Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1442results about "Multiple motor speed/torque control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
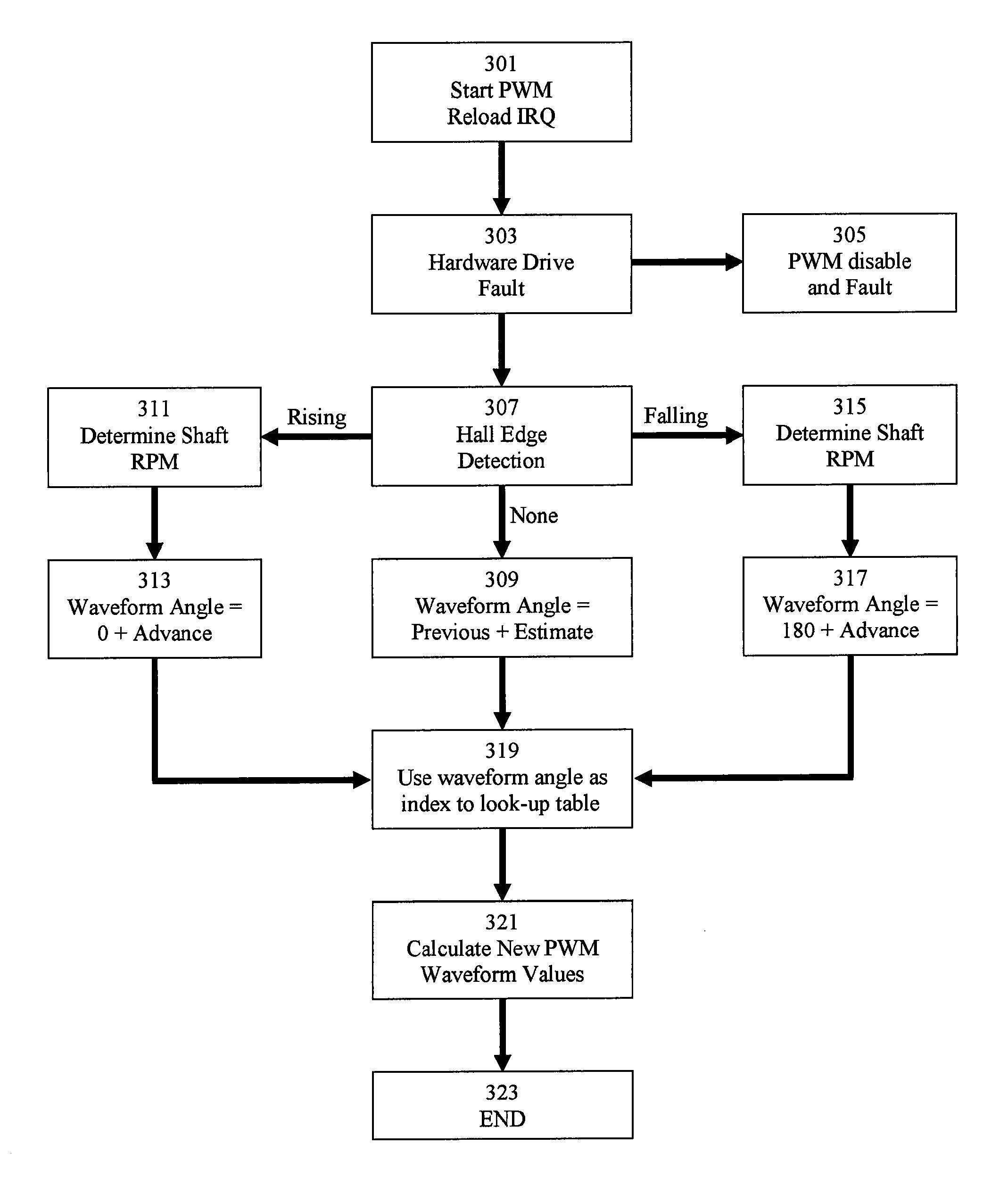
Method and arrangement for control of direct current motor
InactiveUS7567045B2Efficient coordinationLow costVehicle seatsMultiple motor speed/torque controlTelecommunications linkControl signal
Owner:KONGSBERG AUTOMOTIVE AB (SE)
Motor drive circuit with short startup time
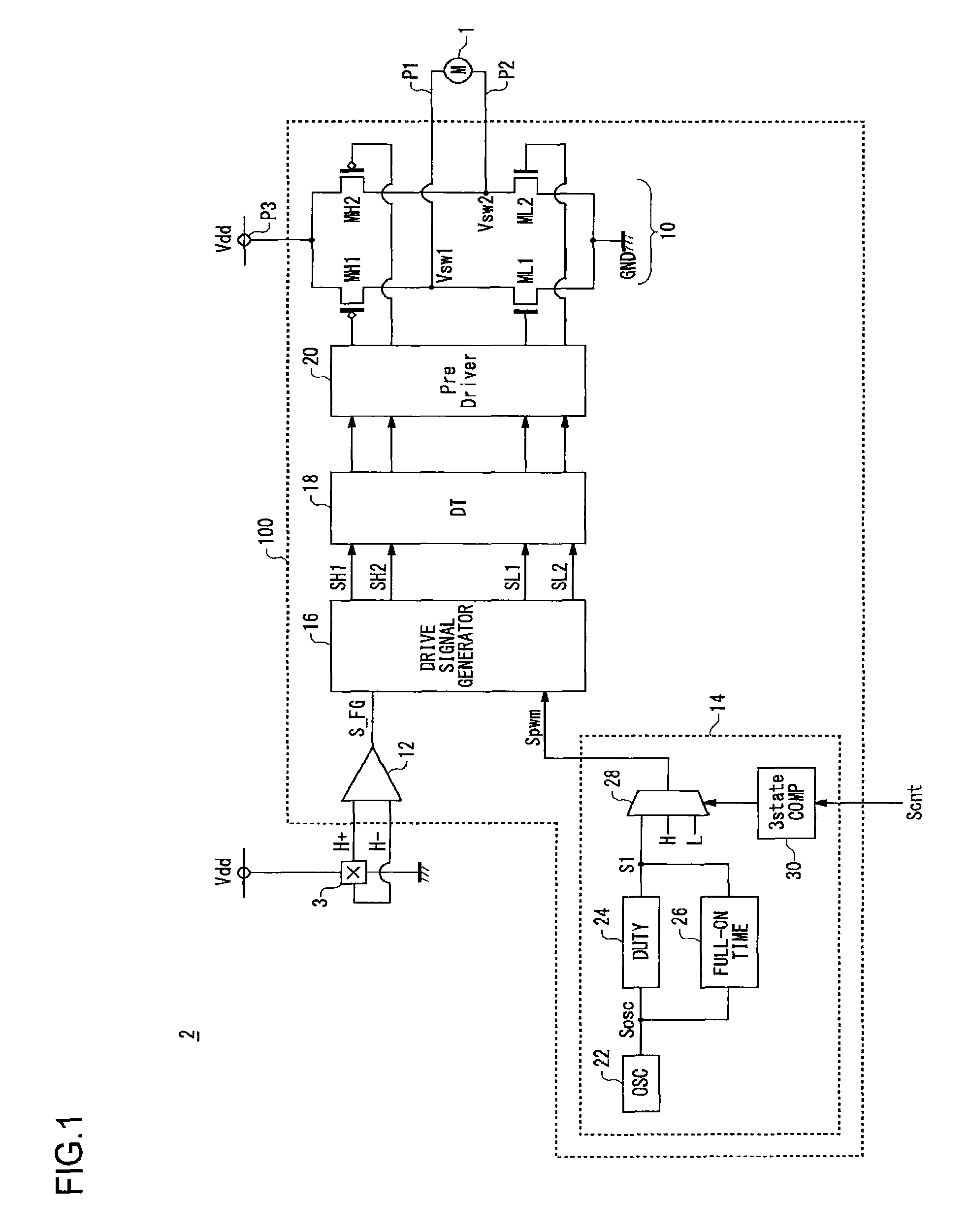
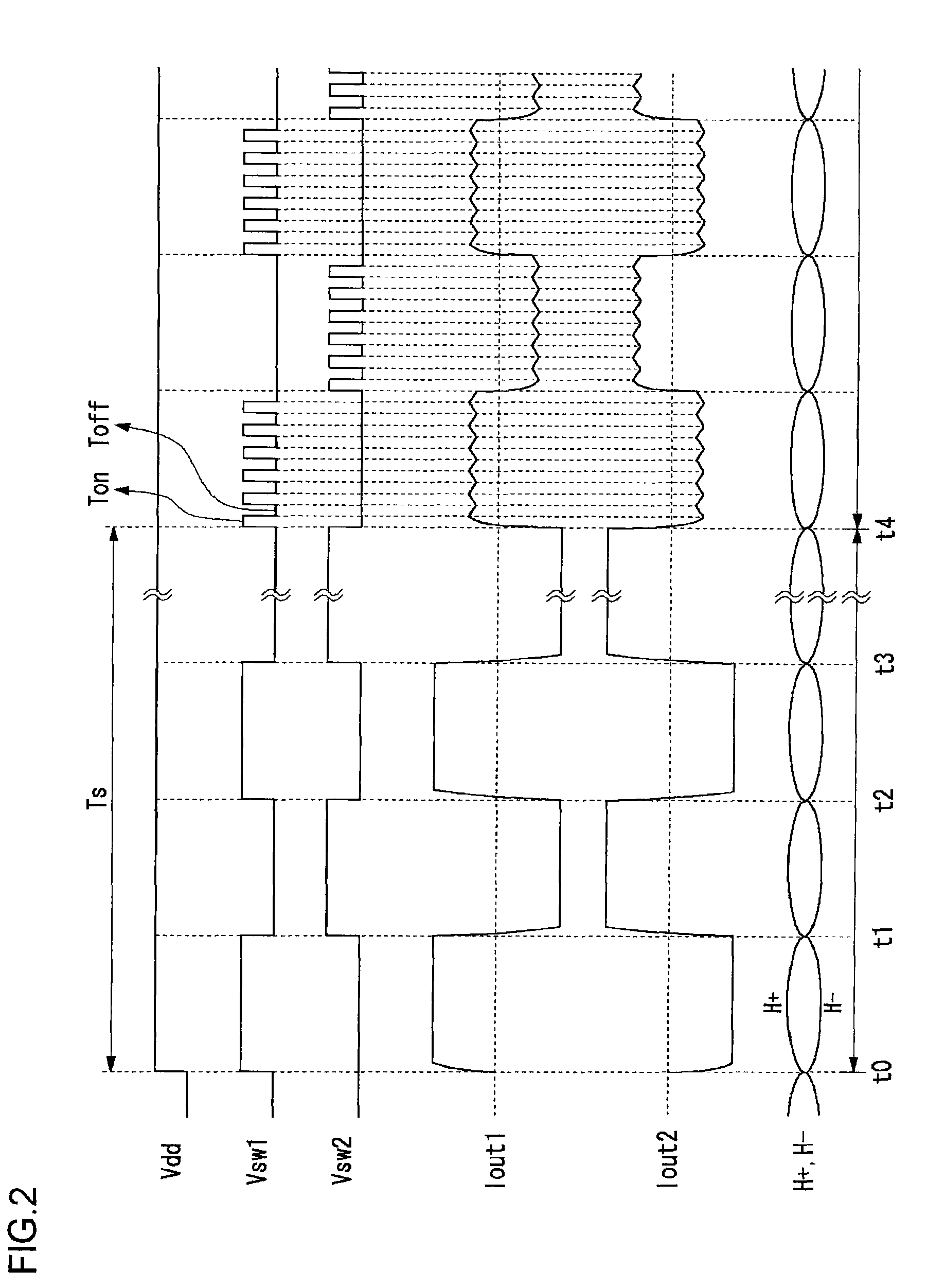
An H-bridge circuit is connected to a coil of the vibration motor that is to be driven. A comparator receives Hall signals indicating position information of a rotor of the vibration motor, and converts to an FG signal. A pulse width modulator generates a pulse-modulated pulse signal specifying energization time of the coil of the vibration motor. The pulse width modulator, in a first mode, after commencing start-up of the vibration motor, sets a duty ratio of the pulse signal to 100%, and after that, switches the duty ratio to a predetermined value in accordance with rotational frequency of the motor. In a second mode, the duty ratio of the pulse signal continues to be set to 100%. In a third mode, frequency and the duty ratio of the pulse signal are set based on a control signal of a pulse form inputted from outside. The control signal is used also in switching mode.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
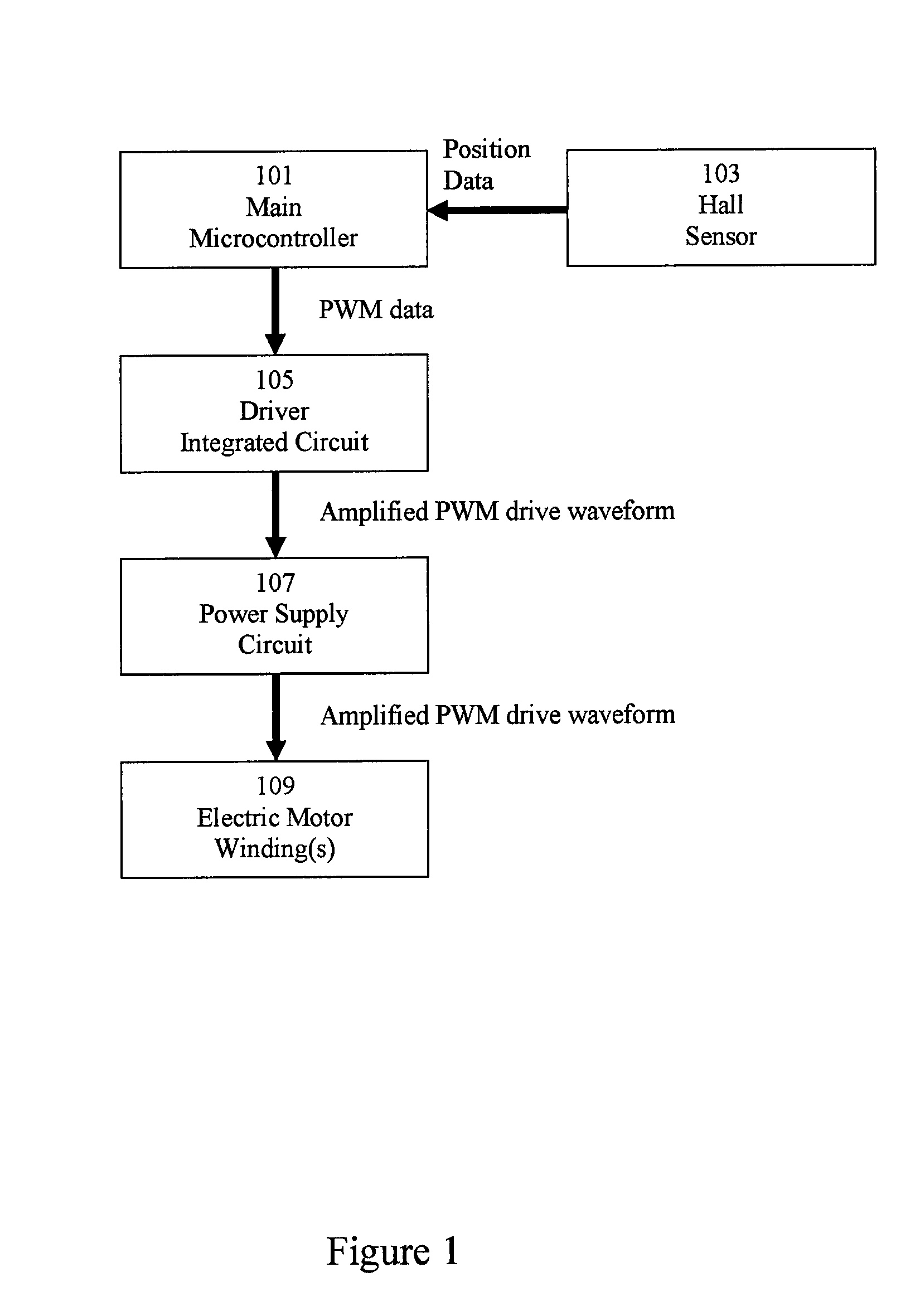
Method and apparatus for controlling electronically commutated motor operating characteristics
InactiveUS6895176B2Operation controlSingle-phase induction motor startersAC motor controlBrushless motorsControl electronics
A permanent magnet DC brushless motor control assembly permits a user to select the permanent magnet DC brushless motor operating characteristics by selecting appropriate control circuits to interface with the motor. The assembly includes a permanent magnet DC brushless motor, a commutator electrically coupled to the motor, and at least one control module electrically coupled to the commutator, to control operating characteristics of the permanent magnet DC brushless motor.
Owner:REGAL BELOIT AMERICA
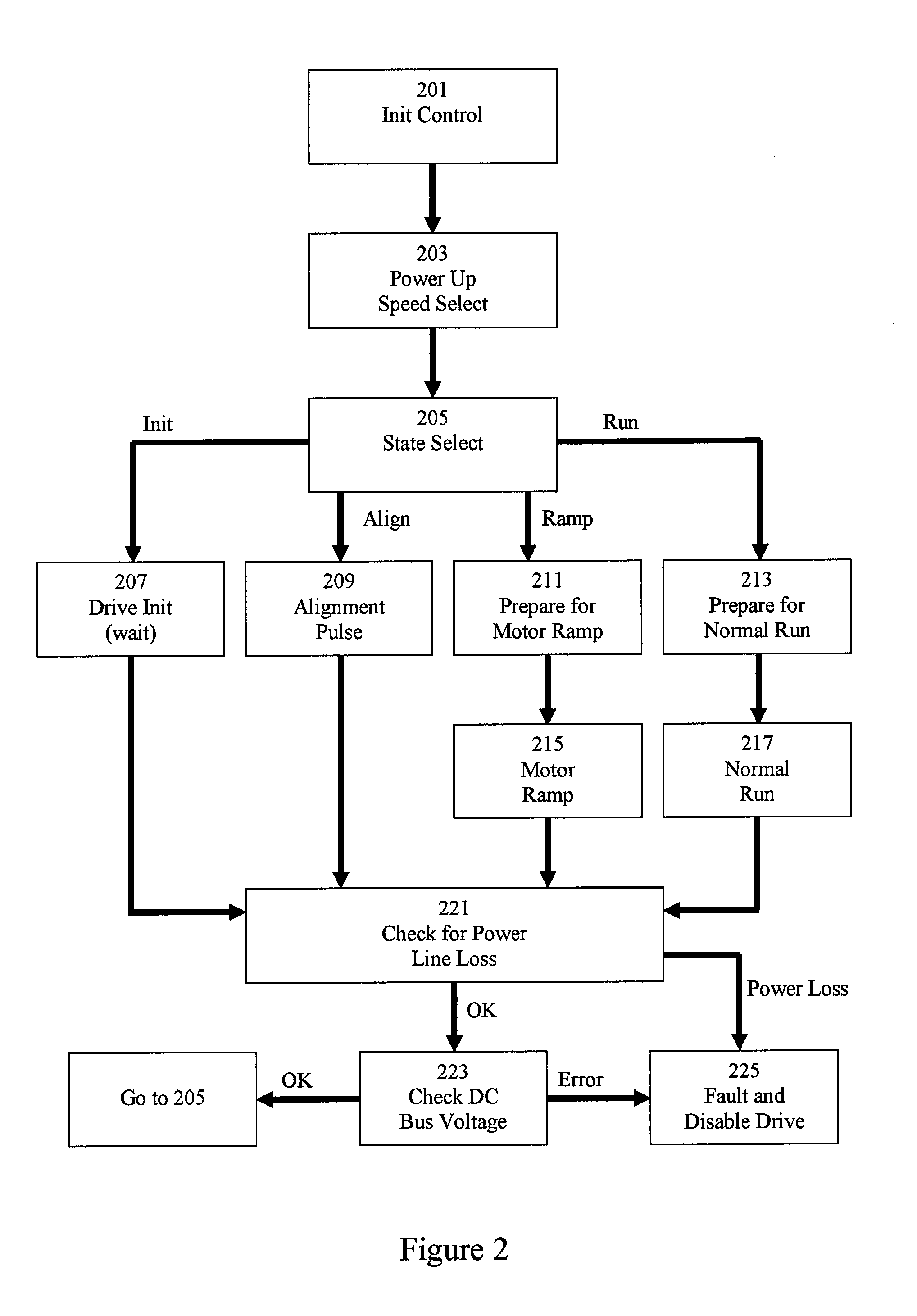
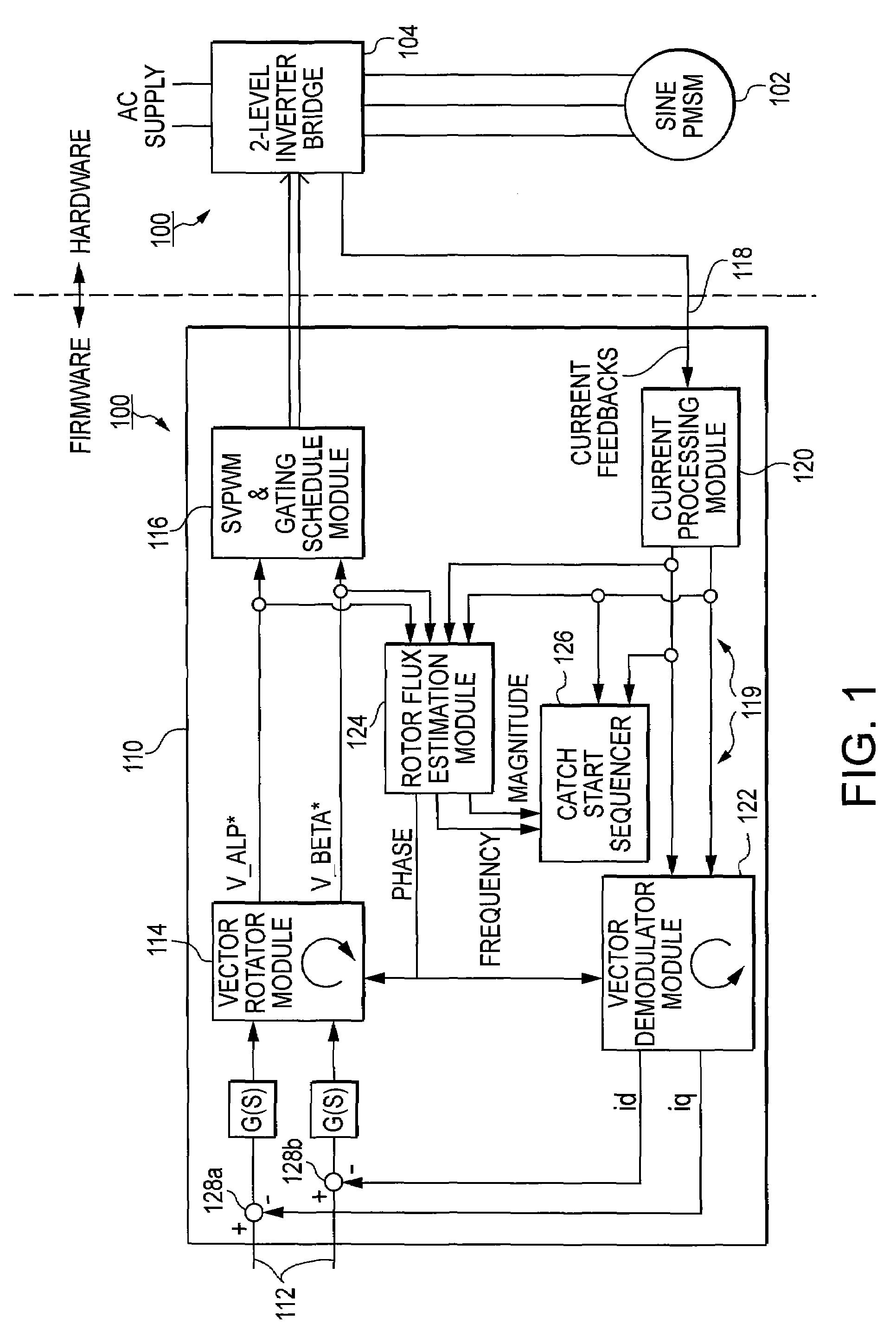
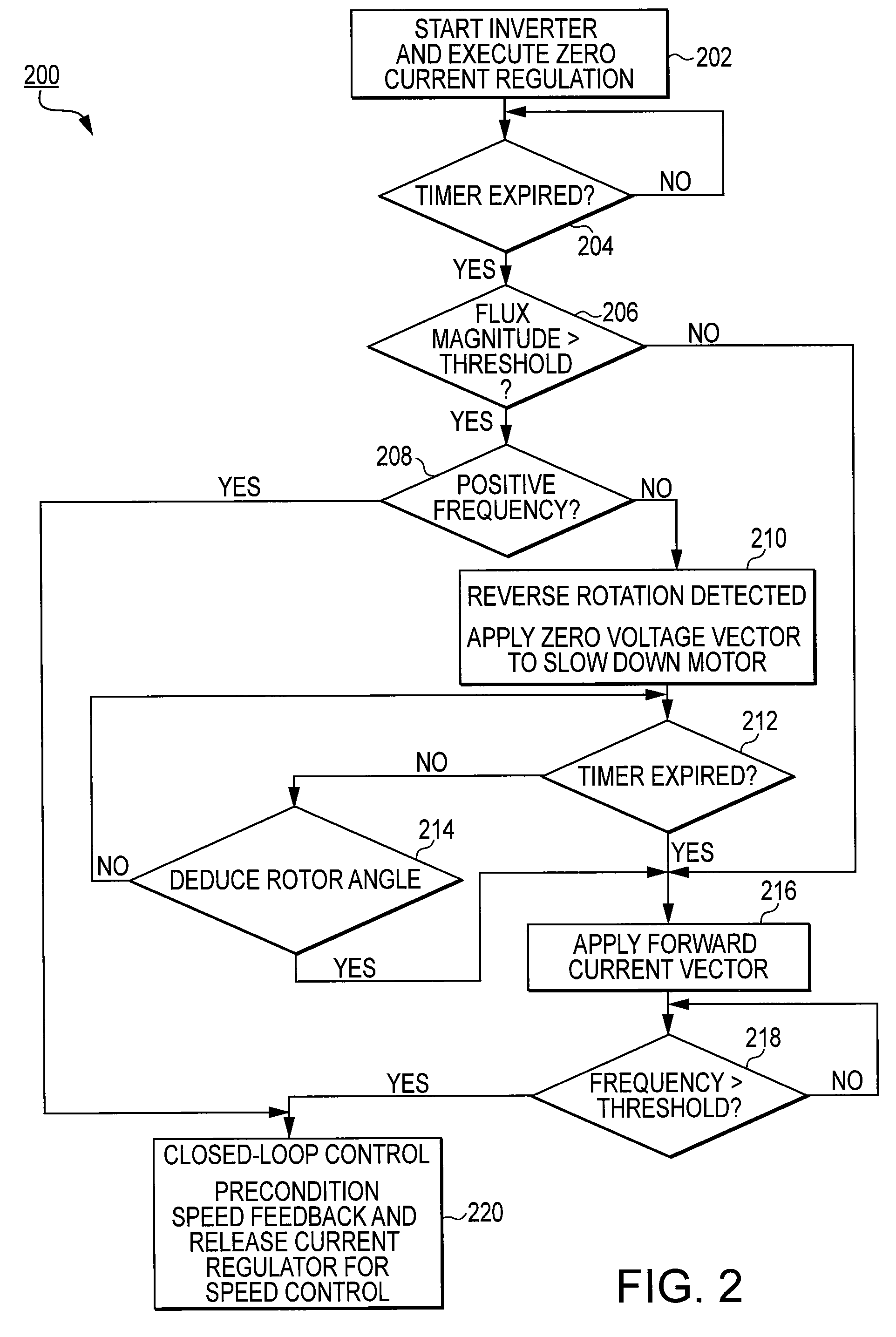
Method and system for starting a sensorless motor
ActiveUS20070001635A1Preventing over current shutdownHigh currentAC motor controlSynchronous motors startersMotor driveEngineering
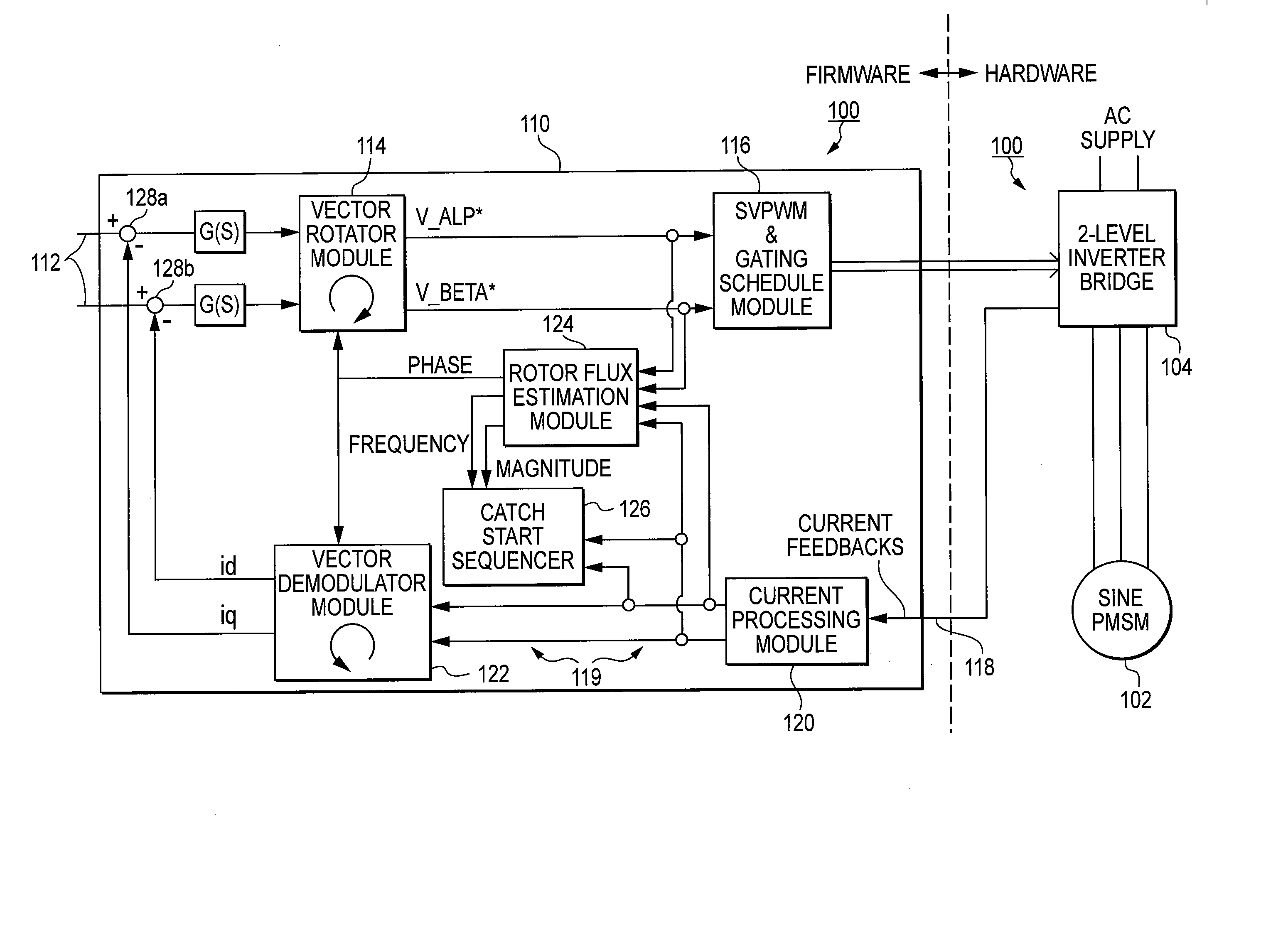
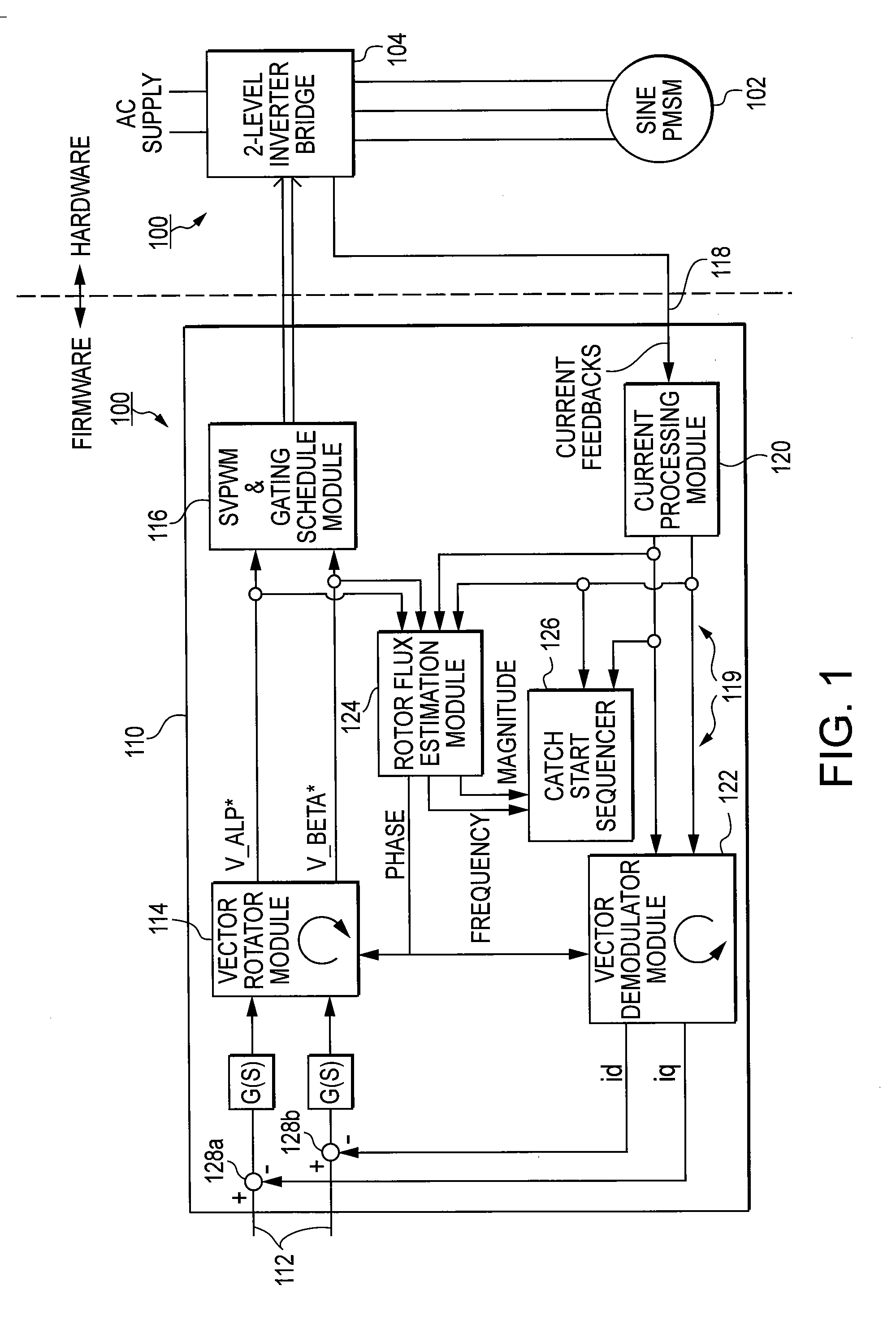
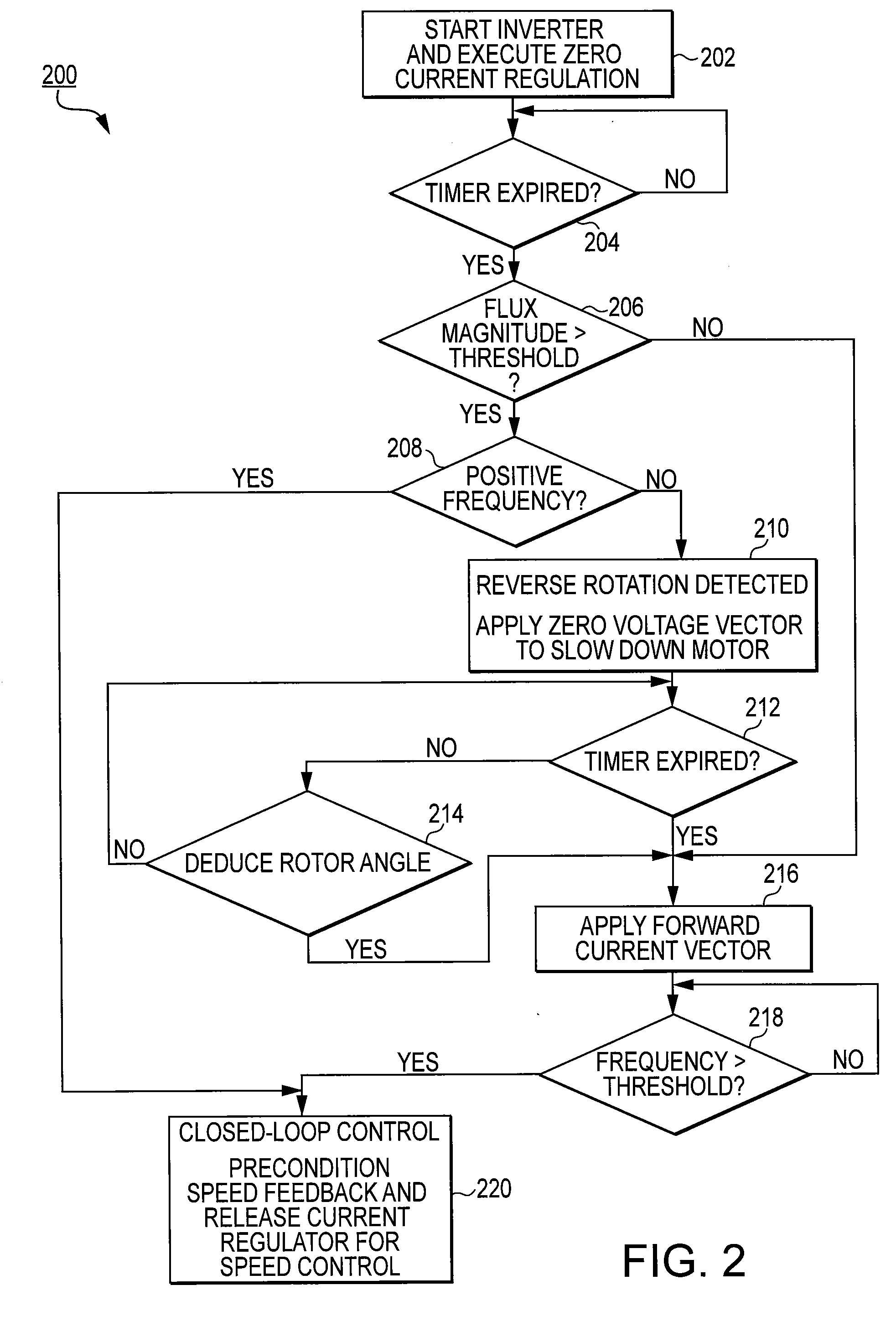
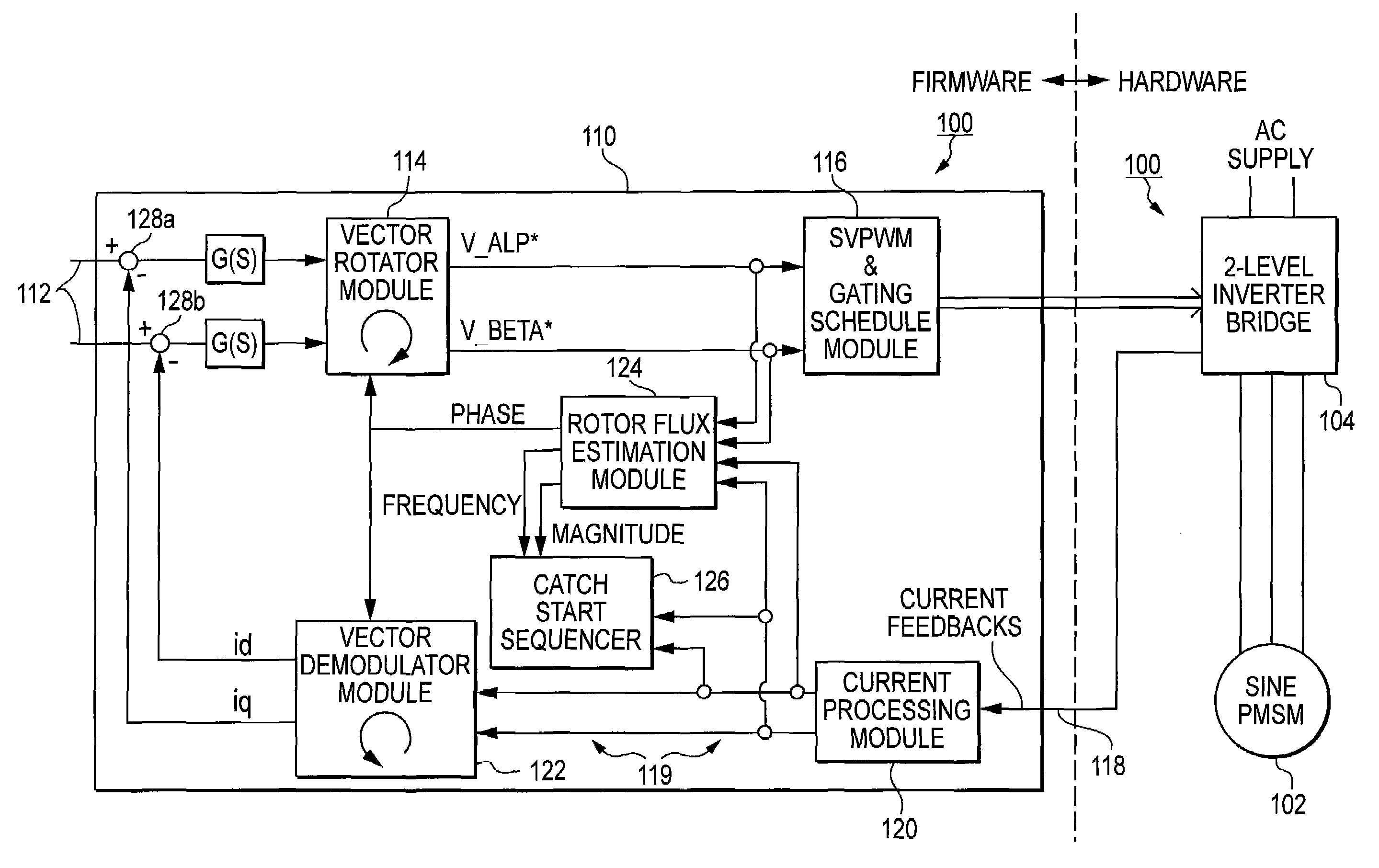
A motor drive system for a sensorless motor includes a catch start sequencer that controls the motor drive system to robustly start the motor in the event the motor rotor is rotating in forward or reverse direction prior to activating the motor drive system. In particular, the catch start sequencer causes the motor drive system to initially find and track the rotor position, and then determines the speed and possibly the direction of rotation of the rotor. If the rotor is rotating in the reverse direction, the catch start sequencer controls the motor drive system to slow the speed of rotation and to then start the rotor rotating in the forward direction.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Electric motor and motor control
InactiveUS8575873B2Reduce noiseHigh complexitySingle-phase induction motor startersTorque ripple controlElectric machinePermanent magnet motor
Various embodiments of an electric motor and electronic control for an electric motor are disclosed. An exemplary electric motor comprises a single-phase brushless permanent magnet electric motor. In exemplary embodiments, the electronic motor control is configured to commutate an electric motor at a frequency other than line frequency, perform pulse width modulation, and drive the electric motor with a drive waveform that approximates the counter-electromotive force of the motor.
Owner:NIDEC MOTOR CORP
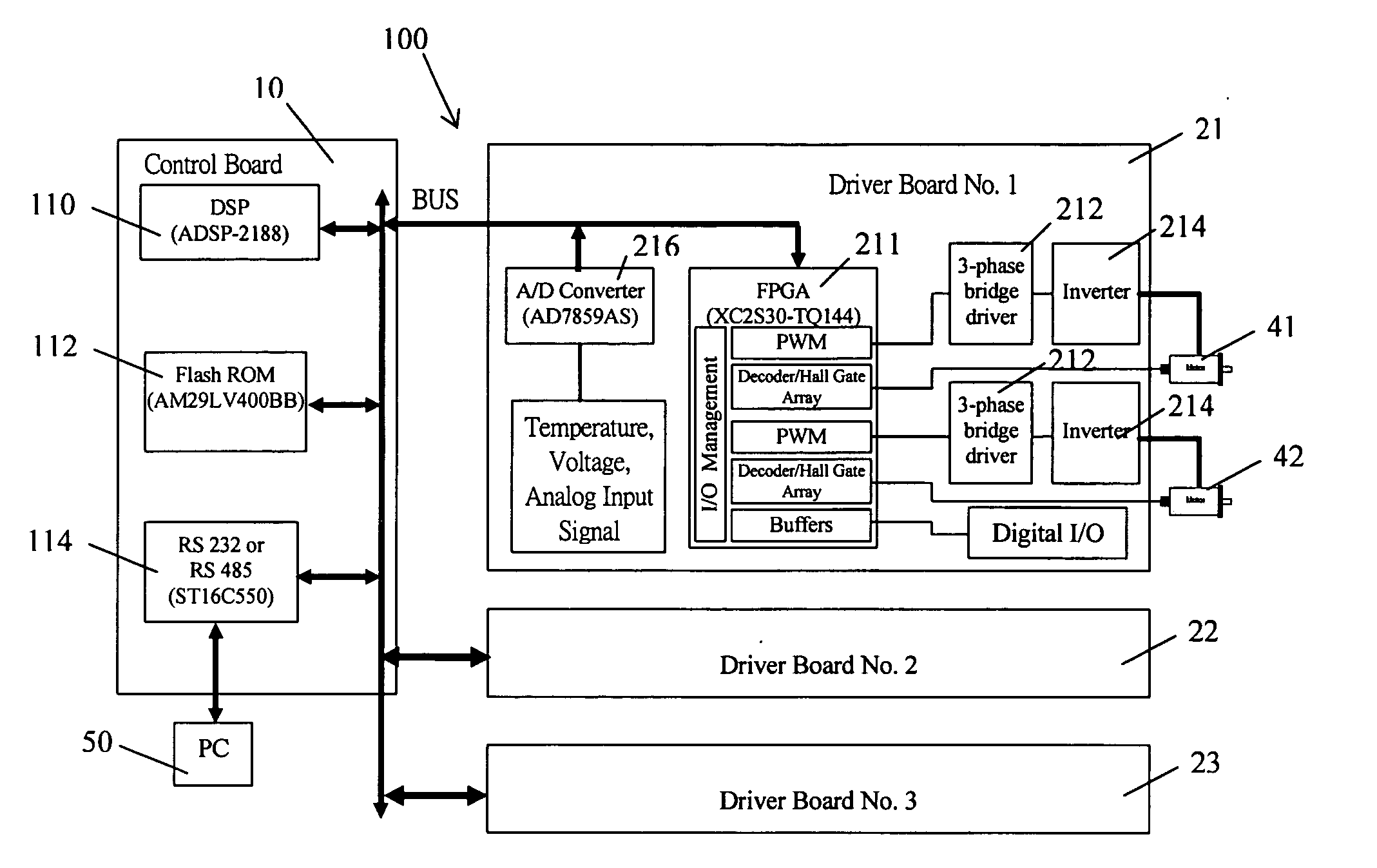
Modular multi-axis motion control and driving system and method thereof
InactiveUS20060100723A1Improve performanceReduced dimensionSynchronous motors startersAC motor controlMOSFETNetwork service
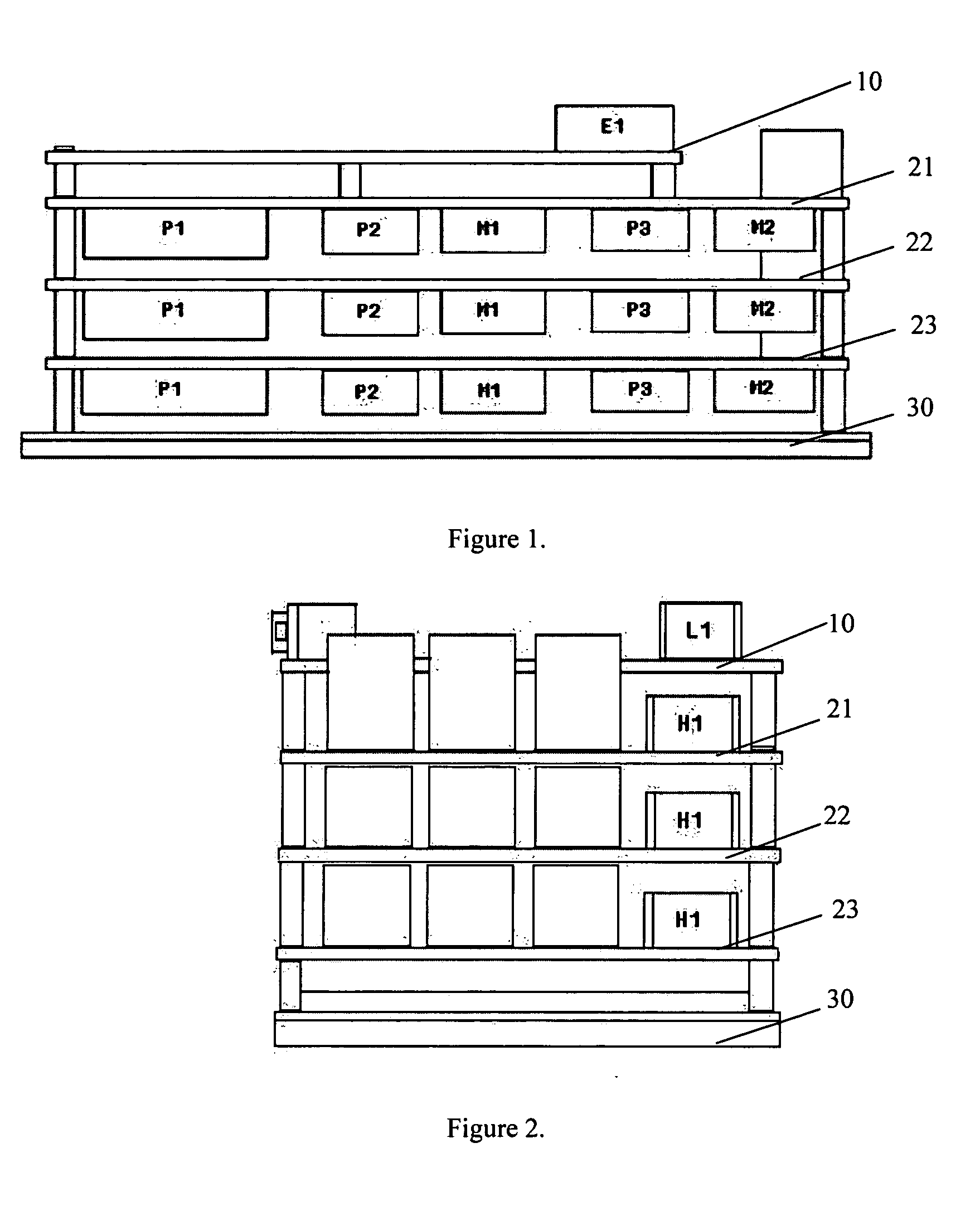
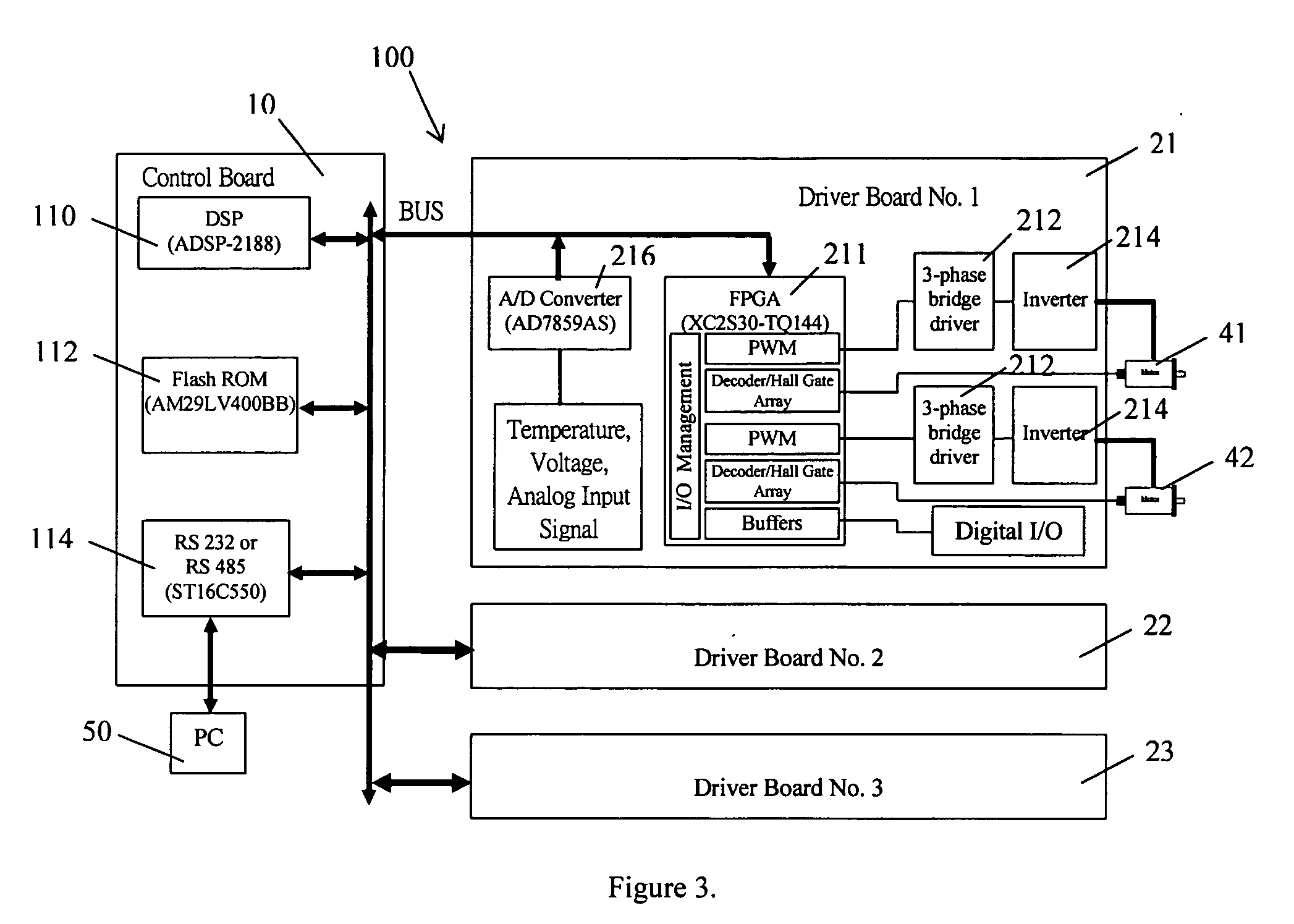
A modular multi-axis motion control and driving system is developed by using advanced Digital Signal Processor (DSP) and Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) technologies. A modular multi-axis motion control and driving system comprises: a control board comprising a DSP and Flash ROM connected to each other, for performing position control and current control of said system; a plurality of driver boards, connected to the control board through a bus, each of which comprise a FPGA device and a plurality of MOSFET power amplifier, for driving a plurality of servo motors; a computer, connected to said control board, for providing graphic user interface, through which motor setting, current and position loop tuning and diagnostic can be performed; Wherein, a control program, system parameters and FPGA configuration file are stored in said Flash ROM, when the system power is on, the DSP automatically executes an loader firmware to transfer the control program from said Flash ROM to the memory of DSP for execution, then the DSP reads the FPGA configuration file from the Flash ROM and configure the FPGA in the driver board, after that, the control program runs into a circulation loop to do system diagnose, network service and check command queue, while the current and position controls are implemented in an interrupt service.
Owner:DYNACITY TECH HK
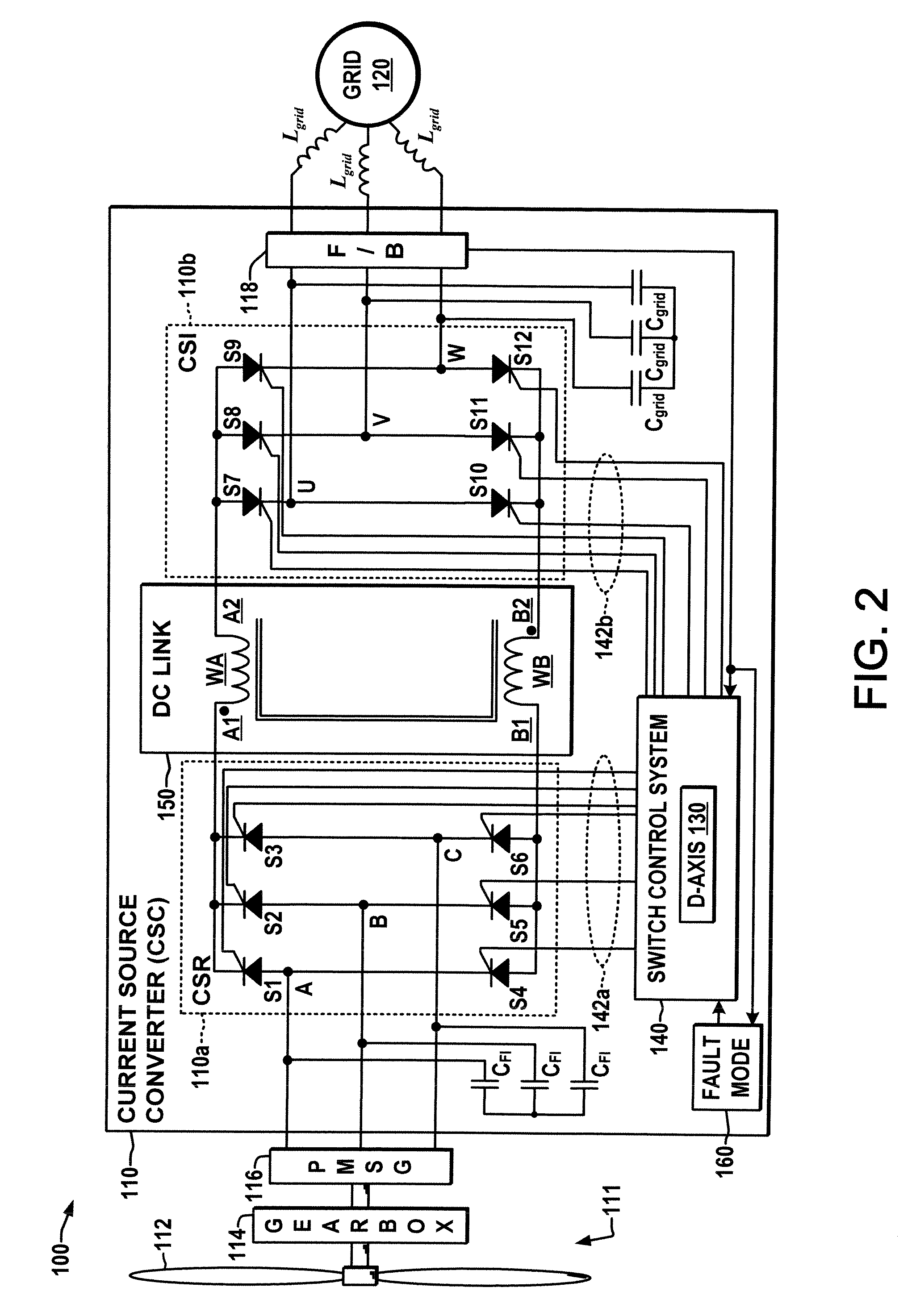
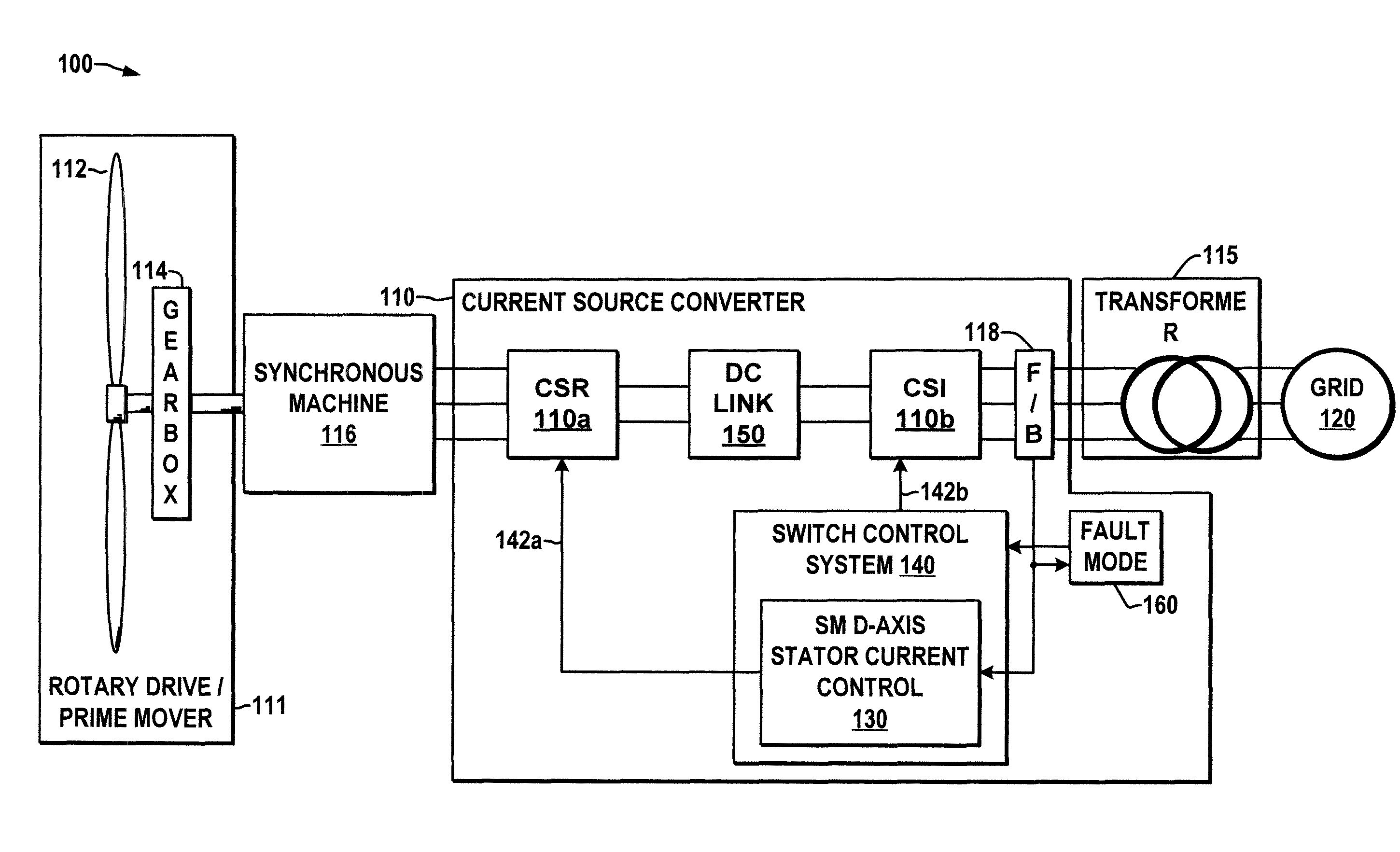
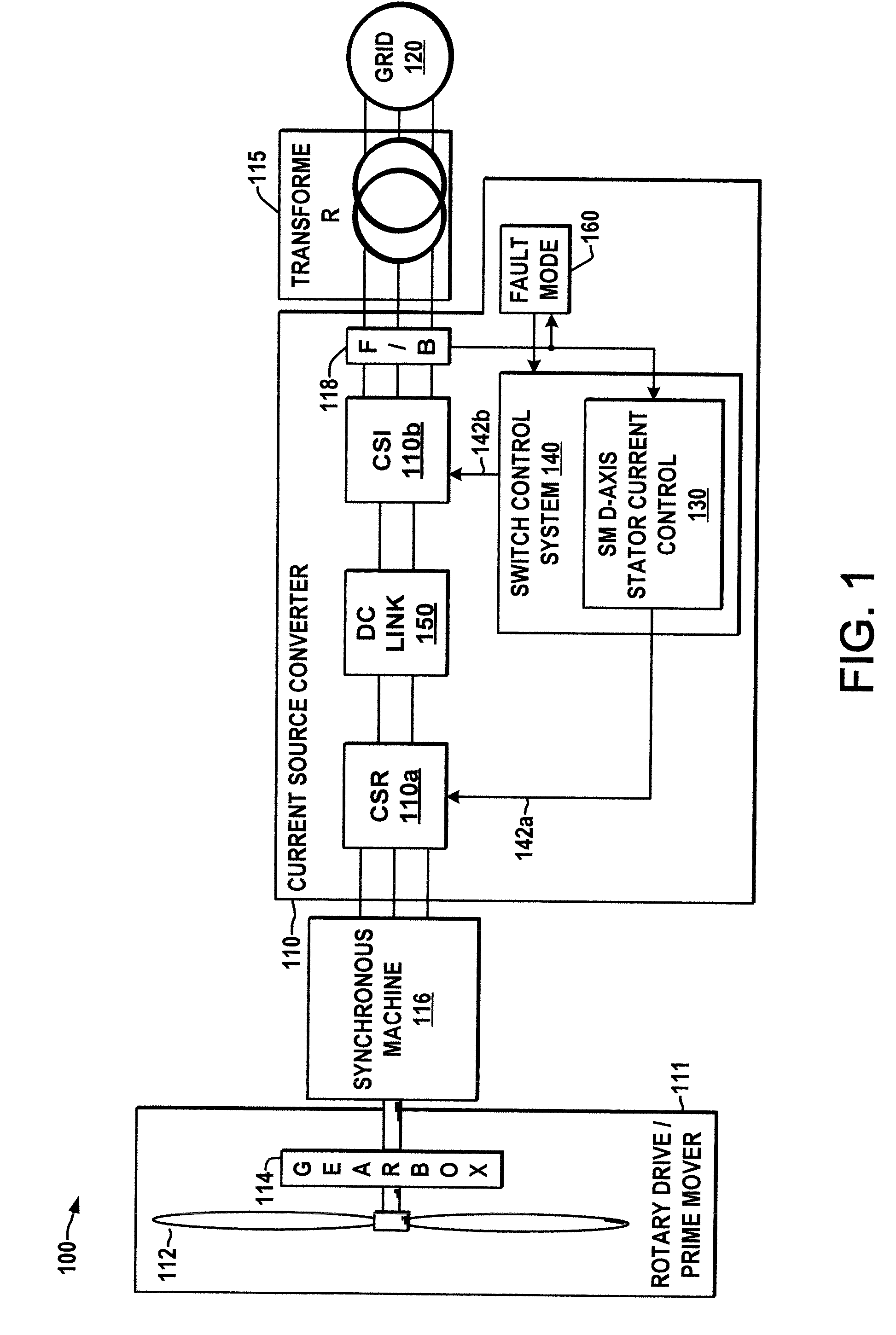
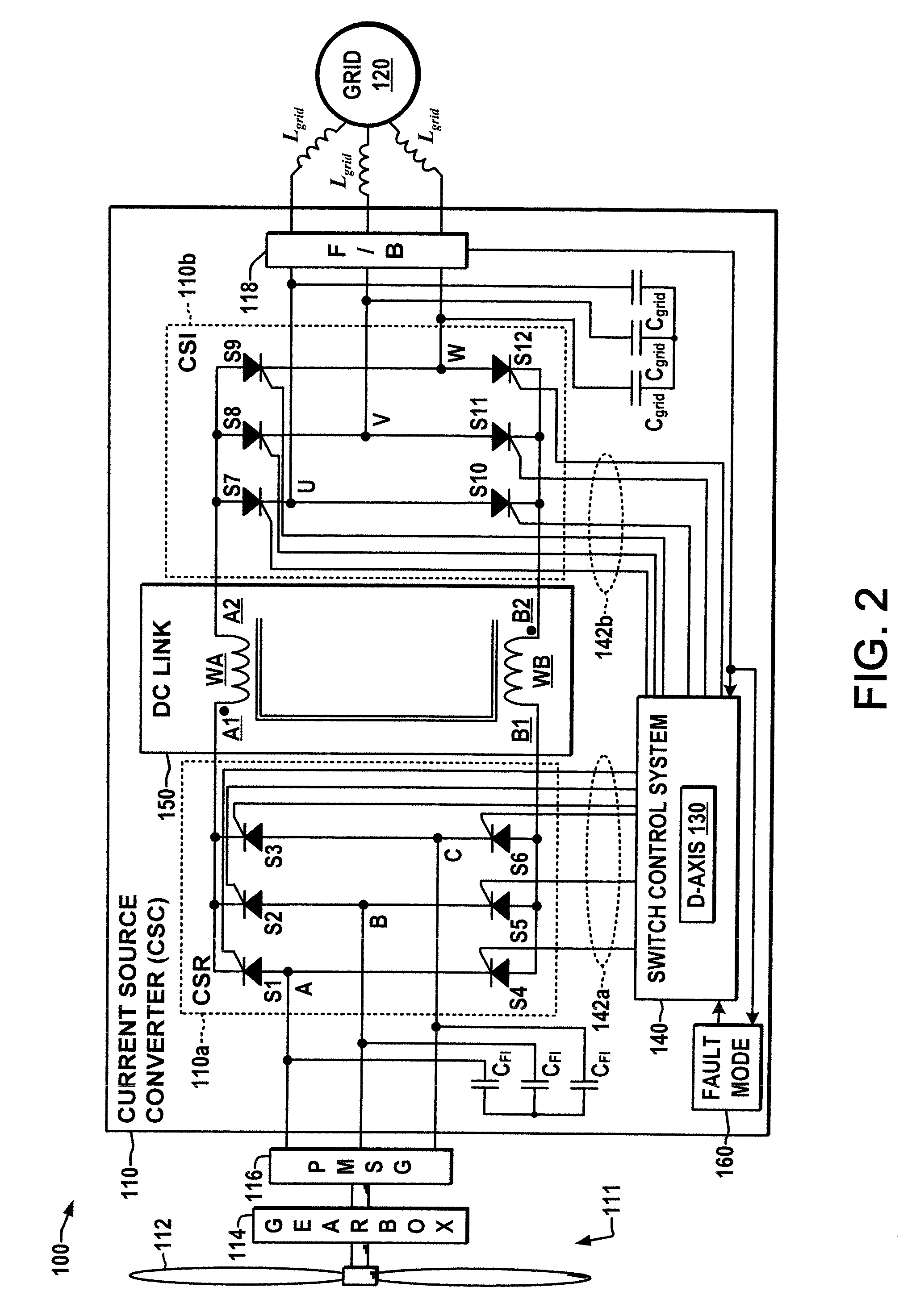
Current source converter-based wind energy system
ActiveUS20100025995A1Excess power being dissipatedAC motor controlSynchronous motors startersResistEngineering
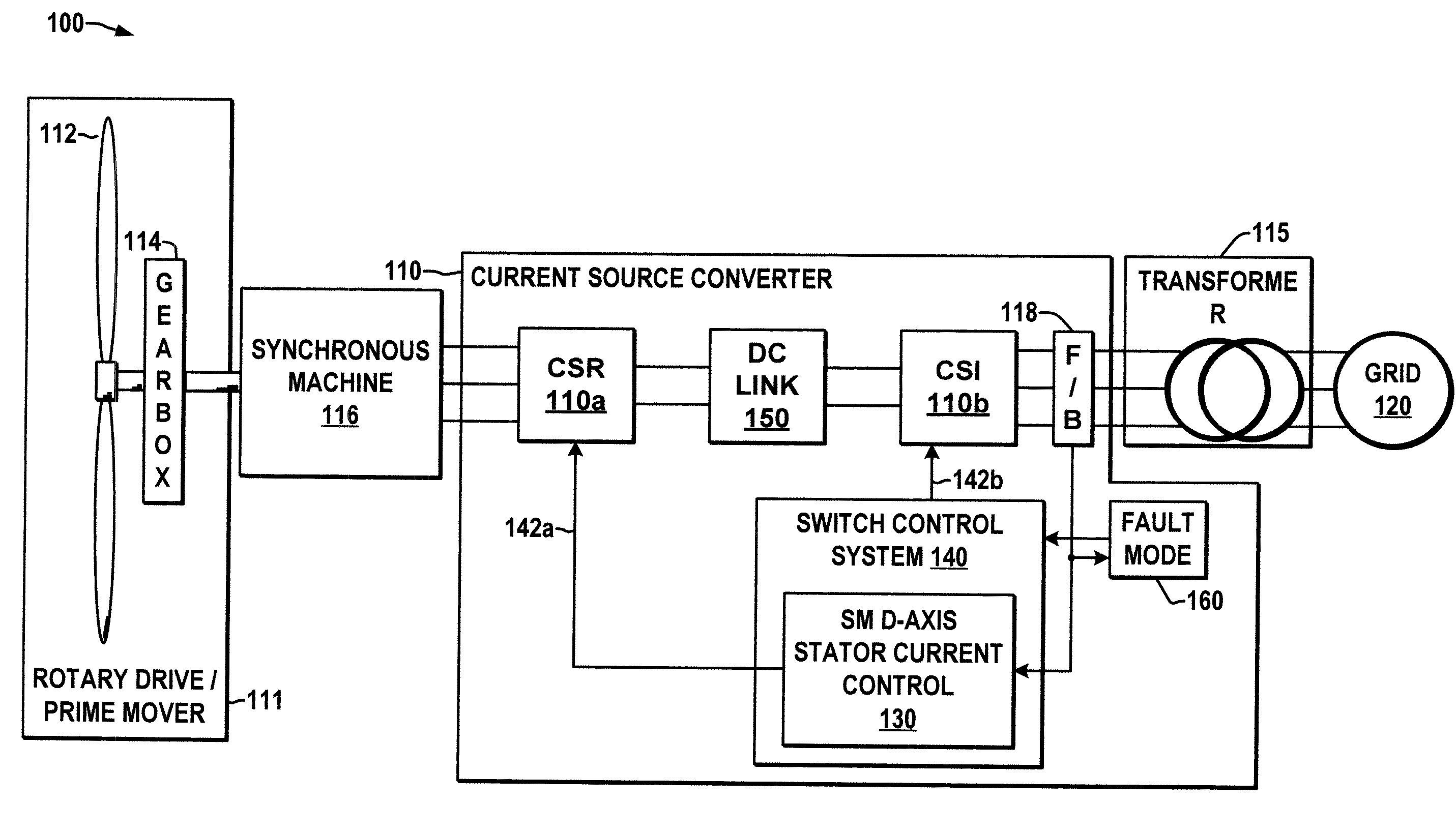
Power conversion apparatus and methods are presented for providing electrical power to a grid or other load in which a synchronous machine is driven by a wind turbine or other prime mover to provide generator power to a switching type current source converter (CSC), with a current source rectifier (CSR) of the CSC being switched to provide d-axis control of the synchronous machine current based on grid power factor feedback, and with a current source inverter (CSI) of the CSC being switched to provide leading firing angle control and selective employment of dumping resists to dissipate excess generator energy in a fault mode when a grid voltage drops below a predetermined level.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
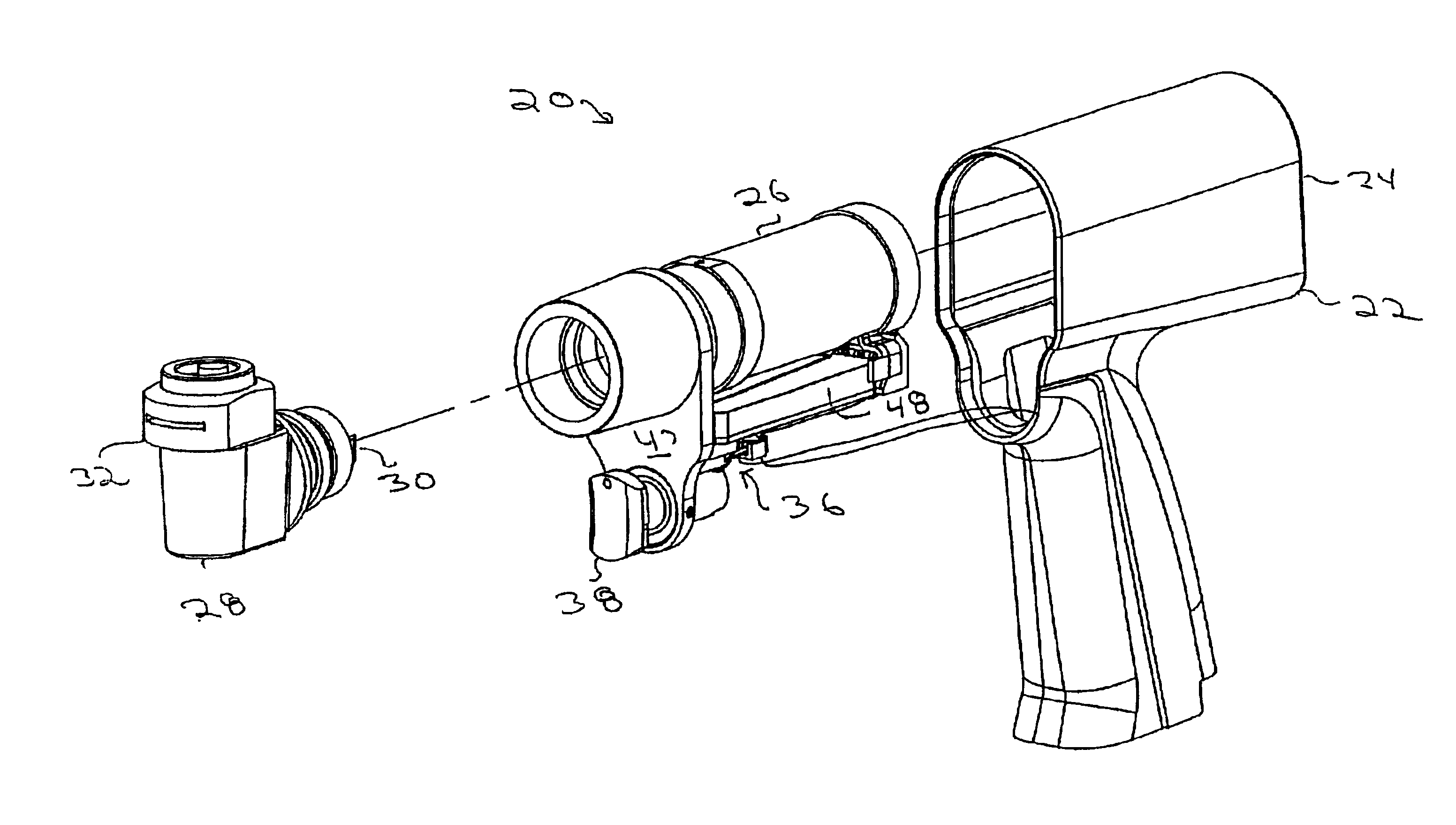
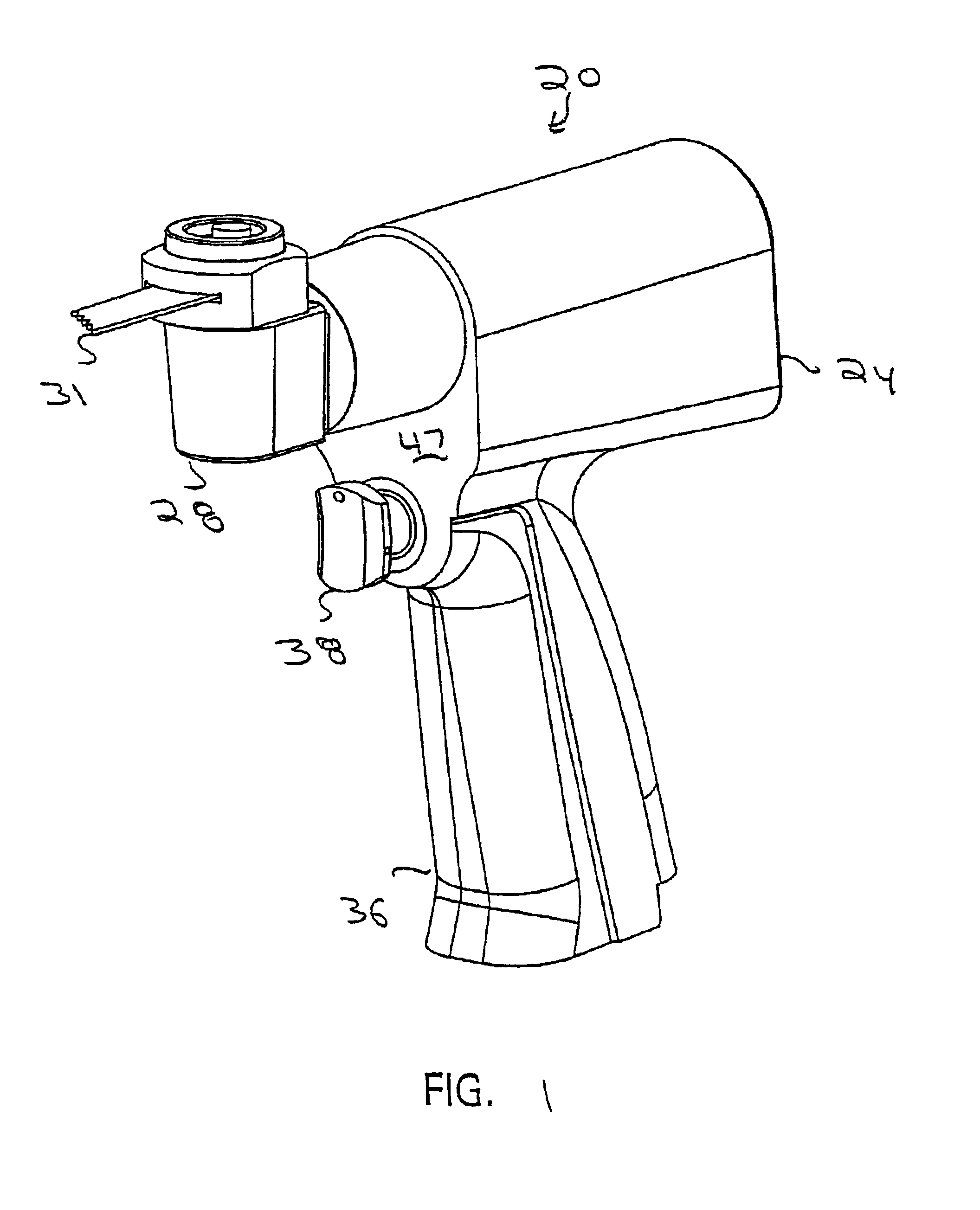
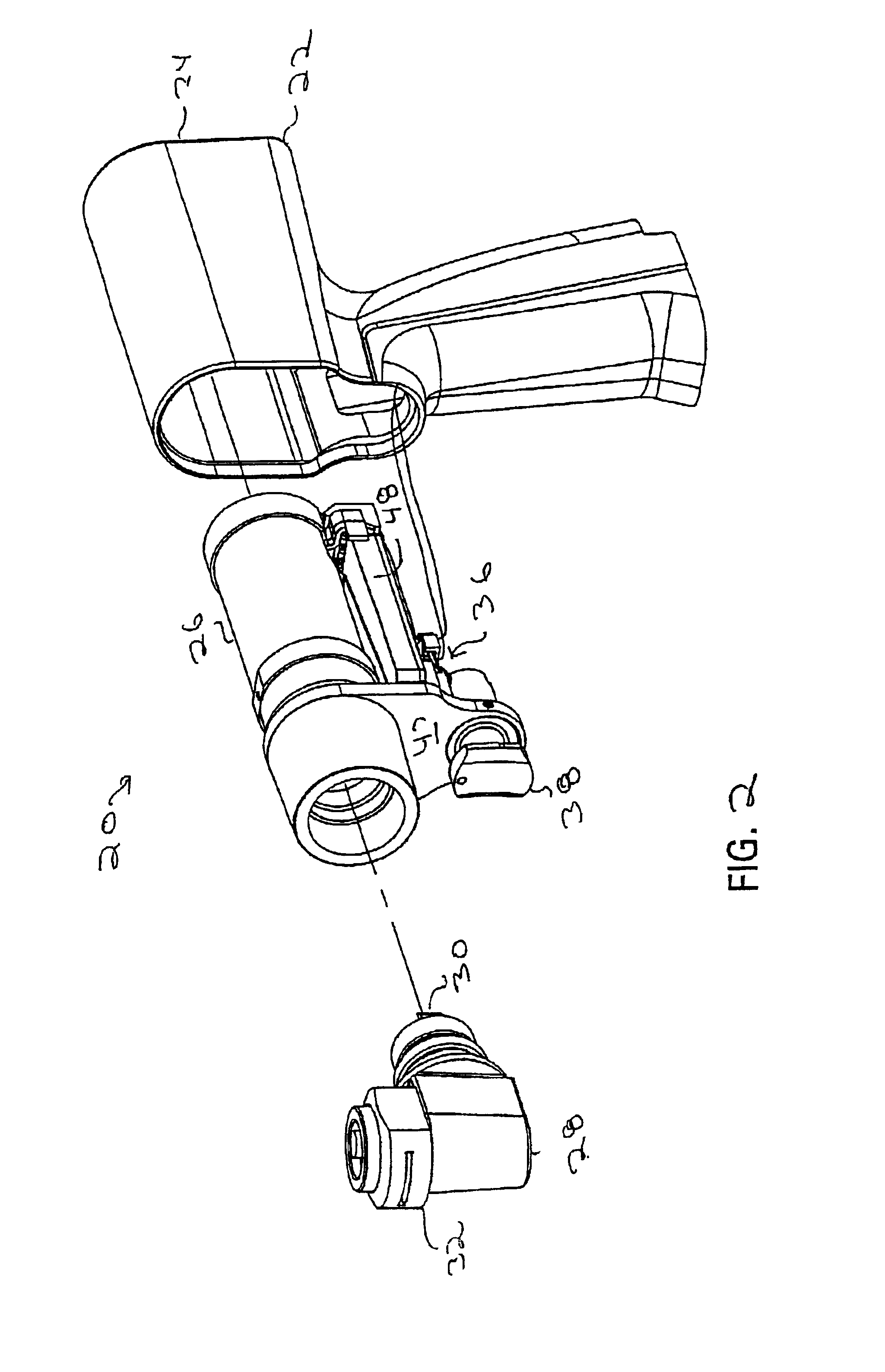
Cordless, powered surgical tool
InactiveUS6960894B2Reduce noiseAvoid difficult choicesSynchronous motors startersAC motor controlComputer moduleControl theory
A powered tool for performing surgical procedures. The tool includes a handpiece in which a power generating unit is housed. A control member is mounted to the handpiece. The control member is mounted to the handpiece so that the orientation of the control member can be selectively set relative to the point to which it is mounted to the handpiece and so it can move relative to a reference point on the handpiece. A control module monitors the orientation of the control member and its position relative to the reference point. Based on the control member orientation and position, the control module generates signals to regulate the operation of the power generating unit. When the power generating unit is a motor, the control module generates signals to ensure that the maximum speed at which the motor can be driven is less than the no load speed.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Hub motors
InactiveUS20060273686A1Raise countIncrease surface areaSingle-phase induction motor startersSynchronous motors startersDrive wheelStator coil
The present invention discloses small compact motor systems which may be located inside a vehicle drive wheel, and which allow a drive motor to provide the necessary torque with reasonable system mass. The motor systems of the invention utilize polyphase electric motors, and are preferably connected to appropriate drive systems via mesh connections, to provide variable V / Hz ratios. In one embodiment the stator coils are wound around the inside and outside of the stator. In a further embodiment, the machine contains a high number of phases, greater than three. In a further embodiment, the phases are connected in a mesh connection. In a further embodiment, each half-phase is independently driven to enable second harmonic drive for an impedance effect. Improvements are apparent in efficiency and packing density.
Owner:BOREALIS TECH LTD
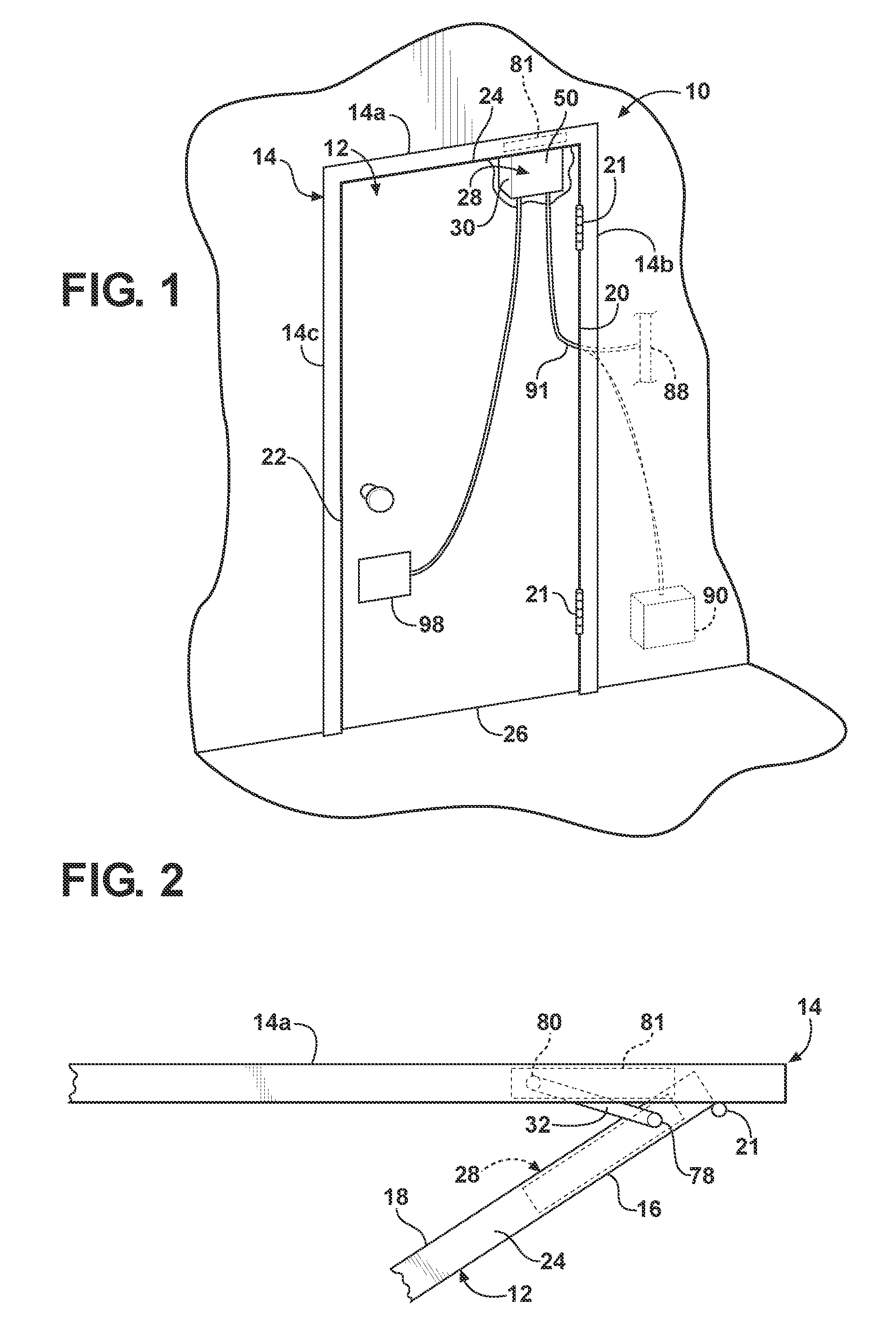
Method of controlling an automatic door system
A door position control including an electric door actuator having a motor and a motor controller in communication with a system controller. A motor actuation operation is selected from a plurality of predetermined motor actuation operations to provide control signals to the motor controller for controlling actuation of the motor for control of door movement. Control of door movement is effected with reference to parameters specific to an installation location including an angular sweep of the door between open and closed positions and with reference to an available bus voltage for supplying power to the motor.
Owner:GLOBE MOTORS
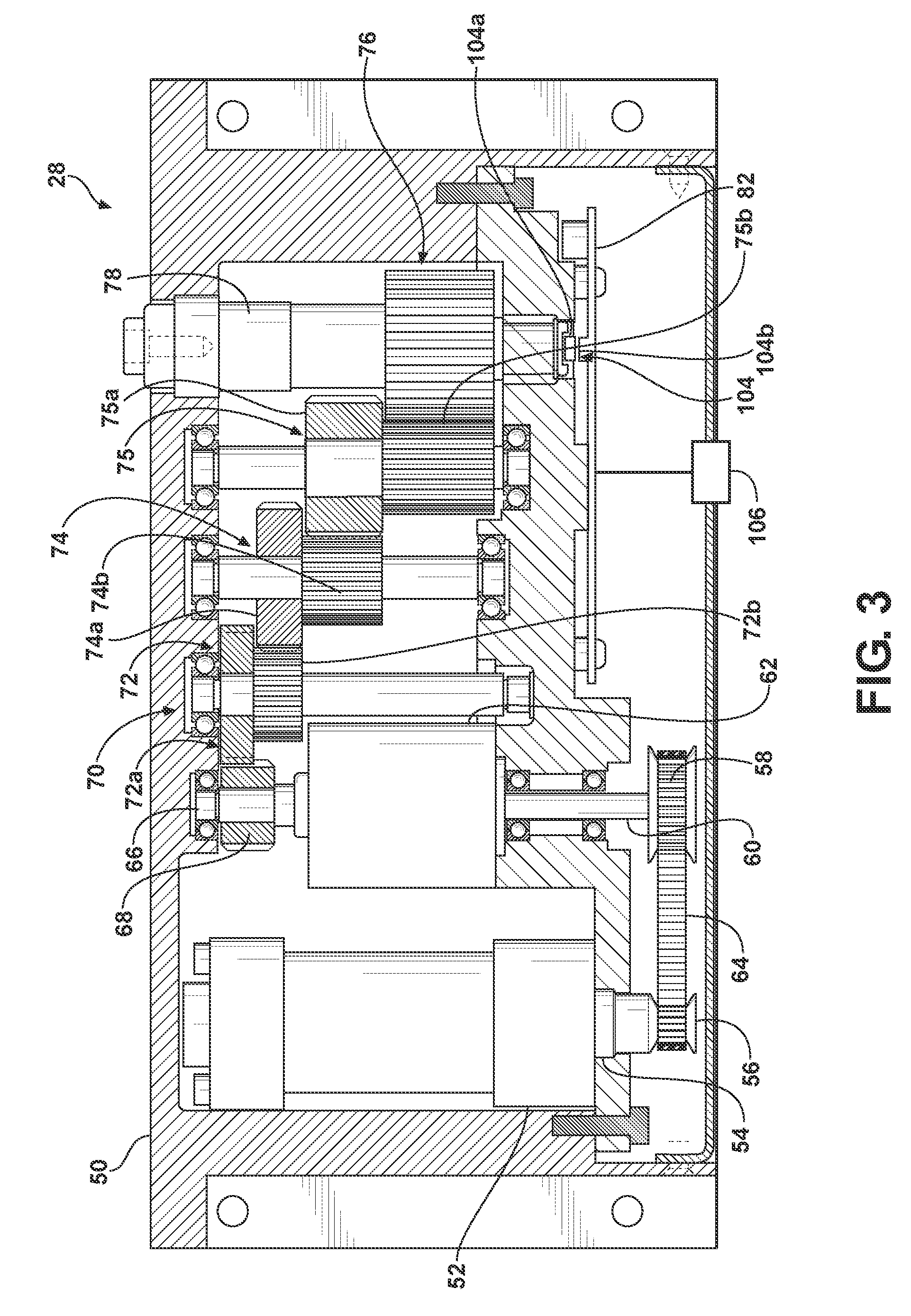
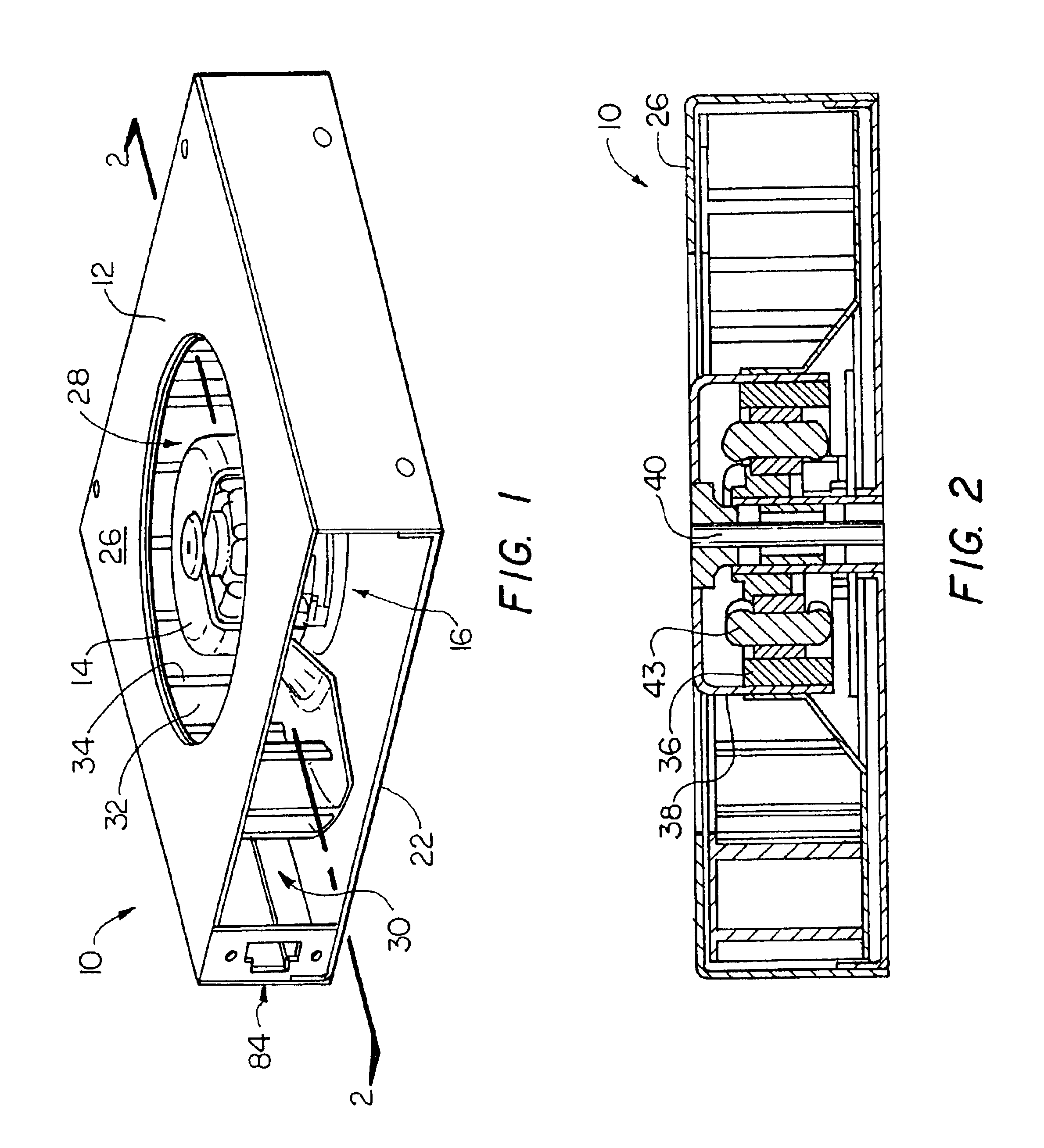
Low profile motor
InactiveUS6841957B2Monitor performanceAC motor controlSynchronous motors startersSurface mountingElectronic component
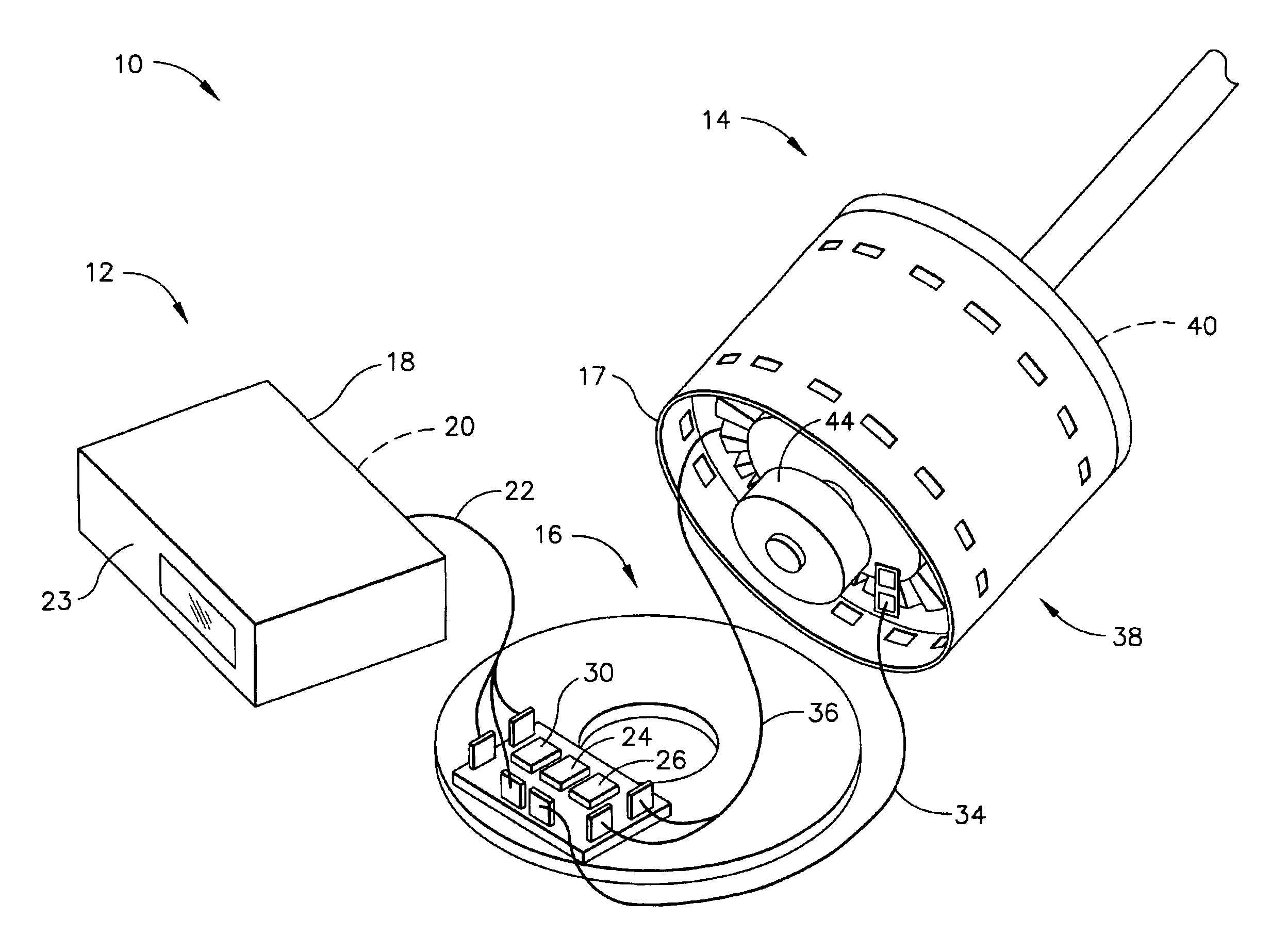
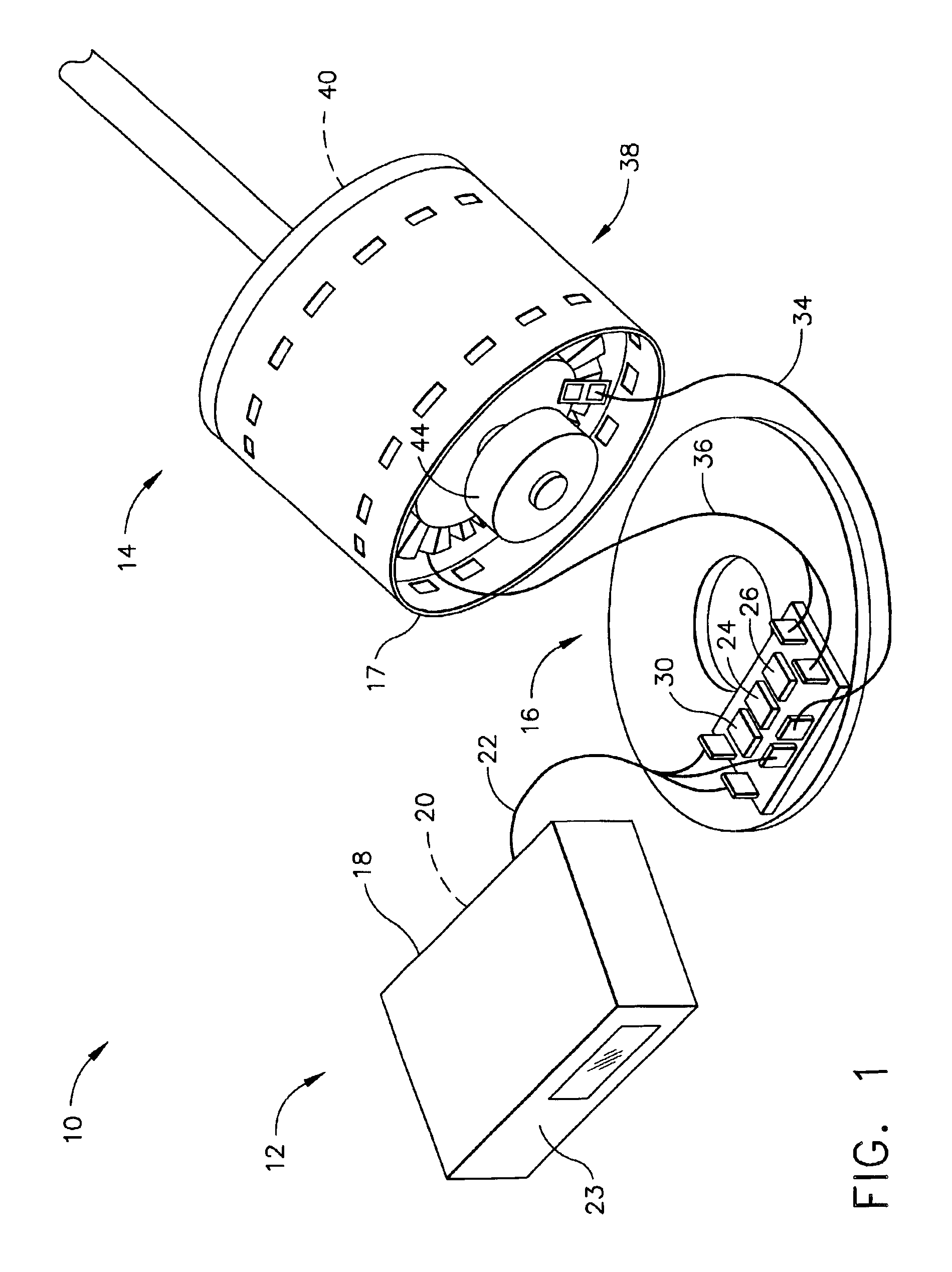
A flat pack blower utilizes surface mounting techniques for mounting the blower electronics on a thin laminated circuit board to reduce the blower profile. To that end, the blower includes a stator, and a rotor rotatably coupled to the stator. The stator includes a coil, a pole coupled with the coil, and a laminated circuit board having blower control circuitry and pads for electrically connecting the blower control circuitry to the coil. Use of surface mounting techniques on the laminated circuit board thus eliminates the discrete electronic components and the wires connecting such components.
Owner:MOTION HLDG
Double-motor controller with electronic differential function
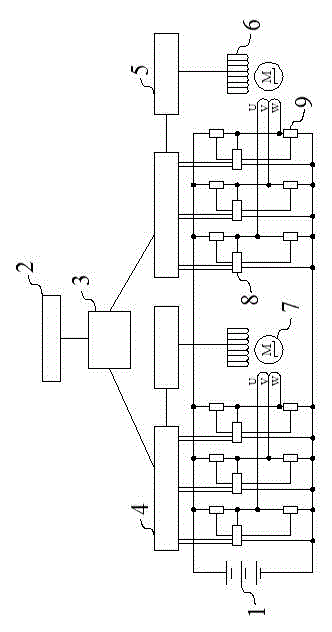
InactiveCN102874129AReduce volumeOptimize layoutSpeed controllerMultiple motor speed/torque controlCapacitanceDrive wheel
The invention discloses a double-motor controller with an electronic differential function. The double-motor controller comprises a main control chip integrated with an electronic differential module, two groups of drive motor control chips, two groups of rotary transformer decoding chips, two groups of power drive modules for controlling a motor to operate, a capacitor bank, an angle decoding and conditioning circuit, two permanent magnet motors with built-in rotary transformers, and an active force battery pack, wherein the main control chip is used for processing a received signal; and a left drive wheel control signal and a right drive wheel control signal are transmitted into the drive motor control chips corresponding to wheels respectively through the operation of an electronic differential operation module. The drive motor control chips receive information of position values, speed values and the like of the drive motor returned by corresponding rotary transformer decoding chips; information provided by the main control chip is combined so as to be processed comprehensively; and a waveform is output to a corresponding power drive module so as to operate the wheels through the drive motor. The double-motor controller with the electronic differential function has the advantages of high drive efficiency, small volume, convenience in arrangement and installation, and capability of active differential.
Owner:CHENGDU LAINTEM MOTORS CONTROL TECH
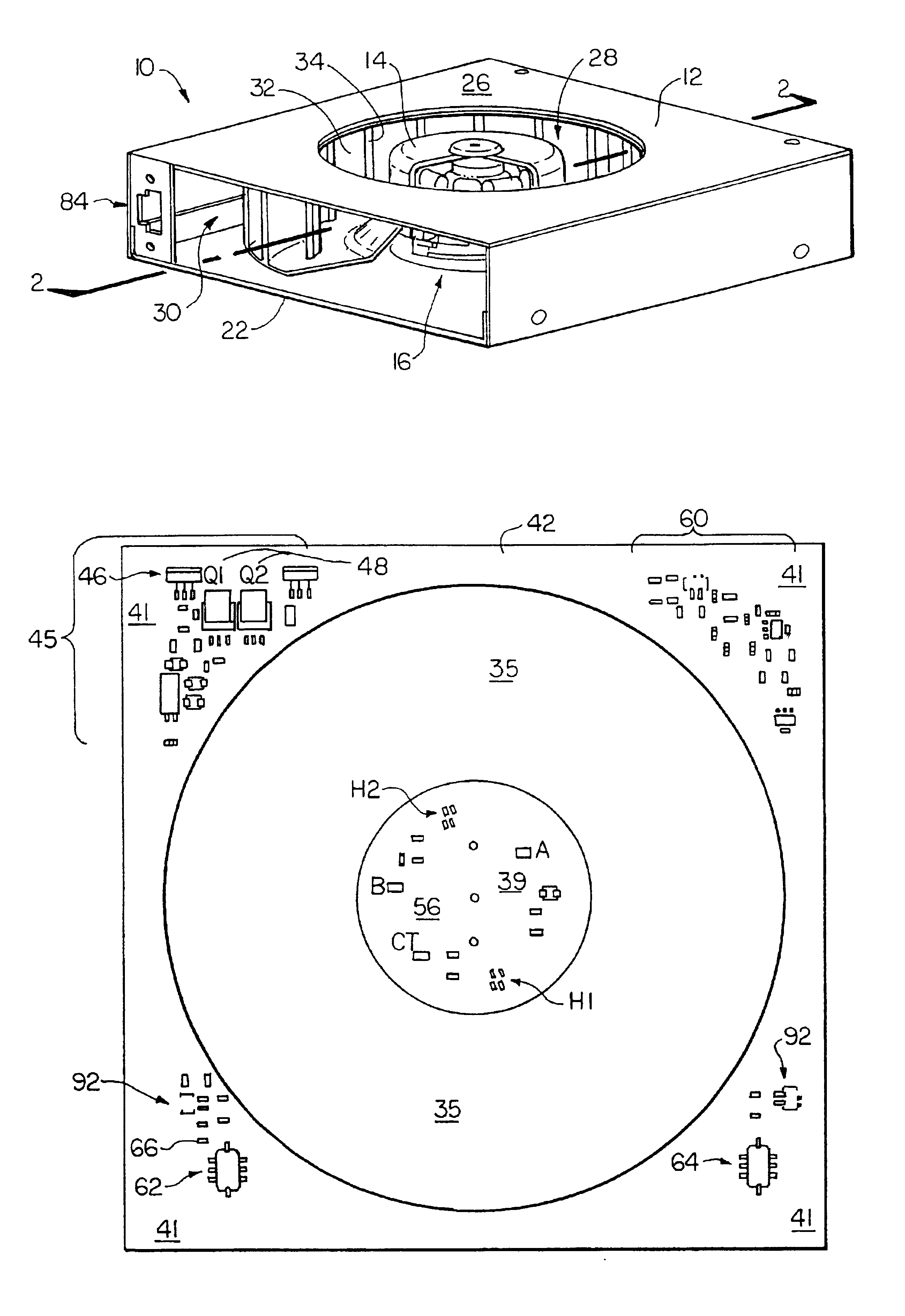
Electric saw communication
ActiveUS20110056716A1Easy to handleEasy to adjust the positionSynchronous motors startersAC motor controlMulticore cablePermanent magnet motor
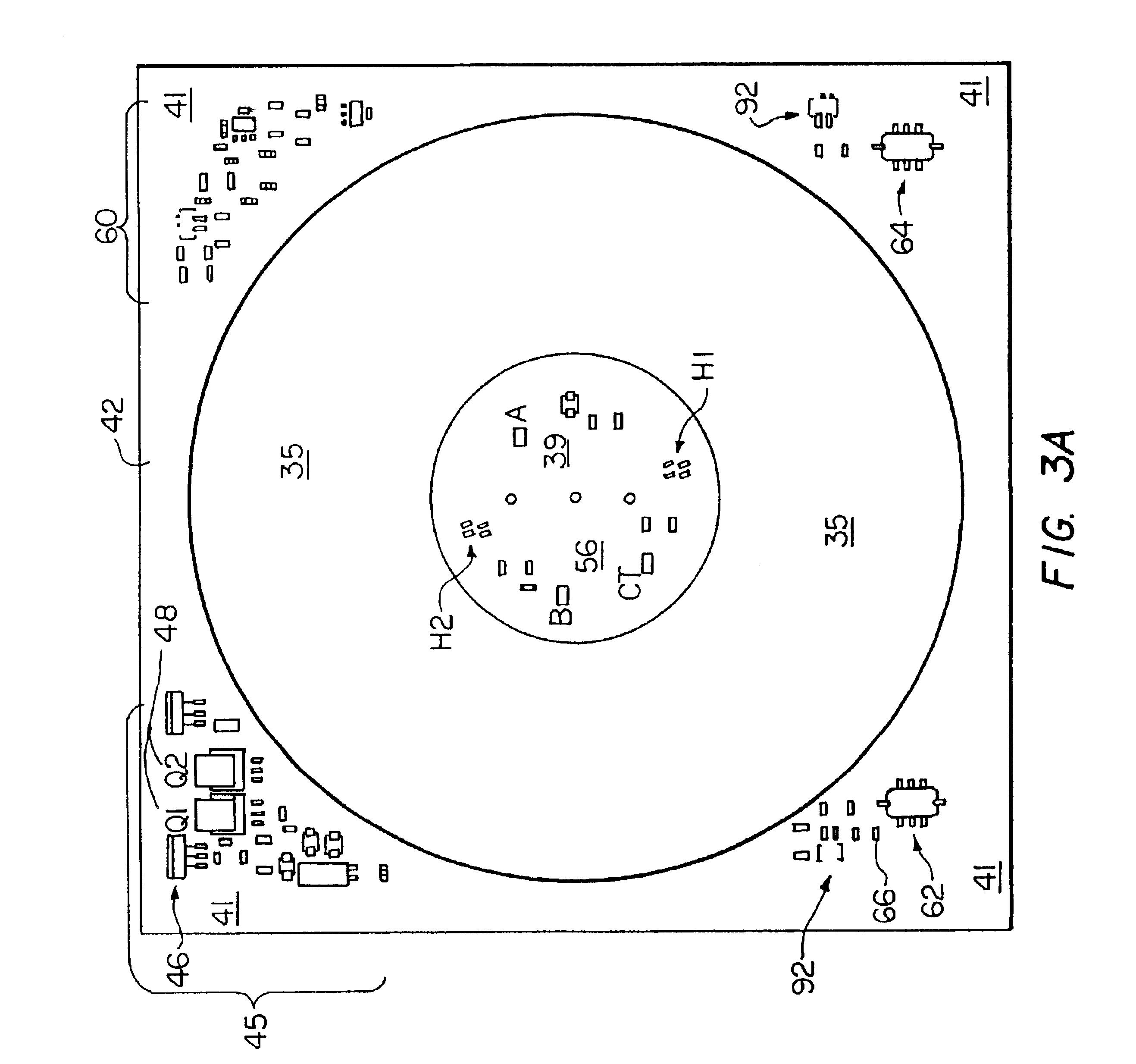
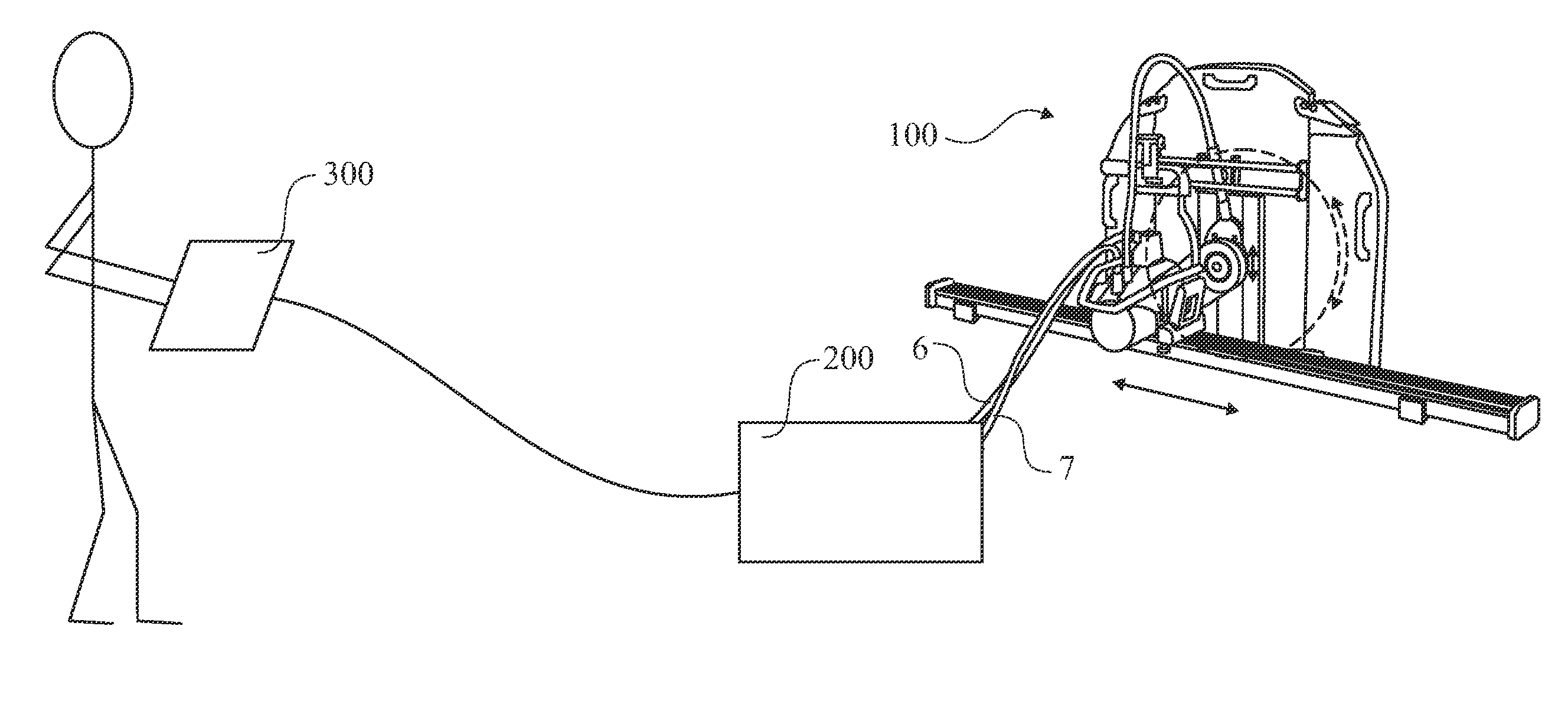
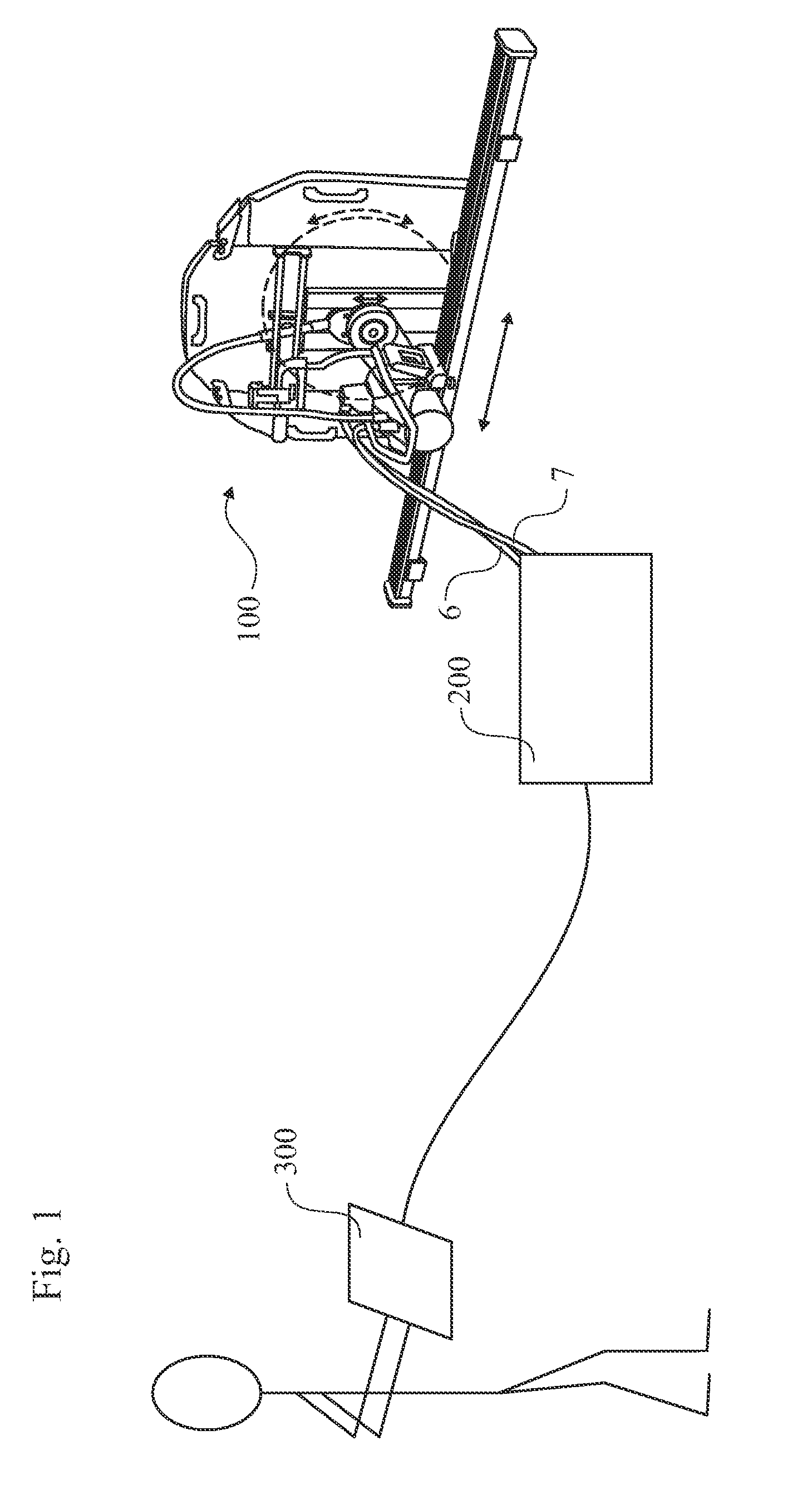
The present invention relates to an electric saw (1) being powered by an external power supply (200) through a multicore cable (6). The multicore cable (6) includes electrical wires (24, 25, 27) for supplying power to the motors (5, 12, 13) of the electric saw (1) and communication wires (26) for data communication between the electric saw (1) and the power supply (200). Two motors (12, 13) of the electric saw are three phase permanent magnet motors (12, 13), with an outer rotor (31) and an inner stator (30). Each of the two motors (12, 13) has three Hall Effect sensors (H1, H2, H3) located around the outer rotor (31).
Owner:HUSQVARNA AB
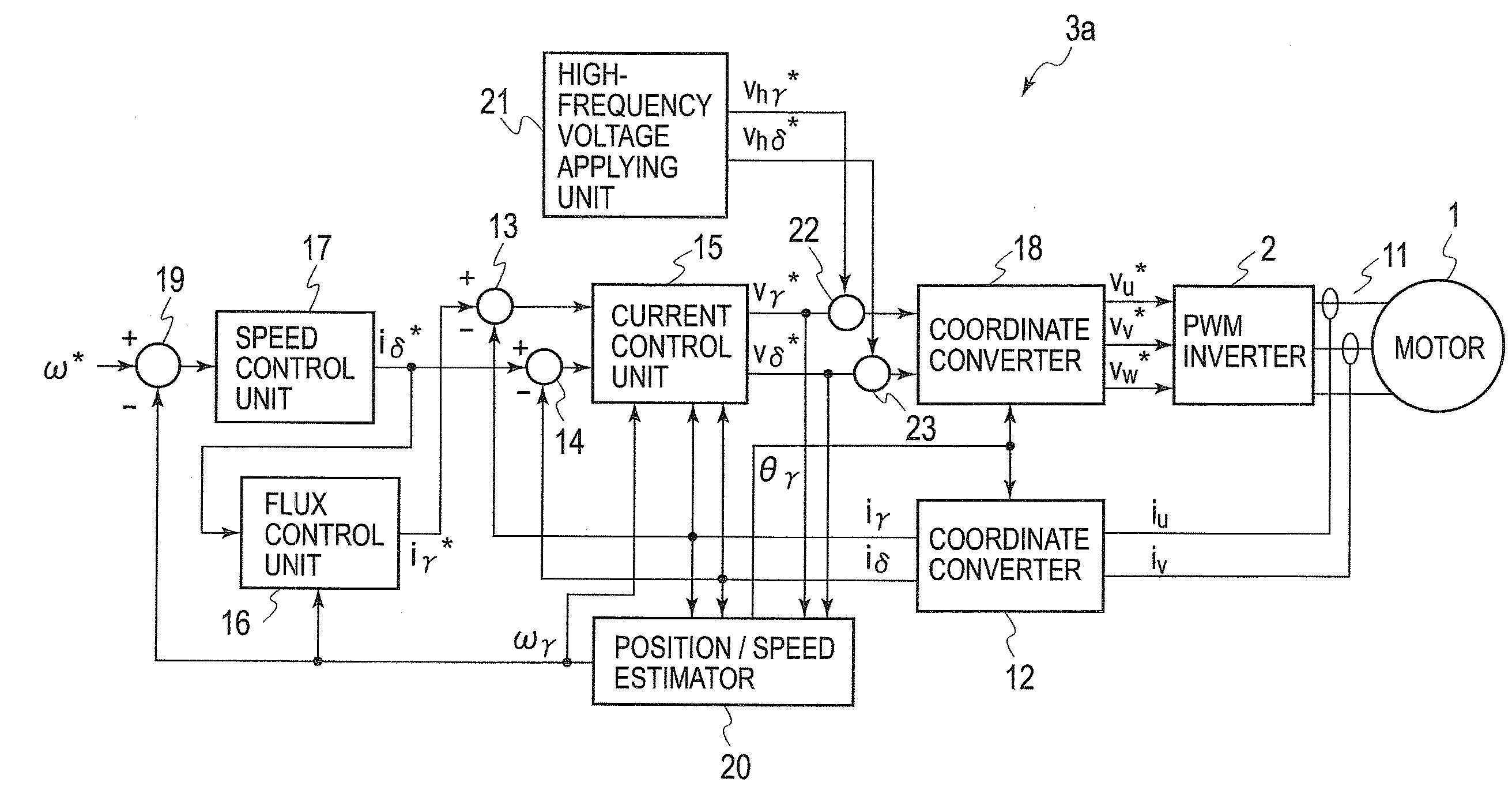
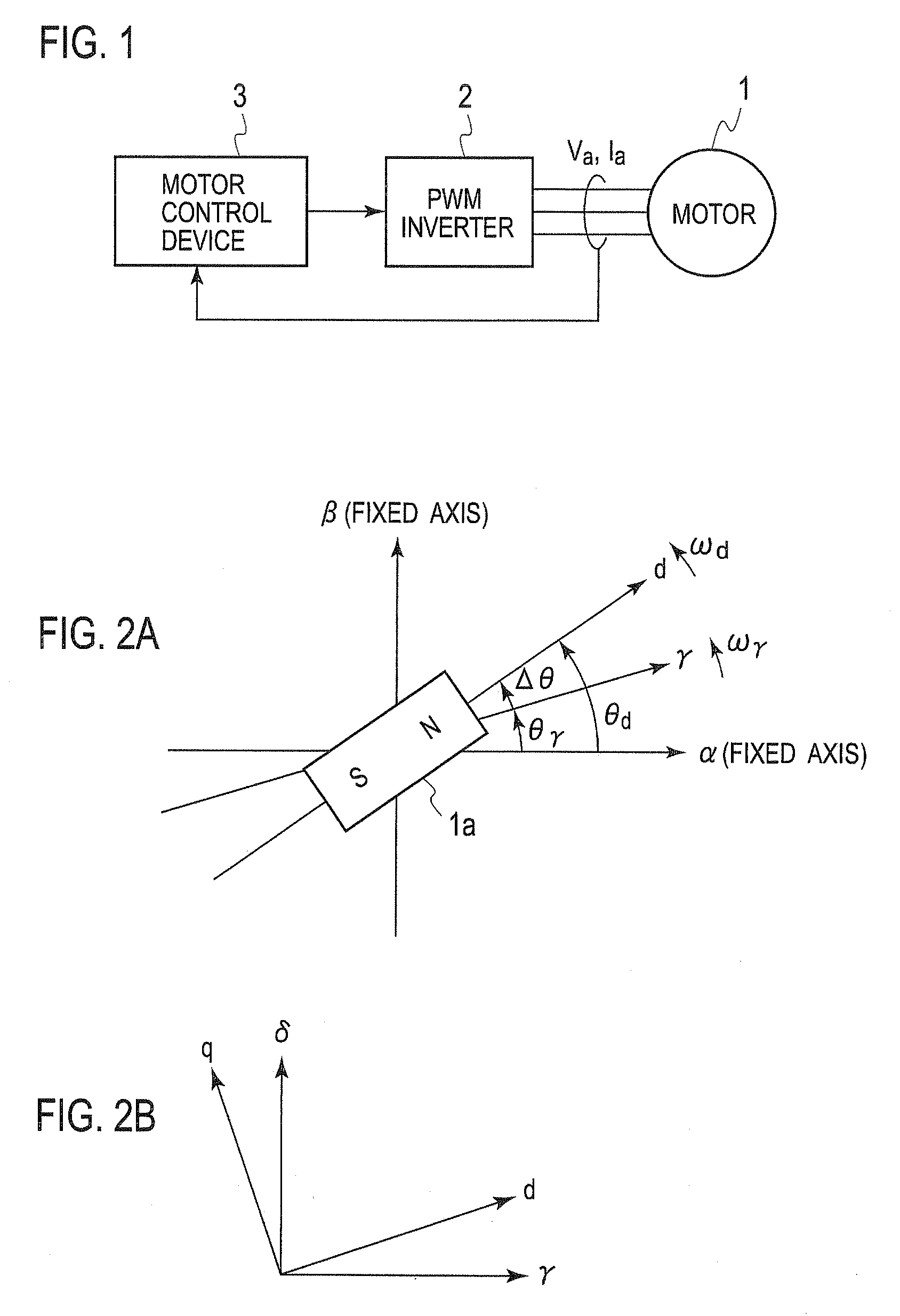
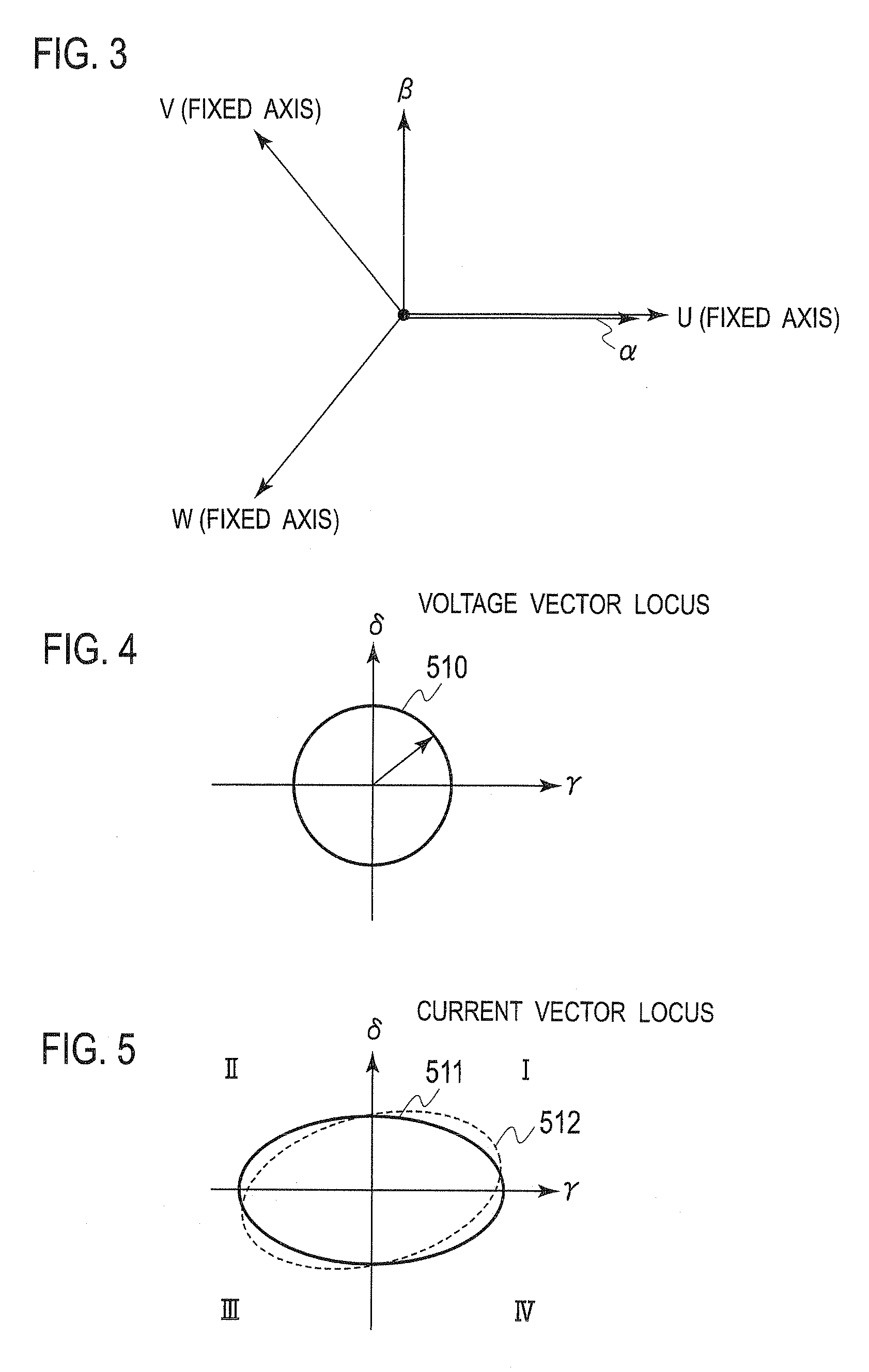
Motor Control Device
ActiveUS20100045218A1Stable positionShort amount of timeSynchronous motors startersVector control systemsMagnetic polesEngineering
To estimate an initial magnetic pole position in a short time, estimated axes for control that correspond to the d-axis and the q-axis are set as the γ-axis and the d-axis, and a high frequency rotation voltage or alternating voltage on the γδ coordinate system is applied to the motor. A high frequency current ih that flows in the motor due to the application of the high frequency voltage is extracted from a detected motor current (armature current) and a direct current component (ihγ×ihd)DC of a product of the γ-axis and d-axis components of the high frequency current ih is derived. On the other hand, the γ′-axis component ichγ and the δ′-axis component ichd of the high frequency current ih that are shifted by p / 4 in electric angle from the γ-axis and the d-axis are obtained and a direct current component of their product (ichγ×ichd)DC is obtained. Thereafter, the magnetic pole position is estimated by computing the axial error Δθ between the γ-d axes utilizing the two direct current components.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
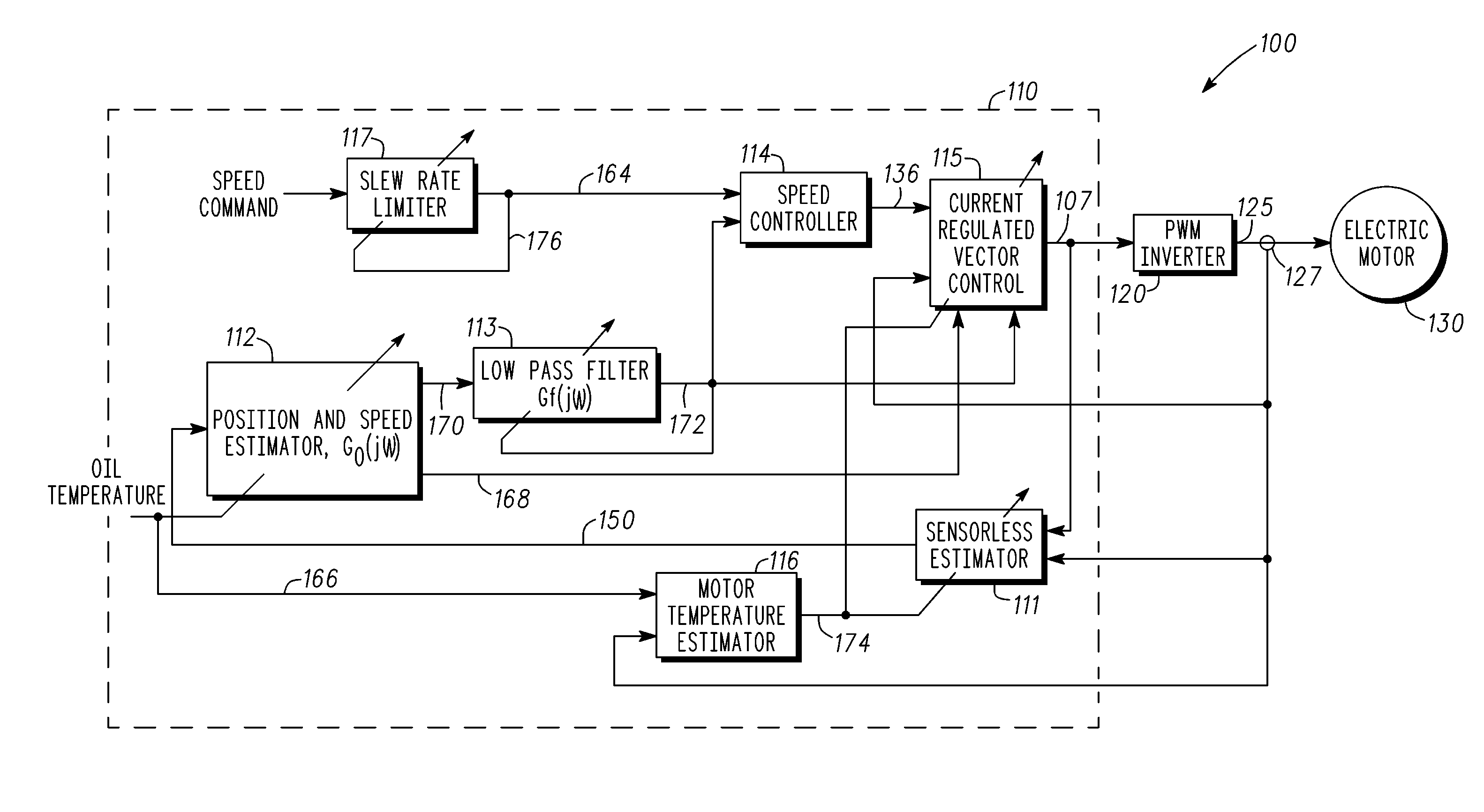
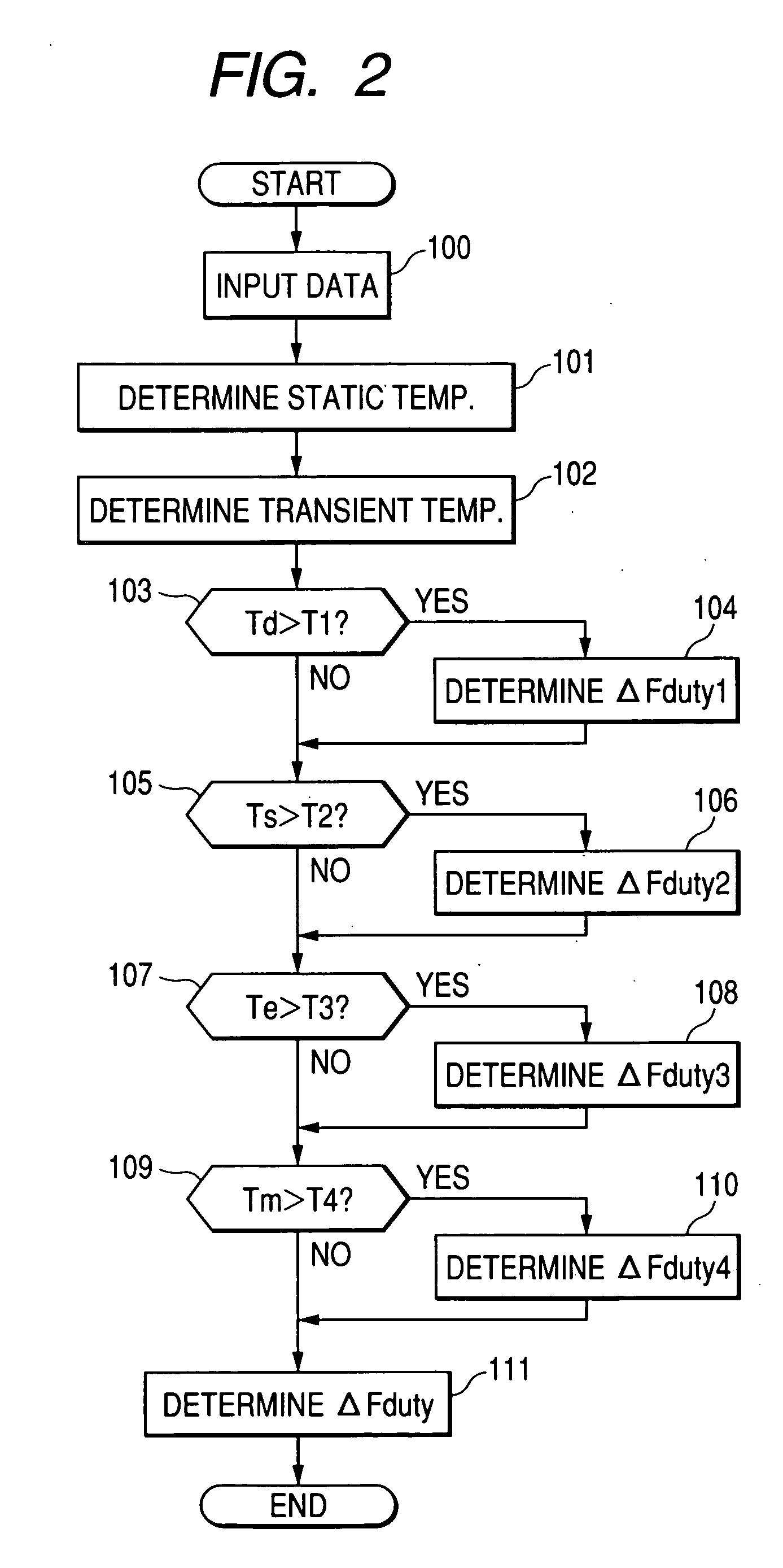
Electric motor stator winding temperature estimation
ActiveUS20090189561A1Avoid overall overheatingSynchronous motors startersDC motor speed/torque controlLow speedPermanent magnet motor
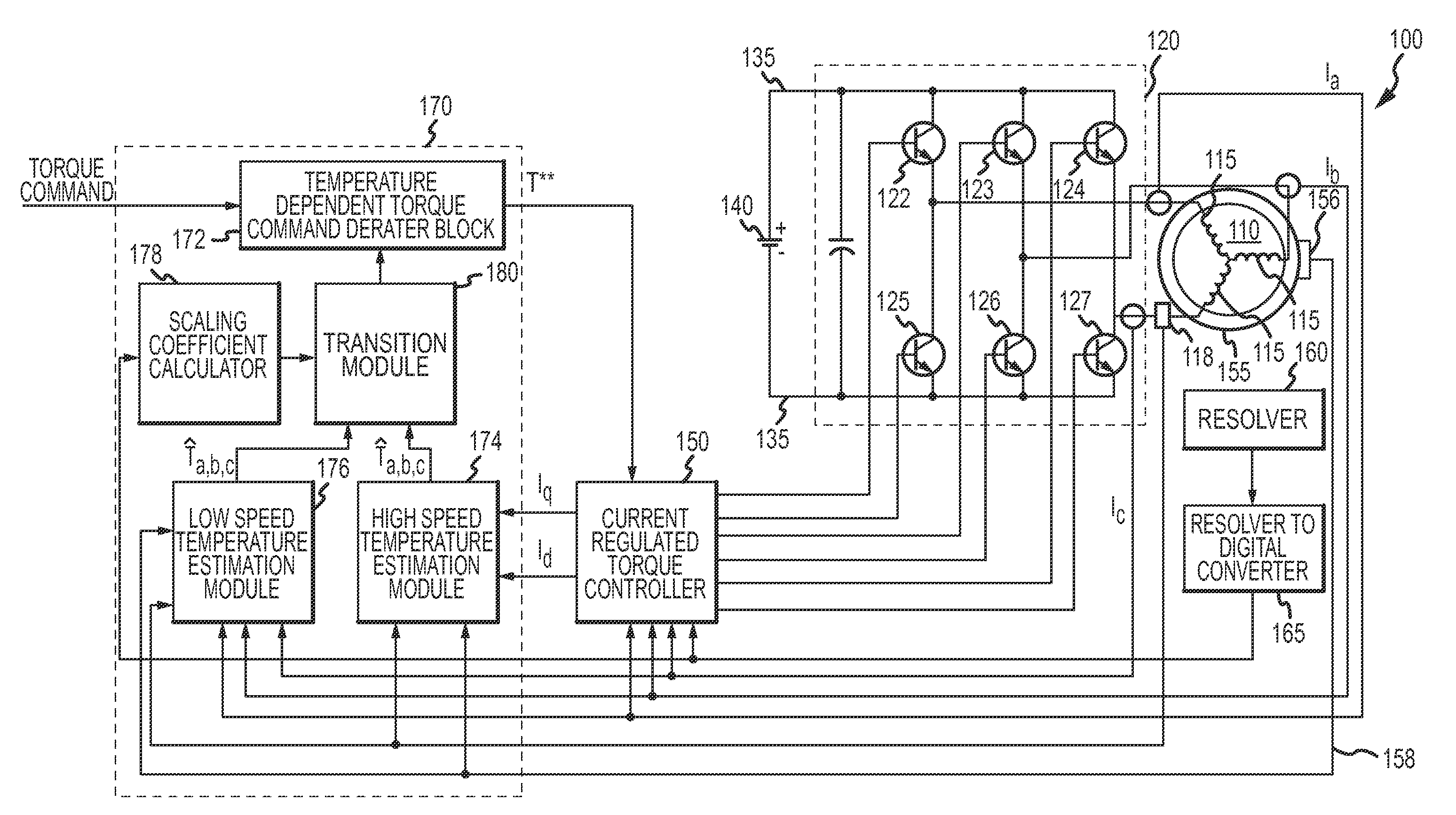
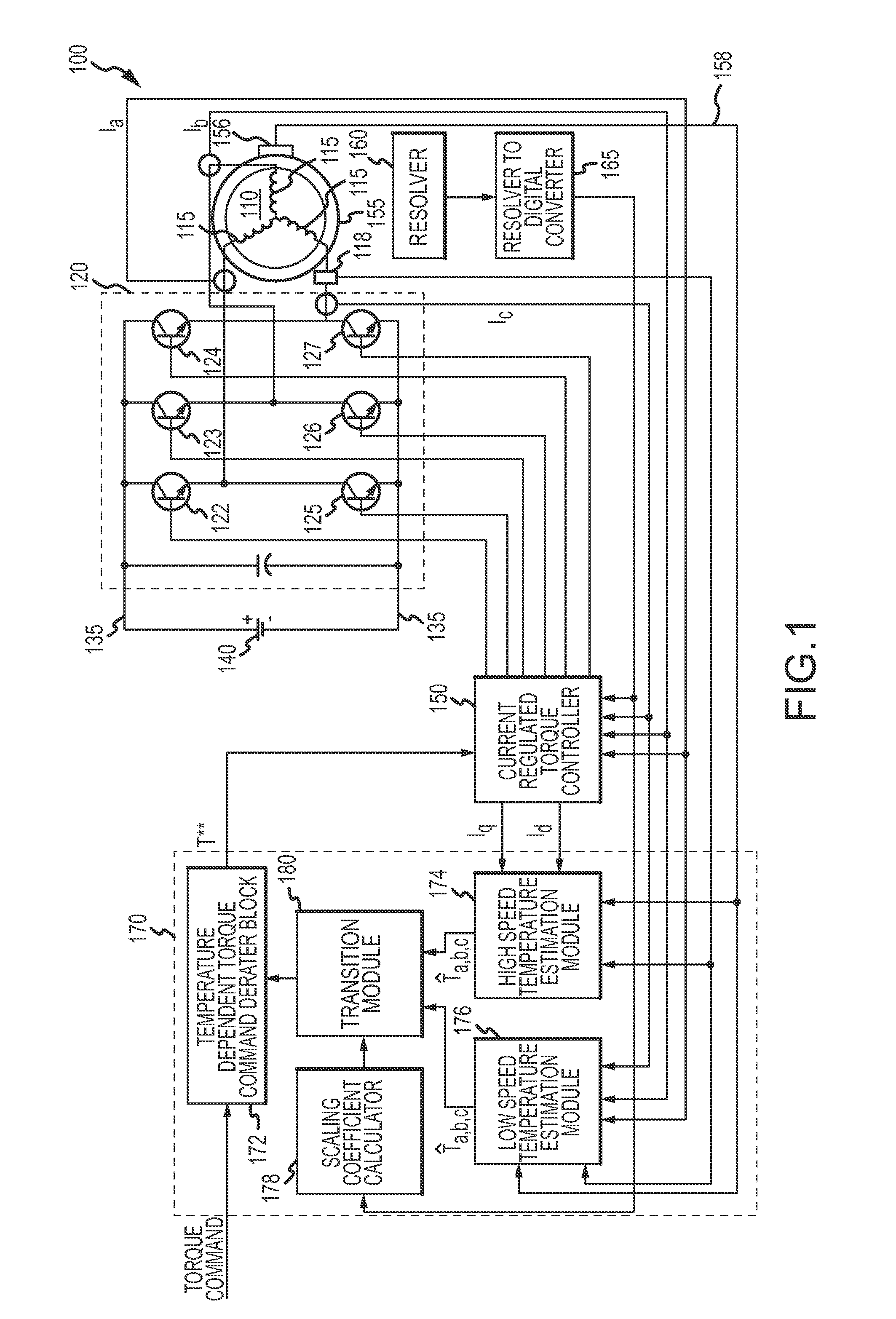
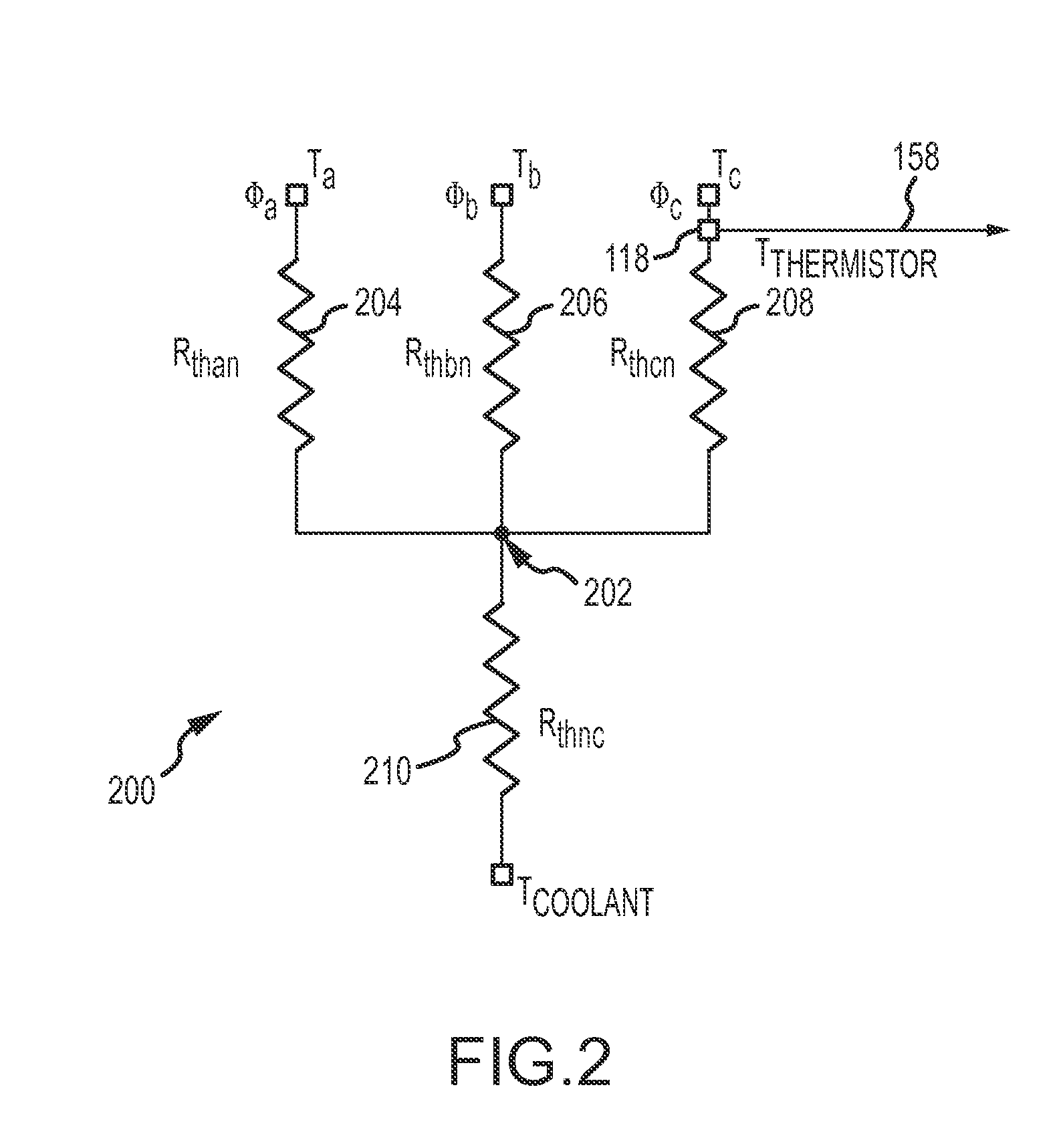
A temperature estimation controller and methods are provided for controlling a torque command to prevent overheating of one or more of a plurality of phases of a permanent magnet motor. The temperature estimation controller includes a low speed temperature estimation module, a transition module and a temperature dependent torque command derater block. The low speed temperature estimation module determines a stator temperature of each of a plurality of phases of the permanent magnet motor in response to first thermal impedances measured for each of the plurality of phases with respect to a thermal neutral. The transition module is coupled to the low speed temperature estimation module and outputs the stator temperature of each of a plurality of phases of the permanent magnet motor as determined by the low speed temperature estimation module when a detected speed of the permanent magnet motor is less than a first predetermined speed. The temperature dependent torque command derater block is coupled to the transition module and derates the torque command in response to the stator temperature of one or more of the plurality of phases.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method and system for starting a sensorless motor
ActiveUS7652441B2Preventing over current shutdownHigh currentAC motor controlSynchronous motors startersMotor driveControl theory
A motor drive system for a sensorless motor includes a catch start sequencer that controls the motor drive system to robustly start the motor in the event the motor rotor is rotating in forward or reverse direction prior to activating the motor drive system. In particular, the catch start sequencer causes the motor drive system to initially find and track the rotor position, and then determines the speed and possibly the direction of rotation of the rotor. If the rotor is rotating in the reverse direction, the catch start sequencer controls the motor drive system to slow the speed of rotation and to then start the rotor rotating in the forward direction.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Current source converter-based wind energy system
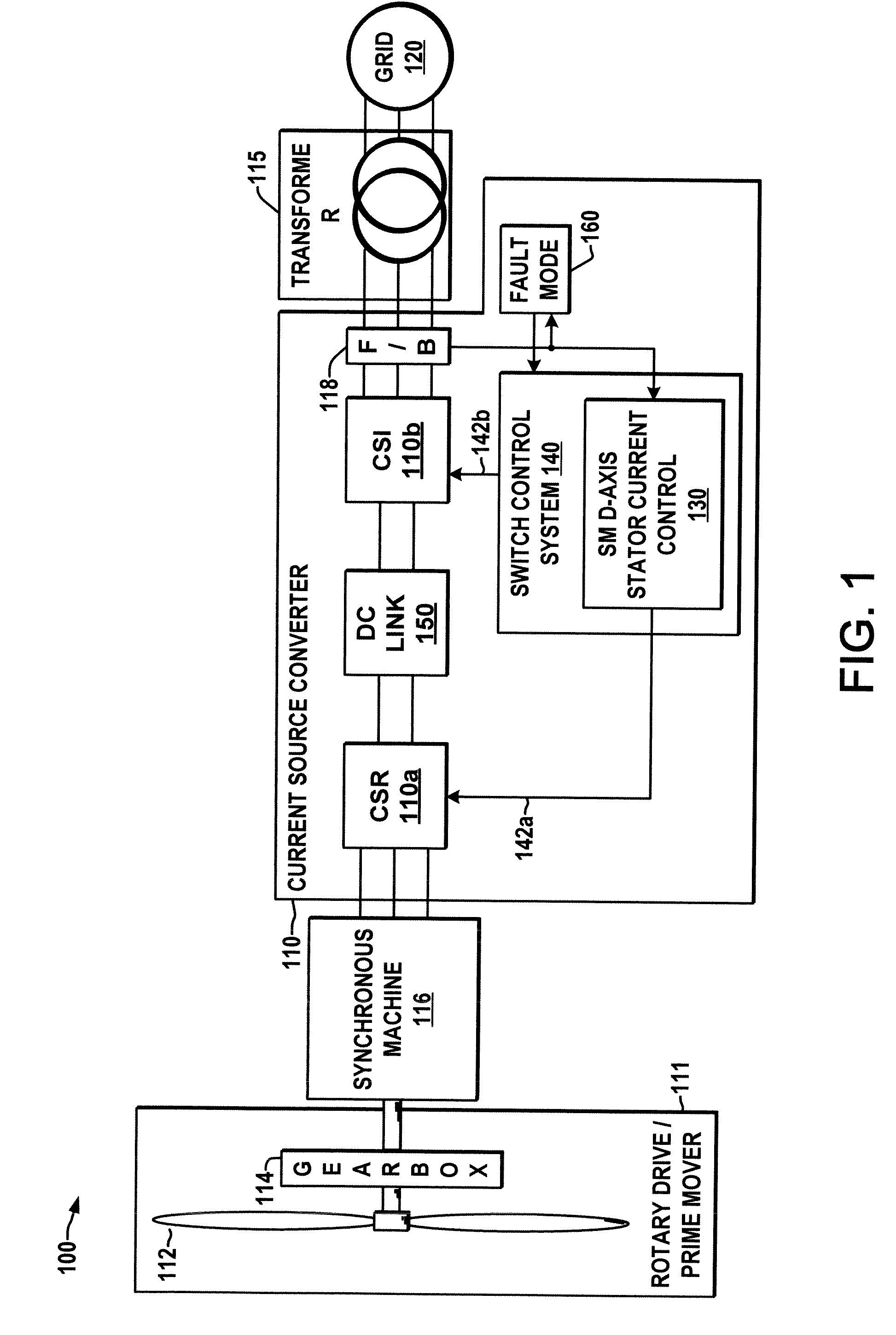
Power conversion apparatus and methods are presented for providing electrical power to a grid or other load in which a synchronous machine is driven by a wind turbine or other prime mover to provide generator power to a switching type current source converter (CSC), with a current source rectifier (CSR) of the CSC being switched to provide d-axis control of the synchronous machine current based on grid power factor feedback, and with a current source inverter (CSI) of the CSC being switched to provide leading firing angle control and selective employment of dumping resists to dissipate excess generator energy in a fault mode when a grid voltage drops below a predetermined level.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
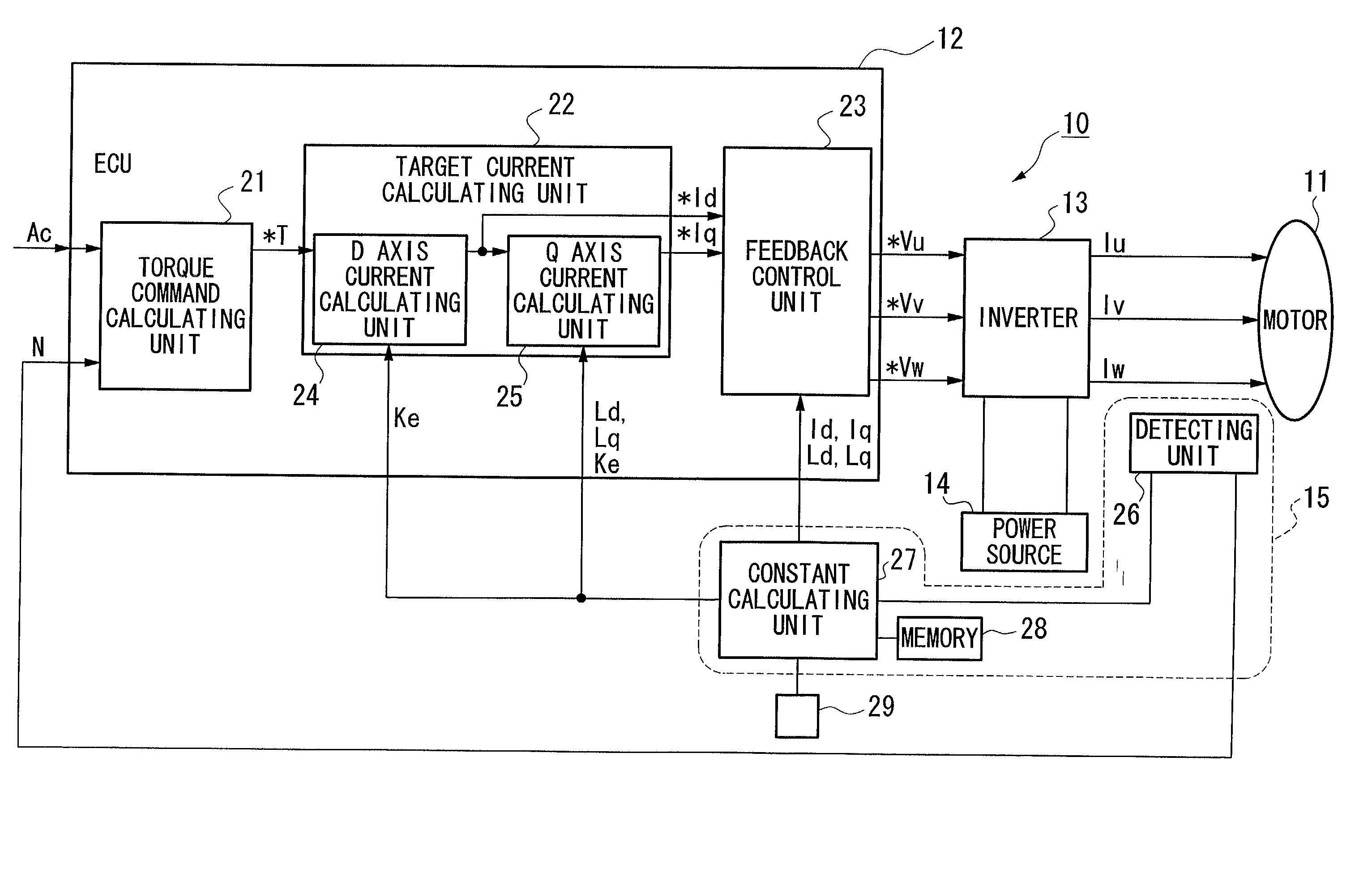
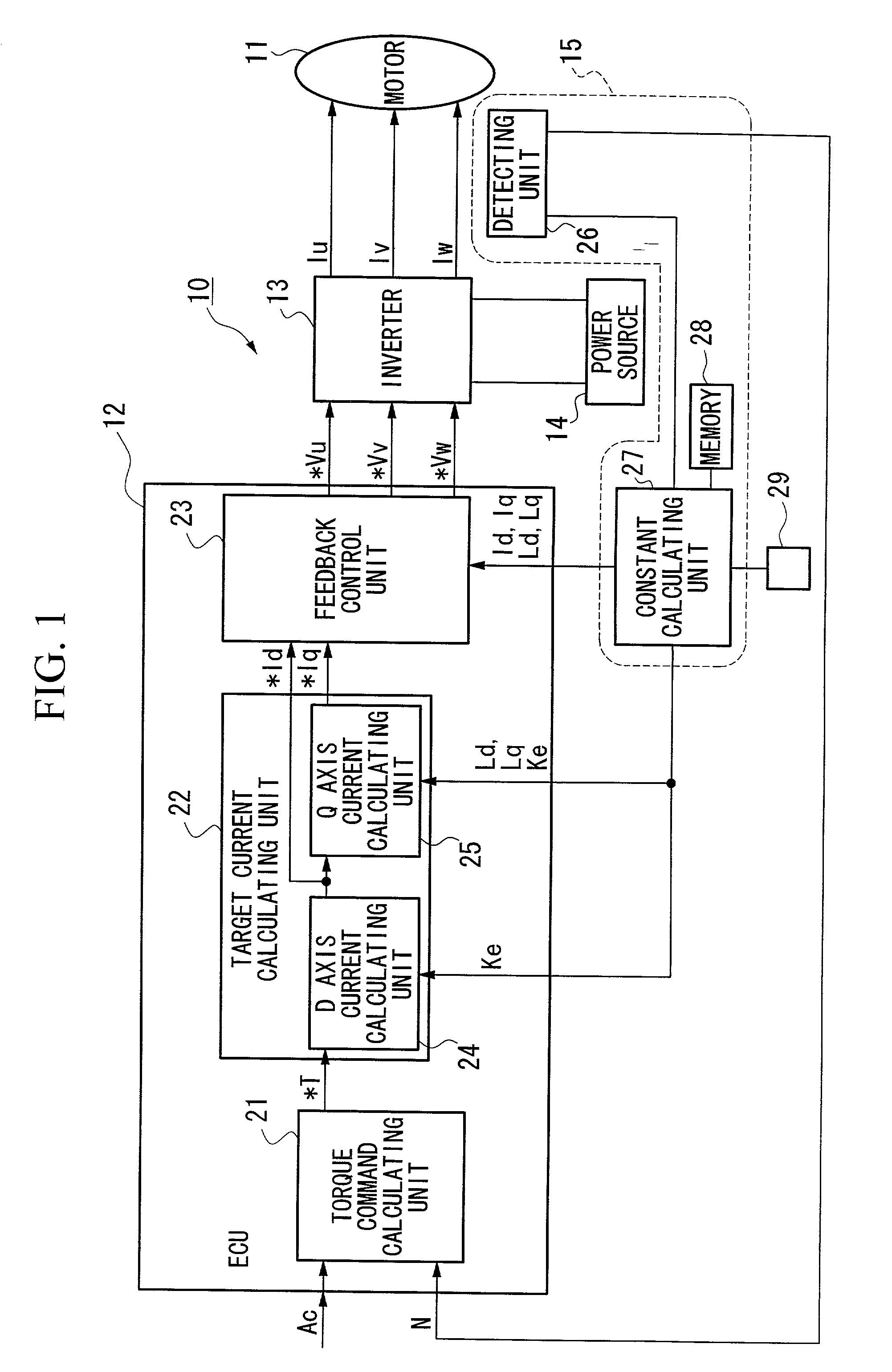
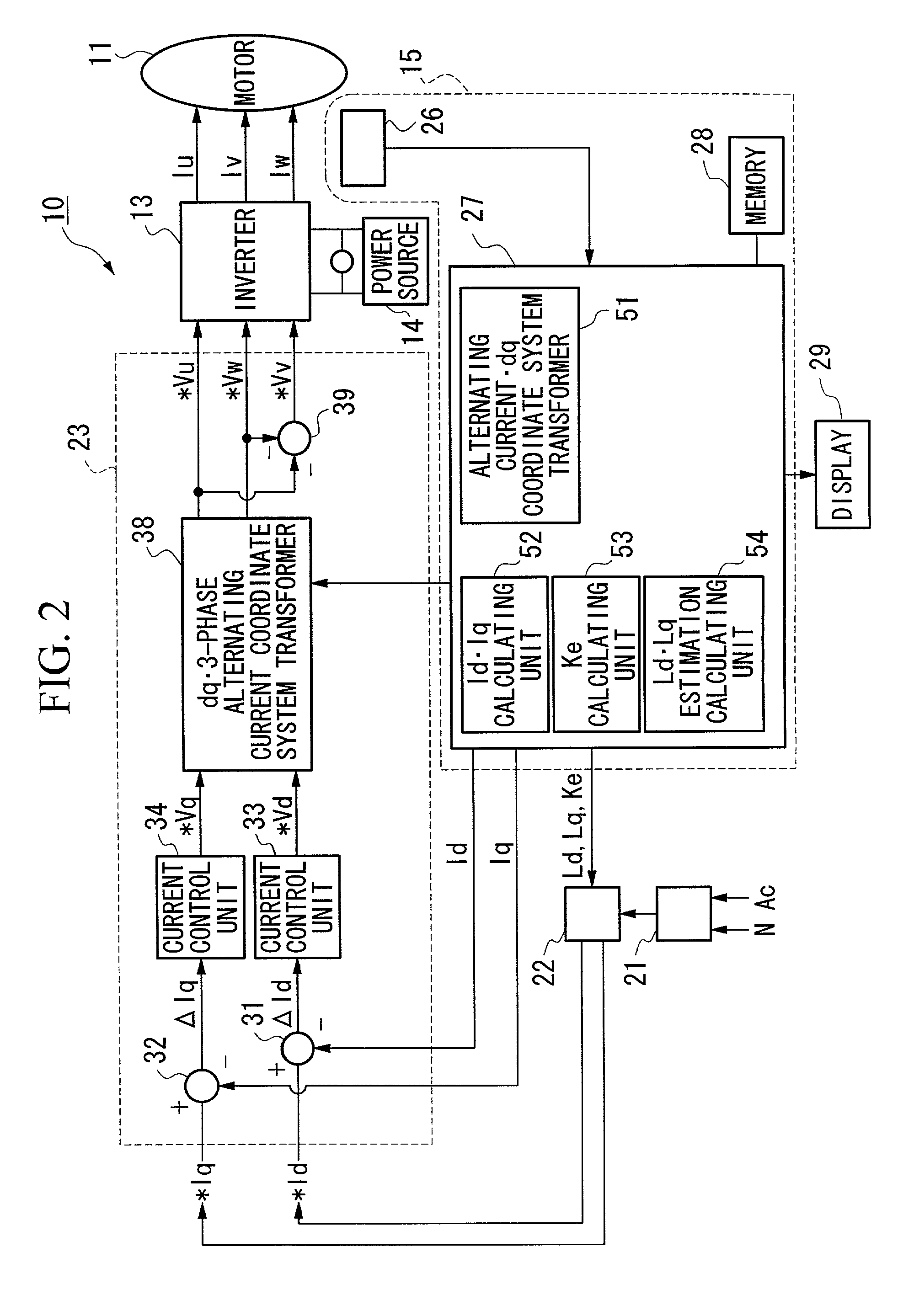
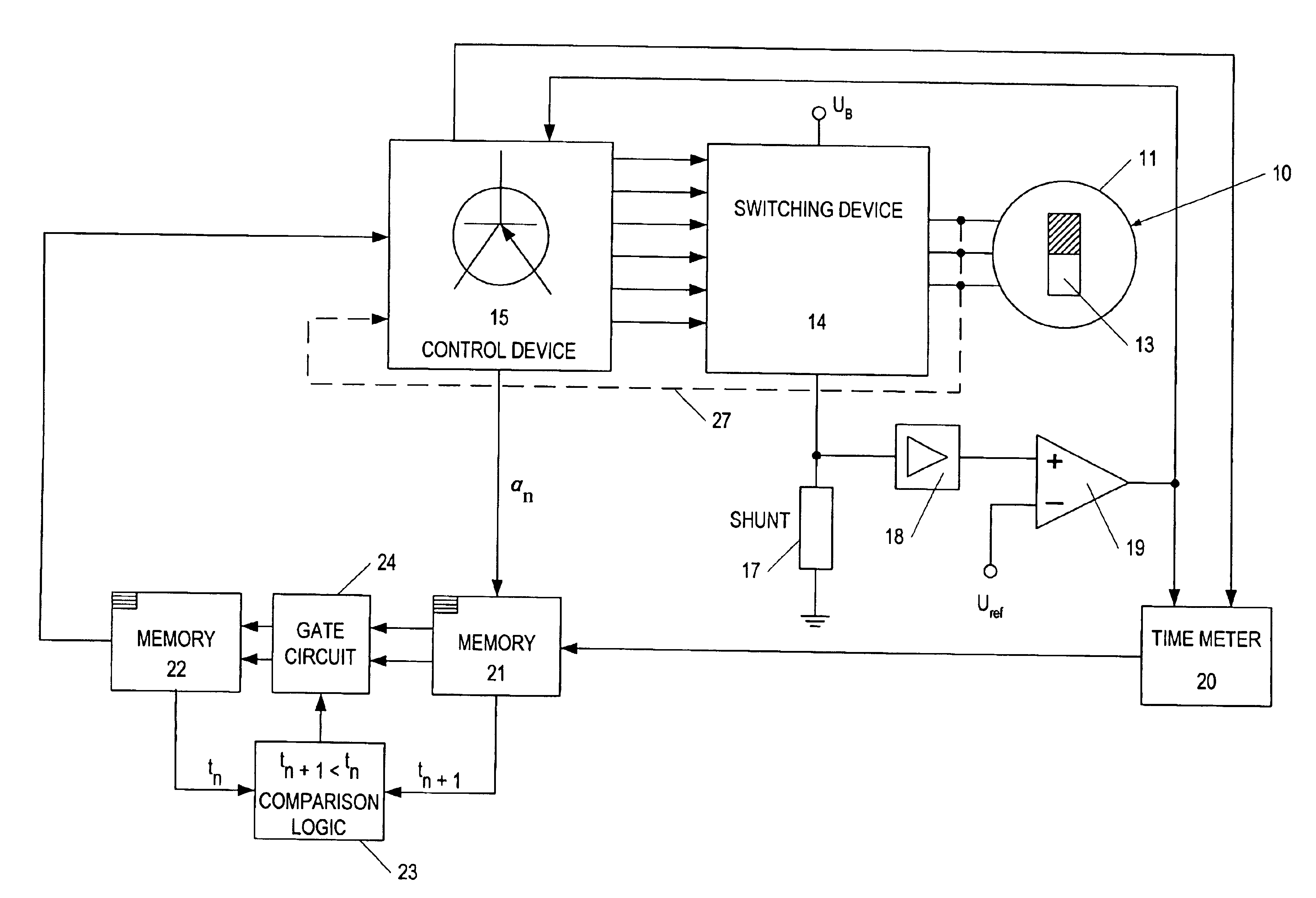
Constant detecting apparatus for brushless DC motor, control apparatus for brushless DC motor, and program for detecting constant of brushless DC motor
InactiveUS20020113615A1Easy to calculateImprove errorAnalogue computers for vehiclesSynchronous motors startersPhase currentsConductor Coil
A constant detecting apparatus 15 comprising a detecting unit 26 and a calculating unit 27. The detecting unit 26 is structured comprising a rotation sensor 41, a torque sensor 42, a position sensor 43, a rotor temperature sensor 44, a winding temperature sensor 45, a phase voltage detector 46, and phase current detectors 47 and 47. The calculating unit 27 calculates the induced voltage constant Ke that changes depending on the motor temperature Tmag while the motor 11 is being driven based on each of the detected signals from the detecting unit 26, and at the same time, the d axis current Id and the q axis current Iq are calculated after elimination of the iron loss, and the d axis inductance Ld and the q axis inductance Lq in the actual operating state of the motor 11 are calculated.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Apparatus for carrying out improved control of rotary machine
ActiveUS20090322264A1Easy maintenanceHigh levelCommutation monitoringDC motor speed/torque controlControl variableVoltage
In an apparatus, a first drive unit drives, in a first range of a voltage utilization factor, a switching member to thereby control an output voltage of the power converter to be matched with a command voltage. A second drive unit drives, in a second range of the voltage utilization factor, the switching member to thereby generate a value of a controlled variable of a rotary machine. The second range of the voltage utilization factor is higher than the first range thereof. An estimating unit estimates, during the switching member being driven by the second drive unit, a value of a parameter associated with the output voltage of the power converter. The estimated value is required for the first drive unit to generate the value of the controlled variable generated by the second drive unit.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Methods, systems and apparatus for dynamically controlling an electric motor that drives an oil pump
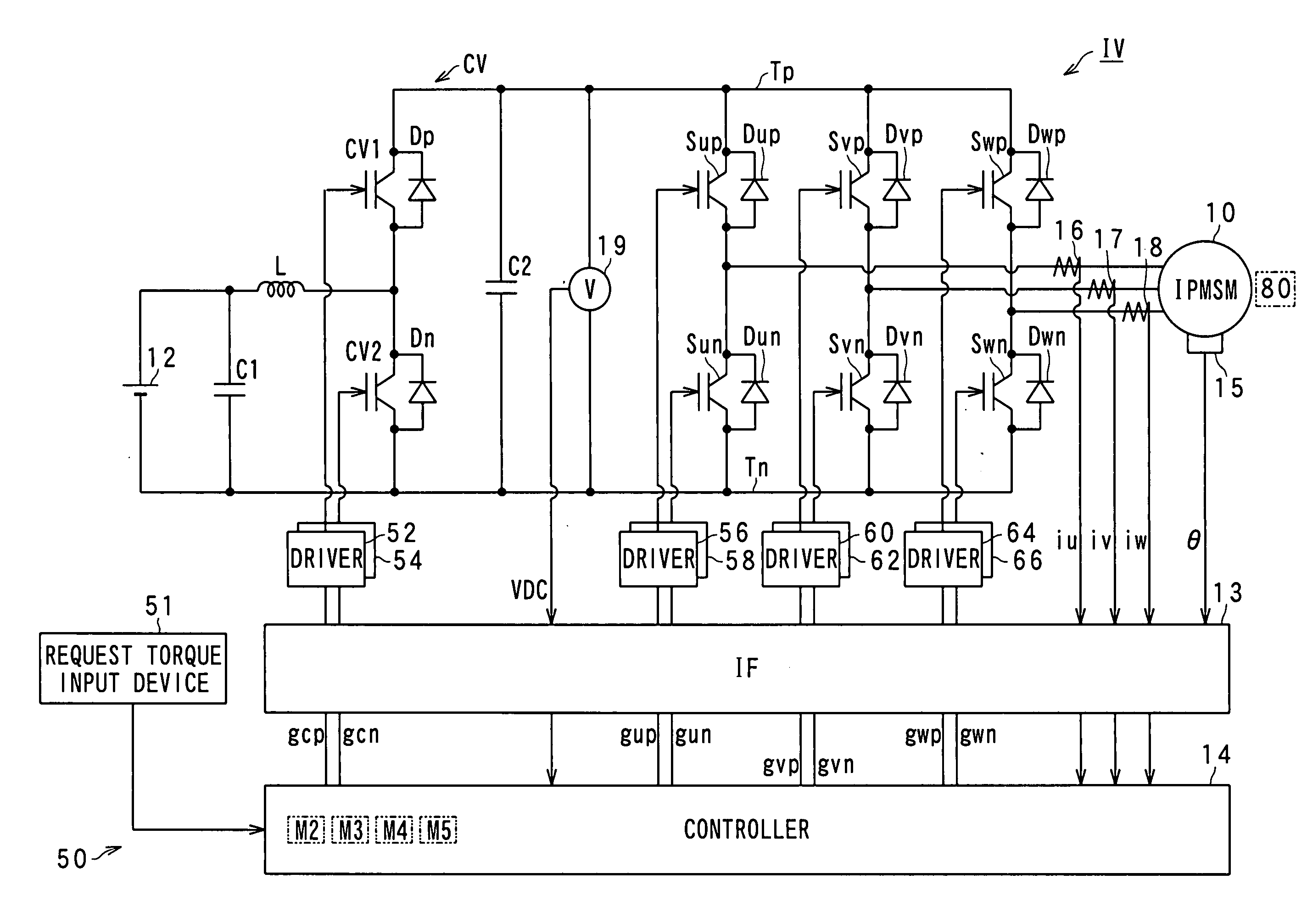
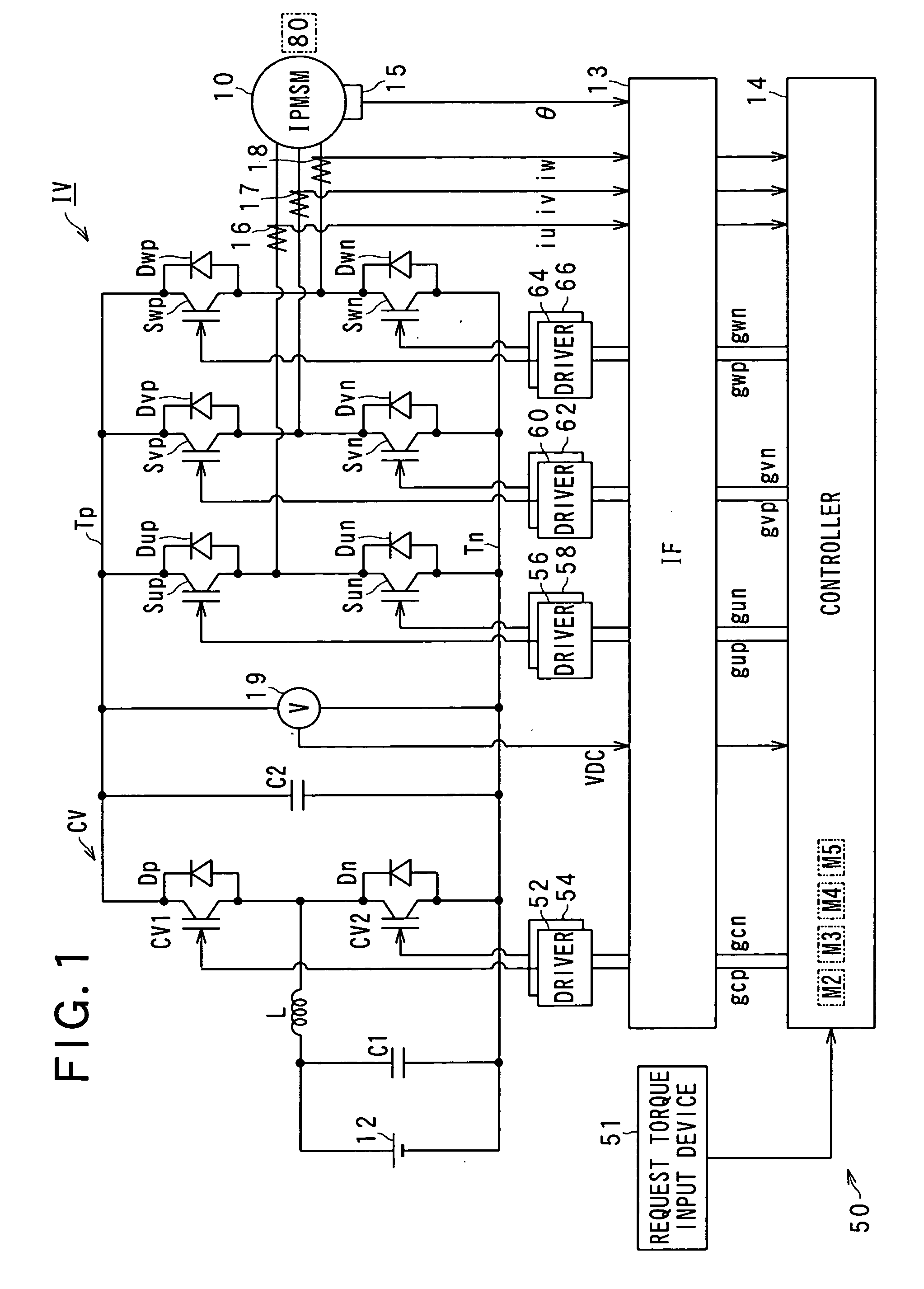
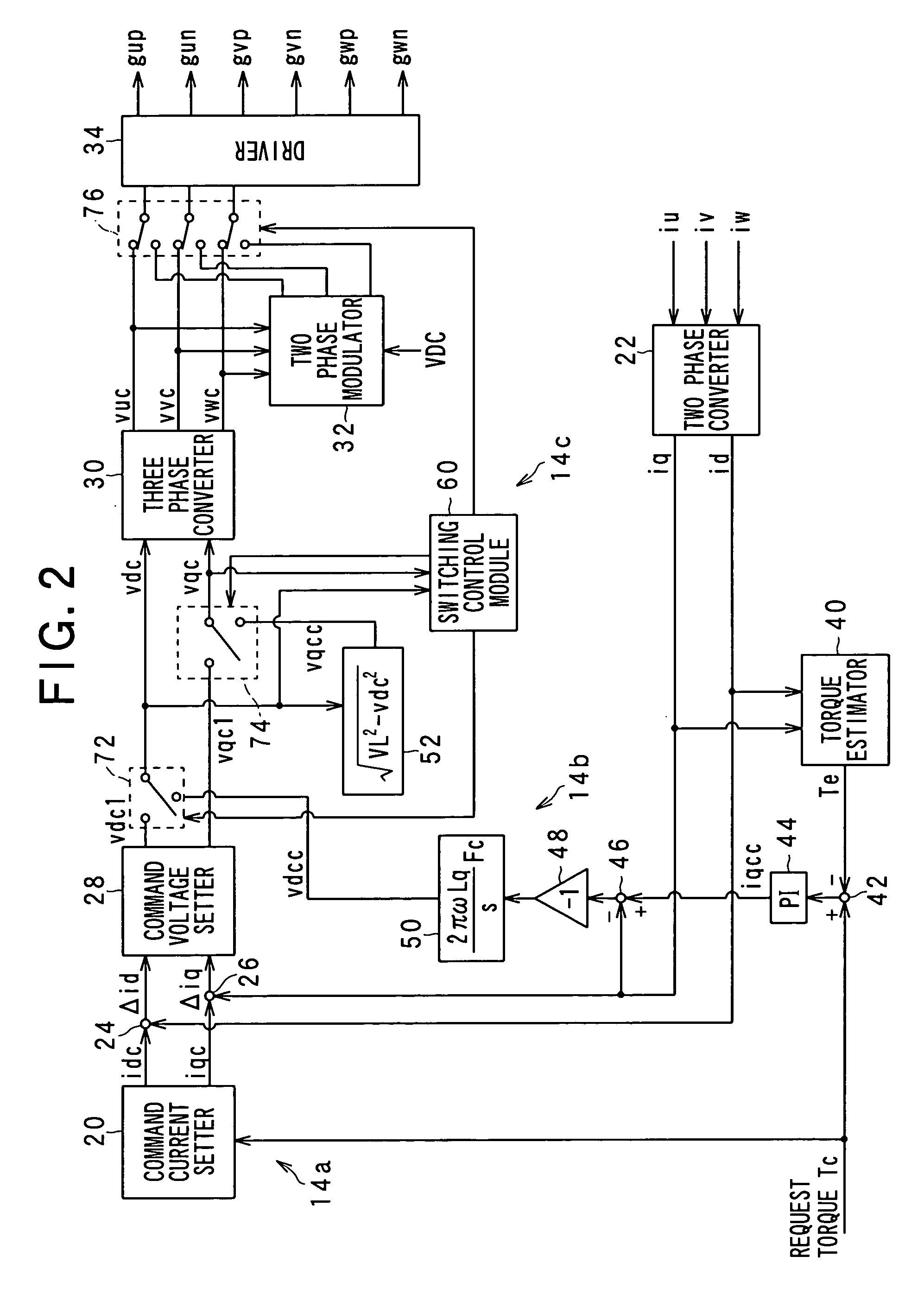
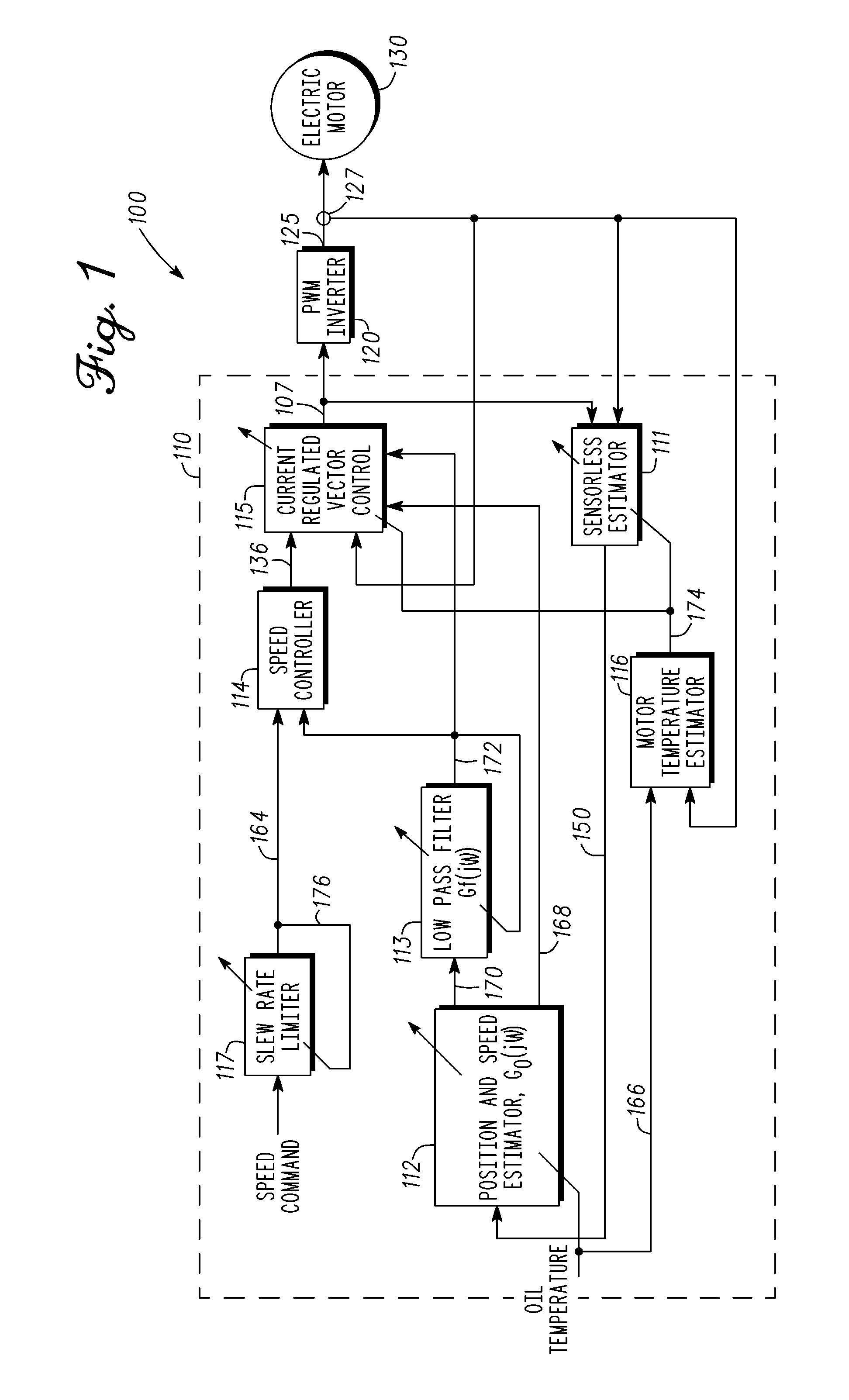
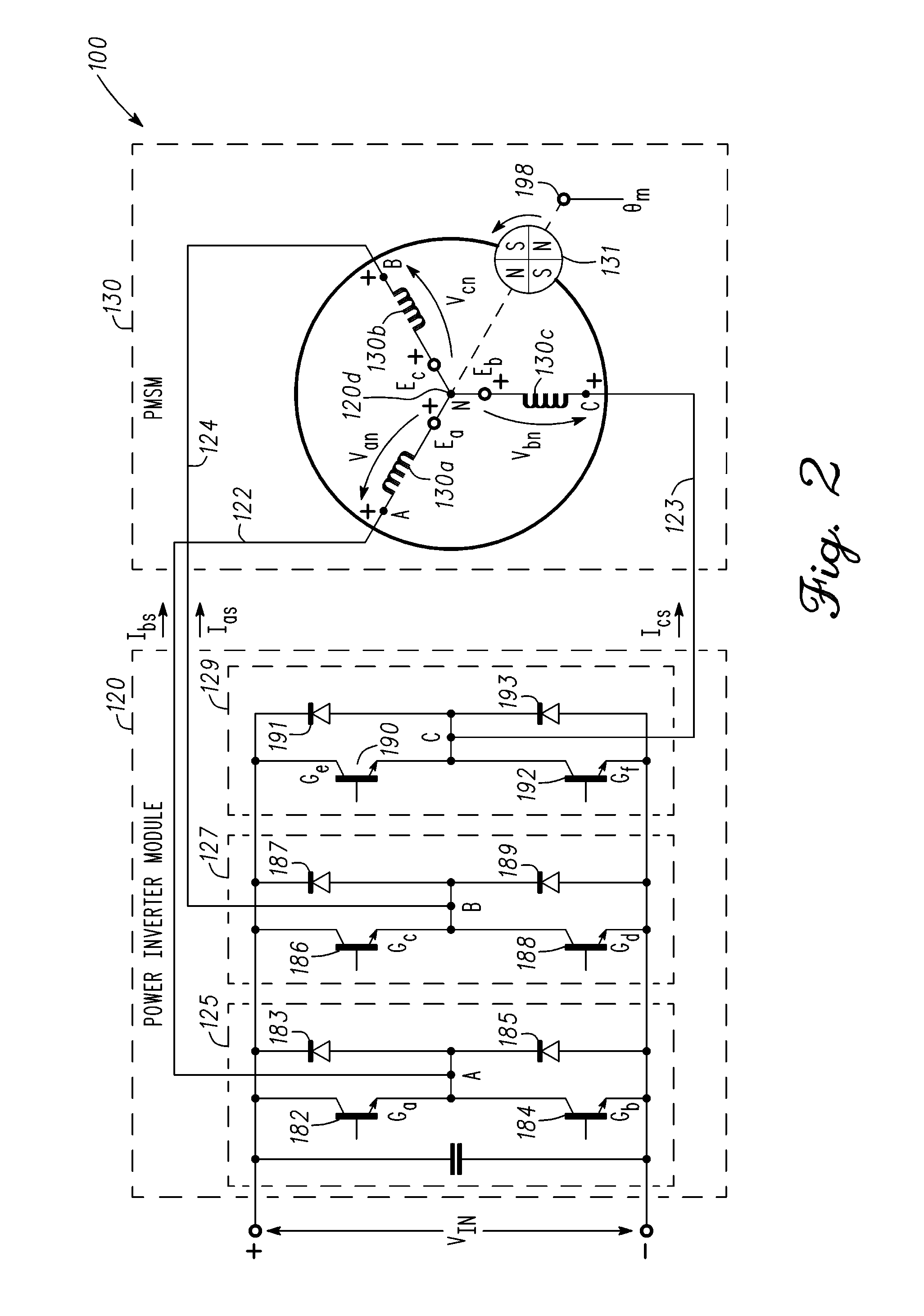
ActiveUS20110084638A1Multiple motor speed/torque controlSingle motor speed/torque controlMotor driveEngineering
Methods, system and apparatus are provided for sensorless control of a vector controlled motor drive system that includes an electric motor used to drive an auxiliary oil pump.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
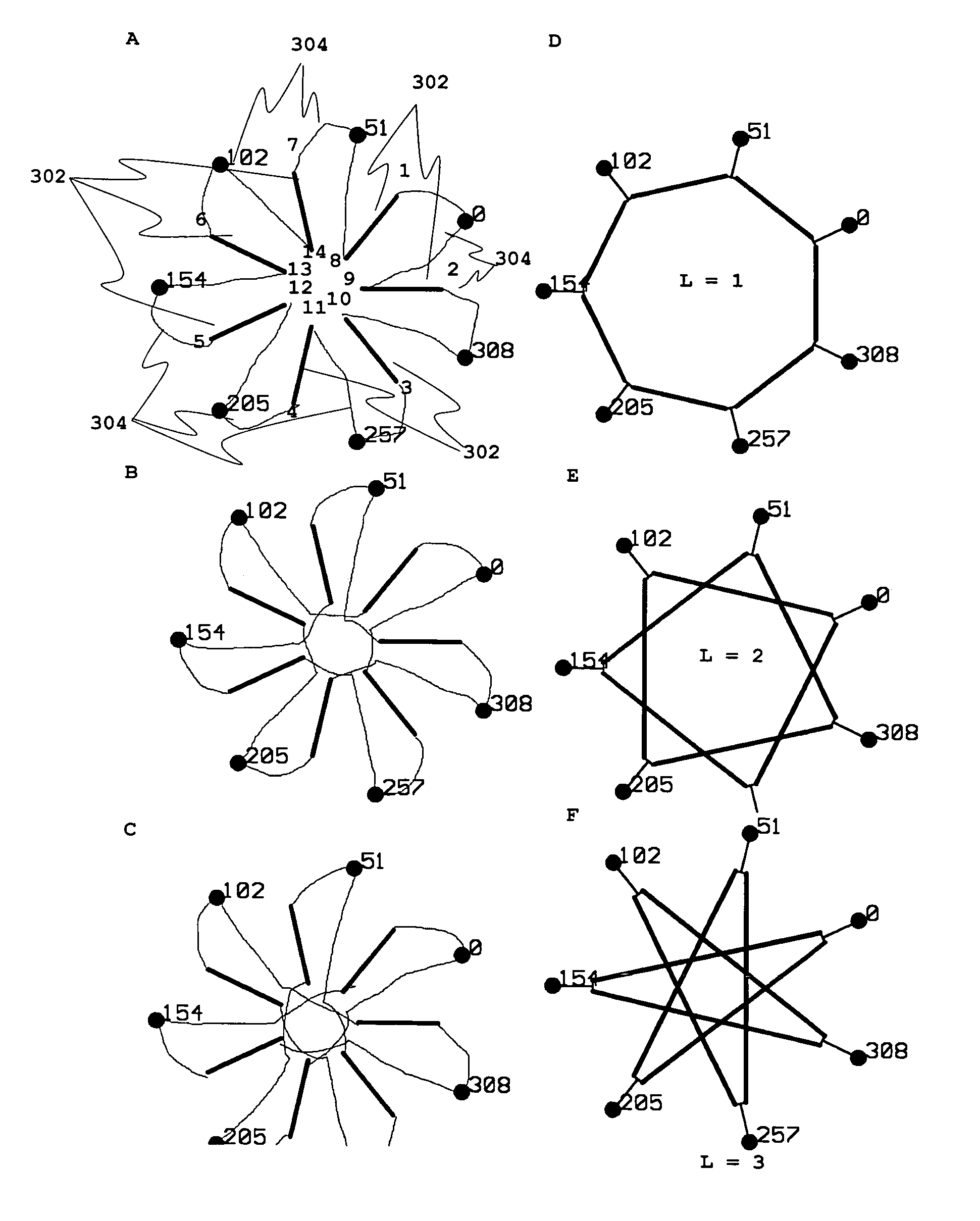
Mesh connected electrical rotating machine with span changing
InactiveUS7116019B2High torque overloadSufficient voltageAssociation with control/drive circuitsMotor/generator/converter stoppersHarmonicNetwork connection
An electrical rotating apparatus is provided that has variable impedance. This is achieved by connecting one of the polyphase components of the apparatus in a mesh connection. The spanning value, L, of such a mesh connection may be varied by changing the harmonic content supplied by an inverter component. Also provided is a method for connecting an inverter to a motor, wherein a switching arrangement permits the simple alteration between various mesh connections of different span value, changing thereby the Volts / Hertz ratio of the motor.
Owner:BOREALIS TECH LTD
Electrical machine and method of controlling the same
InactiveUS20060284581A1Synchronous motors startersAC motor controlElectric machineCounter-electromotive force
An electrical machine having a stator and a rotor. The stator includes a core and a plurality of windings disposed on the core in a multiple-phase arrangement. The rotor is disposed adjacent to the stator to interact with the stator. A method of operating the motor includes applying a pulsed voltage differential to first and second terminals of the windings resulting in movement of the rotor; monitoring the back electromotive force (BEMF) of the windings to sense rotor movement; after the applying and monitoring steps, monitoring the BEMF of the windings to determine whether the rotor is rotating in a desired direction, and electrically commutating the motor when the rotor is rotating in the desired direction and zero or more other conditions exist.
Owner:REGAL BELOIT AMERICA
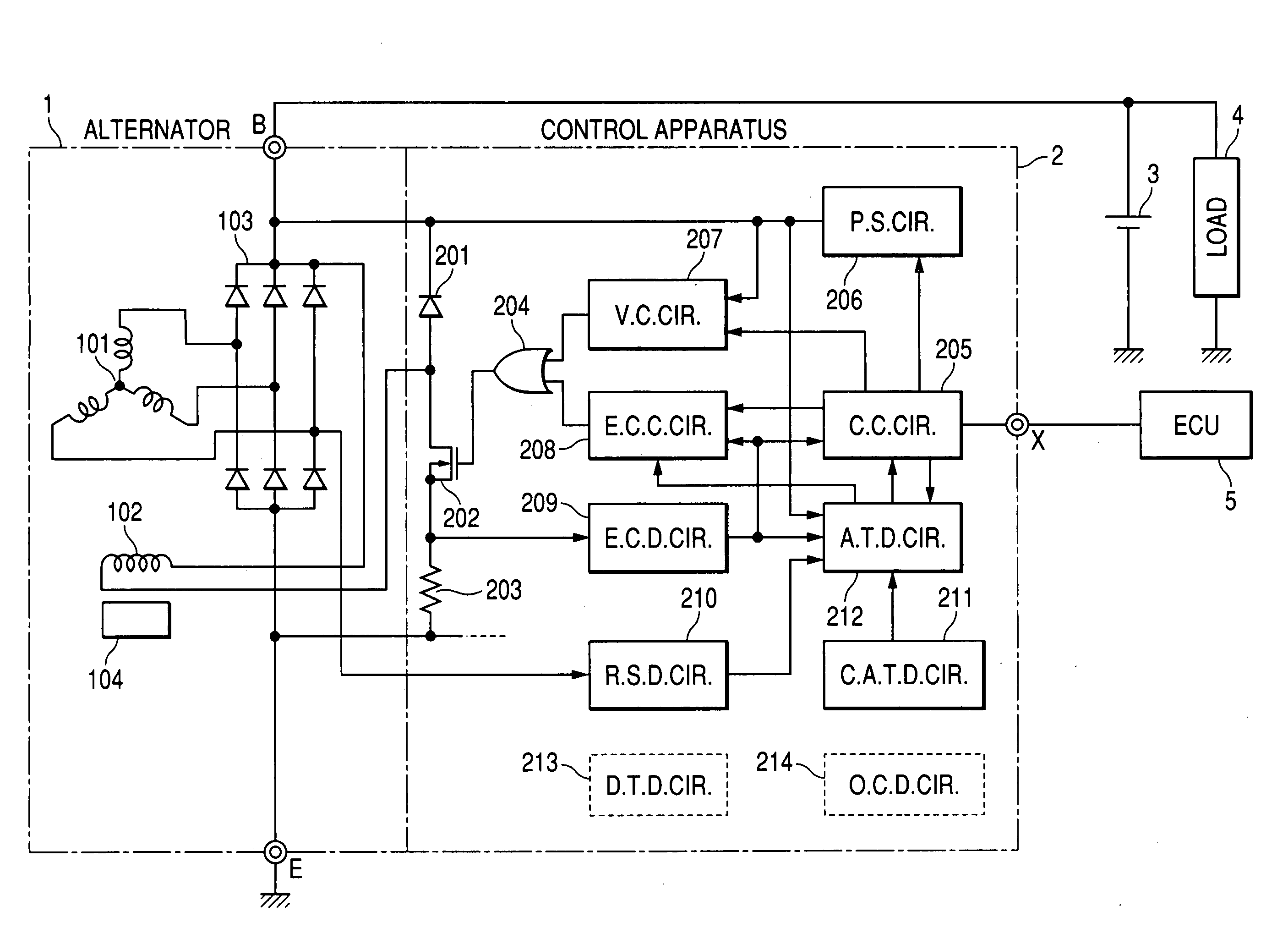
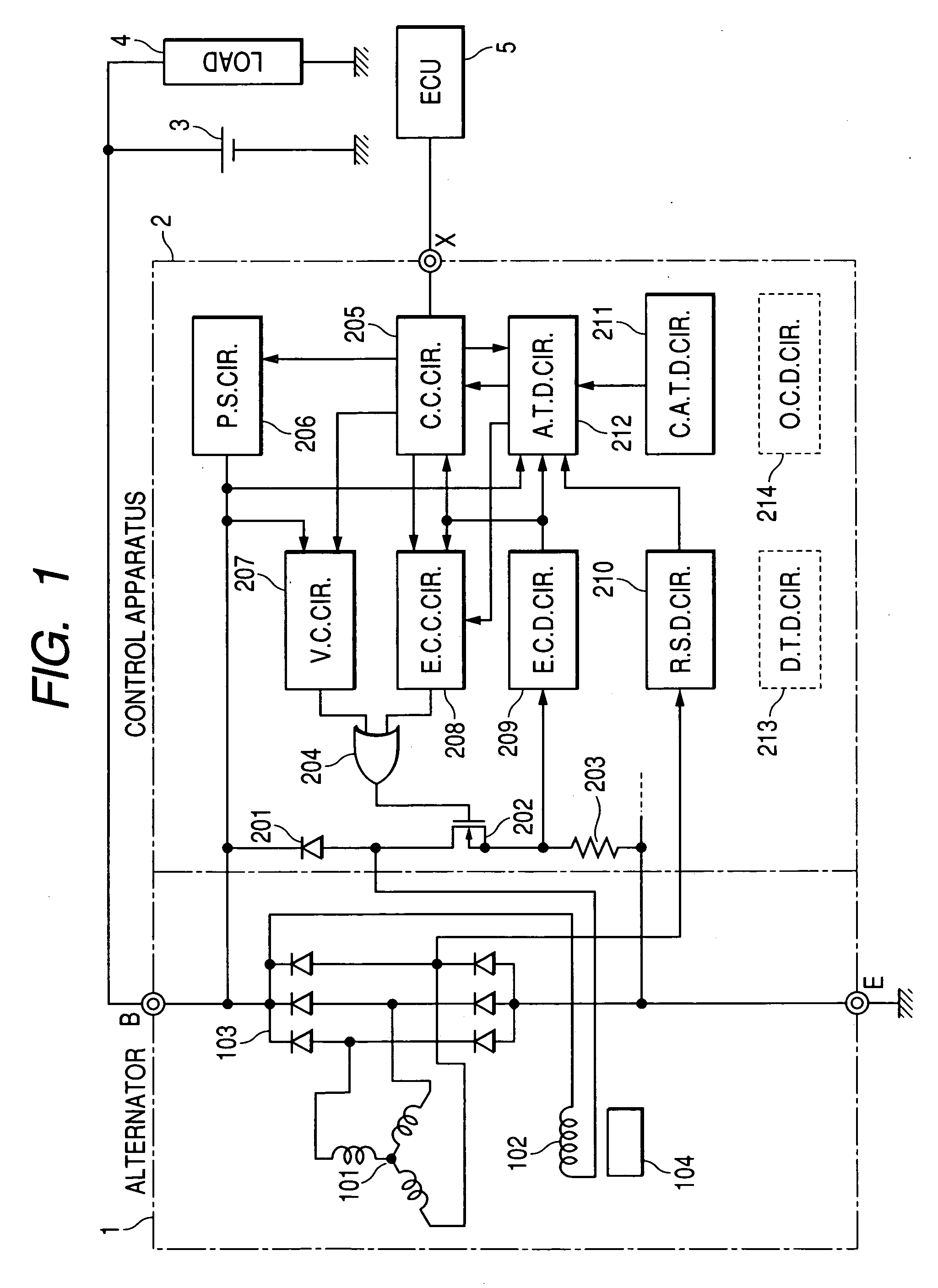
Control apparatus for automotive alternator having capability to accurately detect temperature of alternator
ActiveUS20060238172A1Improve accuracyControl outputMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersAlternatorSignal generator
A control apparatus for a vehicle generator includes a switch, a regulator, a fault condition detector, and a PWM signal generator. The switch is selectively turned on and off so as to intermittently excite the generator. The regulator controls on / off operation of the switch so as to bring an output of the generator into agreement with a target value. The fault condition detector detects a fault condition of the generator. The PWM signal generator generates and outputs a PWM signal that has a duty determined as a function of a duty of the on / off operation of the switch and a frequency determined based on if the fault condition of the generator is detected by the fault condition detector. Consequently, the control apparatus can inform an external control apparatus of the duty of the on / off operation of the switch and the fault condition of the generator with the single PWM signal.
Owner:DENSO CORP
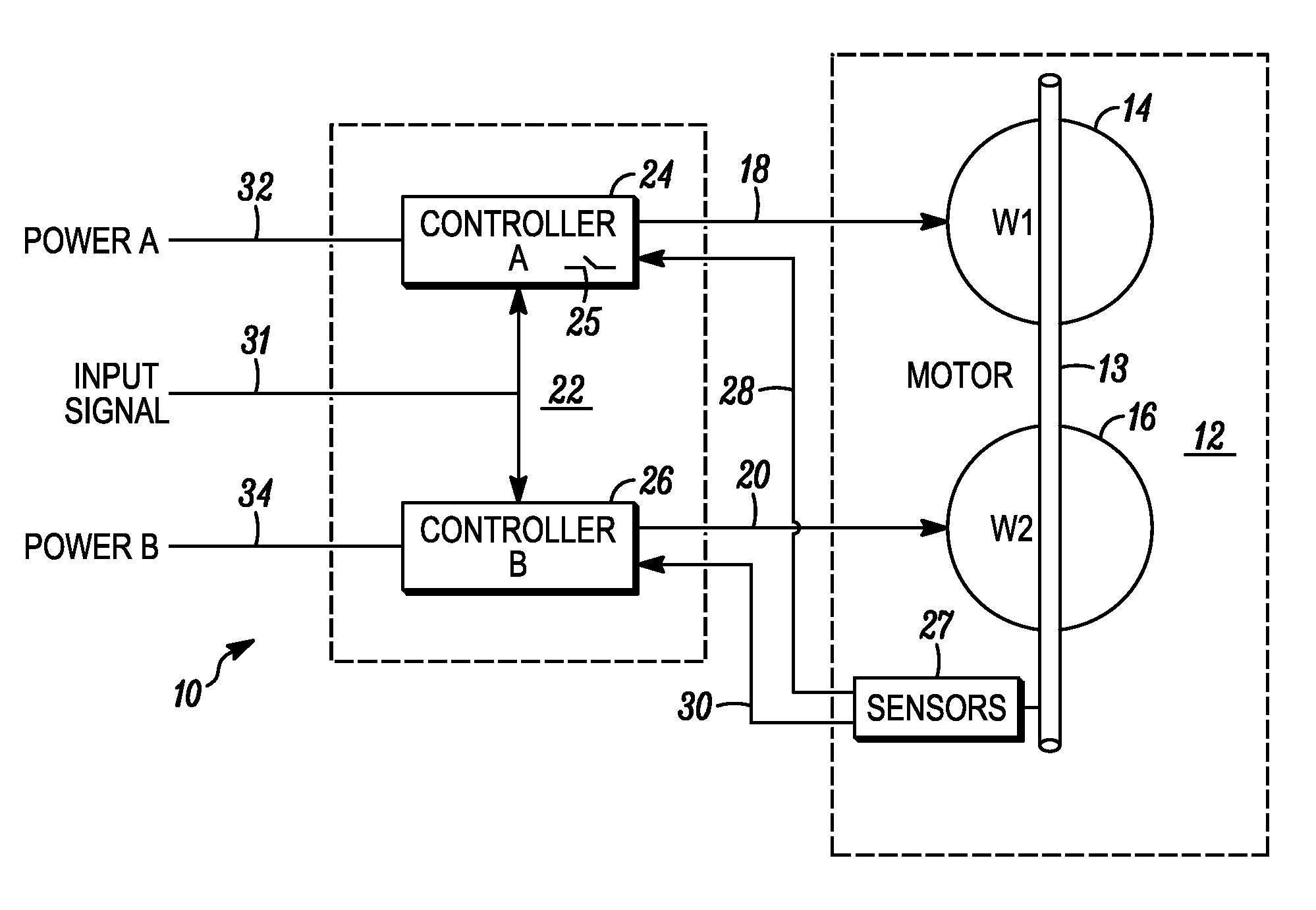
Motor having controllable torque
InactiveUS20090128084A1Increase in sizeSingle-phase induction motor startersCommutation monitoringEngineeringControl theory
A controllable motor includes a rotor. A first stator winding set is operable, upon being energized, to generate and apply a first torque to the rotor. A second stator winding set independent of the first stator winding set is operable, upon being energized, to generate and apply a second torque to the rotor. A motor control is coupled to the first and second stator winding sets. The motor control is operable to selectively energize one of the first or second stator winding sets to thereby generate and apply one of the first or second torques to the rotor, and simultaneously energize both the first and second stator winding sets to thereby generate and apply a third torque greater than the first or the second torque.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Initial rotor position detection for permanent magnet synchronous motors
ActiveUS20100181952A1High sensitivityAvoid uneven performanceMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersFall timeVoltage vector
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
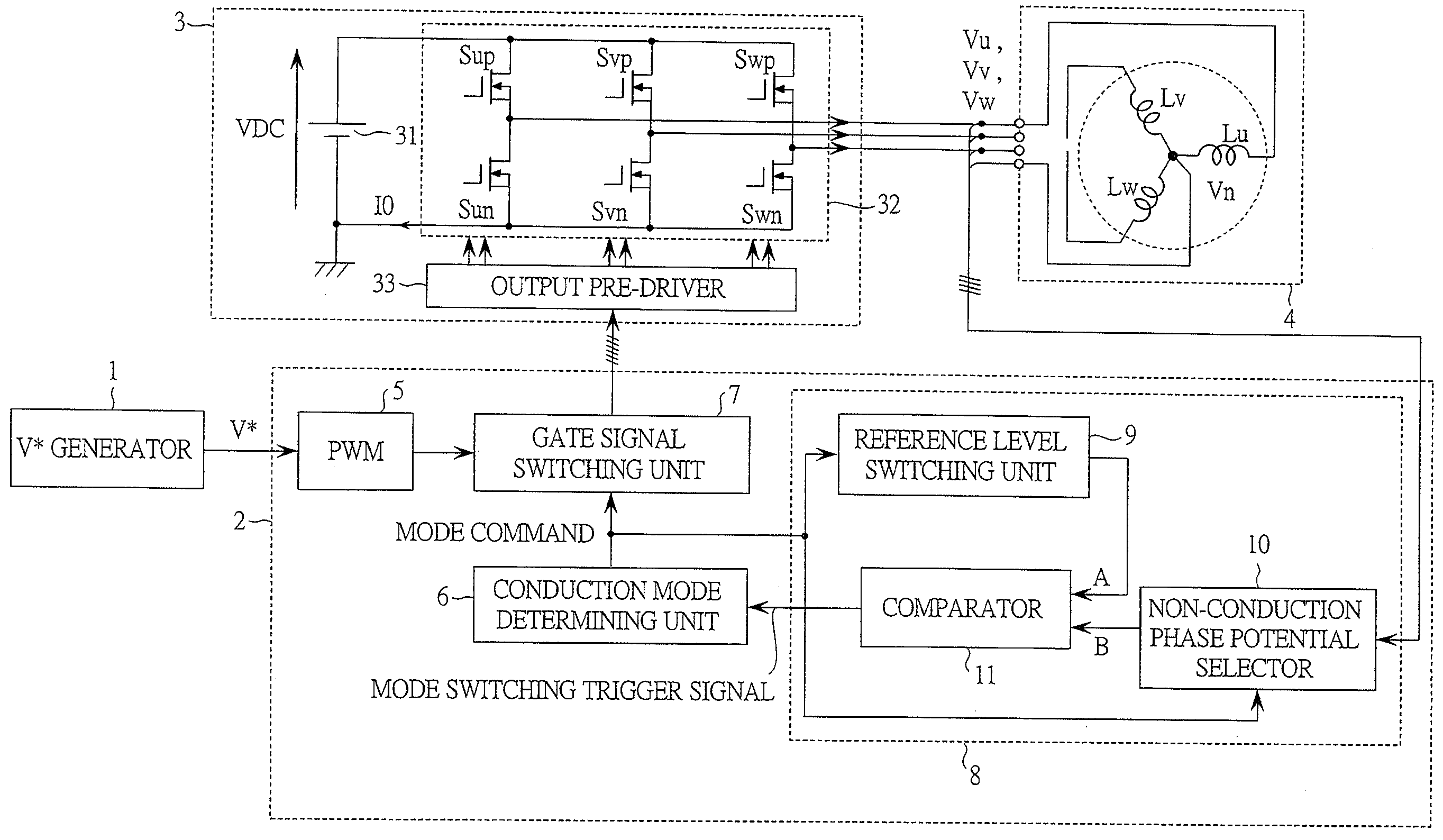
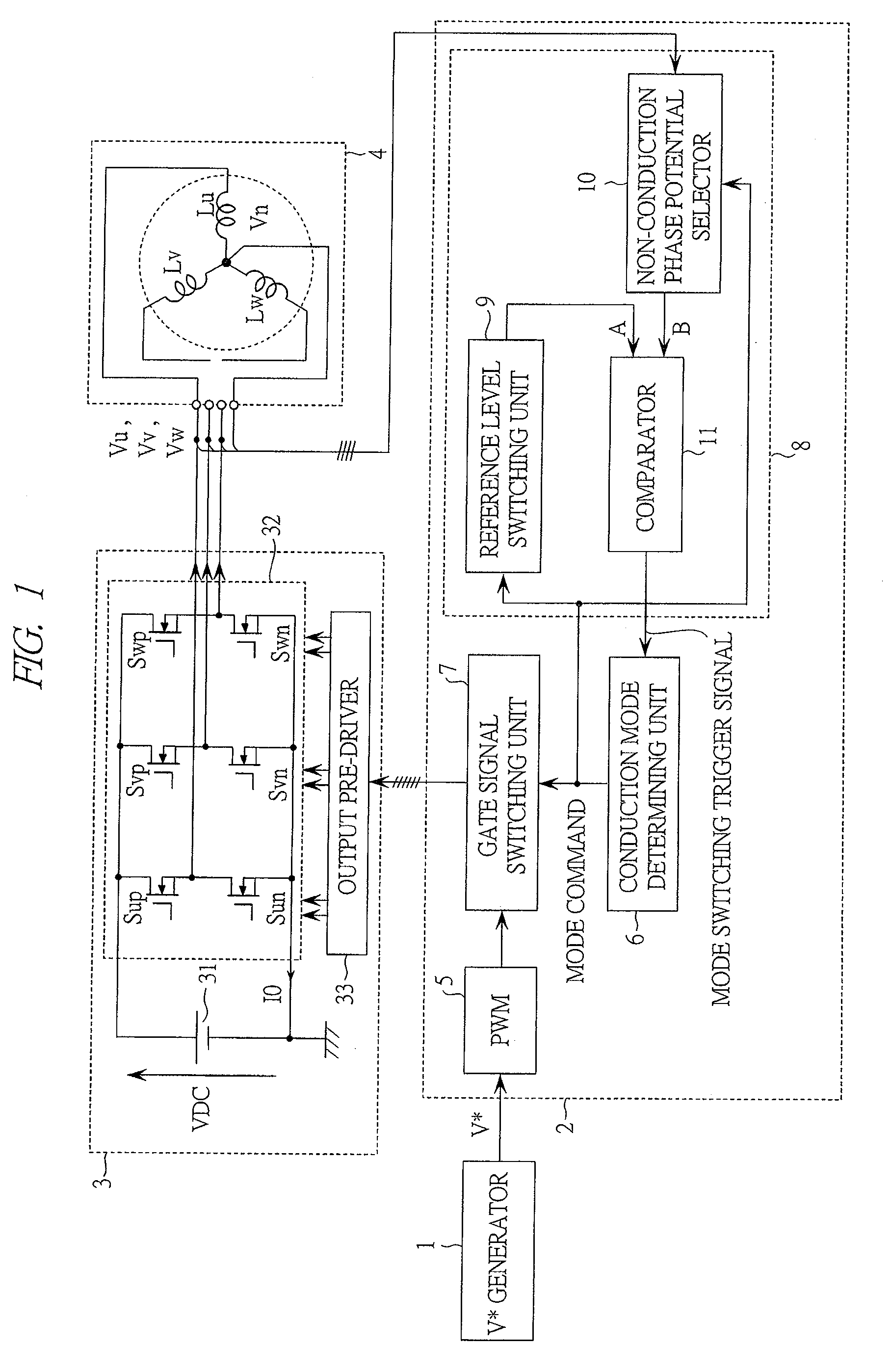
Control device for electric motor drive apparatus
InactiveUS20110080125A1Suppress aliasingCalculation load increaseAC motor controlSynchronous motors startersPower inverterControl signal
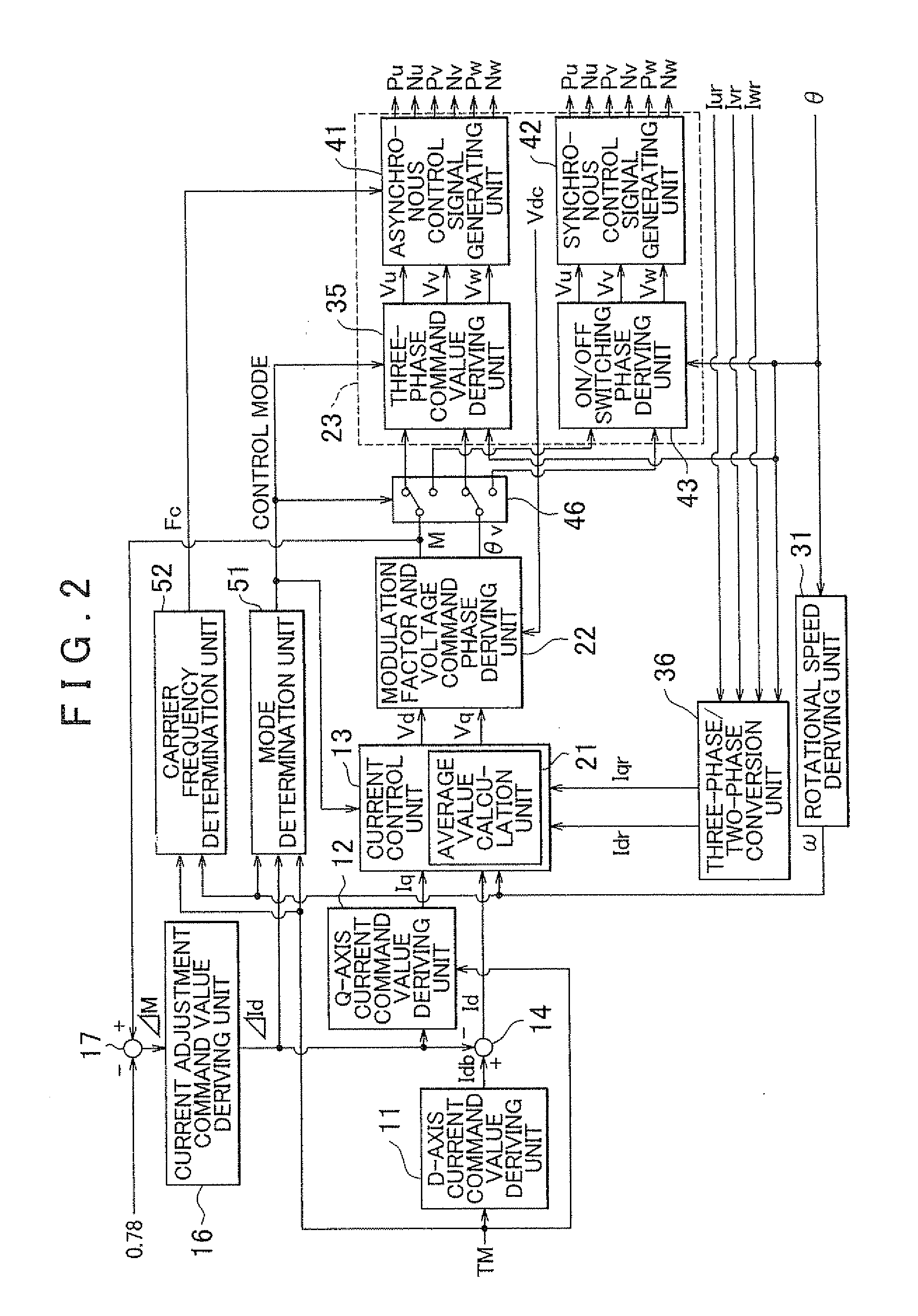
A electric motor drive apparatus comprising a voltage control unit performing voltage control processing that determines alternating-current voltage command values serving as command values of the alternating-current voltages to be supplied to the alternating-current electric motor and generates switching control signals for the inverter; and a control mode selection unit selecting a synchronous control mode in which a cycle of electric angle of the alternating-current electric motor is synchronized with a switching cycle of the inverter, or an asynchronous control mode in which the cycles are not synchronized with each other. Current detection processing is performed to detect currents flowing in coils of the alternating-current electric motor in every standard calculation cycle that is set to a half of a cycle of the carrier.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
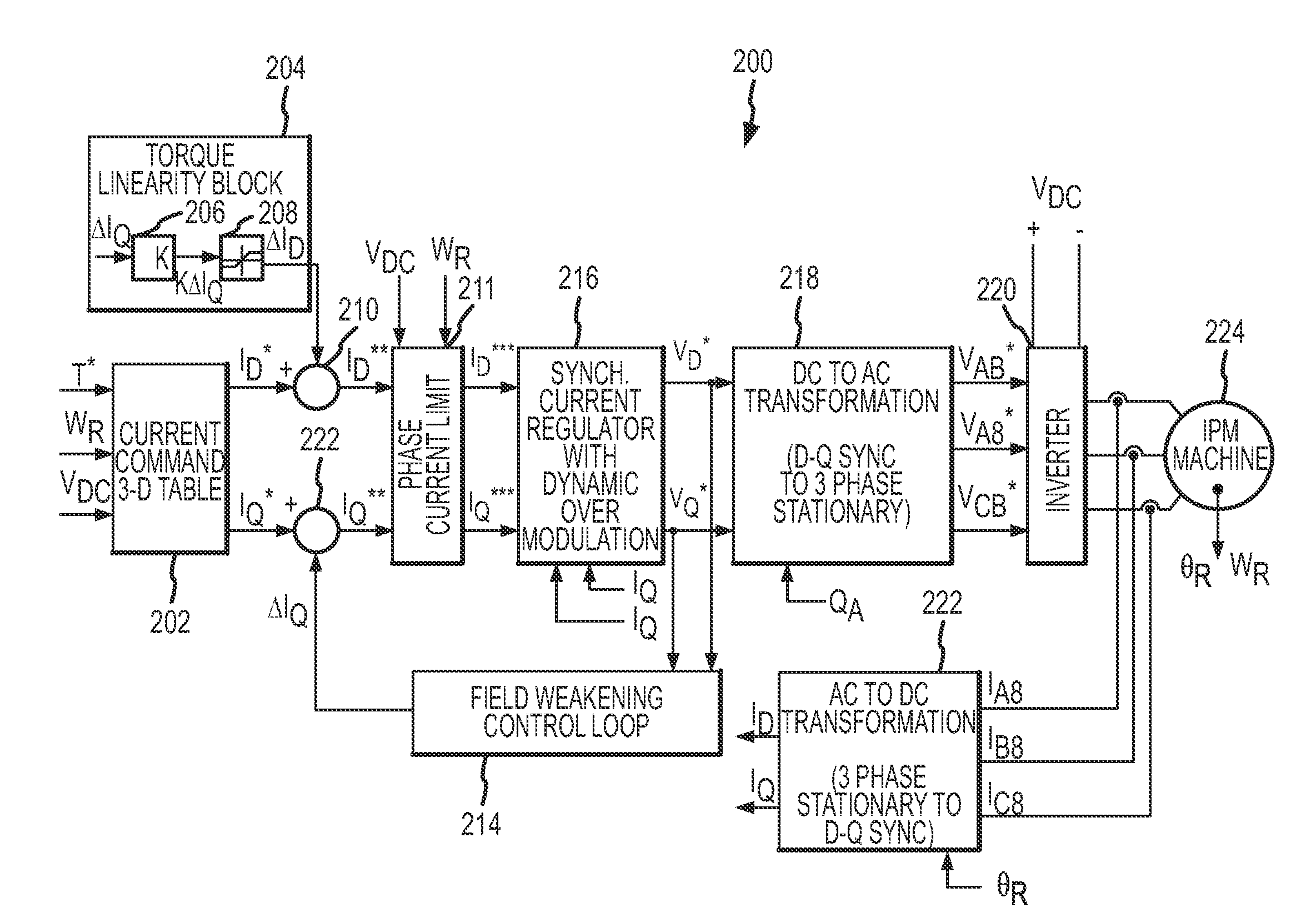
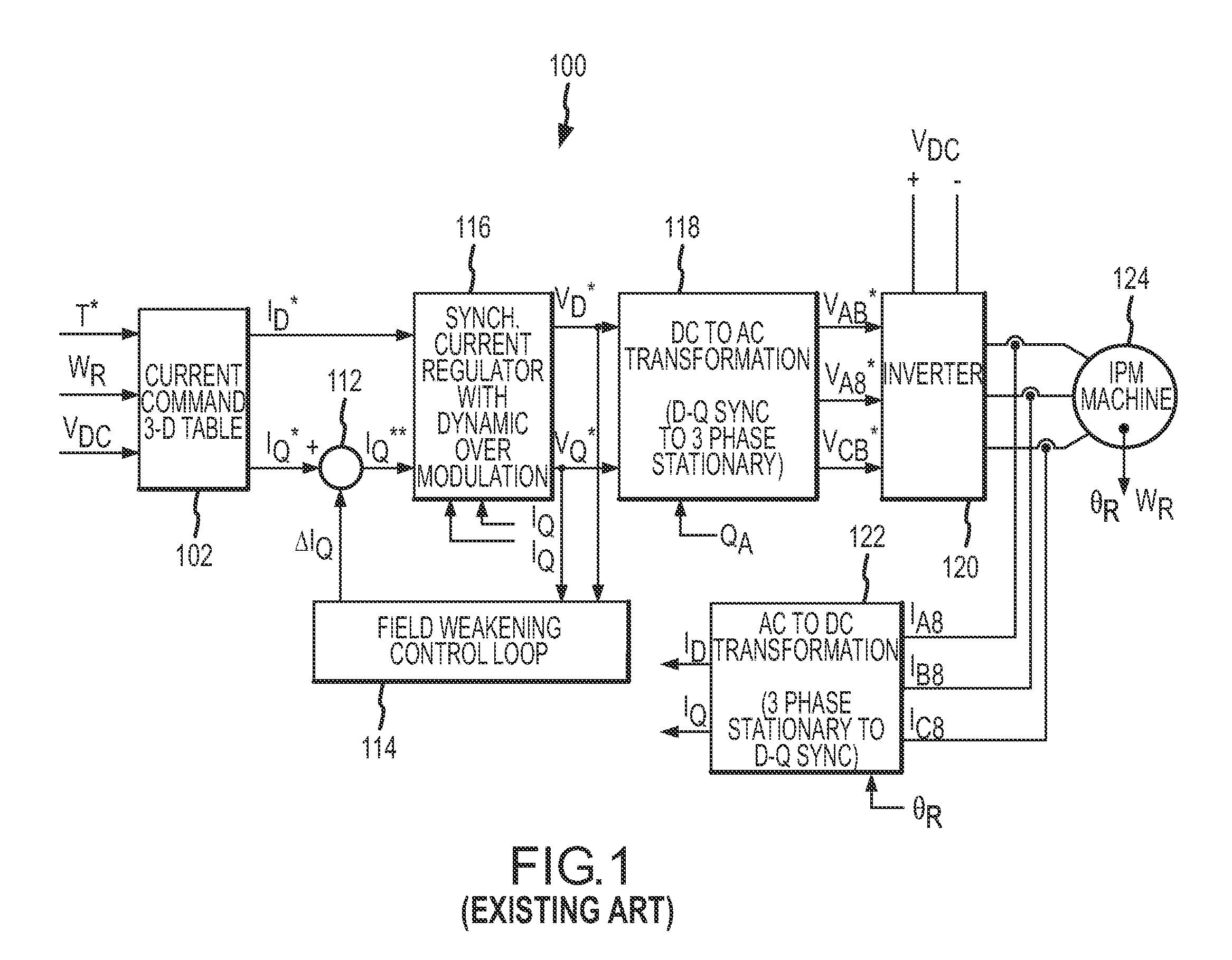
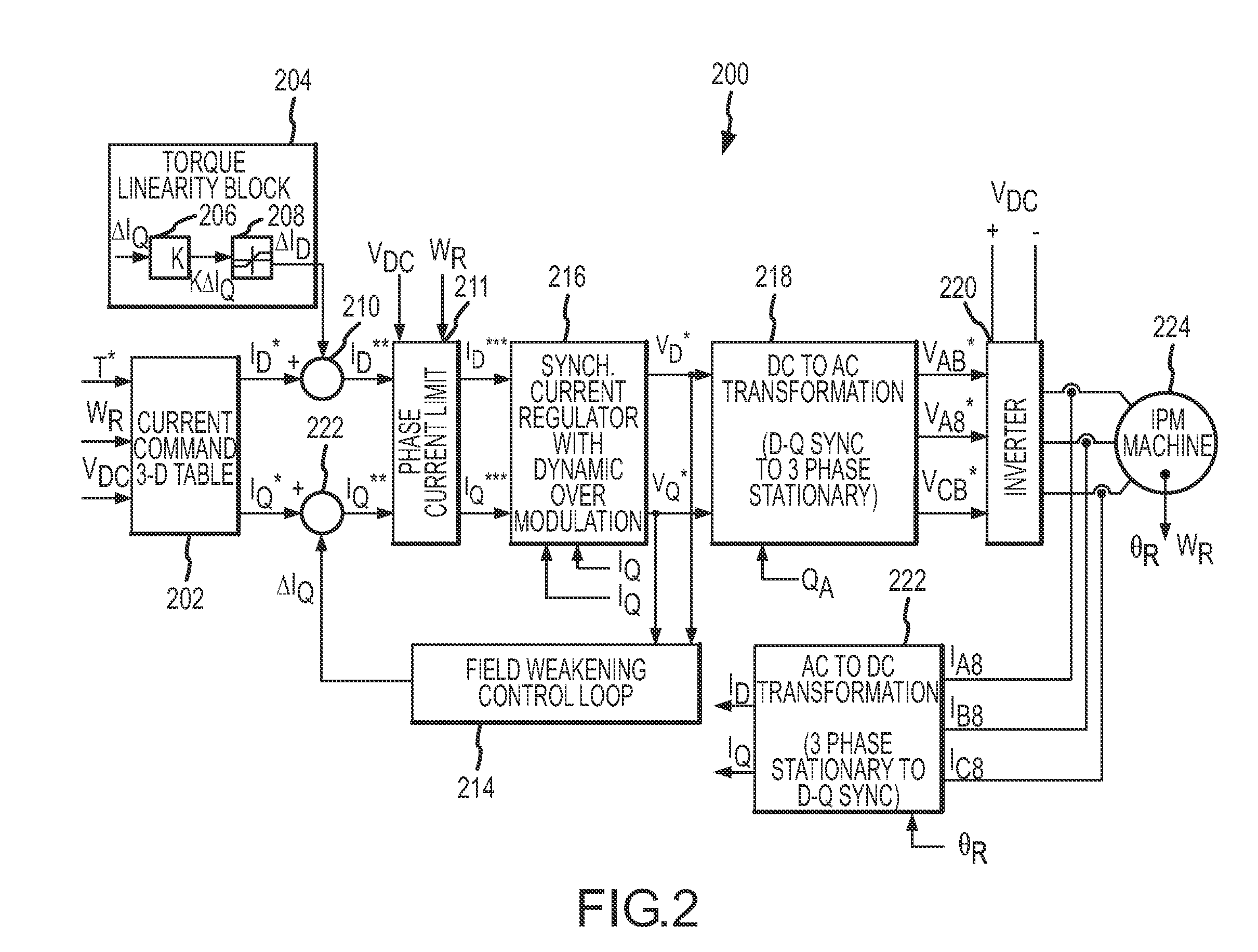
Linearity for field weakening in an interior permanent magnet machine
InactiveUS20090027000A1Speed controllerMotor/generator/converter stoppersMachining systemControl theory
Systems and methods are disclosed to provide torque linearity in the field-weakening region for an IPM machine. The systems and methods adjust the q-axis and the d-axis components of the stator current commands of the IPM machine using a flux weakening and a torque linearity control loop respectively. Thereby, torque linearity is maintained during the field weakening region of operation of the IPM machine.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method for starting a brushless d.c. motor
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
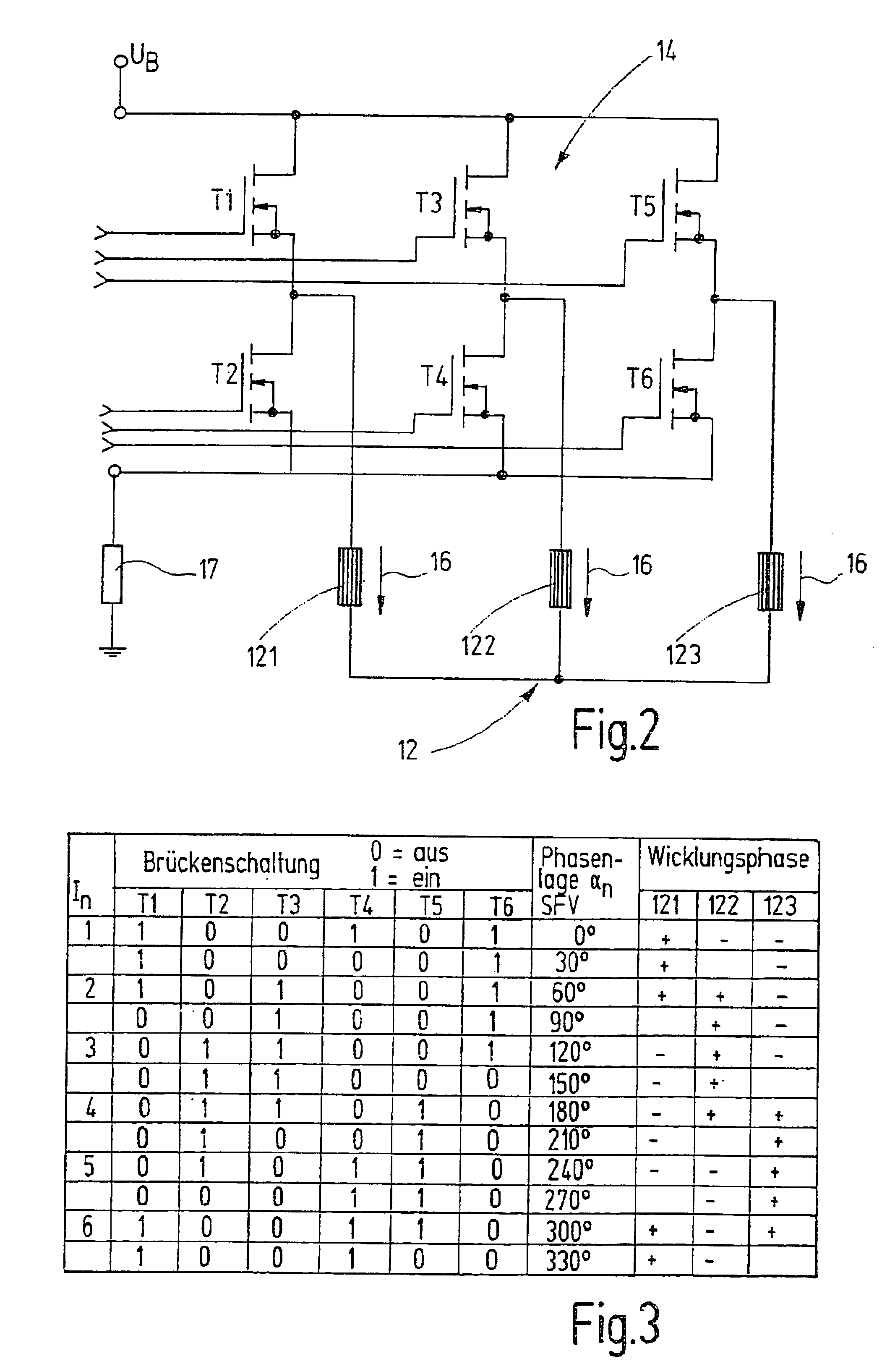
Drive system of synchronous motor
InactiveUS20090200971A1Acceleration time shortenedEfficiently formedMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersSynchronous motorPermanent magnet motor
A drive system of a permanent magnet motor is constituted of a mode switching trigger generator which monitors a state of a permanent magnet motor and issues a mode switching trigger, a conduction mode determining unit which receives the mode switching trigger and switches the mode of the permanent magnet motor, and a PWM generator which outputs a PWM signal to an inverter in accordance with the output of the conduction mode determining unit. The mode switching trigger is generated on condition that the speed electromotive force of the permanent magnet motor exceeds a constant or variable threshold value.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
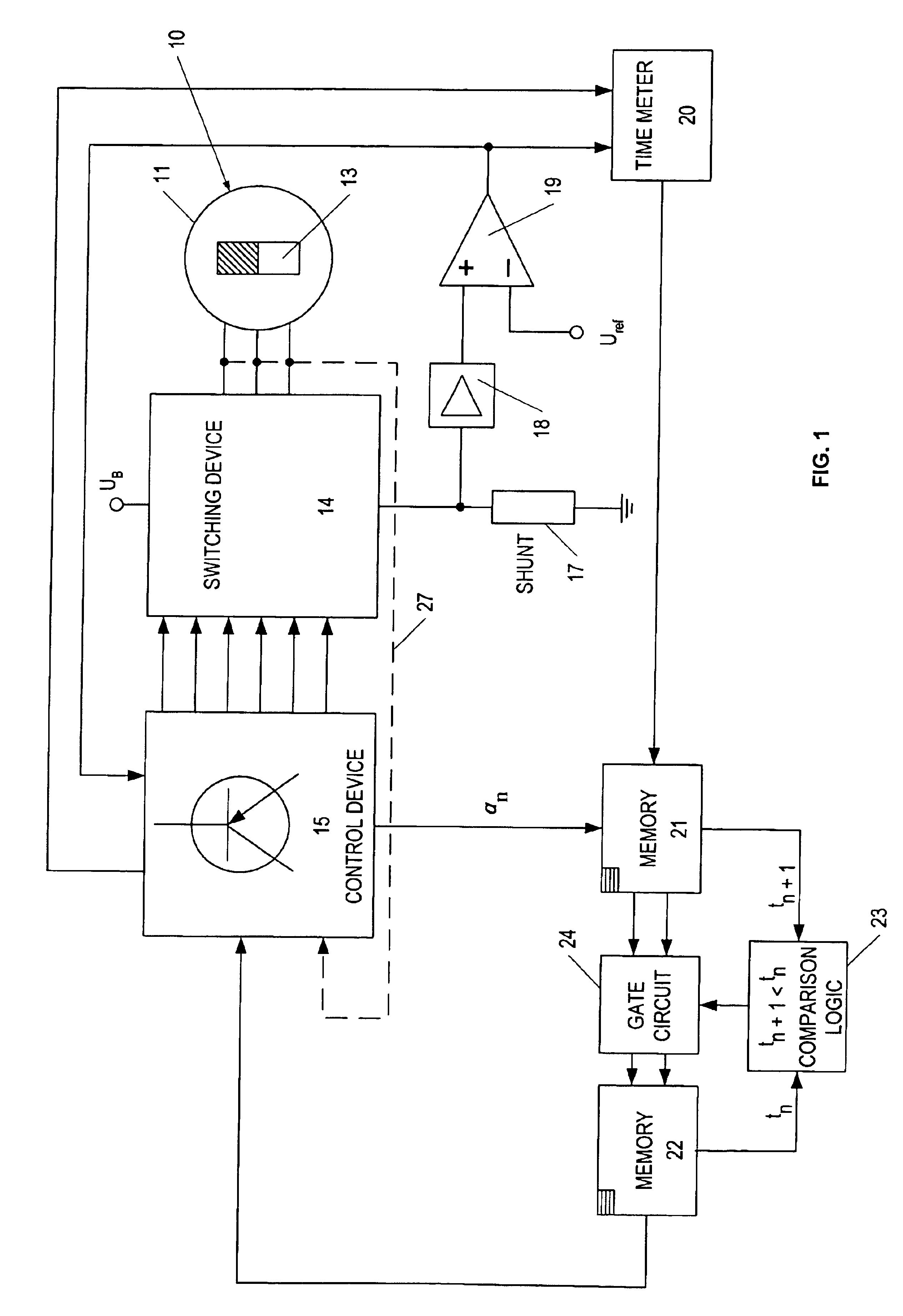
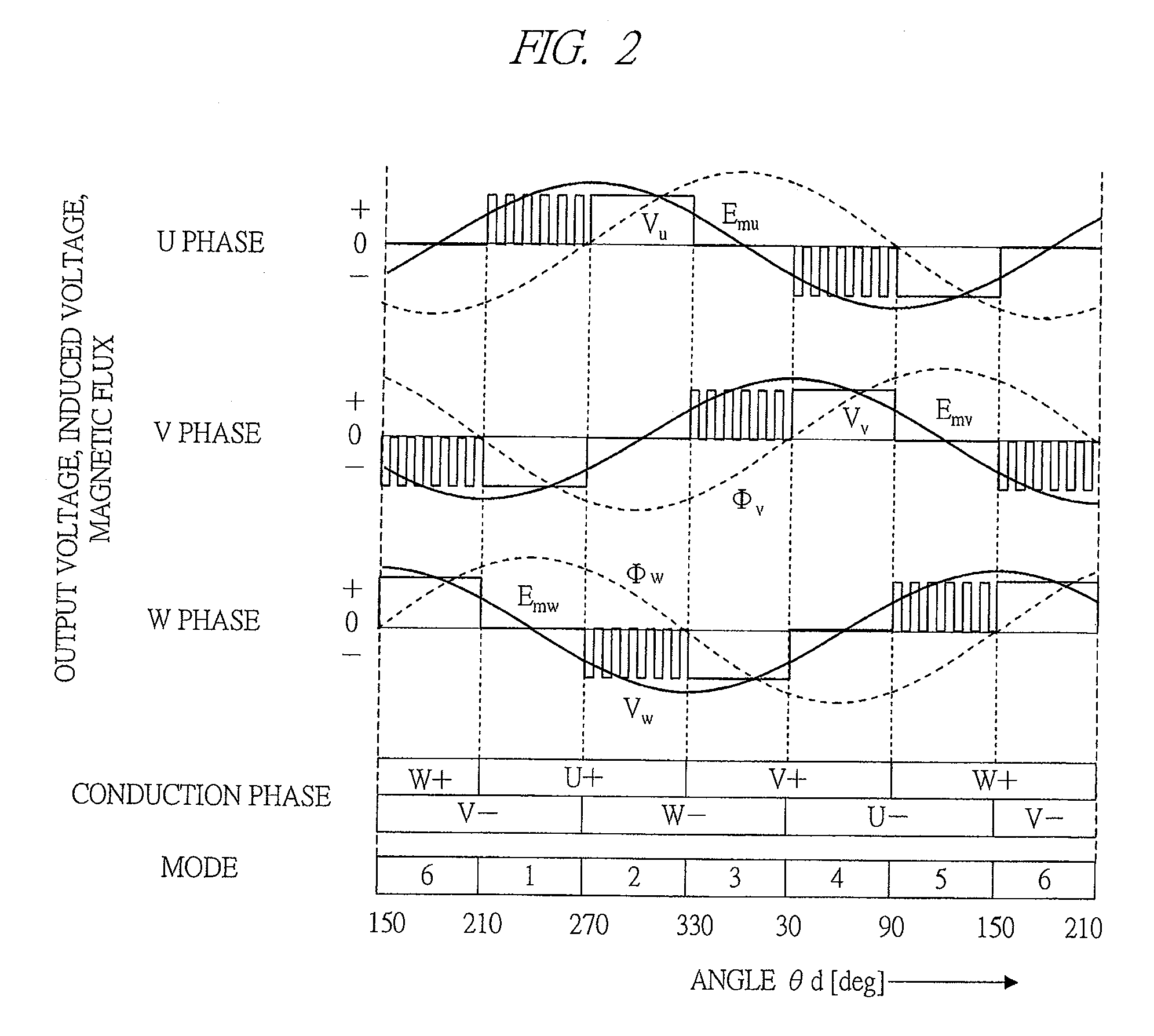
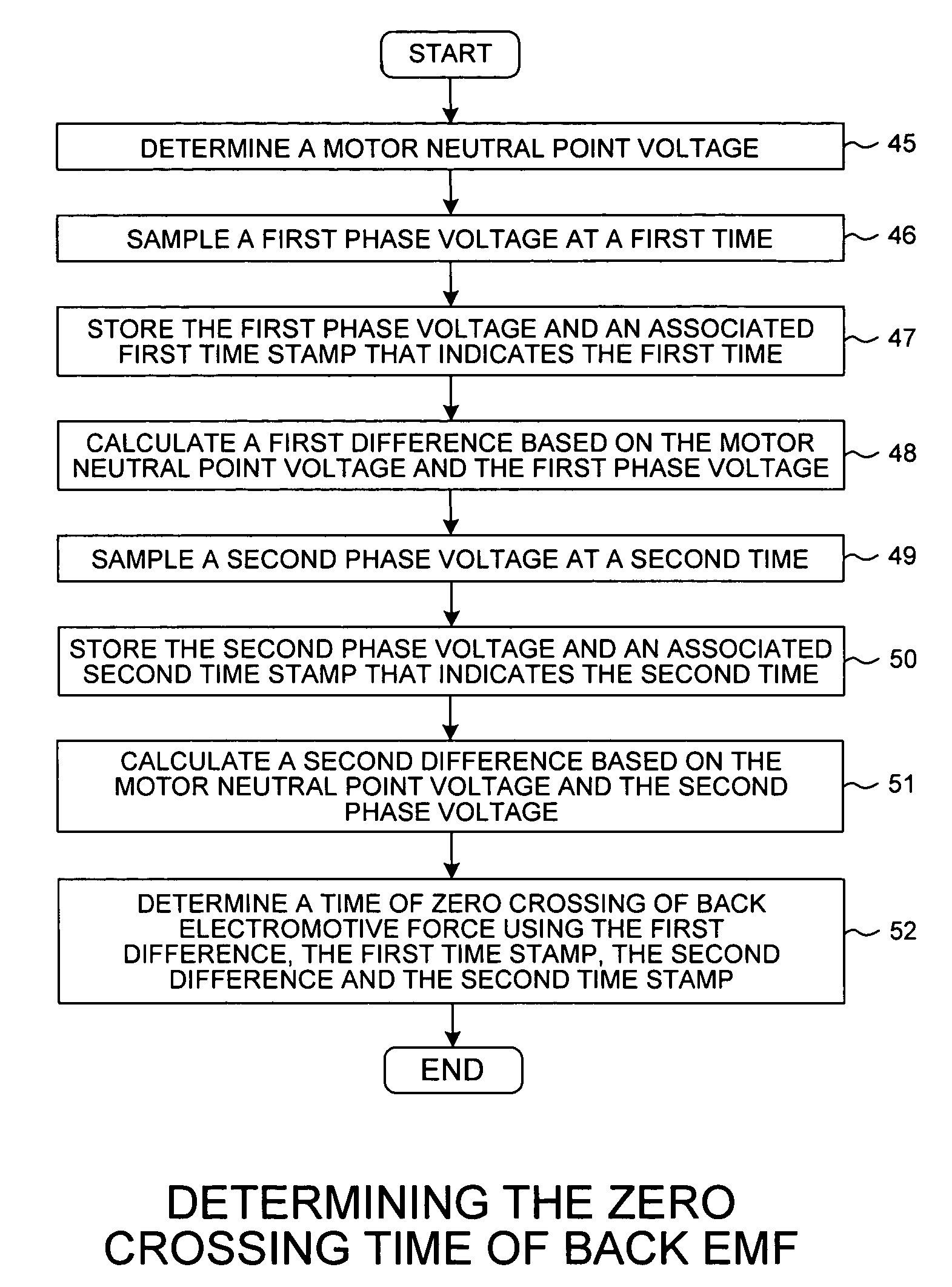
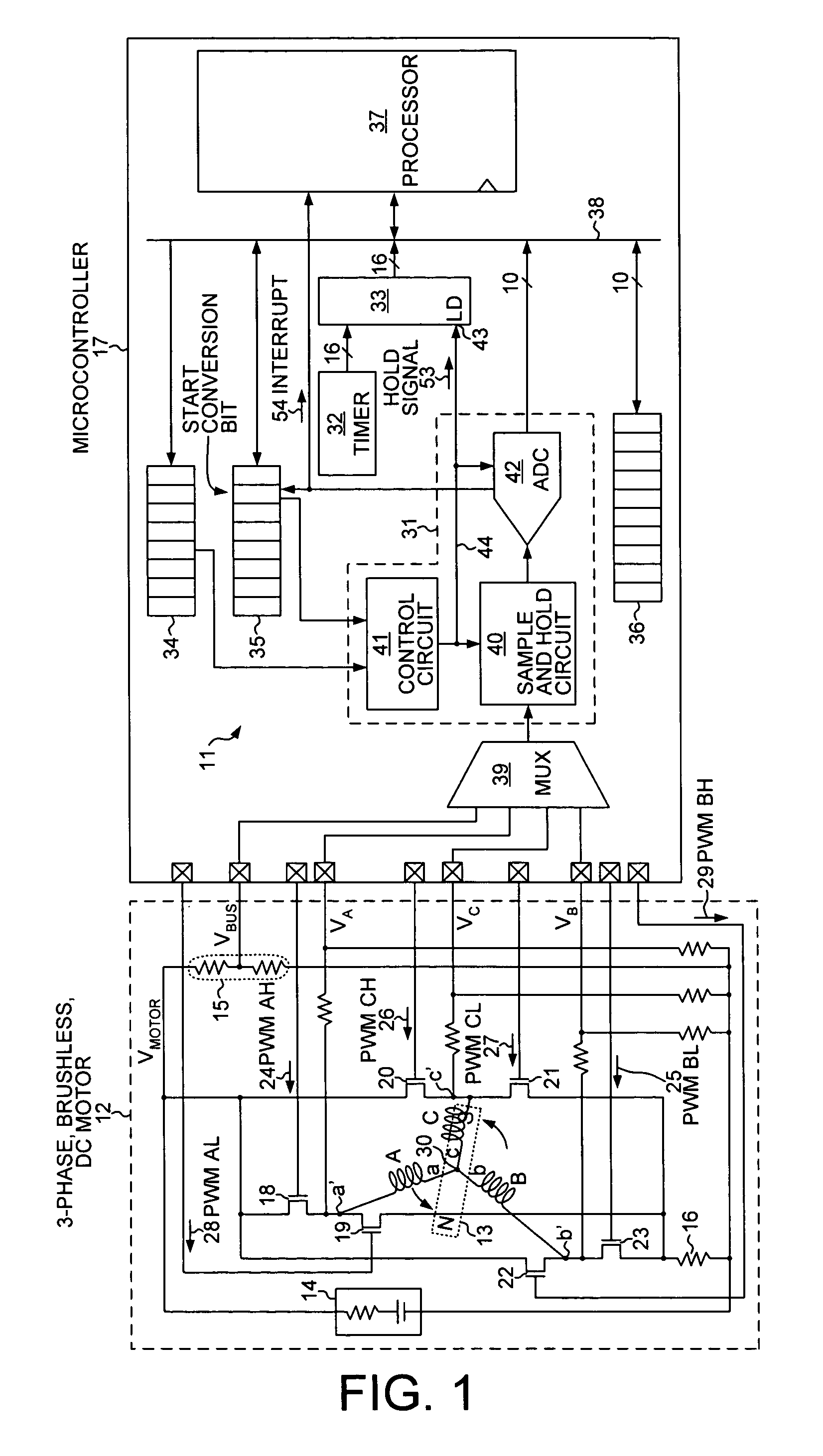
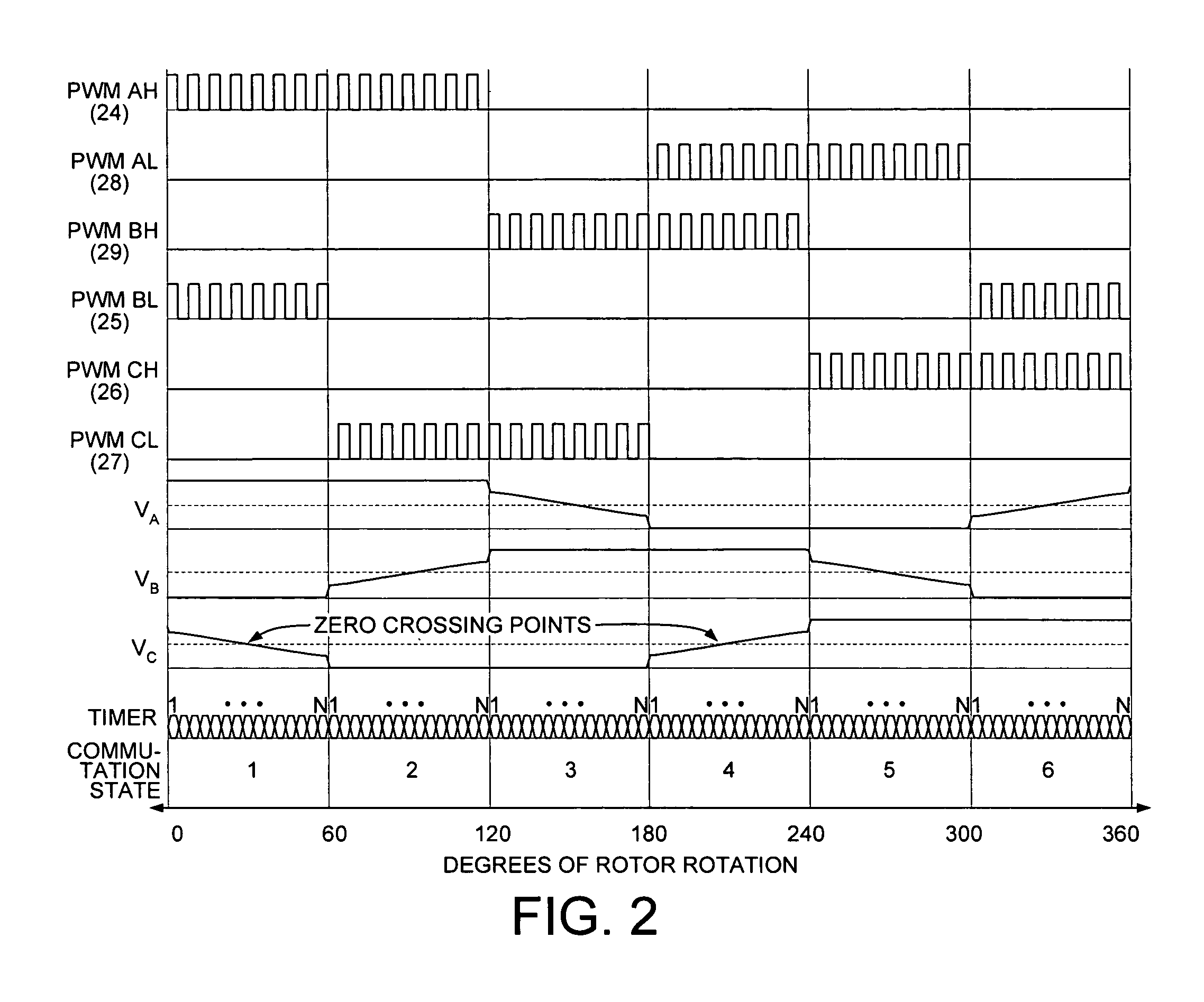
Sample and hold time stamp for sensing zero crossing of back electromotive force in 3-phase brushless DC motors
InactiveUS8030867B1Motor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersMicrocontrollerEngineering
A microcontroller determines the position of the rotor of a brushless, direct-current motor by determining the time of zero crossing of back electromotive force (EMF) emanating from the non-driven phase winding. The zero crossing point is determined by interpolating voltage differentials that are time stamped. Each voltage differential is the difference between the phase voltage of the phase winding and the motor neutral point voltage. The time of zero crossing is determined without using a comparator and without interrupting the processor at each zero crossing point. The processor interpolates the time of zero crossing independently of when the zero crossing point occurs. A hold signal conductor is connected both to a sample and hold circuit and to the load input lead of a time stamp register. The microcontroller simultaneously captures a phase voltage in the sample and hold circuit and a timer count in the time stamp register.
Owner:IXYS INTL LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com