Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4694results about "Support for heads" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
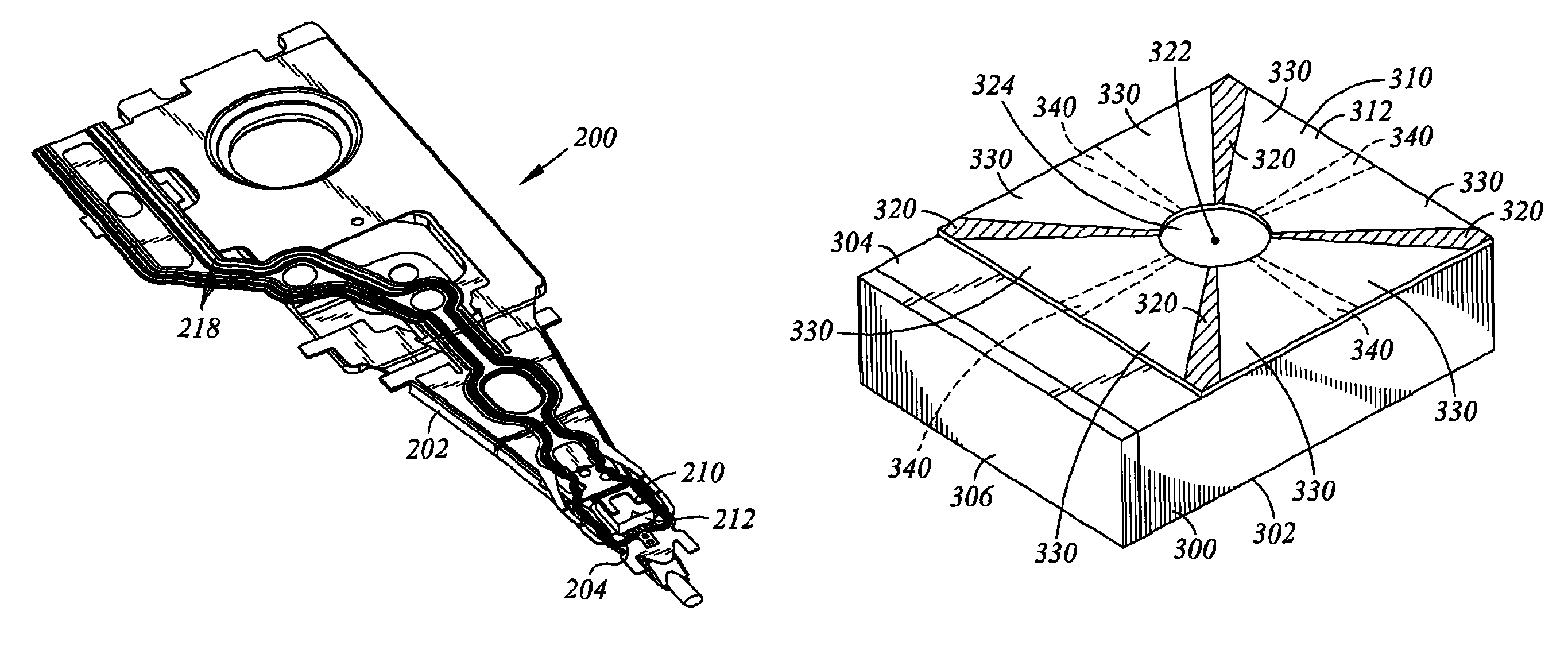
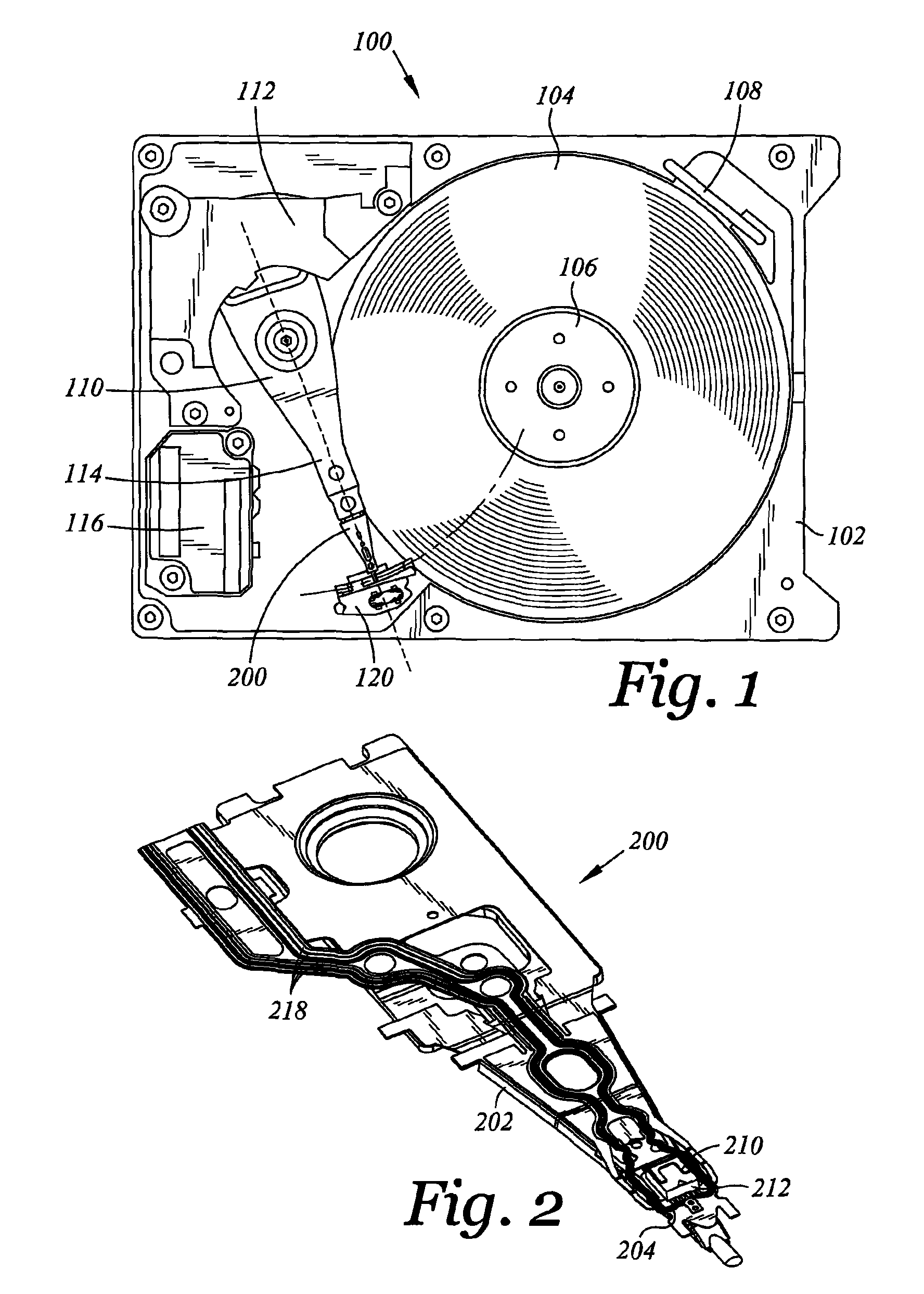
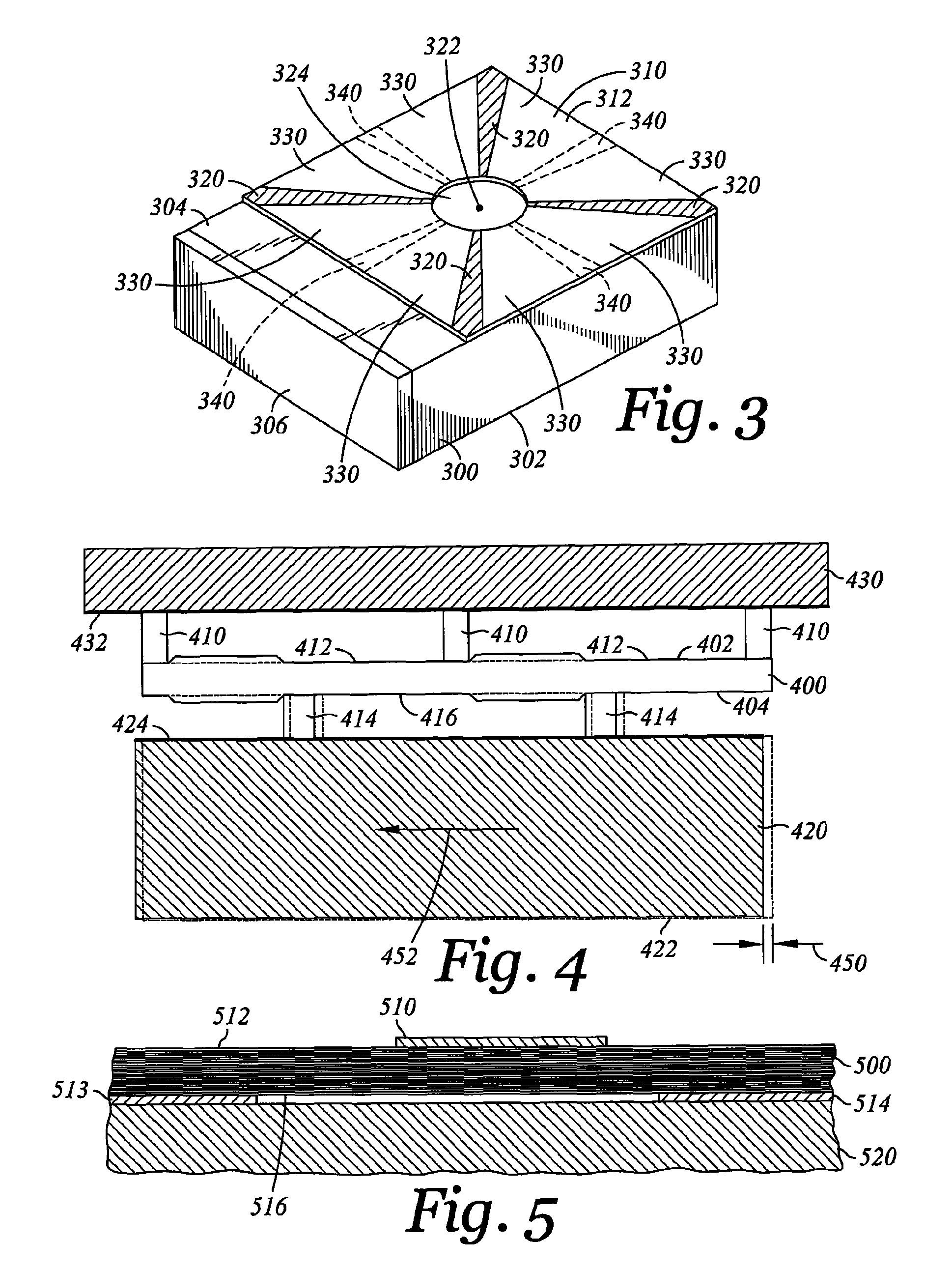
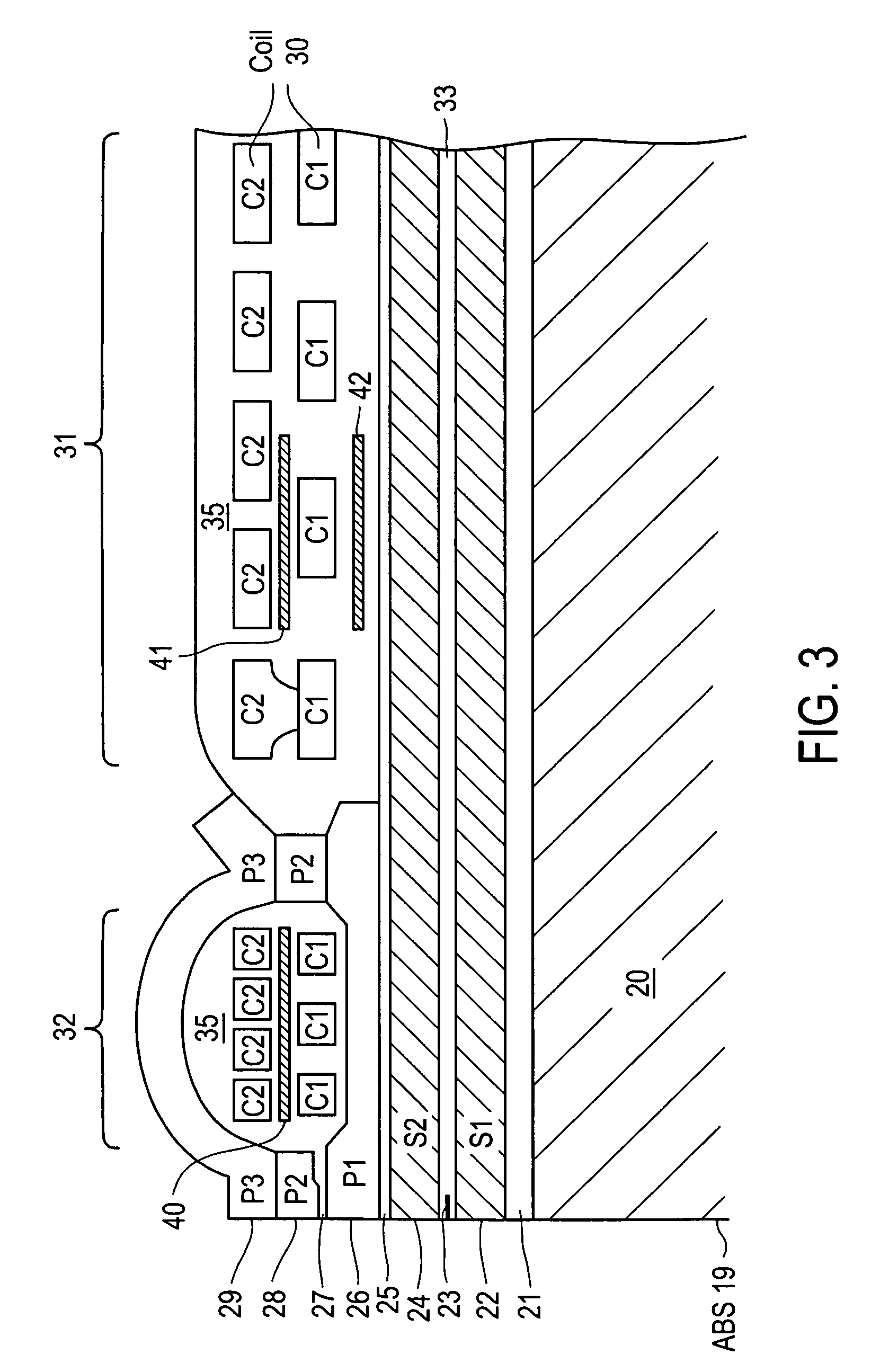
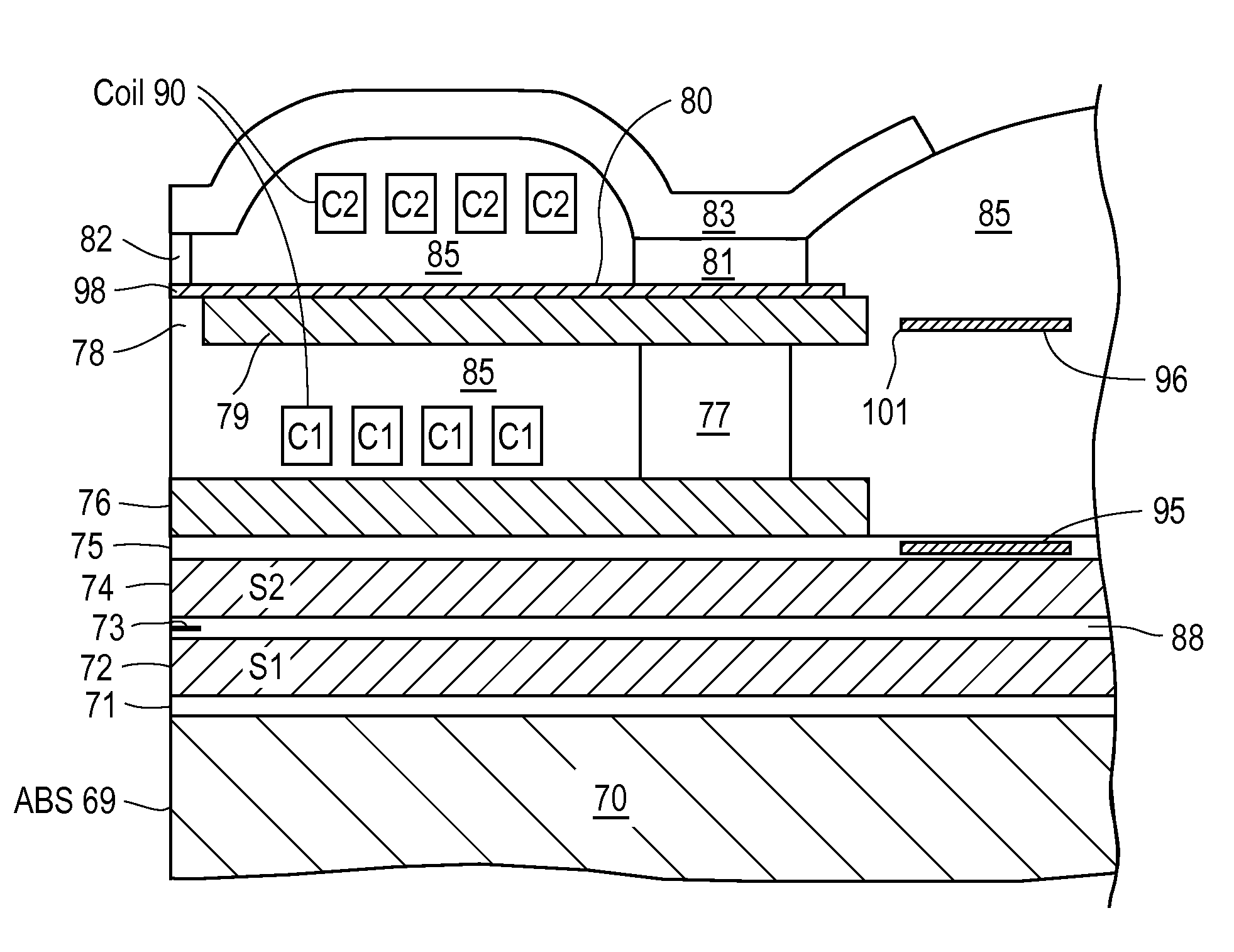
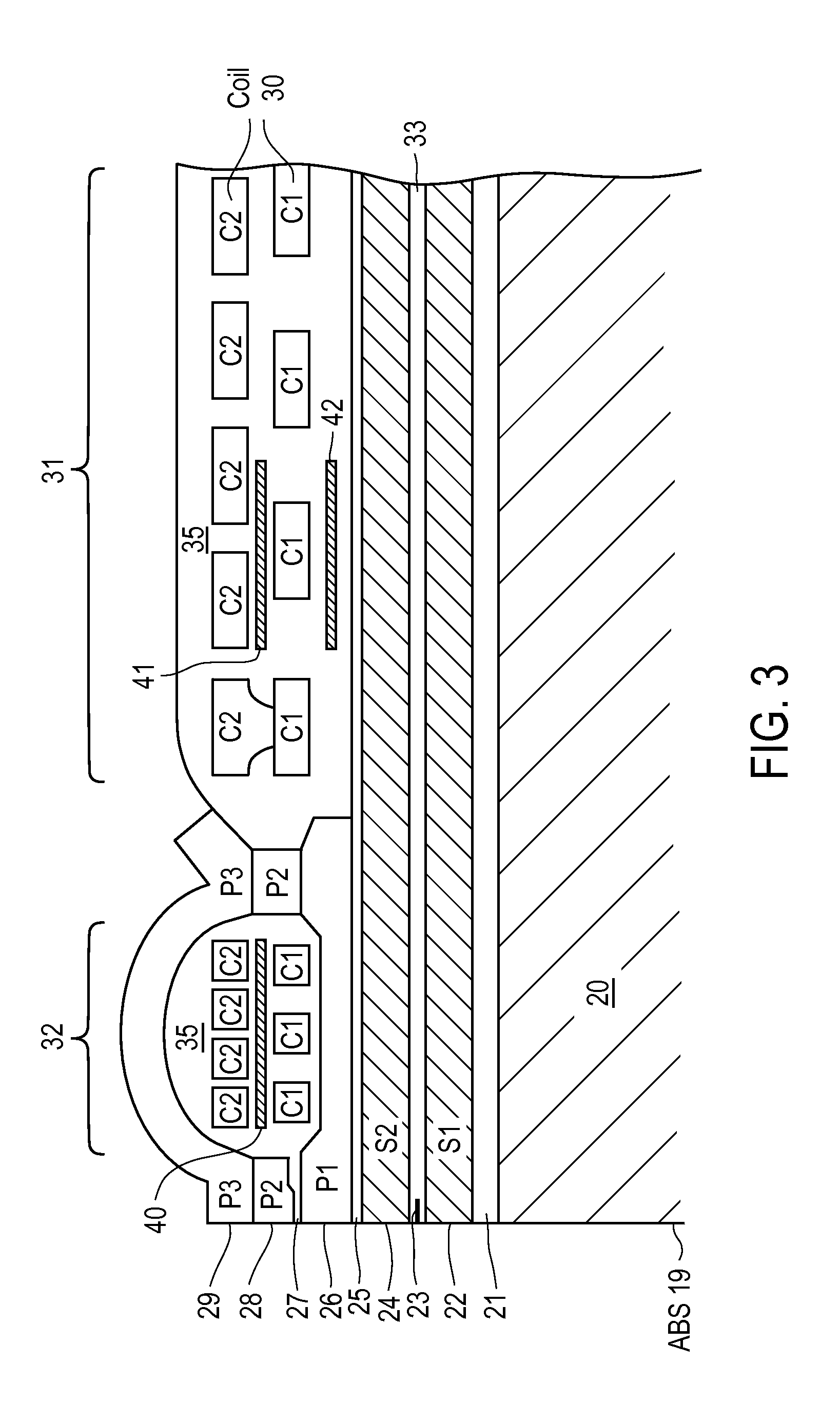
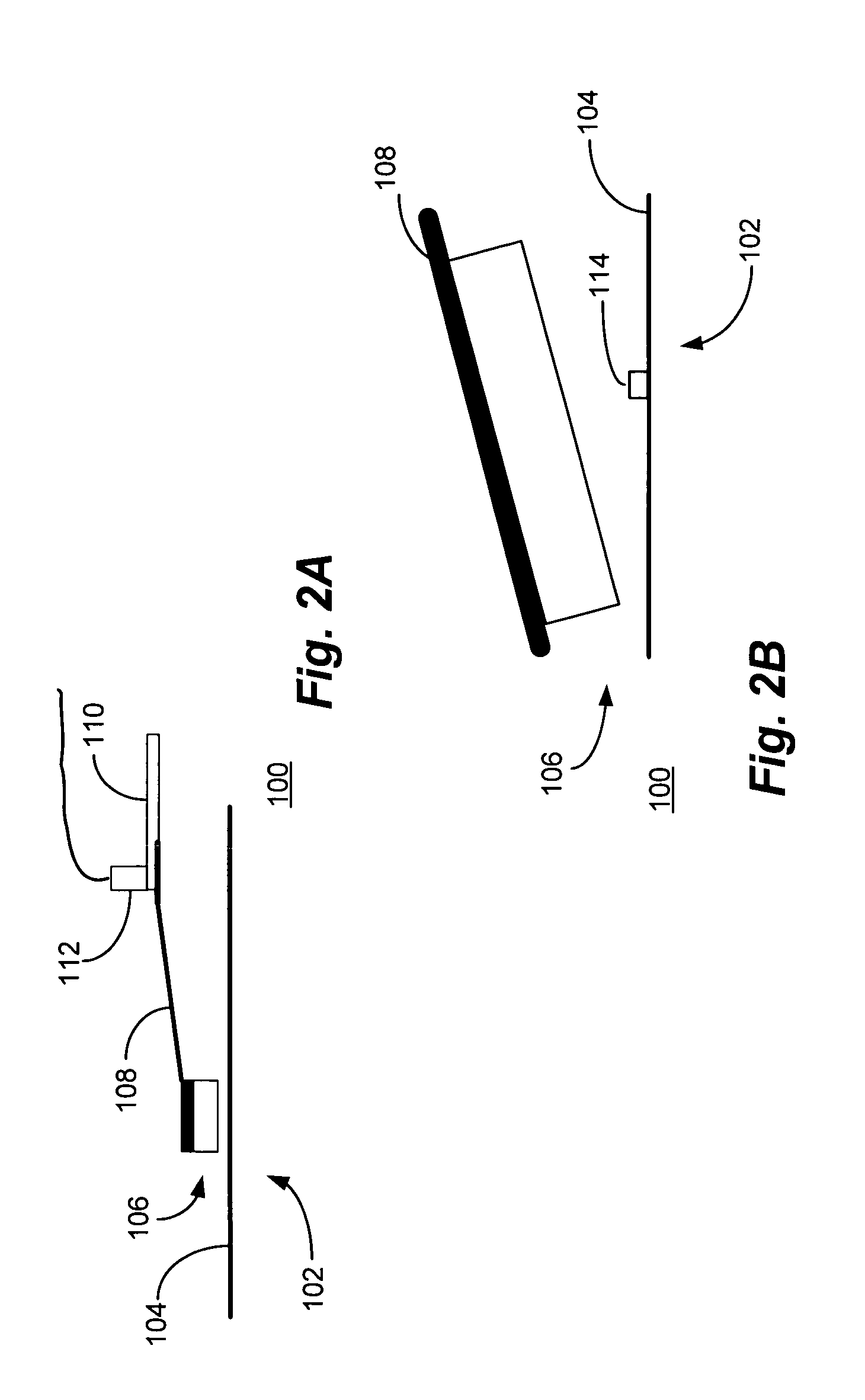
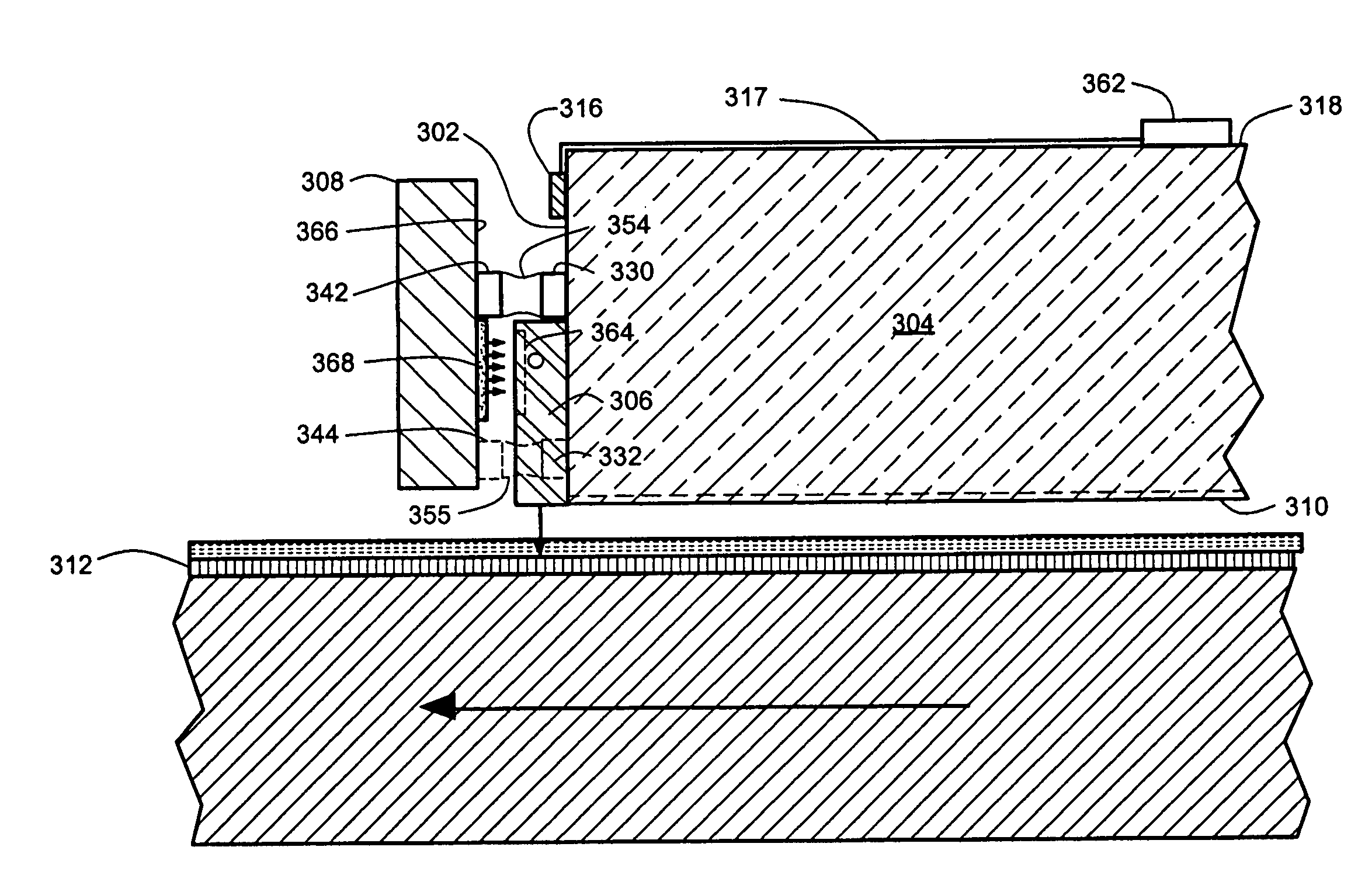
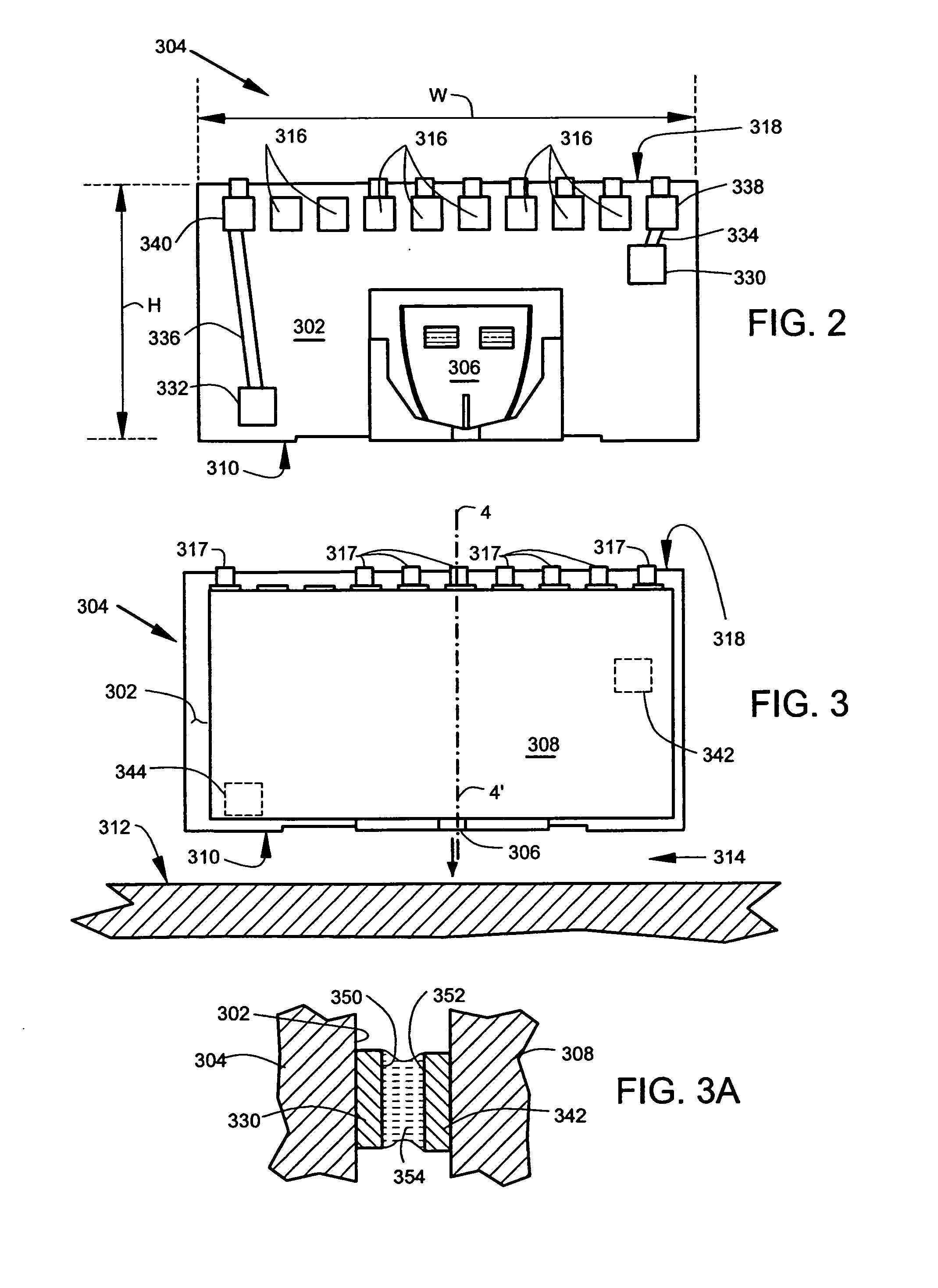
Active fly height control crown actuator
InactiveUS6950266B1Improve production efficiencyReduced altitude sensitivityAnalogue recording/reproducingDriving/moving recording headsData integrityMicro actuator
A micro-actuator is comprised of a piezoelectric motor mounted on a flexure tongue with offsetting hinges, to perform a fine positioning of the magnetic read / write head. The substantial gain in the frequency response greatly improves the performance and accuracy of the track-follow control for fine positioning. The simplicity of the enhanced micro-actuator design results in a manufacturing efficiency that enables a high-volume, low-cost production. The micro-actuator is interposed between a flexure tongue and a slider to perform an active control of the fly height of the magnetic read / write head. The induced slider crown and camber are used to compensate for thermal expansion of the magnetic read / write head, which causes the slider to be displaced at an unintended fly height position relative to the surface of the magnetic recording disk. The enhanced micro-actuator design results in reduced altitude sensitivity, ABS tolerances, and reduced stiction. The controlled fly height of the magnetic read / write head prevents a possibility of a head crash, while improving the performance and data integrity.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
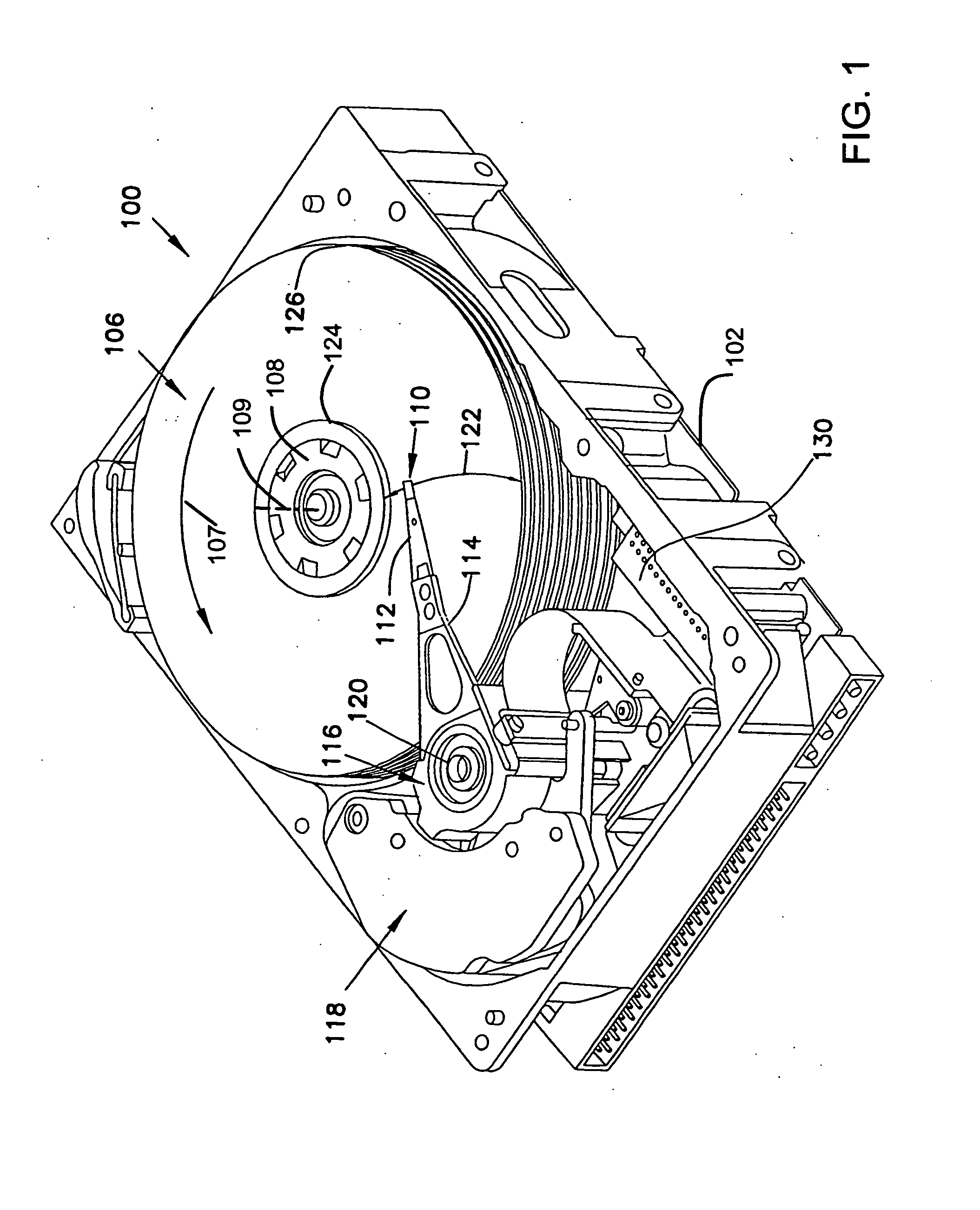
Dimple pivot post for a rotary co-located microactuator
InactiveUS7057857B1Eliminate deformationImprove performanceRecord information storageMounting/attachment of transducer headAdhesiveEngineering
A rotary microactuator-based head-gimbal assembly design controls the unwanted deflection of a flexure in a data storage device and eliminates hinge deformation. The head-gimbal assembly maintains the co-planarity of the hinged islands in the microactuator under the applied load acting on the flexure and two associated hinged islands. The dimple post is placed at the dimple loading region of the flexure tongue and has the same height as adhesive dams on paddles secured to the hinged islands. The dimple post is formed by branching one of the existing conductive traces covered by a photoresist layer to the dimple loading region on flexure tongue. In an alternative embodiment, the dimple post is secured to the dimple loading region of the flexure tongue by means of adhesives with a variety of viscosity and elastic moduli.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Read/write head including displacement generating means that elongates and contracts by inverse piezoelectric effect of electrostrictive effect
A read / write head includes a slider provided with an electromagnetic transducer element (or an optical module), an actuator, and a suspension. The actuator includes a fixed part, a movable part, and at least two beam members for coupling them together. The beam members have a displacement generating means that elongates and contracts by inverse piezoelectric effect or electrostrictive effect. The fixed part is fixed to the suspension, and the movable part is fixed to the slider. Upon the elongation and contraction of the displacement generator, the displacement generator deflects and the movable part displaces linearly, circularly or rotationally with respect to the fixed part, and the electromagnetic transducer element displaces in a linear or circular orbit, so that the electromagnetic transducer element intersects recording tracks. In the actuator, the fixed part, movable part and beam members are formed as an integrated single piece by providing a hole and / or a cutout in a sheet-like member constructed of a piezoelectric or electrostrictive material. The actuator of the structure illustrated is used for the positioning of a direction intersecting recording tracks. In this case, the total sum of voltages applied on the displacement generating means is controlled in such a manner that it is constant at any time, thereby controlling position fluctuations of the electromagnetic transducer element in the direction vertical to the recording medium surface.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
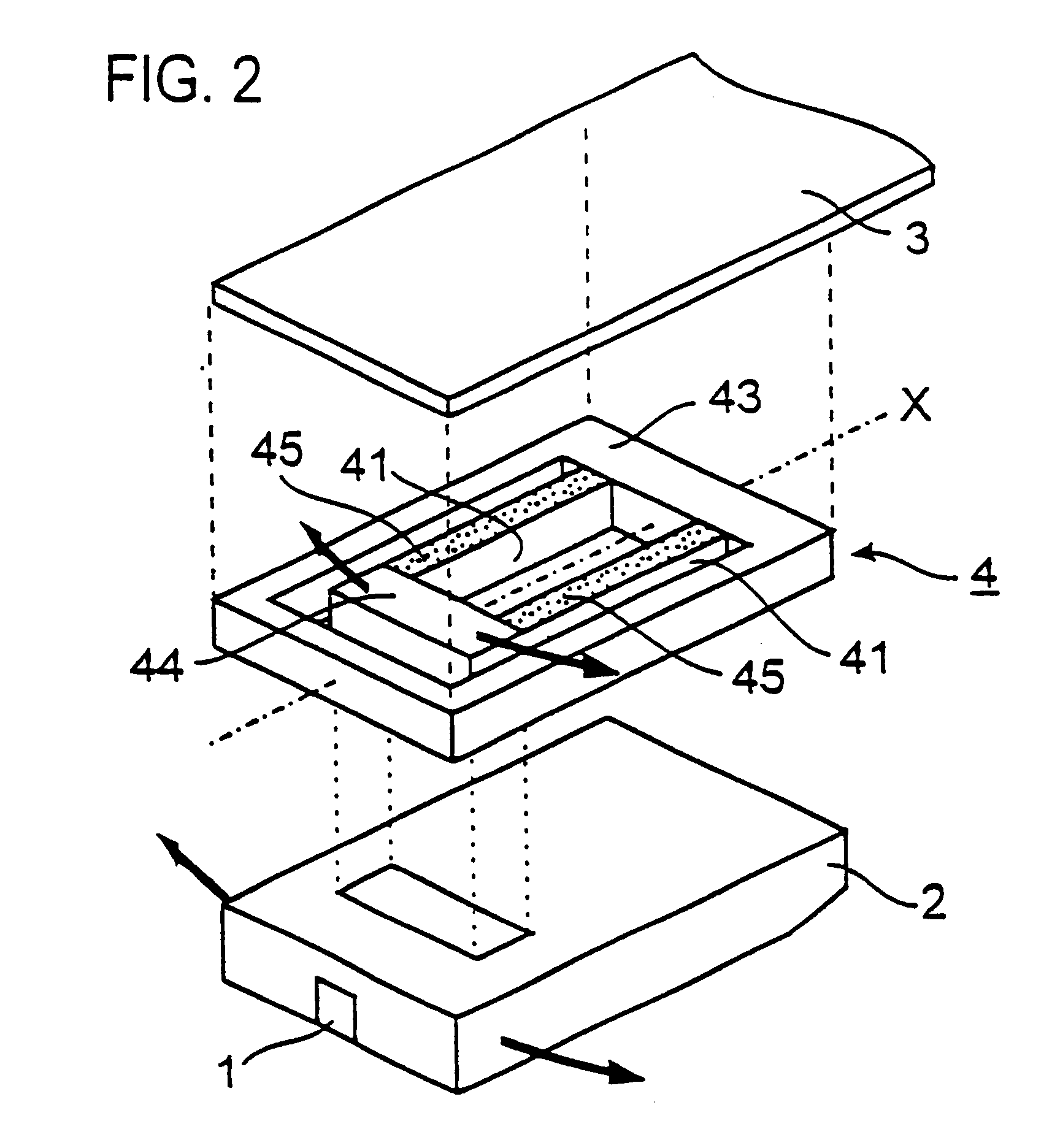
Magnetic recording head with resistive heating element located near the write coil
InactiveUS7372665B1Disposition/mounting of recording headsRecord information storageTransducerTrailing edge
A magnetic head includes a slider body having a trailing surface meeting an air-bearing surface at a trailing edge, with a thin-film transducer disposed on the trailing surface of the slider body near the trailing edge. The thin-film transducer includes a coil embedded between first and second poles. A resistive heating element is disposed adjacent and electrically insulated from, the coil. Application of power to the resistive heating element causes expansion of at least the first and second poles.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
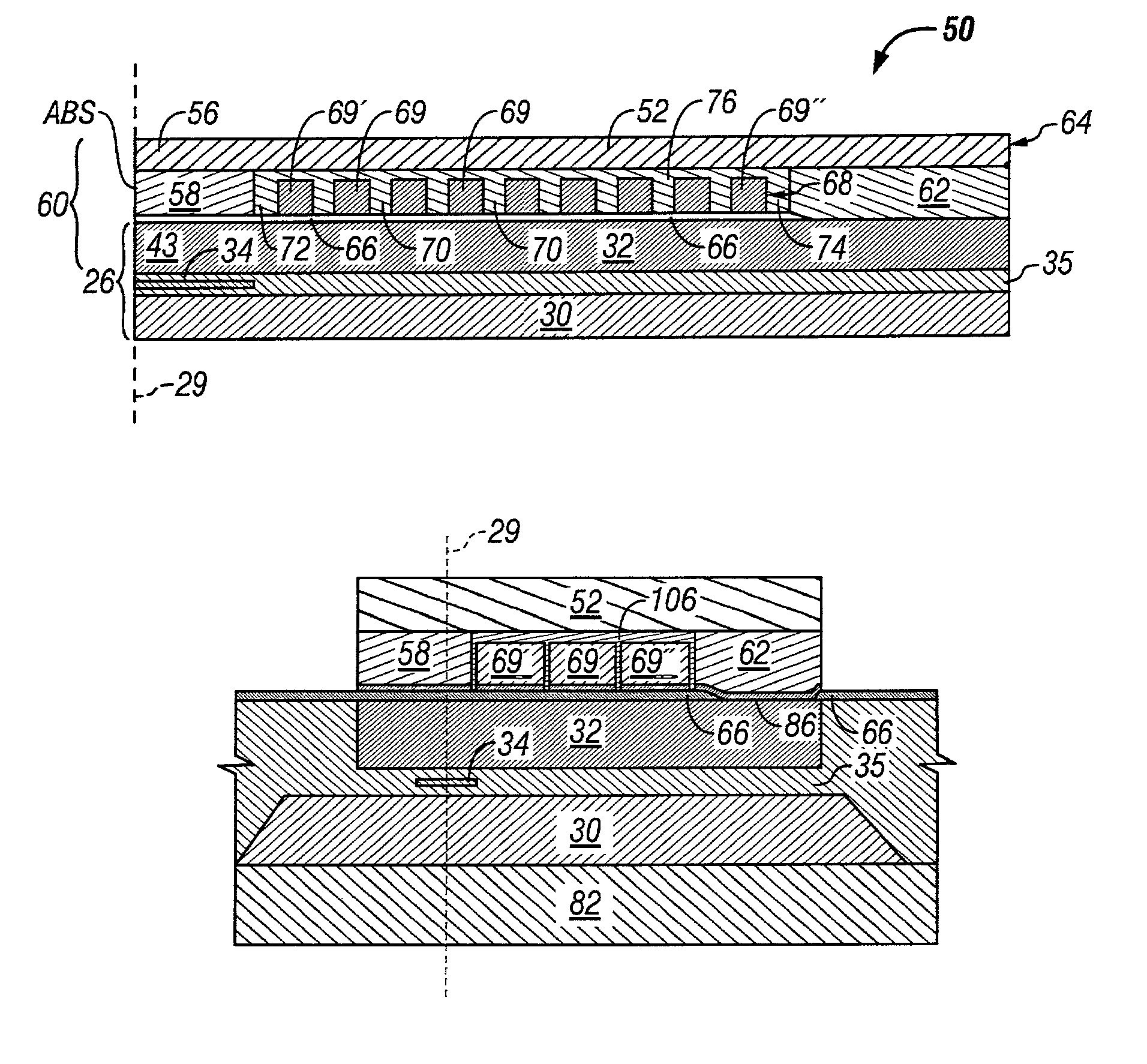
Head gimbal assembly having a radial rotary piezoelectric microactuator between a read head and a flexure tongue
A novel head gimbal assembly (HGA) includes a piezoelectric microactuator having a first side and an opposing second side. The first side includes a plurality of anchor regions that extend radially from a center point and are bonded to the gimbal tongue. The first side also includes a first plurality of non-bonded regions lying between the anchor regions. The second side includes a plurality of link regions that extend radially from the center point and are bonded to a top surface of the read head. The second side also includes a second plurality of non-bonded regions lying between the link regions. Each of the plurality of link regions is angularly spaced between two of the plurality of anchor regions.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
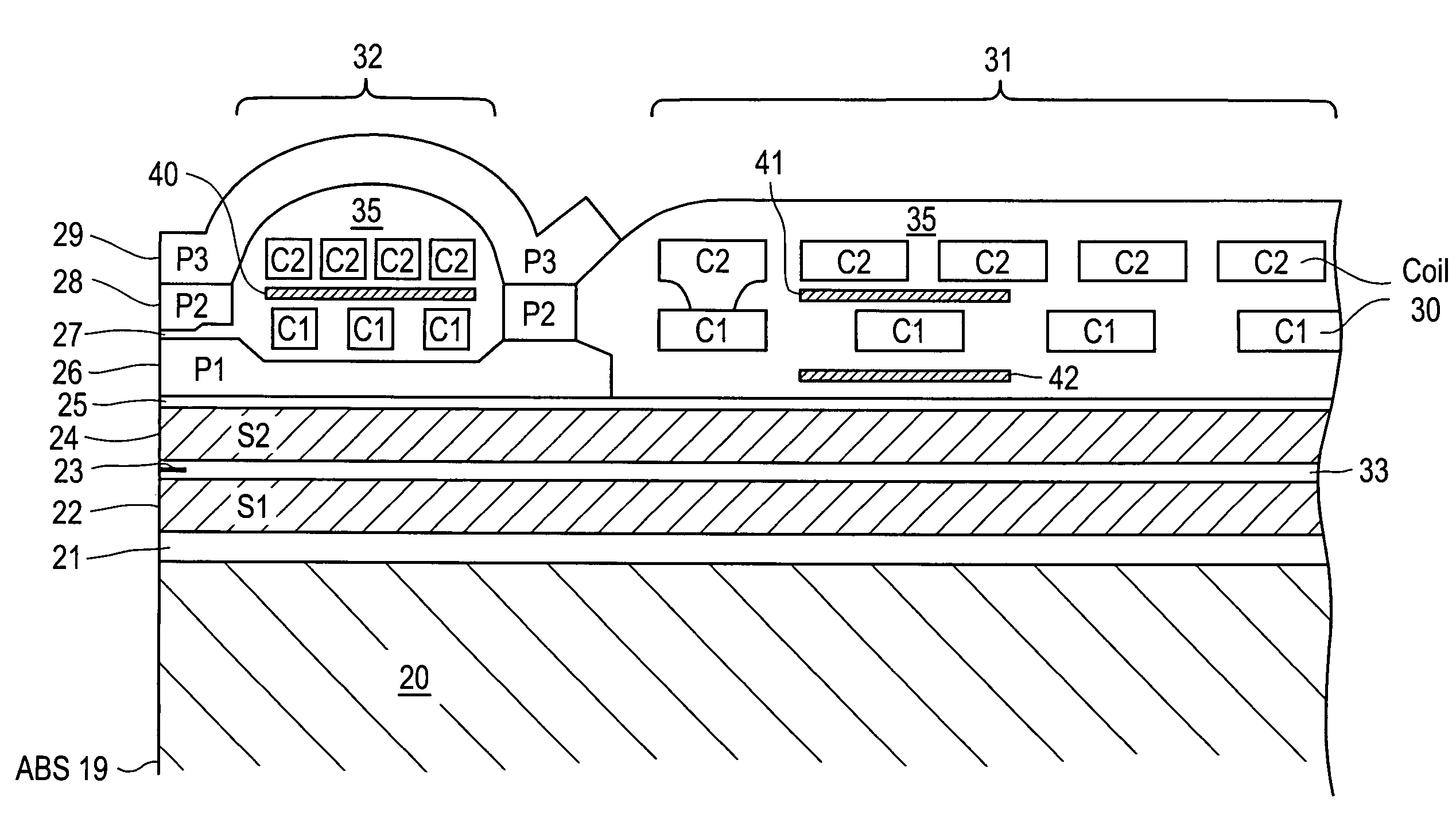
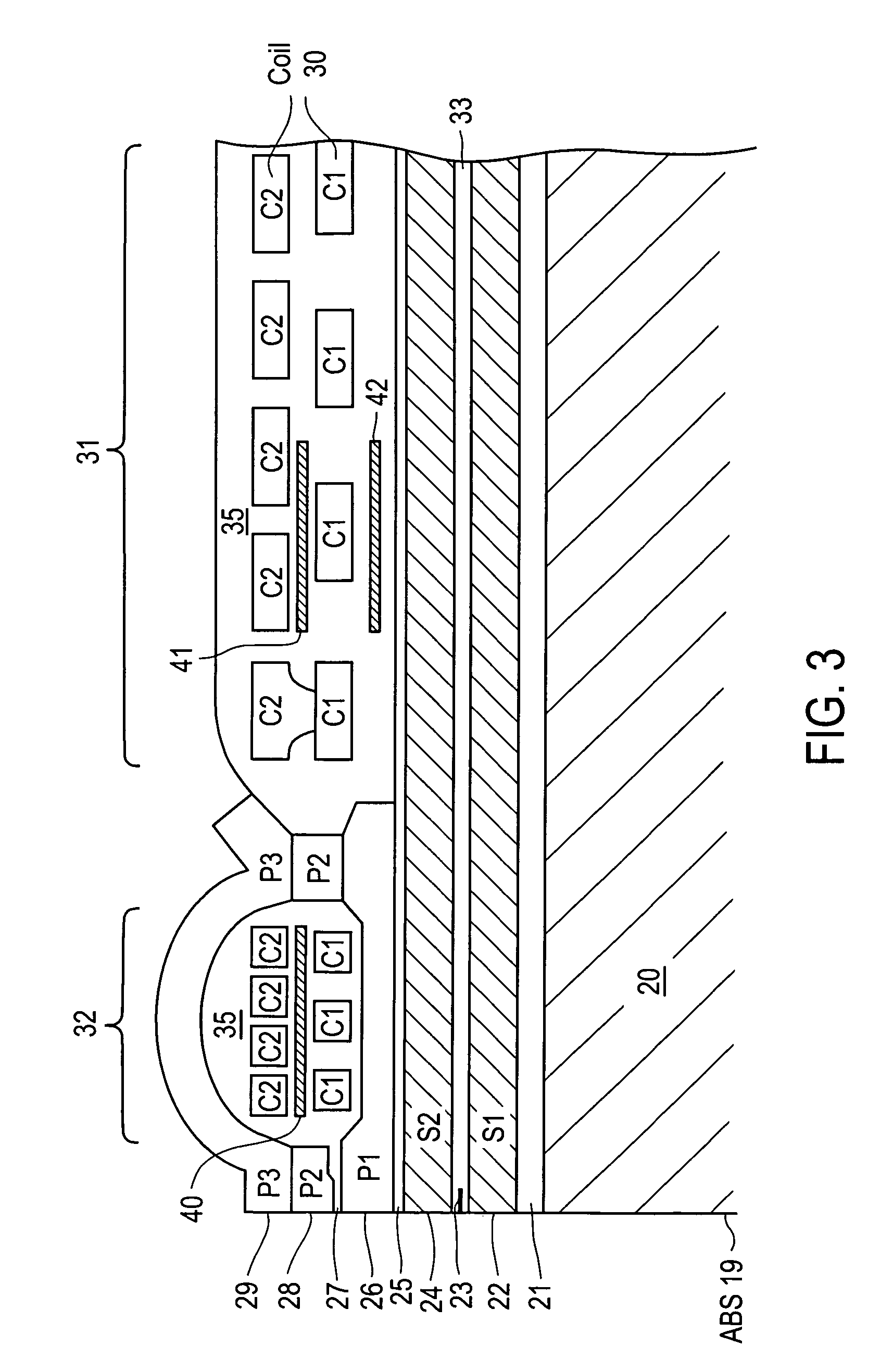
Perpendicular magnetic recording head with dynamic flying height heating element
ActiveUS7430098B1Disposition/mounting of recording headsRecord information storageTransducerFlying height
A magnetic head includes a slider having an air bearing surface (ABS) and a trailing surface, with a transducer fabricated on the trailing surface. The transducer includes an adjunct pole disposed in a first general plane, the adjunct pole having a front edge that is recessed from the ABS and a rear edge. A main pole of the transducer is formed adjacent the adjunct pole, the main pole having a write tip that extends approximately to the ABS. A write coil having a first layer of turns is disposed in a second general plane below the adjunct pole. The magnetic head further includes a heating element, a portion of the heating element being disposed in the first general plane behind the rear edge of the adjunct pole.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Perpendicular magnetic recording head with dynamic flying height heating element disposed below turns of a write coil
ActiveUS7729086B1Disposition/mounting of recording headsRecord information storageTransducerFlying height
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
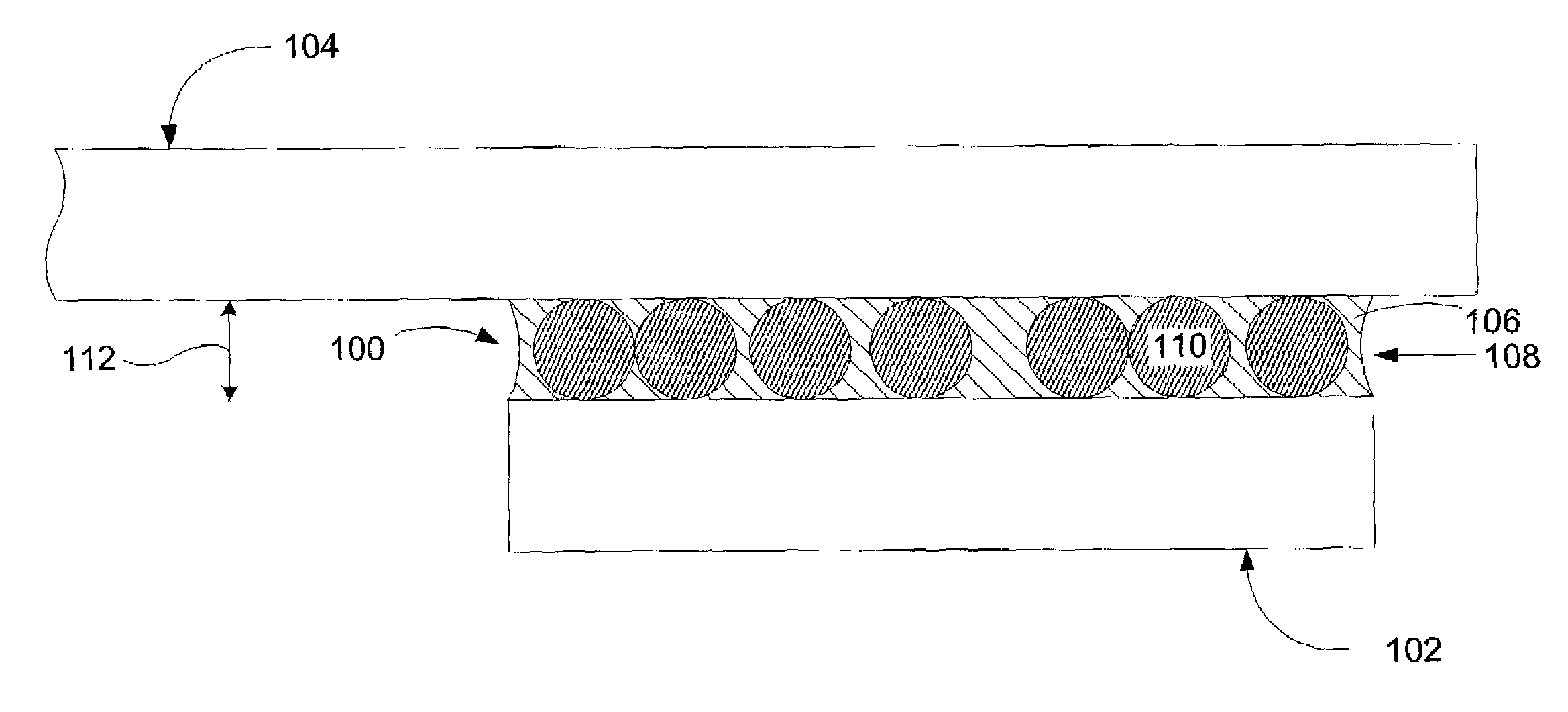
UV curable and electrically conductive adhesive for bonding magnetic disk drive components
An electrically conductive adhesive includes a resin component, a photoinitiator, and metal-coated polymer beads. The beads have an average diameter and a very narrow size distribution around the average diameter. The adhesive is applied between a read / write head and a suspension to attach the two, and the adhesive is cured by exposure to an illumination and / or heat. A pad spacer is included between the read / write head and the suspension to define a spacing and parallelism therebetween. The beads in the adhesive can form one or more layers between the read / write head and the suspension or can be disordered. The metal coating of the beads provide electrical conductivity between the read / write head and the suspension.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Read/write head with dynamic flying height control by magnetostriction
InactiveUS7660080B1Easy to controlDisposition/mounting of recording headsRecord information storageFlying heightData recording
A read / write head for use in a data storage device to control the low dynamic flying height in order to achieve high data recording storage capacity of magnetic hard drives. The read / write head is designed for use in a data storage device that includes a storage medium having a recording surface. The head comprises a pole tip region and an actuator. In turn, the actuator includes an excitation source for generating a magnetic field, and a magnetostrictive plate for expanding in response to the magnetic field, resulting in a protrusion in a section of the pole tip region along a direction towards the recording surface, so that the head flies above the recording surface at a flying height lower than a nominal flying height.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
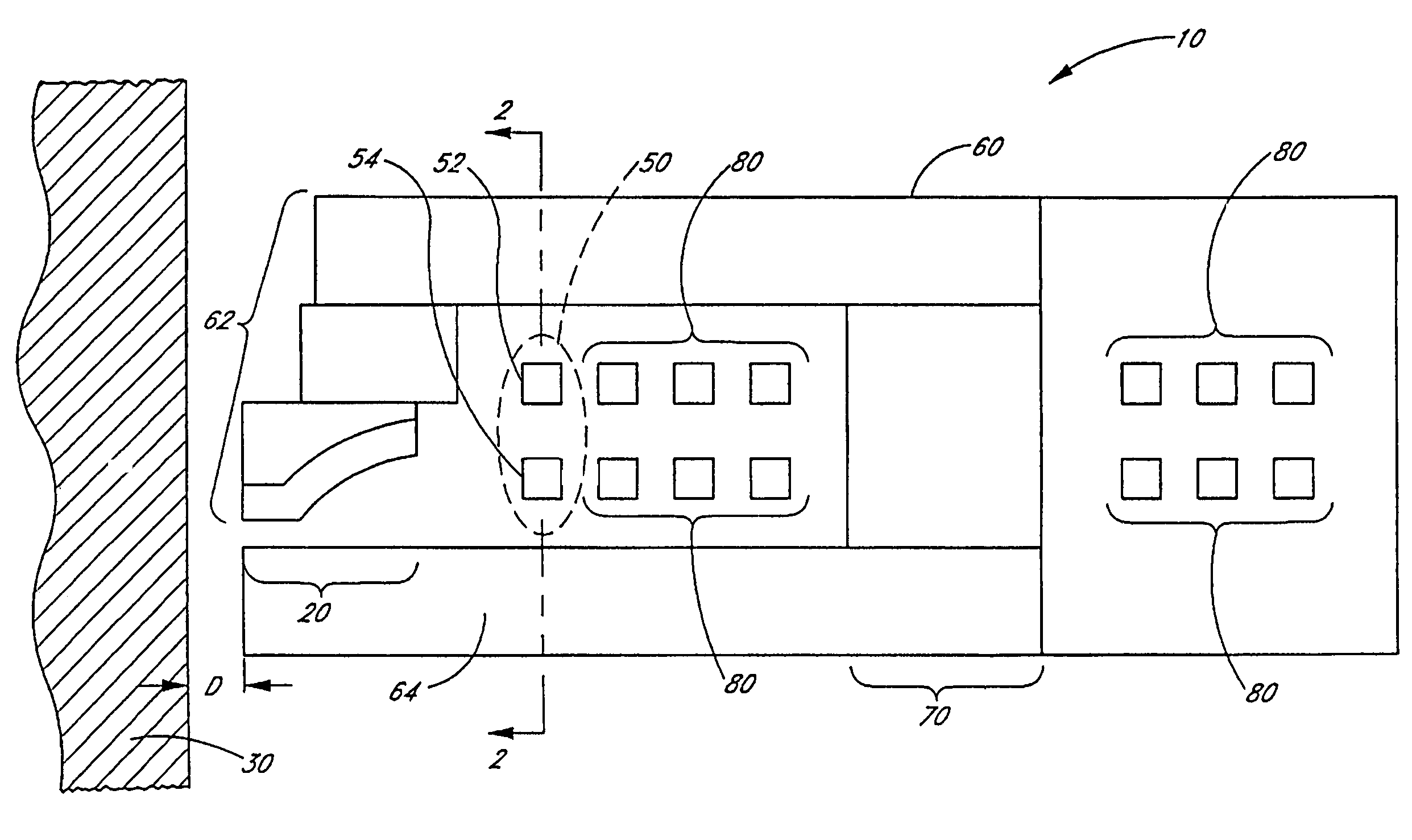
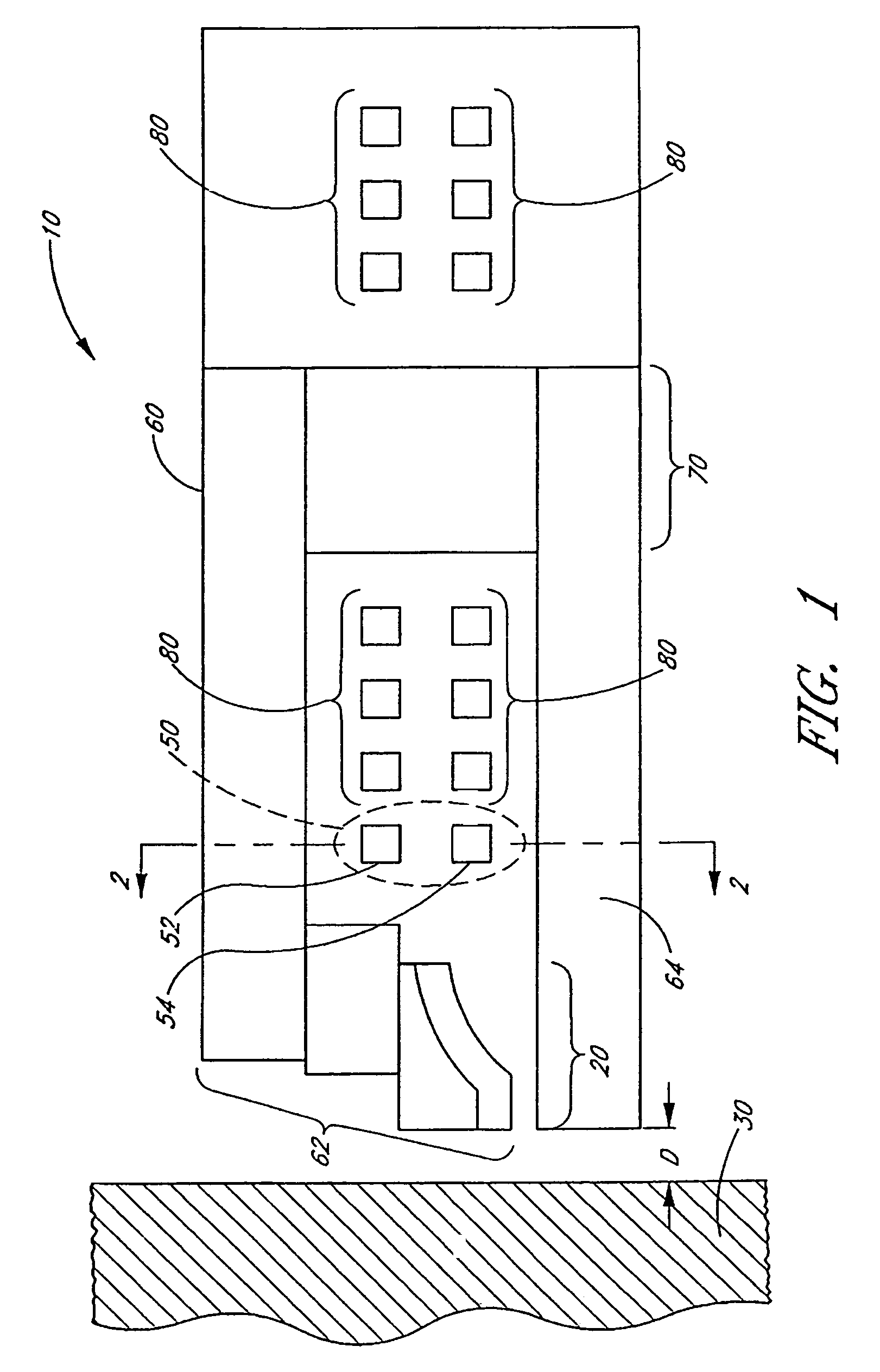
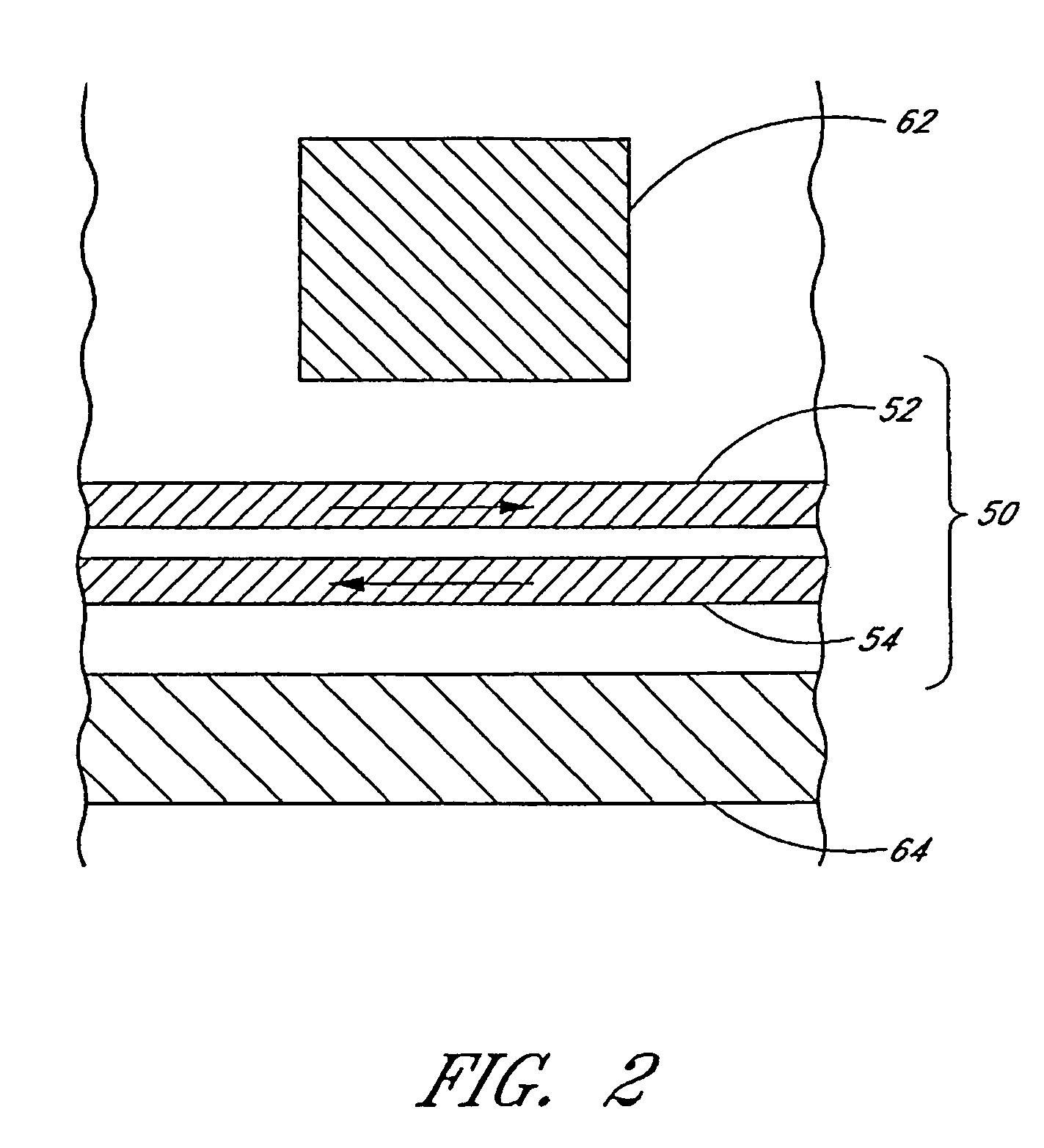
Air bearing having a cavity patch surface coplanar with a leading edge pad surface
InactiveUS6879464B2Improved air bearing surface designIncrease insensitivityFluid-dynamic spacing of headsRecord information storageLeading edgeAir bearing
An air bearing surface for read / write head of a magnetic disk drive is disclosed. The air bearing surface includes a trailing edge pad and a leading edge pad with trailing portions. A cavity is defined between the trailing edge pad and the trailing portions of the leading edge pad. A cavity patch is disposed within the cavity. The cavity patch can be disposed within the cavity towards one side of the read / write head.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
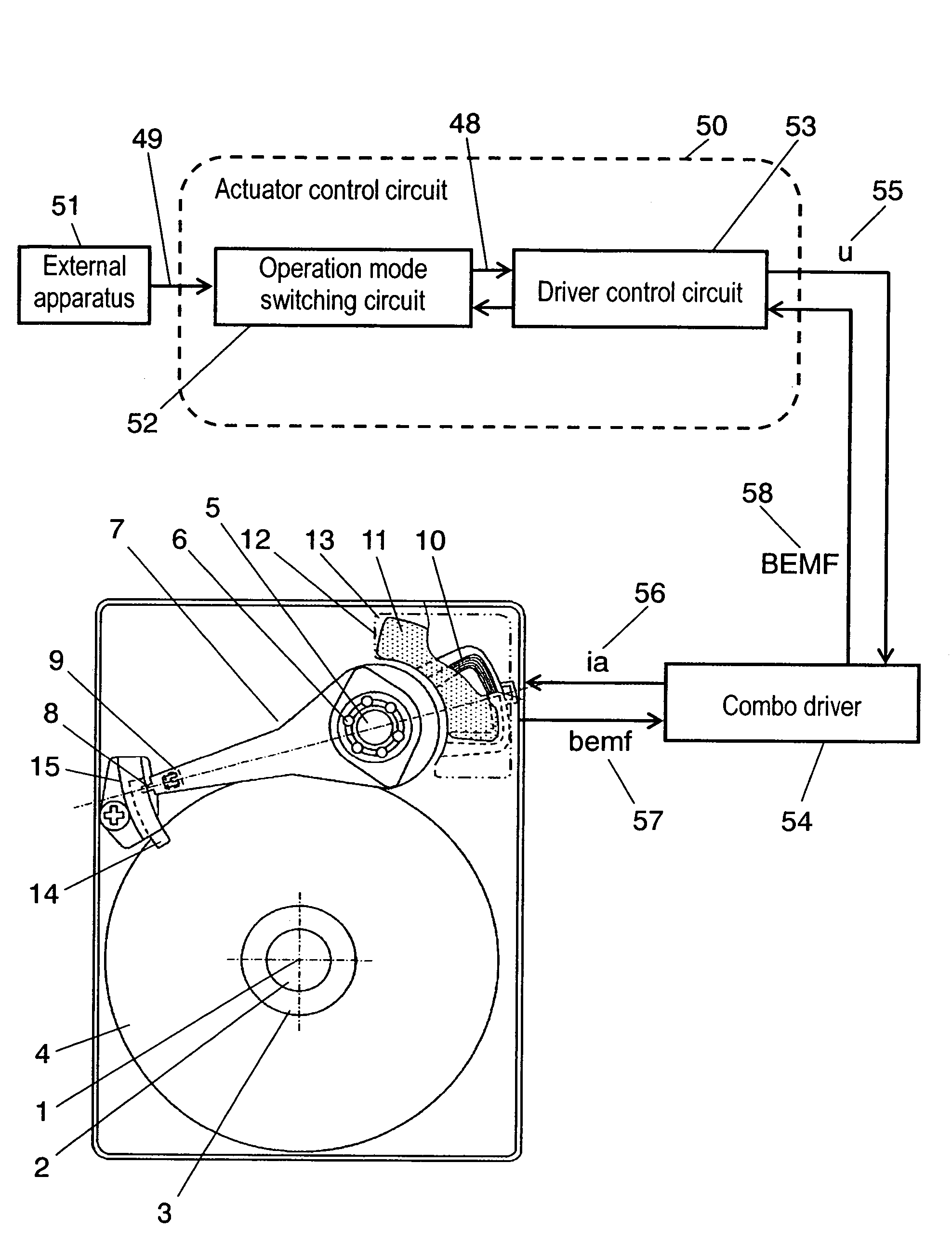
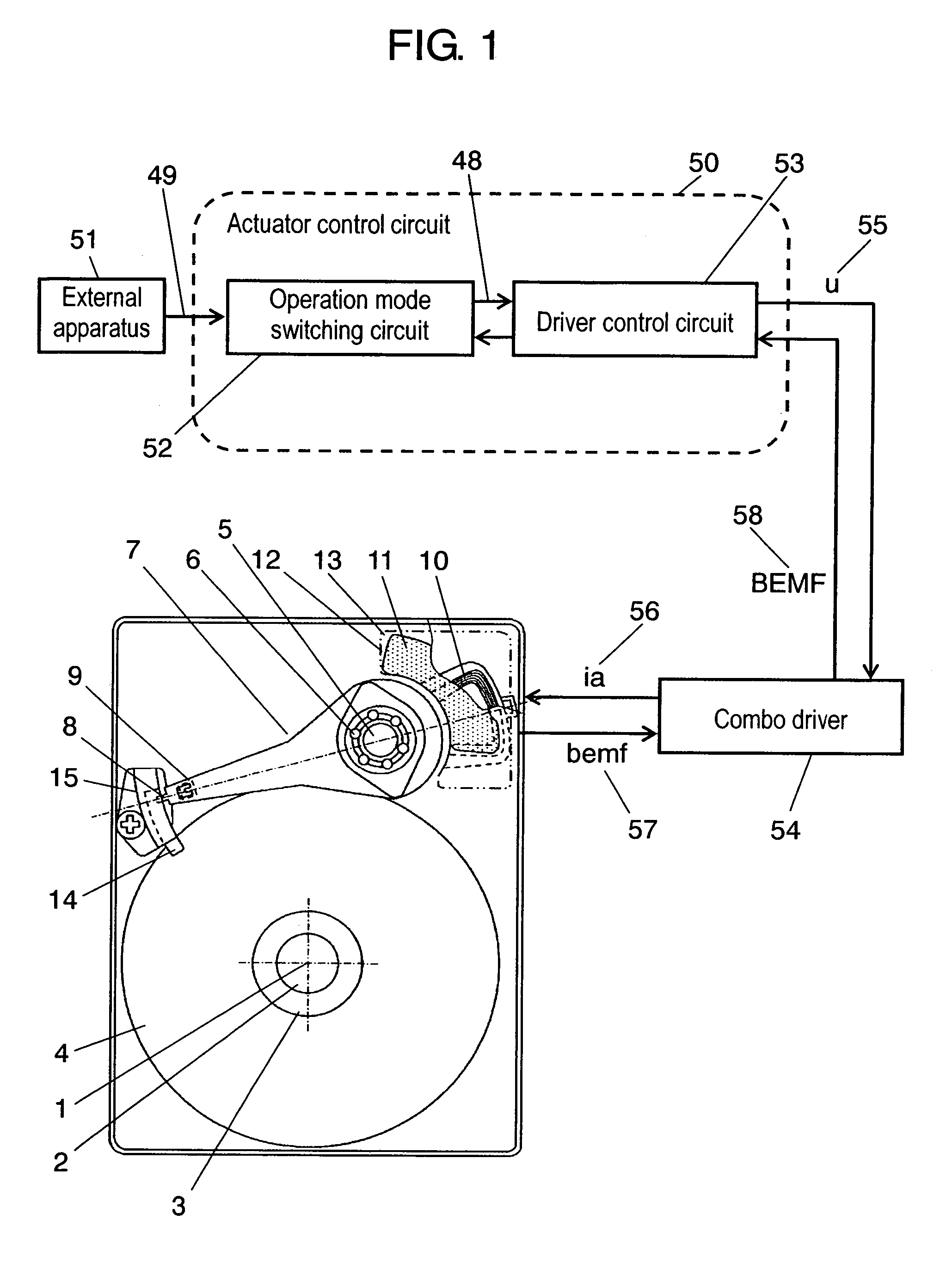
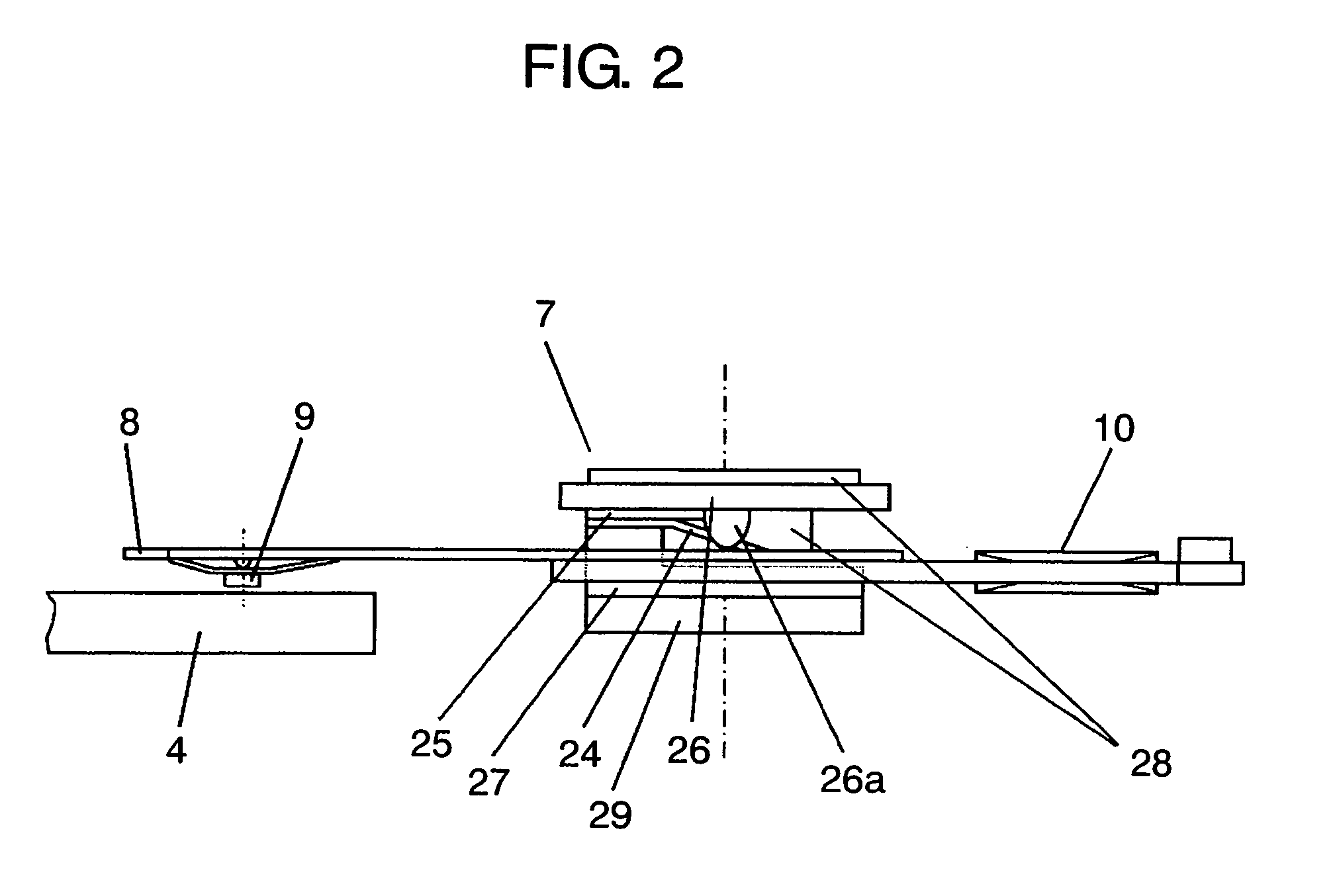
Method of controlling an actuator, and disk apparatus using the same method
InactiveUS7265929B2Power saving and downsizingReduce placementDisposition/mounting of recording headsDriving/moving recording headsDriving currentRepulsion force
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
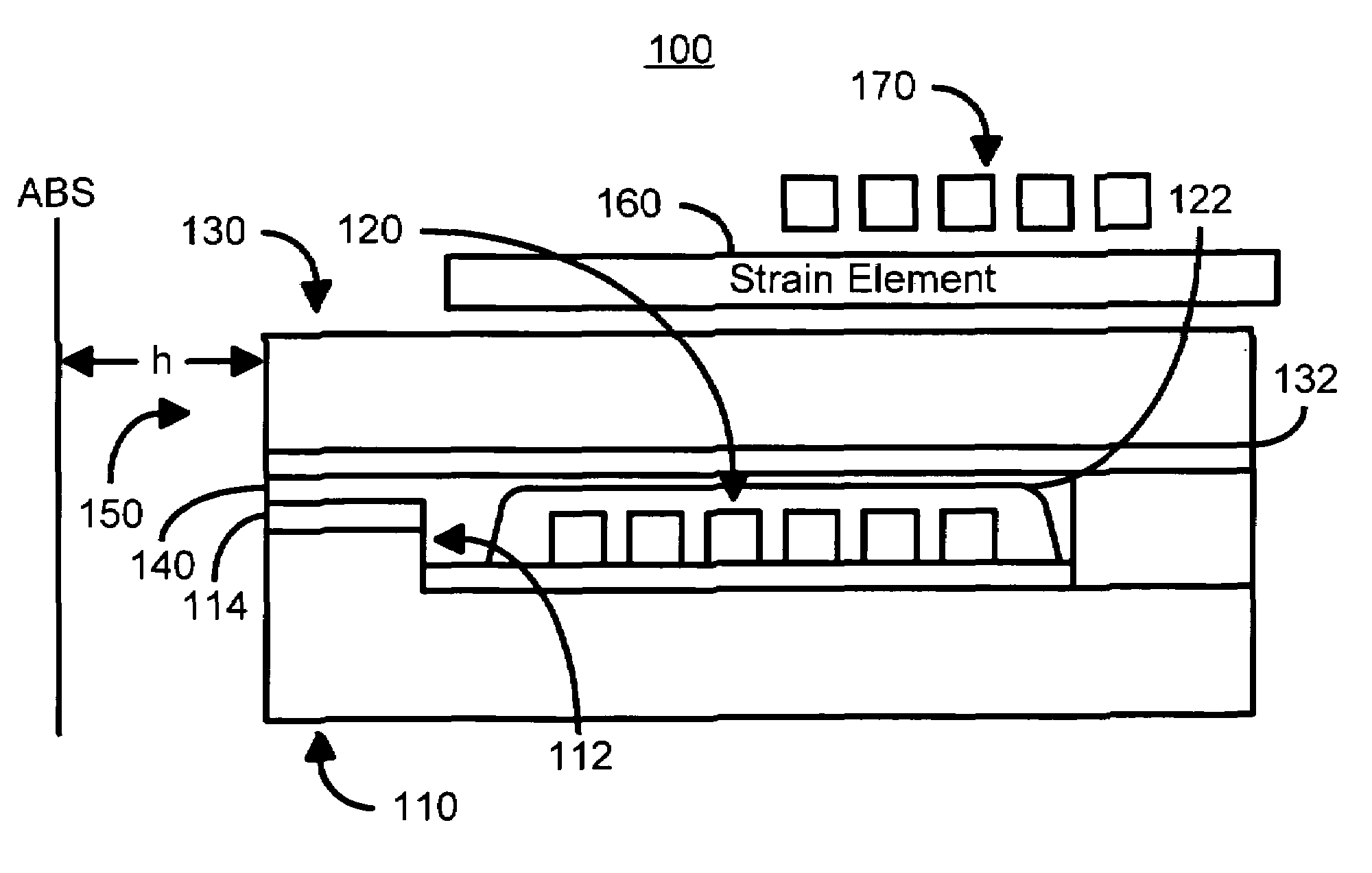
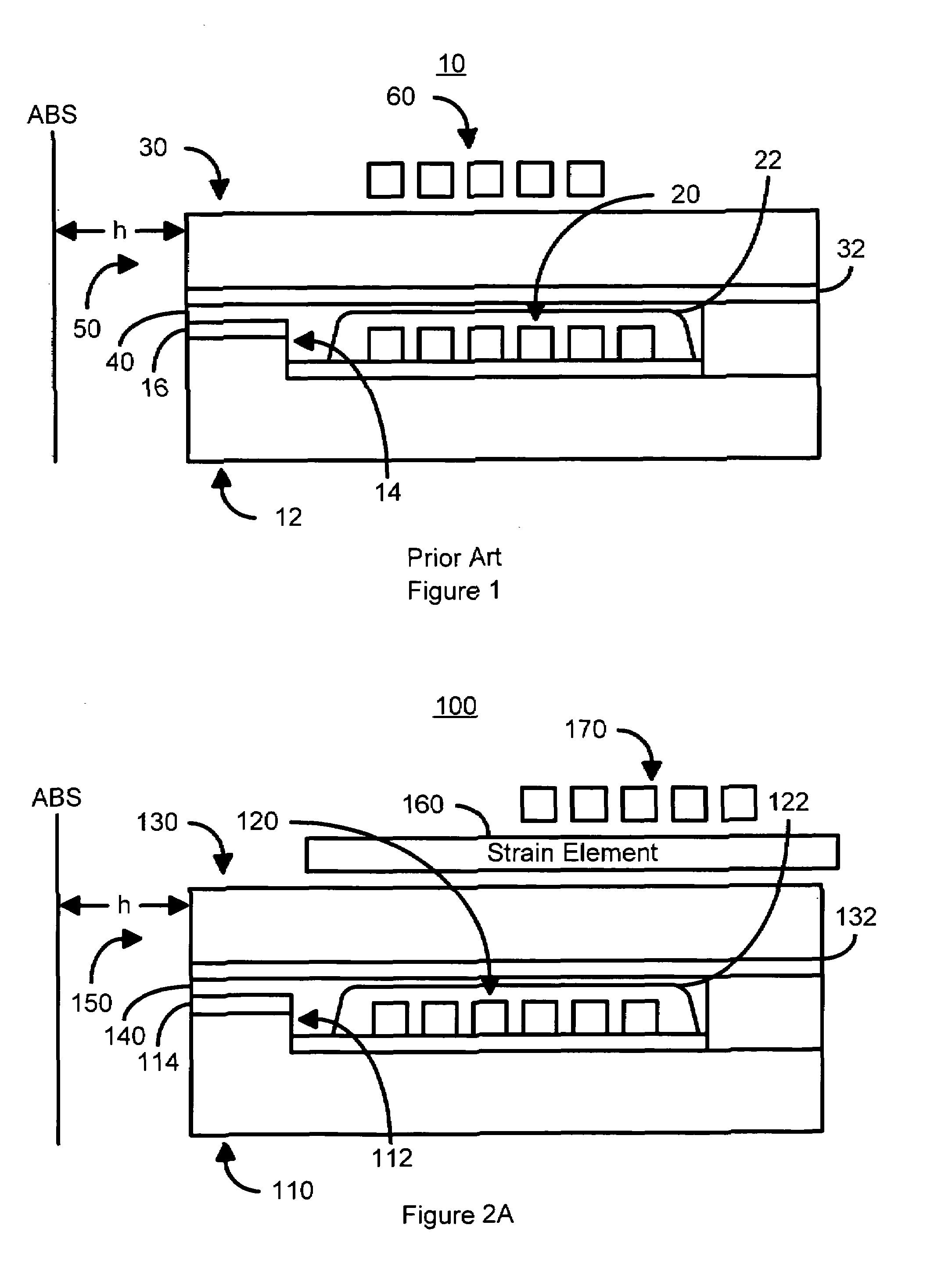
Method and system for providing dynamic actuation of a write head using a strain element
InactiveUS6934113B1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageEngineeringElectrical current
A method and system for actuating a pole tip of a write head is disclosed. The write head includes a first pole and a second pole. The method and system include providing a strain element and providing a coil. The strain element is electrically insulated from the first pole and the second pole. The strain element is further configured to produce a strain for actuating the pole tip in response to a magnetic field. The coil carries a current capable of producing the magnetic field at the strain element.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Magnetic write head having resistive heater coil
InactiveUS7283327B1Construction of head windingsDriving/moving recording headsEngineeringElectrical conduction
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Compact MR write structure
InactiveUS6894877B1Less spaceCompact structureConstruction of head windingsManufacture head surfaceEngineeringBackplane
A compact write element includes a conductive shield layer, an insulating write gap layer, a pole pedestal, a coil, and a conductive pole layer, and, in some embodiments also includes a backgap. The pole pedestal and the coil, and, in some embodiments the backgap, constitute a self-aligned array of components that may be formed in a single masking operation to allow for very tight tolerances between the components for a shorter yoke length. The pole layer is substantially flat and parallel to the conductive shield layer, providing for a shorter stack height. Also, a compact MR read / write head includes such a write element and a magnetic data storage and retrieval system includes the compact MR read / write head having such a write element.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
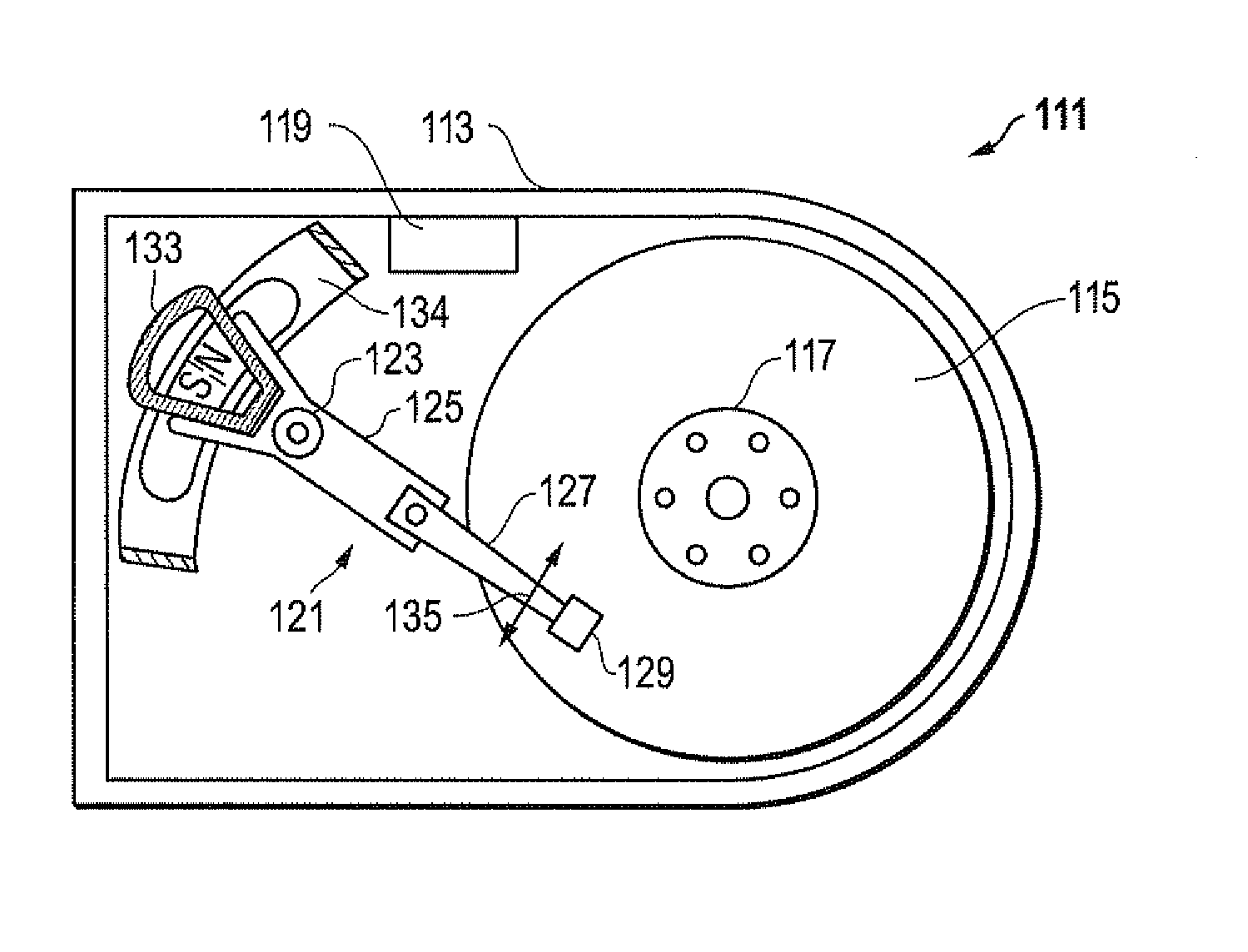
Method for manufacturing a group of head gimbal assemblies
InactiveUS7363697B1Electrical transducersDisposition/mounting of recording headsRotation testBiomedical engineering
A system and method for the production level screening of low flying magnetic heads in the manufacture of disk drive head disk assemblies (HDAs) is disclosed. A test disk is provided and has a plurality of bumps extending from at least one surface thereof. The test disk is rotated to fly a head of a head gimbal assembly selected from the group adjacent the surface of the test disk. An interaction of the head with one or more of the plurality of bumps may be sensed and the head gimbal assembly may be screened out from the group in response to the sensing of the interaction.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method of manufacturing a magnetic head device
InactiveUS7114241B2Electrical transducersManufacture head surfaceSubject matterElectrical and Electronics engineering
A method of manufacturing a magnetic head device includes forming a thin film magnetic head element over a substrate, the thin film magnetic head element including a magnetoresistance (MR) element. The substrate is cut such that the MR element is exposed on a side surface of the substrate. The side surface is then polished. Afterward, a magnetically degenerated layer is removed from the thin film magnetic head element along the side surface. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
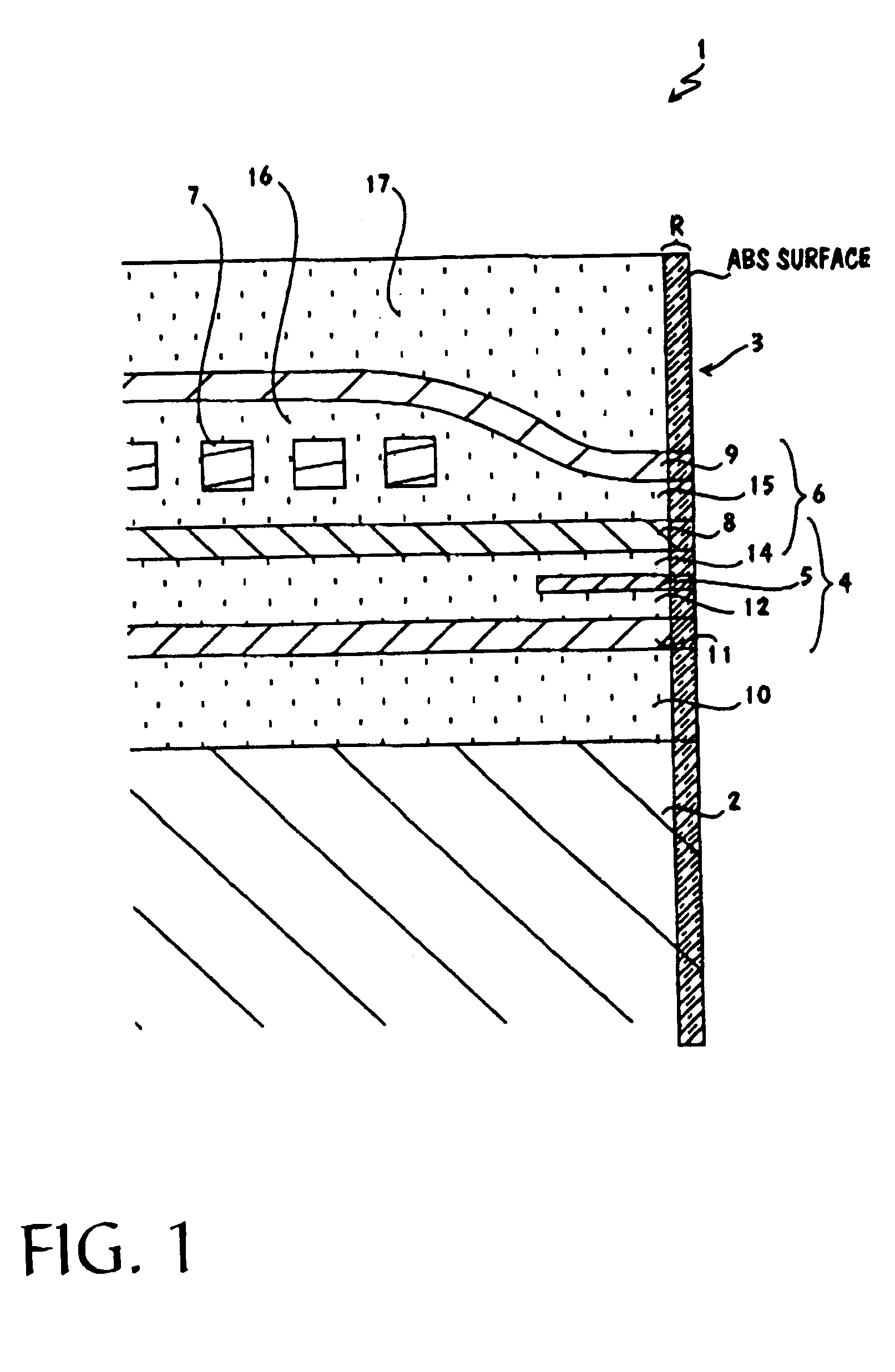
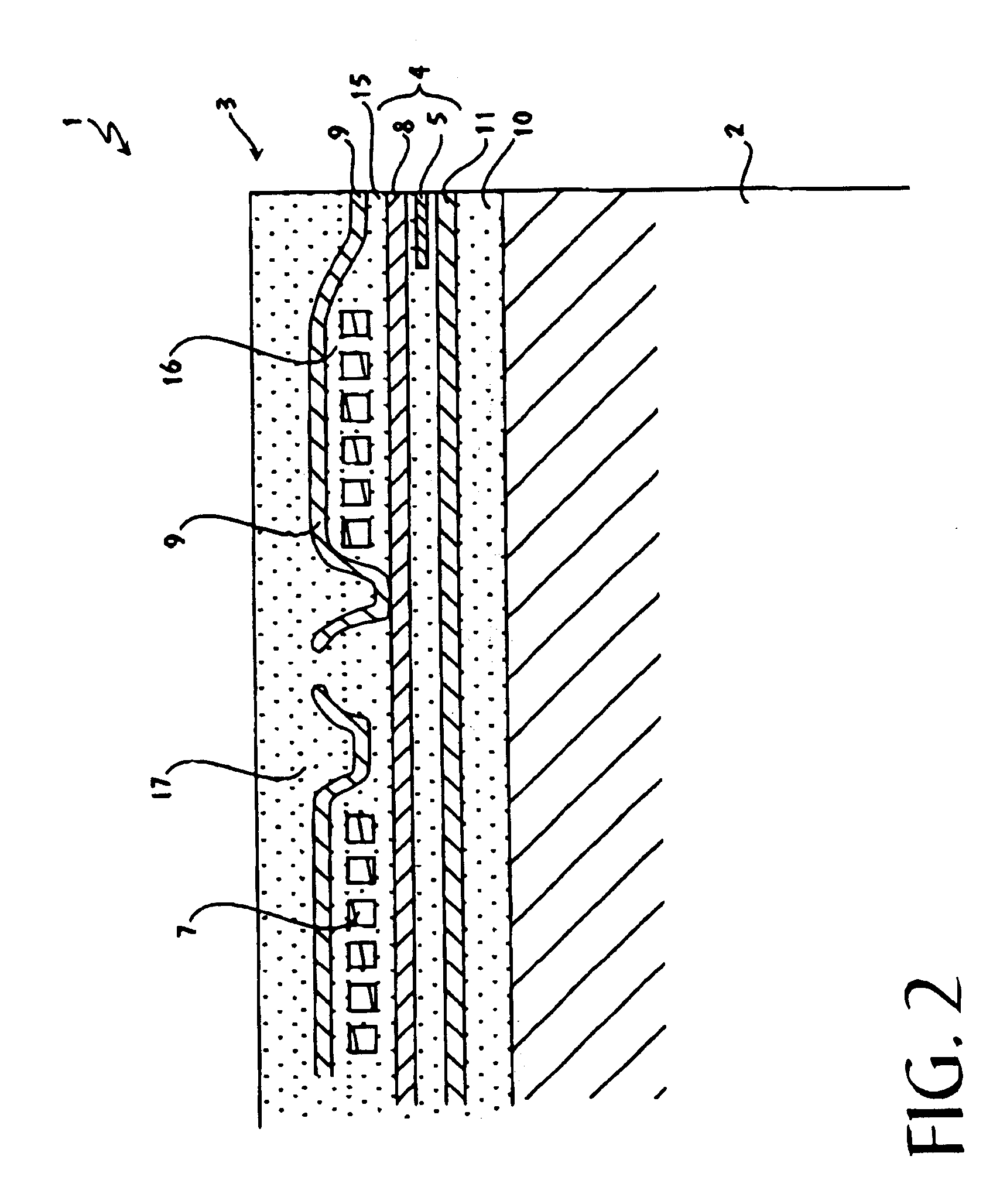
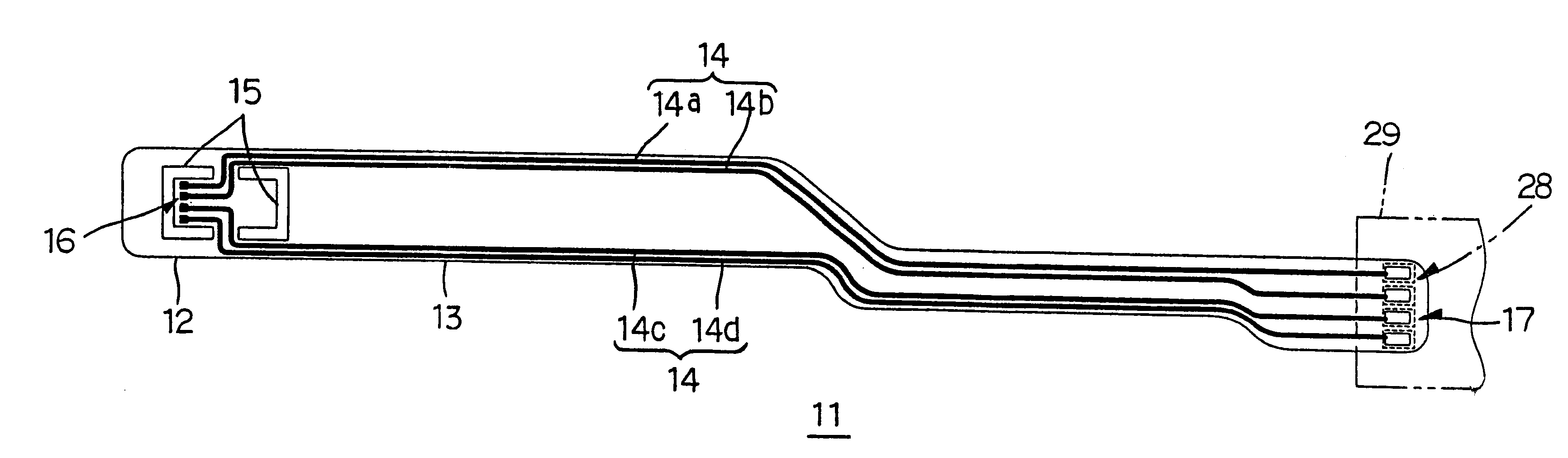
Suspension board with circuit
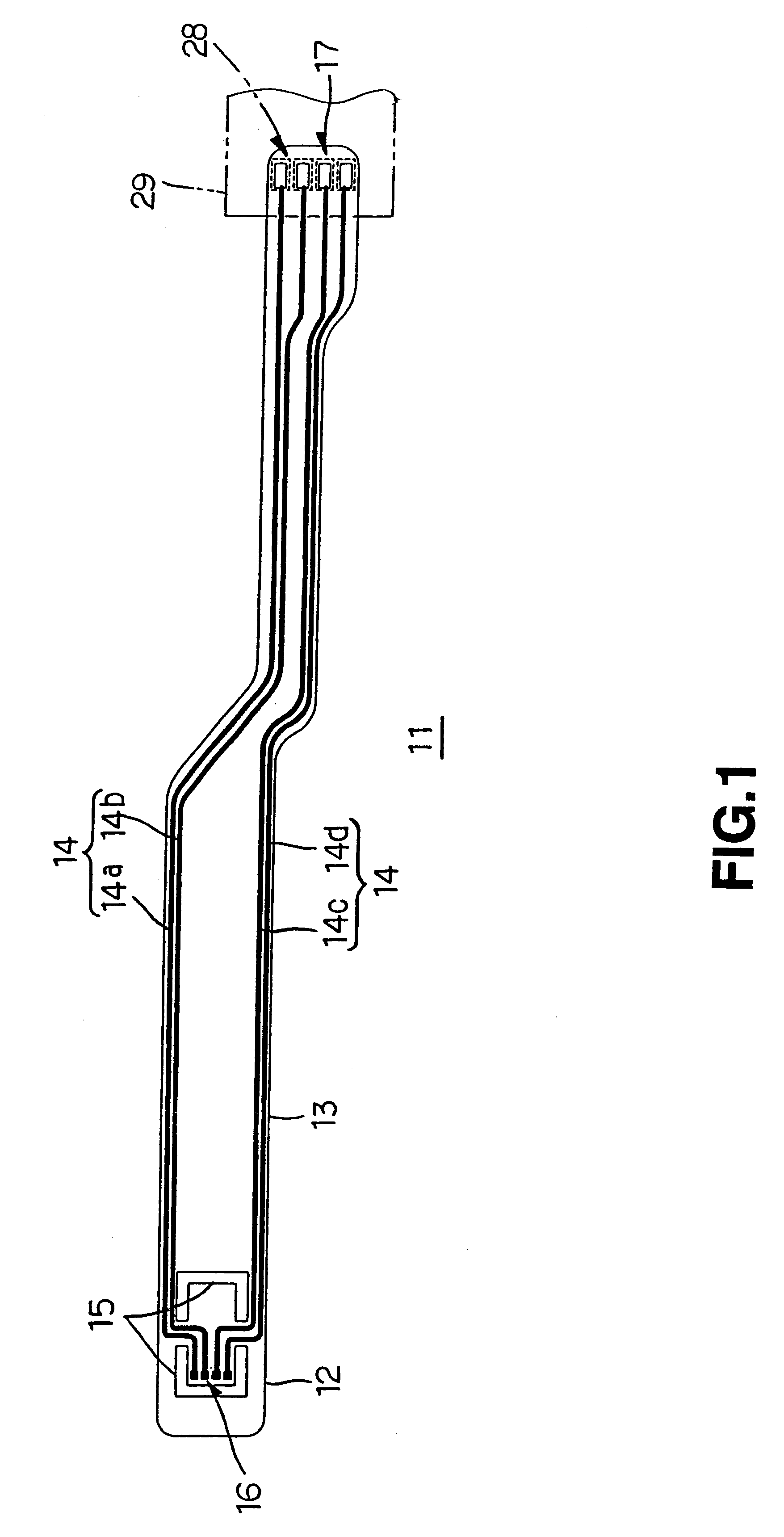
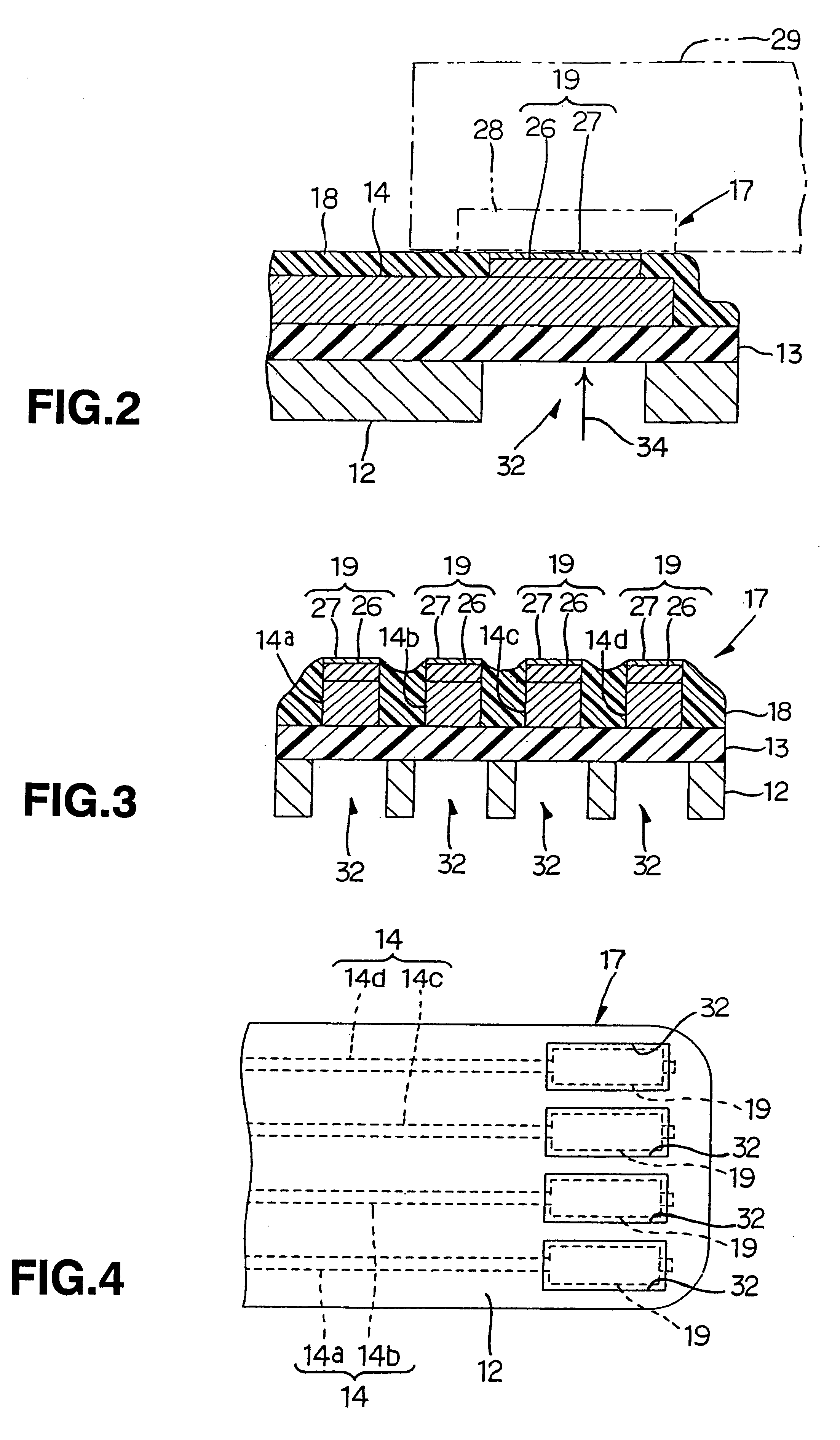
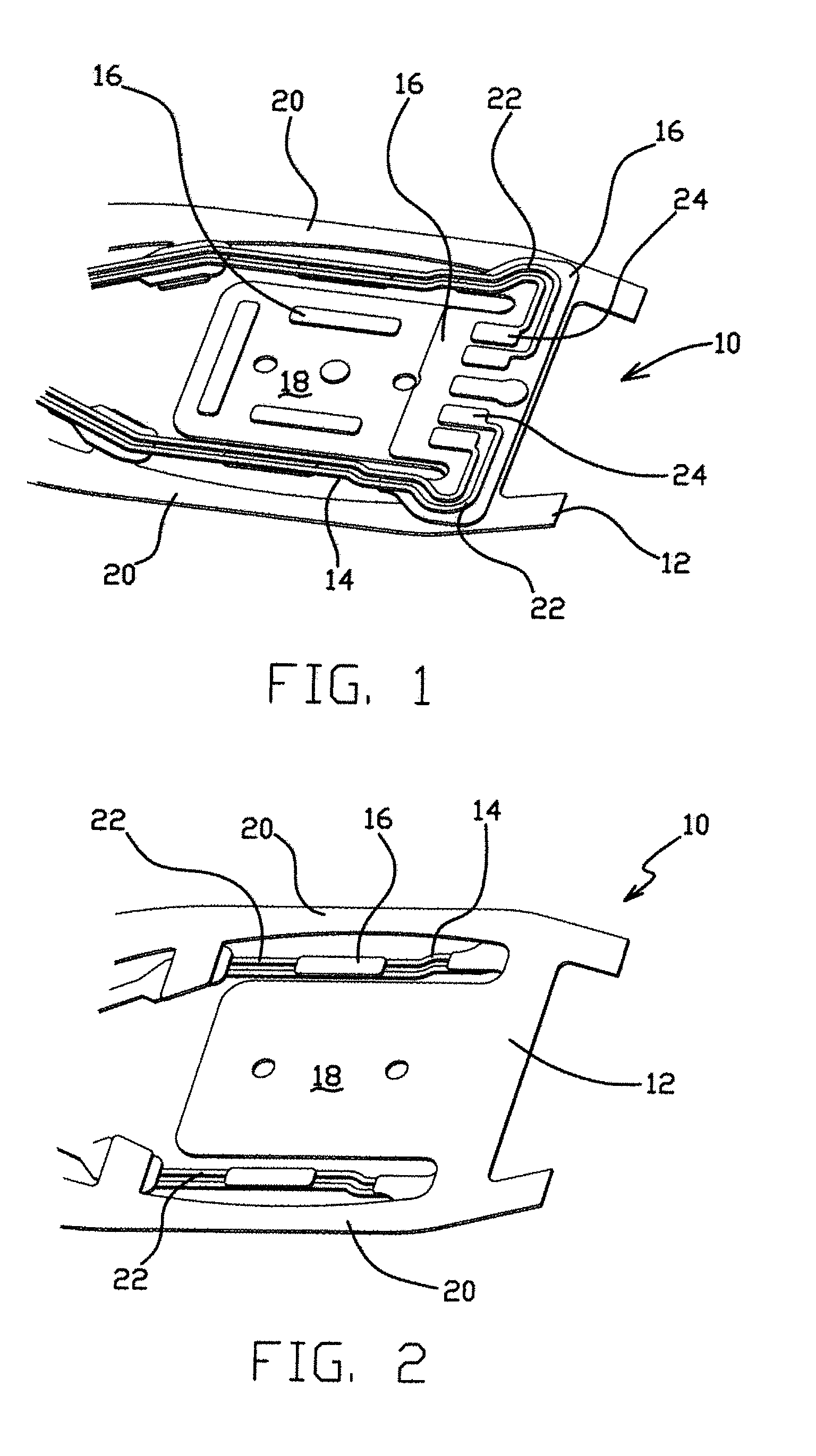
InactiveUS6399899B1High strengthSimple structureRelieving strain on wire connectionRecord information storageExternal connectionEngineering
To provide a suspension board with circuit that enables its terminals to be bonded to the other terminals with sufficient strength with simple structure, to ensure sufficient bonding reliability, the suspension board with circuit 11 includes a suspension board 12, a base layer 13 formed on the suspension board 12, and a conductive layer 14 formed on the base layer 13 and a cover layer 18 with which the conductive layer 14 is covered, wherein external connection terminals 17 to be bonded to terminals 28 of a read / write board 29 are formed without the suspension board 12 and / or the base layer 13 being formed.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
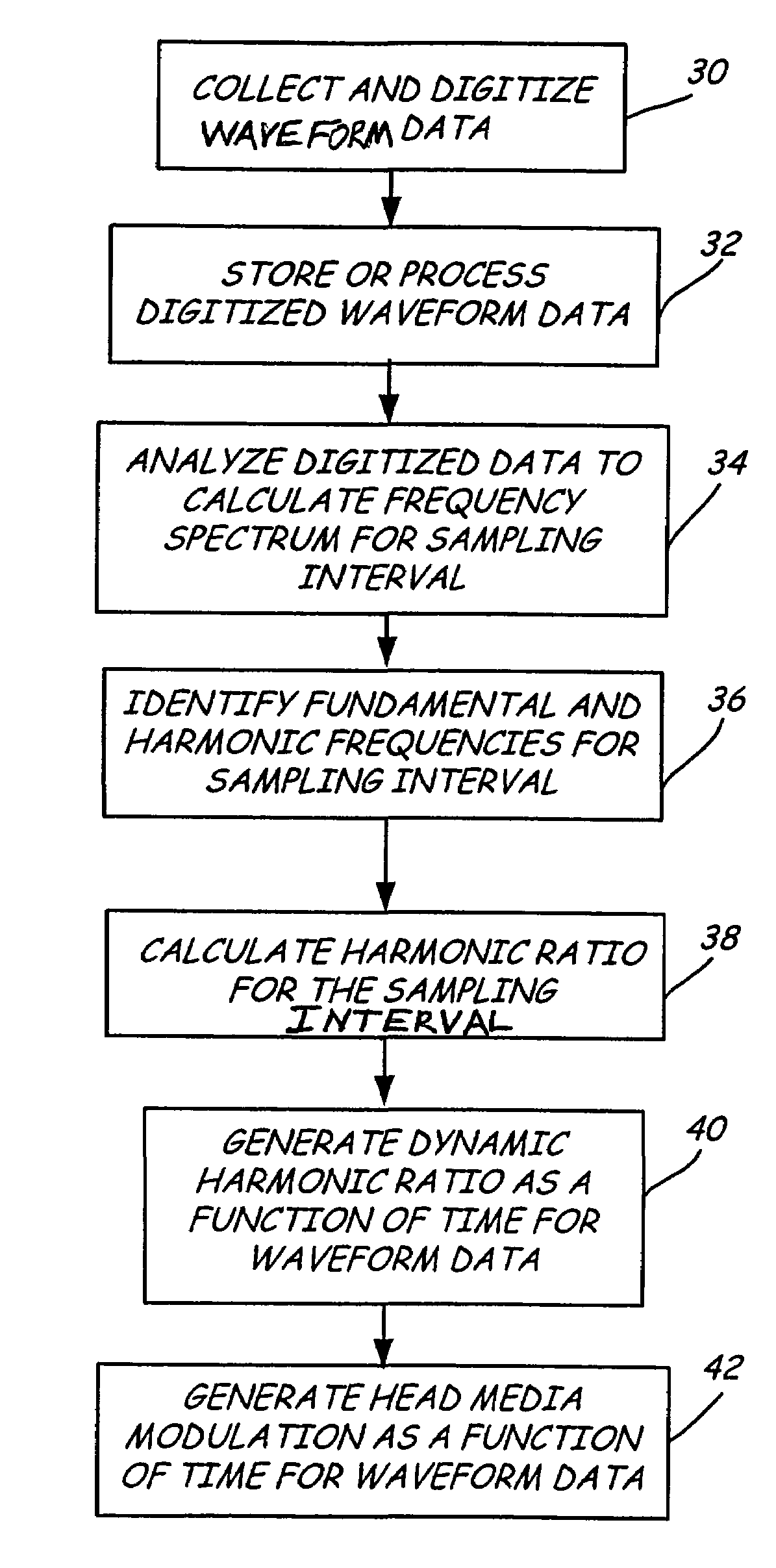
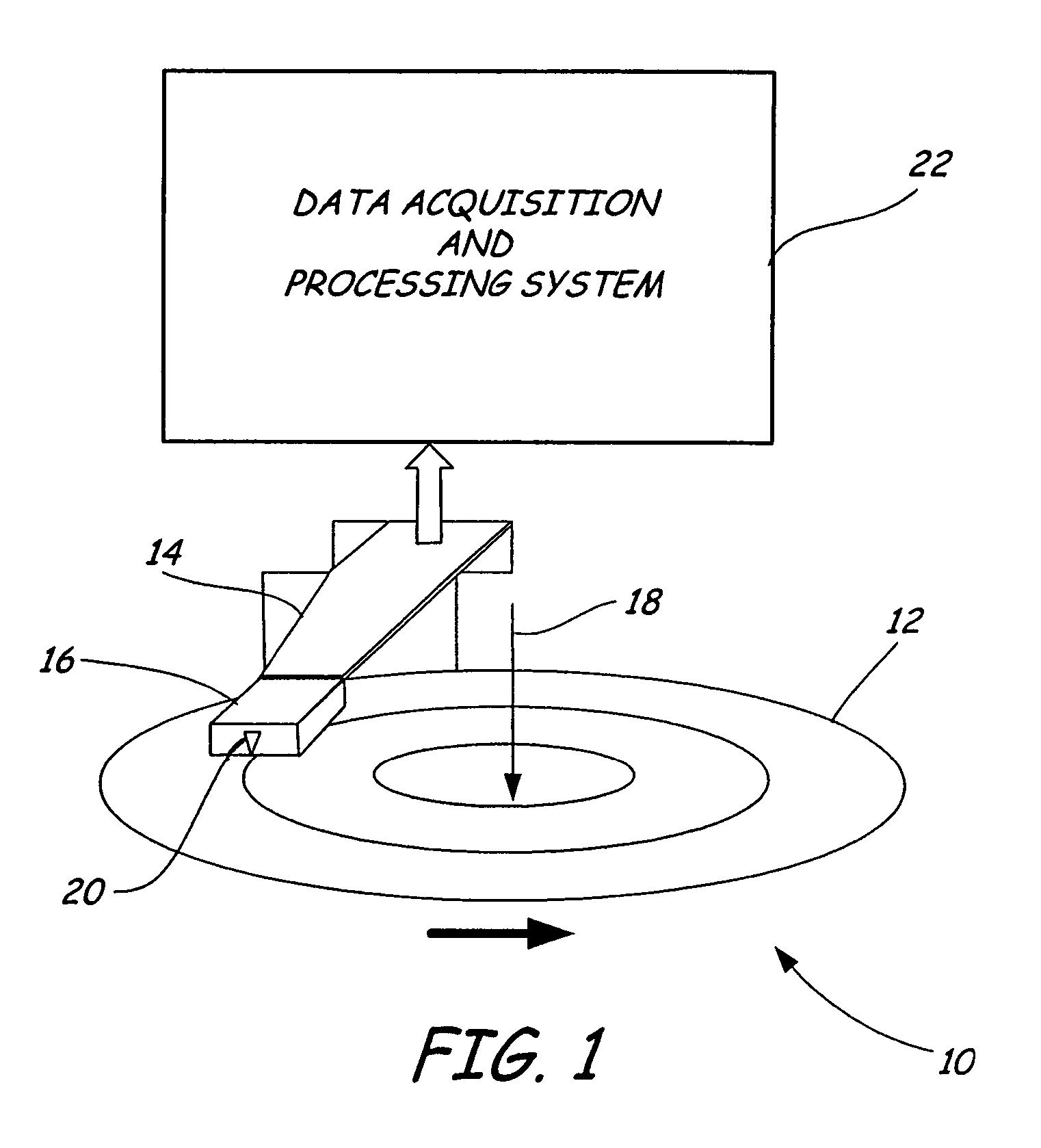
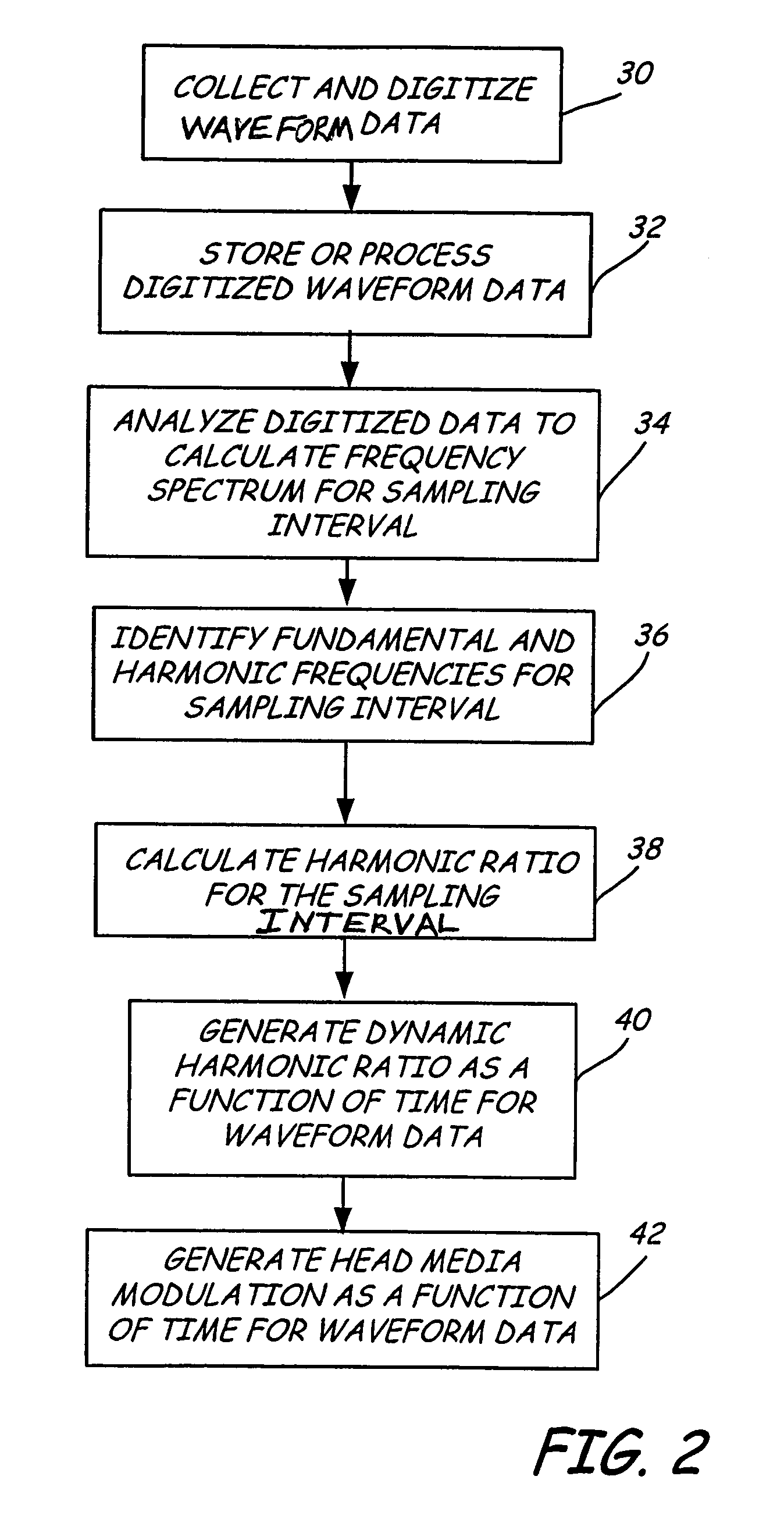
Dynamic measurement of head media spacing modulation
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
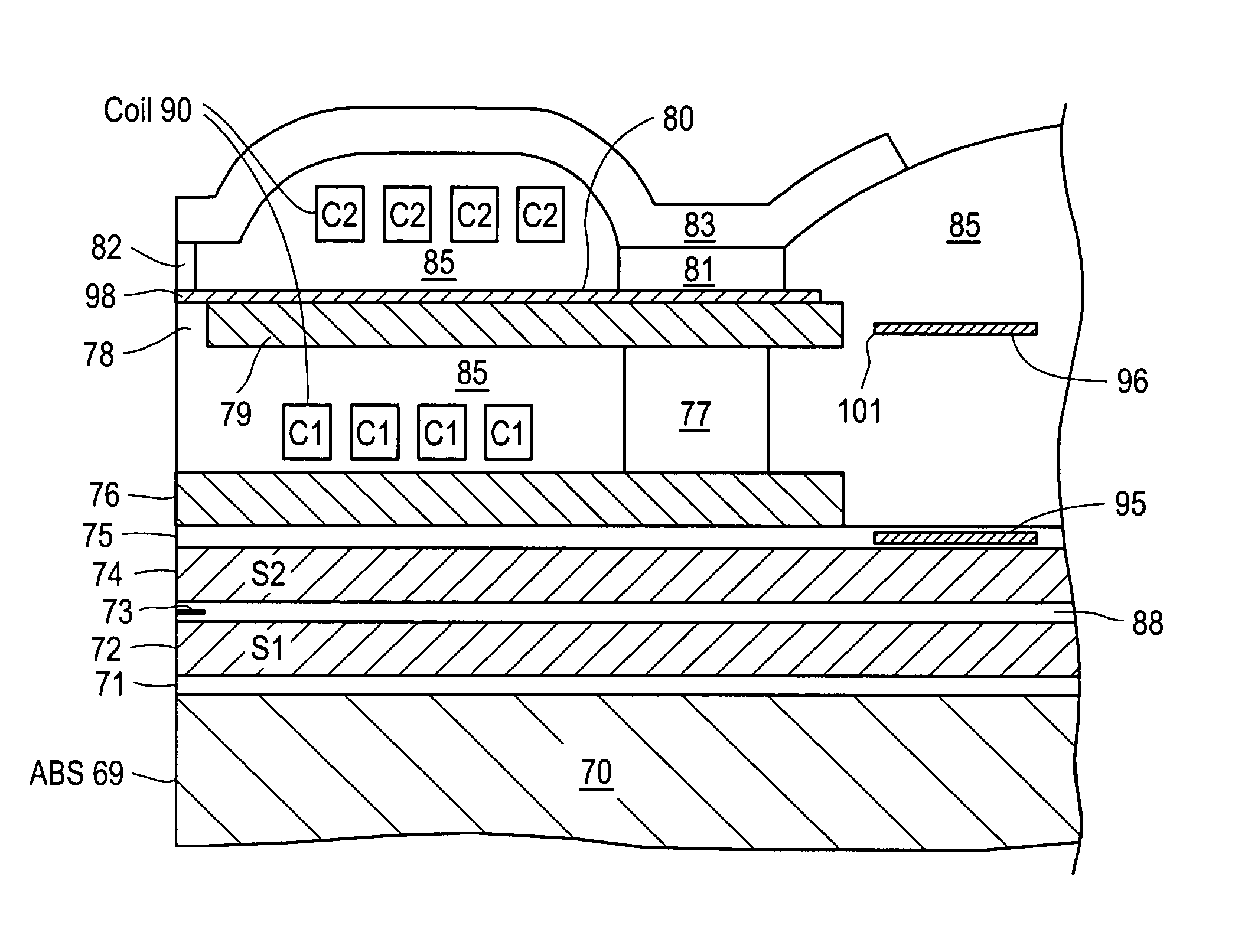
Transducer for heat assisted magnetic recording
ActiveUS7272079B2Combination recordingNanoinformaticsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingMagnetic storage
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
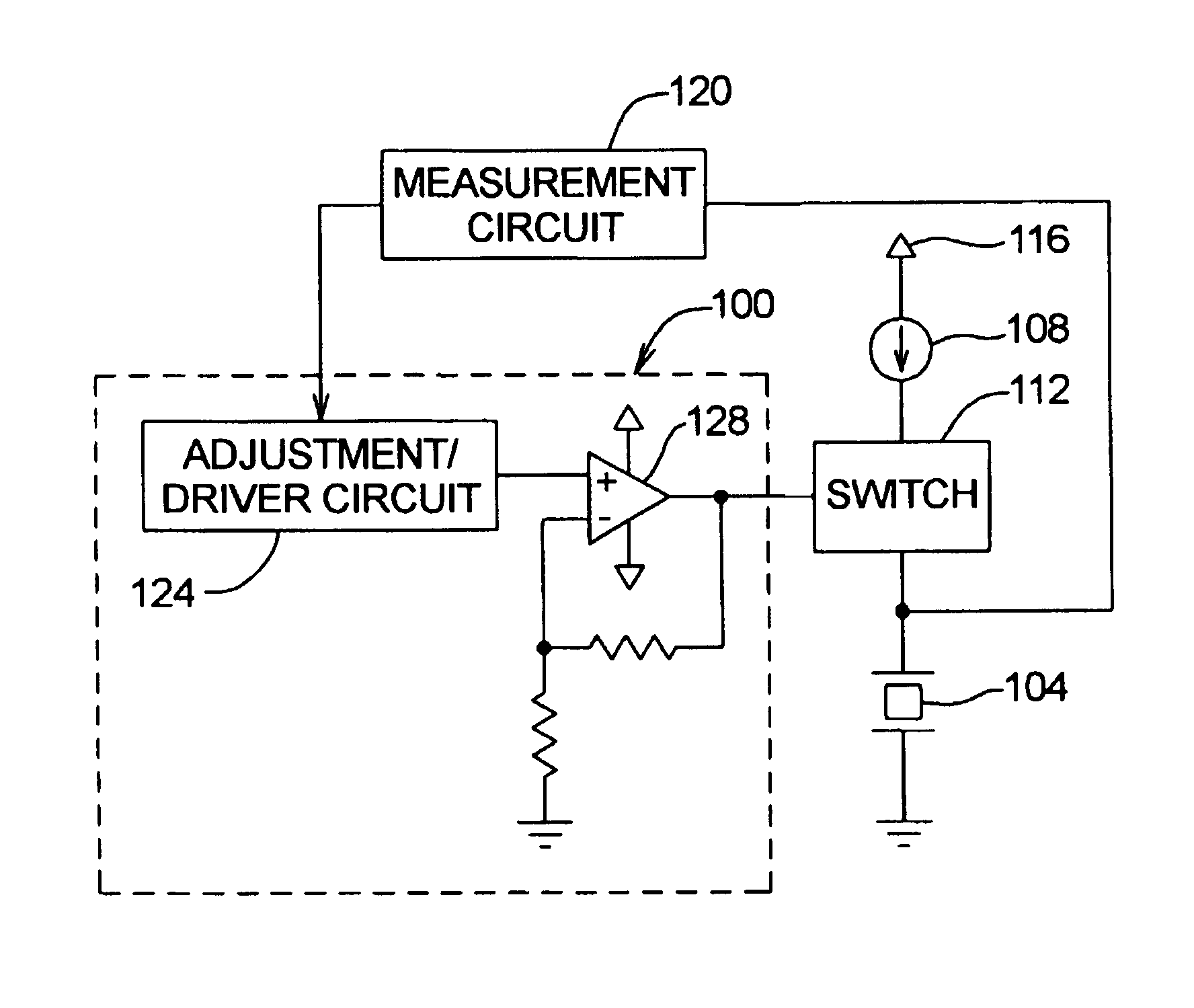
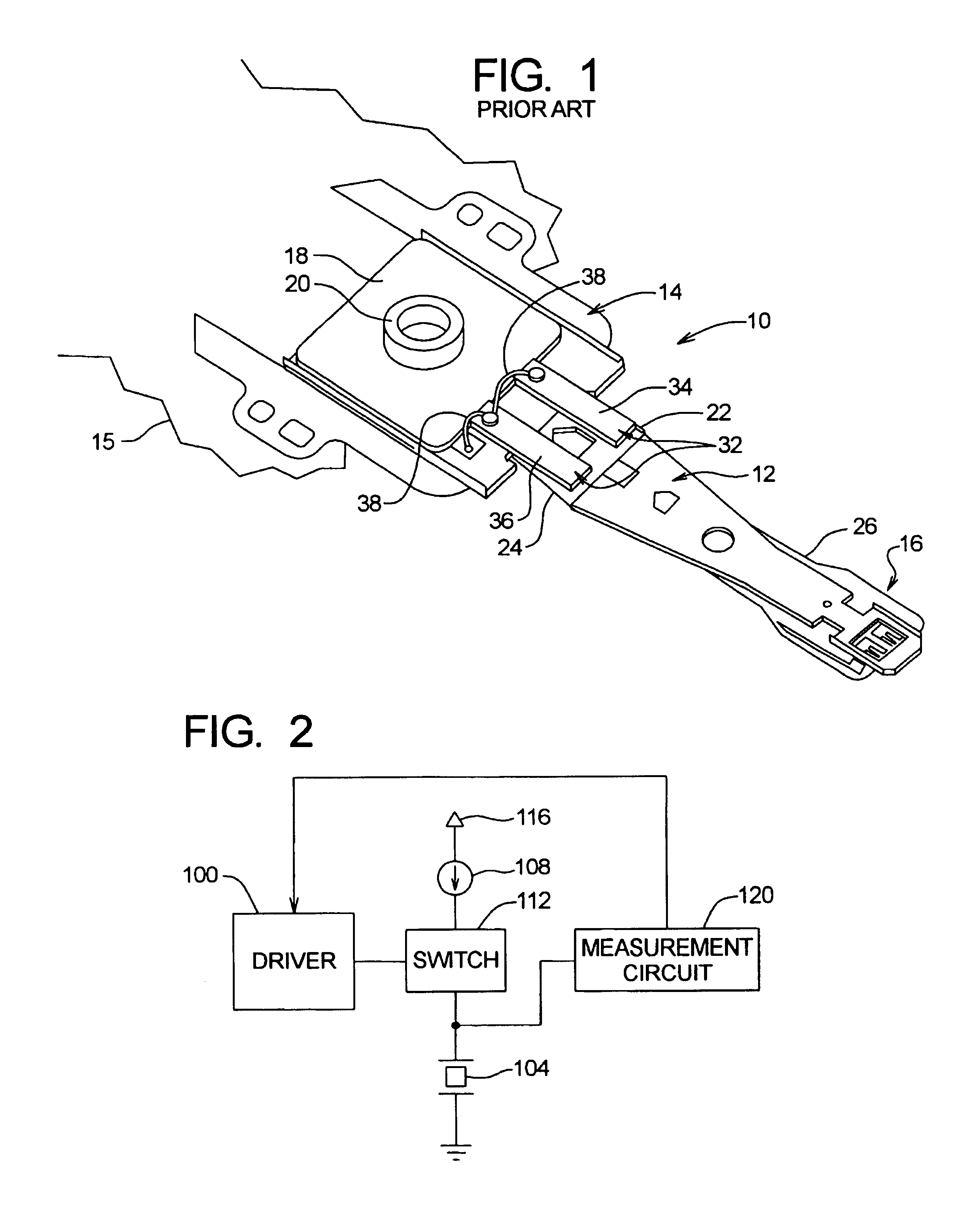
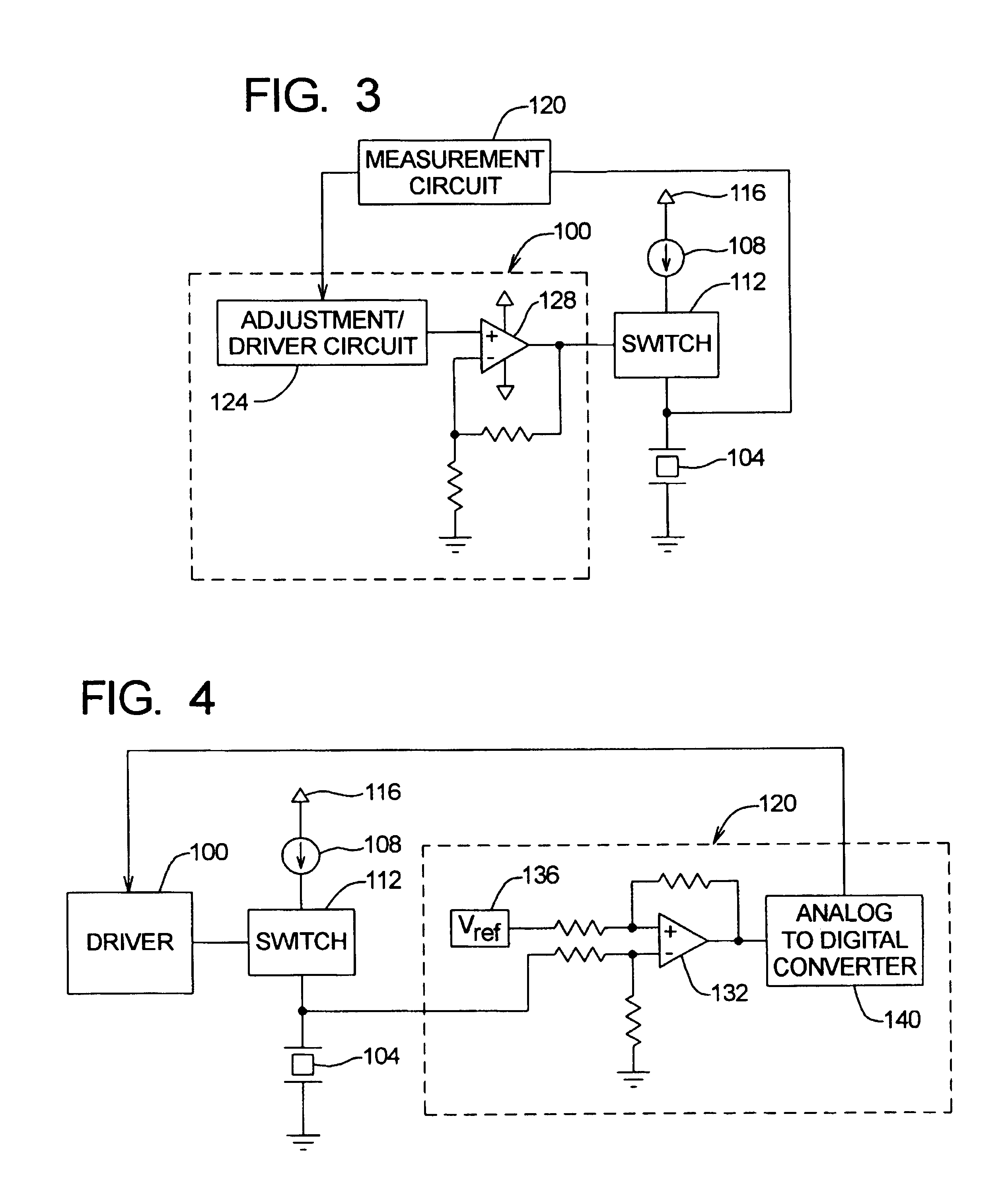
Method and apparatus for calibrating piezoelectric driver in dual actuator disk drive
InactiveUS6975123B1Precise positioningResistance/reactance/impedenceRecord information storageCapacitanceElectricity
A method and apparatus are disclosed which are operable to determine a capacitance associated with at least one piezoelectric element in an dual actuator disk drive. The capacitance information is used to adjust a driver used to drive the piezoelectric element. Capacitance is determined by supplying a predetermined current into the piezoelectric element(s) for a predetermined time period. A voltage associated with the piezoelectric element(s) is measured following the predetermined time period. The capacitance of the piezoelectric element(s) is then calculated based on the measured voltage, the current supplied, and the predetermined time period.
Owner:MAXTOR
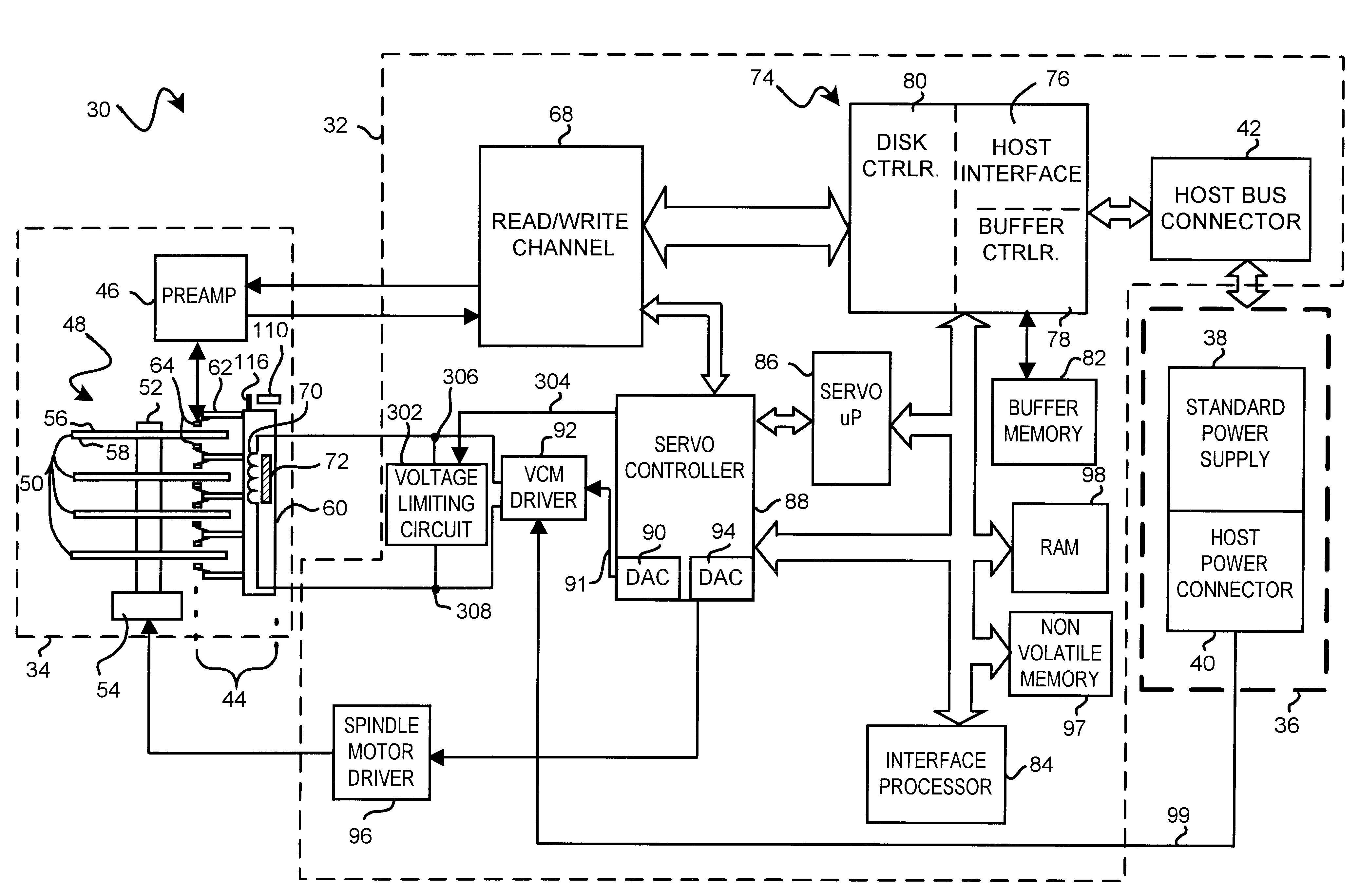
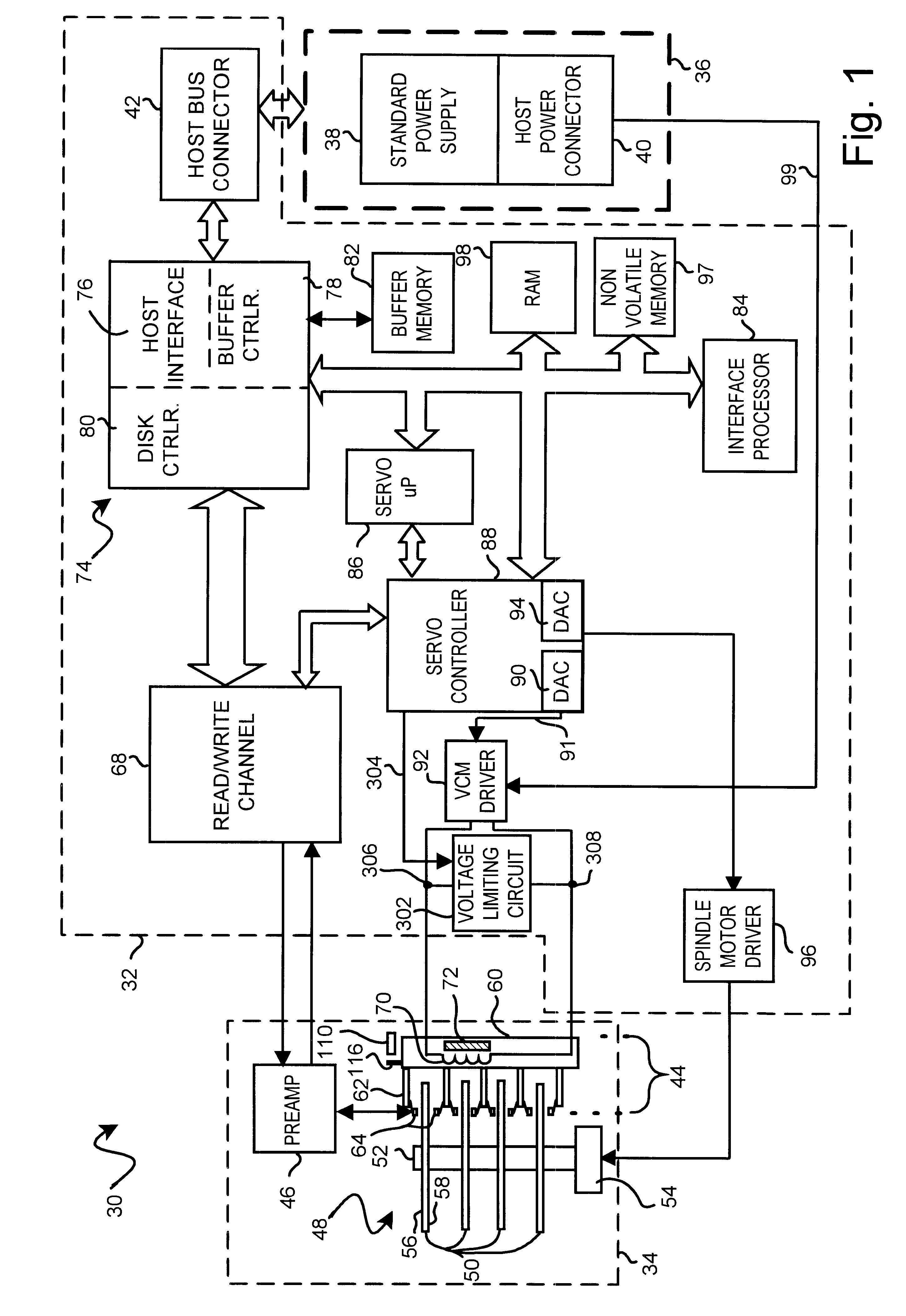
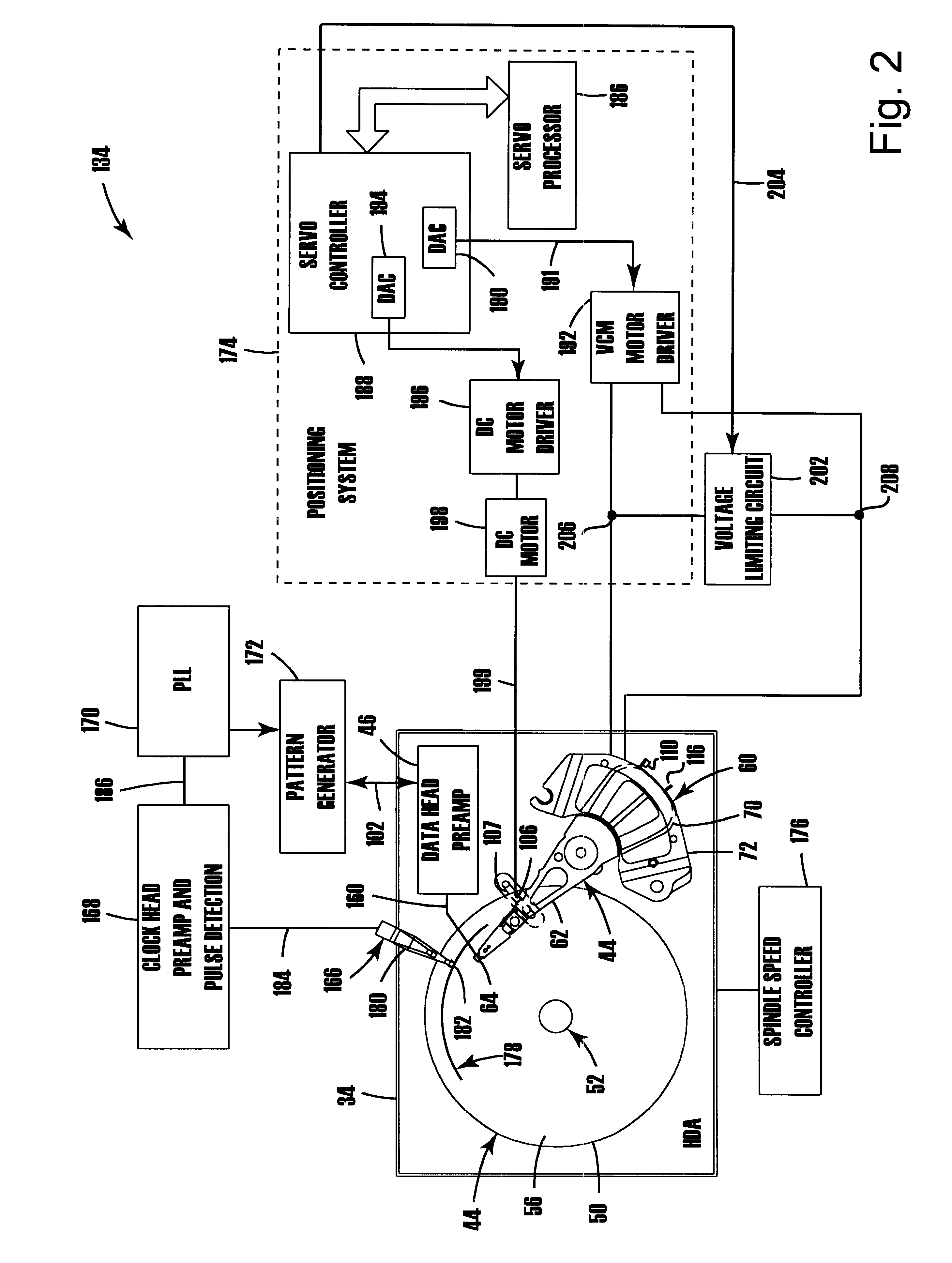
Disk drive employing method of unlatching actuator arm using VCM voltage limiting circuit to limit actuator arm velocity
InactiveUS6496324B1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageControl signalElectric machine
A disk drive employs a method of unlatching an actuator arm from a latch restraining the actuator arm in a disk drive. The disk drive includes a first node, a second node, and a voice coil motor (VCM) coupled to the actuator arm. The VCM includes a coil connected between the first node and the second node. The method includes applying a voltage between the first node and the second node to cause current to flow through the coil in order to move the actuator arm away from the latch at a variable actuator arm velocity. The method includes temporarily activating a VCM velocity control signal to enable a VCM voltage limiting circuit connected in parallel with the coil between the first node and the second node. The method further includes limiting the voltage applied across the coil to a predetermined VCM voltage level with the enabled VCM voltage limiting circuit in order to limit the actuator arm velocity.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
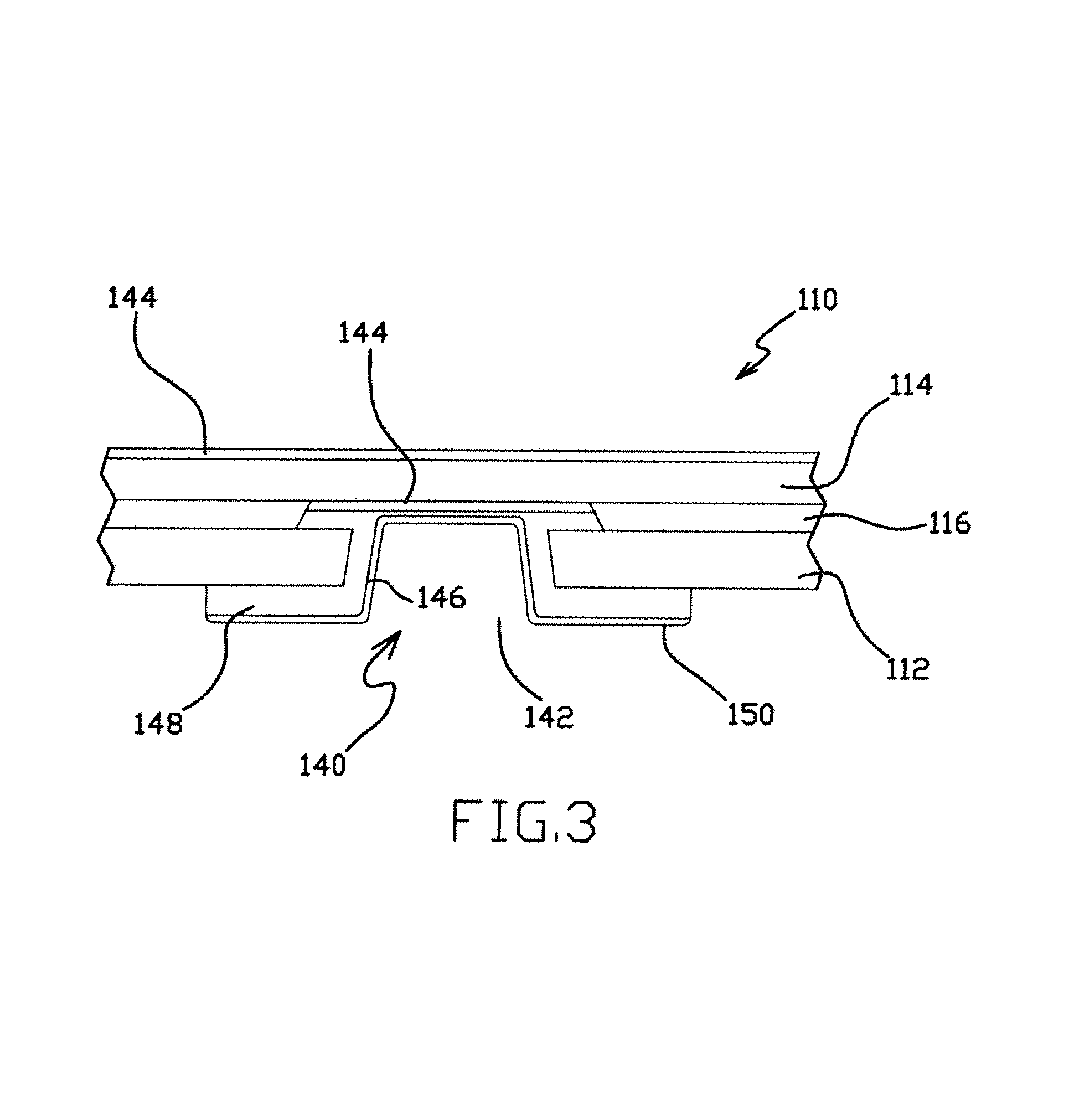
Multi-layer ground plane structures for integrated lead suspensions
ActiveUS7929252B1Additive manufacturing apparatusHigh frequency circuit adaptationsStructure of the EarthGround plane
Multi-layer ground plane structures and methods of manufacture for integrated lead suspension flexures. A flexure in accordance with one embodiment of the invention includes an insulating layer, a plurality of traces on the insulating layer and a stainless steel base layer on the side of the insulating layer opposite the traces. The stainless steel base layer includes one or more void portions with voids in the base layer opposite the insulating layer from the traces and one or more backed portions with the base layer backing the traces. A plurality of patterned and transversely-spaced first conductive ground planes are located opposite the insulating layer from the traces at the void portions and backed portions of the stainless steel base layer. A continuous gold second conductive ground plane is located opposite the insulating layer and the first ground planes from the side of the insulating layer adjacent to the traces at the void portions and backed portions of the stainless steel base layer. The gold ground plane can be used as an etch stop during formation of the voids in the base layer.
Owner:HUTCHINSON TECH
CPP-type thin film magnetic head provided with side shields
ActiveUS20110051291A1High track densityLinearityNanomagnetismDisposition/mounting of recording headsControl layerCoupling
A thin film magnetic head includes first and second shield layers that are positioned on both sides of a magnetoresistive (MR) stack with respect to a film surface orthogonal direction; a first exchange-coupling layer that is positioned between the MR stack and the first shield layer and that generates an exchange-coupling between a first magnetoresistive (MR) magnetic layer and a first magnetic control layer of the first shield layer; a second exchange-coupling layer that is positioned between the MR stack and the second shield layer and that generates an exchange-coupling between a second magnetoresistive (MR) magnetic layer and a second magnetic control layer of the second shield layer; a bias magnetic field application layer that is disposed at an opposite surface of the MR stack from an air bearing surface (ABS) and that applies a bias magnetic field to the MR stack in a direction orthogonal to the ABS; and pair of side shield layers that are positioned at both sides of the MR stack with respect to a track width direction. Each of the side shield layers includes a pair of magnetic layers that are antiferromagnetically exchange-coupled through a side shield ruthenium layer.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
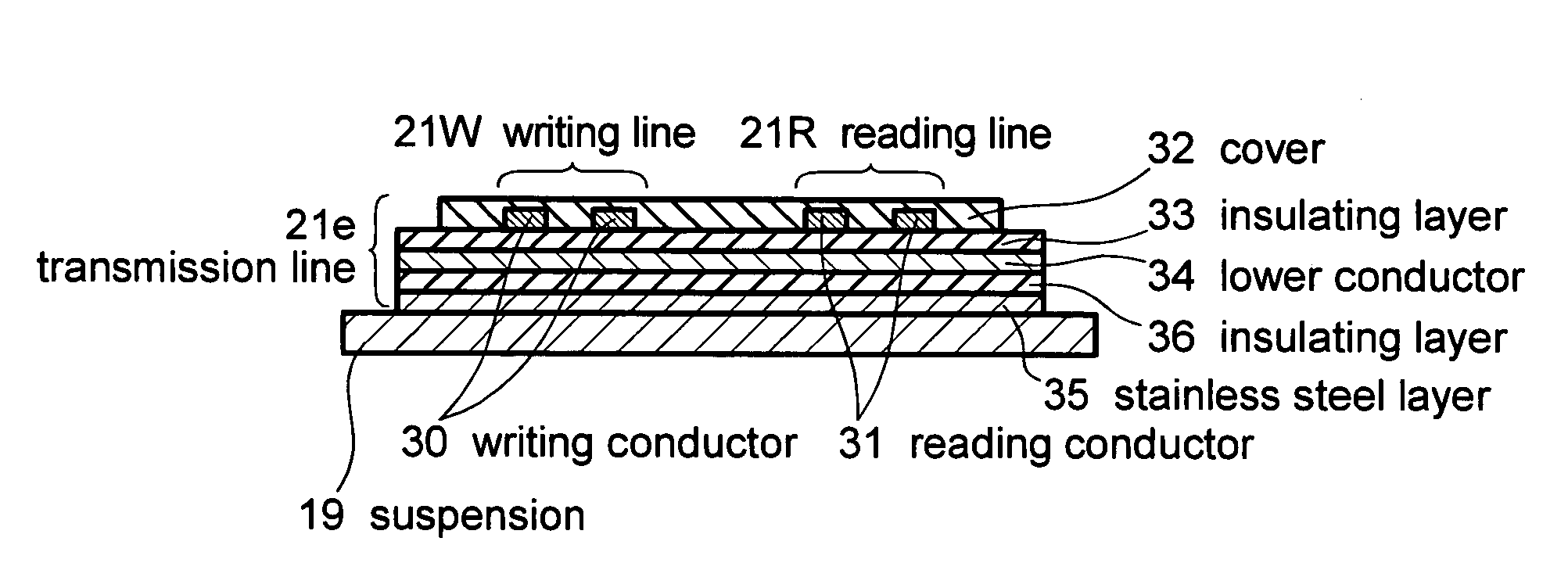
Magnetic disk drive having a suspension mounted transmission line including read and write conductors and a lower conductor
InactiveUS7319573B2Improve electrical performanceReduce transmission lossElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsElectrical conductorAlloy
Embodiments of the invention provide a magnetic disk drive which has improved electrical properties owing to a reduction in the loss of transmission line, improved vibration properties owing to a reduction in the stiffness of wiring around the head, and a flat impedance in the transmission line. In one embodiment, a magnetic disk drive comprises a suspension; a magnetic head coupled with the suspension and configured to write and read information to and from a magnetic recording medium; and a transmission line disposed on the suspension to transmit writing and reading information to and from the magnetic head. The transmission line includes a writing line and a reading line, a lower conductor disposed underneath the writing line and the reading line, and an insulating layer interposed between the lower conductor and the writing and reading lines. The lower conductor comprises copper or copper-based alloy and has a thickness of substantially less than 25 μm, desirably about 2-12 μm, and more desirably about 5 μm.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH JAPAN LTD
Thin-film magnetic head for microwave assist and microwave-assisted magnetic recording method
InactiveUS20090310244A1Stably generate electromagnetic fieldDisposition/mounting of recording headsDriving/moving recording headsExcitation currentMagnetization
Provided is a thin-film magnetic head that can stably generate electromagnetic field with a desired frequency, even under the existence of significantly strong write field with frequently reversed direction. The head comprises an electromagnetic-field generating element between the first and second magnetic poles. The electromagnetic-field generating element comprises a spin-wave excitation layer provided adjacent to the first magnetic pole and having a magnetization with its direction varied according to external magnetic fields, for generating an high frequency electromagnetic field by an excitation of spin wave. And a magnetization of the spin-wave excitation layer is biased in a direction substantially perpendicular to its layer surface by a portion of magnetic field generated from the first magnetic pole, and pin-wave excitation current flows in the electromagnetic-field generating element in a direction from the second pole to the first pole.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
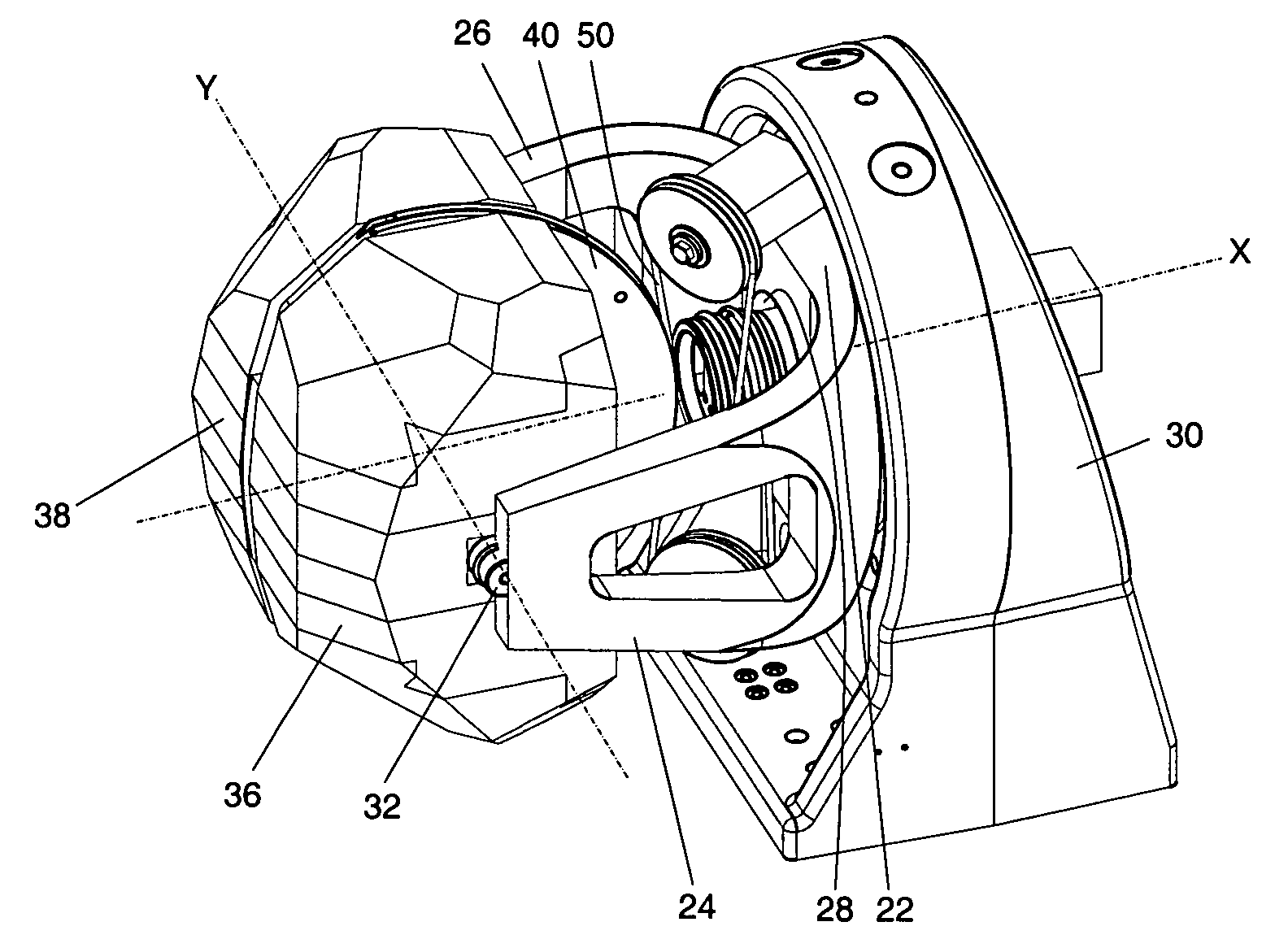
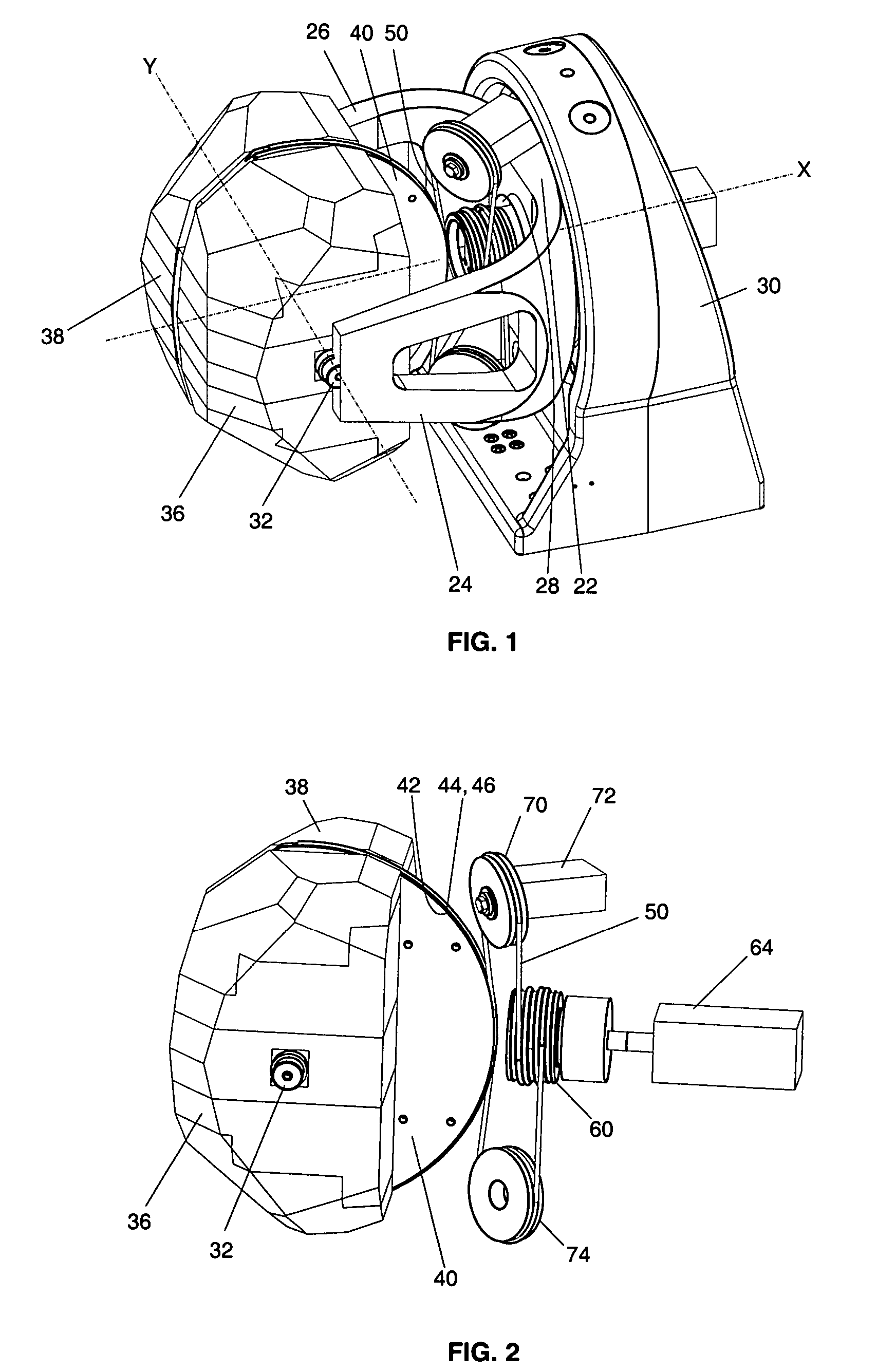
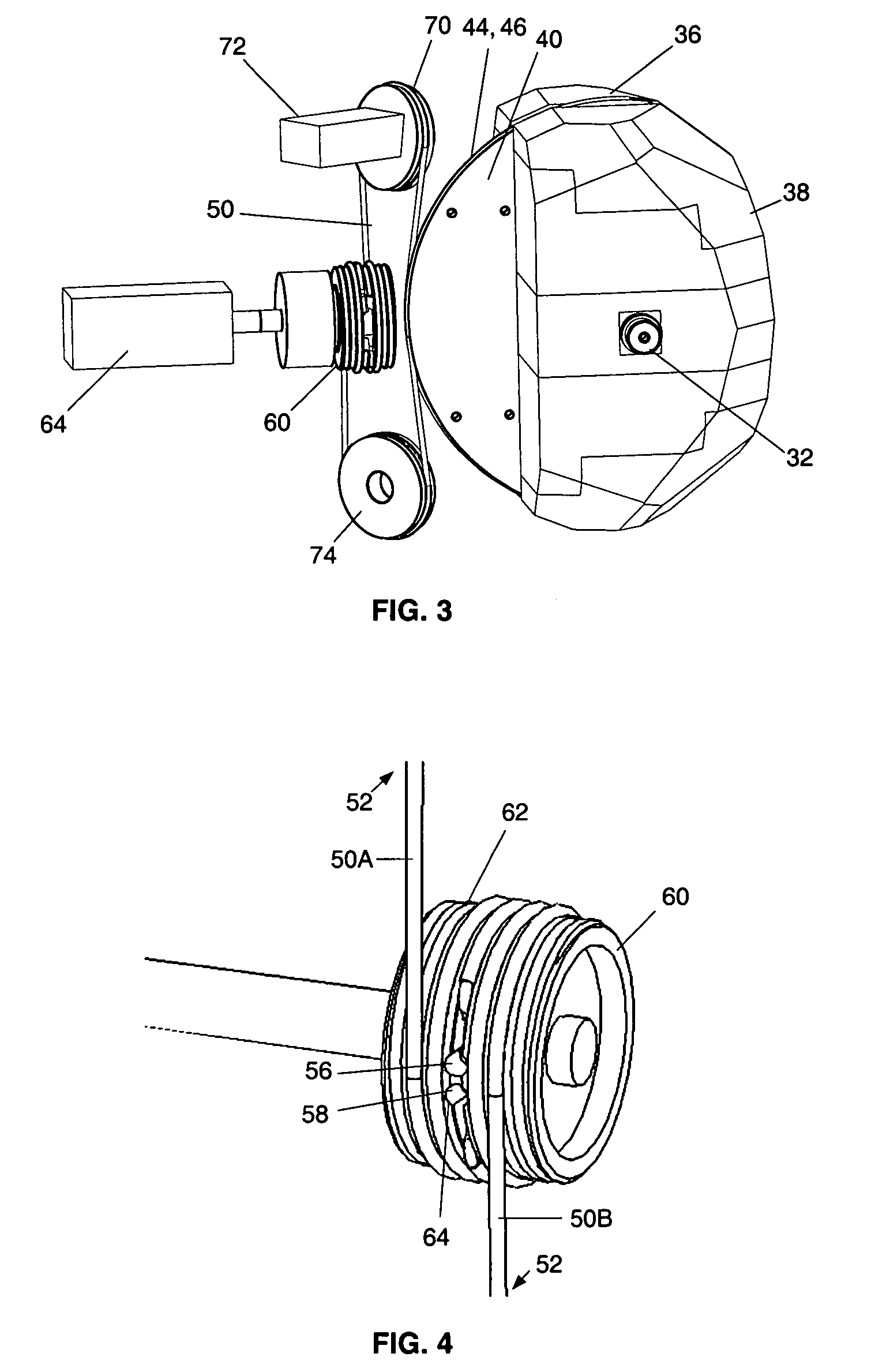
Apparatus for pivotally orienting a projection device
An apparatus that provides for rotation about two axes orthogonal to each other includes a gimbal having two arms adjoining a portion that is mounted to a base for rotation about a first axis. A shaft defining a second axis orthogonal to the first pivotally couples a mounting plate to the arms. The mounting plate has an arcuate edge with first and second parallel grooves therein adapted to receiving a drive cable. A drive cable that is engaged with a drive pulley is aligned by at least one idler pulley with the first and second grooves of the mounting plate. The drive cable has opposing free ends that are received in the first and second grooves of the mounting plate. A motor is coupled to the drive pulley for controlling the drive cable travel, to accordingly rotate the mounting plate to provide for orientating a device in a desired direction.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
Optoelectronic emitter mounted on a slider
InactiveUS20080002298A1Combination recordingFluid-dynamic spacing of headsEngineeringOpto electronic
An apparatus comprising a slider including a slider substrate with a trailing side and a writer with bond pads disposed on the trailing side. The writer has an optic input for receiving an optic output. The apparatus comprises an optoelectronic substrate having a substrate surface facing the trailing side, and having contacts on the substrate surface that are joined to the bond pads by conductive bridges, and having an optoelectronic emitter adjacent the substrate surface for generating the optic output.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
System, method and apparatus for flexure-integrated microactuator
ActiveUS20090244786A1Overcome costsOvercomes manufacturabilityDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageTrack densityHard disc drive
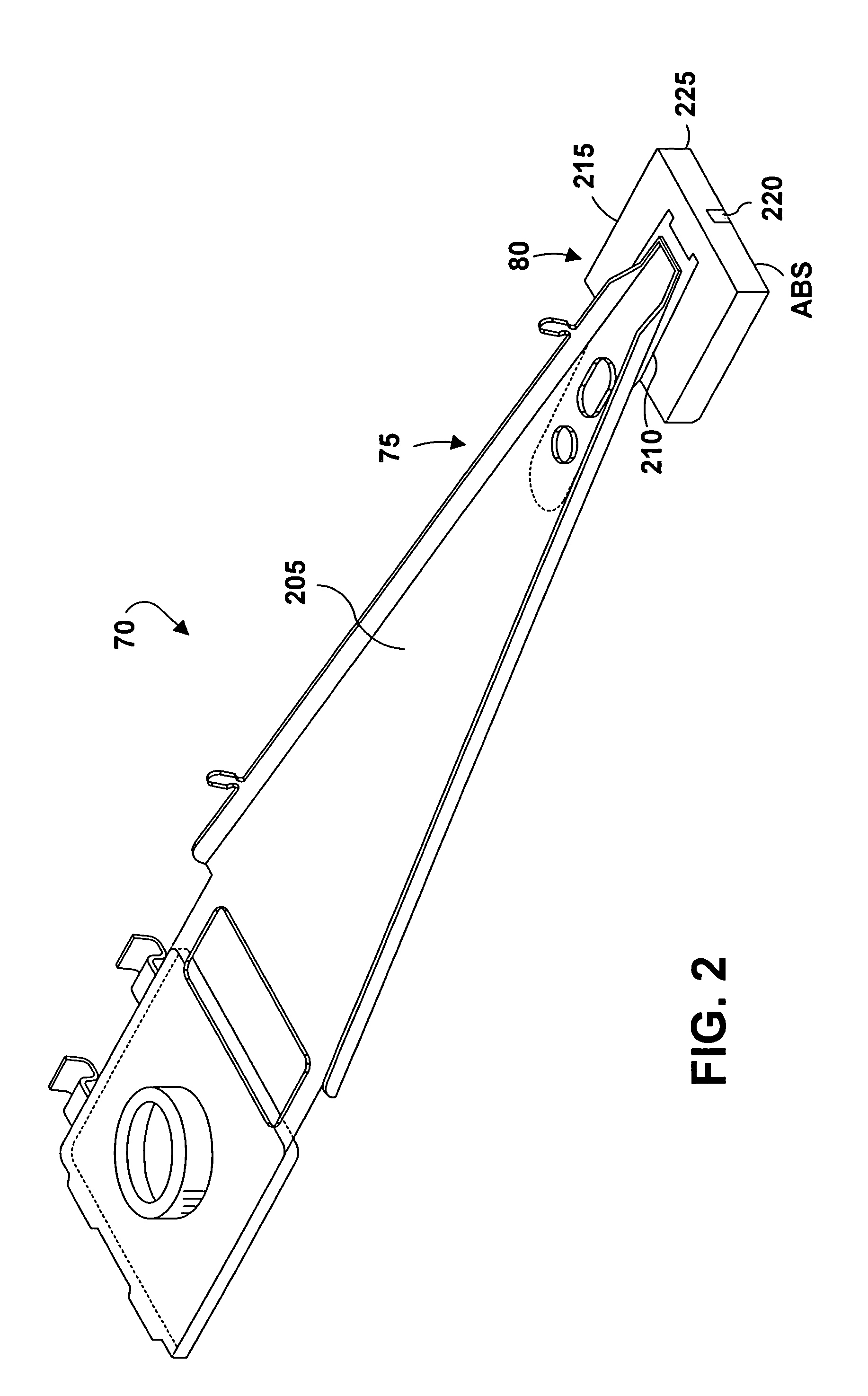
A piezo in-tongue microactuator includes a suspension assembly with a flexure tongue. The tongue has two slots that accept piezo actuators. The tongue also has multiple hinge flexible elements that translate the extension and / or contraction of the piezo actuators into rotary motion of the recording head. This rotary motion is then used to precisely position the recording element over the desired track on the hard disk drive and permits higher track density to be achieved.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
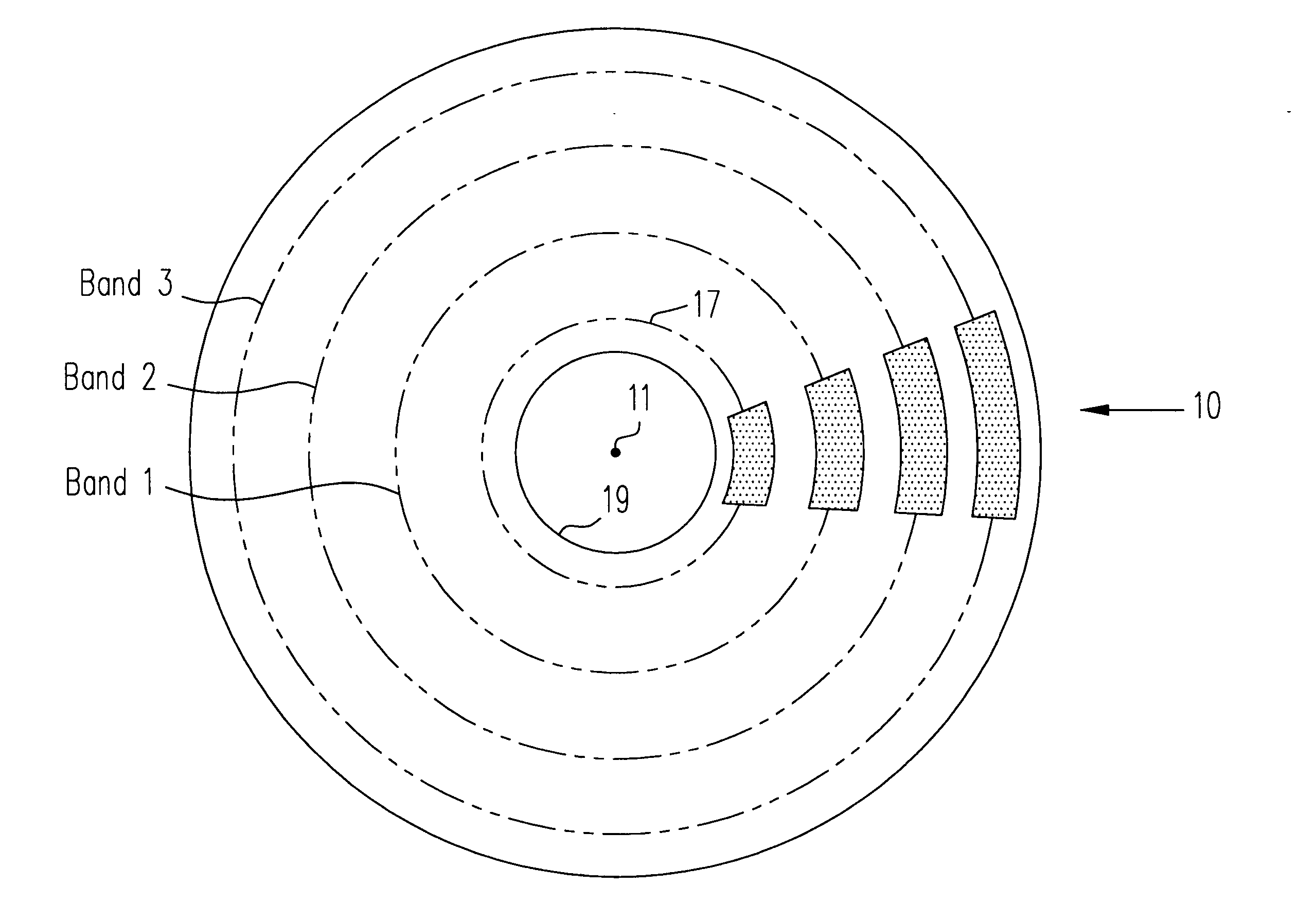
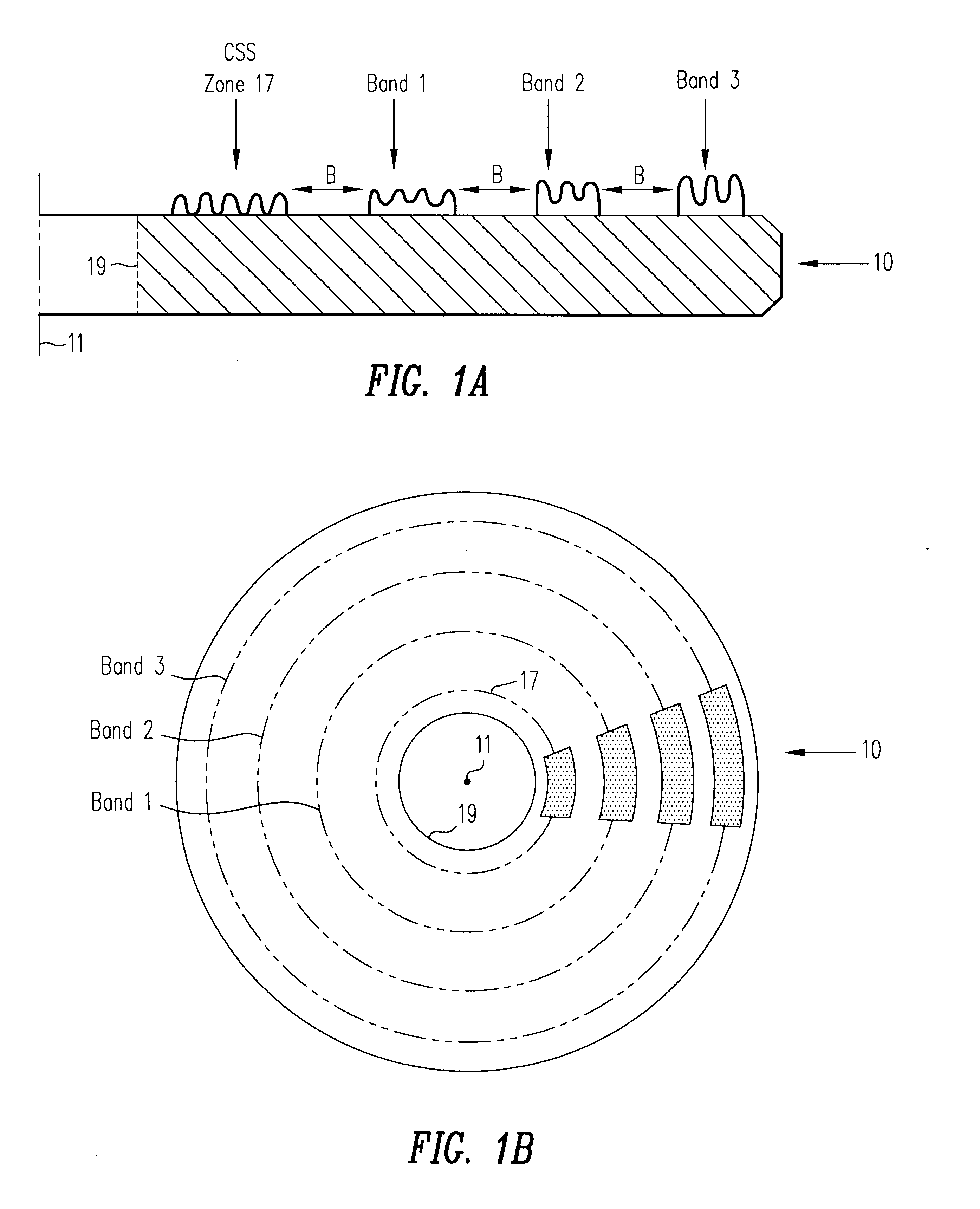
Calibration disk having discrete bands of composite roughness
InactiveUS6408677B1Carrier indicating/warning arrangementsRecord information storageEngineeringFlying height
A calibration disk includes calibration areas that allow a glide head to be calibrated as to the glide's head's avalanche height, fly height and the like. The calibration areas may be, for example, configured in a circumferential band (or, alternatively, a series of circumferential bands extending substantially concentric to one another), one or more spiral bands or some other suitable configuration. Such bands can, for example, extend from adjacent an outer diameter of the calibration disk to adjacent an inner portion of the calibration disk. Each of the circumferential bands is a textured area on the calibration disk having a given degree of composite roughness, as measured by the given circumferential band's average composite roughness height, and as such is referred to herein as a calibration band. Preferably, the given circumferential band is textured in a uniform manner, sufficient to produce a constant and continuous output signal from a sensor mounted on a glide head when the glide head flies lower than a maximum composite roughness height. Also preferably, the average composite roughness height within an individual calibration band is substantially uniform, and the average composite roughness height of each calibration band is slightly different from that of the other calibration bands.
Owner:KOMAG CORP
Plated ground features for integrated lead suspensions
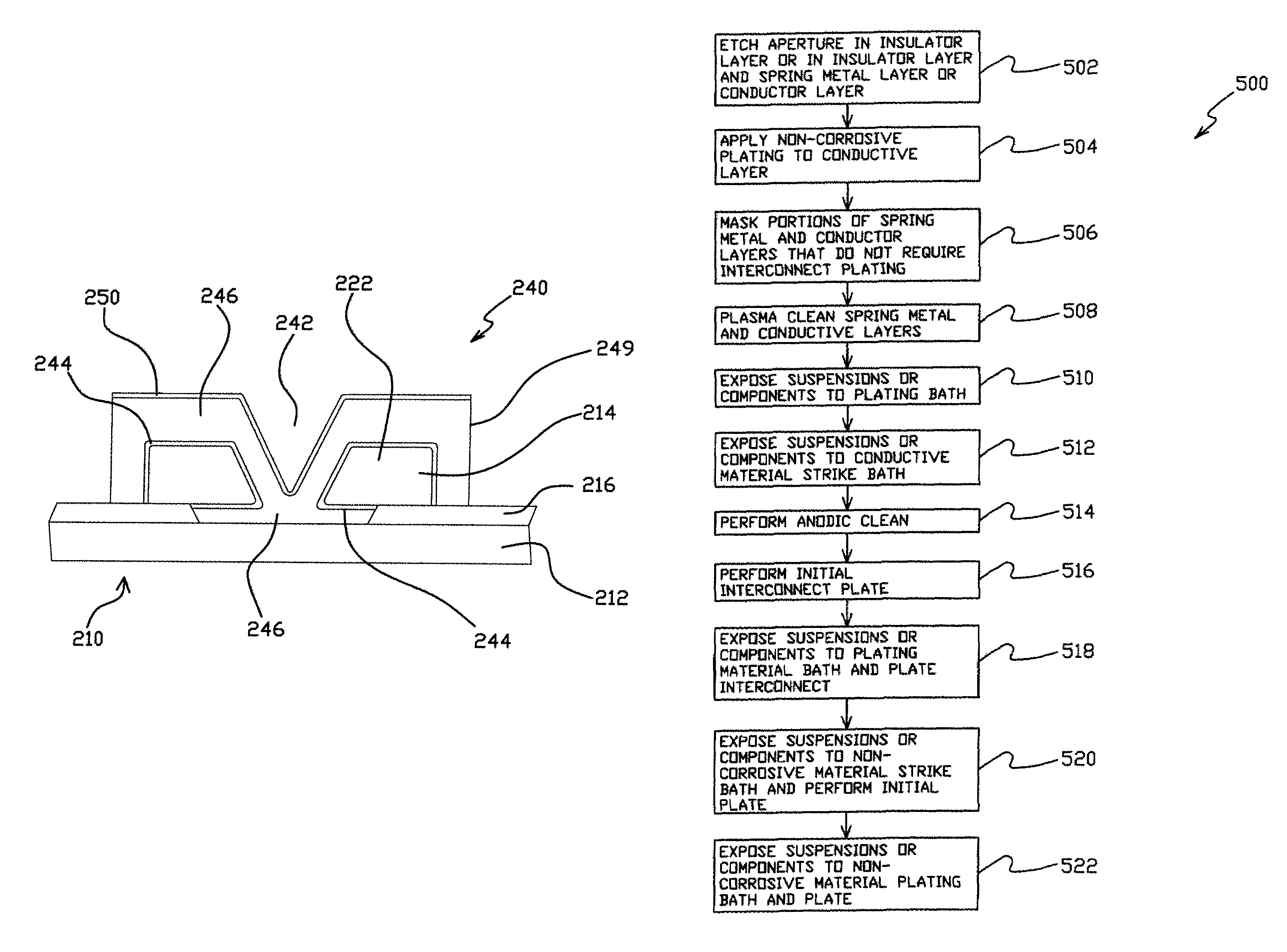
ActiveUS7384531B1Quality improvementAnodisationElectrical connection between head and armConductive materialsElectroplating
A method for forming an electrical interconnect on an integrated lead suspension or suspension component of the type formed from a laminated sheet of material having a stainless steel layer, a conductive lead layer and an insulating layer separating the stainless steel and conductive lead layers. An aperture is formed through at least the insulating layer to expose the stainless steel layer at an interconnect site. An interconnect mask is applied around the interconnect site. Conductive material is electroplated onto the stainless steel layer at the interconnect site to form a plated interconnect. The mask is then removed. The method is used to form an interconnect bond pad on the same side of the stainless steel layer as the conductive lead layer in one embodiment. In another embodiment the aperture is formed through the insulator layer and the stainless steel layer, and conductive material is built up on the stainless steel layer during the electroplating step until it meets and plates onto the conductive lead layer to form a stainless steel side interconnect. In yet another embodiment the aperture is formed through the insulator layer and the conductive lead layer, and conductive material is built up on the stainless steel layer during the electroplating step until it meets and plates onto the conductive lead layer to form a conductive lead side interconnect.
Owner:HUTCHINSON TECH
Popular searches
Analogue recording Record carrier guidance Support for heads Maintaining head carrier alignment Disposition/mounting of heads Heads with metal sheet cores Heads for perpendicular magnetisations Non-conductive material with dispersed conductive material Heads using thin films Manufacture of flux-sensitive heads
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com