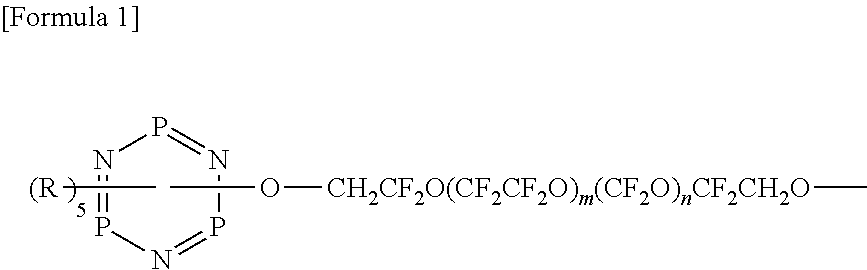Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
569 results about "Heat-assisted magnetic recording" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
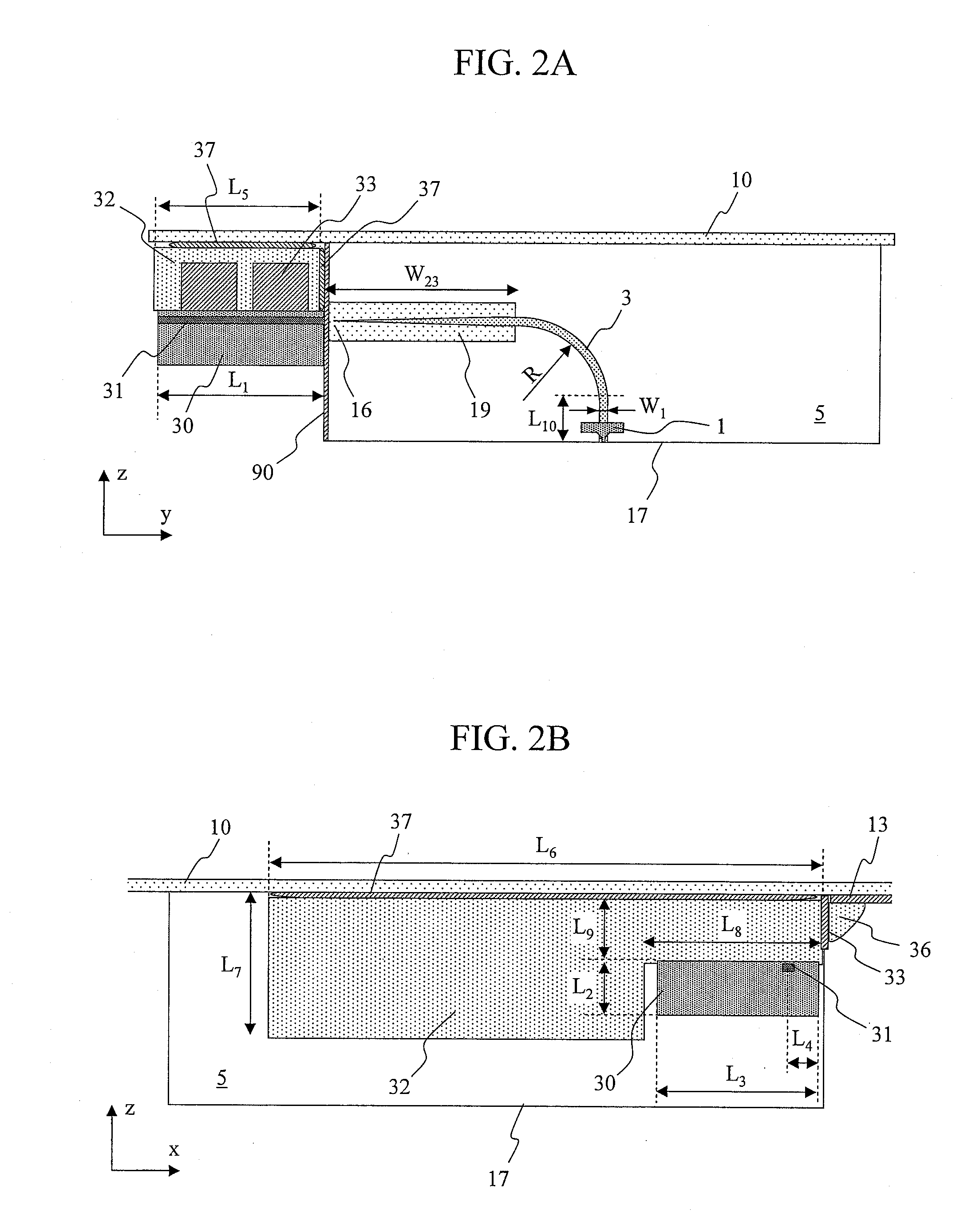
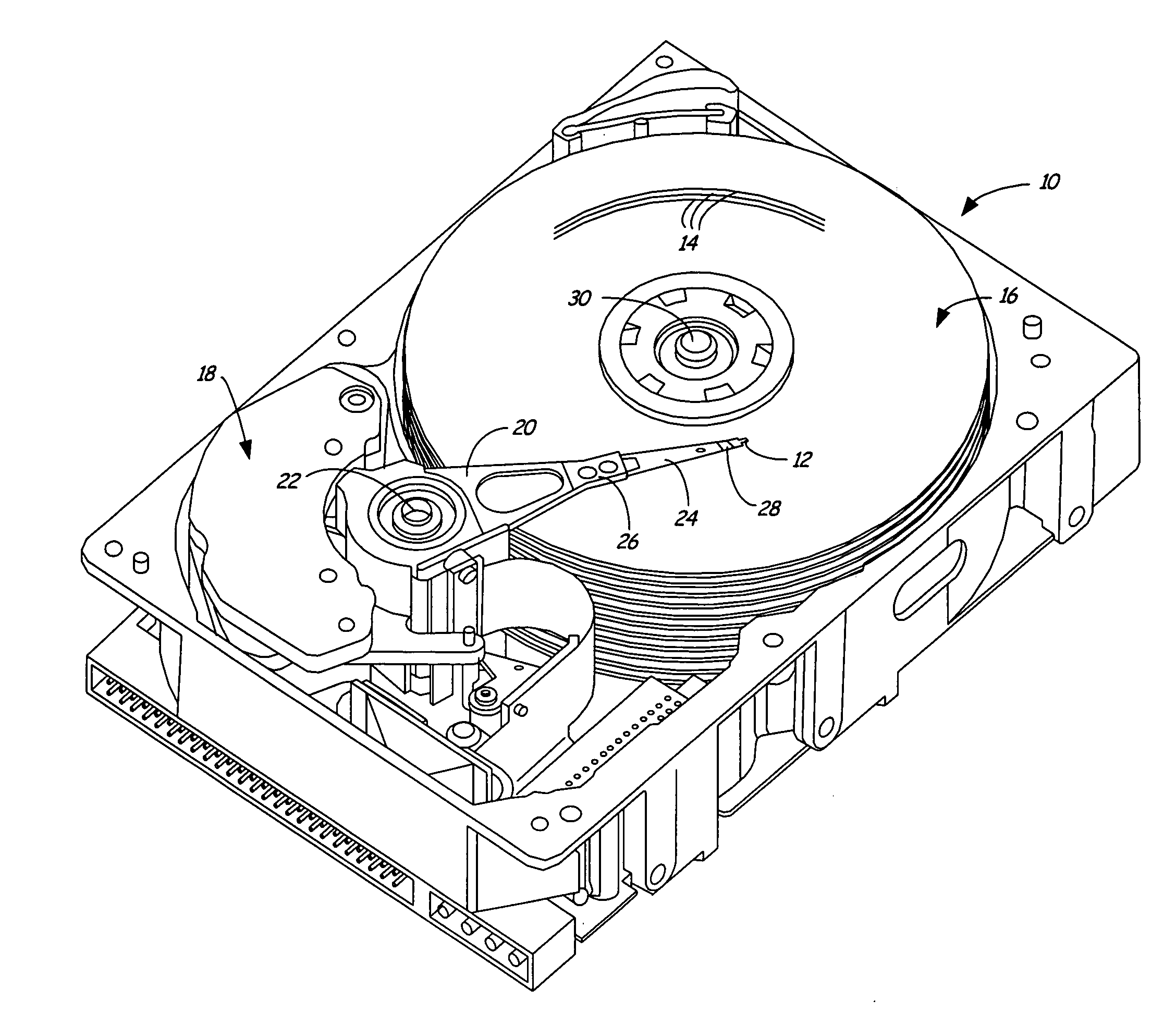
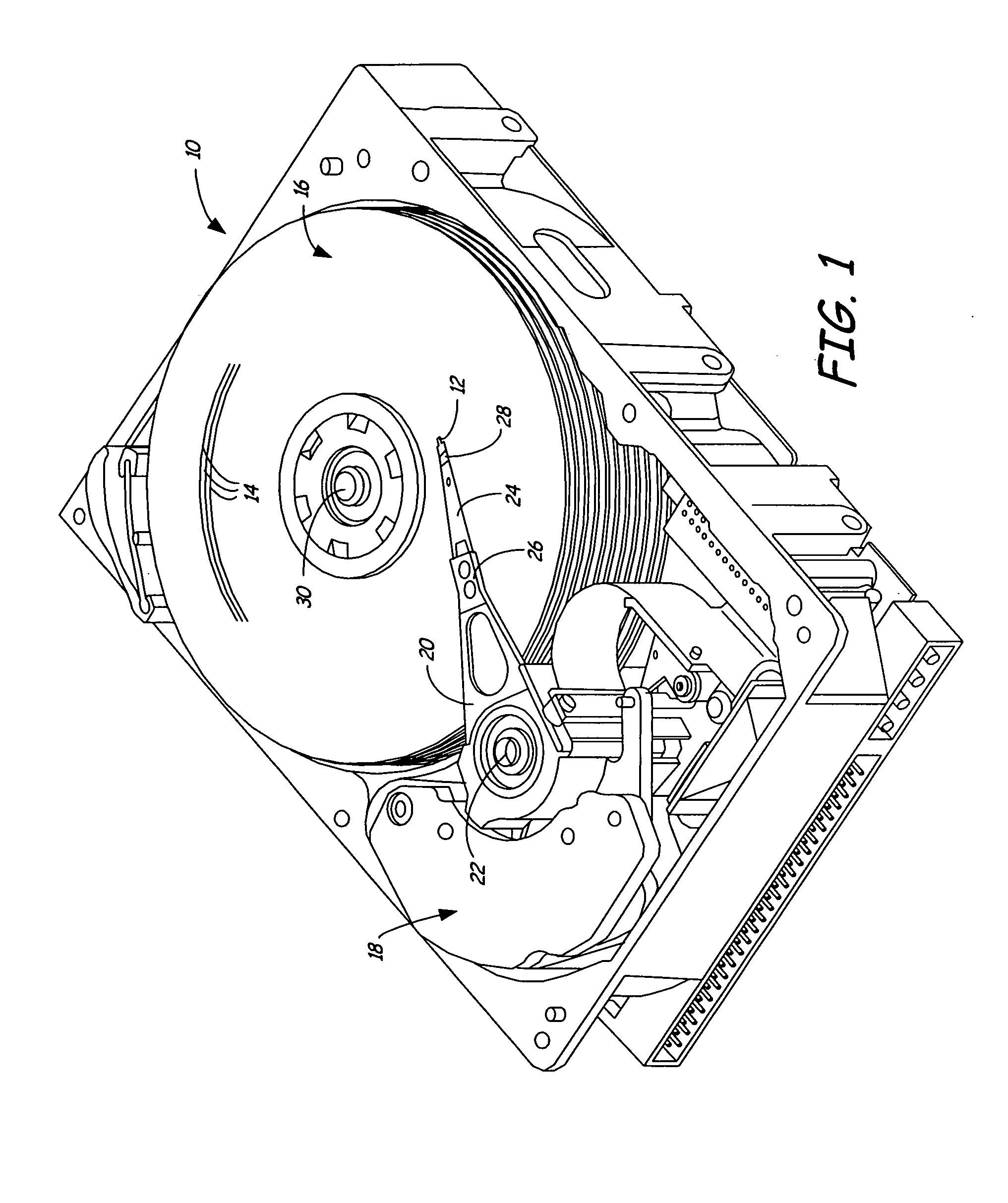
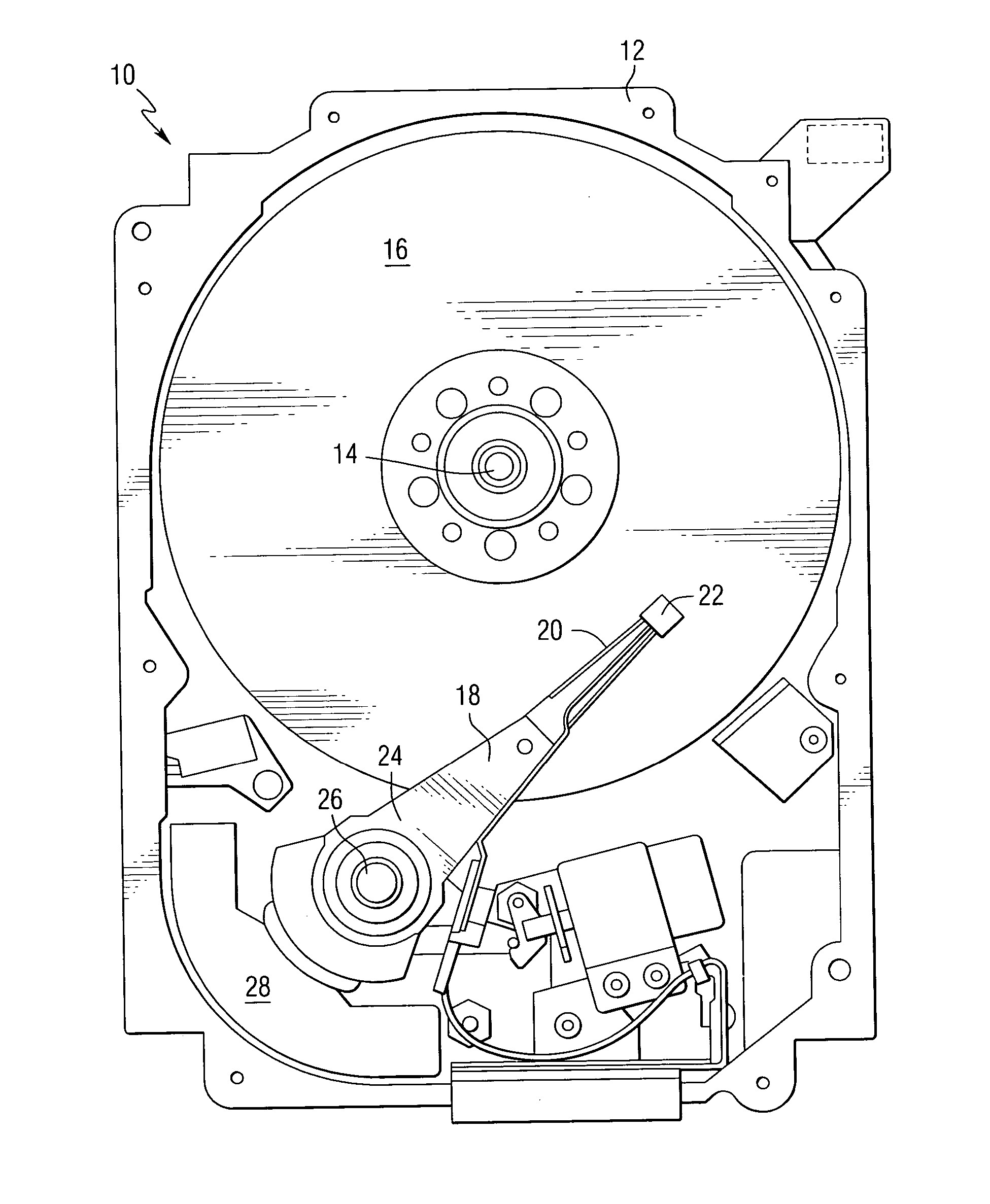
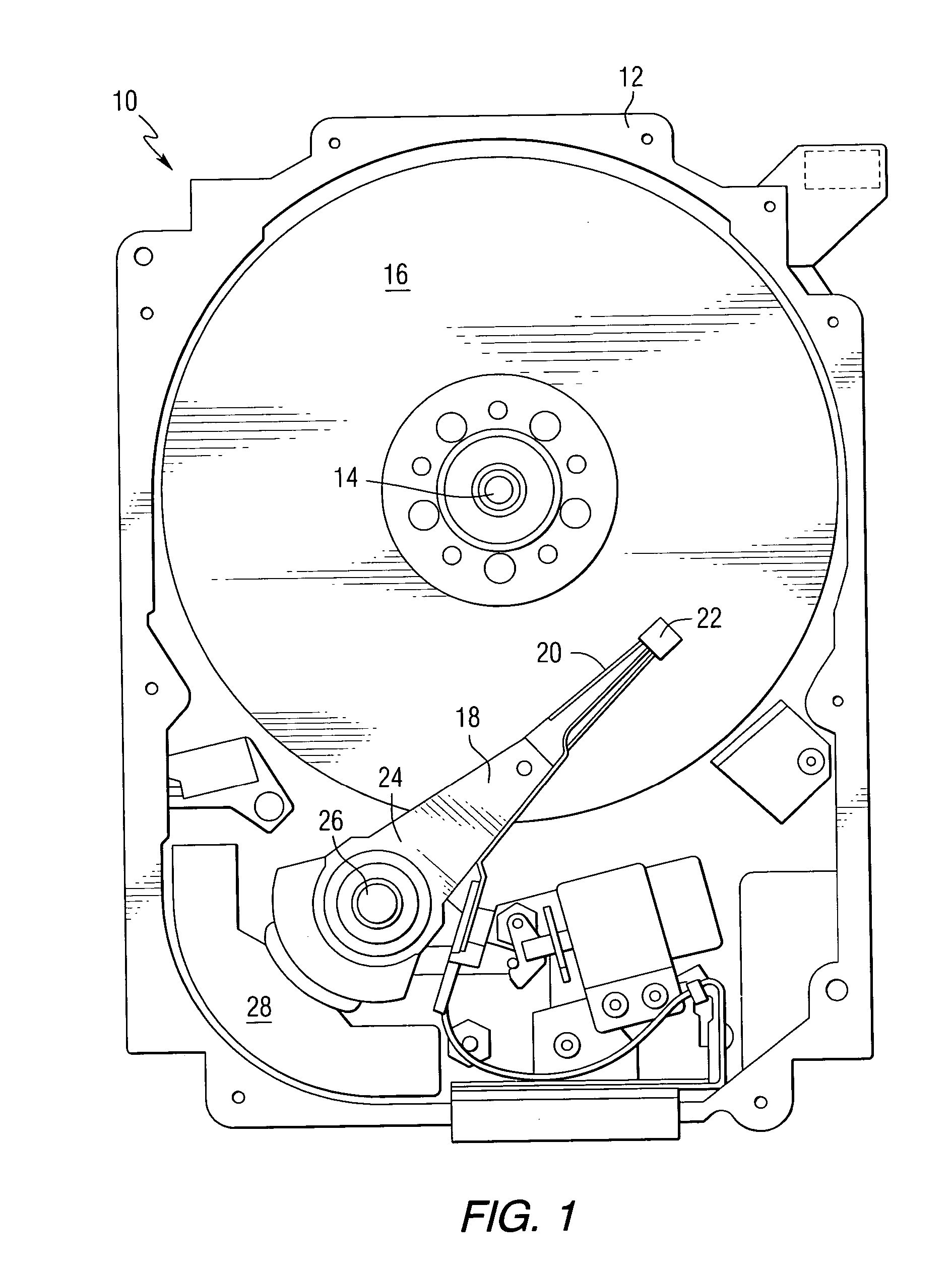
Heat-assisted magnetic recording (HAMR) is a magnetic storage technology for greatly increasing the amount of data that can be stored on a magnetic device such as a hard disk drive by temporarily heating the disk material during writing, which makes it much more receptive to magnetic effects and allows writing to much smaller regions (and much higher levels of data on a disk).
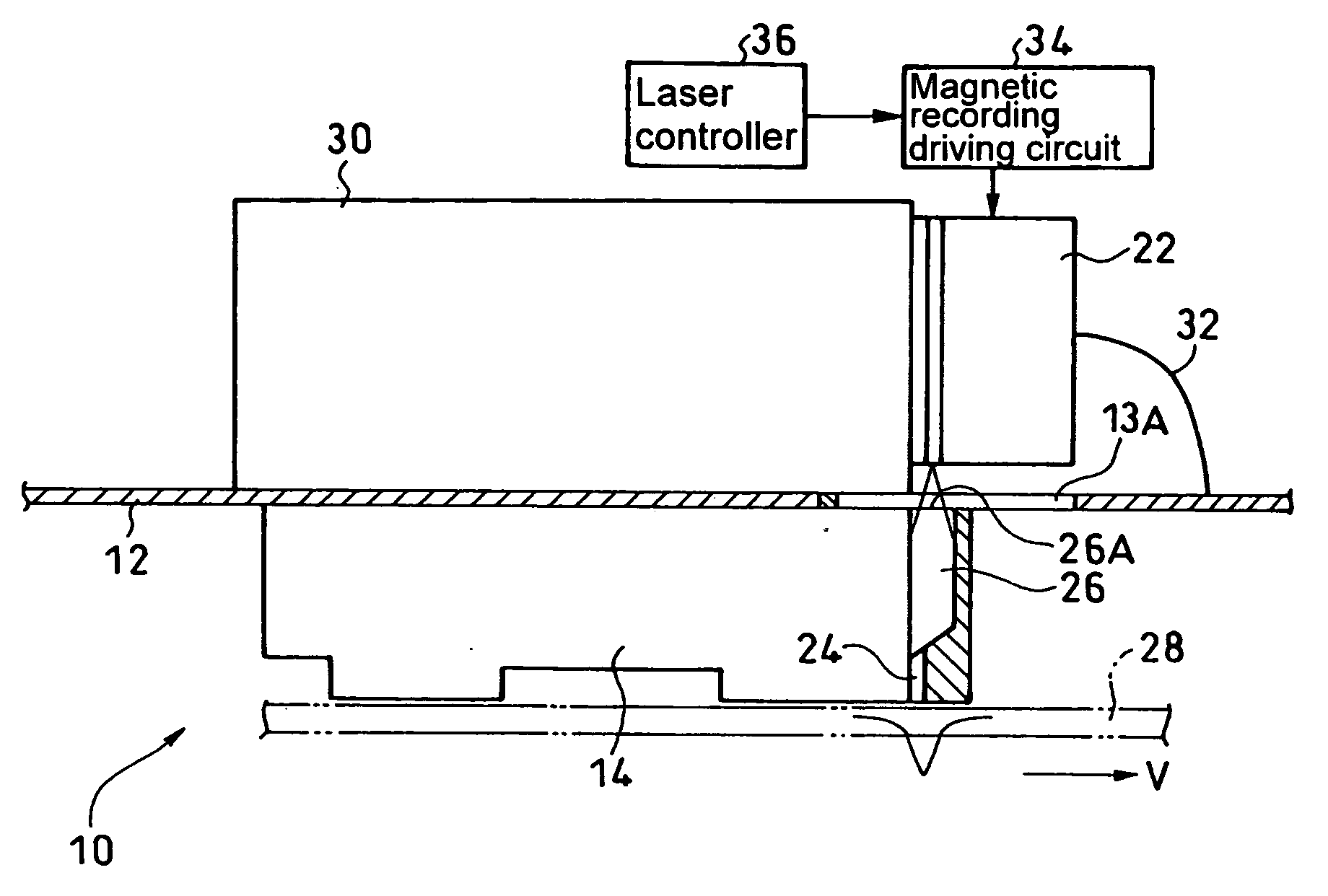
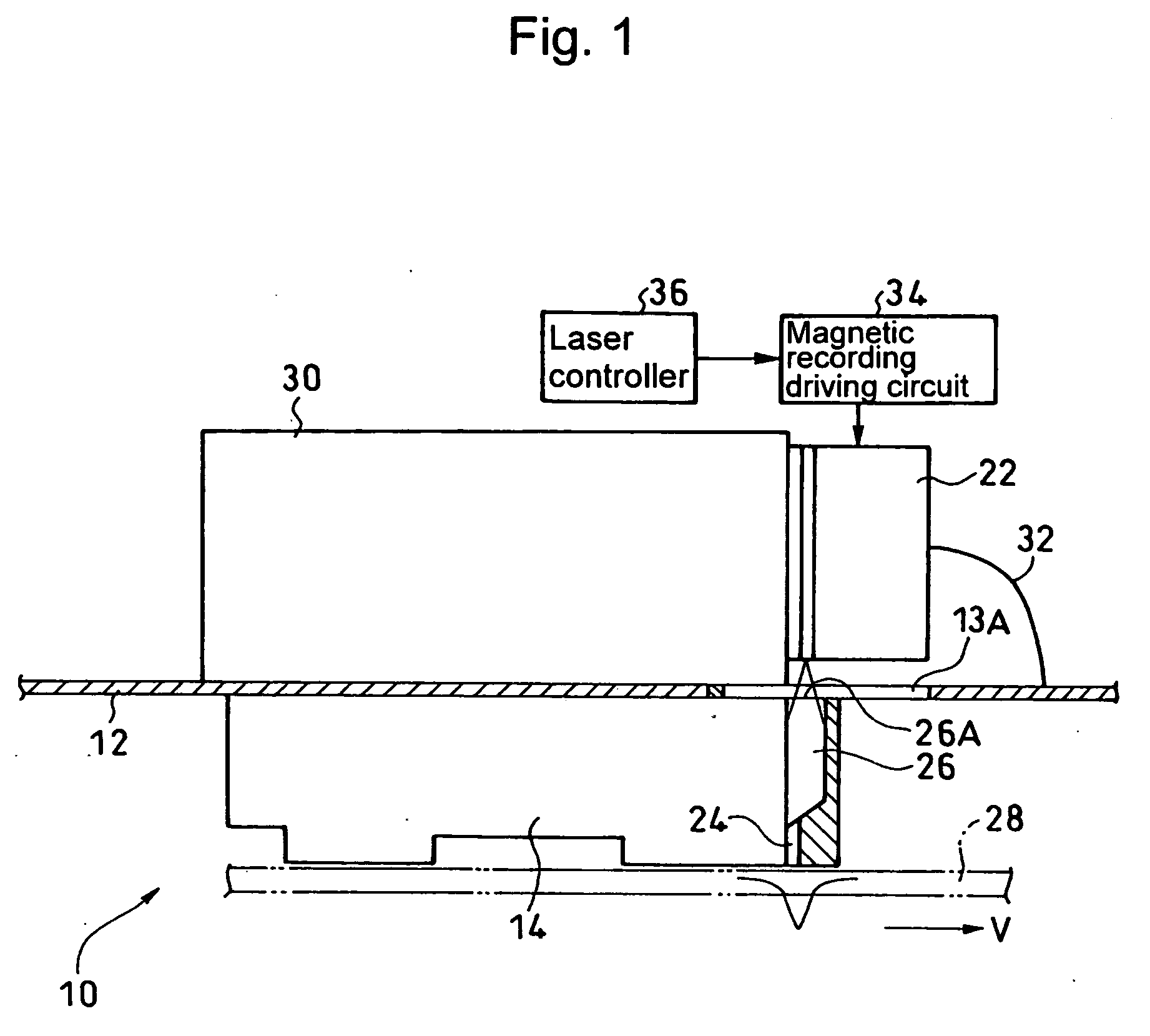
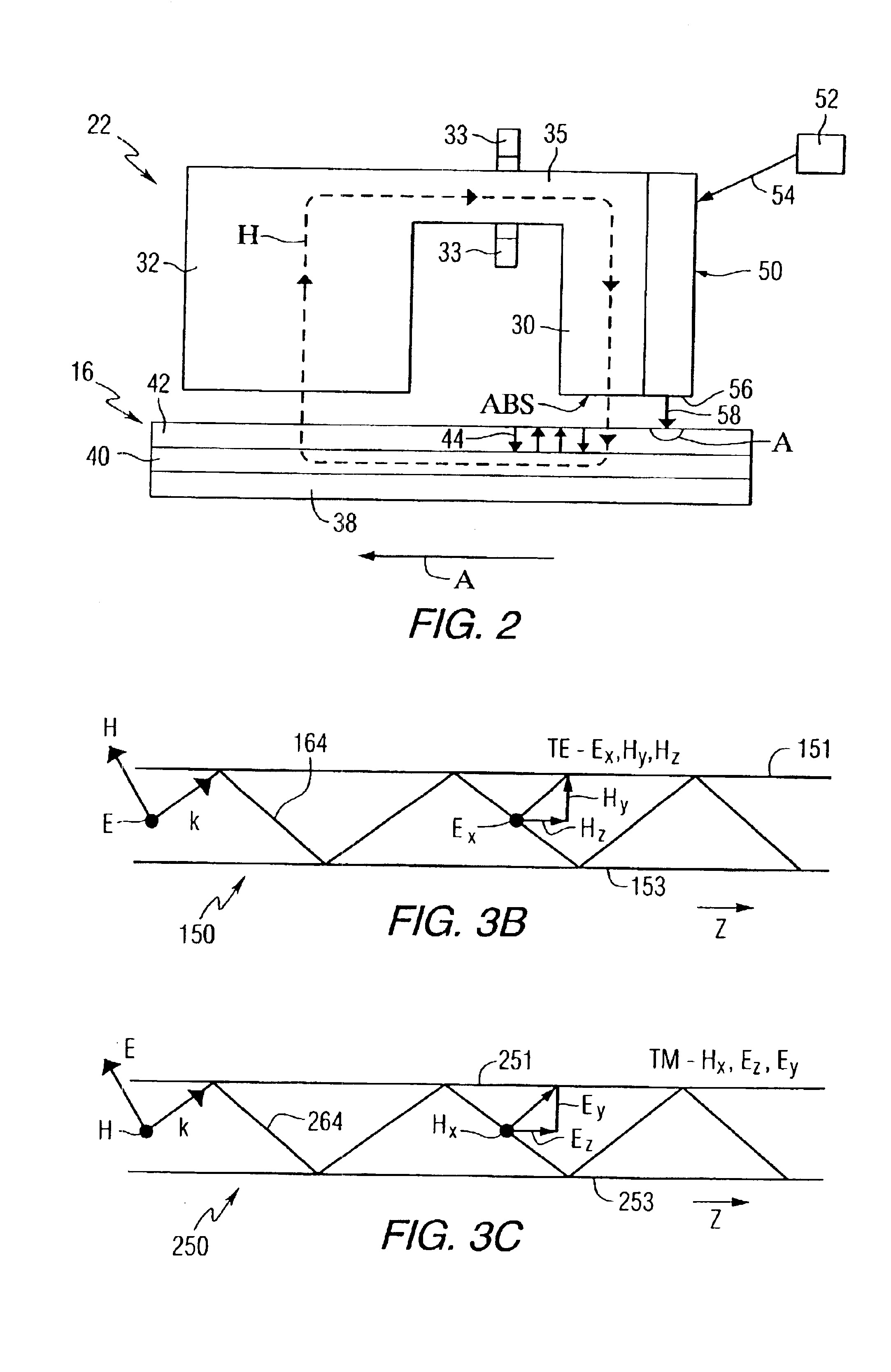
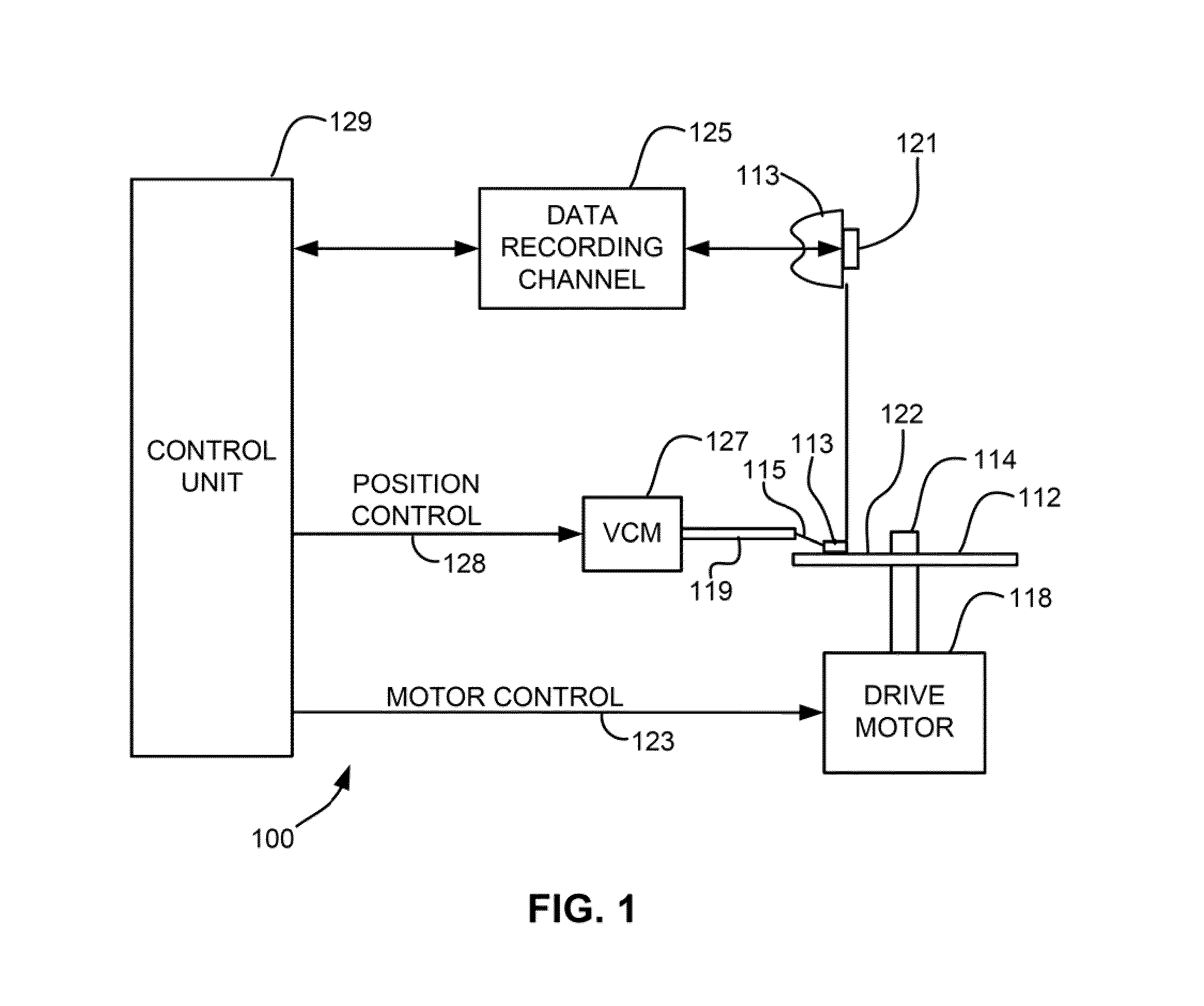
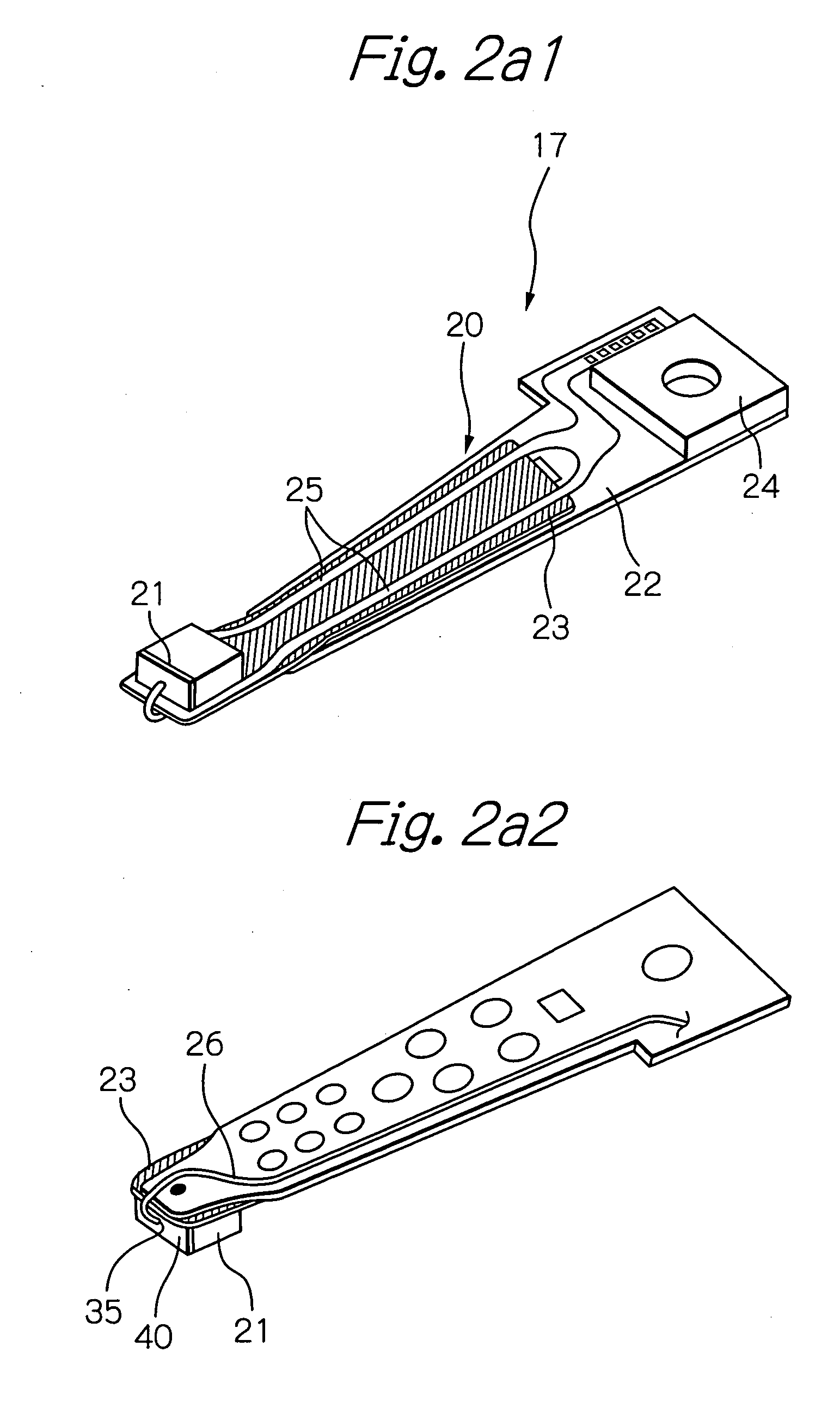
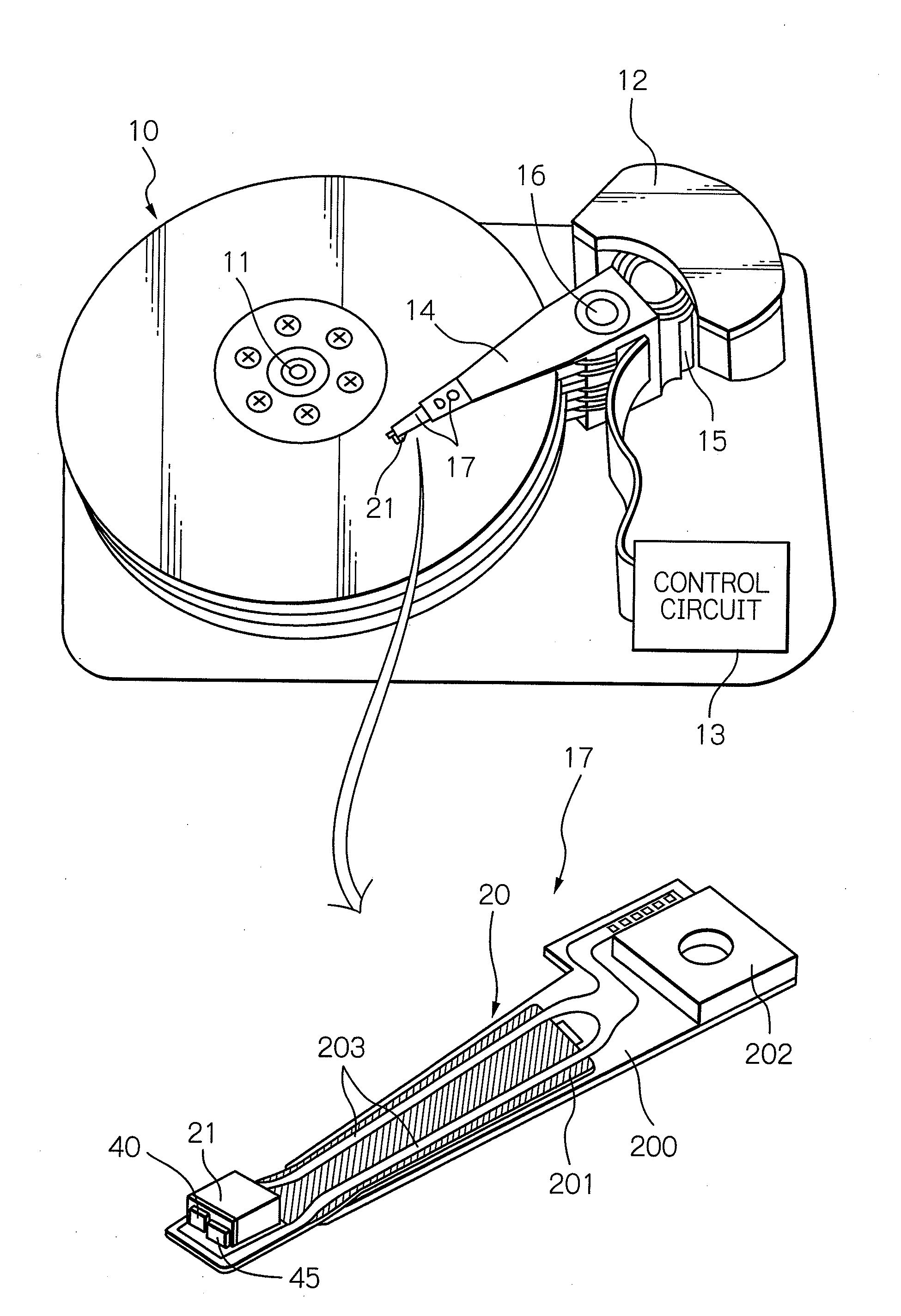
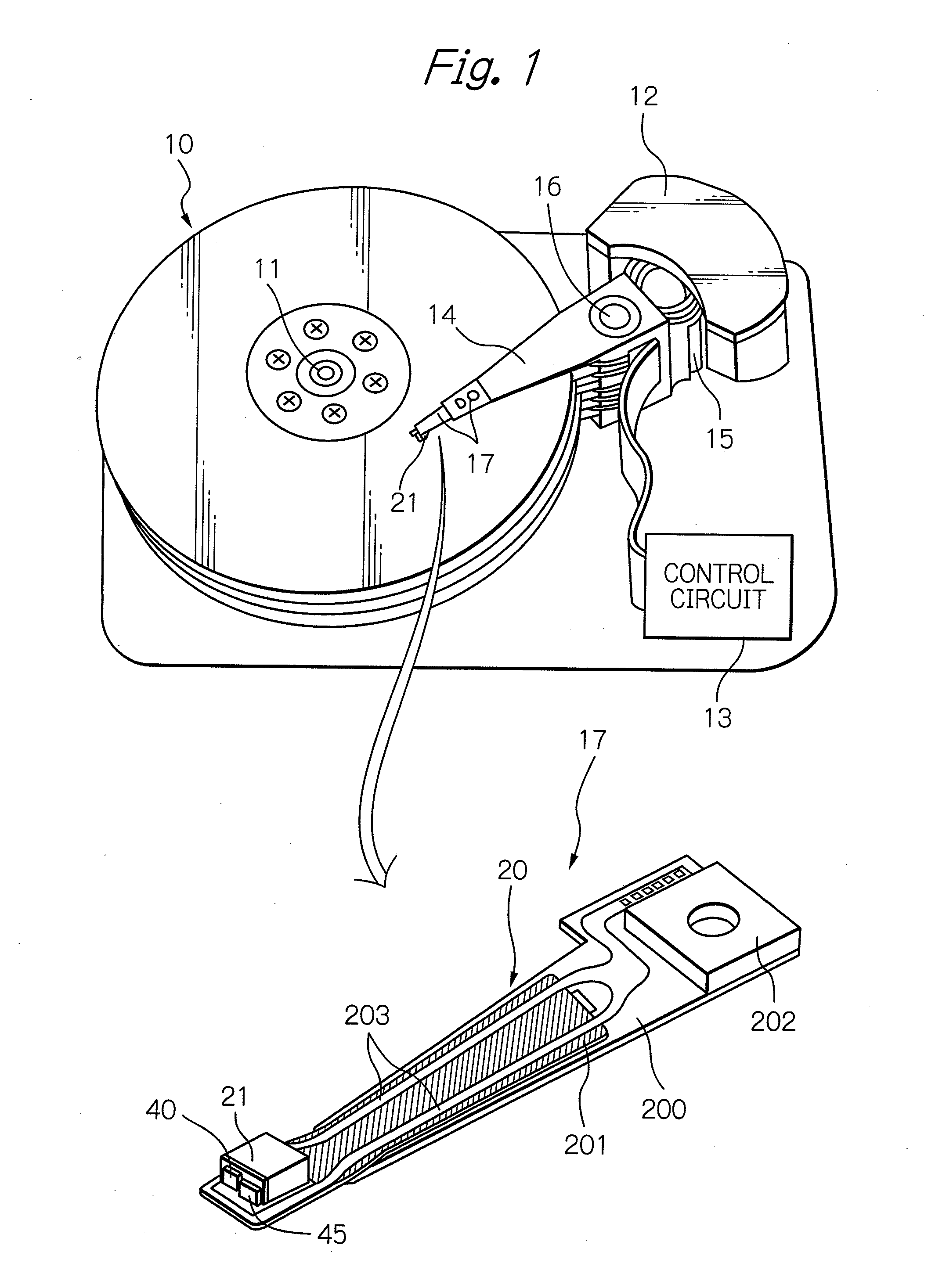
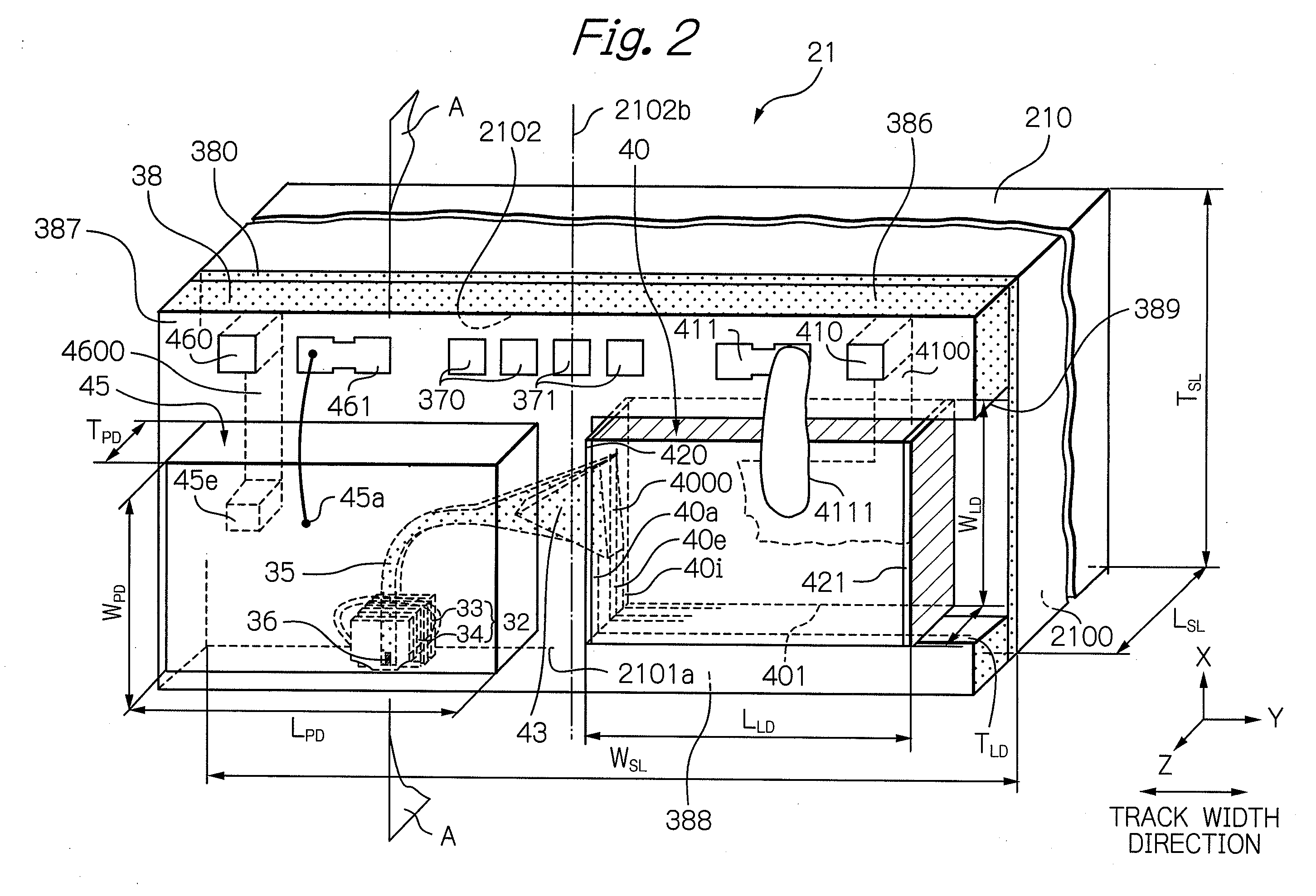
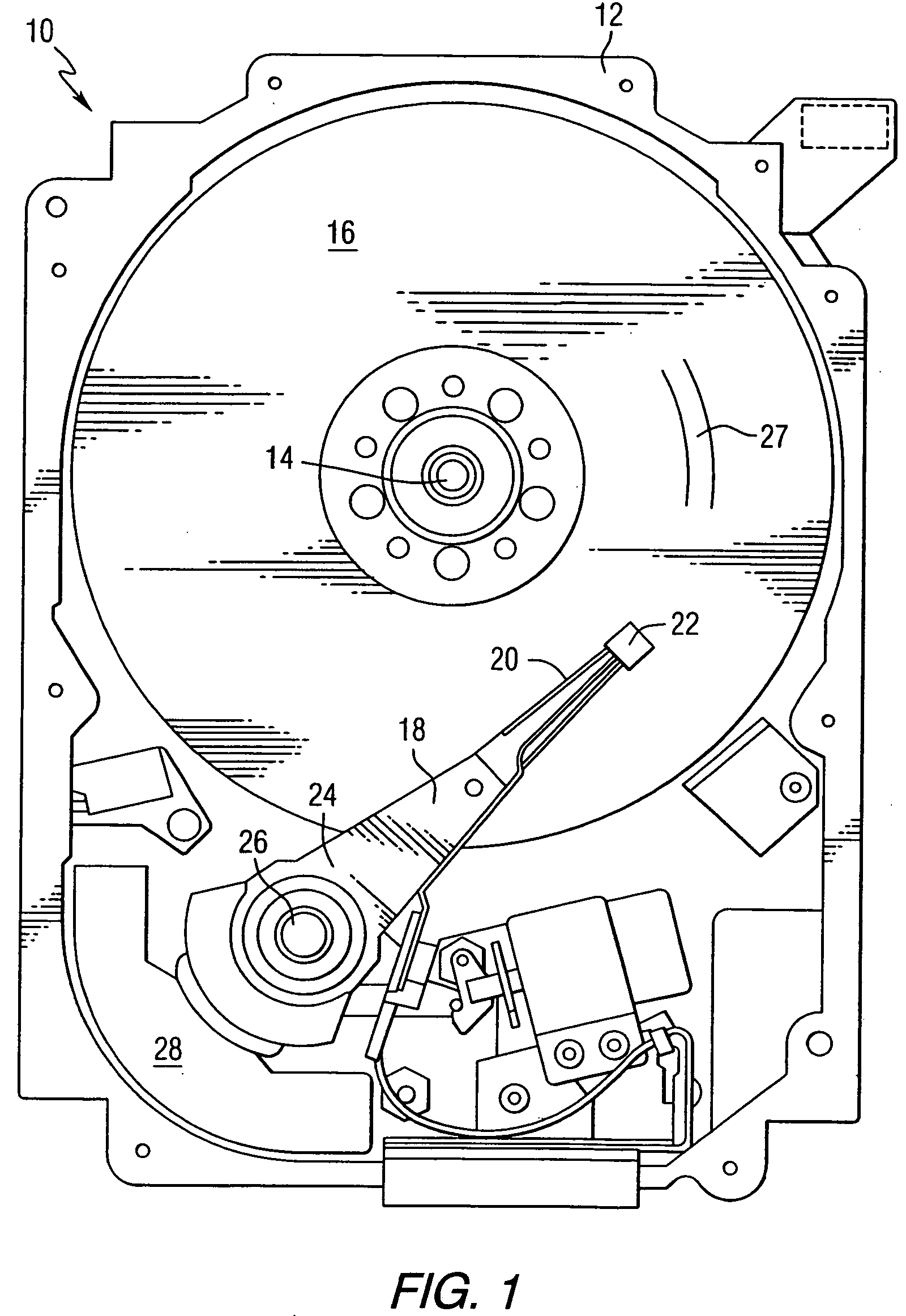
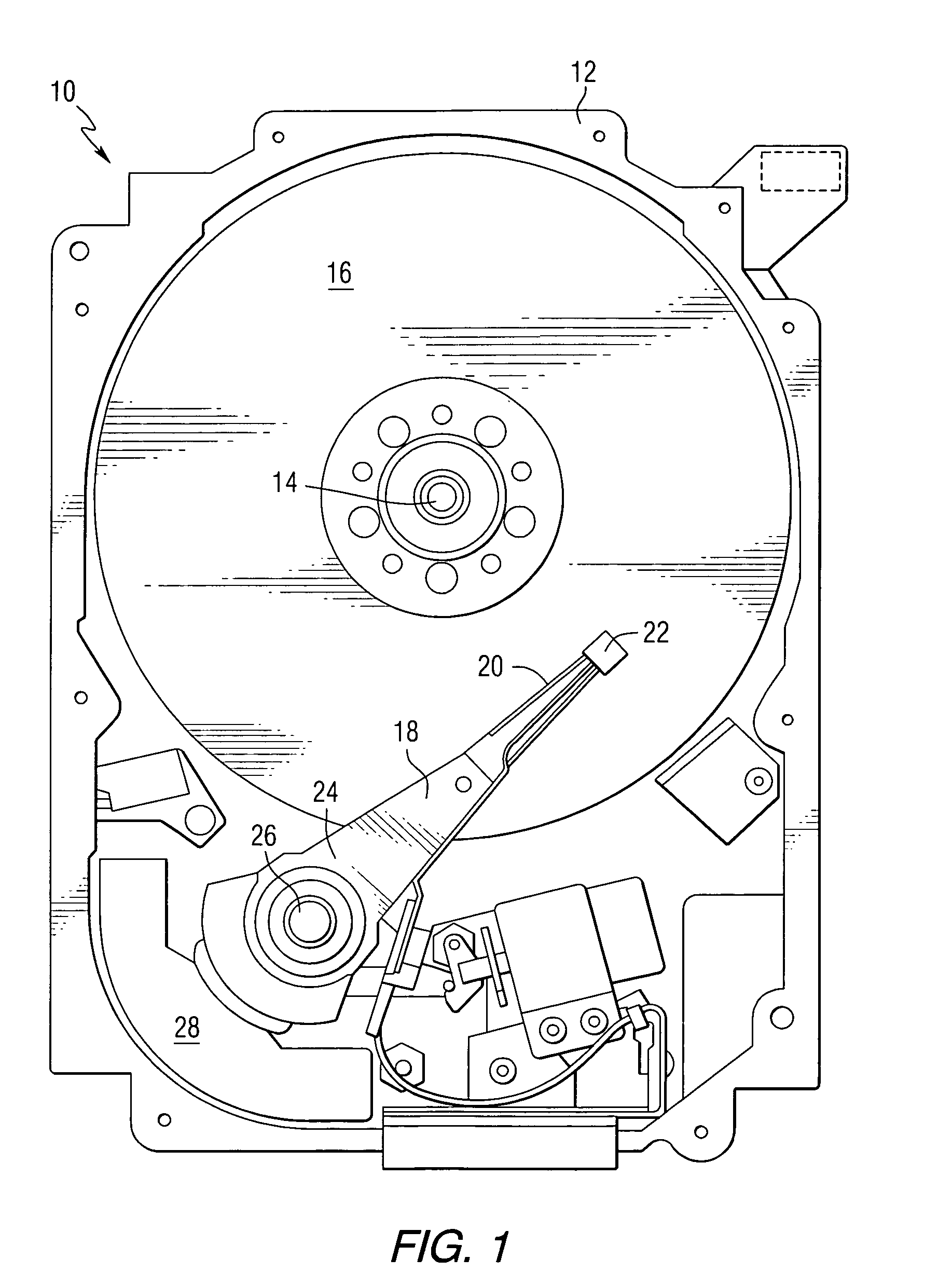
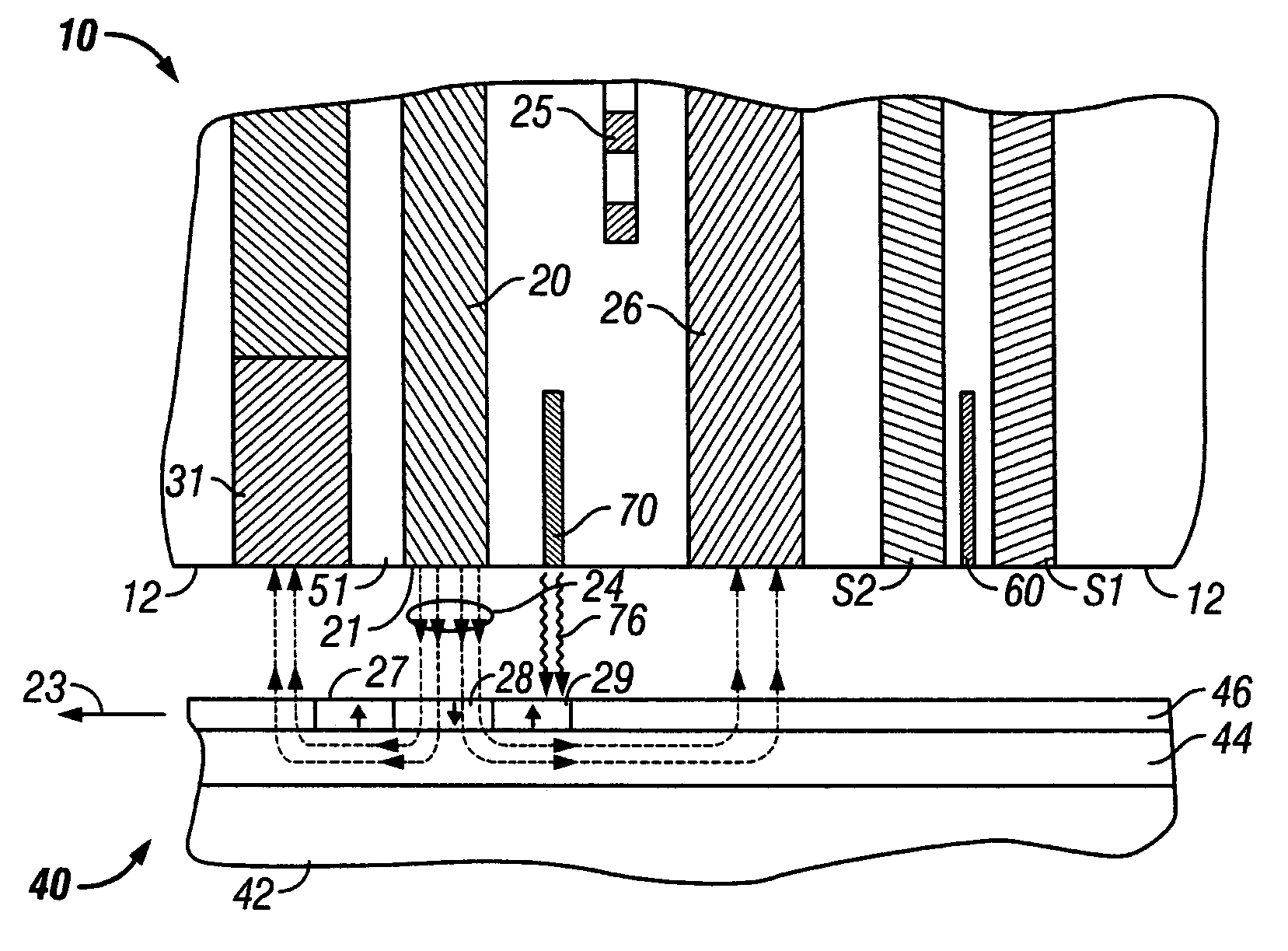
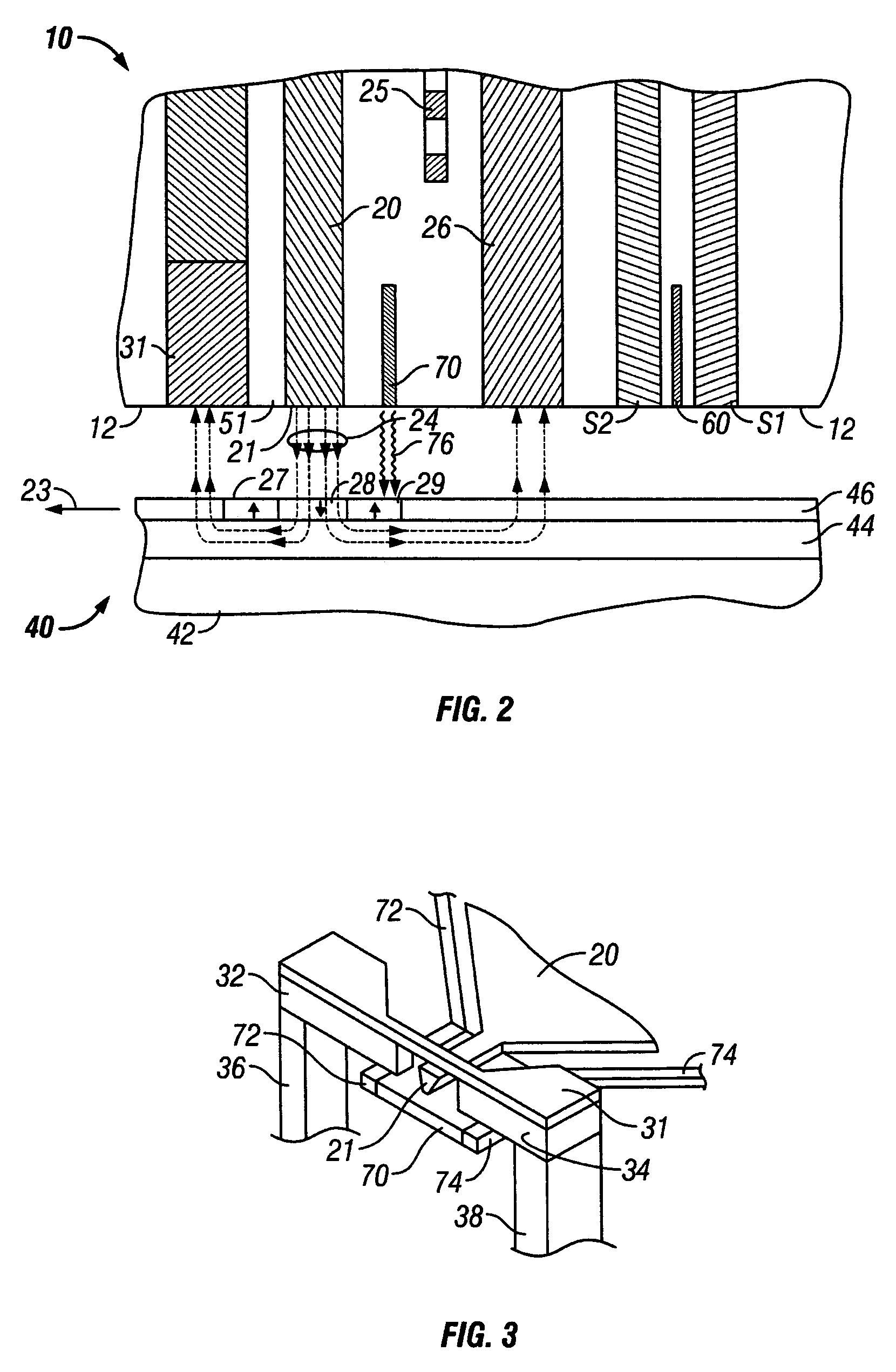
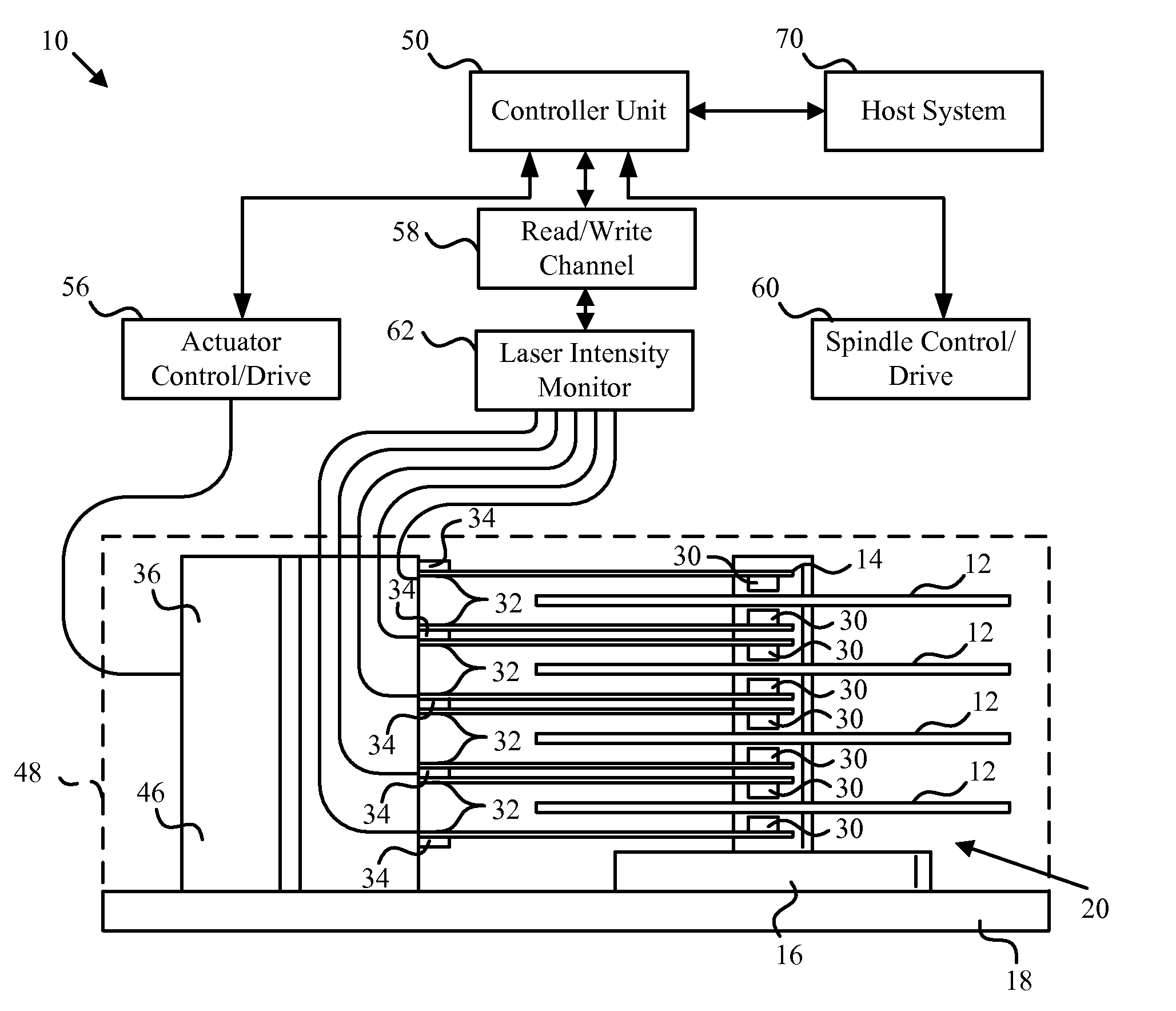
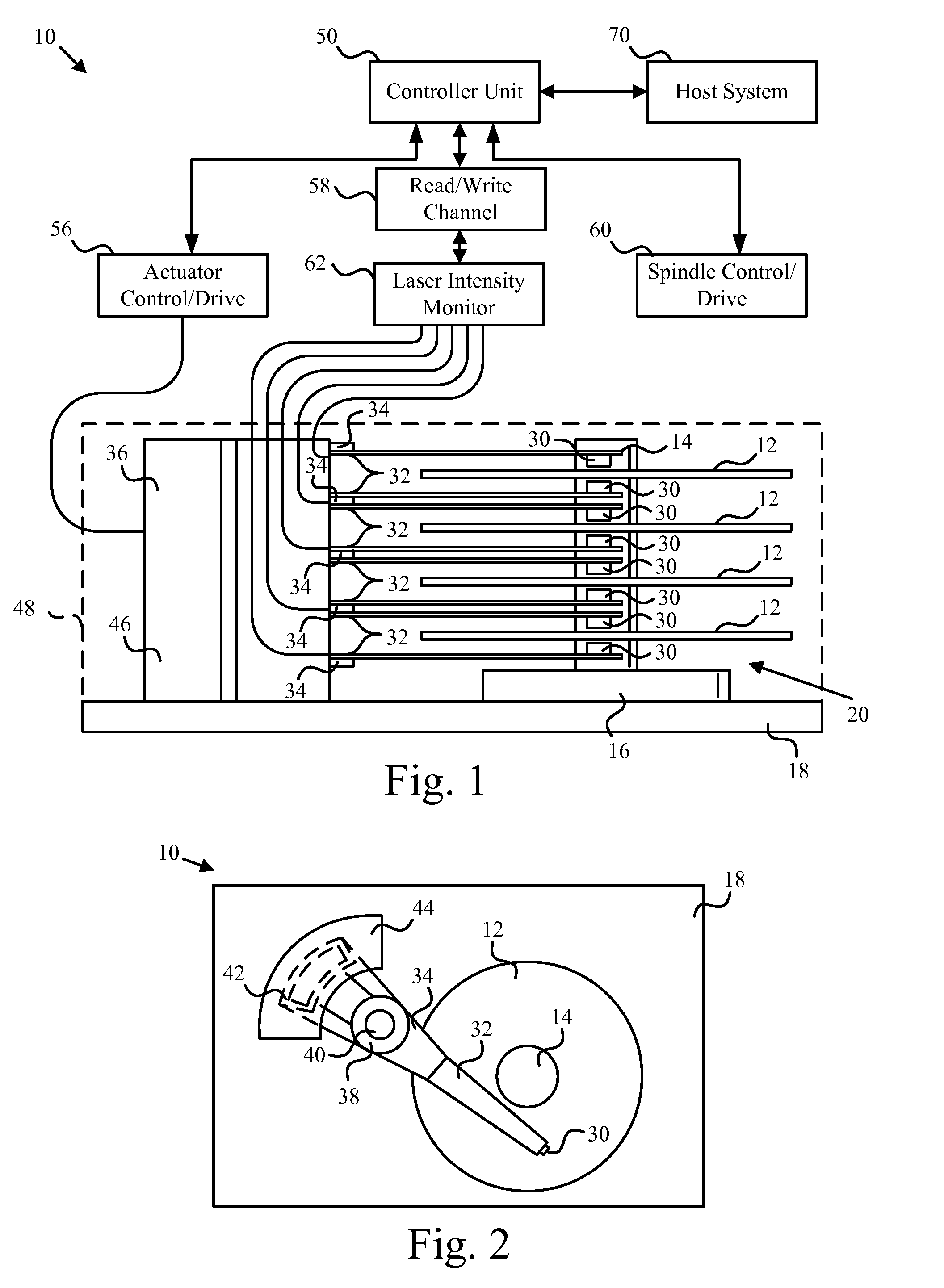
Heat assisted magnetic recording head and heat assisted magnetic recording apparatus
ActiveUS20060187564A1Compact mountingLess crosstalkRecord information storageRecording/reproducing/erasing methodsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingMagnetic poles
A heat assisted magnetic recording head is provided, which can prevent an effect of a heat in a laser diode when a magnetic recording region is heated by a heating laser beam and which can reduce its size and weight. In the heat assisted magnetic recording head, a recording magnetic pole, a magnetic recording element, a magnetic read element, an optical waveguide, and an irradiating optical waveguide are attached to a floating slider provided below a suspension. The laser diode is arranged on an opposite side of the suspension to the floating slider. The heating laser beam emitted from the laser diode is directed to the irradiating optical waveguide through the optical waveguide, so that a magnetic recording medium is irradiated with the heating laser beam exiting from the irradiating optical waveguide.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Transducer for heat assisted magnetic recording
ActiveUS7272079B2Combination recordingNanoinformaticsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingMagnetic storage
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Heat assisted magnetic recording head with a planar waveguide
InactiveUS6944112B2Combination recordingRecord information storageHeat-assisted magnetic recordingWaveguide
A heat assisted magnetic recording head having a planar waveguide for heating a recording medium proximate to where a write pole of the recording head applies a magnetic write field thereto. The planar waveguide includes at least one edge, which may have a substantially parabolic shape, that is shaped to reflect an electromagnetic wave to a focal point within the planar waveguide. The planar waveguide includes a truncated end adjacent the focal point such that the truncated end intersects the focal point.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Heat assisted magnetic recording head and heat assisted magnetic recording apparatus for heating a recording region in a magnetic recording medium during magnetic recording
ActiveUS7538978B2Compact mountingLess crosstalkRecord information storageRecording/reproducing/erasing methodsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingMagnetic poles
A heat assisted magnetic recording head is provided, which can prevent an effect of a heat in a laser diode when a magnetic recording region is heated by a heating laser beam and which can reduce its size and weight. In the heat assisted magnetic recording head, a recording magnetic pole, a magnetic recording element, a magnetic read element, an optical waveguide, and an irradiating optical waveguide are attached to a floating slider provided below a suspension. The laser diode is arranged on an opposite side of the suspension to the floating slider. The heating laser beam emitted from the laser diode is directed to the irradiating optical waveguide through the optical waveguide, so that a magnetic recording medium is irradiated with the heating laser beam exiting from the irradiating optical waveguide.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Recording head
InactiveUS20080056073A1Reduce lossesEffective guidanceCombination recordingIntegrated optical head arrangementsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingLight beam
It is an objective that the optical loss and the number of optical components are reduced in an optical recording head using a near-field where a laser beam is guided from a light source to the tip of the head and a thermally assisted magnetic recording head. A structure where the traveling direction of emitted beam is rotated in the direction of the cavity of the laser diode element and a reflector for guiding the beam to the surface of the surface of the laser diode element is monolithically integrated in the laser diode element is mounted over the slider so that the direction of the cavity of the laser diode element is parallel to the surface of the recording medium, and the substrate side of the laser diode element is mounted to be in the direction opposite the face adjacent to the upper face of the slider.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Alignment features for heat assisted magnetic recording transducers
ActiveUS20060233061A1Combination recordingRecord information storageGratingHeat-assisted magnetic recording
An apparatus comprises an optical transducer positioned adjacent to a storage medium and including a waveguide and a grating for coupling light into the waveguide, a light source transmitting light to the grating, and a detector for detecting a portion of the light, wherein the detected portion of the light has a magnitude that varies in response to the amount of light coupled into the waveguide.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Thermally assisted magnetic recording head and magnetic recording apparatus
InactiveUS20080204916A1Coupling efficiency is improvedOptical power in fluctuatesDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageHeat-assisted magnetic recordingPhotodetector
A second waveguide is formed near a first waveguide for guiding light to the vicinity of a main pole of a thermally assisted magnetic recording head, and a portion of light propagated through the waveguide 1 is branched to the second waveguide. The light transmitting in the second waveguide is detected by a photodetector to detect an intensity of the light propagated through the first waveguide. In the magnetic recording apparatus, an intensity of a semiconductor laser is decreased when an amount of light incident to the photodetector is large and the intensity of the semiconductor laser is increased when the amount of light incident to the photodetector is small. By constituting a feedback loop as described above, the intensity of the light propagated through the first waveguide is kept constant.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Head for thermal assisted magnetic recording device, and thermal assisted magnetic recording device
InactiveUS20110170381A1Improve performanceInhibit temperature riseCombination recordingRecord information storageHeat-assisted magnetic recordingSurface plasmon
An optical near-field generating efficiency of an optical near-field generating element is improved and a temperature rise of the element is suppressed. An optical near-field is generated using a conductive structure having a cross-sectional shape whose width in a direction perpendicular to a polarization direction of incident light transmitted through a waveguide gradually becomes shorter toward a vertex where an optical near-field is generated and having a shape whose width gradually, or in stages, becomes smaller in a traveling direction of the incident light toward the vertex where an optical near-field is generated. The waveguide is arranged beside the conductive structure and an optical near-field is generated via a surface plasmon generated on a lateral face of the conductive structure.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Heatsink films for magnetic recording media
ActiveUS20070026263A1Improve thermal conductivityImprove mechanical propertiesRecord information storageMagnetic recordingHeat-assisted magnetic recordingMetal alloy
Metal alloy heatsink films for magnetic recording media are disclosed. The metal alloy heatsink films possess both high thermal conductivity and improved mechanical properties such as relatively high hardness. The metal alloy heatsink films also have controlled microstructures which are compatible with subsequently deposited crystalline magnetic recording layers. The films may comprise single phase CuZr or AgPd alloys having a selected crystal structure and orientation. The combination of high thermal conductivity, good mechanical properties and controlled microstructures makes the metal alloy heatsink films suitable for various applications including heat assisted magnetic recording systems.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Lubricant for magnetic disk and magnetic disk
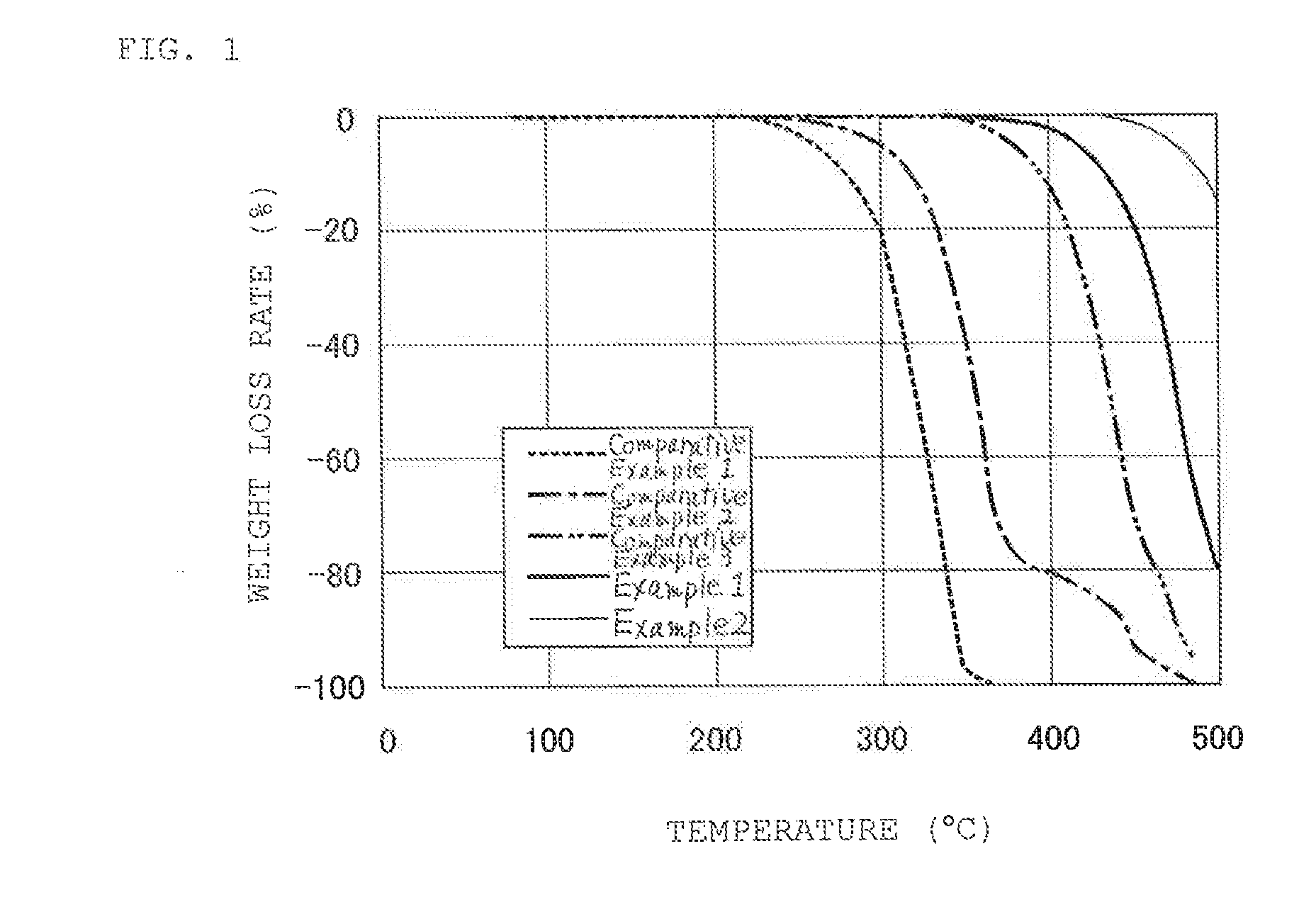
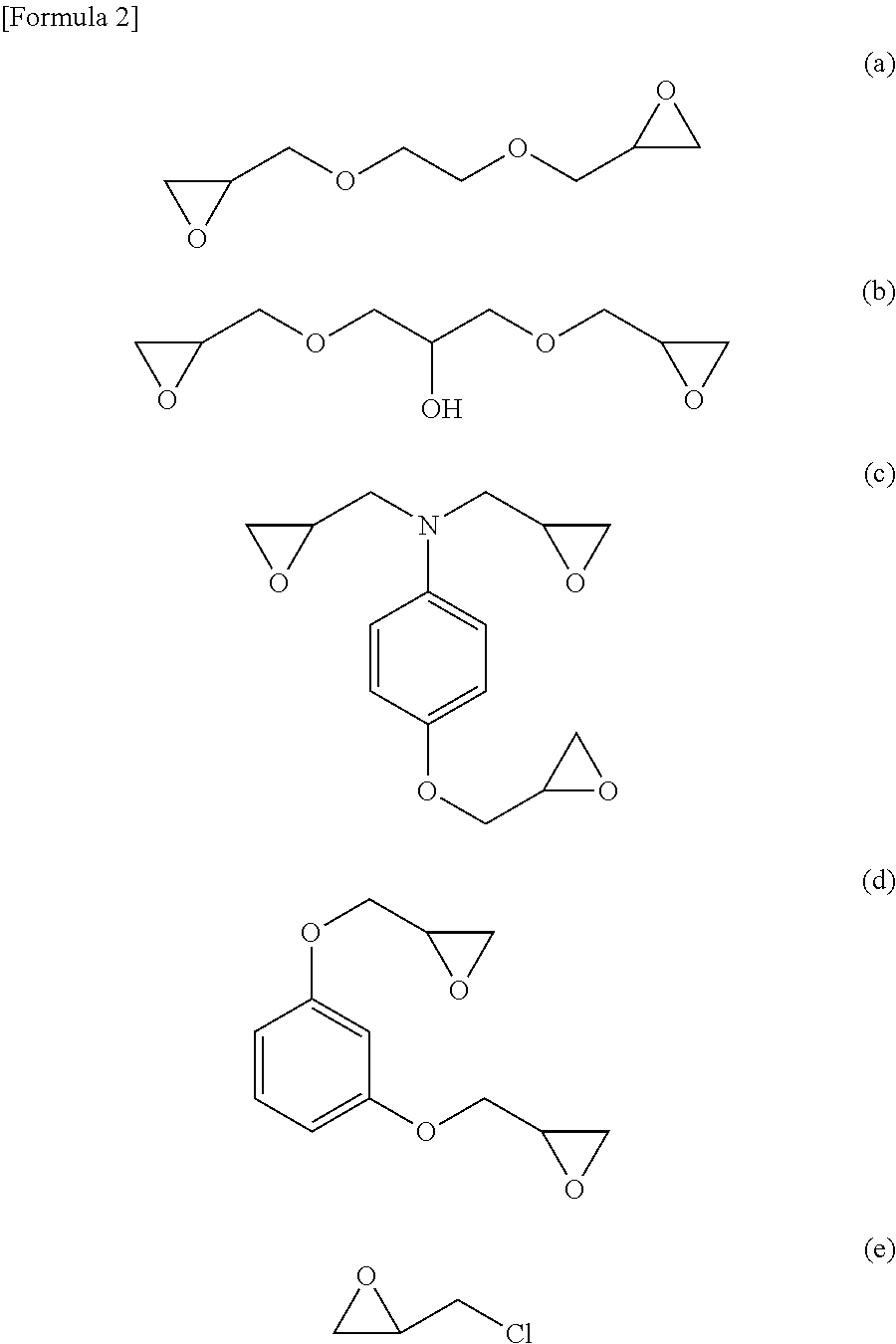
InactiveUS20120276417A1Improve heat resistanceHigh heat resistanceProtective coatings for layersMagnetic materials for record carriersHeat-assisted magnetic recordingPerfluoropolyether
A lubricant for a magnetic disk that is excellent in heat resistance and is suitably used in a magnetic disk to be mounted on a magnetic recording device of a thermally assisted magnetic recording system and a magnetic disk provided with a lubricant layer containing this lubricant. The lubricant for a magnetic disk contains a compound where perfluoropolyether groups each having a perfluoropolyether main chain in its structure and a phosphazene ring at an end are linked to each other through a linking group. The linking group is an aliphatic group or a phosphazene ring. In a magnetic disk having at least a magnetic recording layer, a protective layer, and a lubricant layer on a substrate, the lubricant layer contains the lubricant for a magnetic disk.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Spot size converter and thermal assist magnetic recording head therewith
ActiveUS20110205660A1Shortening waveguide lengthSmall sizeCombination recordingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingHeat-assisted magnetic recordingEngineering
A spot size converter according to the present invention is capable of shortening the waveguide length in the spot size converter and of promoting a size reduction of the optical waveguide itself because two cores having a taper portion are combined and those tapering angles are mutually aligned. Furthermore, spot size conversion efficiency is favorable even in a small size.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Head for thermal assisted magnetic recording device, and thermal assisted magnetic recording device
ActiveUS20110216635A1Increase head heightImprove floating stabilityCombination recordingRecord information storageHeat-assisted magnetic recordingEngineering
In a head for thermal assisted magnetic recording device, a semiconductor laser is mounted so that the total height of the head does not become larger and light power fluctuation due to wavelength fluctuation occurs less frequently. In addition, the rise in temperature of the mounted semiconductor laser is suppressed. A semiconductor laser is placed on a side surface which is different from surfaces on an inflow end side and a trailing side, of four side surfaces of a floating slider. An entrance of a waveguide is placed on the side surface of the floating slider, to thereby cause emitted light from the semiconductor laser to directly enter the waveguide. A curved line part or a reflective mirror is formed in the middle of the waveguide so that the light which has entered the waveguide travels toward an optical near-field generating element.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
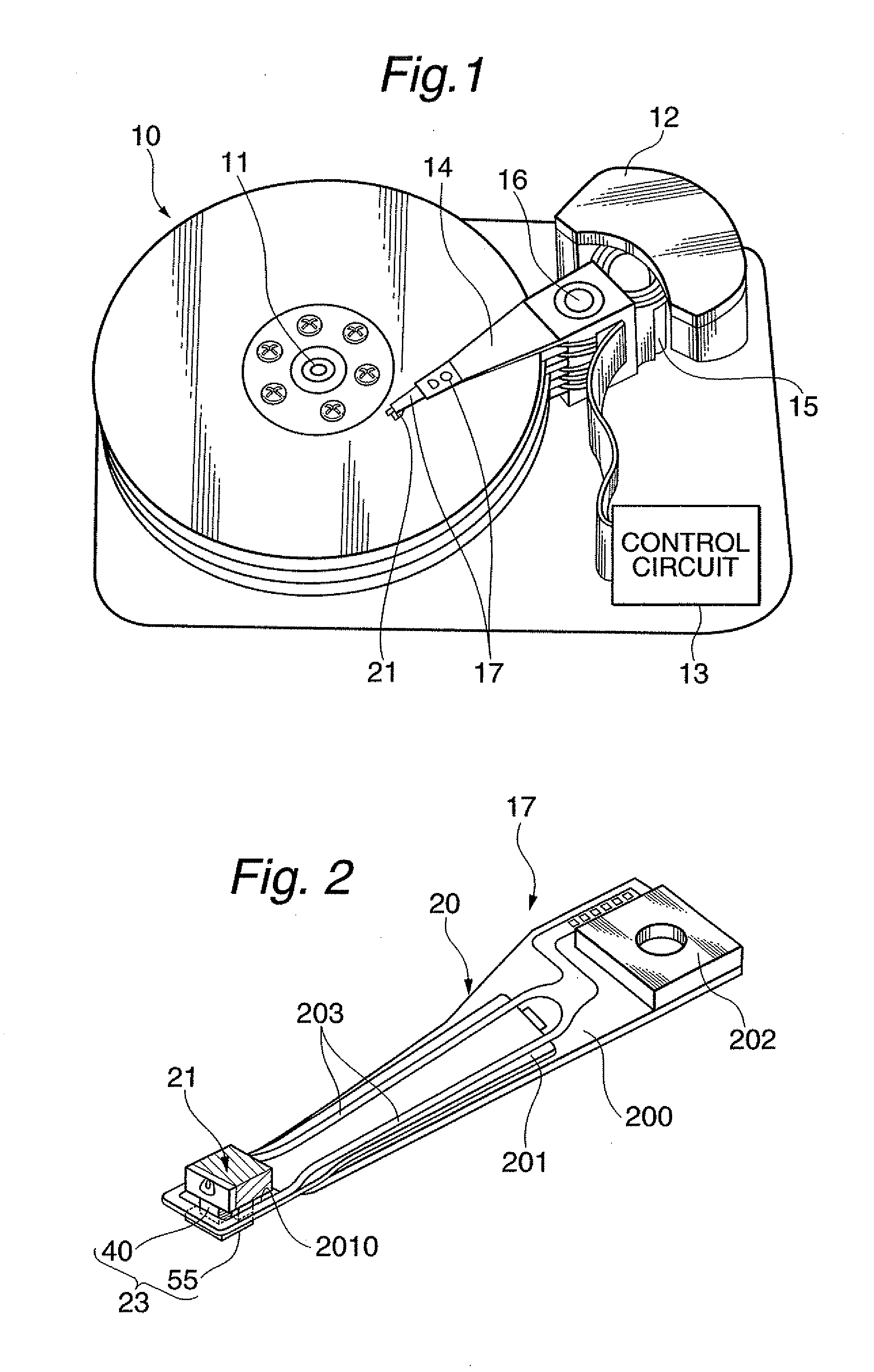
Read/write device, storage medium, driving method of read/write device, semiconductor laser life estimation method, program, program storage medium, and semiconductor laser
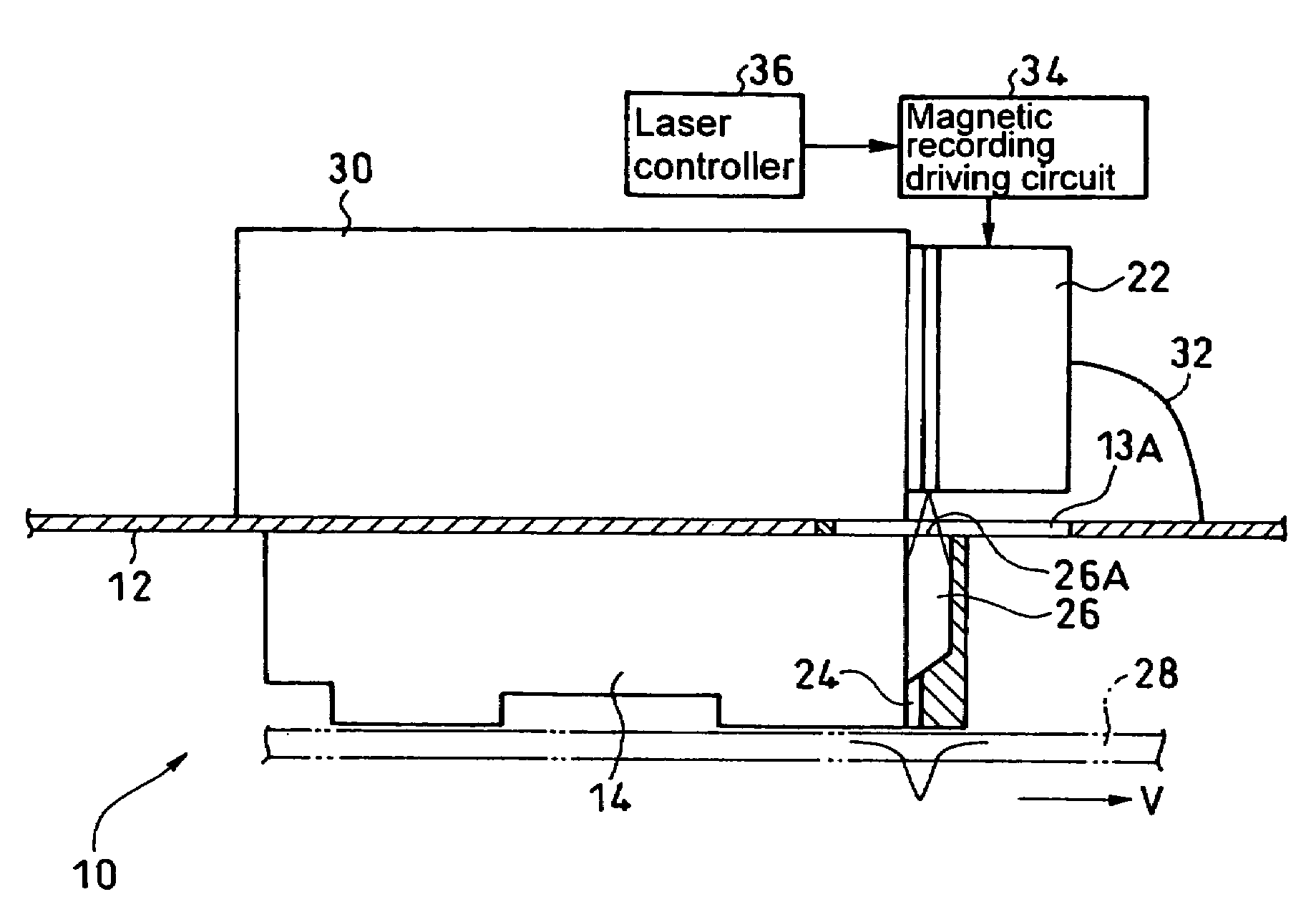
InactiveUS20050213436A1Shorten access timeDrive stabilityApparatus for flat record carriersHeads using thin filmsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingEstimation methods
In a read / write device for writing and reading a storage medium by way of a heat assisted magnetic recording / reproduction scheme, the read / write device including an elevated slider provided with a semiconductor laser, provided is a heat dissipation mechanism for dissipating heat generated in the elevated slider to an outside of a housing of the read / write device. Further, the storage medium has a second heatsink layer formed of an Al film having a thickness of 50 μm, a backing layer, a heat barrier layer, a first heatsink layer, a magnetic recording layer, and a protection film on a glass substrate. With this arrangement, in a read / write device which performs a heat assisted magnetic recording and reproduction by a semiconductor laser provided on the elevated slider, the occurrence of malfunction due to temperature rises in the storage medium is prevented.
Owner:SHARP KK
Thermally assisted magnetic recording disk with ion-implant facilitated non-magnetic regions, manufacturing method thereof, and magnetic recording method
ActiveUS8634155B2Low coercivityPatterned record carriersNanoinformaticsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingThermal expansion
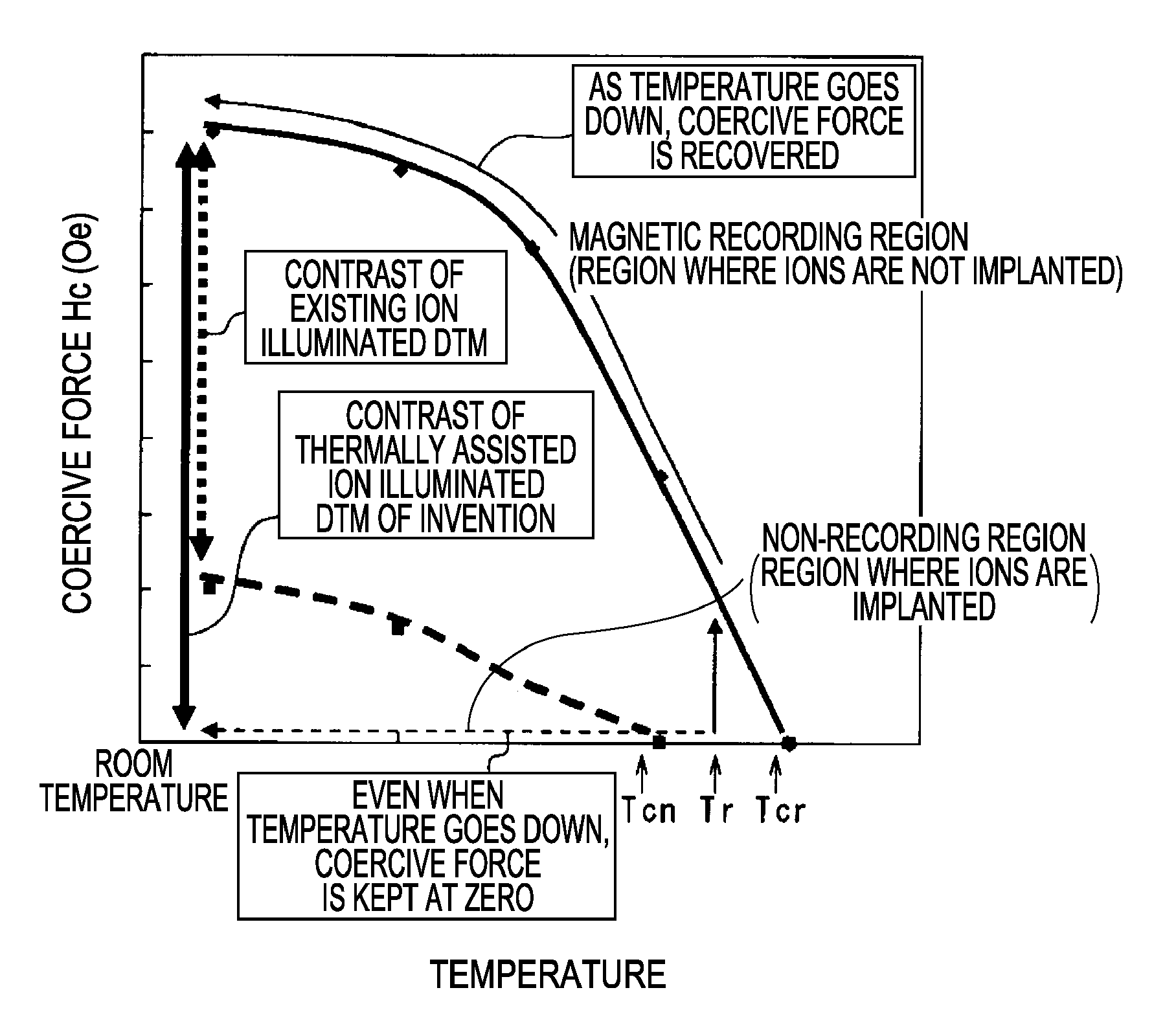
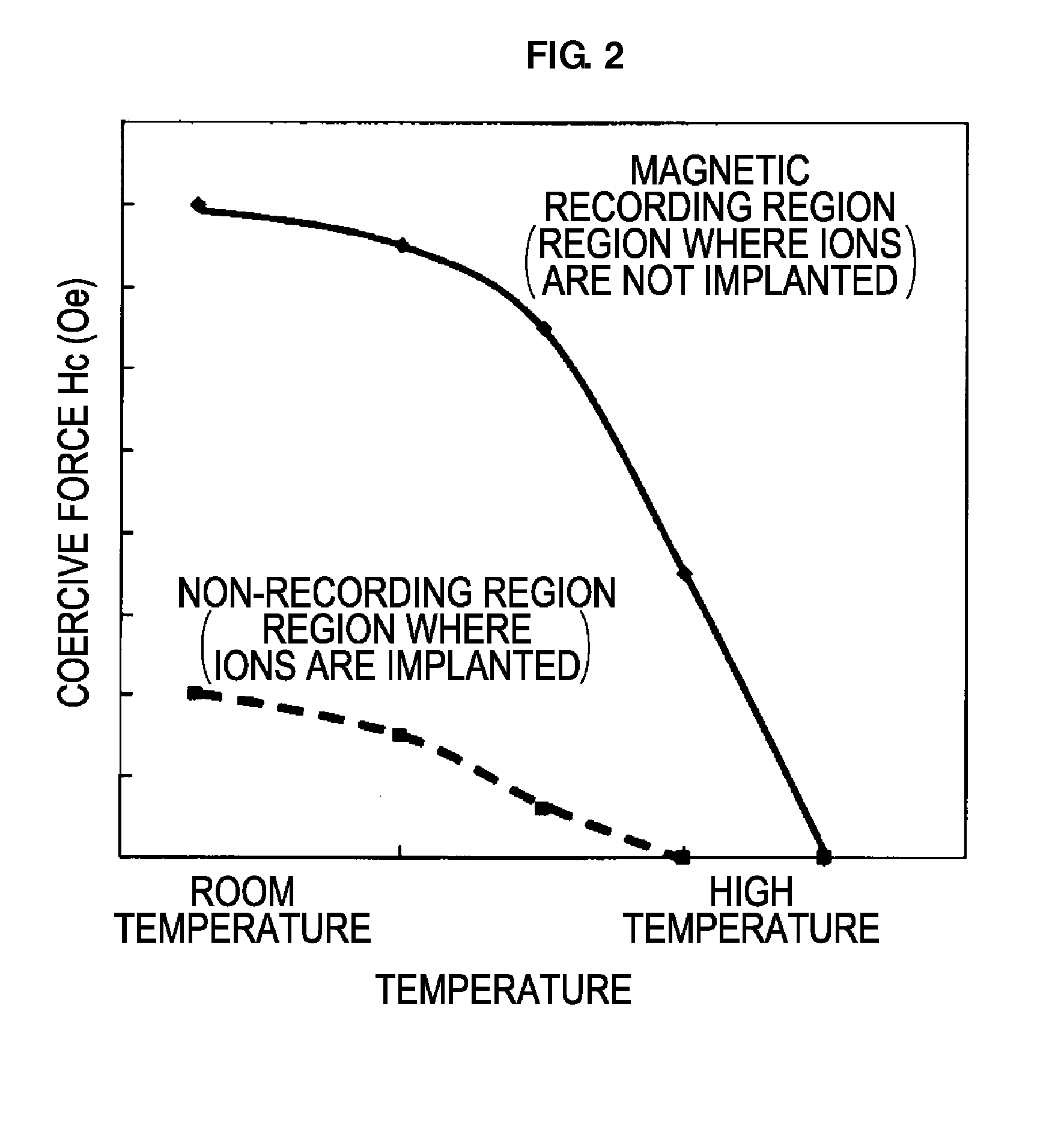
The invention provides a magnetic disk that solves (1) a problem of cross-talk that cannot be solved even by an existing thermally assisted recording method or a discrete method (DTM or the like), (2) a problem of surface flatness, which an existing embedding type DTM or the like has, and (3) a problem of a difference in thermal expansion coefficient between materials when a thermally assisted method is applied to the DTM, and that (4) does not necessitate a special medium structure, and is excellent in a surface flatness and economically and functionally high in realizability. A DTM manufactured by ion implantation is excellent in the surface flatness, and can solve the cross-talk problem by conducting the thermally assisted recording at a temperature between a Curie temperature (Tcn) of a portion where ions are implanted (non-recording region) and a Curie temperature (Tcr) of a portion where ions are not implanted (recording region).
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
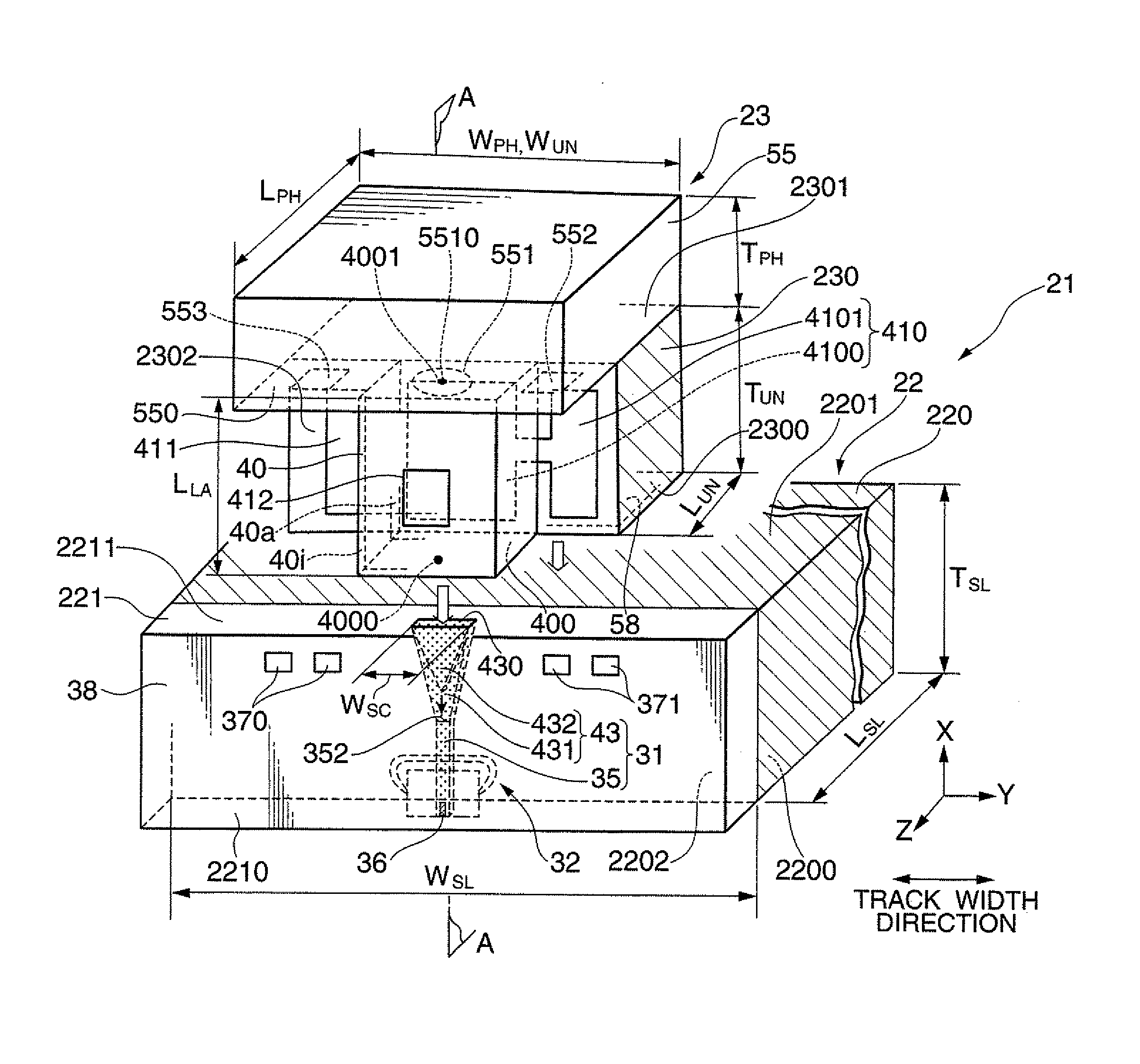
Joint design of thermally-assisted magnetic recording head and patterned media for high optical efficiency
ActiveUS20110096431A1Combination recordingPatterned record carriersHeat-assisted magnetic recordingEngineering
A system according to one embodiment includes a magnetic recording medium having a magnetic layer with features in a discrete track configuration or a bit patterned configuration and an underlayer adjacent the magnetic layer, the underlayer comprising a material capable of forming surface plasmon resonance; and a magnetic head having: a writer for writing to the medium; and a near-field transducer for heating the medium for thermally assisted recording. Additional systems and methods are also presented.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
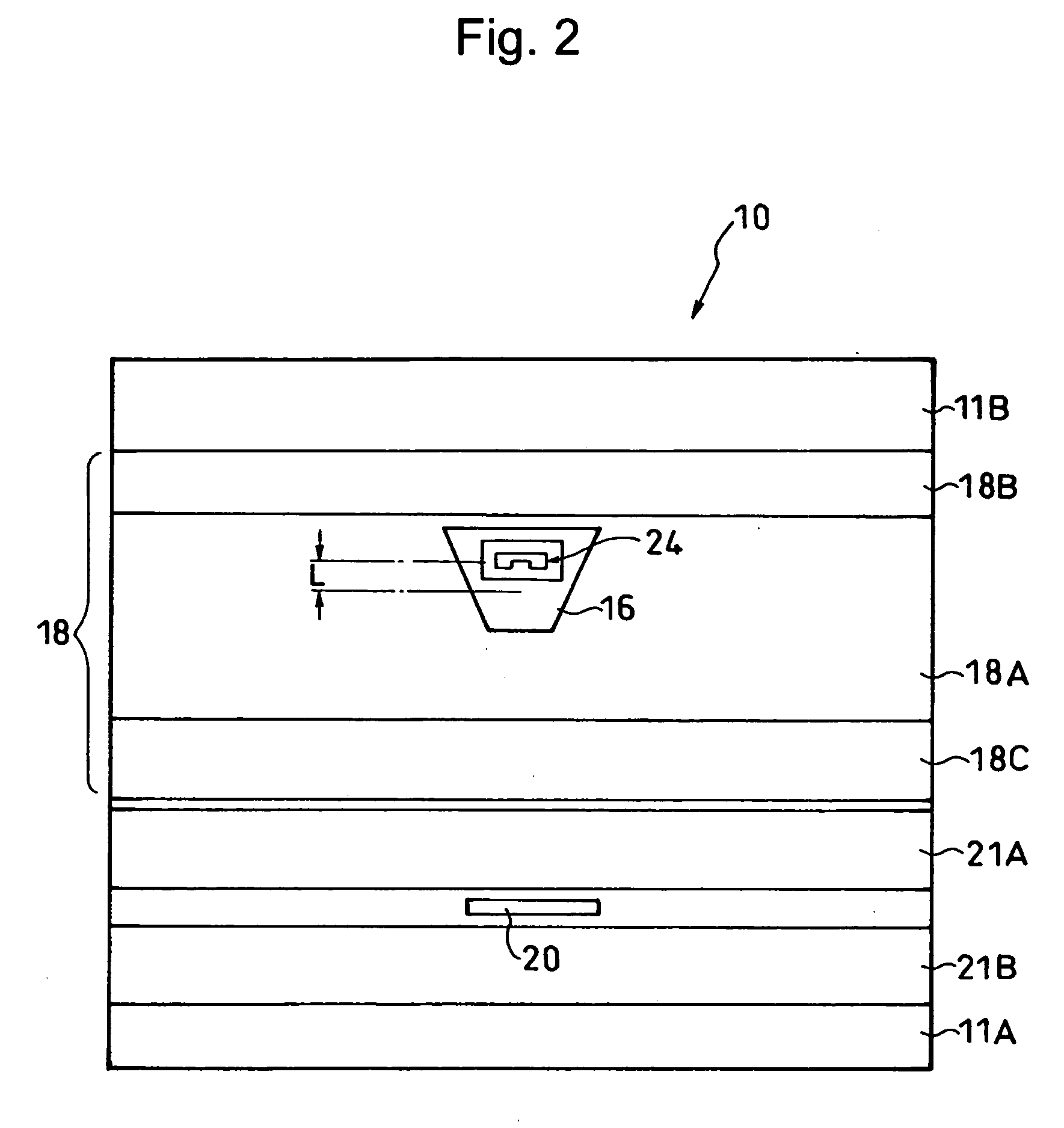
Thin-film magnetic head having near-field-light-generating portion with trapezoidal end
ActiveUS20070177302A1Write reliablyEffective lightingRecord information storageRecording/reproducing/erasing methodsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingData signal
A thin-film magnetic head for a heat-assisted magnetic recording which can perform a reliable writing immediately only on a desired track by applying a near-field light to a desired position and range is provided. The head comprises: an electromagnetic coil element for writing data signals, having a pole end reaching a head end surface; and a near-field-light-generating portion for heating a portion of a magnetic recording medium during write operation by generating a near-field light, having a generation end reaching the head end surface and provided adjacent to the pole end and in the leading side of the pole end, and a shape of the generation end on the head end surface being a trapezoid with a shorter edge on the trailing side, or being a triangle with an apex on the trailing side and with a bottom on the leading side.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Thermally-Assisted Magnetic Recording Head with Light Detector in Element-Integration Surface
ActiveUS20110122737A1Write reliablyReliable read operationCombination recordingDisposition/mounting of recording headsEnvironmental effectHeat-assisted magnetic recording
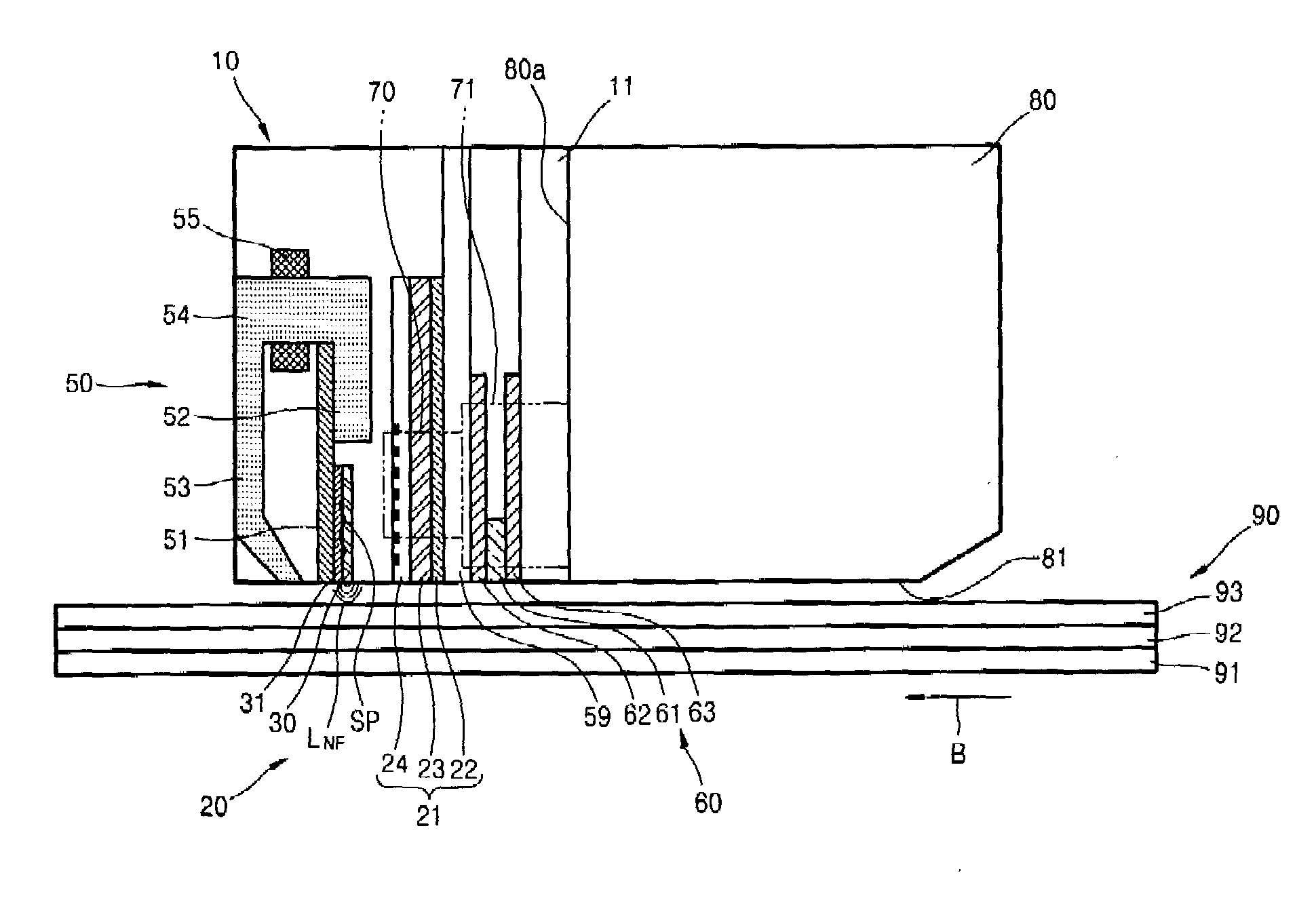
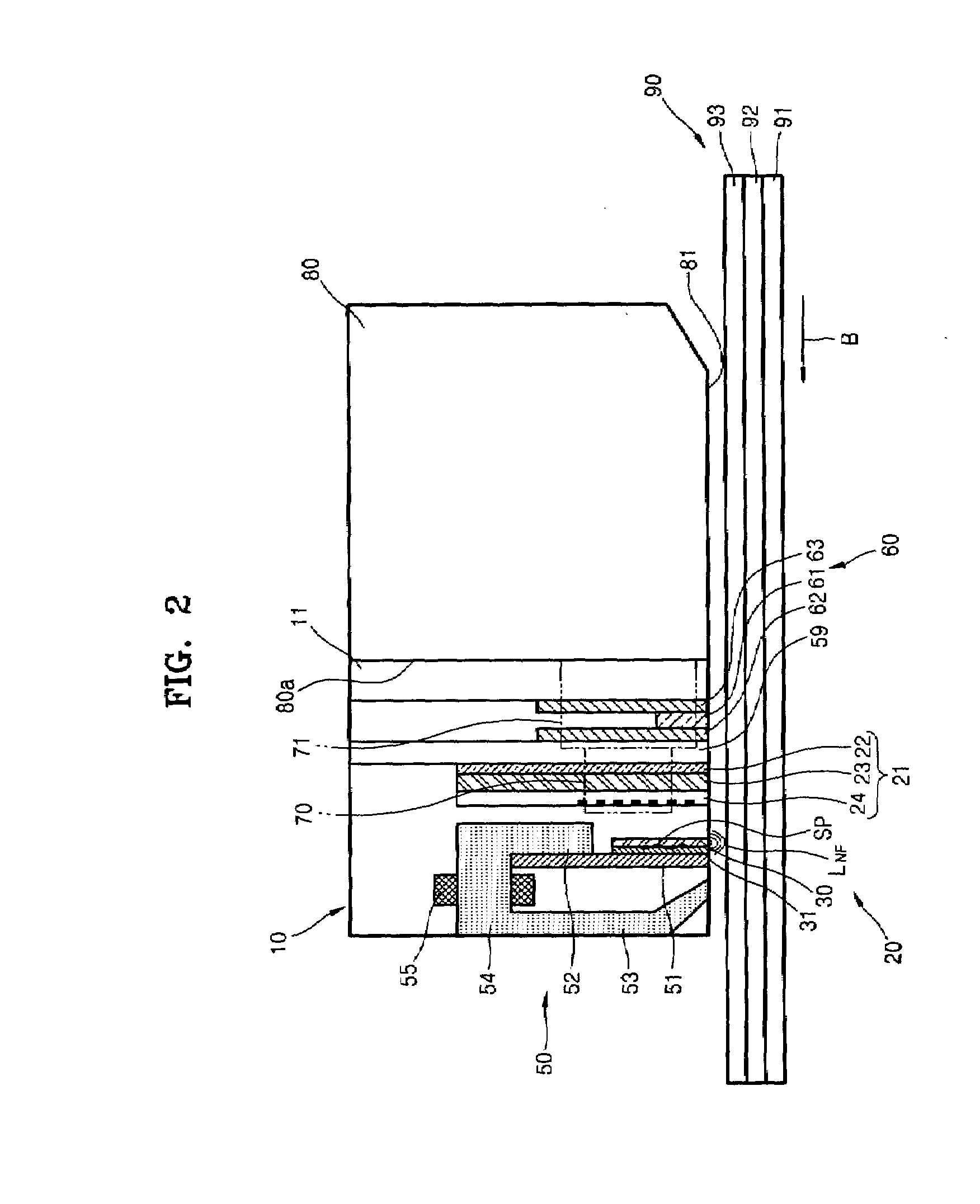
A thermally-assisted magnetic recording head is provided, in which the light-source output can be adjusted according to its variation by environmental influences and over time. The head comprises: a light source; a write head element provided in a element-integration surface; an optical system provided in the element-integration surface and configured to guide a light emitted from the light source to the vicinity of one end of the write head element; and a light detector for monitoring the light-source output, provided in the element-integration surface and comprising a light-receiving surface covering an area directly above at least a portion of the optical system. This light detector with such a light-receiving surface can detect a leakage light emitted from the optical system as a monitoring light. Therefore, feedback adjustment of the light-source output can be realized to stabilize the intensity of light for thermal-assist applied to a magnetic recording medium.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Transducer for heat assisted magnetic recording
ActiveUS20050289576A1Combination recordingNanoinformaticsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingMagnetic storage
An apparatus for concentrating electromagnetic energy comprises a metallic transducer including a first section and a second section, wherein the first section is wider than the second section and has a width to length aspect ratio greater than or equal to a width to length aspect ratio of the second section, and a condenser for directing electromagnetic radiation onto the transducer. A magnetic storage device that includes the apparatus is also provided.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Patterned thin films and use of such films as thermal control layers in heat assisted magnetic recording media
ActiveUS20060154110A1Reduce heat transferImprove heat transfer performanceRecording by magnetic meansNanoinformaticsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingOptoelectronics
Patterned thin films comprise regions of relatively low thermal conductivity material separated by regions of relatively high thermal conductivity material. The low thermal conductivity regions may be provided in the form of cylinders or cuboids which are arranged in a continuous matrix of the high thermal conductivity material. The thin film may be used as thermal control layers in data recording media such as heat assisted magnetic recording media.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
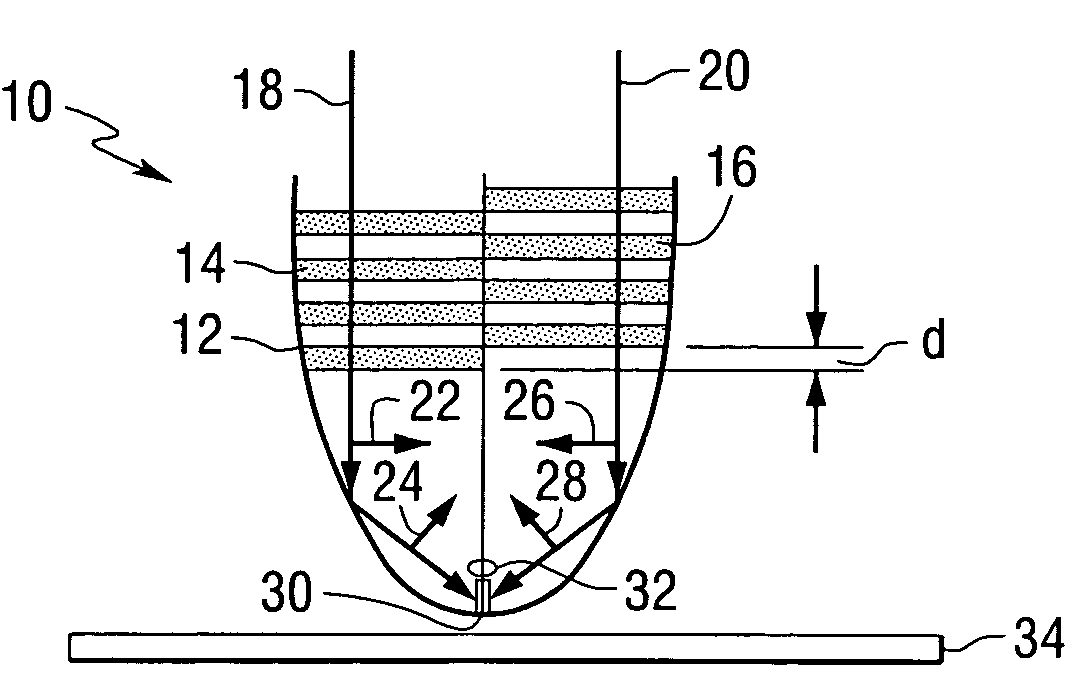
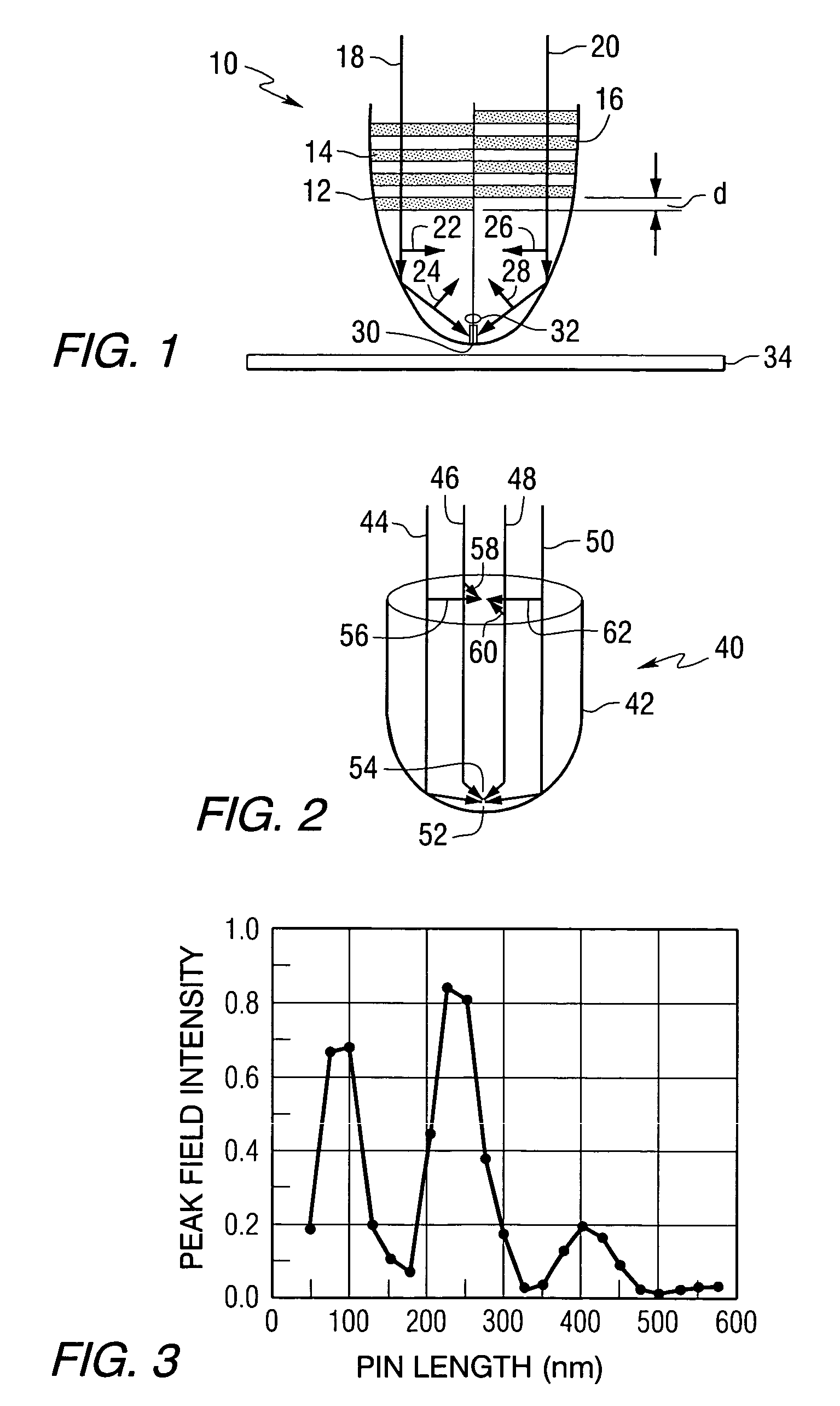
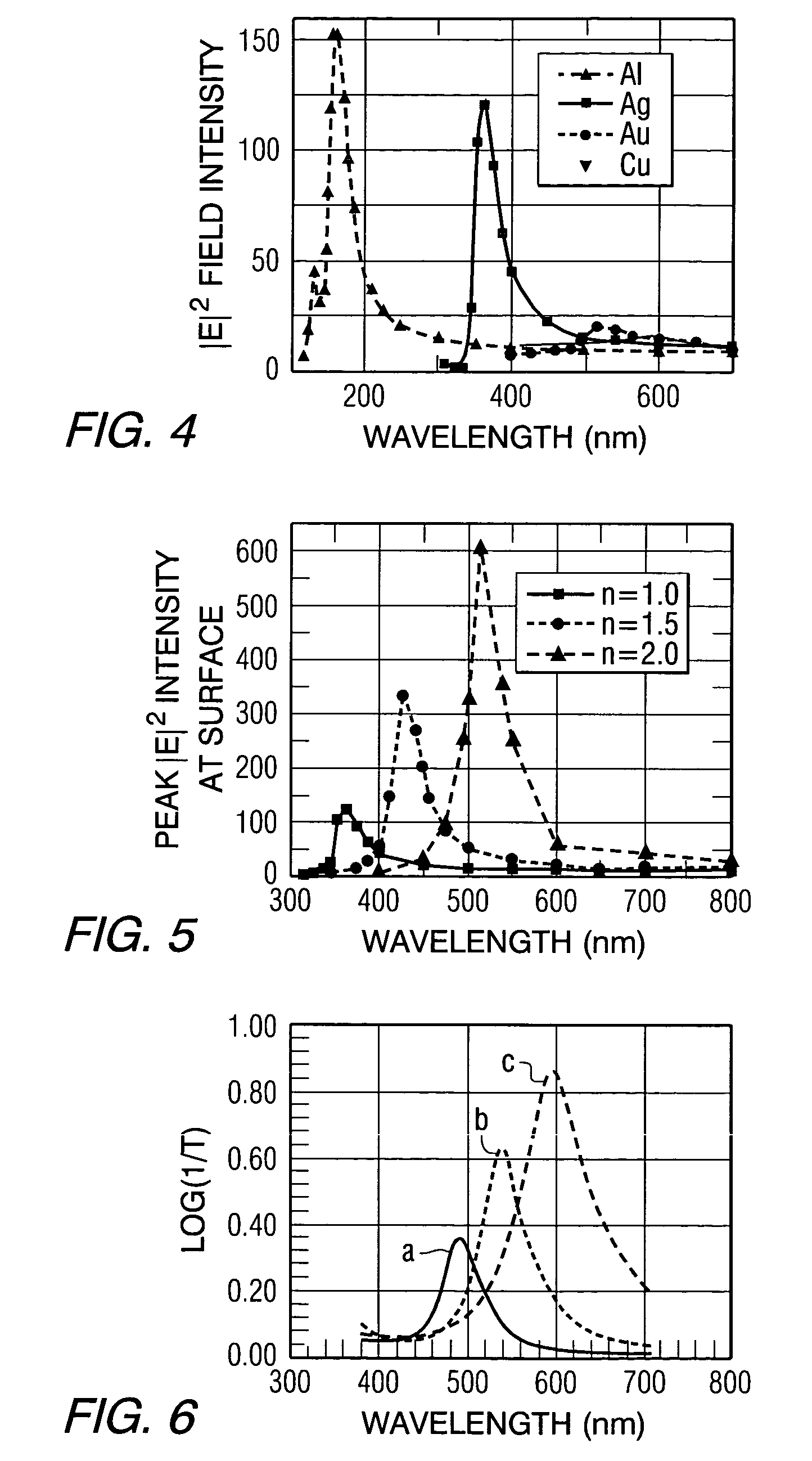
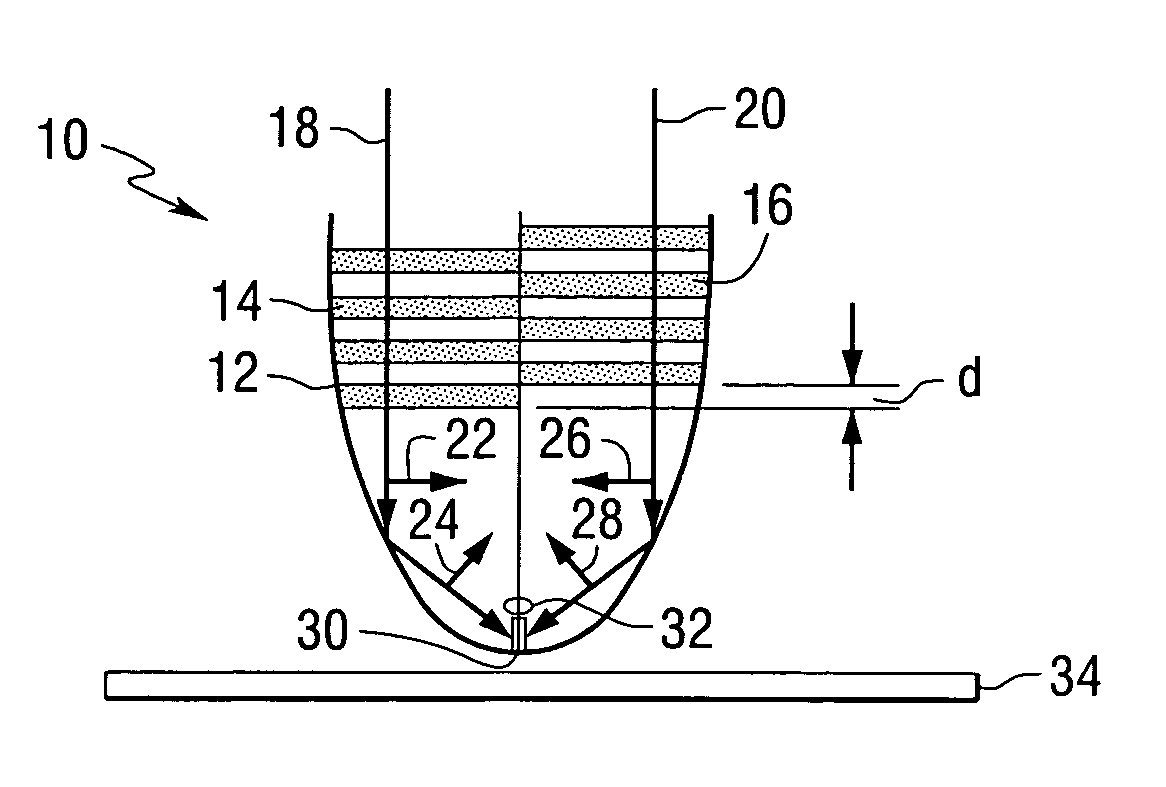
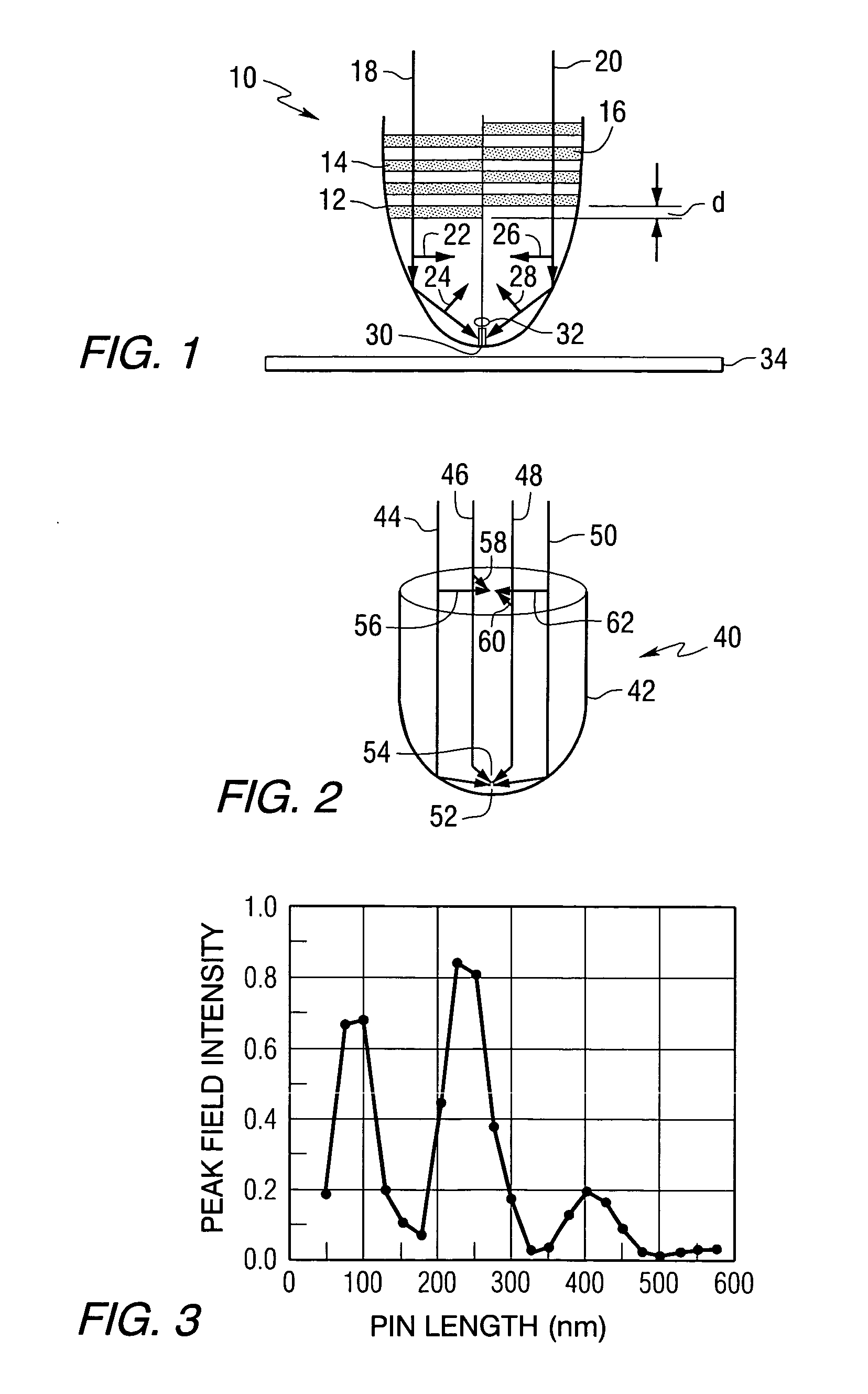
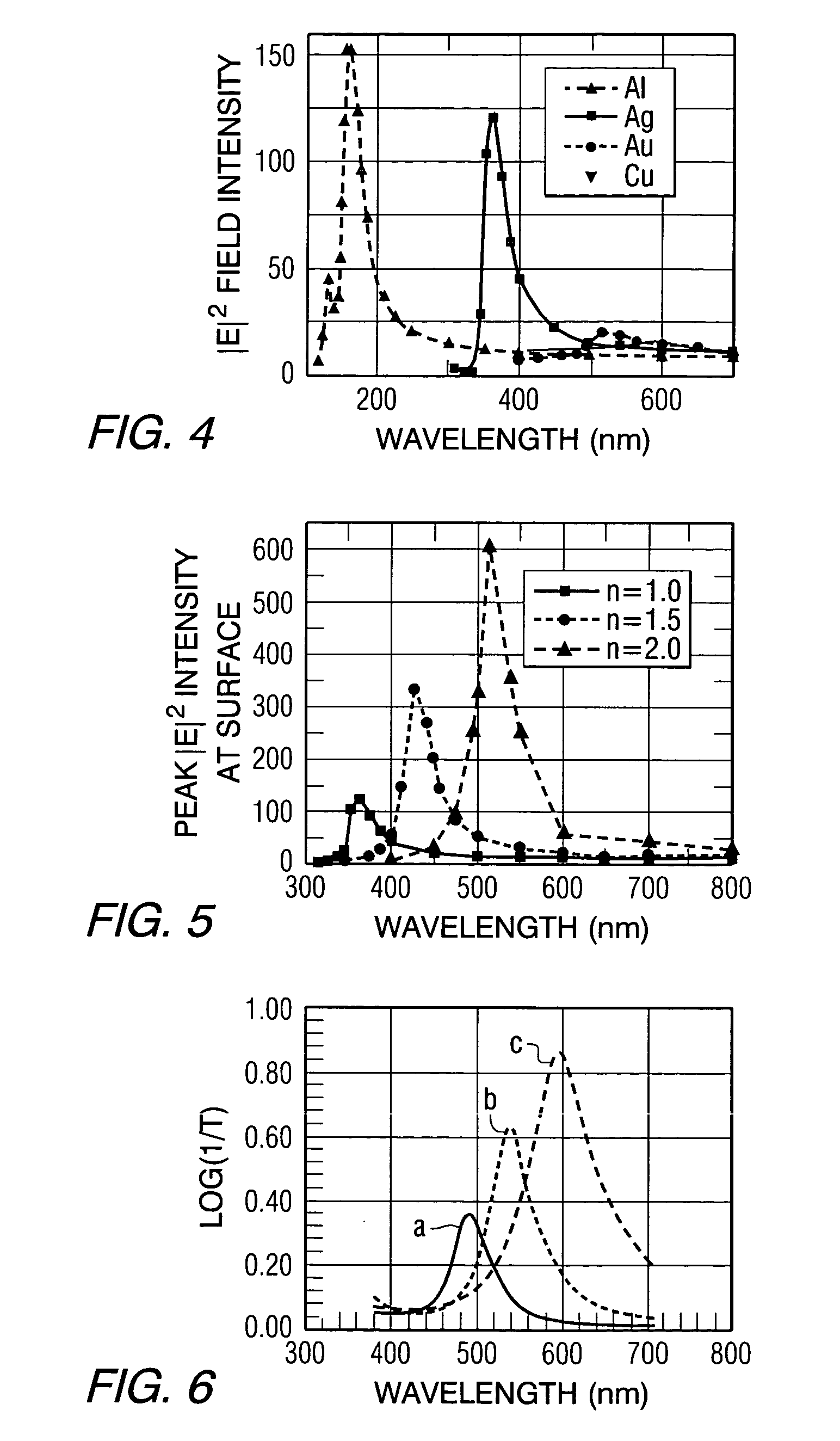
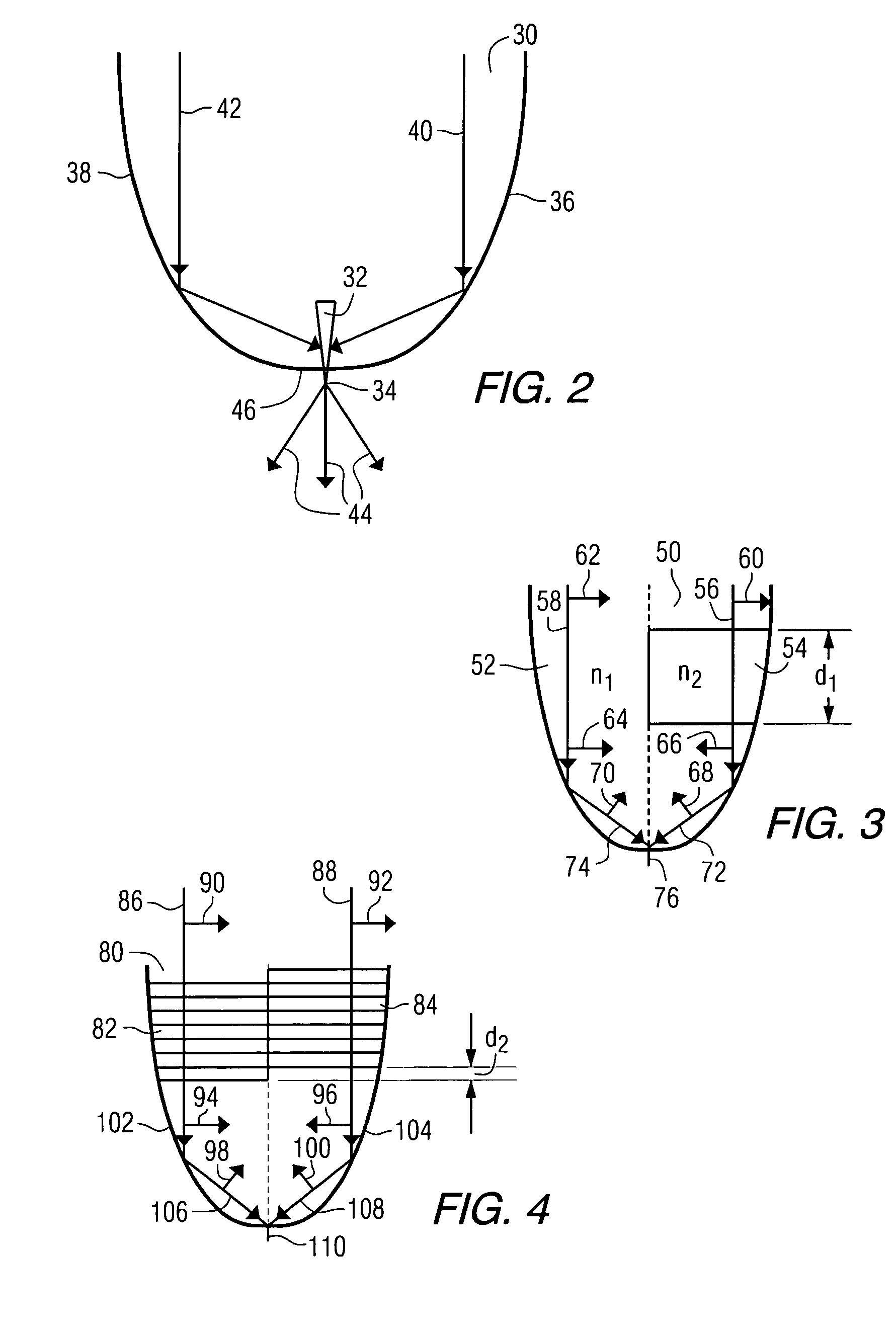
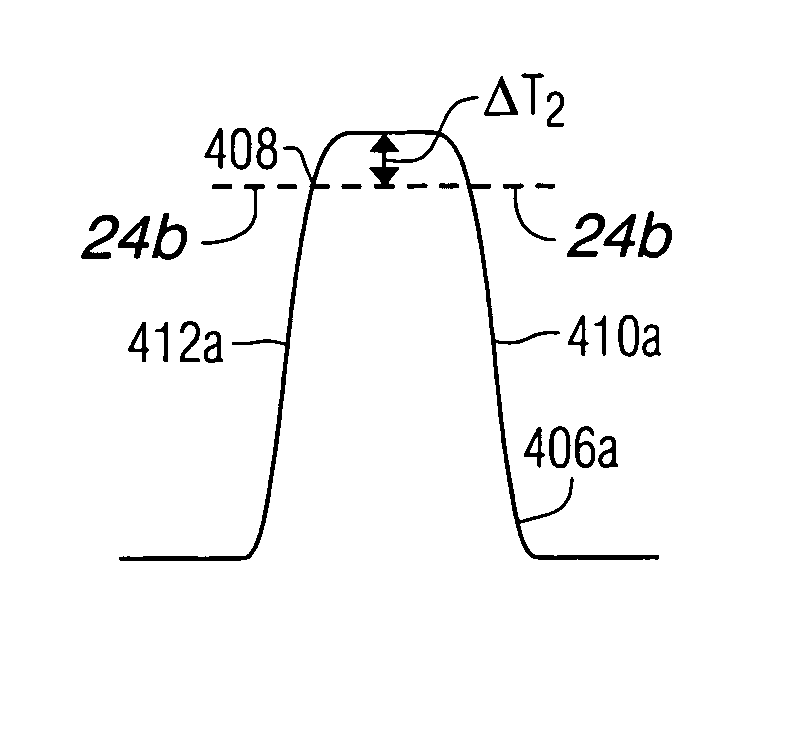
Heat assisted magnetic recording with heat profile shaping
ActiveUS7412143B2Combination recordingRecord information storageHeat-assisted magnetic recordingElectromagnetic radiation
A transducer comprises a conductive pin and a waveguide for directing electromagnetic radiation onto the pin, wherein the pin is configured to create a rectangular flat top field distribution at a surface of a storage medium positioned adjacent to an end of the pin, leading to a flat top thermal profile within the storage medium. A second pin can be included in the transducer. Recording heads that include the transducer, disc drives that include the recording head, and a method of heating a portion of a storage medium that is performed by the recording head, are also included.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Heat assisted magnetic recording with heat profile shaping
ActiveUS20050041950A1Combination recordingRecord information storageHeat-assisted magnetic recordingEngineering
A transducer comprises a conductive pin and a waveguide for directing electromagnetic radiation onto the pin, wherein the pin is configured to create a rectangular flat top field distribution at a surface of a storage medium positioned adjacent to an end of the pin, leading to a flat top thermal profile within the storage medium. A second pin can be included in the transducer. Recording heads that include the transducer, disc drives that include the recording head, and a method of heating a portion of a storage medium that is performed by the recording head, are also included.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Thermally-assisted magnetic recording head, method of manufacturing the same, and thermally-assisted magnetic recording apparatus
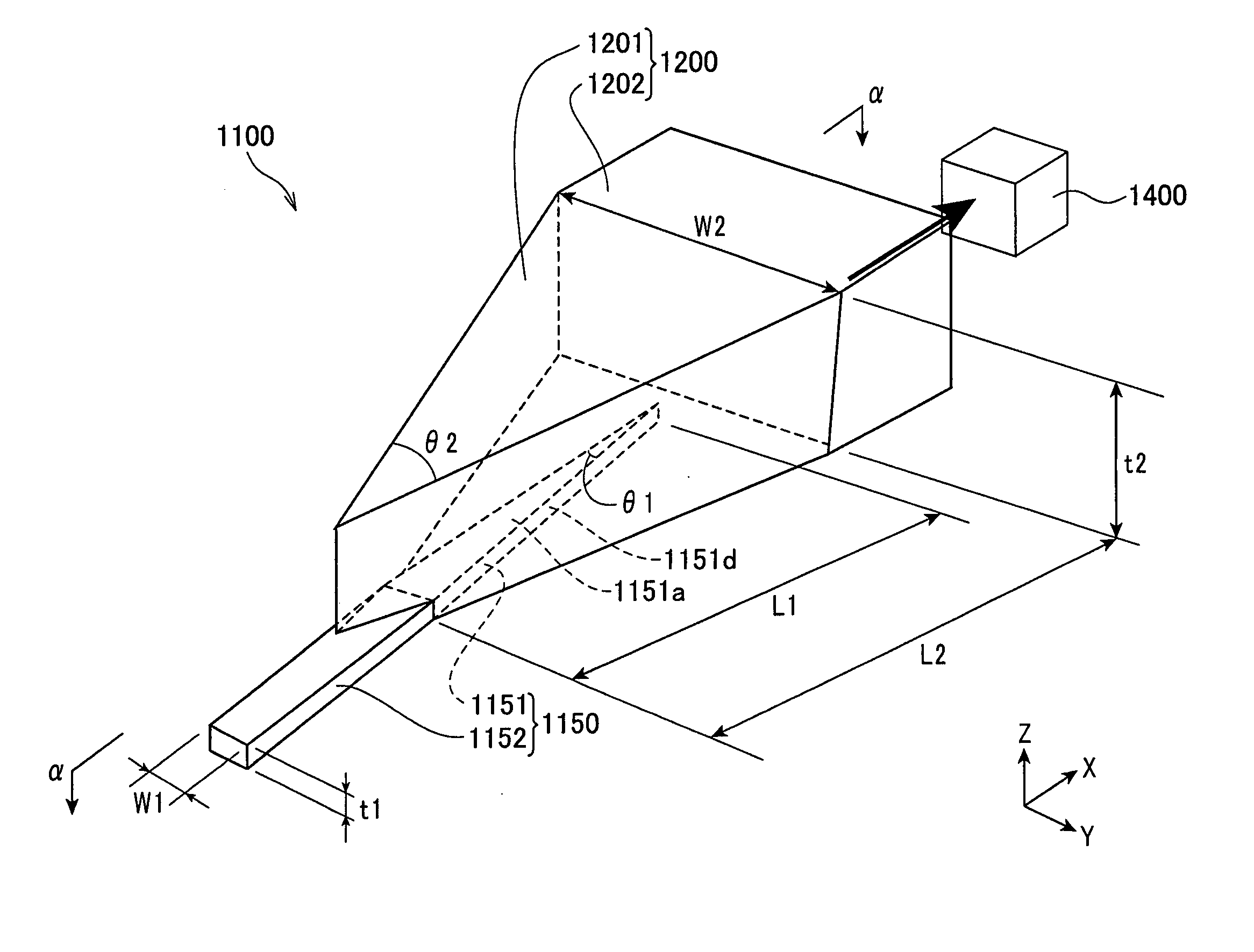
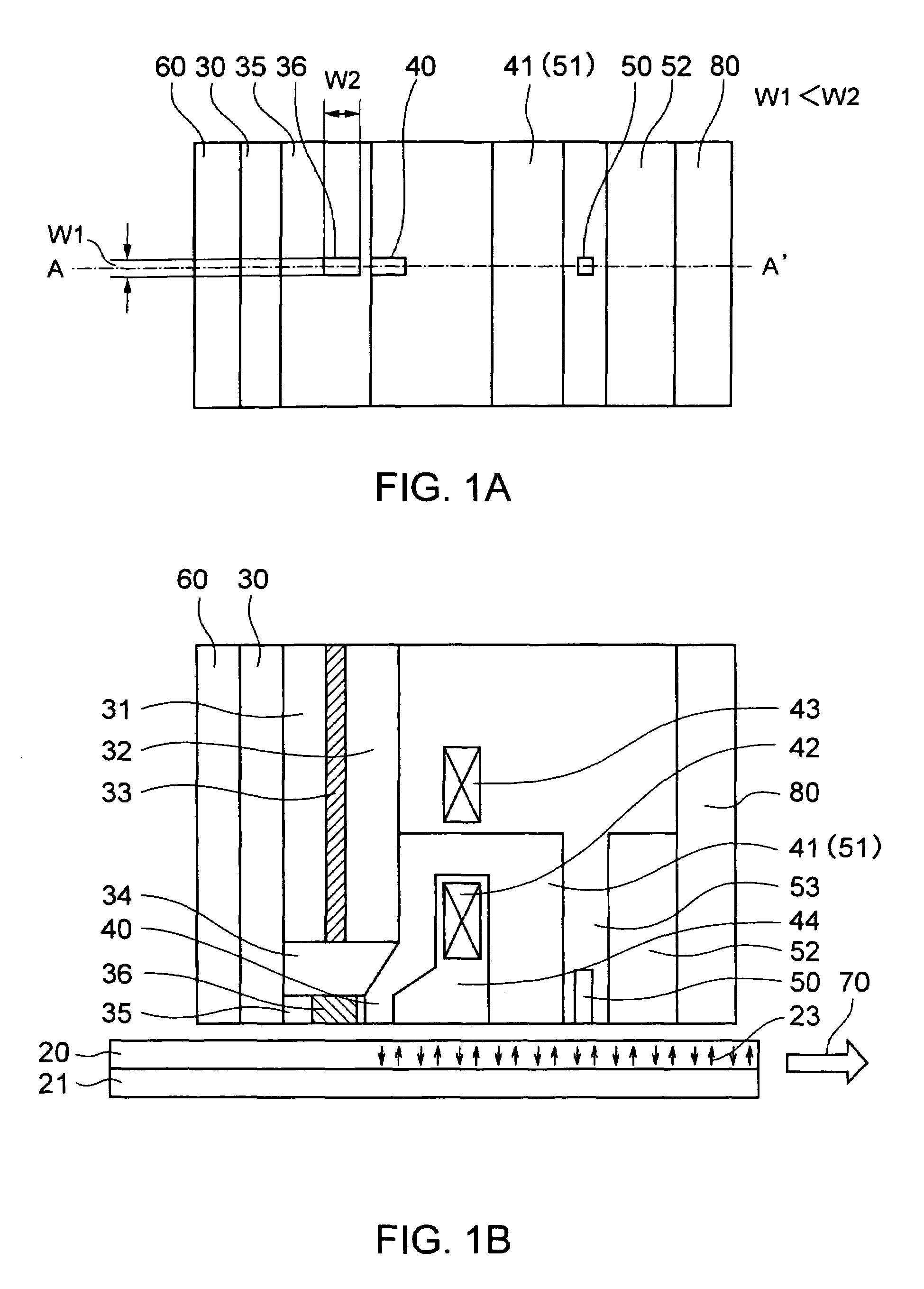
InactiveUS7042810B2Optimize timingEfficient and stable recordingElectron beam carrier recordingNanoinformaticsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingMagnetic poles
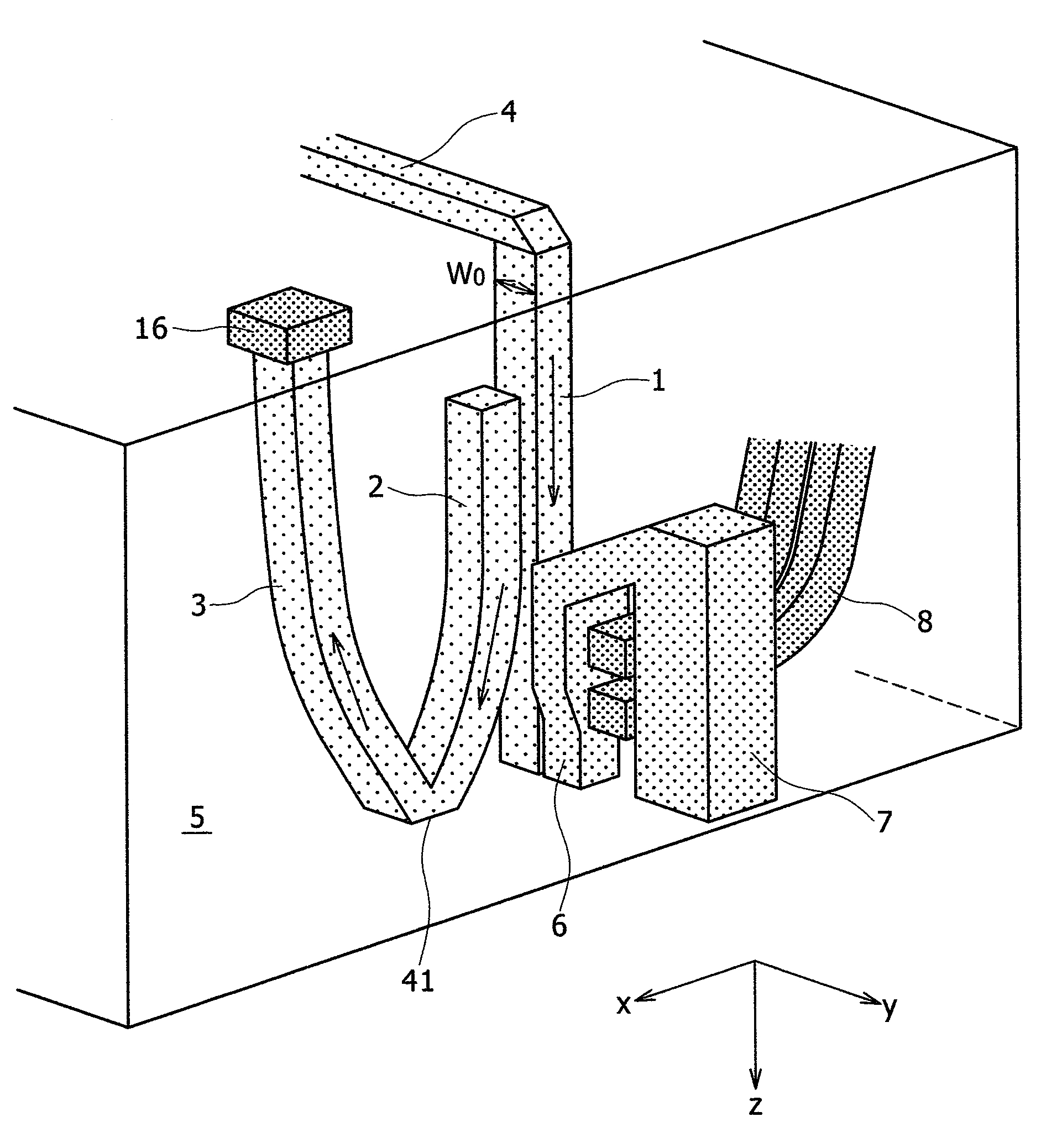
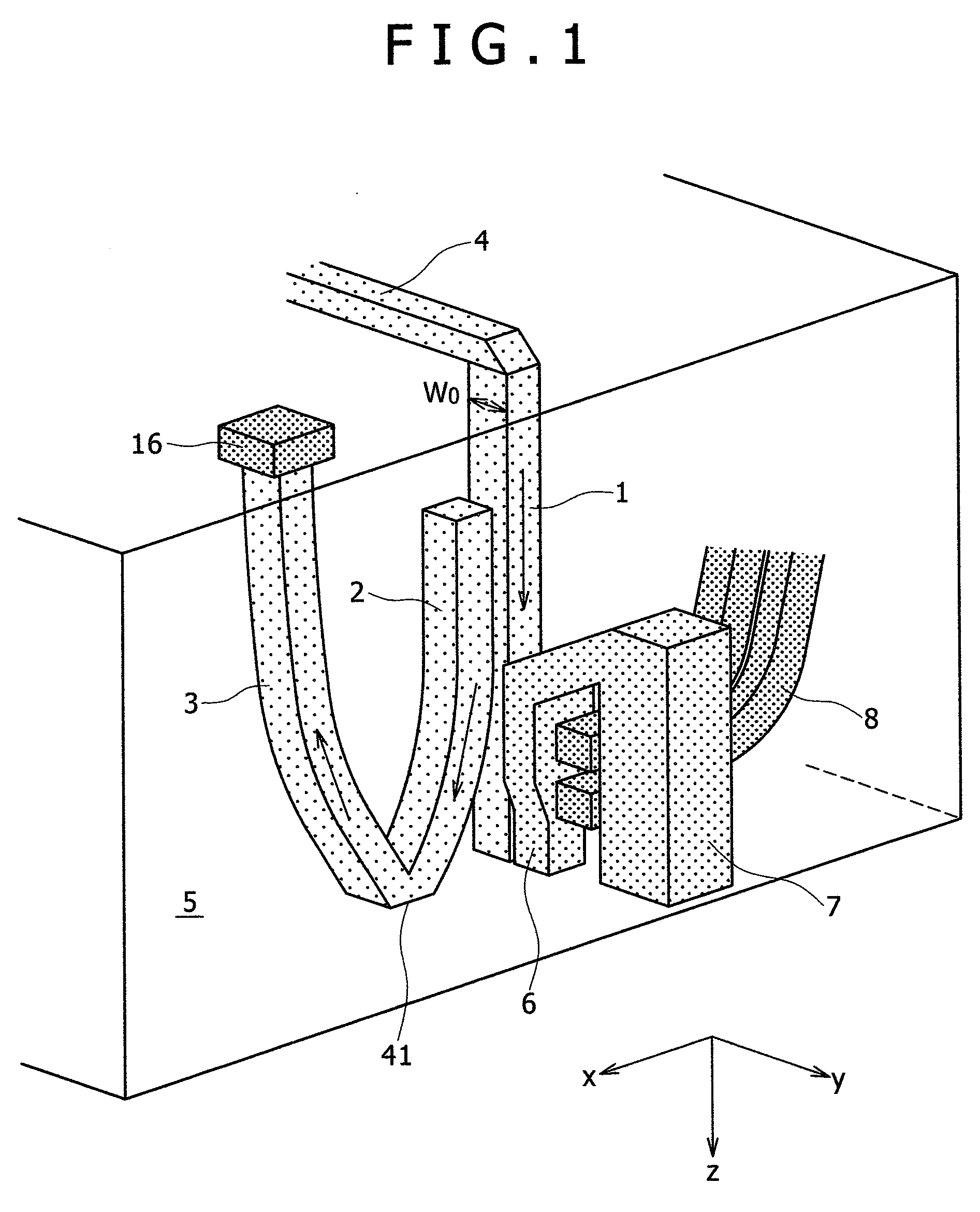
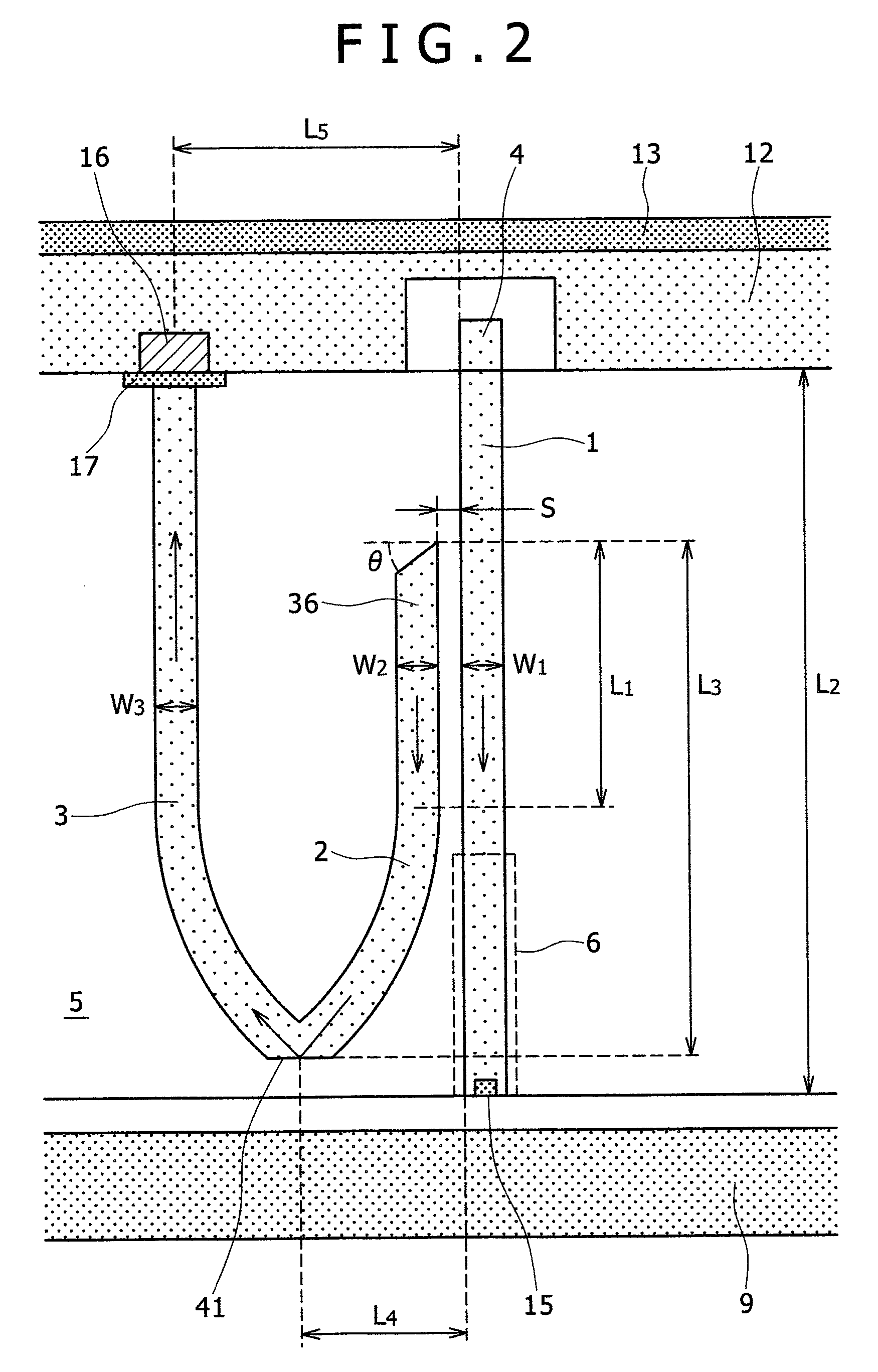
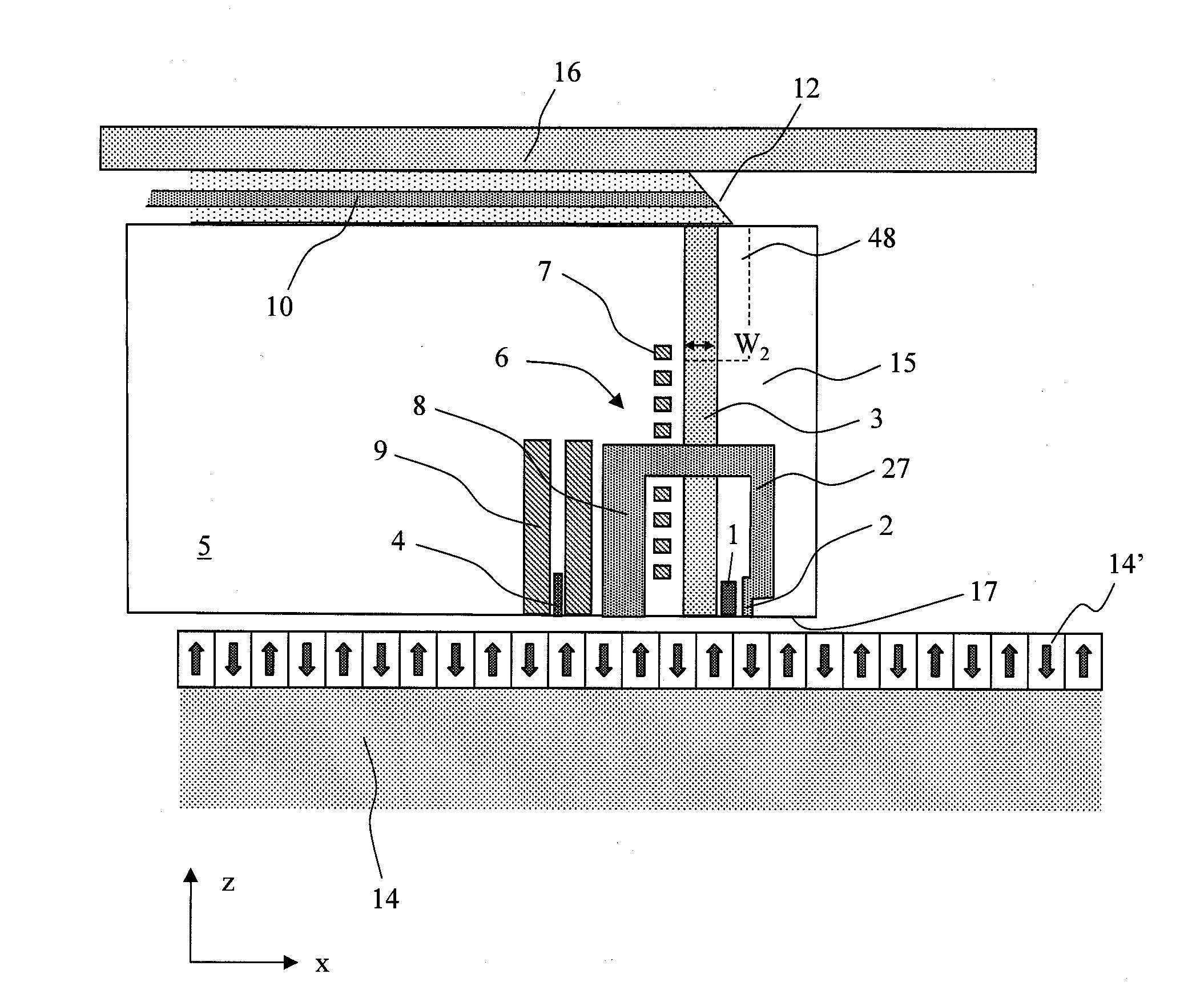
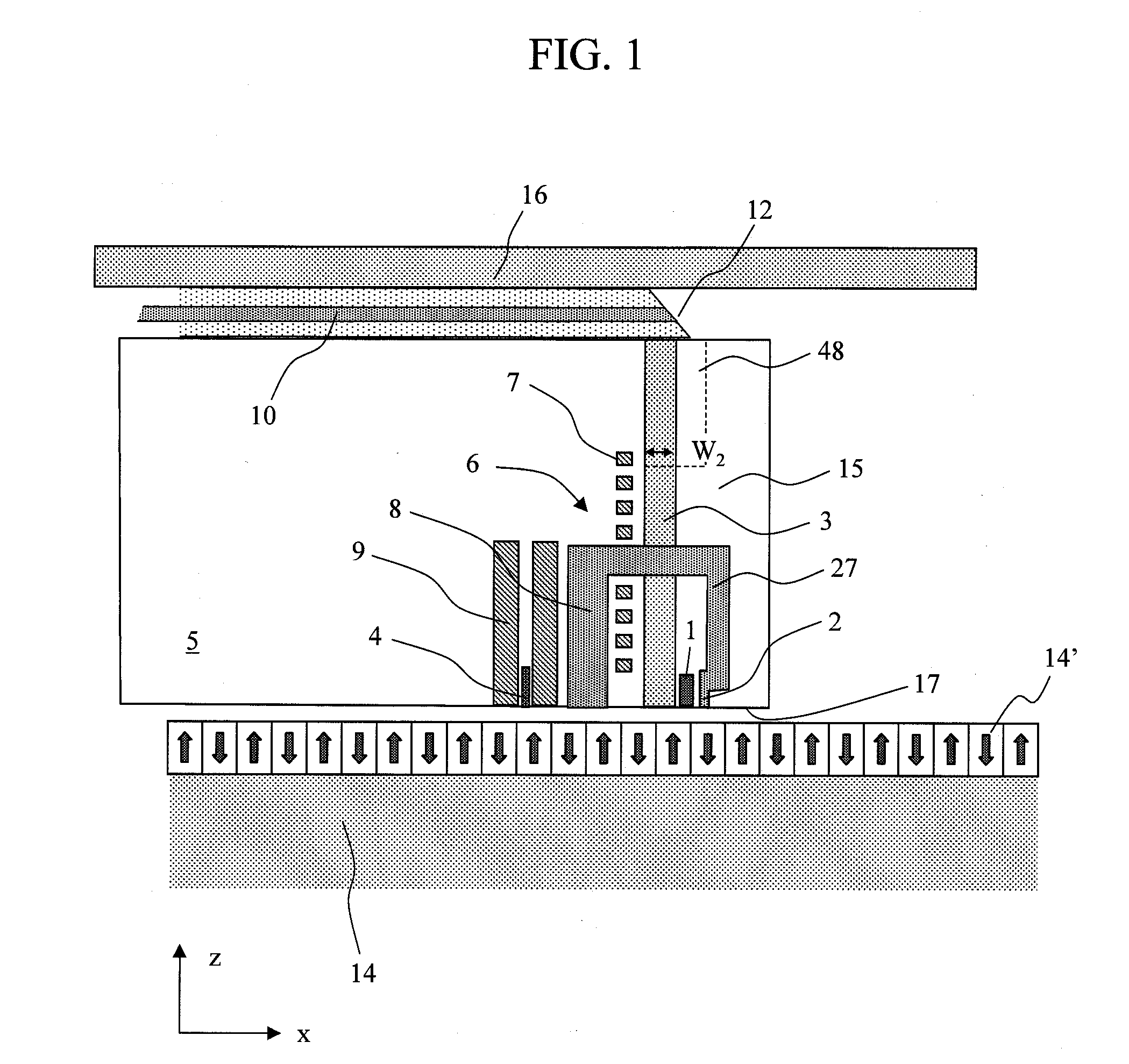
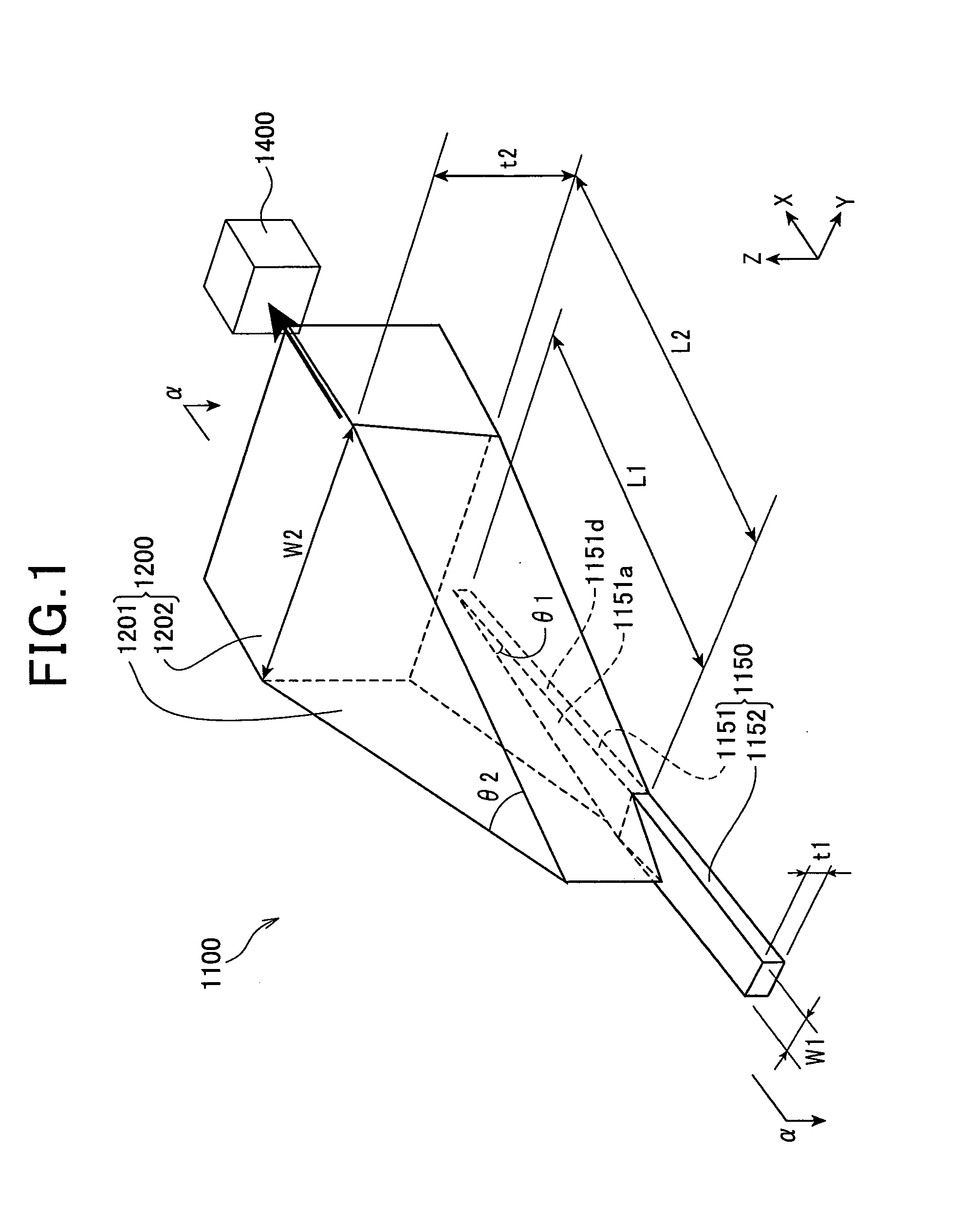
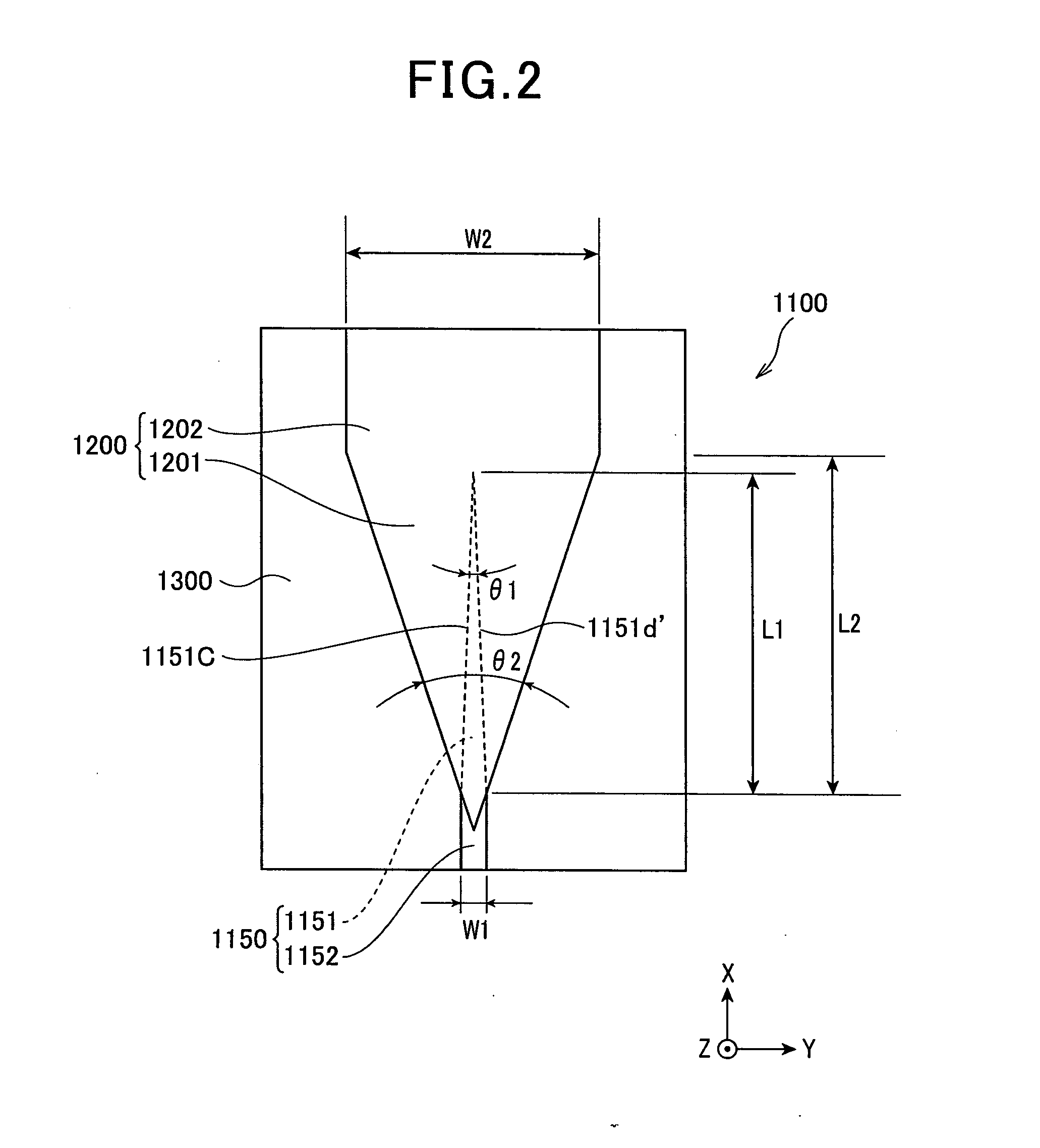
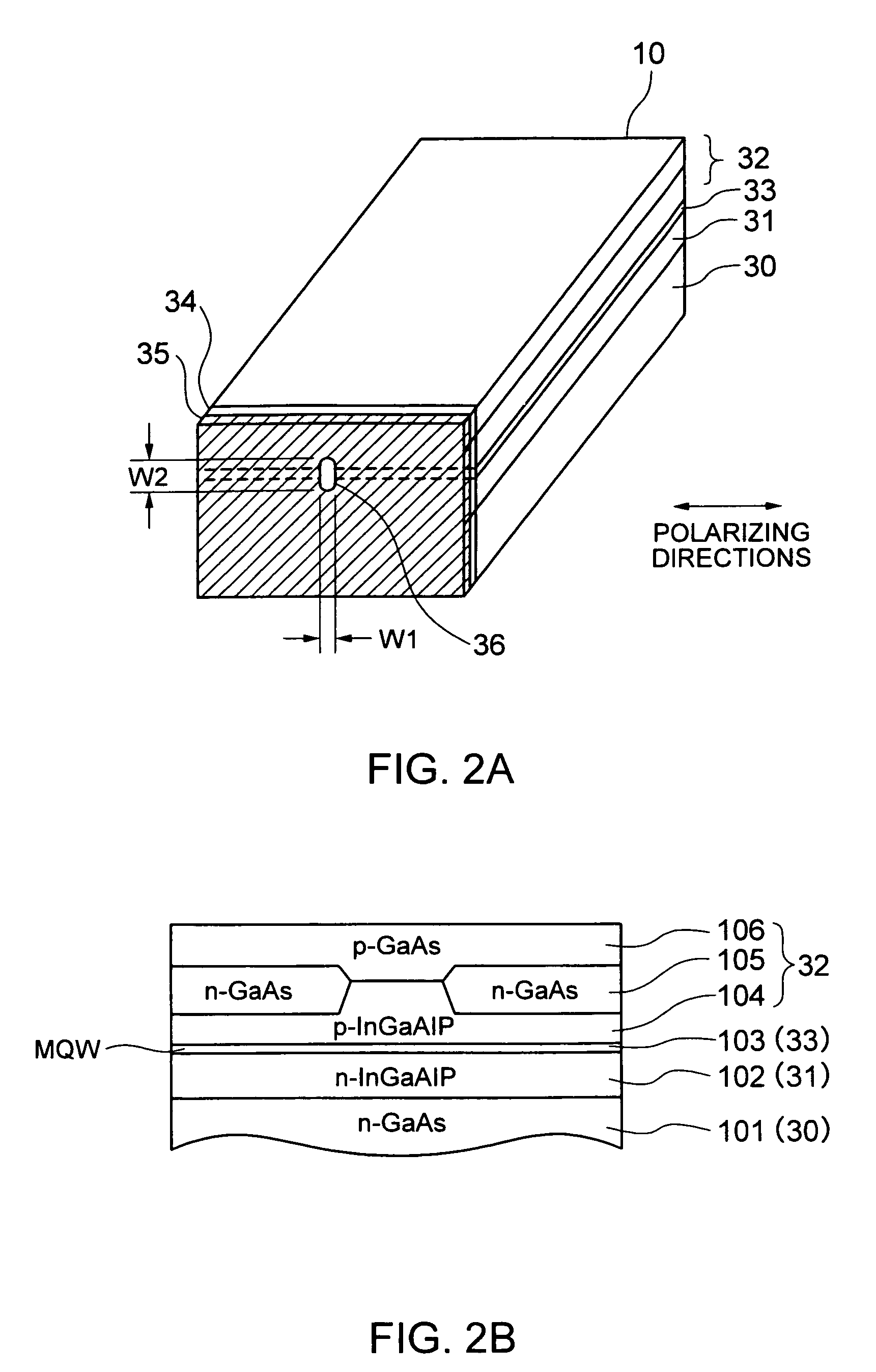
A thermally-assisted magnetic recording head and a magnetic recording apparatus having the magnetic recording head built in are disclosed. The magnetic recording head is capable of recording magnetic information by heating a recording unit of a recording medium and raising its temperature to reduce magnetic coercive force and then applying recording magnetic field to the recording unit having the reduced coercive force. The magnetic recording head has a light absorbing film having an aperture, a laser device emitting and directing light through the aperture to the recording medium to head the recording unit and raise its temperature, and a recording magnetic pole for applying the recording magnetic field to the recording unit. In the aperture, an aperture width W1 is along a polarizing direction of the light emitted from the laser device while an aperture width W2 is approximately perpendicular to the polarizing direction of the aperture width W1, and the aperture width W1 is shorter than the aperture width W2. The heating source such as a laser device recedes from the medium to provide a unique configuration where a tip of the recording magnetic pole protrudes ahead of the heating source, and hence, heating beam and the recording magnetic pole can be located close to each other without losing sufficient energy density to heat the medium.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
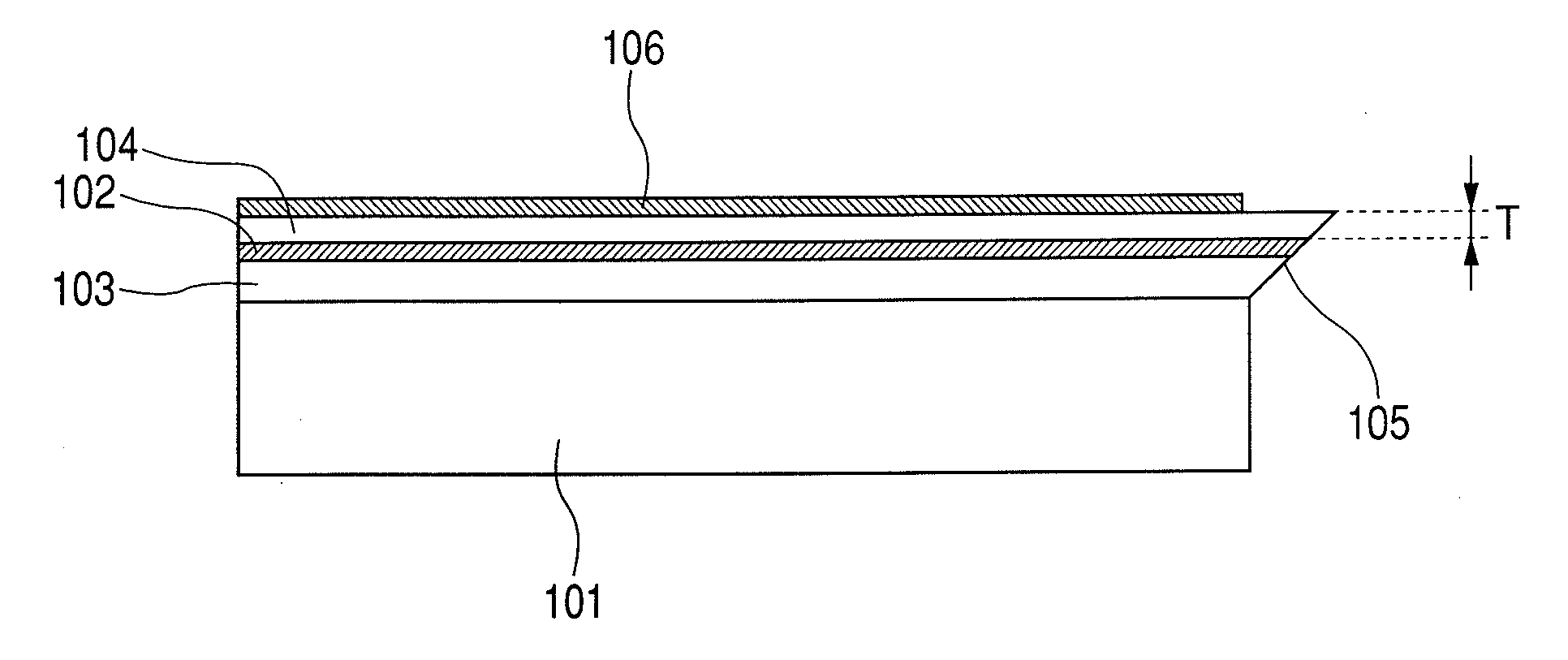
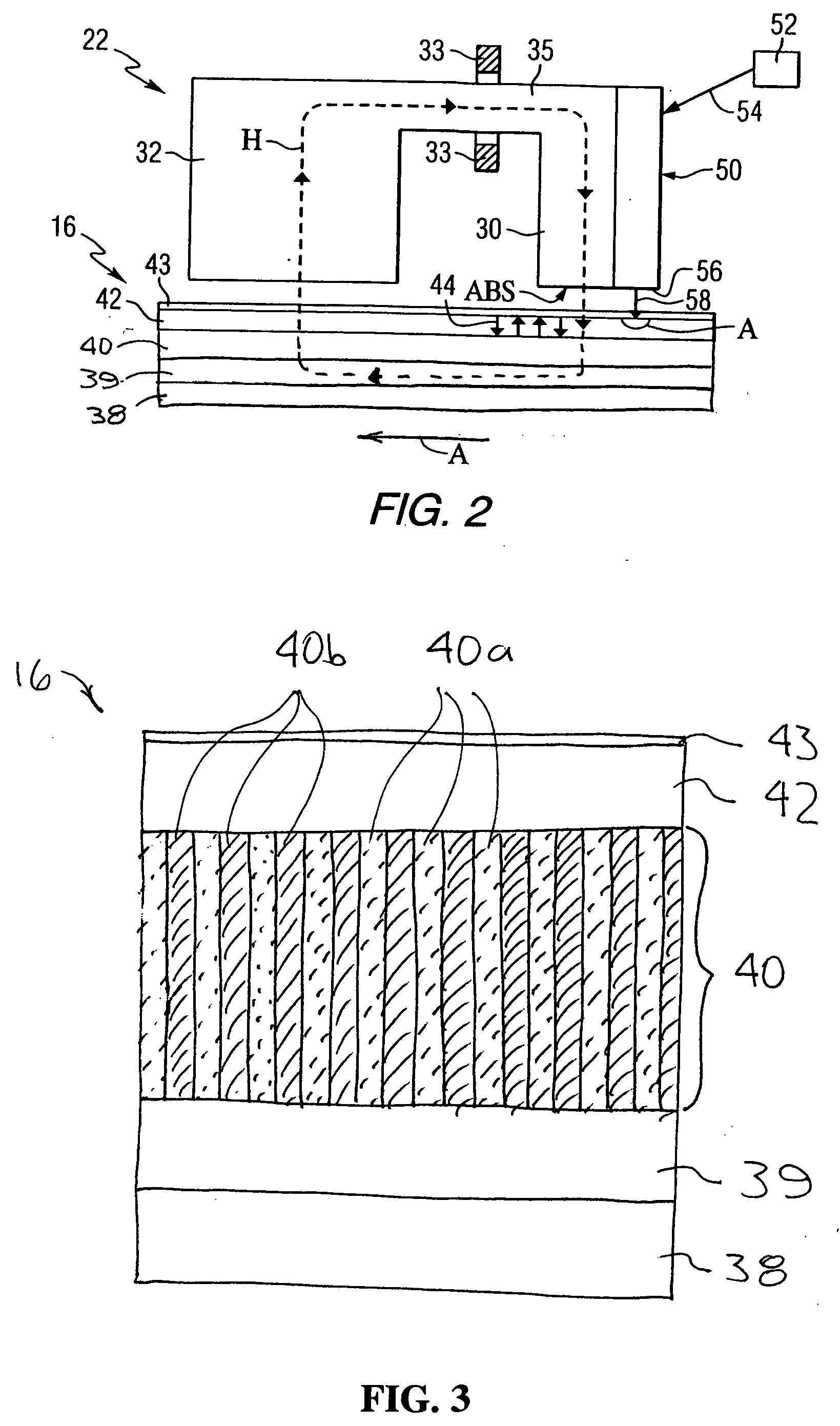
Heat assisted magnetic recording head
InactiveUS20070165495A1Easy to manufactureImprove power generation efficiencyCombination recordingManufacture head surfaceHeat-assisted magnetic recordingWaveguide
A heat assisted magnetic recording (HAMR) head is provided. The HAMR head is mounted in a slider having an ABS that faces a recording medium and illuminates light on the local area of the recording medium, and includes a recording unit that performs recording and a near field light emitter that illuminates near field light onto the local area of the recording medium, the near field light emitter including a light source, a waveguide, and a near field light emission (NFE) pole located between the recording unit and the waveguide, and which generates near field light that is illuminated on the recording medium using light transmitted through the waveguide.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Thermally-assisted perpendicular magnetic recording system and head
InactiveUS7068453B2Combination recordingHeads using thin filmsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingMagnetic shield
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Integrated head for heat assisted magnetic recording
ActiveUS20080170319A1Record information storageRecording/reproducing/erasing methodsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingMagnetic media
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Heat assisted magnetic recording head and method
ActiveUS20050052771A1Combination recordingRecord information storageHeat-assisted magnetic recordingMagnetic storage
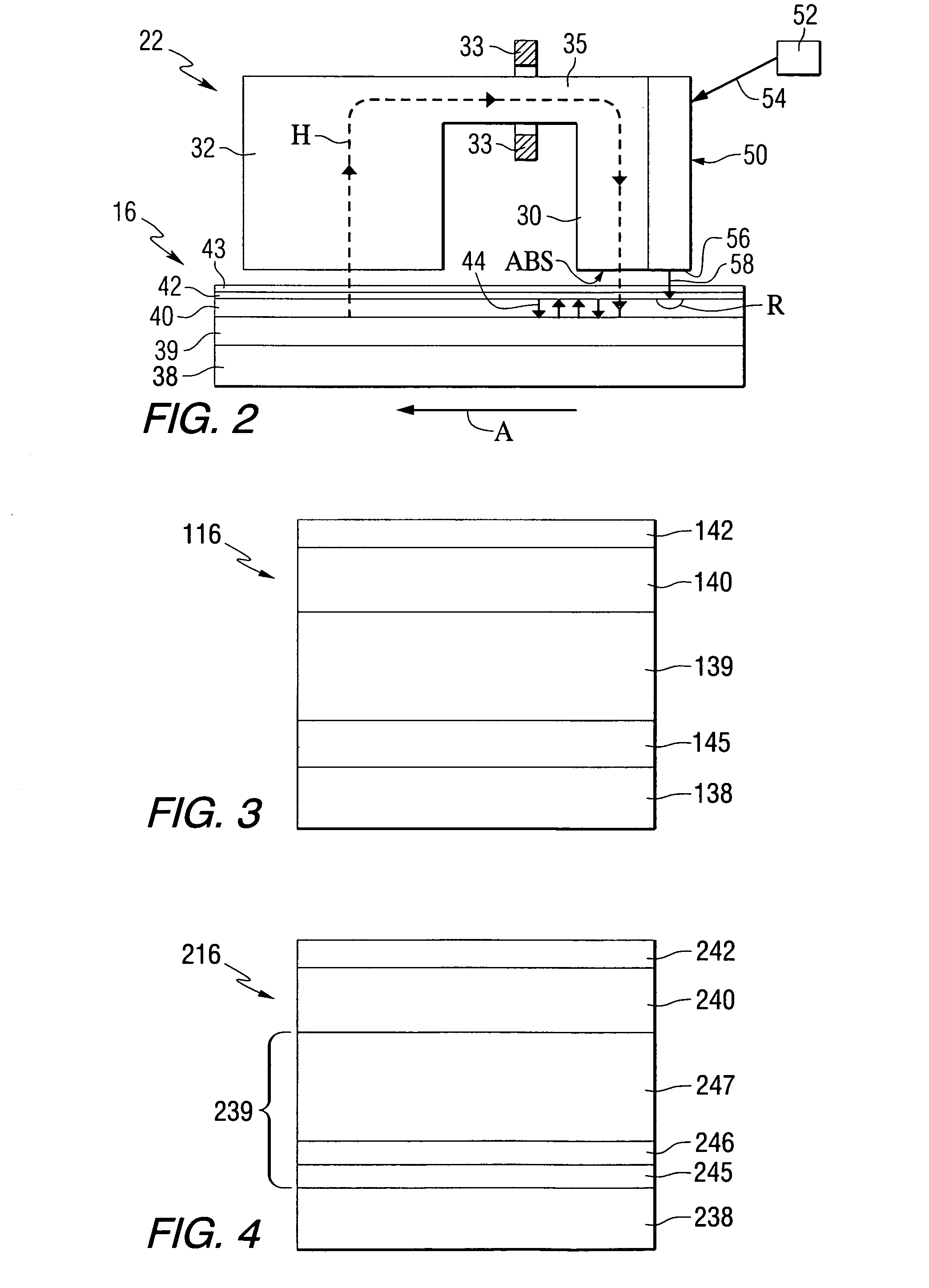
A magnetic recording head comprises a write pole having a pole tip adjacent to an air bearing surface, a return pole, a near field transducer positioned adjacent to the air bearing surface for producing near field radiation for heating a portion of a magnetic storage medium, wherein a thermal profile of the portion of the magnetic storage medium has a maximum gradient at a location subject to a magnetic write field produced by the write pole. A disc drive that includes the magnetic recording head and a method of recording using the magnetic recording head are also provided.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
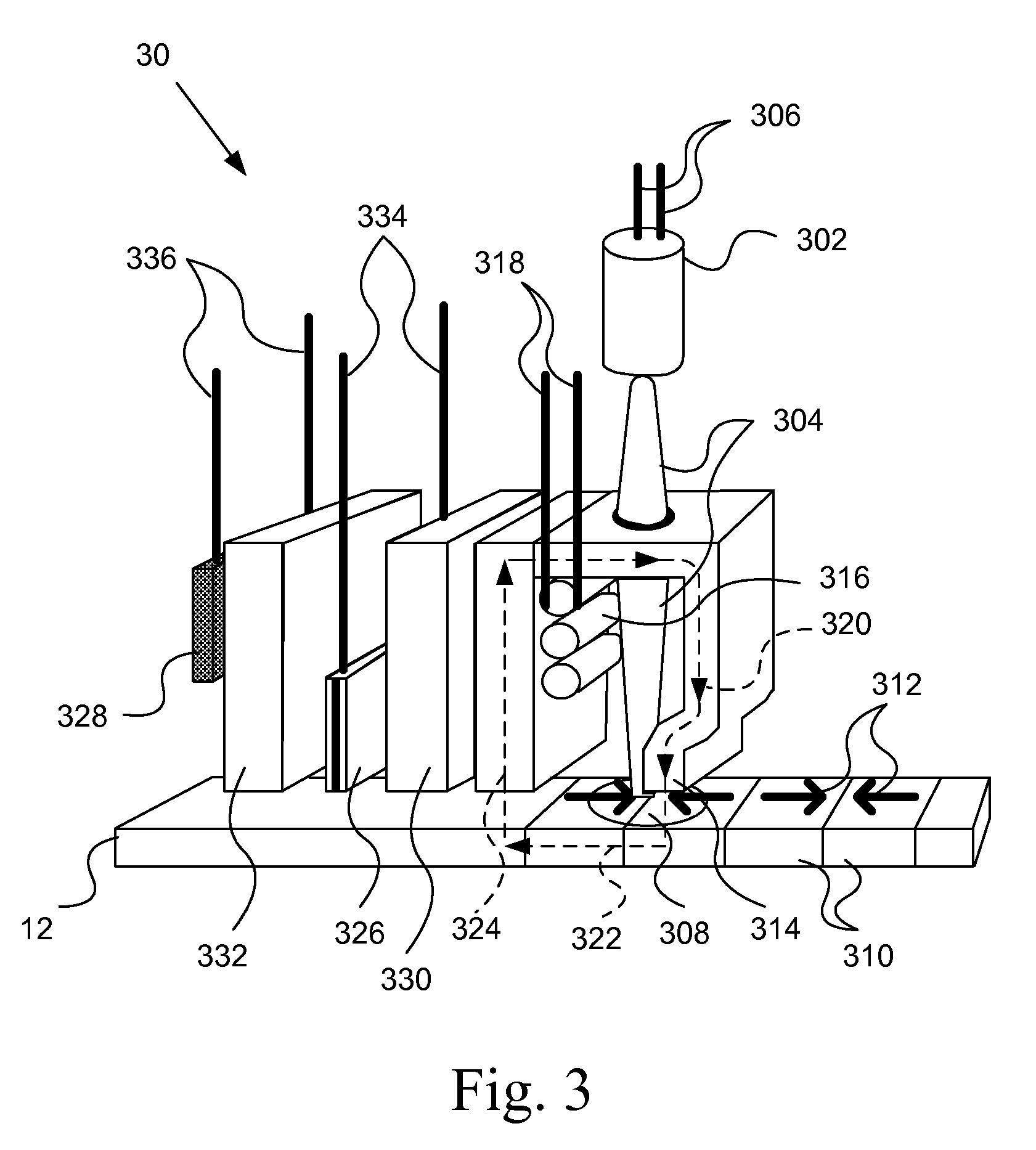
Laser power sensor for thermally assisted magnetic recording
ActiveUS20090225464A1Record information storageRecording/reproducing/erasing methodsPower sensorHeat-assisted magnetic recording
An apparatus, system, and method for measuring thermally induced electric resistance changes in thermally assisted magnetic recording are disclosed for monitoring laser light output in thermally assisted magnetic recording disk drives. An electrical lead is coupled to a read / write head element. A first electrical resistance in the read / write head element is measured. The read / write head is heated by a laser and a second electrical resistance in the read / write head element is measured. The electrical resistance may be monitored at regular intervals when the read / write head element is on the ramp or the electrical resistance measurements may be continuously monitored as the read / write head flies over the magnetic media.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Heat assisted magnetic recording light delivery with fixed laser and rotating mirror
ActiveUS20060233062A1Combination recordingRecord information storageHeat-assisted magnetic recordingLight delivery
An apparatus comprises a moveable arm for positioning an optical transducer adjacent to a storage medium, a stationary light source, and a moveable mirror mounted at a pivot axis of the arm for reflecting light from the light source to the optical transducer. An actuator can be provided for rotating the moveable mirror through an angle of about one half of an angle of rotation of the moveable arm.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Light source unit for thermally-assisted magnetic recording capable of monitoring of light output
ActiveUS20110228653A1Properly and stably heatedImprove efficiencyCombination recordingPhotometry using reference valuePhotovoltaic detectorsHeat-assisted magnetic recording
Provided is a light source unit that is to be joined to a slider to form a thermally-assisted magnetic recording head. The light source unit comprises: a unit substrate having a source-installation surface; a light source provided in the source-installation surface and emitting thermal-assist light; and a photodetector bonded to a rear joining surface of the unit substrate in such a manner that a rear light-emission center of the light source is covered with a light-receiving surface of the photodetector. The photodetector can be sufficiently close to the light source; thus, constant feedback adjustment with high efficiency for the light output of the light source can be performed. This adjustment enables light output from the light source to be controlled in response to changes in light output due to surroundings and to changes with time to stabilize the intensity of light with which a magnetic recording medium is irradiated.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION +1
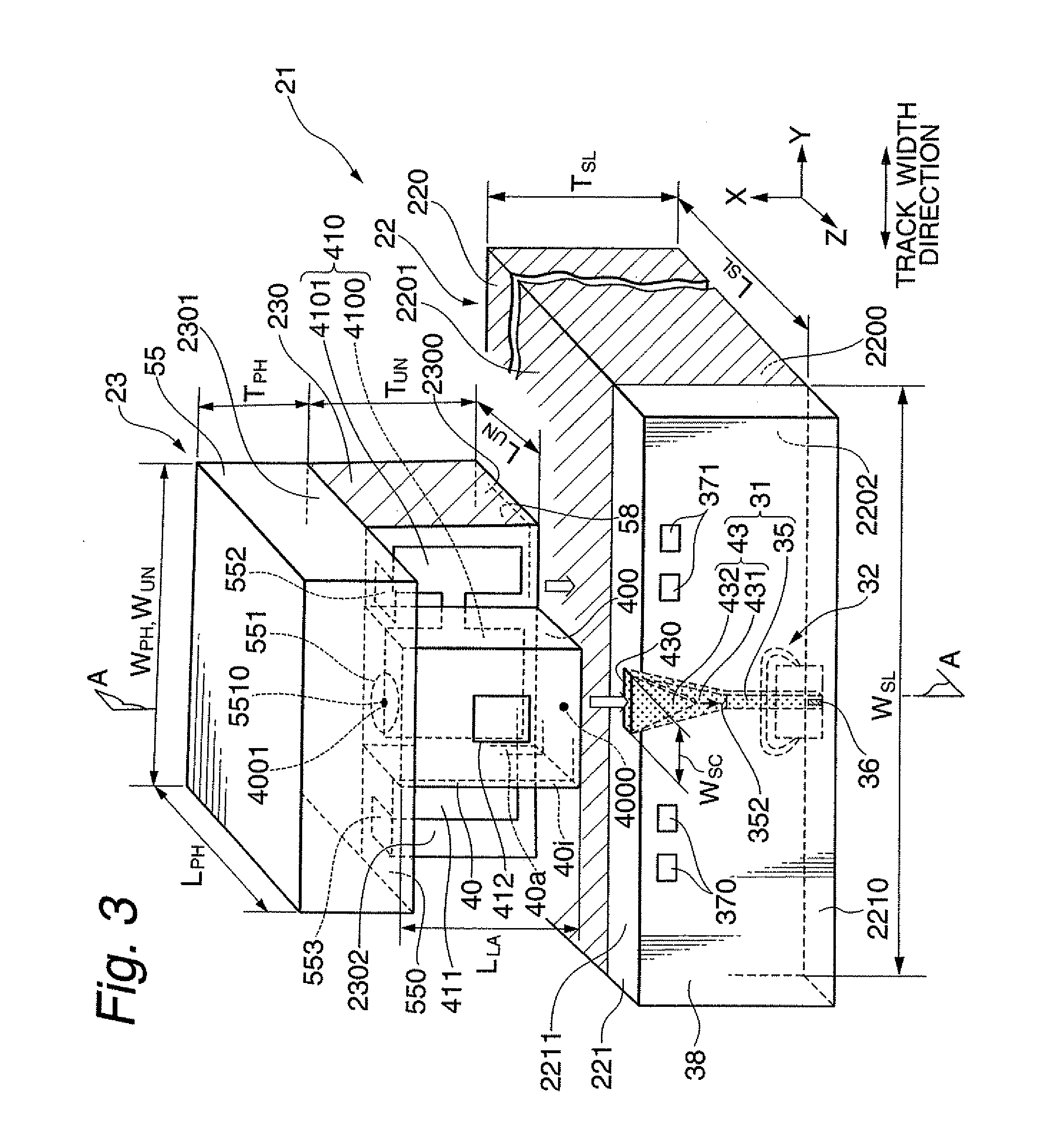
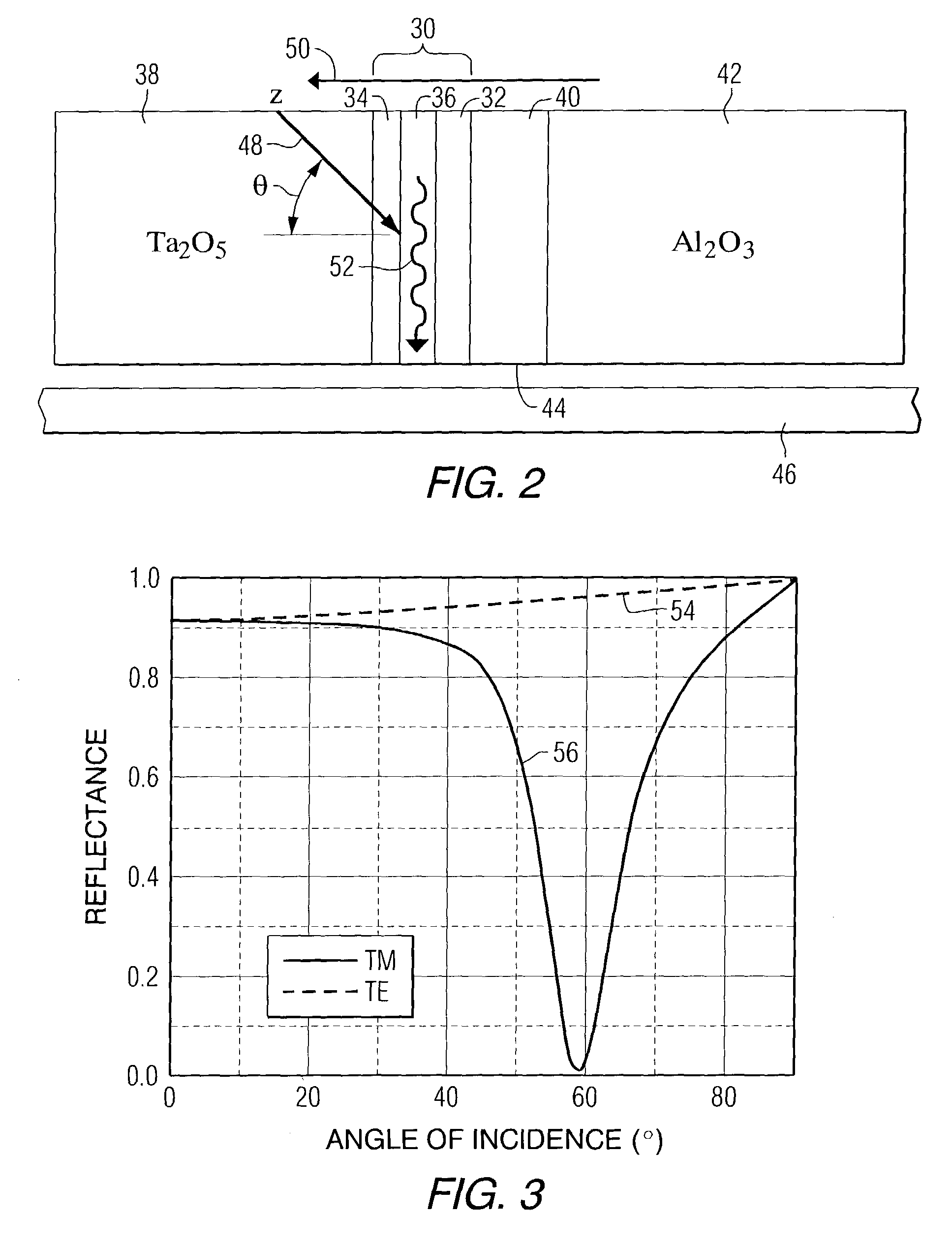
Planar waveguide for heat assisted magnetic recording
Recording heads are provided that comprise a magnetic write pole, and a planar waveguide positioned adjacent to the magnetic write pole, the planar waveguide including a first metal layer, a second metal layer, a first optical layer positioned between the first and second metal layers, and a second optical layer for coupling an electromagnetic wave to the first optical layer at a resonant incident angle. The second optical layer for coupling an electromagnetic wave to the first optical layer at a resonant incident angle is positioned adjacent to a surface of the second metal layer opposite the first optical layer and / or a diffraction grating. A mode index lens can also be provided for confining the electromagnetic wave in a direction parallel to the plane of the first optical layer. Disc drives incorporating the recording heads and a method of magnetic recording performed by the recording heads are also disclosed.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com