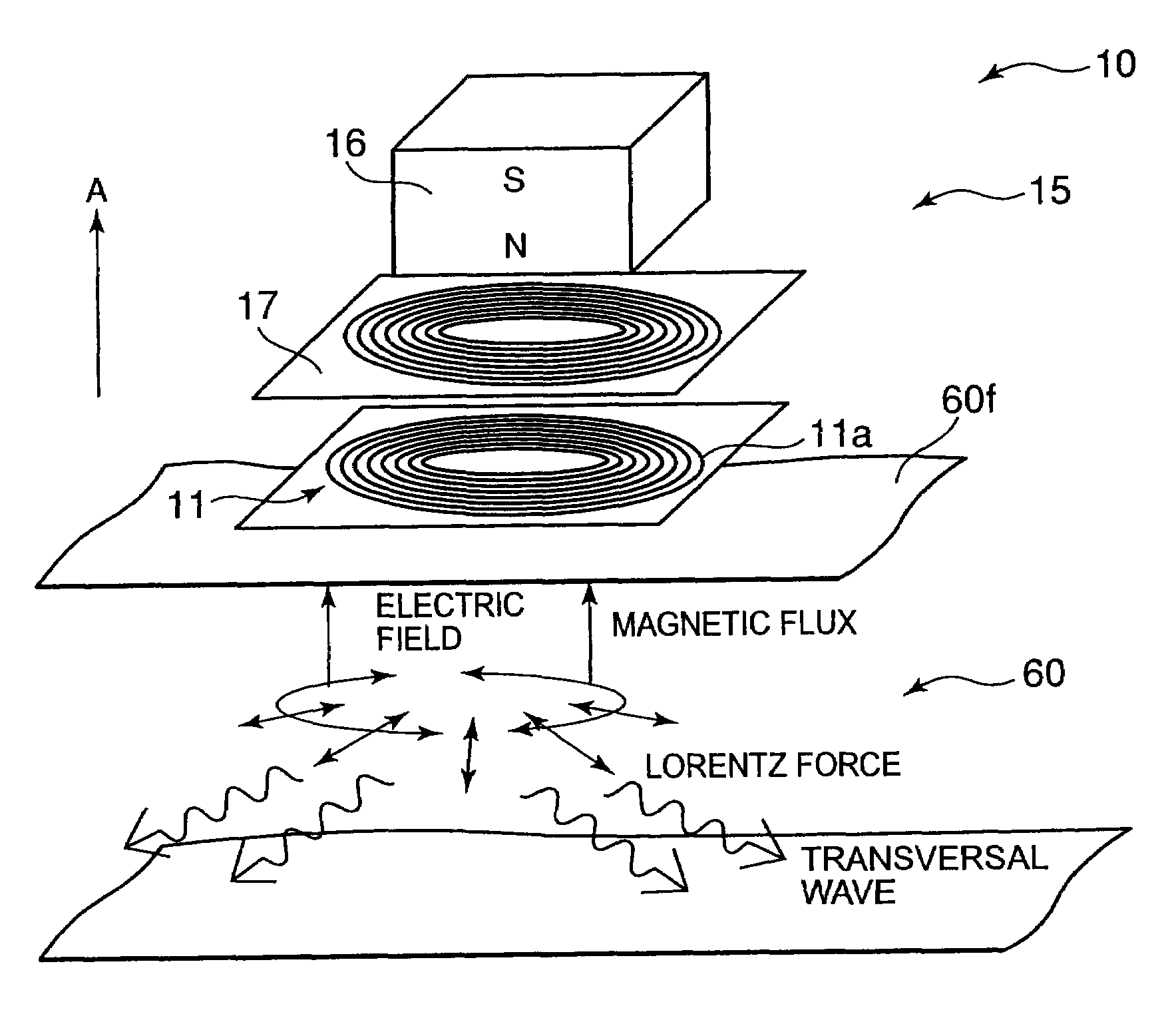
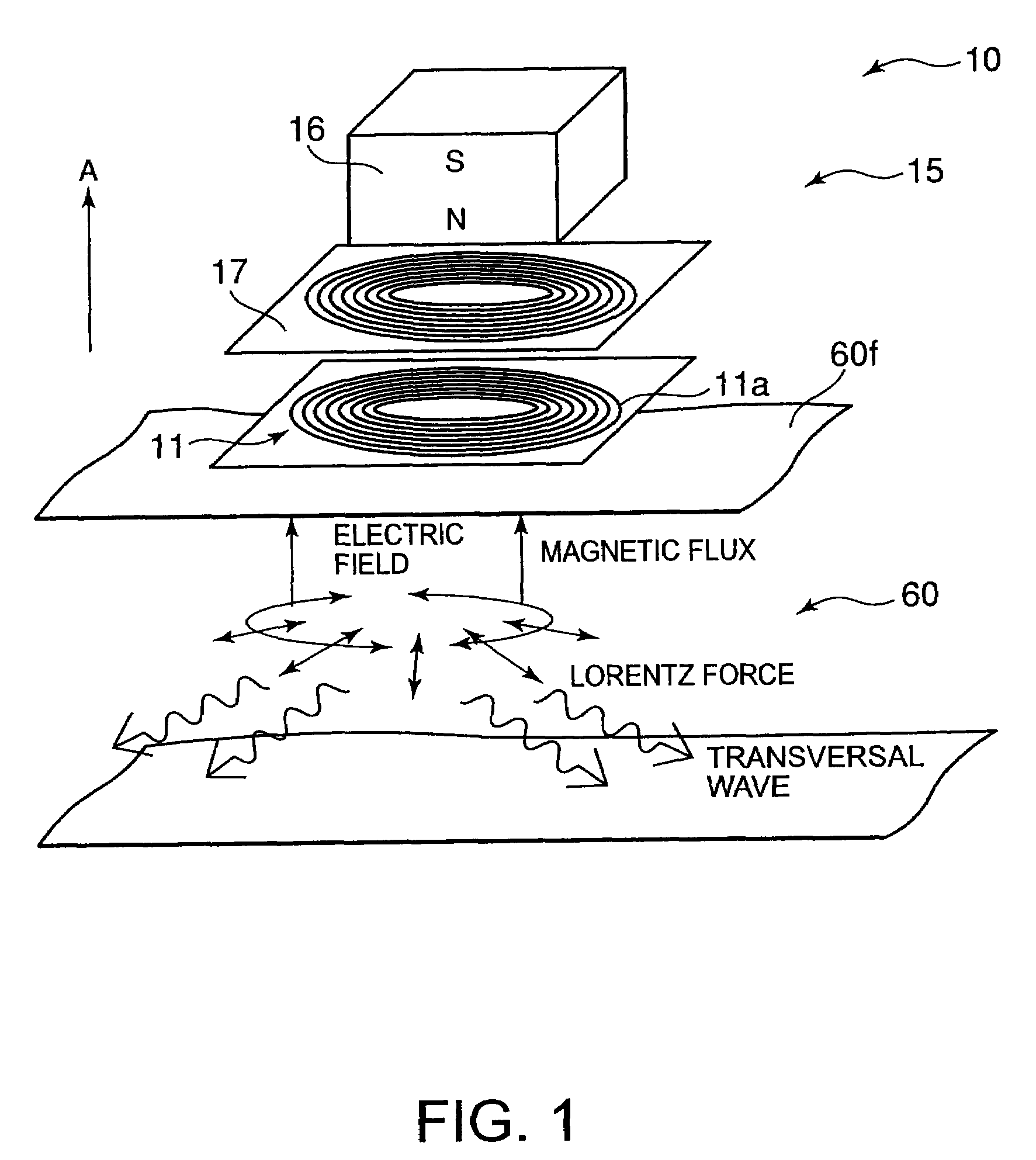
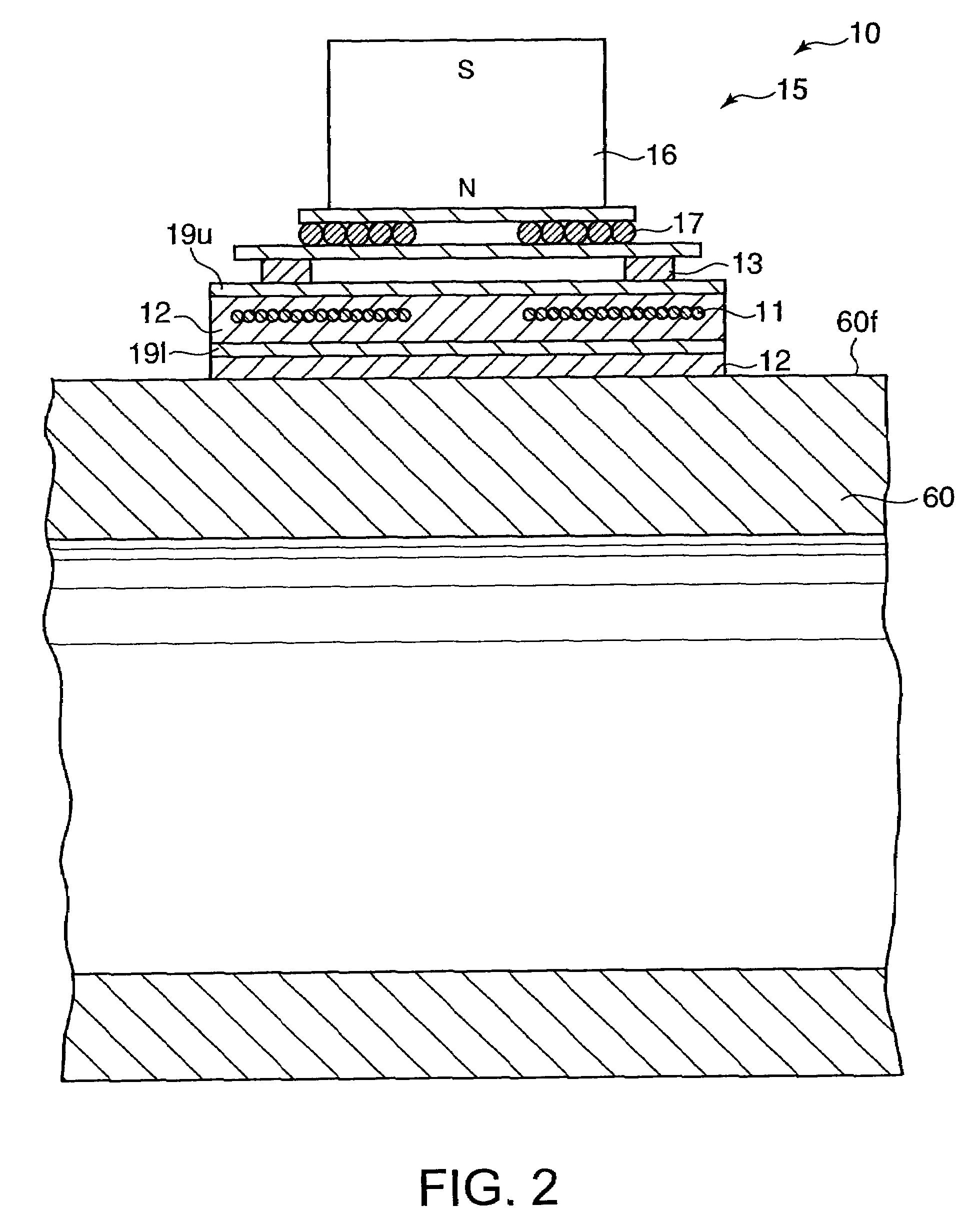
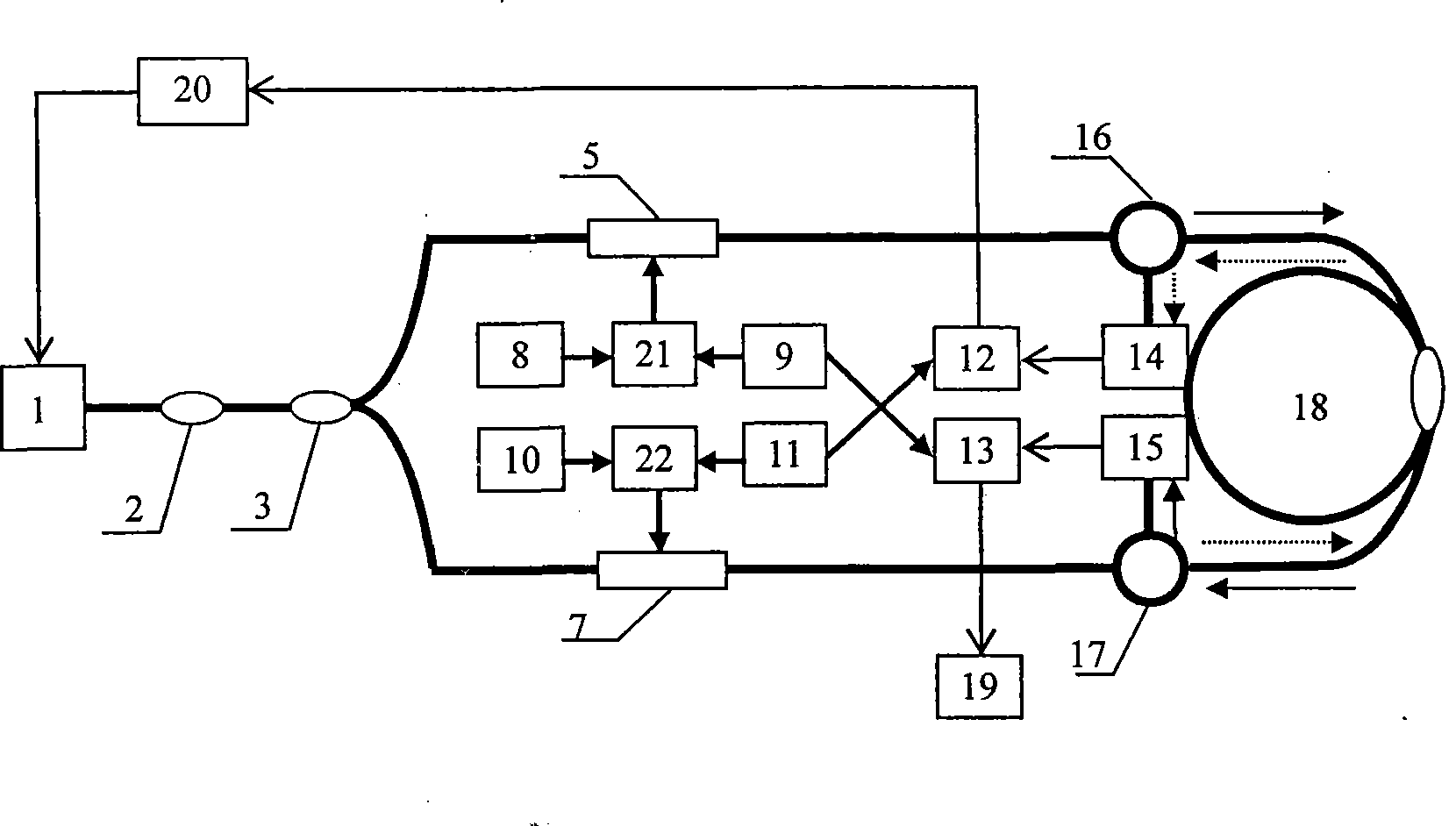
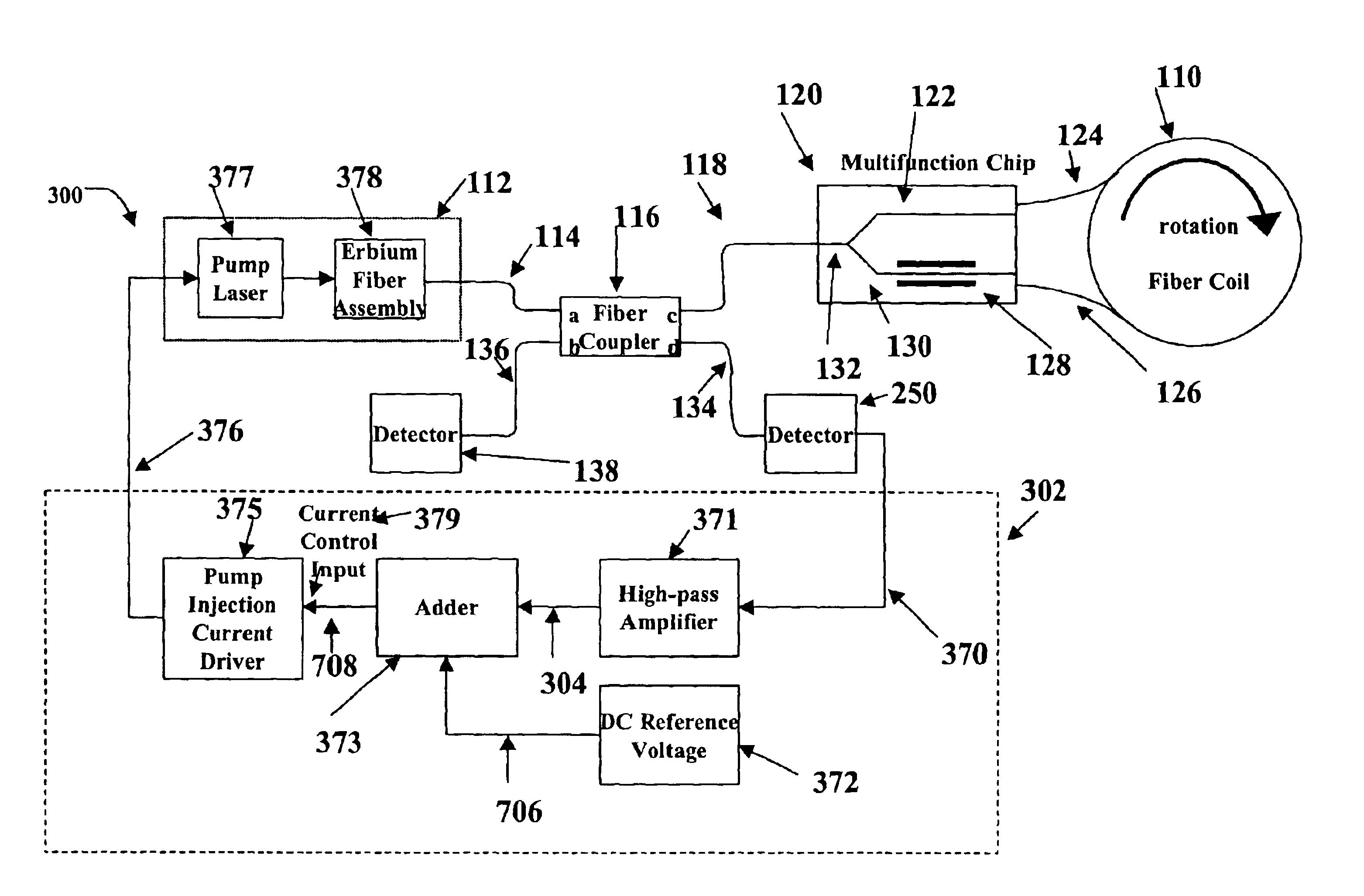
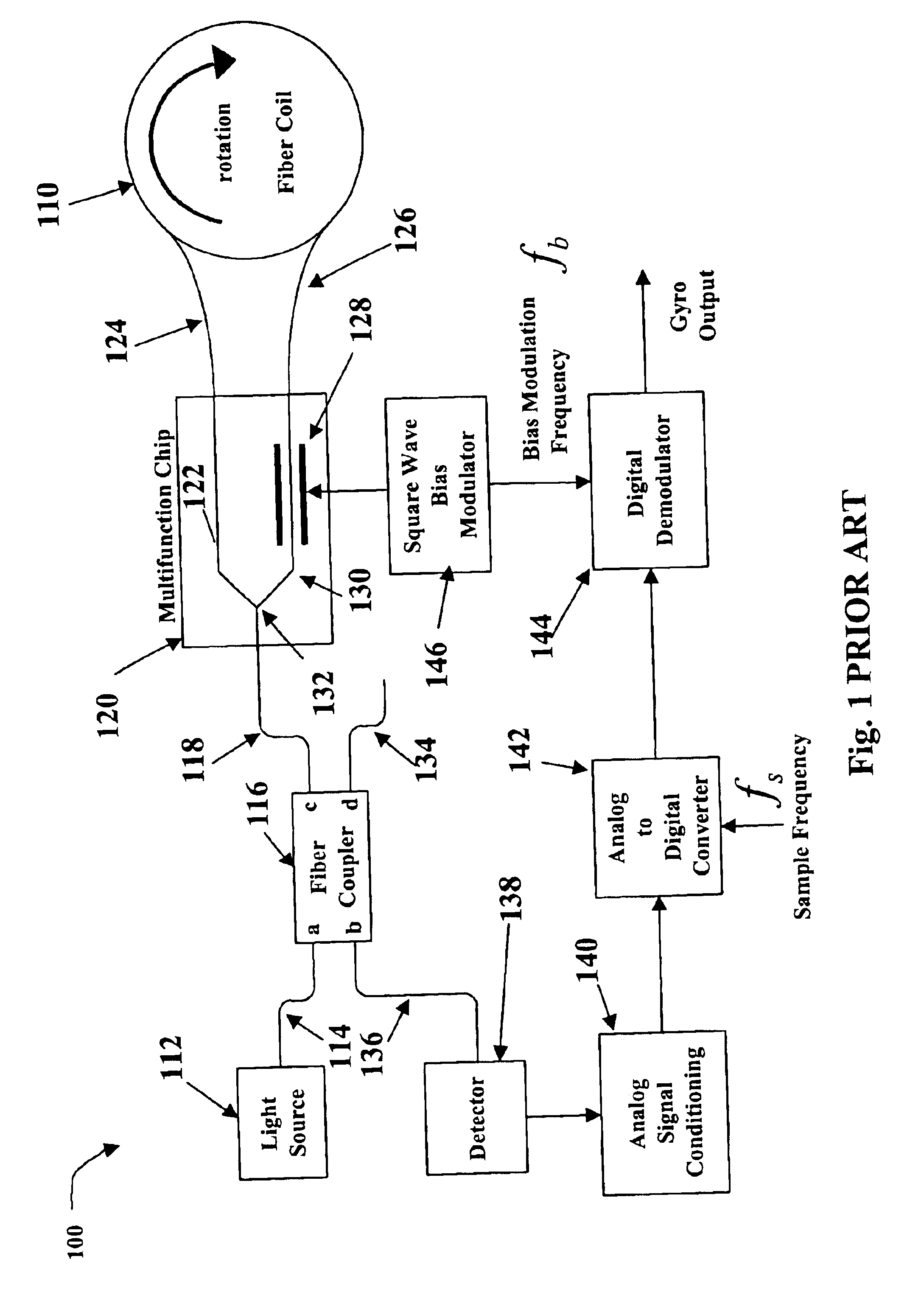
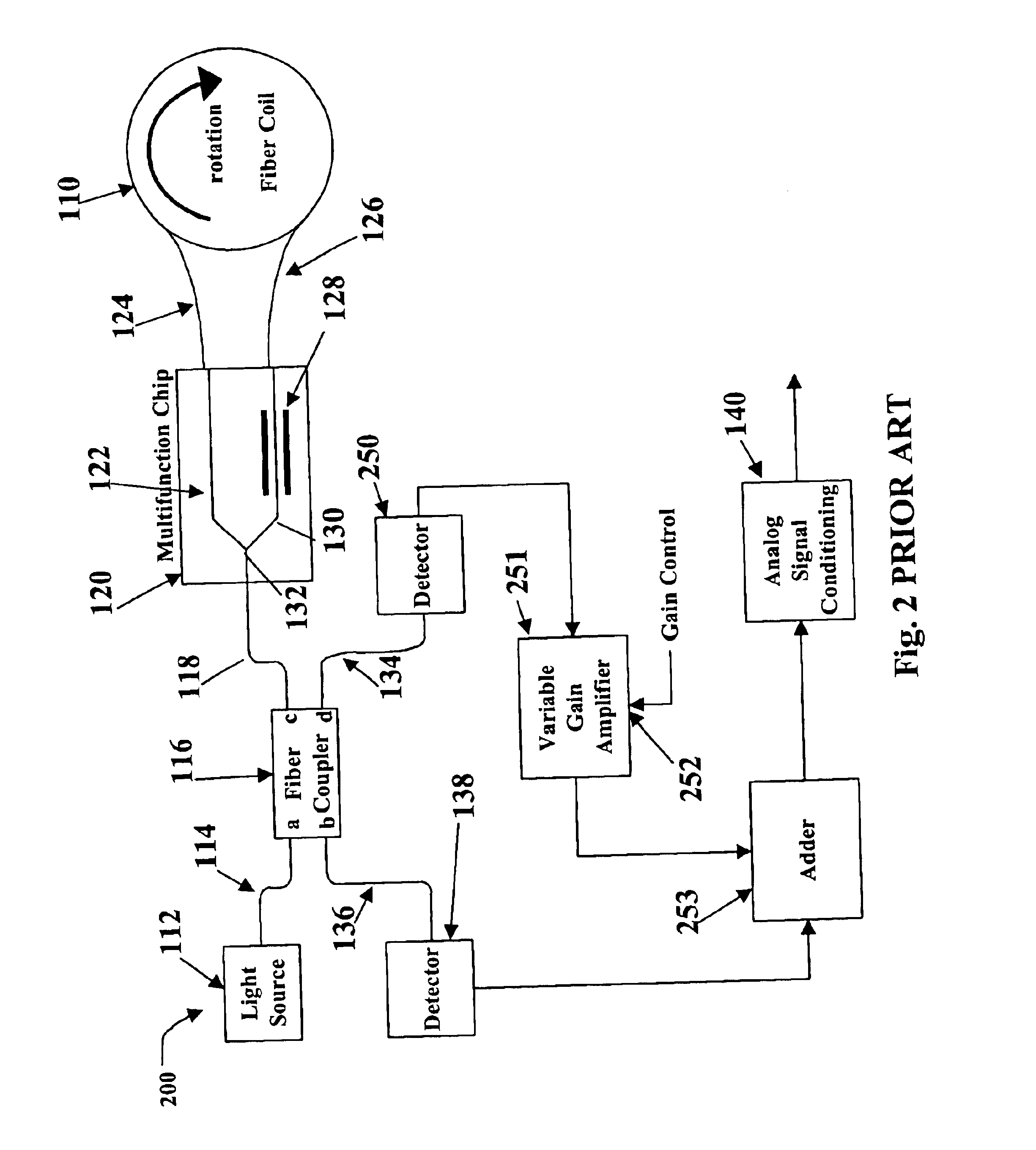
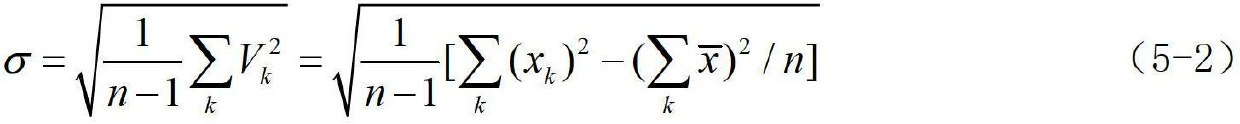Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2277results about "Sagnac effect gyrometers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
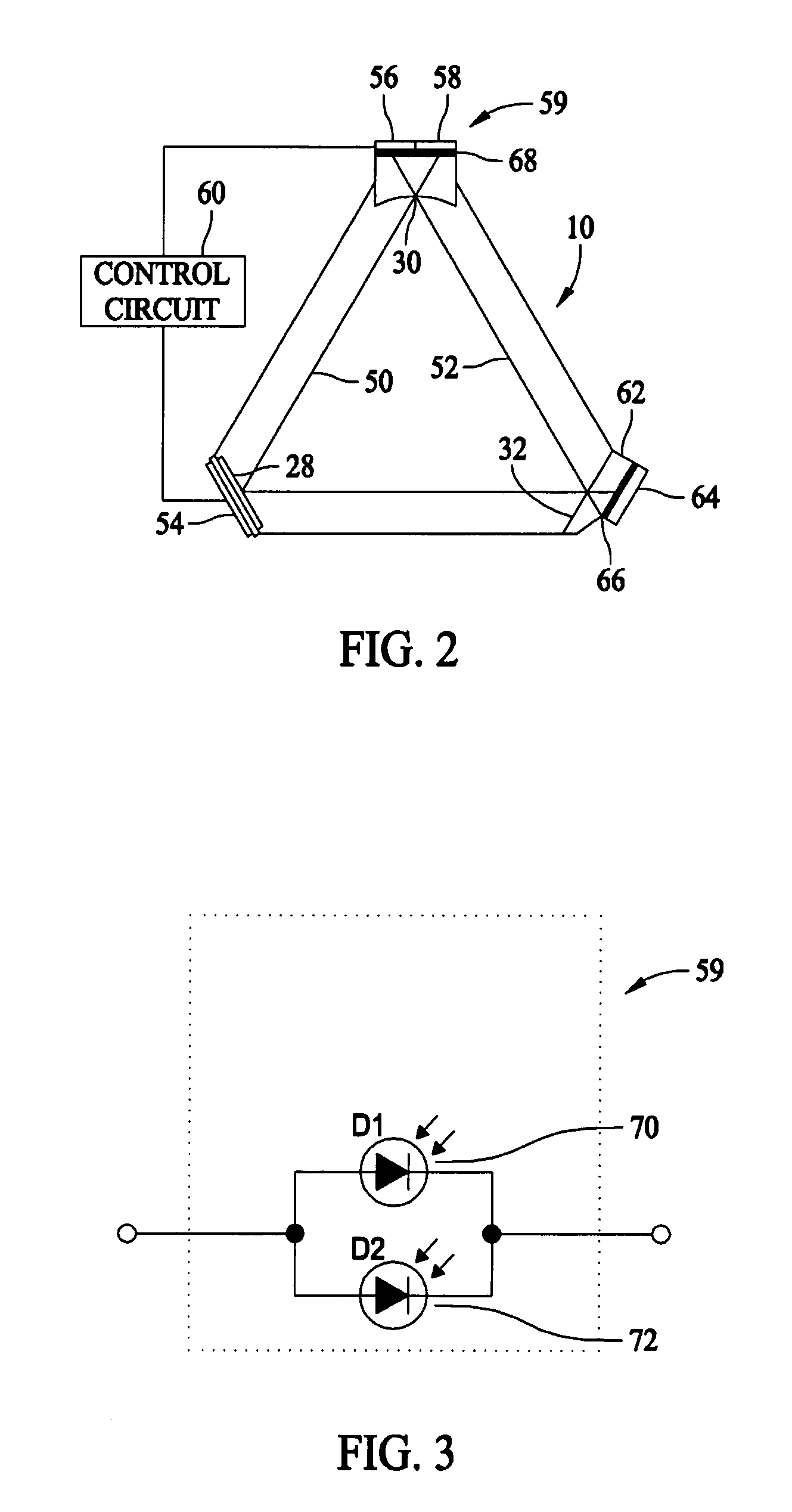
Systems and methods for implementing path length control for quantum cryptographic systems
ActiveUS7627126B1Reduce impactReduce QBERKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationPath lengthKey distribution
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP
Optical member for biological information measurement, biological information calculation apparatus, biological information calculation method, computer-executable program, and recording medium
ActiveUS7236814B2Eliminate the effects ofSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsSagnac effect gyrometersBiological bodyPrism cover
An optical member for biological information measurement has a prism, which has a light incident surface being injected with emitted light, a living body tissue measuring section which a living body tissue contacts, and a light emitting surface which emits the light reflected by the living body tissue measuring section which the living body tissue contacts, or the light which has passed the living body tissue through the living body tissue measuring section which the living body tissue has contacted. A prism cover is provided so as to expose the living body tissue measuring section and to surround all or a part of the outer circumferential portion of the prism.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
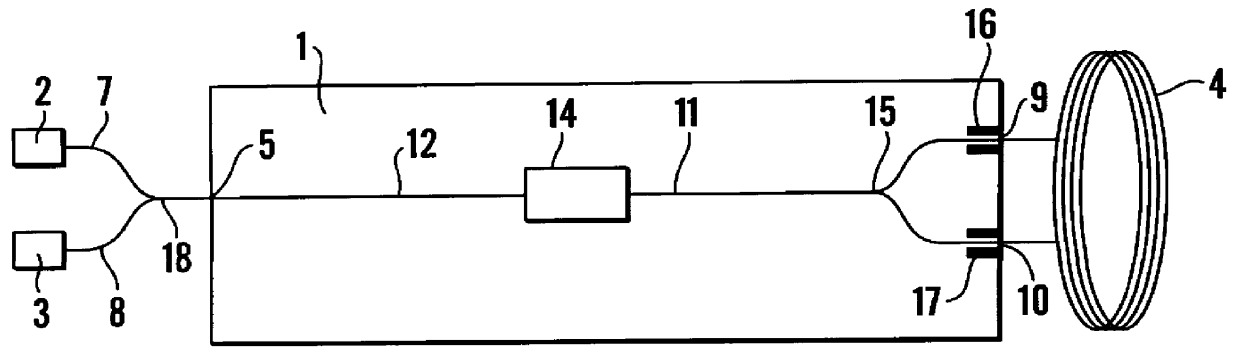
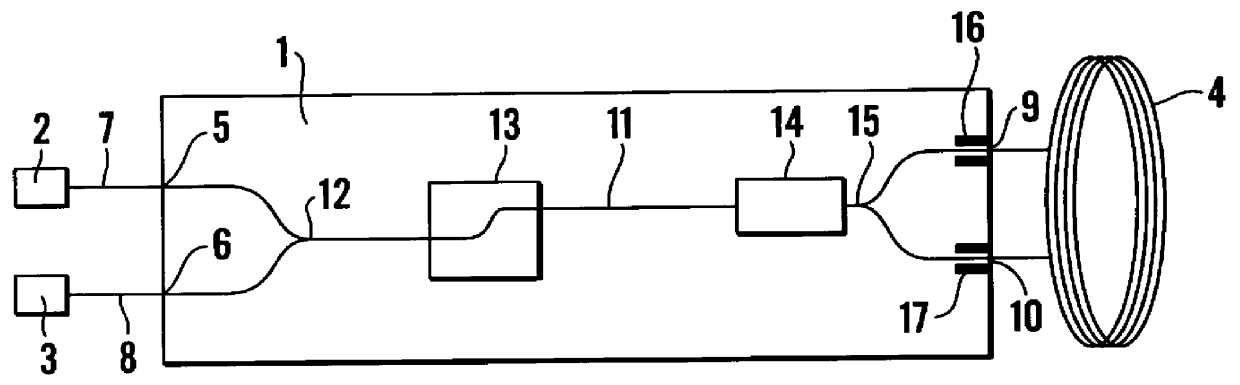
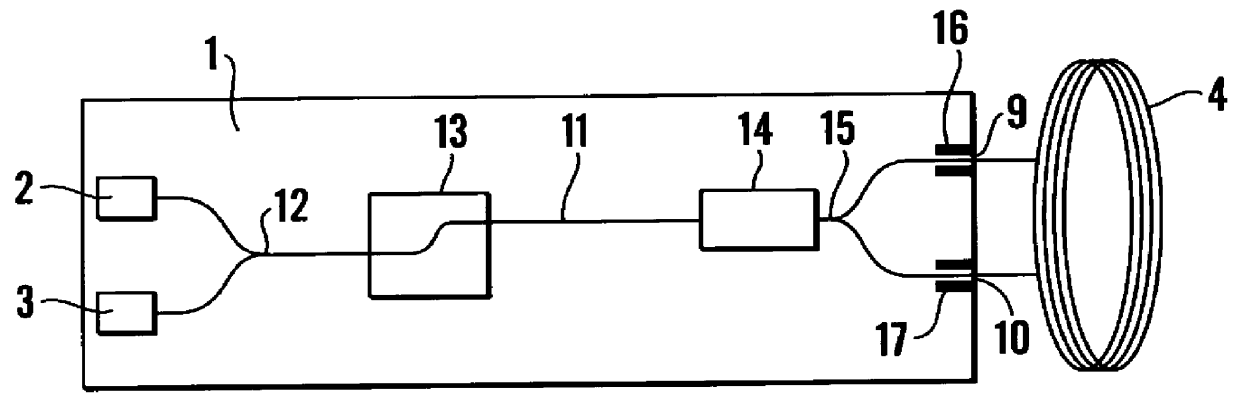
Bifilar optical fiber stowage for fiber-optic gyroscope
ActiveUS20100092126A1Speed measurement using gyroscopic effectsSagnac effect gyrometersFiberGyroscope
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
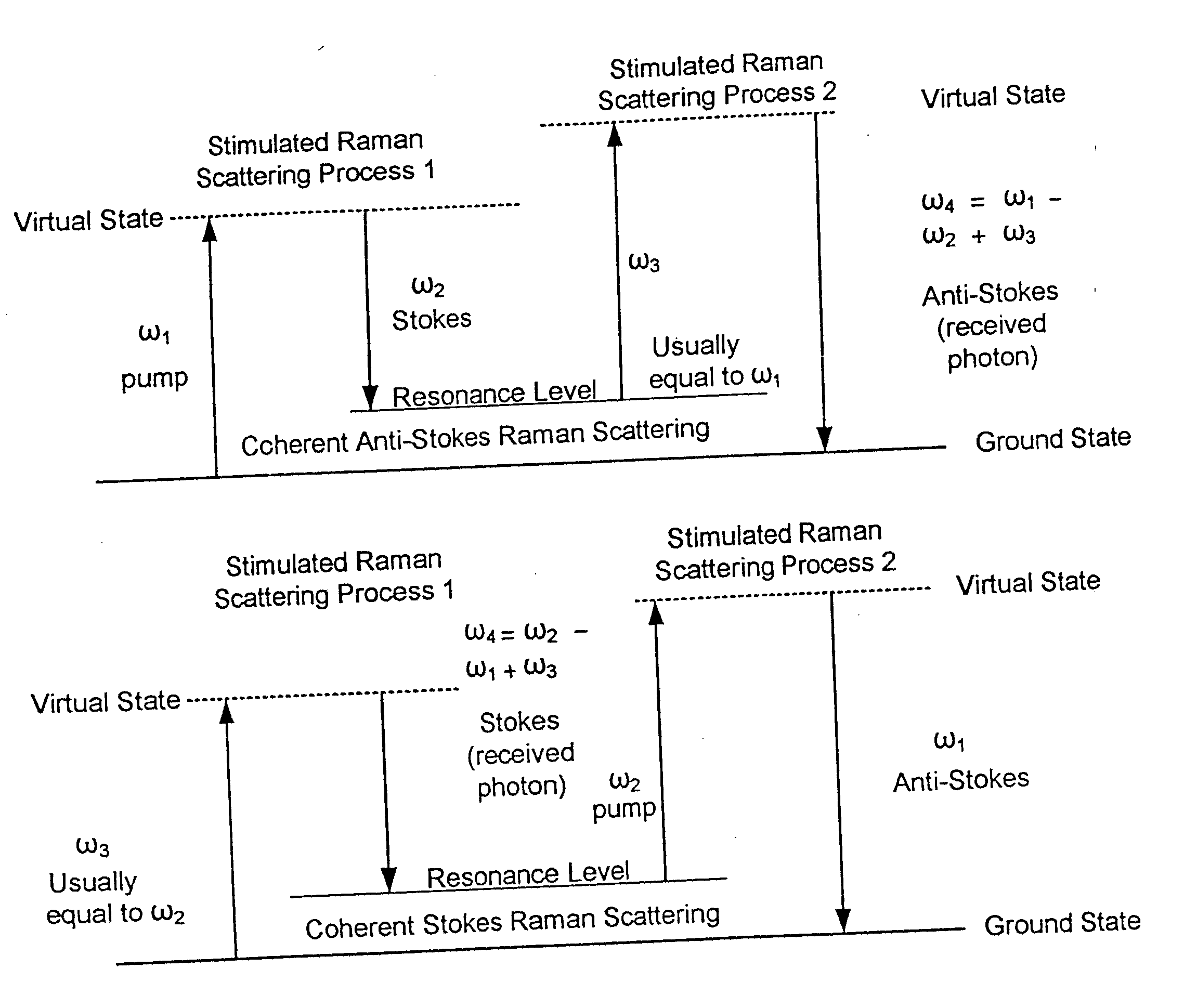
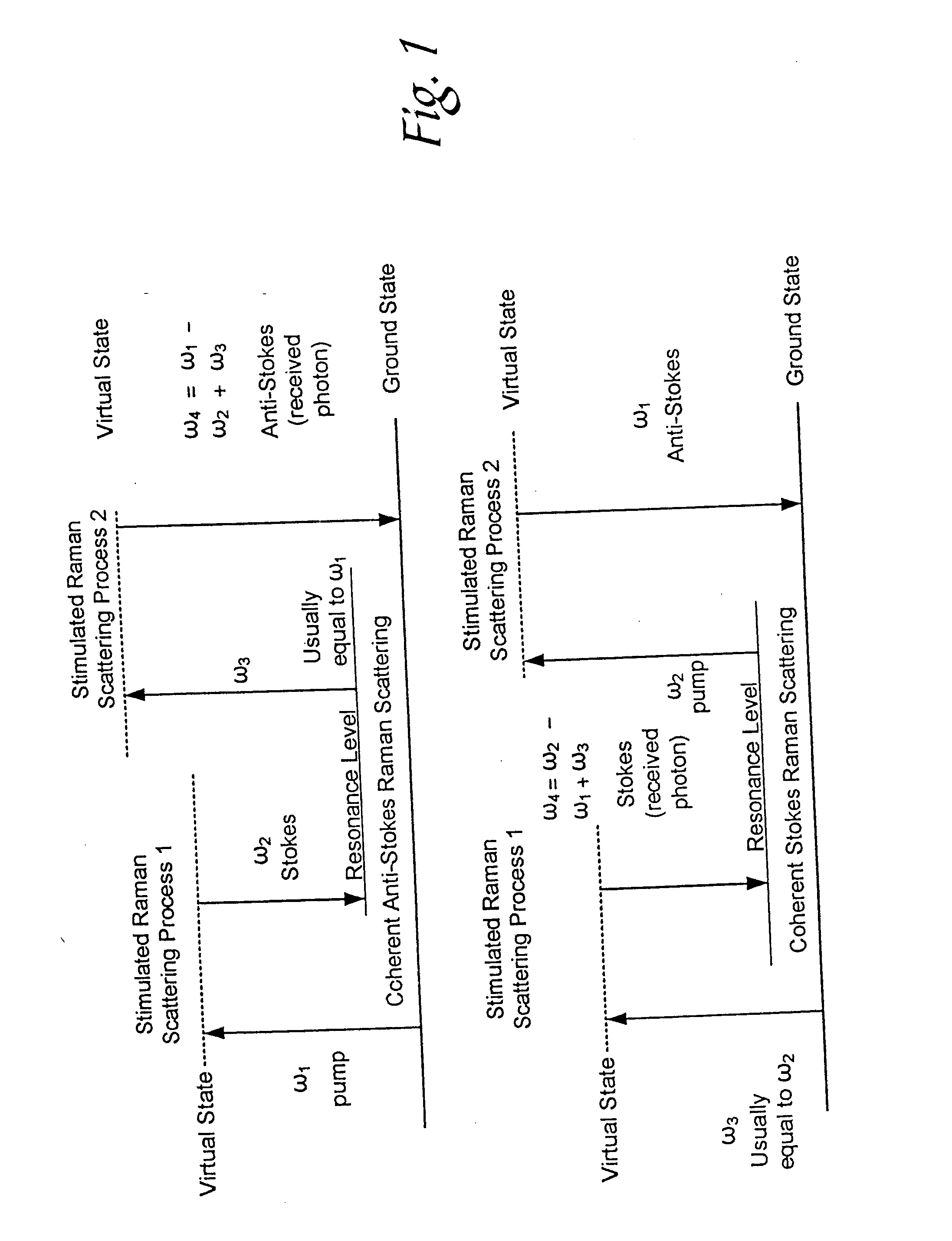
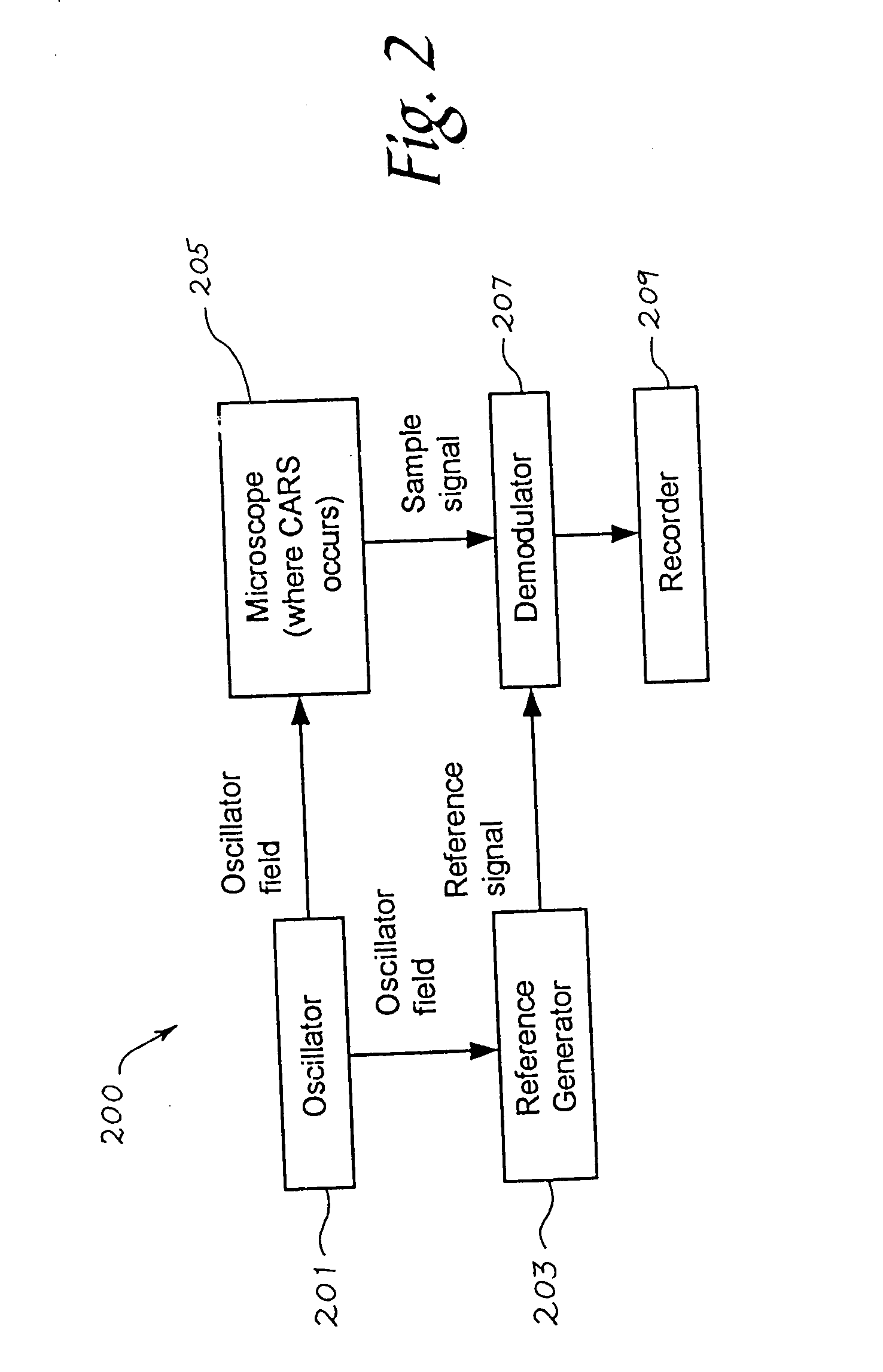
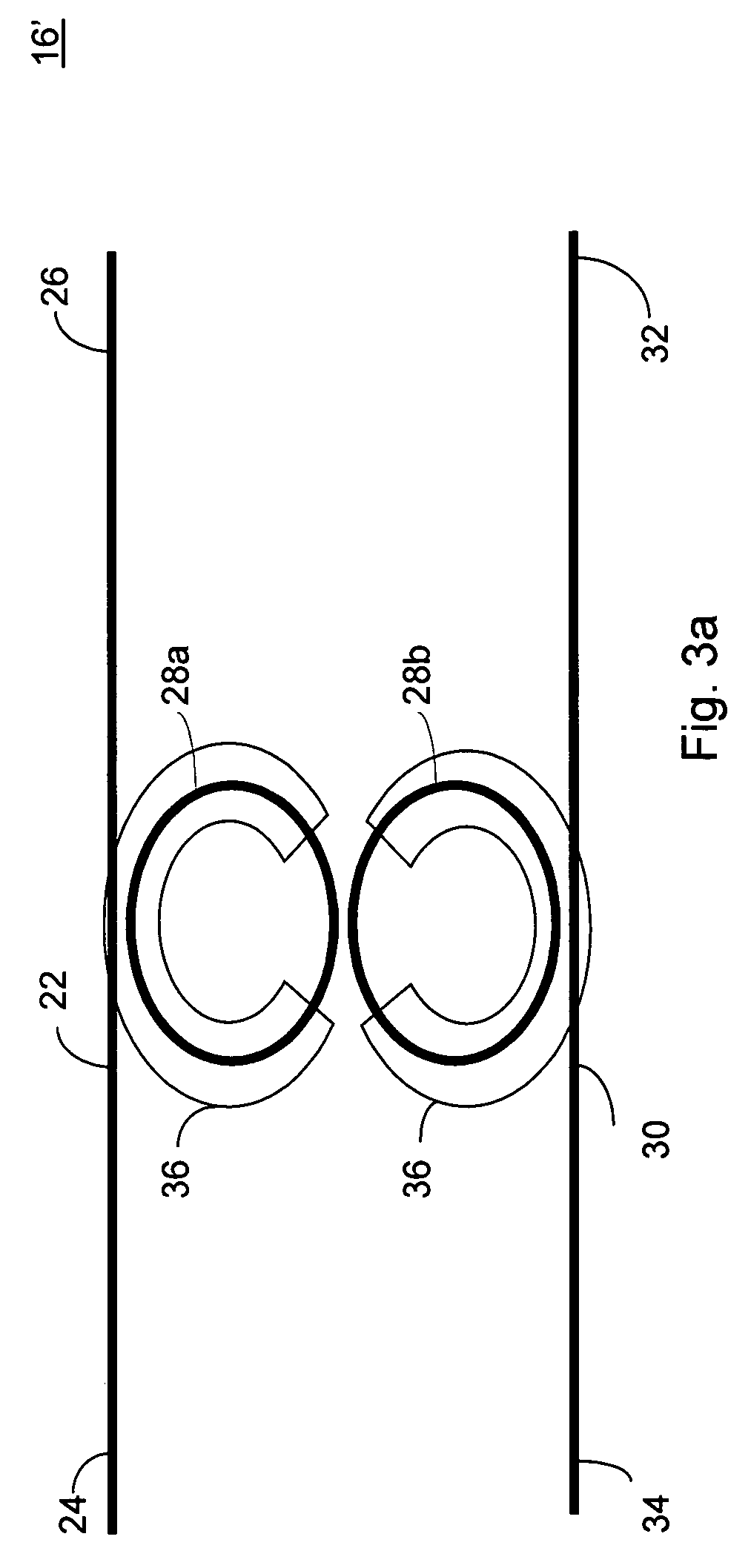
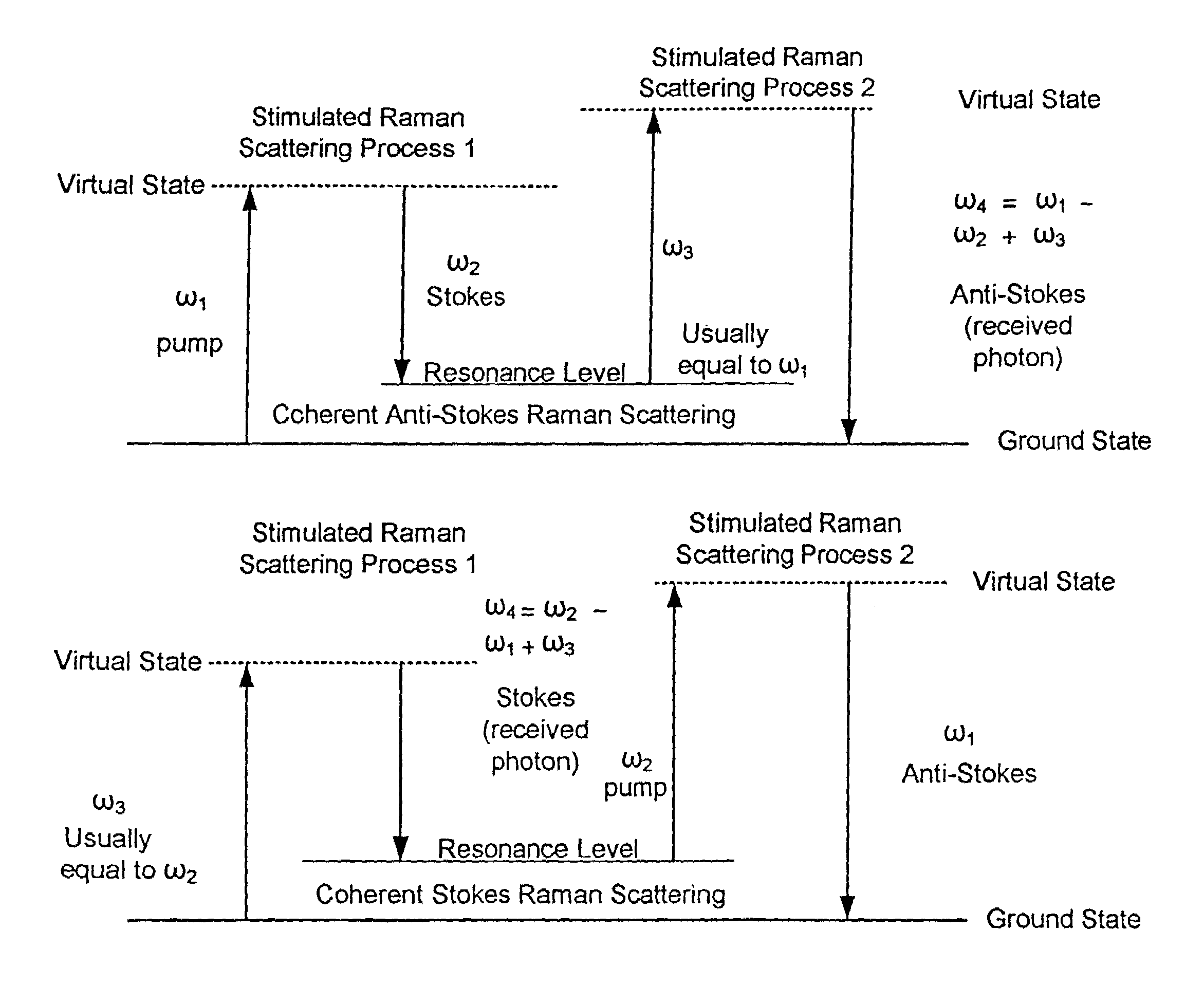
Nonlinear interferometric vibrational imaging
ActiveUS20050168735A1Radiation pyrometryAdditive manufacturing apparatusElectromagnetic radiationPhysics
A method of examining a sample, which includes: exposing a reference to a first set of electromagnetic radiation, to form a second set of electromagnetic radiation scattered from the reference; exposing a sample to a third set of electromagnetic radiation to form a fourth set of electromagnetic radiation scattered from the sample; and interfering the second set of electromagnetic radiation and the fourth set of electromagnetic radiation. The first set and the third set of electromagnetic radiation are generated from a source; at least a portion of the second set of electromagnetic radiation is of a frequency different from that of the first set of electromagnetic radiation; and at least a portion of the fourth set of electromagnetic radiation is of a frequency different from that of the third set of electromagnetic radiation.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
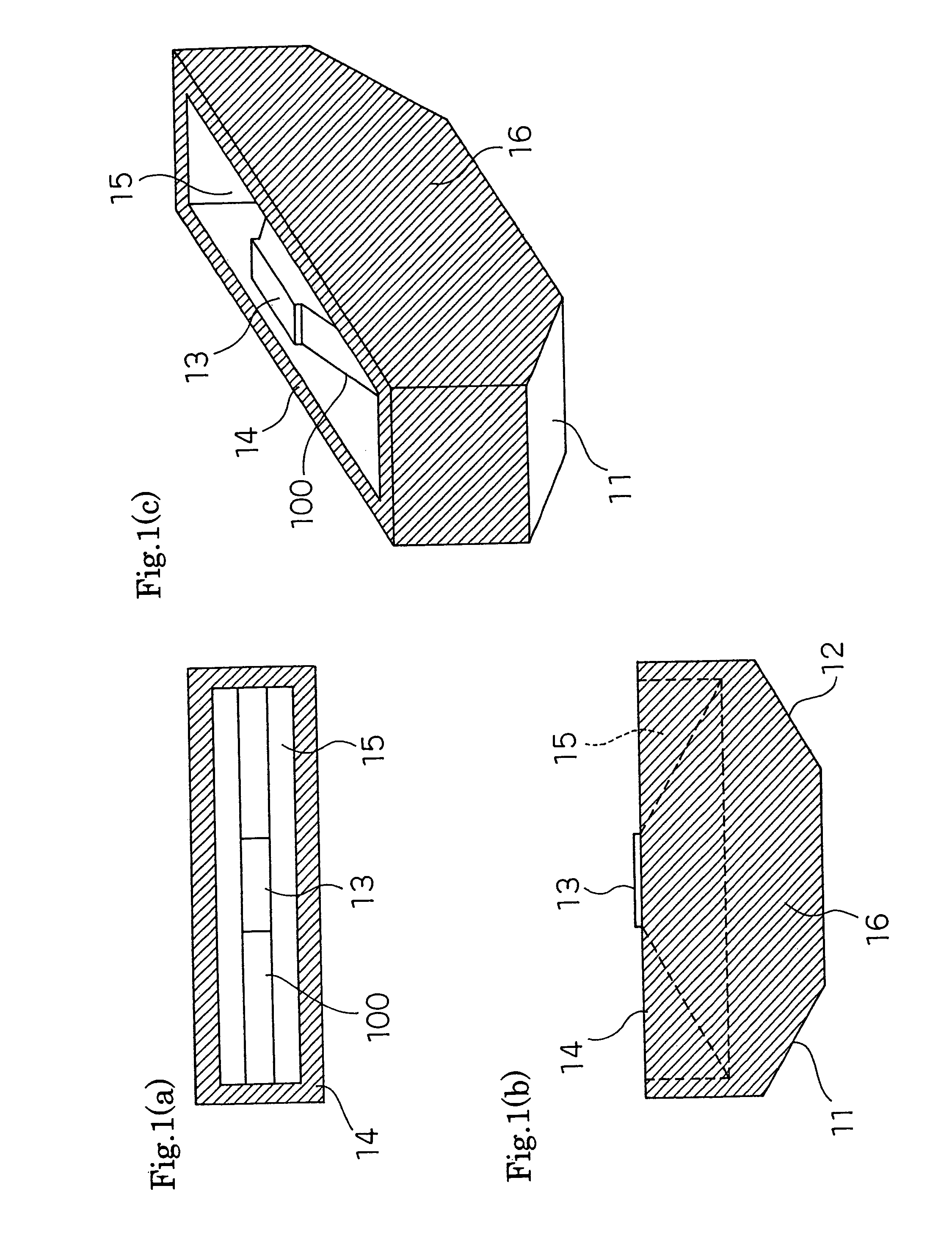
Integrated optical circuit
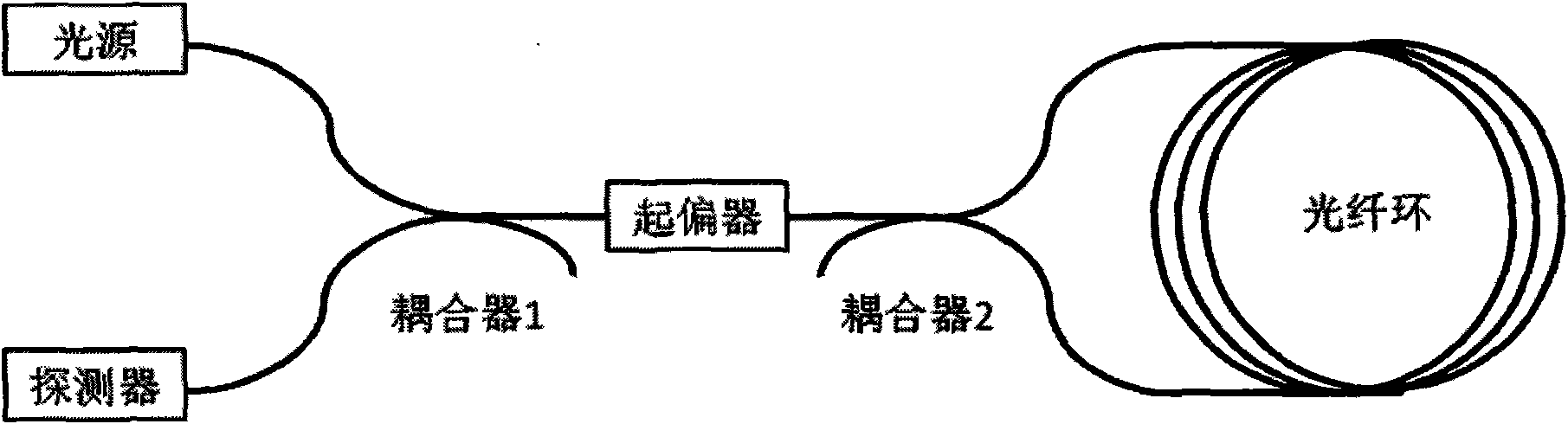
InactiveUS6163632ASagnac effect gyrometersSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsFiberPhase shifted
An integrated optical circuit for use in a fibre optic gyroscope which senses rotation rates by determining a phase shift due to the Sagnac Effect between light beams travelling around an optical fibre sensing loop (4) in opposite directions, the circuit being provided on a silicon-on-insulator chip comprising a layer of silicon separated from a substrate by an insulating layer, the circuit comprising: rib waveguides (11) formed in the silicon layer for receiving light from a light source (2) and transmitting light to a light detector (3), fibre optic connectors (9) in the form of grooves etched in the silicon layer for receiving the respective ends of the optical fibre sensing loop (4); rib waveguides (11) formed in the silicon layer for transmitting light to and from said fibre optic connectors (9) so as to direct light beams in opposite directions around the sensing loop (4) and receive light beams returning therefrom, phase determining means and (13,17,31) integrated in silicon layer for determining a phase shift between the light beams returning from the sensing loop (4).
Owner:BOOKHAM TECH
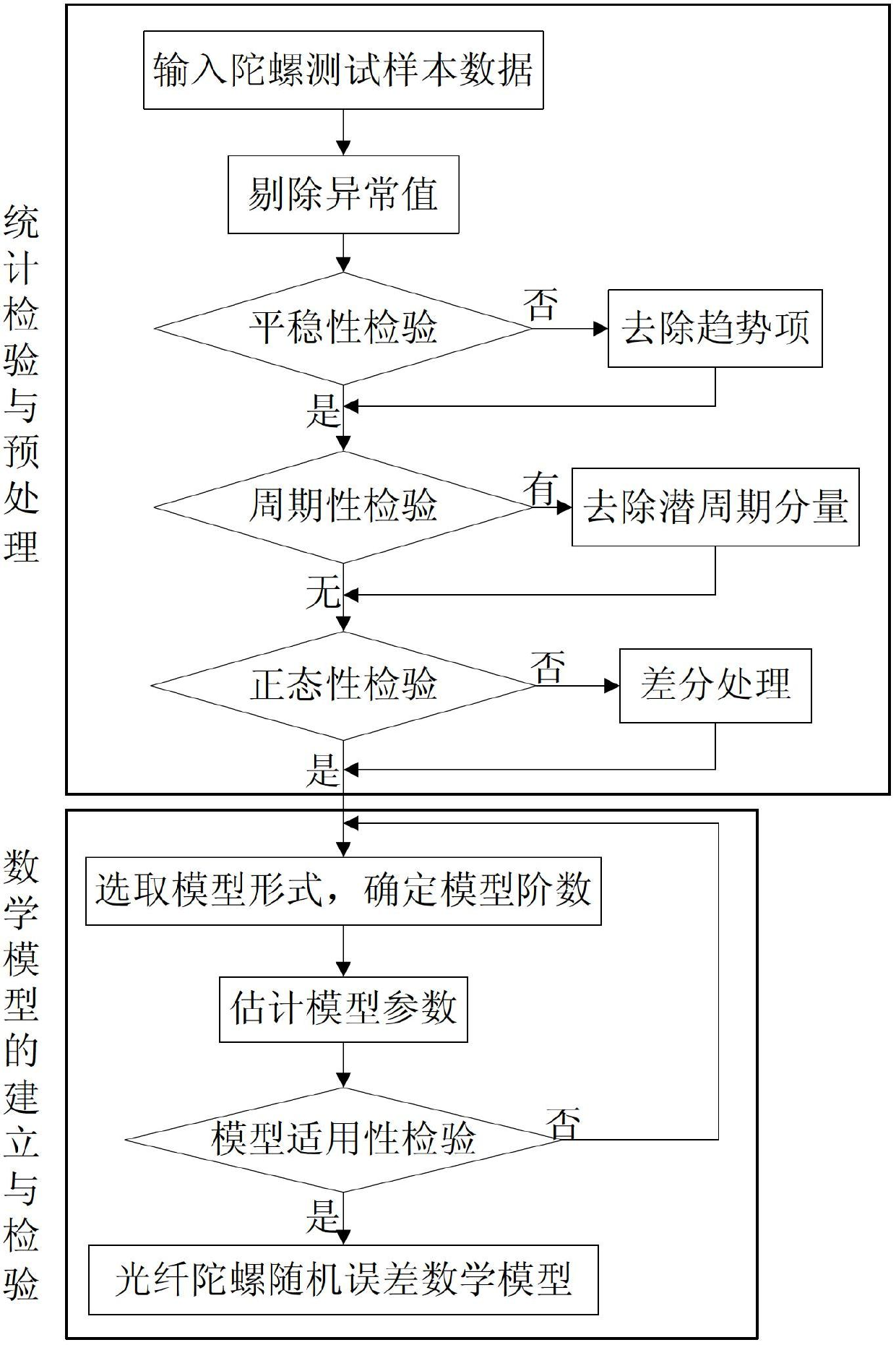
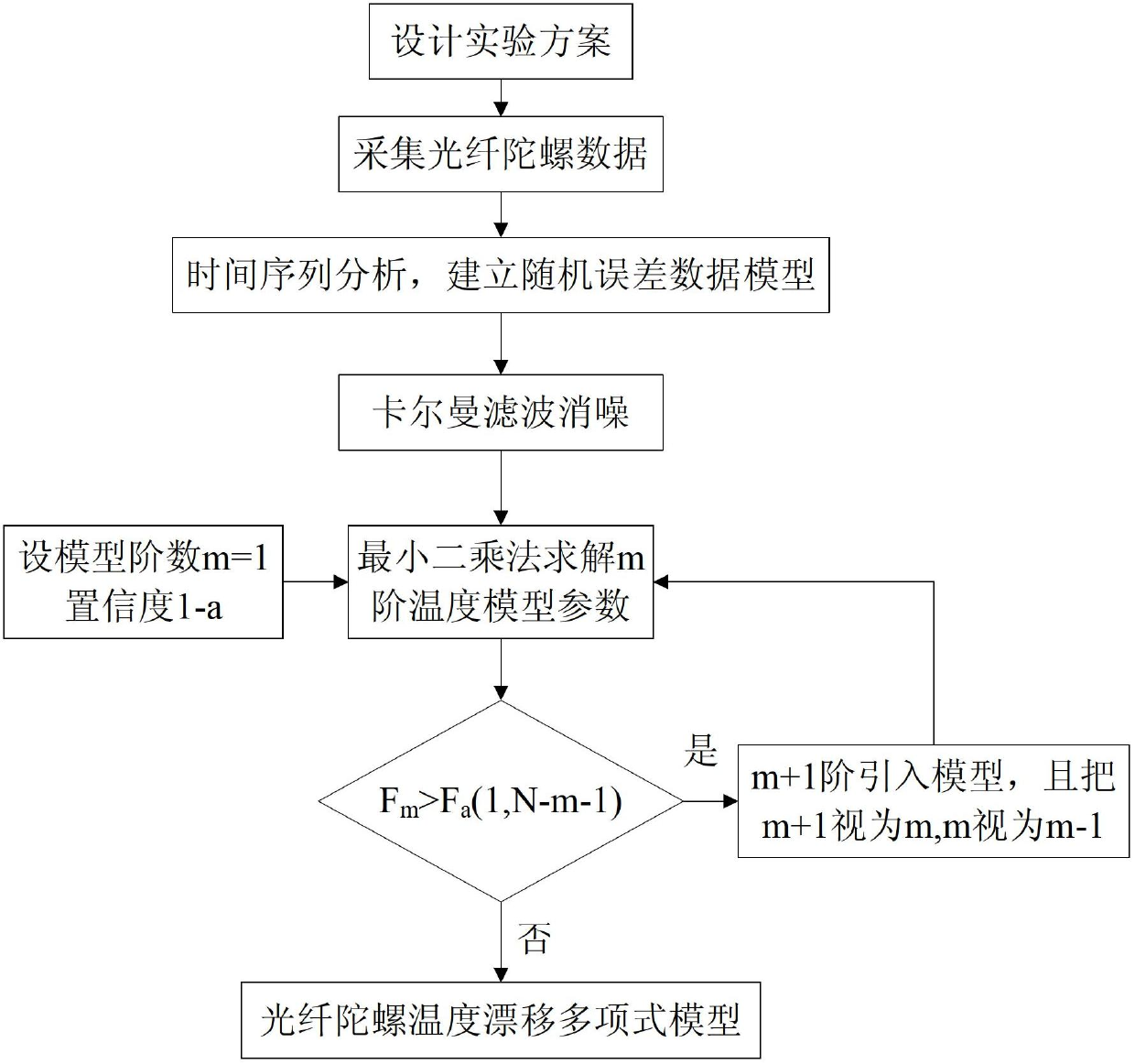
Temperature compensation method for denoising fiber-optic gyroscope on basis of time series analysis
A temperature compensation method for denoising a fiber-optic gyroscope on the basis of time series analysis comprises four steps of: step 1, designing an experimental scheme, performing fixed point low and high temperature testing experiment on the fiber-optic gyroscope, and utilizing acquisition software for data acquisition; step 2, performing time series analysis on the zero offset data of the gyroscope, and establishing the mathematical model of the random error of the fiber-optic gyroscope; step 3, adopting a kalman filtering algorithm to filter random noise in the zero offset data of the fiber-optic gyroscope; and step 4, utilizing the data which is de-noised by the kalman filtering to identify the model structure of the temperature shift error of the fiber-optic gyroscope, and calculating the parameters of the identified model. The method establishes the multinomial model of the static temperature shift error of the fiber-optic gyroscope through time series analysis, kalman filtering denoising treatment and identification of the temperature shift error model structure and parameters. The method completely meets the real-time compensation requirement on the project, and has a better practicable value and a wide application prospect in the technical field of aerospace navigation.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
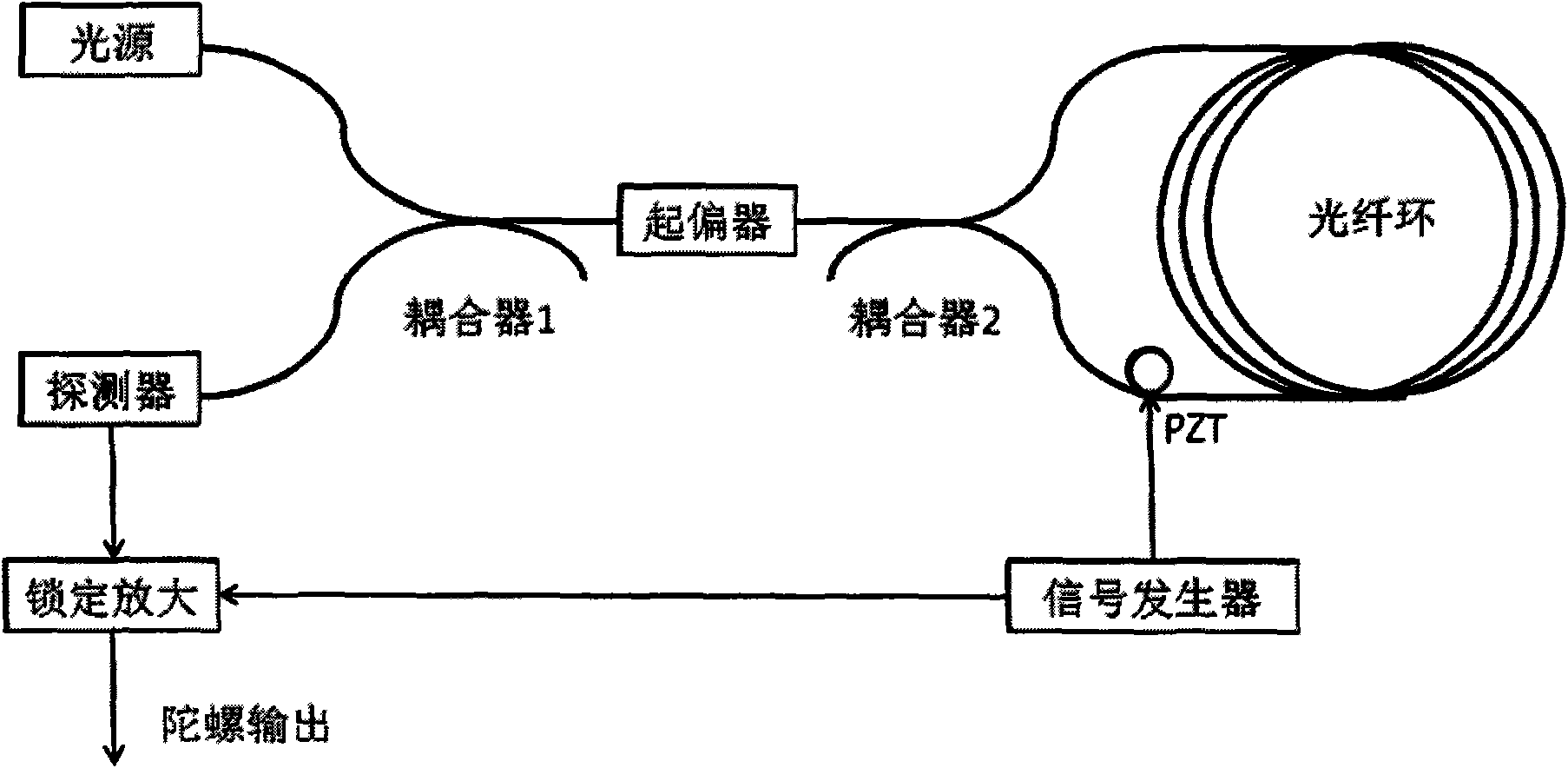
System and method for stabilizing light sources in resonator gyro
ActiveUS7372574B2Speed measurement using gyroscopic effectsSagnac effect gyrometersResonanceLaser light
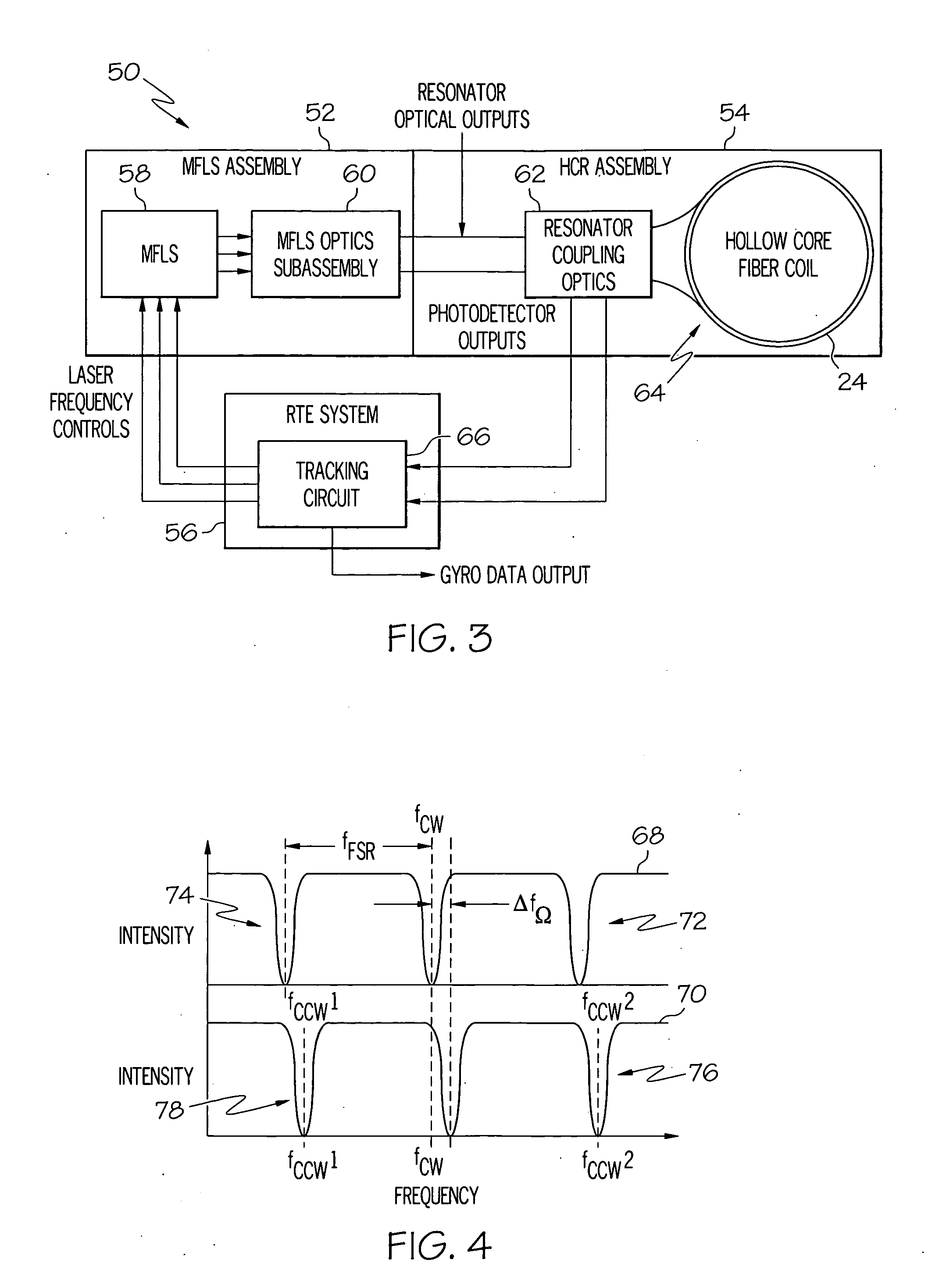
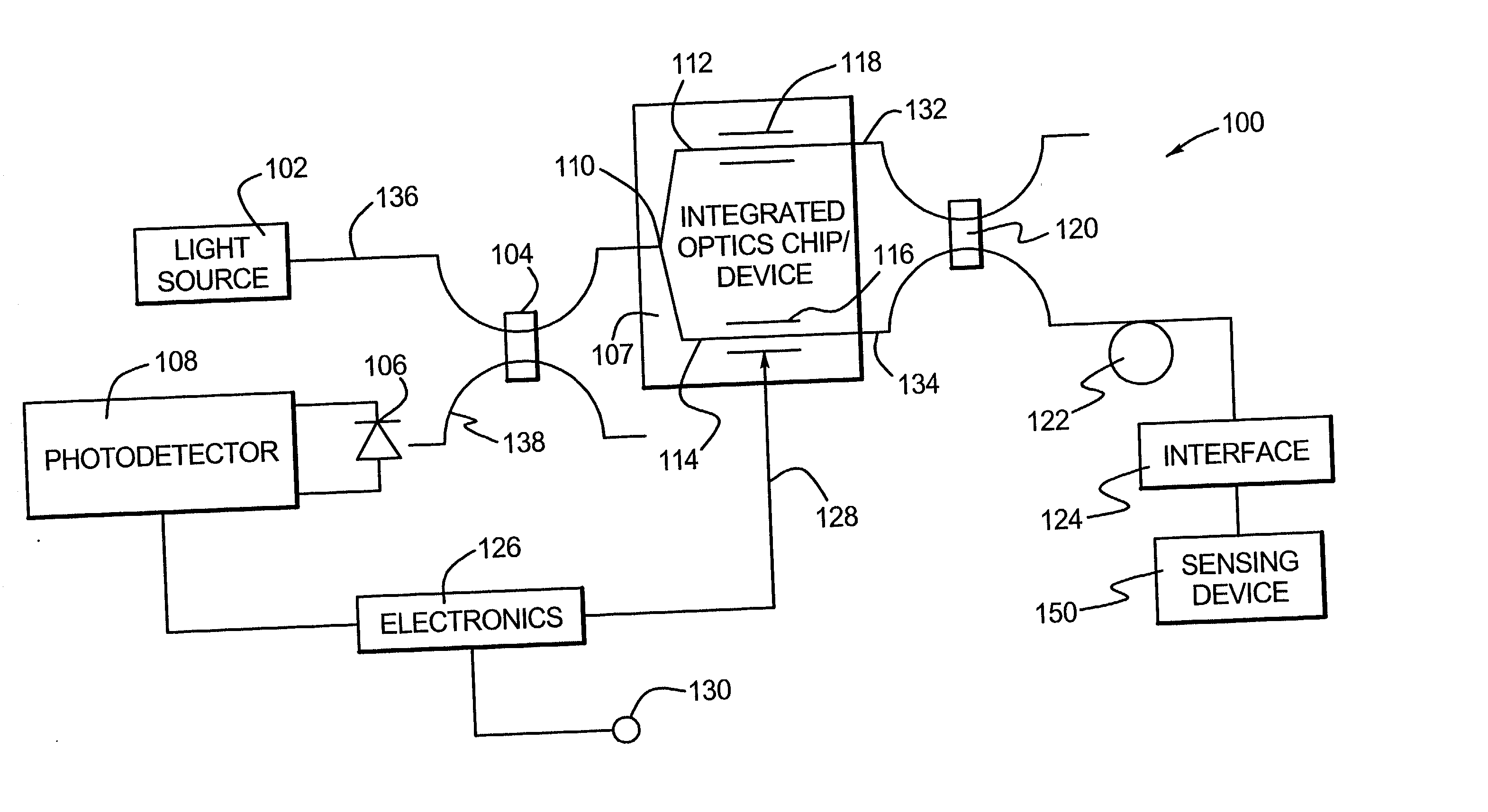
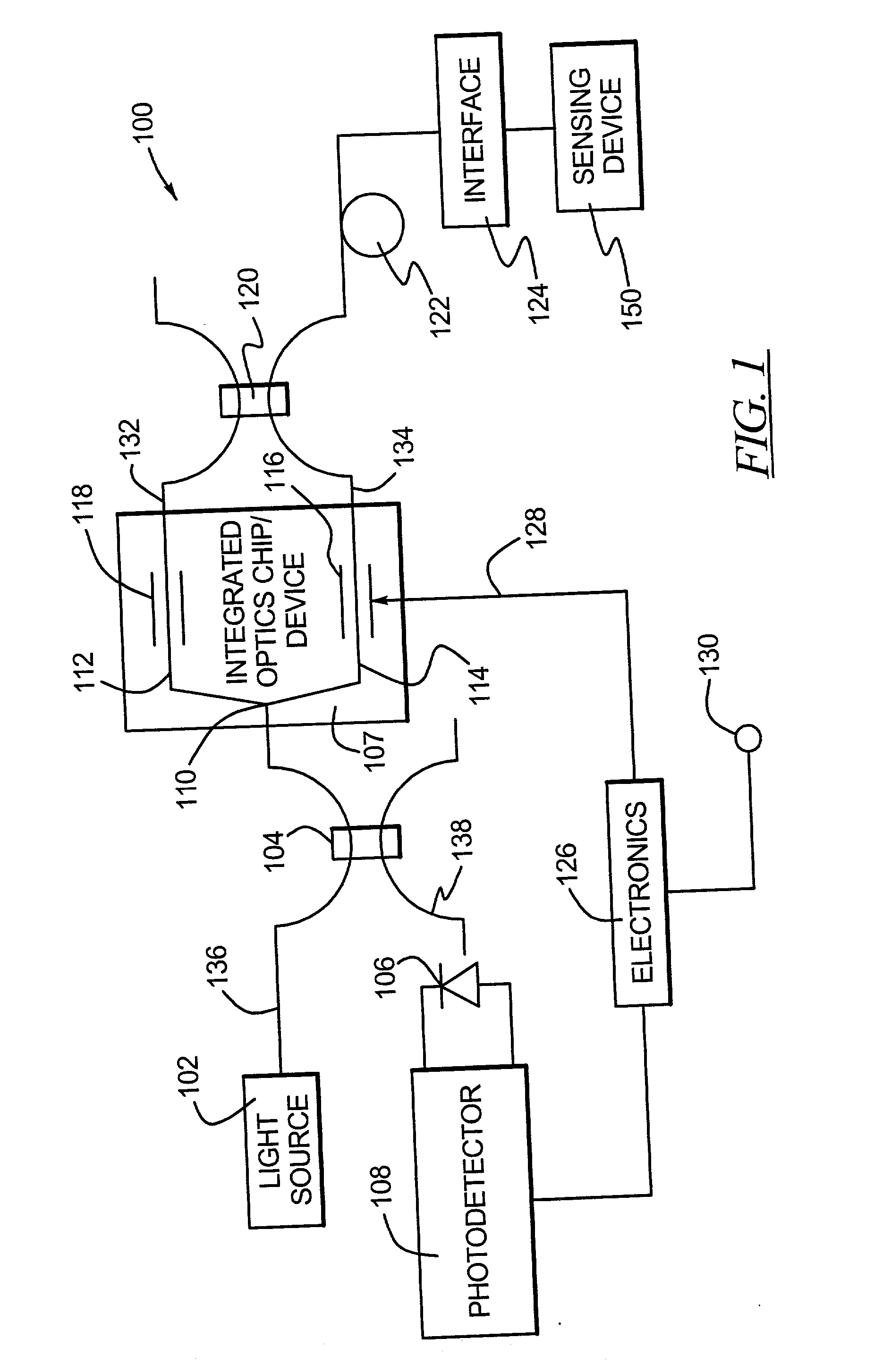
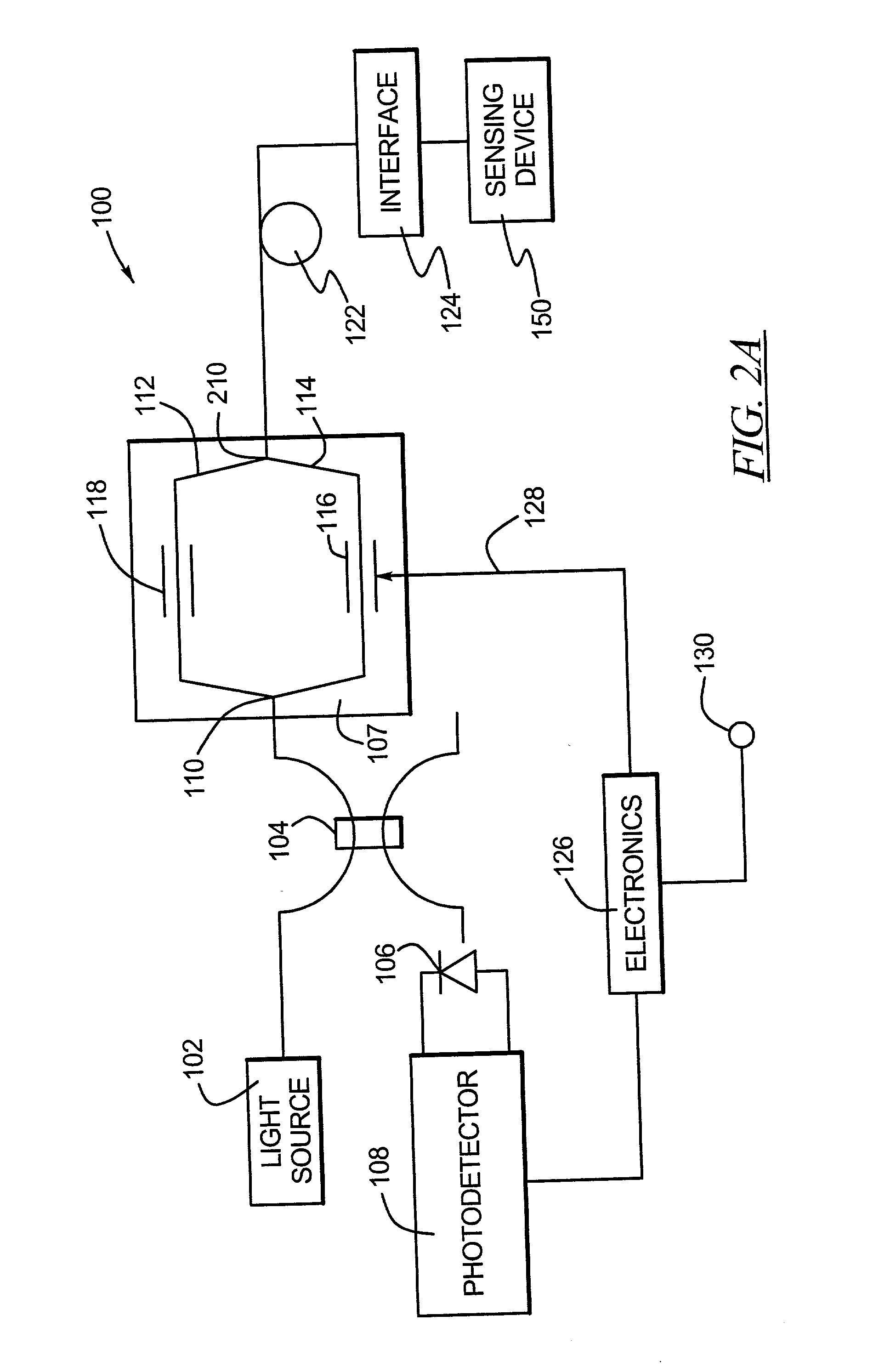
Methods and apparatus are provided for stabilizing laser light sources of a resonator gyro. A resonator gyro comprises a first light source configured to produce a first input light, a second light source configured to produce a second input light, a resonator coupled to the first and second light sources, a resonance detection circuit coupled to the resonator, and a controller coupled to the resonance detection circuit and the first and second light sources. The resonance detection circuit detects a resonance frequency for each of the counter-propagating directions of the resonator. The controller tunes the first input light to a clockwise resonance frequency, and tunes the second input light to a counter-clockwise resonance frequency. A difference between the resonance frequencies is proportional to a rotational rate of the resonator gyro.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
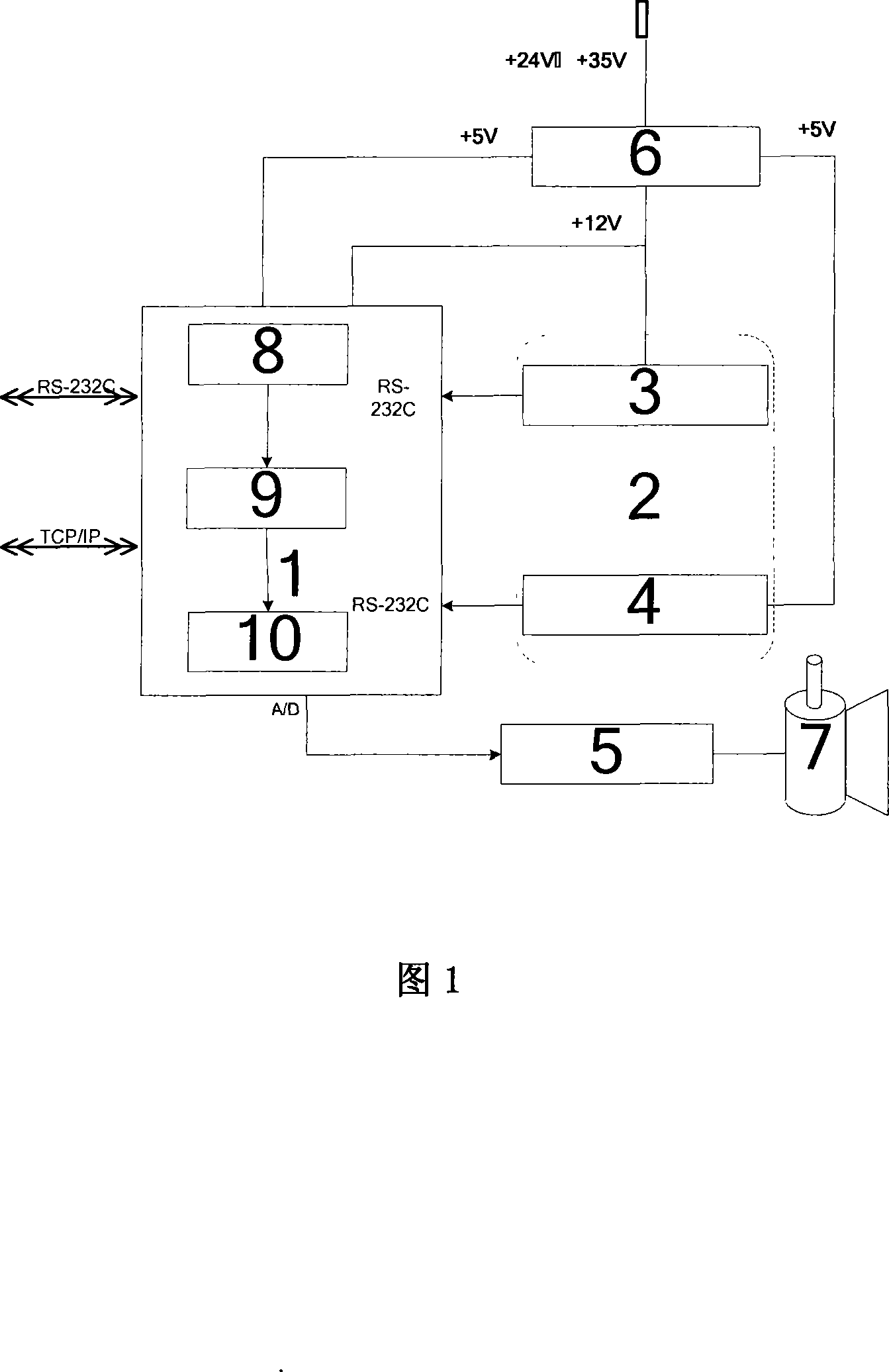
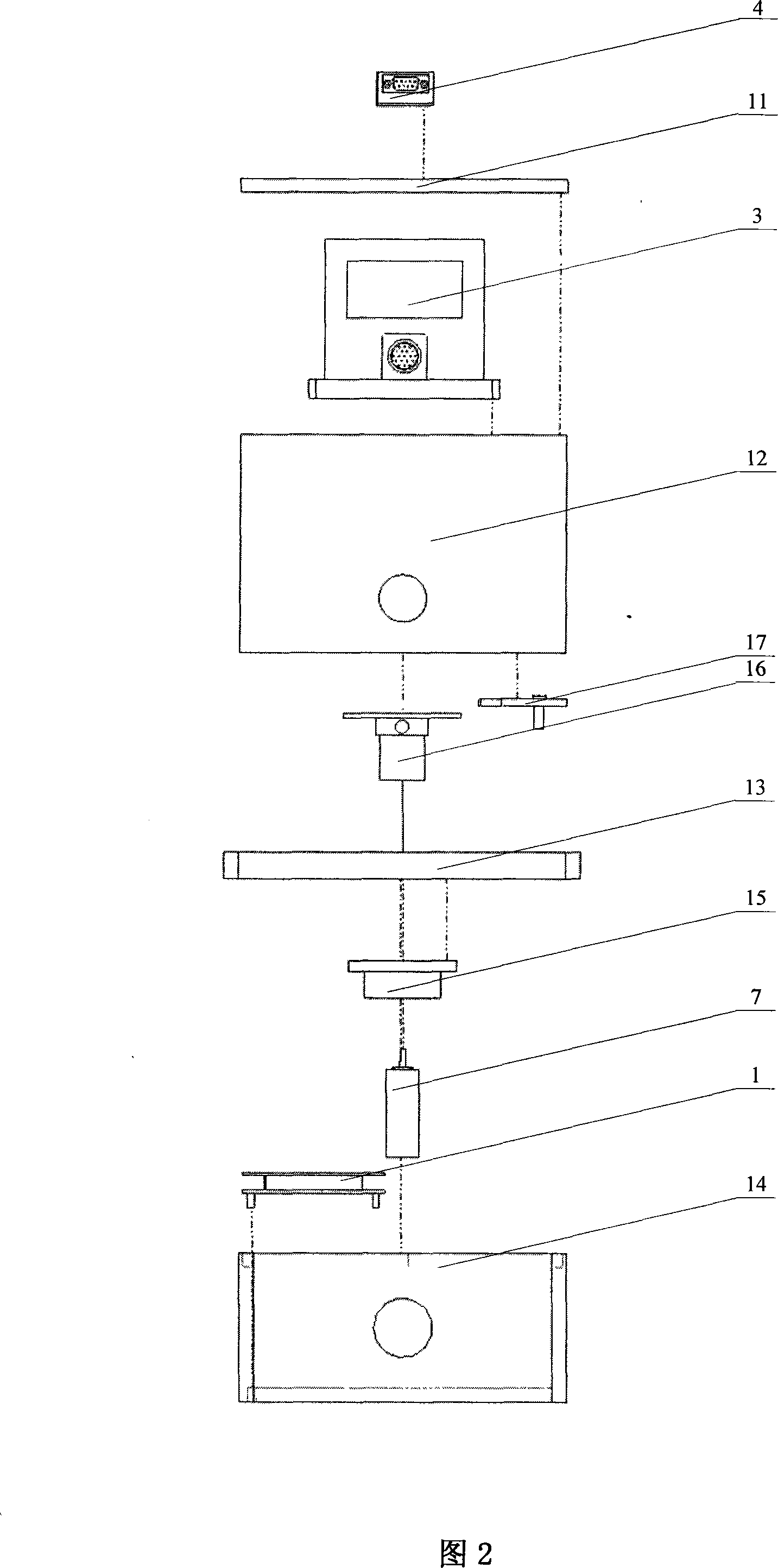
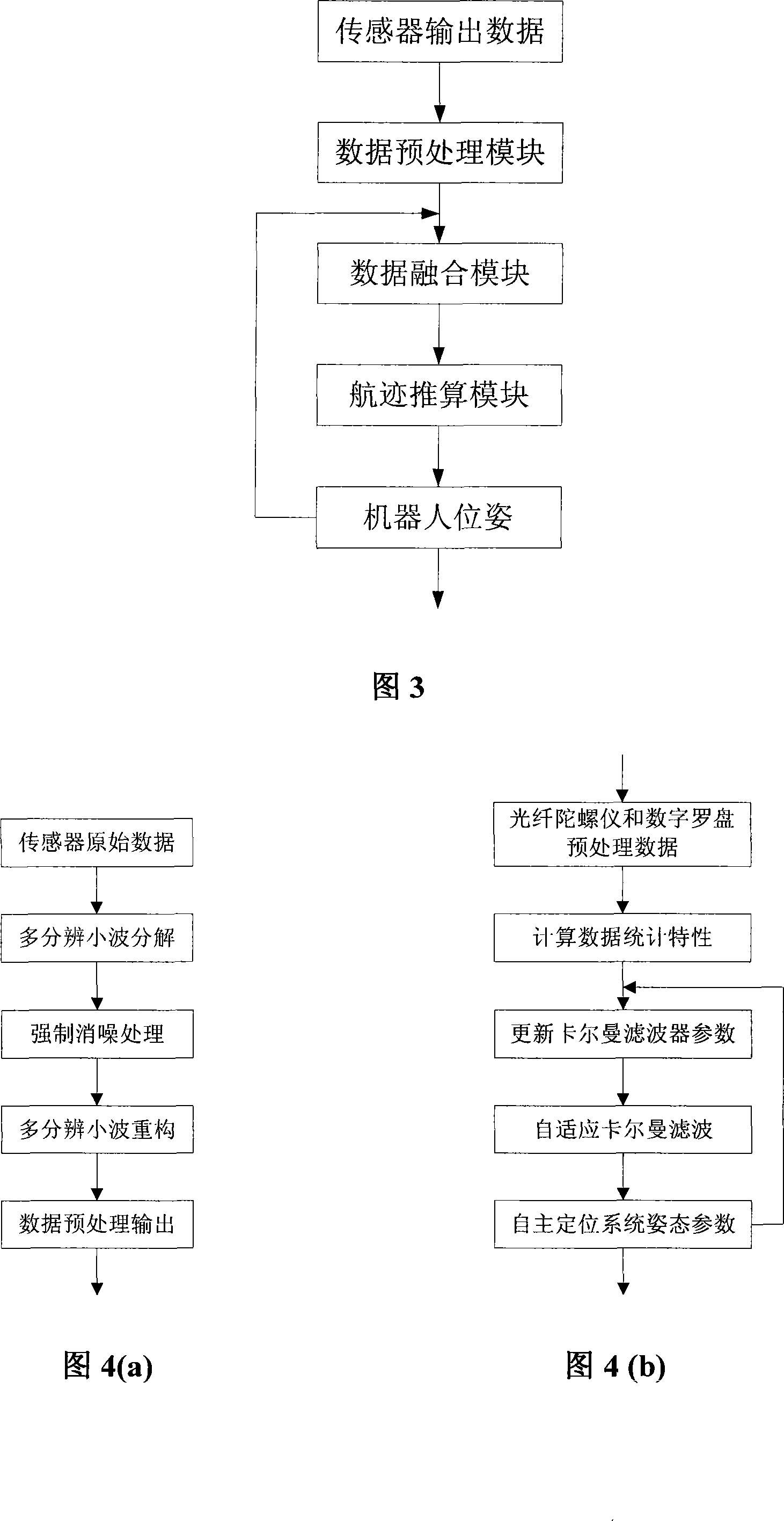
Freedom positioning system for robot
InactiveCN101201626ASolve the self-positioning problemEffective pose informationInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationEngineeringCoal
The invention provides a robot independent positioning system and belongs to a robot intelligent control device. The invention solves the high-precision and independent positioning problem of the robot in the underground operation. The invention comprises an installation platform, a sensor subsystem, a data processing subsystem and a voltage conversion module; the sensor subsystem, the data processing subsystem and the voltage conversion module are arranged on the installation platform; the upper part of the installation platform is a turntable carrying the sensor subsystem; a fixed base on the lower part of the installation platform has a structure of a sealed cavity; the inside of the fixed base is provided with the data processing subsystem and the voltage conversion module; the sensor subsystem comprises an inertial sensor module and a three-dimensional digital compass; the data processing subsystem comprises a central controller, a data preprocessing module, a data integration module and a dead reckoning module; the data preprocessing module, the data integration module and the dead reckoning module are arranged in the central controller. The invention can be used for the intelligent robot working in the underground environment such as coal mines, tunnels, caverns and so on; the invention can be used for the independent positioning of robots, shield machines, underground locomotives and so on; the invention provides effective pose information for intelligent robots to finish such tasks as reconnaissance, exploration and search in the underground environment.
Owner:湖北鹰特飞智能科技有限公司
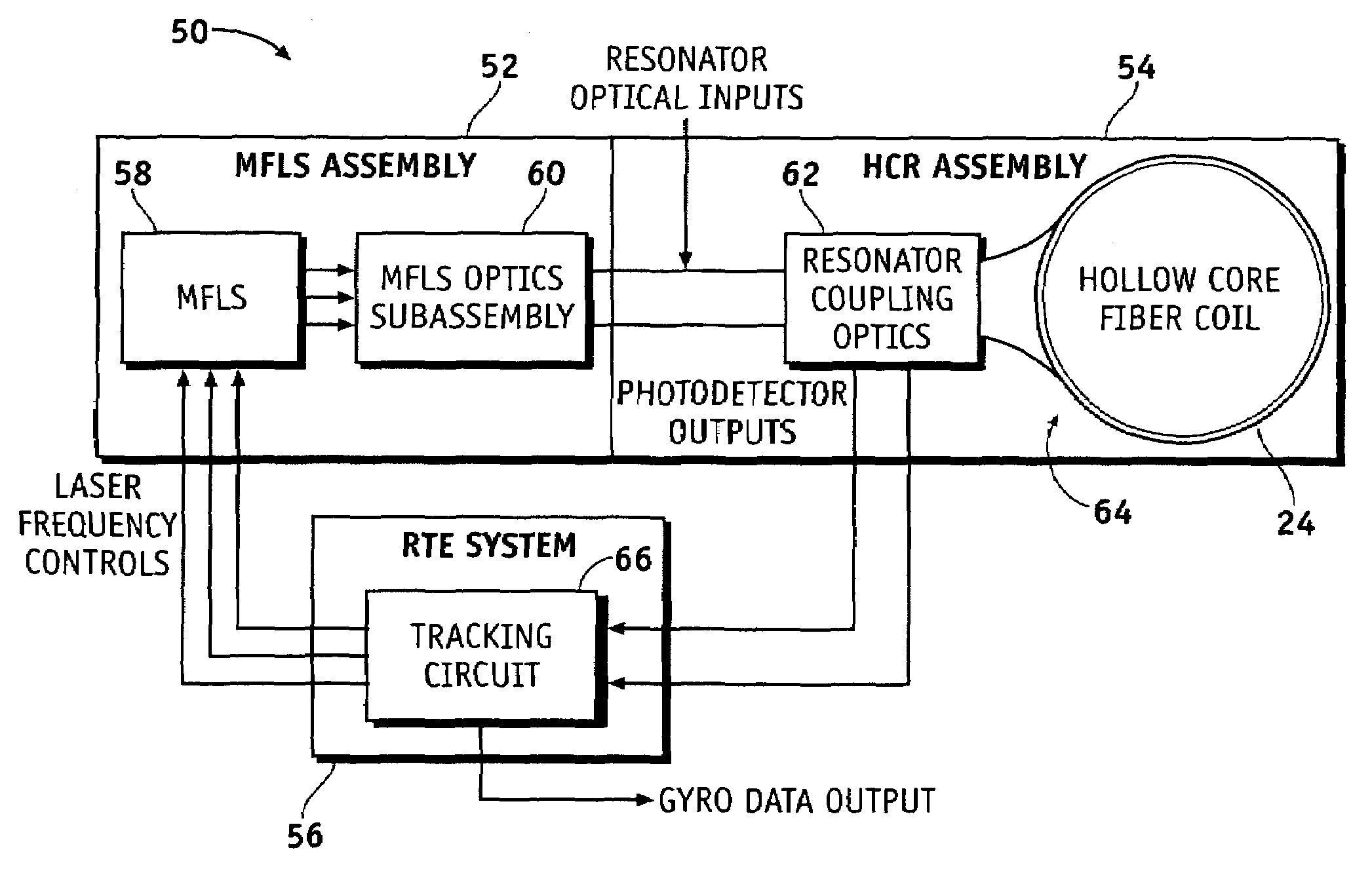
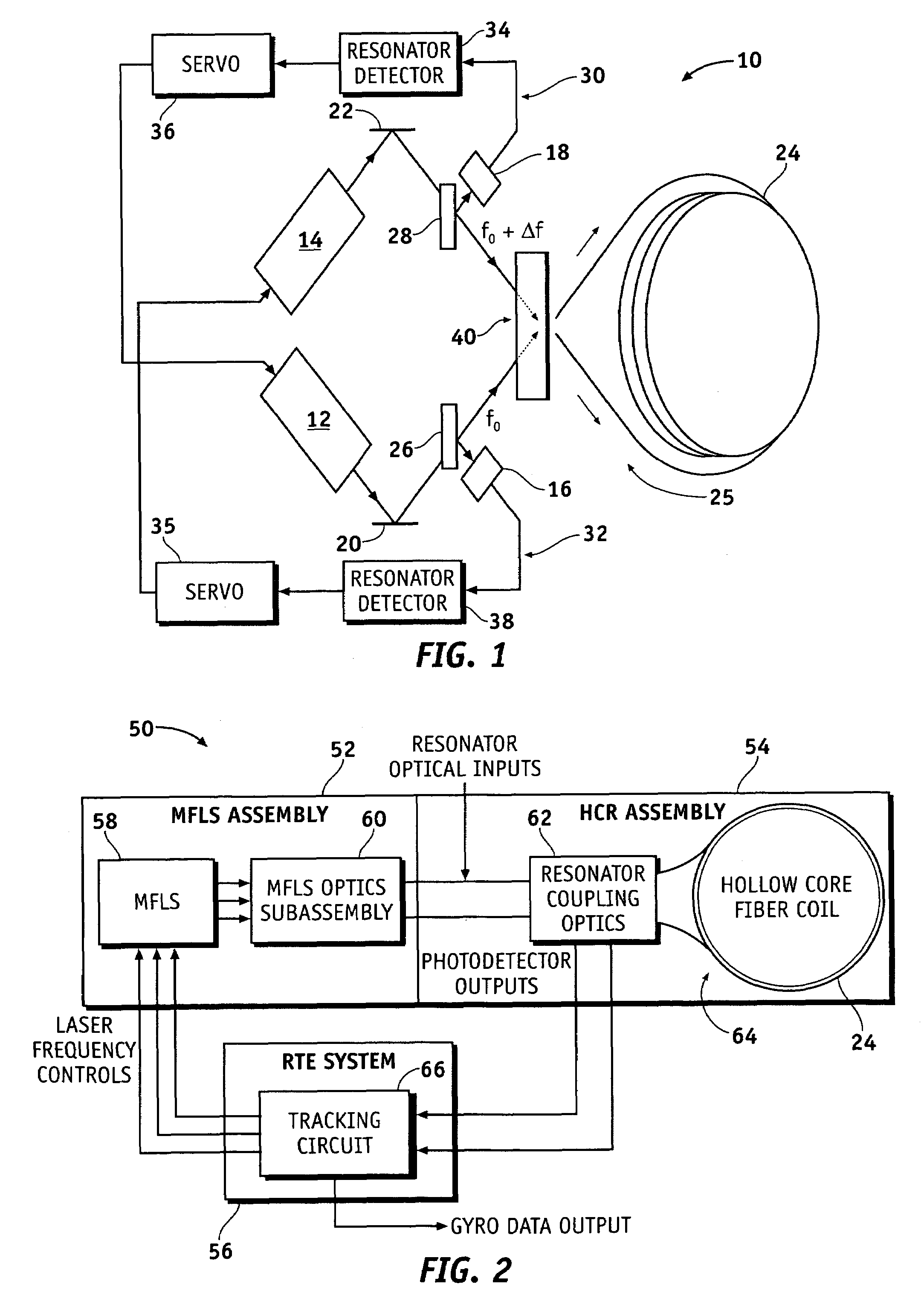
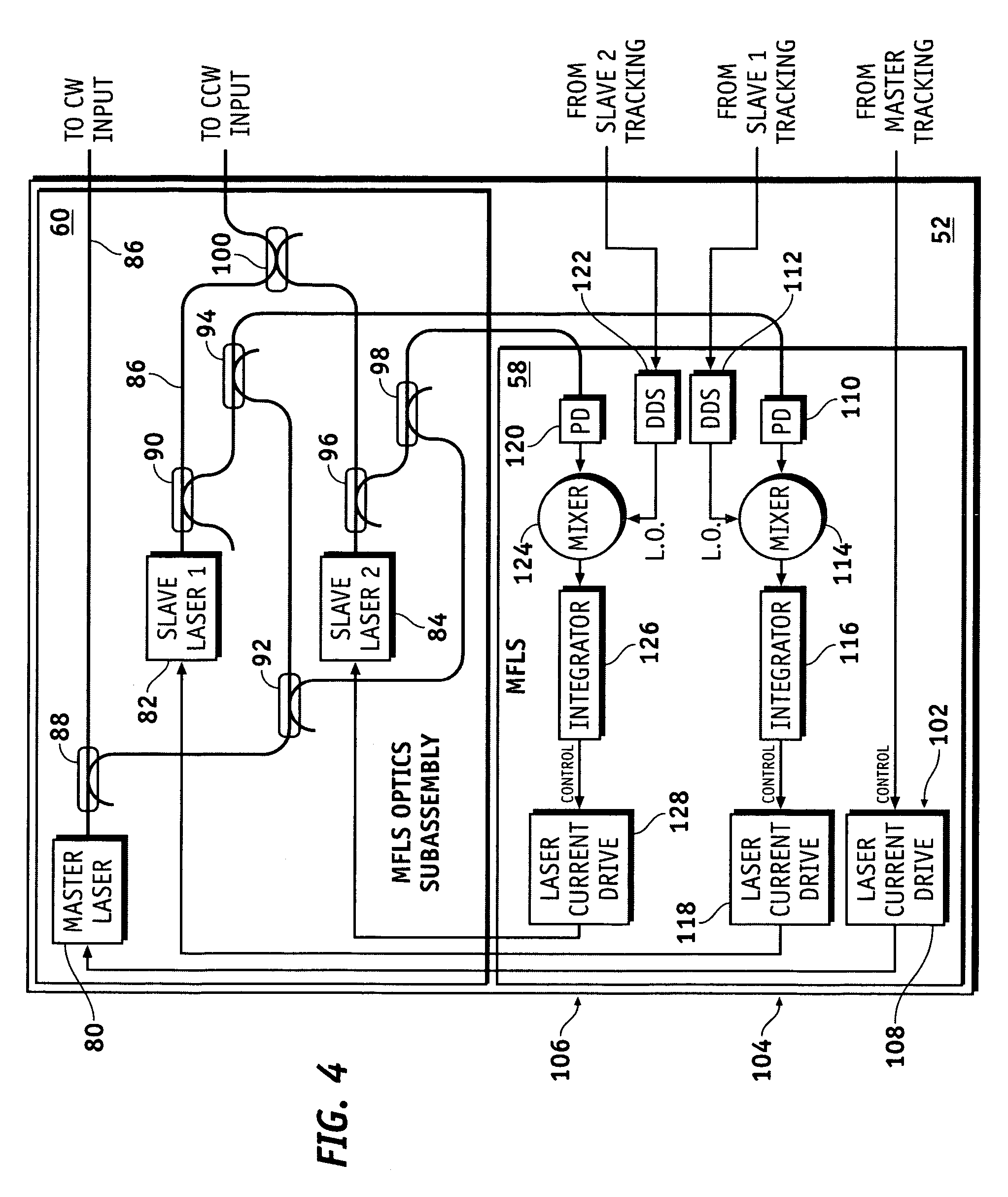
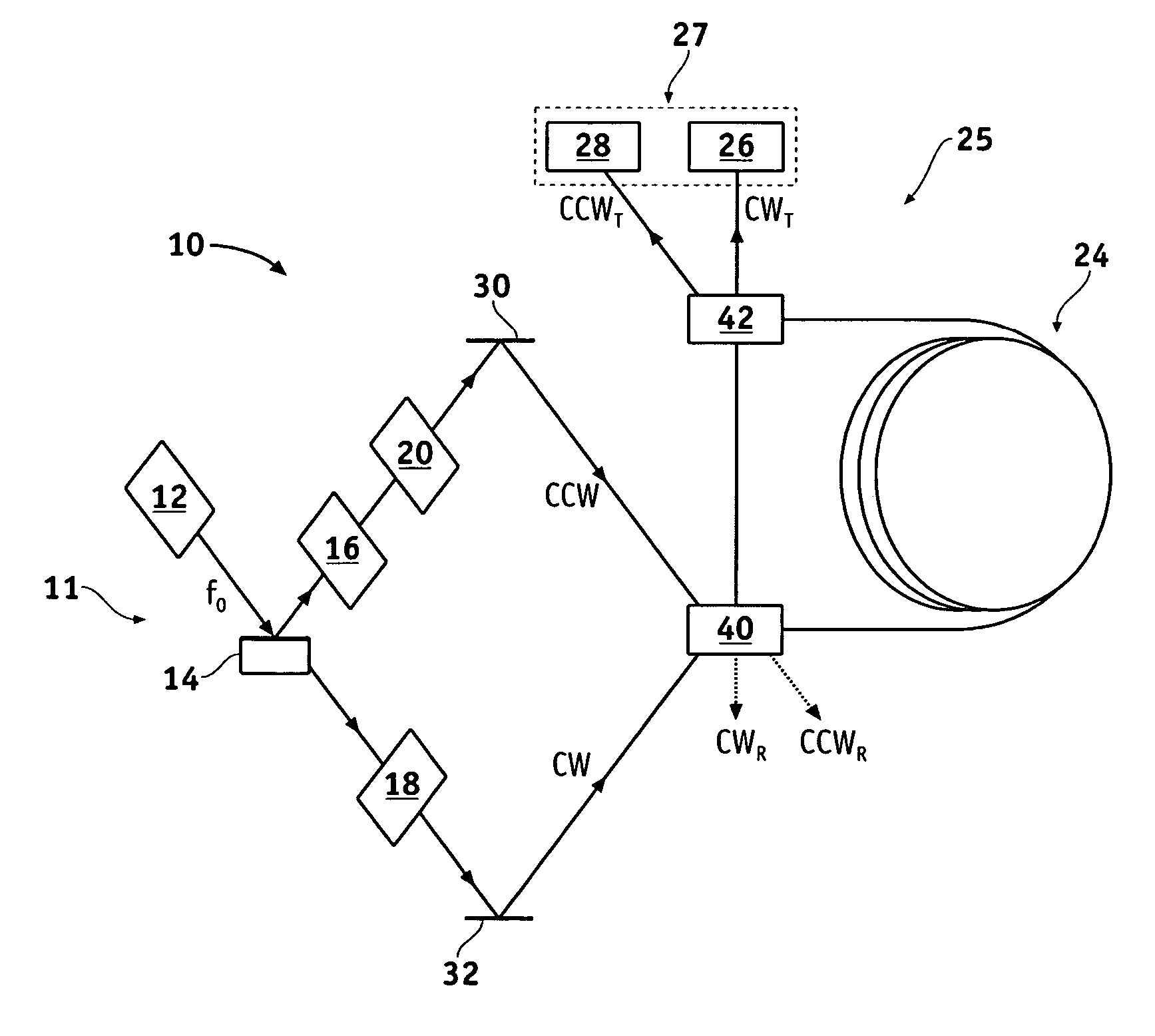
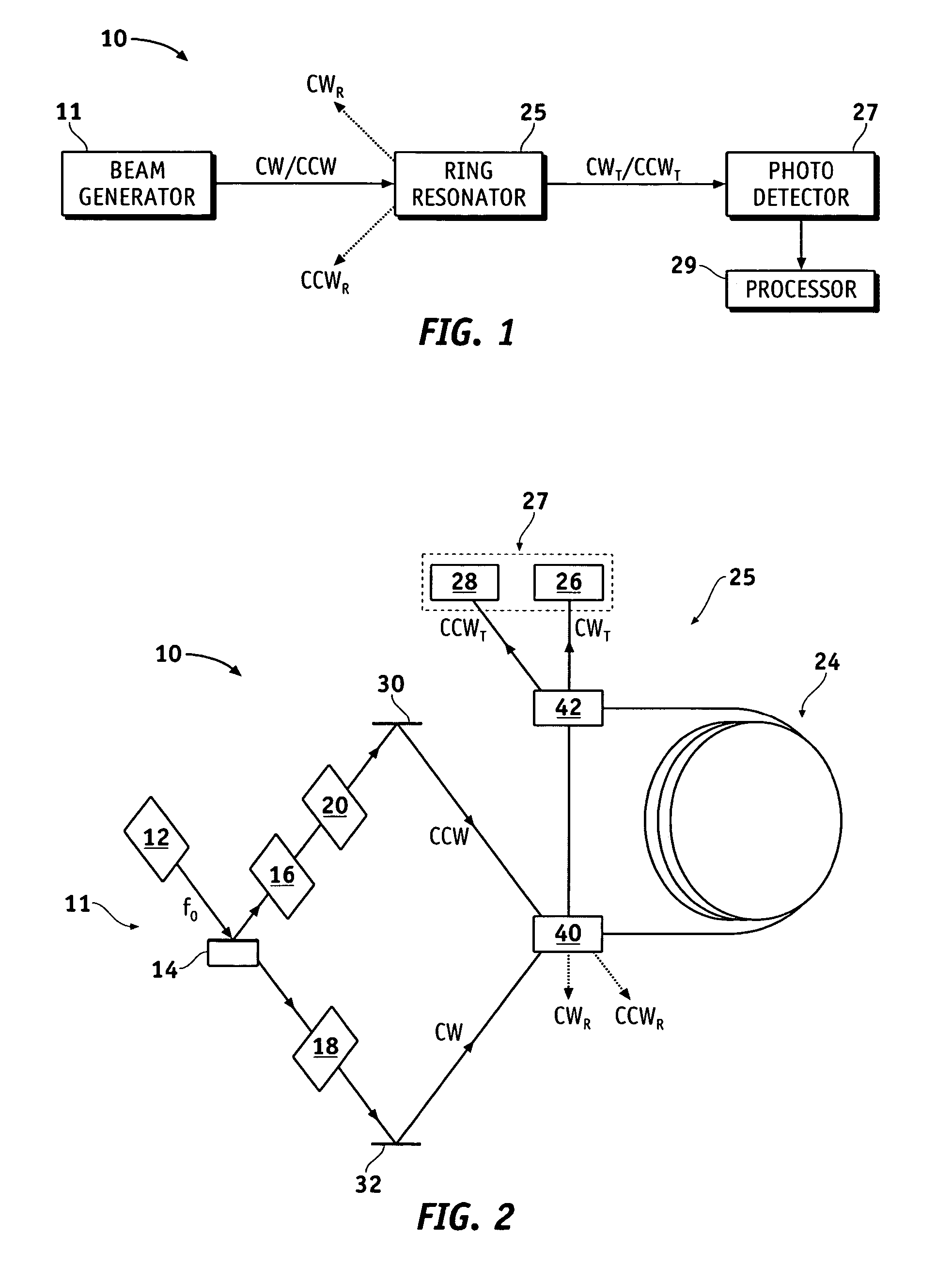
Optical resonator gyro with external cavity beam generator
ActiveUS20070242276A1Sagnac effect gyrometersSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsOptical gyroscopeLight beam
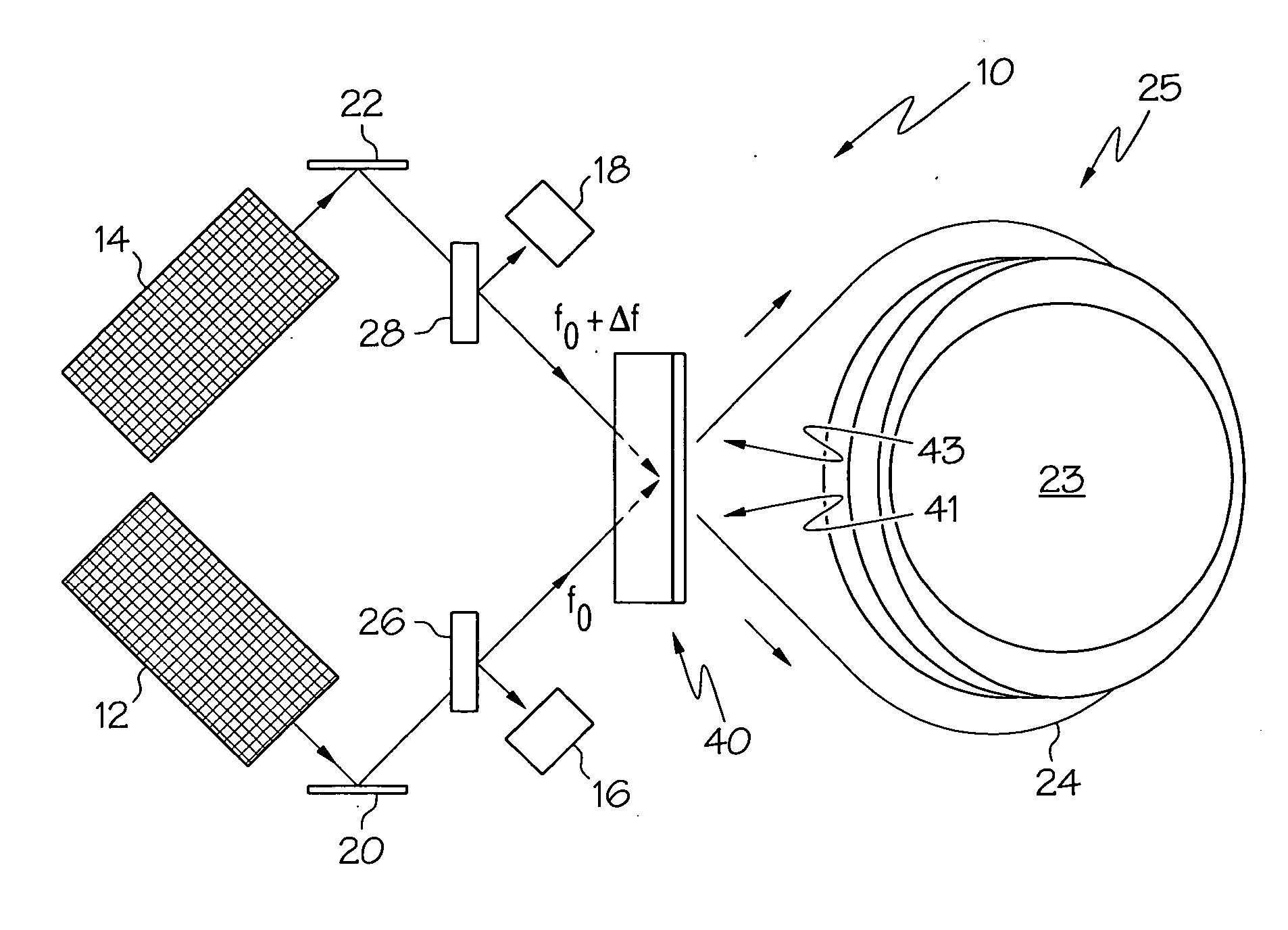
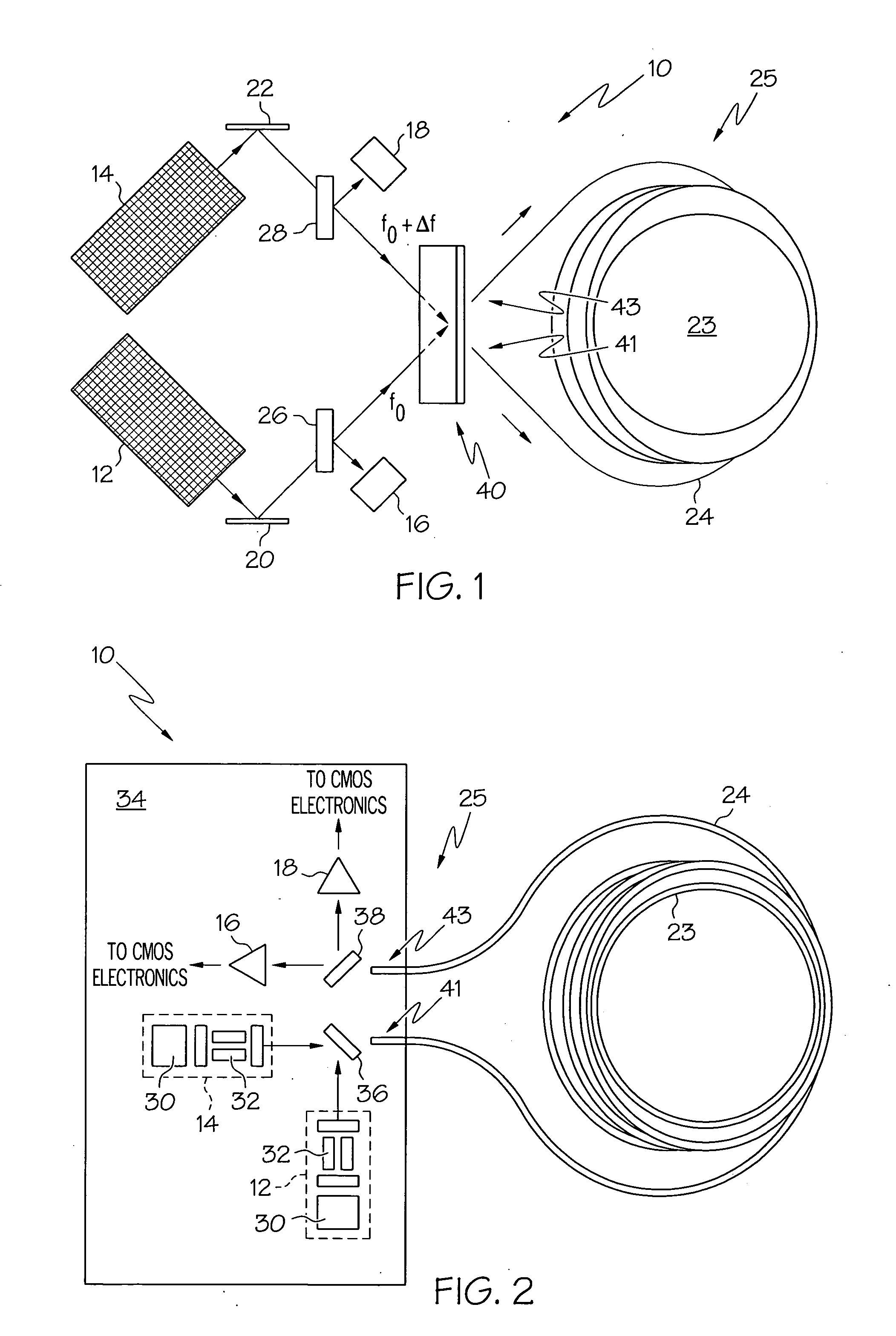
Methods and apparatus are provided for determining the rotational rate of an optical gyro. An optical gyro comprises at least one substrate, a multi-frequency light source (MFLS) mounted on the substrate, and a resonator coupled to the MFLS. The MFLS is configured to produce a first light beam having a first frequency and a second light beam having a second frequency and phase locked with the first light beam. The resonator comprises an optical fiber coil having a hollow core. The resonator is configured to circulate a portion of each of the first and second light beams through the hollow core. The portion of the first light beam propagates in a first counter-propagating direction, and the portion of the second light beam propagates in a second counter-propagating direction. A measured difference between the first and second frequencies indicates a frequency shift proportional to the rotation rate of the optical gyro.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
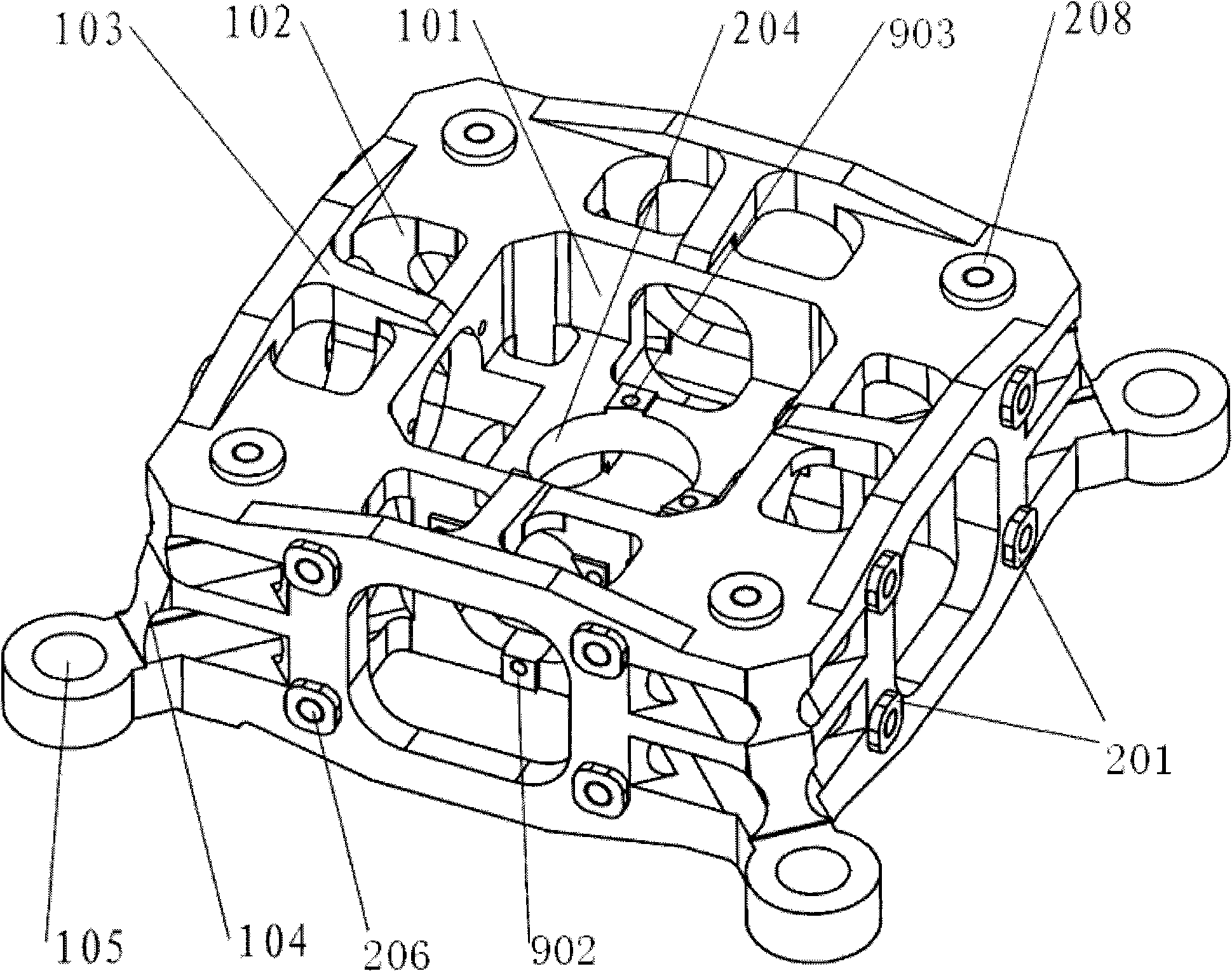
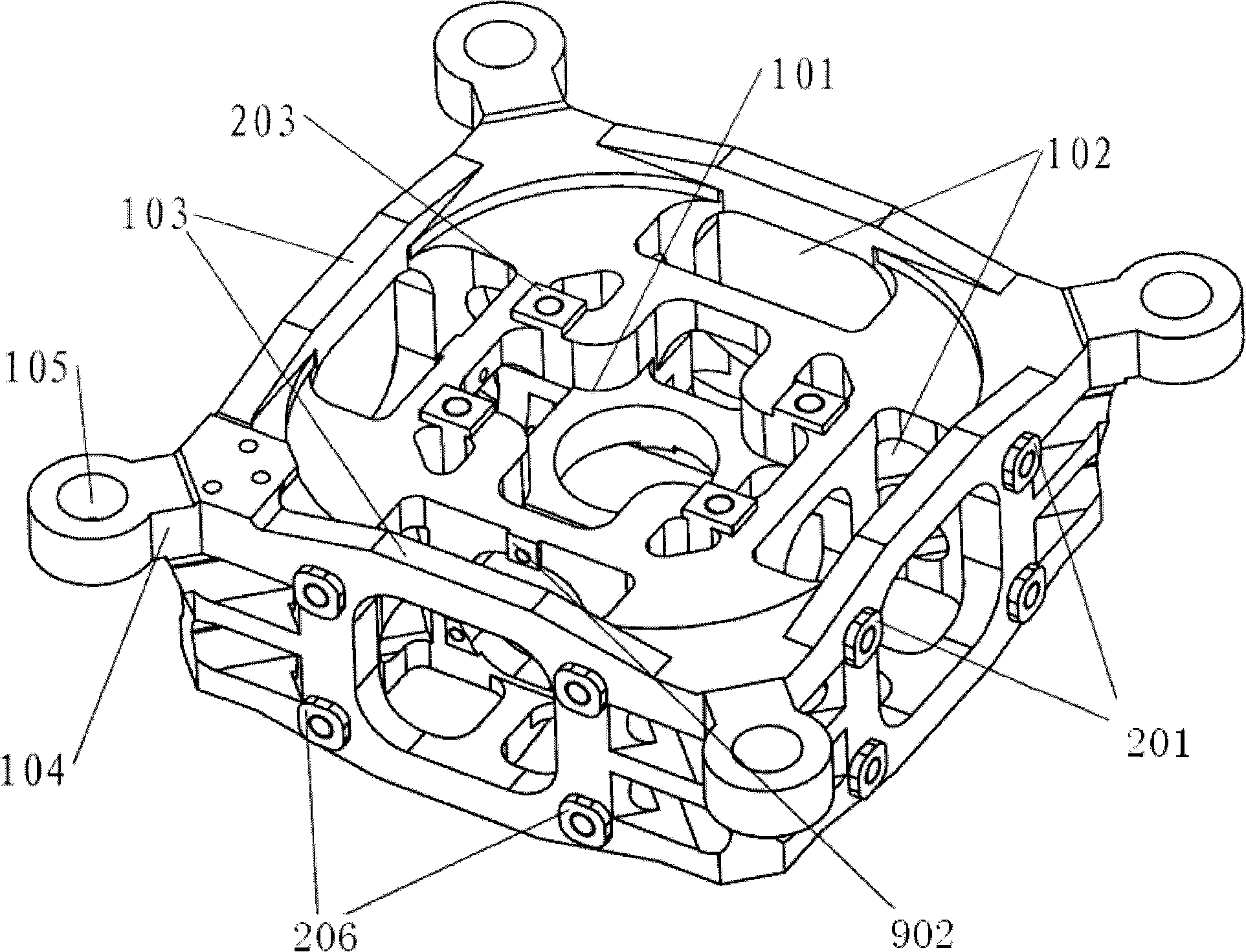
Three axis optical fibre gyroscope inertia measurement unit integral structure
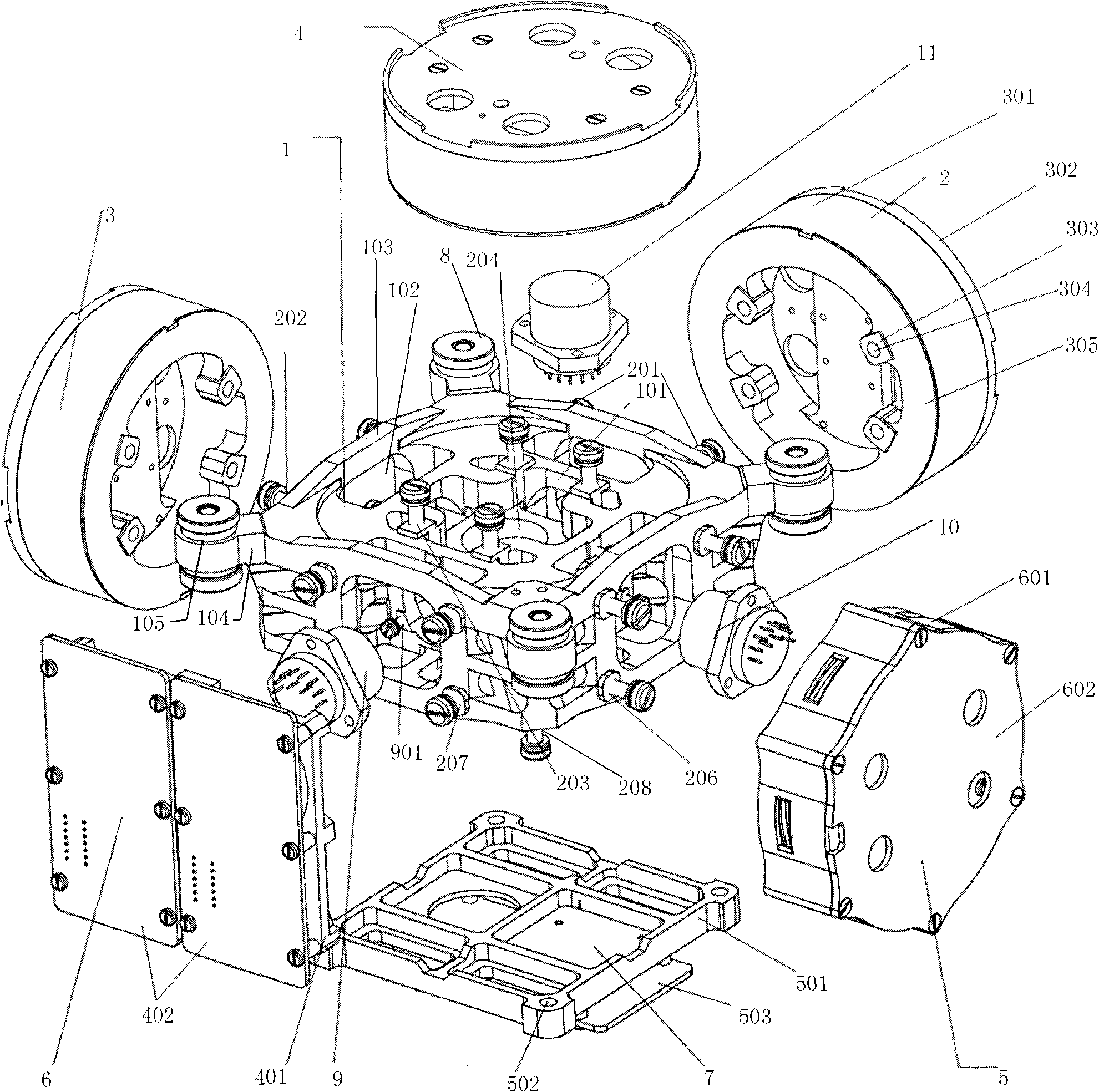
The invention relates to an integral structure of a triaxial optical fiber gyro inertia measuring unit, which comprises a mounting skeleton, three fiber optic gyro scopes, three accelerometers, a light source, a circuit board and a vibration damper. The mounting skeleton adopts a hollow hexahedron frame structure, each group of mounting holes are symmetrically arranged, and mounting lug bosses are arranged on the positioning end surface of the mounting holes. Three fiber optic gyro scopes form mutual space and are orthogonally arranged on the outer surface of the mounting skeleton, the light source and the circuit board are respectively arranged on the outer surface of the mounting skeleton which is corresponding to the three fiber optic gyro scopes, the three accelerometers form the mutual space and are orthogonally arranged on the inner surface of the mounting skeleton which is corresponding to the three fiber optic gyro scopes and near the geometric center of the mounting skeleton, and the vibration damper is arranged on the outer surface of the mounting skeleton. The measuring unit has the advantages that the quality is light; the degree of deviation between the mass center of an inertia measuring unit and the geometric mounting center is very small; the dynamic testing precision is high; the temperature field distribution of the inertia measuring unit is beneficial for the temperature compensation and control of each component, and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Micro-resonator based optical sensor
InactiveUS7145660B2Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorResonant cavityOptical communication
Owner:LAMBDA CROSSING
Nonlinear interferometric vibrational imaging
A method of examining a sample, which includes: exposing a reference to a first set of electromagnetic radiation, to form a second set of electromagnetic radiation scattered from the reference; exposing a sample to a third set of electromagnetic radiation to form a fourth set of electromagnetic radiation scattered from the sample; and interfering the second set of electromagnetic radiation and the fourth set of electromagnetic radiation. The first set and the third set of electromagnetic radiation are generated from a source; at least a portion of the second set of electromagnetic radiation is of a frequency different from that of the first set of electromagnetic radiation; and at least a portion of the fourth set of electromagnetic radiation is of a frequency different from that of the third set of electromagnetic radiation.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
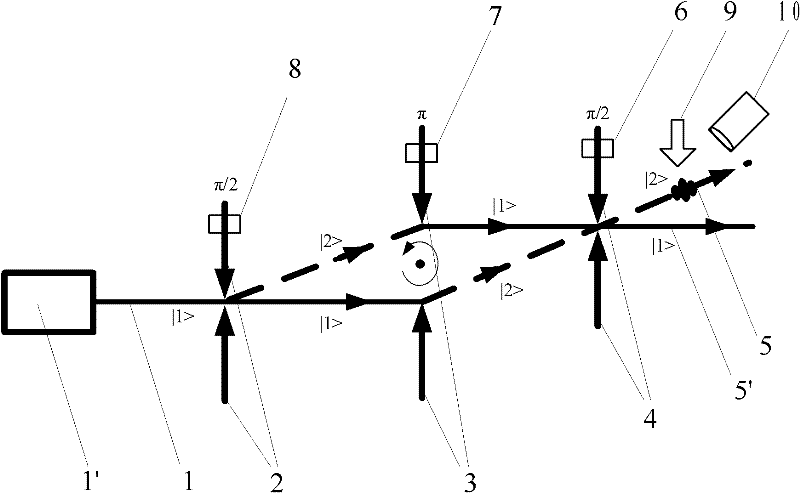
Cold atom beam interference gyro device
ActiveCN102538775AShorten speedExcellent optical propertiesSagnac effect gyrometersSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGratingFluorescence
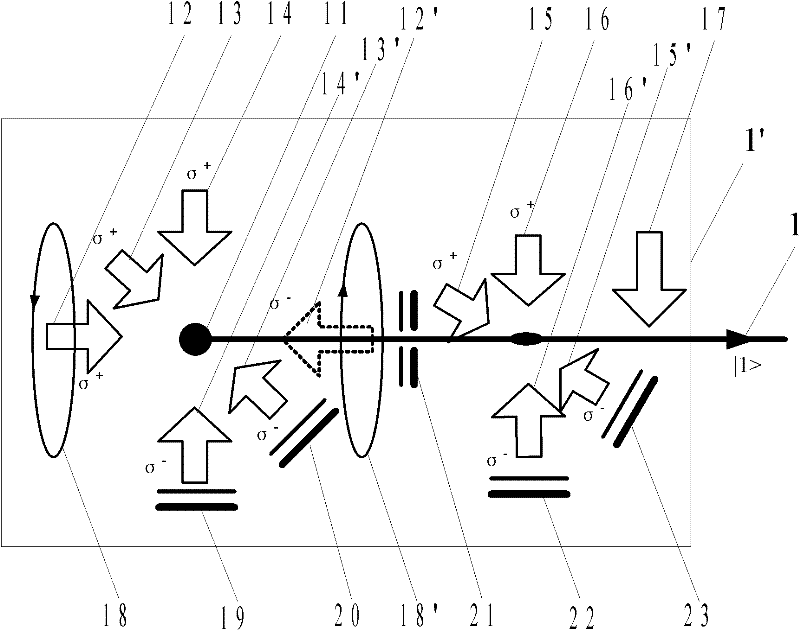
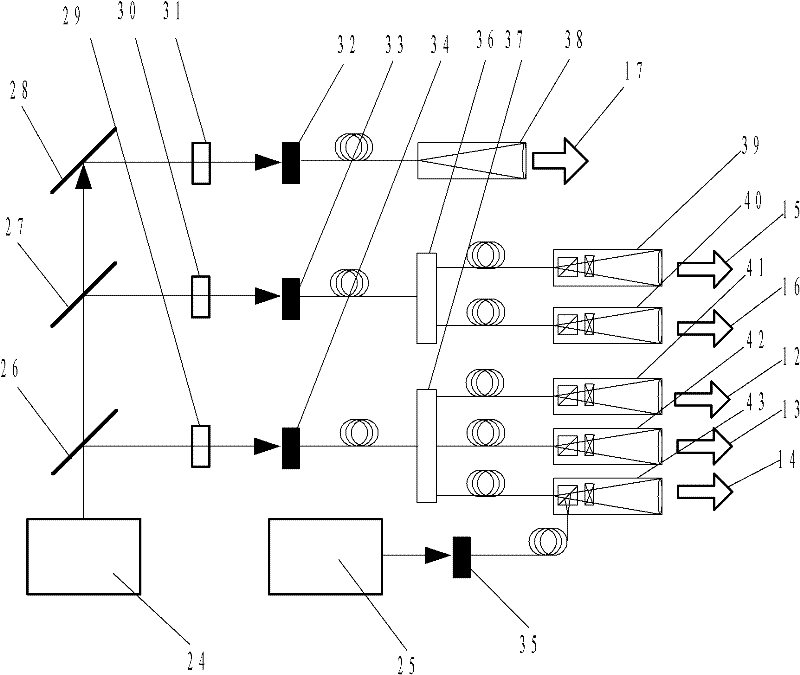
The invention discloses a cold atom beam interference gyro device, which comprises a cold atom beam system, a coherent atom beam operating system, and a gyro rotating signal extracting system. The cold atom beam system continuously emits | 1 > state cold atom beams as a matter wave source; the coherent atom beam operating system is composed of three gratings placed on the emitting path of | 1 > state cold atom beams in turn, and three phase modulators for modulating the phases of three gratings, respectively; | 1 > state cold atom beams orderly enter the three grating for splitting, reflecting and splitting again so as to obtain | 2 > energy state atom beam and | 1 > state cold atom beam interference signals; the | 2 > energy state atom beam interference signals are induced to produce fluorescent signals by the probing laser of the gyro rotating signal extracting system, a photoelectric detecting device detects the fluorescent signals and transmits the signals to a computer for processing to obtain gyro rotating angular-speed signals. With this device disclosed by the invention, high-precision gyro absolute rotating signals relative to inertial space and with high requirement on environment can be obtained.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Single sensor ring laser gyroscope
InactiveUS7330269B2Speed measurement using gyroscopic effectsSagnac effect gyrometersPath lengthControl signal
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
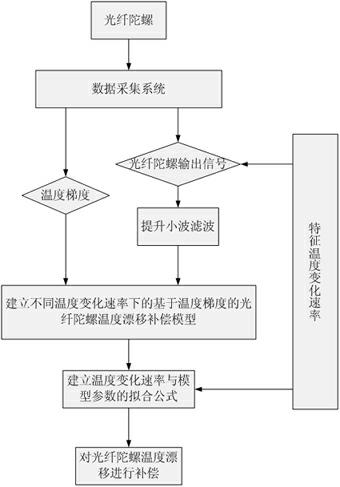
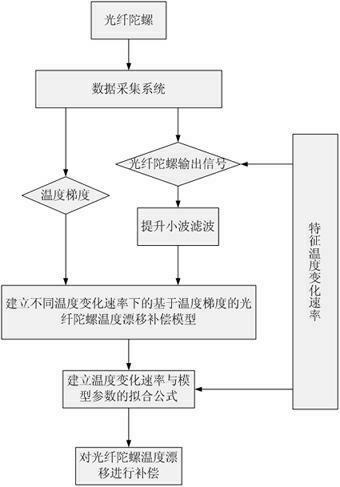
Method for modeling and error compensation of temperature drift of fiber optic gyroscope
ActiveCN102095419AComprehensive analysis to study the effects of temperature driftAnalyzing the effects of temperature driftSagnac effect gyrometersThermodynamicsFibre optic gyroscope
The invention discloses a method for modeling and error compensation of temperature drift of a fiber optic gyroscope, which comprises the following steps of: obtaining a learning sample and denoising the learning sample; establishing a fiber optic gyroscope temperature drift error compensation model based on temperature gradient; establishing a parameter formula based on a temperature change rate so as to determine the relations between the temperature change rate and various parameters of the fiber optic gyroscope temperature drift error compensation model; and subtracting a temperature drift compensation value, obtained by the fiber optic gyroscope temperature drift error compensation model, from the real-time output data of the fiber optic gyroscope to realize temperature compensation to the fiber optic gyroscope. The invention not only realizes modeling for the temperature drift of the fiber optic gyroscope in mechanism, but also simultaneously and greatly improves the convenience and accuracy of modeling, and has important significance to performance research and improvement of the fiber optic gyroscope in constantly variable temperature environments.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
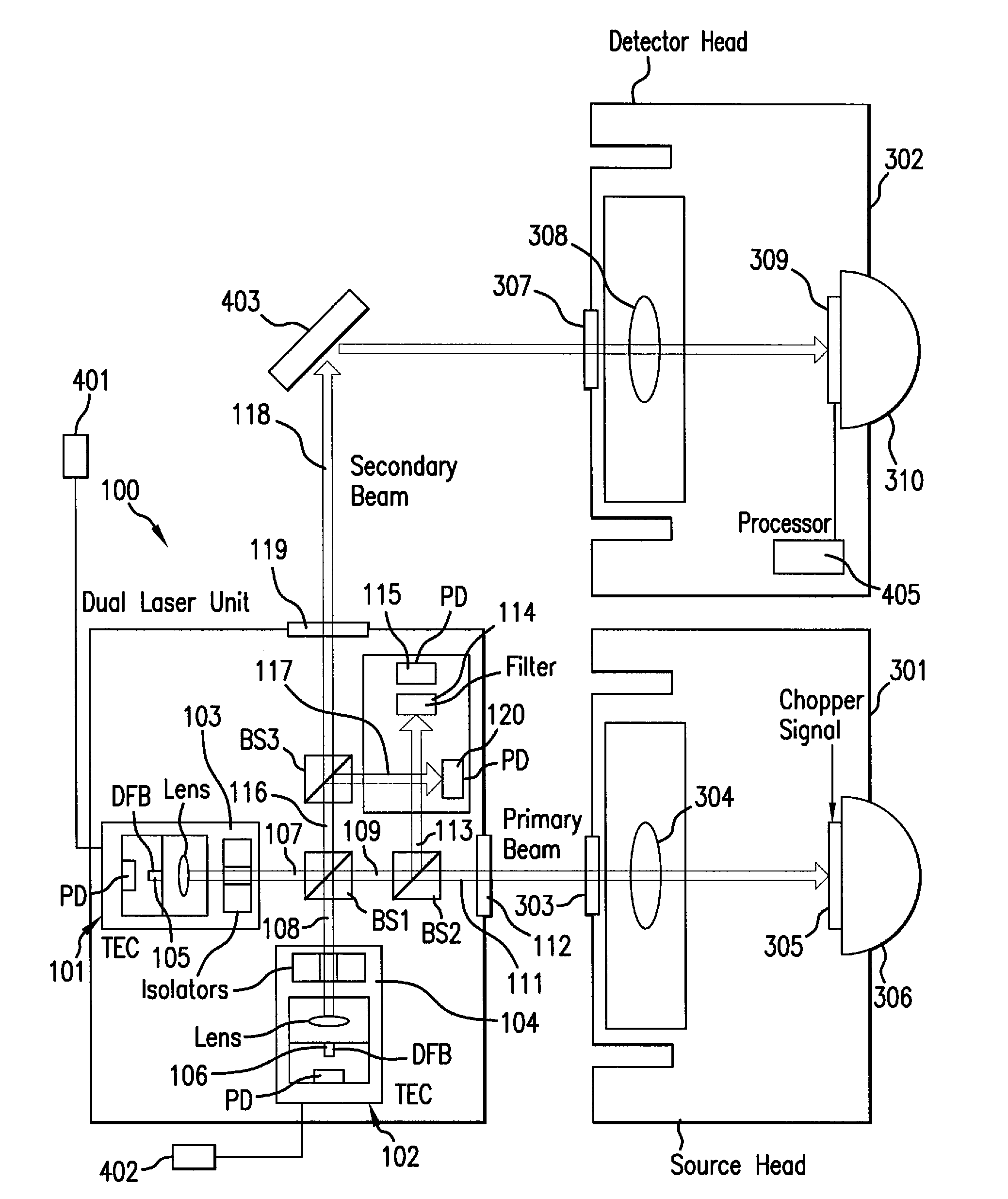
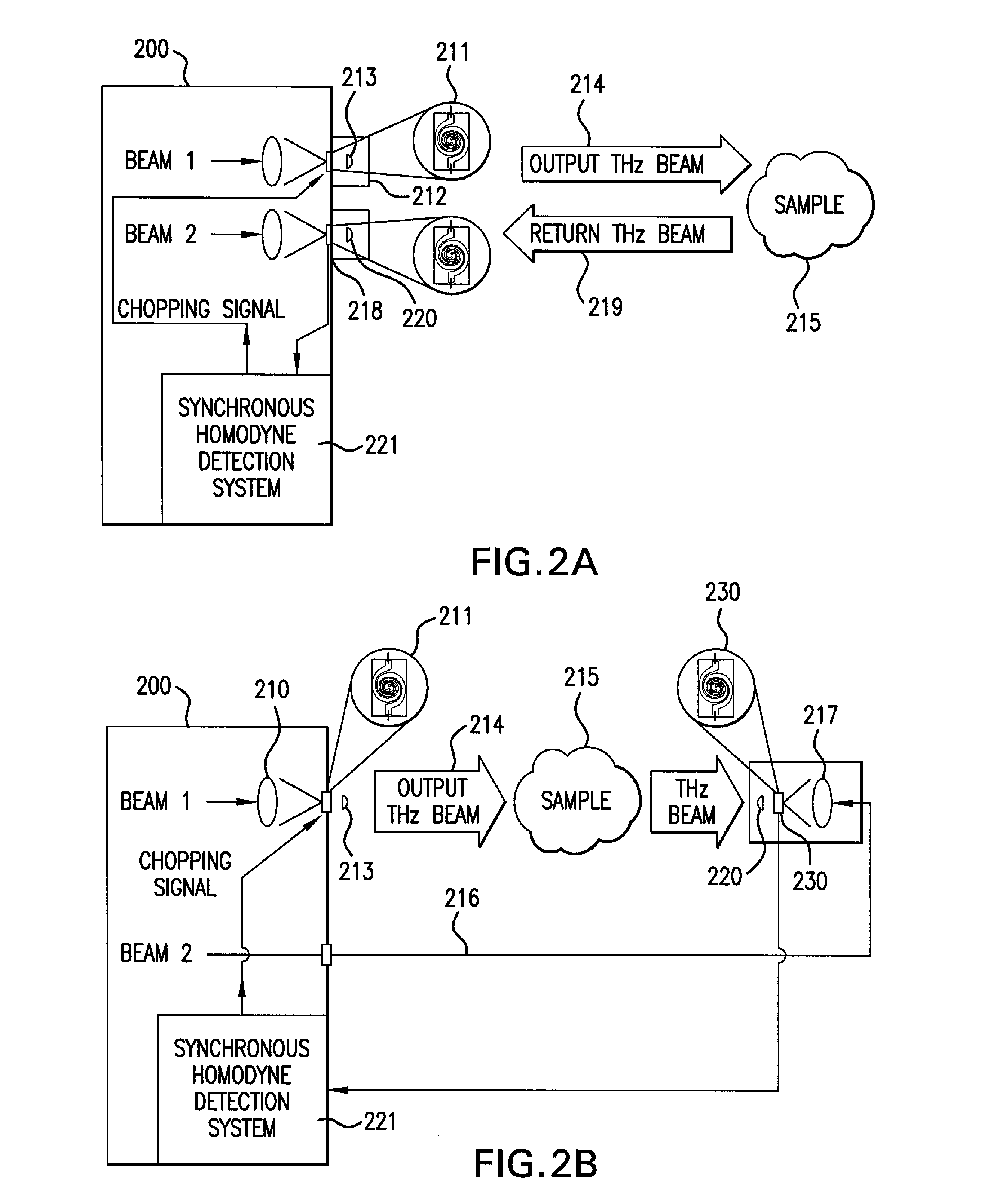
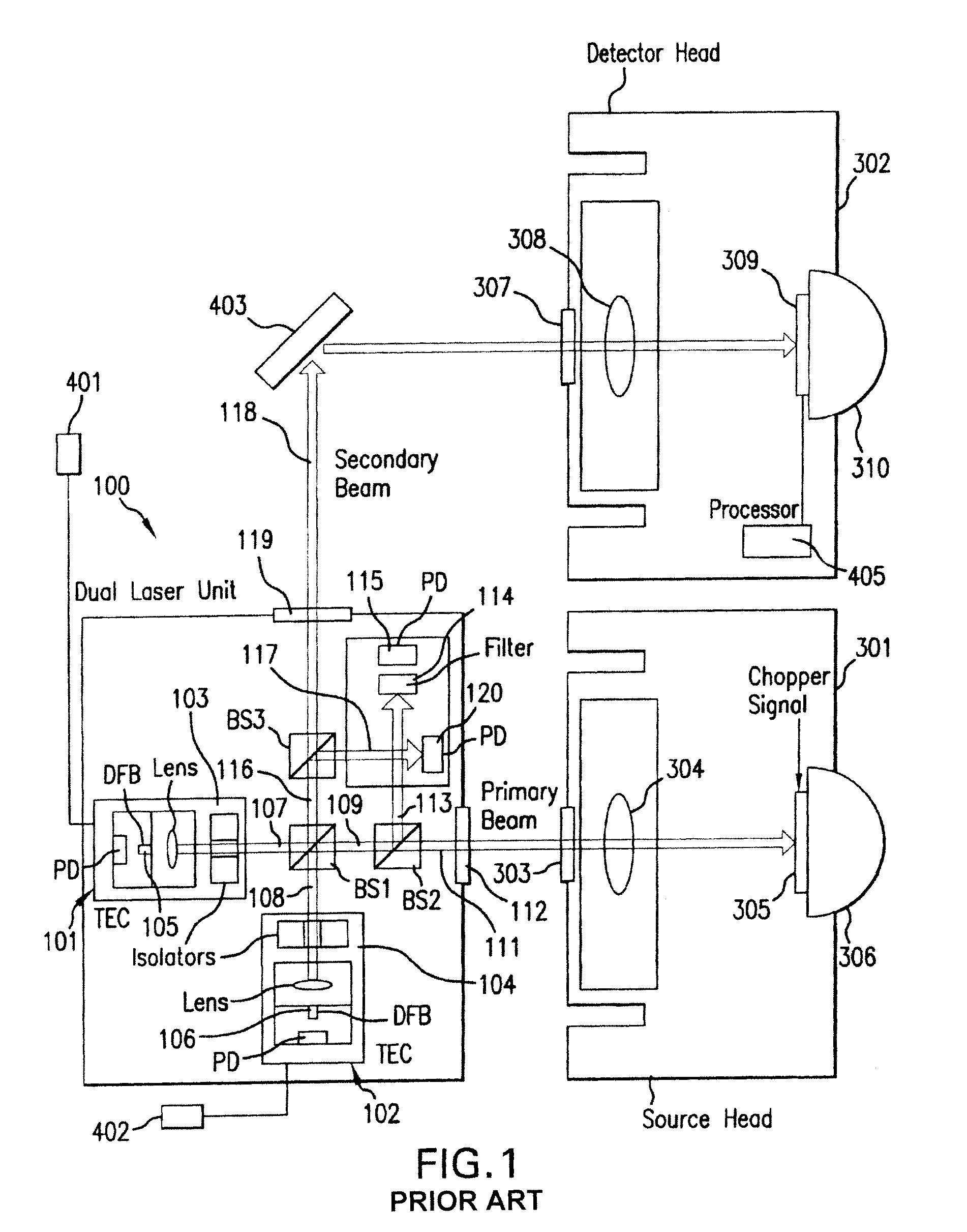
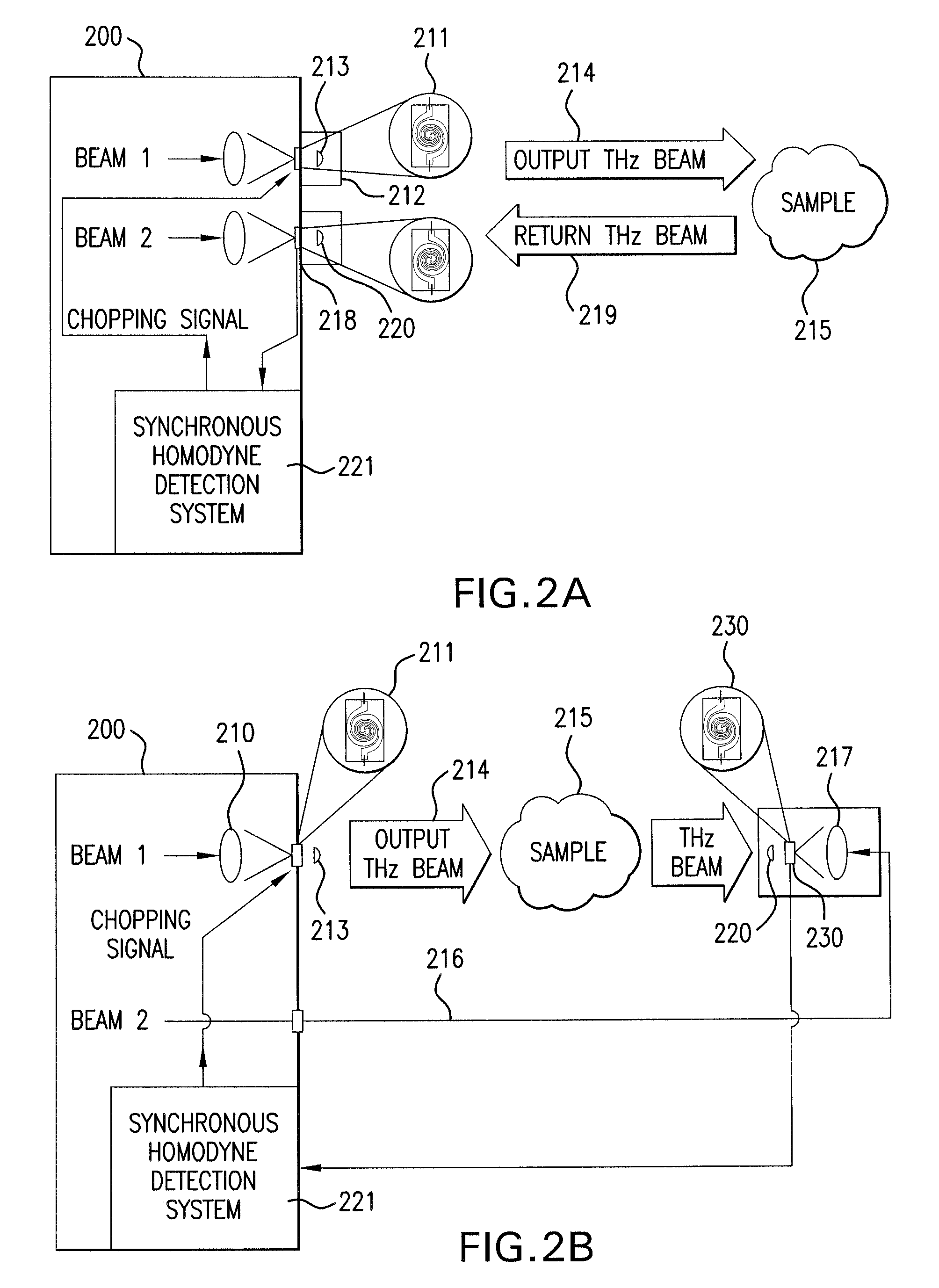
Terahertz Frequency Domain Spectrometer with Controllable Phase Shift
InactiveUS20090283680A1High resolutionHigh detection sensitivityRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansPhase shiftedPhase difference
An apparatus for analyzing, identifying or imaging an target including an integrated dual laser module coupled to a pair of photoconductive switches to produce cw signals in the range of frequencies from 100 GHz to over 2 THz focused on and transmitted through or reflected from the target; and a detector for acquiring spectral information from signals received from the target and using a multi-spectral homodyne process to generate an electrical signal representative of some characteristics of the target with resolution less than 250 MHz. The photoconductive switches are activated by laser beams from the dual laser module. The lasers in the module are tuned to different frequencies and a phase shifter in the path of one beam allows the beams to have an adjustable phase difference.
Owner:DEMERS JOSEPH R
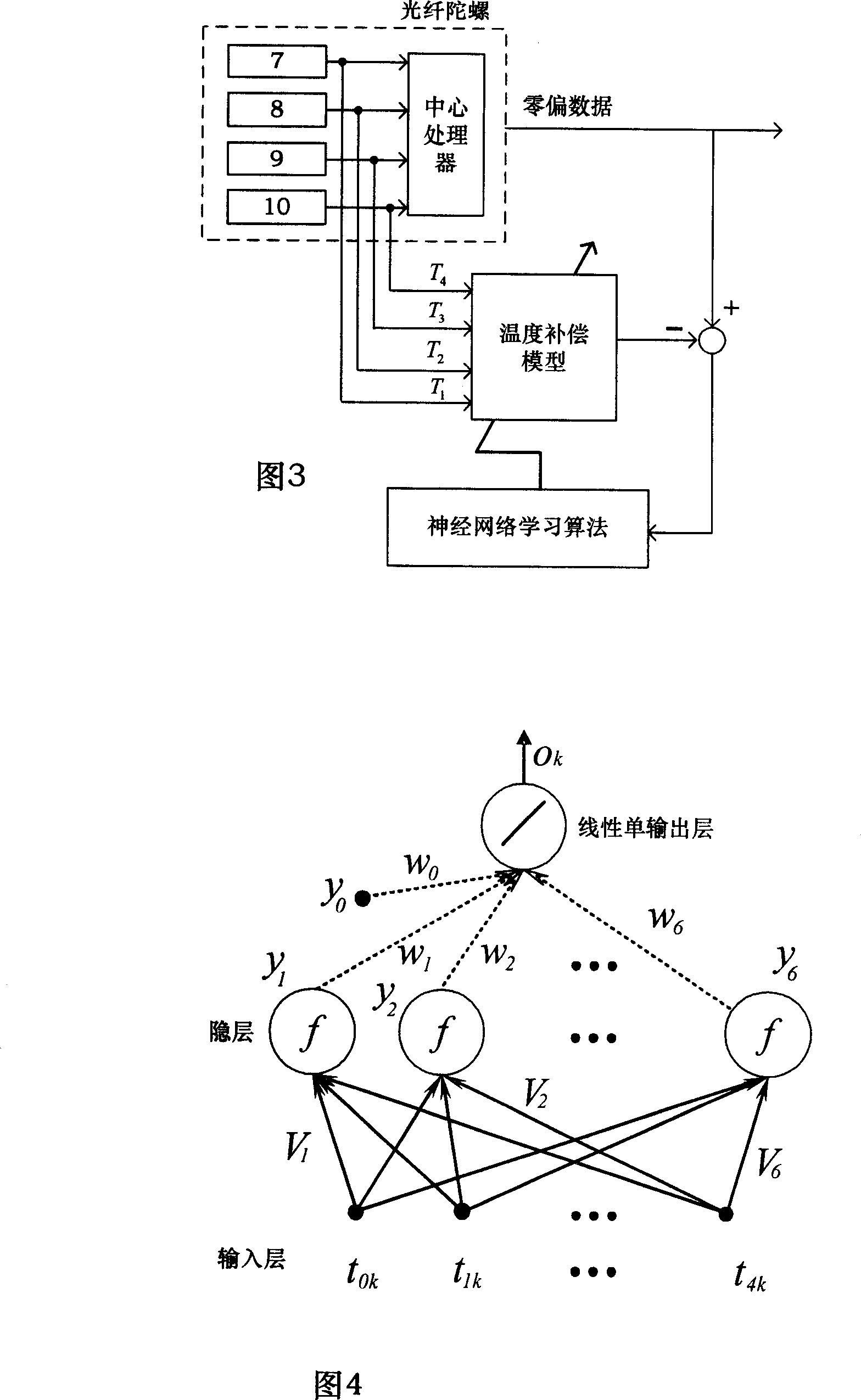
Neural net based temperature compensating optical fibre gyroscope
InactiveCN101013035AReduce computationGood nonlinear mapping abilitySagnac effect gyrometersSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopeThermodynamics
The invention discloses an FOG based on neural network to do temperature compensation, using the neural network learning algorithm for the temperature drift compensation method, and the temperature compensation method obtains the amendment temperature compensation coefficient to provide parameters for FOG high precision output. According to the effect of the temperature to the FOG output when the FOG working, it respectively installs a temperature sensor A on the light source, a temperature sensor B at the Y waveguide, a temperature sensor C at the fiber ring inside and a temperature sensor D at the fiber ring outside, and through temperature change of the four temperature sensors, and using the neural network learning algorithm for temperature compensation model training, it makes the built temperature drift compensation having good nonlinear mapping ability, self-learning ability and the generalization ability; the temperature drift compensation coefficient measurement is measured in the debugging phase, reducing the gyro computing volume when using.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Relative intensity noise controller for fiber light sources
InactiveUS20030128365A1Sagnac effect gyrometersSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsFiberOctave
A system and method is provided which suppresses relative intensity noise in a fiber optic gyroscope by taking advantage of the frequency response of erbium fiber. In operation, the gain provided by the erbium fiber is added to the gain of the other components in the feedback loop to provide for stable loop performance up to about 250 kHz. The frequency response of the erbium fiber of about 3 kHz also provides a 6 db per octave roll-off, which, when used in a negative feedback control loop for controlling the current flowing to the gyroscope light source, allows for a relative intensity noise control loop with a bandwidth much greater than 3 kHz; this may be used in high performance gyroscope applications.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Transmission mode RFOG and method for detecting rotation with RFOG
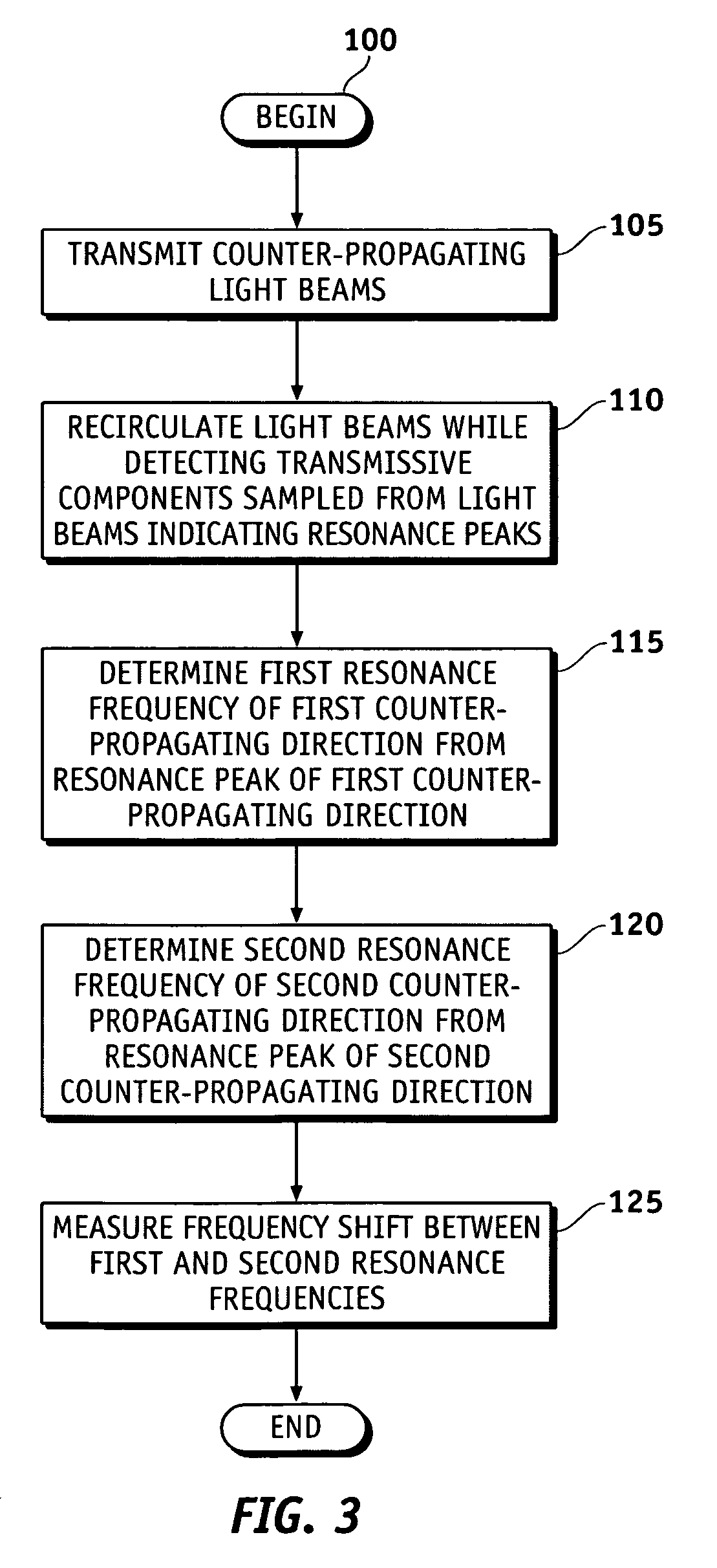
ActiveUS7327460B2Speed measurement using gyroscopic effectsSagnac effect gyrometersResonanceLight beam
Methods and apparatus are provided for sensing a rotation rate of a ring resonator in a transmission mode. A ring resonator for circulating light beams in counter-propagating directions comprises an optical fiber coil having a hollow core and first and second ends. A first optical element is configured to receive an input light beam and direct a portion of the input light beam in a counter-propagating direction of the ring resonator. A second optical element is configured to direct with the first optical element a majority of a circulating light beam in the counter-propagating direction of the ring resonator and derive a transmission mode component of the circulating light beam at one of the ends. The portion of the input light beam enters one of the first and second ends. The circulating light beam is based on the input light beam. The transmission mode component indicates a resonance peak of the counter-propagating direction of the ring resonator.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Fiber optic sensor
InactiveUS20030169956A1Force measurement by measuring optical property variationMaterial analysis by optical meansEnvironmental effectPath length
A method is provided for sensing an environmental effect upon a sensing element and includes exposing the sensing element into the environmental effect, producing a light signal in the sensing element, modulating the light signal with a modulation signal, and determining a path length of the light signal as a function of the modulation signal. A fiber optic sensor is provided that includes a light source producing a light, a sensing element optically coupled to the light source such that the light propagates through the sensing element, a detector optically coupled to the sensing element. The detector detects light intensity propagating in the sensing element. An electronics processor receives the detector output and produces a modulation signal for the light. The processor further produces an output signal indicative of the environmental effect as a function of the modulation signal.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Active sensor, multipoint active sensor, method for diagnosing deterioration of pipe, and apparatus for diagnosing deterioration of pipe, and apparatus for diagnosis deterioration of pipe
ActiveUS7711217B2Reduce the numberShorten the timeAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansEngineeringOscillatory waves
An active sensor 10 is positioned on an outside of a pipe 60 so as to detect a thickness of the pipe. The active sensor comprises: an oscillator 15 capable of inputting oscillatory waves into the pipe and sweeping a frequency of the oscillatory waves within a desired range; and an optical fiber sensor mounted on the pipe, the optical fiber sensor detecting the oscillatory waves generated in the pipe.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
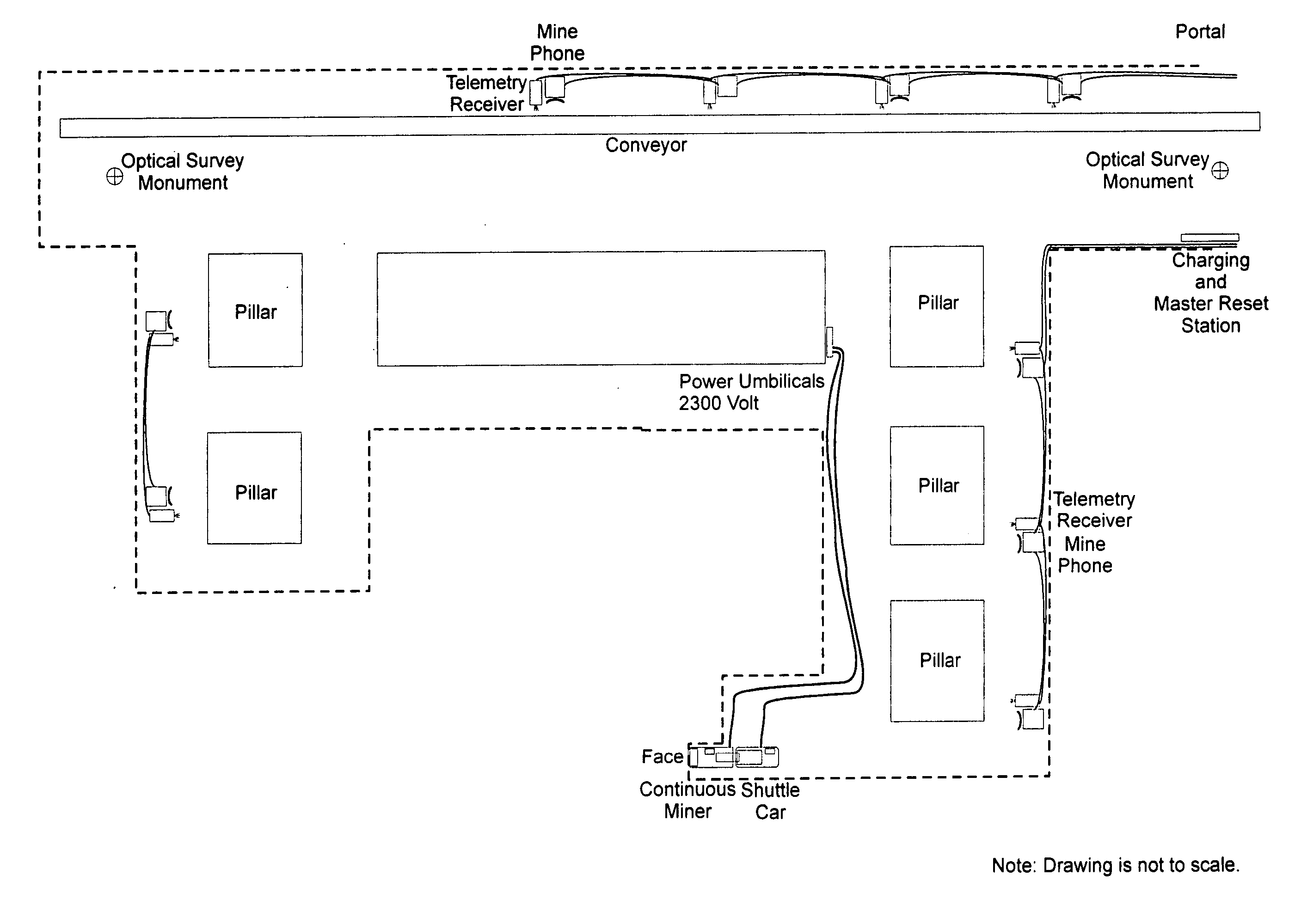
Inertial sensor tracking system
InactiveUS20070241886A1Direction finders using radio wavesRoad vehicles traffic controlGyroscopeAccelerometer
The INERTIAL SENSOR TRACKING SYSTEM is an overall system installation consisting of wireless body pack transmitters, broadband telemetry transceivers, computer and monitoring equipment, and emergency power generation for tracking personnel in an underground mine environment. The system is designed to function with normal primary power and on battery operation in the event of an emergency. In the past inertial sensors have been large spinning mass gyroscopes and large mass-based accelerometers. These inertial sensors have required high voltage three phase electrical supplies. The “wearable” body pack must be battery operated and the sensors must be small and lightweight. Micro-Electro-Mechanical (MEM) sensors fulfill both the requirements of low weight and low power consumption. The accuracy of the MEM sensor has been developed sufficiently to incorporate, with de-noising algorithms, an accurate position-sensing device. The proliferation of broadband TCP / IP protocol based RF systems provides a standardized medium of transmission, which will work in an underground environment.
Owner:INSET SYST
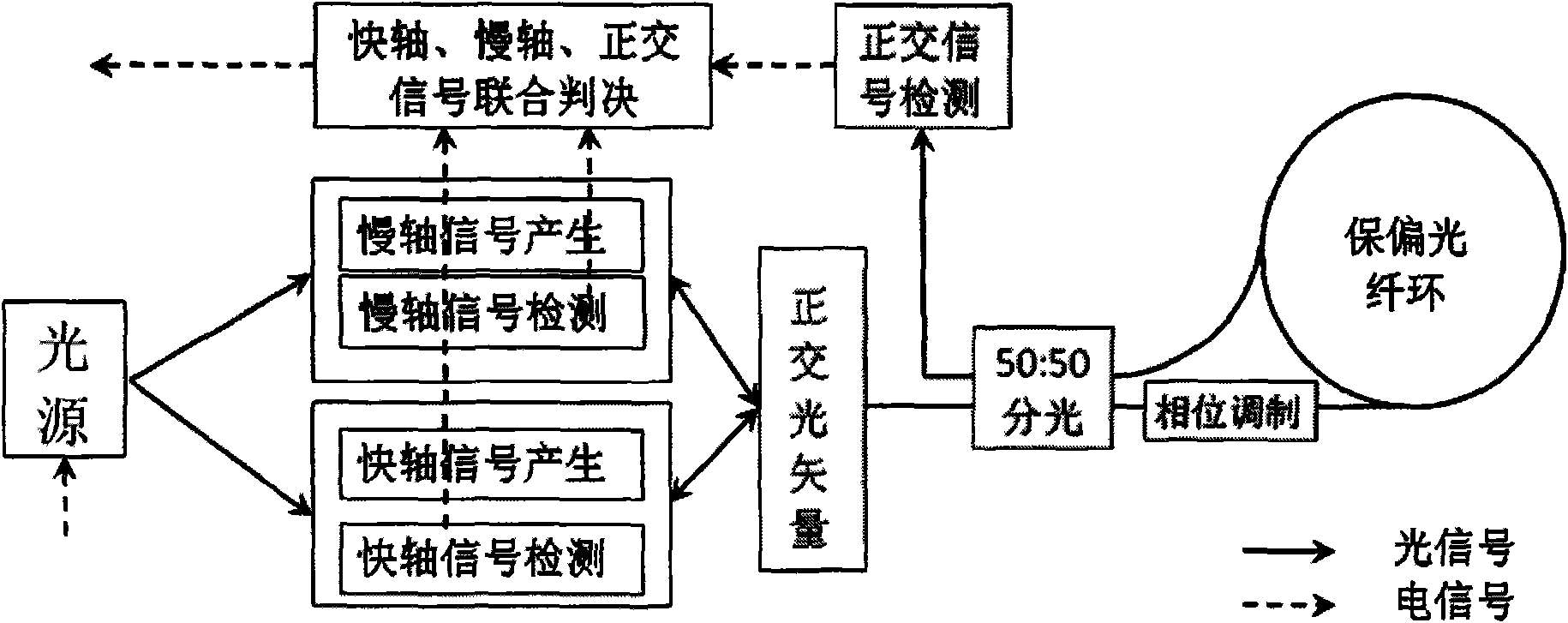
Dual-polarization interferometric fiber-optic gyro
InactiveCN101629825AHigh measurement accuracyImprove measurement stabilitySagnac effect gyrometersBeam splitterAngular velocity
The invention discloses a dual-polarization interferometric fiber-optic gyro which belongs to the field of communication technology. The fiber-optic gyro comprises a light source, two linear polarized light generating circuits, two signal detection light paths, a polarized beam splitter / combiner, a polarization-maintaining coupler, a phase modulator and a polarization-maintaining fiber-optic ring; wherein the light source is connected with the input ends of the two linear polarized light generating circuits by optic fibers; two output ends of the two linear polarized light generating circuits are respectively connected with two ports at the same side of the polarized beam splitter / combiner by optic fibers through one signal detection light path; the port at the other side of the polarized beam splitter / combiner is connected with the polarization-maintaining fiber-optic ring through the polarization-maintaining coupler; and the phase modulator is connected between the polarization-maintaining fiber-optic ring and the polarization-maintaining coupler by optic fibers. Compared with the prior art, the fiber-optic utilizes the dual-polarized light to carry out the detection, thereby greatly improving the measuring precision and the measuring stability of the rotating angular velocity; meanwhile, the fiber-optic gyro has the advantages of simple structure, low cost, small volume, high sensitivity and wide application range simultaneously.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Terahertz frequency domain spectrometer with controllable phase shift
InactiveUS7781736B2High resolutionDetection sensitivityRadiation pyrometryPolarisation-affecting propertiesPhase shiftedPhase difference
An apparatus for analyzing, identifying or imaging an target including an integrated dual laser module coupled to a pair of photoconductive switches to produce cw signals in the range of frequencies from 100 GHz to over 2 THz focused on and transmitted through or reflected from the target; and a detector for acquiring spectral information from signals received from the target and using a multi-spectral homodyne process to generate an electrical signal representative of some characteristics of the target with resolution less than 250 MHz. The photoconductive switches are activated by laser beams from the dual laser module. The lasers in the module are tuned to different frequencies and a phase shifter in the path of one beam allows the beams to have an adjustable phase difference.
Owner:DEMERS JOSEPH R
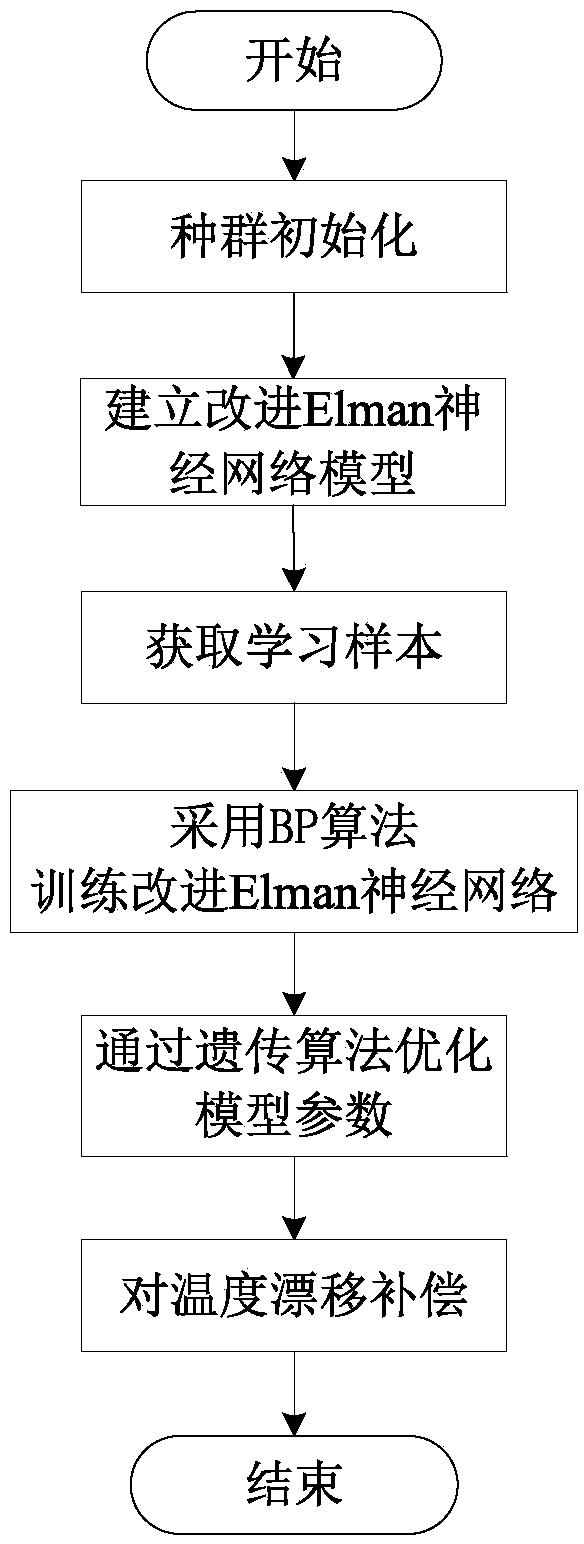
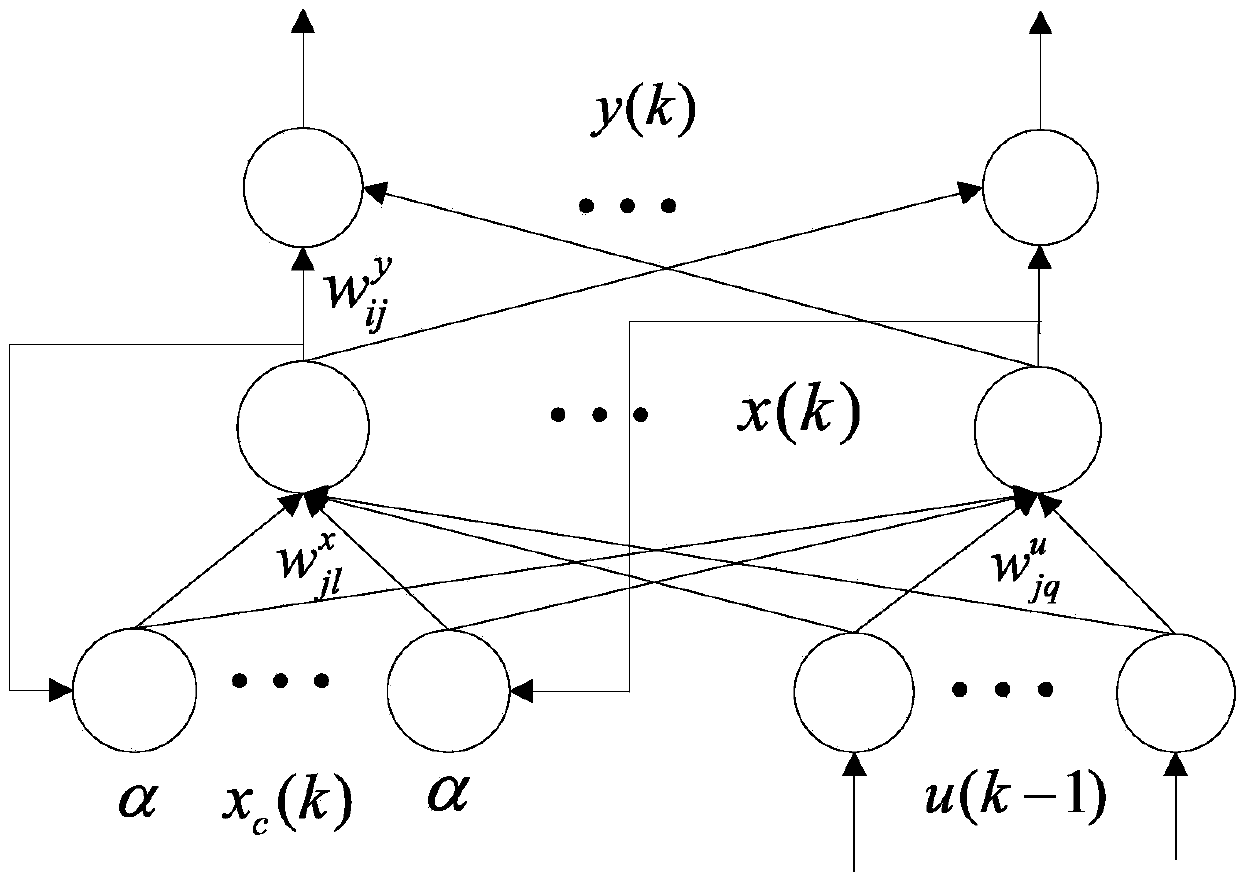
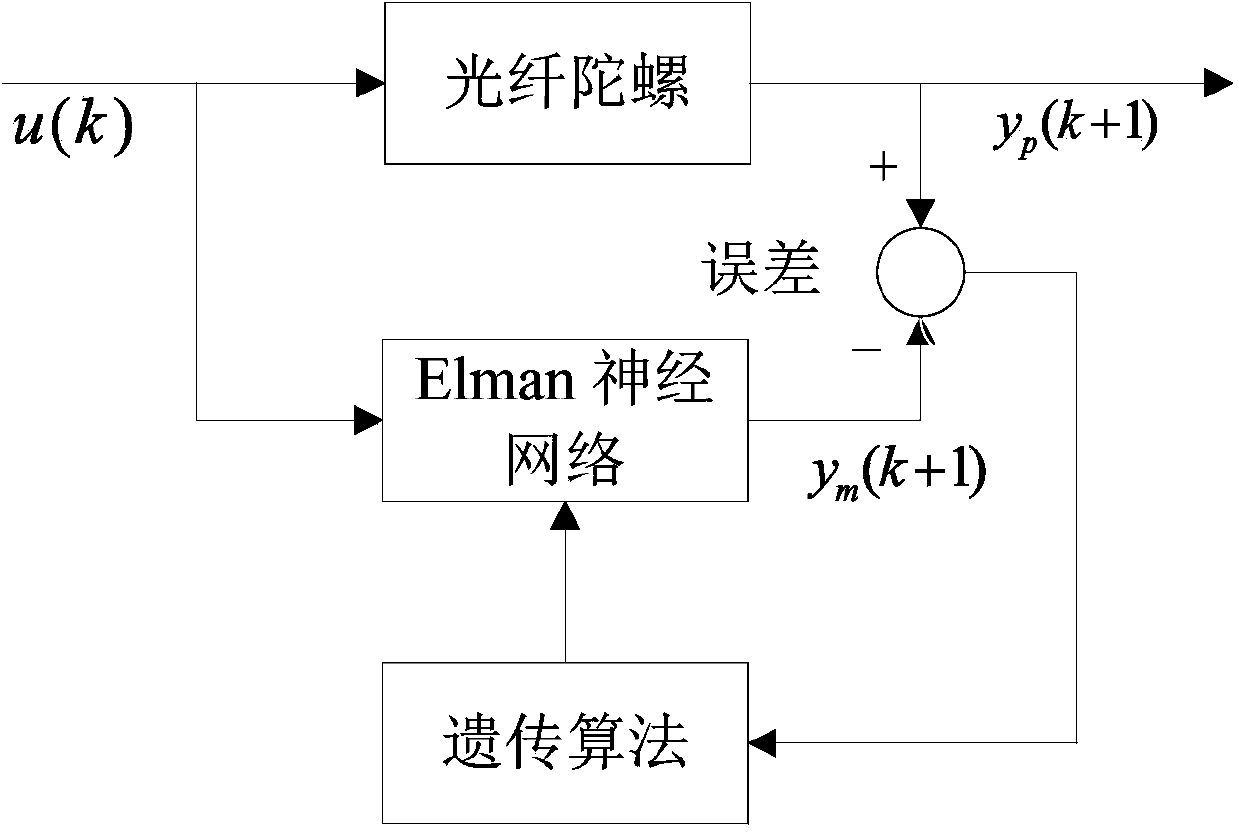
Fiber optic gyroscope temperature drift modeling method by optimizing dynamic recurrent neural network through genetic algorithm
ActiveCN103593538AWith dynamic memorySimplify the scaleBiological neural network modelsSagnac effect gyrometersFiberGyroscope
The invention discloses a fiber optic gyroscope temperature drift modeling method by optimizing a dynamic recurrent neural network through a genetic algorithm. The fiber optic gyroscope temperature drift modeling method by optimizing the dynamic recurrent neural network through the genetic algorithm comprises the following steps of (1) initializing network parameters, and establishing an improved Elman neural network model; (2) obtaining a training and testing sample; (3) training an improved Elman neural network, and optimizing model parameters through the genetic algorithm; (4) outputting forecasts of an fiber optic gyroscope, and compensating errors. The output of the fiber optic gyroscope processed through a denoising algorithm is trained by introducing the improved Elman neural model with self-feedback connection weight, constant iterative optimization is carried out on the model parameters through the genetic algorithm, and the optimal model is obtained according to the magnitude of the errors of the model under different parameters. According to the fiber optic gyroscope temperature drift modeling method by optimizing the dynamic recurrent neural network through the genetic algorithm, the complexity of the algorithm is taken into consideration, the accuracy of the fiber optic gyroscope temperature drift model is improved, the application of the fiber optic gyroscope temperature drift model in engineering is expanded, and certain practical significance is achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
High gain resonant modulator system and method
InactiveUS20060083456A1Improve slope efficiencyIncreased analog link gainLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingMach–Zehnder interferometerResonator
An optical resonant modulator includes an optical ring resonator and an optical loop that is coupled to the optical ring resonator by two couplers. The optical ring resonator can have a hybrid design in which the ring resonator is formed on an electro-optically passive material and the optical loop is formed on an electro-optically active material. An amplification section can be inserted between the electro-optically passive and the electro-optically active sections. In analog applications, an optical resonator includes a Mach Zehnder interferometer section having an input and an output, with a feedback path coupling the output to the input. Applications of the optical modulator of the invention, and a method for modulating an optical signal also are disclosed.
Owner:PHOTONICSYST
Photoelectric detector amplitude versus frequency character test method for optical fiber peg-top
InactiveCN101126784AAccurate Frequency CharacteristicsAccurately obtain frequency characteristicsSagnac effect gyrometersContactless testingGyroscopePhotodetector
The utility model discloses a method for testing the frequency properties of the photoelectric detector used for fiber optic gyroscopes. A signal generator produces sinusoidal signals and adds the signal to a light intensity modulator to carry out sinusoidal modulation on the optical power of the optical signal from the fiber source in order to produce an optical signal with sinusoidal components. The measured photodetector converts the modulated optical signal into an electrical signal and samples the electric signal by means of high-speed data acquisition card, then conducts narrowband filter and signal processing over the collected samples and calculates the corresponding frequency response. The frequency sequence pre-selected by a numerical control system changes the frequency at which the sine wave generator (NC) system sends out signals , tests a series of frequency point responses, which can be combined into an amplitude frequency response curve of the measured photodetector, and the curve is transmitted to the terminal computer for displaying and storage. By controlling all the test processes by numerical control system, the utility model has the advantages of automatic measurement, fast testing speed, high testing precision, and therefore is suitable for carefully weighing the photodetector frequency performance in the whole operating frequency range.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Detection apparatus and method for miniature resonance type optical gyroscope with double-signal combined modulation
InactiveCN101464151AEasy to implementMiniaturizationSagnac effect gyrometersResonant cavityOptical gyroscope
The invention discloses a device and a method for detecting a micro resonant mode optical gyro in dual-signal combined modulation. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out the dual-signal combined modulation to a laser input into the chip of a micro optical ring-shaped resonant cavity, and synchronously demodulating the clockwise and counterclockwise output signals of the optical ring-shaped resonant cavity, wherein, one demodulated signal controls the frequency of a laser device through a servo loop, so that the frequency of the output light of the laser device can be tracked and locked on the resonant frequency; and the other demodulated signal extracts the difference of the two resonant frequencies and outputs the difference as a gyro signal. The invention is favorable for realizing the micro resonant mode optical gyro in an integrated optical device and the miniaturization of the system, improves the output signal-to-noise ratio of the micro resonant mode optical gyro, suppresses the noise caused by backscattering, and reduces the control precision in modulation amplitude required by the system and improves the stability of the system at the same time.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Relative intensity noise controller with maximum gain at frequencies at or above the bias modulation frequency or with second order feedback for fiber light sources
InactiveUS6765678B2Speed measurement using gyroscopic effectsSagnac effect gyrometersFiberNegative feedback
A system and method is provided which suppresses relative intensity noise in a fiber optic gyroscope by taking advantage of the frequency response of erbium fiber. In operation, the gain provided by the erbium fiber is added to the gain of the other components in the feedback loop to provide for stable loop performance up to about 250 kHz. The frequency response of the erbium fiber of about 3 kHz also provides a 6 db per octave roll-off, which, when used in a negative feedback control loop for controlling the current flowing to the gyroscope light source, allows for a relative intensity noise control loop with a bandwidth much greater than 3 kHz; this may be used in high performance gyroscope applications.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Fiber gas lasers and fiber ring laser gyroscopes based on these gas lasers
InactiveUS20080094636A1Good amplification performanceSimple structureLaser using scattering effectsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsFiber couplerGyroscope
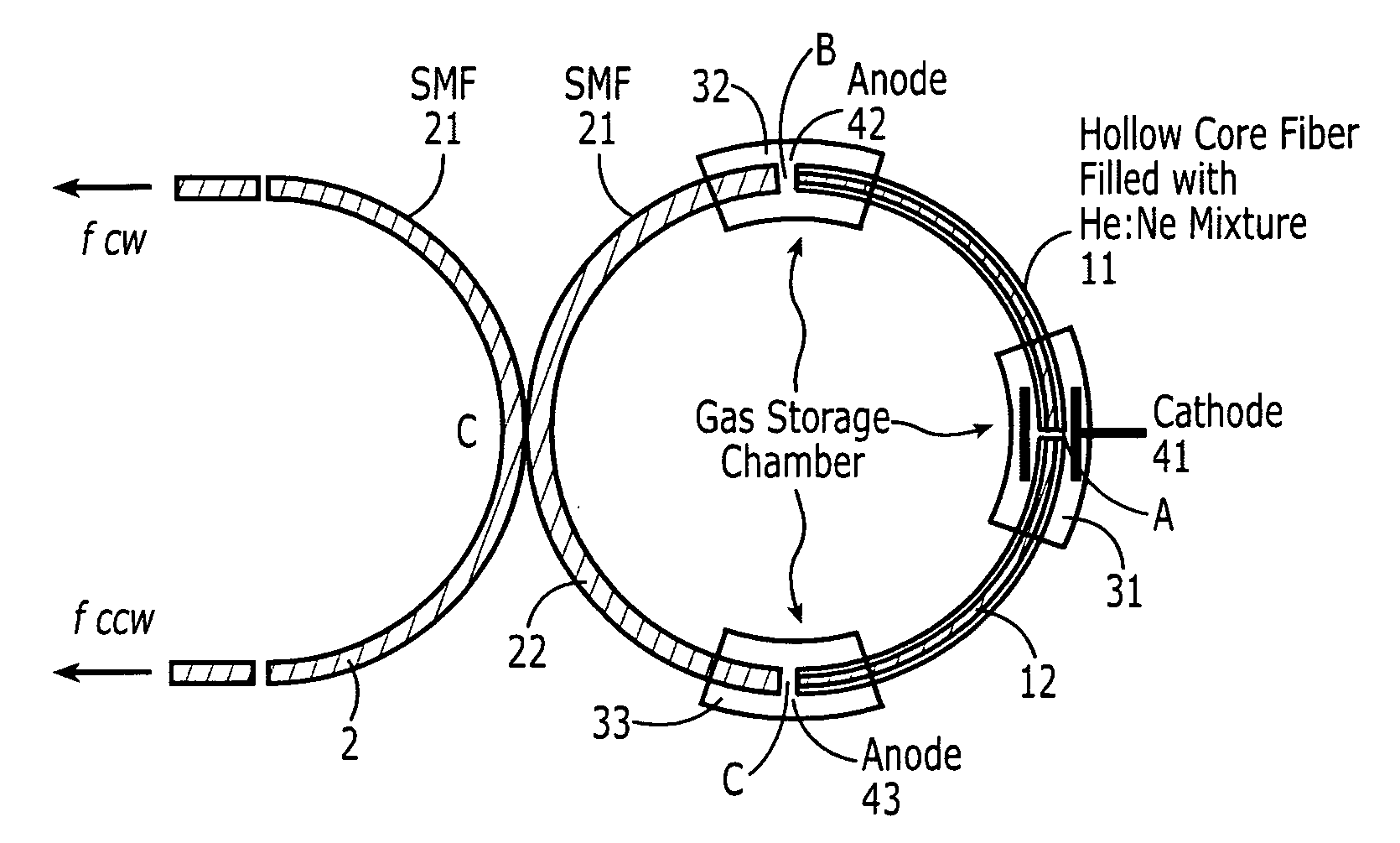
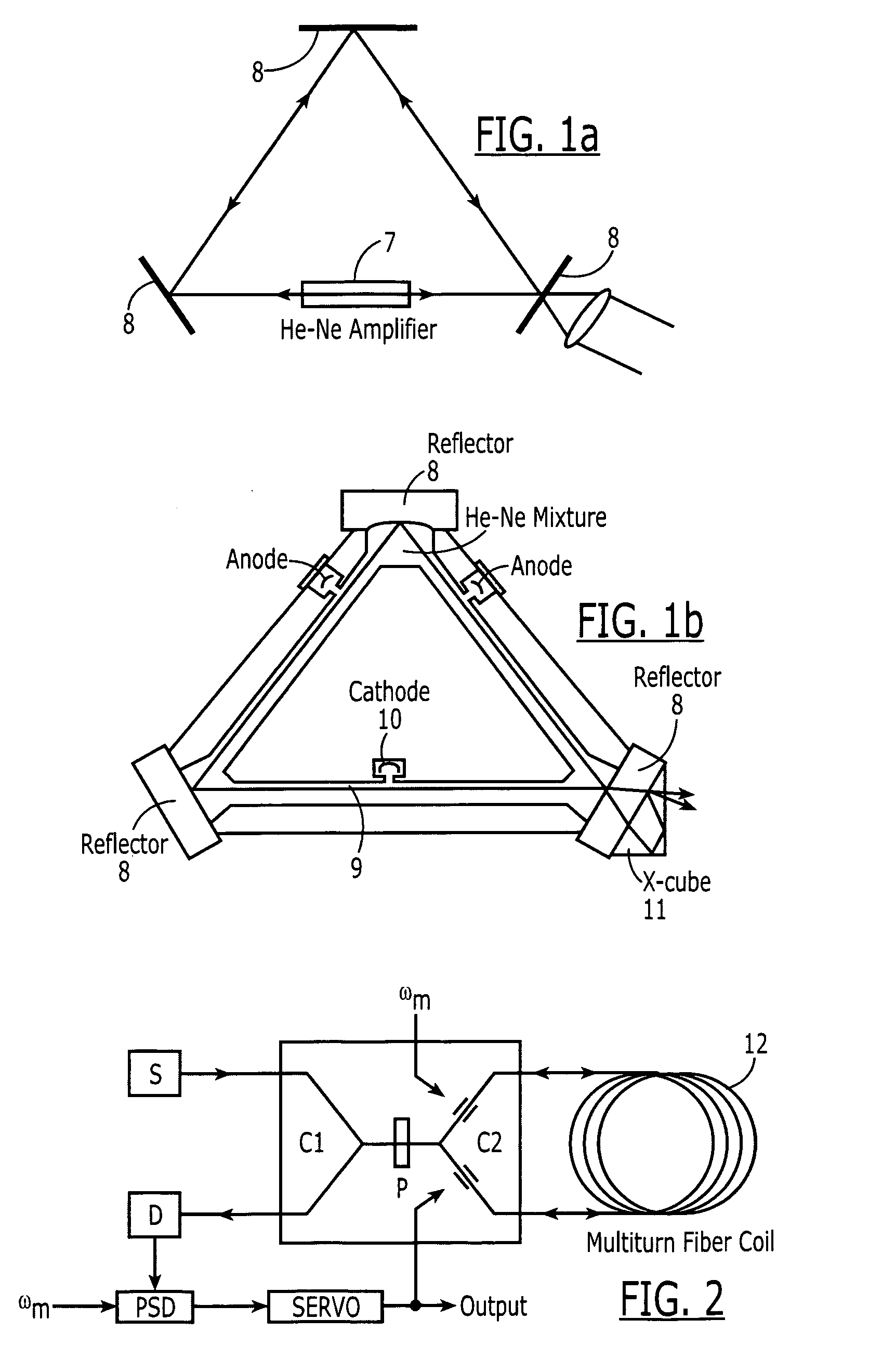
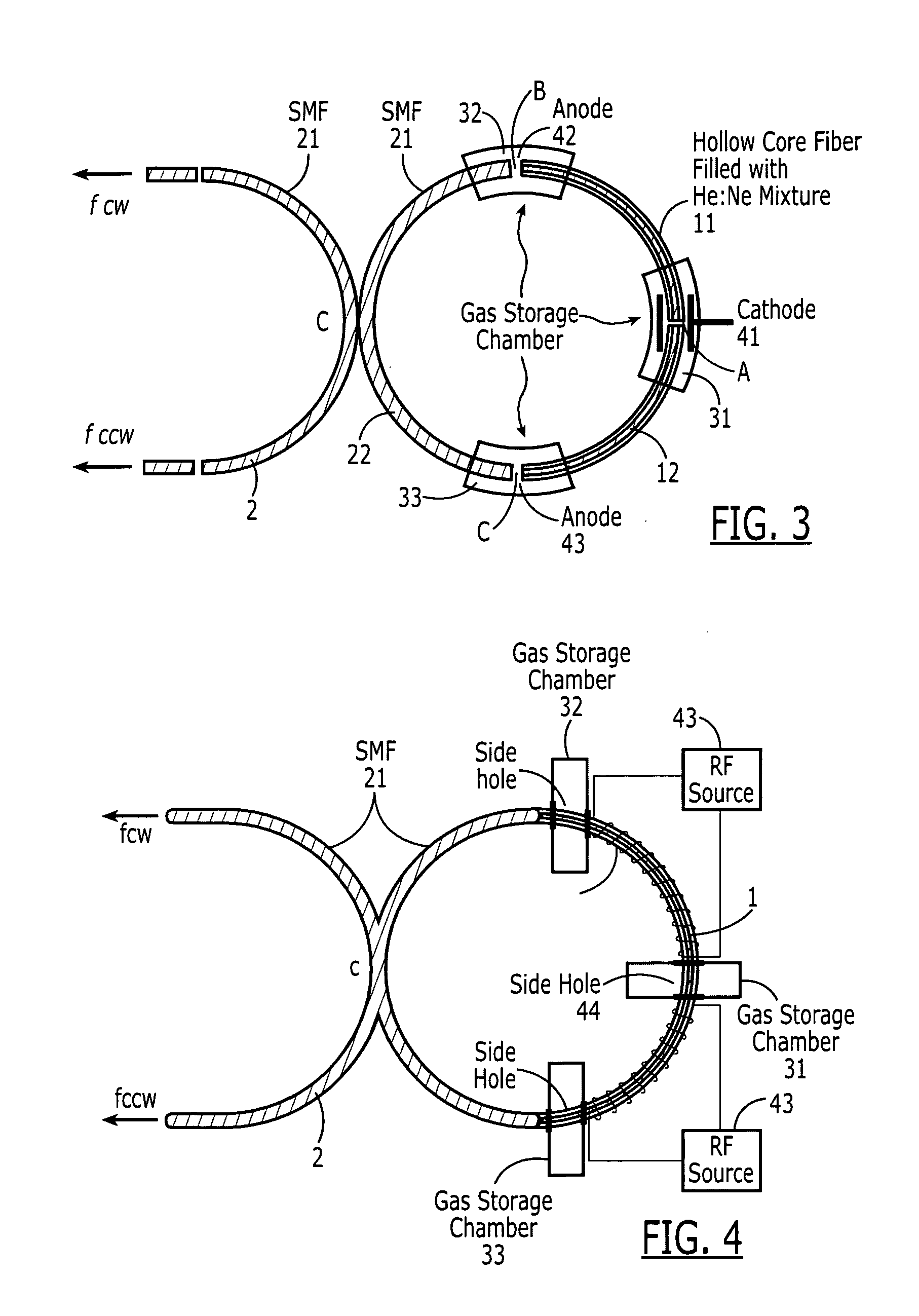
This invention discloses to a type of fiber gas lasers and fiber ring laser gyroscopes based on these fiber gas lasers. The fiber gas lasers comprise of excitation gases, optical resonator and excitation source, etc. The optical resonator is made by connecting two selected arms of a single mode fiber coupler to the two ends of hollow-core fiber to form a ring resonator. The hollow-core of the fiber is filled with excitation gases to act as gain medium. The fiber laser is simple to construct, lower cost, and has adjustable size and good amplification performance. The fiber ring laser gyroscopes based on this novel type of gas lasers can be applied on robotics, automobile navigation, etc.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com