Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
155results about How to "Short pulse width" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Delivery of macromolecules into cells
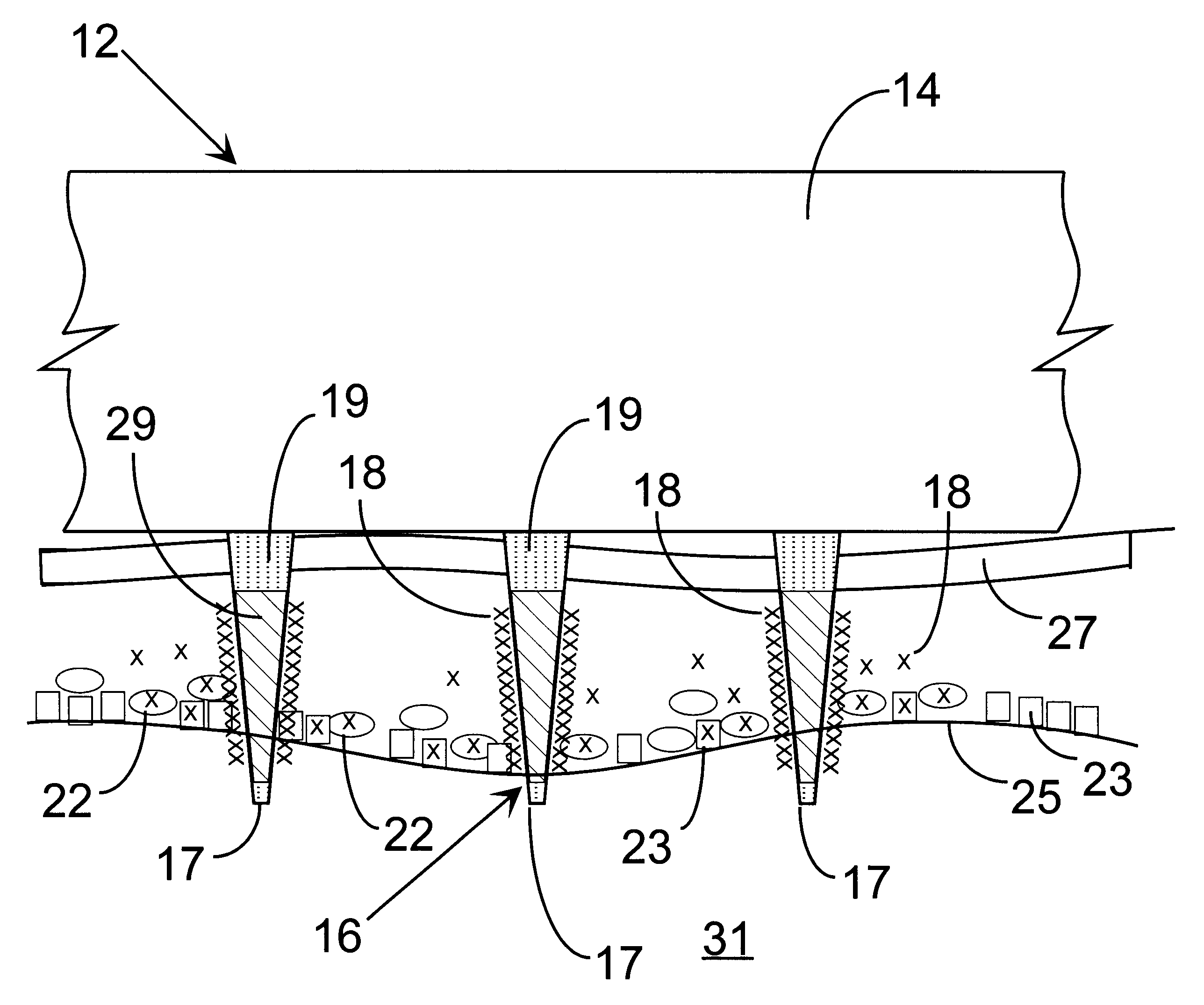
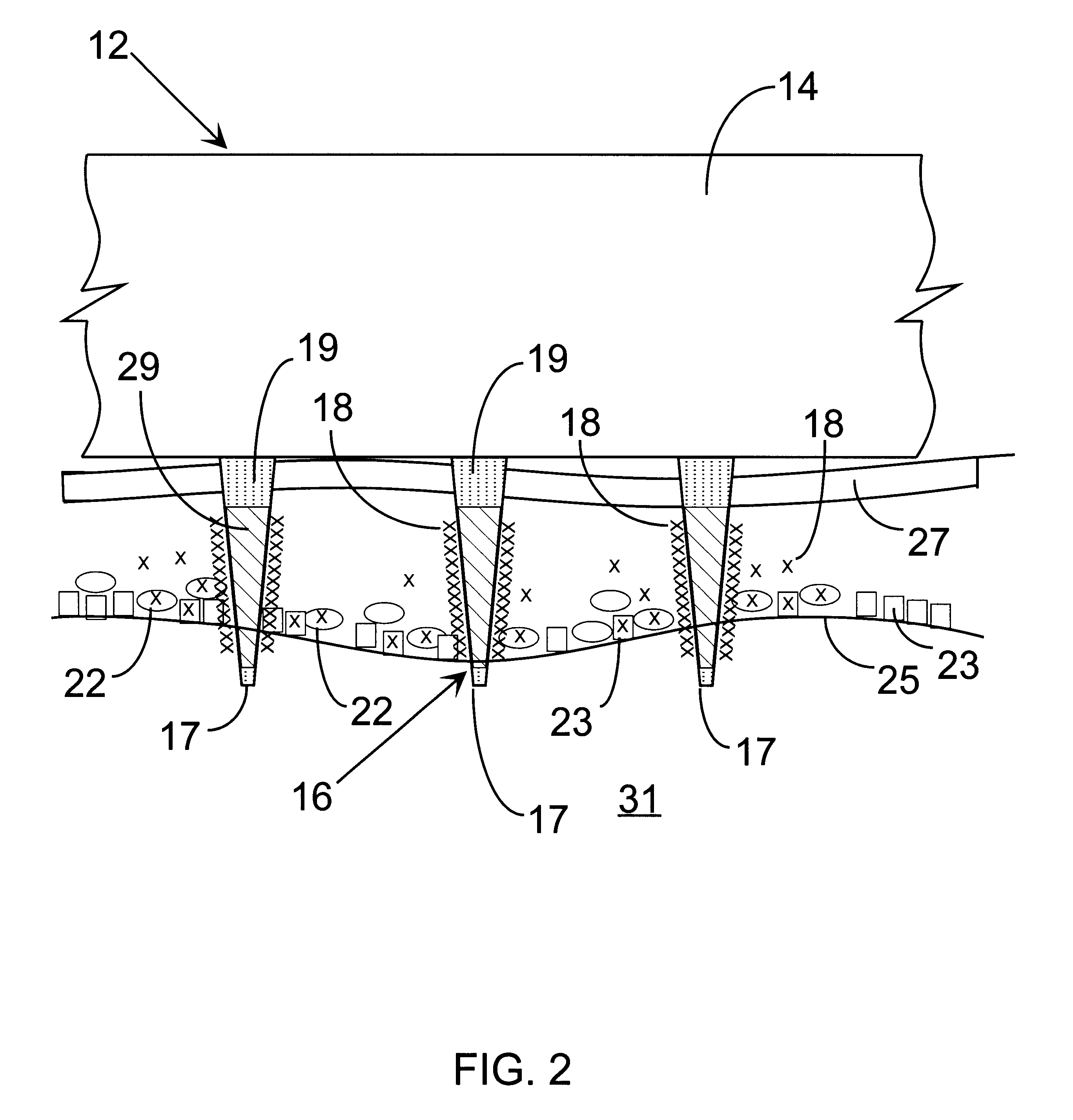
InactiveUS6603998B1Raise the threshold voltageReducing pulse widthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrotherapyLangerhan cellA-DNA
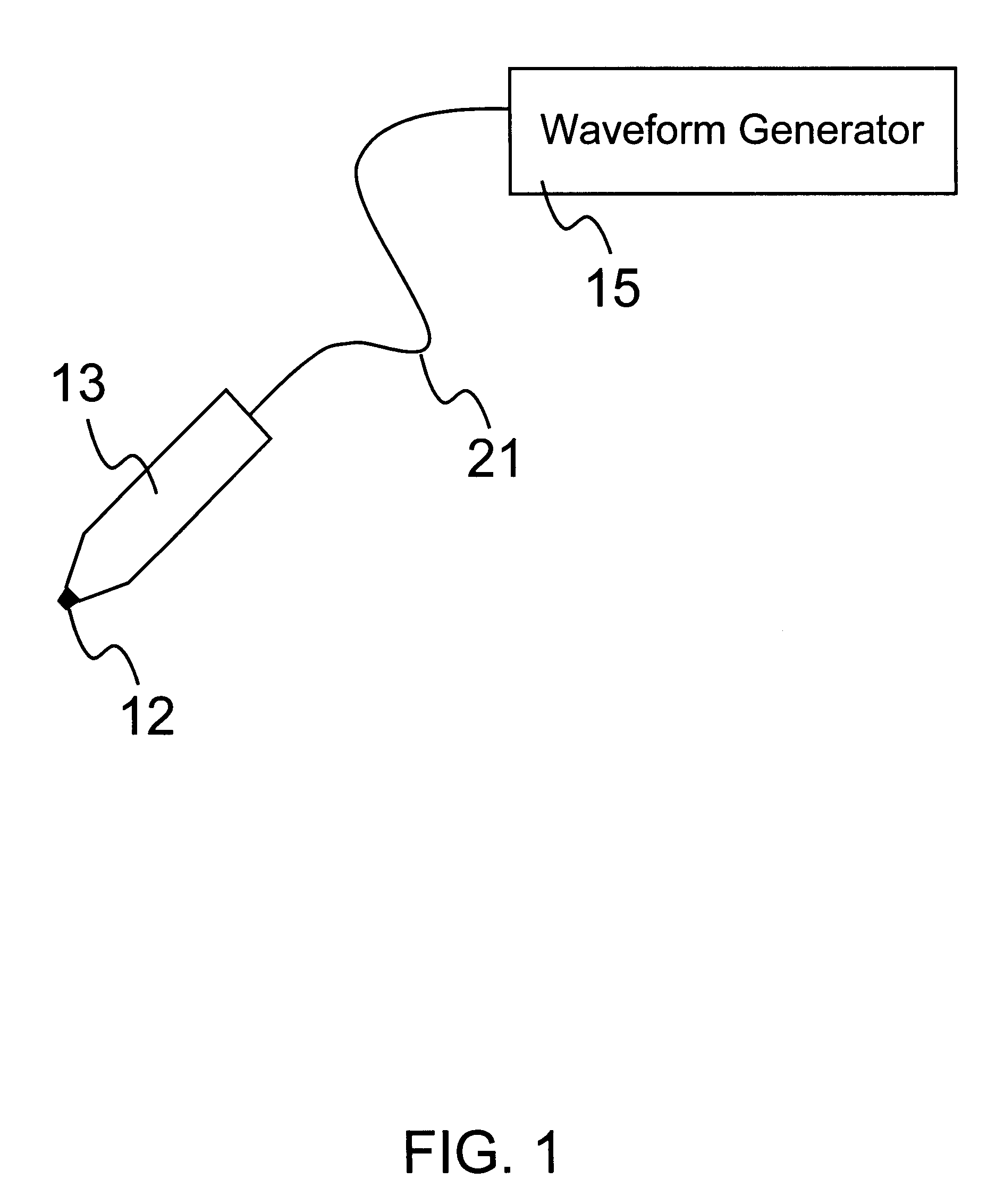
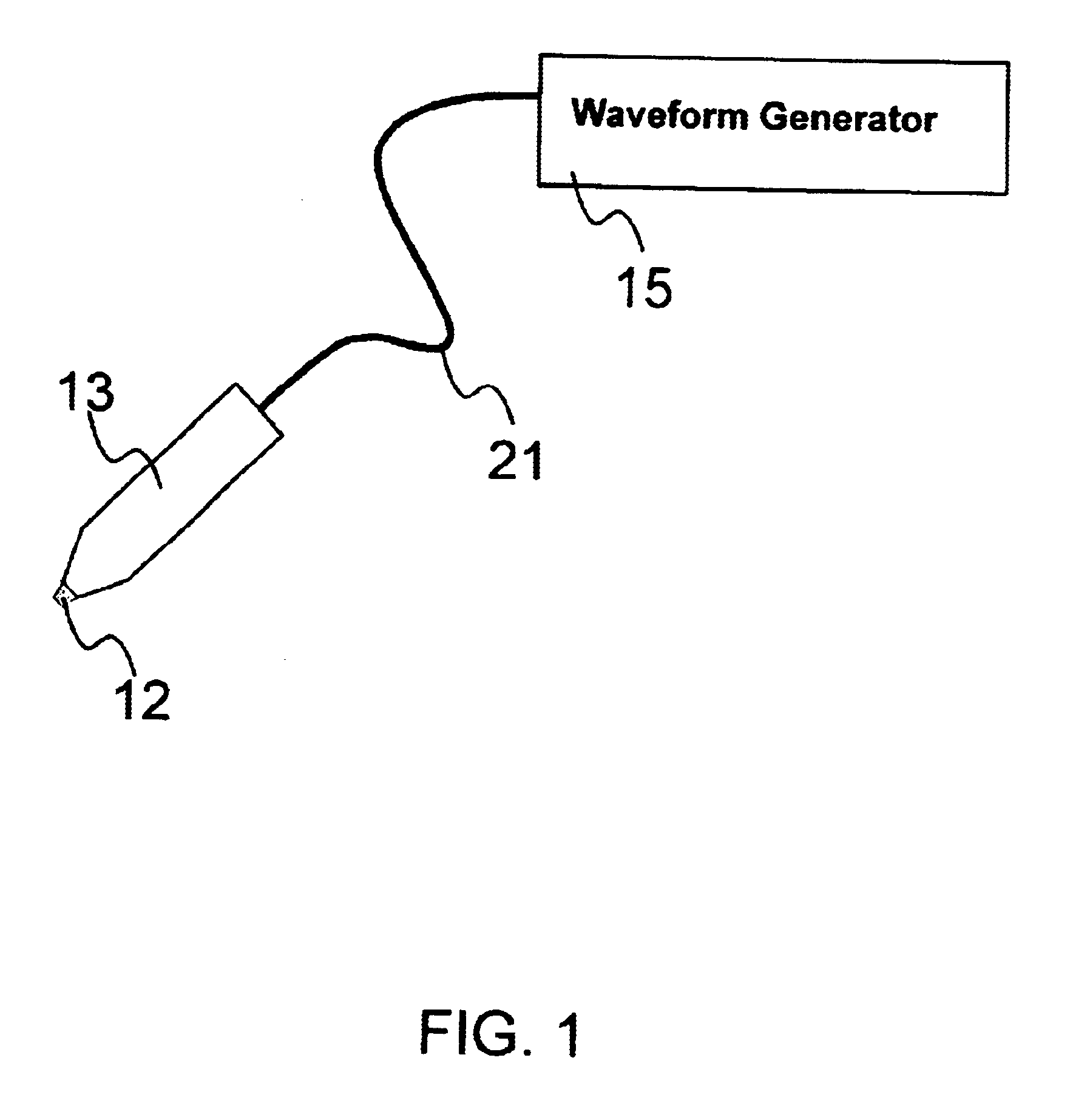
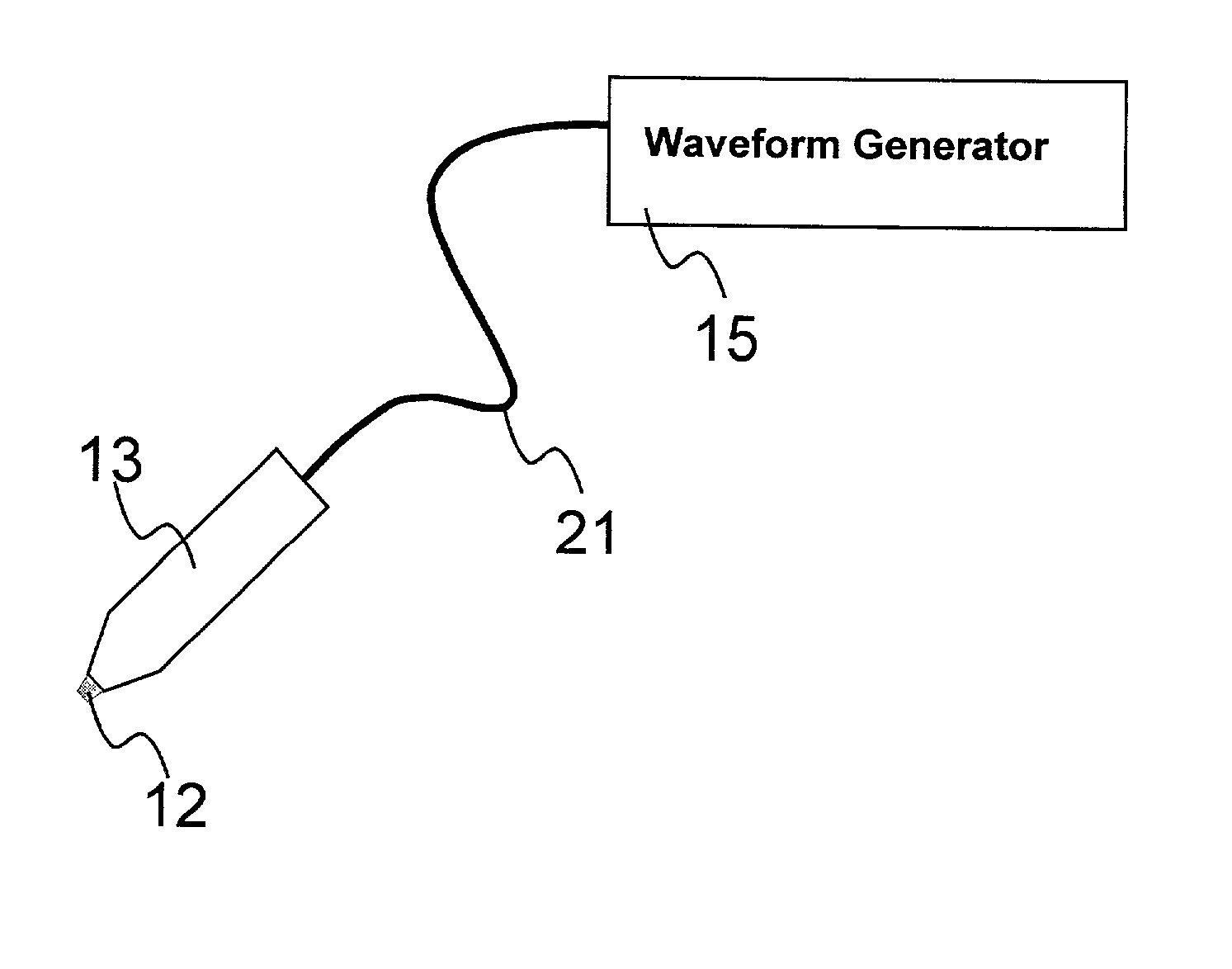
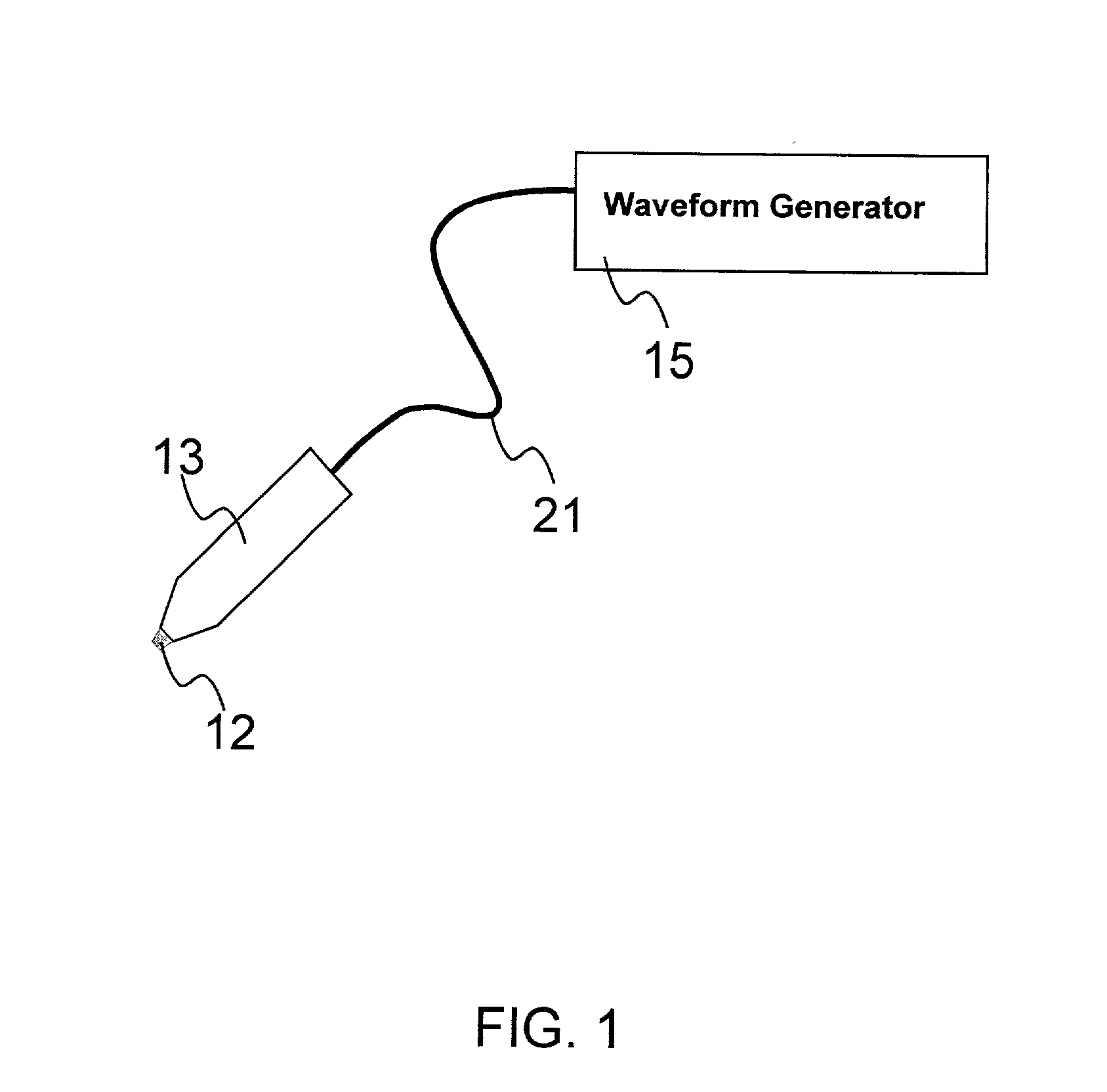
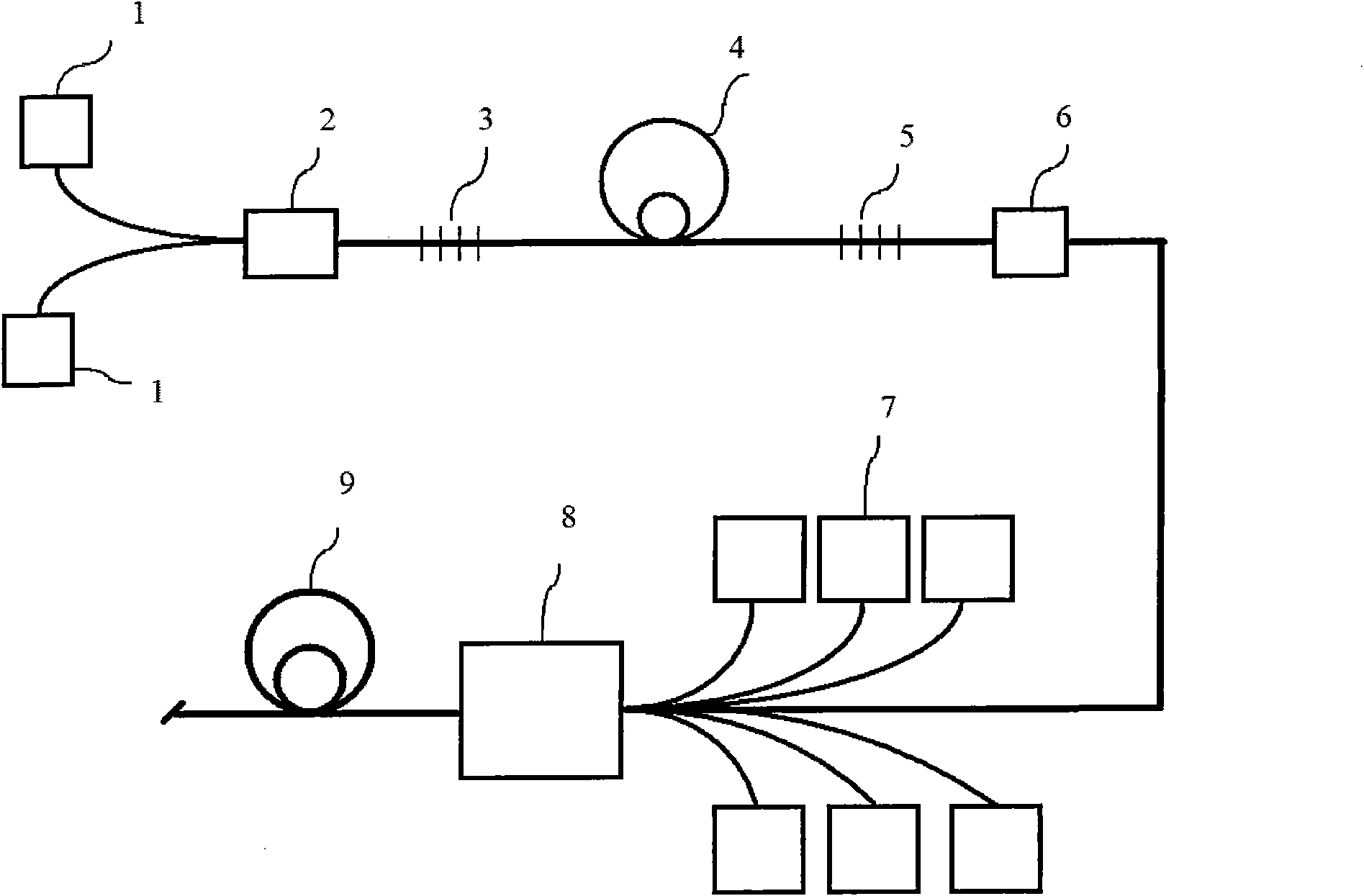
An object of the invention is to provide a method for delivery of macromolecules into biological cells, such as Langerhans cells (22) in the epidermis (20) of a patient, which includes the steps of coating electodes (16) in an electrode assembly (12) with solid phase macromolecules to be delivered, such as a DNA, and / or RNA vaccine or a protein-based vaccine, attaching the electrode assembly (12) having the coated electrodes (16) to an electrode assembly holder (13), providing a waveform generator (15), establishing electrically conductive pathways between the electrodes (16), and the waveform generator (15), locating the electrodes (16) such that the biological cells are situated therebetween, such as by penetrating the needle electrode (16) into the epidermis (20) above the epidermal basal lamina, and providing pulse waveform from the waveform generator (15) to the electrodes (16), such that macromolecule on the electrodes (16) is driven off of the electrodes (16), and delivered into the biological cells, such as the Langerhans cells (22).
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
Electrodes coated with treating agent and uses thereof
InactiveUS6713291B2Rapidly ready for useShort pulse widthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological cellCoated electrodes
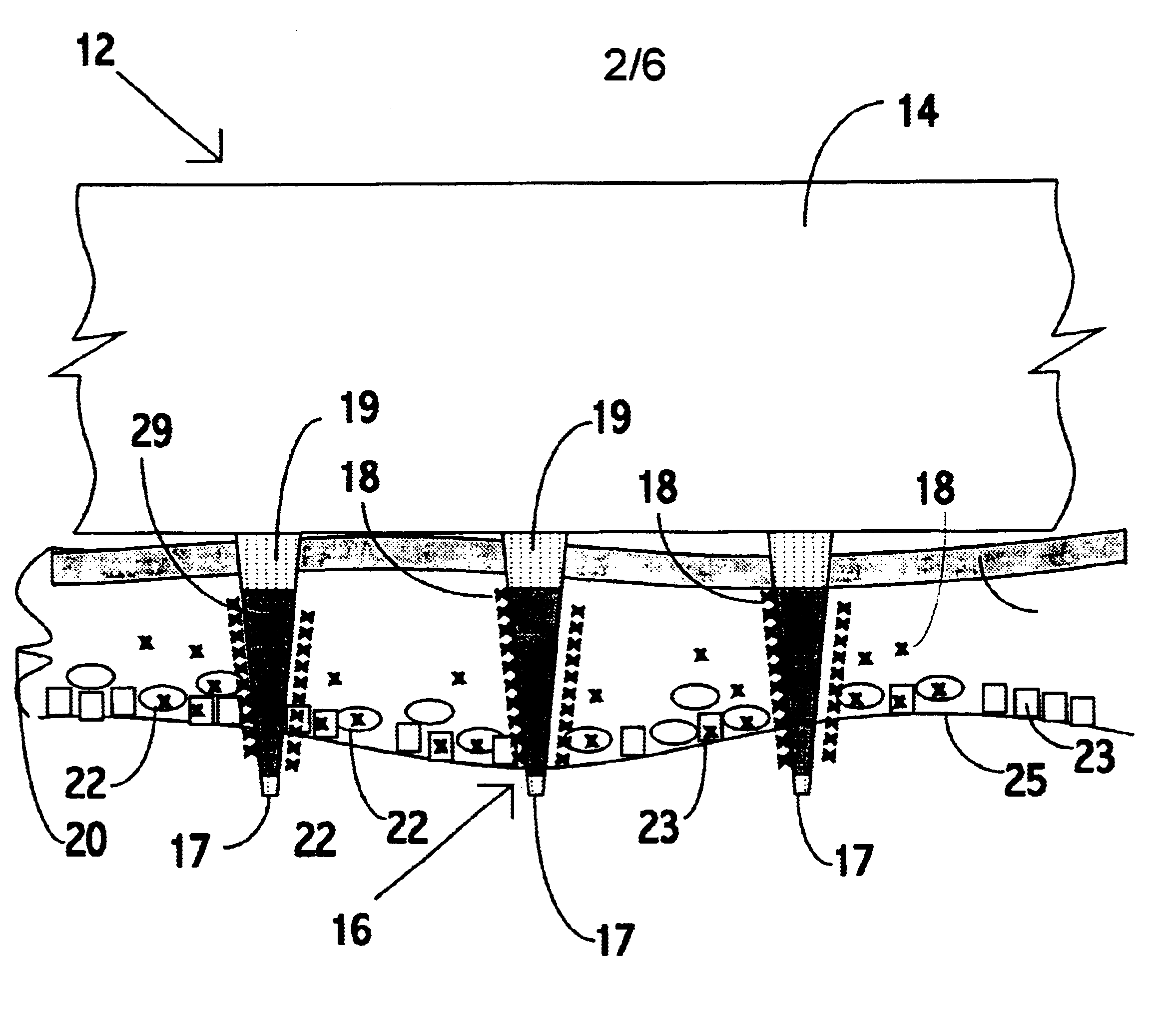
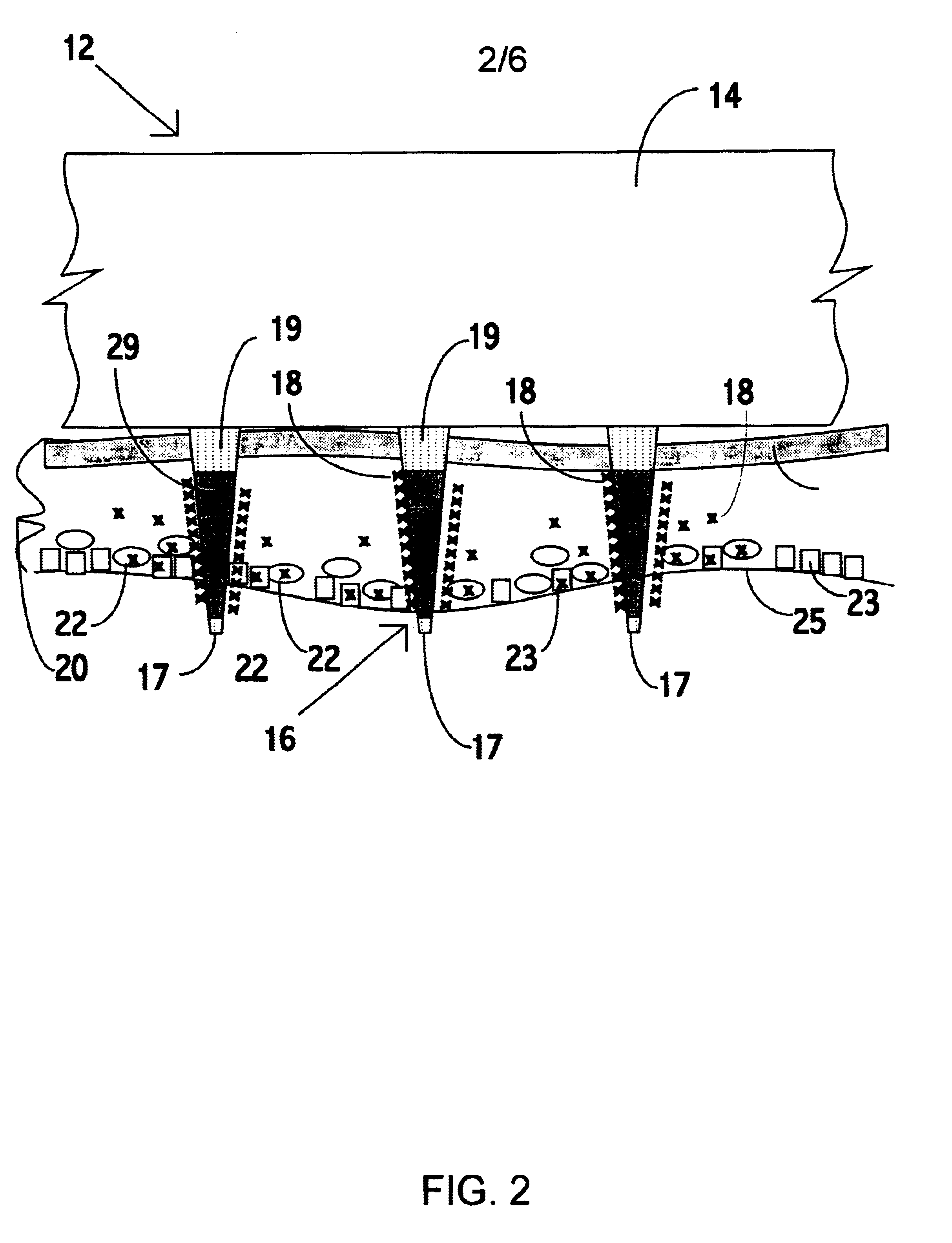
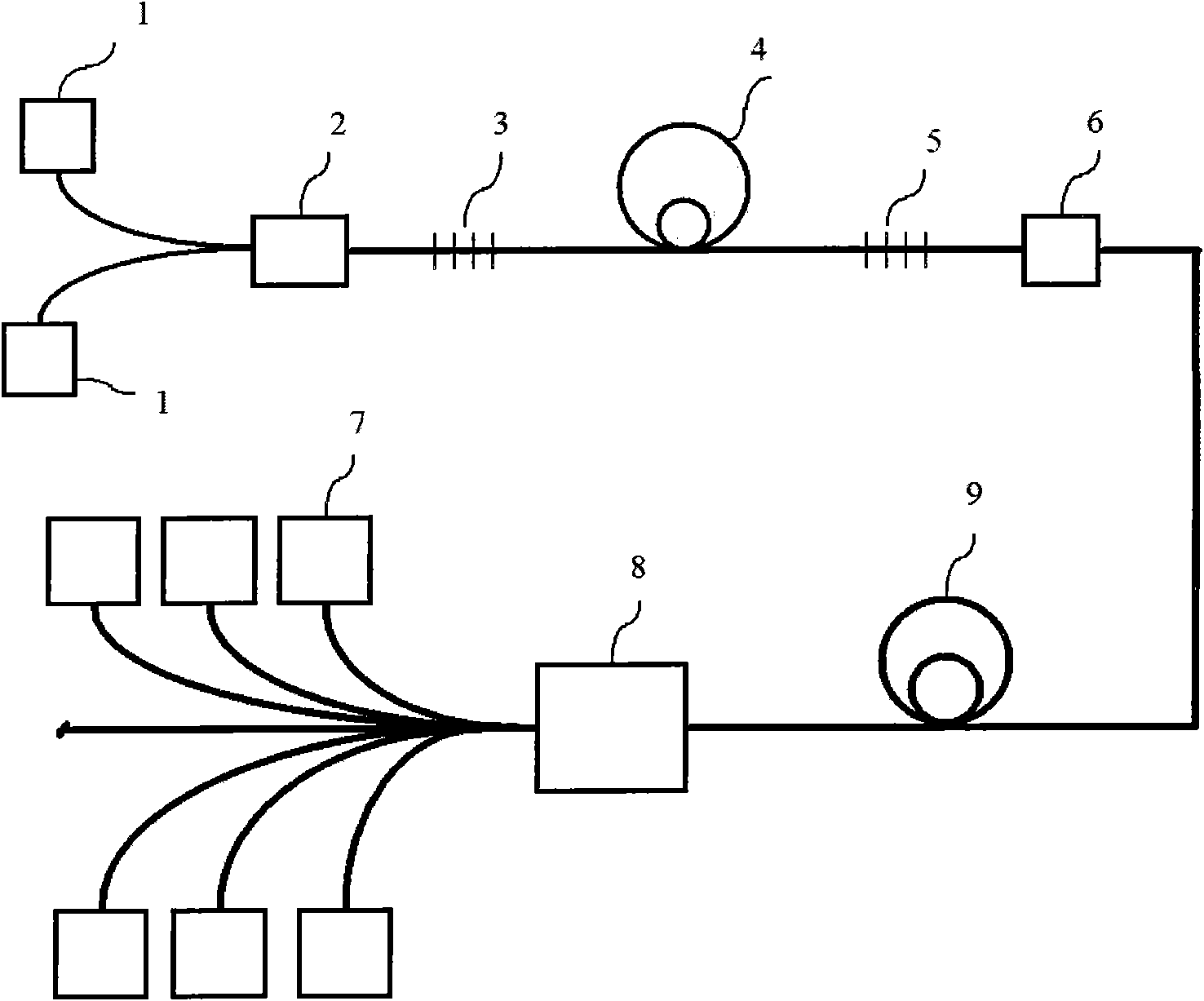
An object of the invention is to provide a method for delivery of macromolecules into biological cells in the tissues of a patient and includes the steps of: (a) providing electrodes (16) in an electrode assembly (12), wherein the electrodes have fixed electrode surfaces (42) which are coated with at least one static layer of electrode releasable molecules (44) to be delivered; (b) providing a waveform generator (15) for generating electric fields; (c) establishing electrically conductive pathways between the electrodes (16) and the waveform generator (15); (d) locating the electrodes (16) such that the biological cells are situated therebetween, and (g) providing electric fields in the form of pulse waveforms from the waveform generator (15) to the electrodes (16), such that molecules in the at least one static layer of the electrode releasable molecules (44) on the electrodes (16) are delivered into the biological cells. The electrode releasable molecules (44) can be either electric field separable molecules and / or solvent separable material. Another object of the invention is to provide an apparatus for carrying out the method of the invention. The static-coated electrode assembly (12) can be provided in a sterile package (24), from which the electrode assembly (12) is removed prior to use. The statically-coated electrode assembly (12) can be in a form of a disposable assembly (12) which is removable and replaceable from an electrode assembly holder (13).
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
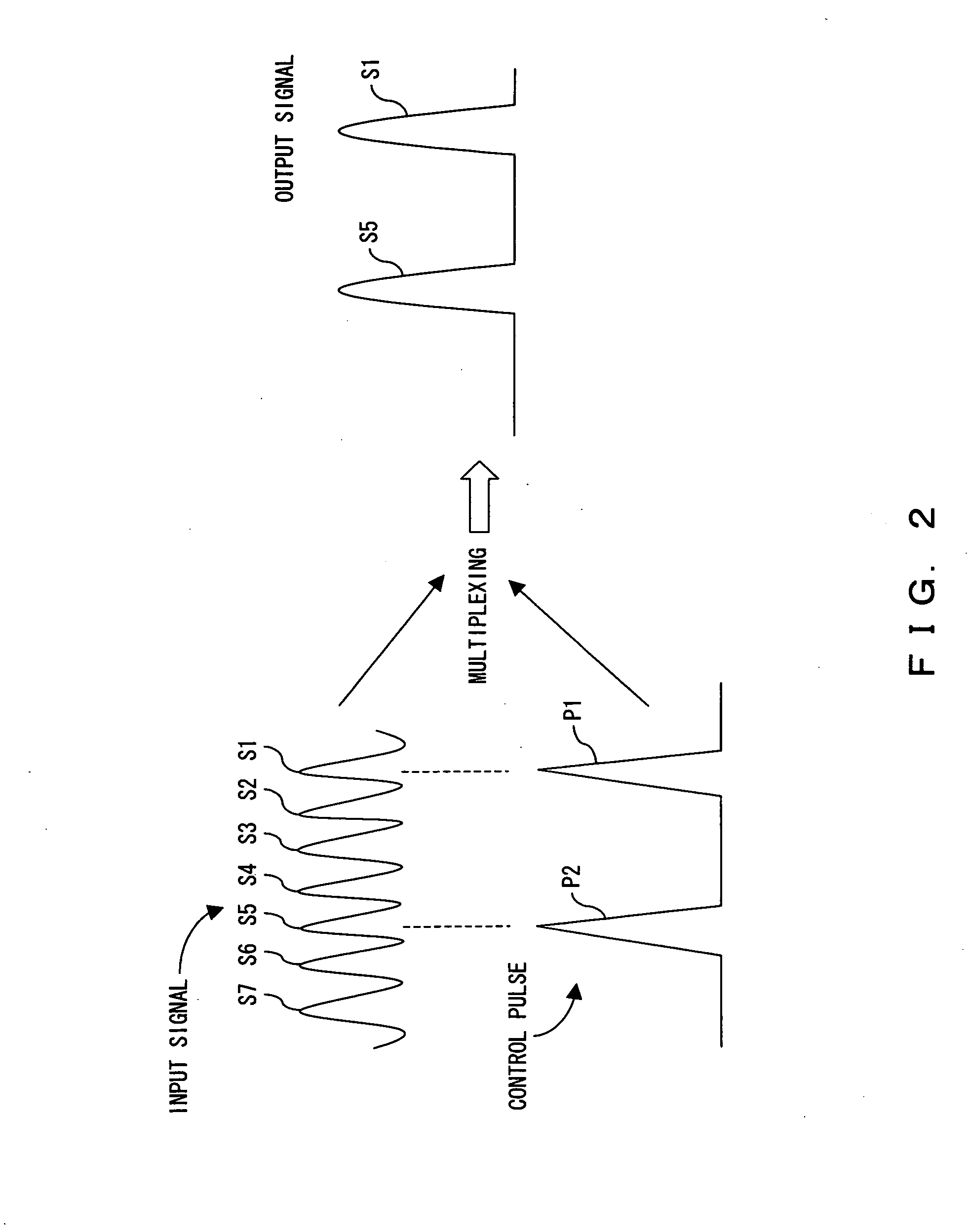
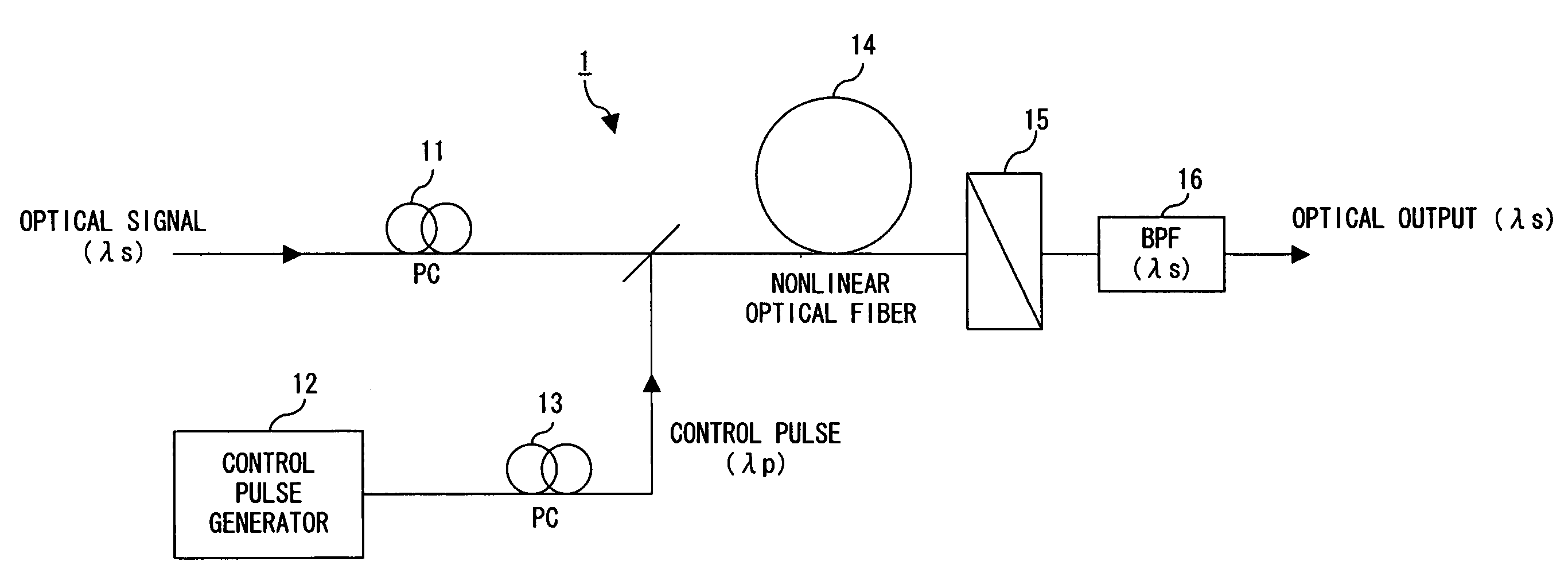
Optical switch and optical waveform monitoring device utilizing optical switch
ActiveUS20060051100A1Improve switching efficiencyExcellent optical S/N ratioLaser detailsPolarisation multiplex systemsPolarizerLength wave
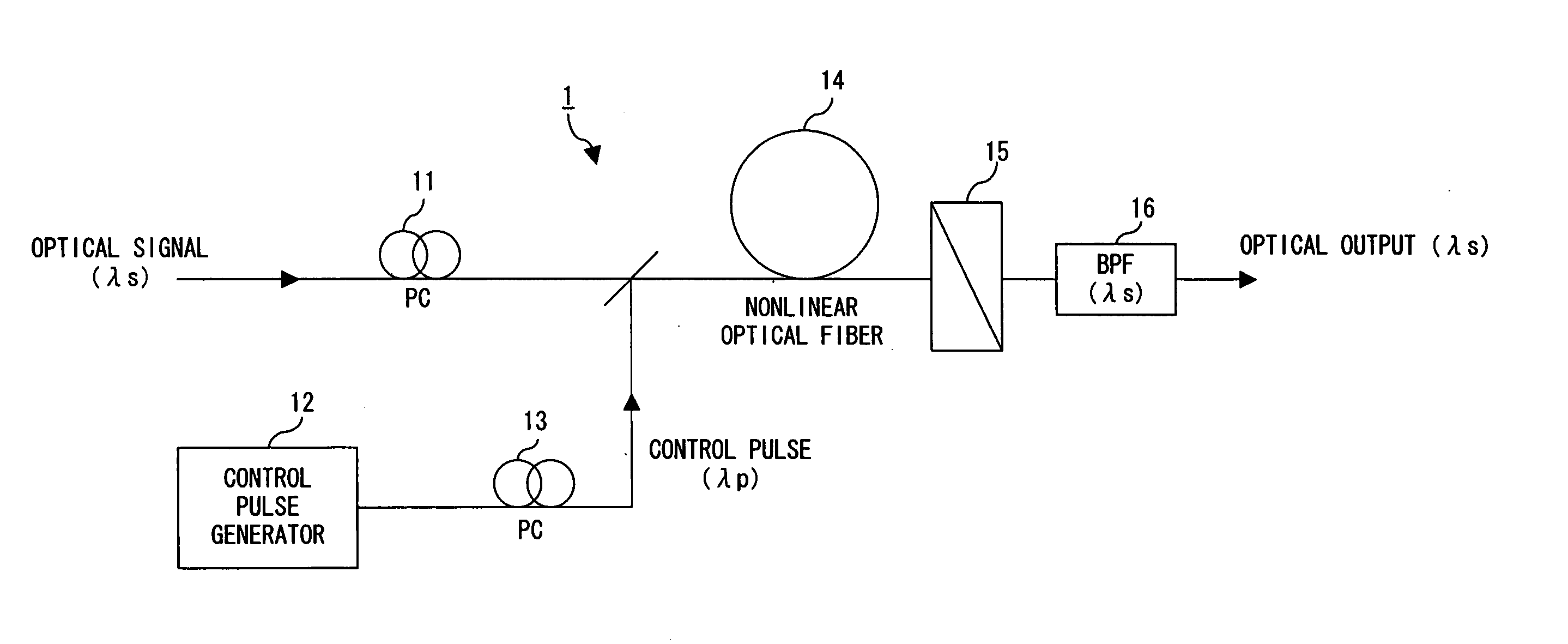
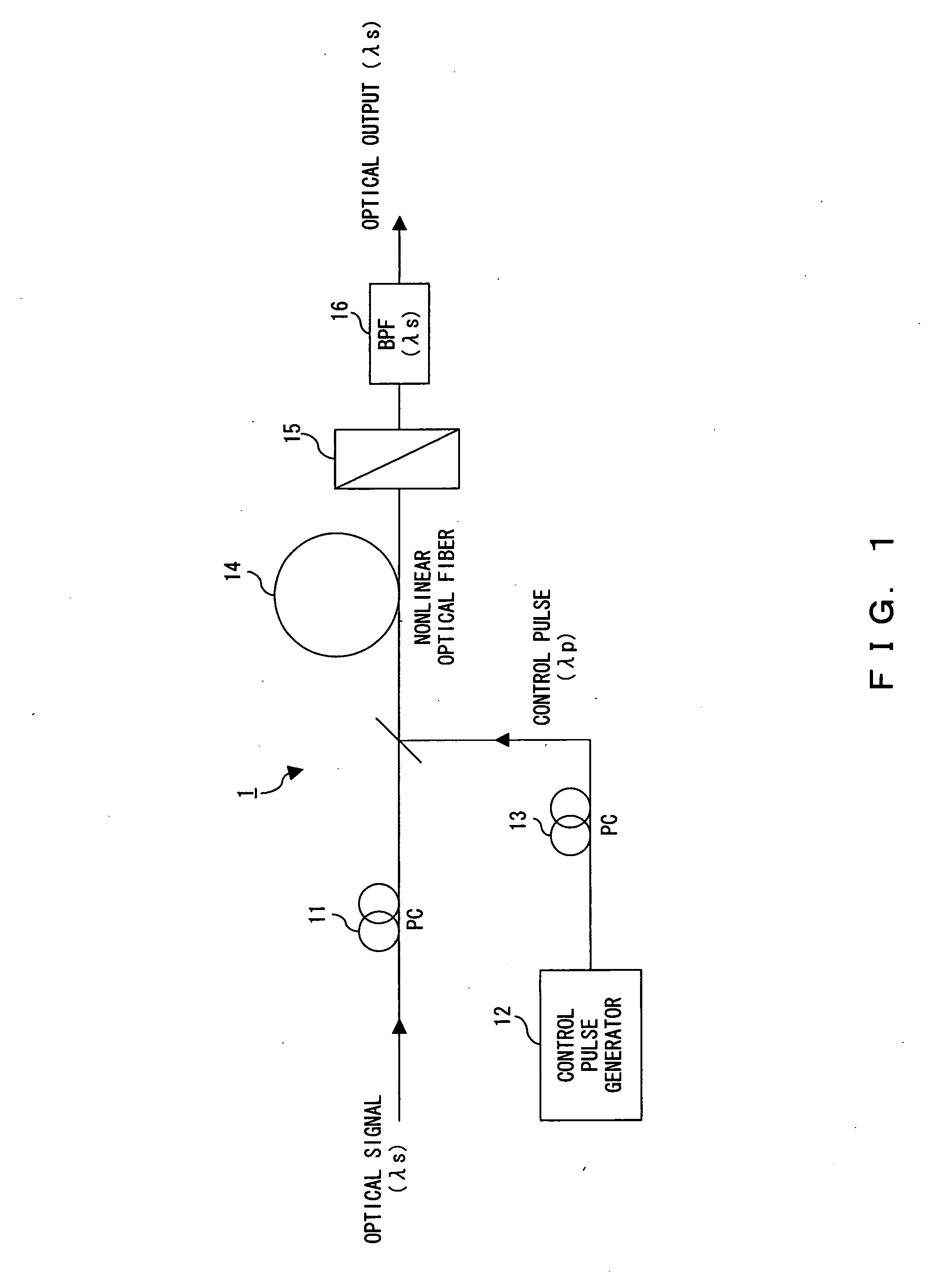
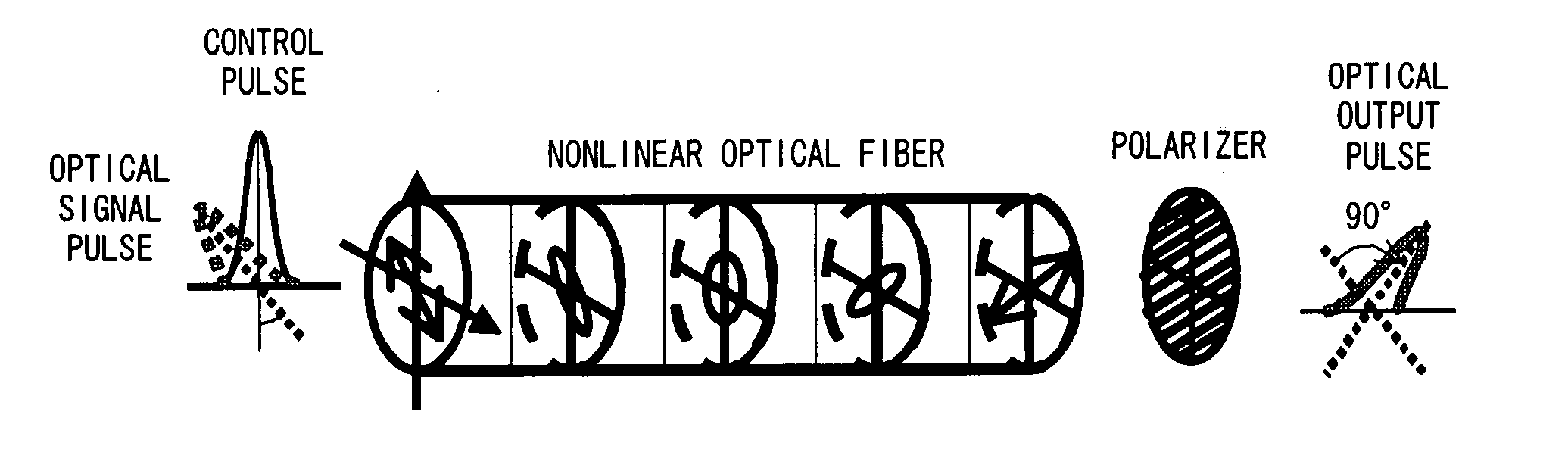
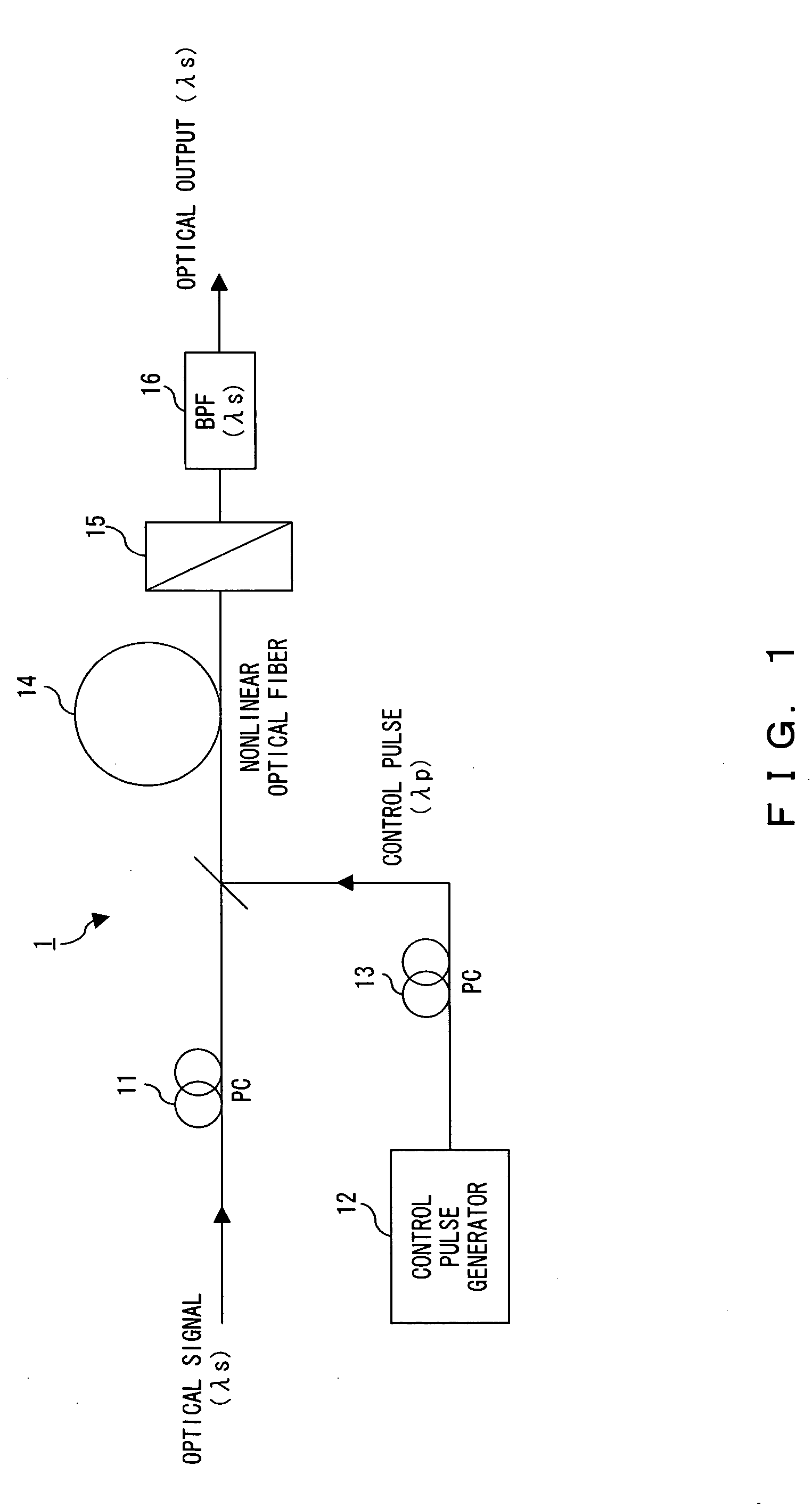
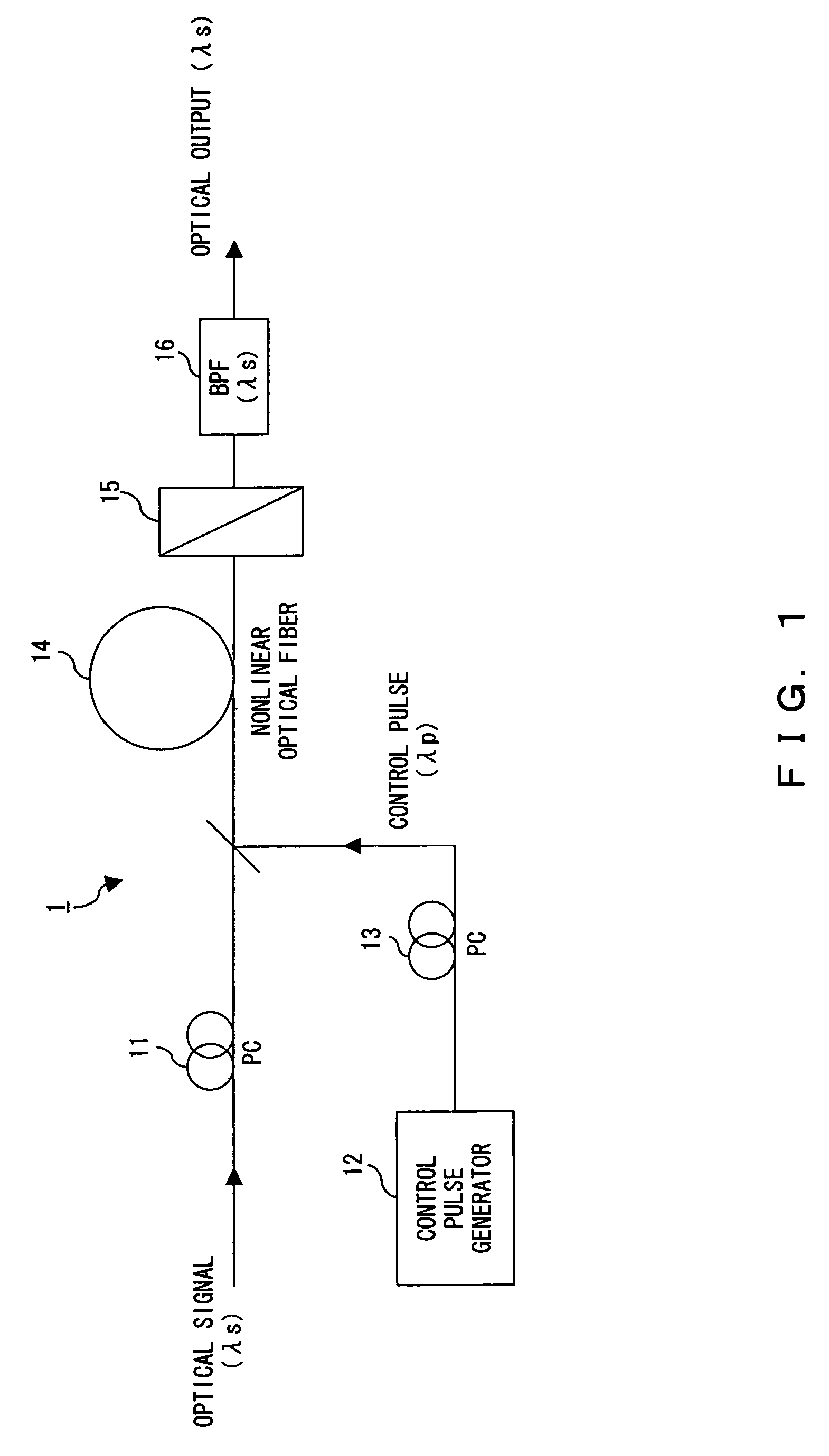
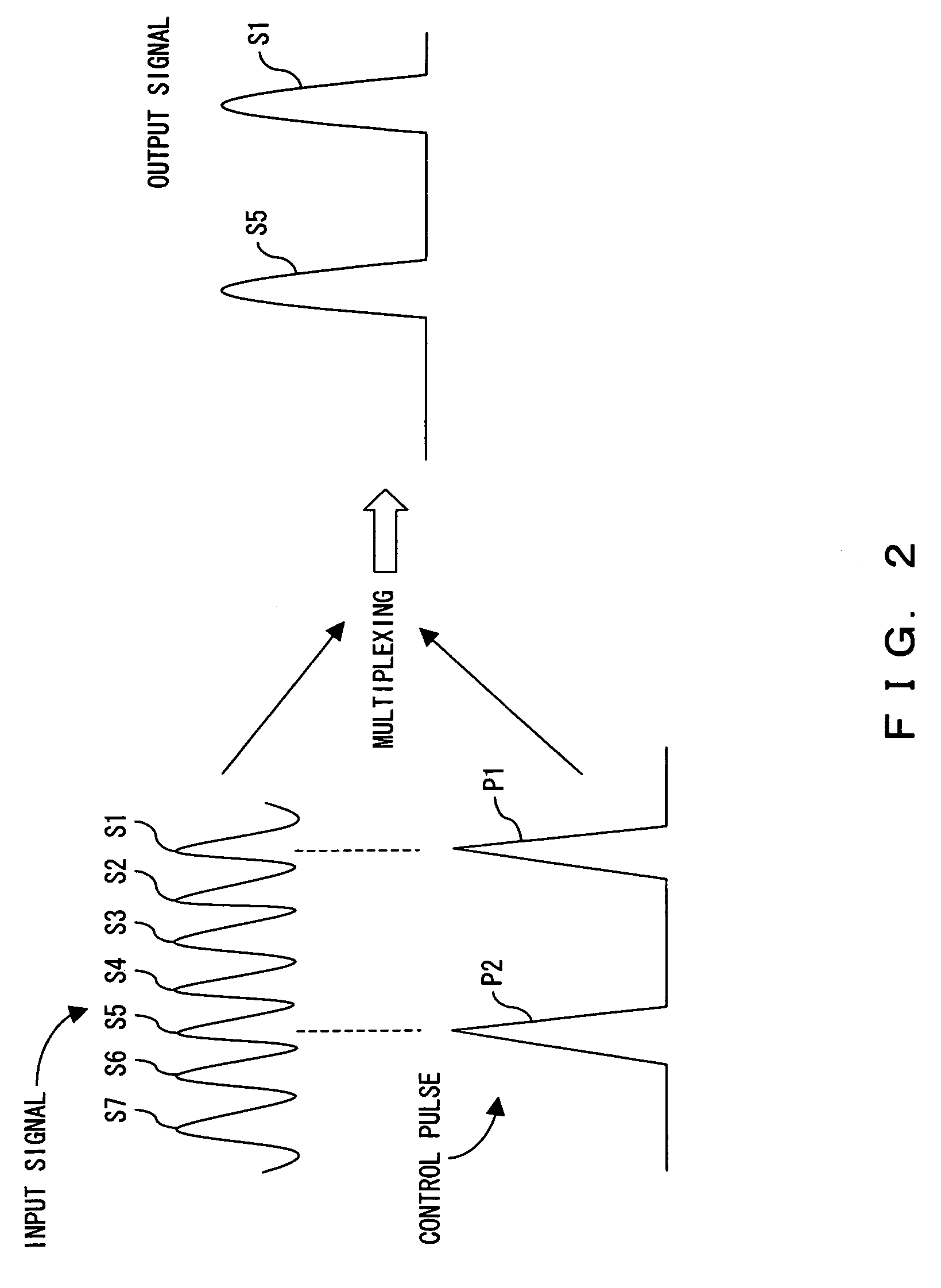
The polarization direction of an optical signal is changed by a polarization controller so as to be orthogonal to a main axis of a polarizer. A control pulse generator generates control pulses from control beam with a wavelength which is different from the wavelength of the optical signal. The optical signal and the control pulse are input to a nonlinear optical fiber. In the nonlinear optical fiber, the optical signal, during a time period in which the optical signal and the control pulse coincide, is amplified with optical parametric amplification around a polarization direction of the control pulse. The optical signal, during the time period in which the optical signal and the control pulse coincide, passes through the polarizer.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
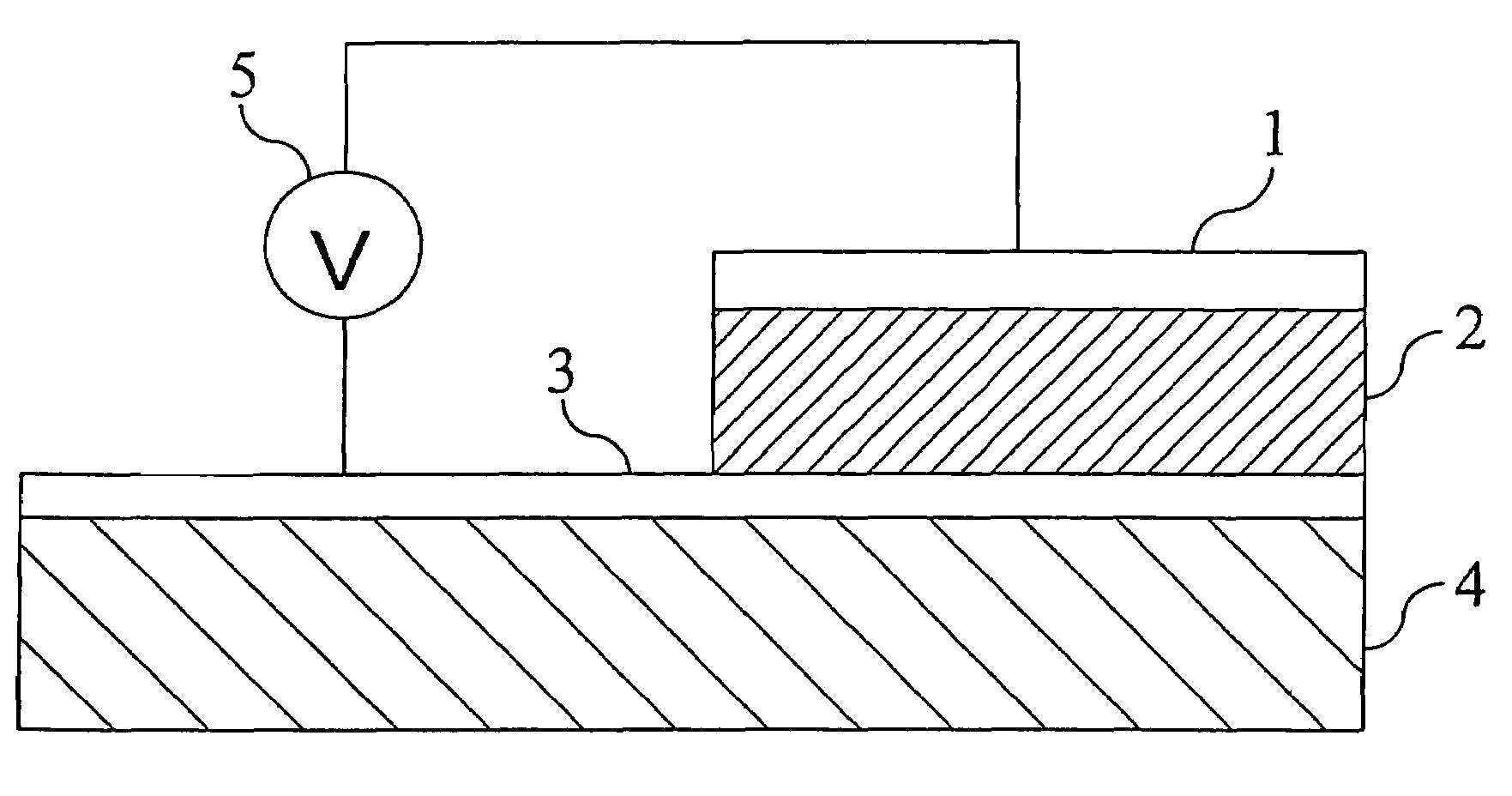
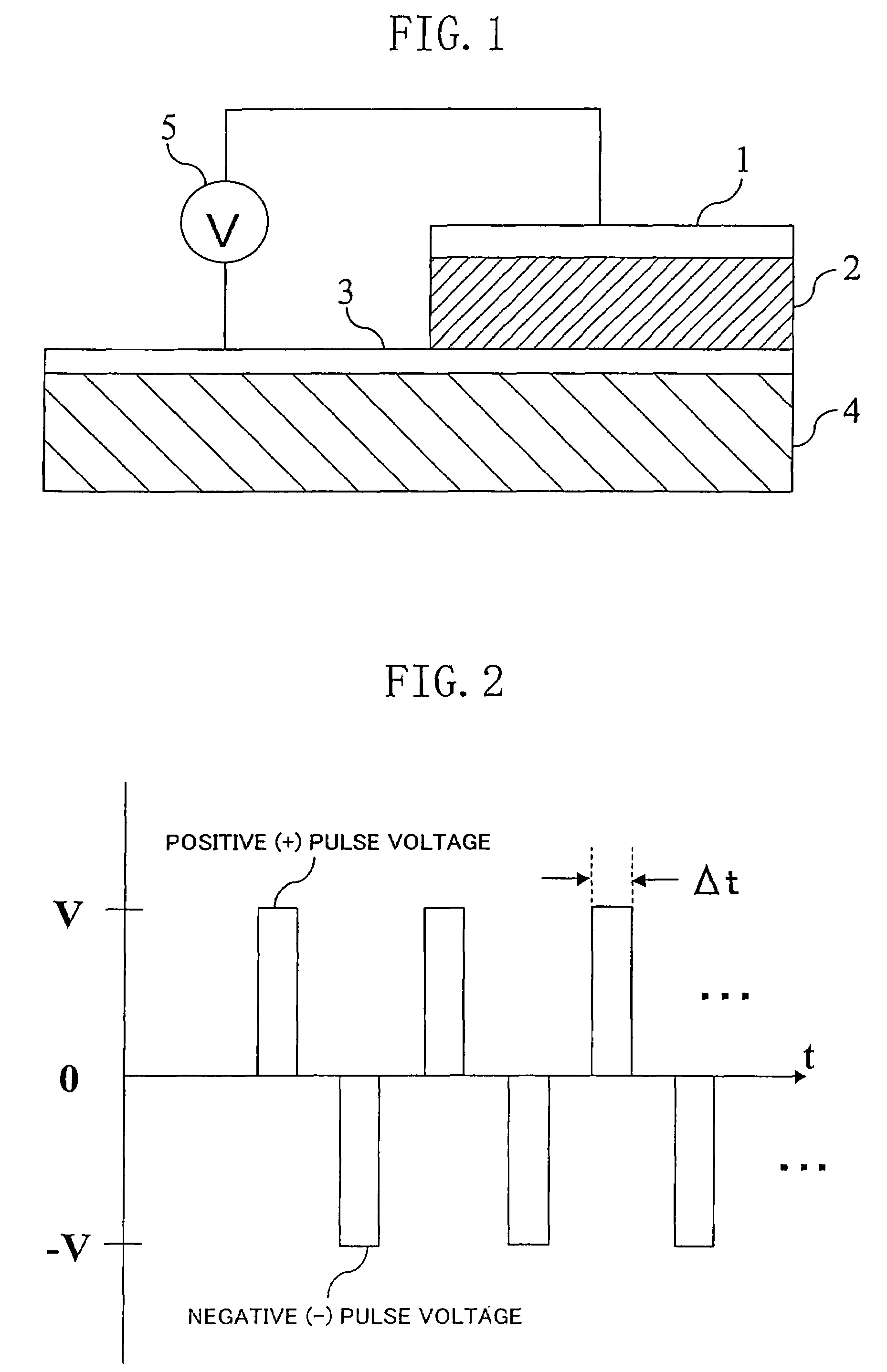
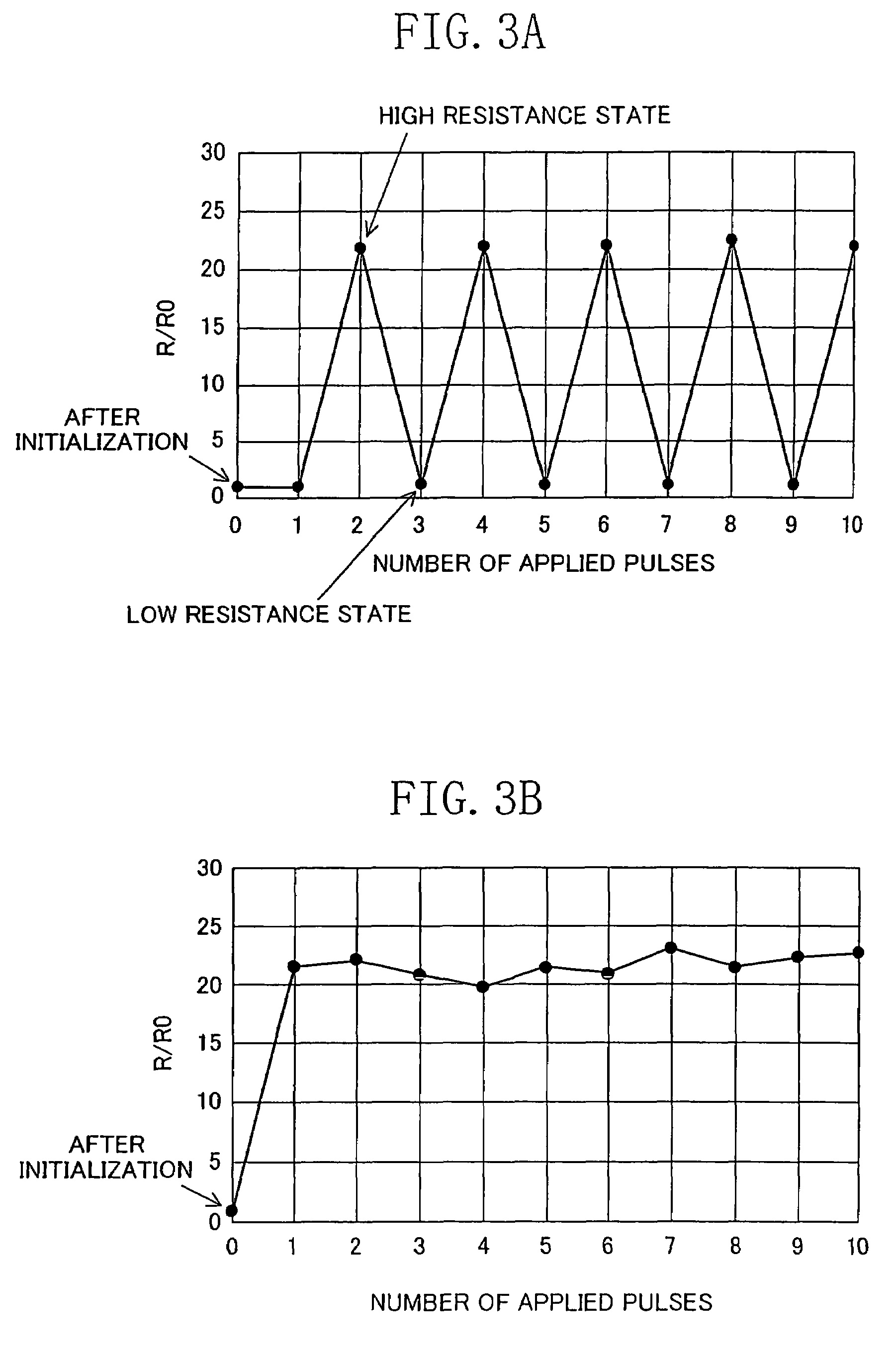
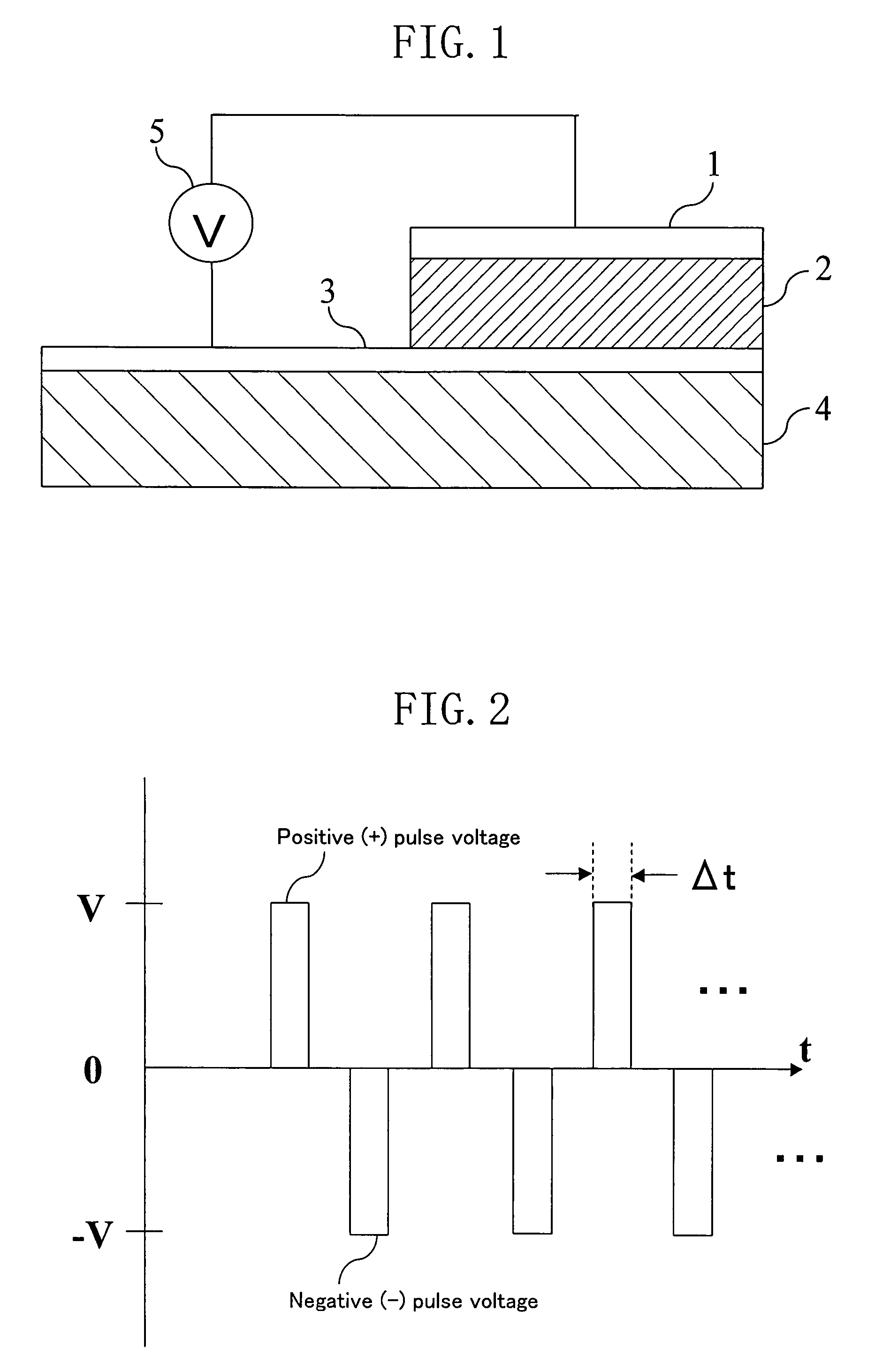
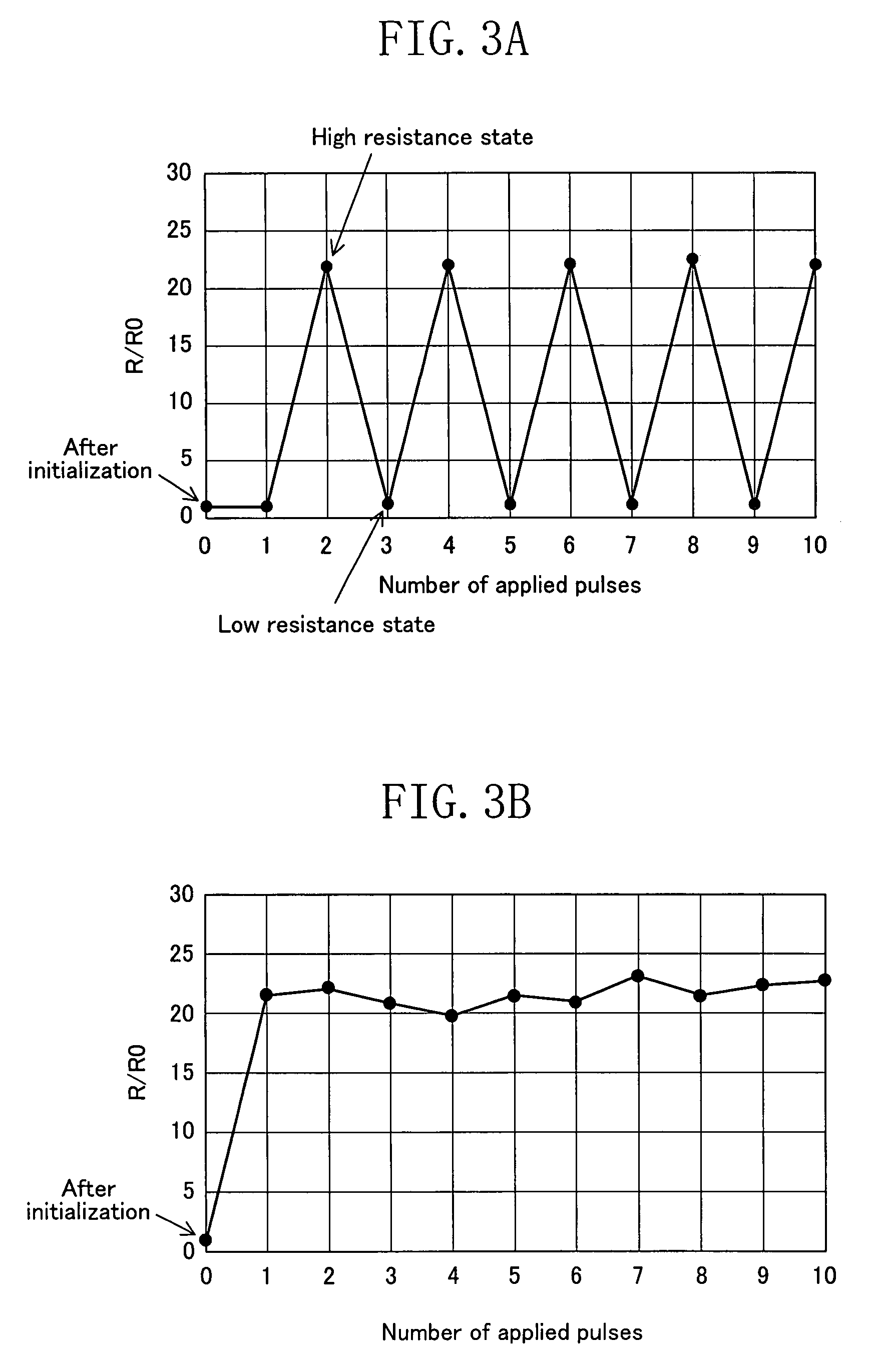
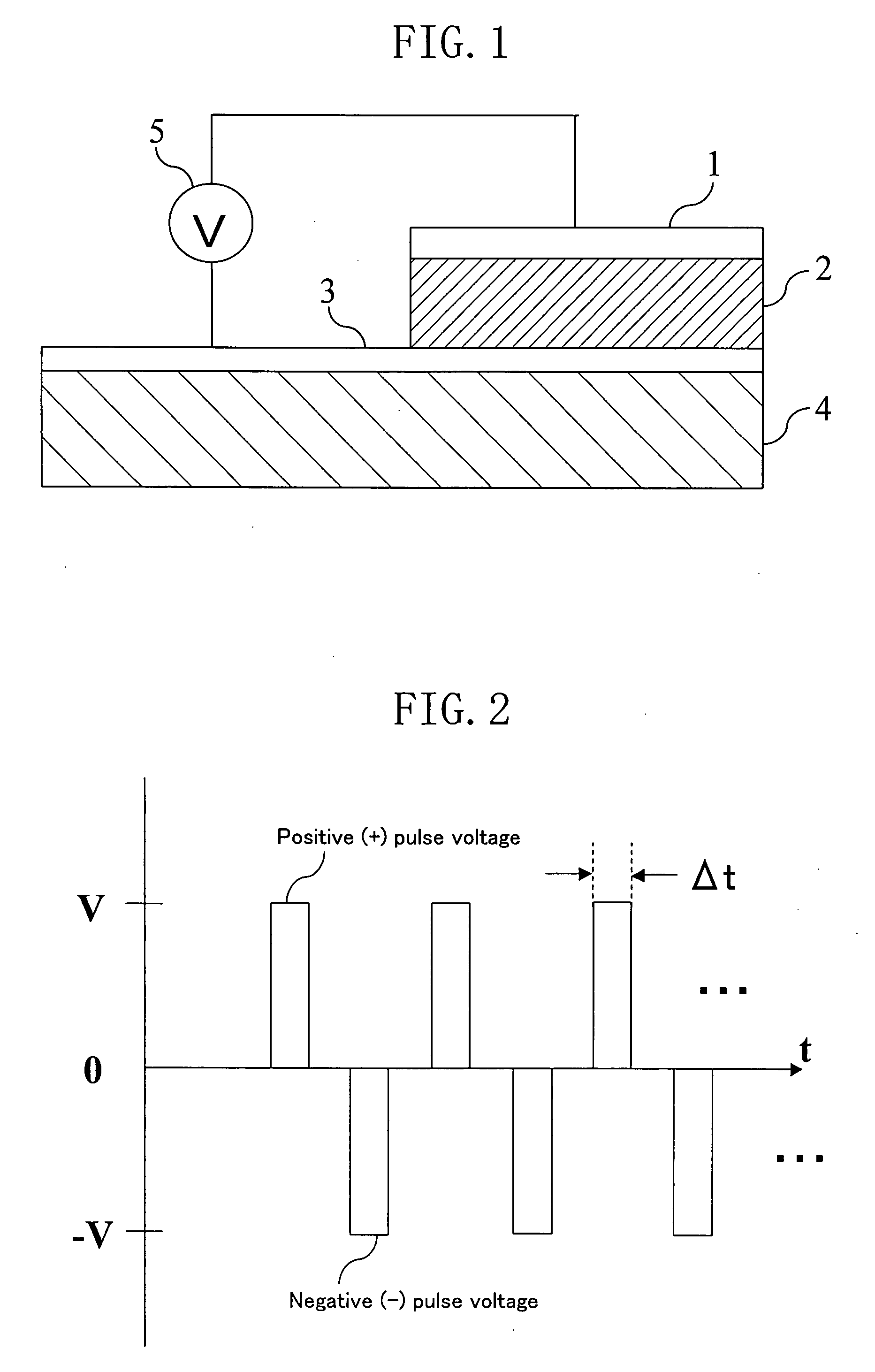
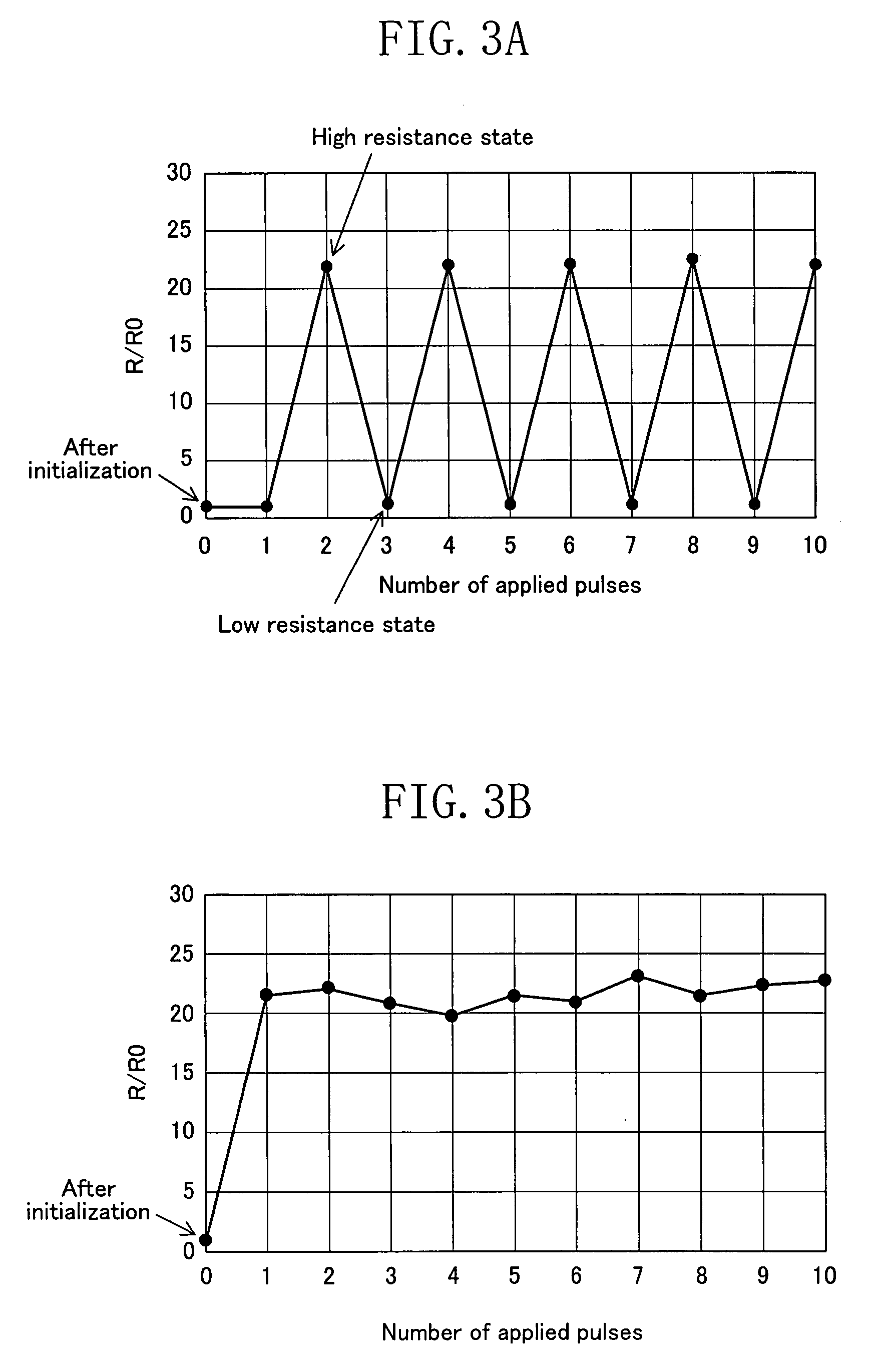
Electric element, memory device, and semiconductor integrated circuit formed using a state-variable material whose resistance value varies according to an applied pulse voltage
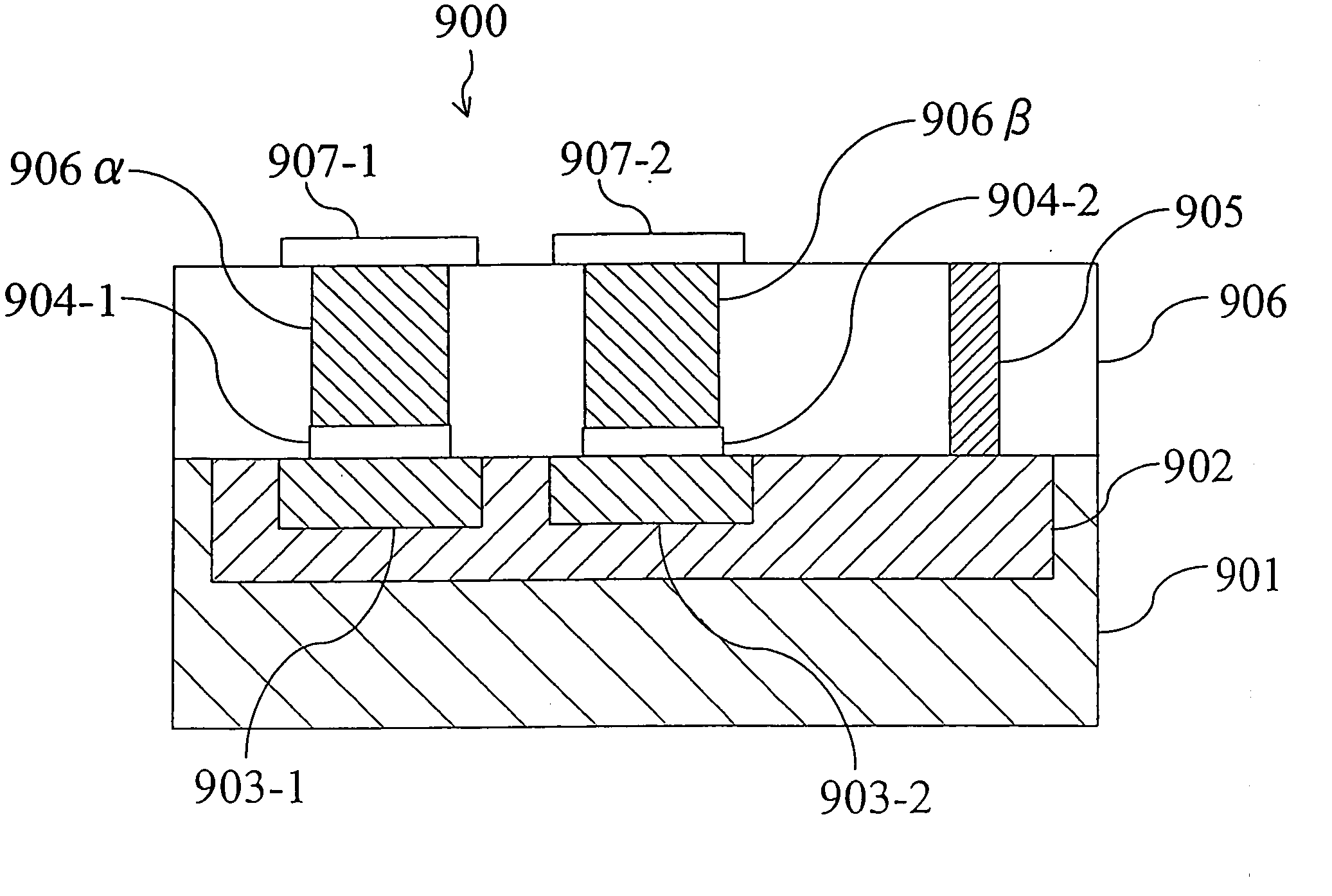
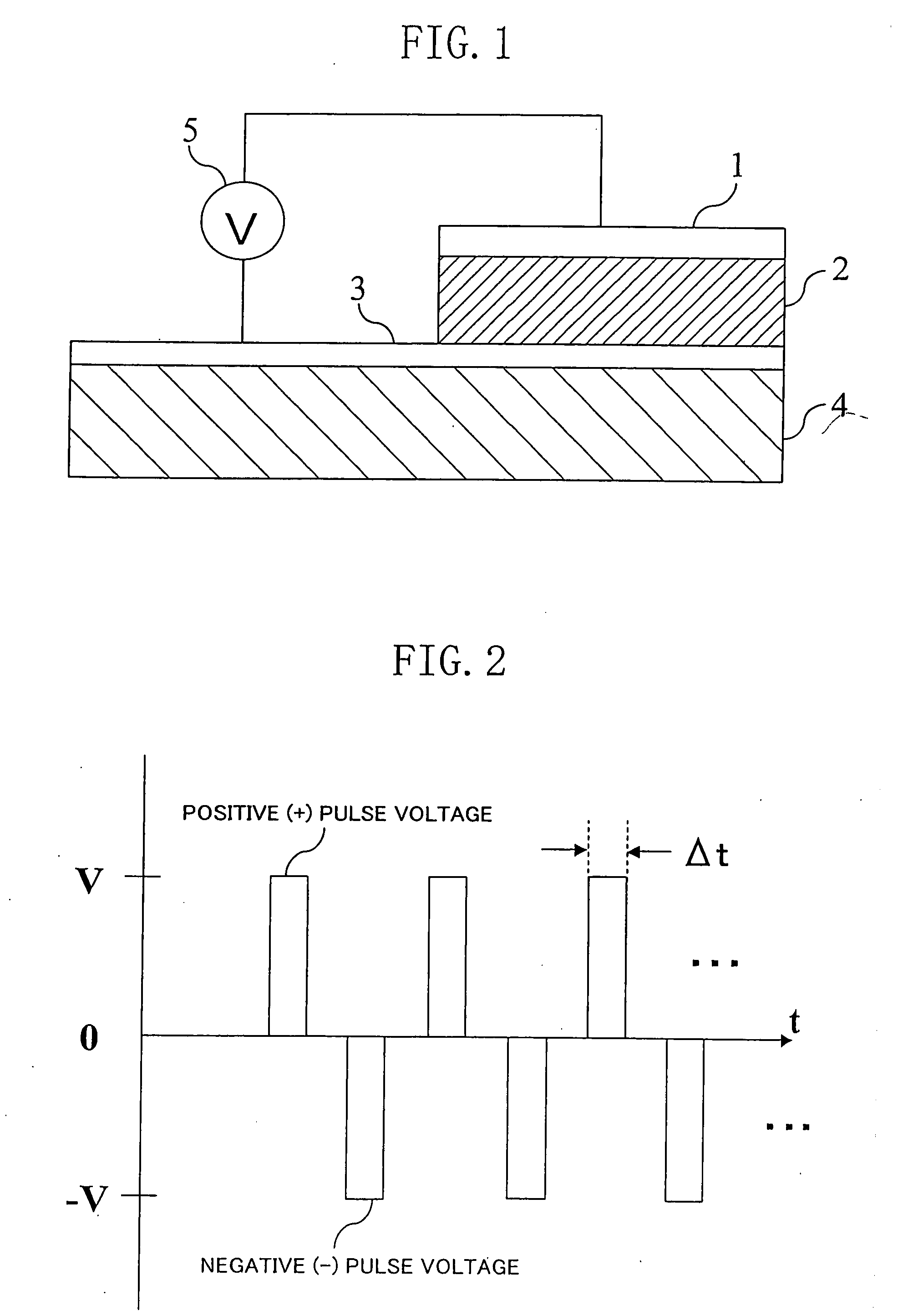
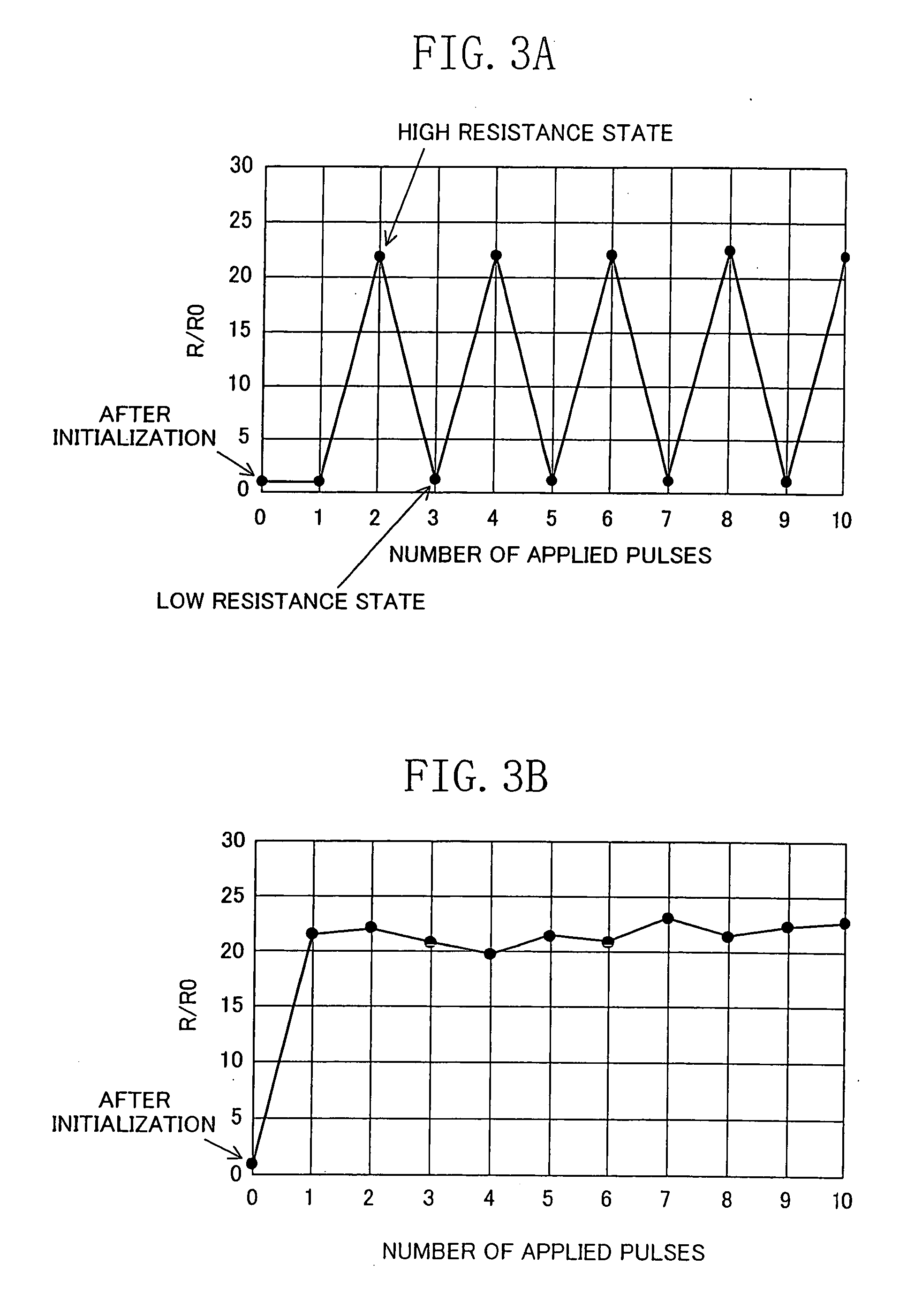
ActiveUS7577022B2Simple processShort pulse widthSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingState variableEngineering
An electric element includes: a first electrode (1); a second electrode (3); and a layer (2) connected between the first electrode and the second electrode and having a diode characteristic and a variable resistance characteristic. The layer (2) conducts a substantial electric current in a forward direction extending from one of the first electrode (1) and the second electrode (3) to the other electrode as compared to a reverse direction opposite of the forward direction. The resistance value of the layer (2) for the forward direction increases or decreases according to a predetermined pulse voltage applied between the first electrode (1) and the second electrode (3).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Optical switch and optical waveform monitoring device utilizing optical switch
InactiveUS20060045445A1Improve switching efficiencyReduce lossesTime-division optical multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesOptical parametric amplifierPolarizer
The polarization direction of a signal is rotated by a polarization controller so as to be orthogonal to the main axis of a polarizer. A control pulse generator generates control pulses from control source with a wavelength which is different from the wavelength of the signal. The signal and the control pulse are input to a nonlinear optical fiber. In the nonlinear optical fiber, the signal, during the time period in which the signal and the control pulse coincide, has its polarization direction rotated by cross phase modulation, and is amplified by optical parametric amplification. The signal, during the time period in which the signal and the control pulse coincide, passes through the polarizer.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
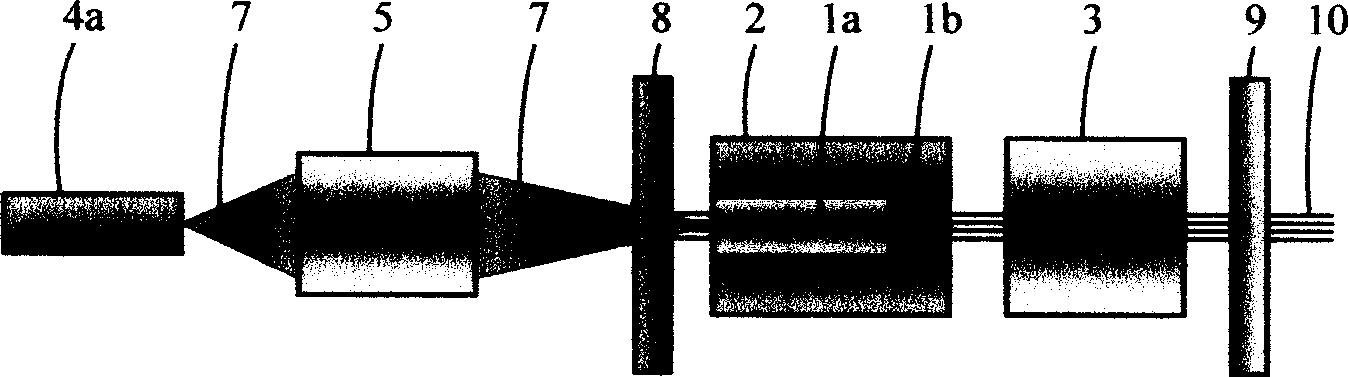
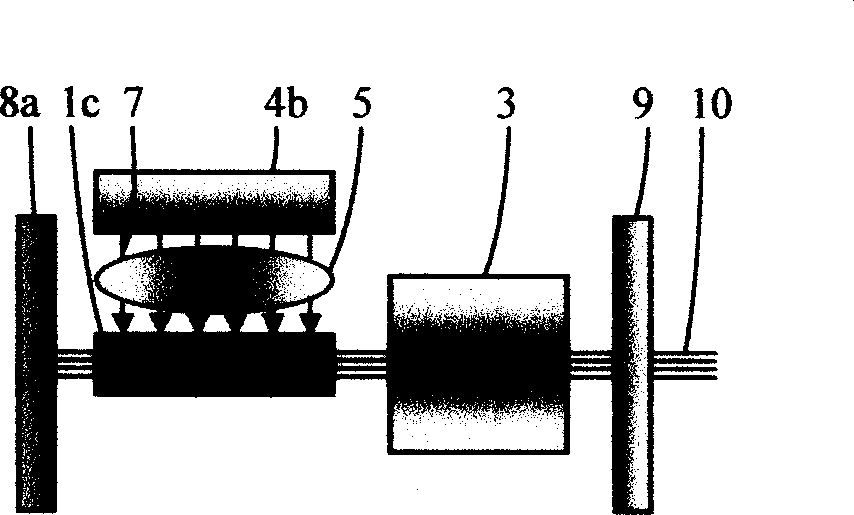
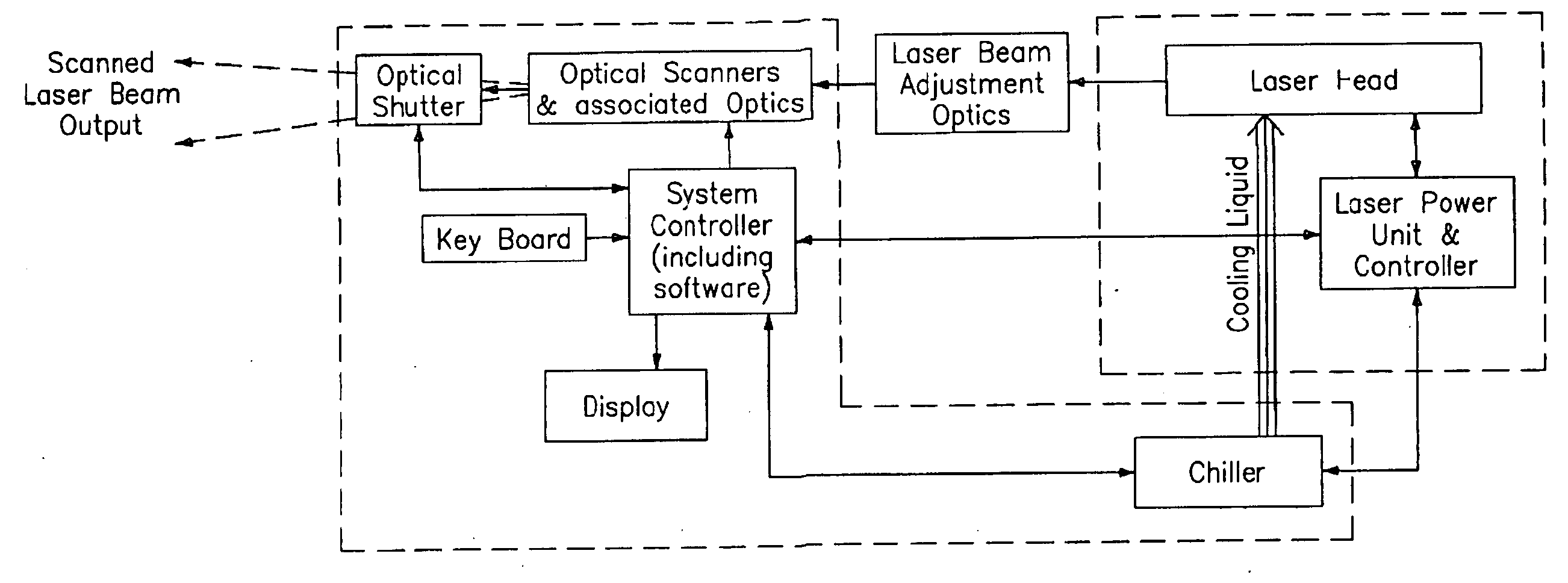
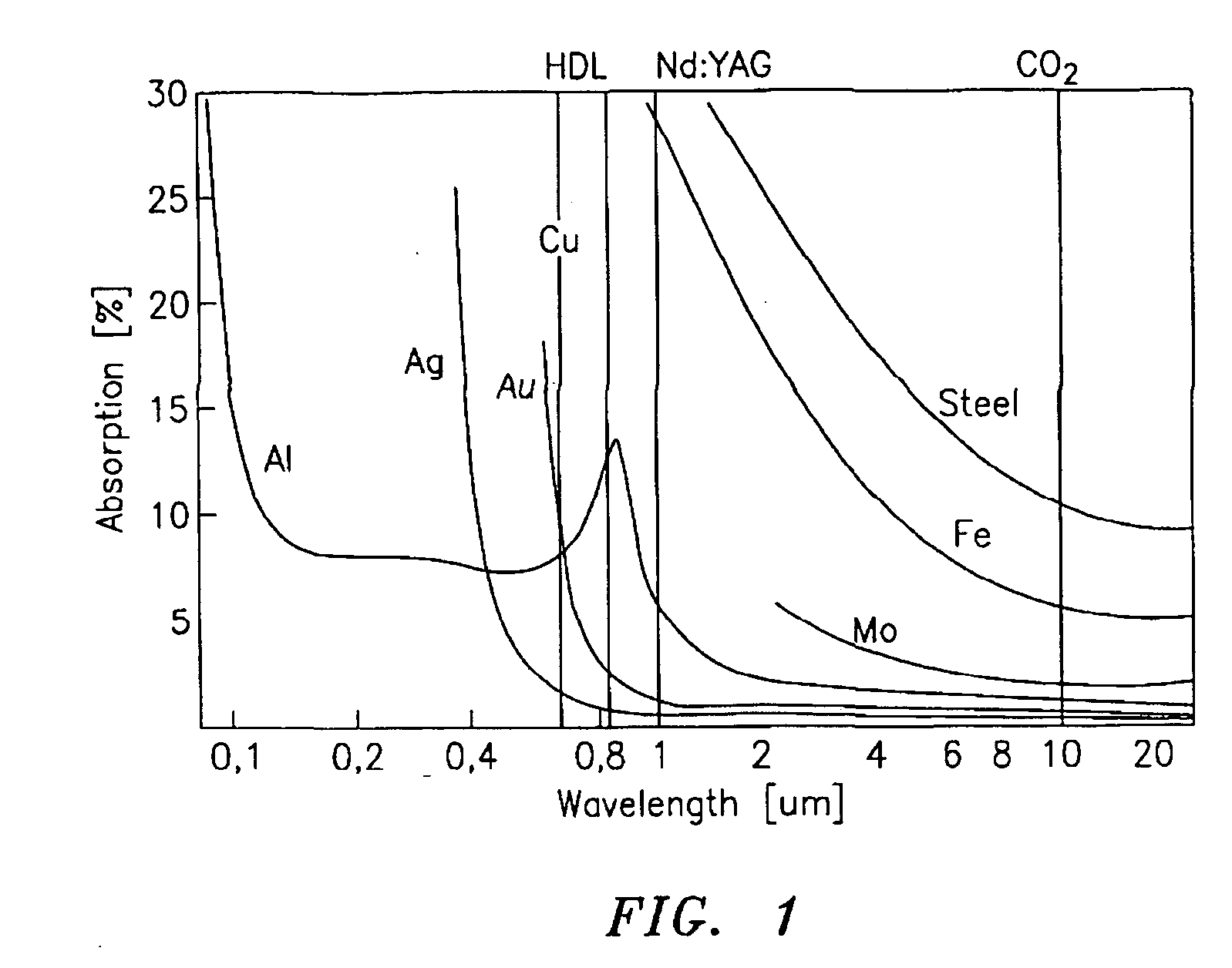
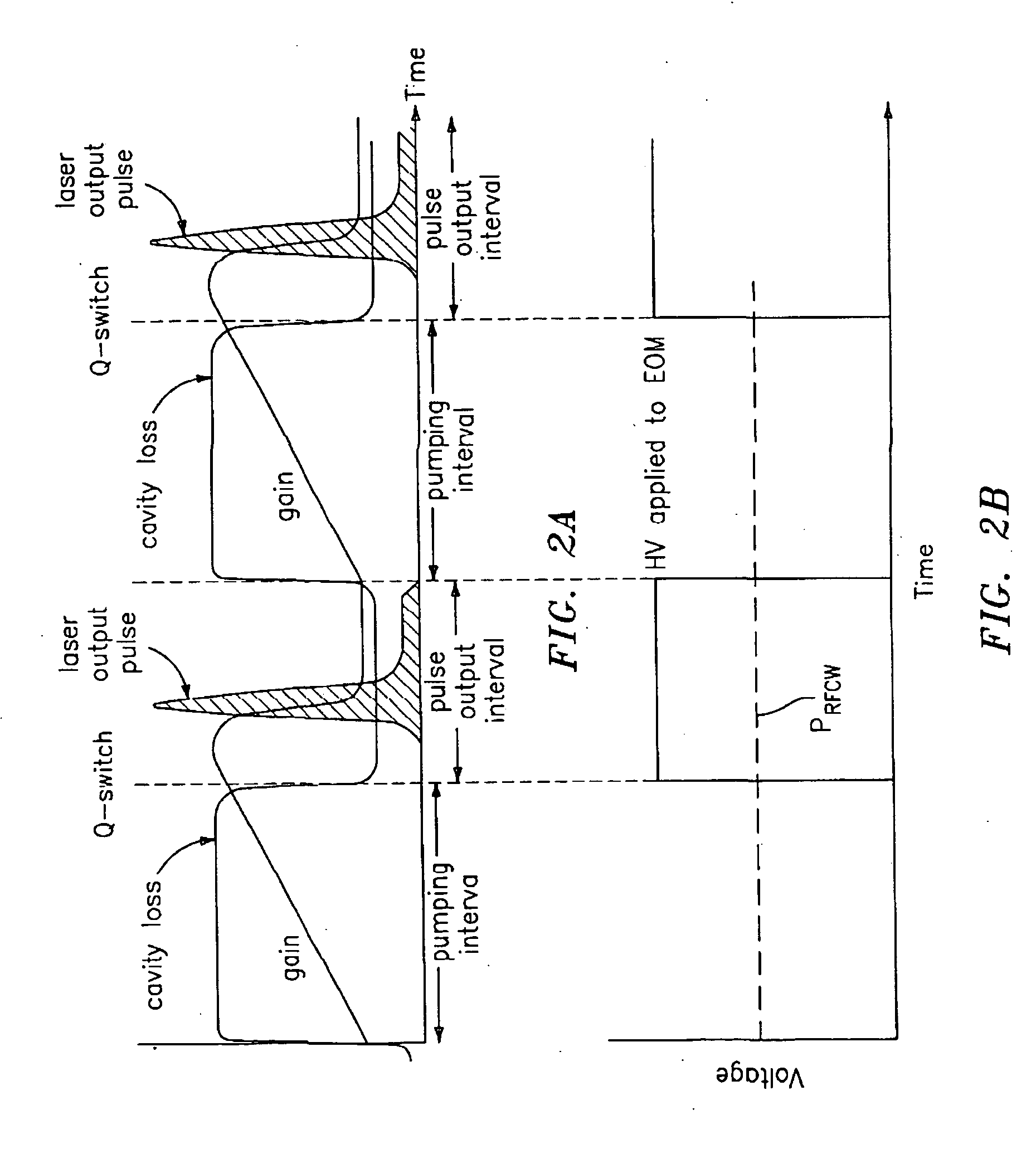
Q-switched, cavity dumped laser systems for material processing
InactiveUS7058093B2High strengthLow powerActive medium materialGas laser constructional detailsEngravingPeak value
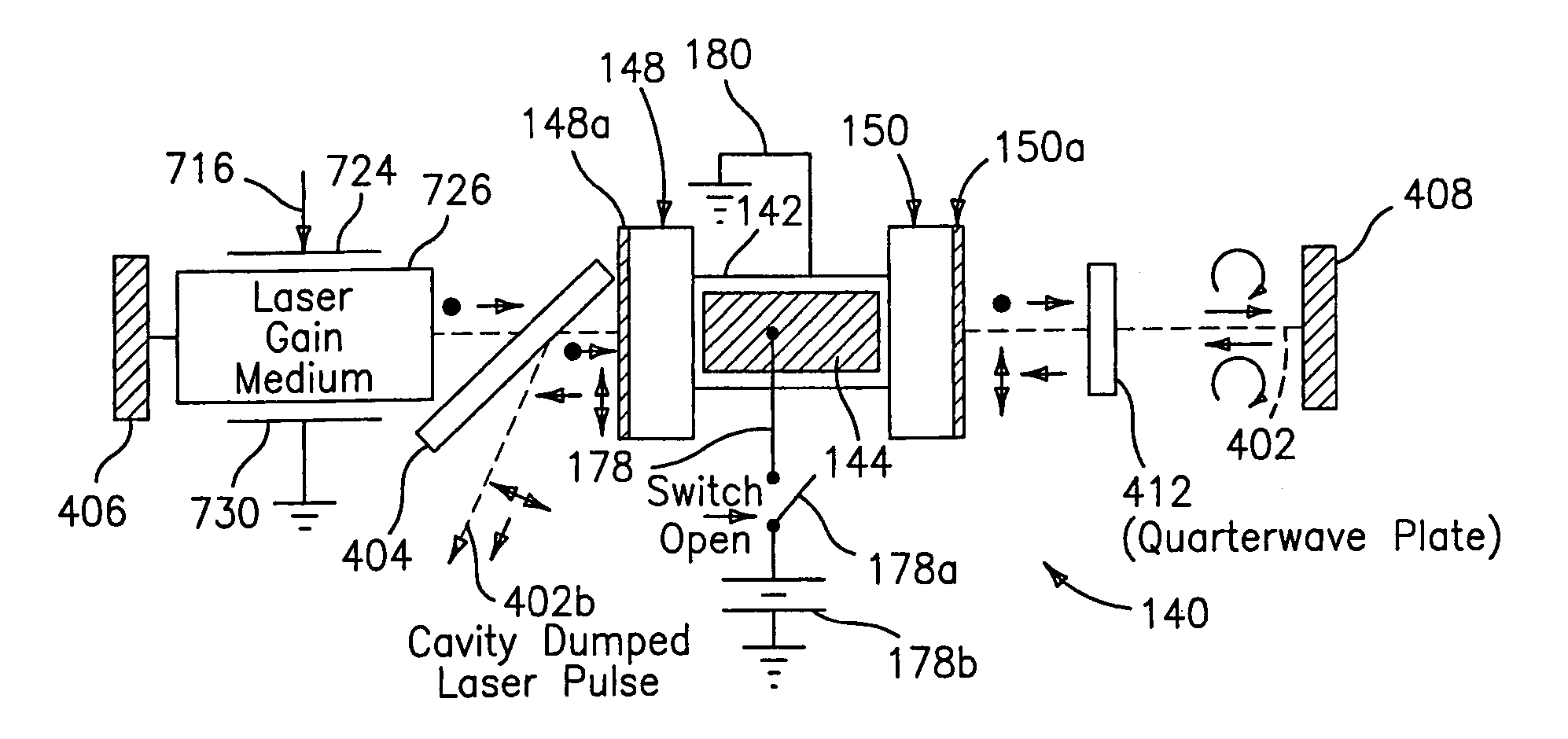
This disclosure discusses techniques for obtaining wavelength selected simultaneously super pulsed Q-switched and cavity dumped laser pulses utilizing high optical damage threshold electro-optic modulators, maintaining a zero DC voltage bias on the CdTe electro-optic modulator (EOM) so as to minimize polarization variations depending on the location of the laser beam propagating through the CdSe EOM crystal, as well as the addition of one or more laser amplifiers in a compact package and the use of simultaneous gain switched, Q-switched and cavity dumped operation of CO2 lasers for generating shorter pulses and higher peak power for the hole drilling, engraving and perforation applications.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Electrodes coated with treating agent and uses thereof
InactiveUS20020061589A1Rapidly ready for useEfficient processingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological cellCoated electrodes
An object of the invention is to provide a method for delivery of macromolecules into biological cells in the tissues of a patient and includes the steps of: (a) providing electrodes (16) in an electrode assembly (12), wherein the electrodes have fixed electrode surfaces (42) which are coated with at least one static layer of electrode releasable molecules (44) to be delivered; (b) providing a waveform generator (15) for generating electric fields; (c) establishing electrically conductive pathways between the electrodes (16) and the waveform generator (15); (d) locating the electrodes (16) such that the biological cells are situated therebetween, and (g) providing electric fields in the form of pulse waveforms from the waveform generator (15) to the electrodes (16), such that molecules in the at least one static layer of the electrode releasable molecules (44) on the electrodes (16) are delivered into the biological cells. The electrode releasable molecules (44) can be either electric field separable molecules and / or solvent separable material. Another object of the invention is to provide an apparatus for carrying out the method of the invention. The static-coated electrode assembly (12) can be provided in a sterile package (24), from which the electrode assembly (12) is removed prior to use. The statically-coated electrode assembly (12) can be in a form of a disposable assembly (12) which is removable and replaceable from an electrode assembly holder (13).
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
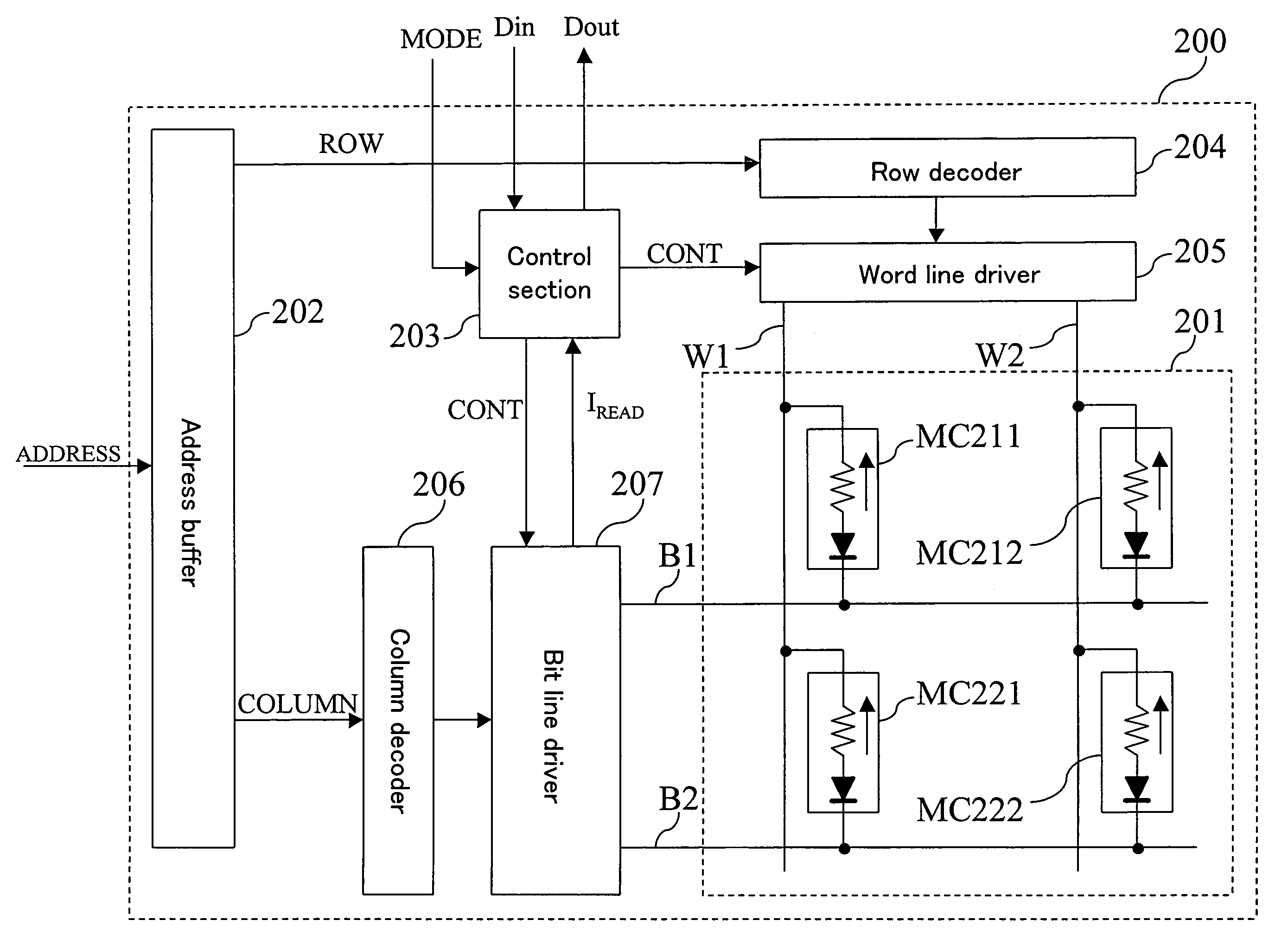
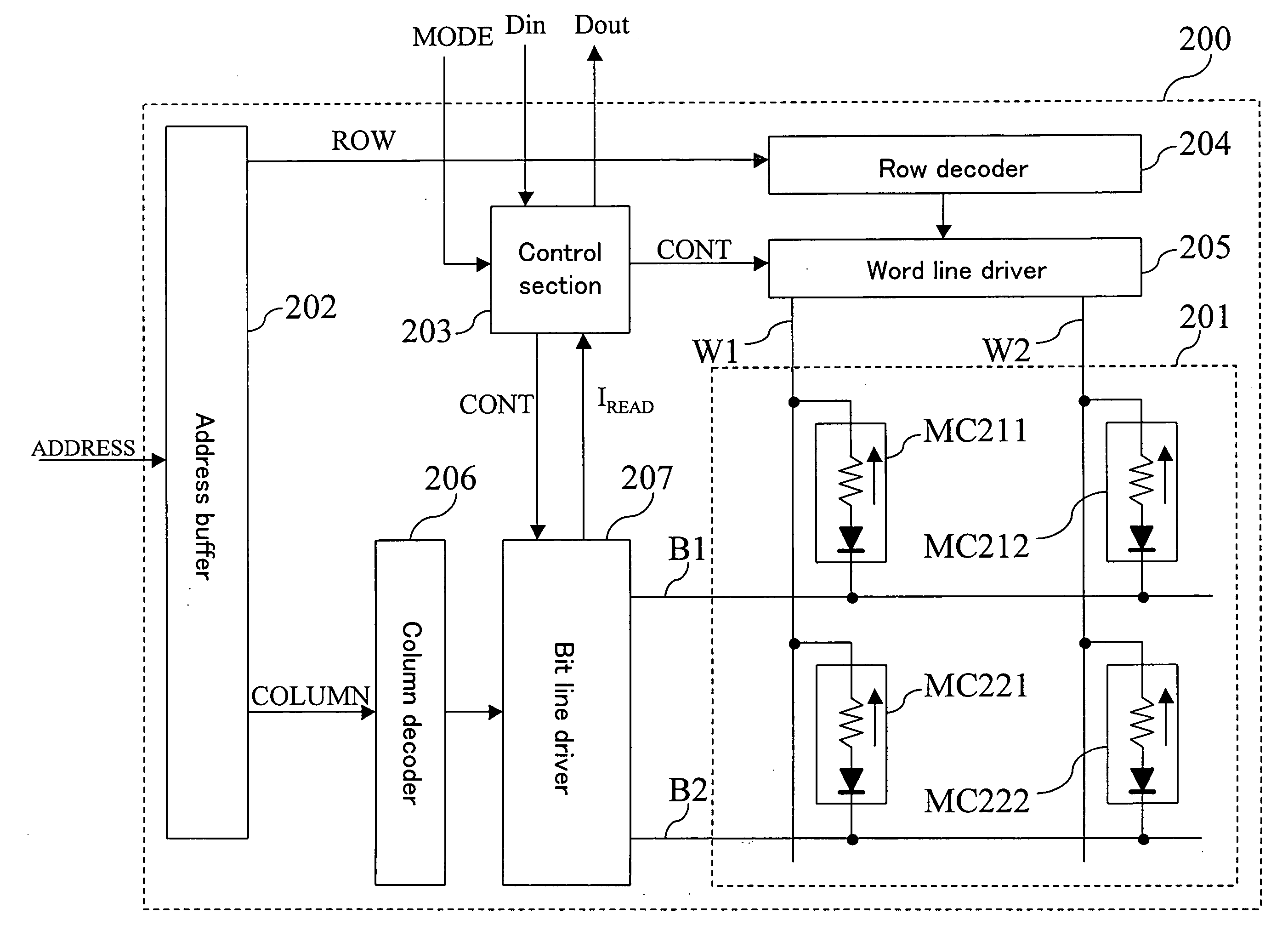
Memory device and semiconductor integrated circuit
ActiveUS7525832B2Simple processShorten the timeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingState variableSemiconductor
First electrode layer includes a plurality of first electrode lines (W1, W2) extending parallel to each other. State-variable layer lying on the first electrode layer includes a plurality of state-variable portions (60-11, 60-12, 60-21, 60-22) which exhibits a diode characteristic and a variable-resistance characteristic. Second electrode layer lying on the state-variable layer includes a plurality of second electrode lines (B1, B2) extending parallel to each other. The plurality of first electrode lines and the plurality of second electrode lines are crossing each other when seen in a layer-stacking direction with the state-variable layer interposed therebetween. State-variable portion (60-11) is provided at an intersection of the first electrode line (W1) and the second electrode line (B1) between the first electrode line and the second electrode line.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Active and passive Q-adjusted single longitudinal mode laser
InactiveCN1645691AShort pulse widthHigh degree of polarizationOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialResonant cavityLongitudinal mode
The invention consists of pumping source, cavity, and a group of coupling device set between the pumping source and cavity, and connected with pumping source through optical fiber. The cavity consists of front cavity mirror and back cavity mirror coated with film. The double-doped crystals and active Q-switch are set between the front and back mirrors. A cooling device is set on the double-doped crystals. The invention features using active Q-switch to control the passive Q-switch for getting prelase pulse, and using saturable absorption crystals as longitudinal mode selector for making the solid single longitudinal mode laser work under higher pumping power.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Memory Device and Semiconductor Integrated Circuit
ActiveUS20080212359A1Simple processShorten the timeSolid-state devicesDiodeState variableSemiconductor
First electrode layer includes a plurality of first electrode lines (W1, W2) extending parallel to each other. State-variable layer lying on the first electrode layer includes a plurality of state-variable portions (60-11, 60-12, 60-21, 60-22) which exhibits a diode characteristic and a variable-resistance characteristic. Second electrode layer lying on the state-variable layer includes a plurality of second electrode lines (B1, B2) extending parallel to each other. The plurality of first electrode lines and the plurality of second electrode lines are crossing each other when seen in a layer-stacking direction with the state-variable layer interposed therebetween. State-variable portion (60-11) is provided at an intersection of the first electrode line (W1) and the second electrode line (B1) between the first electrode line and the second electrode line.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for machining micro holes in ceramic matrix composite through femtosecond lasers
ActiveCN104607808AHigh peak powerShort pulse widthWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser beam welding apparatusWavelengthLayer removal
The invention relates to a method for machining micro holes in a ceramic matrix composite through femtosecond lasers. According to the method, the silicon carbide ceramic matrix composite sample is placed on a working table and machined layer by layer in a spiral line mode through the femtosecond lasers or machined in a linear scanning mode, wherein the thickness of the sample is smaller than 3 mm; in the micro-machining process, the wave length of femtosecond laser machining ranges from 400 nm-1500 nm, the pulse width ranges from 80 fs to 500 fs, the output power of the lasers is determined according to the requirements of micro-machining and ranges from 20 mW to 20 W, and the repetition frequency of the lasers is determined according to the requirements of micro-machining and ranges from 50 K to 25 MHz; the sample is machined in a layer-by-layer removal mode, wherein the rotation speed of a machining head is 2400 rev / s. In the machining process, the method has the advantages that machining damage is small, and because material around the damage region is still in a cold state after machining, the heat effect is small; machining precision is high, energy of the femtosecond lasers is in Gaussian distribution, absorption and action of the energy in the machining process are limited within the size of which the focus center is quite small, and the machining dimension is expressed from a micro form to a sub-micro form.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Yb-doped fiber laser based on pulse laser seeds in gain modulation technology
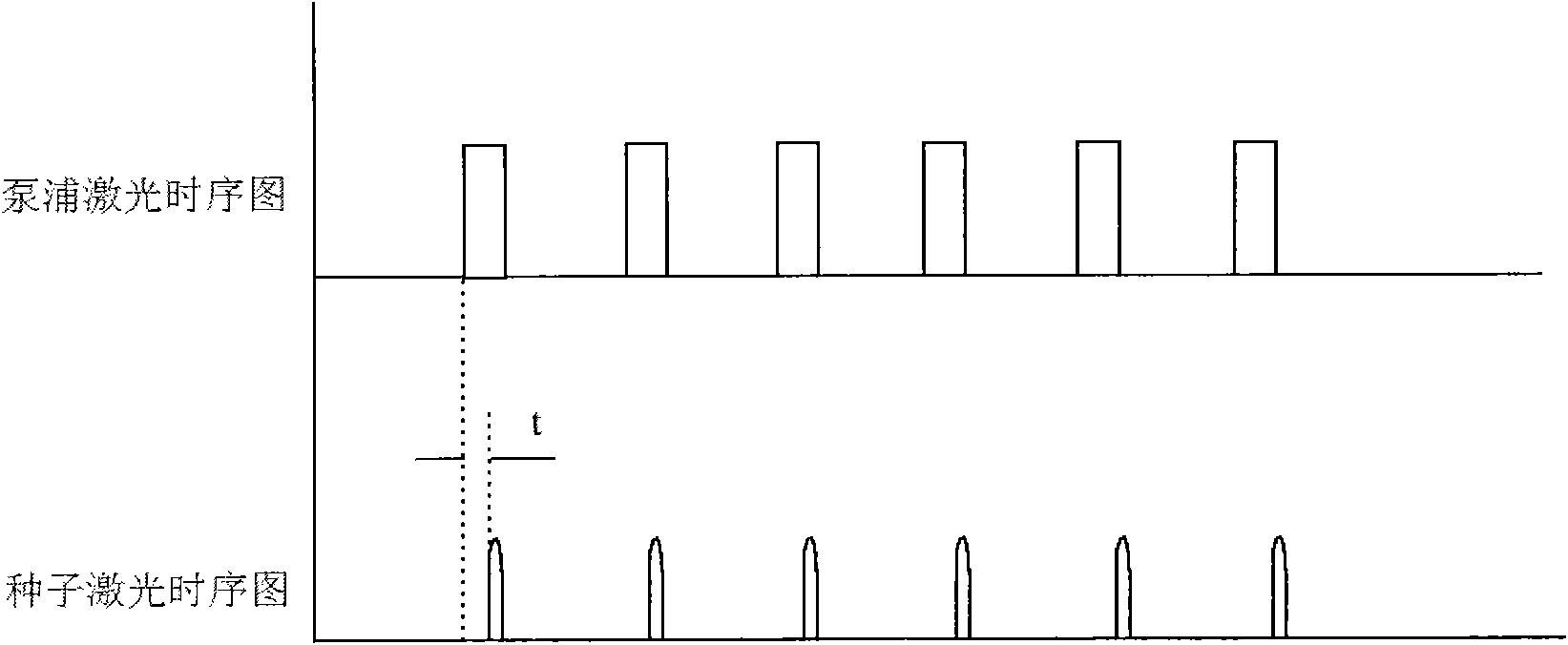
InactiveCN101969172AIncrease powerLow costActive medium shape and constructionSeeds sourcePulsed laser
The invention discloses a Yb-doped fiber laser based on pulse laser seeds in a gain modulation technology, which is composed of a pulse-modulated laser pumping source, a multimode fiber combiner, a fiber grating pair, a Yb-doped double clad fiber, an amplification-stage pumping source, a high-power combiner and a double clad Yb-doped fiber for amplifying laser power, wherein the pulse-modulated laser pumping source is coupled into the Yb-doped double clad gain fiber through the multimode fiber combiner so as to generate a pulse laser of which the wavelength is limited by the fiber grating pair; the generated pulse laser as a seed source is amplified by a one-stage or multistage fiber amplifier; the laser amplifier pumping source is coupled into the double clad Yb-doped fiber with large mode field diameter through the high-power combiner; and after power-level amplification, a high-power pulse laser output with adjustable repetition frequency is obtained. The invention can be used for obtaining novel high-power fiber laser pulse seeds with simple structure, low cost and high long-term stability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Optical diagnosis and treatment apparatus
InactiveUS20070027391A1Short pulse widthHigh temporal resolution light detectionCatheterSurgical instrument detailsTherapeutic DevicesTomographic image
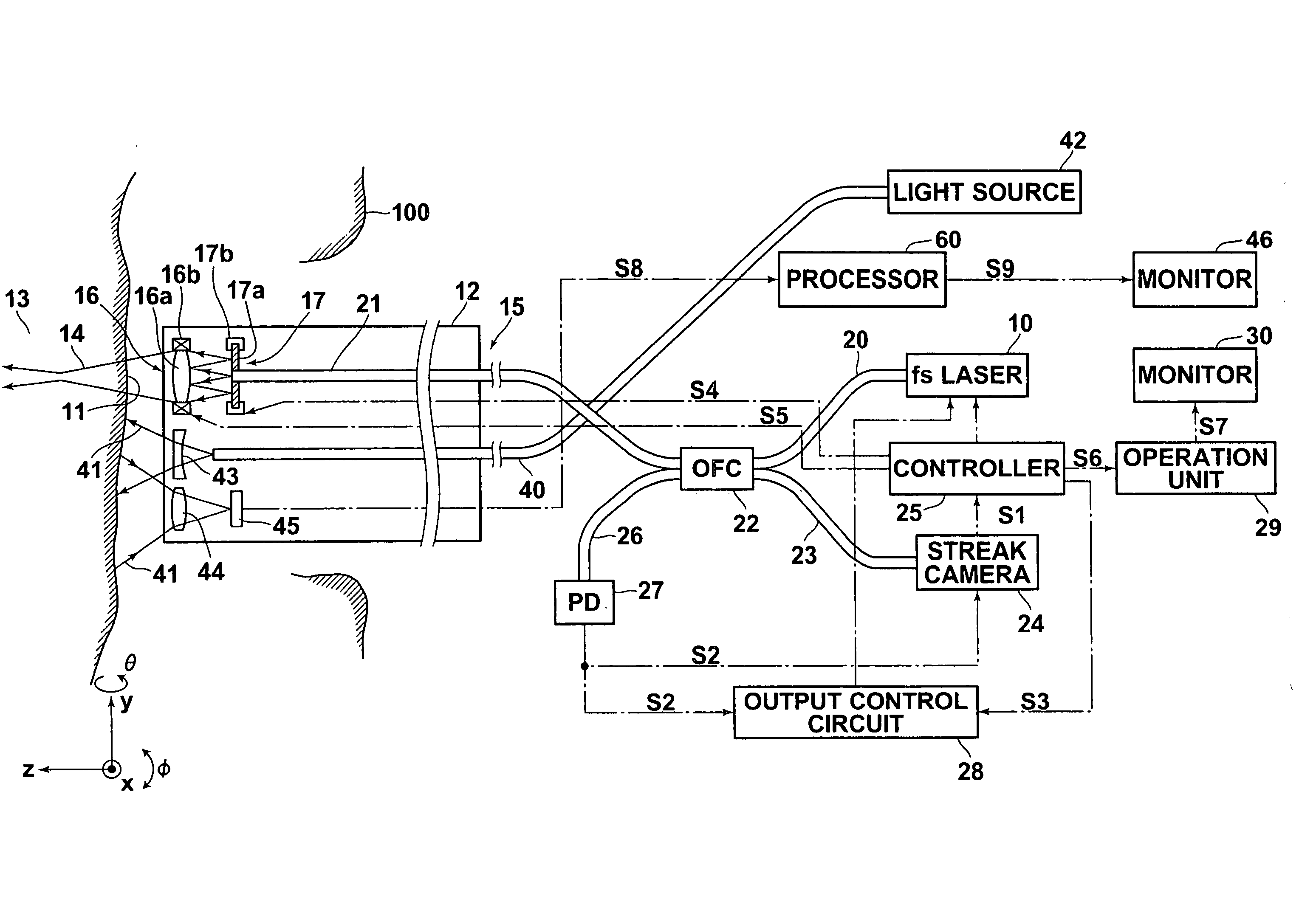
An optical diagnosis and treatment apparatus includes a pulsed light source, an illumination optical system for illuminating a region of a living body through a guide tube, a light condensing means for condensing pulsed light, an optical scan means for two-dimensionally scanning the region, a light detection means for detecting the pulsed light reflected from the region, an operation means for reconstructing, based on an output from the light detection means, a tomographic image of the region, an image display means for displaying the tomographic image based on an output from the operation means and a light intensity switching means for switching the intensity of the pulsed light at least between two levels. The two levels are a level at which vaporization of living body tissue due to multi-photon absorption occurs at a convergence position of the pulsed light and a level at which vaporization does not occur.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Method and apparatus for producing UV laser from all-solid-state system
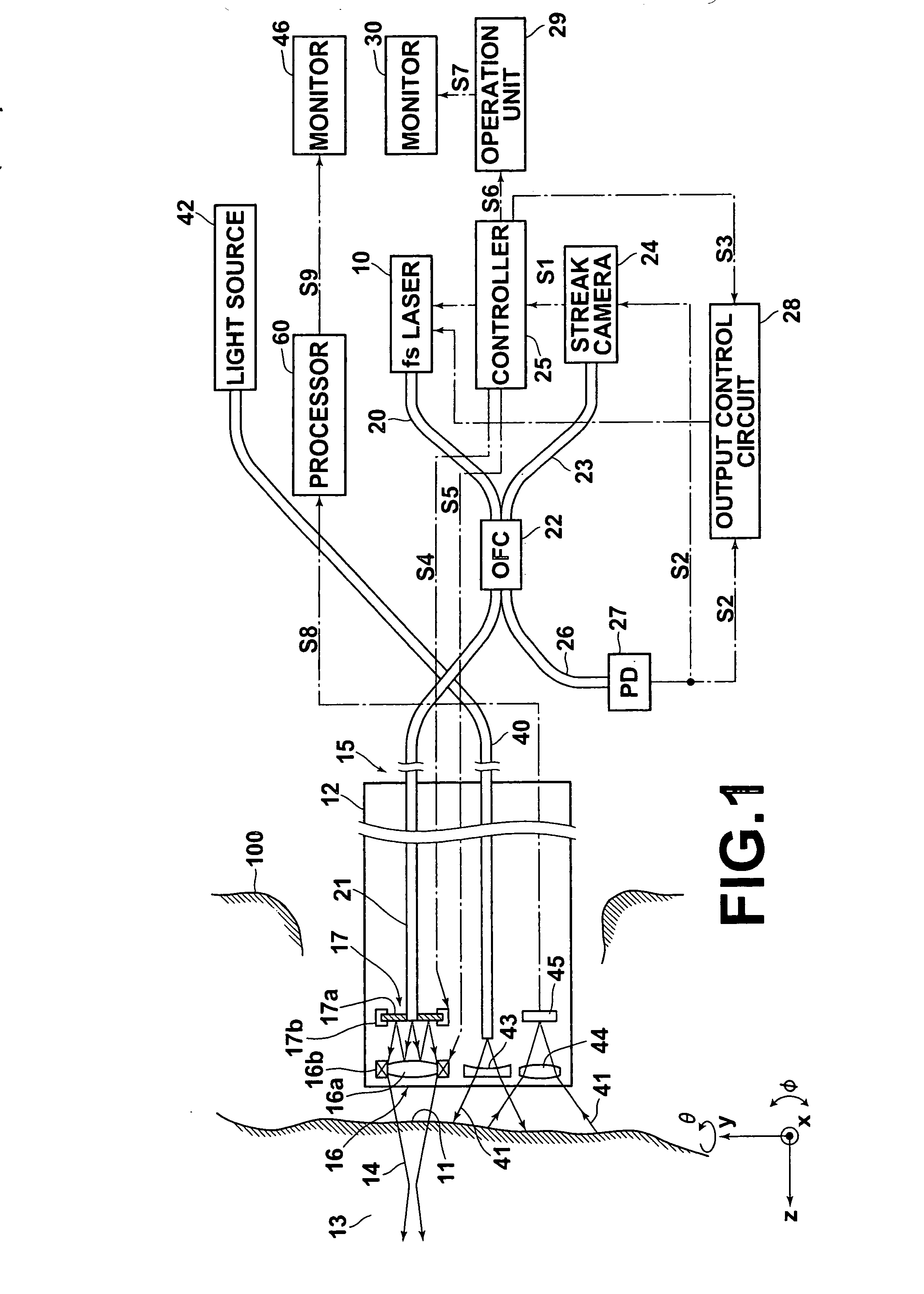
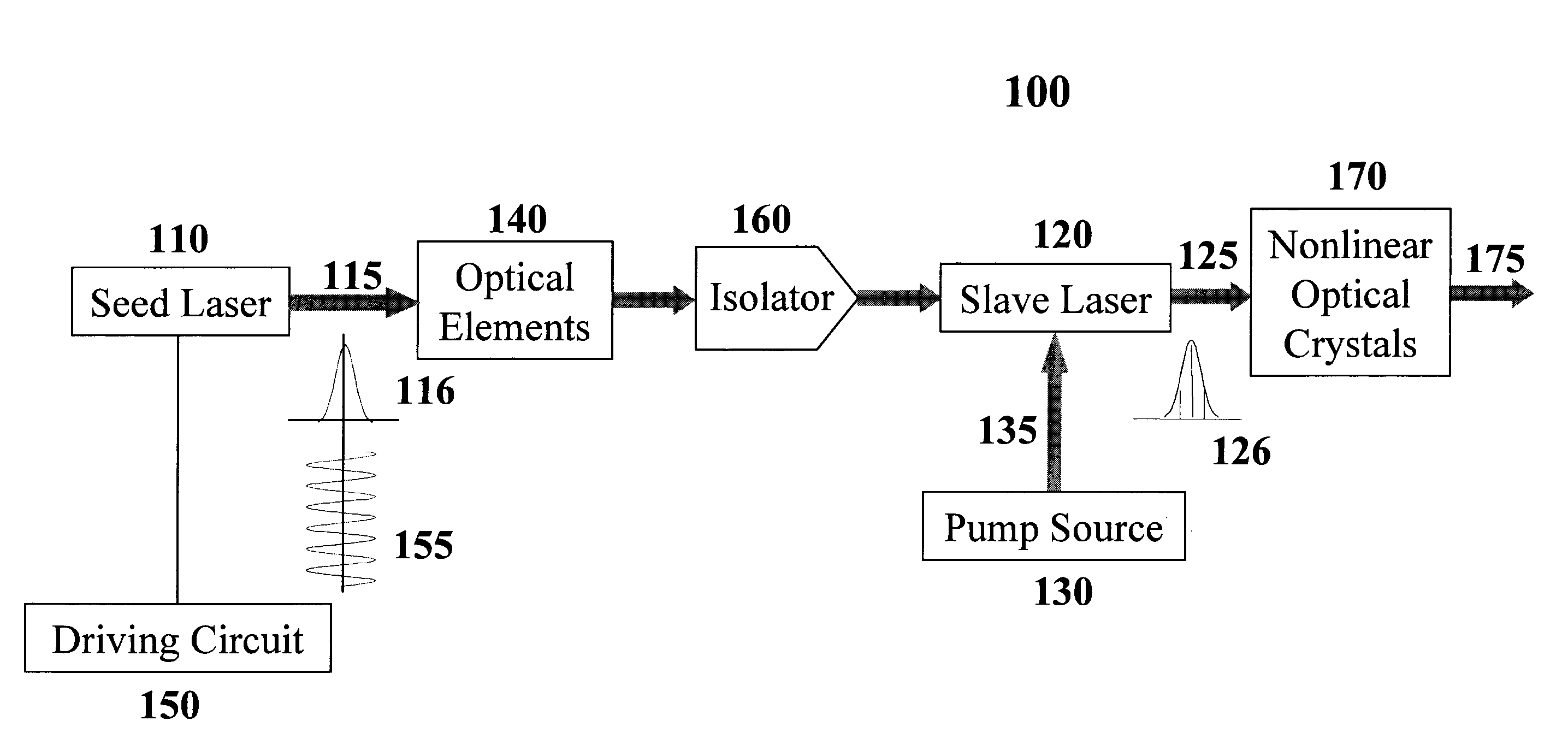
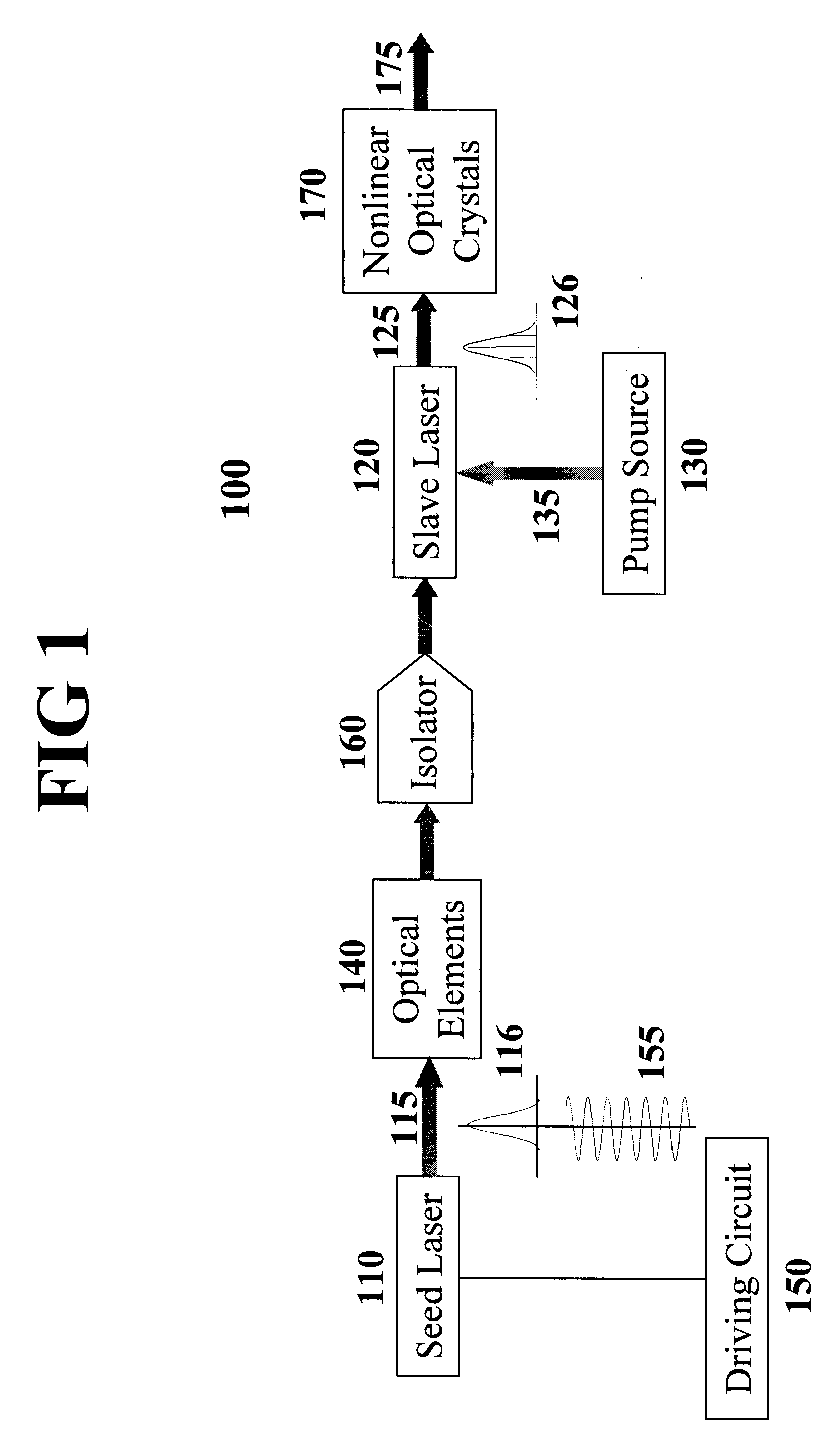
ActiveUS20090201952A1Improve efficiencyLow costLaser using scattering effectsExcitation process/apparatusAll solid stateUv laser
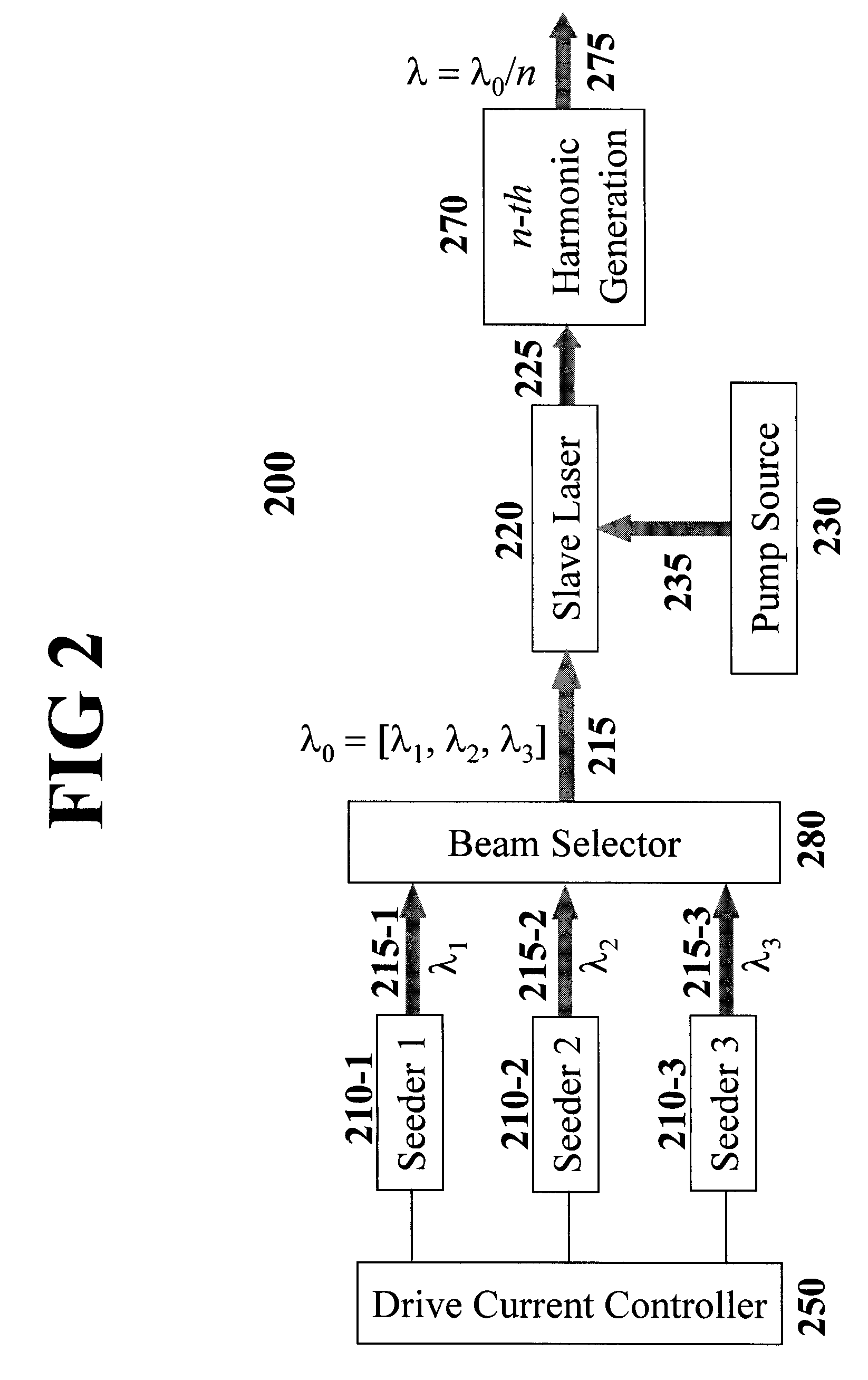
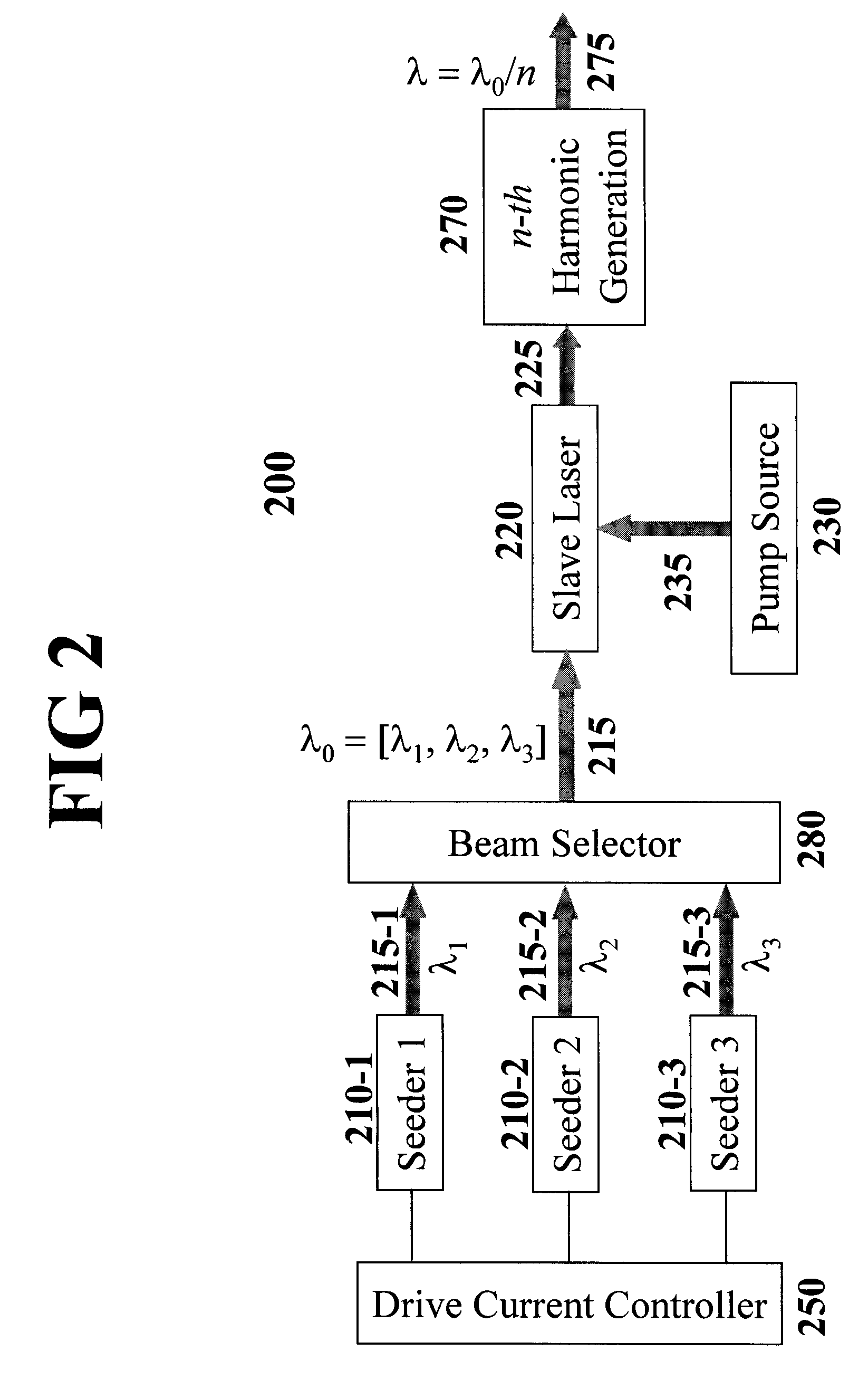
An all-solid-state laser system produces coherent DUV radiation through a third or fourth harmonic generation. The fundamental wavelength is generated by a slave laser optically pumped by one or more light source(s) of high density array(s) and is stabilized by injecting optical seeds whose wavelength is rapidly swept to cover the fundamental wavelength. The pump effects are enhanced by a pump chamber that recycles unabsorbed pump light. The present invention enables DUV pulses with a width shorter than 1 ns and a repetition rate higher than 100 kHz. The output DUV wavelength is adjustable by selecting an appropriate seeder.
Owner:PAVILION INTEGRATION
Electric element, memory device, and semiconductor integrated circuit
ActiveUS20090067215A1Increase the resistance valueLower the resistance valueSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectricityEngineering
An electric element comprises: a first electrode (1); a second electrode (3); and a layer (2) connected between the first electrode and the second electrode and having a diode characteristic and a variable resistance characteristic. The layer (2) conducts a substantial electric current in a forward direction extending from one of the first electrode (1) and the second electrode (3) to the other electrode as compared to a reverse direction opposite of the forward direction. The resistance value of the layer (2) for the forward direction increases or decreases according to a predetermined pulse voltage applied between the first electrode (1) and the second electrode (3).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
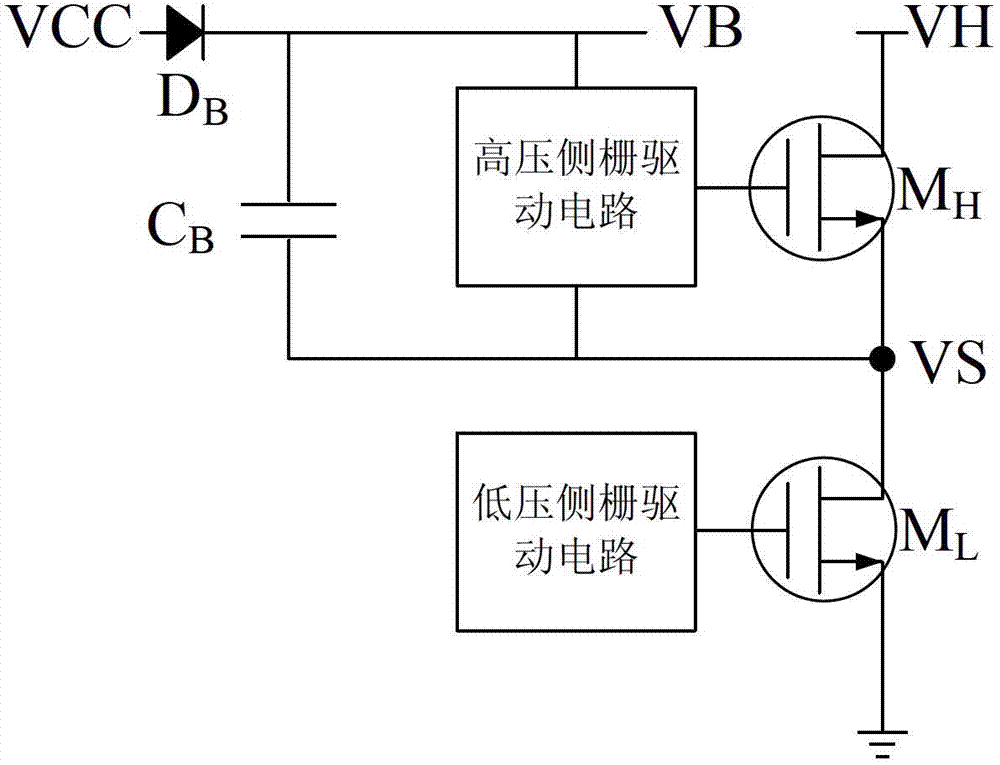
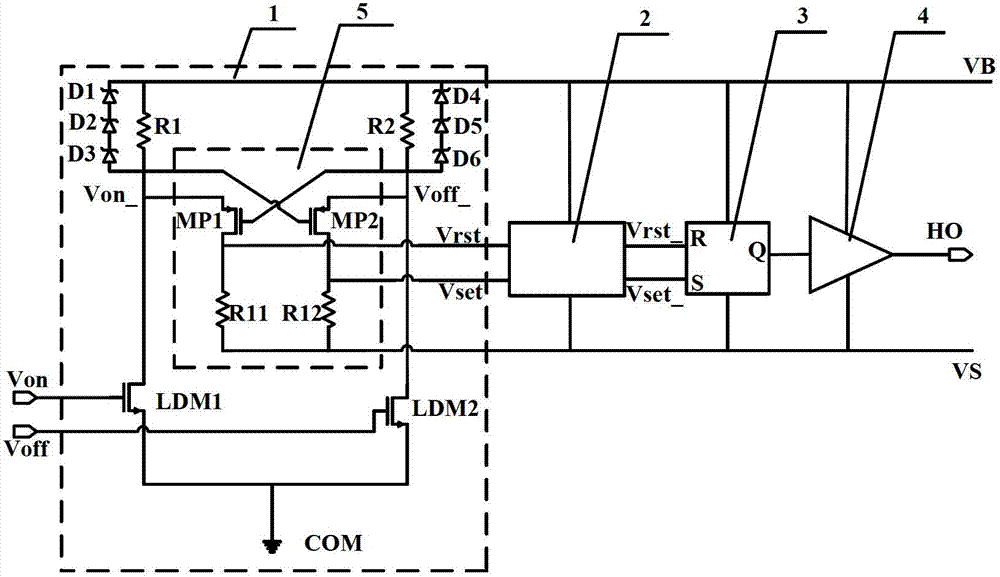
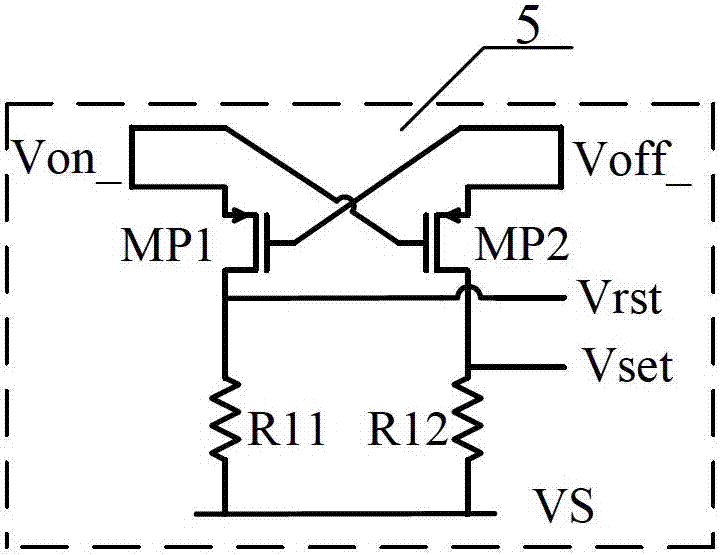
High-voltage side gate drive circuit capable of resisting noise interference
ActiveCN102769453AEliminate the effects of working statusDoes not affect deliveryReliability increasing modificationsProcess deviationsHigh voltage pulse
The invention provides a high-voltage side gate drive circuit capable of resisting noise interference. The high-voltage side gate drive circuit comprises a high-voltage level shift circuit, a differential-mode noise elimination circuit, an RS trigger and an output drive level circuit, wherein a low-side pulse signal is converted into a high-voltage pulse signal for output through the high-voltage level shift circuit; a common mode noise elimination circuit is connected between the output of the high-voltage level shift circuit and the input of the differential-mode noise elimination circuit; the common mode noise elimination circuit is used for eliminating a common mode noise signal generated in application; and the differential-mode noise elimination circuit eliminates the differential-mode noise introduced by process variations, outputs a normal pulse signal, reduces the normal pulse signal into a normal square signal through the RS trigger, outputs the square signal from the output drive level circuit and drives an external high-side power tube.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
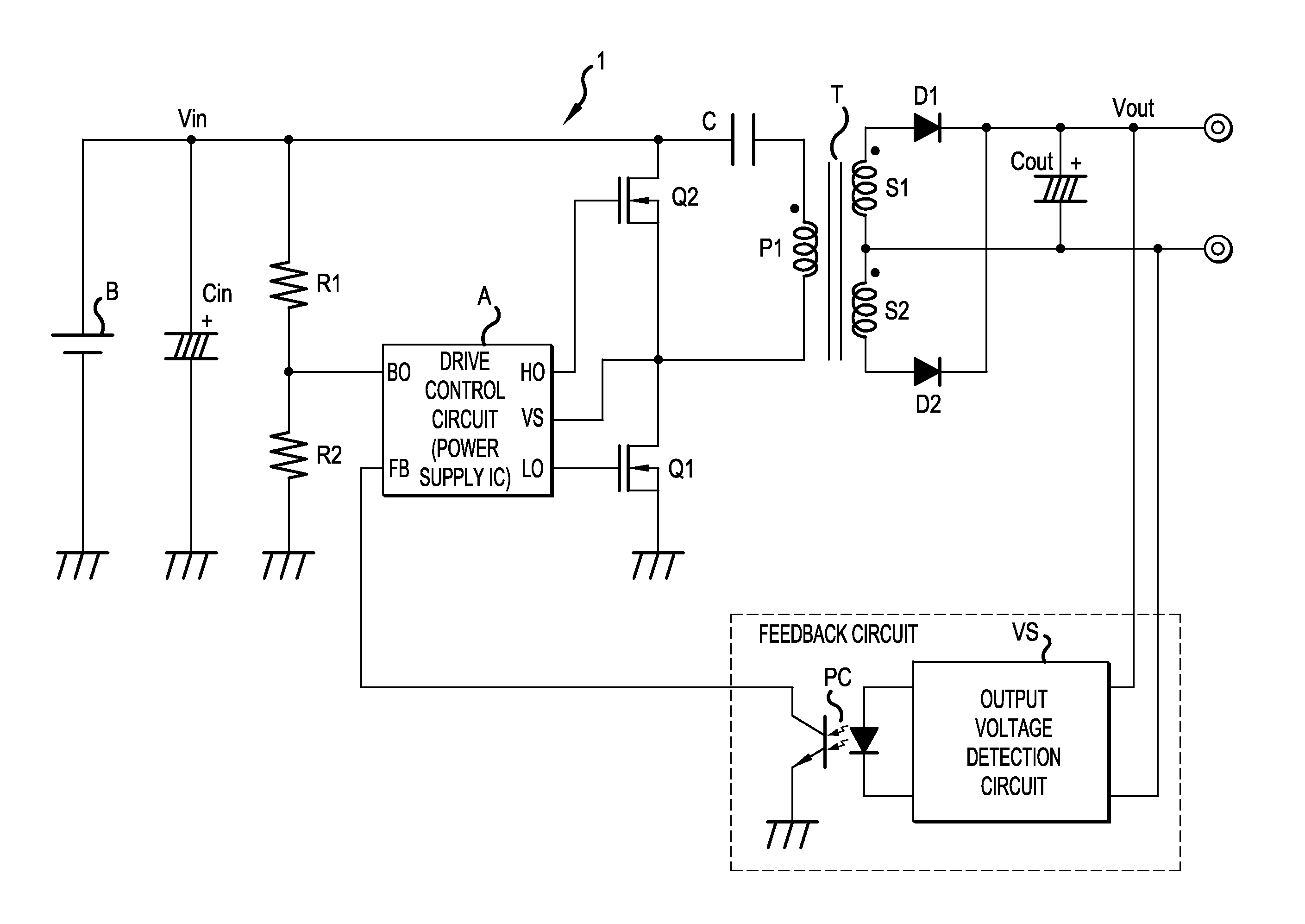
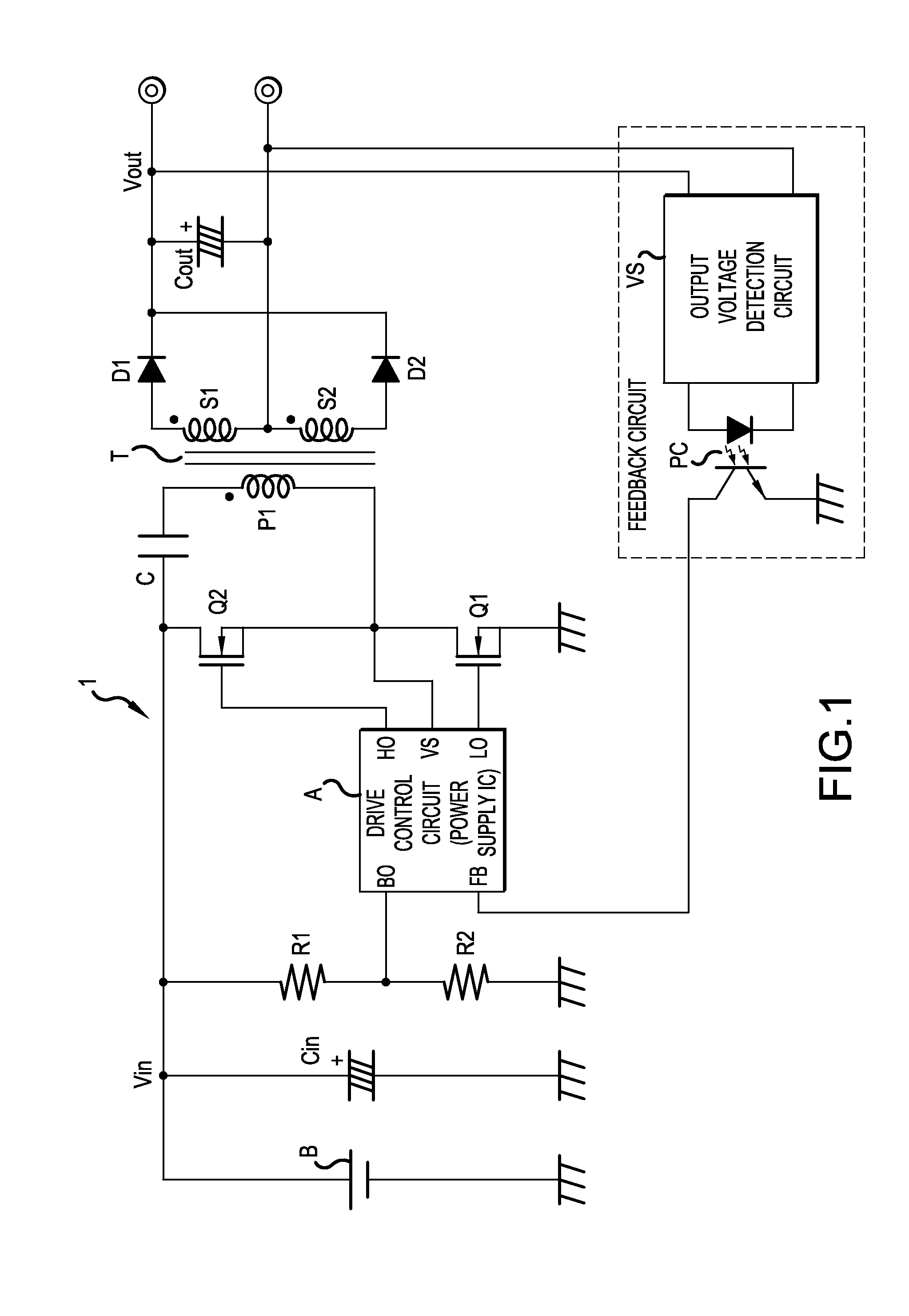
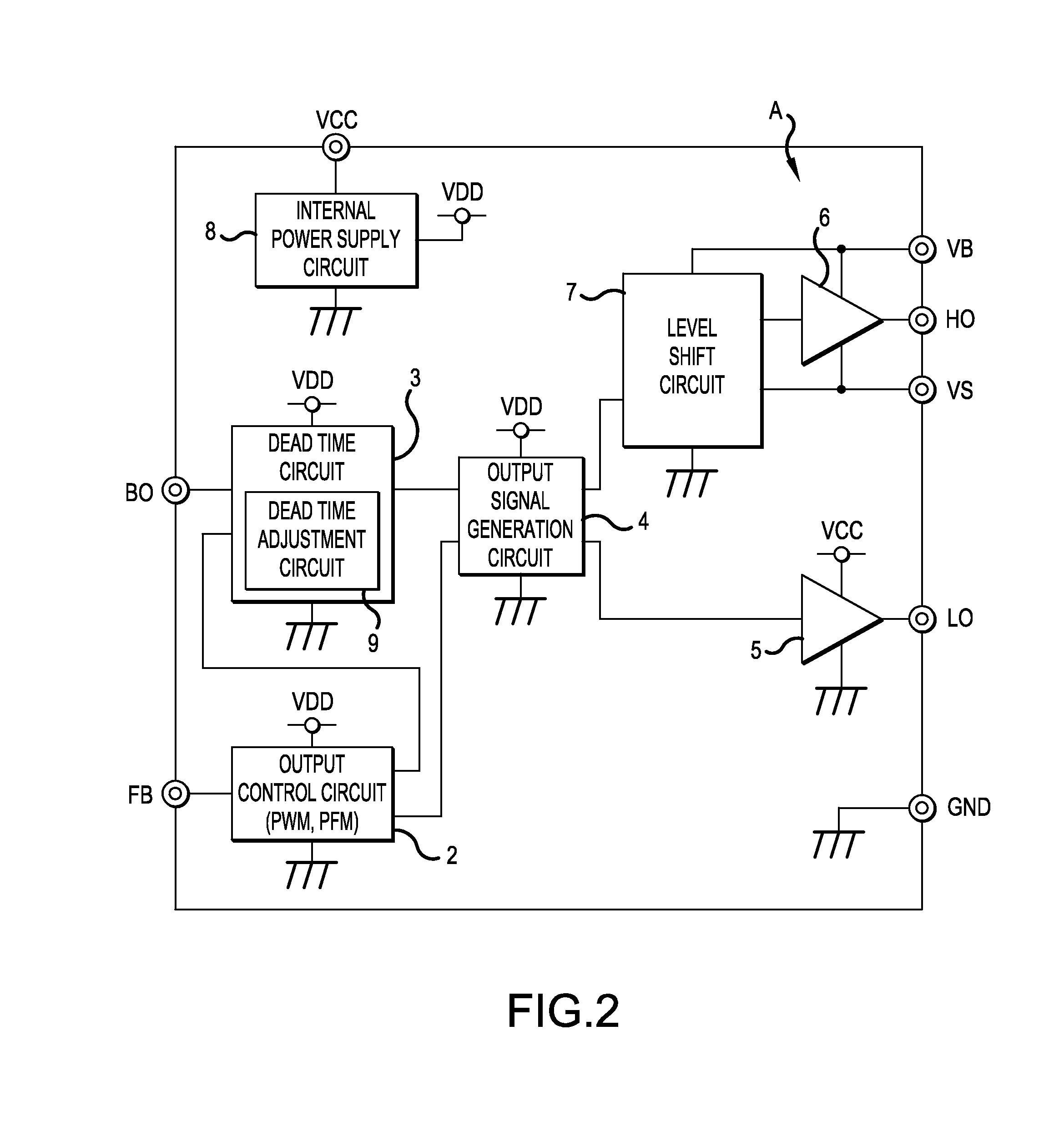
Switching power supply apparatus
ActiveUS20140376275A1Drop in conversion efficiency can be preventedZero voltage switchingEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionCapacitanceControl signal
A switching power supply apparatus includes: a dead time circuit that receives an output control signal and generates dead time signal to specify a time width when both first and second switching elements are turned OFF; an output signal generation circuit that generates first and second output signals which specify the ON time of the first and second switching elements respectively in accordance with the output control signal and the dead time signal; and a dead time adjustment circuit that adjusts the turn ON timings of the first and second switching elements by changing the time width of the dead time signal in accordance with the change of voltage of the DC input power or the change of the output voltage of the capacitor.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Mode-locked quantum dot laser with controllable gain properties by multiple stacking
InactiveUS20060227825A1Easy to controlImprove efficiencyLaser detailsNanoinformaticsMode-lockingQuantum dot
The optical gain and the differential gain of a quantum dot gain region in a gain section of a passive or hybrid mode-locked laser is varied by stacking at least two planes of quantum dots. All quantum dot planes are preferably formed by the same fabrication method and under the same fabrication conditions. The number of stacked planes of quantum dots is selected such that the optical gain and the differential gain are both in their optimal range with respect to the optical loss in the laser resonator and to the differential gain in the saturable absorber element. This results in a device with a short pulse width, stable mode-locking, high-power, and temperature-independent operation.
Owner:INNOLUME
Method and apparatus for verifying semiconductor integrated circuits
InactiveUS7299438B2Short pulse widthSpeed up design timeElectrical testingOscillations comparator circuitsSemiconductorIntegrated circuit
Owner:FUJITSU MICROELECTRONICS LTD
Method and apparatus for producing UV laser from all-solid-state system
ActiveUS7633979B2Improve efficiencyLow costLaser using scattering effectsExcitation process/apparatusAll solid stateUv laser
Owner:PAVILION INTEGRATION CORP
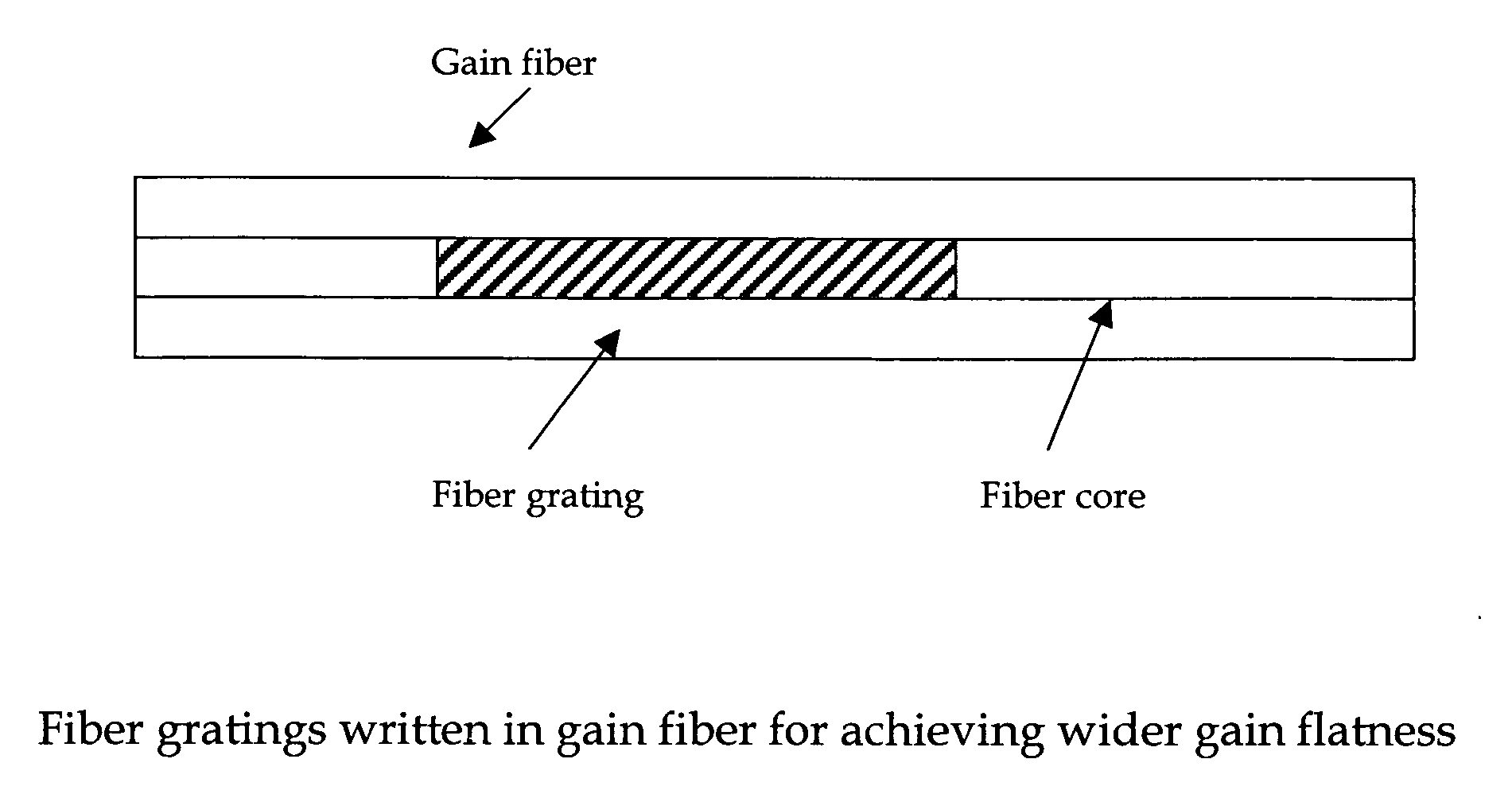
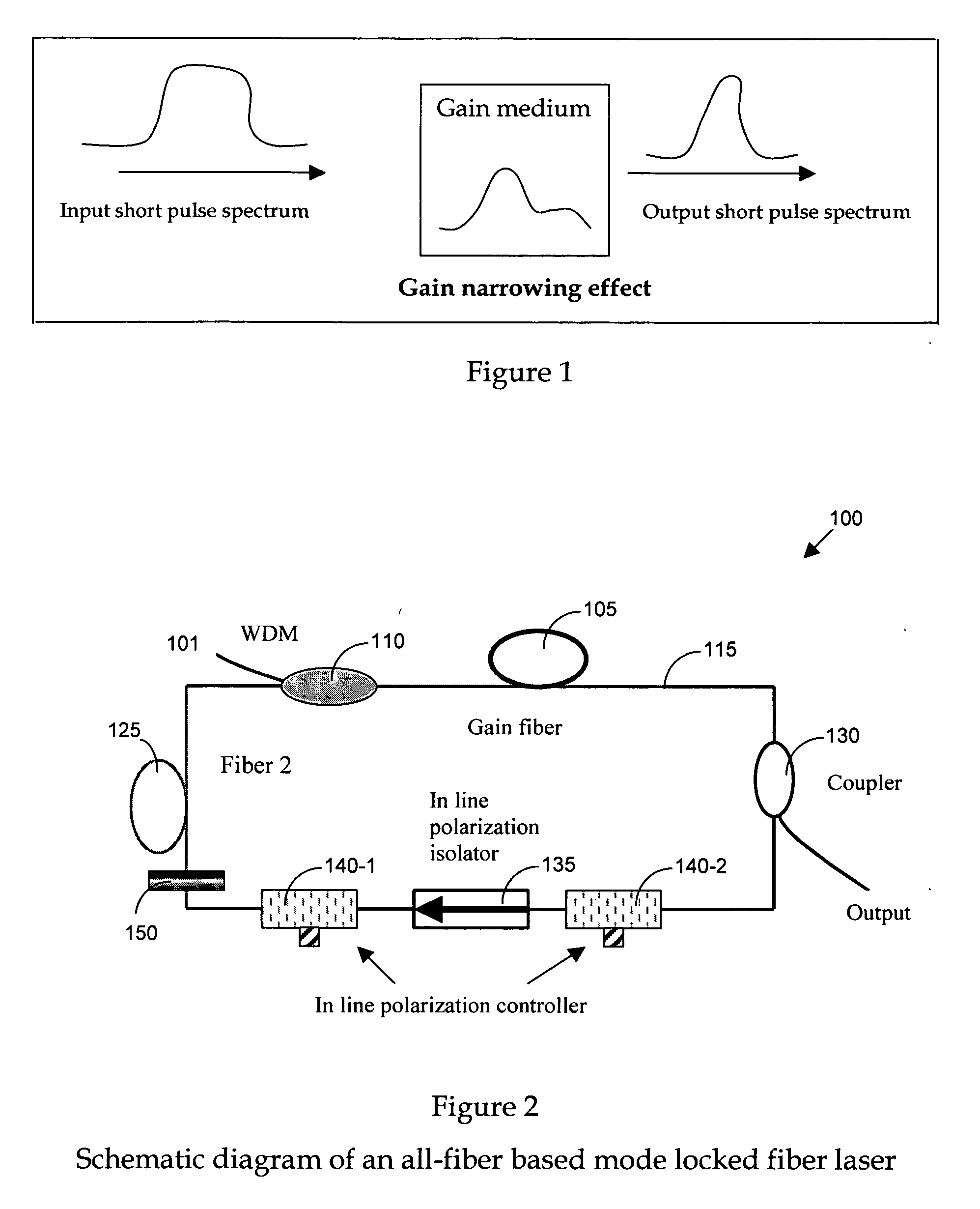
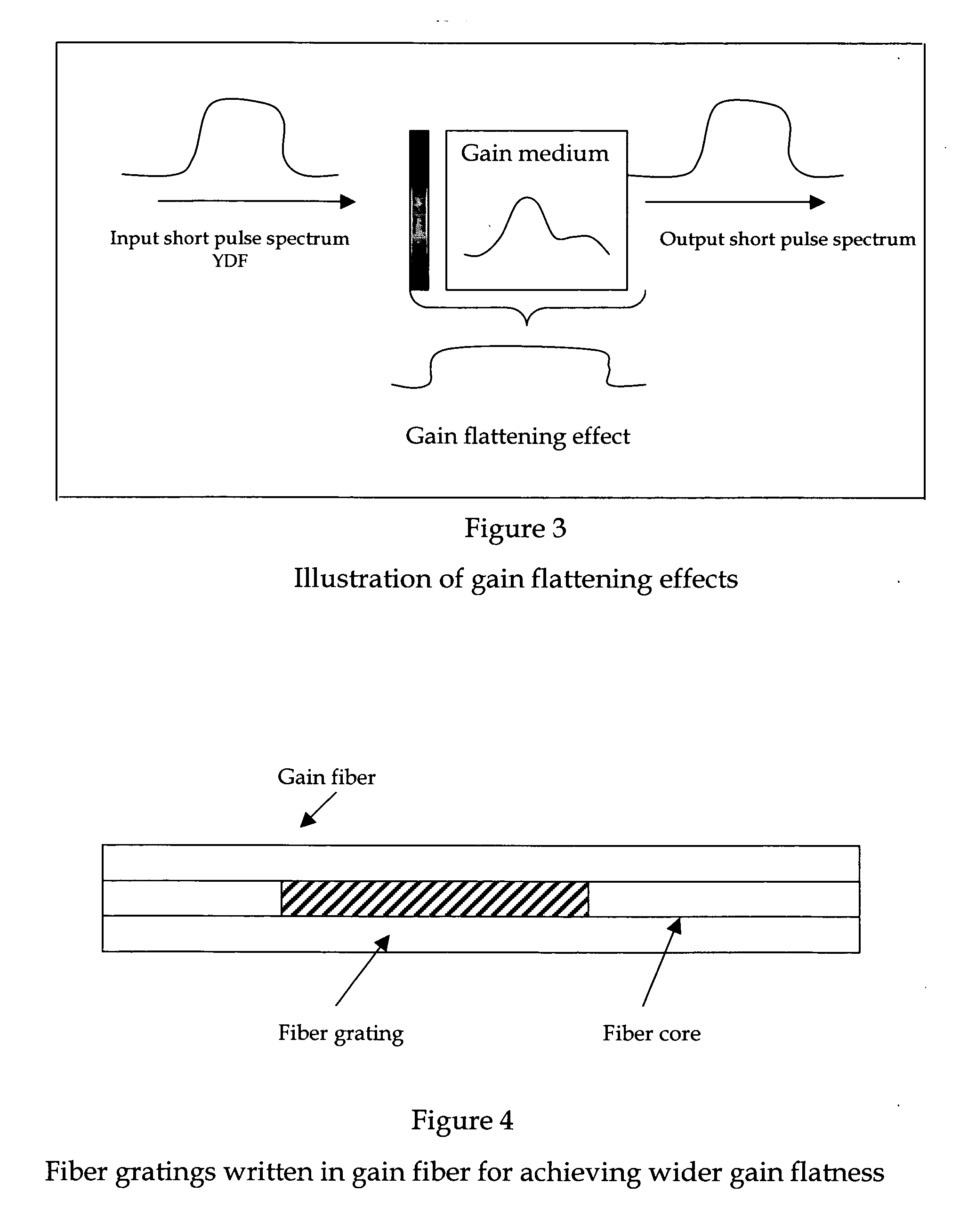
Achieving ultra-short pulse in mode locked fiber lasers by flattening gain shape
InactiveUS20070177642A1Easy to shapeShort pulse widthLaser detailsMode locked fiber laserPulse broadening
A fiber laser cavity that includes a fiber laser cavity that includes a laser gain medium for receiving an optical input projection from a laser pump. The fiber laser cavity further includes a positive dispersion fiber segment and a negative dispersion fiber segment for generating a net negative dispersion for balancing a self-phase modulation (SPM) and a dispersion induced pulse broadening-compression in the fiber laser cavity for generating an output laser with a transform-limited pulse shape wherein the laser gain medium further amplifying and compacting a laser pulse. The fiber laser cavity further includes a gain-flattening filter for flattening a gain over a range of wavelengths whereby the laser cavity is enabled to amplify a laser with improved pulse shape over the range of wavelengths.
Owner:POLARONYX
Q-switched CO2 laser for material processing
InactiveUS20050069007A1Reduce layeringReduce thicknessLaser arrangementsActive medium materialMaterials processingLength wave
A simultaneously super pulsed Q-switched CO2 laser system for material processing comprises sealed-off folded waveguides with folded mirrors that are thin film coated to select the output wavelength of the laser. The system also comprises a plurality of reflective devices defining a cavity; a gain medium positioned within the cavity for generating a laser beam; a cavity loss modulator for modulating the laser beam, generating thereby one or more laser pulses; a pulsed signal generation system connected to the cavity loss modulator for delivering pulsed signals to the cavity loss modulator thereby controlling the state of optical loss within the cavity; a control unit connected to the pulsed signal generation system for controlling the pulsed signal generation system; and a pulse clipping circuit receptive of a portion of the laser beam and connected to the pulsed signal generation system for truncating a part of the laser pulses.
Owner:KENNEDY JOHN T +6
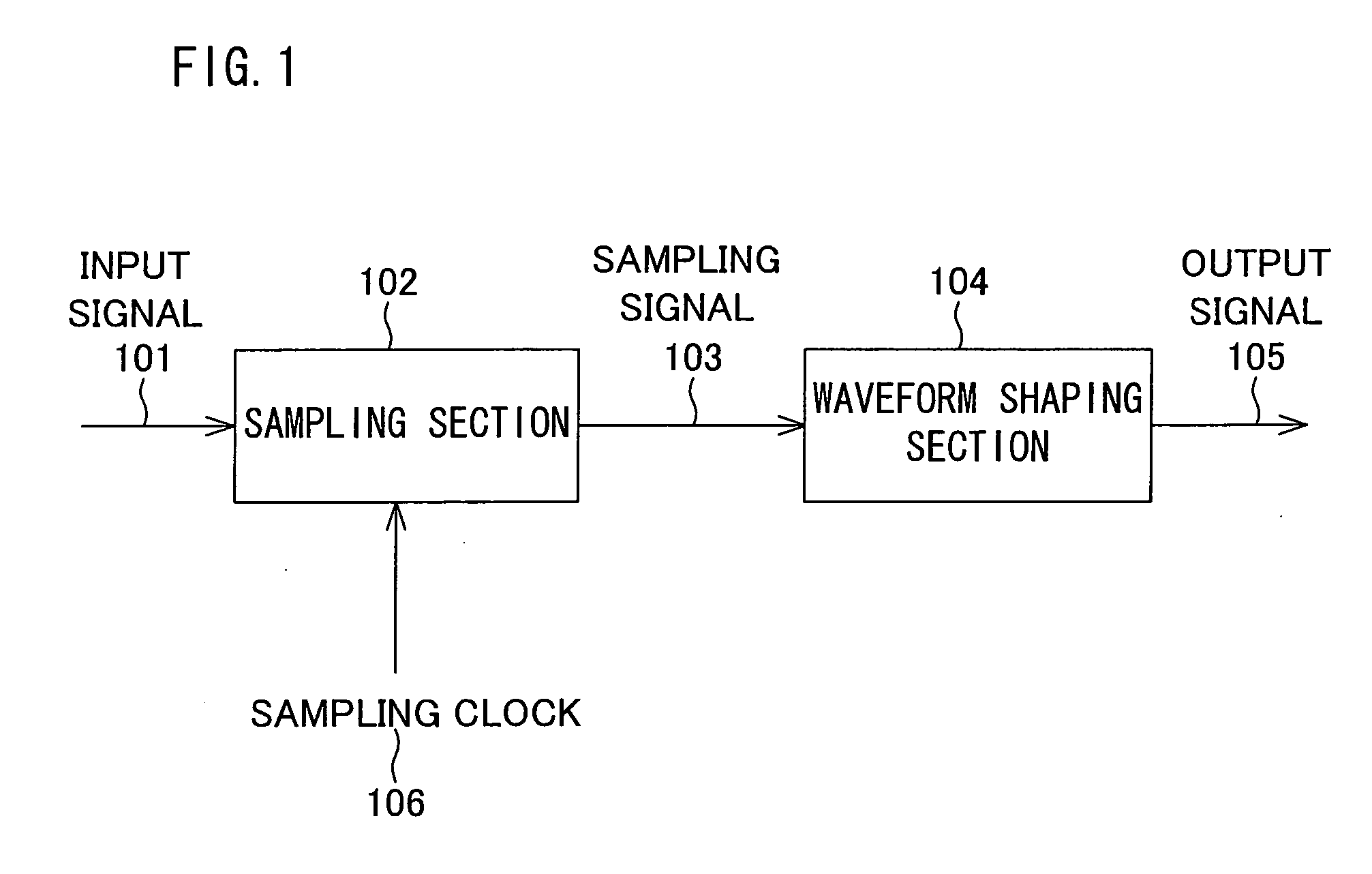
Waveform shaping method, waveform shaping device, electronic device, waveform shaping program and recording medium
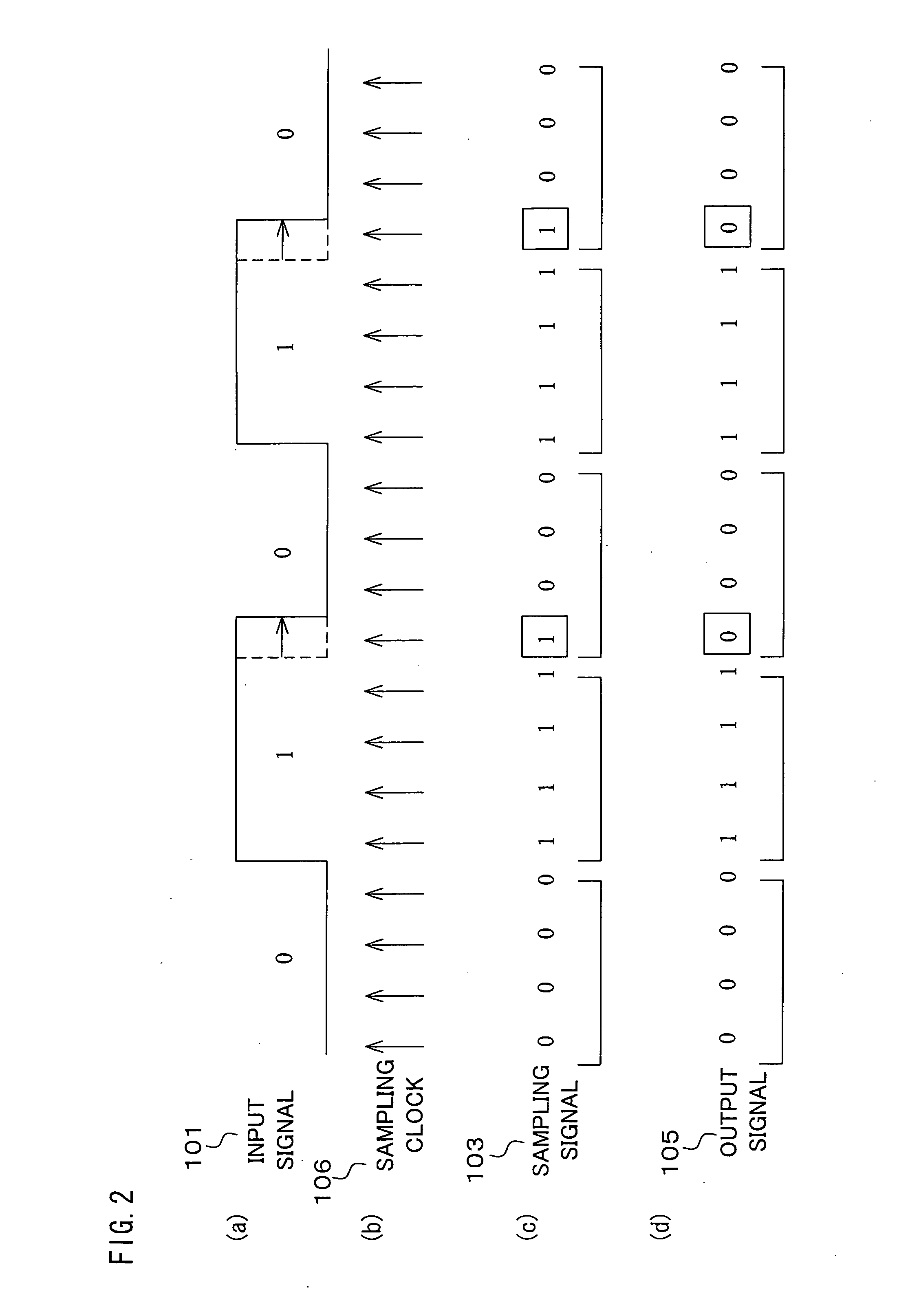
InactiveUS20060274872A1Prevent information contained in input signalAccurate informationModification of read/write signalsTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsWaveform shapingEngineering
A sampling section (102) is provided for generating a sampling signal (103) by sampling an input signal (101) using a sampling clock (106) which is faster than a data speed of the input signal (101). A waveform shaping section (104) is provided for I) processing (e.g. inverting a pulse) the sampling signal (103), so as to shape a restored digital signal obtained from a pulse of the input signal (101), and II) outputting the restored digital signal as an output signal (105). In this way, it becomes possible to provide: A) a waveform shaping method and a waveform shaping device, each of which is capable of correcting distortion in an input signal by means of a simple method or configuration; B) a waveform shaping program that realizes the waveform shaping method or the waveform shaping device; and C) a recording medium storing therein the waveform shaping program.
Owner:SHARP KK
Underwater detection device and underwater detecting method
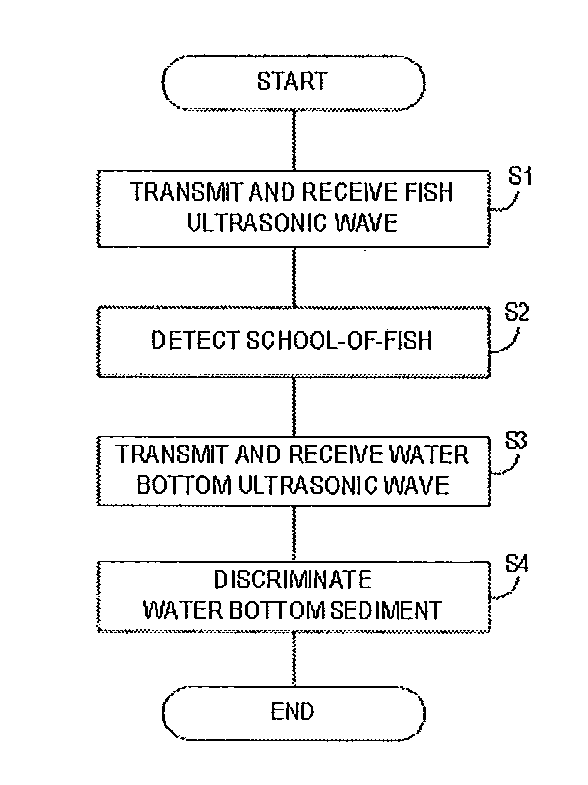
ActiveUS20120263018A1High range resolutionShort pulse widthAcoustic wave reradiationDiscriminatorTransducer
This disclosure provides an underwater detection device, which includes a first generator for generating a first transmission signal, a second generator for generating a second transmission signal having a longer pulse width than that of the first transmission signal, an output unit for outputting the transmission signals generated by the first and second generators to a transducer for transmitting underwater ultrasonic waves based on the first and second transmission signals, respectively, receiving the reflection waves caused by the ultrasonic waves, respectively, and converting the reflection waves into a first reception signal and a second reception signal, respectively, an underwater detector for detecting at least one of a presence of a target object and a water bottom depth based on the first reception signal, and a bottom sediment discriminator for discriminating a water bottom sediment type based on the second reception signal.
Owner:FURUNO ELECTRIC CO LTD
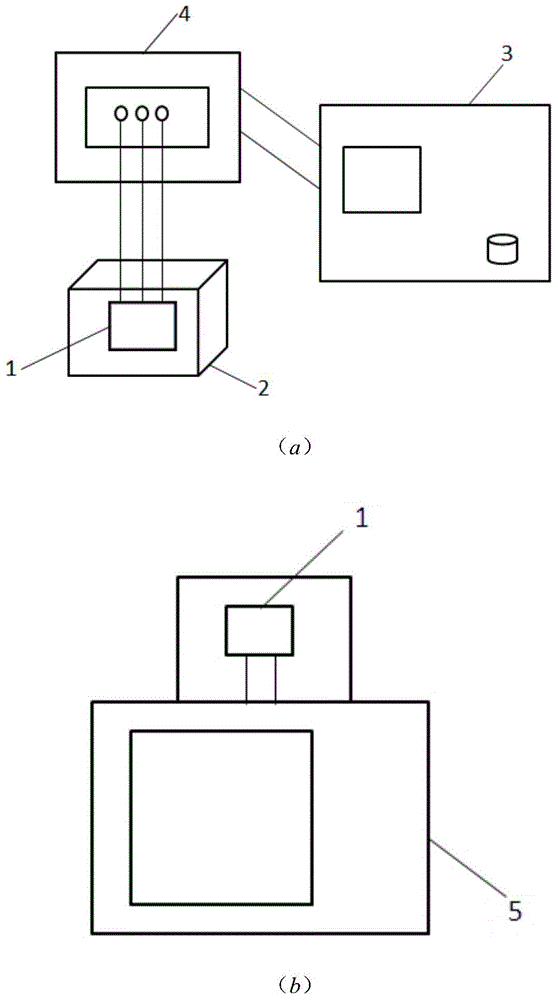
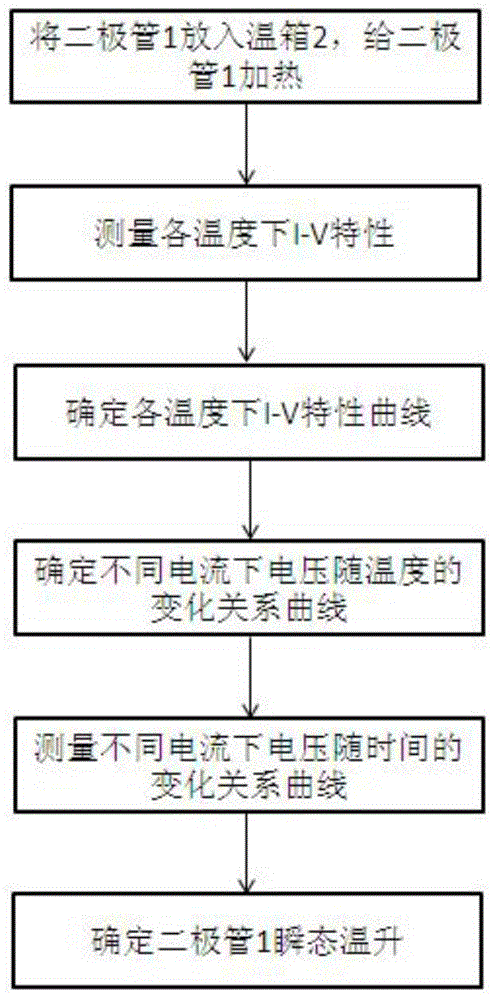
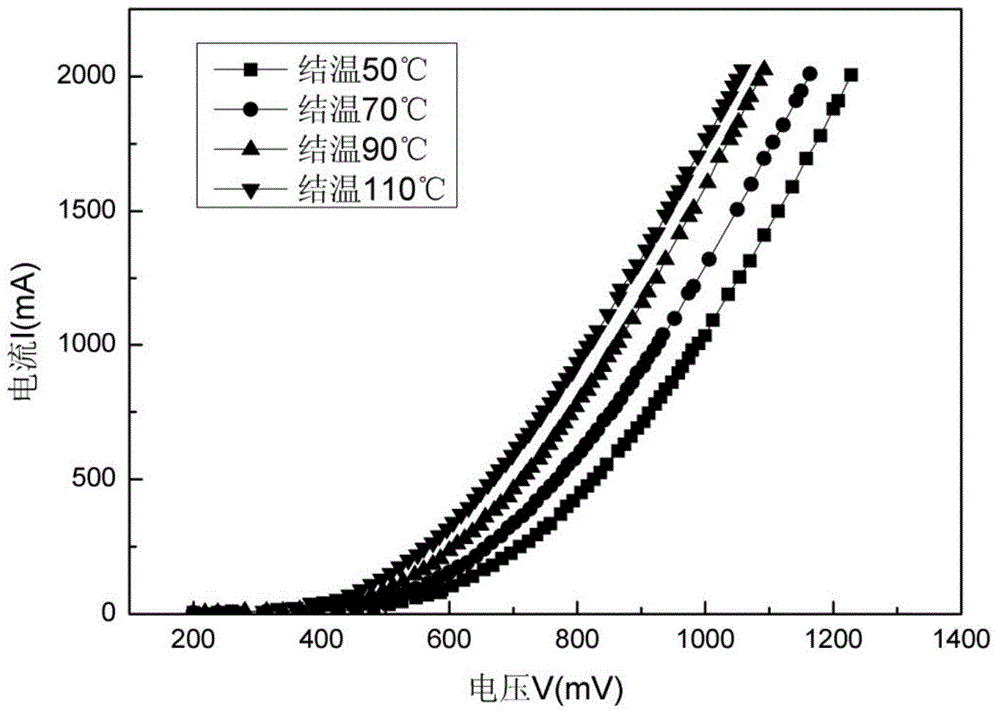
Method for measuring diode transient temperature rise in real time
InactiveCN103954899AEliminate temperature rise errorsShort pulse widthIndividual semiconductor device testingTime changesSemiconductor
The invention relates to a method for measuring the diode transient temperature rise in real time. The method includes the steps of firstly conducting I-V characteristic measurement on a measured diode at different temperatures to obtain an I-V characteristic curve, wherein electric currents applied to the diode are narrow pulse electric currents, and the self temperature rise of the diode can be avoided; then obtaining a curve of the relation between voltages under different electric currents and temperature changes according to the I-V characteristic curve; then collecting a relation, between the voltages under different electric currents and time changes, of the diode through semiconductor parameter analysis meters; finally obtaining the diode transient temperature rise in cooperation with the prior-obtained curve of the relation between the voltages under the different electric currents and the temperature changes. By means of the method, a switch-free measuring device is adopted for measuring the diode transient temperature rise in real time; compared with an existing measurement method related to a switching device with a switch, temperature rise errors caused by switching delaying are eliminated. Meanwhile, the narrow pulse electric currents generated by graphic instruments are small enough in pulse width, influences of the diode self temperature rise on the temperature rise can be effectively avoided, and the measurement accuracy is greatly improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Optical switch and optical waveform monitoring device utilizing optical switch
ActiveUS7848647B2Improve switching efficiencyReduce lossesLaser detailsPolarisation multiplex systemsOptical parametric amplifierLight beam
The polarization direction of an optical signal is changed by a polarization controller so as to be orthogonal to a main axis of a polarizer. A control pulse generator generates control pulses from control beam with a wavelength which is different from the wavelength of the optical signal. The optical signal and the control pulse are input to a nonlinear optical fiber. In the nonlinear optical fiber, the optical signal, during a time period in which the optical signal and the control pulse coincide, is amplified with optical parametric amplification around a polarization direction of the control pulse. The optical signal, during the time period in which the optical signal and the control pulse coincide, passes through the polarizer.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Drag reduction device used for water surface and underwater vehicle and manufacturing method of drag reduction device
InactiveCN106043591AEfficient coupling drag reduction effectReach a high degree of biomimicryWatercraft hull designGlass shaping apparatusViscous liquidManufacturing technology
The invention discloses a drag reduction device used for a water surface and underwater vehicle and a manufacturing method of the drag reduction device, and belongs to the technical field of ship manufacturing. The drag reduction device provided by the invention comprises a placoid layer, a supporting layer and a slow release layer, wherein the placoid layer and the supporting layer are arranged in parallel; the slow release layer is located between the placoid layer and the supporting layer; a channel layer is machined on the supporting layer; overflowing holes communicating with the slow release layer are formed in the surface of the placoid layer; the slow release layer communicates with the channel layer through communicating holes and comprises a plurality of sawtooth-shaped maze flow channels; the channel layer is composed of multi-stage channels with different widths, and the multi-stage channels are distributed dendritically; and the channel with the smallest width communicates with the slow release layer through the communicating holes. Meanwhile, the invention provides the method for manufacturing the drag reduction device. The highly lifelike shark-imitated drag reduction structure manufactured through the manufacturing method is in highly lifelike shark-imitated scale groove shapes and can slowly release a drag reducer, so that the efficient coupling and drag reducing effects of the scale grooves and self-lubricating viscous liquid are achieved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
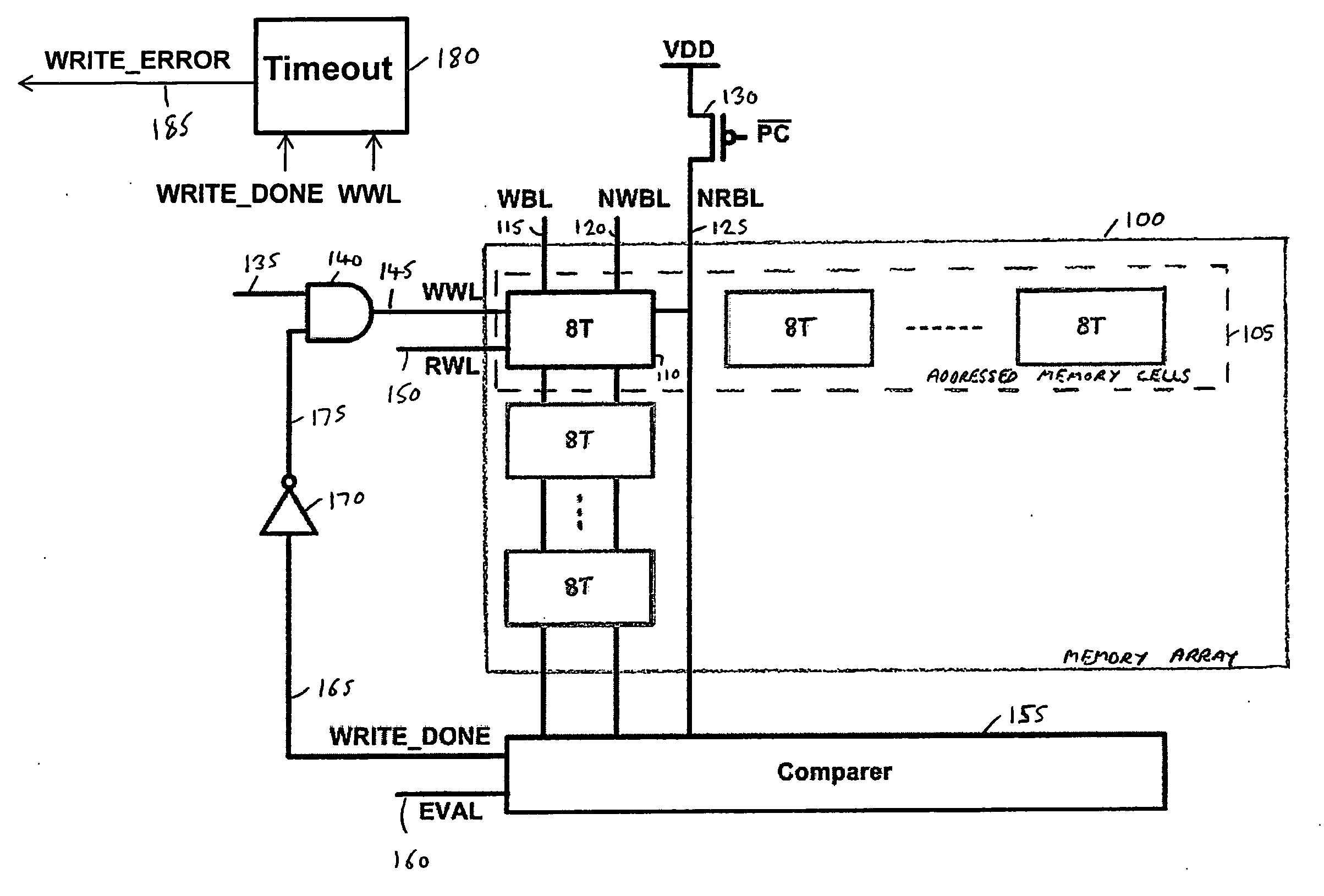
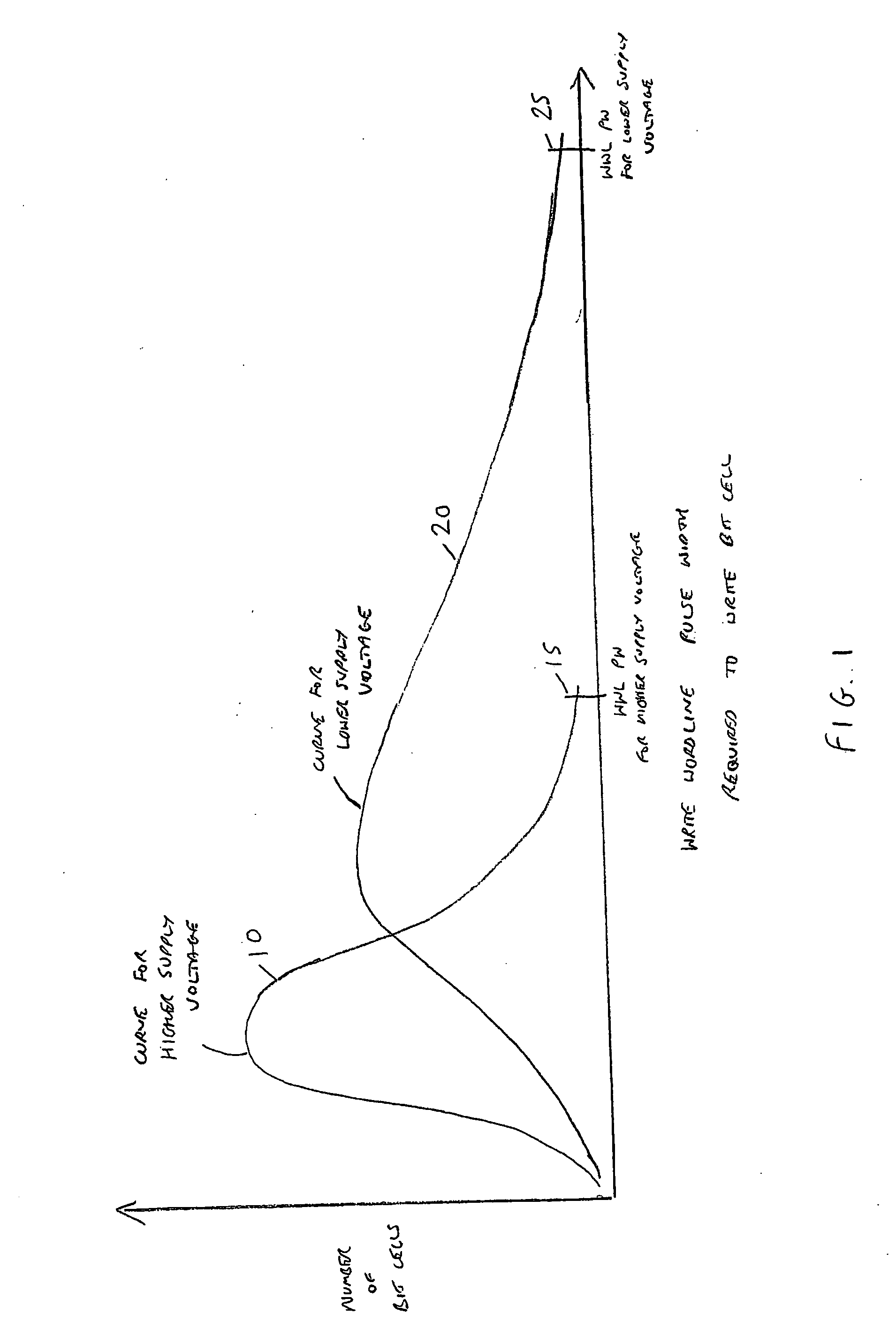
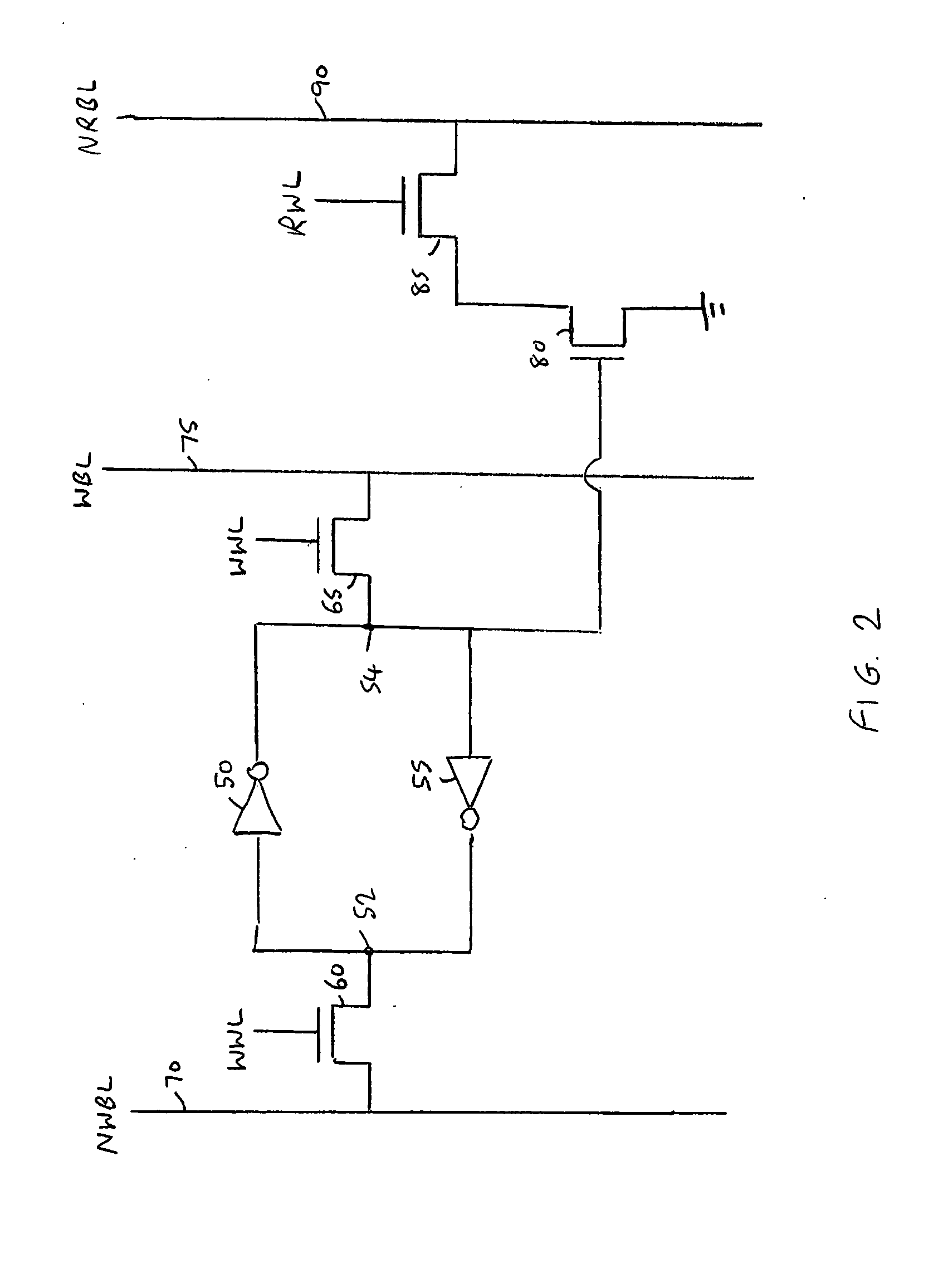
Memory device and method of controlling a write operation within a memory device
A memory device and method are provided incorporating a technique for controlling a write operation within the memory device. The memory device has an array of memory cells, each memory cell supporting writing and simultaneous reading of that memory cell. Write circuitry is arranged, during a write operation, to provide write data to a number of addressed memory cells within the array, whilst word line select circuitry is responsive to the start of the write operation to assert a write word line signal that enables those addressed memory cells to store the write data. Comparing circuitry is arranged, during the write operation, to compare the write data with data currently stored in the addressed memory cells. On detecting that the write data matches the data currently stored in the addressed memory cells, the comparing circuitry asserts a control signal to the word line select circuitry to cause the word line select circuitry to de-assert the write word line signal. As a result, the pulse width of the asserted write word line signal is dependent on time taken by the addressed memory cells to store the write data, thereby leading to a significant reduction in the size of the pulse width when compared with known prior art techniques.
Owner:ARM LTD
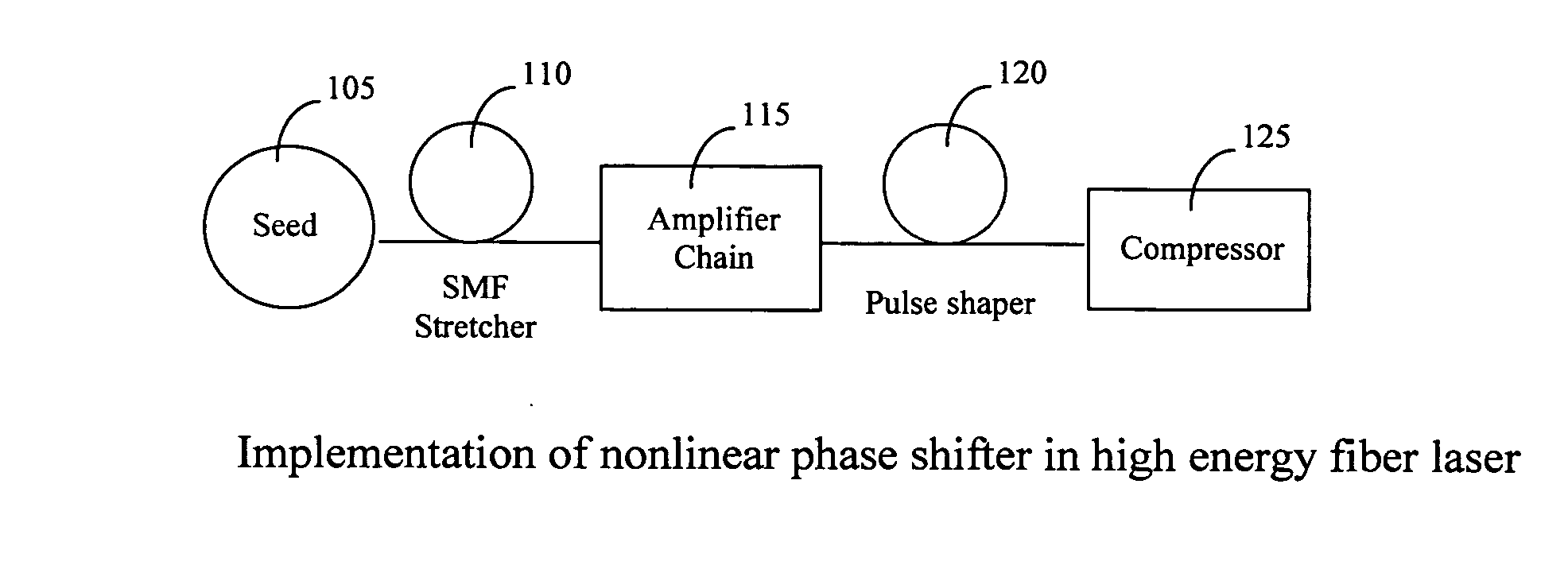
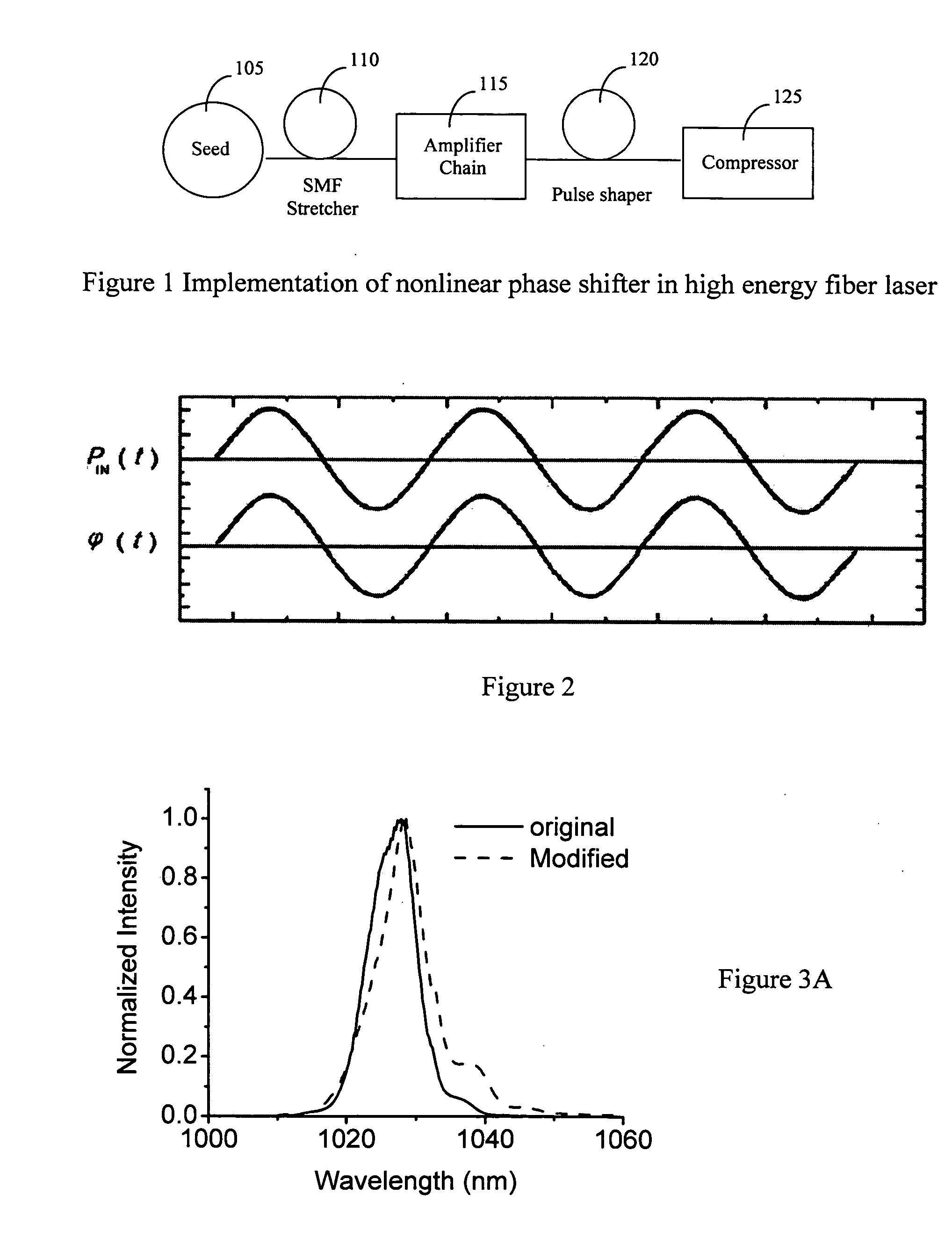
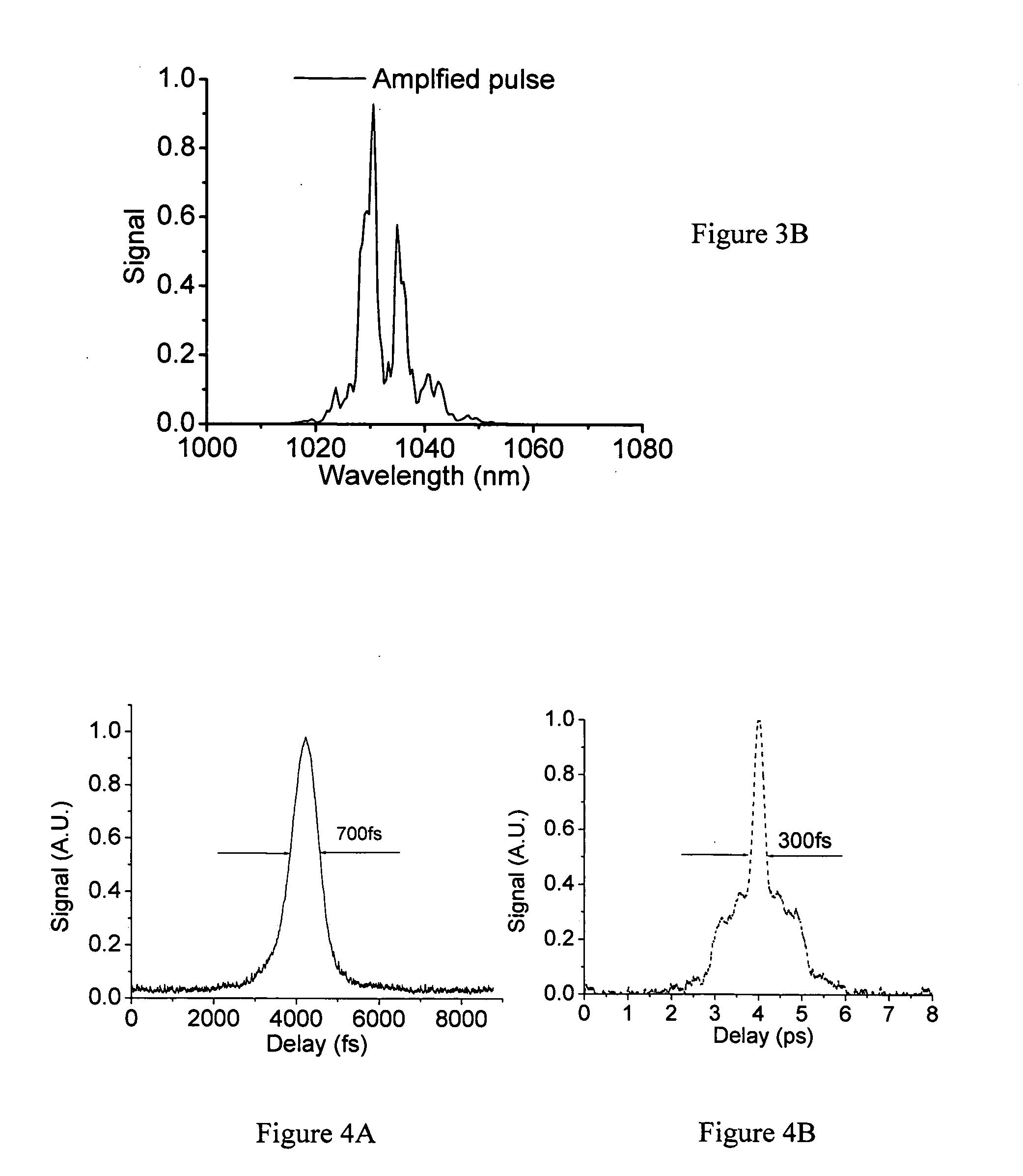
Spectrum broadening and recompression in high-energy fiber laser system
InactiveUS20070047595A1Improve controllabilityHigh bandwidthLaser using scattering effectsAudio power amplifierHigh energy
A fiber Chirped Pulse Amplification (CPA) laser system includes a fiber mode-locking oscillator for generating a laser for projecting to a fiber stretcher for stretching a pulse width of the laser. The fiber CPA laser further includes a multistage amplifier for amplifying the laser for projecting into a pulse shaper then to a compressor having a nonlinear phase generator for compensating high order dispersions and compressing the pulse width of the laser. The pulse shaper is further provided to minimize a nonlinear phase shift inside the multistage amplifier for reducing a Stimulated Raman Scattering (SRS
Owner:POLARONYX
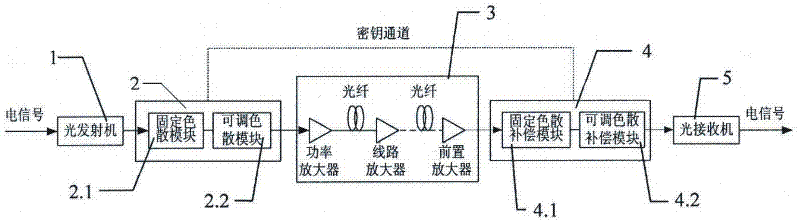
Secret optical communication system based on dynamic strong dispersion management
InactiveCN102347800AImprove transmission qualityRealize confidential transmissionElectromagnetic transmissionGratingDispersion compensation
The invention discloses a secret optical communication system based on dynamic strong dispersion management, belonging to the technical field of secret communication, and comprising an optical signal emission part, an optical signal encryption part, an optical signal transmission part, an optical signal receiving part and an optical signal decryption part; the optical signal encryption part is provided with a fixed and adjustable dispersion module; the optical signal decryption part is provided with a fixed and adjustable dispersion compensation module; the dispersion module and the dispersion compensation module are formed by any one of a fiber bragg grating, a G-T etalon, an MEMS (Micro-Electromechanical System), a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) annular resonant cavity; one end of the optical signal encryption part is connected to an optical signal transmitter, and the other end of the optical signal encryption part is connected to the optical signal transmission part; secret keys are transmitted to the optical signal decryption part through key secrete channels; one end of the optical signal decryption part is connected to the optical signal transmission part, and the other end of the optical signal decryption part is connected to an optical signal receiver; and the optical signal decryption part carries out real-time, synchronous and precise compensation on the transmitted optical pulse according to information provided by the secrete keys for releasing signals. In the secret communication, a dynamic dispersion management technology is used in the optical communication system for the first time to realize the secret transmission of information.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF INFORMATION TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com