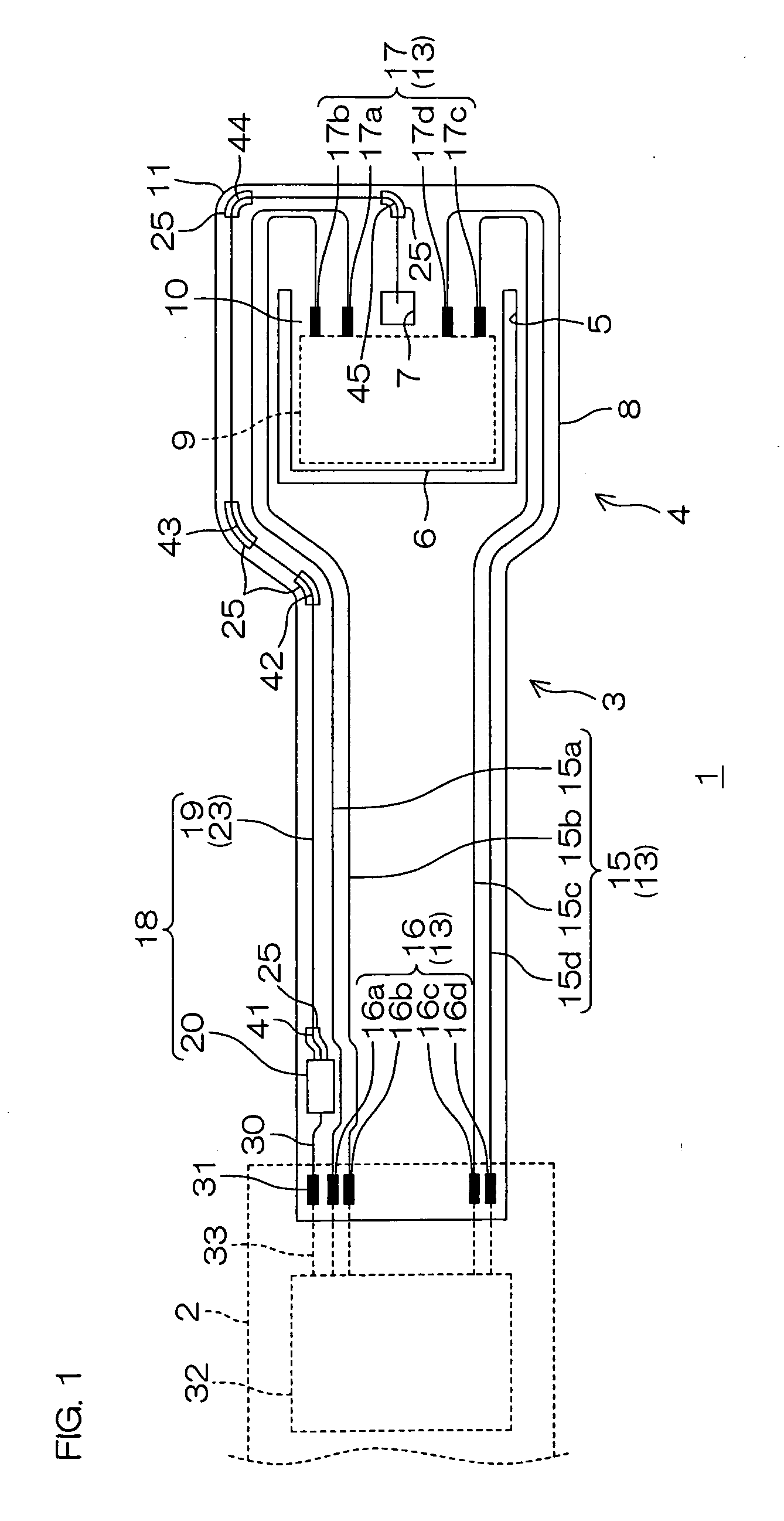
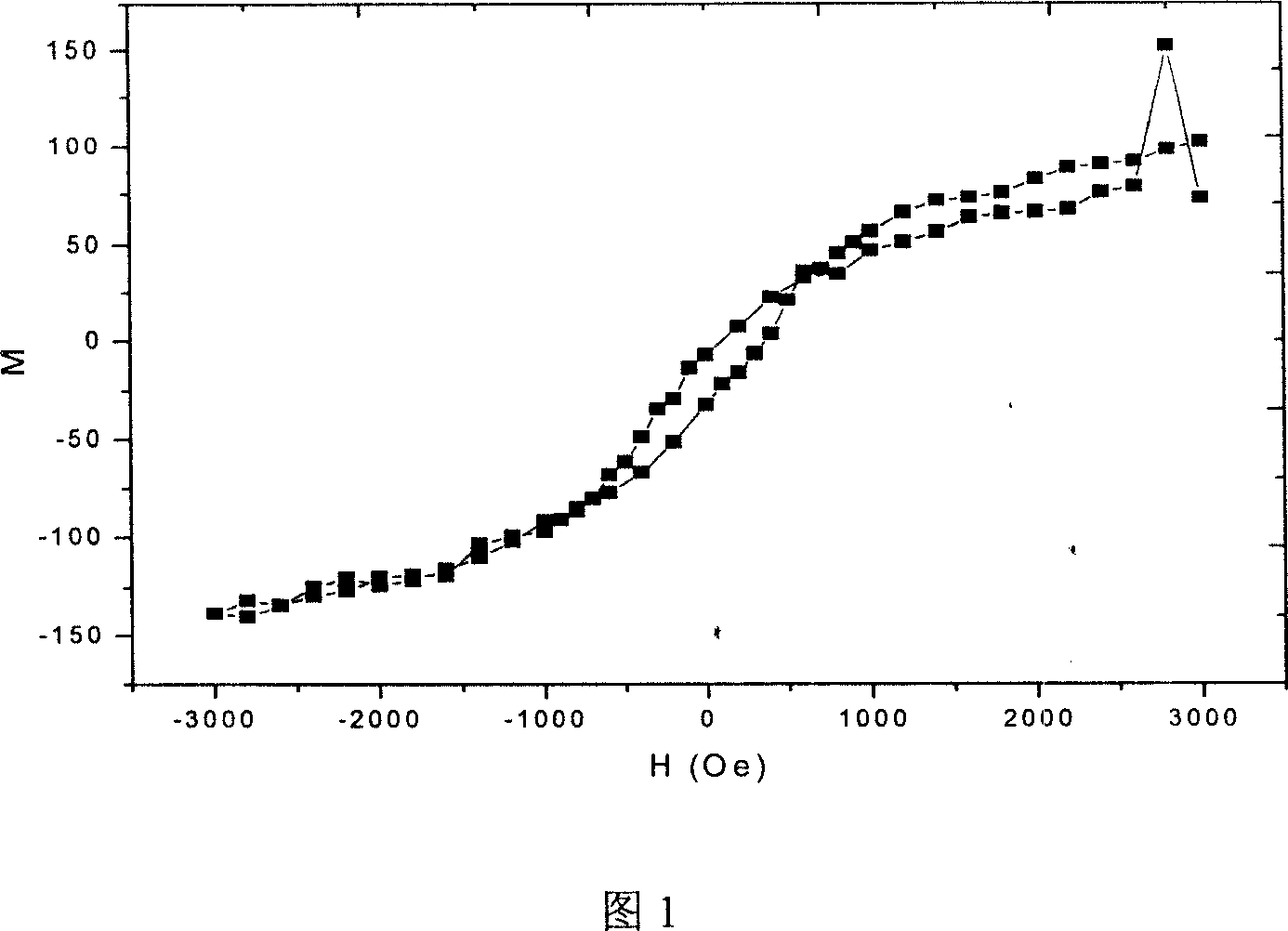
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
105results about "Recording by magnetic means" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
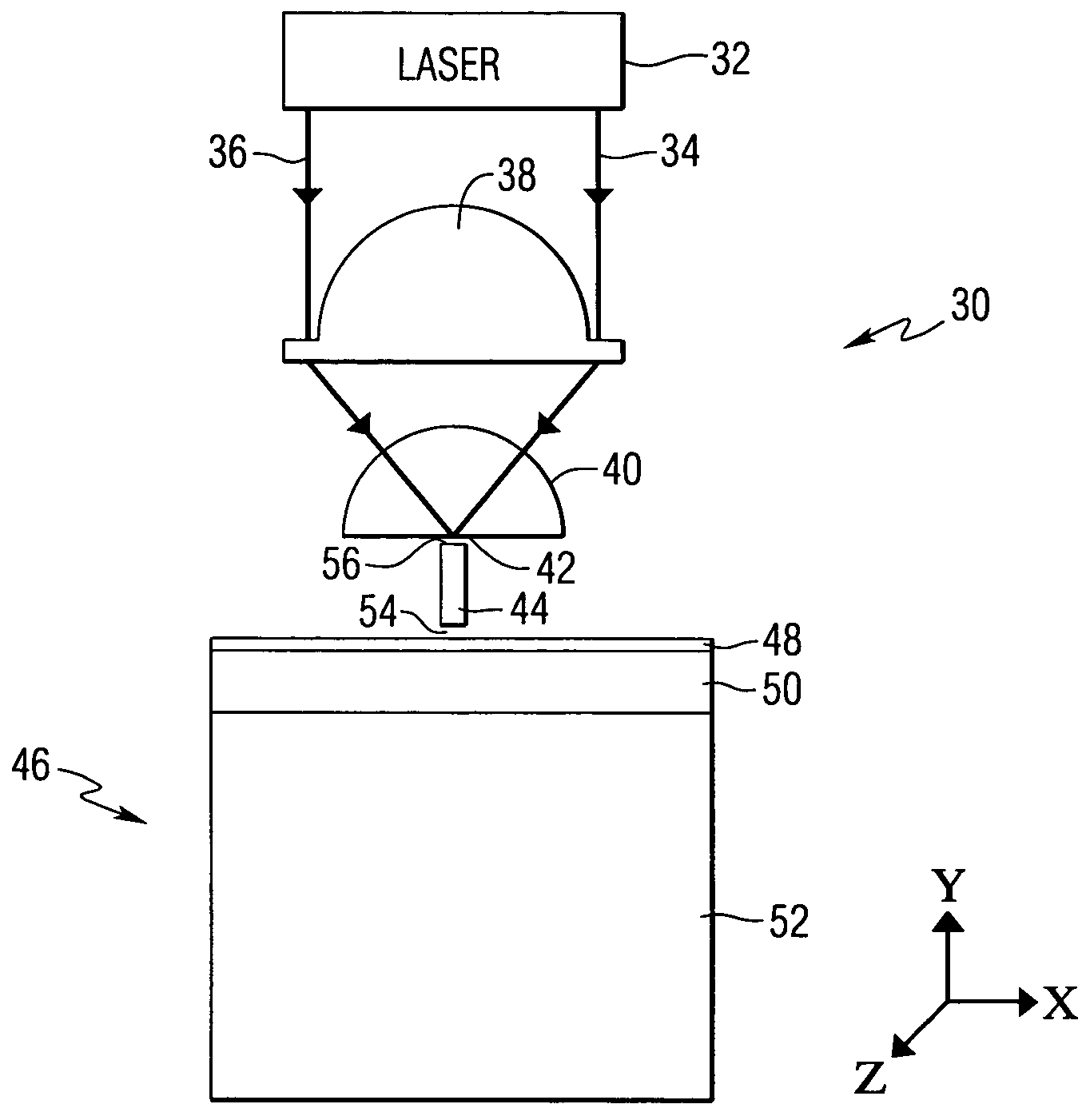
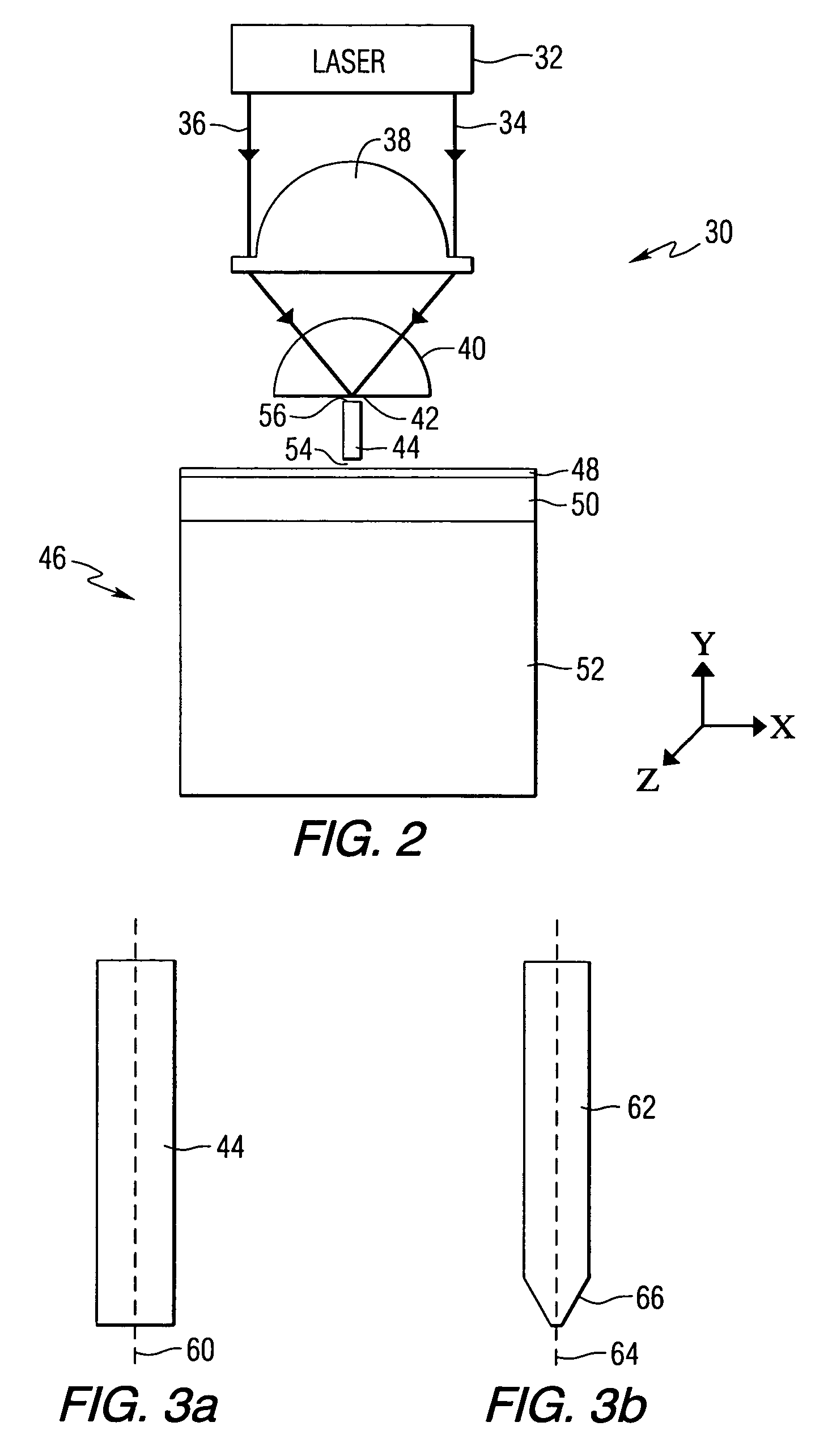
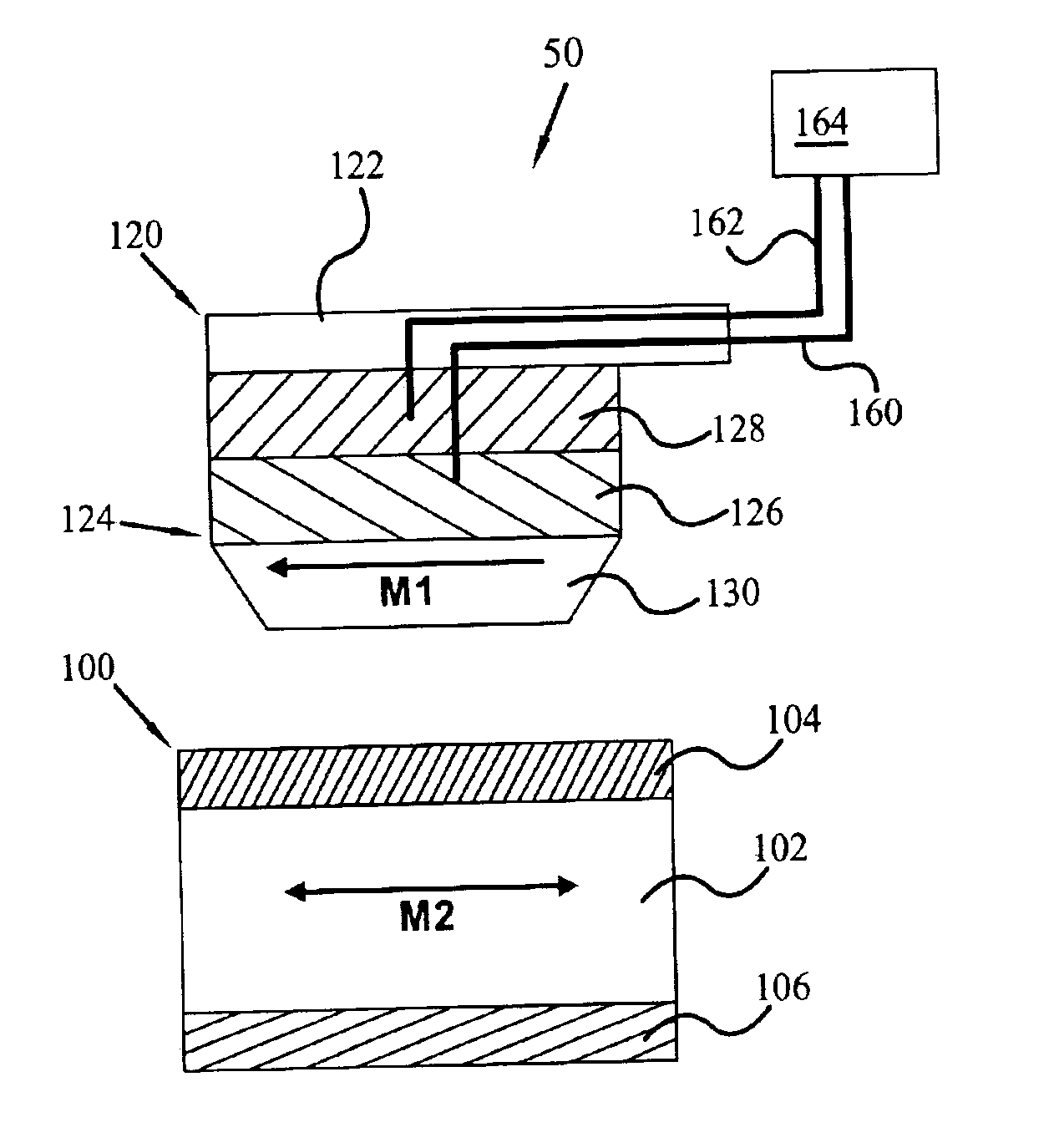
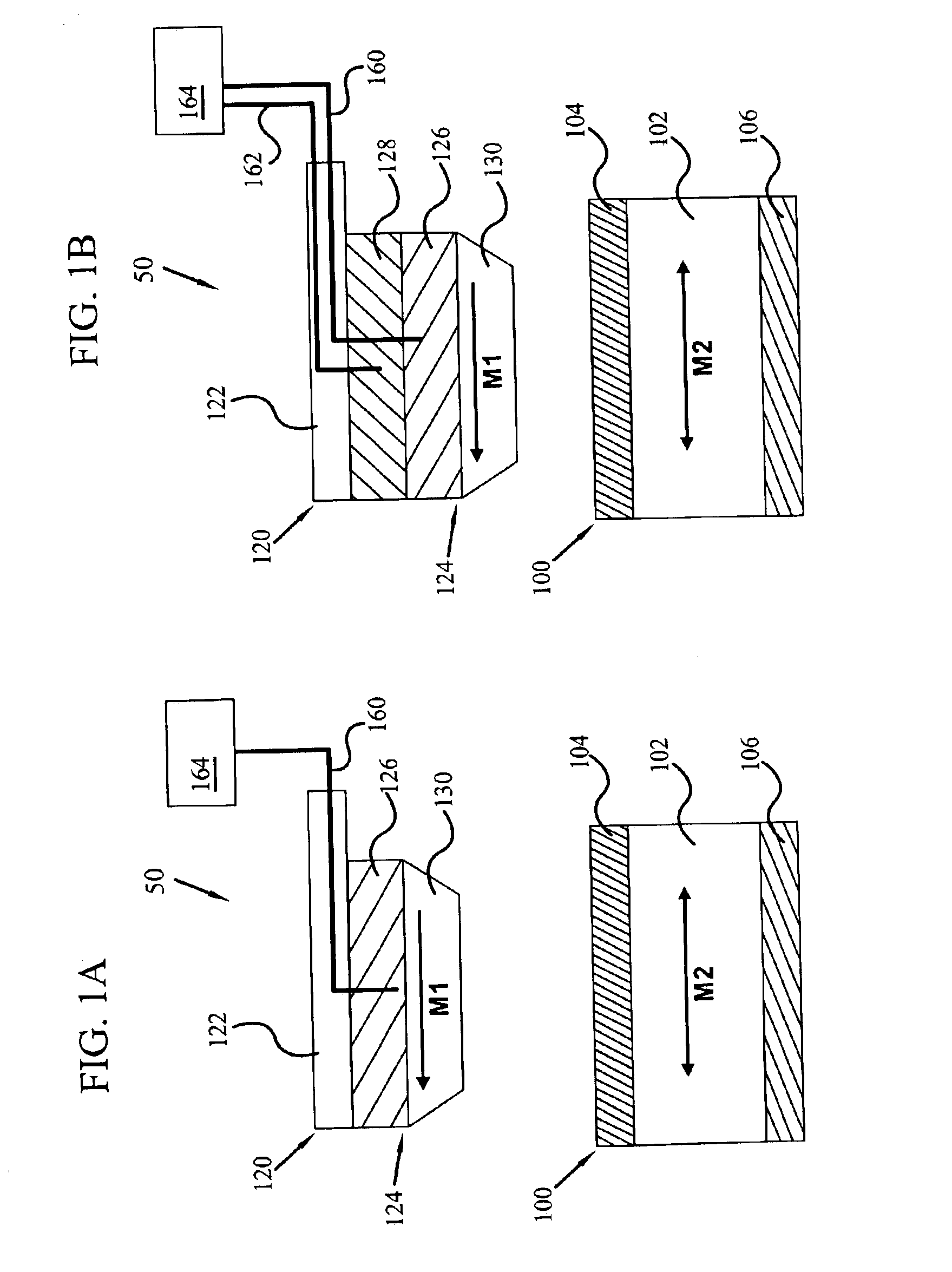
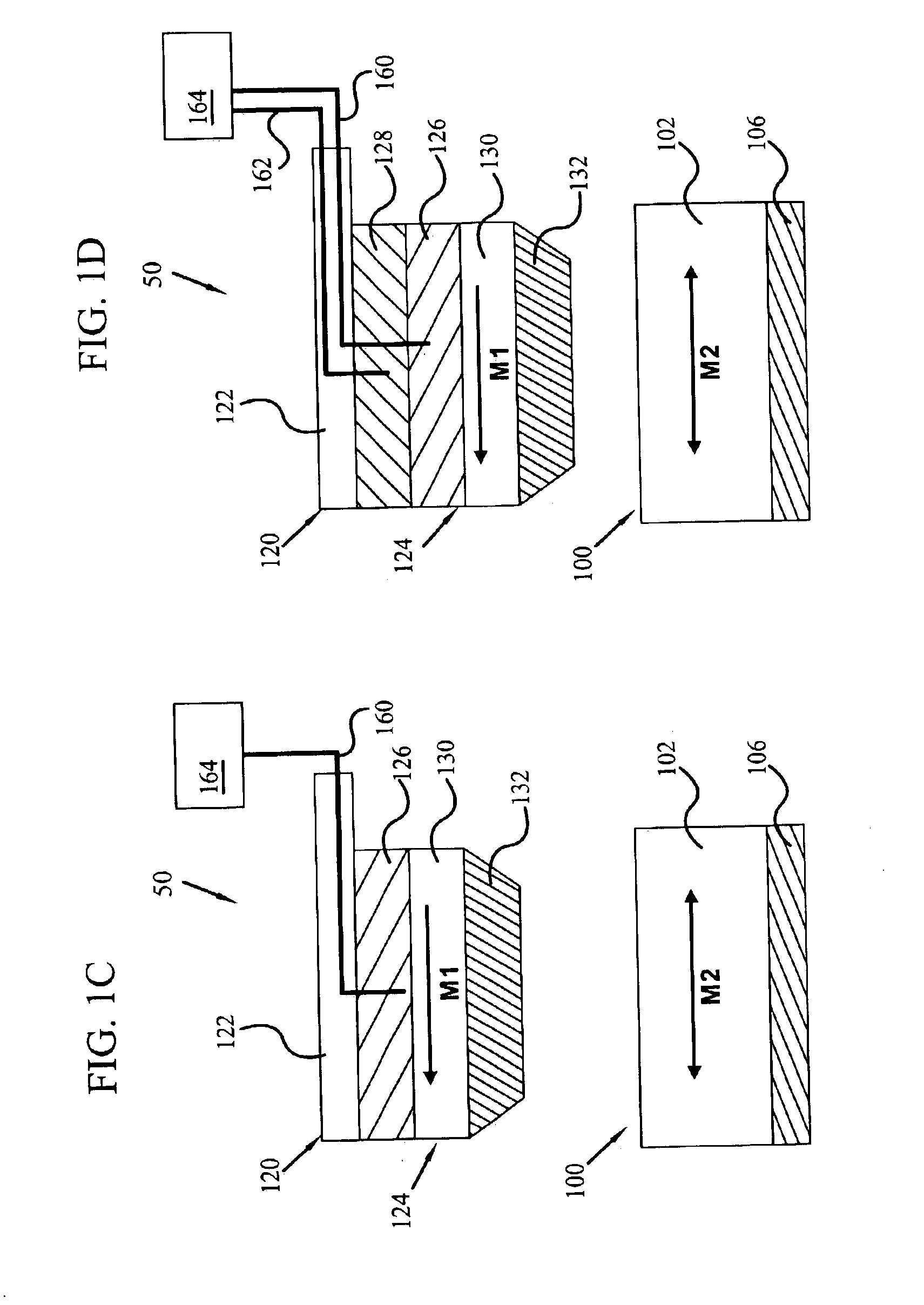
Near-field optical transducers for thermal assisted magnetic and optical data storage
ActiveUS7330404B2Recording by magnetic meansRecord information storageSurface plasmonRefractive index
An optical transducer comprises an optical element for directing an electromagnetic wave to a focal region and a metallic nano-structure having a longitudinal axis substantially parallel to an electric field of the electromagnetic wave, the metallic nano-structure being positioned outside of the optical element, wherein the electromagnetic wave produces surface plasmons on the metallic nano-structure. A cladding material having a refractive index differing from the refractive index of the optical element can be positioned adjacent to a surface of the metallic nano-structure. Magneto-optical recording heads that include the transducers and disc drives that include the magneto-optical recording heads are also included.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Patterned thin films and use of such films as thermal control layers in heat assisted magnetic recording media
ActiveUS20060154110A1Reduce heat transferImprove heat transfer performanceRecording by magnetic meansNanoinformaticsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingOptoelectronics
Patterned thin films comprise regions of relatively low thermal conductivity material separated by regions of relatively high thermal conductivity material. The low thermal conductivity regions may be provided in the form of cylinders or cuboids which are arranged in a continuous matrix of the high thermal conductivity material. The thin film may be used as thermal control layers in data recording media such as heat assisted magnetic recording media.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Thin-film magnetic head with near-field-light-generating layer
ActiveUS7911882B2Improve reliabilityLow coercivityRecording by magnetic meansArm with optical waveguideMagnetic mediaEngineering
A thin-film magnetic head that has a configuration in which the element-formed surface and the opposed-to-medium surface are perpendicular to each other, and a light source is sufficiently distanced from the medium surface is provided. The head comprises at least one near-field-light-generating layer for heating a part of a magnetic medium during write operation by generating a near-field light, having a shape tapered toward a head end surface on the opposed-to-medium surface side, and comprising a near-field-light-generating portion having a light-received surface and a tip reaching the head end surface on the opposed-to-medium surface side, and the light-received surface being sloped in respect to the element-formed surface and being provided in a position where an incident light propagating from a head end surface opposite to the opposed-to-medium surface can reach at least a part of the light-received surface.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
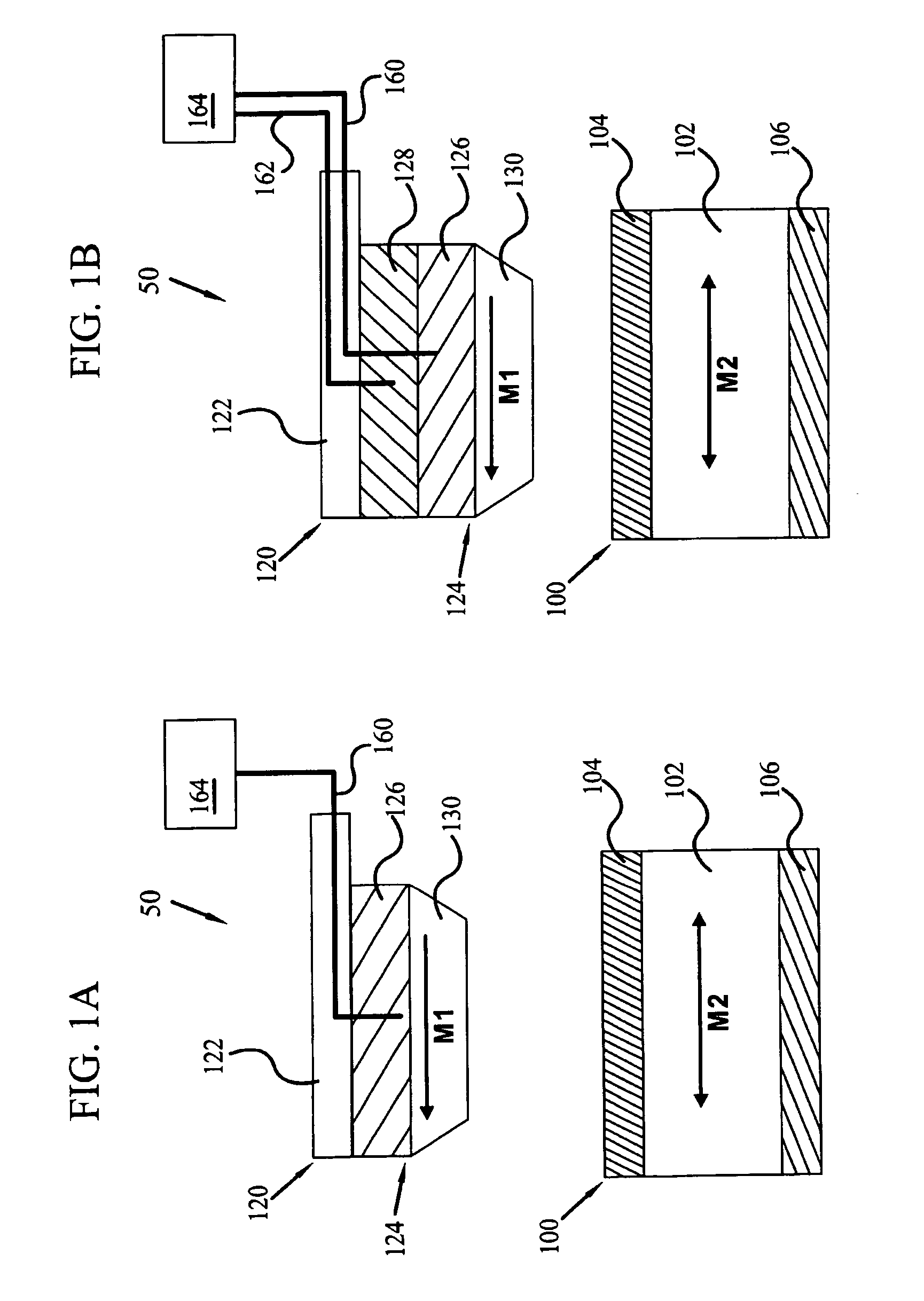
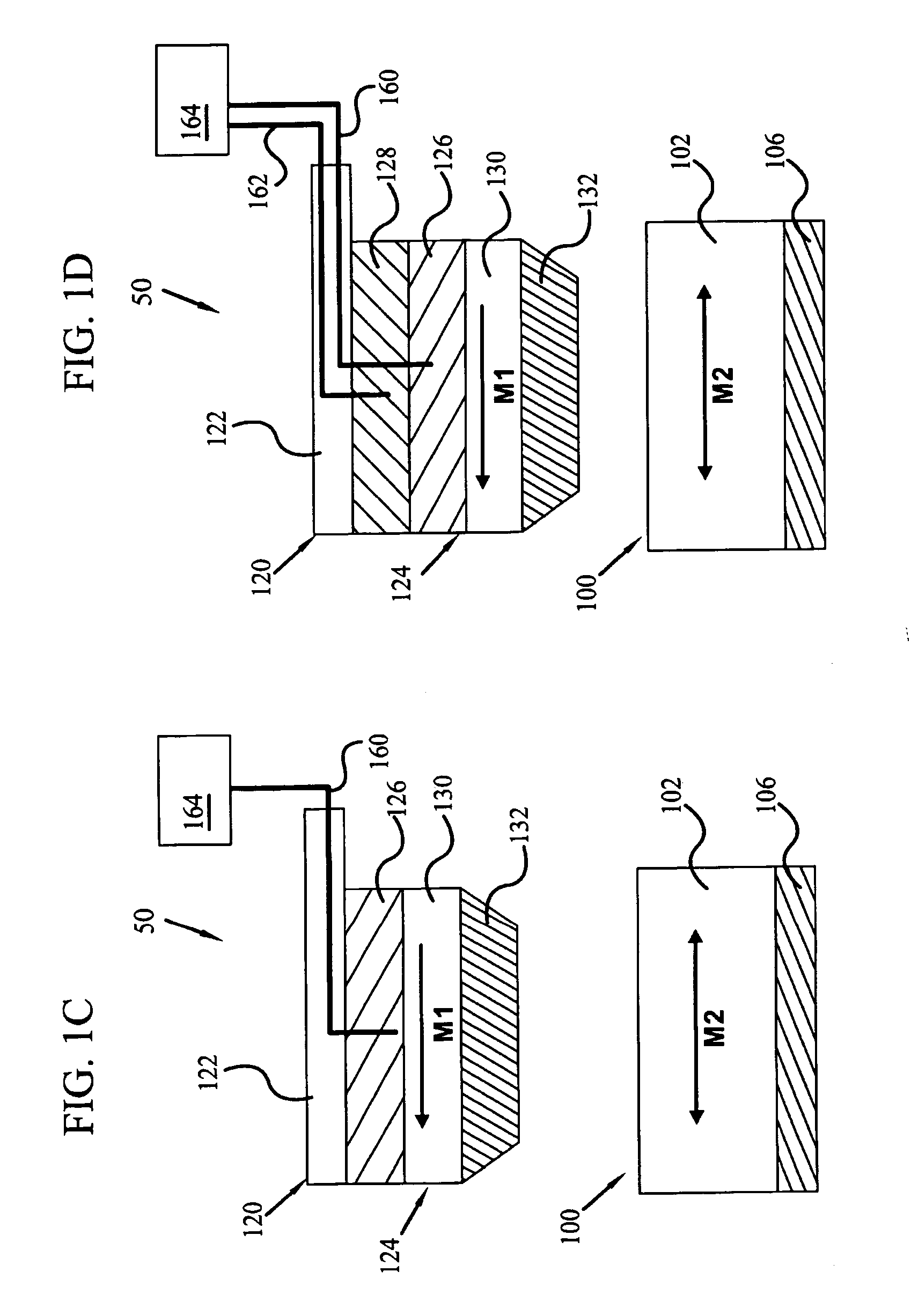
Magnetic memory storage device
This invention provides a probe based magnetic memory storage device. In a particular embodiment, magnetic memory cells are provided in an array. Each cell provides a magnetic data layer and a conductor. At least one movable probe having a tip characterized by a conductor and a soft reference layer is also provided. In addition, an intermediate layer joined to either the movable probe or each memory cell is provided. The movable probe may be placed in contact with a given memory cell, the probe and cell thereby forming a tunnel junction memory cell with the intermediate layer serving as the tunnel junction. The magnetic field provided by the probe conductor may be combined with a field provided by the cell conductor to produce a switching field to alter the orientation of the data layer. The memory cells may include a material wherein the coercivity is decreased upon an increase in temperature. The probe may also include a heat generator. The magnetic field provided by the probe connector will not alter the orientation of an unheated cell, but may alter the orientation of a heated cell.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Magnetic recording apparatus and magnetic recording method
ActiveUS6982845B2High sensitivityMerit on industry is greatRecording by magnetic meansVariable resistance carrier recordingMagnetizationElectrical current
A magnetic recording apparatus comprises a magnetic field impression unit, a current supplying unit and a controlling unit t. The magnetic field impression unit impresses a magnetic field to a magnetic recording medium. The current supplying unit supplies a current to the magnetic recording medium. The controlling unit makes the current supplying unit supply the current to the magnetic recording medium while making the magnetic field impression unit impress the magnetic field to at least a unit of a magnetic recording unit of the magnetic recording medium. Thus, a information is recorded magnetically by making a direction of a magnetization of the magnetic recording unit of the magnetic recording medium in a predetermined direction.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Magnetic recording medium including functional and recording layers orthogonally exchange coupled
InactiveUS6881495B2Increase effective volumeReduce fluctuationRecording by magnetic meansNanomagnetismRoom temperatureRecording density
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Magnetic recording medium, magnetic recording apparatus and magnetic recording method
InactiveUS20050041335A1Increase effective volumeAlleviation of thermal fluctuationRecording by magnetic meansNanomagnetismRoom temperatureRecording density
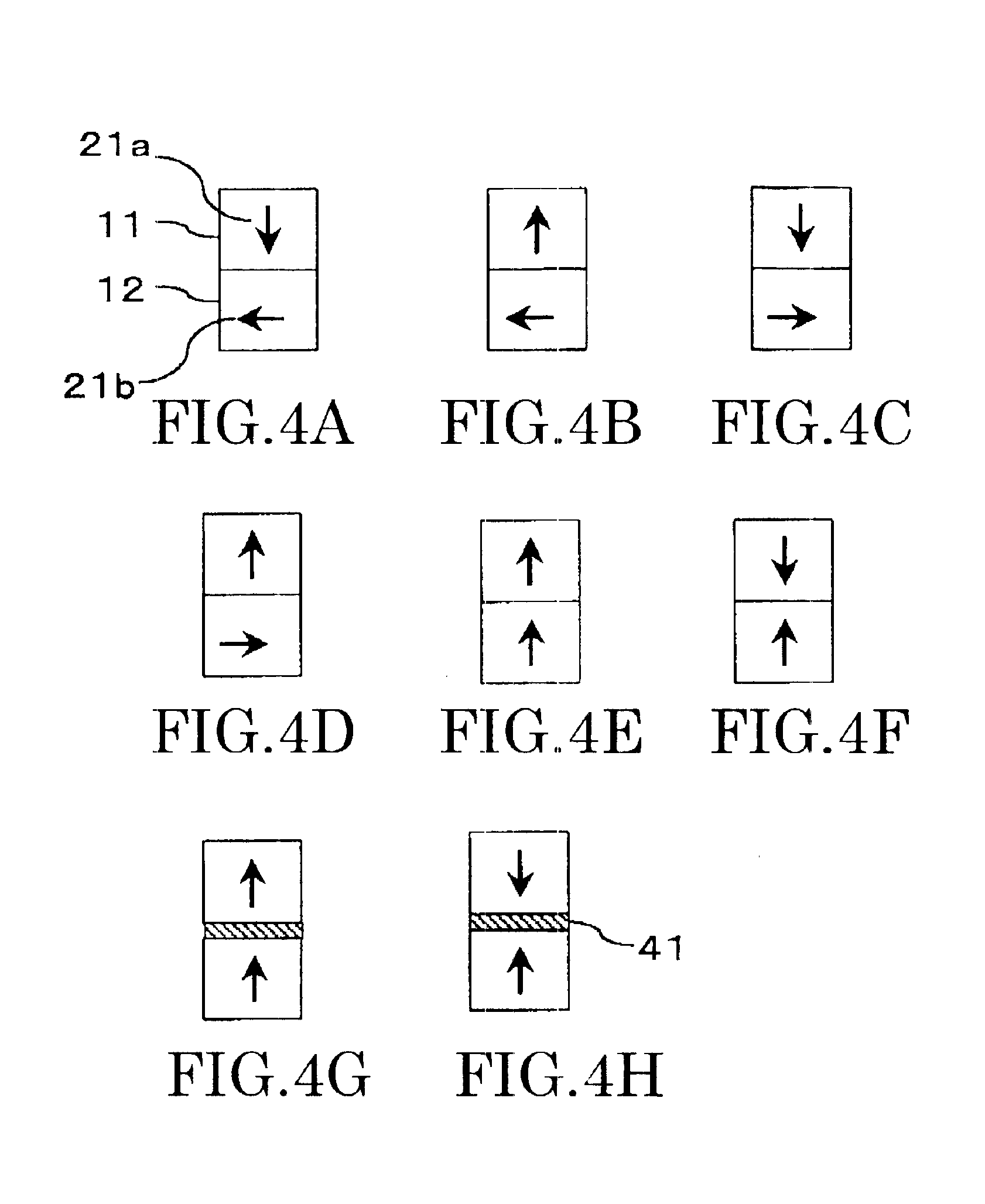
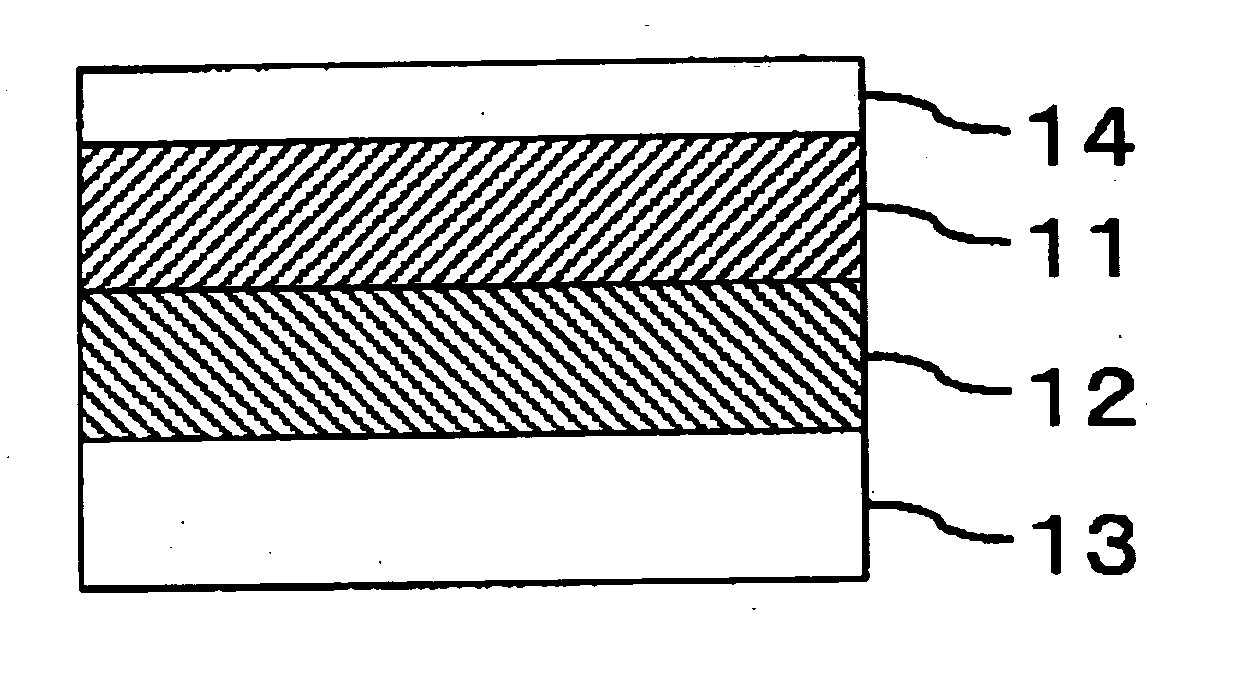
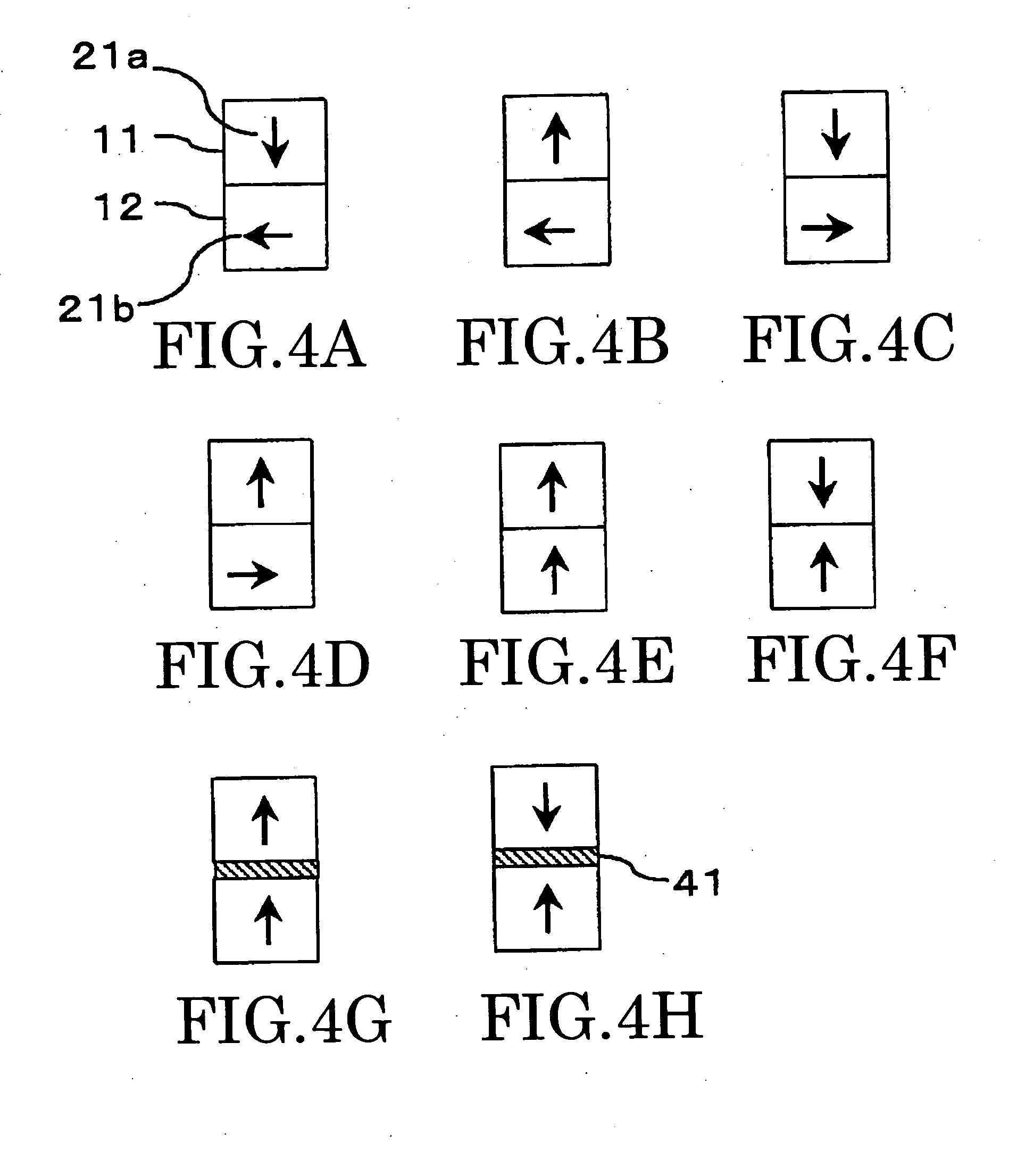
A magnetic recording medium capable of alleviating thermal fluctuation and improving the recording density includes a functional layer (12) containing a magnetic material, and a recording layer (11) overlying the functional layer and containing a magnetic material. The recording layer contains a plurality of magnetic grains (51) and a nonmagnetic material (52) existing among the magnetic grains, and the functional layer and the recording layer exert exchange coupling interaction in a direction making a substantially orthogonal relation with each other at the room temperature.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
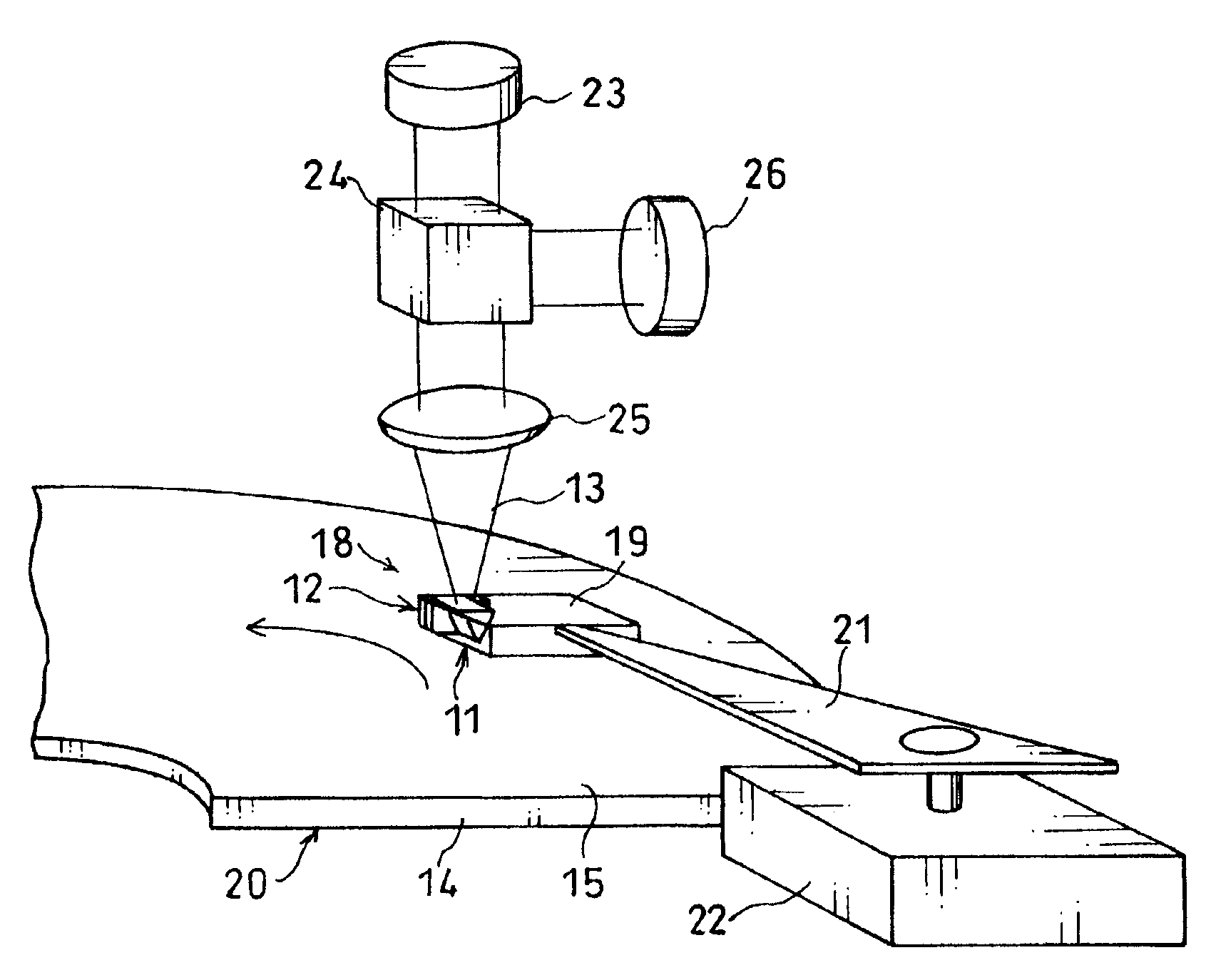
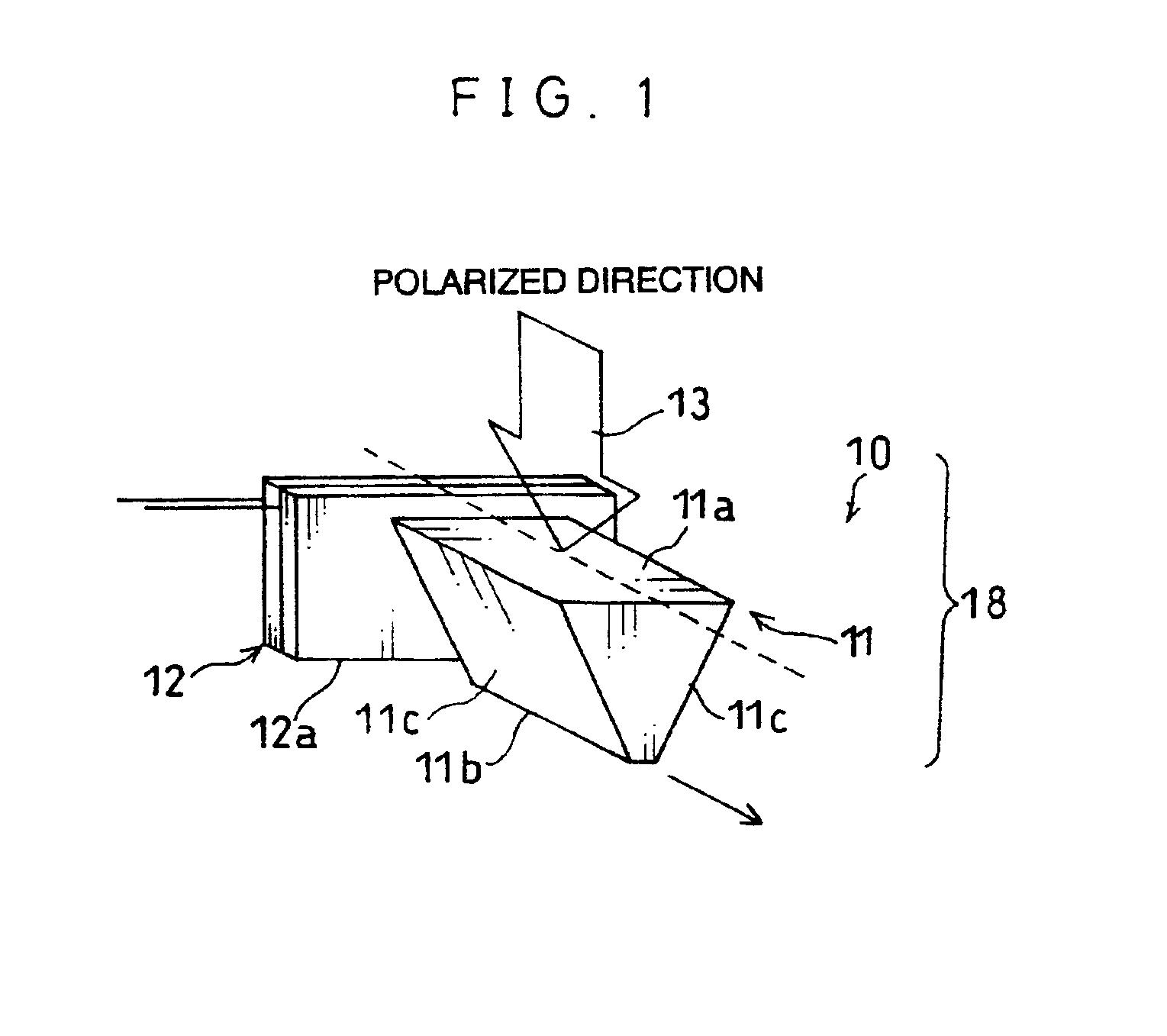
Optically-assisted magnetic recording head and optically-assisted magnetic recording apparatus
InactiveUS20050018547A1Stable magnetic recordingUltra-high densityRecording by magnetic meansHeads using thin filmsHigh intensityLength wave
A pair of members opposed to each other via a gap are commonly used as an evanescent light probe and a writing magnetic head. When the spacing and width of the gap are smaller than the wavelength λ of injected light, highly intensive evanescent light is generated from the gap position of the opposite surface. Magnetic writing is carried out by applying a recording magnetic field from the pair of members to a medium heated by the evanescent light.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Patterned thin films and use of such films as thermal control layers in heat assisted magnetic recording media
ActiveUS7521137B2Reduce heat transferImprove heat transfer performanceRecording by magnetic meansPatterned record carriersHeat-assisted magnetic recordingOptoelectronics
Patterned thin films comprise regions of relatively low thermal conductivity material separated by regions of relatively high thermal conductivity material. The low thermal conductivity regions may be provided in the form of cylinders or cuboids which are arranged in a continuous matrix of the high thermal conductivity material. The thin film may be used as thermal control layers in data recording media such as heat assisted magnetic recording media.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Aluminum-alloy reflective film for optical information recording and target material and recording medium for its formation
InactiveCN1612243ALow thermal conductivityLower melting temperatureRecording by magnetic meansVacuum evaporation coatingRare-earth elementOptoelectronics
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Optical information recording medium and method for manufacturing the medium
InactiveCN1627401AIncrease productionAvoid stopRecording by magnetic meansRecord information storageInformation layerComputer science
The present invention provides a method of properly performing initialization of an optical information recording medium in which the stop of the initialization process is avoided, thereby improving the yield of manufacturing the optical information recording medium. In initializing the information layer with a burst recording area (hereinafter referred to as "BCA"), the laser power, linear velocity and laser light used for the information layer are changed between the BCA range and the data area of the area for recording and reproducing information. At least one initialization condition in the focus of the bundle. In initializing the information layer without BCA, at least one initialization condition including laser power, linear velocity, and laser beam focus and feeding pitch for the information layer is changed between an area corresponding to the BCA and an area corresponding to the data area.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Magnetic recording and reproducing device and magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS20050193405A1Valid recordReliable recordRecording by magnetic meansProtective coatings for layersDouble ValueRecording layer
A magnetic recording and reproducing device includes: a magnetic recording medium in which a magnetic recording layer is formed in a concavo-convex pattern so that tracks are formed by convex portions of a predetermined track width and arranged in parallel in the track width direction; a heating head for heating the magnetic recording medium to partially reduce coercivity of the tracks; a recording head for applying a recording magnetic field to a heated portion of the magnetic recording medium to record magnetic data on the tracks; and a reproducing head for detecting a reproducing magnetic field of the tracks. In this configuration, an effective recording area has an effective recording width that is equal to or more than the track width, and equal to or less than a sum of the track width and a doubled value of width of concave portions between the tracks.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Portable storage device
ActiveUS7088575B2Recording by magnetic meansDigital data processing detailsElectricityElectrical battery
Owner:WISTRON CORP
Magnetic recording medium and hard disk drive using the same, and manufacturing method thereof
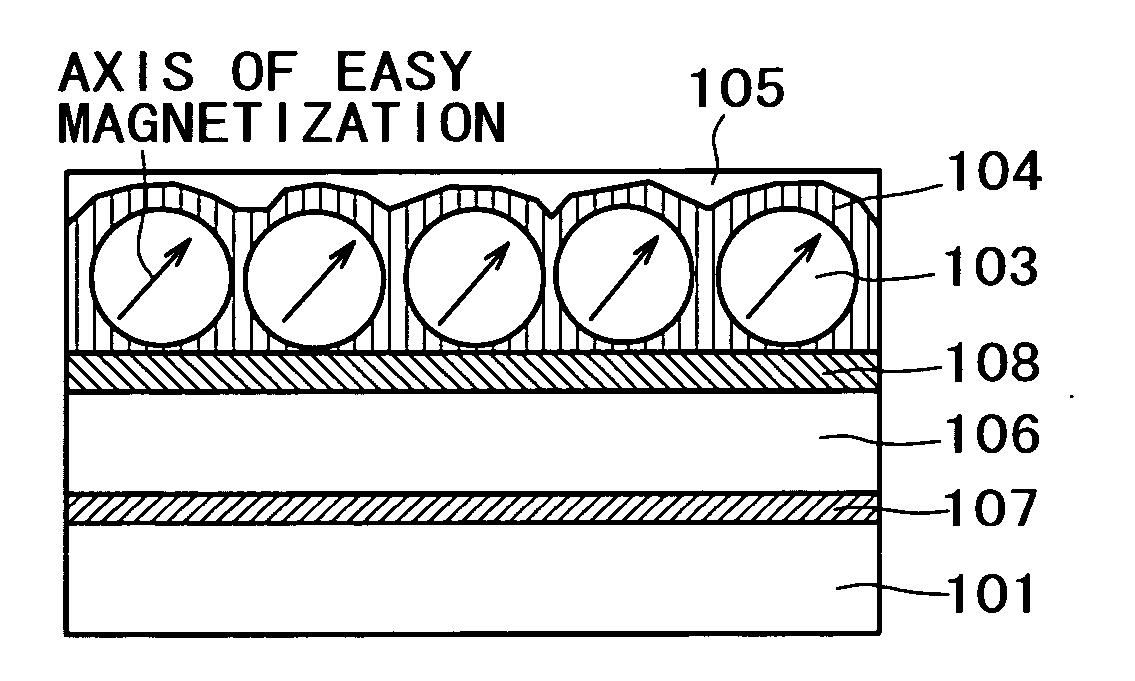
InactiveUS20060153976A1Reduce the overall diameterReduce dispersionRecording by magnetic meansNanomagnetismNanometreHard disc drive
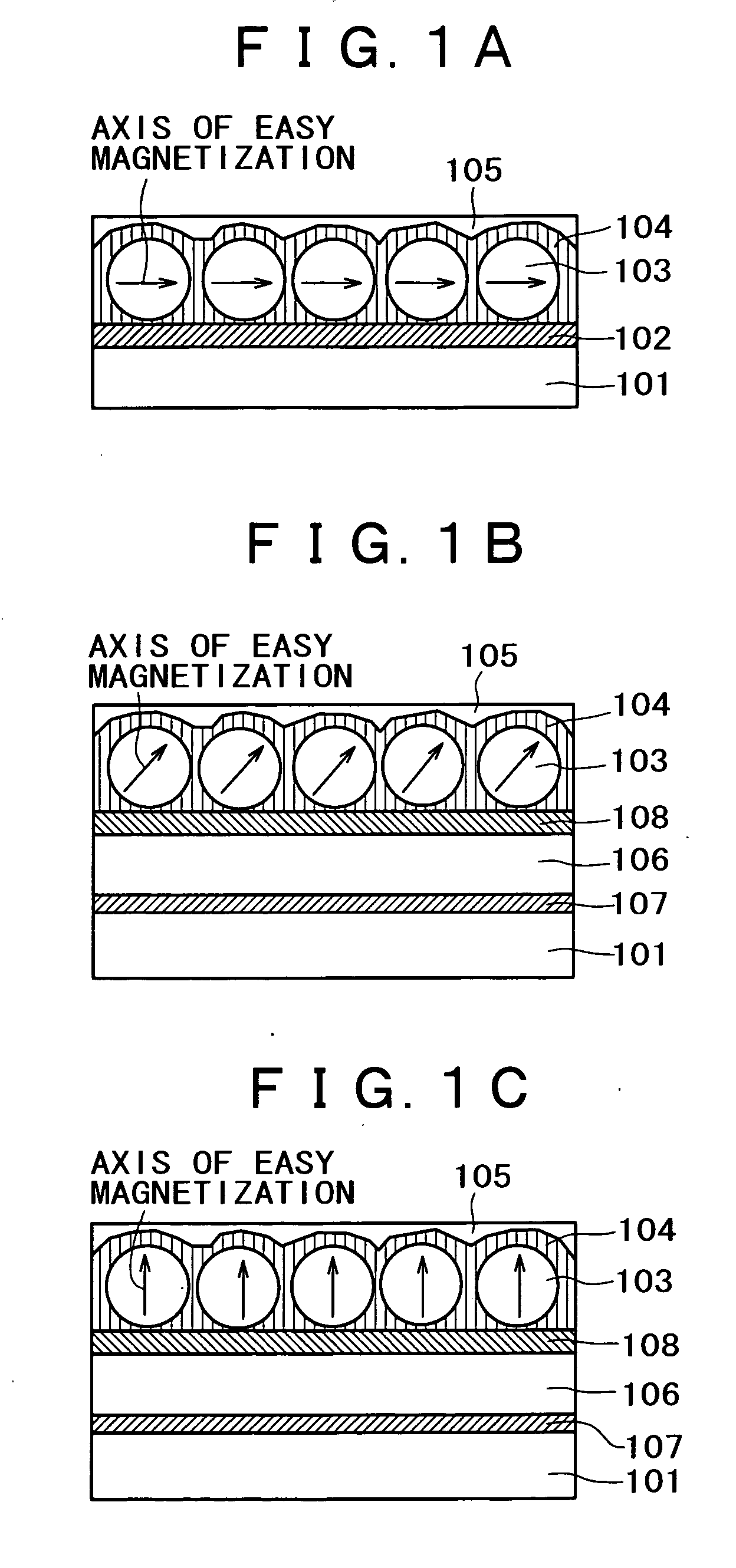
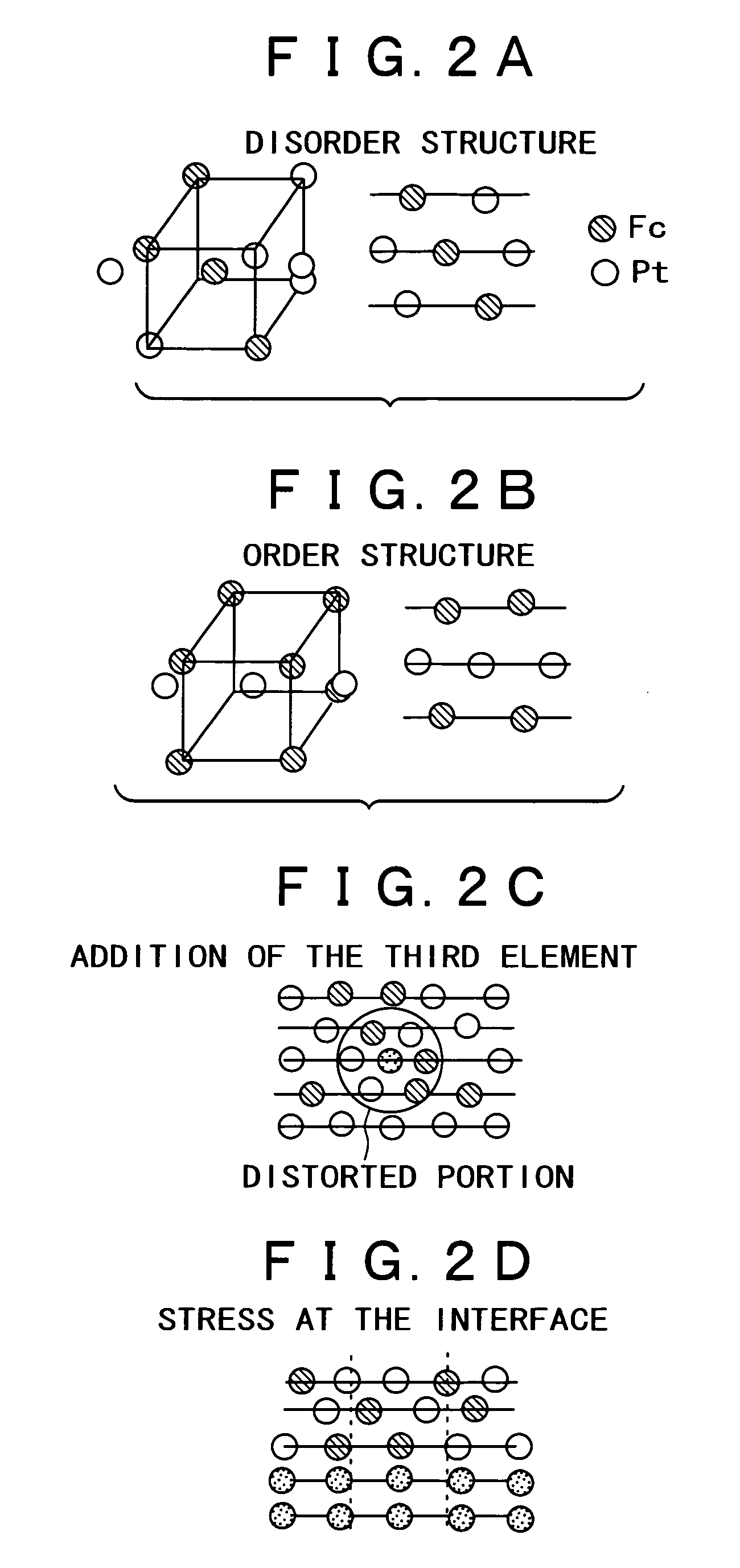
A magnetic recording medium, a hard disk using the same, and a manufacturing method thereof are provided. In one example, the magnetic nano-particle medium is formed by depositing a magnetic nano-particle colloid on a substrate, wherein the axes of easy magnetization of respective crystalline particles are aligned with high accuracy. A layer of L10 alloy nano-particles which will exhibit magnetic properties through an order-disorder transition, and arranged at a substantially uniform spacing on a substrate, and a carbon-containing covering film for surrounding these nano-particles and making the spacing substantially uniform are provided. To the L10 alloy of the nano-particles, at least one non-magnetic element is added, or a covered layer comprising at least one non-magnetic layer is formed therearound. This makes it possible to implement a magnetic recording medium wherein the average diameter of nano-particles is small, and the nano-particle diameter dispersion is small, and the axes of magnetic anisotropy are aligned.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Optically-assisted magnetic recording head and optically-assisted magnetic recording apparatus
InactiveUS7372648B2Stable magnetic recordingUltra-high densityRecording by magnetic meansHeads using thin filmsHigh intensityLength wave
A pair of members opposed to each other via a gap are commonly used as an evanescent light probe and a writing magnetic head. When the spacing and width of the gap are smaller than the wavelength λ of injected light, highly intensive evanescent light is generated from the gap position of the opposite surface. Magnetic writing is carried out by applying a recording magnetic field from the pair of members to a medium heated by the evanescent light.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Metal layer having aperture, method of forming the same, light delivery module including metal layer having aperture, and heat assisted magnetic recording head including the same
InactiveUS20080055343A1Power throughput can be diminishedSmall spot sizeRecording by magnetic meansLayered productsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingLight delivery
A metal layer having an aperture for delivering light, a method of forming the same, a light delivery module including the metal layer having the aperture, and a heat assisted magnetic recording head including the same are provided. The aperture of the metal layer has an inlet and an outlet of different sizes, and also has curved side surfaces. Also, the light delivery module includes the metal layer at an output end thereof, and the heat assisted magnetic recording head includes the light delivery module as an optical heating unit.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH INT
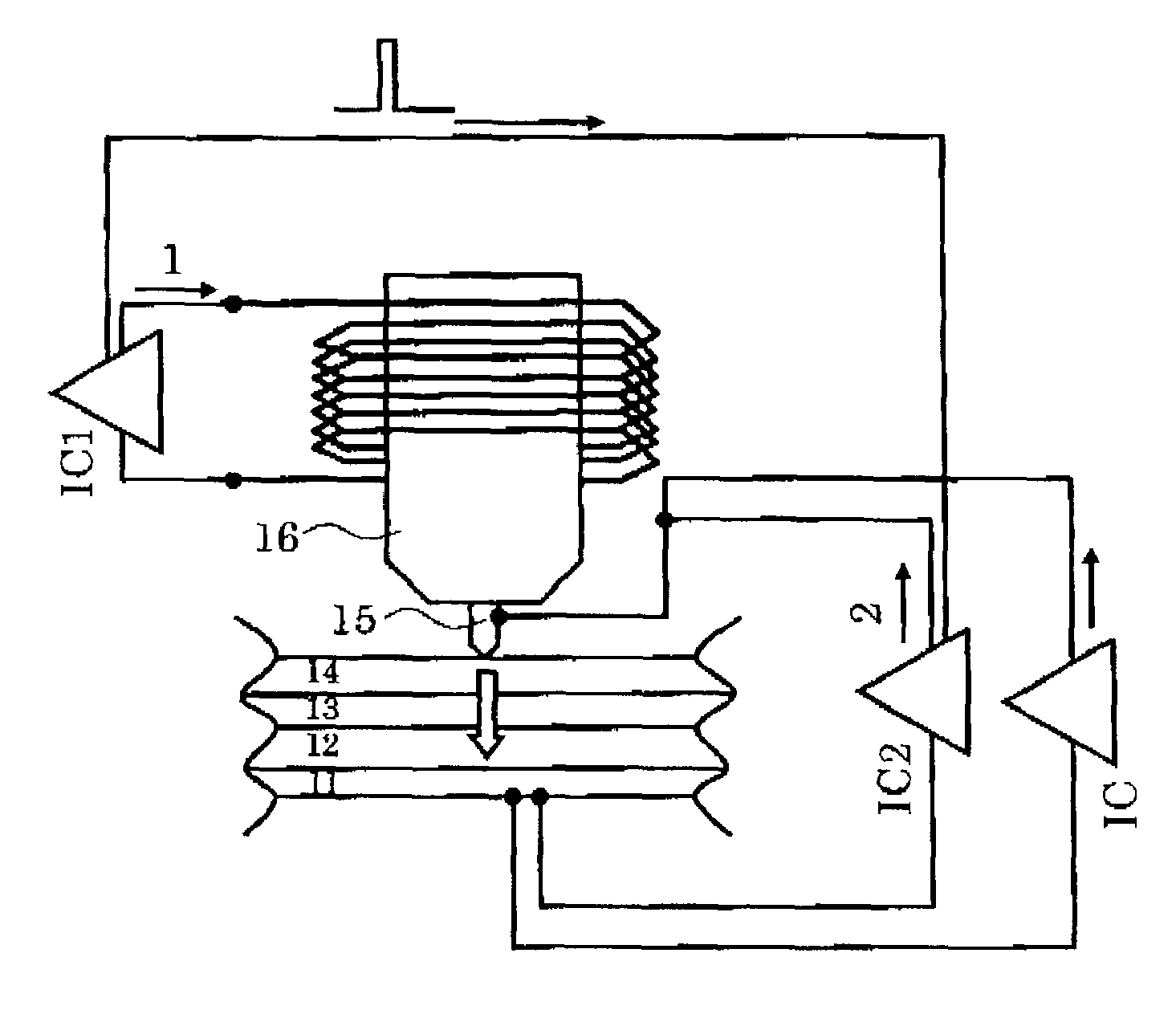
Method and apparatus for initializing recording films of optical recording medium and optical recording medium
InactiveUS20050259552A1Simple structureEfficiently simultaneously crystallized and initializedRecording by magnetic meansMechanical record carriersLight beamFocal position
A method for initializing recording films of an optical recording medium includes two recording layers each including a recording film and which is formed so that a transparent intermediate layer is interposed between each adjacent pair of the recording layers, by projecting a laser beam whose power can be controlled within a predetermined range onto the recording films and simultaneously crystallizing and initializing the recording films, the method for initializing recording films of an optical recording medium including steps of setting a power of the laser beam and a position of a focus of the laser beam so that energy of the laser beam projected onto each of the recording films is equal to or higher than a minimum initialization energy which can crystallize and initialize the recording film irradiated with the laser beam, and projecting the laser beam onto the recording films of the optical recording medium. According to this method, it is possible to efficiently simultaneously crystallize and initialize recording films of the two recording layers of an optical recording medium with an apparatus of simple structure.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optical-disk reproducing apparatus, optical pickup apparatus and optical-disk recording and reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS6940798B2Optical pickup apparatus even smaller and even thinnerSmall sizeRecording by magnetic meansOptical beam sourcesOptical pickupEngineering
The present invention is capable of selectively reproducing an information signal from an optical disk with any of a plurality of types having different track pitches of recording tracks, that is, capable of selectively reproducing an information signal from an optical disk having a low or high recording density by determining the type of the optical disk, that is, determining whether a mounted optical disk is a low-recording-density optical disk or a high-recording-density optical disk. The present invention deliberately generates aberration in an optical beam by controlling a voltage applied to a liquid-crystal device in order to vary the diameter of the optical beam in accordance with the determined type of the optical disk. The present invention is thus characterized in that it is applicable to an optical pickup apparatus for changing the diameter of an optical beam in accordance with whether a mounted optical disk is a low-recording-density optical disk or a high-recording-density optical disk, as well as applicable to an optical-disk reproducing apparatus and an optical-disk recording & reproducing apparatus that employ the optical pickup apparatus.
Owner:SONY CORP
Magnetic memory storage device
InactiveUS6885582B2Low coercivityRecording by magnetic meansMechanical recordingElectrical conductorInter layer
This invention provides a probe based magnetic memory storage device. In a particular embodiment, magnetic memory cells are provided in an array. Each cell provides a magnetic data layer and a conductor. At least one movable probe having a tip characterized by a conductor and a soft reference layer is also provided. In addition, an intermediate layer joined to either the movable probe or each memory cell is provided. The movable probe may be placed in contact with a given memory cell, the probe and cell thereby forming a tunnel junction memory cell with the intermediate layer serving as the tunnel junction. The magnetic field provided by the probe conductor may be combined with a field provided by the cell conductor to produce a switching field to alter the orientation of the data layer. The memory cells may include a material wherein the coercivity is decreased upon an increase in temperature. The probe may also include a heat generator. The magnetic field provided by the probe connector will not alter the orientation of an unheated cell, but may alter the orientation of a heated cell.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
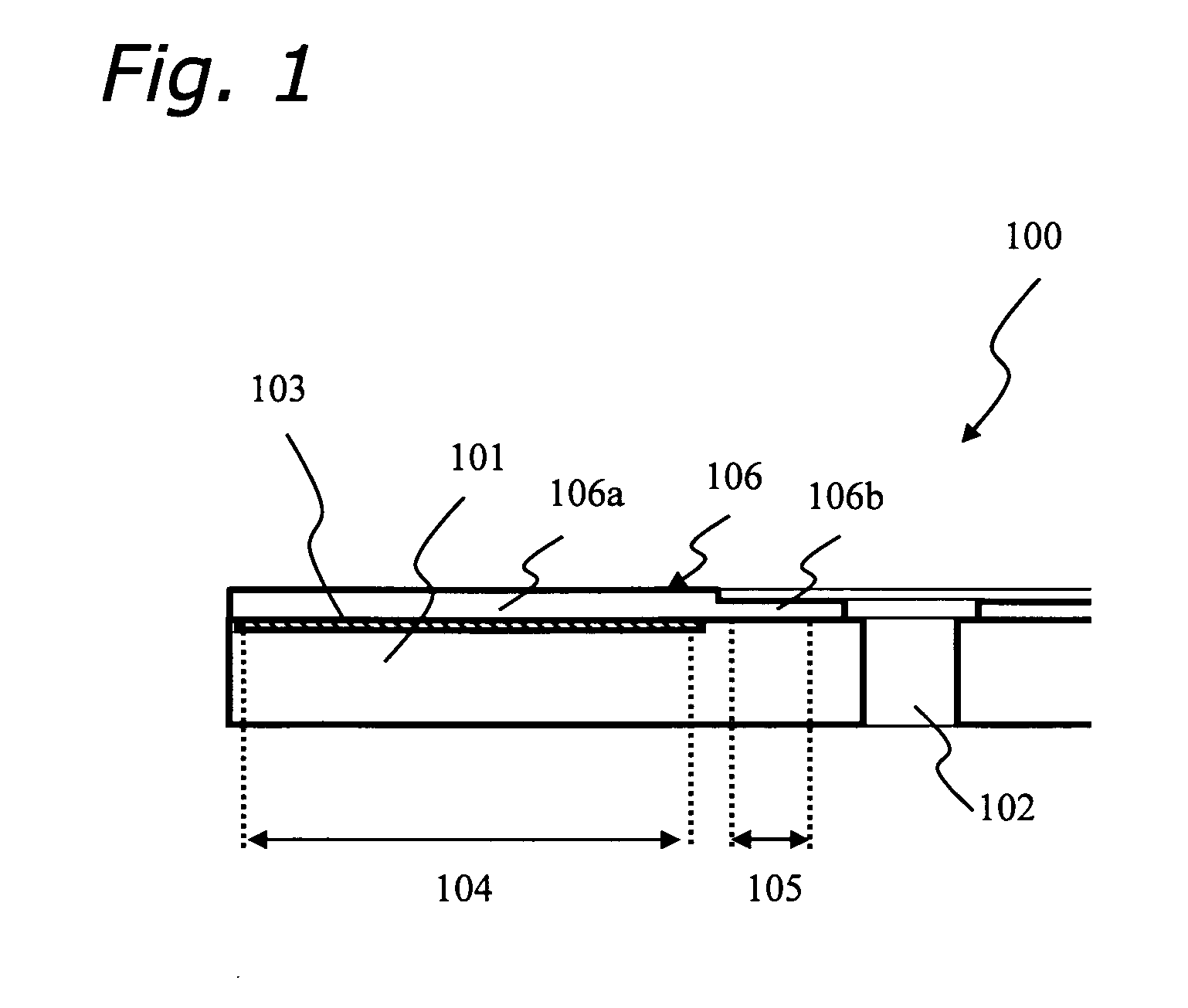
Optical information recording medium
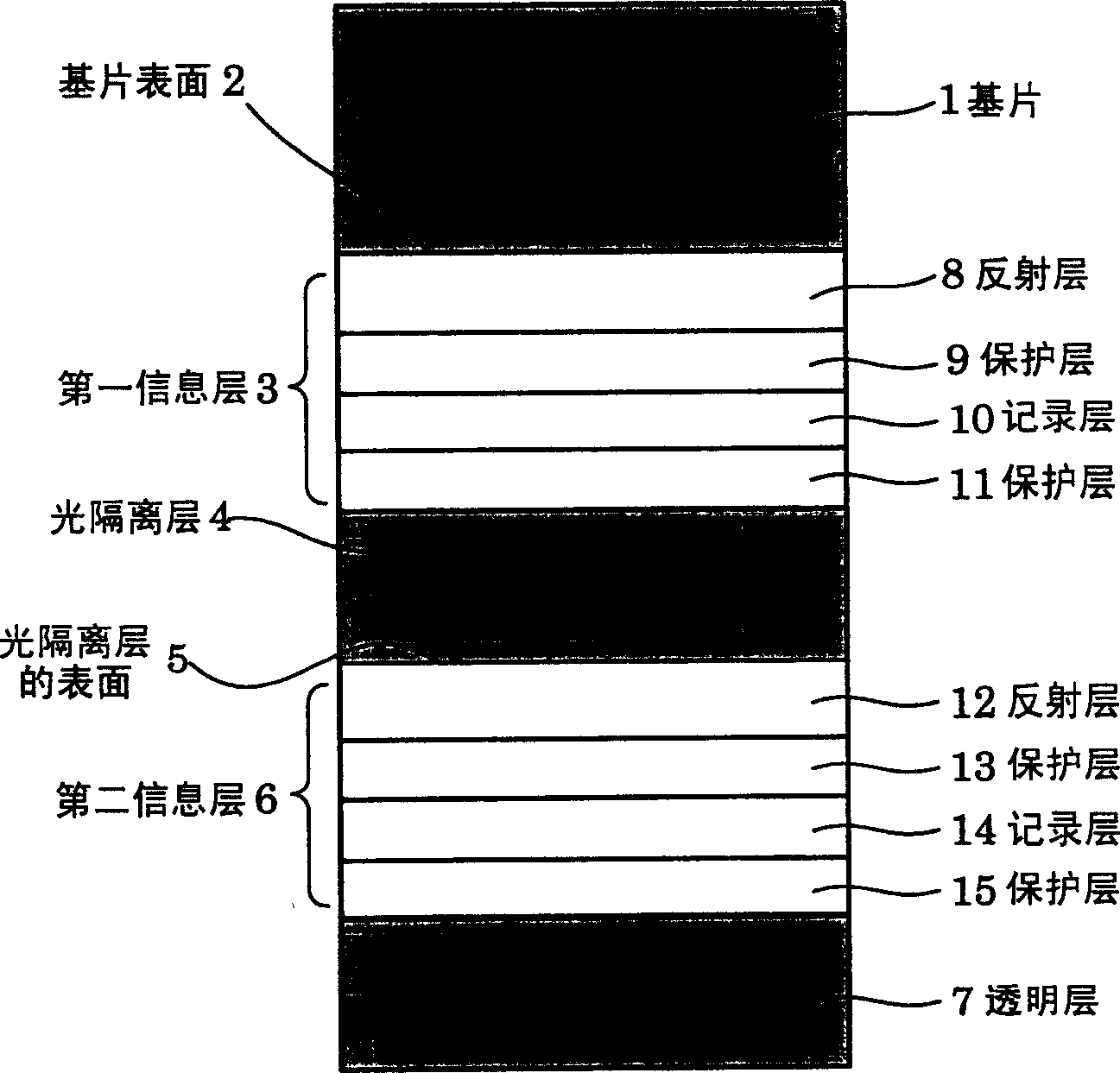
ActiveUS20050132395A1Recording by magnetic meansRecord information storageRecording layerComputer science
The object of the present invention is to provide an optical information recording medium which has tolerance to warping. To achieve the object above, an optical information recording medium 100 of the present invention includes at least one information recording layer 103 on a main surface of a substrate 101 and a light-transmitting layer 106. The substrate 101 includes a clamp area 105 and an information recording area 104 in accordance with the information recording layer 103. In the light-transmitting layer 106, the average thickness of a second area 106b corresponding to the clamp area 105 is thinner than the average thickness of a first area 106a corresponding to the information recording area 104.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Magnetic head and production method for magnetic heads
InactiveUS7140094B2Improve efficiencyReduce outflowRecording by magnetic meansNanomagnetismImage resolutionMagnetic shield
Magnetic heads capable of recording and reading with high sensitivity and resolution are provided by minimizing the outflow of magnetic fluxes from a flux guide to magnetic shields while using a flux guide structure for an MR element. In the magnetic head, magnetic shields exposed on a surface opposite a magnetic recording medium (air bearing surface) and a flux guide exposed between the magnetic heads via a non-magnetic layer are provided, and magnetic fluxes are guided by the flux guide to a magnetoresistive (MR) element formed in a position not exposed on the air bearing surface. The height of the magnetic shields in direction perpendicular to the air bearing surface is less than the distance from the air bearing surface to the MR element.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Apparatus and method for recording information
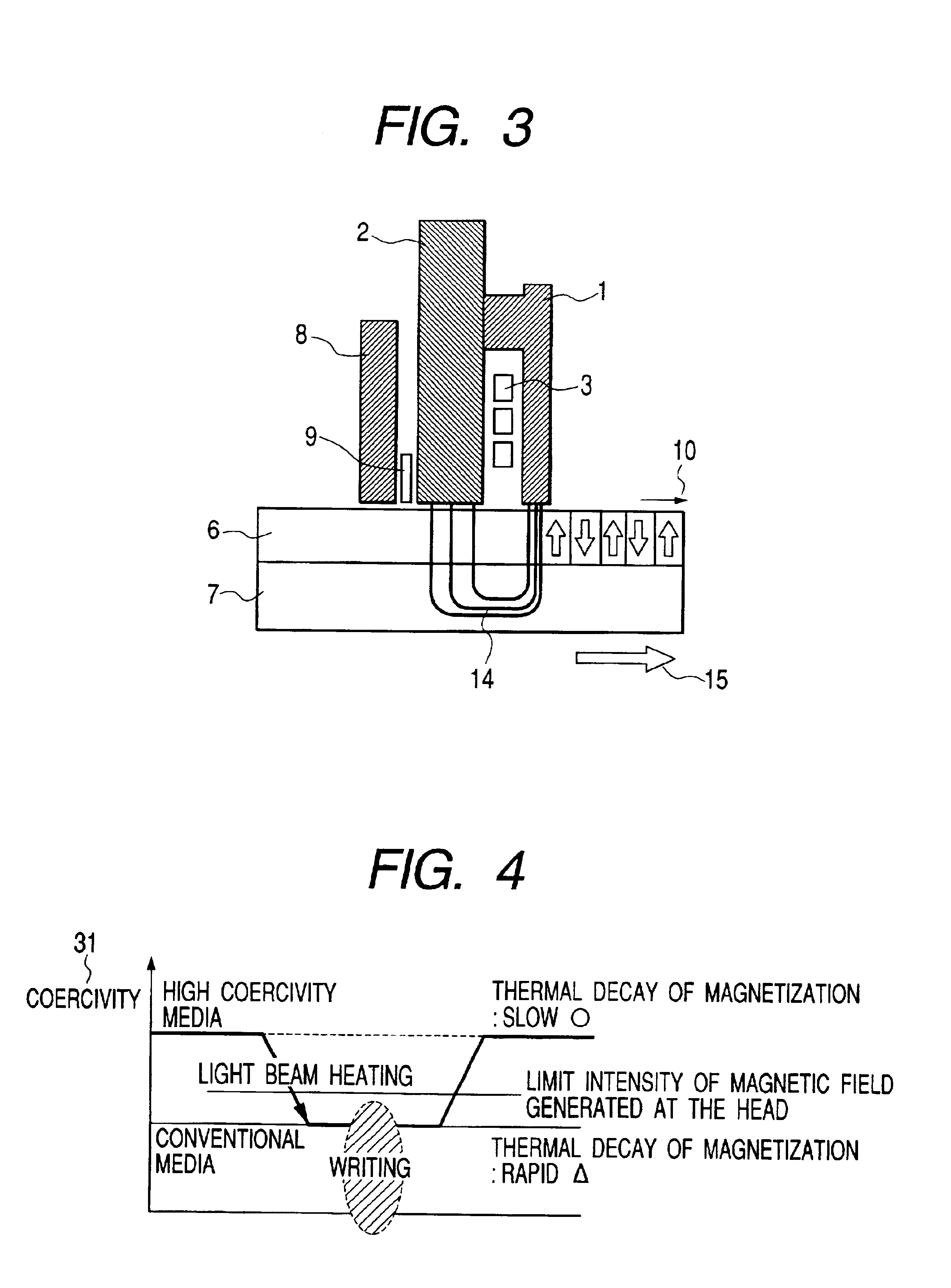
ActiveUS6952380B2Reduce magnetizationImprove reliabilityRecording by magnetic meansRecord information storageRoom temperatureThermal decay
A vertical magnetic recording apparatus is provided which can diminish thermal decay of magnetization to ensure a high reliability of the life of recorded information and which can stably effect the write of magnetic information. Light assist is performed by obliquely applying light to a gap between a main pole of a vertical recording head and a medium. The light is radiated from the head side of the apparatus with respect to the medium. Utilizing the present invention, the thermal decay of magnetization at room temperature is diminished, the life of the recorded information is increased, and the storage reliability of the disk is increased.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Thermal-assisted magnetic memory storage device
ActiveUS7161875B2Low coercivityRecording by magnetic meansNanoinformaticsElectricityElectrical conductor
A thermal-assisted probe based magnetic memory storage device. In a particular embodiment, magnetic tunnel junction memory cells and at least one movable probe with a tip characterized by a conductor and a heat generator are provided. The movable probe may be placed in electrical and thermal contact with a given memory cell. The memory cells include a material wherein the coercivity is decreased upon an increase in temperature. The magnetic field provided by the read conductor will not alter the orientation of an unheated cell, but may alter the orientation of a heated cell. A related method of use is also provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
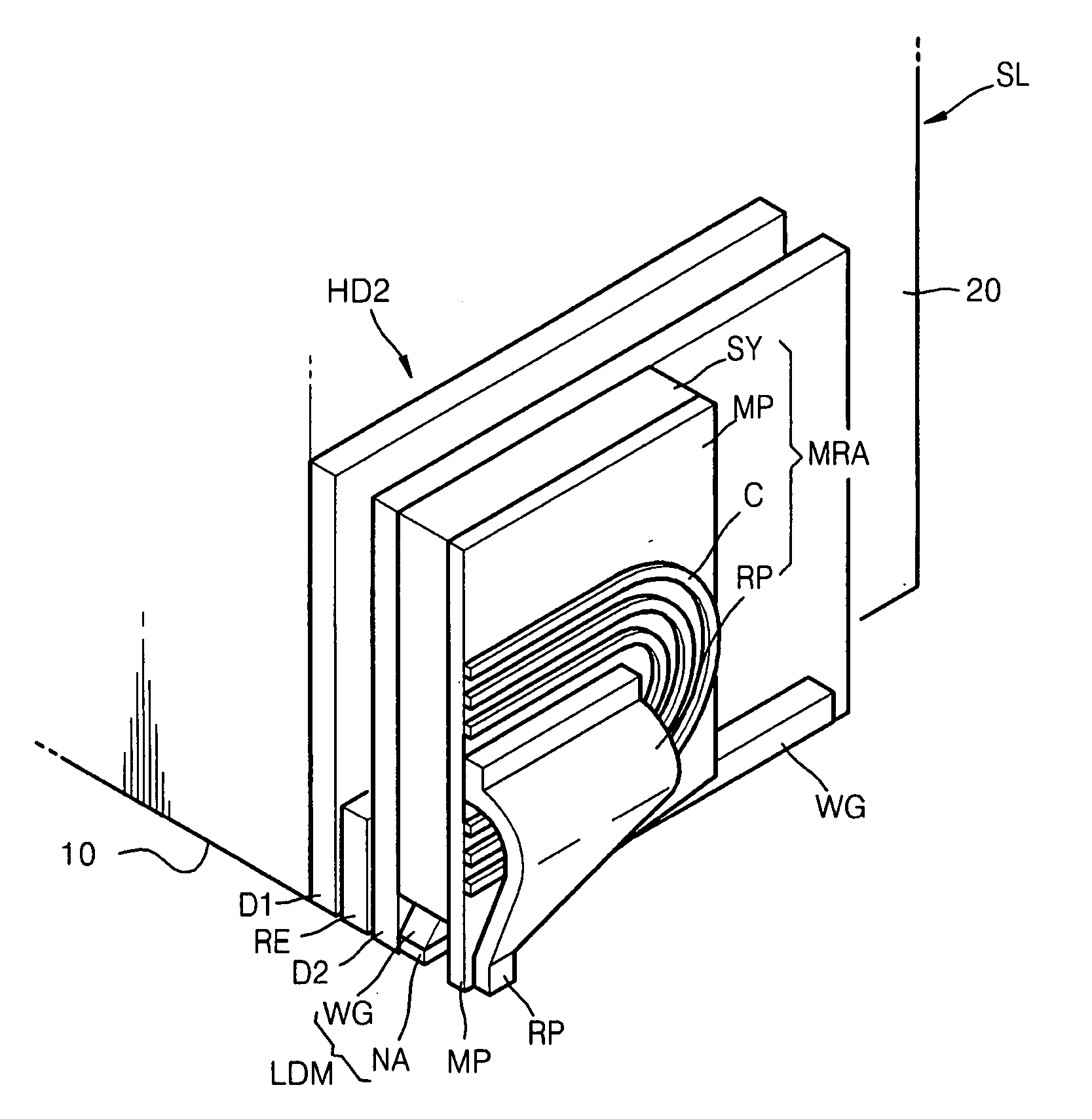
Thermally-assisted magnetic recording head
InactiveUS8300503B2Recording by magnetic meansArm with optical waveguideHeat-assisted magnetic recordingOptical axis
In a thermally assisted magnetic recording head having a light source and a waveguide to lead a laser beam radiated from the light source to a front end of the magnetic head, while blocking an adverse effect of heat generated in the light source and securing a good floating characteristic, the light source and the magnetic head are optically coupled with high efficiency and the magnetic head itself is reduced in size. This invention provides a reflection mirror that is formed of a part or whole of one inclined end surface of the semiconductor laser mounted on the first submount. Near one end surface of the slider is provided the optical waveguide that pierces through the slider in a direction of the thickness thereof. The slider is mounted on the second submount and the positions of the first submount and the second submount are adjusted to practically align the light axis of the beam emitted from the mirror with the light axis of the optical waveguide, thereby realizing a novel thermally assisted magnetic recording head.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
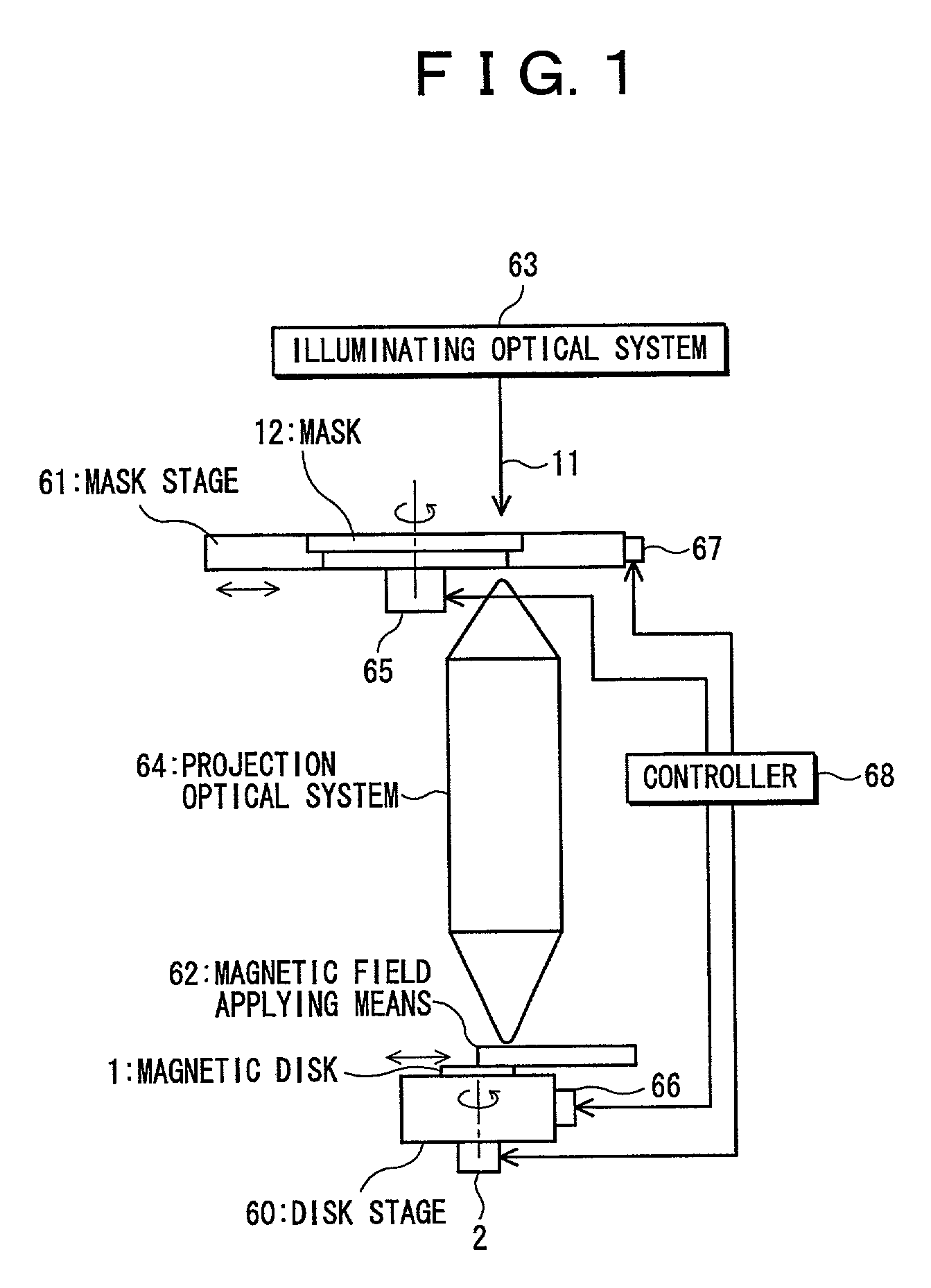
Magnetic pattern forming method, magnetic pattern forming apparatus, magnetic disk, and magnetic recording apparatus
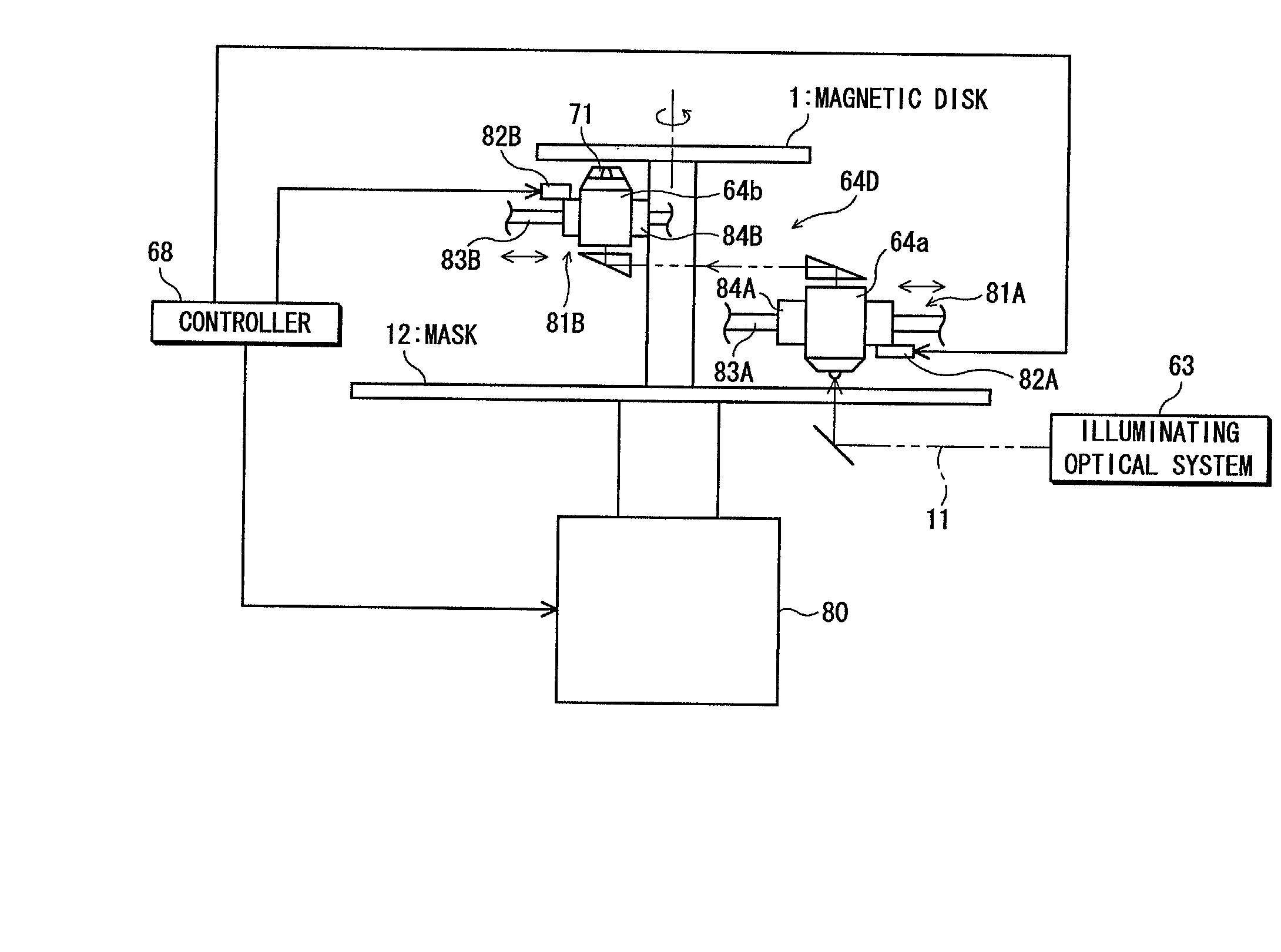
InactiveUS20020097640A1Effectively and efficiently formedImprove accuracyRecording by magnetic meansNanoinformaticsReduction ratioMagnetic layer
A magnetic pattern forming apparatus, which is designed to form a desired magnetic pattern on a magnetic disk having a magnetic layer on a substrate, is made up of a mask having a pattern identical or similar to the desired magnetic pattern, a projection optical system for exposing the magnetic disk to a spot-like energy beam coming through the mask to heat the magnetic layer for projecting the mask pattern to the magnetic disk at a one-to-one ratio or a predetermined reduction ratio, a magnetic field applying device for applying an external magnetic field to the magnetic disk, a control unit for conducting scanning with the spot-like energy beam with respect to the magnetic disk and the mask in their radial directions while rotating the magnetic disk and the mask.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Information write/read head including an optical slit having a light emitting section whose width is shorter than a light beam diffraction limit
InactiveUS6876603B2High track densityNarrow widthRecording by magnetic meansTrack finding/aligningLight beamEngineering
An information write / read head writes or reads information on or from recording tracks by the heat-assisted system. The information write / read head includes a magnetic head provided in such a manner that a longitudinal direction of a magnetic gap crosses a scanning direction. Further, the information write / read head includes an aperture slit having a length of not less than a diffraction limit of a light beam, and a width shorter than the diffraction limit in the direction orthogonal to the recording track, which is formed in such a manner that the longitudinal direction thereof is aligned in a scanning direction of the recording track.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
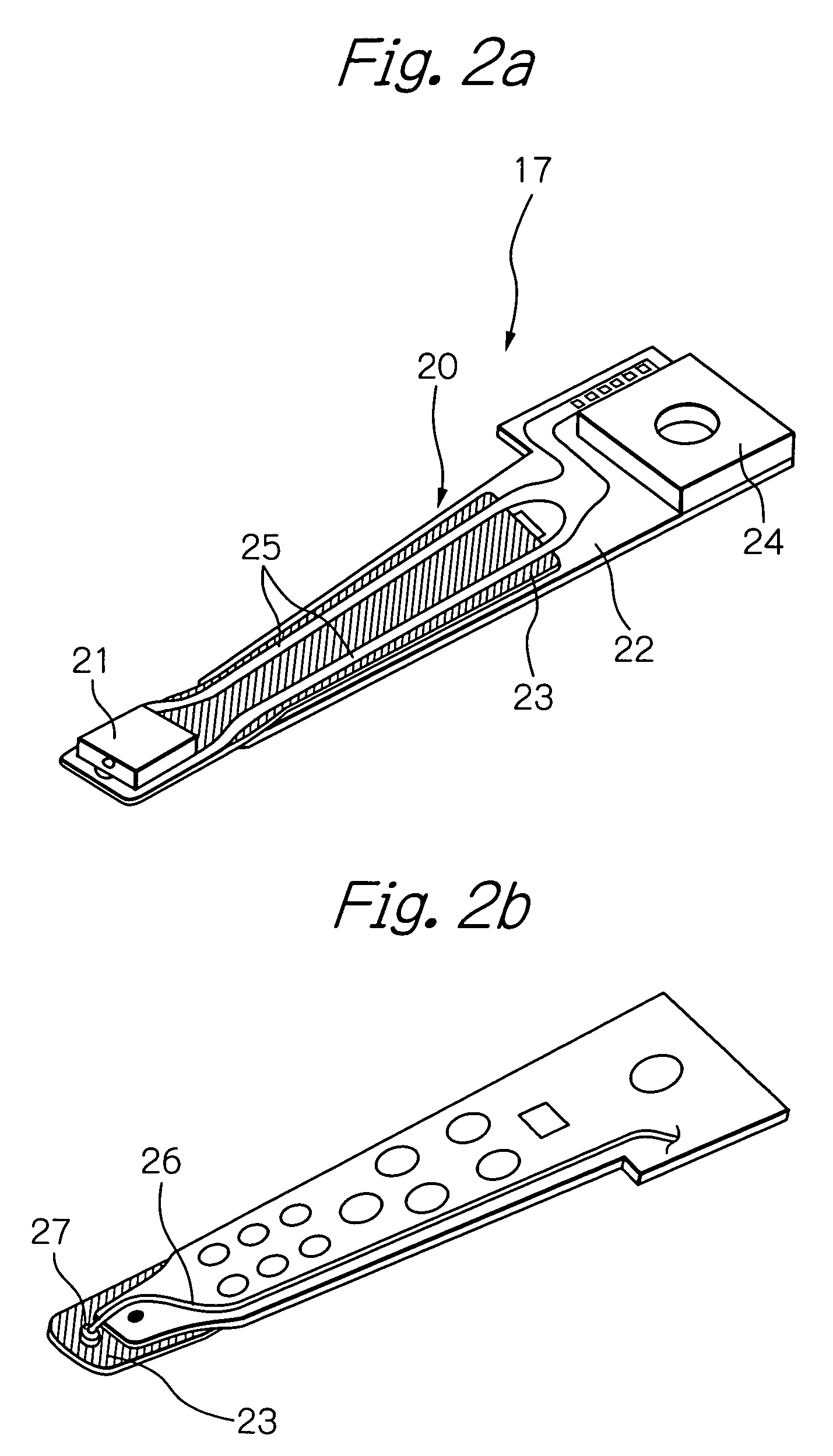
Suspension board with circuit
InactiveUS20090032299A1Improve leakageAvoid light leakageRecording by magnetic meansRecord information storageEngineeringWaveguide
A suspension board with circuit includes a metal supporting board, an insulating base layer formed on the metal supporting board, a conductive pattern formed on the insulating base layer, an insulating cover layer formed on the insulating base layer so as to cover the conductive pattern, and an optical waveguide including a core layer having a curved portion and a metal thin film covering a surface of the curved portion.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Thermally-assisted magnetic recording head including first and second cladding sections having different characteristics
ActiveUS8767348B1Improve recording effectLarge coefficientRecording by magnetic meansManufacture head surfaceHeat-assisted magnetic recordingPlasma generator
The thermally-assisted magnetic recording head of the invention includes: a waveguide; a magnetic pole; a cladding layer provided between the waveguide and the magnetic pole; and a plasmon generator embedded in the cladding layer. The cladding layer includes a first cladding section located on a side close to an air-bearing surface and a second cladding section located on a side far from the air-bearing surface, and a thermal expansion coefficient of the first cladding section is larger than a thermal expansion coefficient of the second cladding section.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Multi-order recordable CD of run-length limiting and making method thereof
InactiveCN1687991AReduce order requirementsIncrease storage capacityRecording by magnetic meansRecord information storageOptical disk storageEngineering
1A multi-stage record disk with limited travel lengths and its manufacturing method characterizes that the width of the recording symbol on said multi-stage record disk is multi-stage and decided by recorded laser power, at the same time, the travel length is limited, there are d 'o' at the least and k 'o' at the most between two non-o data, parameters d, k decide the smallest and largest travel lengths possibly appearing in the channel series determined by the exposing time for caving and recording lasers. A manufacture method is disclosed including multi-stage addition record disk of dye material or multi-stage duped disk of phase change or magneto-optic material, which obviously increases the storage volume of record disks and data transmission rate.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Photomagnetic mixed storing material with high-coercive fore and producing method thereof
InactiveCN1975892AImprove coercive forceImprovement and enhancement of storageRecording by magnetic meansRecord information storageRadio frequency magnetron sputteringThermal stability
A method for preparing photo-magnetic mixed storage material with high coercive force includes utilizing radio-frequency magnetic control to sputter a layer of Mg O buffer layer first and than utilizing DC magnetic control to sputter a layer of Tb Fe Co to form a film with double layers for raising coercive force of film material.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com