Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1257 results about "Electron injection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electron injection. The emission of electrons from one solid into another. The process of injecting a beam of electrons with an electron gun into the vacuum chamber of a mass spectrometer, betatron, or other large electron accelerator.
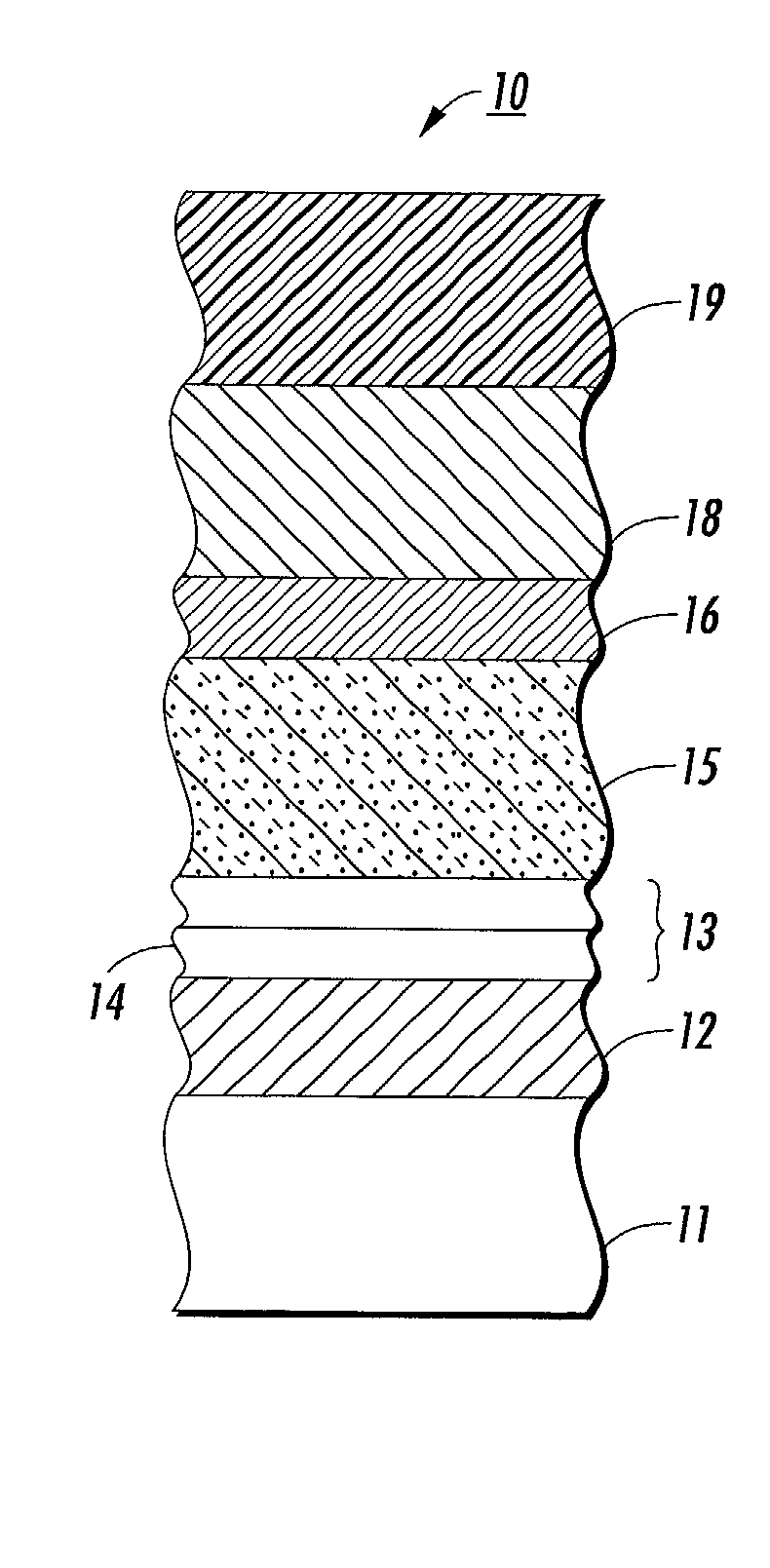
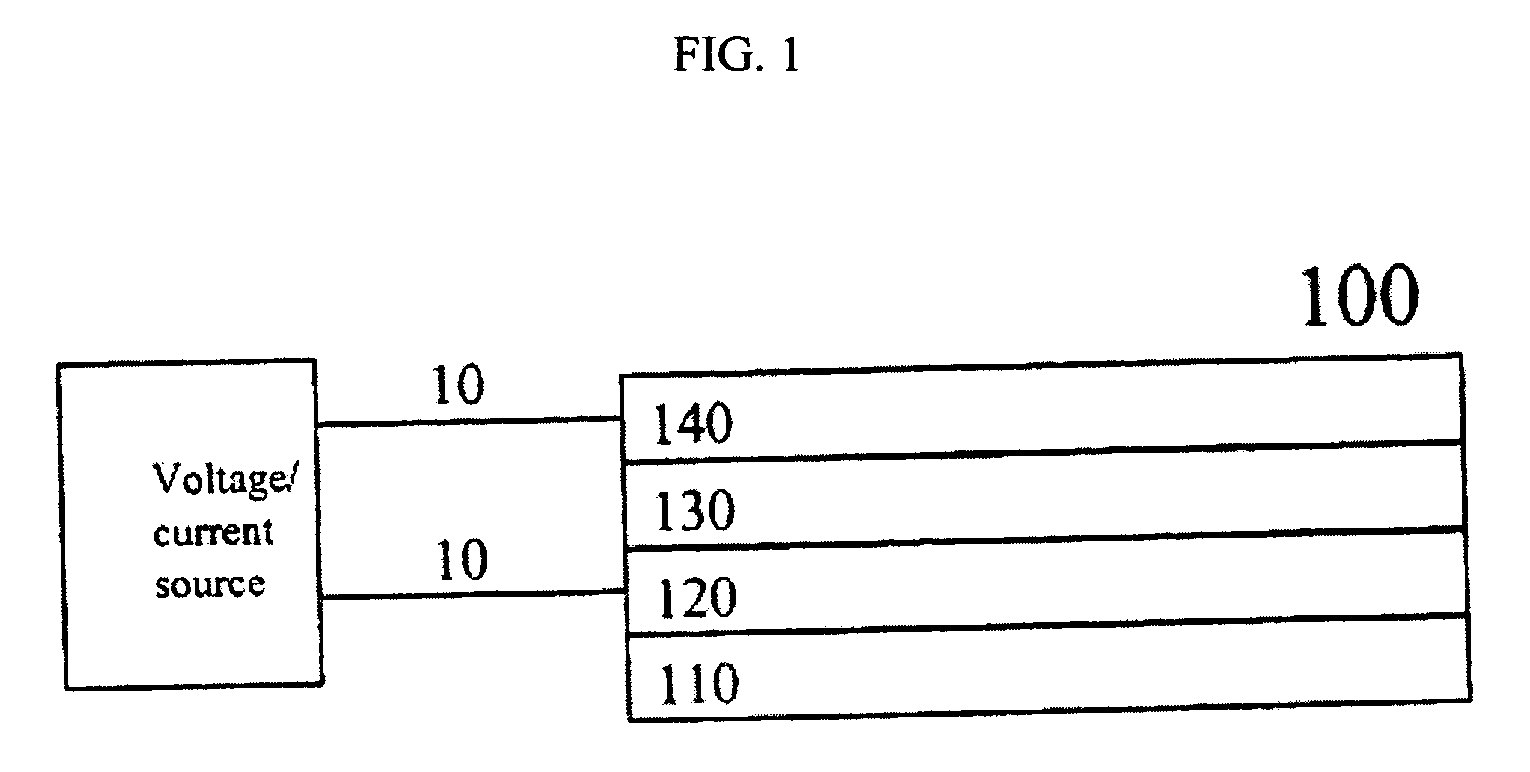
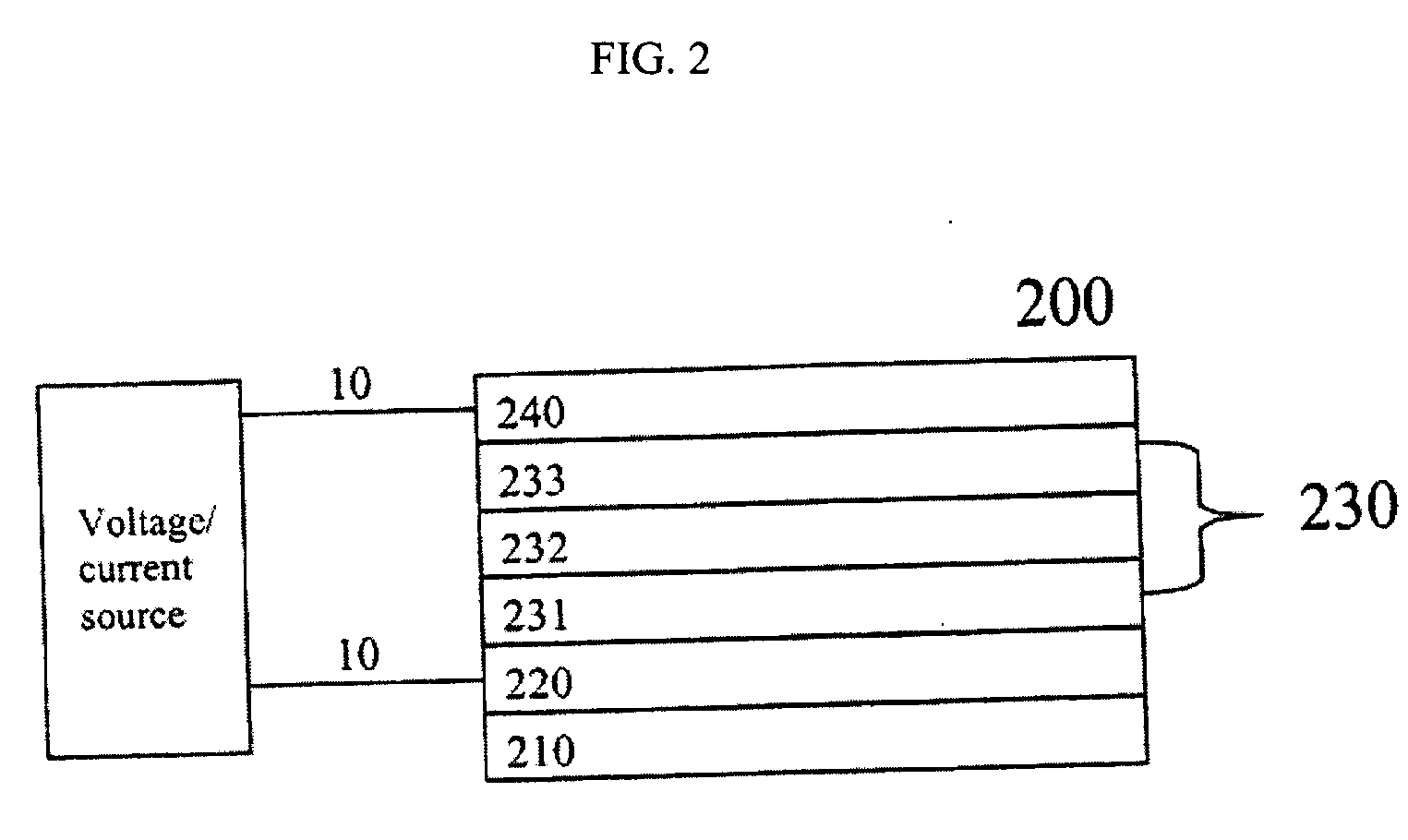
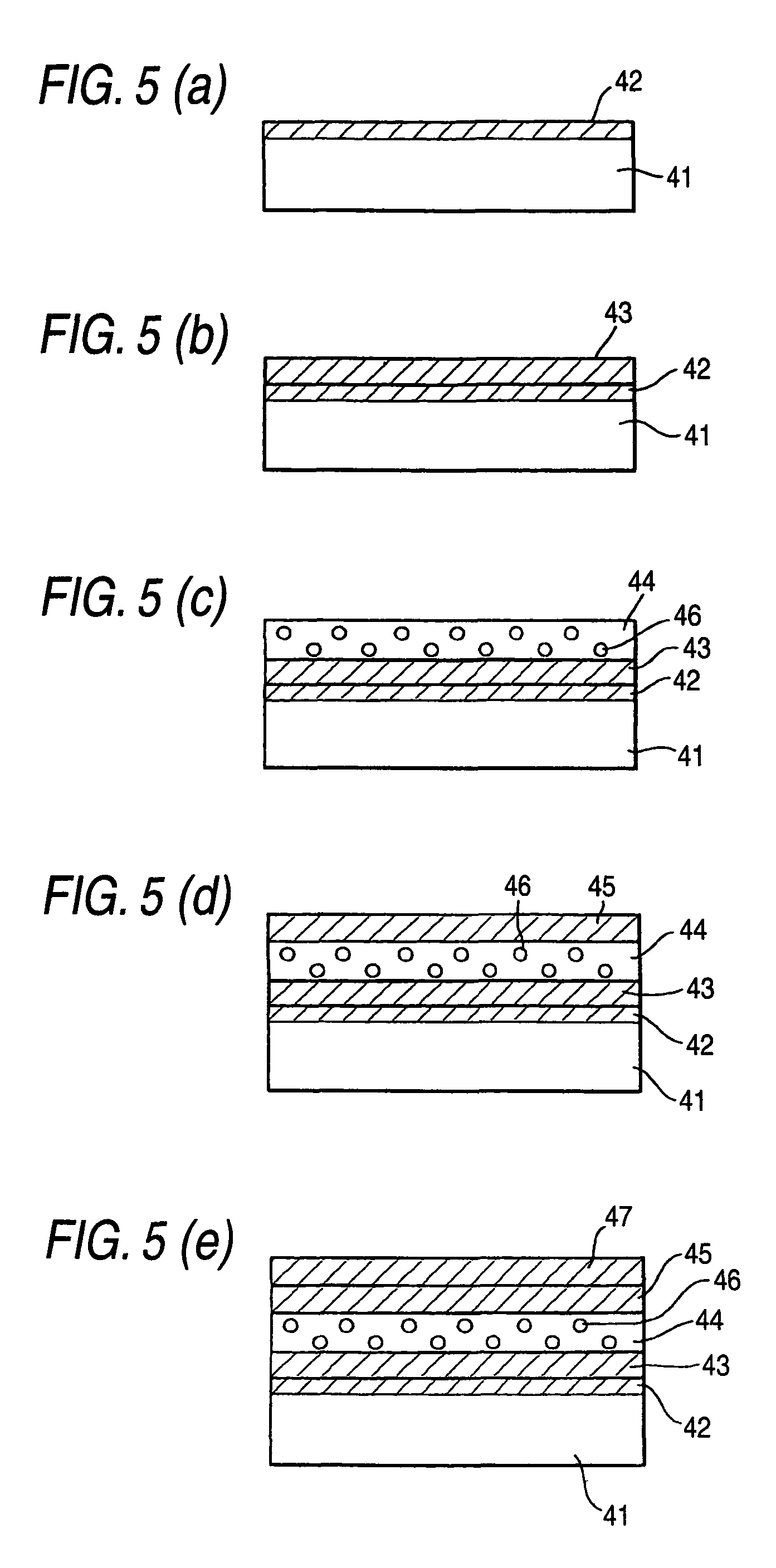
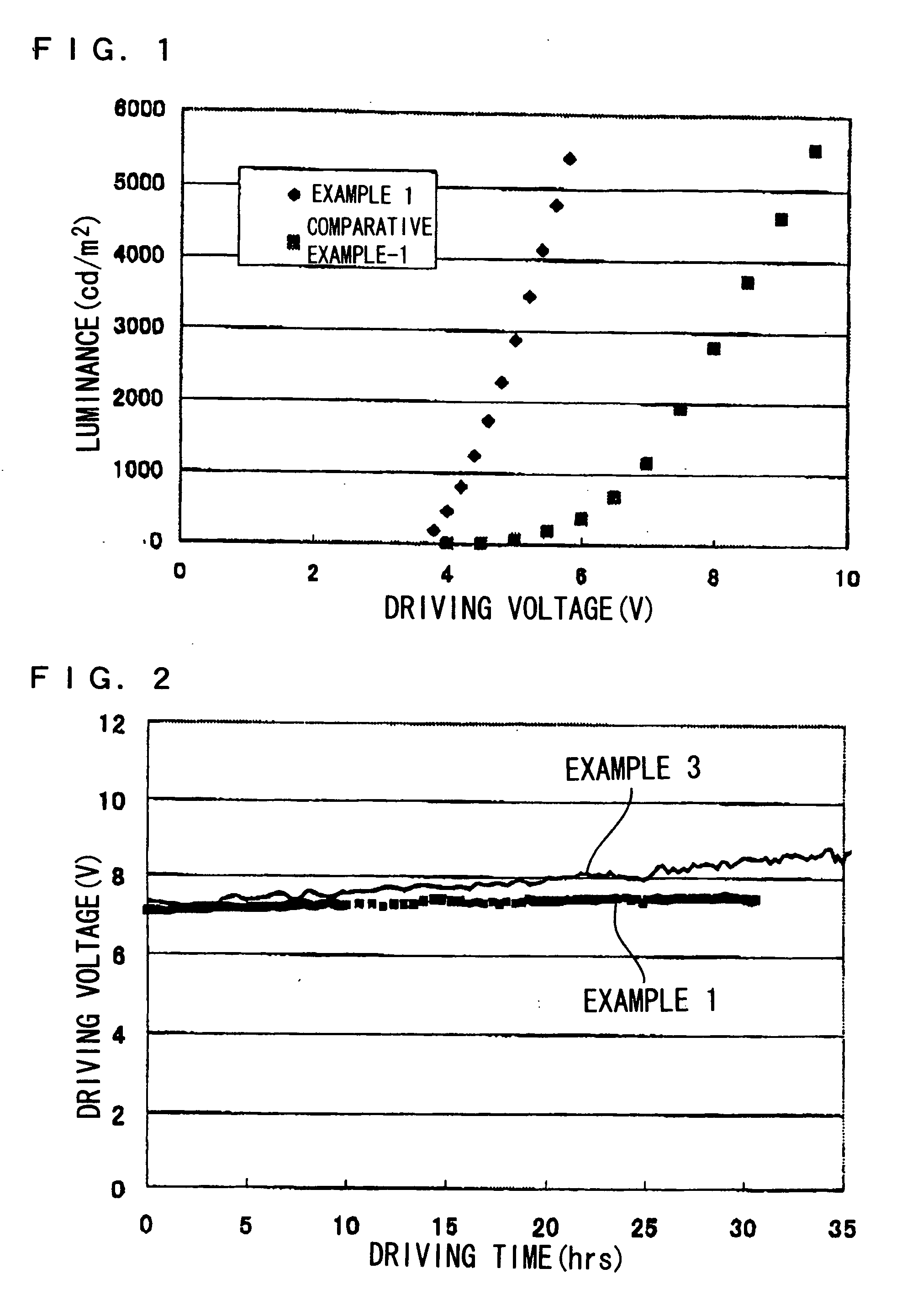
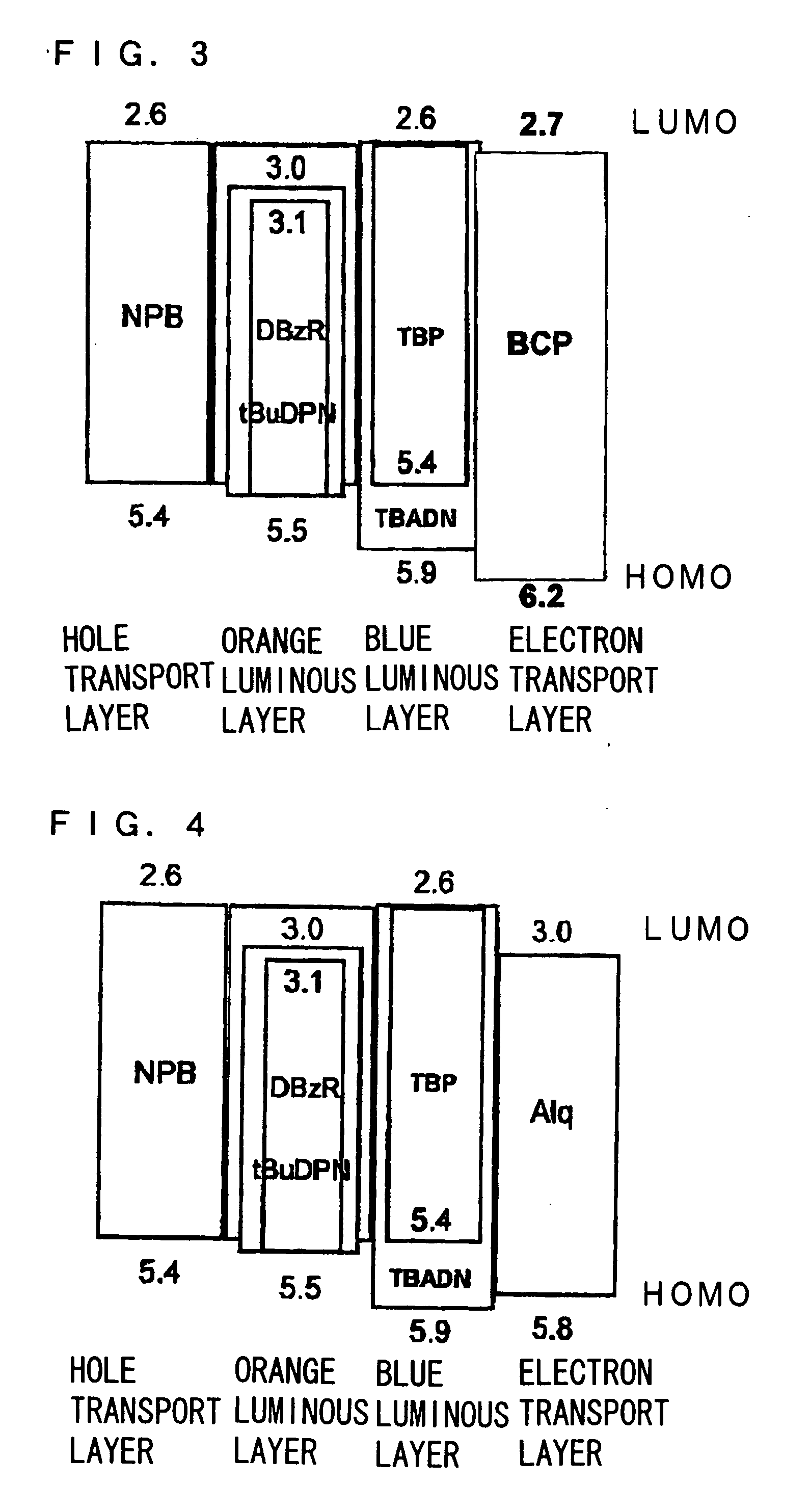
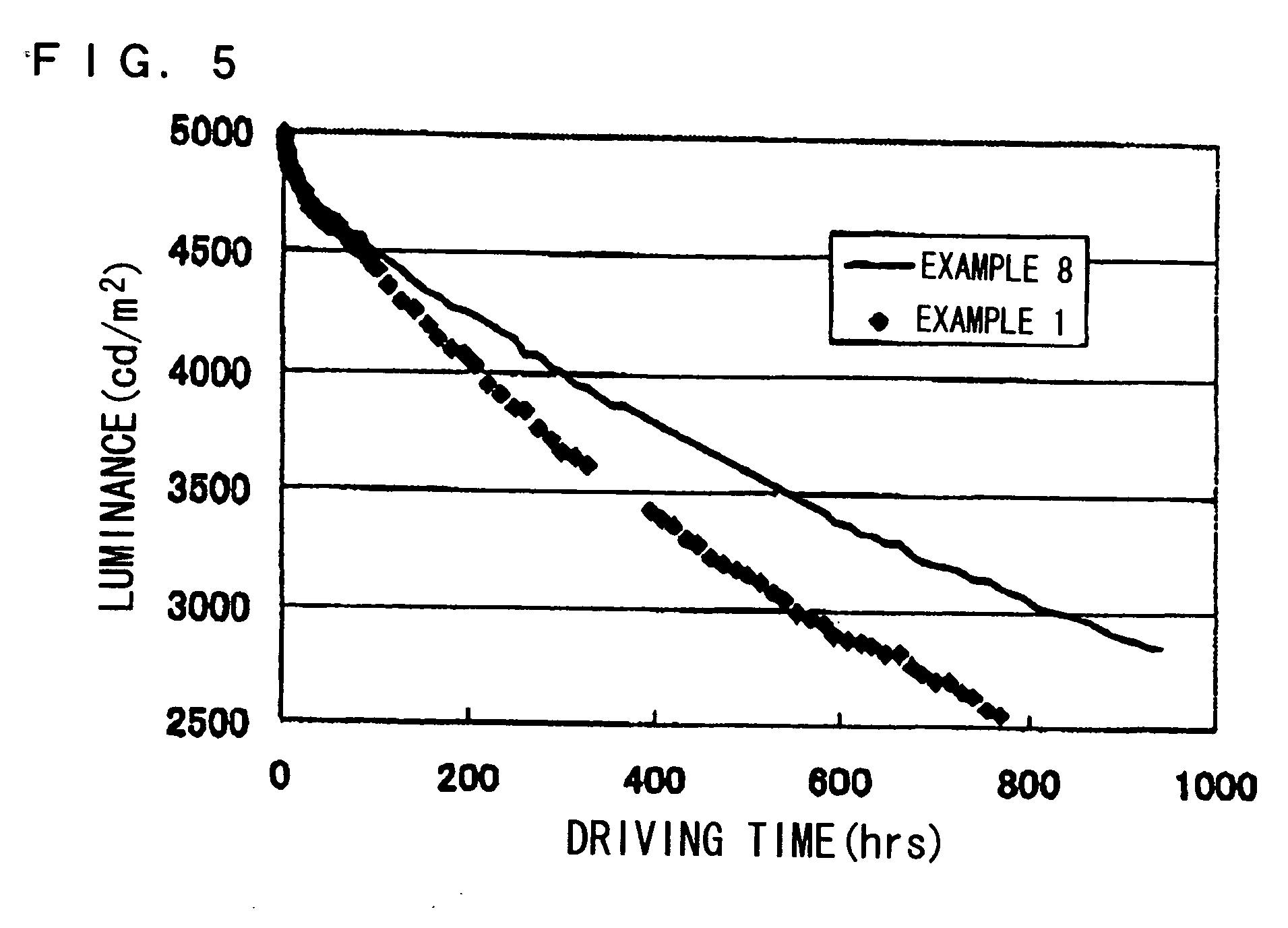
Electron transporting compounds and organic electroluminescent devices using the same
InactiveUS20140284580A1Prolonged lifetime stabilityLow working voltageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectronic transmissionPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
Disclosed is a novel compound of Formula 1 and an organic electroluminescent device using the same. In Formula 1, X and Y independently represents a hydrogen, an aromatic or a hetero aromatic hydrocarbon having C5 to C10 carbons; X and Y may be the same or different; Ar1 to Ar2 each represent a hydrogen, an unsubstituted or substituted aromatic hydrocarbon having C4 to C12 carbons, or an unsubstituted or substituted condensed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon having C4 to C12 carbons; Ar1 to Ar2 can form a fused aromatic ring system with the adjacent aromatic hydrocarbons. The compound of Formula 1 is present in the electron injection or a transport material, or an exciton blocking layer in the organic light emitting device, and thereby improving the device stability, lowering the operational voltage.
Owner:E RAY OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
Material for transporting electrons and organic electroluminescent display using the same
InactiveUS6878469B2Improve the display effectImprove efficiencyOrganic chemistryDischarge tube luminescnet screensAnthraceneElectron injection
Novel materials for electron injection / transportation and emitting layers can greatly improve the stability of an organic electroluminescent display. Electroluminescent displays incorporating these materials produce blue light at low voltage levels. These novel organic materials include compounds in which 1 to 2 imidazole functional groups are introduced in the 2 or 2,6-site of 9,10 substituted anthracene. An organic electroluminescent display with an organic compound layer of these materials has high efficiency, thermal stability, operationally stability and maintains driving voltage before and after operation.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Organic electroluminescent devices
InactiveUS20050106419A1Low resistivityReduced stabilityDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesSimple Organic CompoundsElectron injection
An organic electroluminescent device includes an anode electrode layer, a cathode electrode layer opposed to the anode electrode layer, and a luminous layer containing an organic compound disposed between the anode electrode layer and the cathode electrode layer. An excitation state of the organic compound in the luminous layer is created upon a hole injection from the anode electrode layer, and an electron injection from the cathode electrode layer, thereby causing light emission in the organic electroluminescent device. An electron-accepting material is provided in at least one hole transportation layer capable of transporting holes injected from the anode electrode layer disposed between the anode electrode layer and the cathode electrode layer, and the electron-accepting material is positioned at a site which is not adjacent to the anode electrode layer.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Organic electroluminescence element and an exposure unit and image-forming apparatus both using the element
ActiveUS20050248267A1Large quantity of lightOrganic electroluminescence element can be enhancedDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesElectron injectionWork function
The invention has an object of providing an organic electroluminescence element with a large emitted light quantity, an exposure unit and an image-forming apparatus both using the element. The organic electroluminescence element in accordance with the invention has, on a substrate, an anode acting as a hole injection electrode, a cathode acting as an electron injection electrode, a plurality of light emission layers each having a light emission region and a charge generation layer injecting electrons into the light emission layer lying close to the anode and injecting holes into the light emission layer lying close to the cathode, these layers being arranged between the anode and the cathode, and is configured so that the work function of the charge generation layer is set higher than the ionization potential of the light emission layer lying close to the anode.
Owner:JOLED INC
Organic electroluminescence element and an exposure unit and image-forming apparatus both using the element
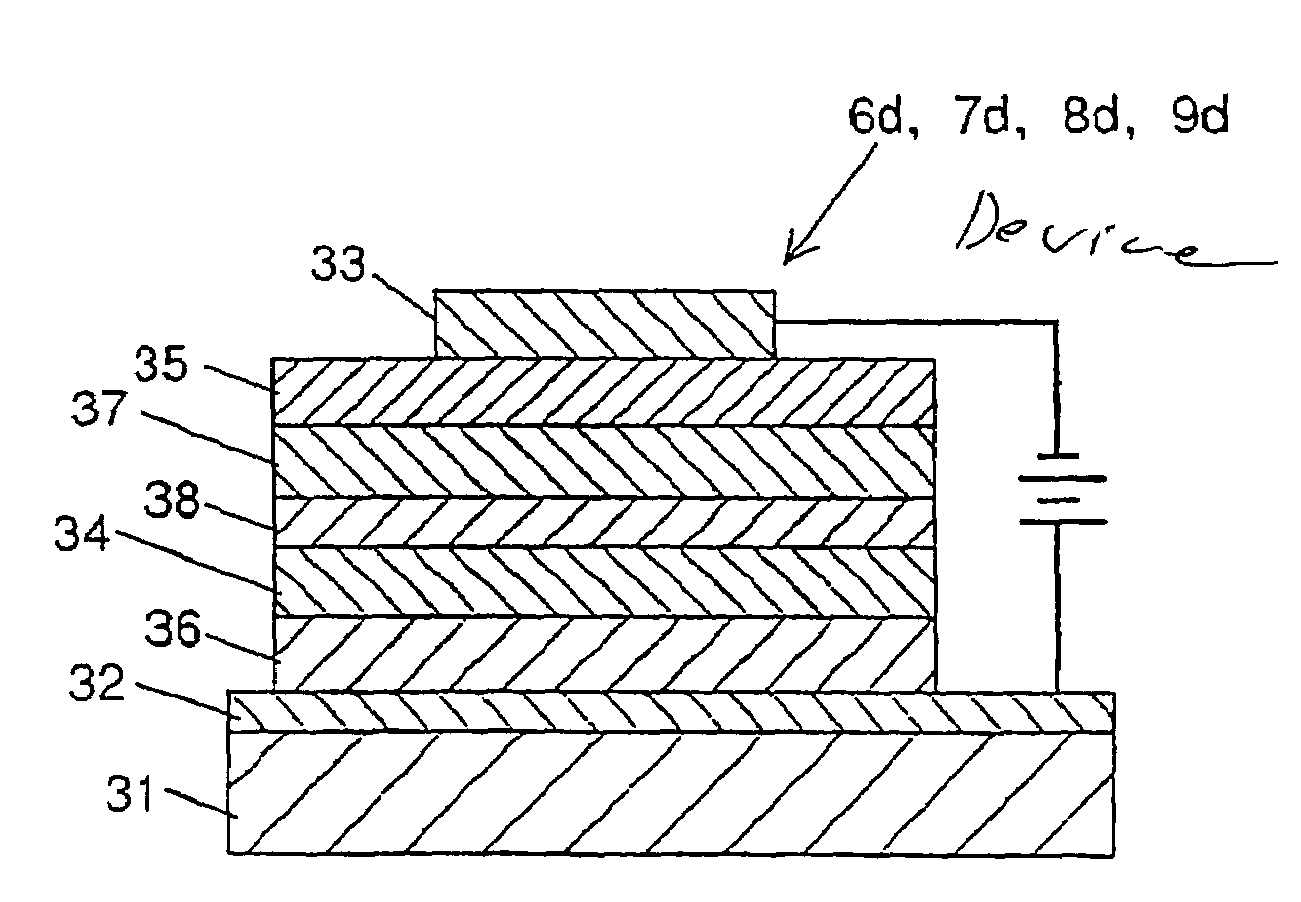
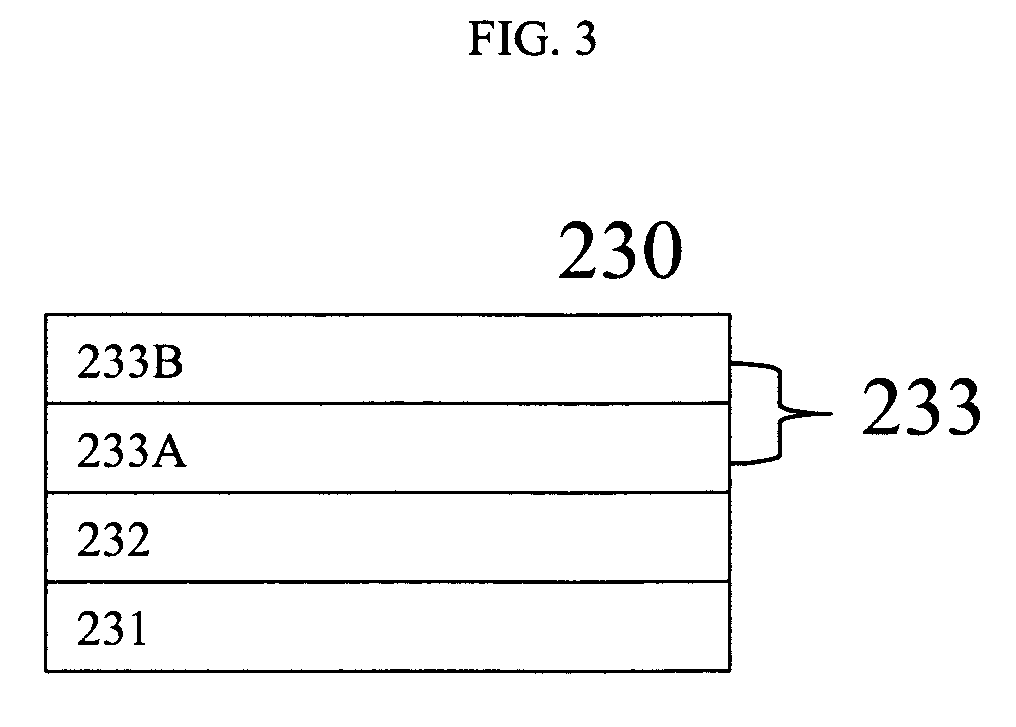
ActiveUS7158161B2Organic electroluminescence element can be enhancedIncrease the amount of lightElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesElectron injectionOrganic electroluminescence
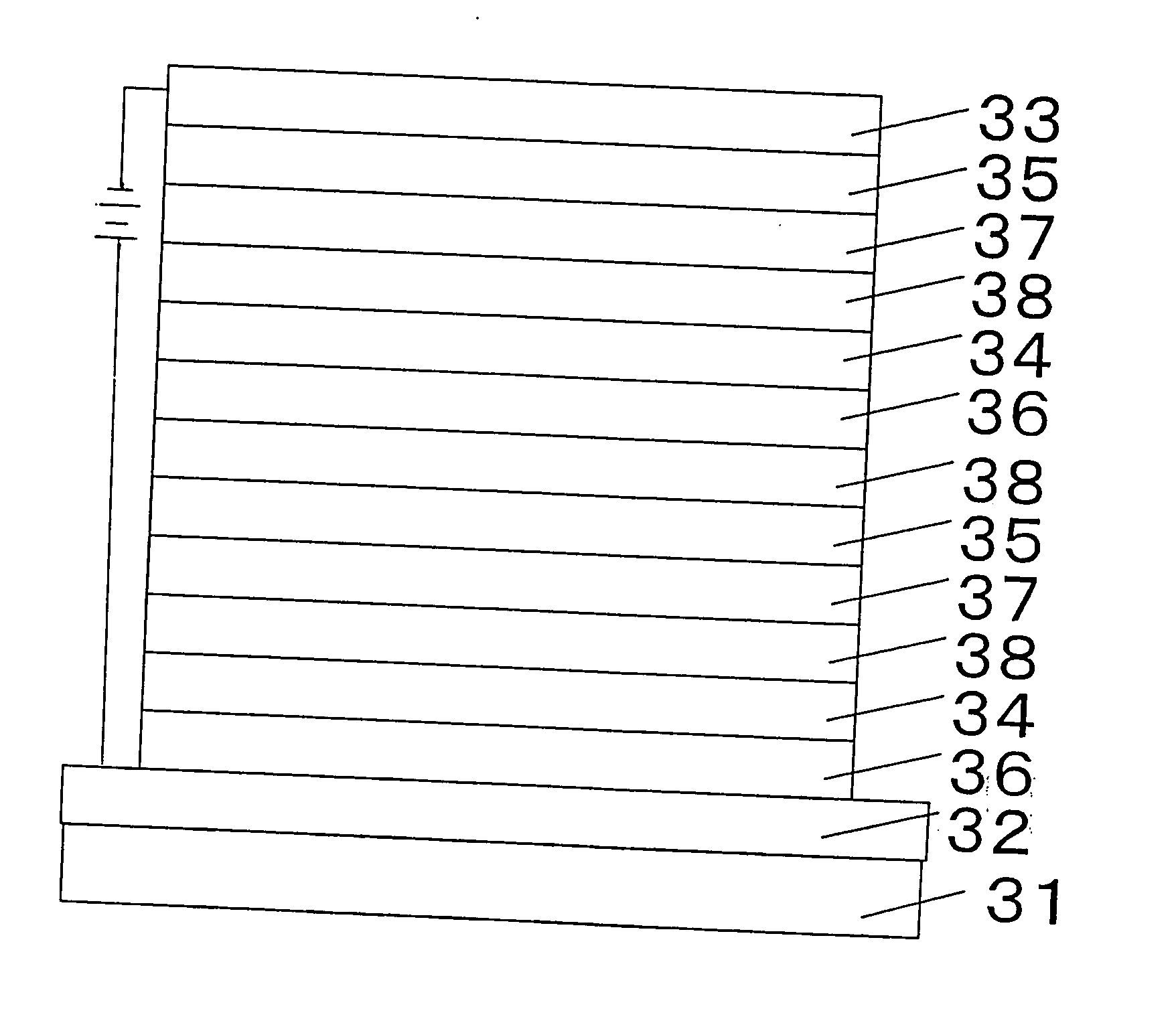
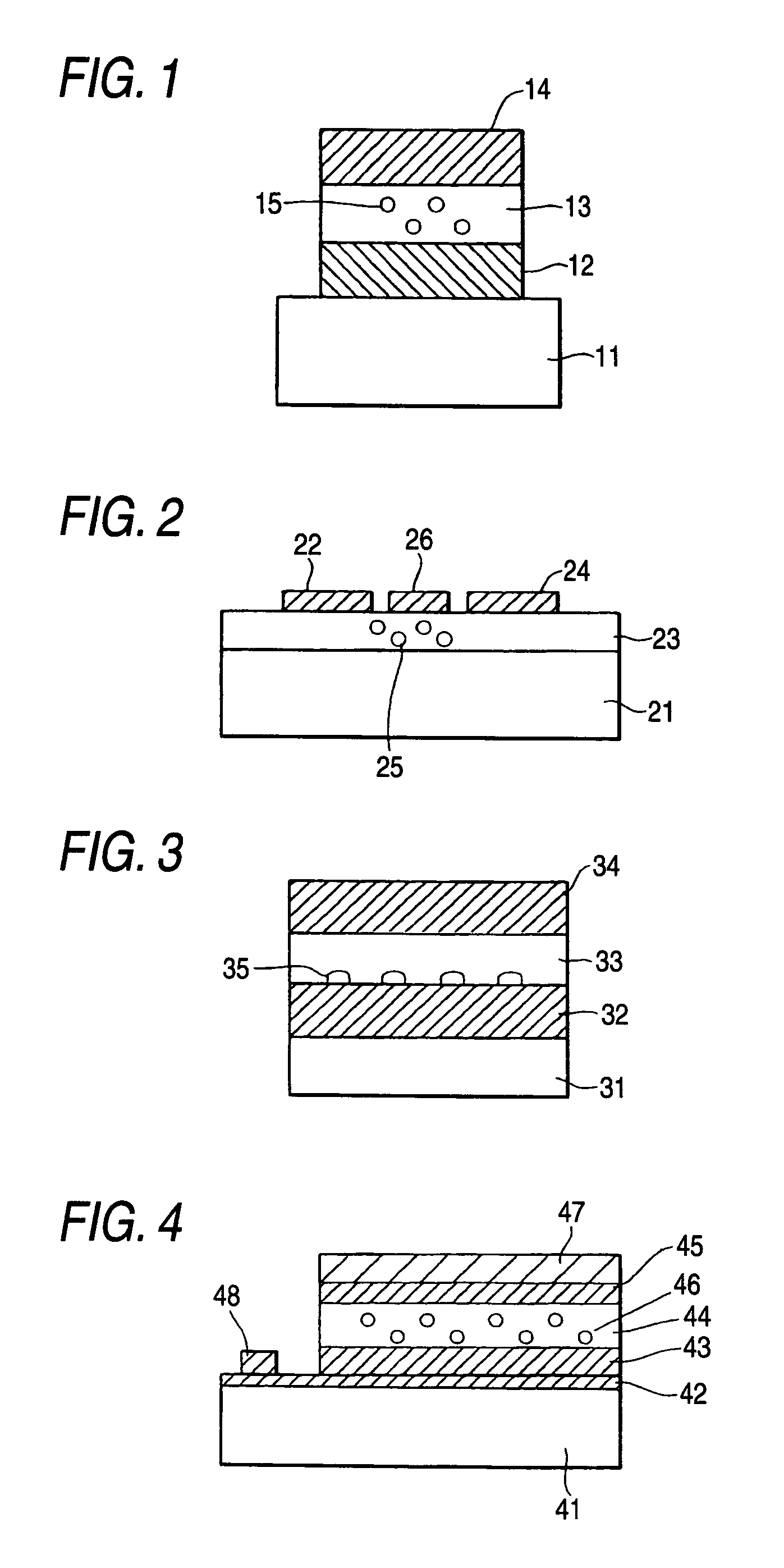
Providing an exposure unit using an organic electroluminescence element with a large emitted light quantity.The organic electroluminescence element has, on a substrate 31, an anode 32 acting as a hole injection electrode, a cathode 33 acting as an electron injection electrode, a first and second emission layers 34 and 35 each having a light emission region, and a charge generation layer 38 injecting electrons into the light emission layer 34 lying close to the anode 32 and injecting holes into the light emission layer 35 lying close to the cathode 33, these layers being arranged between the anode 32 and the cathode 33.
Owner:JOLED INC
Organic el display unit, method of manufacturing the same, and solution used in method
ActiveUS20110248247A1Improve emission efficiencyReduce emission efficiencyElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesElectron holeElectron injection
An organic electroluminescence display unit includes: a lower electrode for each device; a first hole injection / transport layer provided on the lower electrode for each device; a second organic light emitting layer of the first color provided on the first hole injection / transport layer for the second organic electroluminescence device; a second hole injection / transport layer provided on the entire surfaces of the second organic light emitting layer and the first hole injection / transport layer for the first organic electroluminescence device, and being made of a low molecular material; a blue first organic light emitting layer provided on the entire surface of the second hole injection / transport layer; and an electron injection / transport layer having at least one of electron injection characteristics and electron transport characteristics, and an upper electrode that are provided in sequence on the entire surface of first organic light emitting layer.
Owner:JOLED INC
OLEDs with improved operational lifetime
InactiveUS20060141287A1Adversely reducing purity of colorImprove efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesSimple Organic CompoundsDopant
An organic light-emitting device includes a substrate, an anode and a cathode disposed over the substrate, and a light-emitting layer disposed between the anode and the cathode wherein the light-emitting layer includes a host and at least one dopant. The host of the light-emitting layer is selected to include a solid organic material including a mixture of at least two components wherein the first host component is an organic compound capable of transporting electrical charges and also forms an aggregate, and the second component of the mixture is an organic compound capable, of transporting electrical charges and, upon mixing with the first host component, is capable of forming a continuous and substantially pin-hole-free layer. The dopant of the light-emitting layer is selected to collect excitons and produce colored light, and an electron-transporting layer is disposed between the light-emitting layer and the cathode for providing improved electron injection and transport.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Light emitting device
InactiveUS7141817B2Improve injectionAvoid quenchingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectron injectionElectron donor
By doping an organic compound functioning as an electron donor (hereinafter referred to as donor molecules) into an organic compound layer contacting a cathode, donor levels can be formed between respective LUMO (lowest unoccupied molecular orbital) levels between the cathode and the organic compound layer, and therefore electrons can be injected from the cathode, and transmission of the injected electrons can be performed with good efficiency. Further, there are no problems such as excessive energy loss, deterioration of the organic compound layer itself, and the like accompanying electron movement, and therefore an increase in the electron injecting characteristics and a decrease in the driver voltage can both be achieved without depending on the work function of the cathode material.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
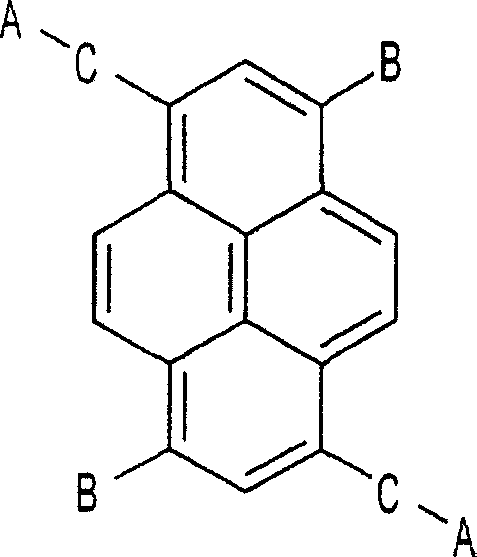
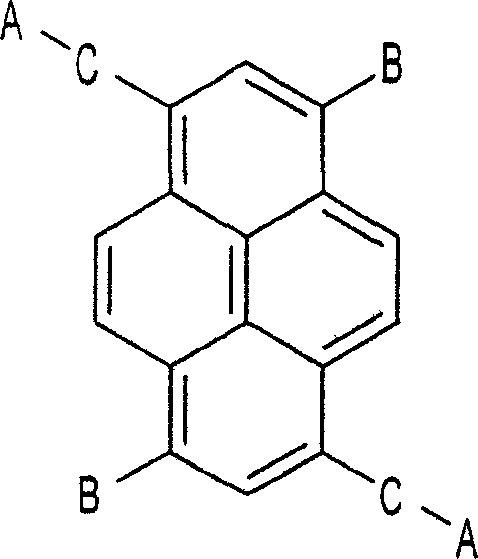
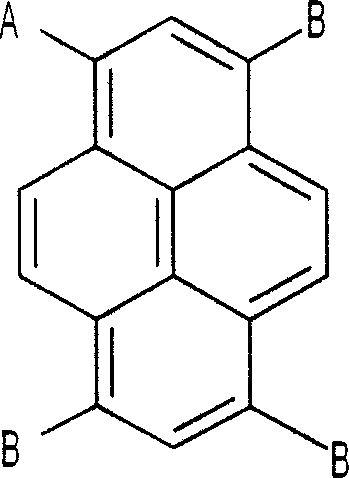
Electron transport compound and organic light emitting device comprising the same
An organic light emitting device having a pyrene based electron transport compound and an electron injecting and transport layer comprising the electron transport compound is provided.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Organic light emitting devices
InactiveUS20020135296A1Minimize and reduce changeEnable stabilizationDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsElectronic transmissionElectron injection
An organic light emitting device containing (i) a substrate; (ii) a first electrode, such as an anode; (iii) a mixed region comprising a mixture of a hole transport material and an electron transport material, and wherein this mixed region includes at least one organic luminescent material; (iv) a second electrode, such as a cathode; (v) a thermal protective element coated on the second electrode; wherein, one of the two said first and second electrodes is a hole injection anode, and one of the two electrodes is an electron injection cathode, and wherein the organic light emitting device further comprises; (vi) a hole transport region, interposed between the anode and the mixed region, wherein the hole transport region optionally includes a buffer layer; and (vii) an electron transport region interposed between the cathode and the mixed region.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
OLEDs with improved operational lifetime
InactiveUS20060040131A1Adversely reducing purity of colorImprove efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesSimple Organic CompoundsDopant
An organic light-emitting device includes a substrate, an anode and a cathode disposed over the substrate, and a light-emitting layer disposed between the anode and the cathode wherein the light-emitting layer includes a host and at least one dopant. The host of the light-emitting layer is selected to include a solid organic material including a mixture of at least two components wherein the first host component is an organic compound capable of transporting electrical charges and also forms an aggregate, and the second component of the mixture is an organic compound capable of transporting electrical charges and, upon mixing with the first host component, is capable of forming a continuous and substantially pin-hole-free layer. The dopant of the light-emitting layer is selected to collect excitons and produce colored light, and an electron-transporting layer is disposed between the light-emitting layer and the cathode for providing improved electron injection and transport.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Organic light emitting devices
ActiveUS20040209117A1Improve efficiencyEnhanced operational lifetimeOrganic chemistryDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectron injectionDisplay device
The present invention is an organic light emitting device (OLED) comprising an anode, a cathode and a luminescent region provided between the anode and the cathode. The luminescent region comprises an electron injection and transporting zone and at least one of a hole injection and transporting zone and a mixed charge transport layer. One or both of the electron injection and transporting zone and the mixed charge transporting layer comprises an azole compound represented by formula I and / or II. The provision of the novel azole compounds of the invention as electron transport materials within an organic electroluminescent device advantageously reduces power consumption and increases power conversion efficiency within the device and as such, are suitable for a variety of display applications.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
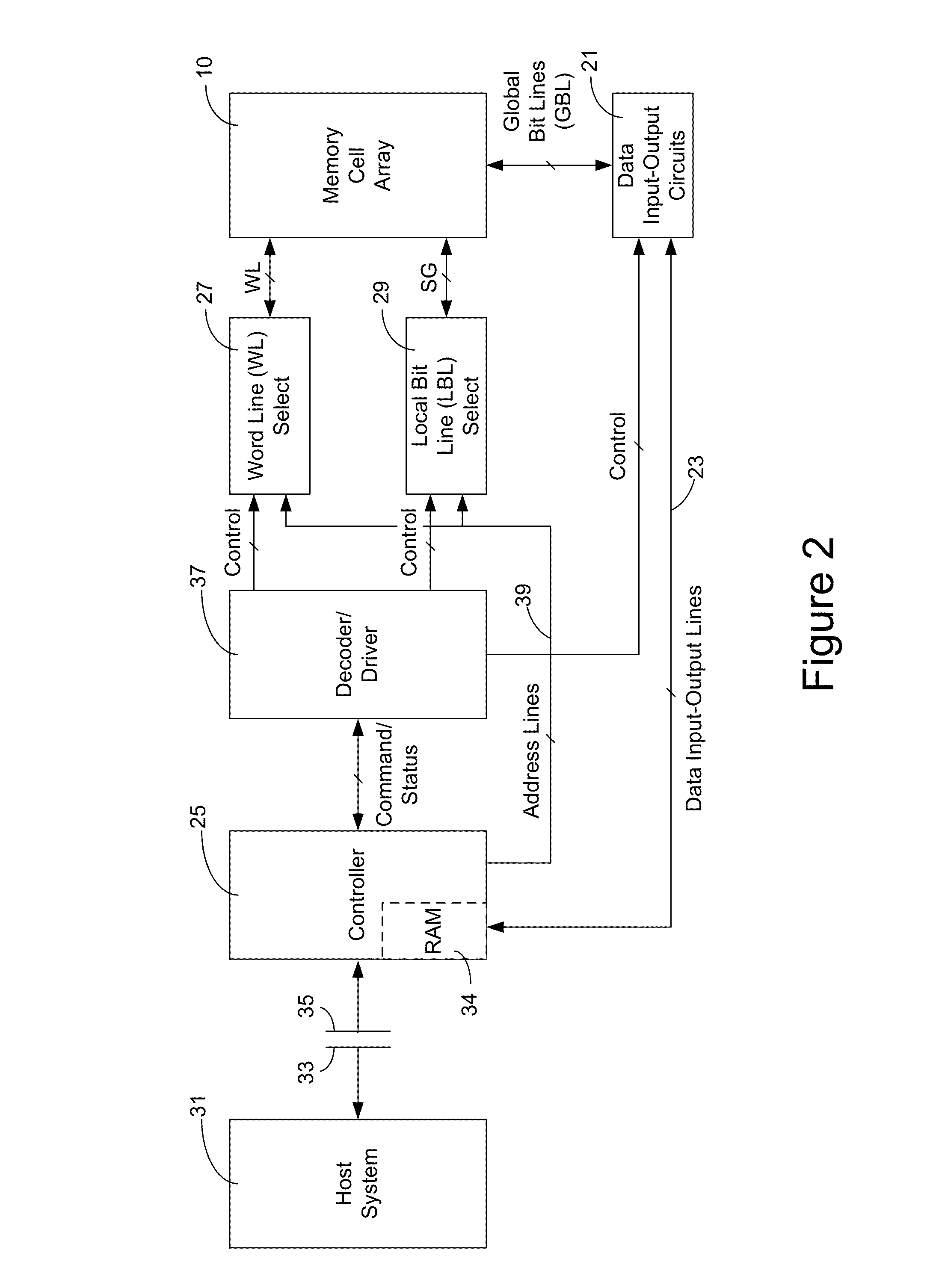
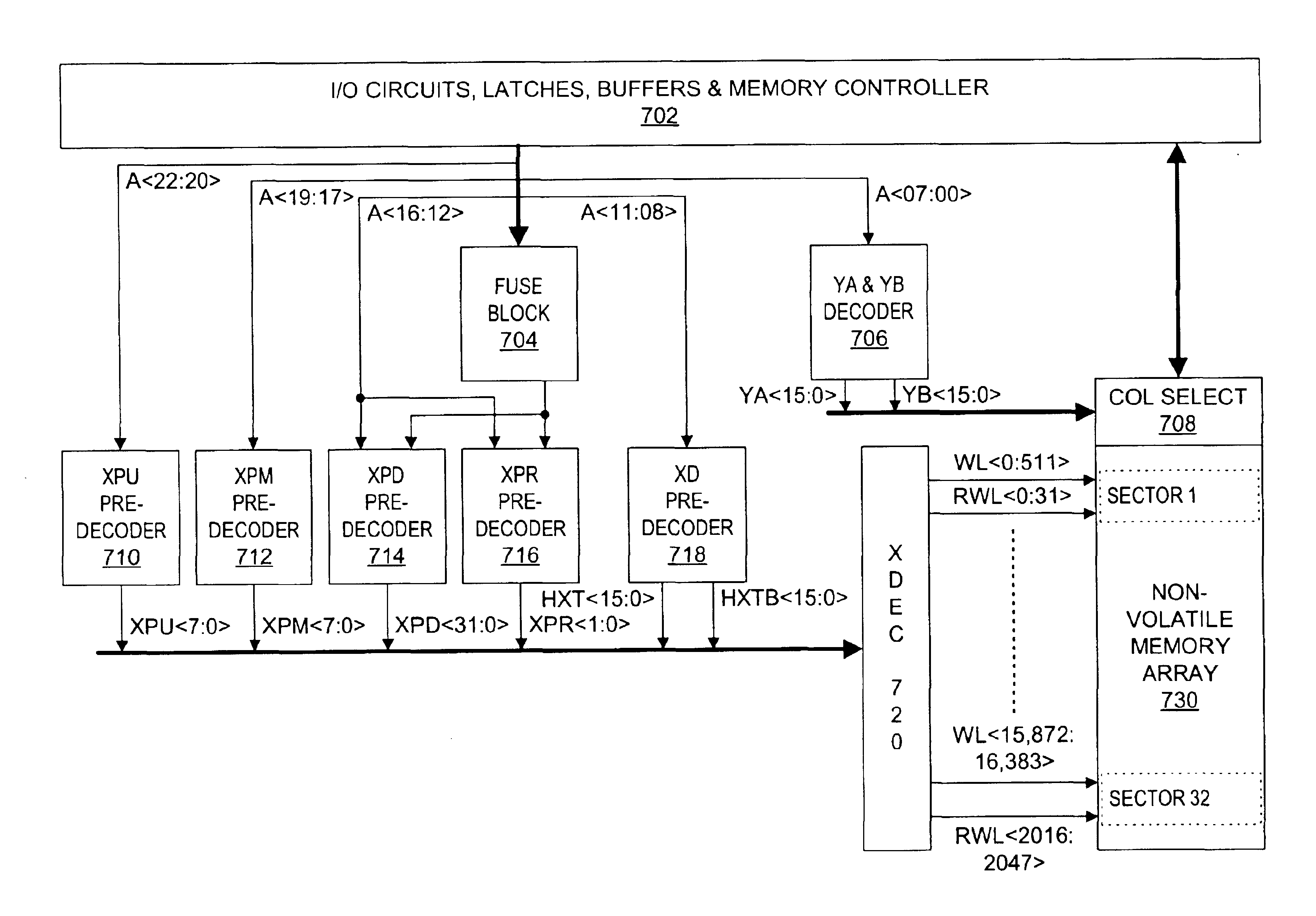
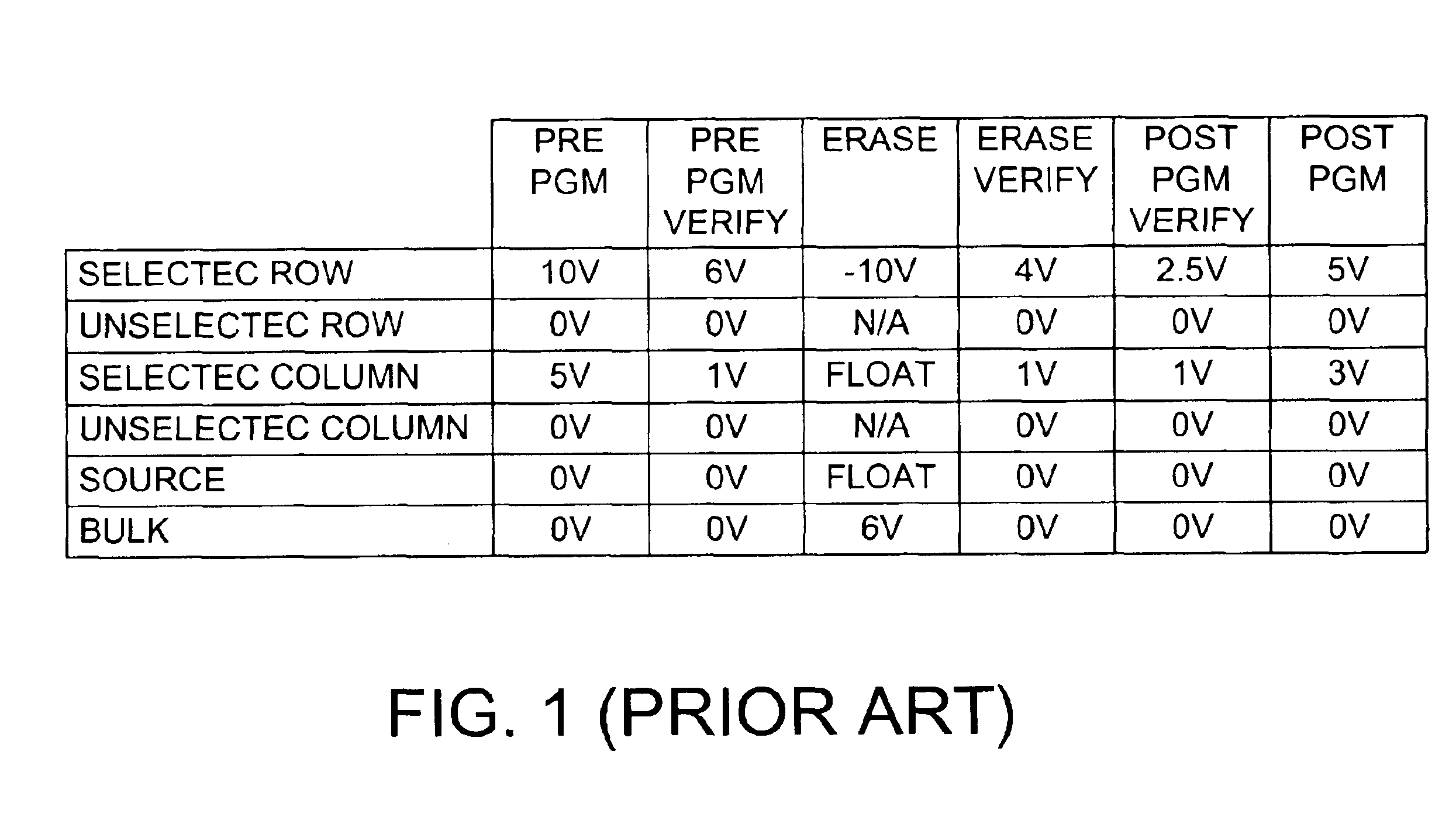
Method and apparatus for providing row redundancy in nonvolatile semiconductor memory
In a NOR-type flash memory of either the ETOX or virtual ground type that is programmed using electron injection and erased using FN tunneling, and that has row redundancy, the typical sequence of operations used for an embedded sector erase, namely the Preprogram, Preprogram Verify, Erase, Erase Verify, Post-Program Verify, and Post-Program operations, need not be performed for the data cells on bad or shorted rows or in unused redundant rows. Instead, the bad or shorted rows or the unused redundant rows are suitably biased so that the threshold voltages of the data cells in these rows tend to converge to a threshold voltage near the UV erased threshold.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
Organic electroluminescence element
InactiveUS6358633B1Increase brightnessStable brightnessDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDopantElectron hole
In an organic electroluminescent device constructed by providing at least an emitting layer using an organic material between a hole injection electrode and an electron injection electrode, in forming an emitting layer having a dopant doped into a host material, a dopant having a condensed ring obtained by condensing three or more rings is used, and the difference between the highest occupied molecular orbital in the host material and the highest occupied molecular orbital in the dopant is in a range from -0.3 eV to +0.3 eV.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Quantum dot-dispersed light emitting device, and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS7880377B2Control freedomDischarge tube luminescnet screensLayered productsElectron injectionSemiconductor materials
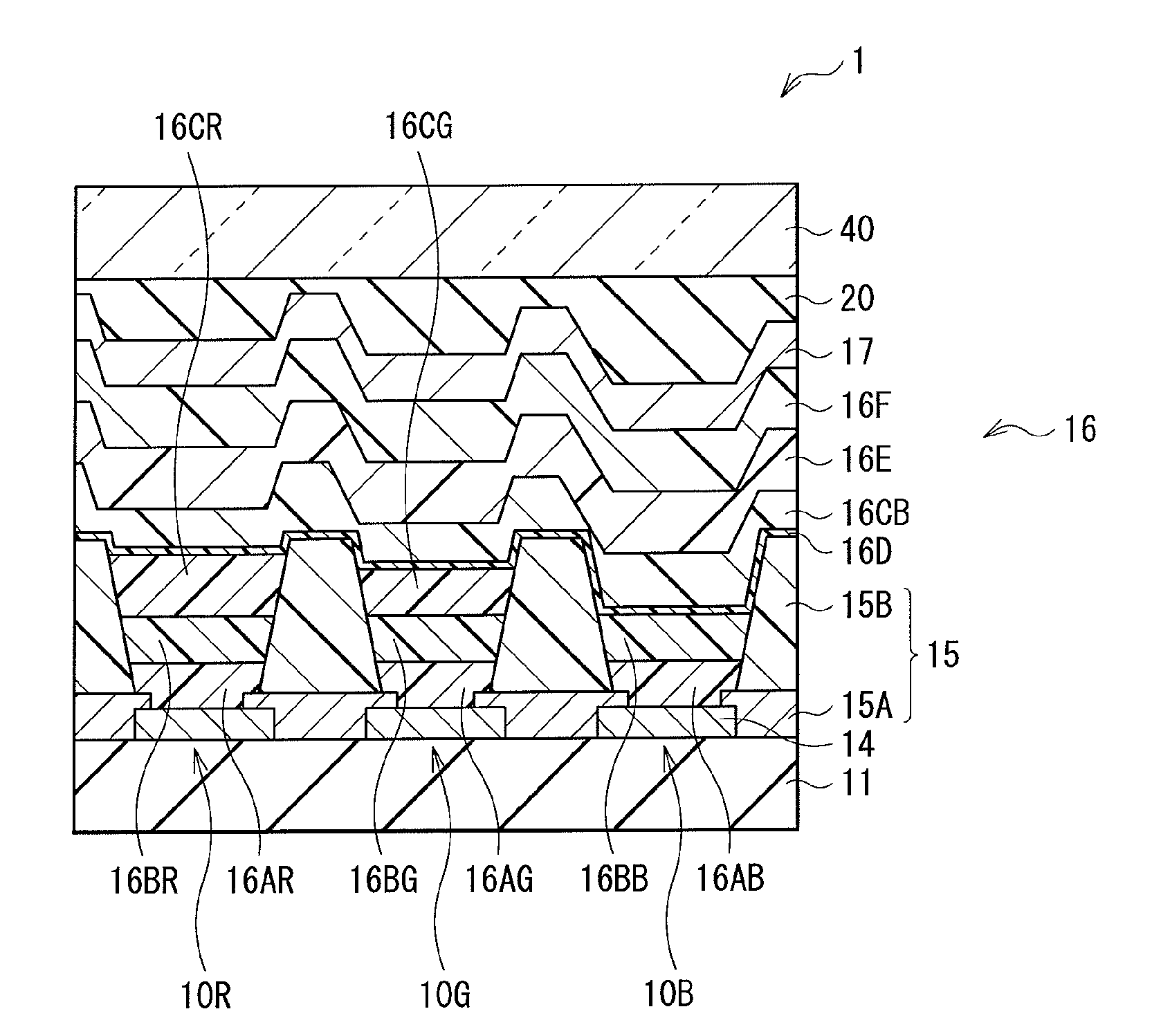
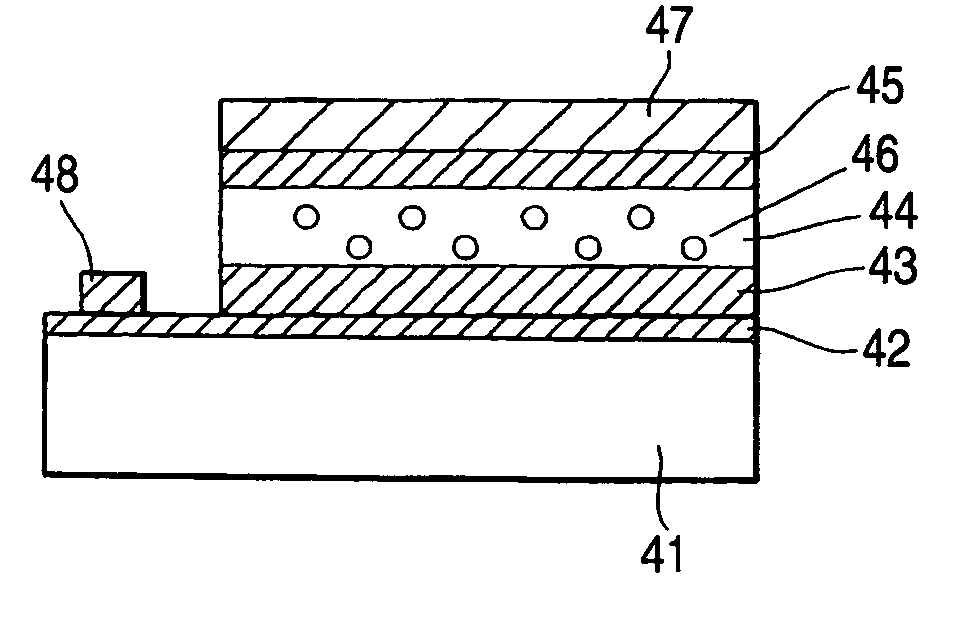
A light emitting device having practical light emission characteristics is obtained without epitaxial growth.A quantum dot-dispersed light emitting device of the invention includes a substrate 11, an electron injection electrode 12, a hole injection electrode 14, and an inorganic light emitting layer 13 disposed so as to be in contact with both the electrodes. The inorganic light emitting layer 13 contains an ambipolar inorganic semiconductor material and nanocrystals 15 dispersed as luminescent centers in the ambipolar inorganic semiconductor material and is configured so as to be capable of light emission without having, at the interface with the electron injection electrode and / or the hole injection electrode, epitaxial relation therewith.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Organic electroluminescent element
InactiveUS20060051615A1Improve balanceImprove luminous efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesElectron holeHole injection layer
In an organic electroluminescent element in which a light emitting layer is disposed between a hole injection electrode and an electron injection electrode, and a hole injection layer is provided between the hole injection electrode and the light emitting layer, and an electron transport layer is provided between the electron injection electrode and the light emitting layer, the organic electroluminescent element is characterized in that a fluorocarbon layer is provided between the hole injection layer and the light emitting layer, and the electron transport layer is formed from a phenanthroline compound.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Organic electroluminescent device and method for preparing the same
InactiveUS20080284325A1Improved electron injection characteristicAvoid damageDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsThiazoleElectron injection
The present invention relates to an organic electroluminescent device comprising a substrate, a cathode, at least two organic material layers comprising a light-emitting layer, and an anode in the sequentially laminated form, in which the organic material layers comprise an organic material layer comprising a compound having a functional group selected from the group consisting of an imidazole group, an oxazole group and a thiazole group between the cathode and the light-emitting layer. The organic electroluminescent device according to the present invention comprises an organic material layer comprising a compound having a functional group selected from the group consisting of an imidazole group, an oxazole group and a thiazole group between a cathode and a light-emitting layer, thus having an improved electron injection characteristic to provide an organic electroluminescent device of an inverted structure operating at a low voltage.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Organic electroluminescent device having a conjugated polymer and an inorganic insulative electron injecting and transporting layer
InactiveUS6404126B1Improve efficiencyLong lastingDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesRubidium oxideLithium oxide
An organic electroluminescent device having high efficiency, a long life time, and low cost, includes a substrate, a hole injecting electrode and an electron injecting electrode formed on the substrate, an organic material-containing organic layer between the electrodes, and an inorganic insulative electron injecting and transporting layer between the light emitting layer and the electron injecting electrode. The organic layer includes a light emitting layer containing a conjugated polymer, and the inorganic insulative electron injecting and transporting layer comprises three components. The first component is at least one oxide selected from the group consisting of lithium oxide, rubidium oxide, potassium oxide, sodium oxide, and cesium oxide. The second component is at least one of strontium oxide, magnesium oxide, and calcium oxide. The third component consists of silicon oxide, germanium oxide, or mixtures thereof.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Organic electroluminescent light emitting devices
InactiveUS6118212AHigh luminance and efficiencyHigh quality imagingDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesLithiumElectron injection
An organic EL device of the invention comprises a hole injecting electrode, an electron injecting electrode and at least one organic layer interleaved between them. The electron injecting electrode is a film of an aluminum lithium alloy formed by a sputtering technique and comprising 0.4 to 14 at % of lithium. The electron injecting electrode further includes on a side of the electron injecting electrode that is not opposite to the organic layer a protective electrode comprising at least one of aluminum, aluminum and a transition metal except titanium, titanium, and titanium nitride.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
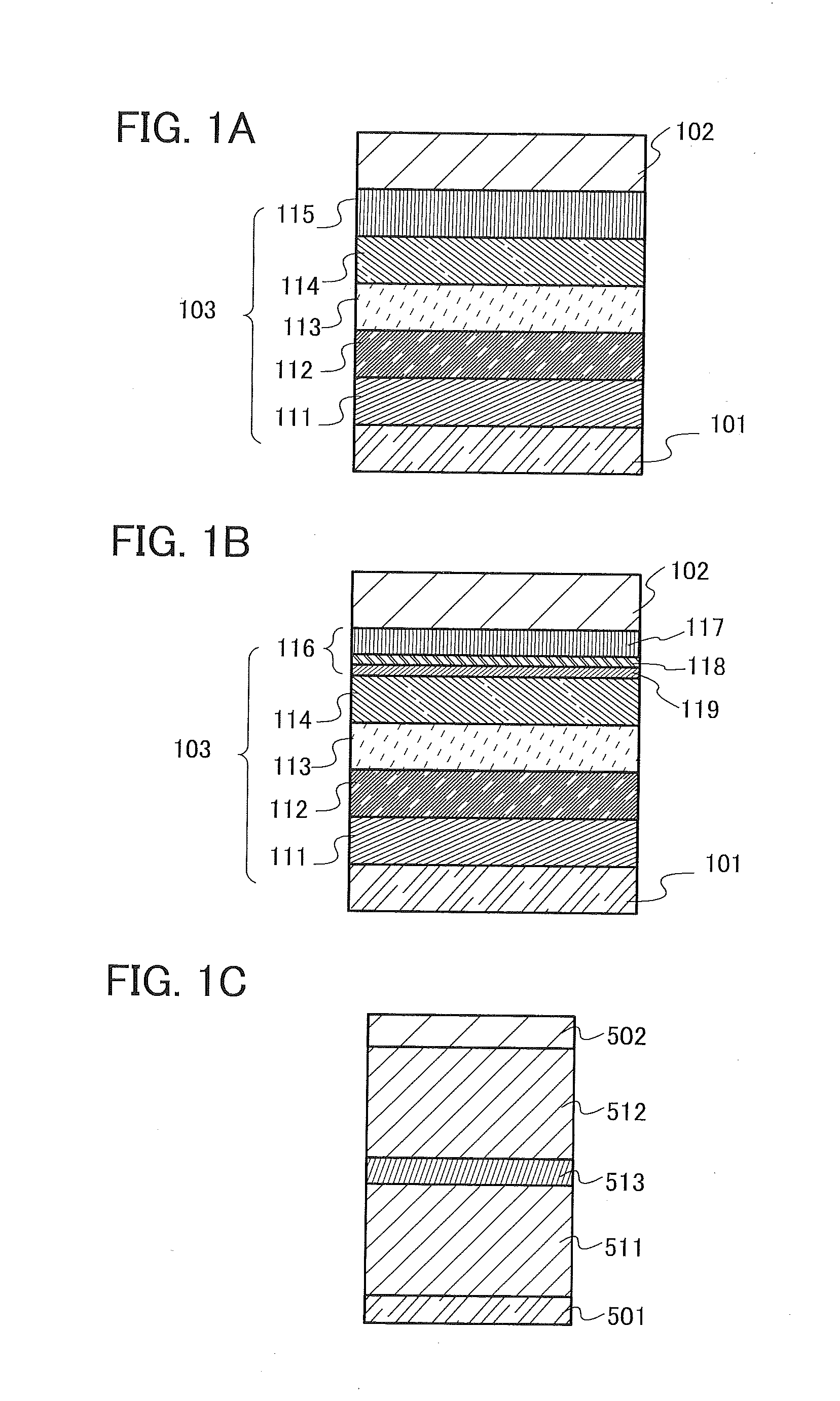
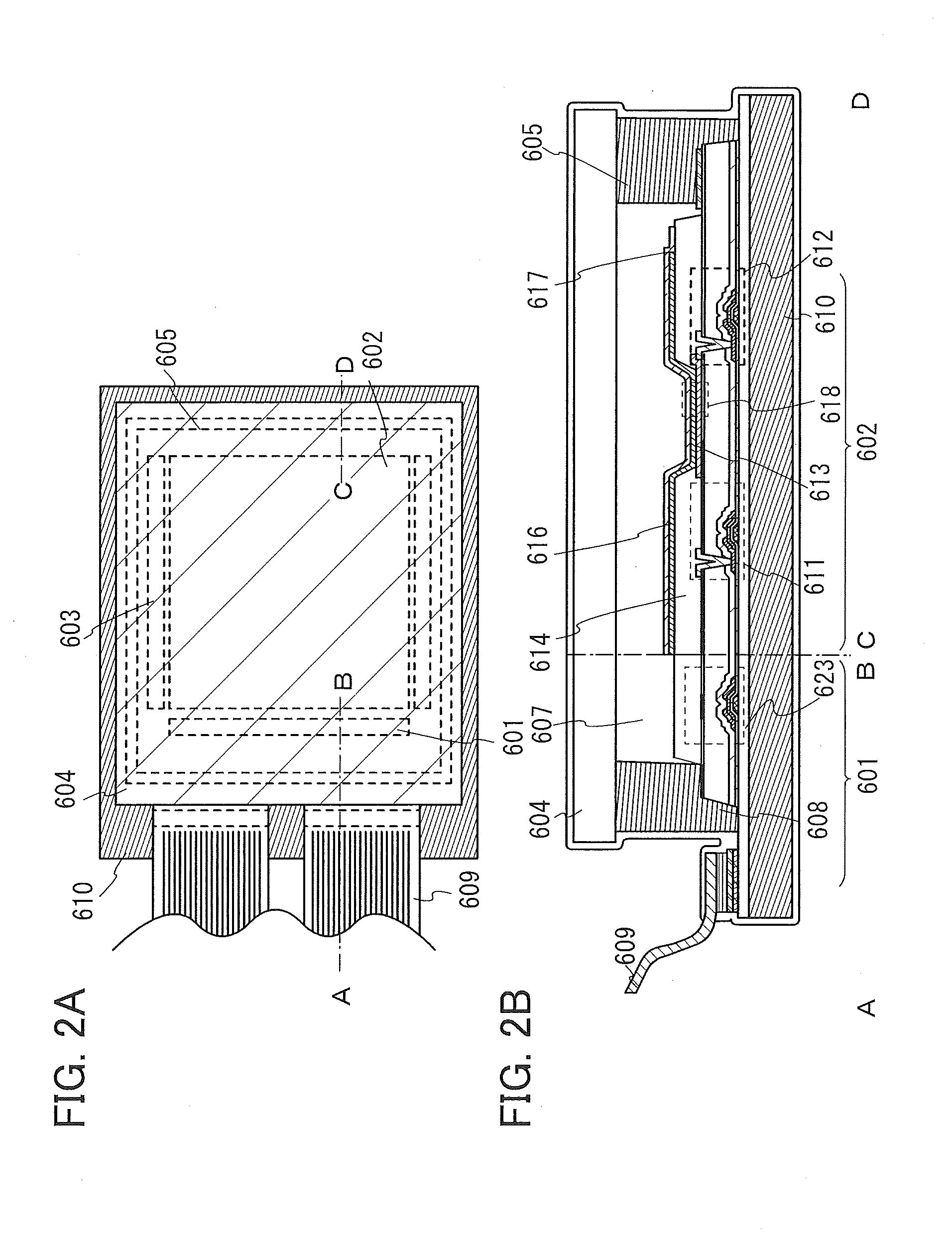
Organic Compound, Light-Emitting Element, Display Module, Lighting Module, Light-Emitting Device, Display Device, Electronic Device, and Lighting Device
ActiveUS20160240794A1Improve heat resistanceLess crosstalkOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesElectron injectionDisplay device
A novel organic compound that can be used as an electron-injection material or an electron-transport material of a light-emitting element is provided. An organic compound with which a display device having less crosstalk can be obtained is provided. A light-emitting device, a display device, and an electronic device each having less crosstalk are provided. An organic compound including two or three benzo[h]quinazoline rings is provided. In the organic compound, two or three benzo[h]quinazoline rings are preferably included in the substituent including an aromatic ring or a heteroaromatic ring and having 3 to 30 carbon atoms. When two or three benzo[h]quinazoline rings are included in a substituent particularly including a heteroaromatic ring and having 3 to 30 carbon atoms, a high electron-transport property can be obtained.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Light-emitting device of field-effect transistor type
InactiveUS20060043380A1Long-term reliabilityHigh selectivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesElectron injectionSemiconductor materials
A theme is to provide a field-effect light-emitting device that can obtain a long-term reliability and broaden a selectivity of emission wavelength. The invention of this application is a field-effect transistor type light-emitting device having an electron injection electrode, i.e. a source electrode, a hole injection electrode, i.e. a drain electrode, an emission active member disposed between the source electrode and the drain electrode so as to contact with both electrodes, and a field application electrode, i.e. a gate electrode, for inducing electrons and holes in the emission active member, which is disposed in the vicinity of the emission active member via an electrically insulating member or an insulation gap. The emission active member is made of an inorganic semiconductor material having both an electron transporting property and a hole transporting property.
Owner:HOYA CORP
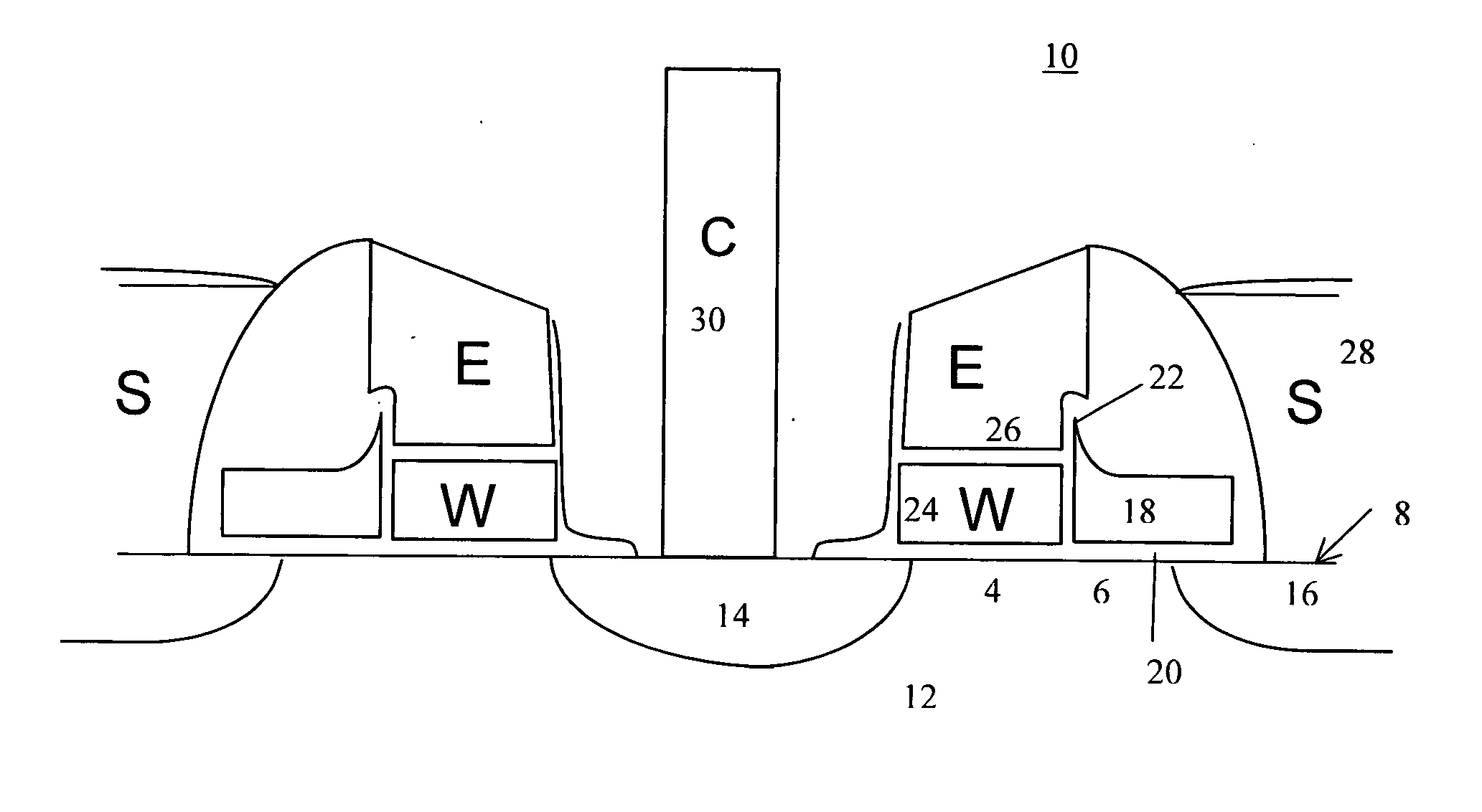
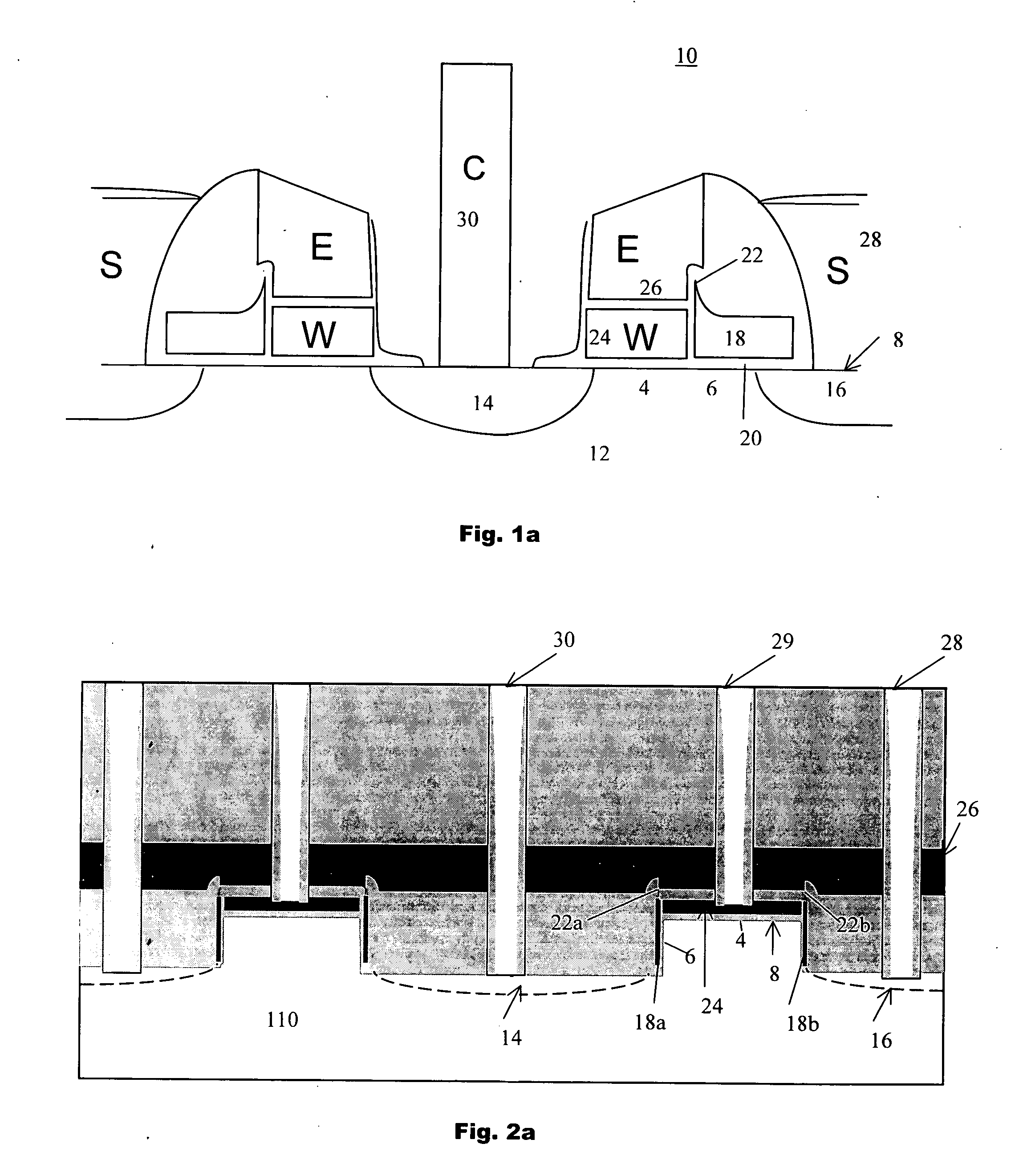
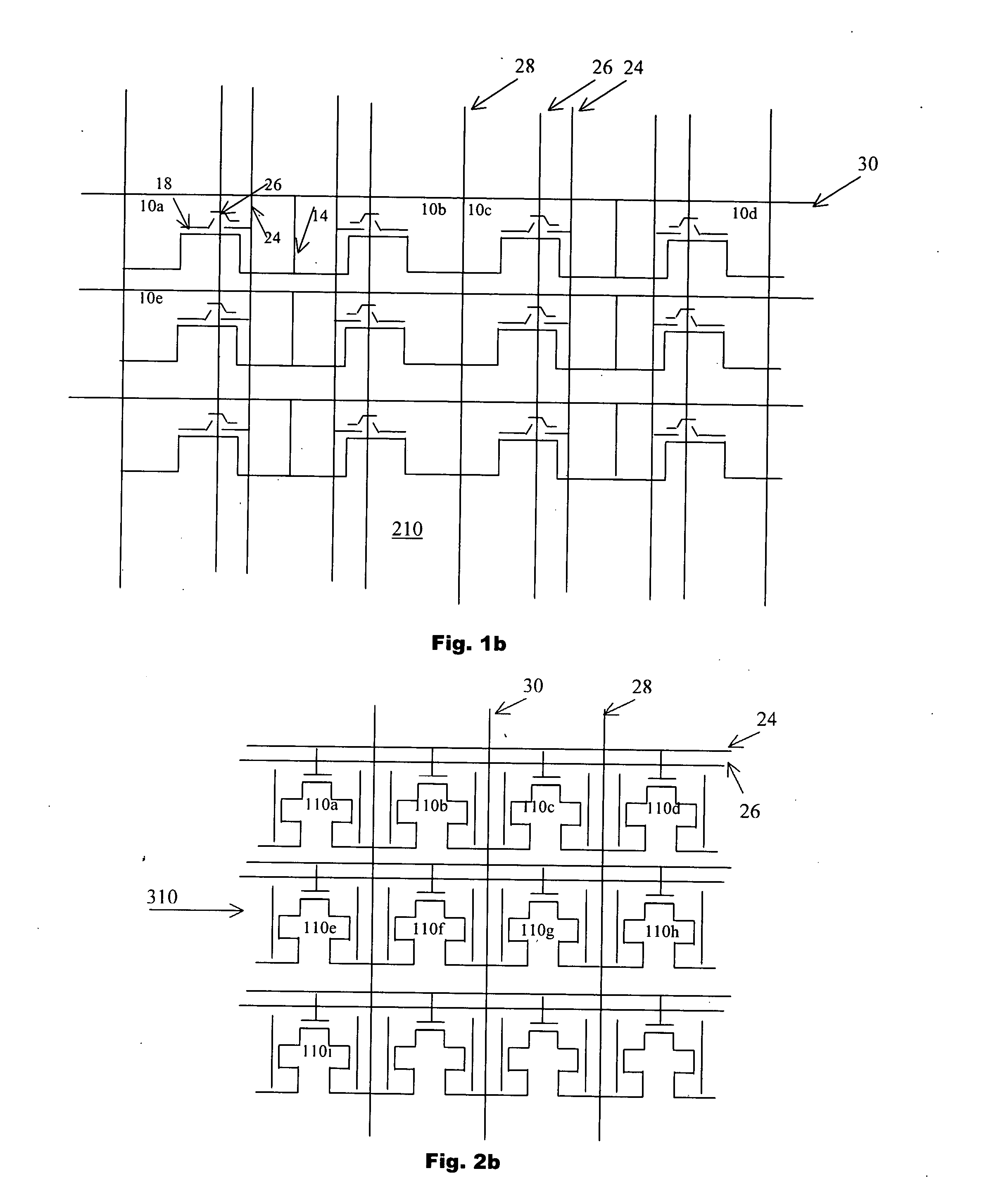
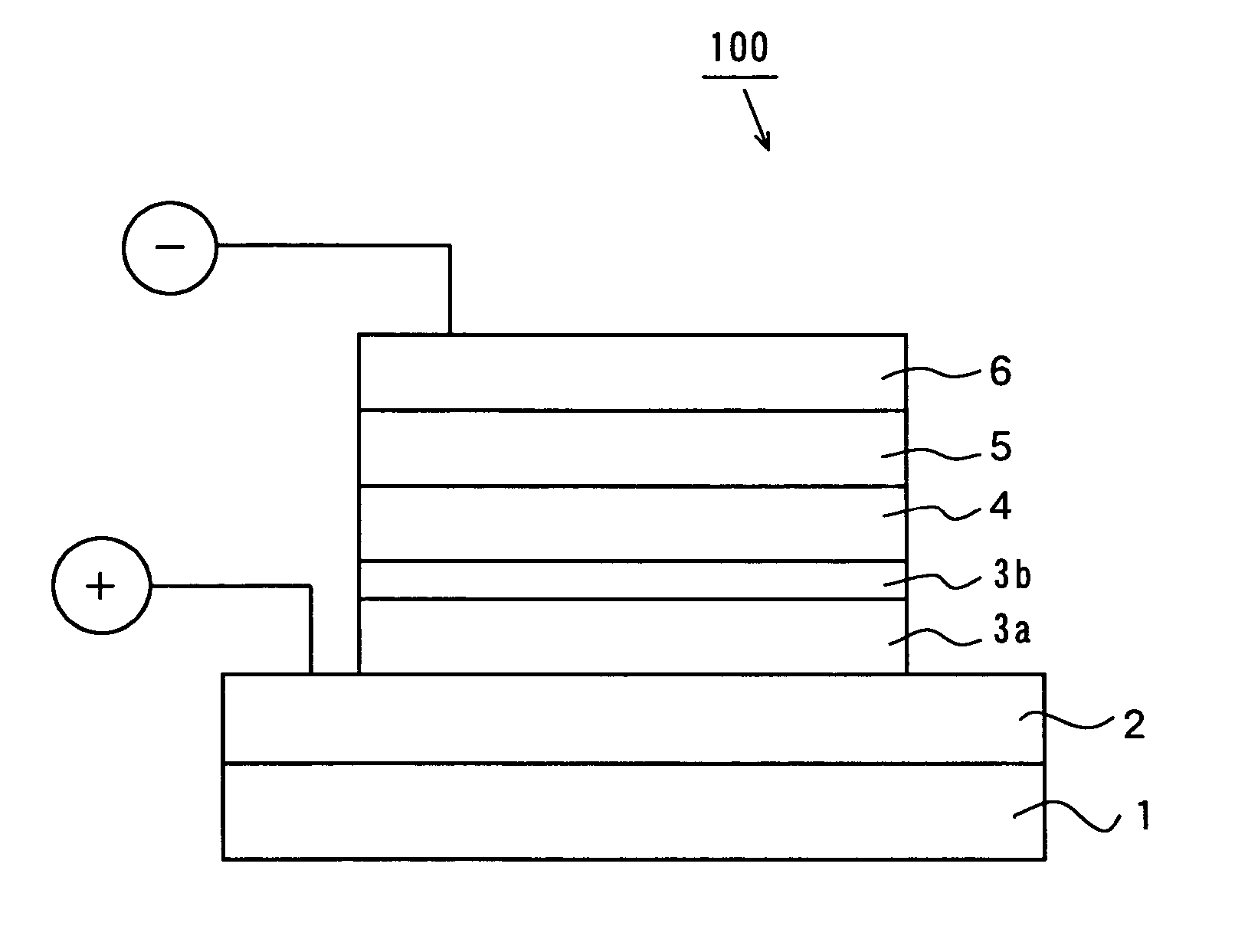
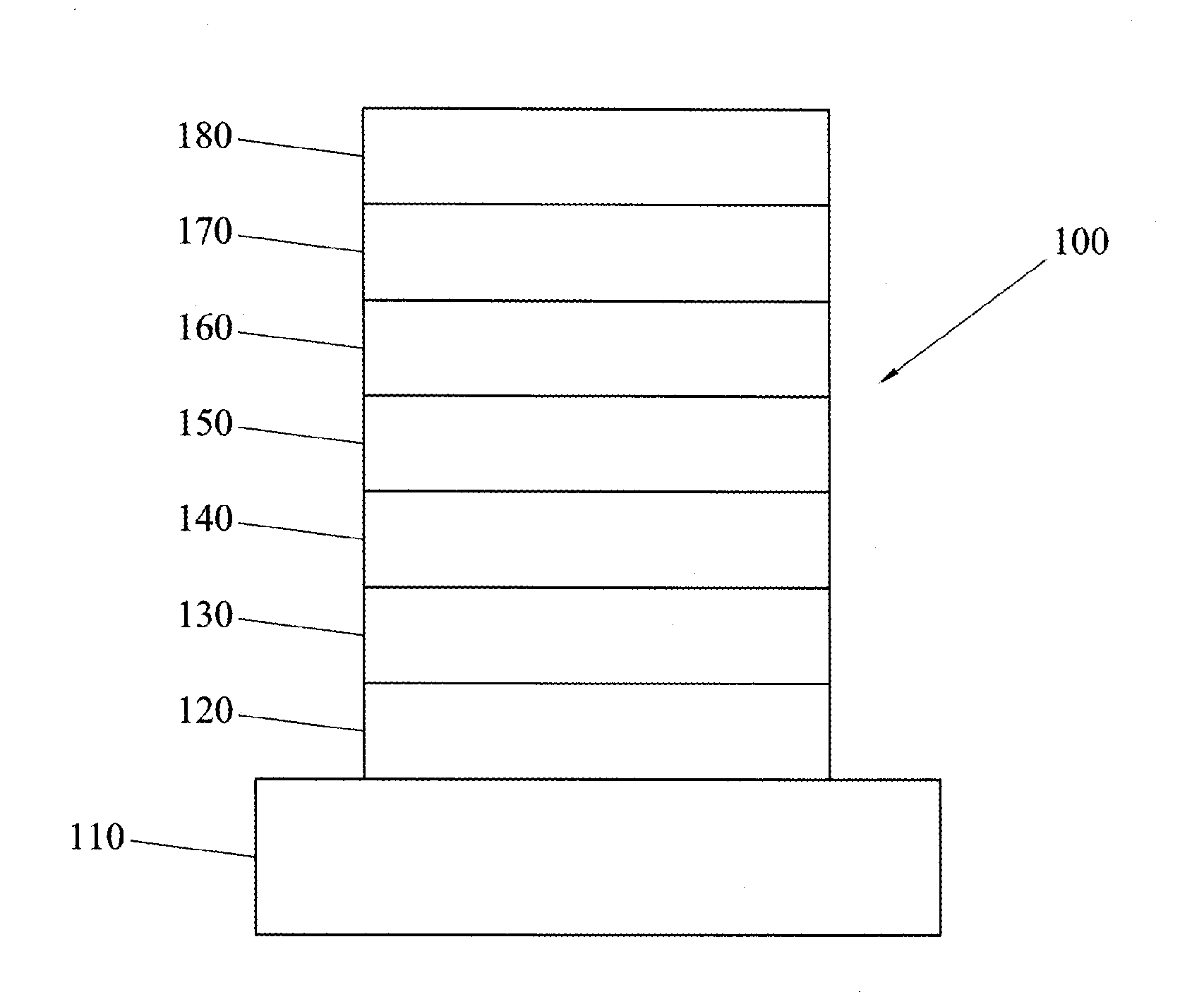
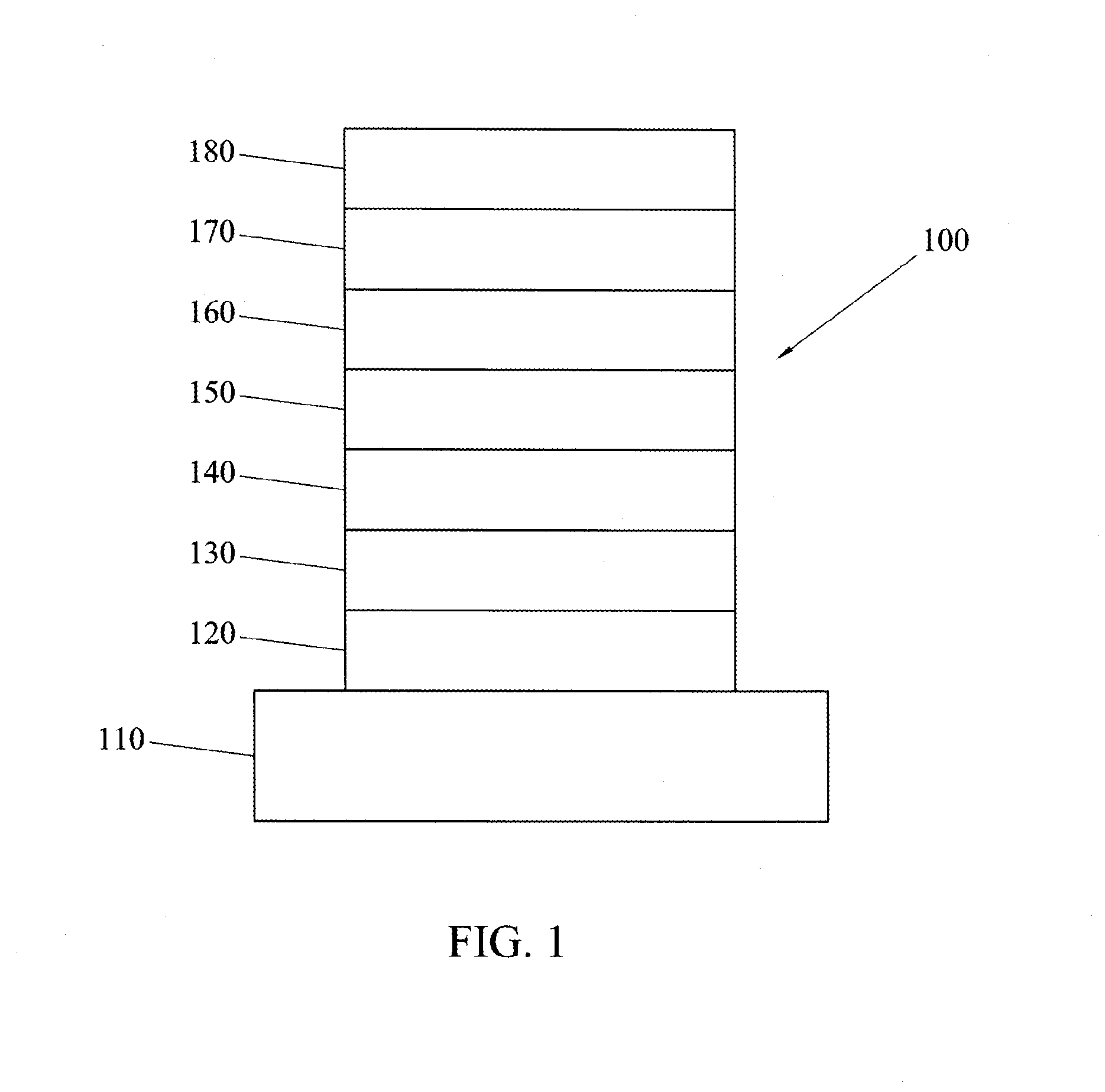
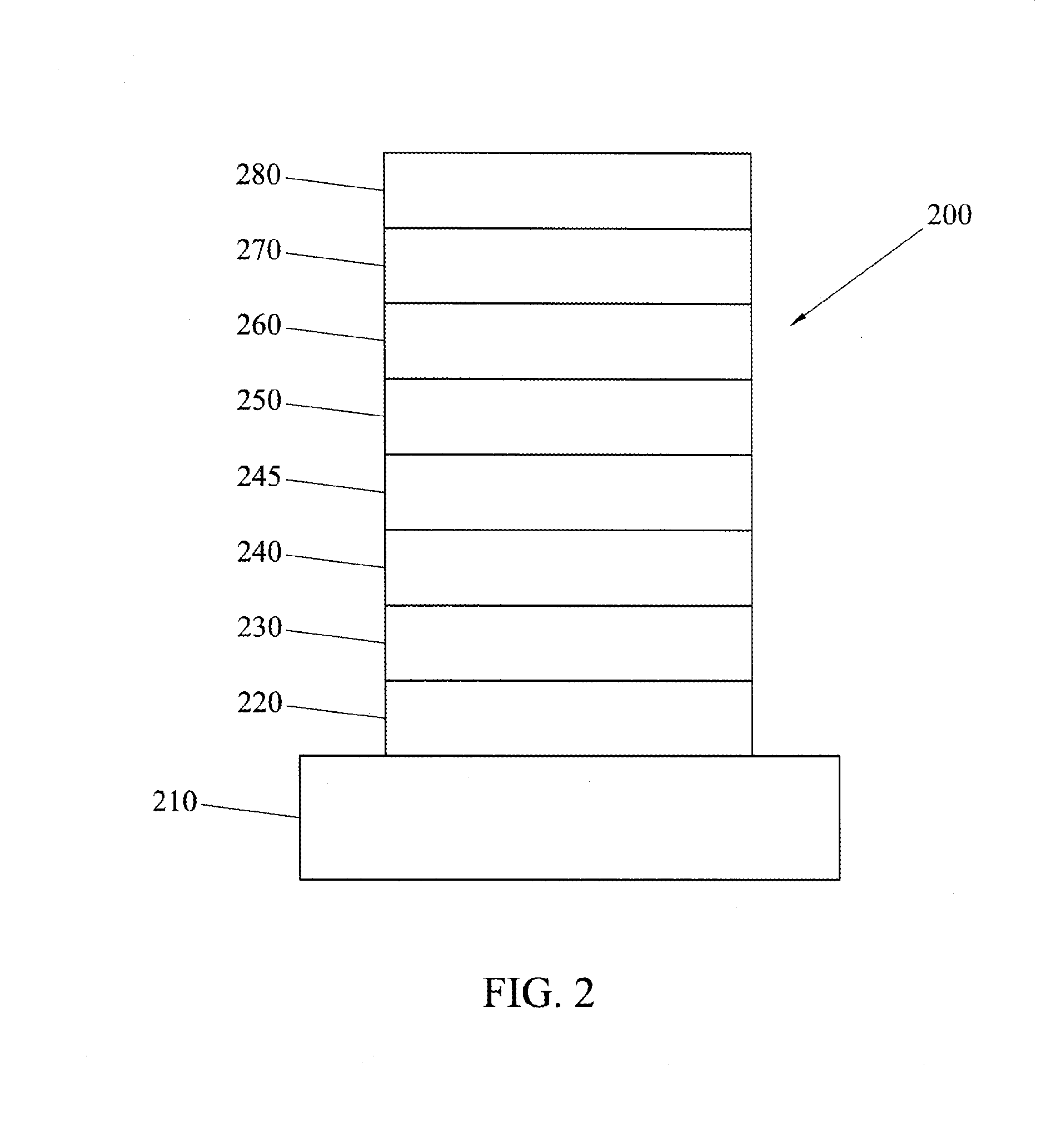
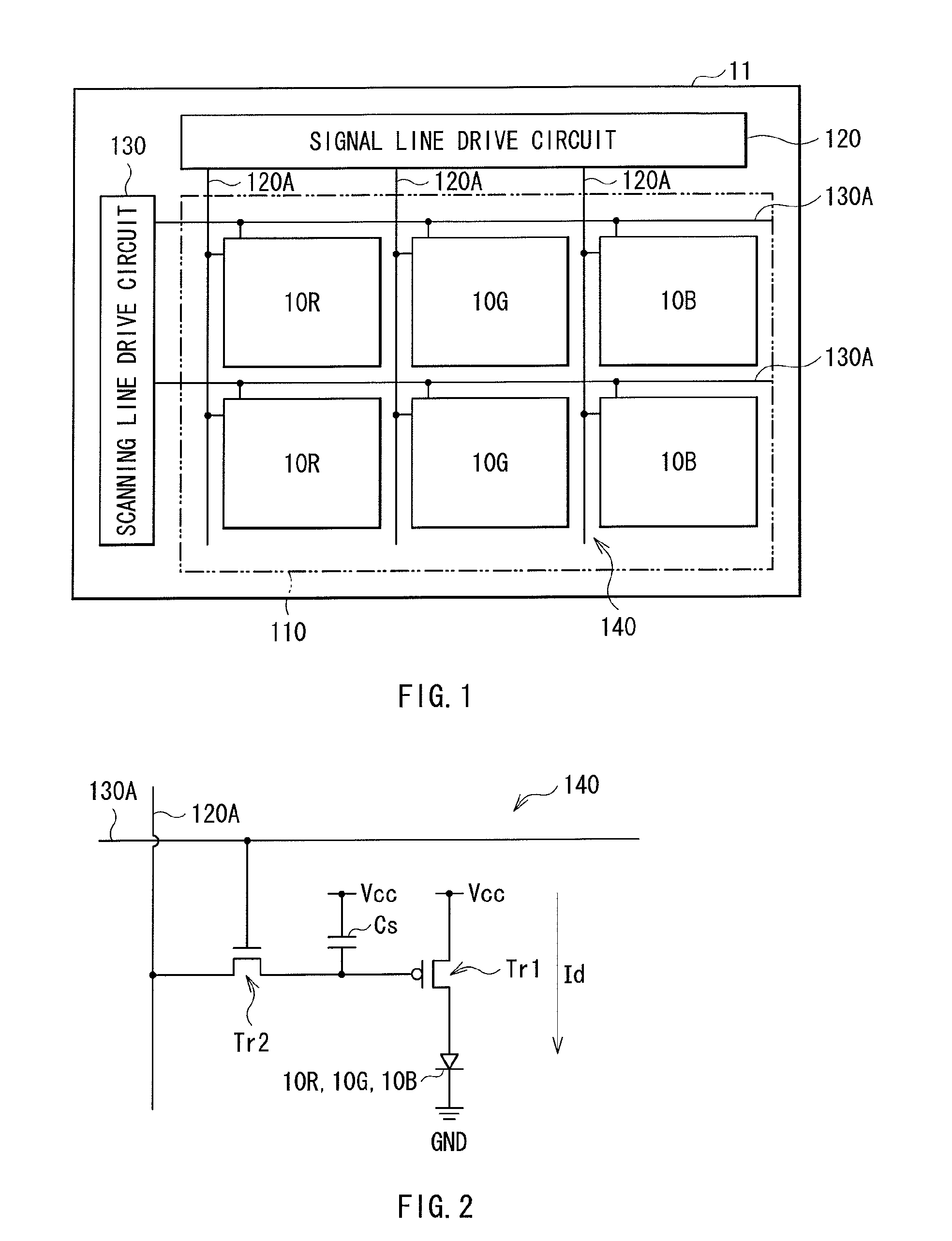
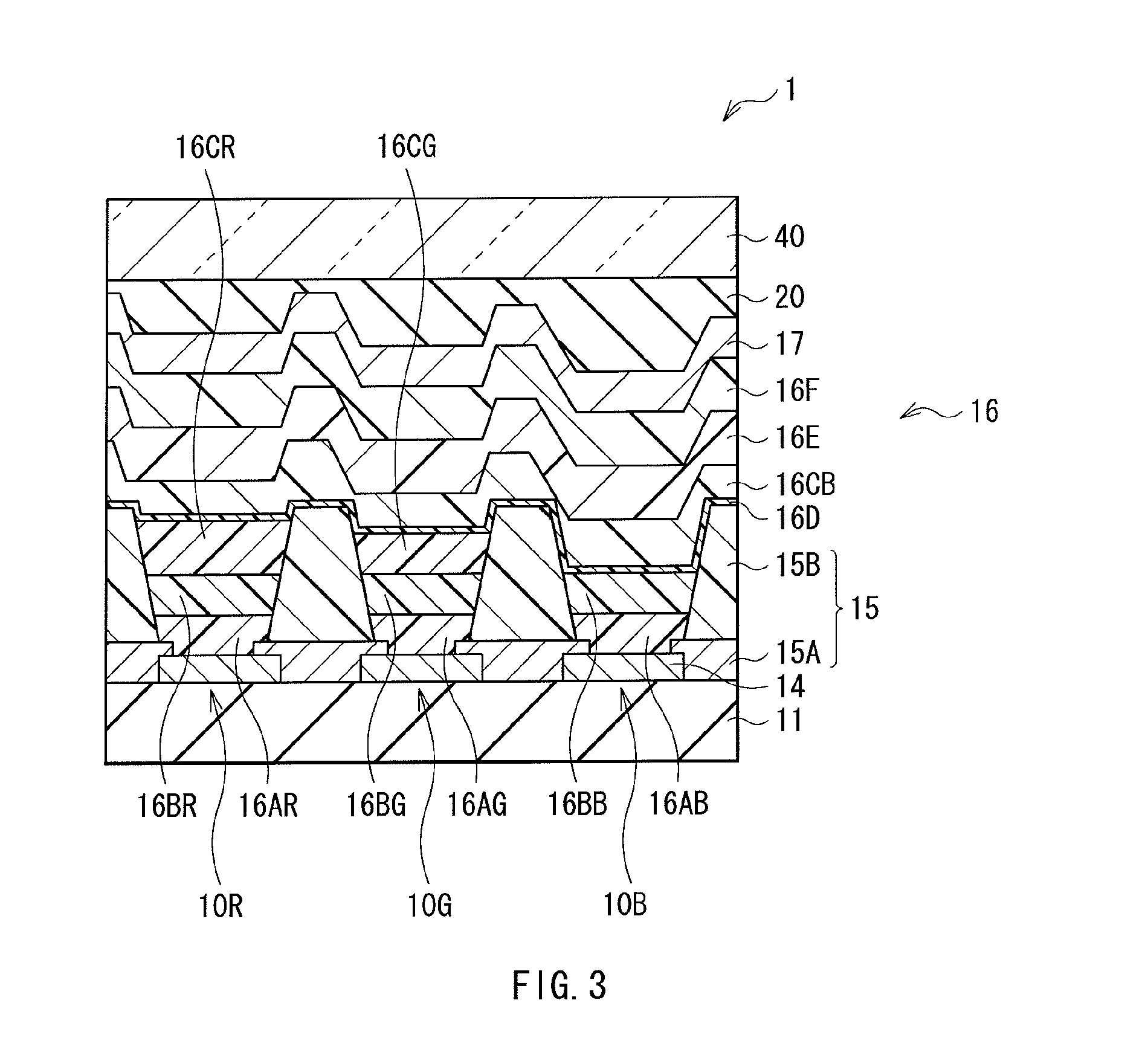
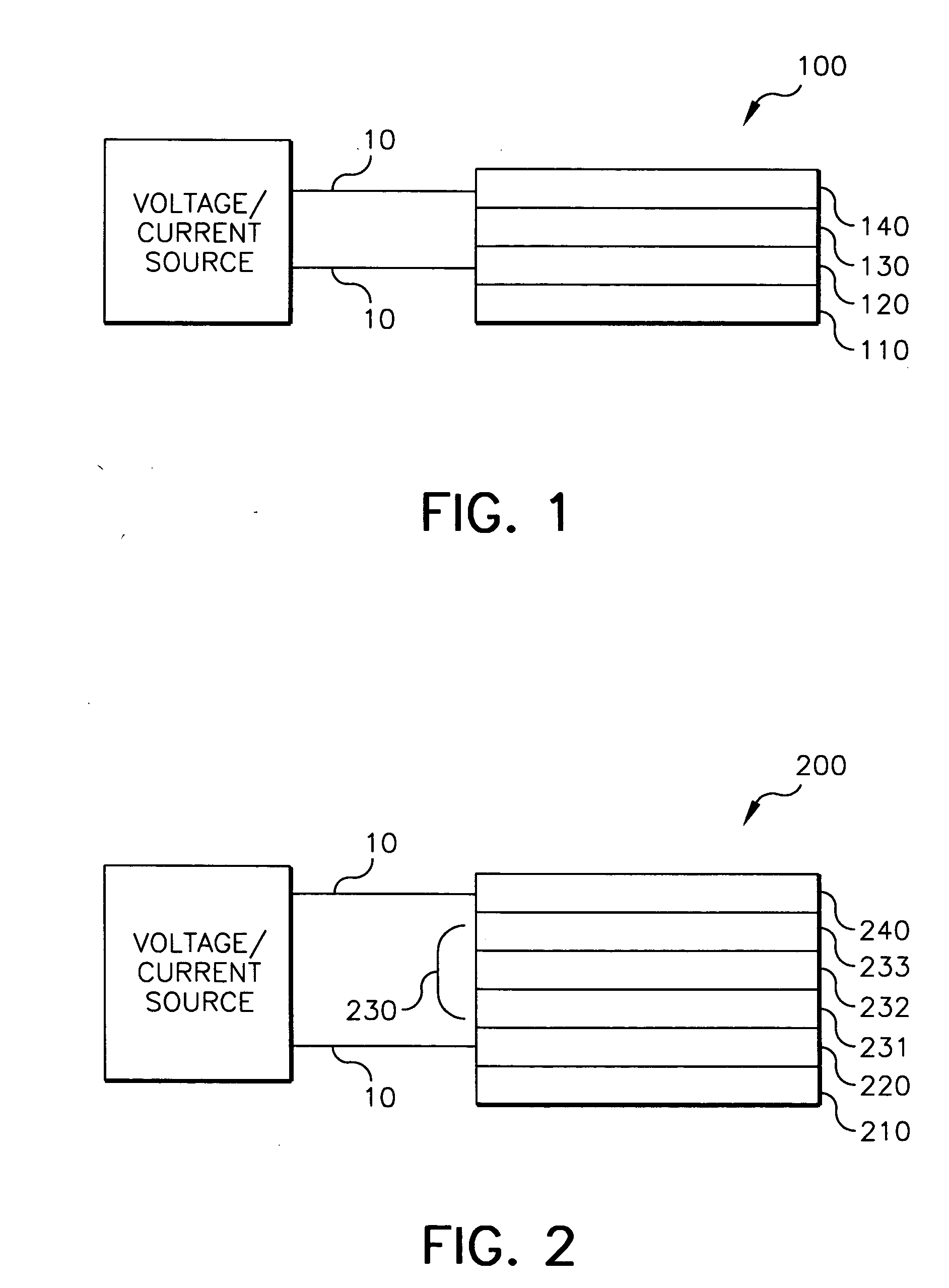
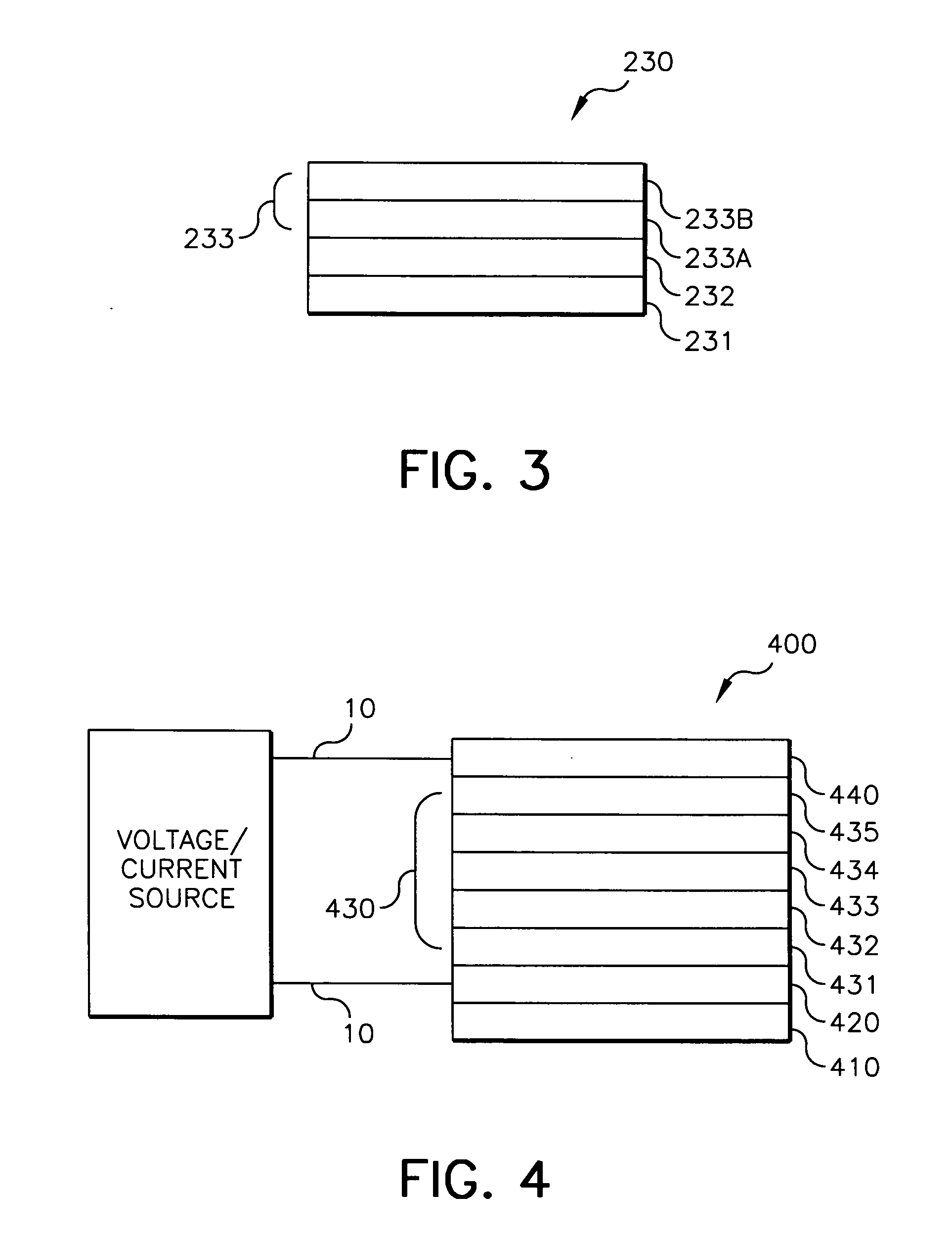
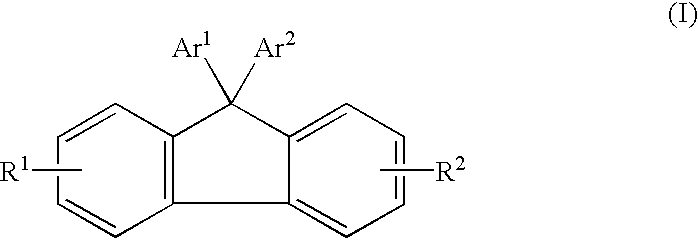
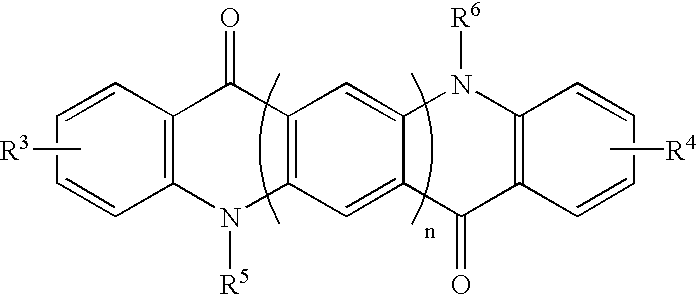
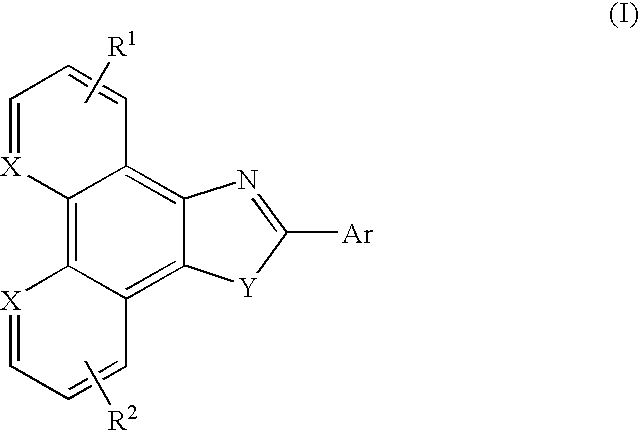
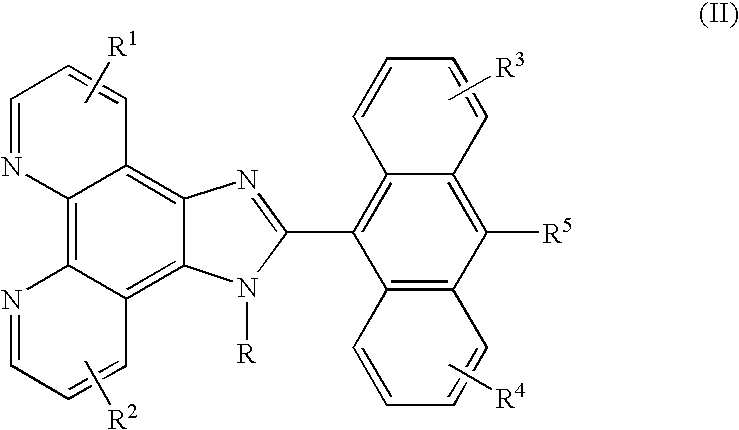
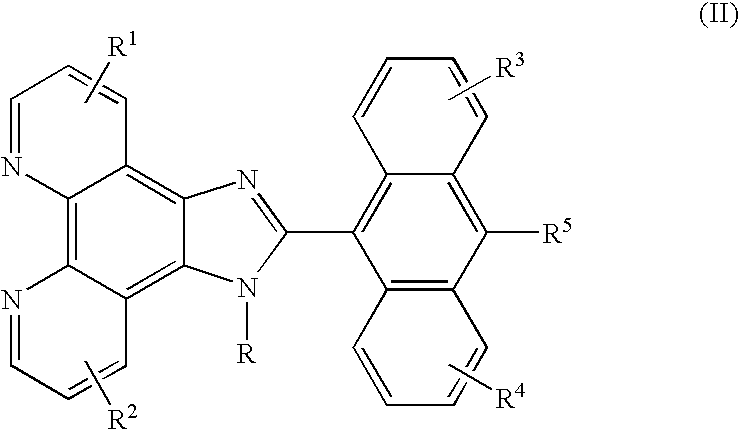
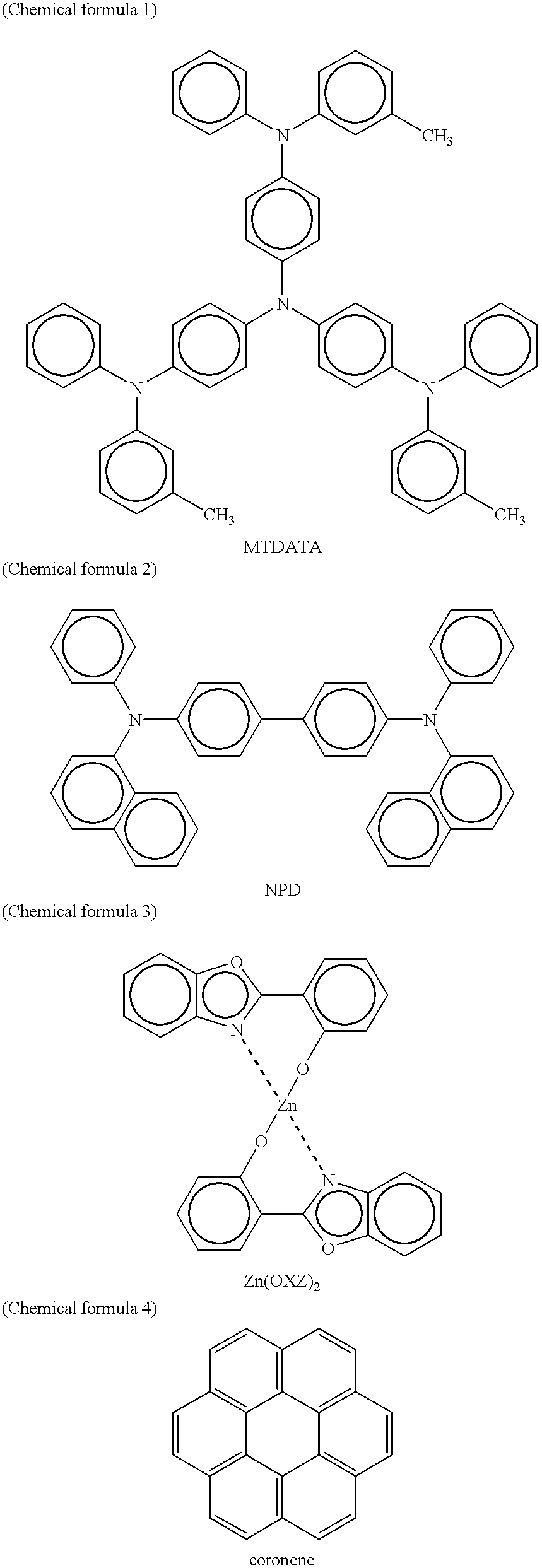
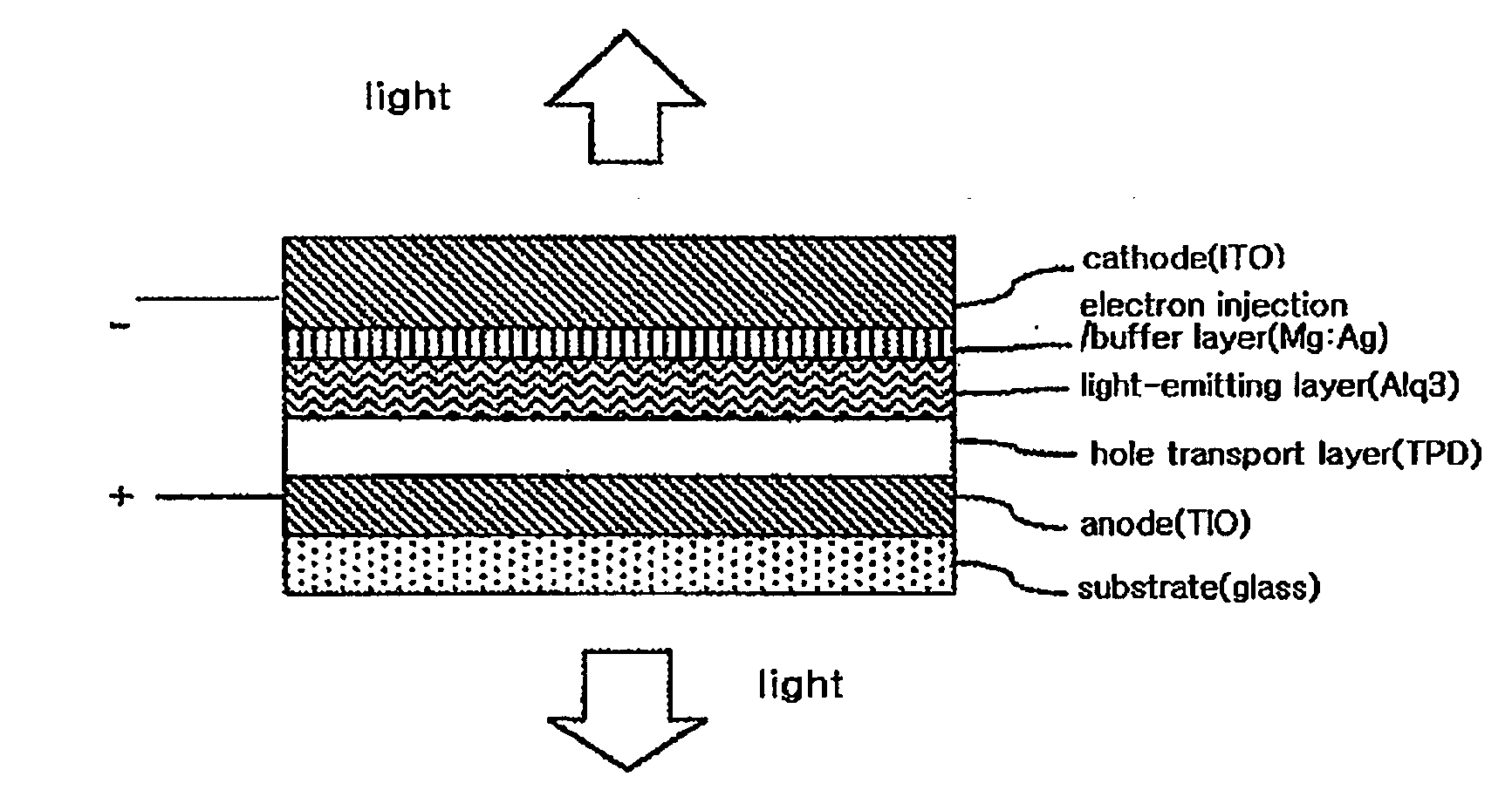
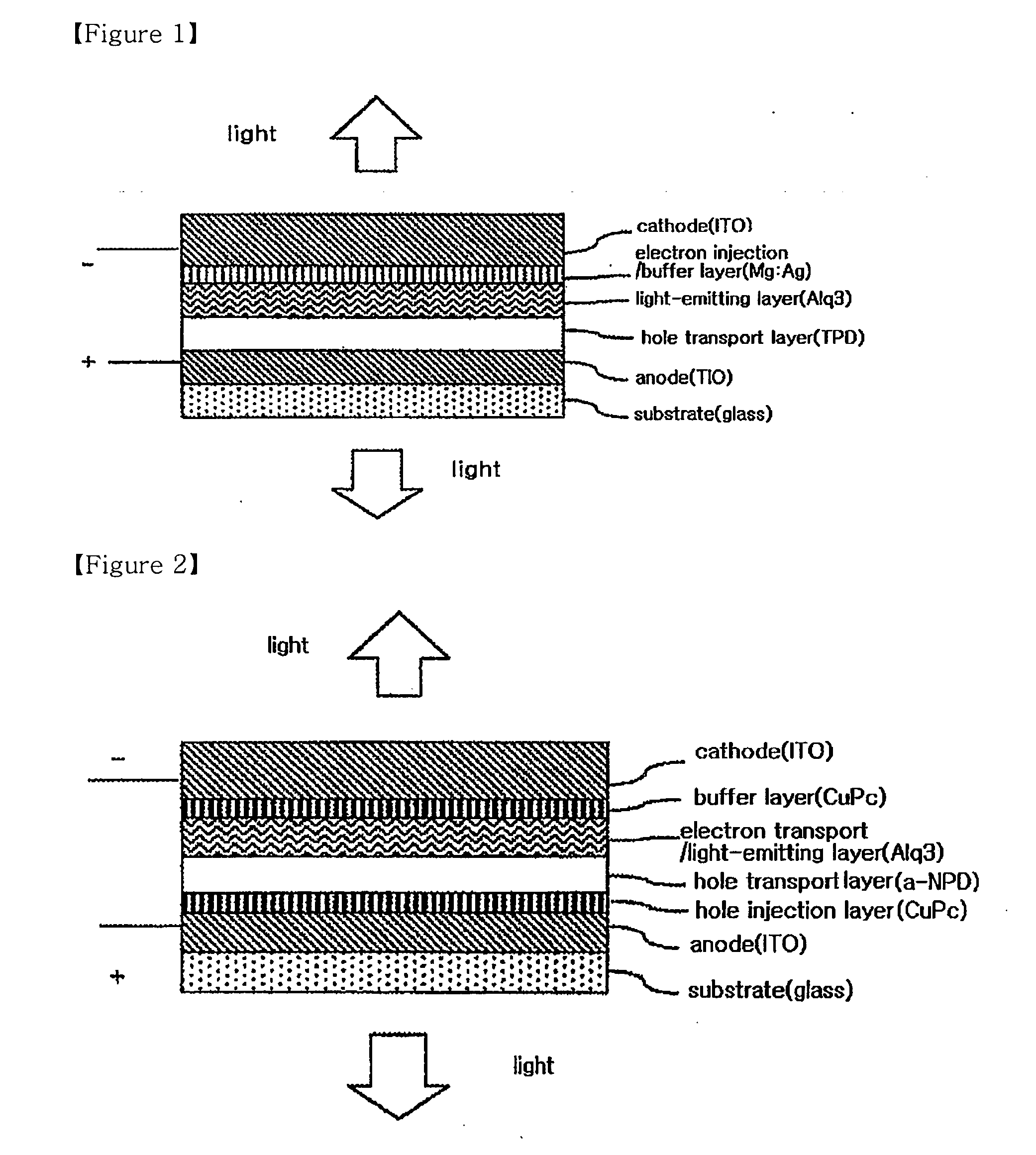
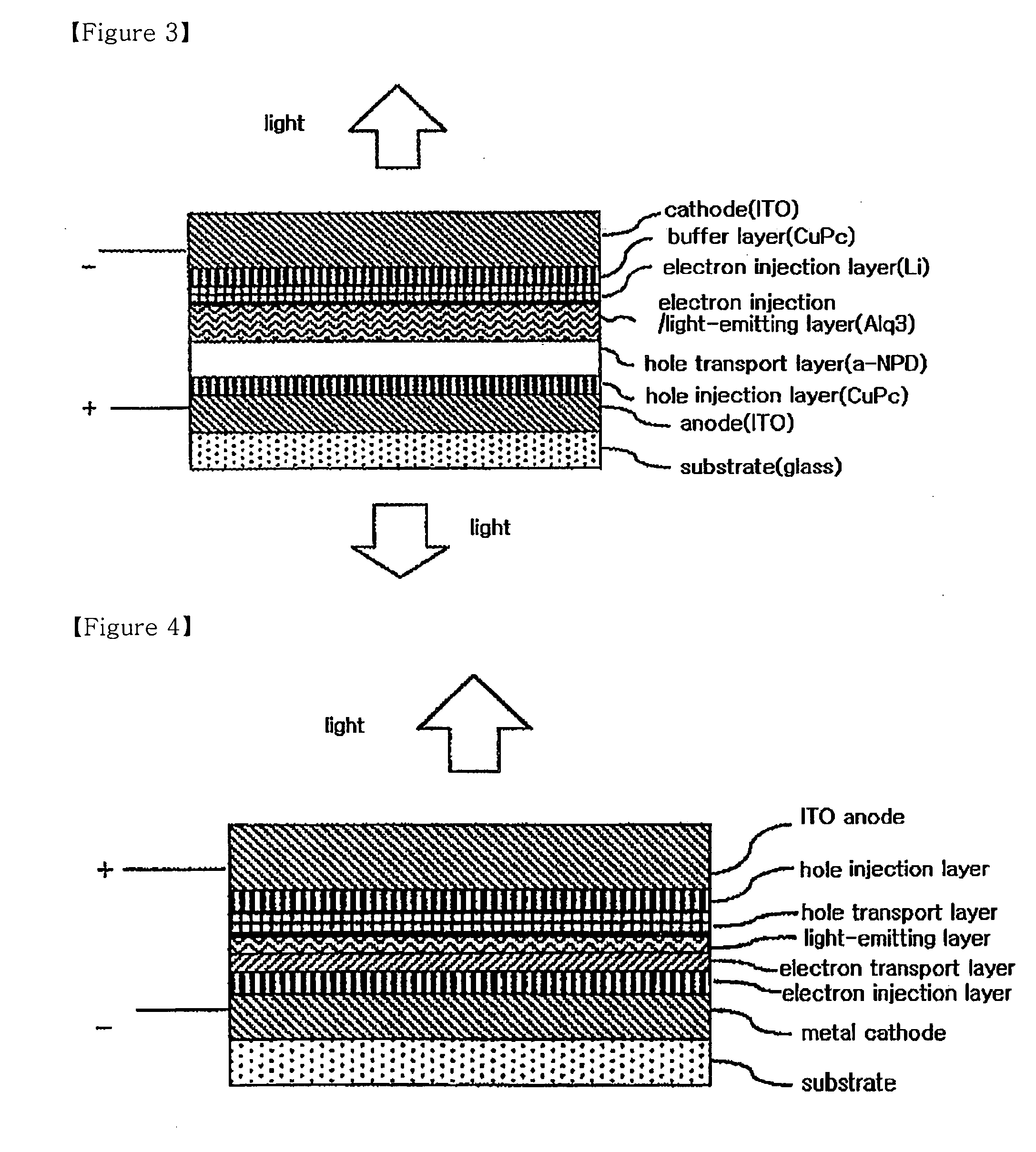
6H-INDOLO[2,3-b]QUINOXALINE DERIVATIVES AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE USING THE SAME
ActiveUS20110303901A1Group 4/14 element organic compoundsSolid-state devicesQuinoxalineElectron injection
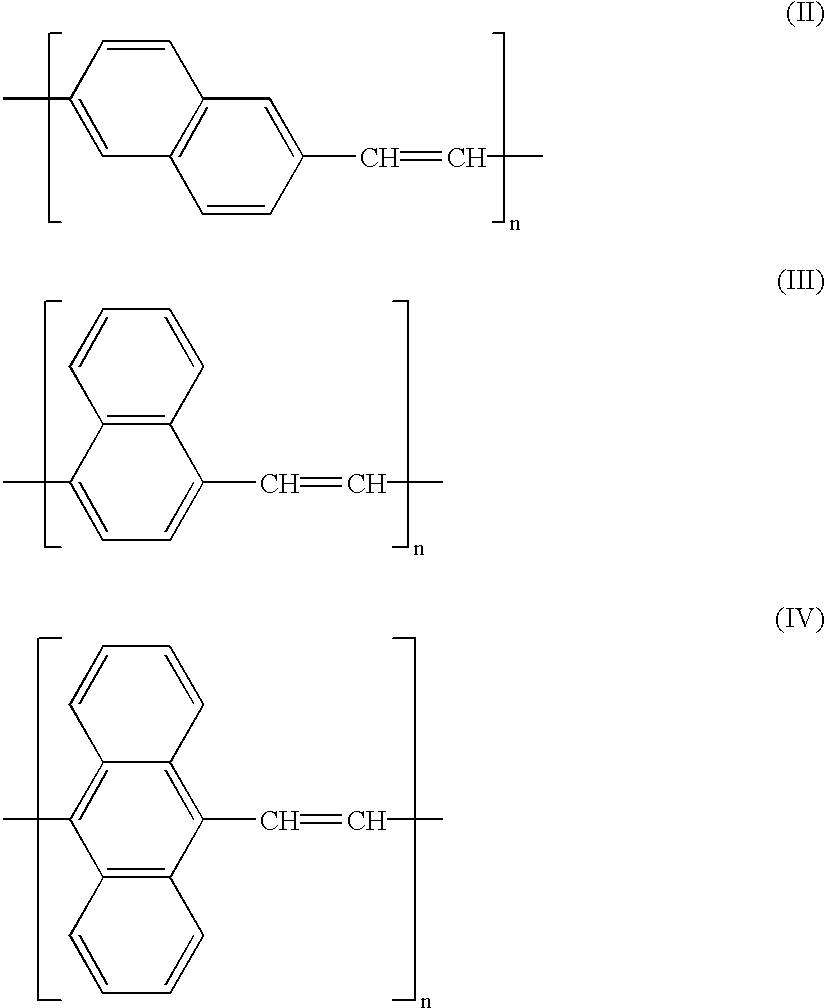
A 6H-indolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline derivative has a structure of formula (I). R9 is a member selected from the group consisted of an aryl group having one or more substituents and a heteroaryl group having one or more substituents, and R1 to R8 are substituents. The 6H-indolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline derivative of the present invention incorporates an indole and a quinoxaline group therefore inherits good energy transfer ability from indole and good electron-injection ability from quinoxaline. The compound of the present invention may function as a host material or a dopant in the light-emitting layer. In addition, the compound of the present invention may function as hole transport material, electron transport material, hole blocking material, electron blocking material, hole injecting material or electron injecting material.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Organic el display device and method of manufacturing the same
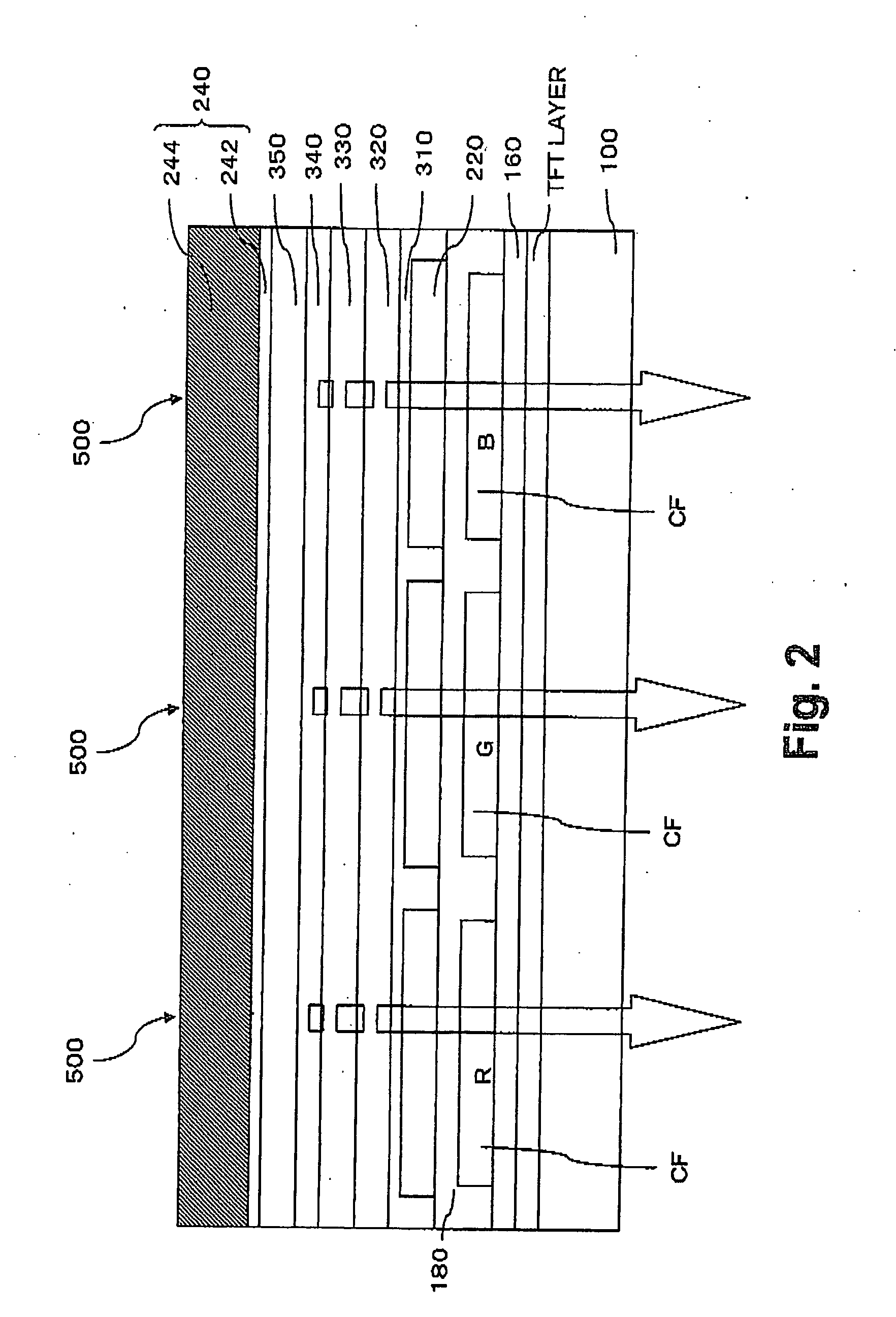
ActiveCN102655164AImprove luminous efficiencyHigh color puritySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTransport layerElectron injection
Disclosed herein is an organic EL display device, including: a lower electrode provided every first organic EL element for a blue color and every second organic EL element for another color on a substrate; a hole injection / transport layer provided every first and second organic EL elements; a second organic light emitting layer for another color provided on said hole injection / transport layer for said second organic EL element; a connection layer made of a low-molecular material and provided over an entire surface of said hole injection / transport layer for said second organic light emitting layer and said first organic EL element; a first organic light emitting layer for a blue color provided over an entire surface of said connection layer; and an electron injection / transport layer and an upper electrode provided over an entire surface of said organic light emitting layer in order.
Owner:JOLED INC
Electroluminescence element
InactiveUS20060066231A1Uniform light emission easilyImprove light emission balanceDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesElectron injectionOrganic layer
An EL element includes, between an anode and a cathode, an emissive element layer including a plurality of emissive layers. The emissive element layer includes two or more organic layers containing a hole transporting compound, and one or more of the plurality of emissive layers contain the hole transporting compound. The concentration of the hole transporting compound in the organic layer which is formed closest to the electron injecting electrode among the organic layers containing the hole transporting compound is lower than the concentration of the hole transporting compound in the organic layer which is formed closest to the hole injecting electrode. When three or more organic layers contain a hole transporting compound, the concentration of the hole transporting compound contained in each organic layer can be set such that, as the organic layer is further away from the hole injecting electrode, the concentration is lower. With this setting, the supply amount and supply timing of holes and electrons can be optimized easily with regard to each of the plurality of emissive layers, so that uniform light emission can be generated in any one of the emissive layers.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
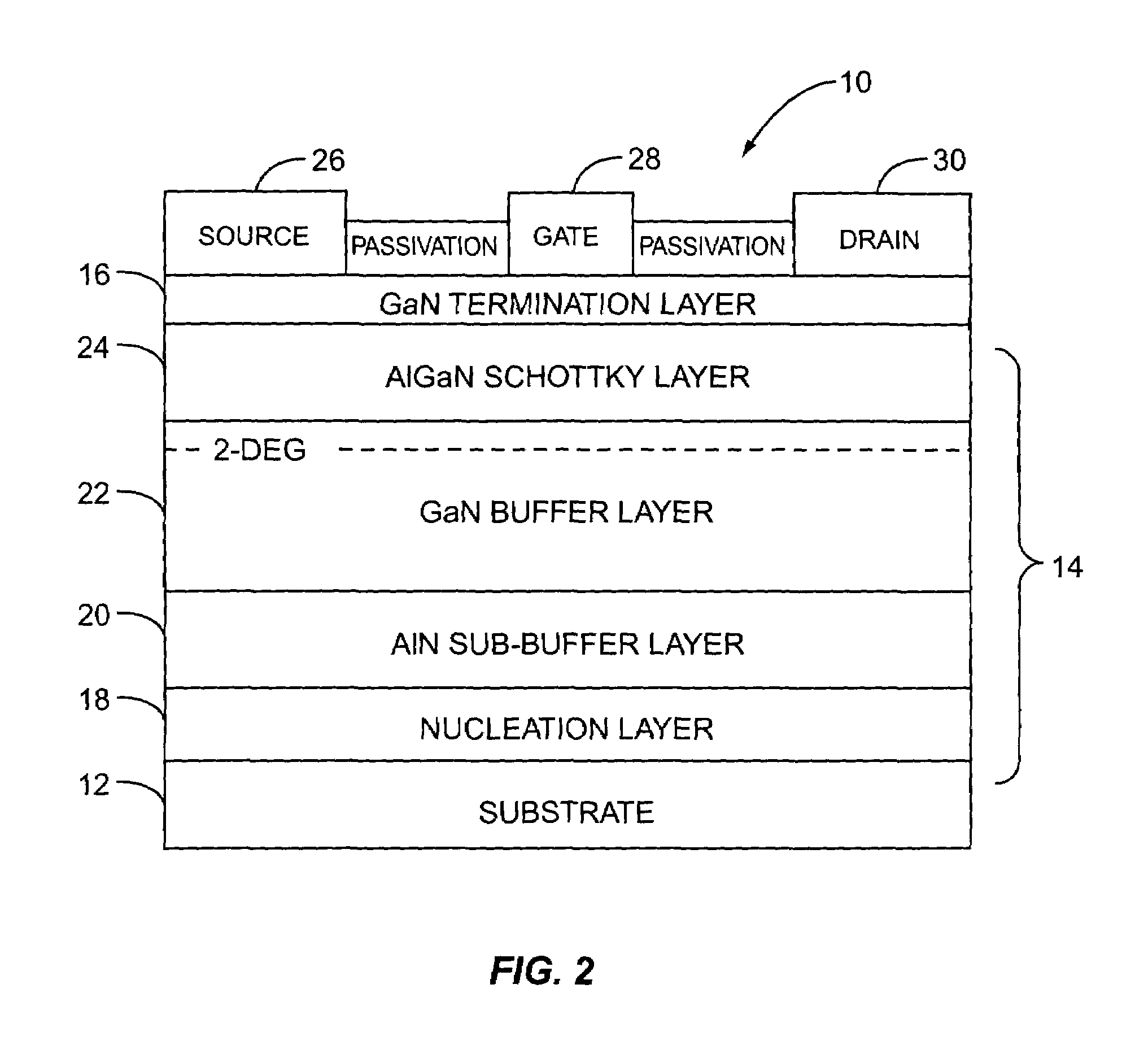
High voltage GaN-based transistor structure
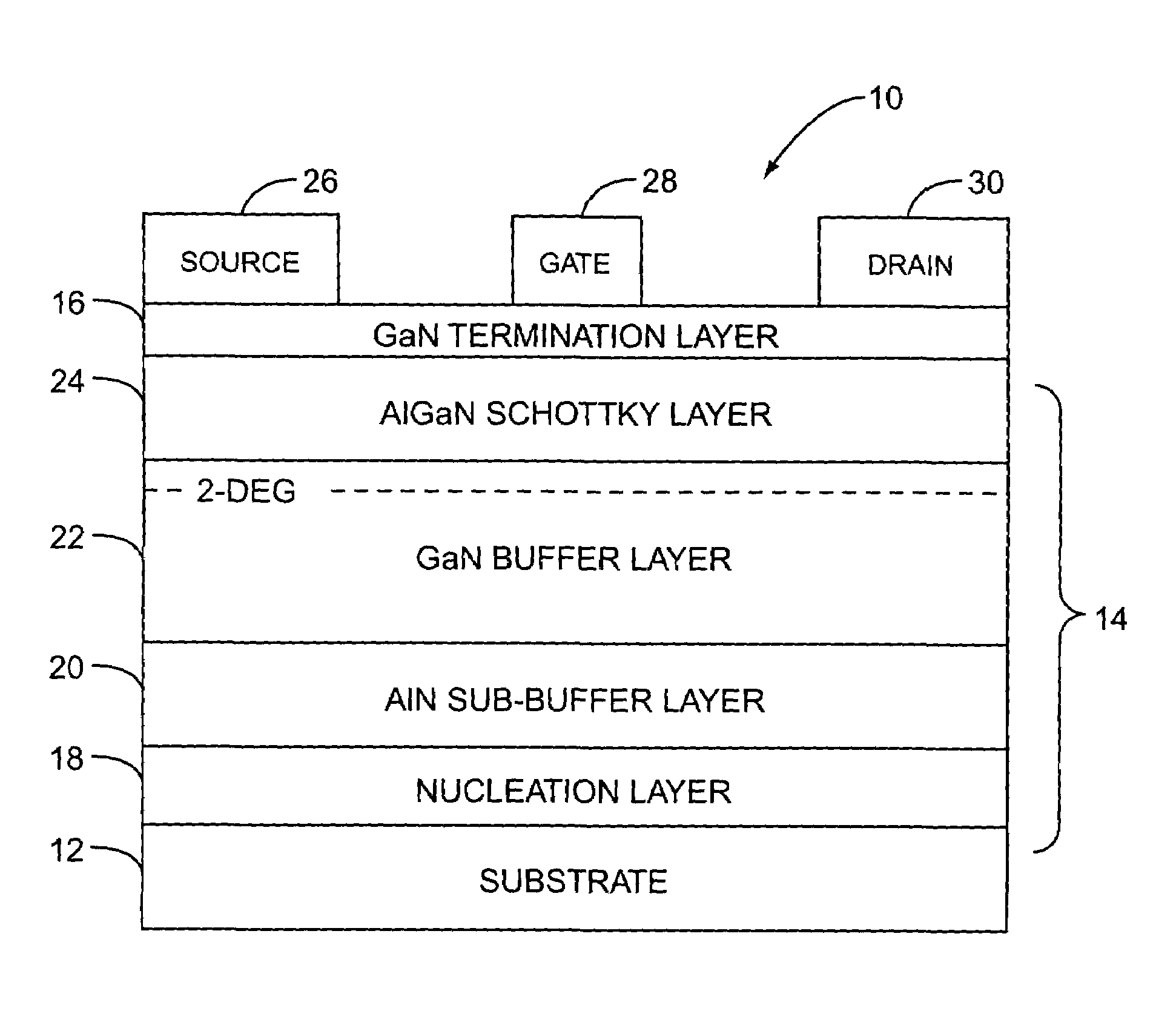
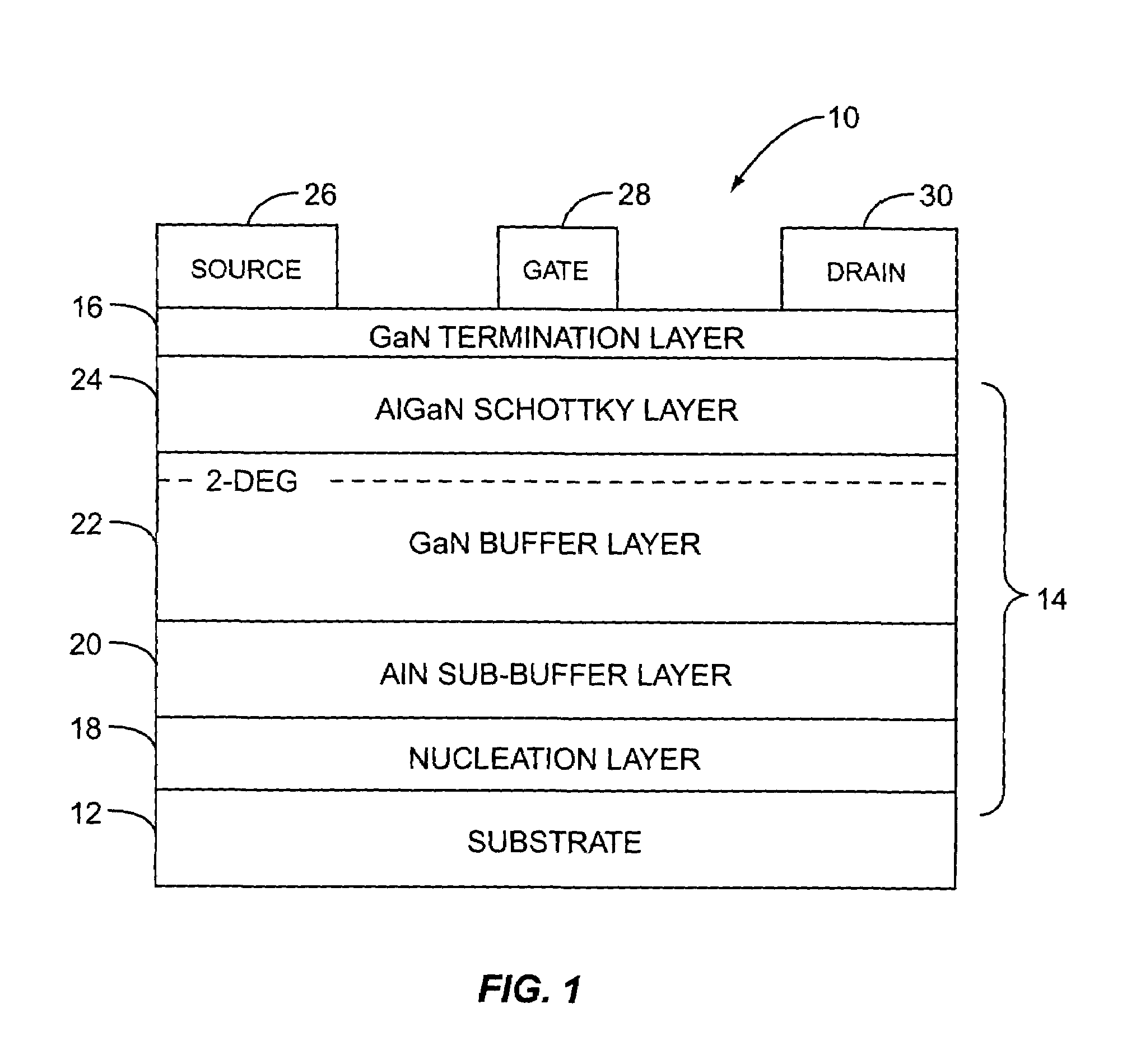
ActiveUS7026665B1Improve performanceImprove passivation effectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGallium nitrideHigh pressure
The present invention relates to a high voltage and high power gallium nitride (GaN) transistor structure. In general, the GaN transistor structure includes a sub-buffer layer that serves to prevent injection of electrons into a substrate during high voltage operation, thereby improving performance of the GaN transistor structure during high voltage operation. Preferably, the sub-buffer layer is aluminum nitride, and the GaN transistor structure further includes a transitional layer, a GaN buffer layer, and an aluminum gallium nitride Schottky layer.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Floating-gate semiconductor structures
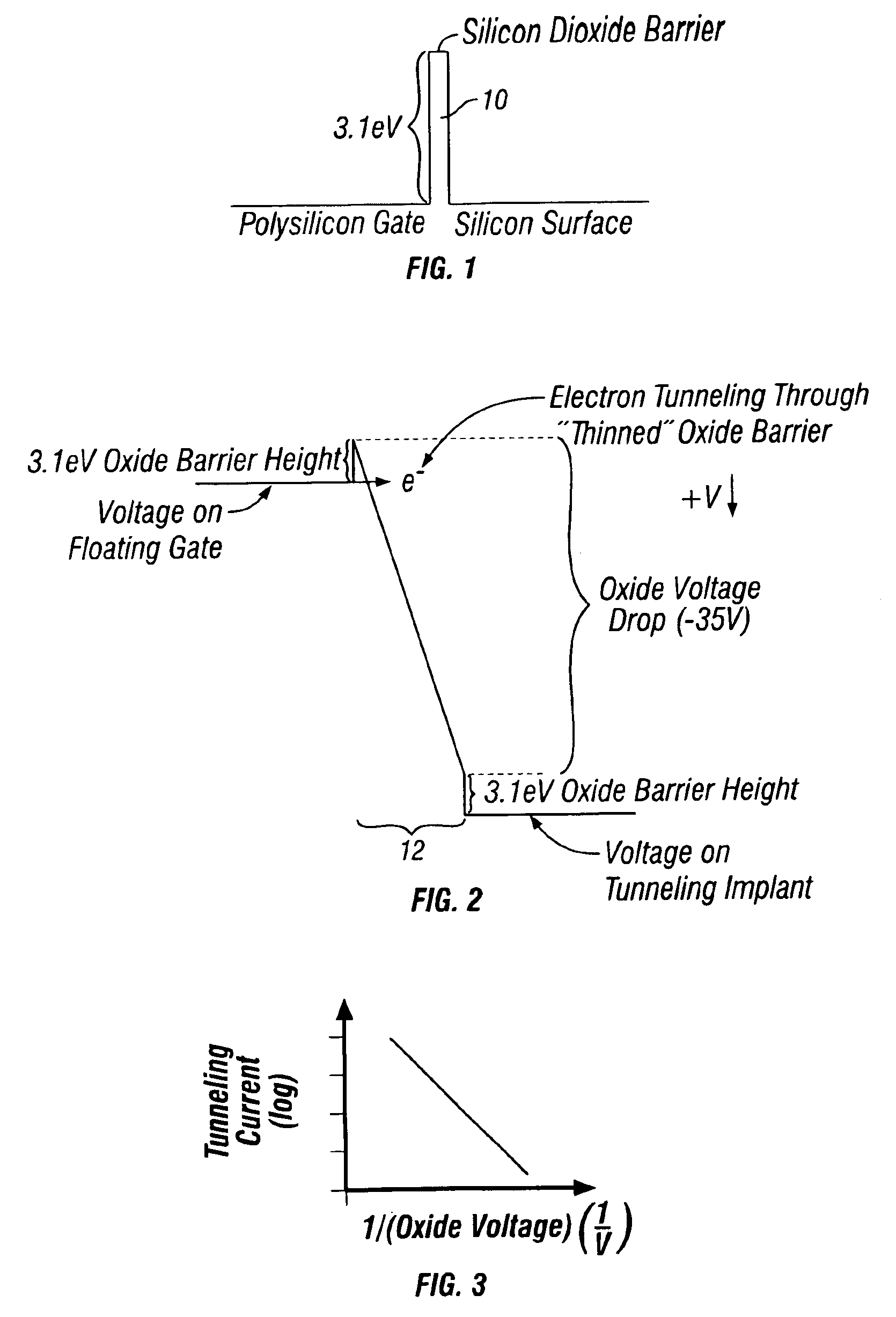
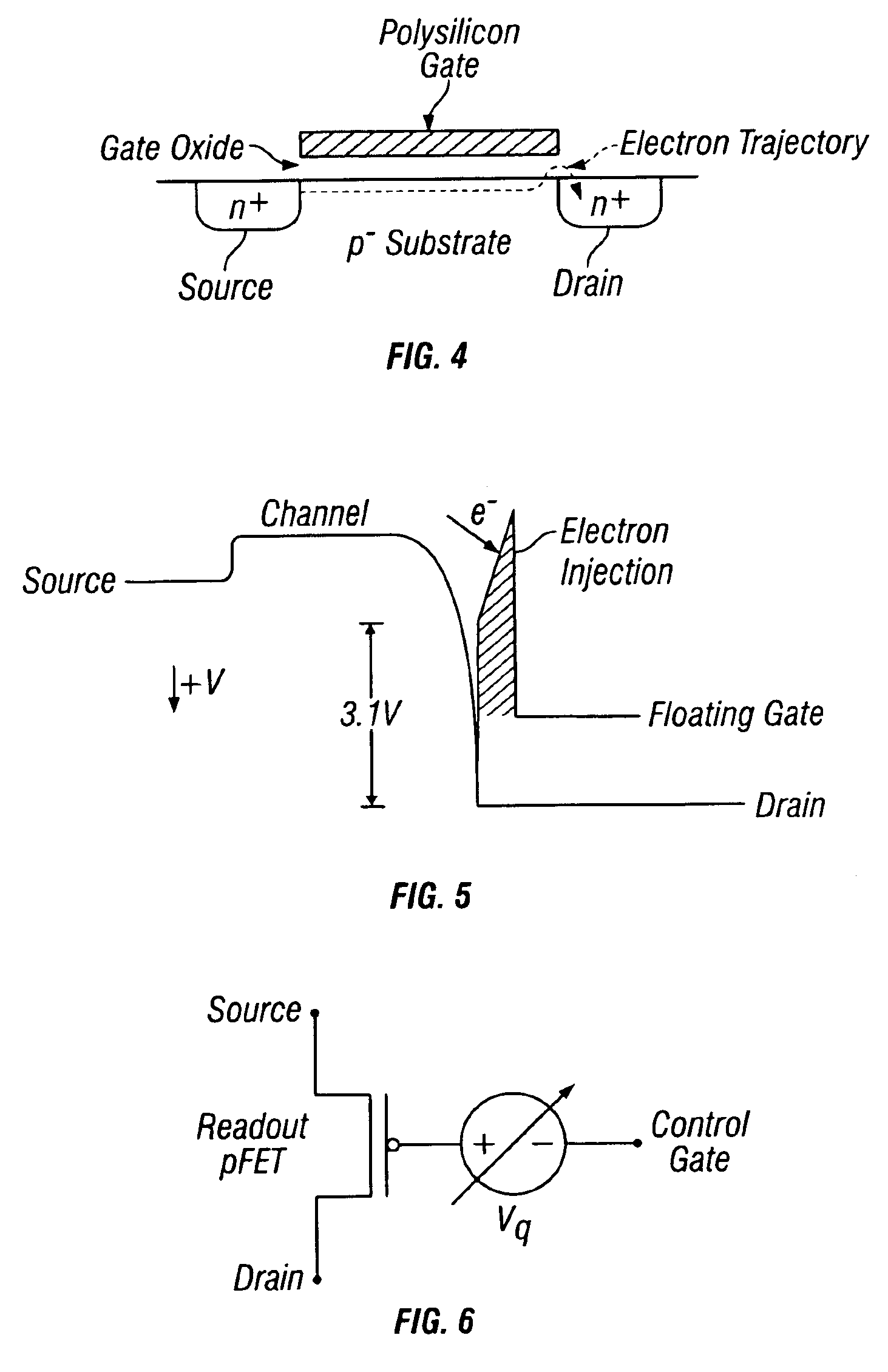
Hot-electron injection driven by hole impact ionization in the channel-to-drain junction of a p-channel MOSFET provides a new mechanism for writing a floating-gate memory. Various pFET floating-gate structures use a combination of this mechanism and electron tunneling to implement nonvolatile analog memory, nonvolatile digital memory, or on-line learning in silicon. The memory is nonvolatile because the devices use electrically isolated floating gates to store electronic charge. The devices enable on-line learning because the electron injection and tunneling mechanisms that write the memory can occur during normal device operation. The memory updates and learning are bidirectional because the injection and tunneling mechanisms add and remove electrons from the floating gate, respectively. Because the memory updates depend on both the stored memory and the pFETs terminal voltages, and because they are bidirectional, the devices can implement on-line learning functions.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC +1
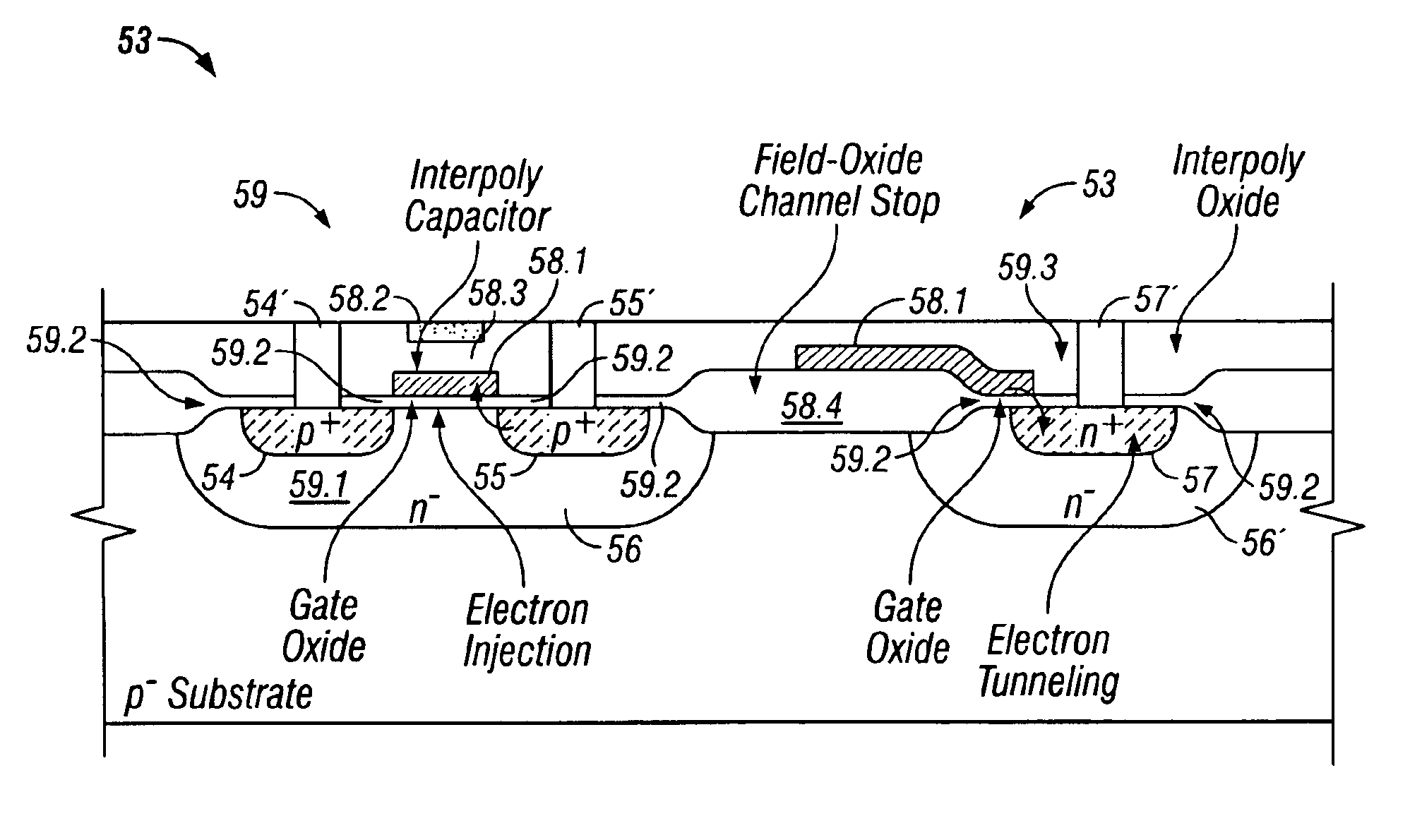
Nonvolatile memory cell having floating gate, control gate and separate erase gate, an array of such memory cells, and method of manufacturing
A nonvolatile memory cell having a floating gate for the storage of charges thereon has a control gate and a separate erase gate. The cell is programmed by hot channel electron injection and is erased by poly to poly Fowler-Nordheim tunneling. A method for making an array of unidirectional cells in a planar substrate, as well as an array of bidirectional cells in a substrate having a trench, is disclosed. An array of such cells and a method of making such an array is also disclosed.
Owner:SILICON STORAGE TECHNOLOGY
Organic electroluminescent device and manufacturing method thereof
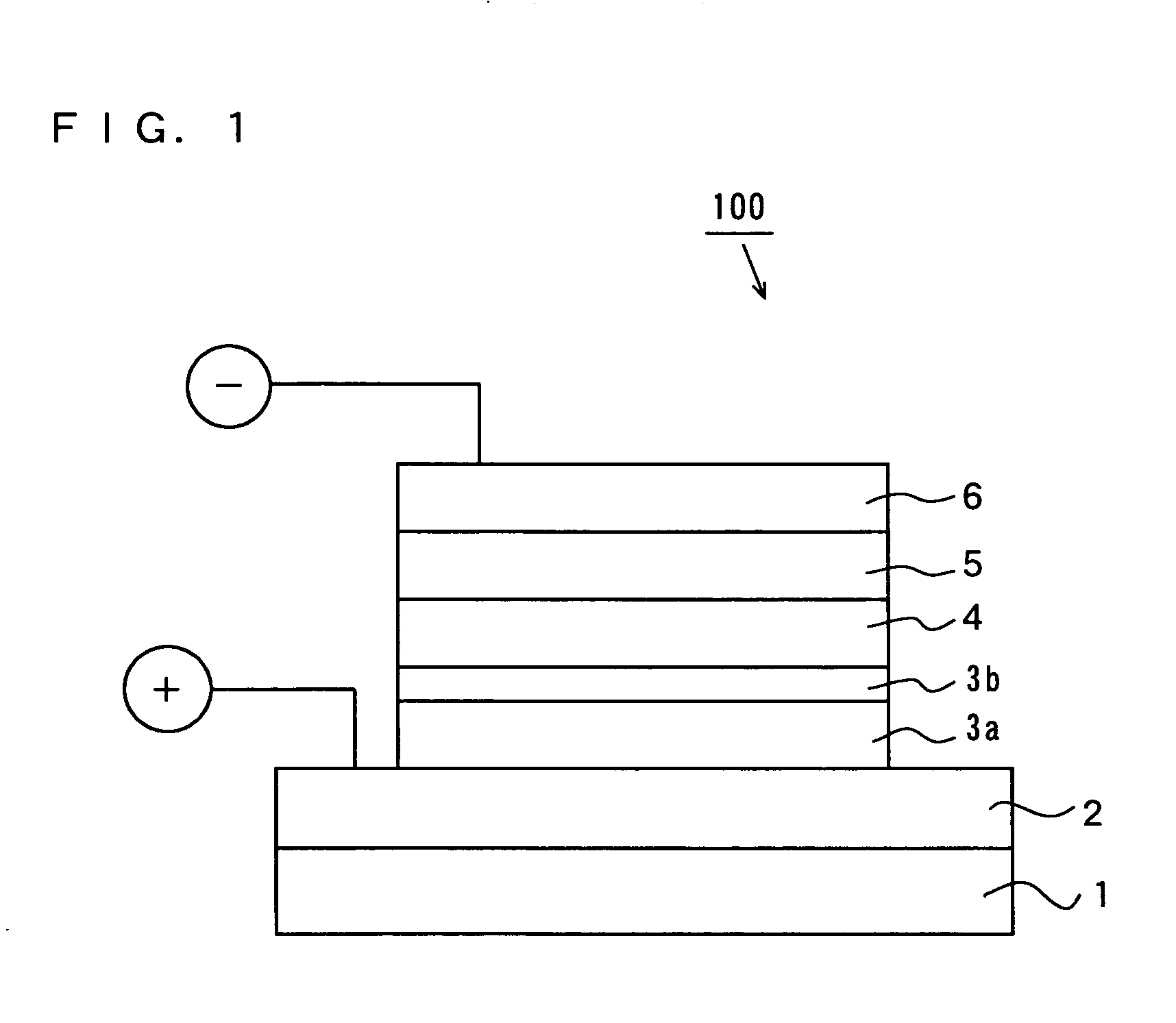
ActiveUS20050062406A1Avoid light deteriorationReduced initial drive voltageBatteries circuit arrangementsDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectron injectionHole injection layer
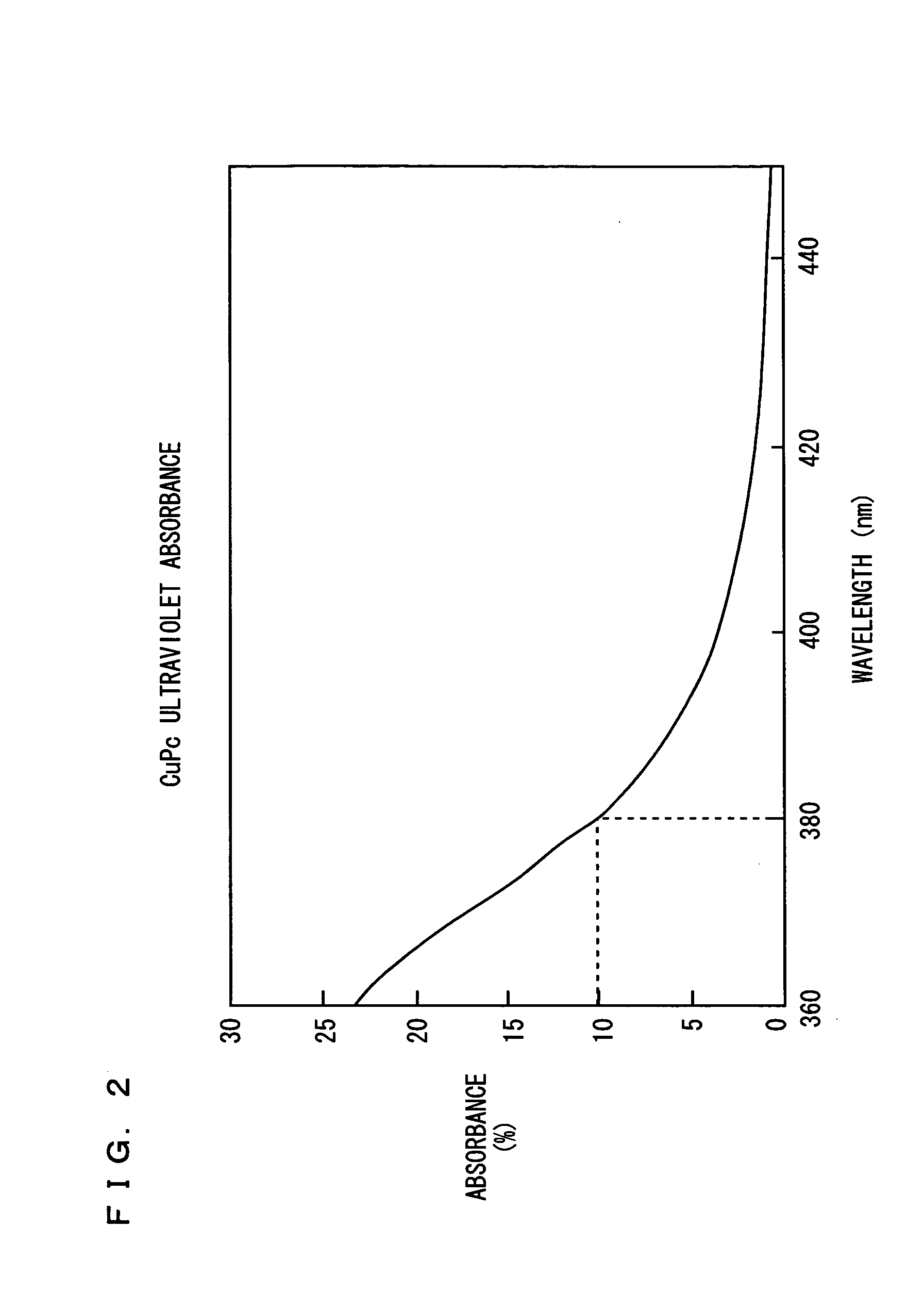
In an organic EL device, a hole injection electrode (anode) made of a transparent electrode. A first hole injection layer made of CuPc, a second hole injection layer made of CFx, a hole transport layer and alight emitting layer each made of an organic material are formed in this order on the hole injection electrode. An electron injection electrode (cathode) is further formed on the light emitting layer. The first hole injection layer made of CuPc absorbs ultraviolet light, so that the organic EL device can be prevented from deterioration by the ultraviolet light. The second hole injection layer made of CFx promotes injection of holes, so that the initial drive voltage can be reduced.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
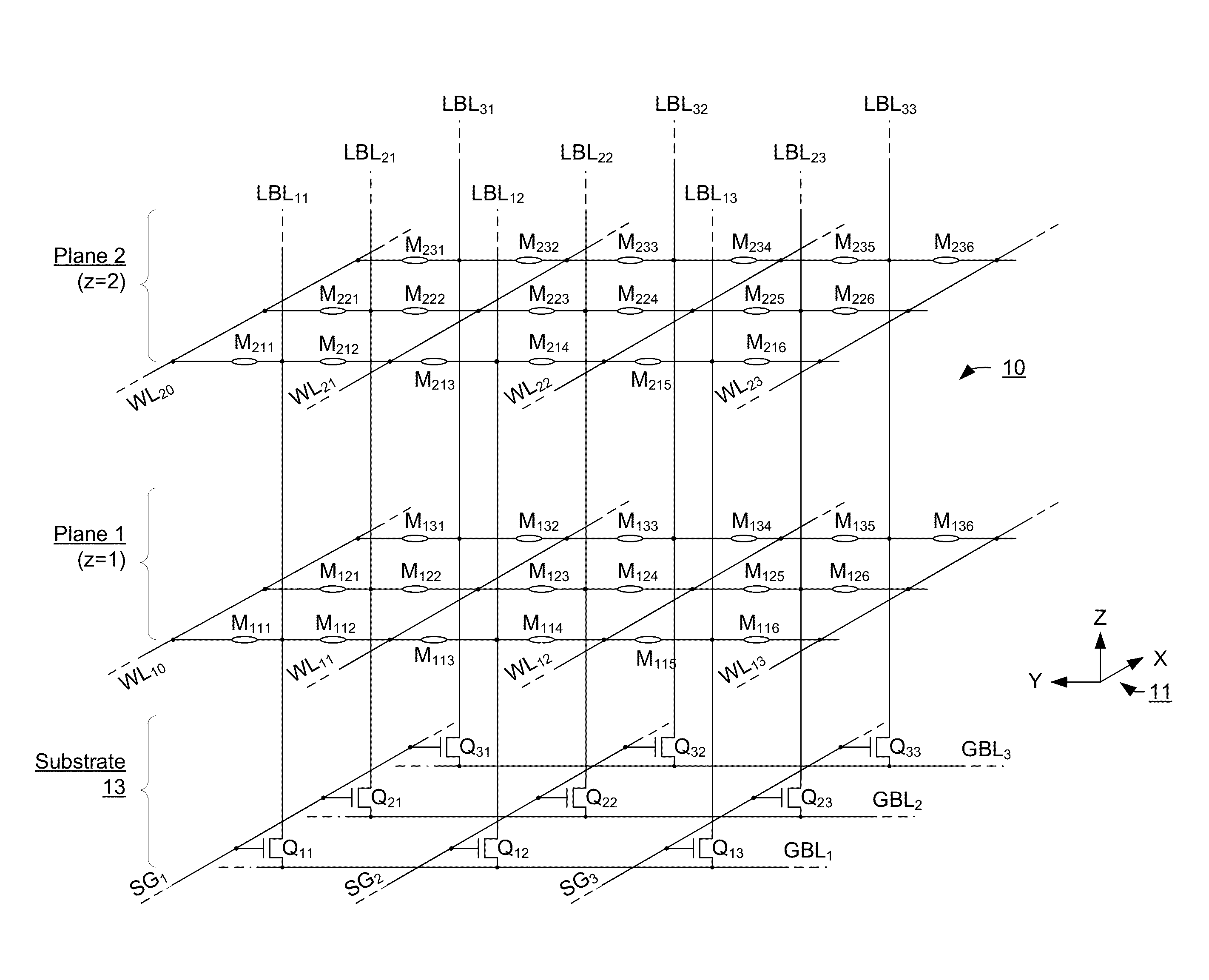
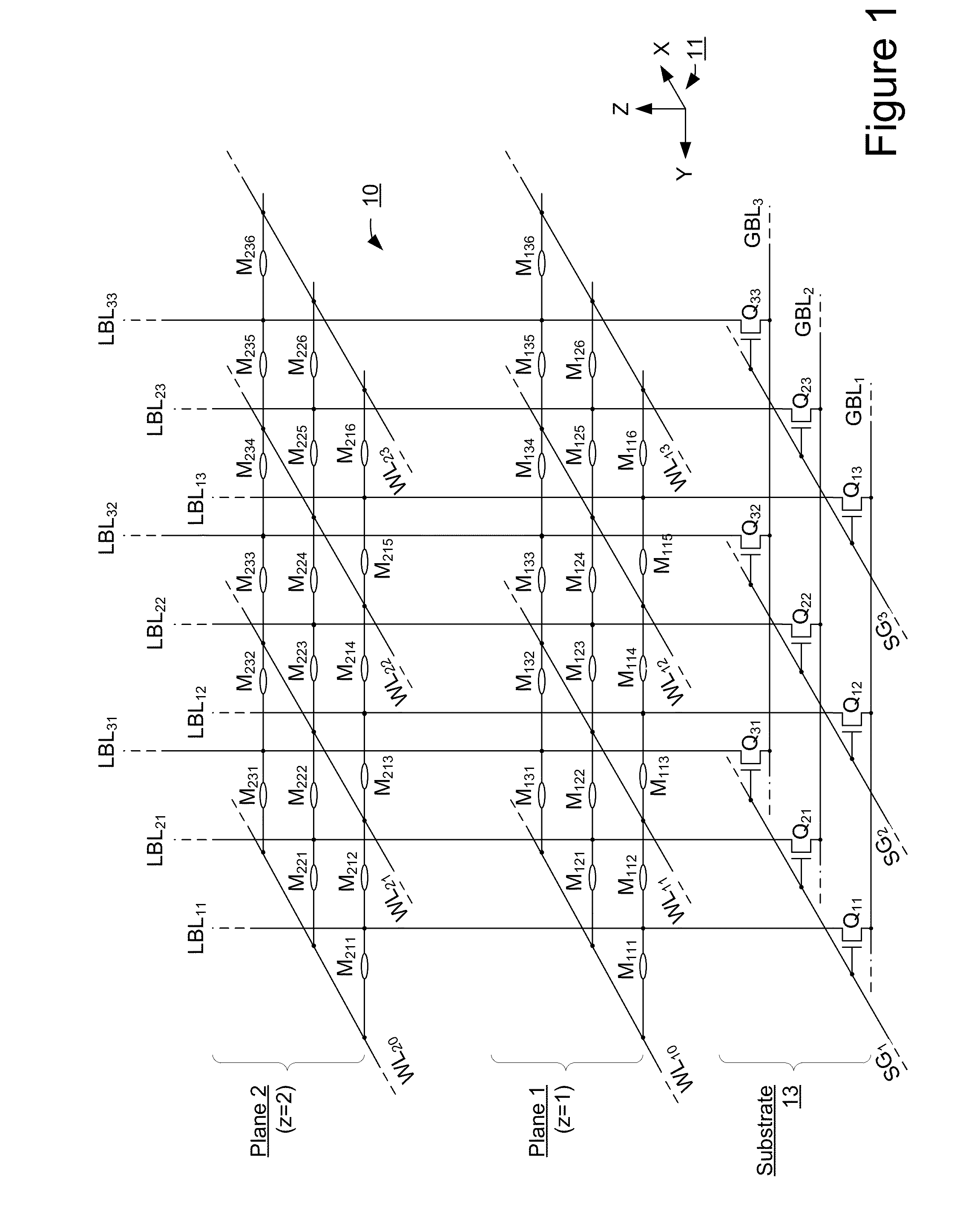
Low forming voltage non-volatile storage device
A three-dimensional array of memory elements that reversibly change a level of electrical conductance in response to a voltage difference being applied across them. Memory elements are provided across a plurality of planes positioned different distances above a semiconductor substrate. Bit lines to which the memory elements of all planes are connected are oriented vertically from the substrate and through the plurality of planes. The memory elements can be set to a low resistance state and reset to a high resistance state during standard operation by biasing appropriate voltages on the word lines and bit lines. Prior to standard operation, the memory elements undergo a forming operation, during which current through the bit lines is limited. A forming voltage is applied to the memory elements during forming with a polarity such that the bit line acts as a cathode and the word line acts as an anode, with the cathode having a lower electron injection energy barrier to the switching material than the anode.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Organic electroluminescent display with filter layer
InactiveUS6114805AIncadescent screens/filtersDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectron injectionSolid structure
An organic electroluminescent display includes a substrate (1), and, in order from the substrate, a hole injection electrode, at least one organic layer, an electron injecting electrode, and a sealing plate, and wherein the substrate further includes thereon an element-isolating structure (7,8) for isolating planar structures of the organic layer and the electron injection electrode from each other during film formation, the element isolating structure being a solid structure containing a base part formed on the substrate side and an overhang part larger in width than the base part, and provided on a portion where the organic layer is isolated from the electron injecting electrode as well as other portions, so that the element isolating structure can function as a spacer for the sealing plate, and at least one type of filter layer (14a-14c) is interleaved between the element-isolating structure serving as the spacer and the substrate.
Owner:FUTABA CORPORATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
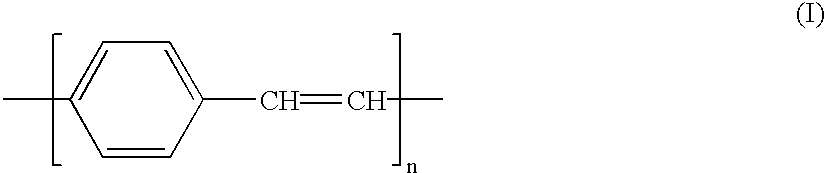


![6H-INDOLO[2,3-b]QUINOXALINE DERIVATIVES AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE USING THE SAME 6H-INDOLO[2,3-b]QUINOXALINE DERIVATIVES AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE USING THE SAME](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/a2b10734-5e12-45d6-ae2f-1c7f2da5b0b4/US20110303901A1-20111215-D00000.png)
![6H-INDOLO[2,3-b]QUINOXALINE DERIVATIVES AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE USING THE SAME 6H-INDOLO[2,3-b]QUINOXALINE DERIVATIVES AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE USING THE SAME](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/a2b10734-5e12-45d6-ae2f-1c7f2da5b0b4/US20110303901A1-20111215-D00001.png)
![6H-INDOLO[2,3-b]QUINOXALINE DERIVATIVES AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE USING THE SAME 6H-INDOLO[2,3-b]QUINOXALINE DERIVATIVES AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE USING THE SAME](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/a2b10734-5e12-45d6-ae2f-1c7f2da5b0b4/US20110303901A1-20111215-C00001.png)