Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33results about How to "Less crosstalk" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
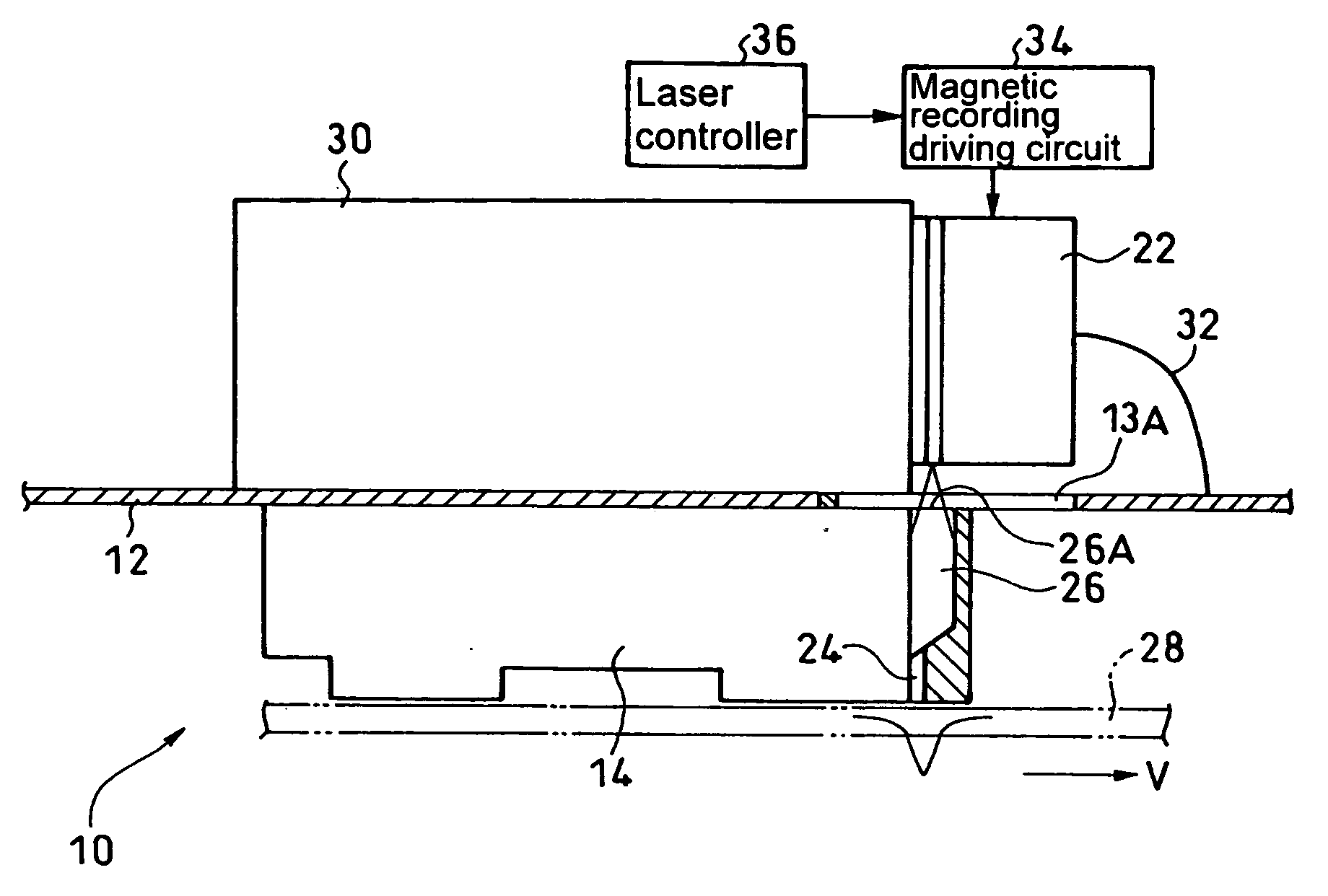
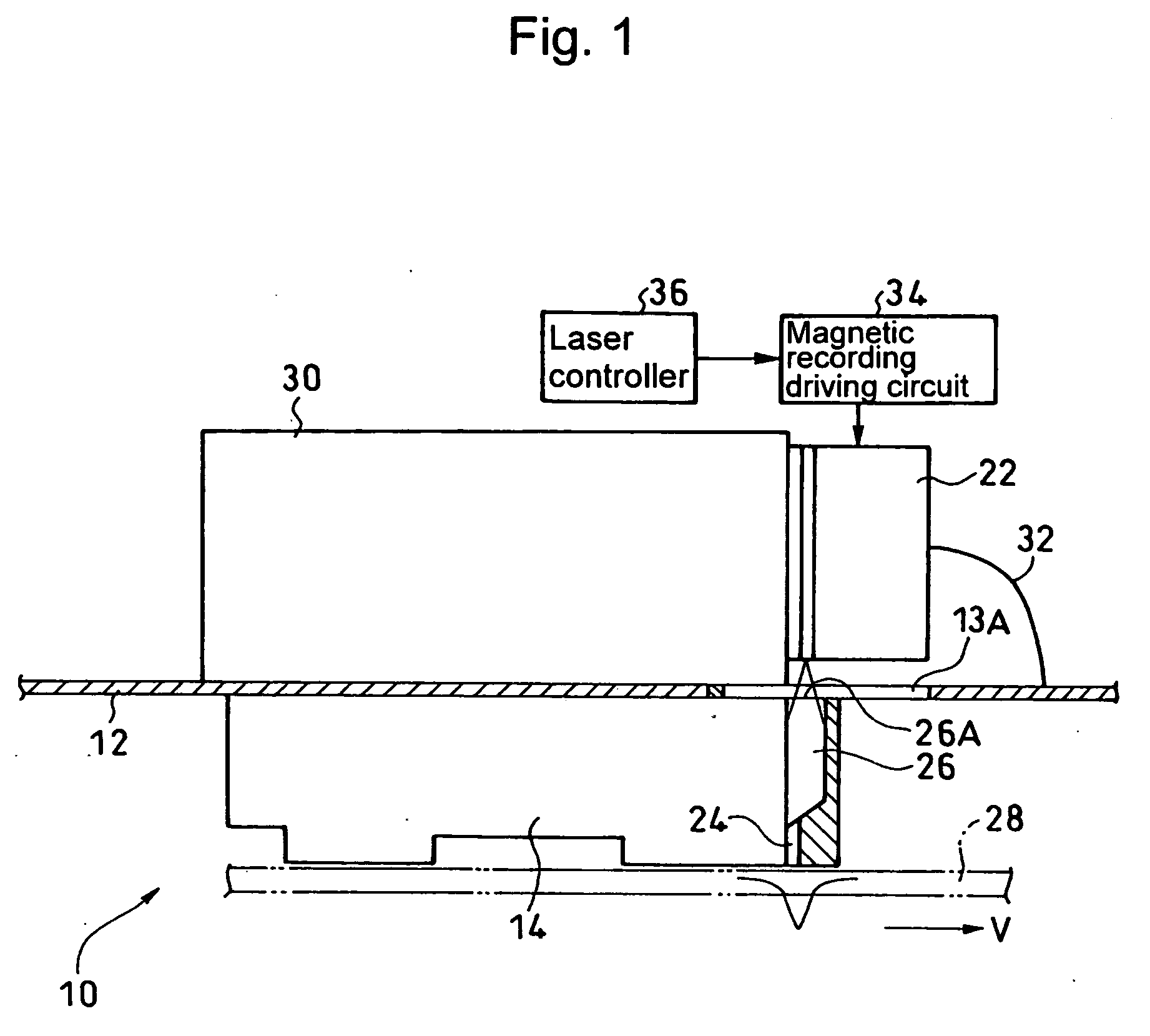
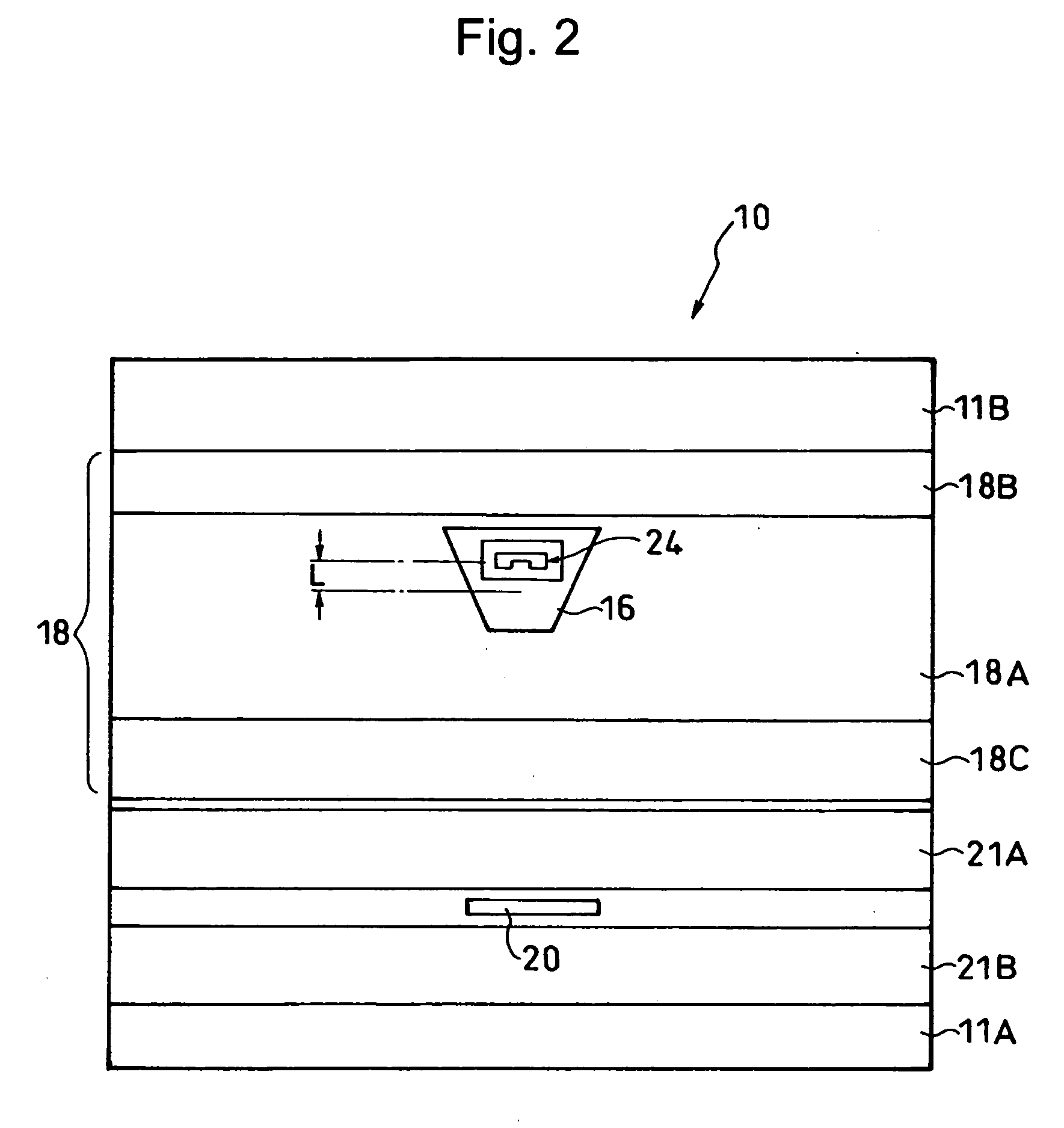
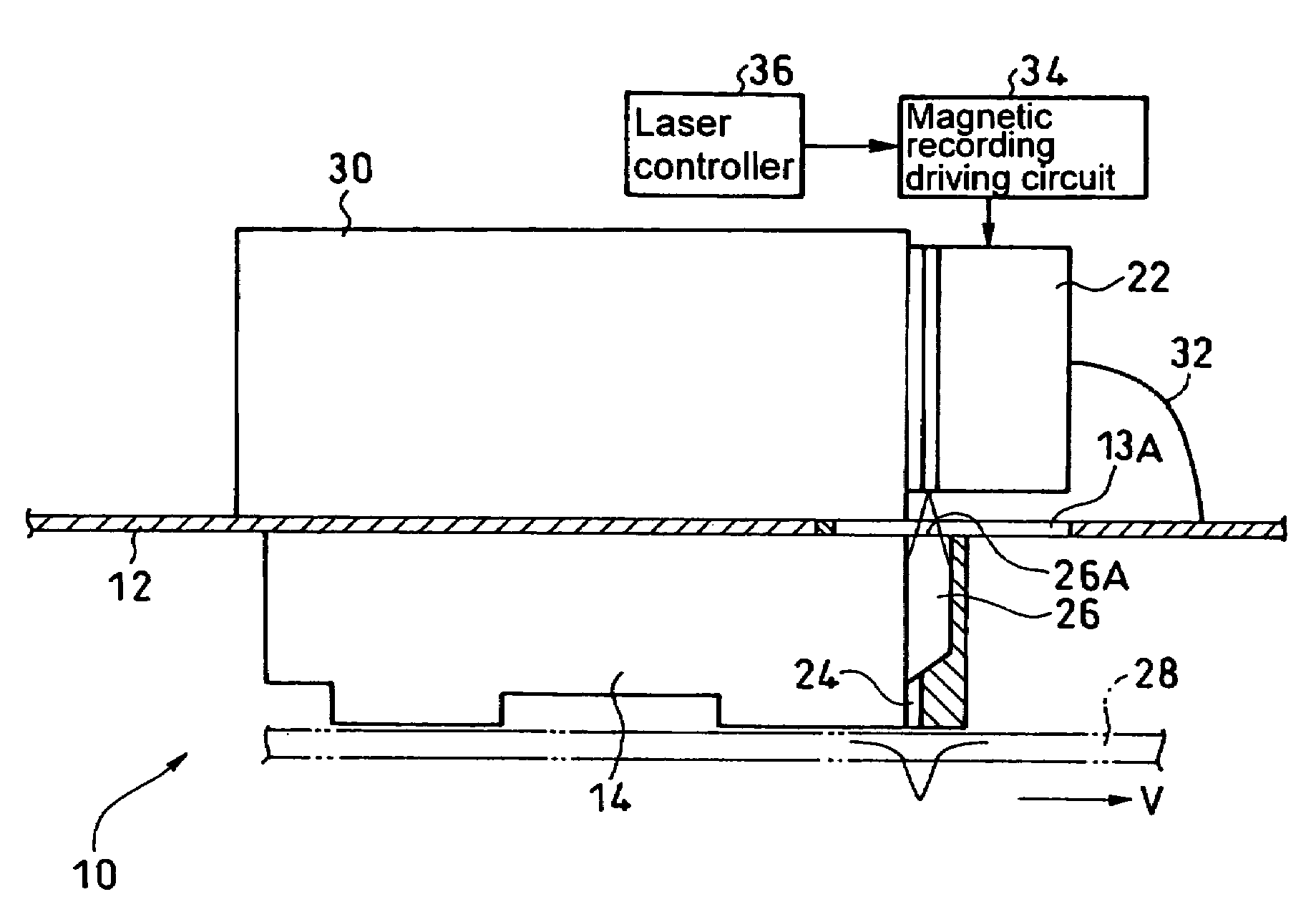
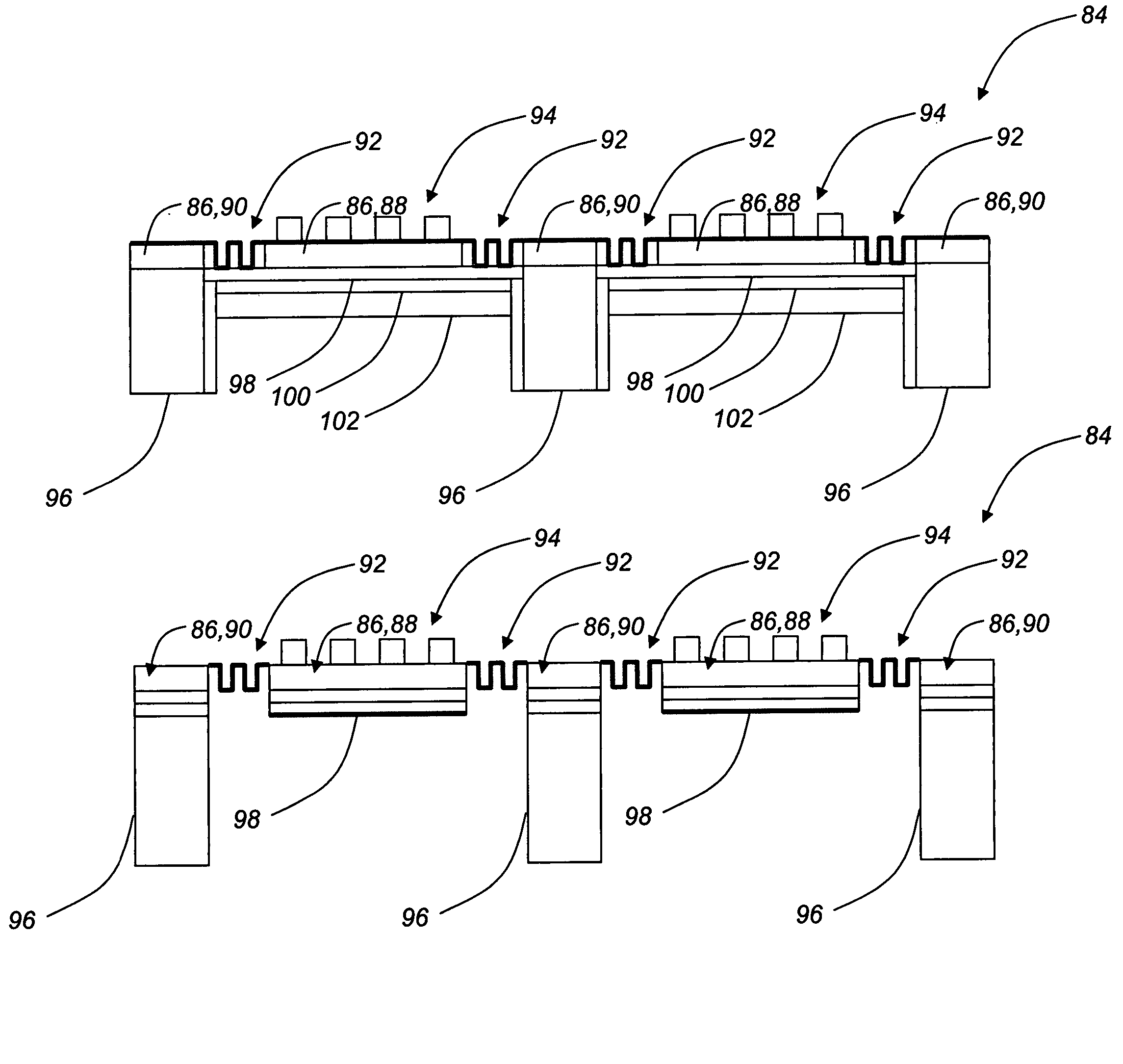
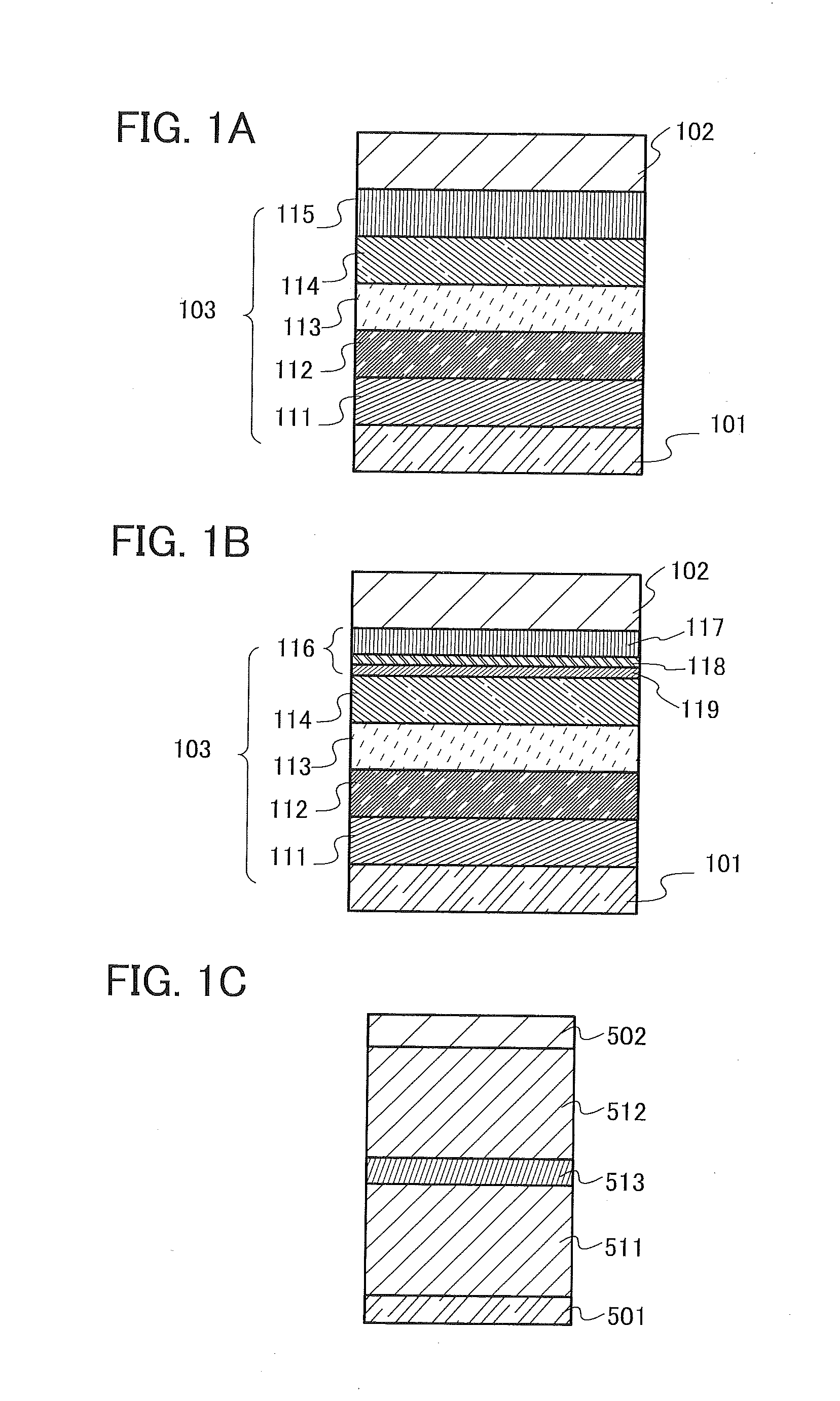
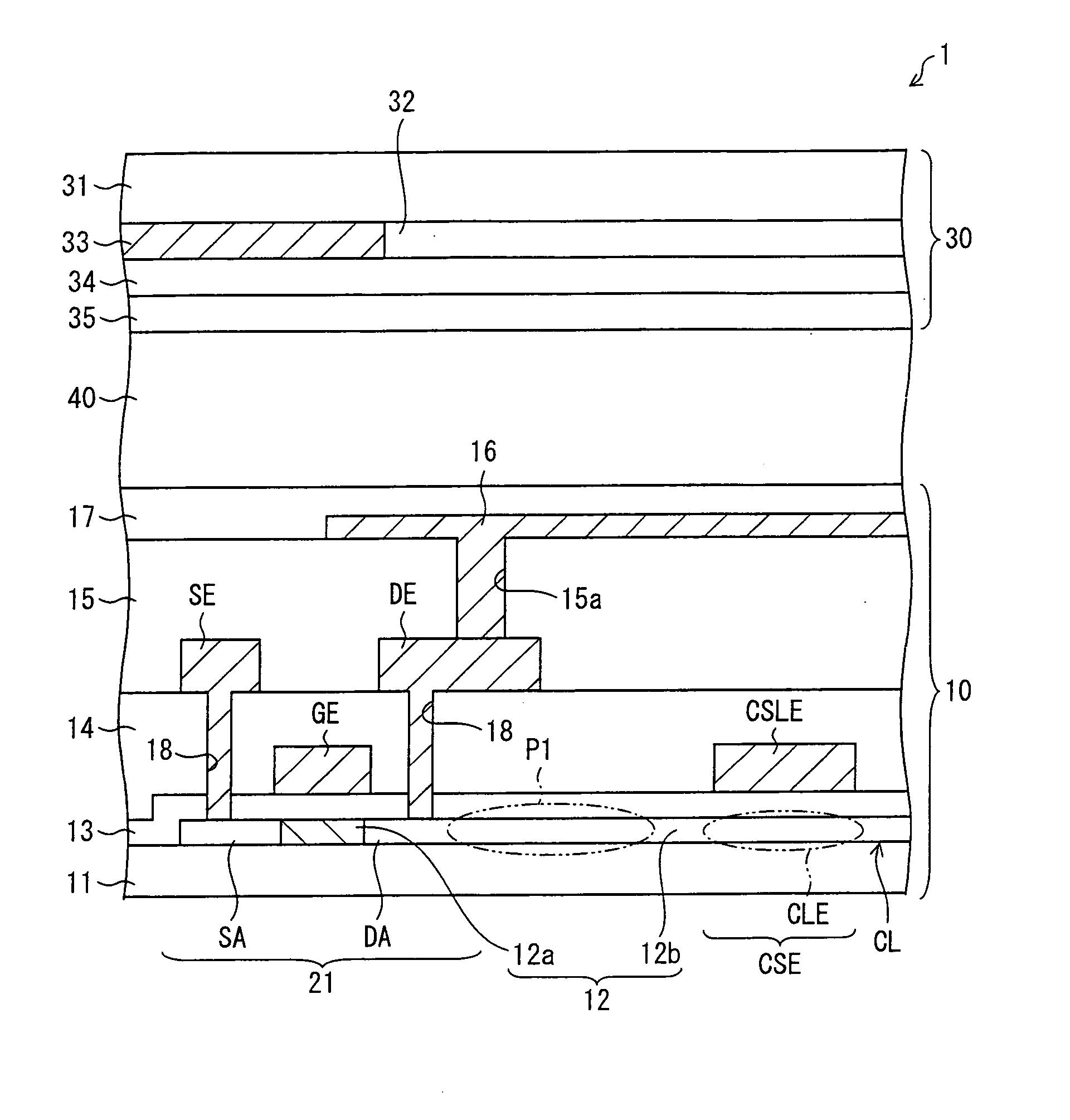
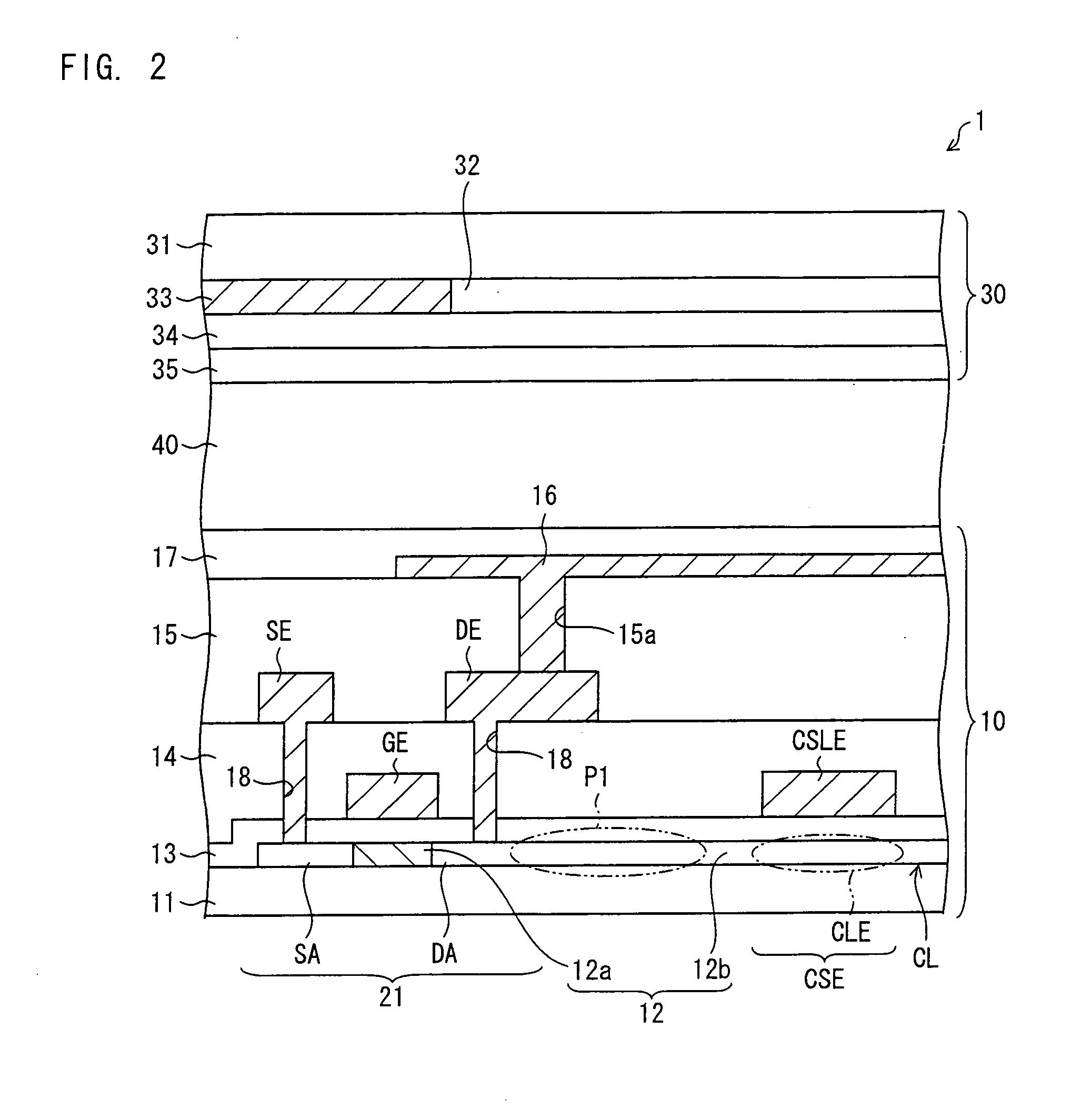
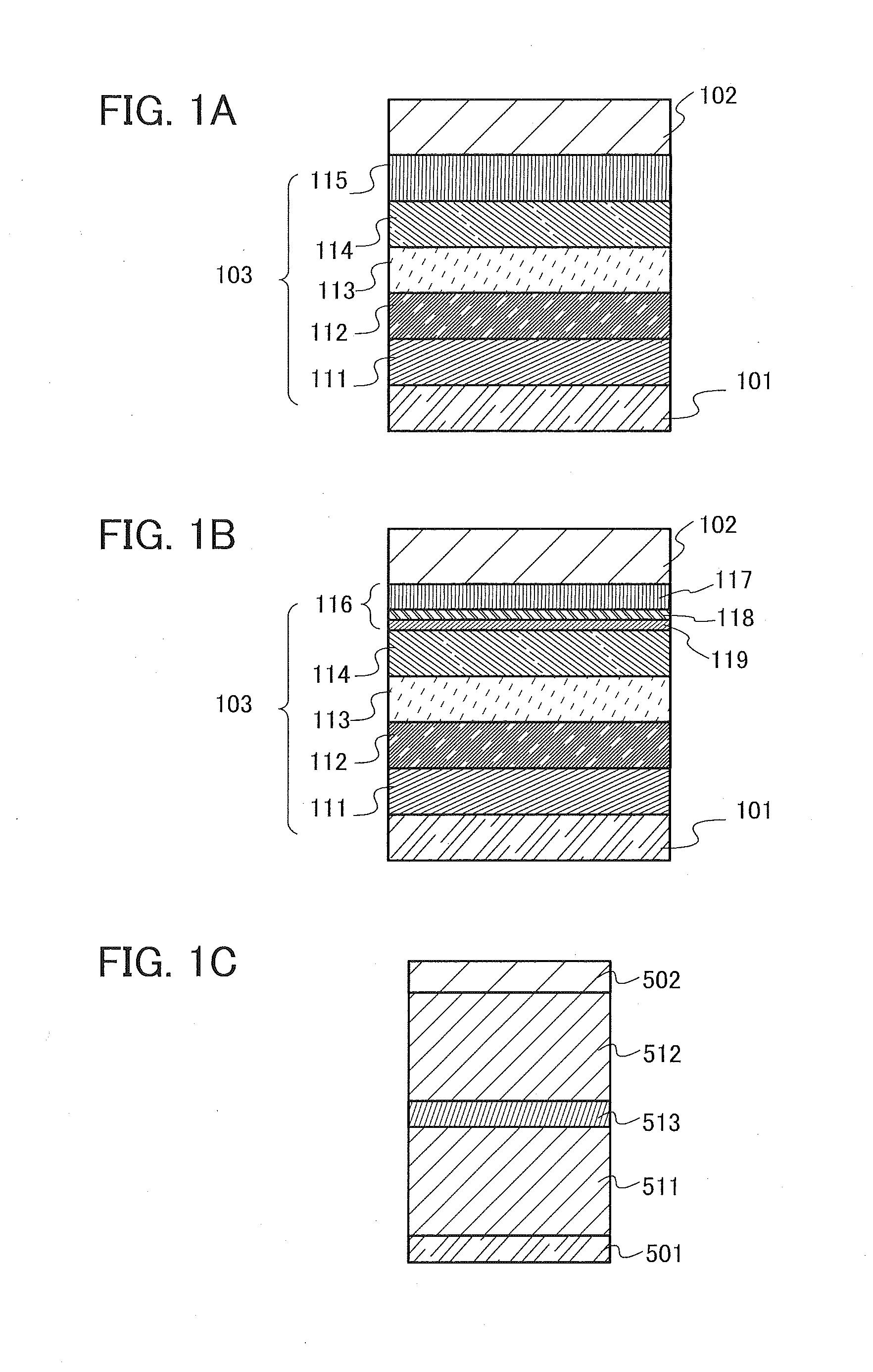
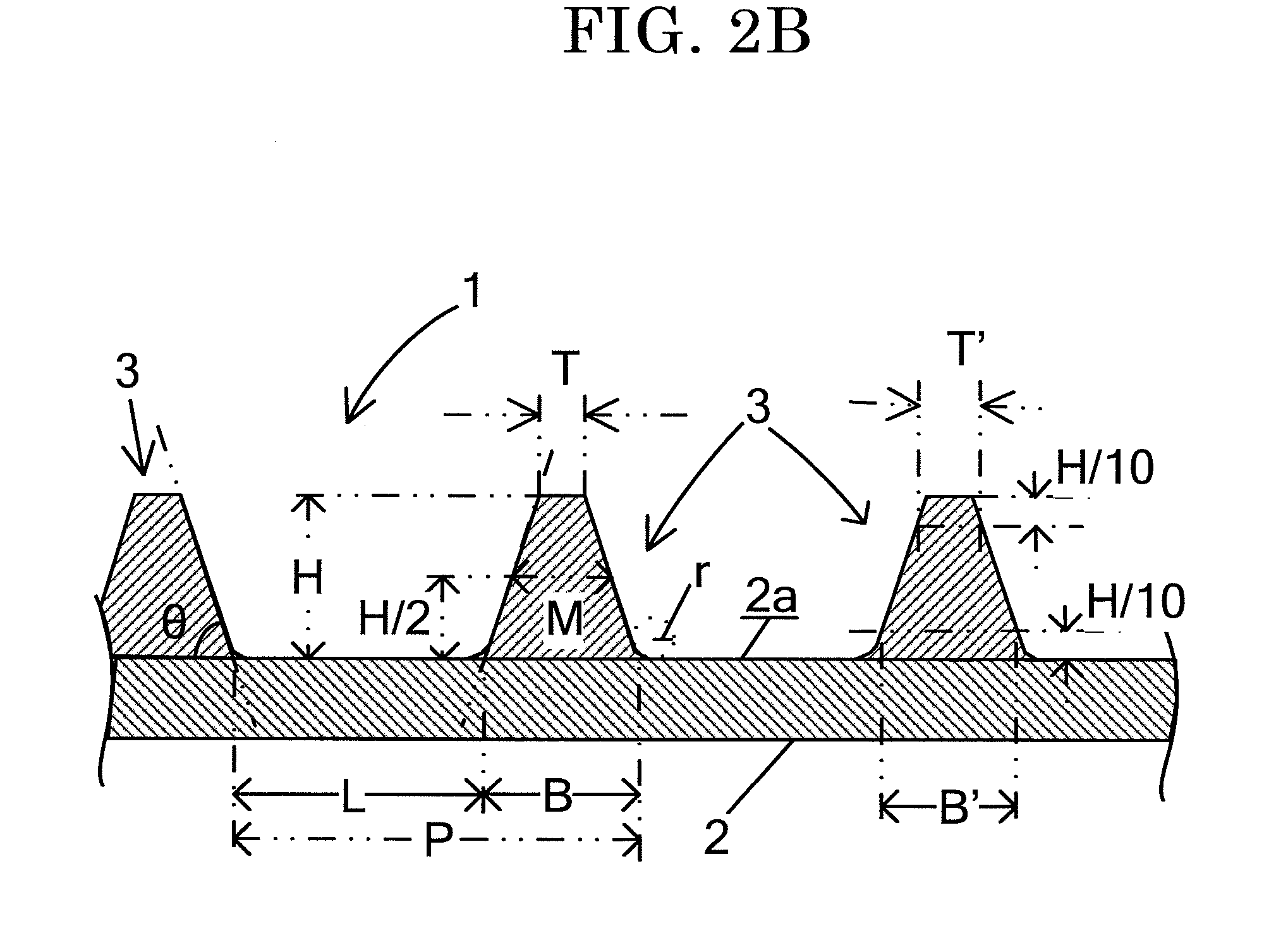
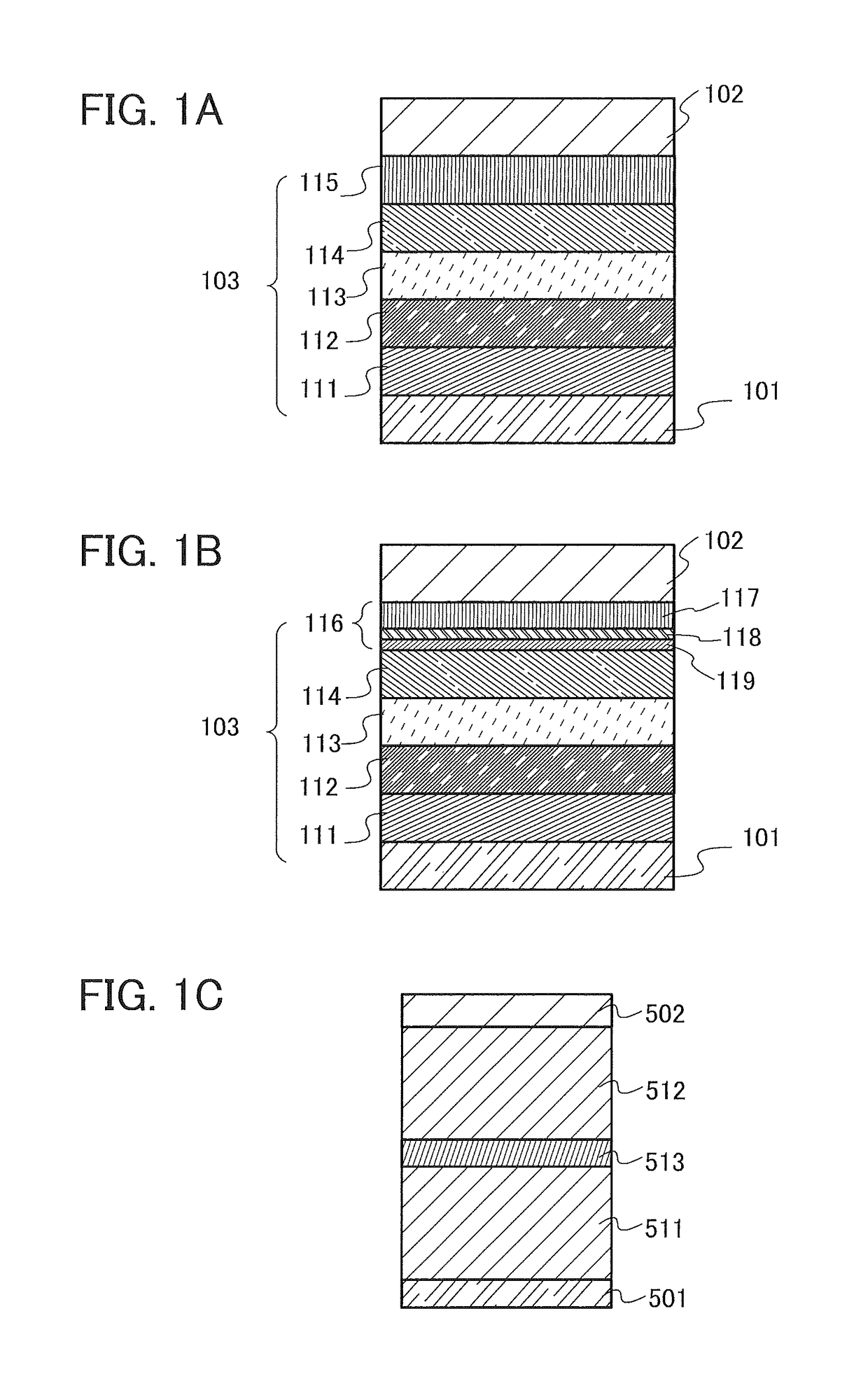
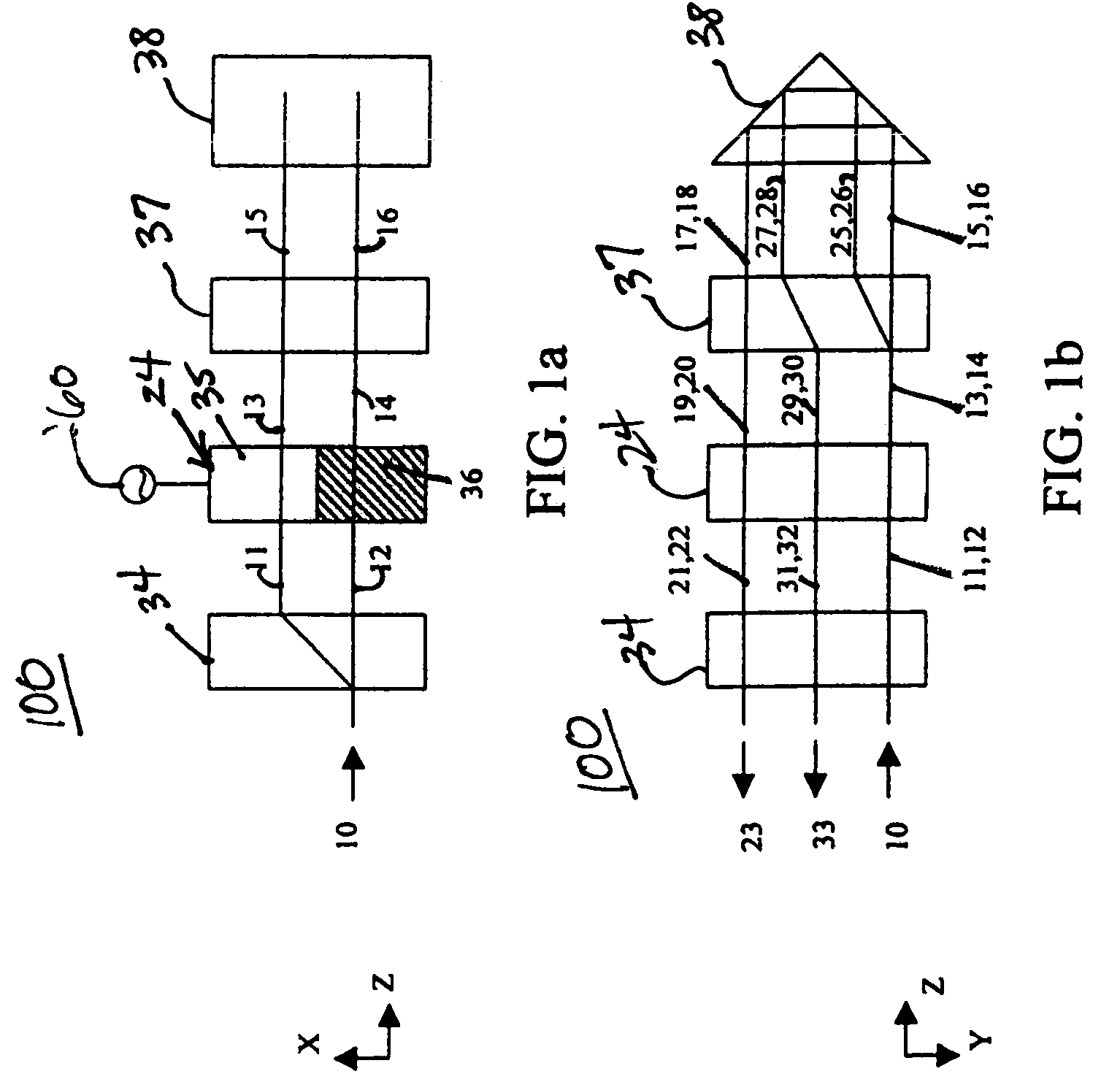
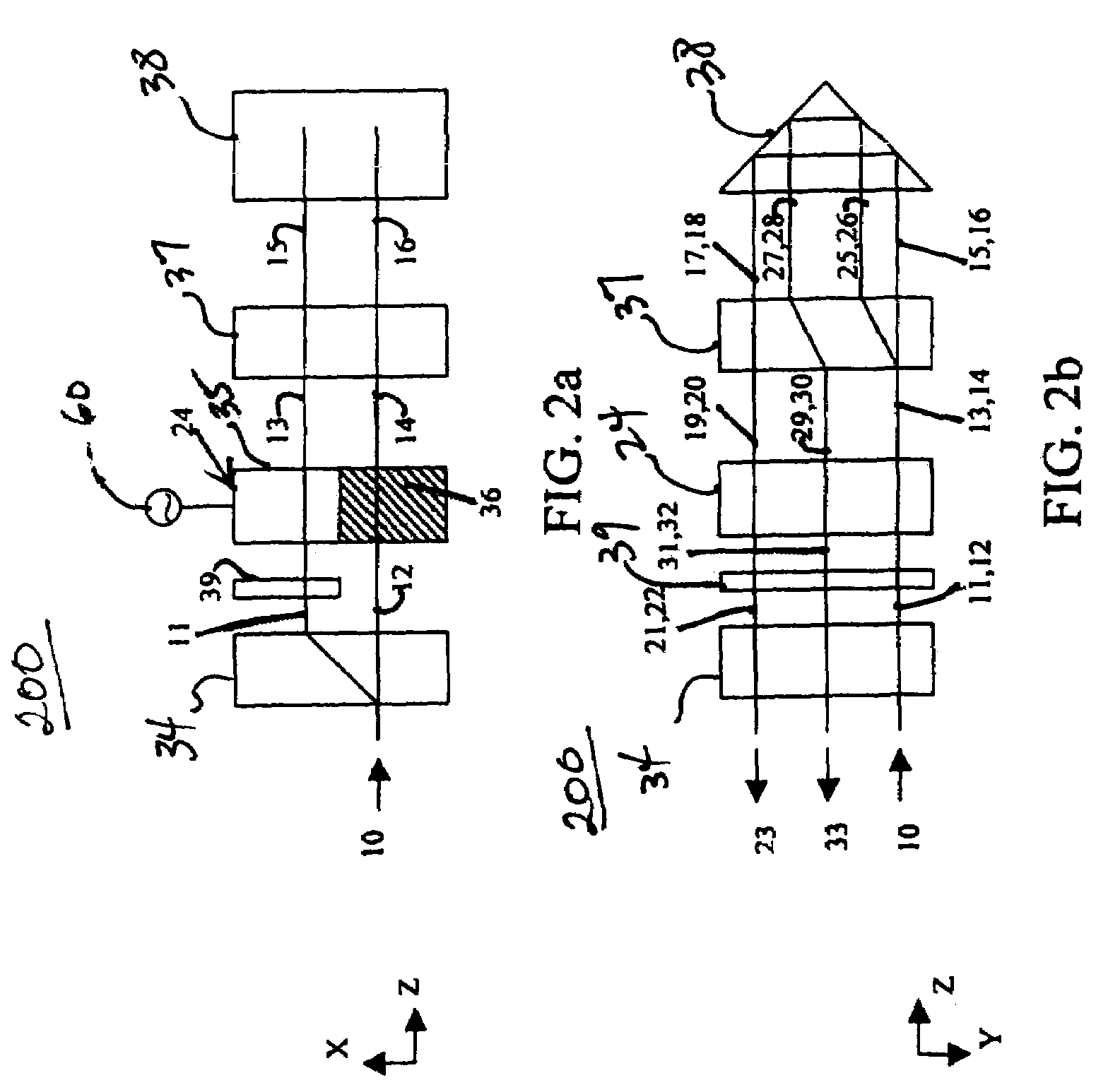
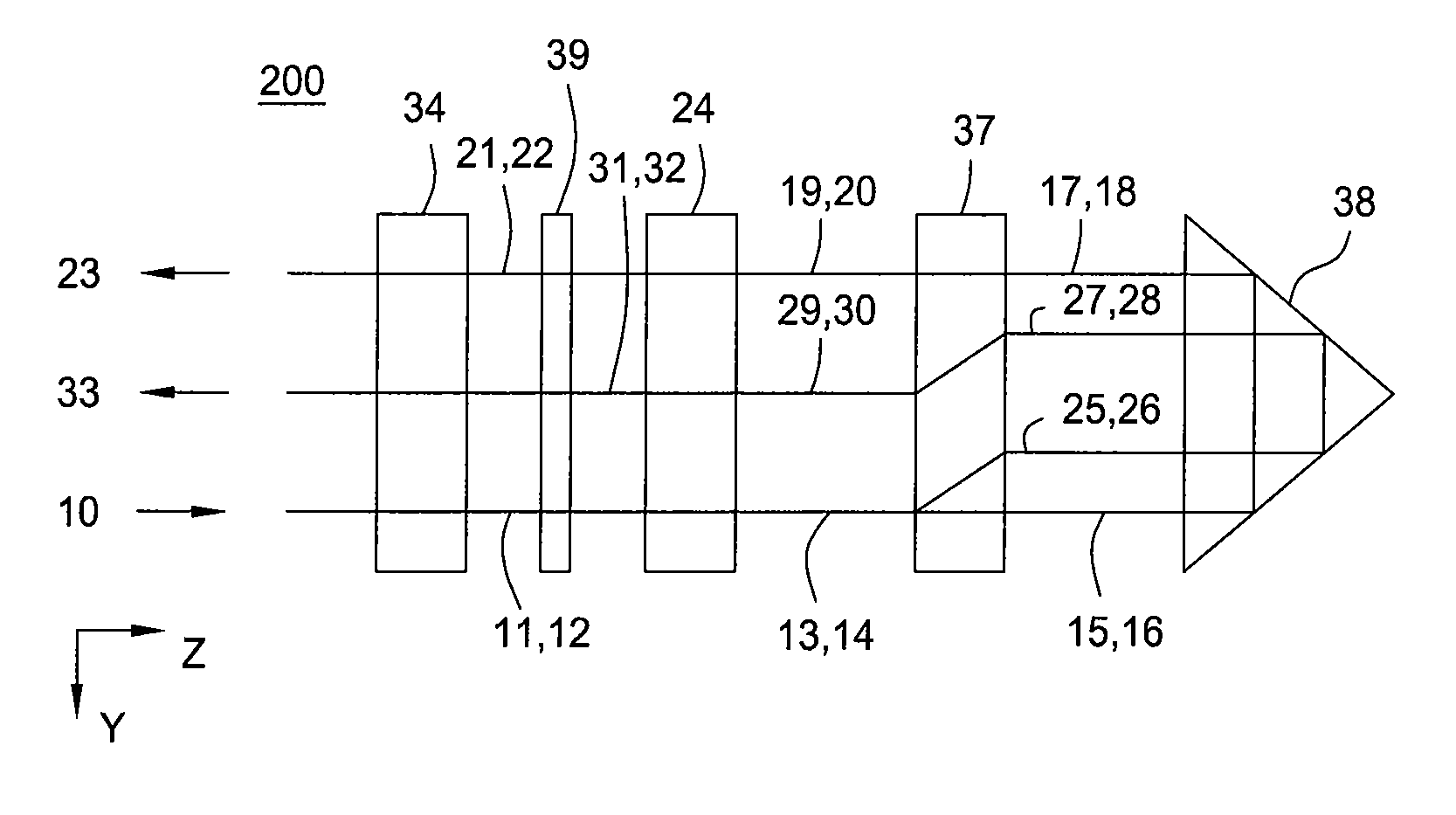
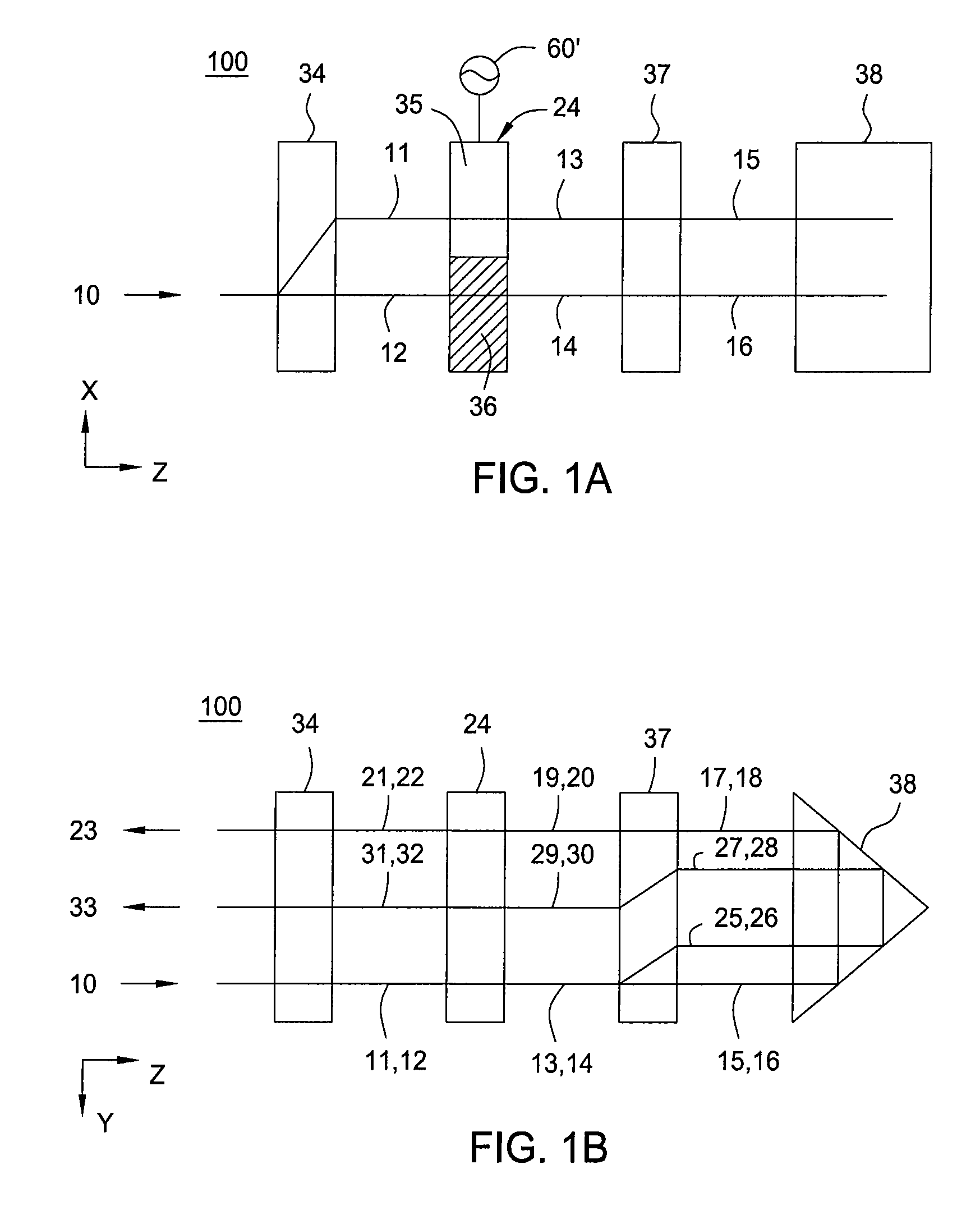
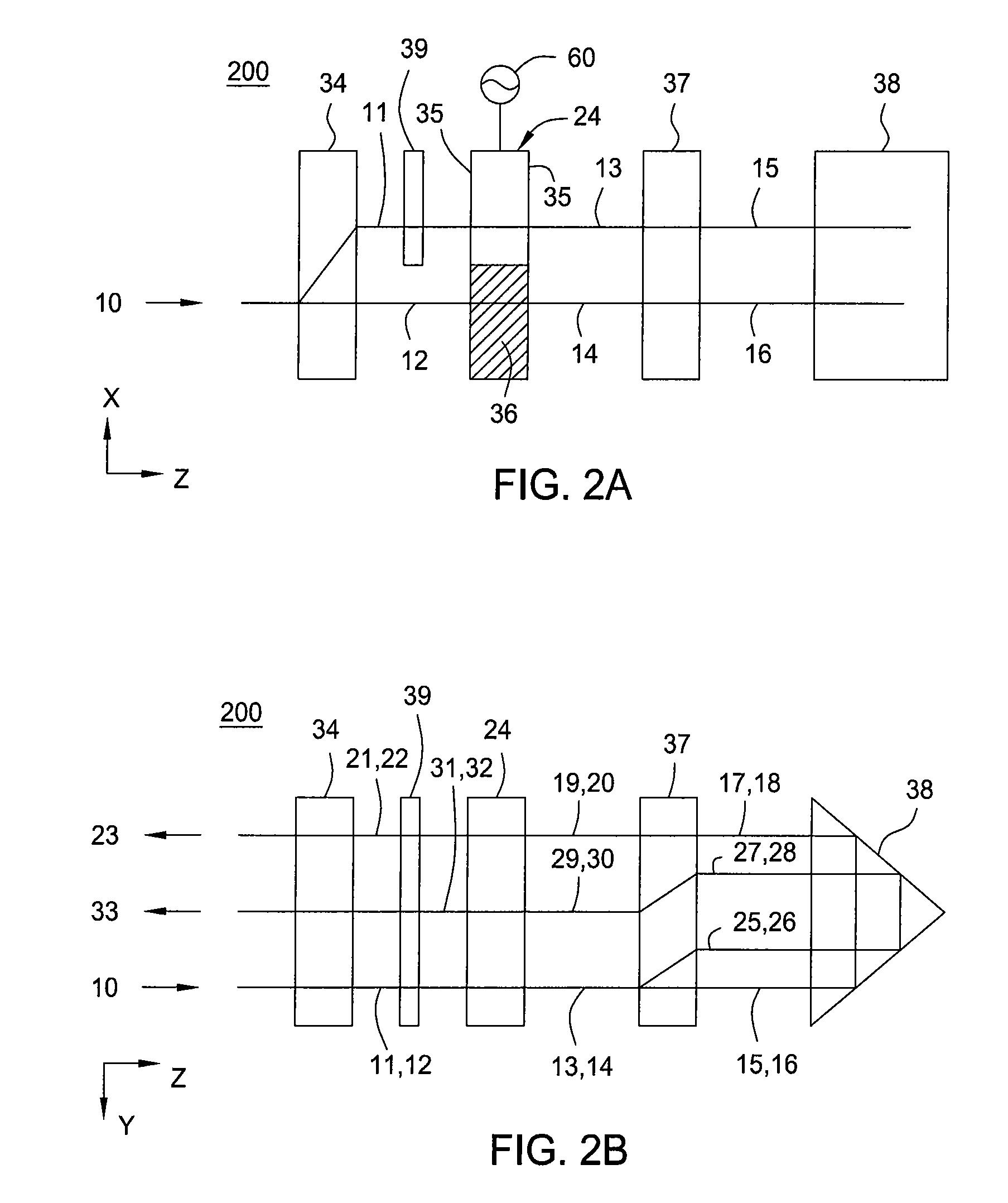
Heat assisted magnetic recording head and heat assisted magnetic recording apparatus
ActiveUS20060187564A1Compact mountingLess crosstalkRecord information storageRecording/reproducing/erasing methodsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingMagnetic poles
A heat assisted magnetic recording head is provided, which can prevent an effect of a heat in a laser diode when a magnetic recording region is heated by a heating laser beam and which can reduce its size and weight. In the heat assisted magnetic recording head, a recording magnetic pole, a magnetic recording element, a magnetic read element, an optical waveguide, and an irradiating optical waveguide are attached to a floating slider provided below a suspension. The laser diode is arranged on an opposite side of the suspension to the floating slider. The heating laser beam emitted from the laser diode is directed to the irradiating optical waveguide through the optical waveguide, so that a magnetic recording medium is irradiated with the heating laser beam exiting from the irradiating optical waveguide.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Heat assisted magnetic recording head and heat assisted magnetic recording apparatus for heating a recording region in a magnetic recording medium during magnetic recording
ActiveUS7538978B2Compact mountingLess crosstalkRecord information storageRecording/reproducing/erasing methodsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingMagnetic poles
A heat assisted magnetic recording head is provided, which can prevent an effect of a heat in a laser diode when a magnetic recording region is heated by a heating laser beam and which can reduce its size and weight. In the heat assisted magnetic recording head, a recording magnetic pole, a magnetic recording element, a magnetic read element, an optical waveguide, and an irradiating optical waveguide are attached to a floating slider provided below a suspension. The laser diode is arranged on an opposite side of the suspension to the floating slider. The heating laser beam emitted from the laser diode is directed to the irradiating optical waveguide through the optical waveguide, so that a magnetic recording medium is irradiated with the heating laser beam exiting from the irradiating optical waveguide.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Miniaturized multi-gas and vapor sensor devices and associated methods of fabrication
InactiveUS20050109081A1High sensitivityHigh adsorption rateMaterial nanotechnologyMaterial heat developmentMiniaturizationEngineering
The invention provides a miniaturized sensor device including a thin film membrane having a first surface and a second surface, one or more resistive thin film heater / thermometer devices disposed directly or indirectly adjacent to the first surface of the thin film membrane, and a frame disposed directly or indirectly adjacent to the second surface of the thin film membrane, wherein one or more internal surfaces of the frame define at least one cell having at least one opening. The sensor device also includes a thin film layer disposed directly or indirectly adjacent to the frame. The sensor device further includes a sensing layer disposed directly or indirectly adjacent to the thin film membrane.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Front illuminated back side contact thin wafer detectors
InactiveUS20060255420A1Reduce impactReduce susceptibilitySolid-state devicesDiodeHigh densityContact pad
Owner:OSI OPTOELECTRONICS
Organic Compound, Light-Emitting Element, Display Module, Lighting Module, Light-Emitting Device, Display Device, Electronic Device, and Lighting Device
ActiveUS20160240794A1Improve heat resistanceLess crosstalkOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesElectron injectionDisplay device
A novel organic compound that can be used as an electron-injection material or an electron-transport material of a light-emitting element is provided. An organic compound with which a display device having less crosstalk can be obtained is provided. A light-emitting device, a display device, and an electronic device each having less crosstalk are provided. An organic compound including two or three benzo[h]quinazoline rings is provided. In the organic compound, two or three benzo[h]quinazoline rings are preferably included in the substituent including an aromatic ring or a heteroaromatic ring and having 3 to 30 carbon atoms. When two or three benzo[h]quinazoline rings are included in a substituent particularly including a heteroaromatic ring and having 3 to 30 carbon atoms, a high electron-transport property can be obtained.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
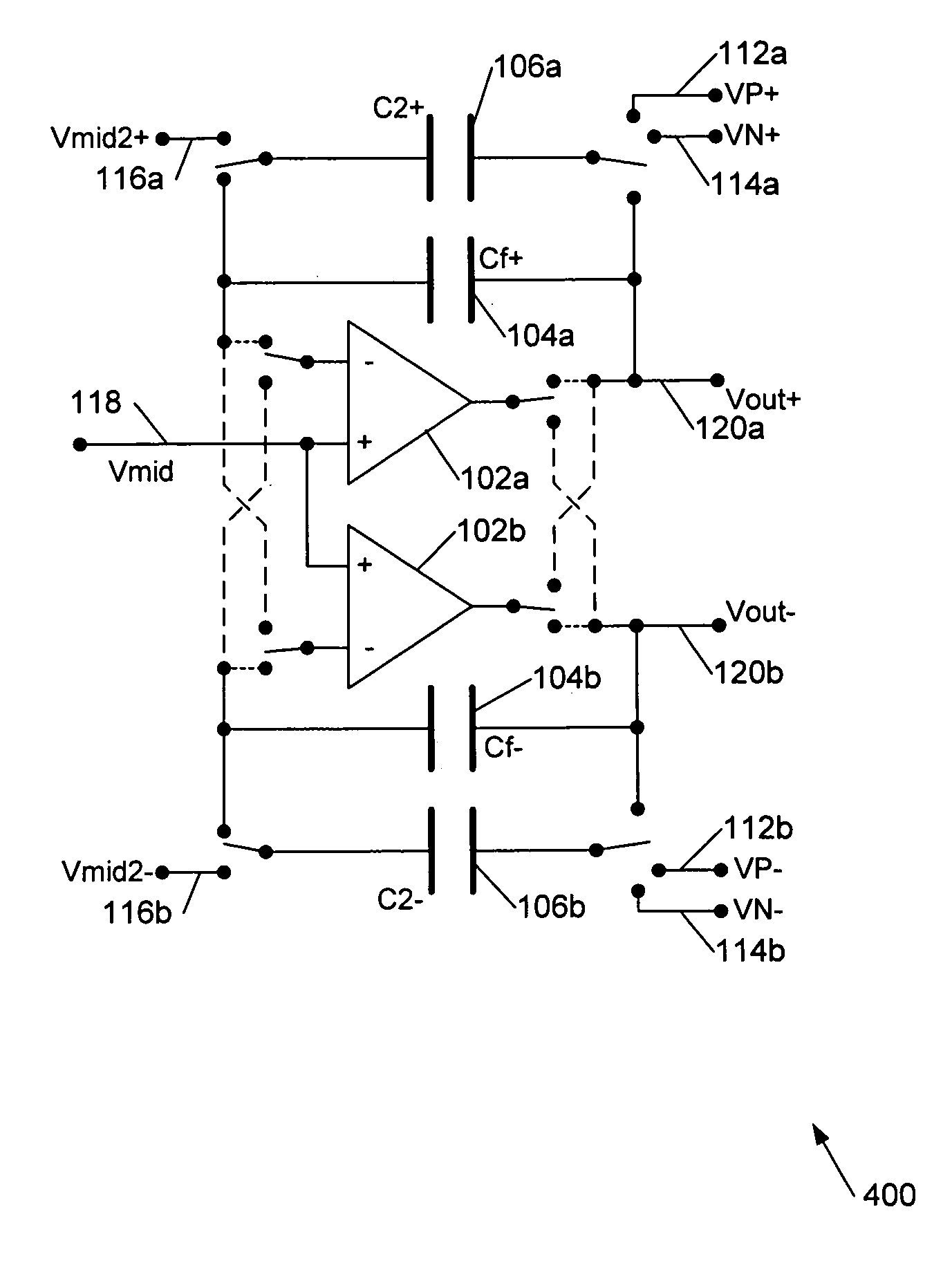
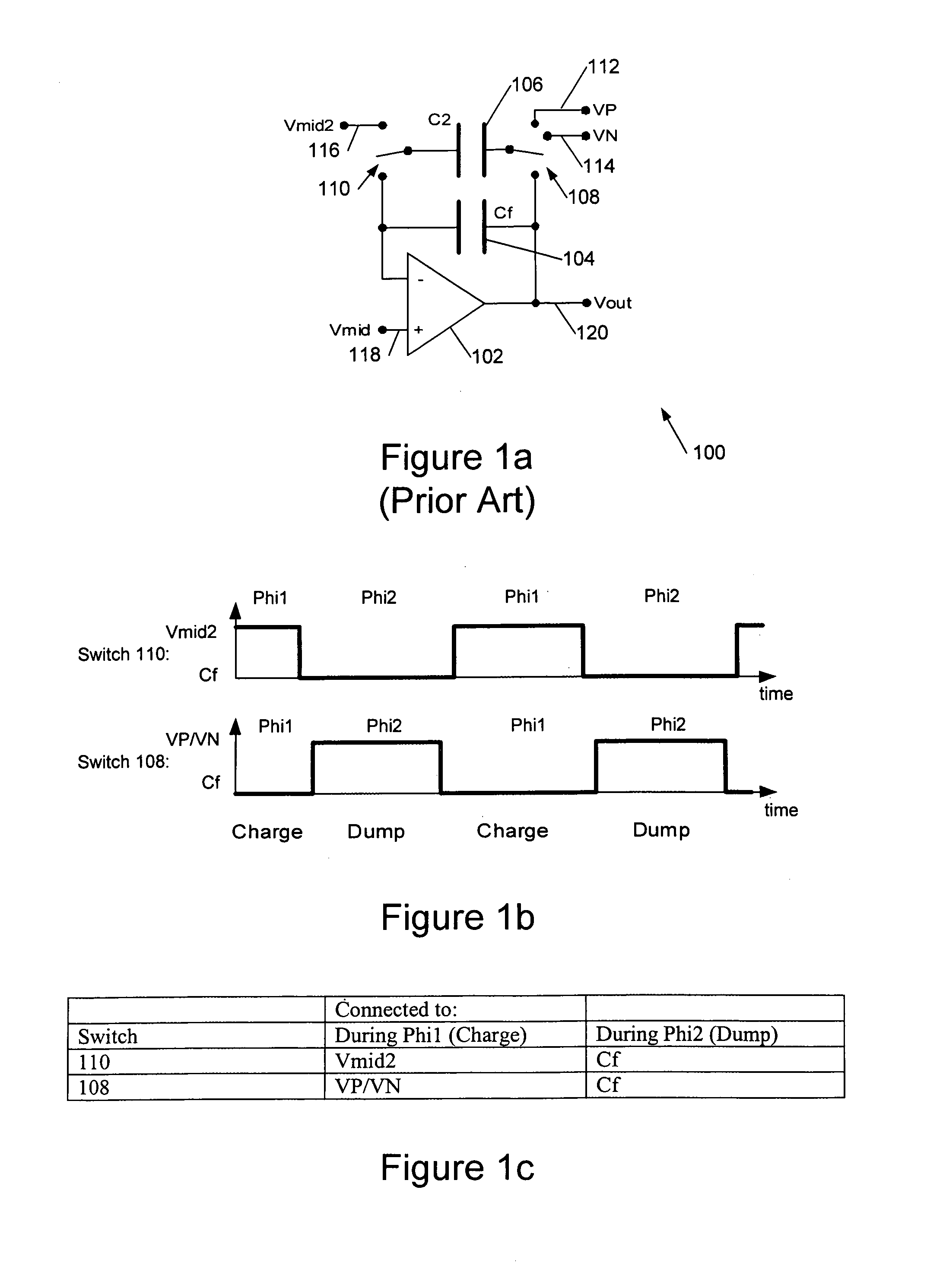
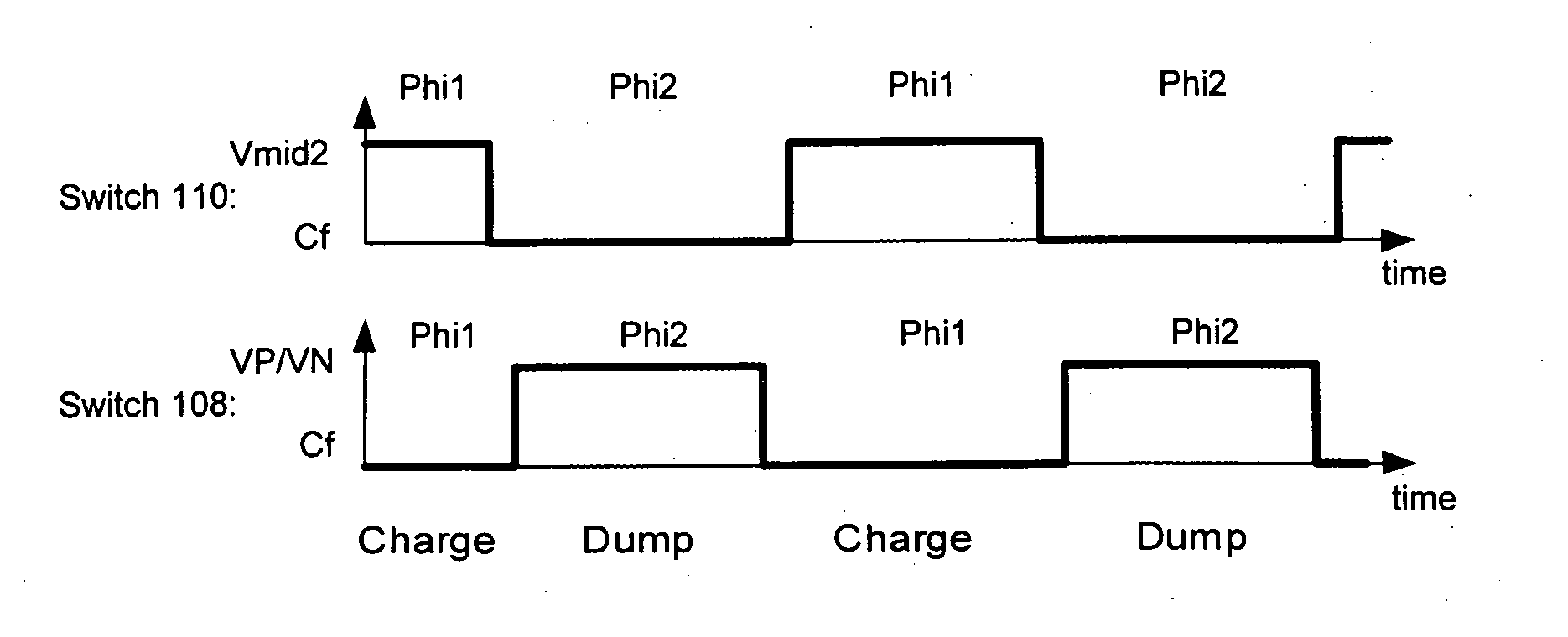
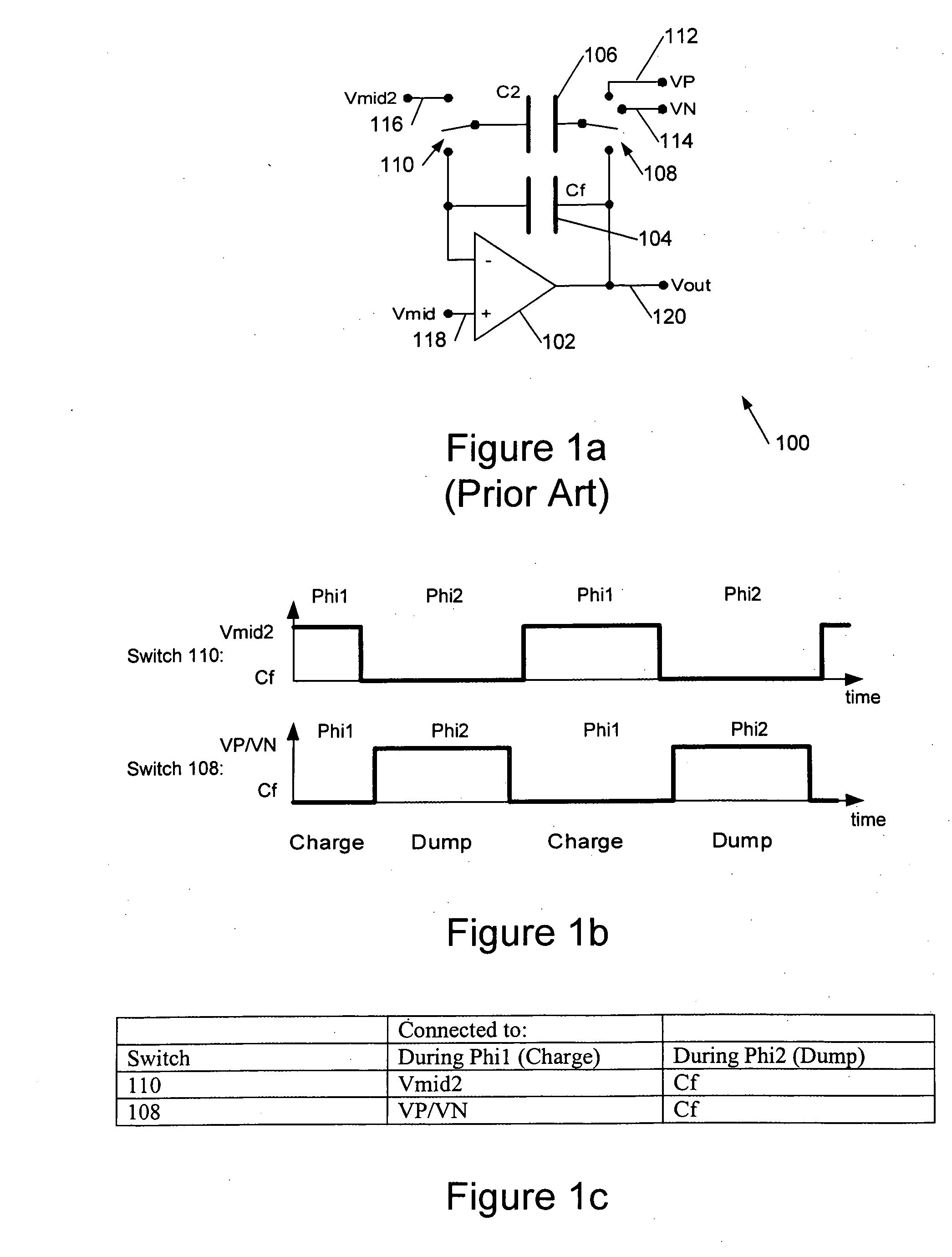
Digital-to-analogue converter circuits
ActiveUS6952176B2Reduce loadIncreased rejectElectric signal transmission systemsDelta modulationDigital analog converterAudio power amplifier
This invention is generally concerned with digital-to-analogue converters and more particularly relates to techniques for reducing signal dependent loading of reference voltage sources used by these converters.A differential switched capacitor digital-to-analogue (DAC) circuit (500) comprises first and second differential signal circuit portions (500a,b) for providing respective positive and negative signal outputs with respect to a reference level, and has first and second reference voltage inputs (112,114) for receiving respective positive and negative references. Each of said first and second circuit portions comprises an amplifier (102a,b) with a feedback capacitor (104a,b), a second capacitor (106a,b), and a switch (108a,b, 110a,b) to switchably couple said second capacitor to a selected one of said reference voltage inputs to charge the second capacitor and to said feedback capacitor to share charge with the feedback capacitor. The switch of said first circuit portion is further configured to connect said second capacitor (106a) of said first circuit portion to share charge with said feedback capacitor (104b) of said second circuit portion; and the switch of said second circuit portion is further configured to connect said second capacitor (106b) of said second circuit portion to share charge with said feedback capacitor (104a) of said first circuit portion. This enables the second capacitors to in effect be alternately pre-charged to positive and negative signal-dependent nodes so that, on average, signal dependent loading of the references is approximately constant.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
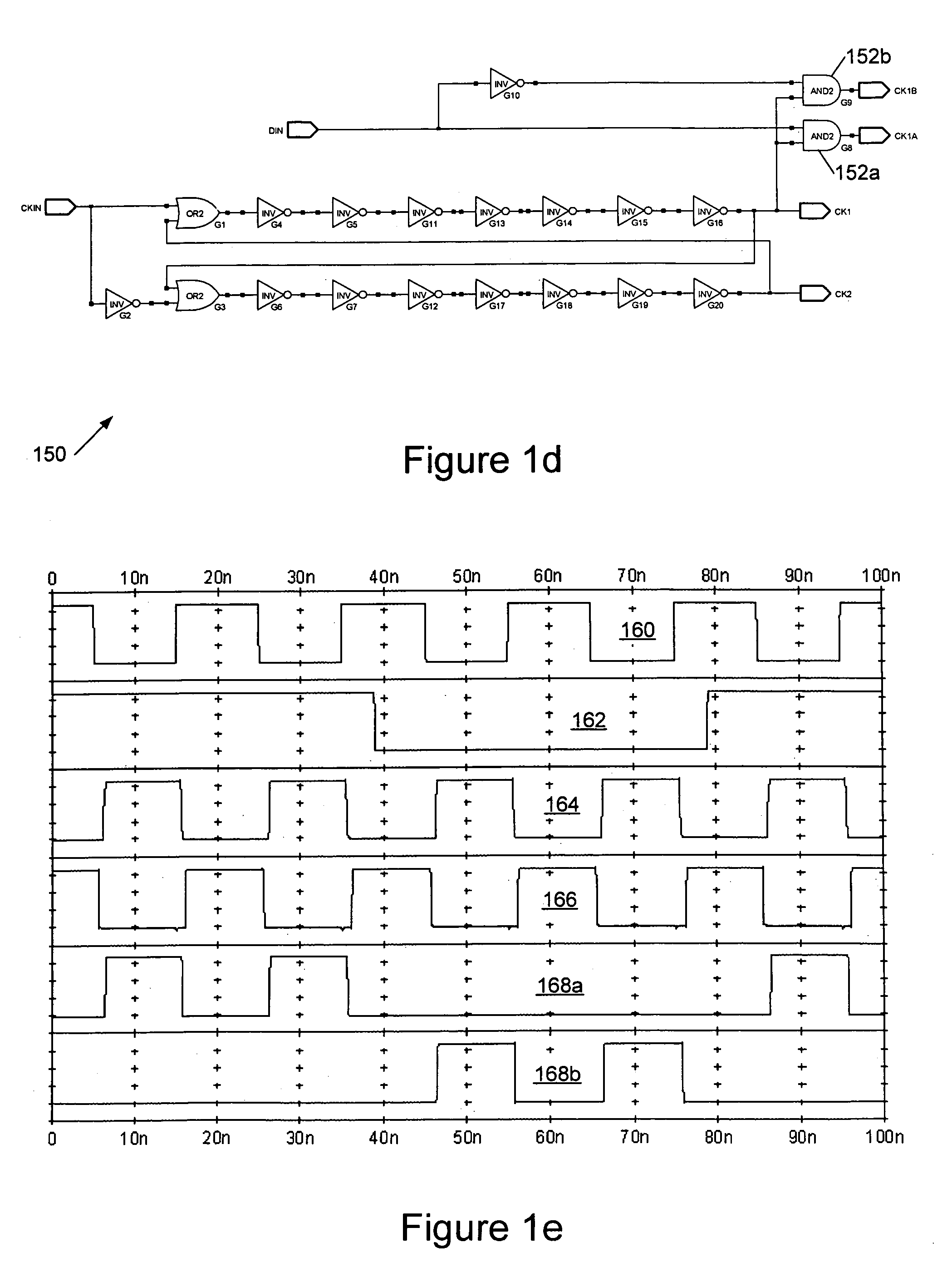
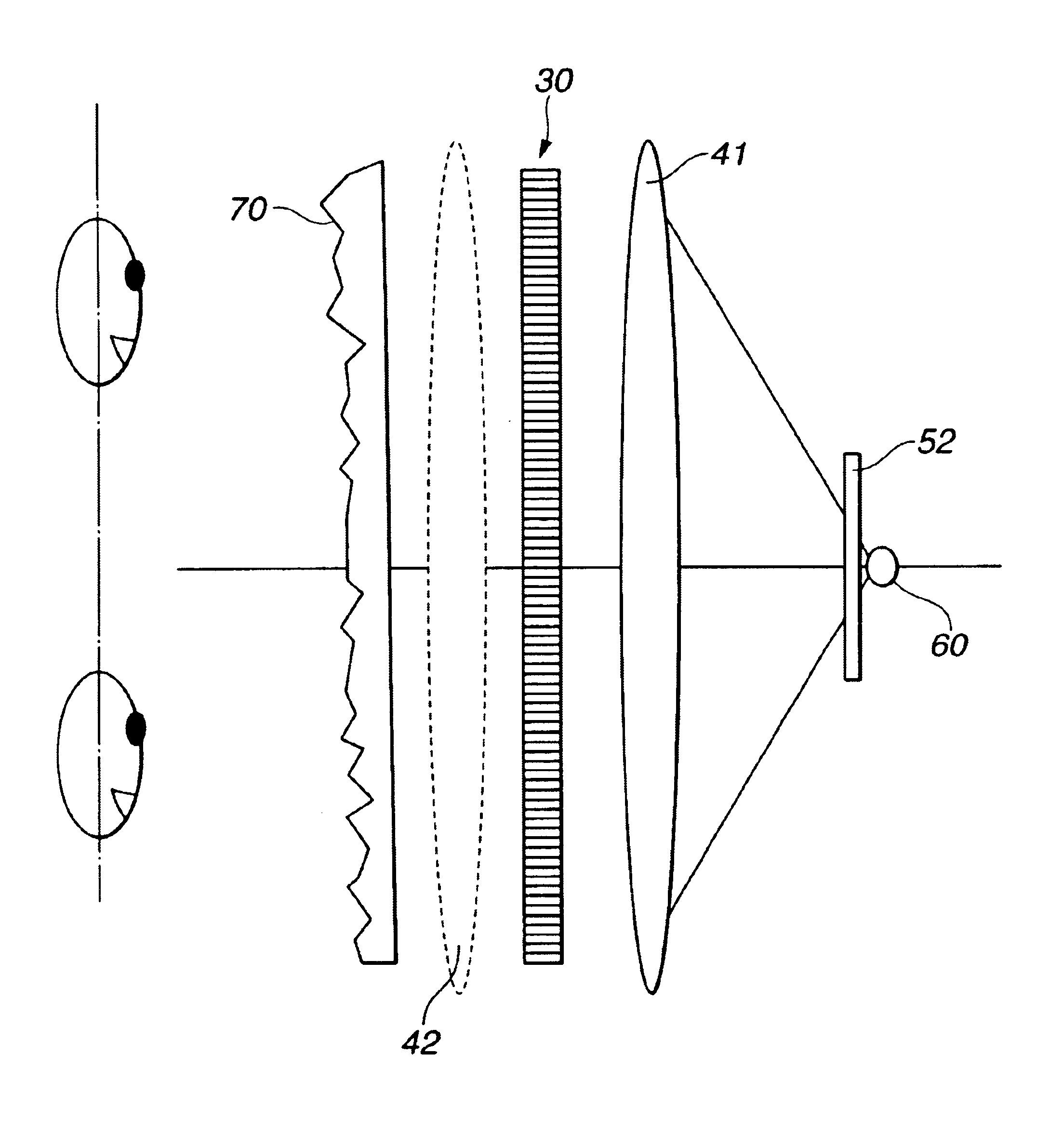
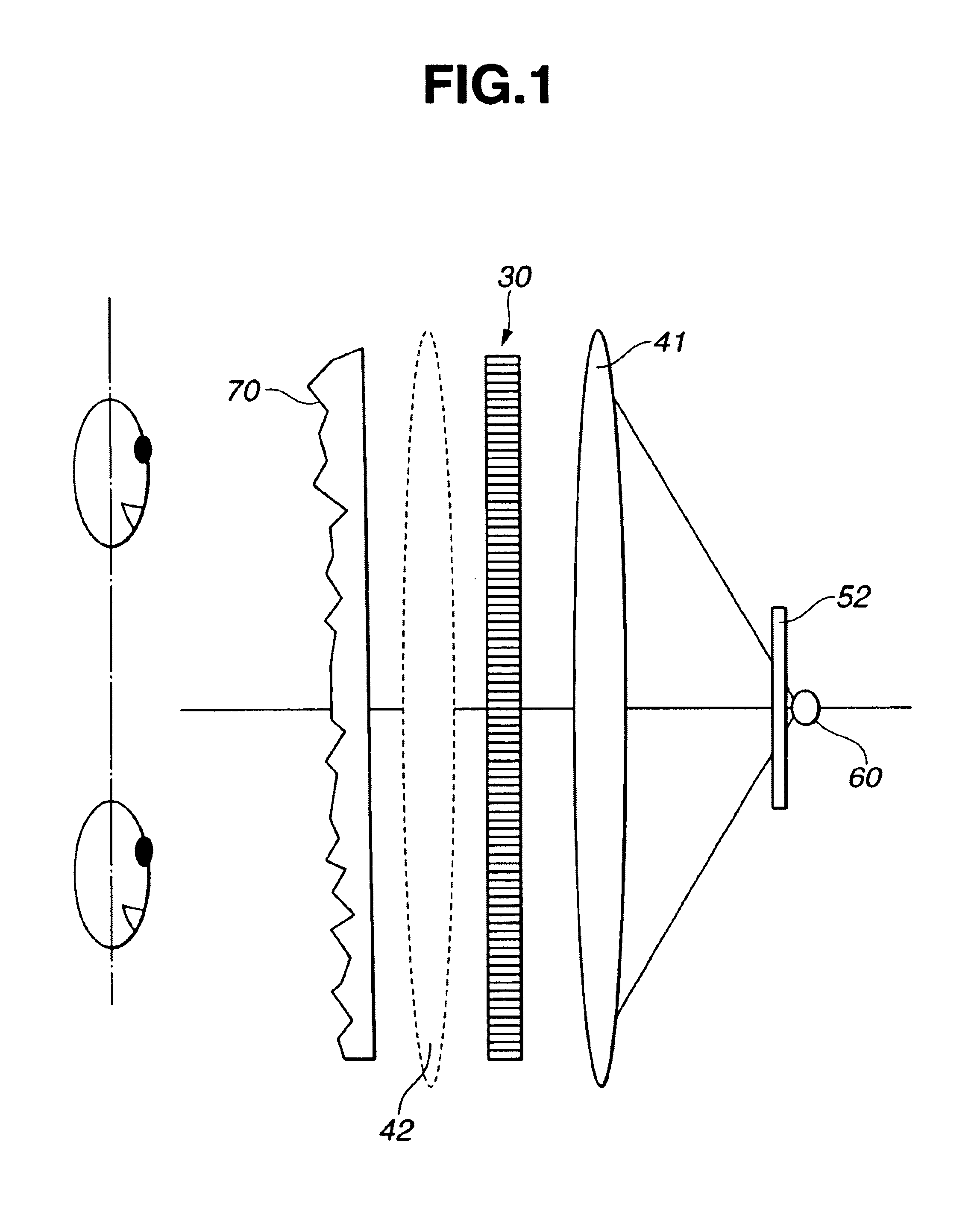
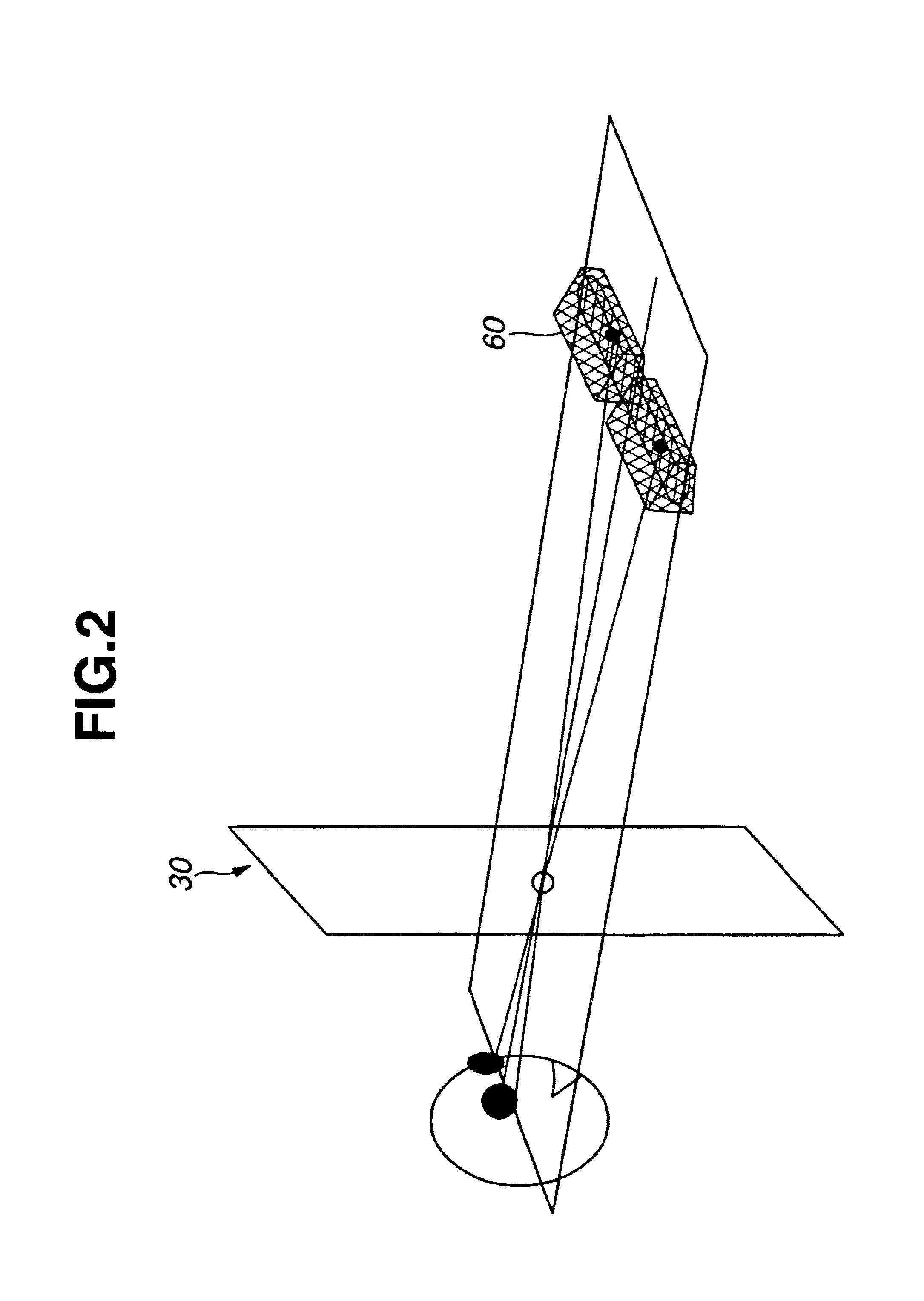
Stereoscopic display system for viewing without spectacles
InactiveUS6864862B2Accurate separationIncrease freedomStatic indicating devicesSteroscopic systemsDisplay deviceEyewear
A light source (60) is provided in the rear of display means (30), which has a light transmission type display and is made up of pixels (31) for left and right eyes and a first image separation mechanism (32) for the left and right eyes, with a lens unit (41) having a collecting power in a vertical direction and a second image separation mechanism (52) therebetween. The transmission light from the light source (60) spreads in the vertical direction as shown in the drawing. Such spread of the light occurs over the whole of a display surface. It is therefore possible to view the image on the display surface, when the viewer's head is located at any of positions 1 to 4. Accordingly, it becomes possible to make a degree of freedom in vertical (up-and-down) positional movement of the viewer's head.
Owner:SONY CORP
Multi-fiber core single-mode optical fiber and manufacturing method thereof
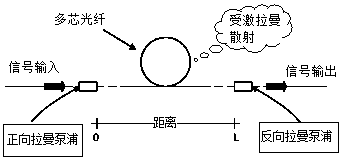
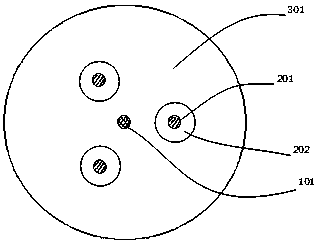
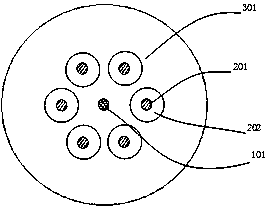
ActiveCN104678484AReduce crosstalkRaman amplification is possibleOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingGlass fibre drawing apparatusCommunications systemEngineering
The invention relates to a multi-fiber core single-mode optical fiber and a manufacturing method thereof. The multi-fiber core single-mode optical fiber comprises claddings and a plurality of fiber cores. The multi-fiber core single-mode optical fiber is characterized in that the fiber cores include a pumping fiber core and a plurality of signal fiber cores, wherein the pumping fiber core is arranged in the center of the optical fiber, the signal fiber cores are distributed on one to three circumferences around the center at equal intervals, so as to form one to three layers of signal fiber cores, sunken claddings tightly cover each signal fiber core, and common claddings are arranged outside the sunken claddings. The multi-fiber core single-mode optical fiber has the characteristics of low signal crosstalk among all of the signal fiber cores, easiness in online light amplification, simplicity and convenience in manufacturing and low manufacturing cost and is suitable for large-scale production. A distributed Raman amplification technique of the multi-fiber core single-mode optical fiber is used in an ultrahigh-speed communication system, so that effective light amplification can be realized, and the harm of a non-linear effect to the performance of a high-speed optical transmission system is further reduced.
Owner:YANGTZE OPTICAL FIBRE & CABLE CO LTD
Front illuminated back side contact thin wafer detectors
InactiveUS7579666B2Reduce impactReduce susceptibilitySolid-state devicesDiodeHigh densityContact pad
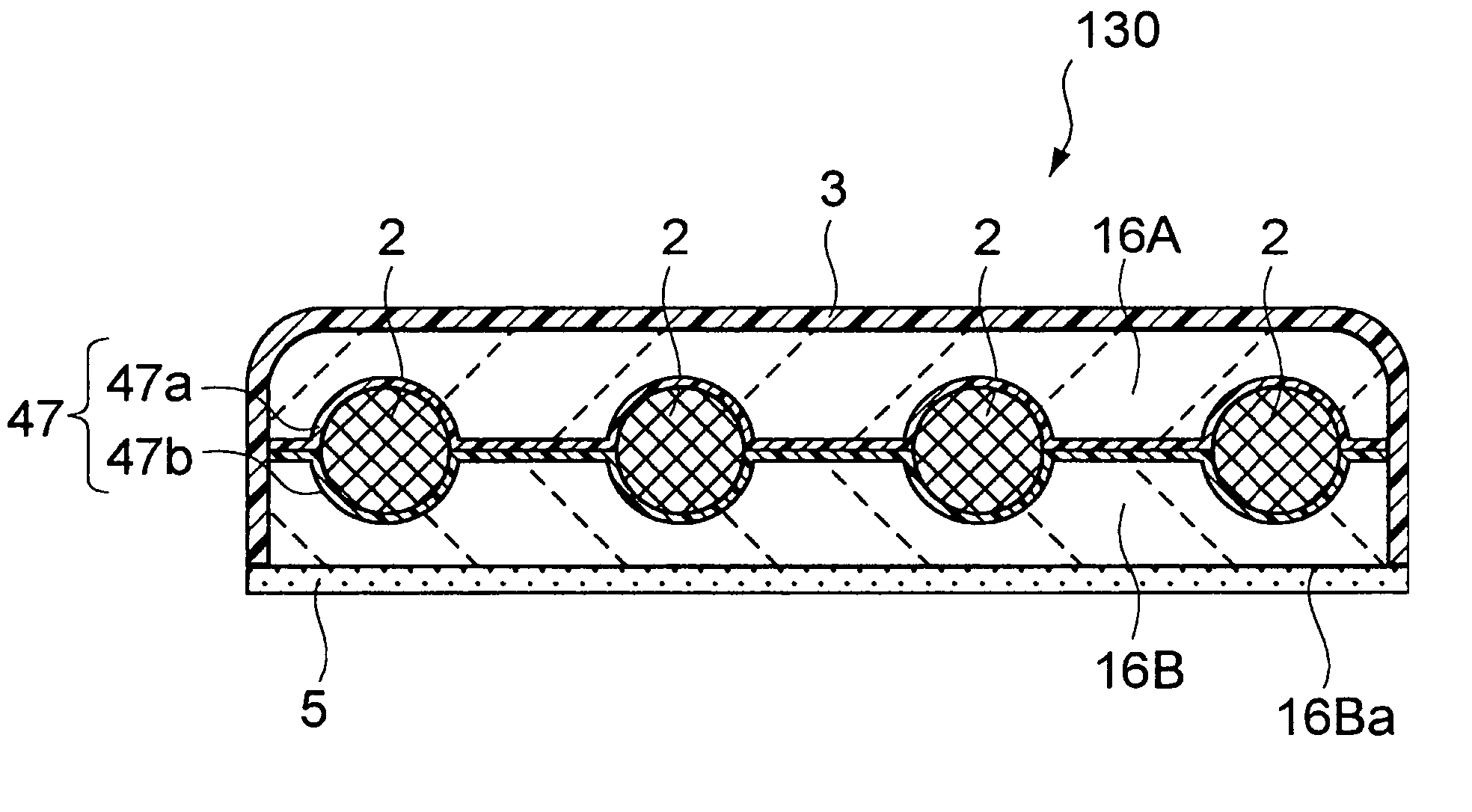
The present invention is directed toward a detector structure, detector arrays, a method of detecting incident radiation, and a method of manufacturing the detectors. The present invention comprises several embodiments that provide for reduced radiation damage susceptibility, decreased affects of cross-talk, and increased flexibility in application. In one embodiment, the present invention comprises a plurality of front side illuminated photodiodes, optionally organized in the form of an array, with both the anode and cathode contact pads on the back side. The front side illuminated, back side contact photodiodes have superior performance characteristics, including less radiation damage, less crosstalk using a suction diode, and reliance on reasonably thin wafers. Another advantage of the photodiodes of the present invention is that high density with high bandwidth applications can be effectuated.
Owner:OSI OPTOELECTRONICS
Mobile radio communication system
InactiveCN1422447ANarrow beam widthAvoid alignment problemsAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesJet aeroplaneCommunications system
This disclosure provides a communication system using a high-altitude aircraft traveling at relatively slow speeds, which can remain airborne for long periods of time. The communication system uses the airplane as a long term high altitude platform that relays signals between one or more ground-stations and / or satellites, aircraft, and the like. The ground-stations have narrow-beam antennas that are aimable, permitting the aircraft to maintain a larger station than would otherwise be possible using the narrow-beam antennas. The ground-stations adjust their aim based on information either gained by tracking the aircraft's signal, or transmitted by the aircraft to the ground-station.
Owner:AEROVIRONMENT INC
Miniaturized multi-gas and vapor sensor devices and associated methods of fabrication
InactiveUS7104113B2High sensitivityHigh selectivityMaterial nanotechnologyMaterial heat developmentEngineeringMembrane configuration
The invention provides a miniaturized sensor device including a thin film membrane having a first surface and a second surface, one or more resistive thin film heater / thermometer devices disposed directly or indirectly adjacent to the first surface of the thin film membrane, and a frame disposed directly or indirectly adjacent to the second surface of the thin film membrane, wherein one or more internal surfaces of the frame define at least one cell having at least one opening. The sensor device also includes a thin film layer disposed directly or indirectly adjacent to the frame. The sensor device further includes a sensing layer disposed directly or indirectly adjacent to the thin film membrane.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Data transmission cable
InactiveUS7112746B2Less crosstalkReduce crosstalkFlat/ribbon cablesFibre mechanical structuresEngineeringData transmission
Owner:SONY CORP
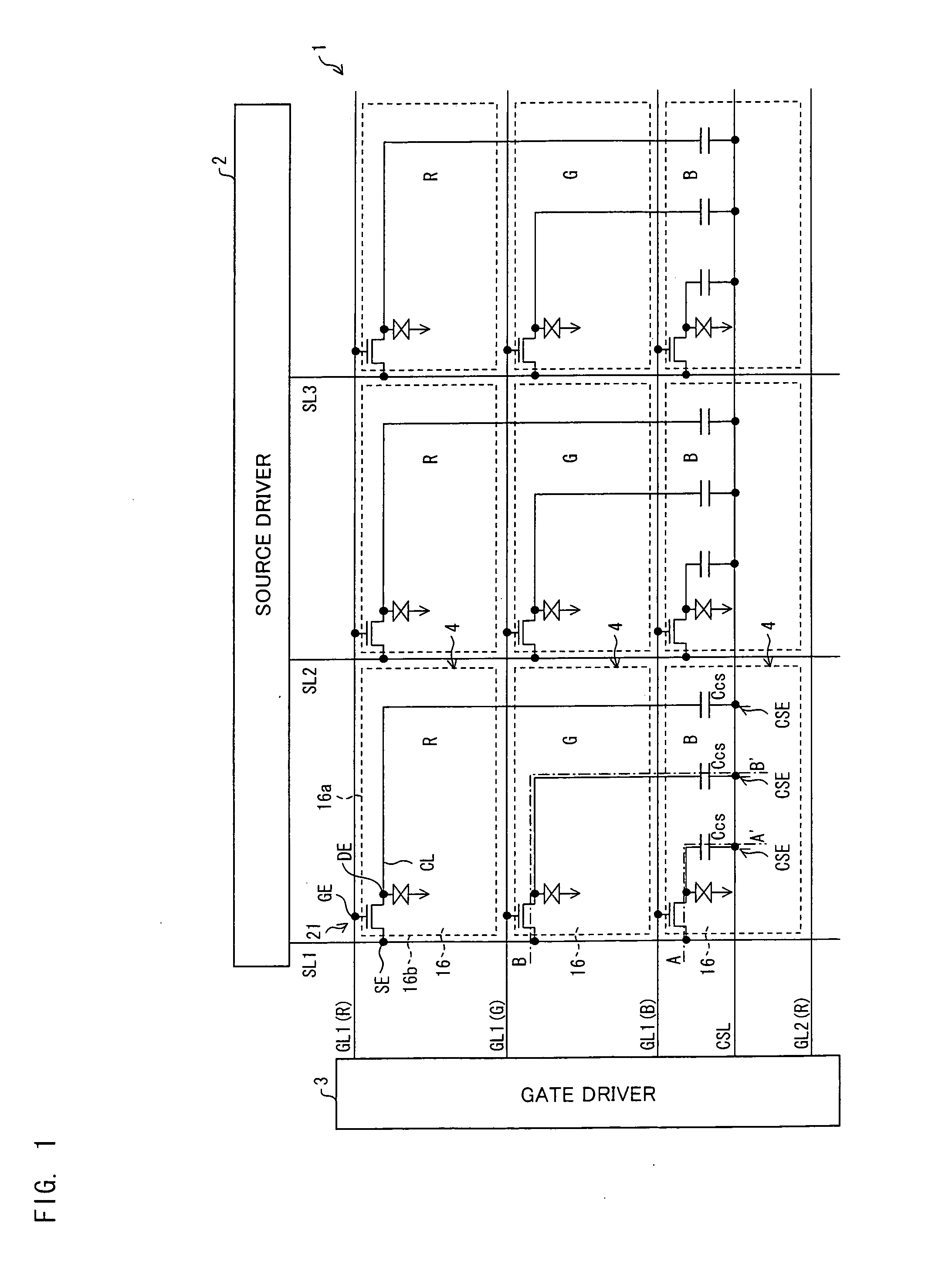
Active matrix substrate, display panel, display device, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20110170028A1Avoid crosstalkReduce loadStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsActive matrixDisplay device
The TFT substrate includes (i) gate lines and data lines which are provided in a matrix manner, (ii) a plurality of pixel electrodes each of which has a side which extends in parallel with the gate lines and a side which extends in parallel with the data lines and is shorter than the side, (iii) storage capacitor lines extending in parallel with the gate lines, and (iv) connection lines which are electrically connected to the respective pixel electrodes. In at least one embodiment, the number of the storage capacitor lines is smaller than that of the gate lines. A single one of the storage capacitor lines overlap a plurality of connection lines which are electrically connected to respective of the plurality of pixel electrodes which are arranged in a direction in parallel with the data lines. The single one of the storage capacitor lines and the plurality of connection lines overlap each other via the insulating film so as to form storage capacitor elements.
Owner:SHARP KK
Organic Compound, Light-Emitting Element, Display Module, Lighting Module, Light-Emitting Device, Display Device, Electronic Device, and Lighting Device
ActiveUS20160190471A1High heat resistanceLess crosstalkOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesChemistrySimple Organic Compounds
An object is to provide an organic compound having high heat resistance and a light-emitting element, a light-emitting device, an electronic device, and a display device each having high reliability. Provided are an organic compound having a 2,2′-(pyridine-2,6-diyl)bipyrimidine skeleton in which the 2-positions of pyrimidine skeletons are bonded to the 2- and 6-positions of a pyridine skeleton, and having a structure in which at least one aryl group having a fused structure with 10 to 16 carbon atoms is bonded to the 2,2′-(pyridine-2,6-diyl)bipyrimidine skeleton, and a light-emitting element, a light-emitting device, an electronic device, and a display device each containing the organic compound.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Mold structure
InactiveUS20080142680A1Efficiently transferring high-quality patternLess crosstalkNanoinformaticsConfectioneryEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Digital-to-analogue converter circuits
ActiveUS20050122245A1Increased rejectSave chip areaElectric signal transmission systemsDelta modulationAudio power amplifierPre-charge
This invention is generally concerned with digital-to-analogue converters and more particularly relates to techniques for reducing signal dependent loading of reference voltage sources used by these converters. A differential switched capacitor digital-to-analogue (DAC) circuit (500) comprises first and second differential signal circuit portions (500a,b) for providing respective positive and negative signal outputs with respect to a reference level, and has first and second reference voltage inputs (112,114) for receiving respective positive and negative references. Each of said first and second circuit portions comprises an amplifier (102a,b) with a feedback capacitor (104a,b), a second capacitor (106a,b), and a switch (108a,b, 110a,b) to switchably couple said second capacitor to a selected one of said reference voltage inputs to charge the second capacitor and to said feedback capacitor to share charge with the feedback capacitor. The switch of said first circuit portion is further configured to connect said second capacitor (106a) of said first circuit portion to share charge with said feedback capacitor (104b) of said second circuit portion; and the switch of said second circuit portion is further configured to connect said second capacitor (106b) of said second circuit portion to share charge with said feedback capacitor (104a) of said first circuit portion. This enables the second capacitors to in effect be alternately pre-charged to positive and negative signal-dependent nodes so that, on average, signal dependent loading of the references is approximately constant.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Liquid crystal display device
A liquid crystal display device is constituted such that sub-pixels are disposed in an array form in a first direction and a second direction orthogonal to each other, a plurality of gate lines are disposed in the second direction, an optical element for distributing the light to the second direction is disposed on the liquid crystal display device, liquid crystal molecules of the liquid crystal display device are controlled by an electric field almost in parallel to the surface of the liquid crystal display device, and a data line is disposed to obliquely divide the sub-pixels at a position different from the boundary between the sub-pixels neighboring in the second direction, where the data line can have a small angle with respect to the second direction, and the numerical aperture is not deteriorated greatly even when the lengths of apertures of the sub-pixels in the first direction are constant.
Owner:NEC LCD TECH CORP
Mold structure
InactiveUS7850441B2Efficiently transferring high-quality patternLess crosstalkRecord carriersNanoinformaticsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
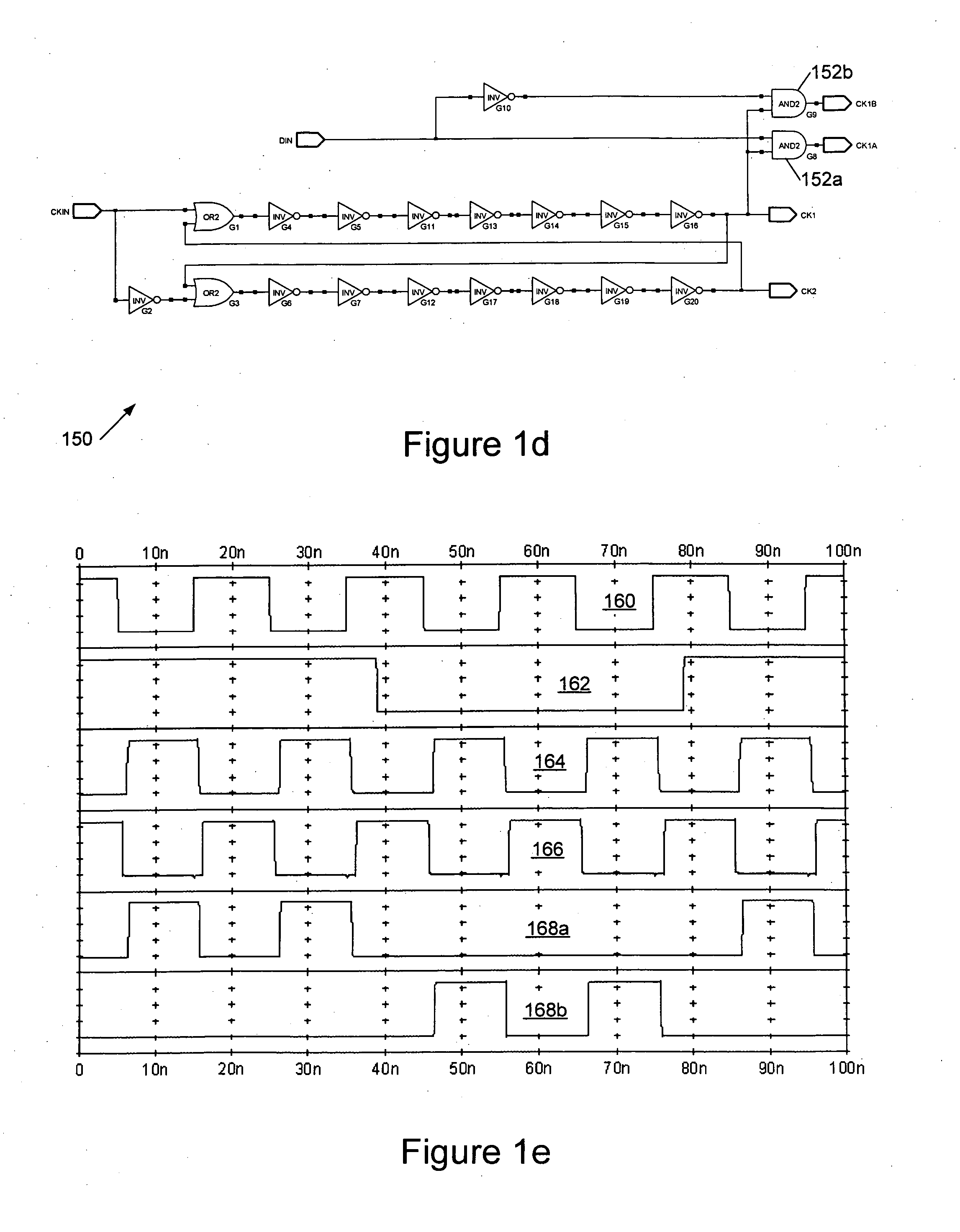
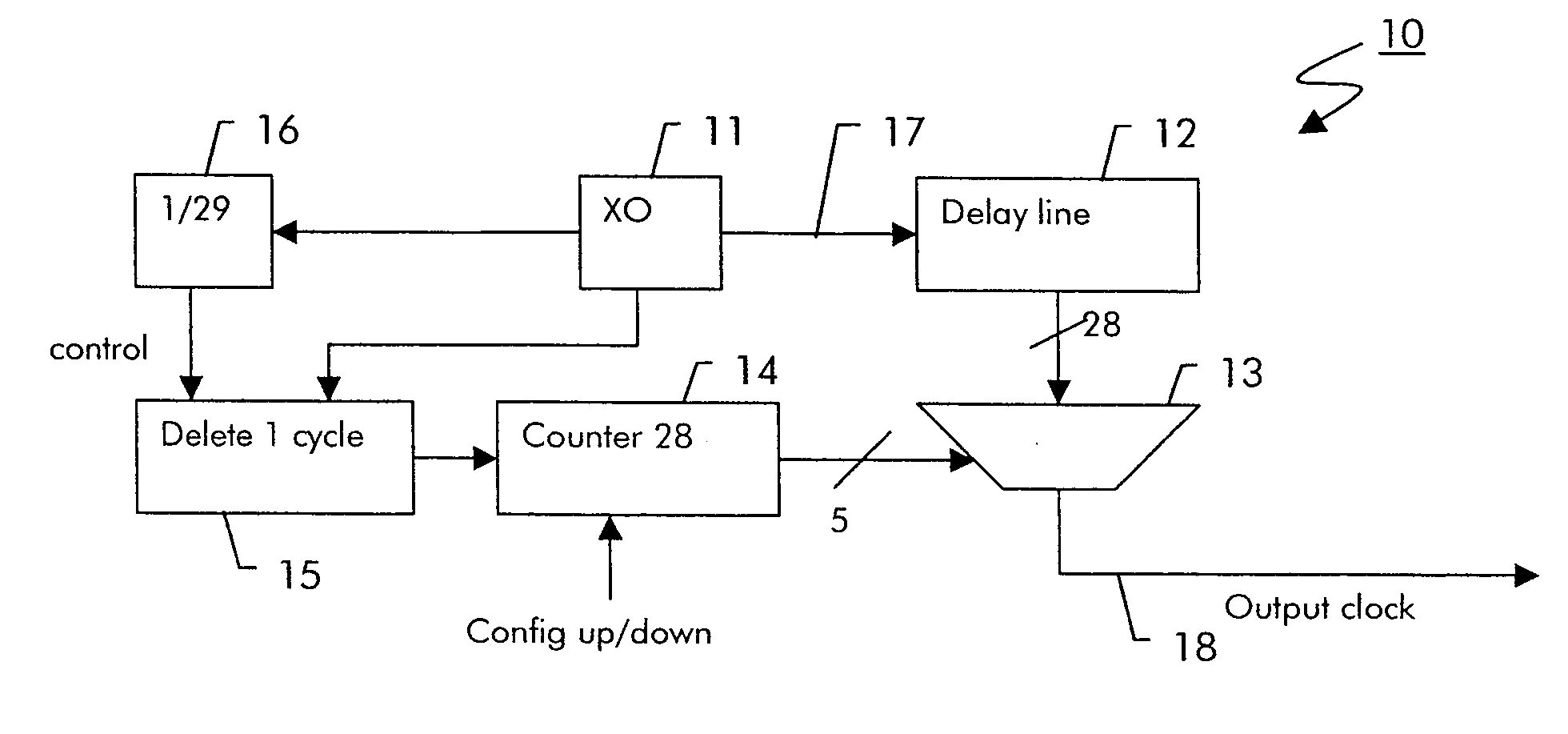
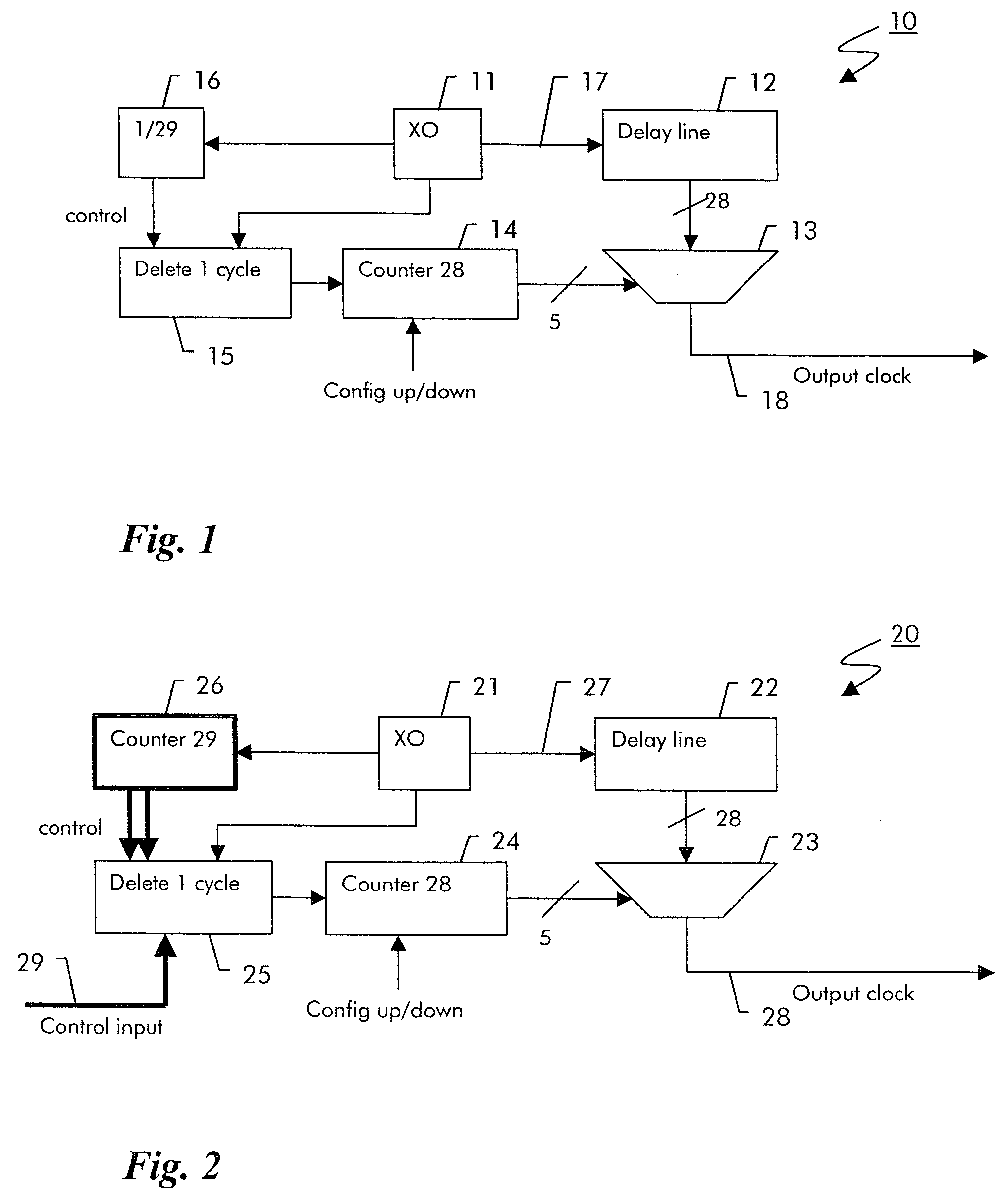
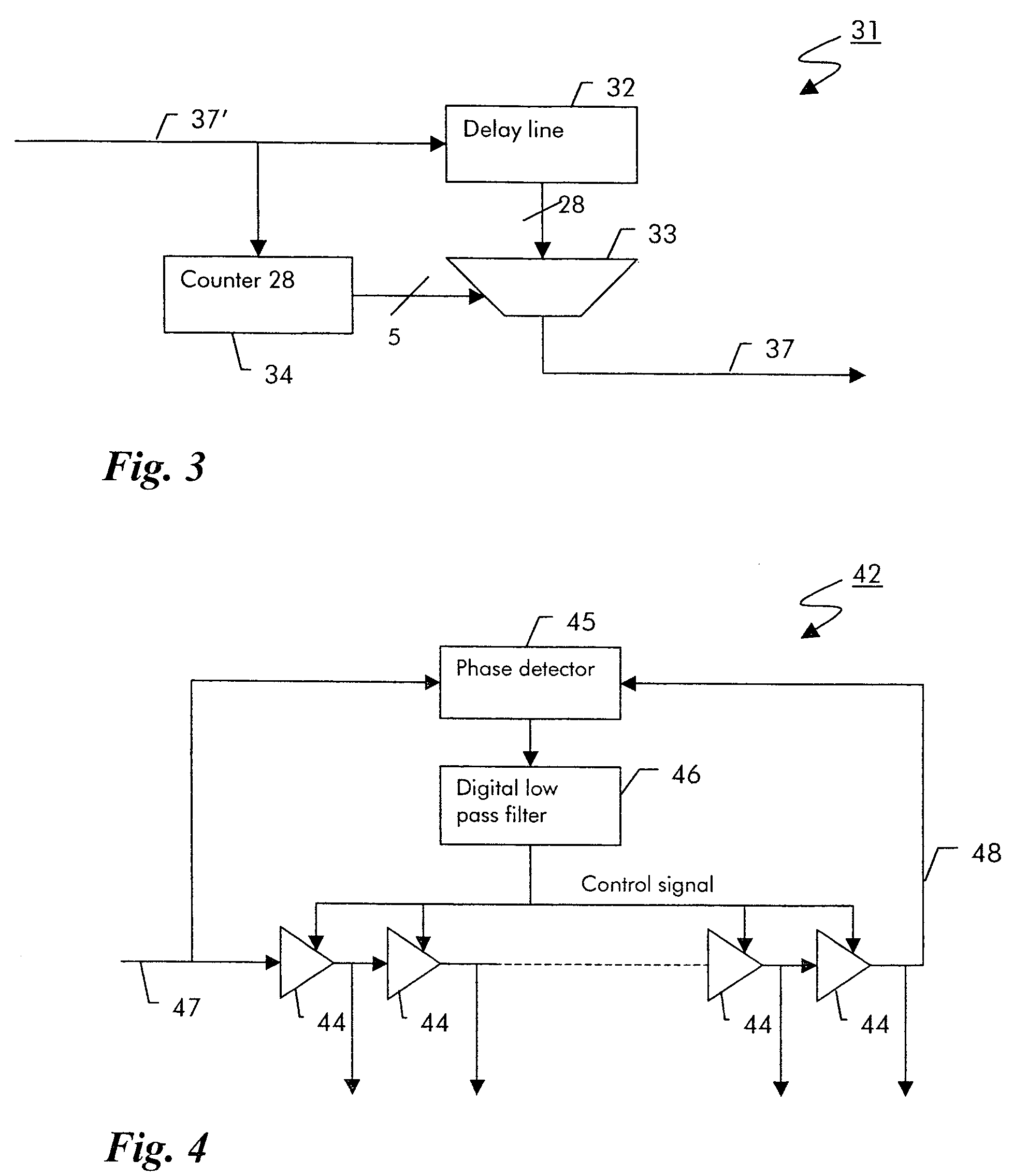
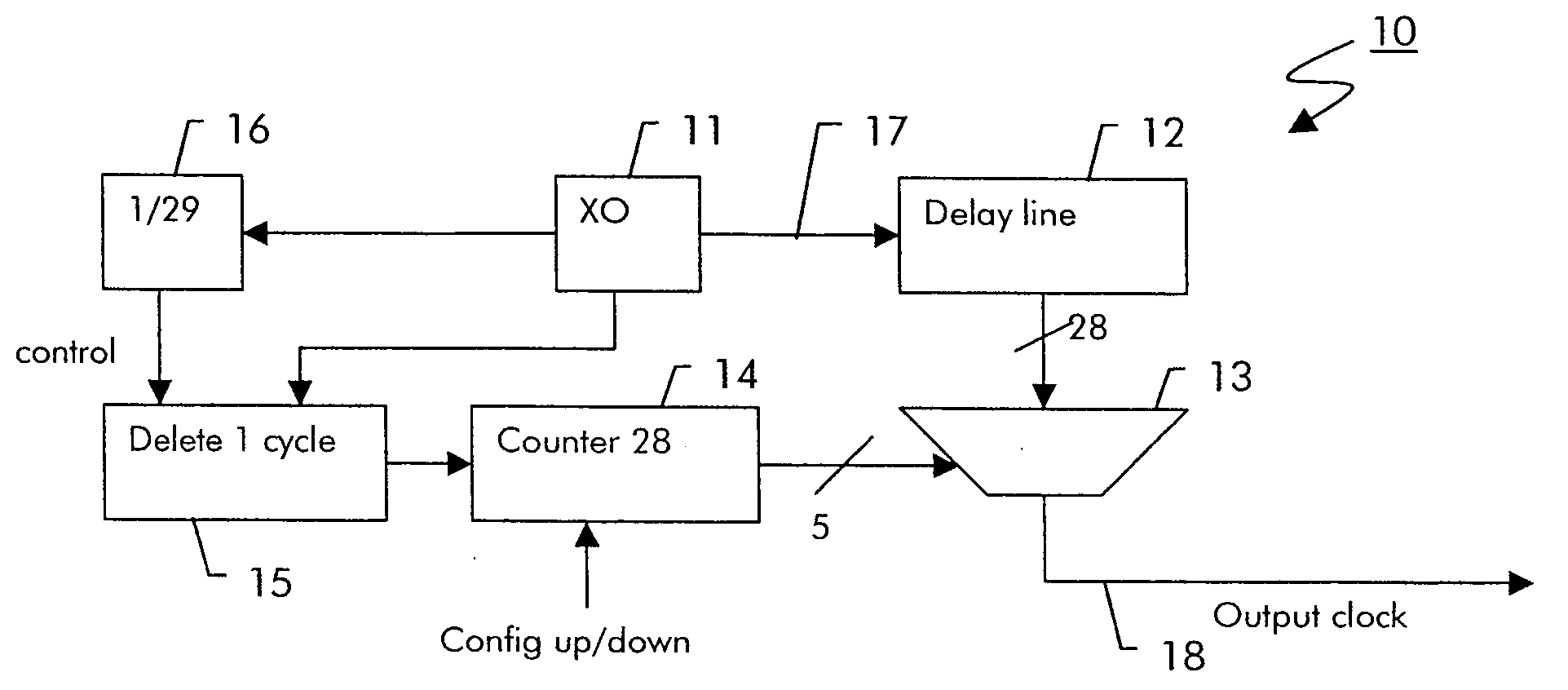
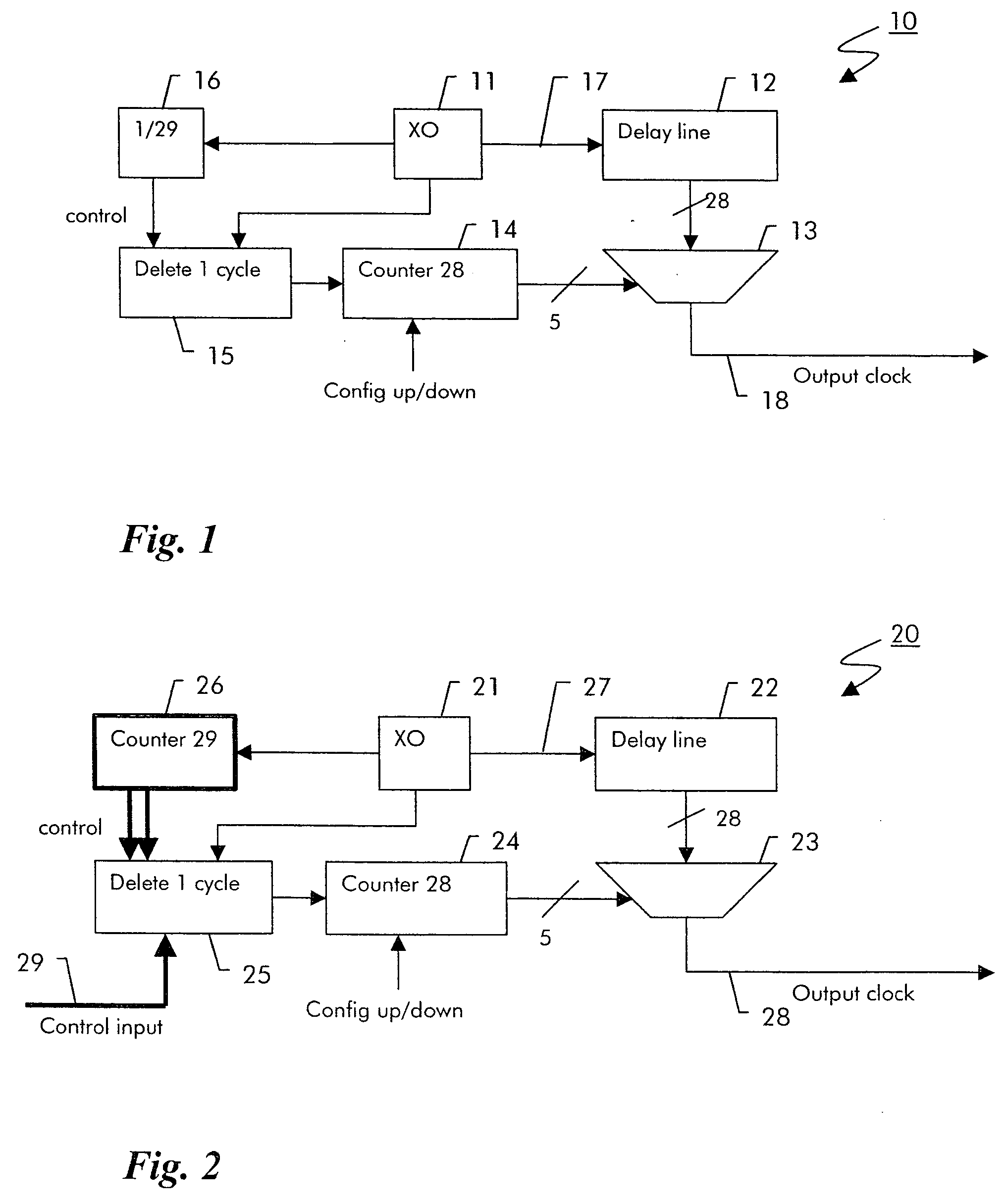
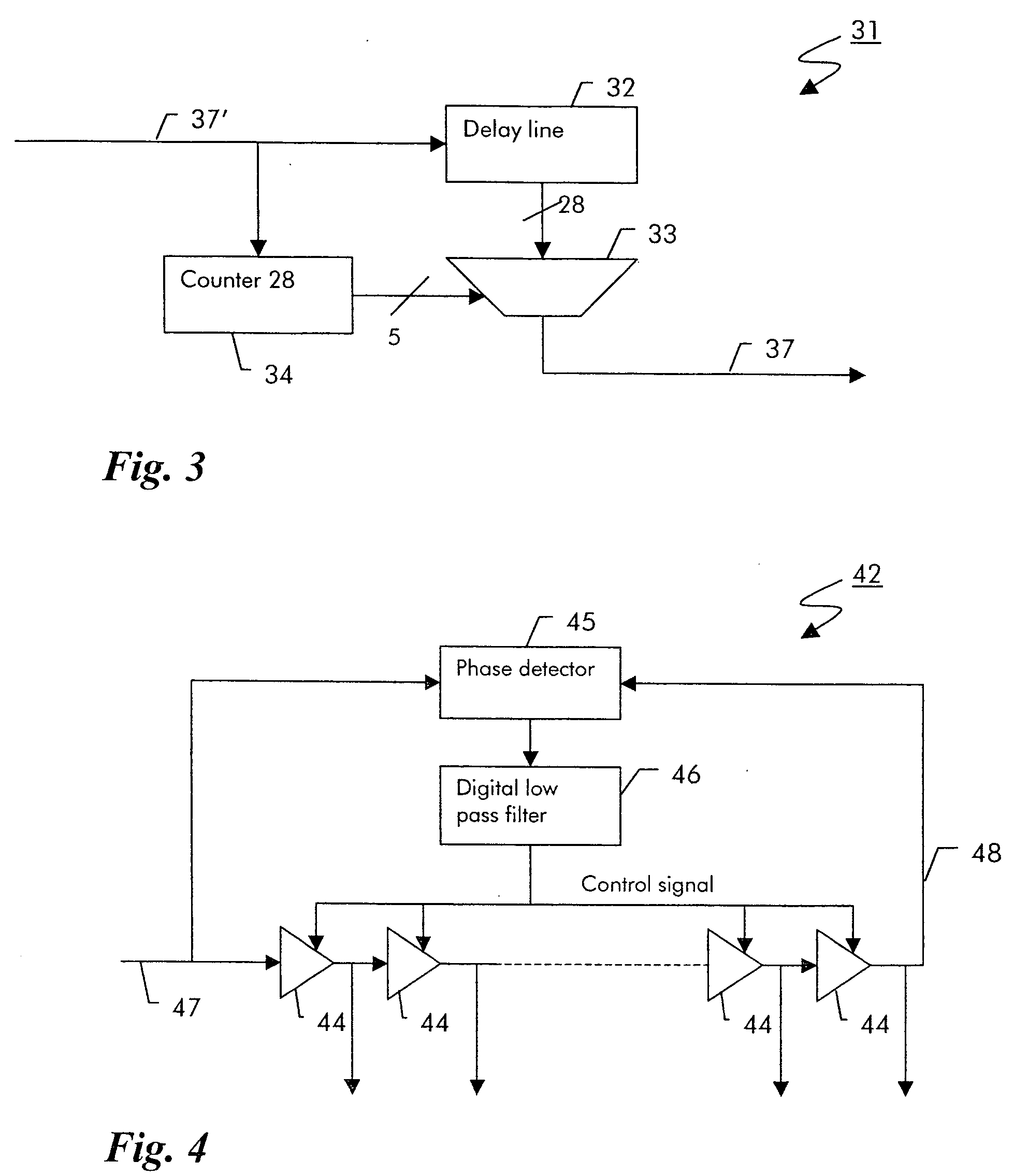
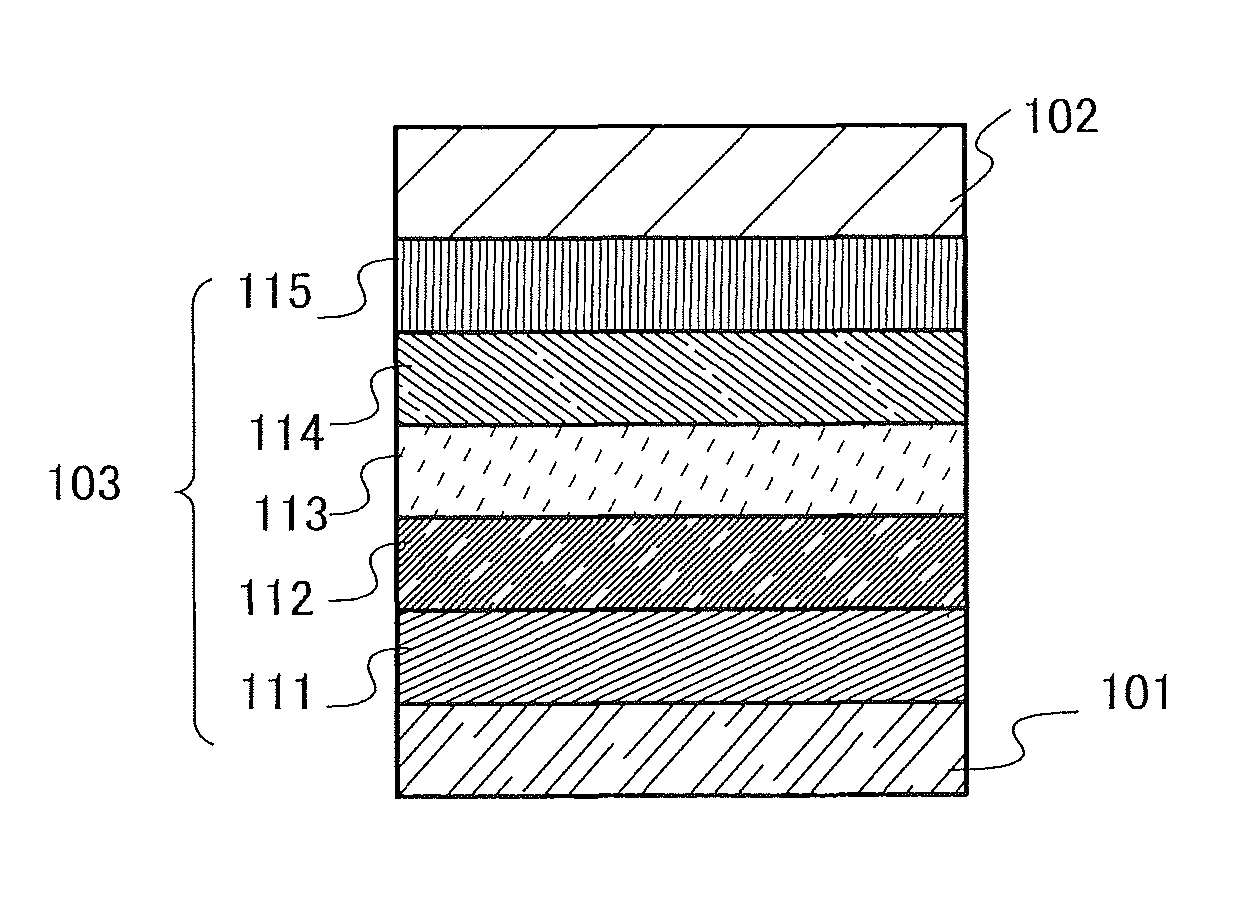
Digital clock filter circuit for a gapped clock of a non-isochronous data signal having a selected one of at least two nominal data rates
InactiveUS7702946B2Reduce areaSimple configurationPulse automatic controlError detection/correctionMultiplexerDigital clock
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Digital clock filter
InactiveUS20060140222A1Reduce areaSimple configurationPulse automatic controlError detection/correctionMultiplexerDigital clock
A clock filter circuit (20), which serves for filtering the clock of non-isochronous data signals having a selected one of at least two nominal data rates, has an auxiliary clock source (21) that generates an auxiliary clock signal (27) with a pulse repetition rate which is in the range between the at least two predetermined data rates, a delay line (22).connected to the auxiliary clock source (21) for creating a set of mutually delayed copies of the auxiliary clock signal and a multiplexer (23) that switches in a cyclic order between the delayed copies according to predetermined rules, which depend on the selected data rate to generate a filtered clock signal (28). A control circuit determines whether the rate of the filtered clock (28) signal must be increased or decreased as compared to said data signal and controls the multiplexer (23) to delay or advance the cyclical switching accordingly.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Organic compound, light-emitting element, display module, lighting module, light-emitting device, display device, electronic device, and lighting device
ActiveUS9929352B2Improve heat resistanceImprove reliabilityOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesDisplay deviceOrganic compound
An object is to provide an organic compound having high heat resistance and a light-emitting element, a light-emitting device, an electronic device, and a display device each having high reliability. Provided are an organic compound having a 2,2′-(pyridine-2,6-diyl)bipyrimidine skeleton in which the 2-positions of pyrimidine skeletons are bonded to the 2- and 6-positions of a pyridine skeleton, and having a structure in which at least one aryl group having a fused structure with 10 to 16 carbon atoms is bonded to the 2,2′-(pyridine-2,6-diyl)bipyrimidine skeleton, and a light-emitting element, a light-emitting device, an electronic device, and a display device each containing the organic compound.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
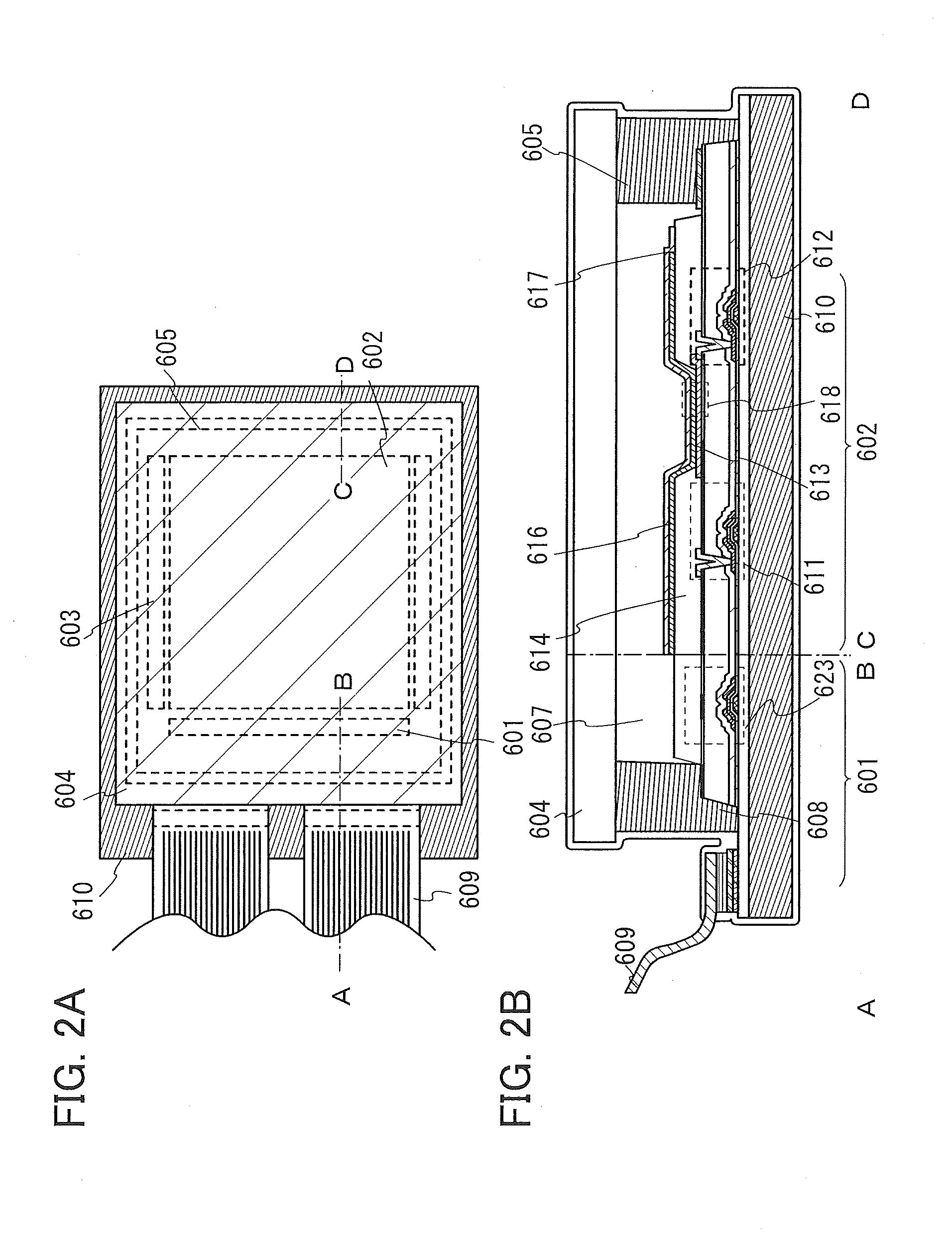
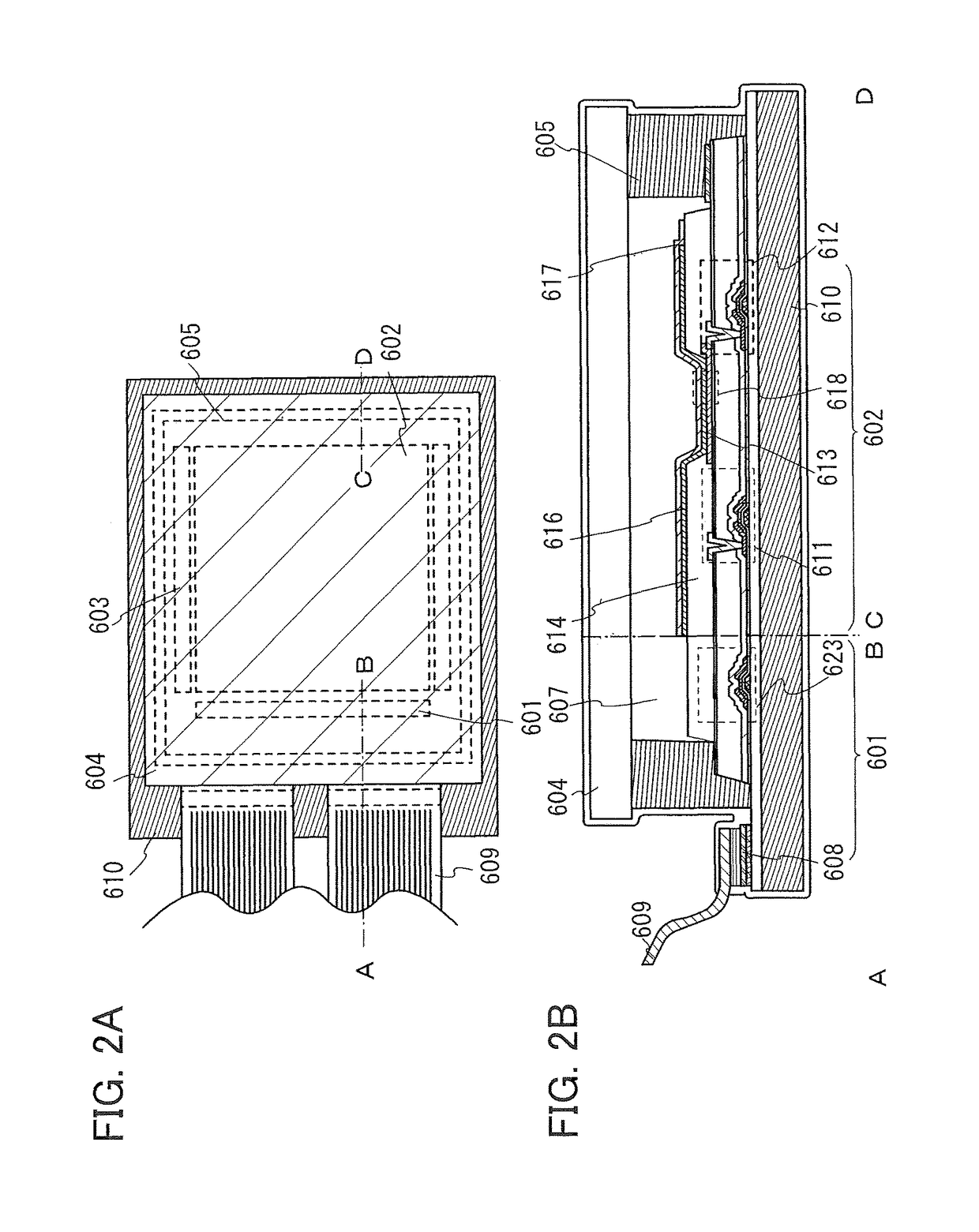
Proximity sensor and mobile device using the same
ActiveUS10107911B1High sensitivityLess crosstalkRadiation pyrometryPrinted circuit aspectsProximity sensorEngineering
A proximity sensor and a mobile device using the same are provided. The proximity sensor includes a circuit board, an emitter package, a receiver package, a plastic casing and a lens. The emitter package is disposed on the circuit board and includes an emitter and an emitter housing. The receiver package is disposed on the circuit board and includes a receiver and a receiver housing. The plastic casing covers the emitter package and the receiver package. The plastic casing includes a first opening corresponding to the emitter package and a second opening corresponding to the receiver package. The first opening has a first geometric centerline and the second opening has a second geometric centerline. The height of the emitter package is smaller than that of the receiver package, and the emitter is disposed between the first geometric centerline and the second geometric centerline.
Owner:LITE ON SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Organic compound, light-emitting element, display module, lighting module, light-emitting device, display device, electronic device, and lighting device
ActiveUS10476009B2Improve heat resistanceLess crosstalkOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesElectron injectionDisplay device
A novel organic compound that can be used as an electron-injection material or an electron-transport material of a light-emitting element is provided. An organic compound with which a display device having less crosstalk can be obtained is provided. A light-emitting device, a display device, and an electronic device each having less crosstalk are provided. An organic compound including two or three benzo[h]quinazoline rings is provided. In the organic compound, two or three benzo[h]quinazoline rings are preferably included in the substituent including an aromatic ring or a heteroaromatic ring and having 3 to 30 carbon atoms. When two or three benzo[h]quinazoline rings are included in a substituent particularly including a heteroaromatic ring and having 3 to 30 carbon atoms, a high electron-transport property can be obtained.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
A kind of multi-core single-mode optical fiber and its manufacturing method
ActiveCN104678484BRaman amplification is possibleReduce optical powerOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingGlass fibre drawing apparatusUltra high speedCommunications system
Owner:YANGTZE OPTICAL FIBRE & CABLE CO LTD
High extinction ratio and low crosstalk compact optical switches
InactiveUS7486443B1Low costExtinction ratioMultiplex system selection arrangementsPolarising elementsLight beamEngineering
An improved optical switch utilizes one polarization modulator, with the beam components traversing it twice. Because of the twice traverse, the extinction ratio of the switch is doubled without the addition of another polarization modulator, thus avoiding the costs of additional optical components. With no additional components, the switch is more compact than conventional switches with the same extinction ratio. Fewer components also result in more thermal and long-term stability and less crosstalk.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Organic compound, light-emitting element, display module, lighting module, light-emitting device, display device, electronic device, and lighting device
ActiveUS10333080B2Improve heat resistanceLess crosstalkOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesElectron injectionDisplay device
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
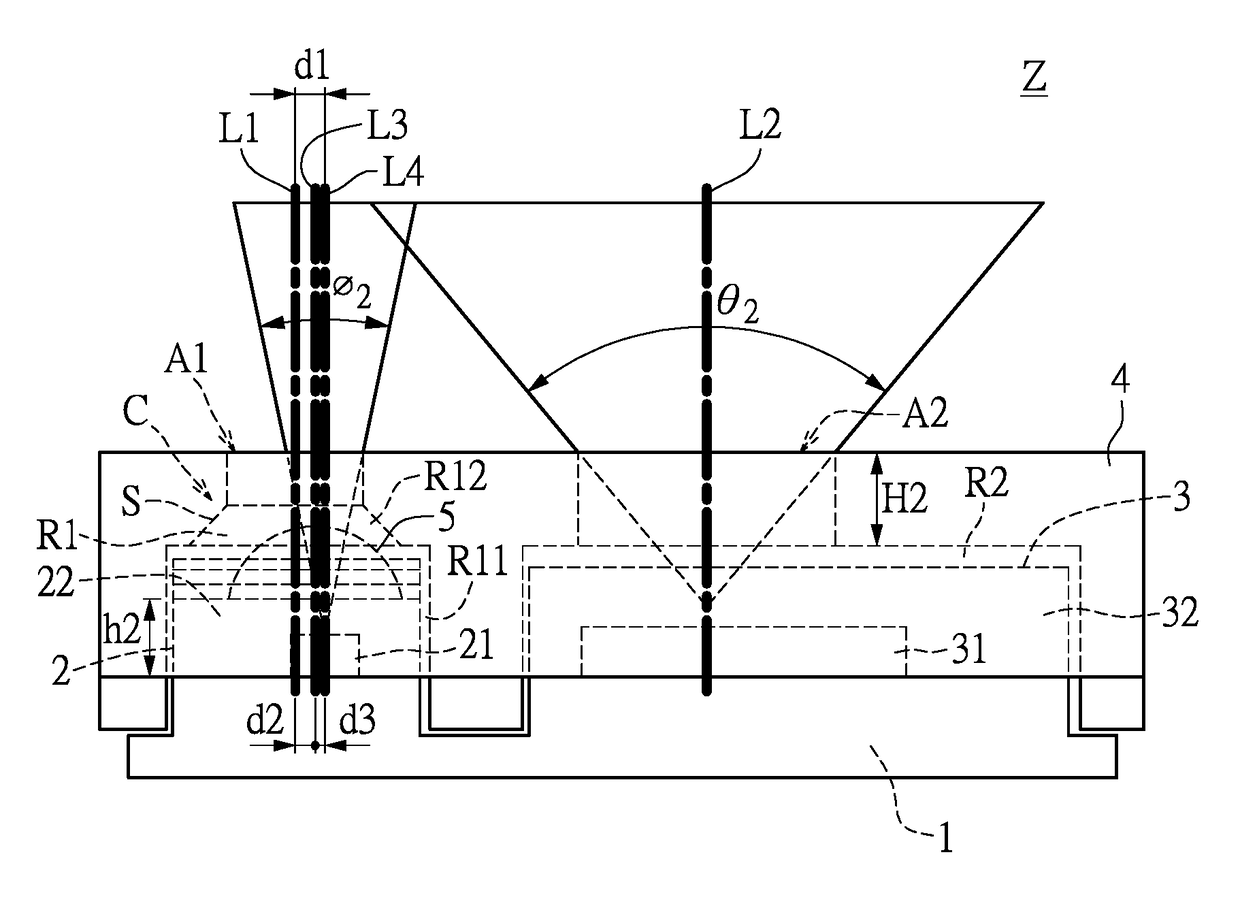
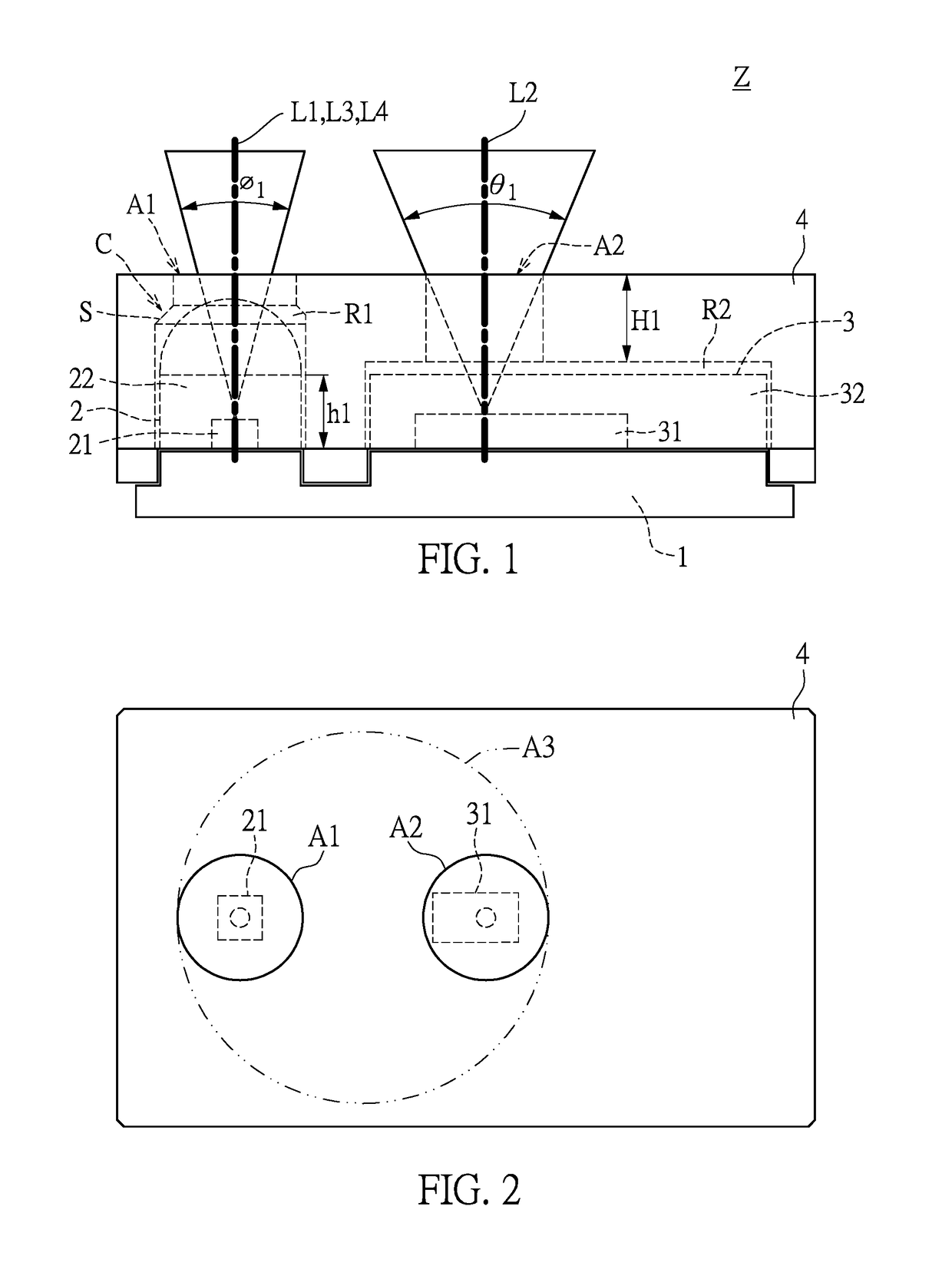
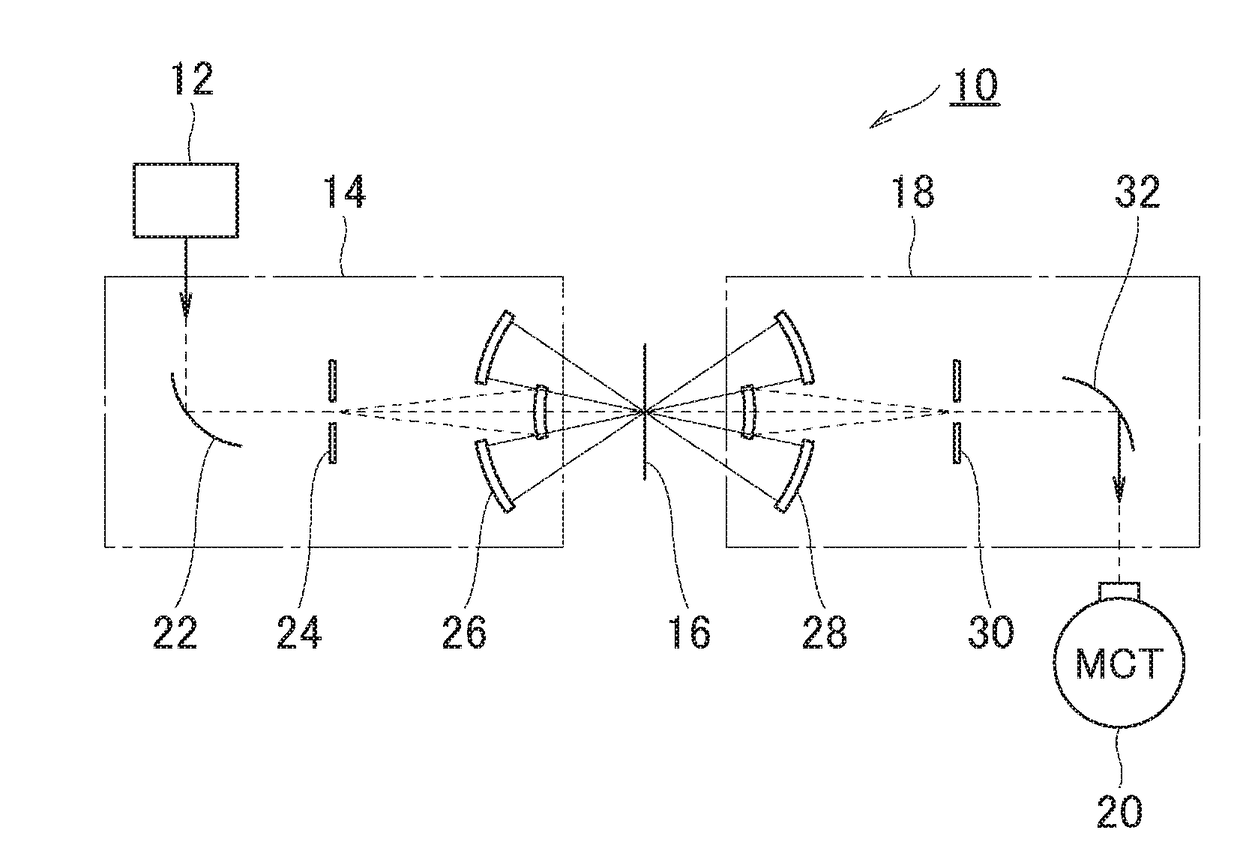
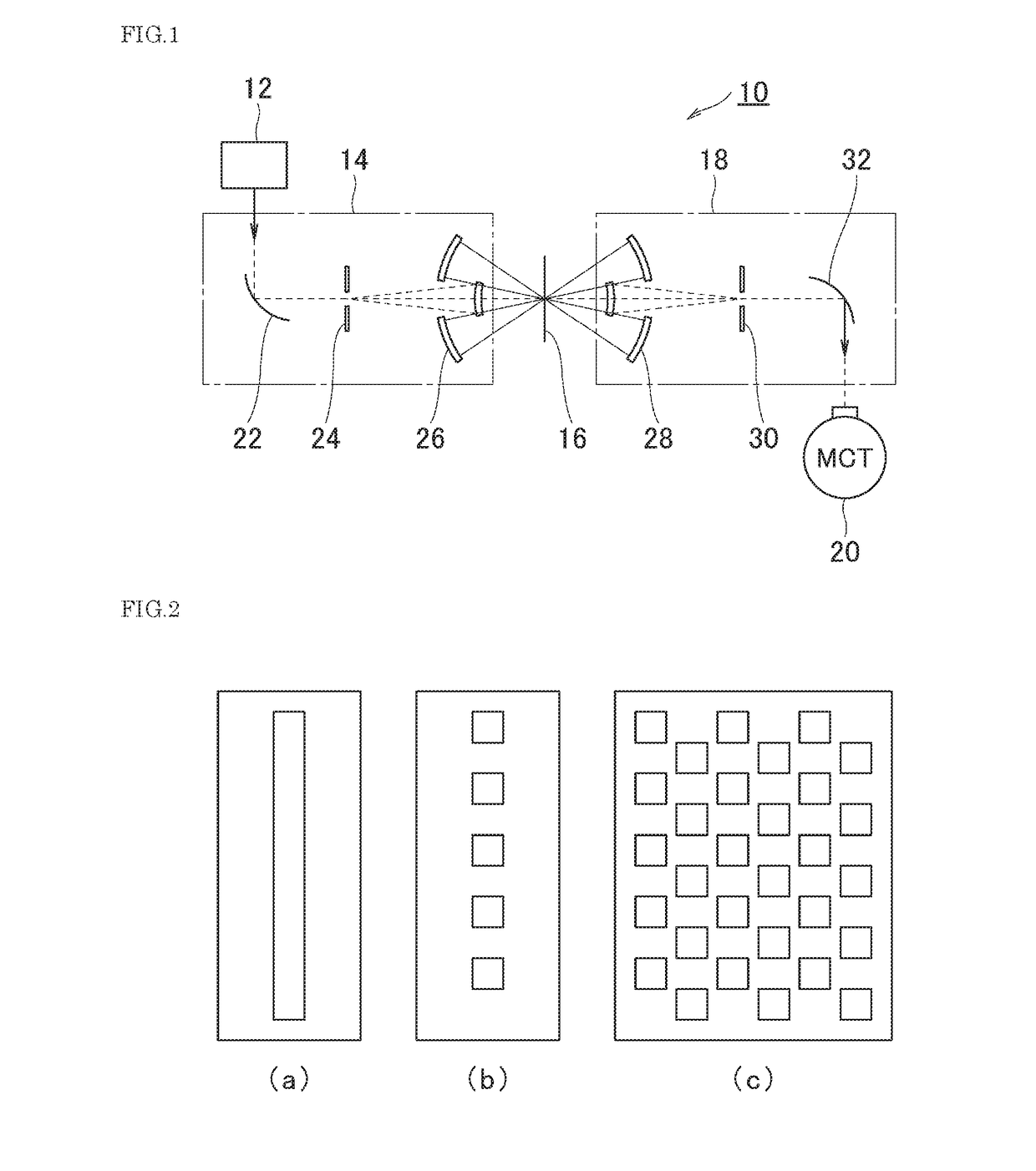
Infrared microscope
ActiveUS20180307018A1Good accuracyLess crosstalkMicroscopesColor/spectral properties measurementsInfraredMicroscope
The problem to be solved by the present invention is to provide an infrared microscope with good measuring accuracy and less crosstalk.The infrared microscope 10 comprises a light source 12, an irradiating unit 14 for irradiating the infrared light from the light source to a sample 16, a focusing unit 18 for focusing the infrared light transmitted through or reflected by the sample 16, and a detector 20 for detecting the focused infrared light. The irradiating unit 14 comprises a first aperture 24, and the first aperture is disposed at a position where the infrared light from the light source passes therethrough. The focusing unit 18 comprises a second aperture 30, and the second aperture is disposed at an imaging position of the infrared light at the first aperture 24. The first aperture has a plurality of holes, and the holes are disposed at intervals corresponding to the arrangement of the light-receiving elements provided in the detector 20 to detect the infrared light as a detecting light. The second aperture 30 has holes that have the same size and arrangement as the first aperture 24.
Owner:JASCO CORP
Liquid crystal display device
A liquid crystal display device is constituted such that sub-pixels are disposed in an array form in a first direction and a second direction orthogonal to each other, a plurality of gate lines are disposed in the second direction, an optical element for distributing the light to the second direction is disposed on the liquid crystal display device, liquid crystal molecules of the liquid crystal display device are controlled by an electric field almost in parallel to the surface of the liquid crystal display device, and a data line is disposed to obliquely divide the sub-pixels at a position different from the boundary between the sub-pixels neighboring in the second direction, where the data line can have a small angle with respect to the second direction, and the numerical aperture is not deteriorated greatly even when the lengths of apertures of the sub-pixels in the first direction are constant.
Owner:NEC LCD TECH CORP
High extinction ratio and low crosstalk compact optical switches
InactiveUS8014067B2Low costExtinction ratioMultiplex system selection arrangementsPolarising elementsLight beamLight extinction
An improved optical switch utilizes one polarization modulator, with the beam components traversing it twice. Because of the twice traverse, the extinction ratio of the switch is doubled without the addition of another polarization modulator, thus avoiding the costs of additional optical components. With no additional components, the switch is more compact than conventional switches with the same extinction ratio. Fewer components also result in more thermal and long-term stability and less crosstalk.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
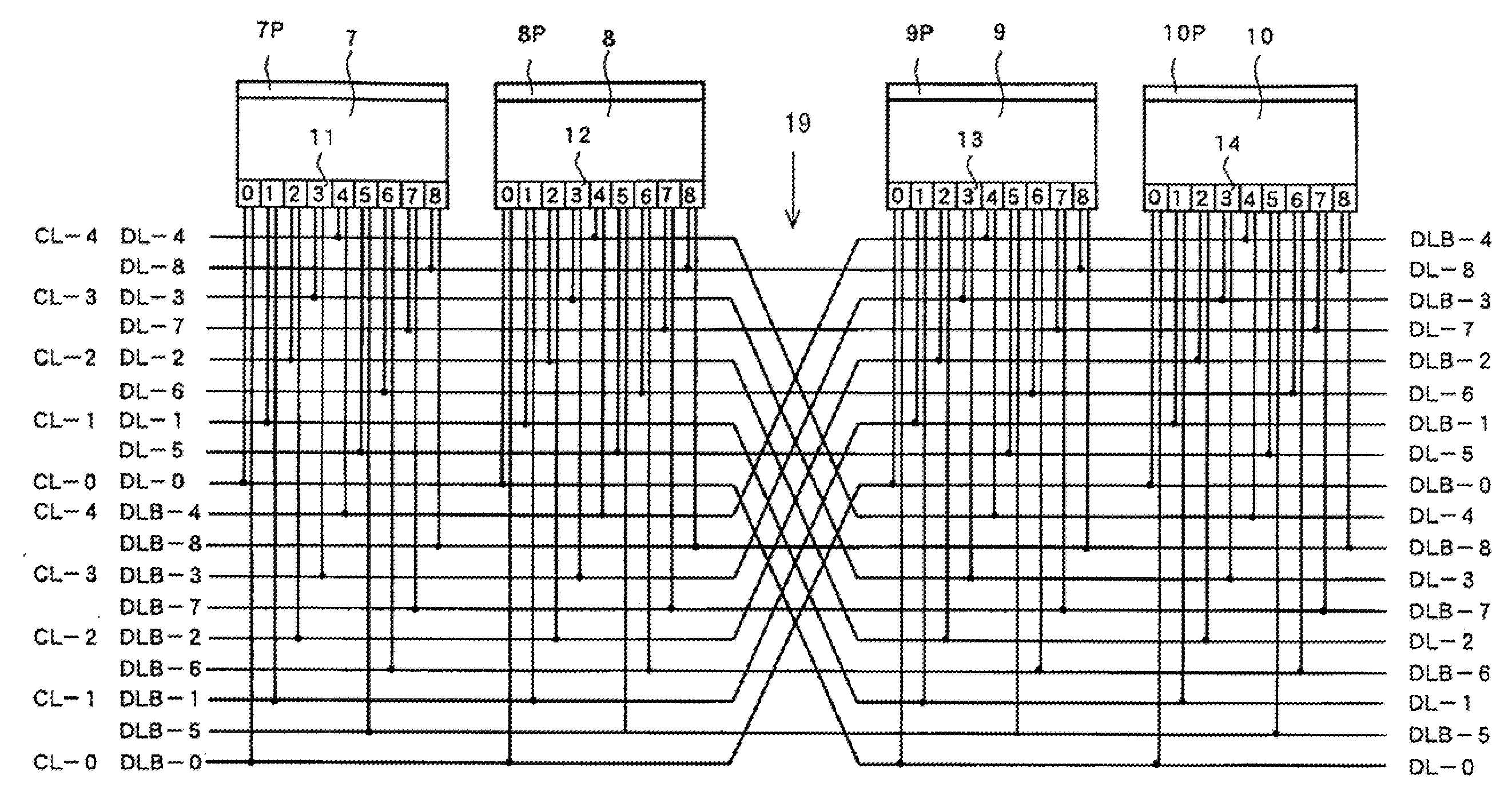
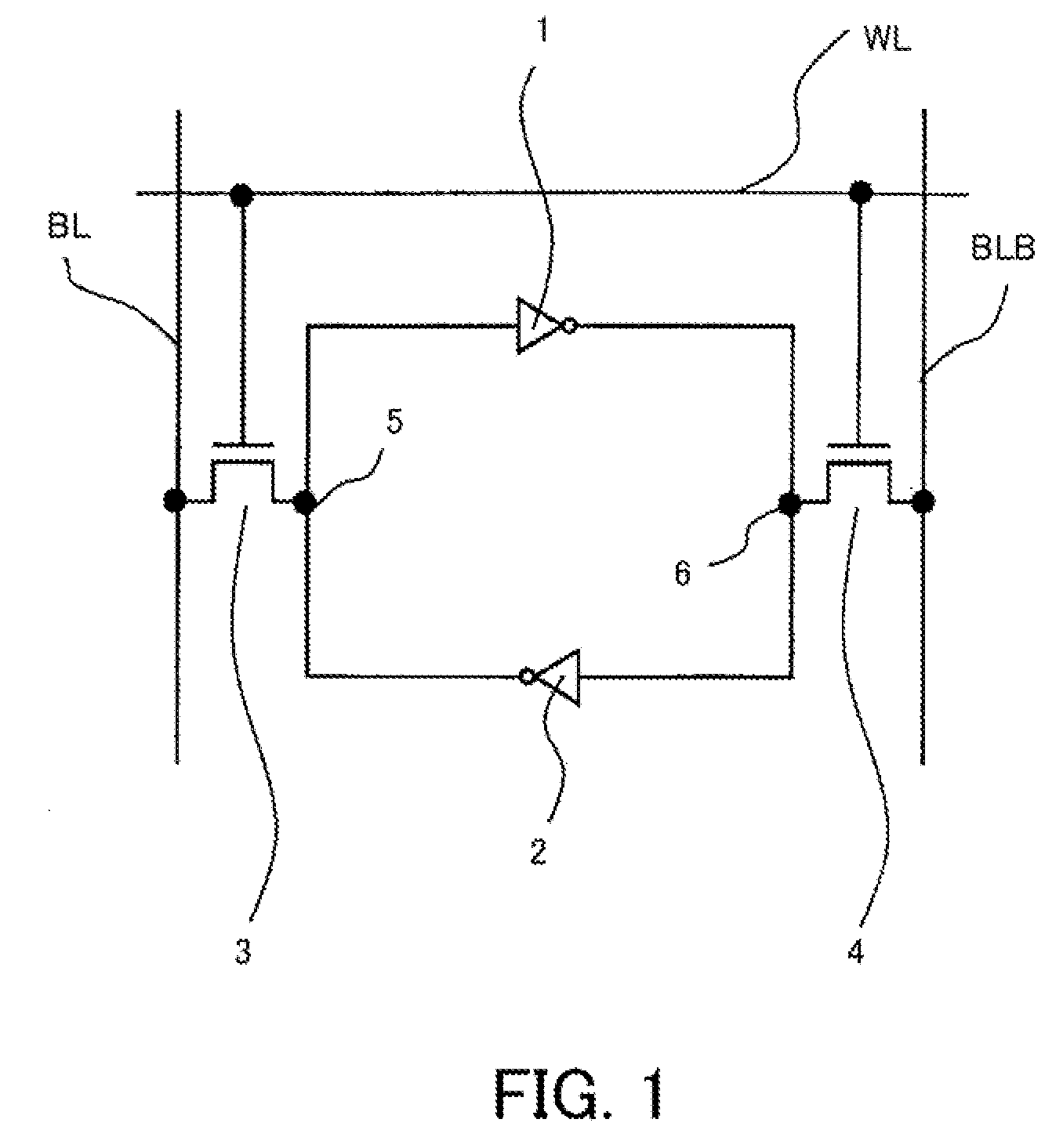
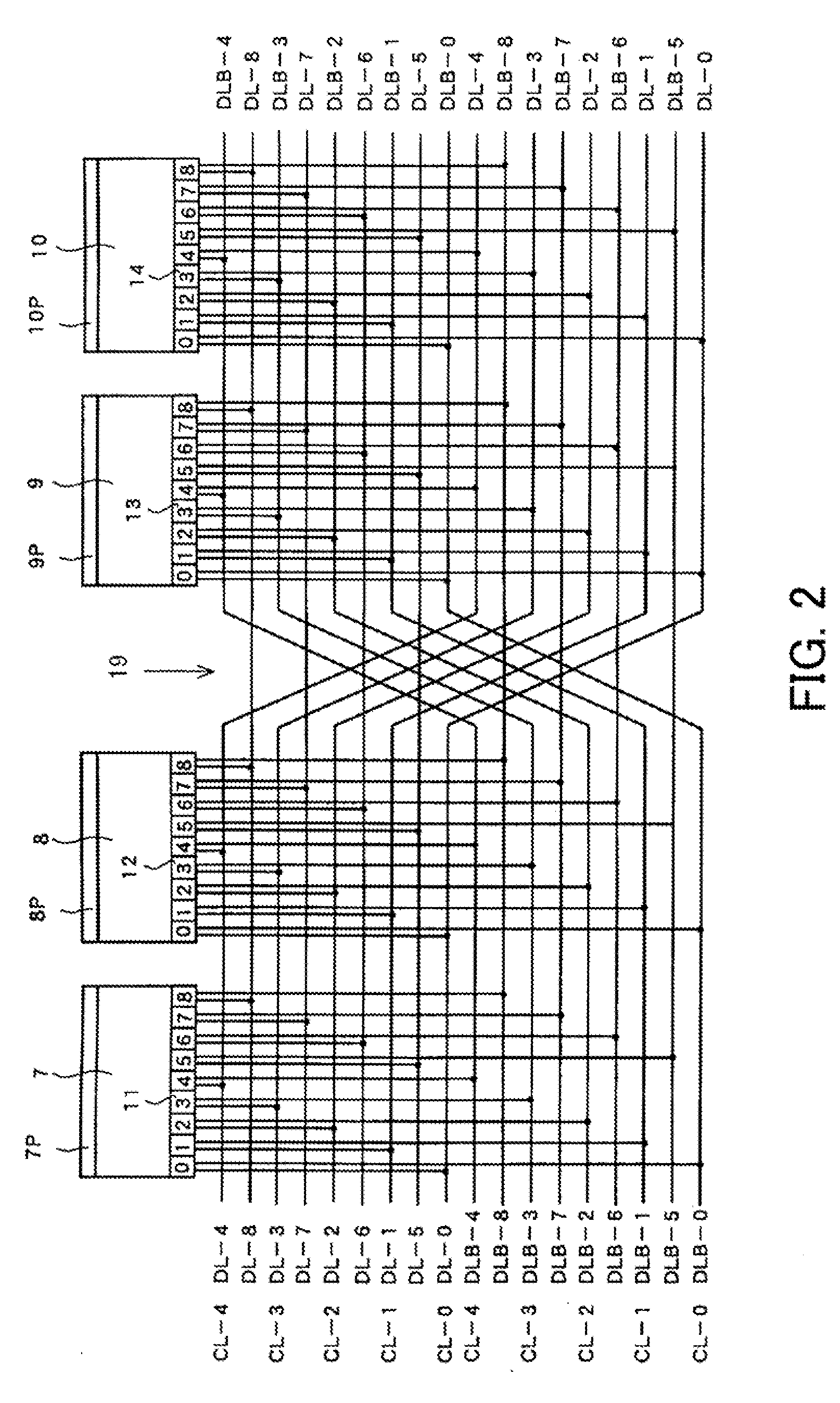
Semiconductor memory device
According to some preferred embodiments of the present invention, a semiconductor memory device includes an array of memory cells and plural pairs of complementary bit lines, each pair of the complementary bit lines being connected to the memory cells arranged in the same column. The array is divided into plural memory blocks each including plural memory cells arranged in the same column. The corresponding complementary bit lines of the plural memory blocks are connected to corresponding common complementary data lines, respectively. Some pairs of the complementary data lines are crossed at least one time so that the complementary data lines of each pair of the some pairs of the complementary data lines are reversed in position and that the crossed data line and a non-cross data line are arranged alternately whereby crosstalk to be generated between adjacent data lines are reduced.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com