Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
50results about How to "Write reliably" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
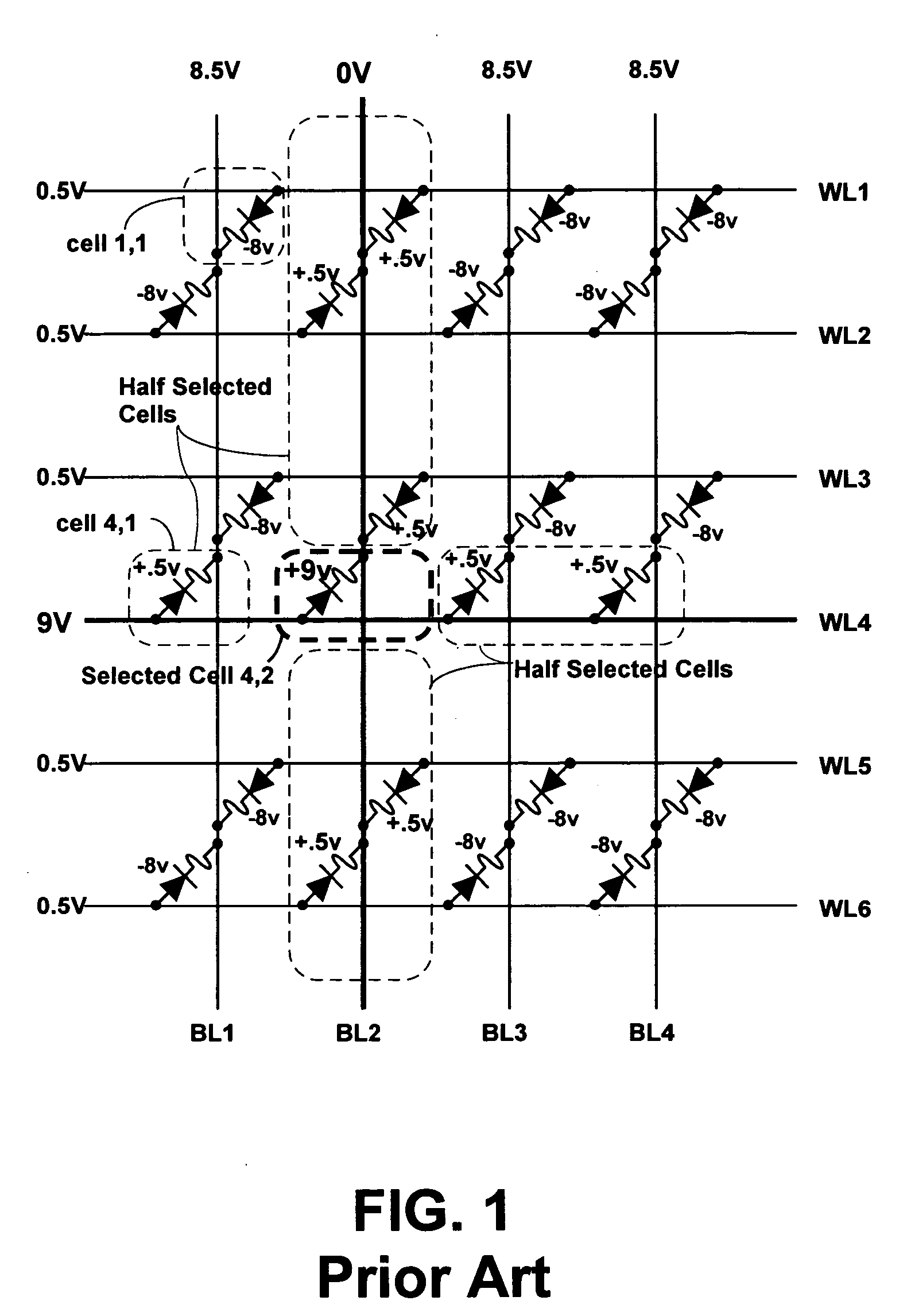
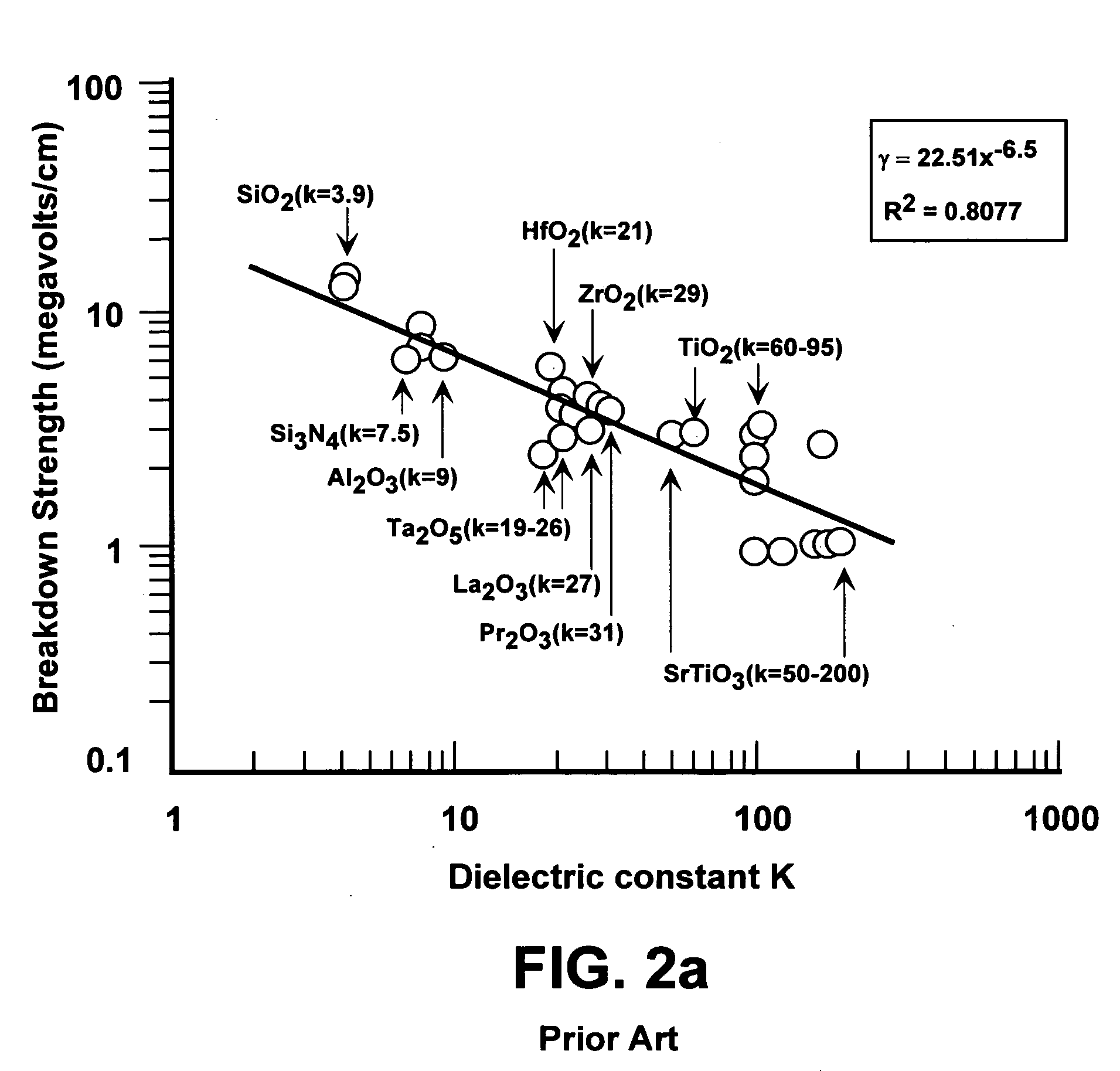
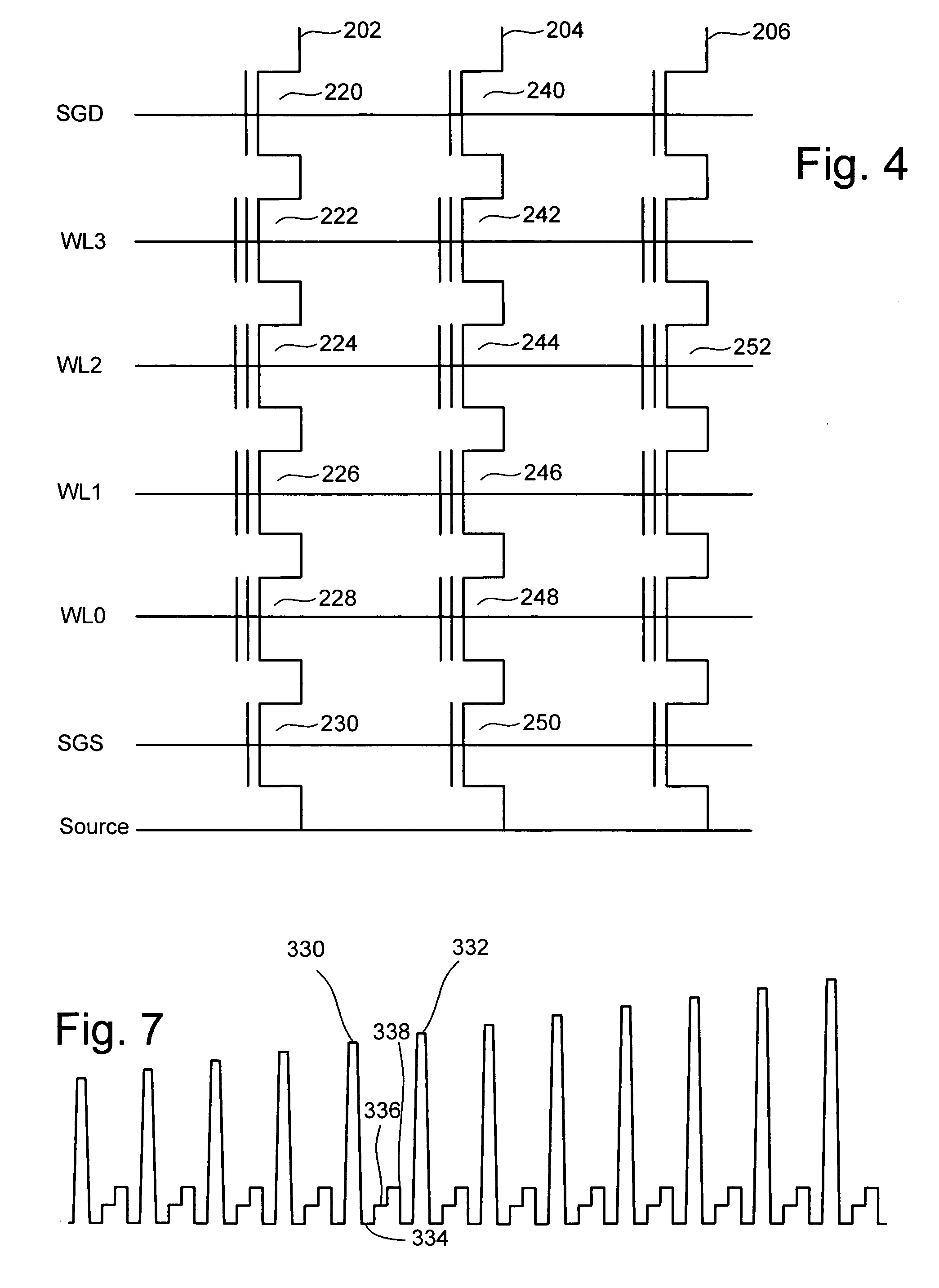
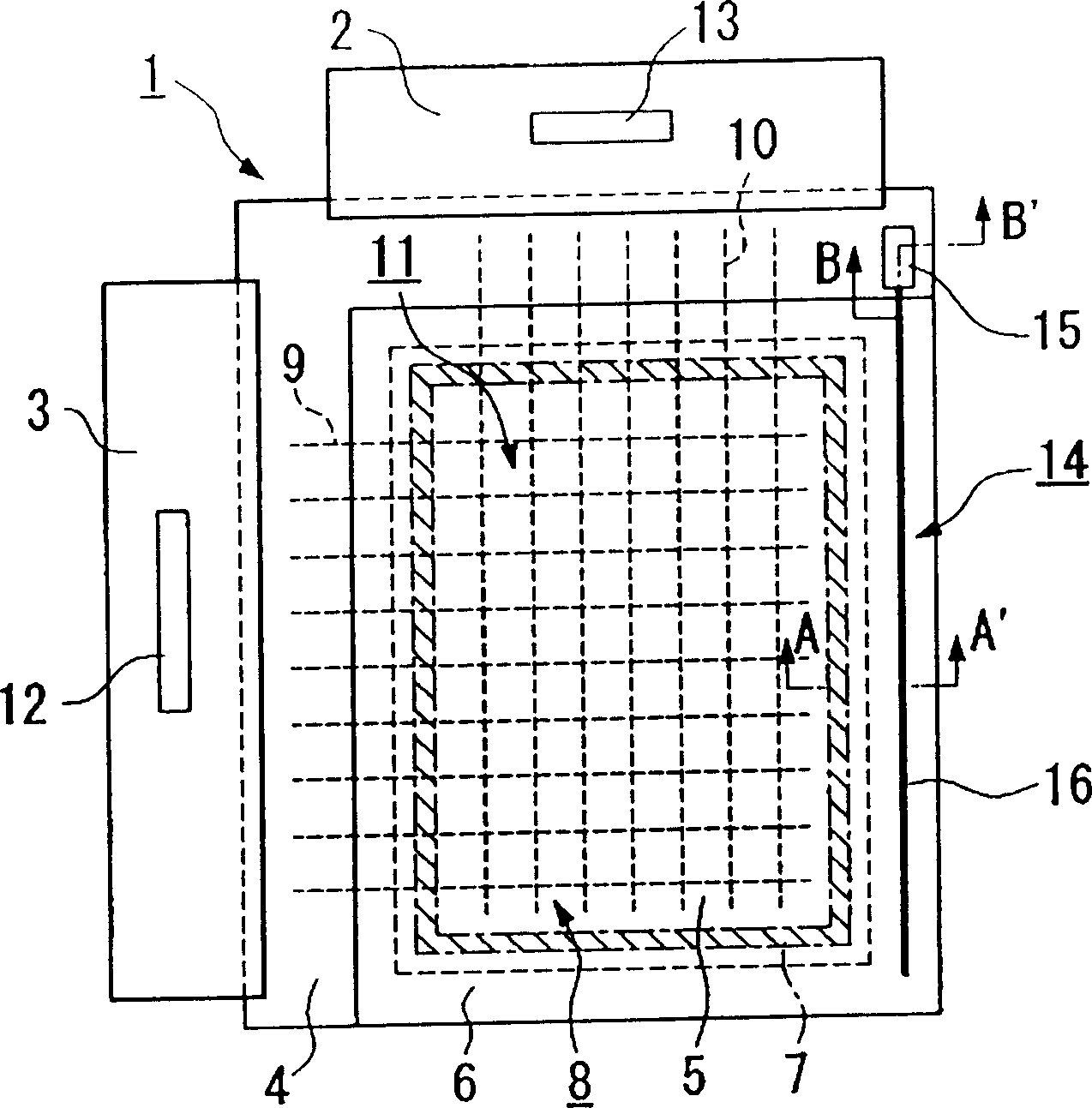
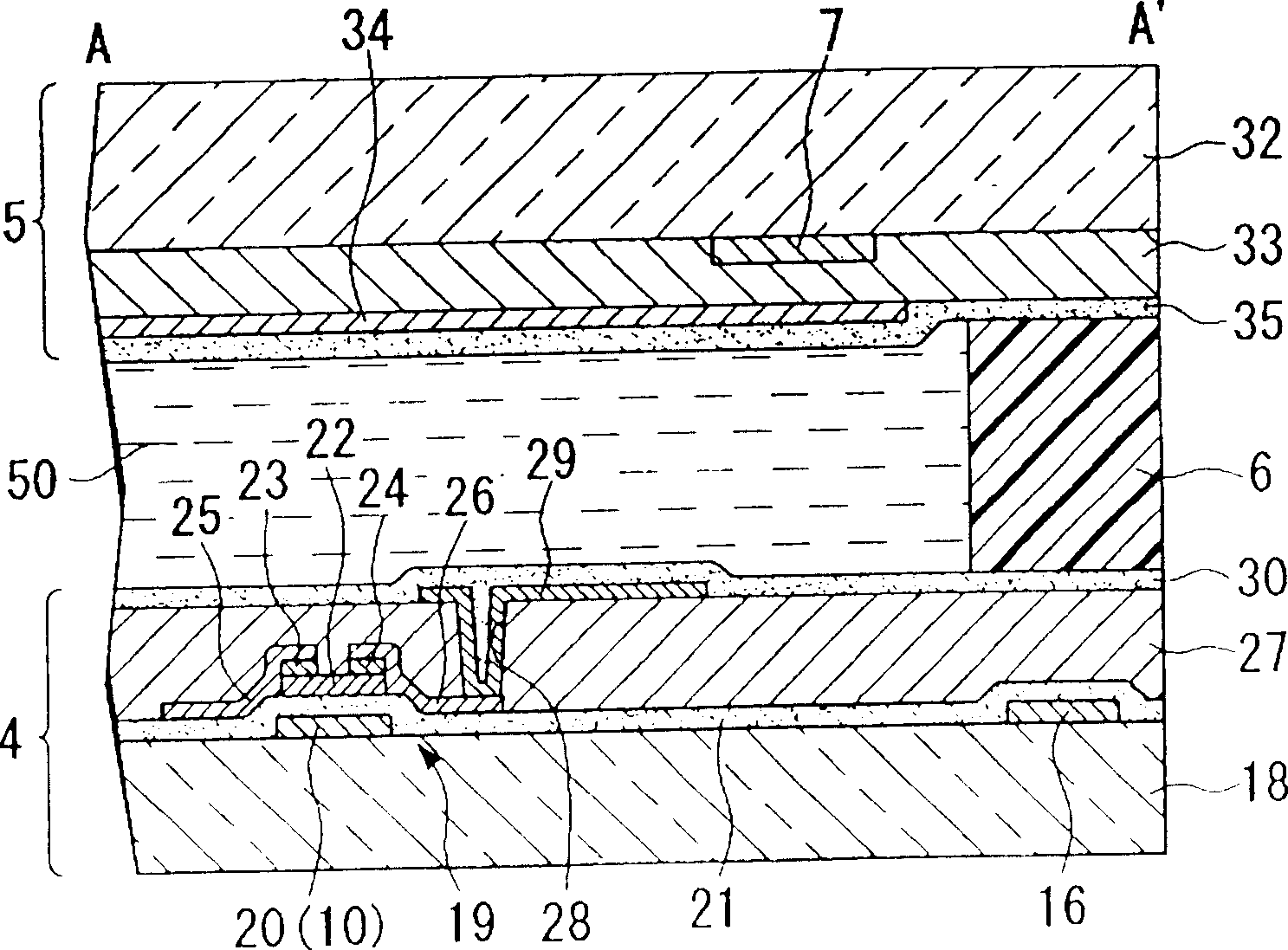
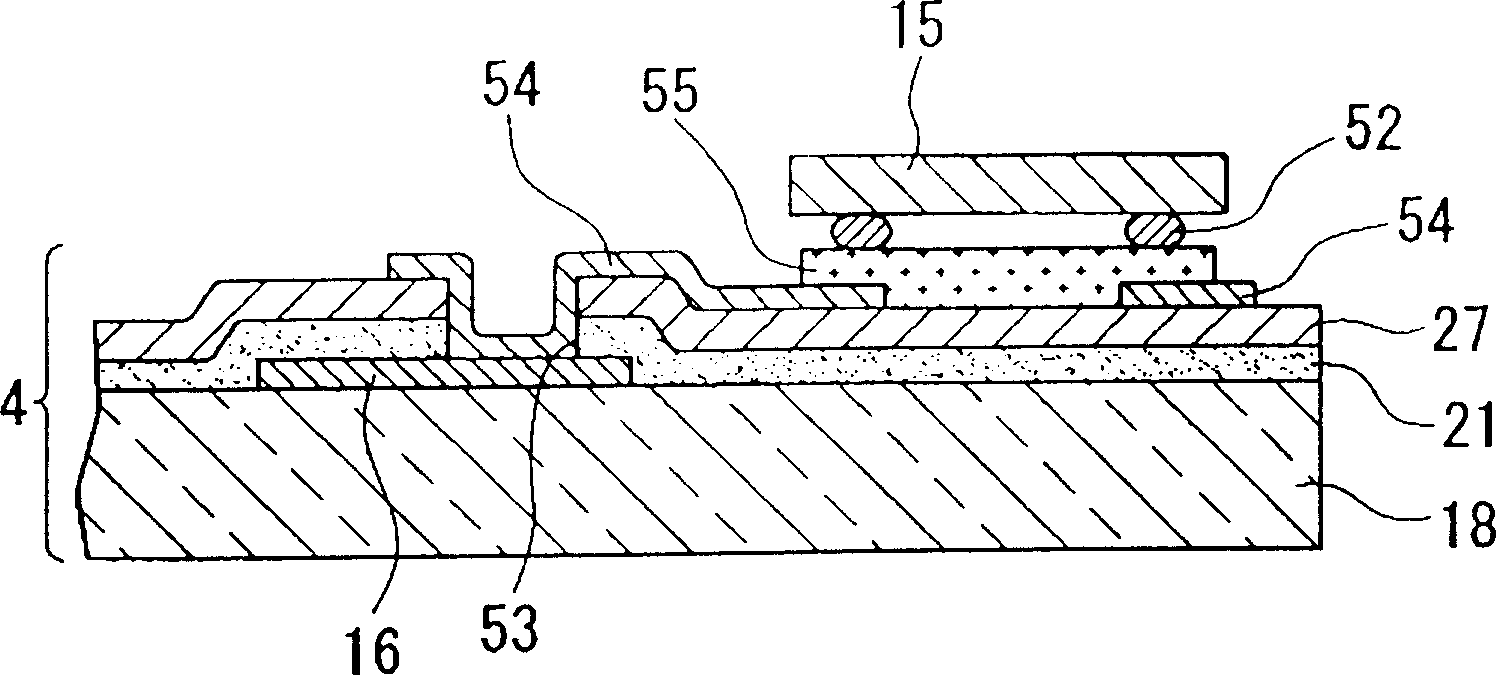
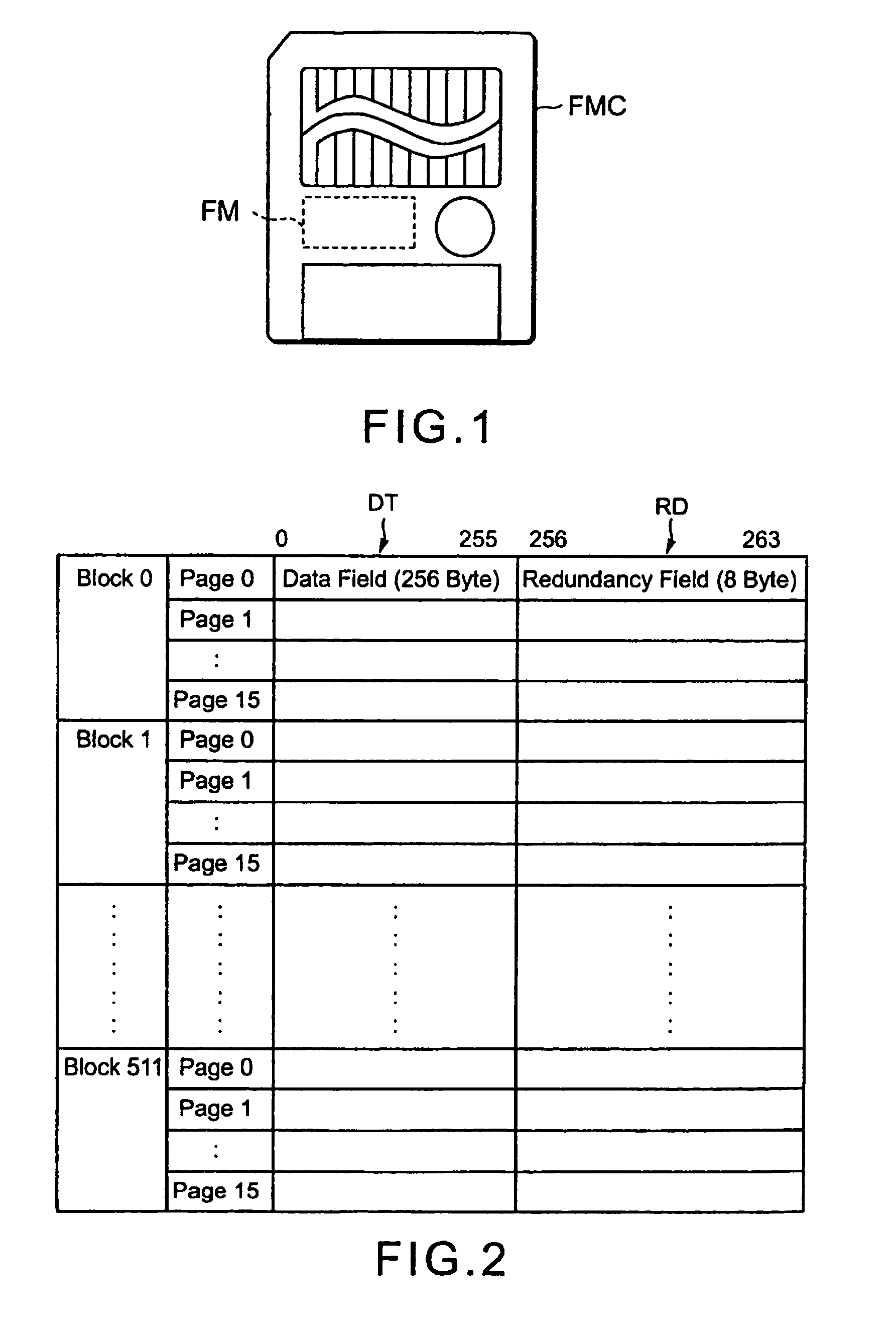
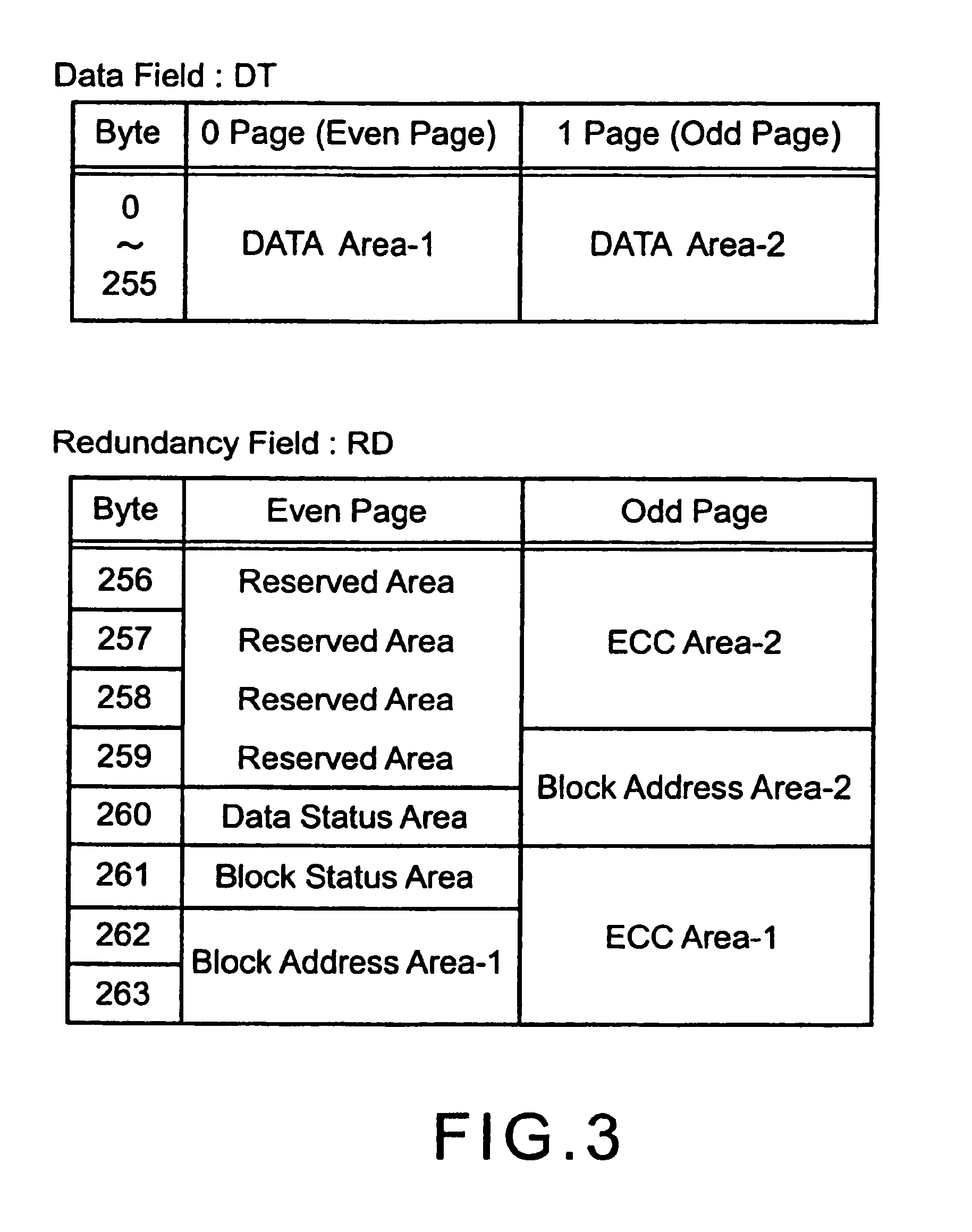
Memory with high dielectric constant antifuses and method for using at low voltage
InactiveUS20070069241A1Reliable readWrite reliablySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLow voltageAlloy
A memory array having memory cells comprising a diode and an antifuse can be made smaller and programmed at lower voltage by using antifuse materials having higher dielectric constant and higher acceleration factor than silicon dioxide, and by using diodes having lower band gaps than silicon. Such memory arrays can be made to have long operating lifetimes by using the high acceleration factor and lower band gap materials. Antifuse materials having dielectric constants between 5 and 27, for example hafnium silicon oxynitride or hafnium silicon oxide are particularly effective. Diode materials with band gaps lower than silicon, such as germanium or a silicon-germanium alloy are particularly effective.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Thermally-Assisted Magnetic Recording Head with Light Detector in Element-Integration Surface
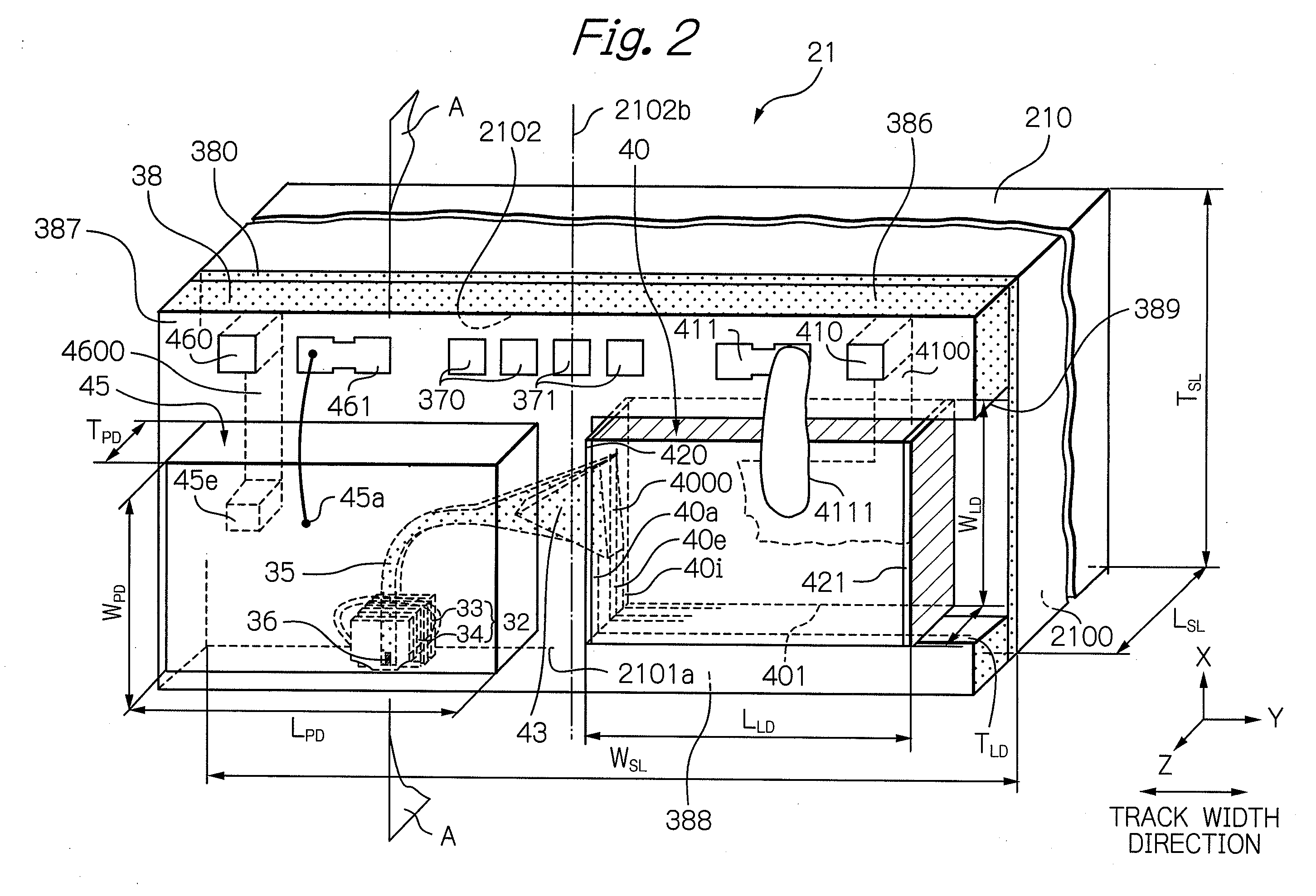
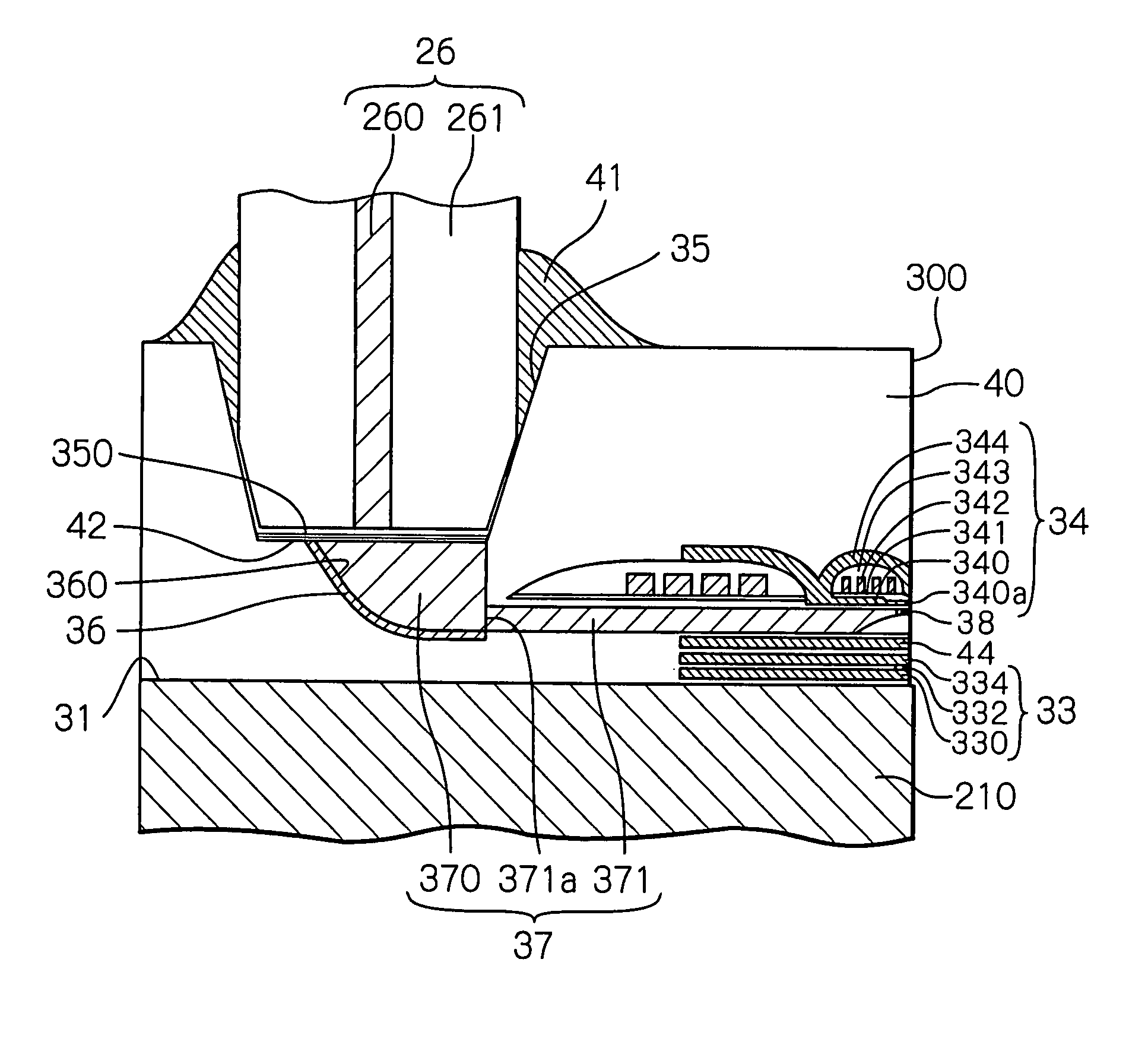
ActiveUS20110122737A1Write reliablyReliable read operationCombination recordingDisposition/mounting of recording headsEnvironmental effectHeat-assisted magnetic recording
A thermally-assisted magnetic recording head is provided, in which the light-source output can be adjusted according to its variation by environmental influences and over time. The head comprises: a light source; a write head element provided in a element-integration surface; an optical system provided in the element-integration surface and configured to guide a light emitted from the light source to the vicinity of one end of the write head element; and a light detector for monitoring the light-source output, provided in the element-integration surface and comprising a light-receiving surface covering an area directly above at least a portion of the optical system. This light detector with such a light-receiving surface can detect a leakage light emitted from the optical system as a monitoring light. Therefore, feedback adjustment of the light-source output can be realized to stabilize the intensity of light for thermal-assist applied to a magnetic recording medium.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
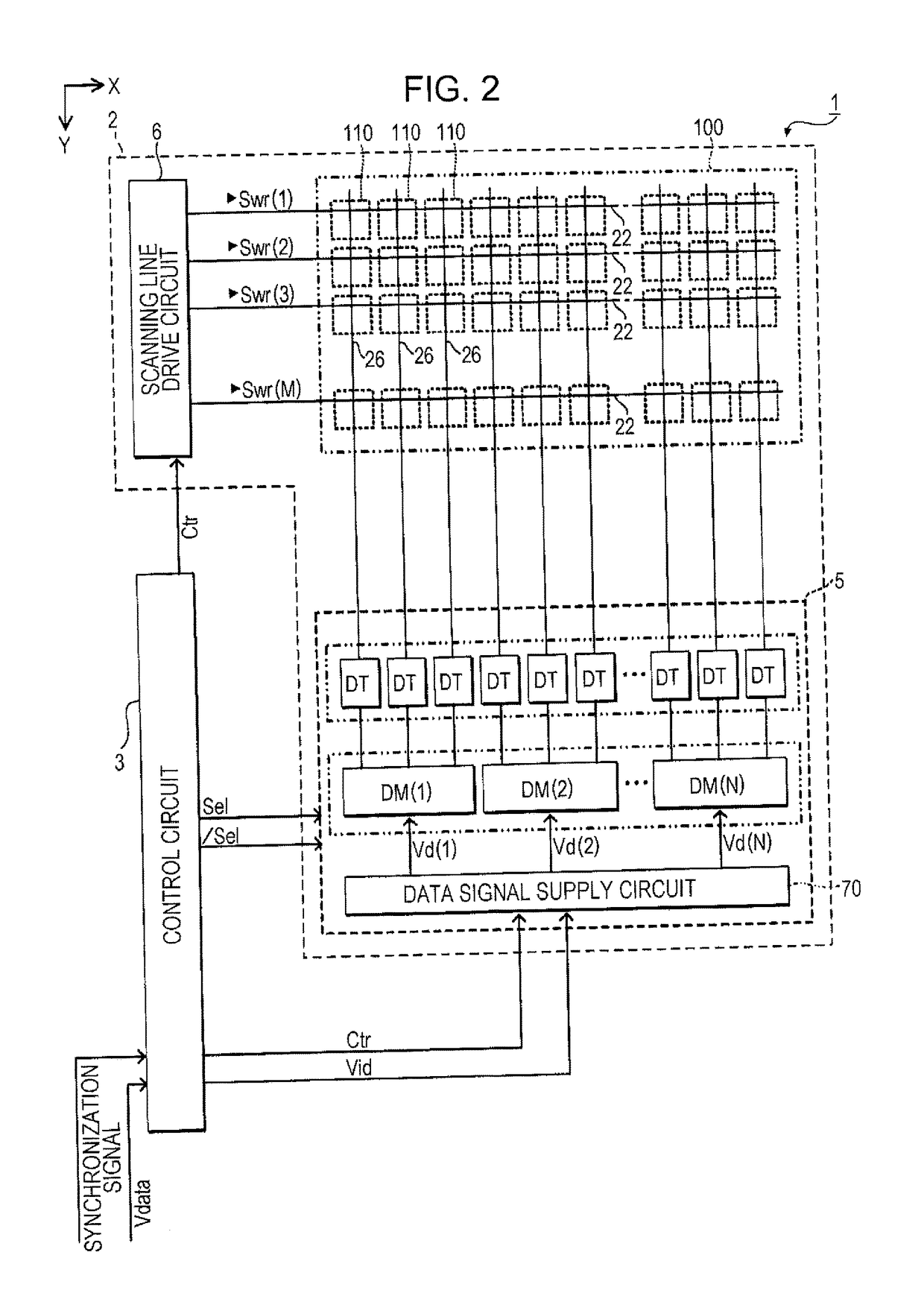
Unit circuit, electro-optical device, and electronic apparatus
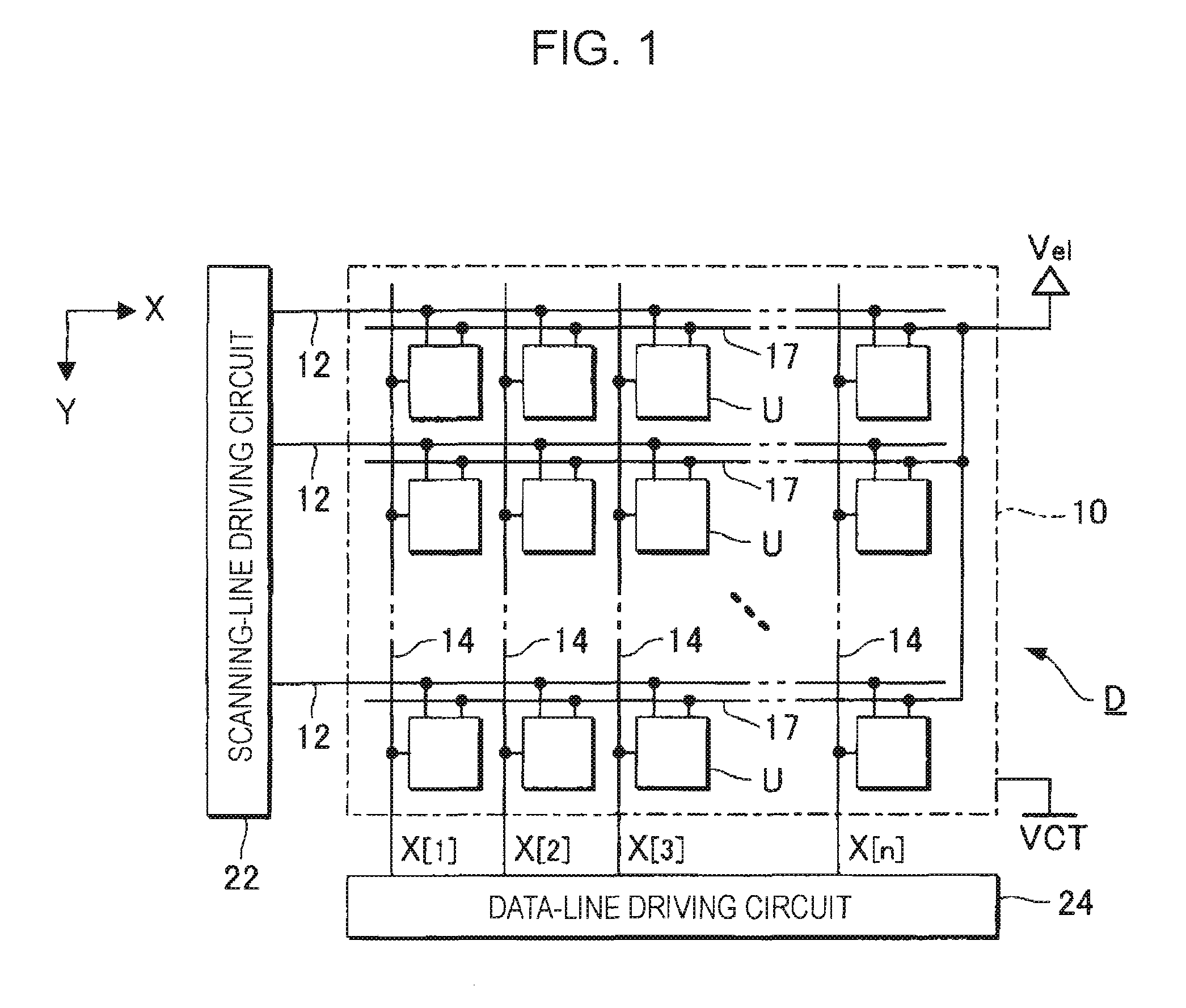
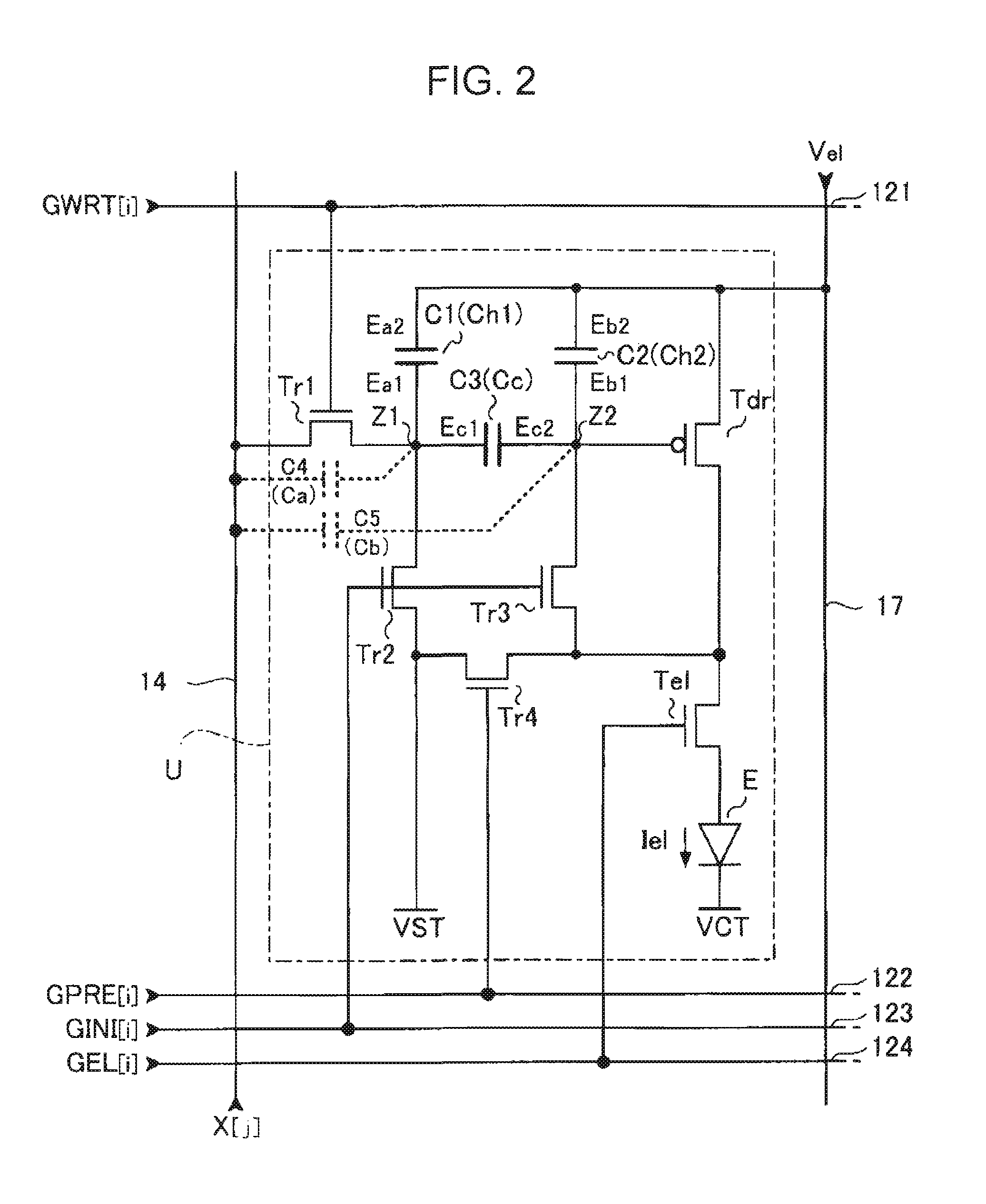
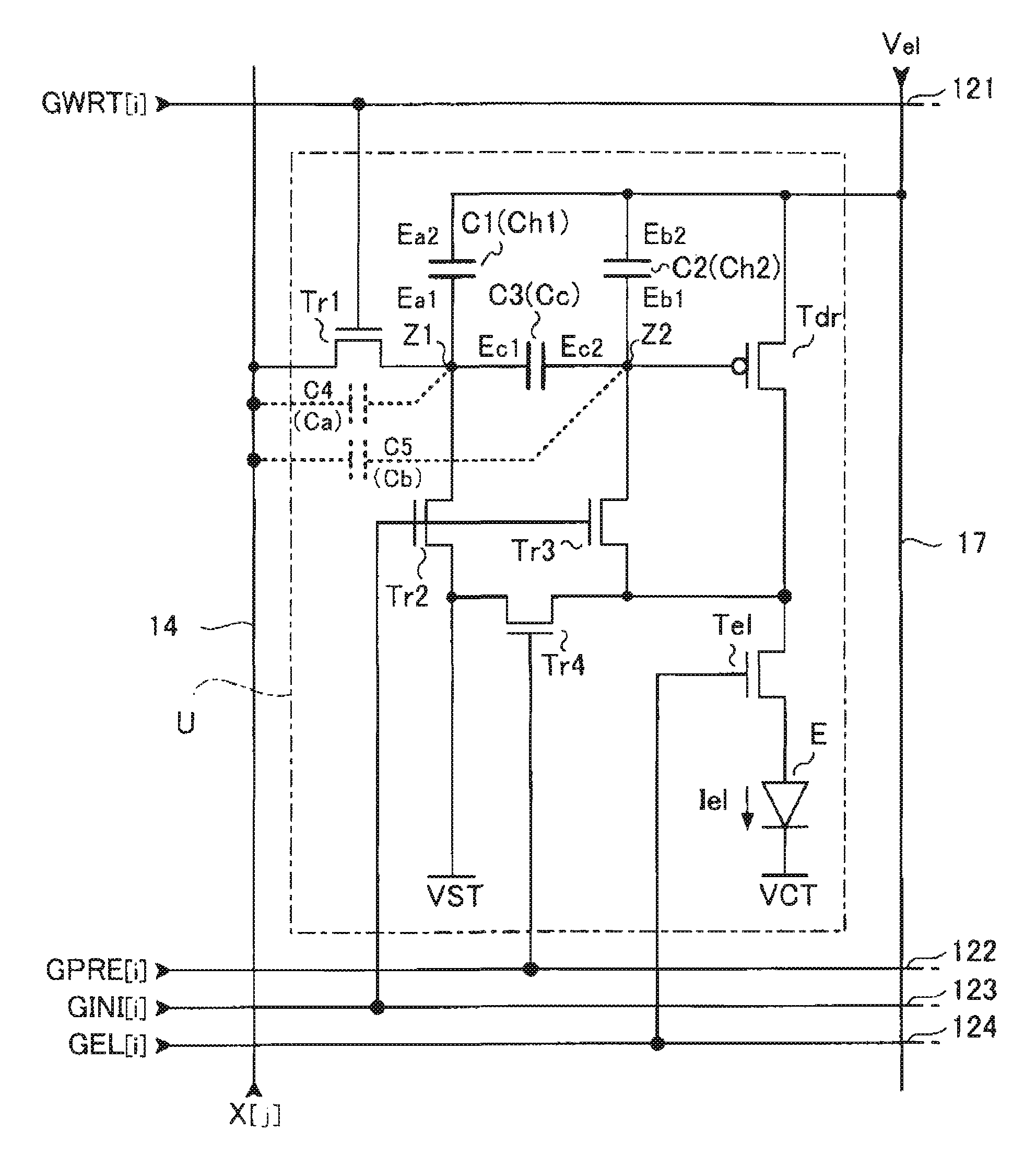
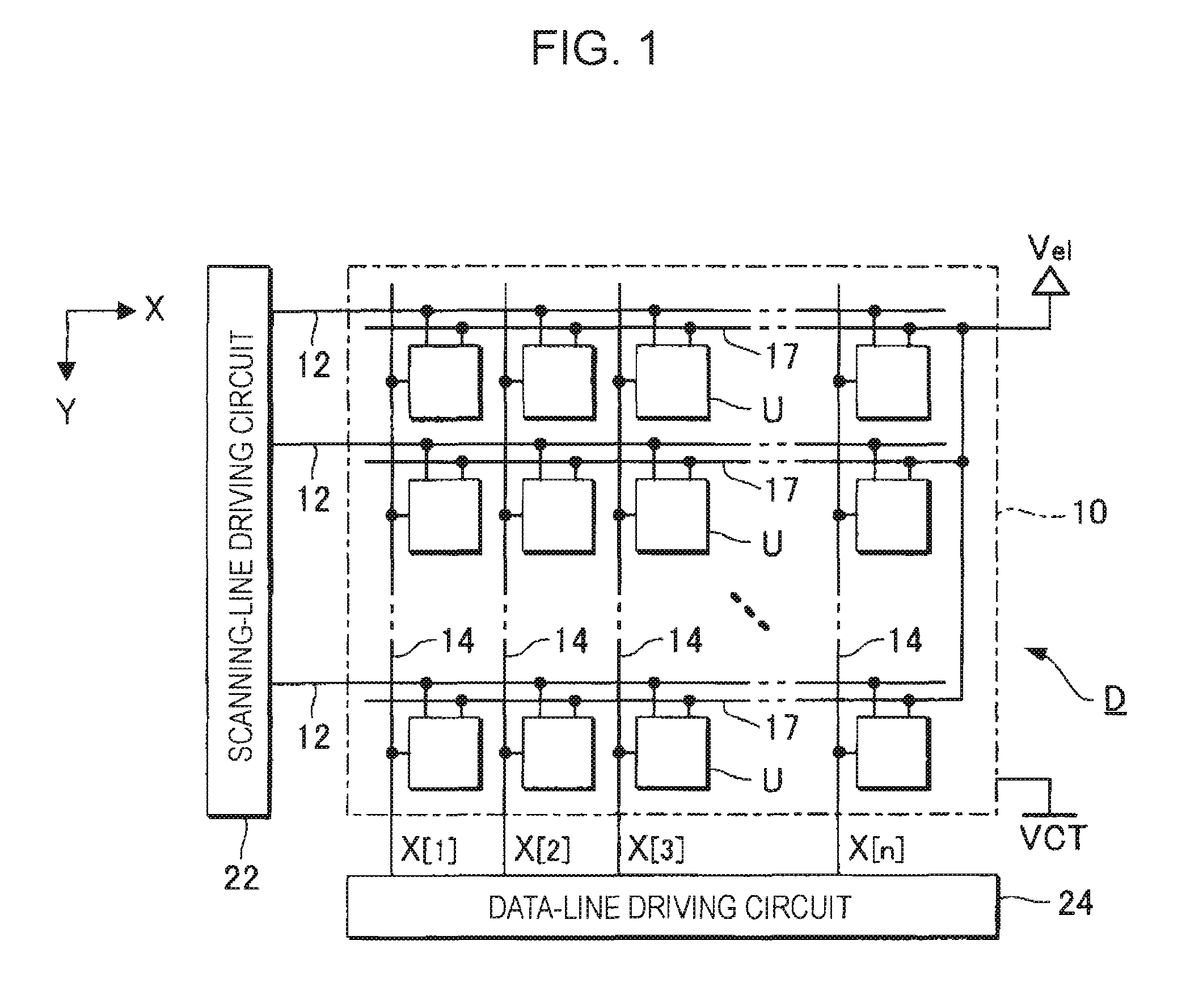
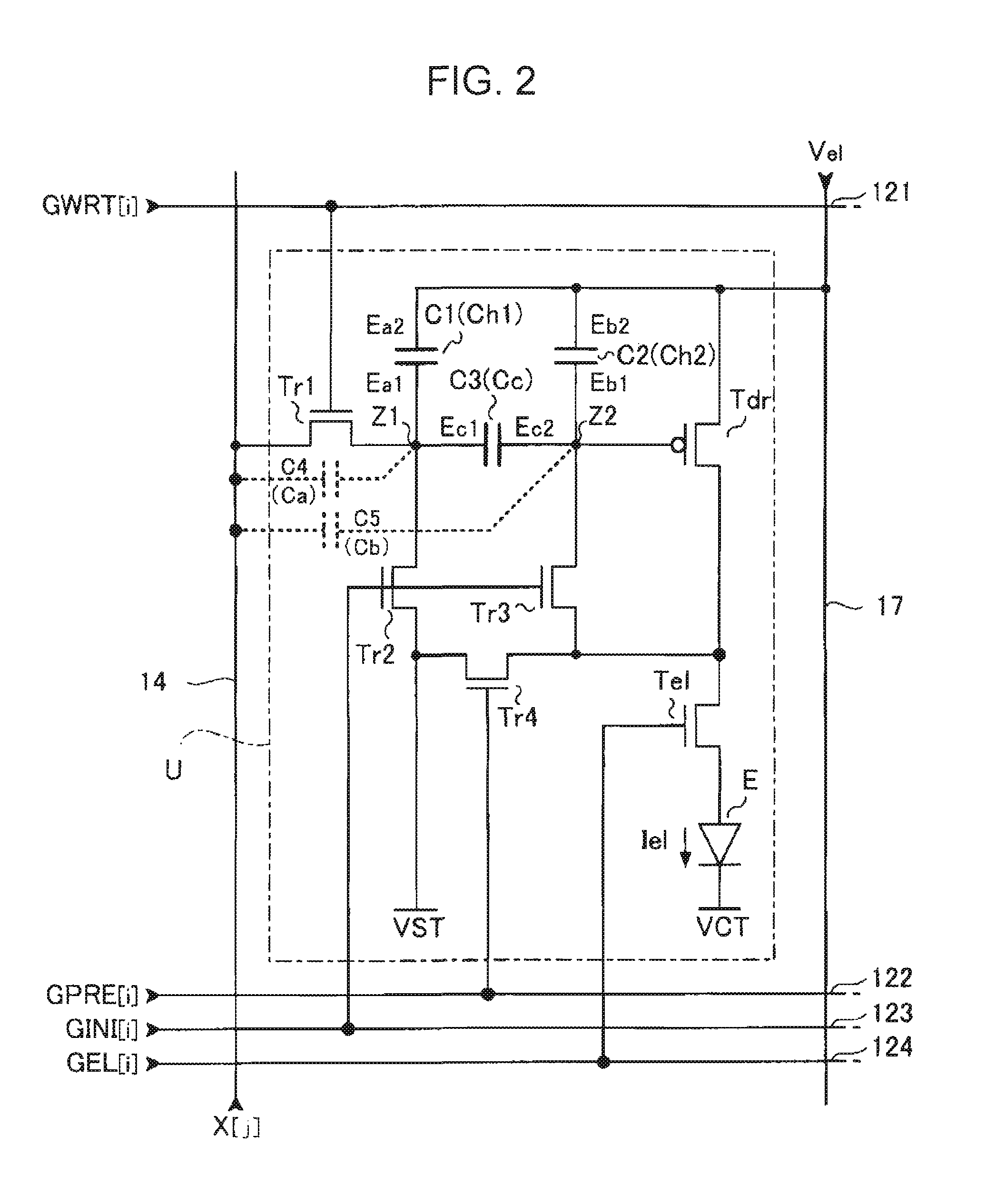
ActiveUS20070273619A1Accurately compensate variationAccurate compensationElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesCapacitanceElectricity
A unit circuit includes an electro-optical element, a first capacitive element, a second capacitive element, a third capacitive element, a drive transistor, a first switching element, an initialization unit, and a compensation unit. The electro-optical element emits an amount of light in accordance with a magnitude of a drive current. The first capacitive element includes a first electrode and a second electrode, the first electrode is electrically connected to a first node, and the second electrode is capable of receiving a fixed potential. The second capacitive element includes a third electrode and a fourth electrode, the third electrode is electrically connected to a second node, and the fourth electrode is capable of receiving a fixed potential. The third capacitive element includes a fifth electrode and a sixth electrode, the fifth electrode is electrically connected to the first node, and the sixth electrode is electrically connected to the second node. The drive transistor includes a gate, a source, and a drain and outputs the drive current in a driving period. The gate thereof is electrically connected to the second node. In a data writing period, the first switching element is in an on state and supplies to the first node a data potential supplied via a data line. The initialization unit causes the third capacitive element to discharge charges stored therein in an initialization period. The compensation unit electrically connects the source and the drain of the drive transistor together in a compensation period.
Owner:ELEMENT CAPITAL COMMERCIAL CO PTE LTD
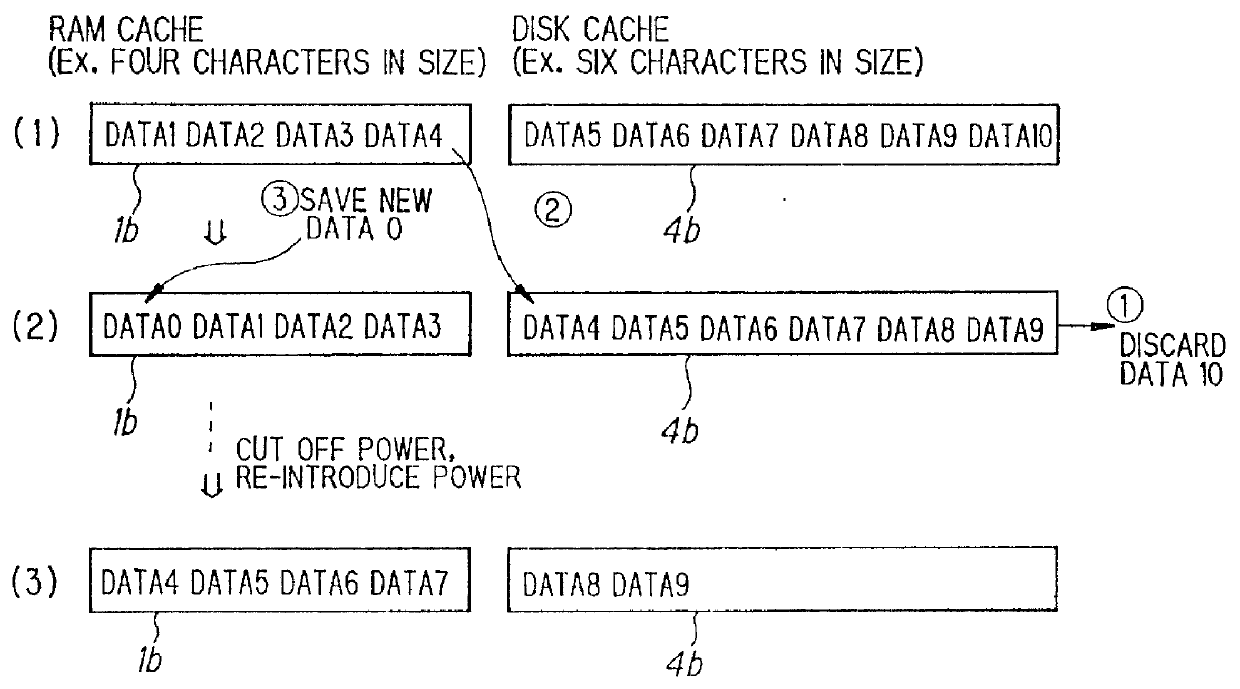
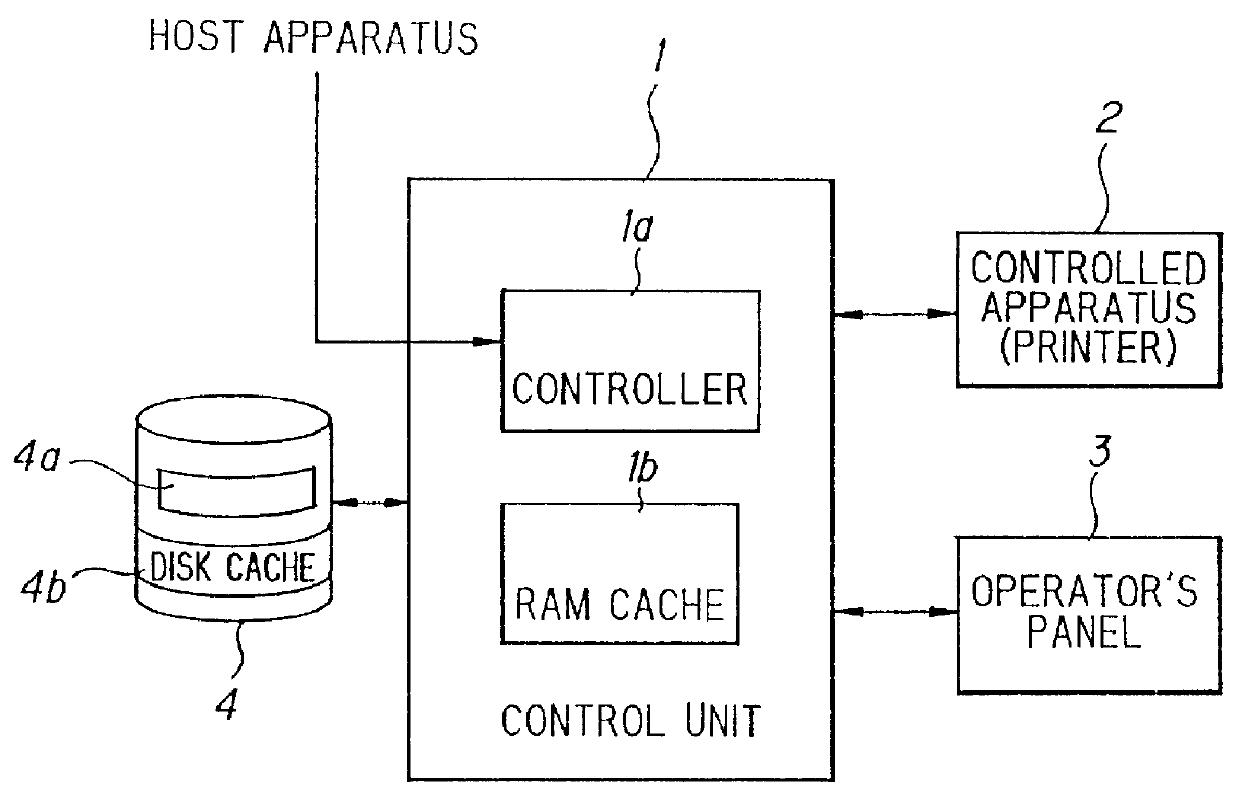
Method for saving generated character image in a cache system including a backup cache
InactiveUS6101576AWrite reliablyData processing applicationsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationHit ratioImaging data
When a control unit is in a non-operating (non-printing) state, data to be saved (character-image data) in a RAM cache memory is transferred to a disk cache memory at regular intervals in order of priority, thereby saving the data in the disk cache memory. If a power supply is cut off and then power is reintroduced, high-priority character-image data, which has been transferred from the RAM cache memory to the disk cache memory and saved in the disk cache memory when printing is not being carried out, is restored in the RAM cache memory. As a result, the high-priority data saved in the RAM cache memory when the power supply was cut off can be restored in the RAM cache memory, thereby raising the hit rate.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Continued verification in non-volatile memory write operations
ActiveUS20070153594A1Good maintenanceEasy maintenanceRead-only memoriesRecord information storageProgramming processThreshold voltage
Temporary lock-out is provided while programming a group of nonvolatile memory cells to more accurately program the memory cells. After successfully verifying that the threshold voltage of a memory cell has reached the level for its intended state, it is possible that the threshold voltage will subsequently decrease to below the verify level during additional iterations of the programming process needed to complete programming of other memory cells of the group. Memory cells are monitored (e.g., after each iteration) to determine if they fall below the verify level after previously verifying that the target threshold voltage has been reached. Cells that pass verification and then subsequently fail verification can be subjected to further programming. For example, the bit line voltage for the memory cell of interest may be set to a moderately high voltage to slow down or reduce the amount of programming accomplished by each subsequent programming pulse. In this manner, a memory cell that falls out of verification can be placed back in the normal programming flow without risking over-programming of the cell.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
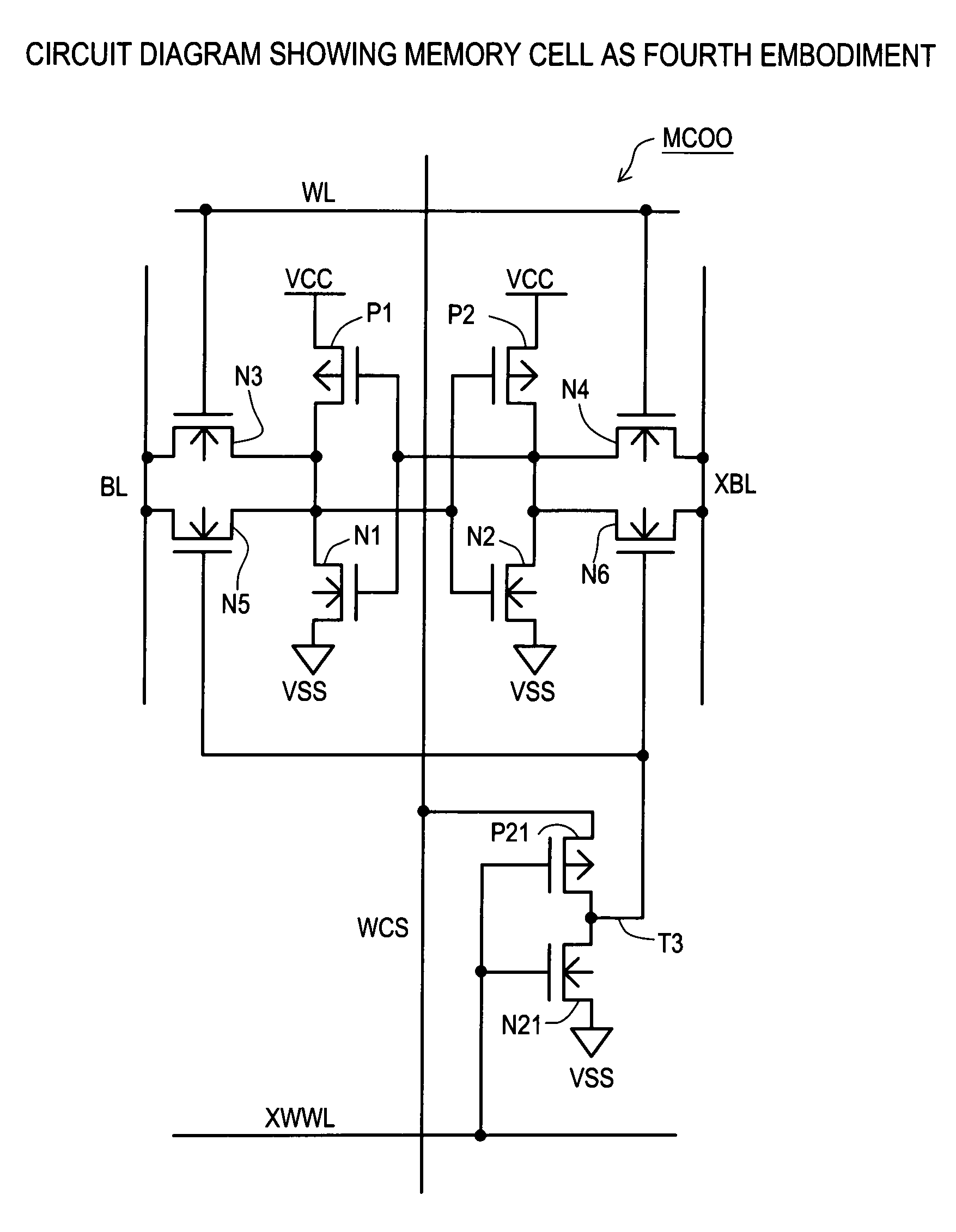
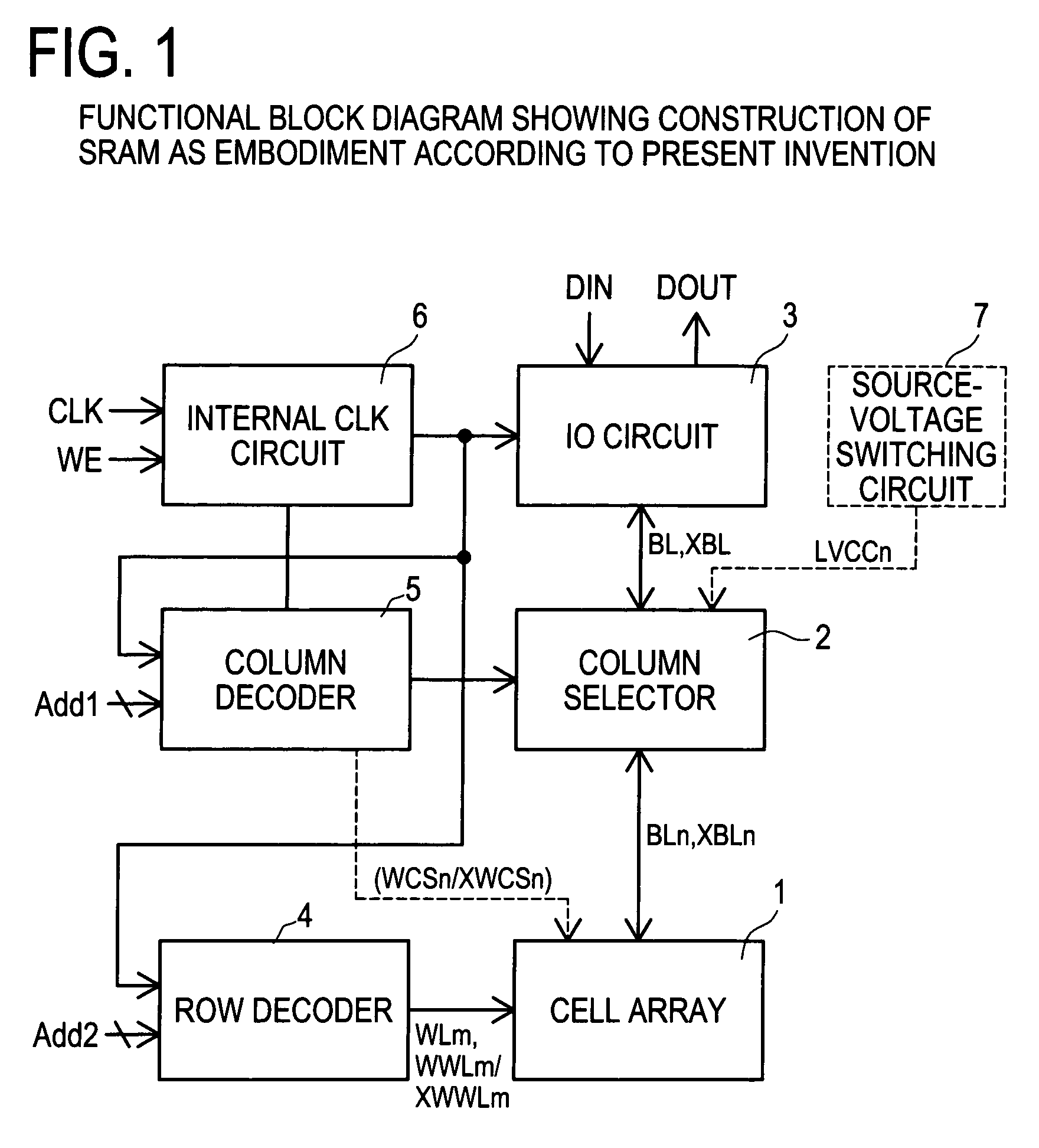
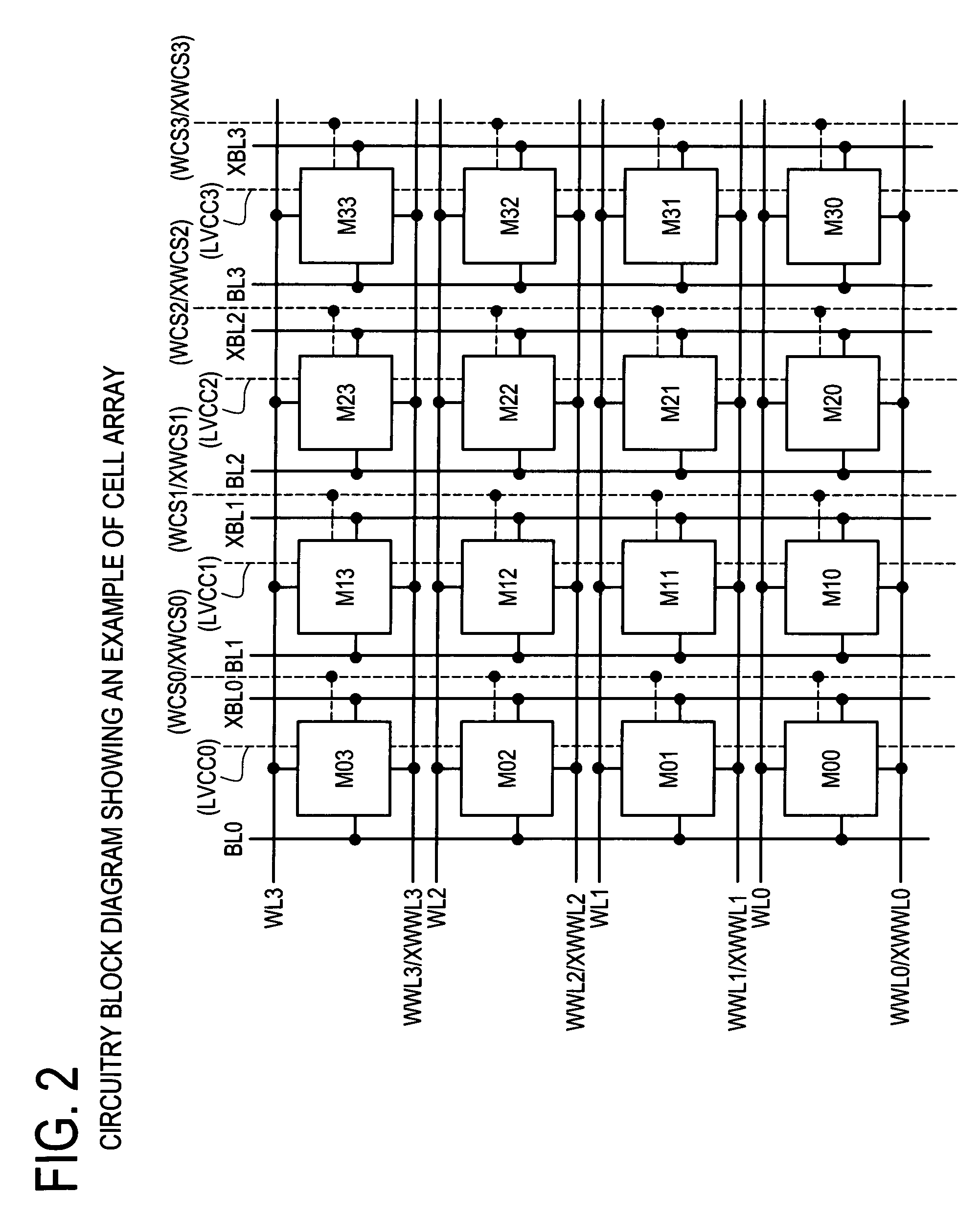
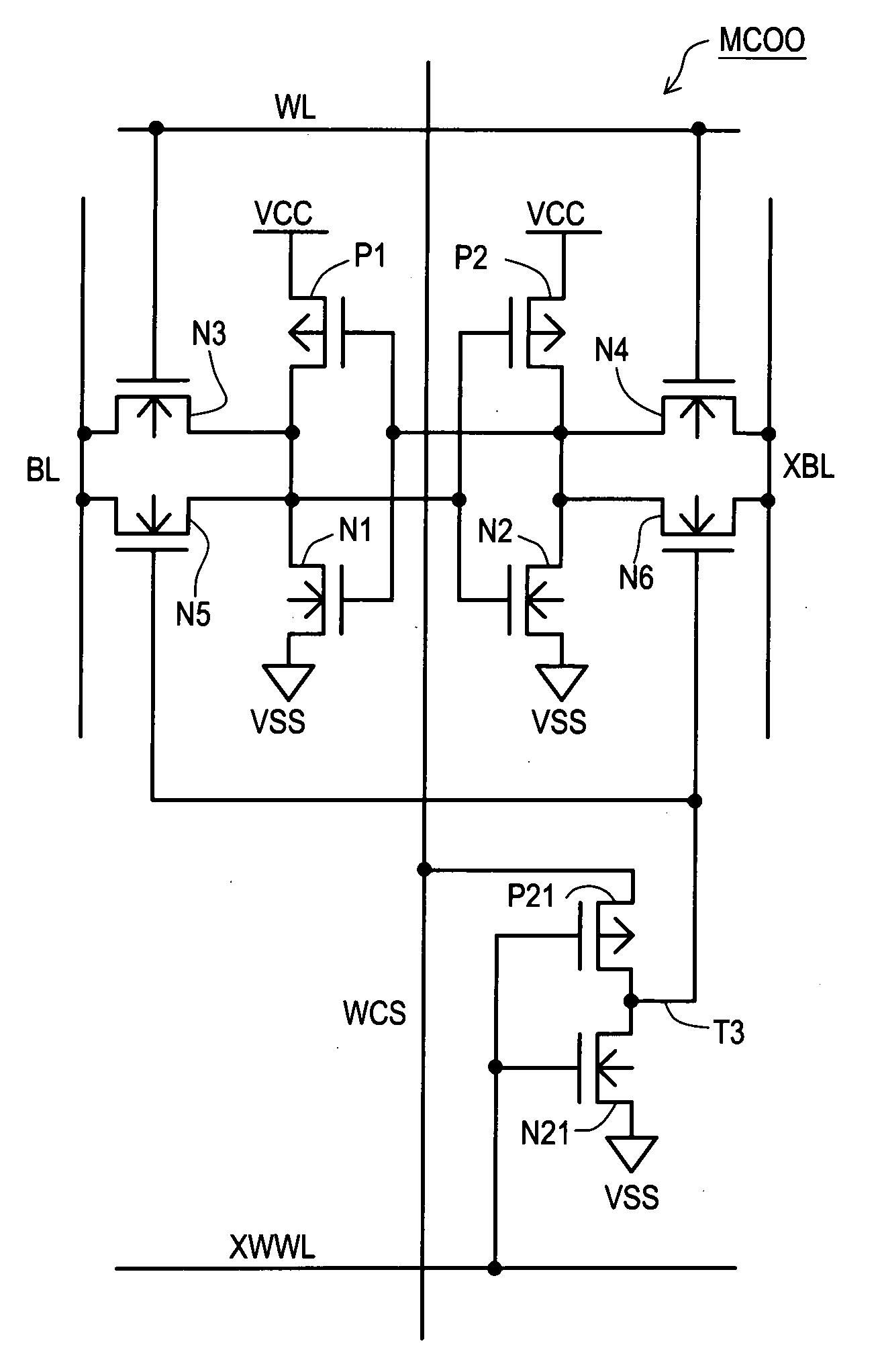
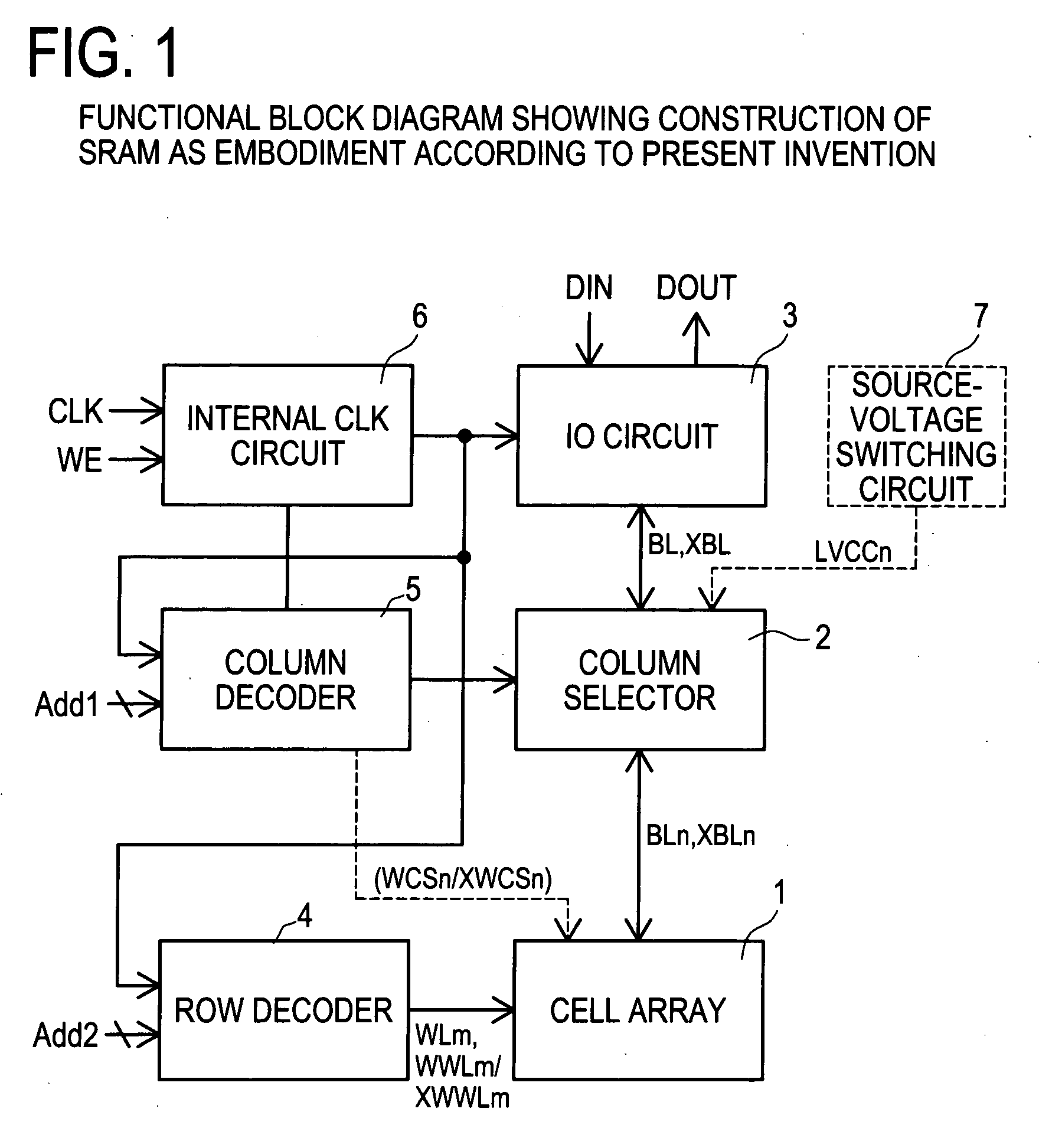
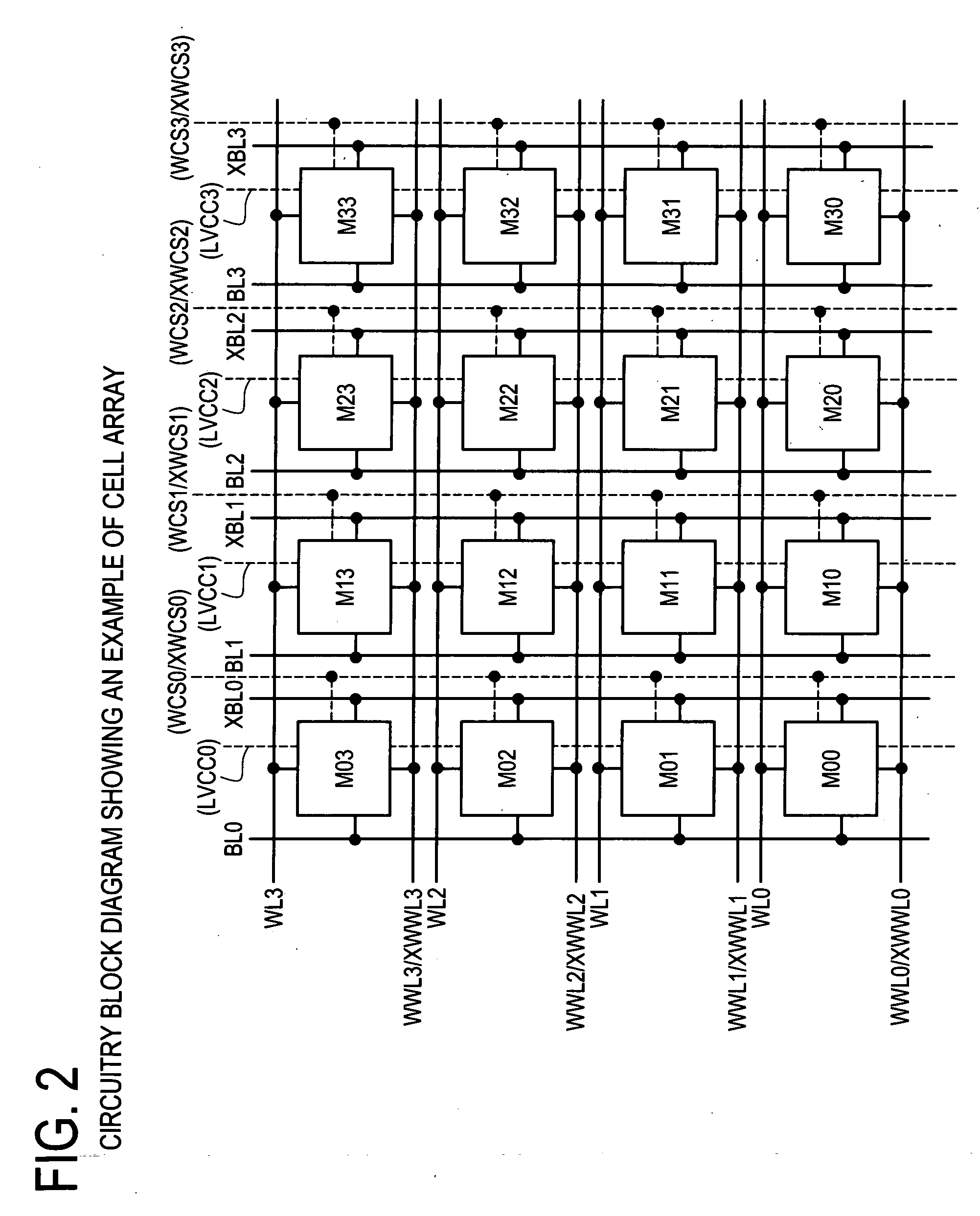
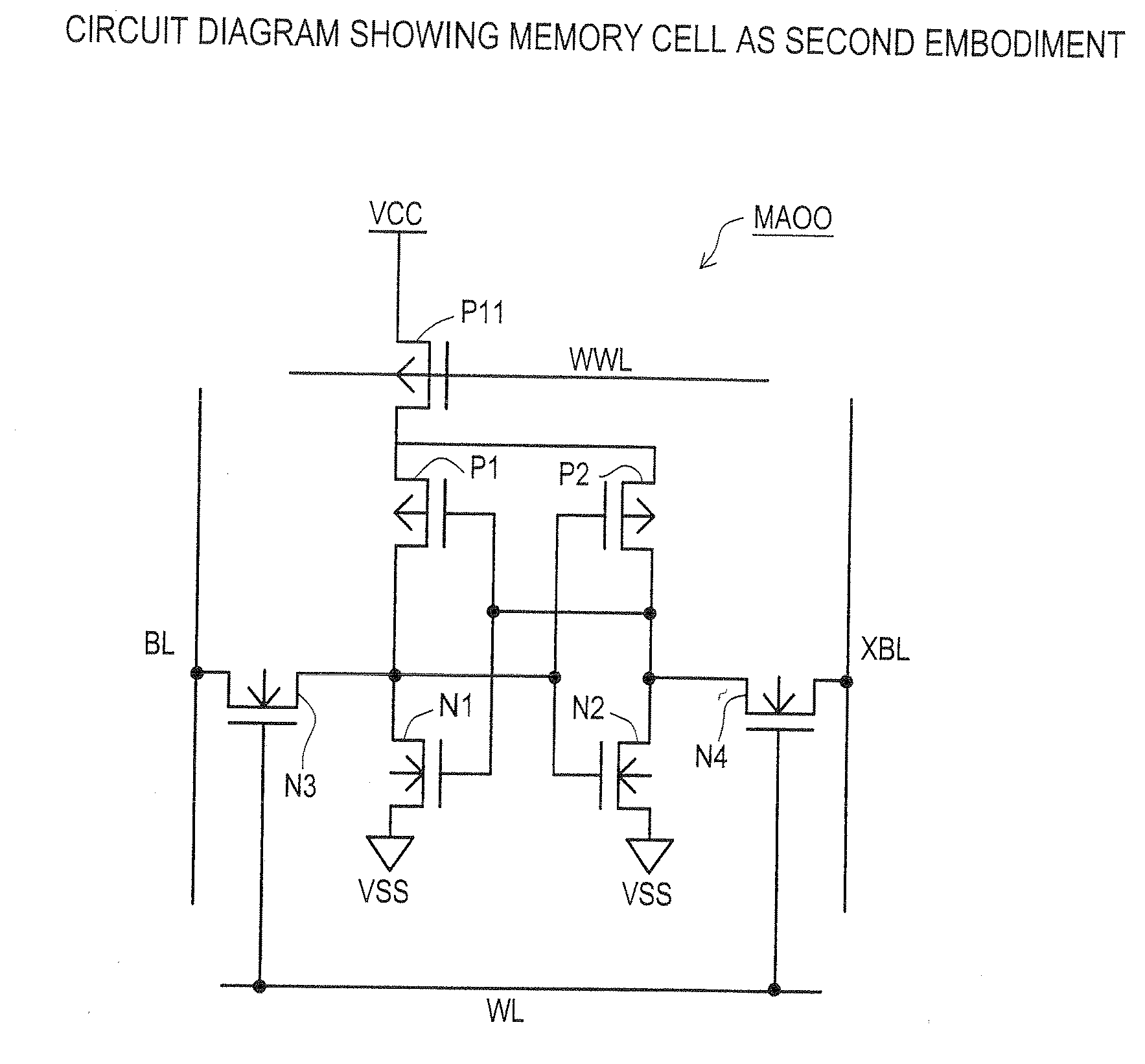
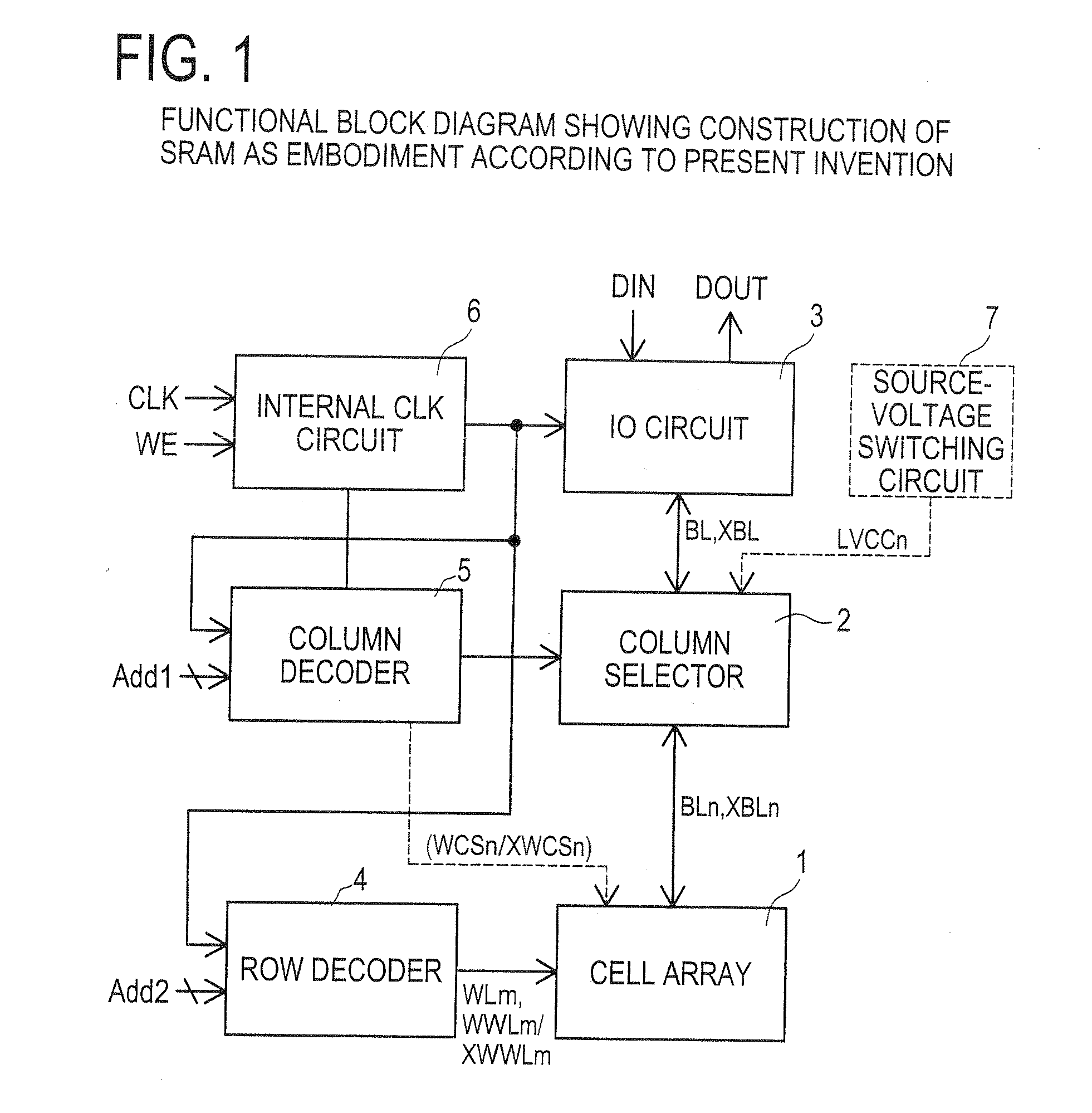
Semiconductor memory which enables reliable data writing with low supply voltage by improving the conductance via access transistors during write operation
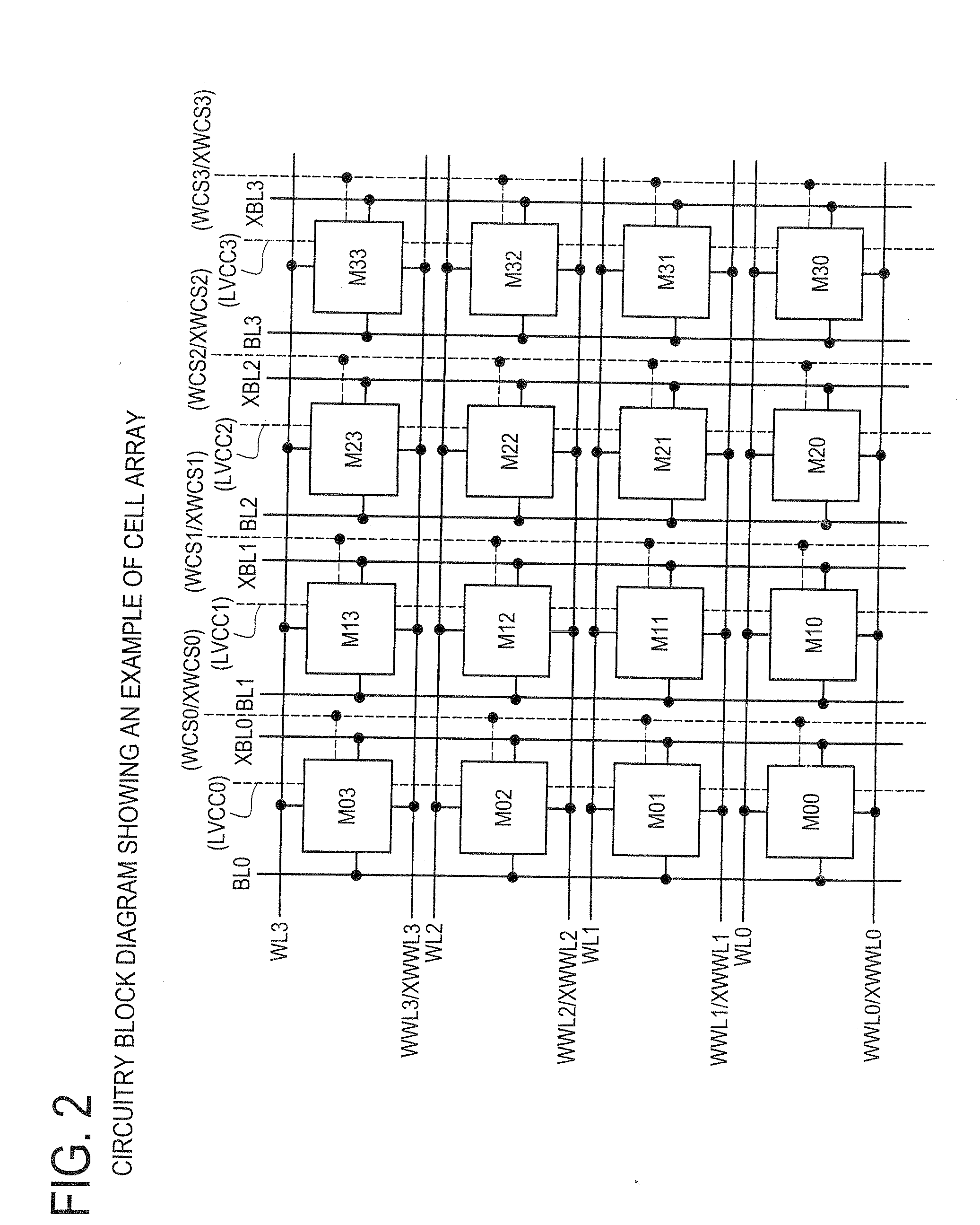
A semiconductor memory maintains securely the stored contents in the memory cells, and it is written with data reliably even in a case where a relatively low supply voltage is applied. A memory cell M00 comprises a pair of inverters cross-coupled with each other, a first switching unit provided between bit line BL and the output terminal of one of the inverters, and a second switching unit provided between bit line XBL and the output terminal of the other inverter. The first switching unit and the second switching unit are controlled to be conductive such that the conductance of the switches be larger for the writing operation than for the reading operation.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Continued verification in non-volatile memory write operations
ActiveUS7307887B2Easy maintenanceWrite reliablyRead-only memoriesRecord information storageBit lineParallel computing
Temporary lock-out is provided while programming a group of non-volatile memory cells to more accurately program the memory cells. After successfully verifying that the threshold voltage of a memory cell has reached the level for its intended state, it is possible that the threshold voltage will subsequently decrease to below the verify level during additional iterations of the programming process needed to complete programming of other memory cells of the group. Memory cells are monitored (e.g., after each iteration) to determine if they fall below the verify level after previously verifying that the target threshold voltage has been reached. Cells that pass verification and then subsequently fail verification can be subjected to further programming. For example, the bit line voltage for the memory cell of interest may be set to a moderately high voltage to slow down or reduce the amount of programming accomplished by each subsequent programming pulse. In this manner, a memory cell that falls out of verification can be placed back in the normal programming flow without risking over-programming of the cell.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
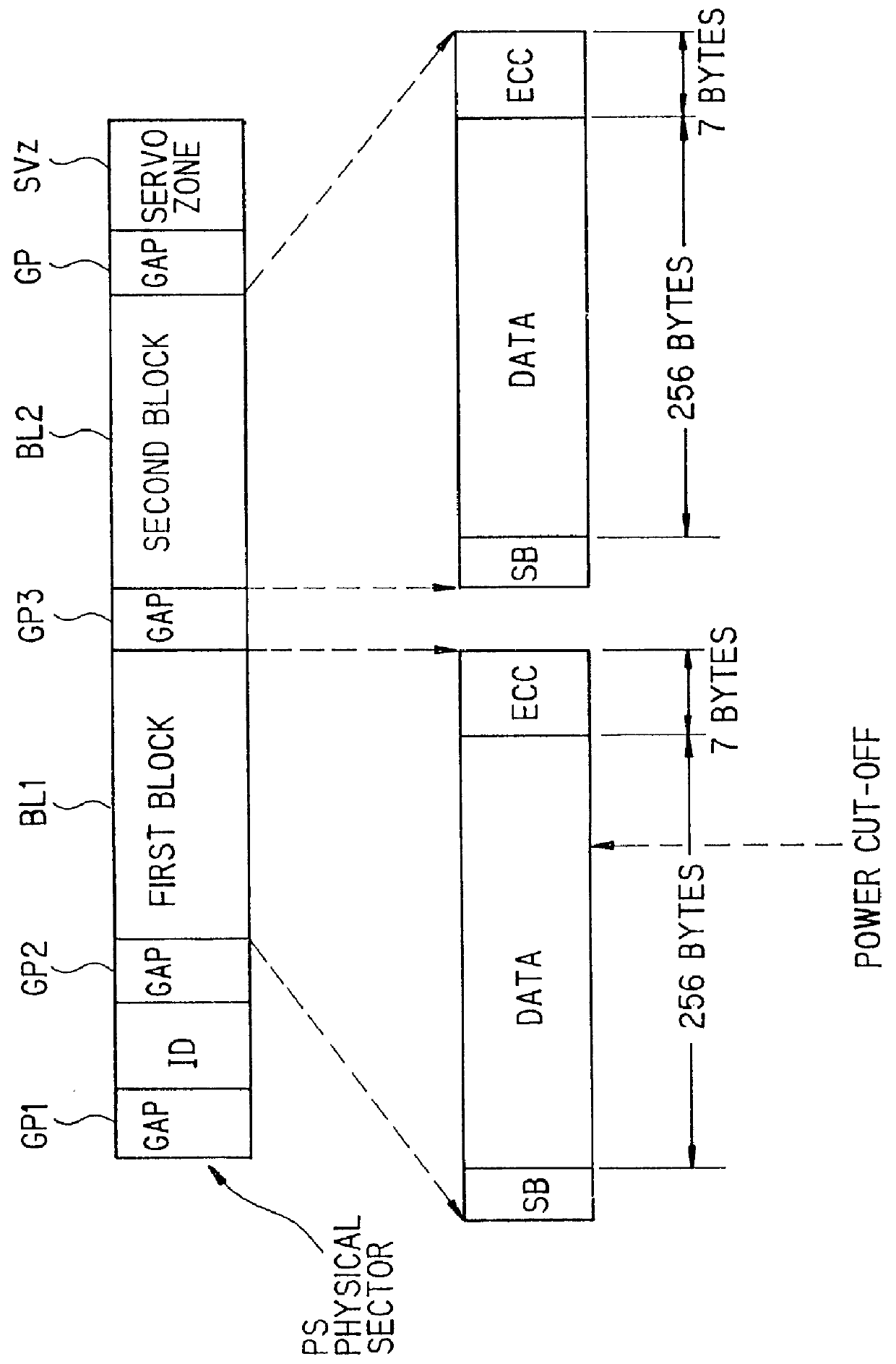
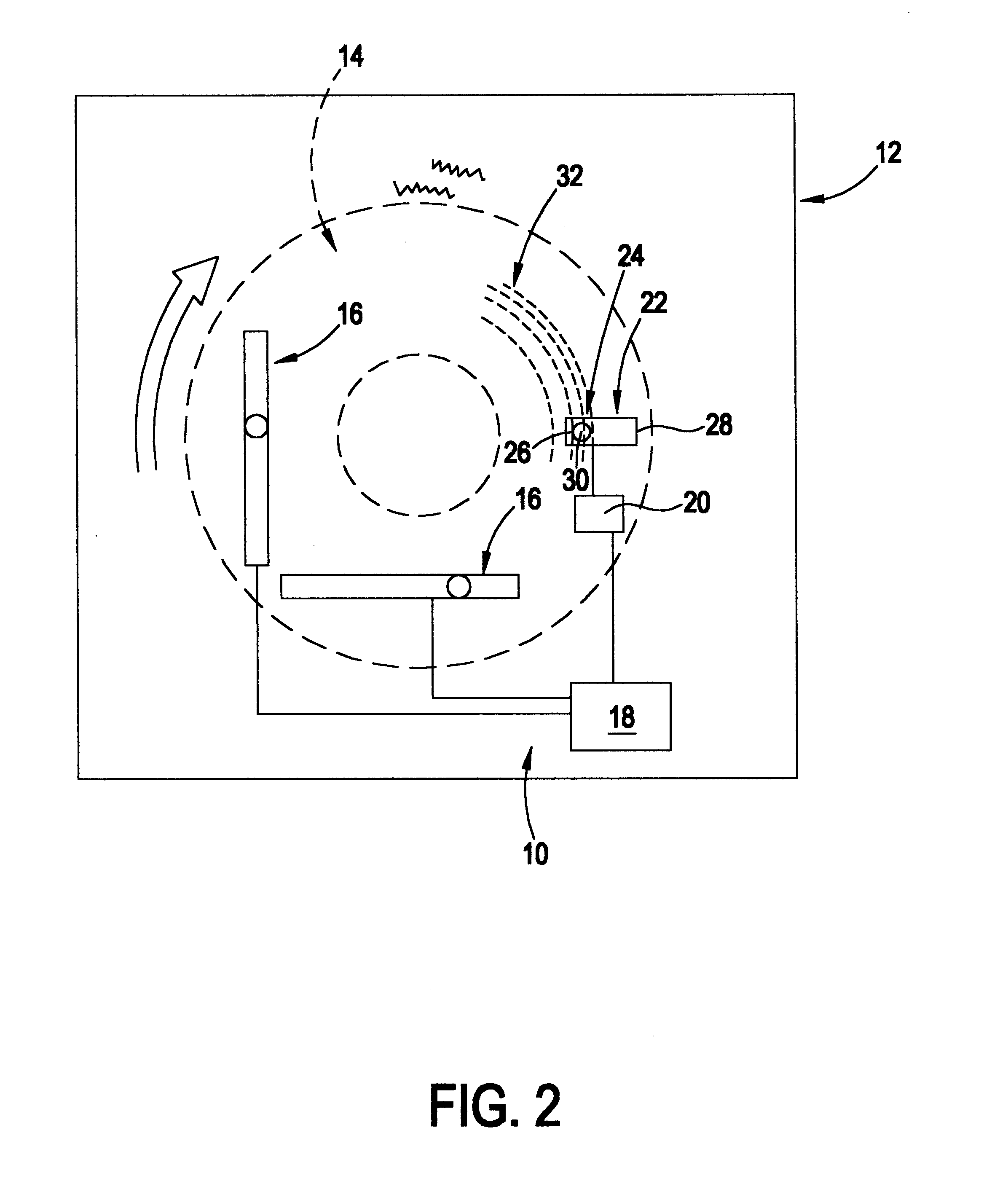
System for accommodating vibrations resulting from rotating a data storage medium
InactiveUS6185171B1Reliable readWrite reliablyCombination recordingFilamentary/web record carriersControl systemControl data
A control system in a data storage apparatus and associated methods for attempting to accommodate the vibrations resulting from rotating a data storage medium. The control system comprises a neural network which utilizes detected vibrations resulting from the rotation of data storage media to learn the characteristics of the rotational imbalance of rotating data storage media. Thereafter, the rotation of a data storage medium and / or movement of a data head is controlled based on the characteristics learned.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Data storage and reading method
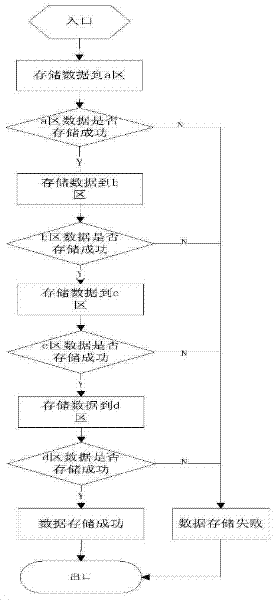
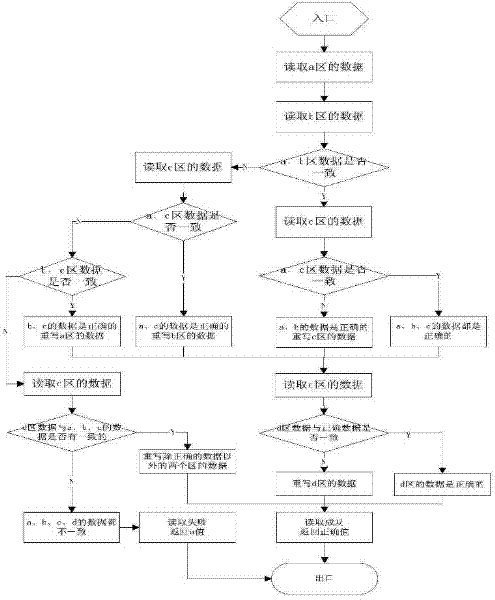
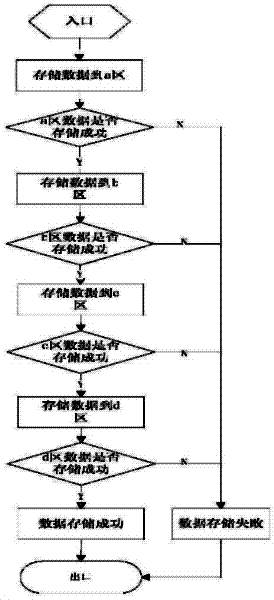
ActiveCN102521084AHigh data reliabilityImprove vandal resistanceRedundant operation error correctionData reliabilitySoftware engineering
The invention relates to a data storage and reading method in an improvement scheme, which includes a data storage step and a data reading step. The data storage and reading method is used for storing, reading and recovering data by means of multi-redundant backup and successive writing, providing a multi-backup mechanism on a storage, ensuring reliable writing of the data and improving data reliability and destruction resistance. When the data are read, even if parts of the data are destructed, the destructed data can be recovered by the aid of normal data, so that accuracy of data reading is ensured.
Owner:HUIZHOU EPOWER ELECTRONICS
Displaying device and electronic apparatus
To provide a display device and an electronic apparatus including a radio communication device, an embodiment of the radio communication device being an IC tag, which do not need a special space to attach the IC tag and is capable of reducing the amount of time and effort required for attaching the IC tag, a display device including a radio communication device having at least one substrate provided with a display unit and display-unit-driving wiring lines 9 and 10 , a communication integrated-circuit unit, and an antenna is provided. At least a part of the antenna is formed on the substrate and formed of a conductor formed in the same layer as a conductor that constitute the display unit or conductors that constitute the display-unit-driving wiring lines.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Systems for continued verification in non-volatile memory write operations
ActiveUS7352629B2Easy maintenanceWrite reliablyRead-only memoriesRecord information storageBit lineParallel computing
Temporary lock-out is provided while programming a group of non-volatile memory cells to more accurately program the memory cells. After successfully verifying that the threshold voltage of a memory cell has reached the level for its intended state, it is possible that the threshold voltage will subsequently decrease to below the verify level during additional iterations of the programming process needed to complete programming of other memory cells of the group. Memory cells are monitored (e.g., after each iteration) to determine if they fall below the verify level after previously verifying that the target threshold voltage has been reached. Cells that pass verification and then subsequently fail verification can be subjected to further programming. For example, the bit line voltage for the memory cell of interest may be set to a moderately high voltage to slow down or reduce the amount of programming accomplished by each subsequent programming pulse. In this manner, a memory cell that falls out of verification can be placed back in the normal programming flow without risking over-programming of the cell.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20170236885A1Avoid lightAvoid applicationStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesReflective layerData transmission
Subpixels of R, G, and B corresponding to a scanning line as a first conductive layer extended in a row direction and a data transfer line as a second conductive layer extended in a column direction are provided. A plurality of transistors in the subpixel of each of the colors is disposed along the column direction, and a reflective layer in the subpixel of at least one color is disposed along the row direction so as to overlap any transistor of subpixels of each display color. A center position of a disposition region of a reflective layer in one pixel unit including the subpixels of R, G, and B is different from a center position of a disposition region of a transistor in one pixel unit.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Writer for head positioning information over recording medium
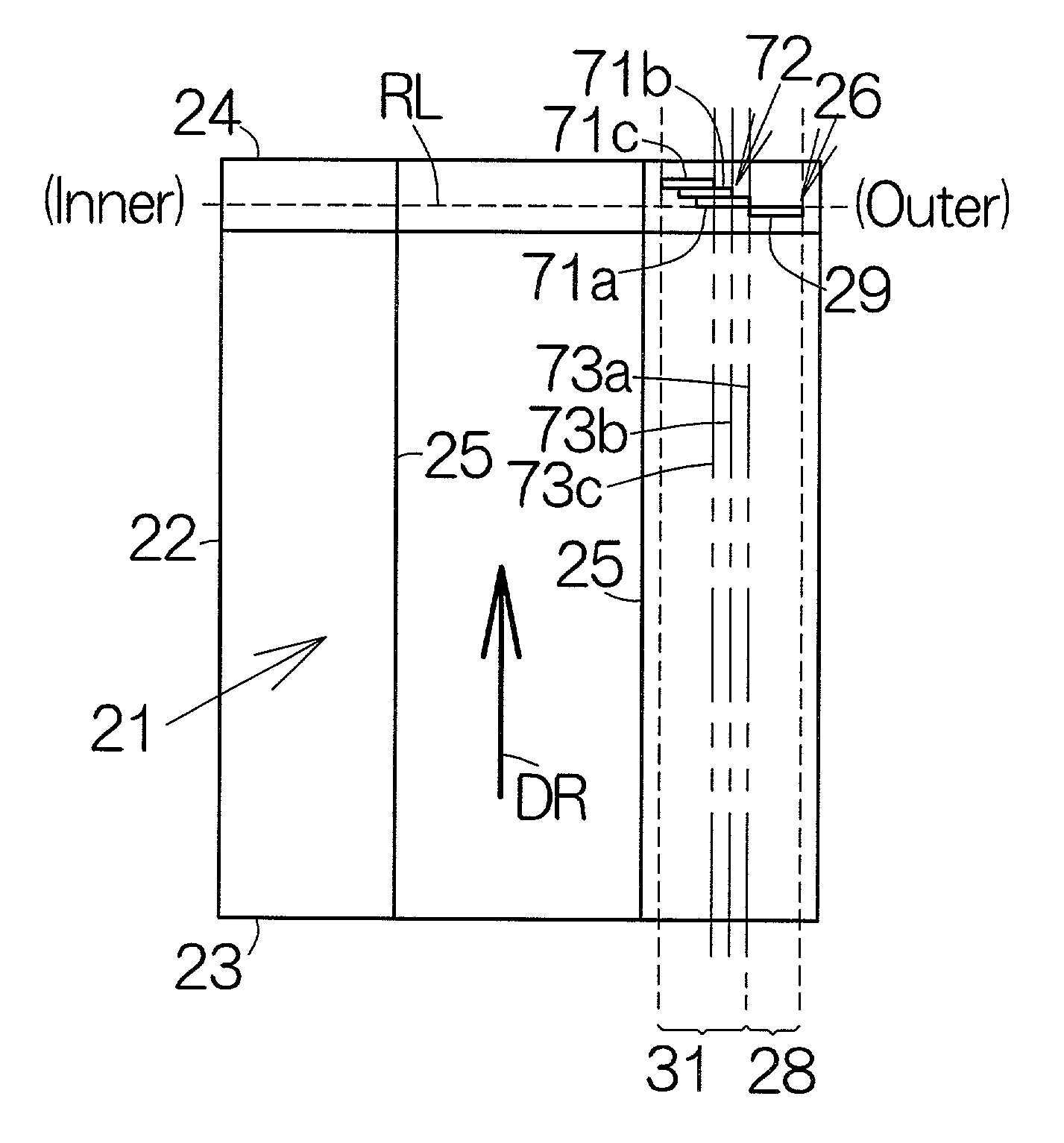
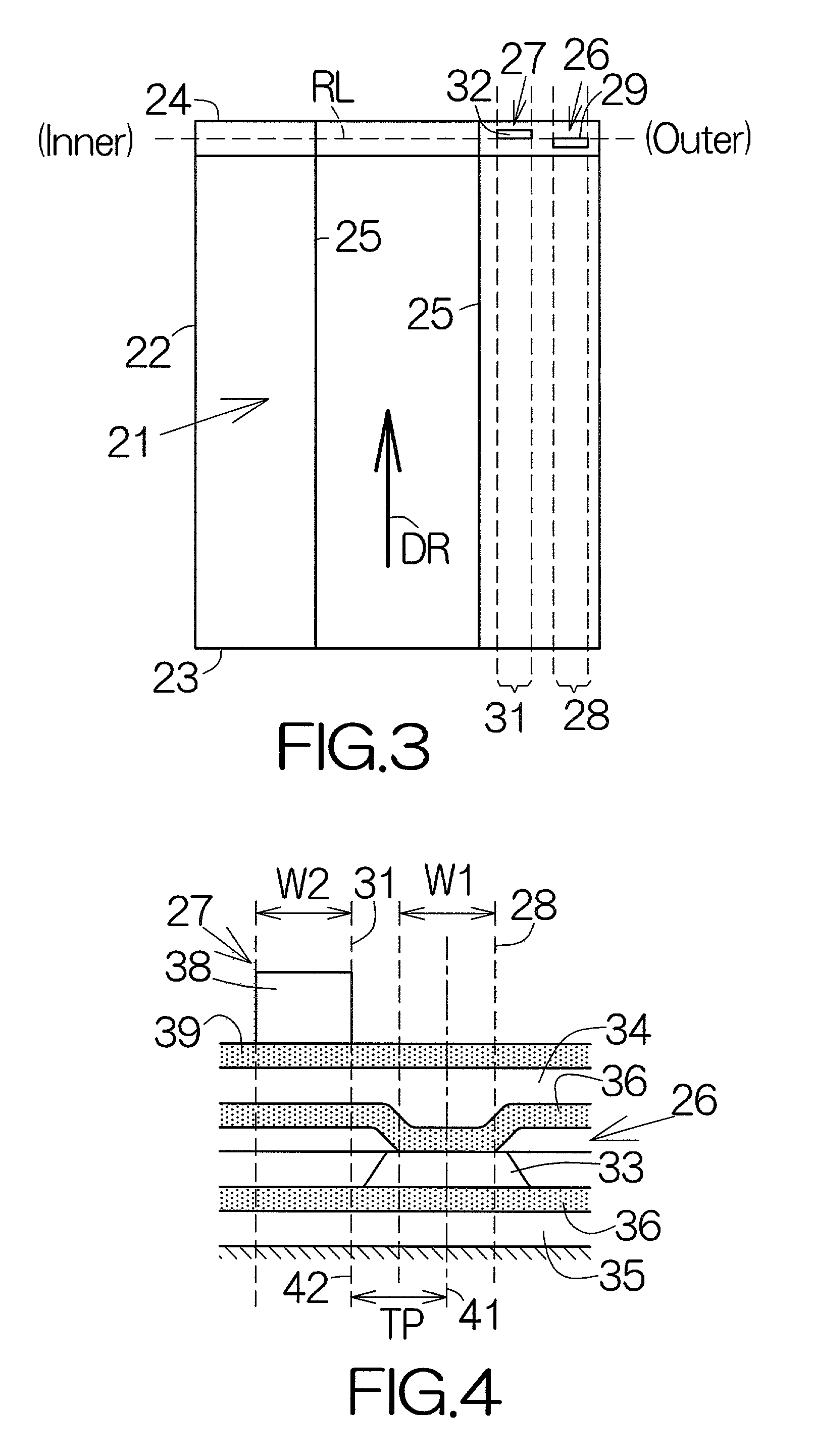
InactiveUS7012775B2Write reliablyHigh positioning accuracyTrack finding/aligningFilamentary/web carriers operation controlEngineeringRecording media
A writer for head positioning information, or a so-called servo track writer allows the read gap to follow a track which has been established on a recording medium or disk. As long as the read gap keeps following the existing track, the write gap is allowed to move along a path extending in parallel with the existing track. The write gap is utilized to write head positioning or servo information into the recording medium along the path. Even when the recording medium suffers from vibration or the like, the read gap can follow the track. The head positioning information can thus be written into the recording medium so as to establish a head positioning pattern at a higher positional accuracy.
Owner:TOSHIBA STORAGE DEVICE CORP
Multi-channel flash memory controller
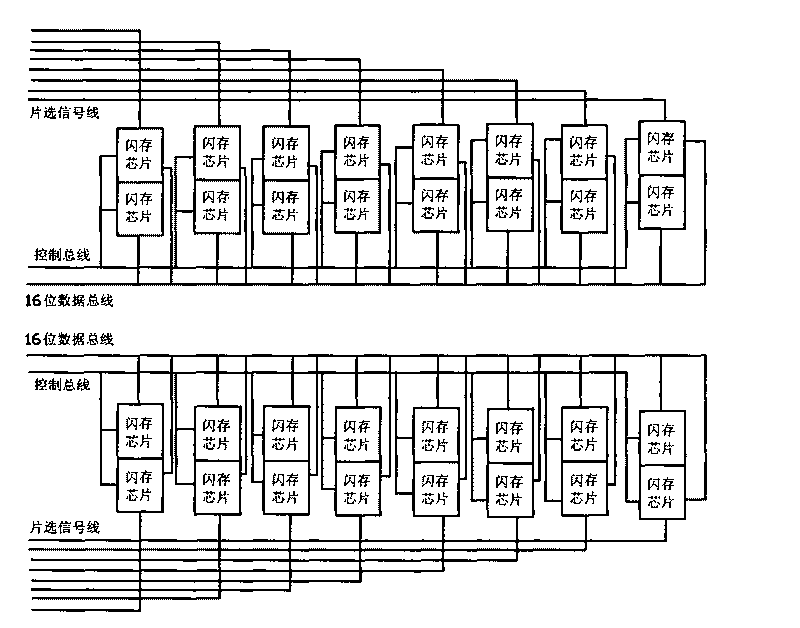
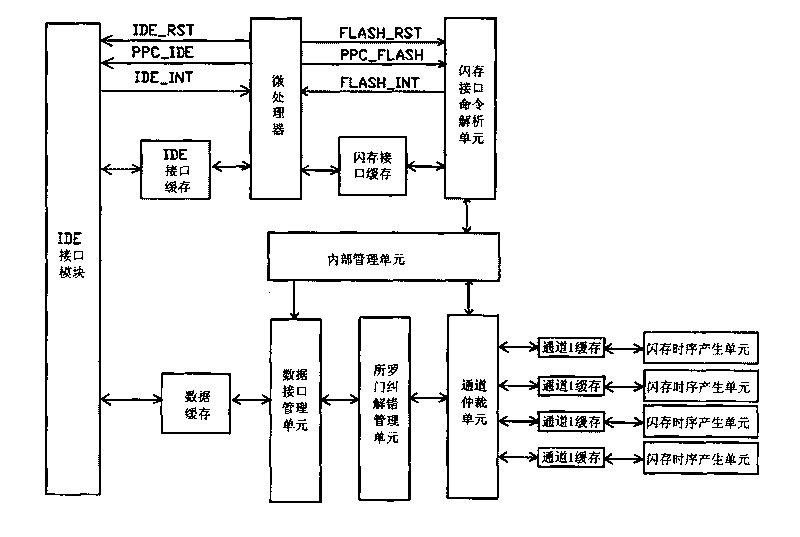
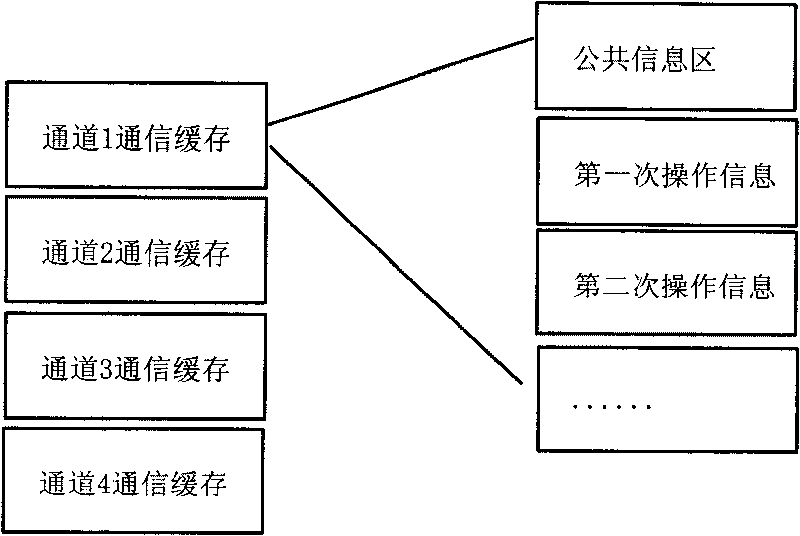
InactiveCN101740103AFast reading and writingFast transmissionDigital storageManagement unitTransmission channel
The invention relates to a multi-channel flash memory controller, which solves the defect of slow data read-write speed of a flash memory data in the prior art. The controller comprises an IDE interface module, a microprocessor and a flash memory management module which are connected with one another through two-port caches, wherein the flash memory management module comprises a flash memory interface command resolving unit, an inner management unit, a data interface management unit, a channel arbitration unit, a channel cache and a flash memory sequence unit; the data interface management unit, the channel arbitration unit and the flash memory sequence unit are sequentially connected; the data interface management unit and the channel arbitration unit are connected with the flash memory interface command resolving unit through the inner management unit; and a data transmission channel is independent of a command transmission channel. The multi-channel flash memory controller has the advantages of fast flash memory read-write speed, high data read-write reliability, high error correcting capacity, and long flash memory service life.
Owner:XIAN KEYWAY TECH
Semiconductor memory and method for controlling semiconductor memory
A semiconductor memory maintains securely the stored contents in the memory cells, and it is written with data reliably even in a case where a relatively low supply voltage is applied. A memory cell M00 comprises a pair of inverters cross-coupled with each other, a first switching unit provided between bit line BL and the output terminal of one of the inverters, and a second switching unit provided between bit line XBL and the output terminal of the other inverter. The first switching unit and the second switching unit are controlled to be conductive such that the conductance of the switches be larger for the writing operation than for the reading operation.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
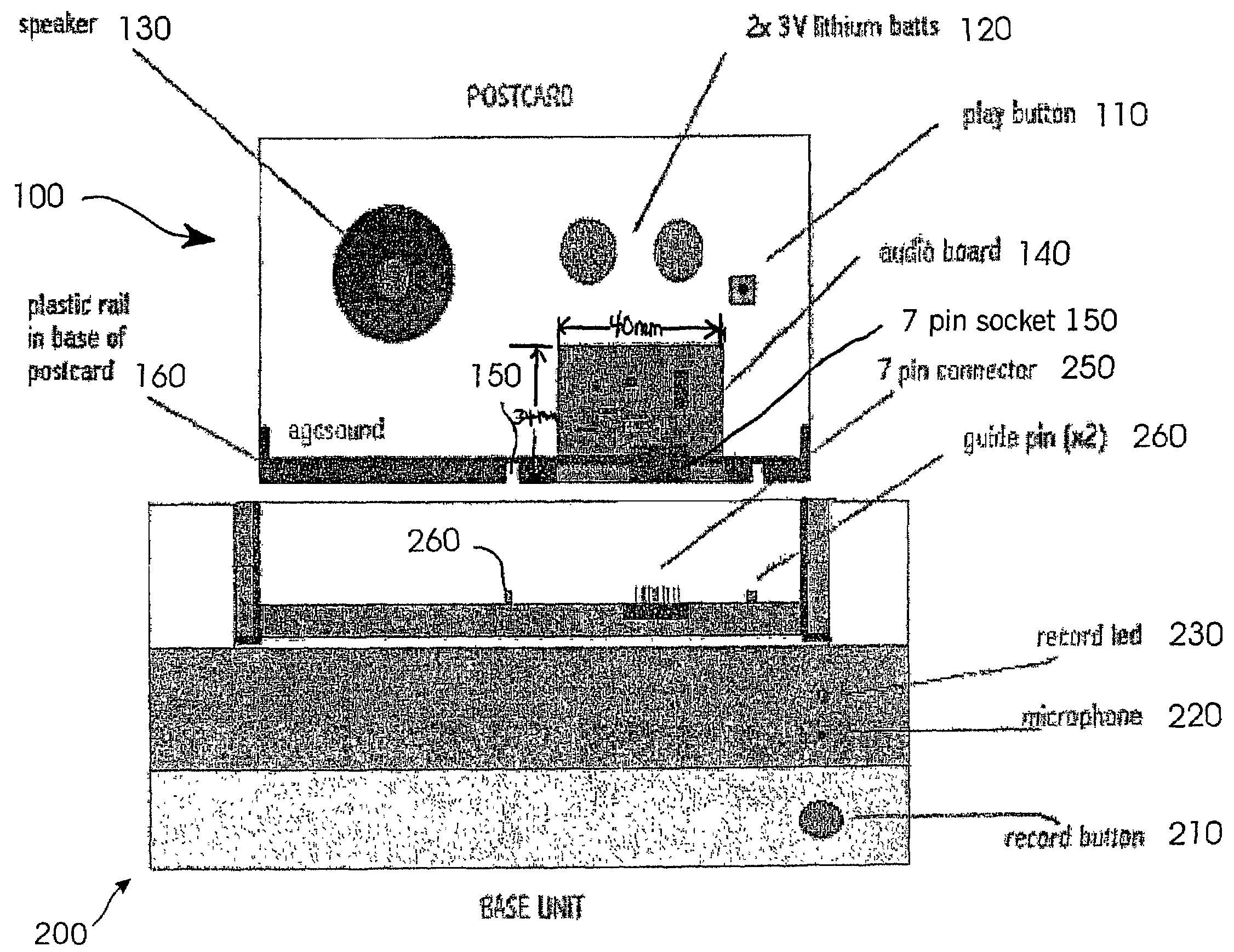
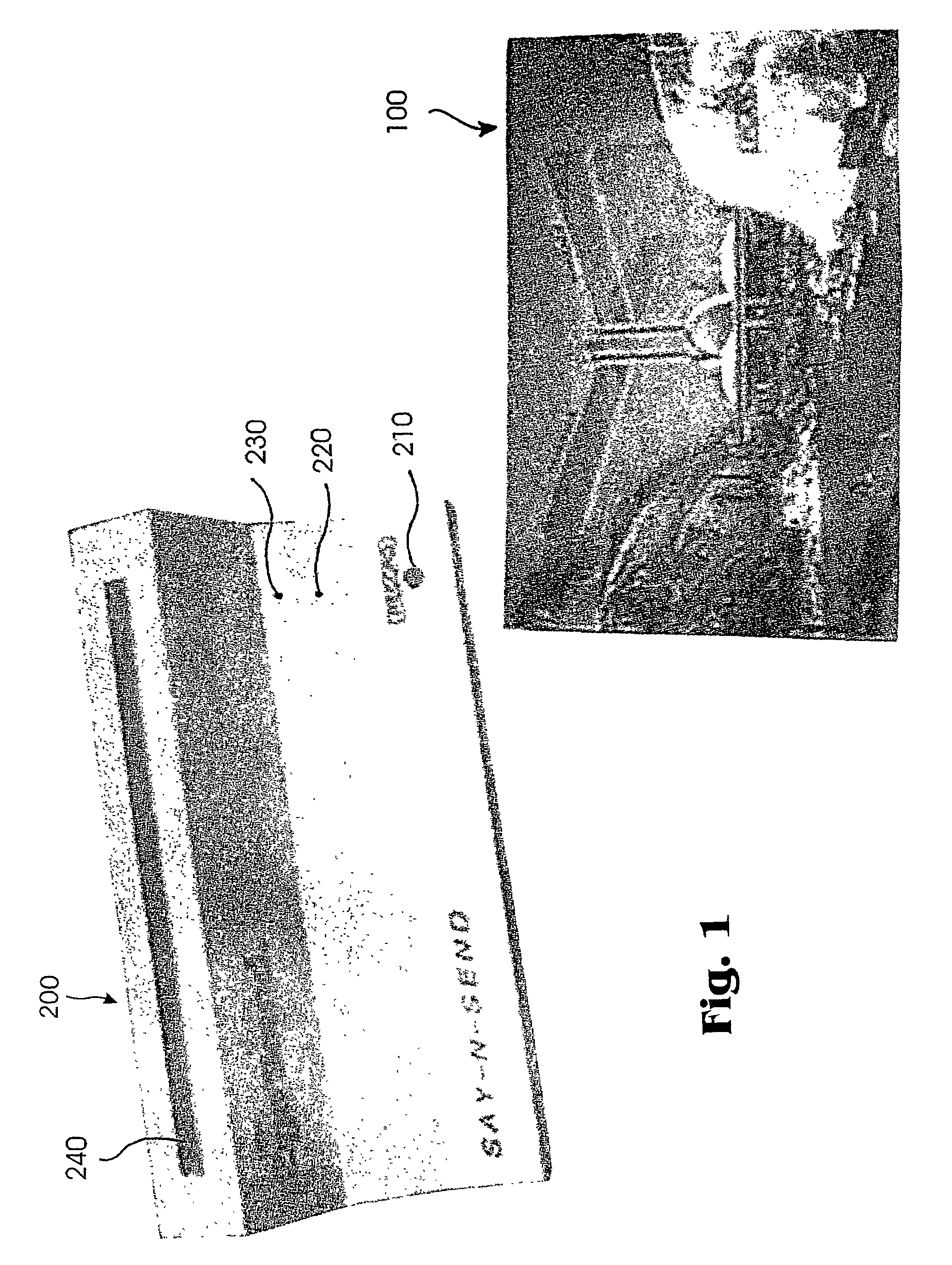
Technique and an apparatus for producing postcards having an audio message for playback by recipient
A system having a postcard having a thickness not to exceed 5.5 mm while containing an audio message for playback and a power supply, the system also having a base recording unit for recording a message to the postcard when the postcard is inserted into the base recording unit. The base recording unit has no power supply and draws power from the power supply on the postcard. The postcard is suitable for mailing using the postal service. The unit for recording is compact, has no power supply, is easily portable and is attractive. The card has a play-back button, a compact battery power source to drive play-back and recording of audio messages. The postcard is absent a record button allowing the postcard with an audio message to be sent through the postal system without the risk of accidental erasure of the recorded message. The card may be recorded and re-recorded when placed in the recording unit. The card contains an audio board that has an IC chip having memory for storing an audio message. The card and the recording unit are both absent a central processing unit.
Owner:APPLE CORP TECH
Unit circuit, electro-optical device, and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS8072396B2Accurate compensationReliablyElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesCapacitanceHemt circuits
A unit circuit includes an electro-optical element, a first capacitive element, a second capacitive element, a third capacitive element, a drive transistor, a first switching element, an initialization unit, and a compensation unit. The electro-optical element emits an amount of light in accordance with a magnitude of a drive current. The first capacitive element includes a first electrode and a second electrode, the first electrode is electrically connected to a first node, and the second electrode is capable of receiving a fixed potential. The second capacitive element includes a third electrode and a fourth electrode, the third electrode is electrically connected to a second node, and the fourth electrode is capable of receiving a fixed potential. The third capacitive element includes a fifth electrode and a sixth electrode, the fifth electrode is electrically connected to the first node, and the sixth electrode is electrically connected to the second node. The drive transistor includes a gate, a source, and a drain and outputs the drive current in a driving period. The gate thereof is electrically connected to the second node. In a data writing period, the first switching element is in an on state and supplies to the first node a data potential supplied via a data line. The initialization unit causes the third capacitive element to discharge charges stored therein in an initialization period. The compensation unit electrically connects the source and the drain of the drive transistor together in a compensation period.
Owner:ELEMENT CAPITAL COMMERCIAL CO PTE LTD
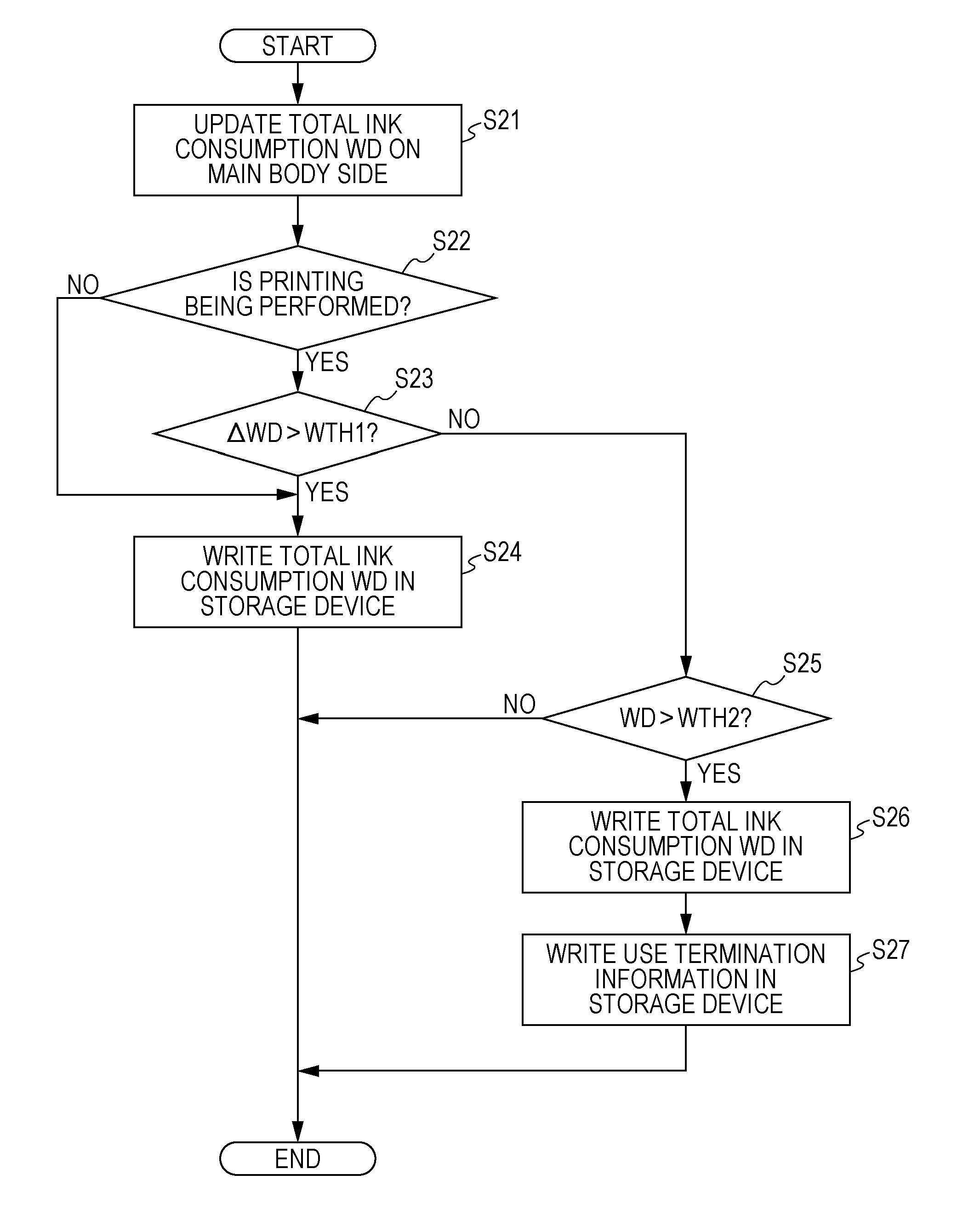
Printing Apparatus
A printing apparatus includes first to n-th (n is an integer equal to or greater than 2) ink tanks in which ink accommodated in an ink pack is filled, slots that respectively correspond to the ink tank, memory units that are packaged together with the ink pack and are respectively installed in the slots, and a processing unit that controls read-out of data from or writing of data to the memory unit. The processing unit updates total ink consumption information on the main body side for each ink color on the basis of the counted ink consumption, and writes the total ink consumption based on the total ink consumption information on the main body side, to the storage device of the memory unit corresponding to the ink color.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Memory system
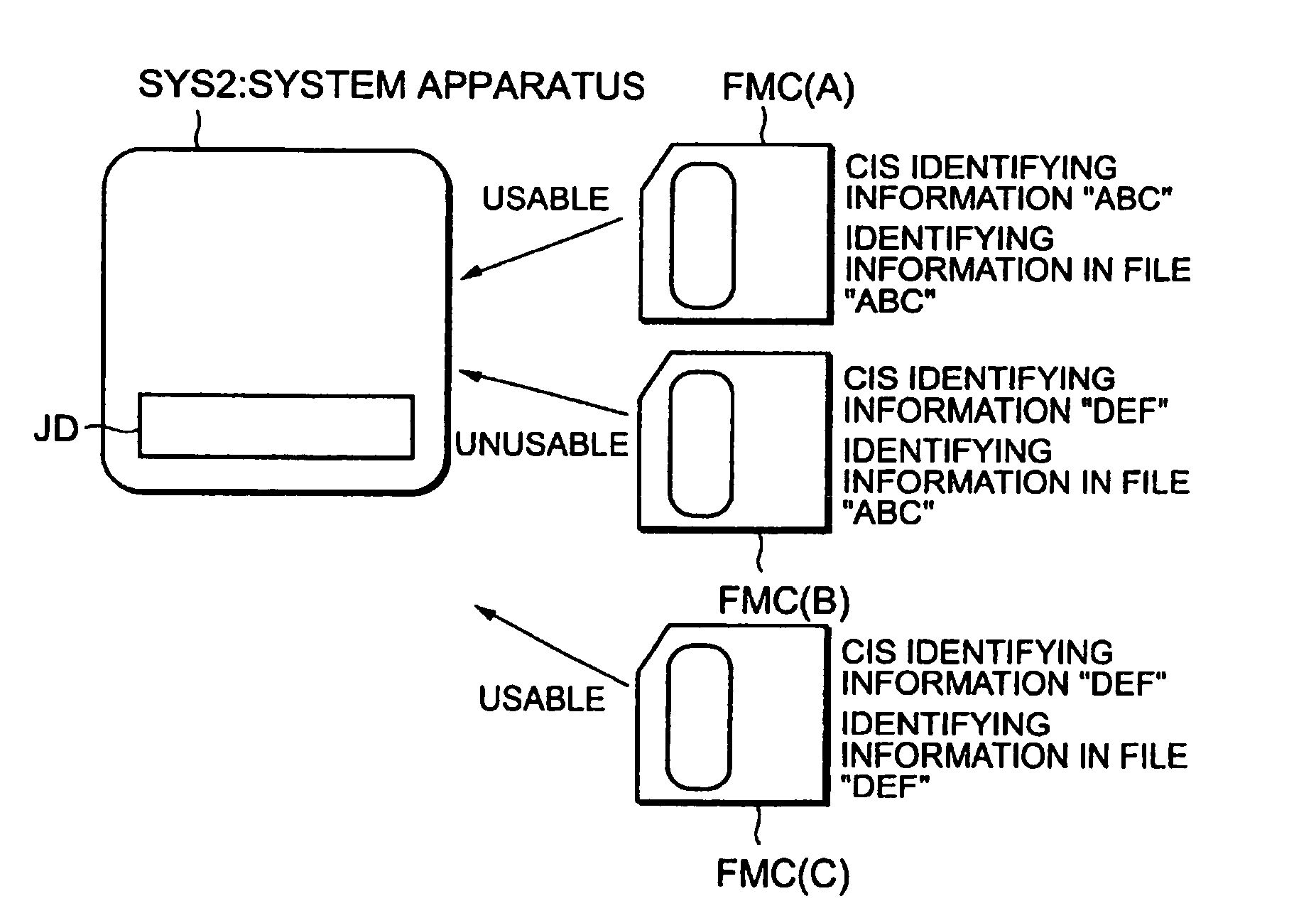
InactiveUSRE42398E1Avoid typosWrite reliablyRead-only memoriesUnauthorized memory use protectionData storingData store
In a memory system using a removable recording medium and data stored in the recording medium, identifying information for identifying each recording medium from others is held in the recording medium, and when data stored in the recording medium is used, the identifying information of the recording medium is required. As a result, when a flash memory card, etc. is used, a copyright is reliably protected.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEMORY CORP
Semiconductor memory which enables reliable data writing with low supply voltage by improving the conductance via access transistors during write operation
A semiconductor memory maintains securely the stored contents in the memory cells, and it is written with data reliably even in a case where a relatively low supply voltage is applied. A memory cell M00 comprises a pair of inverters cross-coupled with each other, a first switching unit provided between bit line BL and the output terminal of one of the inverters, and a second switching unit provided between bit line XBL and the output terminal of the other inverter. The first switching unit and the second switching unit are controlled to be conductive such that the conductance of the switches be larger for the writing operation than for the reading operation.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
Self timed bit and read/write pulse stretchers
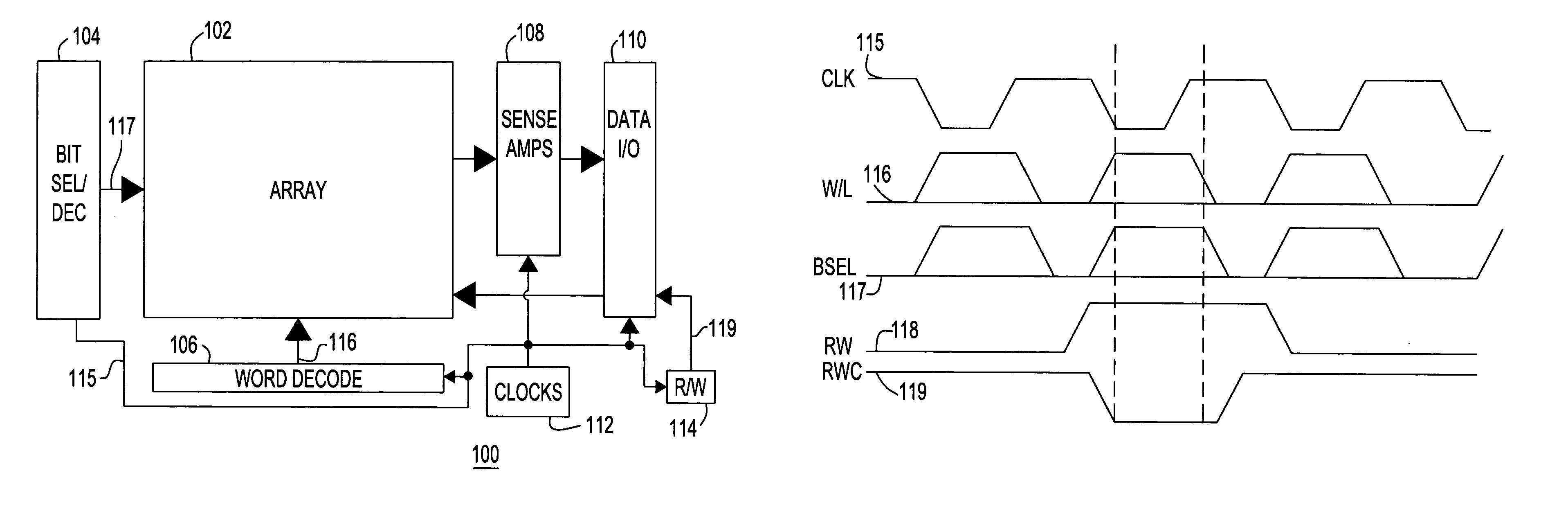
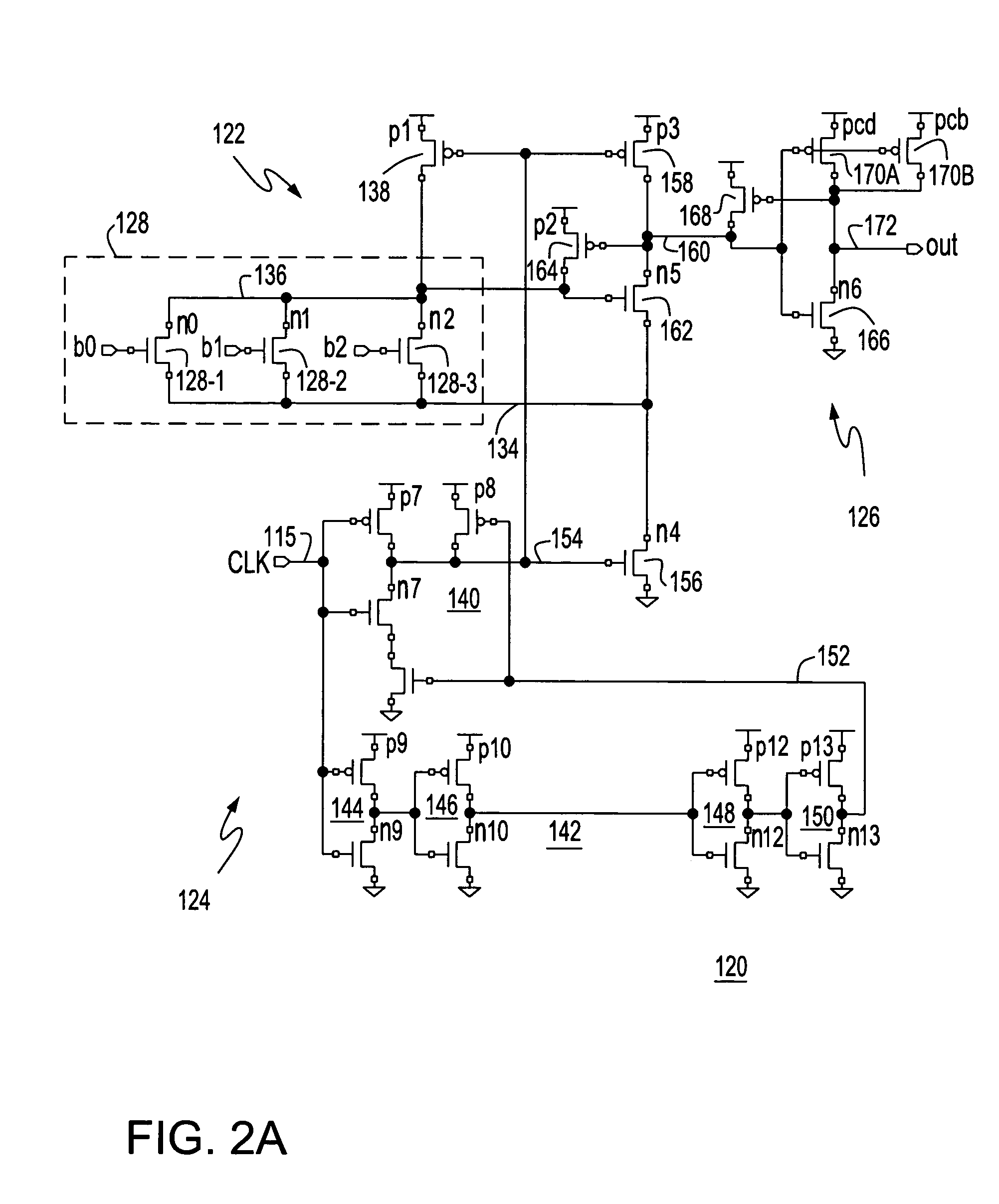
ActiveUS7006403B2High data reliabilityMinimize timeDigital storageRandom access memoryPulse stretcher
Bit and write decode / drivers, a random access memory (RAM) including the decode / drivers and an IC with a static RAM (SRAM) including the decode / drivers. The decode / drivers are clocked by a local clock and each produce access pulses wider than corresponding clock pulses. The bit decode / driver produces bit select pulses that are wider than a word select pulse and the write decode / driver produces write pulses that are wider than the bit select pulses for stable self timed RAM write accesses.
Owner:TWITTER INC
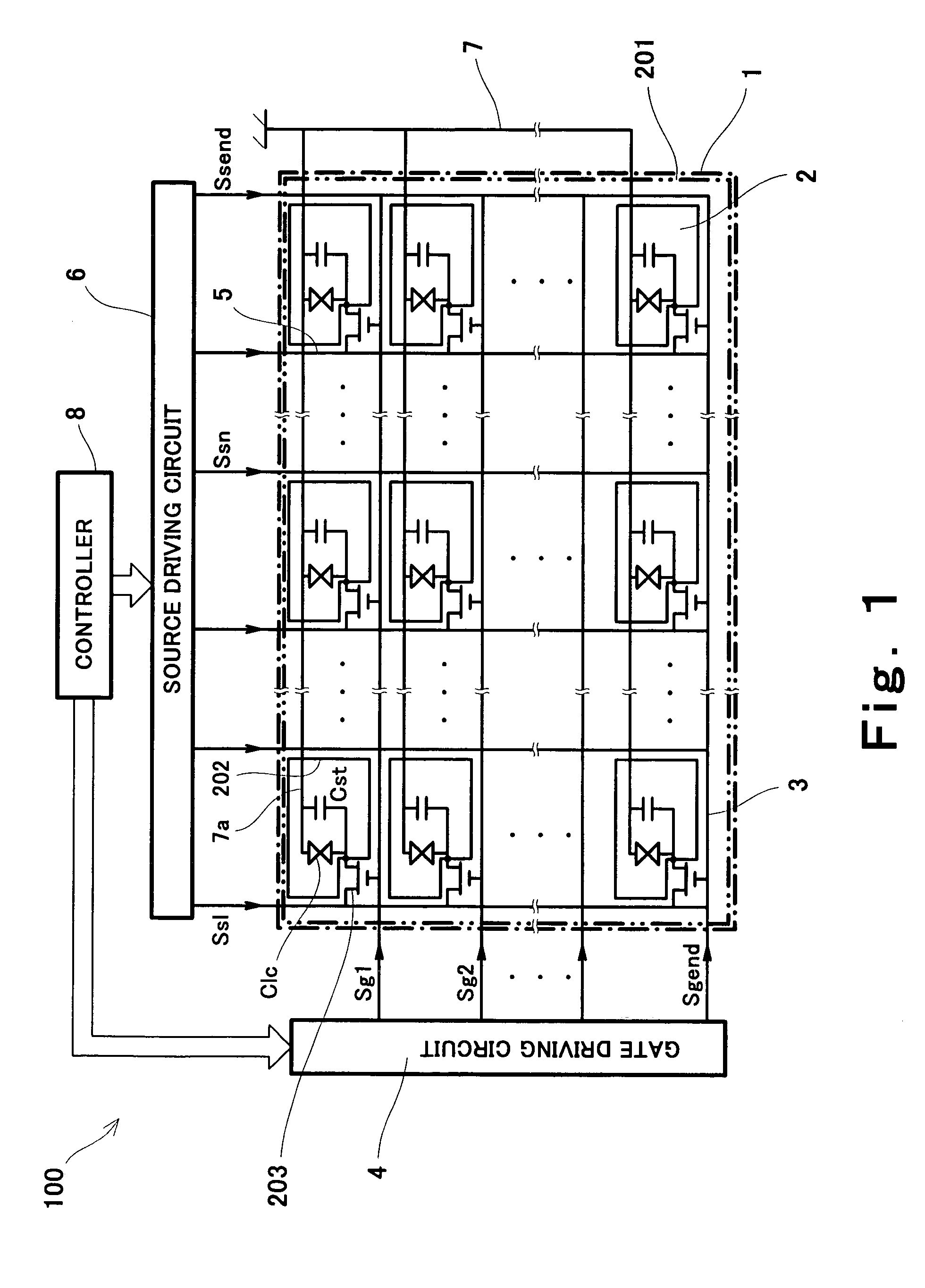
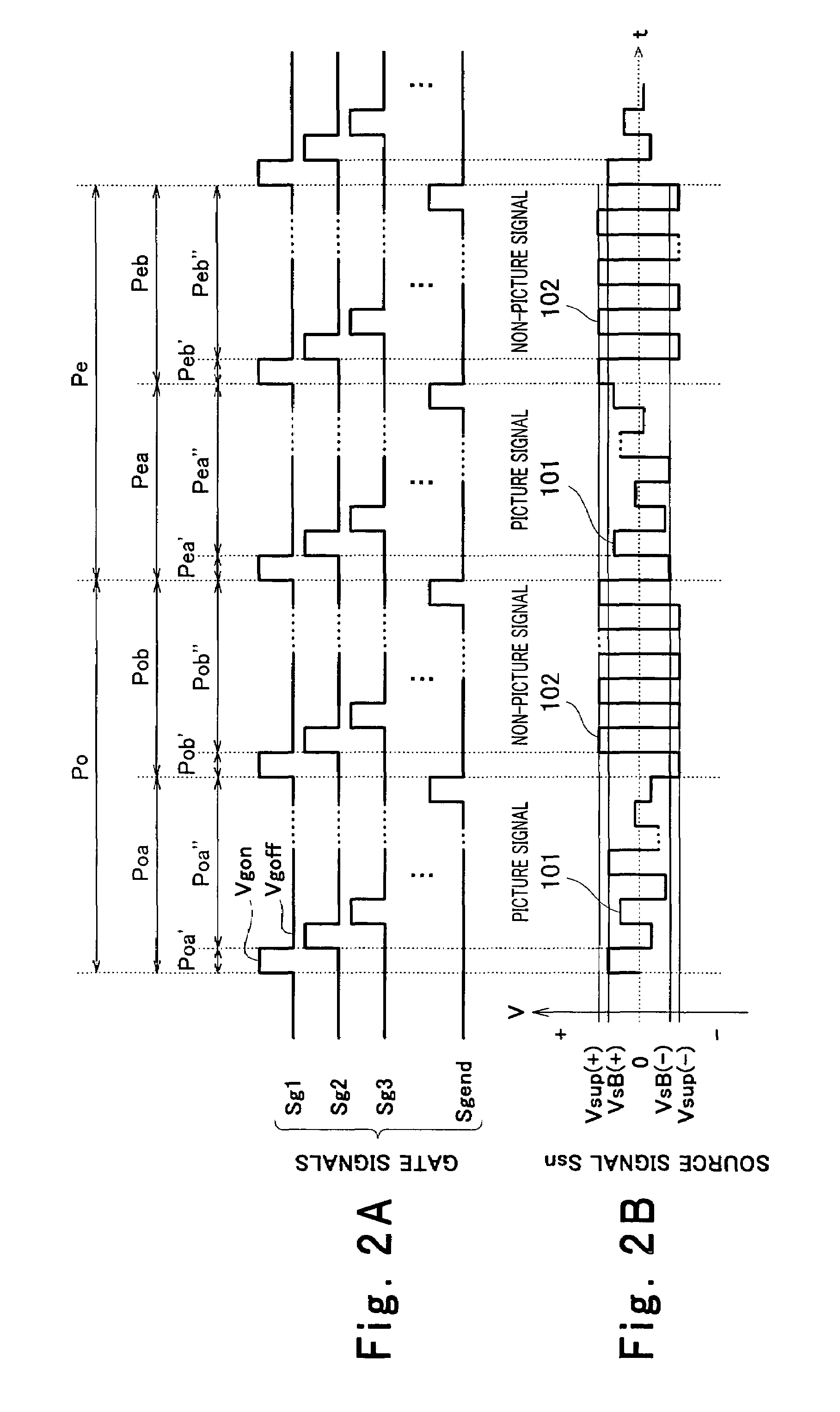
Liquid crystal display element driving method and liquid crystal display using the same
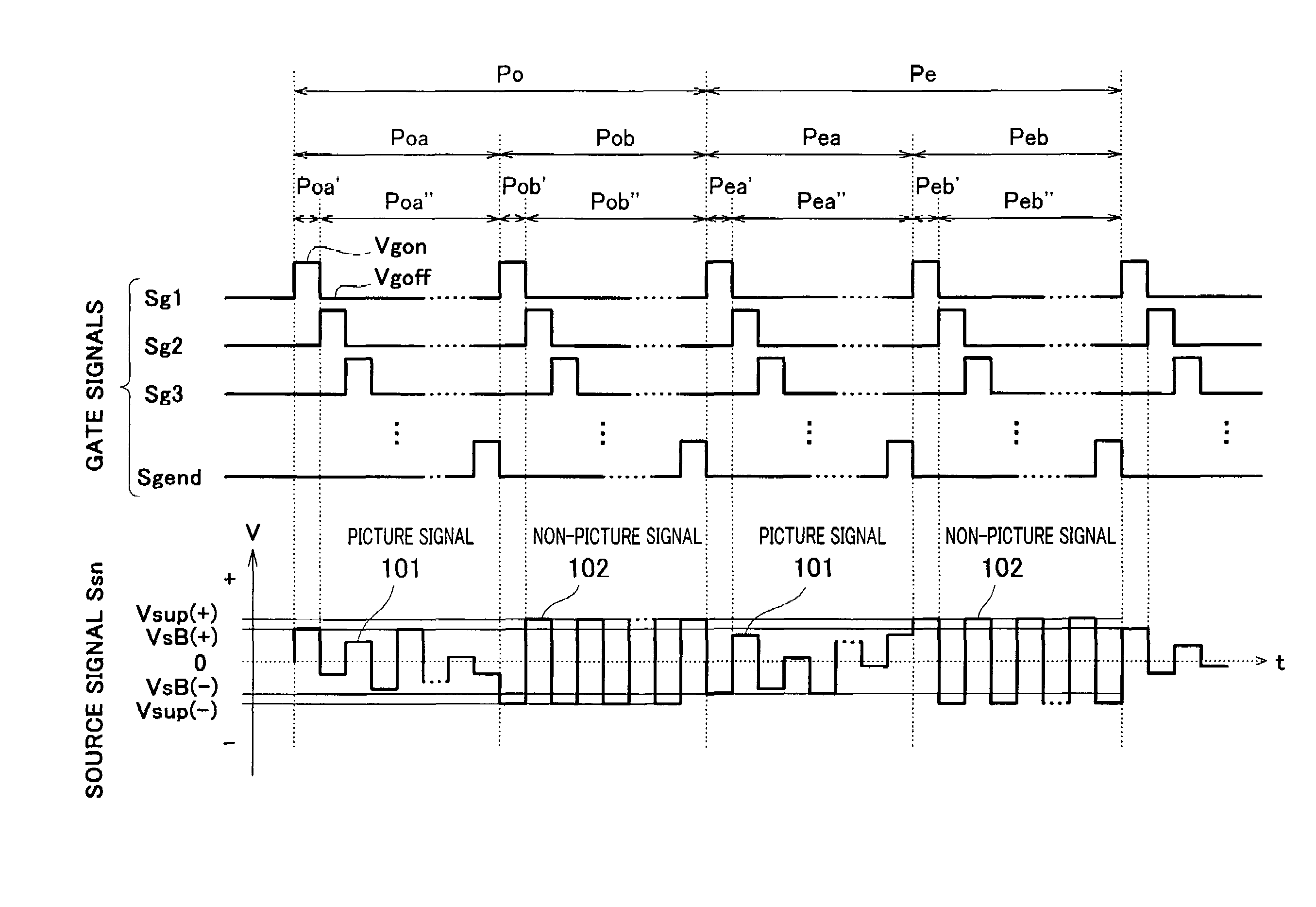
InactiveUS7161574B2Simple constitutionWrite reliablyStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsSignal onTransmittance
A liquid crystal display element driving method or a liquid crystal display device uses a liquid crystal display element having a plurality of pixels constituting a screen; divides a frame period into a plurality of write periods and outputs gate signals to select the pixels sequentially during the write periods; forms each of source signals such that the source signal includes a picture signal and a non-picture signal respectively assigned for the write periods; writes each of the source signals corresponding to the selected pixels to each of the pixels with its polarity being alternated; and displays an image responsive to the source signals on the screen of the liquid crystal display element in such a manner that a transmittivity of liquid crystals of each of the pixels is controlled in accordance with the written source signal, wherein the non-picture signal having a polarity identical to that of the picture signal to be written subsequently is written to the pixels.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY CENT INC
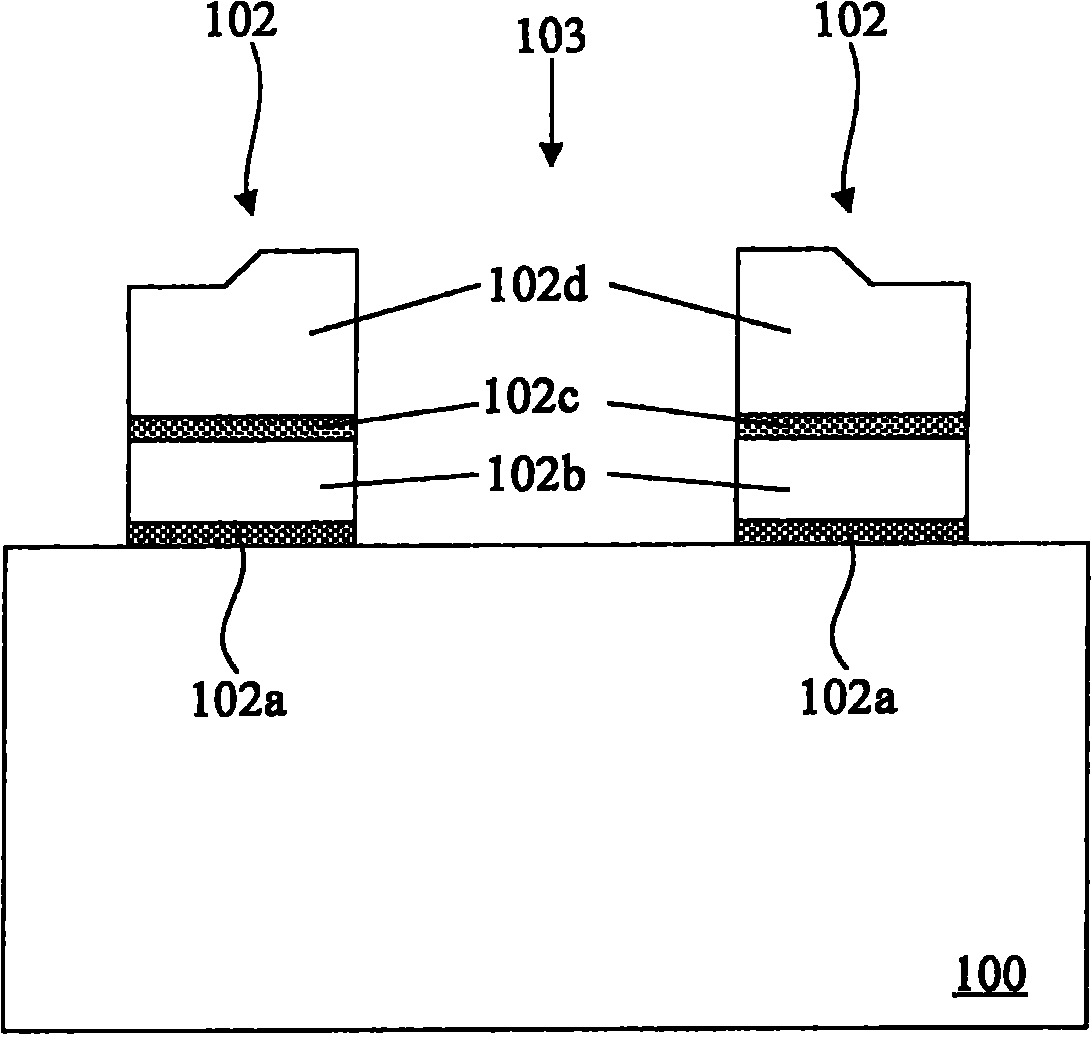
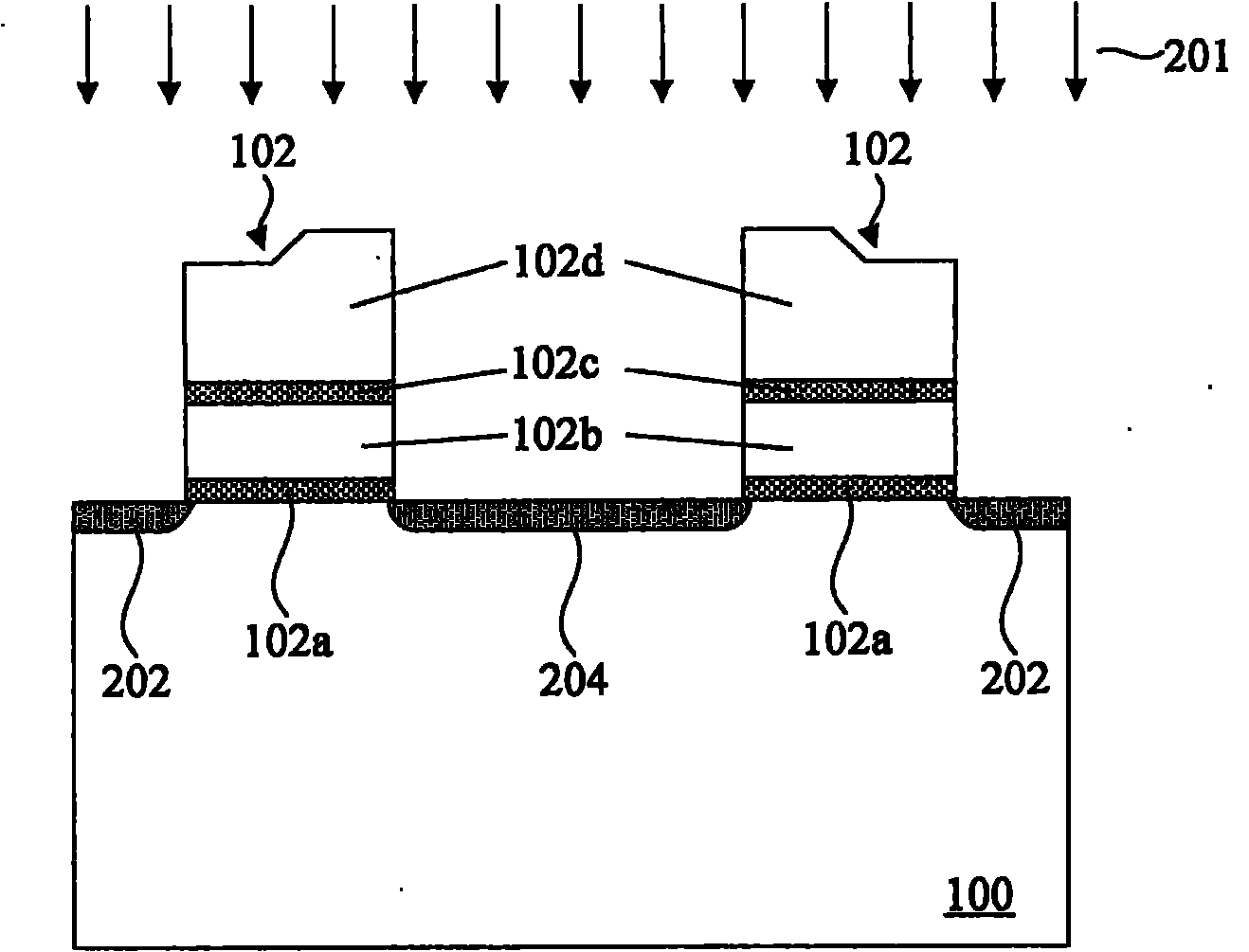
NOR type flash memory structure with double ion implantation and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101826525AAvoid digging throughStable writeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorElectrical connection
The invention provides an NOR type flash memory structure with double ion implantation and a manufacturing method thereof, wherein the NOR type flash memory structure comprises a semiconductor substrate, a lightly doped drain region, a first source region, a highly doped drain region, a phosphorus-doped drain region, two automatic alignment metal silicide layers and a barrier plug. The NOR type flash memory structure can strengthen the electrical connection at the junction of the lightly doped drain region and the highly doped drain region after improving the short channel effect and avoiding the phenomenon that the lightly doped drain region is easy to be dug through when etching, and the mobility of a current carrier in a memory can not be reduced.
Owner:EON SILICON SOLUTION
Self timed bit and read/write pulse stretchers
ActiveUS20050128855A1High data reliabilityMinimize timeDigital storageRandom access memoryPulse stretcher
Bit and write decode / drivers, a random access memory (RAM) including the decode / drivers and an IC with a static RAM (SRAM) including the decode / drivers. The decode / drivers are clocked by a local clock and each produce access pulses wider than corresponding clock pulses. The bit decode / driver produces bit select pulses that are wider than a word select pulse and the write decode / driver produces write pulses that are wider than the bit select pulses for stable self timed RAM write accesses.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Thin-film magnetic head having near-field-light-generating portion with trapezoidal end
ActiveUS7773342B2Write reliablyEffective lightingRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingData signal
A thin-film magnetic head for a heat-assisted magnetic recording which can perform a reliable writing immediately only on a desired track by applying a near-field light to a desired position and range is provided. The head comprises: an electromagnetic coil element for writing data signals, having a pole end reaching a head end surface; and a near-field-light-generating portion for heating a portion of a magnetic recording medium during write operation by generating a near-field light, having a generation end reaching the head end surface and provided adjacent to the pole end and in the leading side of the pole end, and a shape of the generation end on the head end surface being a trapezoid with a shorter edge on the trailing side, or being a triangle with an apex on the trailing side and with a bottom on the leading side.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
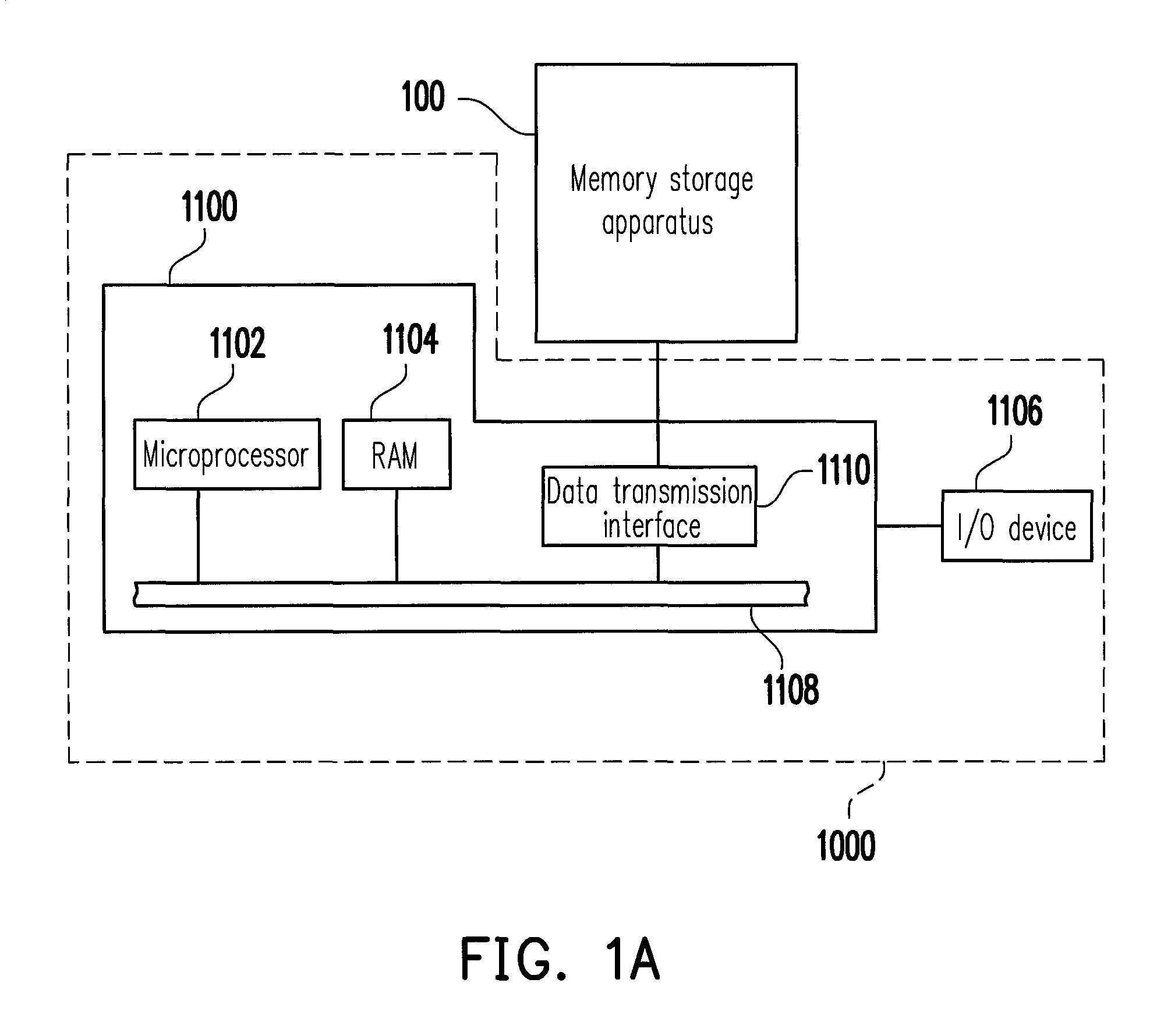
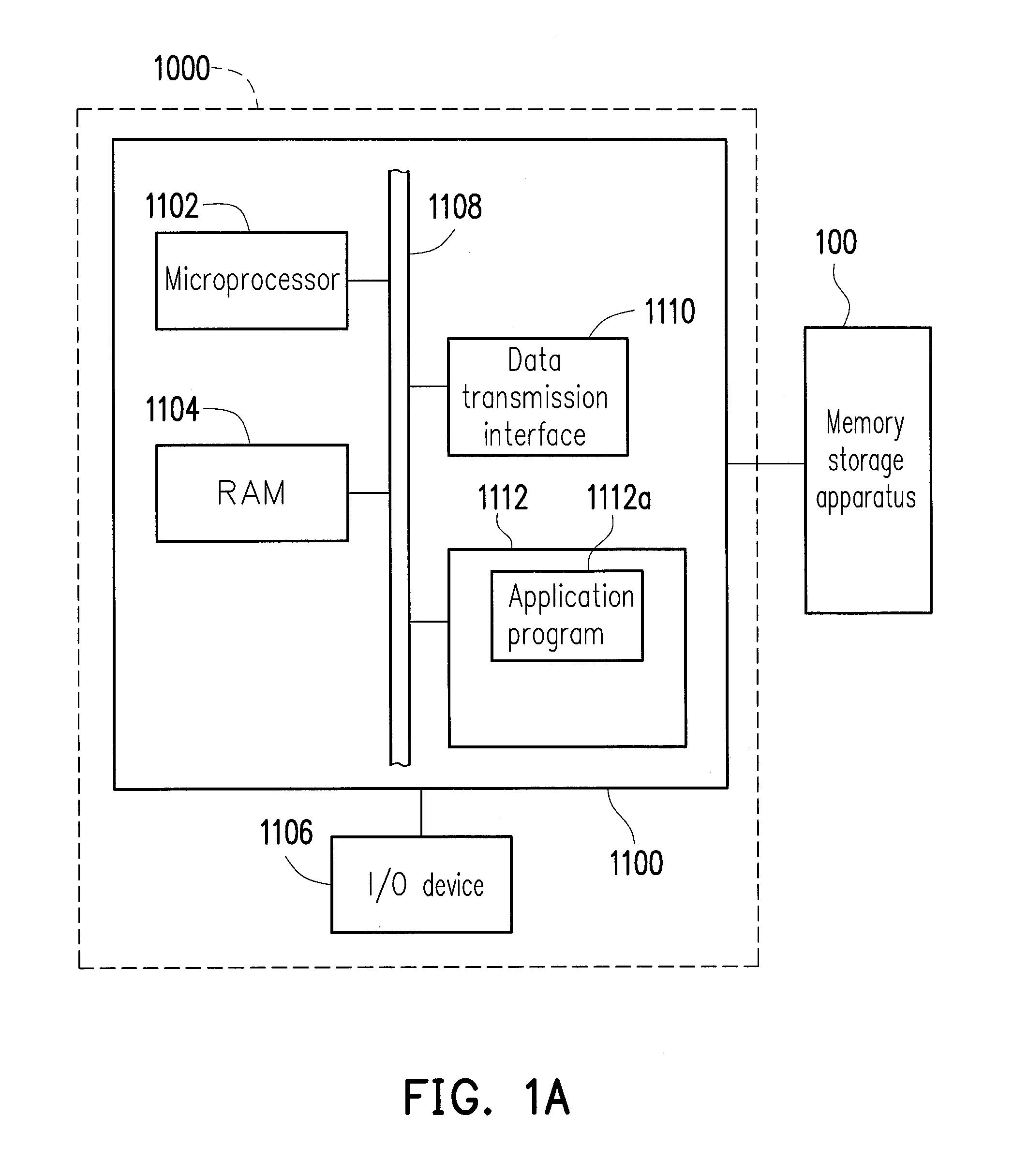
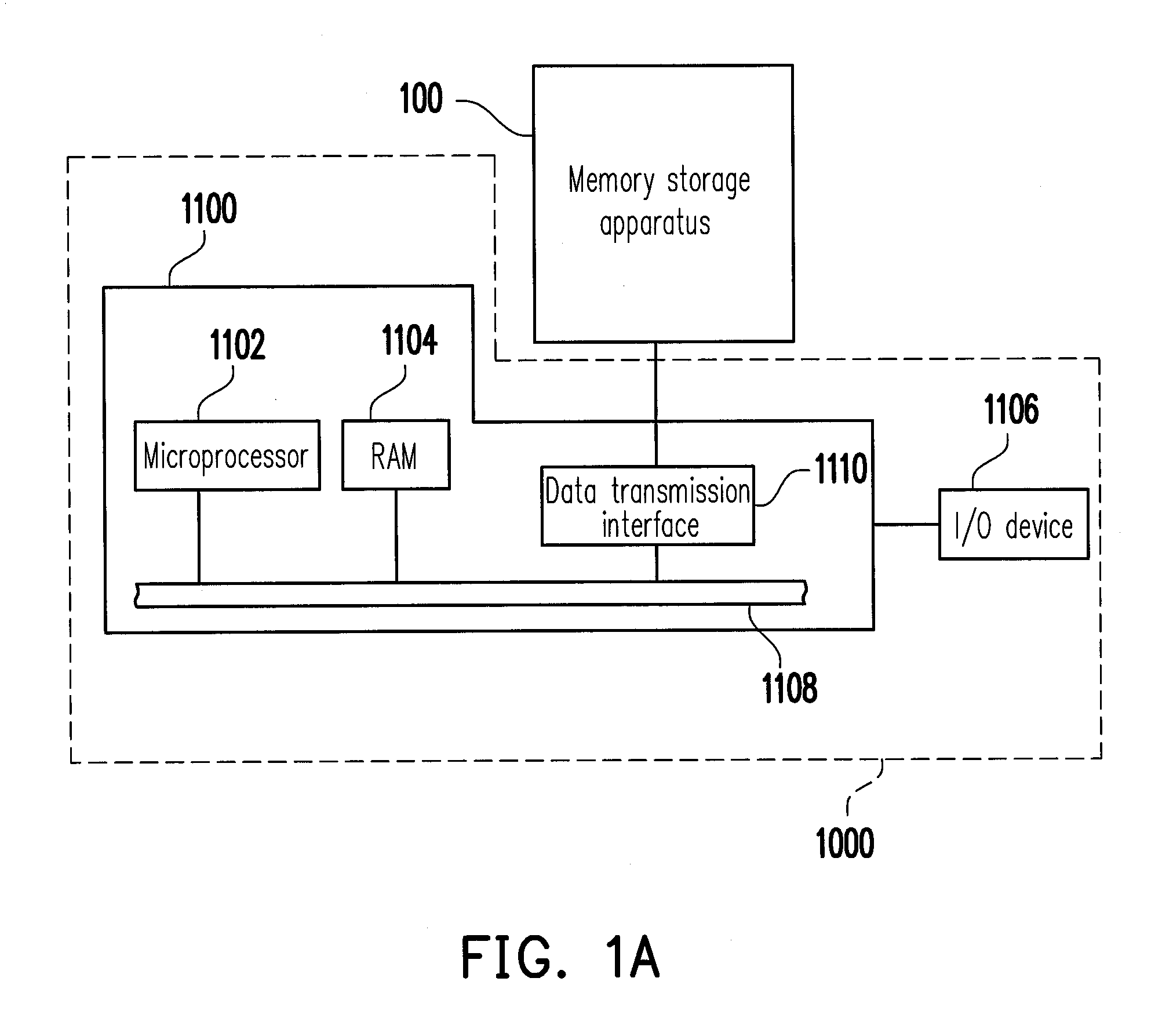
Data writing method, and memory controller and memory storage apparatus using the same
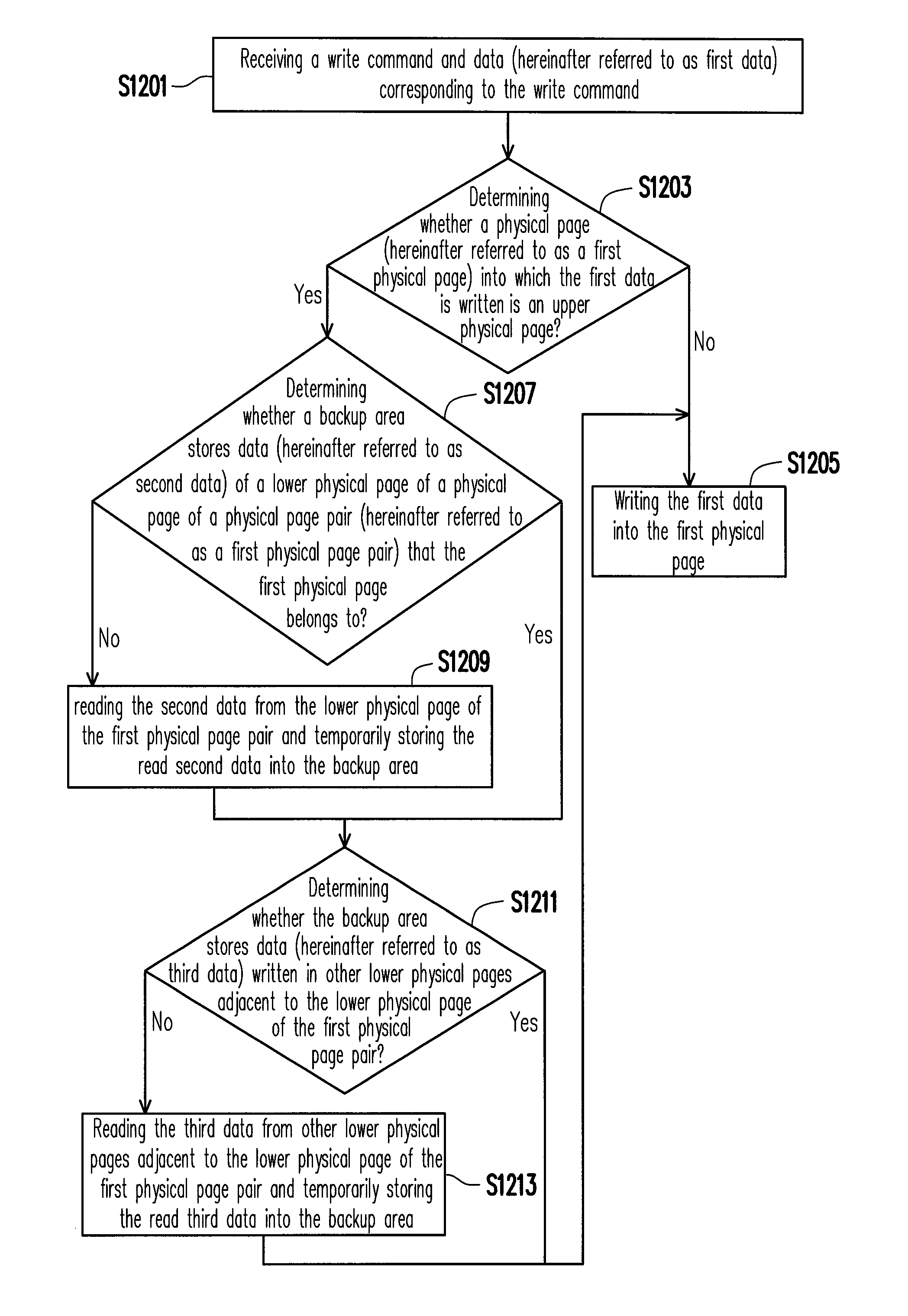
ActiveUS8738847B2Reliable dataHigh speedMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory loss protectionComputer moduleMemory controller
A data writing method for a rewritable non-volatile memory module is provided. The rewritable non-volatile memory module has a plurality of lower physical pages and a plurality of upper physical pages respectively corresponding to the lower physical pages. The method includes determining whether a physical page is one of the upper physical pages before writing first data into the physical page; determining whether a backup area stores second data written into one of the lower physical pages corresponding to the physical page if the physical page is the upper physical page; reading the second data from the lower physical page corresponding to the physical page and backing up the second data into the backup area before writing the first data into the physical page when the backup area does not store the second data. Accordingly, the method may effectively prevent data loss due to a program failure.
Owner:PHISON ELECTRONICS
Data writing method, memory controller and memory storage apparatus
ActiveUS20130246687A1Reliably writing dataReliable dataMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory controllerNon-volatile memory
A data writing method for writing data into a physical block of a rewritable non-volatile memory module is provided. The method includes setting danger distance respectively corresponding to each of the physical pages of the physical block, and setting a secure writing flag in an enable state in response to a secure write command. The method also includes determining whether the secure writing flag is set in the enable state when receiving a write command and updated data thereof; if no, writing the updated data into a predetermined physical page of the physical block; if yes, writing the updated data into a secure physical page of the physical block and re-setting the secure writing flag in a disable state, and the distance between the secure physical page and the predetermined physical page is equal to the danger distance corresponding to the predetermined physical page.
Owner:PHISON ELECTRONICS
Anti-fuse circuit and semiconductor memory device
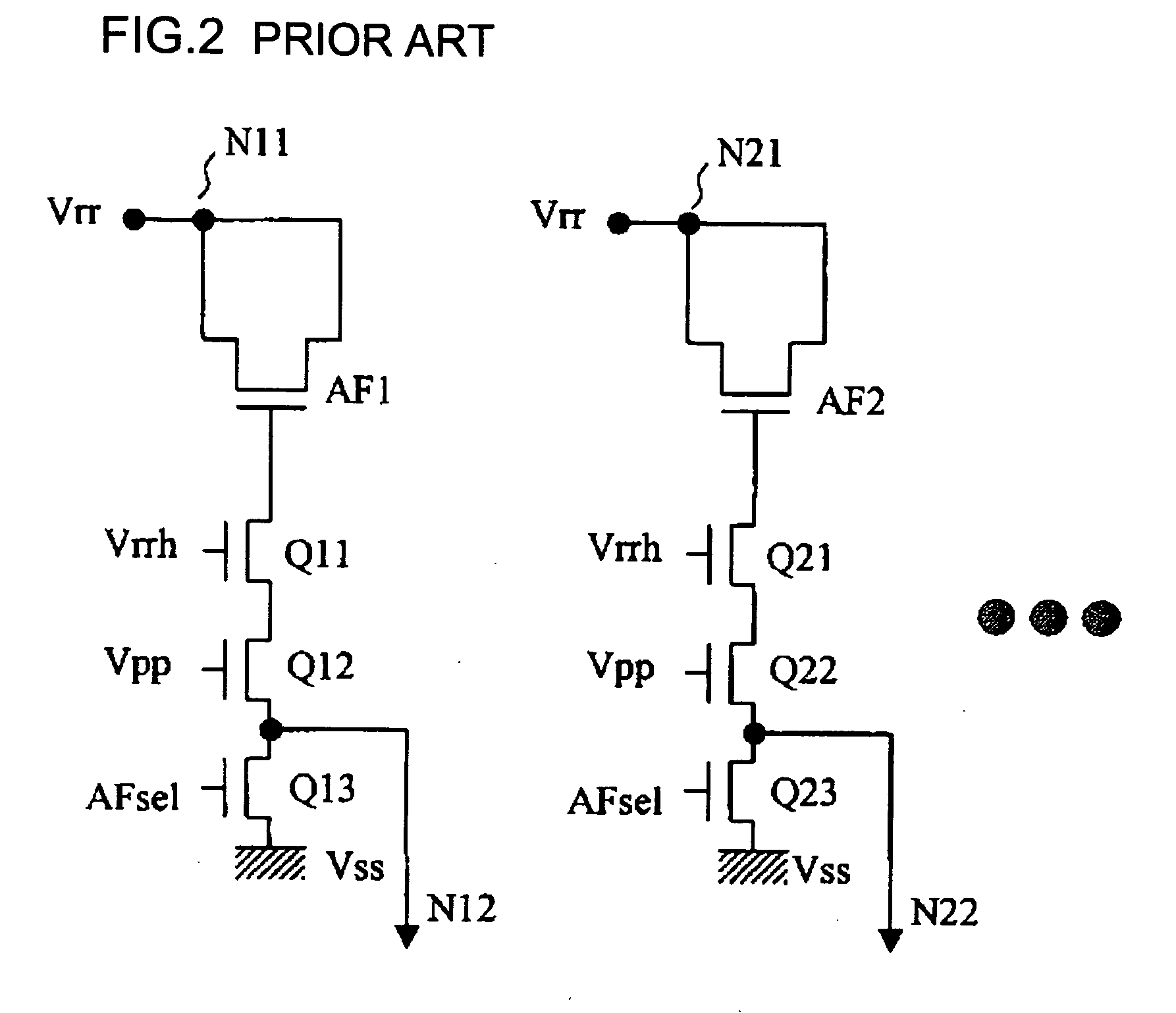
An anti-fuse circuit uses first to fifth power supplies which have first to fifth power supply voltages, respectively, in the order of highest to lowest during writing. The anti-fuse circuit includes: a first level shift circuit which is connected to the second to fourth power supplies and which converts a first logic signal that changes between the third and fourth power supply voltages into a second logic signal that changes between the second and fourth power supply voltages; a second level shift circuit which is connected to the first, second, and fourth power supplies and which converts the second logic signal into a third logic signal that changes between the first and fourth power supply voltages; a transistor having a source connected to the first power supply and a gate connected to the third logic signal; and an anti-fuse element having one end connected to the drain of the transistor and the other end connected to the fifth power supply.
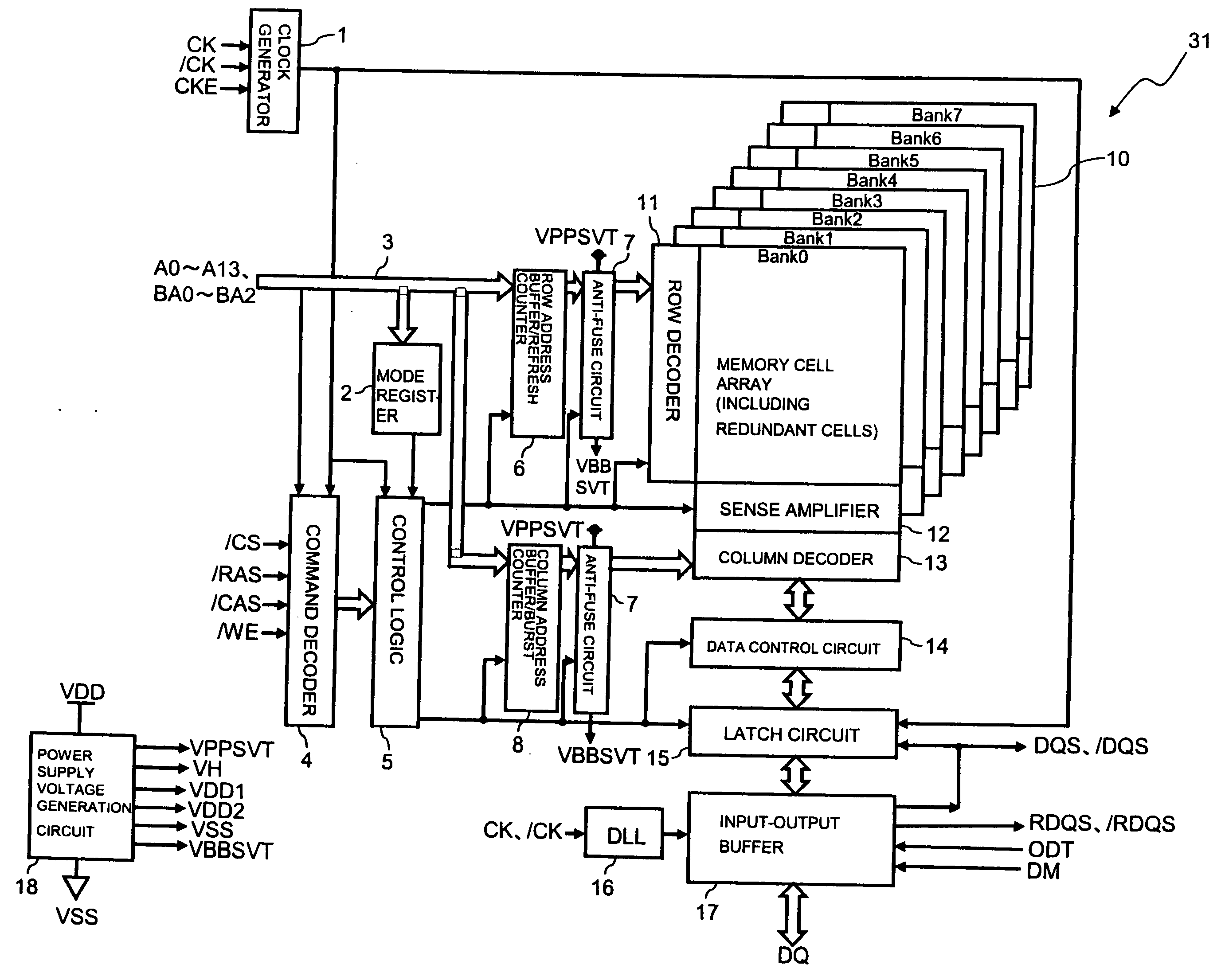
Owner:ELPIDA MEMORY INC
Electronic control apparatus
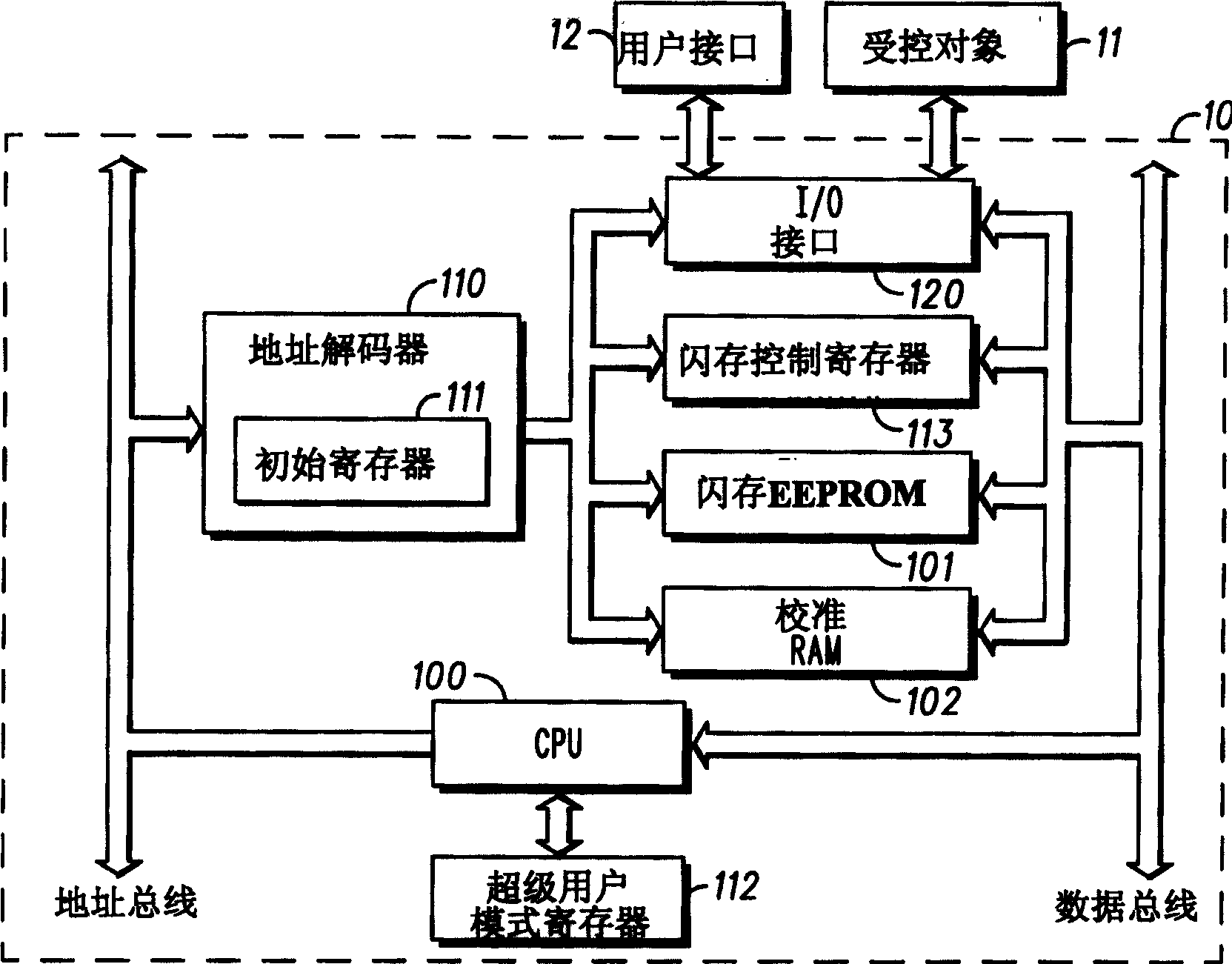
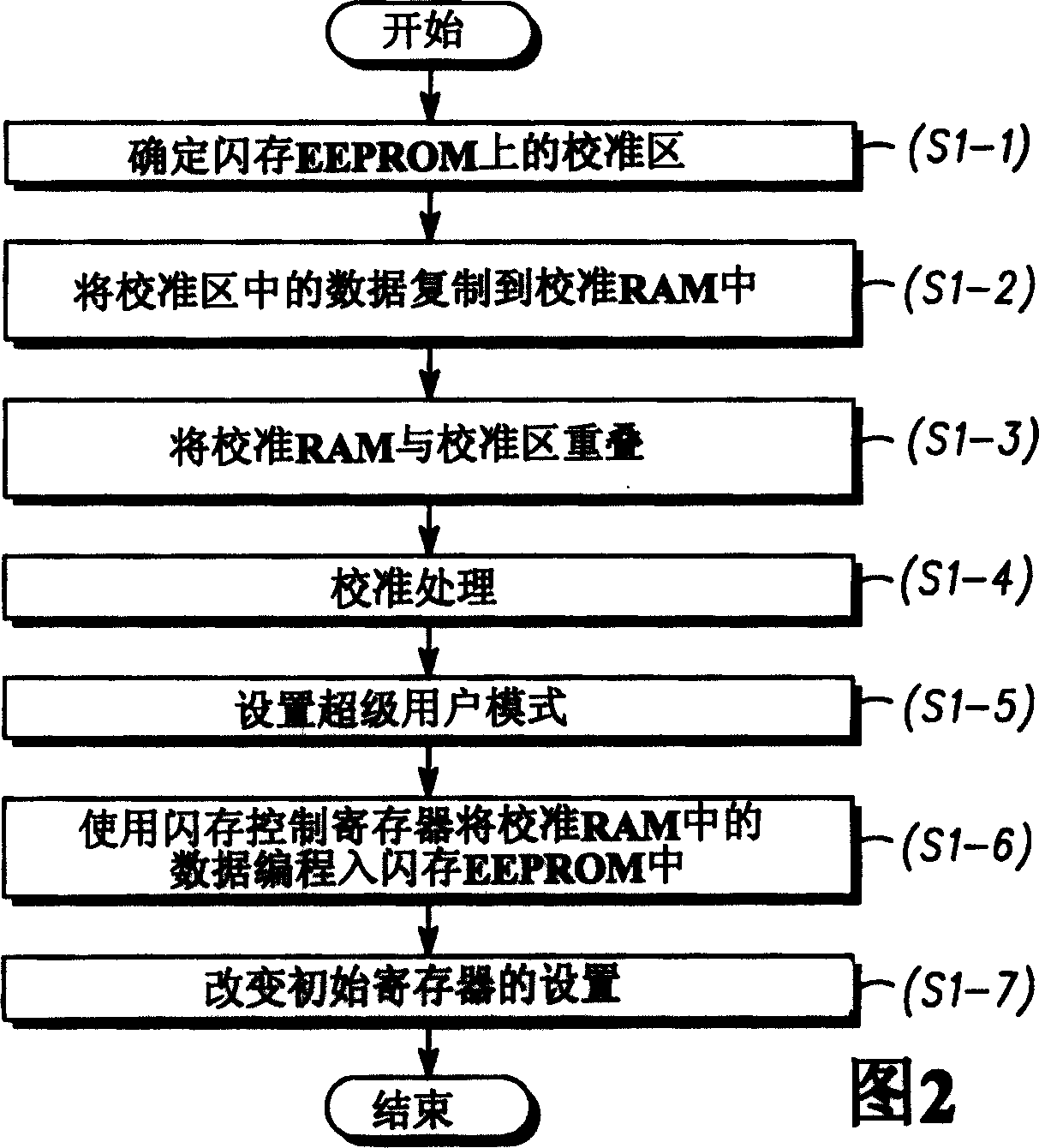
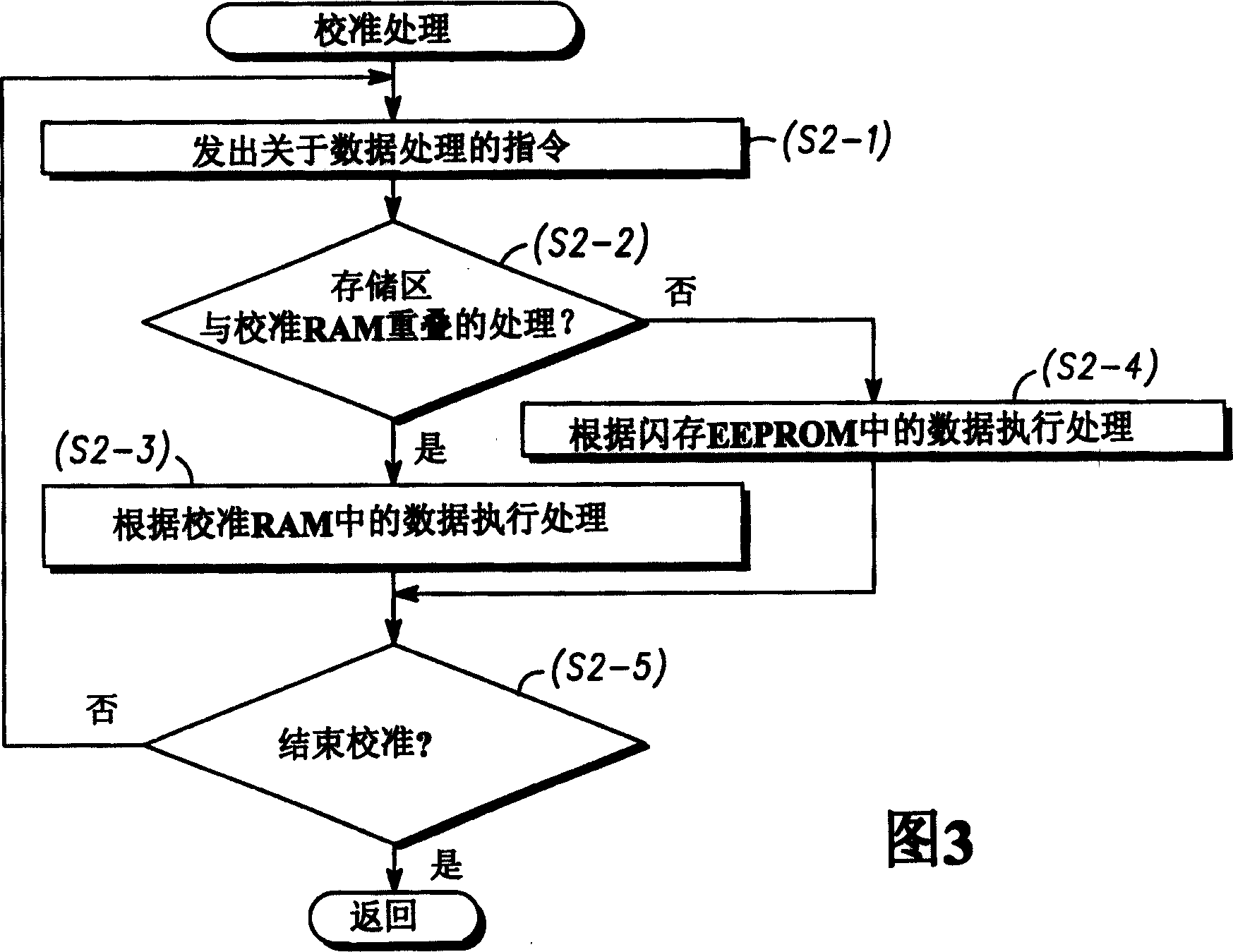
InactiveCN1659662AValid calibrationWrite reliablyElectrical controlError detection/correctionControl registerData storing
The objective is to provide an electronic control apparatus capable of overwriting data in a nonvolatile memory, even during control operation. An ECU ( 10 ) includes a CPU ( 100 ), a flash EEPROM 101, and a calibration RAM ( 102 ). When calibration is performed, data in a calibration area of the flash EEPROM ( 101 ) is stored into the calibration RAM ( 102 ). A memory area of the calibration RAM ( 102 ) is overlapped over the calibration area to perform calibration. The data in the calibration area is written into the calibration RAM ( 102 ). When the calibration is completed, a super-user mode is entered in which the data stored in the calibration RAM ( 102 ) is written into the flash EEPROM ( 101 ) by use of a control register ( 113 ).
Owner:FREESCALE SEMICON INC
Data writing method, and memory controller and memory storage apparatus using the same
ActiveUS20130067141A1Reliably writing dataReliable dataMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesMemory controllerVolatile memory
A data writing method for a rewritable non-volatile memory module is provided. The rewritable non-volatile memory module has a plurality of lower physical pages and a plurality of upper physical pages respectively corresponding to the lower physical pages. The method includes determining whether a physical page is one of the upper physical pages before writing first data into the physical page; determining whether a backup area stores second data written into one of the lower physical pages corresponding to the physical page if the physical page is the upper physical page; reading the second data from the lower physical page corresponding to the physical page and backing up the second data into the backup area before writing the first data into the physical page when the backup area does not store the second data. Accordingly, the method may effectively prevent data loss due to a program failure.
Owner:PHISON ELECTRONICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com