Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1194 results about "Short-channel effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
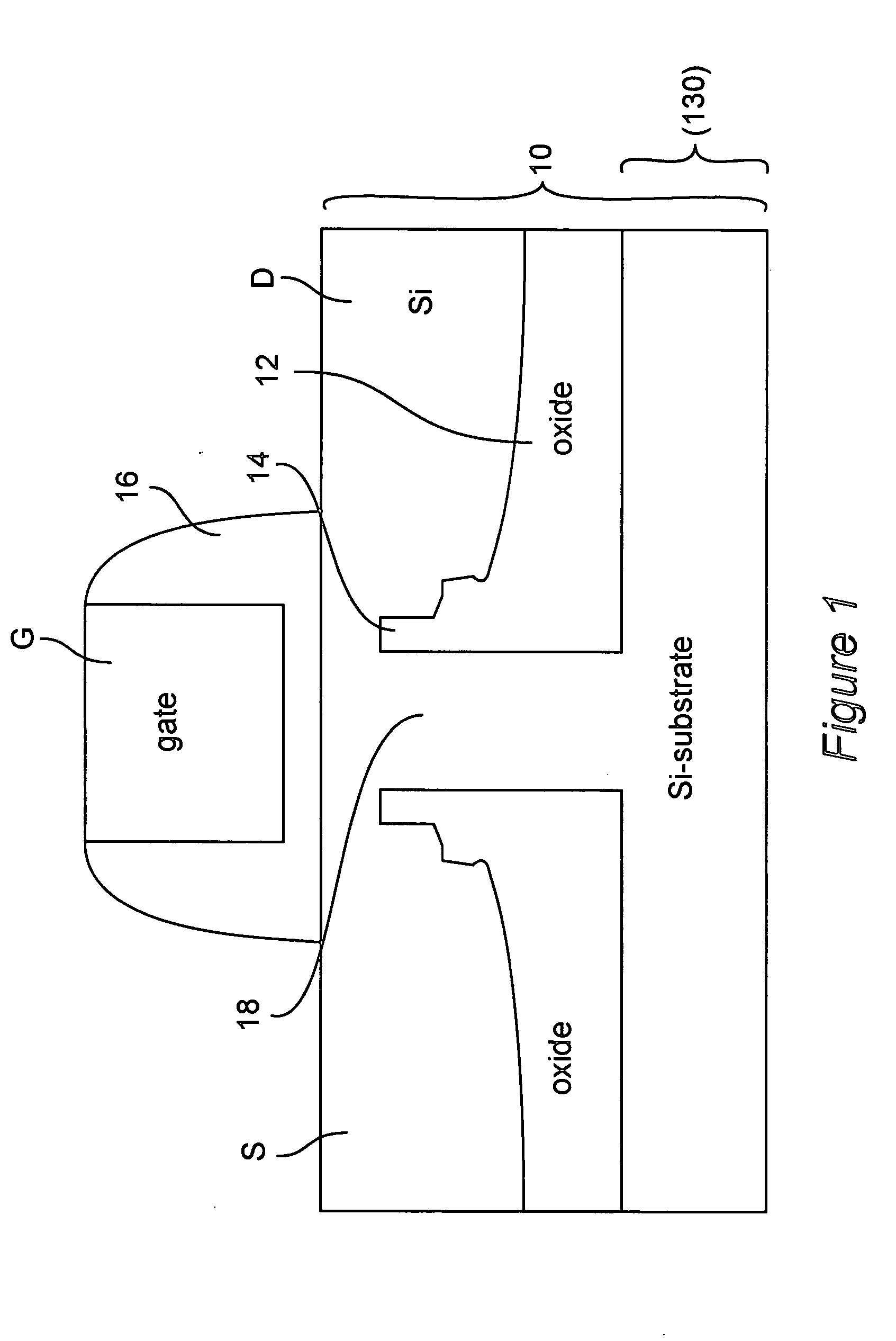
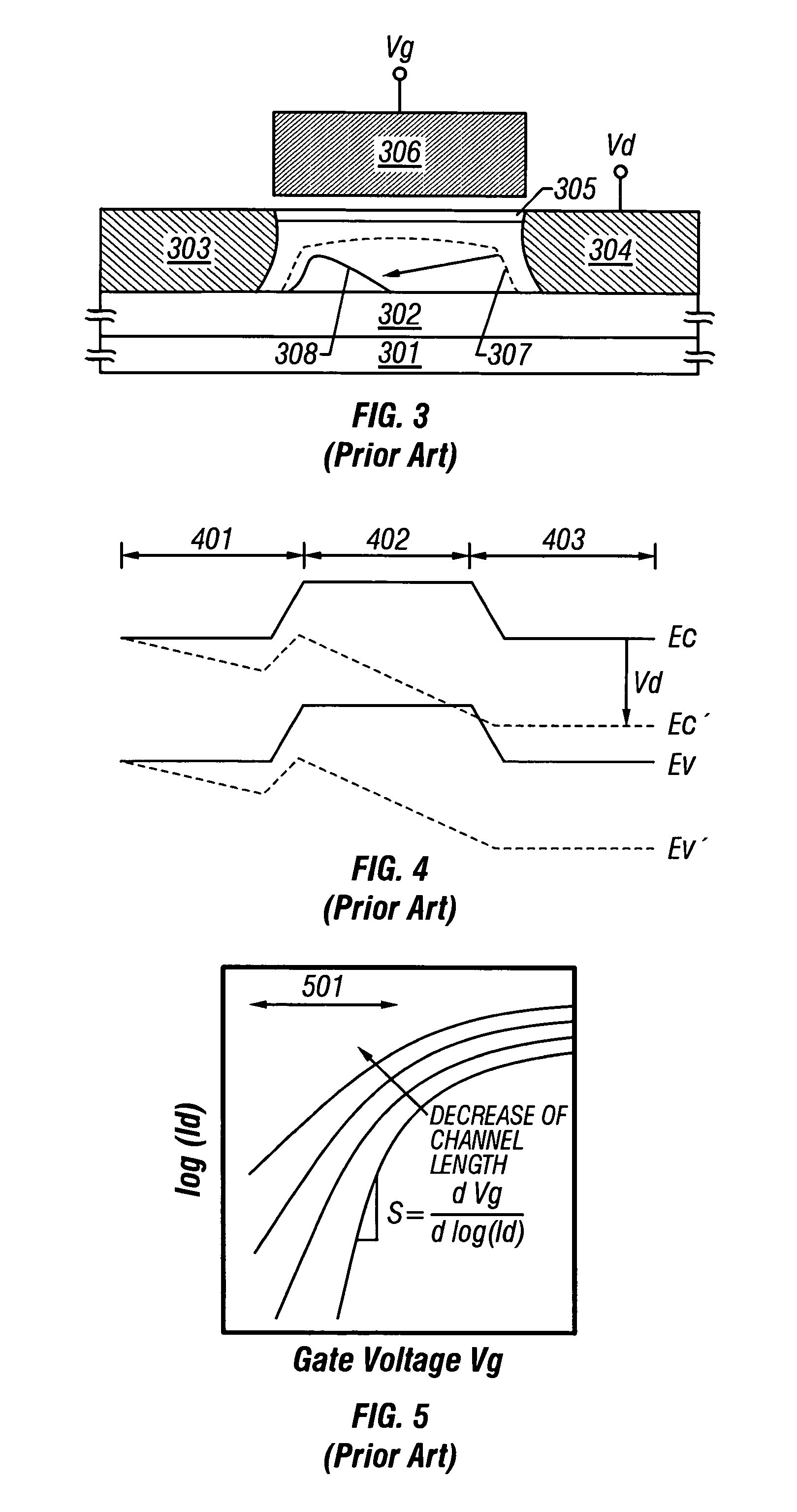
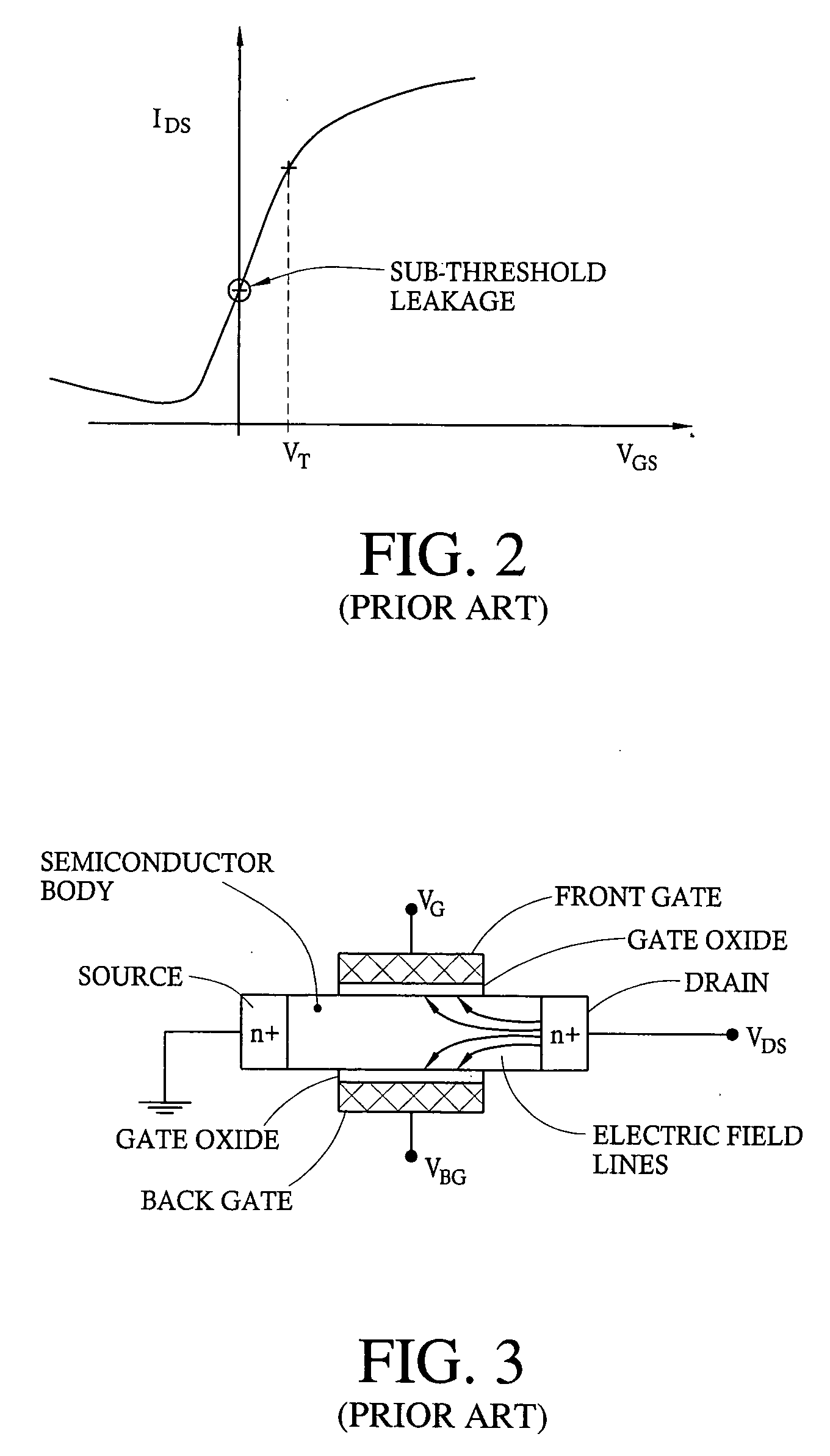
In electronics, short-channel effects occur in MOSFETs in which the channel length is comparable to the depletion layer widths of the source and drain junctions. These effects include, in particular, drain-induced barrier lowering, velocity saturation, and hot carrier degradation.
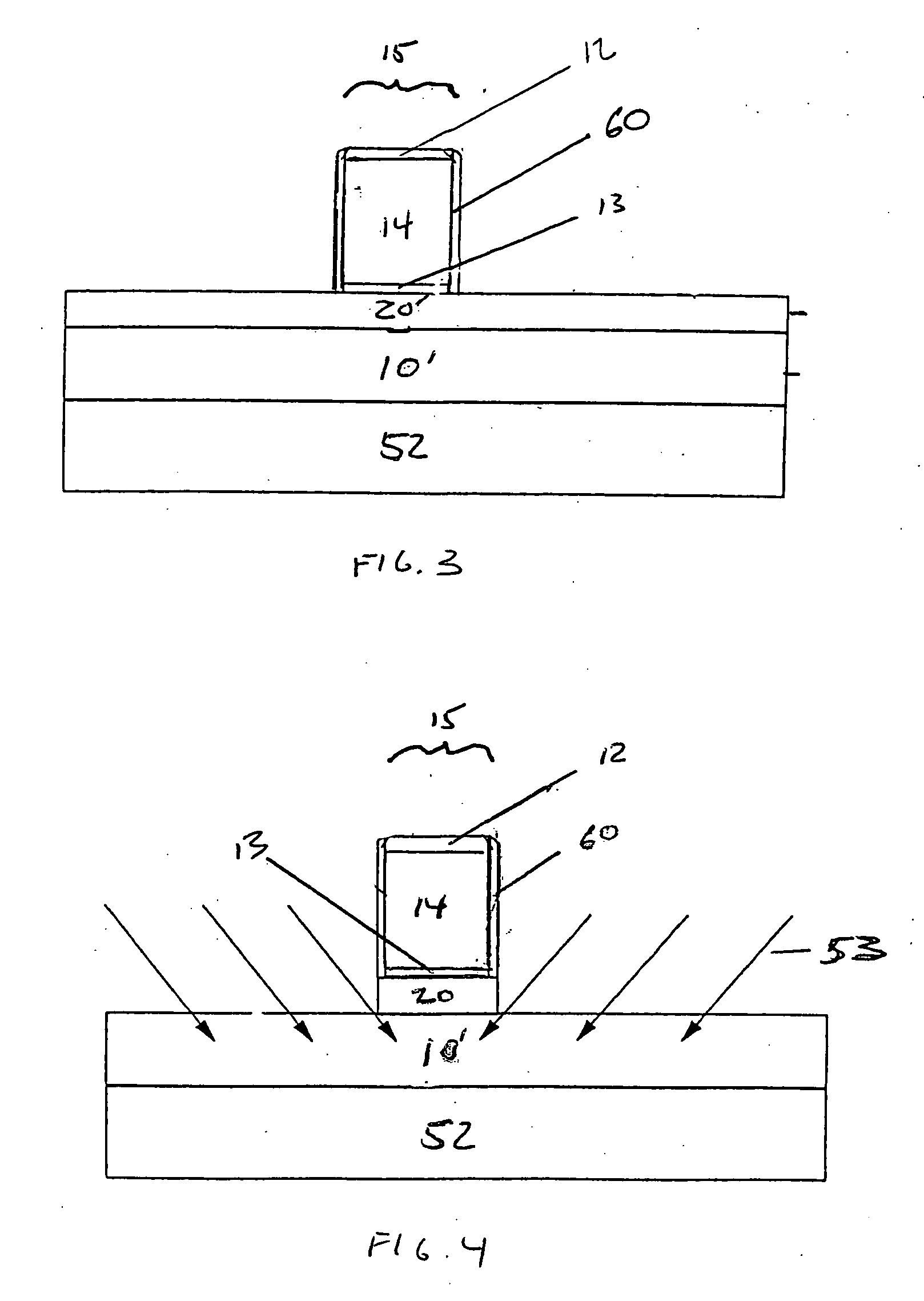
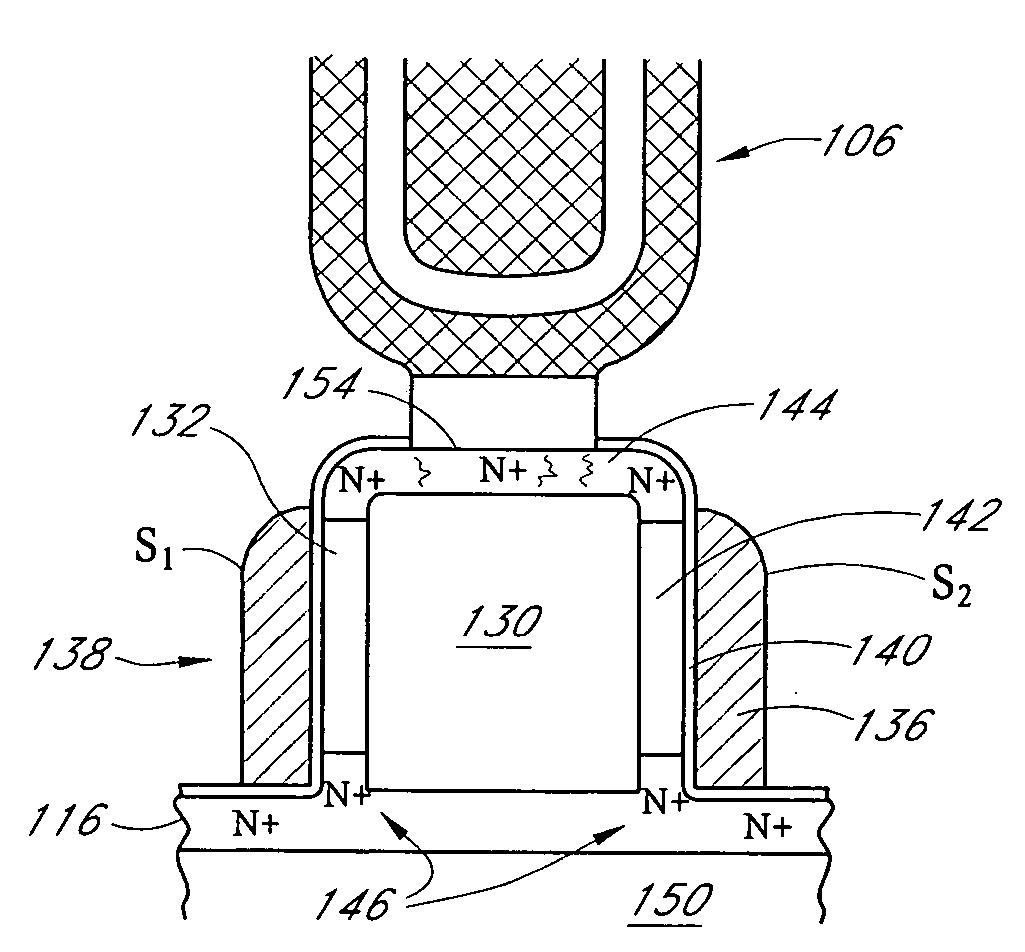
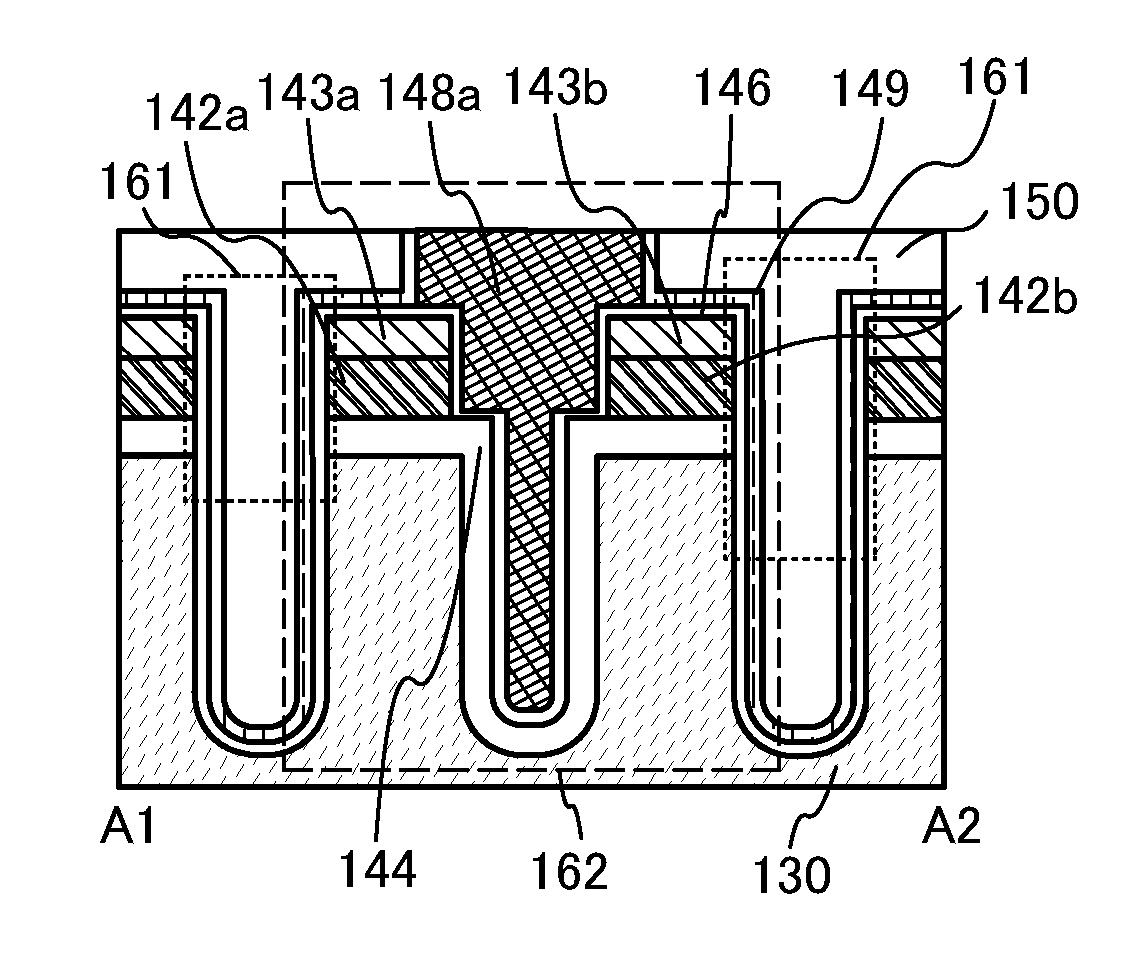
Low leakage heterojunction vertical transistors and high performance devices thereof
InactiveUS6943407B2Superb performanceSuperb scalabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesReverse short-channel effectHeterojunction
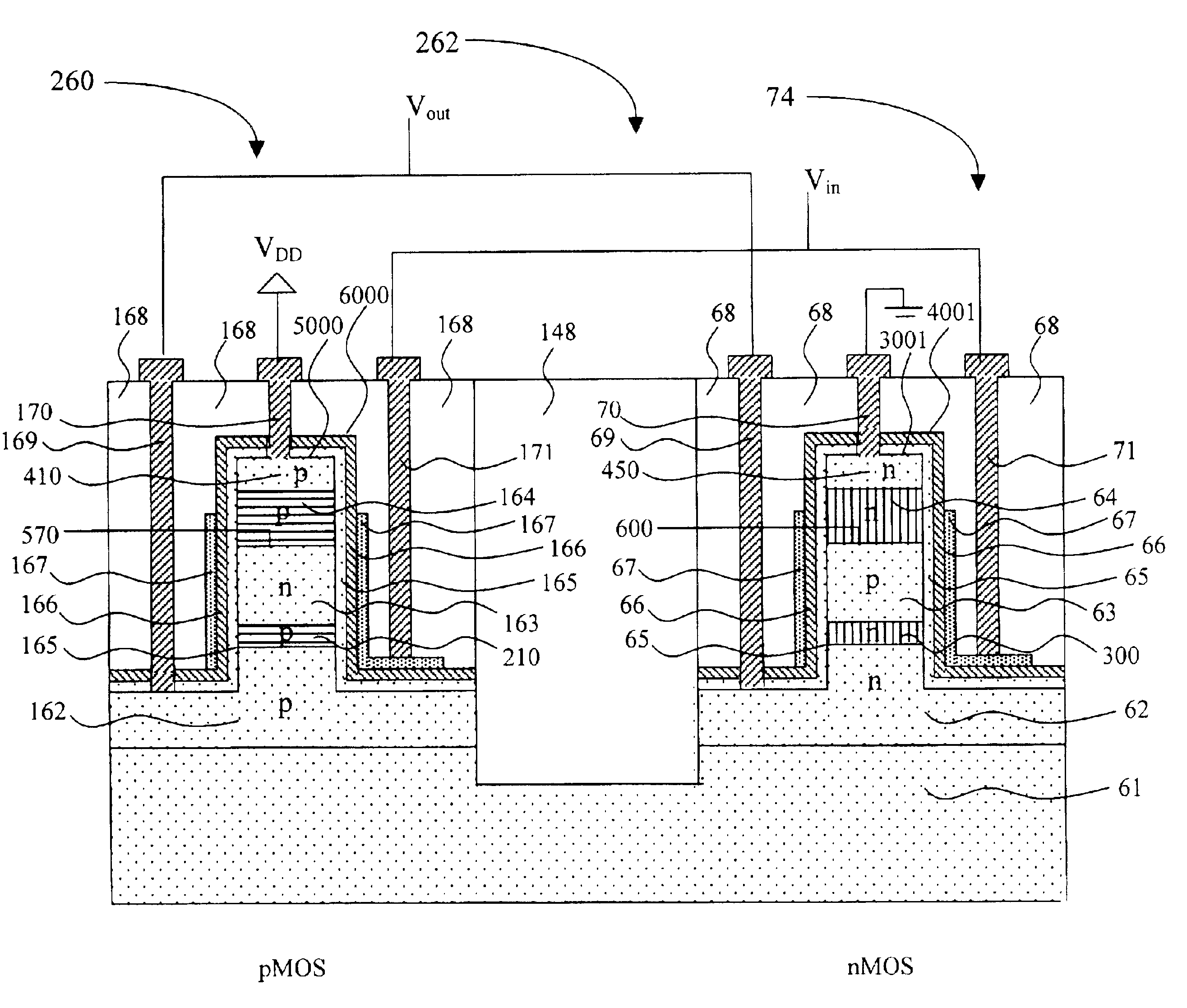
A method for forming and the structure of a vertical channel of a field effect transistor, a field effect transistor and CMOS circuitry are described incorporating a drain, body and source region on a sidewall of a vertical single crystal semiconductor structure wherein a hetero-junction is formed between the source and body of the transistor, wherein the source region and channel are independently lattice strained with respect the body region and wherein the drain region contains a carbon doped region to prevent the diffusion of dopants (i.e., B and P) into the body. The invention reduces the problem of short channel effects such as drain induced barrier lowering and the leakage current from the source to drain regions via the hetero-junction and while independently permitting lattice strain in the channel region for increased mobility via choice of the semiconductor materials. The problem of scalability of the gate length below 100 nm is overcome by the heterojunction between the source and body regions.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20120161126A1Reduce parasitic capacitanceIncrease speedTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialWurtzite crystal structure
A semiconductor device capable of high speed operation is provided. Further, a semiconductor device in which change in electric characteristics due to a short channel effect is hardly caused is provided. An oxide semiconductor having crystallinity is used for a semiconductor layer of a transistor. A channel formation region, a source region, and a drain region are formed in the semiconductor layer. The source region and the drain region are formed by self-aligned process in which one or more elements selected from Group 15 elements are added to the semiconductor layer with the use of a gate electrode as a mask. The source region and the drain region can have a wurtzite crystal structure.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Strained silicon fin structure
InactiveUS20060113522A1Suppression of short channel effectsIncrease currentTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDriving currentLattice mismatch
Disclosing is a strained silicon finFET device having a strained silicon fin channel in a double gate finFET structure. The disclosed finFET device is a double gate MOSFET consisting of a silicon fin channel controlled by a self-aligned double gate for suppressing short channel effect and enhancing drive current. The silicon fin channel of the disclosed finFET device is a strained silicon fin channel, comprising a strained silicon layer deposited on a seed fin having different lattice constant, for example, a silicon layer deposited on a silicon germanium seed fin, or a carbon doped silicon layer deposited on a silicon seed fin. The lattice mismatch between the silicon layer and the seed fin generates the strained silicon fin channel in the disclosed finFET device to improve hole and electron mobility enhancement, in addition to short channel effect reduction characteristic inherently in a finFET device.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC +1
High mobility heterojunction complementary field effect transistors and methods thereof
ActiveUS20050093021A1Minimal toleranceHigh hole mobilityTransistorSolid-state devicesHeterojunctionCMOS
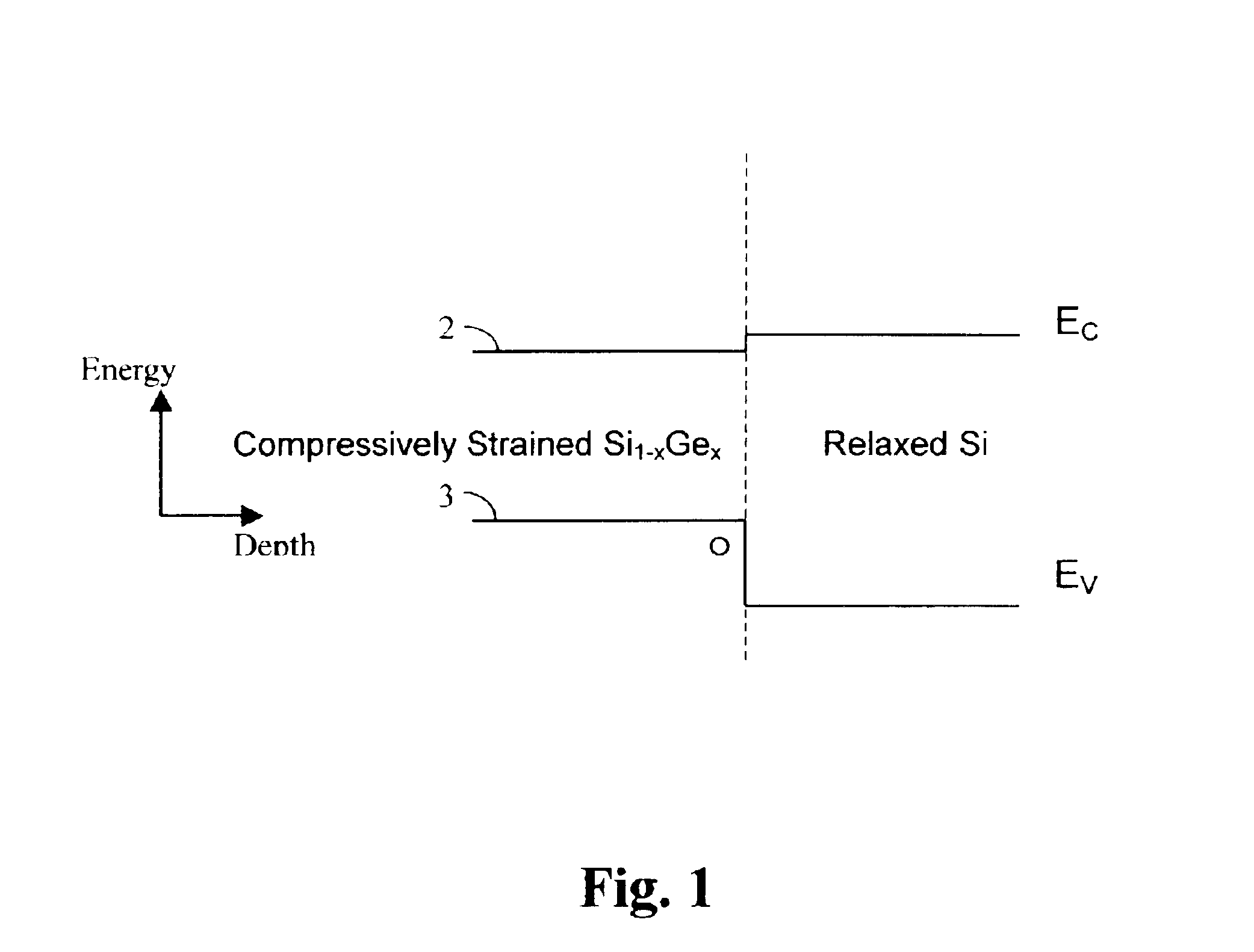
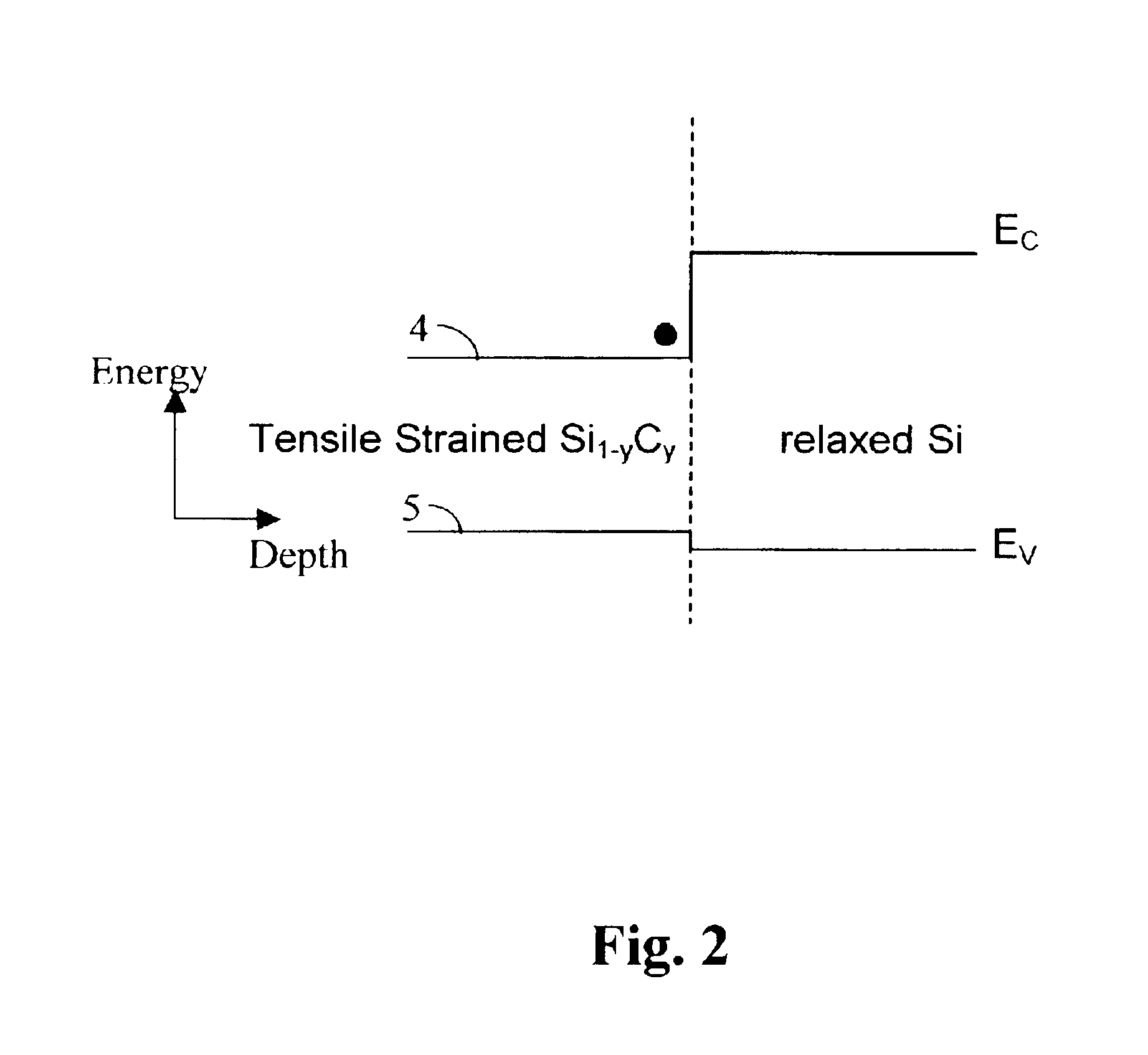
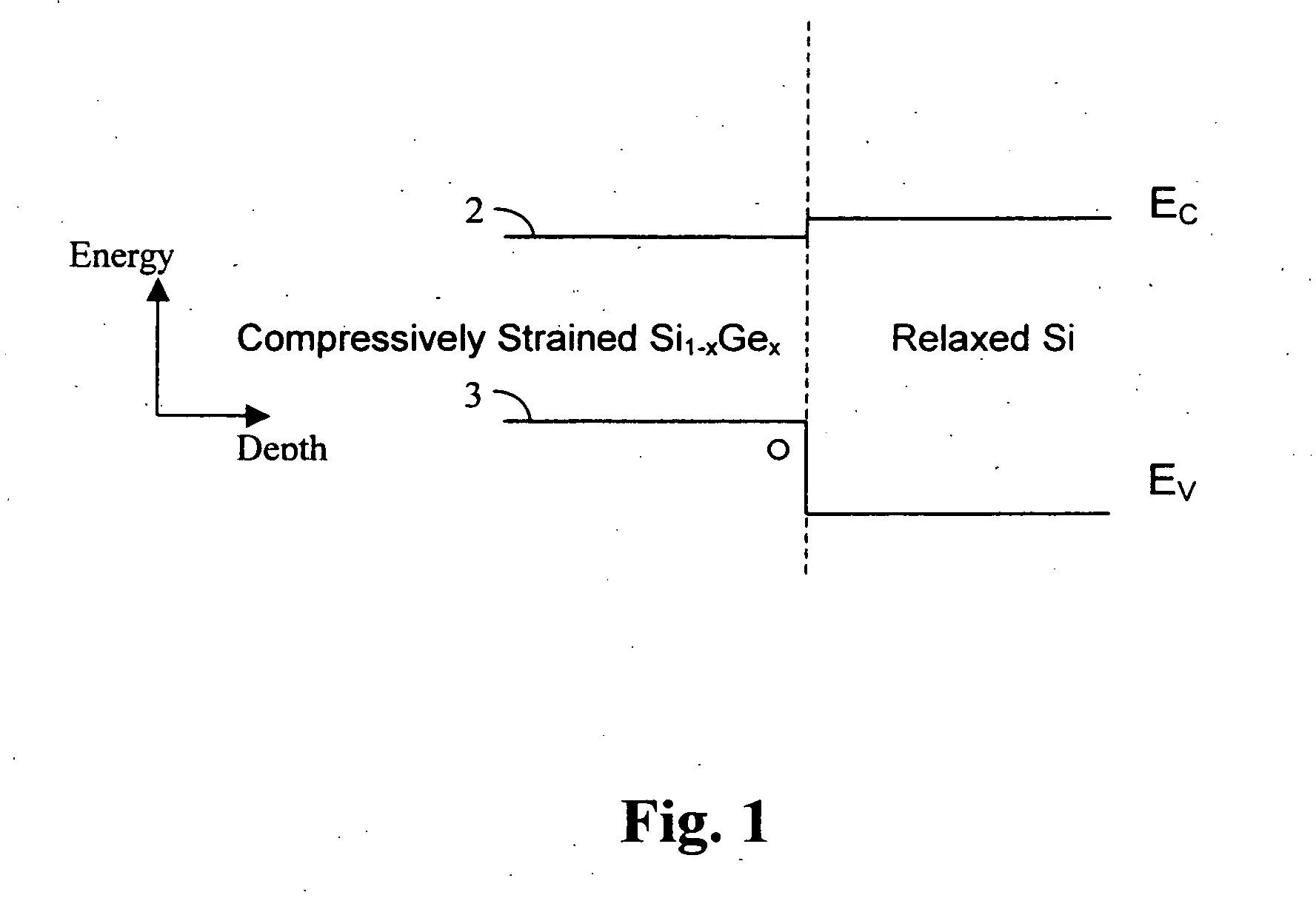
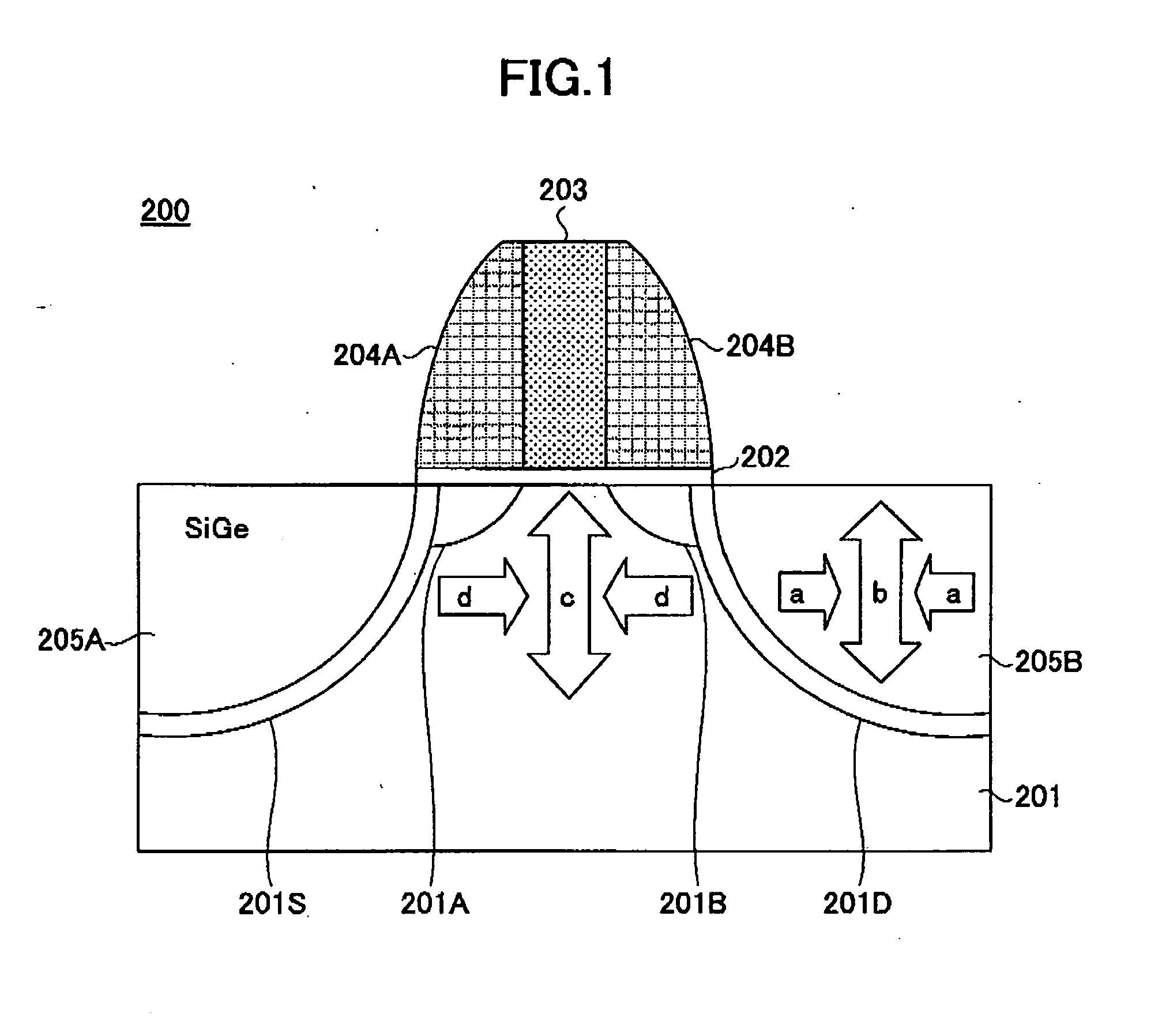
A structure, and method of fabrication, for high performance field effect devices is disclosed. The MOS structures include a crystalline Si body of one conductivity type, a strained SiGe layer epitaxially grown on the Si body serving as a buried channel for holes, a Si layer epitaxially grown on the SiGe layer serving as a surface channel for electrons, and a source and a drain containing an epitaxially deposited, strained SiGe of opposing conductivity type than the Si body. The SiGe source / drain forms a heterojunction and a metallurgical junction with the Si body that coincide with each other with a tolerance of less than about 10 nm, and preferably less than about 5 nm. The heterostructure source / drain is instrumental in reducing short channel effects. These structures are especially advantageous for PMOS due to increased hole mobility in the compressively strained SiGe channel. Representative embodiments include CMOS structures on bulk and on SOI.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20100200919A1Suppression of short channel effectsSpeed up the flowTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSemiconductor packageImpurity
The invention provides a semiconductor device capable of suppressing a short channel effect and fluctuation in a threshold. The semiconductor device includes: a plurality of first transistors formed in a first region in a semiconductor layer in a multilayer substrate having, on a semiconductor substrate, an insulating layer and the semiconductor layer in order from the semiconductor substrate; a plurality of second transistors formed in a second region in the semiconductor layer; a first impurity layer formed in a region opposed to the first region in the semiconductor substrate; a second impurity layer formed in a region opposed to the second region in the semiconductor substrate; and a first isolation part that isolates the first and second regions from each other and electrically isolates the first and second impurity layers from each other to a degree that at least current flowing between the first and second impurity layers is interrupted.
Owner:SONY CORP
Structure and method for manufacturing MOSFET with super-steep retrograded island
InactiveUS20060068555A1Reduce morbidityReduce diffuseTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingKryptonDopant
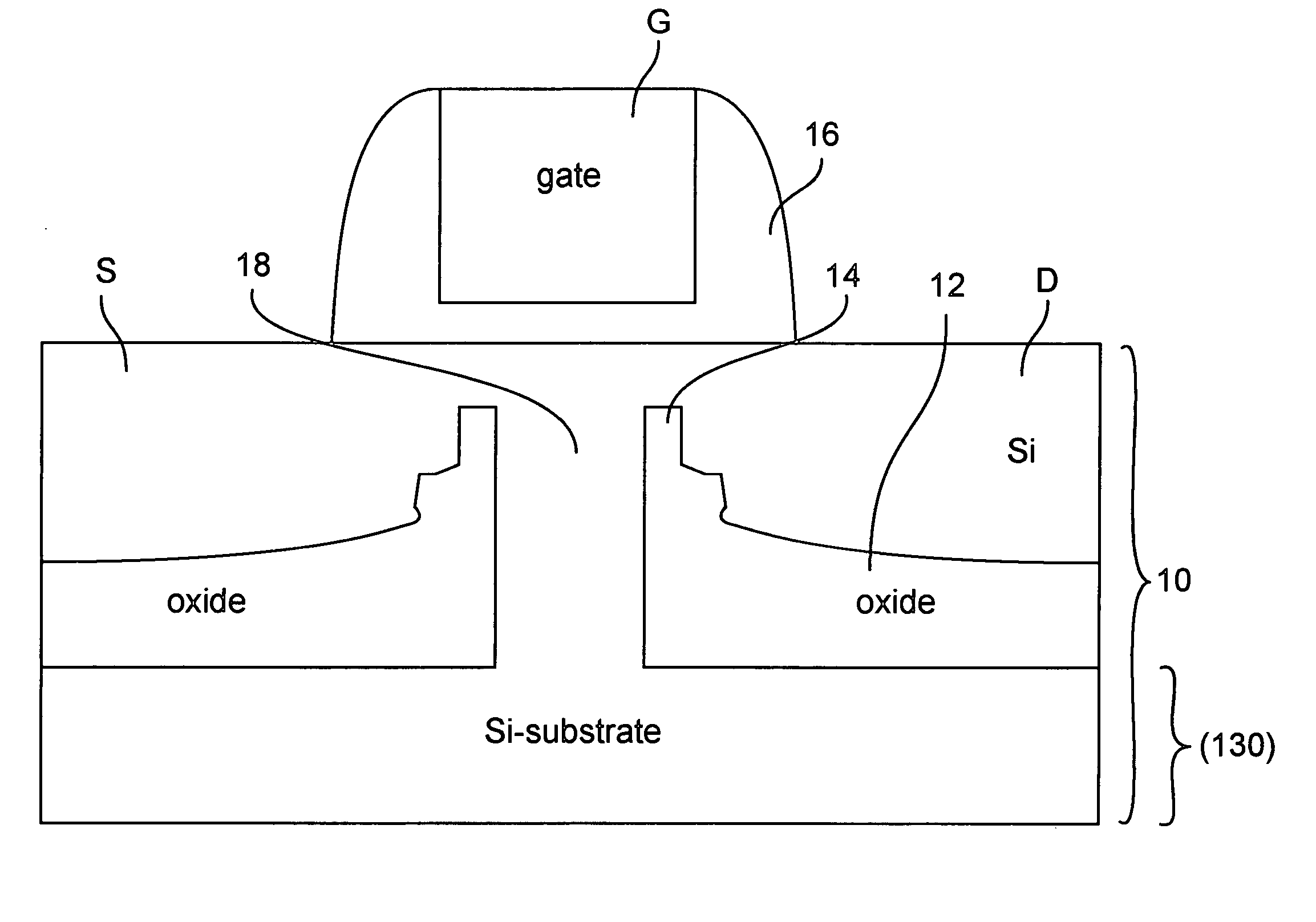
The present invention comprises a method for forming a semiconducting device including the steps of providing a layered structure including a substrate, a low diffusivity layer of a first-conductivity dopant; and a channel layer; forming a gate stack atop a protected surface of the channel layer; etching the layered structure selective to the gate stack to expose a surface of the substrate, where a remaining portion of the low diffusivity layer provides a retrograded island substantially aligned to the gate stack having a first dopant concentration to reduce short-channel effects without increasing leakage; growing a Si-containing material atop the recessed surface of the substrate; and doping the Si-containing material with a second-conductivity dopant at a second dopant concentration. The low diffusivity layer may be Si1-x-yGexZy, where Z can be carbon (C), xenon (Xe), germanium (Ge), krypton (Kr), argon (Ar), nitrogen (N), or combinations thereof.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
High performance CMOS device structure with mid-gap metal gate
InactiveUS6916698B2Improve performanceReduce diffuseTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSWork function
High performance (surface channel) CMOS devices with a mid-gap work function metal gate are disclosed wherein an epitaxial layer is used for a threshold voltage Vt adjust / decrease for the PFET area, for large Vt reductions (˜500 mV), as are required by CMOS devices with a mid-gap metal gate. The present invention provides counter doping using an in situ B doped epitaxial layer or a B and C co-doped epitaxial layer, wherein the C co-doping provides an additional degree of freedom to reduce the diffusion of B (also during subsequent activation thermal cycles) to maintain a shallow B profile, which is critical to provide a surface channel CMOS device with a mid-gap metal gate while maintaining good short channel effects. The B diffusion profiles are satisfactorily shallow, sharp and have a high B concentration for devices with mid-gap metal gates, to provide and maintain a thin, highly doped B layer under the gate oxide.
Owner:IBM CORP
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20110193164A1Reduce parasitic capacitanceLarge thicknessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor deviceGate dielectric
The present application discloses a semiconductor device formed on a SOI substrate which comprises a buried insulating layer and a semiconductor layer on the buried insulating layer and a method for manufacturing the same, wherein a fin of semiconductive material having two opposing sides perpendicular to a main surface of the SOI substrate is provided in the semiconductor layer, said semiconductor device comprising: a source region and a drain region provided at two ends of the fin respectively; a channel region provided at a central portion of the fin; and a stack of gate dielectric and gate conductor provided at one side of the fin, where the gate conductor is isolated from the channel region by the gate dielectric, wherein the gate conductor extends away from the one side of the fin in a direction parallel to the main surface of the SOI substrate. The semiconductor device has an improved short channel effect and a reduced parasitic capacitance and resistance, which contributes to an improved electrical property and facilitates scaling down of the transistor.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Low threshold voltage semiconductor device
InactiveUS7078776B2Easy to changeSuppression of short channel effectsTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorSemiconductor package
A semiconductor device has a first semiconductor region formed in a semiconductor substrate and having a first conductivity type due to first-conductivity-type active impurities contained in the first semiconductor region, and a second semiconductor region formed between the first semiconductor region and the surface of the semiconductor substrate and having a second conductivity type due to second-conductivity-type active impurities contained in the second semiconductor region. The second semiconductor region contains first-conductivity-type active impurities, whose concentration is zero or smaller than a quarter of a concentration of the second-conductivity-type active impurities contained in the second semiconductor region. An insulating film and a conductor are formed on the second semiconductor region. Third and fourth semiconductor regions of the second conductivity type are formed at the semiconductor surface in contact with the side faces of the second semiconductor region. This semiconductor device is capable of suppressing net impurity concentration variations as well as threshold voltage variations to be caused by a short channel effect or manufacturing variations.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
High performance MOSFET
InactiveUS7704844B2Improve device performanceImprove short channel effectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh concentrationDopant
A semiconductor structure which exhibits high device performance and improved short channel effects is provided. In particular, the present invention provides a metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOFET) that includes a low dopant concentration within an inversion layer of the structure; the inversion layer is an epitaxial semiconductor layer that is formed atop a portion of the semiconductor substrate. The inventive structure also includes a well region of a first conductivity type beneath the inversion layer, wherein the well region has a central portion and two horizontally abutting end portions. The central portion has a higher concentration of a first conductivity type dopant than the two horizontally abutting end portions. Such a well region may be referred to as a non-uniform super-steep retrograde well.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Manufacturing method of semiconductor device suppressing short-channel effect
ActiveUS7223646B2Improve reliabilityEliminate the effects ofTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingImpuritySemiconductor
An ideal step-profile in a channel region is realized easily and reliably, whereby suppression of the short-channel effect and prevention of mobility degradation are achieved together. A silicon substrate is amorphized to a predetermined depth from a semiconductor film, and impurities to become the source / drain are introduced in this state. Then the impurities are activated, and the amorphized portion is recrystallized, by low temperature solid-phase epitaxial regrowth. With the processing temperature required for the low temperature solid-phase epitaxial regrowth being within a range of 450° C.–650° C., thermal diffusion of the impurities into the semiconductor film is suppressed, thereby maintaining the initial steep step-profile.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
High performance mosfet
InactiveUS20090090979A1Improve device performanceImprove short channel effectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh concentrationDopant
A semiconductor structure which exhibits high device performance and improved short channel effects is provided. In particular, the present invention provides a metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOFET) that includes a low dopant concentration within an inversion layer of the structure; the inversion layer is an epitaxial semiconductor layer that is formed atop a portion of the semiconductor substrate. The inventive structure also includes a well region of a first conductivity type beneath the inversion layer, wherein the well region has a central portion and two horizontally abutting end portions. The central portion has a higher concentration of a first conductivity type dopant than the two horizontally abutting end portions. Such a well region may be referred to as a non-uniform super-steep retrograde well.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Integrated circuit system for suppressing short channel effects
Owner:CHARTERED SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING
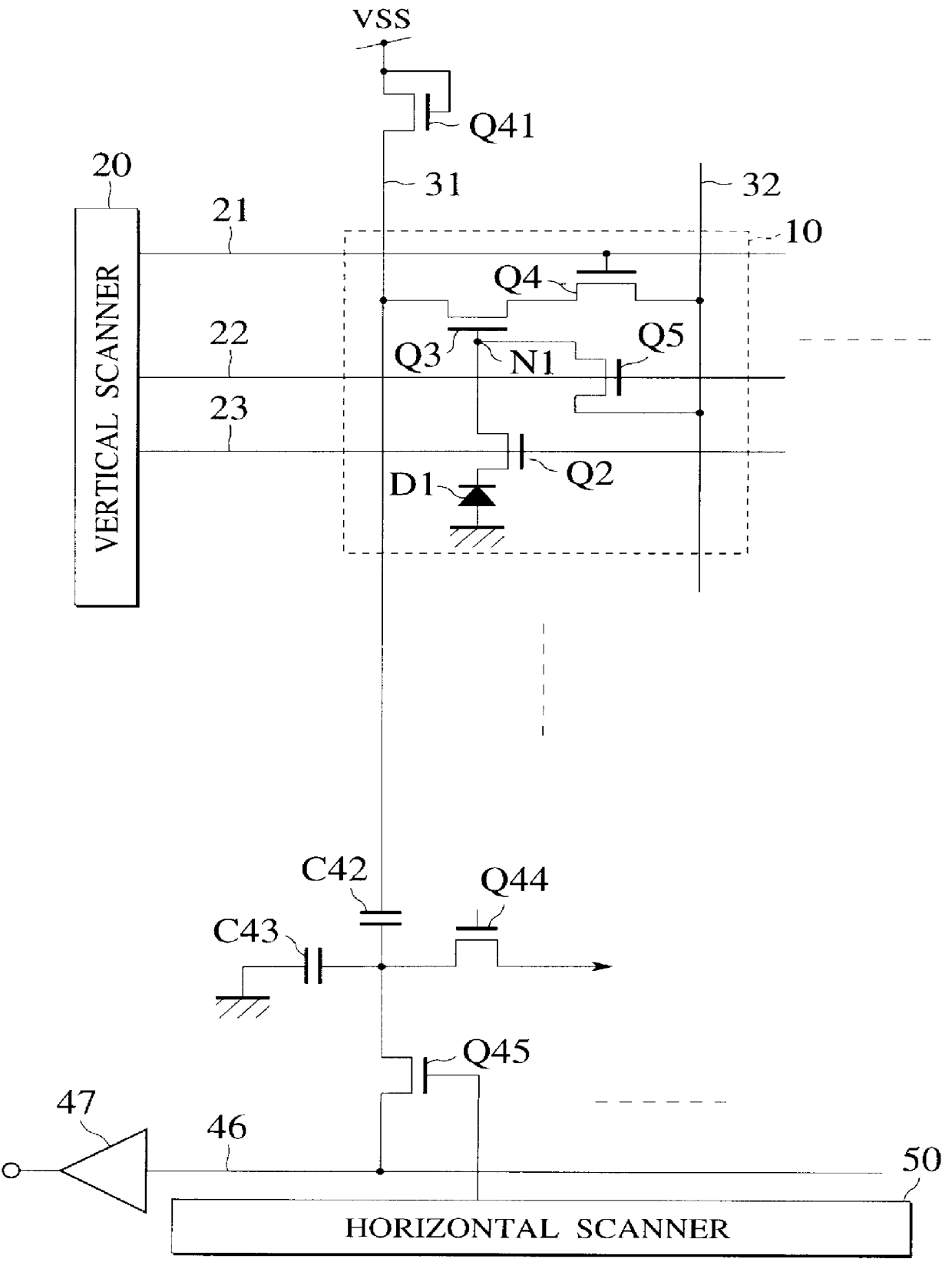
MOS type image sensor
A MOS type image sensor has an image area that consists of a matrix of pixels and a peripheral circuitry area that drives the image area. To make the MOS type image sensor finer, each of the pixels consists of a second p-well region having a lower impurity concentration than a first p-well region disposed in the peripheral circuitry area; a photodiode having a first main electrode region made of the second p-well region and a second main electrode region formed as a first n-diffusion layer disposed at the surface of the second p-well region; a read transistor having a first main electrode region made of the first n-diffusion layer, a second main electrode region formed as a second n-diffusion layer disposed at the surface of the second p-well region, a gate insulation film disposed on the surface of the second p-well region between the first and second n-diffusion layers, and a gate electrode disposed on the gate insulation film and connected to a read signal line; and an amplification transistor disposed in a third p-well region, having a gate electrode connected to the second main electrode region of the read transistor, a first main electrode region connected to an output signal line, and a second main electrode region. Since the impurity concentration of the second p-well region is low, scaled design rules are employable without causing "white pixels", sensitivity deterioration, signal read voltage increase, or short-channel effect.
Owner:NORTH PLATE SEMICON LLC
Low leakage heterojunction vertical transistors and high performance devices thereof
InactiveUS20070148939A1Superb performanceSuperb scalabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionSemiconductor materials
A method for forming and the structure of a vertical channel of a field effect transistor, a field effect transistor and CMOS circuitry are described incorporating a drain, body and source region on a sidewall of a vertical single crystal semiconductor structure wherein a hetero-junction is formed between the source and body of the transistor, wherein the source region and channel are independently lattice strained with respect the body region and wherein the drain region contains a carbon doped region to prevent the diffusion of dopants (i.e., B and P) into the body. The invention reduces the problem of short channel effects such as drain induced barrier lowering and the leakage current from the source to drain regions via the hetero-junction and while independently permitting lattice strain in the channel region for increased mobility via choice of the semiconductor materials. The problem of scalability of the gate length below 100 nm is overcome by the heterojunction between the source and body regions.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Mos transistor for reducing short-channel effects and its production
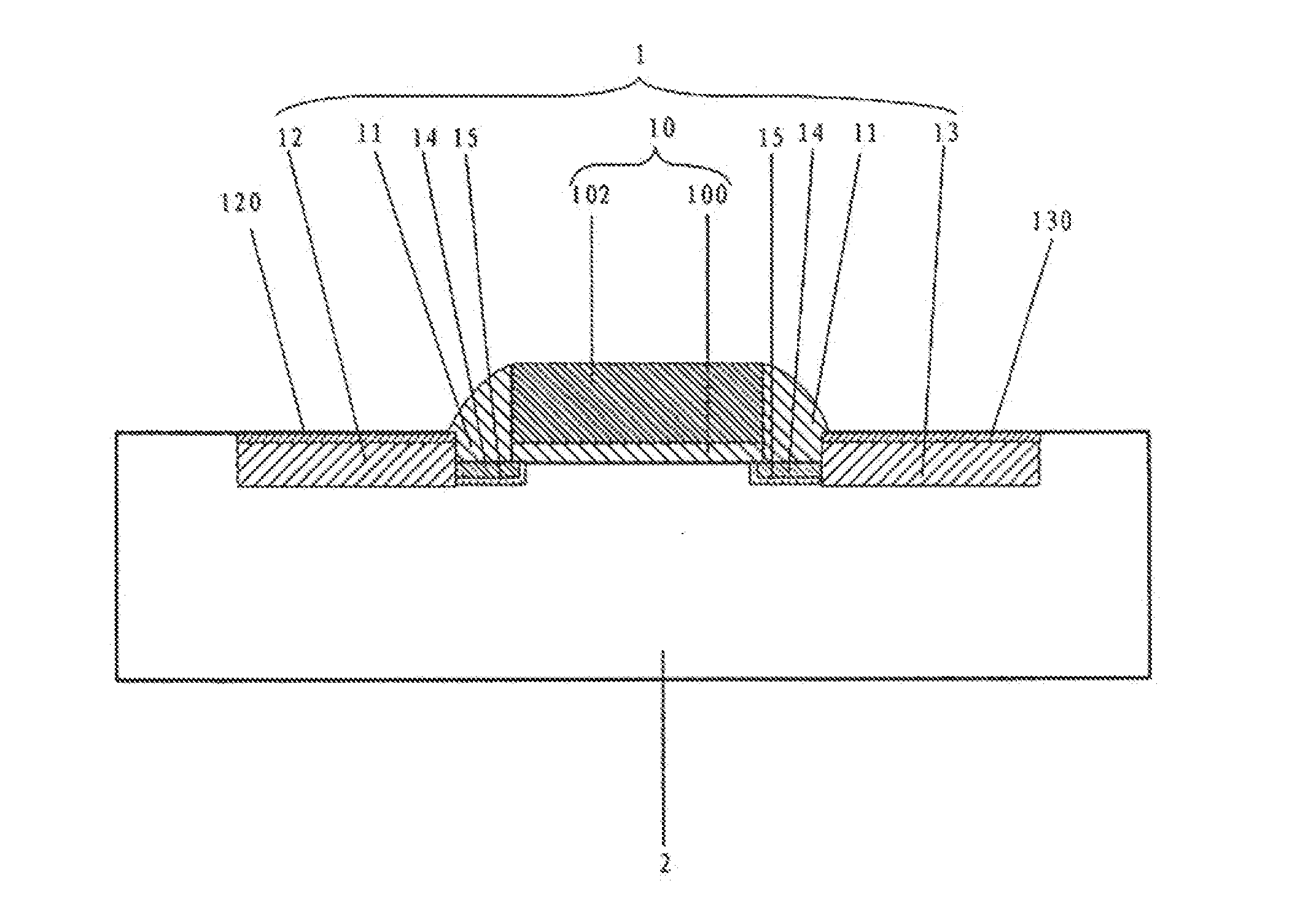
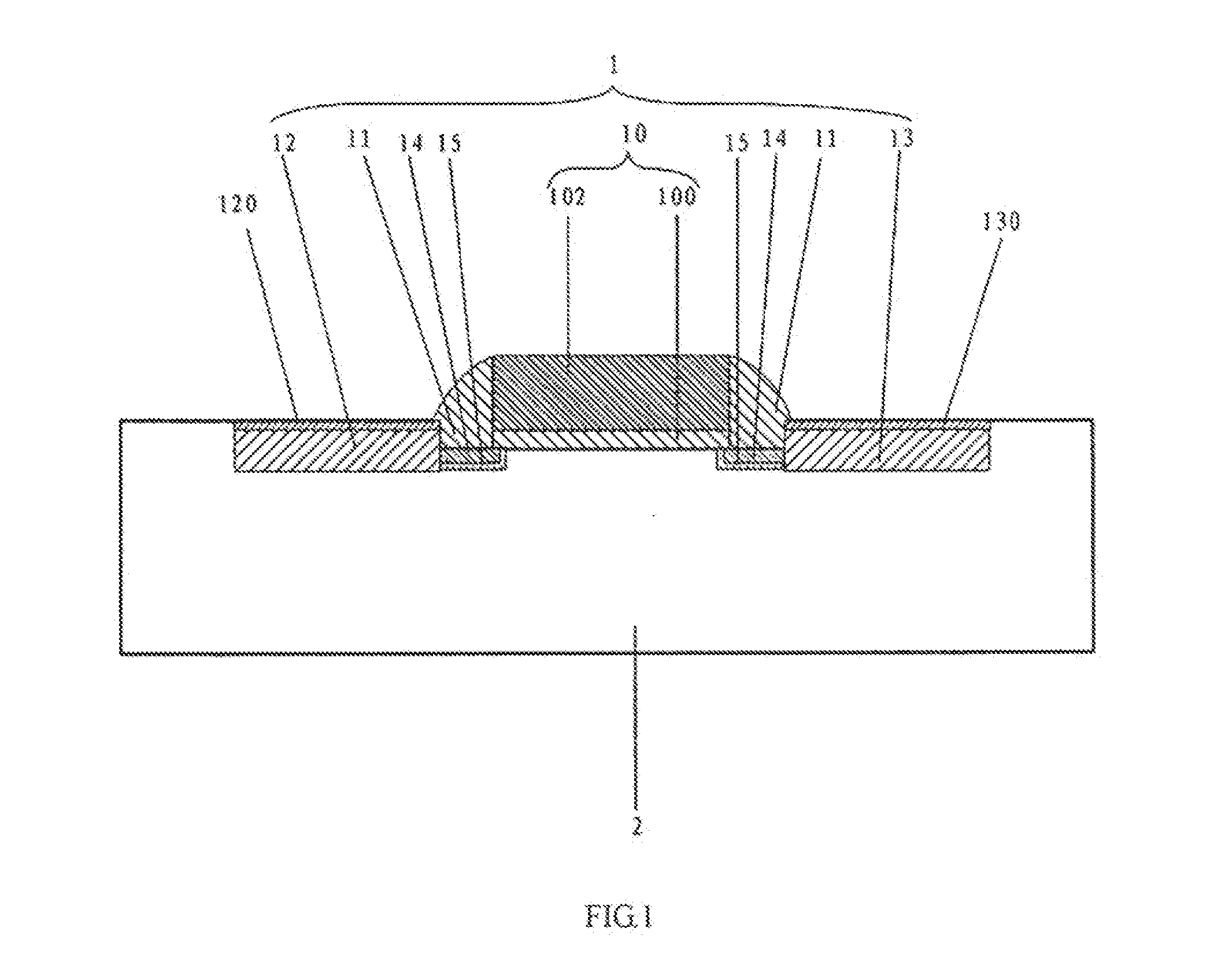
ActiveUS20110059588A1Suppression of short channel effectsReduce impactSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMetal silicideGate stack
Owner:SHANGHAI INTEGRATED CIRCUIT RES & DEV CENT
Hybrid SOI/bulk semiconductor transistors
ActiveUS20050189589A1Increase resistanceDesirable propertyTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
Channel depth in a field effect transistor is limited by an intra-layer structure including a discontinuous film or layer formed within a layer or substrate of semiconductor material. Channel depth can thus be controlled much in the manner of SOI or UT-SOI technology but with less expensive substrates and greater flexibility of channel depth control while avoiding floating body effects characteristic of SOI technology. The profile or cross-sectional shape of the discontinuous film may be controlled to an ogee or staircase shape to improve short channel effects and reduce source / drain and extension resistance without increase of capacitance. Materials for the discontinuous film may also be chosen to impose stress on the transistor channel from within the substrate or layer and provide increased levels of such stress to increase carrier mobility. Carrier mobility may be increased in combination with other meritorious effects.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
High performance CMOS devices and methods for making same
ActiveUS8067280B2Improve performanceImprove short channel effectTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceCMOS
An integrated circuit having high performance CMOS devices with good short channel effects may be made by forming a gate structure over a substrate; forming pocket implant regions and source / drain extensions in the substrate; forming spacers along sides of the gate structure; and thermal annealing the substrate when forming the spacers, the thermal annealing performed at an ultra-low temperature. An integrated circuit having high performance CMOS devices with low parasitic junction capacitance may be made by forming a gate structure over a substrate; forming pocket implant regions and source / drain extensions in the substrate; forming spacers along sides of the gate structure; performing a low dosage source / drain implant; and performing a high dosage source / drain implant.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Insulated gate semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
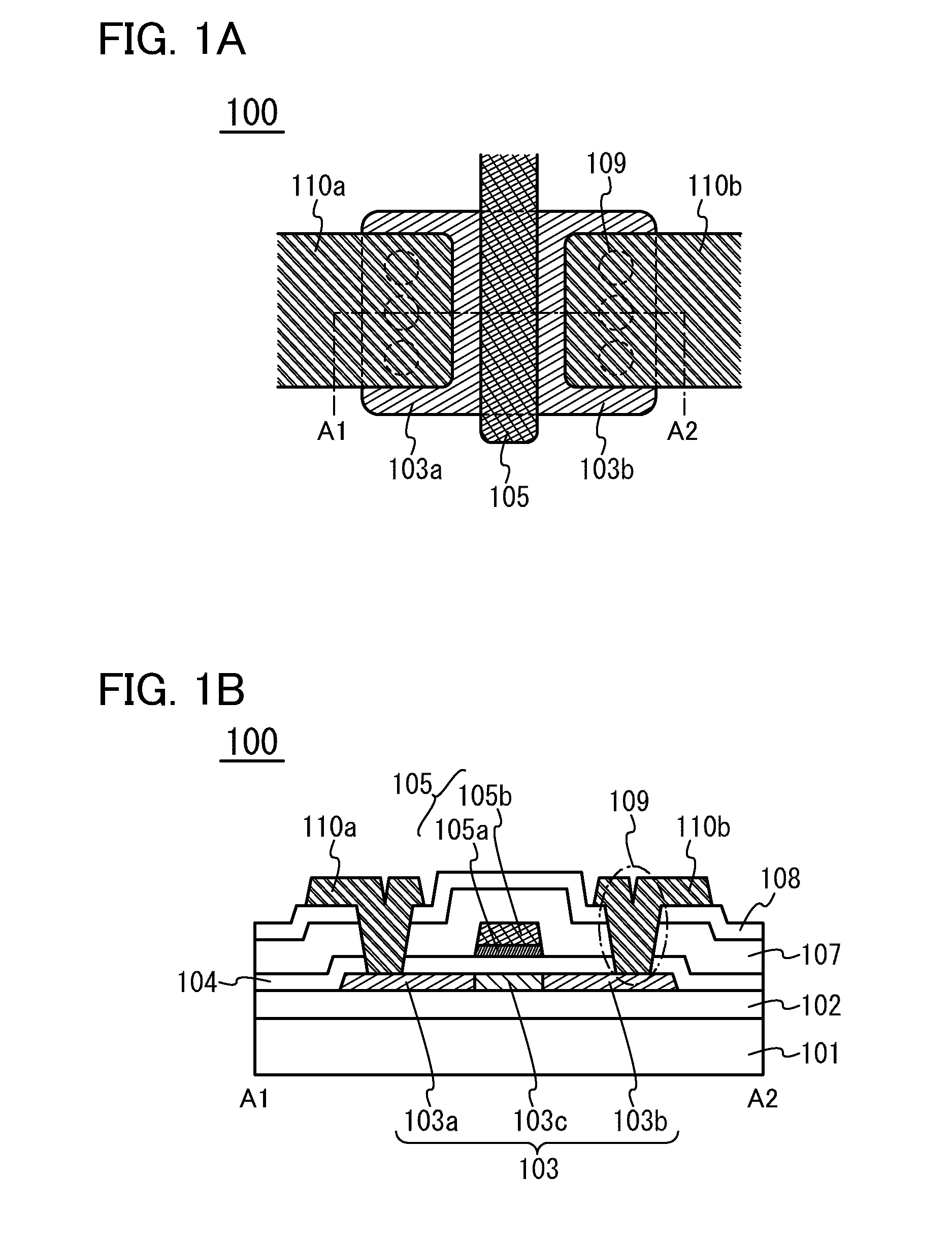
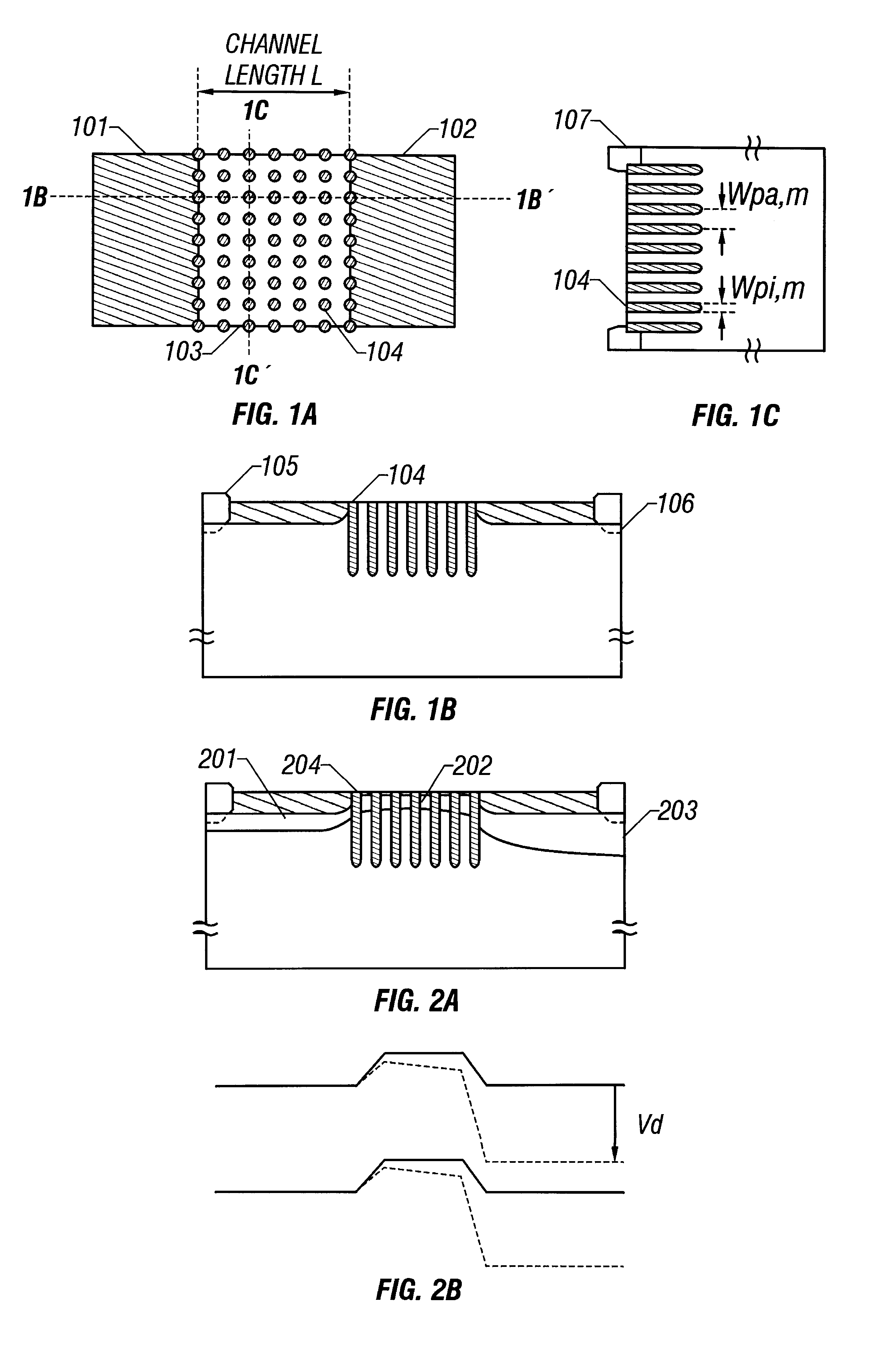
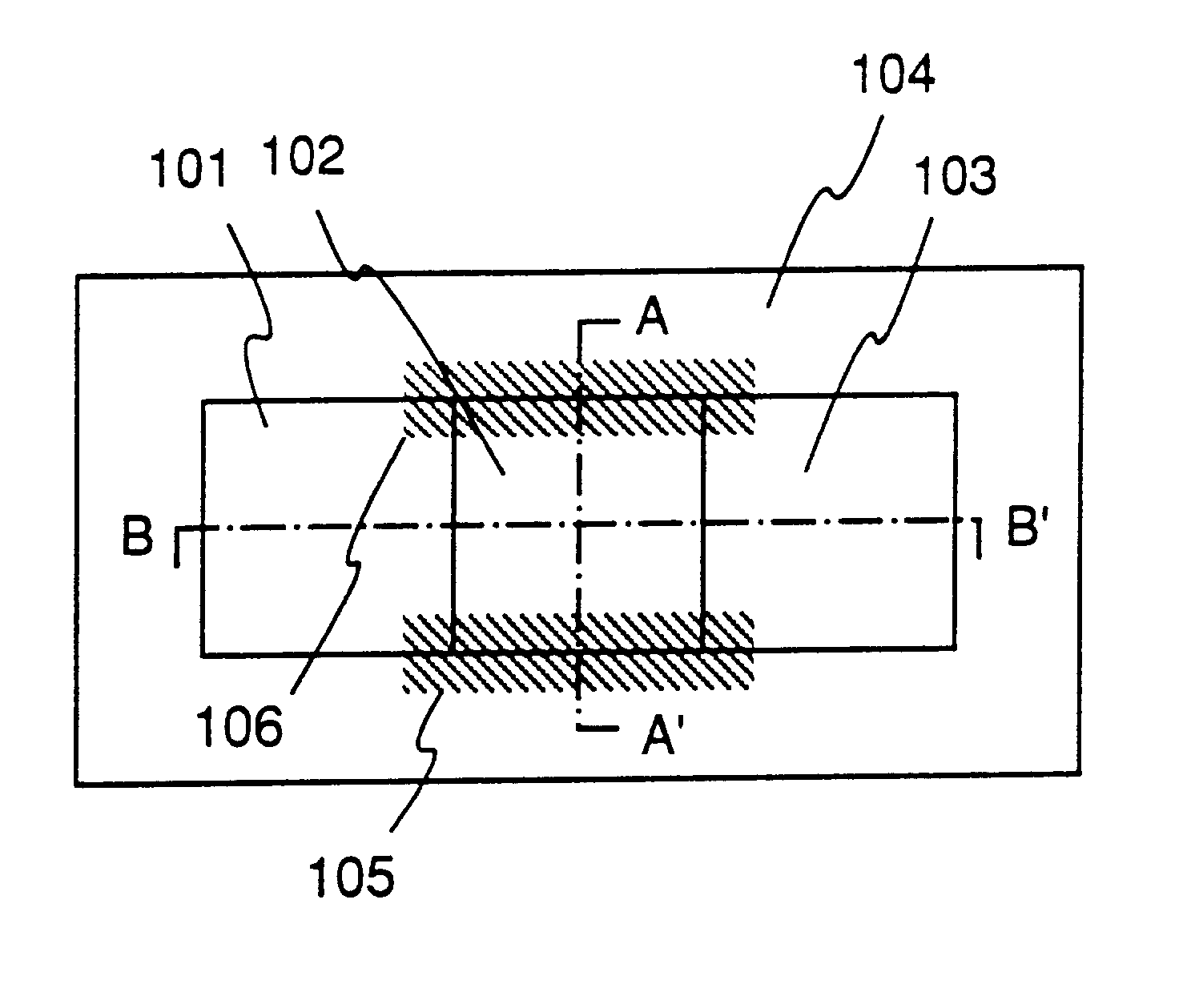
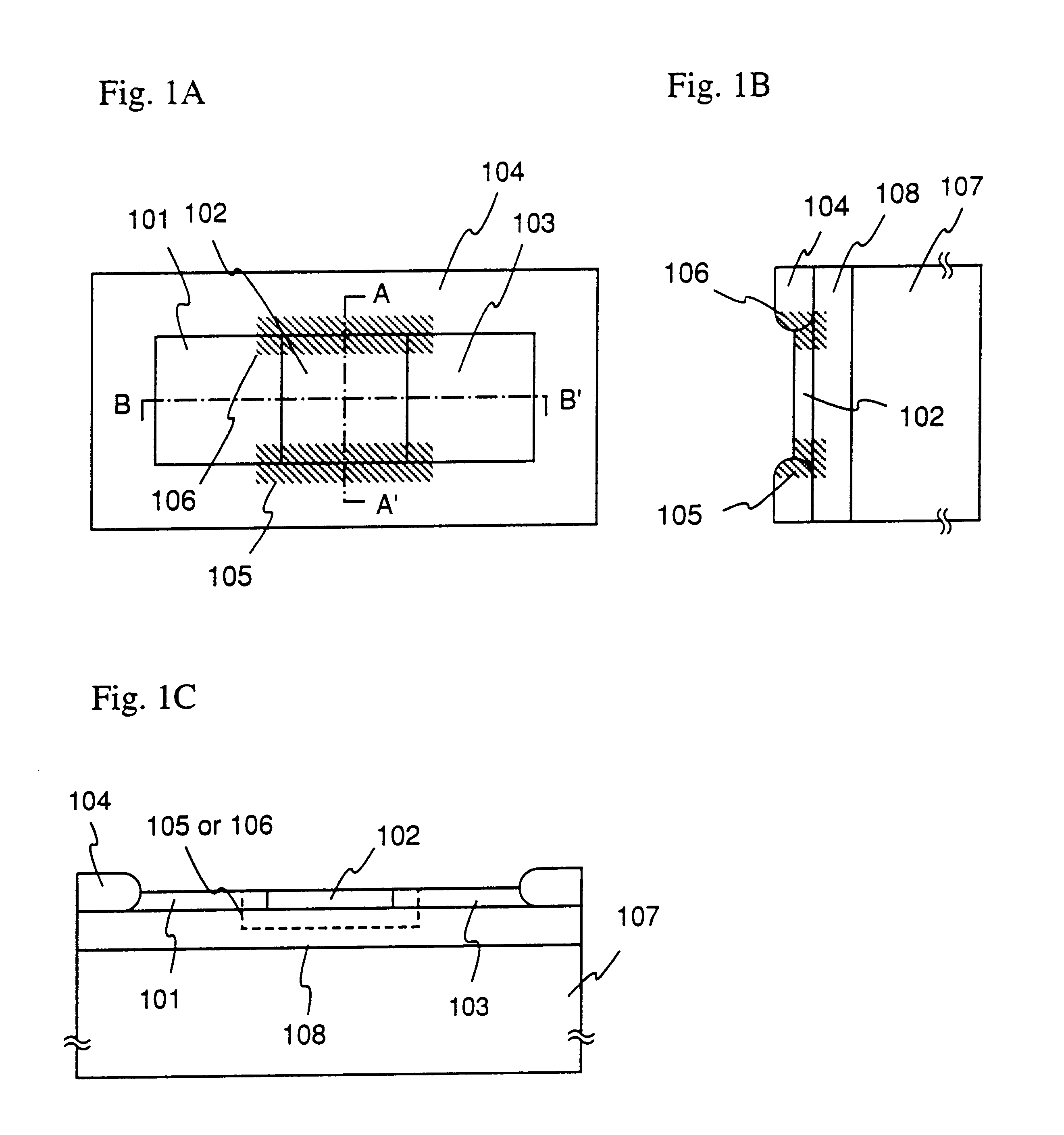
Dot-pattern-like impurity regions are artificially and locally formed in a channel forming region. The impurity regions restrain the expansion of a drain side depletion layer toward the channel forming region to prevent the short channel effect. The impurity regions allow a channel width W to be substantially fined, and the resultant narrow channel effect releases the lowering of a threshold value voltage which is caused by the short channel effect.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device
There is provided a semiconductor device having a new structure which allows a high reliability and a high field effect mobility to be realized in the same time. In an insulated gate transistor having an SOI structure utilizing a mono-crystal semiconductor thin film on an insulating layer, pinning regions are formed at edge portions of a channel forming region. The pinning regions suppress a depletion layer from spreading from the drain side and prevent a short-channel effect. In the same time, they also function as a path for drawing out minority carriers generated by impact ionization to the outside and prevent a substrate floating effect from occurring.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device fabricating method
ActiveUS20050266631A1High speedImprove channel mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice materialSemiconductor
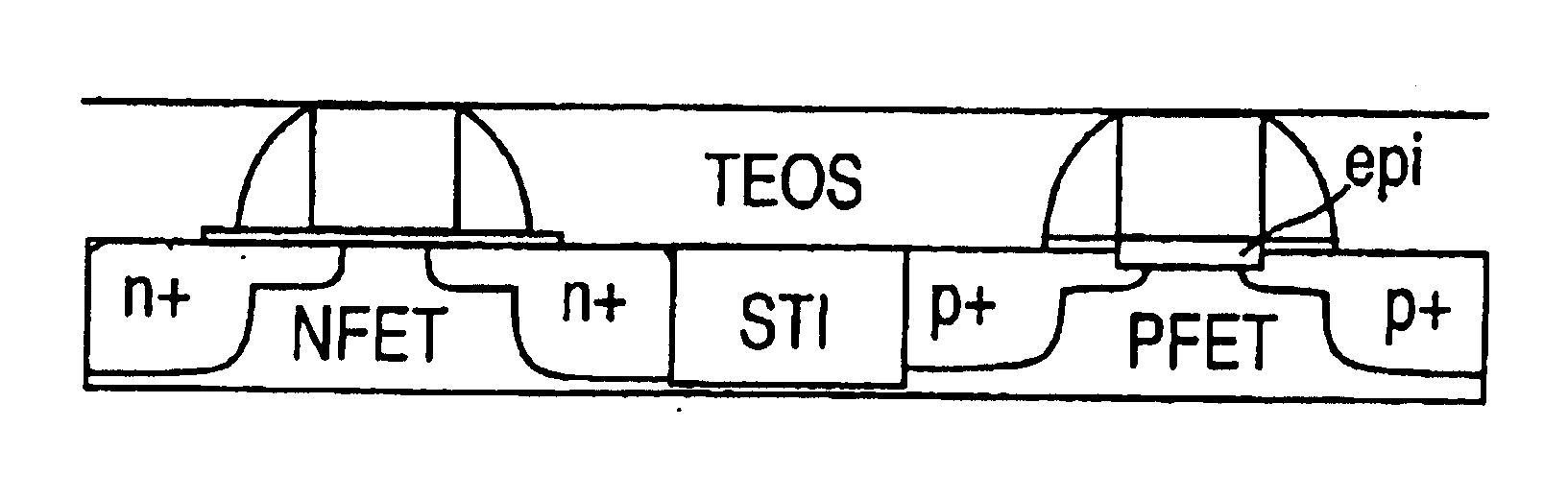
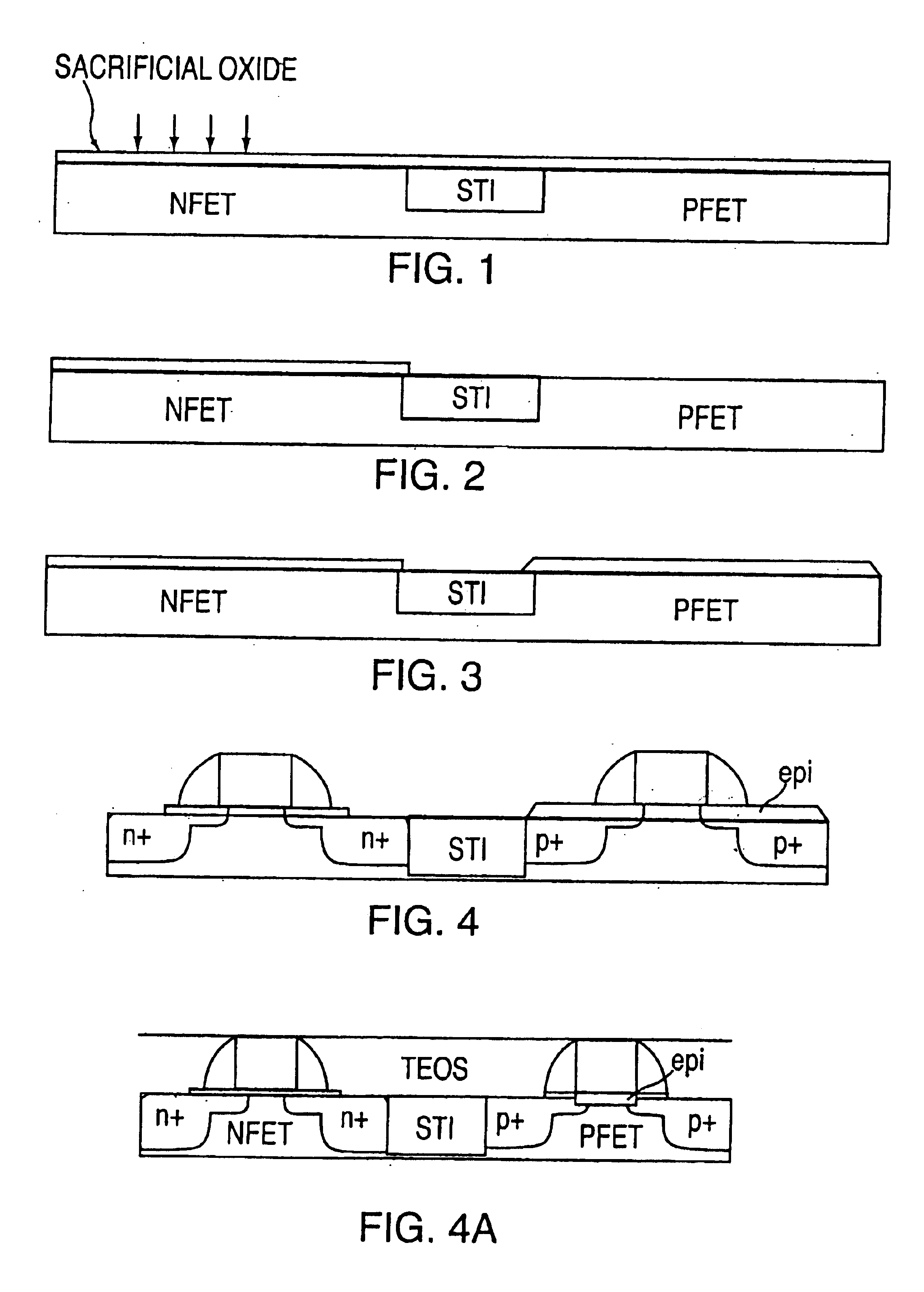
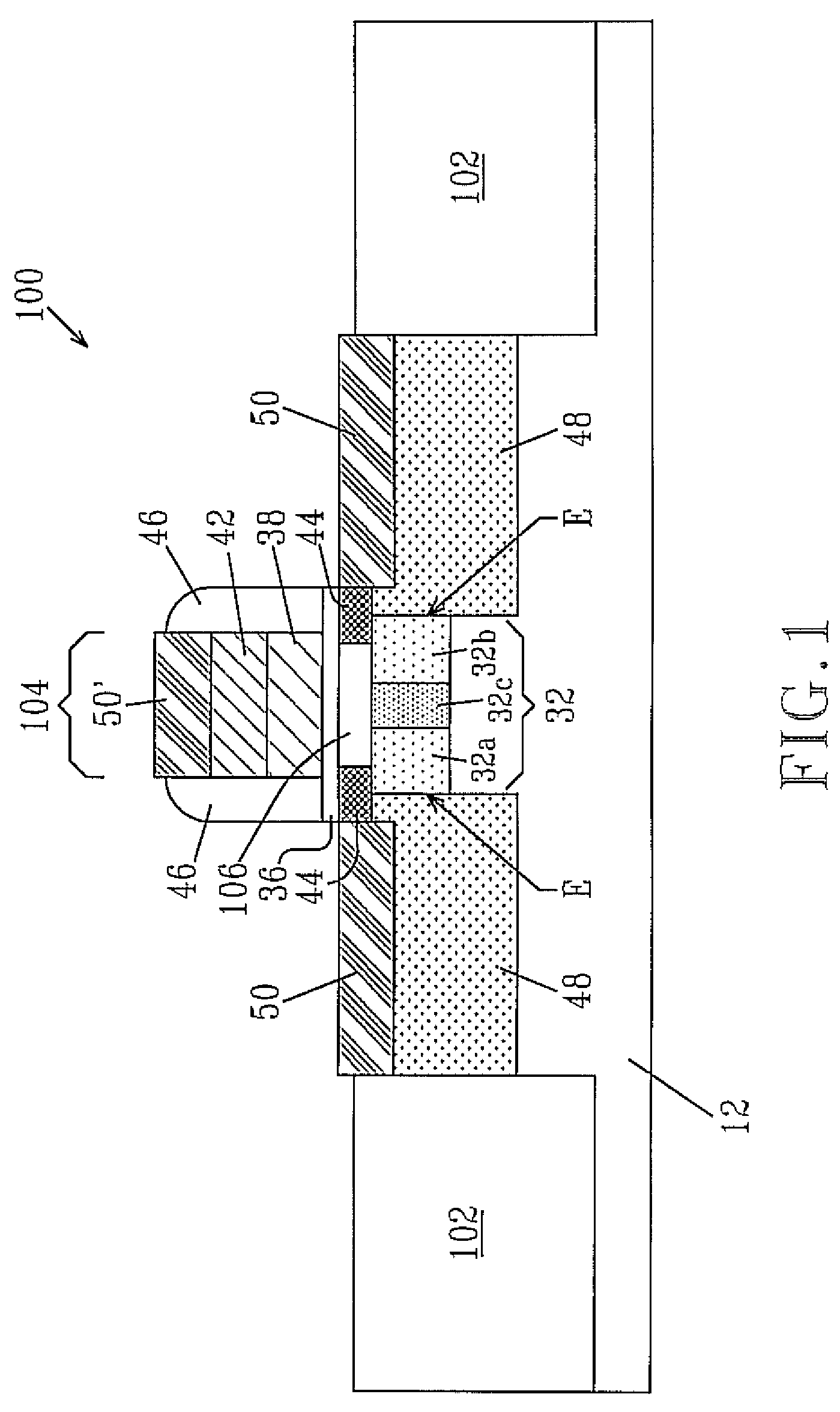
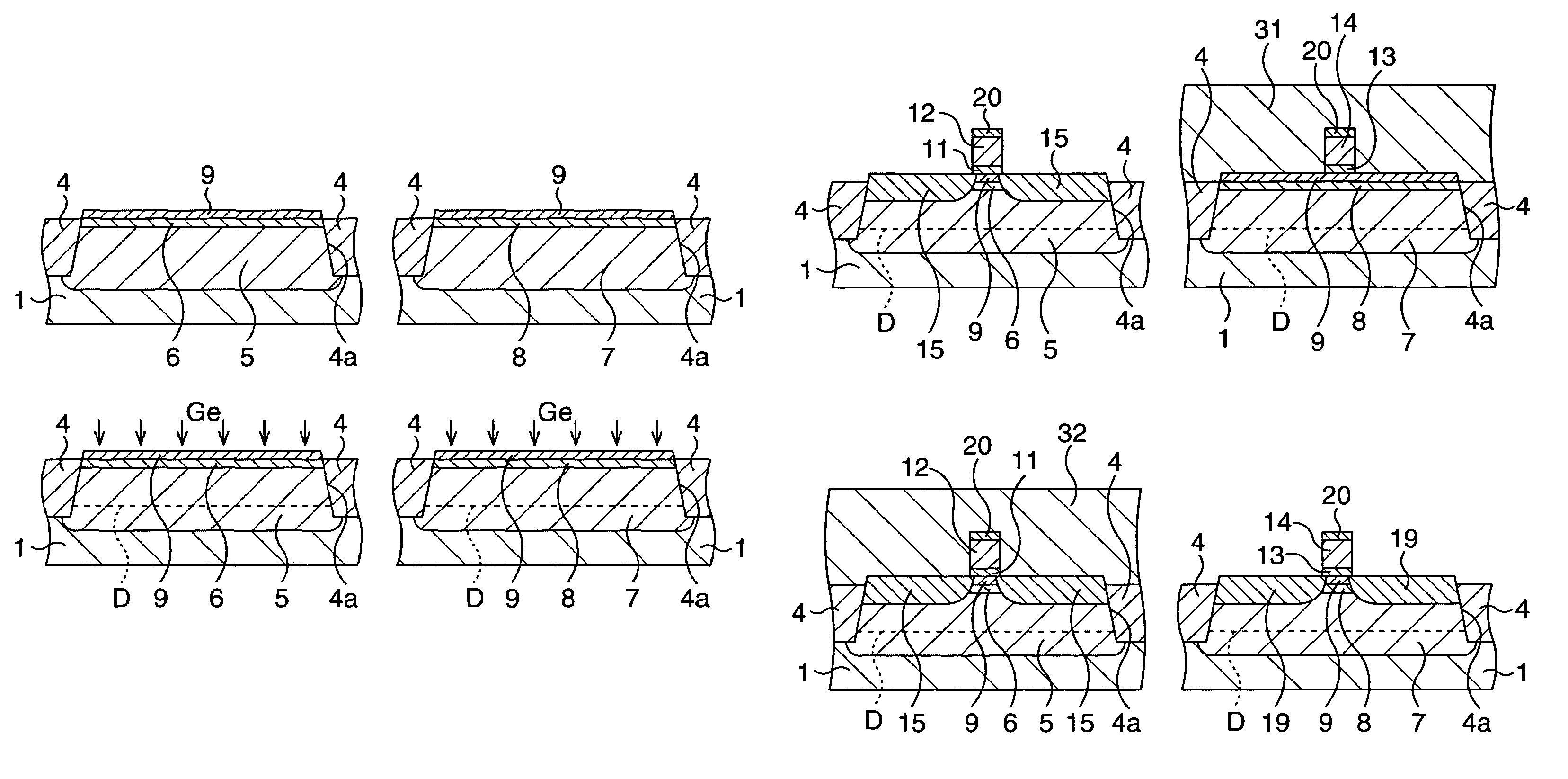
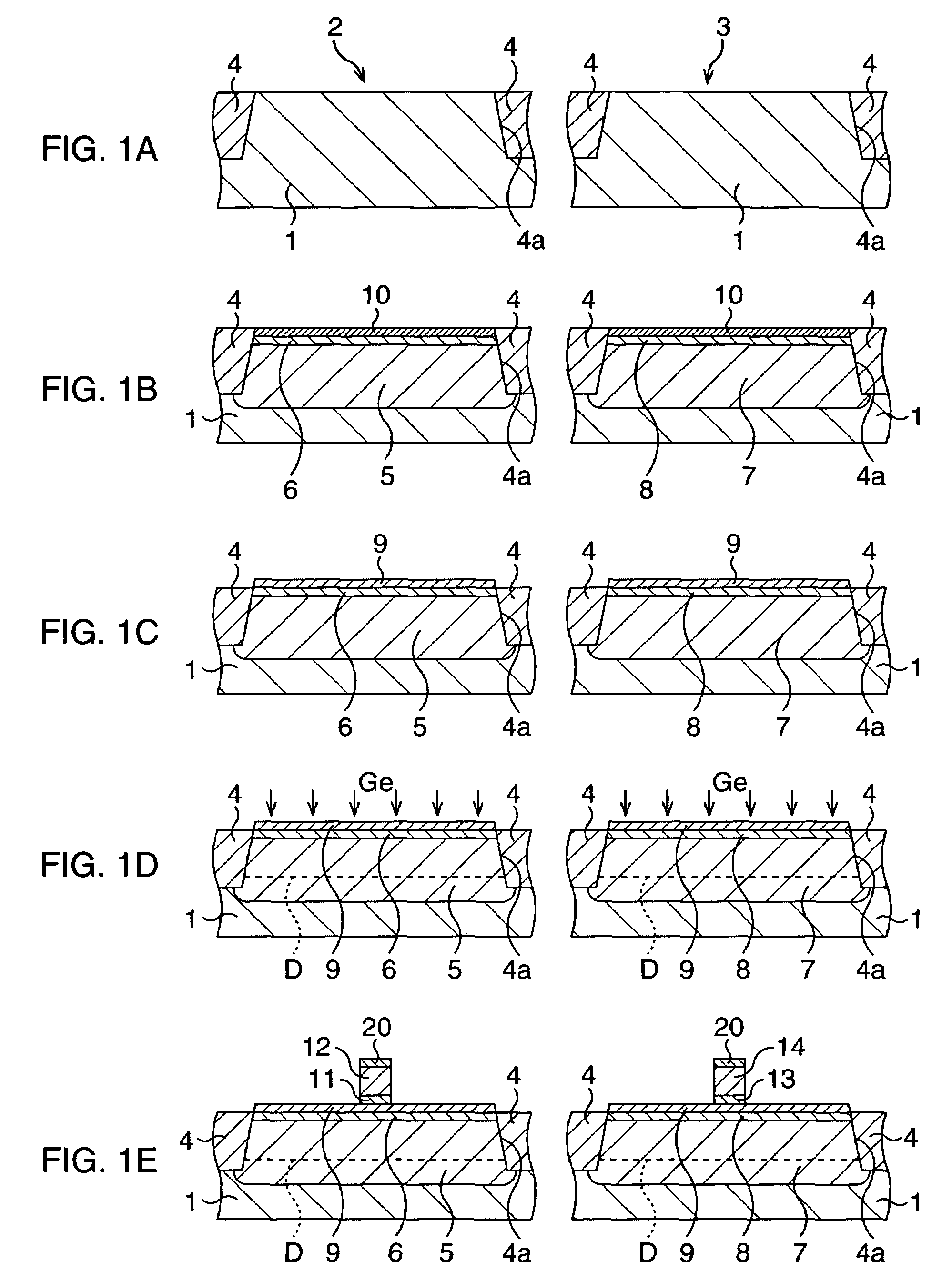
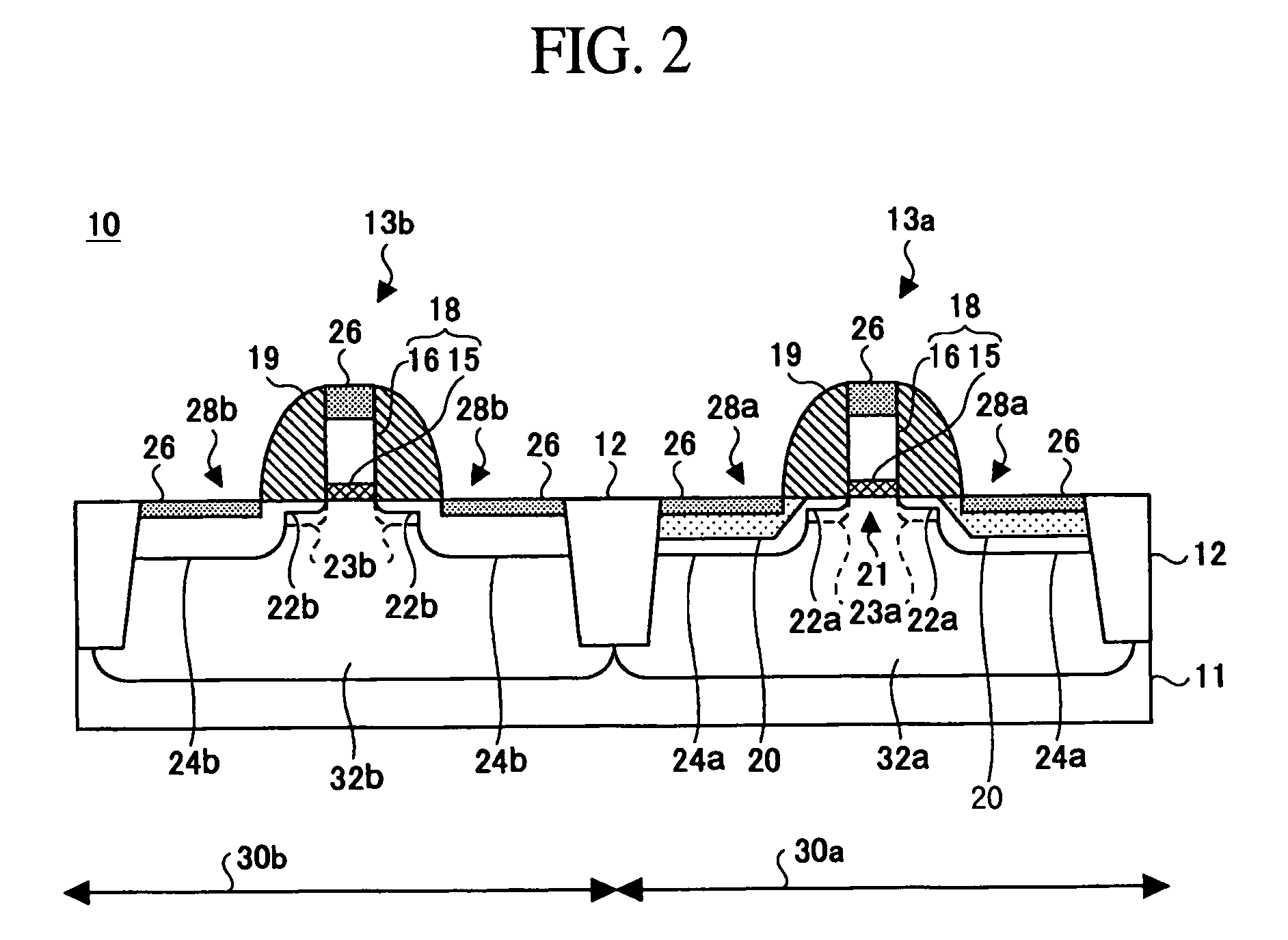
Compression stress applying portions 20 of SiGe film are formed in the source / drain regions of the p-MOSA region 30a. Then, impurities are implanted in the p-MOS region 30a and the n-MOS region 30b to form shallow junction regions 22a, 22b and deep junction regions 23a, 23b. The impurity in the shallow junction regions 22a, 22b is prevented from being diffused immediately below the gate insulation film 15 by the thermal processing in forming the SiGe film, the short channel effect is prevented, and the hole mobility of the channel region of the p-MOS transistor 14a. The operation speed of the p-MOS transistor 13a is balanced with that of the n-MOS transistor, whereby the operation speed of the complementary semiconductor device 10 can be increased. The semiconductor device fabricating method can increase and balance the operation speed of a p-transistor with that of an n-transistor.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
Technique to mitigate short channel effects with vertical gate transistor with different gate materials
InactiveUS20050145959A1Reduce negative impactImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricEngineering
A process of forming a transistor with three vertical gate electrodes including a high-k gate dielectric and the resulting transistor. By forming such a transistor it is possible to maintain an acceptable aspect ratio as MOSFET structures are scaled down to sub-micron sizes. The transistor gate electrodes can be formed of different materials so that the workfunctions of the three electrodes can be tailored. The three electrodes are positioned over a single channel and operate as a single gate having outer and inner gate regions.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
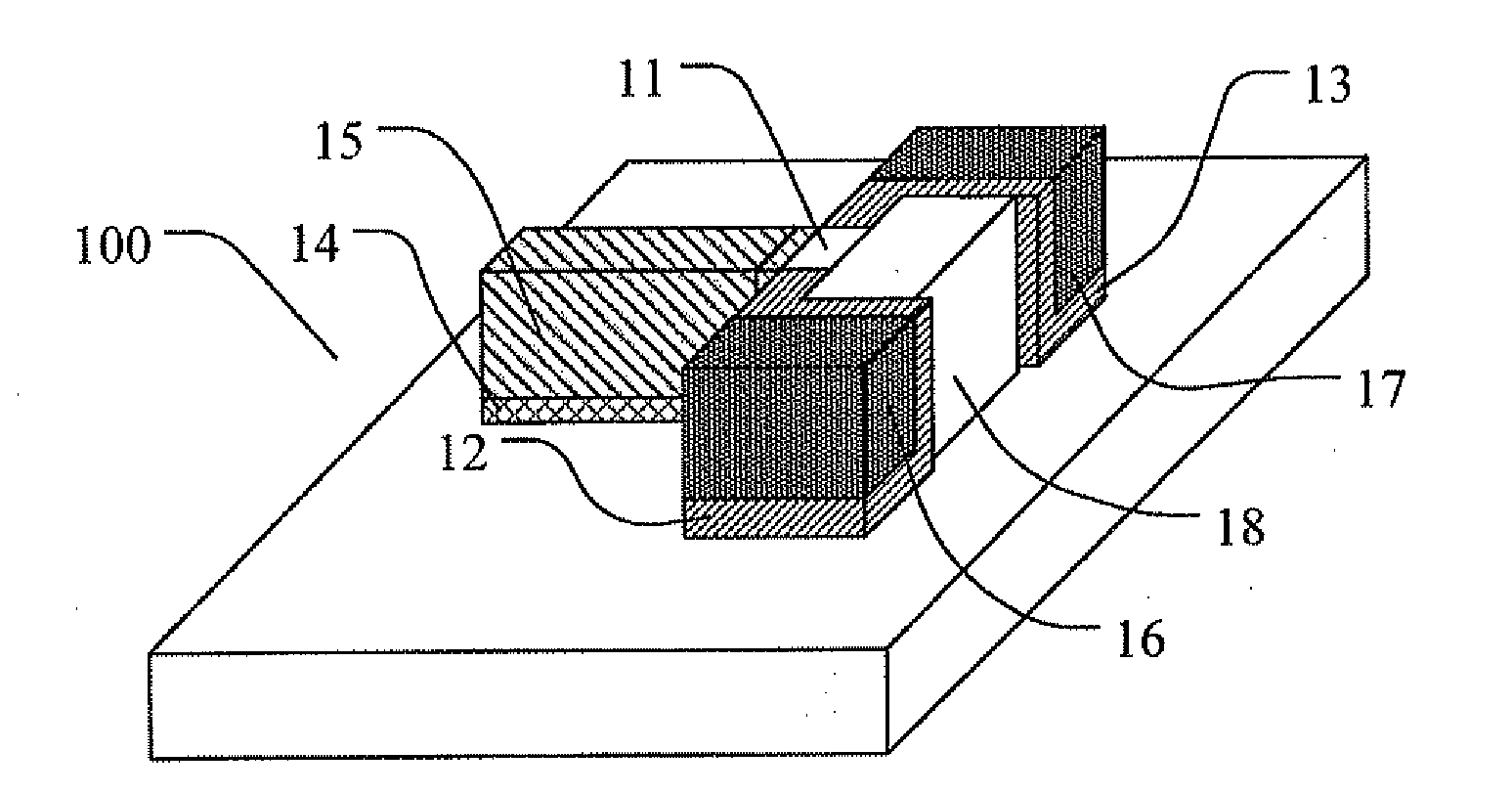
Double-gate field-effect transistor, integrated circuit using the transistor and method of manufacturing the same
A double-gate field-effect transistor includes a substrate, an insulation film formed on the substrate, source, drain and channel regions formed on the insulation film from a semiconductor crystal layer, and two insulated gate electrodes electrically insulated from each other. The gate electrodes are formed opposite each other on the same principal surface as the channel region, with the channel region between the electrodes. The source, drain and channel regions are isolated from the surrounding part by a trench, forming an island. Gate insulation films are formed on the opposing side faces of the channel region exposed in the trench. The island region between the gate electrodes is given a width that is less than the length of the channel region to enhance the short channel effect suppressive property of structure.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Technique to mitigate short channel effects with vertical gate transistor with different gate materials
InactiveUS20020130378A1Improve performanceSuppression of short channel effectsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingReverse short-channel effectScale down
This invention relates to a process of forming a transistor with three vertical gate electrodes and the resulting transistor. By forming such a transistor it is possible to maintain an acceptable aspect ratio as MOSFET structures are scaled down to sub-micron sizes. The transistor gate electrodes can be formed of different materials so that the workfunctions of the three electrodes can be tailored. The three electrodes are positioned over a single channel and operate as a single gate having outer and inner gate regions.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Double-gate field-effect transistor, integrated circuit using the transistor and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20020130354A1Suppression of short channel effectsTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingField-effect transistorDouble gate
A double-gate field-effect transistor includes a substrate, an insulation film formed on the substrate, source, drain and channel regions formed on the insulation film from a semiconductor crystal layer, and two insulated gate electrodes electrically insulated from each other. The gate electrodes are formed opposite each other on the same principal surface as the channel region, with the channel region between the electrodes. The source, drain and channel regions are isolated from the surrounding part by a trench, forming an island. Gate insulation films are formed on the opposing side faces of the channel region exposed in the trench. The island region between the gate electrodes is given a width that is less than the length of the channel region to enhance the short channel effect suppressive property of structure.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Semiconductor device having SOI structure and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS7339235B1Suppression of short channel effectsEffectively suppress a depletion layerTransistorIndividual molecule manipulationEngineeringSemiconductor
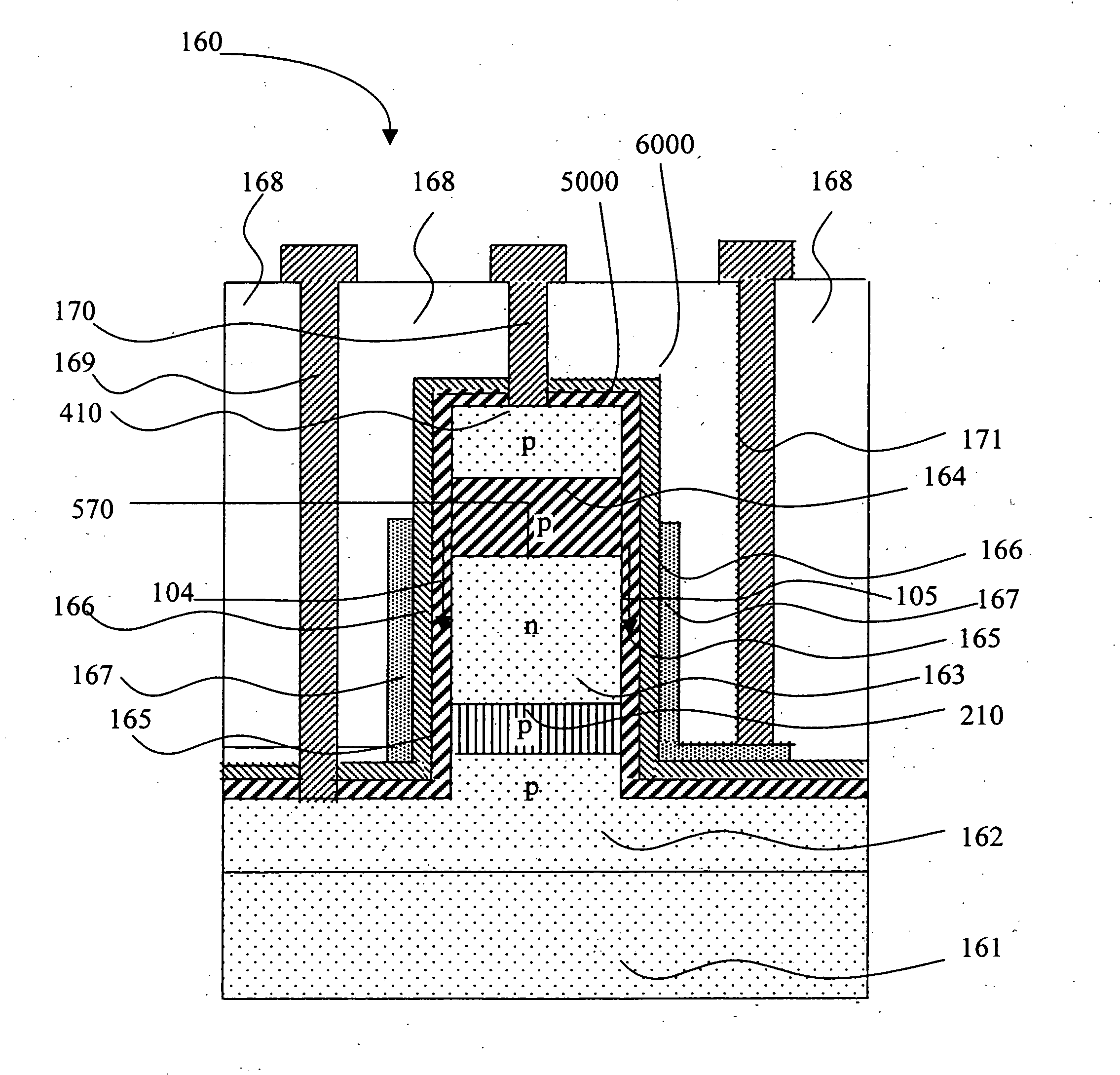
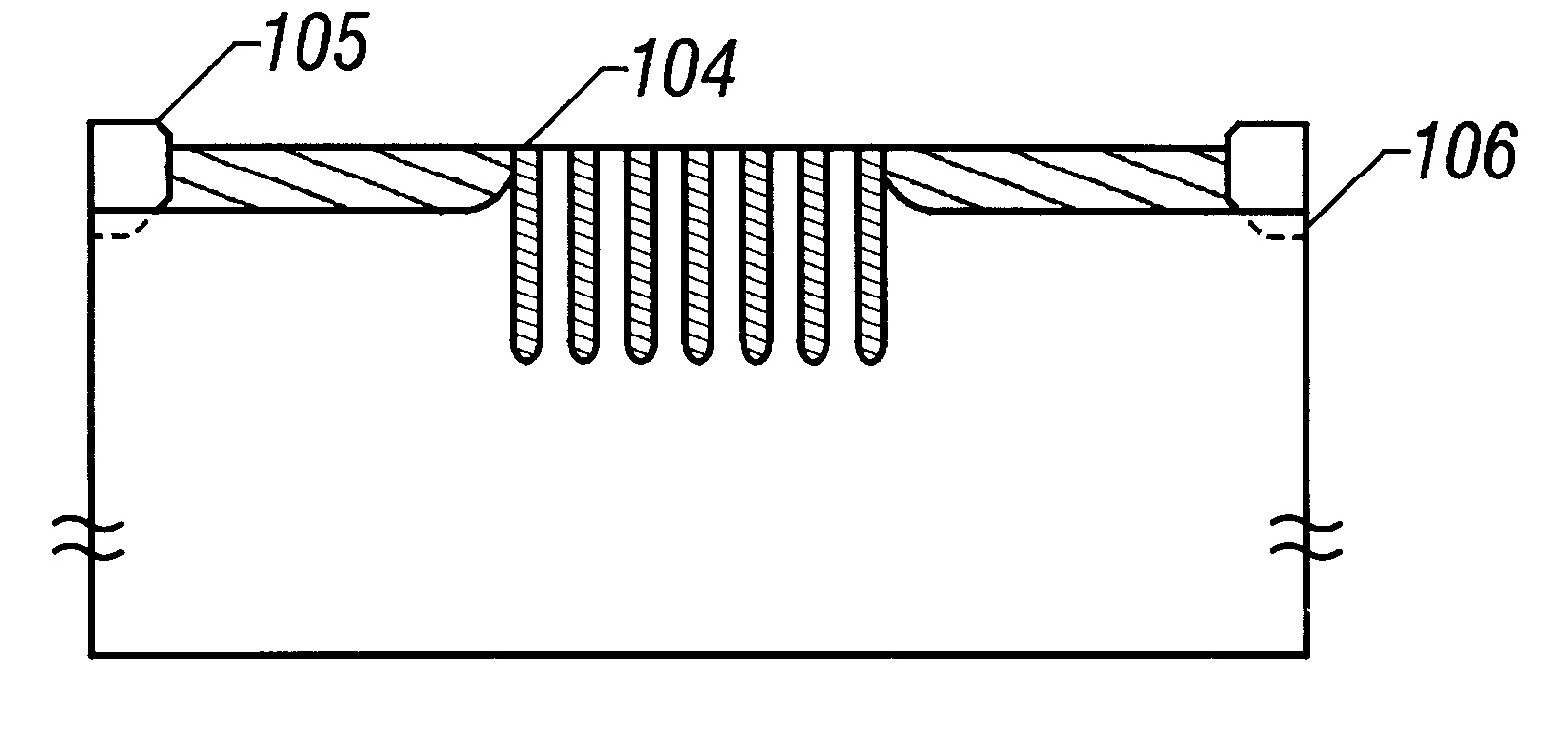
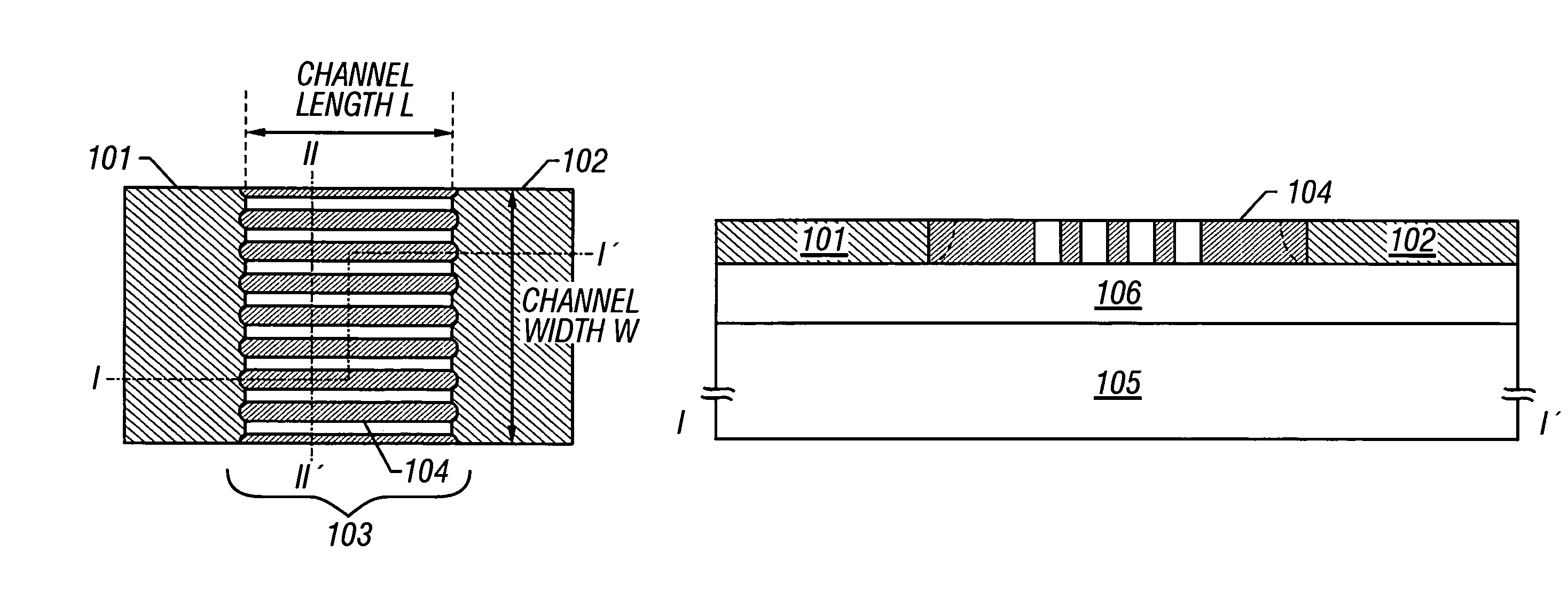
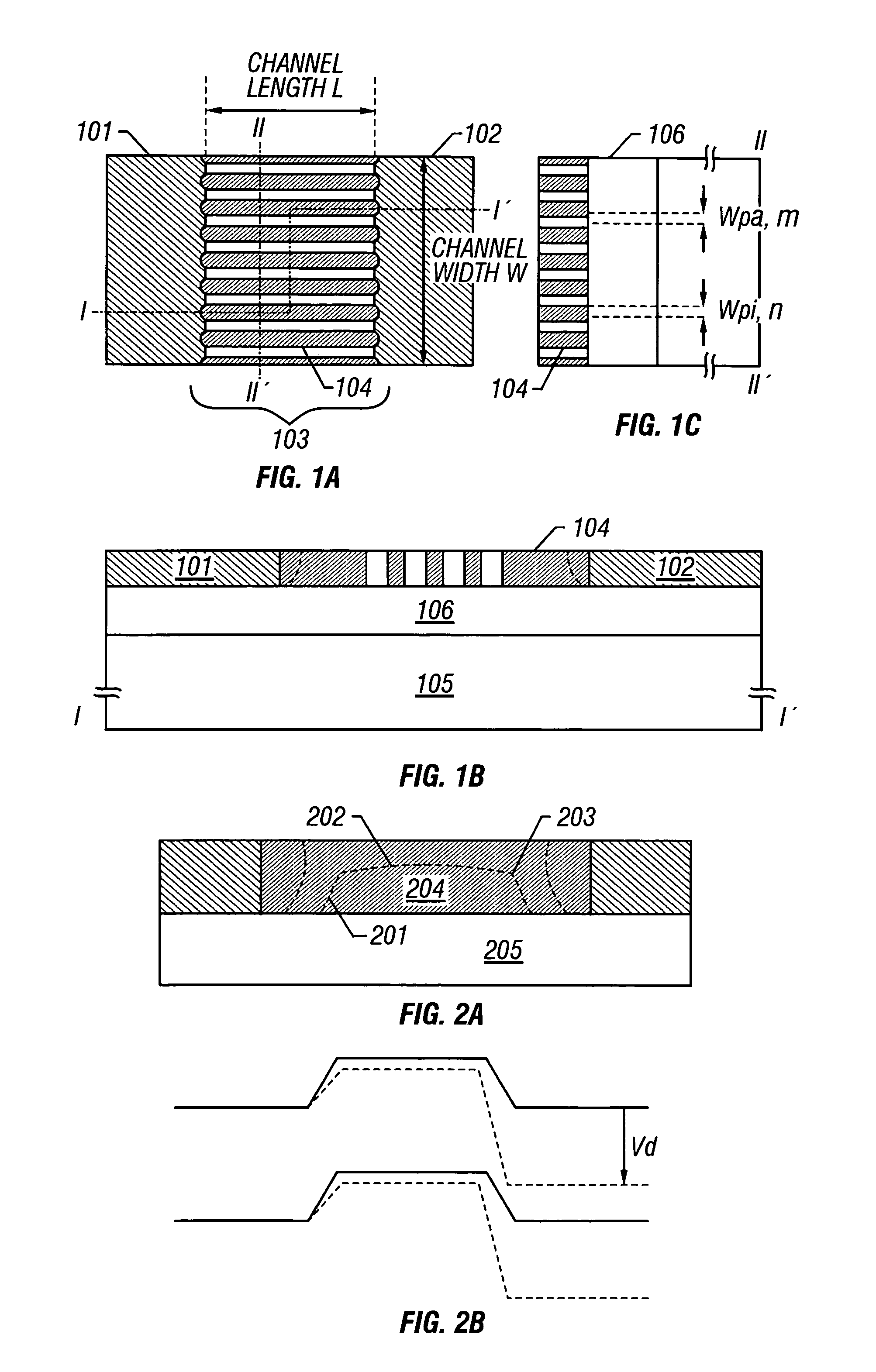
A fine semiconductor device having a short channel length while suppressing a short channel effect. Linearly patterned or dot-patterned impurity regions 104 are formed in a channel forming region 103 so as to be generally parallel with the channel direction. The impurity regions 104 are effective in suppressing the short channel effects. More specifically, the impurity regions 104 suppress expansion of a drain-side depletion layer, so that the punch-through phenomenon can be prevented. Further, the impurity regions cause a narrow channel effect, so that reduction in threshold voltage can be lessened.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20120161123A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenSemiconductor
A miniaturized semiconductor device including a transistor in which a channel formation region is formed using an oxide semiconductor film and variation in electric characteristics due to a short-channel effect is suppressed is provided. In addition, a semiconductor device whose on-state current is improved is provided. A semiconductor device is provided with an oxide semiconductor film including a pair of second oxide semiconductor regions which are amorphous regions and a first oxide semiconductor region located between the pair of second oxide semiconductor regions, a gate insulating film, and a gate electrode provided over the first oxide semiconductor region with the gate insulating film interposed therebetween. Hydrogen or a rare gas is added to the second oxide semiconductor regions.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device and production method thereof
ActiveUS20070012913A1Avoid layeringSuppression of short channel effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice materialCharge carrier mobility
A method of fabricating a semiconductor device is disclosed that is able to suppress a short channel effect and improve carrier mobility. In the method, trenches are formed in a silicon substrate corresponding to a source region and a drain region. When epitaxially growing p-type semiconductor mixed crystal layers to fill up the trenches, the surfaces of the trenches are demarcated by facets, and extended portions of the semiconductor mixed crystal layers are formed between bottom surfaces of second side wall insulating films and a surface of the silicon substrate, and extended portion are in contact with a source extension region and a drain extension region.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Surround gate access transistors with grown ultra-thin bodies
ActiveUS20070018206A1Satisfies needGood conductivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesLateral asymmetryBit line
A vertical transistor having an annular transistor body surrounding a vertical pillar, which can be made from oxide. The transistor body can be grown by a solid phase epitaxial growth process to avoid difficulties with forming sub-lithographic structures via etching processes. The body has ultra-thin dimensions and provides controlled short channel effects with reduced need for high doping levels. Buried data / bit lines are formed in an upper surface of a substrate from which the transistors extend. The transistor can be formed asymmetrically or offset with respect to the data / bit lines. The offset provides laterally asymmetric source regions of the transistors. Continuous conductive paths are provided in the data / bit lines which extend adjacent the source regions to provide better conductive characteristics of the data / bit lines, particularly for aggressively scaled processes.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20120187475A1Occurrence can be suppressedReduce power consumptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringTransistor
A conventional DRAM needs to be refreshed at an interval of several tens of milliseconds to hold data, which results in large power consumption. In addition, a transistor therein is frequently turned on and off; thus, deterioration of the transistor is also a problem. These problems become significant as the memory capacity increases and transistor miniaturization advances. A transistor is provided which includes a wide-gap semiconductor and has a trench structure including a trench for a gate electrode and a trench for element isolation. Even when the distance between a source electrode and a drain electrode is decreased, the occurrence of a short-channel effect can be suppressed by setting the depth of the trench for the gate electrode as appropriate.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com