Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
71 results about "Cavity loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
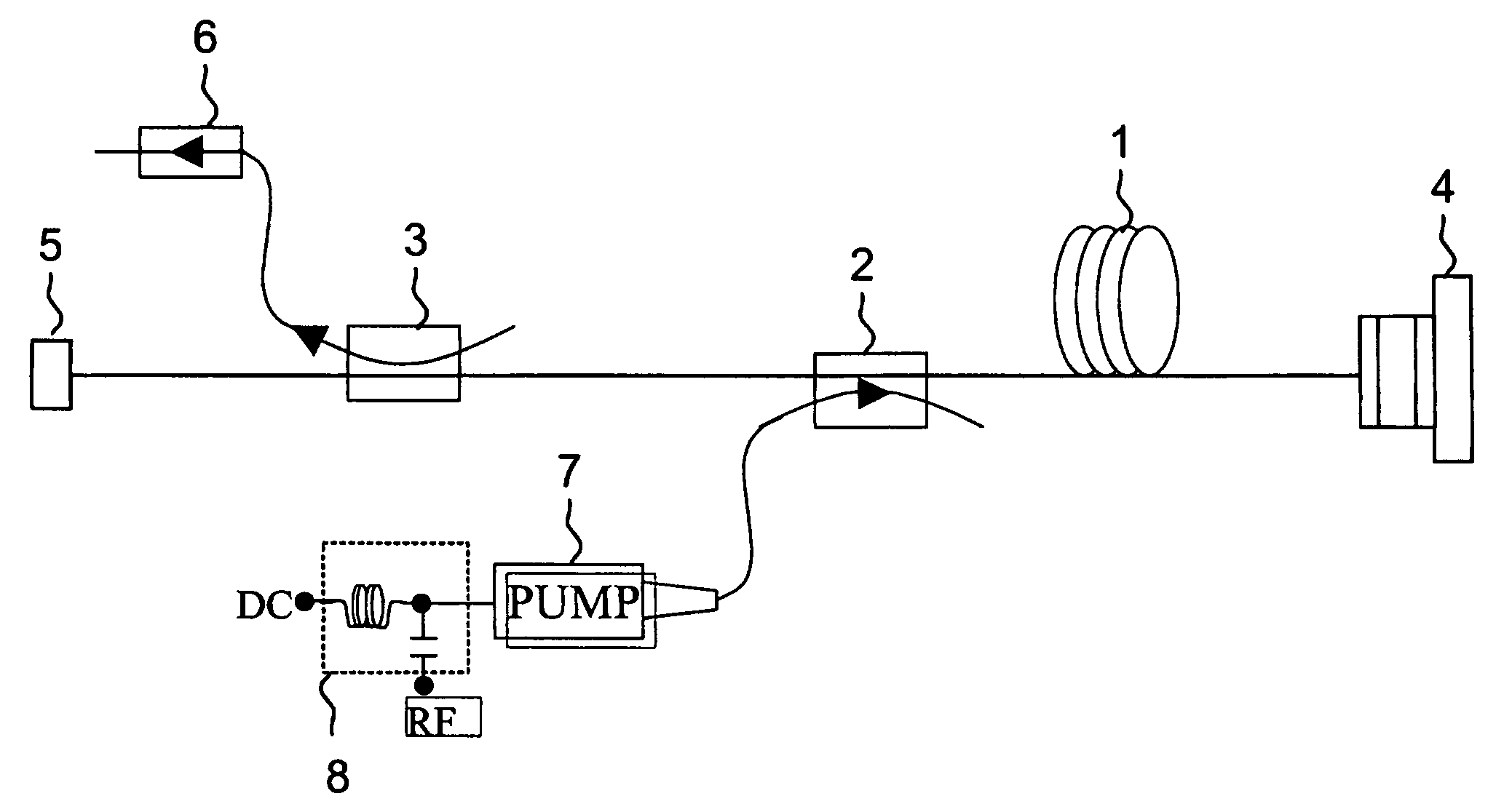
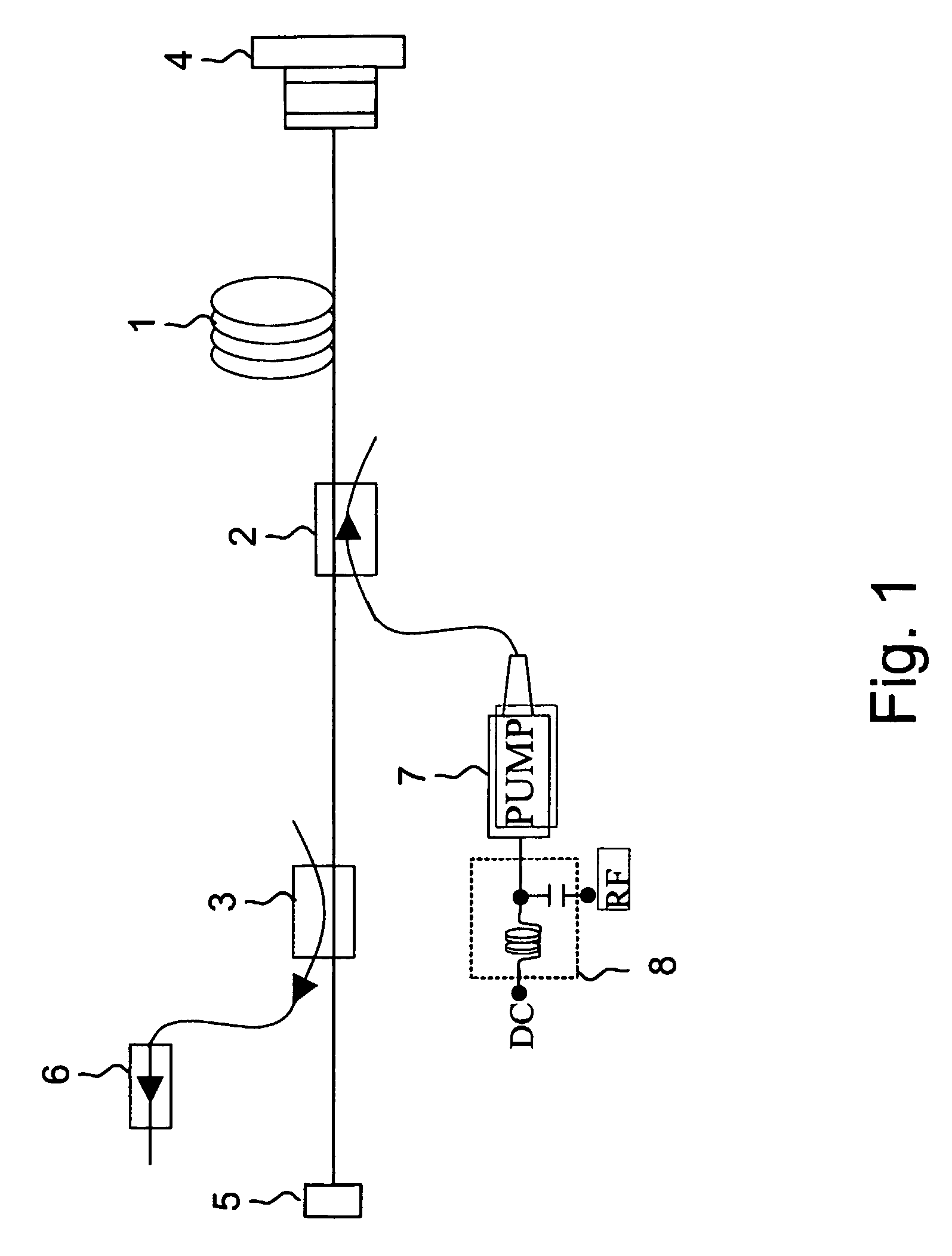
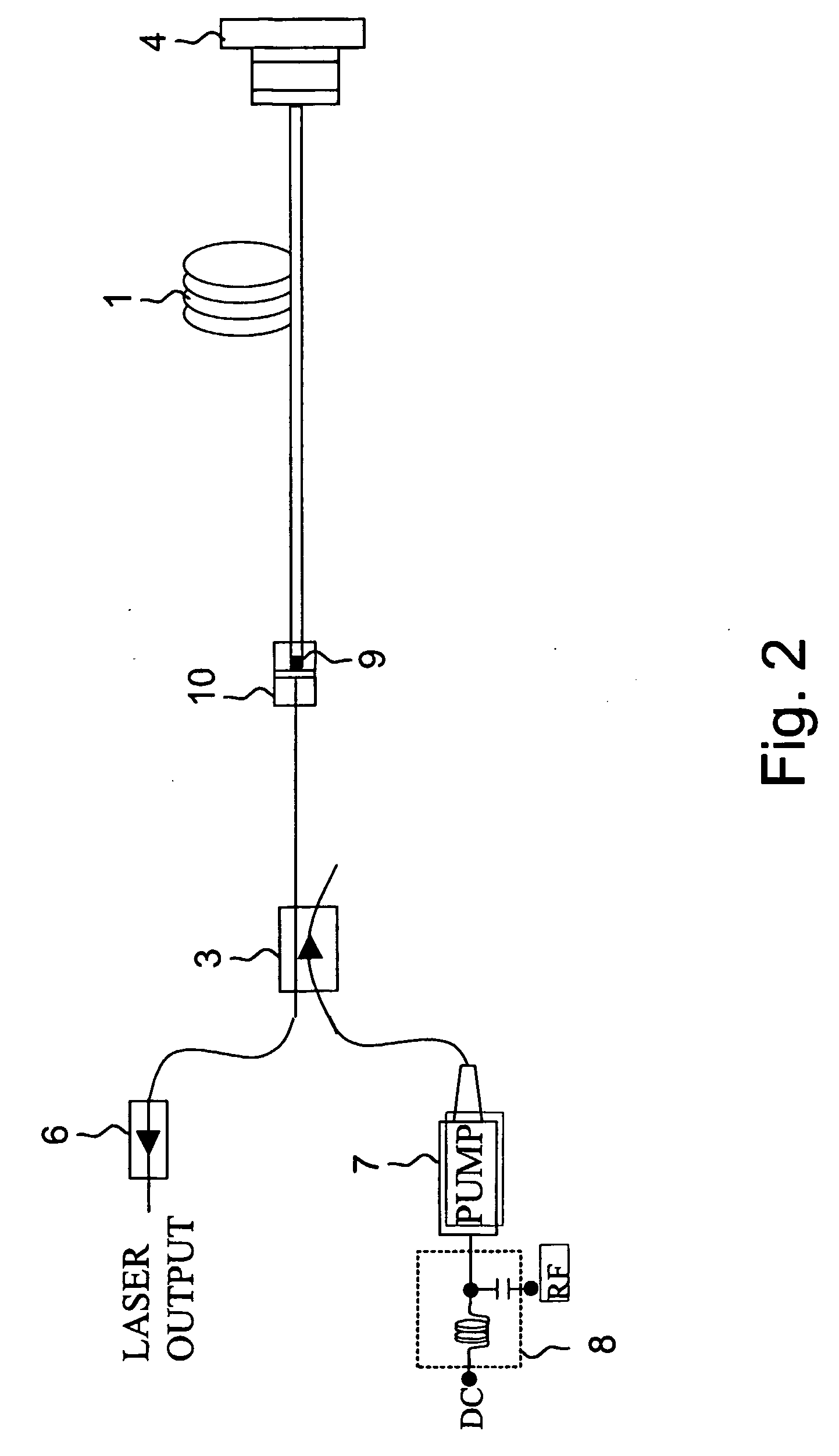
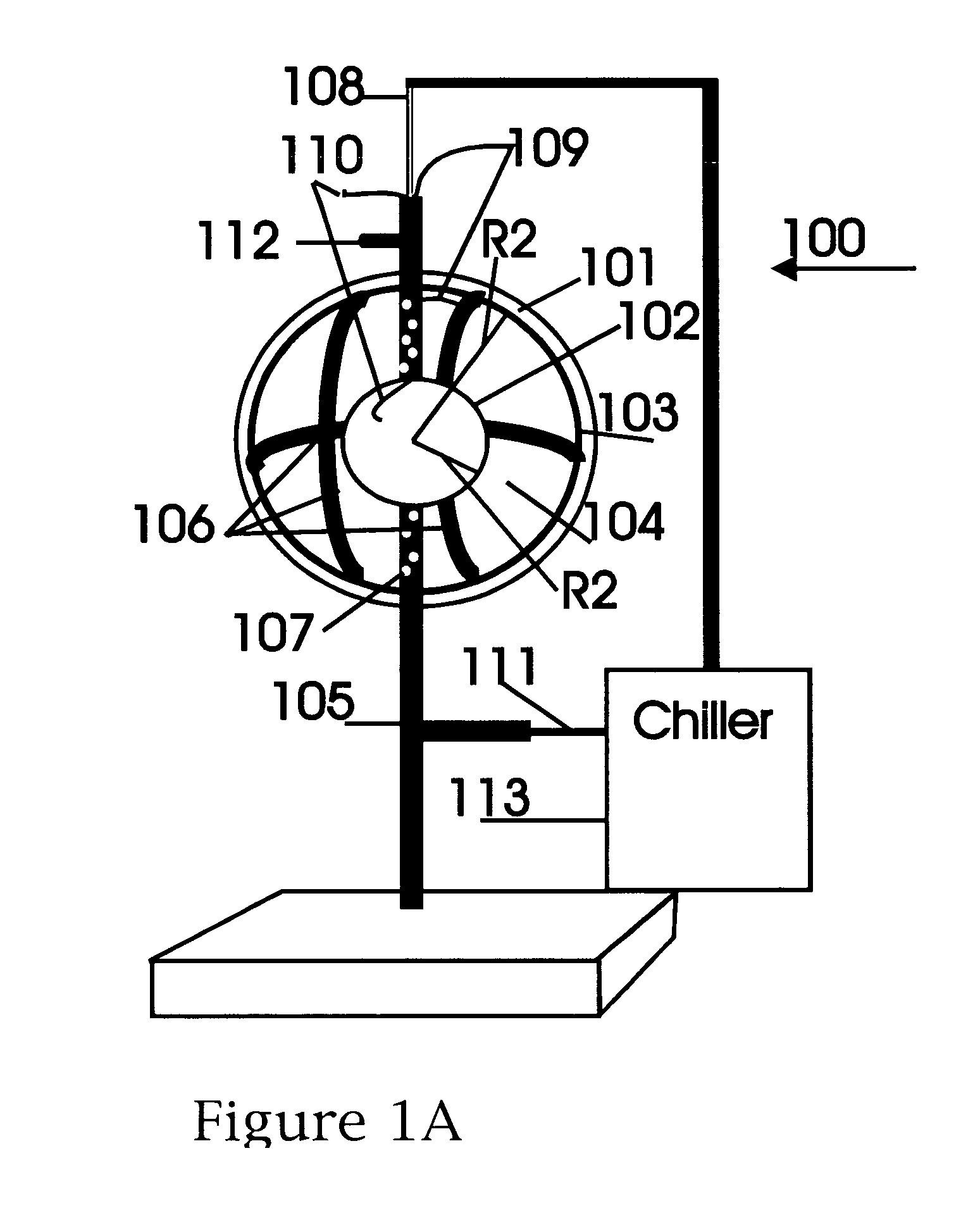
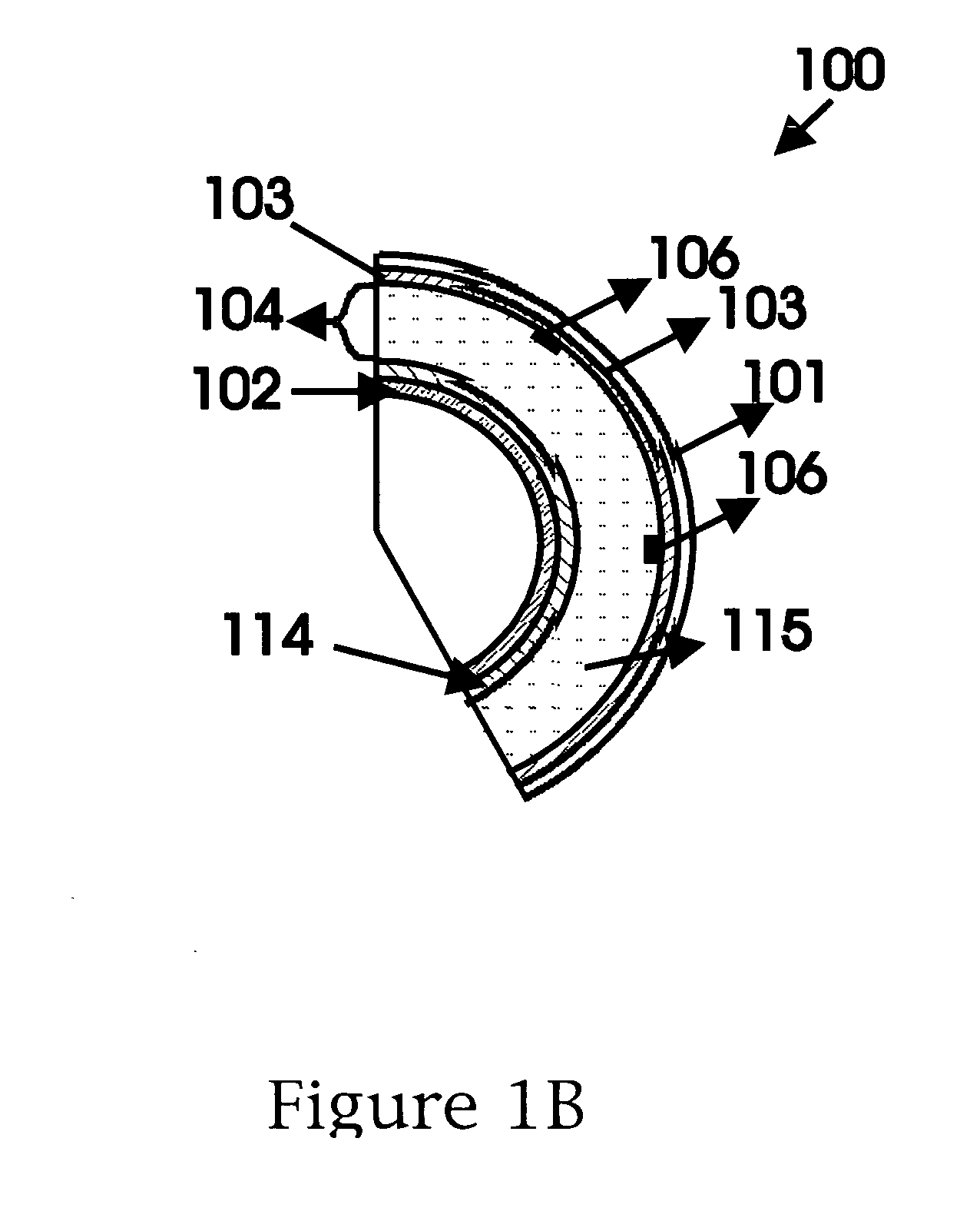
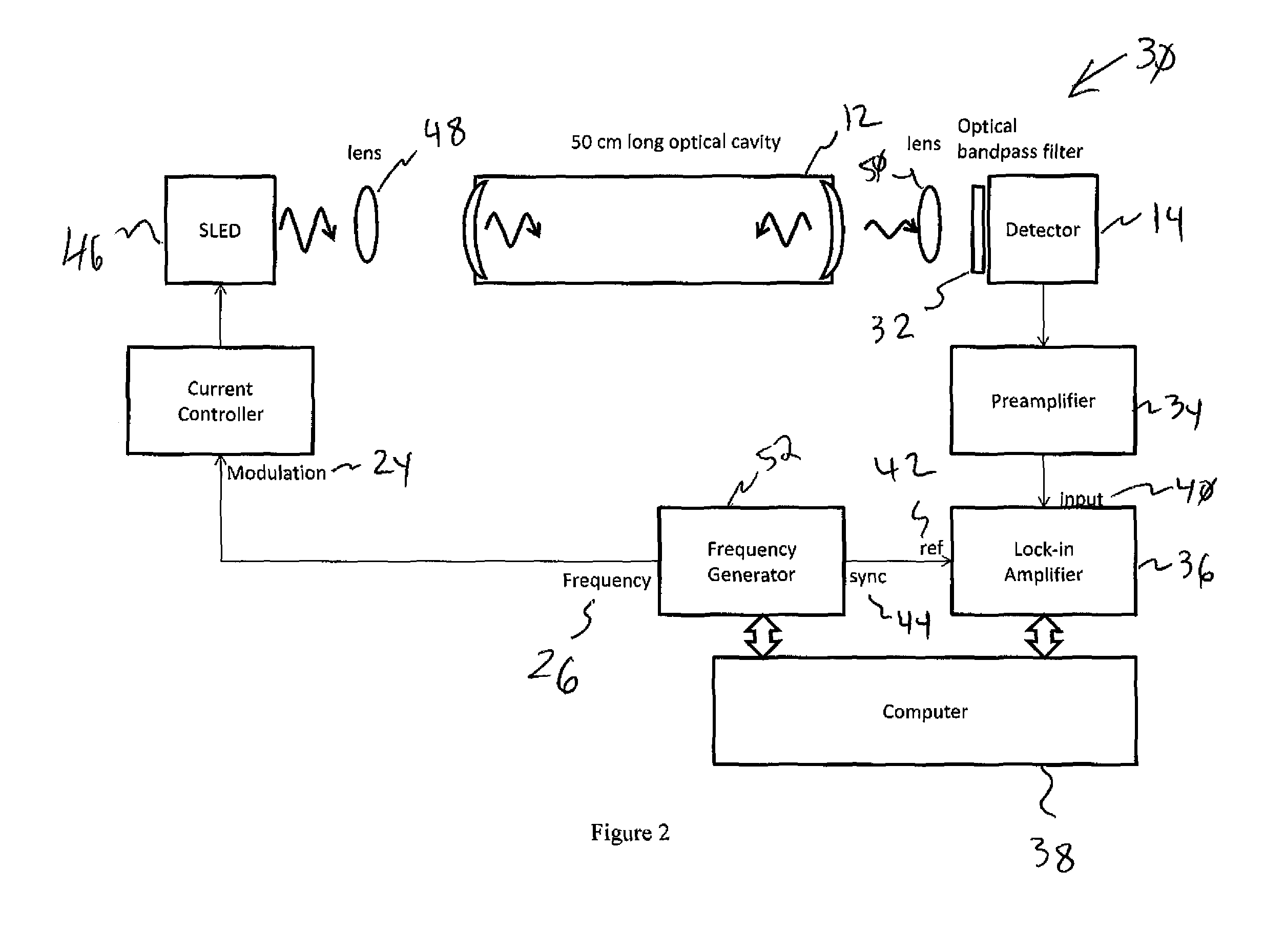
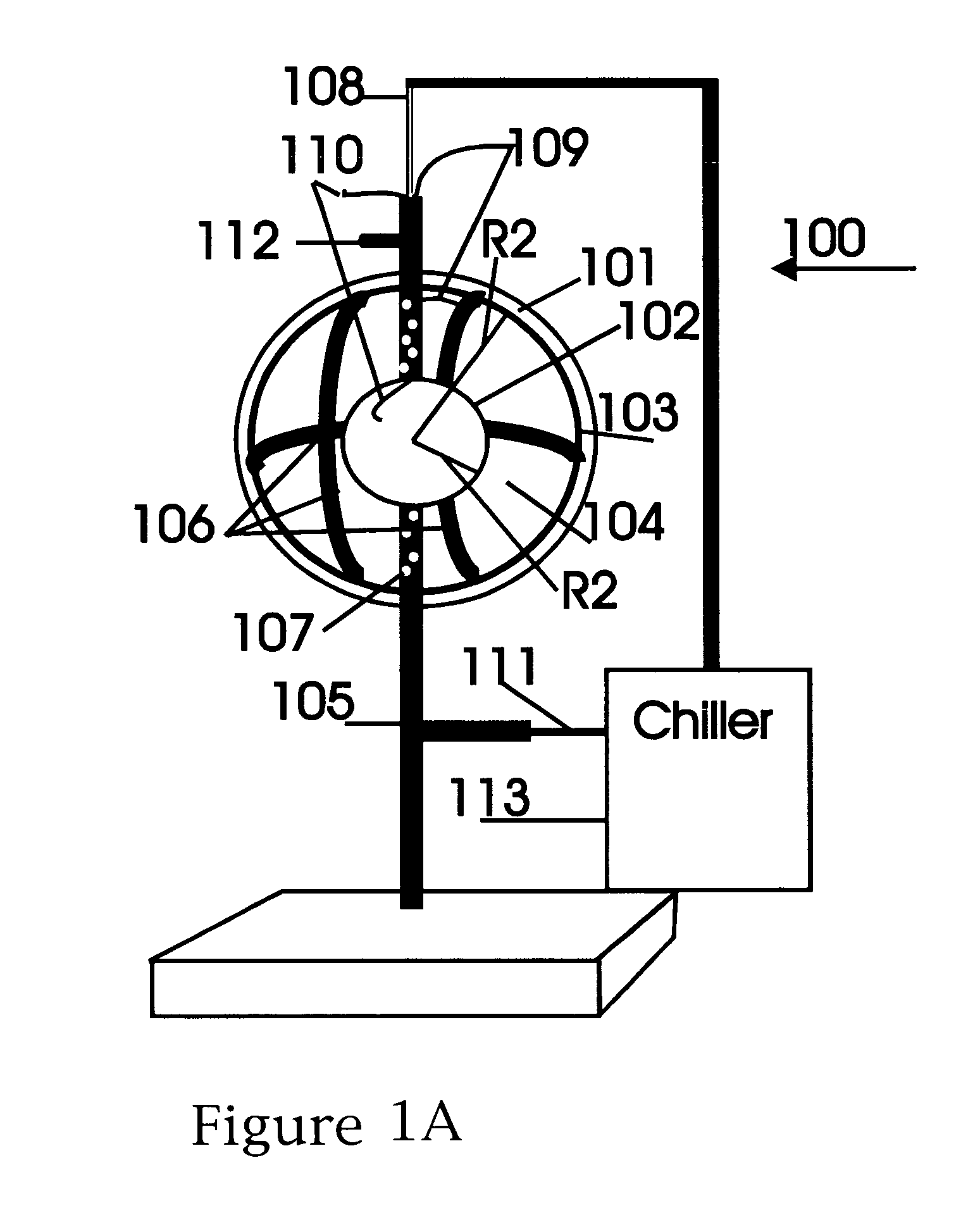
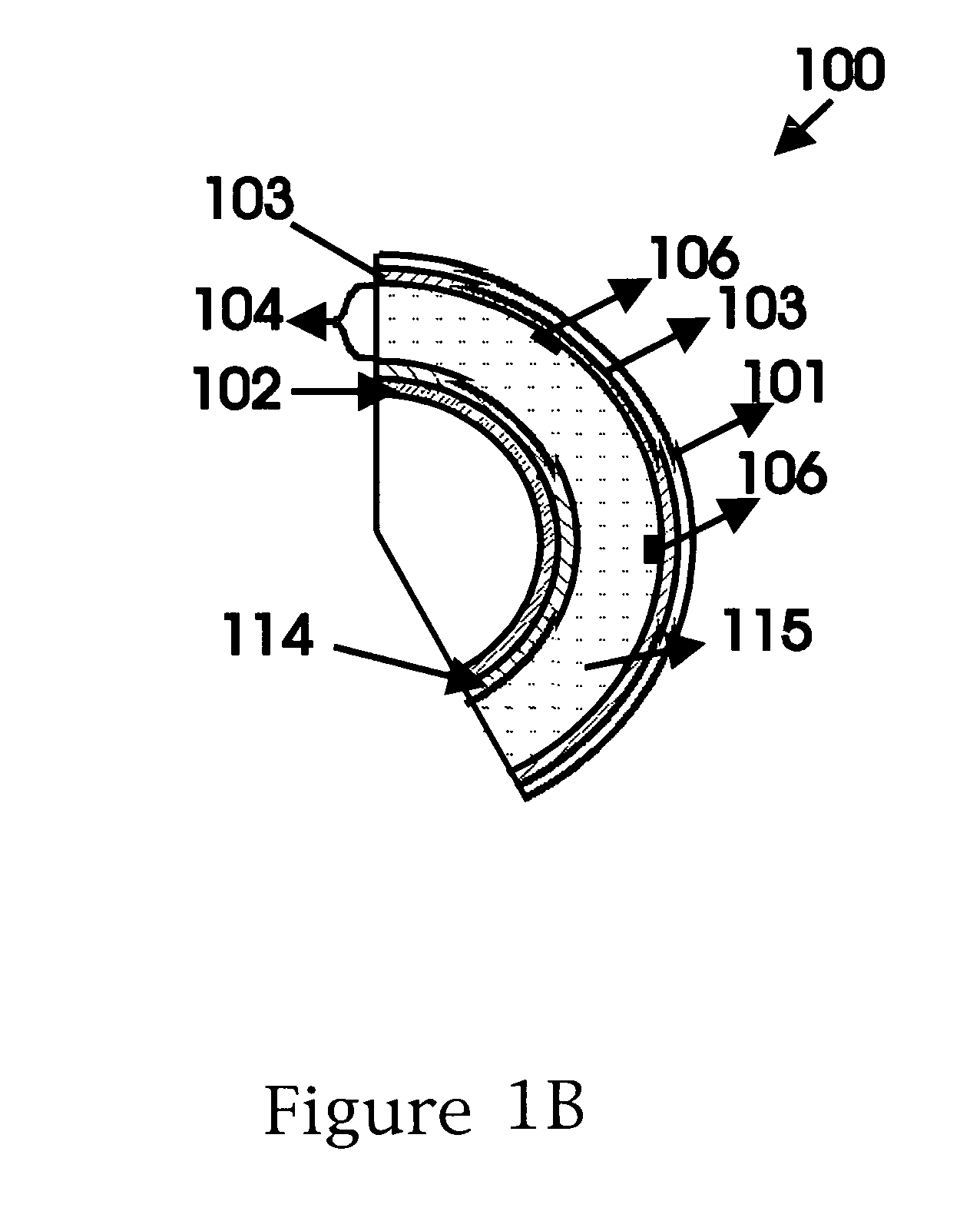
Cavity ring-down detection of surface plasmon resonance in an optical fiber resonator
InactiveUS20050117157A1Simple methodReduce sensitivityRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorRing downOptical cavity
An apparatus and method for use with a coherent optical source to detect environmental changes. The apparatus comprises: an optical cavity, including an input coupling port, and an optical fiber section; a detector optically coupled to the optical cavity to monitor radiation in the optical cavity; and a processor electrically coupled to the detector for analyzing the environmental changes adjacent the detection portion of the optical cavity based on a rate of decay of the radiation in the optical cavity monitored by the detector. The optical fiber section of the optical cavity includes a detection portion coated with a conductive layer capable of supporting a surface plasmon to provide cavity loss. The surface plasmon is responsive to the environmental changes adjacent the detection portion. The coherent optical source is optically coupled to the input coupling port of the optical cavity to provide the radiation in the optical cavity.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Low-repetition-rate ring-cavity passively mode-locked fiber laser
InactiveUS20090003391A1Laser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionMode locked fiber laserFiber disk laser
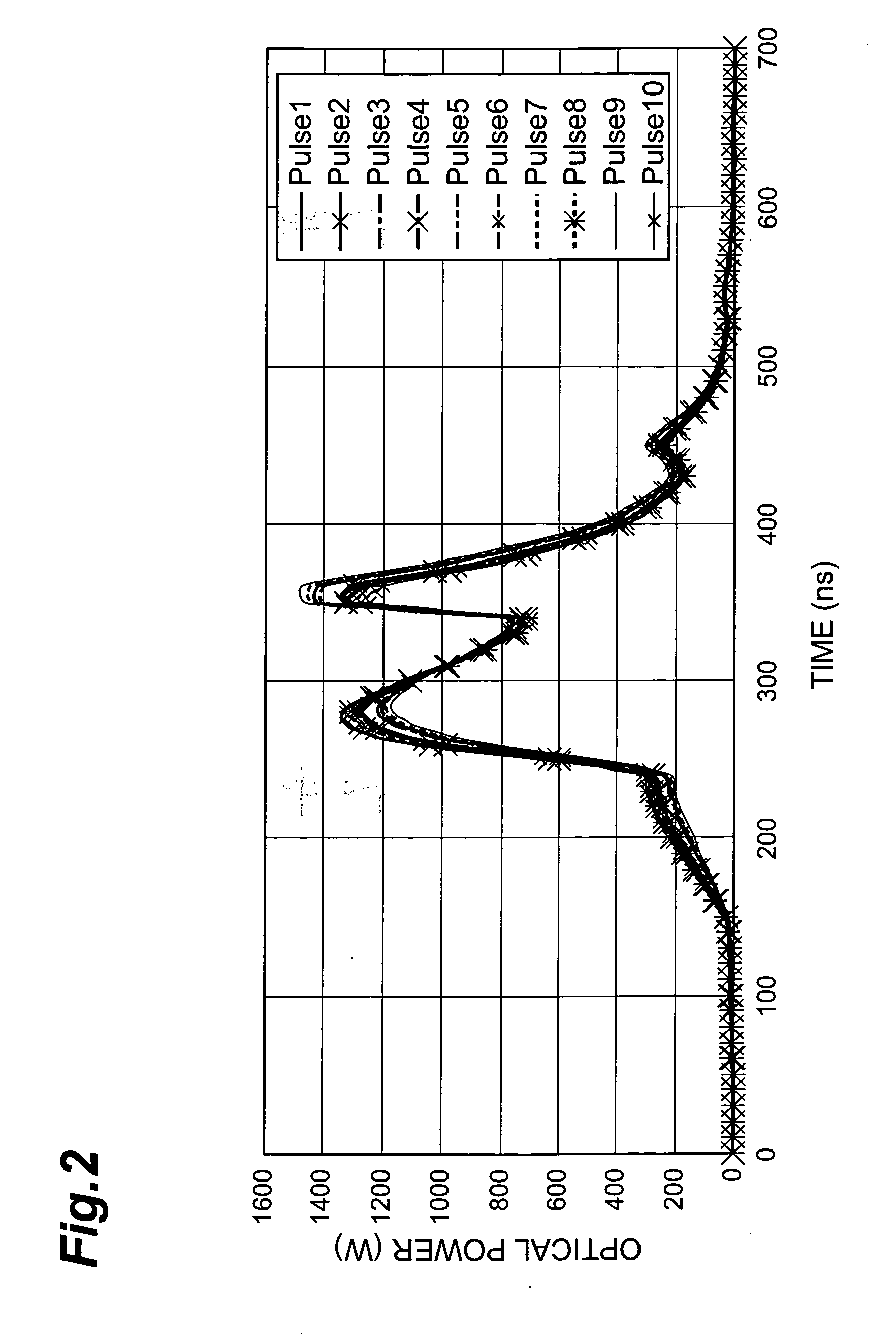
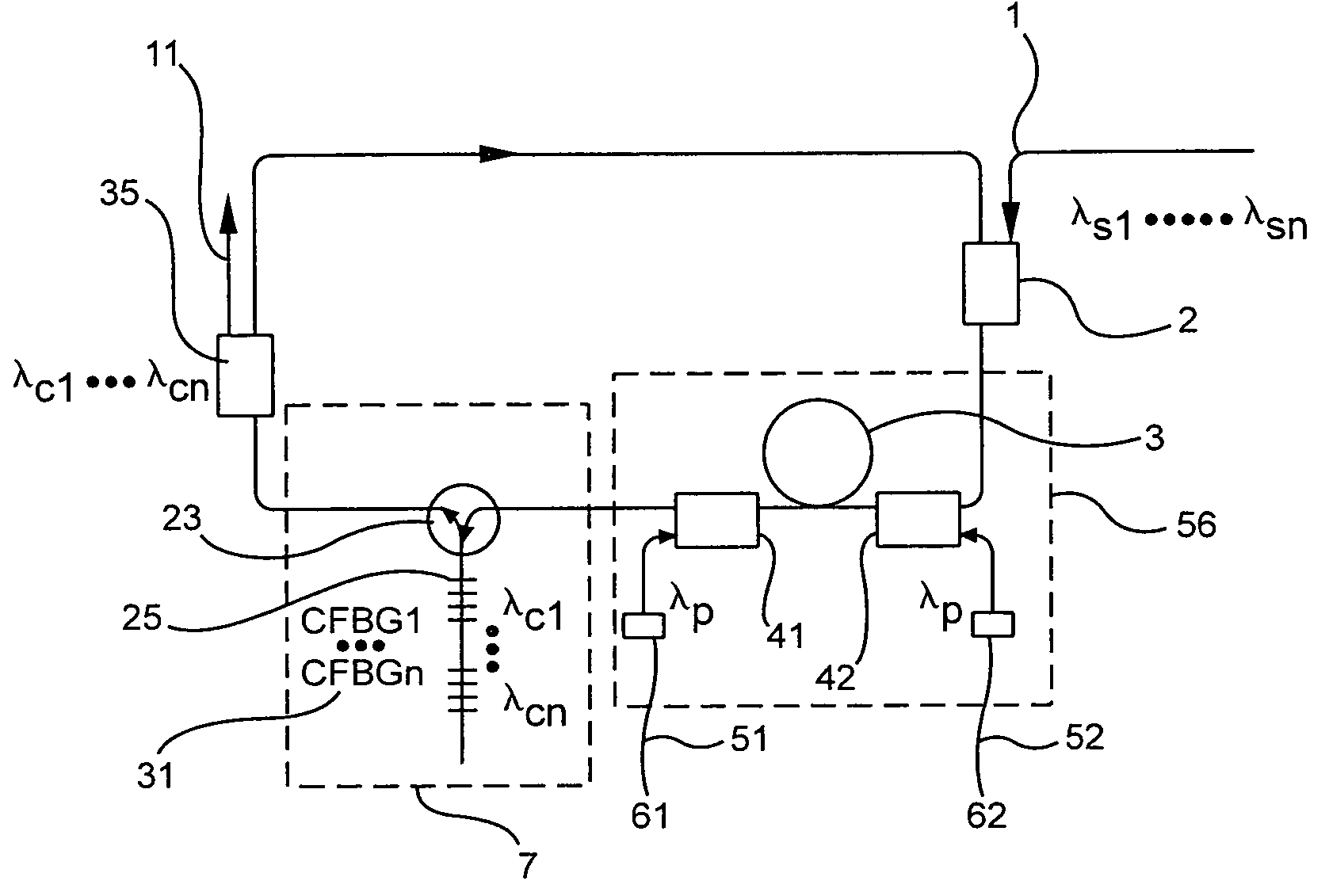
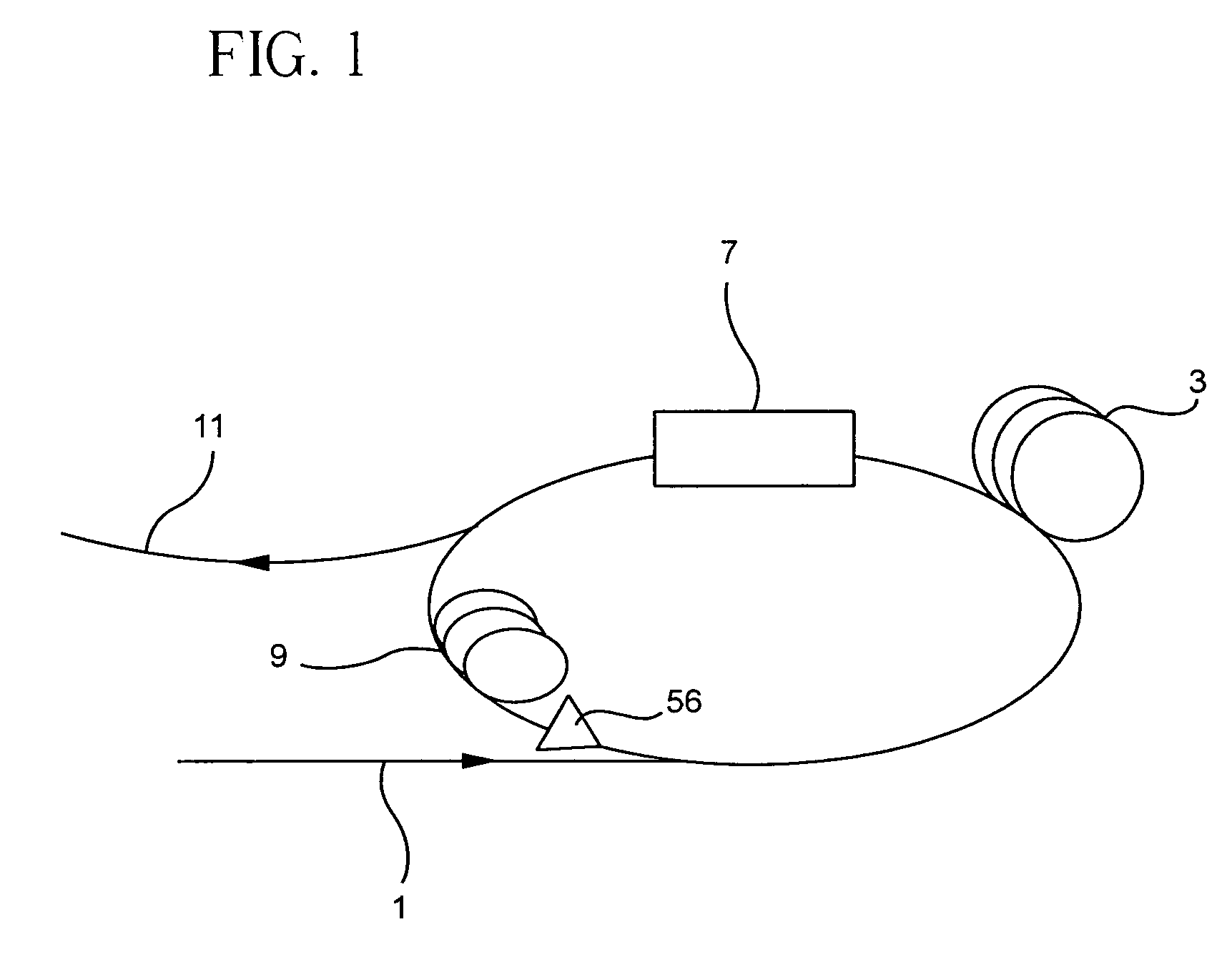
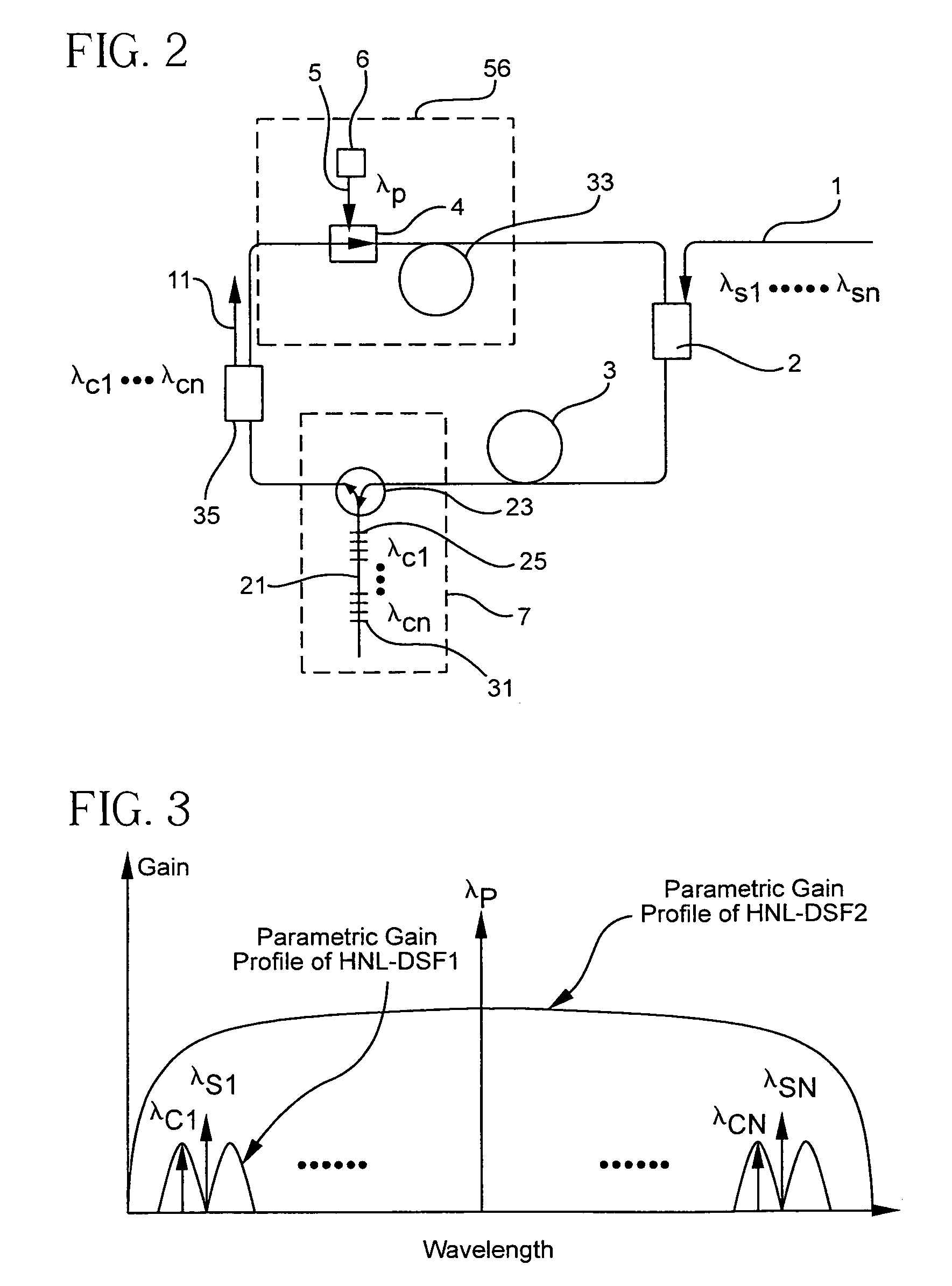
A ring-cavity, passively mode locked fiber laser capable of producing short-pulse-width optical pulses at a relatively low repetition rate. The fiber laser uses a one-way ring-cavity geometry with a chirped fiber Bragg grating (CFBG) at its reflecting member. The CFBG is part of a dispersion compensator that includes an optical circulator that defines a one-way optical path through the ring cavity. A doped optical fiber section is arranged in the optical path and serves as the gain medium. A pump light source provides the pump light to excite the dopants and cause the gain medium to lase. A saturable absorber is operable to effectuate passive mode-locking of the multiple modes supported by the ring cavity. The ring cavity geometry allows to achieve mode locking with single pulse operation in a longer cavity length than conventional linear cavities. Furthermore, the longer cavity length reduces the constraints on the chirp rate of the CFBG. This, in turn, allows the CFBG to have a relatively high reflectivity, which provides the necessary dispersion compensation and cavity loss for generating short optical pulses at a low repetition rate.
Owner:CORNING INC
Laser based cavity enhanced optical absorption gas analyzer
ActiveUS8659759B2Promote absorptionImprove the measurement effectMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis using microwave meansSpectroscopyLaser light
Cavity enhanced absorption spectroscopy systems and methods for detecting trace gases. When the frequency of laser light approaches the frequency of a resonance cavity mode, the laser begins to fill the cavity to that mode. Optical intensity inside the cavity reflects total cavity loss when the laser light frequency coincides with the cavity mode transmission peak. The intra-cavity optical power also depends on the coupling efficiency of the laser beam to the particular cavity mode. Measurement of intensities of three optical signals, namely, intensity of the light incident on to the cavity, intensity of the light reflected from the cavity, and intensity of the intra-cavity optical power, with their appropriate normalization advantageously significantly reduce effects of baseline calibration and drift as the normalized signal only depends on total cavity loss, and not the coupling efficiency, as in traditional approaches.
Owner:LI COR
Method for organizing a mode-locked pulse train by pump modulation
InactiveUS20050163170A1High fundamental repetition rateIncreased stability against noiseLaser using scattering effectsActive medium shape and constructionFiberMode locked fiber laser
The present invention describes a method to achieve stabilization of the repetition rate in a passive harmonic mode-locked fiber laser employing semiconductor saturable absorbers. The pulse organization is accomplished by electrically modulating the amplifier pump source that in turn optically modulates the saturable loss of semiconductor absorber. Moreover owing on an efficient modulation mechanism of the cavity loss, the method can be used to generate an actively mode-lock pulse train. The invention offers the advantages of an actively modulated mode-locked laser while maintaining the simplicity and the cost effectiveness of a passive mode-locked system. We expect that this approach combined with the use of regenerative modulation technique and polarization-maintaining fiber components will permit the generation of the dropout-free pulse trains at gigahertz repetition rates with good long-term stability and minimal cost.
Owner:OPTOELECTRONICS RES CENT
Q-switched CO2 laser for material processing
InactiveUS20050069007A1Reduce layeringReduce thicknessLaser arrangementsActive medium materialMaterials processingLength wave
A simultaneously super pulsed Q-switched CO2 laser system for material processing comprises sealed-off folded waveguides with folded mirrors that are thin film coated to select the output wavelength of the laser. The system also comprises a plurality of reflective devices defining a cavity; a gain medium positioned within the cavity for generating a laser beam; a cavity loss modulator for modulating the laser beam, generating thereby one or more laser pulses; a pulsed signal generation system connected to the cavity loss modulator for delivering pulsed signals to the cavity loss modulator thereby controlling the state of optical loss within the cavity; a control unit connected to the pulsed signal generation system for controlling the pulsed signal generation system; and a pulse clipping circuit receptive of a portion of the laser beam and connected to the pulsed signal generation system for truncating a part of the laser pulses.
Owner:KENNEDY JOHN T +6
Cavity ring-down detection of surface plasmon resonance in an optical fiber resonator
InactiveUS7352468B2Reduce sensitivityRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorRing downOptical cavity
An apparatus and method for use with a coherent optical source to detect environmental changes. The apparatus comprises: an optical cavity, including an input coupling port, and an optical fiber section; a detector optically coupled to the optical cavity to monitor radiation in the optical cavity; and a processor electrically coupled to the detector for analyzing the environmental changes adjacent the detection portion of the optical cavity based on a rate of decay of the radiation in the optical cavity monitored by the detector. The optical fiber section of the optical cavity includes a detection portion coated with a conductive layer capable of supporting a surface plasmon to provide cavity loss. The surface plasmon is responsive to the environmental changes adjacent the detection portion. The coherent optical source is optically coupled to the input coupling port of the optical cavity to provide the radiation in the optical cavity.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Laser based cavity enhanced optical absorption gas analyzer
ActiveUS20130050706A1Improve the measurement effectPromote absorptionTransmissivity measurementsAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopySpectroscopyLaser light
Cavity enhanced absorption spectroscopy systems and methods for detecting trace gases. A laser or other light source that is capable of being frequency-scanned is coupled to a resonance cavity though one of the cavity mirror. When the frequency of the laser light approaches the frequency of one of the cavity modes, the laser begins to fill the cavity to that mode. Optical intensity inside the resonance cavity reflects total cavity loss at the moment when the laser light frequency coincides with the cavity mode transmission peak. The total cavity loss is a sum of the cavity mirror losses and losses caused by absorption of a gas mixture present in the cavity. The intra-cavity optical power also depends on the coupling efficiency of the laser beam to the particular cavity mode. Measurement of intensities of three optical signals, namely, intensity of the light incident on to the cavity, intensity of the light reflected from the cavity, and intensity of the intra-cavity optical power, with their appropriate normalization advantageously significantly reduce effects of baseline calibration and drift as the normalized signal only depends on total cavity loss, and not the coupling efficiency, as in traditional approaches.
Owner:LI COR
Scalable spherical laser
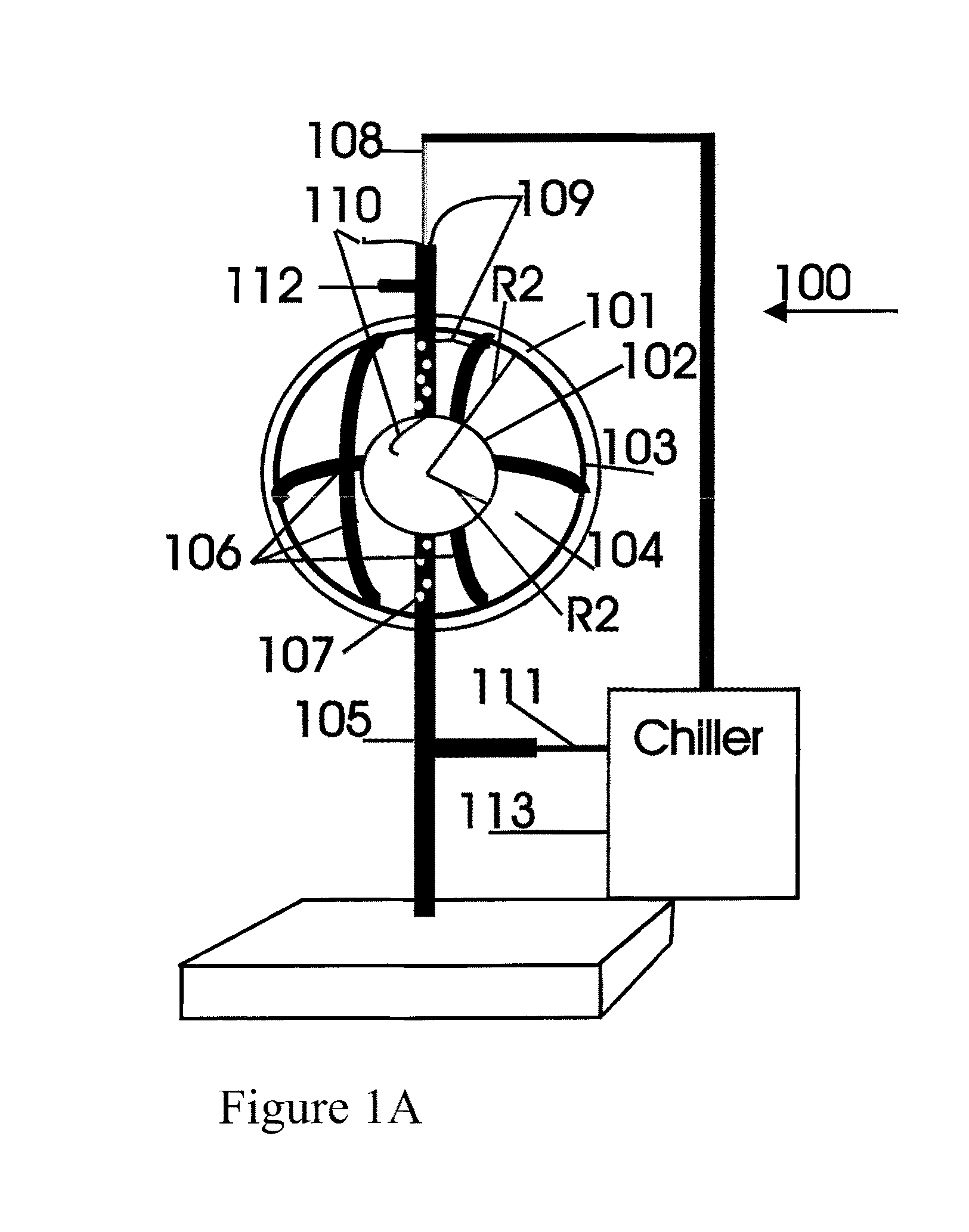
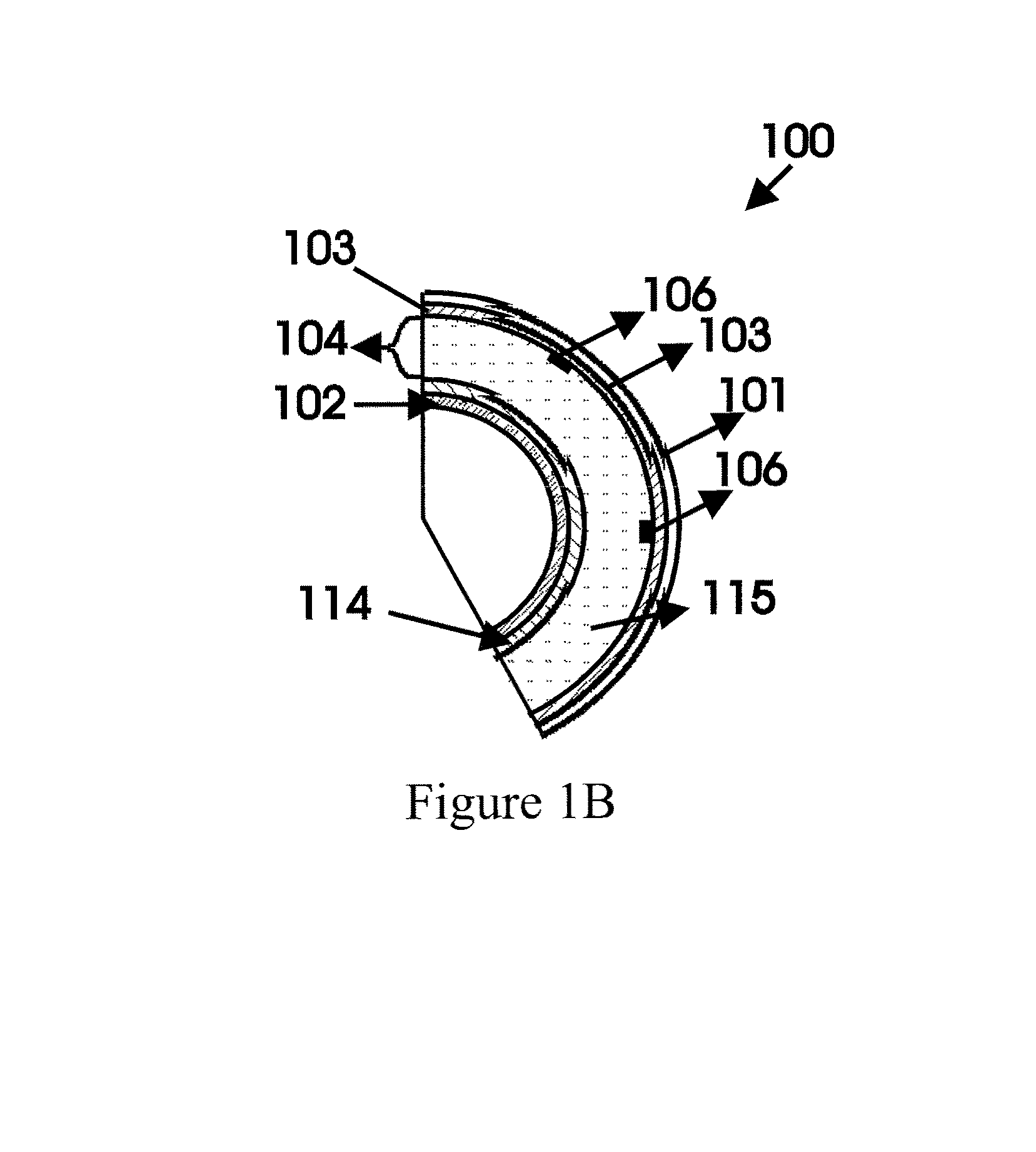
ActiveUS20060227842A1Increasing both radii proportionallyConstant lengthExcitation process/apparatusOptical resonator shape and constructionEllipseCavity loss
A spherical laser includes a transparent or semi-transparent outer spherical vessel having an internal cavity, an amplifying medium in the cavity, and means to excite the amplifying medium. The sphere is provided with a partially reflective coating to act as a spherical optical resonator. Excitation of the amplifying medium produces an optical gain. When the gain exceeds cavity losses and threshold conditions are met, lasing is supported. This creates a three-dimensional, spherically radiating emission, emulating a point source. The output is radially diverging, but is harnessed by enclosing the sphere within a mirrored ellipse to image the output to a point, or within a mirrored parabola to columinate the emission. A concentric, reflective inner sphere may be disposed in the cavity, with the amplifying medium lying between the two spheres. A voltage potential is applied between the spheres to excite the medium.
Owner:RONALD LACOMB
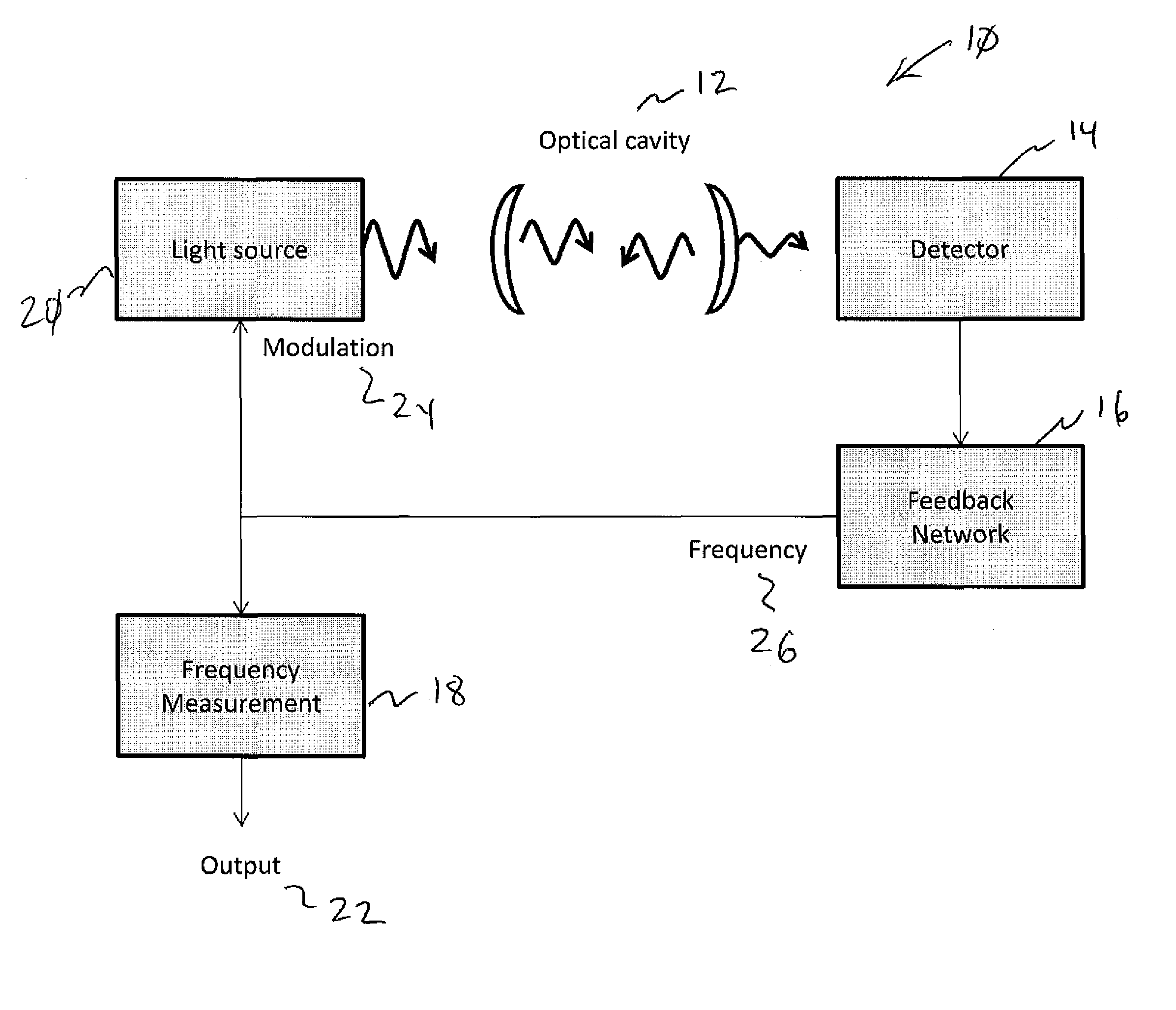
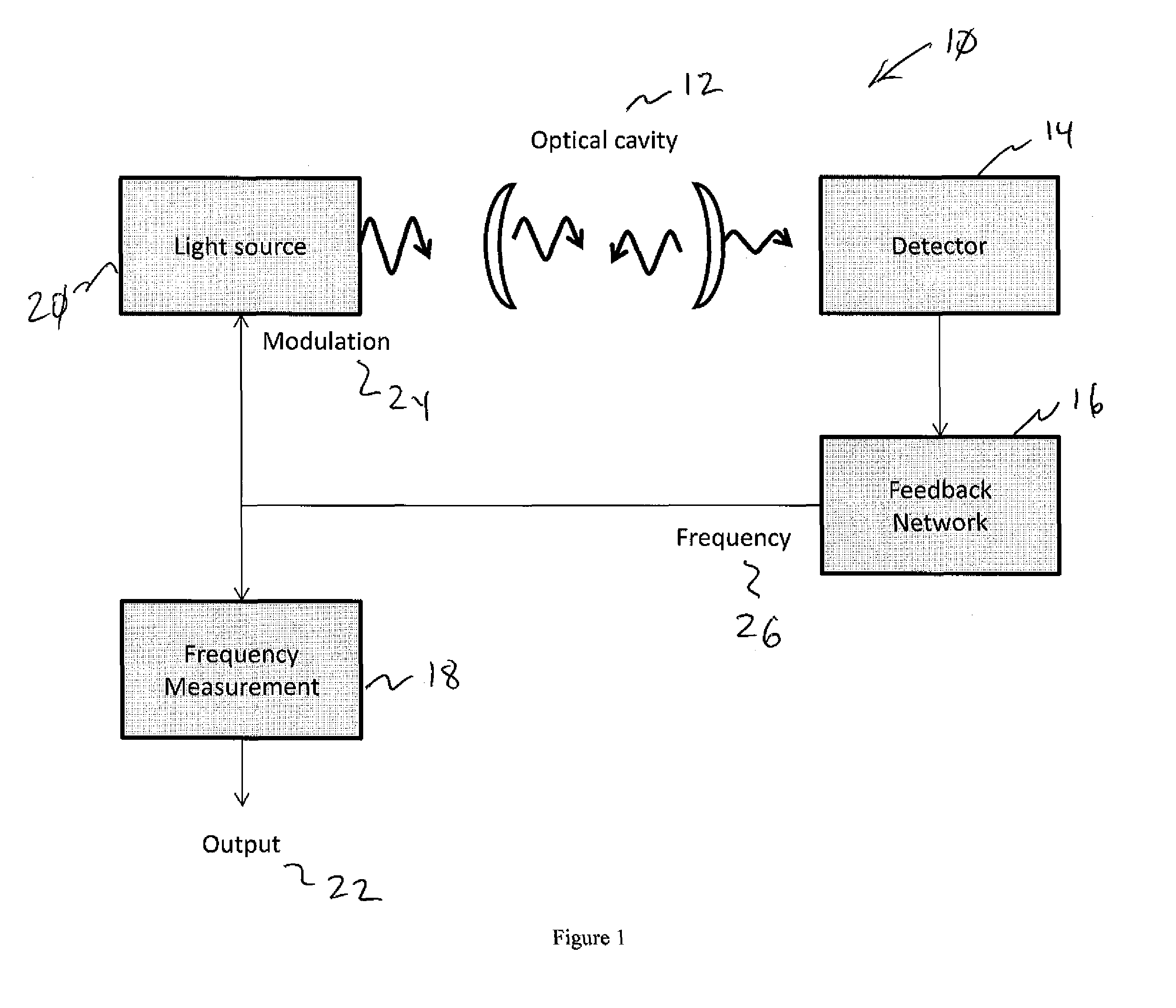
Frequency-feedback cavity enhanced spectrometer
ActiveUS9110006B1Reduce the amplitudePhase shiftRadiation pyrometryAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyOptical cavitySignal on
A spectrometer comprising an optical cavity, a light source capable of producing light at one or more wavelengths transmitted by the cavity and with the light directed at the cavity, a detector and optics positioned to collect light transmitted by the cavity, feedback electronics causing oscillation of amplitude of the optical signal on the detector at a frequency that depends on cavity losses, and a sensor measuring the oscillation frequency to determine the cavity losses.
Owner:SOUTHWEST SCI
Self Raman yellow light laser of composite cavity structure
ActiveCN103996968AIncrease output powerShorten the lengthOptical resonator shape and constructionFiberBeam splitter
The invention discloses a self Raman yellow light laser of a composite cavity structure. A laser diode pumping source emits pump light in an absorption belt of a gain medium, the pump light is focused inside the gain medium through a transmitting energy fiber and a coupling lens set, the gain medium absorbs the pump light to form population inversion, and base frequency laser generation is formed under the feedback action of a laser resonant cavity composed of a resonant cavity shared reflector and a laser total reflector; when base frequency laser passes through the gain medium, Raman gains are generated, and after the Raman gains are greater than the cavity loss of a Raman resonant cavity composed of the resonant cavity shared reflector, a beam splitter and a yellow light output mirror, stable Stokes light generation is formed in the Raman resonant cavity; the frequency of Stokes light is doubled in a frequency doubling crystal, and the generated yellow light secondary harmonic wave is output by the yellow light output mirror. The composite cavity structure is adopted, the length of a base frequency laser resonant cavity is largely decreased, and therefore the stable area of the resonant cavity is effectively enlarged, and the effect of improving the output power of the self Raman yellow light laser is achieved by applying higher pumping power.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Laser gyroscope resonator loss measuring device and method
InactiveCN106342174BSimple designReasonable configurationSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsTurn-sensitive devicesMeasurement costMeasurement device
The present invention first provides a device and method capable of accurately measuring the loss of the laser gyroscope optical resonant cavity in real time. The main components of the basic equipment are sequentially installed with a laser light source assembly, an acousto-optic modulator, and an optical path adjustment assembly according to the direction of light propagation. etc. After the optical path passes through the half-mirror installed in the optical path adjustment component, the laser gyro resonator loss measurement and the real-time imaging of the diaphragm and light spot in the resonant cavity are respectively completed through the photoelectric detection component and the CCD component. The present invention also solves the problem of low accuracy of measuring the loss of the unknown laser gyro resonator by a single method. When the loss of the laser gyro resonator is high, the resonance path is selected for measurement, and when the loss is low, the time attenuation path is selected for measurement by switching the switch. After the device is completed, the relative position of the diaphragm and the laser spot in the resonant cavity can also be measured in real time. High measurement accuracy and low measurement cost. The signal-to-noise ratio of the measuring device is high, the device is easy to debug, compact in structure and small in size.
Owner:XIAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIV
Low-threshold-value femtosecond pulse fiber laser
InactiveCN103401134AReduced diffraction lossImprove stabilityLaser detailsMode-lockingFaraday rotator
The invention relates to a low-threshold-value femtosecond pulse fiber laser. The low-threshold-value femtosecond pulse fiber laser consists of an optical-fiber coupling semiconductor laser, a wavelength division multiplexer, a ytterbium-doped single-mode gain fiber, two optical-fiber collimators, two quarter slides, two half slides, a polarization beam splitter, a faraday rotator, two reflection gratings, a reflection mirror and an optical isolator. The femtosecond laser adopts a semi-space semi-fiber annular cavity structure, the combined action of the faraday rotator and the half slides is adopted, and a group of grating pairs is adopted to carry out intra-cavity chromatic dispersion management on the laser, so that the polarization direction of the laser which passes through the faraday rotator twice is enabled to rotate for 90DEG and to be reflected from a vertical reflection port of the polarization beam splitter, a light path can be prevented from being lowered, and the introduction of an additional reflection mirror can be avoided; The polarization direction of the incident light which radiates on the first reflection grating is adjusted through the half slides, so that the highest diffraction efficiency can be achieved, the intra-cavity loss of the laser can be reduced, and an effect for reducing a mode locking threshold value can be realized.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Mode tailored spherical laser
ActiveUS20130322475A1Increasing both proportionallyConstant cavity lengthExcitation process/apparatusOptical resonator shape and constructionWhispering galleryEllipse
A spherical laser includes a transparent or semi-transparent outer spherical vessel having an internal cavity, an amplifying medium in the cavity, and means to excite the amplifying medium. The sphere is provided with a partially reflective coating to act as a spherical optical resonator. The spherical resonator includes a plurality of optically different regions containing alternative optical media from the cavity medium differing in bulk optical parameters utilized for mode tailoring. The optically different regions work collectively to exclude the whispering gallery modes from those supported by the spherical cavity. Excitation of the amplifying medium produces an optical gain. When the gain exceeds cavity losses and threshold conditions are met, lasing is supported. This creates a three-dimensional, spherically radiating emission, emulating a point source. The sphere is enclosed within a mirrored ellipse to image the output to a point, or within a mirrored parabola to columinate the emission.
Owner:LACOMB RONALD
Polarization continuously adjustable cylindrical vector optical solid-state laser
ActiveCN107681426ALower the thresholdImprove slope efficiencyLaser detailsHalf waveOptical polarization
The invention discloses a polarization continuously adjustable cylindrical vector optical solid-state laser. The laser comprises a laser diode, an optical fiber coupling unit, a film-coating cavity mirror, a gain medium, a polarized element, a vortex half wave plate and a pin hole; the film-coating cavity mirror comprises a film-coating front cavity mirror, a film-coating focusing lens and a film-coating back cavity mirror which form a resonant cavity; the polarization state orientation in different positions in the space is controlled by using a polarization beam splitter, a 1 / 2 wave plate and the vortex half wave plate in the cavity; and cylindrical vector beams in different polarization state distribution are output. By virtue of the laser, the intra-cavity loss is lower, the active mode is higher in flexibility, and the output cylindrical vector beams are higher in quality.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for expanding laser output linewidth
A method for expanding the output linewidth of the laser, used in the technical field of the laser display, includes the following steps: introducing a loss element changing along the wavelength of the laser gain area in the laser cavity, overlapping and compounding the loss curve and the laser medium gain curve in the laser cavity, to cause the laser gain central area with larger cavity loss in the laser cavity, thereby causing the laser wavelength with lower gain in the laser gain bandwidth to obtain the chance of the oscillation starting, consequently widening the output bandwidth of the whole laser. The method of the invention is not only used in the semiconductor pumping intracavity frequency double laser and the fundamental wave output laser in the embodiment, but also is used in the RGB laser of the laser display, which effectively restrains the speckle effect. In addition, the laser has small volume and low cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI BRANCH FUZHOU GAOYI COMM CO LTD
Self-cooling laser optical tweezers device and method based on two-dimensional light trap
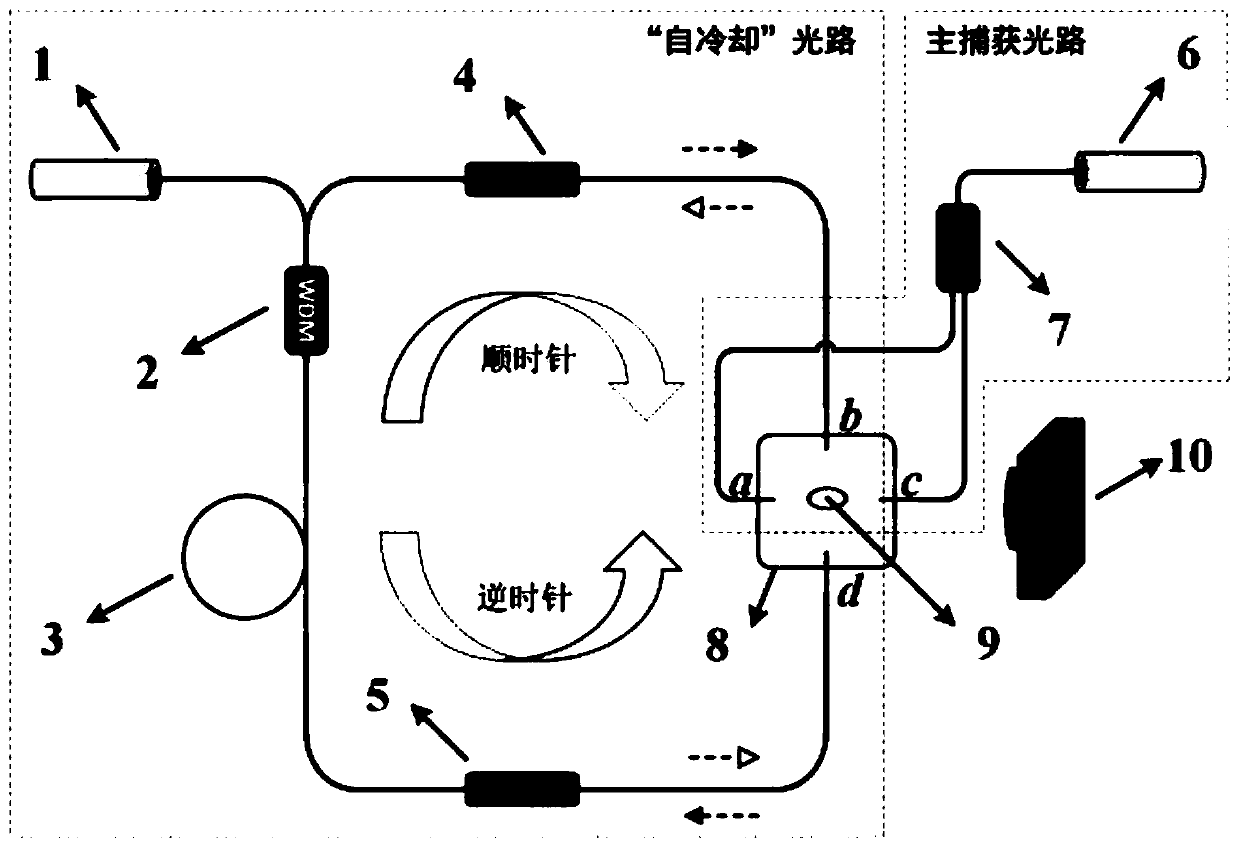
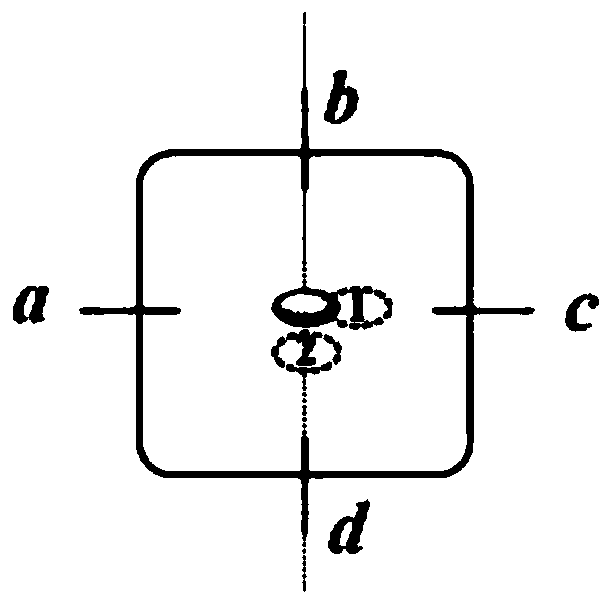
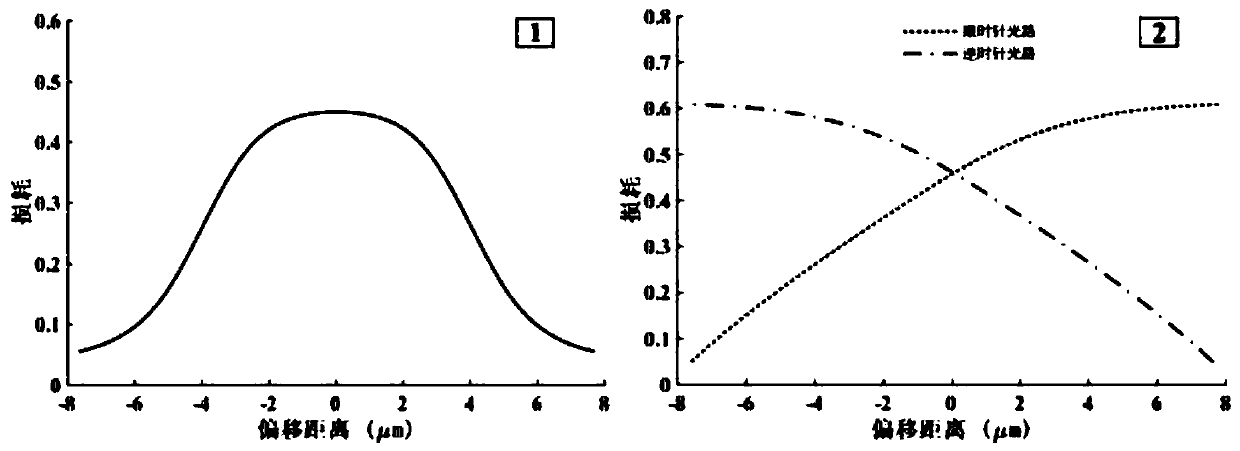
ActiveCN109920575ASimple structureGood repeatabilityRadiation/particle handlingOptoelectronicsSelf feedback
The invention relates to a self-cooling laser optical tweezers device and method based on a two-dimensional light trap. The light tweezers is combined to a light cavity, and the high-speed self-cooling for capturing ellipsoid particles is realized by utilizing the ellipsoid particles location and the characteristics of the cavity loss; the whole cooling process does not involve to the external feedback control, and is realized through the internal self-feedback of a ring cavity. The device has the advantages of being simple in structure, good in repeatability and strong in practicability. Furthermore, the self-cooling laser optical tweezers device is not limited to the light trap structure and the light path structure, and the applicable range is extremely wide.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method for measuring diffraction loss of laser gyro
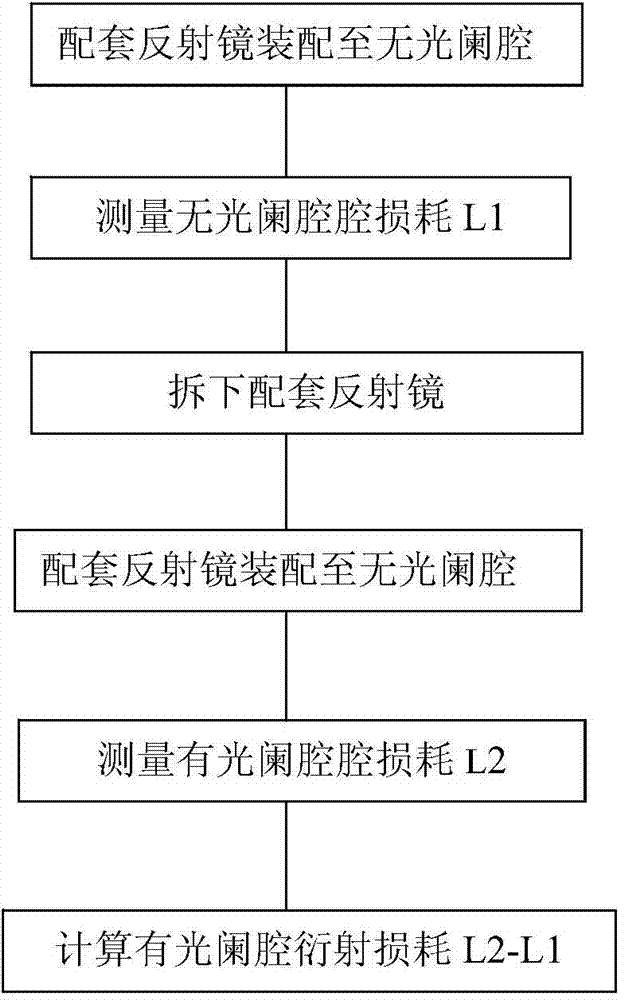
InactiveCN104713573ASolve the problem of inaccurate measurementShort operating cycleMeasurement devicesResonant cavityClassical mechanics
The invention belongs to a method for measuring the loss parameter of a laser gyro, and relates to a method for measuring the diffraction loss of the laser gyro. The measurement method comprises the following steps: assembling a matched reflector to an unapertured cavity, starting a frequency sweep laser, adjusting a light path matching part to make laser enter a resonant cavity composed of an unapertured diaphragm and the reflector, and measuring the initial cavity loss L1 of the unapertured diaphragm resonant cavity through a loss measurement system; disassembling the matched reflector from the unapertured resonant cavity [5], assembling the matched reflector to an apertured cavity, adjusting the light path matching part to make the laser enter a resonant cavity composed of the apertured cavity and the reflector, and measuring the cavity loss L2 of the apertured diaphragm resonant cavity through the loss measurement system [4]; and calculating a difference between the cavity loss L2 and the cavity loss L1 to obtain the diffraction loss of the apertured diaphragm resonant cavity. The method has the advantages of strong operationality, small error and high measurement precision, solves a problem that the measuring diffraction loss of the laser gyro cannot be accurately measured in the prior art, and has good application values.
Owner:FLIGHT AUTOMATIC CONTROL RES INST
Fuel cell system
InactiveUS20070087252A1Increase powerImprove stabilityLaser using scattering effectsReactant parameters controlFuel cellsResonance
The present invention discloses a laser light source for implementing pulsed oscillation of laser light, which has a laser cavity in which a laser medium for generating emitted light with supply of excitation energy is placed on a resonance path; an excitation device for continuously supplying excitation energy to the laser medium; a monitor part for monitoring a power of light extracted at a middle point of the path of the cavity from the laser medium in accordance with the supply of the excitation energy by the excitation device; a Q-switch for modulating a cavity loss of the laser cavity; and a control part for performing such control as to stabilize a peak power or an energy of laser light pulses outputted in a state in which the cavity loss of the laser cavity is set at a second predetermined loss for oscillation of high-power pulses, based on the power of the emitted light monitored by the monitor part in a state in which the cavity loss of the laser cavity is set at a first predetermined loss for non-oscillation of high-power pulses.
Owner:MEGAOPTO
Phase-insensitive recovery of clock pulses of wavelength division multiplexed optical signals
InactiveUS7027468B2Large dispersionEffective gainLaser using scattering effectsSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansRaman amplifiersMode-locking
An optically-pumped mode-locked fiber ring laser for optical clock recovery of multiple wavelength division multiplexed optical signals actively mode-locks a plurality of outputs of the laser as a plurality of recovered clocks for a plurality of the multiple wavelength division multiplexed optical signals. The laser cavity has a cavity length corresponding to an integer multiple of bit periods of at least one of the multiplexed optical signals for receiving a pre-amplified version of the plurality of wavelength division multiplexed optical signals to provide gain modulation through a phase-insensitive parametric amplification and recirculating a proportion of the output from the laser cavity back through the laser cavity for spatially mode-locking the output of the laser cavity as a recovered clock whereby the recovered optical clock each having a periodic train of optical pulses with a repetition rate corresponding to the clock rate of the corresponding multiplexed optical signal is generated by mode-locking of the optically-pumped laser produced by a spatial modulation of the phase-insensitive parametric gain produced by the pulsed nature of the wavelength division multiplexed optical signals. A nonlinear gain medium disposed in the cavity has a sufficiently large dispersion at all of the wavelengths corresponding to the multiple wavelength multiplexed optical signals for minimizing four-wave mixing crosstalk among the multiple wavelength multiplexed optical signals, among the recovered clocks, and between the plurality of multiple wavelength multiplexed optical signals and the recovered clocks. The gain medium is pumped by the plurality of pre-amplified multiplexed optical signals to provide efficient gain modulation through the phase-insensitive parametric amplification at a plurality of narrow wavelength bands, each of the plurality of narrow wavelength bands immediately adjacent to a wavelength of a corresponding optical signal and each of the plurality of narrow wavelength bands including a corresponding recovered optical clock wavelength, and each of the corresponding optical signals copropagating in the laser cavity through the nonlinear gain medium with the recovered optical clocks. A parametric optical amplifier or a Raman amplifier having an inhomogenously broadened gain amplifies the plurality of recovered clocks for compensating a portion of the cavity loss at all wavelengths of the plurality of recovered clocks. A wavelength selector passes the light at the plurality of wavelengths of the recovered clocks for recirculation in the laser cavity and preventing the light from the multiple wavelength division multiplexed optical signals and a plurality of idler waves generated by four wave mixing between the multiple wavelength division multiplexed optical signals and recovered optical clocks from recirculating in the laser cavity.
Owner:CORNING INC
High-efficiency all-optical-fiber column vector light beam laser
PendingCN107872002AEfficient outputImprove portabilityActive medium shape and constructionFiberGrating
The invention discloses a high-efficiency all-optical-fiber column vector light beam laser. Less-mode and long-period fiber bragg grating can realize high-efficiency conversion from a fundamental modeto a first-order mode and has the characteristic of low insertion loss; and by introducing the less-mode and long-period fiber bragg grating into a laser cavity to be used as a mode conversion device, the mode conversion efficiency is improved and intra-cavity loss can be lowered, so that high-efficiency output of the column vector light beam can be realized. The laser comprises an amplifier module used for laser generation and amplification, a resonance cavity module used for realizing laser resonance, a polarization control module used for controlling the intra-cavity laser polarization state, and a mode conversion module, namely the less-mode and long-period fiber bragg grating, used for realizing high-efficiency mode conversion. The column vector light beam output by the laser has thecharacteristics of high efficiency, low threshold value, high purity, mode switchable property and the like, no space coupling structure, high stability, high portability and suitability of productization.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Silicon optical coupling assembly, silicon optical integrated module and integrated resonant fiber-optic gyroscope
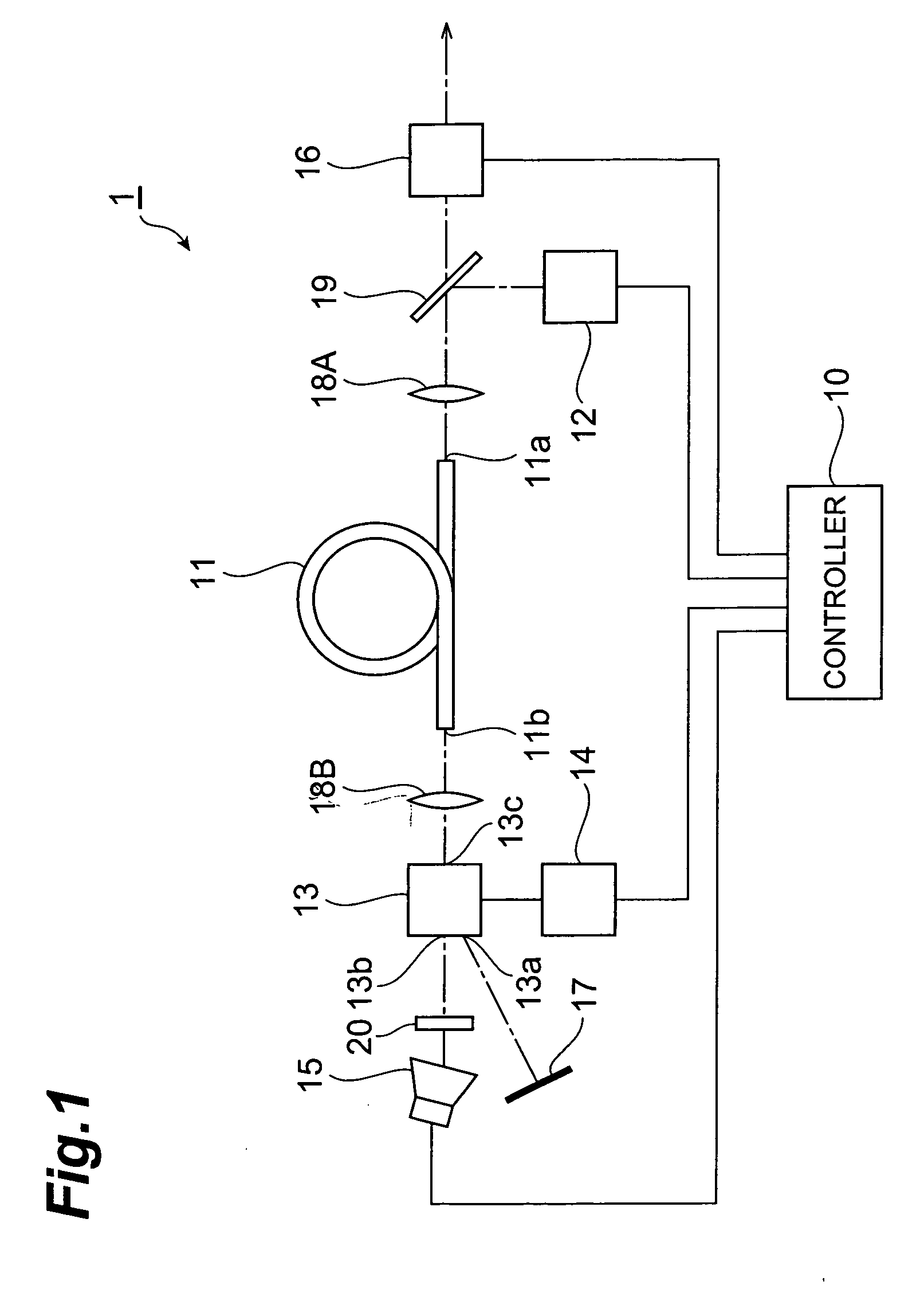
ActiveCN111947640AReduce the volume of the resonatorImprove signal-to-noise ratioSagnac effect gyrometersOptical integrationEngineering
The invention relates to a silicon optical coupling assembly, a silicon optical integrated module and an integrated resonant fiber-optic gyroscope. The integrated resonant fiber-optic gyroscope comprises a silicon light integration module and a photonic crystal fiber. An integrated light source in the silicon optical integration module emits light, the light is divided into two paths from the waveguide to the integrated Y waveguide, and then the light reaches the silicon optical coupling assembly after passing through the integrated optical modulator; a part of light enters the detector through the silicon optical coupling assembly, and the other light is coupled into the photonic crystal fiber and then enters the fiber from the other end through the silicon optical coupling assembly to form circulating light, and part of the circulating light is reflected into the detector. After the integrated optical modulator receives feedback of the detector, optical frequency shift is locked on aforward and reverse resonance peak, a frequency shift difference value is a gyro output signal, and a position error is compensated through the lens and the optical fiber control assembly so as to reduce cavity loss. The silicon optical coupling assembly has the characteristics of no melting point and integration, miniaturization of the gyroscope is facilitated, the signal-to-noise ratio of the gyroscope is high, and the gyroscope has high practical application value.
Owner:XIAN FLIGHT SELF CONTROL INST OF AVIC
Laguerre Gaussian optical parametric oscillator with tunable broadband topological charges
ActiveCN111525379AHigh purityHigh wavelengthOptical resonator shape and constructionParticle physicsQuantum electrodynamics
The invention discloses a Laguerre Gaussian optical parametric oscillator with tunable broadband topological charges. The oscillator comprises a nanosecond pulse laser, a beam shaping device, a coating cavity mirror, a periodically poled lithium niobate crystal, a temperature control device, a polarization element and a vector vortex wave plate, wherein the coating cavity mirror comprises a coating front cavity mirror and a coating rear cavity mirror which form a resonant cavity. The oscillator is advantaged in that relative positions of a vector vortex wave plate and the coating front cavitymirror meet the condition that a ratio of a concave mirror to a concave mirror is 1: 1, a self-reproduction cavity mode with smooth transition from a solid light beam to the hollow Laguerre Gaussian light beam is formed according to the imaging relation of the solid light beam and the hollow Laguerre Gaussian light beam, coupling efficiency of the cavity mode and the pump light is improved, intra-cavity loss is reduced, and finally high-efficiency, high-purity and wavelength and topological charge tunable Laguerre Gaussian light beam output is achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for measuring intra-cavity loss of LD pumping solid state laser device and equipment using the method
InactiveCN101132100AEnable interference-free measurementsAccurate measurementLaser detailsMeasurement devicesSolid-state laser deviceRate equation
Method for measuring the come-and-go loss in the cavity of LD pumping solid laser. The procedures are: first determining the relationship between the laser power and the pumping power measured from the experiment; which experiment result is then substituted in the rate equation to proceed numerical equating to determine the loss in the cavity; in the rate equation, considered are the laser oscillation and other transition steps which affecting the running of a laser, and considering the pumping light and laser being all Gaussian distribution. This invention method is particularly suitable for measuring the come-and-go loss in low gain microchip solid laser cavity.
Bragg grating, preparation method thereof and distributed feedback laser
ActiveCN111769437APrevent injectionLow refractive indexOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionDistributed feedback laserGrating
The invention provides a Bragg grating, a preparation method thereof and a distributed feedback laser, and belongs to the technical field of semiconductor lasers. The Bragg grating is arranged in a distributed feedback laser. The Bragg grating comprises a lower grating waveguide layer, a middle grating waveguide layer and an upper grating waveguide layer which are sequentially formed and have different refractive indexes; the refractive index of the middle grating waveguide layer is lower than the refractive index of the lower grating waveguide layer and the refractive index of the upper grating waveguide layer; the doping types of the lower grating waveguide layer and the middle grating waveguide layer are the same; the doping type of the upper grating waveguide layer is opposite to the doping types of the adjacent layers, so that a reverse biased PN junction can be formed on the upper grating waveguide layer; a plurality of grooves are formed in the upper grating waveguide layer at intervals in the cavity length direction of the distributed feedback laser; and the grooves are filled with buried layers to flatten the upper grating waveguide layer. The coupling coefficient of the Bragg grating can be increased along with the increase of the current of the distributed feedback laser, so that the cavity loss of the distributed feedback laser is reduced, and the response bandwidthis expanded.
Owner:XIAMEN SANAN INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
Optical fiber pressure sensor based on micro ellipsoidal air cavity and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN107300437ASimple preparation processSame coefficient of thermal expansionForce measurement by measuring optical property variationFemto second laserErbium lasers
The present invention relates to an optical fiber pressure sensor based on a micro ellipsoidal air cavity and a manufacturing method of an optical fiber pressure sensor based on a micro ellipsoidal air cavity, belonging to the technical field of optical fiber pressure sensors. The optical fiber pressure sensor comprises a single-mode optical fiber and a pressure-sensitive film; the upper end of the single-mode optical fiber is fixedly connected with the lower end of the pressure-sensitive film; and the single-mode optical fiber and the pressure-sensitive film are connected with an air Fabry-Perot cavity. The materials of the optical fiber pressure sensor are silicon dioxide, so that the thermal expansion coefficients of the optical fiber pressure sensor are the same, thereby avoiding structural failure due to high temperature mismatch of different materials and achieving small temperature crosstalk and low cost. The manufacturing process of the sensor head only needs welding, cutting and grinding, and the process is simple; the confocal Fabry-Perot cavity in the device has the advantages of small interference cavity loss and high interference fringe contrast ratio and high demodulation precision compared with the Fabry-Perot cavity made by the etching process or the femtosecond laser in the prior art.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Automatic self-plugging rivet positioning mechanism
The invention discloses an automatic self-plugging rivet positioning mechanism which comprises a riveter. The riveter comprises a power pipe, the top of the power pipe is communicated with a positioning pipe, a rivet inlet pipe communicated with the positioning pipe is clamped on one side of the positioning pipe, a power device is fixedly mounted in the power pipe and penetrates the power pipe to be inserted into the positioning pipe, the top of the power device is fixedly connected with the bottom of a positioning device in the positioning pipe, the positioning device comprises a riveter pipe, and a moving positioning block is in slide connection with the bottom of the riveter pipe. By matching of the power pipe, the positioning pipe and the rivet inlet pipe, rivet feeding is realized, and problems of time consumption and labor consumption in manual operation are solved; by matching of the power device and the positioning device, rivet positioning is realized; by rivet positioning, the problem of short service life of the riveter due to cavity loss caused by rivets at inappropriate positions is reduced.
Owner:天津镕思铭科技股份有限公司
Three-dimensional self-cooling laser optical tweezers device and method based on lens combination
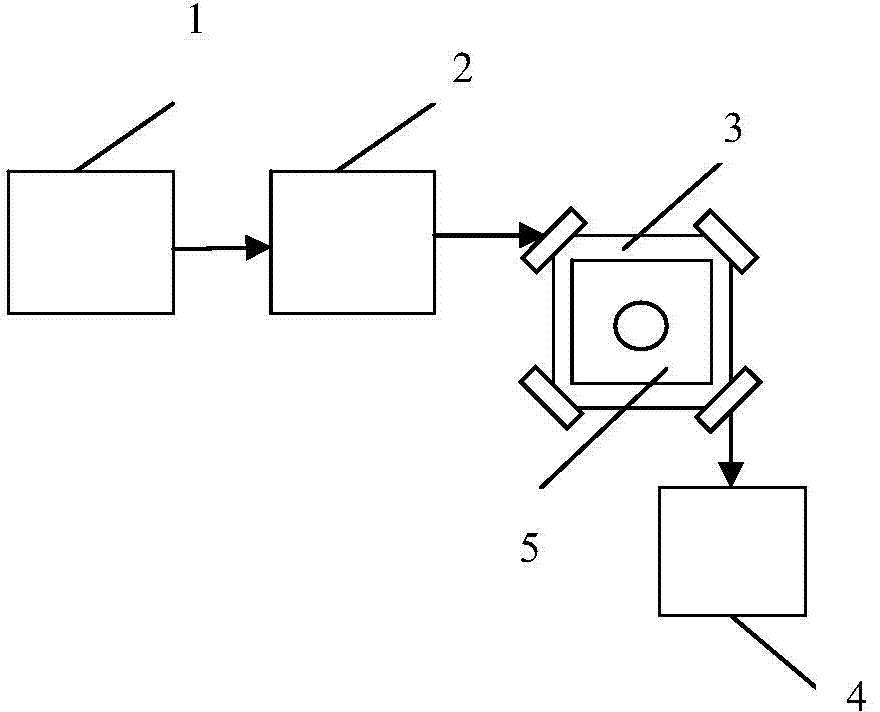
ActiveCN109802287ARealize self-coolingSpeed up coolingRadiation/particle handlingActive medium shape and constructionOptical cavityMicrosphere
The invention relates to a three-dimensional self-cooling laser optical tweezers device and method based on lens combination. The three-dimensional self-cooling laser optical tweezers device based onlens combination is adopted to achieve three-dimensional self-cooling. According to the invention, the method combines optical tweezers into an optical cavity, and achieves the three-dimensional high-speed self-cooling of captured particles by means of the three-dimensional positions of microspheres and the characteristic of cavity loss. The whole cooling process does not involve external feedbackcontrol and is achieved through self feedback in the annular cavity. The device is simple in structure, is good in repeatability, is high practicability and the like. In addition, the device is not limited to an optical trap structure and an optical path structure, and the application range is very wide.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Current biased dual DBR grating semiconductor laser
InactiveUS7339968B2Reduces added cavity lossLower current induced thermal interactionOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionGratingCoupling
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Fiber laser system capable of switching fundamental and second harmonic mode locking
ActiveCN106451048AFlexible adjustment spaceAvoid instabilityActive medium shape and constructionMode-lockingInstability
The invention provides a fiber laser system capable of switching fundamental and second harmonic mode locking. By the aid of all polarization-maintaining fiber mode locking technology based on a reflecting graphene saturable absorption mirror, an all polarization-maintaining fiber resonant cavity can be used for avoiding mode-locking laser instability caused by fiber birefraction change due to external force (such as pressure and bending) in environments, laser can be kept transmitted in the cavity along a polarization-maintaining fiber slow axis along a single linear polarization direction, mode-locking pulse self-starting is more easily realized, usage of elements such as a polarization controller can be decreased, and intra-cavity loss is reduced. The reflecting graphene saturable absorption mirror uses more than five layers of graphene as a saturable absorber, the modulation depth of the graphene is increased along with increase of the number of the layers, fundamental mode locking pulse is obtained at the pumping power ranging from 79mW to 102mW, and second mode locking pulse is obtained when the pumping power reaches 108mW.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV
Scalable spherical laser
ActiveUS7492805B2Increasing both radii proportionallyConstant lengthExcitation process/apparatusOptical resonator shape and constructionEllipseCavity loss
A spherical laser includes a transparent or semi-transparent outer spherical vessel having an internal cavity, an amplifying medium in the cavity, and means to excite the amplifying medium. The sphere is provided with a partially reflective coating to act as a spherical optical resonator. Excitation of the amplifying medium produces an optical gain. When the gain exceeds cavity losses and threshold conditions are met, lasing is supported. This creates a three-dimensional, spherically radiating emission, emulating a point source. The output is radially diverging, but is harnessed by enclosing the sphere within a mirrored ellipse to image the output to a point, or within a mirrored parabola to columinate the emission. A concentric, reflective inner sphere may be disposed in the cavity, with the amplifying medium lying between the two spheres. A voltage potential is applied between the spheres to excite the medium.
Owner:RONALD LACOMB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com