Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
44 results about "Piezoelectric microactuator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
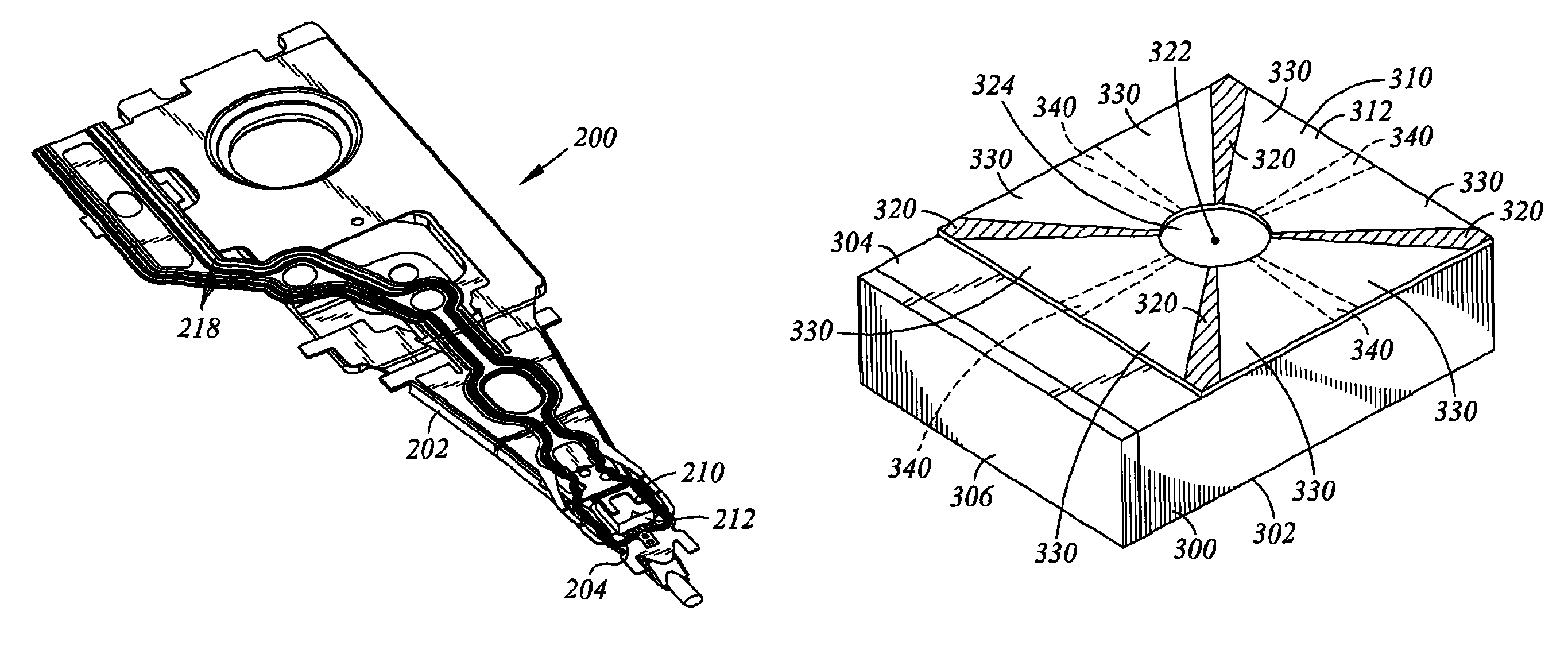
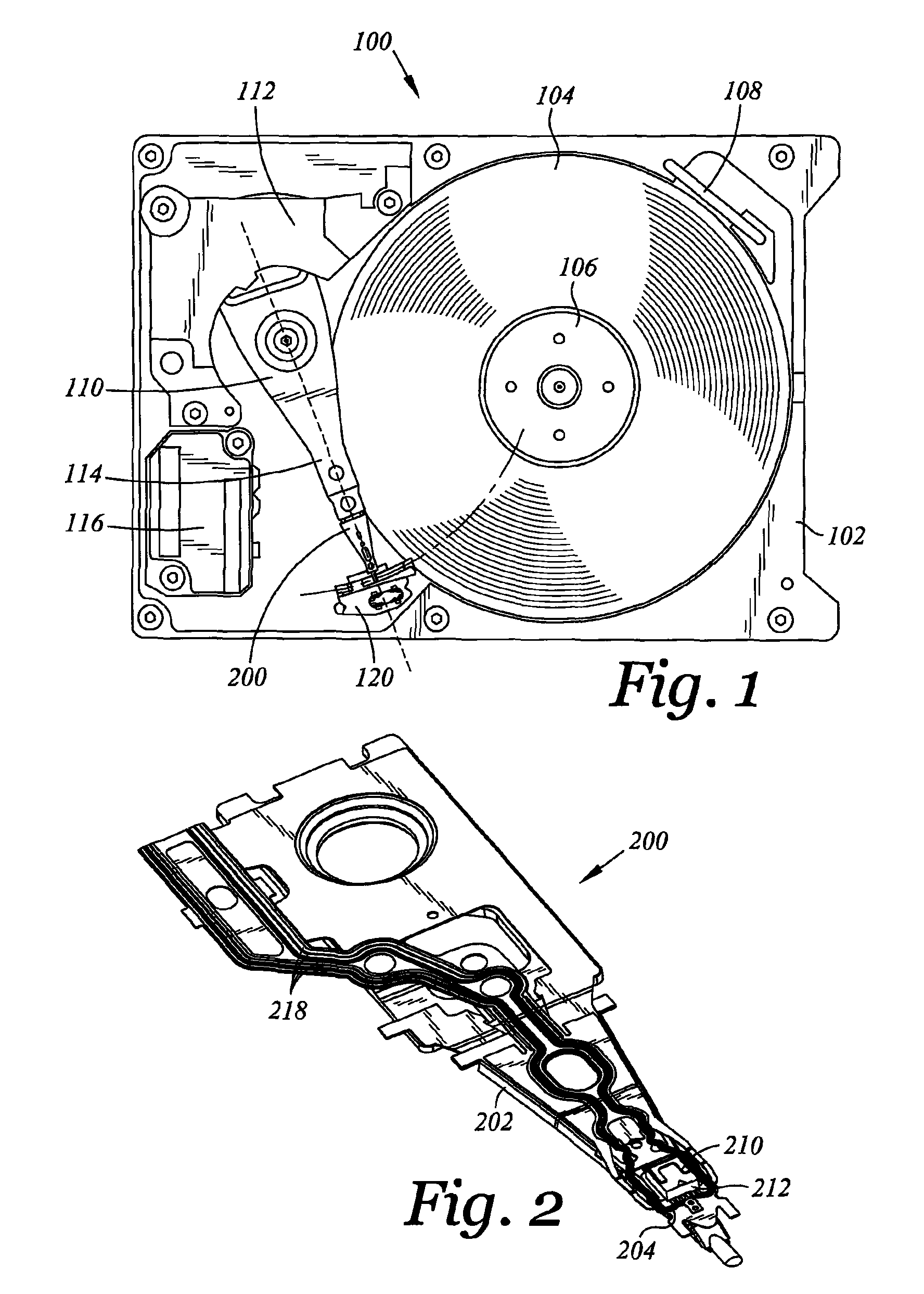
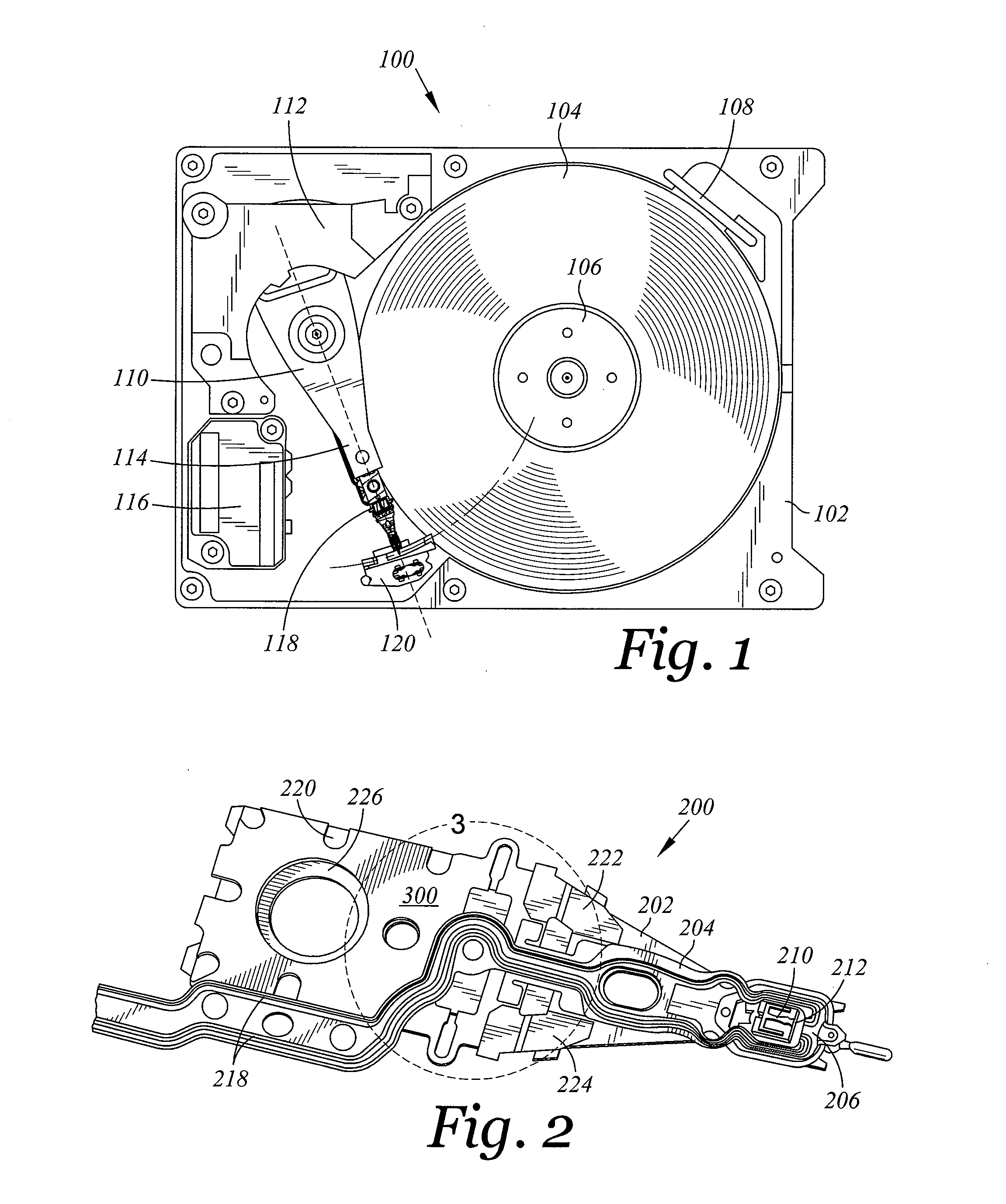
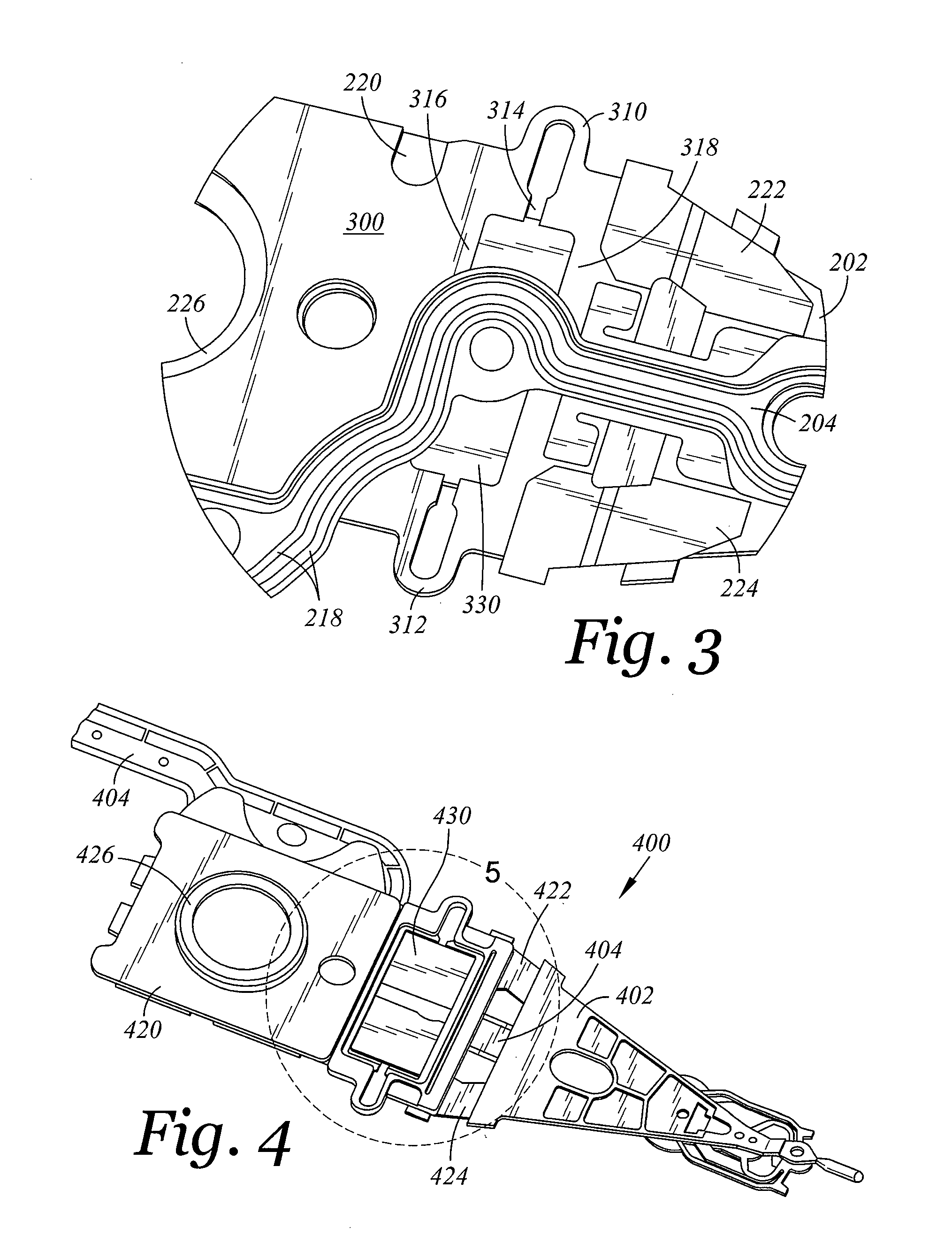
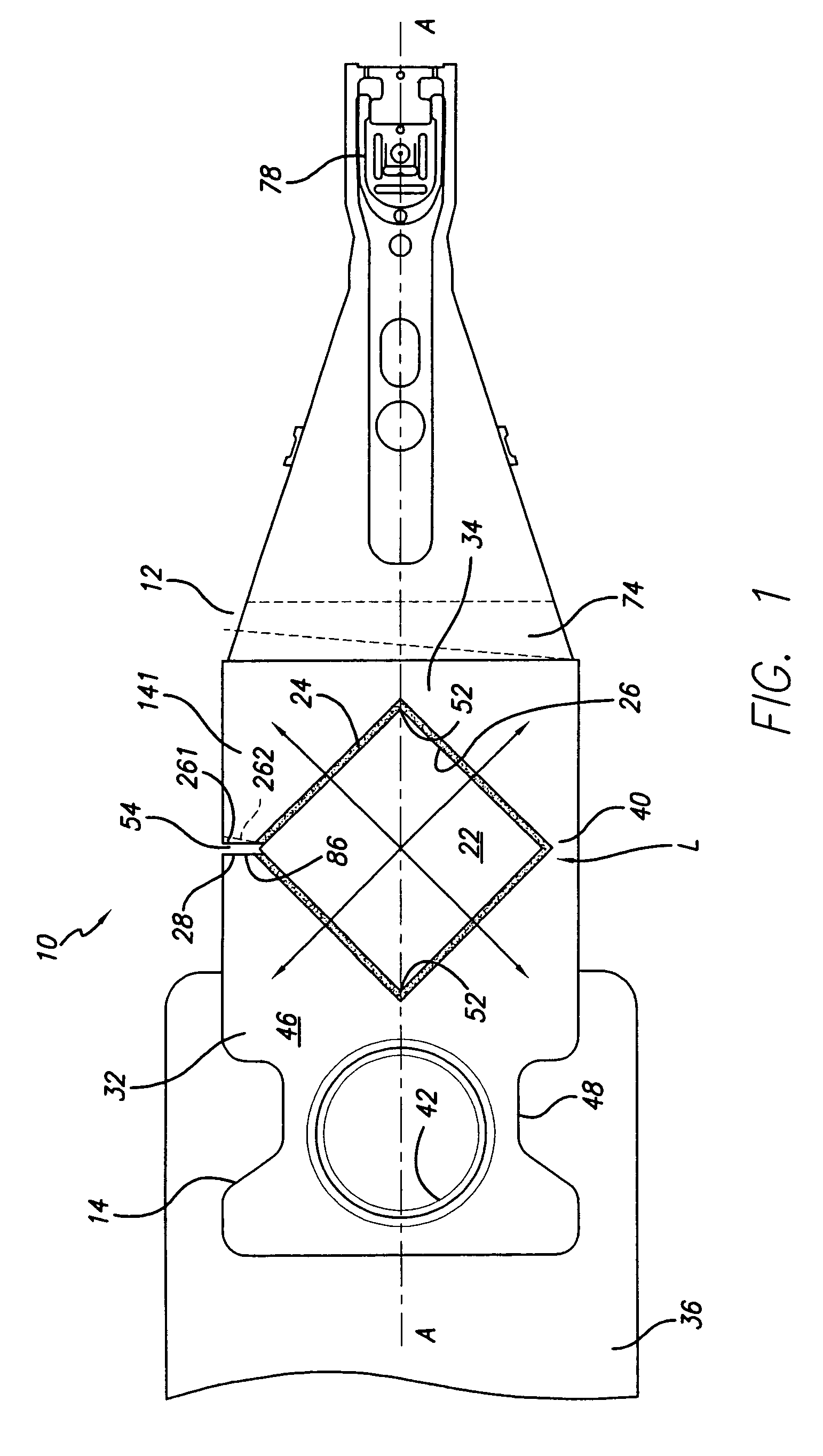
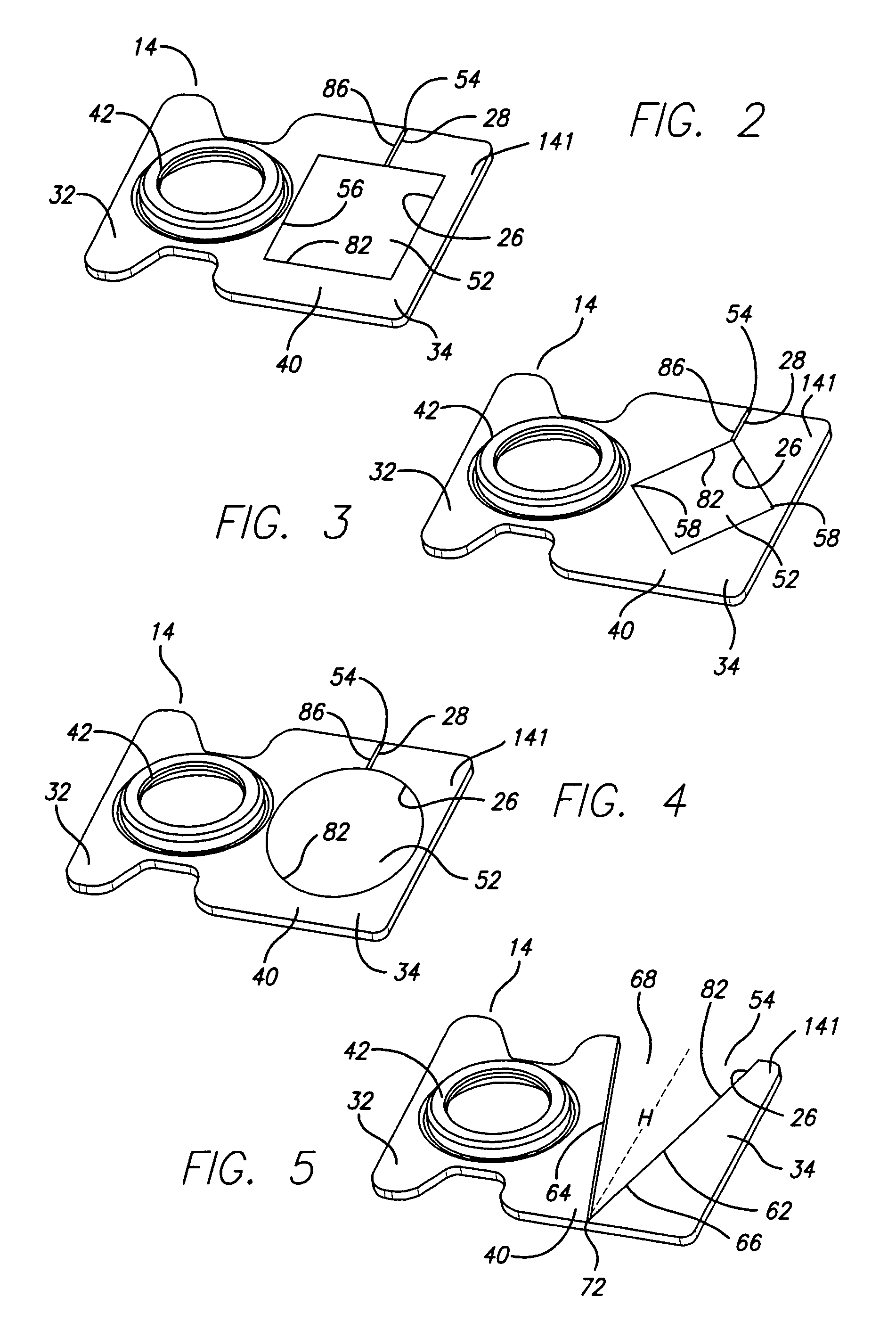
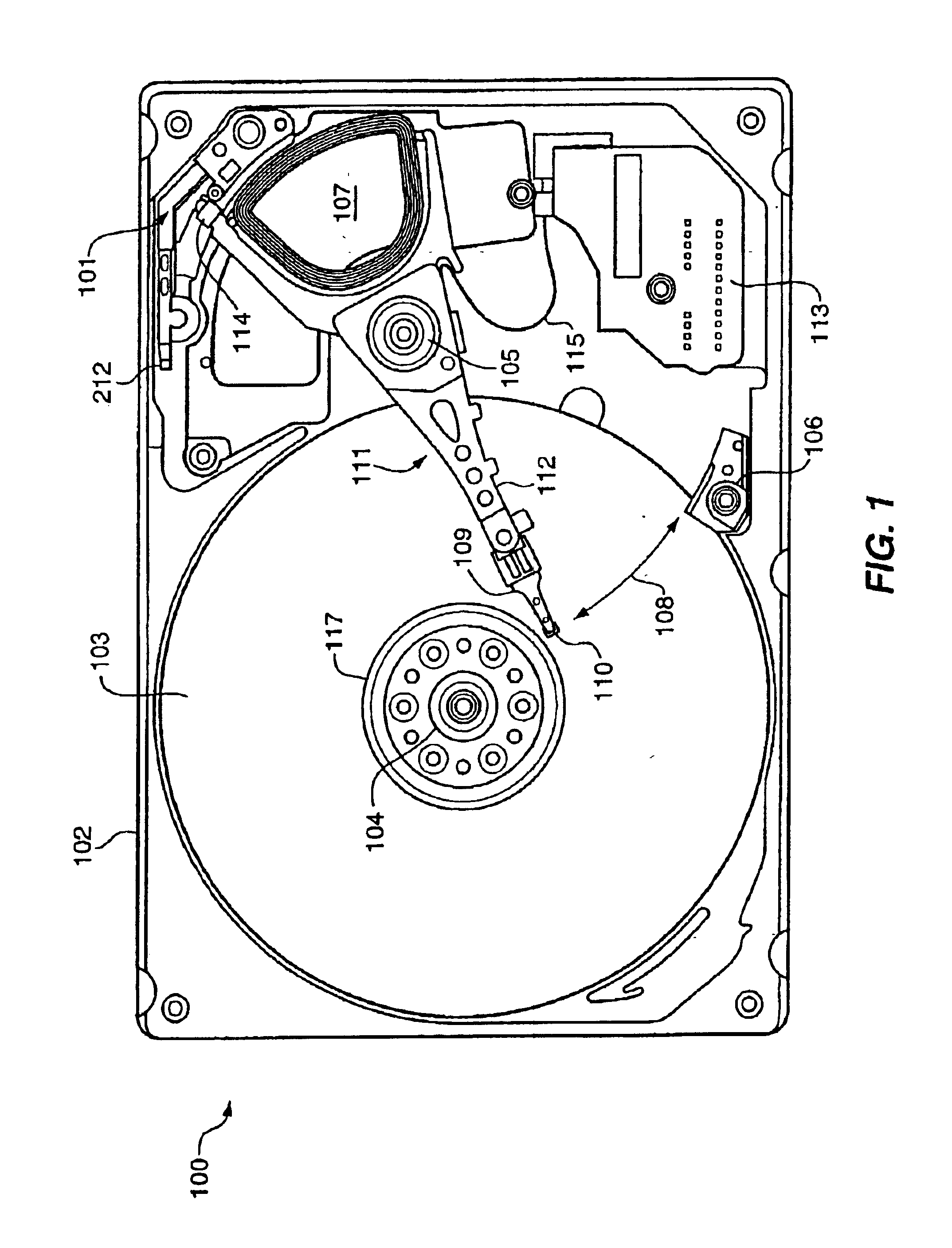
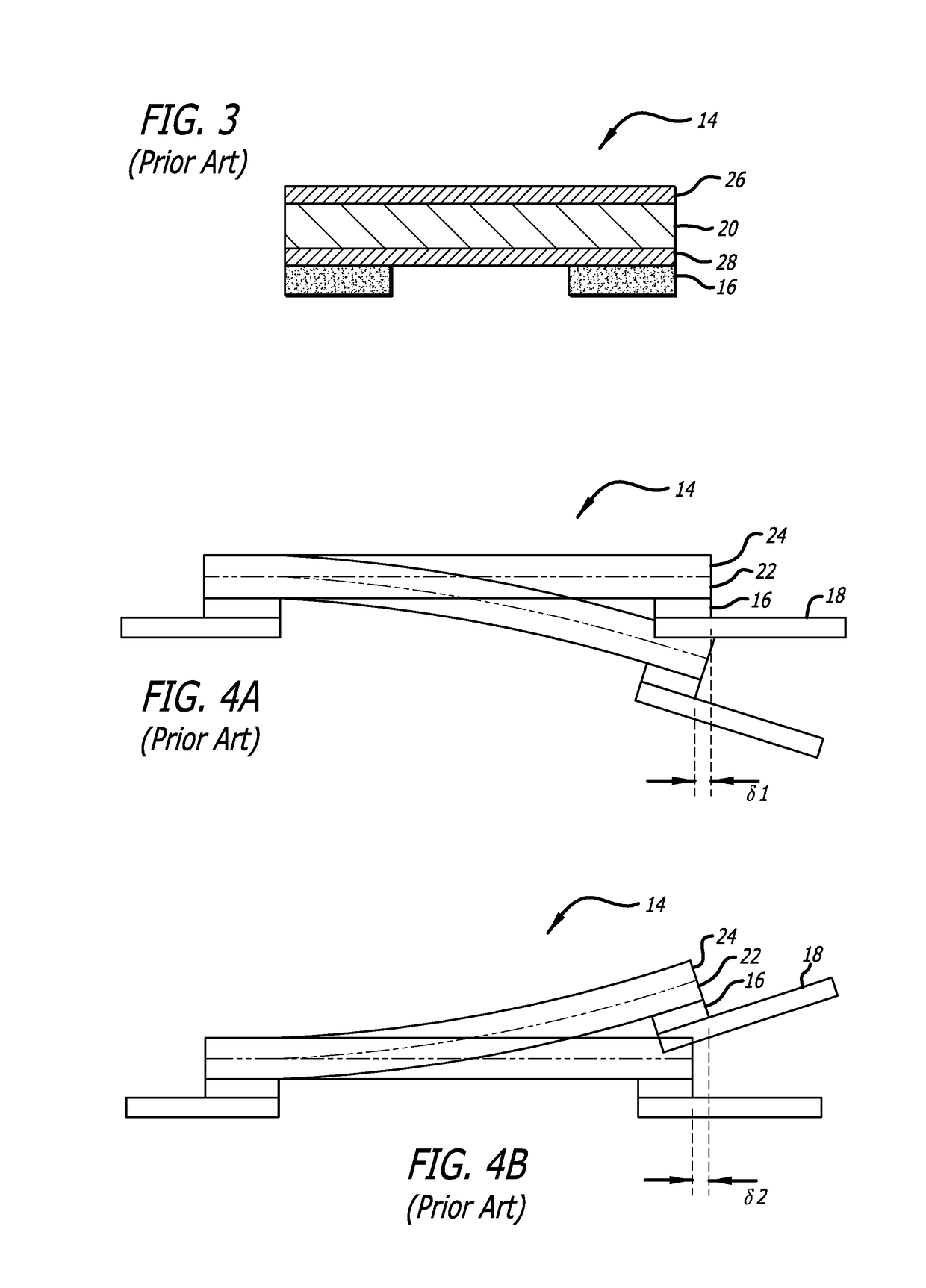
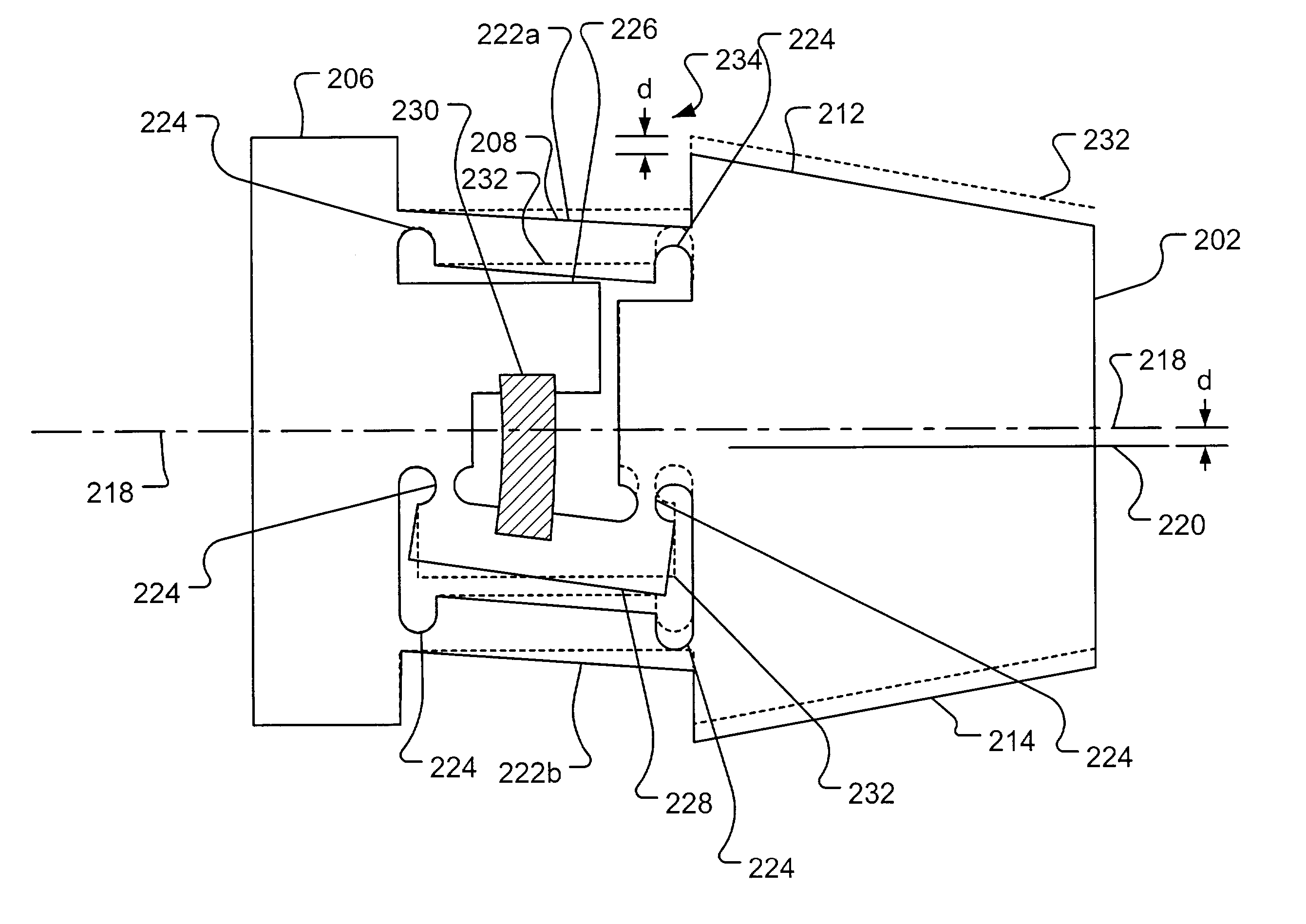
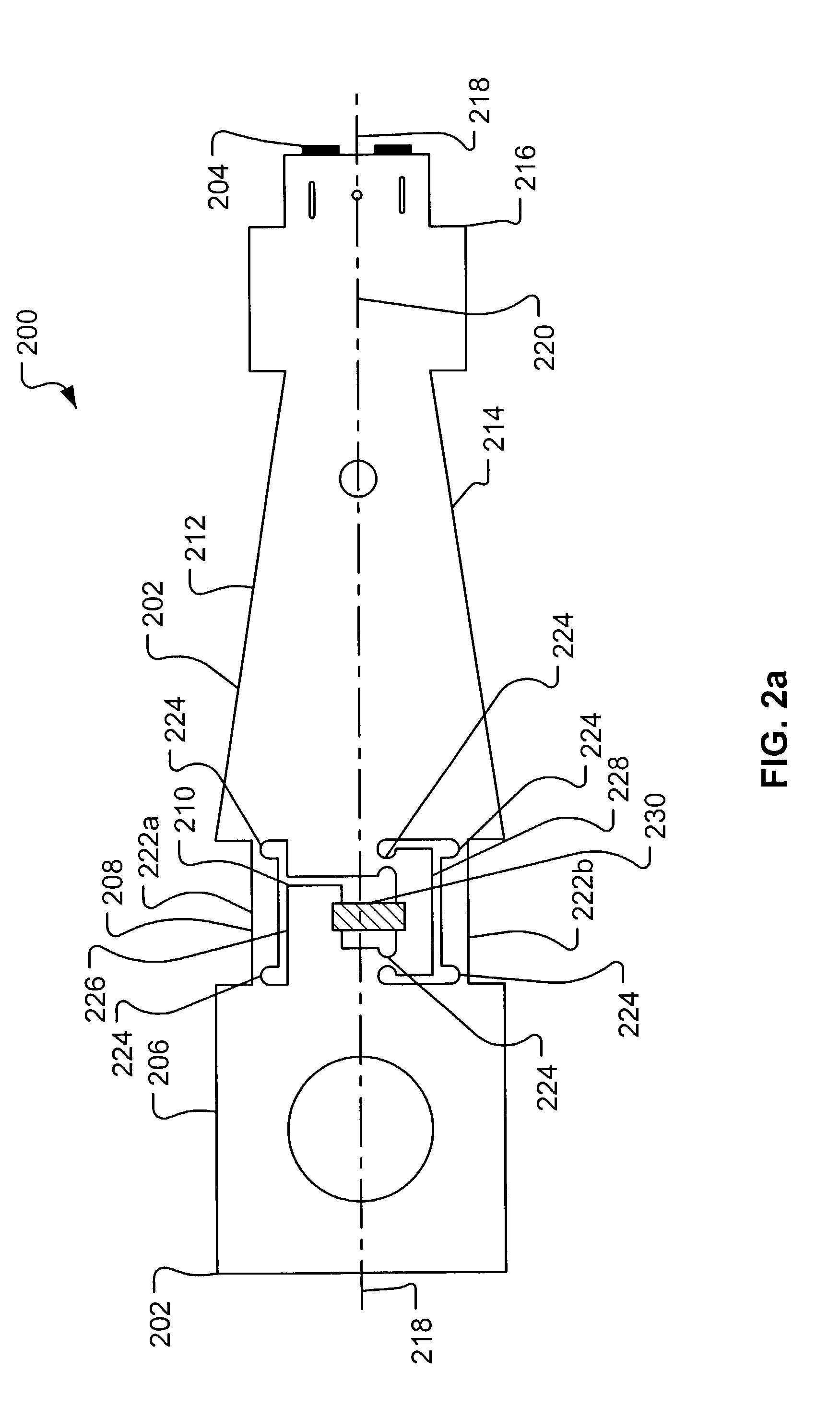
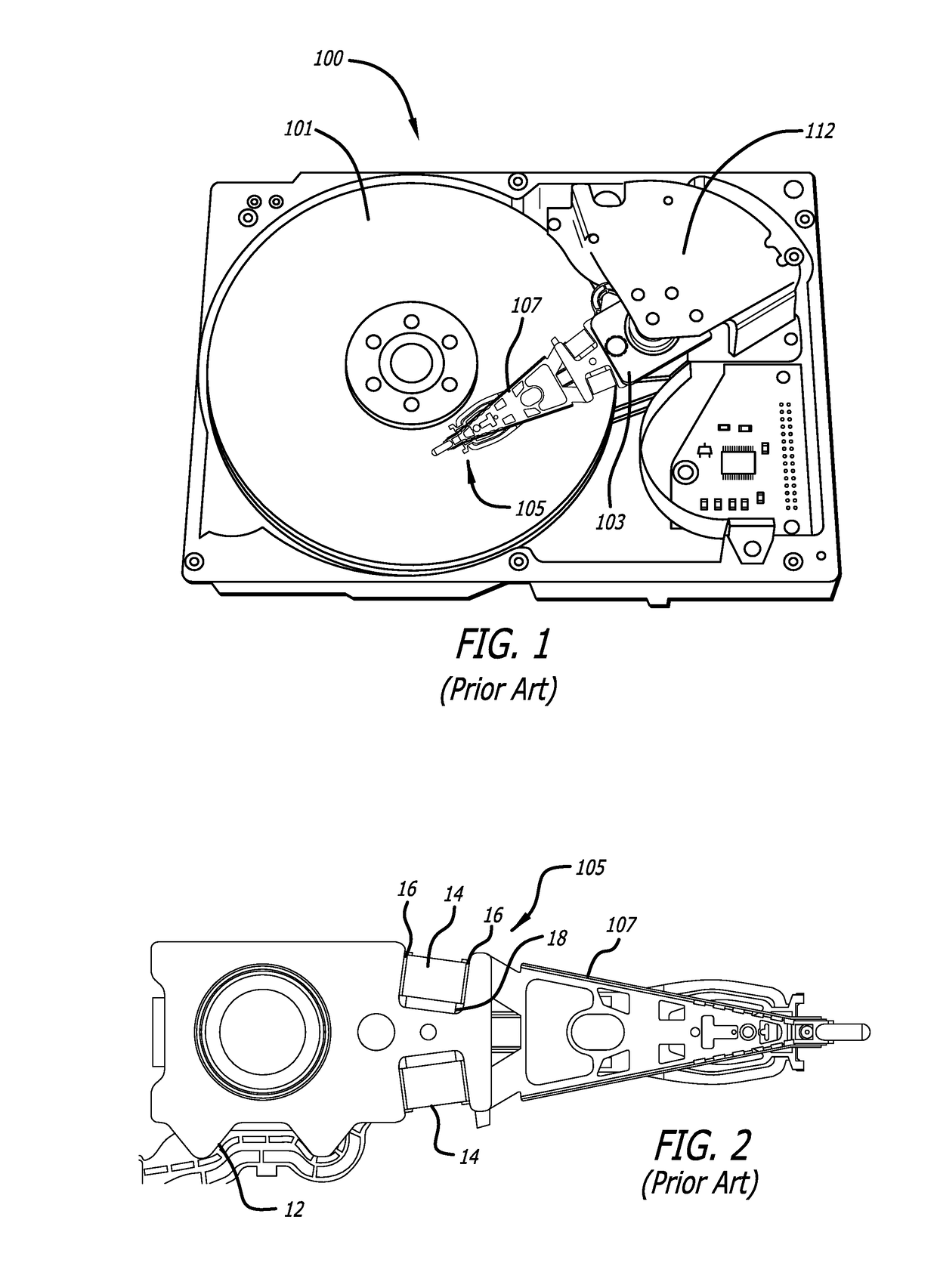
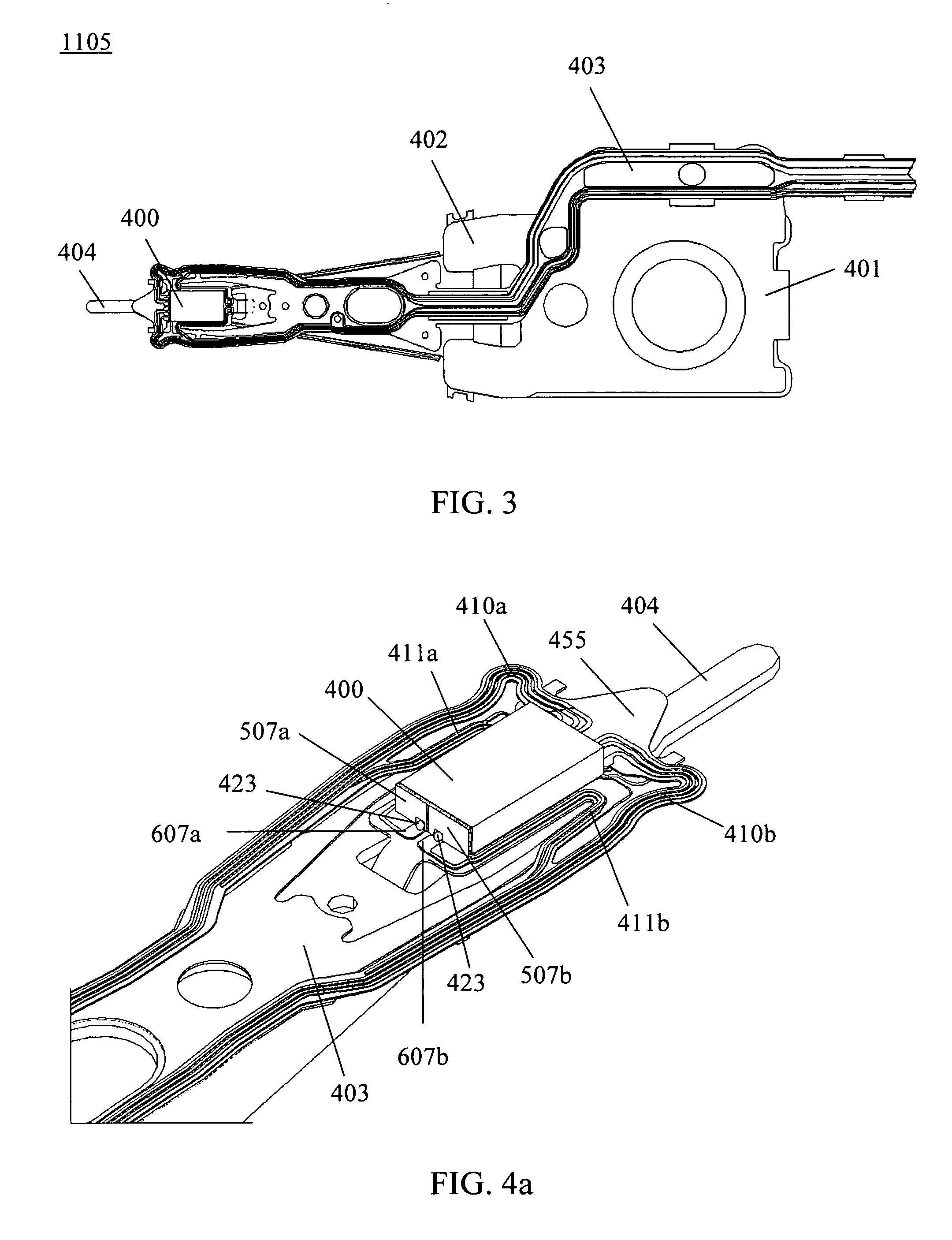
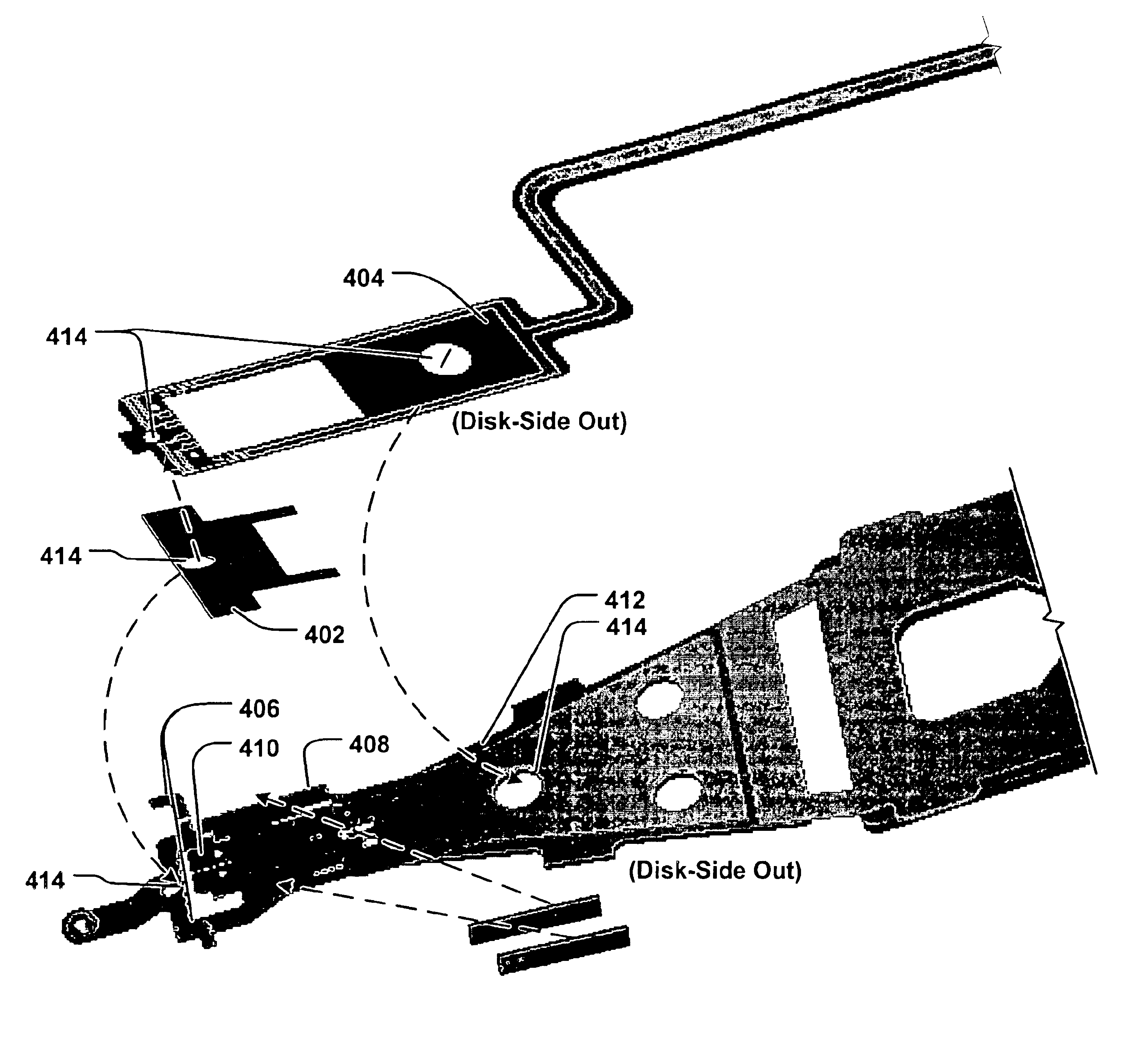
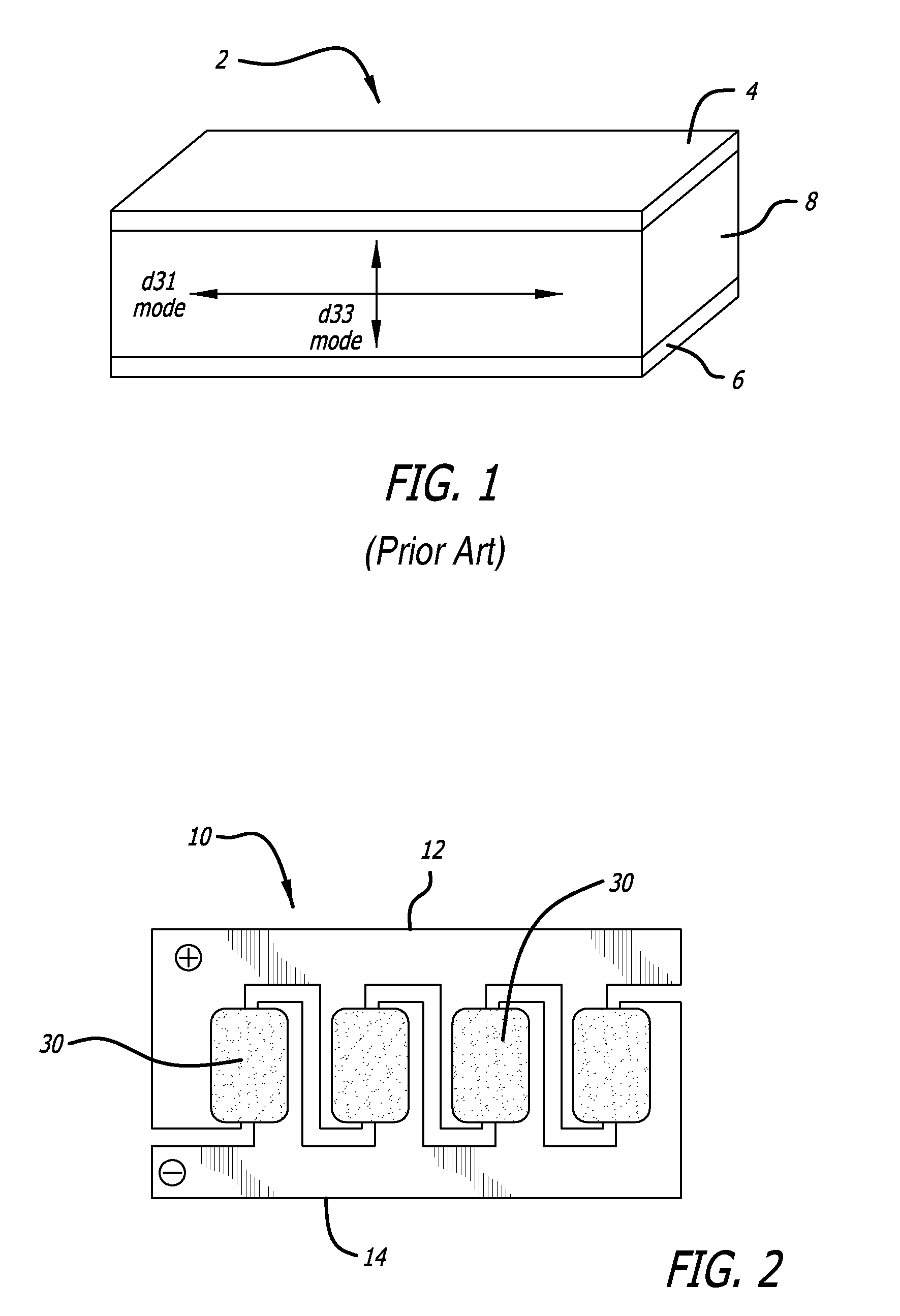
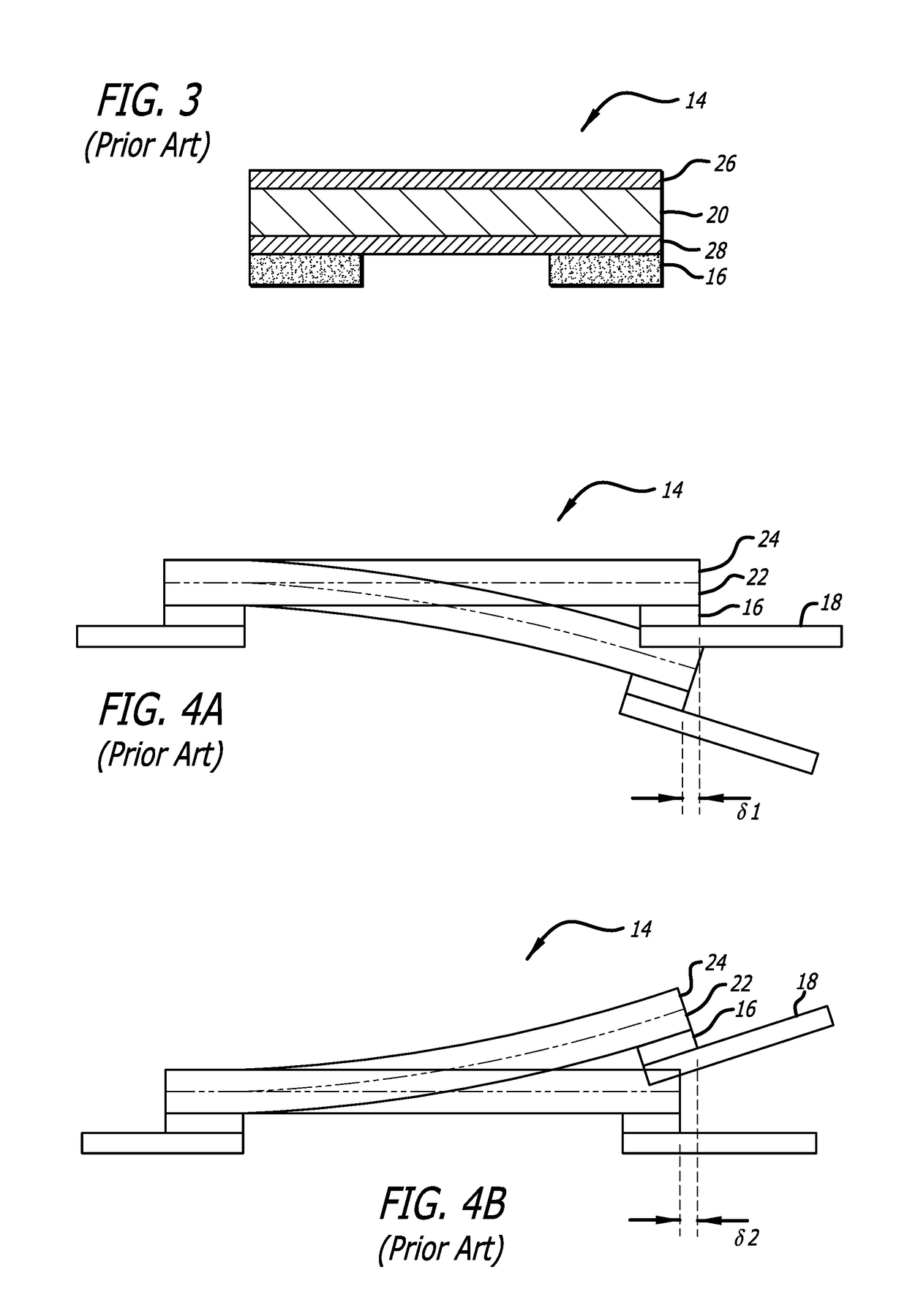
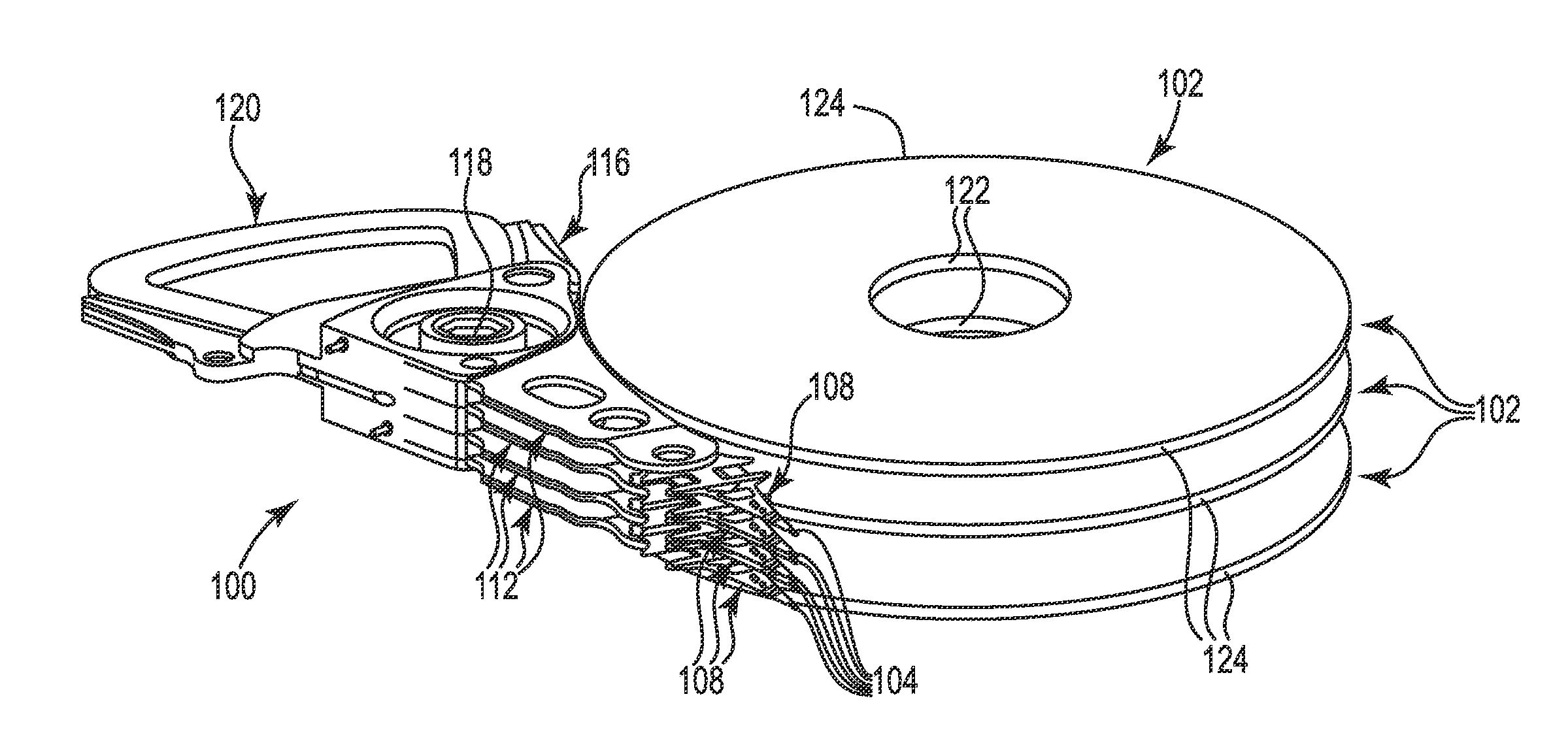
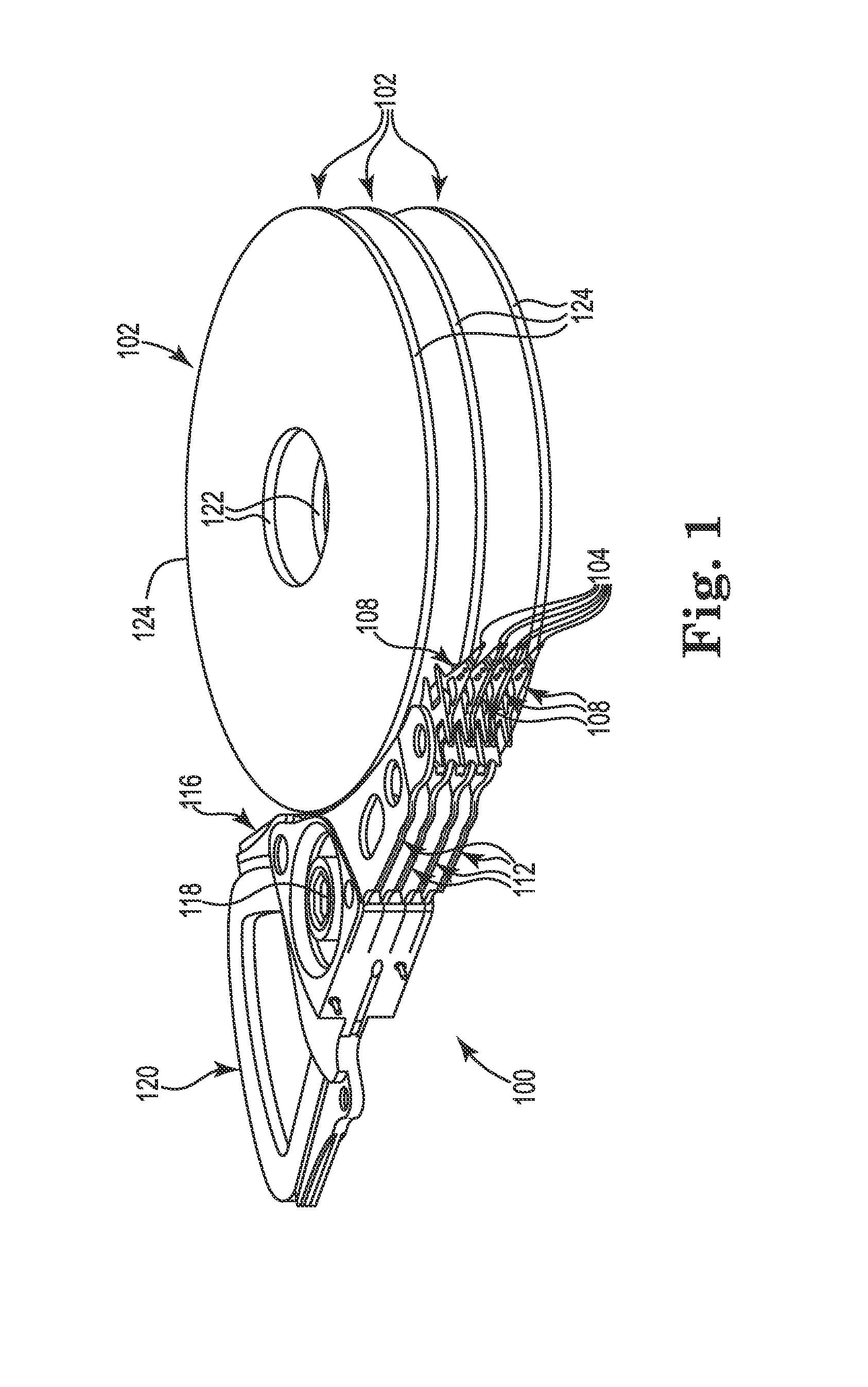
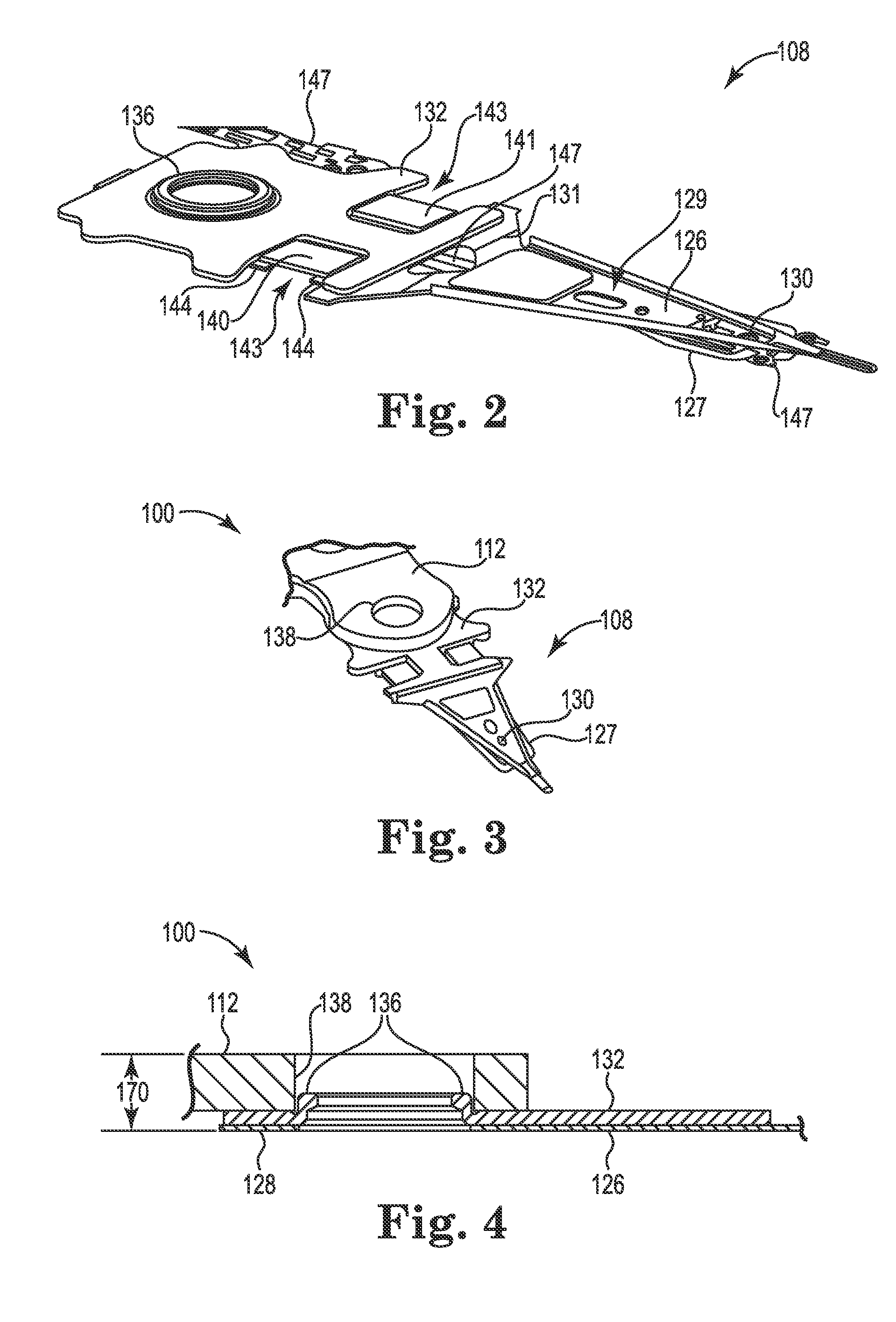
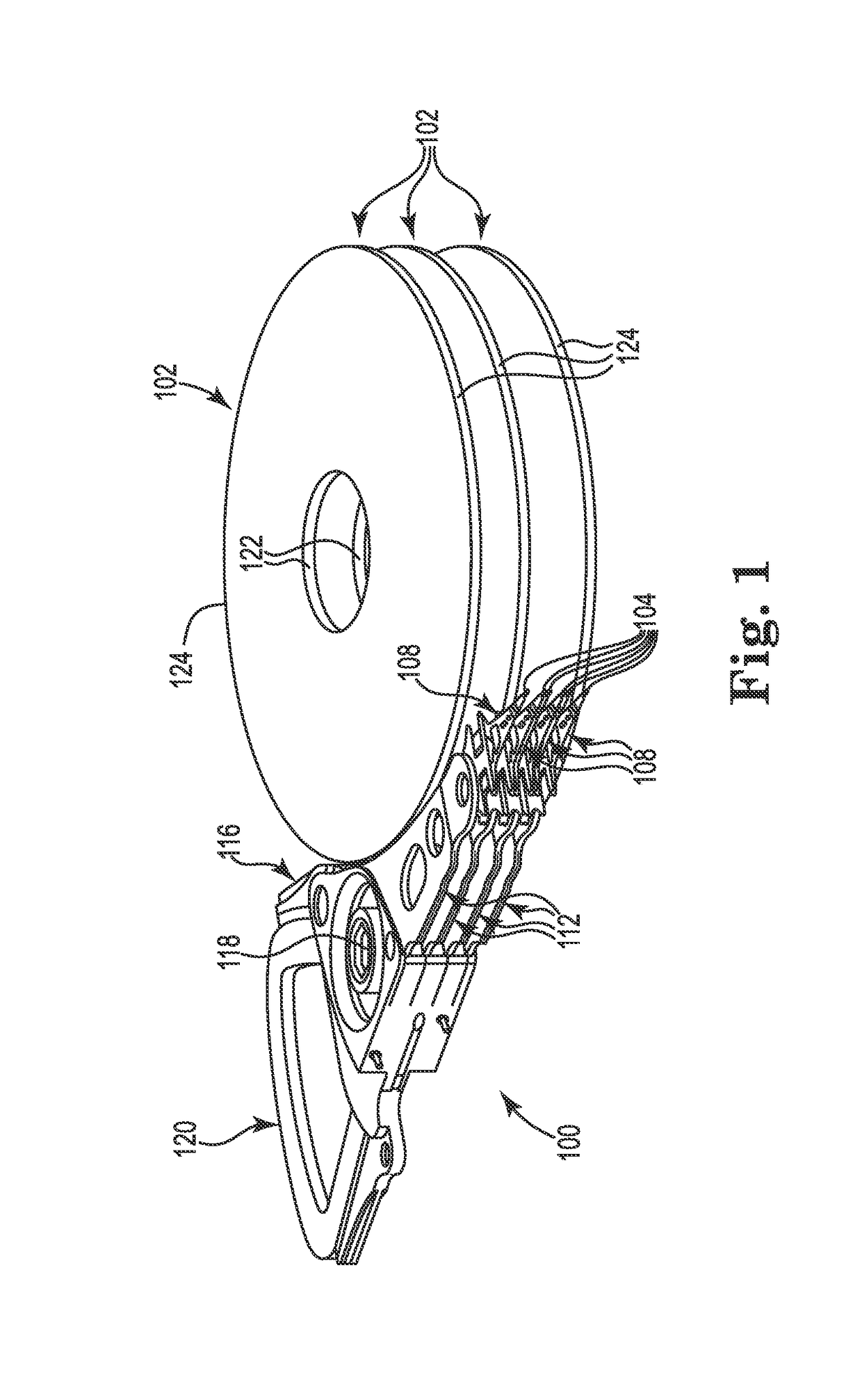
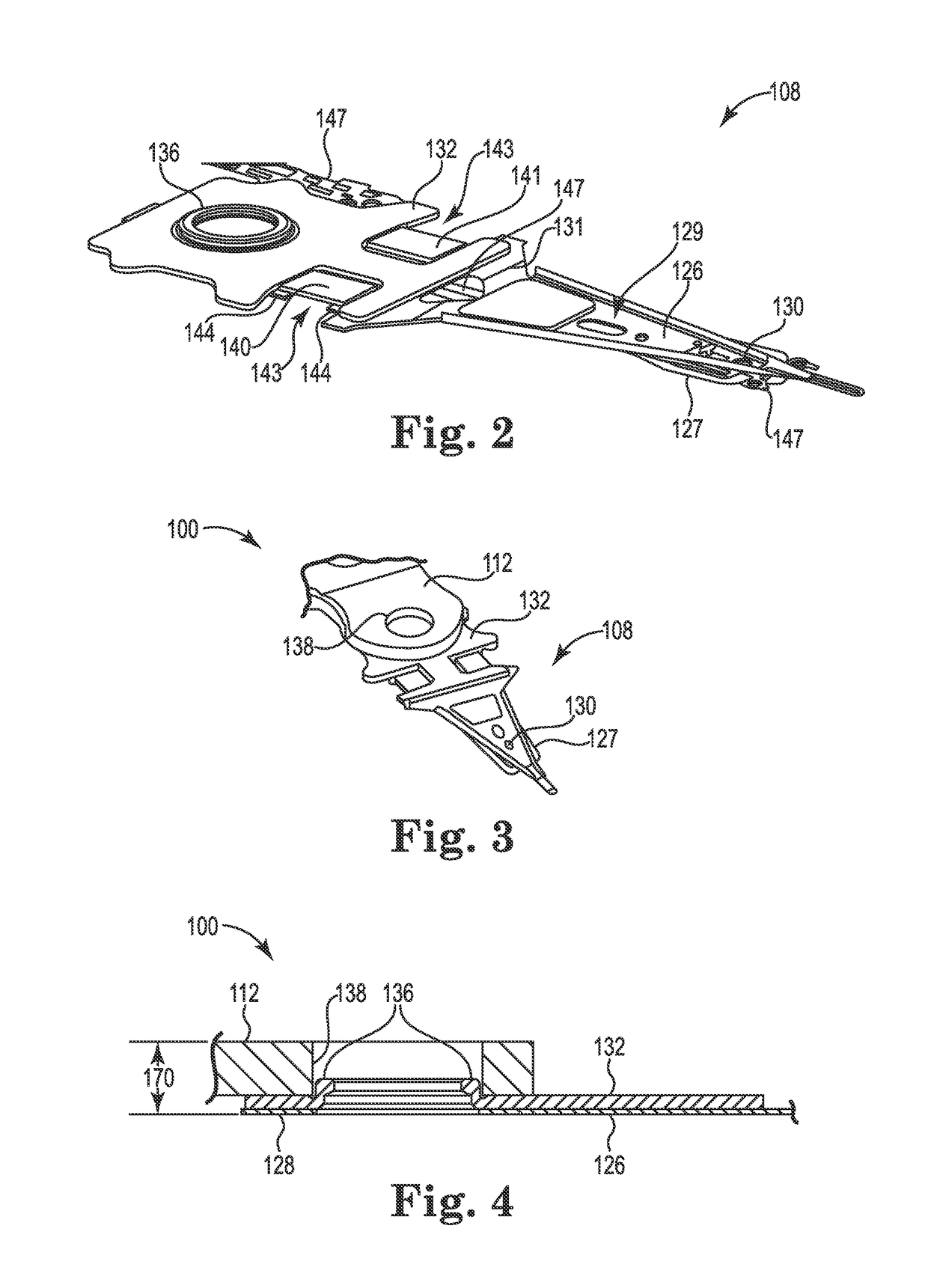
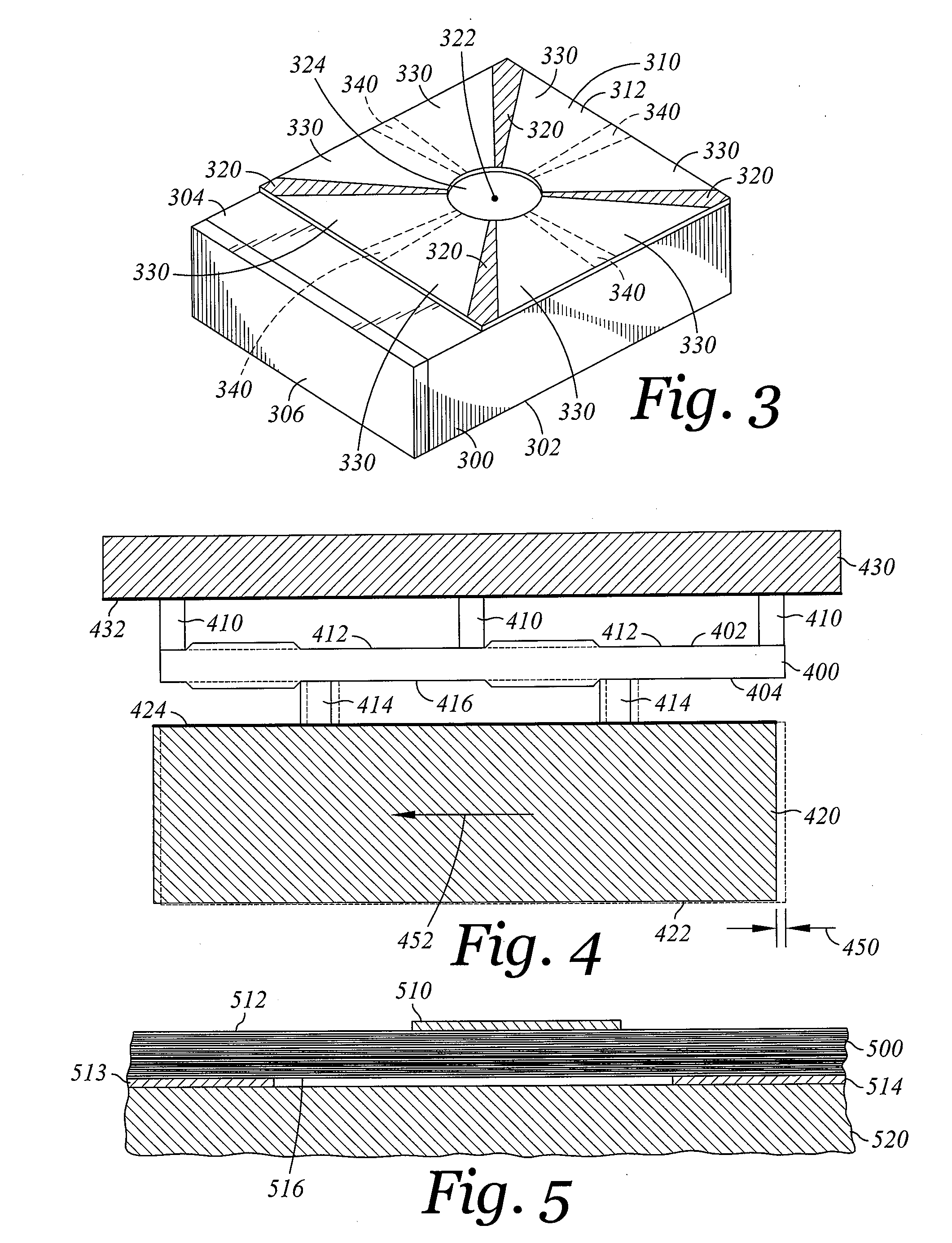
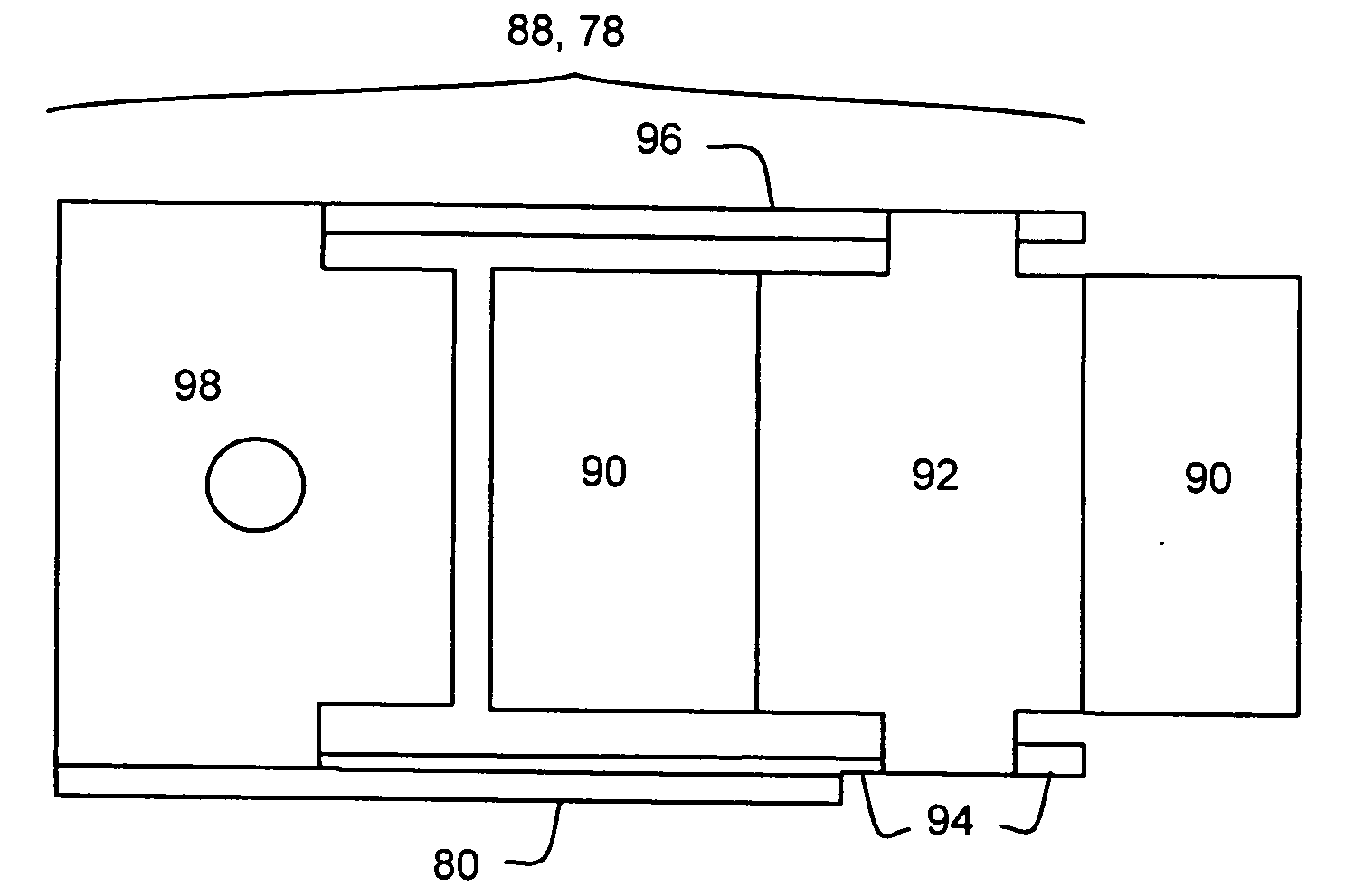
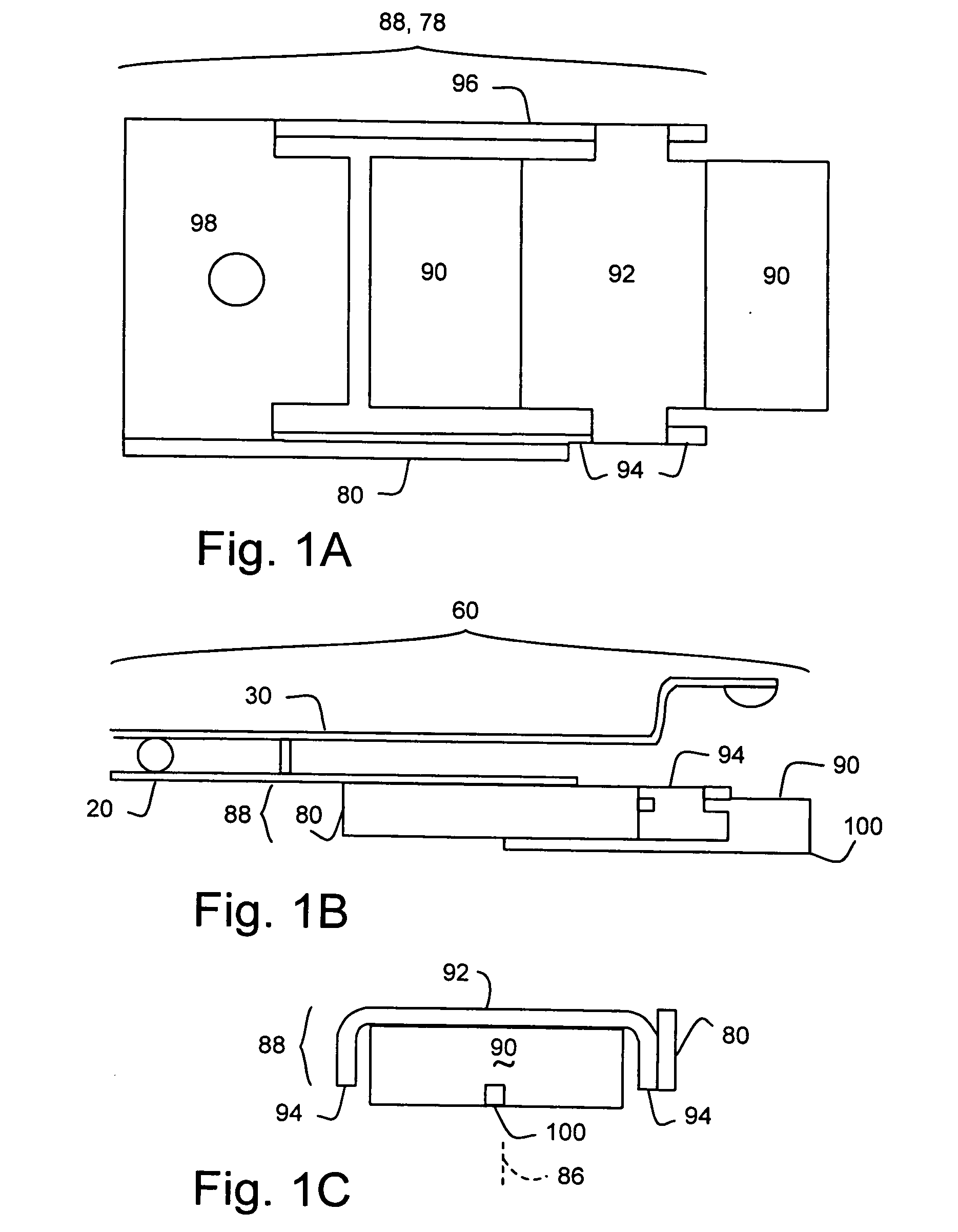
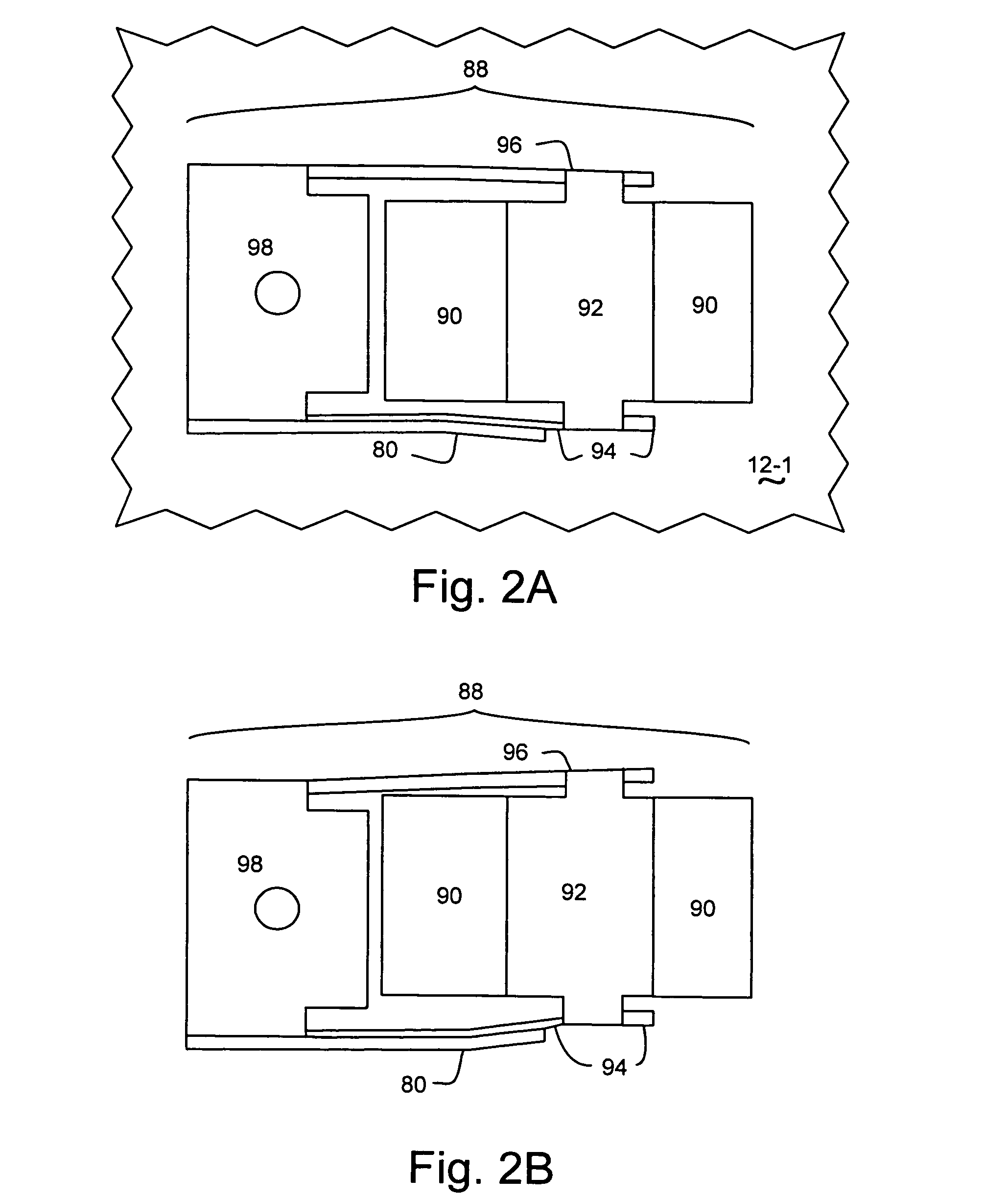
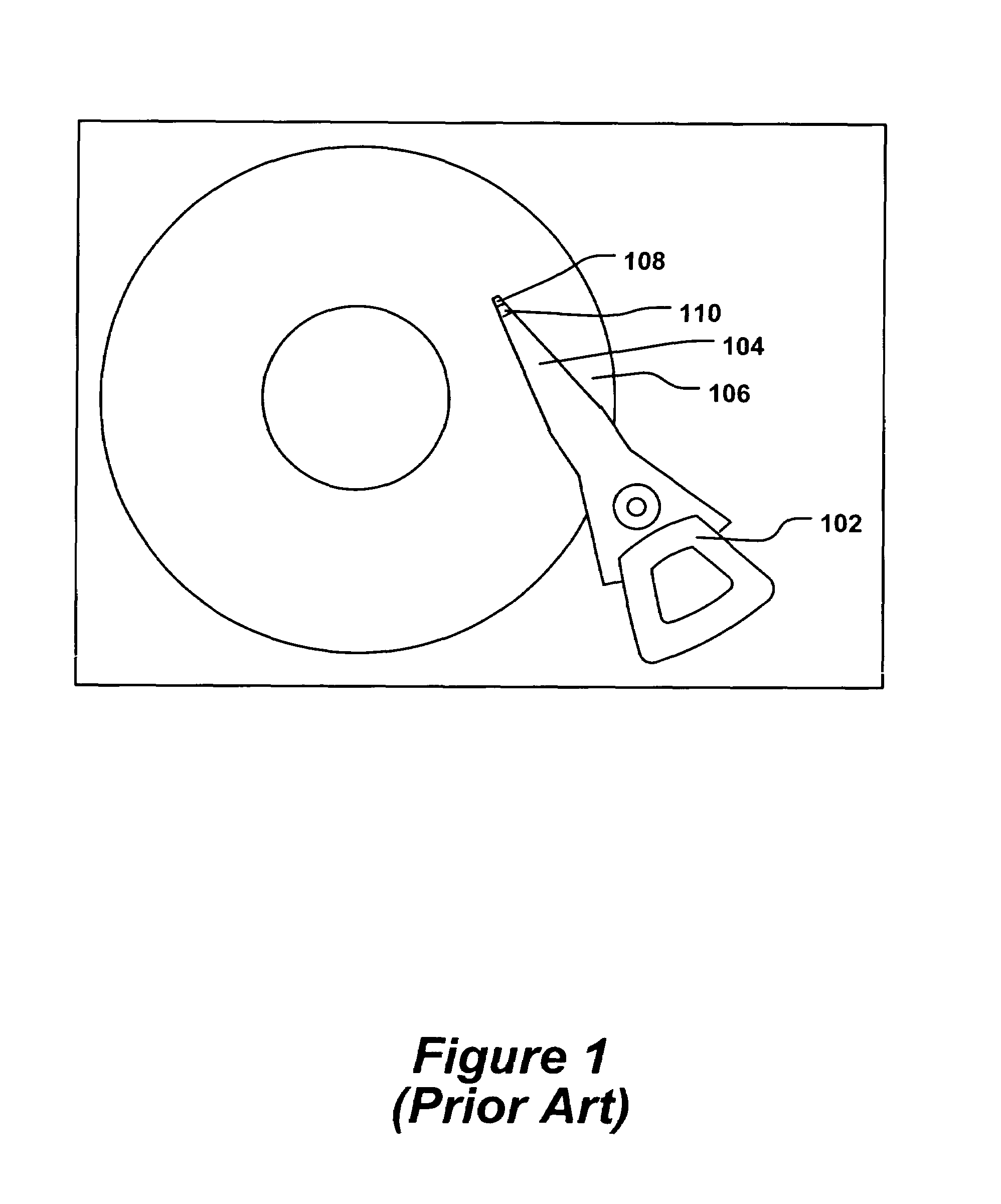
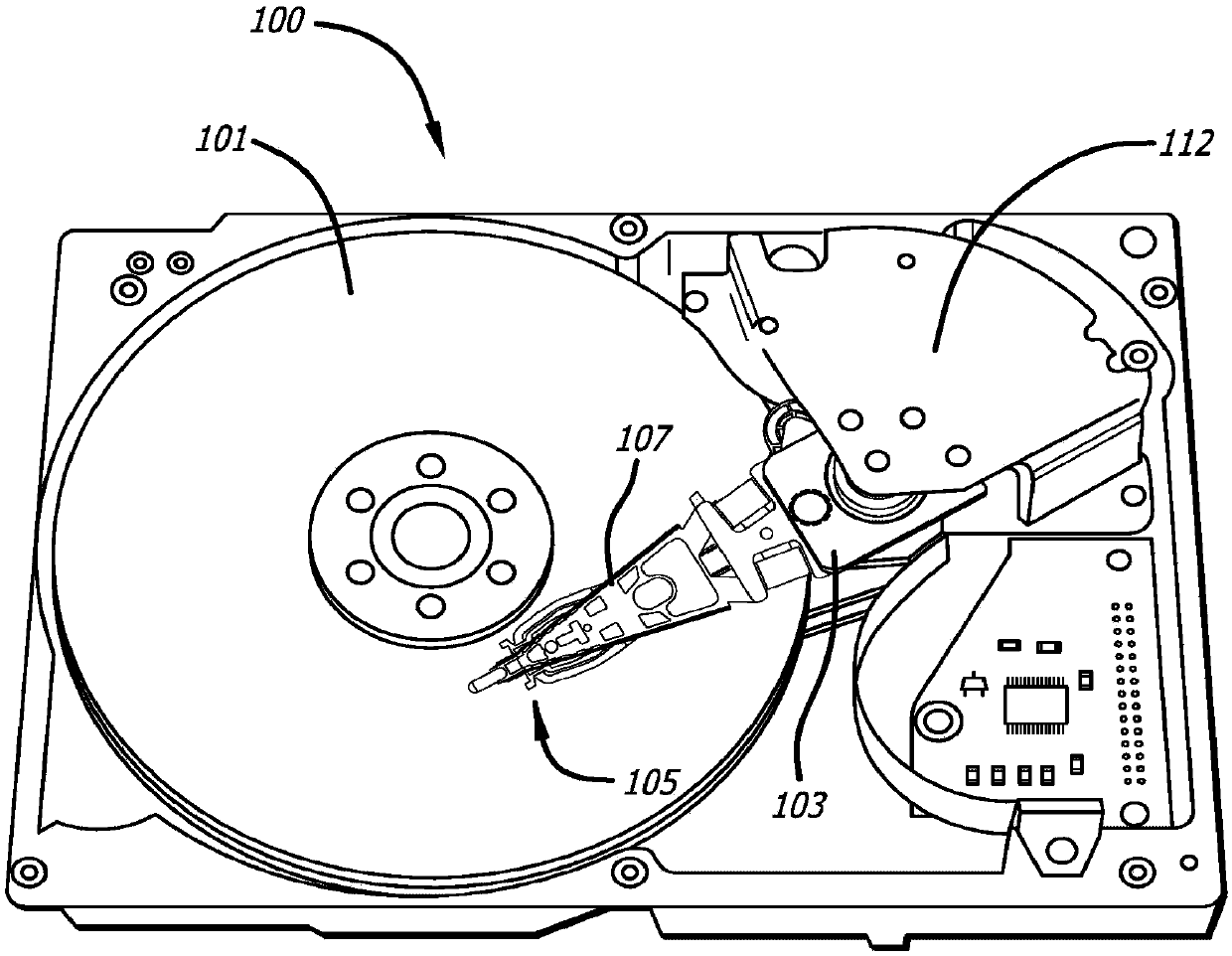
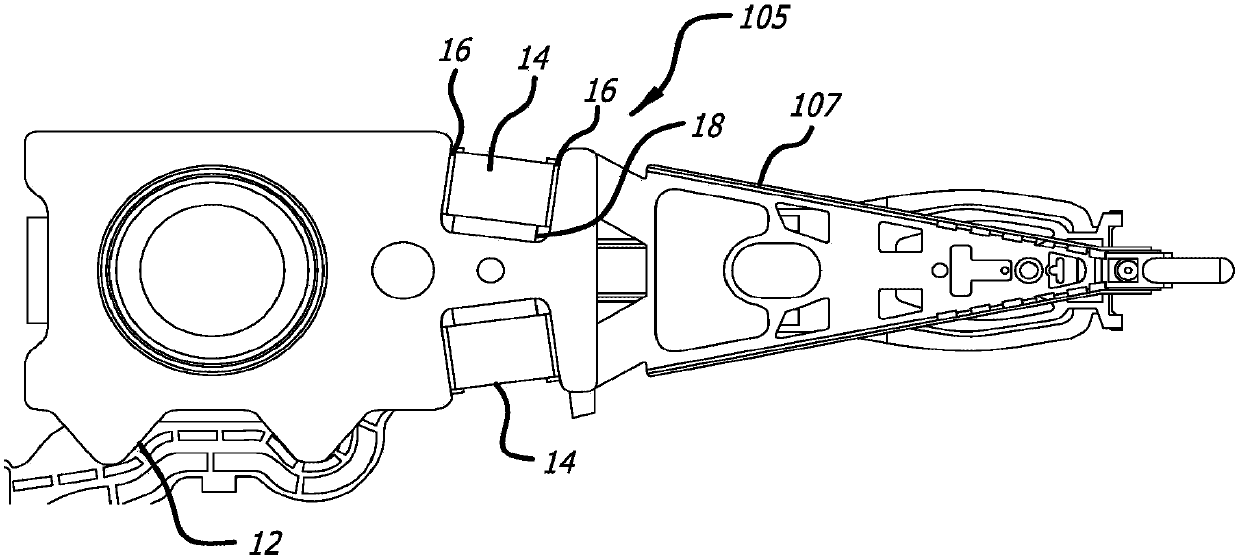
Head gimbal assembly having a radial rotary piezoelectric microactuator between a read head and a flexure tongue
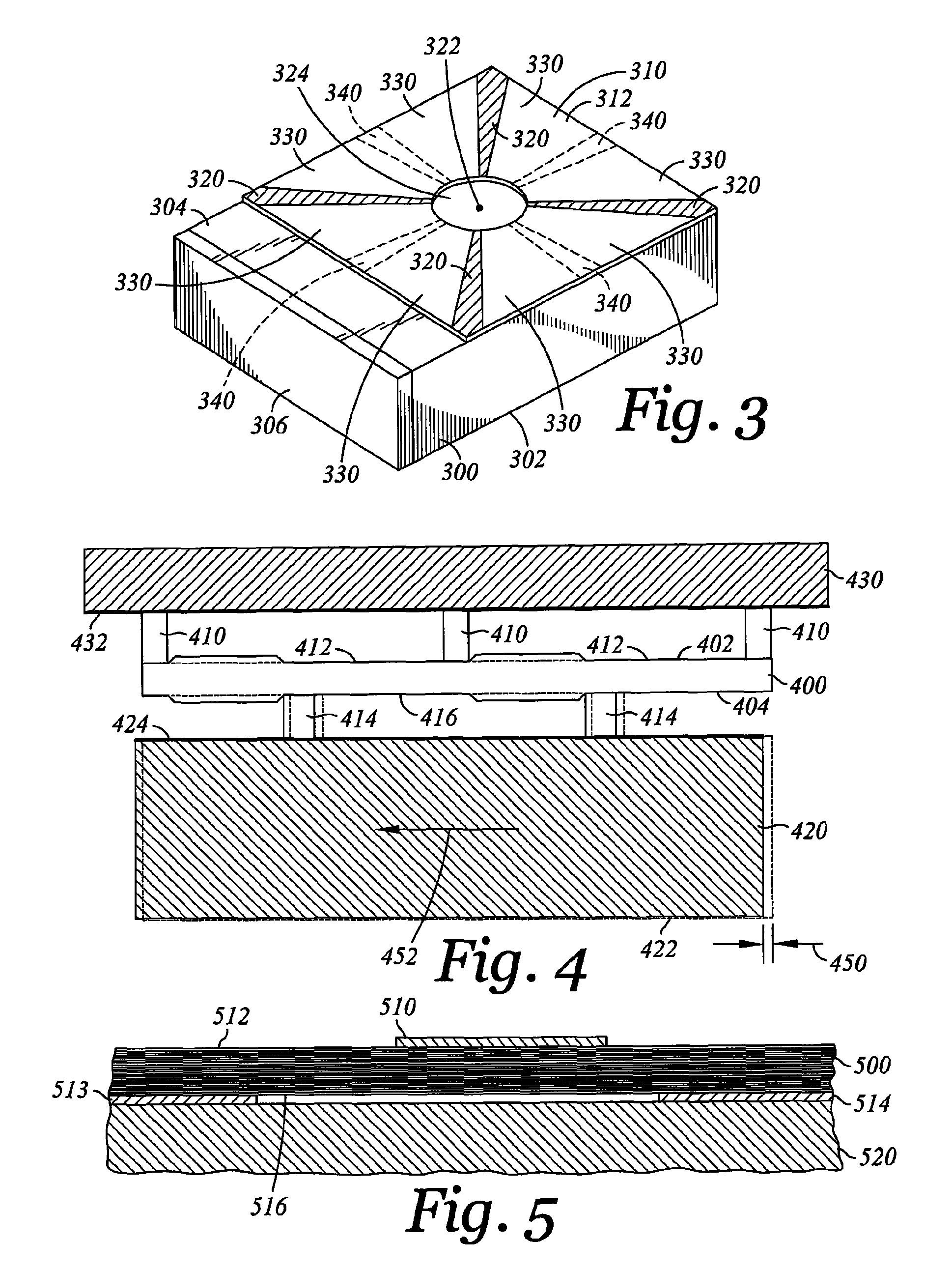
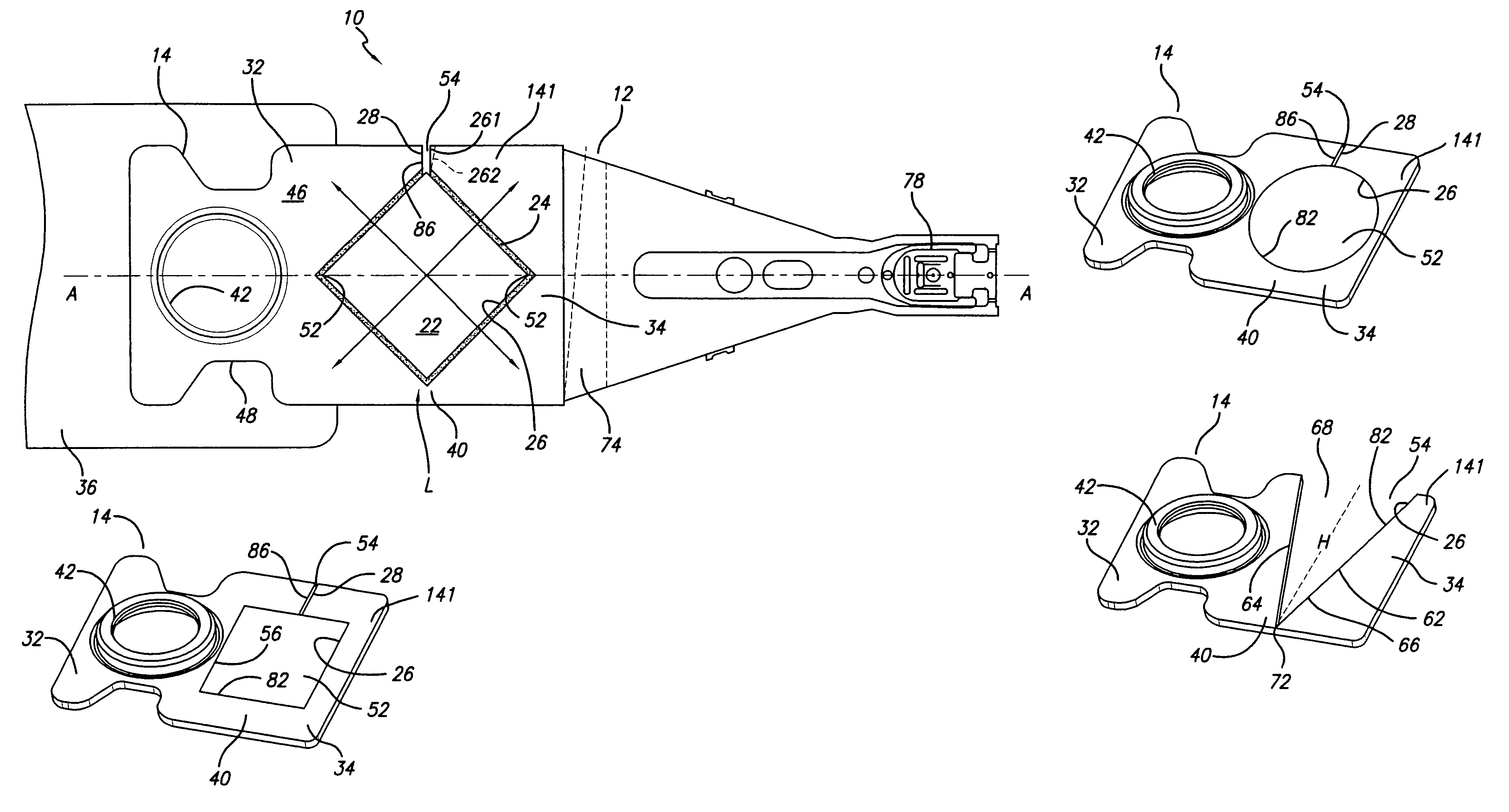
A novel head gimbal assembly (HGA) includes a piezoelectric microactuator having a first side and an opposing second side. The first side includes a plurality of anchor regions that extend radially from a center point and are bonded to the gimbal tongue. The first side also includes a first plurality of non-bonded regions lying between the anchor regions. The second side includes a plurality of link regions that extend radially from the center point and are bonded to a top surface of the read head. The second side also includes a second plurality of non-bonded regions lying between the link regions. Each of the plurality of link regions is angularly spaced between two of the plurality of anchor regions.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
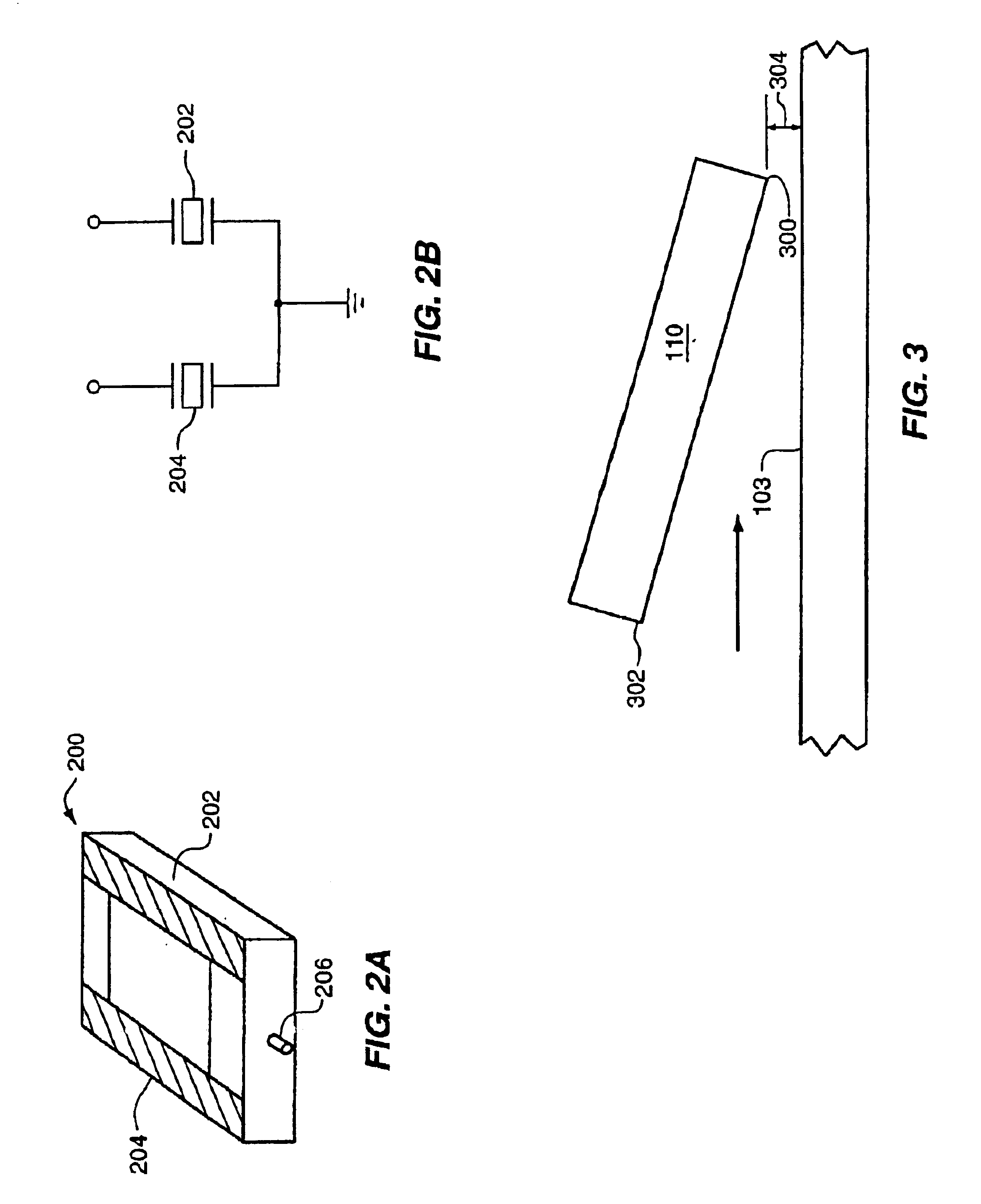
Suspension assembly having a microactuator electrically connected to a gold coating on a stainless steel surface
ActiveUS8542465B2Electrical connection between head and armArm with actuatorsPiezoelectric microactuatorEngineering
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
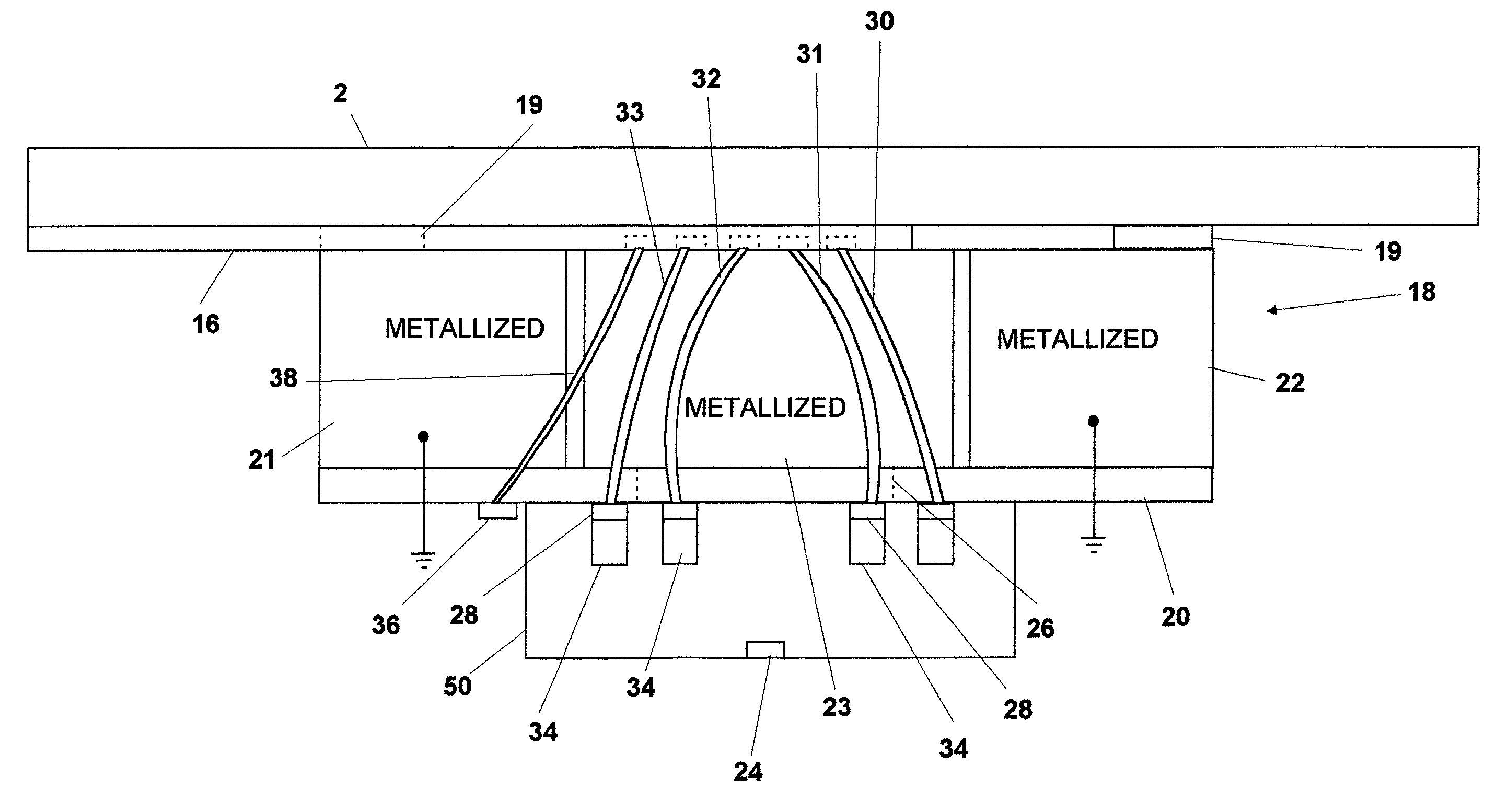
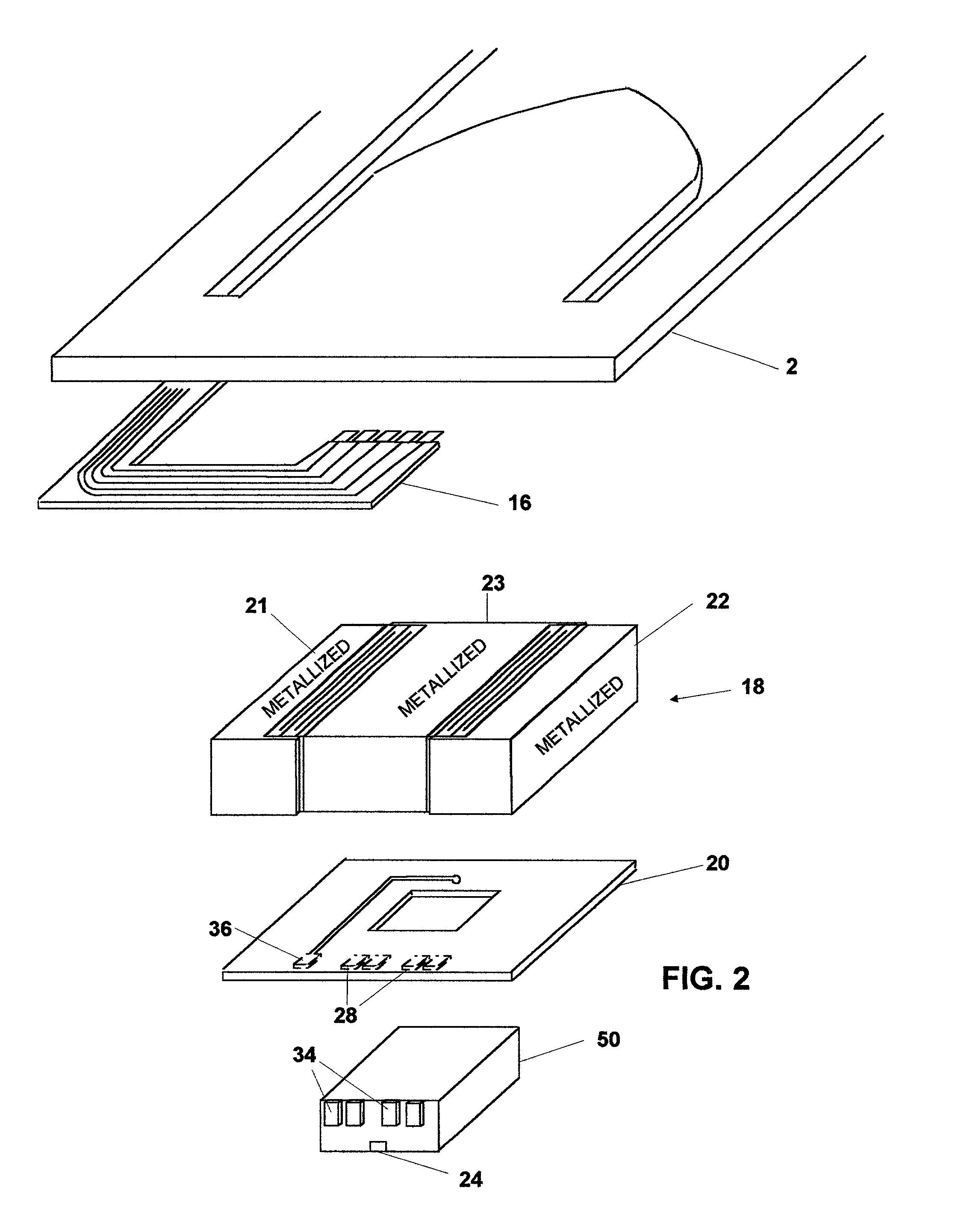
Suspension assembly with piezoelectric microactuators electrically connected to a folded flex circuit segment
ActiveUS7280319B1Electrical connection between head and armRecord information storagePiezoelectric microactuatorFlexible circuits
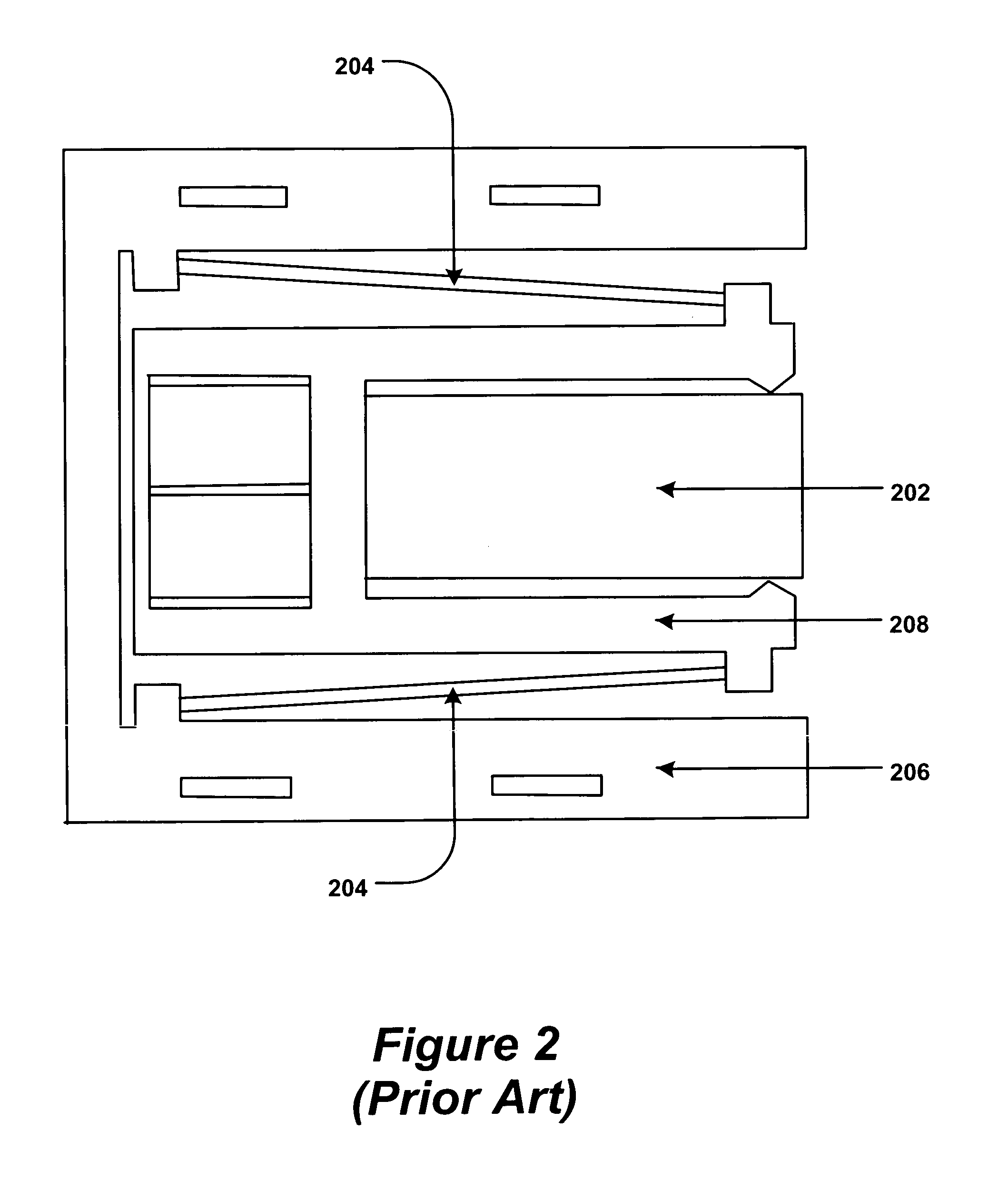
A suspension assembly includes a load beam, a mount plate, first and second piezoelectric microactuators, and a flex circuit segment. The first piezoelectric microactuator is electrically non-conductively attached to the load beam and the mount plate. The first piezoelectric microactuator includes a first piezoelectric element, a first top electrode, and a first bottom electrode. The second piezoelectric microactuator is electrically non-conductively attached to the load beam and the mount plate. The second piezoelectric microactuator includes a second piezoelectric element, a second top electrode, and a second bottom electrode. The flex circuit segment is disposed folded about the first and second piezoelectric microactuators. The flex circuit segment is in electrical communication with the first top electrode, the first bottom electrode, the second top electrode, and the second bottom electrode.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Single PZT actuator for effecting rotation of head suspension loads
ActiveUS7595965B1Easy to routeImprove reliabilityArm with actuatorsRecord information storagePiezoelectric microactuatorEngineering
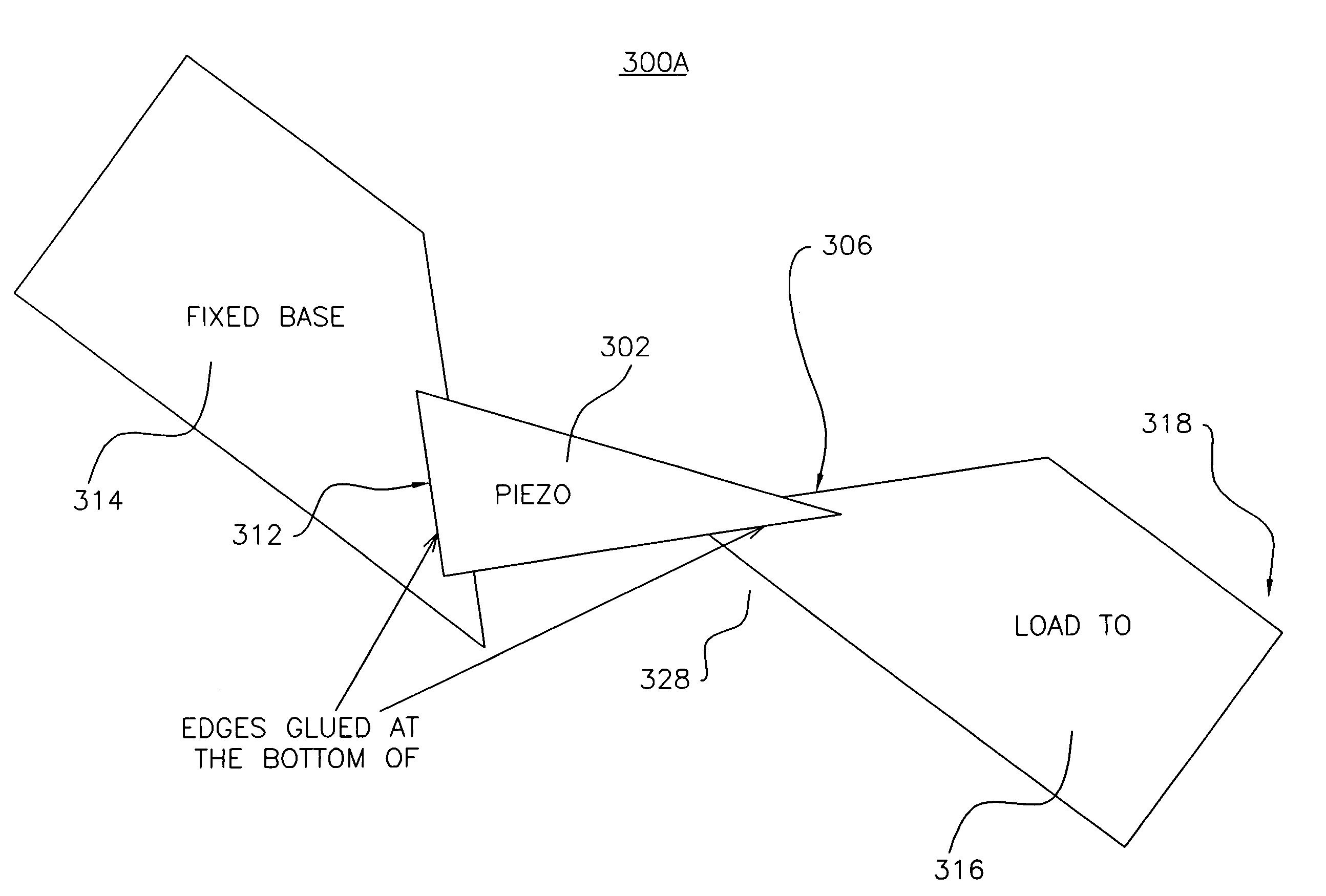
A head suspension assembly couples a baseplate to a rotatable load through a planar triangular piezo microactuator for effecting hingeless rotation of the load. The microactuator expands, responsive to an excitation voltage, with greater magnitude in one direction than in another direction normal to the first direction, resulting in an angular movement of the hypotenuse thereby rotating the load. The upper surface of the microactuator is grounded to a bottom surface of the baseplate or load beam to position the microactuator lead connection surface closest to the load to facilitate trace routing. A load beam grounding surface may be raised to accommodate the microactuator and fix the lead connection surface on a common plane with the unraised surface to further minimize trace routing and provide access for bonding the trace to the load beam.
Owner:MAGNECOMP
Head gimbal assembly with dual-mode piezo microactuator
ActiveUS7417830B1Reduce vibrationAdversely affect shock absorptionArm with actuatorsRecord information storagePiezoelectric microactuatorEngineering
A disk drive suspension has a load beam having a base, a flexure for carrying a slider, and a mount plate. The suspension mount plate has a first portion attachable to an actuator and movable by the actuator as the primary shifting force on the load beam, suitable for larger positioning movements. A second portion of the mount plate is attached to the load beam base and is movable relative to the mount plate first portion. A microactuator moves the second mount plate portion relative to the first mount plate portion as a secondary shifting force on the load beam, suitable for very small positioning movements.
Owner:MAGNECOMP
Suspension assembly having a microactuator electrically connected to a gold coating on a stainless steel surface
ActiveUS20110228425A1Electrical connection between head and armArm with actuatorsPiezoelectric microactuatorMetallurgy
A novel suspension assembly includes a suspension assembly mounting plate, a microactuator mounting structure extending from the suspension assembly mounting plate, a load beam extending from the microactuator mounting structure, and a laminated flexure attached to the load beam. The laminated flexure includes a tongue that has a read head bonding surface. The suspension assembly includes a stainless steel surface having a gold coating, and a piezoelectric microactuator attached to the microactuator mounting structure and electrically connected to the gold coating.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Suspension assembly having recessed actuator with simplified lead connection
ActiveUS7751153B1Easy to routeImprove reliabilityArm with actuatorsRecord information storagePiezoelectric microactuatorEngineering
A head suspension assembly couples a baseplate to a rotatable load through a planar triangular piezo microactuator for effecting hingeless rotation of the load. The microactuator expands, responsive to an excitation voltage, with greater magnitude in one direction than in another direction normal to the first direction, resulting in an angular movement of the hypotenuse thereby rotating the load. The upper surface of the microactuator is grounded to a bottom surface of the baseplate or load beam to position the microactuator lead connection surface closest to the load to facilitate trace routing. A load beam grounding surface may be raised to accommodate the microactuator and fix the lead connection surface on a common plane with the unraised surface to further minimize trace routing and provide access for bonding the trace to the load beam.
Owner:MAGNECOMP
Piezoelectric microactuator for improved tracking control of disk drive read/write heads
InactiveUS7068473B2Easy to controlPrecise positioningDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storagePiezoelectric microactuatorInertial mass
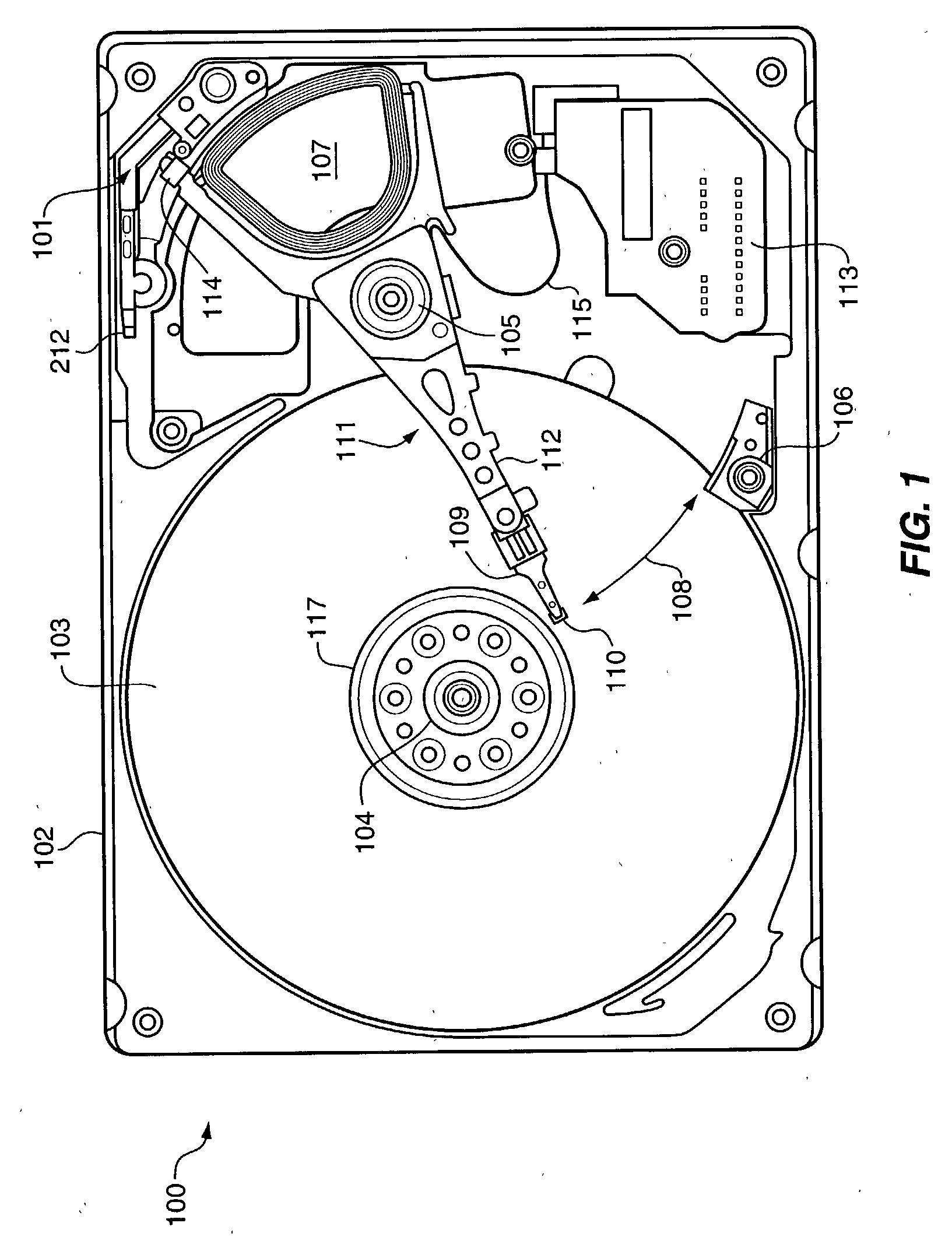
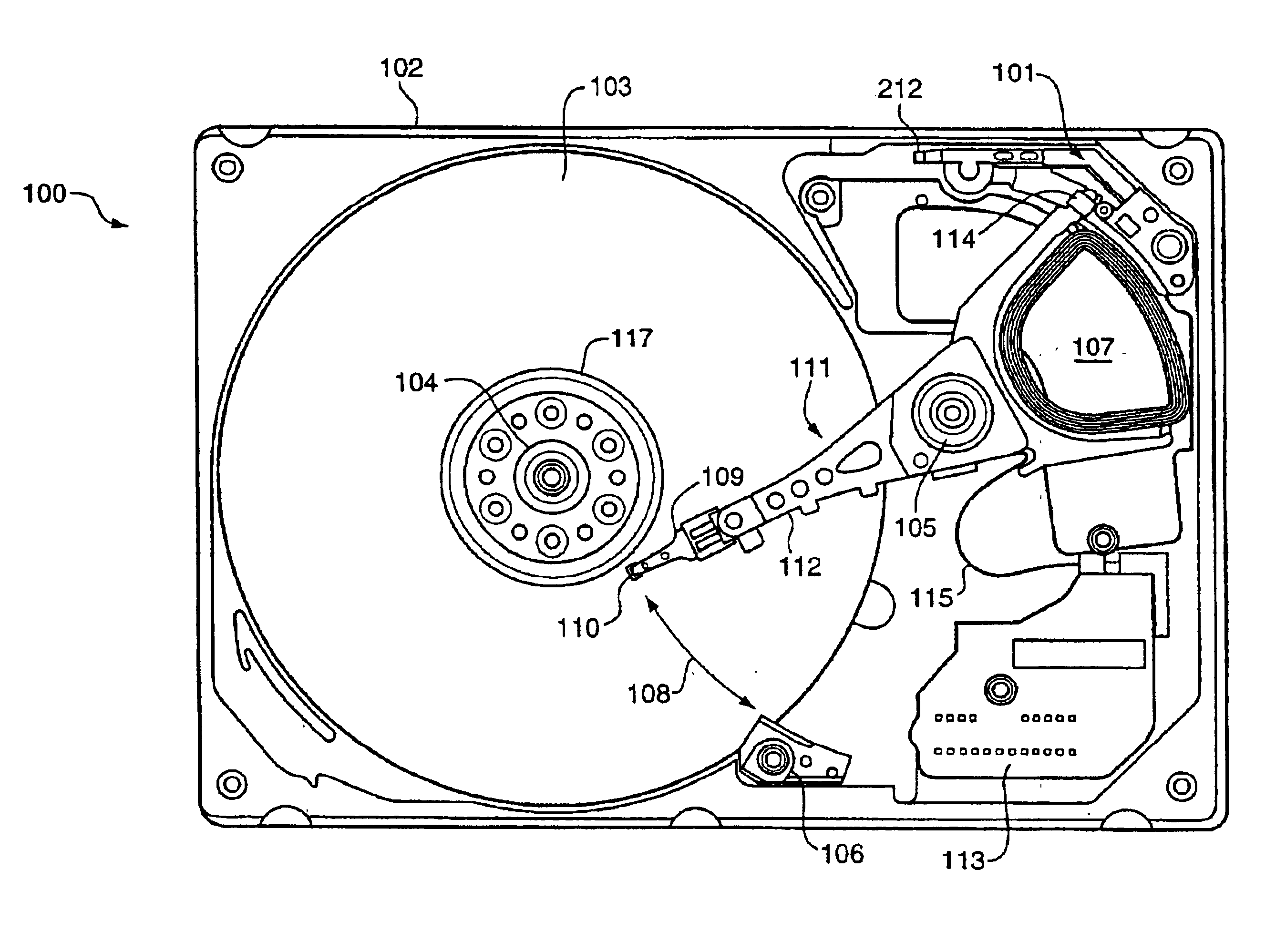
A disc drive actuation system for precisely positioning a read / write head over a selected track of a rotatable disc. The actuation system comprises a flexure, a slider, and a read / write head firmly attached to the slider. A first drive unit is used to pivot the flexure to position the read / write head approximately over a selected track. A microactuator is mounted to the flexure and the slider is mounted to the microactuator. The microactuator comprises an inner inactive region, a first outer inactive region, a second outer inactive region, a first piezoelectric section mounted between the first outer inactive region and the inner inactive region, and a second piezoelectric section mounted between the second outer inactive region and the inner inactive region. The inner inactive region is firmly attached to either the flexure or the slider and both of the outer inactive regions are firmly attached to the other of the flexure or the slider. Also, there is an electrical circuit for energizing the first and the second piezoelectric sections to cause them to expand and contract in order to precisely position the read / write head over the selected track. The circuit and the piezoelectric sections are configured such that the first piezoelectric section expands when the second piezoelectric section contracts and the first piezoelectric section contracts when the second piezoelectric section expands. Since the microactuator has to only overcome the inertial mass of the slider and a portion of its own inertial mass, very precise control at high frequency is possible.
Owner:KINETIC CERAMICS LLC
Peizoelectric microactuator and sensor failure detection in disk drives
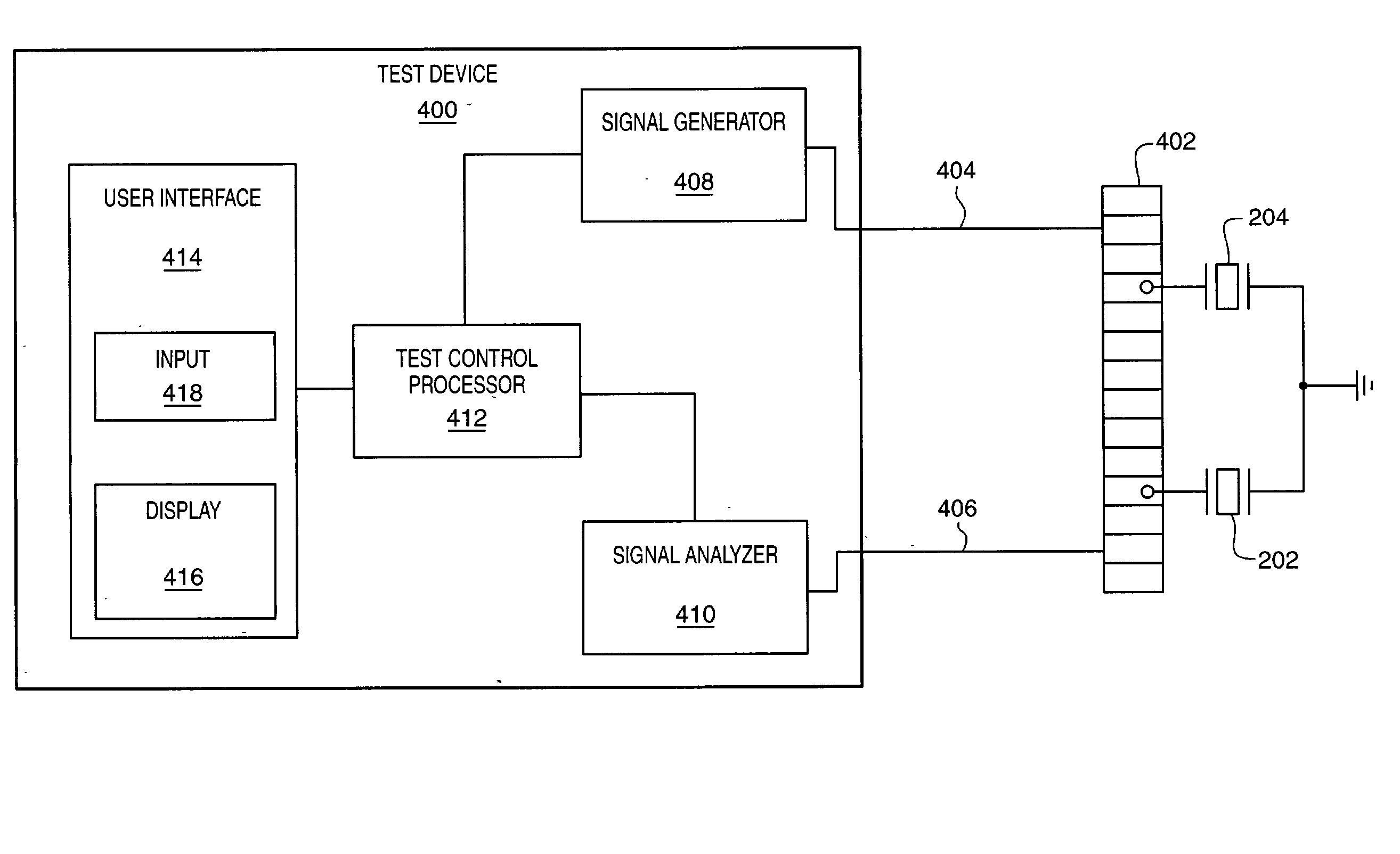
InactiveUS20030076121A1Improve efficiencyEffective reliabilityDisc-shaped record carriersElectronic circuit testingPiezoelectric microactuatorSignal analyzer
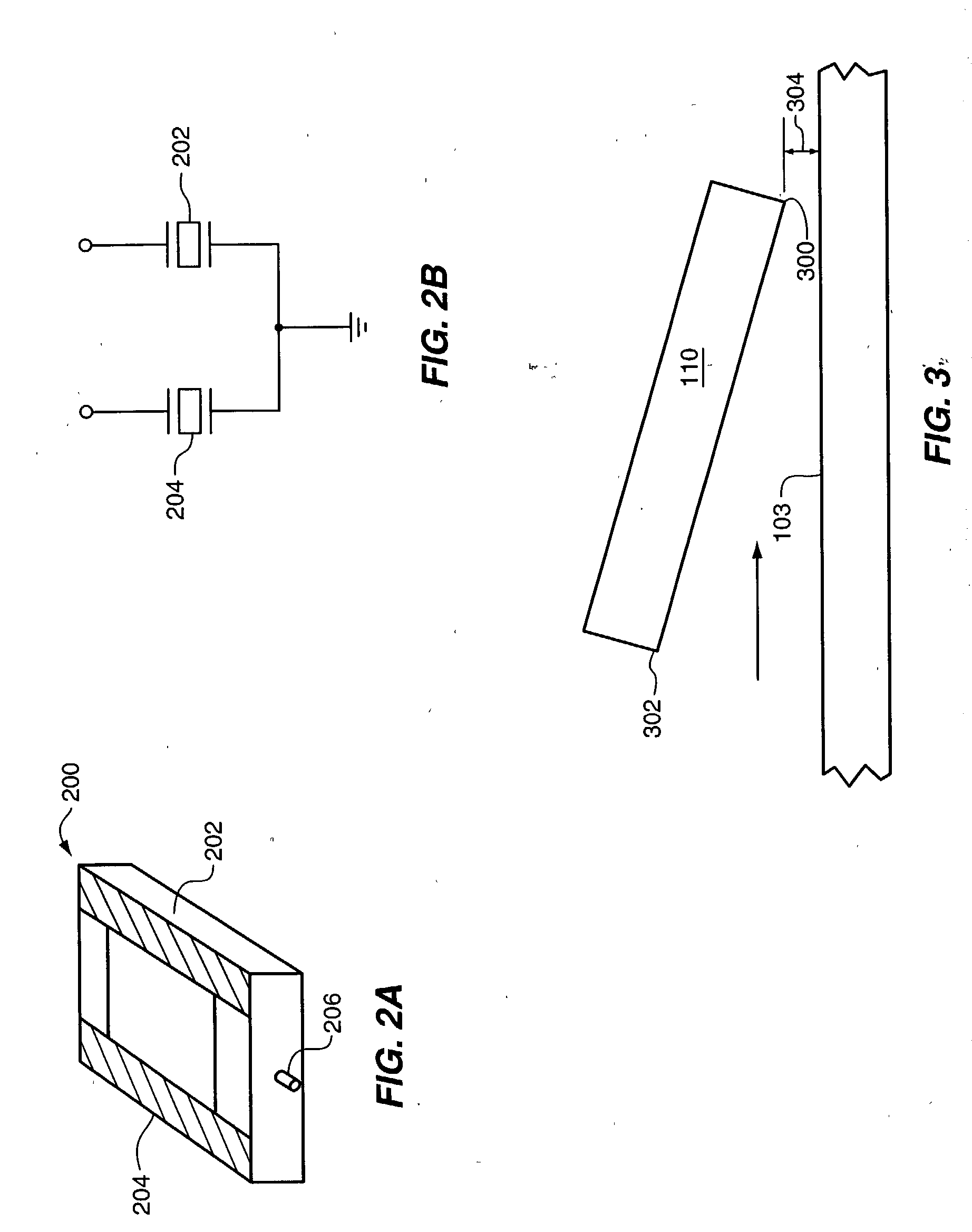
A test device and method for testing one of a disk drive microactuator and a disk drive sensor that includes two piezoelectric elements. The test device includes a signal generator, signal analyzer, and a user interface. The test device is operational to provide a reference signal (e.g. an electrical signal) to one of the piezoelectric elements in the microactuator and obtain a test measure from the other one of the piezoelectric elements. The test measure is then utilized to assess a performance parameter for the microactuator. The test measure is generated by the other one of the piezoelectric elements in response to the reference signal provided to the first one of the piezoelectric elements. In one embodiment of the invention, the test measure is a signal generated in response to the reference signal that may be compared to a known response signal of an operational microactuator to determine operational characteristics of a subject microactuator such as circuitry operation and / or damage to the microactuator.
Owner:GUO WEI +1
Piezoelectric microactuator and sensor failure detection in disk drives
InactiveUS6861854B1Improve efficiencyDisc-shaped record carriersElectronic circuit testingElectricityPiezoelectric microactuator
A test device and method for testing one of a disk drive microactuator and a disk drive sensor that includes two piezoelectric elements. The test device includes a signal generator, signal analyzer, and a user interface. The test device is operational to provide a reference signal (e.g. an electrical signal) to one of the piezoelectric elements in the microactuator and obtain a test measure from the other one of the piezoelectric elements. The test measure is then utilized to assess a performance parameter for the microactuator. The test measure is generated by the other one of the piezoelectric elements in response to the reference signal provided to the first one of the piezoelectric elements. In one embodiment of the invention, the test measure is a signal generated in response to the reference signal that may be compared to a known response signal of an operational microactuator to determine operational characteristics of a subject microactuator such as circuitry operation and / or damage to the microactuator.
Owner:MAXTOR
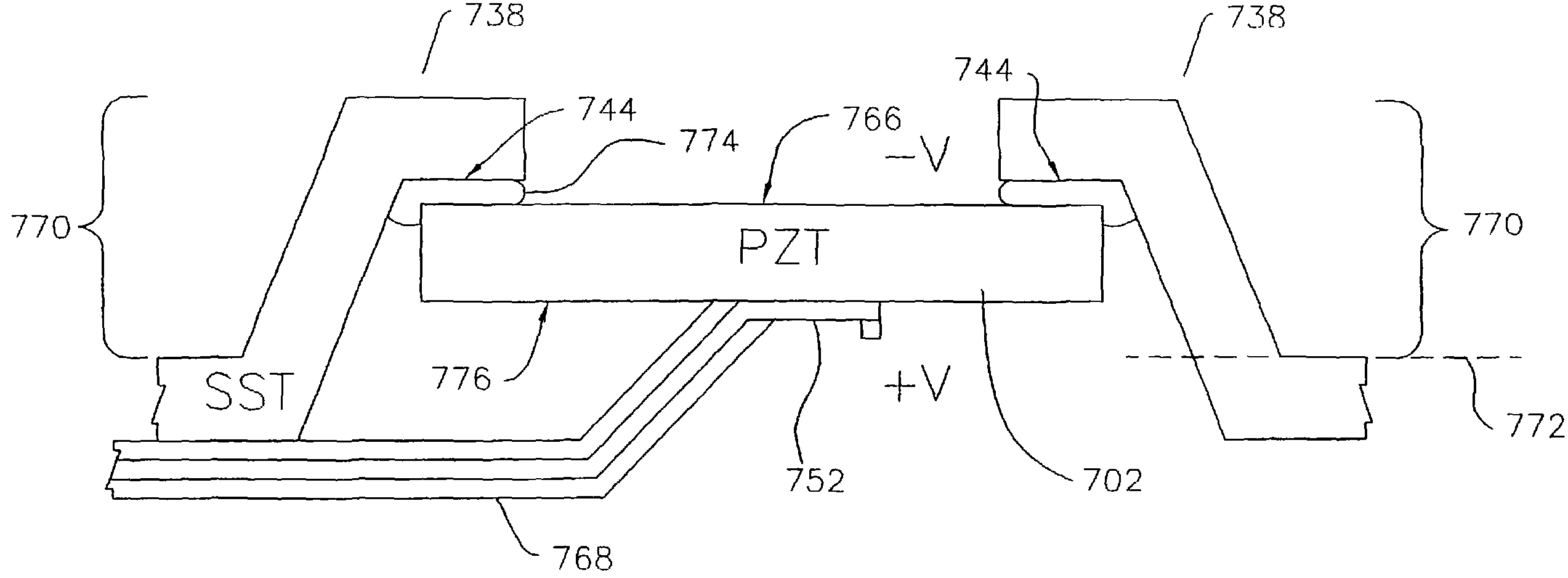
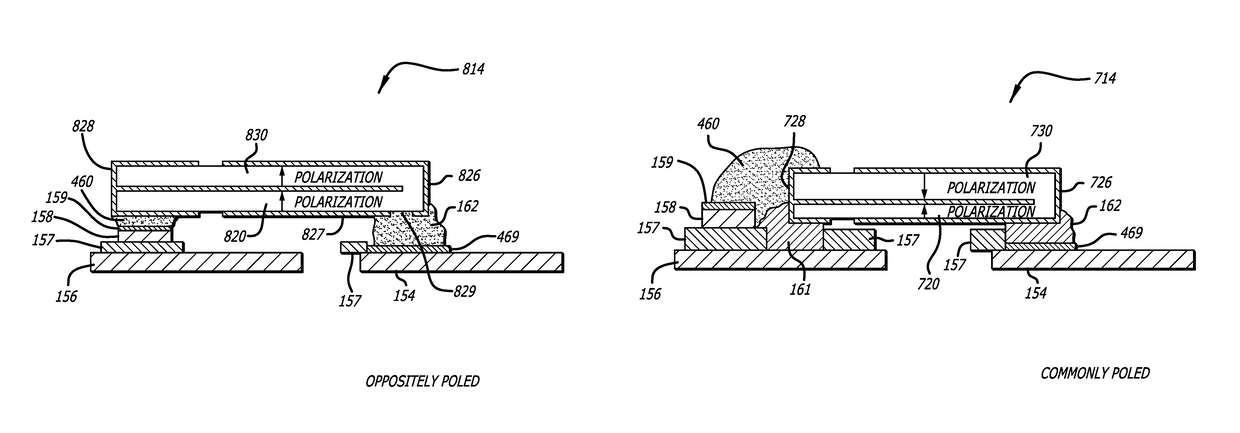
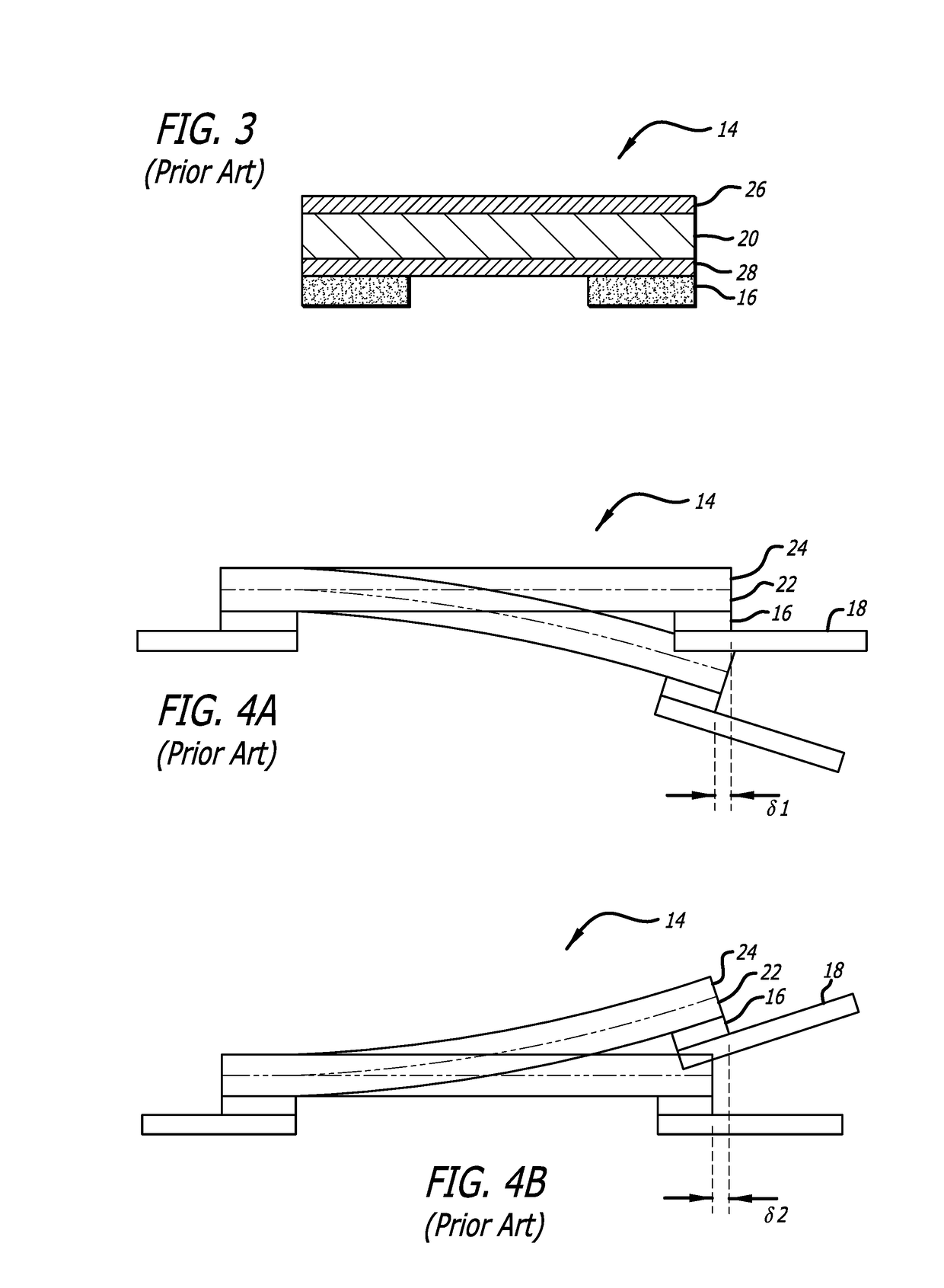
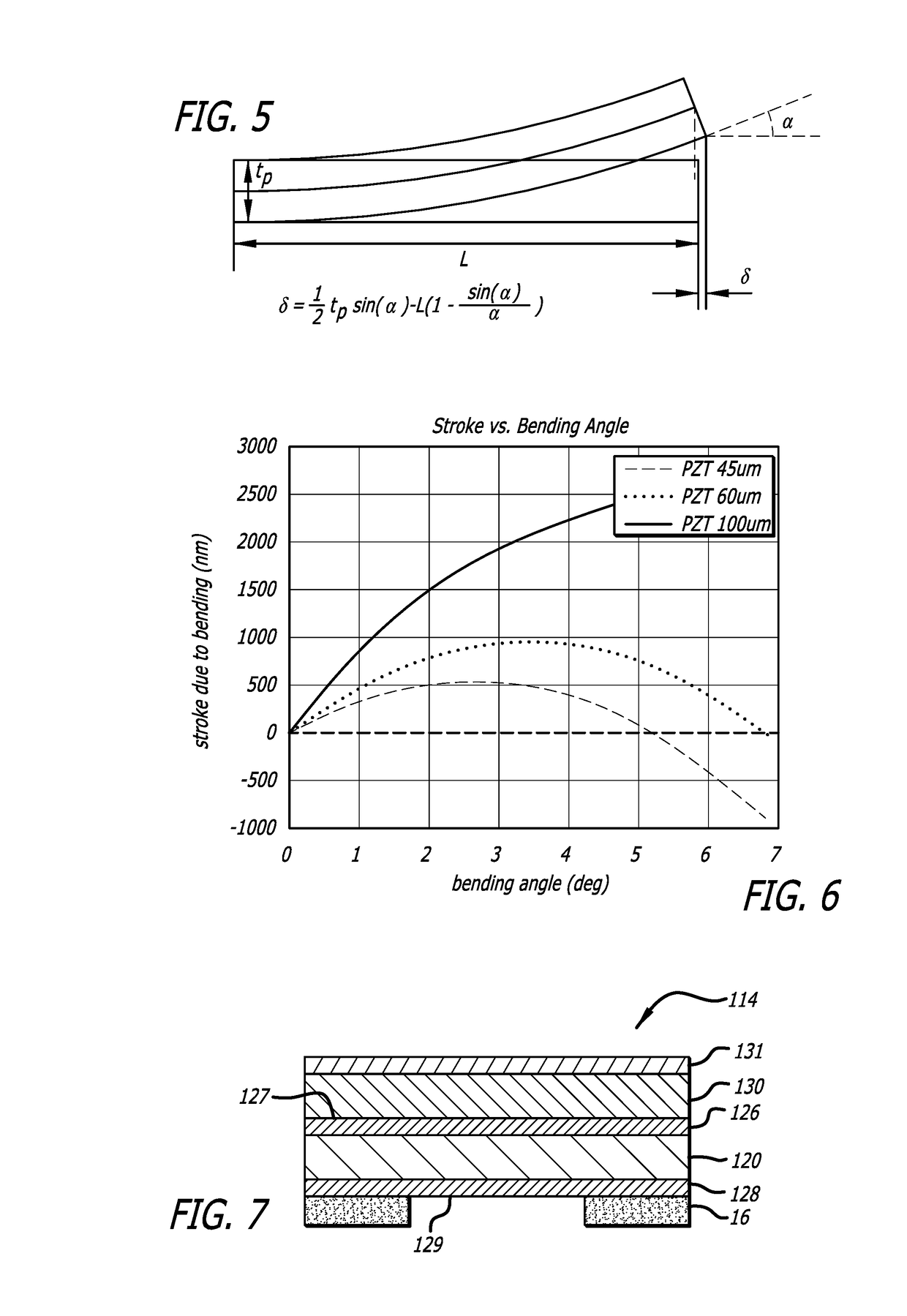
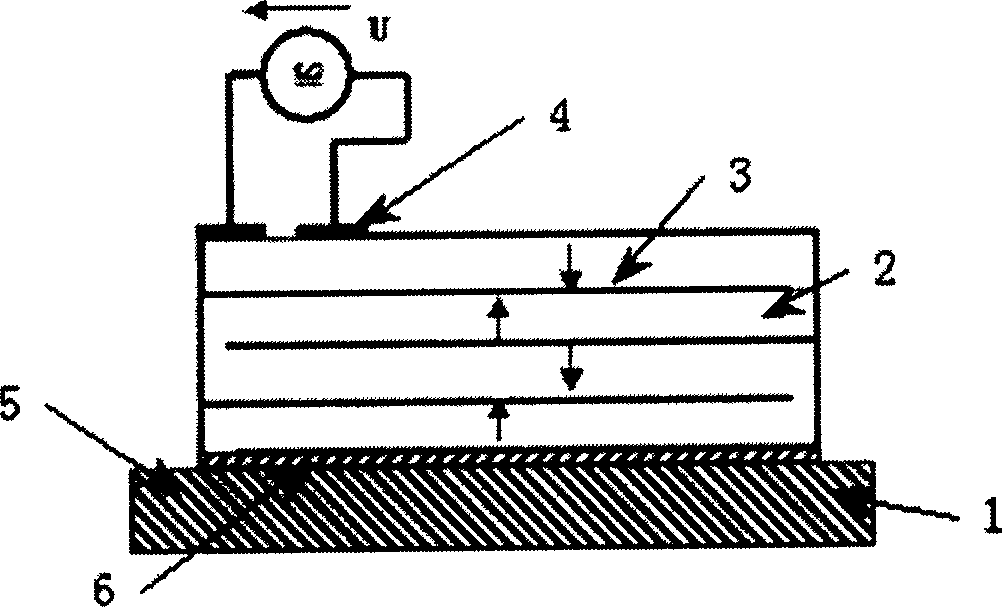
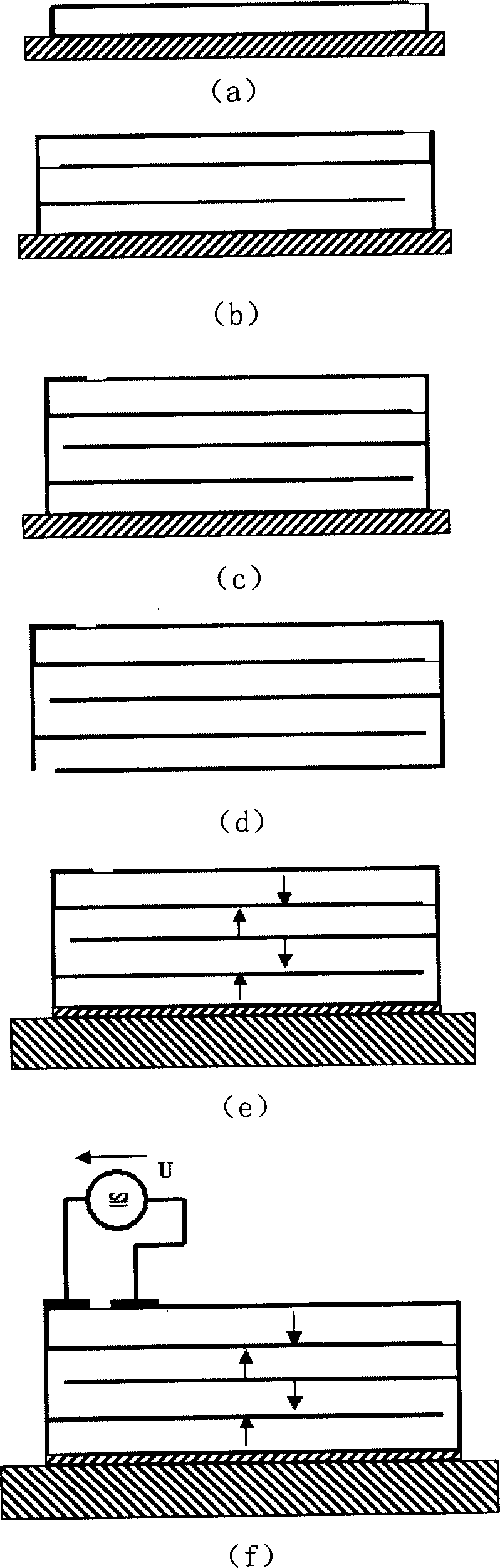
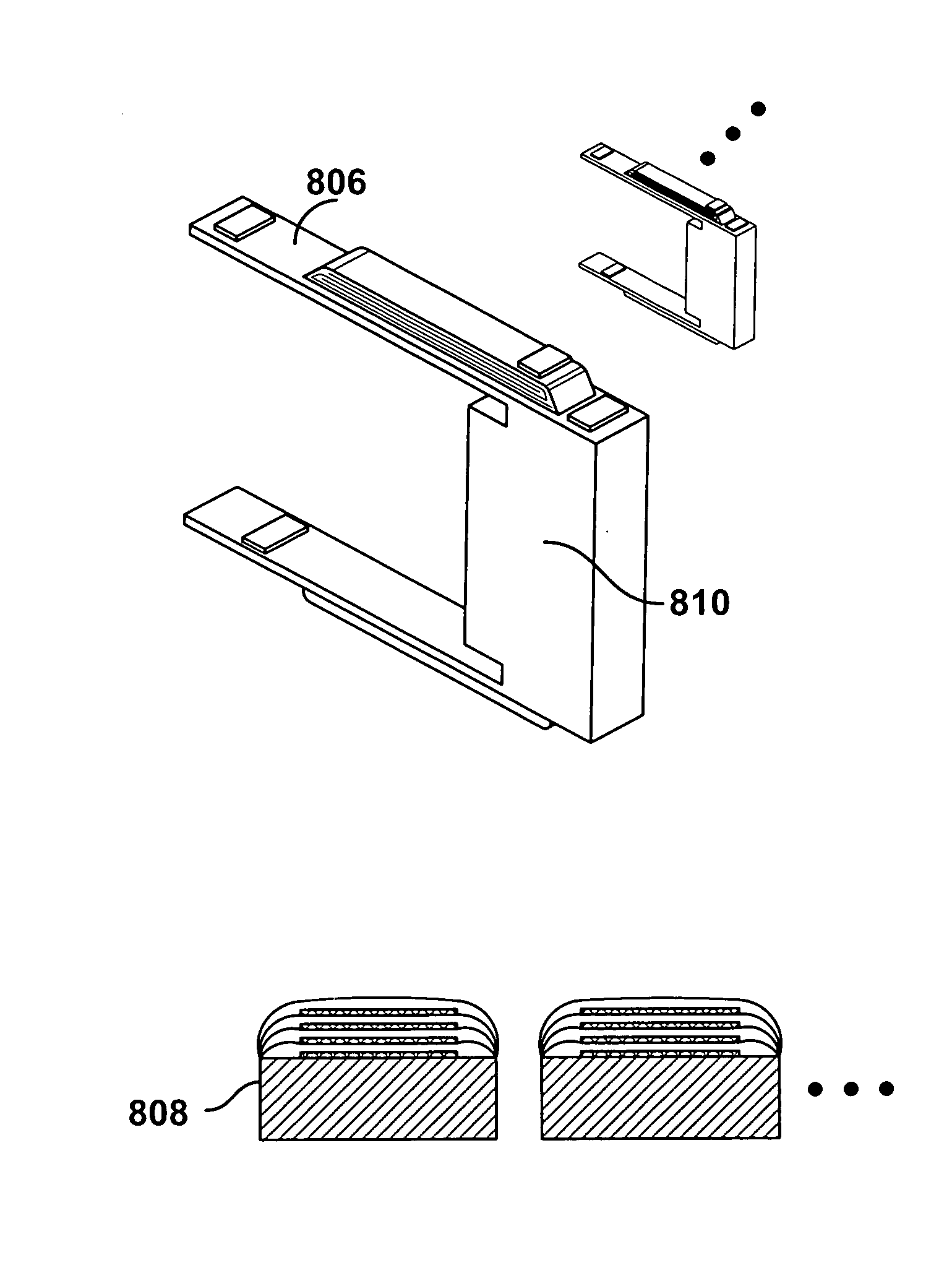
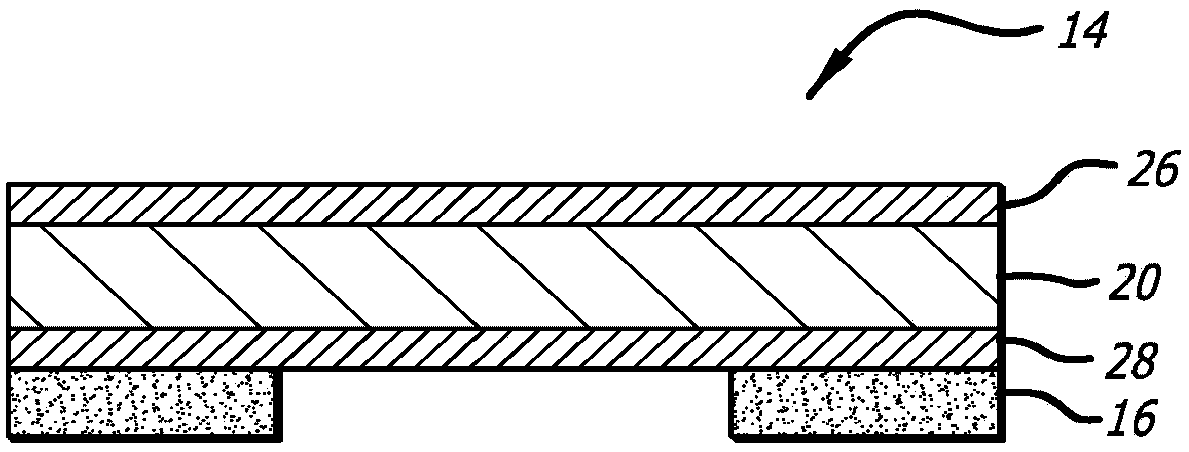
Multi-layer PZT microactuator having a poled but inactive PZT constraining layer
A multi-layer piezoelectric microactuator assembly has at least one poled and active piezoelectric layer and one poled but inactive piezoelectric layer. The poled but inactive layer acts as a constraining layer in resisting expansion or contract of the first piezoelectric layer thereby reducing or eliminating bending of the assembly as installed in an environment, thereby increasing the effective stroke length of the assembly. Poling only a single layer would induce stresses into the device; hence, polling both piezoelectric layers even though only one layer will be active in use reduces stresses in the device and therefore increases reliability.
Owner:MAGNECOMP
Piezoelectric micro-actuator, head gimbal assembly and its assembling method, and disk drive device with the same
ActiveUS20090195938A1Reduce wasteReduce manufacturing costArm with actuatorsRecord information storagePiezoelectric microactuatorMicro actuator
A PZT micro-actuator for a head gimbal assembly includes a pair of separate PZT elements and each PZT element has a body and a plurality of electrical pads. The body has at least two electrode-piezoelectric combination layers laminated together. The at least two electrode-piezoelectric combination layers are physically connected with but electrically isolated from each other. Each electrode-piezoelectric combination layer has at least two of the electrical pads thereon. The electrical pads extend out from the body of the corresponding PZT element. All the electrical pads of each PZT element are offset a predetermined distance therebetween to be electrically isolated. The present invention also discloses a head gimbal assembly (HGA) with the PZT micro-actuator, an assembling method for the head gimbal assembly and a disk drive unit having such HGA.
Owner:SAE MAGNETICS (HK) LTD
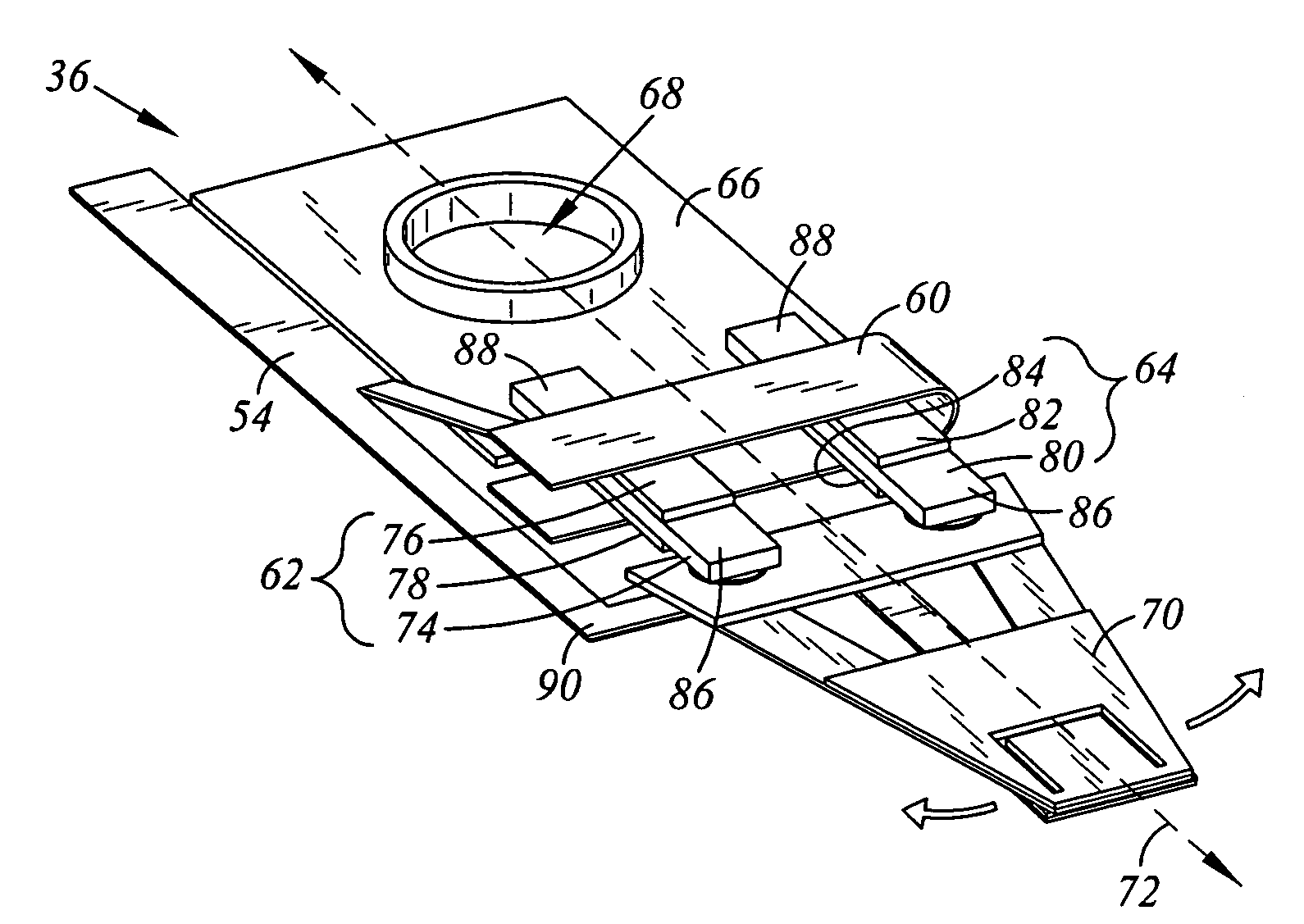
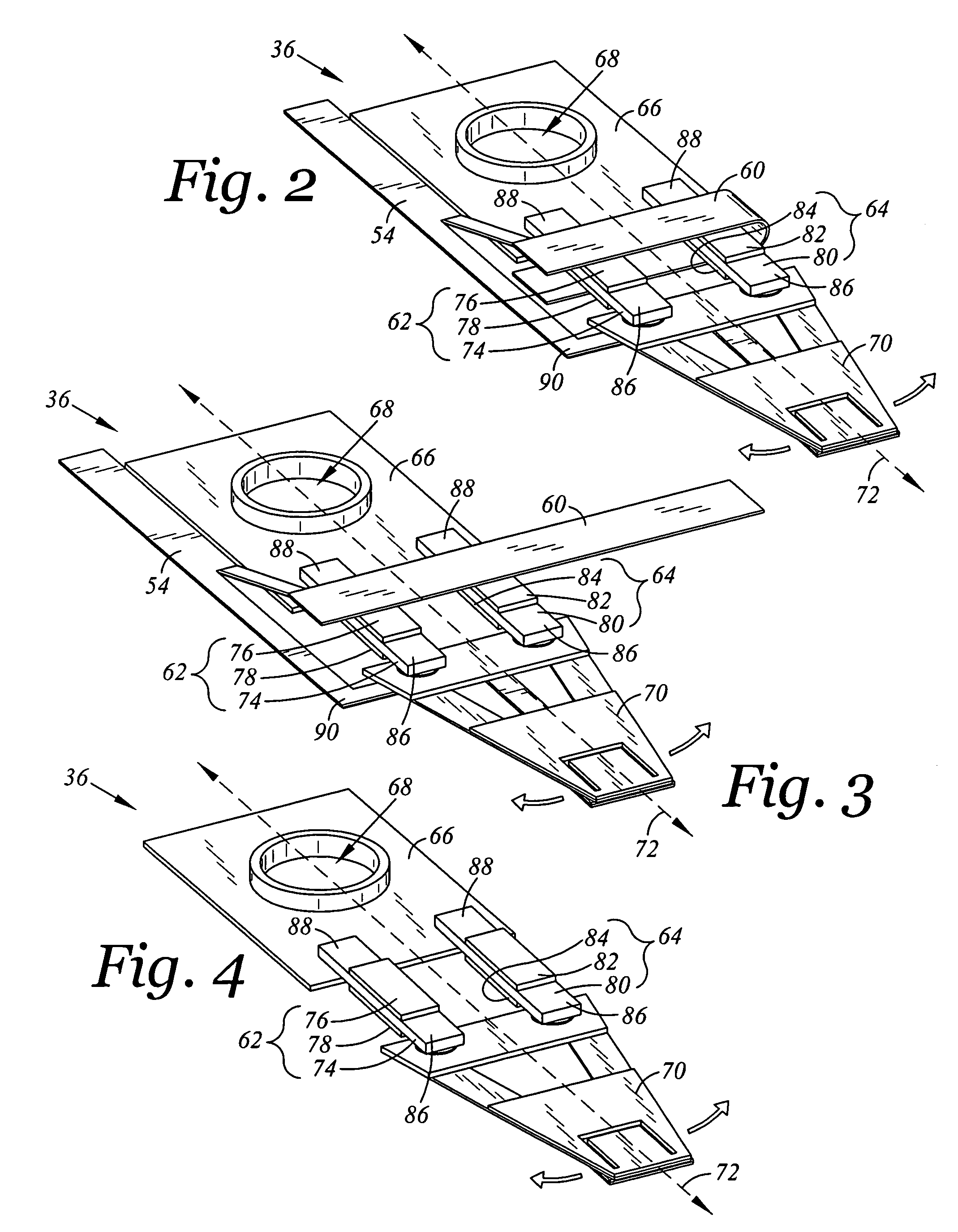
Piezo-electric microactuator for dual stage actuator
InactiveUS7038888B2Disposition/mounting of recording headsRecord information storagePiezoelectric microactuatorDual stage
A head flexure assembly having a flexure with a built in microactuator is disclosed. The flexure is divided into four portions: a base plate portion for attaching the flexure to an actuator arm; a load beam portion for suspending a transducing head; a parallelogram portion connecting the load beam portion and the base plate portion and allowing for the translational movement of the load beam portion with respect to the base plate portion; and a driving frame portion. The parallelogram portion has two substantially parallel members that attach the base plate portion to the load beam portion. The parallel members limit the movement of the load beam portion relative to the base plate portion to translational movement. The driving frame portion has piezoelectric element that in response to a control signal produces a force, orthogonal to the flexure's longitudinal axis, between the base plate portion and the load beam portion.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Piezoelectric microactuator with restraining layer for control of bending
ActiveUS9390739B1Reduce and eliminate and changeIncrease distancePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesArm with actuatorsHard disc drivePiezoelectric microactuator
A PZT microactuator such as for use in a hard disk drive has a restraining layer bonded on its side that is opposite the side on which the PZT will be mounted. The restraining layer comprises a stiff and resilient material such as stainless steel. The restraining layer can cover all of the top of the PZT, or most of the top of the PZT with an electrical connection being made to the PZT where it is not covered by the restraining layer. The restraining layer reduces bending of the PZT as mounted and hence increases effective stroke length, or reverses the sign of the bending which increases the effective stroke length of the PZT even further.
Owner:MAGNECOMP
Multi-layer PZT microactuator having a poled but inactive PZT constraining layer
ActiveUS10236022B2Arm with actuatorsRecord information storagePiezoelectric microactuatorEngineering
A multi-layer piezoelectric microactuator assembly has at least one poled and active piezoelectric layer and one poled but inactive piezoelectric layer. The poled but inactive layer acts as a constraining layer in resisting expansion or contract of the first piezoelectric layer thereby reducing or eliminating bending of the assembly as installed in an environment, thereby increasing the effective stroke length of the assembly. Poling only a single layer would induce stresses into the device; hence, polling both piezoelectric layers even though only one layer will be active in use reduces stresses in the device and therefore increases reliability.
Owner:MAGNECOMP
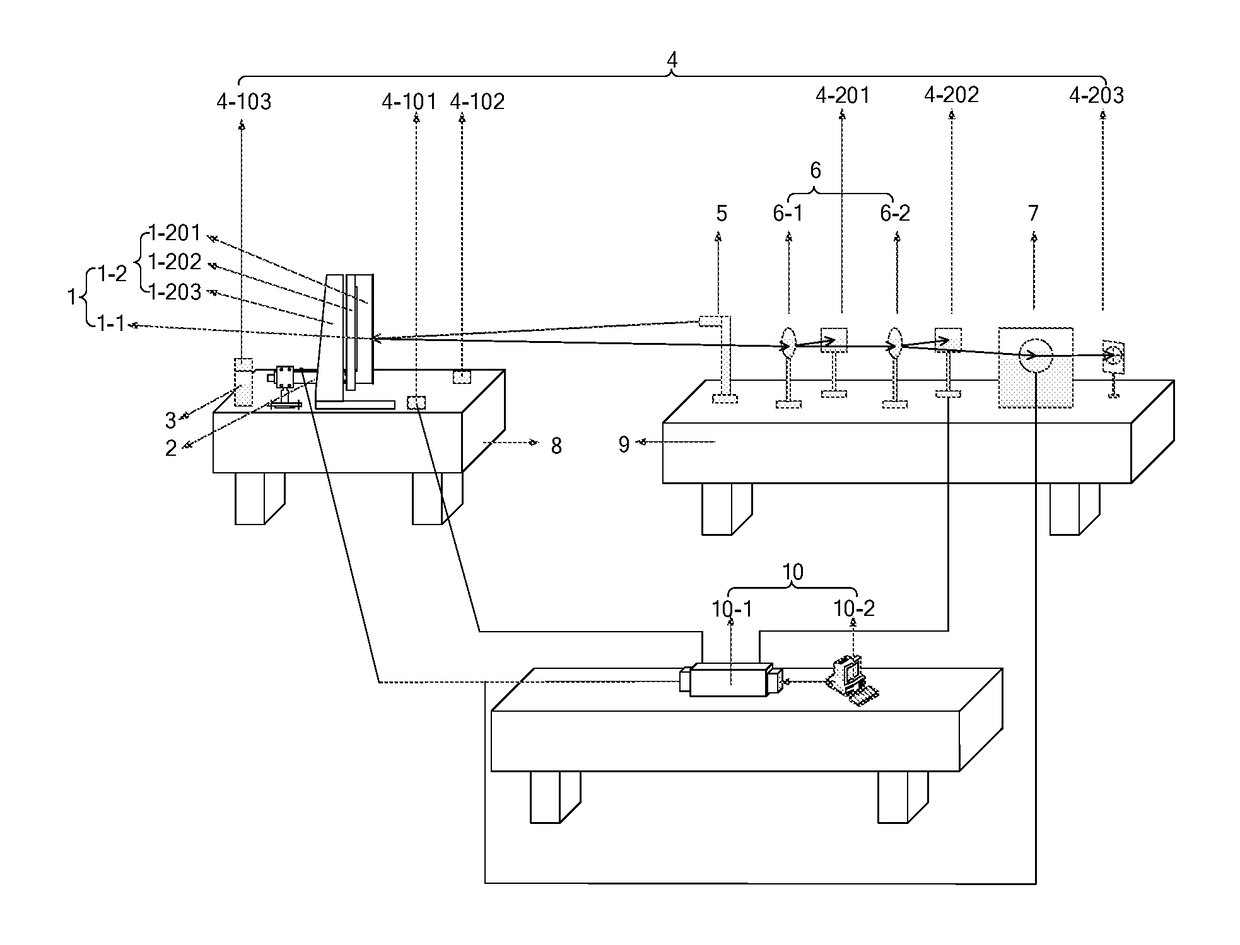
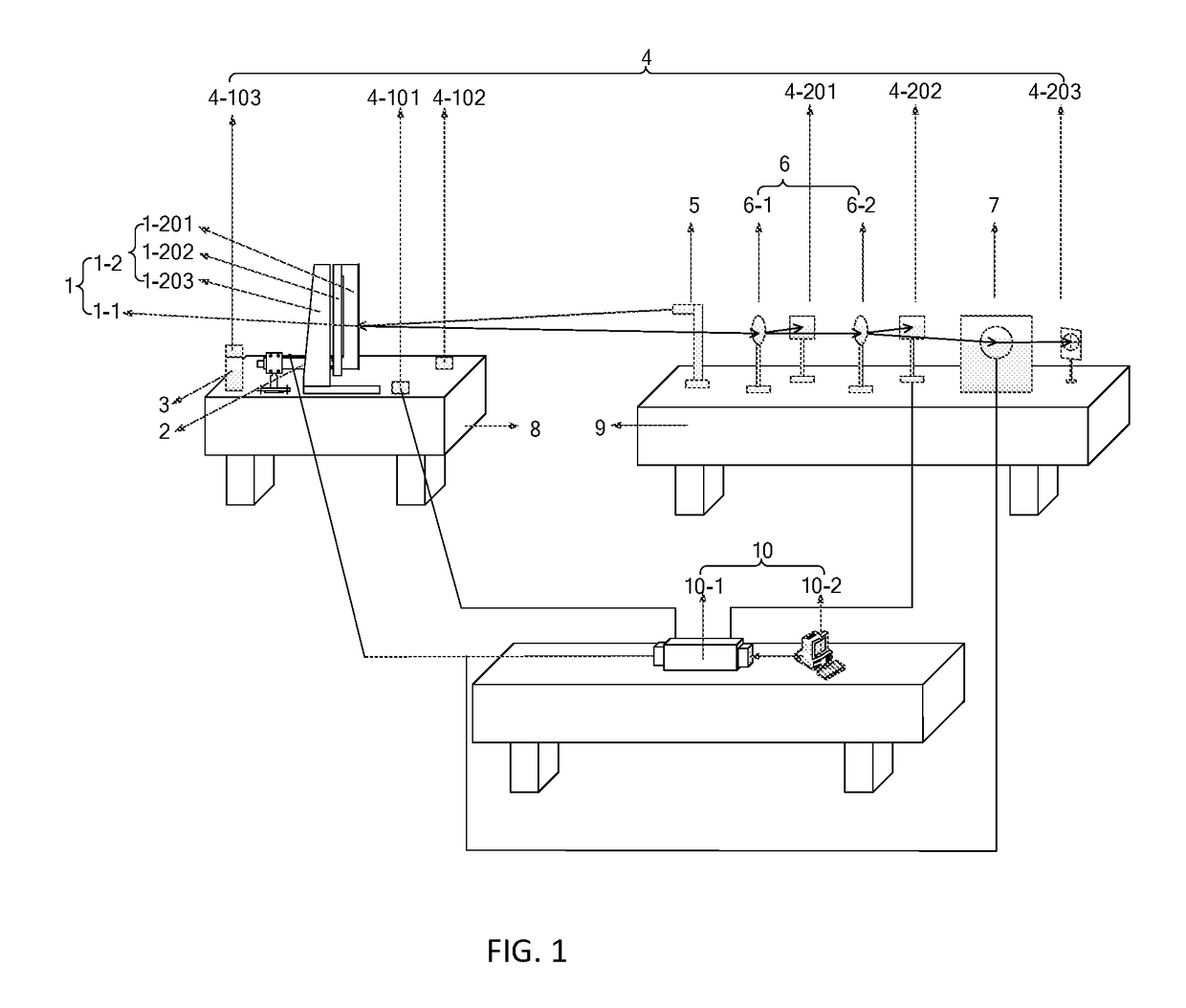
Experimental System for Laser Beam Measurement and Steering Control
ActiveUS20180081146A1Simple structureSmall volumeUsing optical meansControl using feedbackLaser transmitterBeam splitter
An experimental system for laser beam measurement and steering control, and relates to the technical field of optical, mechanical and electronic integration experimental systems. It includes: a high-precision optical mirror, a piezoelectric micro-actuator, a vibration exciter, a signal collection subsystem, a laser emitter, a beam splitter mirror, a fast steering mirror, a mechanical vibration isolation air bearing table, an optical vibration isolation air bearing table, a data processing and analyzing subsystem, and data transmission lines and power supply lines between subsystems and components. It uses a deflection angle of the laser beam as a control variation, can not only precisely measure the deflection angle of the laser beam, but also inhibit vibration of the high-precision optical mirror by using the piezoelectric micro-actuator and directly adjust the steering of the emitted laser beam by using the fast steering mirror, thereby improving precision of beam steering control.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Slider and micro-actuator assembly, head gimbal assembly, and disk drive unit with the same
InactiveUS20100259854A1Guaranteed uptimeAvoid damageArm with actuatorsRecord information storageLeading edgePiezoelectric microactuator
A slider and micro-actuator assembly of the present invention comprises a substrate having a trailing edge and a leading edge opposite the trailing edge; a read / write transducer formed at the trailing edge of the substrate and a piezoelectric micro-actuator formed at the leading edge of the substrate. The piezoelectric micro-actuator connects with the leading edge of the substrate via two spaced insulation layers so as to form a space between the piezoelectric micro-actuator and the leading edge of the substrate, the substrate with the read / write transducer rotates against a center thereof when the piezoelectric micro-actuator is driven to generate a rotation torque to the substrate via the space. The structure of the slider and micro-actuator assembly prevents the read / write transducer from damaged and gets better operation performance when the piezoelectric micro-actuator is driven. The present invention also discloses a method for manufacturing a slider and micro-actuator assembly, a HGA with the slider and micro-actuator assembly and a disk drive unit having such HGA.
Owner:SAE MAGNETICS (HK) LTD
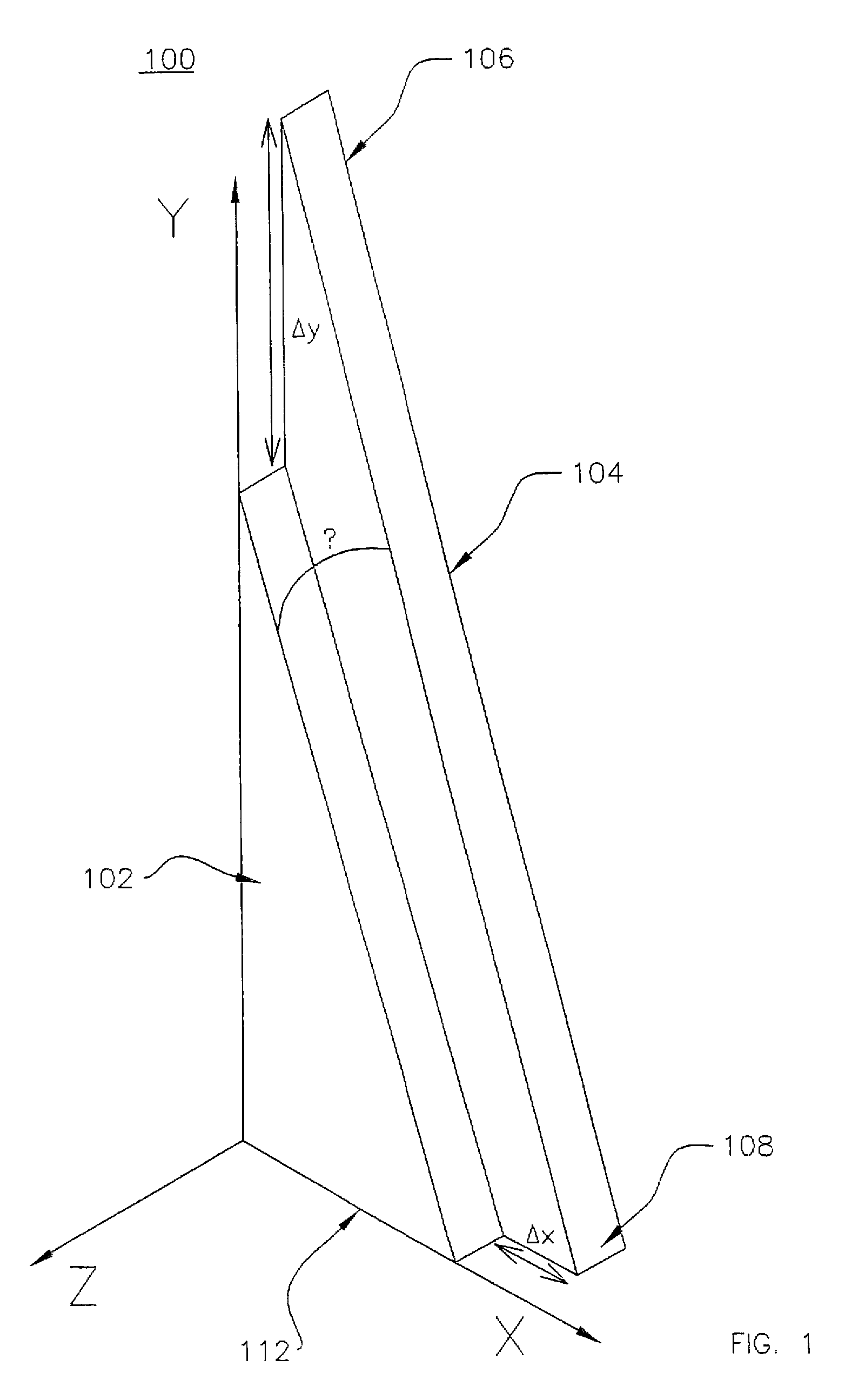
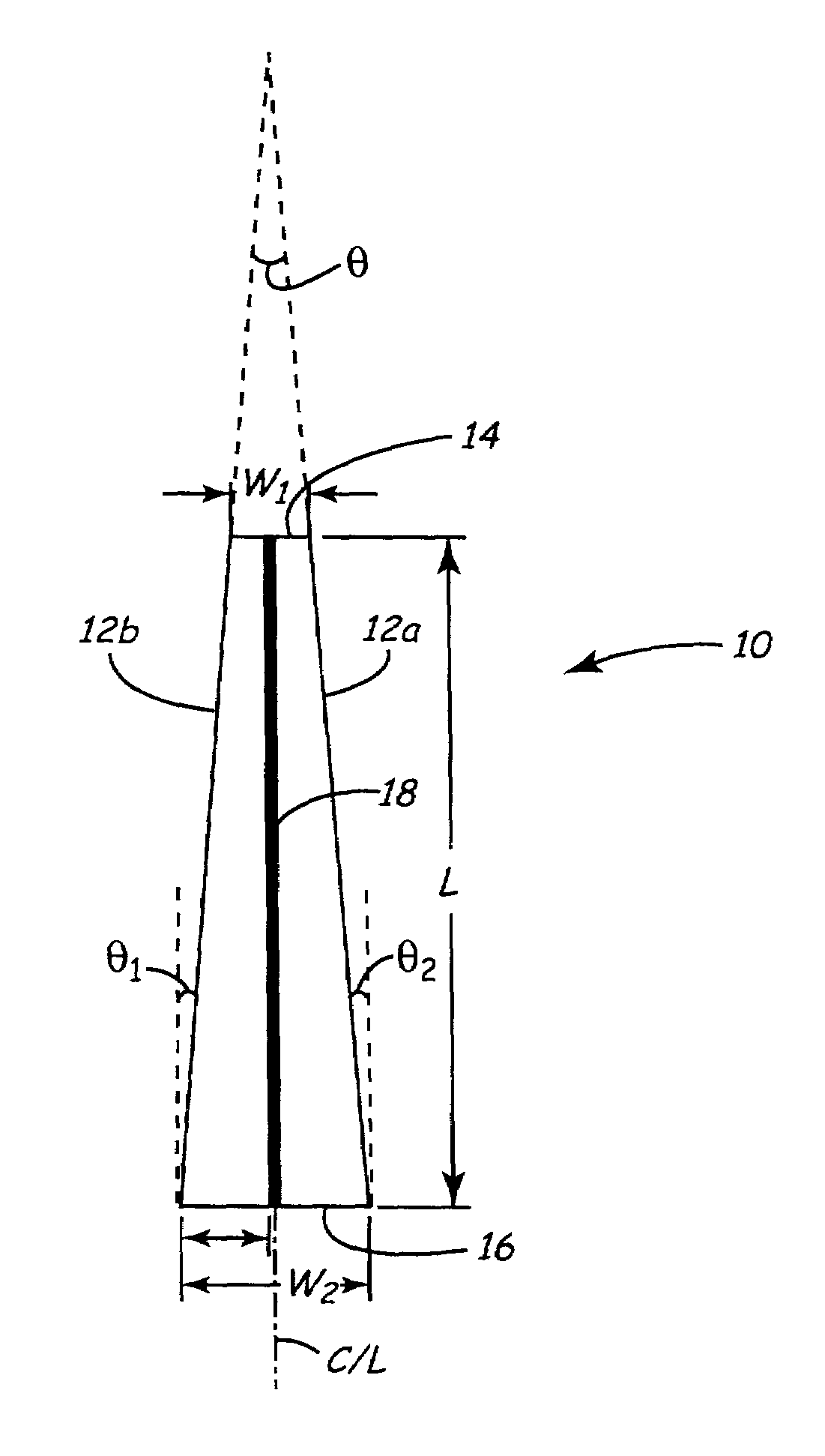
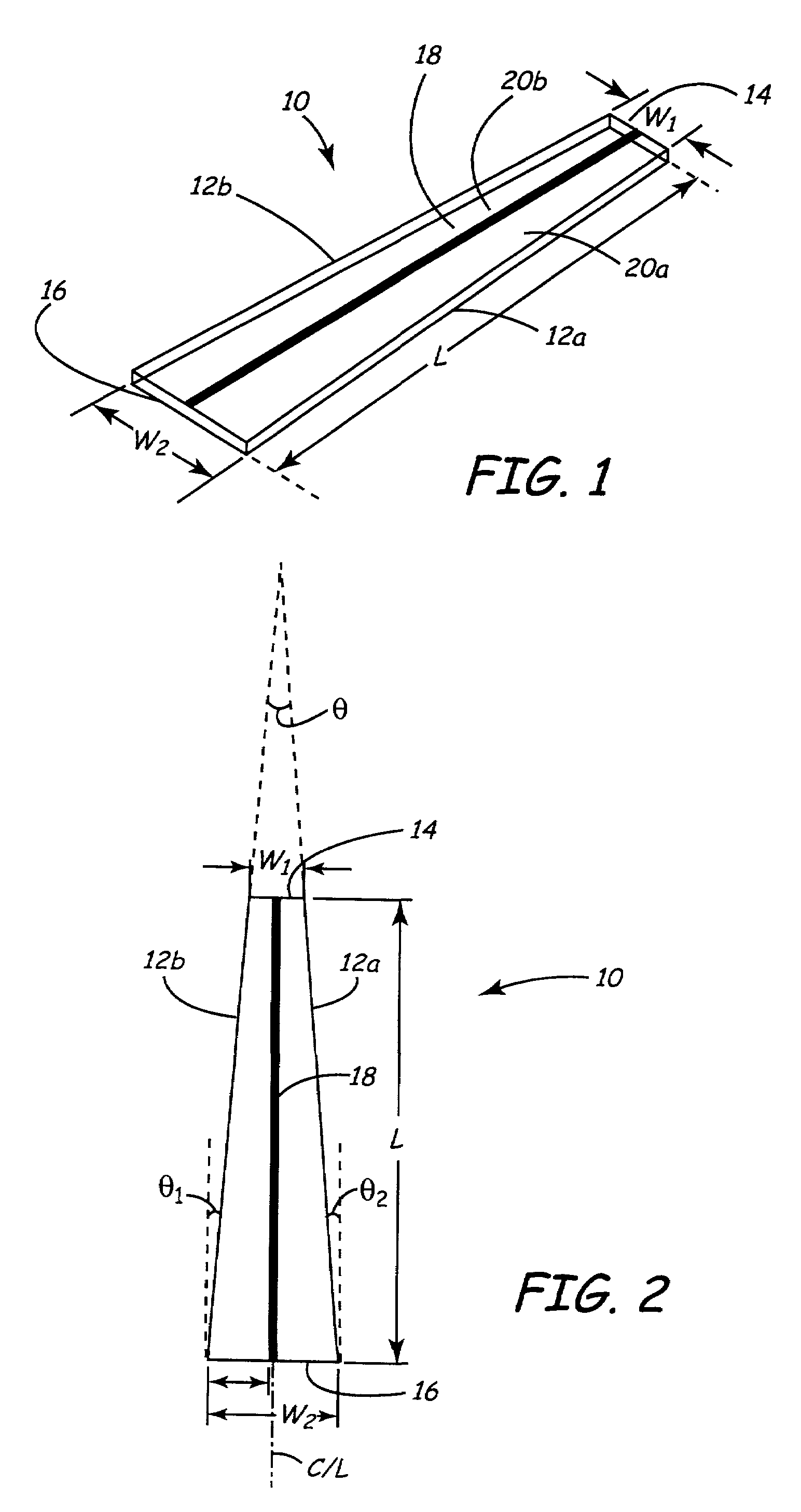
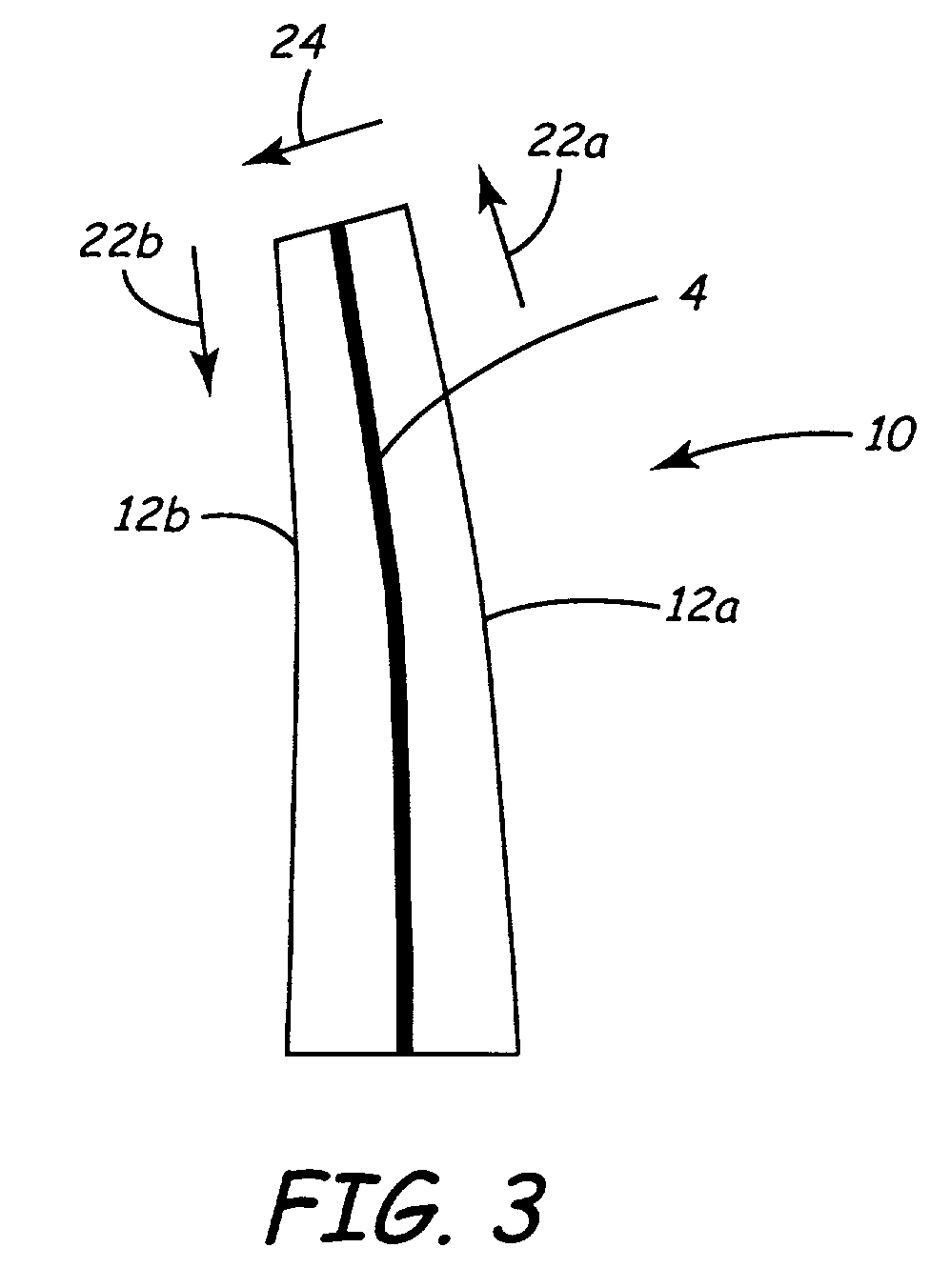
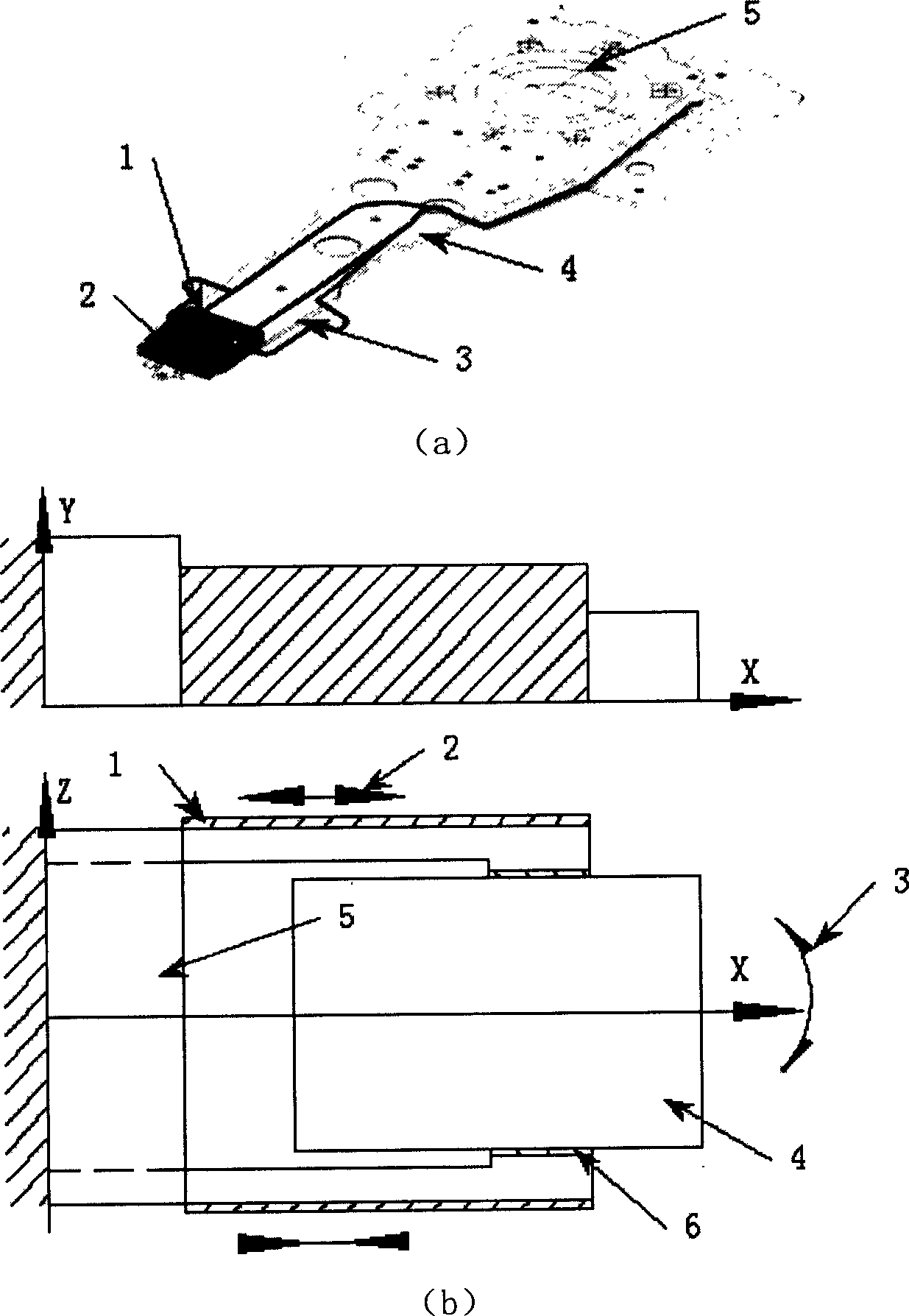
Tapered piezoelectric in-plane bimorph and method of fabricating
InactiveUS7005777B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesIn planePiezoelectric microactuator
Tapered elements fabricated from a substrate of a size many times that of a single element are disclosed. Such tapered elements may be used as piezoelectric microactuators such as in-plane piezoelectric bimorph microactuators. A unique method of fabricating such tapered elements is provided. According to the method, cutting directions are first defined, the substrate is then cut a plurality of times in each cutting direction with adjacent cuts in each cutting direction indexed by proper indexing distances which are determined based on the dimensions of the final tapered elements. In one embodiment of the method, a plurality of optically detectable marks are used to define the cutting directions and cutting means is accordingly optically aligned with the cutting directions.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
System and method for improving piezoelectric micro-actuator operation by preventing undesired micro-actuator motion hindrance and by preventing micro-actuator misalignment and damage during manufacture
InactiveUS6873497B2Disposition/mounting of recording headsRecord information storageElectricityPiezoelectric microactuator
A system and method for improving piezoelectric micro-actuator operation by preventing undesired micro-actuator motion hindrance and by preventing micro-actuator misalignment during manufacture. A shim element is interposed between an electric circuit assembly and a lower portion of an actuator frame. The electric circuit assembly has a generally ‘O’-shaped portion configured so that an upper portion of said actuator frame is able to protrude through the ‘O’-shaped portion. The shim element is coupled between the electric circuit assembly and the lower portion of the actuator frame.
Owner:SAE MAGNETICS (HK) LTD
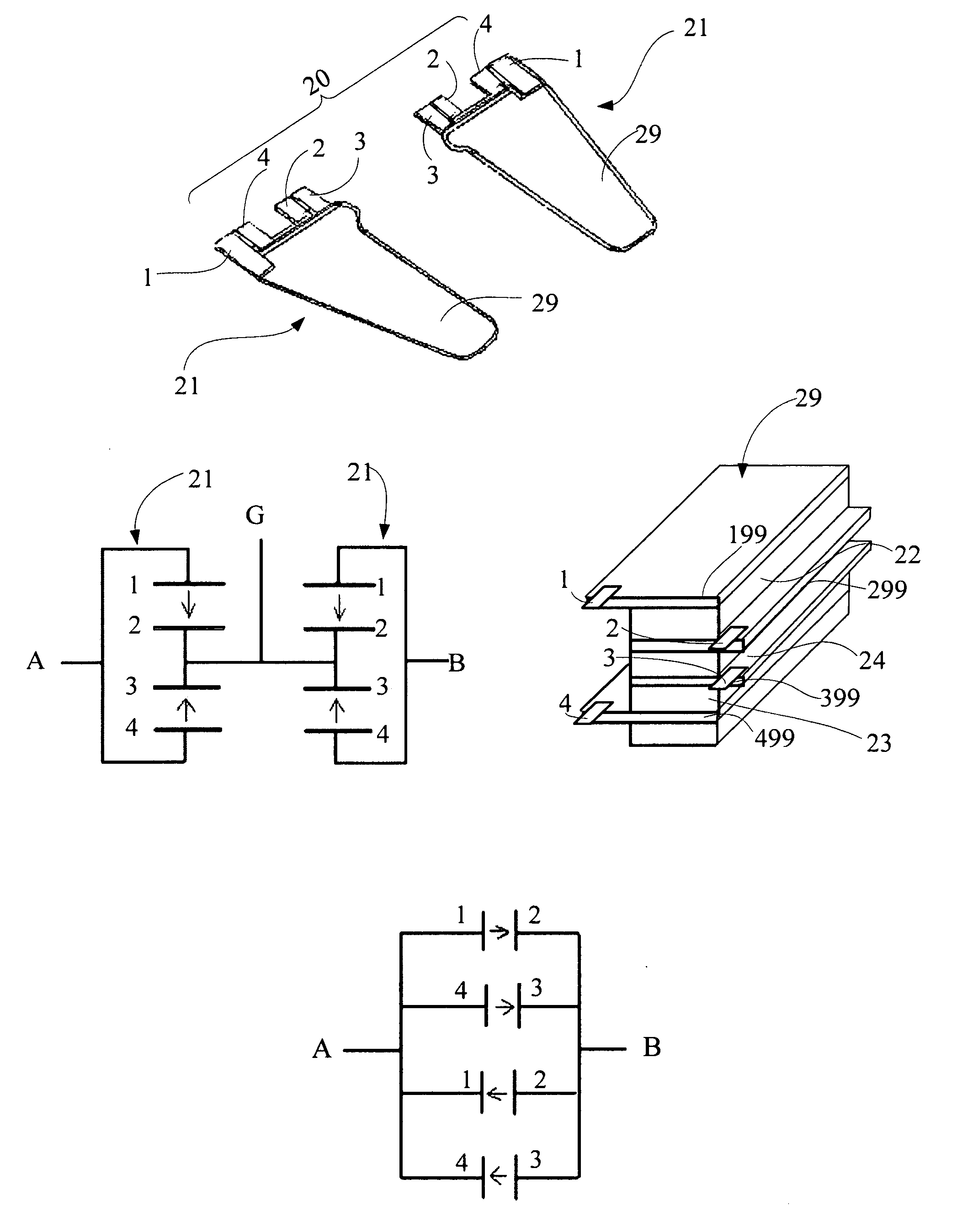
Comb structure for a disk drive suspension piezoelectric microactuator operating in the D33 mode, and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS9431041B1Surface damageSmall electrode gapArm with actuatorsMounting/attachment of transducer headPiezoelectric microactuatorEngineering
A microactuator assembly is formed by depositing PZT material over electrode gaps, the electrode gaps being defined by the spaces between interleaved fingers of metal that define alternating plus and minus electrodes. The PZT material is hardened and poled. The PZT material may be deposited and poled either as isolated islands of PZT material across respective electrode gaps, or as a continuous sheet of PZT material with localized areas of that material being poled and then activated. The individual PZT elements are arranged such that successive PZT elements extend in the same direction as across the electrode gaps. The resulting microactuator assembly acts in the d33 direction of the PZT elements. The electrodes have raised or recessed features such as ribs or castellations, with the PZT material mating with those features, thus anchoring the PZT material to the electrodes.
Owner:MAGNECOMP
Multi-Layer PZT Microactuator Having A Poled But Inactive PZT Constraining Layer
ActiveUS20170345450A1Arm with actuatorsRecord information storagePiezoelectric microactuatorEngineering
A multi-layer piezoelectric microactuator assembly has at least one poled and active piezoelectric layer and one poled but inactive piezoelectric layer. The poled but inactive layer acts as a constraining layer in resisting expansion or contract of the first piezoelectric layer thereby reducing or eliminating bending of the assembly as installed in an environment, thereby increasing the effective stroke length of the assembly. Poling only a single layer would induce stresses into the device; hence, polling both piezoelectric layers even though only one layer will be active in use reduces stresses in the device and therefore increases reliability.
Owner:MAGNECOMP
Circuit connection pad design for improved electrical robustness using conductive epoxy
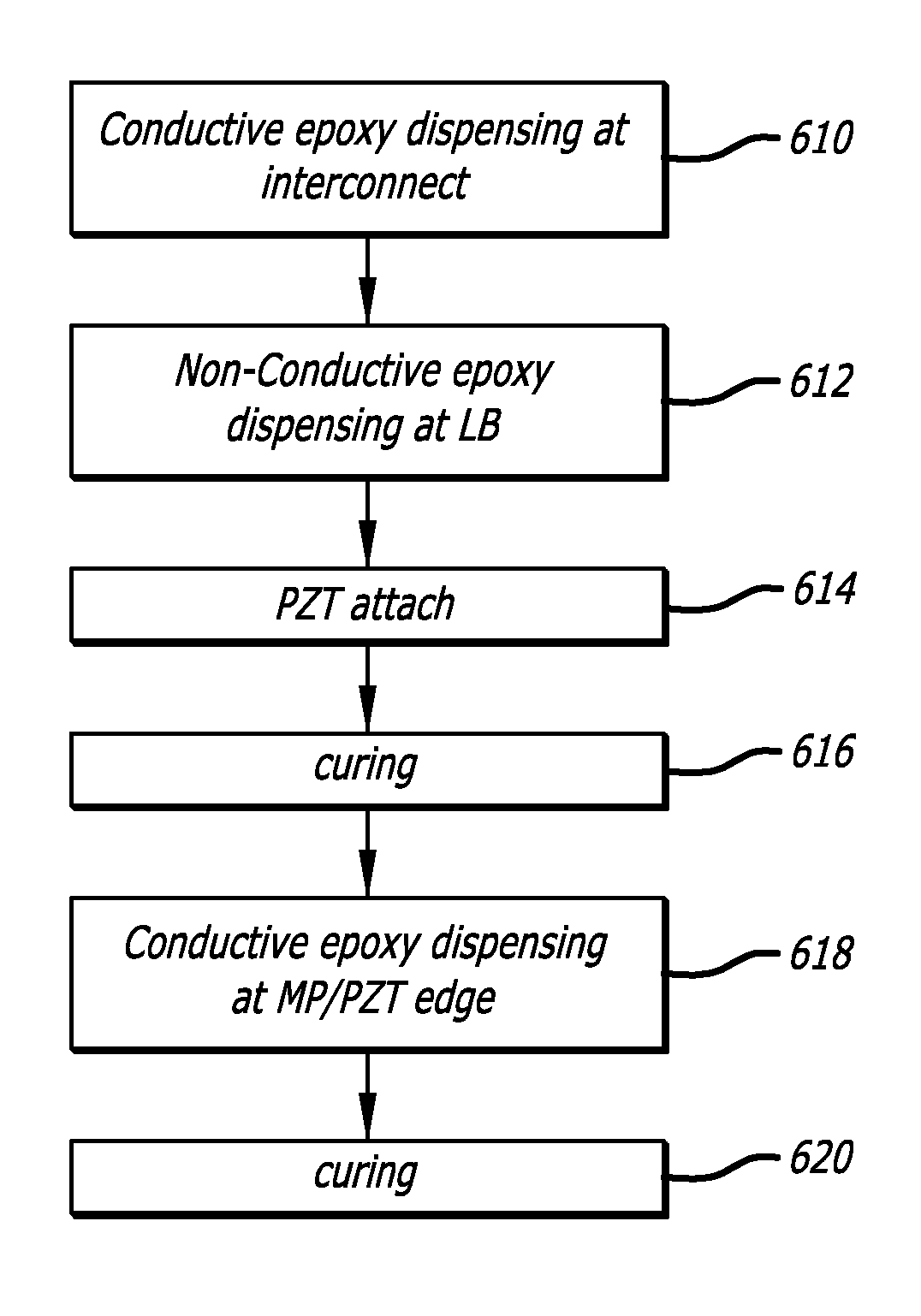
ActiveUS20160086625A1Easy to controlReliable electrical connectionRecord information storageMounting/attachment of transducer headEpoxyElectricity
Disk drives including head suspensions within dual stage actuation systems have improved electrical connectivity between electrical connection pads from flexible circuits as are applied to head suspension assemblies with piezoelectric microactuators as also provided to head suspension assemblies. A more robust electrical connection provides for better control of microactuator actuation for fine movements and positioning of magnetic read / write heads relative to disk data tracks as part of dual stage actuated suspension systems. Electrical connections utilize conductive epoxy for physically and electrically connecting electrically conductive trace connection pads with one or more surfaces of piezoelectric microactuators. Electrical connections include better conductivity by utilizing plural surface portions of electrical connection pads. The result is a more robust and predictable performance for high data resolution within disk drives.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Method of manufacturing piezoelectric microactuators having wrap-around electrodes
ActiveUS9911913B1Simple processSimplifies electrical connectionsTrack finding/aligningPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric microactuatorEngineering
Owner:MAGNECOMP
Circuit connection pad design for improved electrical robustness using conductive epoxy
ActiveUS9679593B2Easy to controlReliable electrical connectionRecord information storageMounting/attachment of transducer headEpoxyElectricity
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Head gimbal assembly having a radial rotary piezoelectric microactuator between a read head and a flexure tongue
ActiveUS20110149439A1Arm with actuatorsRecord information storagePiezoelectric microactuatorEngineering
A novel head gimbal assembly (HGA) includes a piezoelectric microactuator having a first side and an opposing second side. The first side includes a plurality of anchor regions that extend radially from a center point and are bonded to the gimbal tongue. The first side also includes a first plurality of non-bonded regions lying between the anchor regions. The second side includes a plurality of link regions that extend radially from the center point and are bonded to a top surface of the read head. The second side also includes a second plurality of non-bonded regions lying between the link regions. Each of the plurality of link regions is angularly spaced between two of the plurality of anchor regions.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Multilayer film piezoelectric element of micro-actuator for hard disk and method for making same
InactiveCN1571181AExcellent displacement/voltage sensitivityRaise the resonant frequencyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyRecord information storagePiezoelectric microactuatorElectricity
The invention relates to a multifilm piezoelectric element in harddisk micro-actuator and its preparing method. It makes piezoelectric ceramic film by casting method or web printing technique, etc., and makes medium electrode layer by web printing technique, etc. It adopts Ag / Pd electrode and PMN-PZT material to realize low- temperature coburn (reducing from >1300 deg.C to 1030-1190 deg.C). The invention increases the free-end displacement of magnetic head cantilever installed with piezoelectric micro-actuator to >=0.80 mum and resonance frequency to >15KHz (at the condition of external voltage <=40V) to make the micro-actuator have the characters of excellent displacement / voltage sensitivity, resonance frequency, driving force, etc., thus applied to accurate addressing and path location of secondary micro- actuator of a computer harddisk double-stage servo system. It can be widely applied to other technical fields of micro-actuation and position control.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method and apparatus for a single piezoelectric micro-actuator in a head gimbal assembly of a hard disk drive
InactiveUS20070291418A1Low costReduce the total massDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageHard disc drivePiezoelectric microactuator
A slider cradle for lateral positioning slider near rotating disk surface in hard disk drive, consisting essentially of piezoelectric micro-actuator coupling to slider cradle blank, further including piezoelectric micro-actuator coupling to first slider mount arm near slider mount and near slider mount base. A head gimbal assembly including slider cradle coupling to slider, flexure finger, and flexure finger electrically coupling to piezoelectric contacts. An actuator arm coupling to at least one head gimbal assembly. An actuator assembly, comprising voice coil coupling to at least one actuator arm. A hard disk drive containing actuator assembly. The invention includes a method of making slider cradle blank and slider cradle. The products of this process. Making head gimbal assembly, actuator assembly and hard disk drive using the invention's components. The head gimbal assembly, the actuator assembly, and the hard disk drive are products of these processes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for preventing operational and manufacturing imperfections in piezoelectric micro-actuators
InactiveUS7225513B2Piezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric microactuatorMicro actuator
A method of manufacturing an actuator includes applying at least one layer of electrically-conductive material and at least one layer of electrically-insulative material to an actuator block, and separating the actuator block into a plurality of actuators, each actuator having at least one actuator finger. The electrically-conductive material and the electrically-insulative material are applied one layer upon another in an alternating manner to the actuator block in at least one actuator finger location. The layer of insulative material is larger in area than the layer of conductive material such that an insulative layer, applied to the actuator block and sandwiching a conductive layer between the insulative layer and the actuator block, at least partially encloses and electrically isolates the electrically-conductive layer by covering the conductive material on at least three sides.
Owner:SAE MAGNETICS (HK) LTD
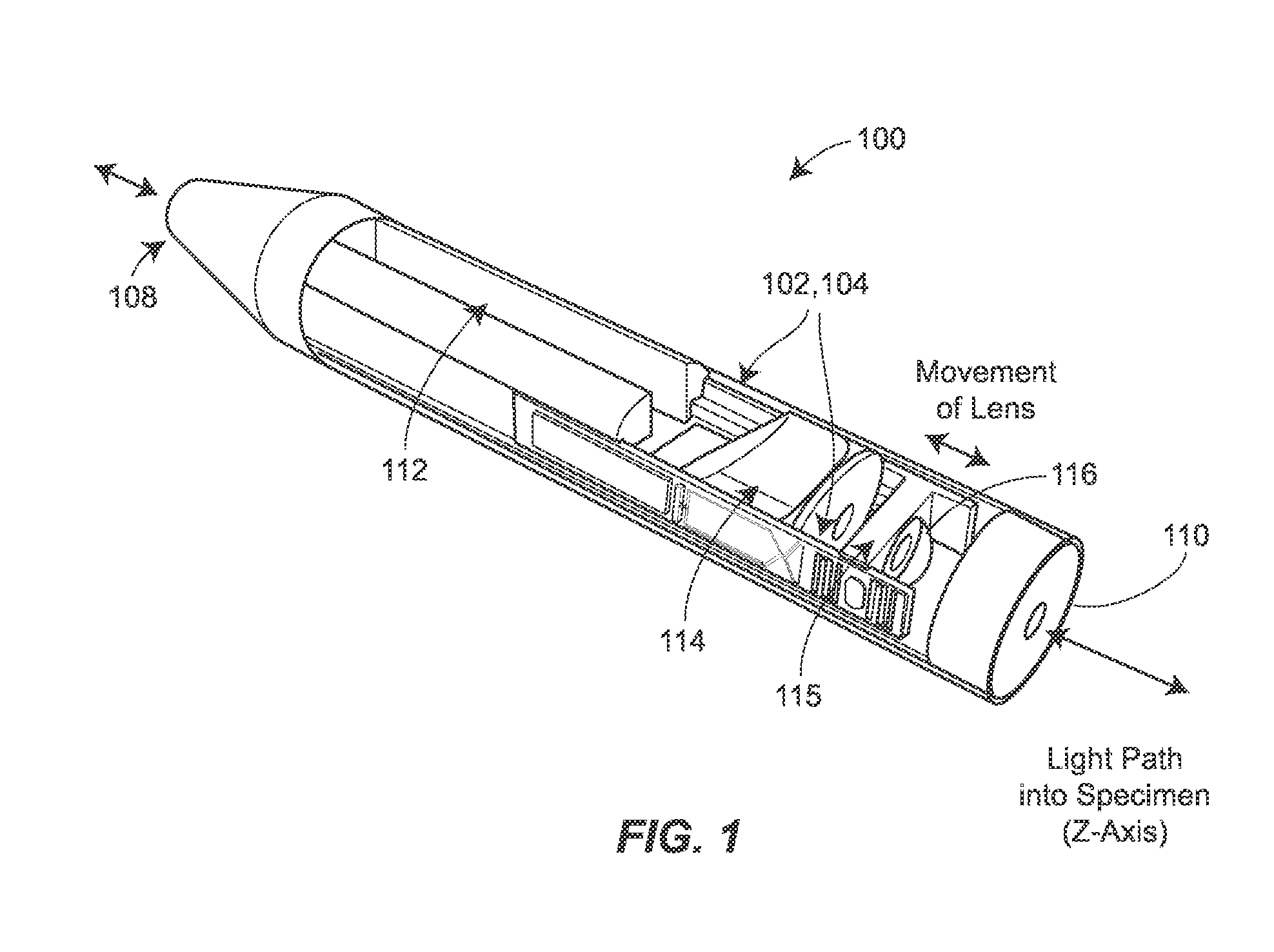
Two-photon endoscopic scanning assembly for inflammatory disease detection
ActiveUS8807801B2Minimize total cross-sectional area and volumeOesophagoscopesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseasePiezoelectric microactuator
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Multi-Layer PZT Microactuator Having A Poled But Inactive PZT Constraining Layer
ActiveCN107689231AEnhanced stroke sensitivityLow data seek timeMounting/attachment of transducer headPiezoelectric microactuatorElectricity
A multi-layer piezoelectric microactuator assembly has at least one poled and active piezoelectric layer and one poled but inactive piezoelectric layer. The poled but inactive layer acts as a constraining layer in resisting expansion or contract of the first piezoelectric layer thereby reducing or eliminating bending of the assembly as installed in an environment, thereby increasing the effectivestroke length of the assembly. Poling only a single layer would induce stresses into the device; hence, polling both piezoelectric layers even though only one layer will be active in use reduces stresses in the device and therefore increases reliability.
Owner:MAGNECOMP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com