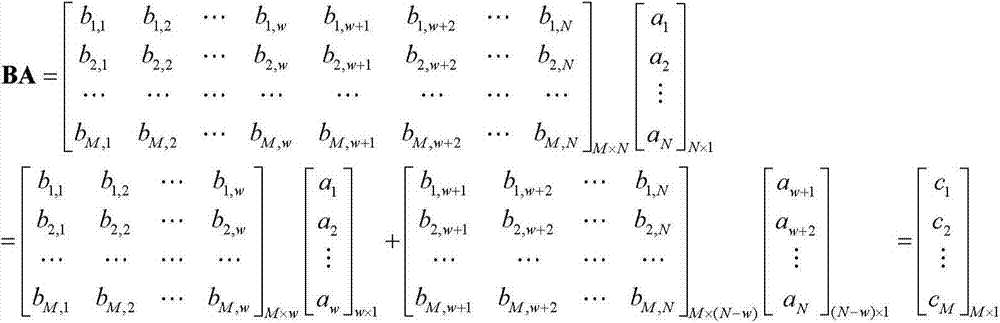Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
302 results about "Data resolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
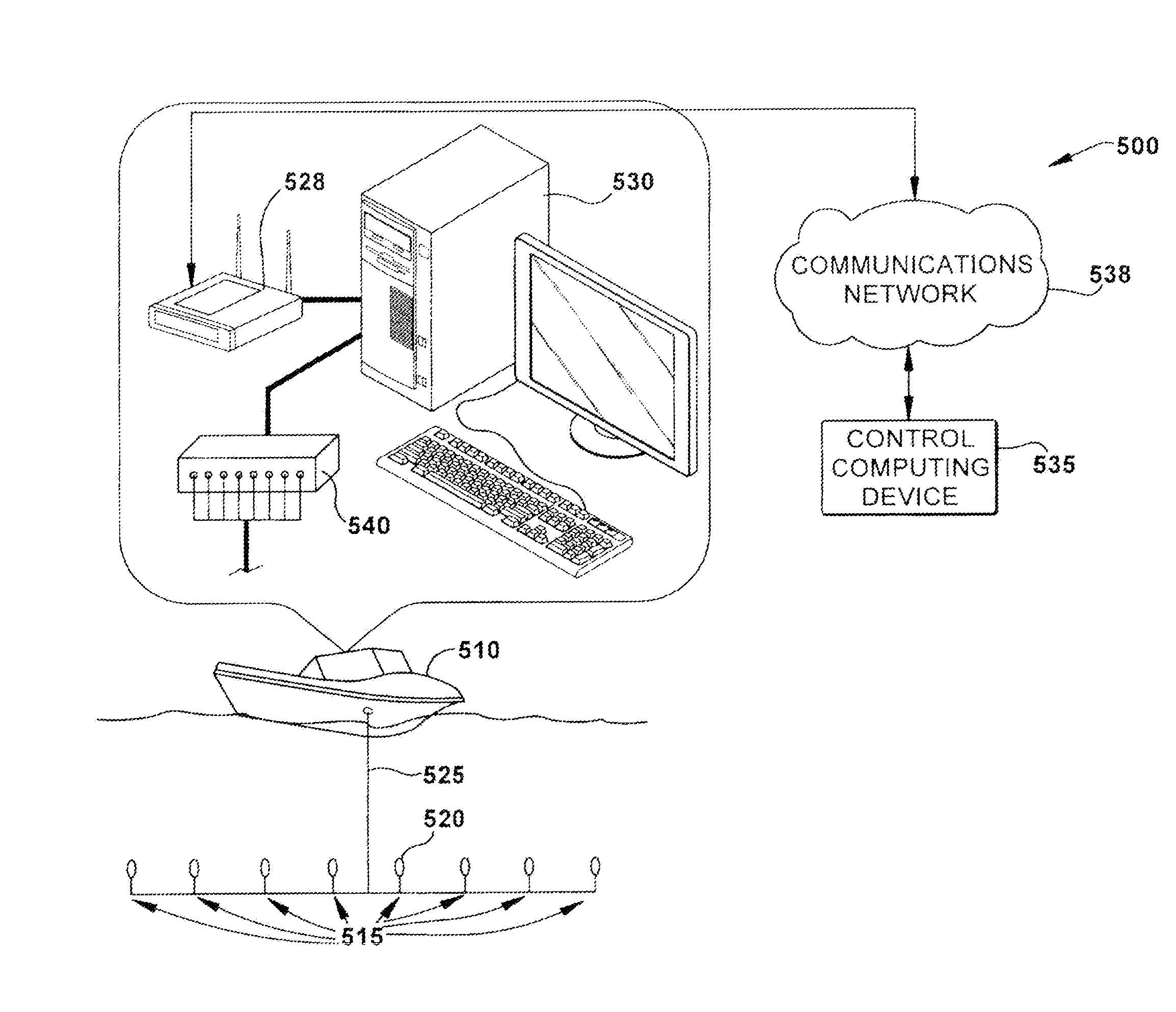
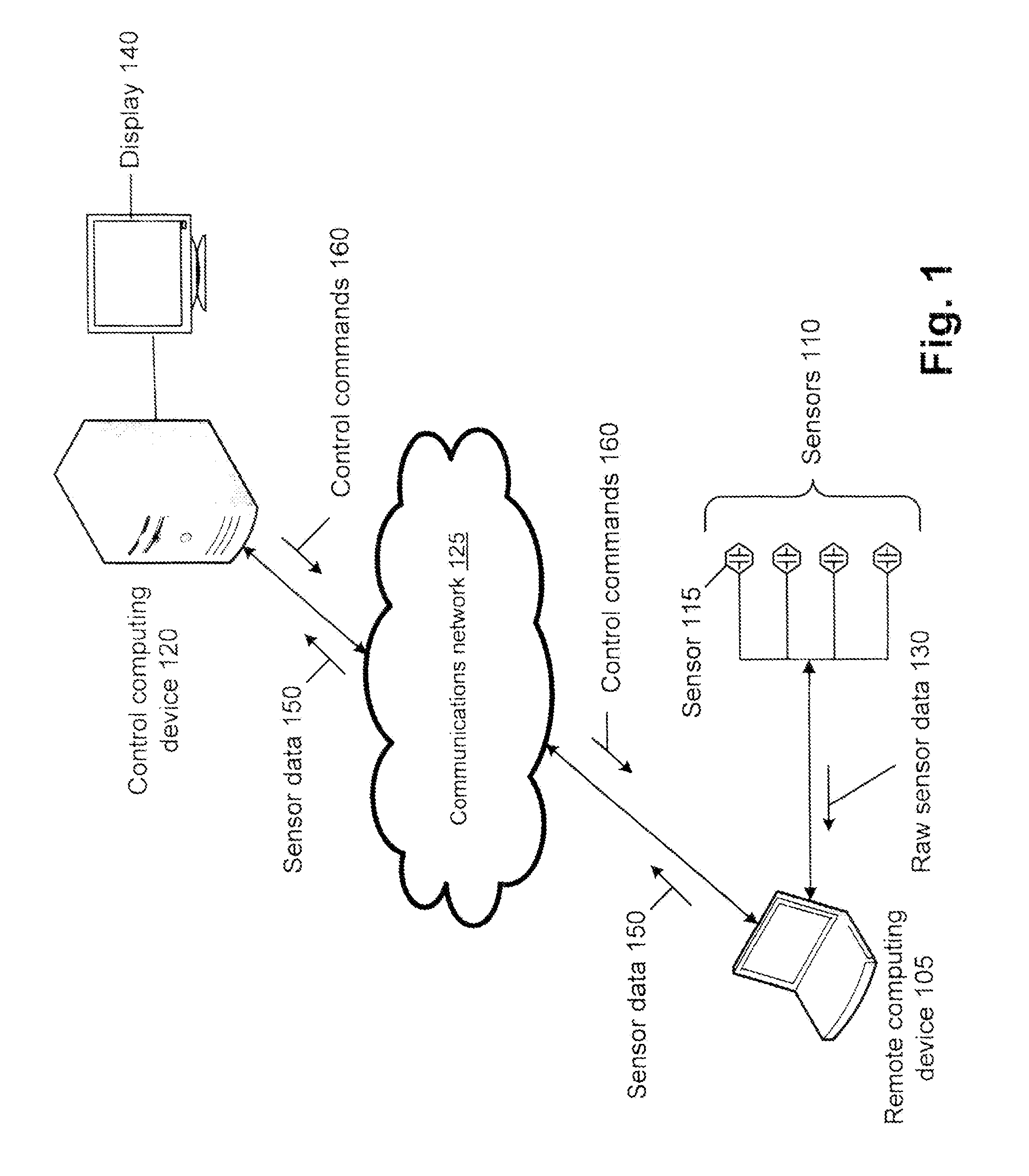
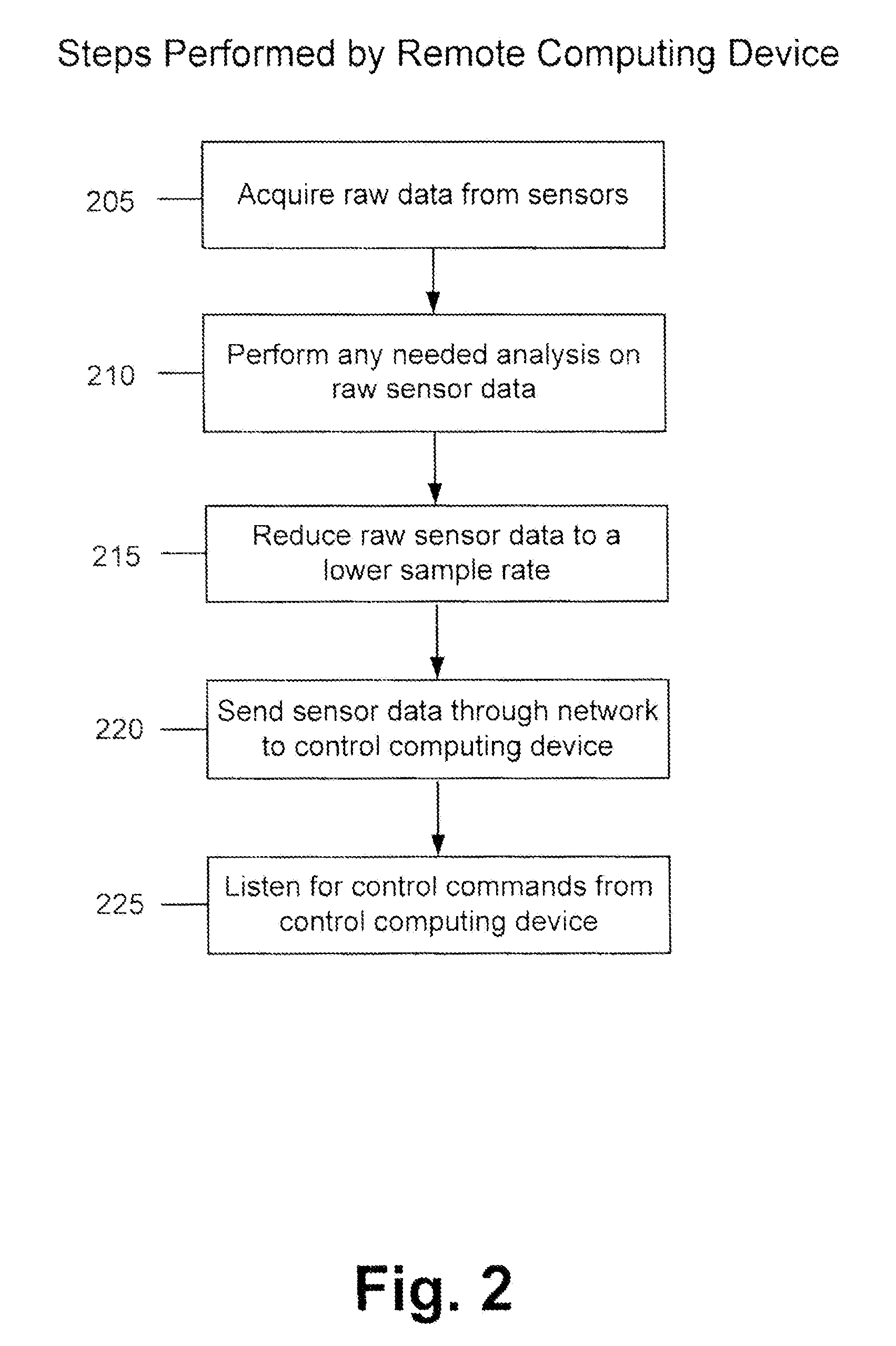
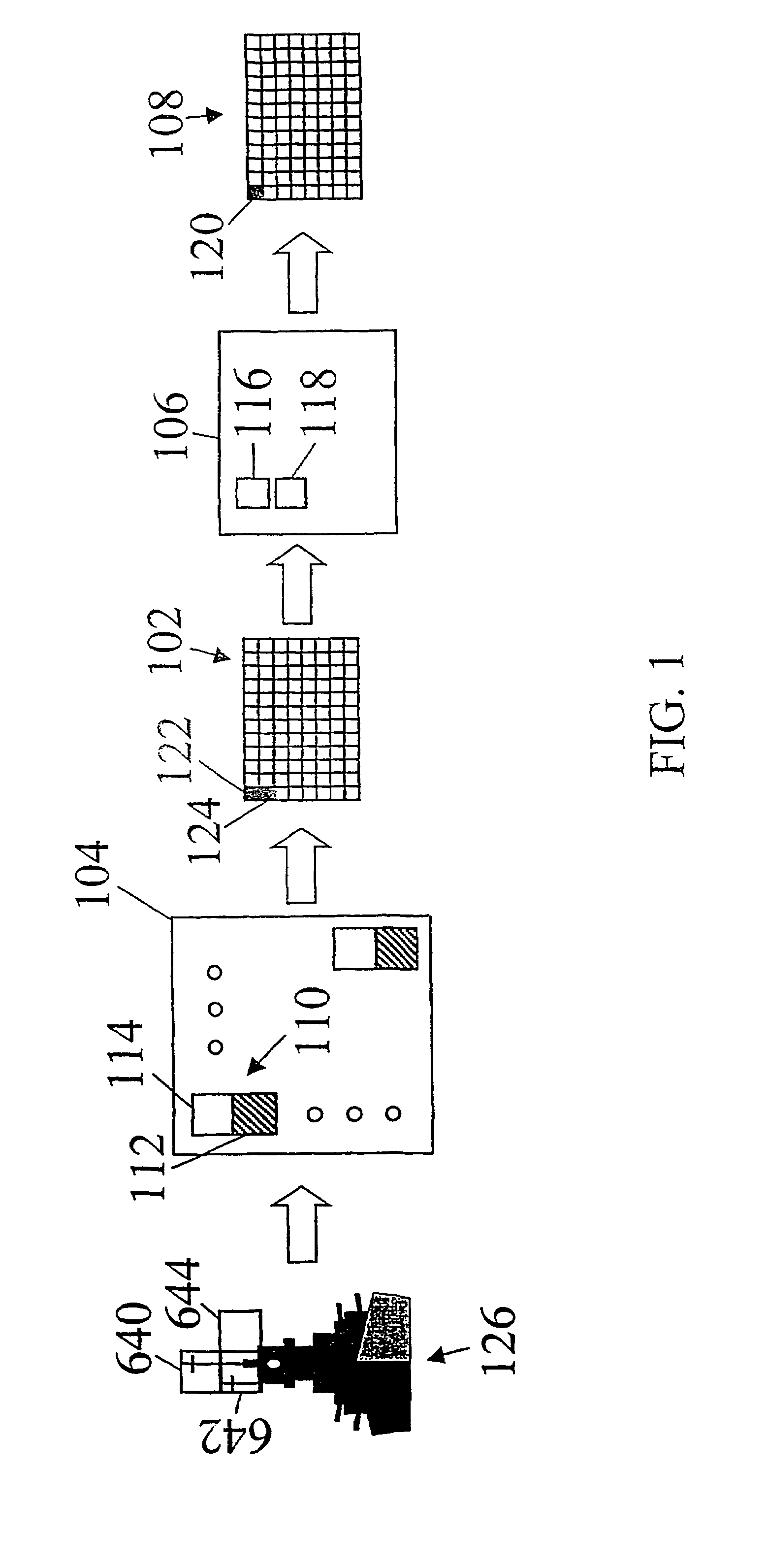
Method and apparatus for adaptive transmission of sensor data with latency controls
ActiveUS20100278086A1High bandwidthData latency is minimizedNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesAutomatic controlThroughput
Disclosed is a method and apparatus to continuously transmit high bandwidth, real-time data, on a communications network (e.g., wired, wireless, and a combination of wired and wireless segments). A control computing device uses user or application requirements to dynamically adjust the throughput of the system to match the bandwidth of the communications network being used, so that data latency is minimized. An operator can visualize the instantaneous characteristic of the link and, if necessary, make a tradeoff between the latency and resolution of the data to help maintain the real-time nature of the system and better utilize the available network resources. Automated control strategies have also been implemented into the system to enable dynamic adjustments of the system throughput to minimize latency while maximizing data resolution. Several applications have been cited in which latency minimization techniques can be employed for enhanced dynamic performance.
Owner:STEVENS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
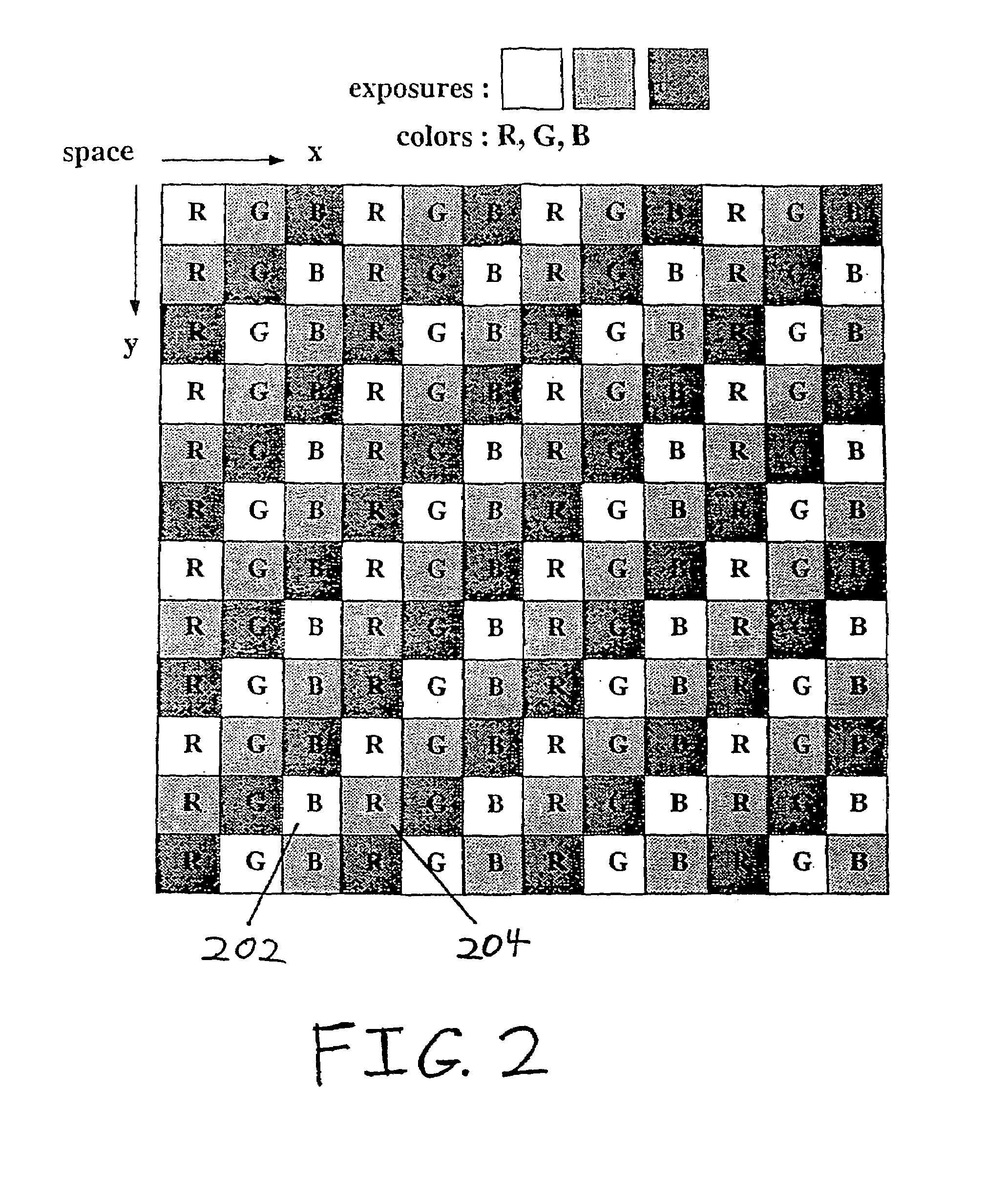
Method and apparatus for enhancing data resolution
InactiveUS7149262B1High data resolutionGeometric image transformationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsImage resolutionSample image
A resolution enhancement algorithm is trained on sample images to obtain a polynomial model mapping of low resolution image data to high resolution image data. The polynomial model mapping is applied to other low resolution images to obtain corresponding higher resolution images. The mapping provides resolution enhancement which is superior to that of conventional image data interpolation techniques.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
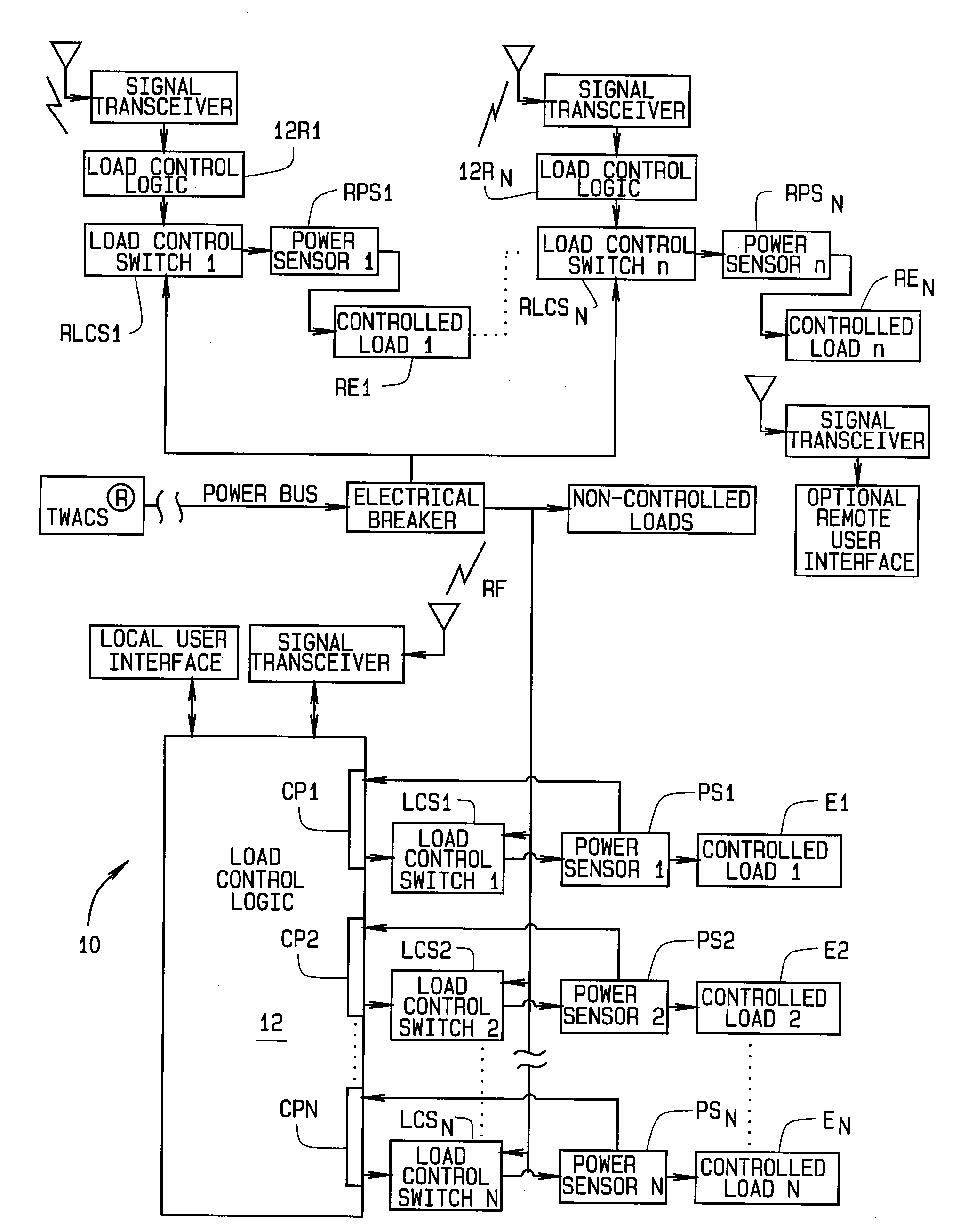
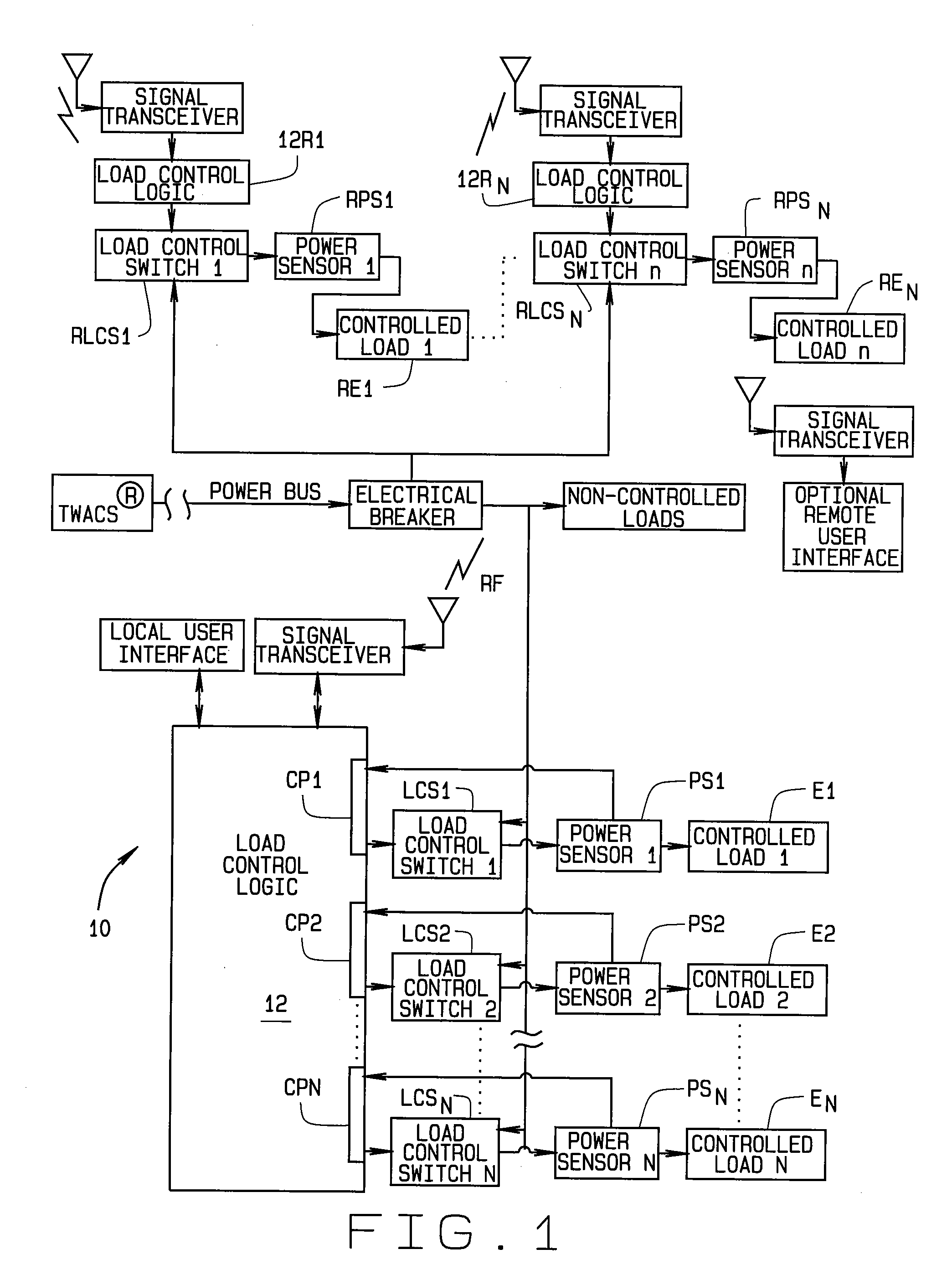
Method for load control using temporal measurements of energy for individual pieces of equipment
ActiveUS20100070103A1Improve efficiencyConducive to loadMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlLoad SheddingDistribution power system
A method for load control in an electrical distribution system using energy usage profiles based on temporal measurements. A load control unit (10) installed at a customer site profiles equipment (E1-En) directly connected to the load control unit and remotely located equipment (RE1-REn) wirelessly connected to the load control unit using measurements of time rather than energy usage. This reduces the cost and complexity of the load control unit. Profiling is done for individual pieces of load controlled equipment rather than for the site as a whole. This improves data resolution. The load control unit controls the load only when the equipment is powered, and adaptively synchronizes load shedding during this time, so to improve local load control performance. Termination of a load control event results in gradual reduction in load shedding so to control the inrush of demand seen by the distribution system. Performance metrics related to the load control are provided to the utility such that complexity of the system is reduced through decreased computations.
Owner:ACLARA TECH LLC
Digital amplifier with improved performance
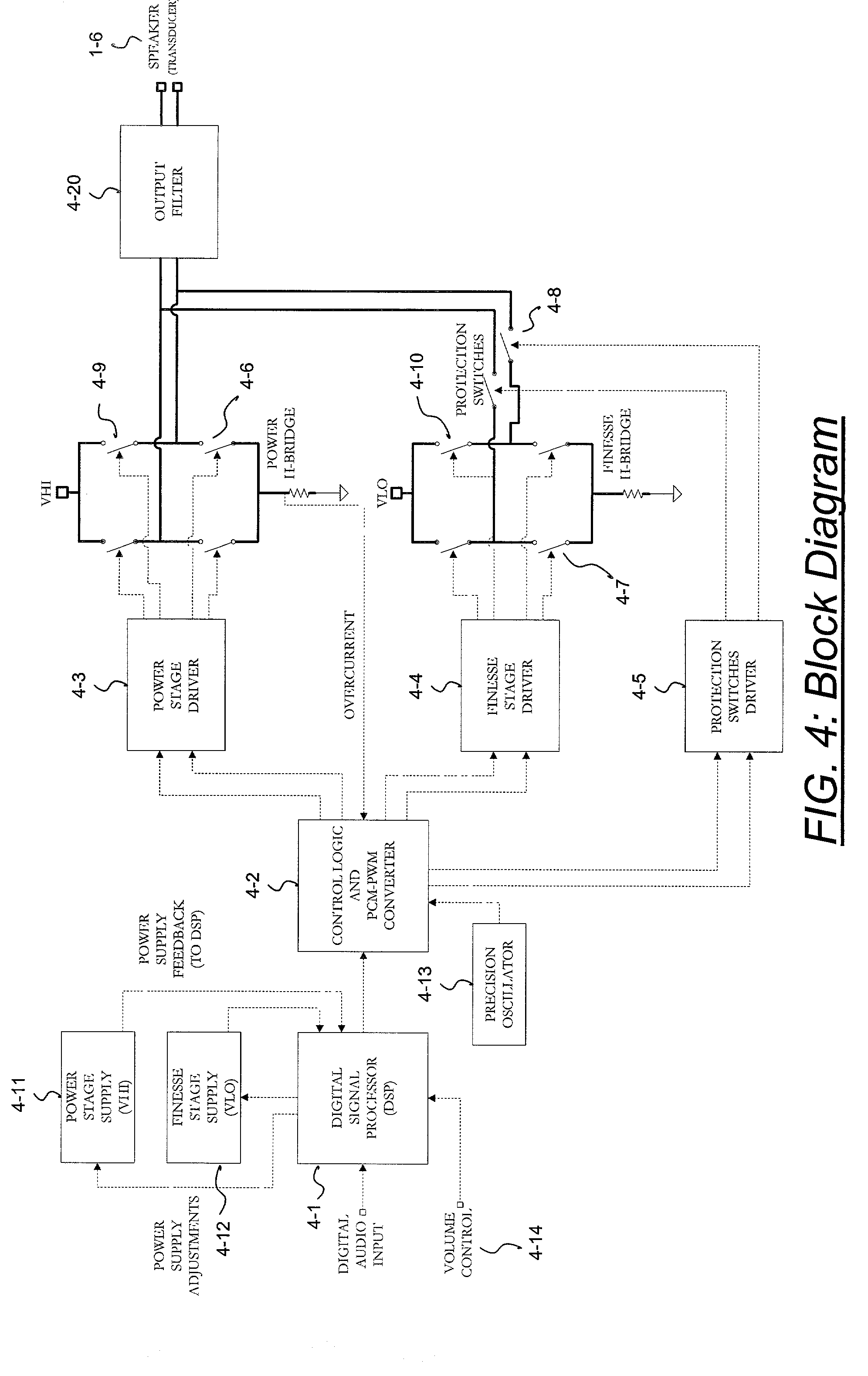
InactiveUS6593807B2Improve dynamic rangeImprove linearityNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsPower amplifiersDigital dataLow-pass filter
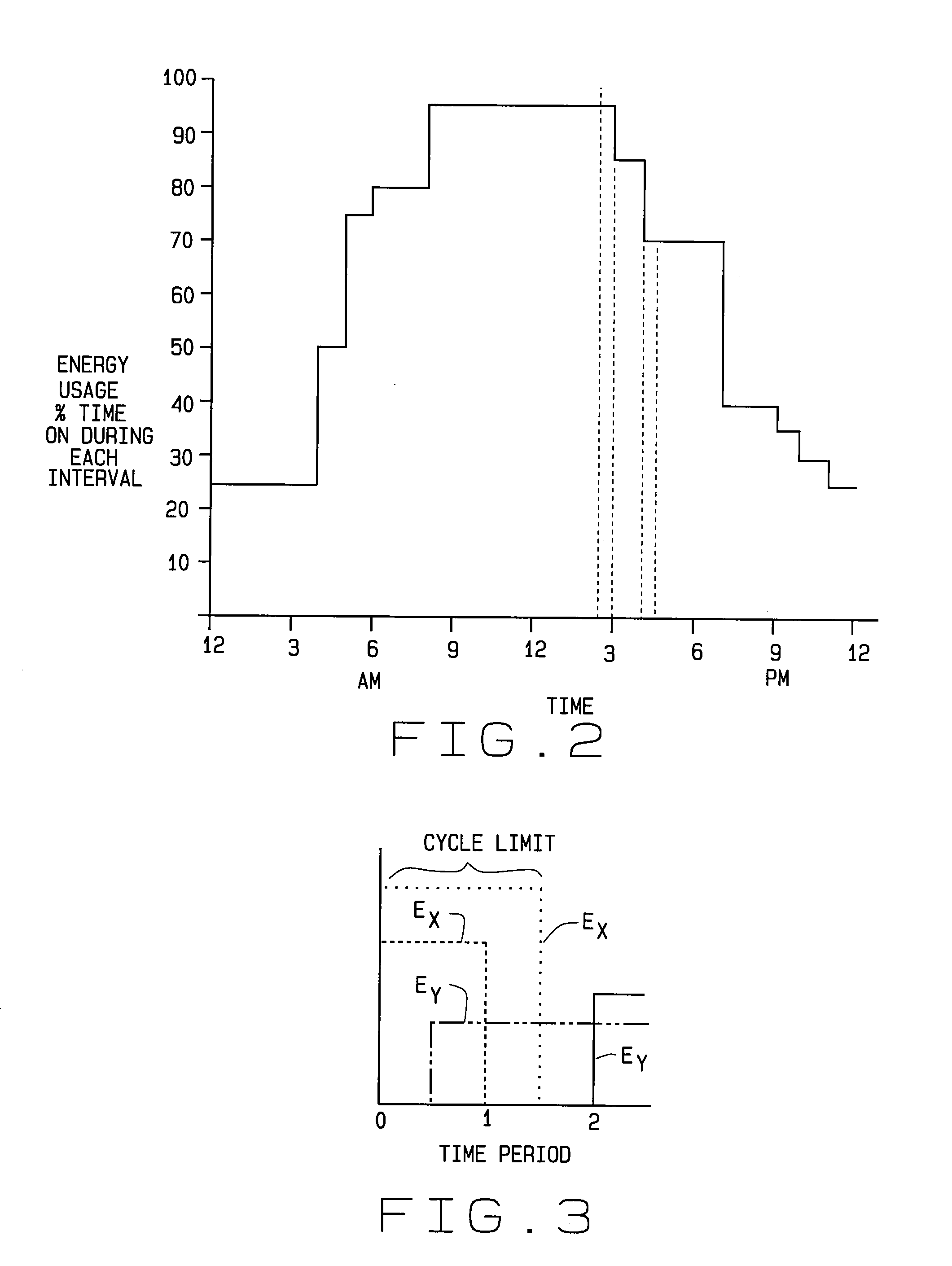
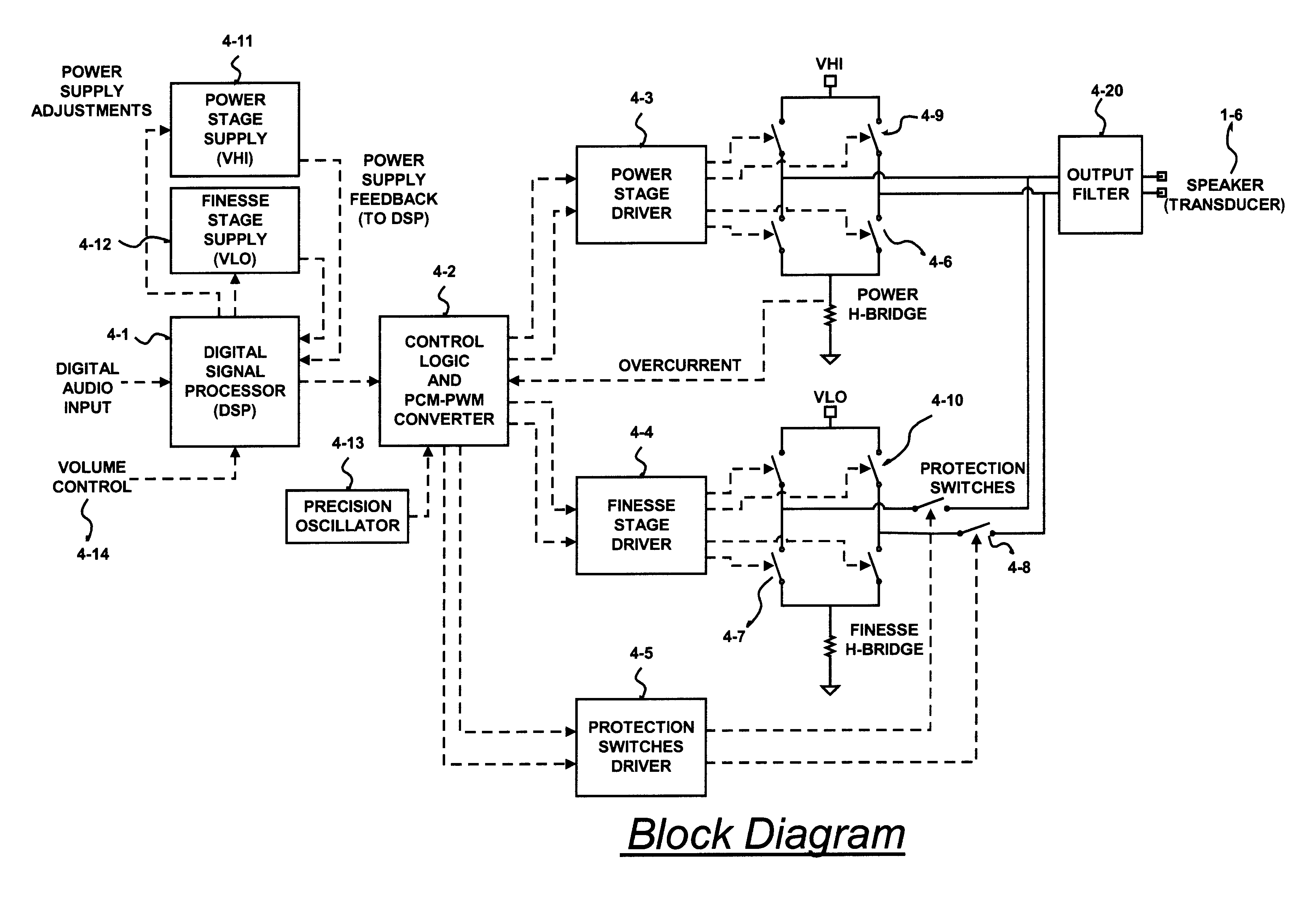
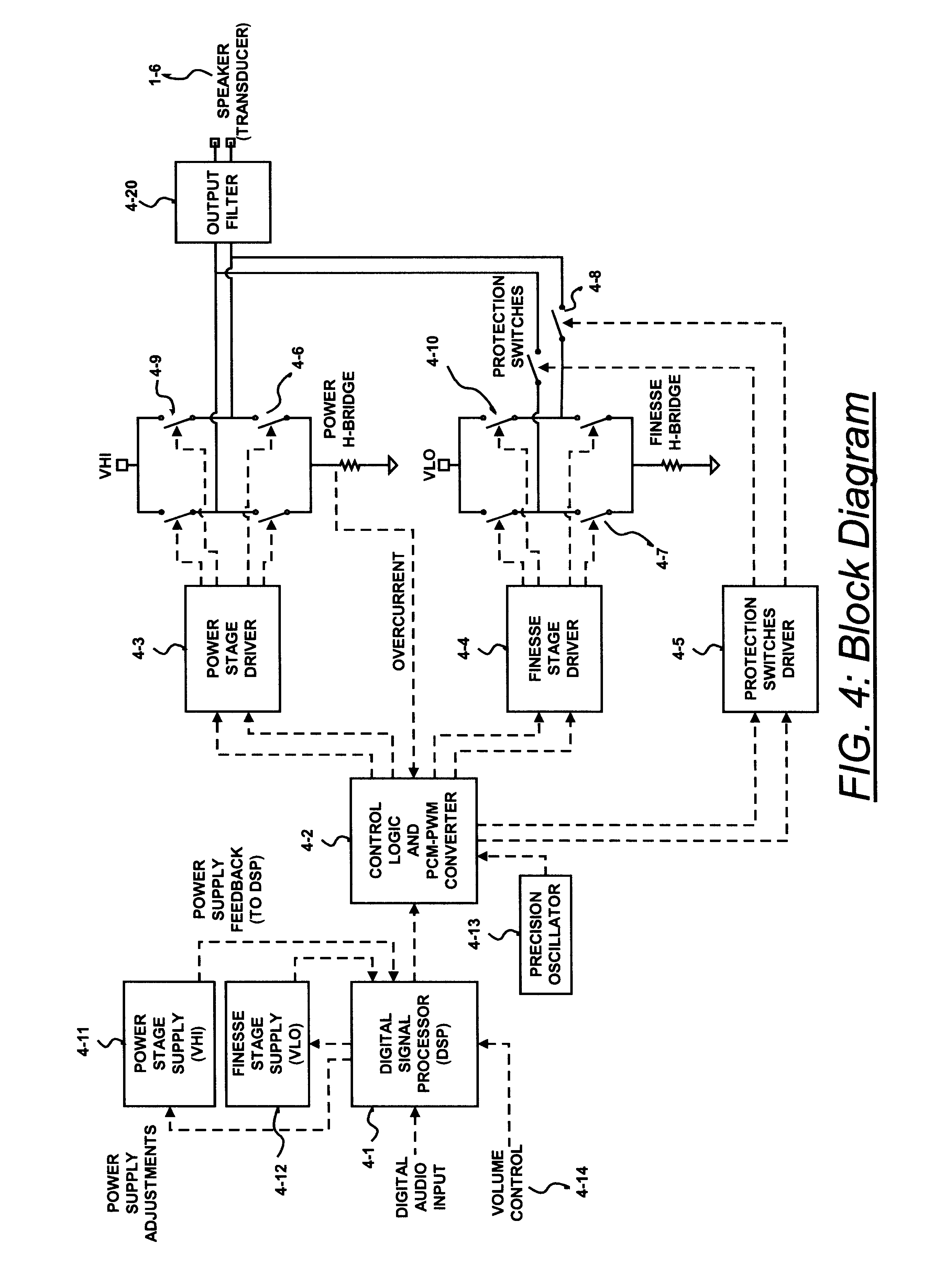
A class D amplifier uses a summation of two or more PWM output stages to achieve an increased dynamic range and improved linearity for any given clock operating speed. The amplifier accepts a digital data stream as its input, such as from a compact disk, or other compatible media, at a data rate, Fa, that could be 44.1 kHz, 96 kHz, or any other rate appropriate for audio data. In the preferred embodiment, the input audio data resolution, N bits, would be split into two data samples, of J and K.Internal switching frequency, Fs, switches the PWM with an over sampling factor M, where Fs=M*Fa. The time resolution of the PWM is determined by a precision oscillator that operates at Fc=Fs*(max(J,K)-log2(M)+1).The J most significant bits would be routed to a power PWM stage operated at a DC voltage of VHI. The K least significant bits are routed to a finesse PWM stage operated at a DC voltage of VLO.The ratio of VLO to VHI will be appropriate for the ratio of K and J so the summation of the power PWM stage and the finesse PWM stage will provide the full range of N bits. This summation is accomplished with a low pass filter and time-division multiplexing of the two PWM stages.A micro controller (MCU) is used to apply a sample packet distribution algorithm to provide more resolution by reducing quantization noise in the audio band of interest. The MCU is also used to calibrate the VLO or VHI, or to calibrate the PWM timing of the two PWM stages to achieve appropriate performance.
Owner:GROVES JR WILLIAM HARRIS +1
Data compression system and method for a weather radar system
A method of compressing data in a weather radar system utilizes a compression system. Weather radar data associated with graphical images provided on a weather radar display is compressed for downloads or downlinks from the airplane or storage on the airplane. The weather radar data can be compressed from any part of the process. In one embodiment, spatial resolution of the data is decreased while data resolution is increased.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
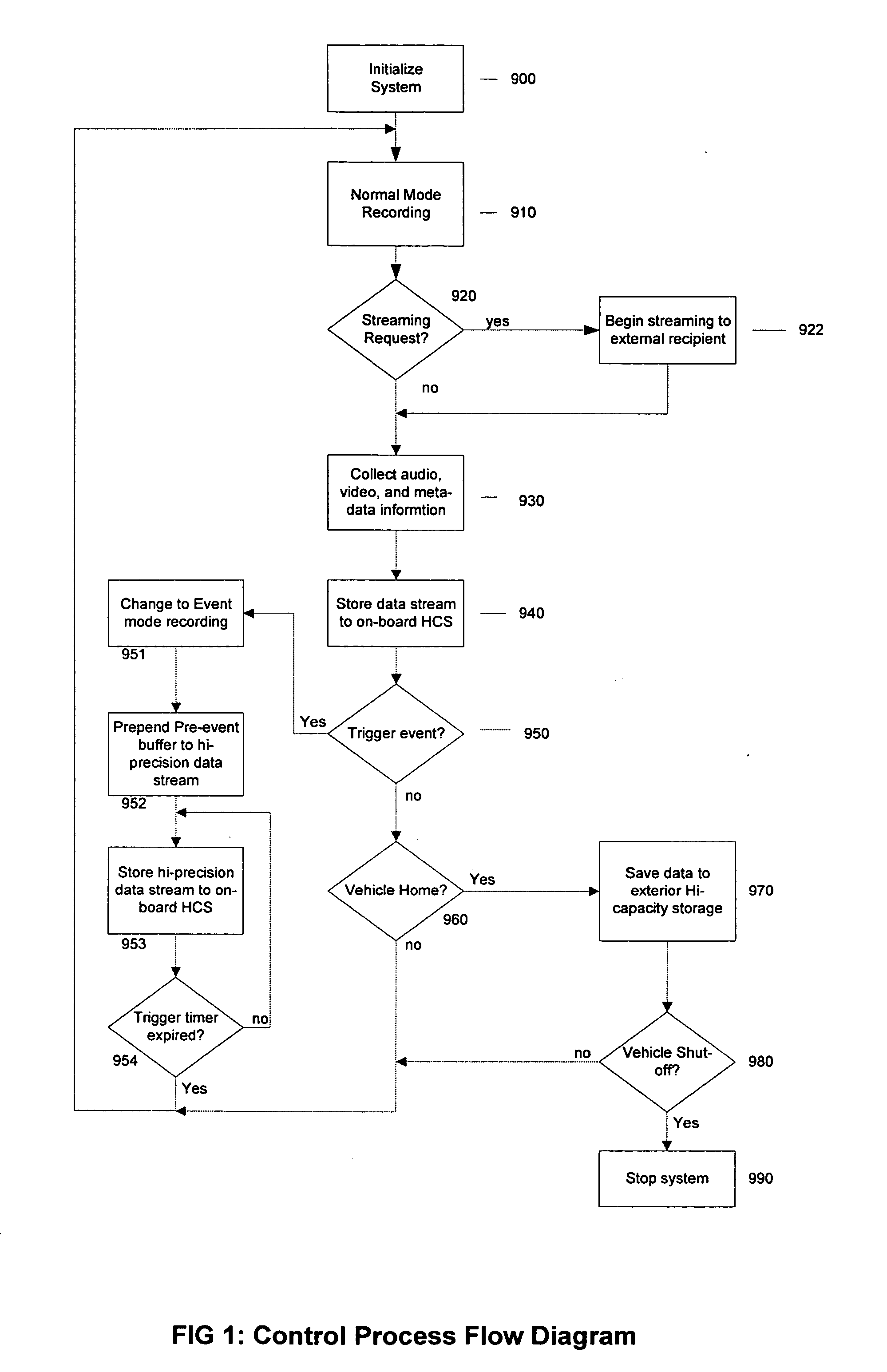
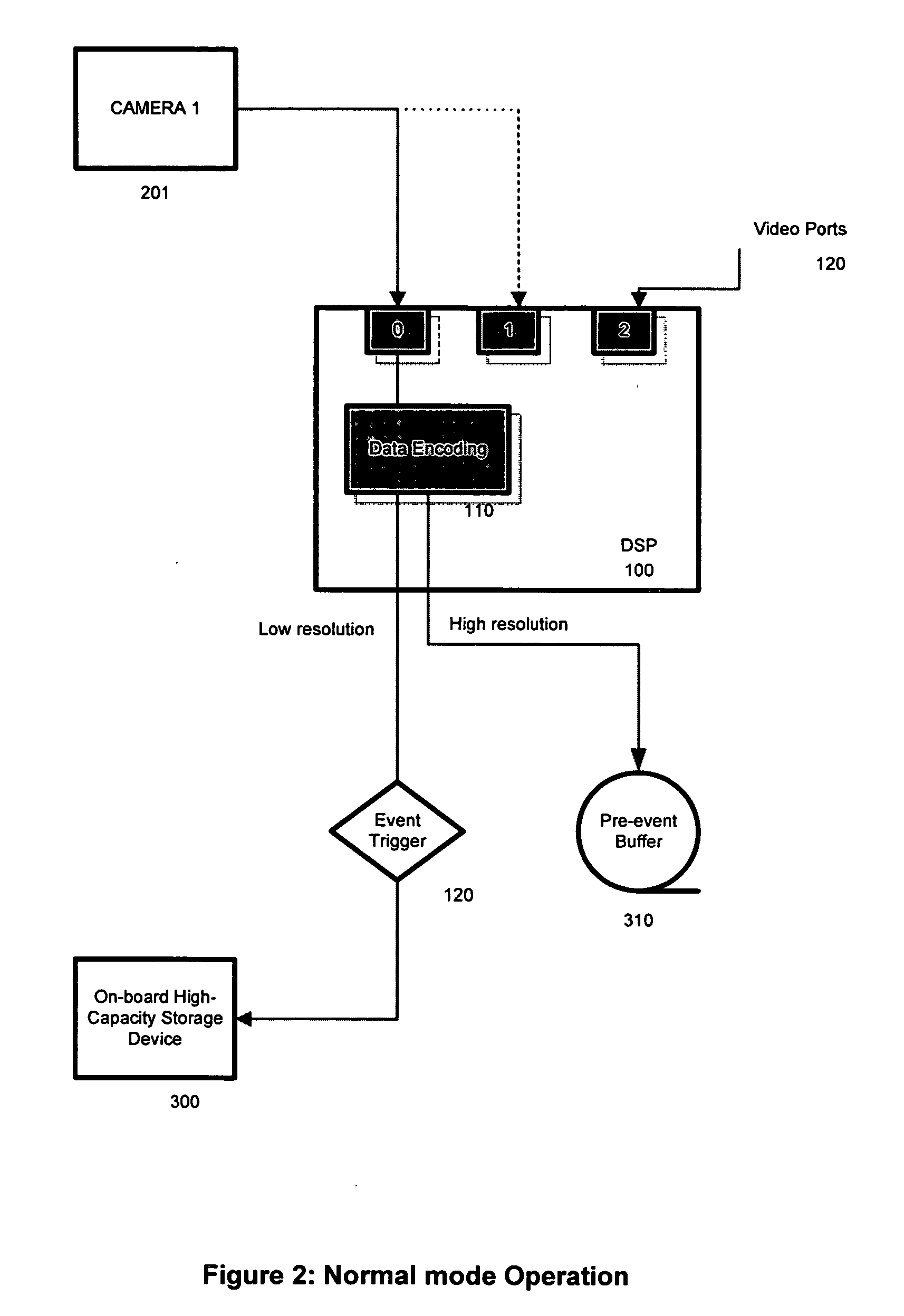
High resolution pre-event record
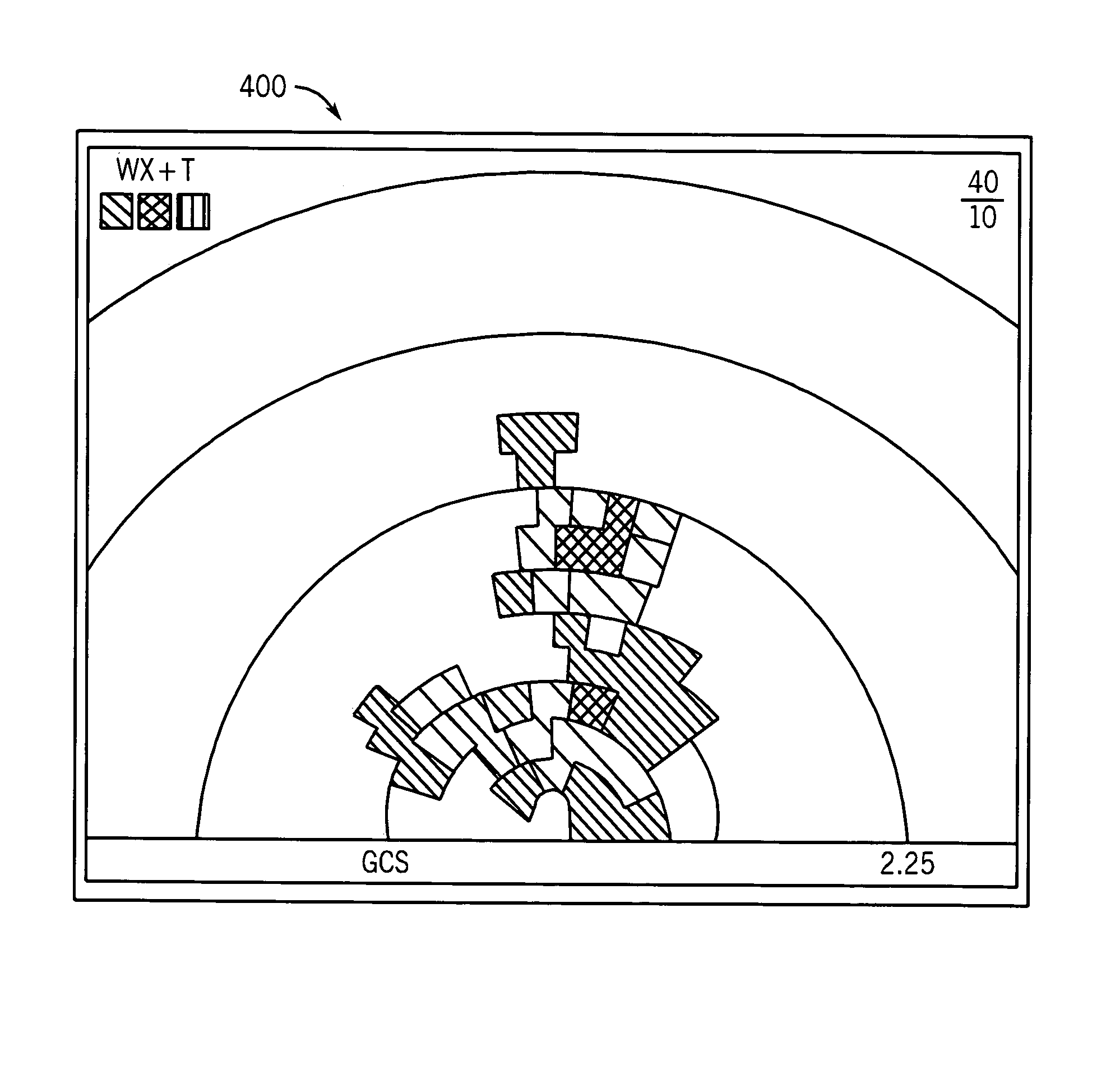
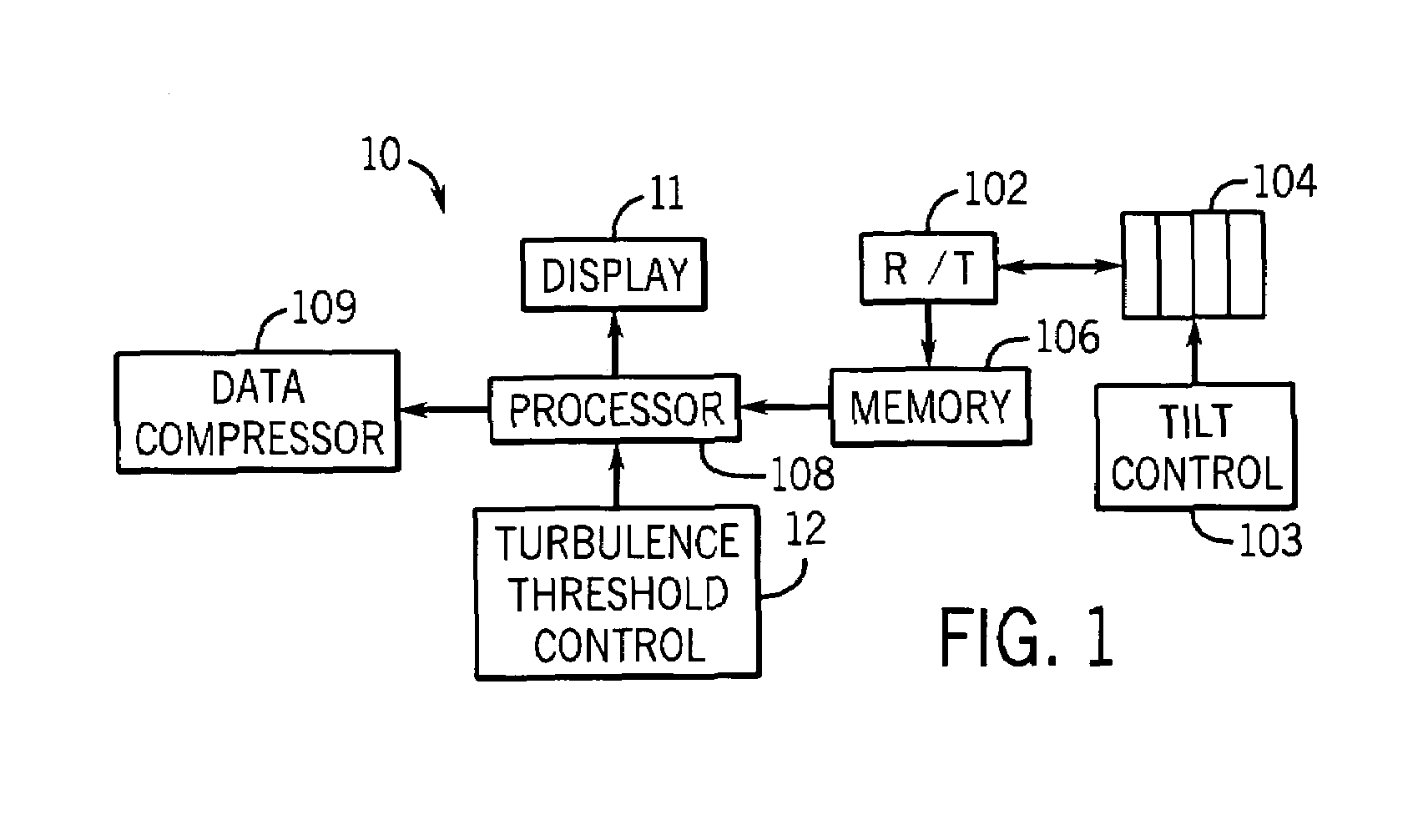
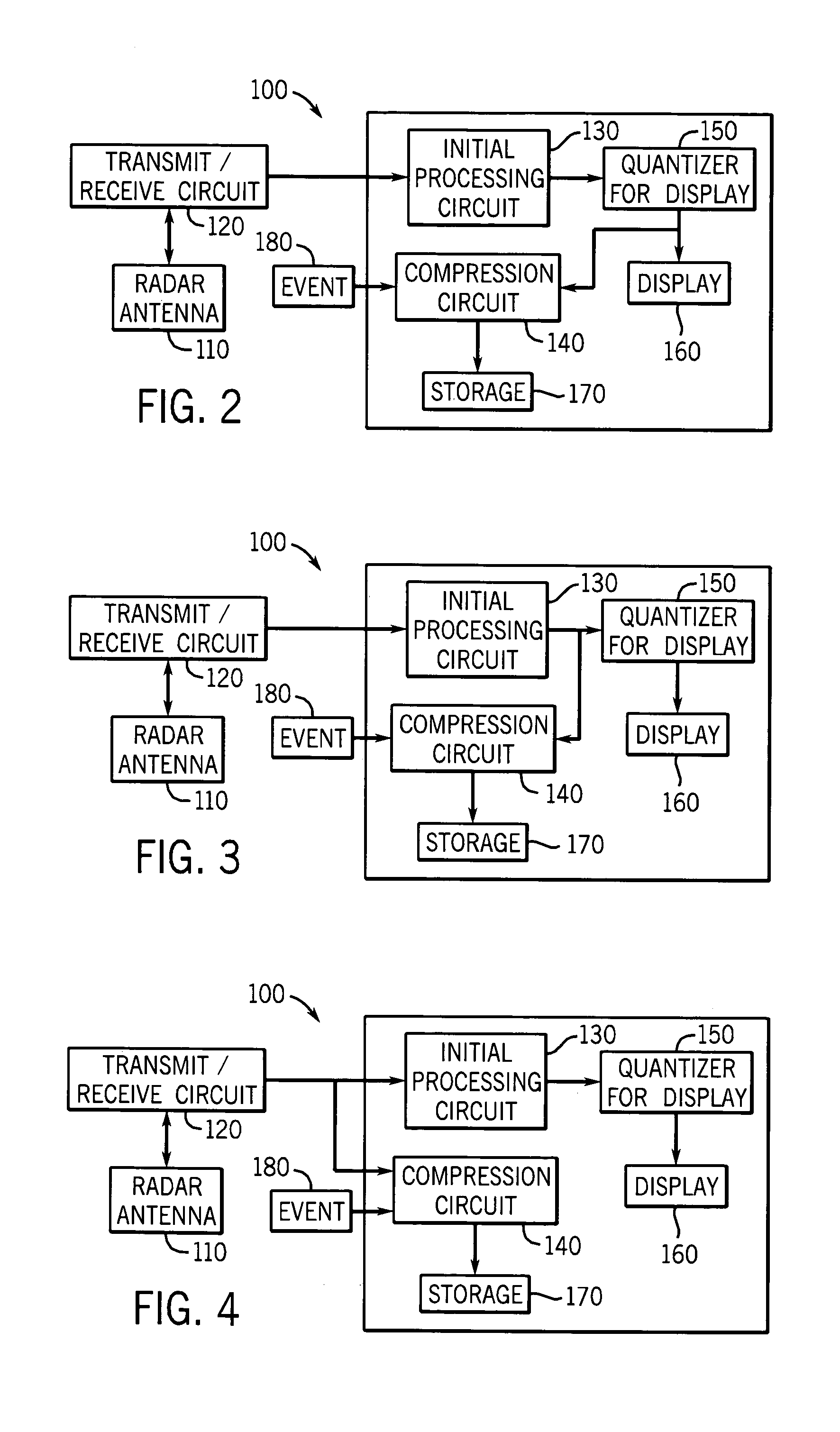
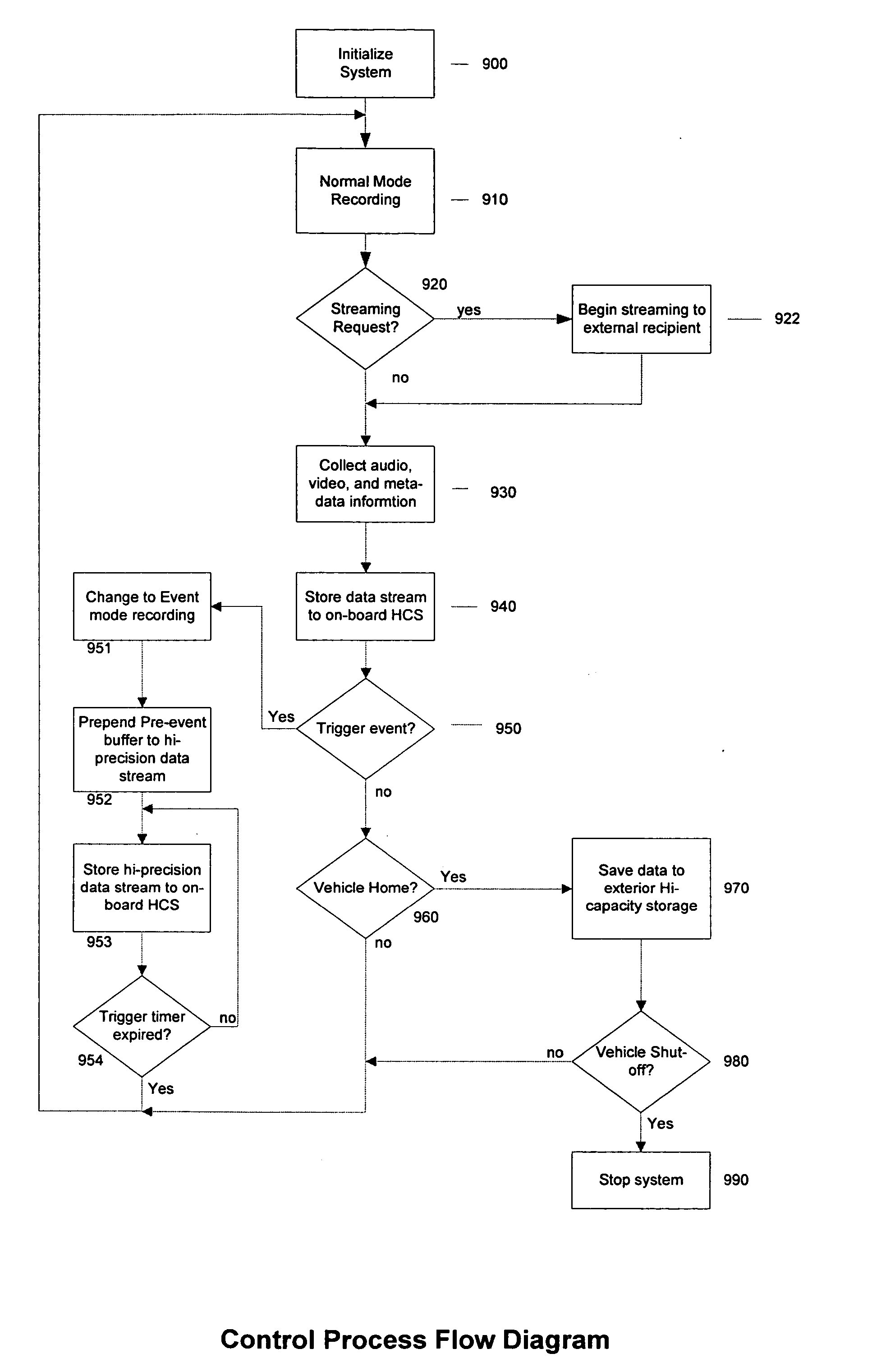
InactiveUS20060077256A1Quality improvementHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesData streamEvent trigger
The High Resolution Pre-Event Record system is an innovative means for collecting audio, video, and meta-data in a mobile vehicle platform and continuously recording this information stream to a high-capacity storage device at different levels of data resolution based upon the status of a trigger event. The occurrence of a trigger event will cause the system to store higher resolution data to an on-board high-capacity storage device prepended by a configurable amount of high resolution data previously recorded into a pre-event data buffer. The data stream may later be downloaded to an external storage device for future review and analysis.
Owner:INTEGRIAN ACQUISITION CORP
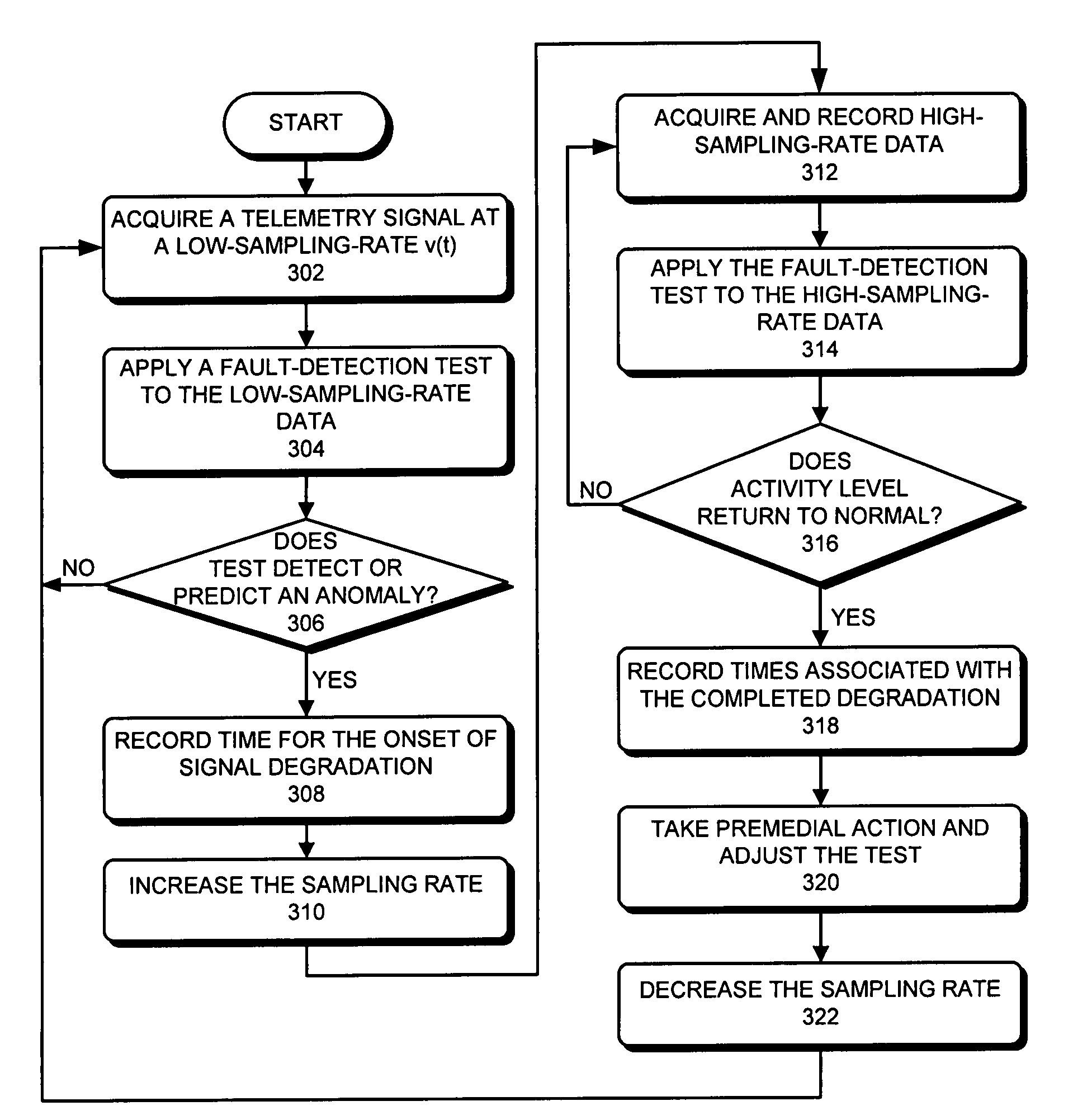
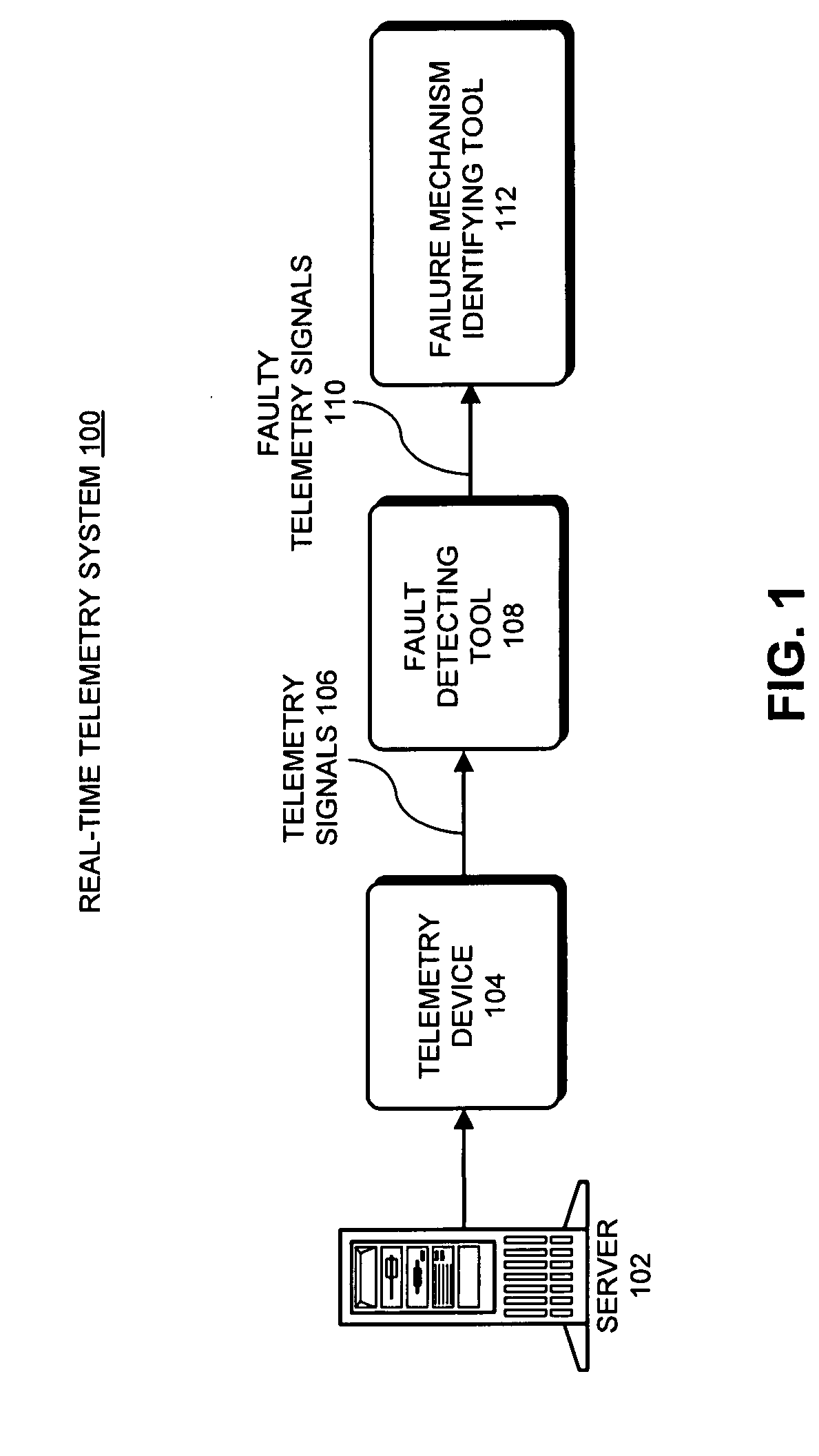
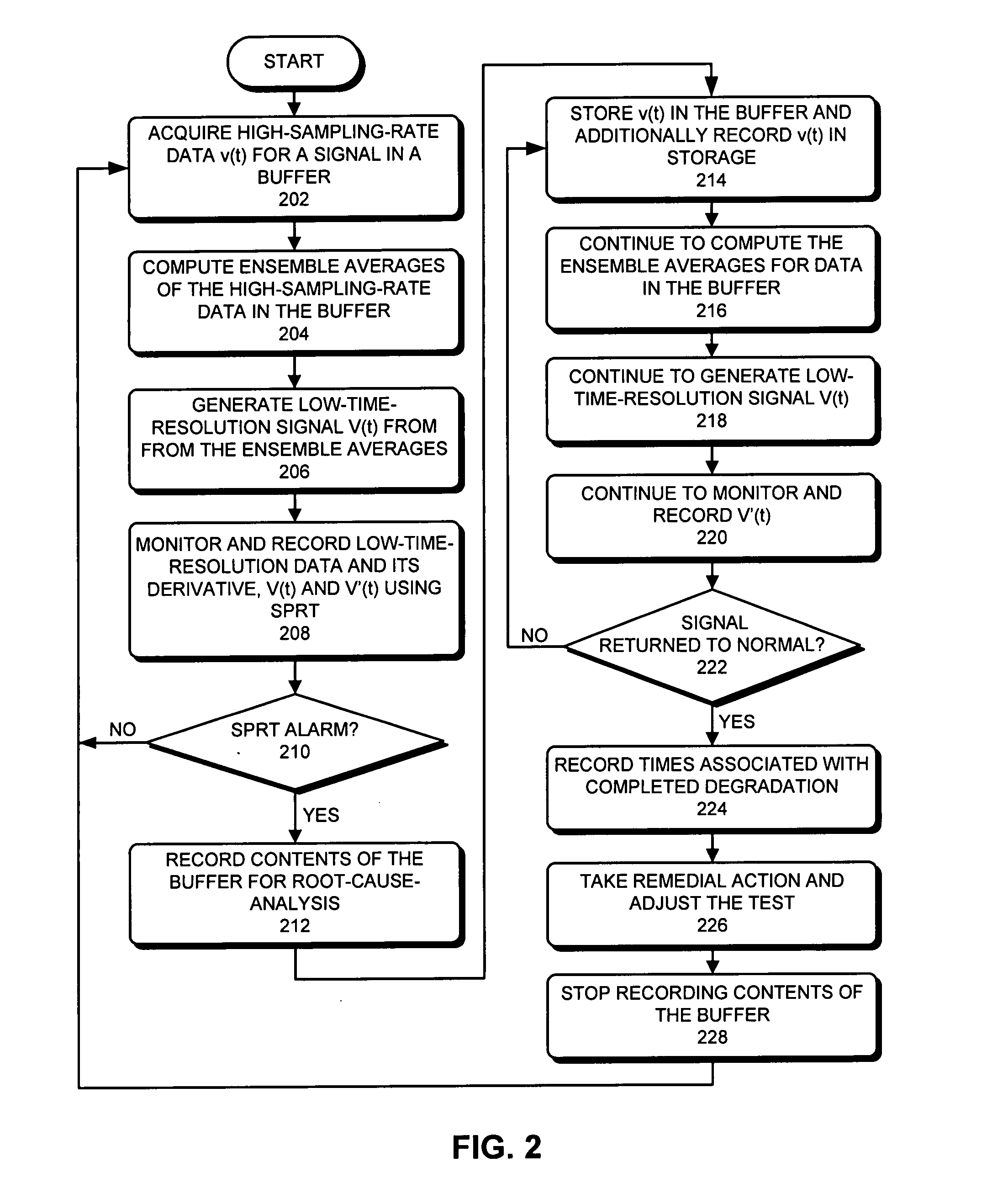
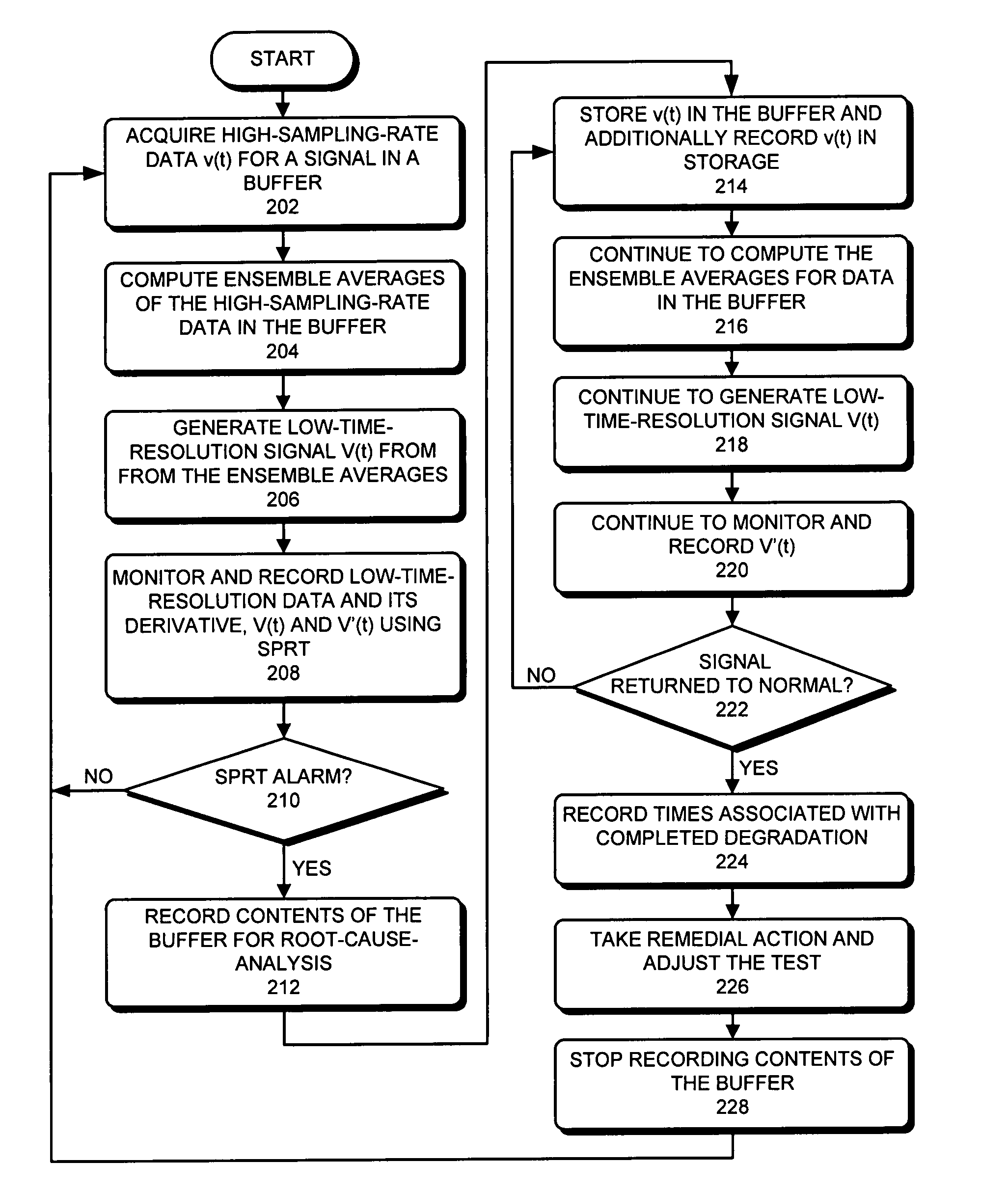
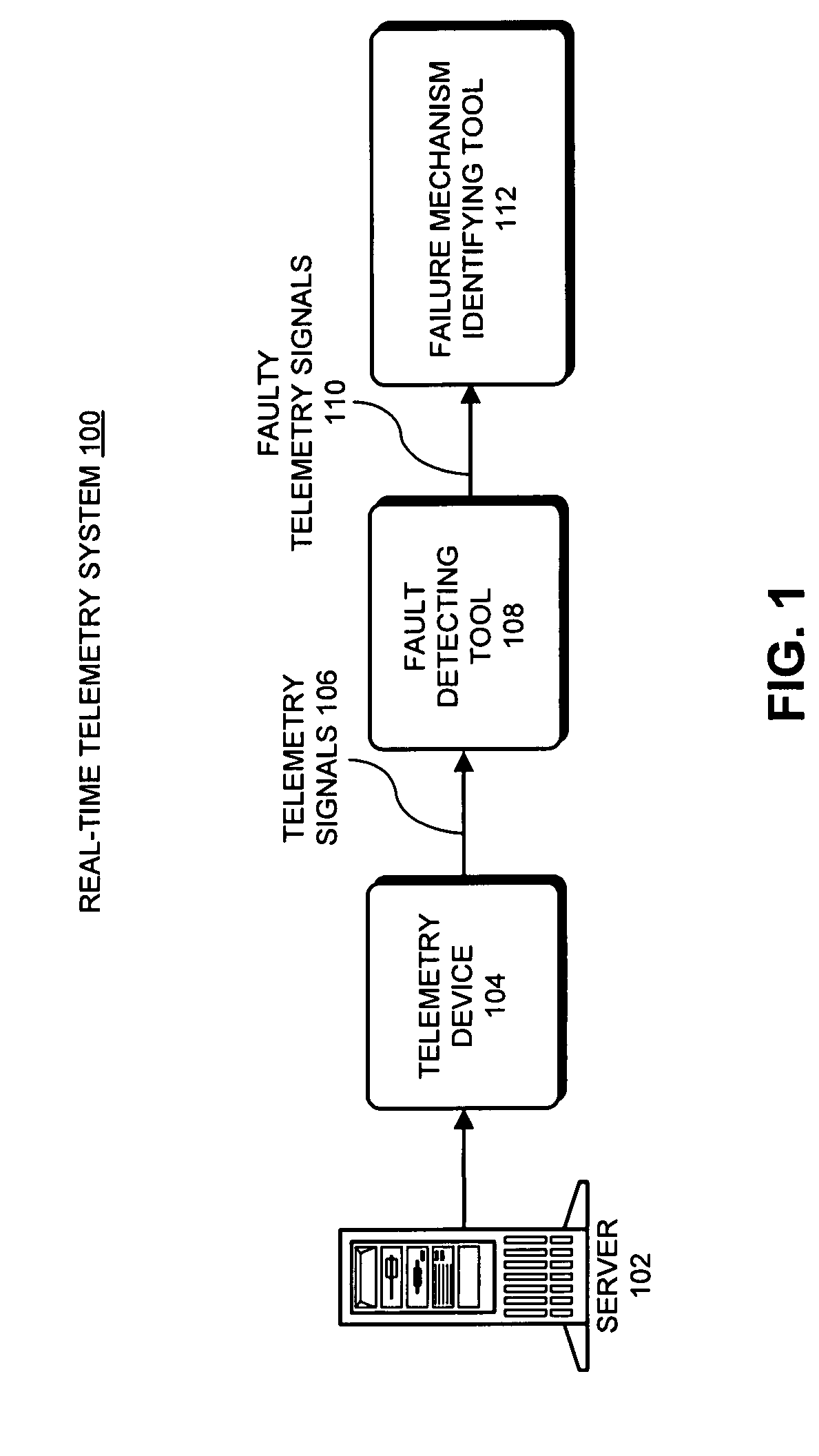
Method and apparatus for dynamically adjusting the resolution of telemetry signals
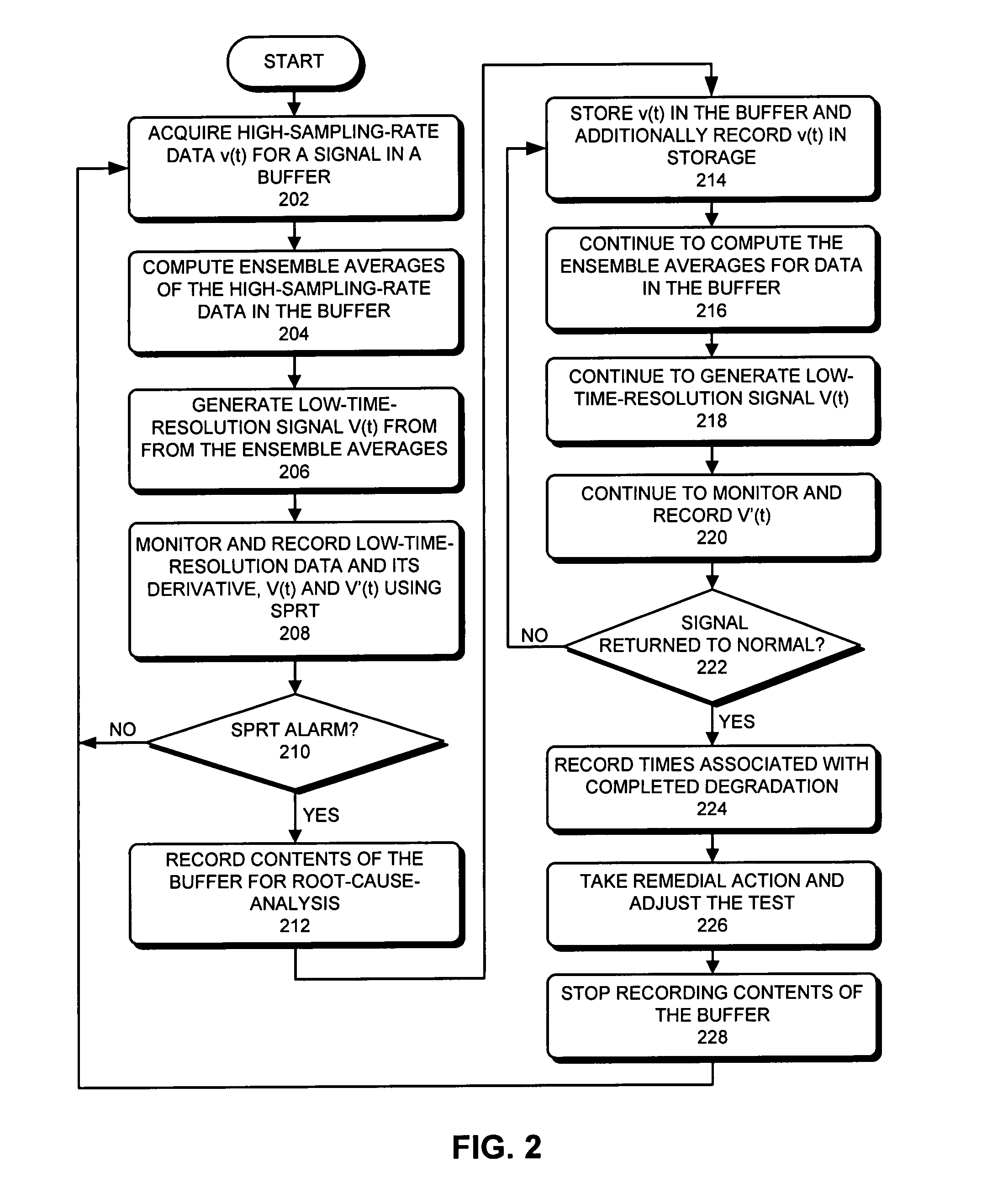
ActiveUS20080252481A1Increase sampling rateIncrease the number ofTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsTransmission systemsImage resolutionComputerized system
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that dynamically adjusts data resolution during proactive-fault-monitoring in a computer system. During operation, the system temporarily stores high-resolution data for a telemetry signal from the computer system in a buffer. The system then generates low-resolution data for the telemetry signal from the high-resolution data. Next, the system monitors the low-resolution data, and while doing so, determines if an anomaly exists in the low-resolution data. If an anomaly exists in the low-resolution data, the system records the high-resolution data from the buffer on a storage device.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
2D code application method and device
ActiveCN101187974AReduce processing difficultyReduce processing complexityDigital data information retrievalCo-operative working arrangementsSoftware engineeringData acquisition
The embodiment of the invention provides a method and a device for two-dimensional code application. The method essentially comprises the following procedures: a terminal acquires two-dimensional code data and conducts resolution of the two-dimensional data to obtain the sign operation flow in the two-dimensional data; the terminal uses a utility model program to execute the sign operation flow in the two-dimensional code data. The device essentially comprises a two-dimensional data acquisition module, a two-dimensional code data resolution module and an operation flow execution module. With the embodiment of the invention, the terminal executes vicinal utility according to execution sequence regulated in the two-dimensional code so as to provide the user with friendly business operation guidance, normalizing feedback information of the client side and reducing the processing difficulty and the complexity of the business platform.
Owner:HUAWEI DEVICE CO LTD
Universal distributed airborne equipment health management simulation platform and implementation method thereof
InactiveCN101901150AReduce difficultyImprove versatilitySpecific program execution arrangementsInteraction design.NET Framework
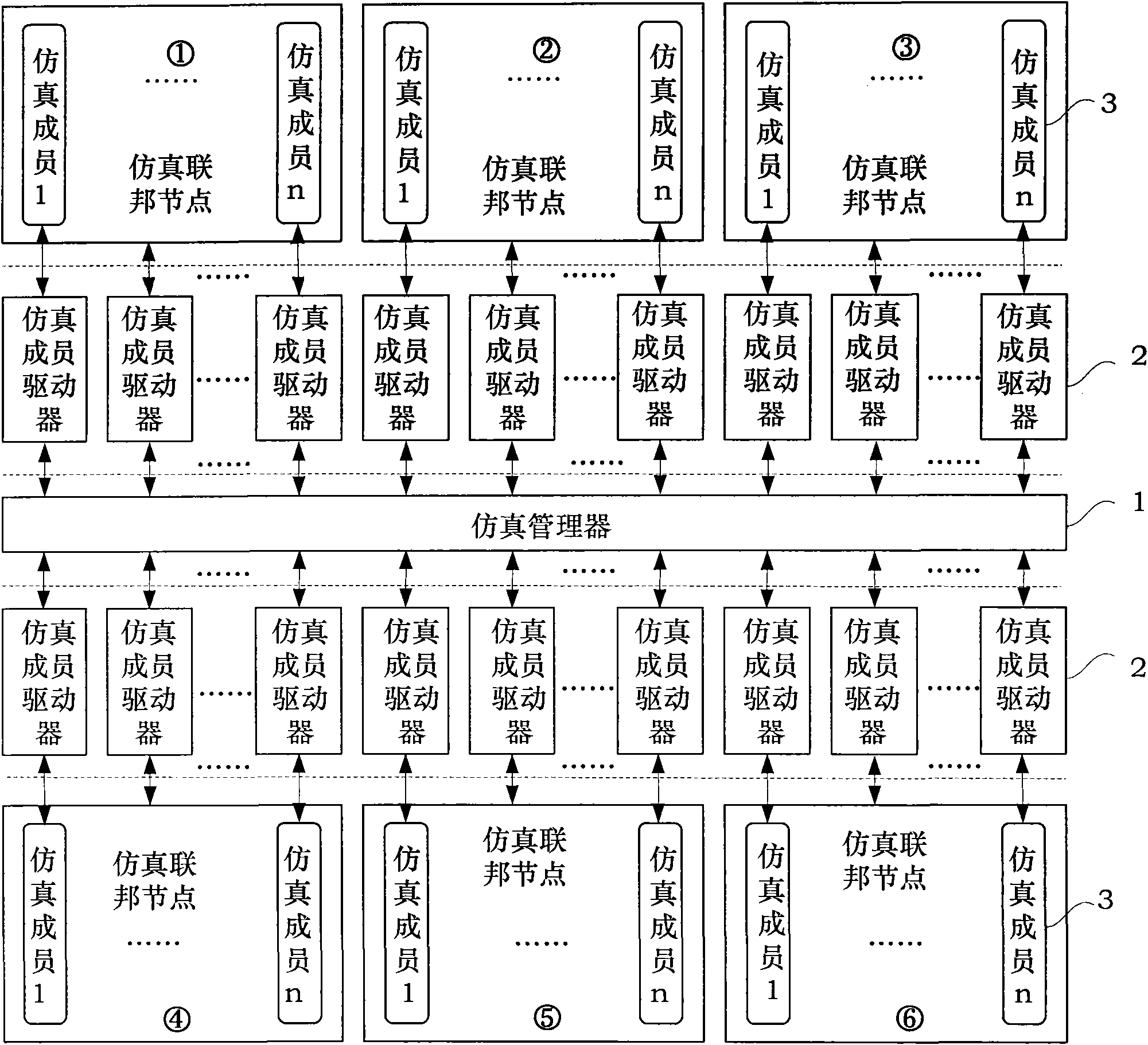
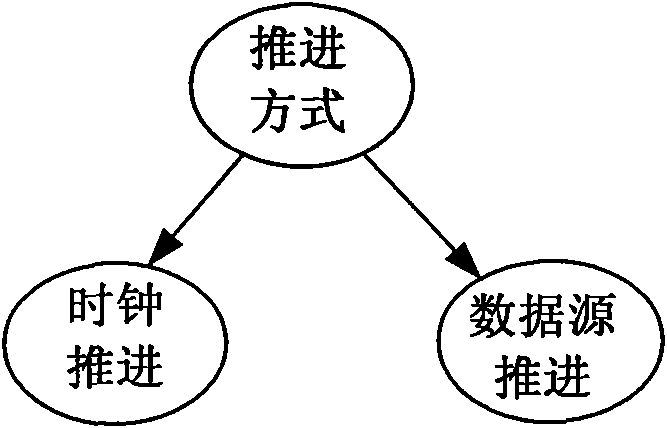
The invention discloses a universal distributed airborne equipment health management simulation platform and an implementation method thereof, and the simulation platform adopts the mediator pattern and mainly comprises three parts of a simulation manager, a simulation member driver and simulation members, wherein the simulation manager is responsible for managing information of all the simulation members, receiving and sending data and carrying out data resolution work; the simulation member driver is used for loading and running all the simulation members and implementing information interaction between the simulation members and the simulation manager; and the simulation members are used for implementing various data calculation and completing the function of the health management technology. The simulation platform is implemented on the basis of a.net framework, on the one hand, the simulation platform can realize the separation between the development of a simulation member object and algorithm model and the interaction design of the simulation members, on the other hand, the simulation platform can highly multiplex the information interaction of the simulation members and software codes for driving the model, thereby not only reducing the workload, but also reducing the complexity in development work.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
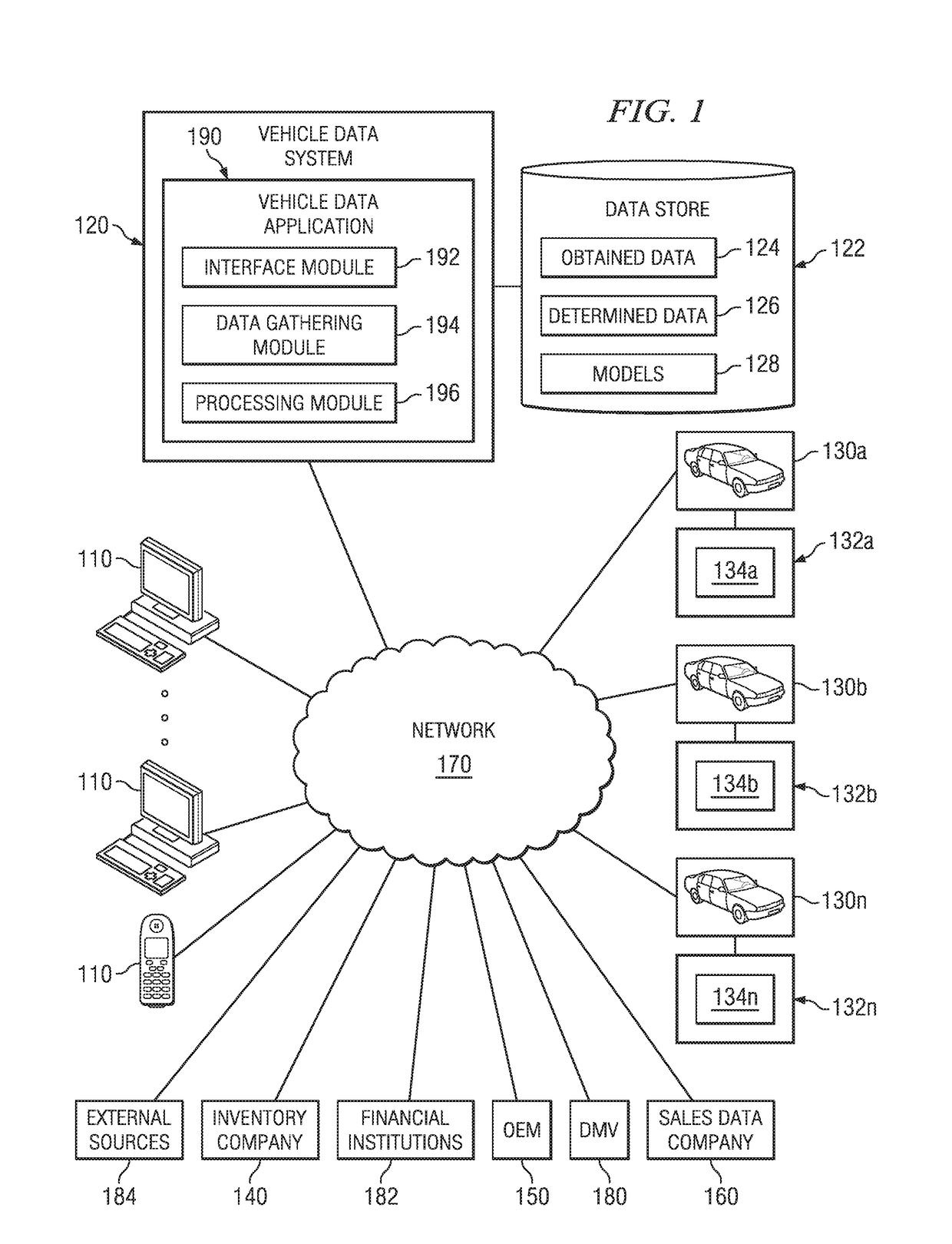
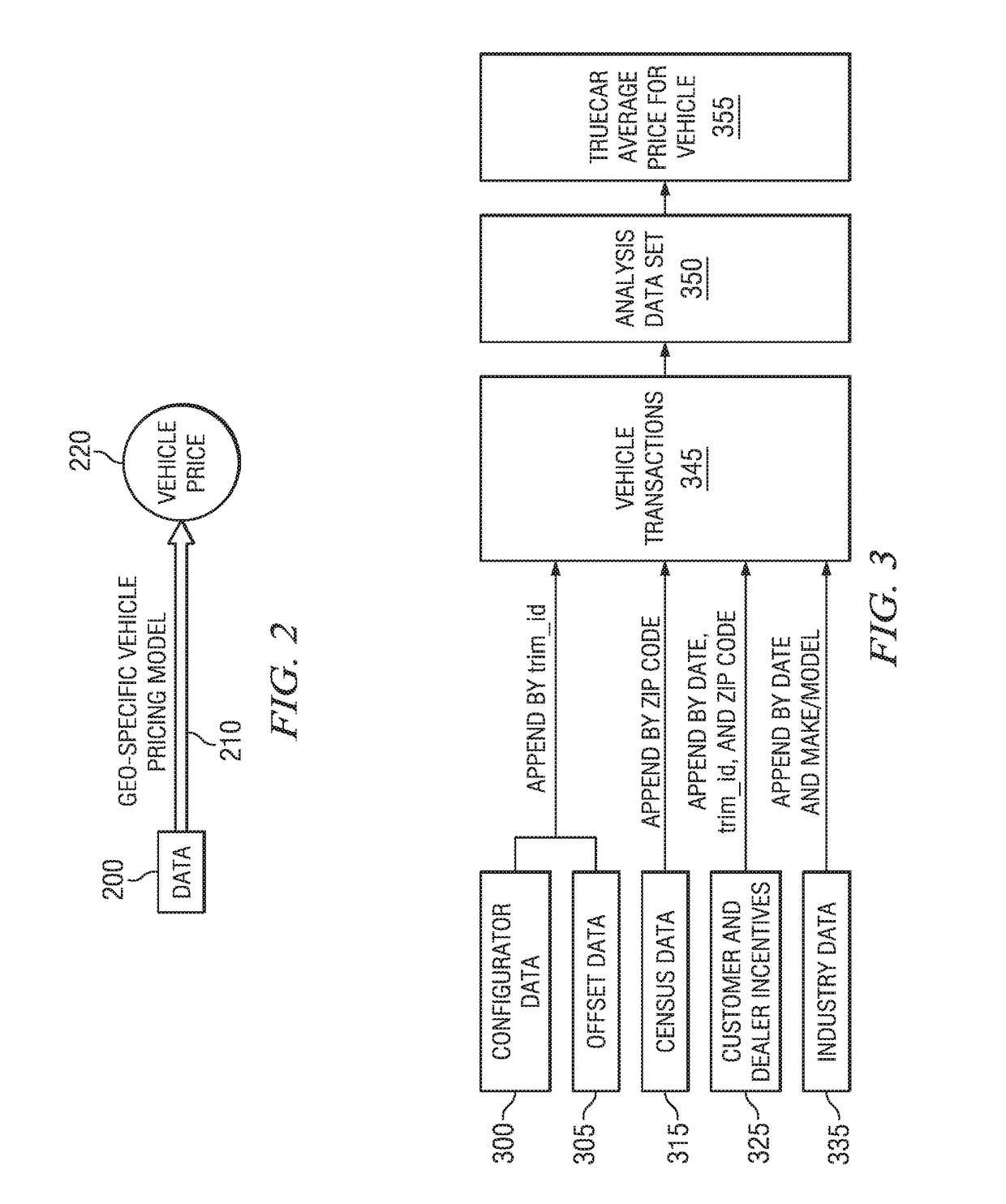
System, method and computer program product for geo-specific vehicle pricing
Disclosed are embodiments for the aggregation and analysis of vehicle prices via a geo-specific model. Data may be collected at various geo-specific levels such as a ZIP-Code level to provide greater data resolution. Data sets taken into account may include demarcation point data sets and data sets based on vehicle transactions. A demarcation point data set may be based on consumer market factors that influence car-buying behavior. Vehicle transactions may be classified into data sets for other vehicles having similar characteristics to the vehicle. A geo-specific statistical pricing model may then be applied to the data sets based on similar characteristics to a particular vehicle to produce a price estimation for the vehicle.
Owner:TRUECAR
Method for improving seismic data resolution based on seismographic record varitron wave model
The invention relates to a based method for improving seismic data resolution based on a seismographic record varitron wave, which is characterized by comprising the steps of: 1, constructing a molecule-Gabor window, adaptively dividing an instable seismographic record into a plurality of stable segments, wherein each segment has an approximately unchangeable equivalent wavelet which is easy to extract from the segment; 2, converting the instable seismographic record into a molecule-Gabor domain by using a molecule-Gabor frame generated by the molecule window obtained by the construction in the step 1; 3, carrying out frequency extension and energy compensation processing on molecule-Gabor coefficients corresponding to the seismographic record segments in each molecule-Gabor window; and 4, inversely transforming the processed molecule-Gabor coefficients into a time domain to obtain the seismographic record after the resolution ratio is increased. In the method, on the basis of the modern quasidifferential operator principle, an adaptive time-frequency analyzing method is used as a tool, and the processed seismic data has high resolution rate and relatively keeps amplitude characteristics.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +2
Time relevance-based visualization of data
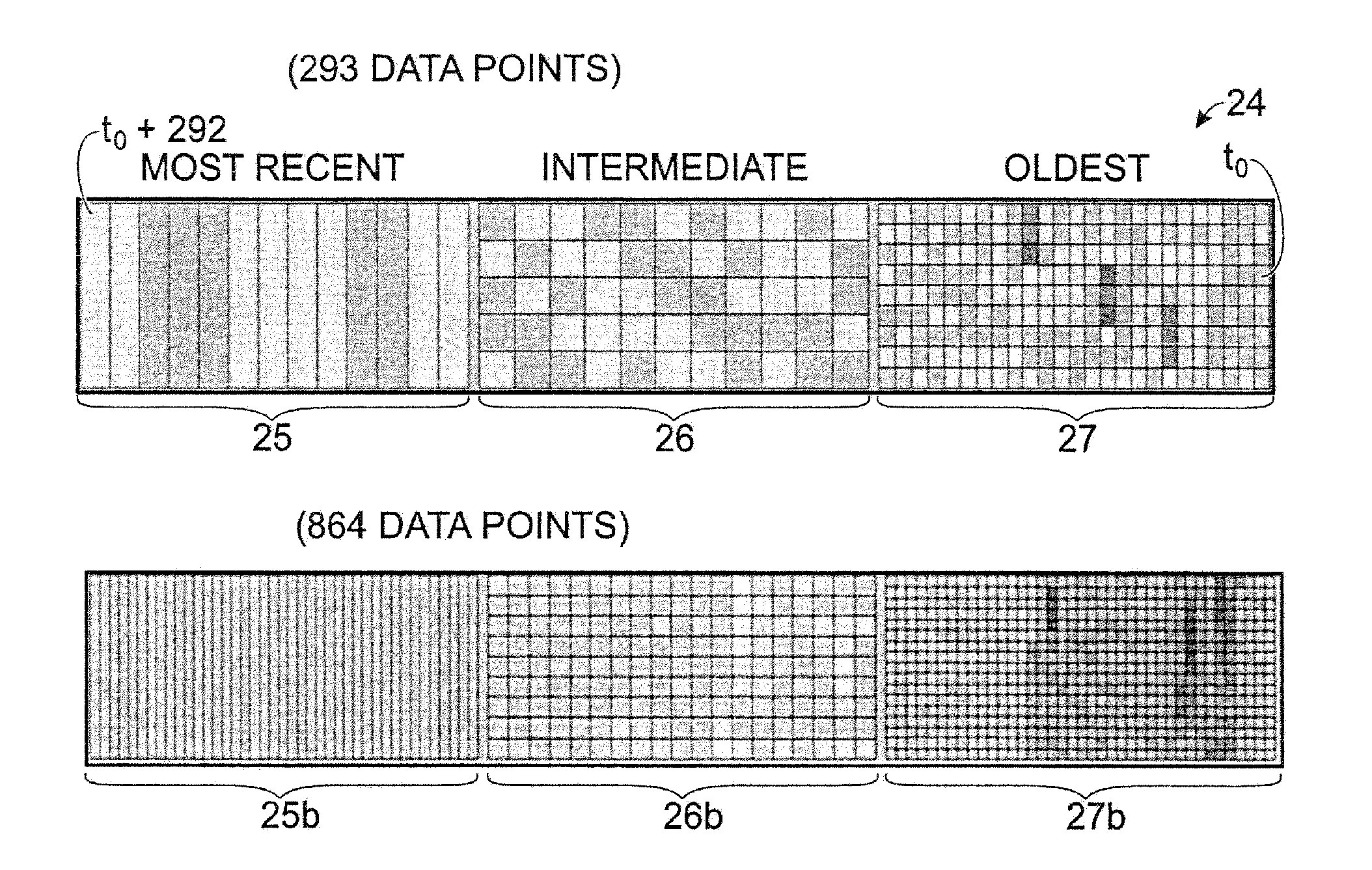
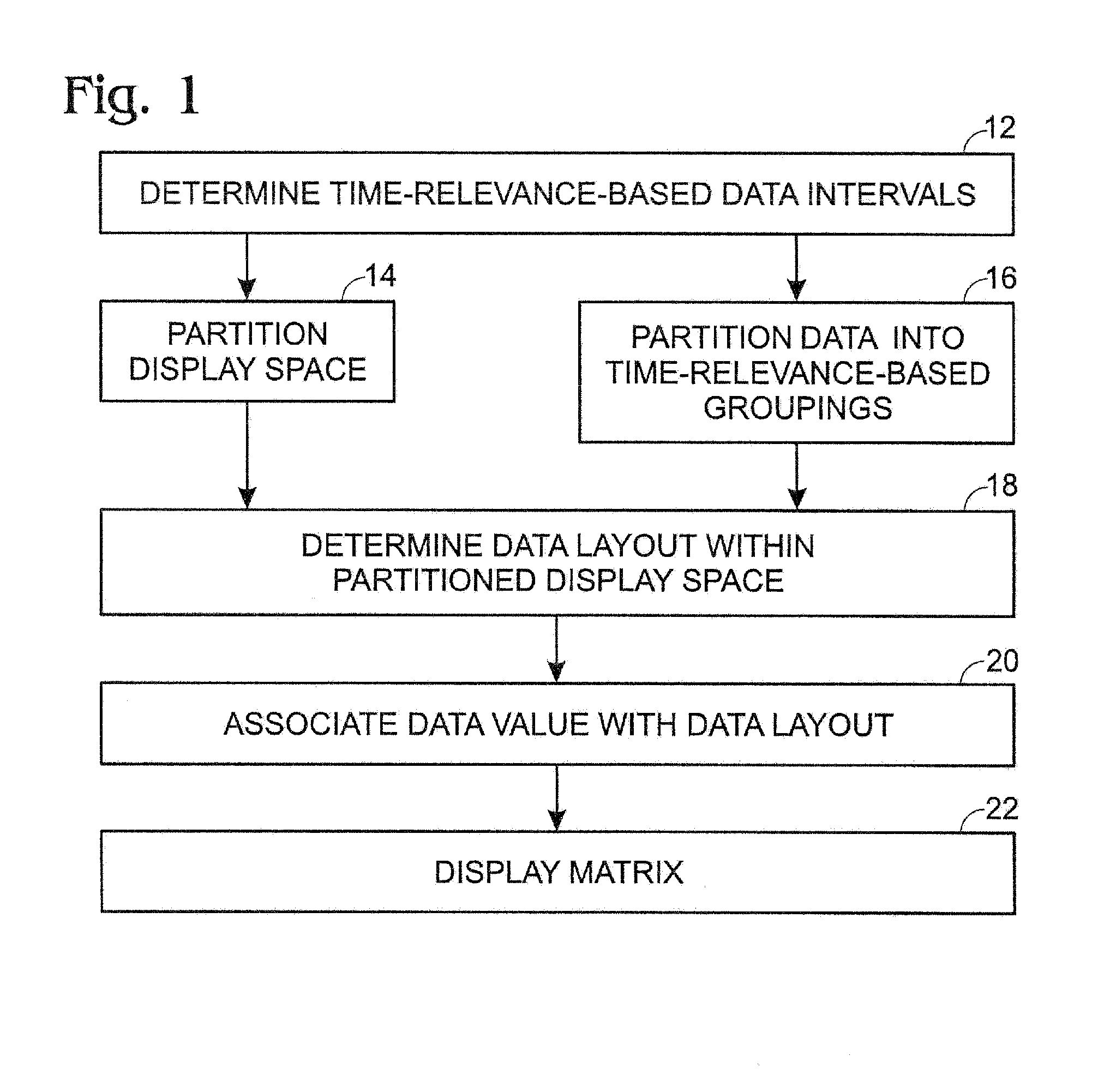
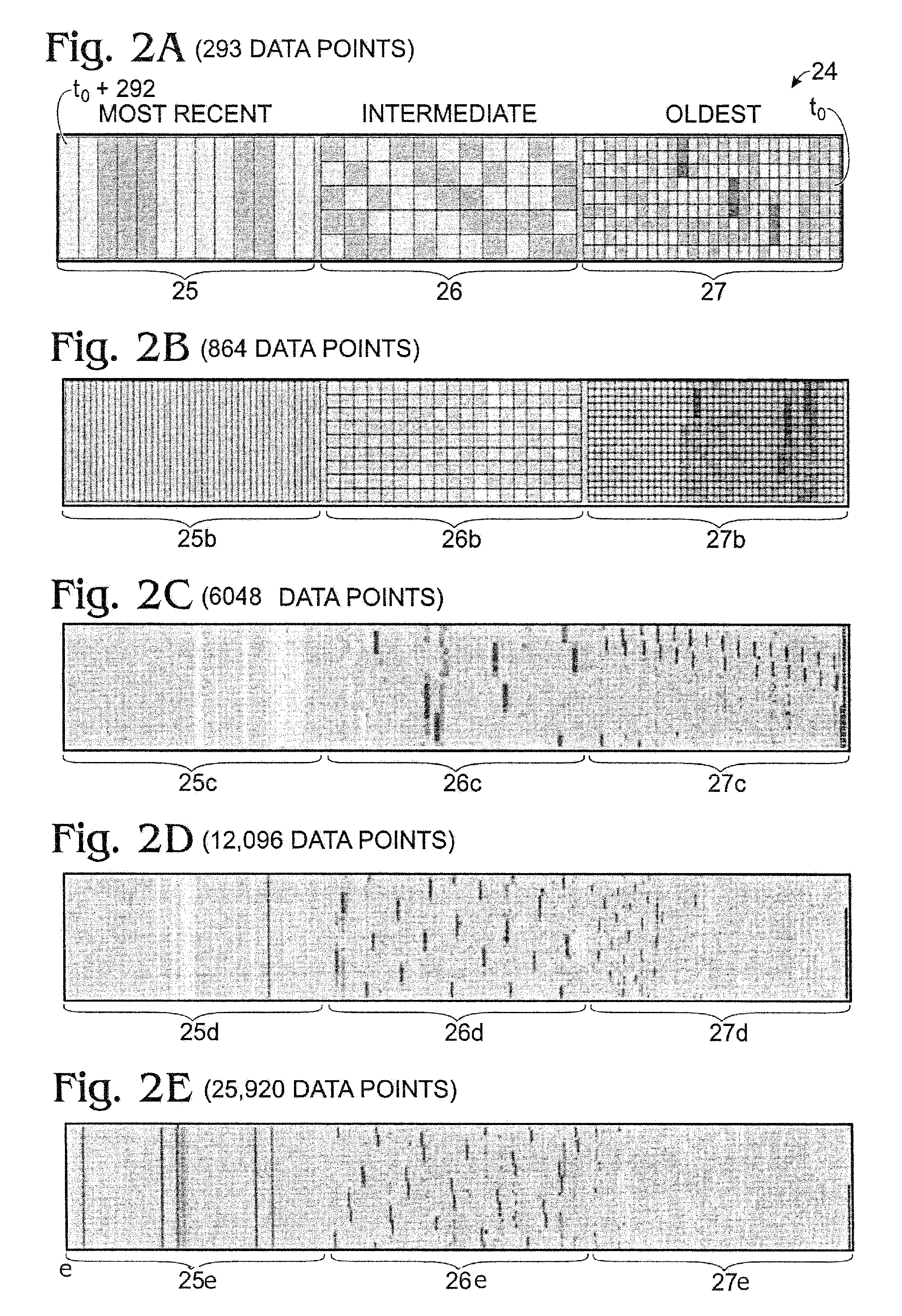
A method for displaying a time-series data set. The method may include determining a number of data intervals for the data set, determining a data resolution for each data interval, partitioning a display space into a number of substantially equally sized partitions equal to the number of data intervals, partitioning the dataset into a number of time-relevance-based subsets equal to the number of partitions based on the currentness of the data and the desired data resolution for each partition, determining a data layout for each partition, and associating the data values for each subset with the corresponding layout. Furthermore, the first subset may consist of more current data at a first resolution and the second subset may consist of data that is less current than the first subset at a lower resolution than the first resolution.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
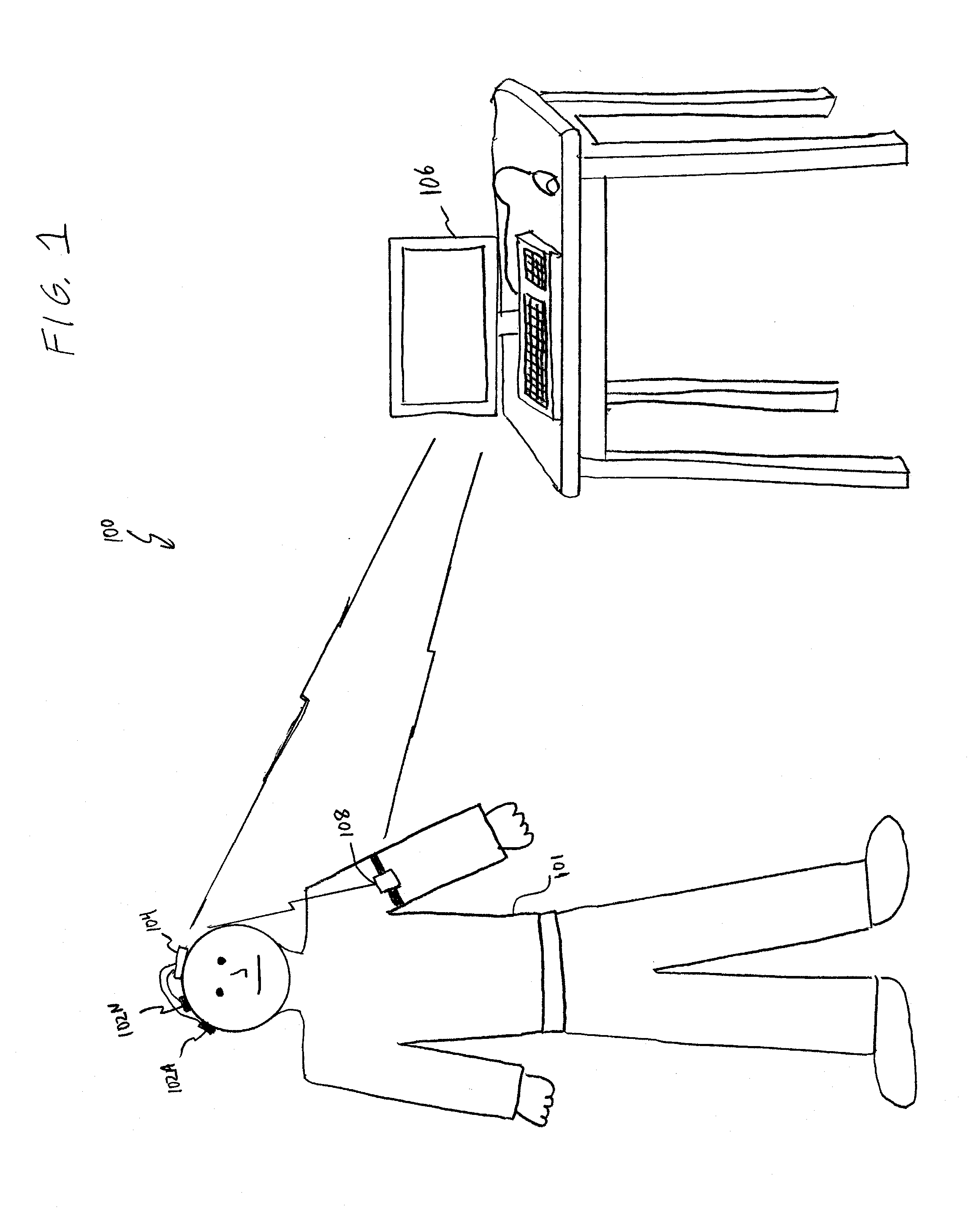
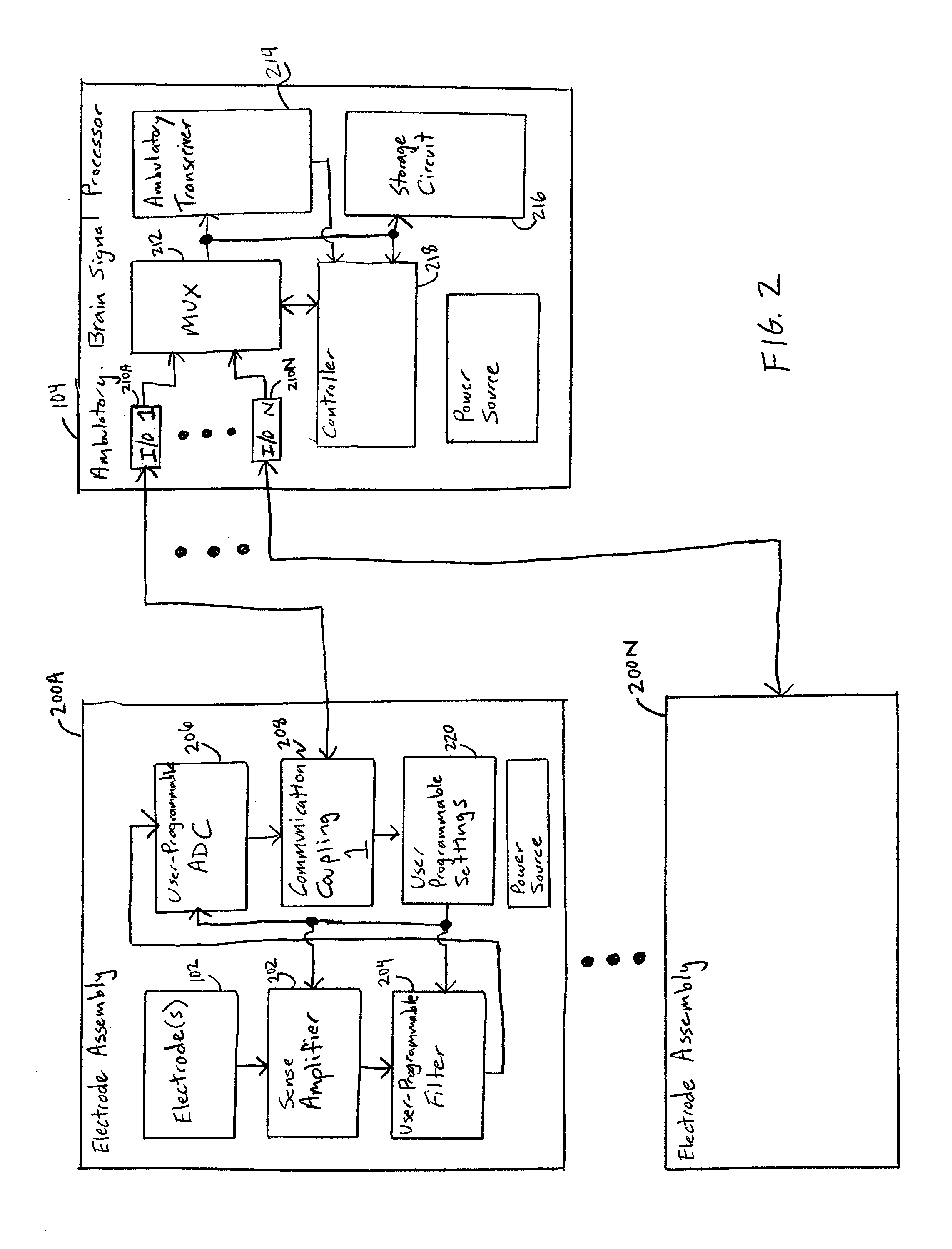
Brain signal telemetry and seizure prediction
An ambulatory intrinsic brain signal processor circuit is coupled to a plurality of electrodes. The signal processor circuit can include a digital multiplexer circuit coupled to the electrodes to multiplex brain signal data from different electrodes together into a multiplexed data stream. An ambulatory transceiver circuit wirelessly communicates information to and from a remote transceiver. A controller circuit permits a user to control which of the electrodes contribute data, a data resolution, and whether the data includes one or both of neural action or local field potential data. Seizure prediction components and methods are also described.
Owner:BIO SIGNAL GROUP CORP
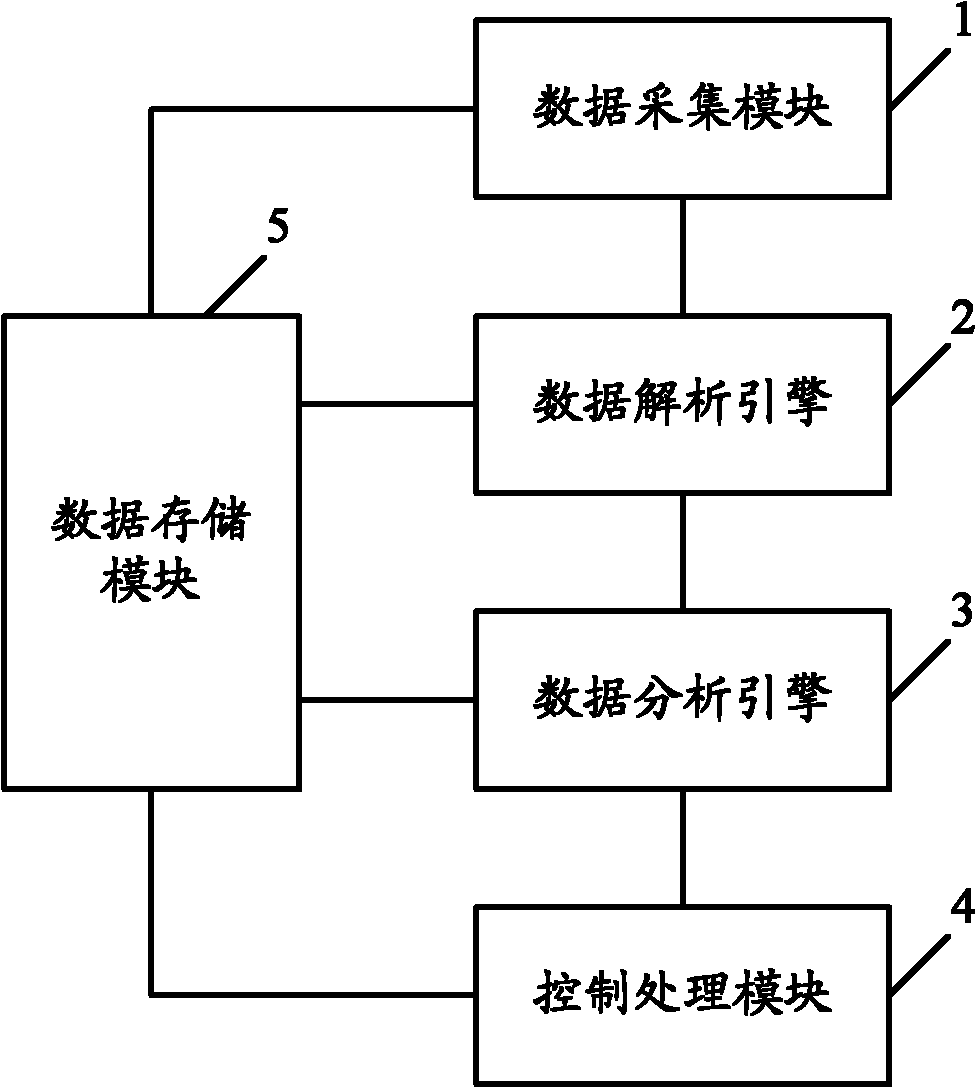
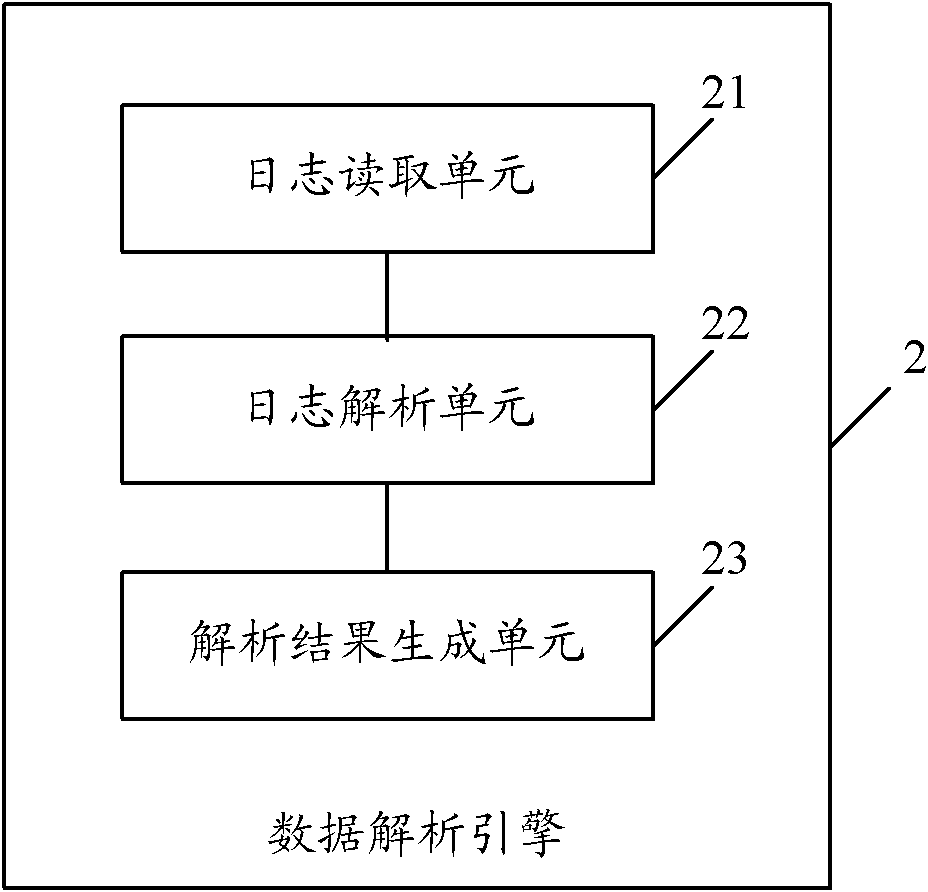
Electronic journal diary intelligent analysis system and method
ActiveCN102163353AControl safe operationReduce downtime costsComplete banking machinesDowntimeSelf-service
The invention discloses an electronic journal diary intelligent analysis system and method. The system comprises a data acquiring module, a data resolution engine, a data analysis engine and a control processing module, wherein the data acquiring module is used for acquiring the electronic journal diary data of a self-service device; the data resolution engine for matching the electronic journal diary data with a predetermined analysis template set to extract the behavior information of the self-service device recorded in the electronic journal diary data; the data analysis engine for analyzing the operation state of the self-service device according to the behavior information; and the control processing module for controlling the safe operation of the self-service device according to the analysis result obtained by the data analysis engine. By using the embodiment of the invention, a plurality of electronic journal diaries in different formats can be analyzed and a self-service terminal can be controlled to operate safely according to the analysis result; and the downtime cost caused by device maintenance can be maximally reduced, and an on-going illegal trade can be effectivelymanaged.
Owner:深圳广电银通金融电子科技有限公司 +1
Frequency division matched filtering method for improving offshore seismic data resolution by utilizing seismic focuses of different depths
InactiveCN102749648AHigh-resolutionIncreased bandwidthSeismic signal processingFrequency spectrumMatched filter
The invention discloses a method for improving offshore seismic data resolution by utilizing air gun seismic focuses of different depths. The method is characterized in that air guns are respectively arranged in positions of different depths to be excited, the near-field wavelet of each seismic focus is recorded, and a far-field wavelet is obtained through simulation; and because of the existence of an offshore strong wave impedance interface, trap points occur on the frequency spectrum of each far-field wavelet, the high-frequency information of air gun seismic focuses at superficial parts is rich, the low-frequency advantages of seismic focuses at deep parts are obvious, and periodic extension is formed. The spectral analysis is carried out on the far-field wavelets to determine the dominant frequency band of each wavelet, the high-frequency dominant section of the wavelet at a superficial part is kept unchanged, the far-field wavelet of the seismic focus at a deep part is expected to be output only at the low-frequency end, and a frequency division matched filter is obtained by calculation and then is applied to all seismic records acquired by the air gun seismic focuses at the superficial parts, thereby realizing the combination of advantages of wavelets of seismic focuses in two different depths, widening the frequency band of the offshore seismic data and improving the resolution.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
System, Method and Computer Program Product for Geo-Specific Vehicle Pricing
Disclosed are embodiments for the aggregation and analysis of vehicle prices via a geo-specific model. Data may be collected at various geo-specific levels such as a ZIP-Code level to provide greater data resolution. Data sets taken into account may include demarcation point data sets and data sets based on vehicle transactions. A demarcation point data set may be based on consumer market factors that influence car-buying behavior. Vehicle transactions may be classified into data sets for other vehicles having similar characteristics to the vehicle. A geo-specific statistical pricing model may then be applied to the data sets based on similar characteristics to a particular vehicle to produce a price estimation for the vehicle.
Owner:TRUECAR
Method and apparatus for dynamically adjusting the resolution of telemetry signals
ActiveUS7577542B2Increase sampling rateIncrease the number ofTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsTransmission systemsImage resolutionComputerized system
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that dynamically adjusts data resolution during proactive-fault-monitoring in a computer system. During operation, the system temporarily stores high-resolution data for a telemetry signal from the computer system in a buffer. The system then generates low-resolution data for the telemetry signal from the high-resolution data. Next, the system monitors the low-resolution data, and while doing so, determines if an anomaly exists in the low-resolution data. If an anomaly exists in the low-resolution data, the system records the high-resolution data from the buffer on a storage device.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method for improving seismic data resolution ratio for well control
ActiveCN102937720AClear overlapping relationshipThe overlapping relationship is accurateSeismic signal processingHorizonEqualization
The invention provides a method for improving a seismic data resolution ratio for well control. The method for improving the seismic data resolution ratio for well control comprises the steps of calculating reflection coefficients at all well positions; calculating deconvolution operators at all well positions according to reflection coefficients at all well positions; conducting reverse distance weighted three-dimensional spatial interpolation on all deconvolution operators to obtain deconvolution operators of all seismic traces in a three-dimensional space; and conducting convolution processing on original seismic trace data according to deconvolution operators of all seismic traces, and obtaining three-dimensional data volumes through phase correction and trace equalization. The method for improving the seismic data resolution ratio for well control solves the problems that seismic data in the prior art are low in resolution ratio and high in limitation of application range, and the method has the advantages that a plurality of weakened horizon information is strengthened, information of structures such as faults is clear and the superimposing relationship of horizons is clear and accurate.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
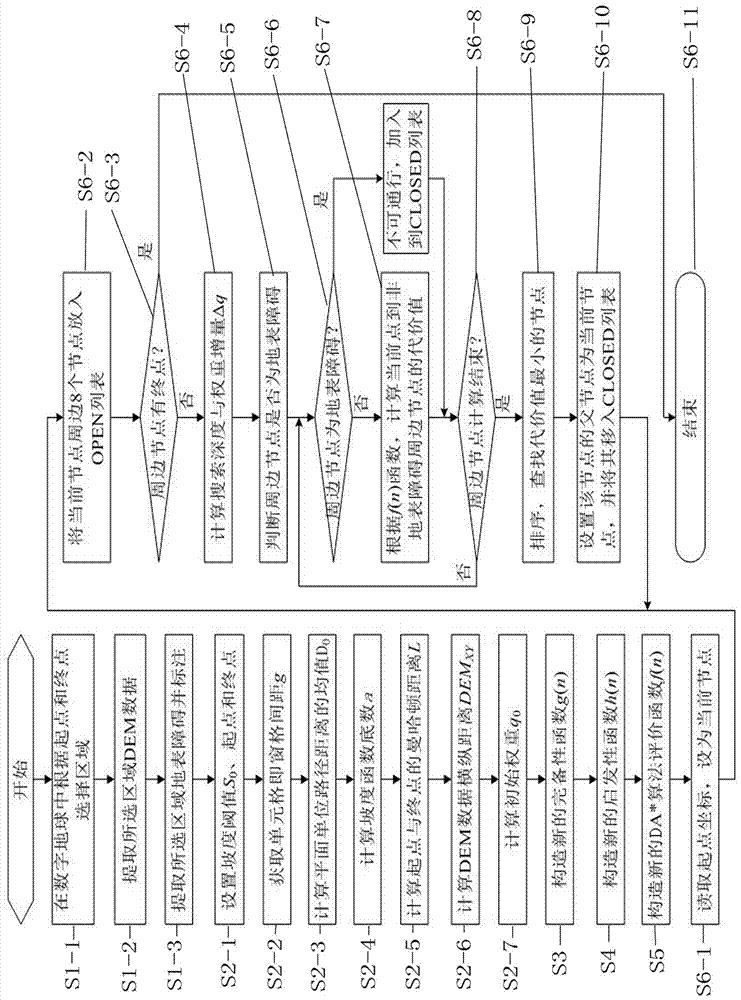
New path planning method based on regular grid DEM data
ActiveCN107228668AImprove efficiencyImprove effectivenessNavigational calculation instrumentsEvaluation resultRegular grid
The present invention discloses a new path planning method based on regular grid DEM data. According to the new path planning method, the distance and the slope are used as the evaluation indexes of the path search; in order to balance the interaction between the distance and the slope, the complete function g(n) of a DA* algorithm is designed based on the distance function of the space path and the slope function constructed with the exponential function; the parameter in the function is calculated with the DEM data, and the new complete function g(n) is optimized so as to be adapted to the change of different resolutions of the DEM data; based on the same strategy and the function construction method, the new heuristic function h(n) of the DA* algorithm is constructed; and in order to improve the search efficiency of the algorithm, by setting the initial weight and dynamically adjusting the weight in the search process, the influence of the complete function and the heuristic function on the evaluation result is changed, such that the new constructed DA* path finding algorithm can efficiently search the appropriate path. According to the preset invention, the new path planning method can self-adapt to the DEM data resolution, and can be used in different application environments.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
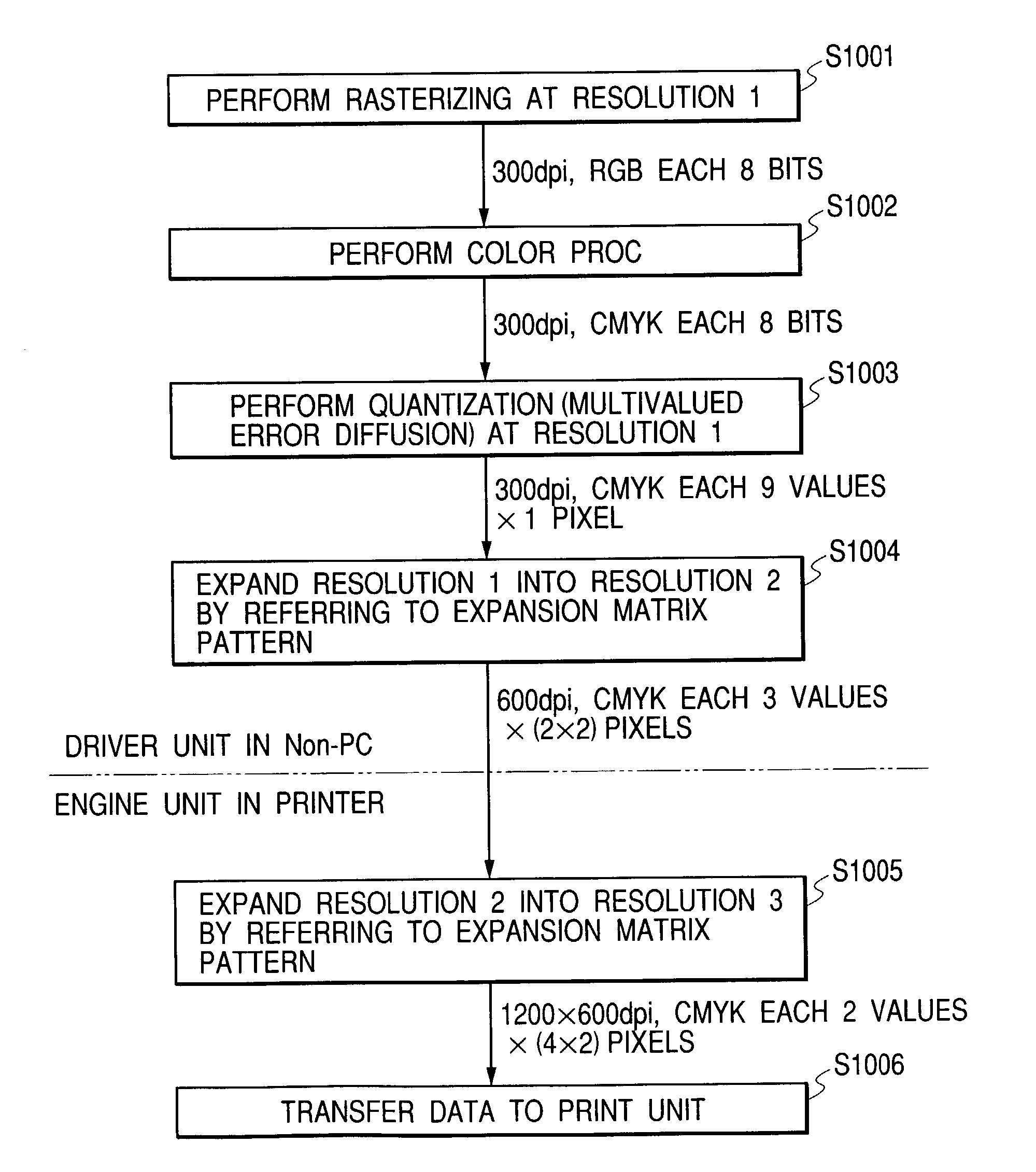
Image recording system, image data resource apparatus, image recording apparatus, image processing method, and program
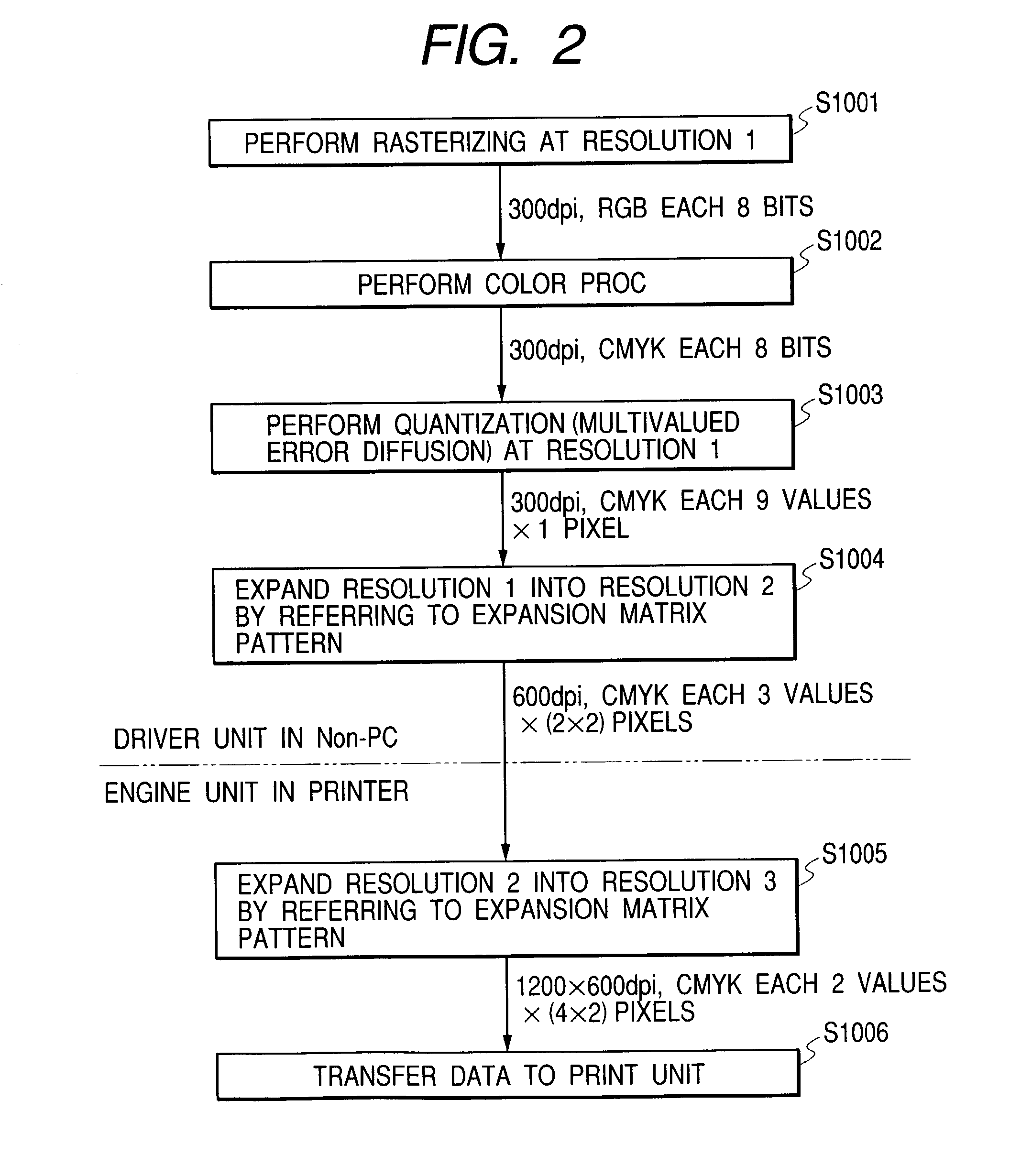
InactiveUS7672011B2Reduce processing loadMaintain image qualityDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsImaging processingImaging quality
A printer driver of a Non-PC controls to quantize image data at quantization resolution (resolution 1), convert the quantized data into data resolution (resolution 2), and then transfer the data of the data resolution to an engine unit of an image output apparatus. The engine unit converts the data resolution of the received data into recording resolution (resolution 3) for a recording medium. Here, the quantization resolution is set to be lower than the data resolution. Thus, processing loads in the image processing unit can be reduced, whereby it is possible to provide image output capable of maintaining image quality and speed even under the circumstance that there is no sufficient memory and high-speed CPU, and to provide image output capable of maintaining image quality and speed according to a matrix recording method flexibly coping with various environments and minimizing the load in the engine unit.
Owner:CANON KK
Digital amplifier with improved performance
InactiveUS20020135419A1Improve dynamic rangeImprove linearityDc amplifiers with modulator-demodulatorDigital dataLow-pass filter
A class D amplifier uses a summation of two or more PWM output stages to achieve an increased dynamic range and improved linearity for any given clock operating speed. The amplifier accepts a digital data stream as its input, such as from a compact disk, or other compatible media, at a data rate, Fa, that could be 44.1 kHz, 96 kHz, or any other rate appropriate for audio data. In the preferred embodiment, the input audio data resolution, N bits, would be split into two data samples, of J and K. Internal switching frequency, Fs, switches the PWM with an over sampling factor M, where Fs=M*Fa. The time resolution of the PWM is determined by a precision oscillator that operates at Fc=Fs*(max(J,K)-log2(+1). The J most significant bits would be routed to a power PWM stage operated at a DC voltage of VHI. The K least significant bits are routed to a finesse PWM stage operated at a DC voltage of VLO. The ratio of VLO to VHI will be appropriate for the ratio of K and J so the summation of the power PWM stage and the finesse PWM stage will provide the full range of N bits. This summation is accomplished with a low pass filter and time-division multiplexing of the two PWM stages. A micro controller (MCU) is used to apply a sample packet distribution algorithm to provide more resolution by reducing quantization noise in the audio band of interest. The MCU is also used to calibrate the VLO or VHI, or to calibrate the PWM timing of the two PWM stages to achieve appropriate performance.
Owner:GROVES JR WILLIAM HARRIS +1
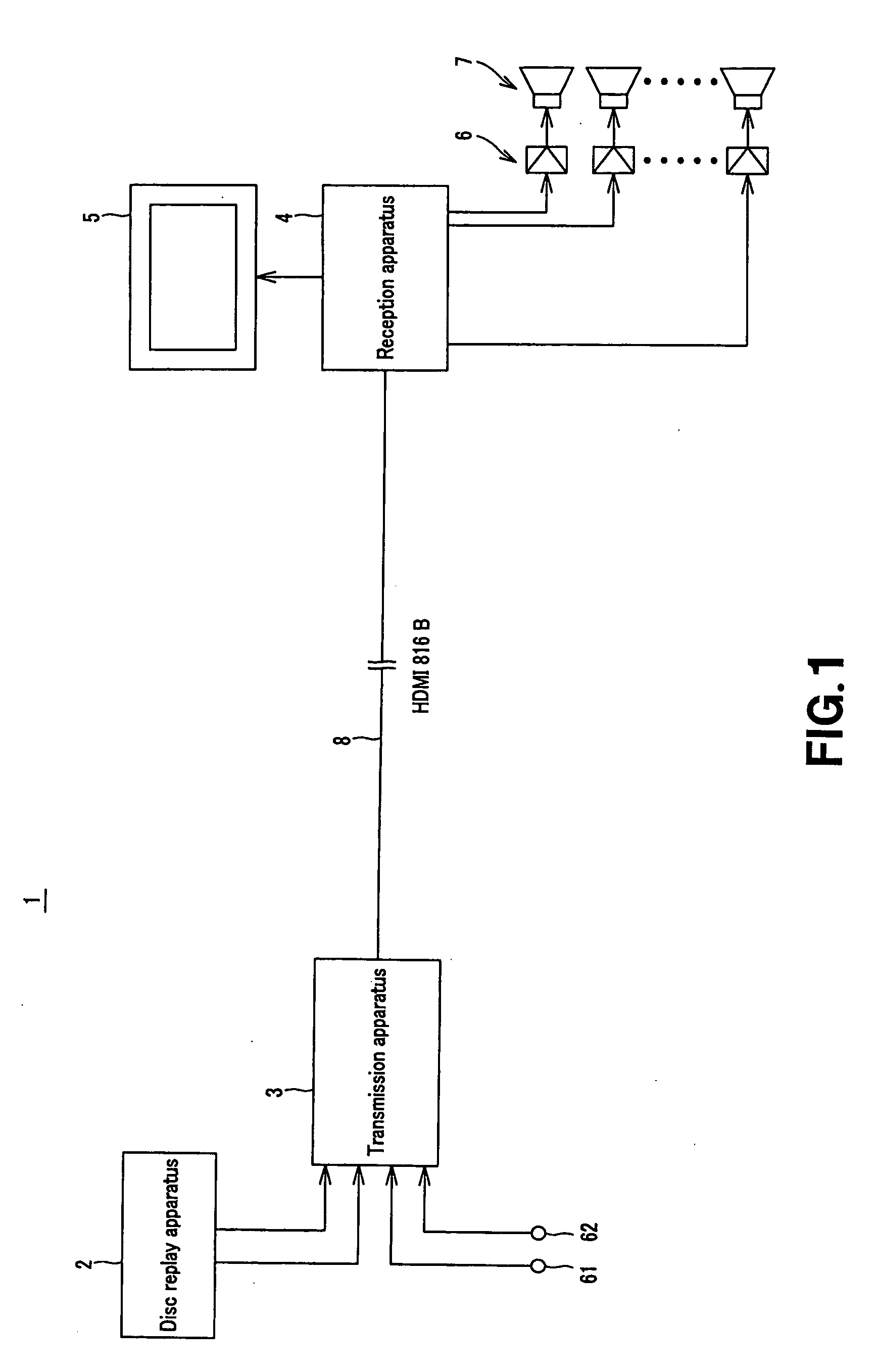
Transmission apparatus, reception apparatus and transmission/reception system
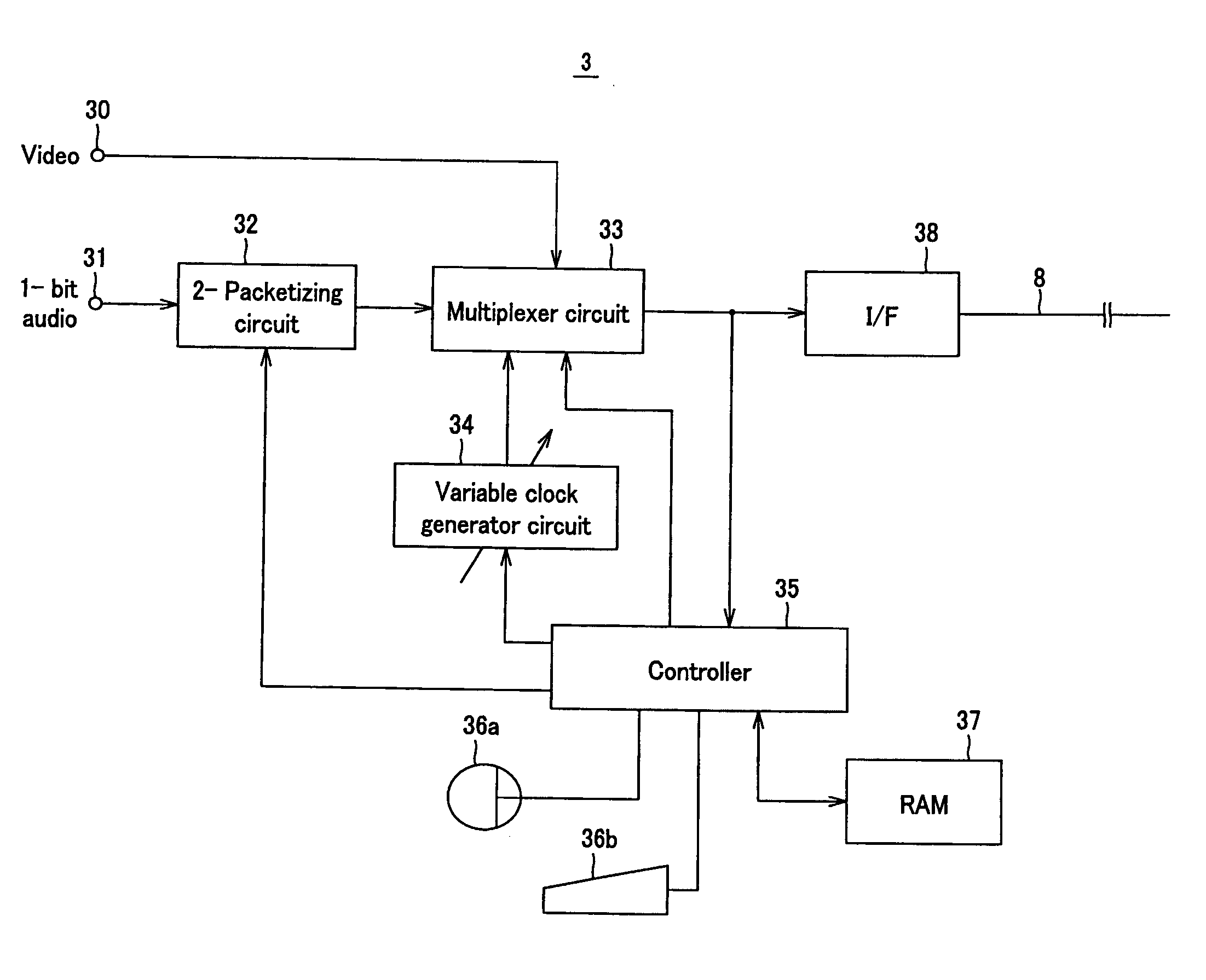
InactiveUS20050220193A1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesImage resolutionDelta-sigma modulation
The present invention relates to a technique of multiplexing a DSD signal with a video signal according to the clock signal generated on the basis of the attributes of the video signal. The present invention provides a transmission apparatus for transmitting audio data and video data to a reception apparatus, which includes a variable clock generating section generating a clock with a variable frequency as a function of the resolution of the video data, a packetizing section packetizing ΔΣ-modulated 1-bit audio data limited for the sampling frequency and the number of channels according to the resolution of the video data, a multiplexing section multiplexing the ΔΣ-modulated 1-bit audio data packetized by the packetizing section and the video data according to the variable clock generated by the variable clock generating section, and a controller controling the process of generating the variable clock by the variable clock generating section according to the resolution of the video data, that of packetizing the ΔΣ-modulated 1-bit audio data by the packetizing section and that of multiplexing the packetized 1-bit audio data and the video data by the multiplexing section.
Owner:SONY CORP
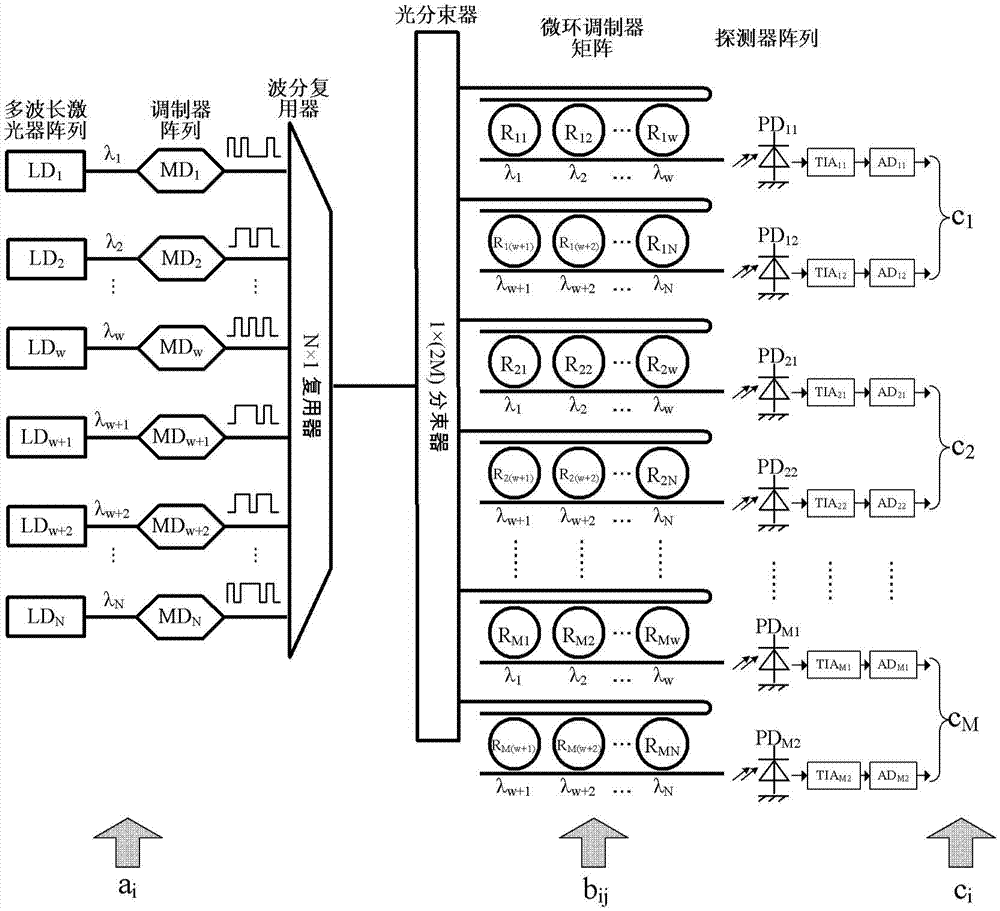
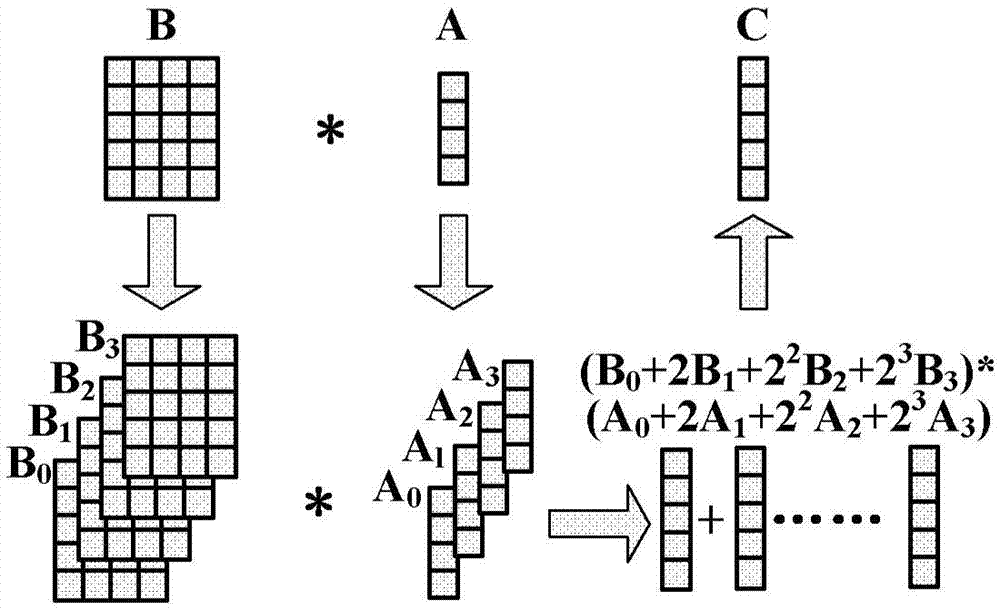
Method for improving data resolution ratio of silica-based optical matrix processor and processor
InactiveCN103678258AReduce resolutionLower requirementComplex mathematical operationsLaser arrayImage resolution
The invention discloses a method for improving the data resolution ratio of a silica-based optical matrix processor and the processor. The method includes the steps that laser signals are output by a laser array and received and modulated by an optical modulator array to an N*1 vector A; a modulator matrix is formed by a micro-ring optical modulator matrix, wherein modulation depths form an M*N matrix B; optical modulation is carried out respectively by dividing the vector A into k subvectors and dividing the matrix B into k submatrixes so as to obtain the product of the k subvectors and the k submatrixes; the obtained product of the subvectors and the k submatrixes is detected by a detector linear array formed by k detectors, and then the product of the vector A and the matrix B is obtained; the element bit wide of each subvector and each submatrix is m, m bit vectors and m bit matrixes are formed after bitwise separation, and the product of the subvectors and the submatrixes is obtained by multiplying the bit vectors by the bit matrixes respectively.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
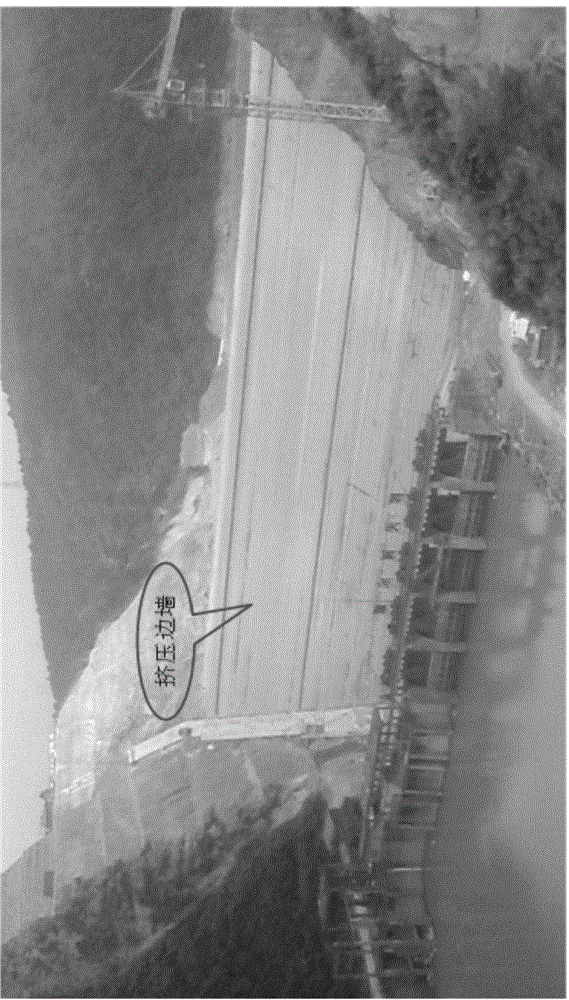
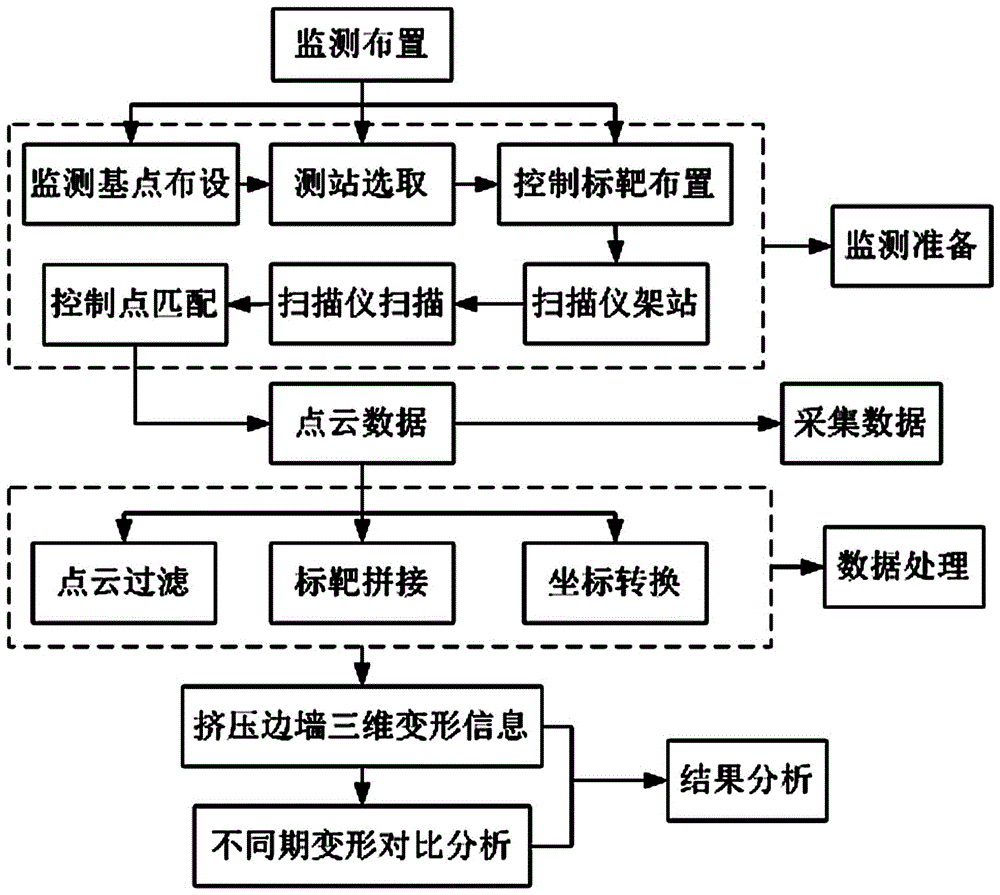
Method for rapidly monitoring high face rockfill dam extrusion sidewall deformation
ActiveCN106225707AAvoid errorsFast Data Acquisition EfficiencyUsing optical meansPoint cloudImage resolution
The invention provides a method for rapidly monitoring high face rockfill dam extrusion sidewall deformation. The method comprises the following steps that step 1: preparation before monitoring and data acquisition are performed; and step 2: processing and analysis are performed based on the point cloud data acquired in the step 1, and an extrusion sidewall relative deformation graph is drawn by using surfer software so that rapid monitoring of high face rockfill dam extrusion sidewall deformation can be realized. According to the method for rapidly monitoring high face rockfill dam extrusion sidewall deformation, the disadvantages that the conventional monitoring means is complex, time-consuming and labor-consuming, low in precision and poor in real-time performance can be solved so that the data acquisition efficiency is high, data acquisition speed is fast and data resolution is high.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Compensation accuracy
ActiveUS20150042703A1Reduce the valueCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDriving currentPattern recognition
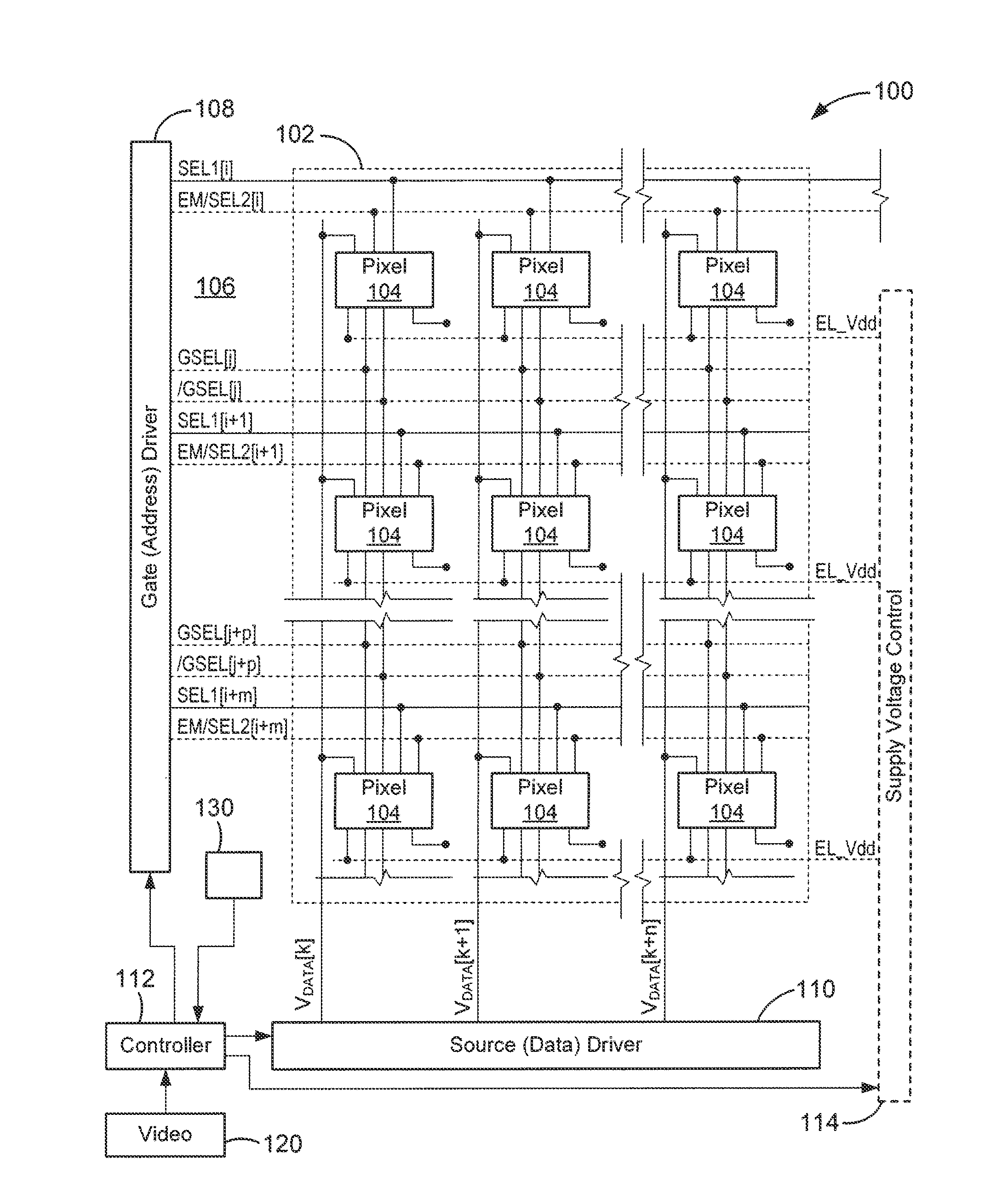
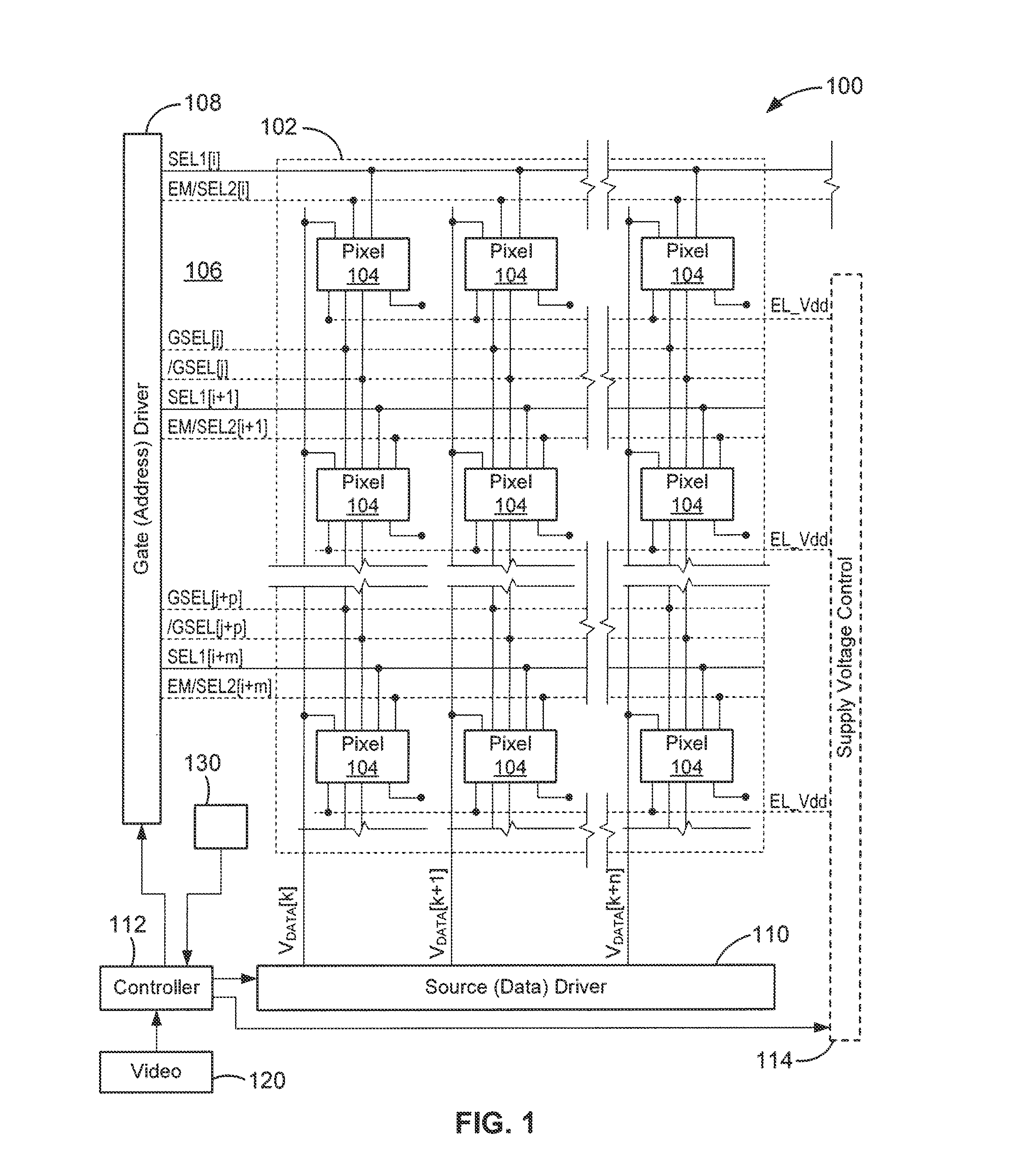
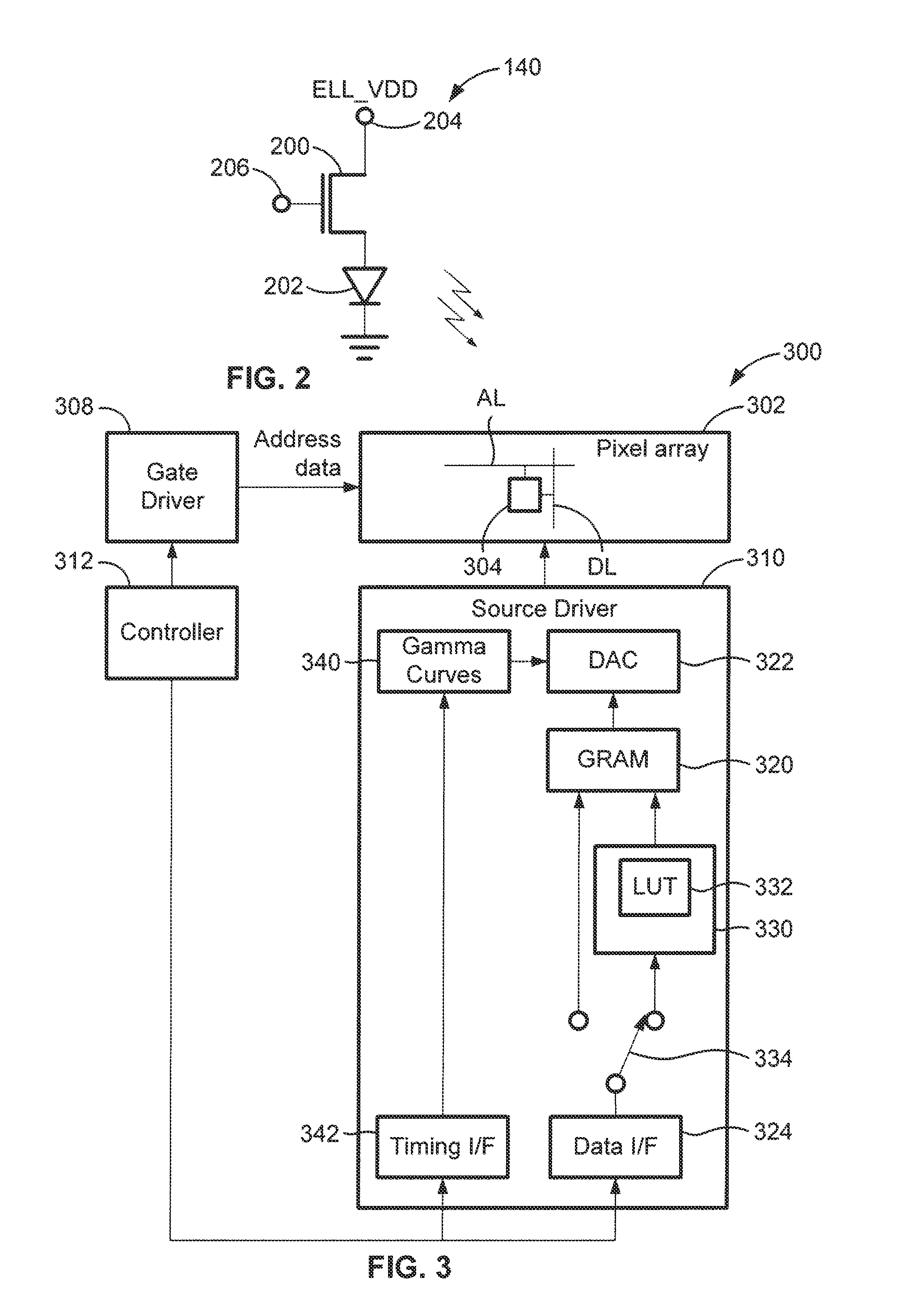
A system uses image data, representing images to be displayed in successive frames, to drive a display having pixels that include a drive transistor and an organic light emitting device by dividing each frame into at least first and second sub-frames, supplying the image data during one of the sub-frames, supplying compensation data during the other of the sub-frames, compensating image data based on the compensation data, and supplying each pixel with a drive current that is based on the compensated image data during each frame. The compensated image data may be supplied from a driver having a preselected data resolution, and the system determines whether the compensated image data is greater than the data resolution of the driver, and if the compensated image data is greater than the data resolution of the driver, transfers the excess compensated image data to a different sub-frame.
Owner:IGNIS INNOVATION
Method for improving seismic data resolution capacity based on system identification
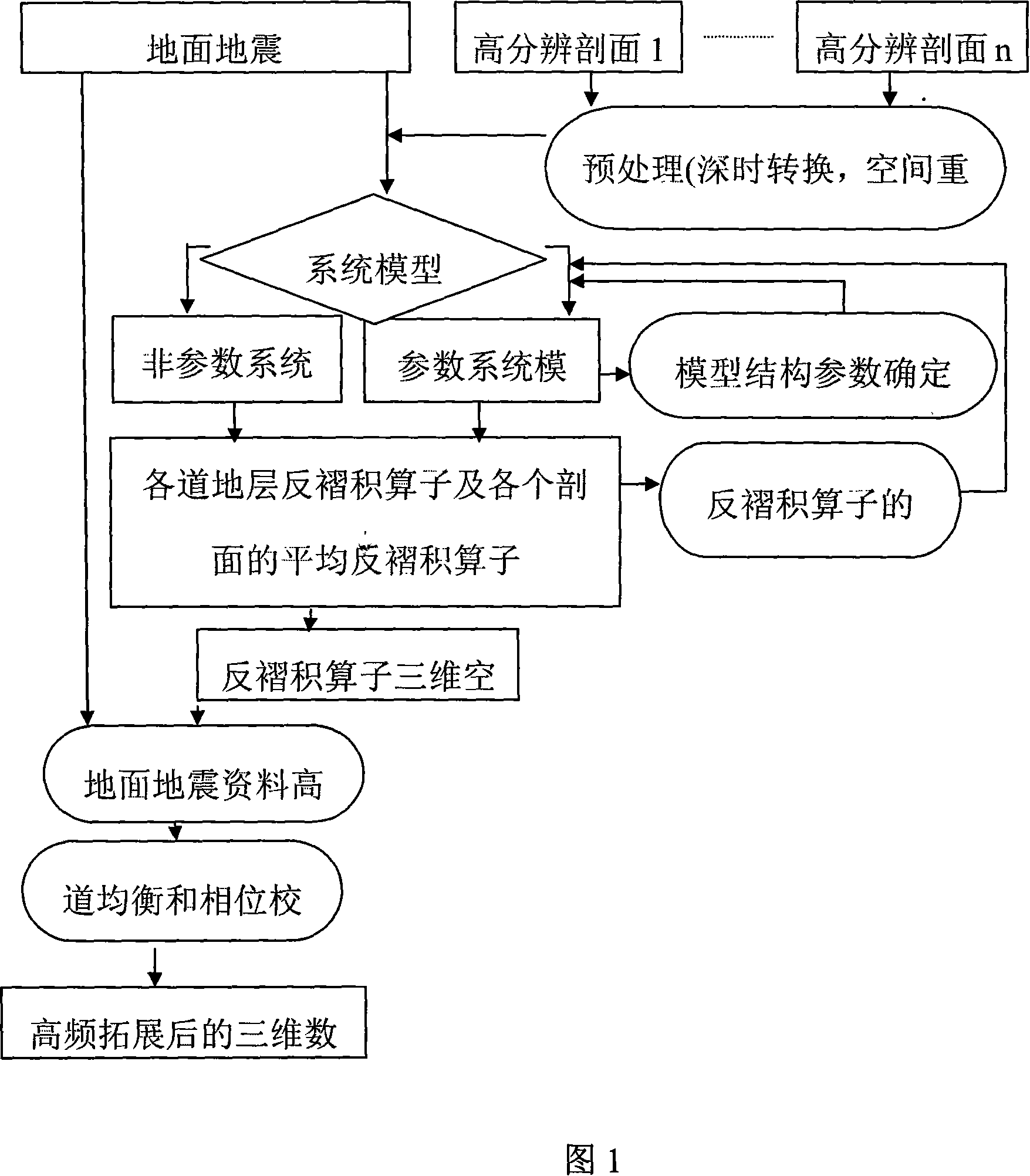
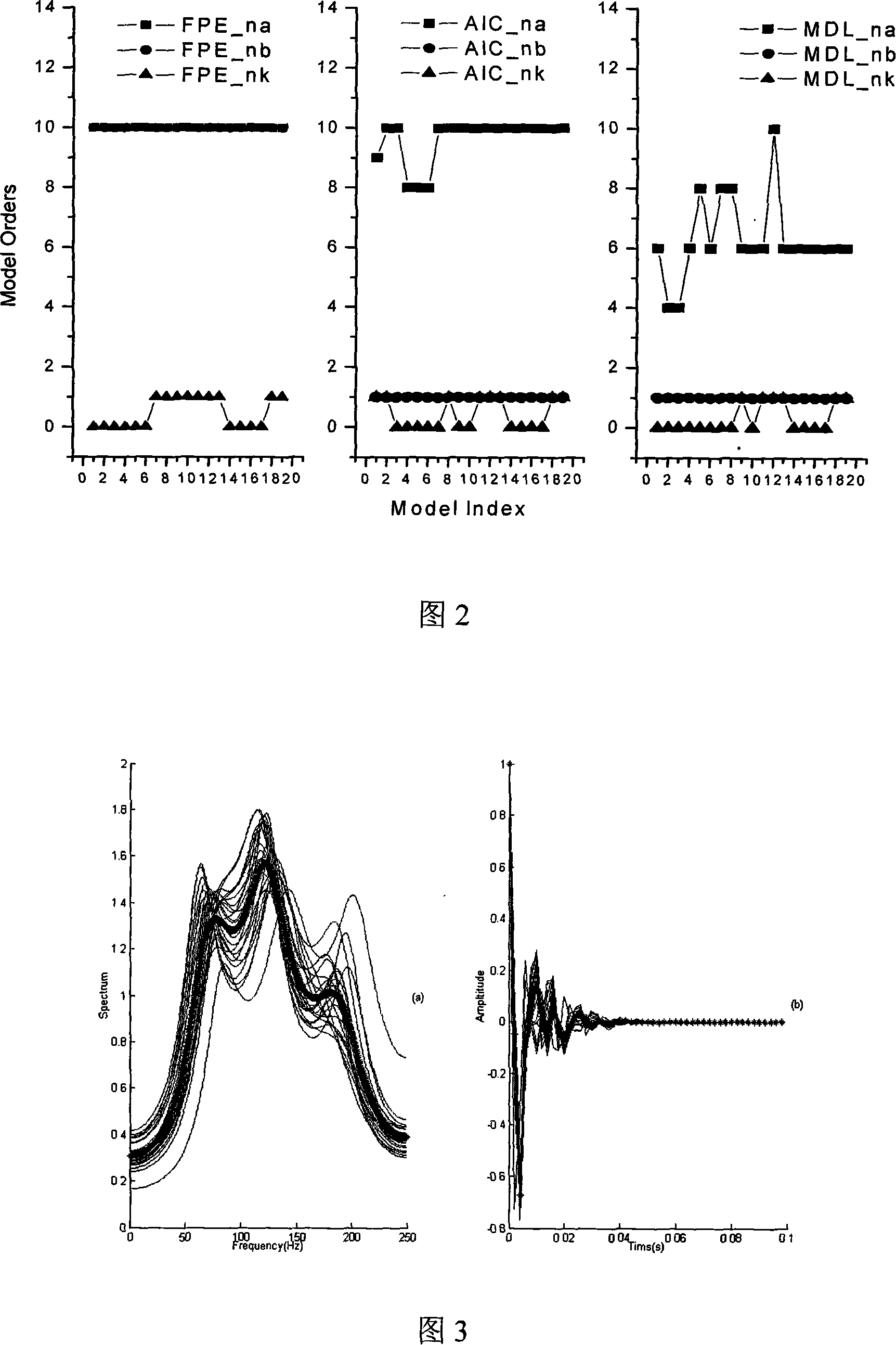
InactiveCN101109821ASeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingMicro structureWell logging
The invention discloses a method for improving the resolution of technical materials for earthquake based on system identification, which essentially comprises the following procedures: (I) a section of high resolution is pre-processed; (II) a model of stratum absorbing system is configured; (III) the system identification of the model of stratum absorbing system is realized, which comprises (1) the realization of the basic structure of system identification, (2) the realization of the non-parameter system model for system identification, and (3) the realization of the parameter system model for system identification; (IV) the system structure of the stratum absorbing model is proved; (V) the system response of the stratum absorbing model is worked out; (VI) the extrapolation of the 3D space of the response of the stratum absorbing model is conducted; (VII) the hi-frequency expansion of the technical materials for the ground earthquake is realized. The invention comprehensively uses the geophysical materials from different dimensions about well logging, between-well earthquake and ground earthquake, etc. to recover with high frequency and high fidelity the technical materials on ground earthquake by using a system identification method, is of great importance for the accurate description and accurate recognization of the micro structure for the reservoir stratum at the after stage of development in an oil field.
Owner:中国石化集团胜利石油管理局有限公司
Method for enhancing images based on multi-scale edge detection in wavelet reconstruction
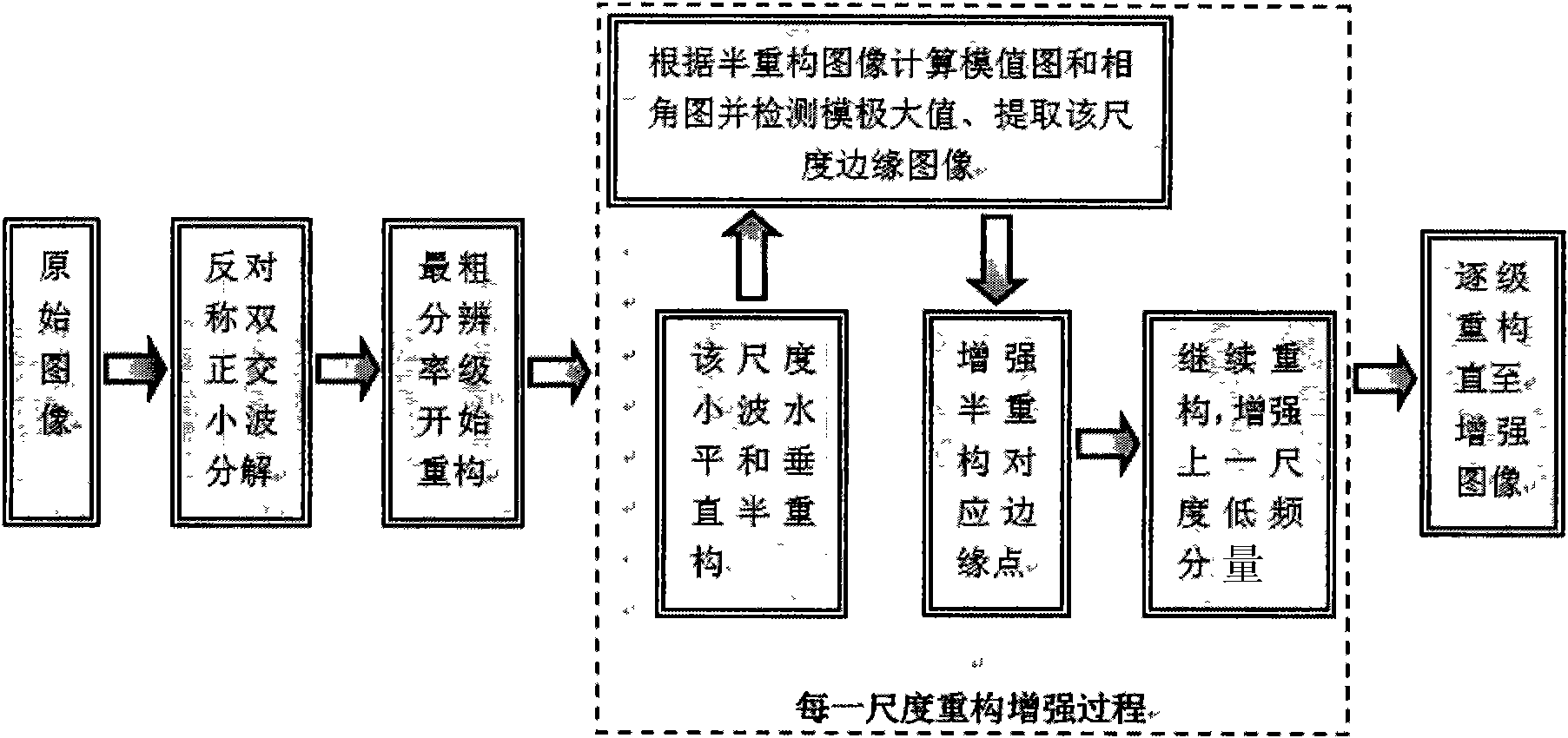
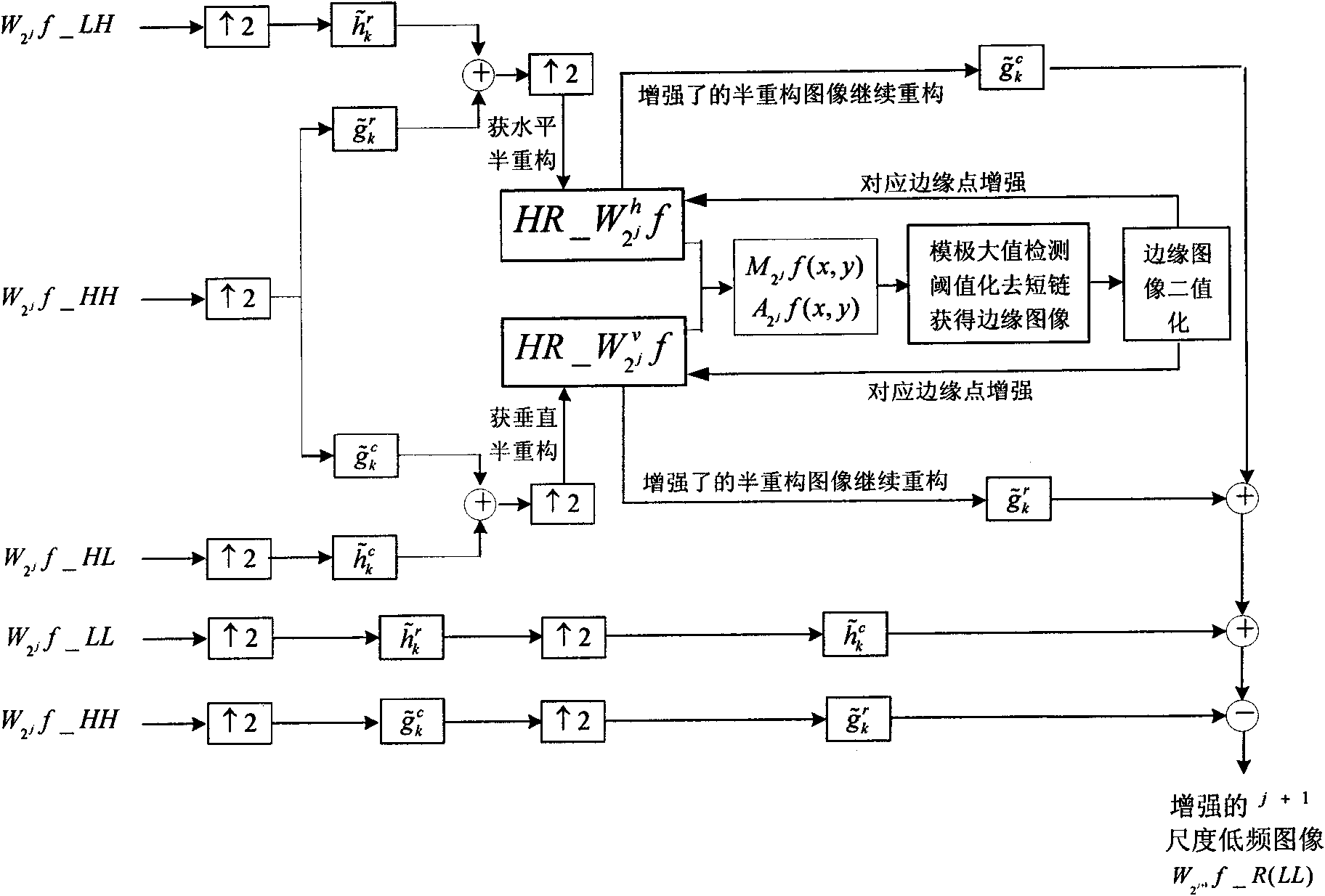
InactiveCN101661616ASmall amount of calculationReduce the amount of calculationImage enhancementHuman–computer interactionImage edge
The invention relates to a method for enhancing images based on multi-scale edge detection in anti-symmetric biorthogonal wavelet reconstruction, aiming at realizing enhancement of image edges in thereconstruction process of wavelet tower-type data resolution. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out multi-scale wavelet decomposition on images; calculating a module value graph and aphase angle graph according to a semi-construction result, carrying out module maximum value detection and threshold value processing and extracting edge images of the scale in the wavelet reconstruction of each level; enhancing corresponding edge points of the semi-reconstruction image according to the edge images; continuing reconstruction to obtain the enhanced low frequency component of the last scale; and carrying out wavelet reconstruction level by level in terms of the reconstruction enhancement process of each level starting from the level of the most coarse resolution to realize image enhancement. The method for enhancing images can be widely used in fields about improving digital images such as medical imaging, biological features recognition, vehicles driving assistance, military, man-machine interaction and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Method for improving seismic data resolution ratio
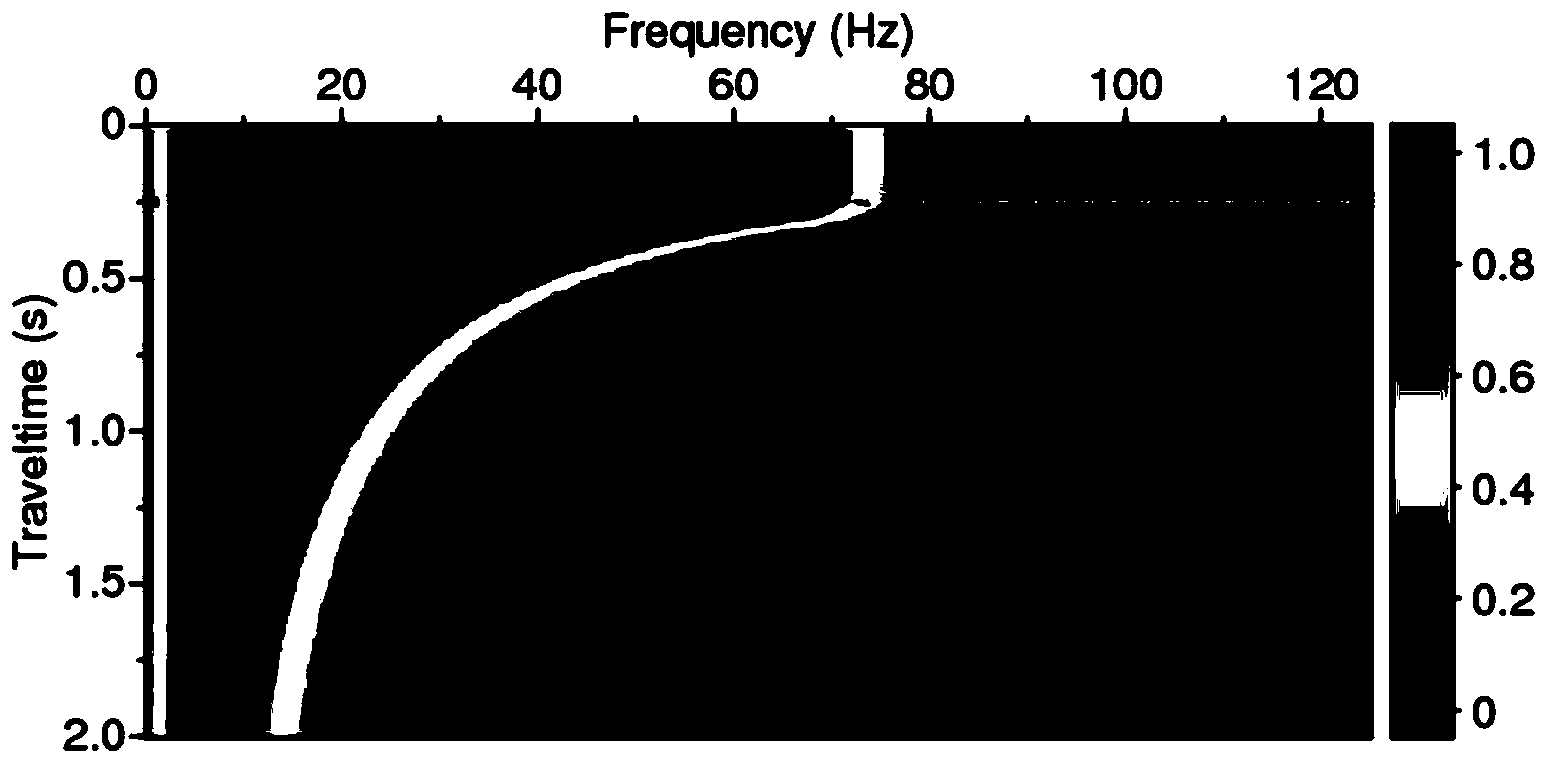
ActiveCN103412329AHigh-resolutionImprove the compensation effectSeismic signal processingTime domainImage resolution
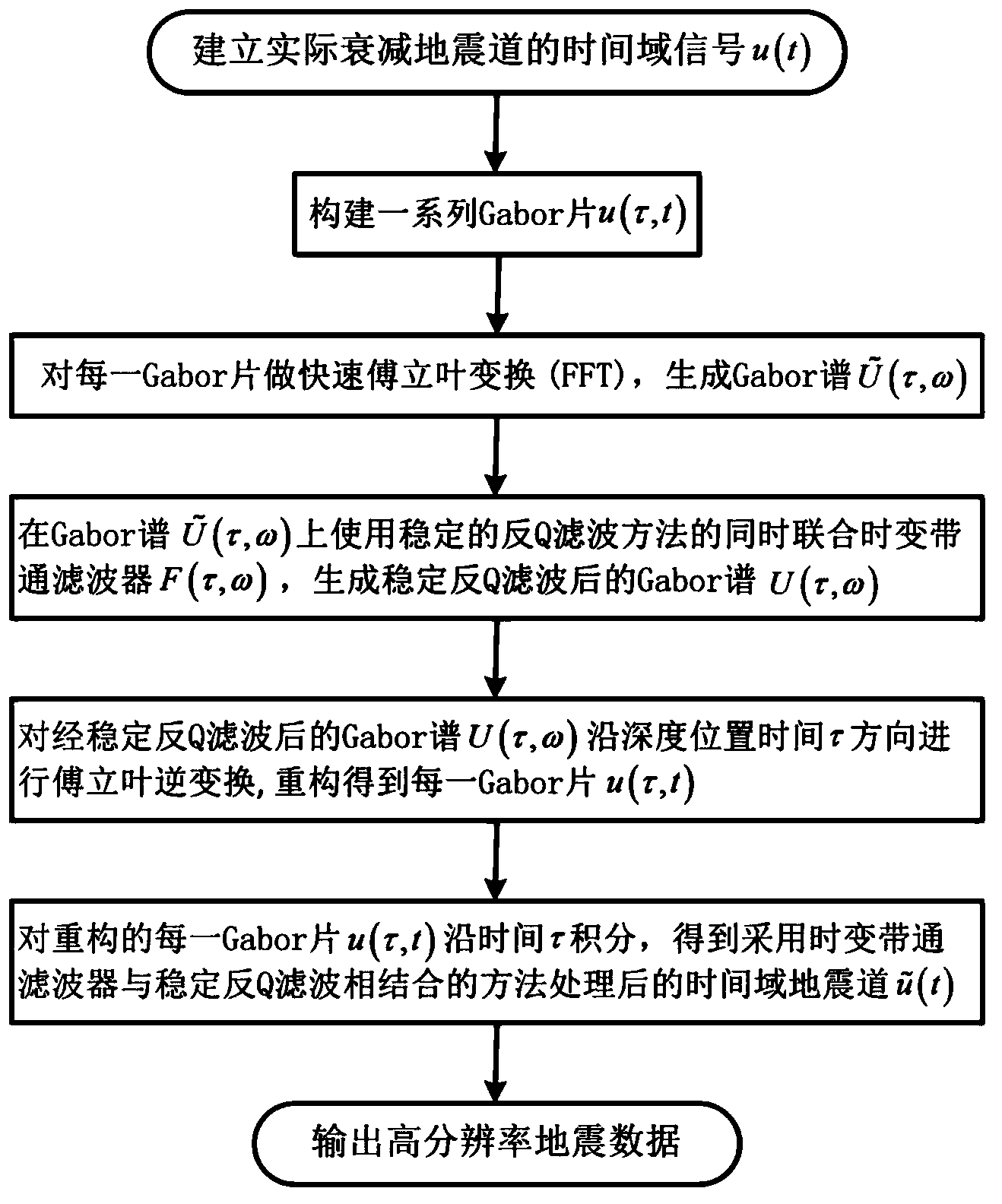
The invention relates to a method for improving the seismic data resolution ratio. The method for improving the seismic data resolution ratio comprises the following steps that a time domain signal u (t) of an actual attenuating seismic trace is established according to input seismic data; a series of Gabor plates u (tau, t) are established according to the established time domain signal u (t) of the actual attenuating seismic trace; FFT conversion is conducted on the Gabor plates u (tau, t) at all time points tau, so that a Gabor spectrum is generated, and the stable reverse Q filtering method compared with a time varying band-pass filter F (tau, omega) is applied to the Gabor spectrum, so that a Gabor spectrum U (tau, omega) after stable reverse Q filtering is generated; Fourier inverse transformation is conducted on the Gabor spectrum U (tau, omega) after stable reverse Q filtering in the depth position time tau direction and each obtained Gabor plate u (tau, t) is reconstituted; the seismic data with the high resolution ratio processed through the stable reverse Q filtering method compared with the time varying band-pass filter. The method for improving the seismic data resolution ratio can be widely applied to processing the seismic data.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
Device and method for observing three-dimensional DC electrical-method simulation experiment
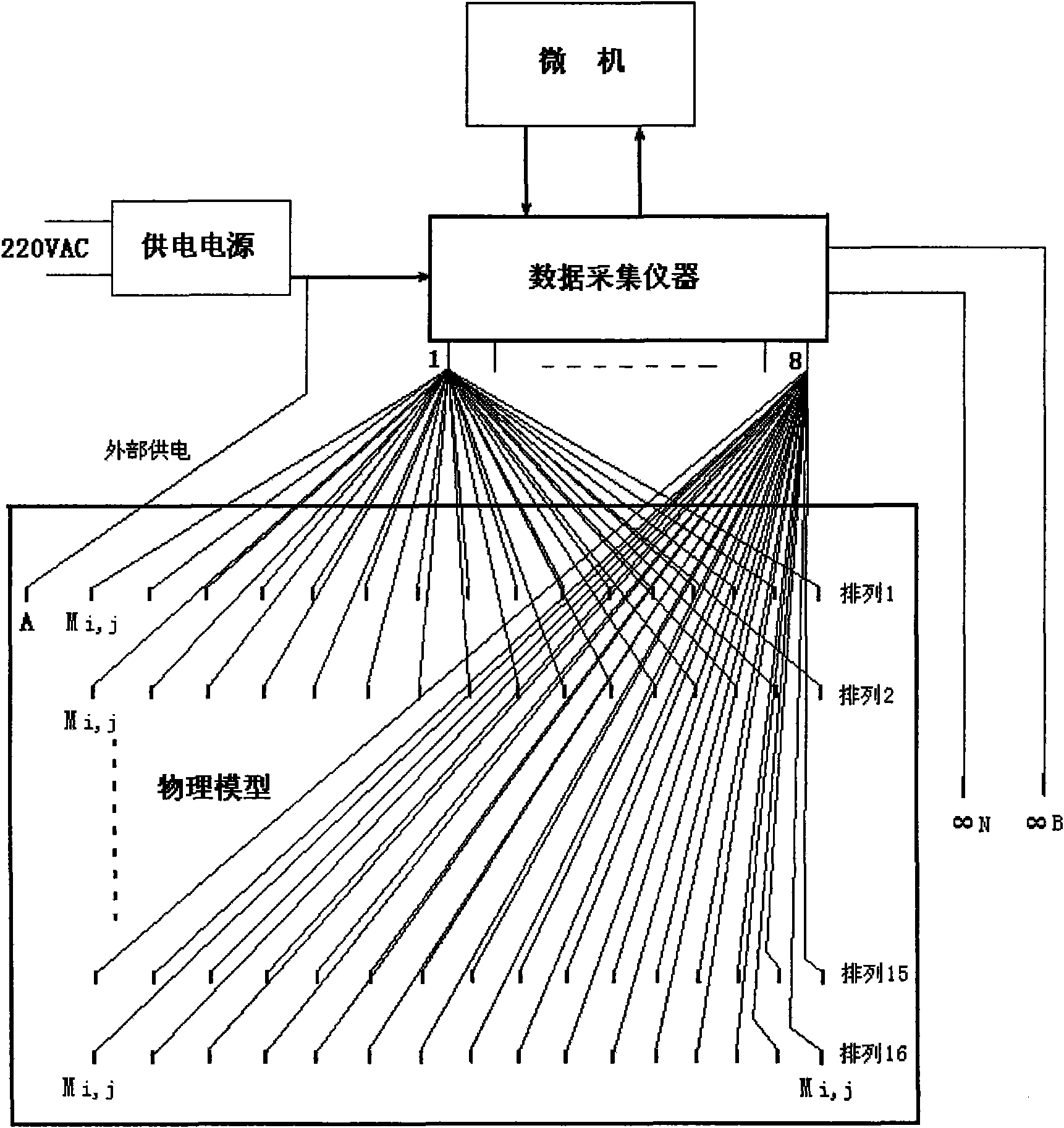
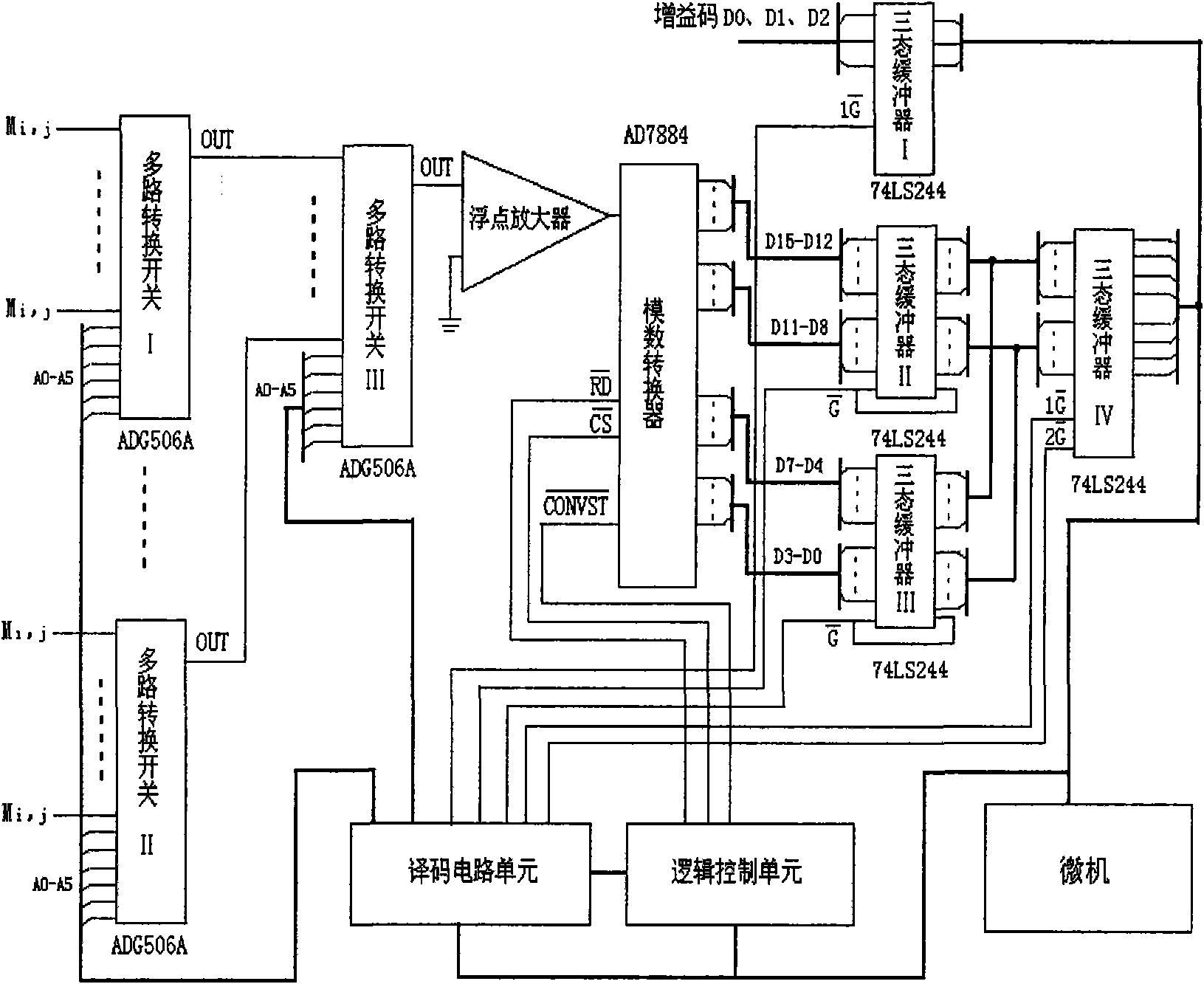
InactiveCN101561513AShort measurement timeHigh degree of automationEducational modelsElectric/magnetic detectionData acquisitionPhysical model
The invention discloses a simulation experiment observation instrument by three-dimensional DC electrical-method and an observation method for simulation experiment teaching. The observation instrument consists of a microcomputer, a DC power supply source and a 256-channel data acquisition instrument. The observation instrument can carry out area observation, two-dimensional observation, four-pole observation and high-density observation. The observation instrument not only retains the measuring function of conventional electrical-method instruments, but also can complete single-electrode power supply and multi-electrode area receiving due to a multi-channel parallel-type receiving mode of the observation instrument. The observation method has the advantages of improving observation efficiency by hundreds of times than the conventional electrical-method instruments, along with simplicity, easy operation, short measuring time, high automation degree and high data resolution, so the observation method is true and reliable in obtained data. The invention can complete study on a special method for multi-electrode power supply and multi-electrode receiving according to different experimental purposes. The observation instrument not only can be used as three-dimensional electrical-method physical-model teaching experiment, but also can be used as a field observation instrument for three-dimensional electrical-method exploration.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
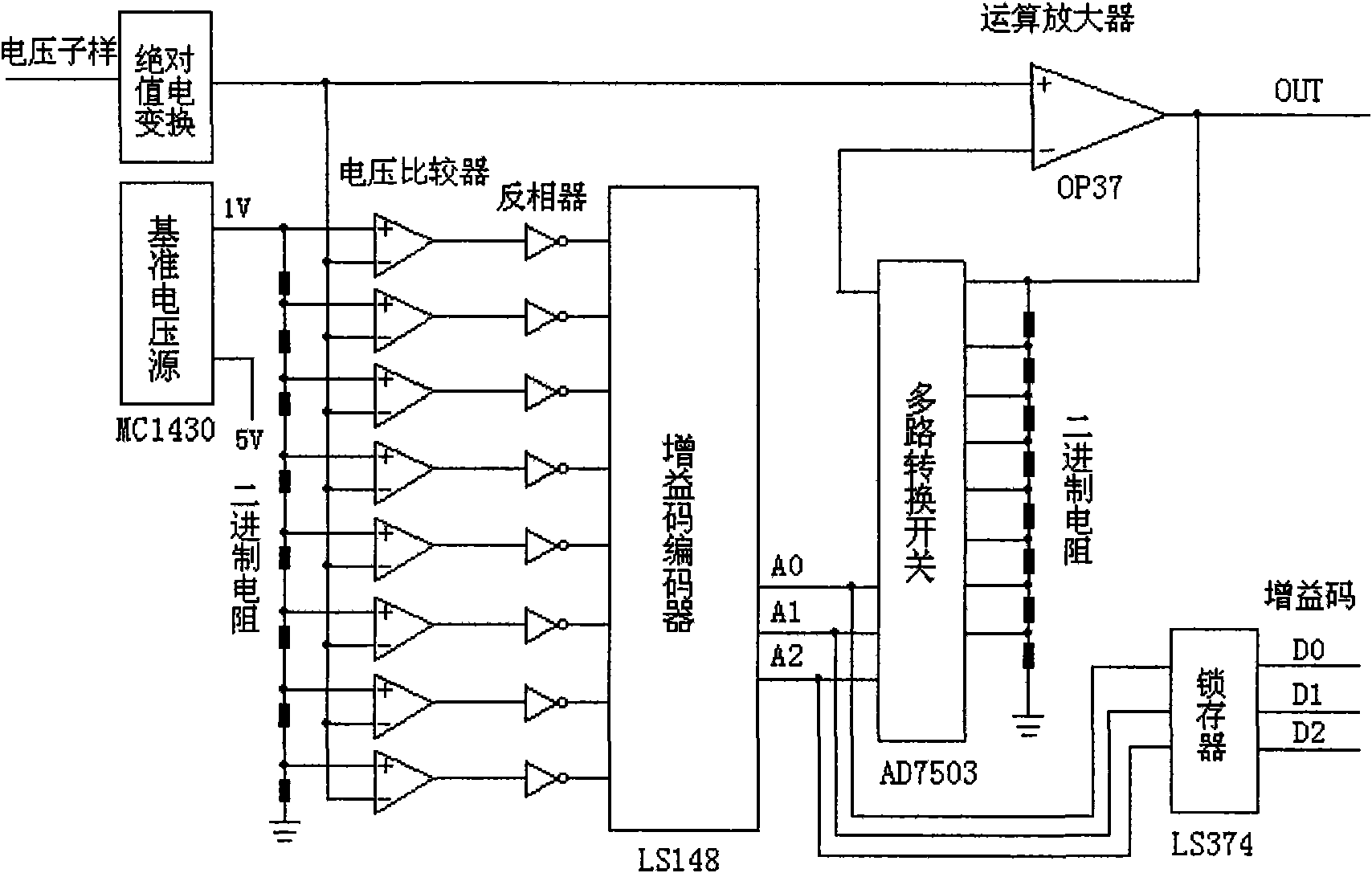
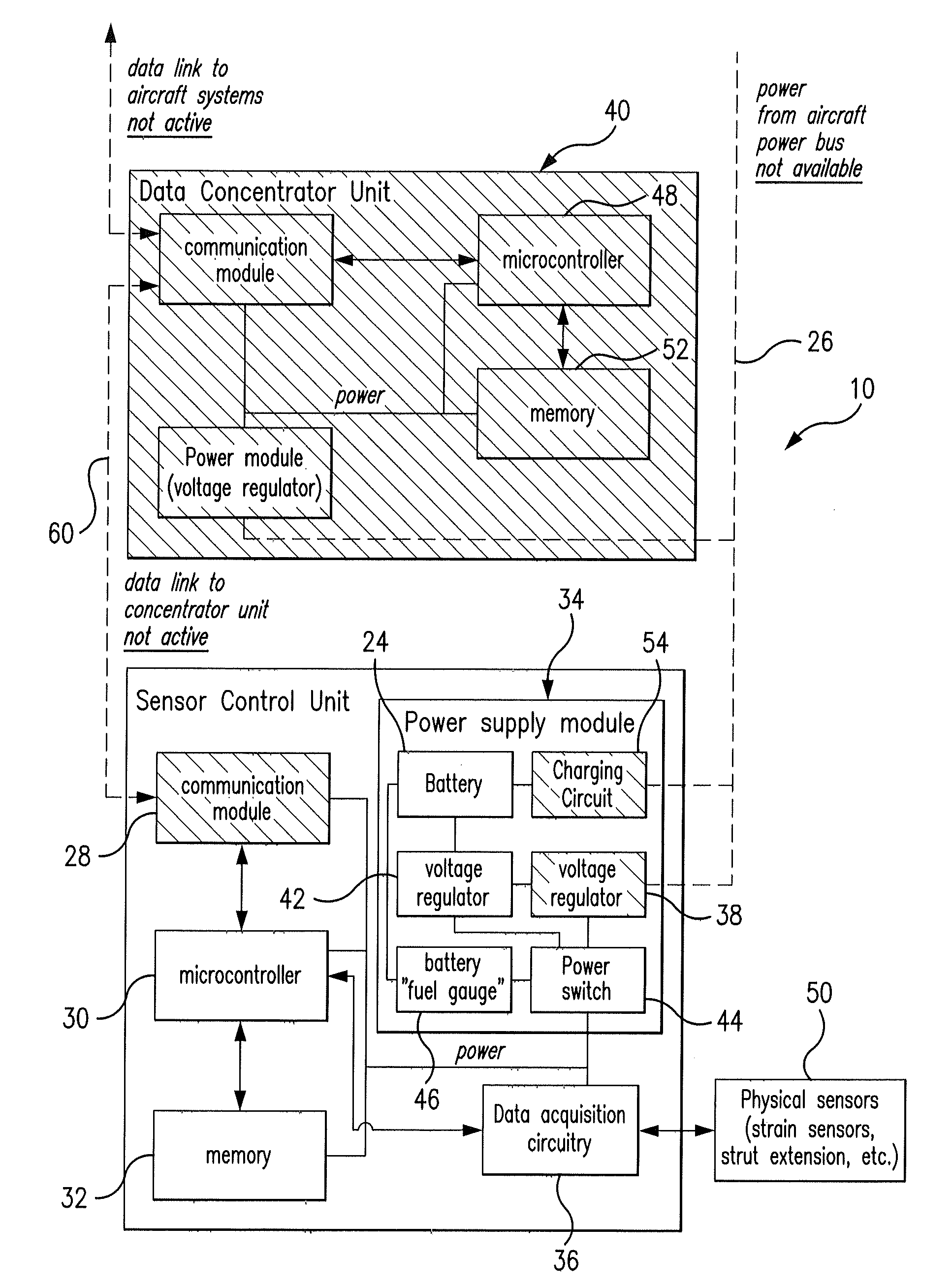
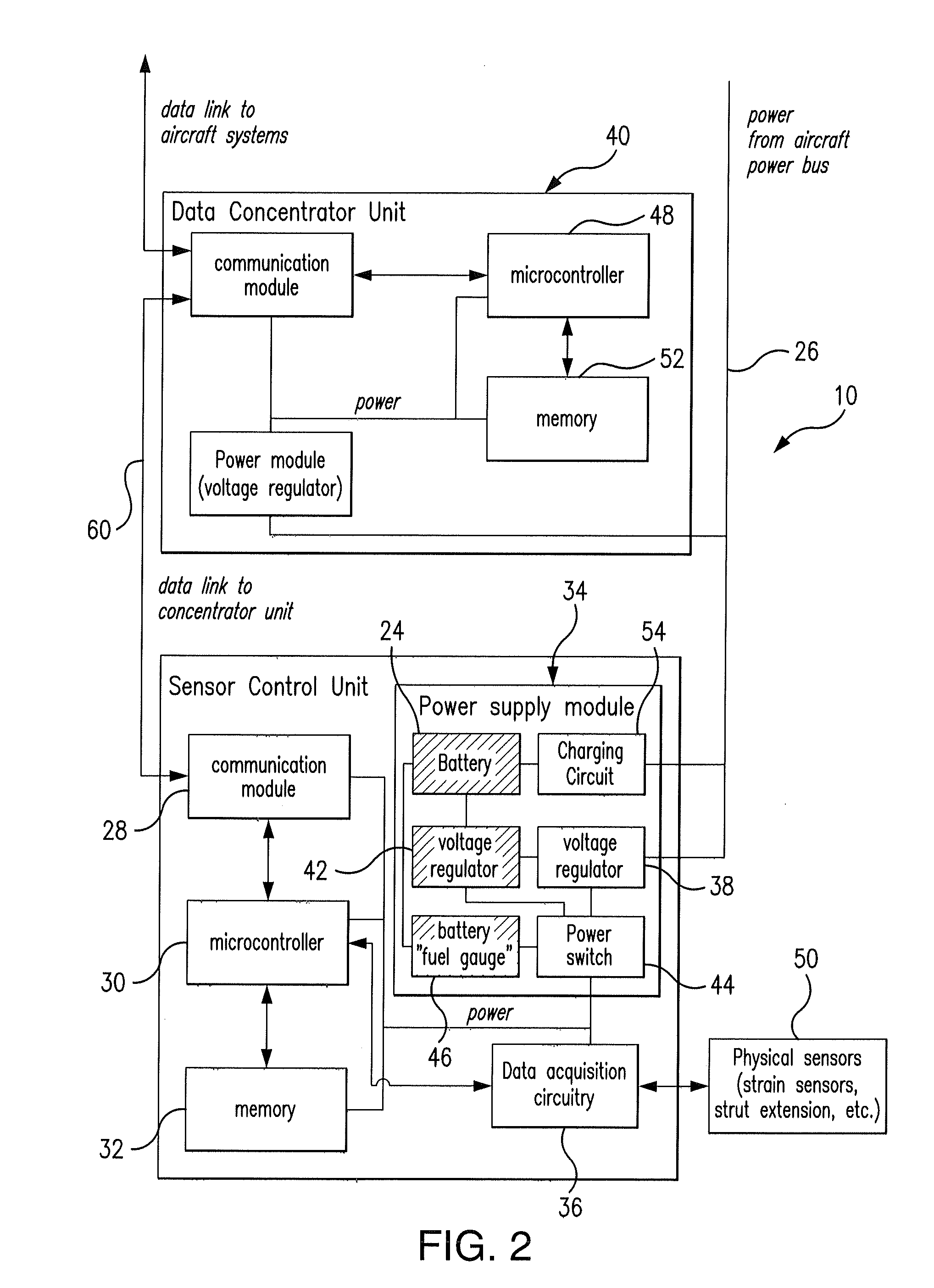
Monitoring systems and methods for aircraft landing gear
ActiveUS20120095703A1Not easy to detectLimiting power drawRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesEnergy efficient board measuresImage resolutionData acquisition
A system and method for monitoring loads applied to aircraft landing gear structure. The method includes the step of interrogating at least one sensor positioned proximate the landing gear structure by way of data acquisition circuitry to yield strain data. The method further includes the step of instructing the data acquisition circuitry with respect to a sampling rate and data resolution for interrogation.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com