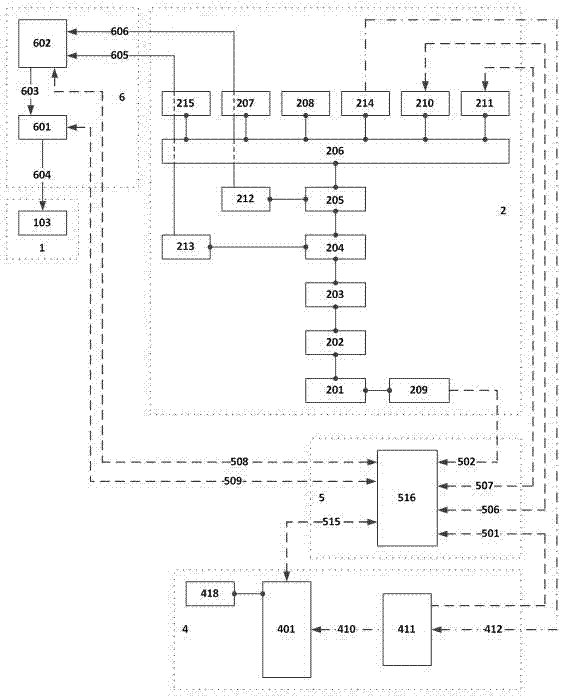
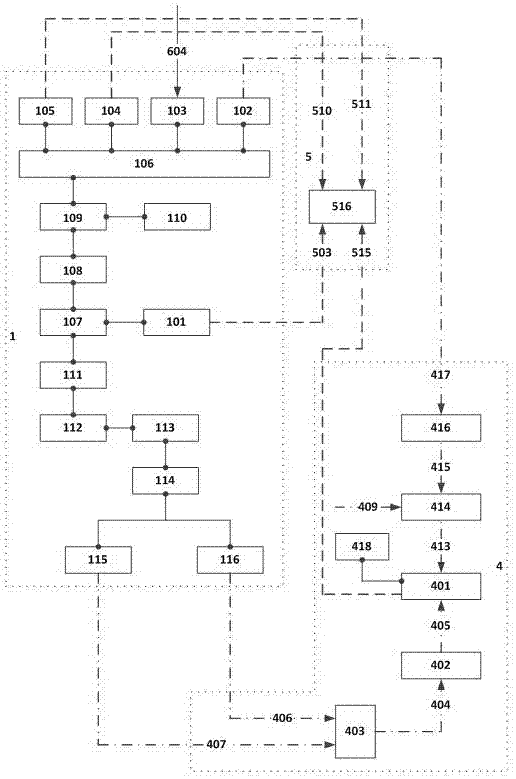
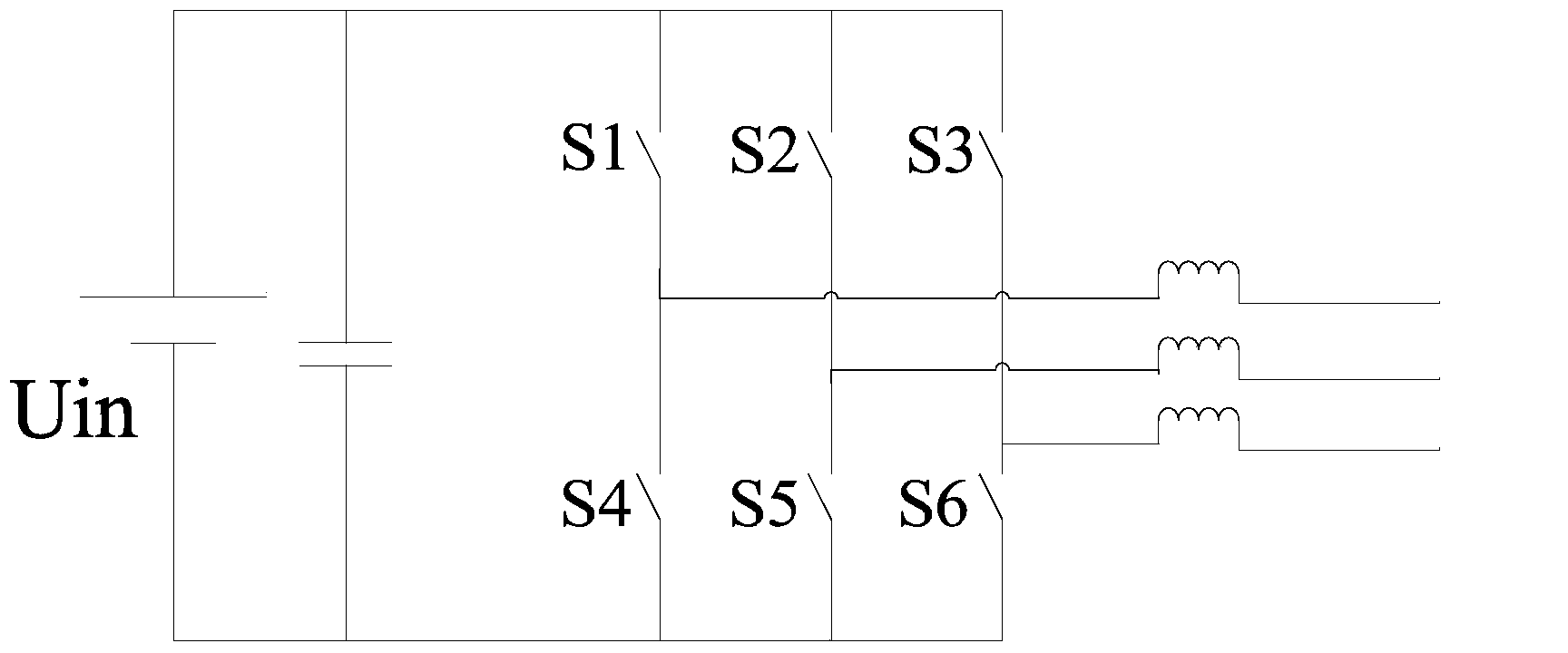
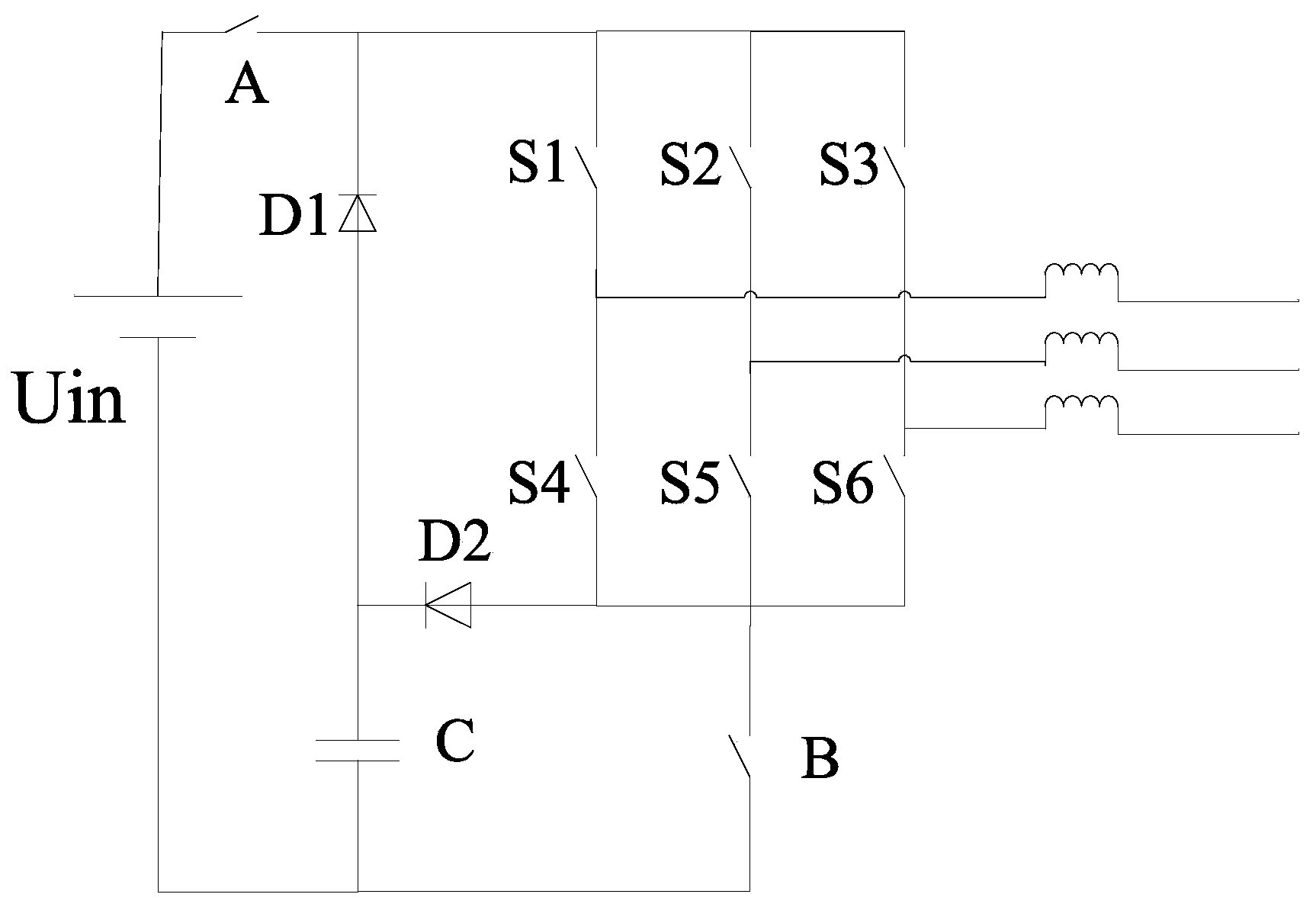
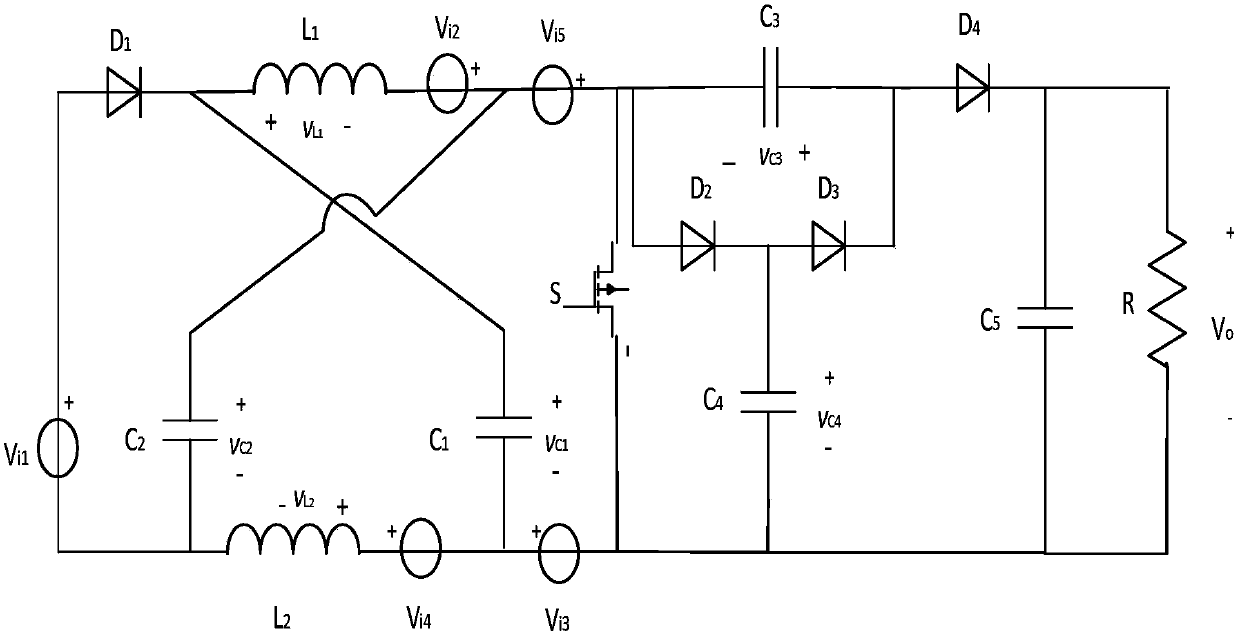
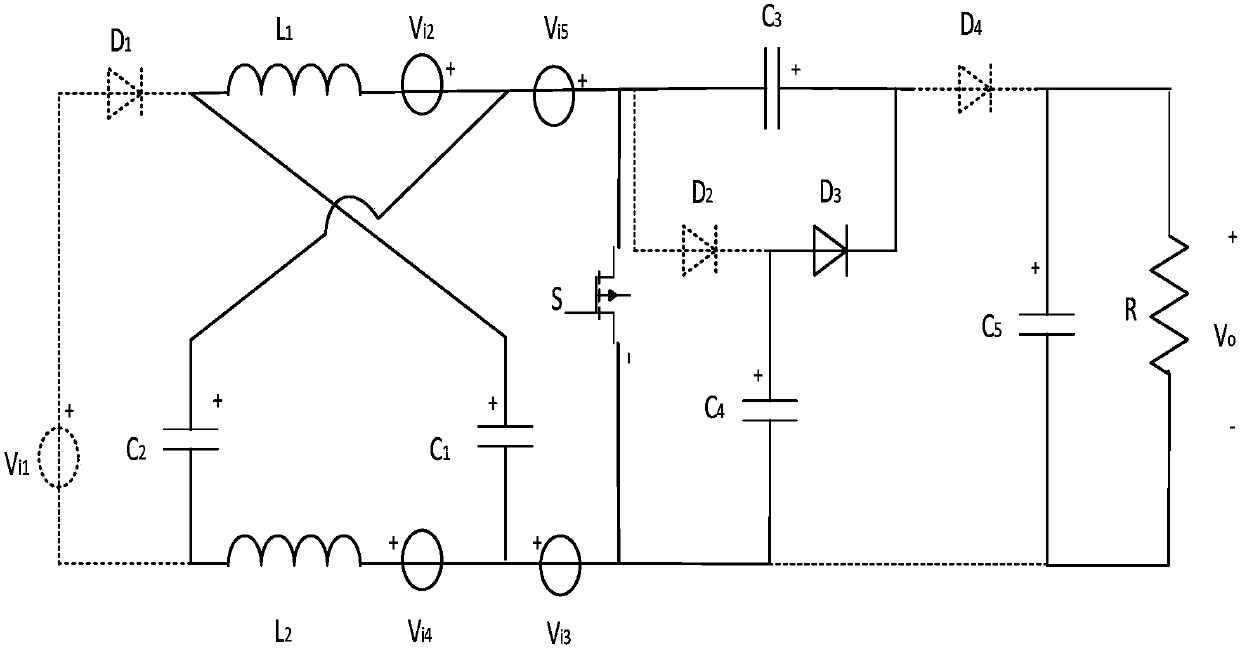
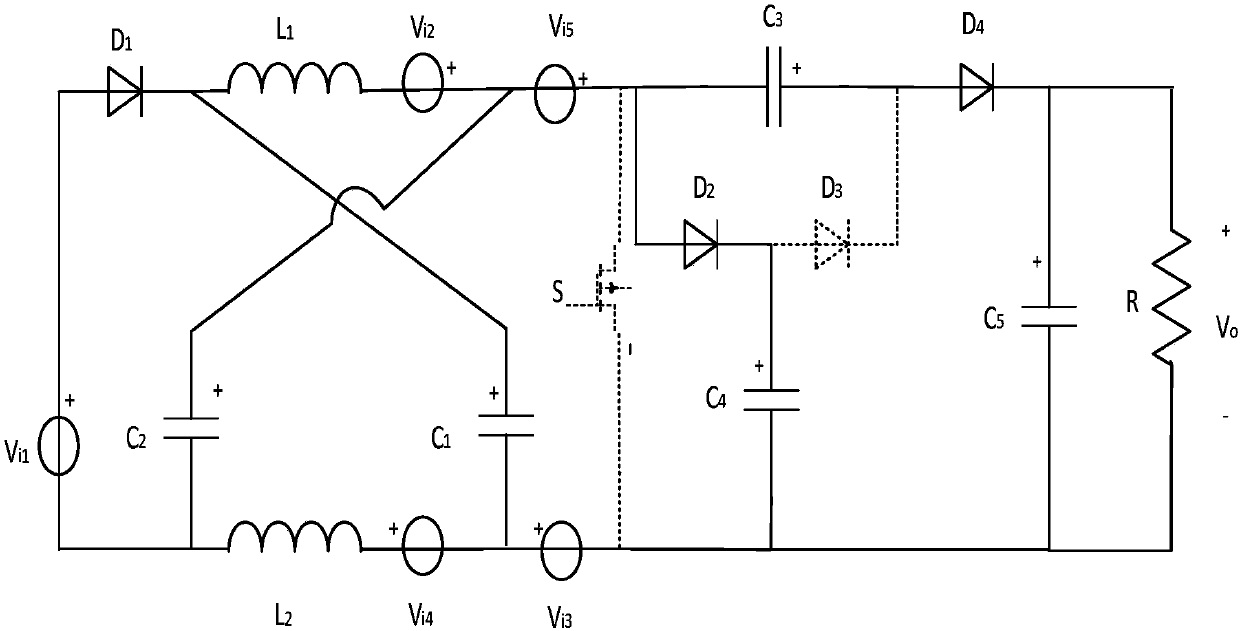
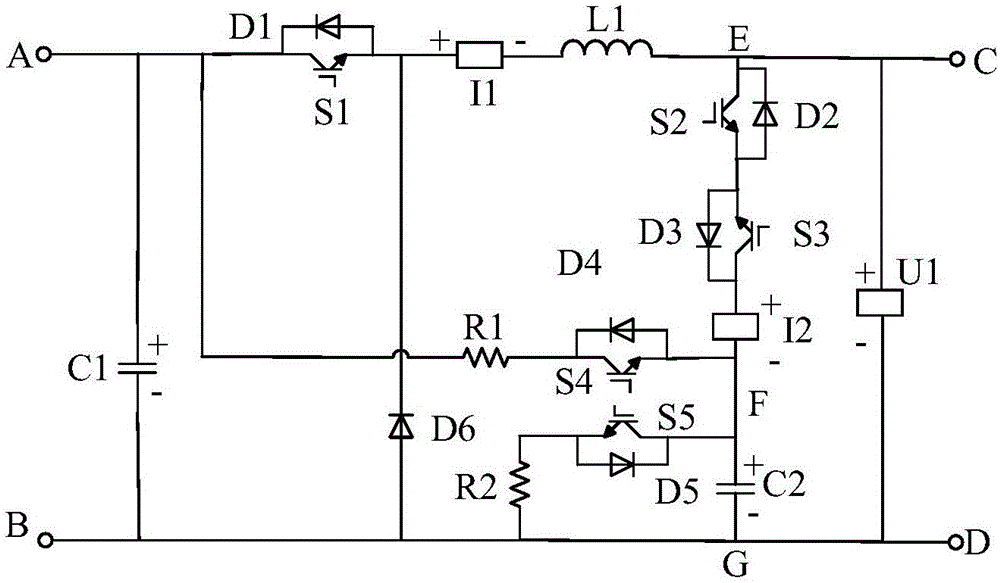
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
45 results about "Fifth power" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The fifth power is a term, apparently created by Ignacio Ramonet, that intends a continuation of the series of the three estates of the realm and the fourth power, the mass media. The term fifth power can be used to refer either to the Internet, public opinion, the Church (which is the First Estate by the original meaning), economic systems or simply money including its creation.
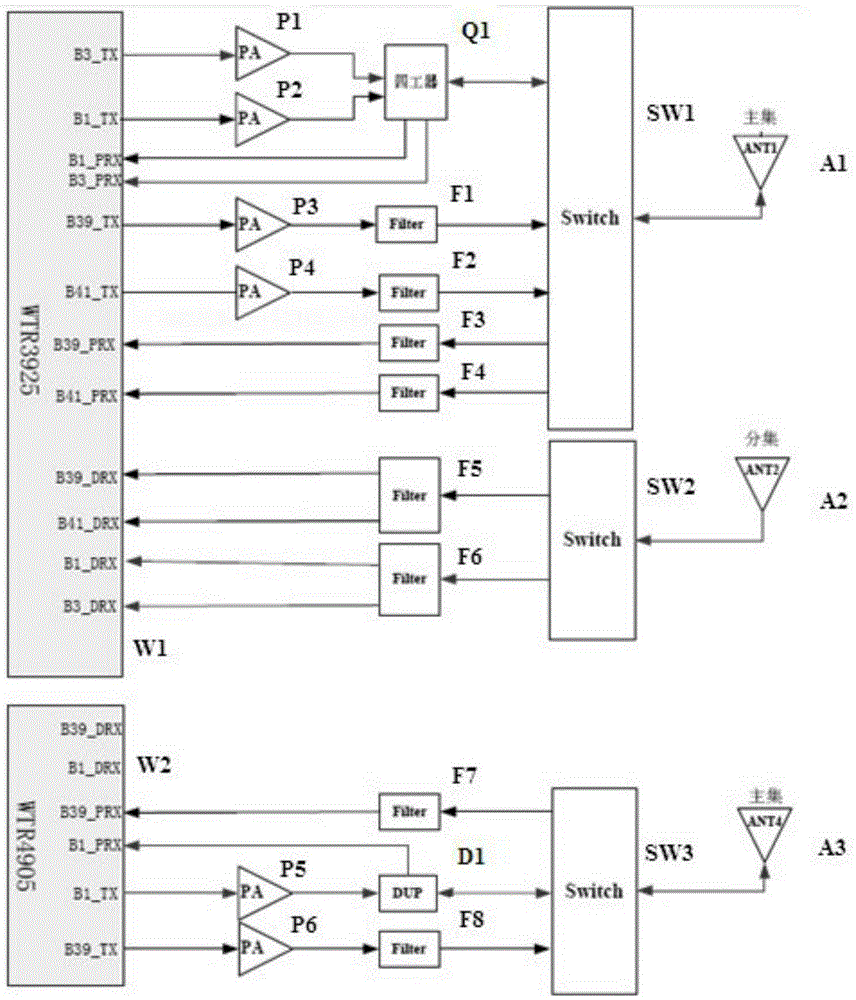
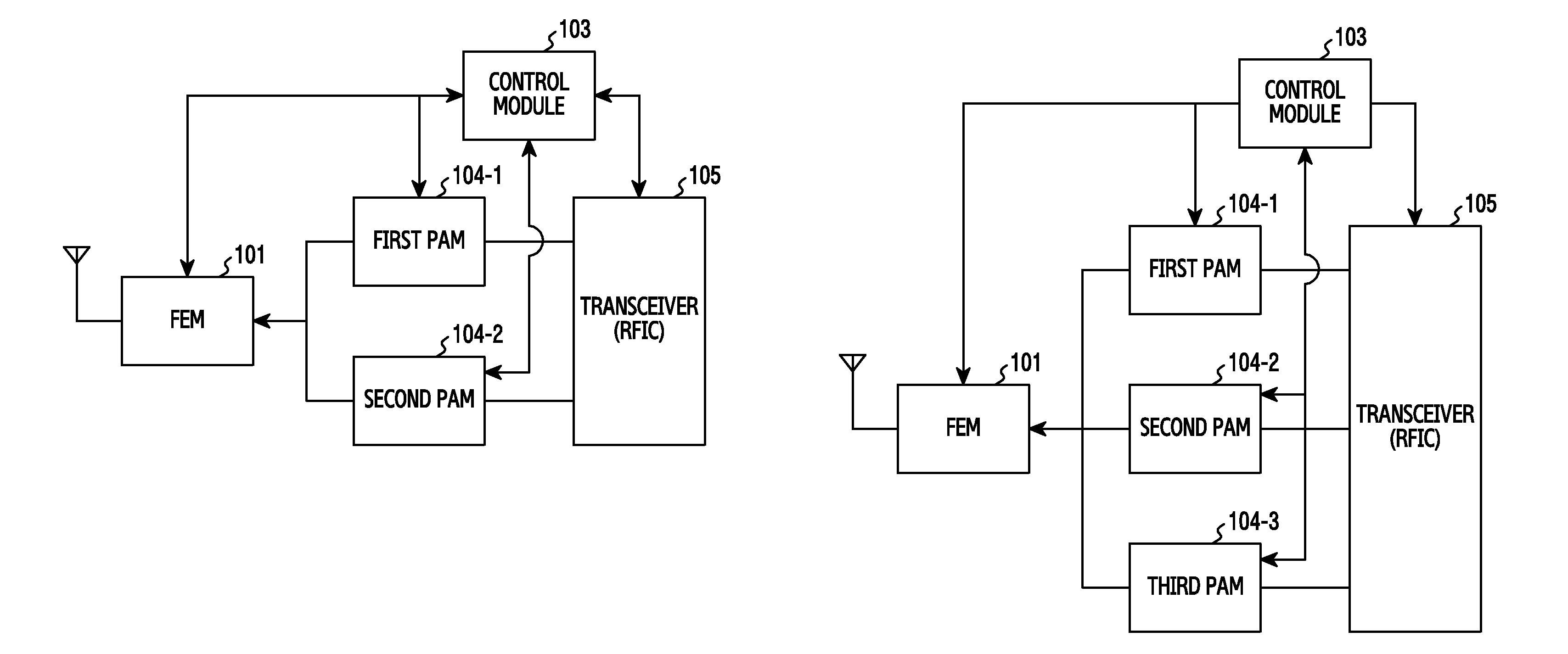
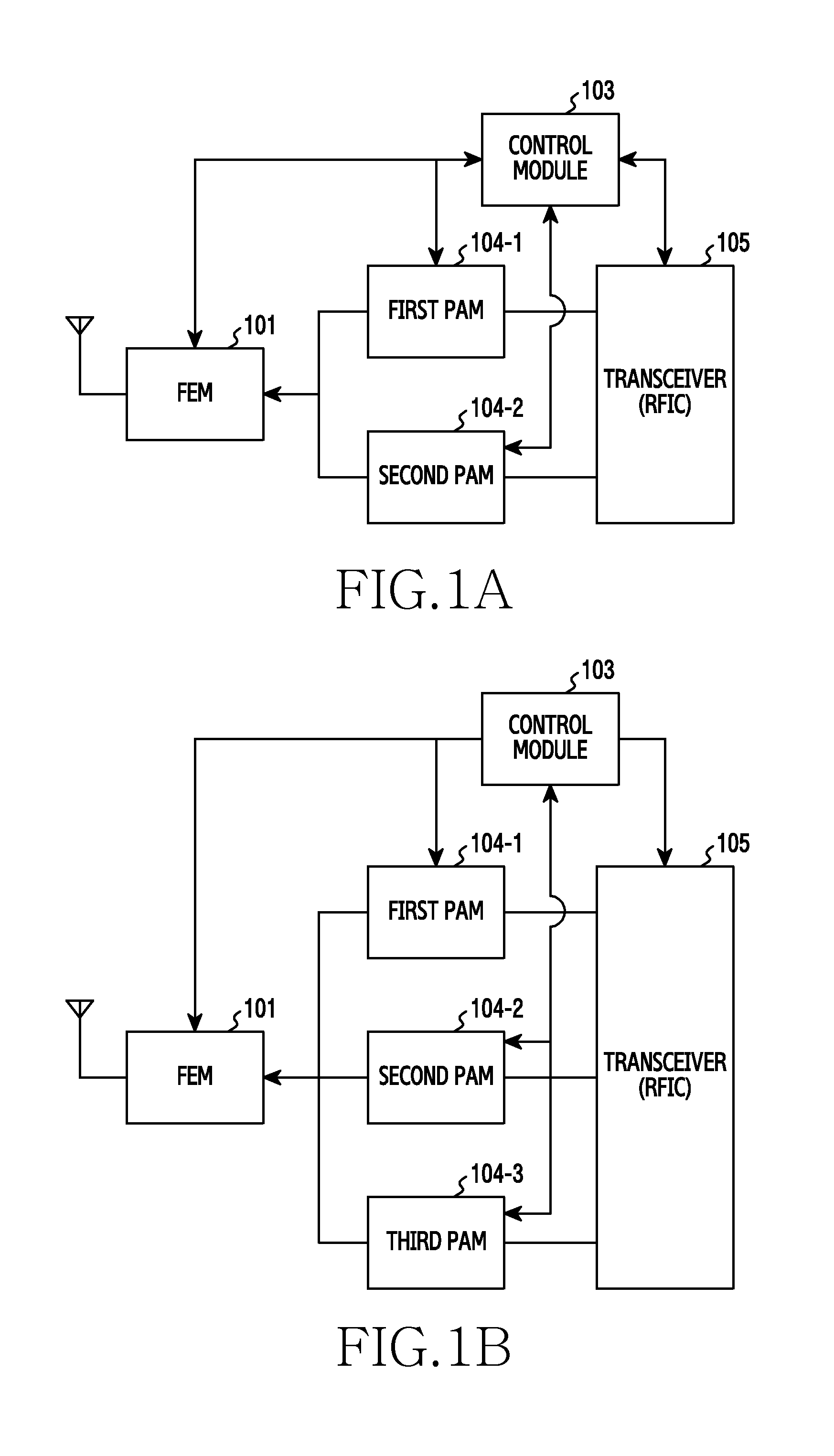
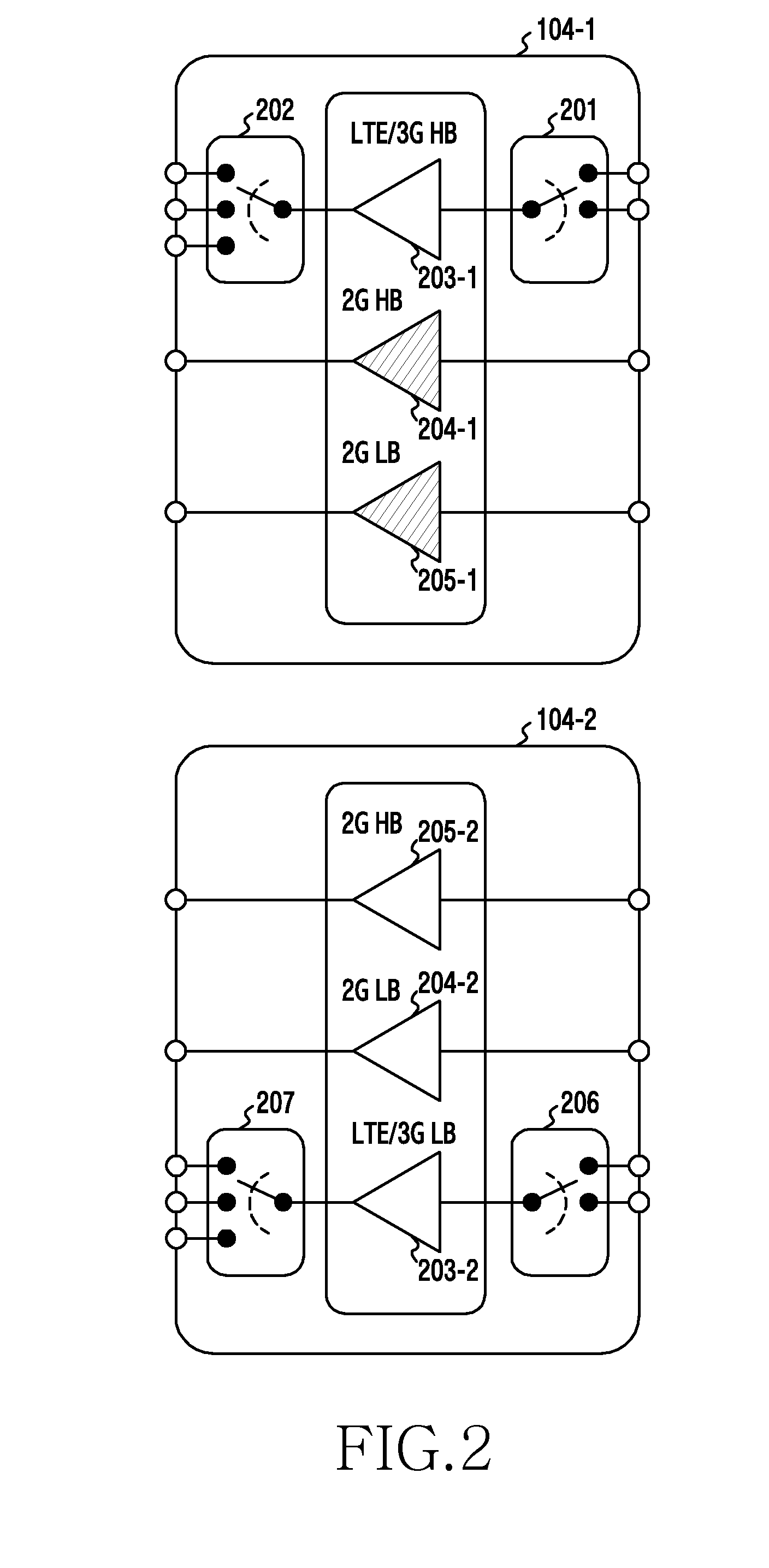
Mobile terminal radio frequency front-end and mobile terminal
The embodiment of the invention discloses a mobile terminal radio frequency front-end comprising a first main antenna, a diversity antenna, a second main antenna, a quadruplexer, a first filter, a second filter, a third filter, a fourth filter, a fifth filter, a sixth filter, a seventh filter, an eighth filter, a first power amplifier, a second power amplifier, a third power amplifier, a fourth power amplifier, a fifth power amplifier, a sixth power amplifier, a quadruplexer, a duplexer, a first radio frequency switch, a second radio frequency switch, a first RF transceiver, a second RF transceiver and a controller. The embodiment of the invention also discloses a mobile terminal. With application of the mobile terminal radio frequency front-end and the mobile terminal, the number of the antennas in the internal part of the mobile terminal can be reduced, and internal interference and complexity of the antenna design can be reduced.
Owner:DONGGUAN COOLPAD SOFTWARE TECH
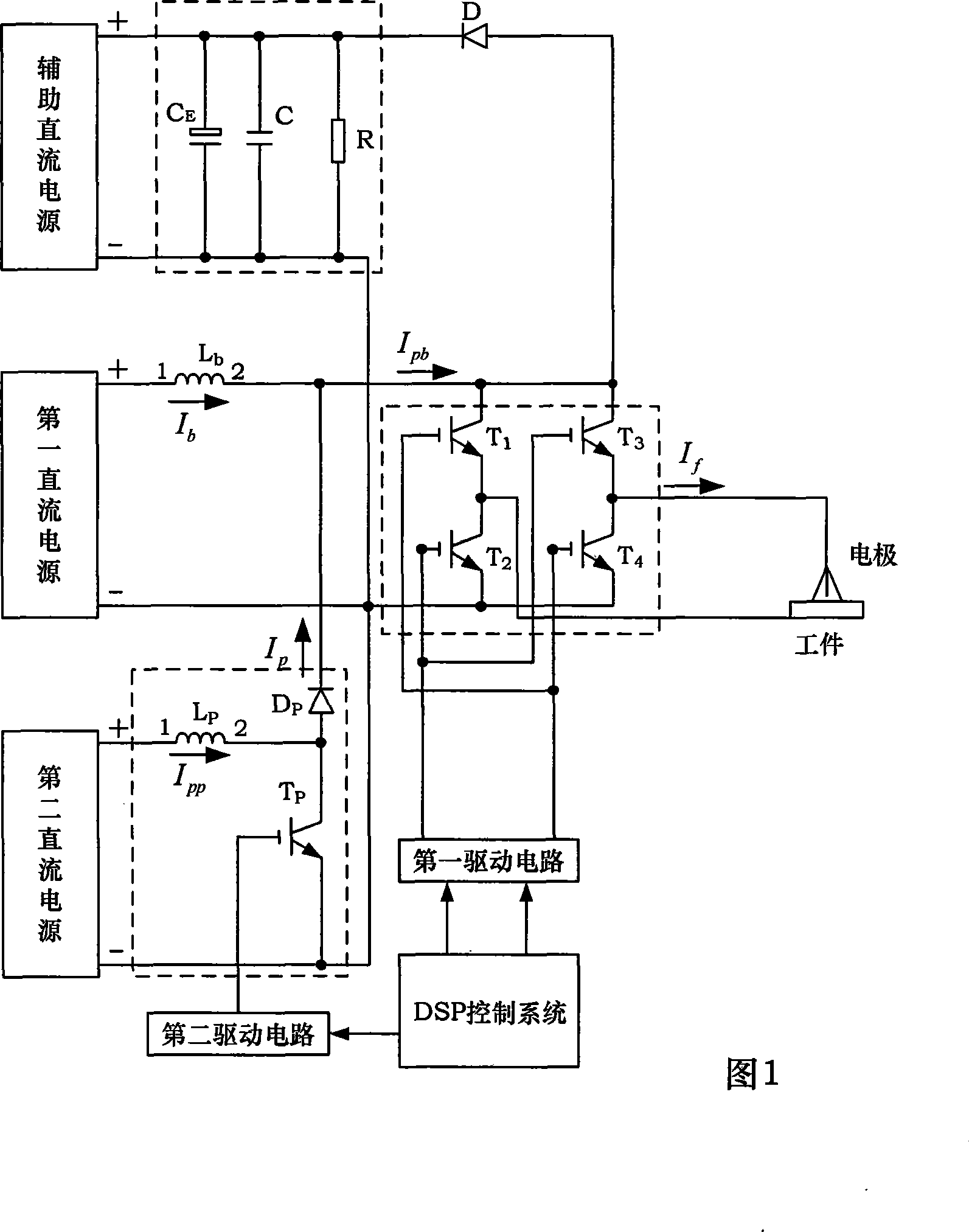
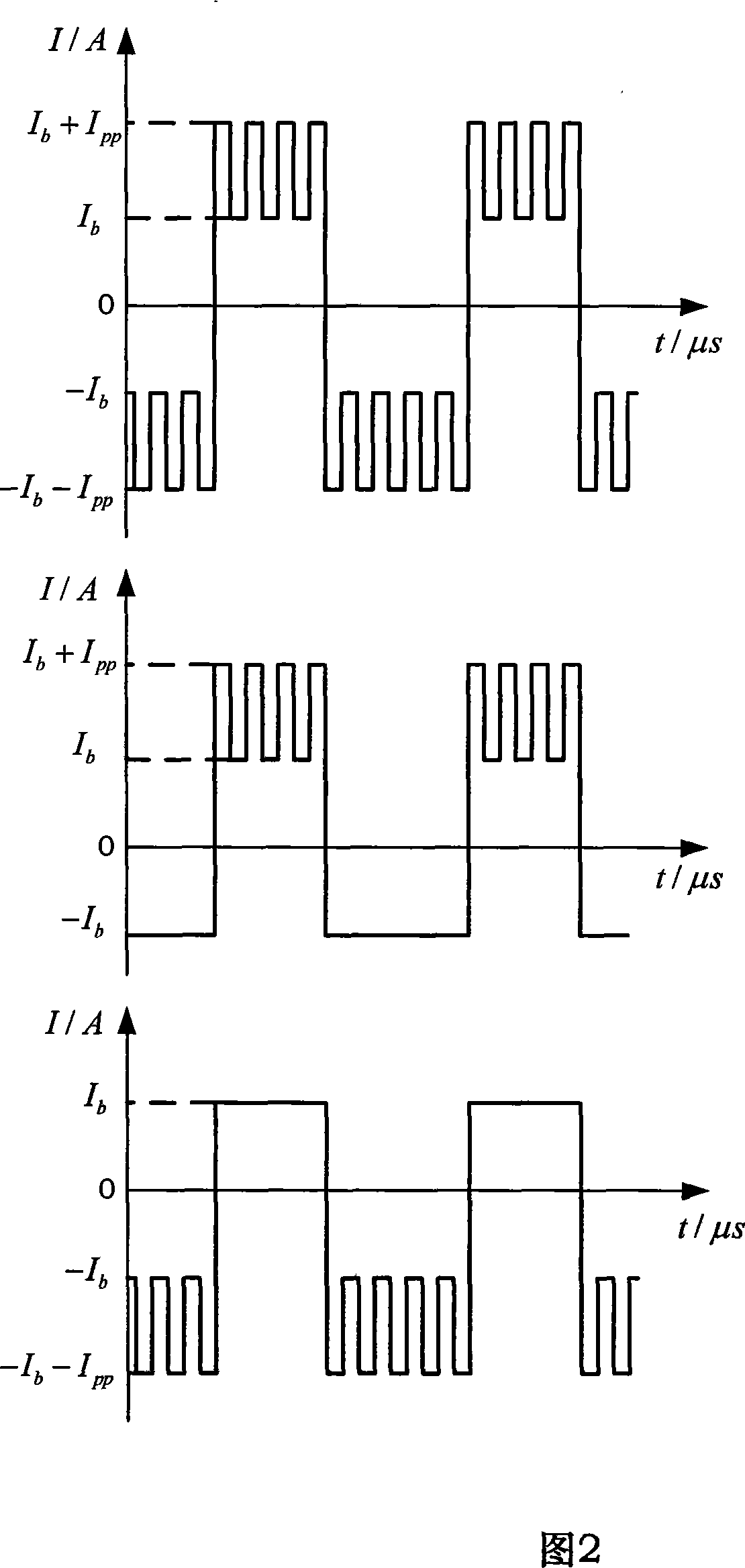
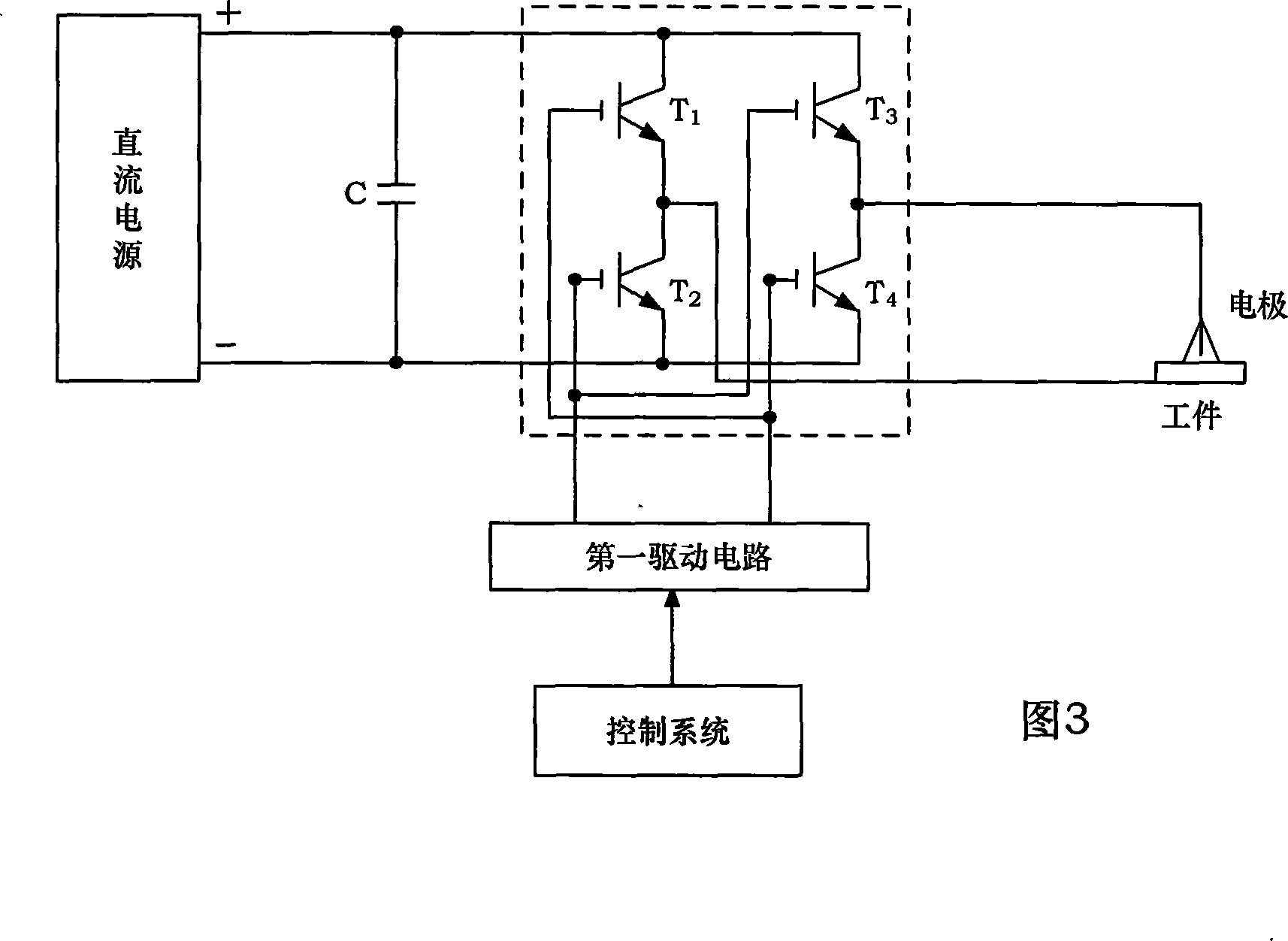
Super speed inverting square wave composite pulse current pole-changing arc-welding power supply device
InactiveCN101125390AUltra-fast current rise rateUltra-fast current fall rateArc welding apparatusCapacitanceFull bridge
The present invention discloses a super rapid exchanging method compound pulse current polarity changing arc welding power supply device used for electric arc welding, which comprises a DC power supply, a full bridge transfer circuit, a control system, a drive circuit, a parallel absorbing protecting circuit and a pulse current output circuit. The parallel absorbing protecting circuit is consists of an electrolytic condenser CE, a high frequency capacitance C and a power resistor R. The pulse current output circuit consists of a second follow current inductance LP, a fifth power switch tube TP and a second power diode DP. The DC power supply comprises an assistant DC power supply, a first DC power supply and a second DC power supply. The first DC power supply is used for providing a background current, and the second DC power supply is used for supplying a peak current Tpp, and the control system adopts a DSP processor chip. The current ascension rate of the power supply equipment output polarity changing square wave current of the present invention is not less than 50A / Mus, and the rate of descent is not less than 50A / Mus, and the current ascension rate of the compound pulse is not less than 50A / Mus, and the current ascension rate is 10 to 15 A / Mus, and the frequency of the compound pulse is 1kHz to 30 kHz, and the duty ratio is 10 percent to 90 percent.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
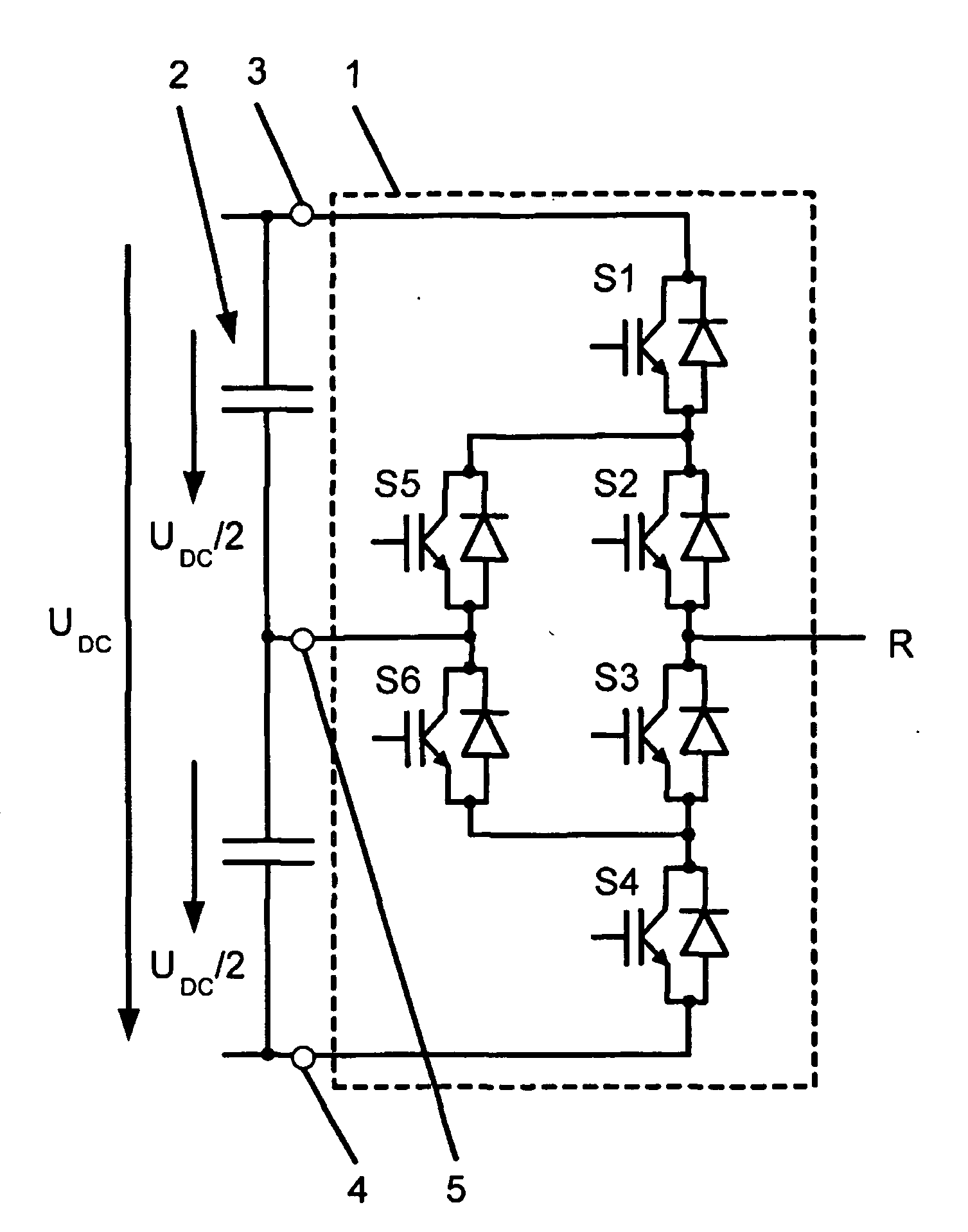
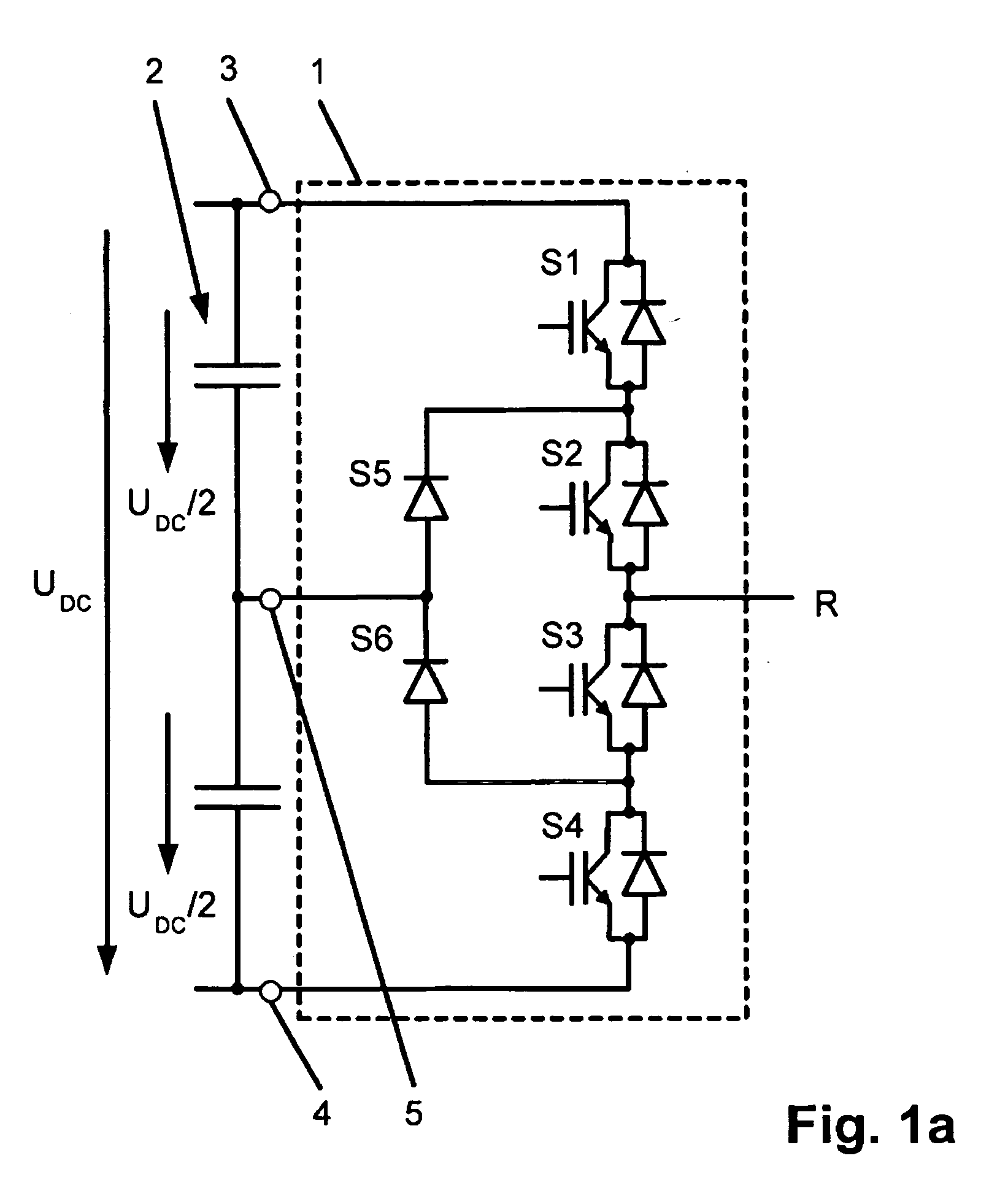
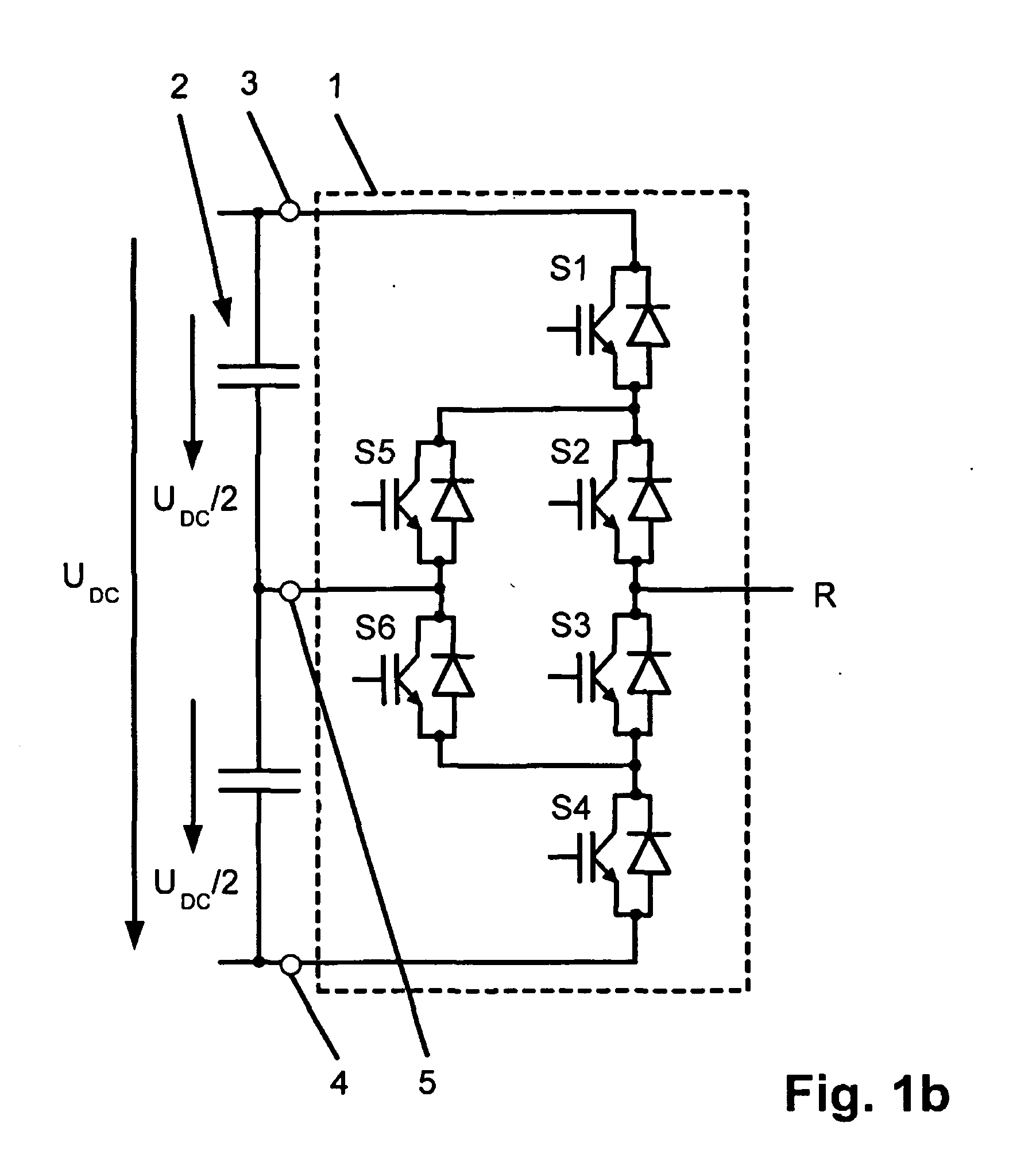
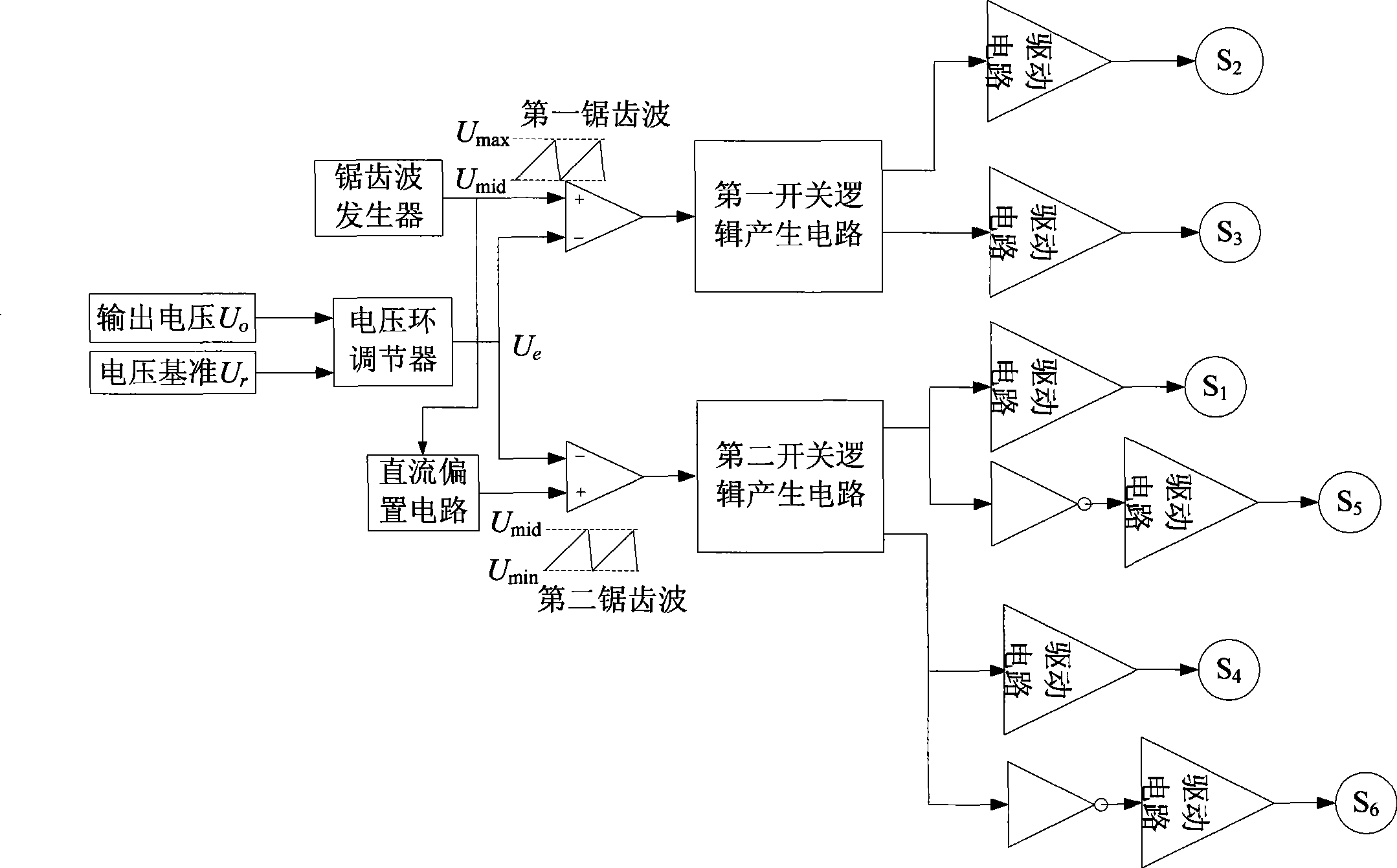
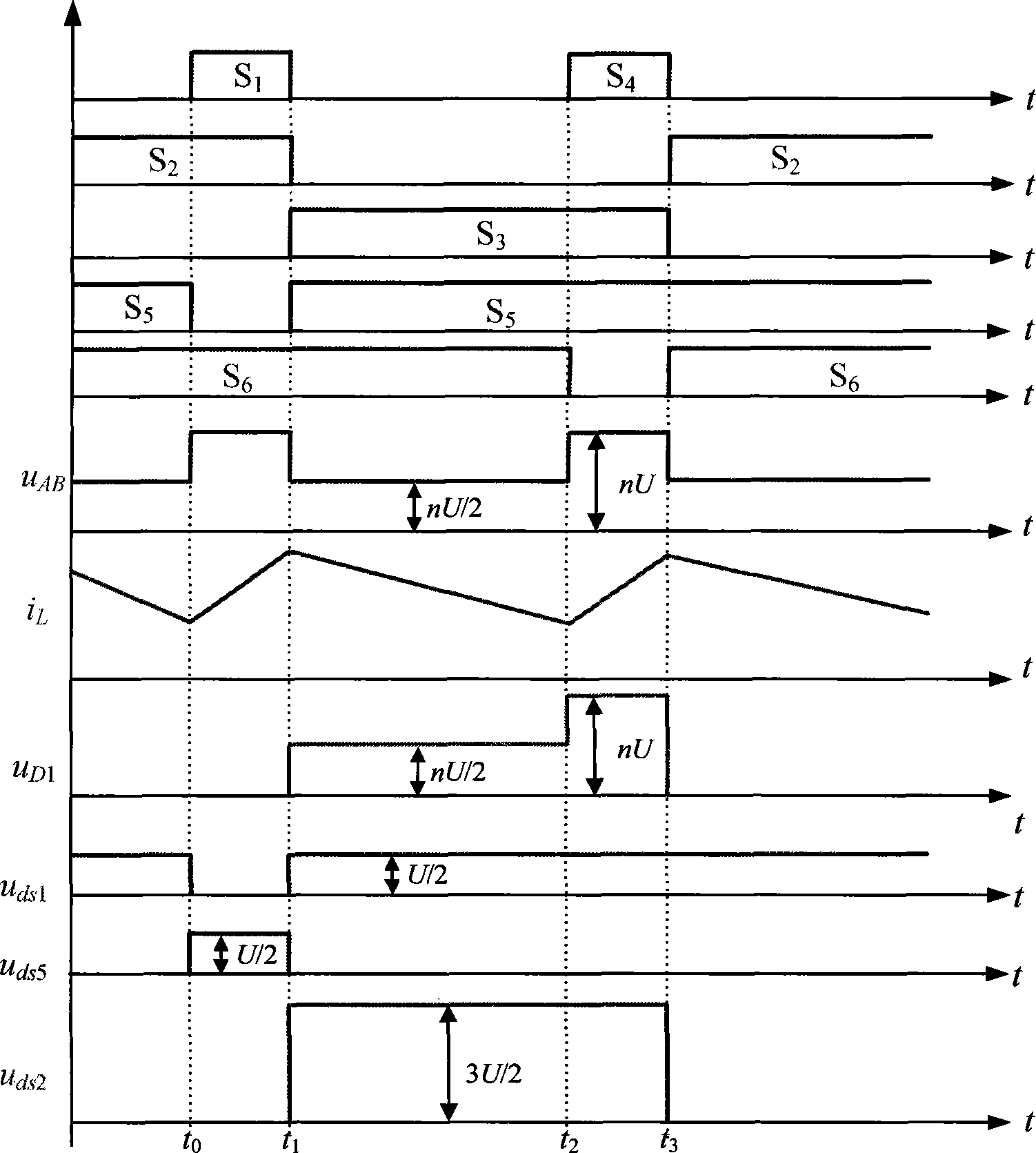
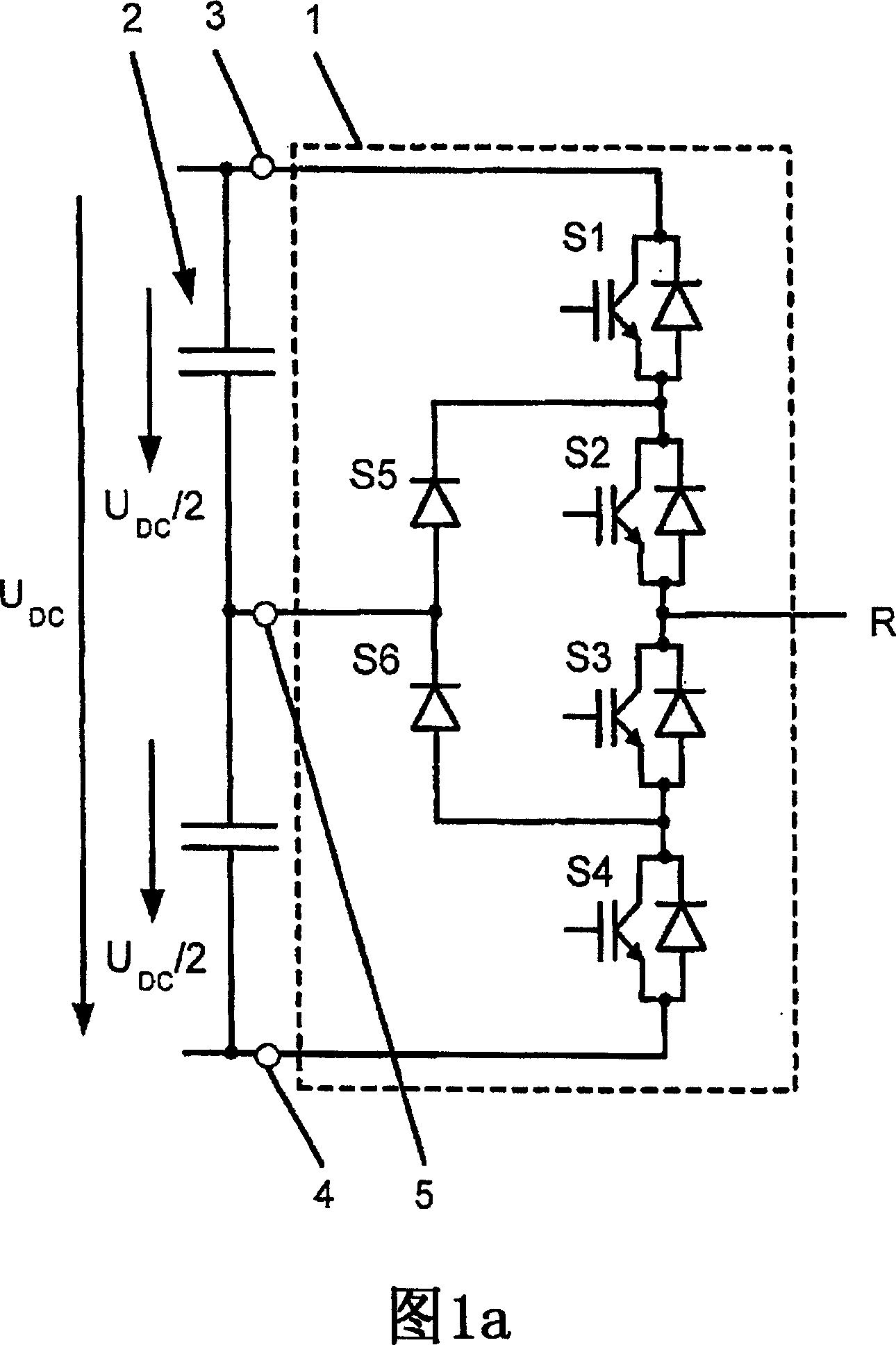
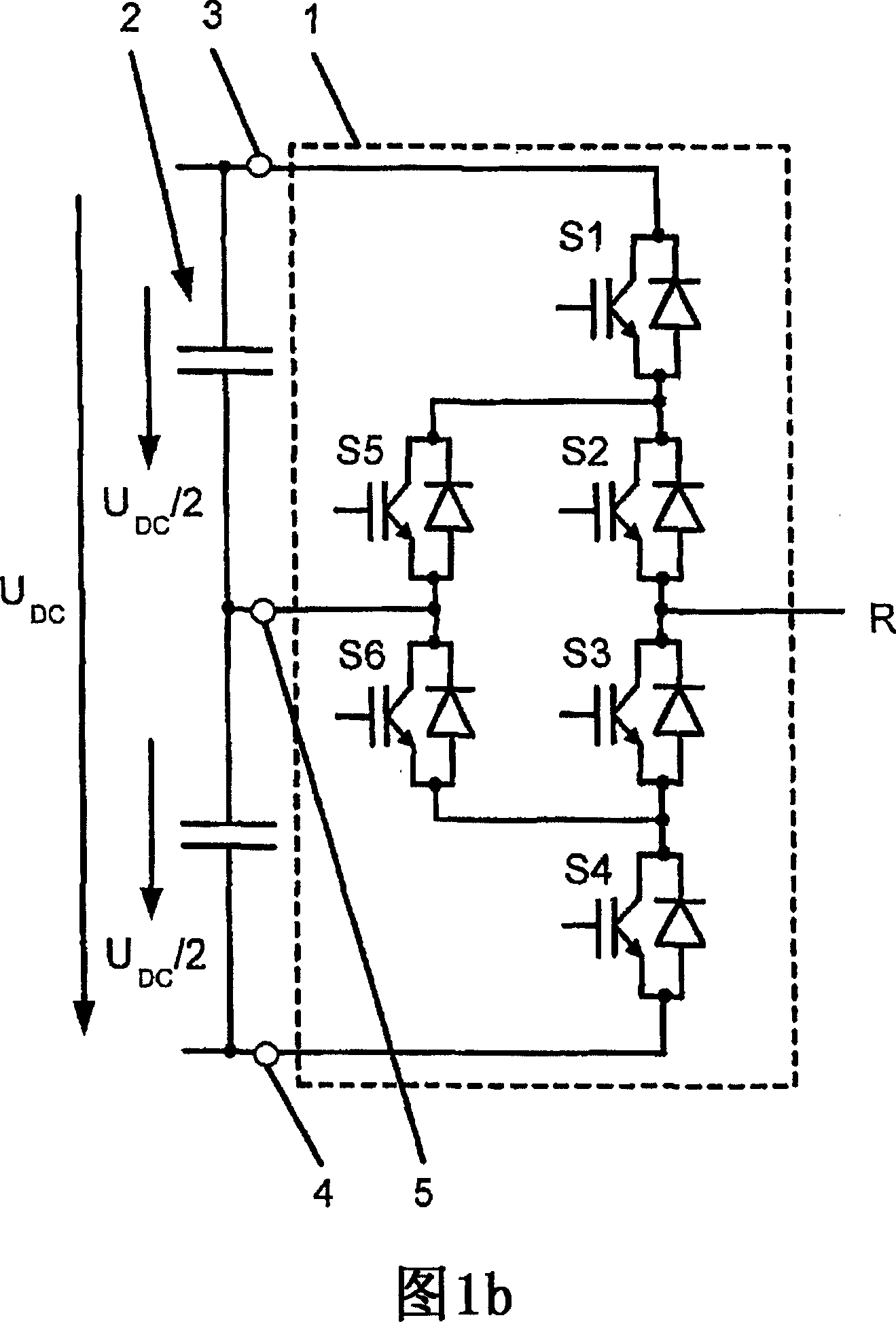
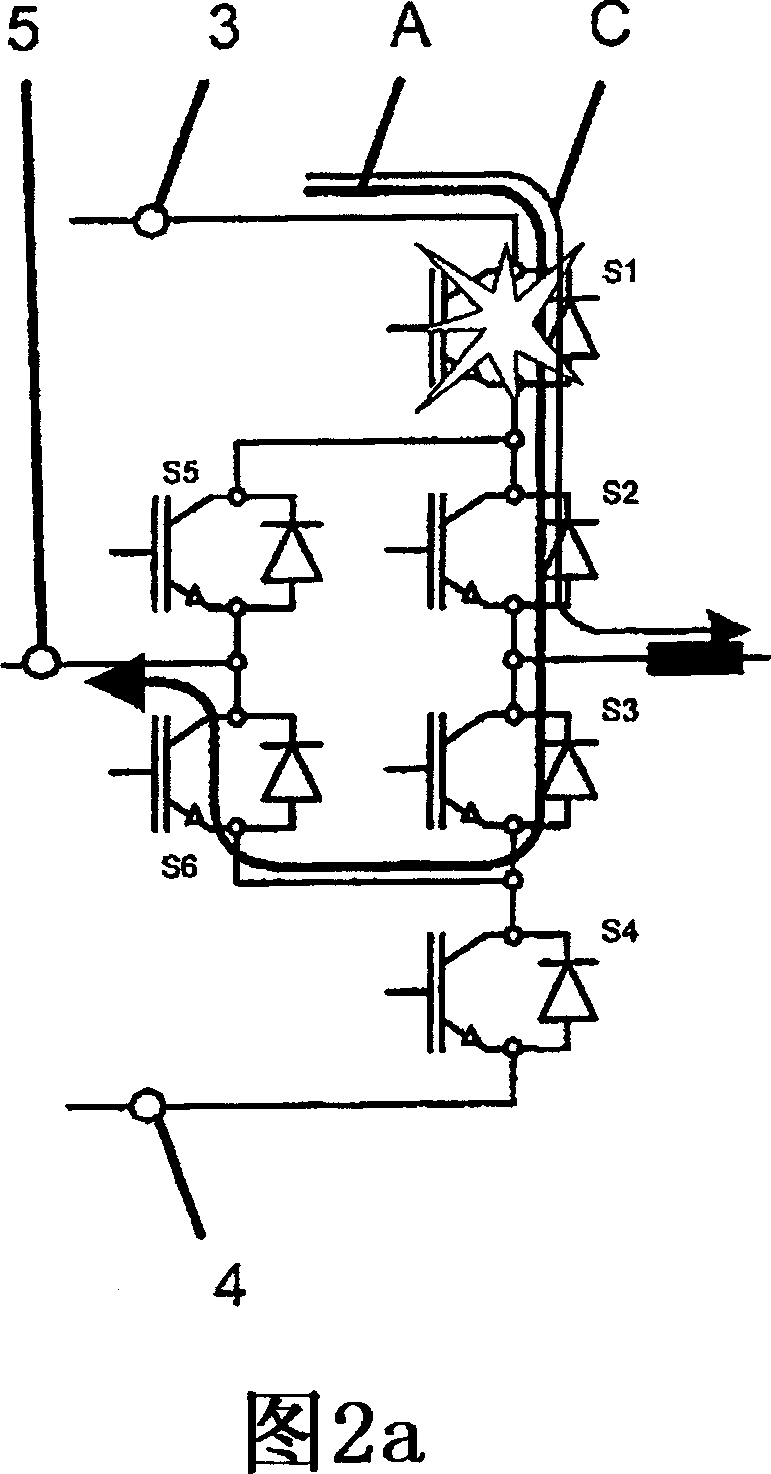
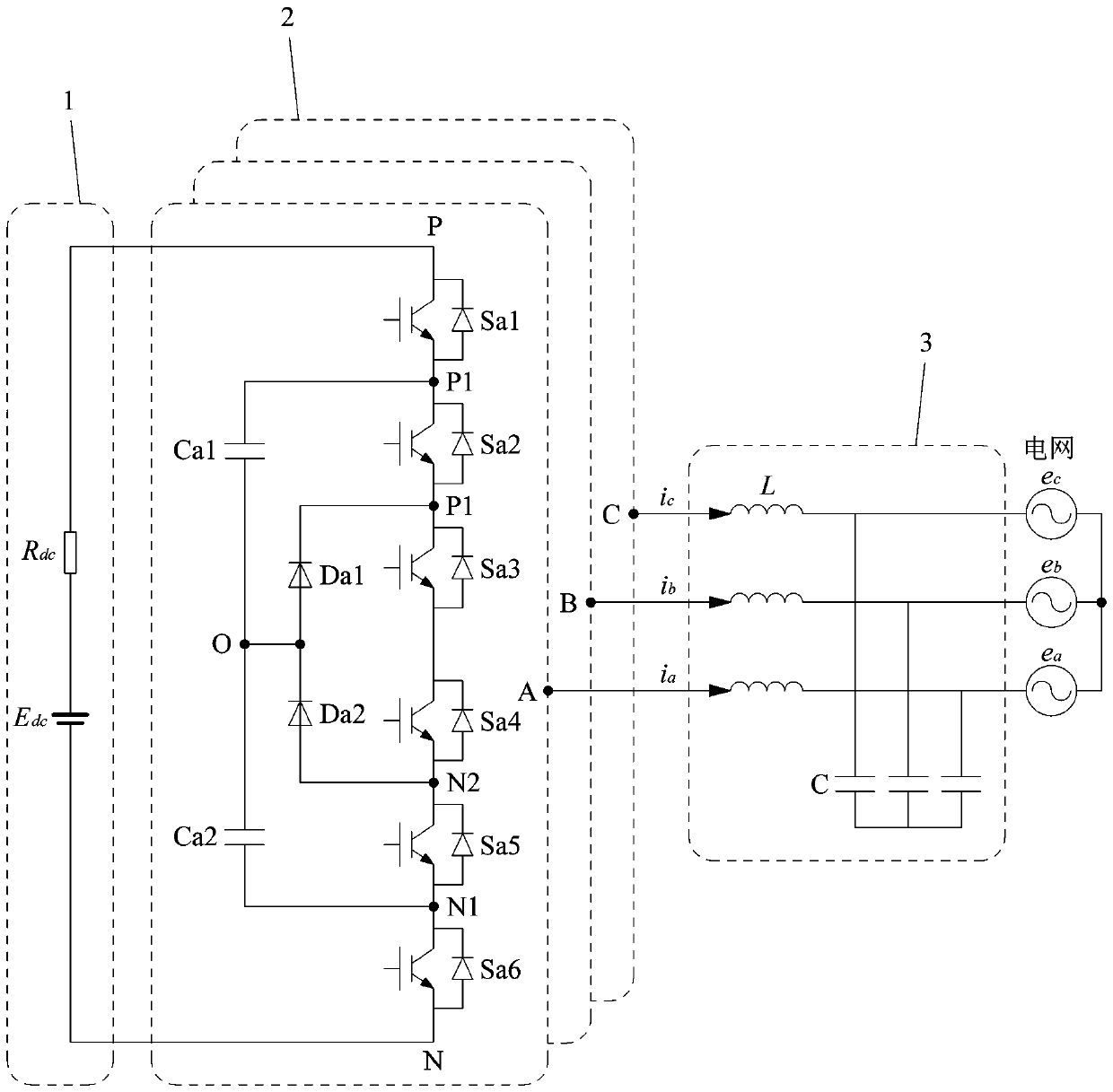
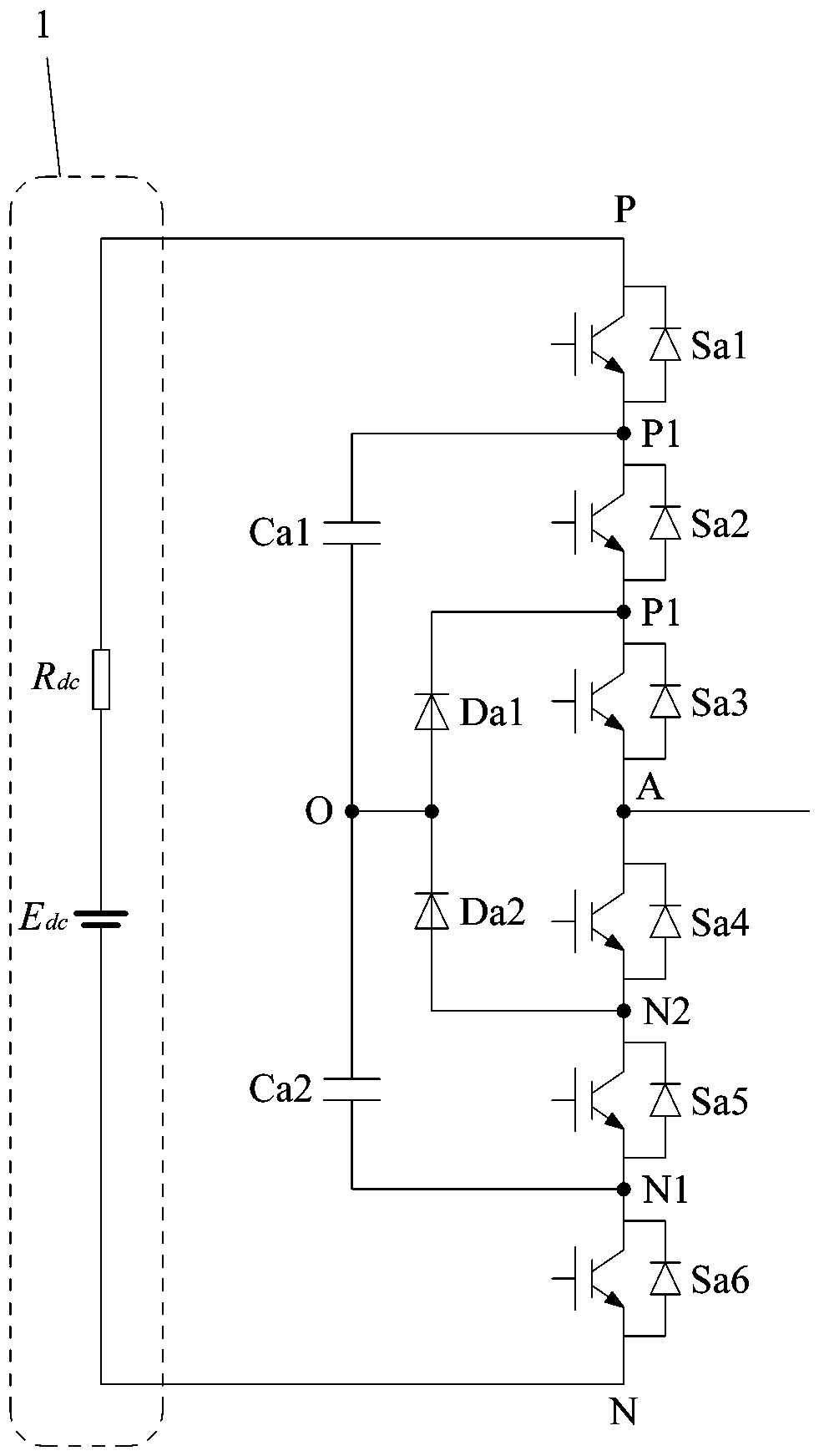
Method for fault handling in a converter circuit for wiring of three voltage levels
ActiveUS20080204959A1Reduce the burden onAccelerated agingAC motor controlElectric devicesFifth powerFault handling
The document specifies a method for fault handling in a converter circuit for switching three voltage levels, in which the converter circuit has a converter subsystem provided for each phase (R,S,T), in which a top fault current path (A) or a bottom fault current path (B) in the converter subsystem is detected, the top fault current path (A) running through the first, second, third and sixth power semiconductor switches in the converter subsystem or through the first and fifth power semiconductor switches (S1, S5) in the converter subsystem, and the bottom fault current path (B) running through the second, third, fourth and fifth power semiconductor switches in the converter subsystem or through the fourth and sixth power semiconductor switches in the converter subsystem, and in which the power semiconductor switches are switched on the basis of a fault switching sequence. To avoid phase shorting of all the phases of the converter circuit in order to achieve a safe operating state for the converter circuit in the event of a fault, the fault switching sequence in the event of detection of the top or the bottom fault current path (A, B) is initially followed by the detection's accompanying switching status of each power semiconductor switch being recorded. In addition, in the event of detection of the top fault current path (A) the first power semiconductor switch and then the third power semiconductor are turned off, and in the event of detection of the bottom fault current path (B) the fourth power semiconductor switch and then the second power semiconductor are turned off.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
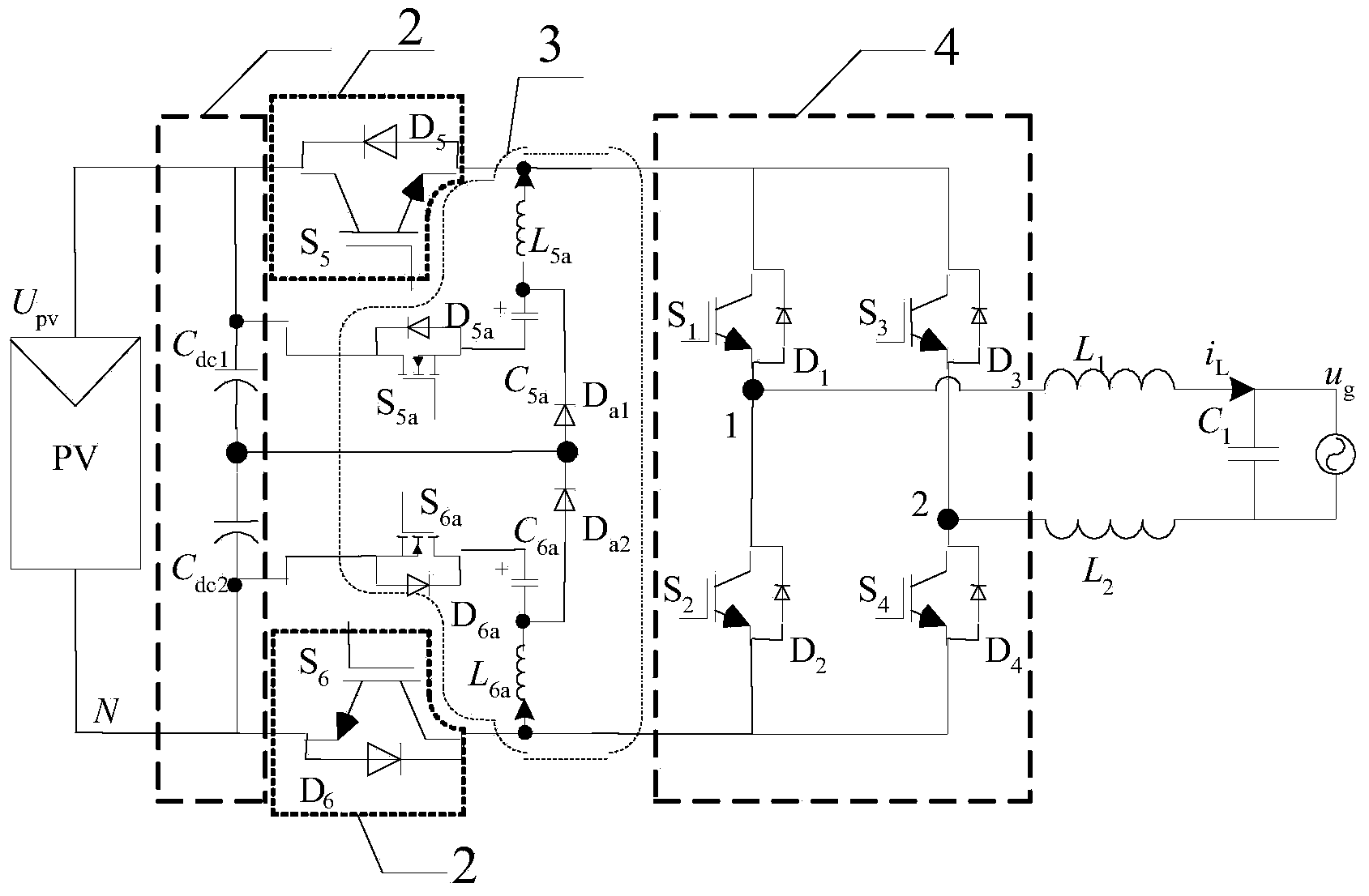
Switching-loss-free full-bridge non-isolated photovoltaic grid-connected inverter and on-off control timing sequence
ActiveCN104242719AAchieve high frequencyMiniaturizationAc-dc conversionPhotovoltaic energy generationCapacitanceFull bridge
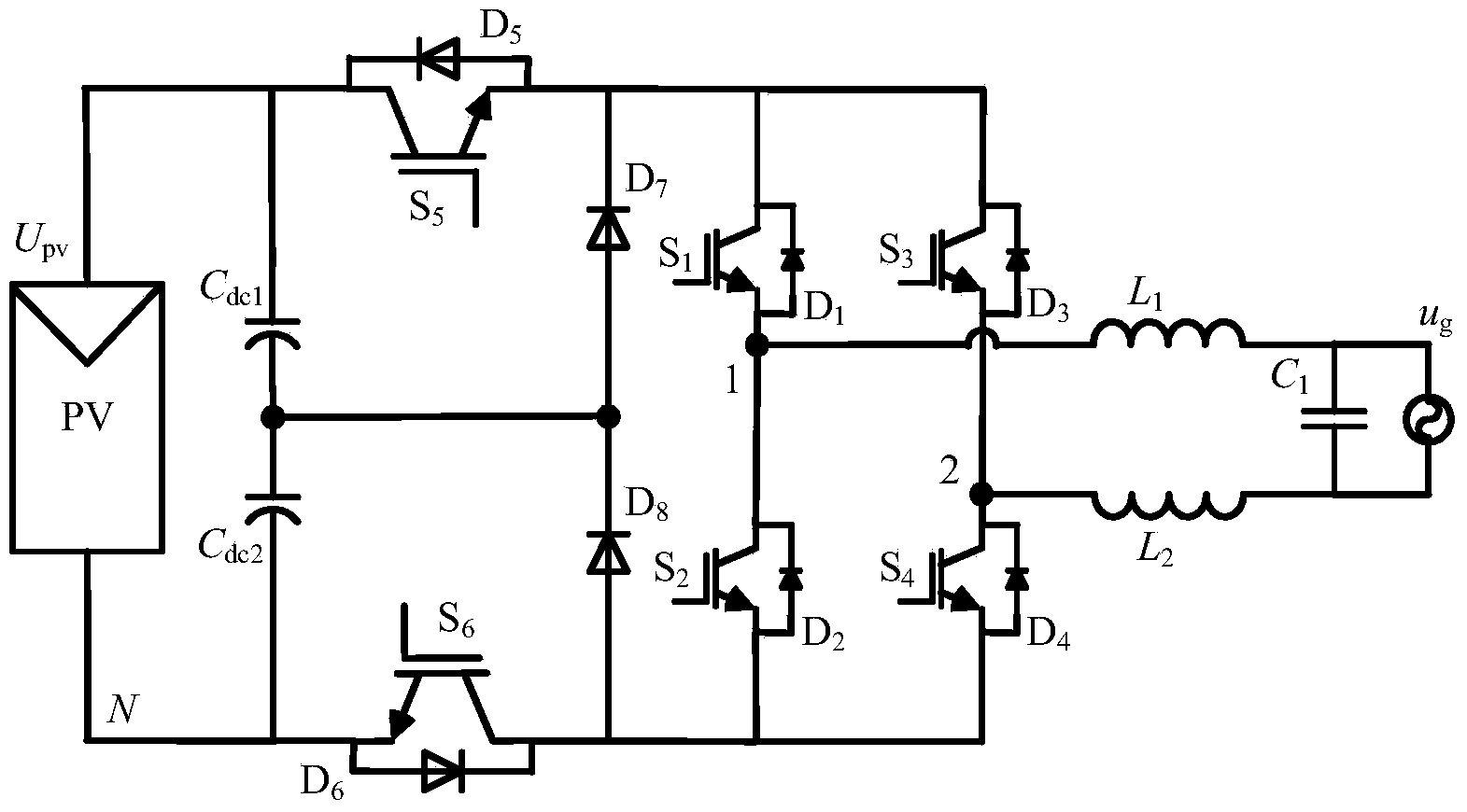
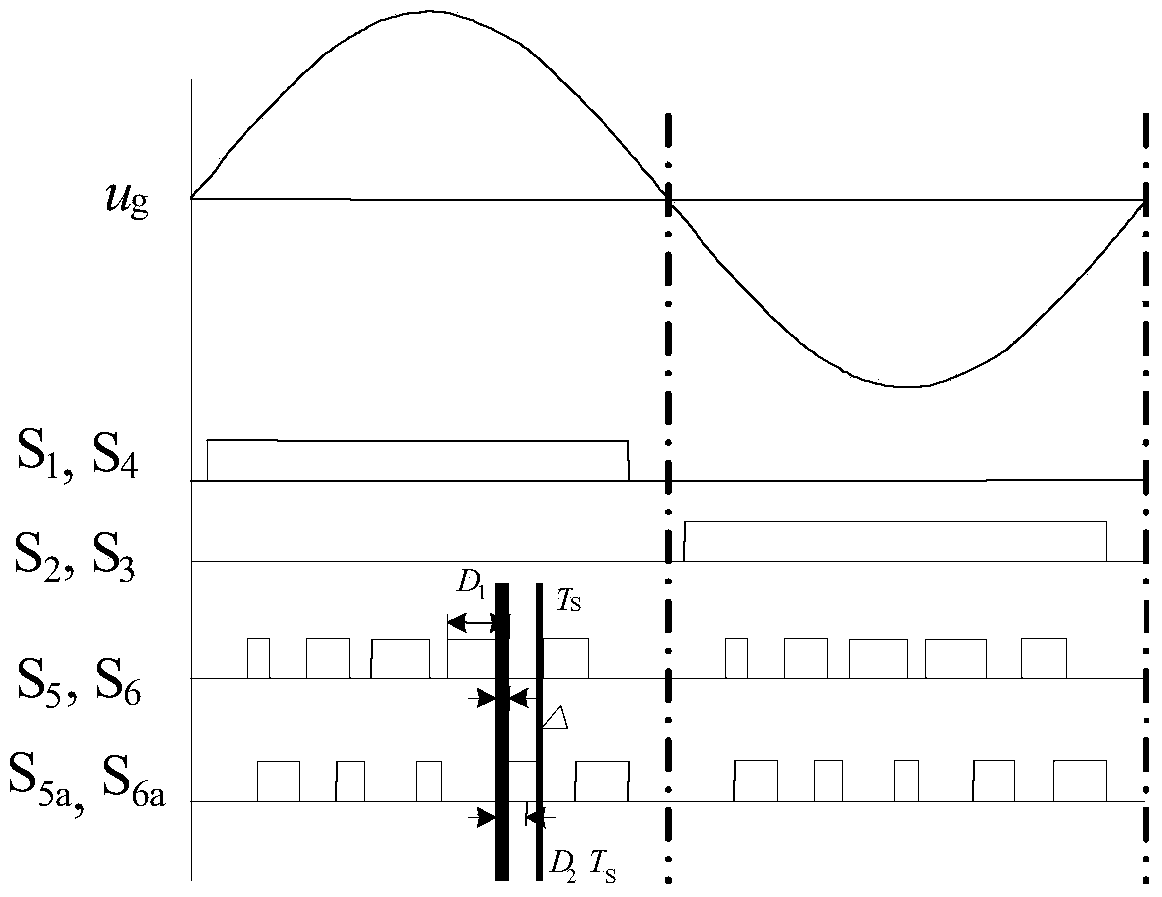
The invention discloses a switching-loss-free full-bridge non-isolated photovoltaic grid-connected inverter and an on-off control timing sequence. The inverter comprises a voltage division capacitance branch, a high-frequency main switching unit, a resonant network and a low-frequency change-over switch unit. Two sets of zero-current switching branches composed of the resonant network composed of full control switches, resonant capacitors and resonant inductors and auxiliary follow current clamping diodes are added, the on-off control timing sequence is matched, the zero-current turning-on and zero-current turning-off conditions of a fifth power switch tube S5 and a sixth power switch tube S6 can be achieved, the zero-current turning-on and zero-current turning-off conditions of a fifth auxiliary power switch tube Sa5 and a sixth auxiliary power switch tube Sa6 can be achieved, the reverse restoration of low-frequency change-over switch unit diodes D1-D4 can be eliminated, it is guaranteed that the common-mode voltage of the inverter is constantly one second of a battery voltage in the power transmission process, the resonance period and the follow current stage to eliminate leak currents, and therefore high frequency and minimization of the non-isolated photovoltaic grid-connected inverter can be achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
T-shaped active clamping type five-level three-phase inverter and grid-connected inversion power generation system
InactiveCN106921306AExtended input voltage rangeImprove performanceAc-dc conversionPower inverterCapacitance
The invention relates to a T-shaped active clamping type five-level three-phase inverter. The T-shaped active clamping type five-level three-phase inverter comprises three same T-shaped active clamping type five-level bridge arms, wherein each T-shaped active clamping type five-level bridge arm comprises a first circuit, a second circuit, a third circuit and a clamping capacitor, the first circuit comprises a first power electronic switch tube, a second power electronic switch tube, a third power electronic switch tube and a fourth power electronic switch tube which are connected in series, a first connection point, a second connection point and a third connection point are contained in the first circuit, the second circuit comprises a fifth power electronic switch tube and a sixth power electronic switch tube which are connected in series, the third circuit comprises a seventh power electronic switch tube and an eighth power electronic switch tube which are connected in series, the clamping capacitor is connected between the first connection point and the third connection point, and the second connection point is an output end. By the T-shaped active clamping type five-level three-phase inverter, the input voltage range of the inverter can be expanded, and the performance of the inverter is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU GOODWE POWER SUPPLY TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
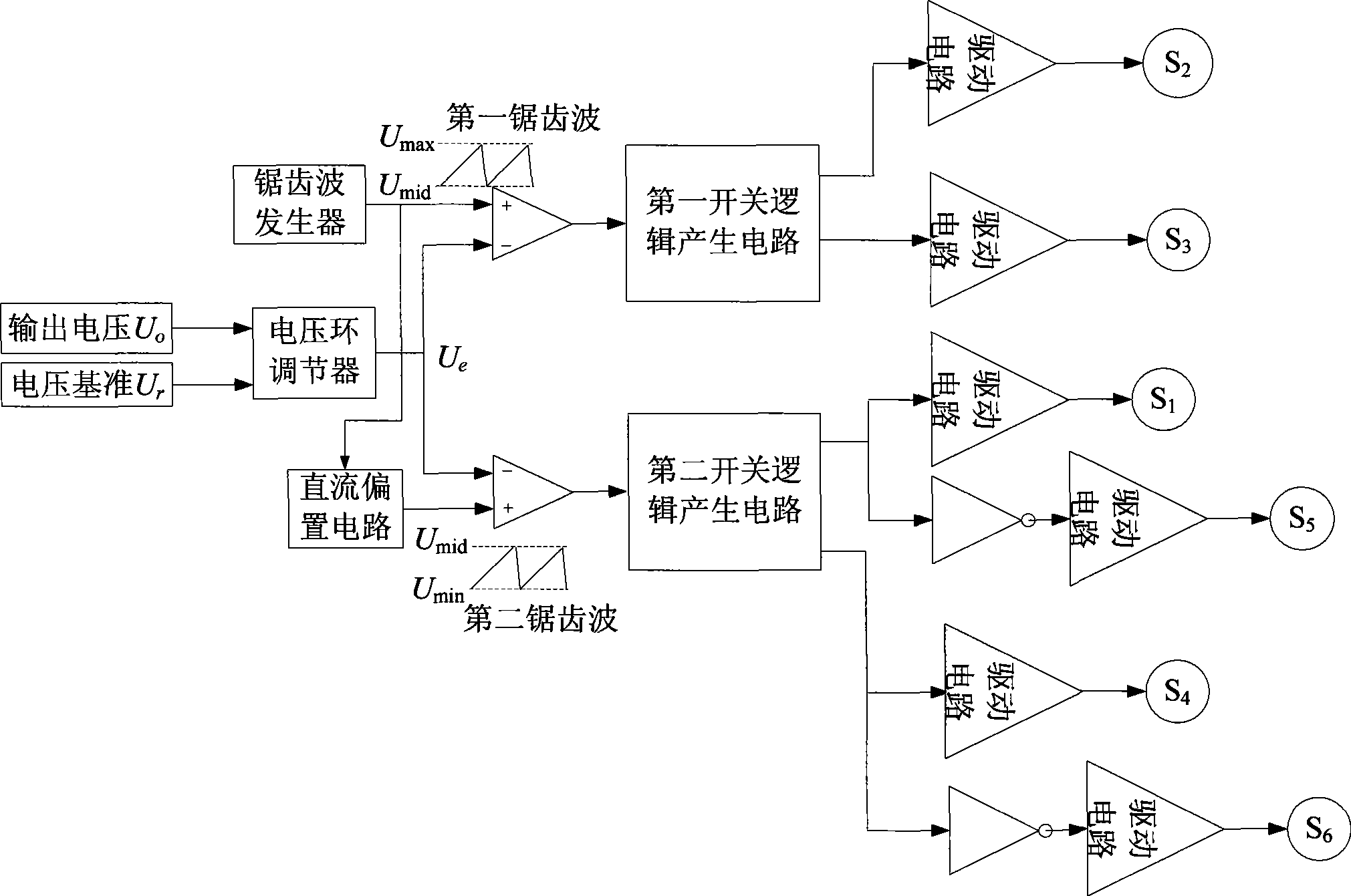
Buck-boost grid-connected inverter and control method thereof
InactiveCN102005962BReduce lossImprove reliabilityAc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsGrid connected inverterFifth power
The invention discloses a buck-boost grid-connected inverter and a control method thereof, belonging to an inverter and a control method thereof. The inverter comprises a power supply, a common circuit, a first bridge arm circuit, a second bridge arm circuit, a first filter inductor and a second filter inductor. The method comprises the following steps: when the setting of an inductive current is less than zero, a first power switching pipe driving signal and a fifth power switching pipe driving signal complement a high-frequency switch, and a second power switching pipe driving signal and a sixth power switching pipe driving signal are switched off; when the setting of an inductive current is more than zero, the second power switching pipe driving signal and the sixth power switching pipe driving signal complement the high-frequency switch, and the first power switching pipe driving signal and the fifth power switching pipe driving signal are switched off; and a third power switching pipe driving signal is the or logic of the second power switching pipe driving signal and the fifth power switching pipe driving signal, and a fourth power switching pipe driving signal is the or logic of the first power switching pipe driving signal and the sixth power switching pipe driving signal.
Owner:黄幼润
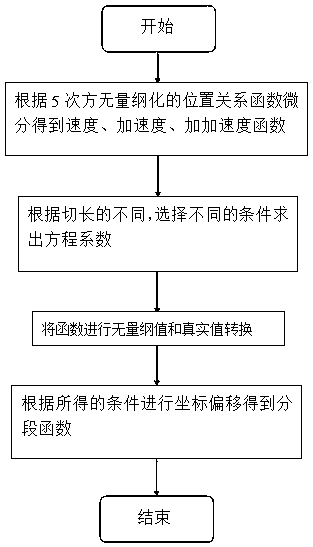
Non-programming electronic cam curve generating method for transection
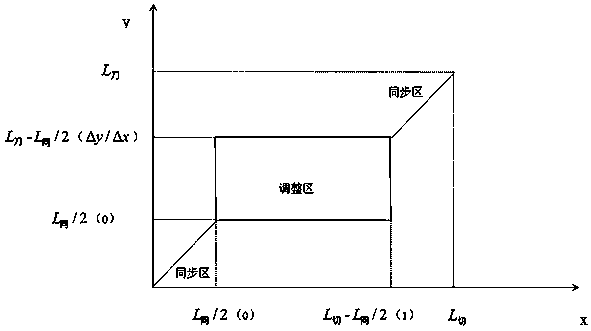
ActiveCN106406219AEasy to operateEasy to debugProgramme control in sequence/logic controllersDrive shaftFifth power
The invention provides a non-programming electronic cam curve generating method for transection. The method comprises: differential processing is carried out based on fifth-power non-dimensionalized position relation function to obtain a speed function, an acceleration function, an accelerated acceleration function; according to different cutting lengths, equation coefficients are calculated by selecting different conditions; conversion between a non-dimensionalized value and a true value is carried out on the functions; and then coordinate offset processing is carried out to obtain piecewise functions. According to the invention, an electronic cam curve can be generated only by setting three parameters: a parameter knife perimeter, a total synchronzi9ation length, and a cutting length; and generation of a reverse speed of a driven shaft is avoided based on calculation. For the electronic cam curve generated by using the method in the transection field, the operation and debugging of the filed operator can be simplified; programming is avoided; and the reliability is high. The speed curve is a fourth-power function that is more flexible and smoother by compared with a third-power function.
Owner:威科达(东莞)智能控制有限公司
Single-phase online inverter with switchable topology
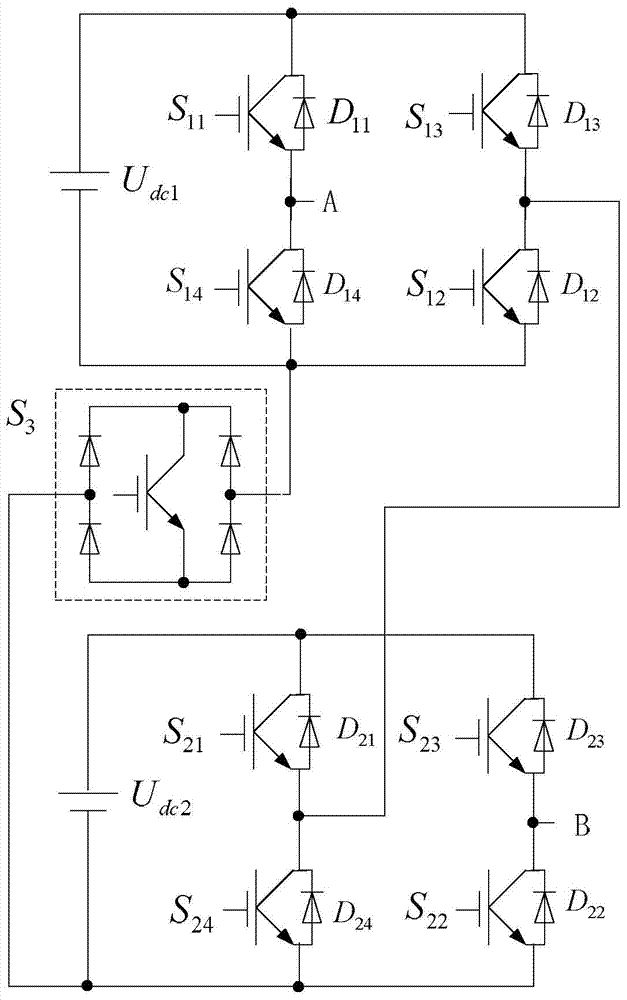
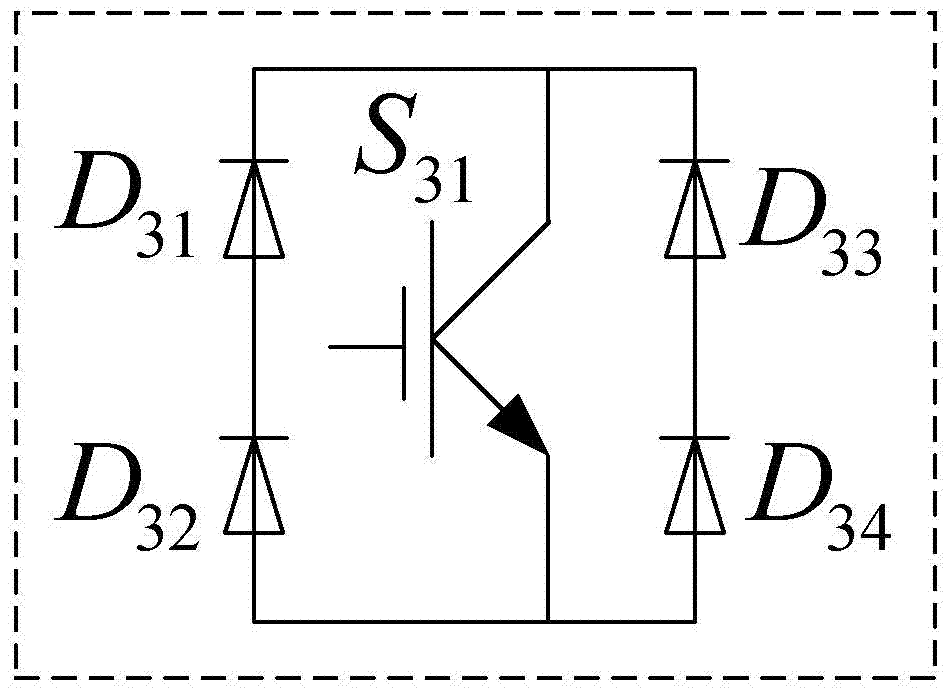
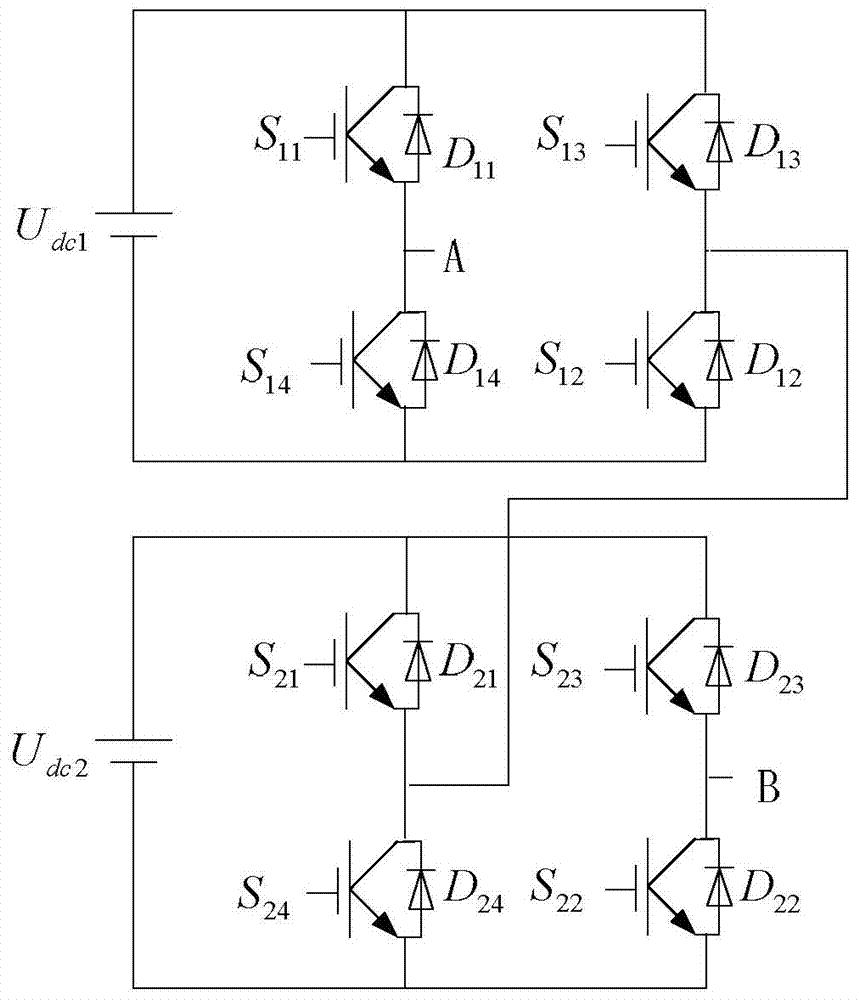
The invention discloses a single-phase online inverter with a switchable topology, relates to the technical field of conversion of electrical energy, and solves the problem that the working efficiency of inverters is influenced due to the fact that the structure of a conventional inverter with a fixed topology is complicated and loss of a power device is serious. According the inverter, a first power switch S11, a first diode D11, a third power switch S13, a third diode D13, a fourth power switch S14, a fourth diode D14, a second power switch S12 and a second diode D12 constitute an H bridge; a fifth power switch S21, a fifth diode D21, a seventh power switch S23, a seventh diode D23, an eighth power switch S24, an eighth diode D24, a sixth power switch S22 and a sixth power switch D22 constitute the other H bridge; and a power output end of the fourth power switch S14 is connected with a power input end of a bilateral switch S3, a power output end of the eighth power switch S24 is connected with a power output end of the bilateral switch S3, a power output end of the third power switch S13 is connected with a power output end of the fifth power switch S21, and a first direct-current power supply Udc1 and a second direct-current power supply Udc2 are connected to outer sides of the two H bridges respectively. The single-phase online inverter is applicable to conversion of electrical energy.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
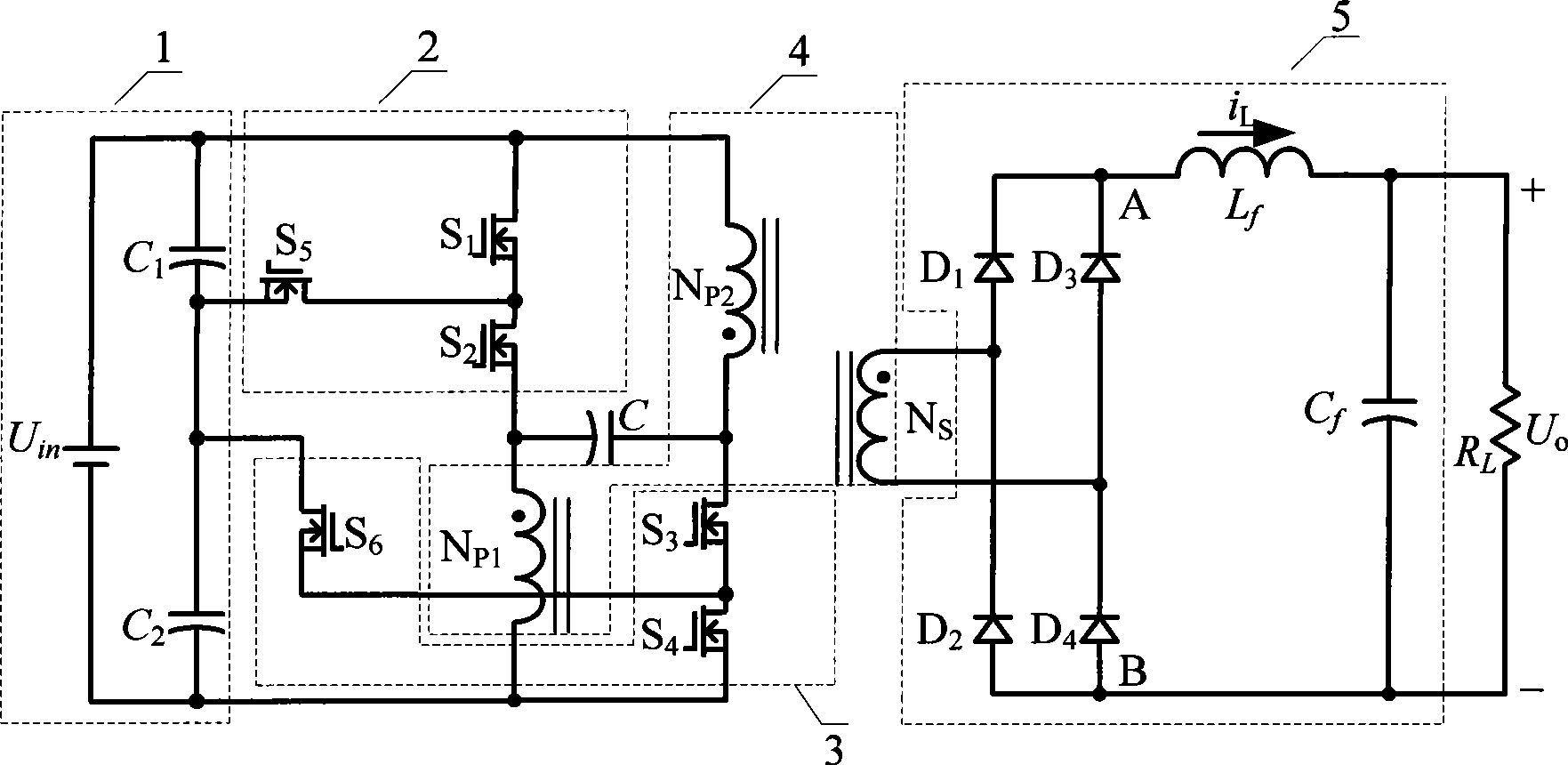
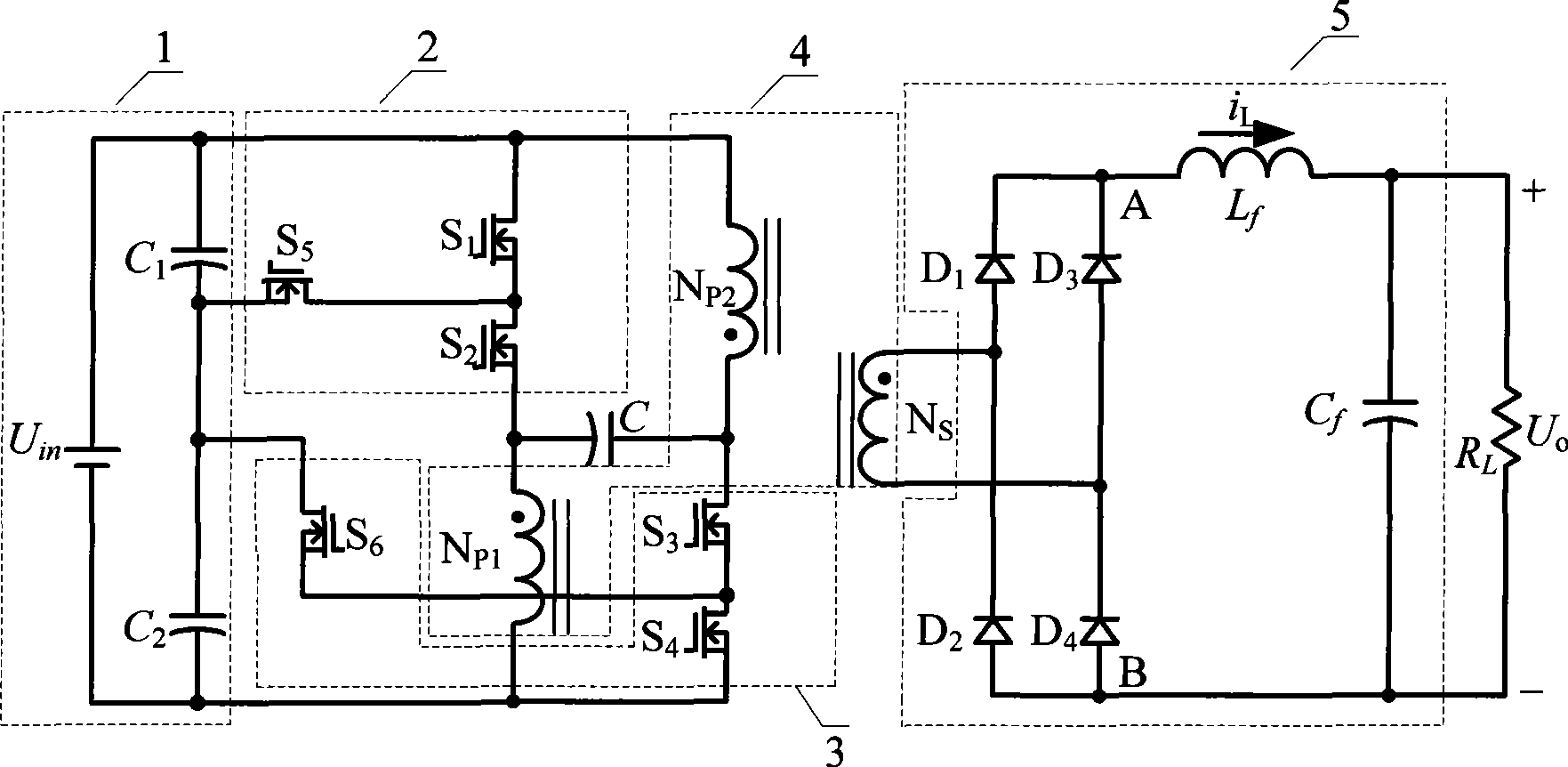
Low voltage wide input push-pull positive stimulate three level DC converter and controlling method thereof
InactiveCN101388609AReduce voltage stressReduce lossDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationThree levelCapacitance
The invention discloses a low voltage wide input push-pull forward three-level direct current convertor and a method for controlling the convertor, which belong to direct current convertors and methods for controlling the convertors. The convertor of the invention is composed of an input dividing capacitance circuit, a first level branch, a second level branch, a third level branch, a clamping capacitor, an insulating transformer, a rectifier bridge and a filter circuit. The method for controlling the convertor of the invention comprises: driving signals of a first power switch tube and a fifth power switch tube are complementary, the driving signals of a fourth power switch tube and a sixth power switch tube are complementary, two working modes of three levels and two levels exist, in the three level working mode, a second power switch tube and a third power switch tube are conducted complementarily for 180 degrees, the first power switch tube and the fourth power switch are modulated by PWM, in two level working mode, the first power switch tube and the fourth power switch tube are cut normally, the fifth power switch tube and the sixth power switch tube are conducted normally, and the second power switch tube and the third power switch tube work by PWM. The invention reduces the conducting loss, improves the conversion efficiency, and saves a flying capacitor.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Inverse-excitation type single-stage inverter for interconnected photovoltaic power generation system
InactiveCN101257263ASimple modulationModulation is simple and easy to implementPhotovoltaic energy generationDc-ac conversion without reversalCapacitancePower inverter
The invention discloses an inverse-excitation type single-stage inverter used in an interconnected photovoltaic power generation system, including an input side circuit, an inverse-excitation transformer and an outlet side circuit, wherein, the input side circuit includes a photovoltaic array, a first filtering capacitance and a first power switch tube, which are connected to the primary side of the transformer; and the outlet side circuit includes a second to fifth power switch tube and a second filtering capacitance, which are connected to the secondary side of the transformer. The invention has the following advantages that the single-stage structure not only realizes voltage boosting inversion output, but also reduces the size, volume weight and cost of the complete machine; high-frequency electric insulation is realized; the entire circuit has no other magnetic components except the high-frequency inverse-excitation transformer, the entire circuit uses less power devices with simple structure and small spending; and the control scheme is more simple and is easy of implementing.
Owner:南京冠亚电源设备有限公司
Method for error handling in a converter circuit for wiring of three voltage levels
ActiveCN1969437AReduce the burden onDelay agingAC motor controlElectric devicesFifth powerWork status
A method for error handling in a converter circuit for wiring of three voltage levels is disclosed, whereby the converter circuit comprises a partial converter system (1), for each phase (R, S, T), in which an upper error current path (A), or a lower error current path (B) is detected in the partial converter system (1). The upper error current path (A) runs over the first, second, third and sixth power semiconductor switch (S1, S2, S3, S6) of the partial converter system (1), or over the first and fifth power semiconductor switch (S1, S5) of the partial converter system (1) and the lower error current path (B) runs over the second, third, fourth and fifth power semiconductor switch (S2, S3, S4, S5) of the partial converter system (1) or over the fourth and sixth power semiconductor switch (S4, S6) of the partial converter system (1) and, after a error switching sequence the power semiconductor switches (S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6) are switched. According to the invention, a phase-side short-circuit of all phases of the converter circuit may be avoided and hence a secure operational state for the converter circuit in the case of an error may be achieved, whereby after the error switch sequence in the case of detection of the upper or the lower error current path (A, B), the switch status of each power semiconductor switch (S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6) on said detection is fixed. Furthermore, on detection of the upper error current path (A), the first power semiconductor switch (S1) and then the third power semiconductor (S3) are switched off and, on detection of the lower error current path (B), the fourth power semiconductor switch (S4) and then the second power semiconductor (S2) are switched off.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
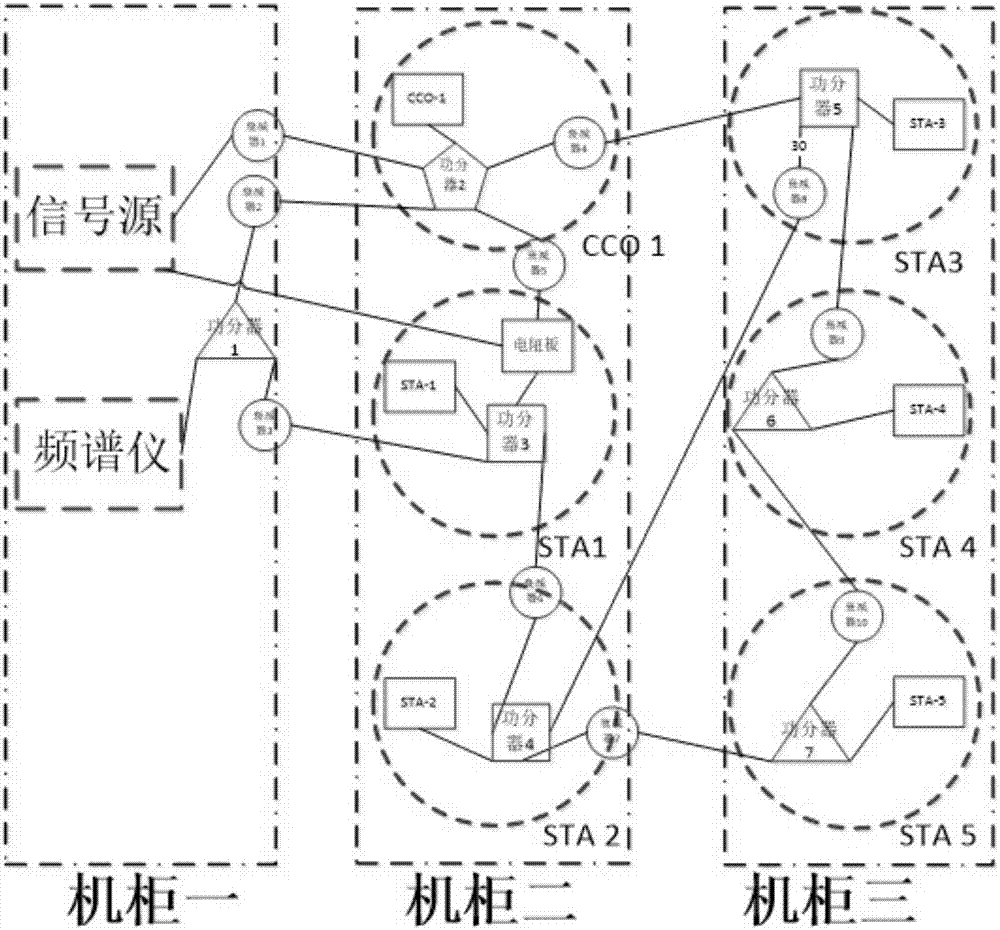
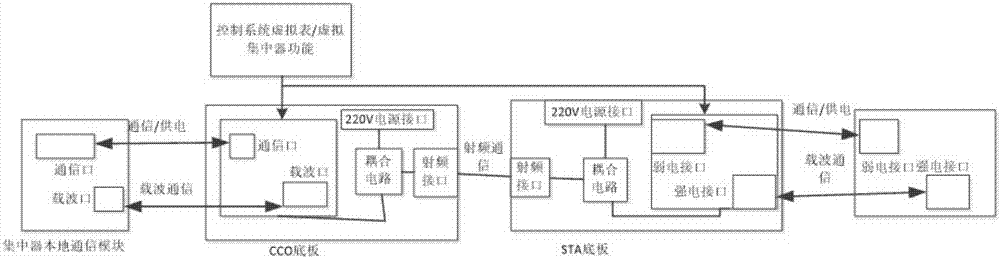
Wiring device of simulation test system
ActiveCN107294565APower distribution line transmissionTransmission monitoringCommunication unitFifth power
The embodiment of the invention discloses a wiring device of a simulation test system, and the device comprises: a signal source, a frequency spectrograph, a first attenuator, a second attenuator, a third attenuator, a forth attenuator, a fifth attenuator, a sixth attenuator, a seventh attenuator, an eighth attenuator, a ninth attenuator, a tenth attenuator, a first power divider, a second power divider, a third power divider, a fourth power divider, a fifth power divider, a sixth power divider, a seventh power divider, a resistance plate, a concentrator communication unit base plate and an ammeter carrier communication unit base plate; the concentrator communication unit base plate and the ammeter carrier communication unit base plate are respectively connected with a concentrator communication unit and an ammeter communication unit, and technical problems that a test mode of one concentrator connecting with a plurality of ammeters only can form a simple network topology structure, can not test the route performance of a carrier communication module in a multi-level route environment and is insufficient to manage and test the network of the communication module are solved.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID +1
Four-level three-phase grid-connection inverter and modulation method and power generation system thereof
ActiveCN107733272AIncrease input voltageImprove current rippleAc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsCapacitanceFifth power
The invention relates to a nested neutral point clamping four-level three-phase grid-connection inverter. The three-phase grid-connection inverter comprises three nested neutral point clamping four-level bridge arms; each bridge arm comprises a first power electronic switching tube, a second power electronic switching tube, a third power electronic switching tube, a fourth power electronic switching tube, a fifth power electronic switching tube and a sixth power electronic switching tube which are connected in sequence, and a first power diode connected between the midpoint of the second powerelectronic switching tube and the third power electronic switching tube and the neutral point, a second power diode connected between the midpoint of the fourth power electronic switching tube and the fifth power electronic switching tube and the neutral point, a first flying capacitor connected between the midpoint of the first power electronic switching tube and the second power electronic switching tube and the neutral point, and a second flying capacitor connected between the midpoint of the fifth power electronic switching tube and the sixth power electronic switching tube and the neutral point. The three-phase grid-connection inverter can improve input voltage and inversion performance and is easy to control.
Owner:JIANGSU GOODWE POWER SUPPLY TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
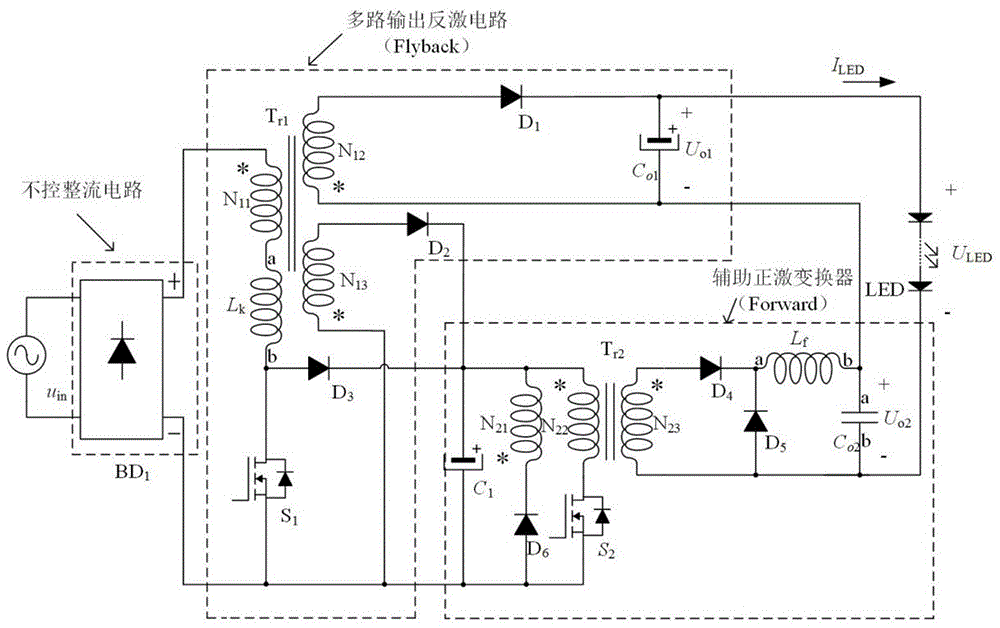
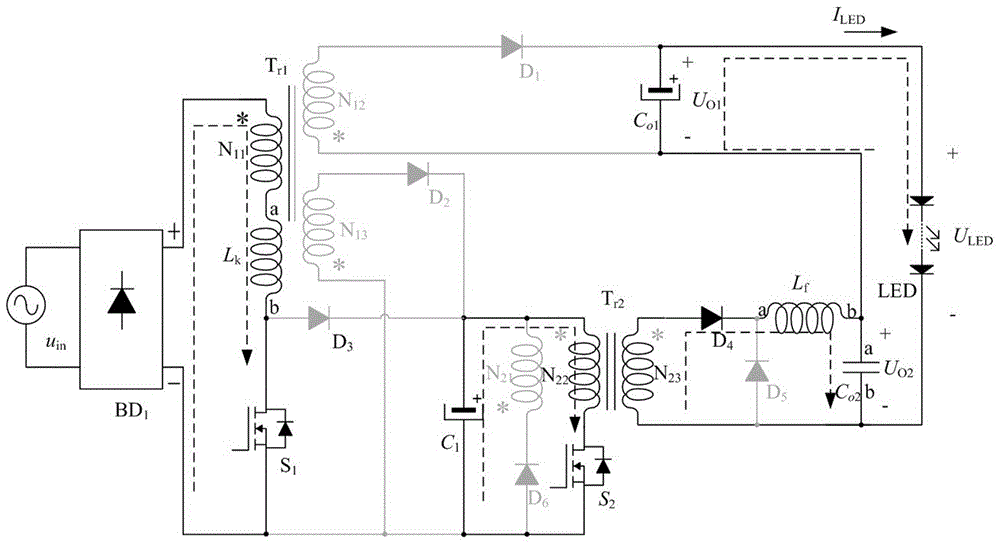
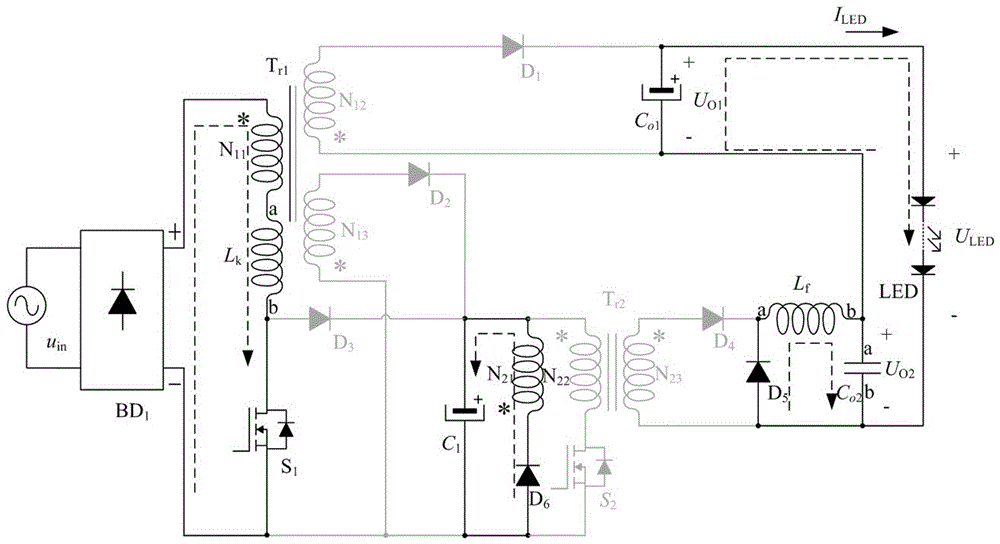
Single-stage low-switch-stress and low-output-ripple LED drive circuit
InactiveCN106535400AReduce voltage stressRealize energy utilizationElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesLow voltageAlternating current
The invention relates to a single-stage low-switch-stress and low-output-ripple LED drive circuit comprising an input alternating-current power supply uin, a diode rectifier bridge BD1, a main transformer Tr1, an auxiliary transformer Tr2, a first power MOS switch tube S1, a second power MOS switch tube S2, a first power diode D1, a second power diode D2, a third power diode D3, a fourth power diode D4, a fifth power diode D5, a sixth power diode D6, an electrolytic capacitor C1, a first output capacitor Co1, a second output capacitor Co2, an output filter inductor Lf, and an LED lamp load. The LED drive circuit based on combination of a single-stage AC-DC converter Flyback and an auxiliary converter Forward is constructed, so that high-efficiency, low-voltage-stress, low-output-ripple, and constant current output functions are realized.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
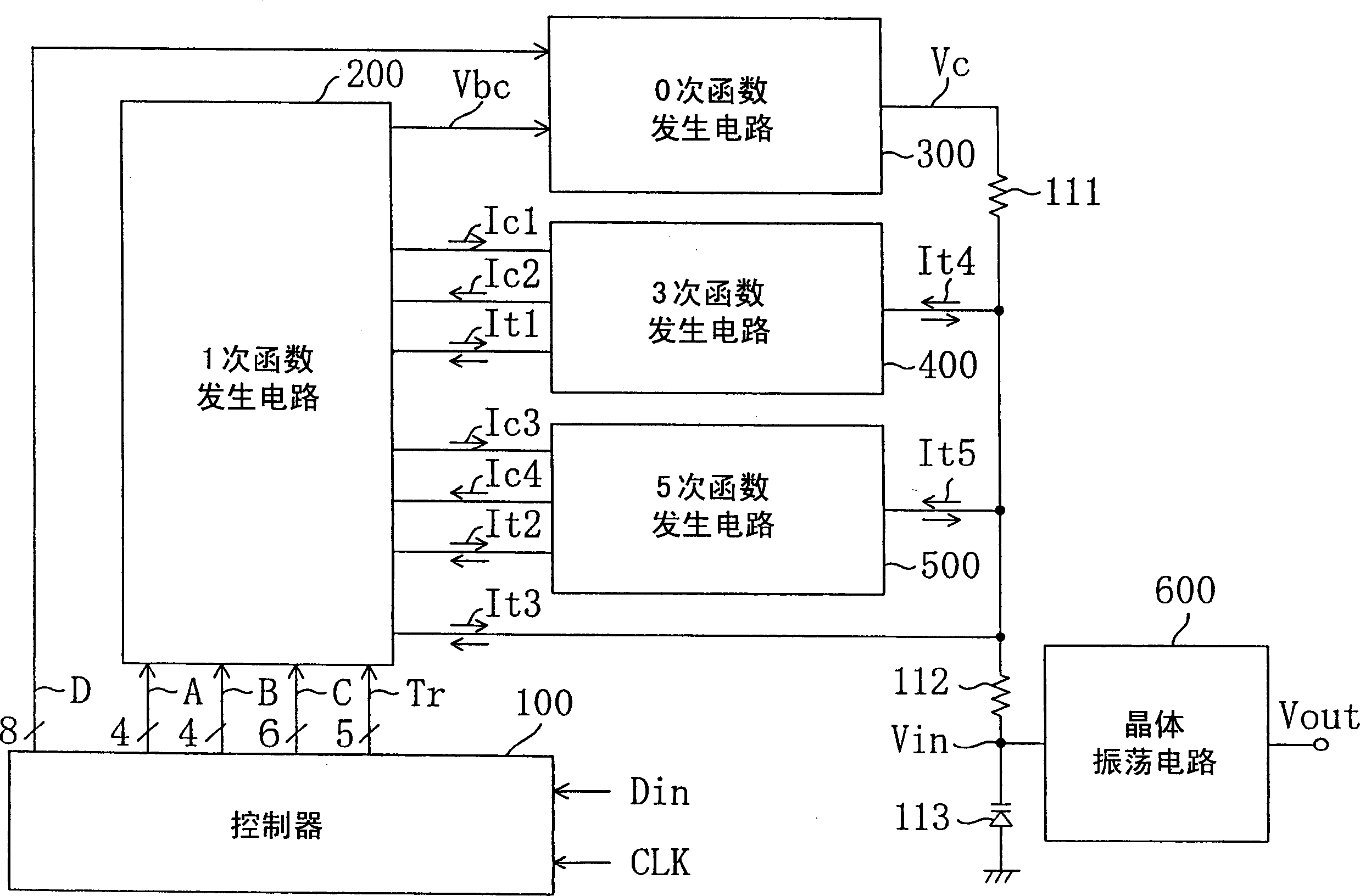
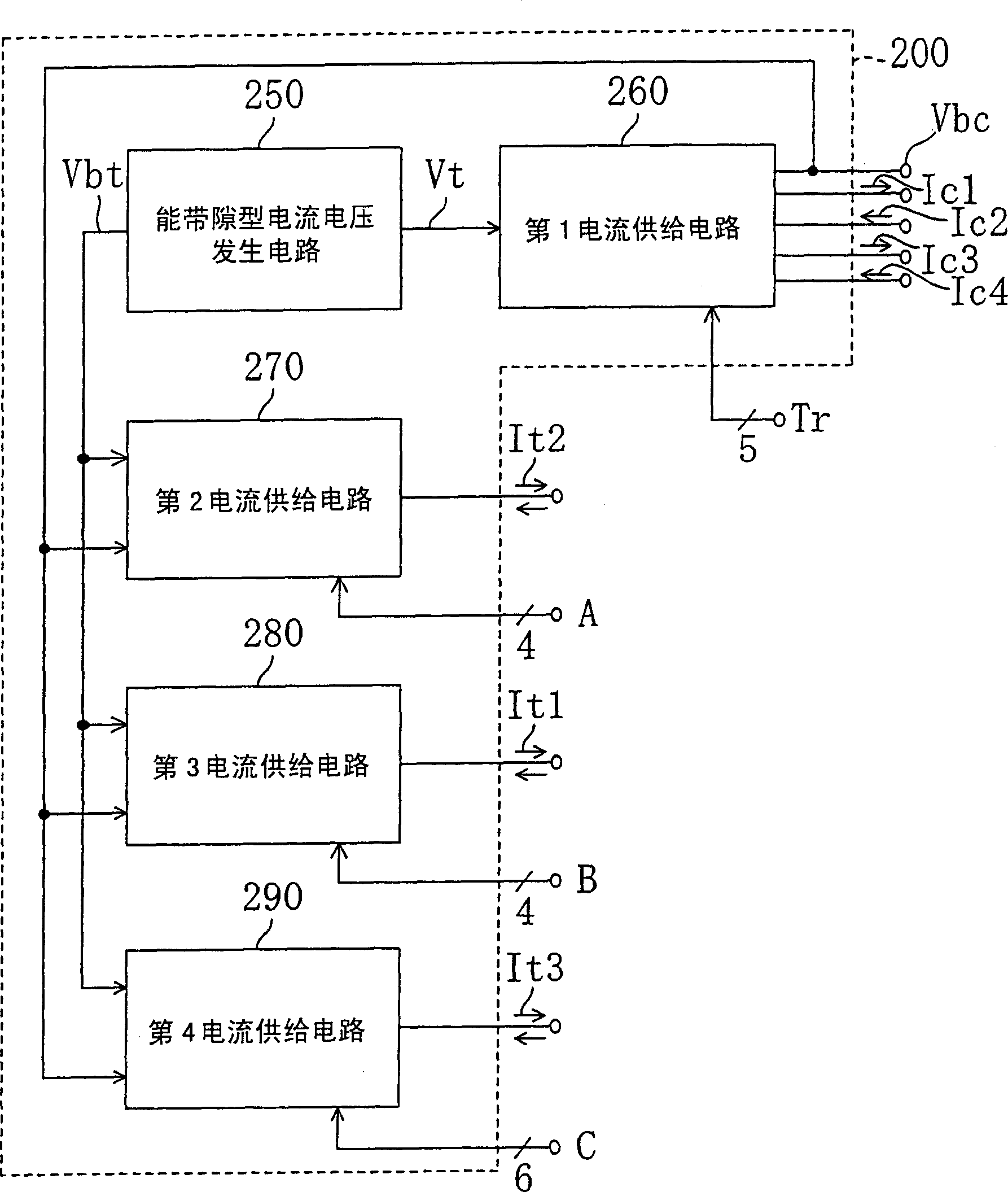
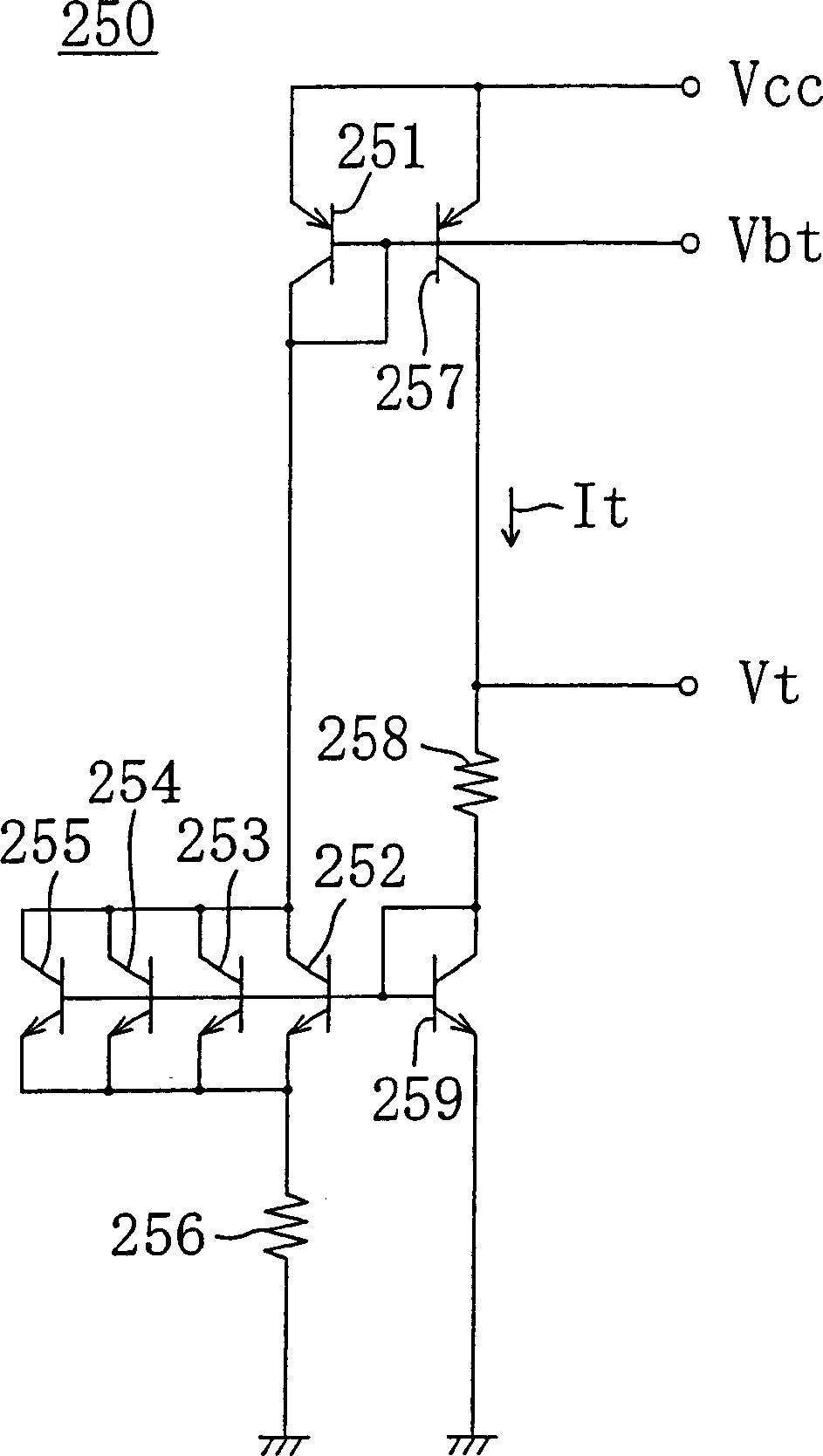
Function generating circuit and temperature compensation type crystal oscillator
With first, second and third current exchanger circuits cascaded, a current in proportion to a difference between an ambient temperature Ta and a reference temperature Tr is input to the first current exchanger circuit. The first current exchanger circuit supplies a current in proportion to the square of Ta-Tr to the second current exchanger circuit, the second current exchanger circuit supplies a current in proportion to the fourth power of Ta-Tr to the third current exchanger circuit, and the third current exchanger circuit outputs a current in proportion to the fifth power of Ta-Tr. Each of the first, second and third current exchanger circuits has a configuration which does not require a high supply voltage enough to drive a series circuit of three or more diodes.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Island-undercurrent underwater power generation device
The invention discloses an island-undercurrent underwater power generation device. The island-undercurrent underwater power generation device comprises a shell, a first power generator, a first gear, a first chain, a first wheel carrier, a first inlet, a second gear, a first propeller, a sliding block, a sliding rail, a first floating board, a first hydraulic cylinder, a first rolling wheel, a second belt, a sixth power generator, a supporting frame, a fourth power generator, a first propeller blade, a rack, an outlet, a first spring, a second floating board, a first flywheel, a second flywheel, a third belt, a connecting block, a third wheel carrier, a second rolling wheel, a third power generator, a second spring, a second propeller blade, a pulling cord, a fifth power generator, a supporting plate, a second hydraulic cylinder, a second inlet, a second power generator and a second wheel carrier; the shell is arranged on a shaft of the sixth power generator; the shaft of the sixth power generator is arranged on the supporting frame; the first inlet is formed in the shell; the first wheel carrier is arranged on the shell; the first wheel carrier is located on the front of the first inlet; and the first wheel carrier is provided with the first propeller. The island-undercurrent underwater power generation device has the advantage that various forms of undercurrent energy can be utilized.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
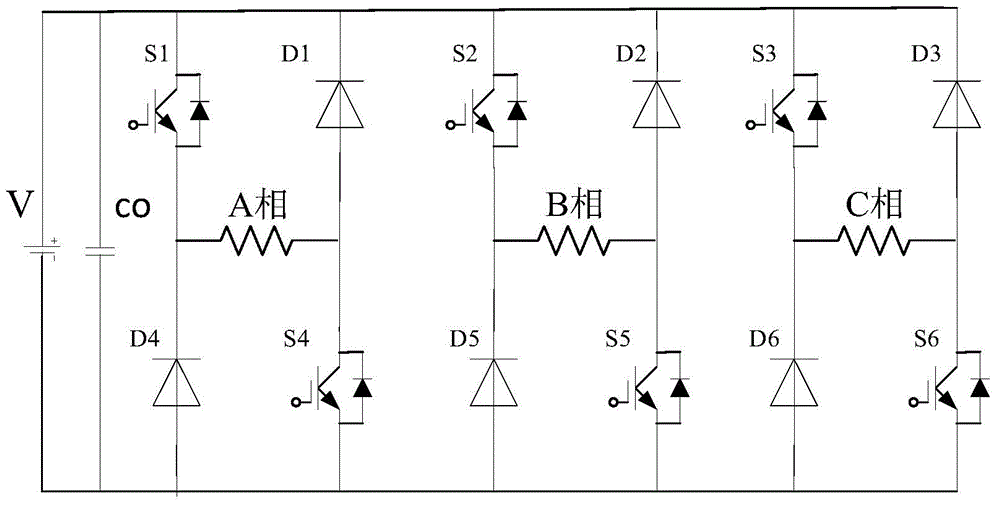
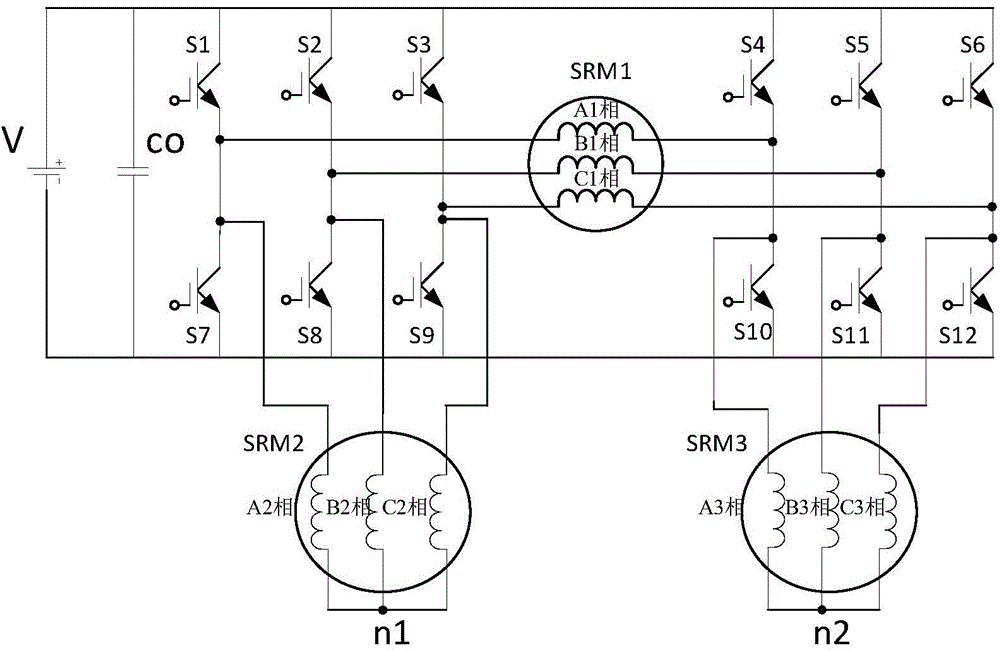
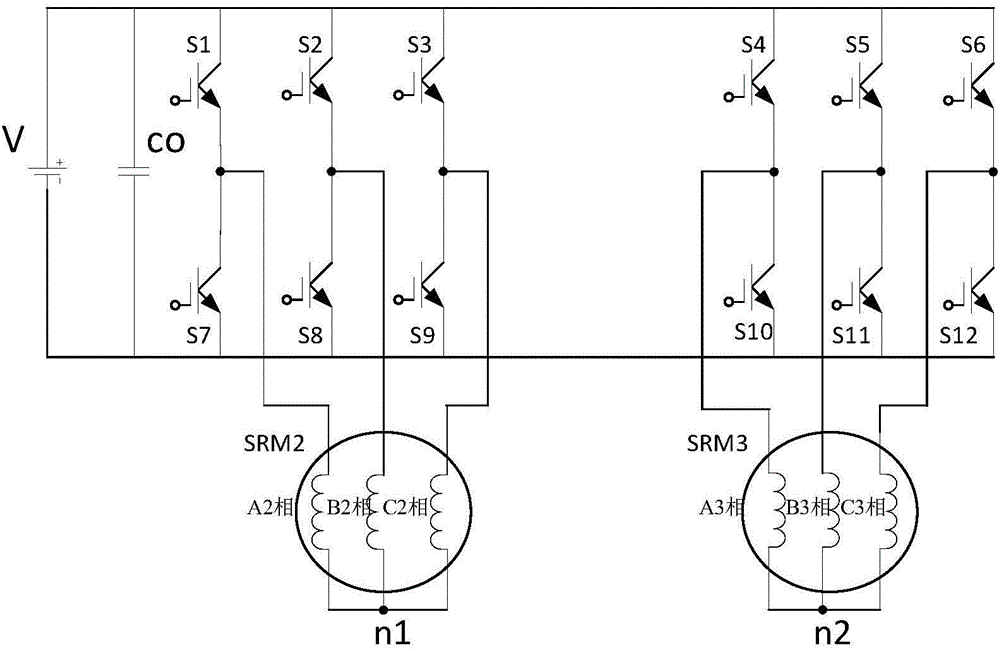
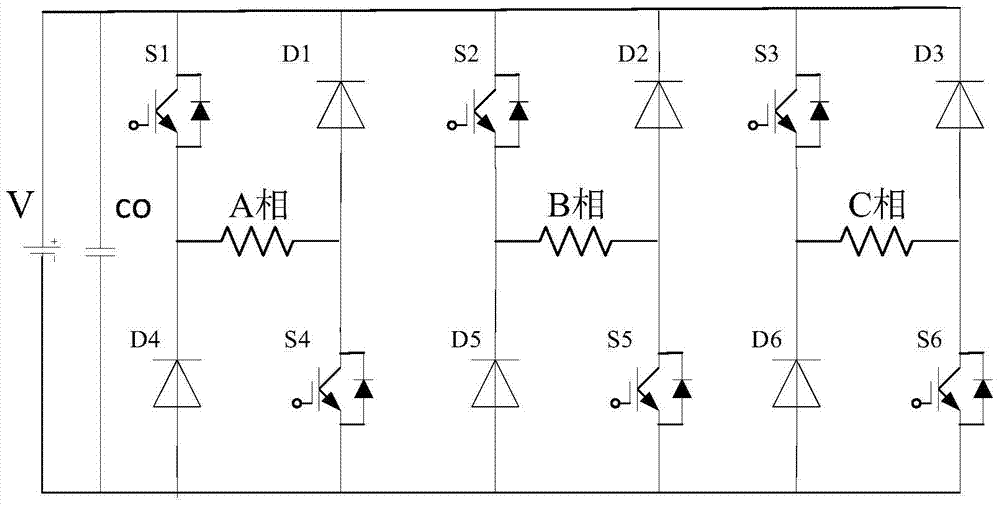
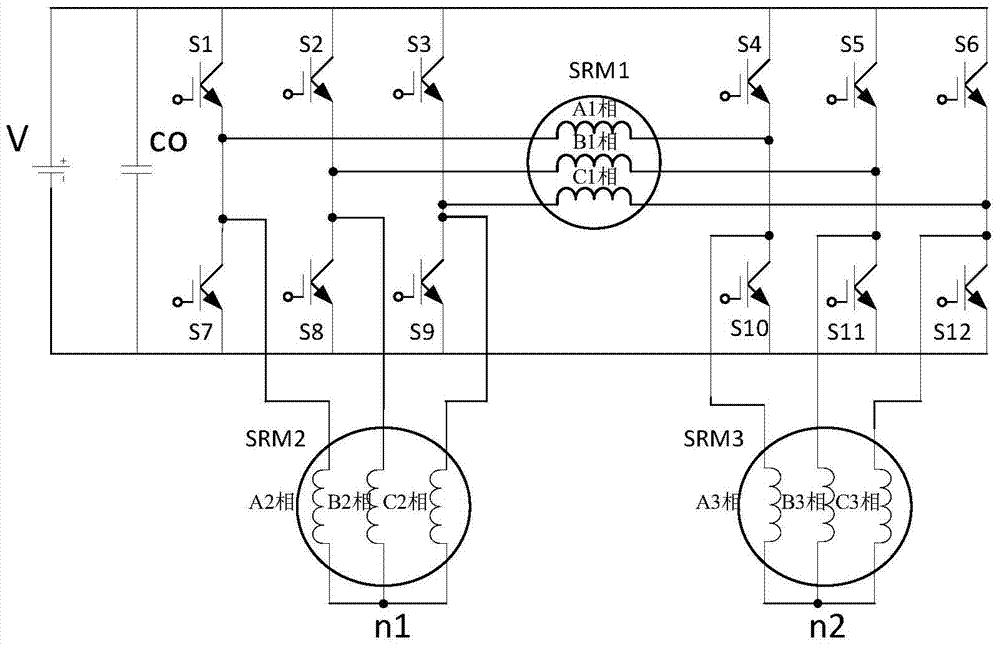
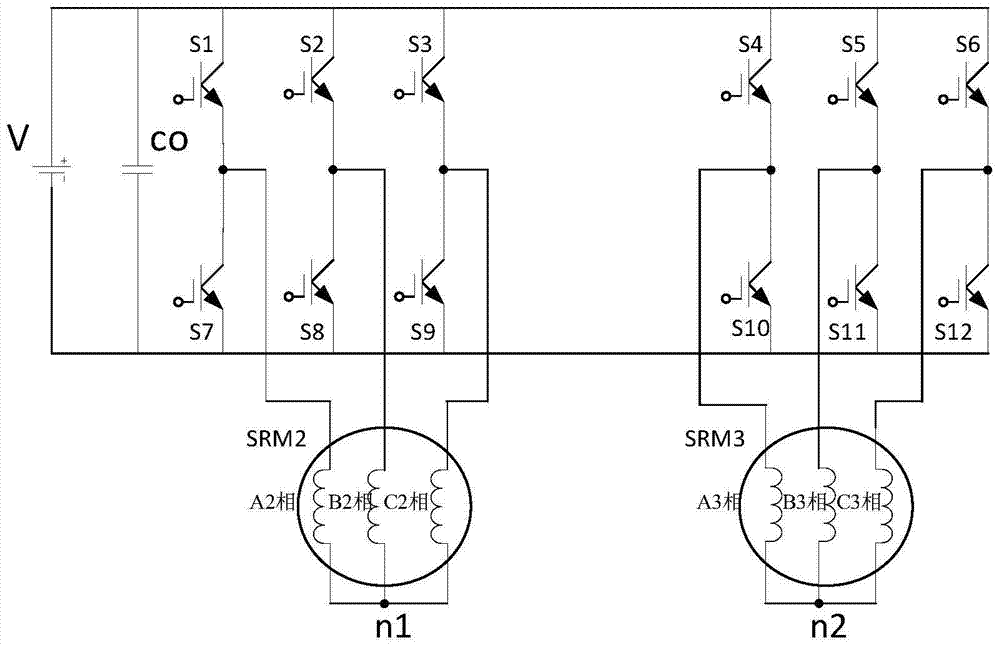
Power topological structure controlling three switch reluctance motors at the same time
ActiveCN104579032ALow costConvenient sourceMultiple motor speed/torque controlCapacitanceEngineering
The invention discloses a power topological structure controlling three switch reluctance motors at the same time. The power topological structure comprises a direct-current power source, the three three-phase switch reluctance motors, a power filter capacitor and 12 power switch tubes. The power filter capacitor is connected with the two electrodes of the direct-current power source in parallel. The positive electrode of the direct-current power source is connected with the collector electrodes of the first power switch tube, the second power switch tube, the third power switch tube, the fourth power switch tube, the fifth power switch tube and the sixth power switch tube at the same time. The negative electrode of the direct-current power source is connected with the emitting electrodes of the seventh power switch tube, the eighth power switch tube, the ninth power switch tube, the tenth power switch tube, the eleventh power switch tube and the twelfth power switch tube at the same time. Through connection of windings of the motors, the three switch reluctance motors are controlled through switching-on and switching-off of a switch, and the idle motor or the faulty motor can be switched off. The problems that an existing switch reluctance motor drive power structure is complicated and high in cost, on some occasions, one or more motors are idler, the utilization rate of a power converter is low, and the work efficiency of a system is low are solved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
FDM type low-melting-point alloy 3D printer spraying head system and application thereof
ActiveCN106956001ASimple designReduce weightAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyControl signalFifth power
Disclosed is an FDM type low-melting-point alloy 3D printer spraying head system and application thereof. A feeding device conveys a printing material prepared by a molten low-melting-point alloy preparing device to a spraying head, an extracting device conveys remaining printing materials collected by a recycling device from the spraying head to the molten low-melting-point alloy preparing device, a purifying device carries out purification treatment on harmful gas collected by the molten low-melting-point alloy preparing device and the recycling device, then the gas is exhausted, a control device provides power source and control signals for the spraying head, the molten low-melting-point alloy preparing device, the recycling device, the gas purifying device, the feeding device and the extracting device through a first power source harness, a second power source harness, a third power source harness, a fourth power source harness, a fifth power source harness, a first power source and signal harness, a second power source and signal harness, a third power source and signal harness, a fourth power source and signal harness, a fifth power source and signal harness, a sixth power source and signal harness, a seventh power source and signal harness, an eighth power source and signal harness, a ninth power source and signal harness and a tenth power source and signal harness; long-time continuous printing is supported, an automatic cooling device is arranged, waste material blockage prevention supplying, printing channel automatic cleaning capacity and the waste material recycling functions are achieved, and harmful gas generated in the printing process can be effectively treated.
Owner:西安航天计量测试研究所
Single-stage inverter
ActiveCN103916035AReduce energy consumptionExtended service lifePhotovoltaic energy generationDc-ac conversion without reversalCapacitancePower inverter
The invention discloses a single-stage inverter. The single-stage inverter comprises an input power source Uin, a first switch A, a second switch B, a first power switch tube S1, a second power switch tube S2, a third power switch tube S3, a fourth power switch tube S4, a fifth power switch tube S5, a sixth power switch tube S6, a first diode D1, a second diode D2 and an energy storage capacitor C. A passive component capacitor serves as an energy exchanging component. According to the novel single-stage inverter structure, the circuit working area is reasonably divided, the input power source energy consumption can be reduced, the service life of the input power source can be prolonged, and the single-stage inverter can be widely applied to the fields of photovoltaic grid-connected inverters, hybrid electric vehicles and the like.
Owner:河北汇聚达节能科技有限公司
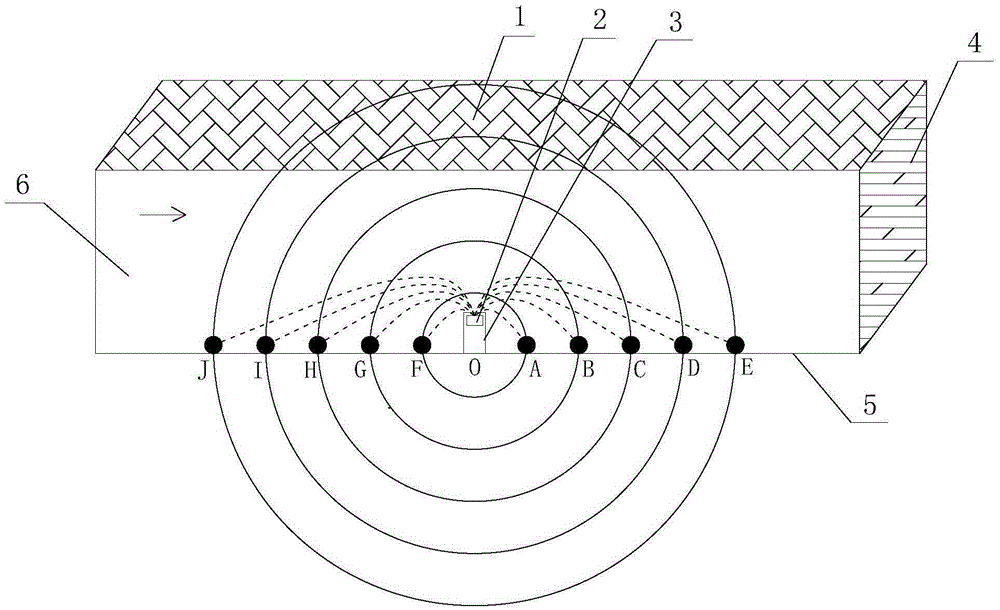
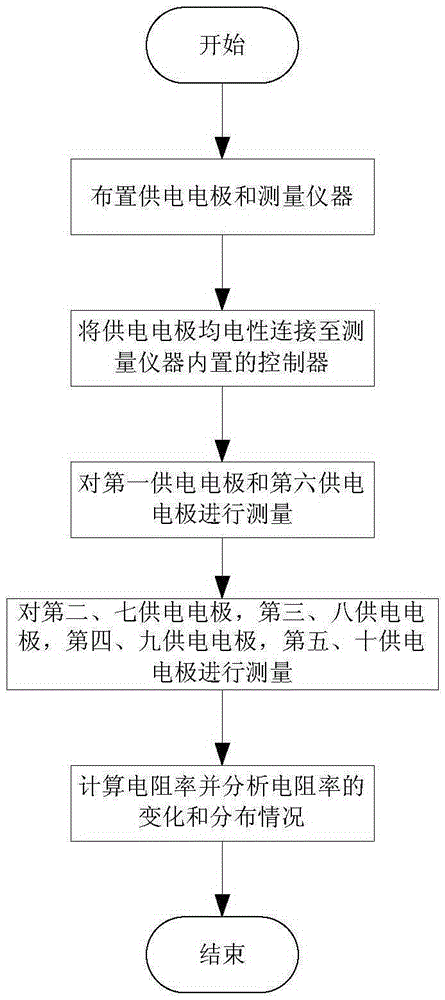
Unknown goaf waterlogged area detection method based on direct-current detection
InactiveCN105388529AReduce laborExpand the effective rangeElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingWater resource assessmentMeasuring instrumentFifth power
The invention provides an unknown goaf waterlogged area detection method based on direct-current detection and belongs to the field of mine detection. The method comprises arranging power supply electrodes and a measuring instrument in an excavation roadway, wherein the power supply electrodes are electrically connected to a controller arranged inside the measuring instrument; sequentially selecting the first power supply electrode and the sixth power supply electrode, the second power supply electrode and the seventh power supply electrode, the third power supply electrode and the eighth power supply electrode, the fourth power supply electrode and the ninth power supply electrode as well as the fifth power supply electrode and the tenth power supply electrode as measuring objects respectively, carrying out measurement and recording data, and summarizing the measured data recorded by the controller; and calculating resistivity and analyzing change of the resistivity and distribution information of unknown goaf waterlogged areas. The method is wide in effective detection range, high in accuracy, flexible and simple to use, and little in labor amount of measuring personnel.
Owner:LIAONING TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY
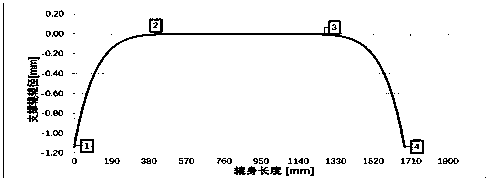
Six-power support roller profile curve
ActiveCN109719136AImprove grinding efficiencyDecrease rate of judgment reductionRevolution surface grinding machinesCounter-pressure devicesReduction rateFifth power
The invention relates to a six-power support roller profile curve, and belongs to the technical field of steel strip production equipment in the metallurgical industry. According to the technical scheme, the equation of the support roller profile curve is f(x)=p1*x^6+p2*x^5+p3*x^4+p4*x^3+p5*x^2+p6*x+p7, wherein x is the support roller body length coordinate, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5 and p6 are coefficients of the sixth power, the fifth power, the fourth power, the third power, the second power and the first power of the equation correspondingly, p7 is the constant term of the equation, and E is thescientific counting method; and the support roller profile curve is ground by a numerically-controlled grinding machine. The six-power support roller profile curve has the beneficial effects that thefinished strip steel plate type can be improved, and the sentence reduction rate of the plate type is reduced from 4.63% to 0.06%. The six-power support roller profile curve is a one-time grinding curve, chamfers on the two sides of a support roller do not need to be separately ground, and the grinding efficiency of the support roller is improved.
Owner:TANGSHAN IRON & STEEL GROUP +1
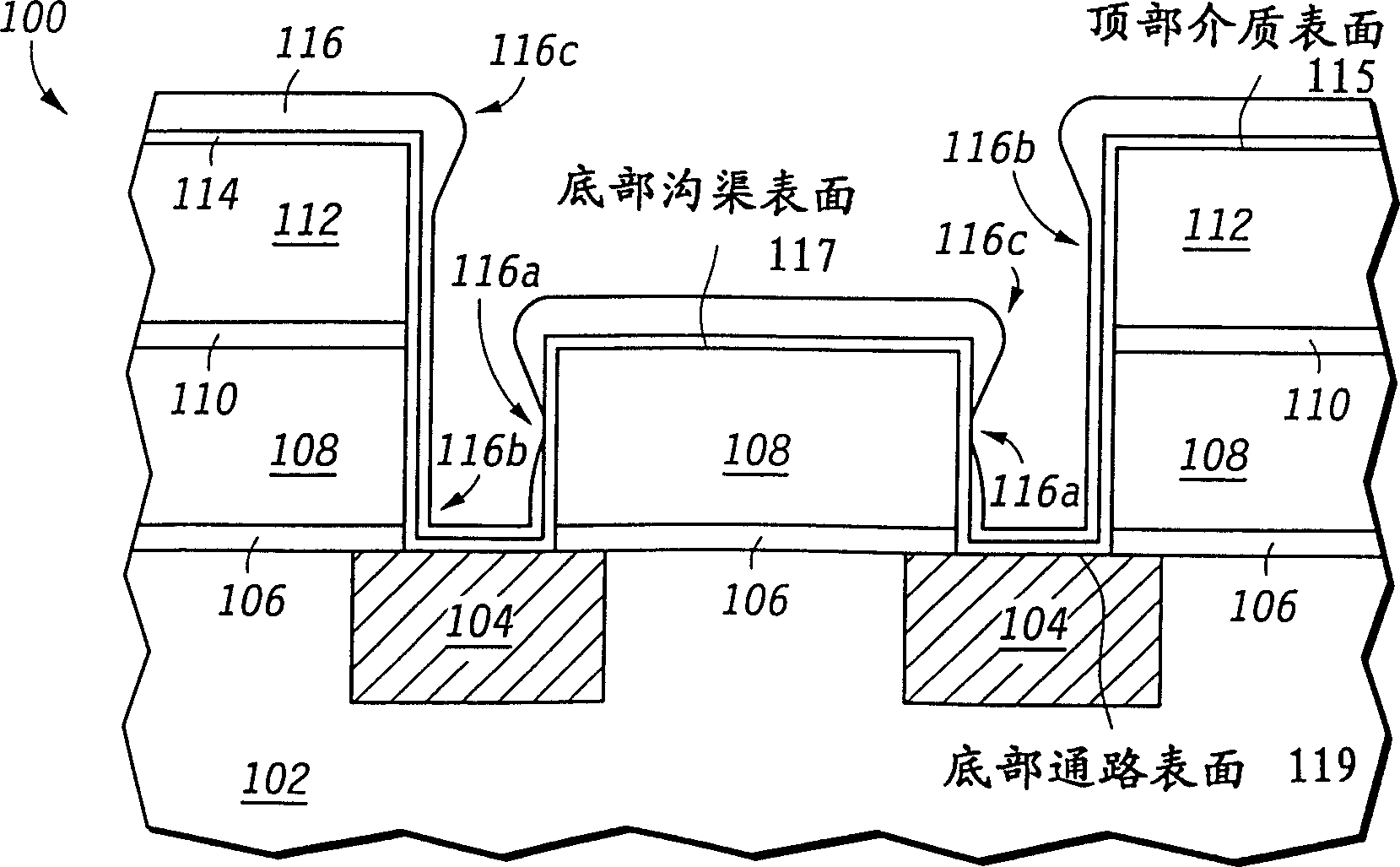
Method for forming copper layer on semiconductor chip
InactiveCN1197128CReduce usageReduce scratchesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesFifth powerSemiconductor chip
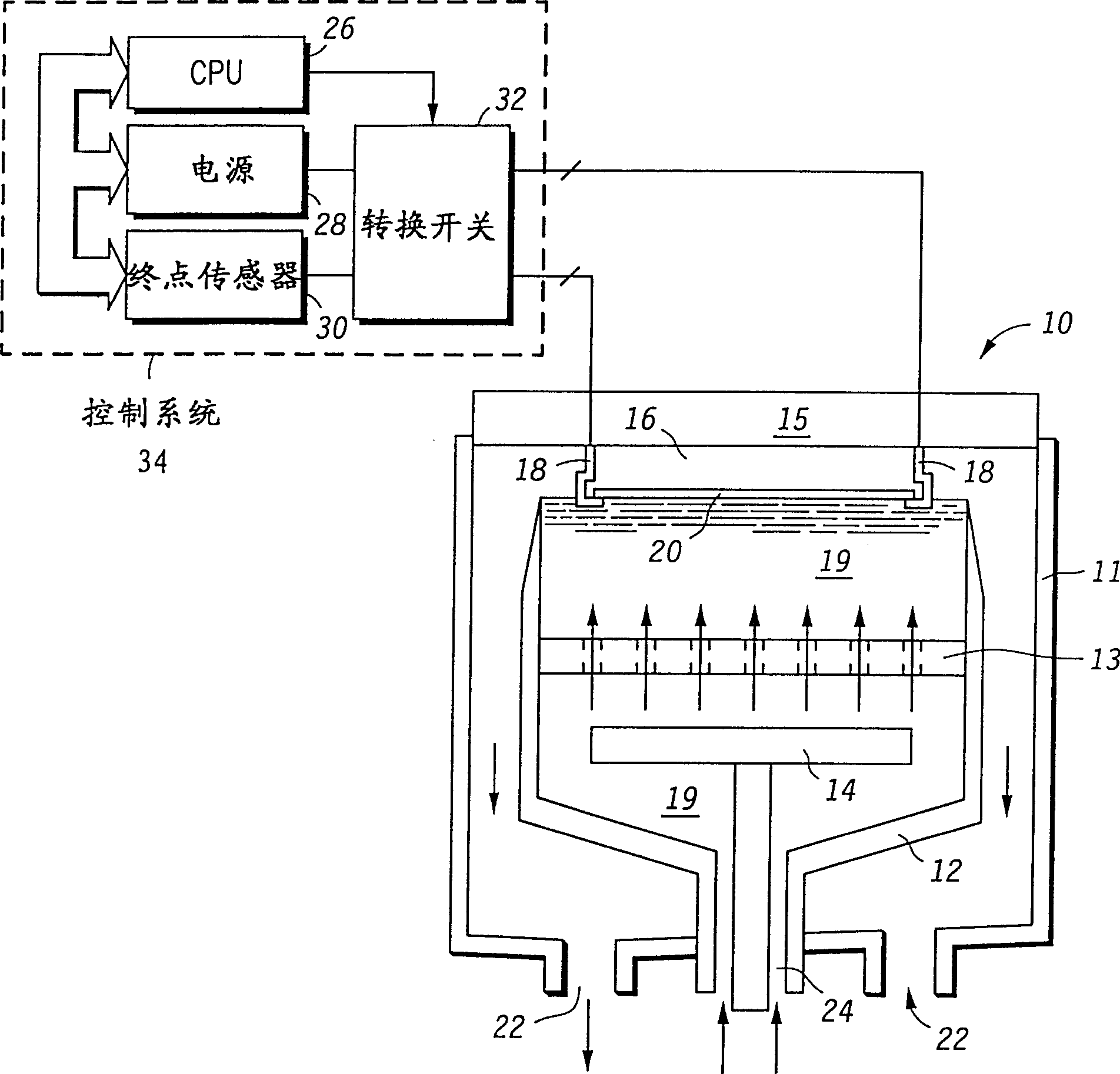
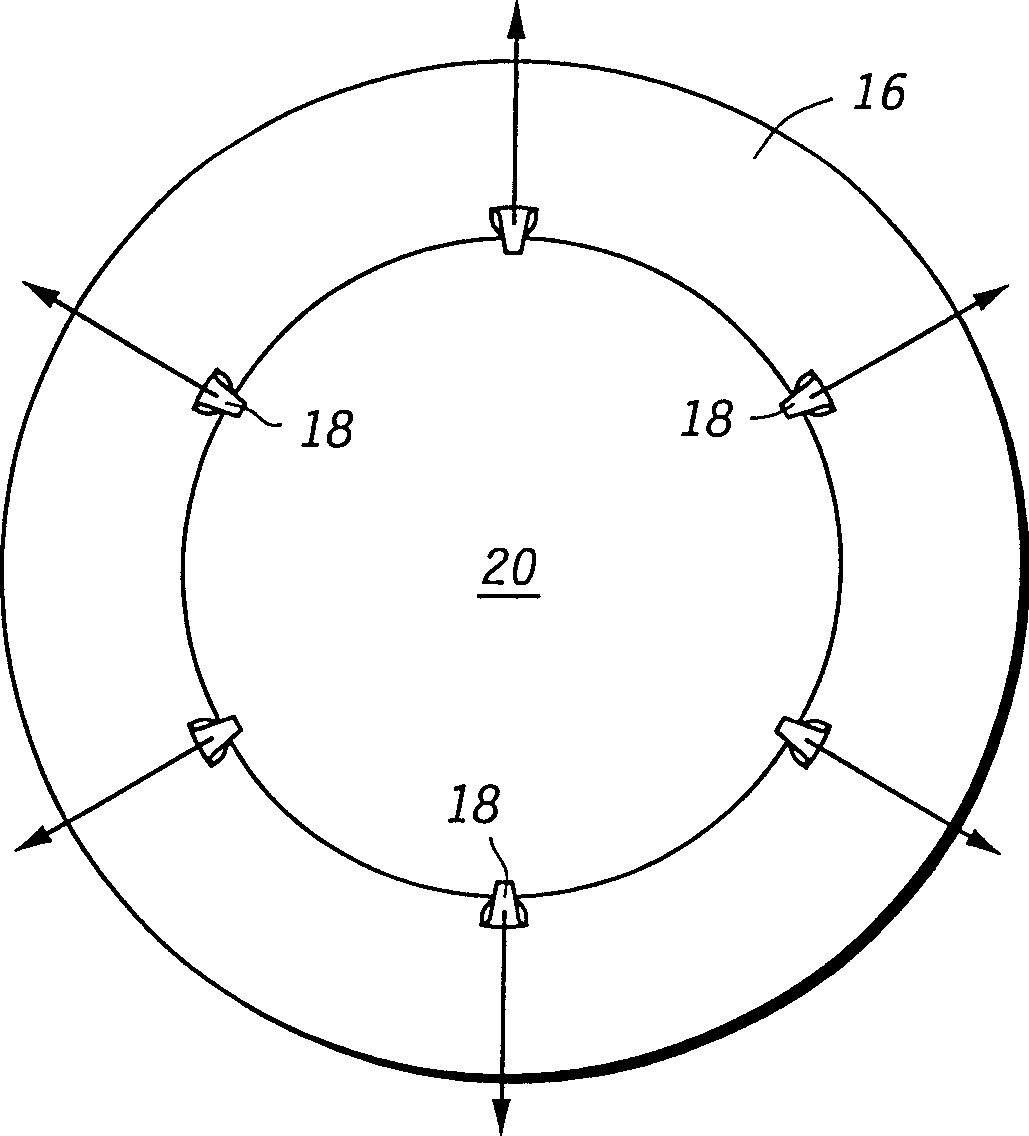
A method for electroplating a copper layer (118) over a wafer (20) powers a cathode of an electroplating system (10) in a manner that obtains improved copper interconnects. A control system (34) powers the cathode of the system (10) with a mix of two or more of: (i) positive low-powered DC cycles (201 or 254); (ii) positive high-powered DC cycles (256 or 310); (iii) low-powered, pulsed, positive-power cycles (306 or 530); (iv) high-powered, pulsed, positive-powered cycles (212, 252, 302, or 352); and / or (v) negative pulsed cycles (214, 304, 510, 528, or 532). The collection of these cycles functions to electroplate copper or a like metal (118) onto the wafer (20). During electroplating, insitu process control and / or endpointing (506, 512, or 520) is performed to further improve the resulting copper interconnect. <IMAGE>
Owner:VLSI TECH LLC
A programming-free electronic cam curve generation method for cross-cutting
ActiveCN106406219BEasy to operateEasy to debugProgramme control in sequence/logic controllersFifth powerDrive shaft
The invention provides a non-programming electronic cam curve generating method for transection. The method comprises: differential processing is carried out based on fifth-power non-dimensionalized position relation function to obtain a speed function, an acceleration function, an accelerated acceleration function; according to different cutting lengths, equation coefficients are calculated by selecting different conditions; conversion between a non-dimensionalized value and a true value is carried out on the functions; and then coordinate offset processing is carried out to obtain piecewise functions. According to the invention, an electronic cam curve can be generated only by setting three parameters: a parameter knife perimeter, a total synchronzi9ation length, and a cutting length; and generation of a reverse speed of a driven shaft is avoided based on calculation. For the electronic cam curve generated by using the method in the transection field, the operation and debugging of the filed operator can be simplified; programming is avoided; and the reliability is high. The speed curve is a fourth-power function that is more flexible and smoother by compared with a third-power function.
Owner:威科达(东莞)智能控制有限公司
LED driving circuit for hybrid control of single-stage bridgeless Sepic and LLC
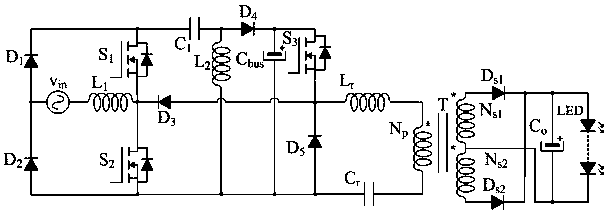
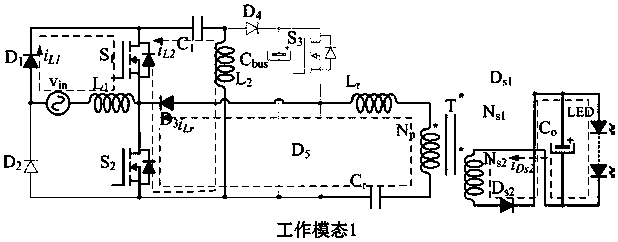
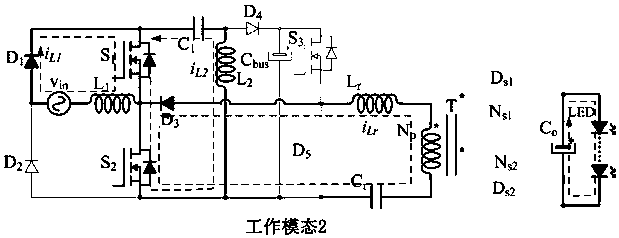
InactiveCN110012574AImprove reliabilityReduce cost lossElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesCapacitancePower factor
The invention relates to an LED driving circuit for hybrid control of a single-stage bridgeless Sepic and an LLC, which comprises a single-phase AC input power supply vin, a first power diode D1, a second power diode D2, a third power diode D3, a fourth power diode D4, a fifth power diode D5, a sixth power diode Ds1, a seventh power diode Ds2, a first power switch tube S1, a power switch tube S2,a third power switch tube S3, a high-frequency capacitor C1, a first output capacitor Cbus, a second output capacitor Co, a resonant capacitor Cr, a first inductor L1, a second inductor L2, a resonantinductor Lr, a high-frequency transformer T including a primary winding Np, a secondary winding Ns1 and a secondary winding Ns2 and an LED lamp load. The LED driving circuit can accomplish adjustableconversion and realize a wide input voltage range, controllable bus voltage, a high power factor, low conduction loss and soft switch conversion, and improves the performance-price ratio of the driving circuit.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Low voltage wide input push-pull positive stimulate three level DC converter and controlling method thereof
InactiveCN101388609BReduce voltage stressReduce lossDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationThree levelCapacitance
The invention discloses a low voltage wide input push-pull forward three-level direct current convertor and a method for controlling the convertor, which belong to direct current convertors and methods for controlling the convertors. The convertor of the invention is composed of an input dividing capacitance circuit, a first level branch, a second level branch, a third level branch, a clamping capacitor, an insulating transformer, a rectifier bridge and a filter circuit. The method for controlling the convertor of the invention comprises: driving signals of a first power switch tube and a fifth power switch tube are complementary, the driving signals of a fourth power switch tube and a sixth power switch tube are complementary, two working modes of three levels and two levels exist, in the three level working mode, a second power switch tube and a third power switch tube are conducted complementarily for 180 degrees, the first power switch tube and the fourth power switch are modulated by PWM, in two level working mode, the first power switch tube and the fourth power switch tube are cut normally, the fifth power switch tube and the sixth power switch tube are conducted normally, and the second power switch tube and the third power switch tube work by PWM. The invention reduces the conducting loss, improves the conversion efficiency, and saves a flying capacitor.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Transmitter and method of processing transmission signals
ActiveUS20160087656A1Simple structureTransmissionWireless communicationAudio power amplifierFifth power
A transmitter and method are provided for processing a transmission signal. The transmitter includes an FEM that switches a plurality of band signals for a first and second communication scheme, wherein the band signals for the first communication scheme include a first HB signal, a second HB signal, a first LB signal, and a second LB signal, and the band signals for the second communication scheme include a third LB and a third HB signal; a first PAM including a first power amplifier that amplifies the third HB signal, a second power amplifier that amplifies the first HB signal, and a third power amplifier that amplifies the first LB signal; and a second PAM including a fourth power amplifier that amplifies the third LB signal, a fifth power amplifier that amplifies the second HB signal, and a sixth power amplifier that amplifies the second LB signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
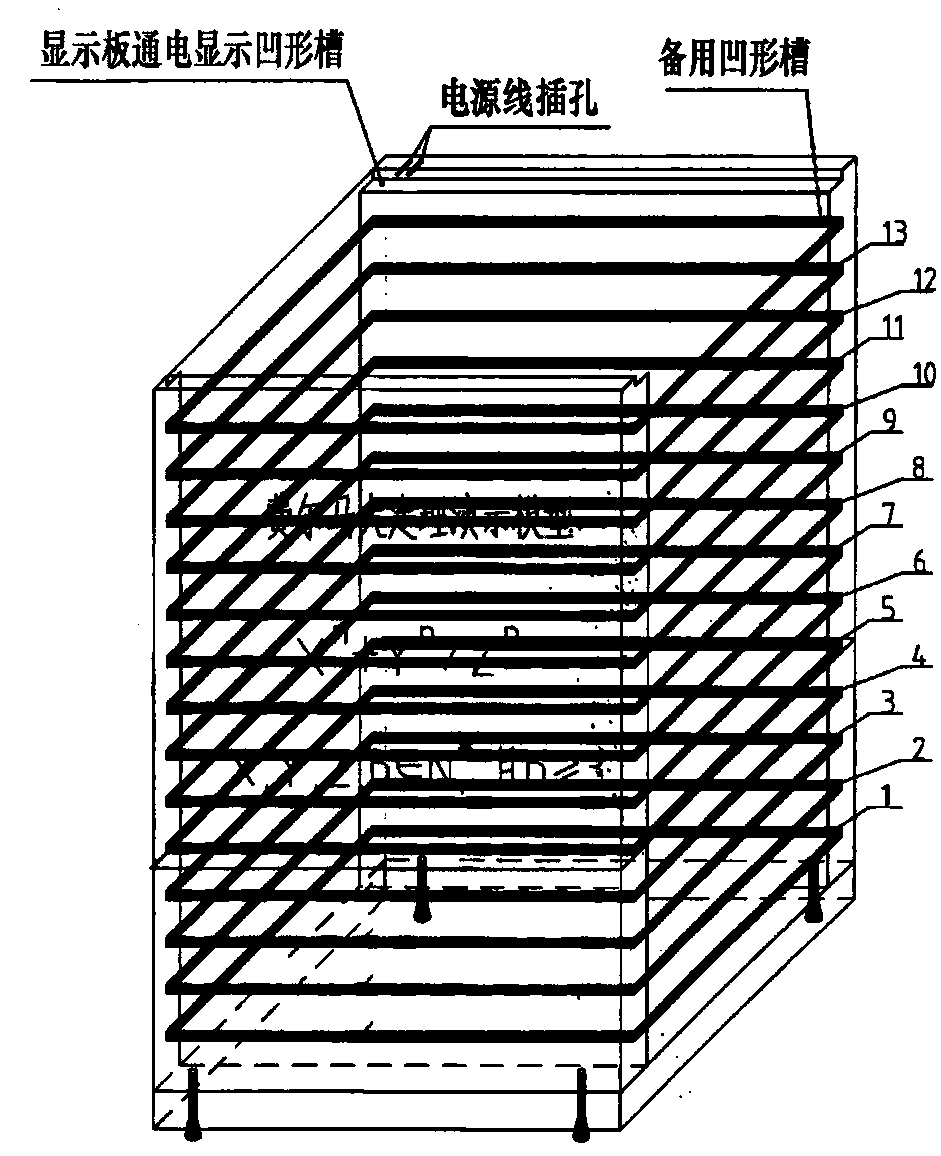
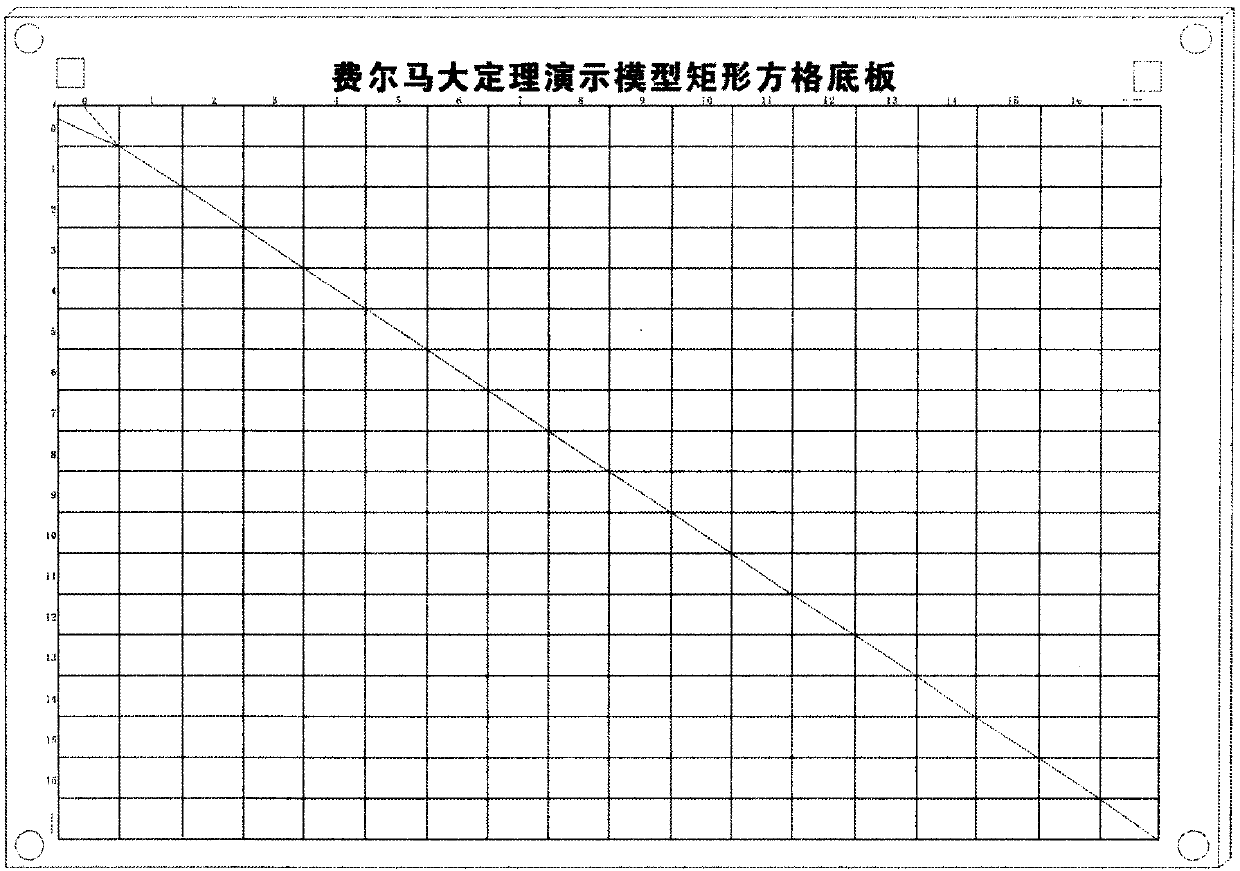
Fermat's grand theorem demonstration model
ActiveCN107919040ASimplify the proof processSave proof timeEducational modelsElectric lightFifth power
A Fermat's grand theorem demonstration model is disclosed and relates to the field of teaching of mathematics in primary, secondary and tertiary schools and the field of scientific research. The invention is aimed at constructing a mathematical model for Fermat's grand theorem and solving two problems of mathematics teaching and popularization of science; the demonstration model consists of a number of rectangular square (1), a number of universal Integrated circuit boards (2), a number of positive Integer nth power formula plates (3), a number of touch screen switch cover plates, a third power display panel (5), a fourth power display panel (6), a fifth power display panel (7), a sixth power display panel (8), a seventh power display panel (9), an eighth power display panel ( 10), a ninthpower display panel (11), an nth power universal display panel (12), an nth power variant four-color display panel (13) and a base seat (14); the third power display panel (5), the fourth power display panel (6), the fifth power display panel (7), the sixth power display panel (8), the seventh power display panel (9), the eighth power display panel (10), the ninth power display panel (11), the nth power universal display panel (12), the nth power variant four-color display panel (13) and the base seat (14) are made via via a Fermat inequality parameter method and an assembly display panel method; all display panels are orderly inserted horizontally into opposite grooves of inner sides of wall panels erected before and after the base seat (14); different colors of the rectangular squares on the display panels or lights of electric lights in an integrated circuit are used to show Fermat inequalities and demonstrate that Fermat's grand theorem is true, and the positive integer n is greater than or equal to 3.
Owner:李中平
Voltage-multiplying unit based multi-input high gain Z-source converter
InactiveCN107070211AReduce voltage stressHigh voltage gainDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationMulti inputCapacitance
The invention discloses a voltage-multiplying unit based multi-input high gain Z-source converter. The Z-source converter includes a Z-source voltage boosting module, a voltage multiplying module and an output module connected in sequence. The Z-source voltage boosting module is composed of a first power source, a second power source, a third power source, a fourth power source, a fifth power source, a first inductor, a second inductor, a first capacitor, a second capacitor, a first diode and a switch tube. The voltage multiplying module is composed of a second diode, a third diode, a third capacitor and a fourth capacitor. The output module is composed of a fourth diode, a fifth capacitor and a load. According to the invention, multiplication of output voltage gain is realized, voltage stress of the switch tube and the diodes is reduced and interfaces for input of the multiple power sources are also provided at the same time.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Constant-voltage and constant-current dual-mode BUCK type direct-current power circuit on basis of compensation topology
ActiveCN106787694AReduce overshootReduce dynamic adjustment timeApparatus without intermediate ac conversionCapacitanceDc current
The invention provides a constant-voltage and constant-current dual-mode BUCK type direct-current power circuit on the basis of compensation topology. The constant-voltage and constant-current dual-mode BUCK type direct-current power circuit comprises a first capacitor, a second capacitor, a first resistor, a second resistor, an inductor, a first diode, a second diode, a third diode, a fourth diode, a fifth diode, a sixth diode, a first power electronic switch device, a second power electronic switch device, a third power electronic switch device, a fourth power electronic switch device, a fifth power electronic switch device, a first current sensor, a second current sensor, a voltage sensor, a first input wiring terminal, a second input wiring terminal, a third input wiring terminal and a fourth input wiring terminal. The constant-voltage and constant-current dual-mode BUCK type direct-current power circuit has the advantages that the problems that most traditional BUCK type direct-current power sources only can work in constant-voltage modes, are long in dynamic regulation time under the condition of sudden change of load, are high in voltage fluctuation amplitude in the constant-voltage modes and are high in current fluctuation amplitude in constant-current modes can be solved; voltages can be reduced on the premise that currents of input direct-current voltages are basically stable, stable direct-current voltages can be provided for load in constant-voltage modes by topological structures of a direct-current power main circuit and corresponding control strategies, and stable direct currents can be provided for the load in constant-current modes by the topological structures of the direct-current power main circuit and the corresponding control strategies.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com