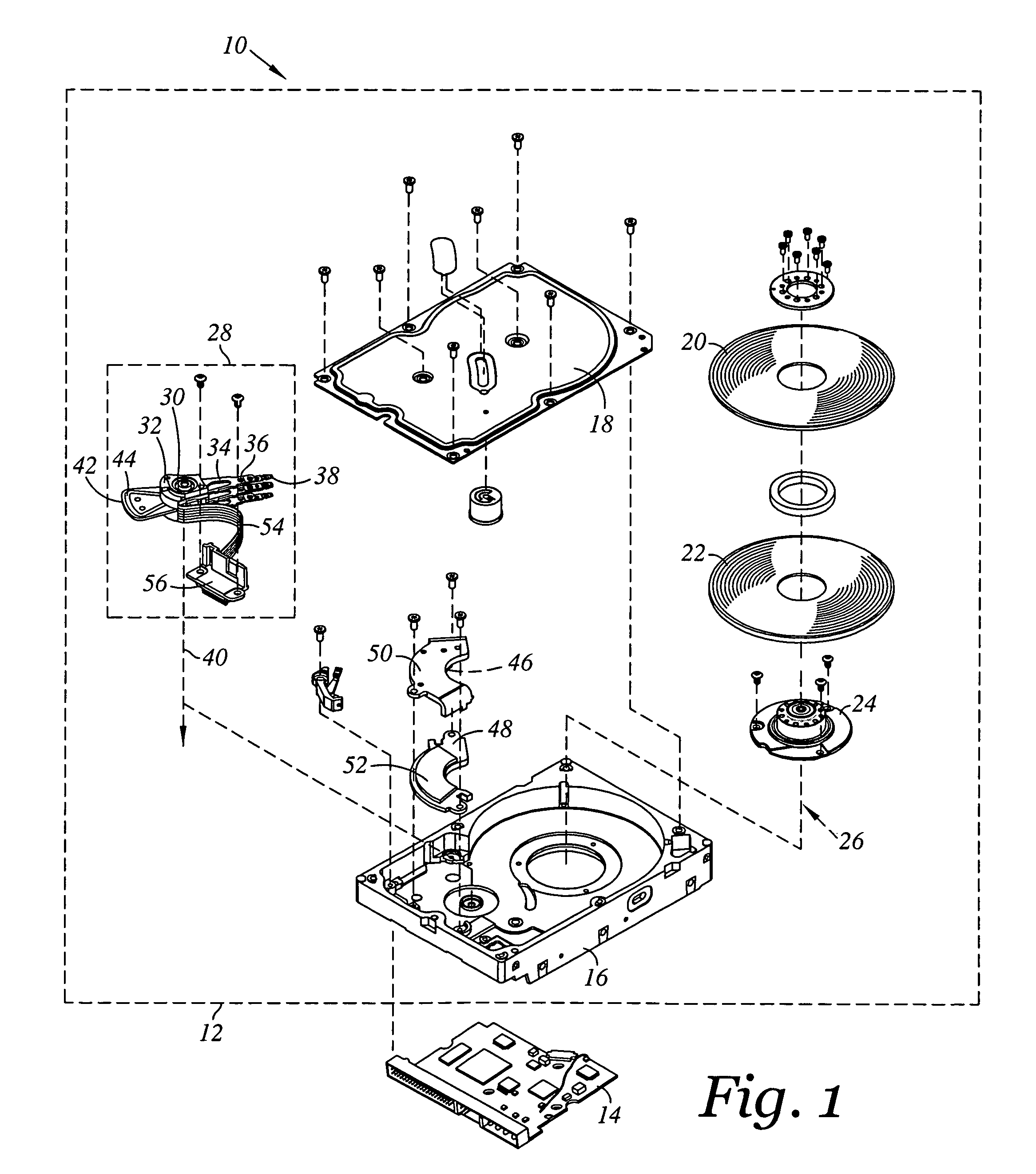
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
984results about "Mounting/attachment of transducer head" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
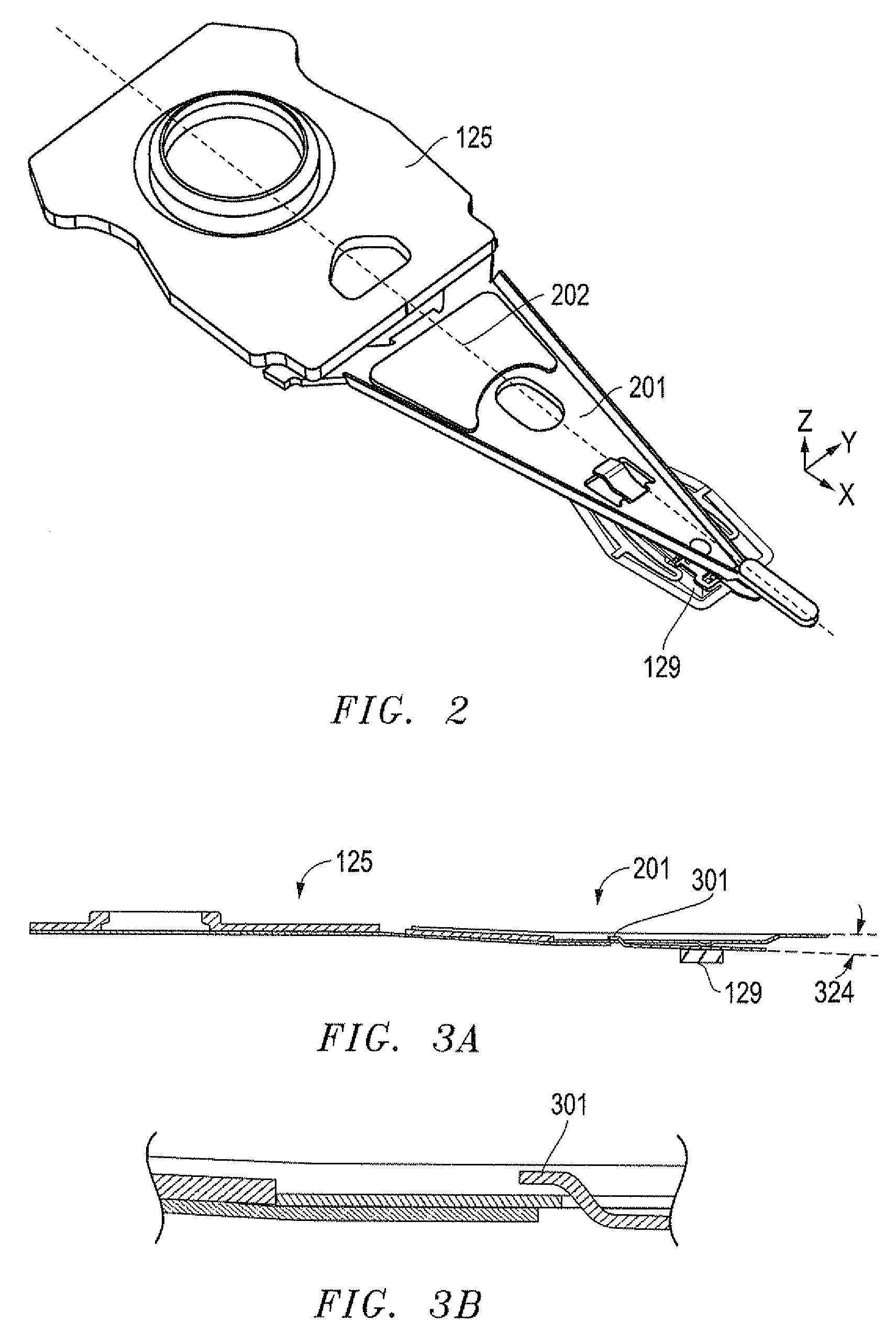
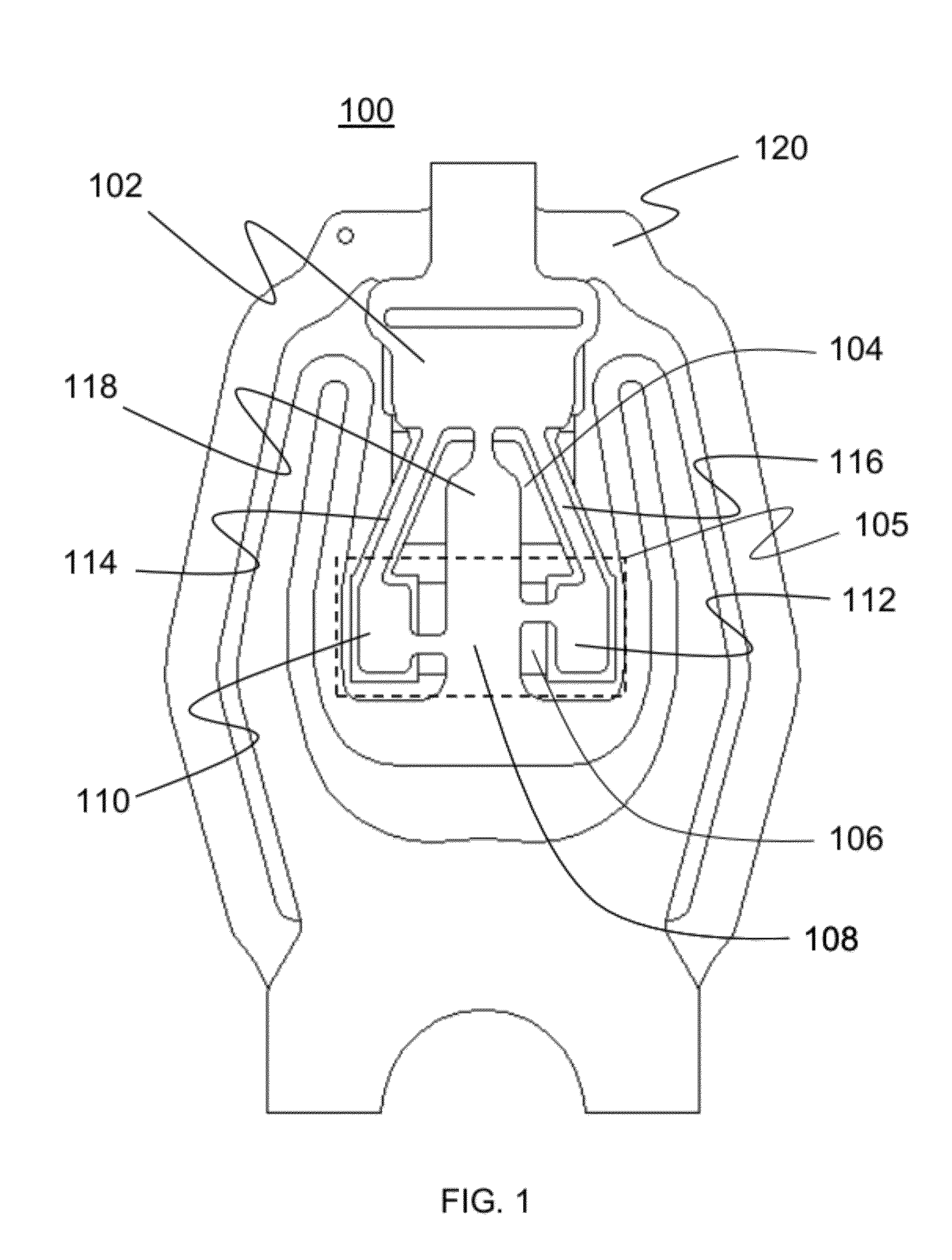
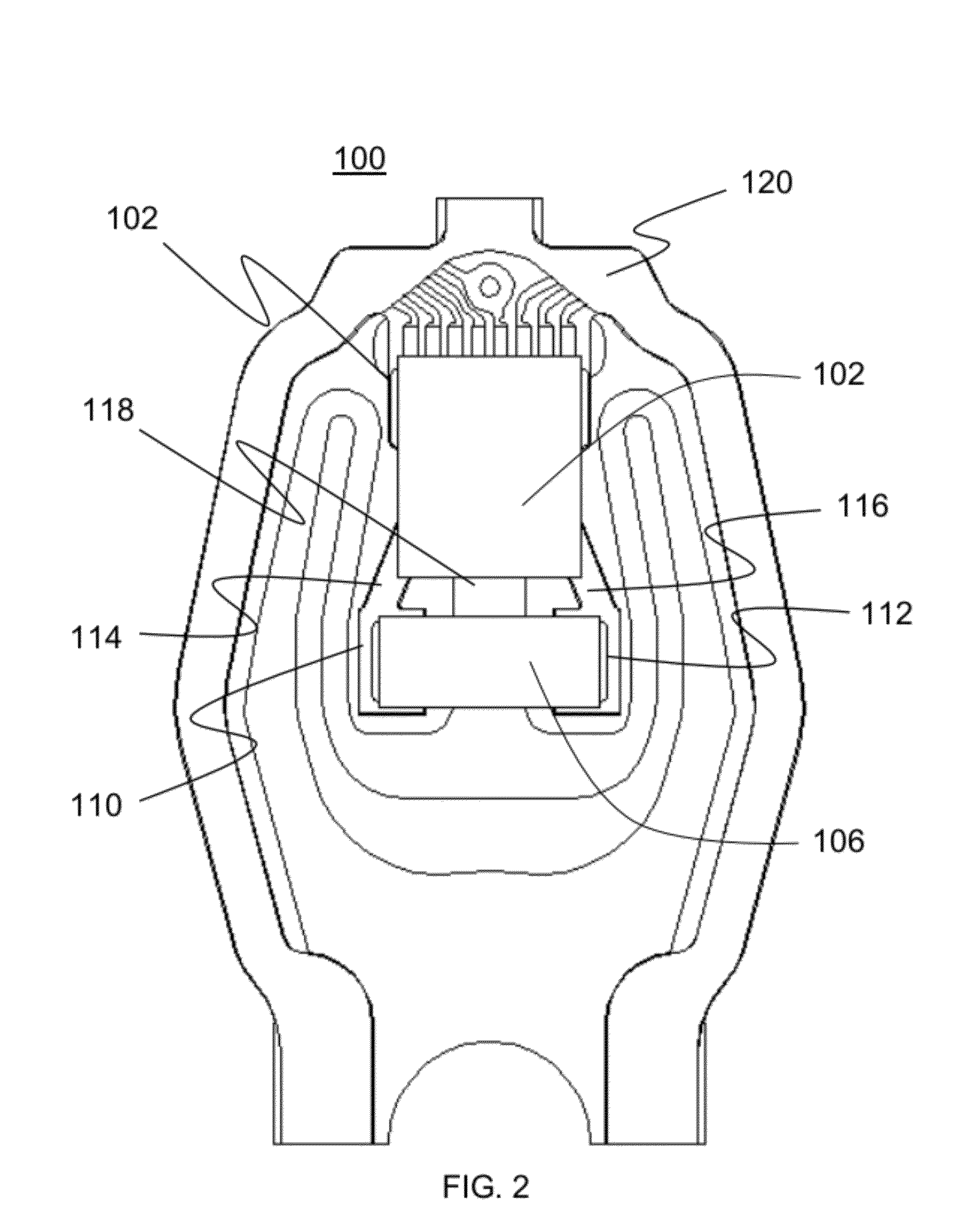
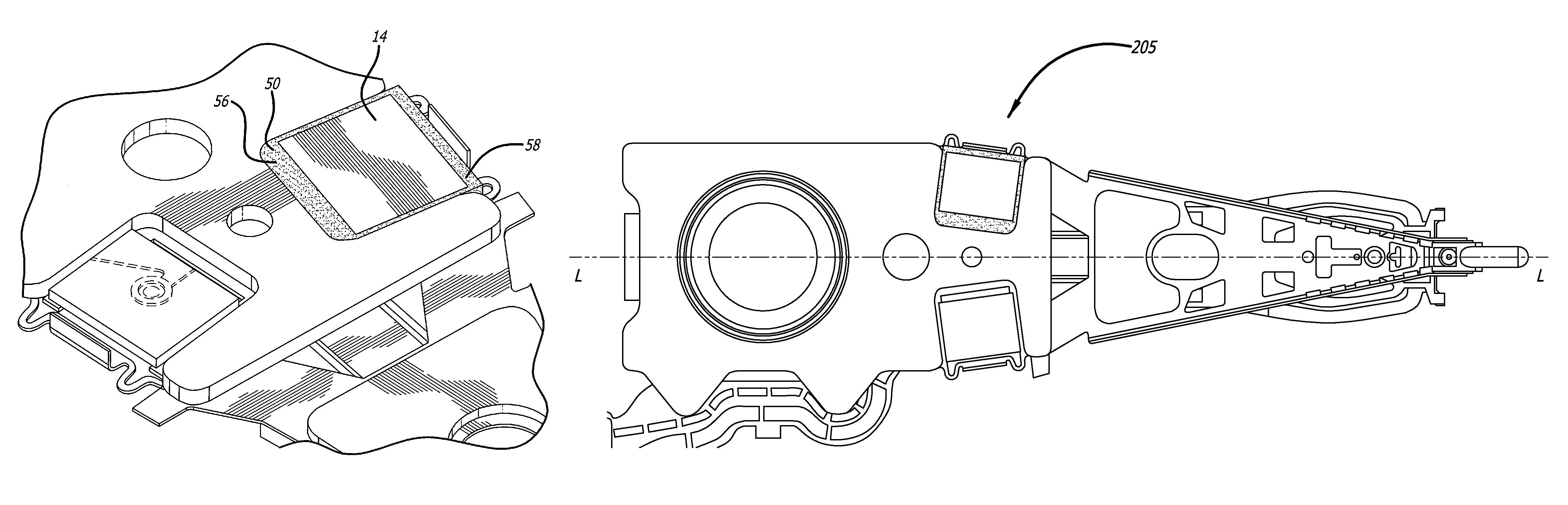
Dimple pivot post for a rotary co-located microactuator
InactiveUS7057857B1Eliminate deformationImprove performanceRecord information storageMounting/attachment of transducer headAdhesiveEngineering
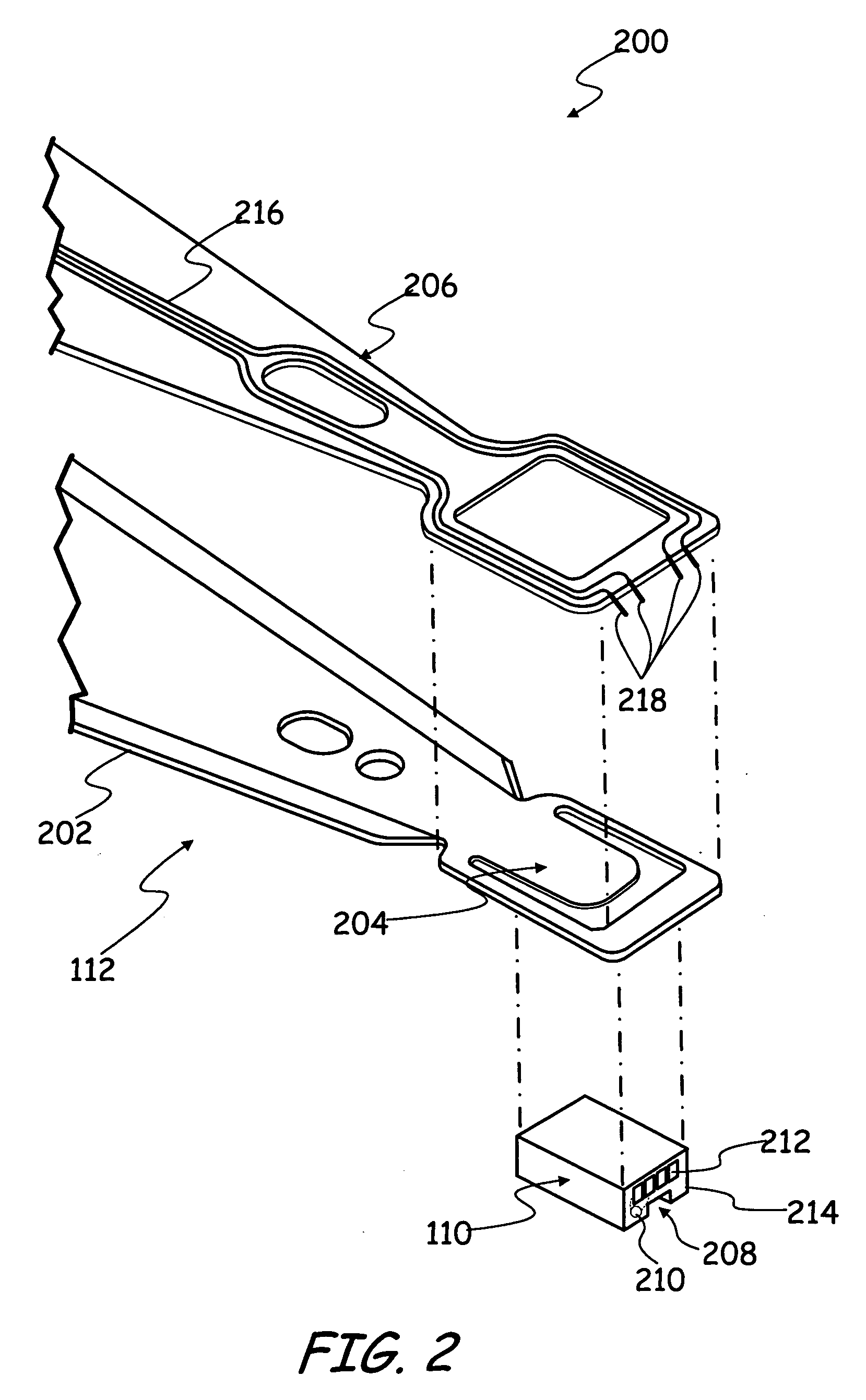
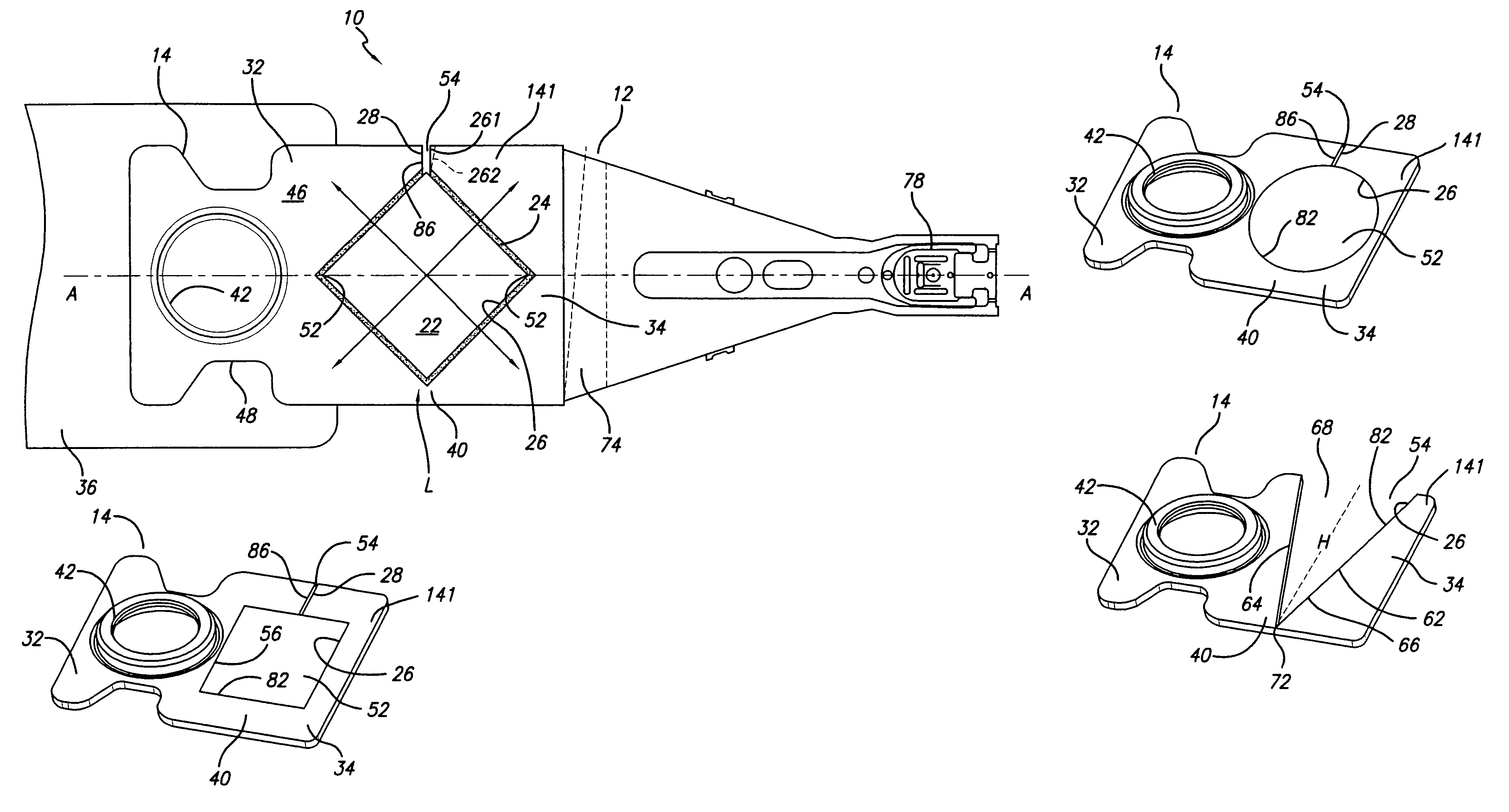
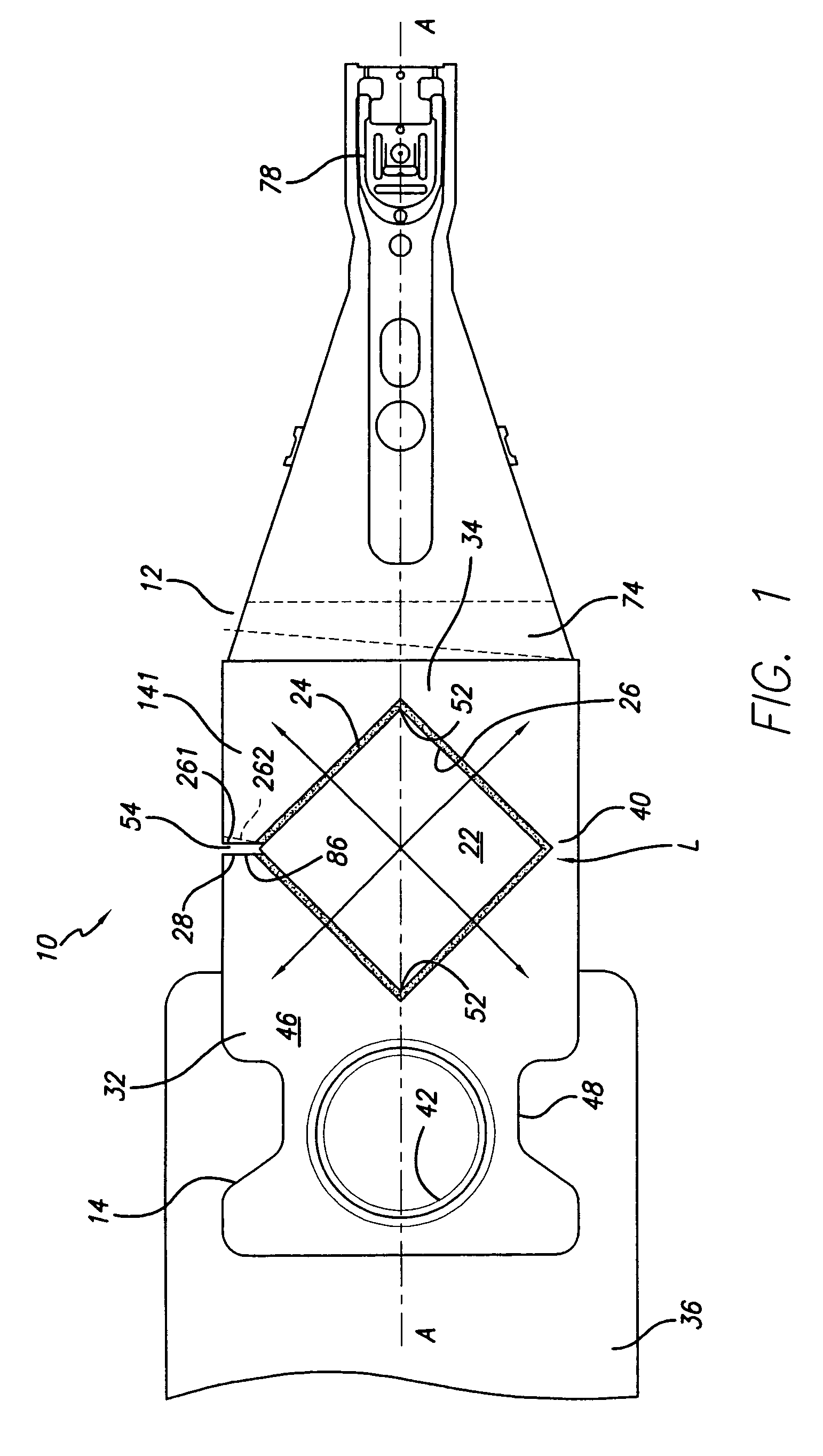
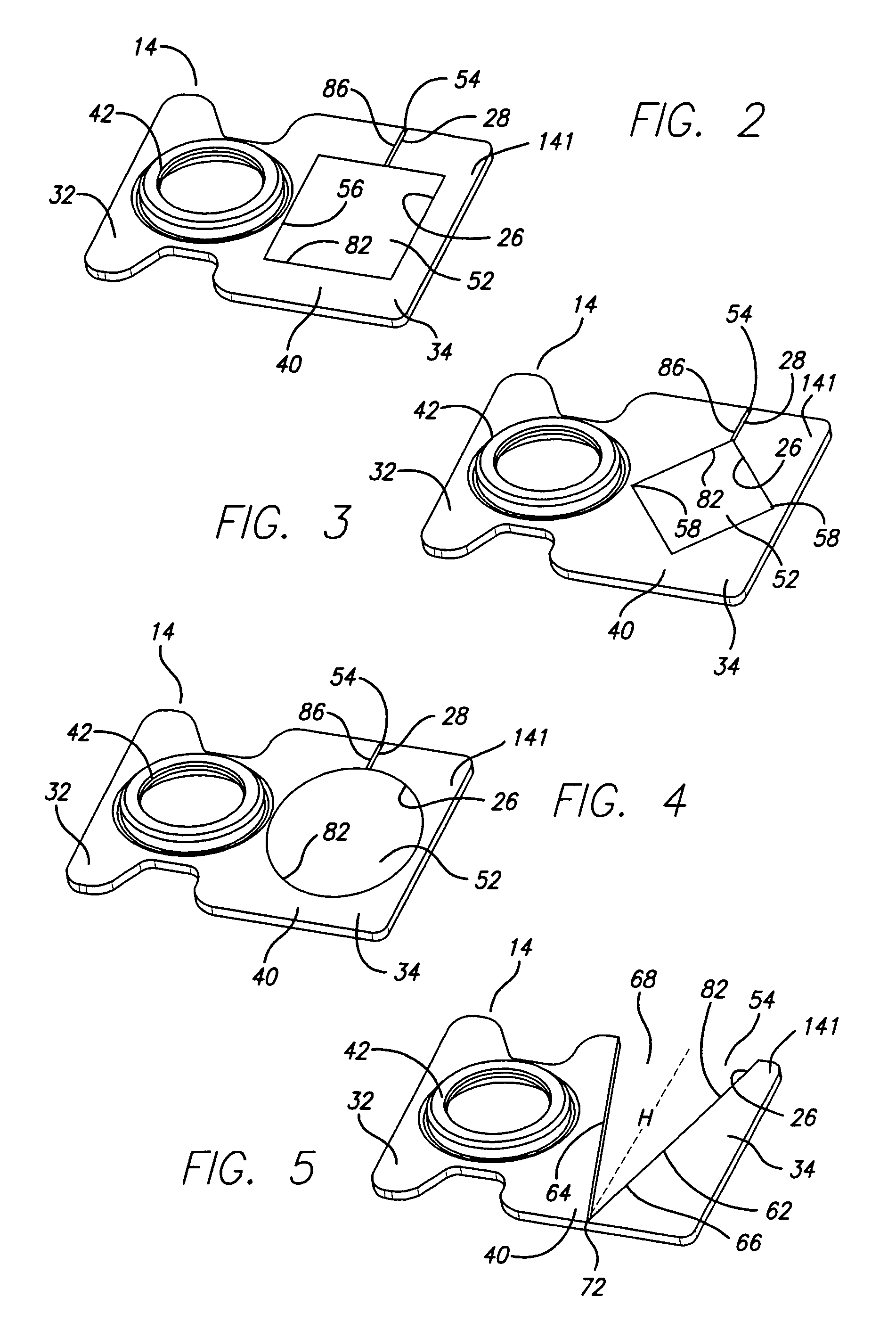
A rotary microactuator-based head-gimbal assembly design controls the unwanted deflection of a flexure in a data storage device and eliminates hinge deformation. The head-gimbal assembly maintains the co-planarity of the hinged islands in the microactuator under the applied load acting on the flexure and two associated hinged islands. The dimple post is placed at the dimple loading region of the flexure tongue and has the same height as adhesive dams on paddles secured to the hinged islands. The dimple post is formed by branching one of the existing conductive traces covered by a photoresist layer to the dimple loading region on flexure tongue. In an alternative embodiment, the dimple post is secured to the dimple loading region of the flexure tongue by means of adhesives with a variety of viscosity and elastic moduli.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
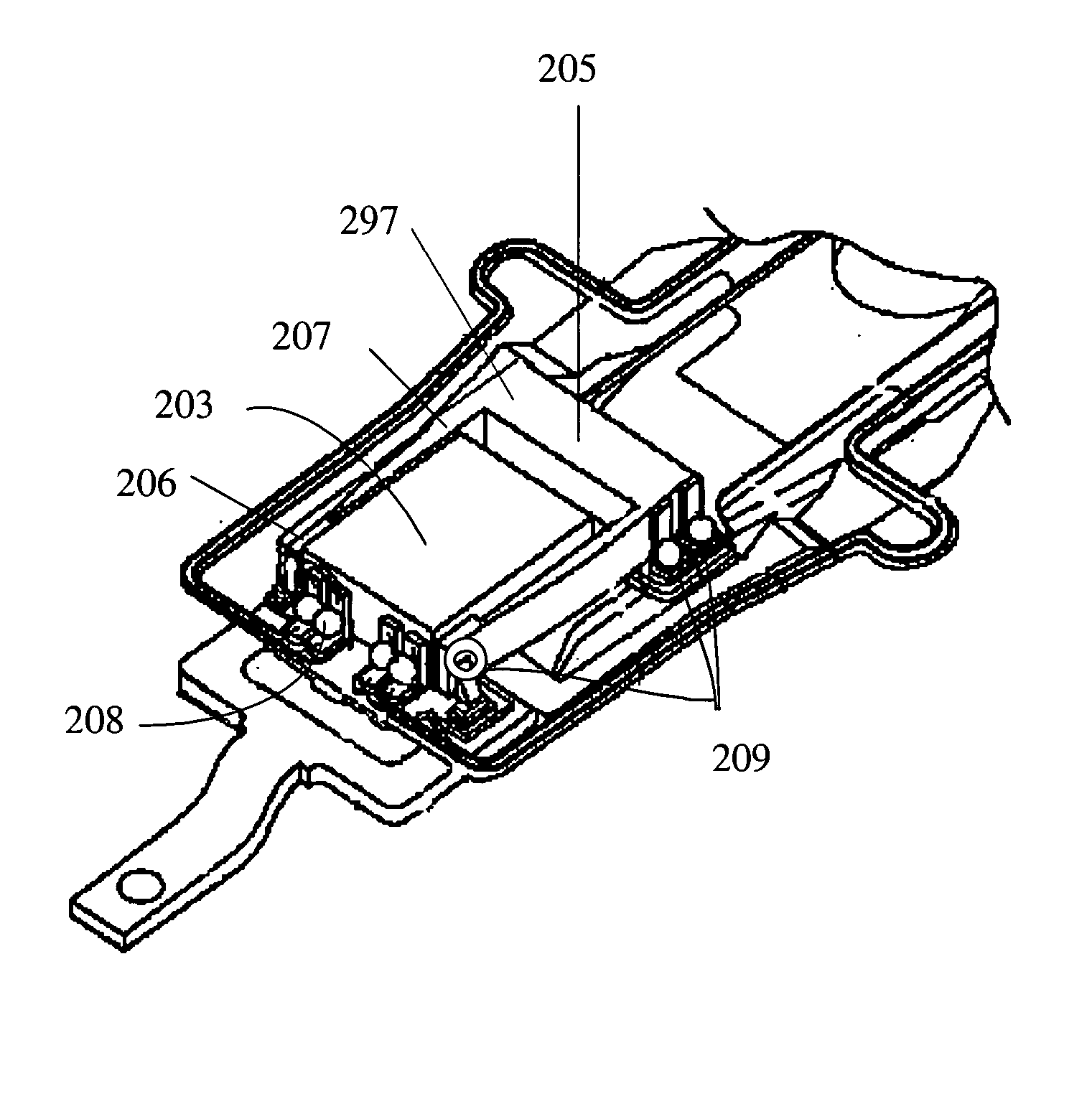
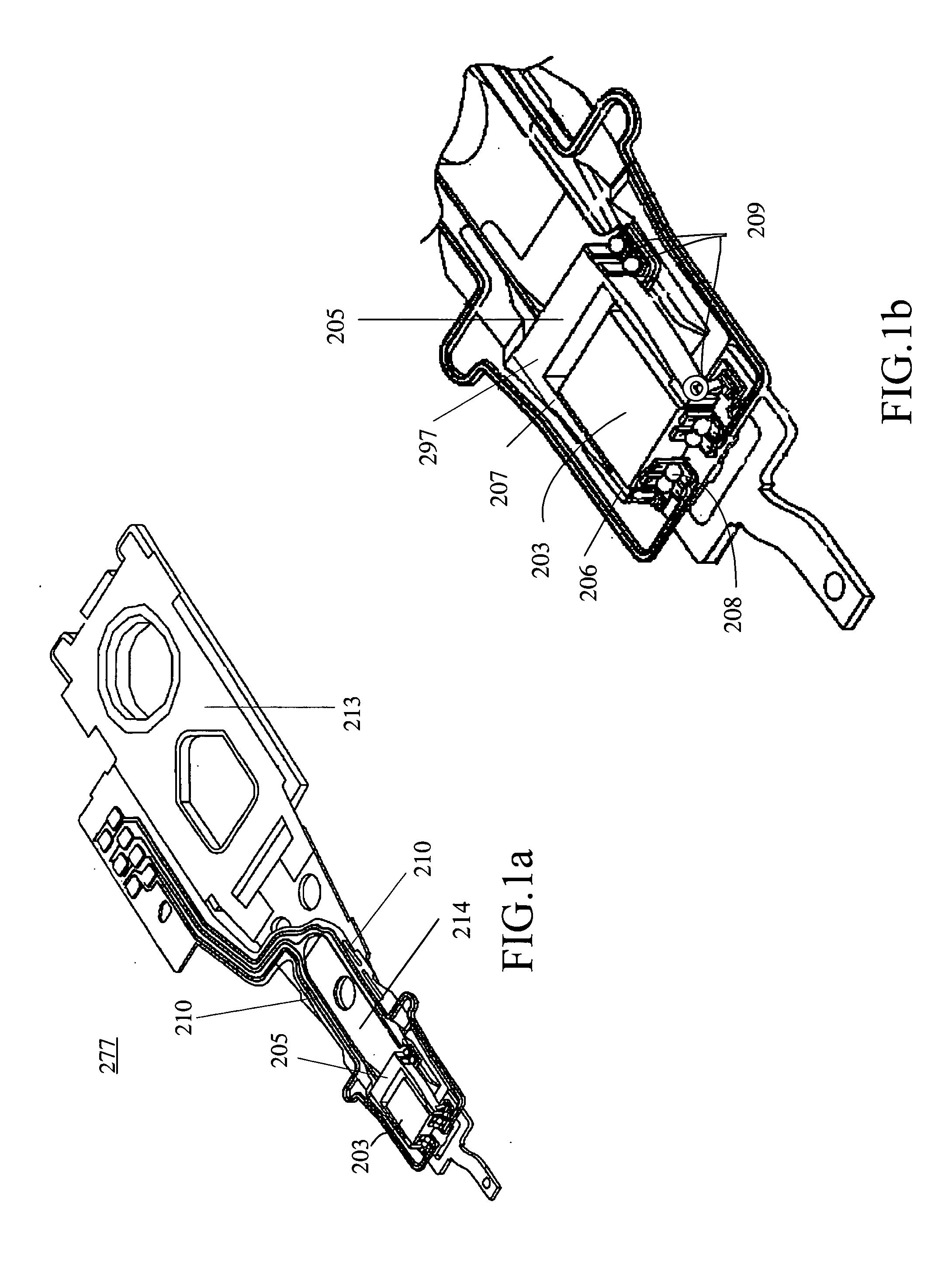
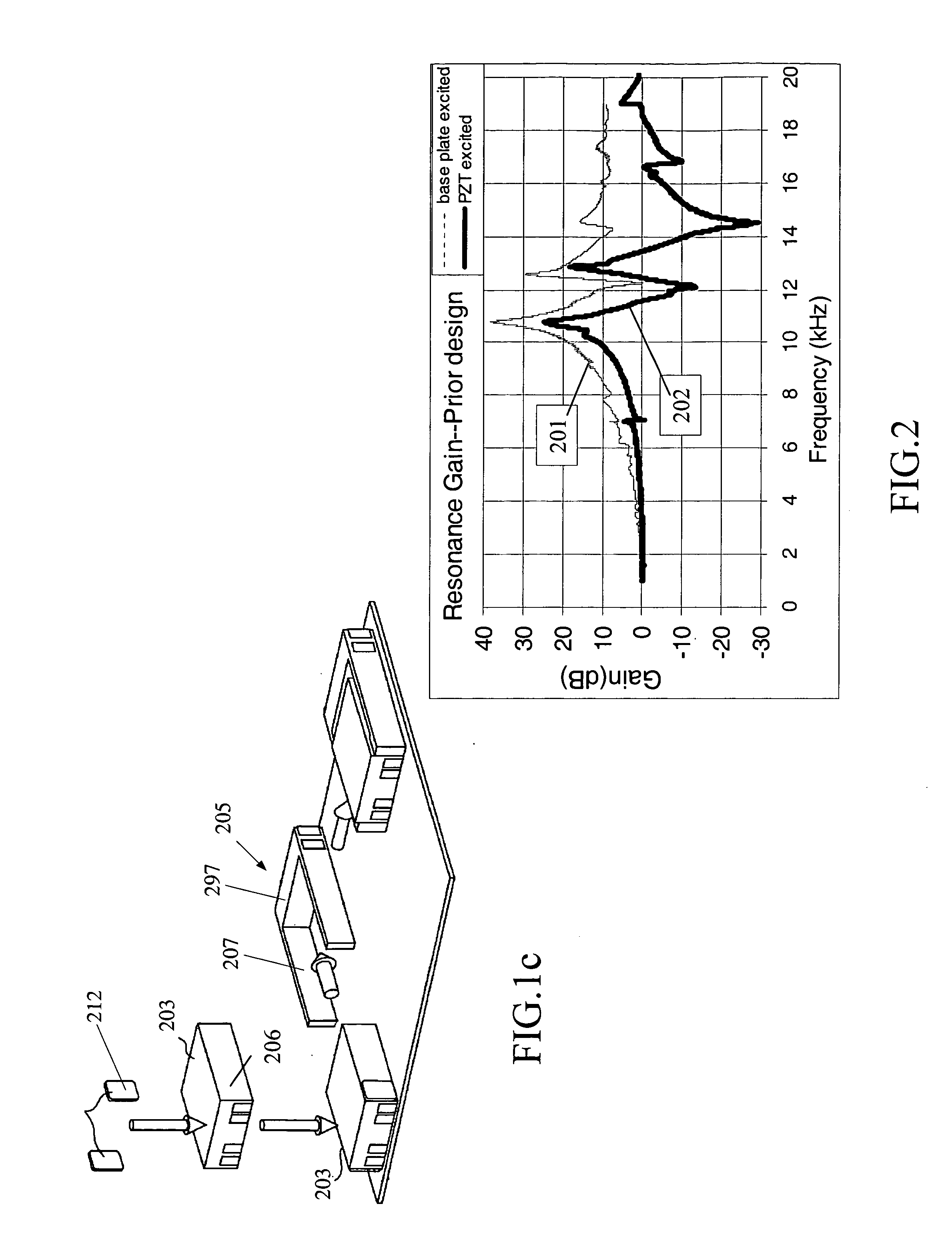
Head gimbal assembly having a radial rotary piezoelectric microactuator between a read head and a flexure tongue
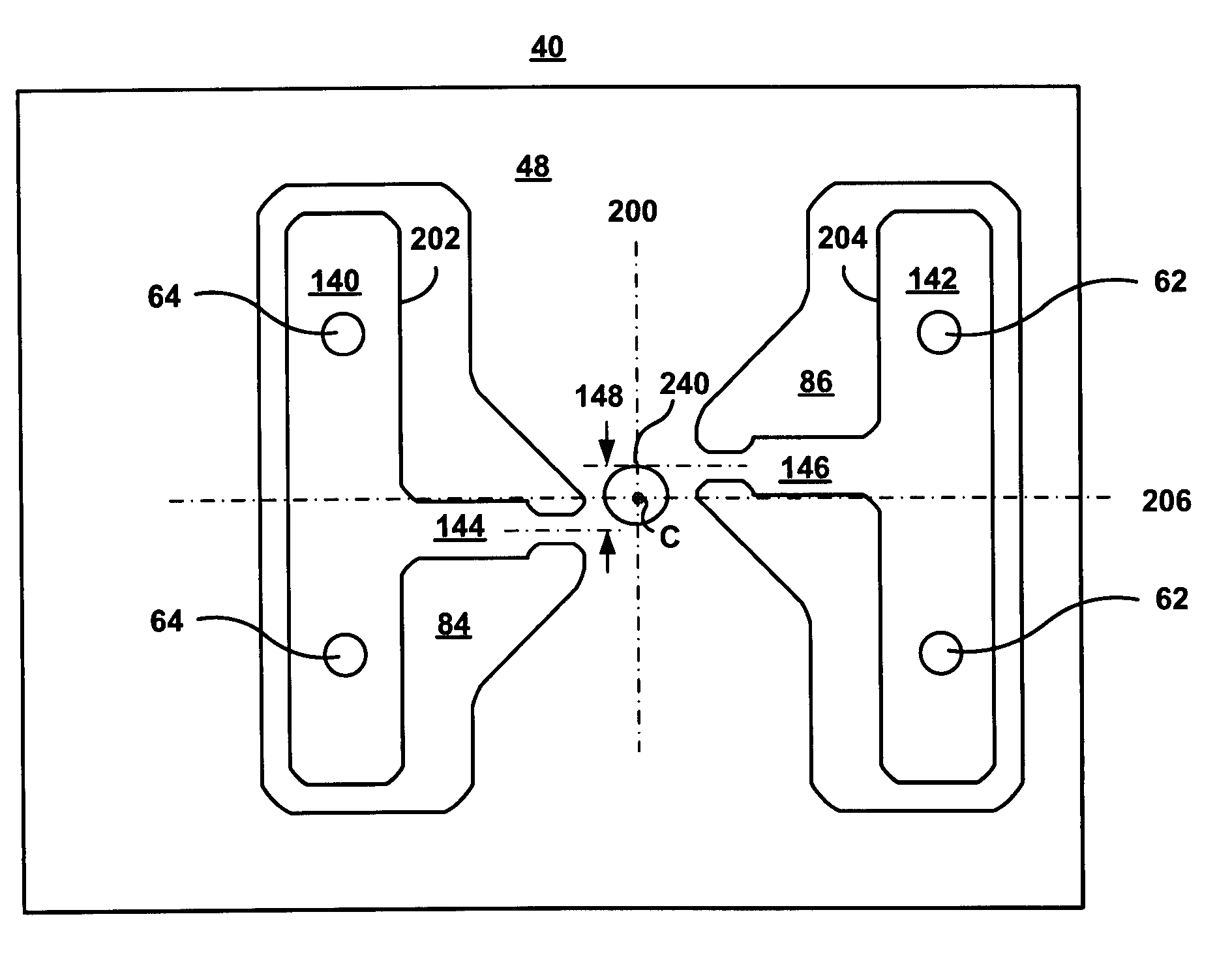
A novel head gimbal assembly (HGA) includes a piezoelectric microactuator having a first side and an opposing second side. The first side includes a plurality of anchor regions that extend radially from a center point and are bonded to the gimbal tongue. The first side also includes a first plurality of non-bonded regions lying between the anchor regions. The second side includes a plurality of link regions that extend radially from the center point and are bonded to a top surface of the read head. The second side also includes a second plurality of non-bonded regions lying between the link regions. Each of the plurality of link regions is angularly spaced between two of the plurality of anchor regions.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Servo writing a disk drive using a secondary actuator to control skew angle
InactiveUS7489464B1Constant skewConstant track densityDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageSkew angleActuator
A method of servo writing a plurality of servo sectors to a disk of a disk drive to define a plurality of data tracks is disclosed. The disk drive comprises the disk, an actuator arm, a head coupled to a distal end of the actuator arm, wherein the head comprises a read element and a write element. A voice coil motor (VCM) rotates the actuator arm about a pivot to actuate the head radially over the disk, and a secondary actuator adjusts a skew angle for the head while using the write element to write the servo sectors to the disk.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
System, method and apparatus for flexure-integrated microactuator
ActiveUS20090244786A1Overcome costsOvercomes manufacturabilityDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageTrack densityHard disc drive
A piezo in-tongue microactuator includes a suspension assembly with a flexure tongue. The tongue has two slots that accept piezo actuators. The tongue also has multiple hinge flexible elements that translate the extension and / or contraction of the piezo actuators into rotary motion of the recording head. This rotary motion is then used to precisely position the recording element over the desired track on the hard disk drive and permits higher track density to be achieved.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Suspension assembly having a microactuator electrically connected to a gold coating on a stainless steel surface
ActiveUS8542465B2Electrical connection between head and armArm with actuatorsPiezoelectric microactuatorEngineering
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
System, method and apparatus for flexure-integrated microactuator
ActiveUS8085508B2Overcome costsOvercomes manufacturabilityTrack finding/aligningRecord information storageHard disc driveTrack density
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
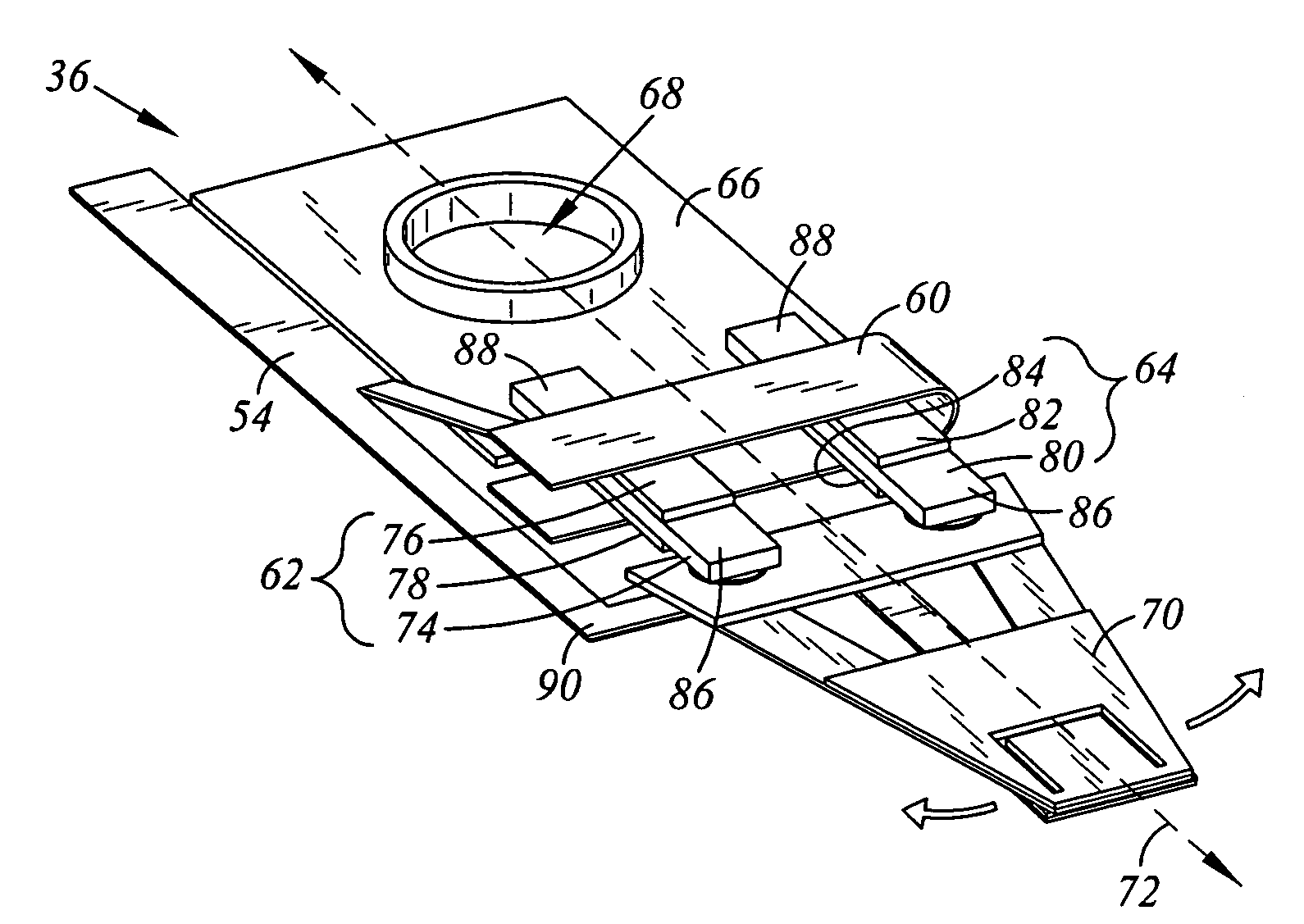
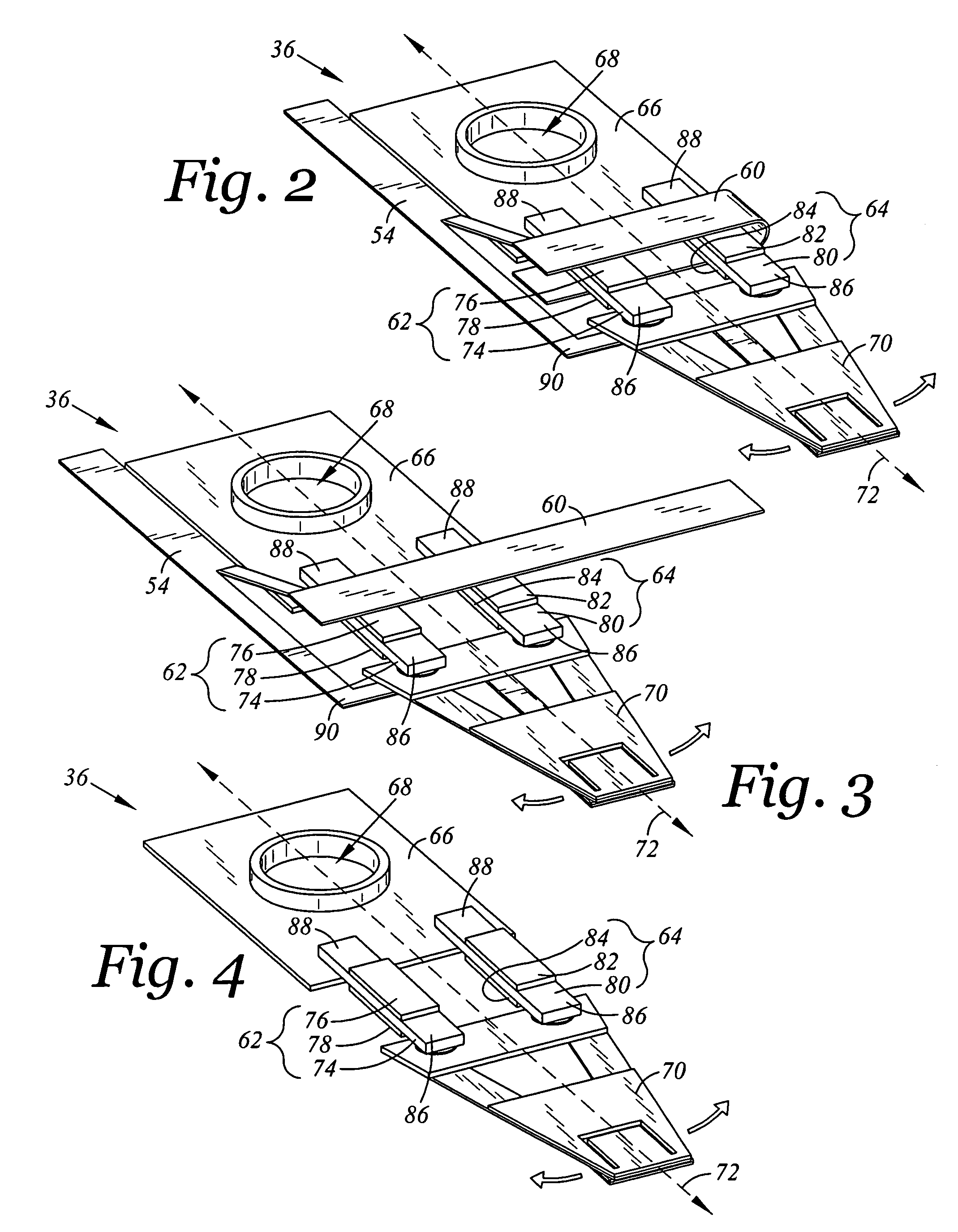
Suspension assembly with piezoelectric microactuators electrically connected to a folded flex circuit segment
ActiveUS7280319B1Electrical connection between head and armRecord information storagePiezoelectric microactuatorFlexible circuits
A suspension assembly includes a load beam, a mount plate, first and second piezoelectric microactuators, and a flex circuit segment. The first piezoelectric microactuator is electrically non-conductively attached to the load beam and the mount plate. The first piezoelectric microactuator includes a first piezoelectric element, a first top electrode, and a first bottom electrode. The second piezoelectric microactuator is electrically non-conductively attached to the load beam and the mount plate. The second piezoelectric microactuator includes a second piezoelectric element, a second top electrode, and a second bottom electrode. The flex circuit segment is disposed folded about the first and second piezoelectric microactuators. The flex circuit segment is in electrical communication with the first top electrode, the first bottom electrode, the second top electrode, and the second bottom electrode.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
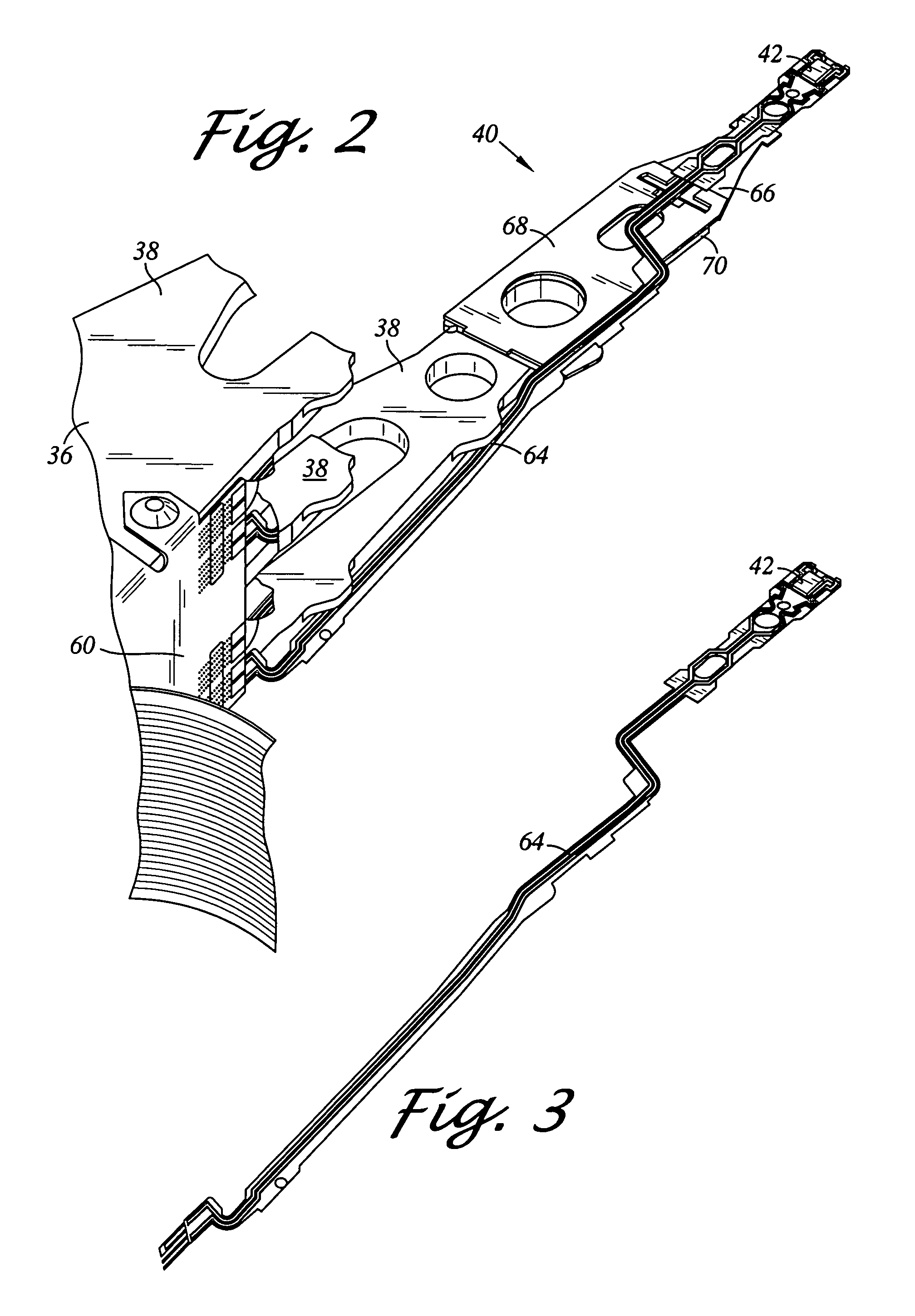
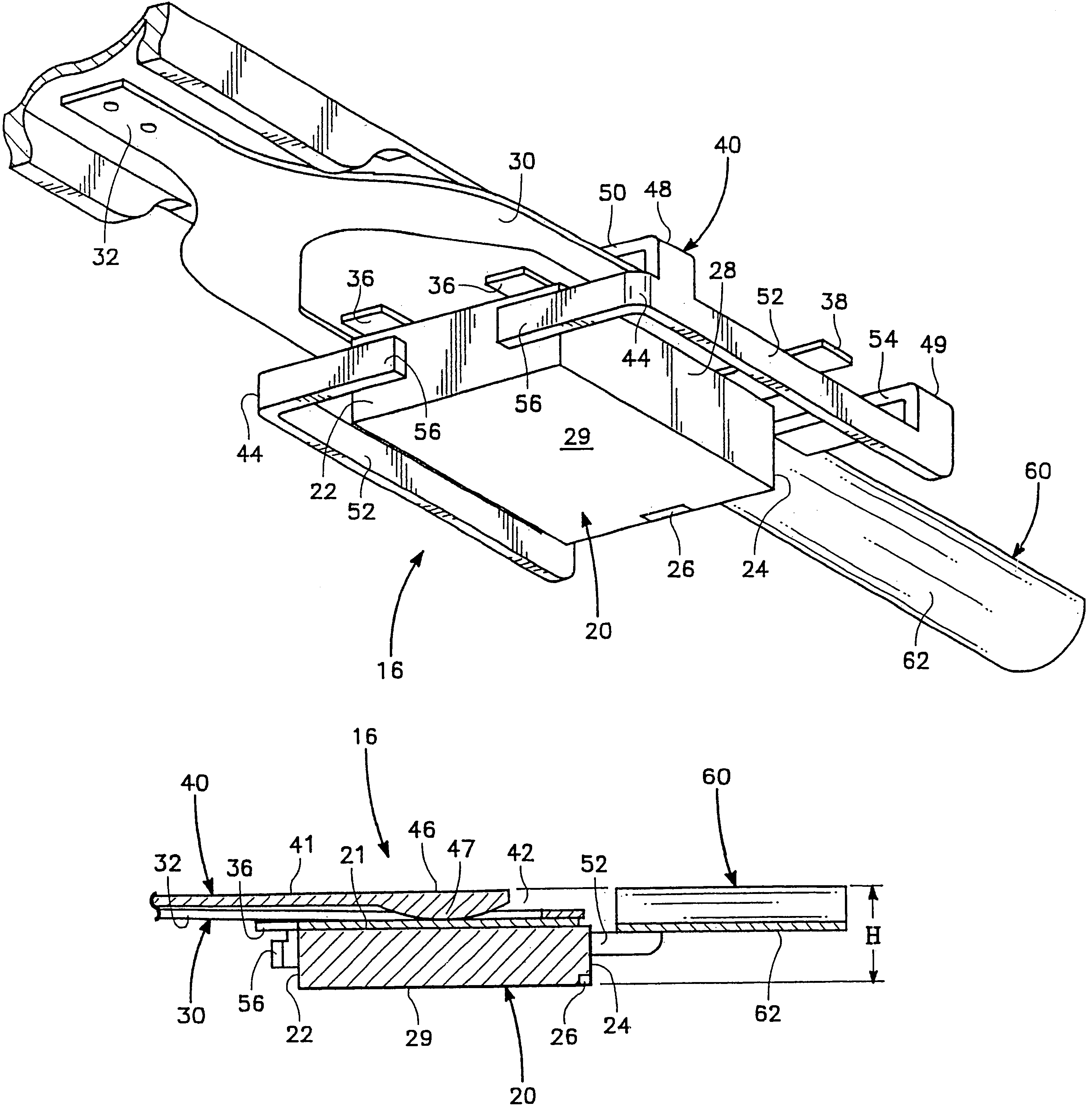
Hard disk drive with slider support structure and head gimbal assembly
InactiveUS6459549B1Electrical connection between head and armRecord information storageHard disc driveEngineering
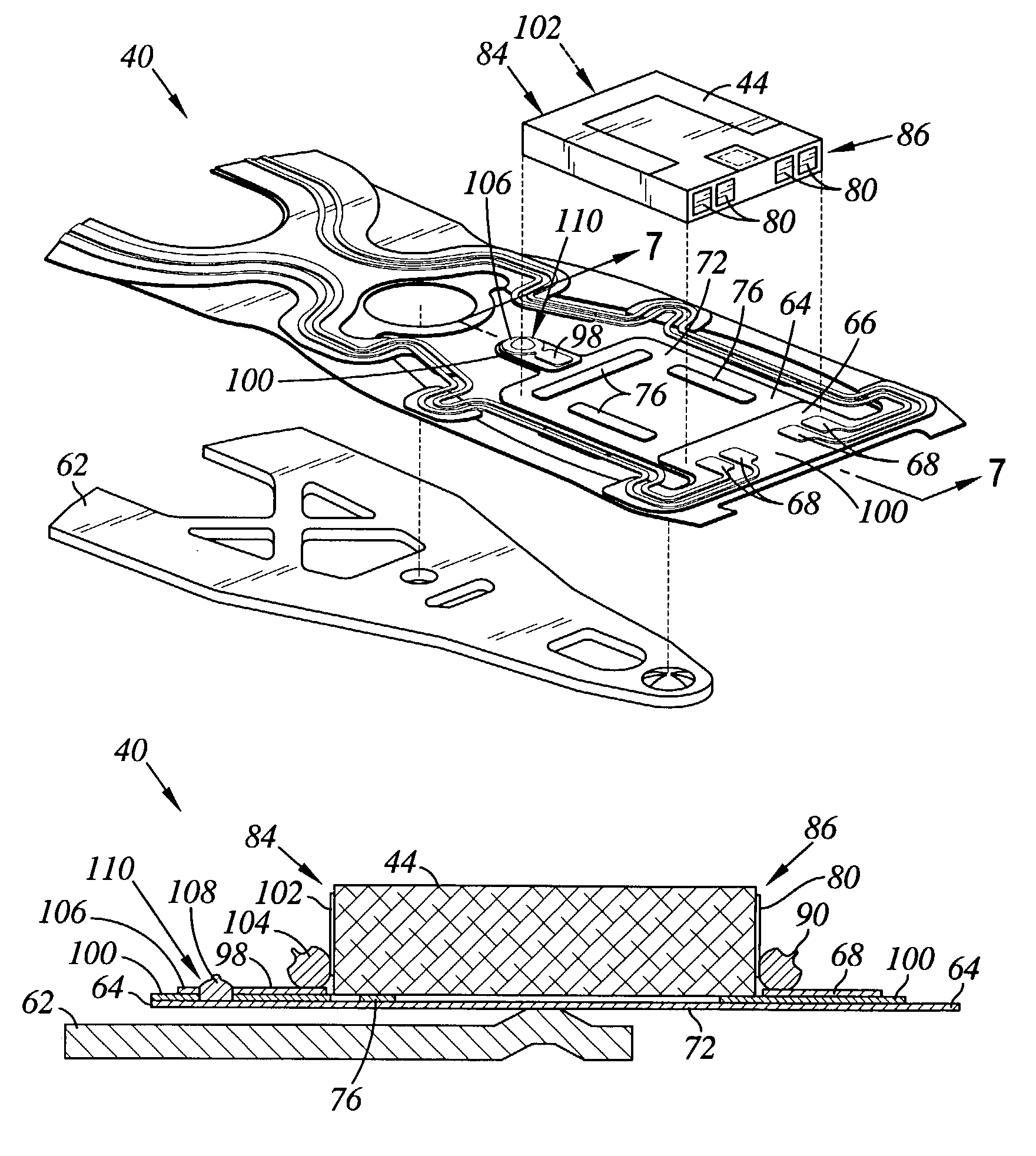
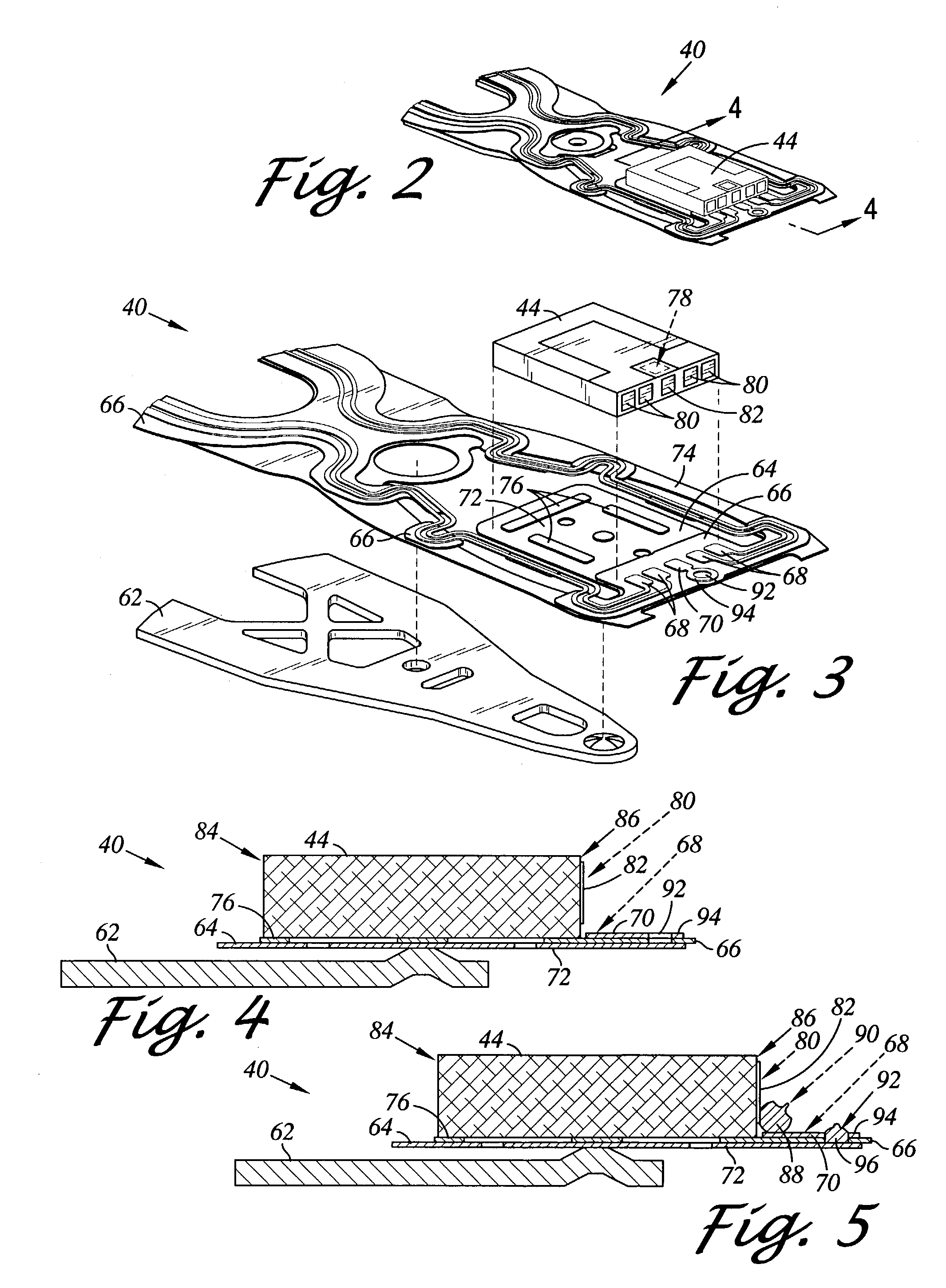
Apertures are formed in the portion of a flexure adjacent to the soldered portions between the bonding pads of the slider and the lead pads of lead end portions. With this, an adhesive agent for bonding the slider to a flexure tongue is moved downward from the apertures so there is no fear that the adhesive agent will contact the lead pads and the bonding pads. This design prevents the protrusion of an adhesive agent from short-circuiting the flexure, and absorbs a warp produced by shrinkage of a soldered portion by decreasing rigidity of the flexure. When both the bonding pad formed on the slider and the lead pad of a lead fixed to the platform of the flexure are disposed and soldered, the quality of the soldered portion is improved by locating the pads as close to each other as possible.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Head gimbal assembly to reduce slider distortion due to thermal stress
InactiveUS20080002299A1Reduce thermal deformationFluid-dynamic spacing of headsRecord information storageThermal expansionThermal distortion
A head gimbal assembly (HGA) is provided. The HGA includes a suspension that has a suspension coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) and a slider that has a slider CTE. A bonding element attaches the slider to the suspension. A compensation layer, having a compensation CTE, is located on the suspension. The compensation layer serves to compensate for a thermal distortion of the slider. A method of forming a HGA is also provided. The method includes providing a suspension having a suspension CTE and forming a slider having a slider CTE. The method further includes attaching the slider to the suspension and depositing a compensation layer, having a compensation CTE, on the suspension. The compensation layer serves to compensate for a thermal distortion of the slider.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
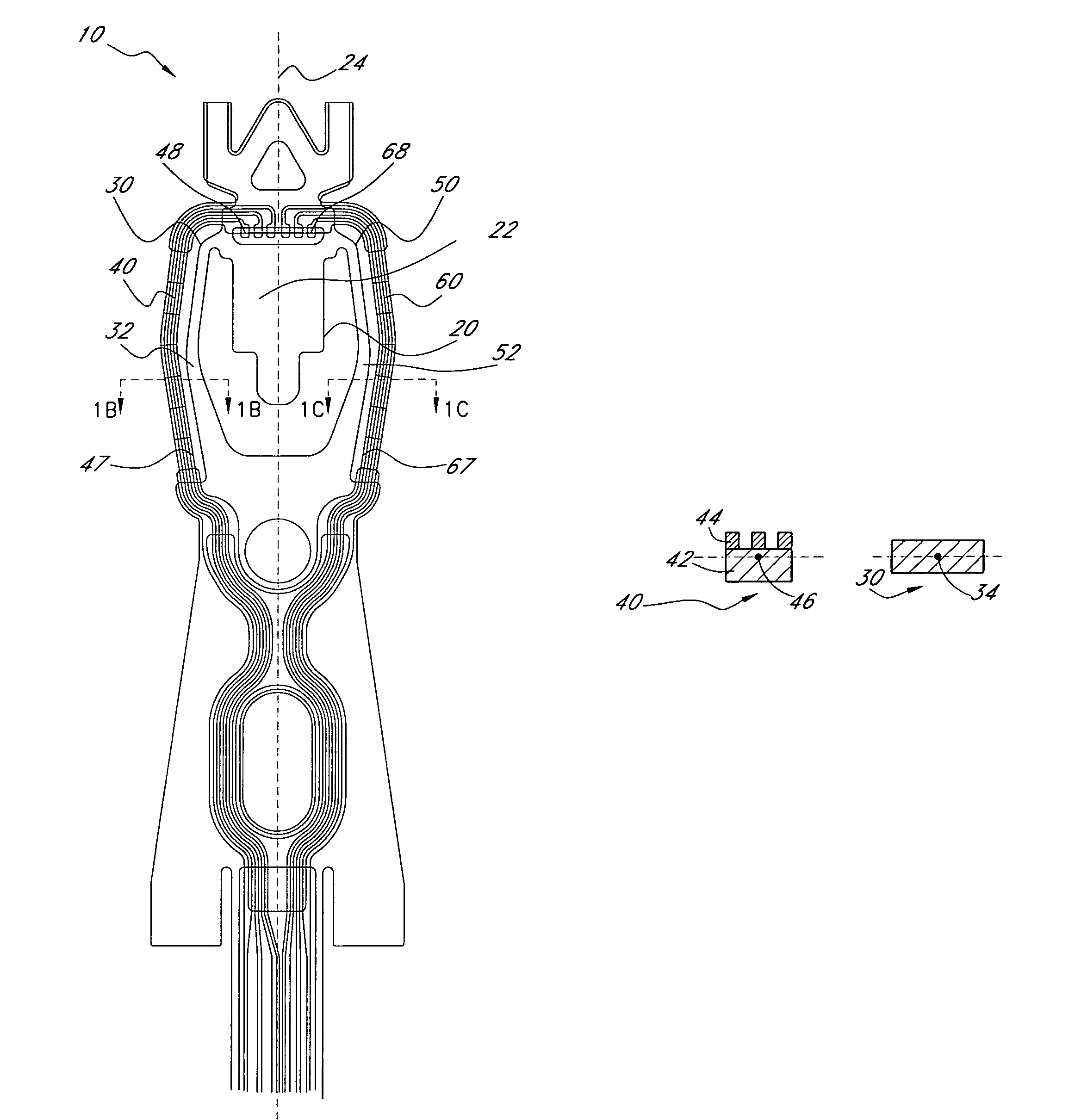
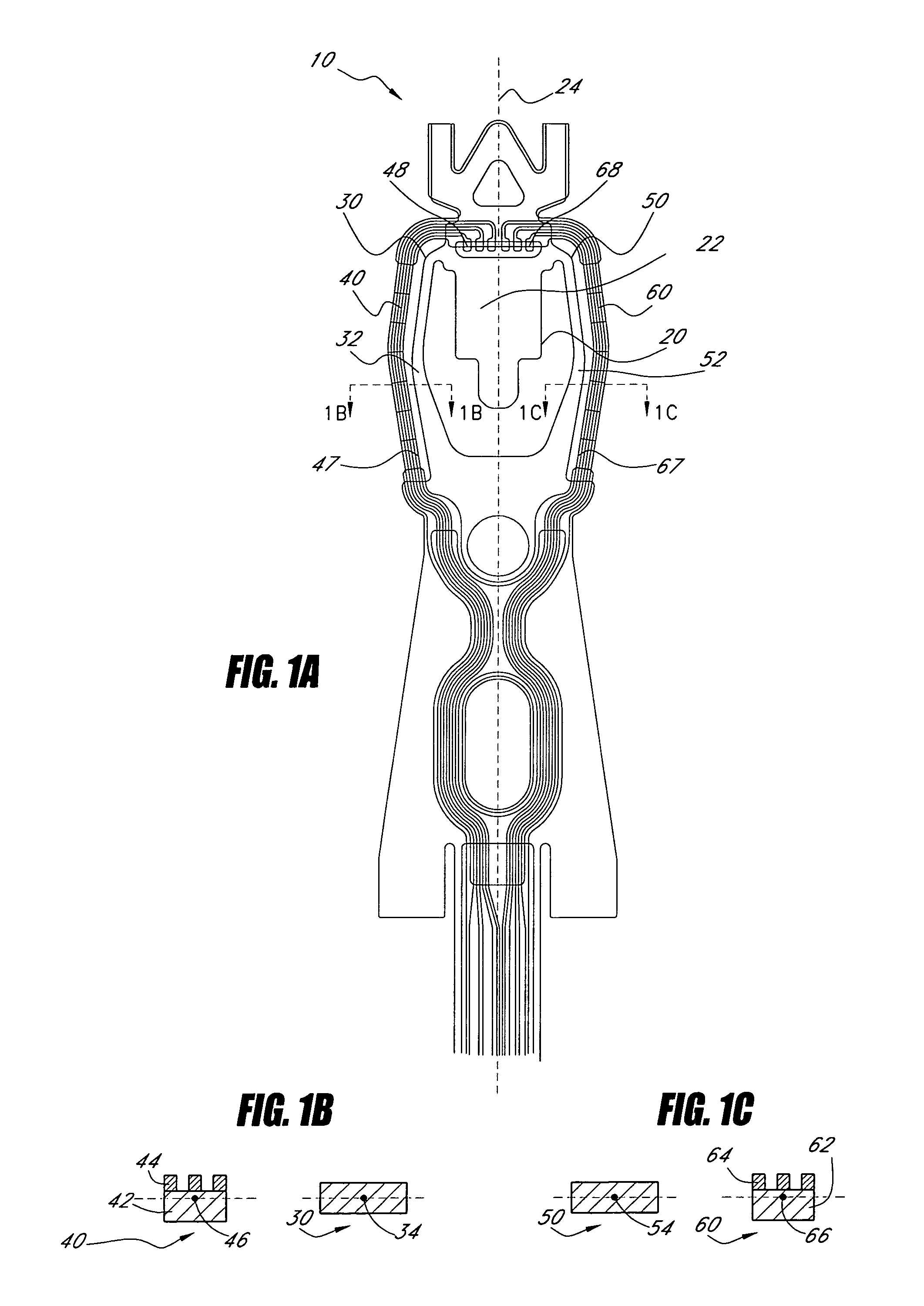
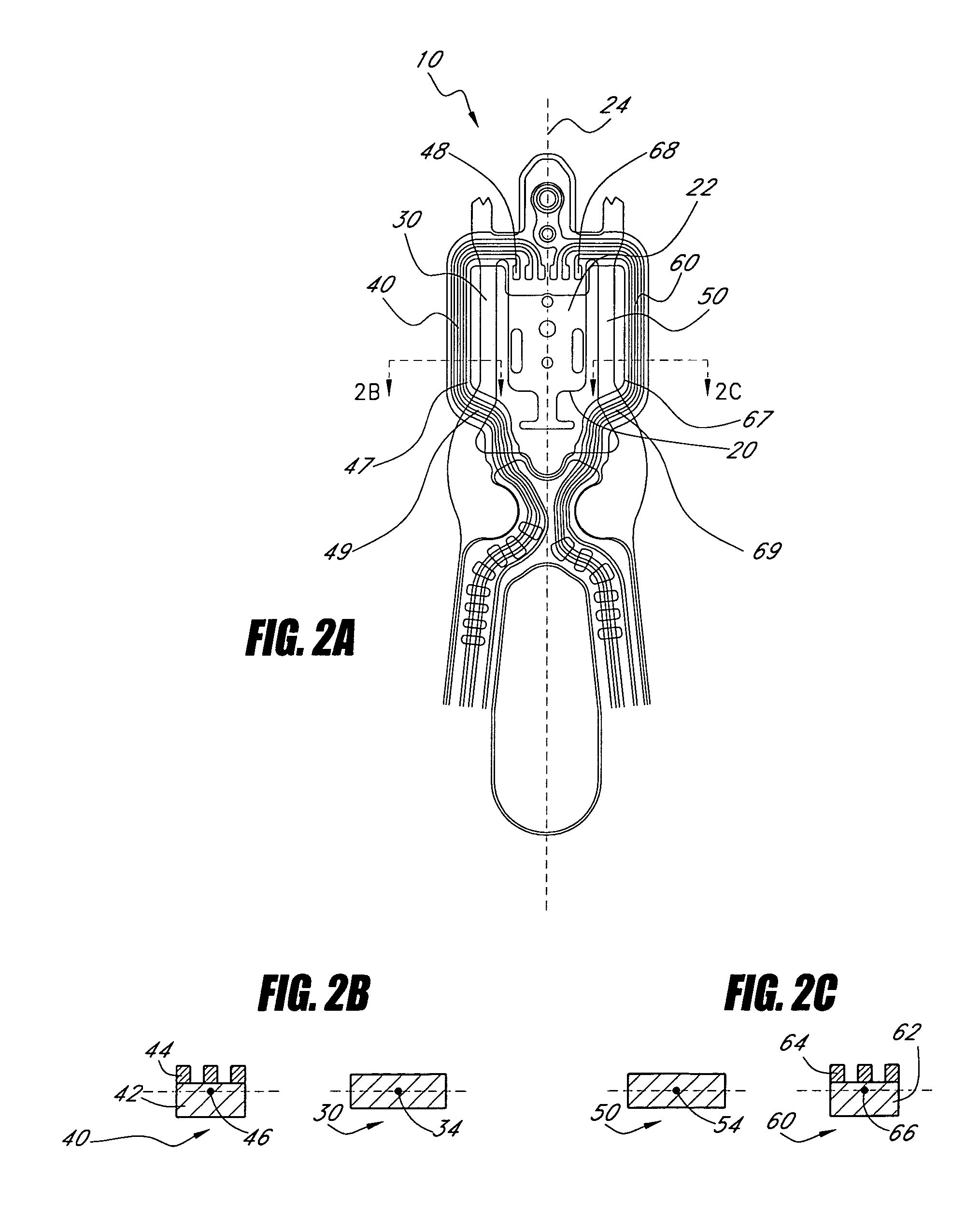
Flexure having arms with reduced centroid offset for supporting a head in a disk drive
ActiveUS7826177B1Record information storageMounting/attachment of transducer headConductive materialsStructural material
A flexure for supporting a head in a disk drive includes a tongue including a head mounting surface for attaching the head. The flexure further includes a first arm on a first side of the tongue. The first arm includes a structural material and has a first cross-sectional area in a plane perpendicular to the head mounting surface. The first cross-sectional area has a first centroid. The flexure further includes a second arm on the first side of the tongue. The second arm includes a conductive material layer. The second arm has a second cross-sectional area in the plane perpendicular to the head mounting surface. The second cross-sectional area has a second centroid. The second centroid is not offset from the first centroid by more than 10 microns in a direction perpendicular to the head mounting surface.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
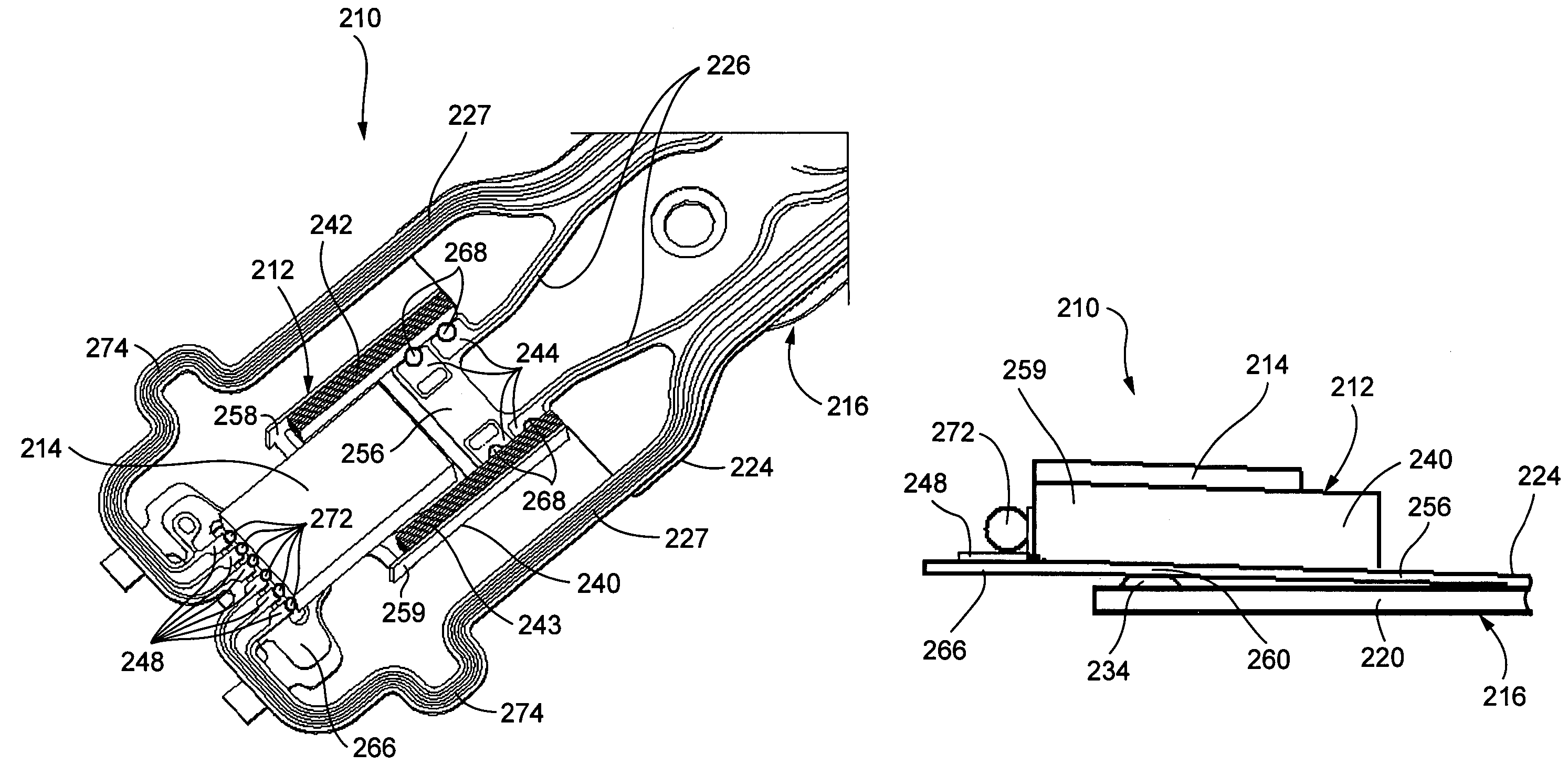
Head stack assembly including a ground conductive pad for grounding a slider to a gimbal
ActiveUS7006330B1Fluid-dynamic spacing of headsRecord information storageConductive materialsActuator
A head stack assembly includes an actuator including an actuator arm, a load beam coupled to the actuator arm, and a gimbal coupled to the load beam. The gimbal is formed of an electrically conductive material. The head stack assembly further includes a dielectric layer disposed upon the gimbal. The head stack assembly further includes a slider supported by the gimbal. The head stack assembly further includes slider conductive pads disposed upon the dielectric layer with the dielectric layer interposed between the slider conductive pads and the gimbal. The slider conductive pads are electrically connected to the slider. The head stack assembly further includes a ground conductive pad disposed upon the dielectric layer with the dielectric layer interposed between the ground conductive pad and the gimbal. The ground conductive pad is electrically connected to the slider and the gimbal for electrically grounding the slider.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Microactuated dimple for head suspensions
InactiveUS7256968B1Move preciselyTrack finding/aligningRecord information storageDynamic storageEngineering
A head suspension for supporting a head slider over a disk in a dynamic storage device and providing precise movement of the head slider relative to tracks on the disk. The head suspension includes a load beam, a flexure having a slider mounting region, and a dimple interface transmitting a load beam force to the slider mounting region. The head suspension further includes a microactuator mounted to the load beam. Movement of the microactuator is transmitted through the dimple interface by action of frictional forces at the dimple interface so as to cause movement of the slider mounting region transverse to tracks on the disk. A method of precisely moving a head slider supported by a head suspension includes providing and driving a microactuator configured to transmit movement of the microactuator to a slider mounting region through a dimple interface by action of frictional forces at the dimple interface.
Owner:HUTCHINSON TECH
Head gimbal assembly including a trace suspension assembly backing layer with a conductive layer formed upon a gimbal having a lower oxidation rate
ActiveUS7006331B1Electrical connection between head and armPrinted circuit groundingEngineeringConductive materials
A head gimbal assembly for a disk drive. The head gimbal assembly includes a trace suspension assembly backing layer including a gimbal. The trace suspension assembly backing layer is formed of a conductive material having a first oxidation rate. The head gimbal assembly further includes a gimbal conductive layer disposed upon the gimbal and formed of a conductive material having a second oxidation rate lower than the first oxidation rate. The head gimbal assembly further includes a slider supported by the gimbal. The head gimbal assembly further includes a conductive compound disposed between the gimbal conductive layer and the slider for electrically grounding the slider to the trace suspension assembly backing layer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Rotational micro-actuator integrated with suspension of head gimbal assembly, and disk drive unit with the same
InactiveUS7719798B2Improve resonance performanceArm with actuatorsRecord information storageMicro actuatorEngineering
A micro-actuator for a head gimbal assembly includes a metal frame including a bottom support integrated with a suspension flexure of the head gimbal assembly, a top support adapted to support a slider of the head gimbal assembly, and a pair of side arms that interconnect the top support and the bottom support. The top support includes a rotatable plate, connection arms that couple the rotatable plate to respective side arms, and an electrical pad support plate that supports bonding pads. A PZT element is mounted to each of the side arms. Each PZT element is excitable to cause selective movement of the side arms.
Owner:SAE MAGNETICS (HK) LTD
Head gimbal assembly with dual-mode piezo microactuator
ActiveUS7417830B1Reduce vibrationAdversely affect shock absorptionArm with actuatorsRecord information storagePiezoelectric microactuatorEngineering
A disk drive suspension has a load beam having a base, a flexure for carrying a slider, and a mount plate. The suspension mount plate has a first portion attachable to an actuator and movable by the actuator as the primary shifting force on the load beam, suitable for larger positioning movements. A second portion of the mount plate is attached to the load beam base and is movable relative to the mount plate first portion. A microactuator moves the second mount plate portion relative to the first mount plate portion as a secondary shifting force on the load beam, suitable for very small positioning movements.
Owner:MAGNECOMP
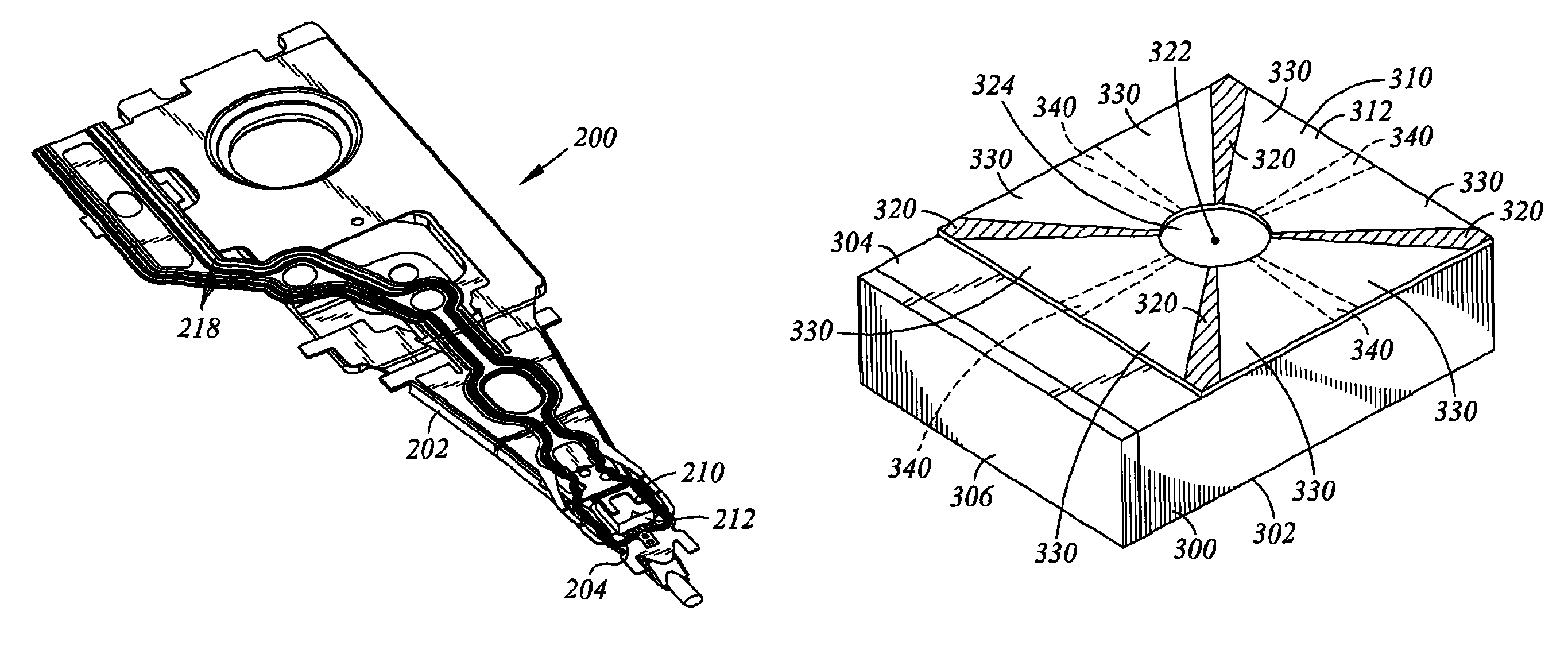
Remote drive rotary head dual stage actuator
ActiveUS8310790B1Electrical connection between head and armRecord information storageDual stageTransducer
A gimbal assembly of a dual-stage microactuator is provided with a remotely-located piezoelectric transducer (PZT) and at least one actuation strut connecting an asymmetrical amplification structure supporting the PZT to a tongue supporting a slider, such that the movement of the PZT over the asymmetrical amplification structure is amplified by the asymmetrical amplification structure and at least one actuation strut into rotation of the tongue and slider. A plurality of actuation struts connect opposing sides of the asymmetrical amplification structure with opposing sides of the tongue, which causes the tongue to rotate about a central portion of the tongue upon which a dimple of a supporting loadbeam contacts the tongue.
Owner:NHK SPRING CO LTD
Suspension assembly having a microactuator electrically connected to a gold coating on a stainless steel surface
ActiveUS20110228425A1Electrical connection between head and armArm with actuatorsPiezoelectric microactuatorMetallurgy
A novel suspension assembly includes a suspension assembly mounting plate, a microactuator mounting structure extending from the suspension assembly mounting plate, a load beam extending from the microactuator mounting structure, and a laminated flexure attached to the load beam. The laminated flexure includes a tongue that has a read head bonding surface. The suspension assembly includes a stainless steel surface having a gold coating, and a piezoelectric microactuator attached to the microactuator mounting structure and electrically connected to the gold coating.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Head gimbal assembly with flying height controller, disk drive unit using the same, and flying height adjusting method and system thereof
InactiveUS20060082917A1Good flying height adjustment capabilityReduce weightElectrical connection between head and armDriving/moving recording headsControl systemFlying height
Owner:SAE MAGNETICS (HK) LTD
Rotational, shear mode, piezoelectric motor integrated into a collocated, rotational, shear mode, piezoelectric micro-actuated suspension, head or head/gimbal assembly for improved tracking in disk drives and disk drive equipment
ActiveUS8125741B2High track densityImprove data storage capacityDriving/moving recording headsArm with actuatorsShock resistanceControl theory
A rotational, shear mode, piezoelectric motor is integrated with a suspension, head or head gimbal assembly (HGA) into a collocated, rotational, shear mode, piezoelectric micro-actuated suspension, head or head gimbal assembly (HGA) for use in disk drives and disk drive manufacturing equipment. When excited by a control voltage, the collocated, shear mode, piezoelectric micro-actuated HGA rotates the head enabling high frequency, high resolution track positioning of the read / write element. The motor is integrated with the head and flexure (collocation). The head rotates about a rotation axis that is ideally located at the center of mass of the head. A shear mode piezoelectric motor rotates the head. A collocated, rotational, shear mode, piezoelectric micro-actuated HGA has high stiffness, high frequency response, high positioning resolution, low mass and low internal vibration for improved tracking, increased track density and greater disk drive storage capacity. Furthermore, its solid integration improves shock resistance and reduces micro-contamination.
Owner:MAGNECOMP +1
Head suspension
ActiveUS20100073825A1Properly keeping rigidity balanceProperly vibration characteristicArm with actuatorsRecord information storageAdhesiveMechanical engineering
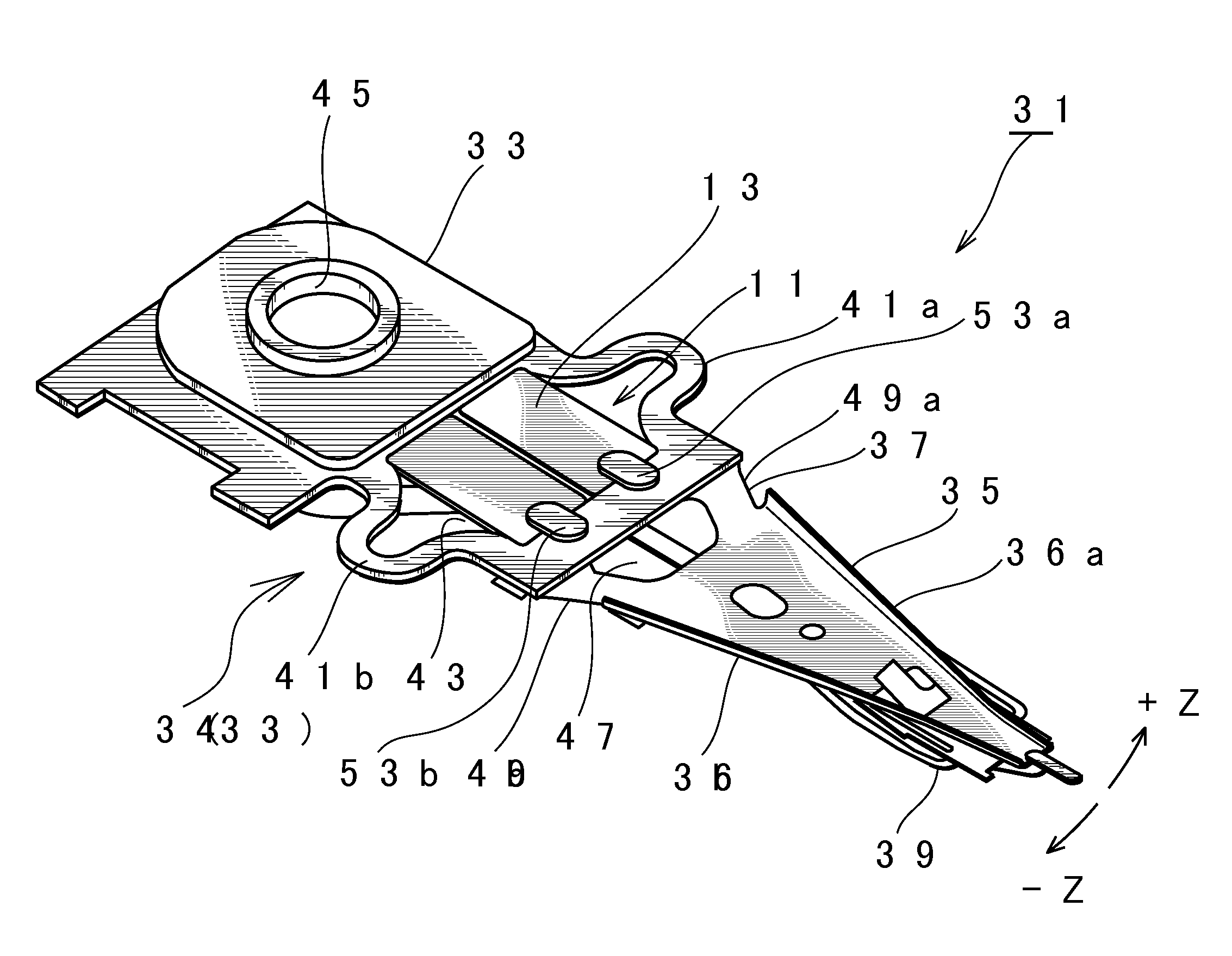
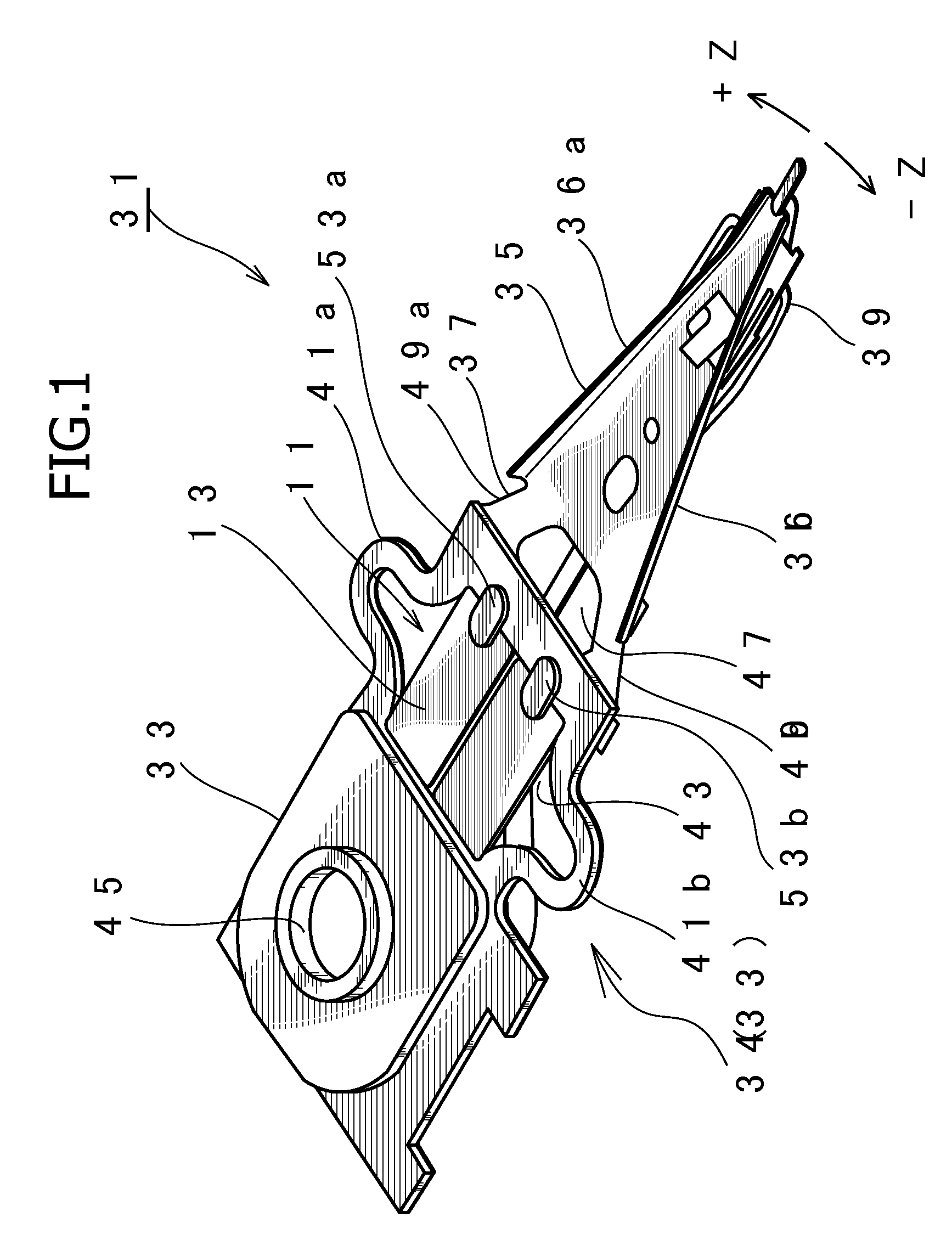
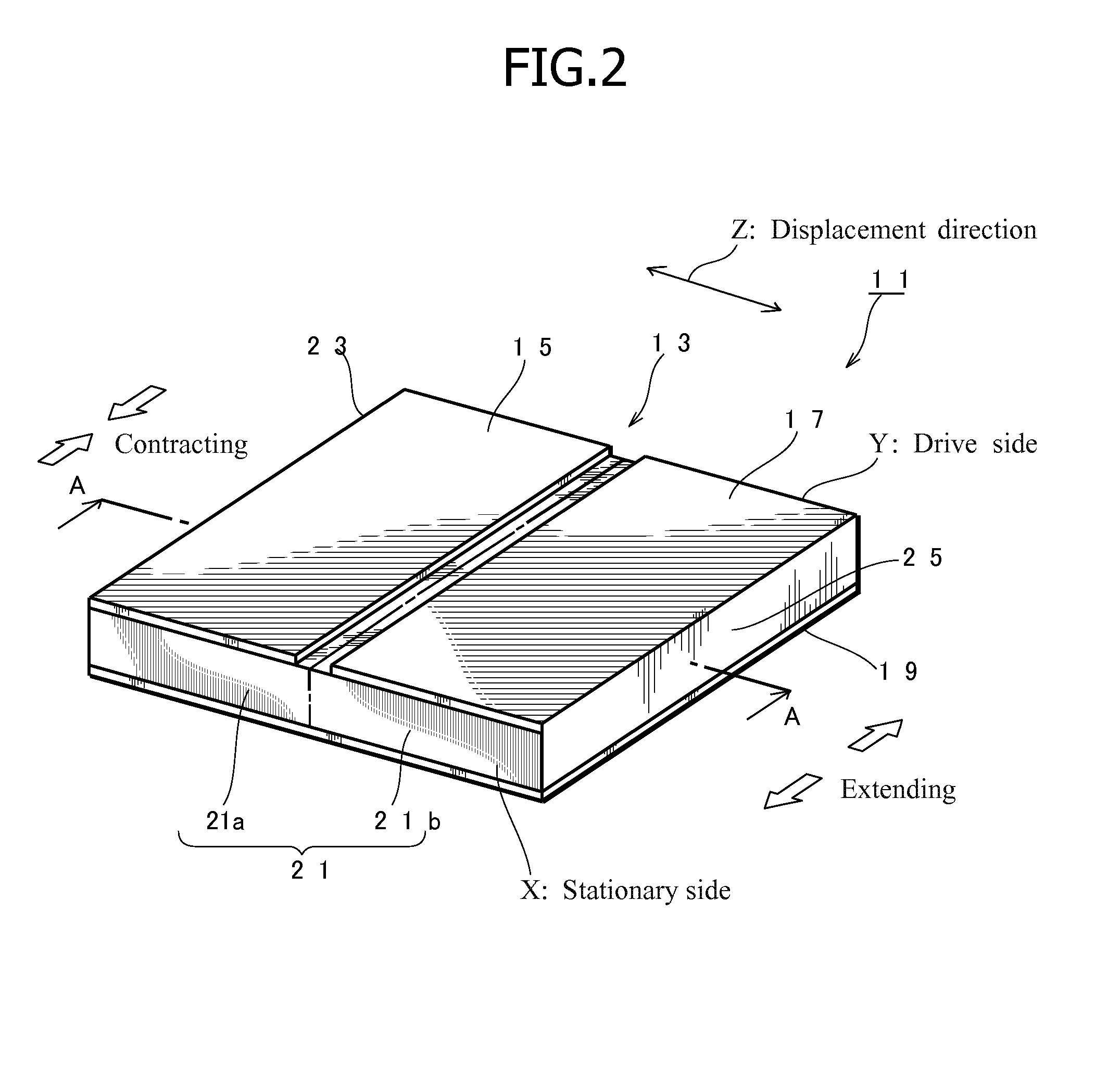
A head suspension has a piezoelectric element 13 that deforms in response to a voltage applied thereto, a base plate 33 provided with an opening 43 to which the piezoelectric element is attached, and a load beam 35 that is fixed to the base plate 33 so that a front end of the load beam 35 moves in a sway direction according to the deformation of the piezoelectric element 13. The head suspension includes an adhesive 51 applied to a gap 50 between the piezoelectric element 13 and the opening 43, to attach the piezoelectric element 13 to the opening 43. The adhesive 51 has a thixotropic characteristic and is sol when applied to the gap 50. A displacement of the piezoelectric element is correctly transmitted to the load beam. The head suspension properly keeps a rigidity balance and vibration characteristic.
Owner:NHK SPRING CO LTD
Electrode structure of piezoelectric element, method of forming electrode of piezoelectric element, piezoelectric actuator, and head suspension
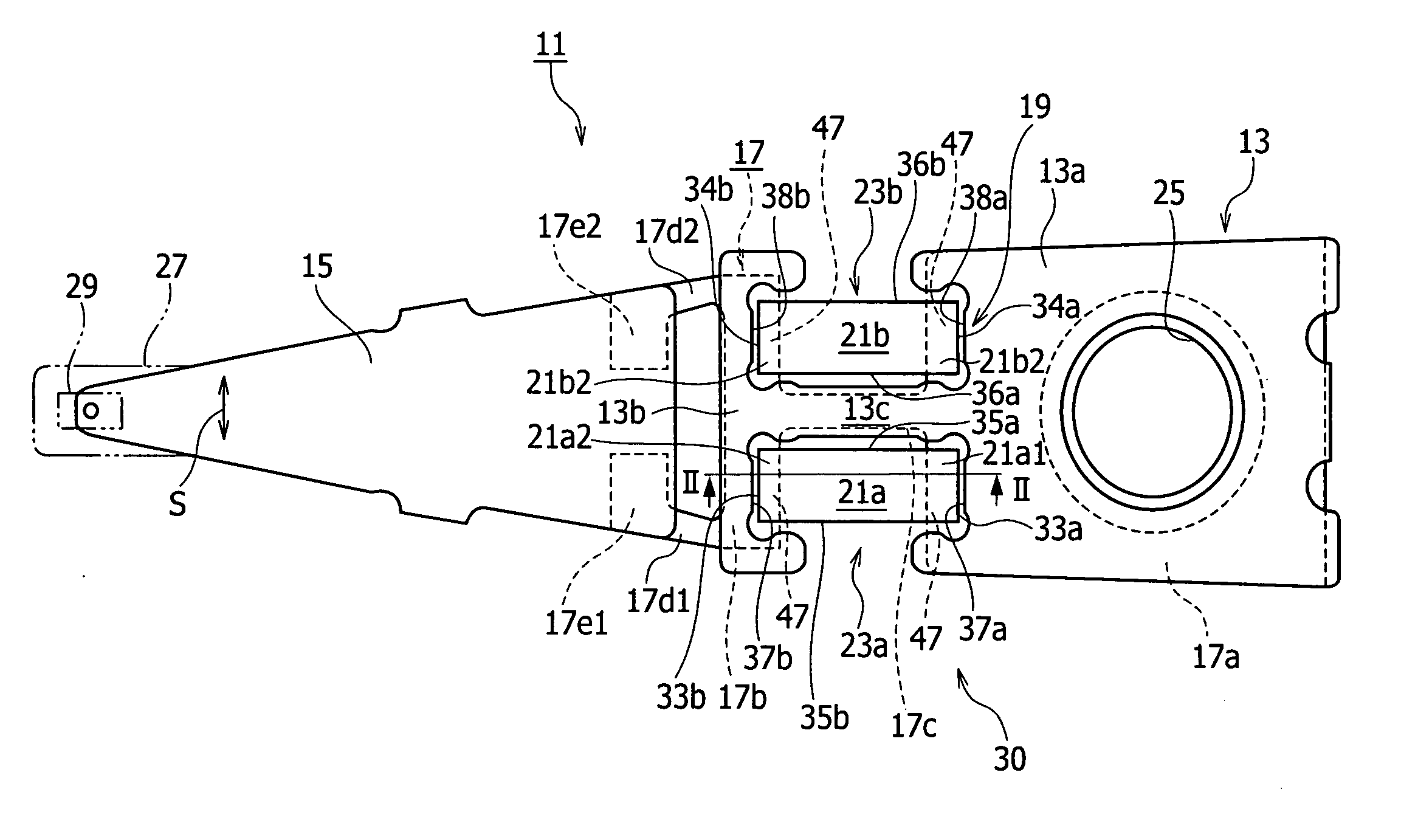
ActiveUS20100195252A1Avoid shortingTrack finding/aligningPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric actuatorsMechanical engineering
An electrode structure of a piezoelectric element is provided. The piezoelectric element 23a (23b) constitutes a piezoelectric actuator 19 attached to an attaching part 30 of an object, to minutely move a movable part 15 of the object relative to a base part 13 of the object according to deformation occurring on the piezoelectric element in response to a power applied state of the piezoelectric element. The electrode structure includes an electrode 41a formed on one of a pair of electrode forming faces 31a and 31b of the piezoelectric element on an inner side of a peripheral zone 31a1, the peripheral zone being defined along the periphery of the electrode forming face 31a on which the electrode is formed. The electrode structure also includes a non-electrode part 51 formed in the peripheral zone. Even if the peripheral zone 31a1 of the electrode forming face 31a having a short-circuit causing possibility touches the attaching part 30, no short circuit occurs.
Owner:NHK SPRING CO LTD
Head suspension with a reinforced limiter tab
ActiveUS7477488B1Record information storageMounting/attachment of transducer headEngineeringTrailing edge
A head suspension for a head / gimbal assembly comprises a flexure attached to a load beam. The load beam includes a lifter tab configured to engage a lifting surface of a load / unload ramp. The flexure includes a limiter tab, extending from a trailing edge thereof, that is configured to engage with a gimbal-limiting surface of the load / unload ramp. The limiter tab comprises a metallic base layer, a metallic stiffening layer, and a non-metallic intermediate layer disposed between the base and stiffening layers. The stiffening layer can include both conductive traces that terminate with a set of bonding pads and an appendage that extends along a length of the limiter tab. The appendage portion of the stiffening layer serves to increase the thickness of the limiter tab to increase the stiffness of the limiter tab.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Microactuated suspension with shear transmission of force
InactiveUS7292413B1Small sizeReduce manufacturing costRecord information storageMounting/attachment of transducer headEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:MAGNECOMP
Micro-actuator, vibration canceller, head gimbal assembly, and disk drive unit with the same
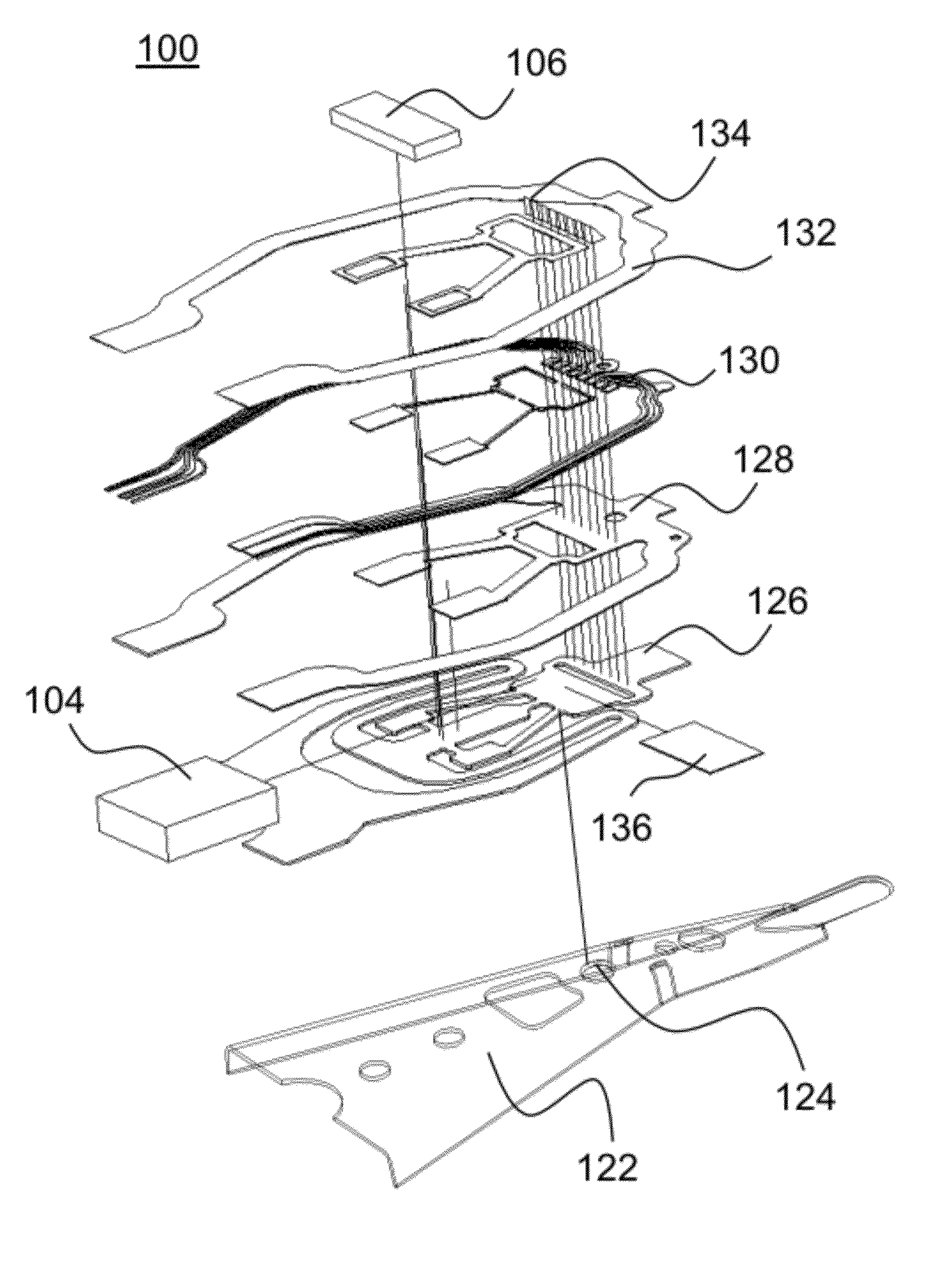
InactiveUS20060146449A1Precise positioningImprove featuresArm with actuatorsRecord information storageMicro actuatorResonance
A head gimbal assembly (HGA) for a disk drive unit that includes a micro-actuator, a slider and a suspension to load the slider and the micro-actuator. The micro-actuator is provided with a vibration canceller that counteracts forces generated by activation of the micro-actuator when making fine head position adjustments. The vibration canceller incorporates PZT elements that generate counteracting forces in the bottom plate of the micro-actuator to cancel the vibration generated by the micro-actuator, thereby providing improved resonance performance for a disk drive unit.
Owner:SAE MAGNETICS (HK) LTD
Low profile head gimbal assembly with shock limiting and load/unload capability
InactiveUS7085104B1Record information storageProtective measures for recording headsLeading edgeEngineering
Head gimbal assemblies are provided that comprise a slider, a load beam, a flexure, and a lifter tab. The flexure holds the slider against a pivot point of the load beam. The lifter tab extends from the load beam to engage a load / unload ramp. The load beam includes a base portion having the pivot point, a first side rail, and a first limiter stop. The first side rail is disposed adjacent to a transverse side of the slider while the first limiter stop is adjacent to a leading side of the slider. The first limiter stop extends from the first side rail and is essentially perpendicular thereto. The flexure includes a first leading edge tab that extends between the first limiter stop and the base portion of the load beam to limit the movement of the flexure especially during loading and unloading.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Rotational PZT micro-actuator, head gimbal assembly, and disk drive unit with the same
InactiveUS7379274B2Precise positioningImprove featuresArm with actuatorsRecord information storageMicro actuatorControl theory
A head gimbal assembly (HGA) for a disk drive unit that includes a micro-actuator, a slider and a suspension to load the slider and the micro-actuator. The micro-actuator includes a pair of actuator side arms, a PZT element extending between and connecting the actuator side arms; a rotatable plate positioned between the actuator side arms, wherein the slider is mounted on the rotatable plate; and a pair of connection elements that connect the rotatable plate to the actuator side arms, respectively. The rotatable plate rotates in a first direction when the PZT element contracts and a second direction when the PZT element expands.
Owner:SAE MAGNETICS (HK) LTD
Rotational PZT micro-actuator, head gimbal assembly, and disk drive unit with same
InactiveUS20070223146A1Good resonance performance and position adjusting performanceSimple structureElectrical connection between head and armRecord information storageMicro actuatorGimbal
A HGA of the invention includes a slider; a micro-actuator to adjust the position of the slider; and a suspension to support the slider and the micro-actuator. The micro-actuator includes two side arms; a load plate for supporting the slider, which is connected with at least one of the side arms; a pair of piezoelectric (PZT) elements connected with the side arms; and a support shaft coupled with the suspension, the support shaft being connected with the side arms and positioned between the PZT elements. The invention also discloses a disk drive unit using such a HGA.
Owner:SAE MAGNETICS (HK) LTD
Hard disk drive DSA suspension having PZT encapsulation dam
ActiveUS8526142B1Sufficient flexibilityIncrease stroke lengthArm with actuatorsRecord information storageEpoxyDual stage
A dual stage actuated (DSA) suspension includes a dam-like structure that holds epoxy along the outside lateral side of the PZT microactuators while that epoxy hardens. In the illustrative embodiment, the dam-like structure is in the form of a wing rail that is integrally formed with the suspension base plate, and extends parallel to the outside face of the PZT. The wing rail has an upturned edge to help contain the epoxy while it hardens. The wing rail has springs at its fore and aft ends so that the rail does not unduly limit movement of the PZTs and hence microactuator stroke length. The wing rail does not touch the PZT electrodes. The encapsulation dam allows epoxy to be dispensed after the PZT has been located on the suspension, so as to substantially cover all sides of the PZT and thus prevent the shedding of contaminating particles during operation.
Owner:MAGNECOMP
Electrical connections to a microactuator in a hard disk drive suspension
ActiveUS8570688B1Elimination of expensive tail weave process stepAccomplished quickly and easilyArm with actuatorsSolid-state devicesHard disc driveContact pad
In a disk drive suspension circuit, an electrical contact from a flexible circuit to a face of a PZT microactuator is provided by a mechanical bias to press a contact pad of the flexible circuit against the PZT surface. The mechanical bias is provided by a piece of stainless steel that is welded to a nearby point or points on the suspension, and which biases the electrical contact pad carrying the PZT driving voltage against the PZT. The piece of stainless steel may be in the form of a flat piece welded on one or more sides of the contact pad, and may include a dimple for pressing against the contact pad. Additional insulation material may be provided between the dimple and the contact pad to prevent the dimple from penetrating through the flexible circuit's cover layer and shorting the driving voltage.
Owner:MAGNECOMP
Magnetic recording head slider comprising bond pad having a probe contact area and a solder contact area
ActiveUS8587901B1Electrical connection between head and armFluid-dynamic spacing of headsDistal portionEngineering
Examples of a magnetic recording head slider, a head gimbal assembly and methods of manufacturing each are disclosed. The magnetic recording head slider may comprise a slider body and a plurality of bond pads formed on a trailing edge of the slider body. Each of the plurality of bond pads may include a probe contact area and a soldering contact area. The probe contact area may be larger than the soldering contact area. The head gimbal assembly may include a suspension arm with conductive leads. A plurality of bond pads may be formed on the suspension arm in contact with the ends of the conductive leads. A width of a proximal portion of each of the bond pads may be greater than a width of a distal portion of each of the plurality of bond pads. The methods may include forming the above-described structures.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com