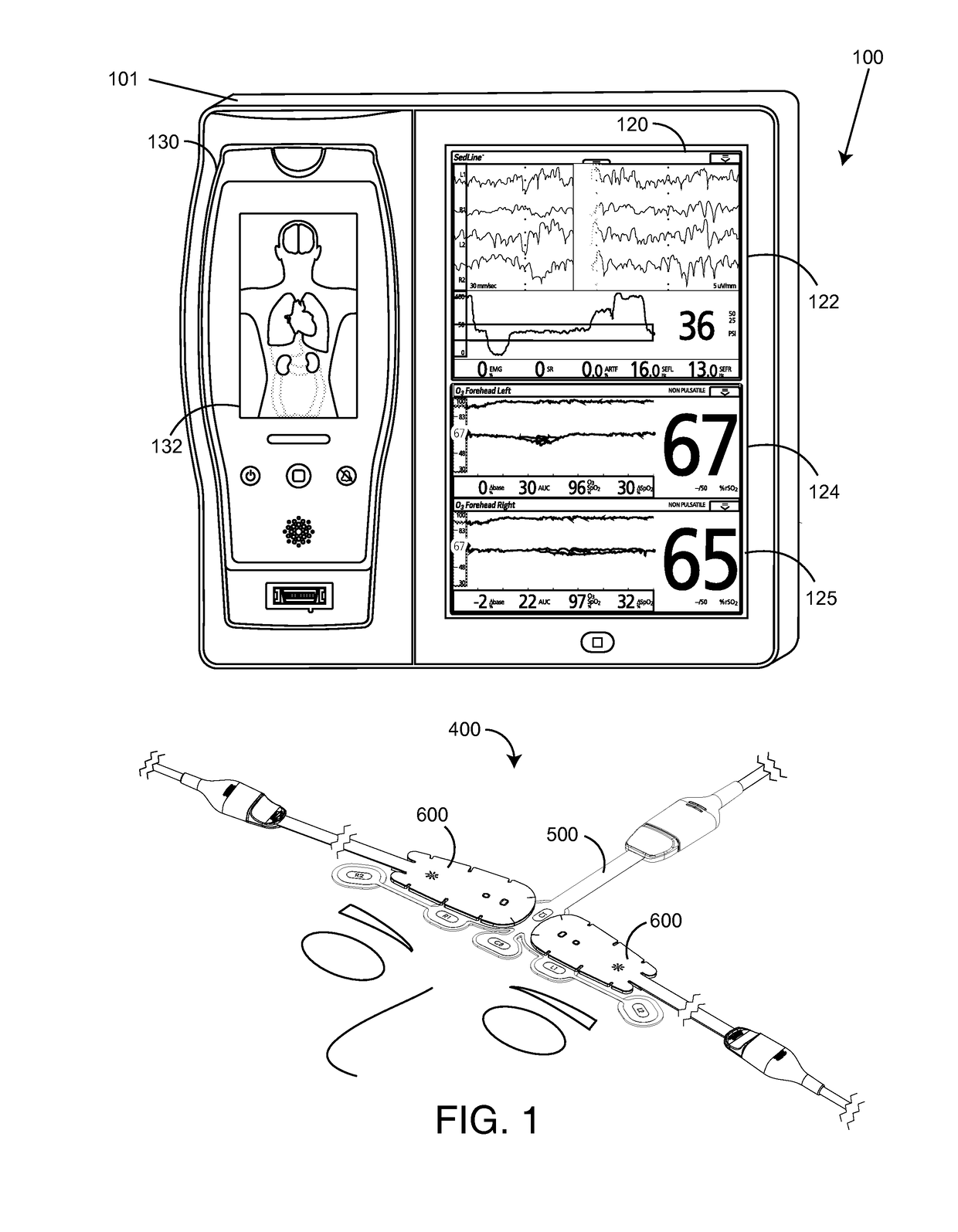
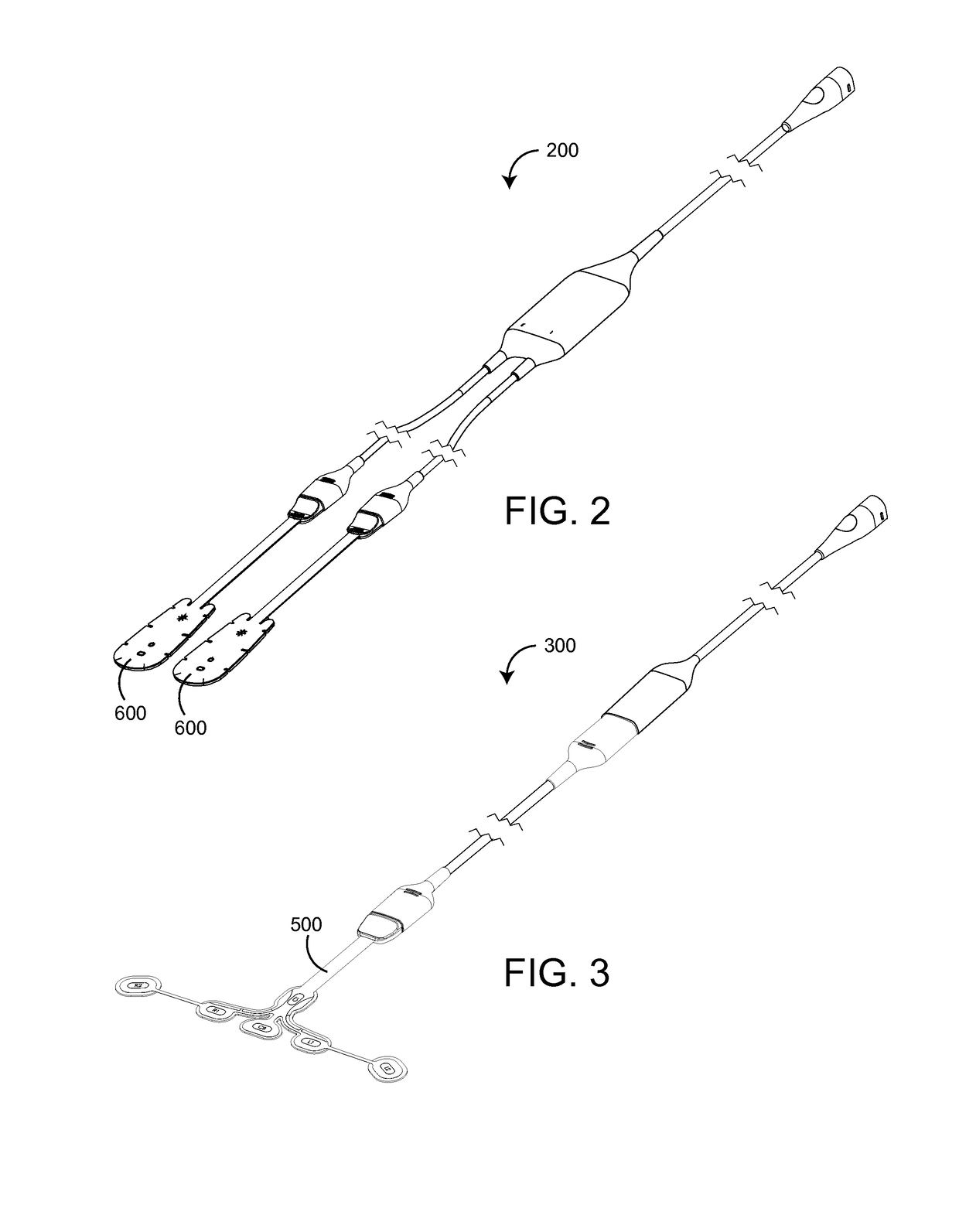
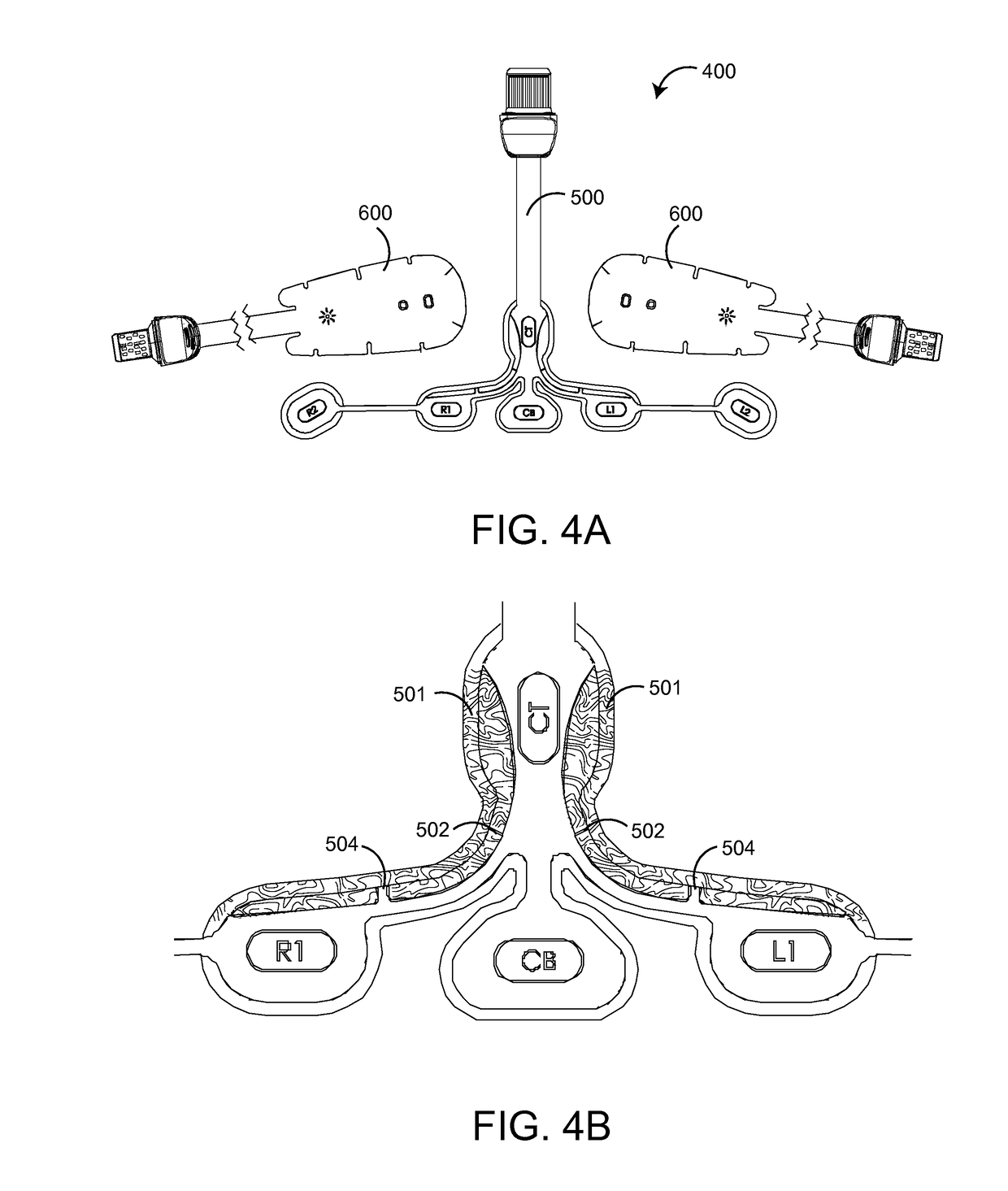
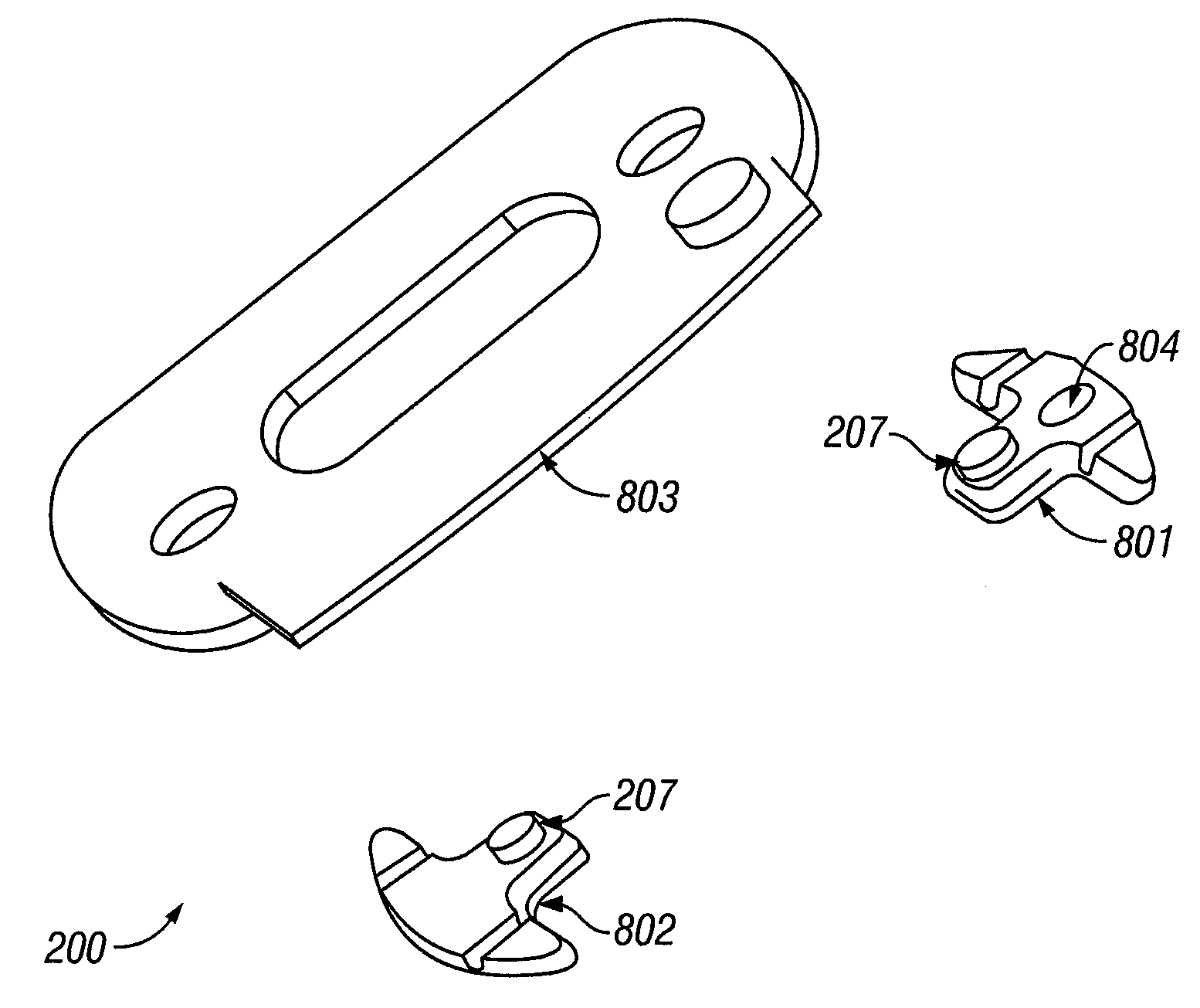
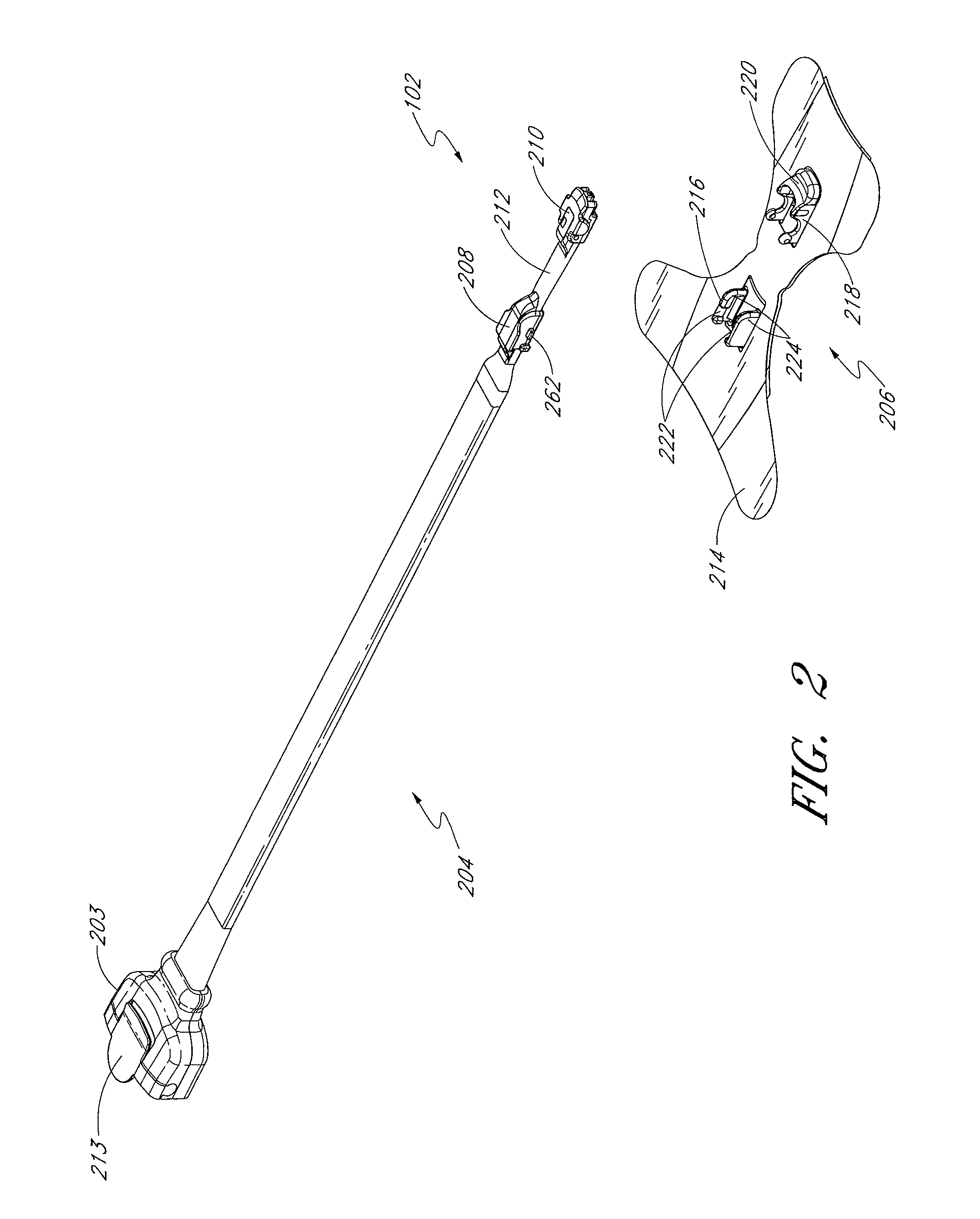Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
534 results about "Measurement site" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
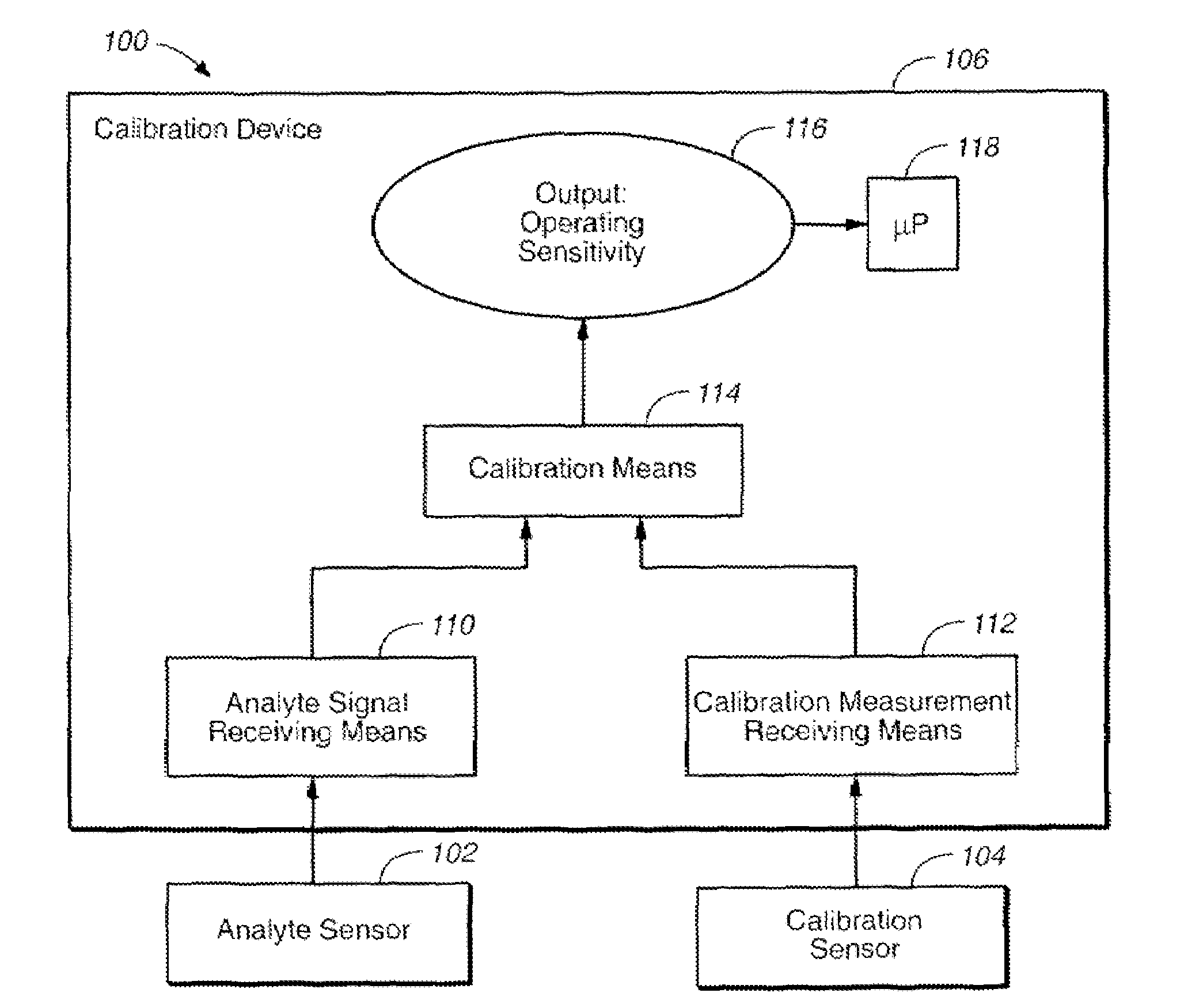
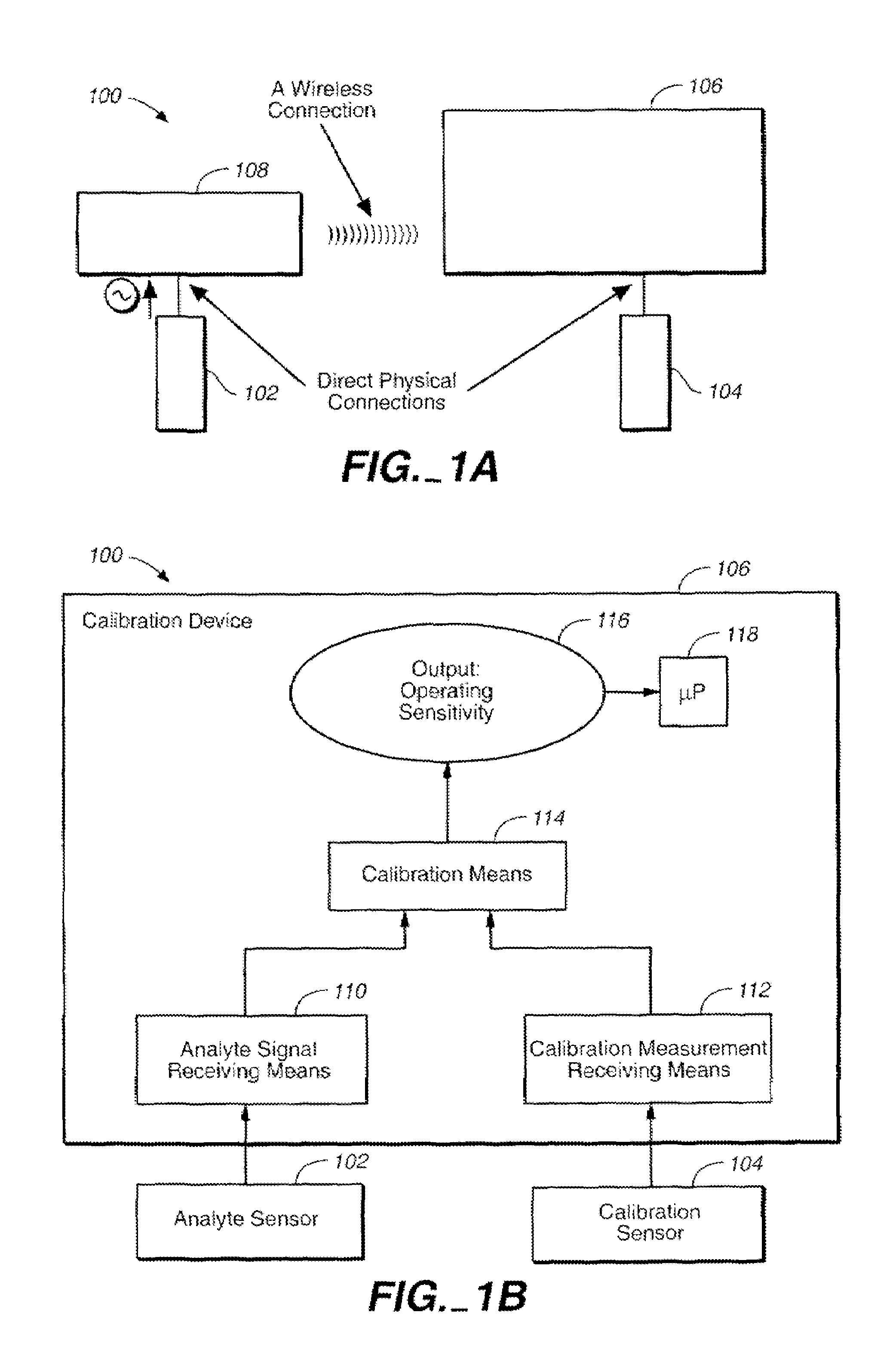
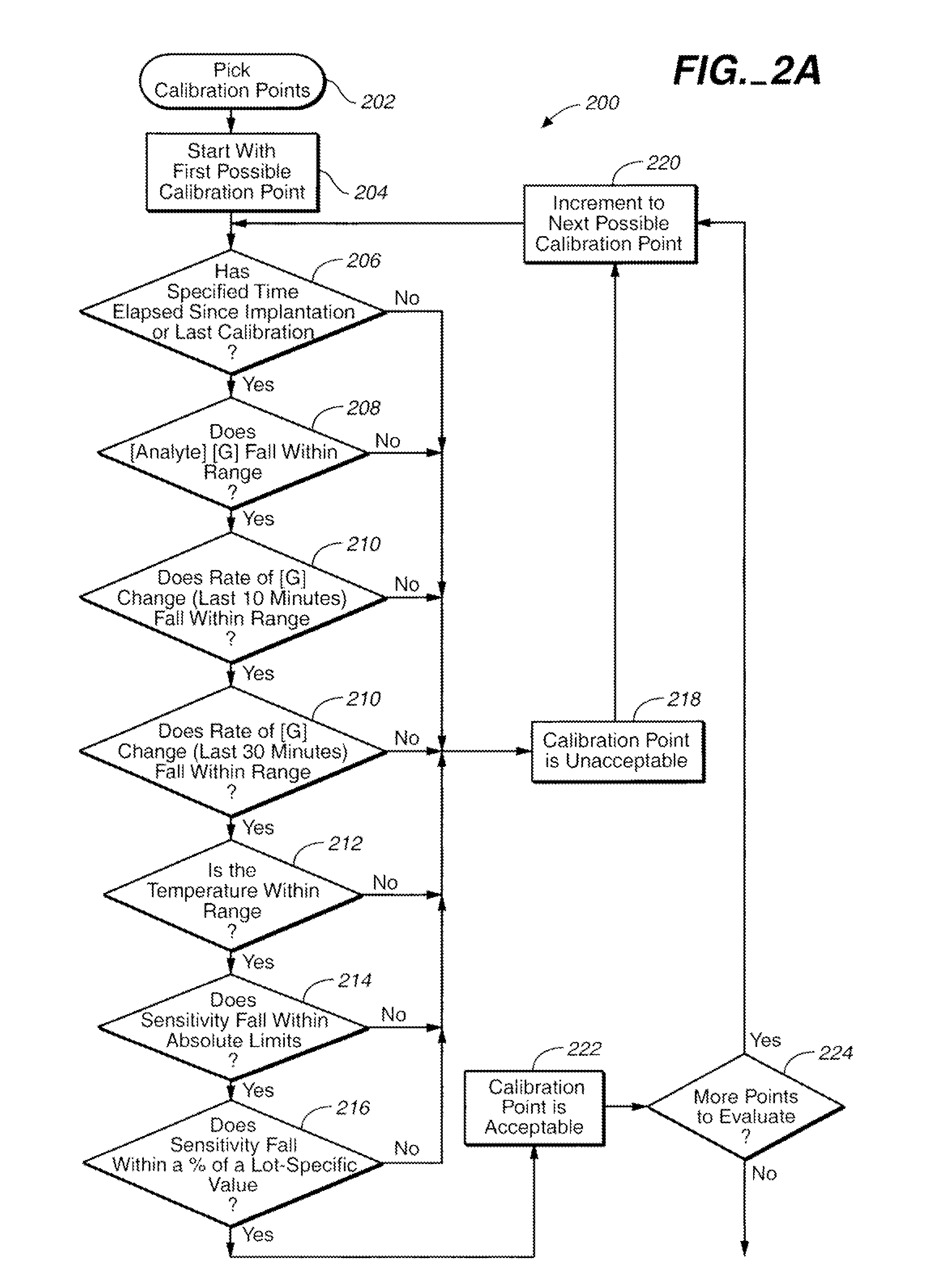
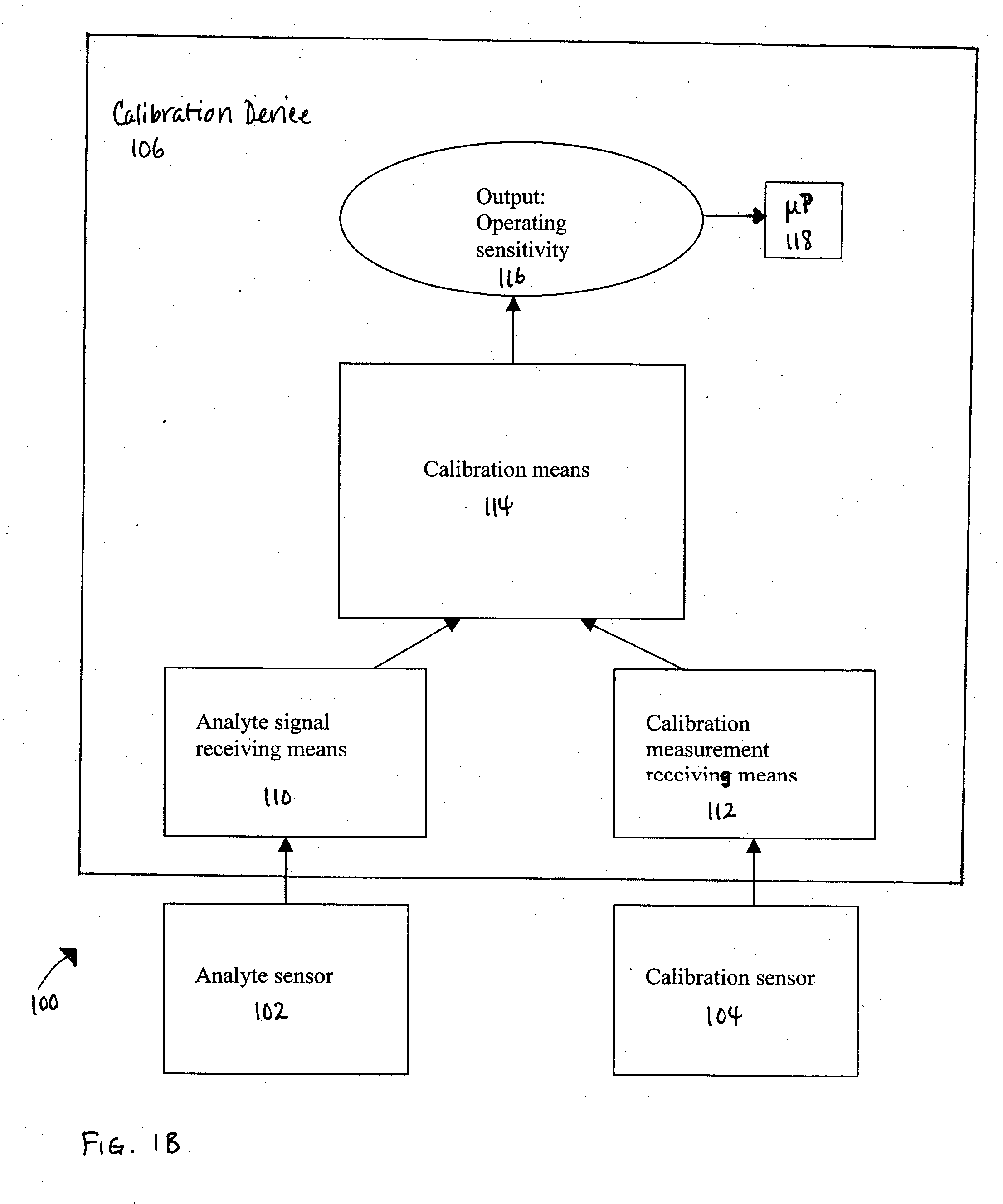
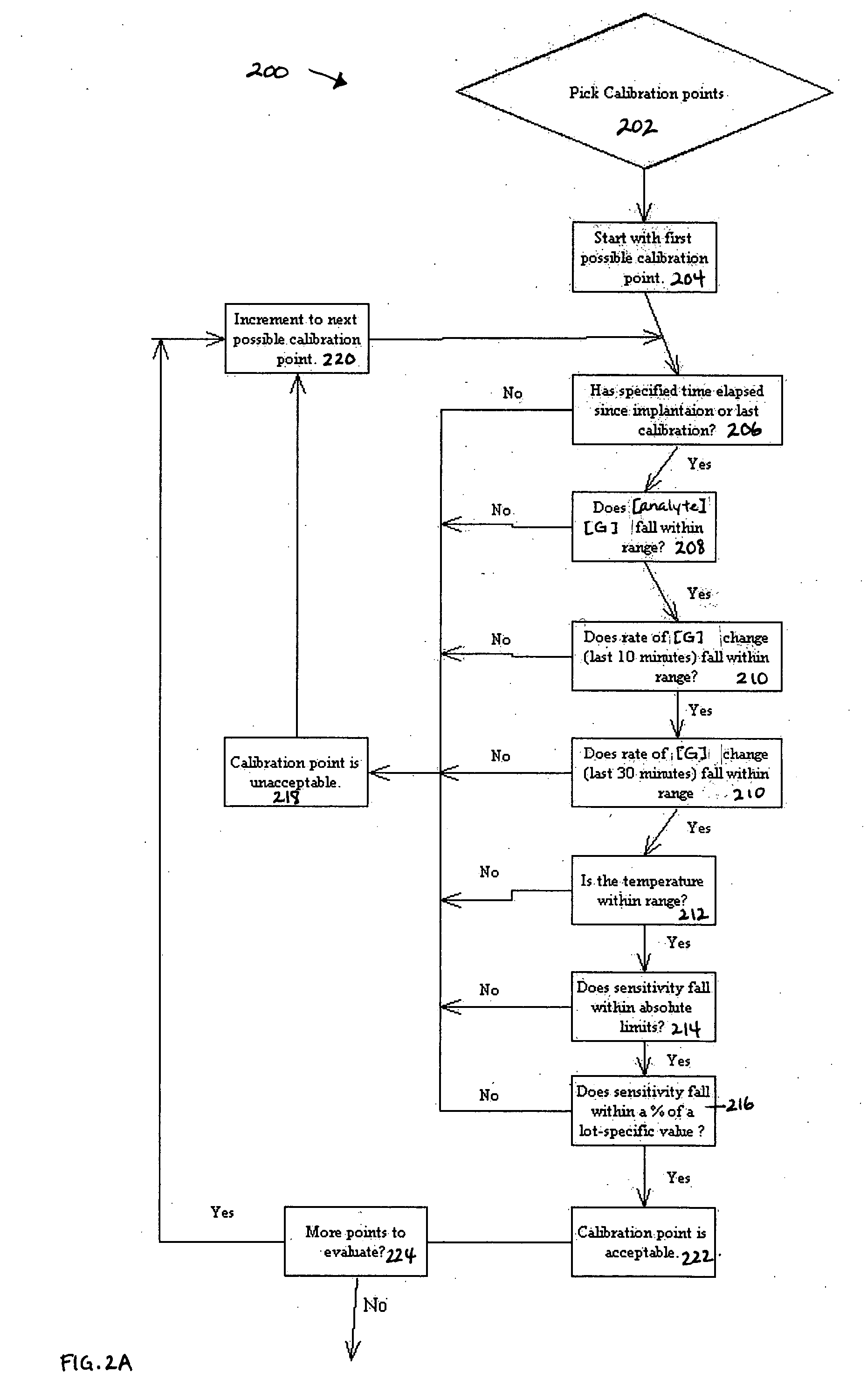
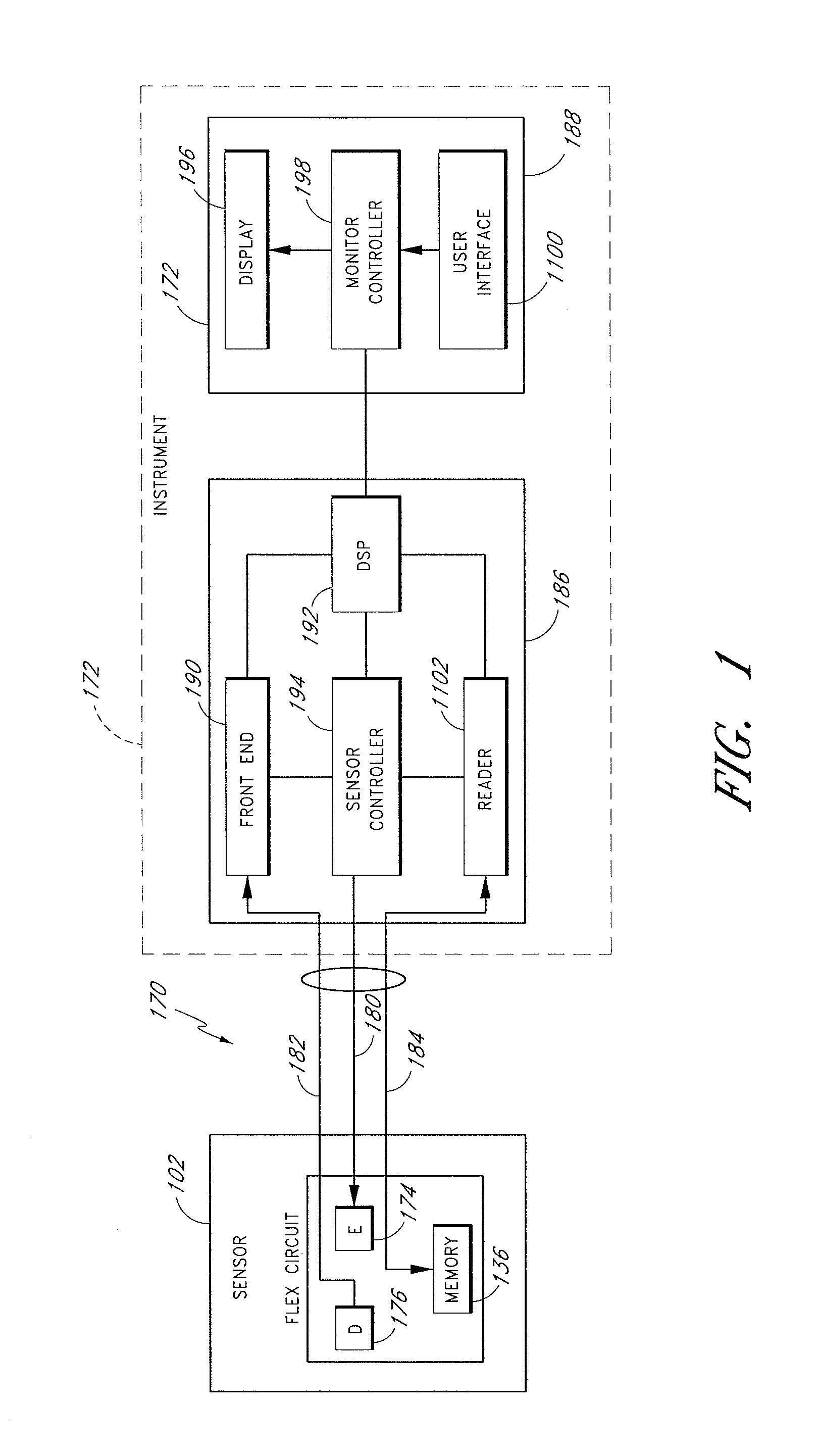
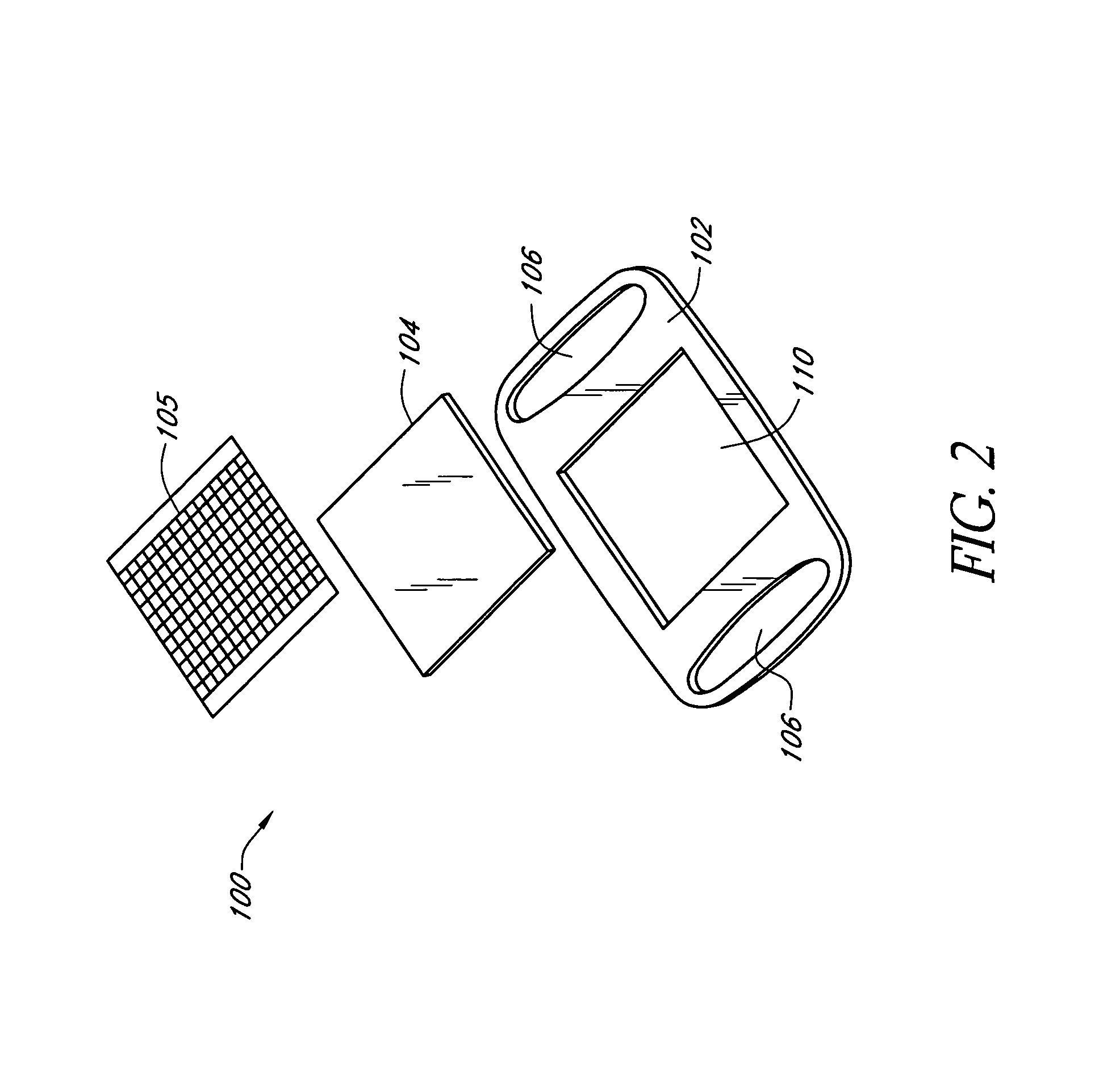
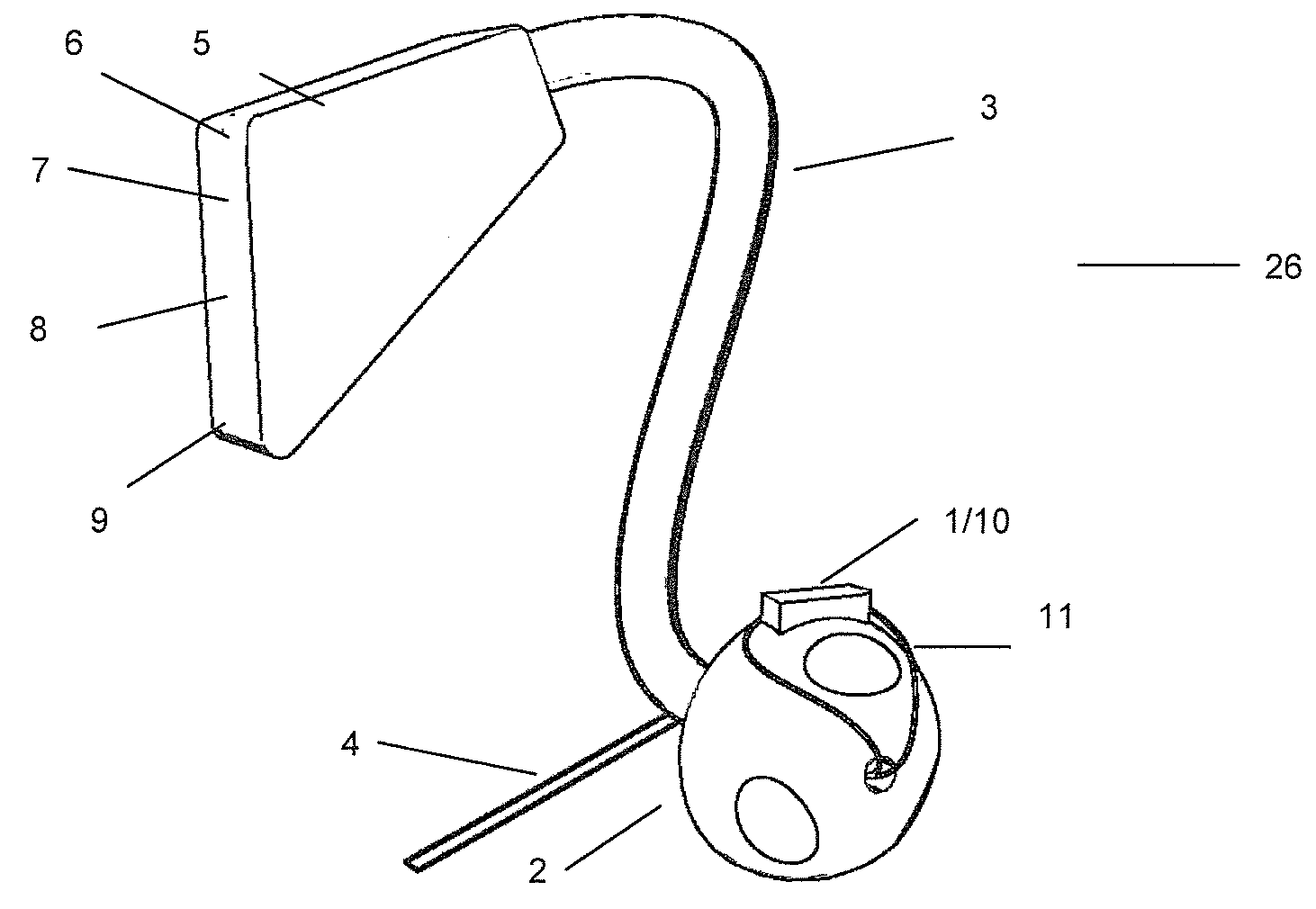
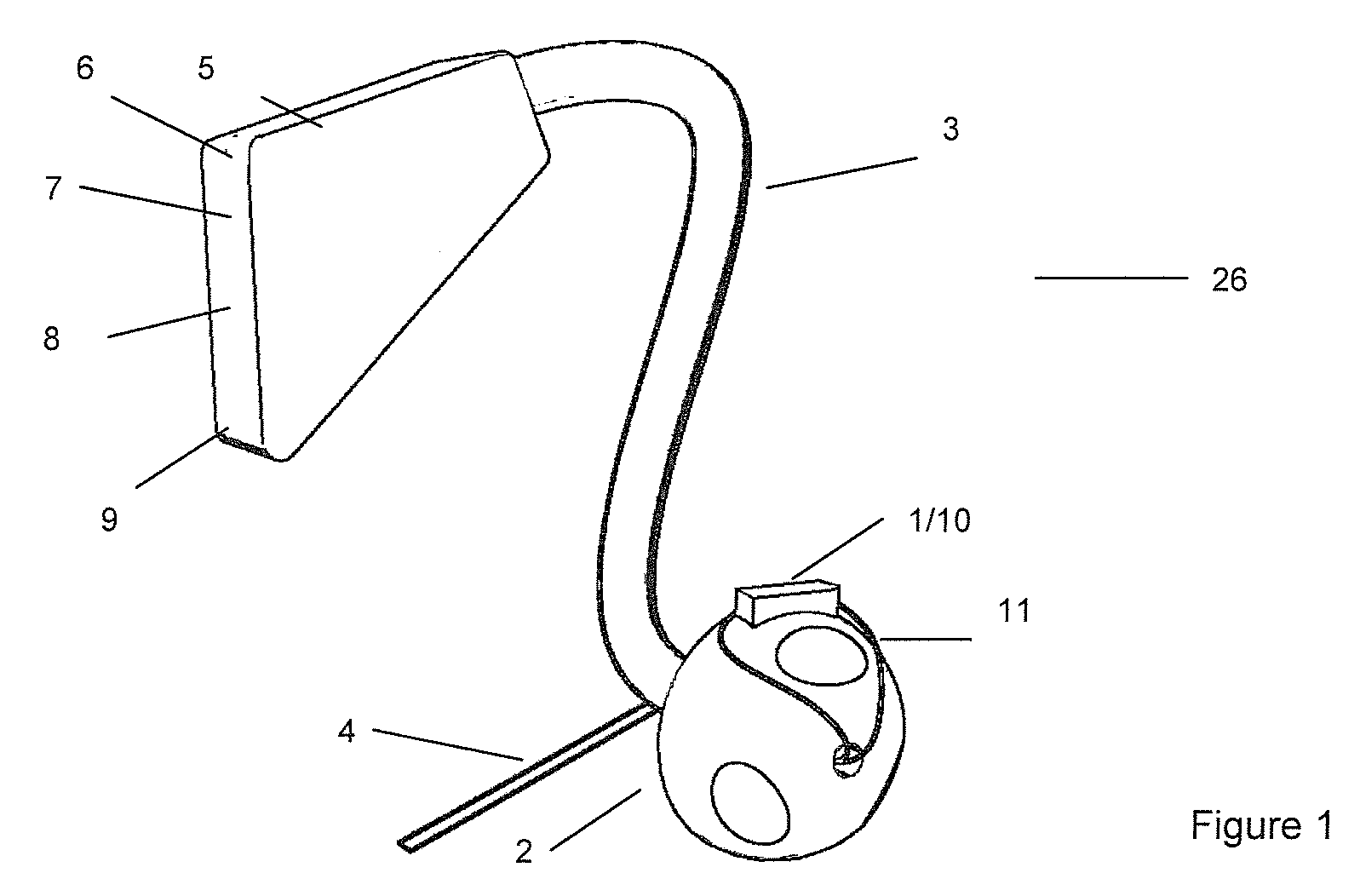
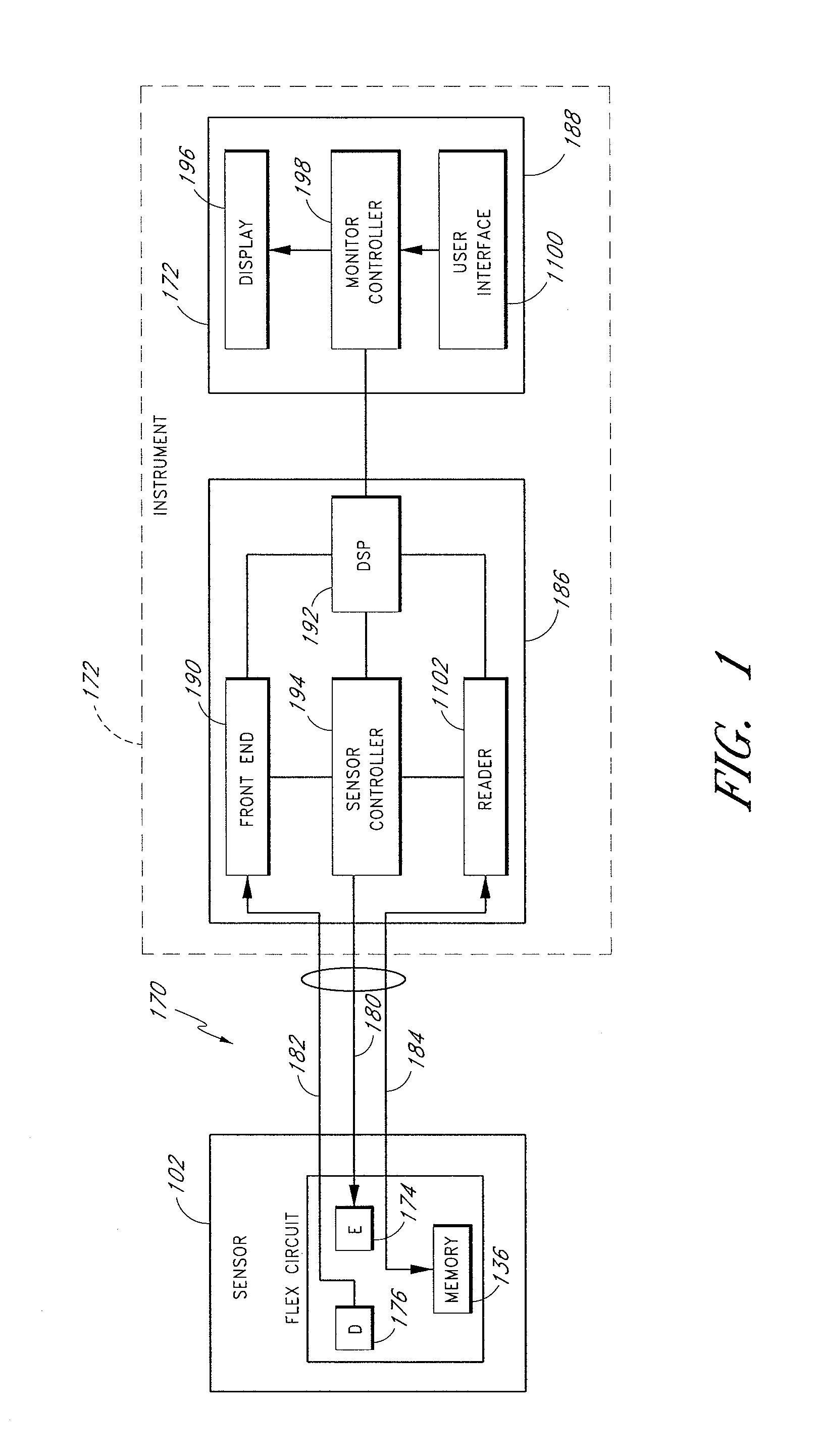
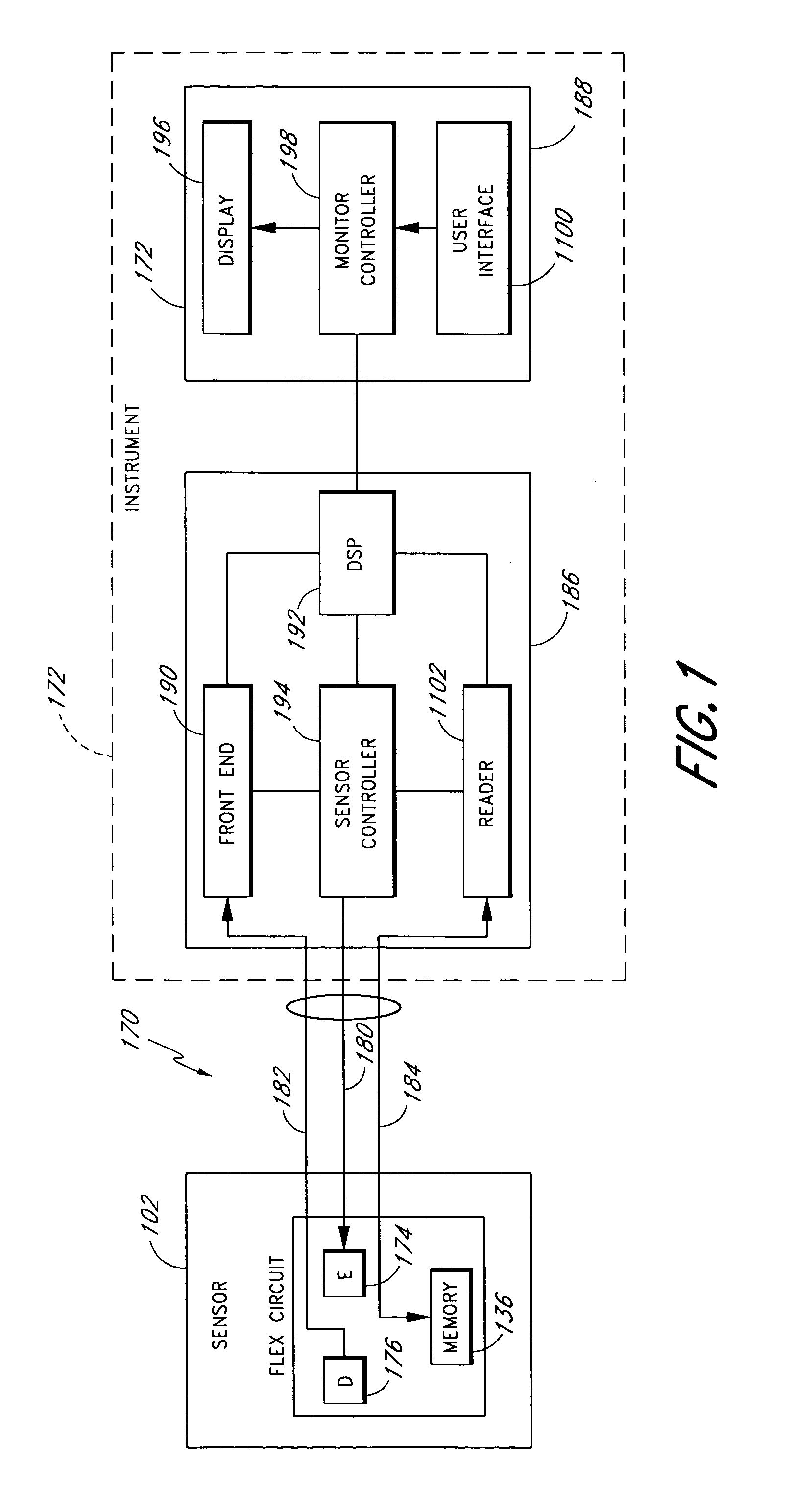
Method of calibrating an analyte-measurement device, and associated methods, devices and systems
ActiveUS7299082B2Improve mobilityAvoid high pressureMicrobiological testing/measurementCatheterMeasurement deviceAnalyte
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
A method of calibrating an analyte-measurement device, and associated methods, devices and systems
ActiveUS20050239154A1Improve mobilityAvoid high pressureMicrobiological testing/measurementCatheterMeasurement deviceAnalyte
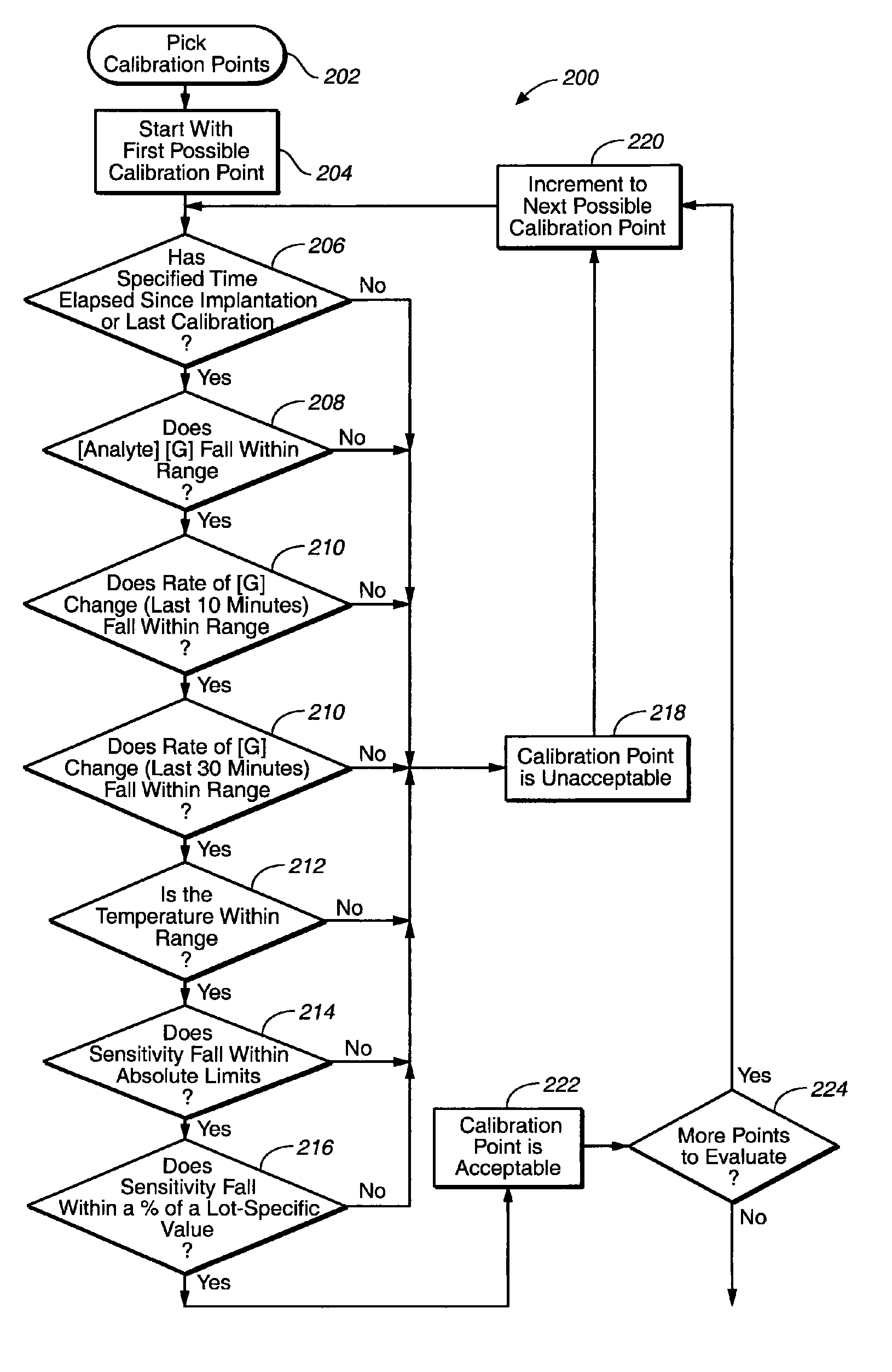
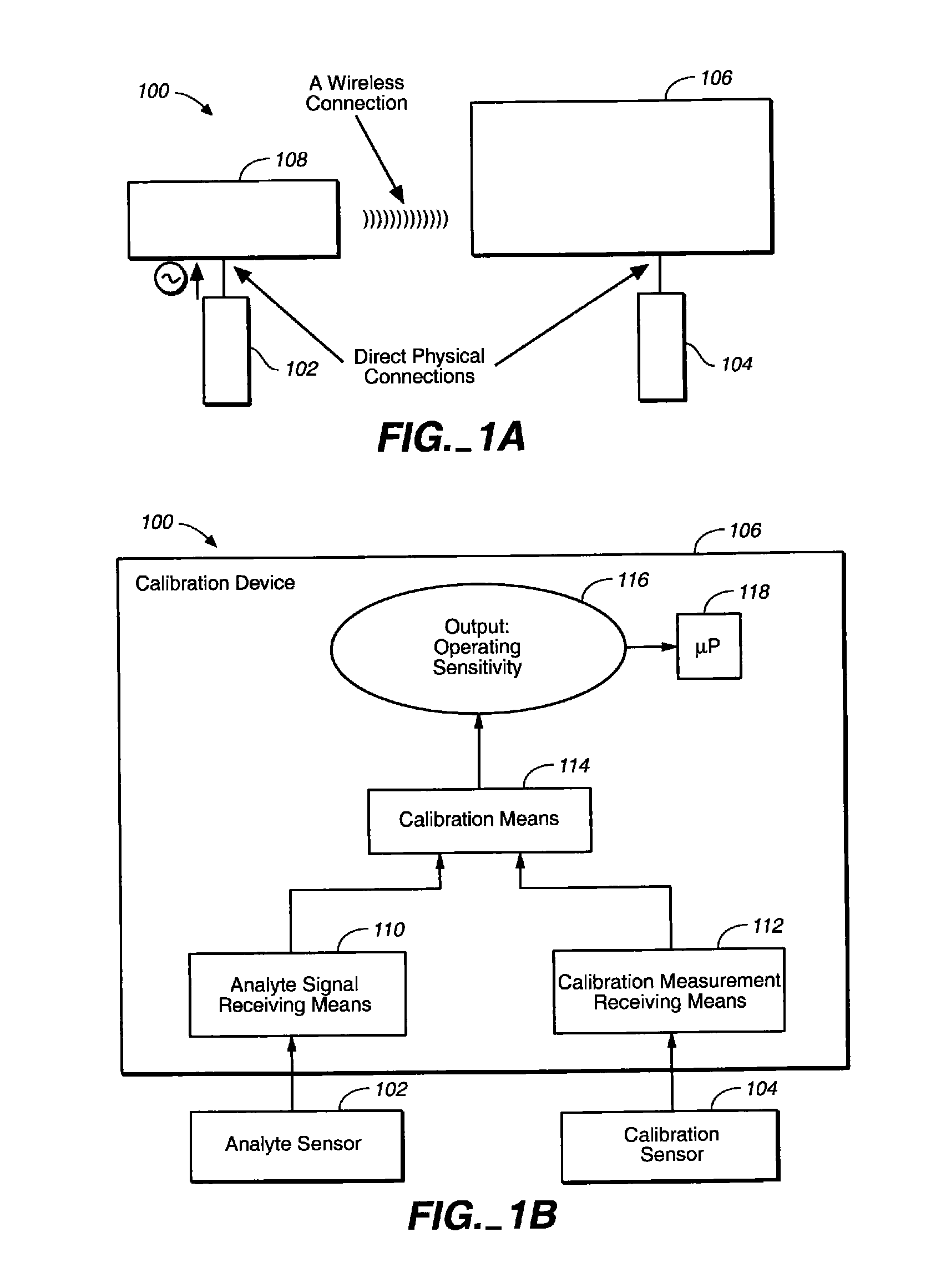
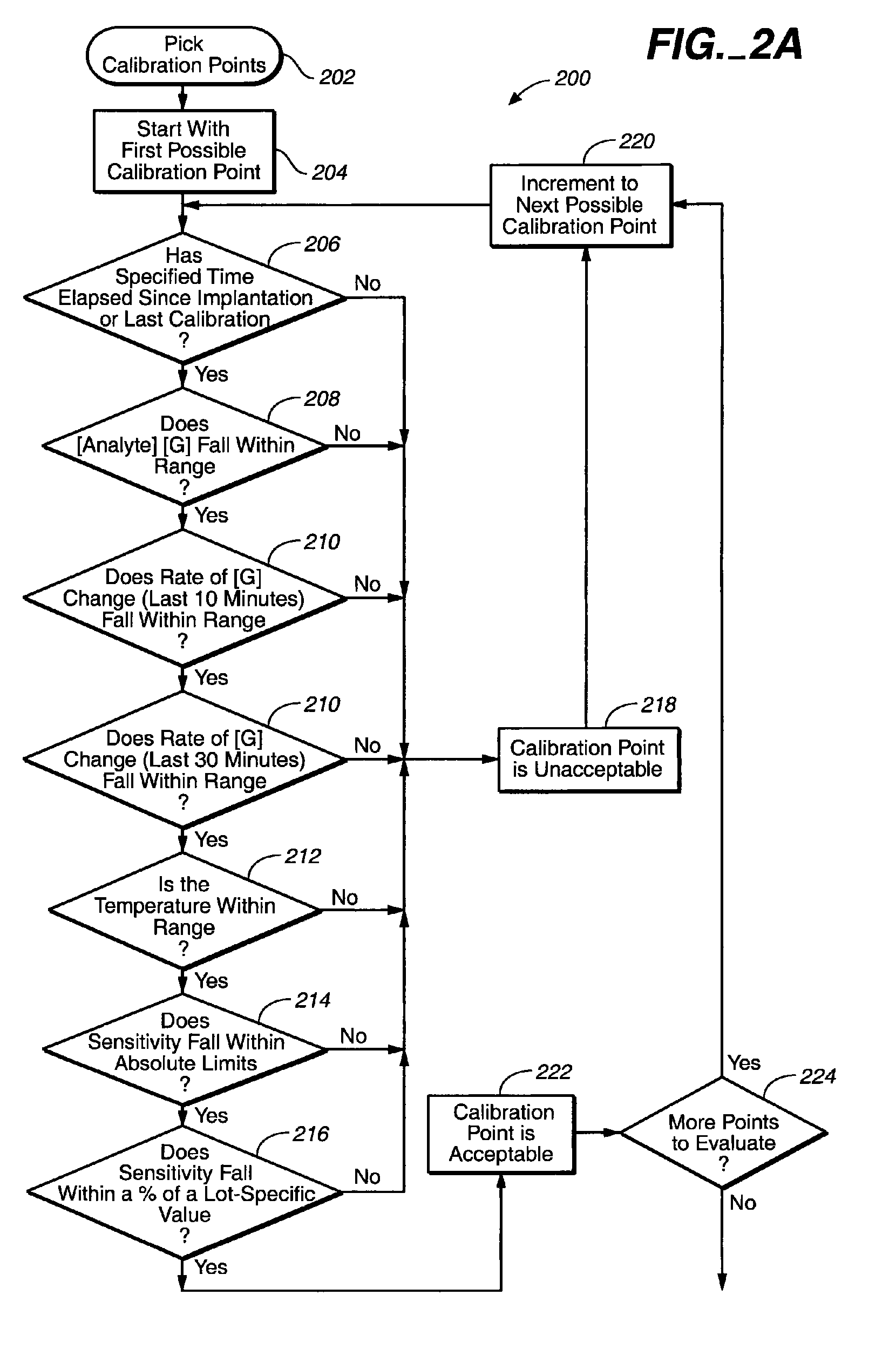
The invention relates to a method for calibrating an analyte-measurement device that is used to evaluate a concentration of analyte in bodily fluid at or from a measurement site in a body. The method involves measuring a concentration, or calibration concentration, of an analyte in blood from an “off-finger” calibration site, and calibrating the analyte-measurement device based on that calibration concentration. The invention also relates to a device, system, or kit for measuring a concentration of an analyte in a body, which employs a calibration device for adjusting analyte concentration measured in bodily fluid based on an analyte concentration measured in blood from an “off-finger” calibration site.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Resposable pulse oximetry sensor
InactiveUS7039449B2Longevity and associated costSensorsBlood characterising devicesAdhesivePulse oximetry
A pulse oximeter sensor has both a reusable and a disposable portion. The reusable portion of the sensor preserves the relatively long-lived and costly emitter, detector and connector components. The disposable portion of the sensor is the relatively inexpensive adhesive tape component that is used to secure the sensor to a measurement site, typically a patient's finger or toe. The disposable portion of the sensor is removably attached to the reusable portion in a manner that allows the disposable portion to be readily replaced when the adhesive is expended or the tape becomes soiled or excessively worn. The disposable portion may also contain an information element useful for sensor identification or for security purposes to insure patient safety. A conductive element that allows a pulse oximeter monitor to read the information element is located on the disposable portion in such a way that continuity is broken when the adhesive tape become torn, such as upon removal from the measurement site.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA +1
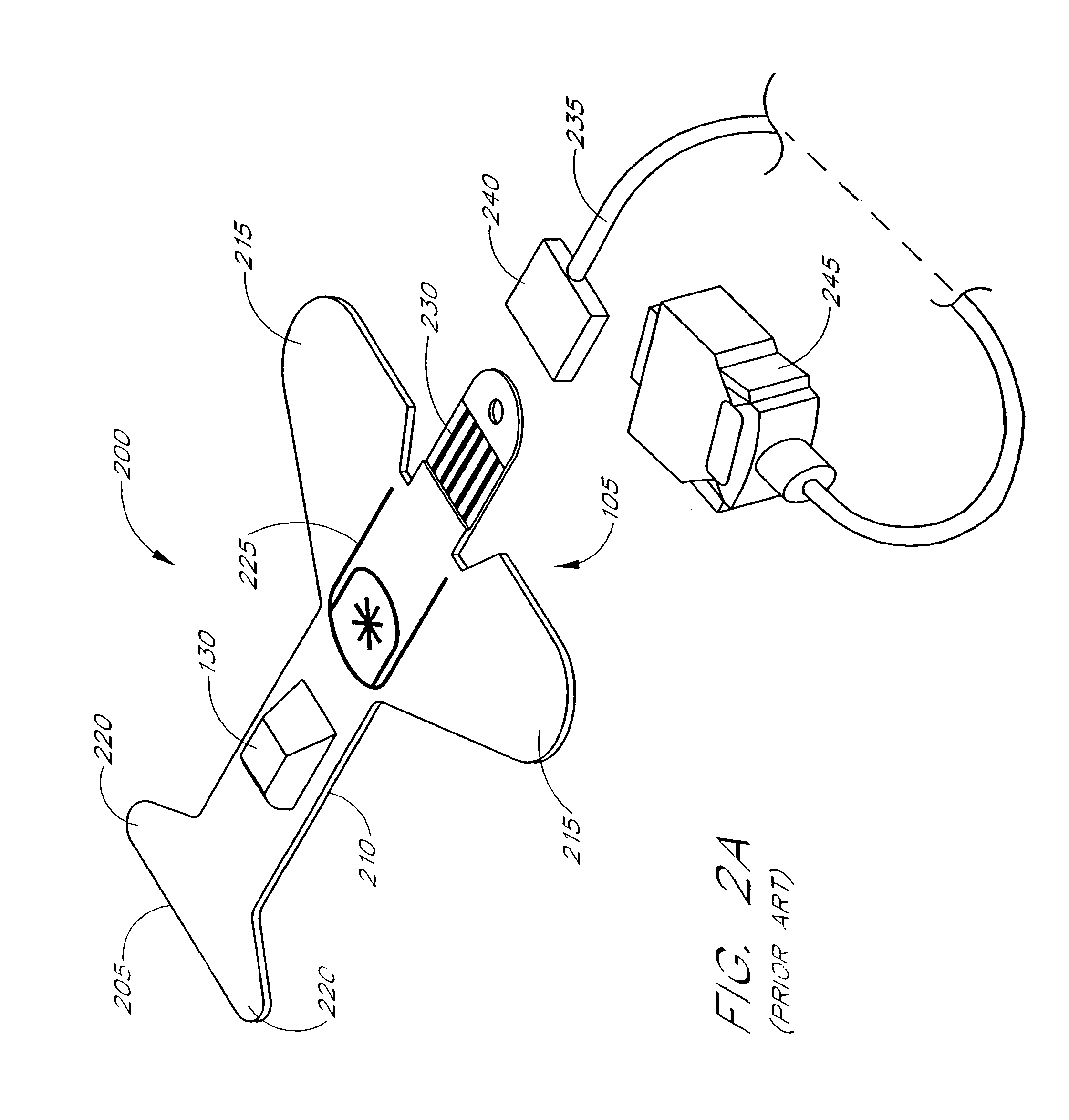
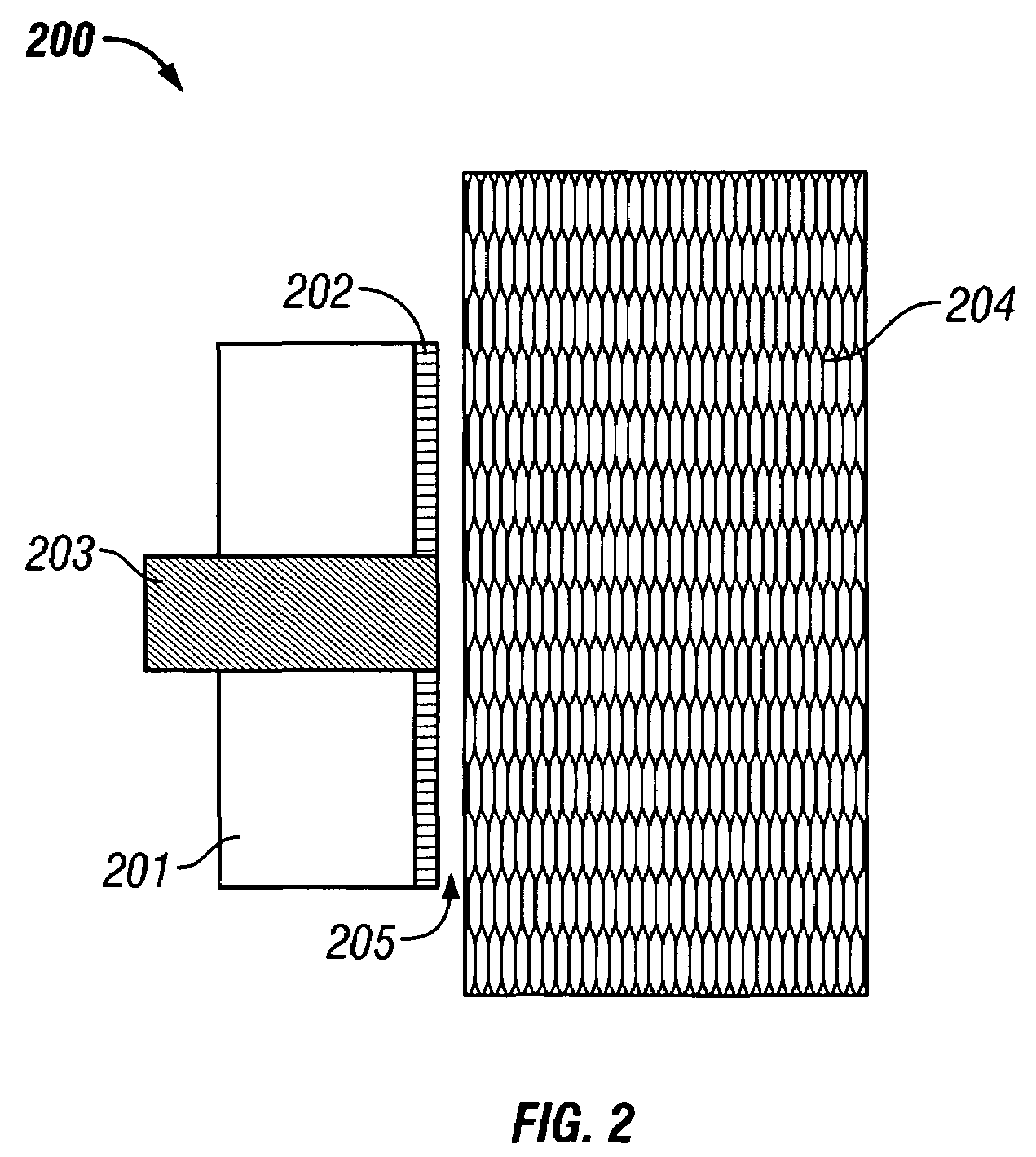
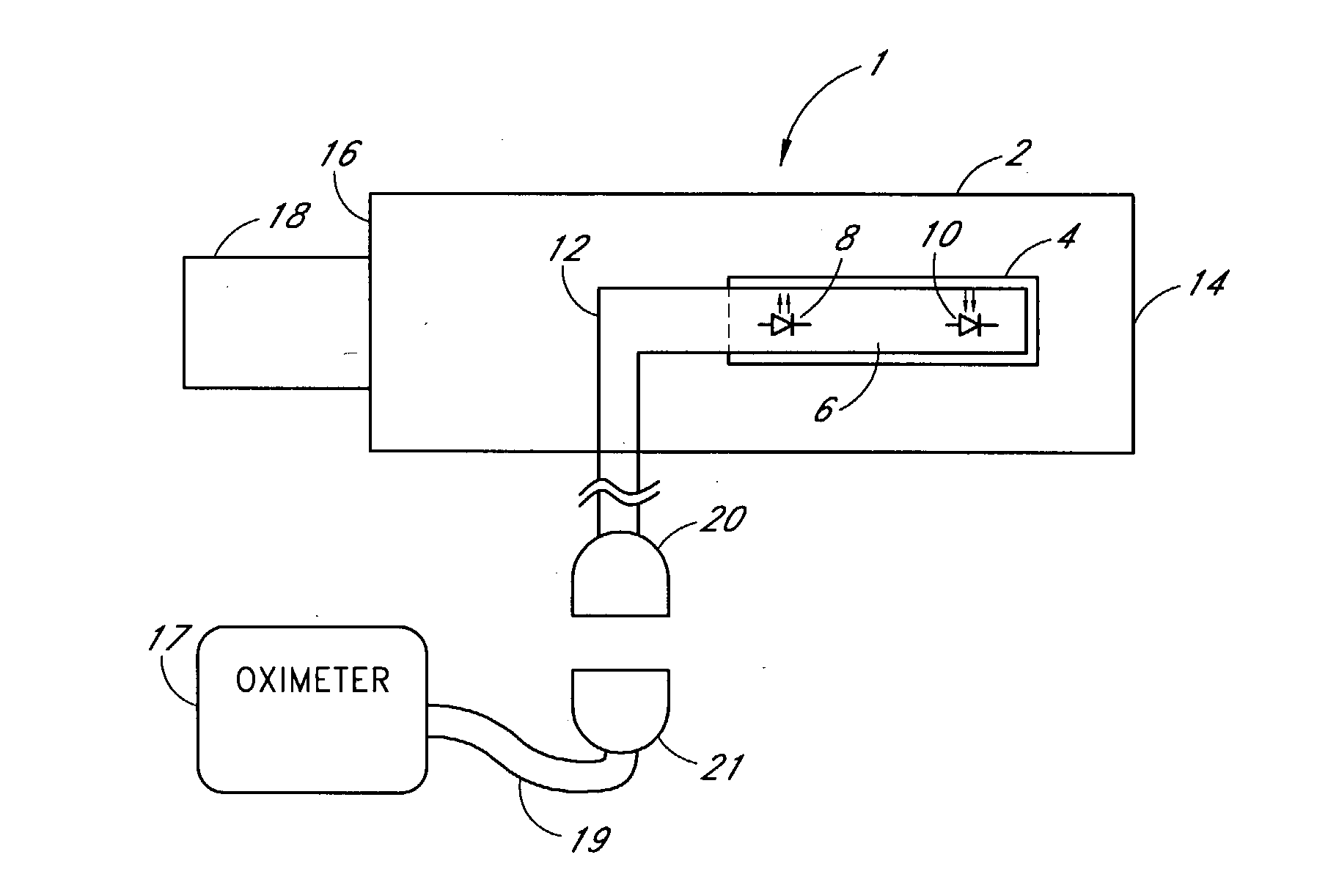
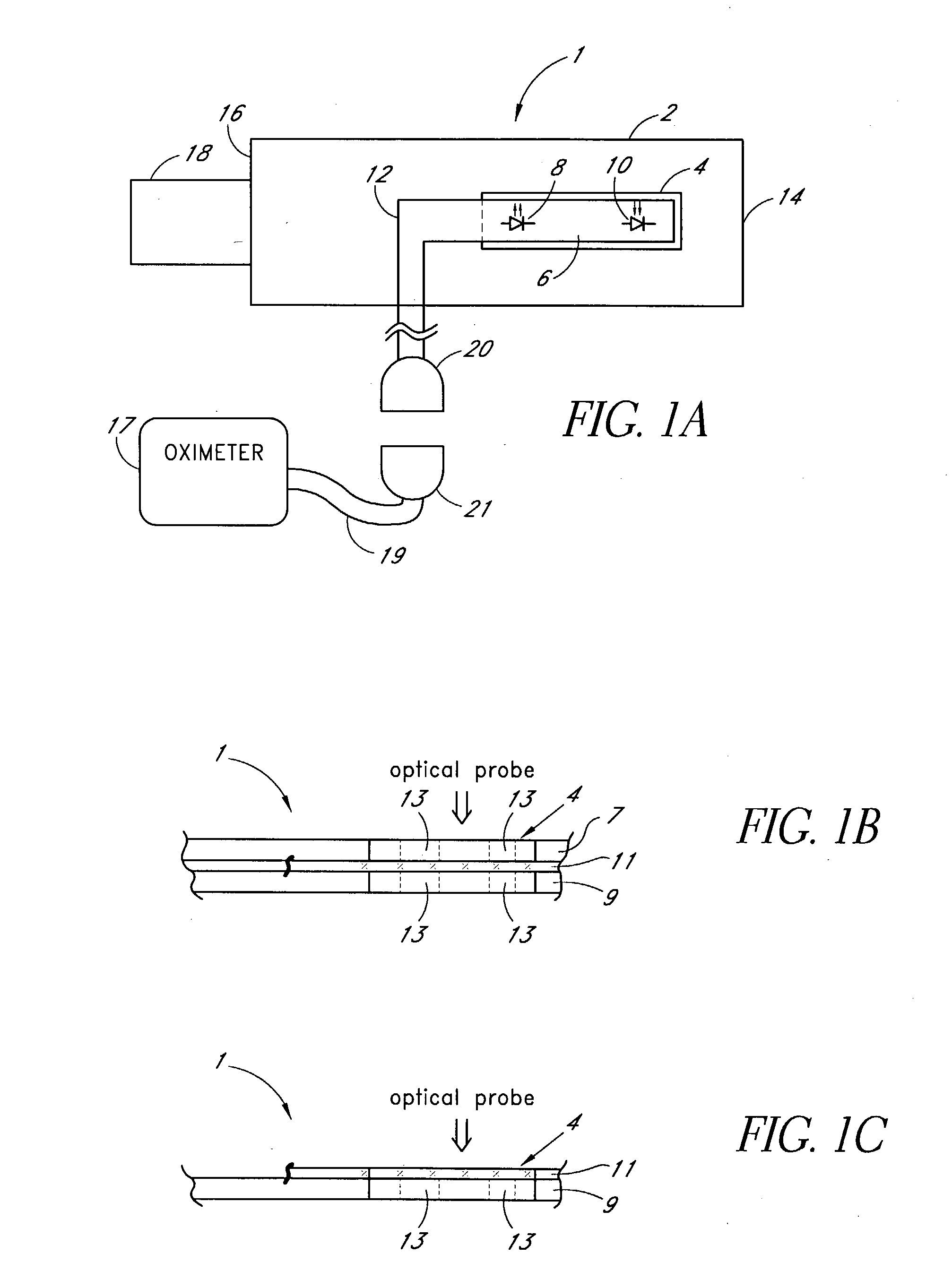
Attachment and optical probe
A medical monitoring system, such as an oximetry system, applies an attachment for securing an optical probe to a measurement site. The attachment has an elongated support with a first end and a second end, and a dedicated area in proximity of the first end. The dedicated area receives an optical probe and includes a material that is transparent for light emitted and received by the optical probe. The dedicated area mountably receives the optical probe on the material so that in use, the material is positioned between the optical probe and a surface of a measurement site. The optical probe may be factory-mounted to the dedicated area of the attachment as a ready-to-use sensor. In the alternative, the attachment may be available as an individual component, or as a part of a kit including the attachment and the optical probe.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Optical probe including predetermined emission wavelength based on patient type
ActiveUS7096052B2Reduce light energyCorrectly employDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsLight energyPatient type
A reflectance sensor which can be applied to a patient in a manner which reduces the light energy reaching the detector without first being attenuated by the tissue at the measurement site. Moreover, the reflectance sensor includes emitting devices adapted for use in legacy patient monitoring systems.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Optical sensor including disposable and reusable elements
ActiveUS8233955B2Reduce chanceComplicate to separateDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBiomedical engineeringMeasurement site
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Resposable pulse oximetry sensor
InactiveUS8000761B2Longevity and associated costSensorsBlood characterising devicesAdhesivePulse oximetry
A pulse oximeter sensor has both a reusable and a disposable portion. The reusable portion of the sensor preserves the relatively long-lived and costly emitter, detector and connector components. The disposable portion of the sensor is the relatively inexpensive adhesive tape component that is used to secure the sensor to a measurement site, typically a patient's finger or toe. The disposable portion of the sensor is removably attached to the reusable portion in a manner that allows the disposable portion to be readily replaced when the adhesive is expended or the tape becomes soiled or excessively worn. The disposable portion may also contain an information element useful for sensor identification or for security purposes to insure patient safety.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Oximeter probe off indicator defining probe off space
ActiveUS8265723B1Accurate measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsComputer scienceMeasurement site
An embodiment of the present disclosure seeks to select characteristics of incoming intensity data that cause comparisons of selected characteristics to produce defined probe off space having reduced crossover with defined probe on space. Once defined, the present disclosure compares characteristics of incoming intensity data with the now defined probe off space, and in some embodiments, defined probe on space, to determine whether a probe off condition exists. When a processor determines a probe off condition exists, the processor may output or trigger an output signal that audibly and / or visually indicates to a user that the optical sensor should be adjusted for a proper application to a measurement site.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Optical sensor including disposable and reusable elements
ActiveUS8600467B2Reduce chanceComplicate to separateWave amplification devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringBiomedical engineeringMeasurement site
An embodiment of the present disclosure provides a noninvasive optical sensor or probe including disposable and reusable components. The assembly of the disposable and reusable components is straightforward, along with the disassembly thereof. During application to a measurement site, the assembled sensor is advantageously secured together while the componentry is advantageously properly positioned.
Owner:CERCACOR LAB INC
Method and apparatus for coupling a channeled sample probe to tissue
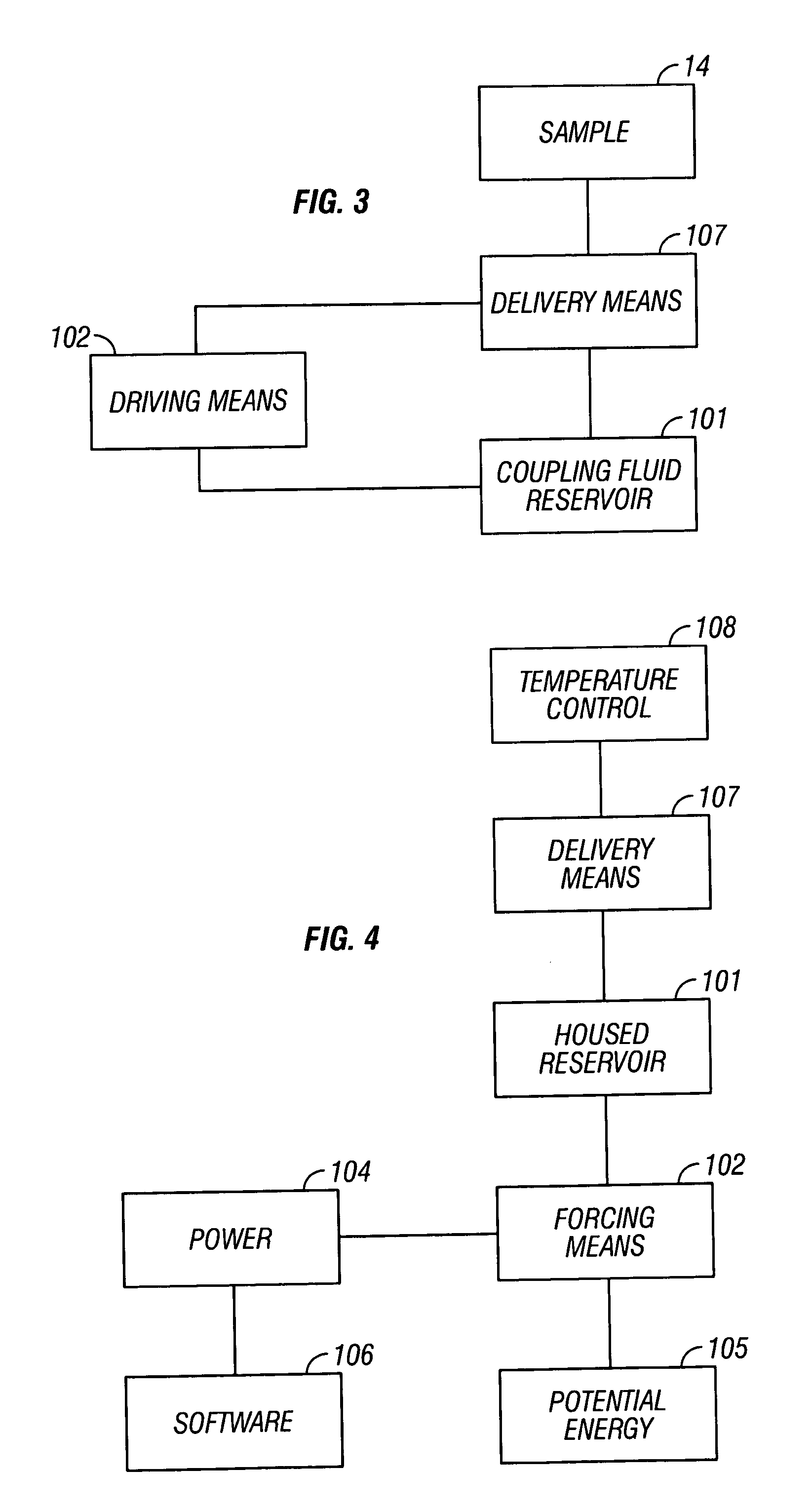
ActiveUS8504128B2Good optical performanceError minimizationMedical devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansAnalyteThin layer
Sampling is controlled in order to enhance analyte concentration estimation derived from noninvasive sampling. More particularly, sampling is controlled using controlled fluid delivery to a region between a tip of a sample probe and a tissue measurement site. The controlled fluid delivery enhances coverage of a skin sample site with the thin layer of fluid. Delivery of contact fluid is controlled in terms of spatial delivery, volume, thickness, distribution, temperature, and / or pressure.
Owner:GLT ACQUISITION
Method for modulating light penetration depth in tissue and diagnostic applications using same
InactiveUS7043287B1Reduce the impactLimit sampling depthDiagnostics using lightOptical sensorsDiseaseAnalyte
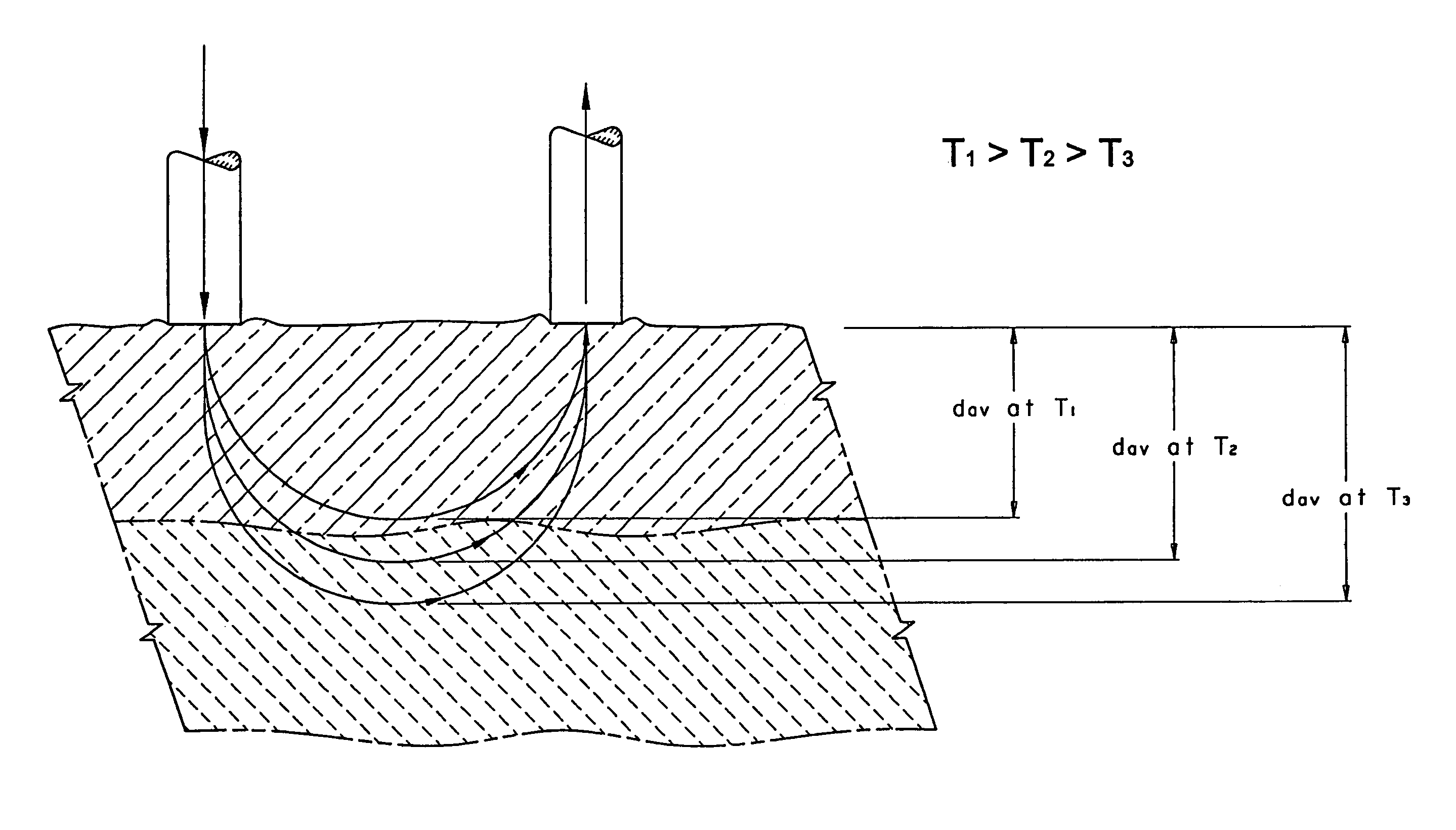
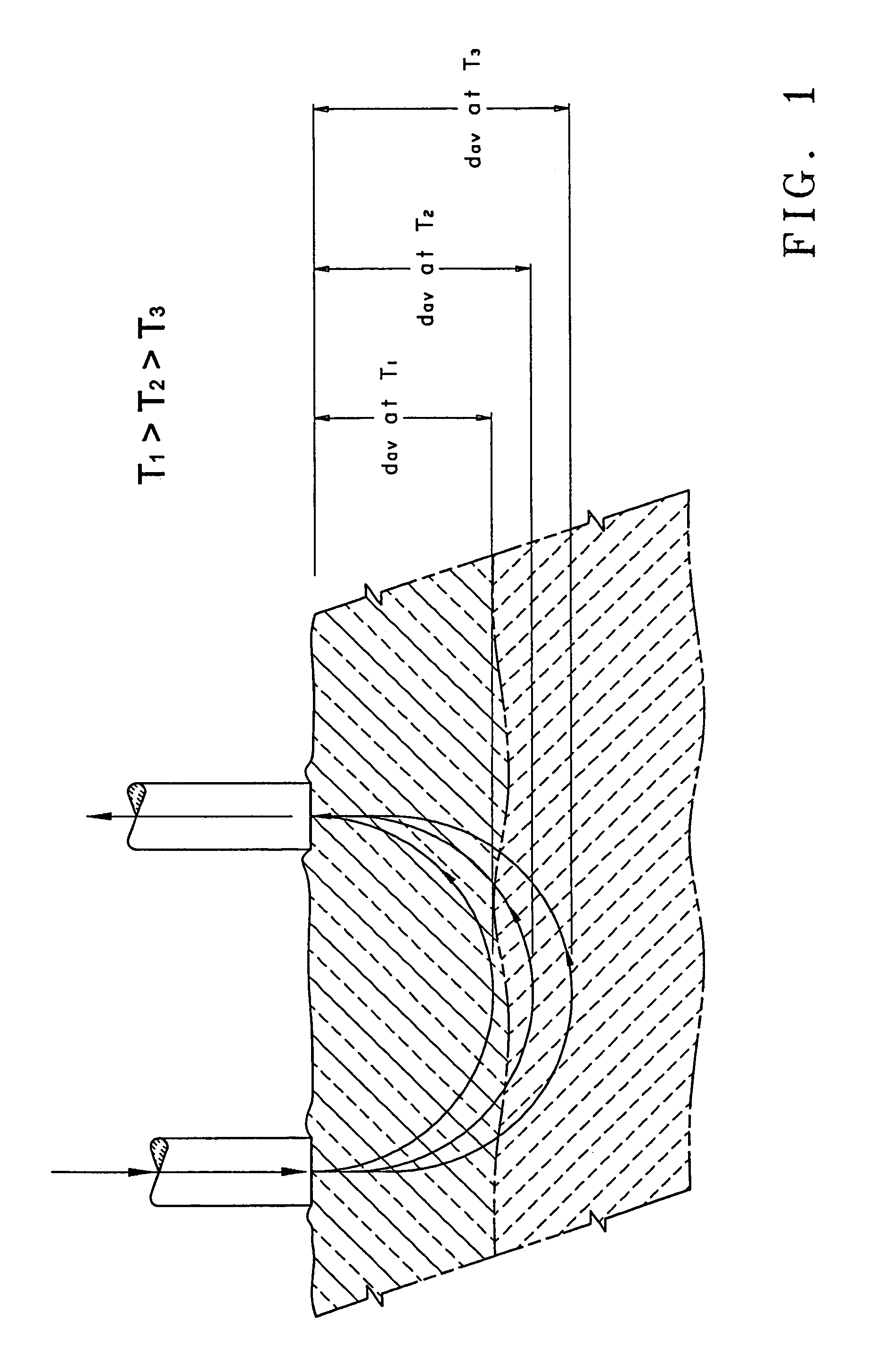
Devices and methods for non-invasively measuring at least one parameter of a sample, such as the presence of a disease condition, progression of a disease state, presence of an analyte, or concentration of an analyte, in a biological sample, such as, for example, a body part. In these devices and methods, temperature is controlled and is varied between preset boundaries. The methods and devices measure light that is reflected, scattered, absorbed, or emitted by the sample from an average sampling depth, dav, that is confined within a region in the sample wherein temperature is controlled. According to the method of this invention, the sampling depth dav, in human tissue is modified by changing the temperature of the tissue. The sampling depth increases as the temperature is lowered below the body core temperature and decreases when the temperature is raised within or above the body core temperature. Changing the temperature at the measurement site changes the light penetration depth in tissue and hence dav. Change in light penetration in tissue as a function of temperature can be used to estimate the presence of a disease condition, progression of a disease state, presence of an analyte, or concentration of an analyte in a biological sample. According to the method of this invention, an optical measurement is performed on a biological sample at a first temperature. Then, when the optical measurement is repeated at a second temperature, light will penetrate into the biological sample to a depth that is different from the depth to which light penetrates at the first temperature by from about 5% to about 20%.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
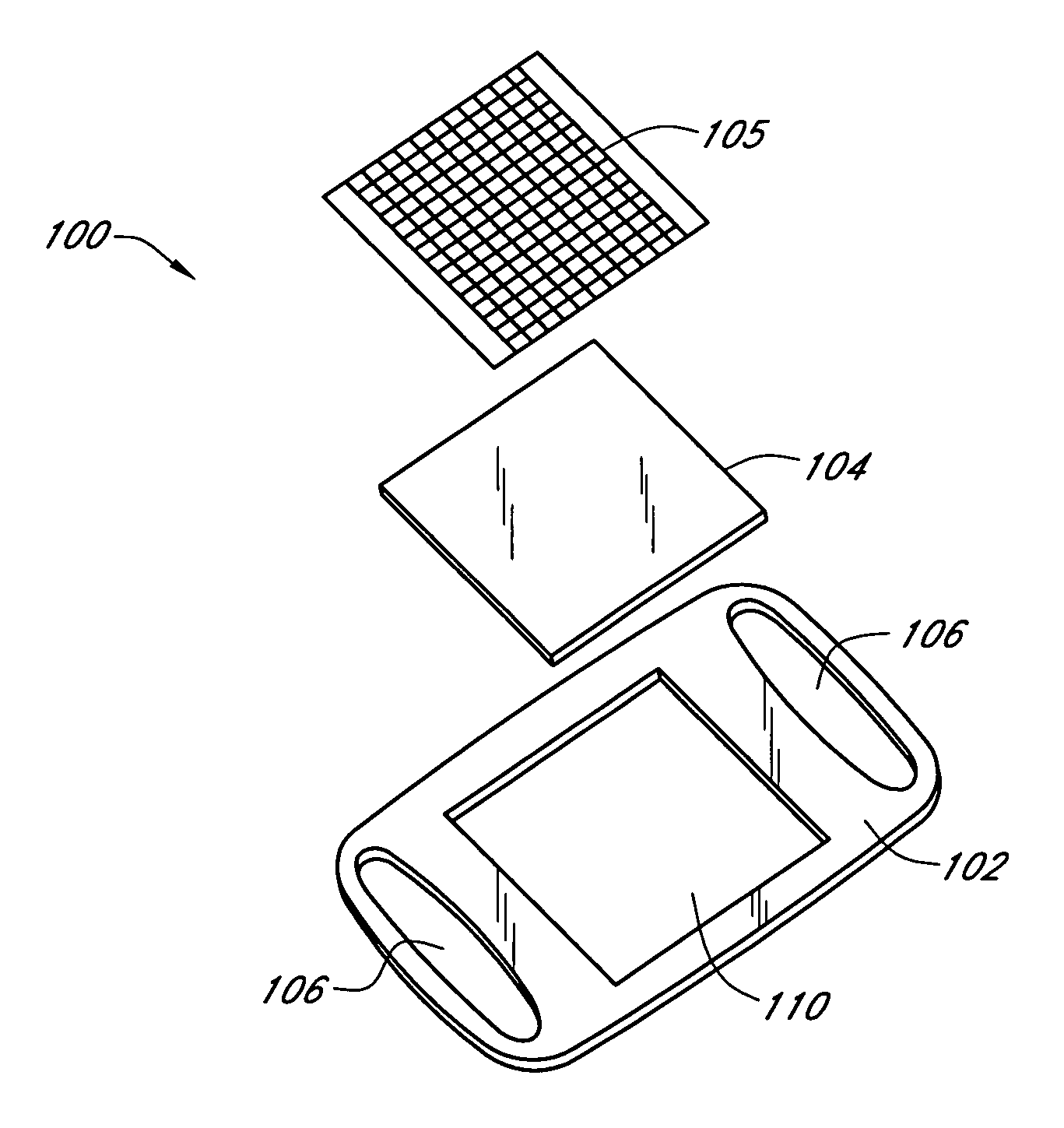
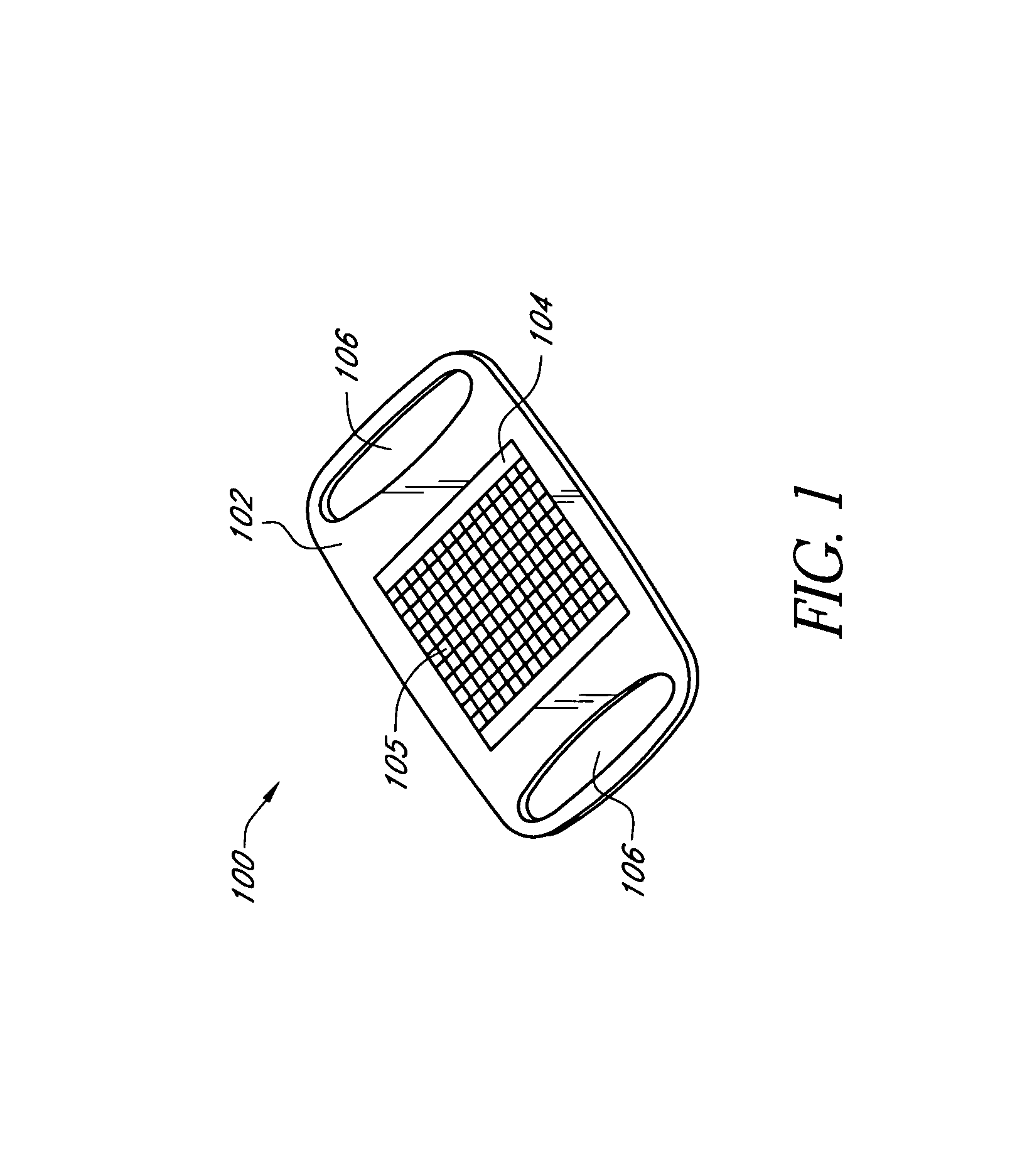
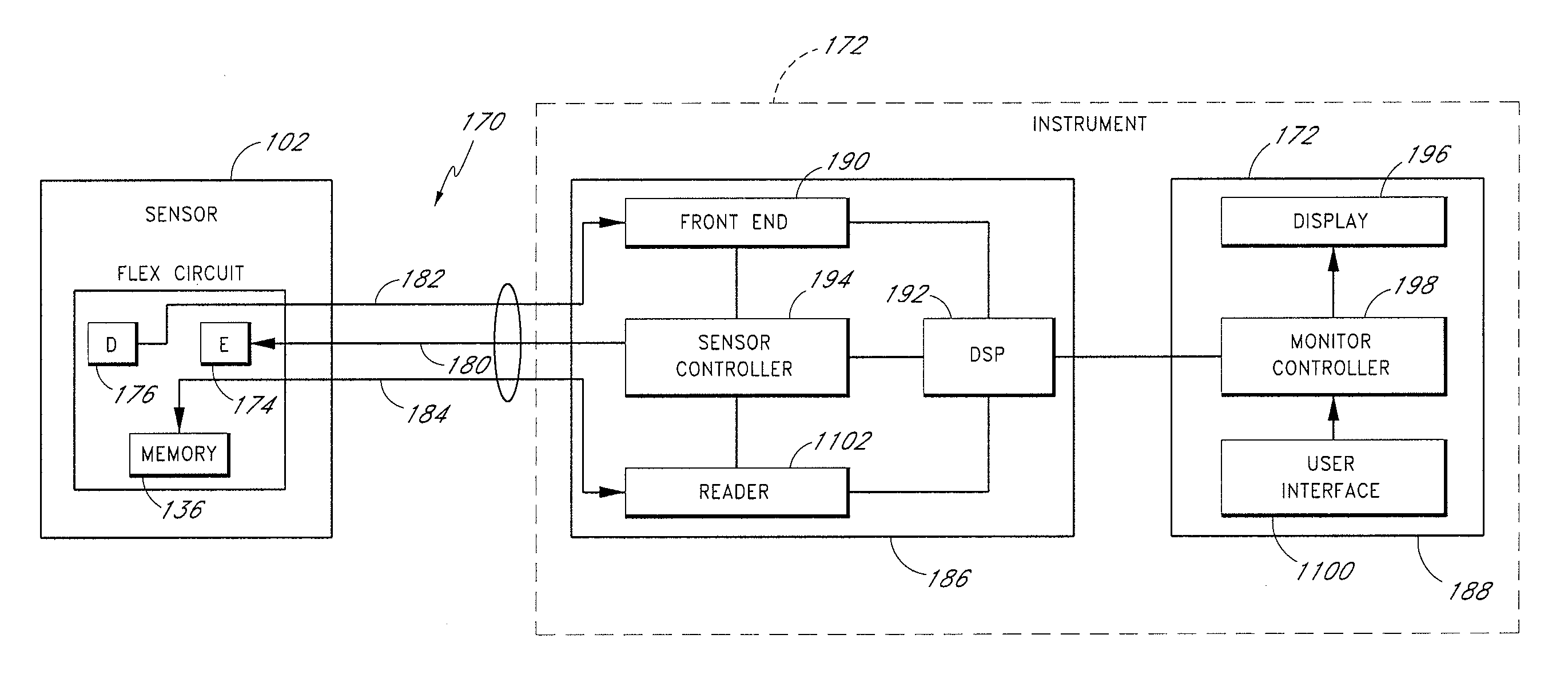
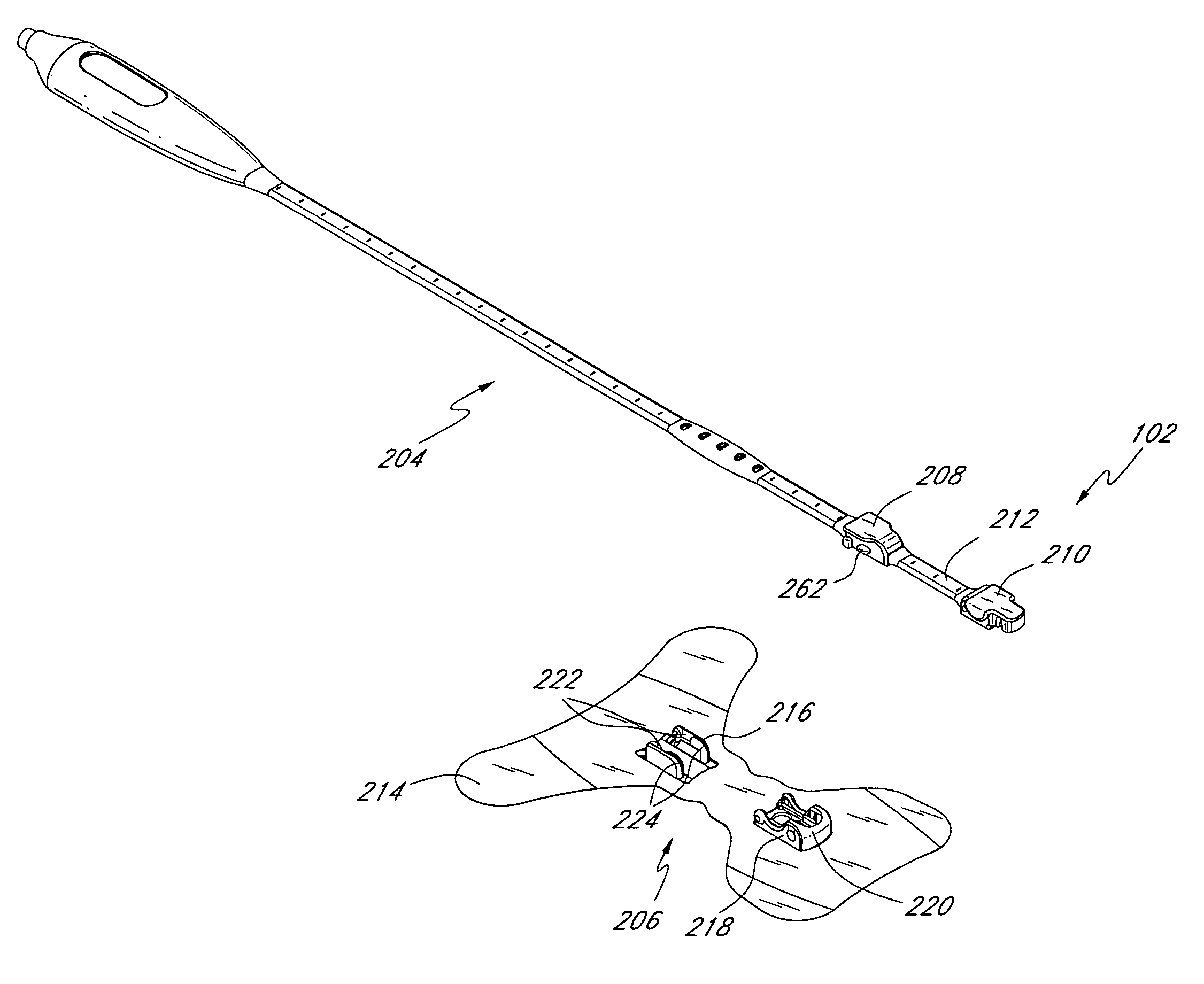
Modular physiological sensors
ActiveUS10154815B2Accurate operationAutomate analysisElectroencephalographySensorsModularityEngineering
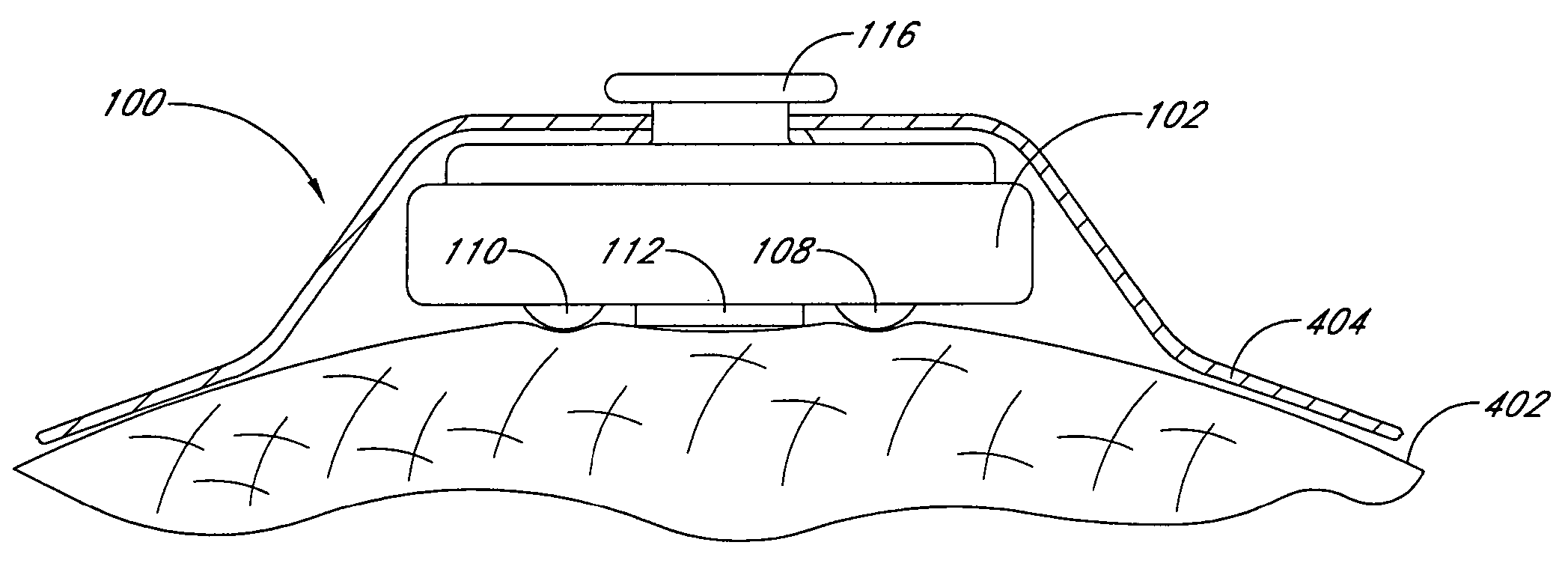
Modular physiological sensors that are physically and / or electrically configured to share a measurement site for the comfort of the patient and / or to ensure proper operation of the sensors without interference from the other sensors. The modular aspect is realized by providing outer housing shapes that generally conform to other physiological sensors; mounting areas for attachment of one sensor to another sensor; providing release liners on the overlapping sensor attachment areas; and / or providing notches, tabs or other mechanical features that provide for the proper placement and interaction of the sensors.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
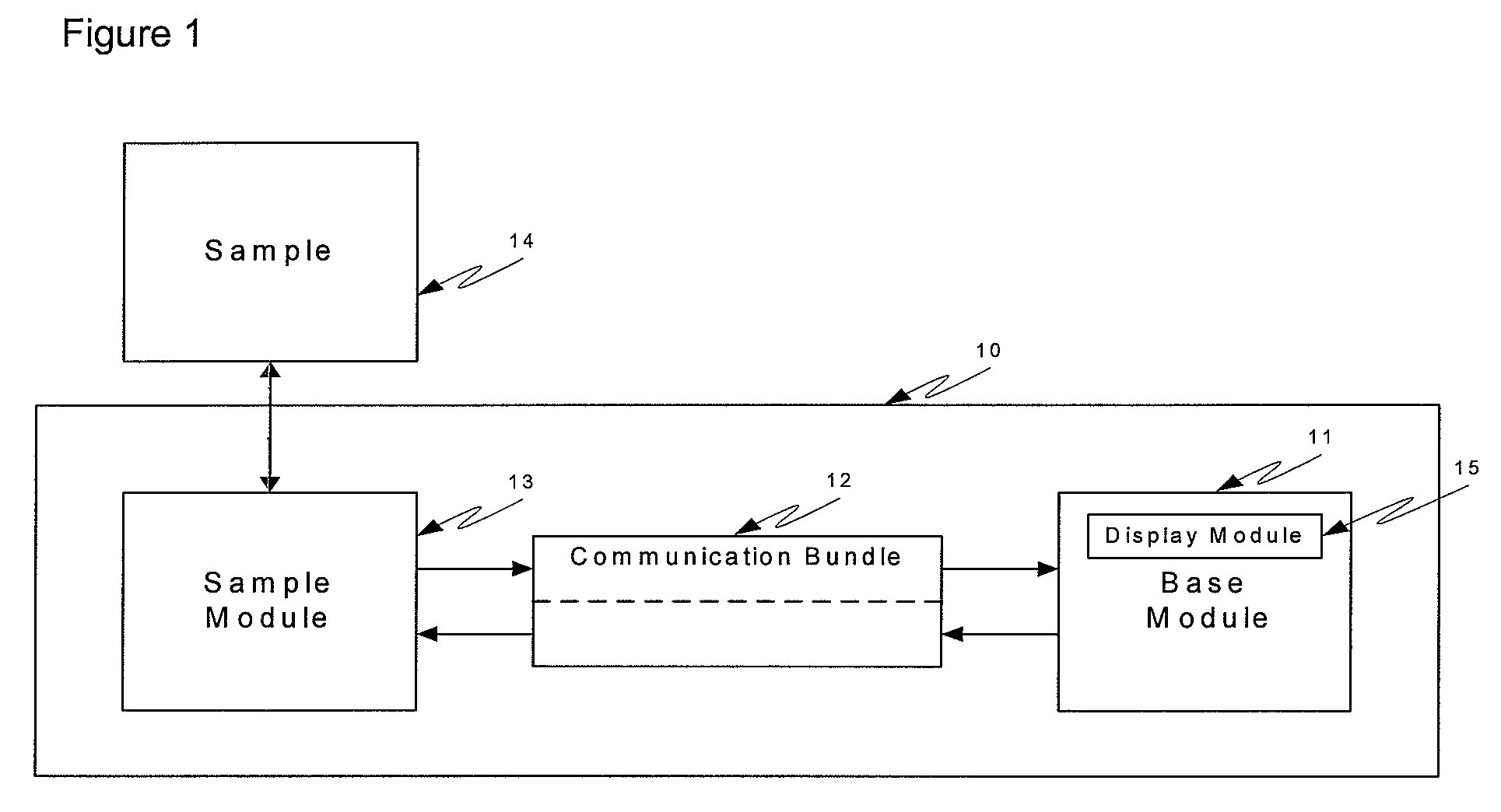
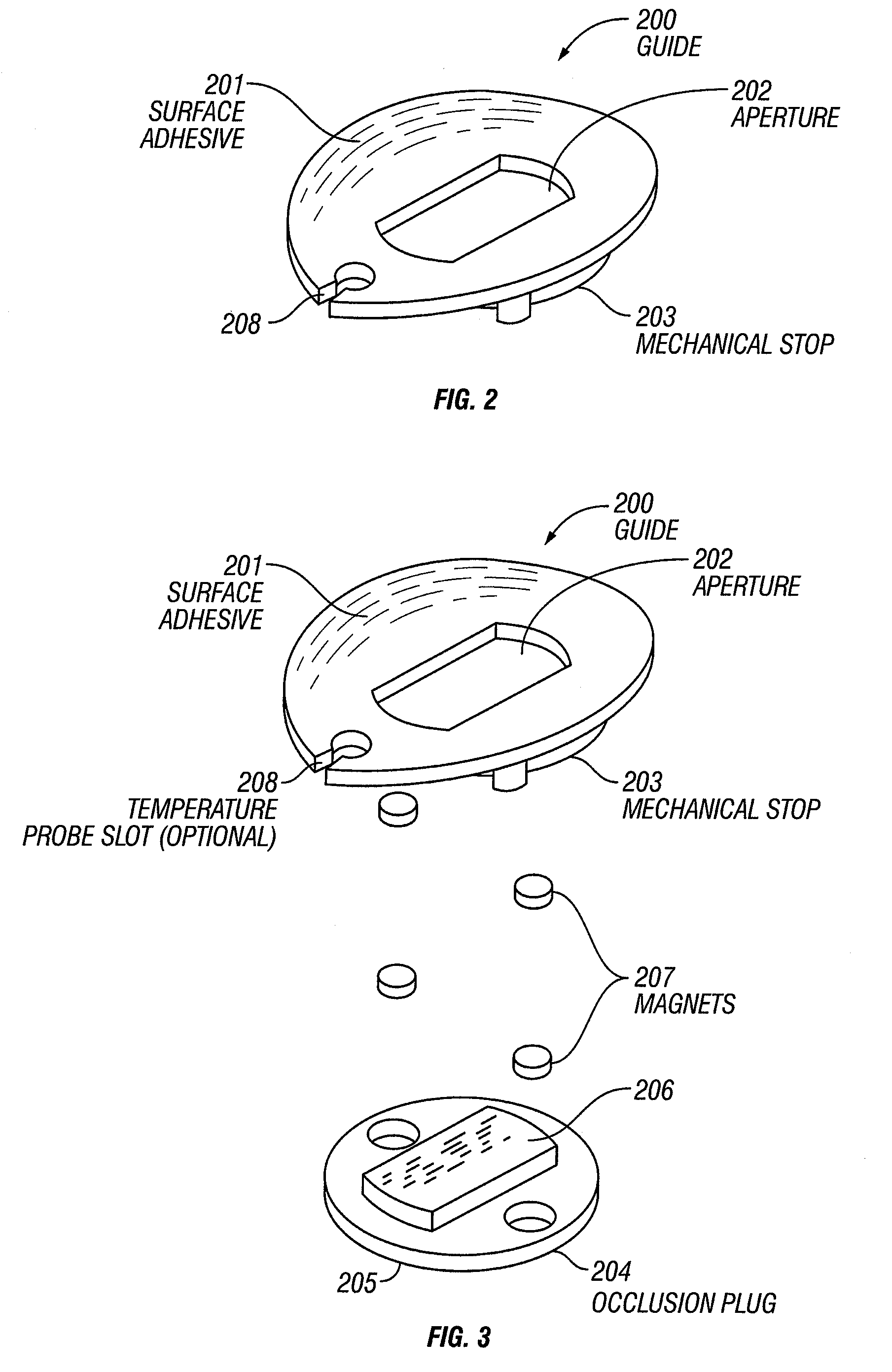
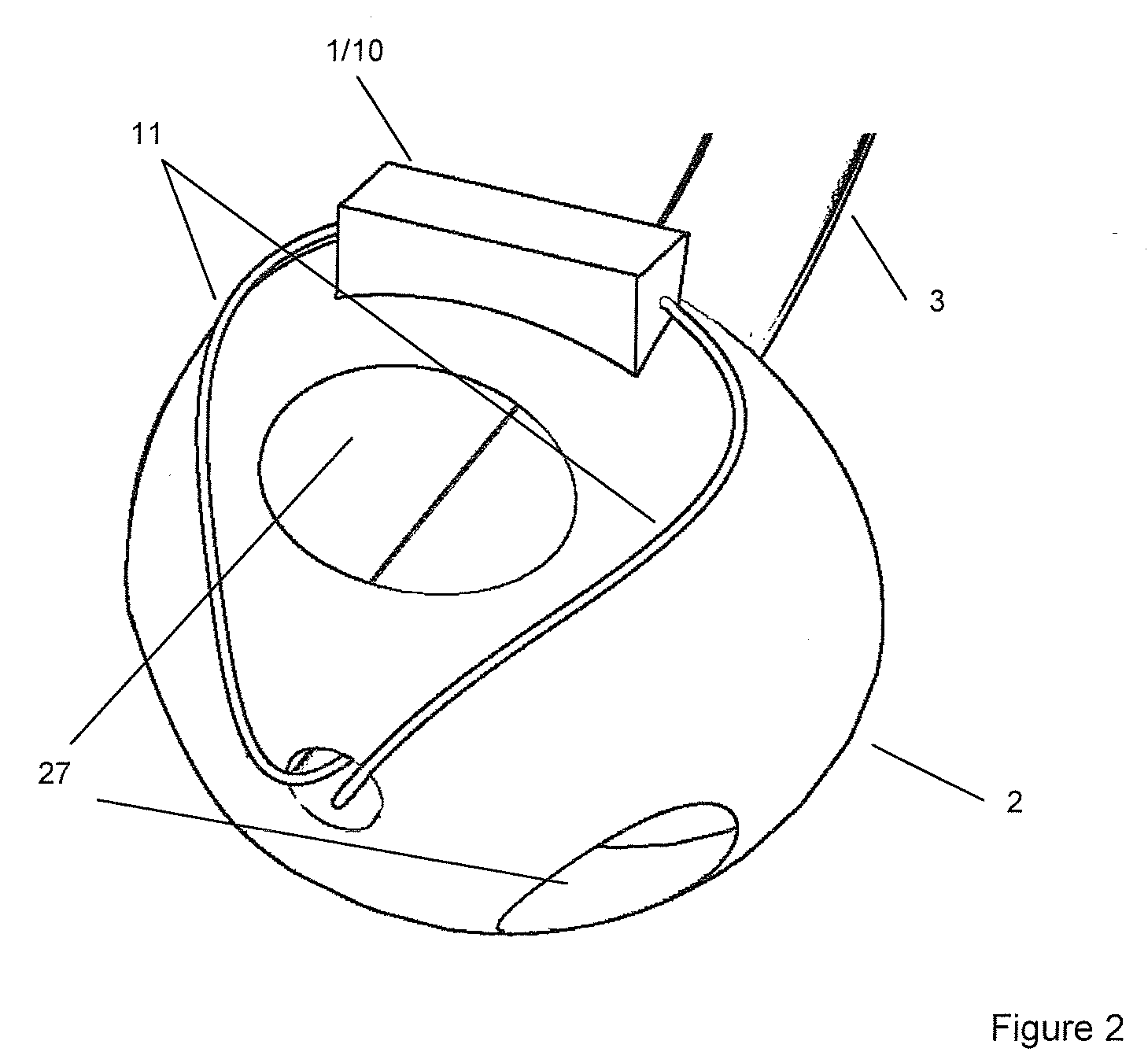
Optical sampling interface system for in-vivo measurement of tissue
InactiveUS7606608B2Minimizes stateMinimizes variationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsCouplingTissue sample
An optical sampling interface system is disclosed that minimizes and compensates for errors that result from sampling variations and measurement site state fluctuations. Embodiments of the invention use a guide that does at least one of, induce the formation of a tissue meniscus, minimize interference due to surface irregularities, control variation in the volume of tissue sampled, use a two-part guide system, use a guide that controls rotation of a sample probe and allows z-axis movement of the probe, use a separate base module and sample module in conjunction with a guide, and use a guide that controls rotation. Optional components include an occlusive element and a coupling fluid.
Owner:GLT ACQUISITION
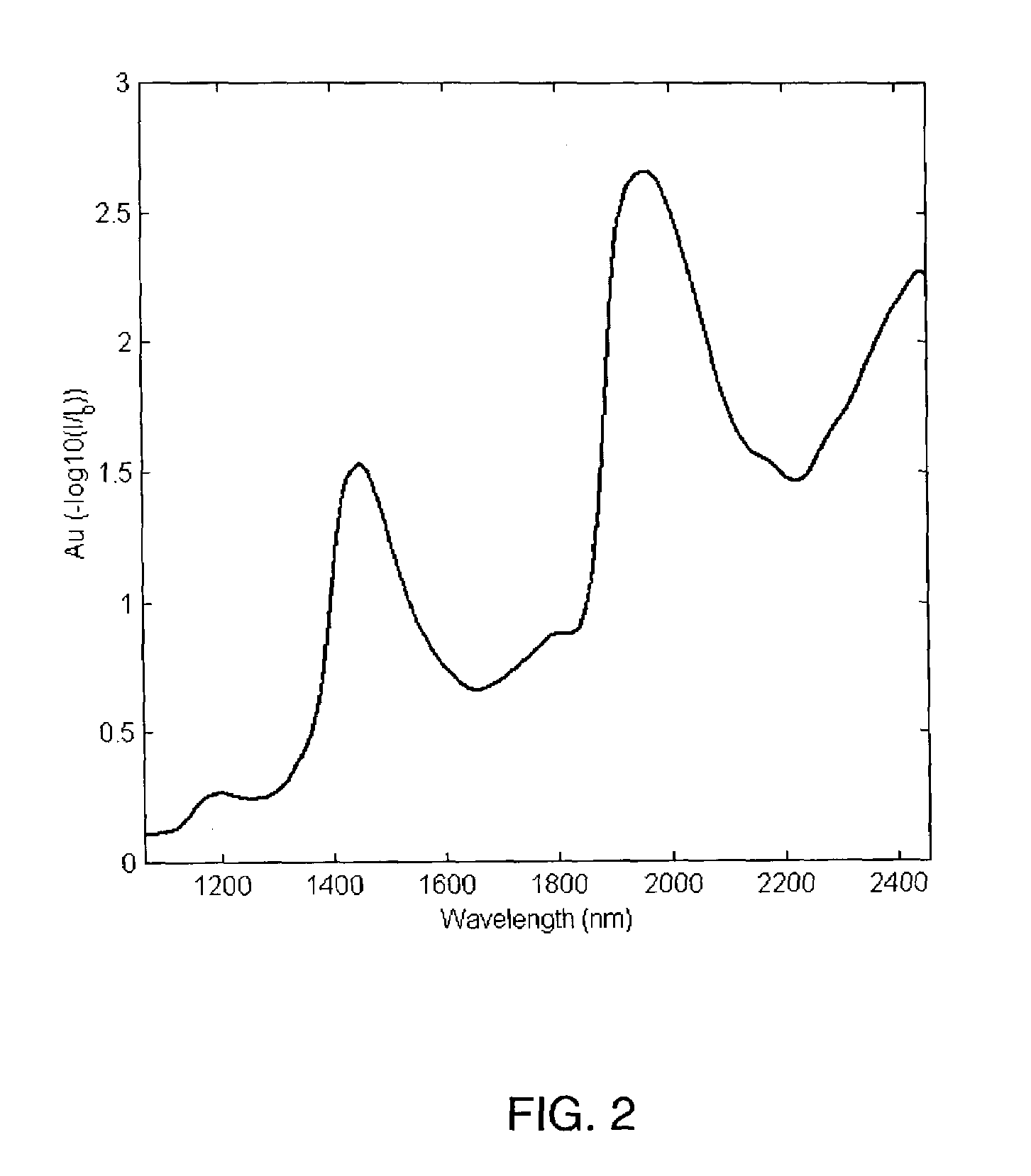
Device for capturing thermal spectra from tissue
InactiveUS6959211B2Improve determinationIsolating measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringColor/spectral properties measurementsAnalyteGlucose polymers
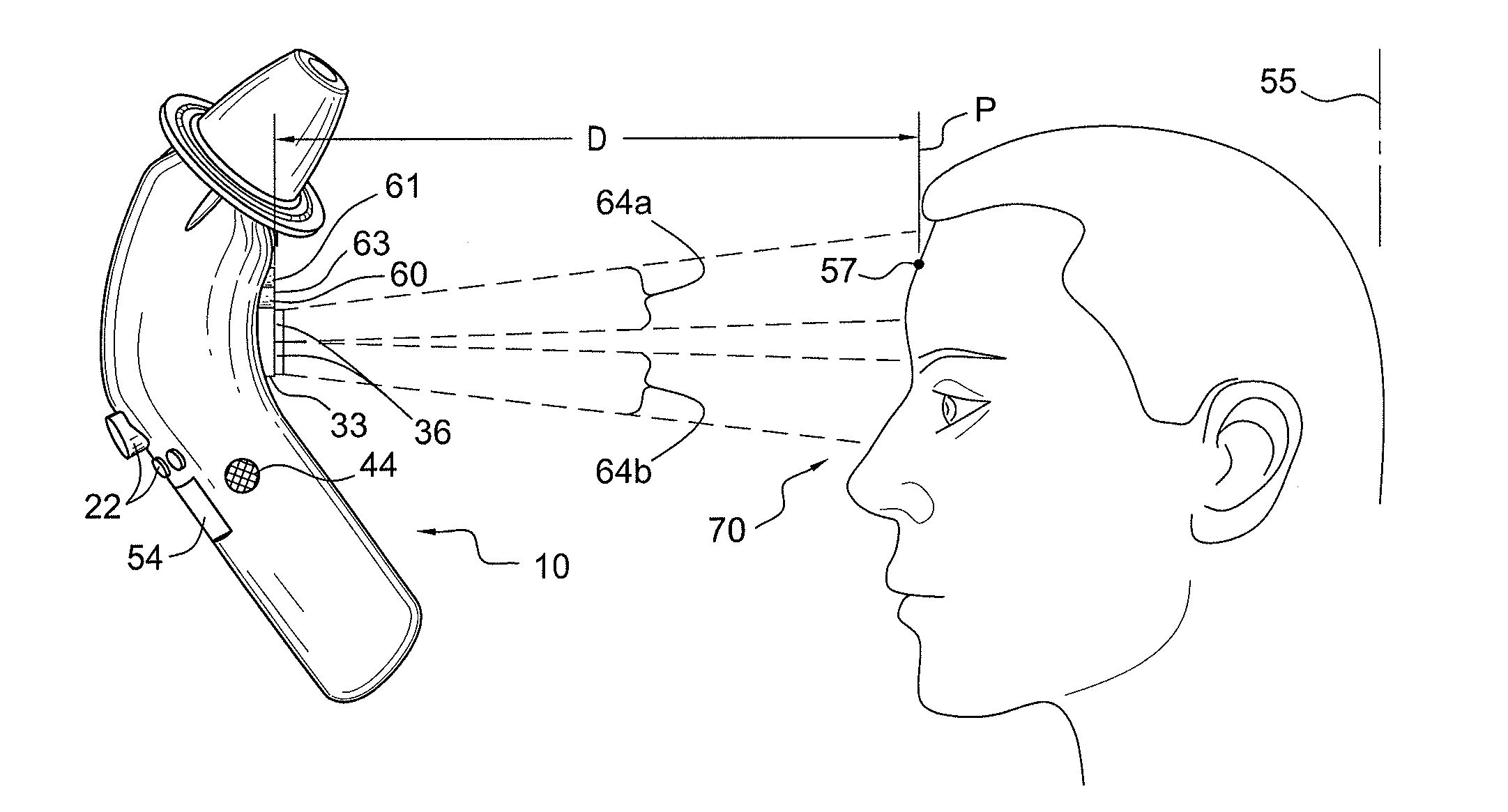
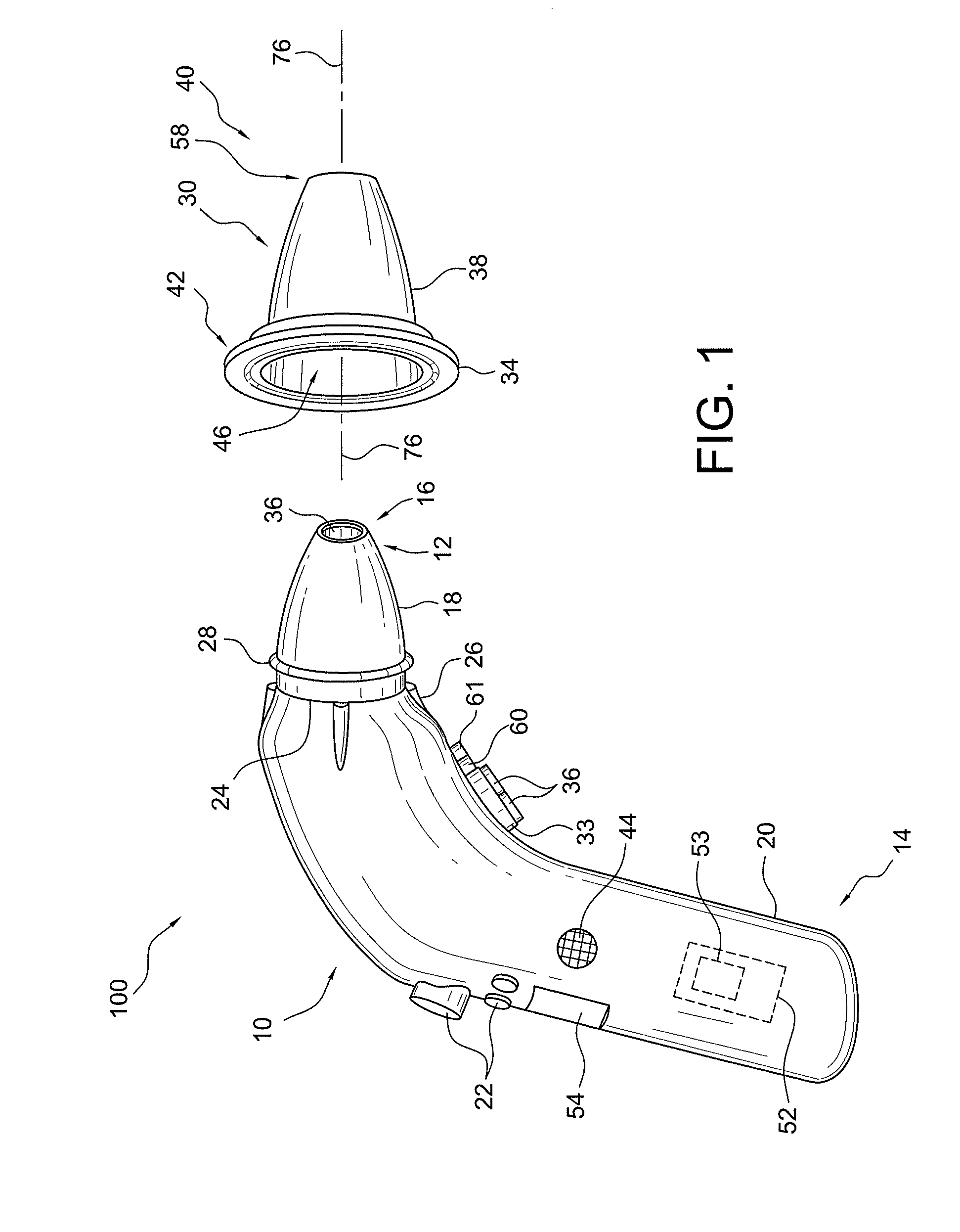
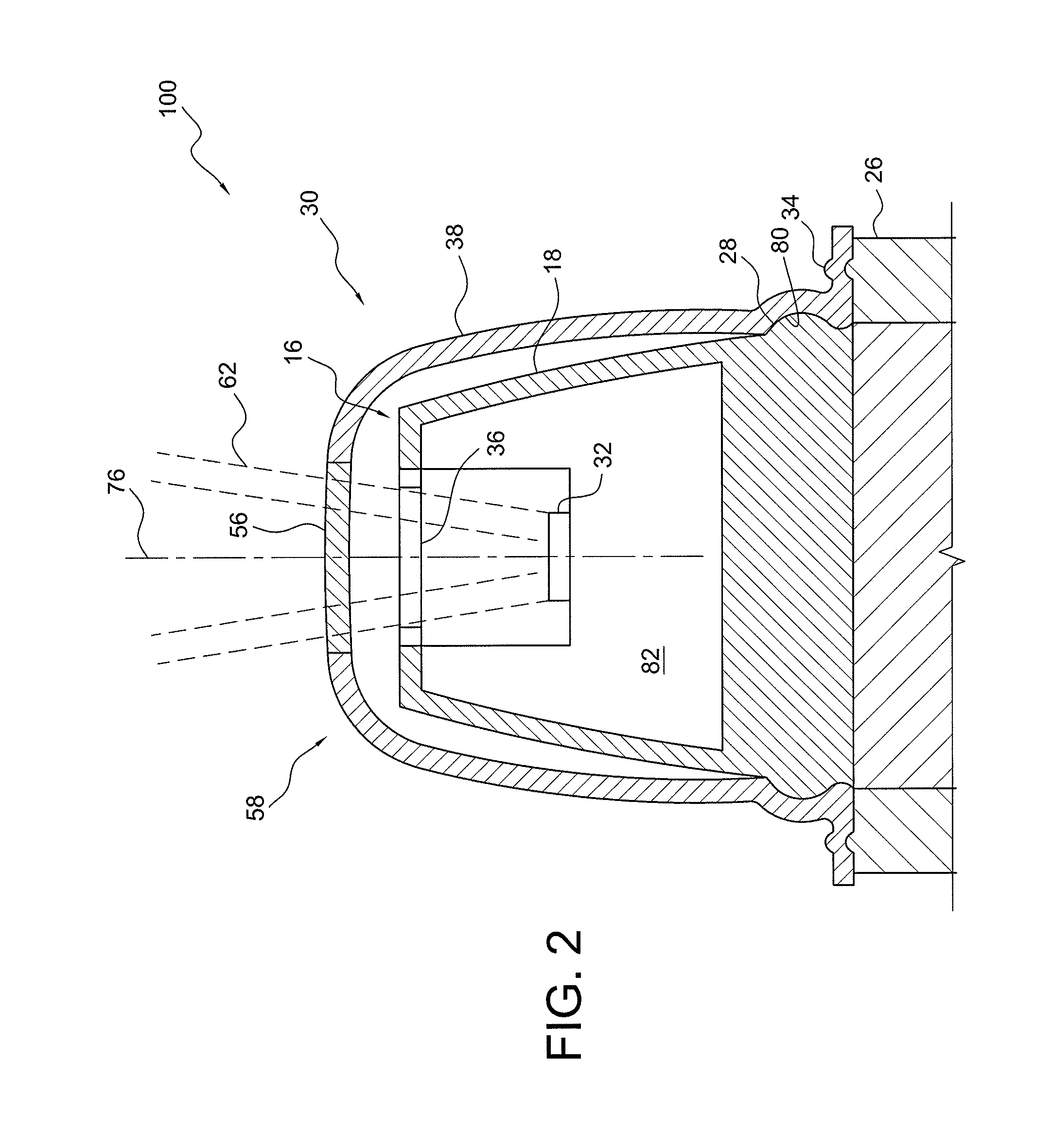
A device and method are provided for use with a noninvasive optical measurement system, such as a thermal gradient spectrometer, for improved determination of analyte concentrations within living tissue. In one embodiment, a wearable window is secured to a patient's forearm thereby isolating a measurement site on the patient's skin for determination of blood glucose levels. The wearable window effectively replaces a window of the spectrometer, and thus forms an interface between the patient's skin and a thermal mass window of the spectrometer. When the spectrometer must be temporarily removed from the patient's skin, such as to allow the patient mobility, the wearable window is left secured to the forearm so as to maintain a consistent measurement site on the skin. When the spectrometer is later reattached to the patient, the wearable window will again form an interface between the spectrometer and the same location of skin as before.
Owner:OPTISCAN BIOMEDICAL
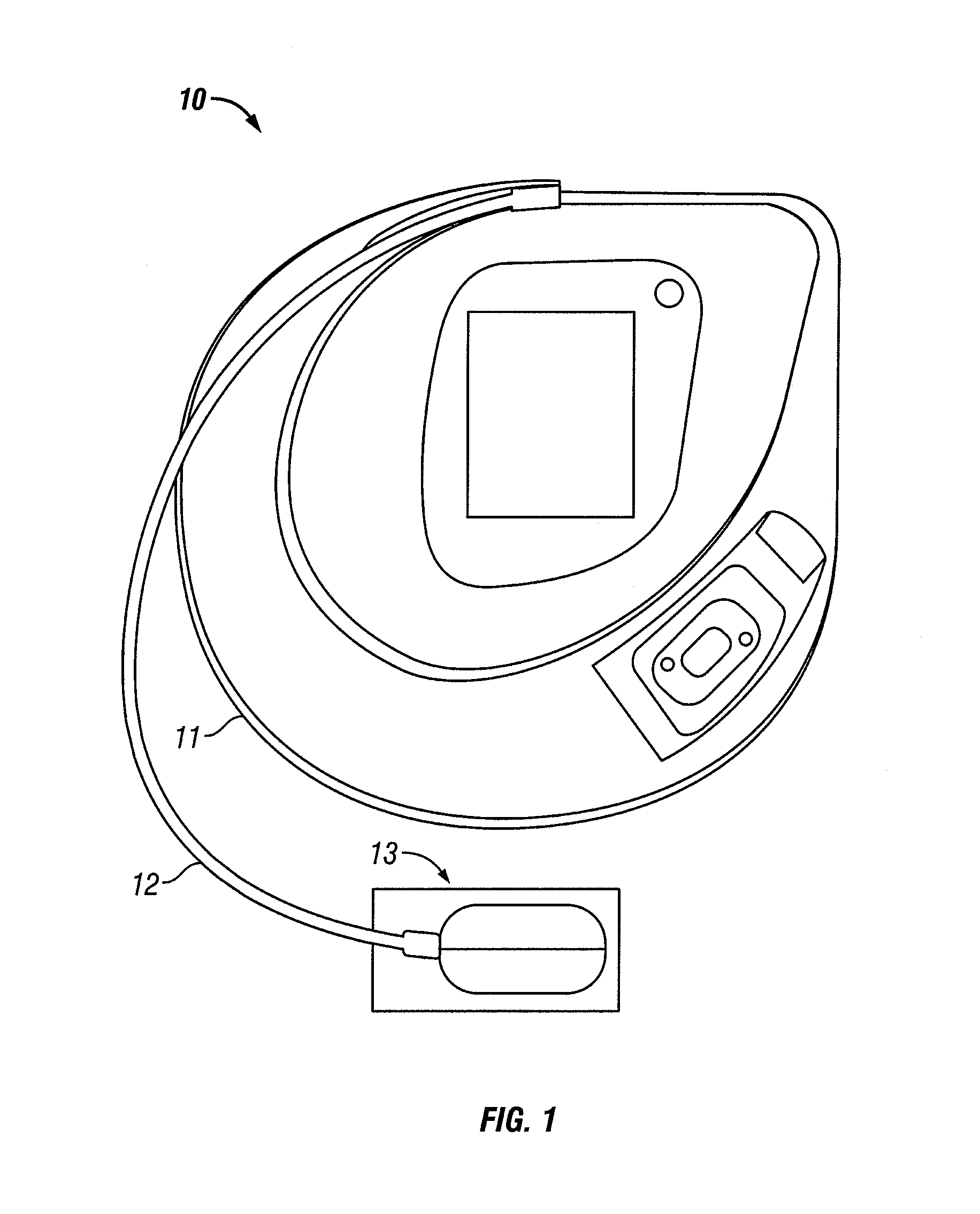
Correlation of alternative site blood and interstitial fluid glucose concentrations to venous glucose concentration
InactiveUS8216138B1Improve mobilityEnhance mobility of fluidImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMeasurement deviceAnalyte
The invention relates to a method for calibrating an analyte-measurement device that is used to evaluate a concentration of analyte in bodily fluid at or from a measurement site in a body. The method involves measuring a concentration, or calibration concentration, of an analyte in blood from an “off-finger” calibration site, and calibrating the analyte-measurement device based on that calibration concentration. The invention also relates to a device, system, or kit for measuring a concentration of an analyte in a body, which employs a calibration device for adjusting analyte concentration measured in bodily fluid based on an analyte concentration measured in blood from an “off-finger” calibration site.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Method of calibrating of an analyte-measurement device, and associated methods, devices and systems
ActiveUS20080081969A1Improve mobilityAvoid high pressureImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteMeasurement device
The invention relates to a method for calibrating an analyte-measurement device that is used to evaluate a concentration of analyte in bodily fluid at or from a measurement site in a body. The method involves measuring a concentration, or calibration concentration, of an analyte in blood from an “off-finger” calibration site, and calibrating the analyte-measurement device based on that calibration concentration. The invention also relates to a device, system, or kit for measuring a concentration of an analyte in a body, which employs a calibration device for adjusting analyte concentration measured in bodily fluid based on an analyte concentration measured in blood from an “off-finger” calibration site.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
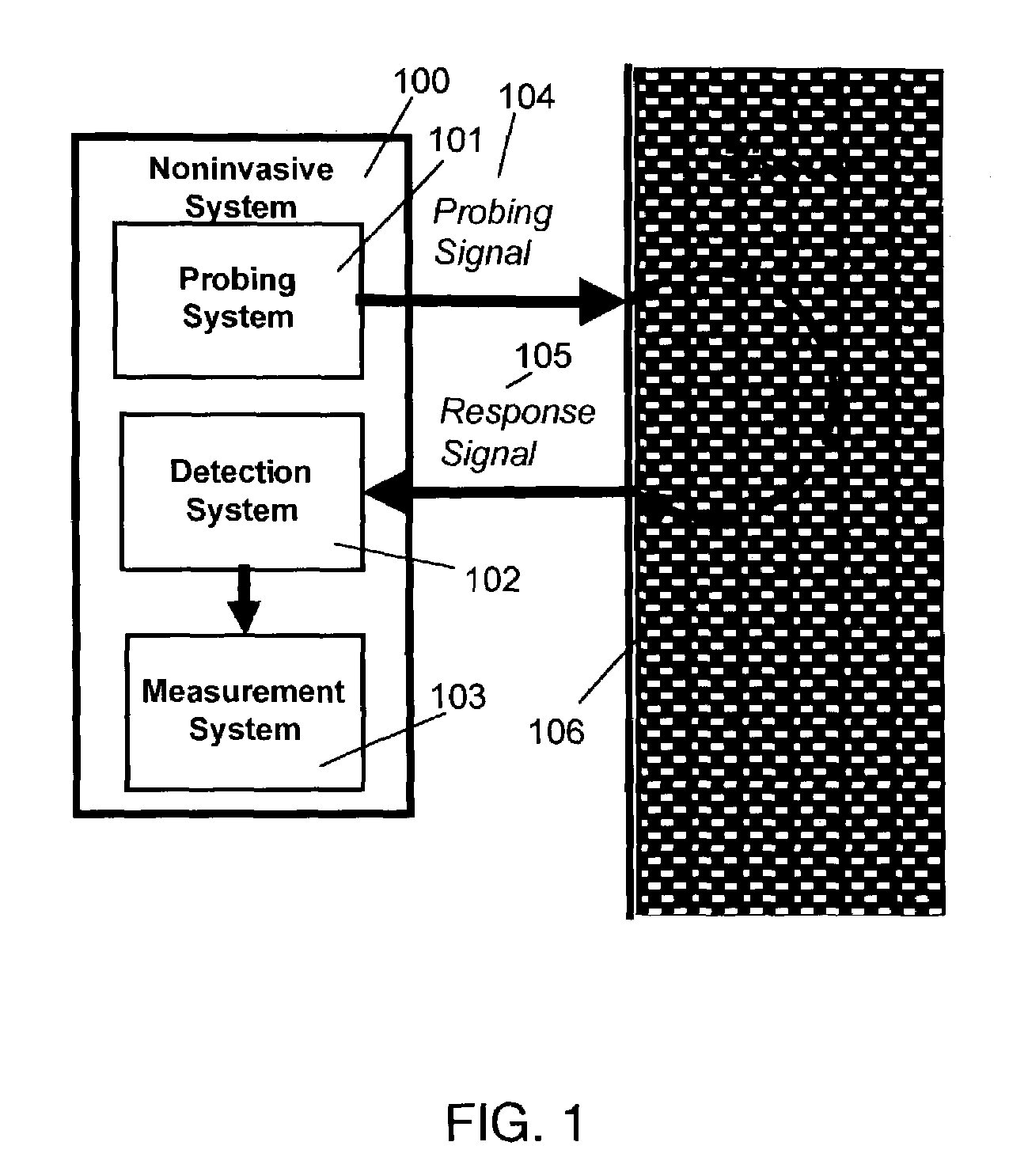
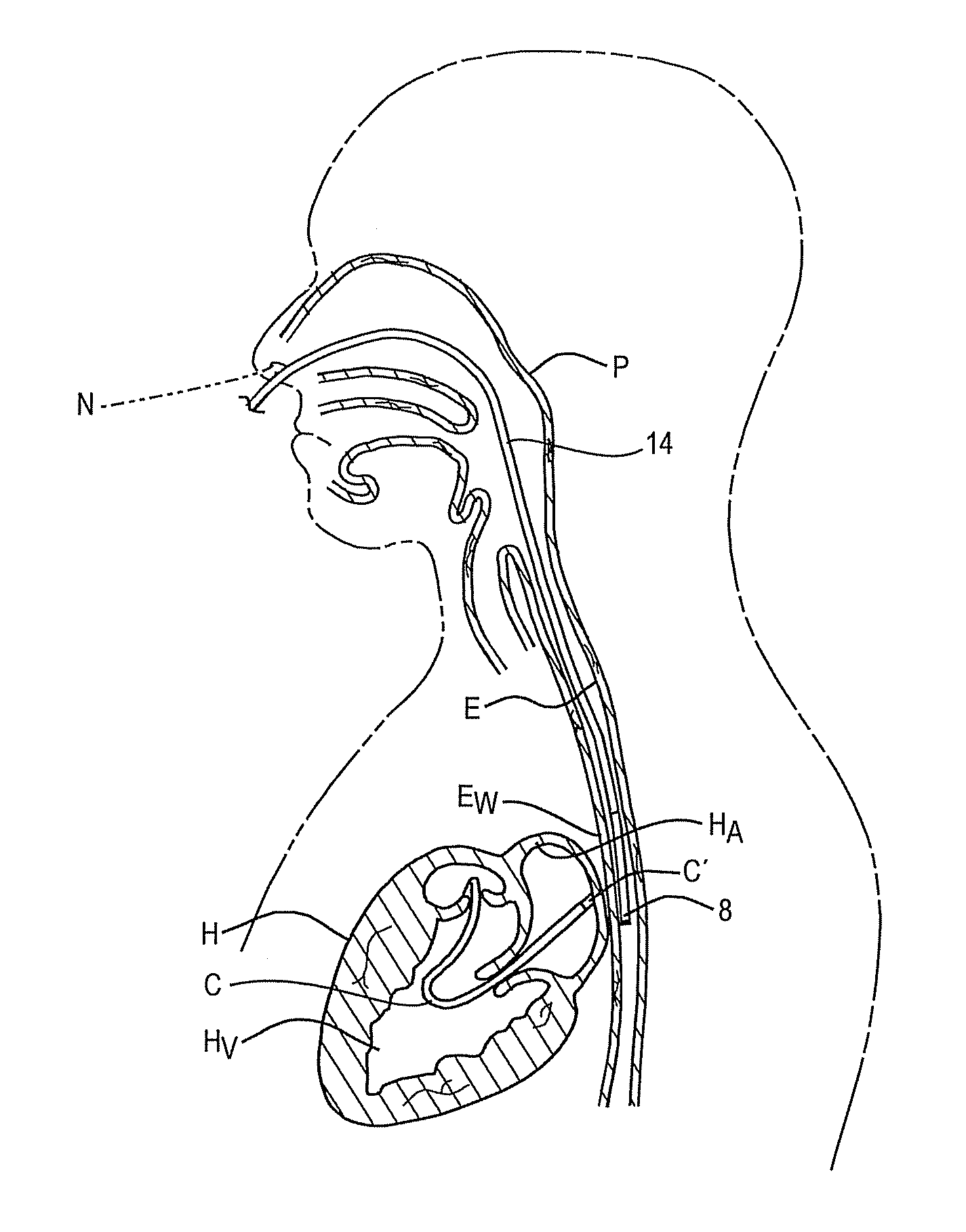
Methods and devices for continuous and mobile measurement of various bio-parameters in the external auditory canal
InactiveUS20090088611A1High frequencyElectrocardiographyCatheterExternal Auditory CanalsPulse oximetry
A method and a device for the continuous, mobile non-invasive and aesthetically unobtrusive measurement of important vital parameters, in particular body(core)temperature, arterial oxygen saturation, heart rate, respiration rate (by pulse oximetry), blood pressure, ECG, and substance concentrations in blood or tissue. The measuring site and the position of the sensor components is the (proximal) auditory canal, whereby there results an unobtrusive sensor technology suitable for a stable monitoring in everyday life i.e. even unaffected by motion. The sensor system includes a small evaluation unit and electronics for signal processing and e.g. means for wireless transmission to a mobile phone. Thus physiological parameters become available for long term diagnostics, for outpatients, for monitoring during rehabilitation, or for monitoring the health status in everyday life, while doing sports and during training, for an increase of the safety of individuals or of people with dangerous occupations or risky hobbies.
Owner:BUSCHMANN JOHANNES
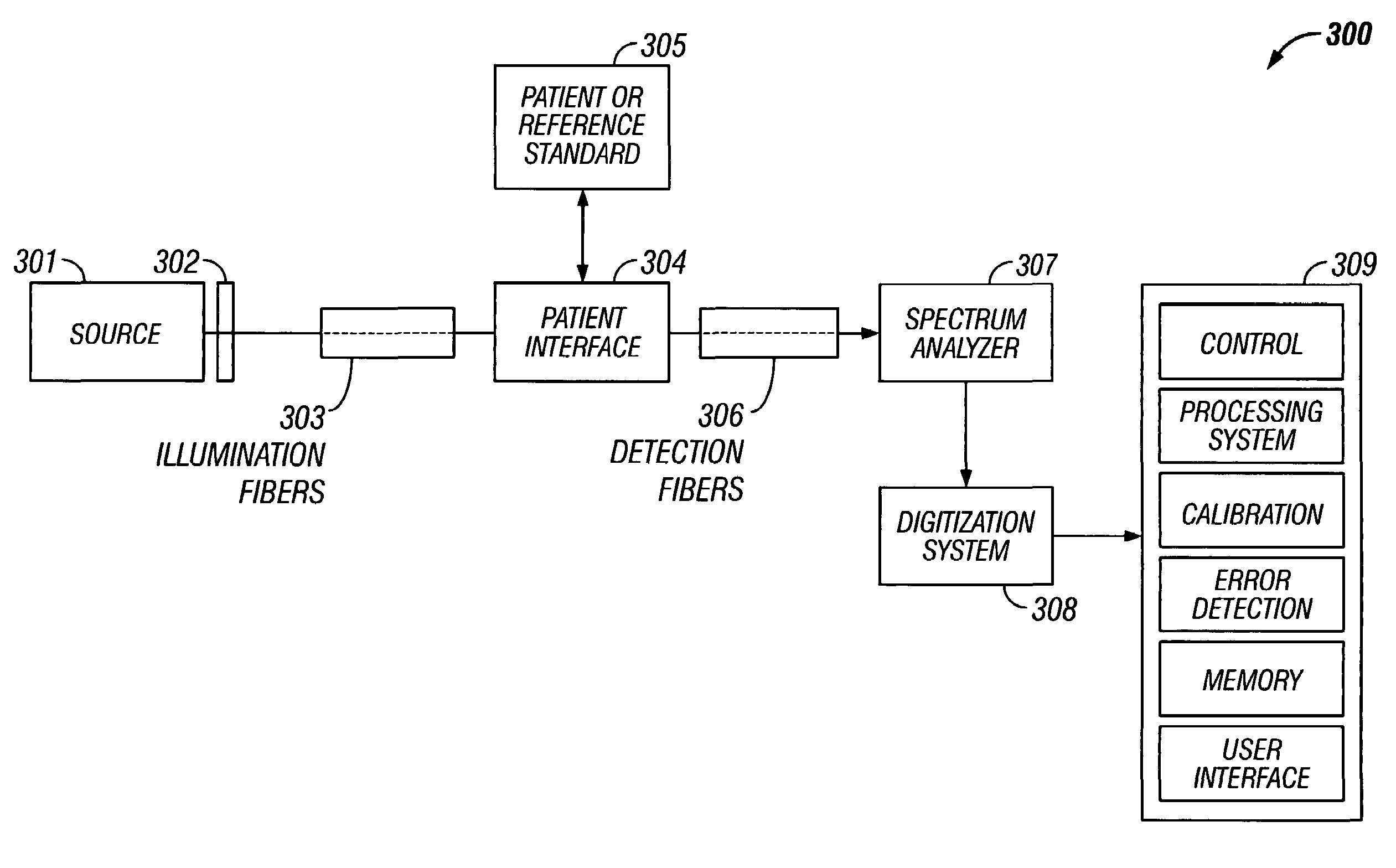
Sampling interface system for in-vivo estimation of tissue analyte concentration
InactiveUS20050187439A1Good optical performanceMinimizing sampling errorDiagnostics using spectroscopyColor/spectral properties measurementsAnalyteCoupling
Sampling is controlled to enhance analyte concentration estimation derived from noninvasive sampling. Means of assuring that the same tissue sample volume is repeatably sampled are presented, thus minimizing sampling errors due to mechanical tissue distortion, specular reflectance, and probe placement. In a first embodiment of the invention, sampling is controlled using automated delivery of a coupling fluid to a region between a tip of a sample probe and a tissue measurement site in a manner requiring minimal user interaction. In a second embodiment of the invention, sampling is controlled by controlling temperature variations, preferably with a coupling fluid, at a region about the tip of a sample probe and a sample site. In a third embodiment, sampling is procedurally controlled via timing and location of coupling fluid delivery to a sample site.
Owner:SENSYS MEDICAL
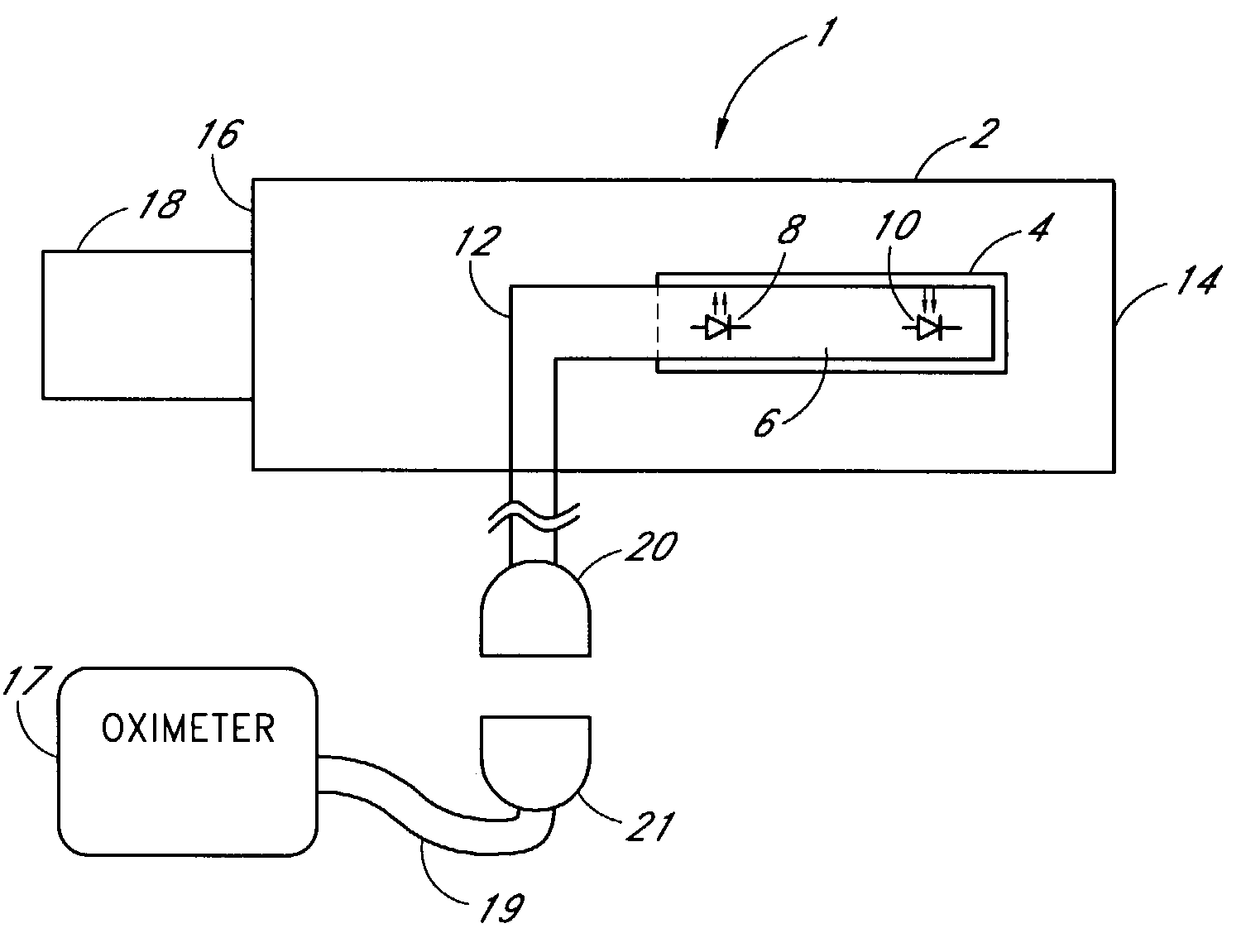
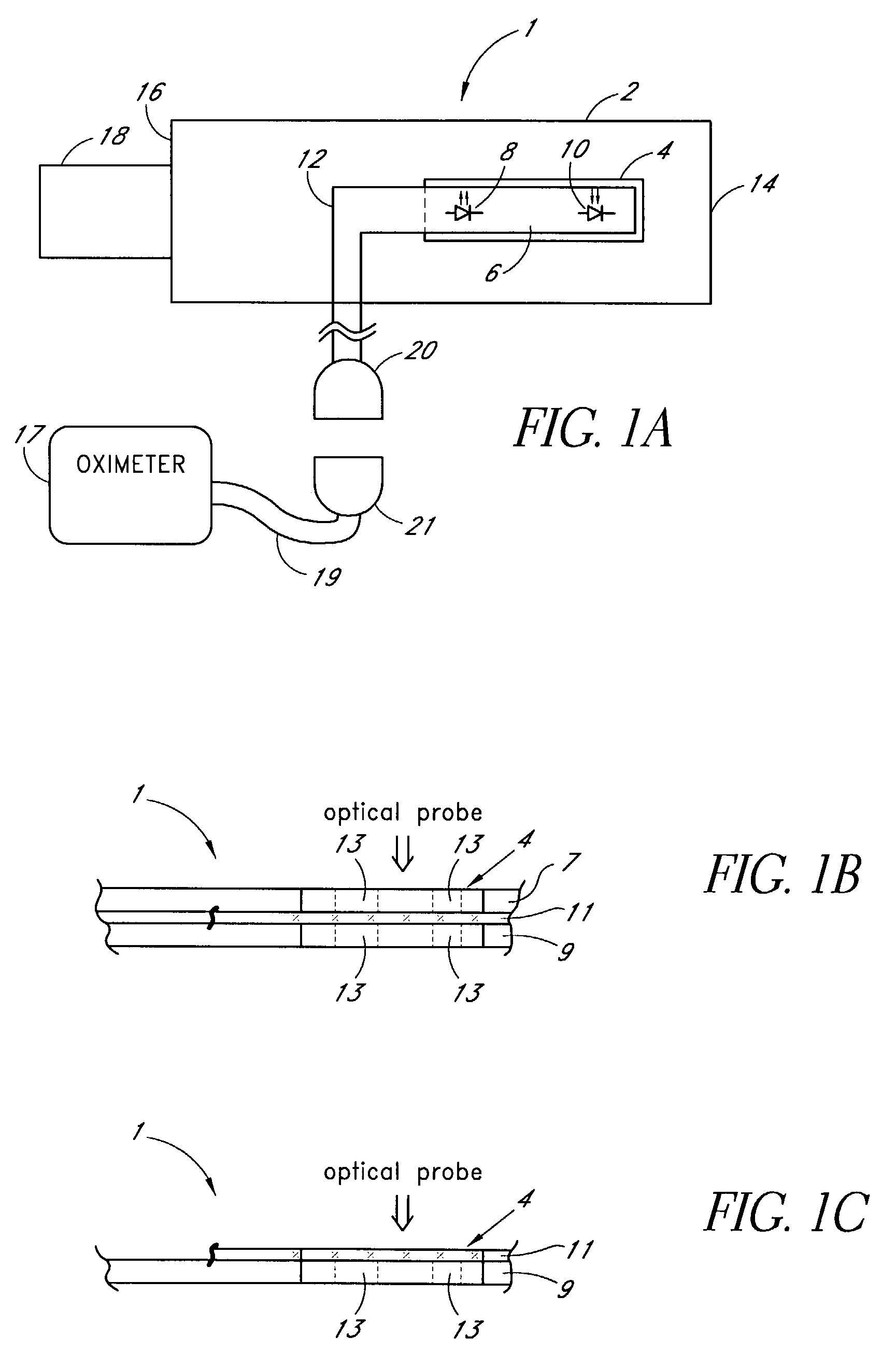
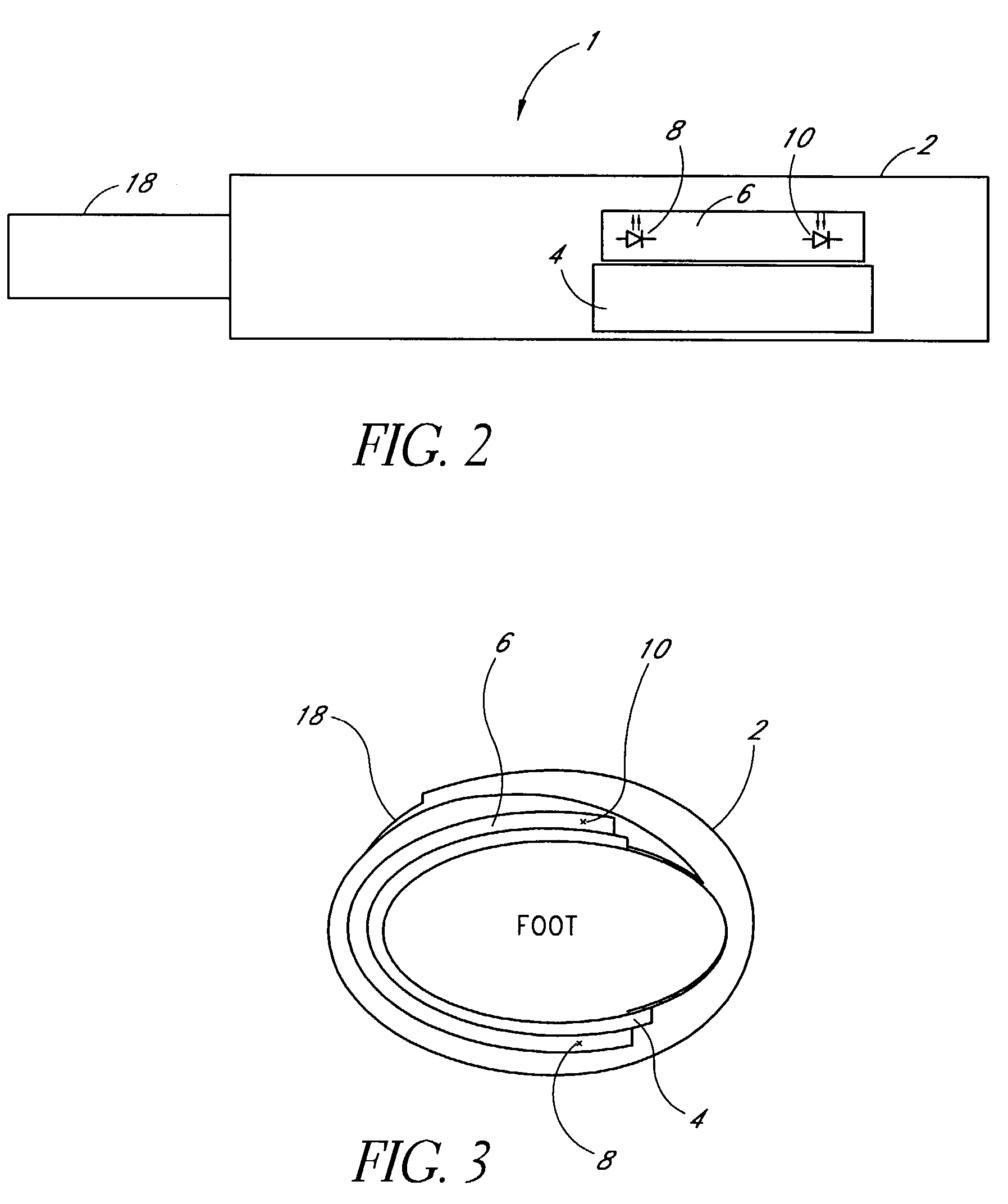
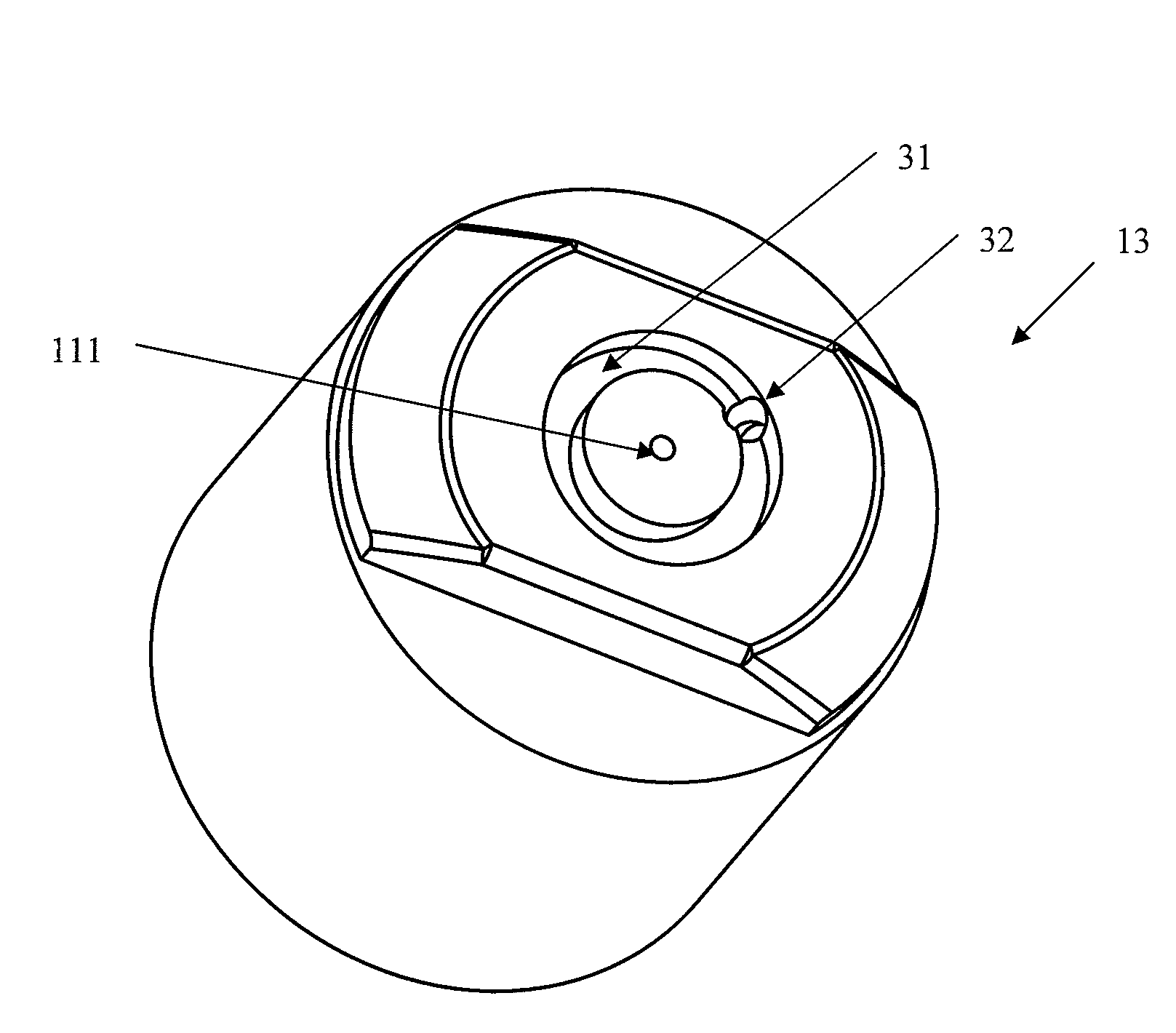
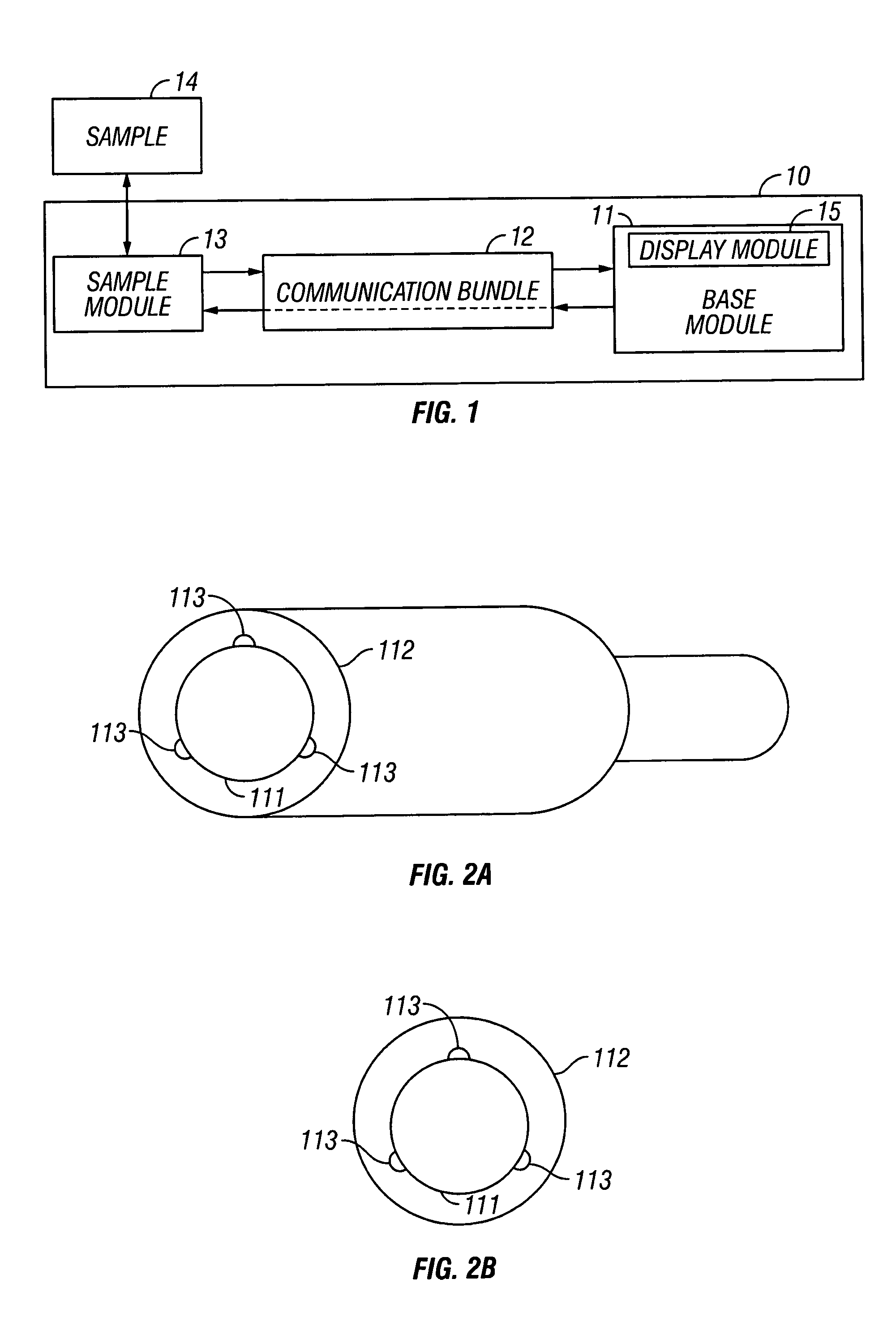
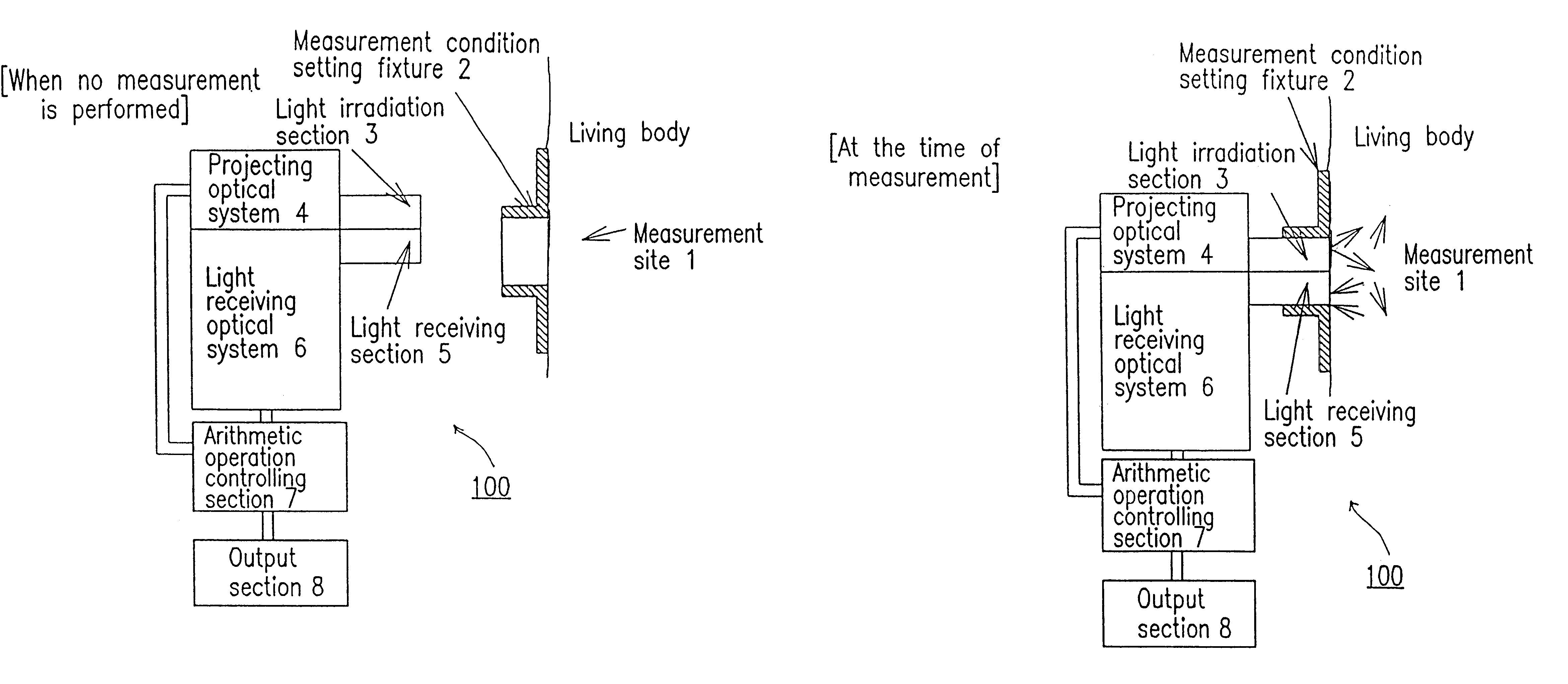
Measuring condition setting jig, measuring condition setting method and biological information measuring instrument
InactiveUS6381489B1Easily and accurately reproducedHighly precise measurement valueDiagnostics using lightSurgeryLight irradiationMeasuring instrument
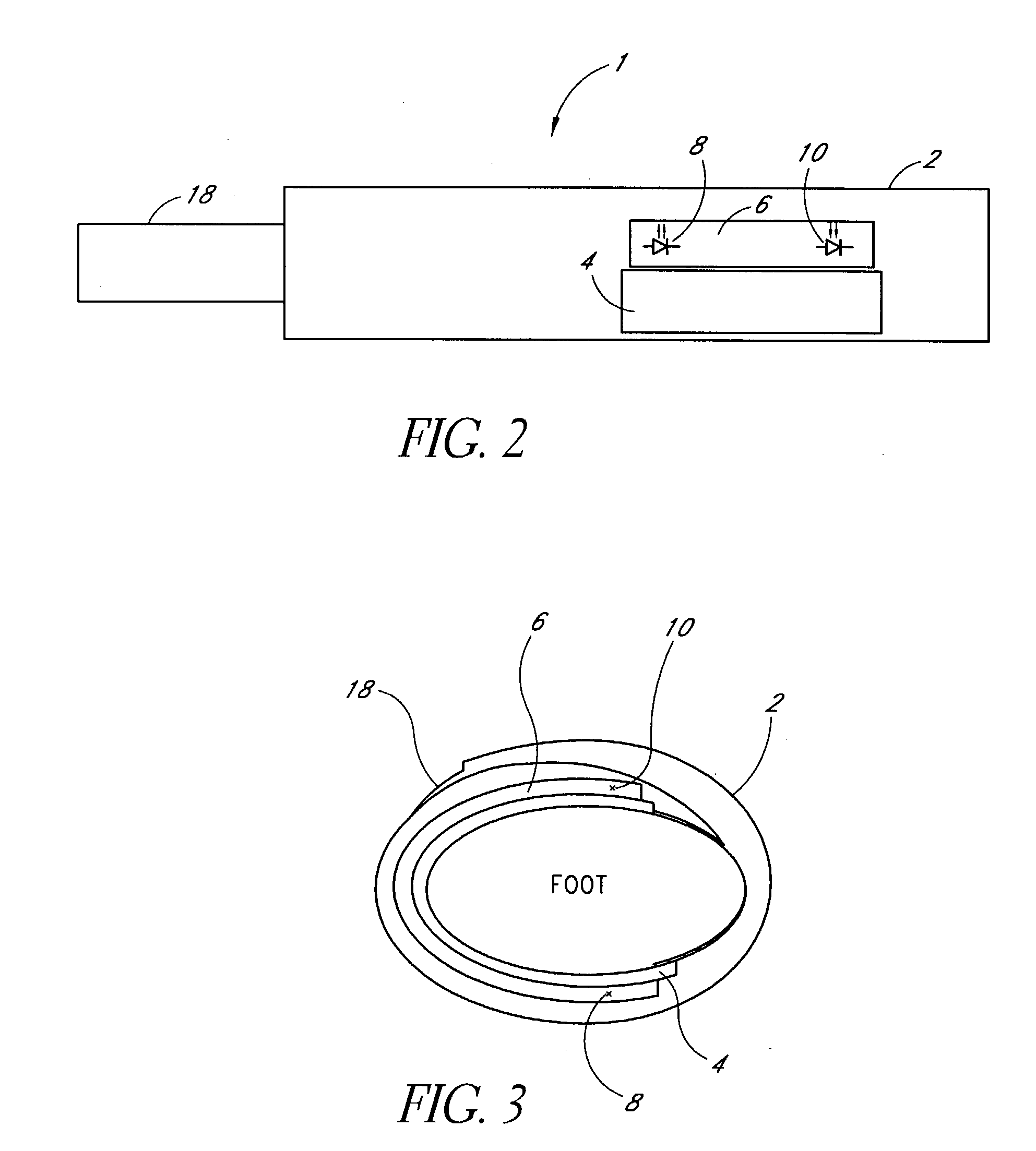
A measurement condition setting fixture 2 is secured to a measurement site 1 of a living body prior to the measurement. At the time of measurement, a light irradiation section 3 and a light receiving section 5 of a measuring optical system are respectively attached and secured to a light irradiation section securing section 10 and a light receiving section securing section 11 of the measurement condition setting fixture 2. Thus, the measurement site 1 and the measuring optical system are secured to each other, and desirable measurement conditions can be realized. Moreover, the measurement conditions can be maintained throughout the measurement. After the measurement is completed, the measurement site 1 can be removed from the measuring optical system by detaching the light irradiation section 3 and the light receiving section 5 from the light irradiation section securing section 10 and the light receiving section securing section 11. When the measurement is performed again, the desirable measurement conditions can be reproduced merely by attaching the light irradiation section 3 and the light receiving section 5 to the light irradiation section securing section 10 and the light receiving section securing section 11.
Owner:KYOTO DAICHI KAGAKU
Method and apparatus for control of skin perfusion for indirect glucose measurement
InactiveUS7509153B2Improve heat transfer performanceImprove measurement reliabilityRaman scatteringDiagnostic recording/measuringConcentrations glucoseDirect effects
A method and apparatus for noninvasive glucose measurement measures glucose indirectly from the natural response of tissue to variations in analyte concentration. The indirect measurement method utilizes factors affected by or correlated with the concentration of glucose, such as refractive index, electrolyte distribution or tissue scattering. Measurement reliability is greatly improved by stabilizing optical properties of the tissue at the measurement site, thus blood perfusion rates at the sample site are regulated. Perfusion is monitored and stabilized by spectroscopically measuring a control parameter, such as skin temperature, that directly affects perfusion. The control parameter is maintained in a range about a set point, thus stabilizing perfusion. Skin temperature is controlled using a variety of means, including the use of active heating and cooling elements, passive devices, such as thermal wraps, and through the use of a heated coupling medium having favorable heat transfer properties.
Owner:GLT ACQUISITION
Attachment and optical probe
A medical monitoring system, such as an oximetry system, applies an attachment for securing an optical probe to a measurement site. The attachment has an elongated support with a first end and a second end, and a dedicated area in proximity of the first end. The dedicated area receives an optical probe and includes a material that is transparent for light emitted and received by the optical probe. The dedicated area mountably receives the optical probe on the material so that in use, the material is positioned between the optical probe and a surface of a measurement site. The optical probe may be factory-mounted to the dedicated area of the attachment as a ready-to-use sensor. In the alternative, the attachment may be available as an individual component, or as a part of a kit including the attachment and the optical probe.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Patient interface with respiratory gas measurement component
InactiveUS20060249160A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesBreathing filtersAirway adaptorCatheter
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
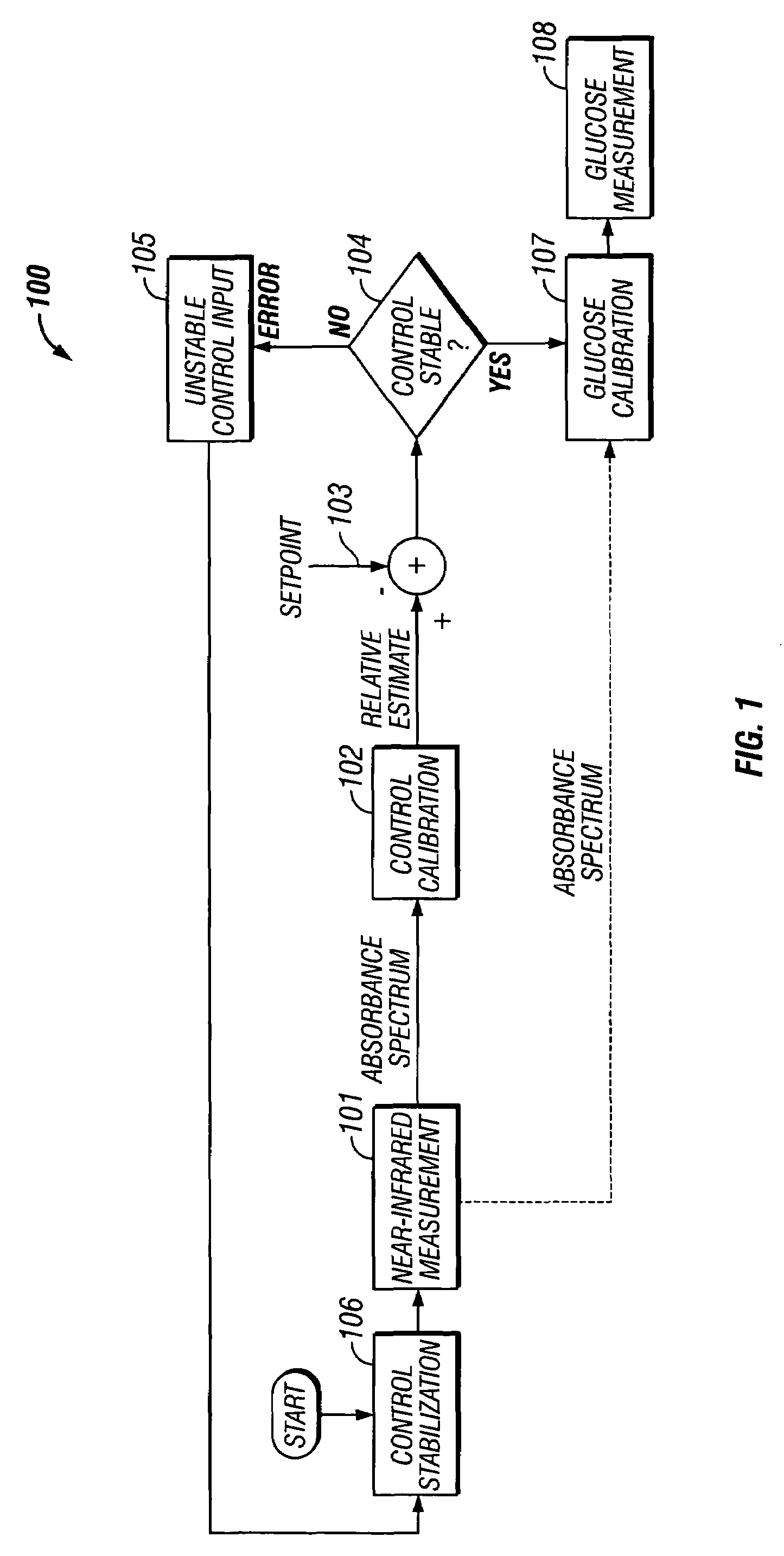
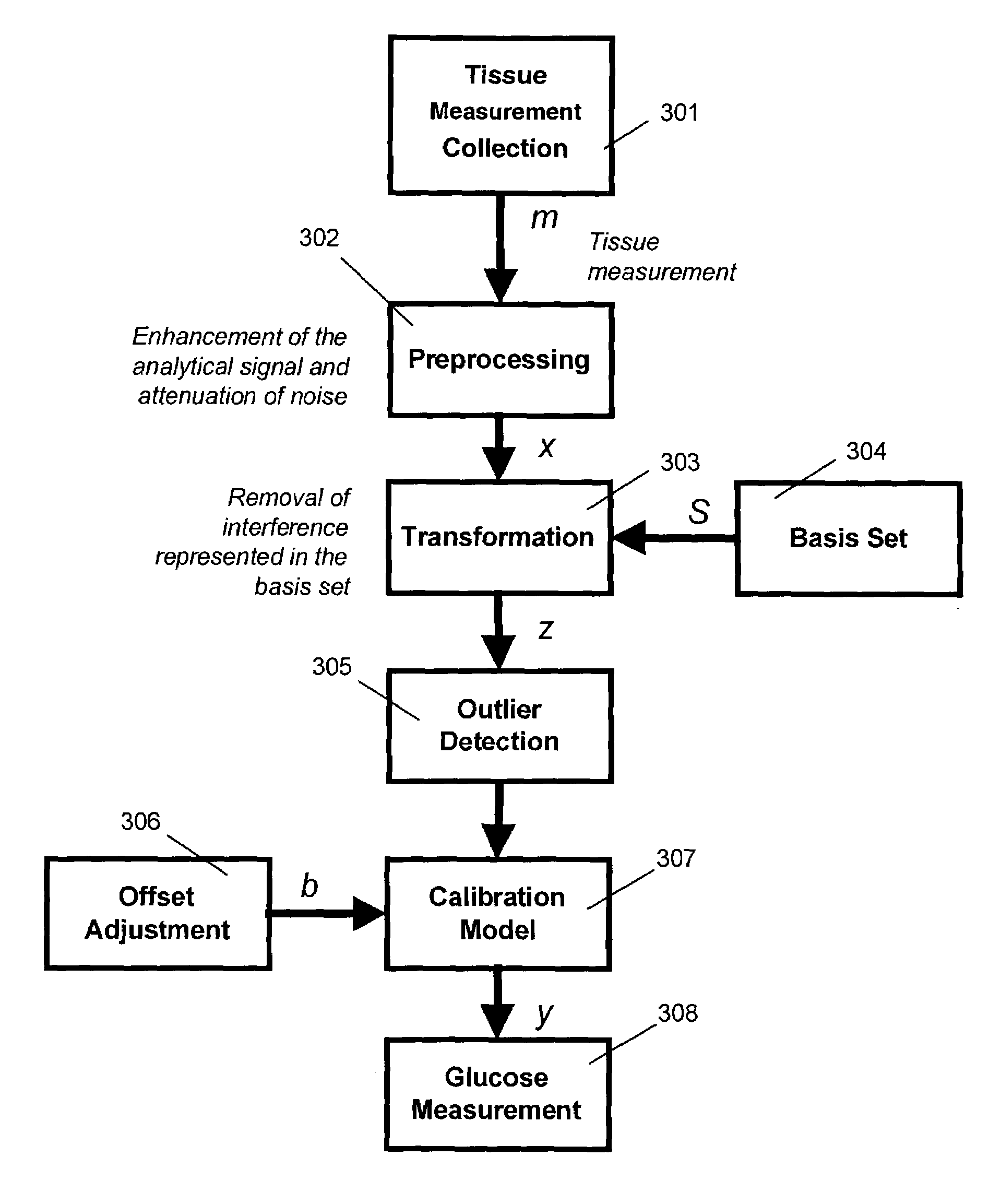
Measurement site dependent data preprocessing method for robust calibration and prediction
InactiveUS7010336B2Low variabilityPromote lowerSpectrum investigationDiagnostics using spectroscopyData setAnalyte
A solution for reducing interference in noninvasive spectroscopic measurements of tissue and blood analytes is provided. By applying a basis set representing various tissue components to a collected sample measurement, measurement interferences resulting from the heterogeneity of tissue, sampling site differences, patient-to-patient variation, physiological variation, and instrumental differences are reduced. Consequently, the transformed sample measurements are more suitable for developing calibrations that are robust with respect to sample-to-sample variation, variation through time, and instrument related differences. In the calibration phase, data associated with a particular tissue sample site is corrected using a selected subset of data within the same data set. This method reduces the complexity of the data and reduces the intra-subject, inter-subject, and inter-instrument variations by removing interference specific to the respective data subset. In the measurement phase, the basis set correction is applied using a minimal number of initial samples collected from the sample site(s) where future samples will be collected.
Owner:GLT ACQUISITION
Optical sensor including disposable and reusable elements
ActiveUS20110004079A1Reduce chanceComplicate to separateLine/current collector detailsWave amplification devicesBiomedical engineeringMeasurement site
An embodiment of the present disclosure provides a noninvasive optical sensor or probe including disposable and reusable components. The assembly of the disposable and reusable components is straightforward, along with the disassembly thereof. During application to a measurement site, the assembled sensor is advantageously secured together while the componentry is advantageously properly positioned.
Owner:CERCACOR LAB INC
Method and apparatus for minimizing thermal trauma to an organ during tissue ablation of a different organ
InactiveUS20120035603A1Accurate measurementImprove cooling effectDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMicrowave radiometryMicrowave
A method of minimizing thermal trauma during tissue ablation includes the steps of placing an ablation catheter at an ablation site on a first organ in a patient's body, providing energy to the ablation catheter to heat first organ tissue at the ablation site, providing microwave radiometry apparatus including a probe containing a microwave antenna and a radiometer responsive to the antenna output for producing a temperature signal corresponding to the thermal radiation picked up by the antenna and positioning the probe in a body passage of a second organ in the patient's body having a wall portion adjacent to the ablation site so that the microwave antenna is located at a measurement site opposite the ablation site. Using the radiometry apparatus, the temperature at depth in the second organ tissue at the measurement site is measured to provide a corresponding temperature signal, and the ablation catheter is controlled in response to the temperature signal to maintain the temperature of the second organ tissue below a predetermined value that does not result in thermal trauma to the second organ tissue. Apparatus for carrying out the method is also disclosed.
Owner:ADVANCED CARDIAC THERAPEUTICS
Optical sensor including disposable and reusable elements
ActiveUS20070123763A1Reduce chanceComplicate to separateDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBiomedical engineeringMeasurement site
An embodiment of the present disclosure provides a noninvasive optical sensor or probe including disposable and reusable components. The assembly of the disposable and reusable components is straightforward, along with the disassembly thereof. During application to a measurement site, the assembled sensor is advantageously secured together while the componentry is advantageously properly positioned.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Temperature measurement system
ActiveUS20140046192A1Body temperature measurementSensing radiation from moving bodiesCore temperatureNuclear medicine
A method of determining a temperature of a patient includes measuring a first temperature of the patient with a temperature device without contacting the patient with the device, and measuring a second temperature of the patient by contacting a measurement site of the patient with the device. The method also includes determining a temperature value indicative of a core temperature of the patient based on the first and second temperatures.
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
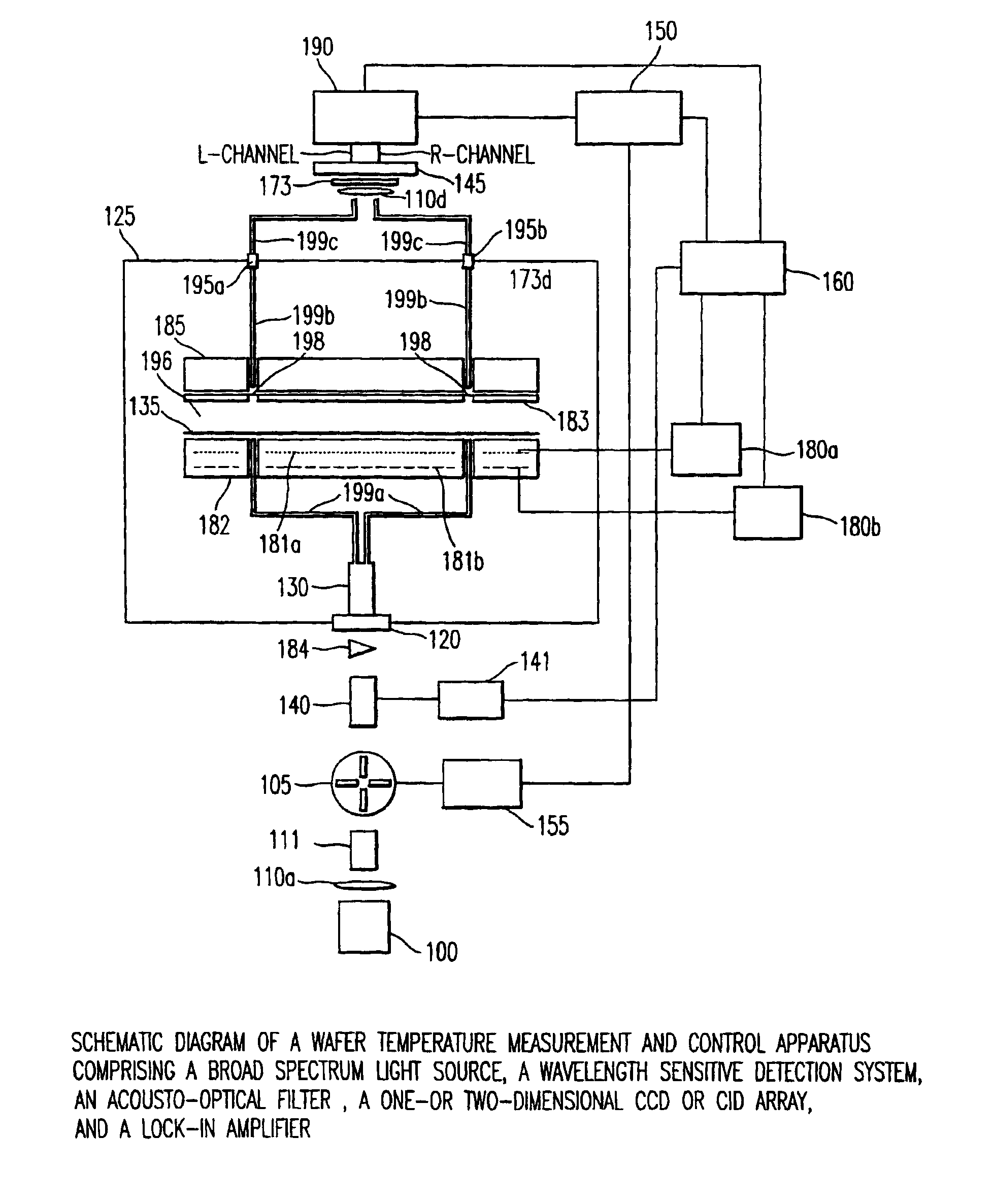
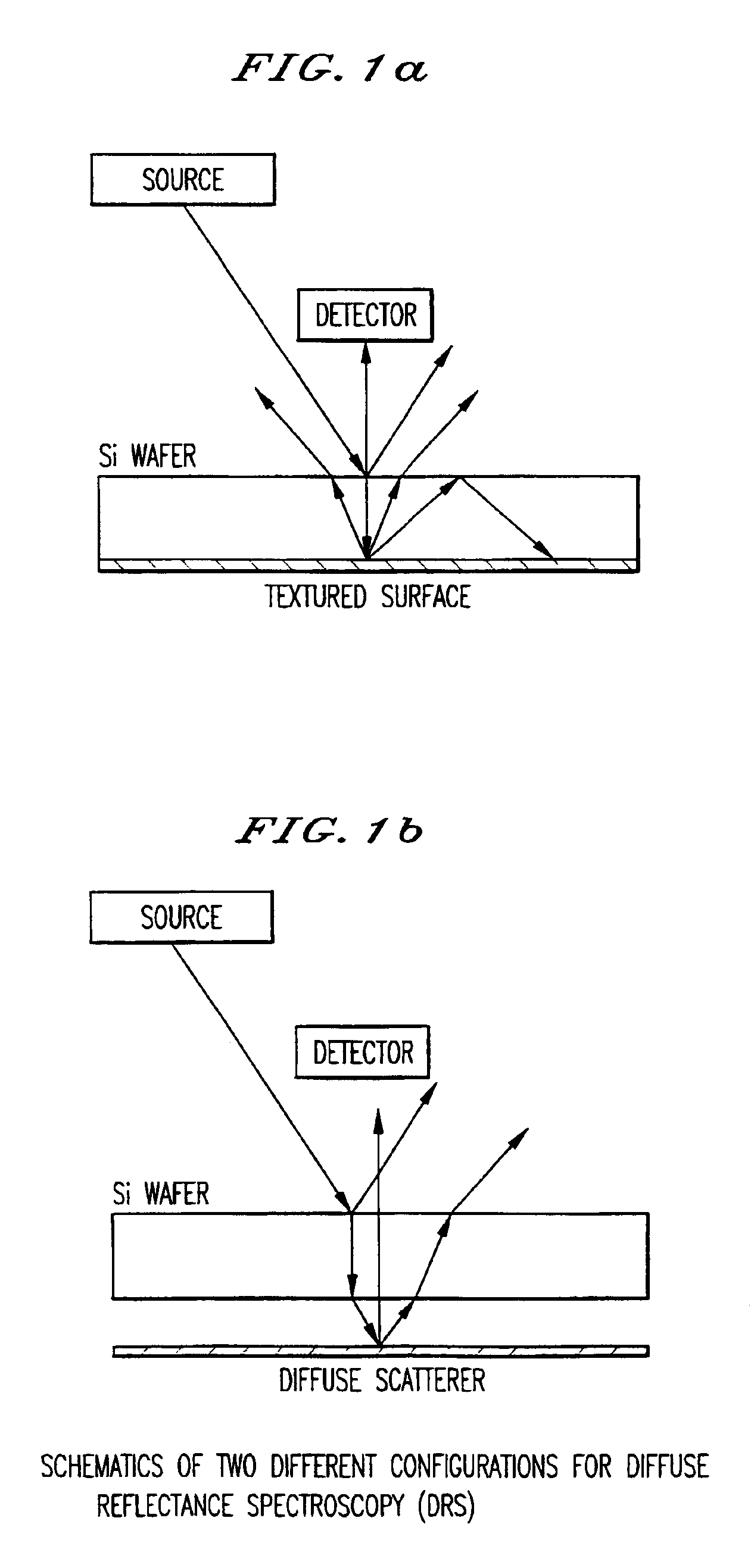
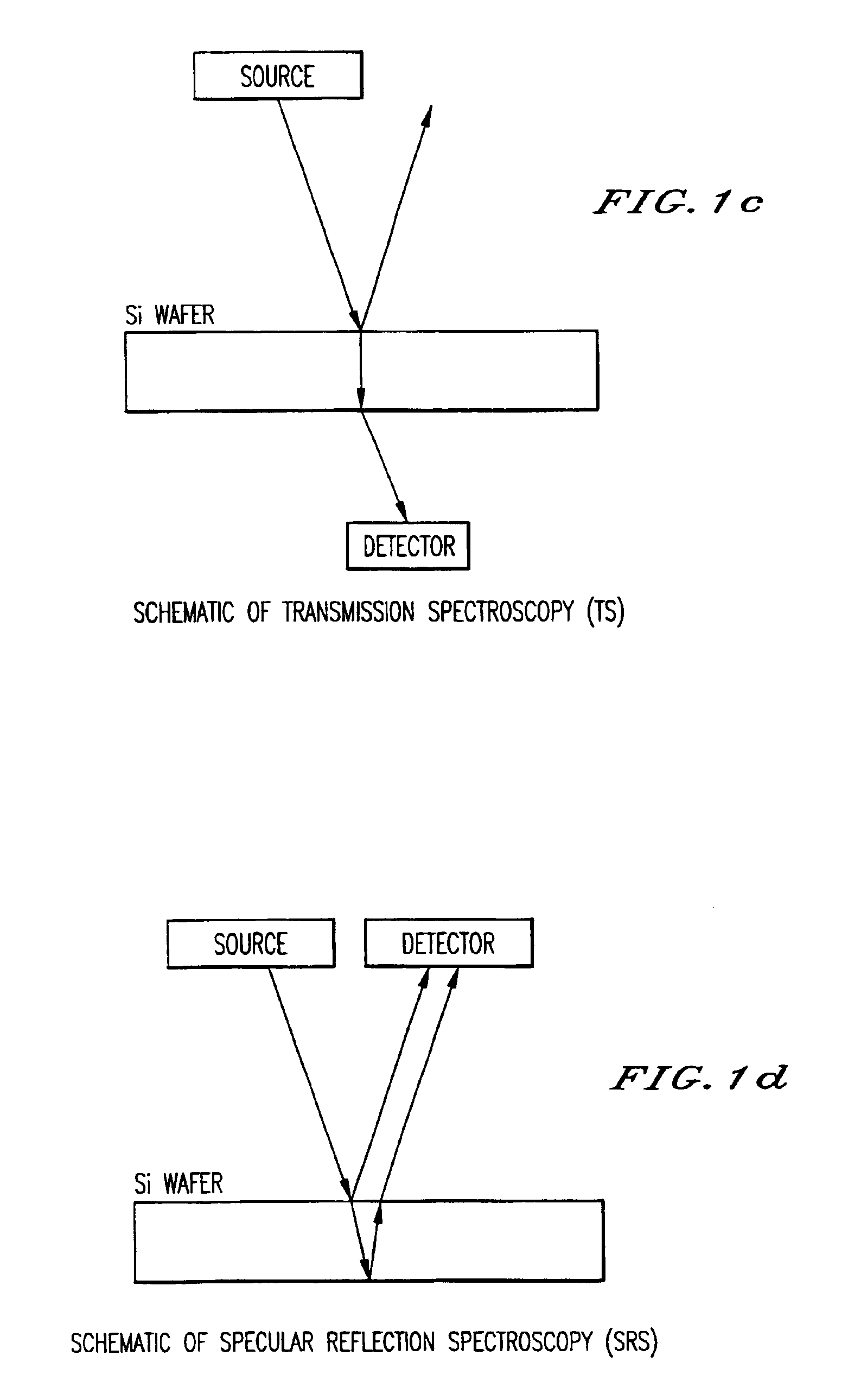
Method of wafer band-edge measurement using transmission spectroscopy and a process for controlling the temperature uniformity of a wafer
InactiveUS6891124B2Precise reproducible measureRadiation pyrometryLiquid surface applicatorsEngineeringFeedback control
A method and system for using transmission spectroscopy to measure a temperature of a substrate (135). By passing light through a substrate, the temperature of the substrate can be determined using the band-edge characteristics of the wafer. This in-situ method and system can be used as a feedback control in combination with a variable temperature substrate holder (182) to more accurately control the processing conditions of the substrate. By utilizing a multiplicity of measurement sites the variation of the temperature across the substrate (135) can also be measured.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
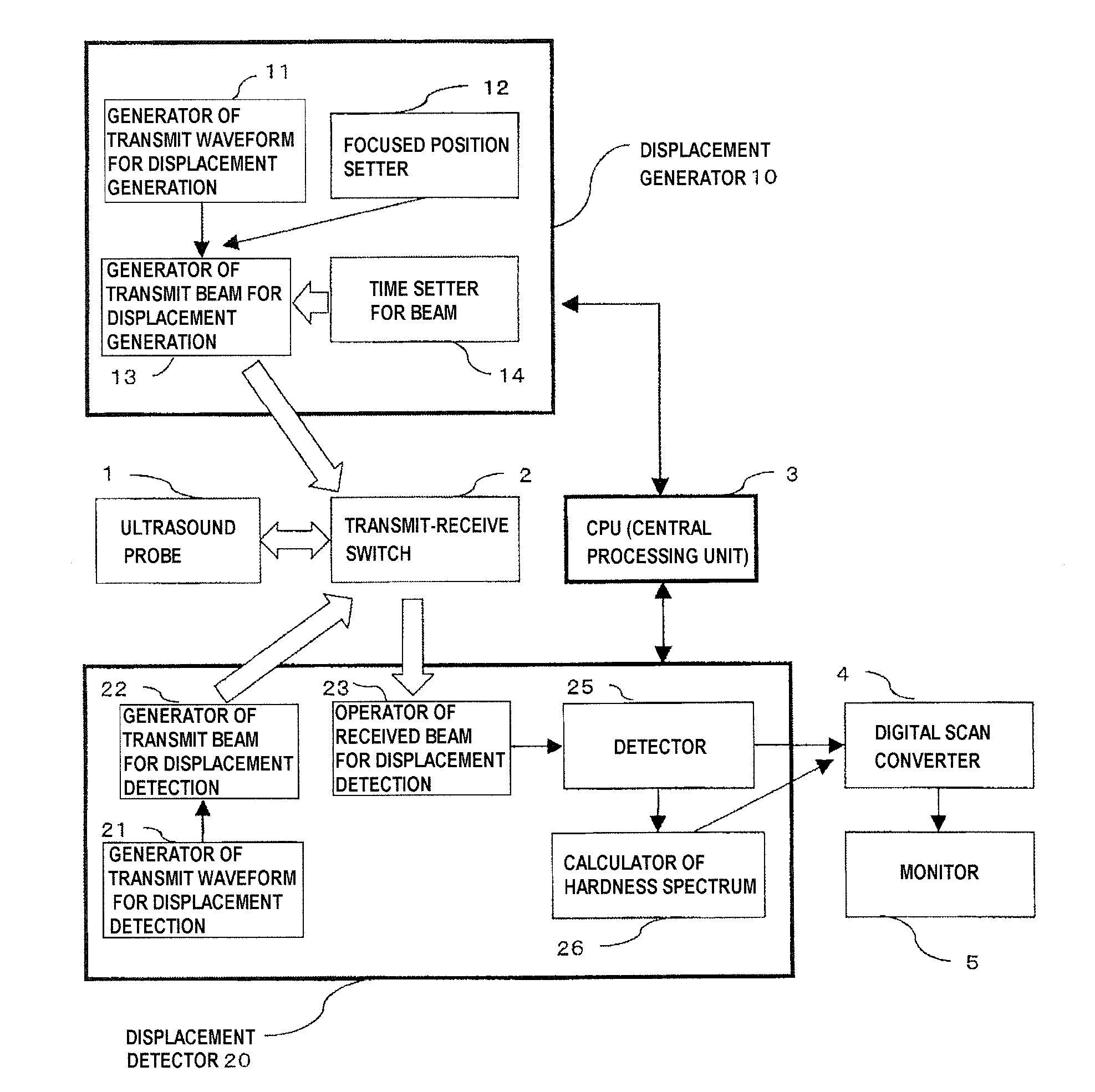
Ultrasonic diagnostic device
InactiveUS20120136250A1Increase displacementImprove securityOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsWide areaSonification
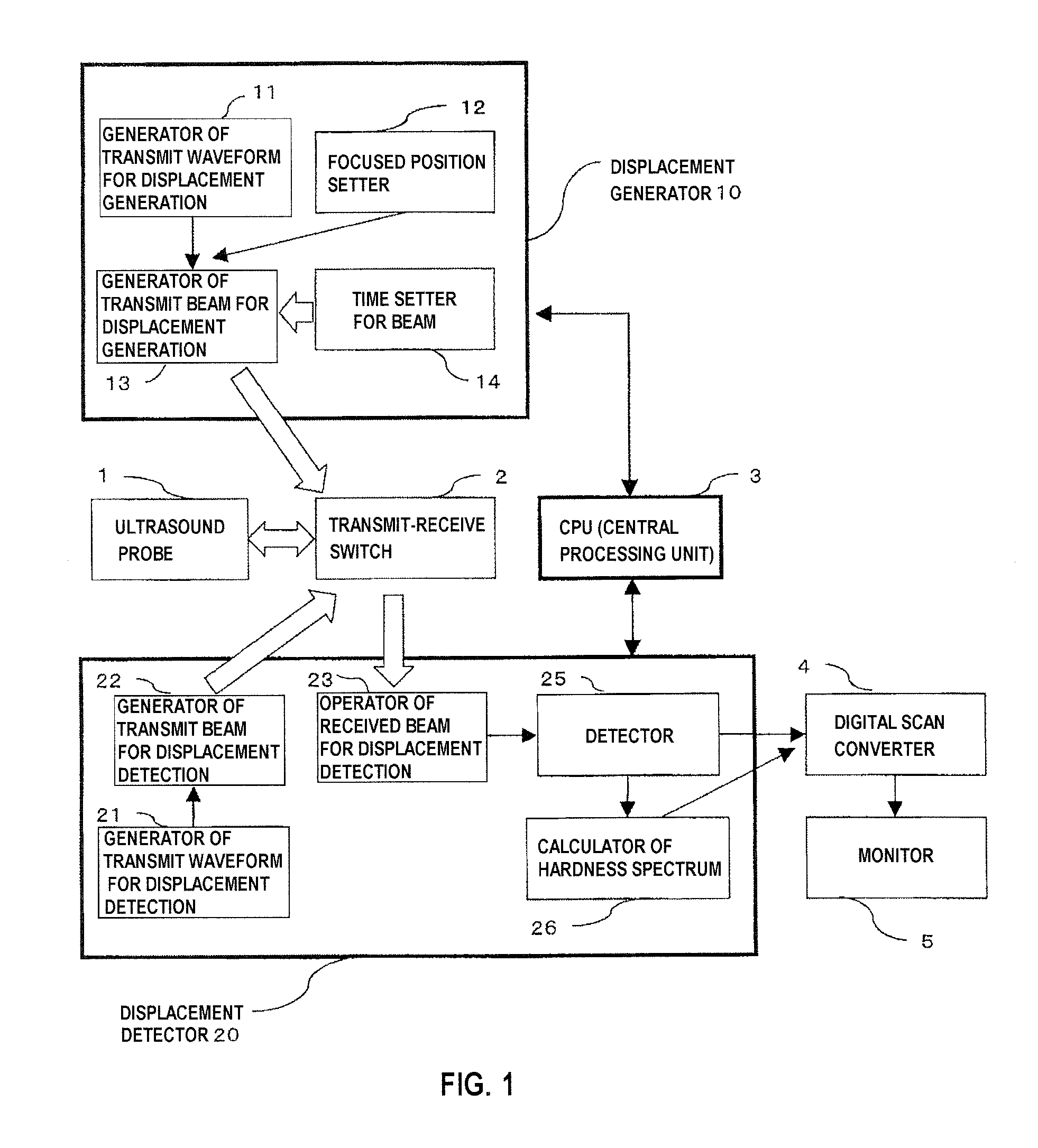
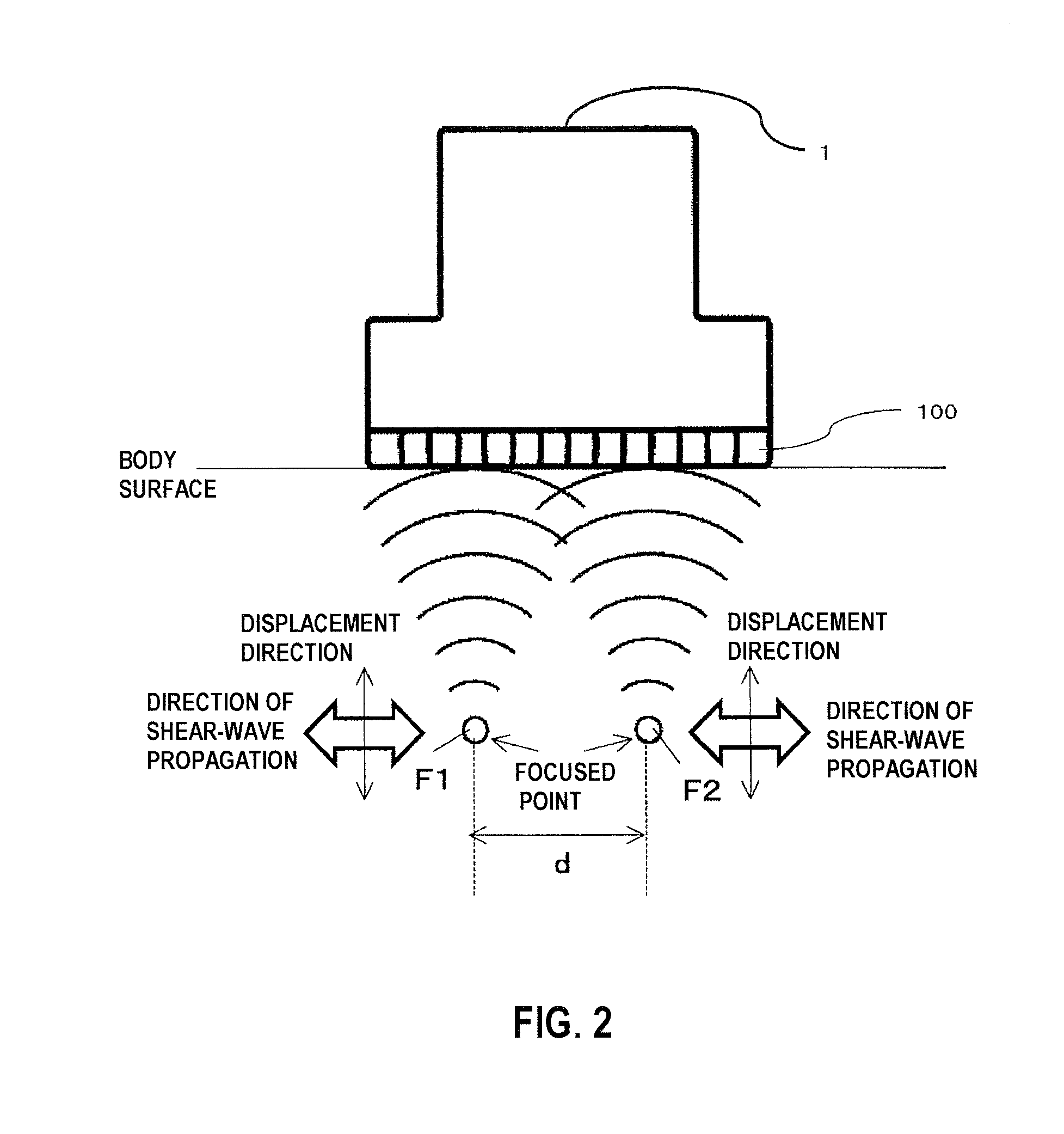
In a radiation-pressure elastography technique for transmitting a ultrasound focused beam into a test object body and diagnosing the hardness thereof, it is required to consider high sensitivity and safety.In the present invention, the focused beam is transmitted to two positions as a means for displacing a tissue and exciting a shear wave. In addition, time control is performed in such a manner that a transmit beam serves as a burst-chirp signal, and ultrasound waves are transmitted and received while sweeping a transmit frequency. On this occasion, when the distance between the two focused points and the transmit frequency become integral multiple of the wavelength, two waves interfere with each other, thereby obtaining a large amplitude. Furthermore, when the transmit frequency becomes equal to a resonance frequency peculiar to the tissue, the amplitude also becomes larger. Accordingly, a small intensity of transmit waveform enhances sensitivity. In addition, transmission using the burst-chirp signal facilitates widening of a bandwidth of the transmit frequency, enabling usage of a frequency highly sensitive for a target measurement site. Optional number of focused points and arbitrary positions thereof allow a wide area to be covered.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Integrated physiological sensor apparatus and system
InactiveUS20100049007A1Improve accuracyIncrease blood perfusionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMedicinePerfusion
A physiological sensor apparatus, system and method for determining a physiological characteristic, comprising providing at least one physiological sensor that is adapted to measure at least one physiological characteristic at a target measurement site on a subject's body, heating an extended tissue region on the subject's body, whereby blood perfusion of the tissue region is enhanced, and measuring at least one physiological characteristic at the target measurement site with the physiological sensor during or within a predetermined period after heating the extended tissue region. In one embodiment, the sensor system includes at least one temperature algorithm that is adapted to adjust the heat applied to the extended tissue region based on the body's response to the heat stimuli.
Owner:WOOLSTHORPE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com