
InactiveUS7215628B2Information arrangementIntegrated optical head arrangementsHolographyComputer science
It is an object of the invention to allow the use of a practical light source to record information in each information recording area of a recording medium having a plurality of information recording areas through the use of holography while moving the recording medium.When recording information in the information recording areas (7) of the recording medium, the irradiating position (101) of information light and recording-specific reference light is moved such that the irradiating position (101) follows a single moving information recording area (7) for a predetermined period. Consequently, the single information recording area (7) keeps being irradiated with the information light and the recording-specific reference light for the predetermined period. Information is thus recorded in this information recording area (7) in the form of an interference pattern as a result of interference between the information light and the recording-specific reference light.
Owner:OPTWARE
Integrated type optical head with sheet waveguide and light coupler
InactiveUS7184386B2Enhanced couplingIntegrated optical head arrangementsRecord information storageOptical pickupOutput coupler
An integrated optical head is provided. In the integrated optical head, a light source emits light. A waveguide guides the light. An input coupler is located at one edge of the waveguide, and couples light emitted from the light source and transmits the coupled light to the waveguide. An output coupler is located at another edge of the waveguide, and couples light emitted from the waveguide and focuses the coupled light on an optical disc. A light path changing unit is installed on the waveguide, and changes the light path of light that has been reflected by the optical disc and then passed through the output coupler. An optical detector receives the light passed through the light path changing unit and converts the received light into an electrical signal in order to detect information from the optical disc Accordingly, an input coupling efficiency and an output coupling efficiency are improved, such that light loss is reduced. Thus, recording and reproduction of an optical head can be improved, and a light, compact, integrated optical head can be obtained.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optical recording using a waveguide structure and a phase change medium
InactiveUS20060133230A1Optical flying-type headsVariable resistance carrier recordingElectromagnetic radiationOptical recording
An apparatus comprises a slider having an air bearing surface, a first waveguide for directing electromagnetic radiation to a focal point adjacent to the air bearing surface, a storage medium position adjacent to the air bearing surface, a detector for detecting electromagnetic radiation reflected from the storage medium, and a structure positioned adjacent to the focal point for collecting the reflected electromagnetic radiation and for transmitted the reflected electromagnetic radiation toward the detector.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
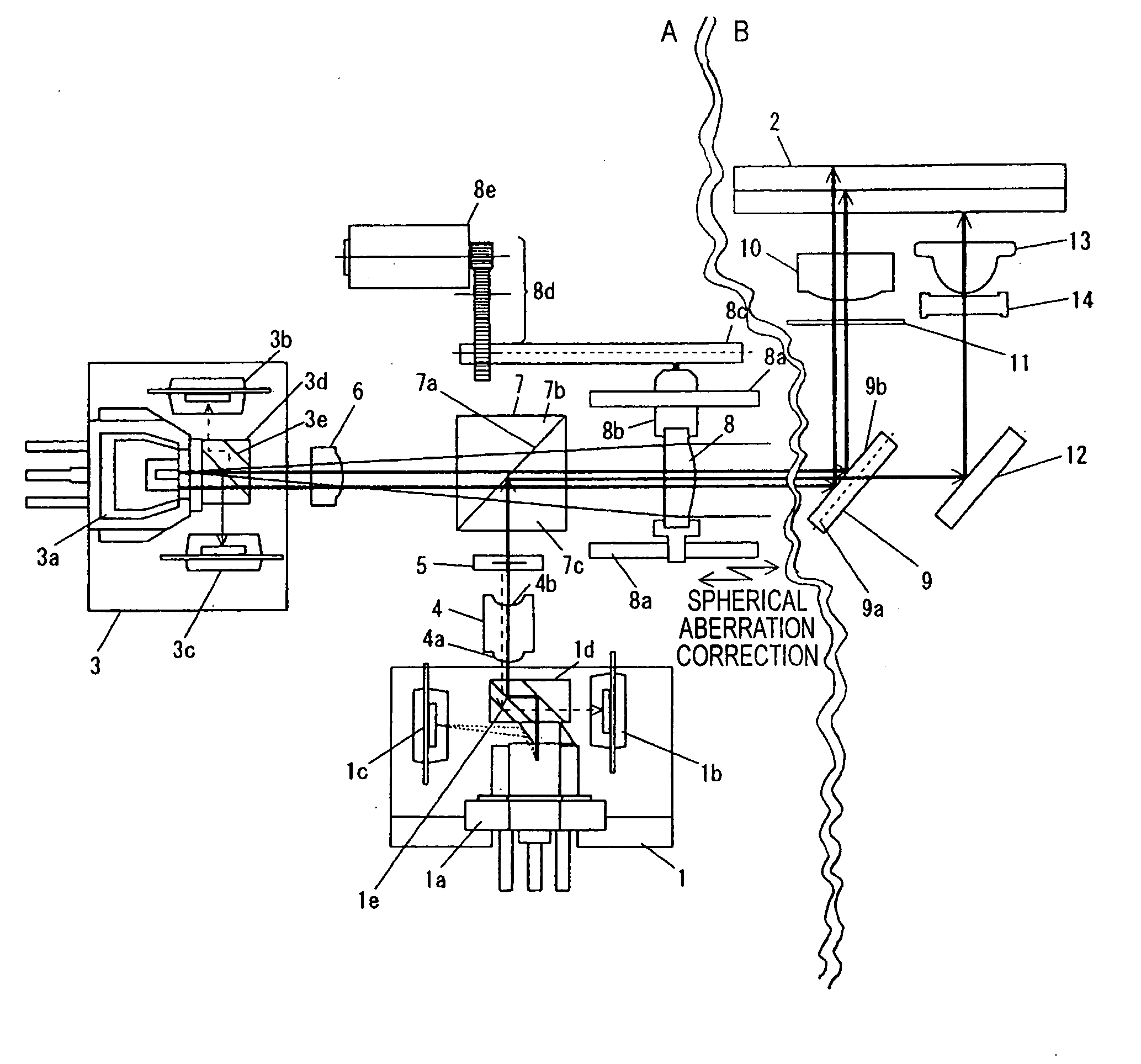
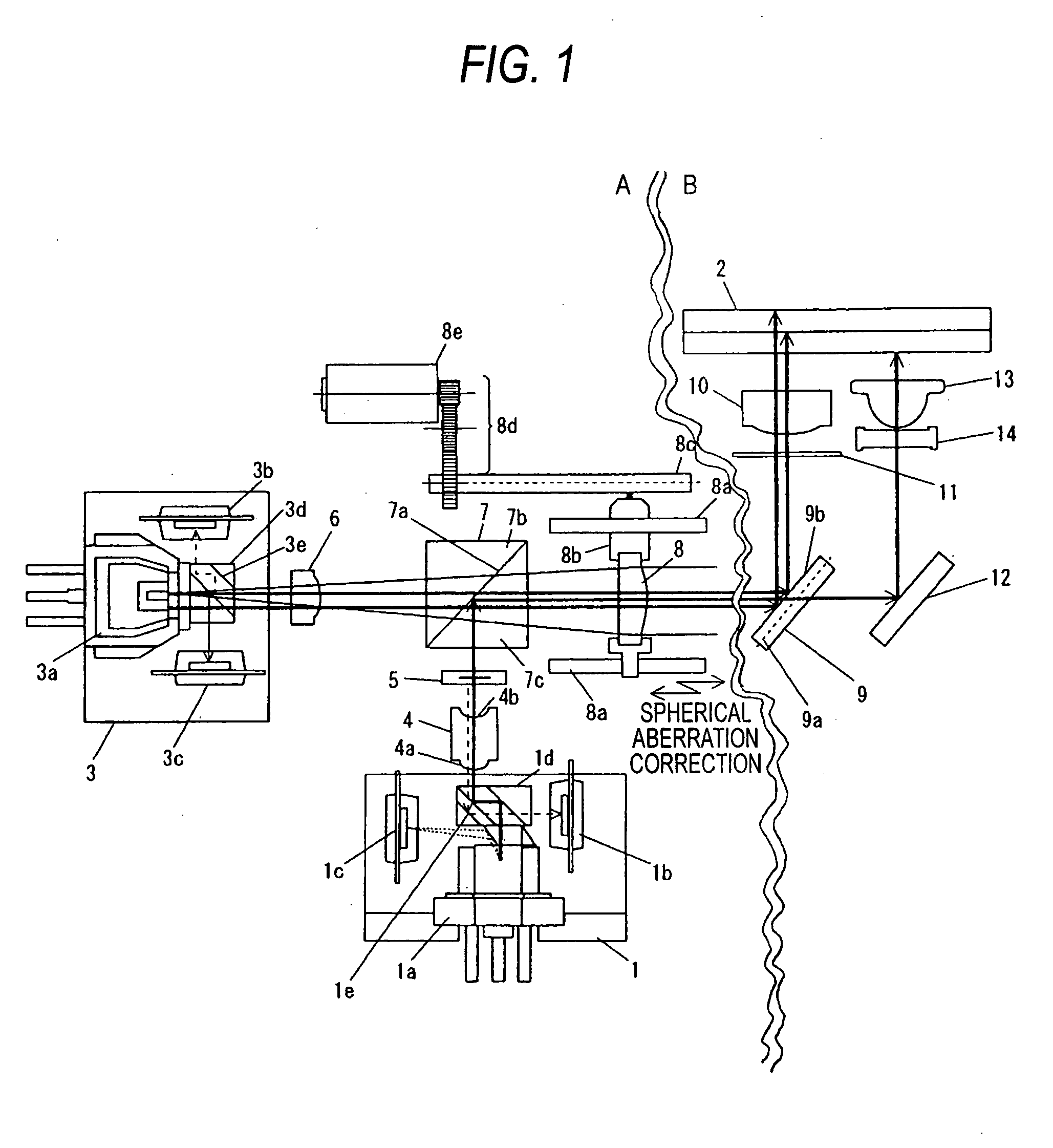
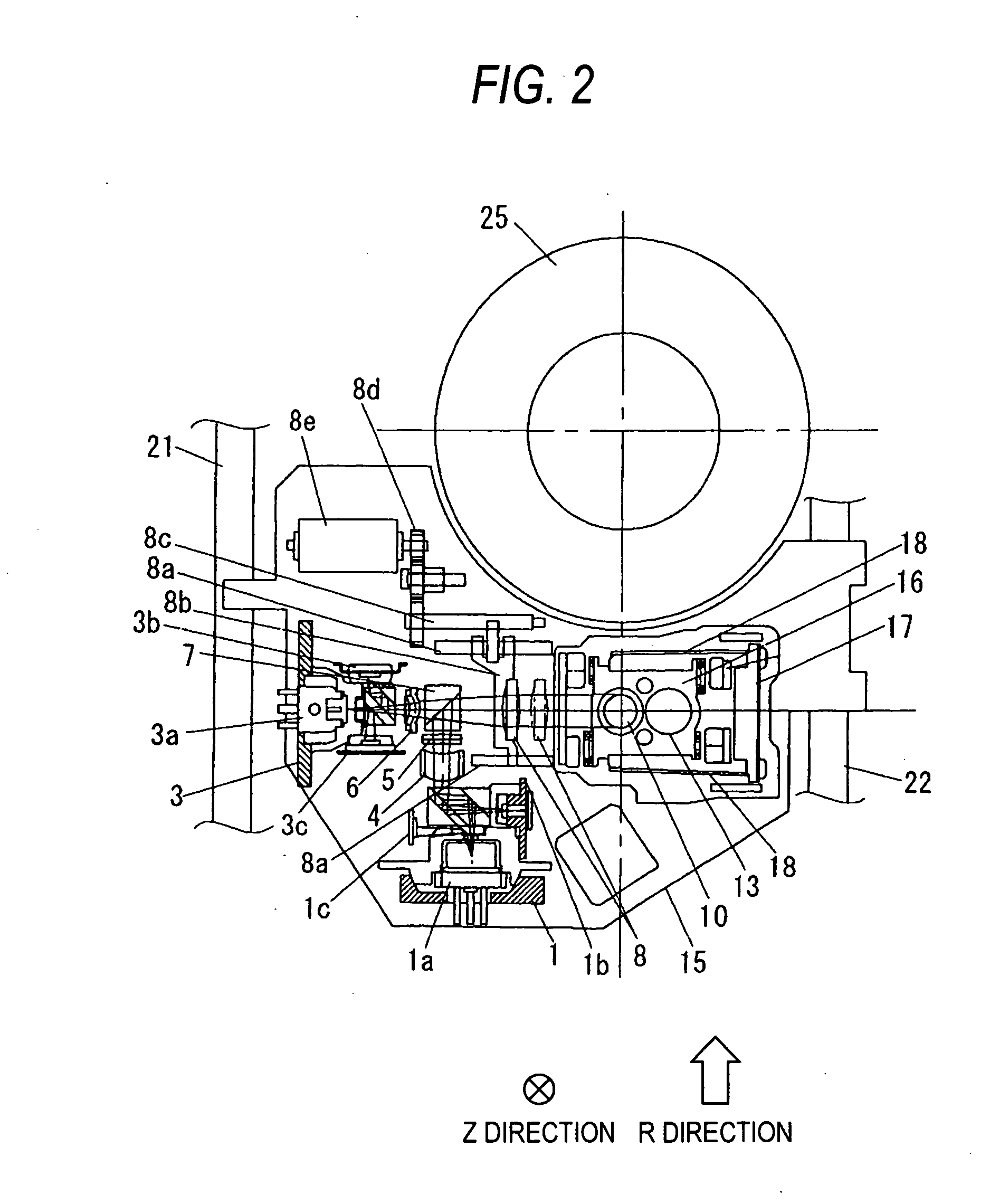
Optical disk apparatus using focal shift signals to control spherical aberration
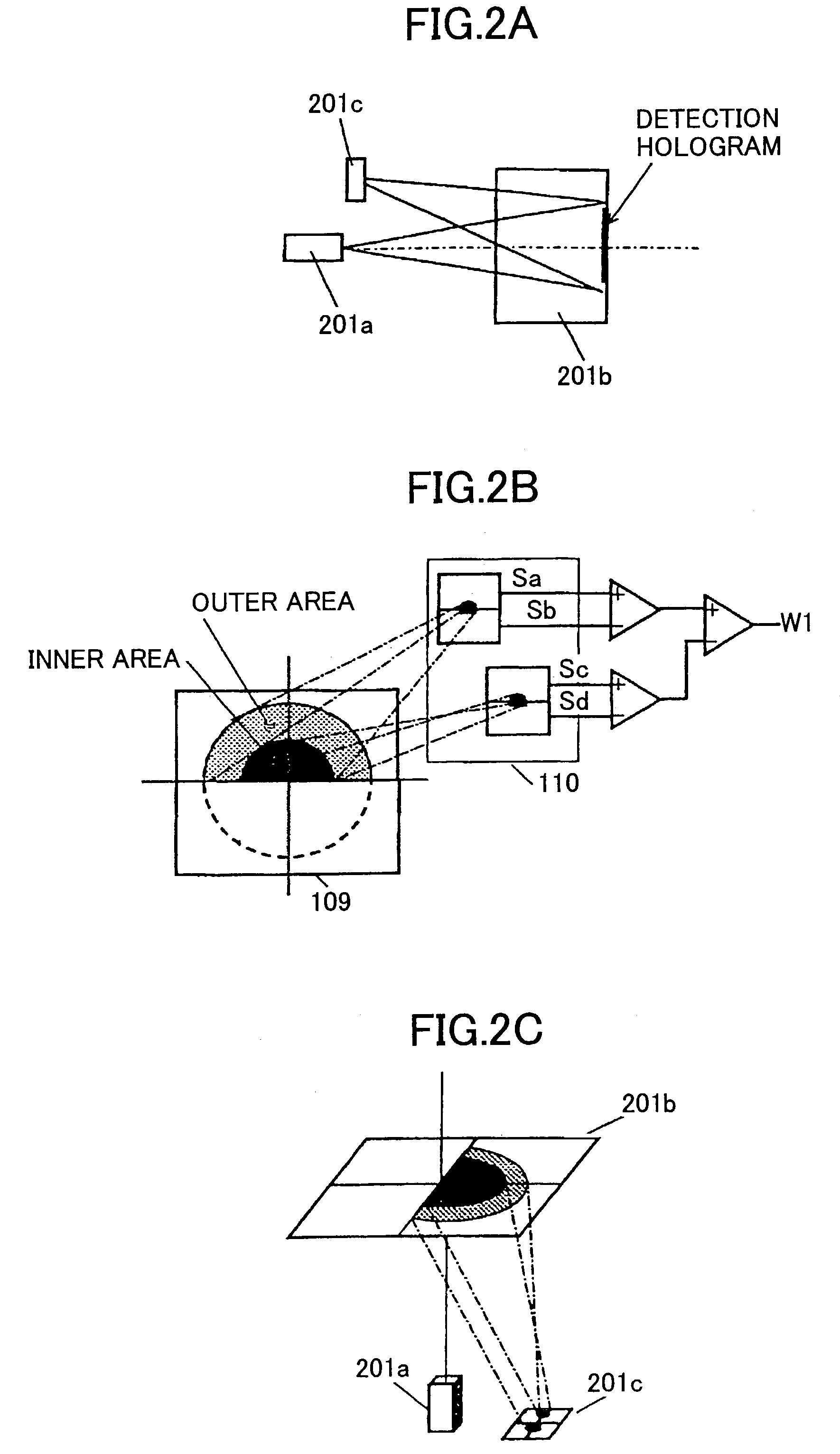
InactiveUS7012875B2Suppress lightIntegrated optical head arrangementsOptical detectorsComputational physicsLuminous flux
In the past there has been a problem that on a detection surface the influence of interference causes a defocusing signal to degrade, narrowing the range in which spherical aberration can be stably detected. Accordingly, a diffraction grating is used to focus the inner and outer sides of luminous flux on separate optical detectors before the optical flux is focused on an optical detector and defocusing signals are independently calculated to find the difference therebetween, thereby providing a spherical aberration signal. This makes it possible to detect spherical aberation signals more stably.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
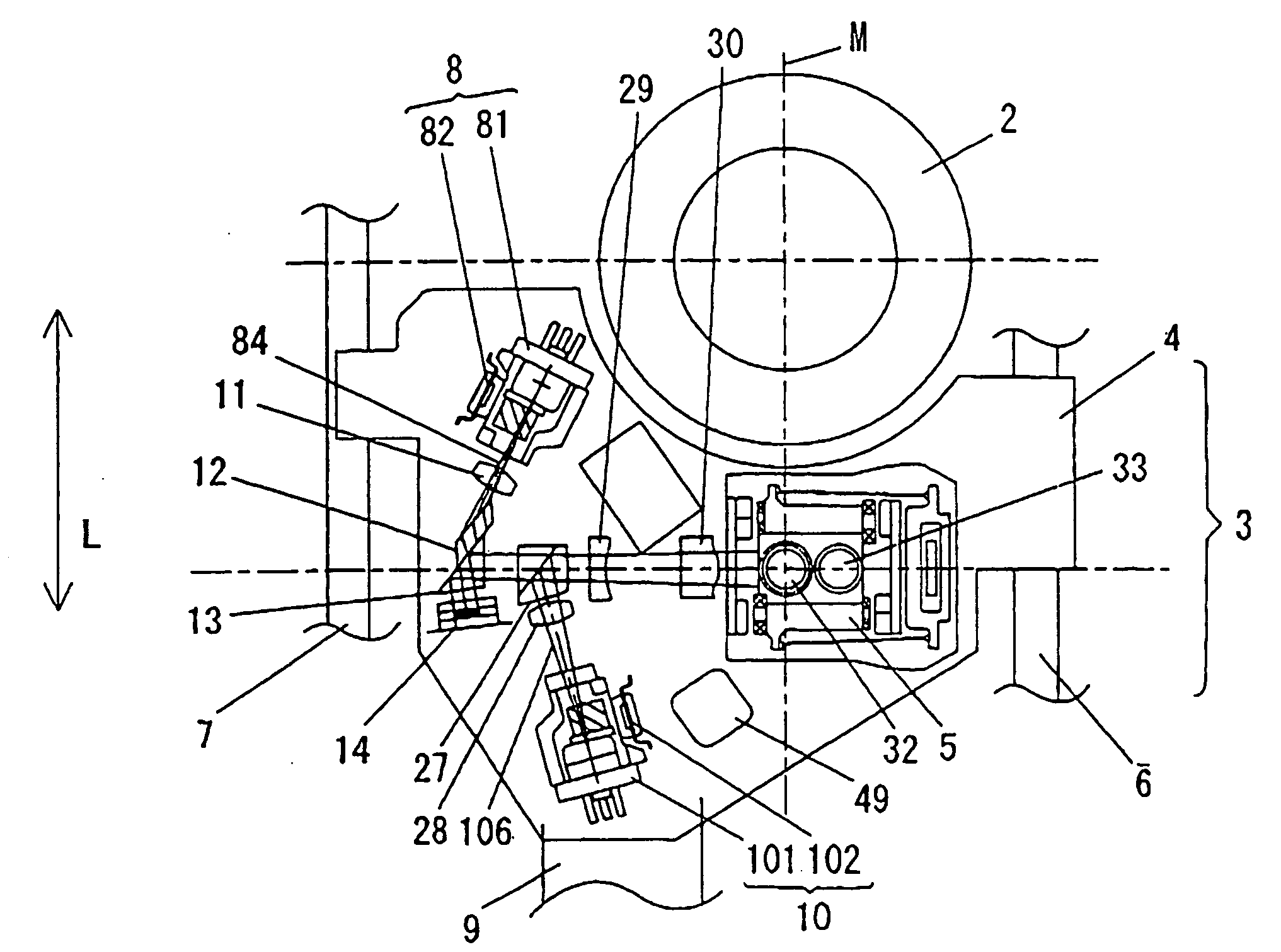
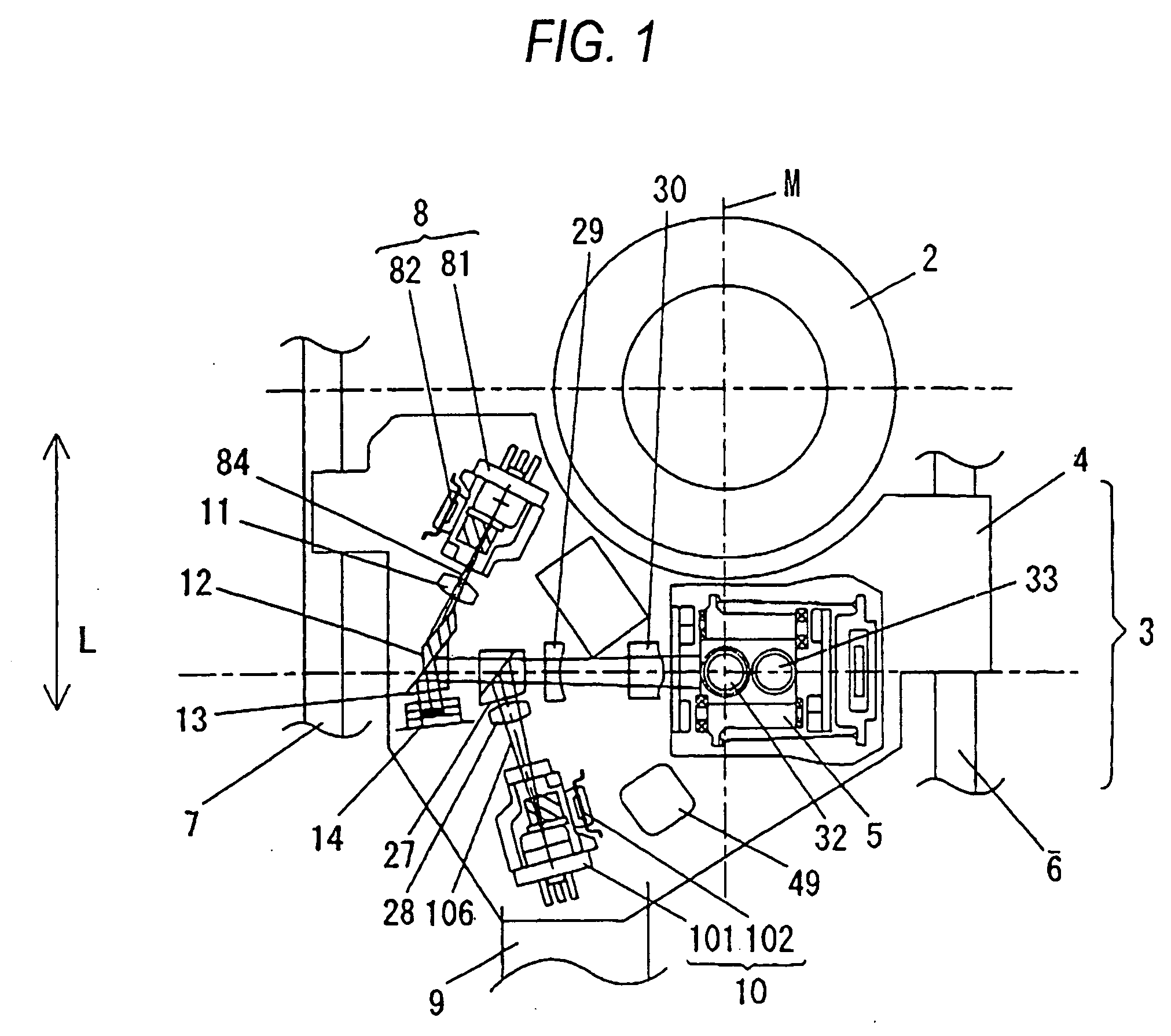
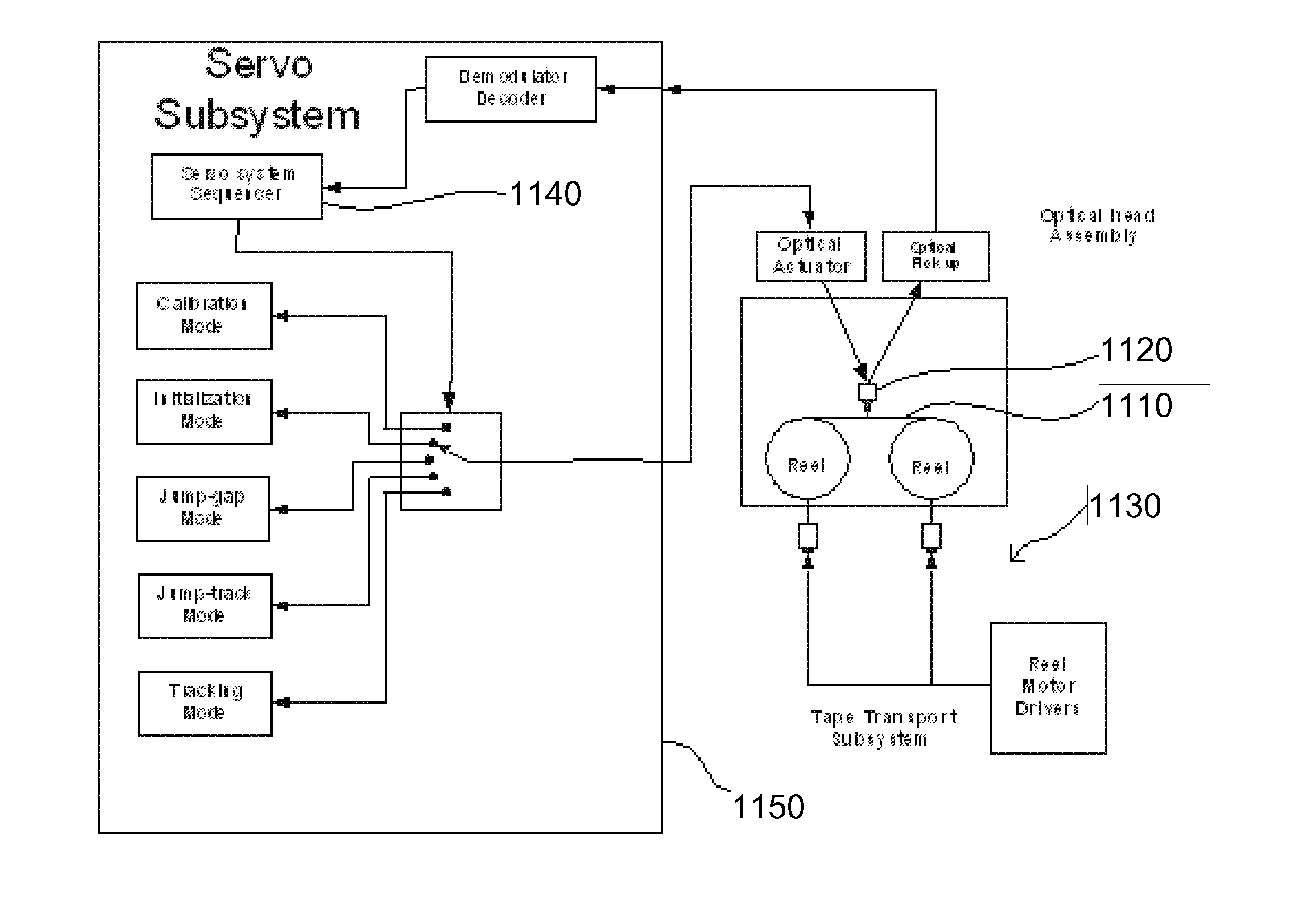
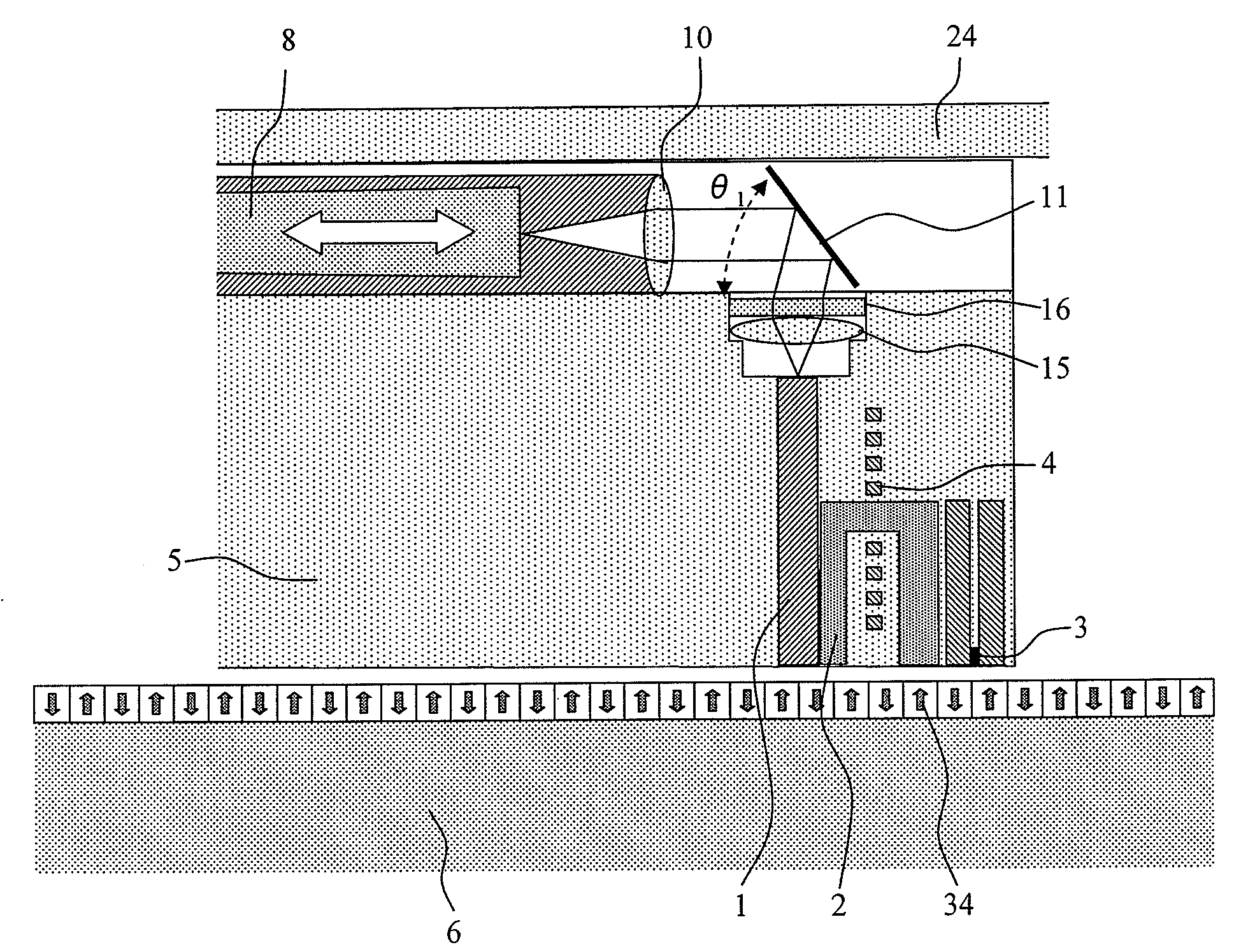
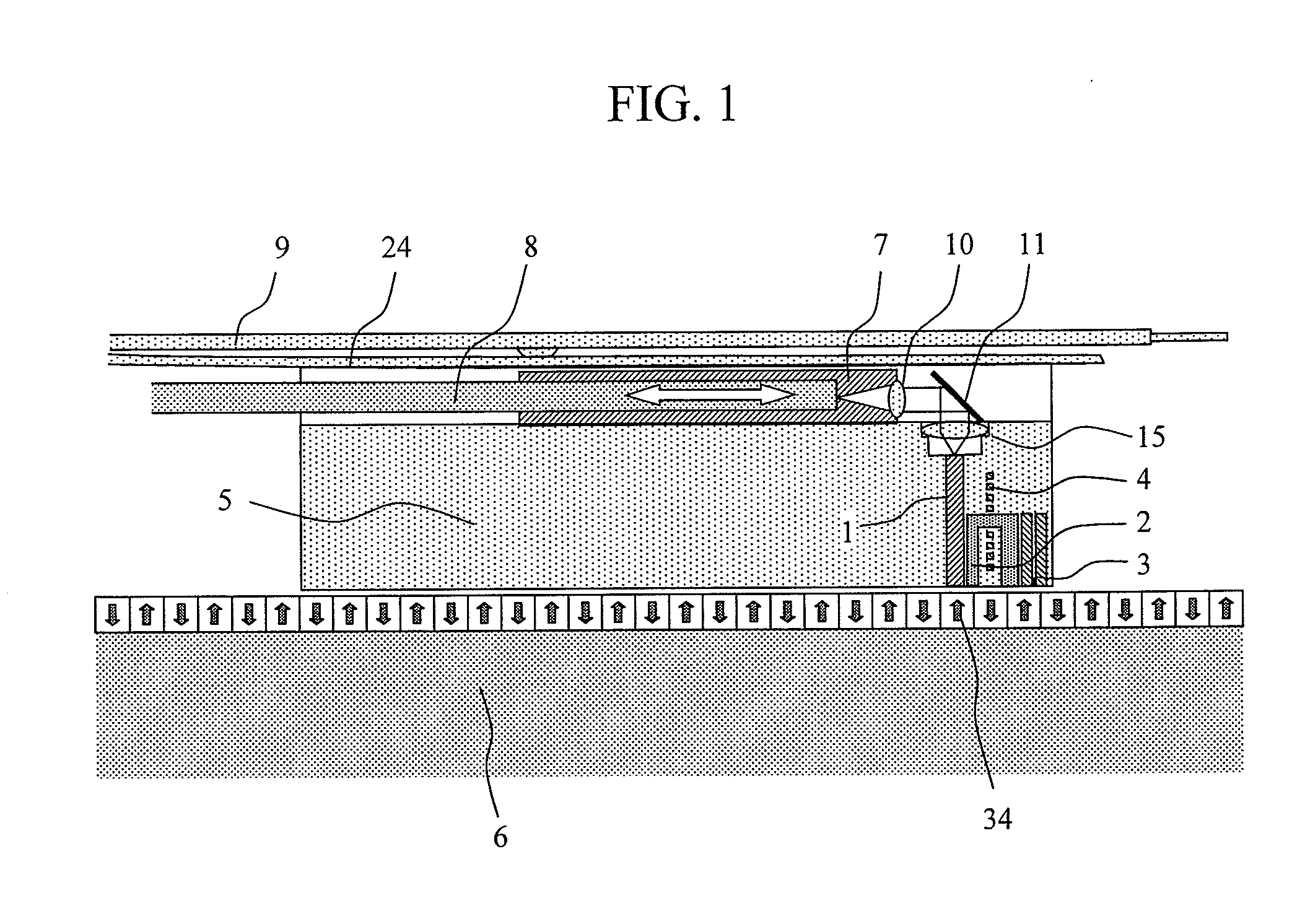
Head, head gimbal assembly and information recording apparatus
InactiveUS20080117727A1Reduce the applied forceSuspension stabilityIntegrated optical head arrangementsRecord information storageLevitationEngineering
In an apparatus wherein a semiconductor laser, which is a light source, is disposed external to a flying slider and the semiconductor laser and the flying slider are coupled with each other using a waveguide, force applied from the waveguide to the flying slider is reduced to stabilize the levitation of the slider. A waveguide coupled with a semiconductor laser is fixed to a moving part disposed on a flying slider. The moving part is adapted to move in parallel with the traveling direction of light. A collimator lens is disposed on the moving part to change light exiting from the waveguide to parallel light. This parallel light is condensed by a lens fixed to the flying slider and is coupled with a waveguide in the flying slider.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Optical head and optical recording apparatus
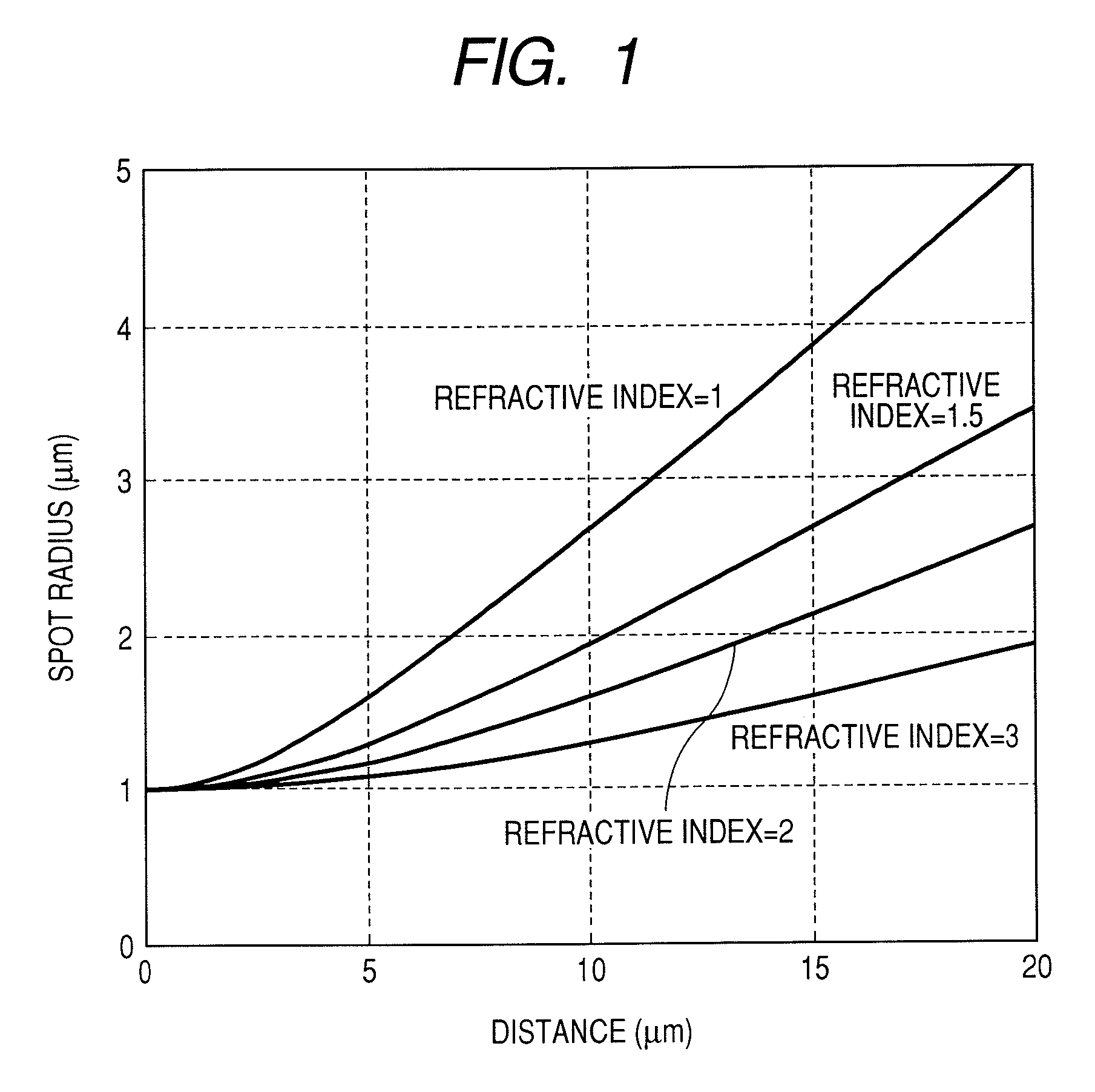
InactiveUS20080002529A1Luminous efficacy greatReduce the overall heightCombination recordingIntegrated optical head arrangementsLight spotRefractive index
An optical head having: a graded index lens which receives incident light radiated from a linear optical guide at one end surface of the graded index lens and transmits the incident light from the other end surface of the graded index lens, the graded index lens is adapted to form a light spot at a position that is away from the other end surface from which the incident light is transmitted; a light path deflection section which deflects light transmitted from the graded index lens, the light path deflection section is arranged between the other end surface from which the incident light is transmitted and the position where the light spot is formed; and a slider which floats on a recording medium while moving relative to the recording medium, wherein at least the graded index lens and the light path deflection section are installed on the slider.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Optical disk apparatus using mechanism for controlling spherical aberration
InactiveUS7283439B2Suppress lightIntegrated optical head arrangementsOptical detectorsComputational physicsLuminous flux
In the past there has been a problem that on a detection surface the influence of interference causes a defocusing signal to degrade, narrowing the range in which spherical aberration can be stably detected. Accordingly, a diffraction grating is used to focus the inner and outer sides of luminous flux on separate optical detectors before the optical flux is focused on an optical detector and defocusing signals are independently calculated to find the difference therebetween, thereby providing a spherical aberration signal. This makes it possible to detect spherical aberration signals more stably.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
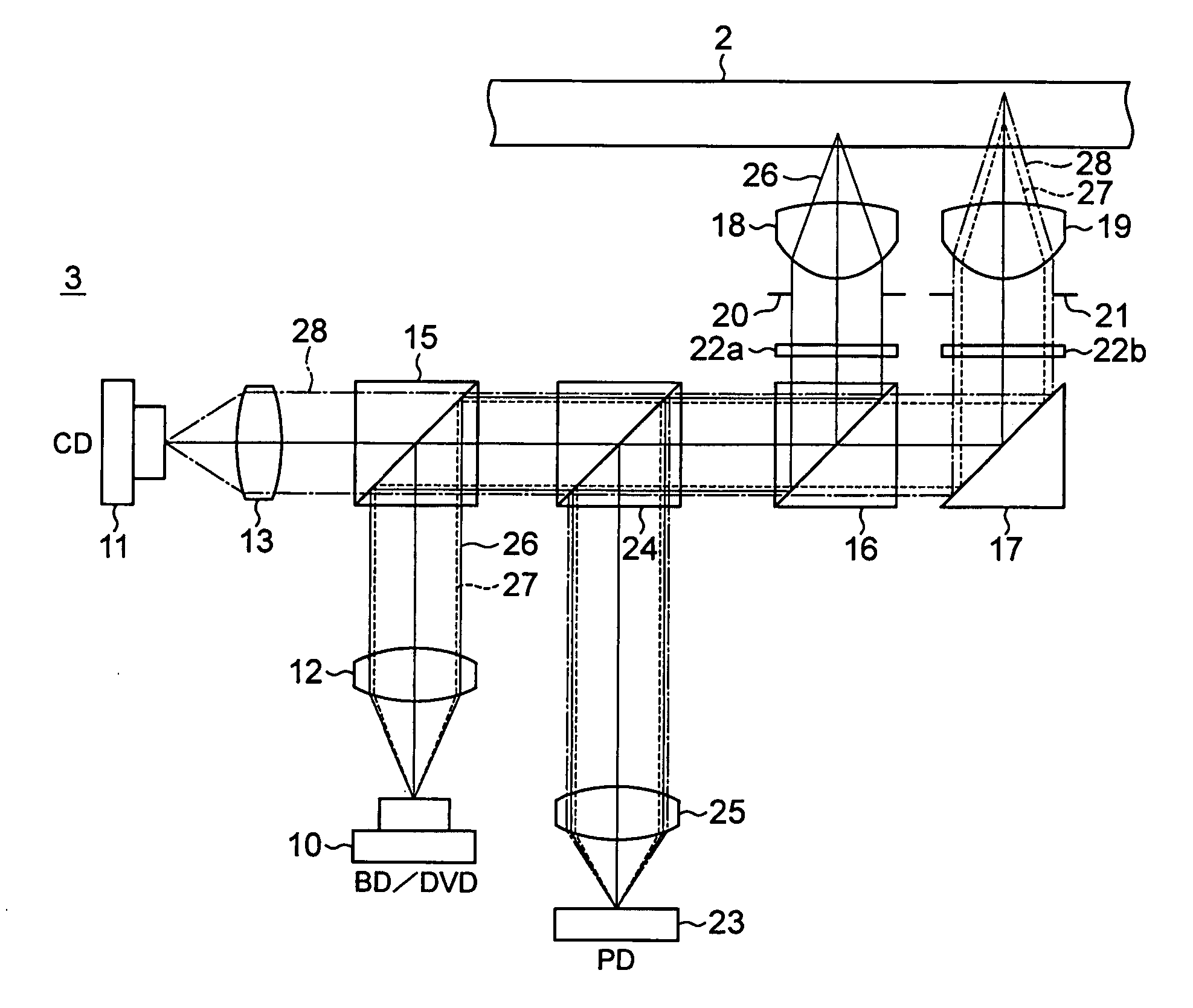
Optical pickup
InactiveUS6868055B2Easy assembly controlIntegrated reductionIntegrated optical head arrangementsOptical beam sourcesOptical pickupLight beam
An optical pickup can be provided, the optical pickup being capable of recording and playback of a plurality of optical disks having different specs by using light beams of different wavelengths, and further being suitable for integrating the semiconductor lasers and light receiving elements into a single package, by including: first and second semiconductor lasers adjacently disposed; a three-beam diffraction grating for generating three beams for tracking control; a second hologram element for diffracting light of the second semiconductor laser to guide it to a photosensor; a complex polarization beam splitter (PBS) for reflecting only light from the first semiconductor laser; and a first hologram element for diffracting light of the first semiconductor laser to guide it to the photosensor.
Owner:SHARP KK
Optical pickup and optical information processing apparatus with light sources of three different wavelengths
InactiveUS7142497B2Reduced beam diameterEffectively controlled and reducedIntegrated optical head arrangementsOptical beam sourcesOptical pickupOptical recording
An optical pickup apparatus for performing recording, reproduction and deletion of information onto each of three types of optical recording mediums including light sources of a blue wavelength zone, light sources of a red wavelength zone and light sources of an infrared wavelength zone. The optical pickup apparatus also has a single object lens which condenses a light from any of the light sources and a single aberration correction device disposed in a common light path between each of the light sources and the object lens.
Owner:RICOH KK
Optical near-field generator and near-field optical recording and reproduction apparatus
InactiveUS7359599B2Improve efficiencyLow efficiencyIntegrated optical head arrangementsNanoinformaticsRefractive indexOptical recording
Decrease in optical near-field intensity is prevented when an light propagating medium made of a high refractive index material, such as a waveguide or a lens, is combined with a scatterer for producing optical near-field. Near the optical near-field generating element, a second light propagating medium is disposed in contact with a first light propagating medium of a high refractive index material, such as a waveguide or a lens. The refractive index of the second light propagating medium is made smaller than the refractive index of the first light propagating medium.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
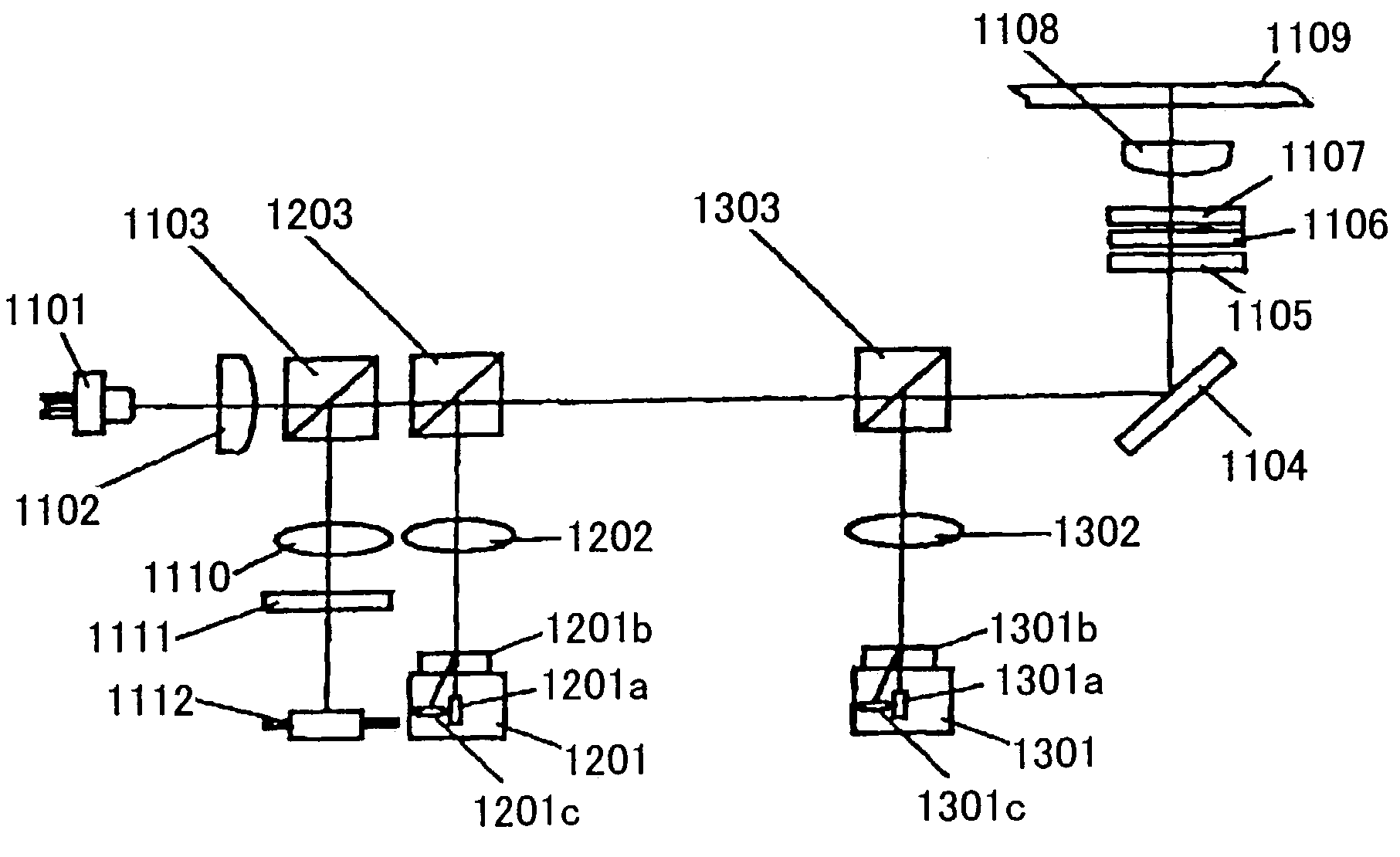
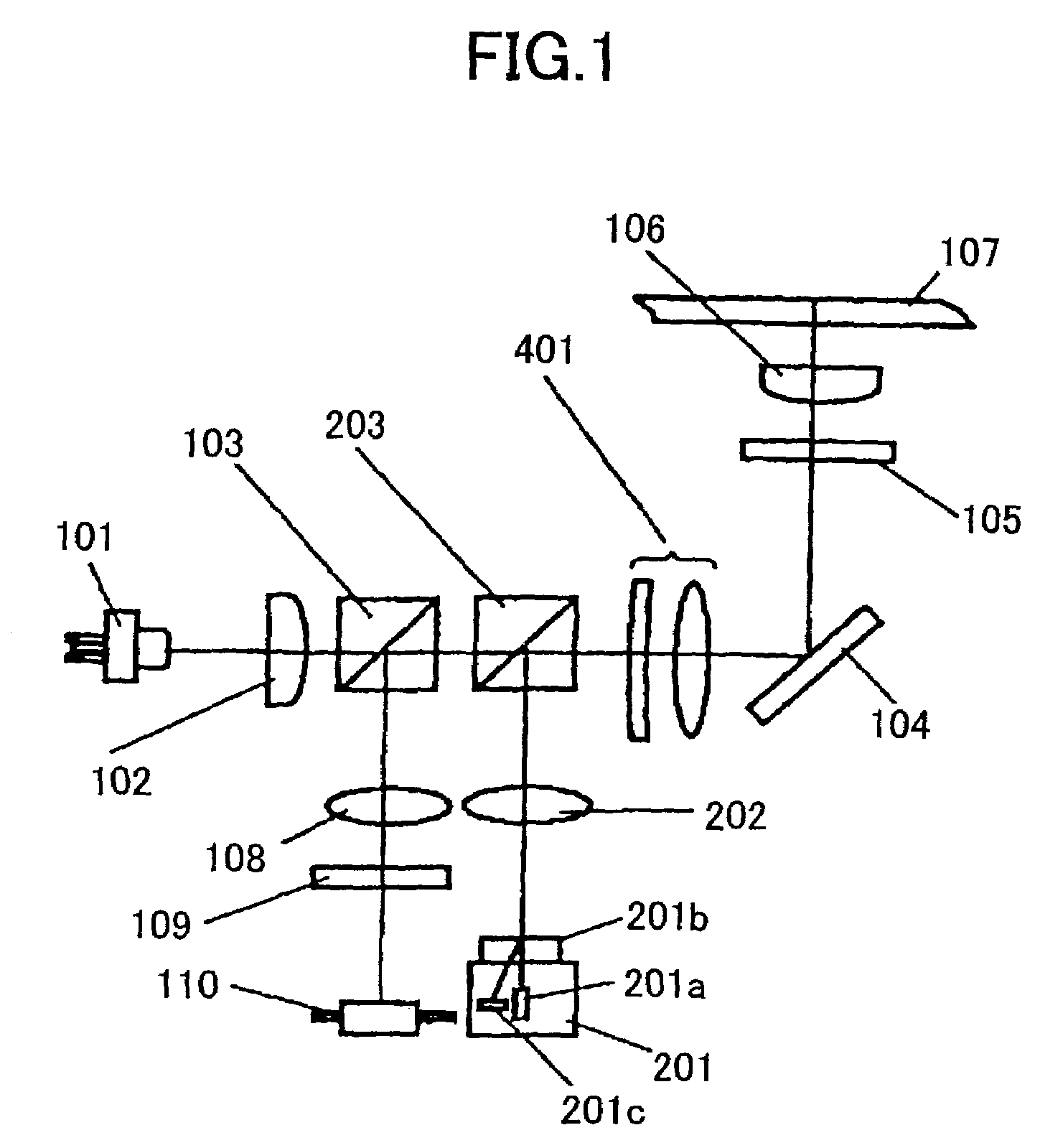
Optical reproducing apparatus
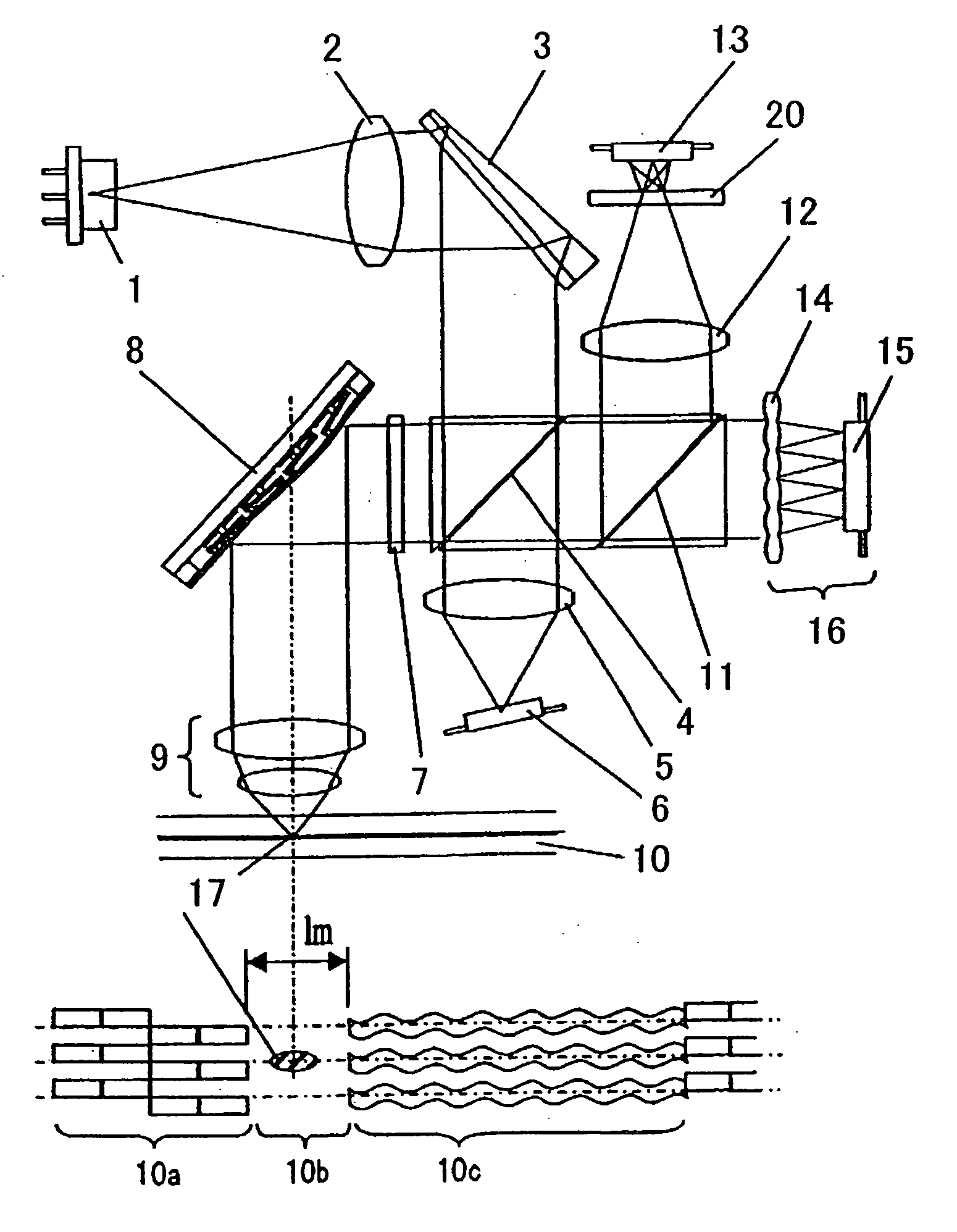
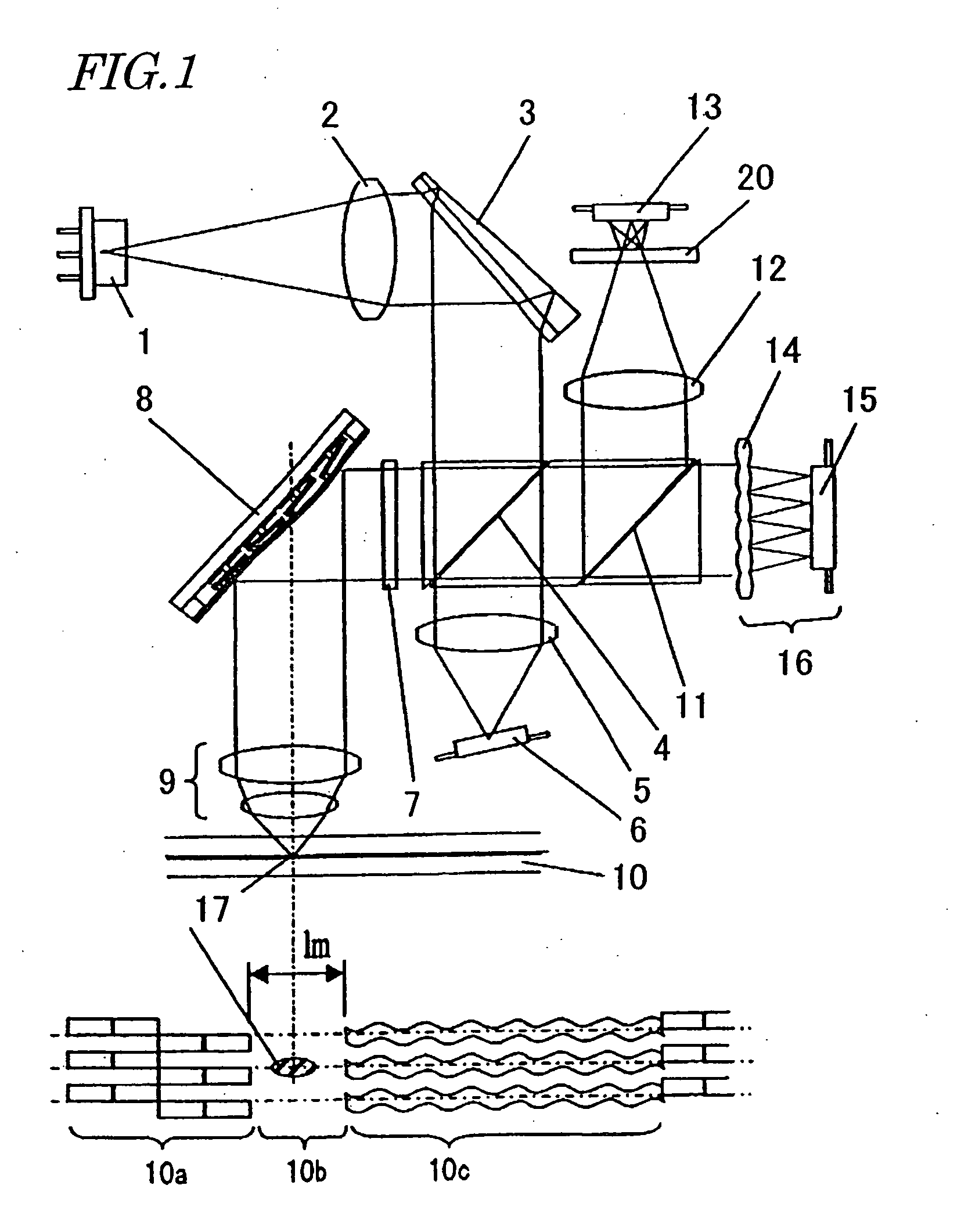
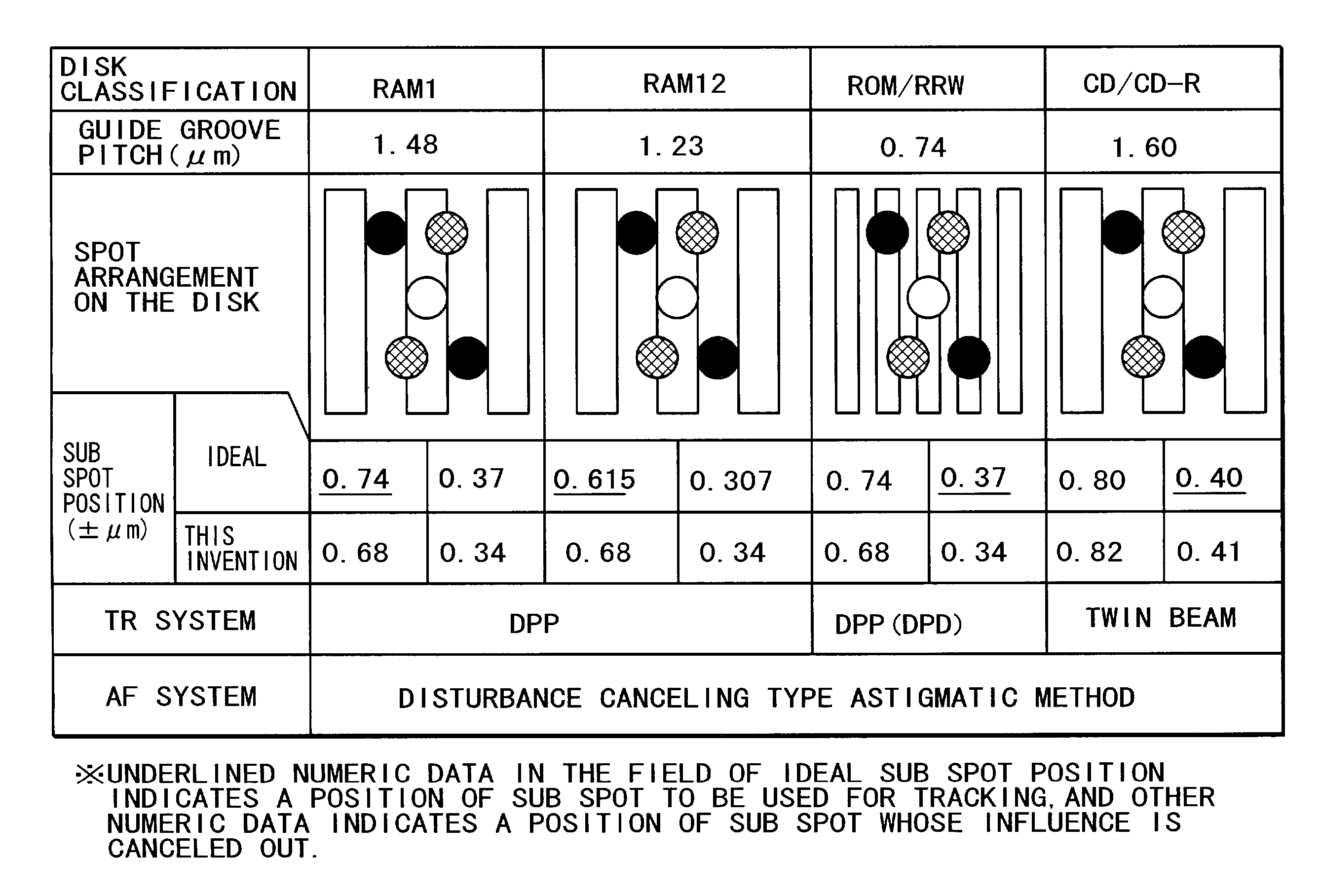
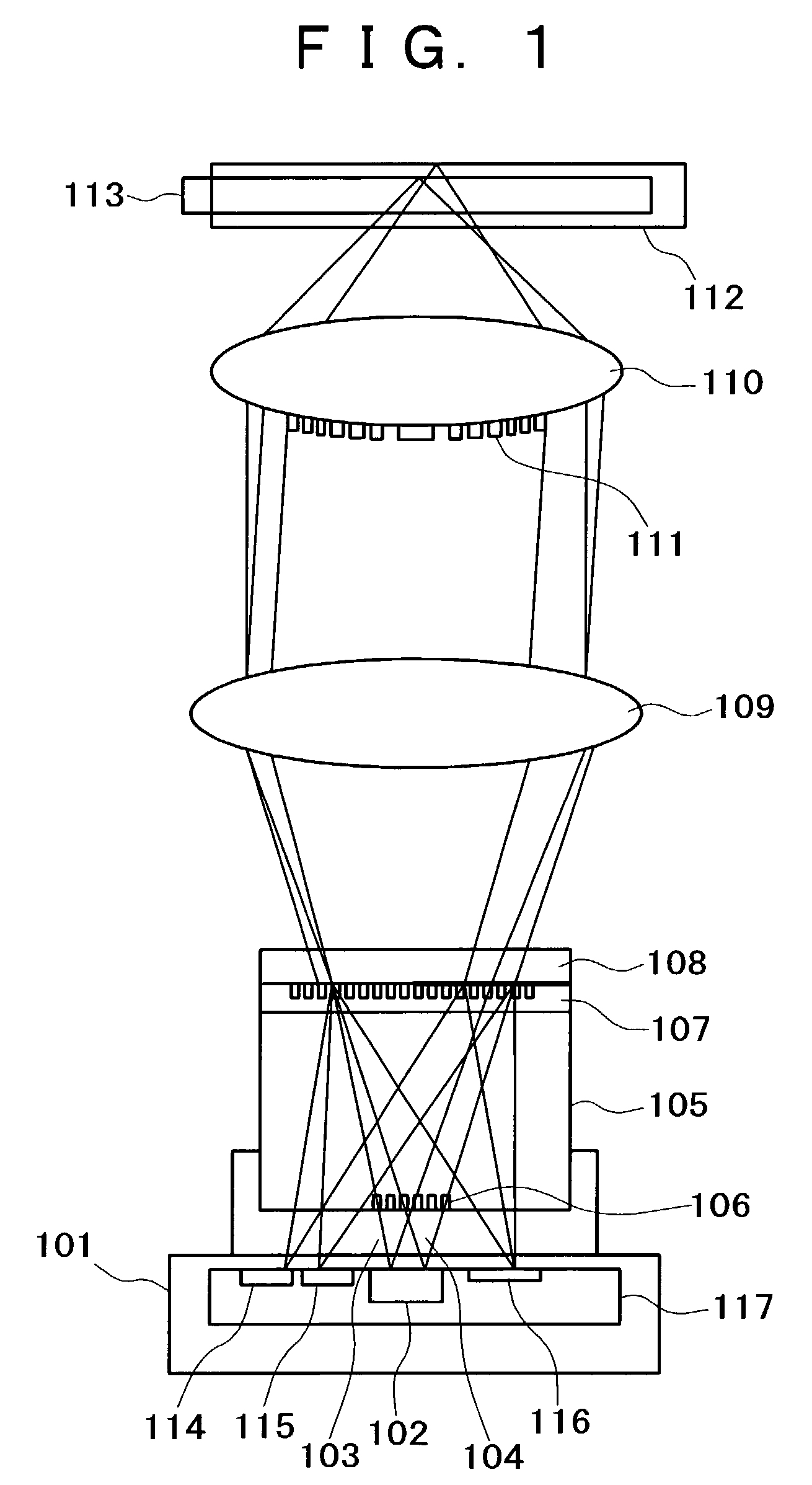
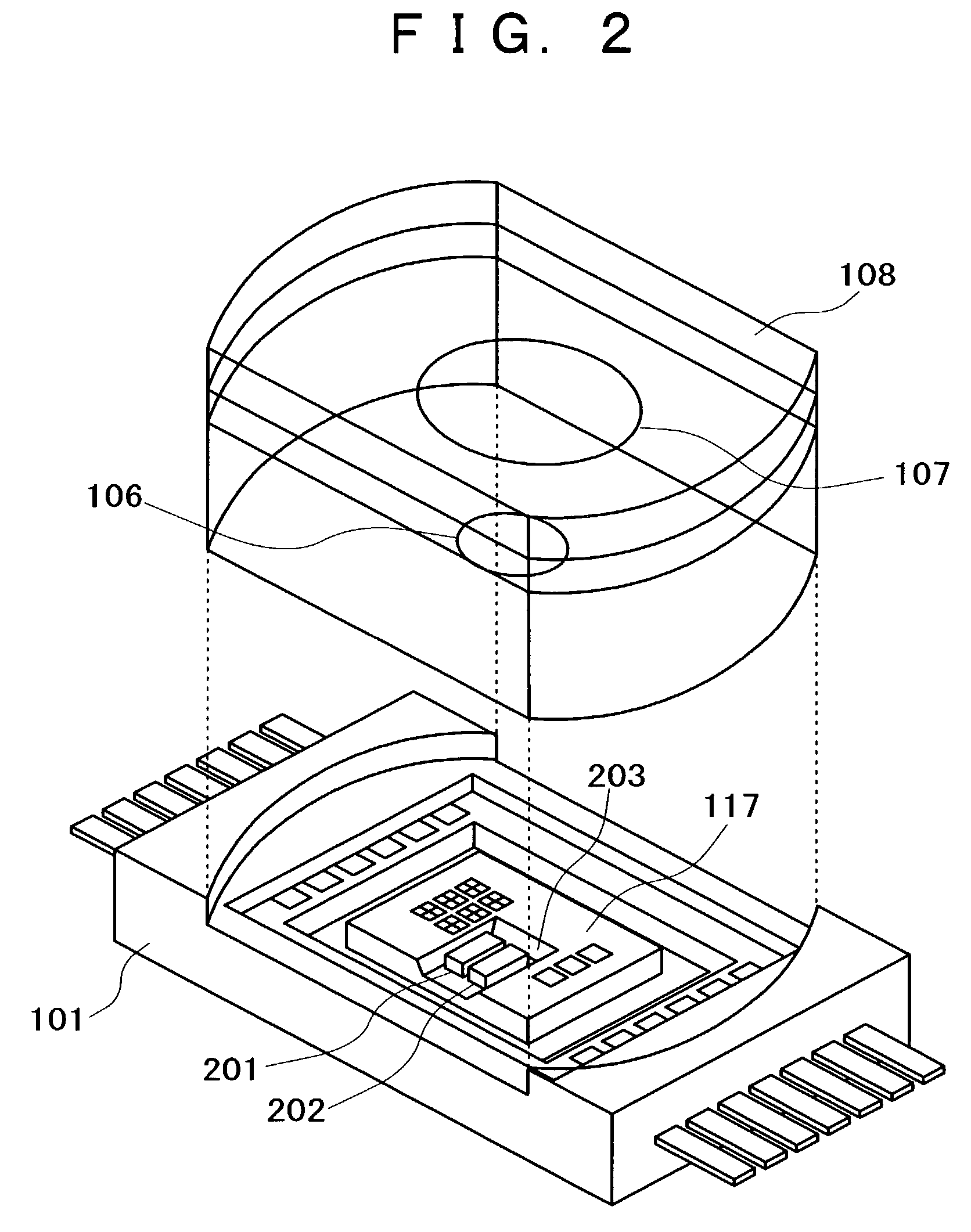
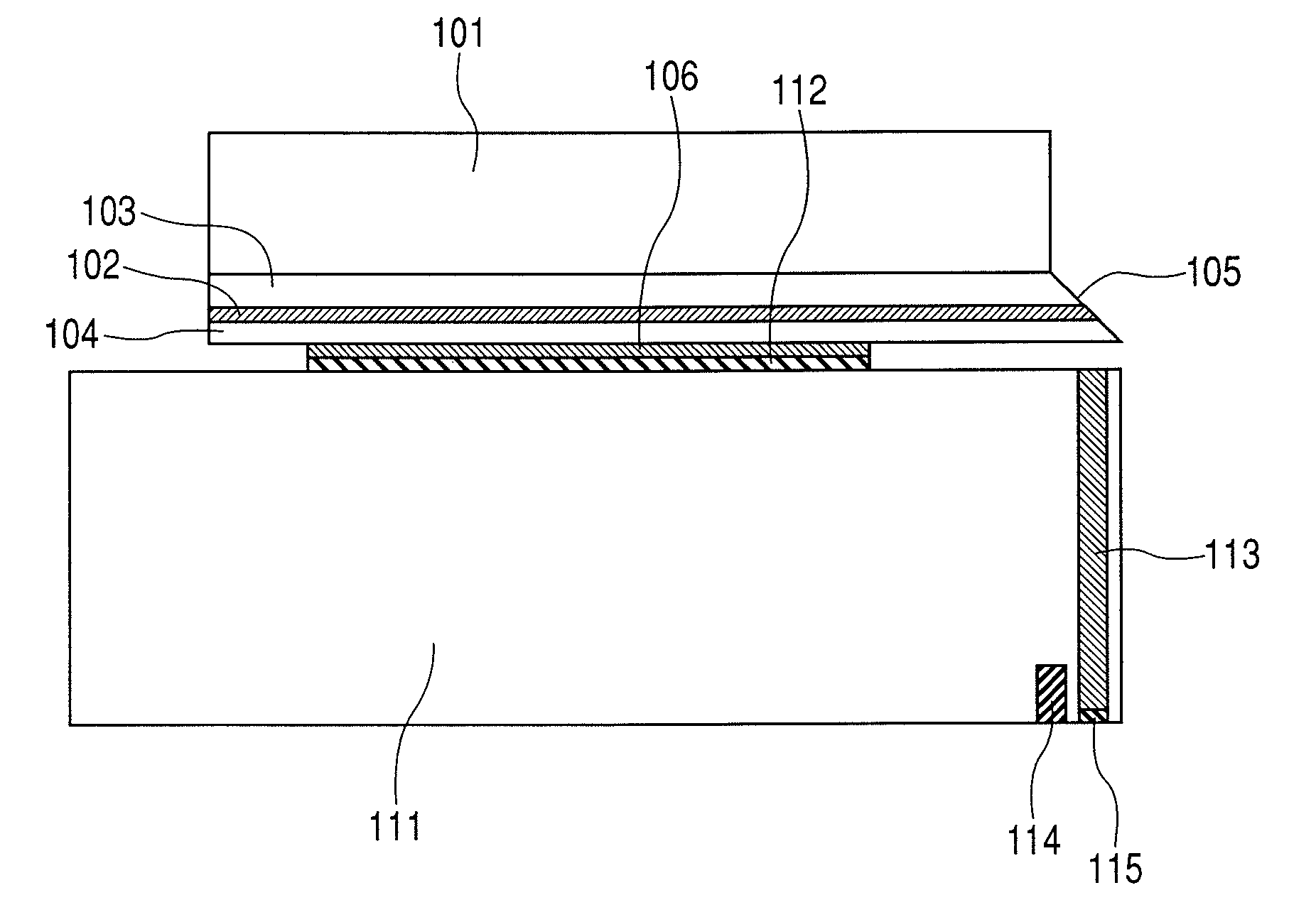
An optical reproducing apparatus that uses a hologram laser module and is applicable to a DVD Multi drive, wherein five sub spots of light in total that are most suitable to perform the differential push-pull tracking both for DVD-RAM and for DVD-R / RW are irradiated on the disk, respectively, and influence of several sub spots that are unnecessary in recording and reproducing a disk is canceled out by calculation, to realize an optical head that is compatible with the DVD Multi drive using a hologram laser module, and thereby providing a small-size, high-performance optical reproducing apparatus.
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP
Recording head
InactiveUS7864635B2Effective guidanceIncrease the number ofCombination recordingIntegrated optical head arrangementsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingLight beam
It is an objective that the optical loss and the number of optical components are reduced in an optical recording head using a near-field where a laser beam is guided from a light source to the tip of the head and a thermally assisted magnetic recording head. A structure where the traveling direction of emitted beam is rotated in the direction of the cavity of the laser diode element and a reflector for guiding the beam to the surface of the surface of the laser diode element is monolithically integrated in the laser diode element is mounted over the slider so that the direction of the cavity of the laser diode element is parallel to the surface of the recording medium, and the substrate side of the laser diode element is mounted to be in the direction opposite the face adjacent to the upper face of the slider.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com