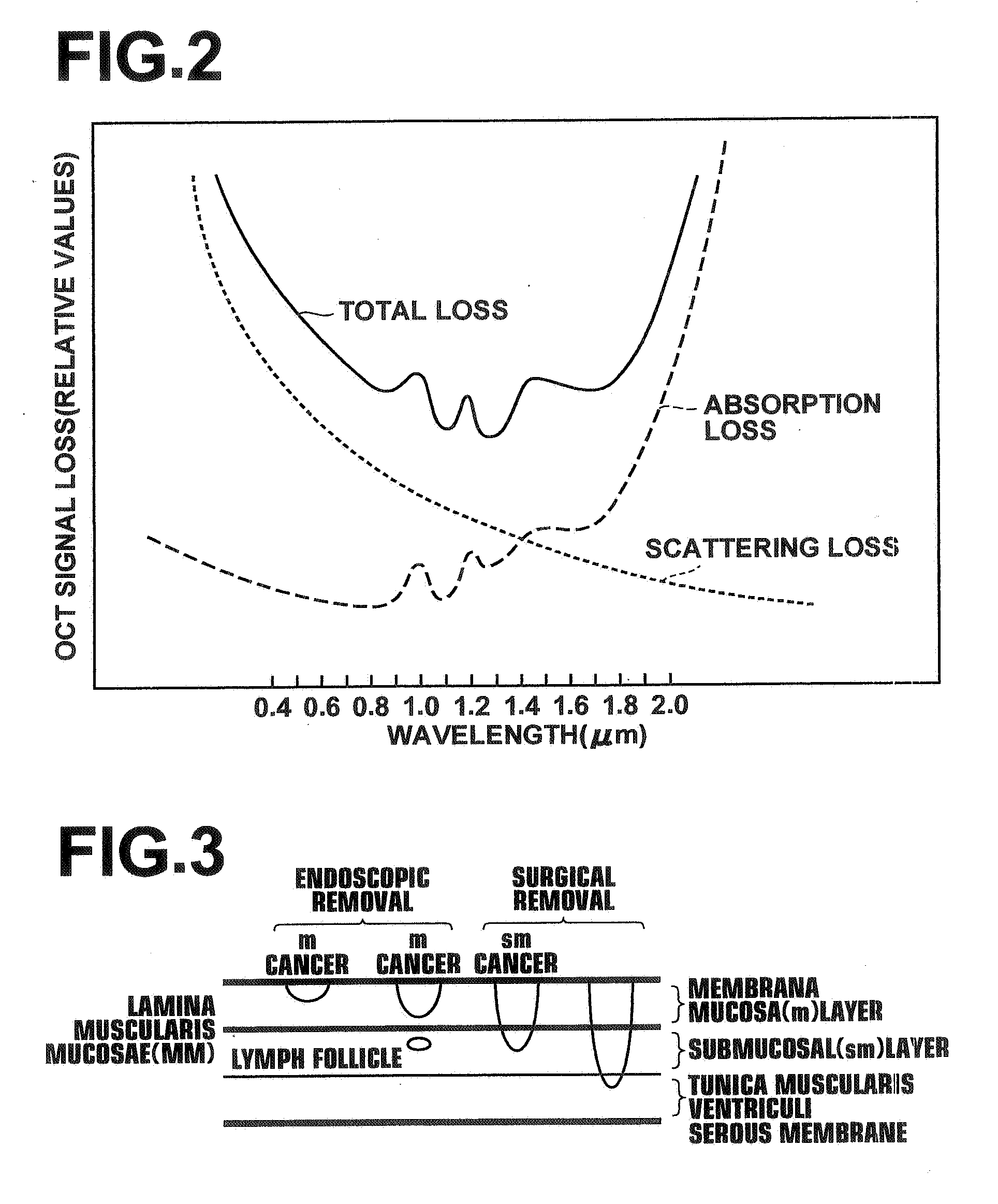
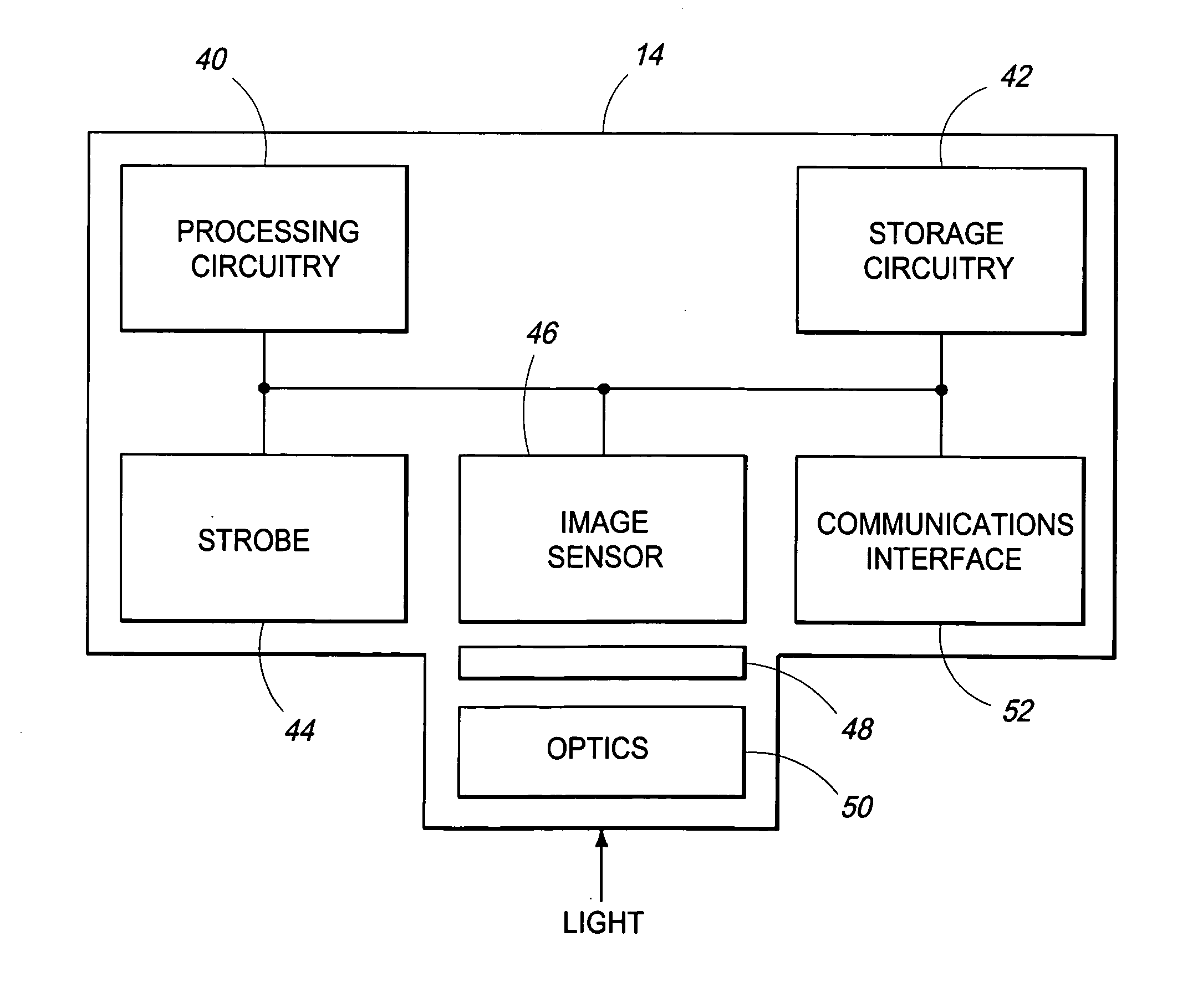
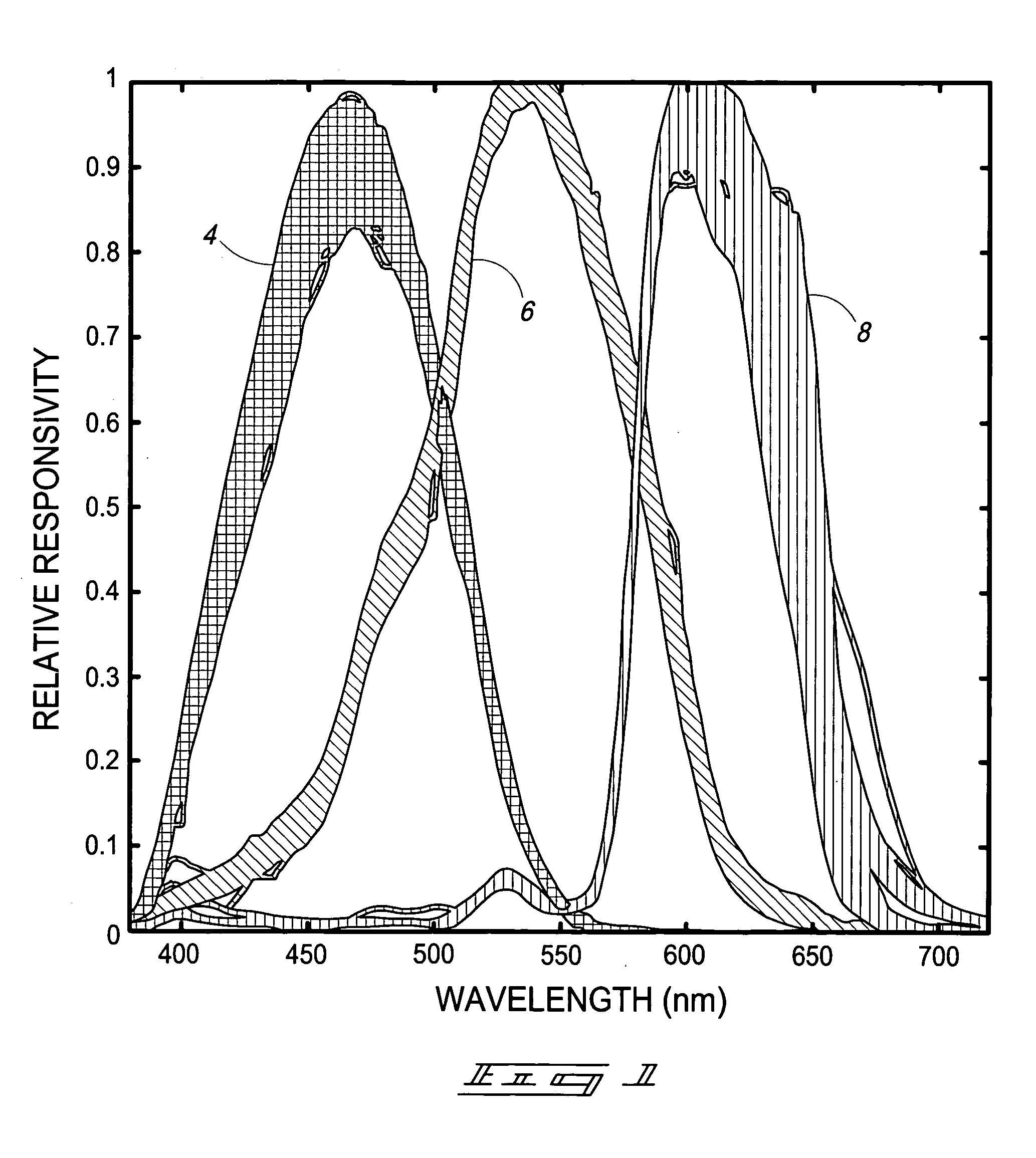
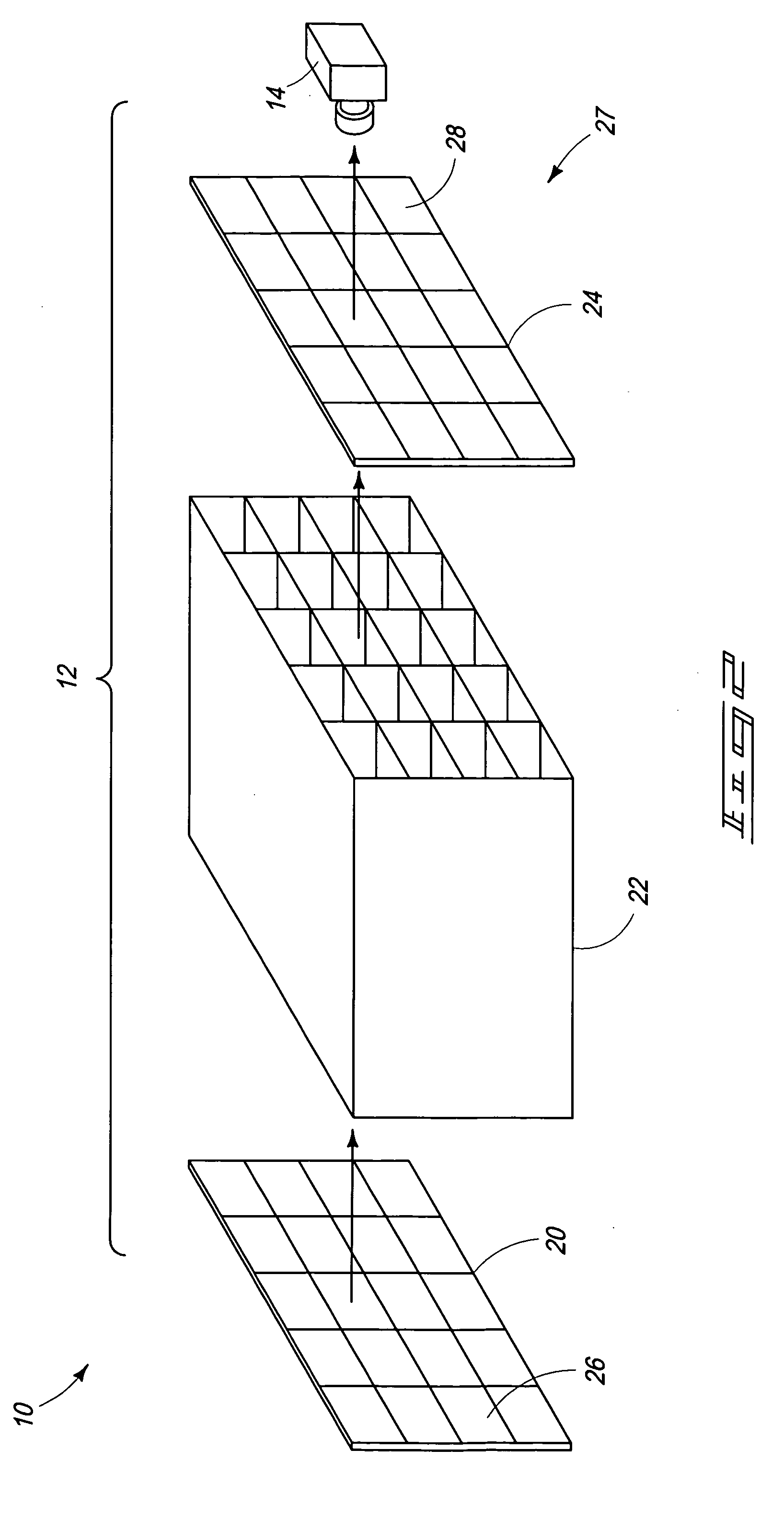
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5636results about "Spectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromators" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
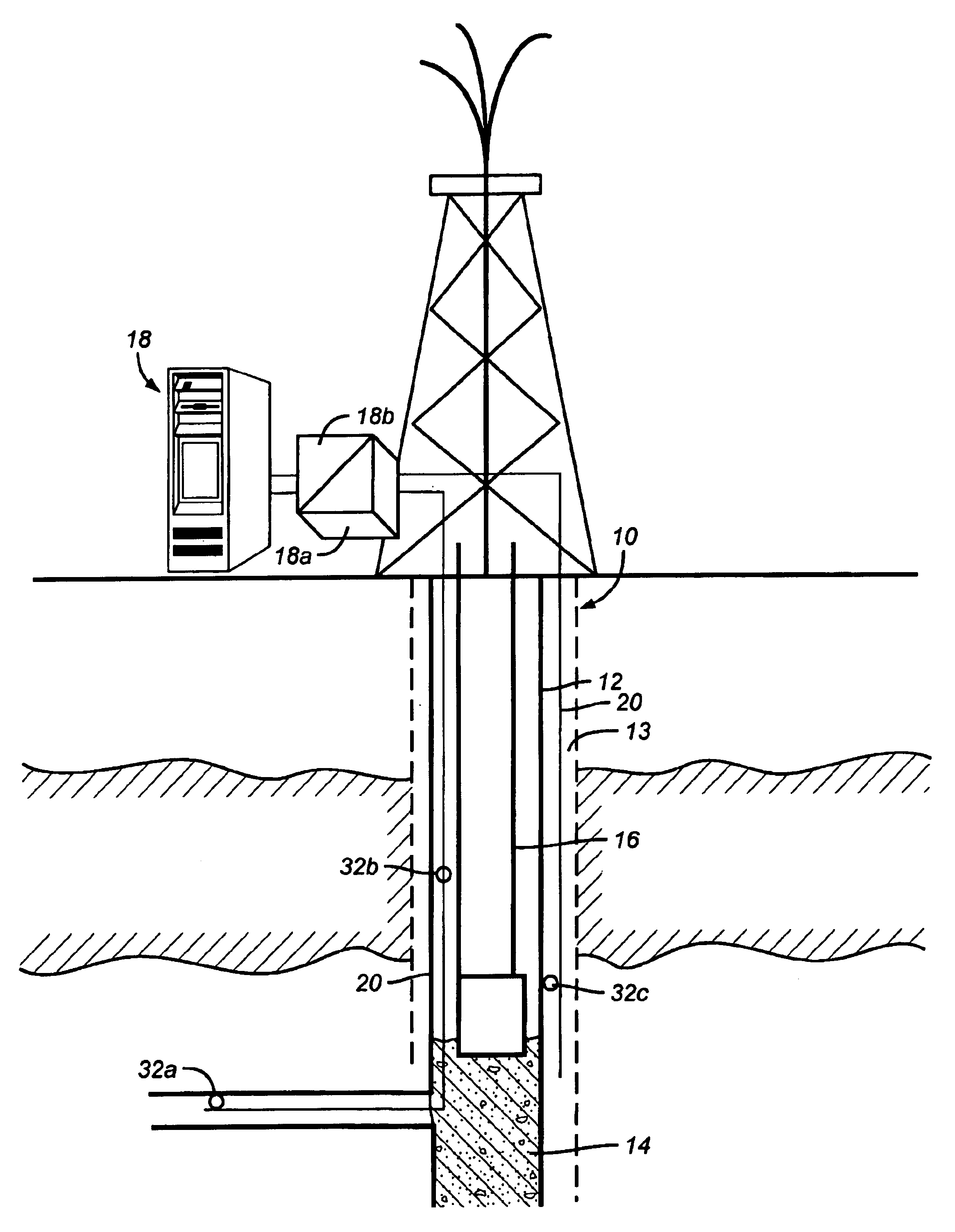
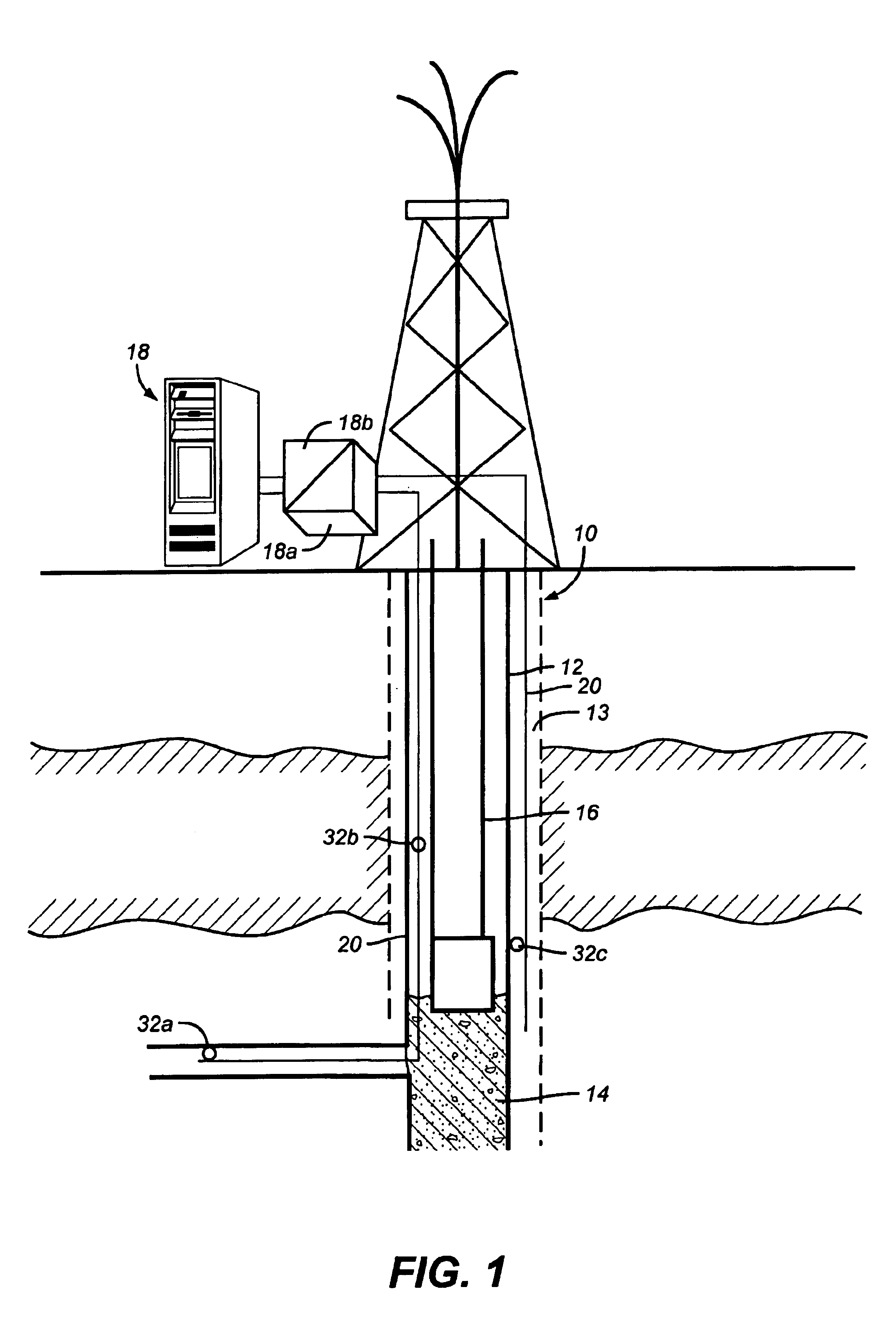
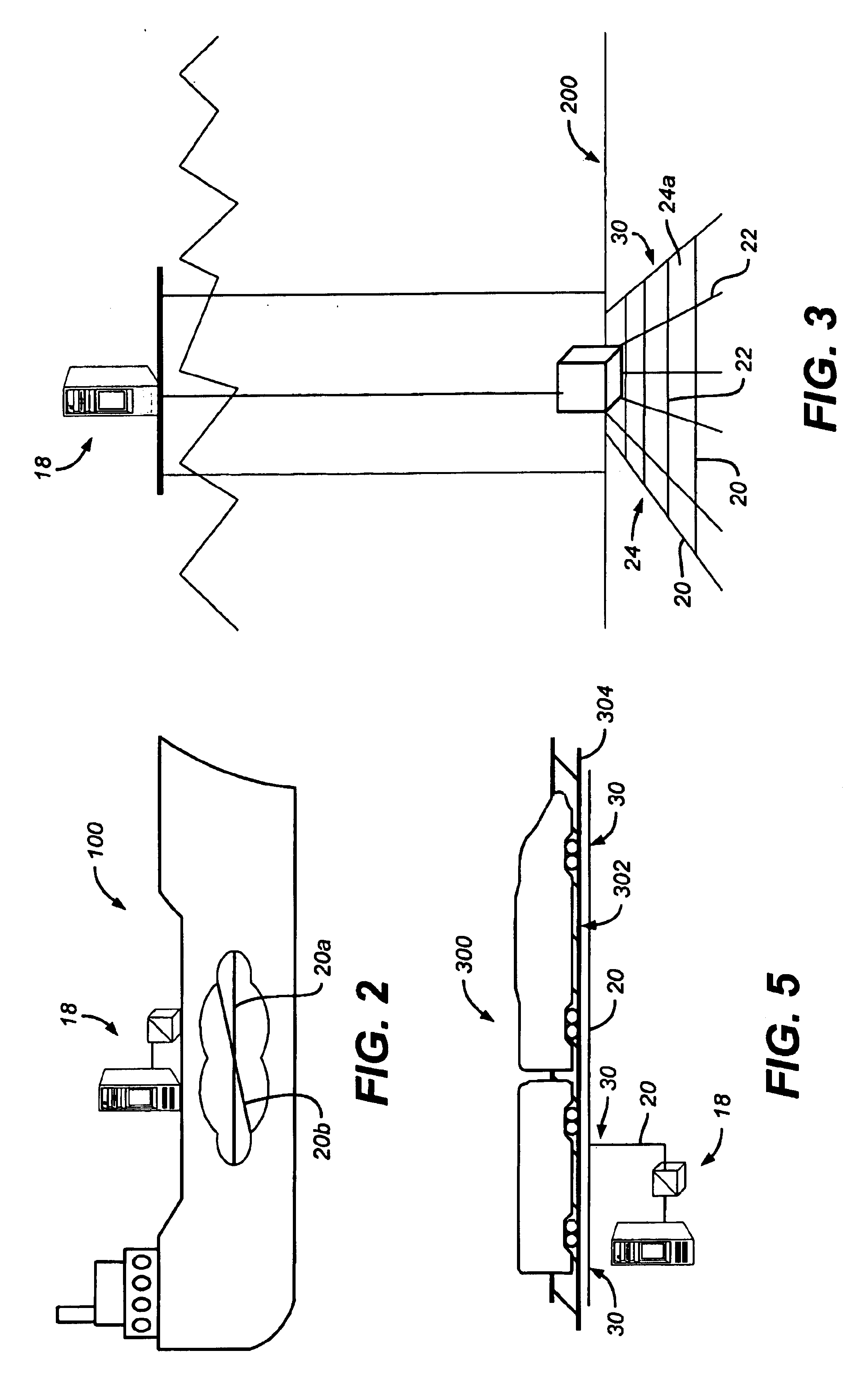
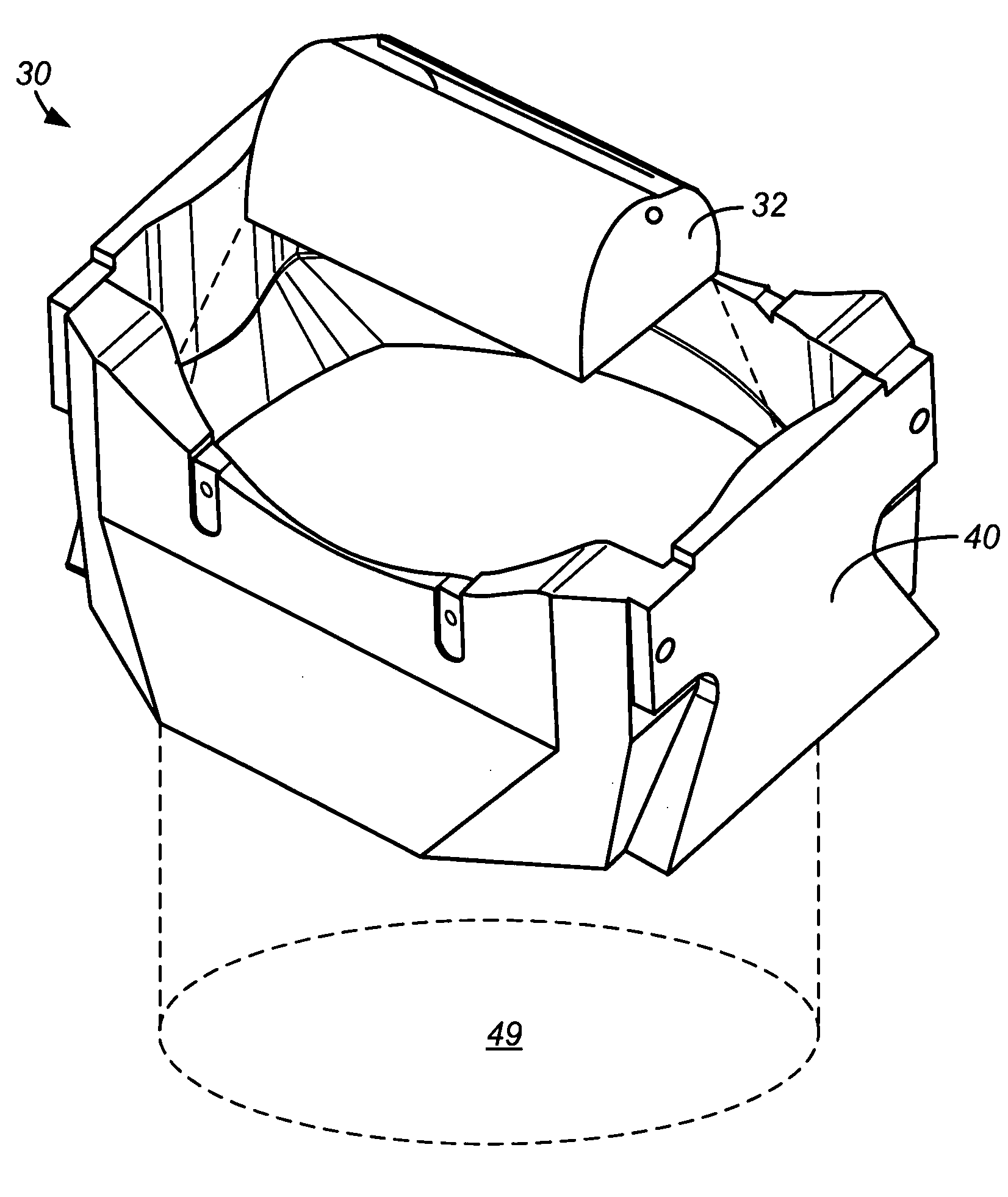
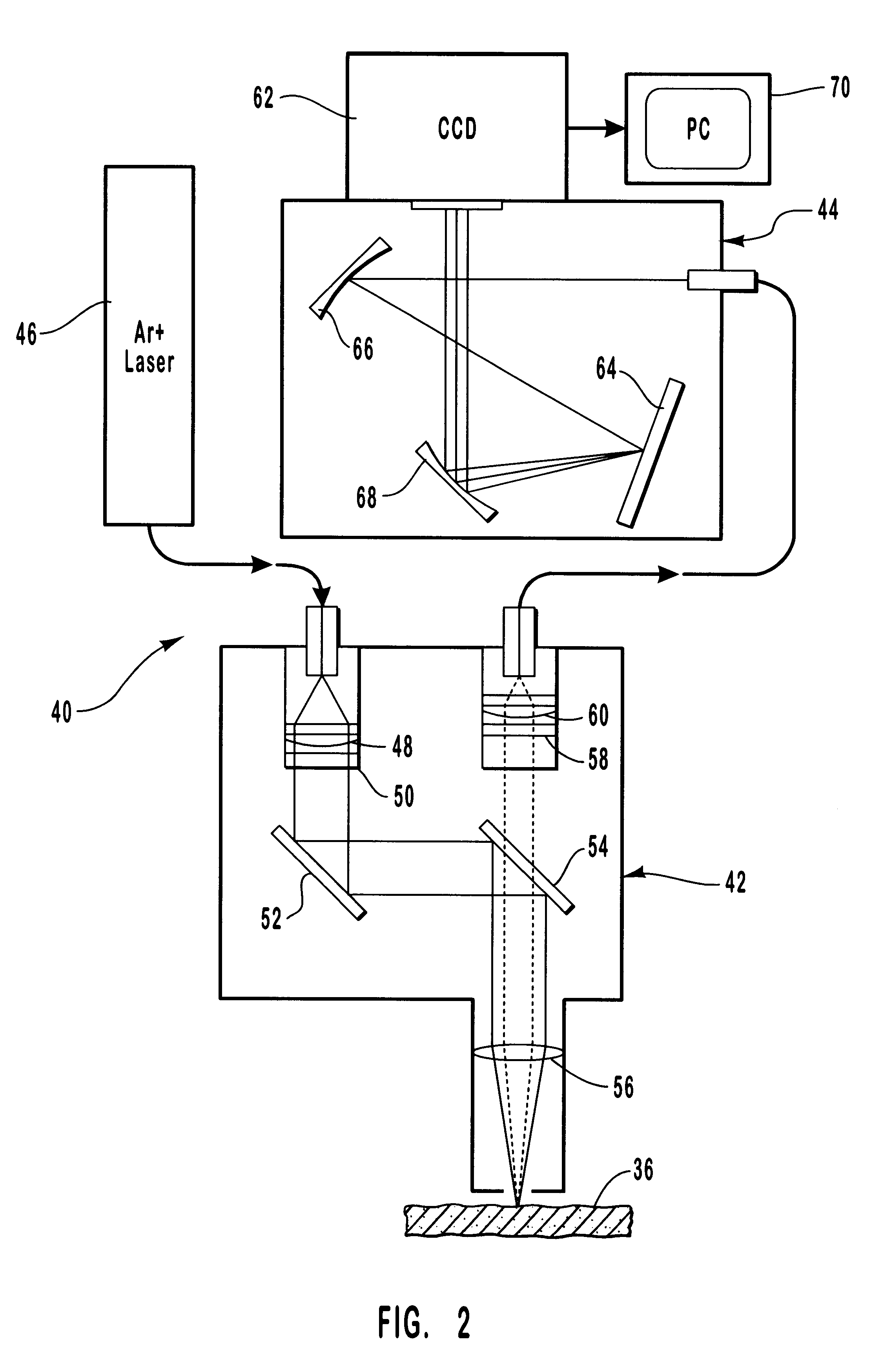
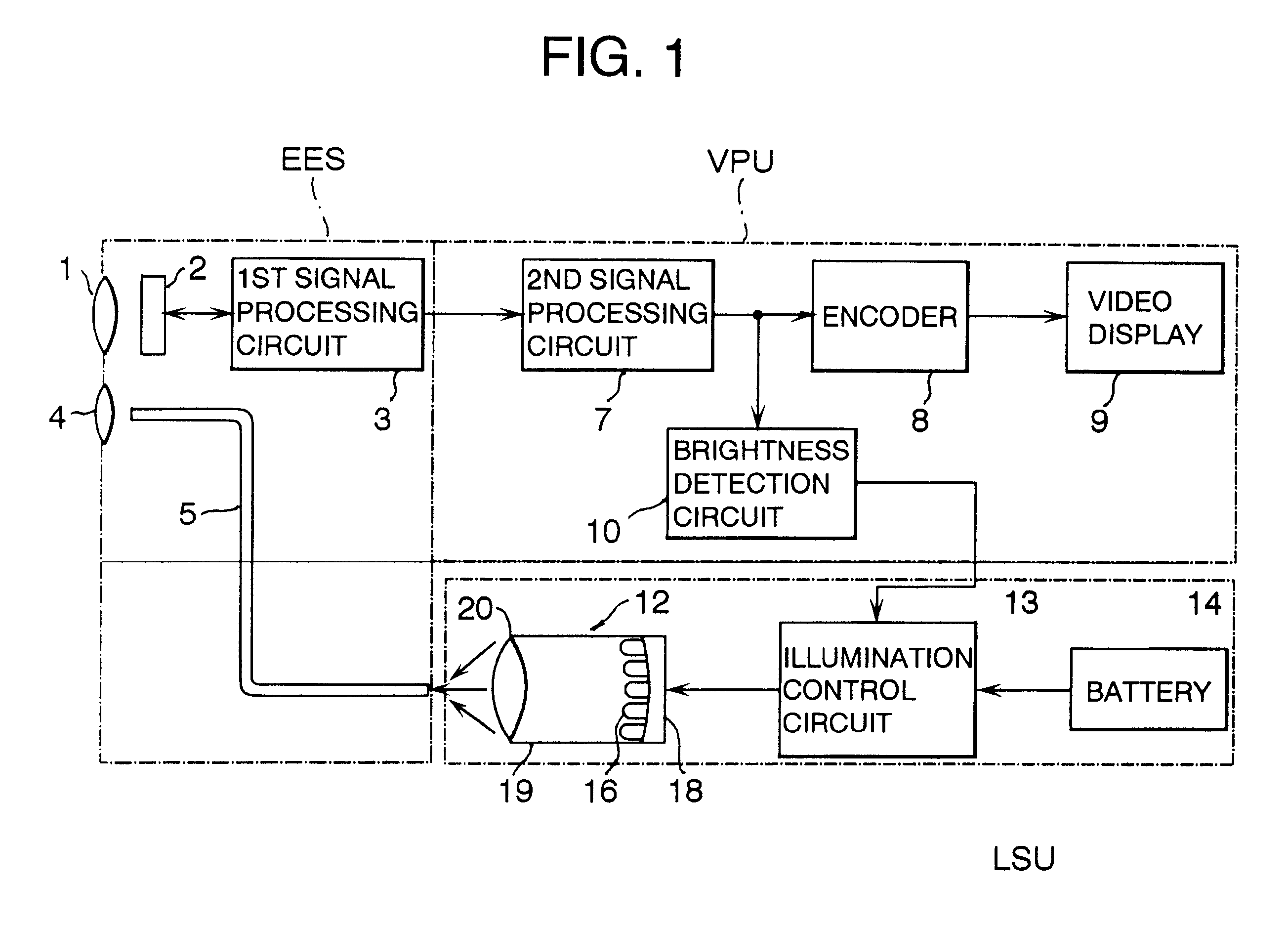
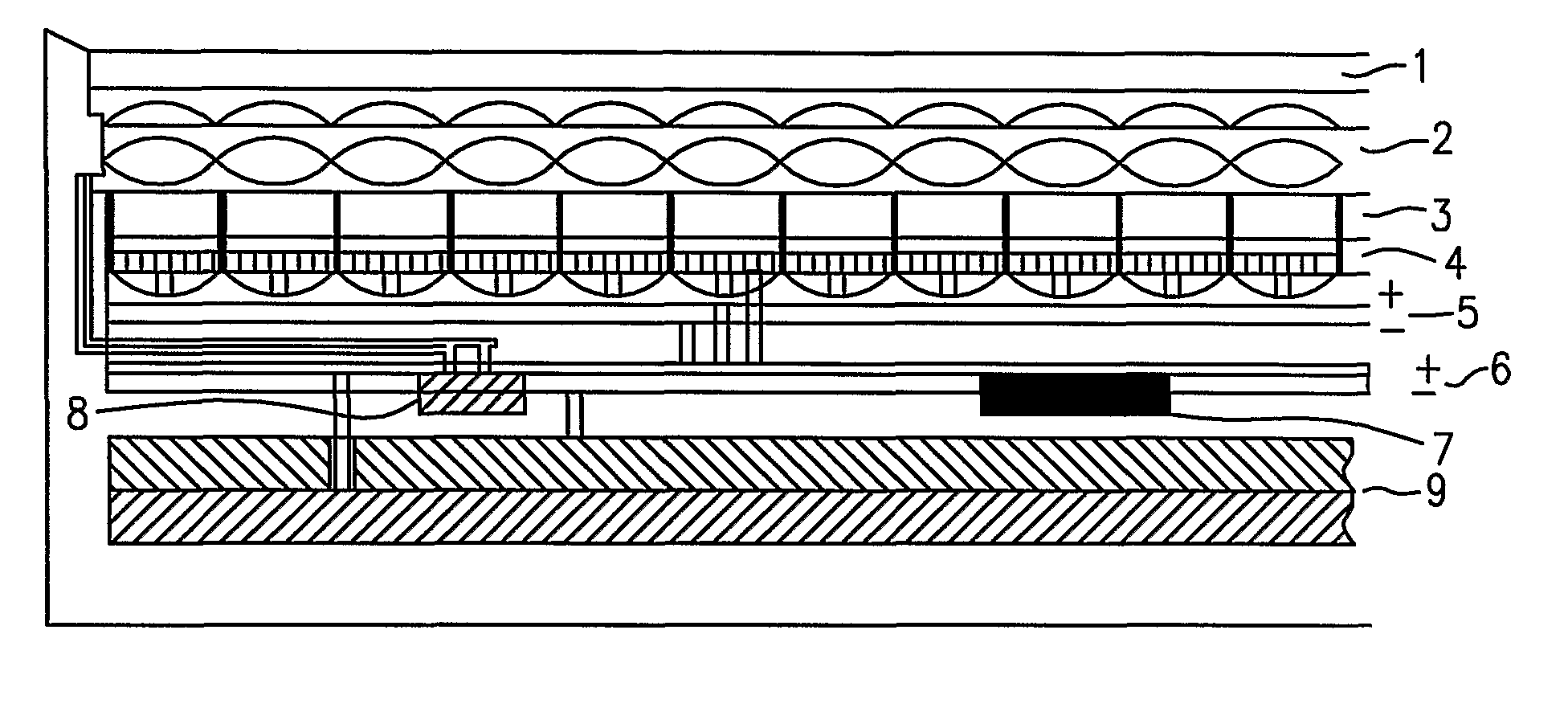
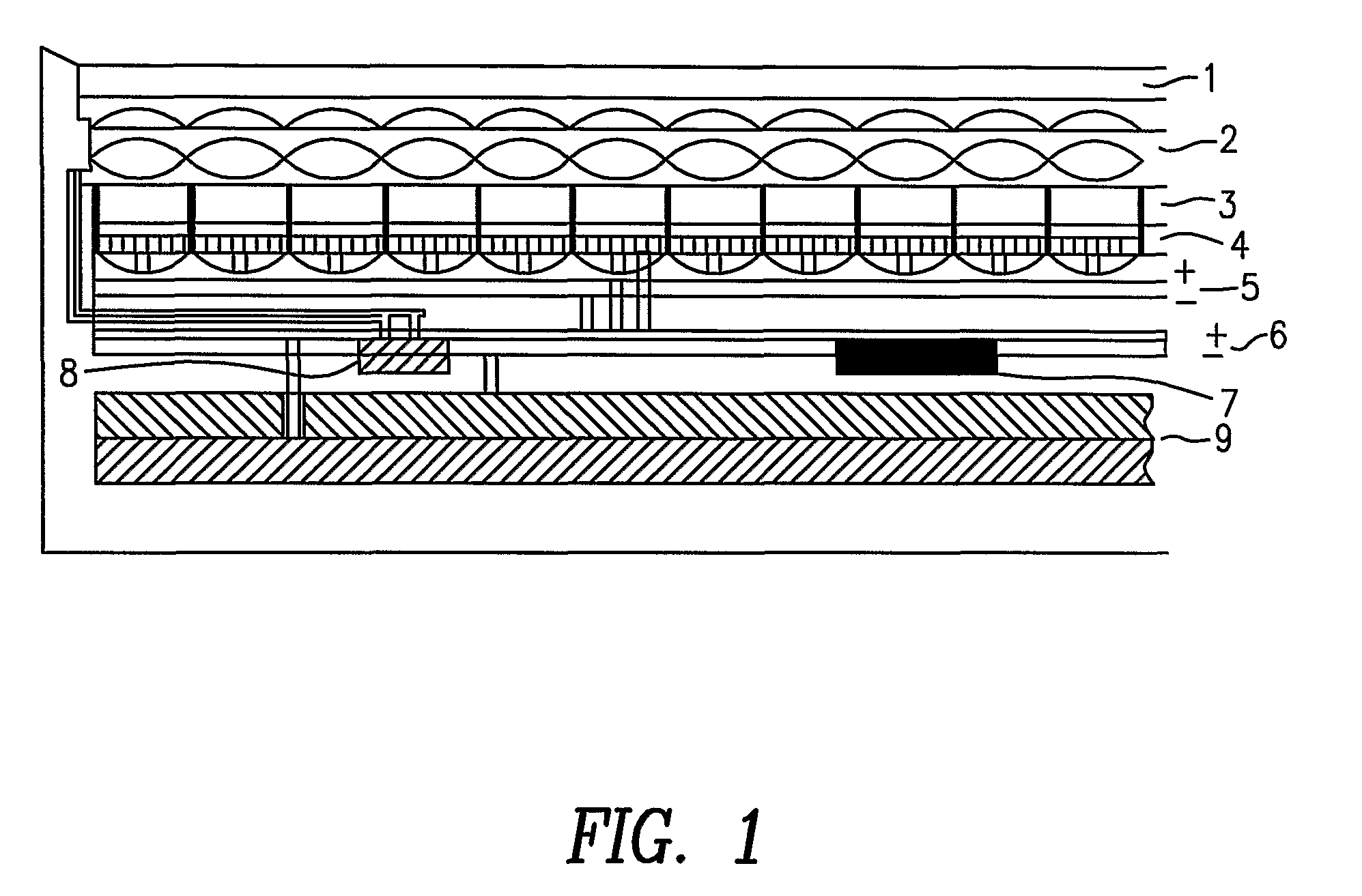
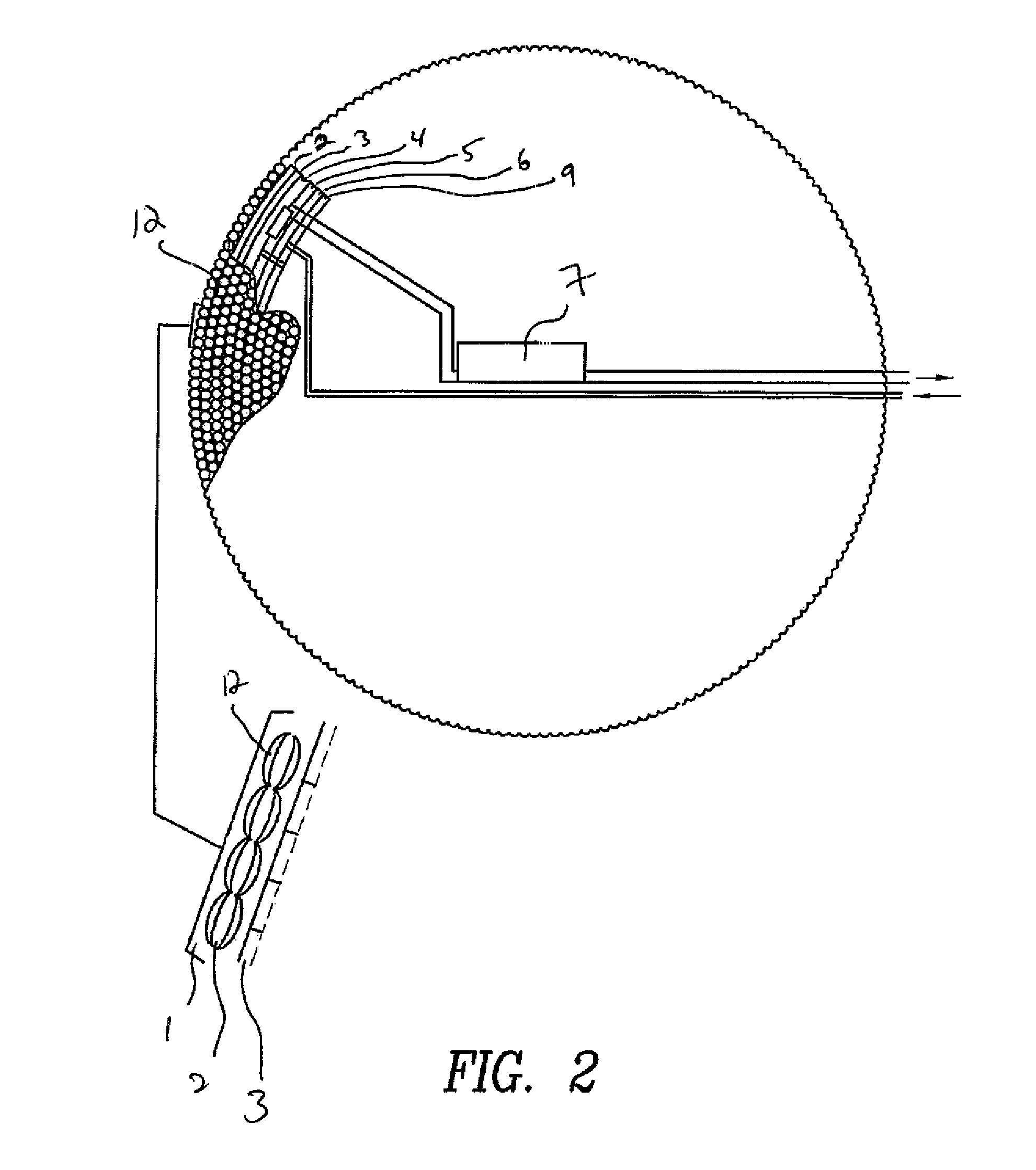
Method and system for monitoring smart structures utilizing distributed optical sensors
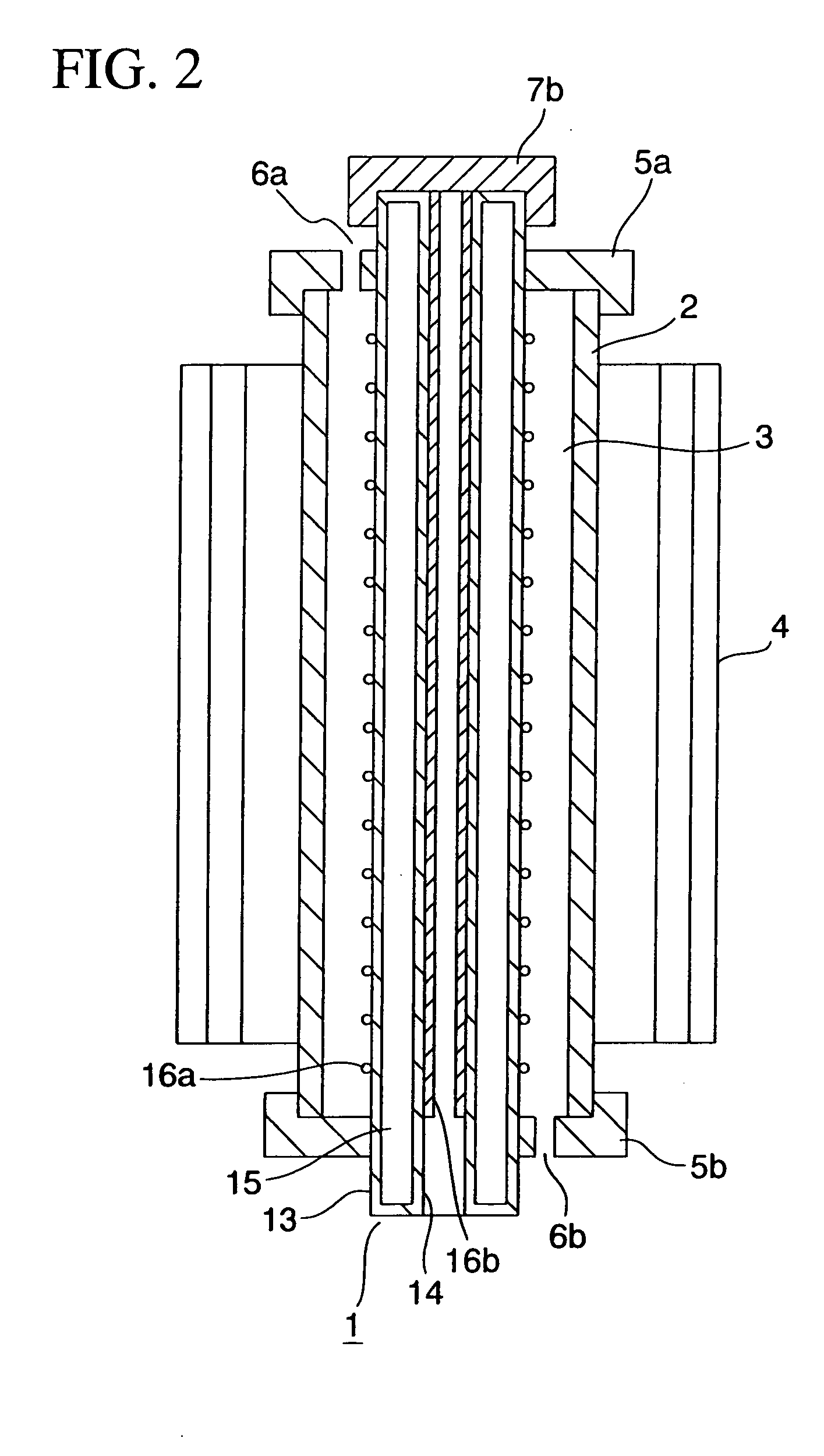
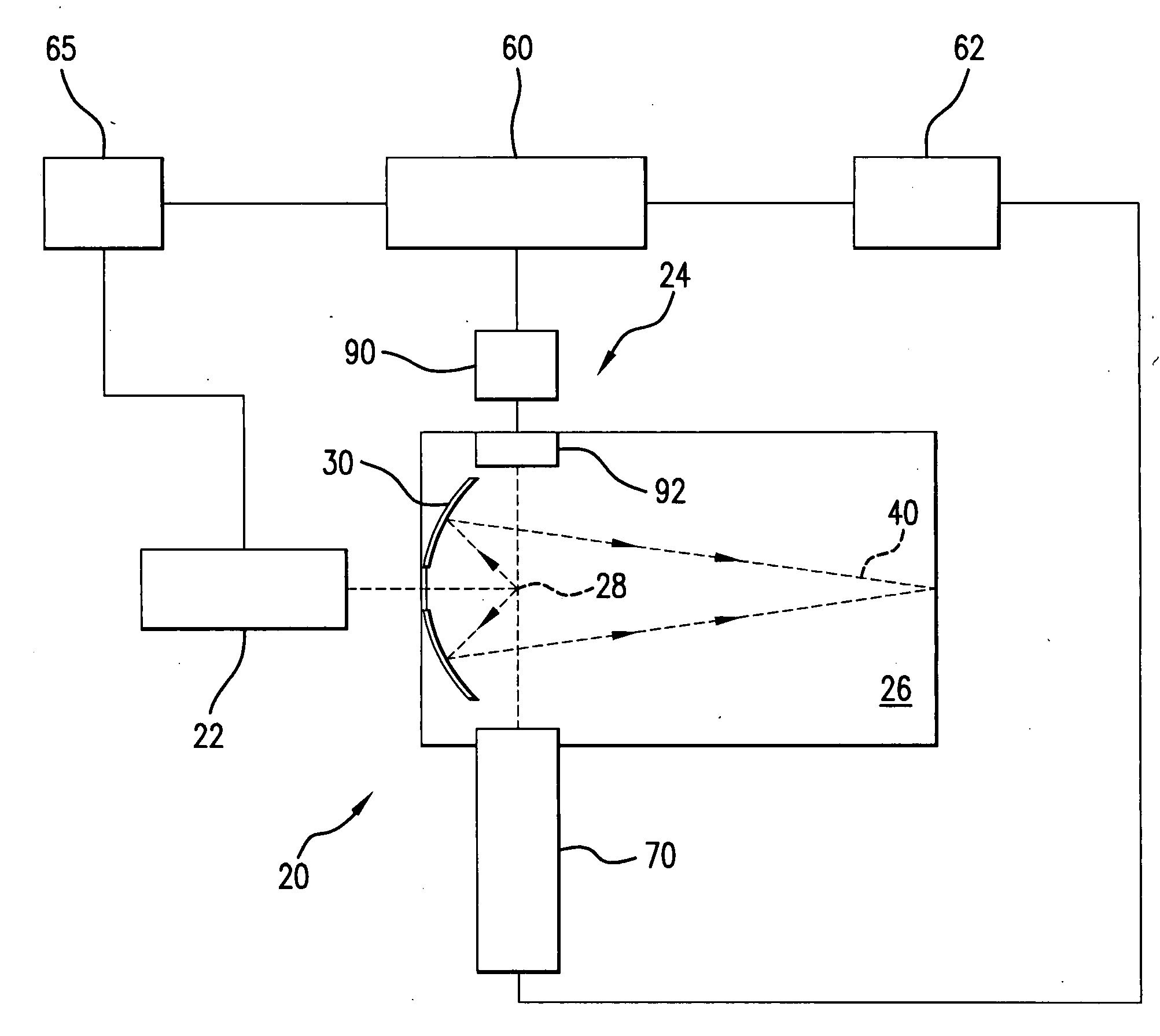
A monitoring system and method for monitoring a predetermined set of physical characteristics associated with a structure using the monitoring system. The system is distributed in the structure and comprises a distributed optical sensing device (30), further comprising a fiber optic cable (20, 22); a light source (18a) operatively in communication with the fiber optic cable (20, 22); a light detection device (18b), operatively in communication with the fiber optic cable (20, 22), for measuring the light received at the light detection device (18b) from the fiber optic cable (20, 22); and a data processor (18) capable of using the light measured to calculate a predetermined set of physical parameters describing the predetermined set of physical characteristics.
Owner:ZIEBEL AS
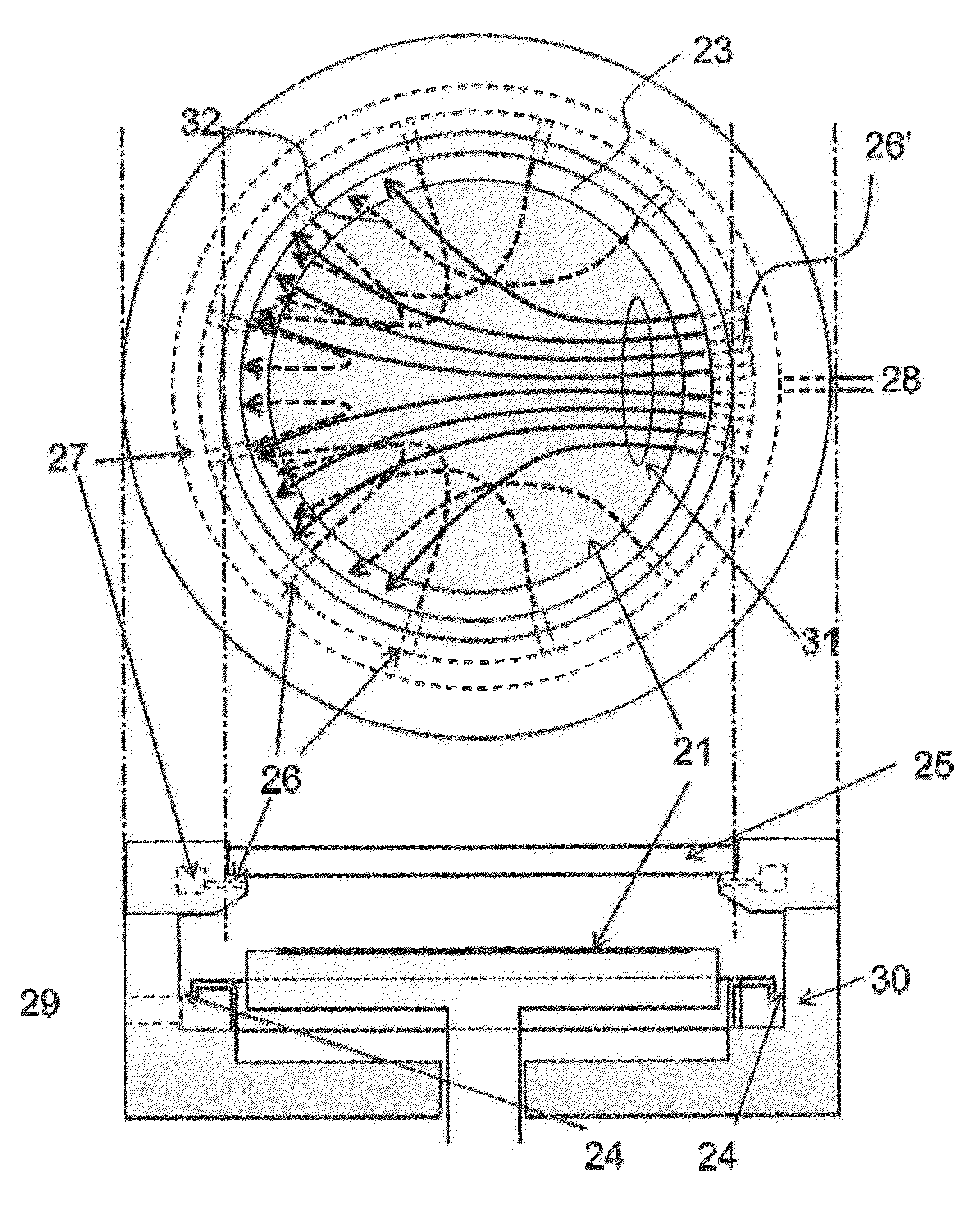
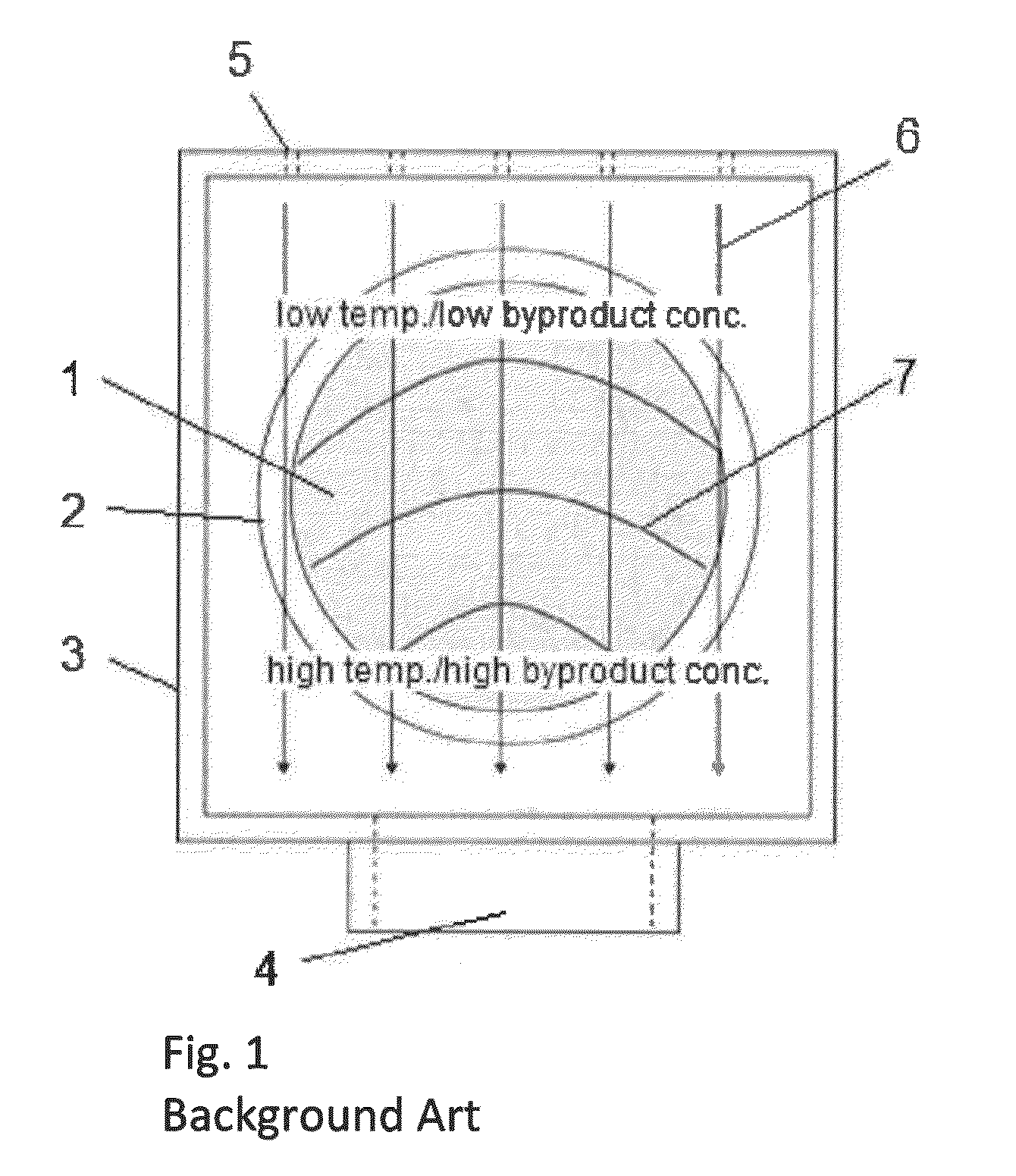
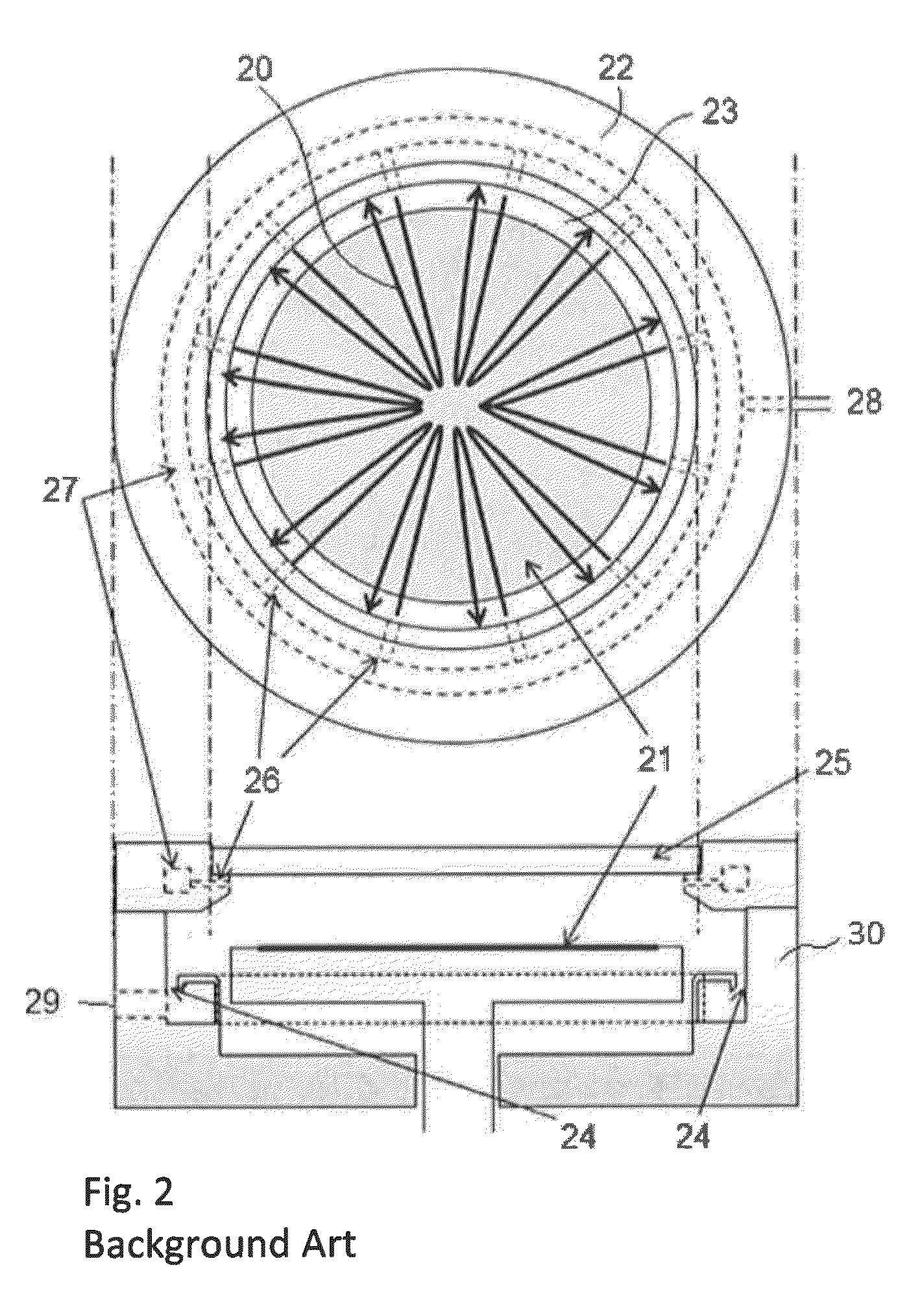
Apparatus and method for treating a substrate with UV radiation using primary and secondary reflectors
ActiveUS7566891B2Reduce light lossRadiation pyrometryPretreated surfacesProcess regionUltraviolet radiation
Embodiments of the invention relate generally to an ultraviolet (UV) cure chamber for curing a dielectric material disposed on a substrate and to methods of curing dielectric materials using UV radiation. A substrate processing tool according to one embodiment comprises a body defining a substrate processing region; a substrate support adapted to support a substrate within the substrate processing region; an ultraviolet radiation lamp spaced apart from the substrate support, the lamp configured to transmit ultraviolet radiation to a substrate positioned on the substrate support; and a motor operatively coupled to rotate at least one of the ultraviolet radiation lamp or substrate support at least 180 degrees relative to each other. The substrate processing tool may further comprise one or more reflectors adapted to generate a flood pattern of ultraviolet radiation over the substrate that has complementary high and low intensity areas which combine to generate a substantially uniform irradiance pattern if rotated. Other embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Advanced surface-enhanced Raman gene probe systems and methods thereof
InactiveUS6174677B1Produce roughnessEffective supportBioreactor/fermenter combinationsRadiation pyrometryNucleotideGene probe
The subject invention is a series of methods and systems for using the Surface-Enhanced Raman (SER)-labeled Gene Probe for hybridization, detection and identification of SER-labeled hybridized target oligonucleotide material comprising the steps of immobilizing SER-labeled hybridized target oligonucleotide material on a support means, wherein the SER-labeled hybridized target oligonucleotide material comprise a SER label attached either to a target oligonucleotide of unknown sequence or to a gene probe of known sequence complementary to the target oligonucleotide sequence, the SER label is unique for the target oligonucleotide strands of a particular sequence wherein the SER-labeled oligonucleotide is hybridized to its complementary oligonucleotide strand, then the support means having the SER-labeled hybridized target oligonucleotide material adsorbed thereon is SERS activated with a SERS activating means, then the support means is analyzed.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN ENERGY SYST INC
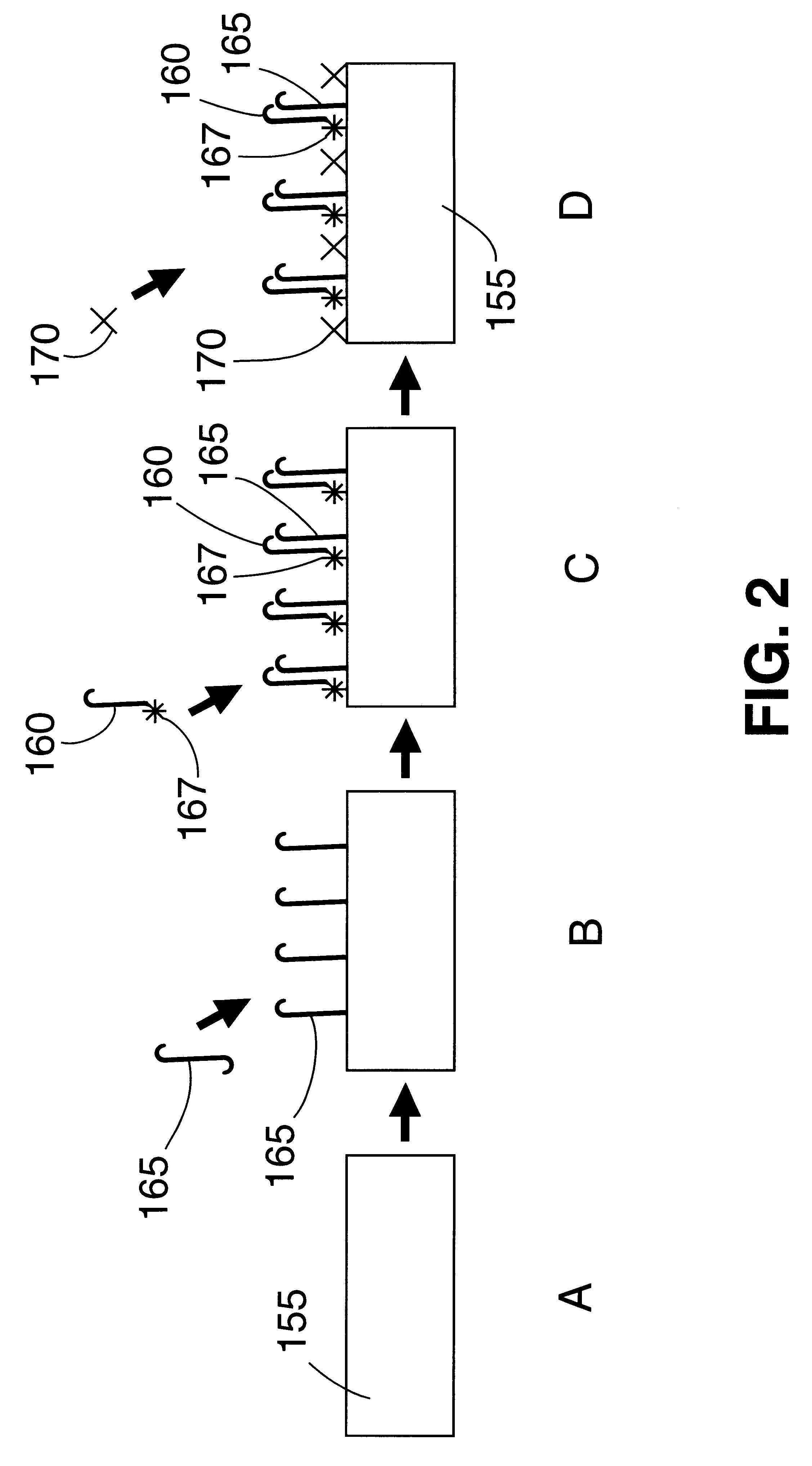
Method for supplying gas with flow rate gradient over substrate
ActiveUS8664627B1Reduce gradientIncrease concentrationMaterial analysis by optical meansPipeline systemsReaction chamberChemistry
A method for supplying gas over a substrate in a reaction chamber wherein a substrate is placed on a pedestal, includes: supplying a first gas from a first side of the reaction chamber to a second side of the reaction chamber opposite to the first side; and adding a second gas to the first gas from sides of the reaction chamber other than the first side of the reaction chamber so that the second gas travels from sides of the substrate other than the first side in a downstream direction.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
UV light irradiating apparatus with liquid filter
ActiveUS7763869B2High mechanical strengthHigh energyMirrorsOptical filtersLiquid layerLight irradiation
A UV light irradiating apparatus for irradiating a semiconductor substrate with UV light includes: a reactor in which a substrate-supporting table is provided; a UV light irradiation unit connected to the reactor for irradiating a semiconductor substrate placed on the substrate-supporting table with UV light through a light transmission window; and a liquid layer forming channel disposed between the light transmission window and at least one UV lamp for forming a liquid layer through which the UV light is transmitted. The liquid layer is formed by a liquid flowing through the liquid layer forming channel.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Highly sensitive, fast pixel for use in an image sensor
ActiveUS7560701B2Overcomes speed limitationReasonable sensitivitySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansElectric signalDemodulation
Owner:AMS SENSORS SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Apparatus and method for exposing a substrate to UV radiation using asymmetric reflectors
ActiveUS7692171B2Reduce light lossNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProcess regionUltraviolet radiation
Embodiments of the invention relate generally to an ultraviolet (UV) cure chamber for curing a dielectric material disposed on a substrate and to methods of curing dielectric materials using UV radiation. A substrate processing tool according to one embodiment comprises a body defining a substrate processing region; a substrate support adapted to support a substrate within the substrate processing region; an ultraviolet radiation lamp spaced apart from the substrate support, the lamp configured to transmit ultraviolet radiation to a substrate positioned on the substrate support; and a motor operatively coupled to rotate at least one of the ultraviolet radiation lamp or substrate support at least 180 degrees relative to each other. The substrate processing tool may further comprise one or more reflectors adapted to generate a flood pattern of ultraviolet radiation over the substrate that has complementary high and low intensity areas which combine to generate a substantially uniform irradiance pattern if rotated. Other embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Systems and methods for reducing the influence of plasma-generated debris on the internal components of an EUV light source
ActiveUS7196342B2Prevented from reachingRadiation pyrometryLaser using scattering effectsSputteringHydrogen
Systems and methods are disclosed for reducing the influence of plasma generated debris on internal components of an EUV light source. In one aspect, an EUV meteorology monitor is provided which may have a heater to heat an internal multi-layer filtering mirror to a temperature sufficient to remove deposited debris from the mirror. In another aspect, a device is disclosed for removing plasma generated debris from an EUV light source collector mirror having a different debris deposition rate at different zones on the collector mirror. In a particular aspect, an EUV collector mirror system may comprise a source of hydrogen to combine with Li debris to create LiH on a collector surface; and a sputtering system to sputter LiH from the collector surface. In another aspect, an apparatus for etching debris from a surface of a EUV light source collector mirror with a controlled plasma etch rate is disclosed.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
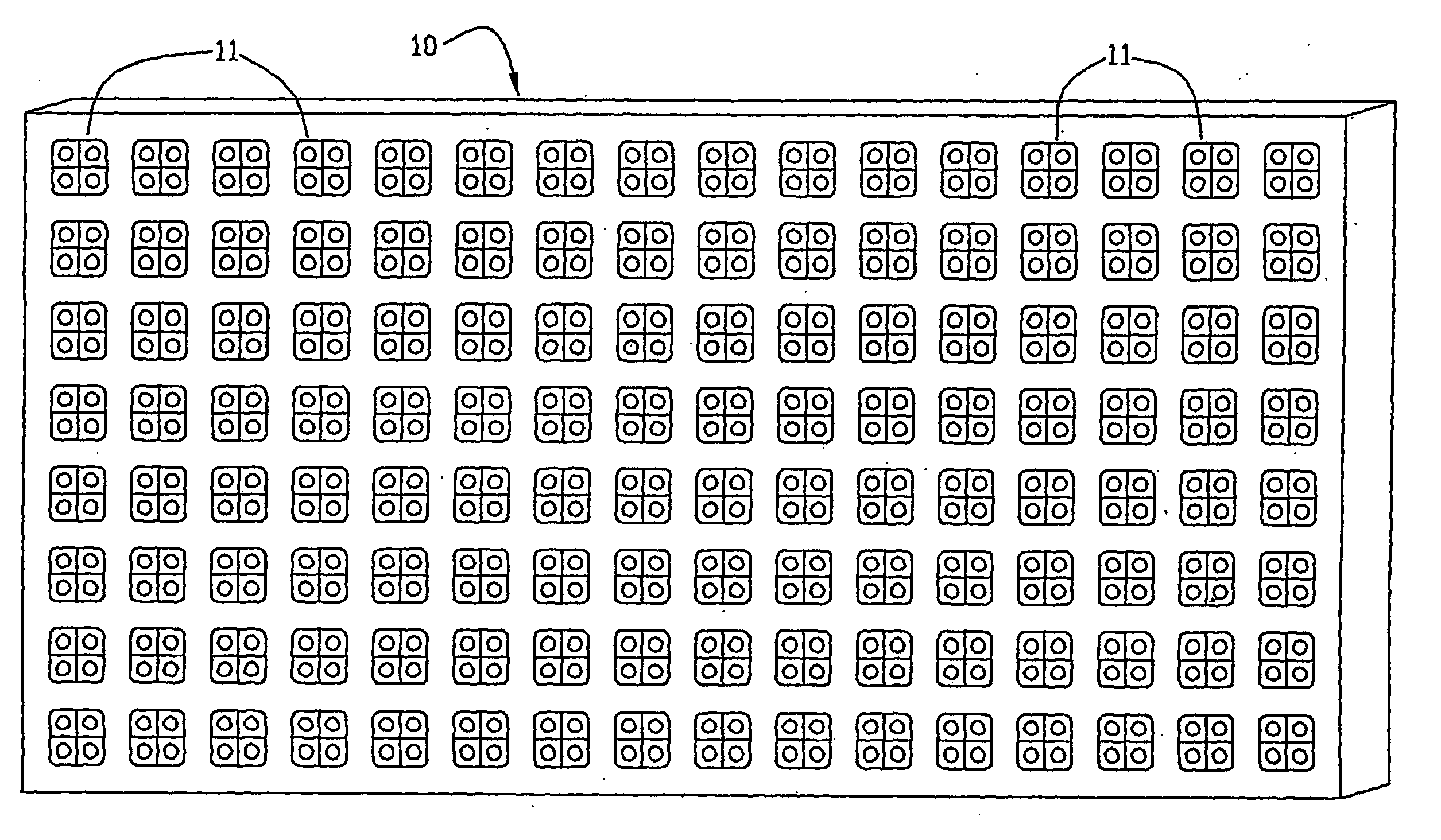
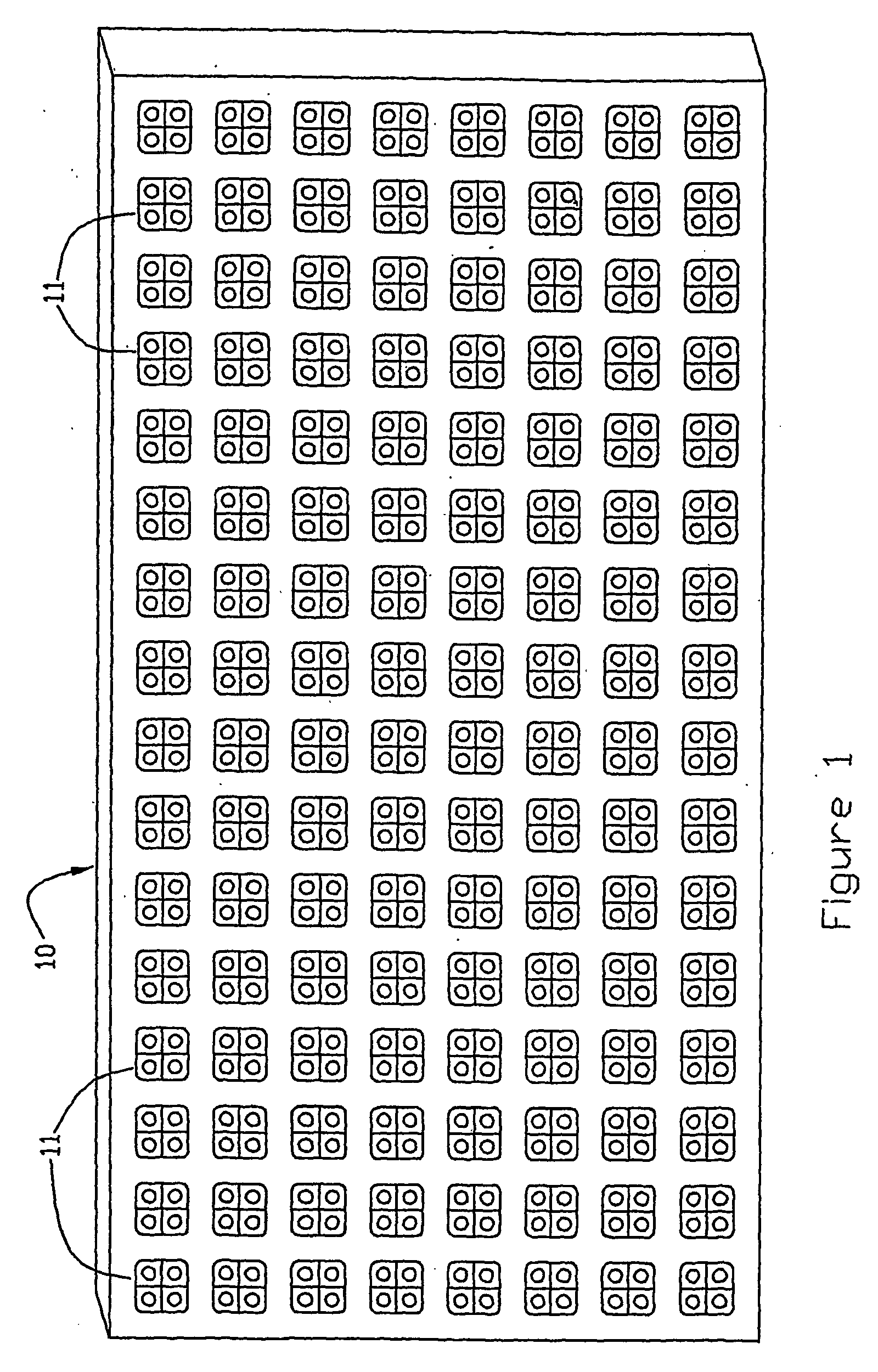
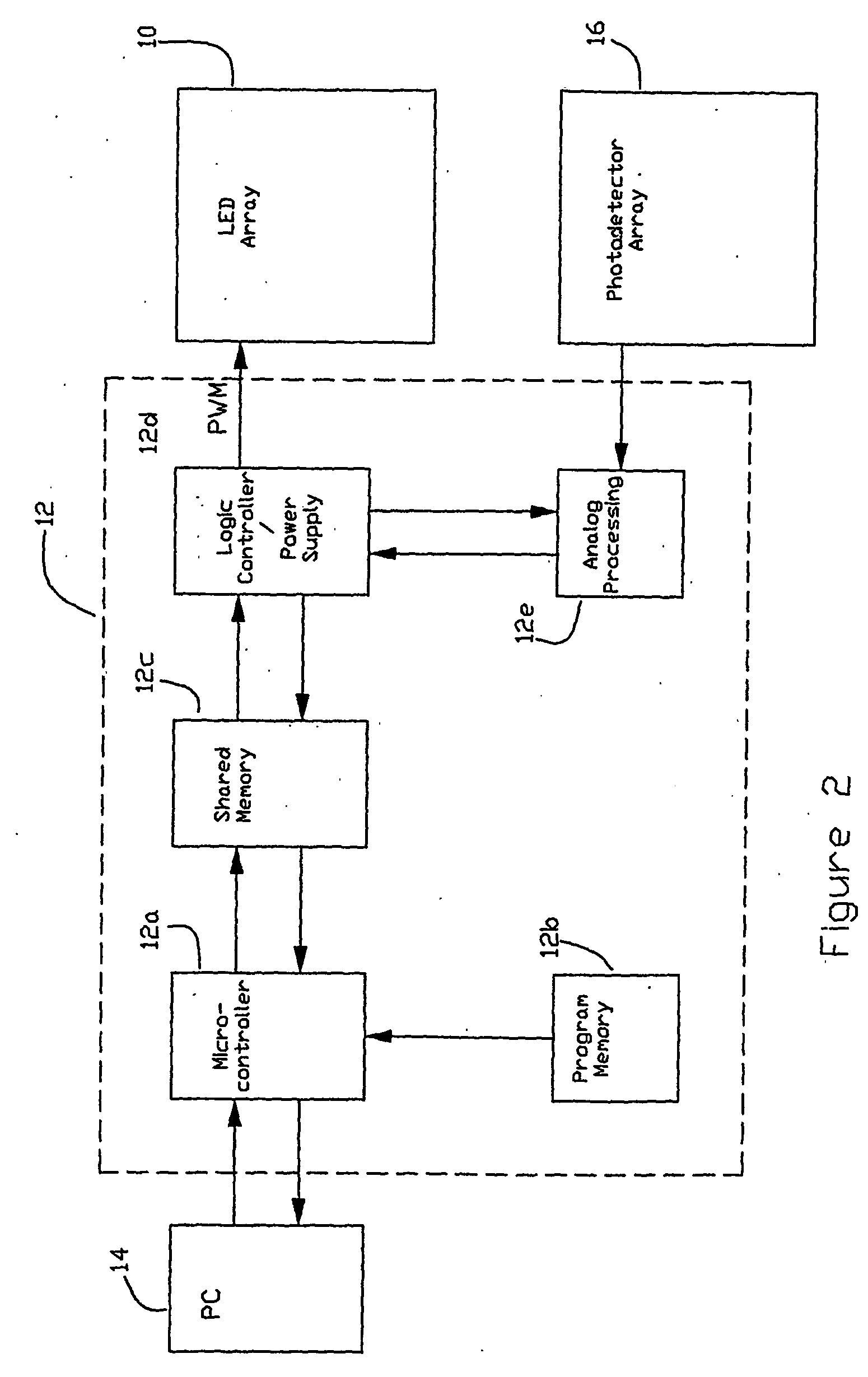
Led illumination source/display with individual led brightness monitoring capability and calibration method
InactiveUS20060227085A1Uniform brightnessUniform colorStatic indicating devicesTelevision systemsMaximum levelDisplay device
An LED area illumination source / display (10) such as an electronic billboard is made up of a number of individual pixels with each pixel including a number of LEDs, e.g., a red (18), blue (19) and green LED (20), with each LED representing a primary color being arranged to be energized separately. At least one light sensor (22) is incorporated into the display for providing a measure of the light emitted from each LED representing a primary color in each pixel. The source / display (10) is susceptible of being self-calibrated by initially energizing the LEDs (18, 19, 20) at less than a maximum level and increasing the energization level as necessary during use to restore the original light output of degraded LEDs.
Owner:VISIONEERED IMAGE SYST
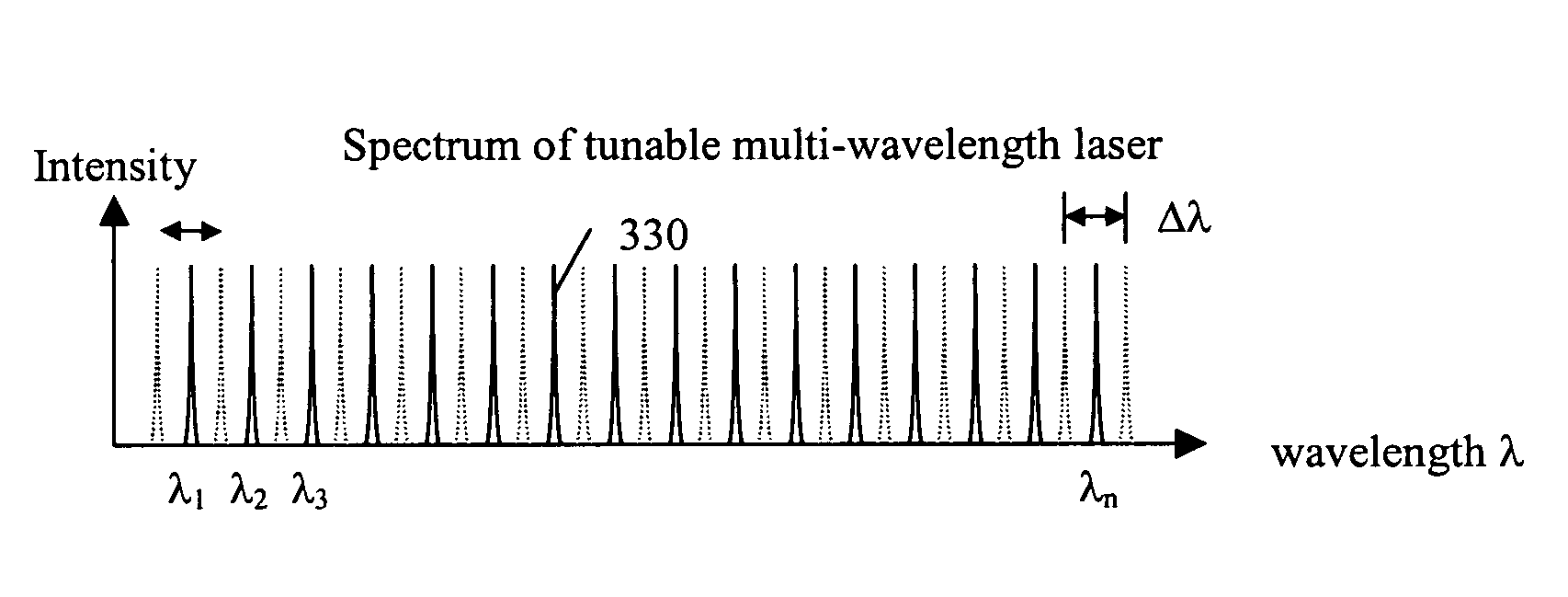
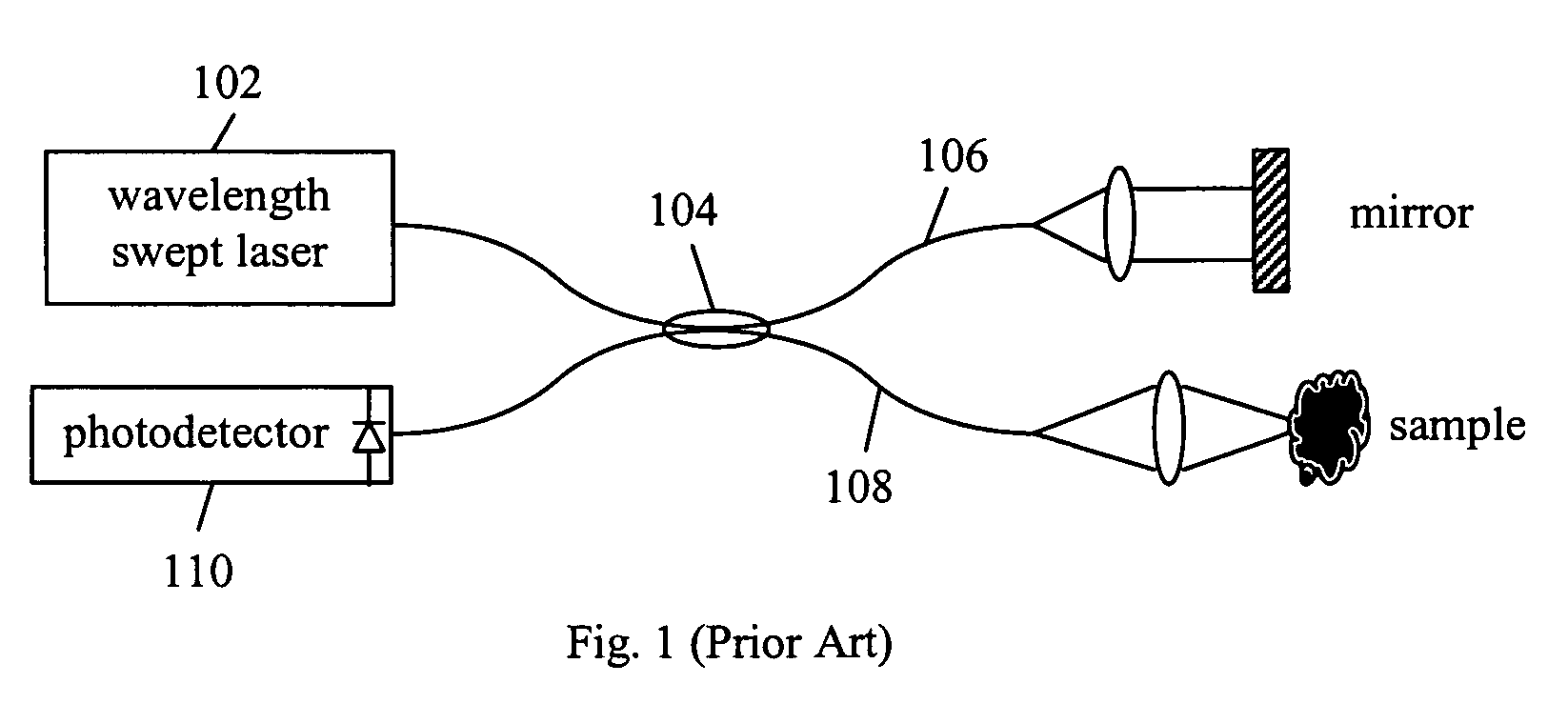
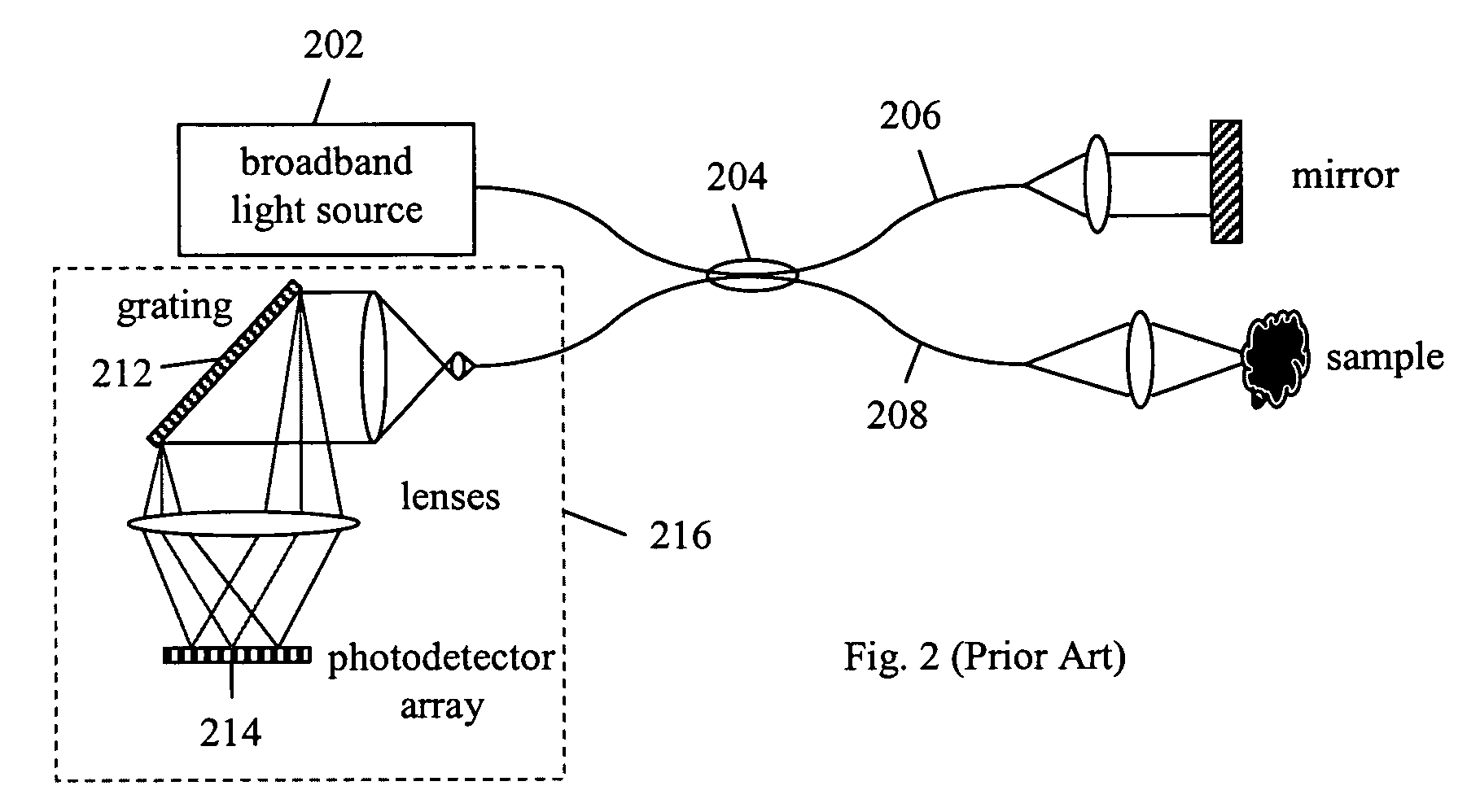
Fourier domain optical coherence tomography employing a swept multi-wavelength laser and a multi-channel receiver
ActiveUS7391520B2Low costIncrease in the speed of each axial scanInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansSpectral domainLasing wavelength
The present invention is an alternative Fourier domain optical coherence system (FD-OCT) and its associated method. The system comprises a swept multi-wavelength laser, an optical interferometer and a multi-channel receiver. By employing a multi-wavelength laser, the sweeping range for each lasing wavelength is substantially reduced as compared to a pure swept single wavelength laser that needs to cover the same overall spectral range. The overall spectral interferogram is divided over the individual channels of the multi-channel receiver and can be re-constructed through processing of the data from each channel detector. In addition to a substantial increase in the speed of each axial scan, the cost of invented FD-OCT system can also be substantially less than that of a pure swept source OCT or a pure spectral domain OCT system.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
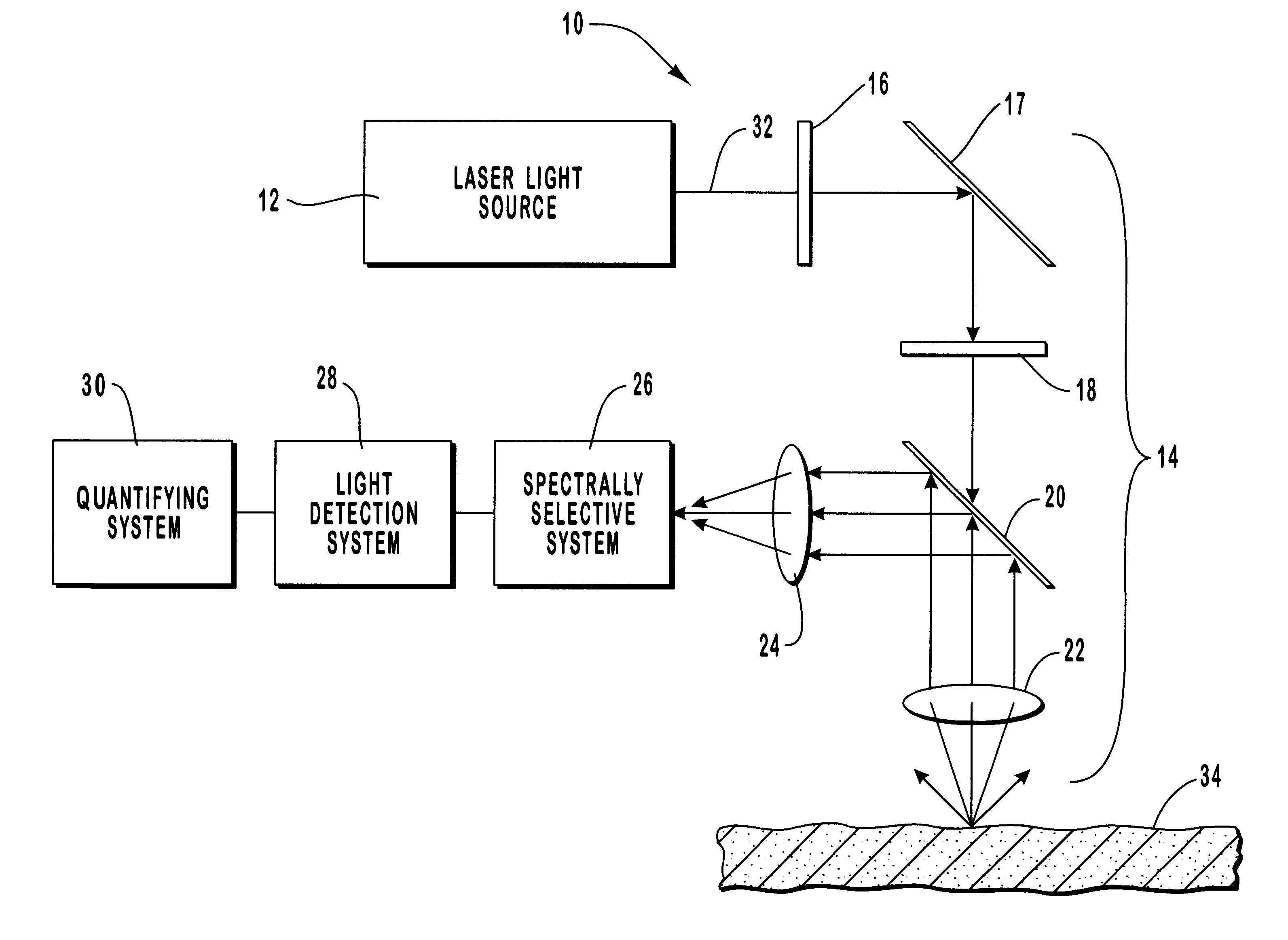
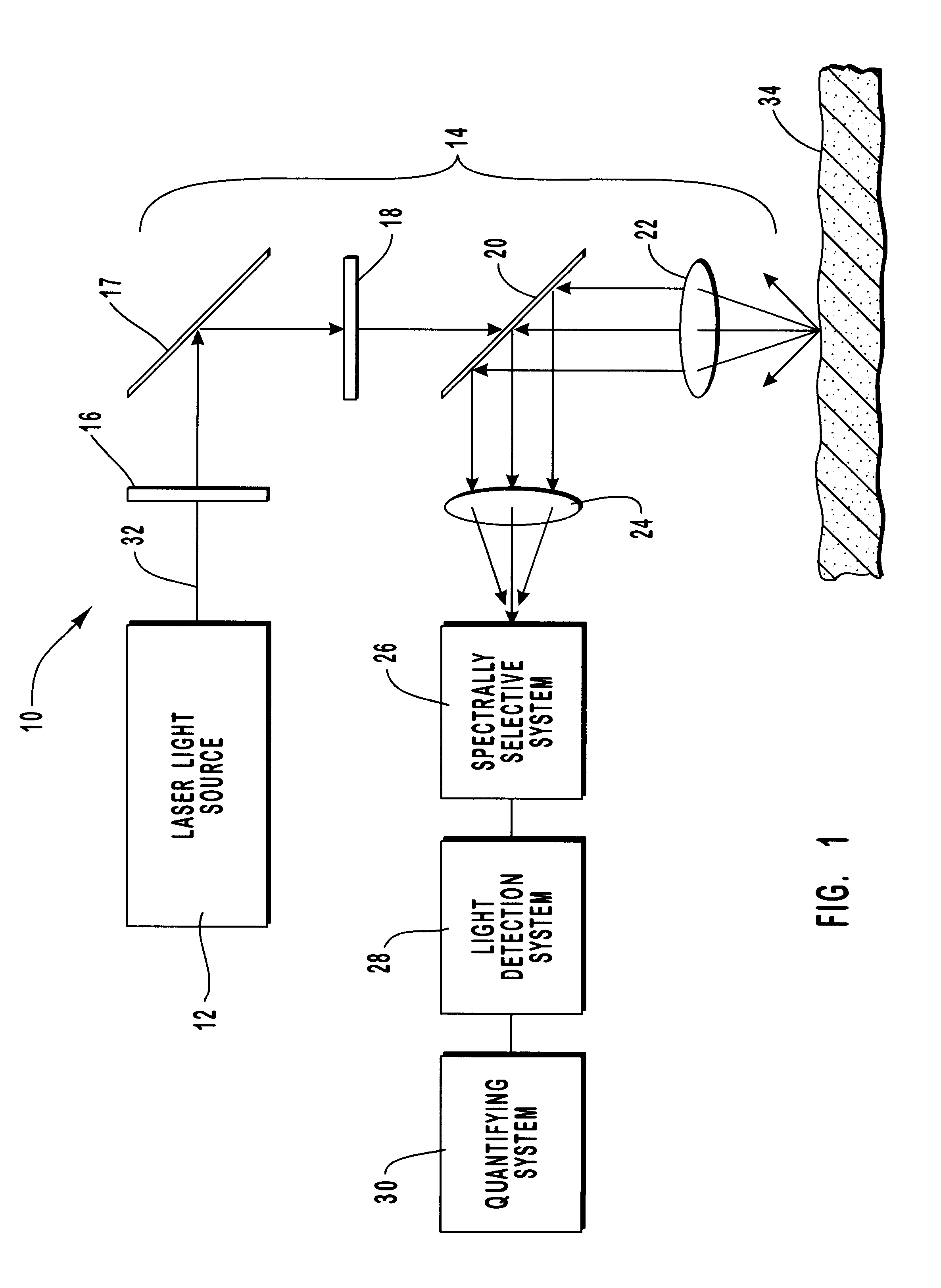
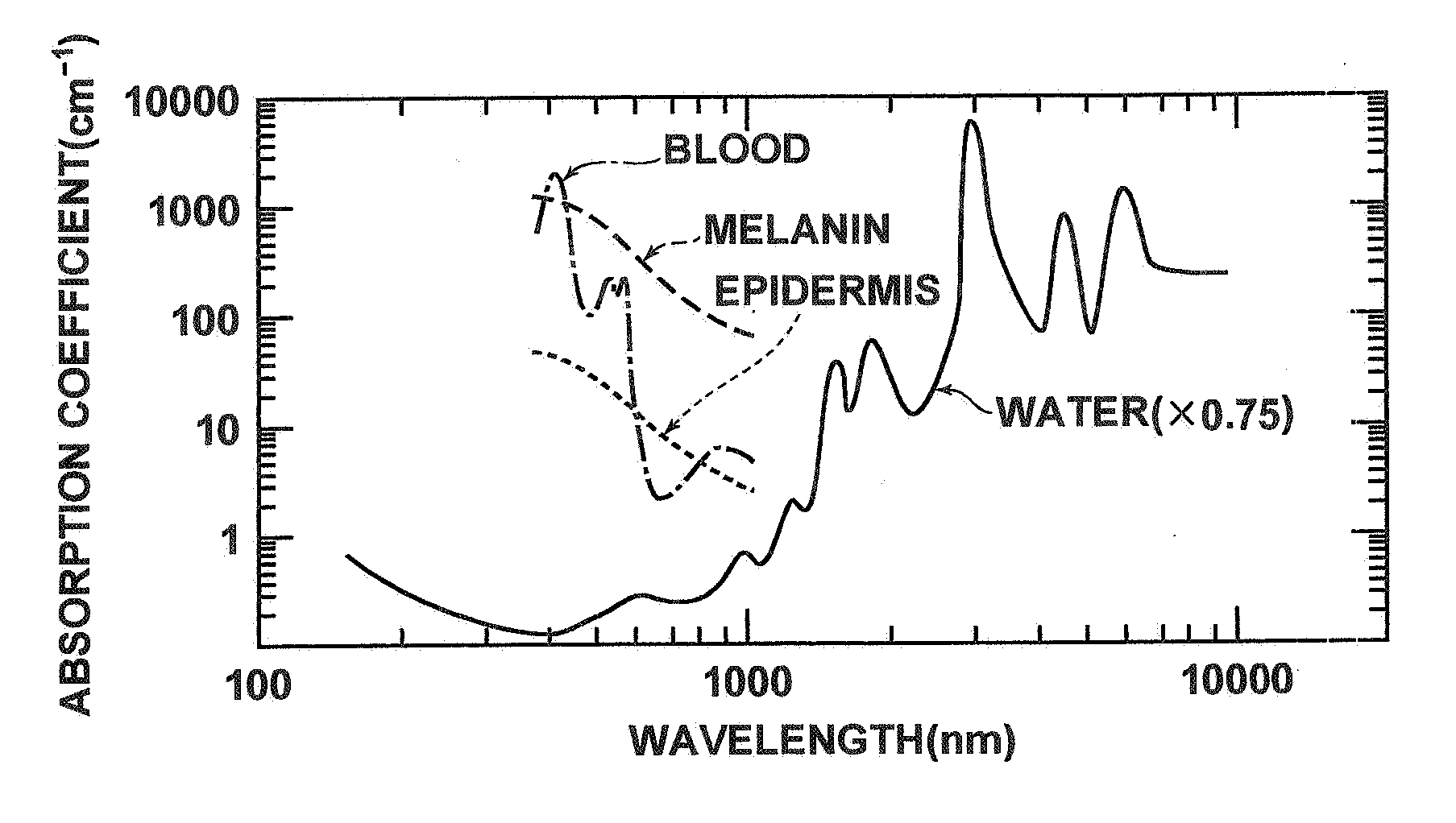
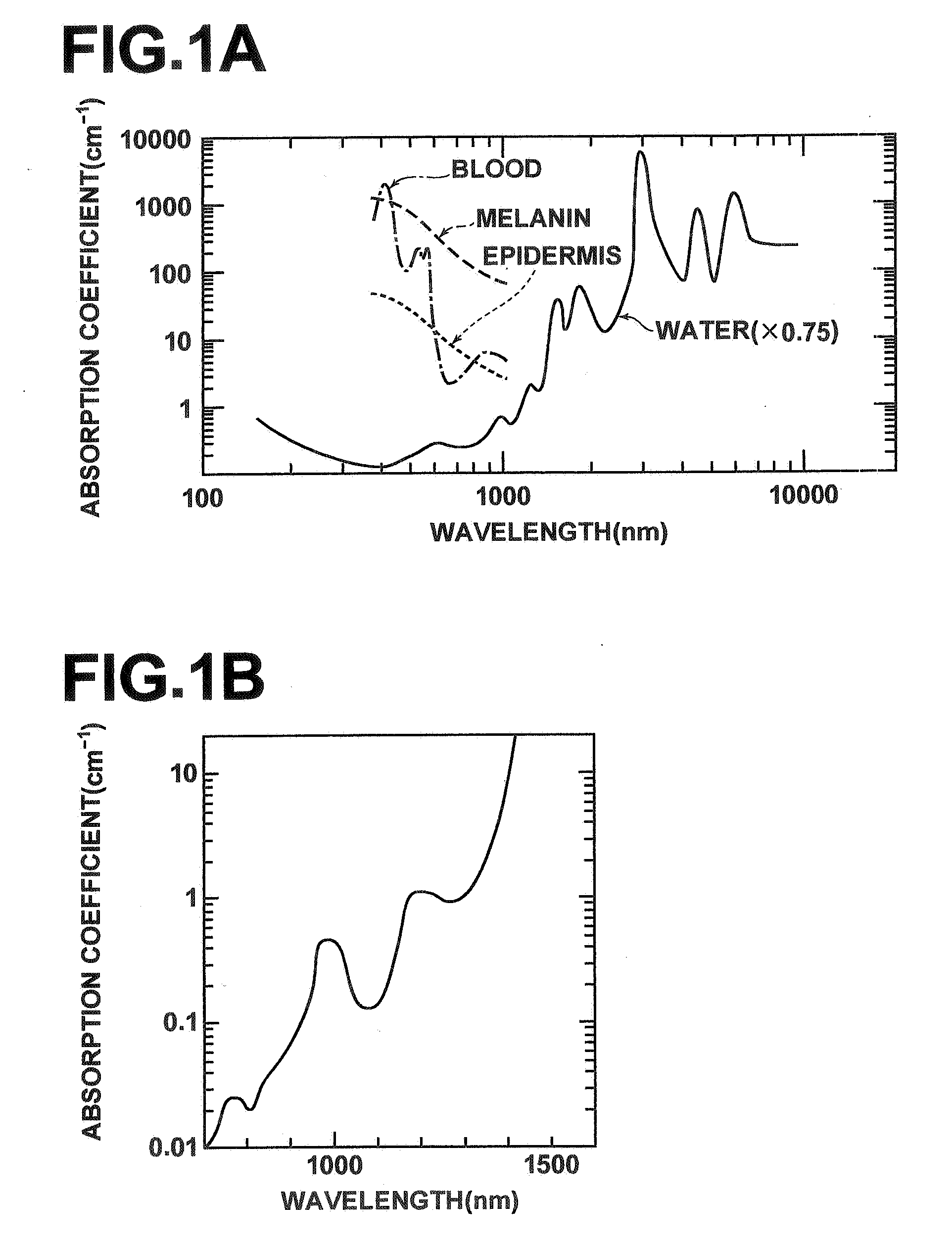
Method and apparatus for noninvasive measurement of carotenoids and related chemical substances in biological tissue
InactiveUS6205354B1Rapid and noninvasive and quantitative measurementRiskRadiation pyrometrySurgeryResonance Raman spectroscopyAntioxidant
A method and apparatus are provided for the determination of levels of carotenoids and similar chemical compounds in biological tissue such as living skin. The method and apparatus provide a noninvasive, rapid, accurate, and safe determination of carotenoid levels which in turn can provide diagnostic information regarding cancer risk, or can be a marker for conditions where carotenoids or other antioxidant compounds may provide diagnostic information. Such early diagnostic information allows for the possibility of preventative intervention. The method and apparatus utilize the technique of resonance Raman spectroscopy to measure the levels of carotenoids and similar substances in tissue. In this technique, laser light is directed upon the area of tissue which is of interest. A small fraction of the scattered light is scattered inelastically, producing the carotenoid Raman signal which is at a different frequency than the incident laser light, and the Raman signal is collected, filtered, and measured. The resulting Raman signal can be analyzed such that the background fluorescence signal is subtracted and the results displayed and compared with known calibration standards.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
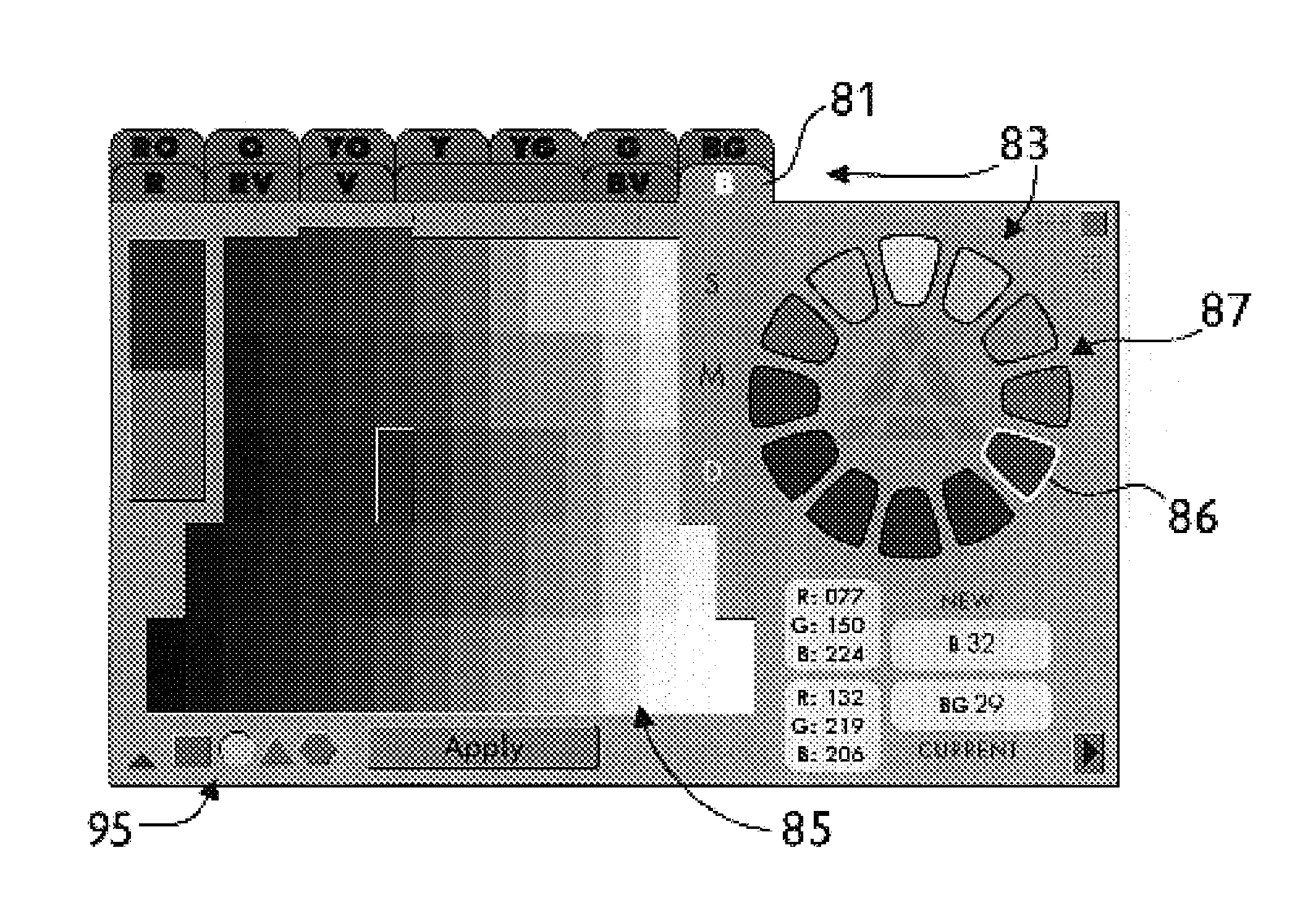
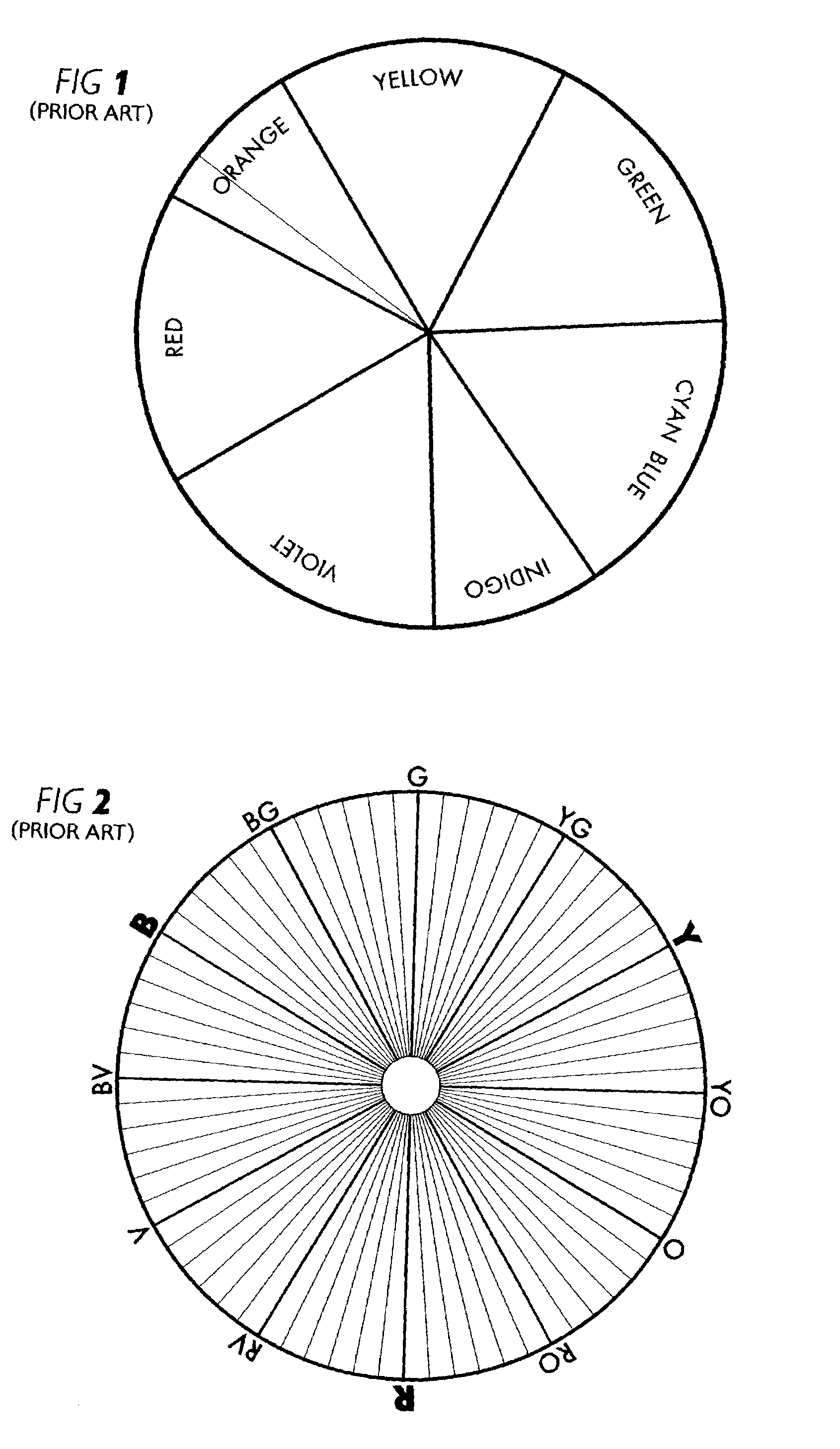
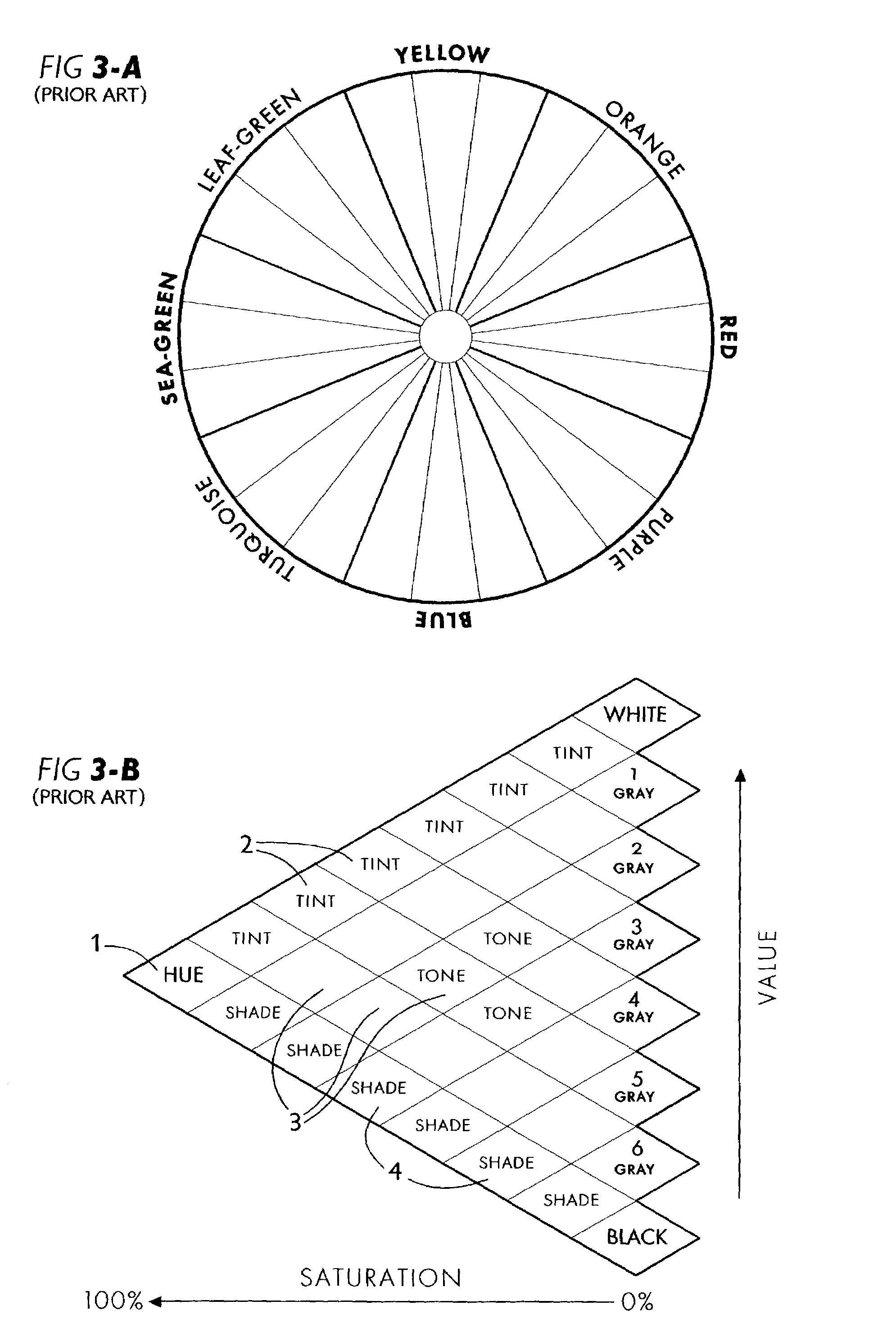
Artists' color display system
InactiveUS7180524B1Improve matchWell mixedTexturing/coloringCharacter and pattern recognitionGraphicsDisplay contrast
An assortment of color elements is grouped within a plurality of color families which are organized in accordance with a circular color chart (FIG. 10-A) and a columnar chart (FIG. 11-A). Except for the neutral-gray color family, a pair of boundary-hues respectively defines the extent of acceptable hue variation within each group, resulting in an included range of hue within each color family, and an excluded range of hue in between neighboring color families. Variant-hue charts enhance color comparison and selection within each main color family by displaying contrasting variations of all three color attributes, that is, value, saturation, and hue, within a single chart. Variant-hue charts also consolidate color elements into a compact format, and provide a graphical user interface for computer color selection.
Owner:AXELROD DALE
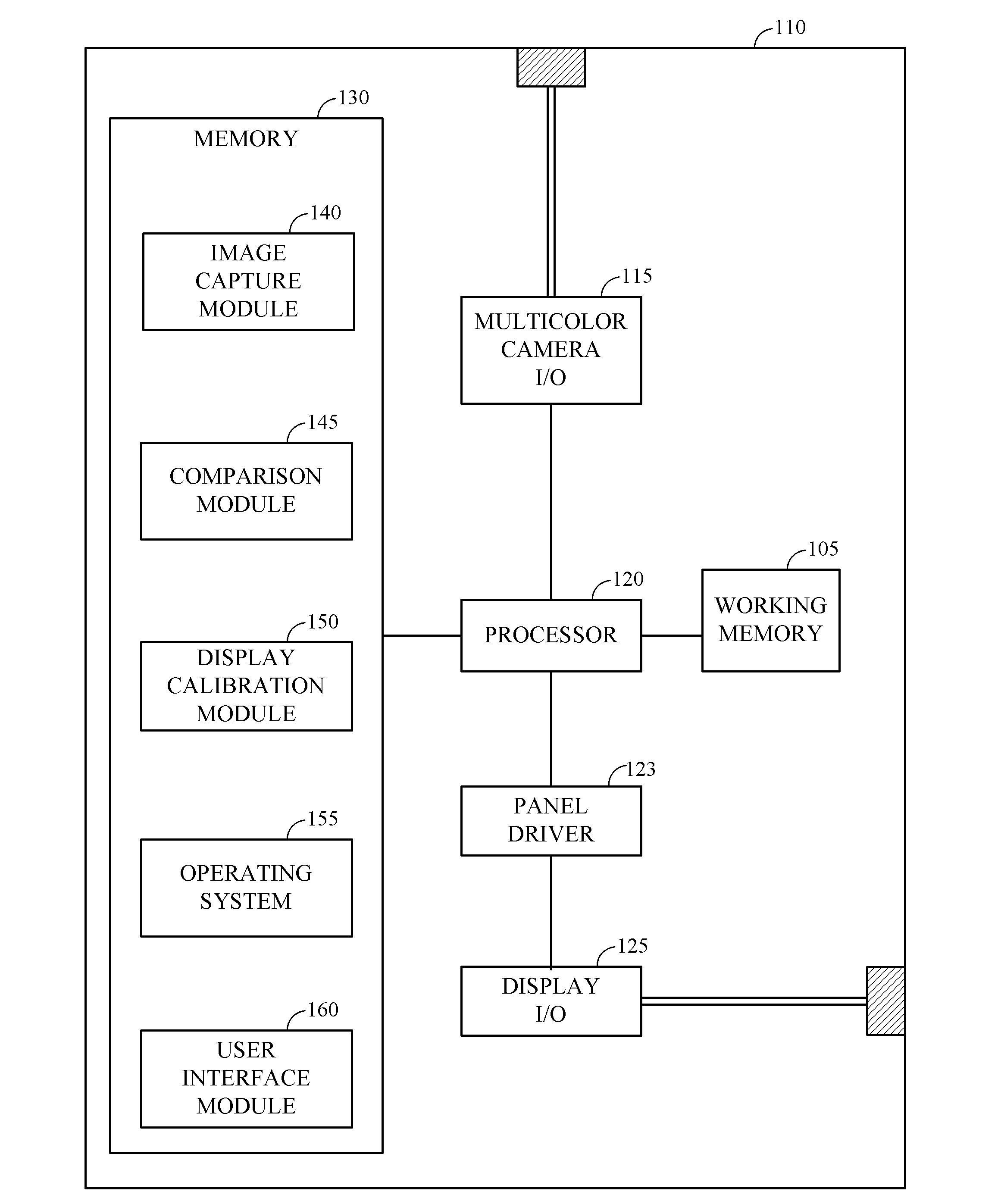
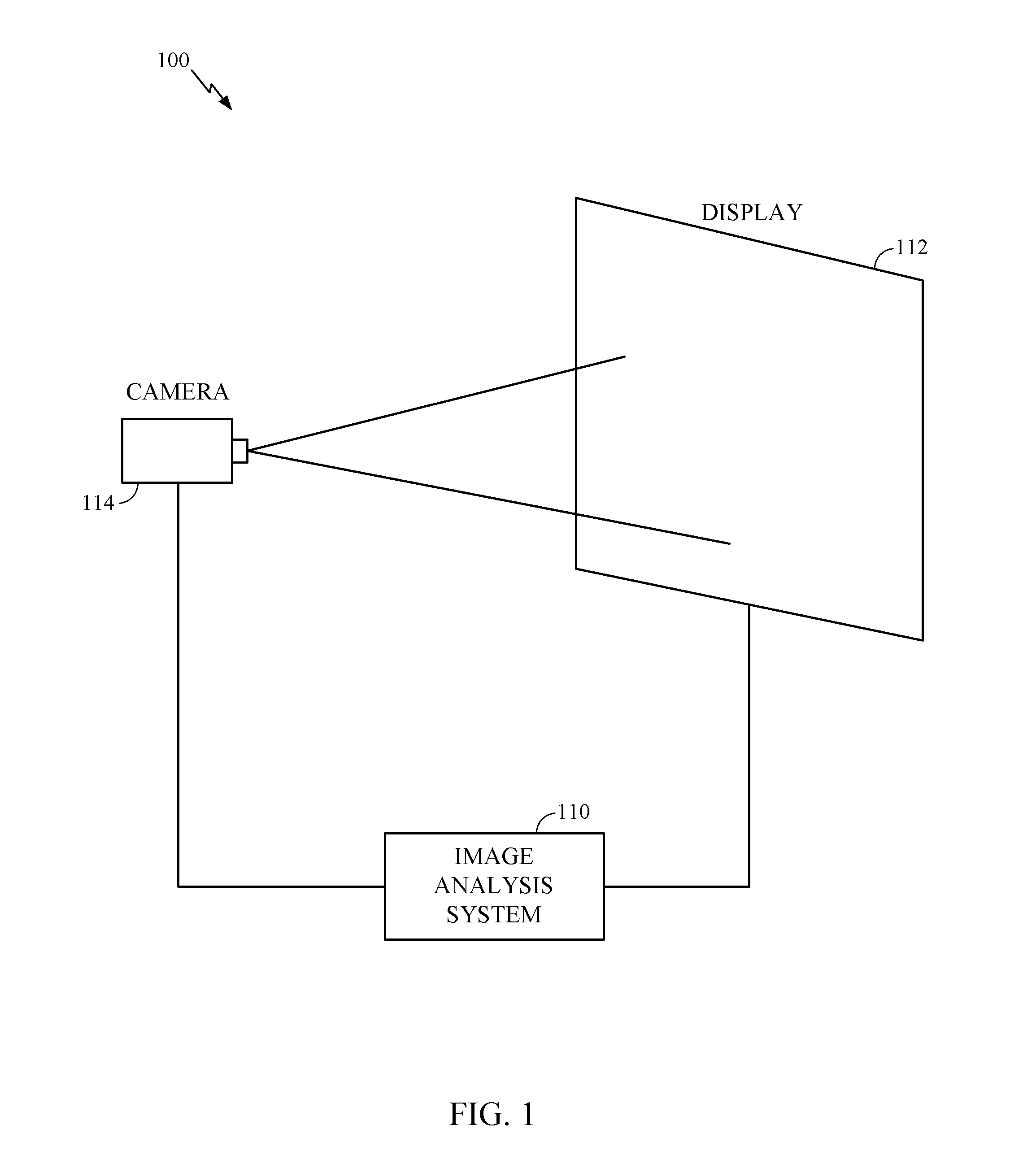
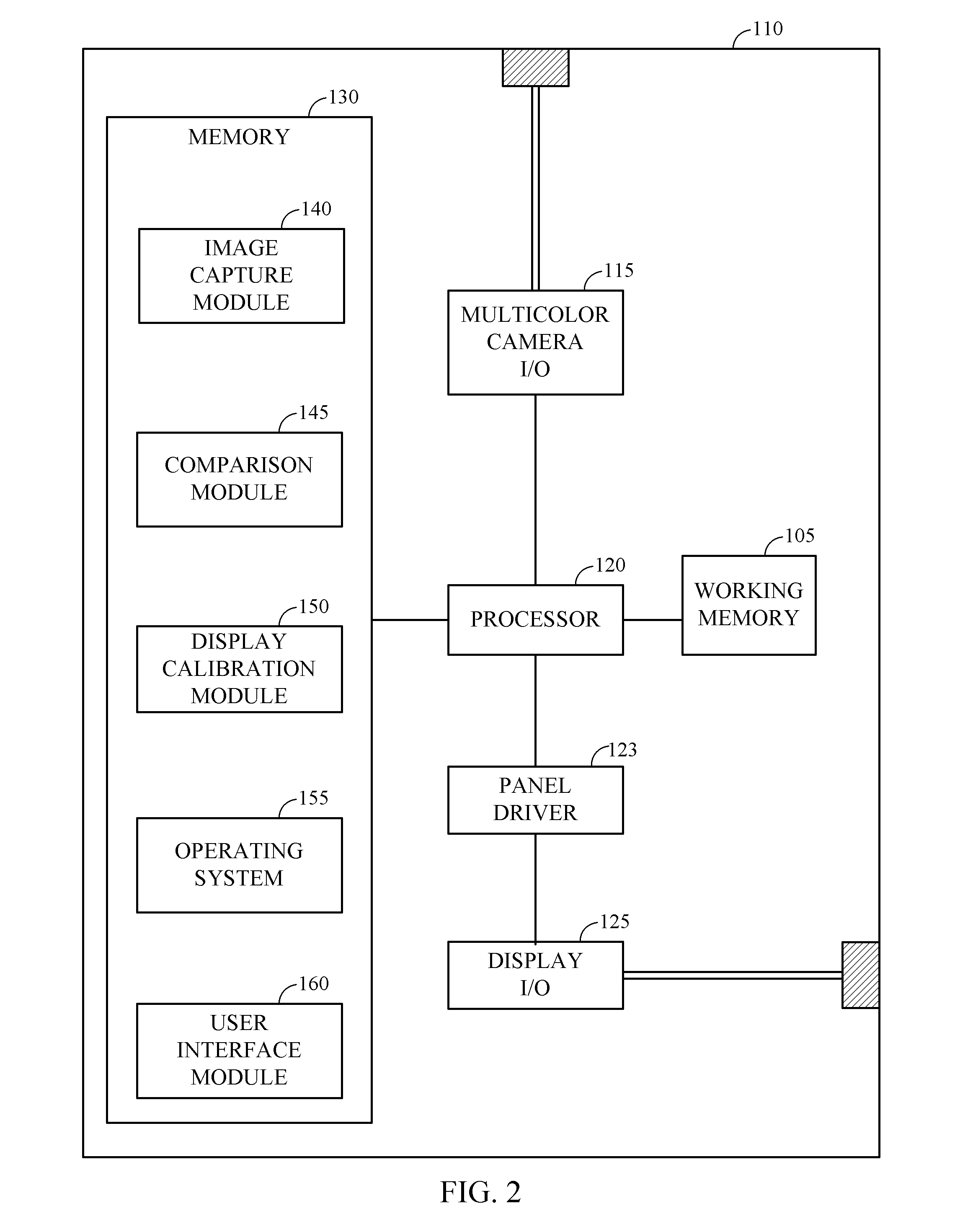
Fast calibration of displays using spectral-based colorimetrically calibrated multicolor camera
Described are a system and method to calibrate displays using a spectral-based colorimetrically calibrated multicolor camera. Particularly, discussed are systems and methods for displaying a multicolor calibration pattern image on a display unit, capturing the multicolor calibration pattern image with a multicolor camera having a plurality of image sensors, with each image sensor configured to capture a predetermined color of light, comparing a set of reference absolute XYZ coordinates of a set of colors from the multicolor calibration pattern with a set of measured XYZ color coordinates captured using the colorimetrically calibrated camera, and calibrating the display unit based on the comparison between the reference coordinates and the measured coordinates.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
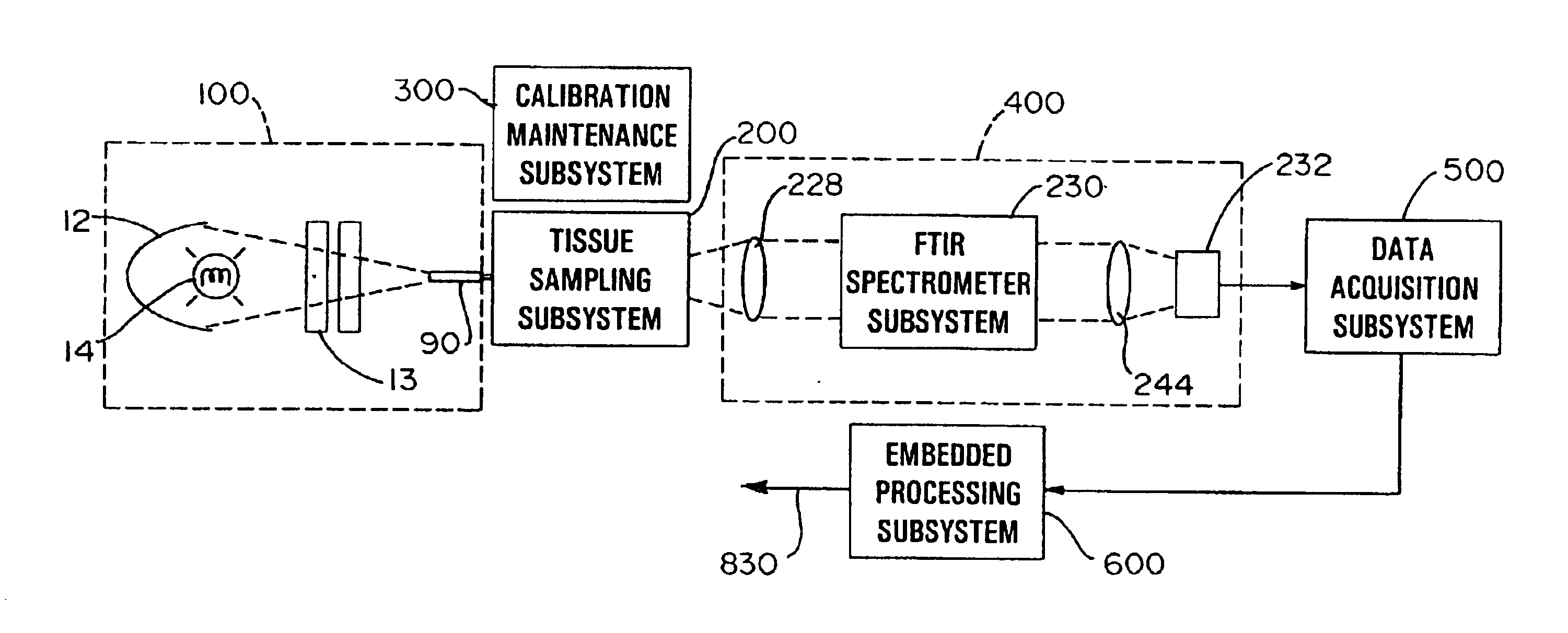
System for non-invasive measurement of glucose in humans
InactiveUS6865408B1Efficient collectionMaximize glucose net analyte signal-to-noise ratioRadiation pyrometryDiagnostics using spectroscopyData acquisitionNon invasive
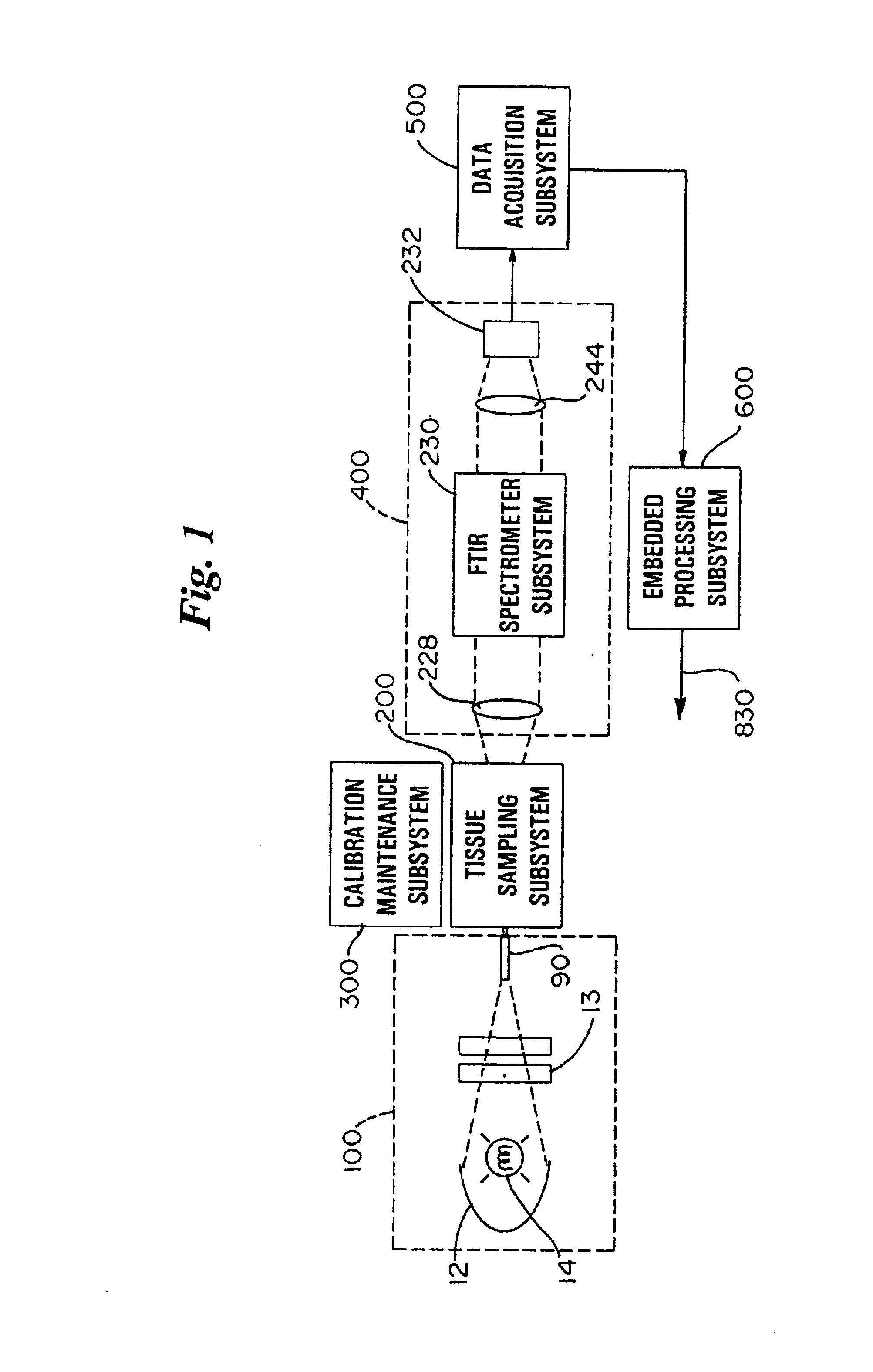
An apparatus and method for non-invasive measurement of glucose in human tissue by quantitative infrared spectroscopy to clinically relevant levels of precision and accuracy. The system includes six subsystems optimized to contend with the complexities of the tissue spectrum, high signal-to-noise ratio and photometric accuracy requirements, tissue sampling errors, calibration maintenance problems, and calibration transfer problems. The six subsystems include an illumination subsystem, a tissue sampling subsystem, a calibration maintenance subsystem, an FTIR spectrometer subsystem, a data acquisition subsystem, and a computing subsystem.
Owner:INLIGHT SOLUTIONS
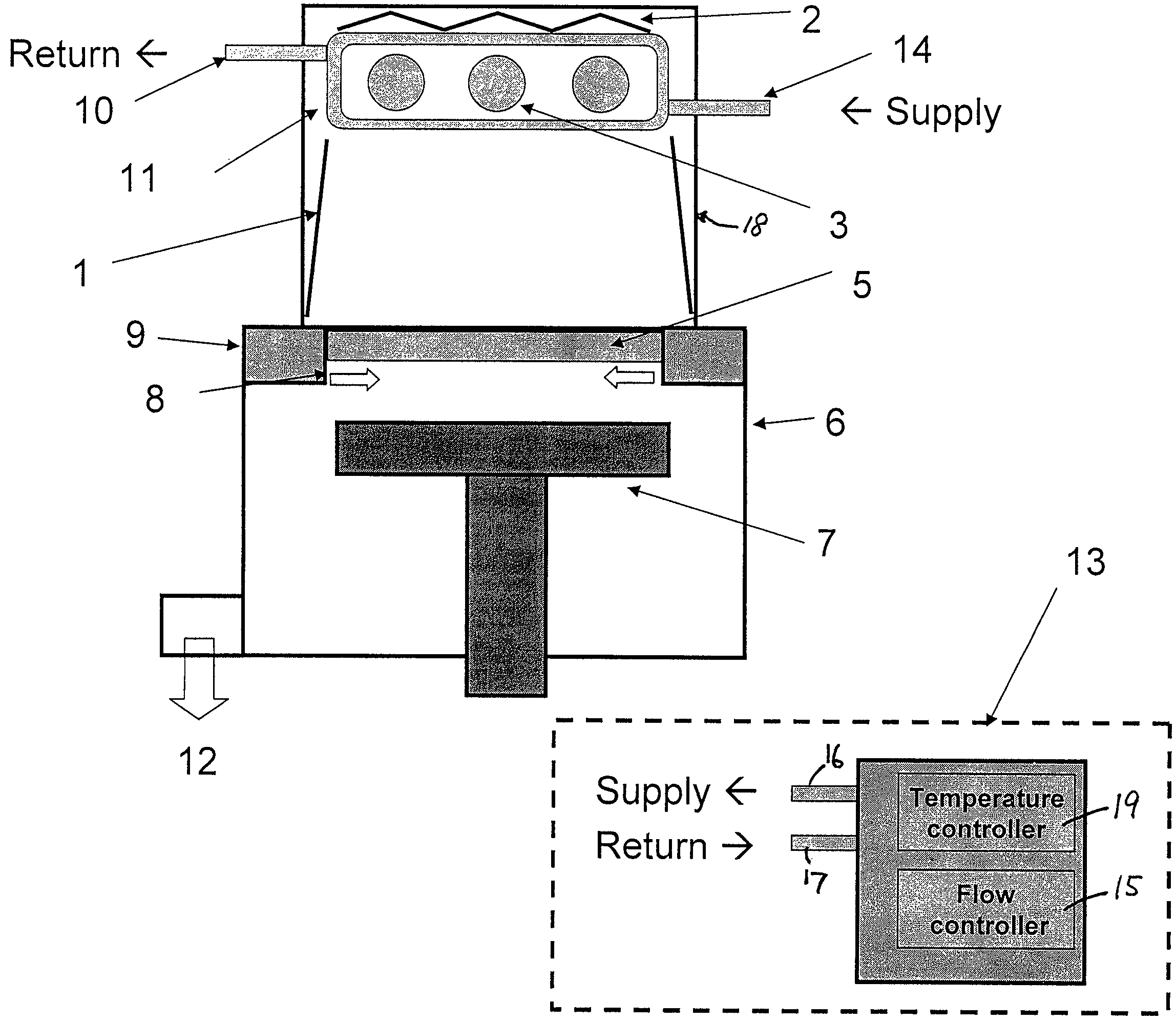
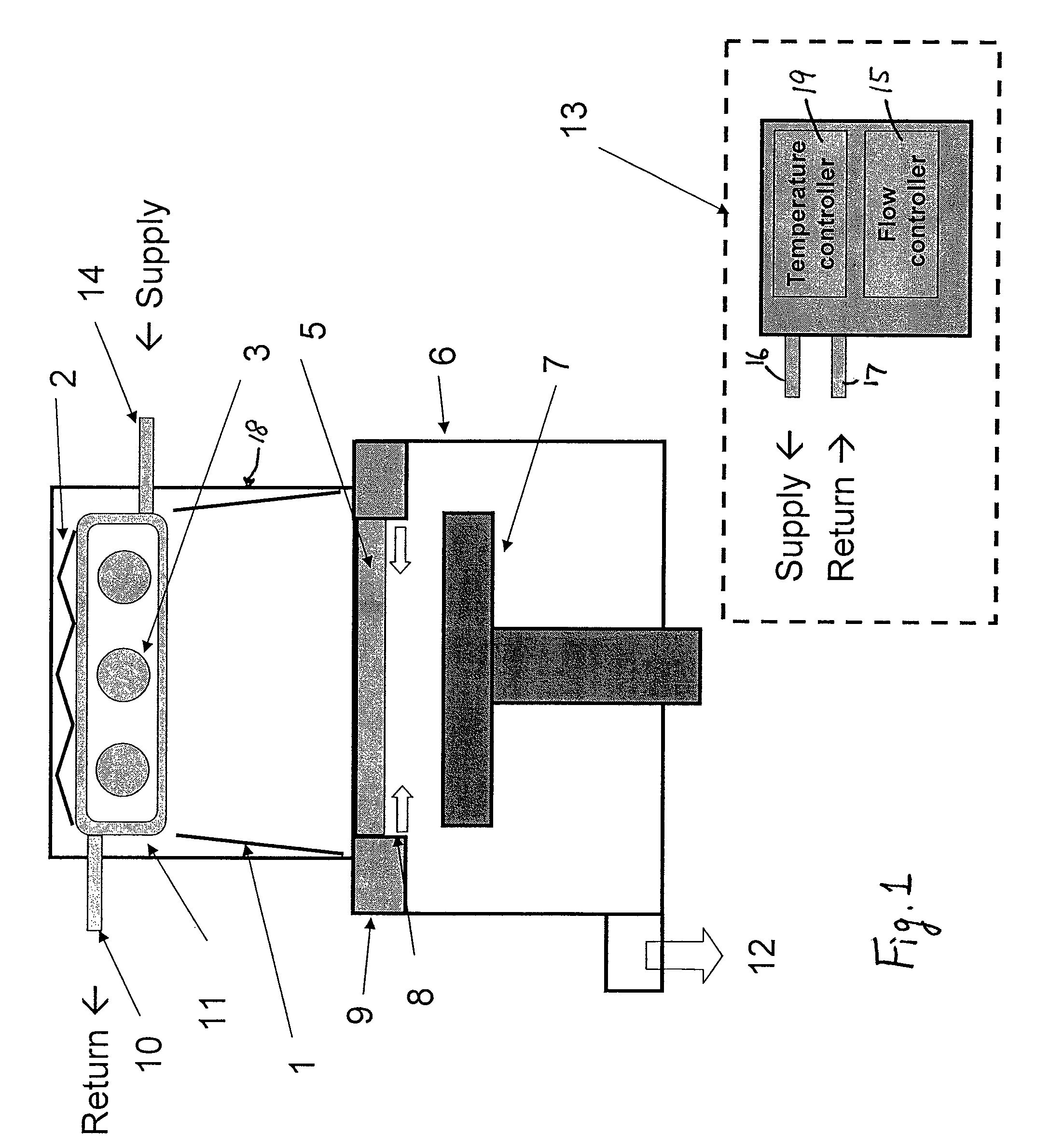
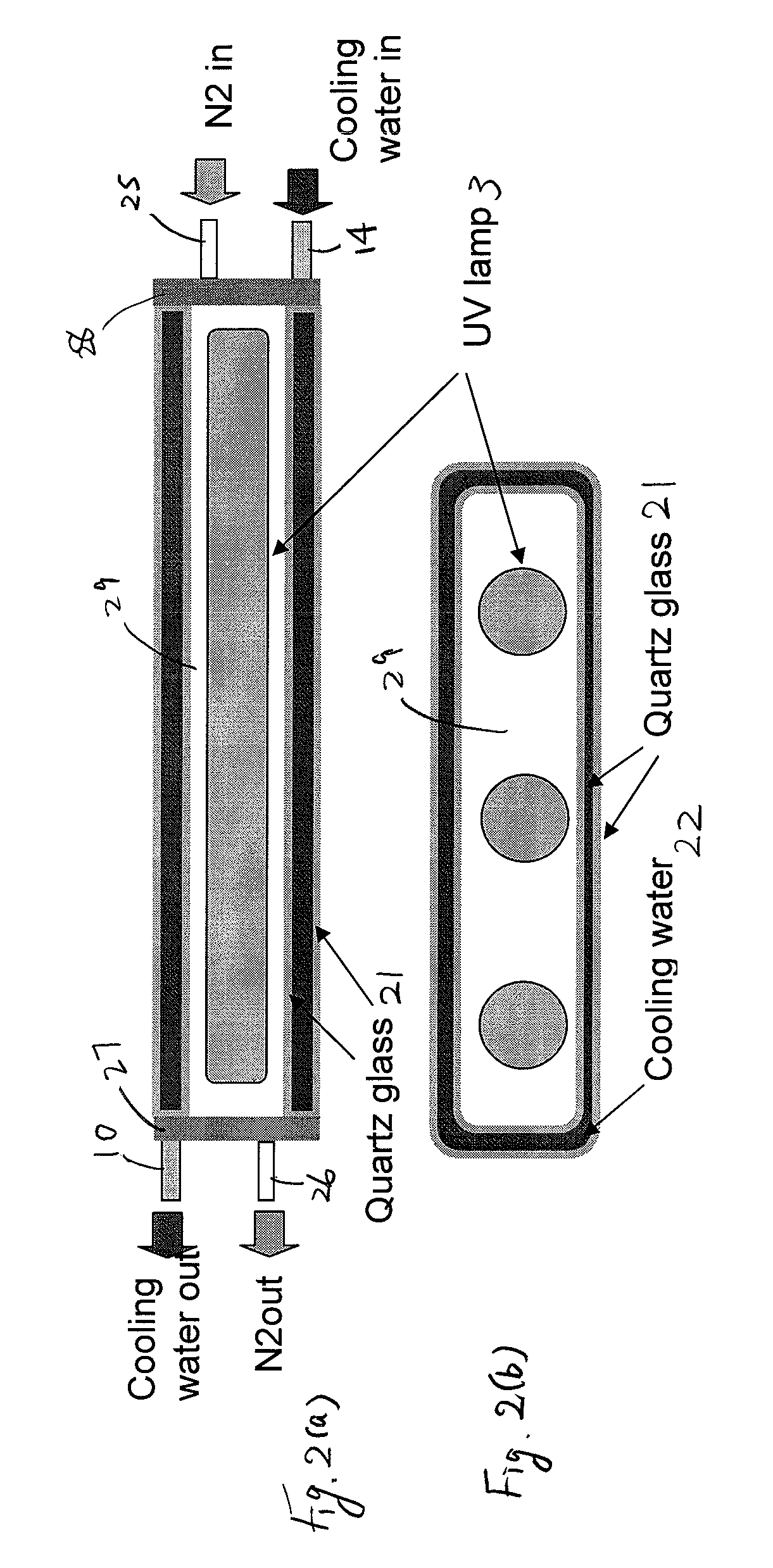
Ultraviolet ray generator, ultraviolet ray irradiation processing apparatus, and semiconductor manufacturing system
InactiveUS20050263719A1High dielectric constantReduce transmission intensityFurnace componentsLiving organism packagingUltravioletNitrogen gas
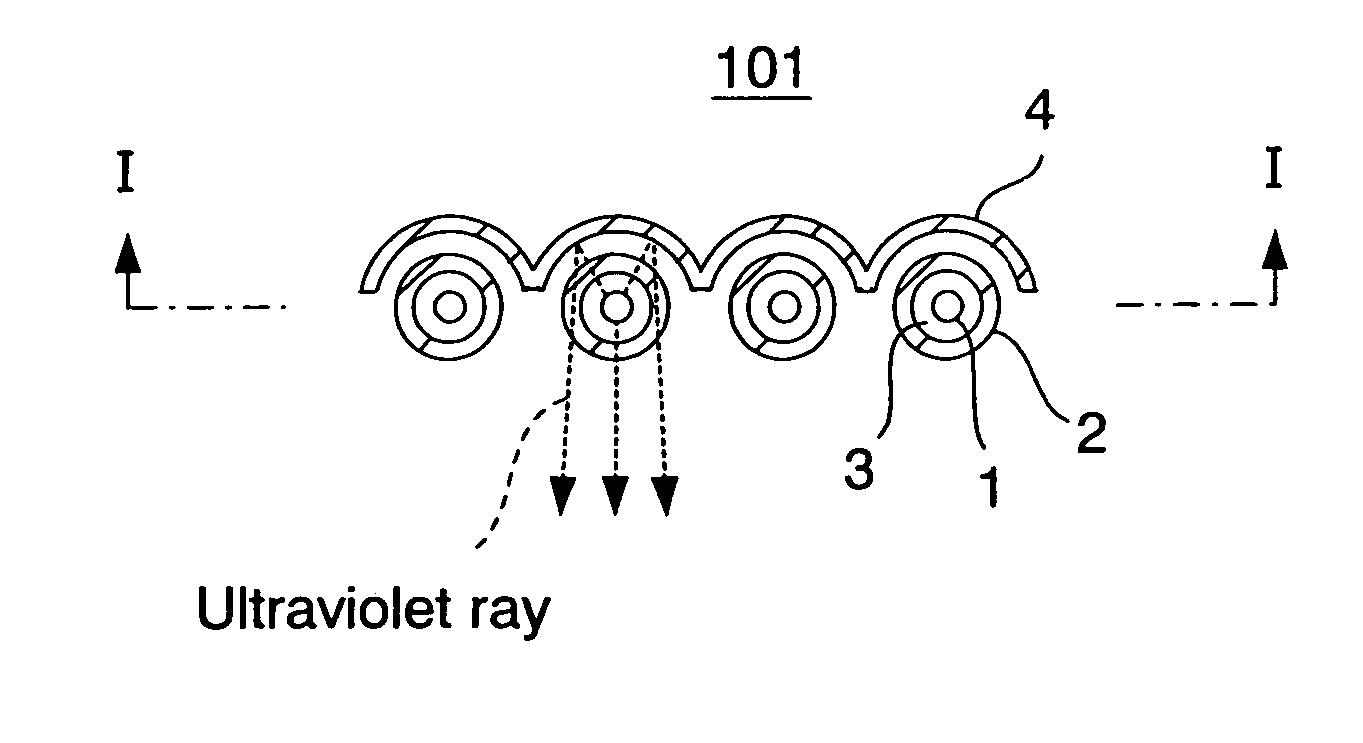
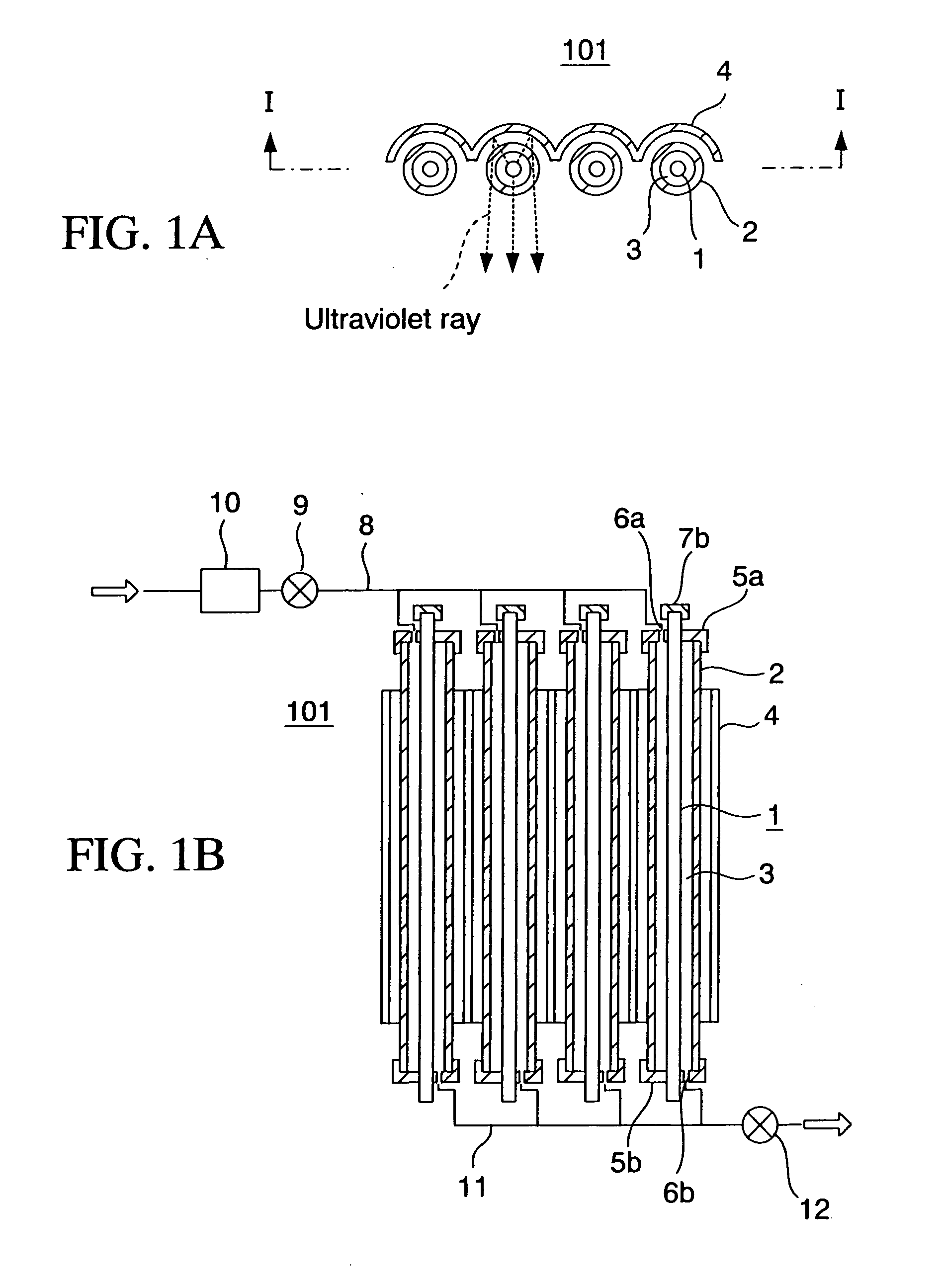
The present invention relates to an ultraviolet ray generator 101, and the generator 101 has an ultraviolet ray lamp 1, a protective tube 2 being made of a material which is transparent with respect to ultraviolet ray and housing the ultraviolet ray lamp 1, and gas introduction port 6a introducing nitrogen gas or inert gas into the protective tube 2.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
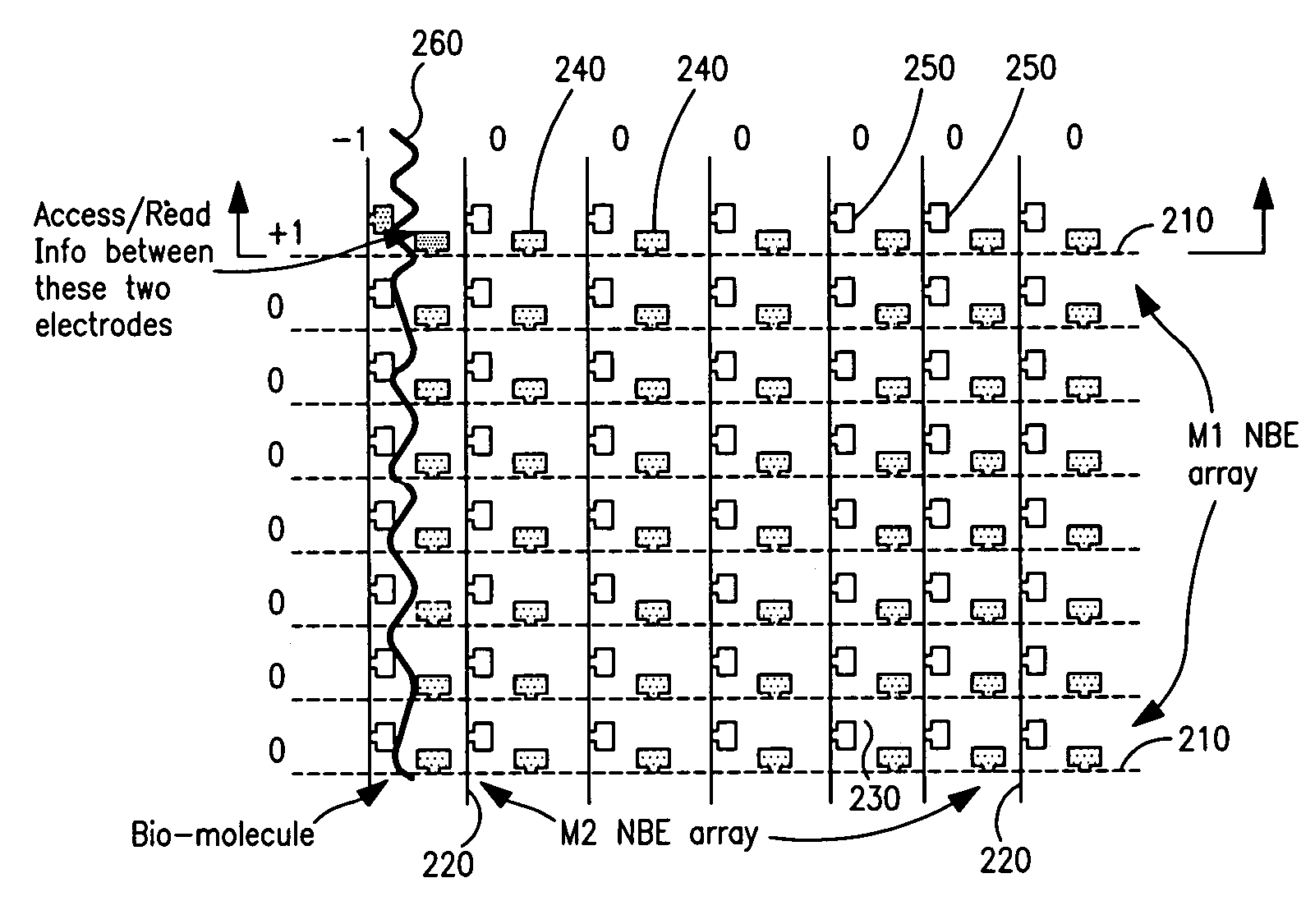
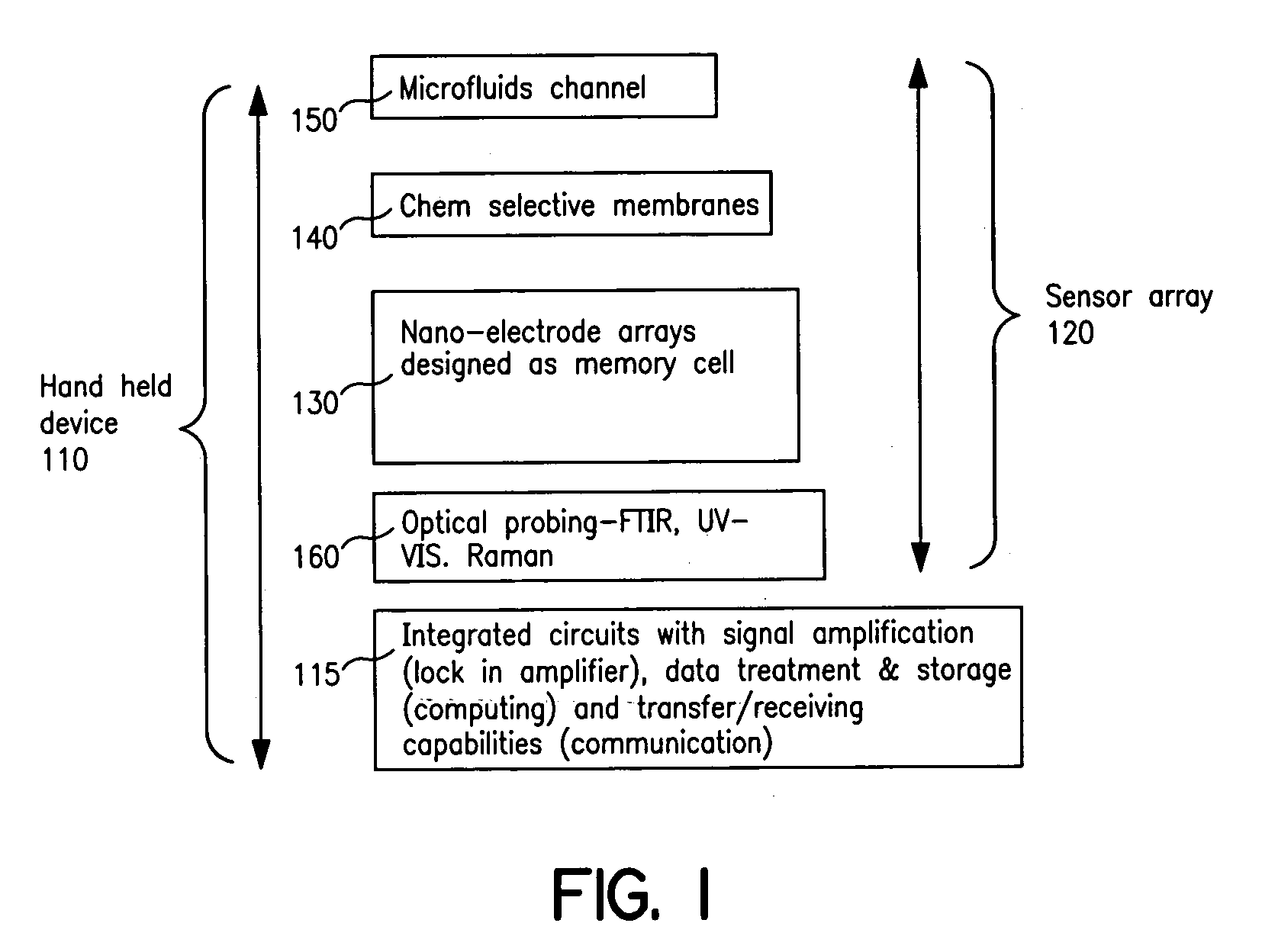
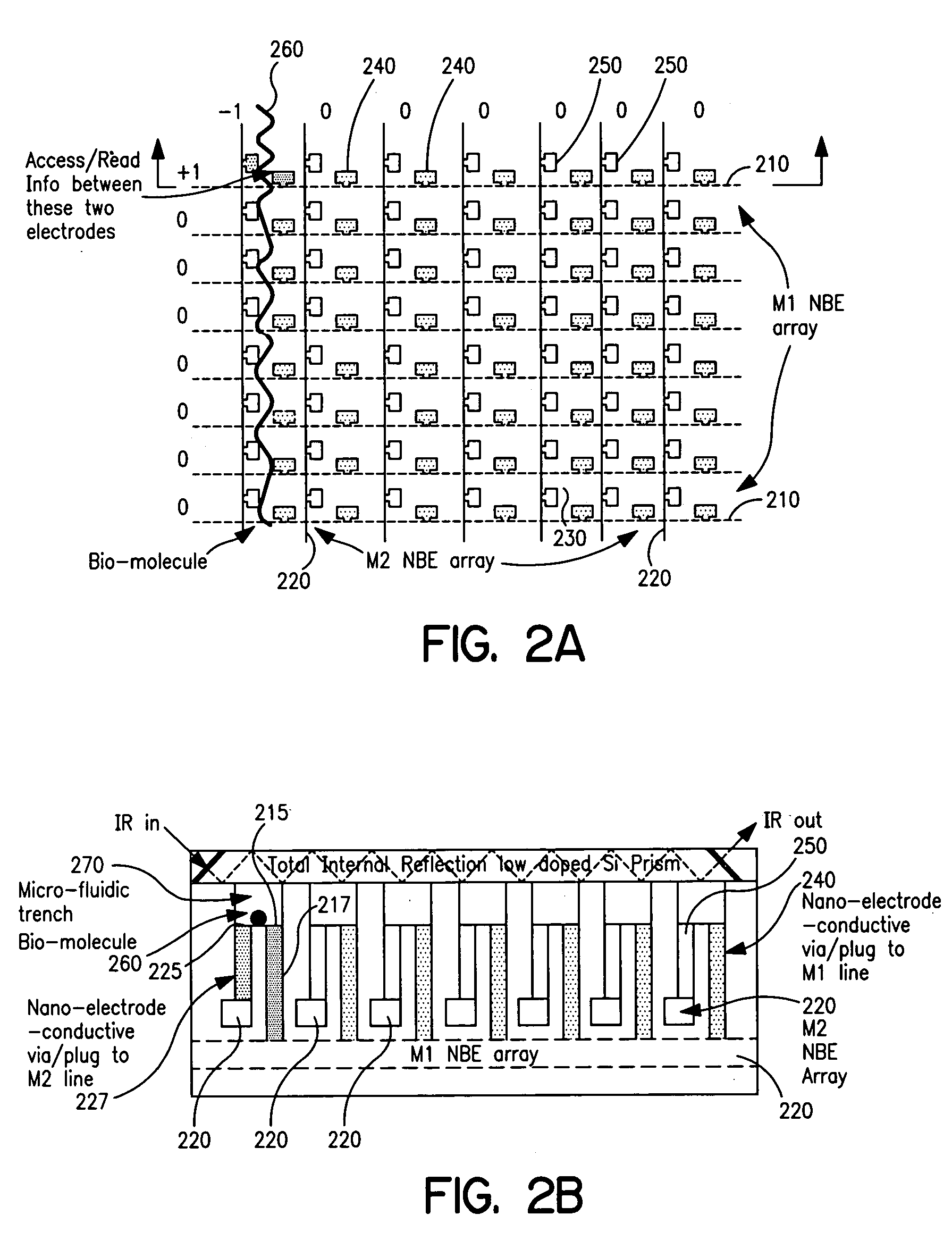
Sensor array integrated circuits
InactiveUS20050221473A1Low reliabilityLow costMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSensor arrayIntegrated circuit
An apparatus includes a condensed array addressed device; and a spectroscope optically coupled to the condensed array addressed device. A method includes determining bonding and / or lack-of-bonding of a target molecule to a condensed array addressed device by characterizing a subsequent rate of electrolysis on the condensed array addressed device. A method includes fabricating a condensed array addressed device using damascene patterning.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Device for capturing thermal spectra from tissue
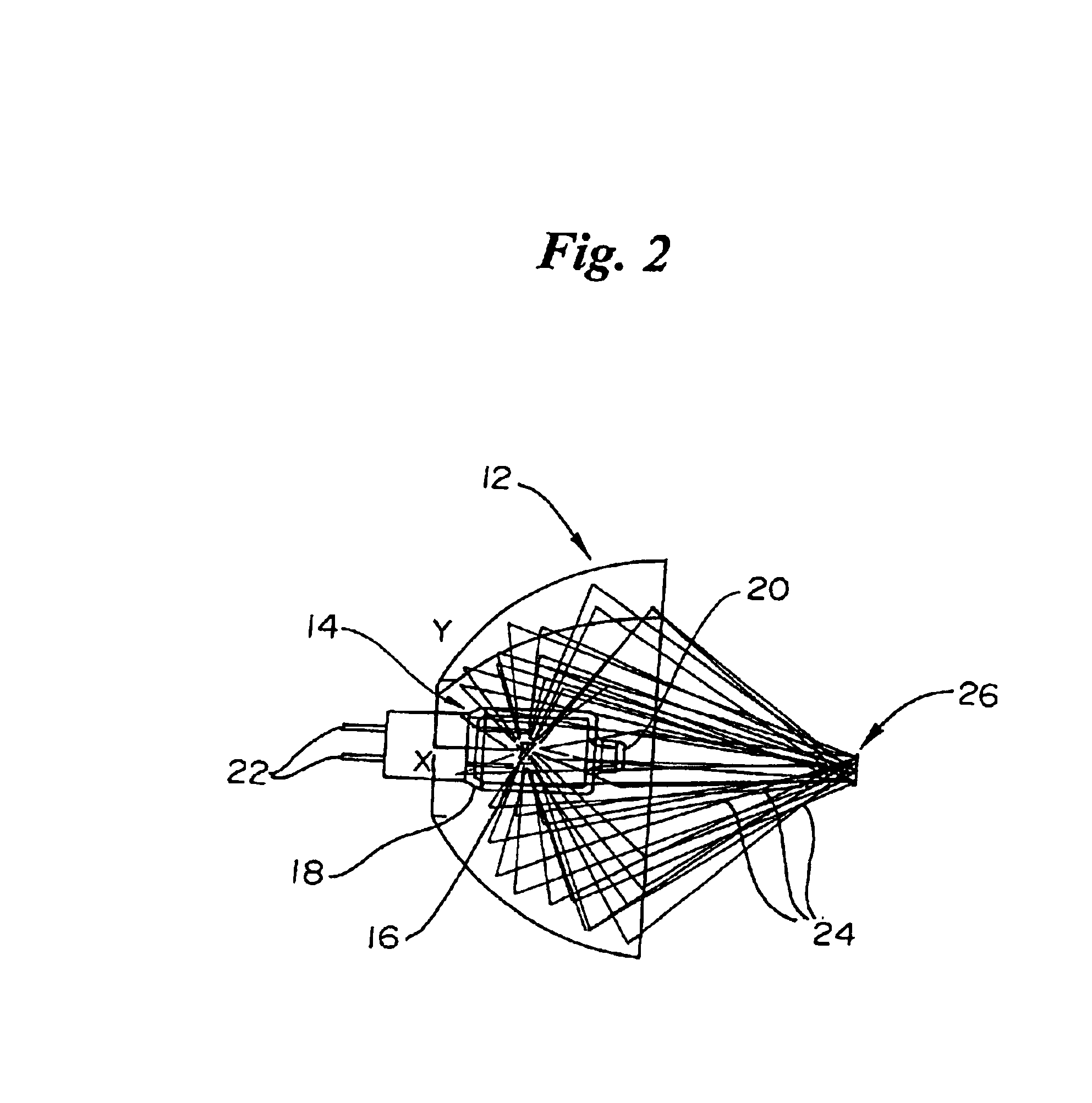
InactiveUS6959211B2Improve determinationIsolating measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringColor/spectral properties measurementsAnalyteGlucose polymers
A device and method are provided for use with a noninvasive optical measurement system, such as a thermal gradient spectrometer, for improved determination of analyte concentrations within living tissue. In one embodiment, a wearable window is secured to a patient's forearm thereby isolating a measurement site on the patient's skin for determination of blood glucose levels. The wearable window effectively replaces a window of the spectrometer, and thus forms an interface between the patient's skin and a thermal mass window of the spectrometer. When the spectrometer must be temporarily removed from the patient's skin, such as to allow the patient mobility, the wearable window is left secured to the forearm so as to maintain a consistent measurement site on the skin. When the spectrometer is later reattached to the patient, the wearable window will again form an interface between the spectrometer and the same location of skin as before.
Owner:OPTISCAN BIOMEDICAL
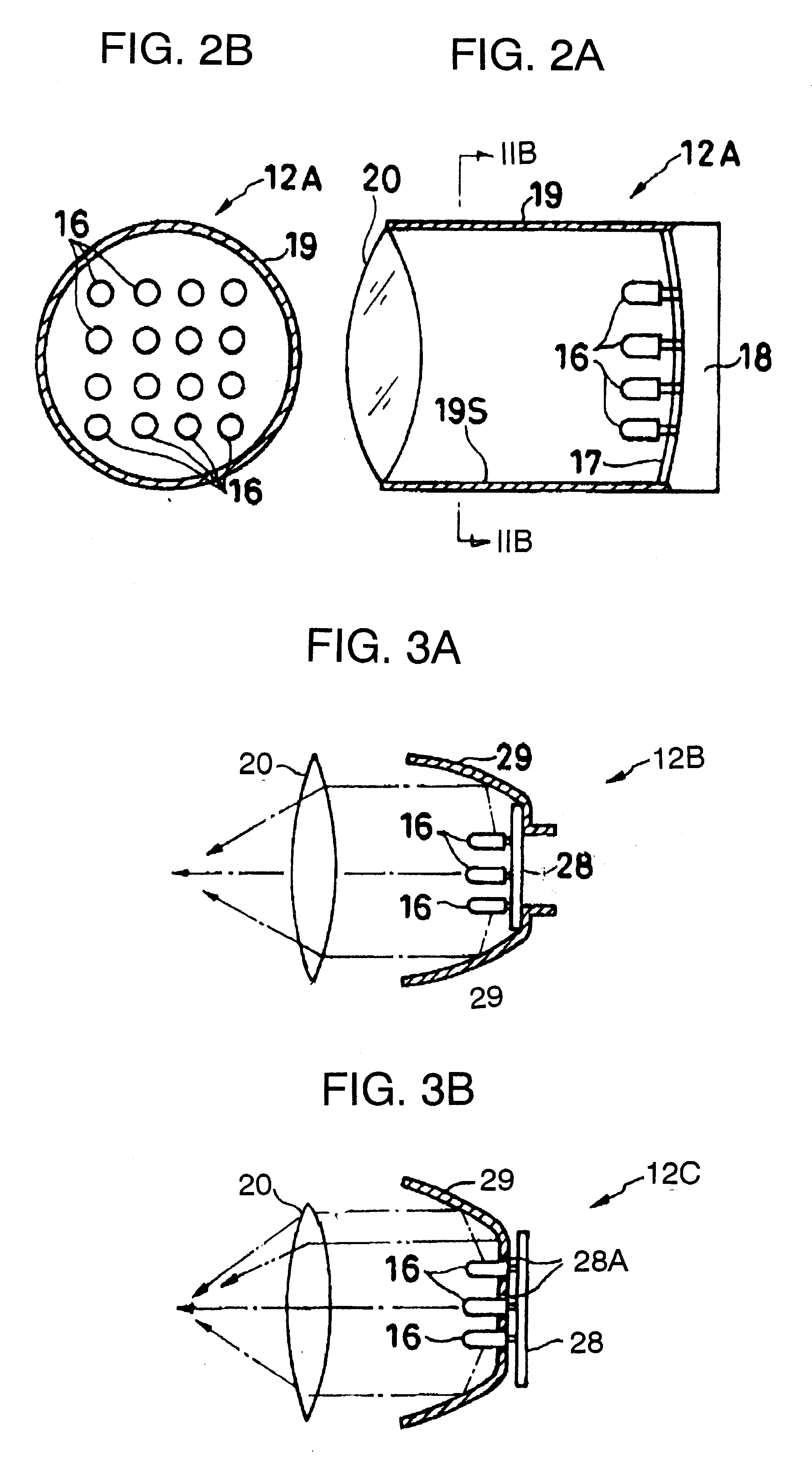
Battery-powered light source arrangement for endoscope
InactiveUS6260994B1Less overall consumptionLittle electrical powerMechanical apparatusPrintersElectrical batteryLight guide
A light source arrangement for a battery-powered light source unit of an endoscope comprises a cylindrical housing, a base disposed at one end of the housing, a plurality of LEDs connected to a flexible circuit board supported on the base and a focusing lens. A light guide for directing light emanating from the LEDs. The light guide comprises a reflective surface formed on an inner wall of the housing, a reflector having a concave reflective surface which is disposed at one end of the housing so as to surround the LEDs or a micro-lens array disposed in front of the LEDs with each micro lens aligned with the LED.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Optical tomography apparatus
ActiveUS20070019208A1High resolutionMaintain good propertiesMaterial analysis by optical meansCatheterMultiplexingDiffusion
Low coherence light having a central wavelength λc of 1.1 μm and a full width at half maximum spectrum Δλ of 90 nm is emitted. The low coherence light has wavelength properties suited for the light absorbing properties, the diffusion properties, and the dispersion properties of living tissue. A light dividing means divides the low coherence light into a measuring light beam, which is irradiated onto a measurement target via an optical probe, and a reference light beam that propagates toward an optical path length adjusting means. A multiplexing means multiplexes a reflected light beam, which is the measuring light beam reflected at a predetermined depth of the measurement target, and the reference light beam, to form coherent light. A coherent light detecting means detects the optical intensity of the multiplexed coherent light. An image obtaining means performs image processes, and displays an optical tomographic image on a display apparatus.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Imaging device analysis systems and imaging device analysis methods
Imaging device analysis systems and imaging device analysis methods are described. According to one embodiment, an imaging device analysis system includes a light source configured to output light for use in analyzing at least one imaging component of an imaging device, wherein the imaging device is configured to generate images responsive to received light, and processing circuitry coupled with the light source and configured to control the light source to optically communicate the light to the imaging device, wherein the processing circuitry is further configured to access image data generated by the imaging device responsive to the reception, by the imaging device, of the light from the light source and to process the image data to analyze an operational status of the at least one imaging component.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Apparatus for imaging using an array of lenses
An imaging system / camera consisting of multiple nano-sized optical elements arranged in an array format with more than one pixel per optical element will have a higher resolution than each element would be capable of individually, since each element being at a different point gathers slightly different overlapping information. Hence by processing such information one can obtain a clear image. Furthermore multiple information from sectors of an array of sensors can be processed to obtain 3-D, stereotypic and panoramic imaging and may be connected to each other allowing seeing around obstacles as well as enabling full 3-D tracking and / or metric determination of an unknown object. Color / spectroscopic imaging can be achieved by utilizing equally sized lenses and multi-wavelength sensing layers below the lenses. However, color / spectroscopic imaging and / or spectroscopy can be achieved by taking advantage of unique optical properties of nano-scaled lenses accepting various wavelengths below their diffraction limits.
Owner:NANOLIGHT TECH
Laser-Driven Light Source
ActiveUS20070228300A1Minimize coolingAvoid low lightRadiation pyrometryNanoinformaticsProduct gasBrightness perception
An apparatus for producing light includes a chamber and an ignition source that ionizes a gas within the chamber. The apparatus also includes at least one laser that provides energy to the ionized gas within the chamber to produce a high brightness light. The laser can provide a substantially continuous amount of energy to the ionized gas to generate a substantially continuous high brightness light.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Raman-active taggants and their recognition
InactiveUS6610351B2Easy to useQuality improvementMaterial nanotechnologyRadiation applicationsMaximum dimensionActive component
An organic or organoelement, linear or branched, monomeric or polymeric composition of matter having a Raman-active component in the form of particles. The particles having a maximum dimension of 50 mum. The Raman-active compound is applied to a substrate. When the Raman-active compound is exposed to a laser light wavelength which is batochromically well beyond a spectral region of maximum absorbance of said Raman-active compound, Raman scattering can be detected.
Owner:QUANTAG SYST
Optical sensor with layered plasmon structure for enhanced detection of chemical groups by SERS
InactiveUS20060034729A1Produced in advanceRadiation pyrometryMicrobiological testing/measurementExcitation beamLight excitation
An optical sensor and method for use with a visible-light laser excitation beam and a Raman spectroscopy detector, for detecting the presence chemical groups in an analyte applied to the sensor are disclosed. The sensor includes a substrate, a plasmon resonance mirror formed on a sensor surface of the substrate, a plasmon resonance particle layer disposed over the mirror, and an optically transparent dielectric layer about 2-40 nm thick separating the mirror and particle layer. The particle layer is composed of a periodic array of plasmon resonance particles having (i) a coating effective to binding analyte molecules, (ii) substantially uniform particle sizes and shapes in a selected size range between 50-200 nm (ii) a regular periodic particle-to-particle spacing less than the wavelength of the laser excitation beam. The device is capable of detecting analyte with an amplification factor of up to 1012-1014, allowing detection of single analyte molecules.
Owner:POPONIN VLADIMIR
Spectroscopic microscopy with image-driven analysis
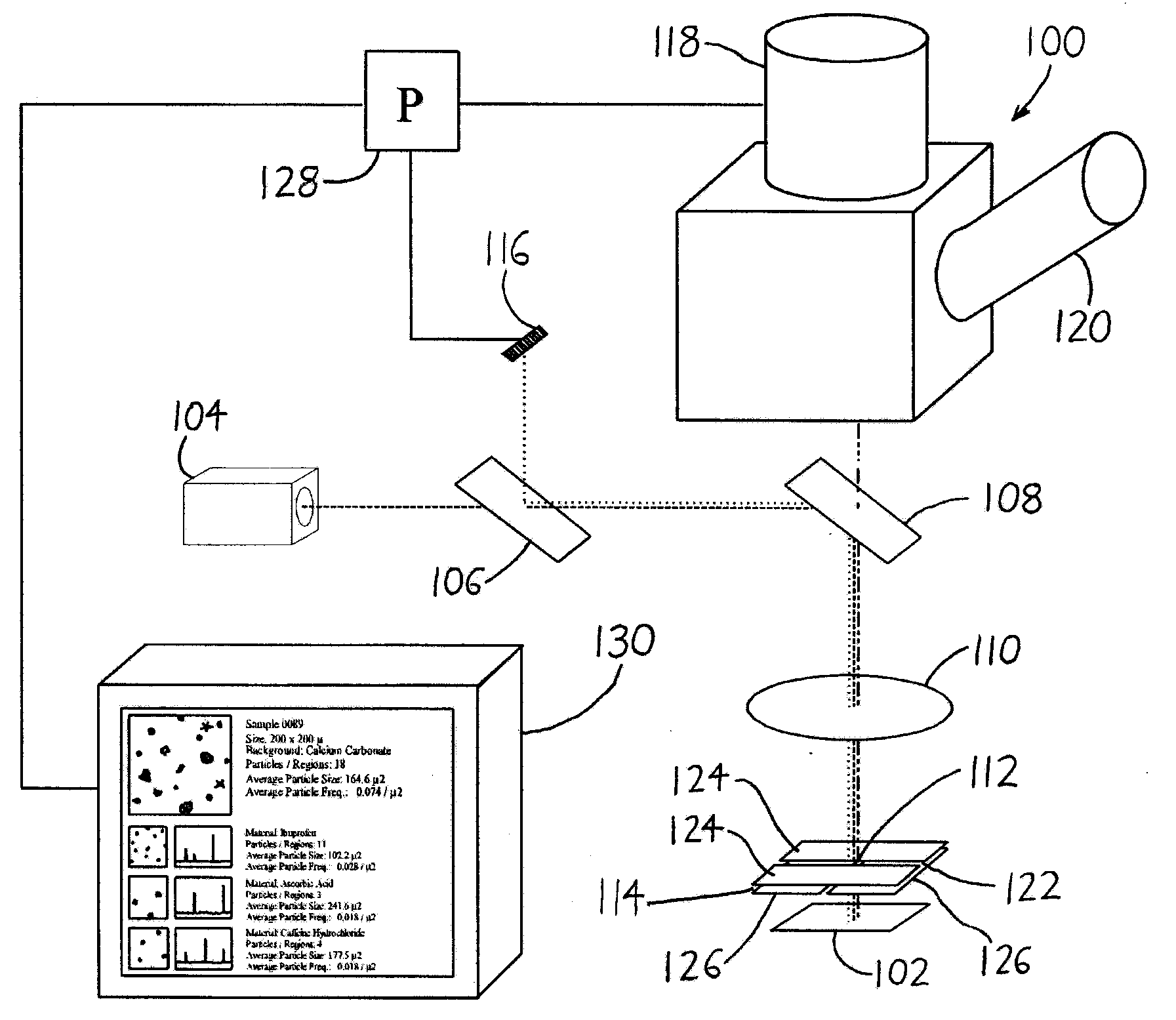
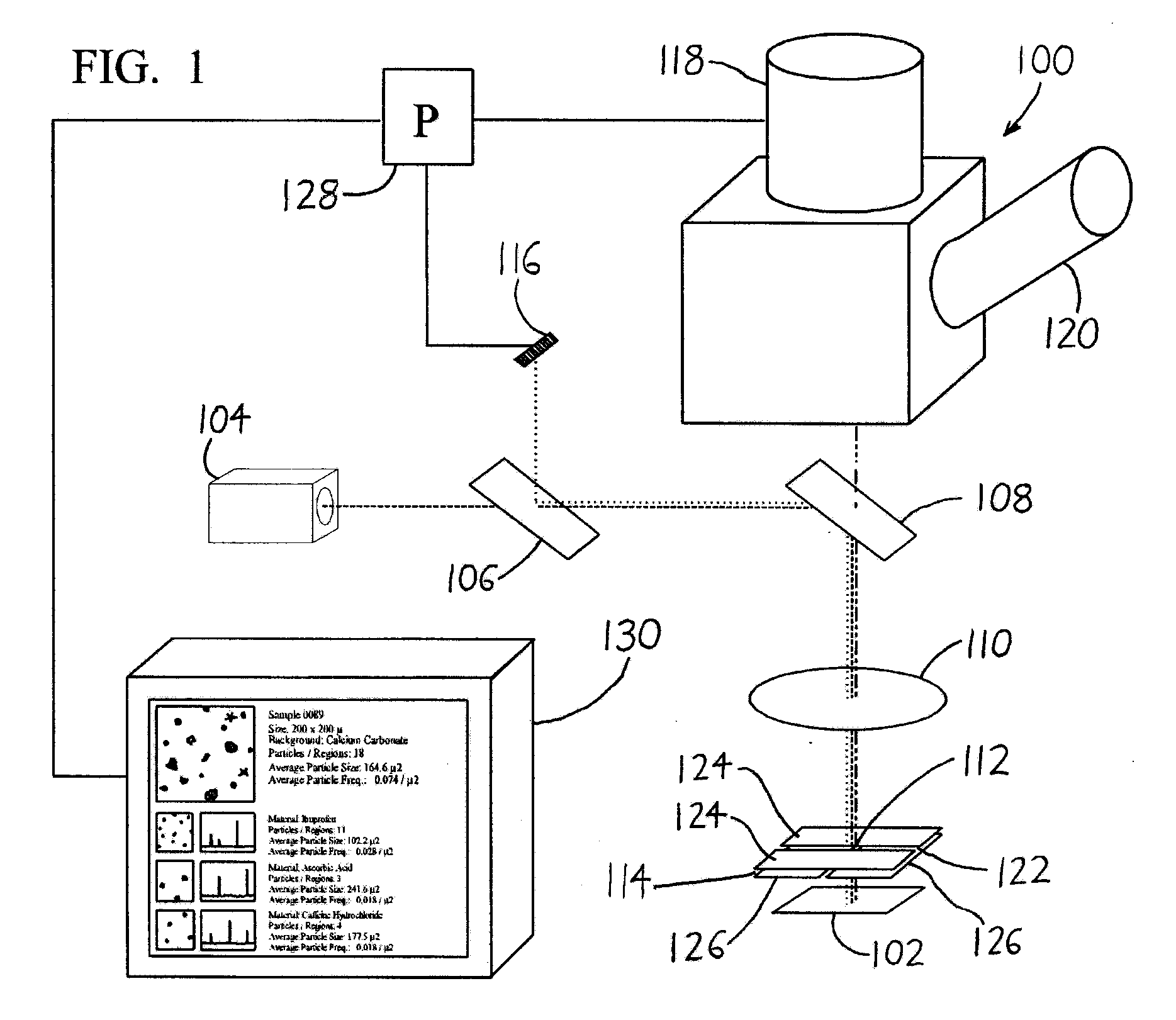
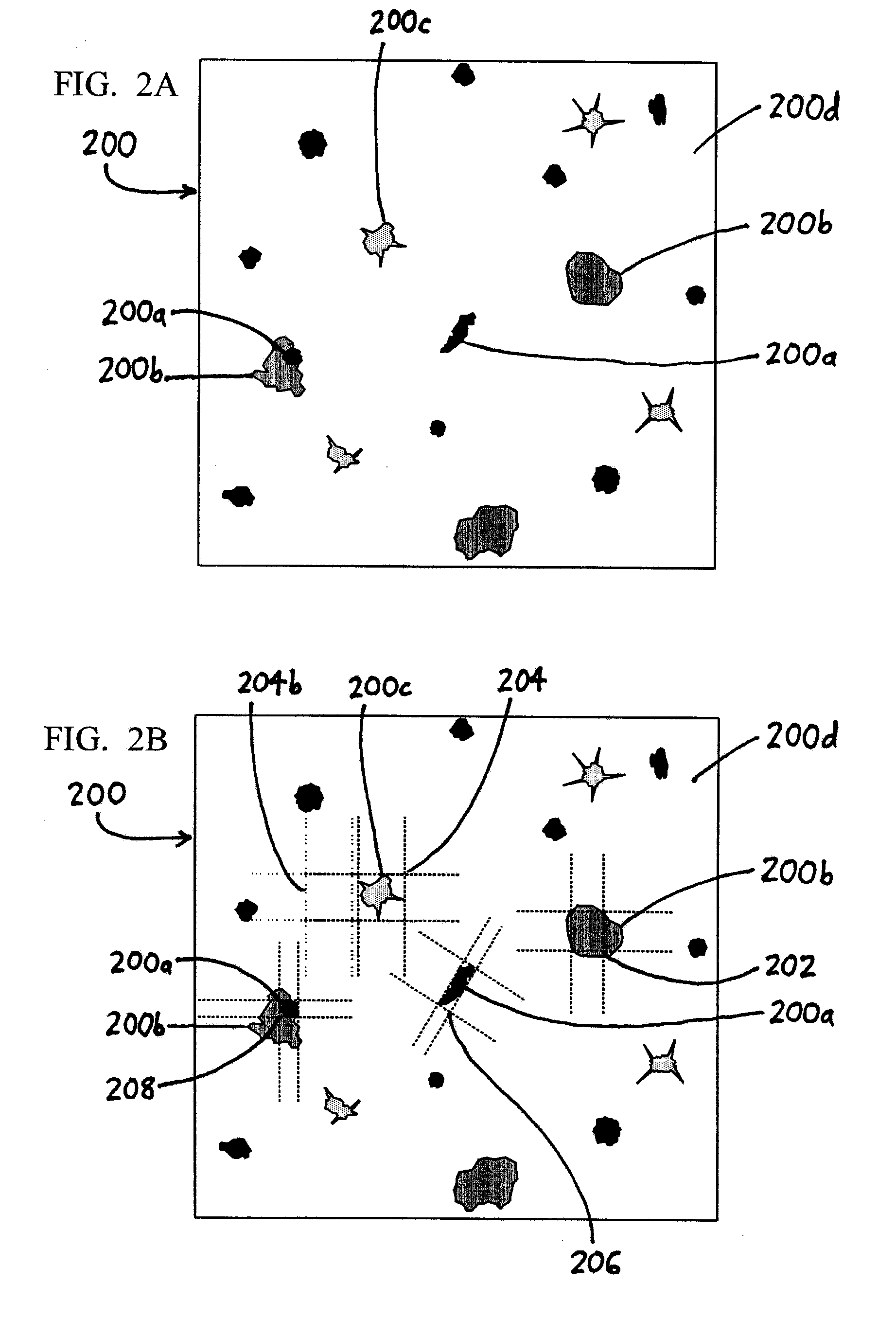
ActiveUS20080049220A1Easy to identifyArea maximizationRadiation pyrometryCharacter and pattern recognitionVideo imageAnalysis sample
In a spectroscopic microscope, a video image of a specimen is analyzed to identify regions having different appearances, and thus presumptively different properties. The sizes and locations of the identified regions are then used to position the specimen to align each region with an aperture, and to set the aperture to a size appropriate for collecting a spectrum from the region in question. The spectra can then be analyzed to identify the substances present within each region of the specimen. Information on the identified substances can then be presented to the user along with the image of the specimen.
Owner:THERMO ELECTRONICS SCI INSTR LLC
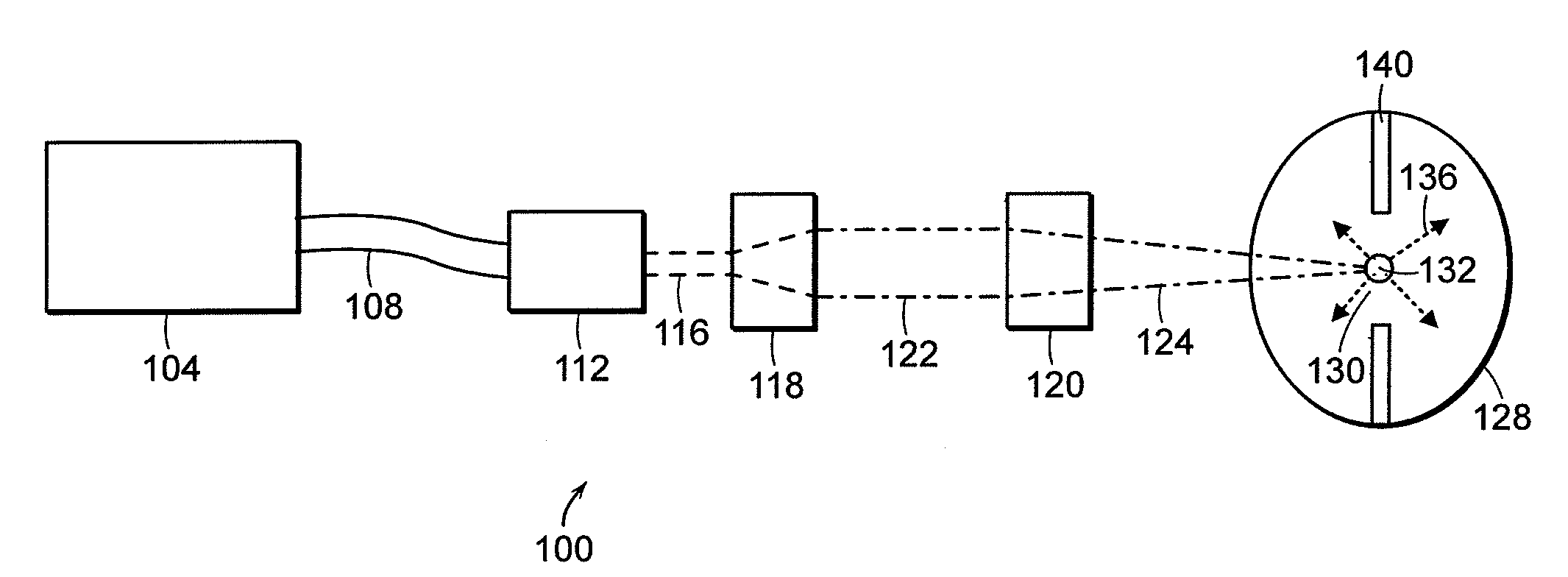
Laser produced plasma EUV light source with pre-pulse
A method for generating EUV light is disclosed which may include the acts / steps of providing a source material; generating a plurality of source material droplets; simultaneously irradiating a plurality of source material droplets with a first light pulse to create irradiated source material; and thereafter exposing the irradiated source material to a second light pulse to generate EUV light, e.g. by generating a plasma of the source material. In another aspect, an EUV light source may include a droplet generator delivering a plurality of source material droplets to a target volume; a source of a first light pulse for simultaneously irradiating a plurality of droplets in the target volume to produce an irradiated source material; and a source of a second light pulse for exposing the irradiated source material to generate EUV light. The droplet generator may comprise a non-modulating droplet generator and may comprise a multi-orifice nozzle.
Owner:CYMER INC
Cleaning tools with UV flash unit
A combination tool for cleaning and sanitizing a surface is disclosed. The tool includes a cleaning device and at least one UV flash unit. The cleaning device can be adapted for either wet or dry cleaning. The combination tool can also include a dispensing unit that can dispense a treatment agent. The tool can also include a sensor that can detect surface properties. In some arrangements, the tool includes a motive component that can propel the tool robotically.
Owner:THE CLOROX CO
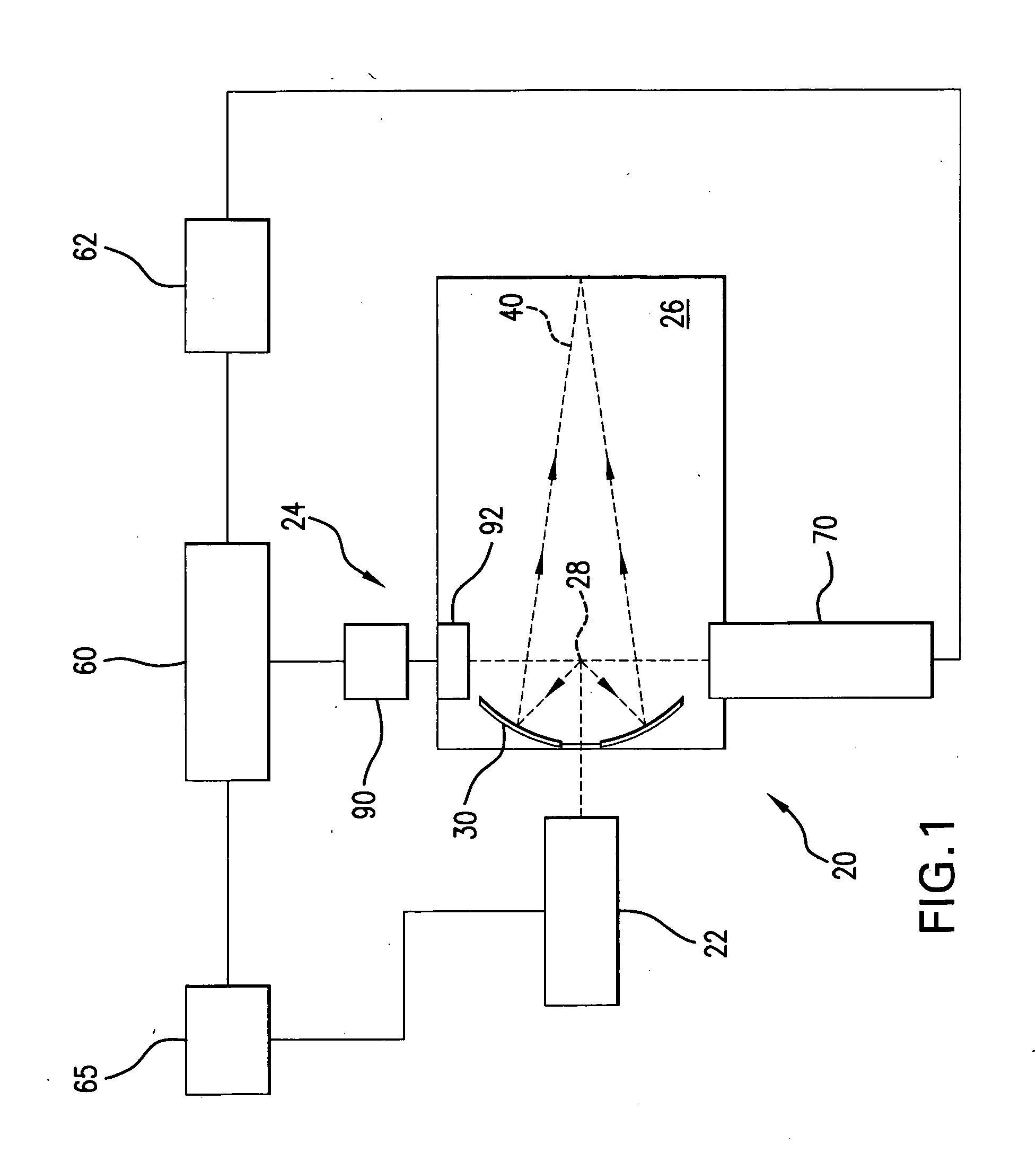
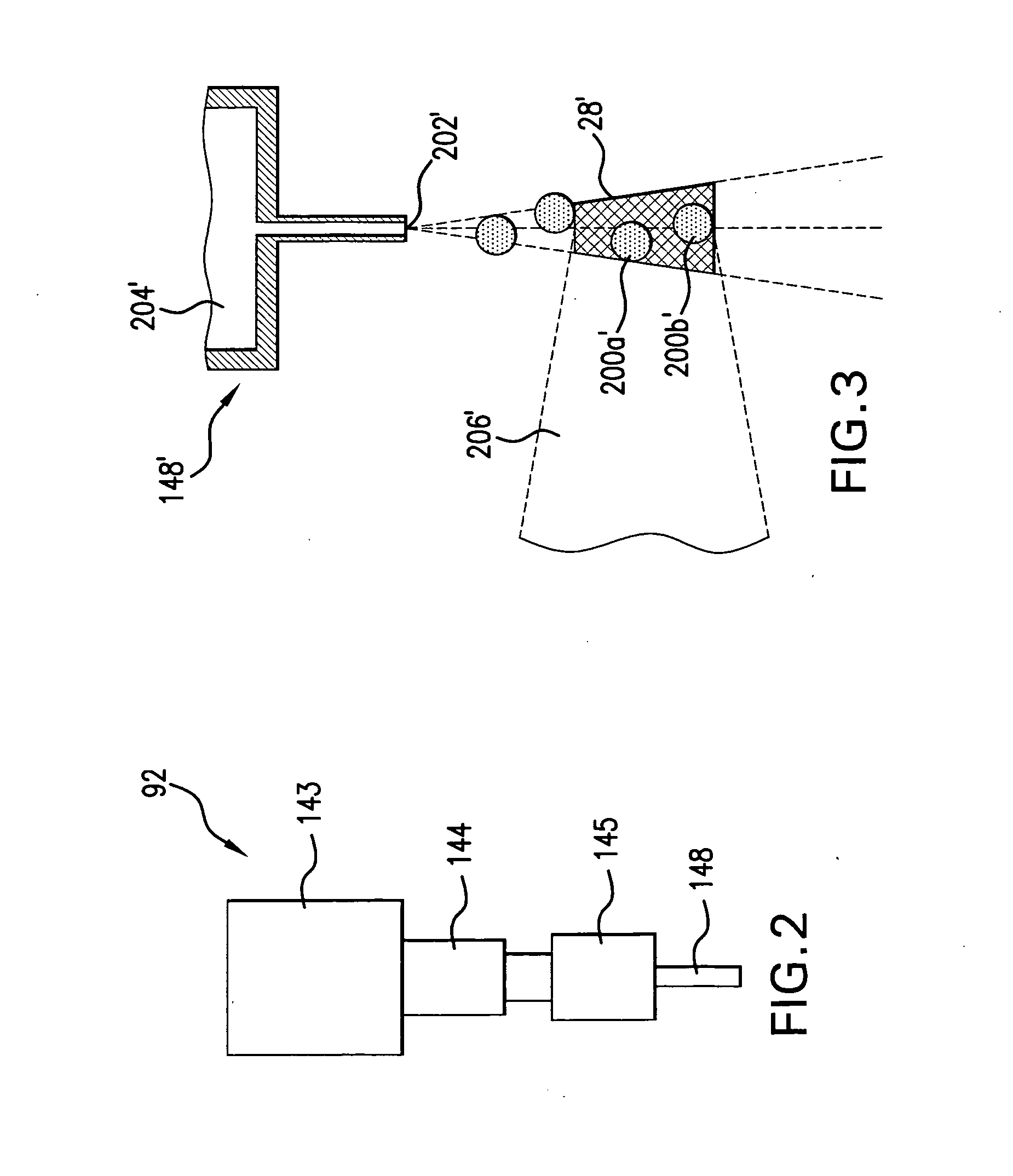
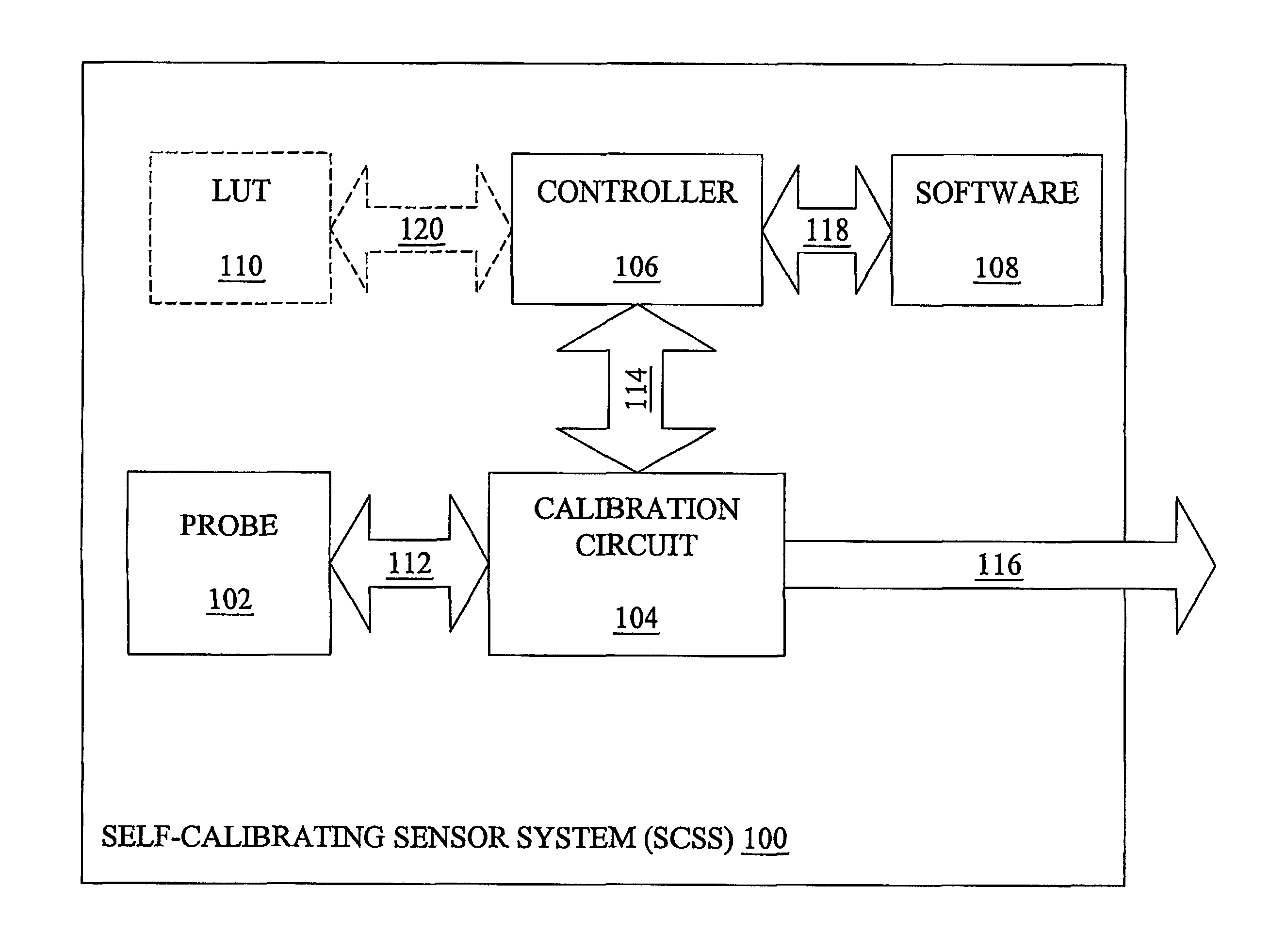
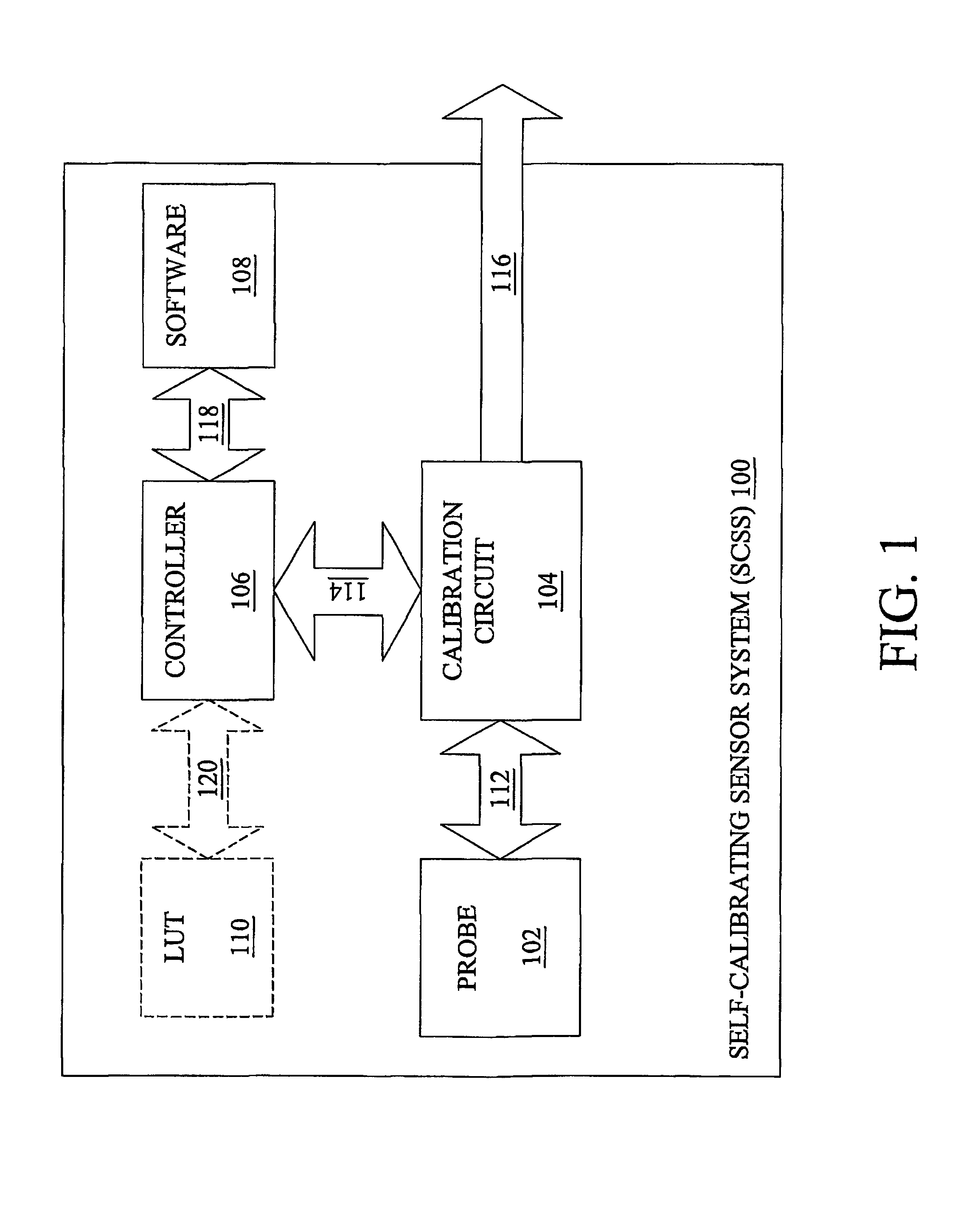
System and method for a self-calibrating non-invasive sensor
A non-invasive emitter-photodiode sensor which is able to provide a data-stream corresponding to the actual wavelength of light emitted thereby allowing calibration of the sensor signal processing equipment and resulting in accurate measurements over a wider variation in emitter wavelength ranges.
Owner:MEDTOR INC
EUV light source
ActiveUS20050199829A1Sufficient sizeSufficient thermal massNanoinformaticsRadioactive sourcesControl systemDisplacement control
An apparatus and method for EUV light production is disclosed which may comprise a laser produced plasma (“LPP”) extreme ultraviolet (“EUV”) light source control system comprising a target delivery system adapted to deliver moving plasma initiation targets and an EUV light collection optic having a focus defining a desired plasma initiation site, comprising: a target tracking and feedback system comprising: at least one imaging device providing as an output an image of a target stream track, wherein the target stream track results from the imaging speed of the camera being too slow to image individual plasma formation targets forming the target stream imaged as the target stream track; a stream track error detector detecting an error in the position of the target stream track in at least one axis generally perpendicular to the target stream track from a desired stream track intersecting the desired plasma initiation site. At least one target crossing detector may be aimed at the target track and detecting the passage of a plasma formation target through a selected point in the target track. A drive laser triggering mechanism utilizing an output of the target crossing detector to determine the timing of a drive laser trigger in order for a drive laser output pulse to intersect the plasma initiation target at a selected plasma initiation site along the target track at generally its closest approach to the desired plasma initiation site. A plasma initiation detector may be aimed at the target track and detecting the location along the target track of a plasma initiation site for a respective target. An intermediate focus illuminator may illuminate an aperture formed at the intermediate focus to image the aperture in the at least one imaging device. The at least one imaging device may be at least two imaging devices each providing an error signal related to the separation of the target track from the vertical centerline axis of the image of the intermediate focus based upon an analysis of the image in the respective one of the at least two imaging devices. A target delivery feedback and control system may comprise a target delivery unit; a target delivery displacement control mechanism displacing the target delivery mechanism at least in an axis corresponding to a first displacement error signal derived from the analysis of the image in the first imaging device and at least in an axis corresponding to a second displacement error signal derived from the analysis of the image in the second imaging device.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Medical hyperspectral imaging for evaluation of tissue and tumor
ActiveUS20060247514A1Diagnostics using lightPolarisation-affecting propertiesRadiologyFungating tumour
Apparatus and methods for hyperspectral imaging analysis that assists in real and near-real time assessment of biological tissue condition, viability, and type, and monitoring the above over time. Embodiments of the invention are particularly useful in surgery, clinical procedures, tissue assessment, diagnostic procedures, health monitoring, and medical evaluations, especially in the detection and treatment of cancer.
Owner:HYPERMED IMAGING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com