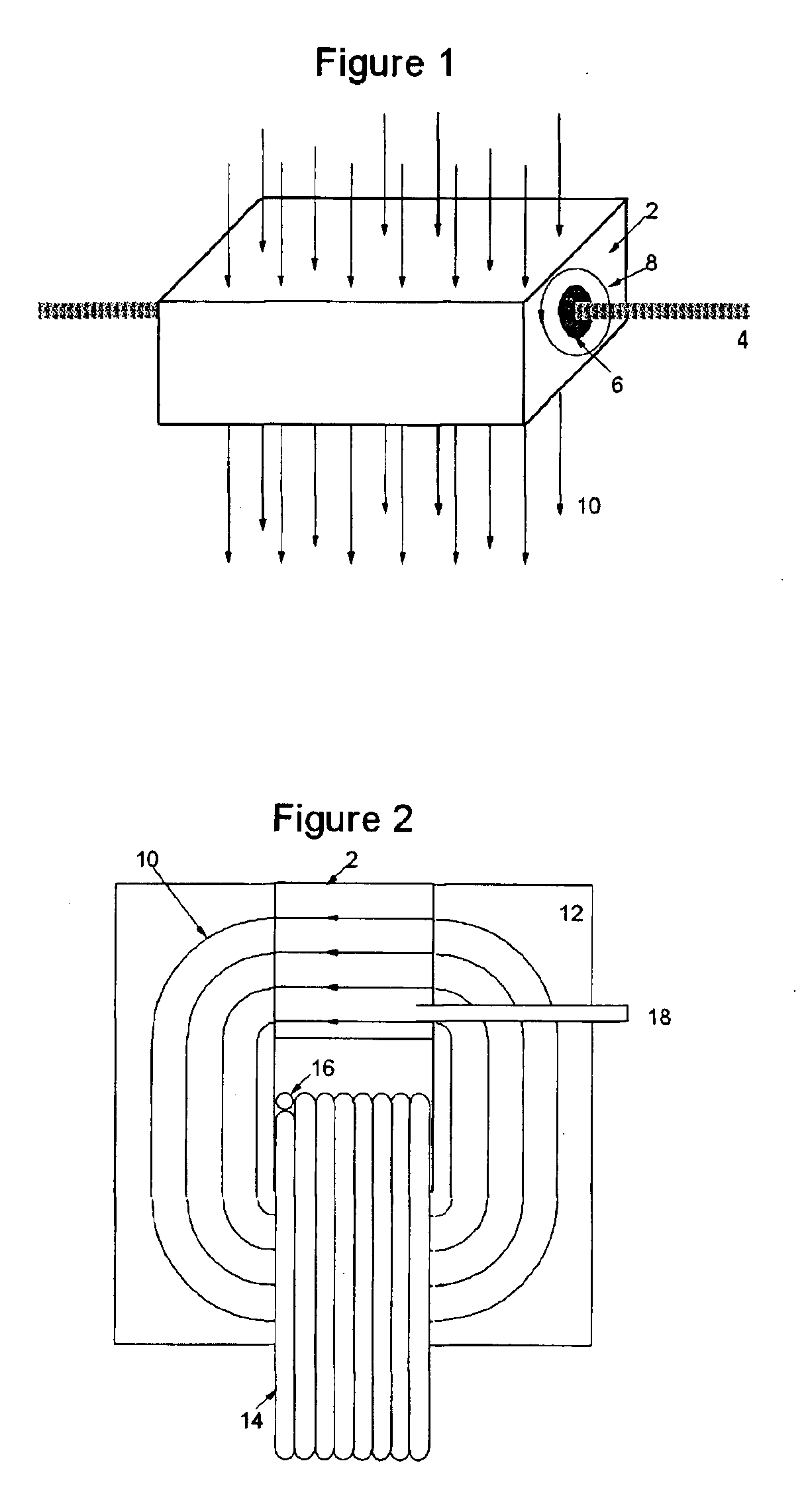
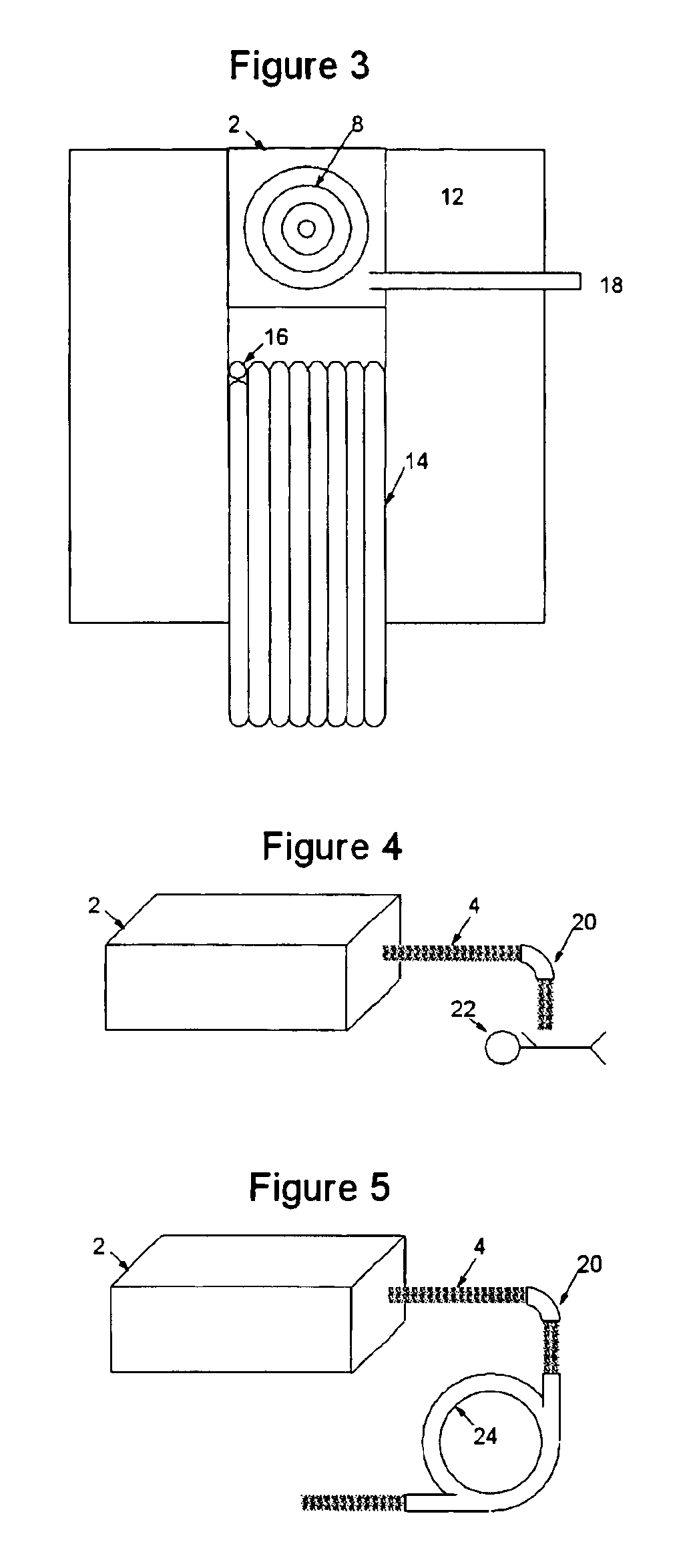
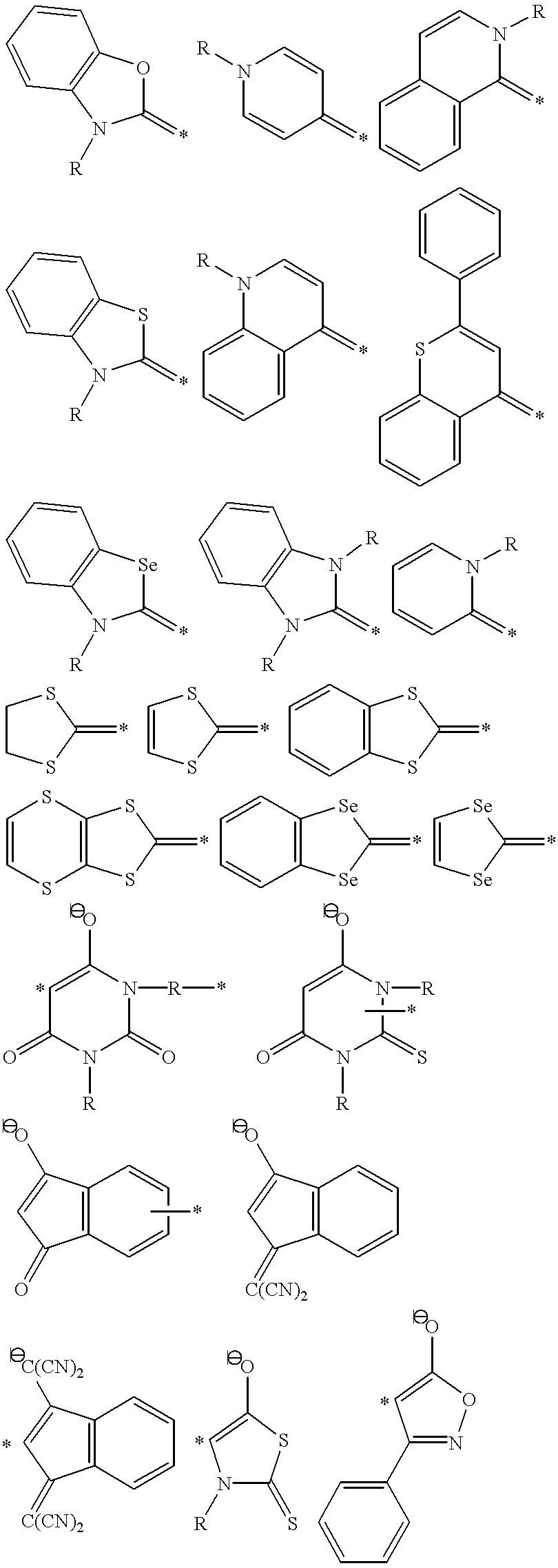
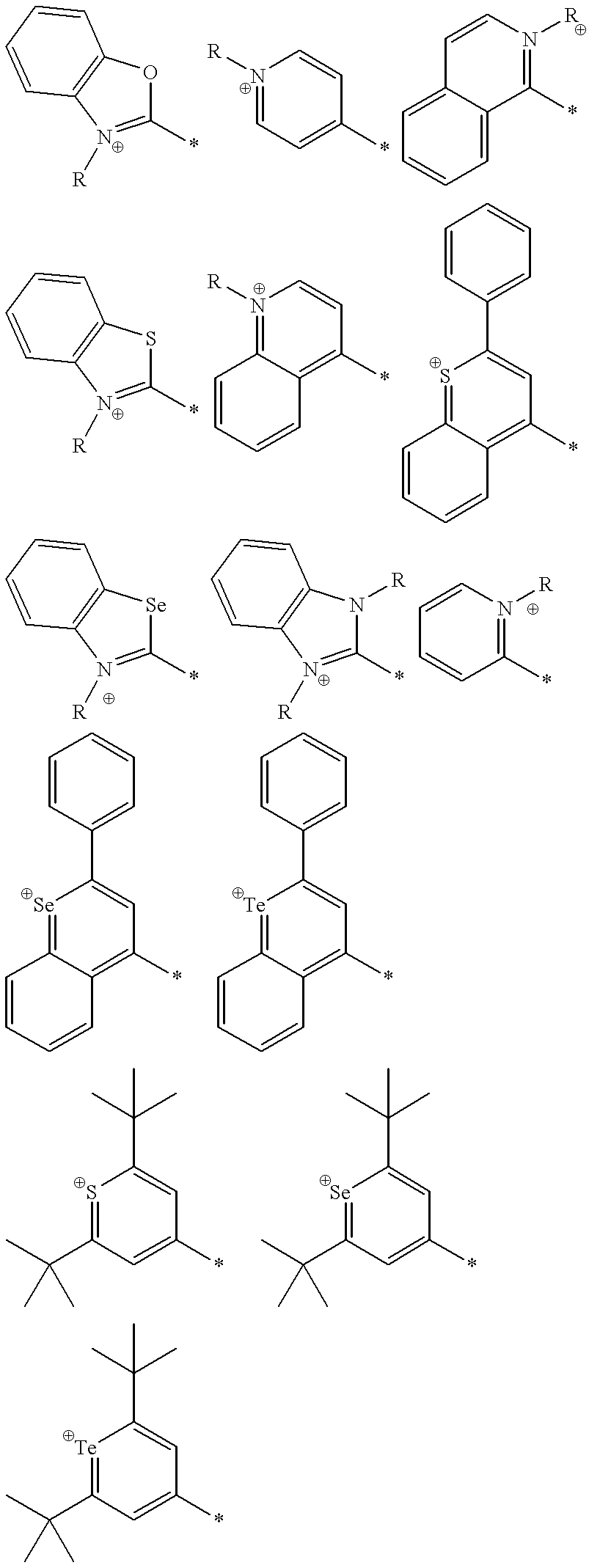
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
12034 results about "Particle physics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Particle physics (also known as high energy physics) is a branch of physics that studies the nature of the particles that constitute matter and radiation. Although the word particle can refer to various types of very small objects (e.g. protons, gas particles, or even household dust), particle physics usually investigates the irreducibly smallest detectable particles and the fundamental interactions necessary to explain their behaviour. By our current understanding, these elementary particles are excitations of the quantum fields that also govern their interactions. The currently dominant theory explaining these fundamental particles and fields, along with their dynamics, is called the Standard Model. Thus, modern particle physics generally investigates the Standard Model and its various possible extensions, e.g. to the newest "known" particle, the Higgs boson, or even to the oldest known force field, gravity.
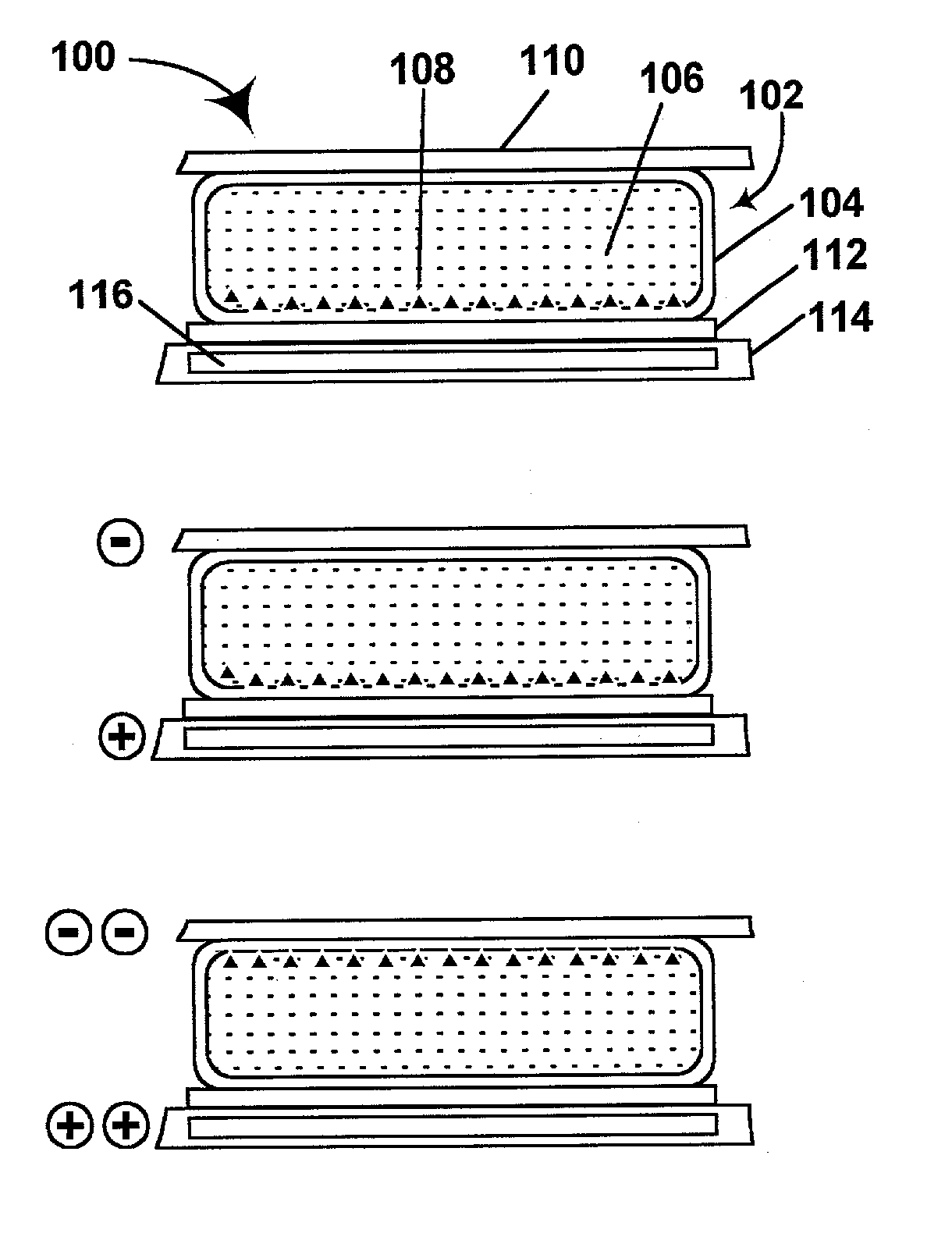
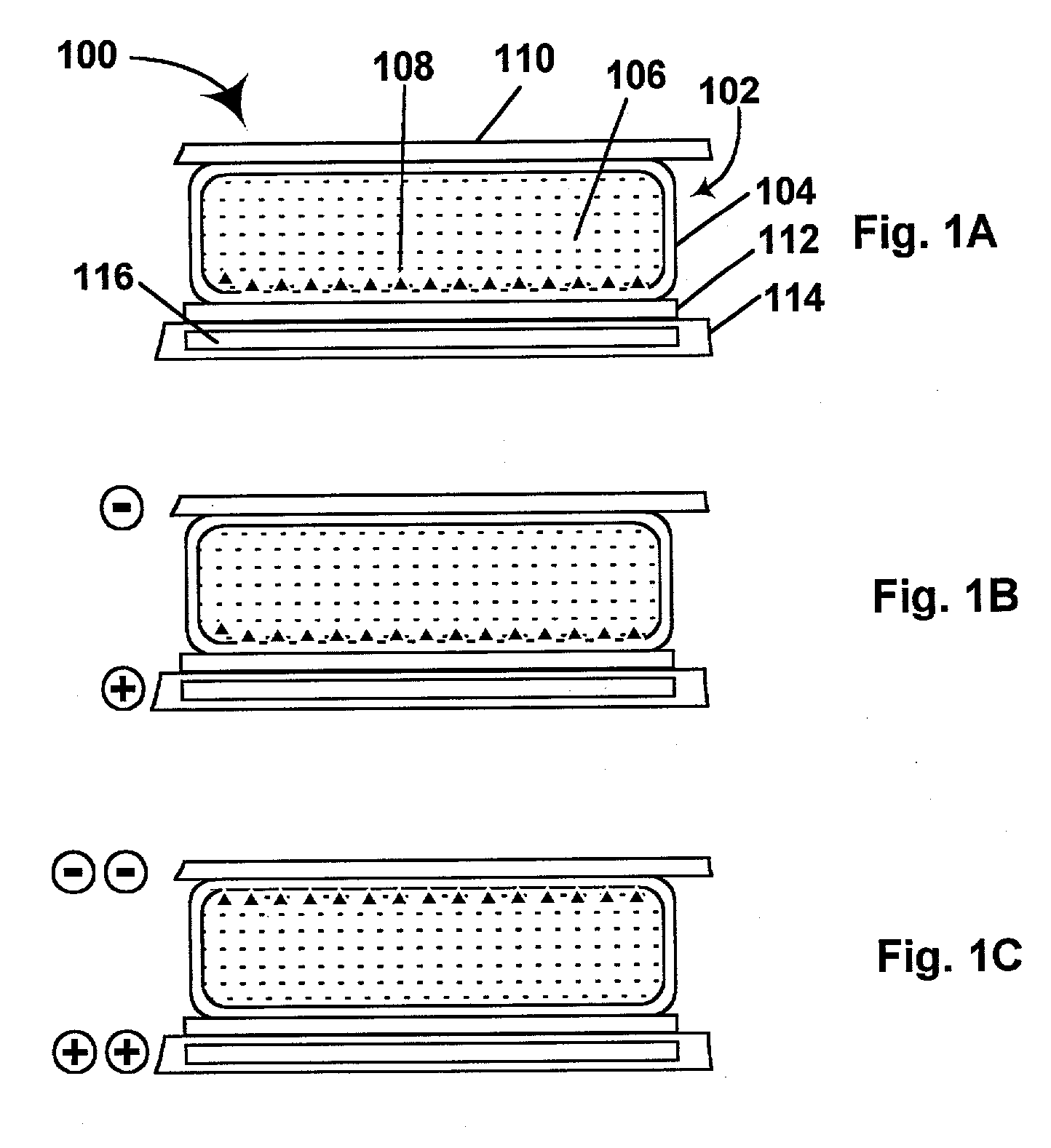
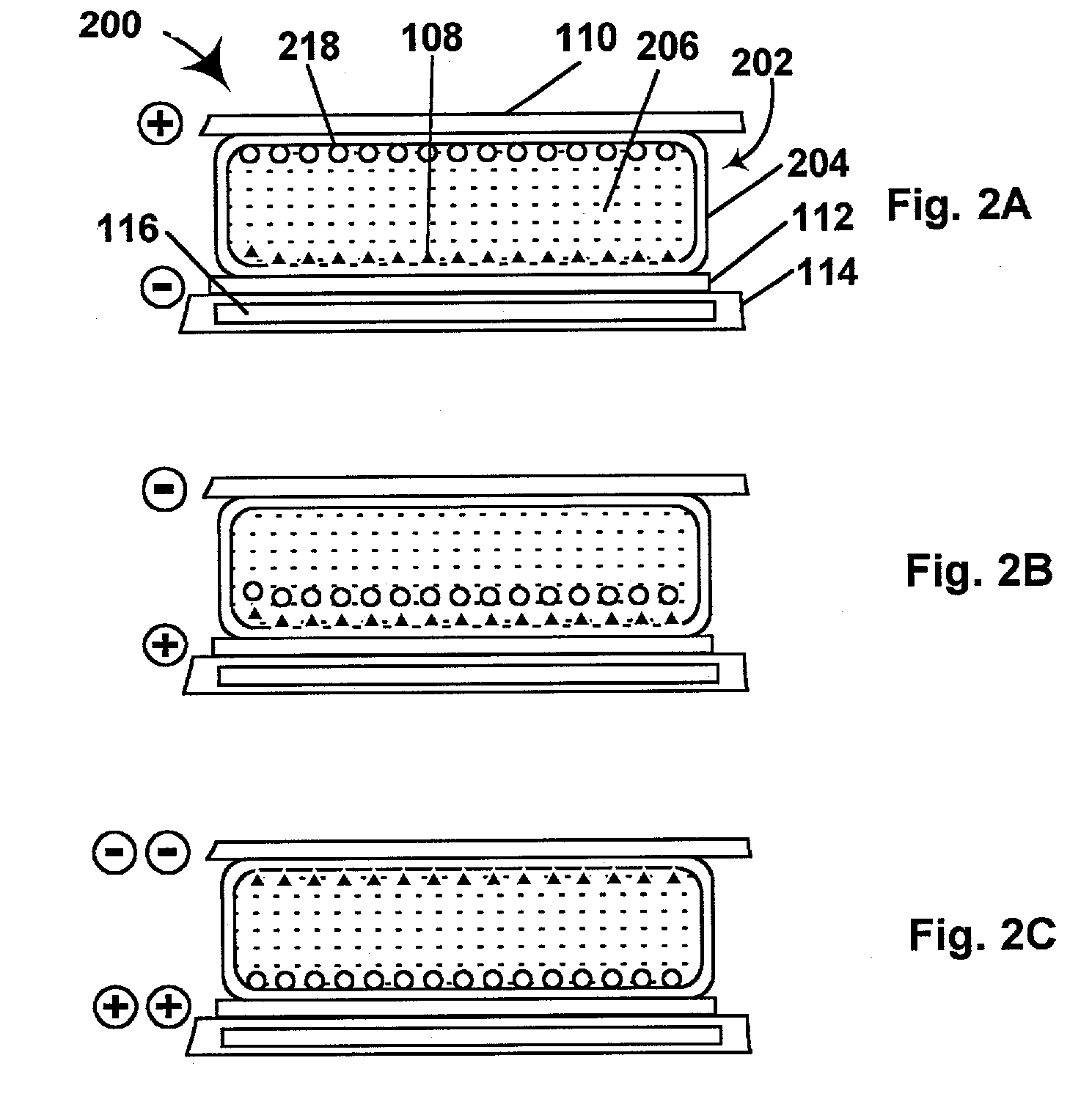
Electrophoretic displays containing magnetic particles
InactiveUS6870661B2Easy to fallImprove stabilitySludge treatmentStatic indicating devicesElectrophoresisDisplay device
An electrophoretic medium comprises a plurality of one or more types of particles suspended in a suspending fluid. The particles include at least one electrically charged, electrophoretically mobile particle capable of translating through the suspending fluid upon application of an electric field to the medium and at least one magnetic particle. A magnet is disposed adjacent the electrophoretic medium to introduce a threshold resistance to magnetic particle movement.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
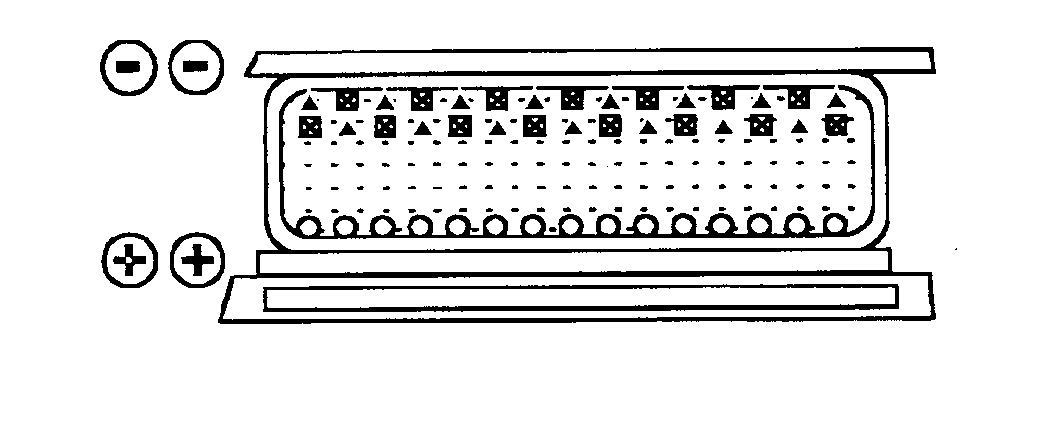
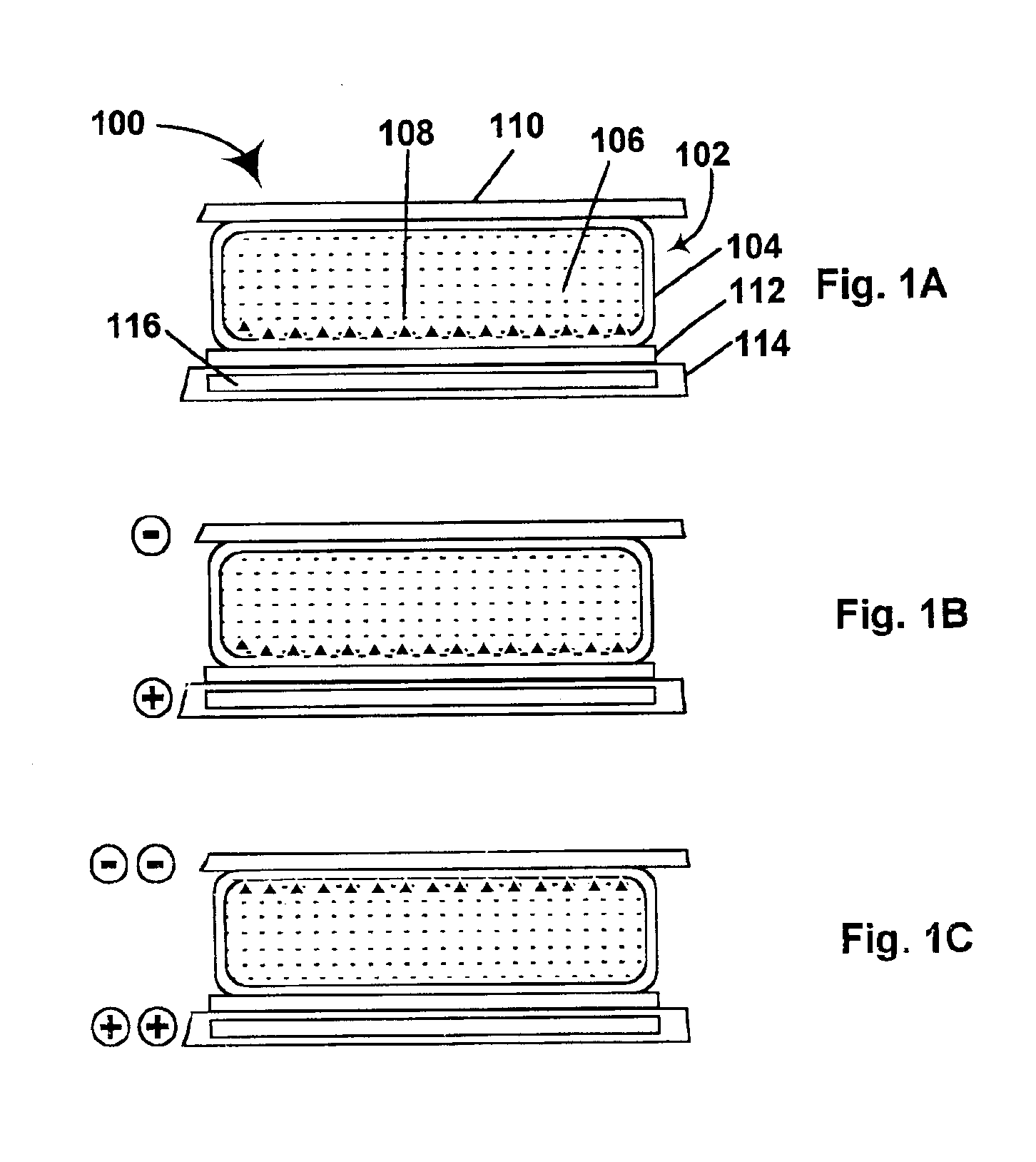
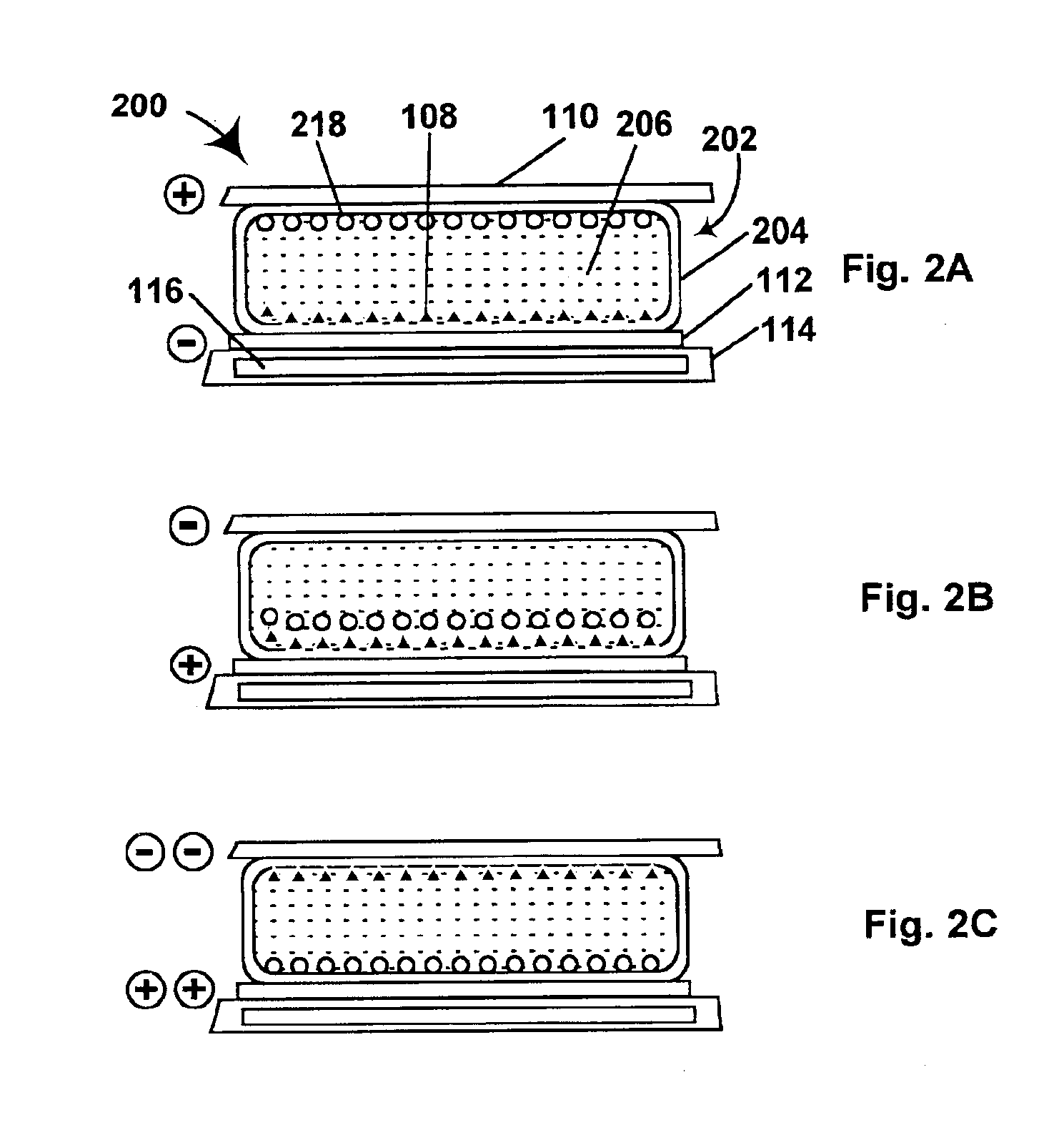
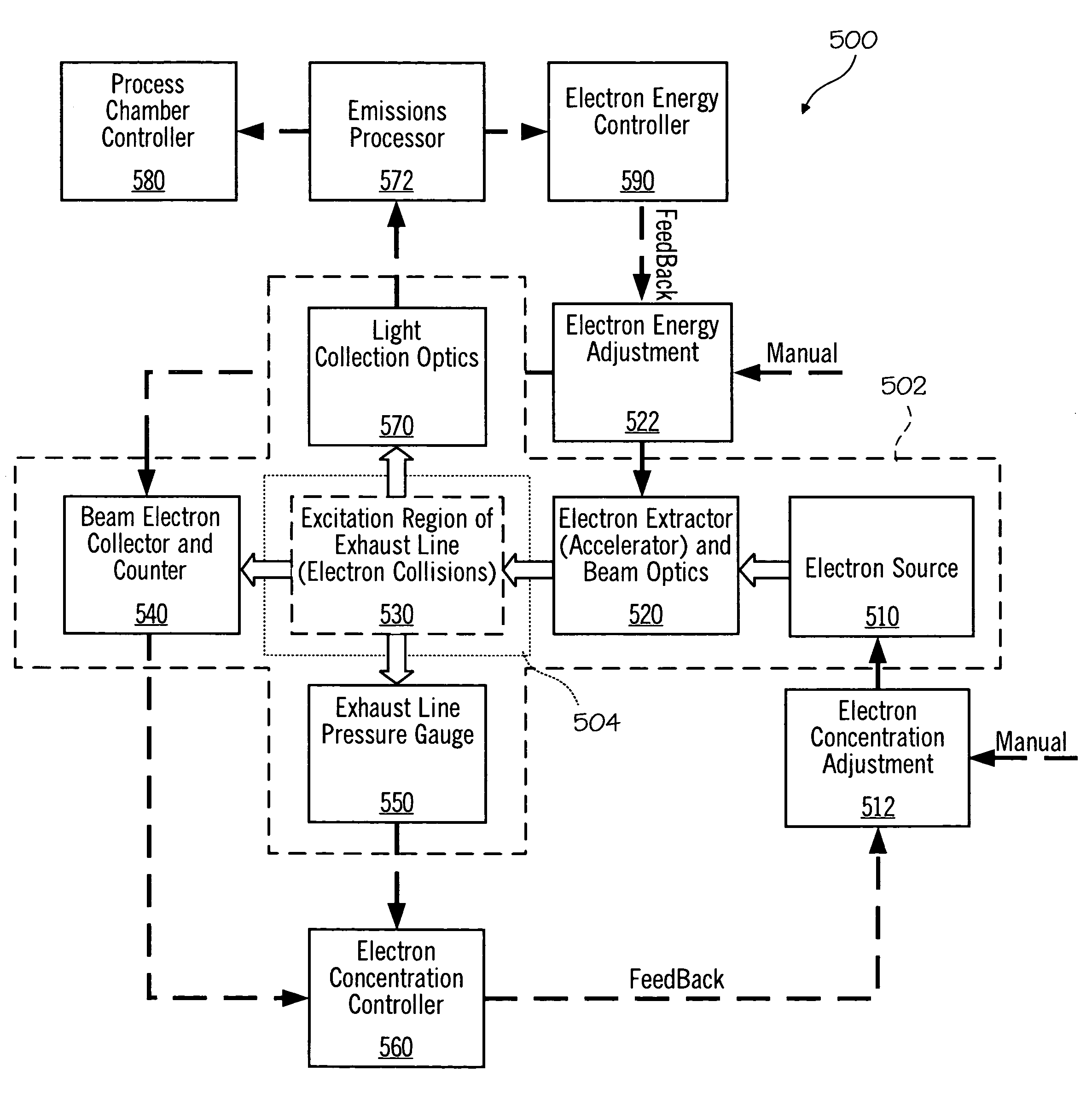
Electron beam exciter for use in chemical analysis in processing systems
ActiveUS20100032587A1Disparity will become so greatHigh electron energyCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesRadiation therapyElectron sourceFluorescence
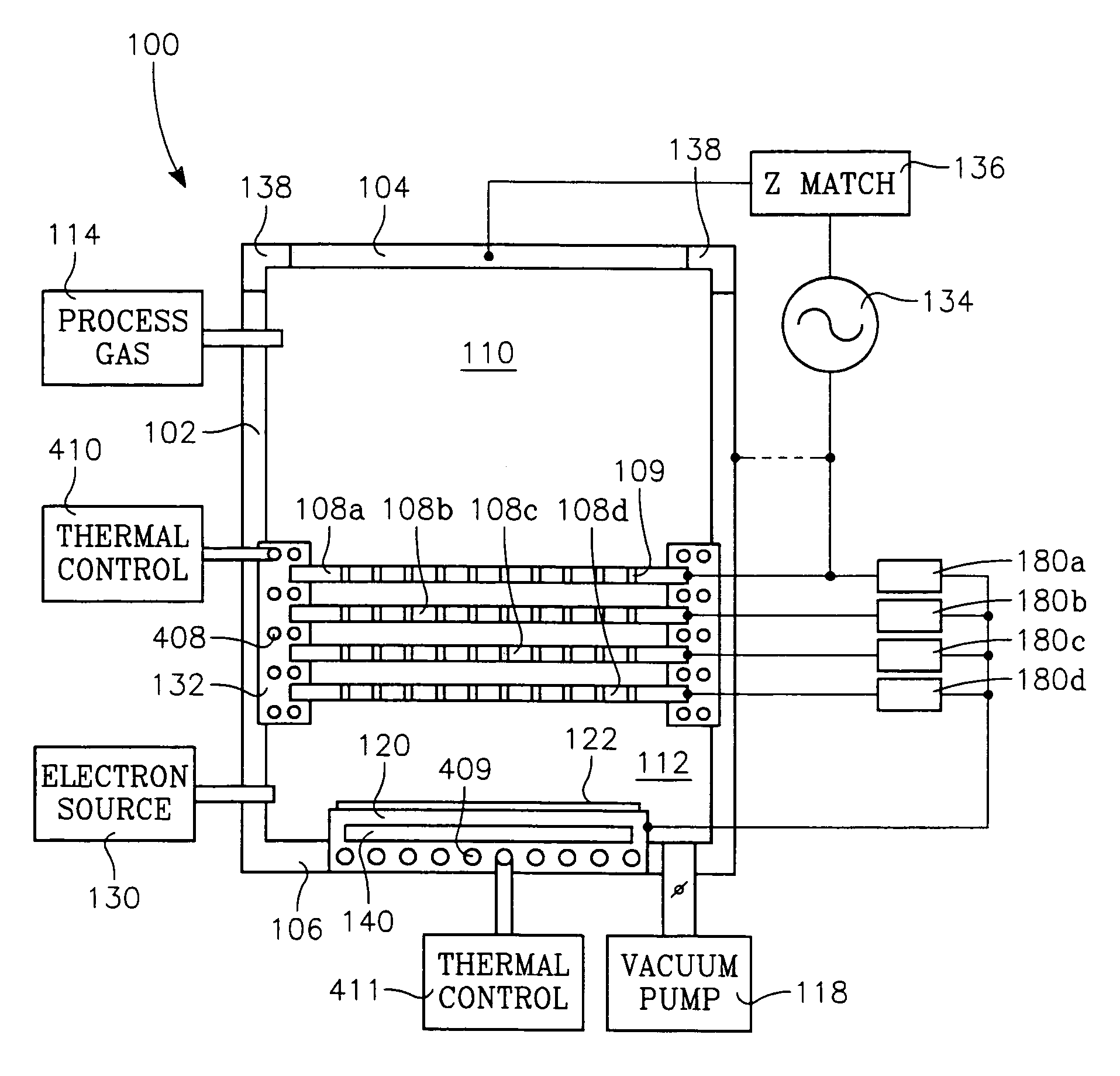
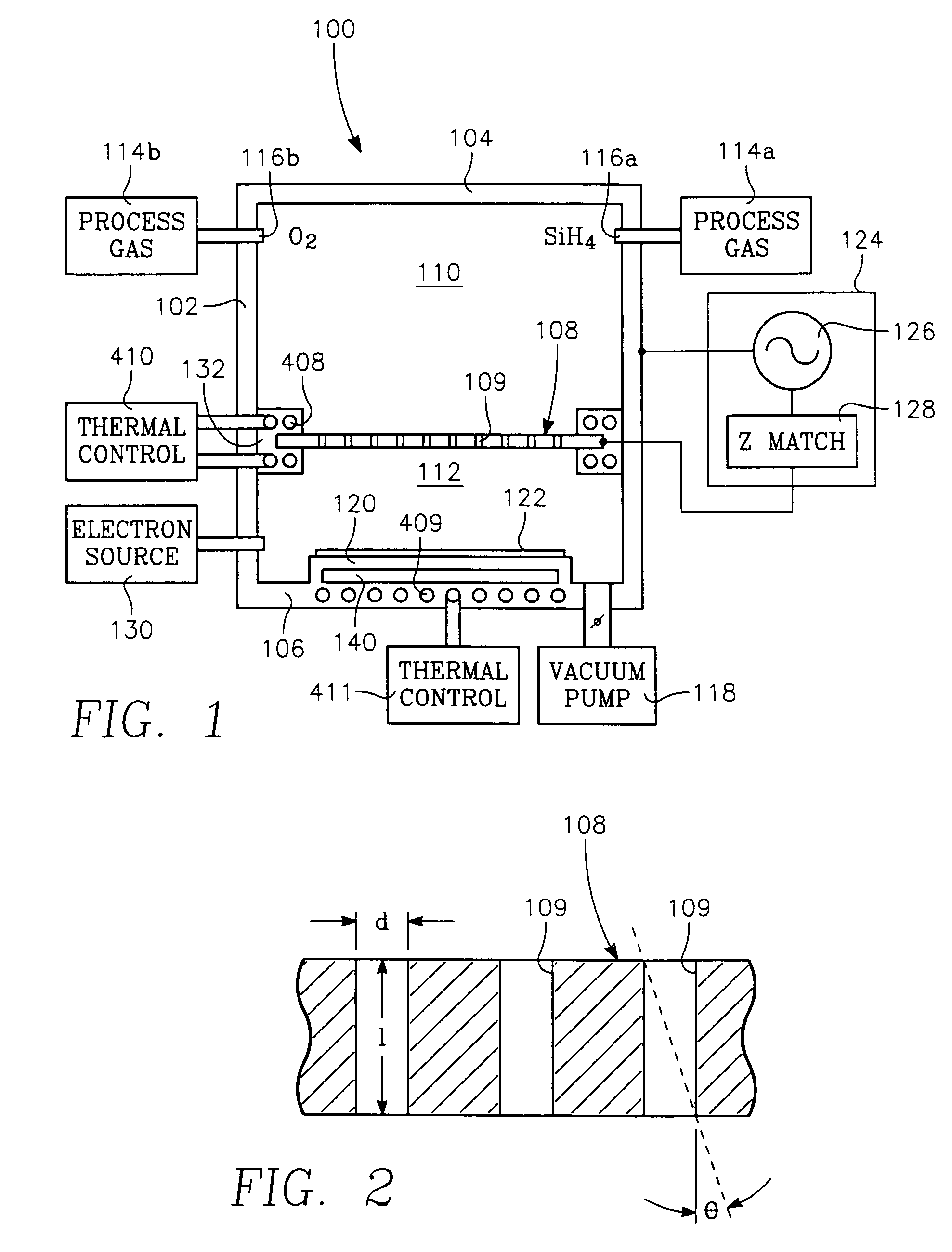
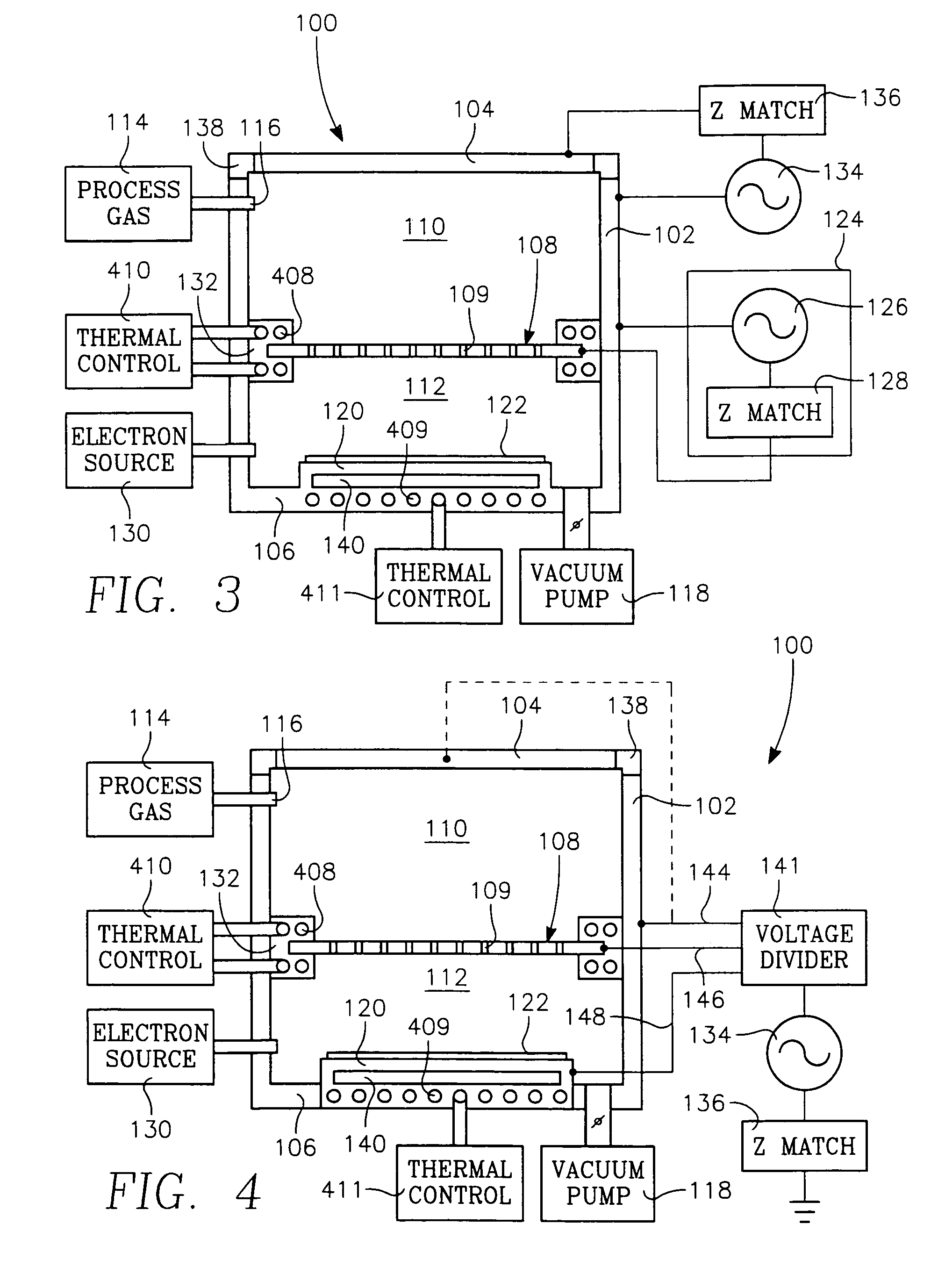
The present invention is directed to a gas line electron beam exciter, gas line electron beam excitation system and method for exciting a gas using an electron beam exciter. The electron beam exciter generally comprises a variable density electron source for generating a cloud of electrons in an electron chamber and a variable energy electron extractor for accelerating electrons from the electron chamber as an electron beam and into an effluent stream for fluorescing species in the effluent. The electron density of the electron beam is variably controlled by adjusting the excitation power applied to the variable density electron source. The electrons in the electron chamber reside at a reference electrical potential of the chamber, typically near ground electrical potential. The electron energy of the electron beam is variably controlled by adjusting an electrical potential across the variable energy electron extractor, which energizes the electrons through an extraction hole of the chamber and toward the extractor. The greater the difference in the electrical potential between the electron extractor and the electron source, the higher the energy imparted to the electrons in the electron beam. The excitation power applied to the electron source can be adjusted independently from the electron energy of the electron beam, thereby altering the electron density of the electron beam without changing the energy level of the electrons of the electron beam.
Owner:VERITY INSTR +1
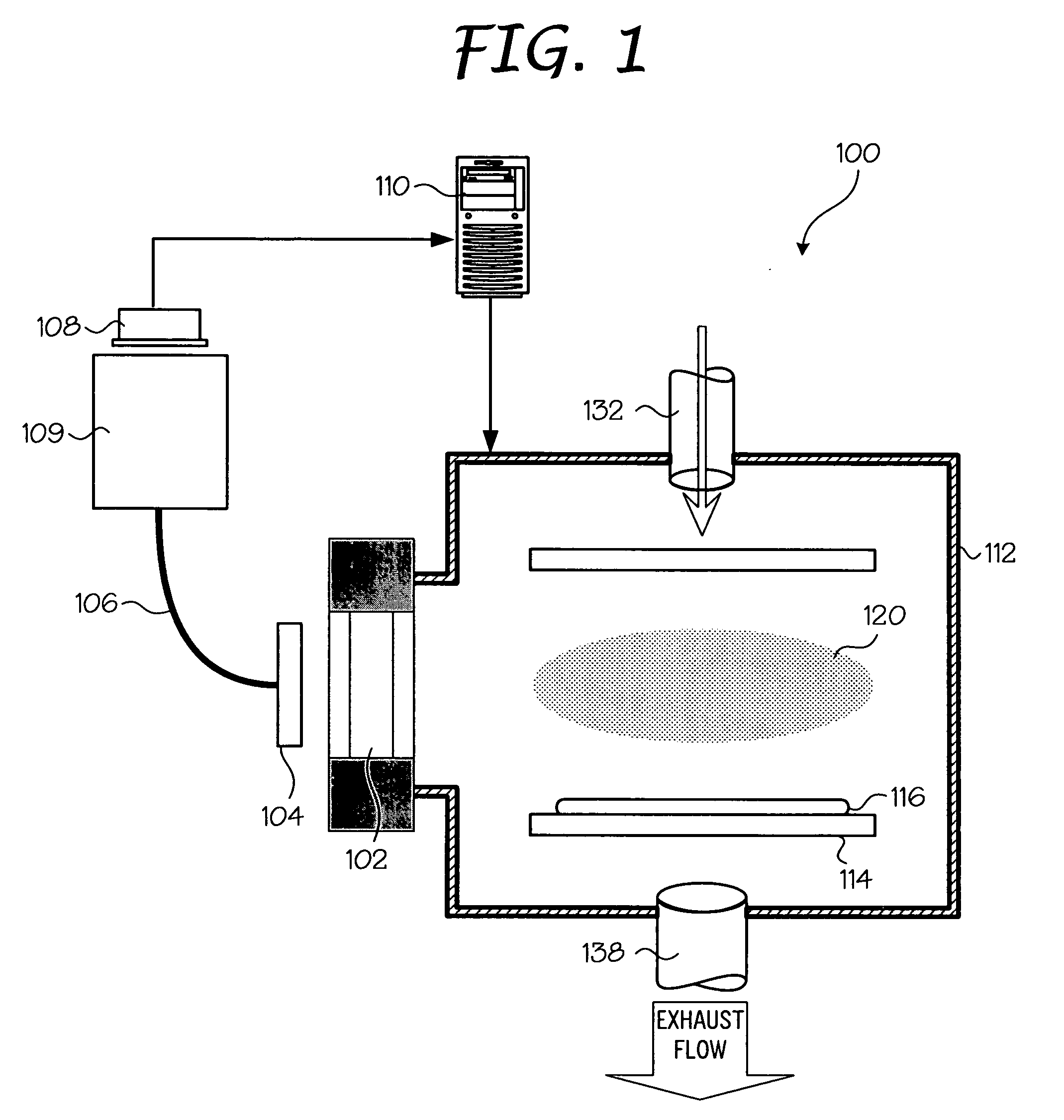
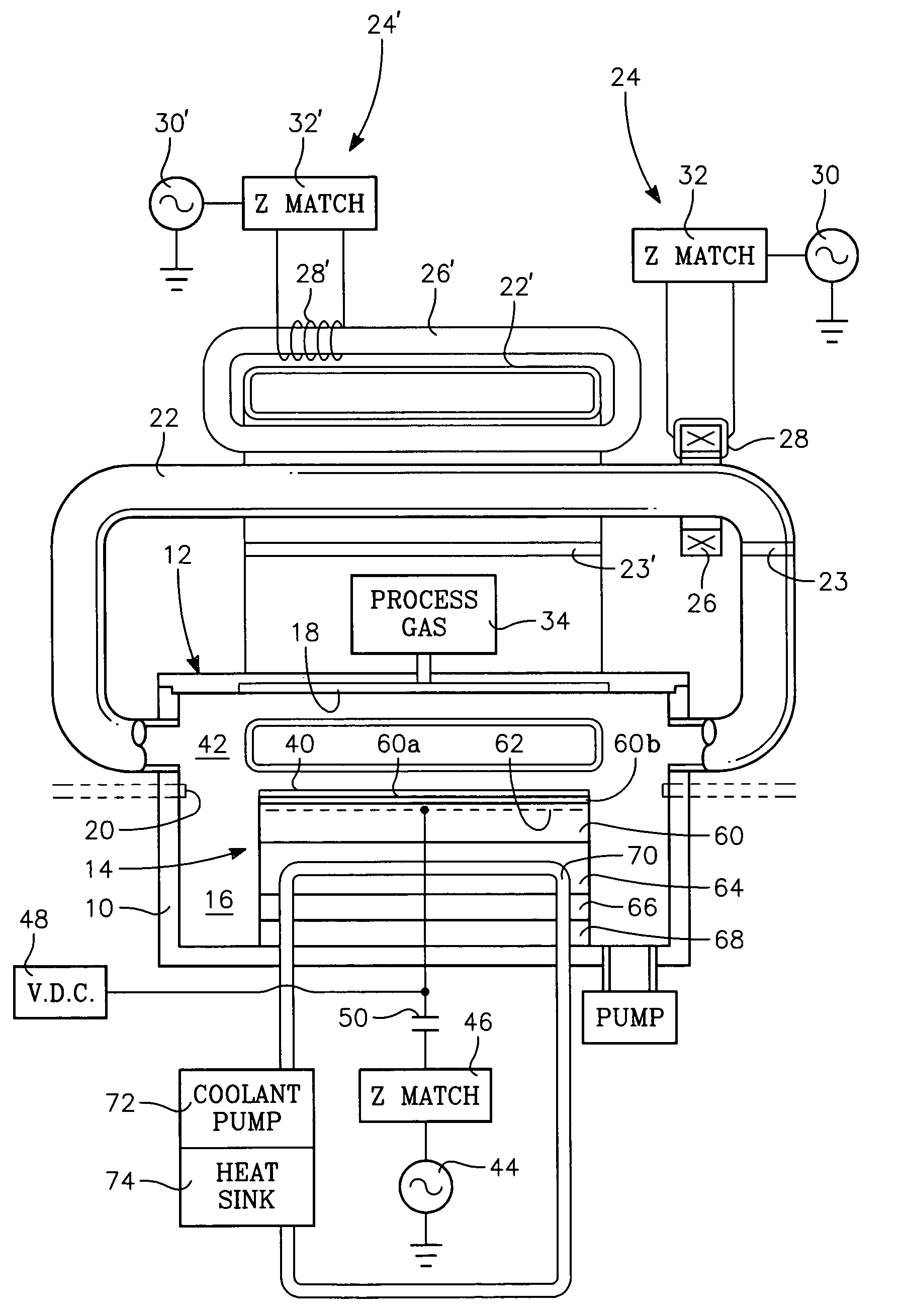
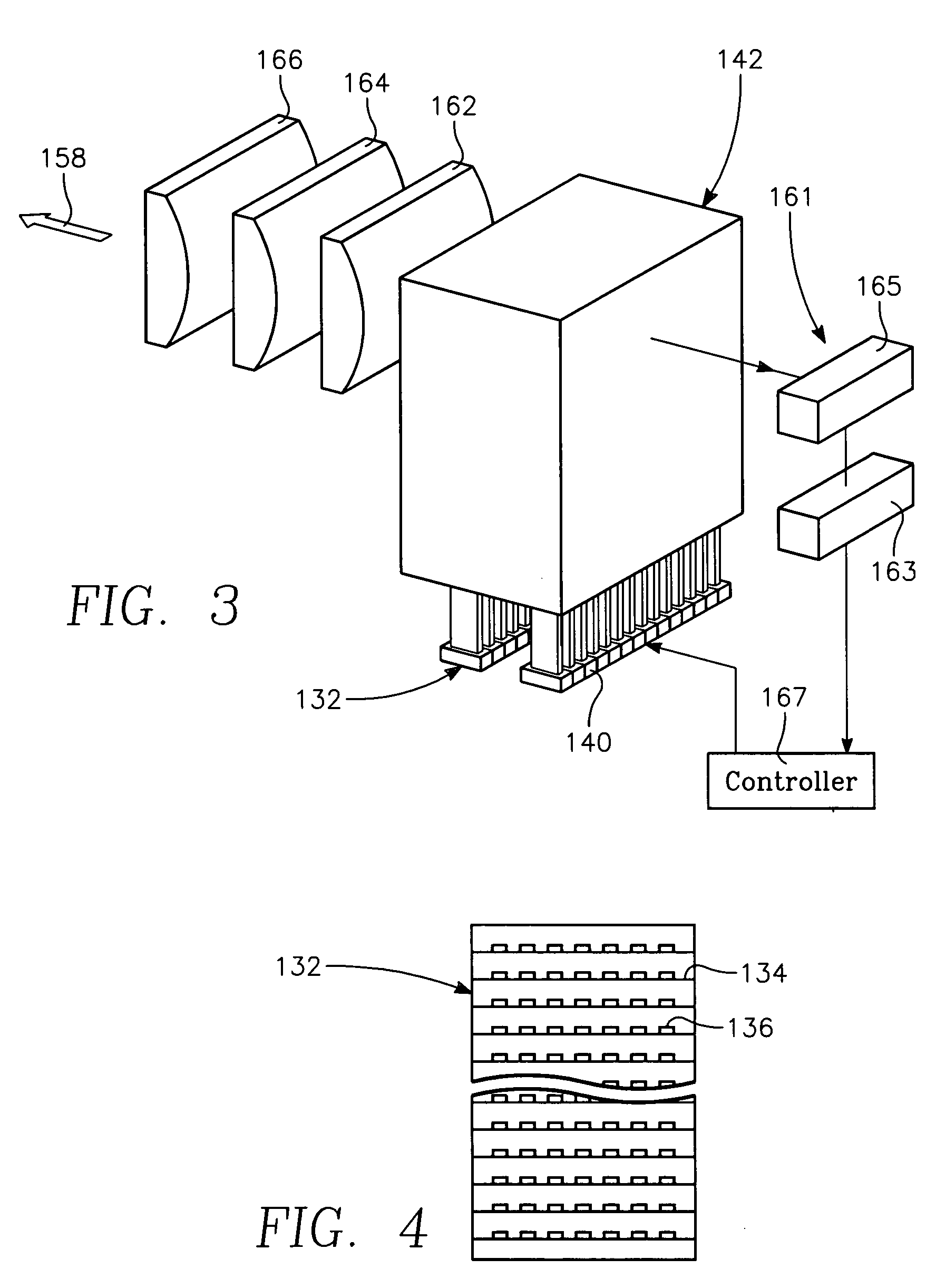
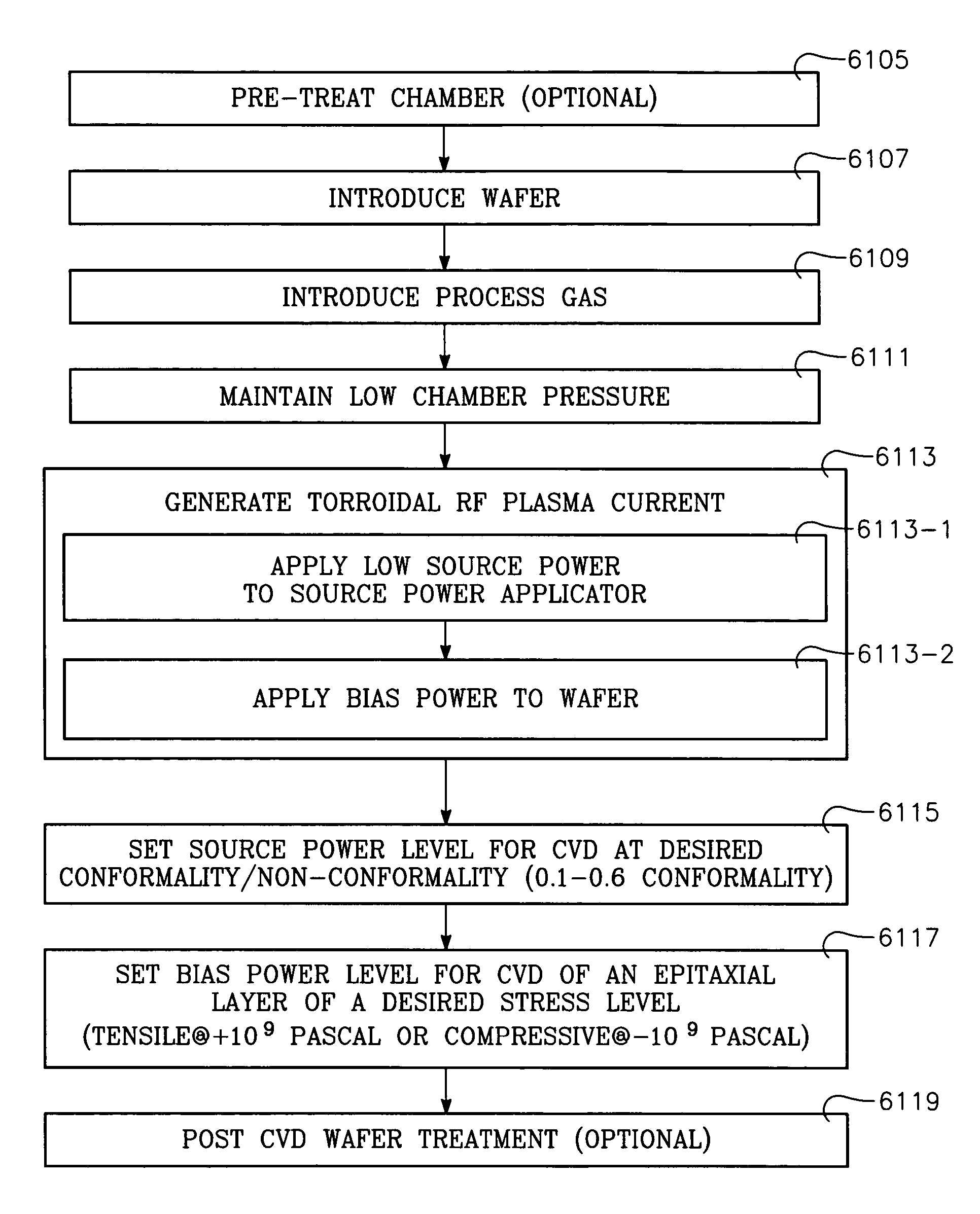
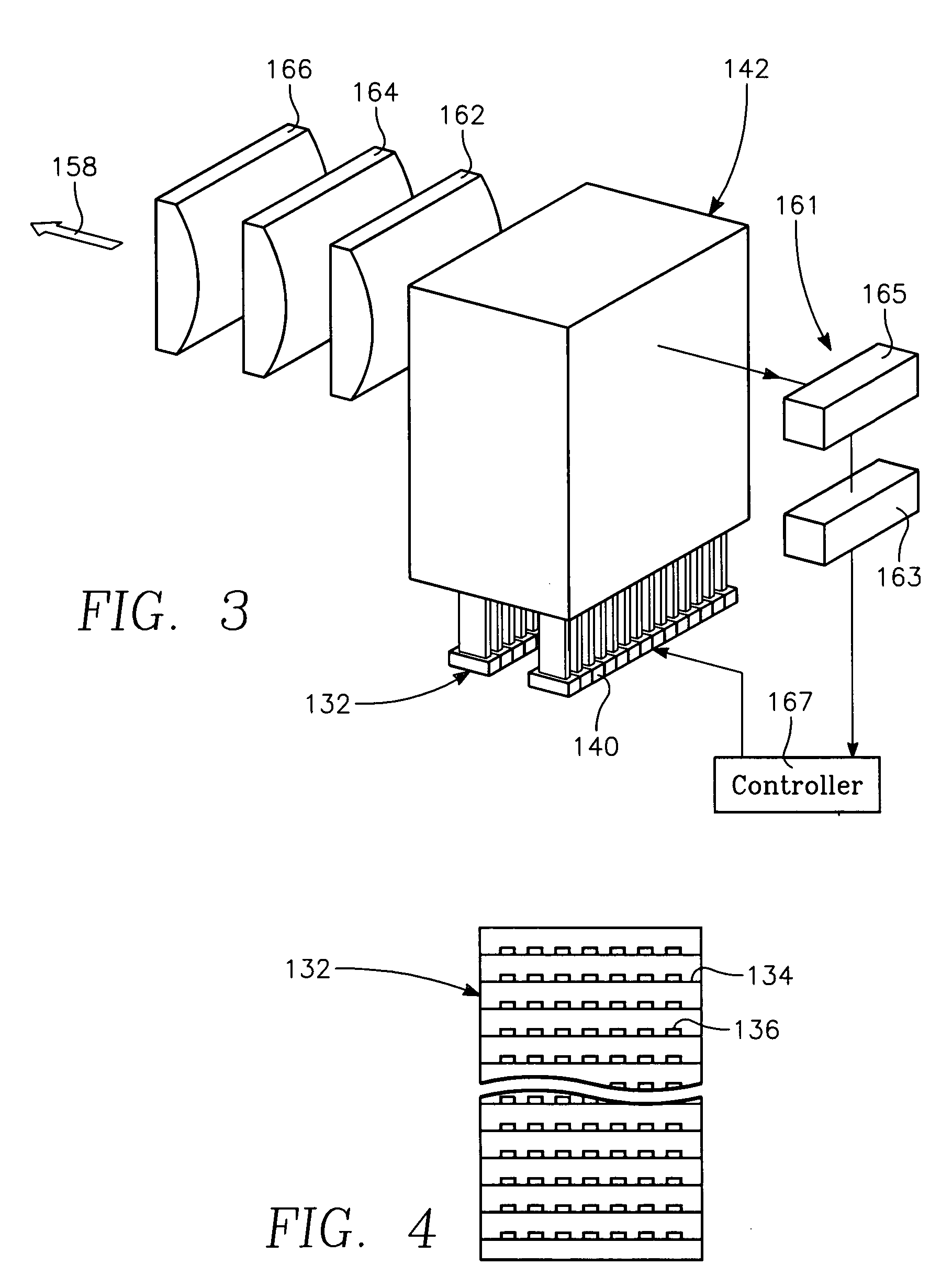
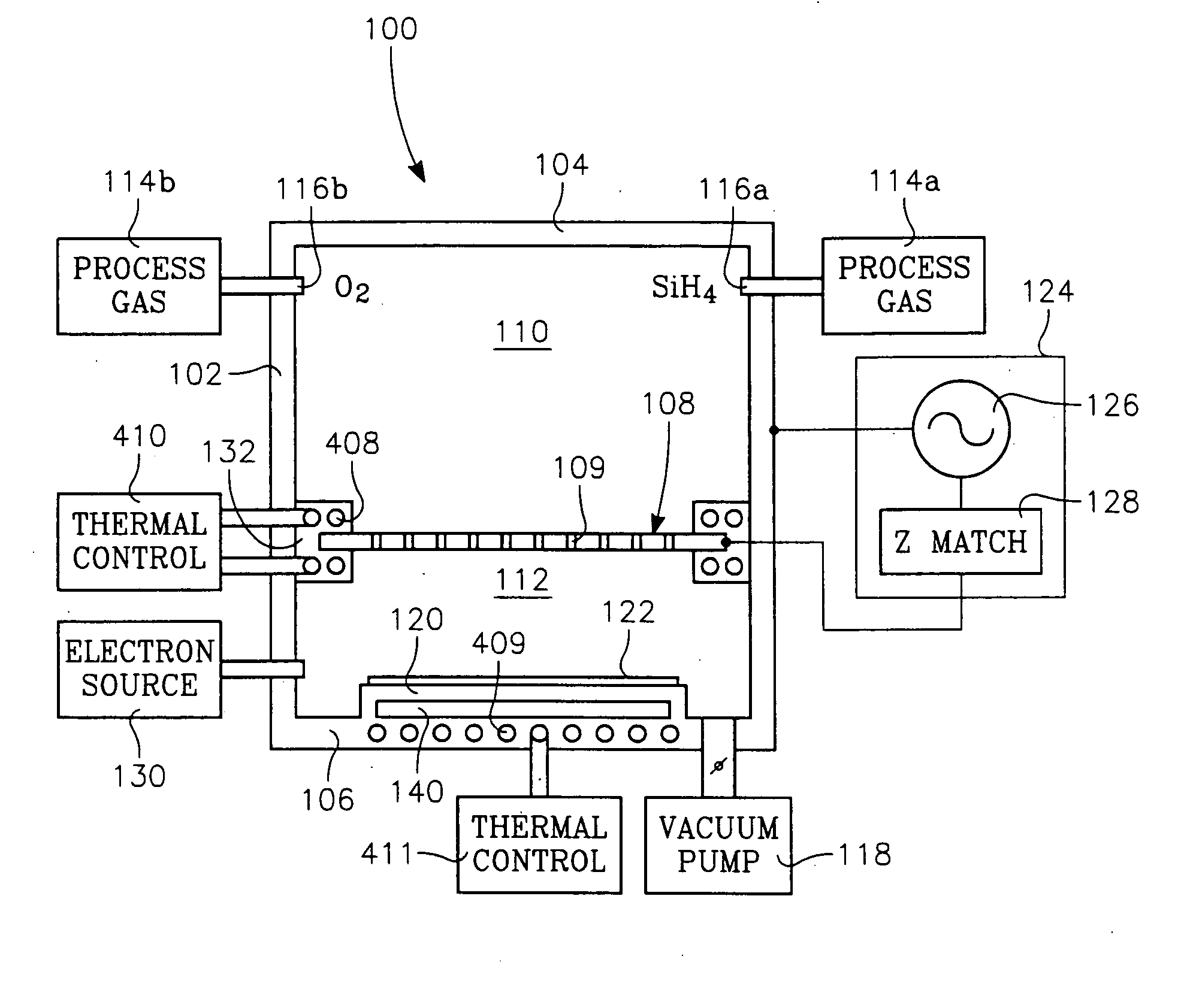
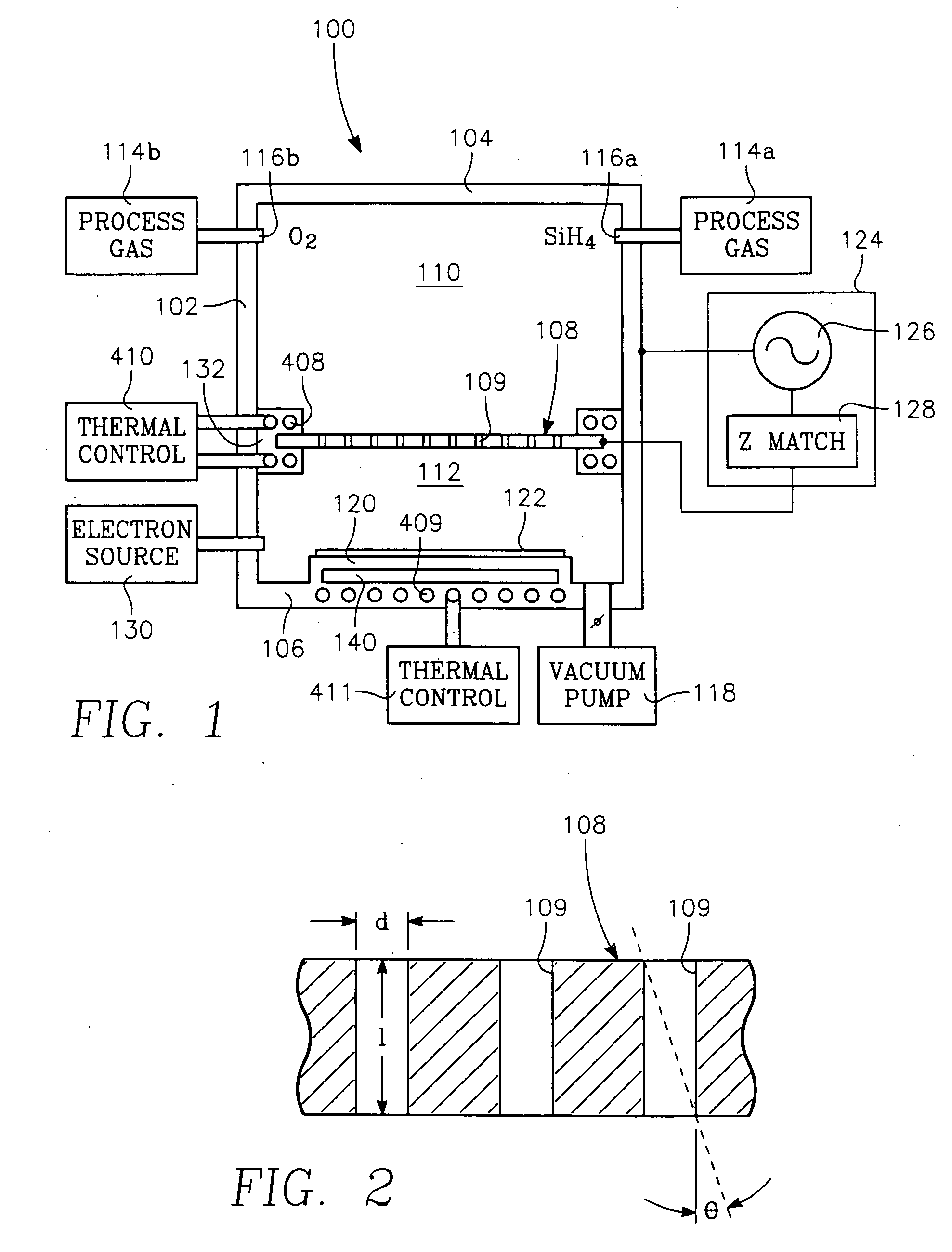
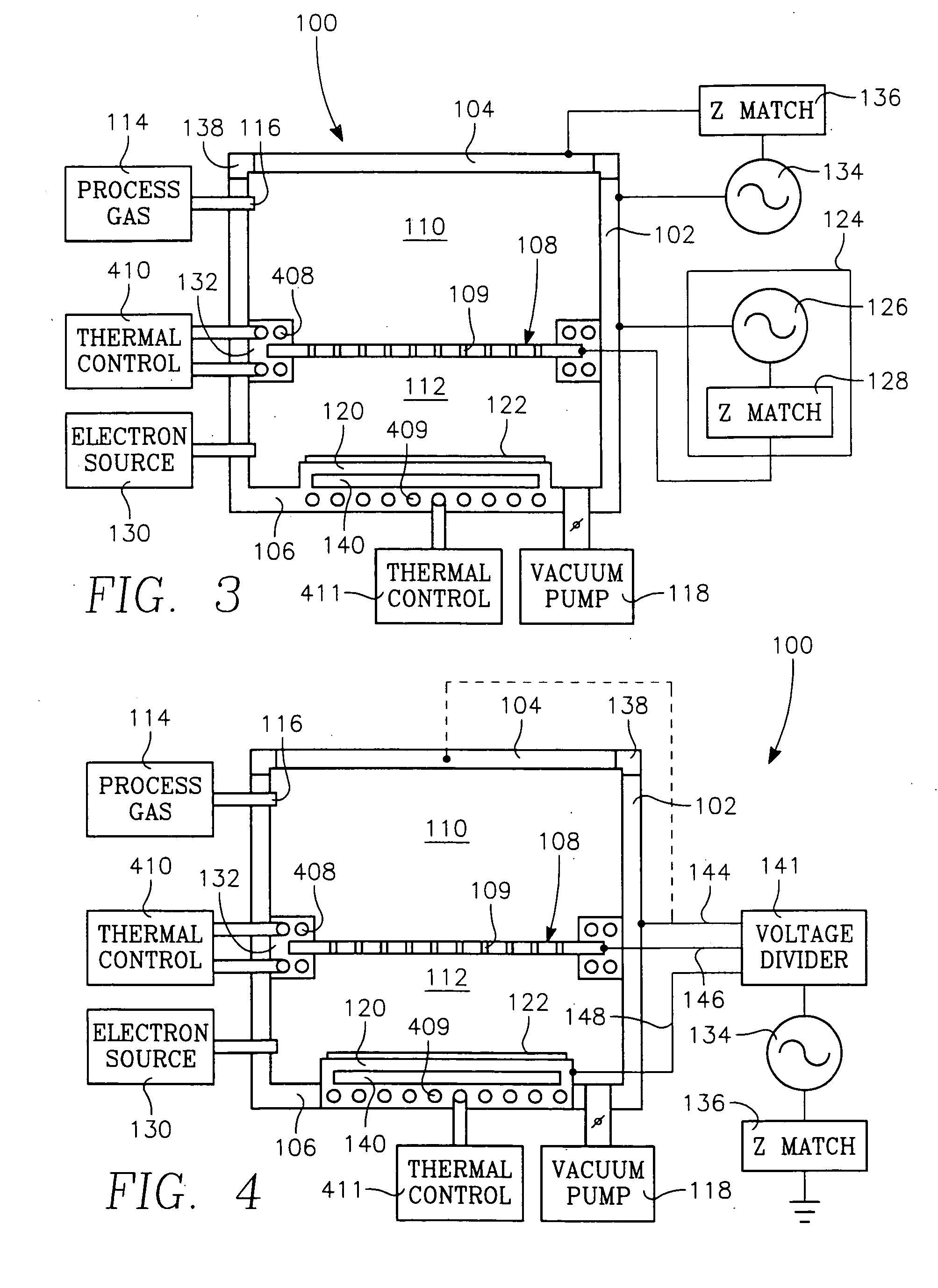
Low temperature plasma deposition process for carbon layer deposition
InactiveUS7312162B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingCarbon layerPlasma current
A method of depositing a carbon layer on a workpiece includes placing the workpiece in a reactor chamber, introducing a carbon-containing process gas into the chamber, generating a reentrant toroidal RF plasma current in a reentrant path that includes a process zone overlying the workpiece by coupling plasma RF source power to an external portion of the reentrant path, and coupling RF plasma bias power or bias voltage to the workpiece.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Low temperature plasma deposition process for carbon layer deposition
InactiveUS20060264060A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingCarbon layerPlasma current
A method of depositing a carbon layer on a workpiece includes placing the workpiece in a reactor chamber, introducing a carbon-containing process gas into the chamber, generating a reentrant toroidal RF plasma current in a reentrant path that includes a process zone overlying the workpiece by coupling plasma RF source power to an external portion of the reentrant path, and coupling RF plasma bias power or bias voltage to the workpiece.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
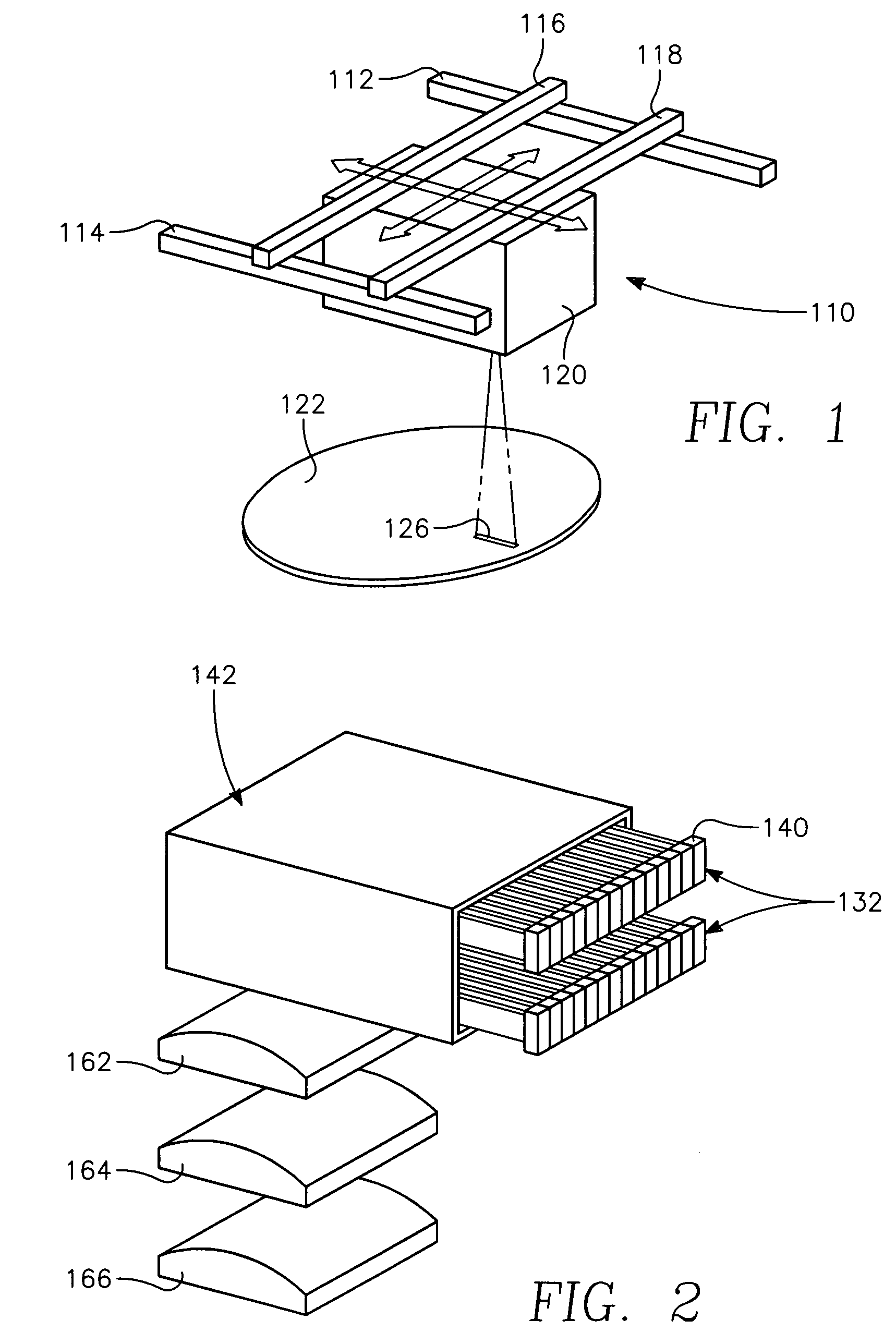
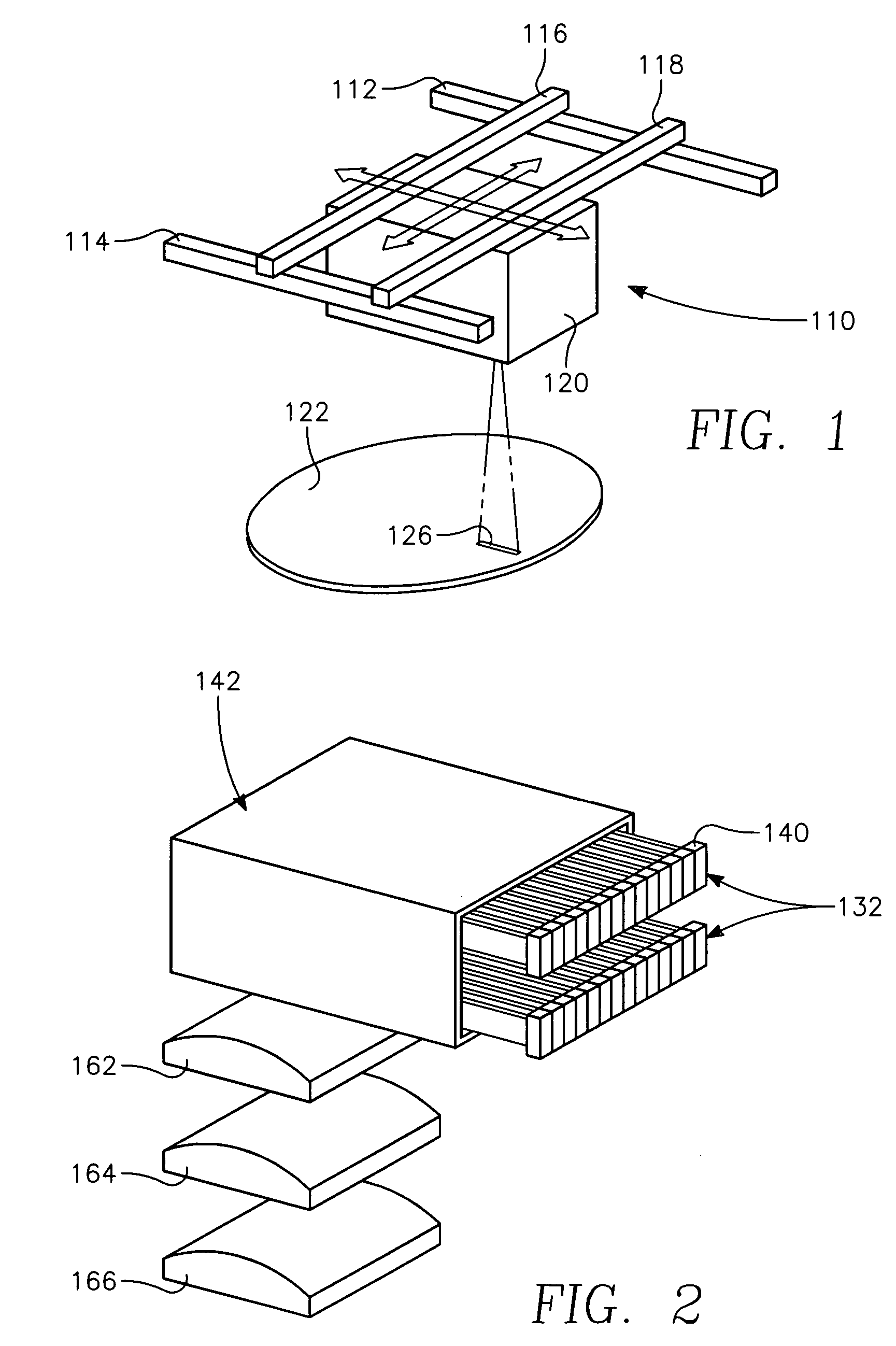
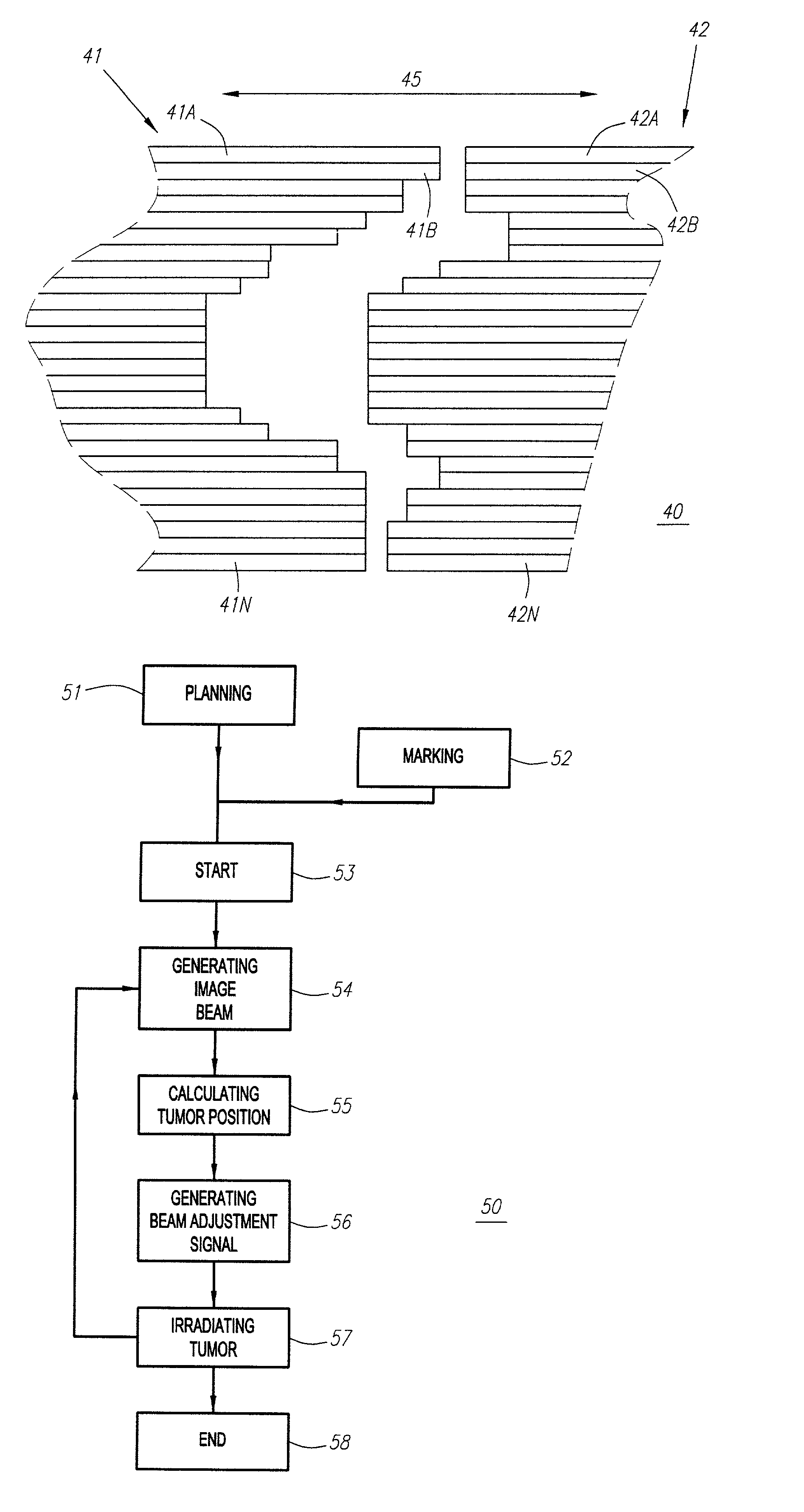
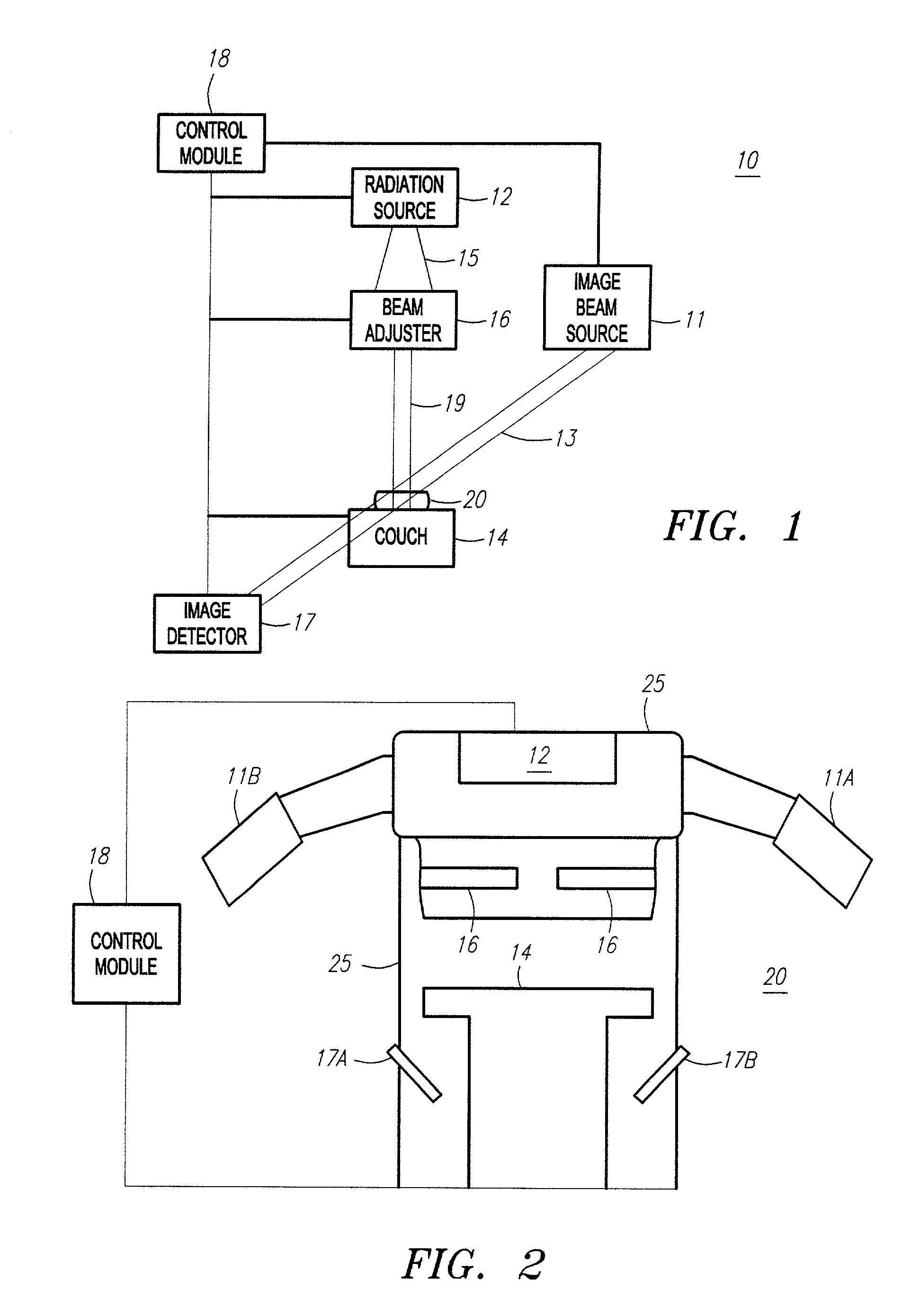
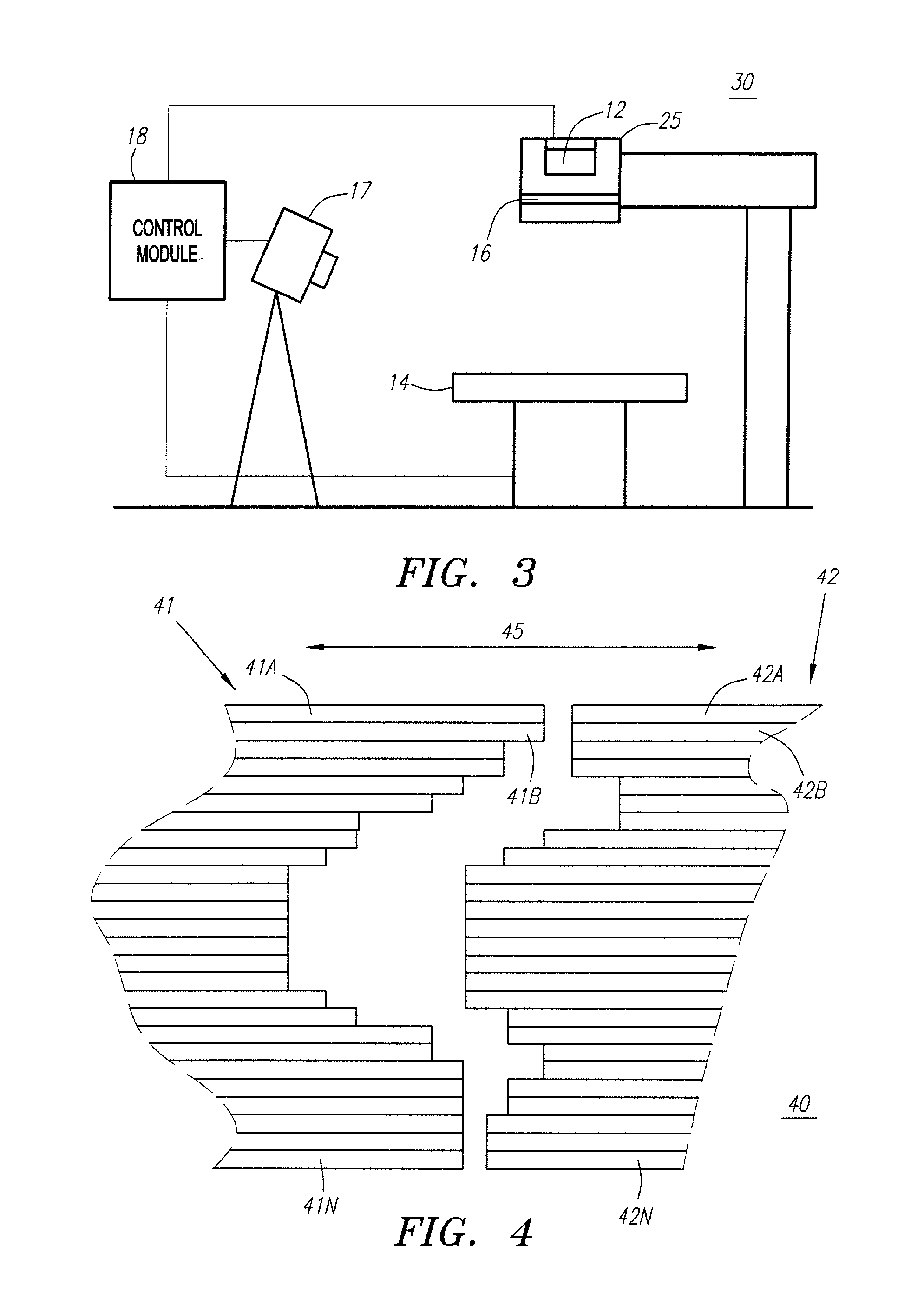
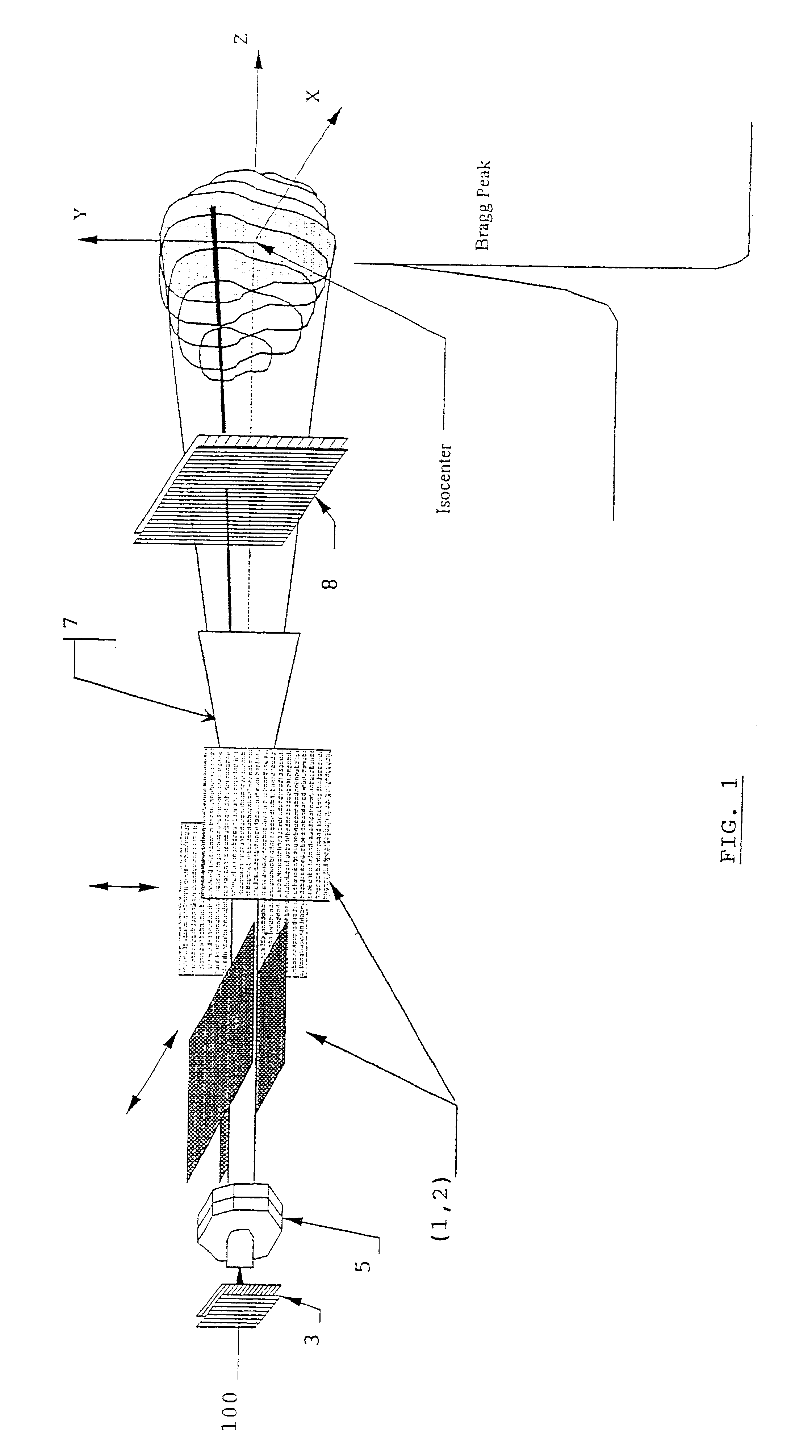
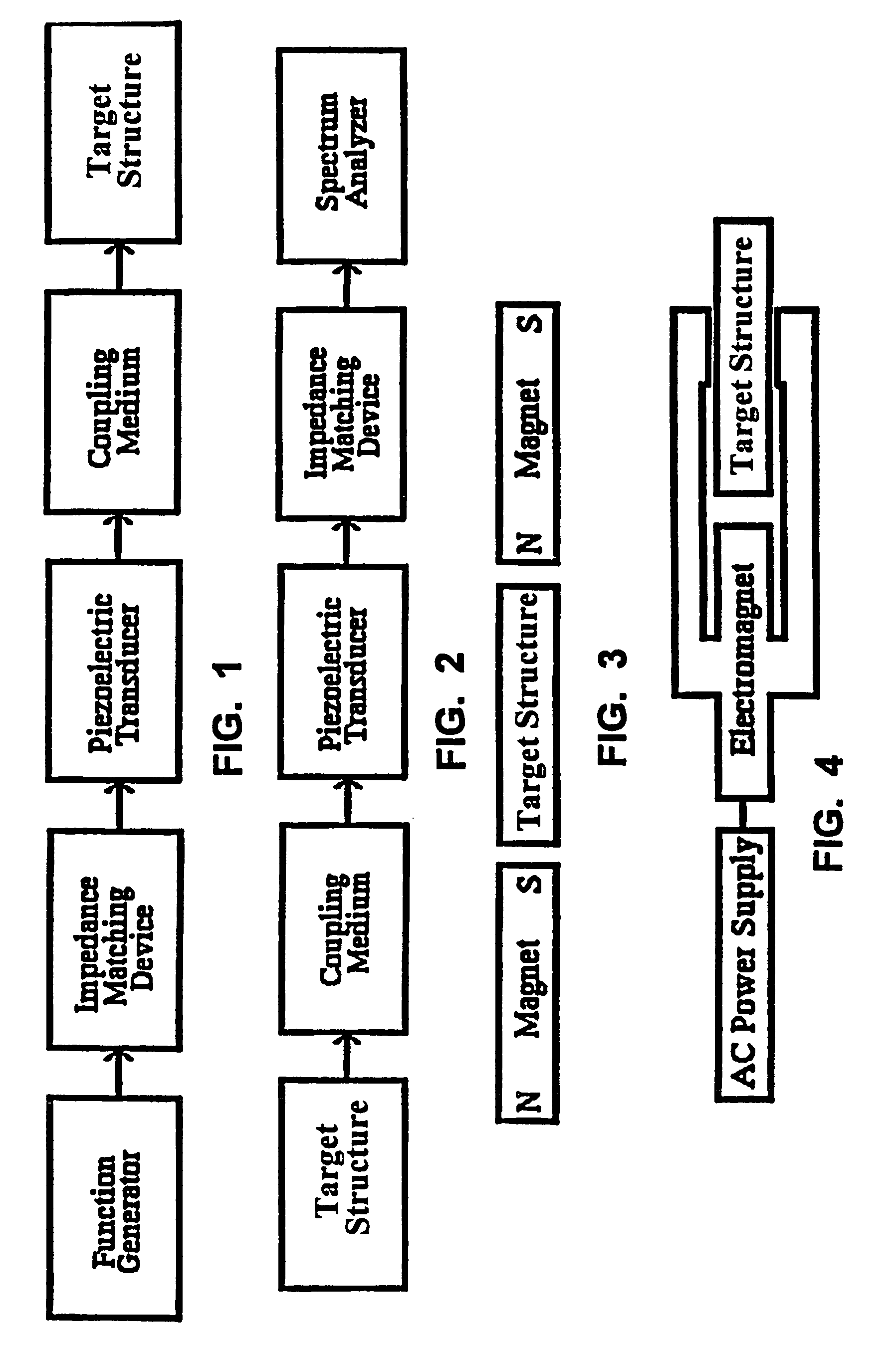
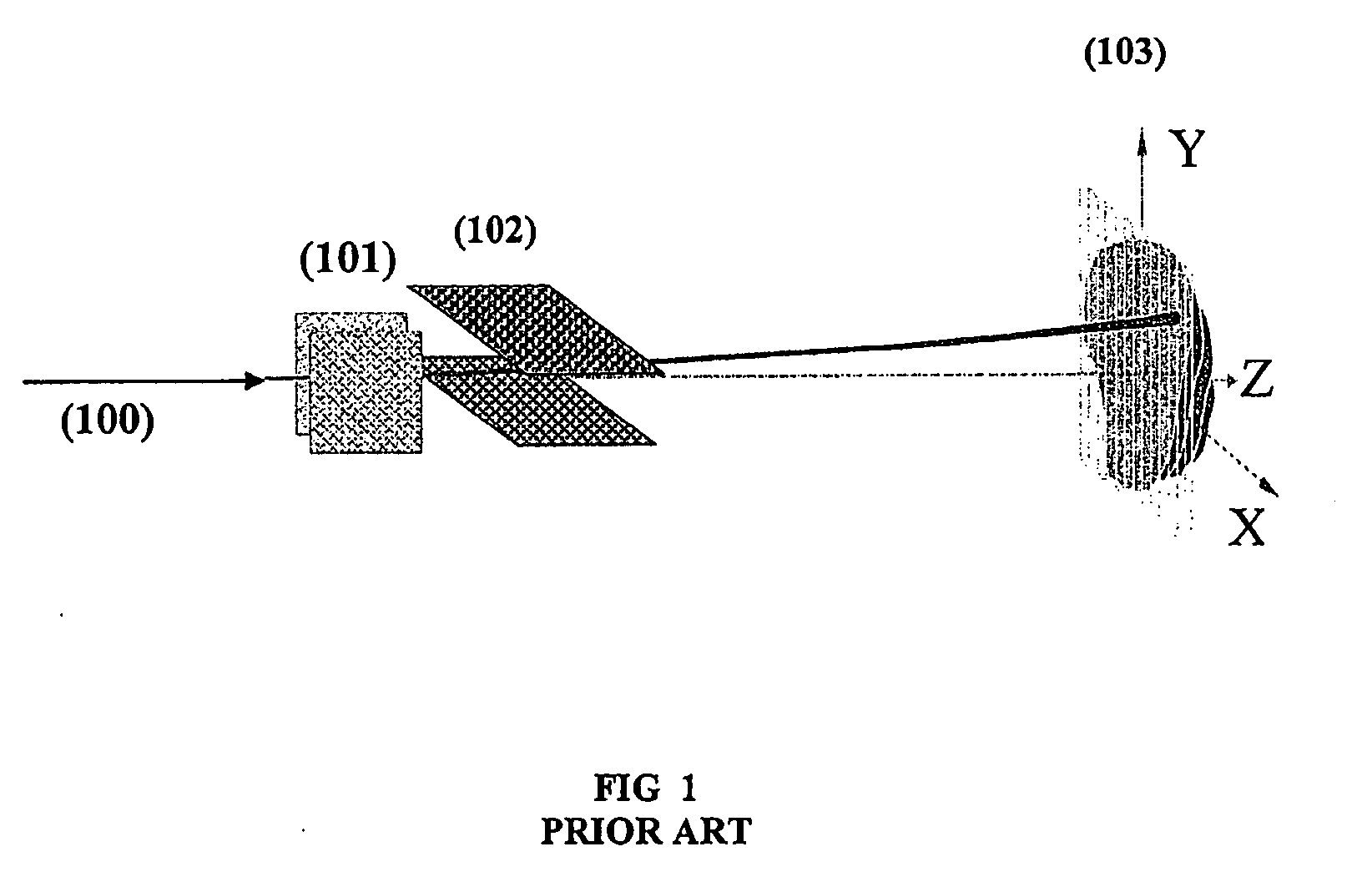
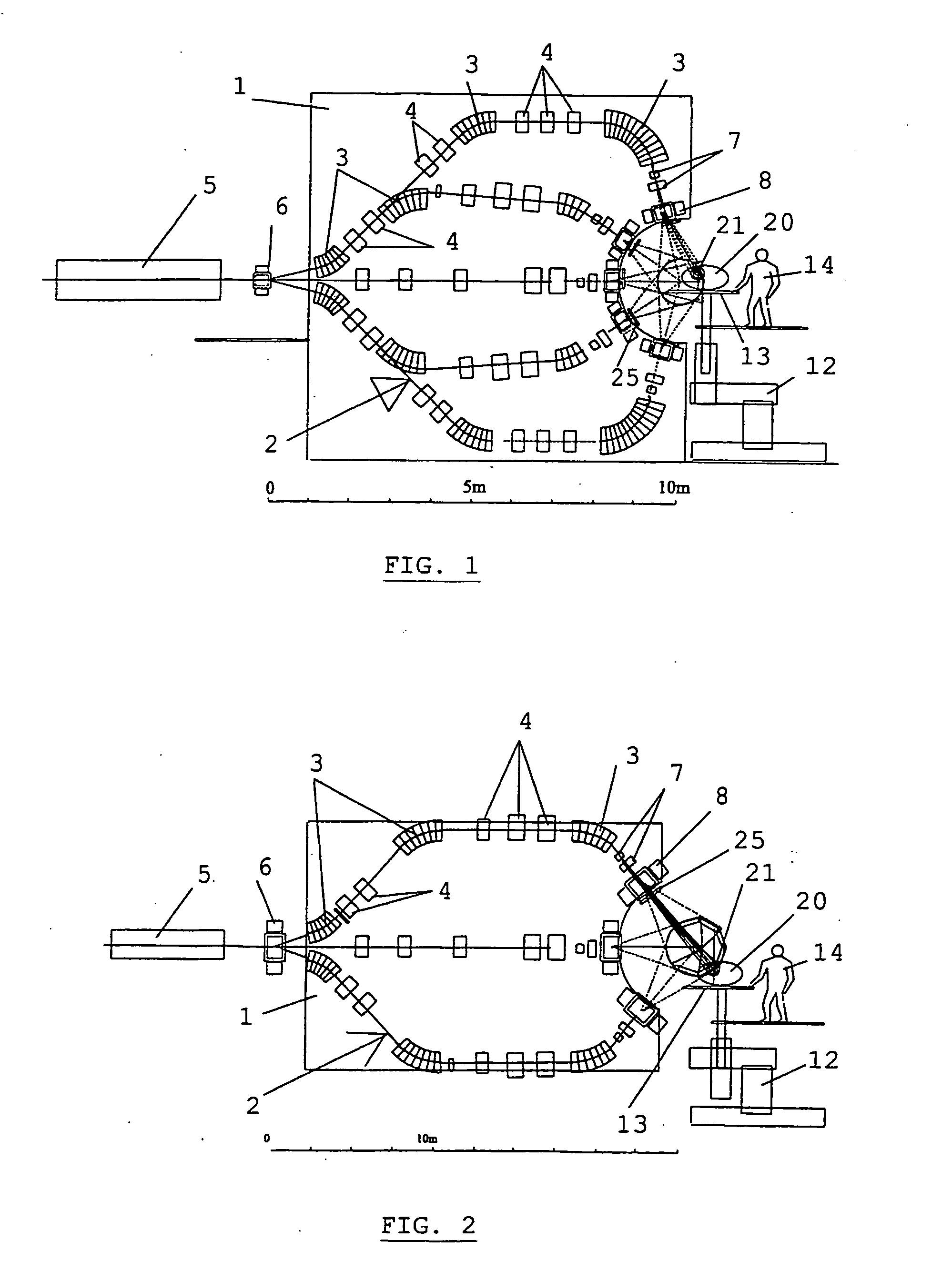
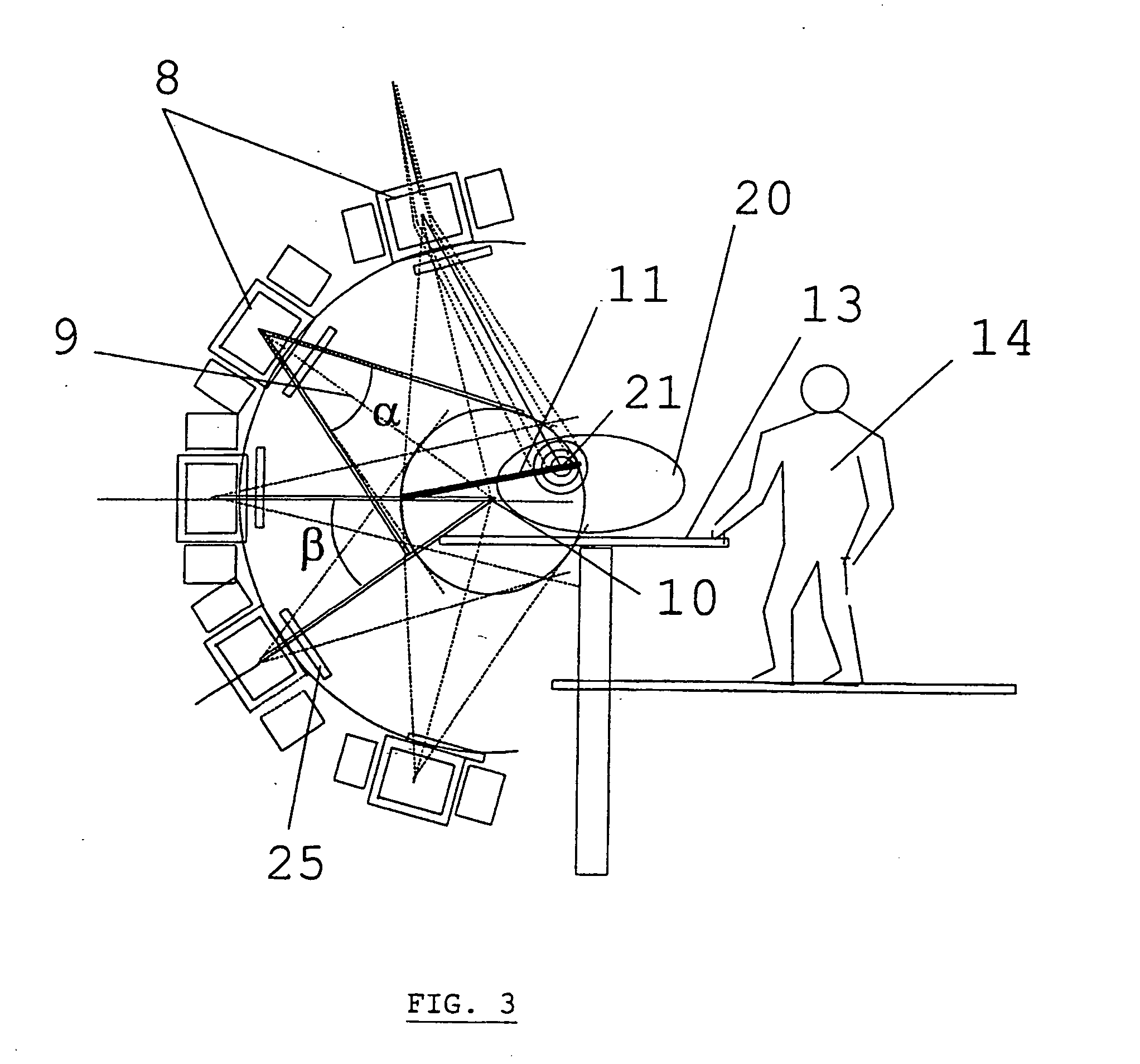
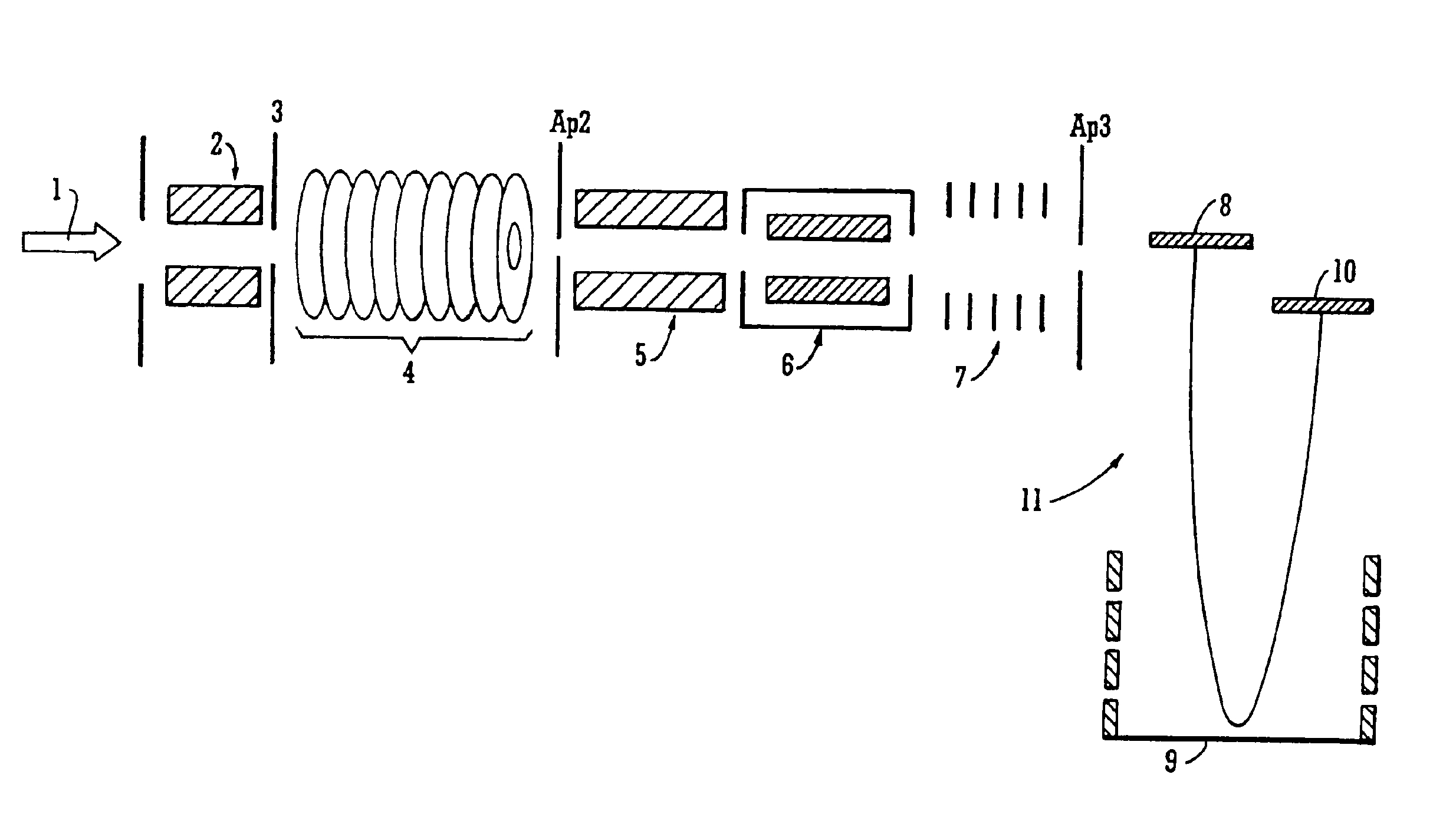
Method and apparatus for irradiating a target
An apparatus (10) for irradiating a target includes a radiation source (12) for generating a radiation beam and a multiple leaf beam adjuster (16) for collimating and adjusting the shape of the radiation beam from the radiation source (12) that would be projected on the target. An image detector (17) detects generates an image signal of the target. In response to the image signal, a control module (18) generate a beam adjustment signal for controlling the beam adjuster (16), thereby enabling the radiation beam from the radiation source (12) to track the movement of the target.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
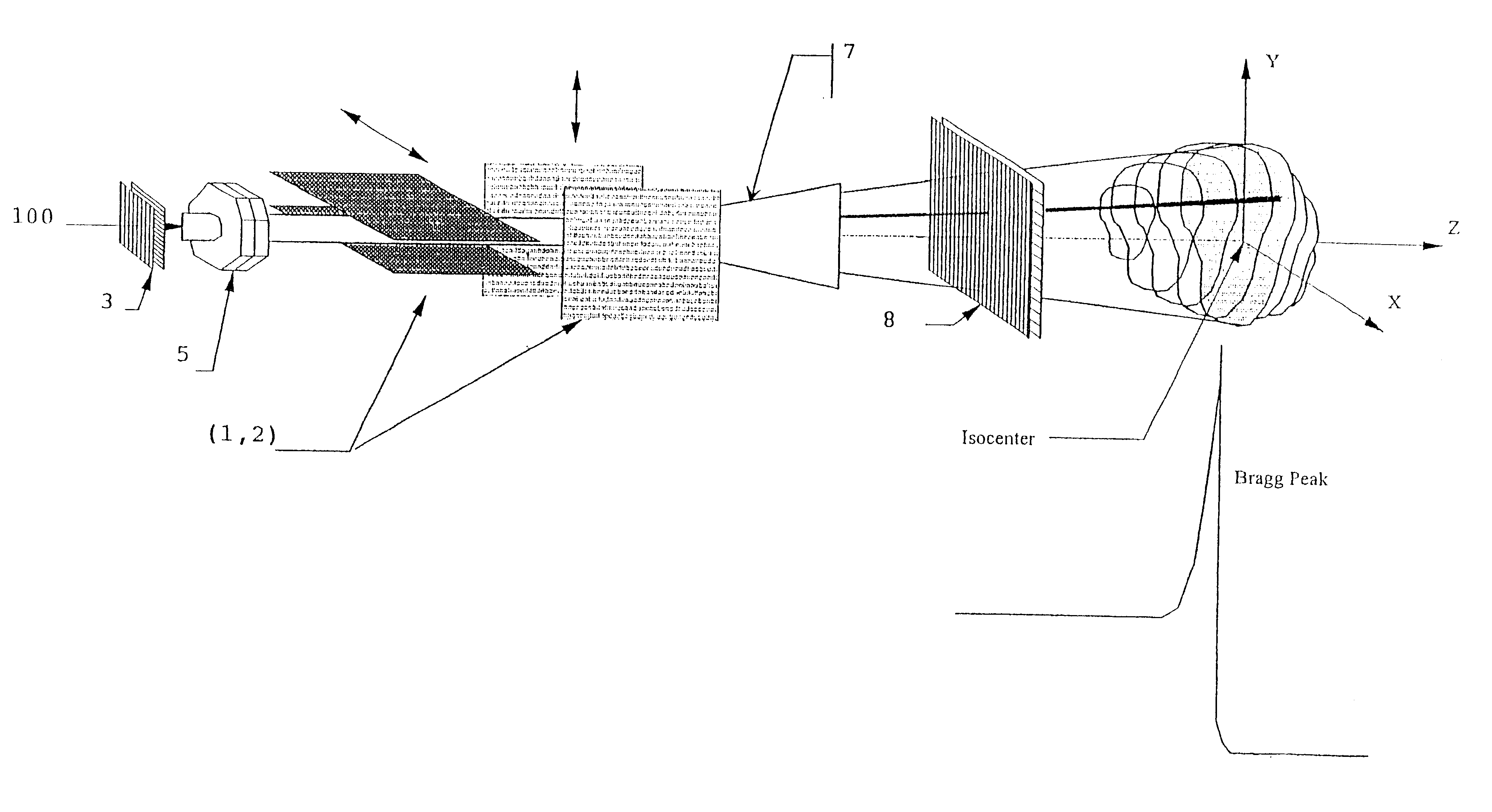
Method for treating a target volume with a particle beam and device implementing same
InactiveUS6717162B1Good flexibilityPossible to obtainRadiation/particle handlingElectrode and associated part arrangementsParticle beamParticle physics
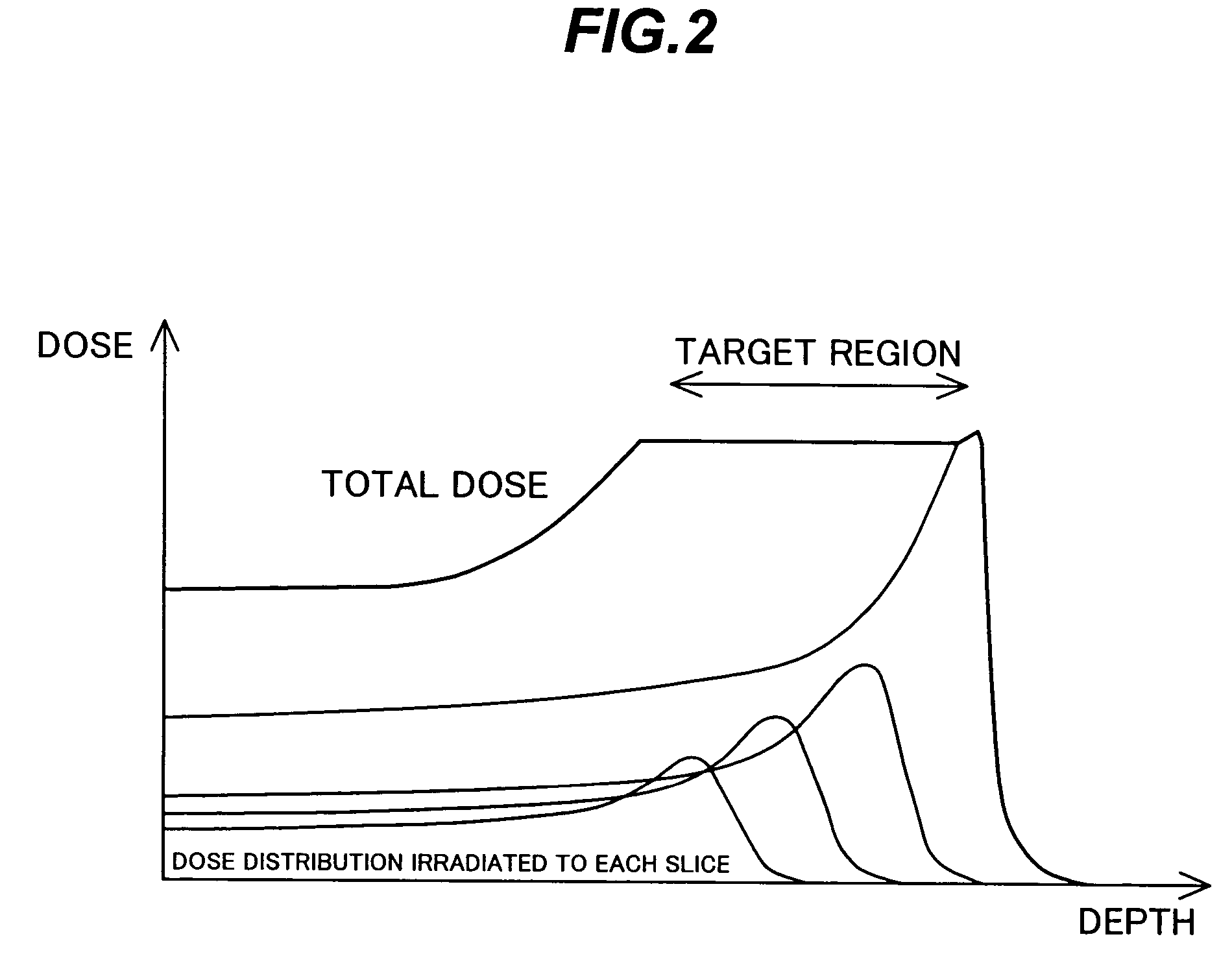
The invention concerns a method for treating a target volume with a particle beam, in particular a proton beam, which consists in generating said particle beam using an accelerator and in producing from said beam a narrow spot directed towards the target volume, characterized in that said spot sweeping speed and the particle beam intensity are simultaneously varied.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
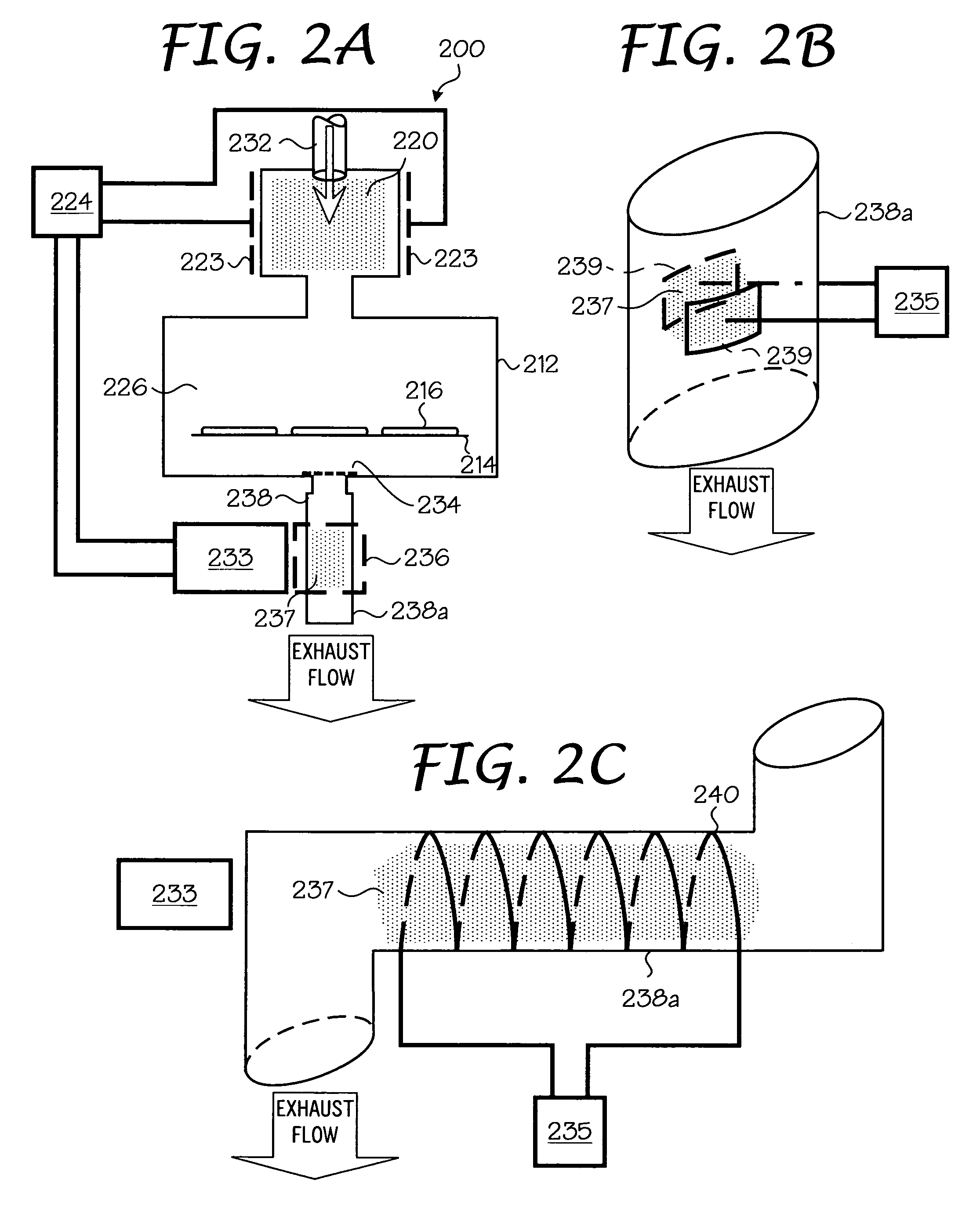
Chemical vapor deposition plasma process using an ion shower grid
A chemical vapor deposition process is carried out in a reactor chamber with an ion shower grid that divides the chamber into an upper ion generation region and a lower process region, the ion shower grid having plural orifices oriented in a non-parallel direction relative to a surface plane of the ion shower grid. A workpiece is placed in the process region facing the ion shower grid, the workpiece having a workpiece surface generally facing the surface plane of the ion shower grid. A gas mixture is furnished comprising deposition precursor species into the ion generation region and the process region is evacuated at an evacuation rate sufficient to create a pressure drop across the ion shower grid from the ion generation region to the process region whereby the pressure in the ion generation region is at least several times the pressure in the process region. A layer of material of a desired thickness is deposited on the workpiece by: (a) applying plasma source power to generate a plasma of the deposition precursor species in the ion generation region, and (b) applying a grid potential to the ion shower grid to create a flux of ions from the plasma through the grid and into the process region.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Electrophoretic displays containing magnetic particles
An electrophoretic medium comprises a plurality of one or more types of particles suspended in a suspending fluid. The particles include at least one electrically charged, electrophoretically mobile particle capable of translating through the suspending fluid upon application of an electric field to the medium and at least one magnetic particle. A magnet is disposed adjacent the electrophoretic medium to introduce a threshold resistance to magnetic particle movement.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
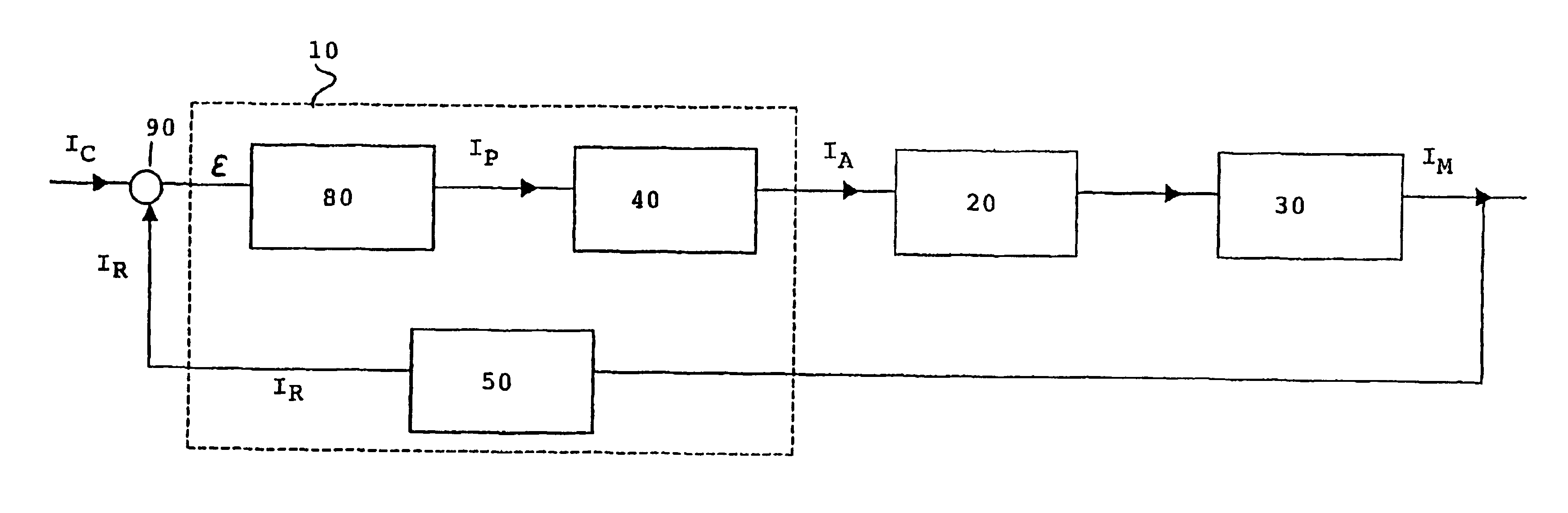
Device and method for regulating intensity of beam extracted from a particle accelerator
InactiveUS6873123B2Thermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersParticle acceleratorAccelerated particle
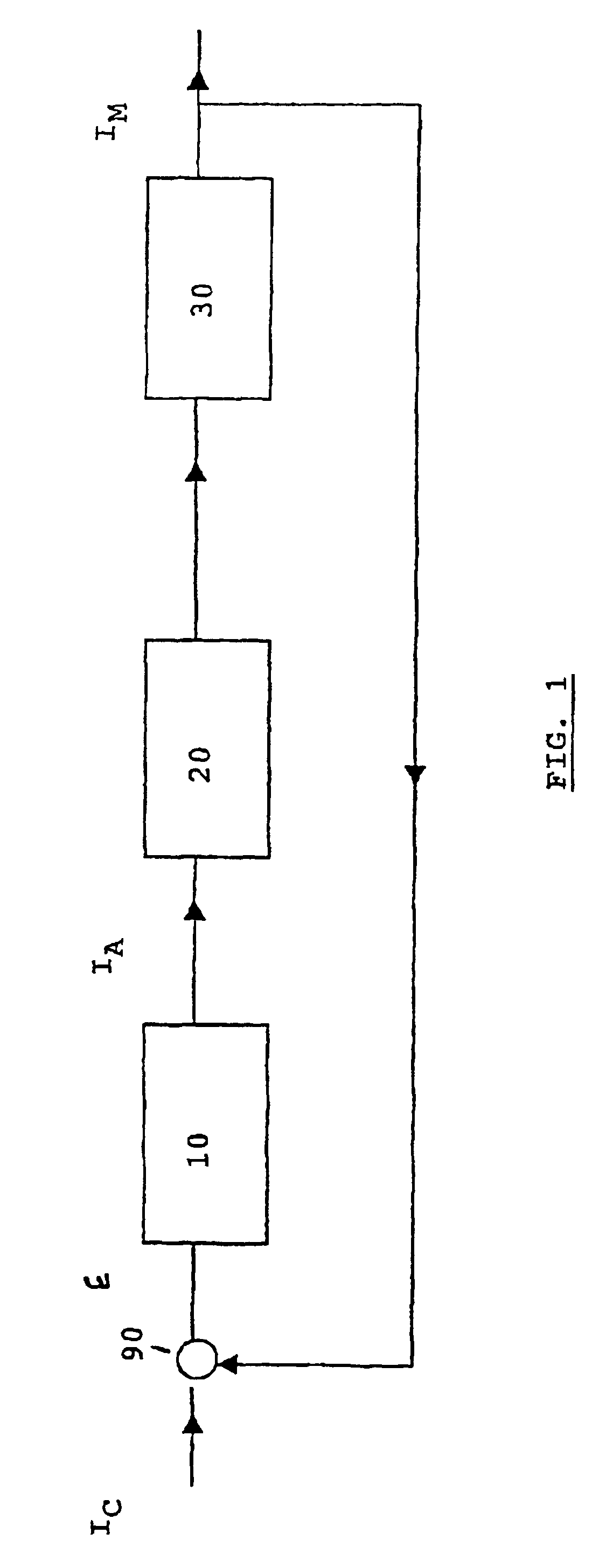
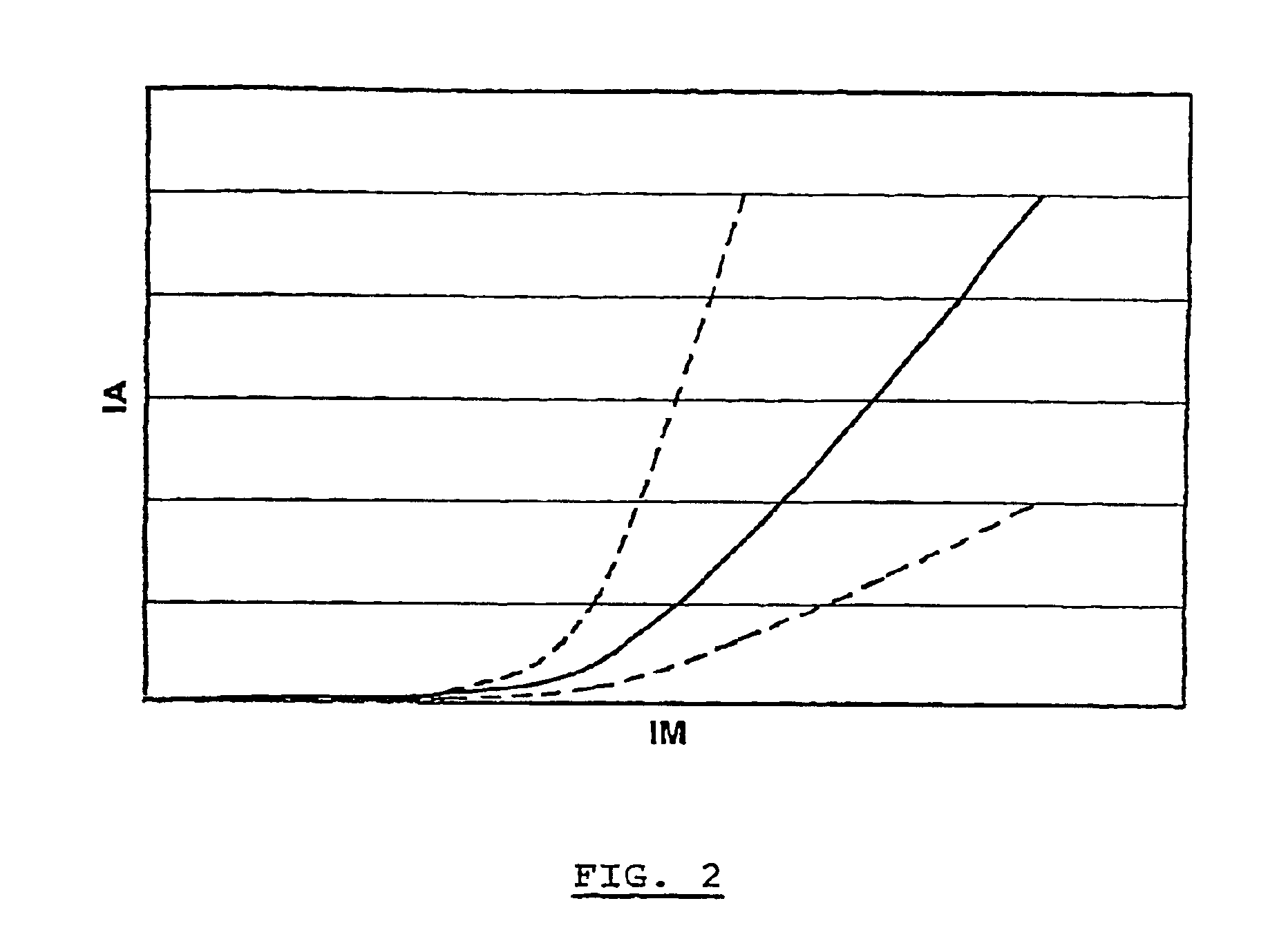
The invention concerns a device (10) for regulating the intensity of a beam extracted from a particle accelerator, such as a cyclotron, used for example for protontherapy, said particles being generated from an ion source. The invention is characterized in that it comprises at least: a comparator (90) determining a difference ε between a digital signal IR representing the intensity of the beam measured at the output of the accelerator and a setpoint value IC of the beam intensity: a Smith predictor (80) which determines on the basis of the difference ε, a correct value of the intensity of the beam IP; an inverted correspondence table (40) supplying, on the basis of the corrected value of the intensity of the beam IP, a setpoint value IA for supply arc current from the ion source (20).
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
Particle therapy system
InactiveUS6936832B2Simply and quickly correctReduce laborRadiation/particle handlingElectrode and associated part arrangementsTransport systemLight beam
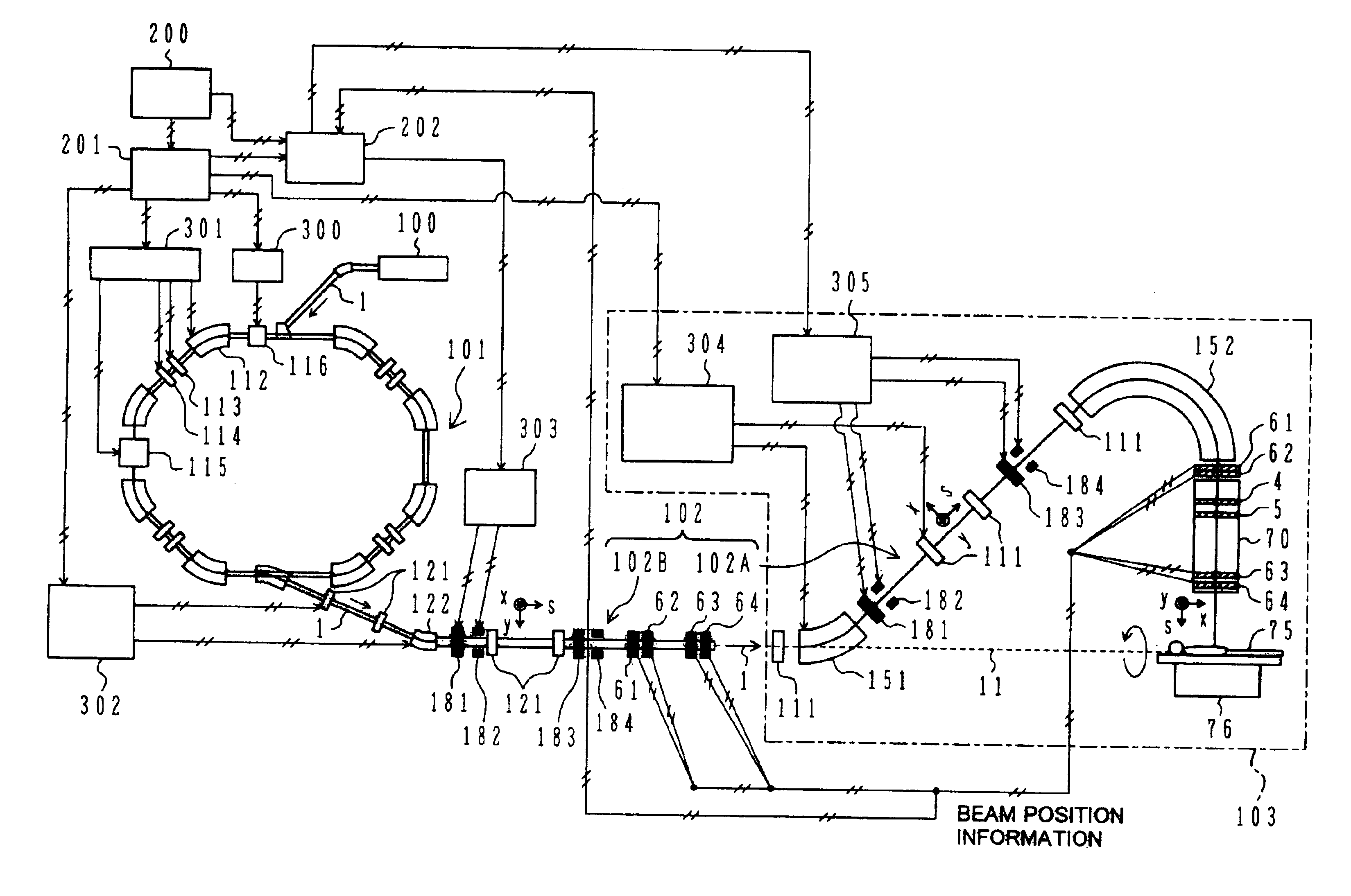
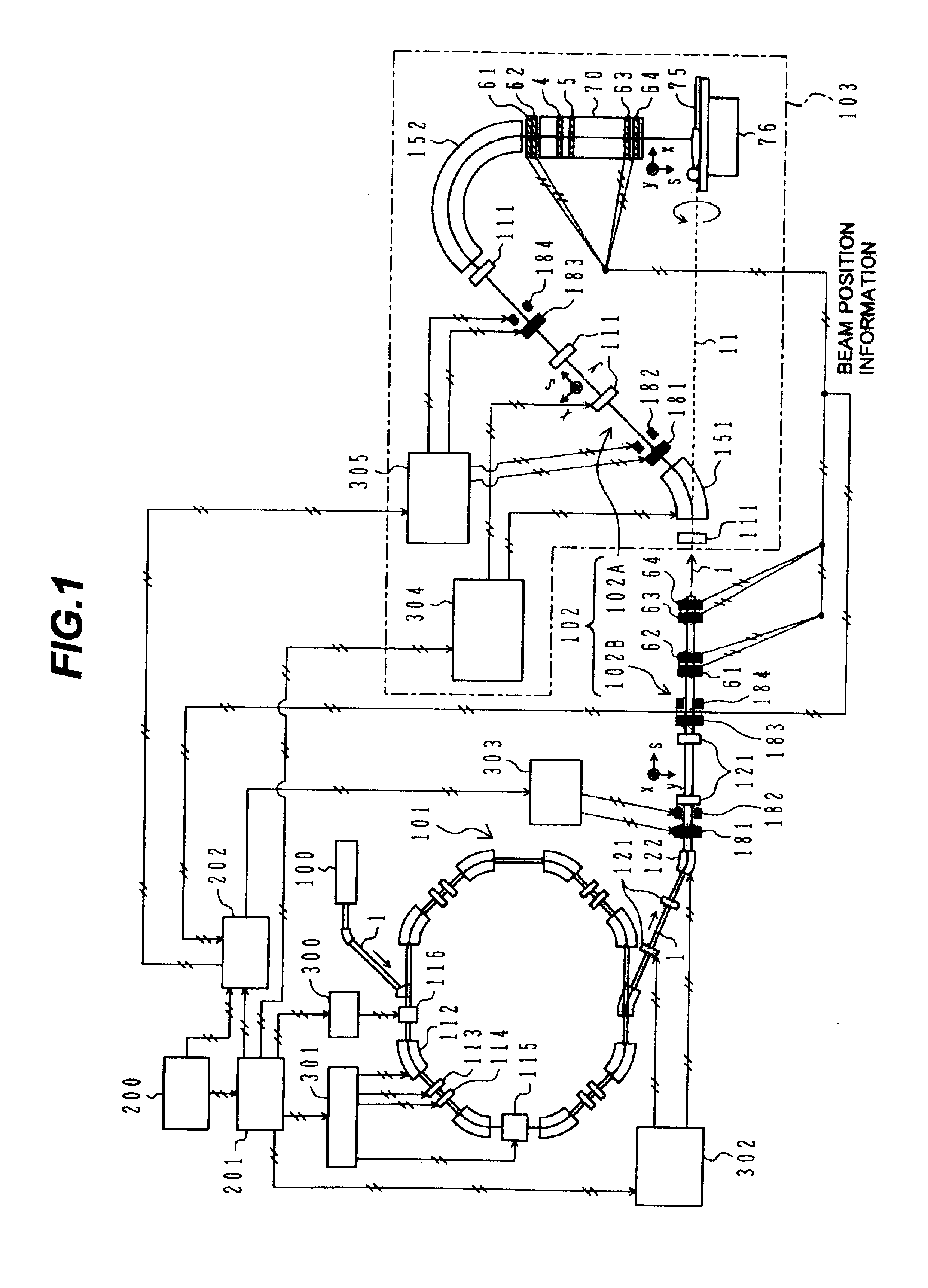
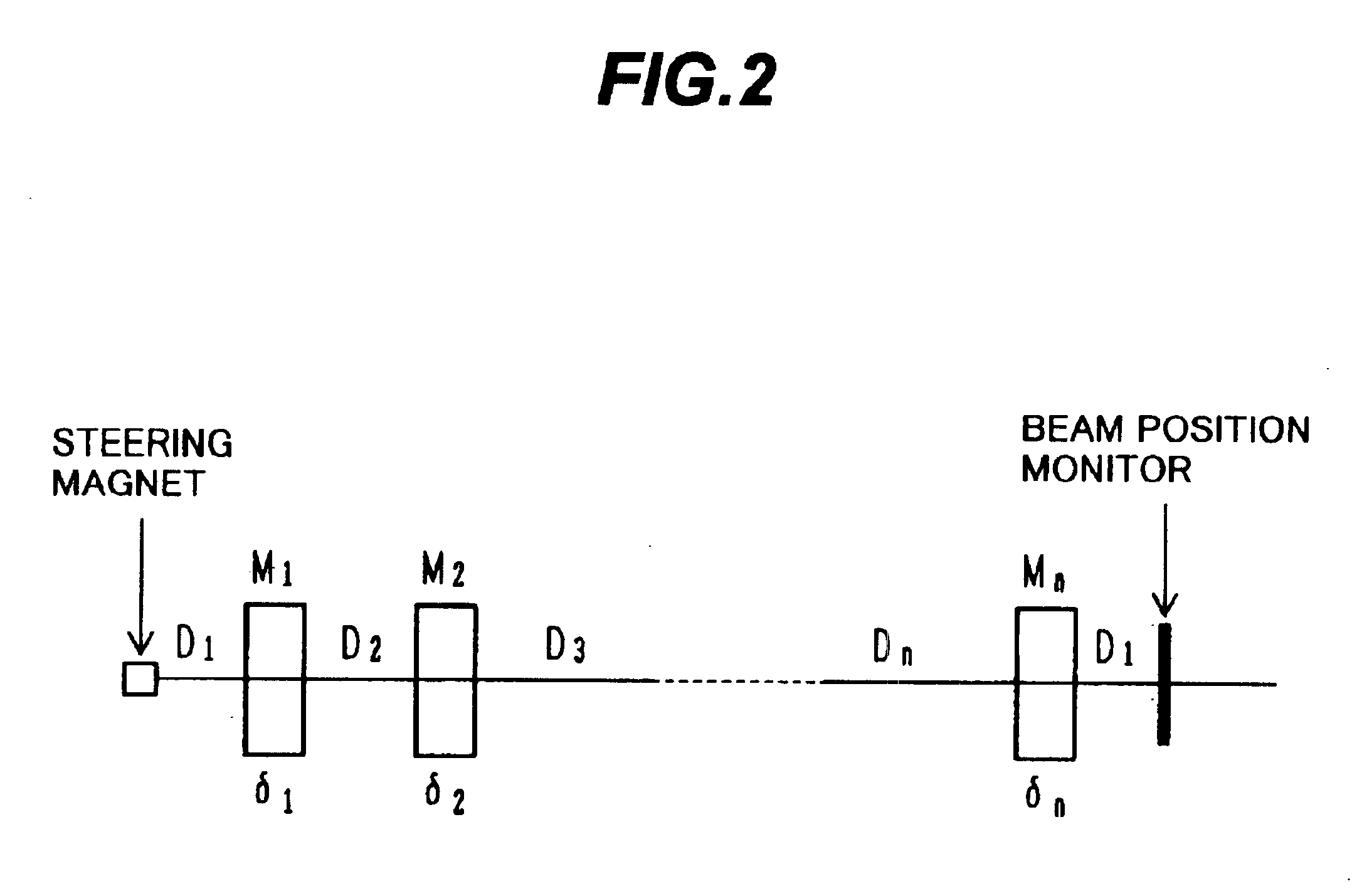
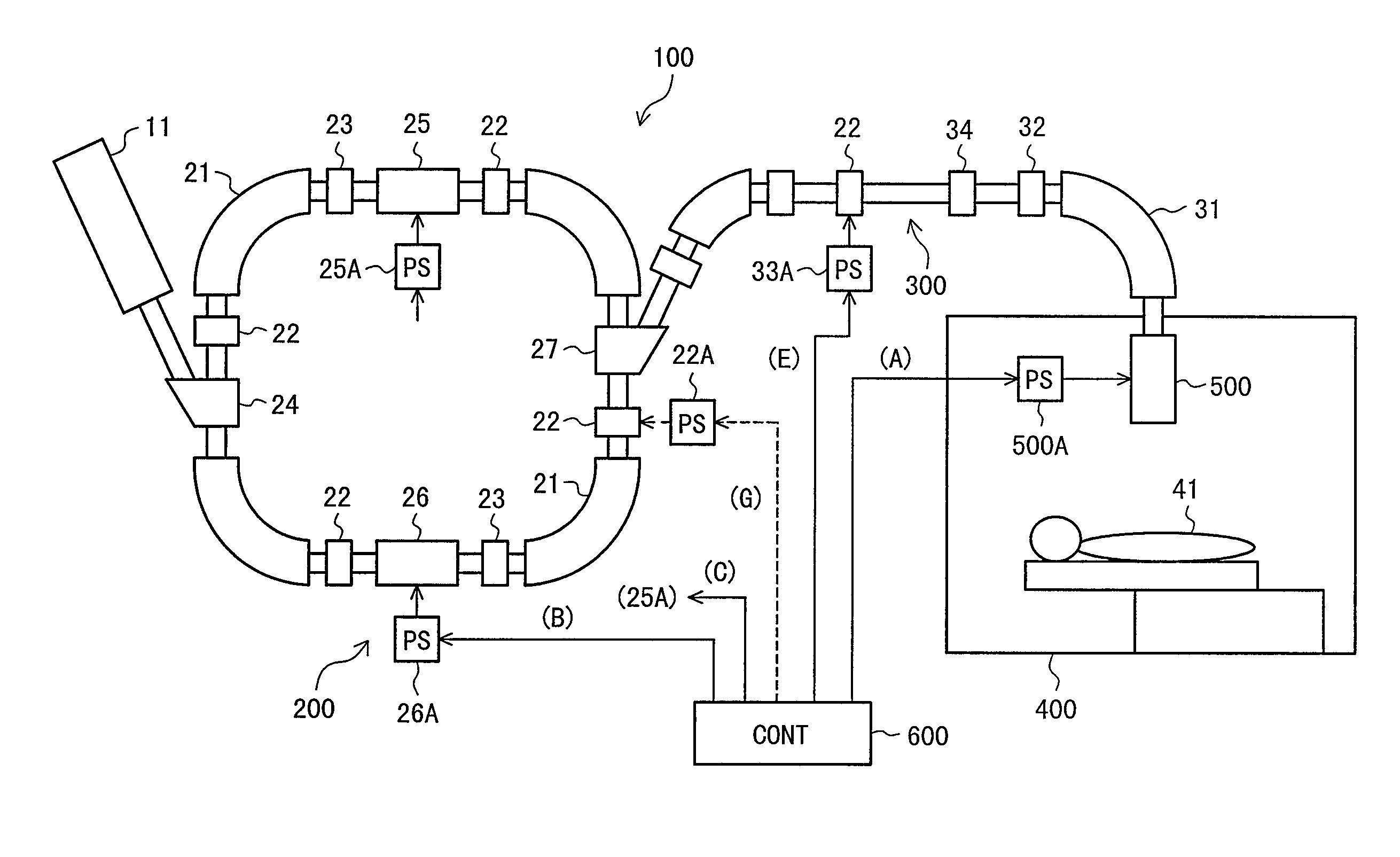
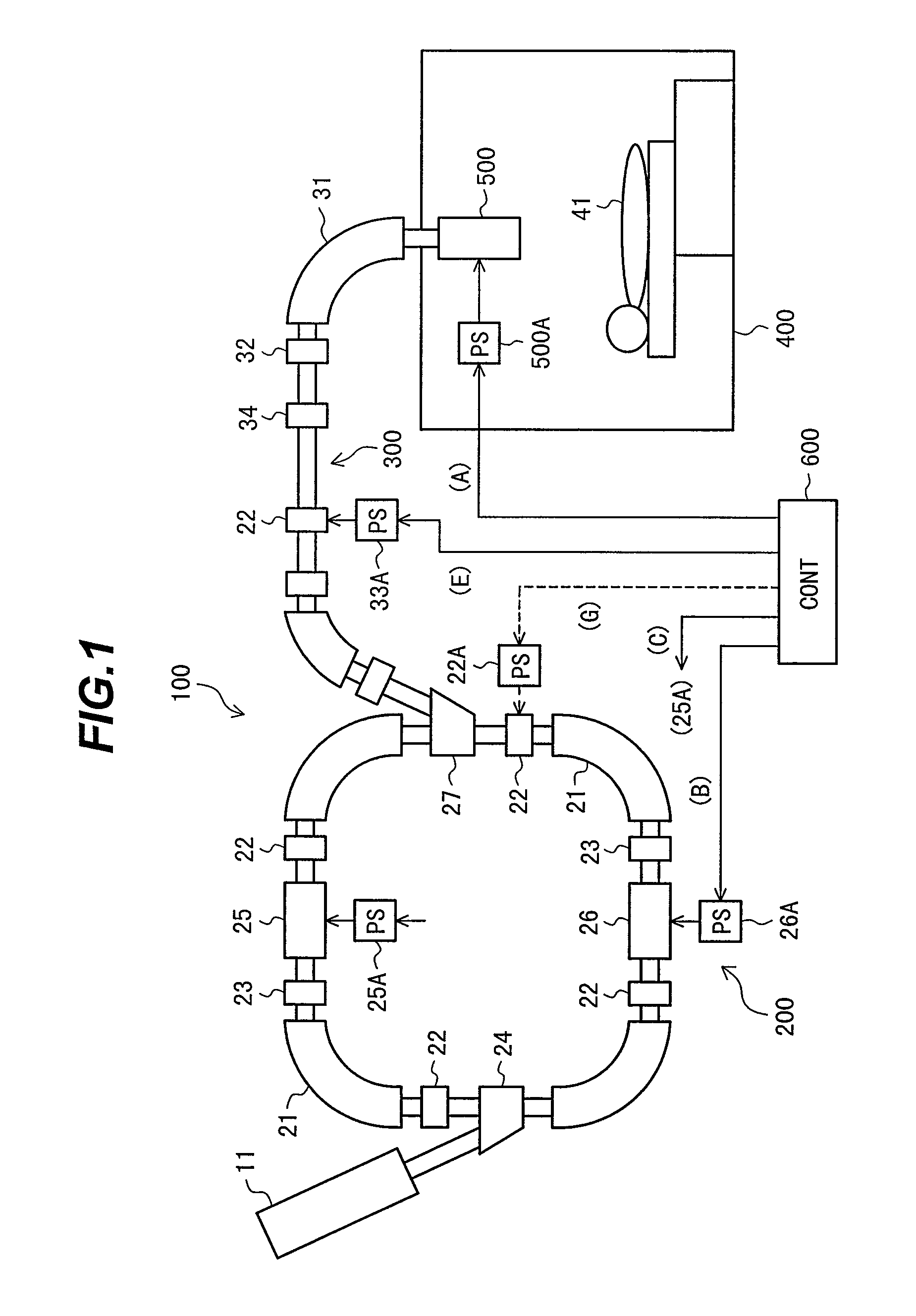
A particle therapy system is provided which can simply and quickly correct a beam orbit. In a particle therapy system provided with an irradiation facility comprising a first beam transport system for receiving a beam and transporting the beam to the patient side, and an irradiation nozzle for forming an irradiation field of the beam, the particle therapy system comprises first beam position monitors for detecting a position upstream of the irradiation nozzle at which the beam passes, second beam position monitors for detecting a position downstream of the irradiation nozzle at which the charged-particle beam passes, and first and second steering magnets. Correction bending amounts for causing the beam to be coincident with a predetermined orbit after the correction are determined in accordance with detected results from the first and second beam position monitors, and first and second steering magnets are excited under control so that the determined correction bending amounts are obtained.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Chemical vapor deposition plasma process using an ion shower grid
A chemical vapor deposition process is carried out in a reactor chamber with an ion shower grid that divides the chamber into an upper ion generation region and a lower process region, the ion shower grid having plural orifices oriented in a non-parallel direction relative to a surface plane of the ion shower grid. A workpiece is placed in the process region facing the ion shower grid, the workpiece having a workpiece surface generally facing the surface plane of the ion shower grid. A gas mixture is furnished comprising deposition precursor species into the ion generation region and the process region is evacuated at an evacuation rate sufficient to create a pressure drop across the ion shower grid from the ion generation region to the process region whereby the pressure in the ion generation region is at least several times the pressure in the process region. A layer of material of a desired thickness is deposited on the workpiece by: (a) applying plasma source power to generate a plasma of the deposition precursor species in the ion generation region, and (b) applying a grid potential to the ion shower grid to create a flux of ions from the plasma through the grid and into the process region.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Methods for using resonant acoustic and/or resonant acousto-EM energy to detect and/or effect structures
InactiveUS7165451B1Avoid damageAccurate detectionVibration measurement in solidsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsParticle physicsQuantum electrodynamics
Owner:GR INTELLECTUAL RESERVE LLC
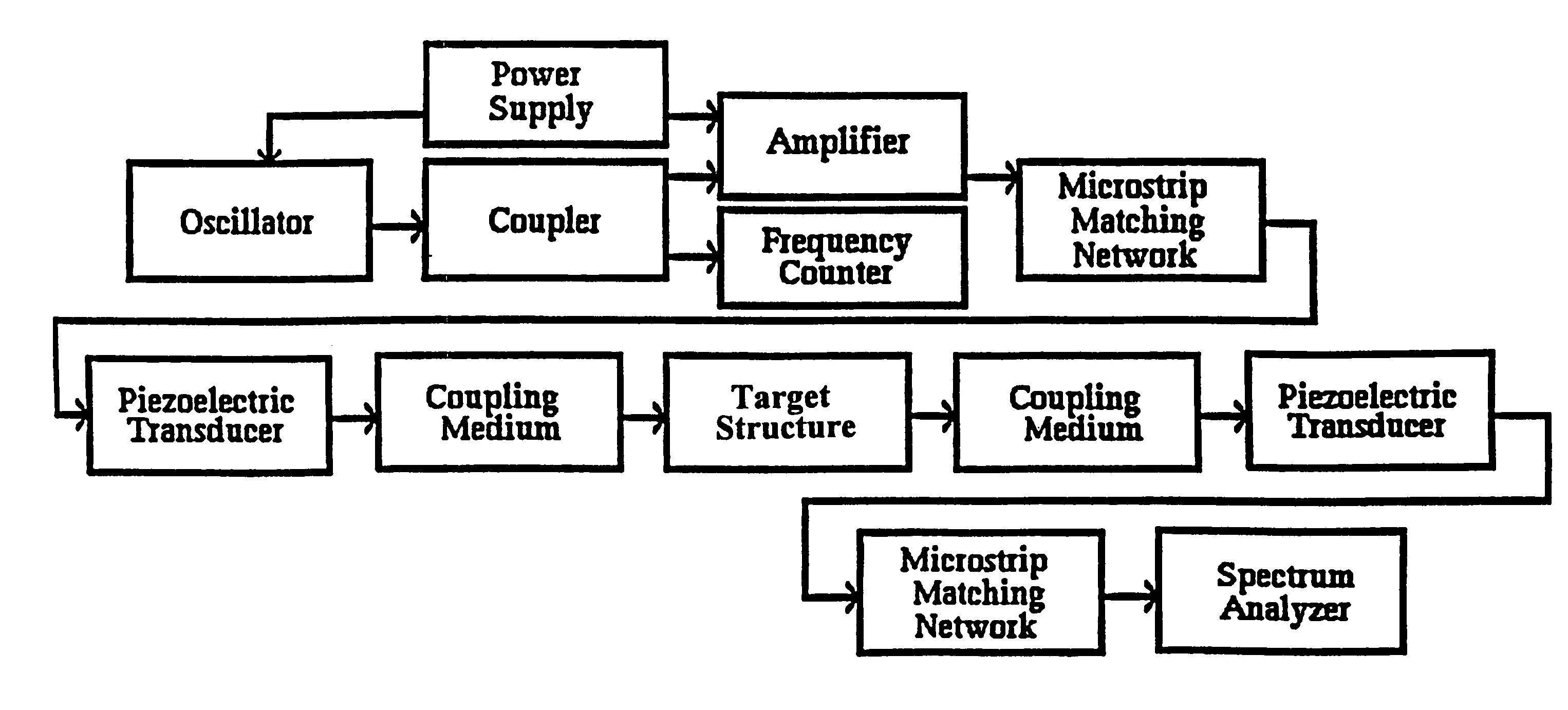
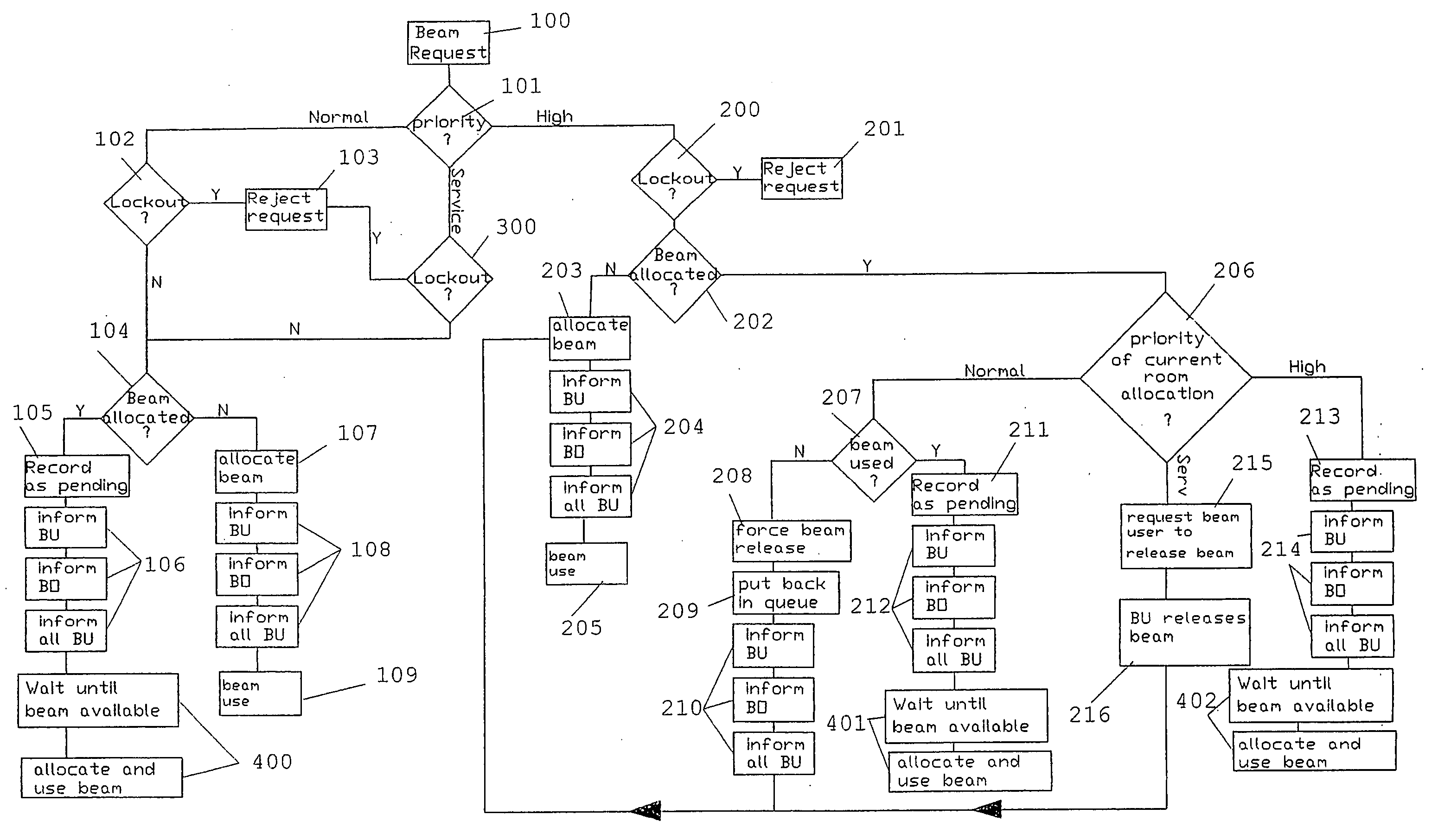
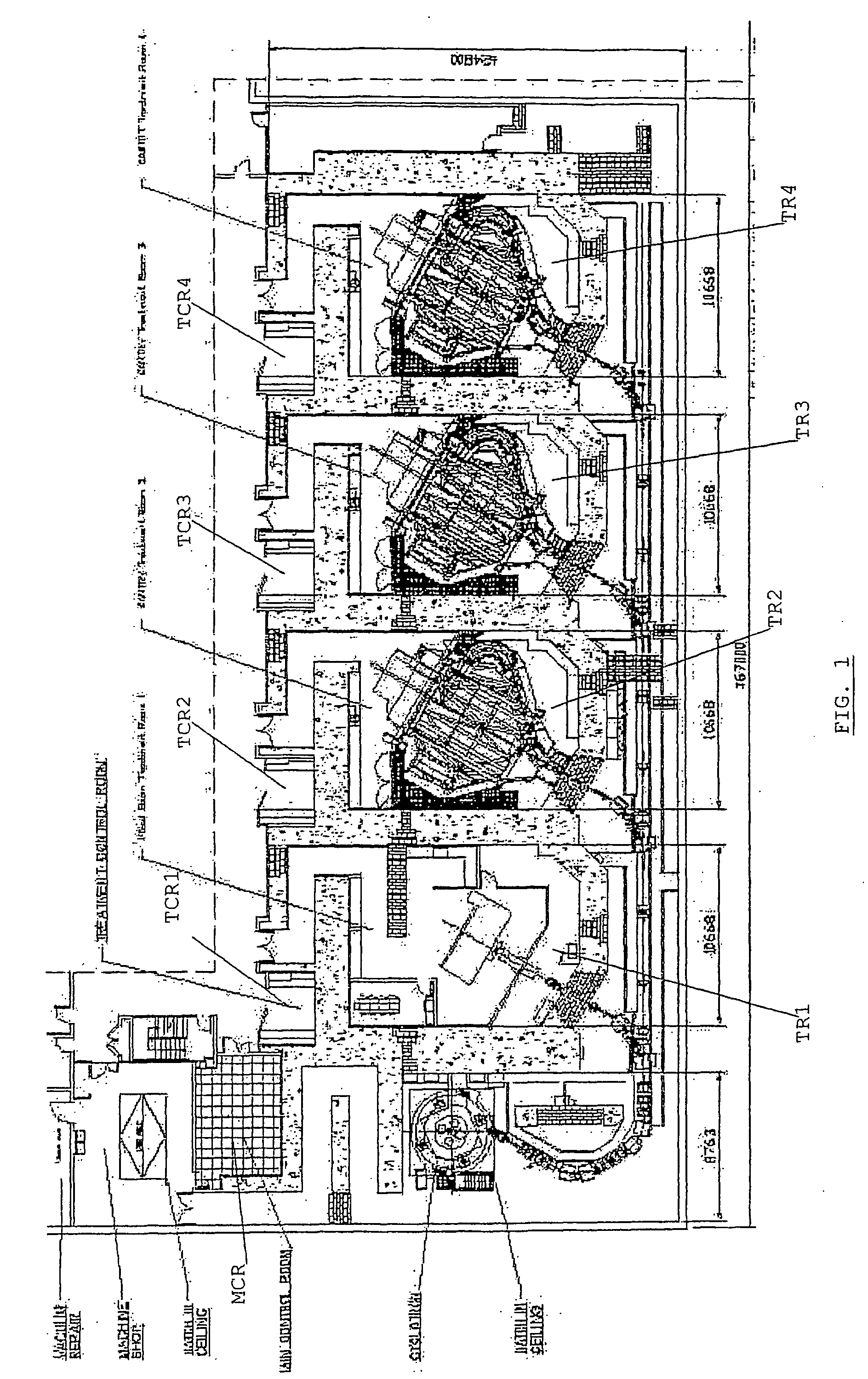
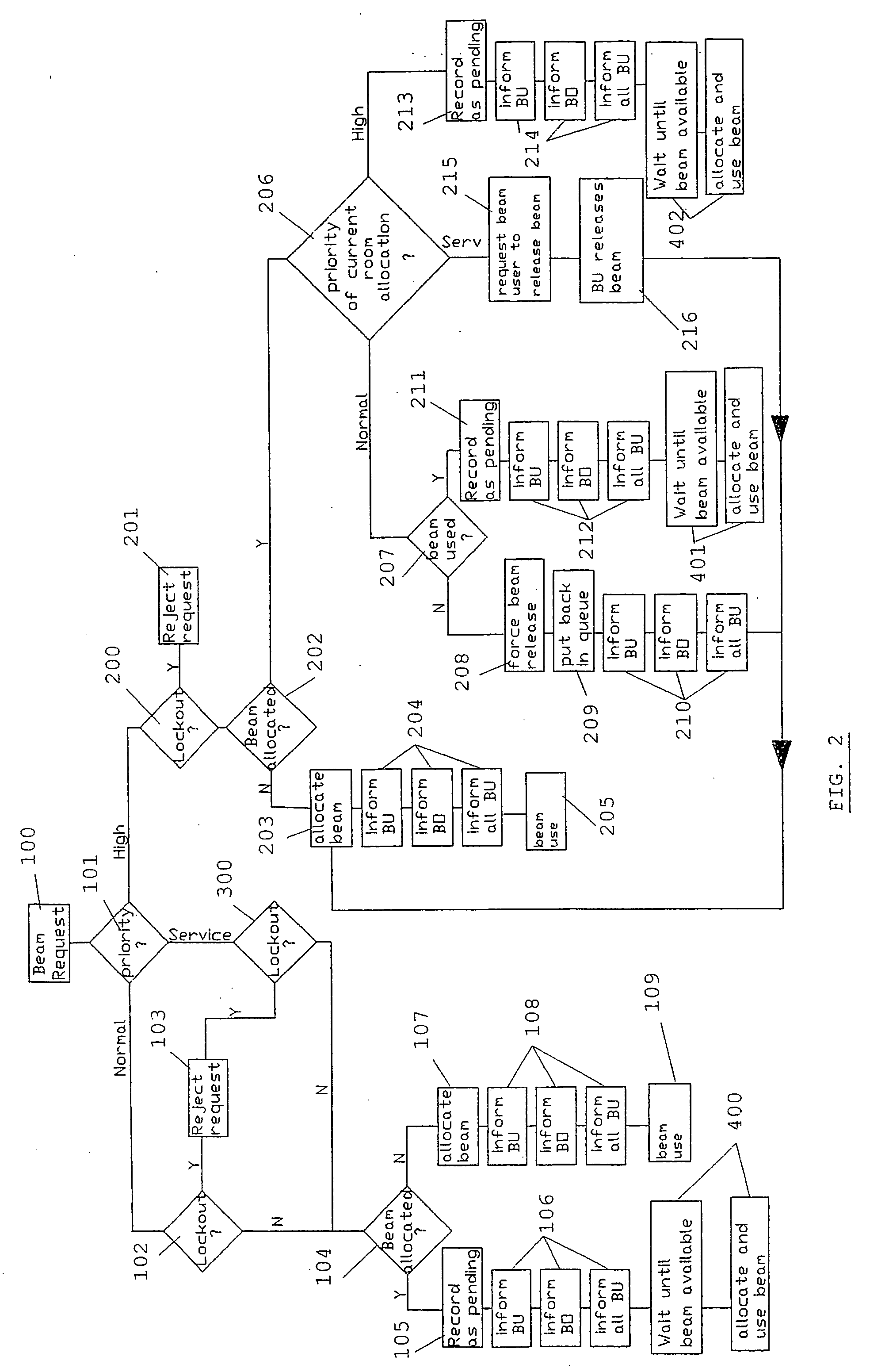
Method and system for automatic beam allocation in a multi-room particle beam treatment facility
InactiveUS20070018121A1Light therapyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyParticle beamLight beam
The present invention is related to a method and a system for automatically allocating a particle beam to one of a plurality of treatment rooms. Upon receiving a request from one of the beam users, the system checks whether the beam is available and may automatically allocate the beam to the requesting room. Otherwise, the request may be put on a waiting list of pending requests, in a position which depends on the priority level (and arrival lime) coupled to said request.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
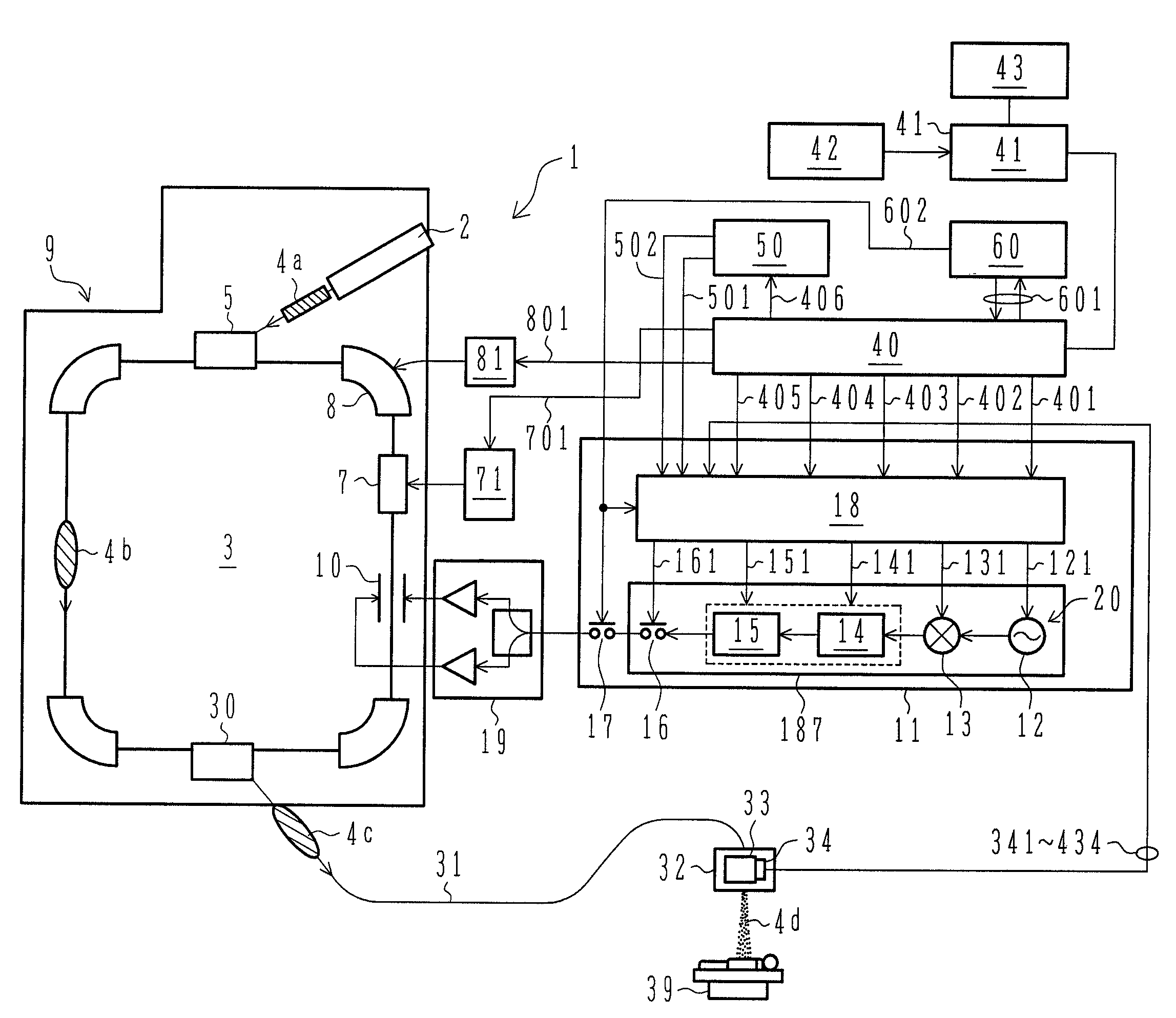
Particle beam irradiation system
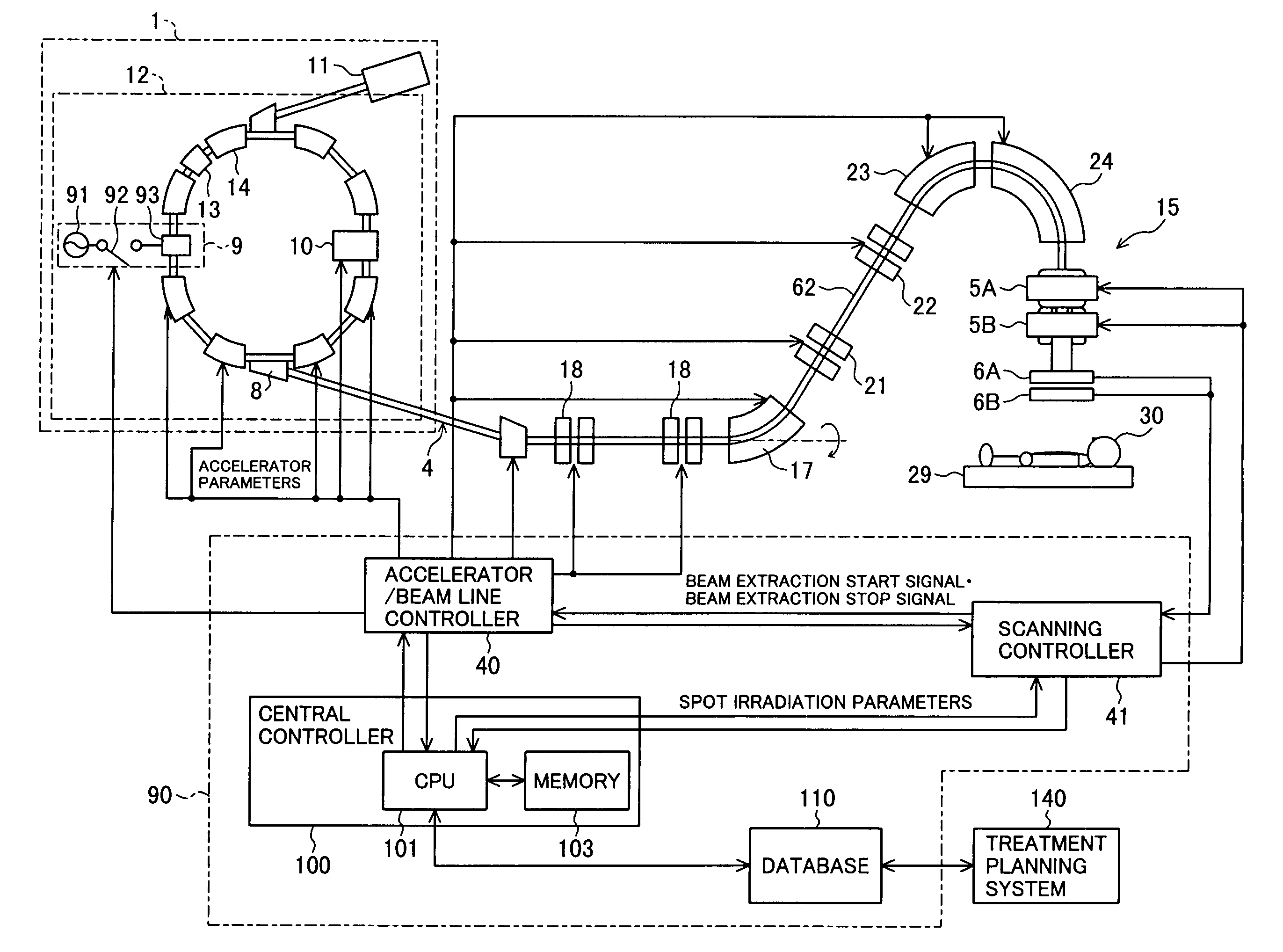
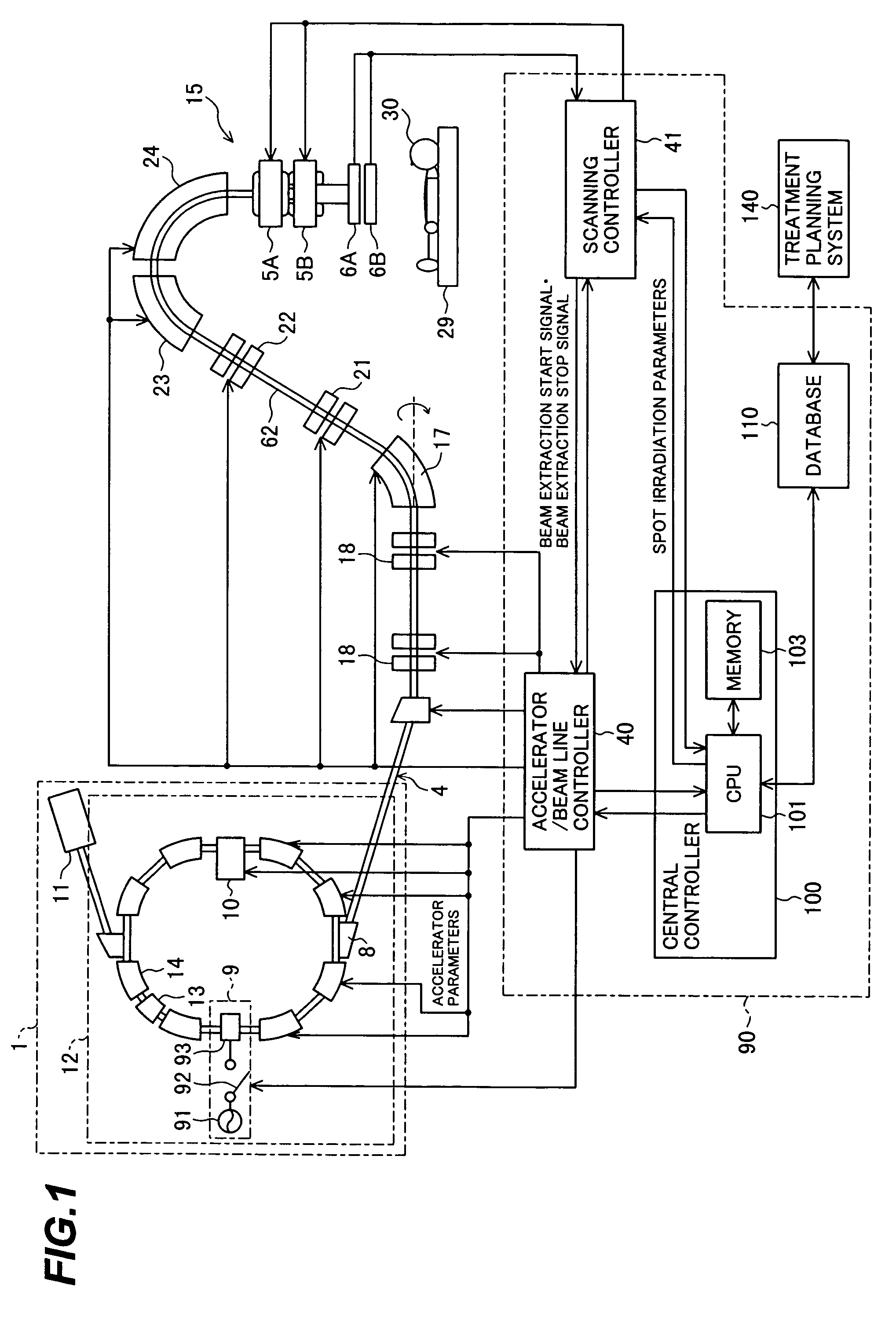
ActiveUS7807982B2Simplify device configurationEasy to controlLaser detailsParticle separator tubesIntensity controlSynchrotron
It is an object of the present invention to provide a charged particle beam extraction method and particle beam irradiation system that make it possible to exercise intensity control over an extracted ion beam while a simple device configuration is employed. To accomplish the above object, there is provided a particle beam irradiation system comprising: a synchrotron for accelerating and extracting an charged particle beam; an irradiation apparatus for extracting the charged particle beam that is extracted from the synchrotron; first beam intensity modulation means for controlling the beam intensity of the charged particle beam extracted from the synchrotron during an extraction control period of an operation cycle of the synchrotron; and second beam intensity modulation means for controlling the beam intensity during each of a plurality of irradiation periods contained in the extraction control period of the operation cycle.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
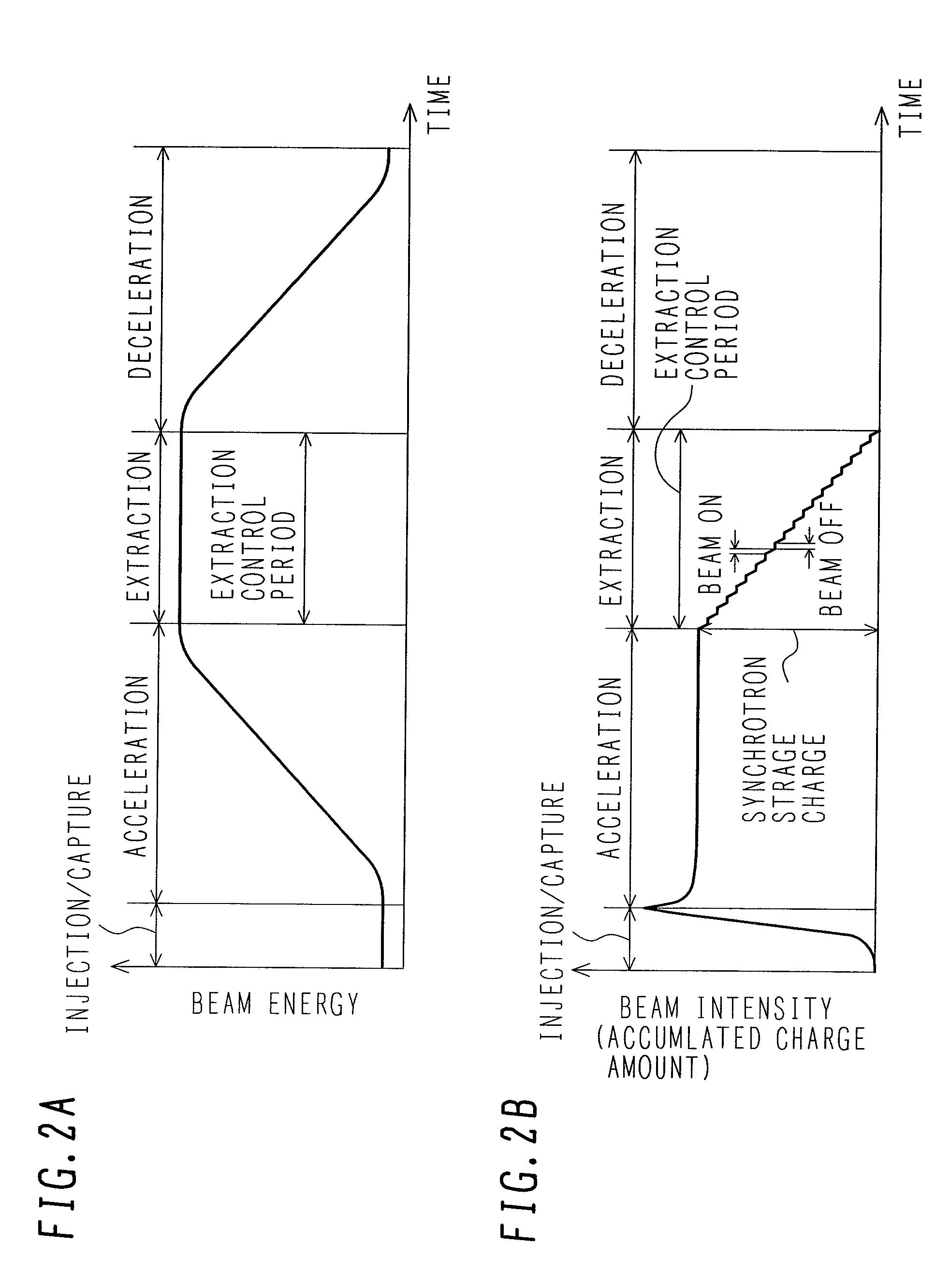
Particle beam irradiation system
ActiveUS7301162B2Minimize exposureUniform dose distributionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingParticle beamLight beam
A particle beam irradiation system capable of ensuring a more uniform dose distribution at an irradiation object even when a certain time is required from output of a beam extraction stop signal to the time when extraction of a charged particle beam from an accelerator is actually stopped. The particle beam irradiation system comprises a synchrotron, an irradiation device including scanning magnets and outputting an ion beam extracted from the synchrotron, and a control unit. The control unit stops the output of the ion beam from the irradiation device in accordance with the beam extraction stop signal, controls the scanning magnets to change an exposure position in a state in which the output of the ion beam is stopped, and after the change of the exposure position, starts the output of the ion beam from the irradiation device again. The control unit further outputs a next beam extraction stop signal when an increment of dose integrated from the time of a preceding beam extraction stop signal as a start point reaches a setting dose stored in advance.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Particle beam processing system
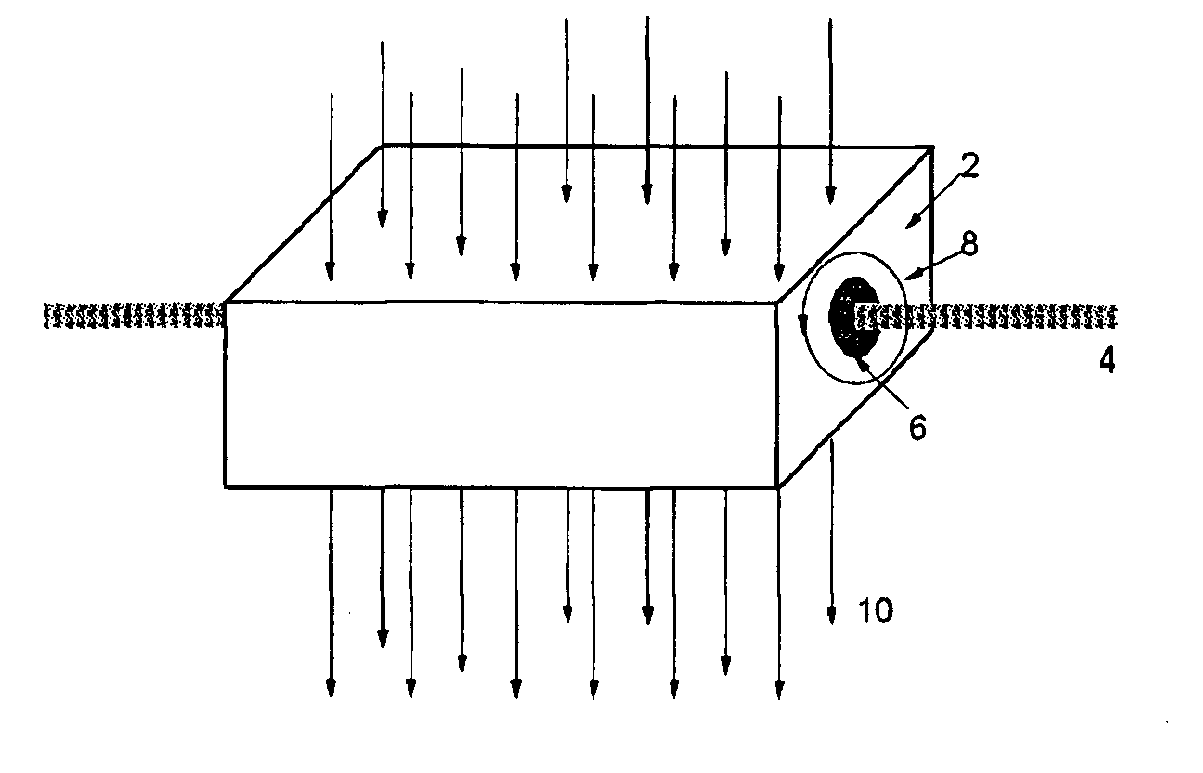
InactiveUS6838676B1Decreased beam sizeLow costStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis by optical meansParticle beamParticle physics
A method for slowing and controlling a beam of charged particles includes the steps of superimposing at least one magnetic field on a mass and passing the beam through the mass and at least one magnetic field such that the beam and the mass slows but does not stop the particles. An apparatus for slowing and controlling a beam of charged particles includes a bending magnetic field superimposed on a focusing magnetic field within a mass.
Owner:HBAR TECH LC
Two-photon or higher-order absorbing optical materials and methods of use
InactiveUS6267913B1Wide bandwidthOrganic chemistryRadiation applicationsChemical compoundElectron donor
Compositions capable of simultaneous two-photon absorption and higher order absorptivities are disclosed. Many of these compositions are compounds satisfying the formulae D-Π-D, A-Π-A, D-A-D and A-D-A, wherein D is an electron donor group, A is an electron acceptor group and Π comprises a bridge of pi-conjugated bonds connecting the electron donor groups and electron acceptor groups. In A-D-A and D-A-D compounds, the pi bridge is substituted with electron donor groups and electron acceptor groups, respectively. Also disclosed are methods that generate an electronically excited state of a compound, including those satisfying one of these formulae. The electronically excited state is achieved in a method that includes irradiating the compound with light. Then, the compound is converted to a multi-photon electronically excited state upon simultaneous absorption of at least two photons of light. The sum of the energies of all of the absorbed photons is greater than or equal to the transition energy from a ground state of the compound to the multi-photon excited state. The energy of each absorbed photon is less than the transition energy between the ground state and the lowest single-photon excited state of the compound is less than the transition energy between the multi-photon excited state and the ground state.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
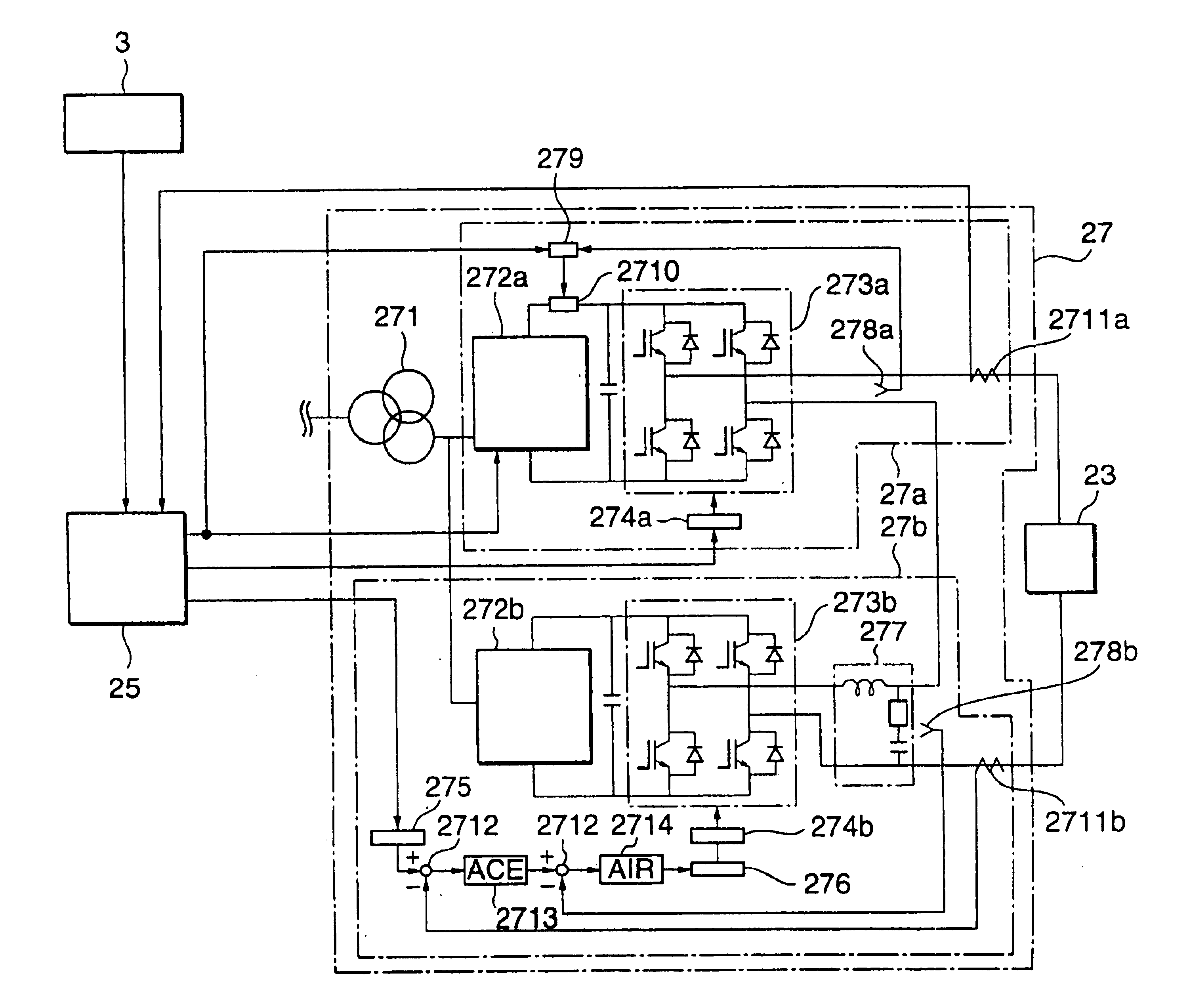
Adiabatic quantum computation with superconducting qubits
ActiveUS20050224784A1Increasing effective charging energyQuantum computersNanoinformaticsAdiabatic quantum computationComputational problem
A method for computing using a quantum system comprising a plurality of superconducting qubits is provided. Quantum system can be in any one of at least two configurations including (i) an initialization Hamiltonian H0 and (ii) a problem Hamiltonian HP. The plurality of superconducting qubits are arranged with respect to one another, with a predetermined number of couplings between respective pairs of superconducting qubits in the plurality of qubits, such that the plurality of superconducting qubits, coupled by the predetermined number of couplings, collectively define a computational problem to be solved. In the method, quantum system is initialized to the initialization Hamiltonian HO. Quantum system is then adiabatically changed until it is described by the ground state of the problem Hamiltonian HP. The quantum state of quantum system is then readout thereby solving the computational problem to be solved.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Tagged particles for downhole application
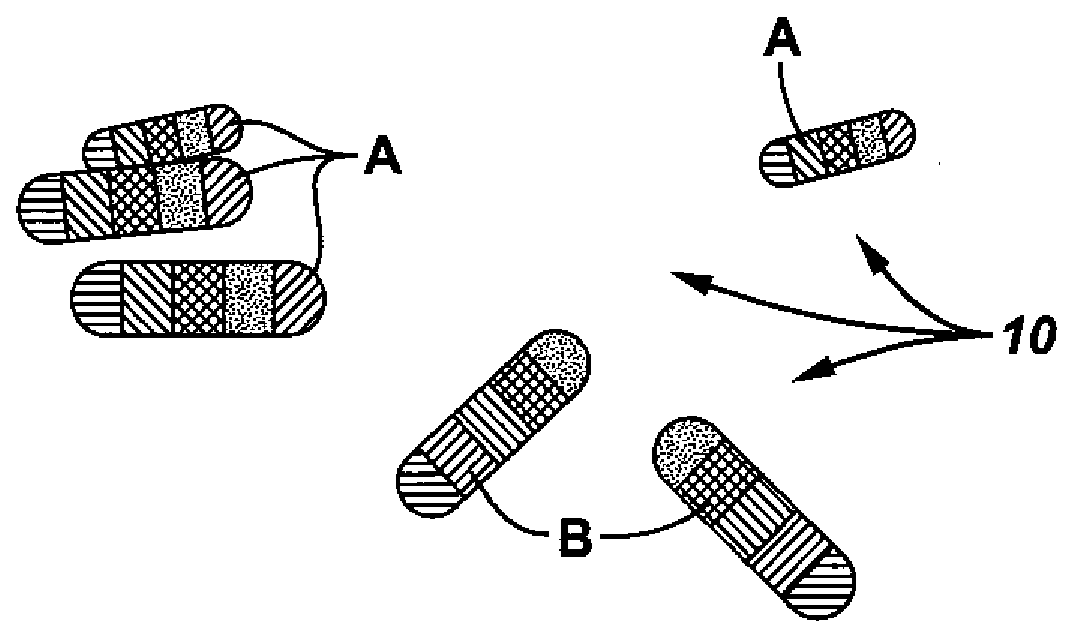
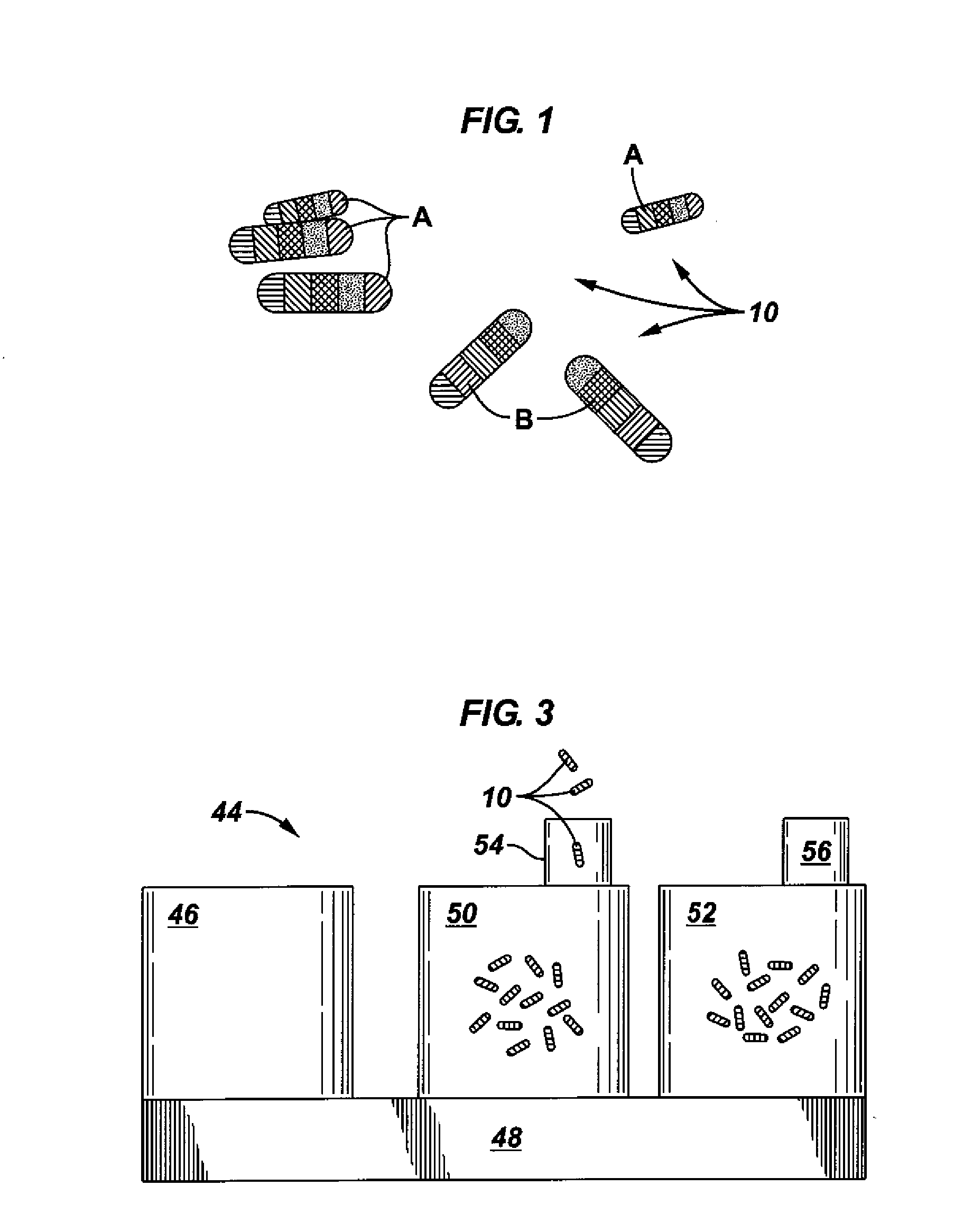
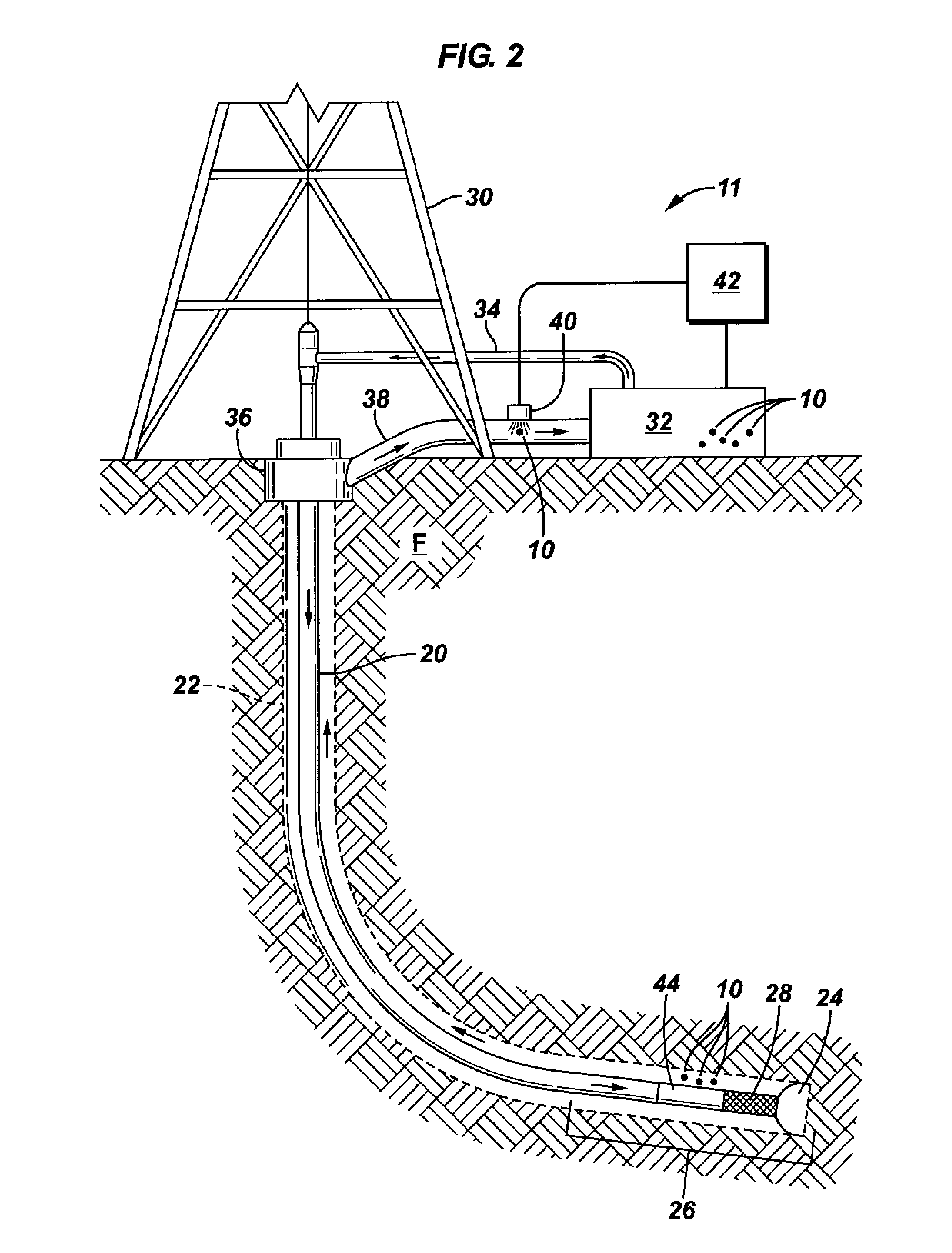
A tagged object includes a main body and a plurality of coded particles. Each coded particle may have a miniature body and be configured to provide a resolvable optical emission pattern when illuminate. The plurality of coded particles may be immobilized to the main body. A method for performing oilfield monitoring may include disposing of different types of tagged objects at different locations, wherein the different types of tagged objects each comprise a plurality of coded particles. Each of the coded particles may have a miniature body containing rare earth elements configured to produce a unique optical emission pattern when illuminated. The method may include allowing an event to trigger the release of one of the different types of tagged objects from one of the different locations. In addition, the method may include identifying the released tagged objects by unique optical emission patterns, in some cases in order to determining an occurrence location of the event.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
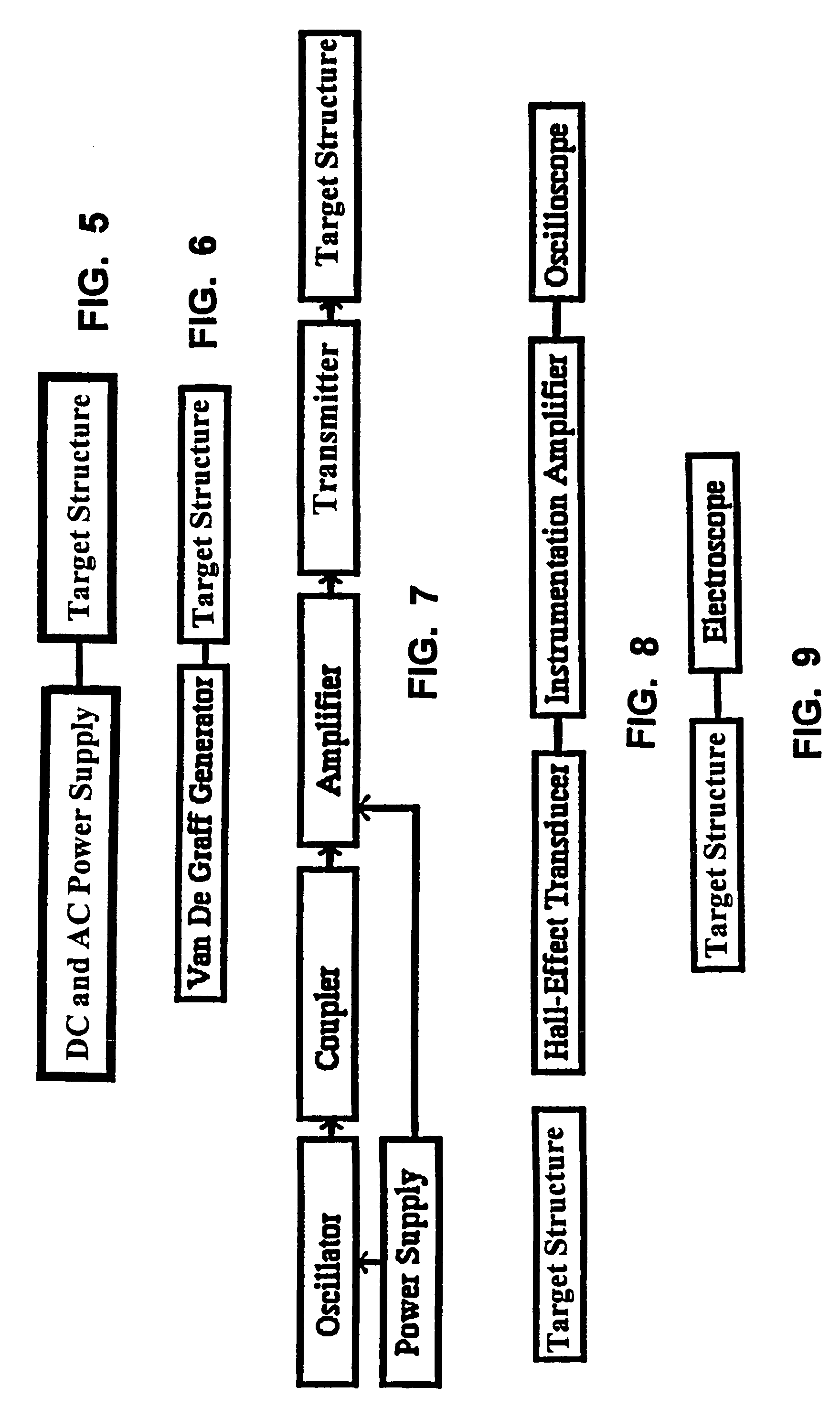
Charged particle beam irradiation equipment and control method thereof
InactiveUS6881970B2Short timeIrradiation time can be shortenedThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersParticle physicsElectrical current
A power supply for applying a voltage to a scanning electromagnet for deflecting a charged particle beam has a first power supply unit having no filter and a second power supply unit having a filter. When an irradiation position of the charged particle beam in an irradiation object is moved, the first power supply unit, namely a power supply unit having no filter, is used to apply the voltage to the scanning electromagnet, so that an exciting current flowing in the scanning electromagnet can be changed in a short time. Further, when the irradiation position of the charged particle beam is maintained, the second power supply is used to apply a voltage whose pulsating component was removed to the scanning electromagnet, so that the exciting current flowing in the scanning electromagnet can be controlled precisely. Consequently, the charged particle beam can be applied uniformly to the irradiation object and an irradiation time of the charged particle beam to the irradiation object can be curtailed.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Testing apparatus using charged particles and device manufacturing method using the testing apparatus
ActiveUS7138629B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesIlluminanceBeam source
Owner:EBARA CORP
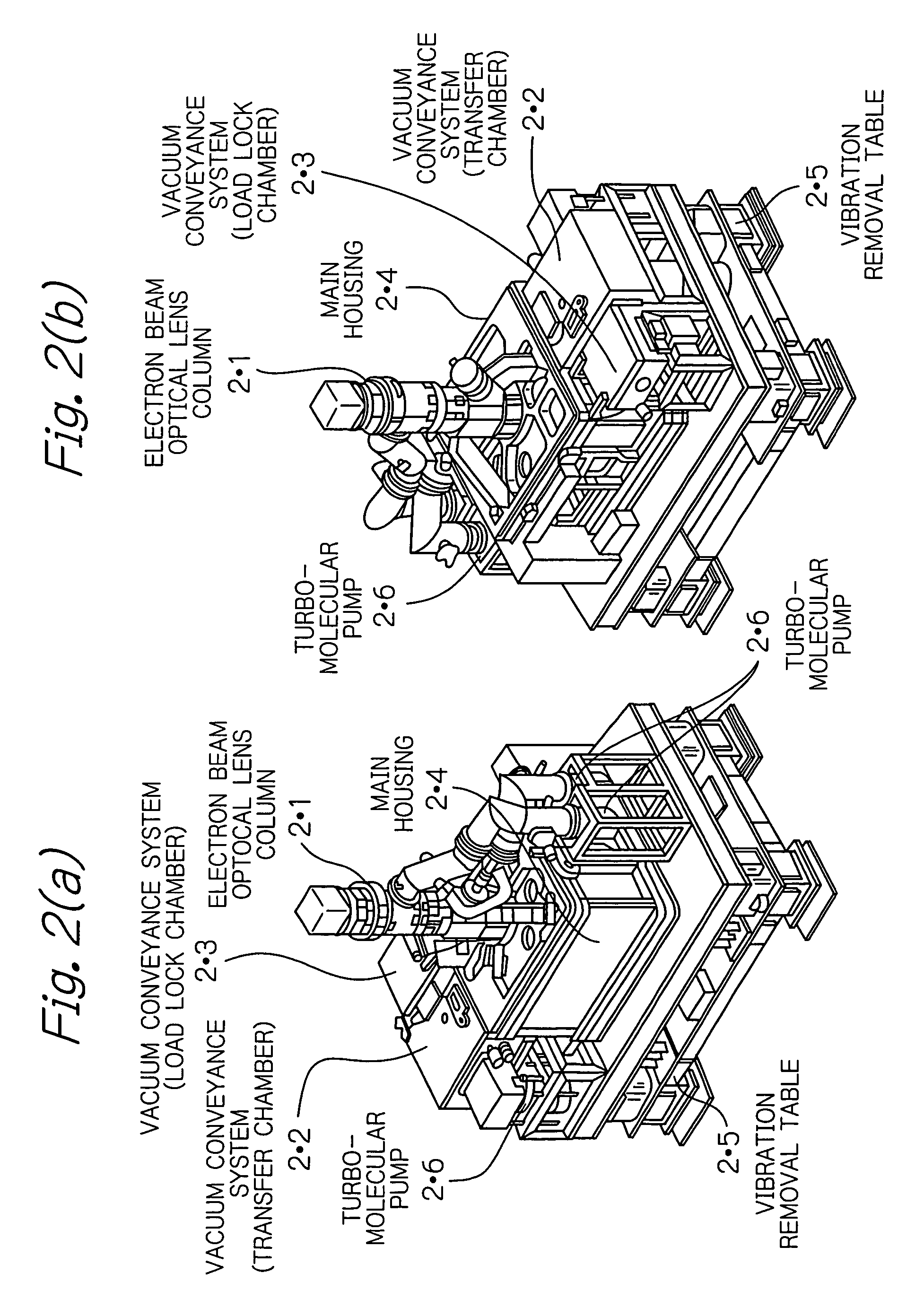
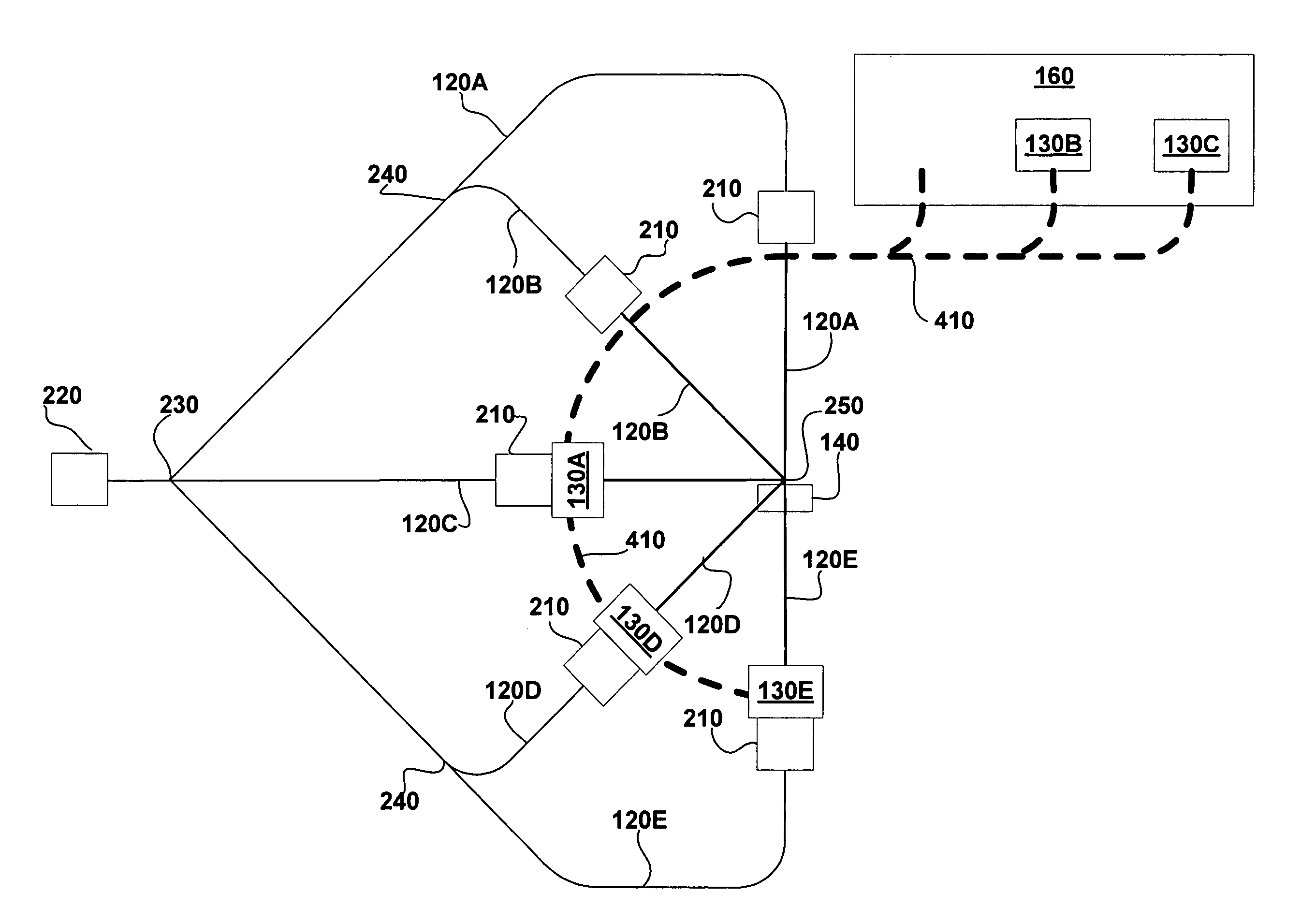
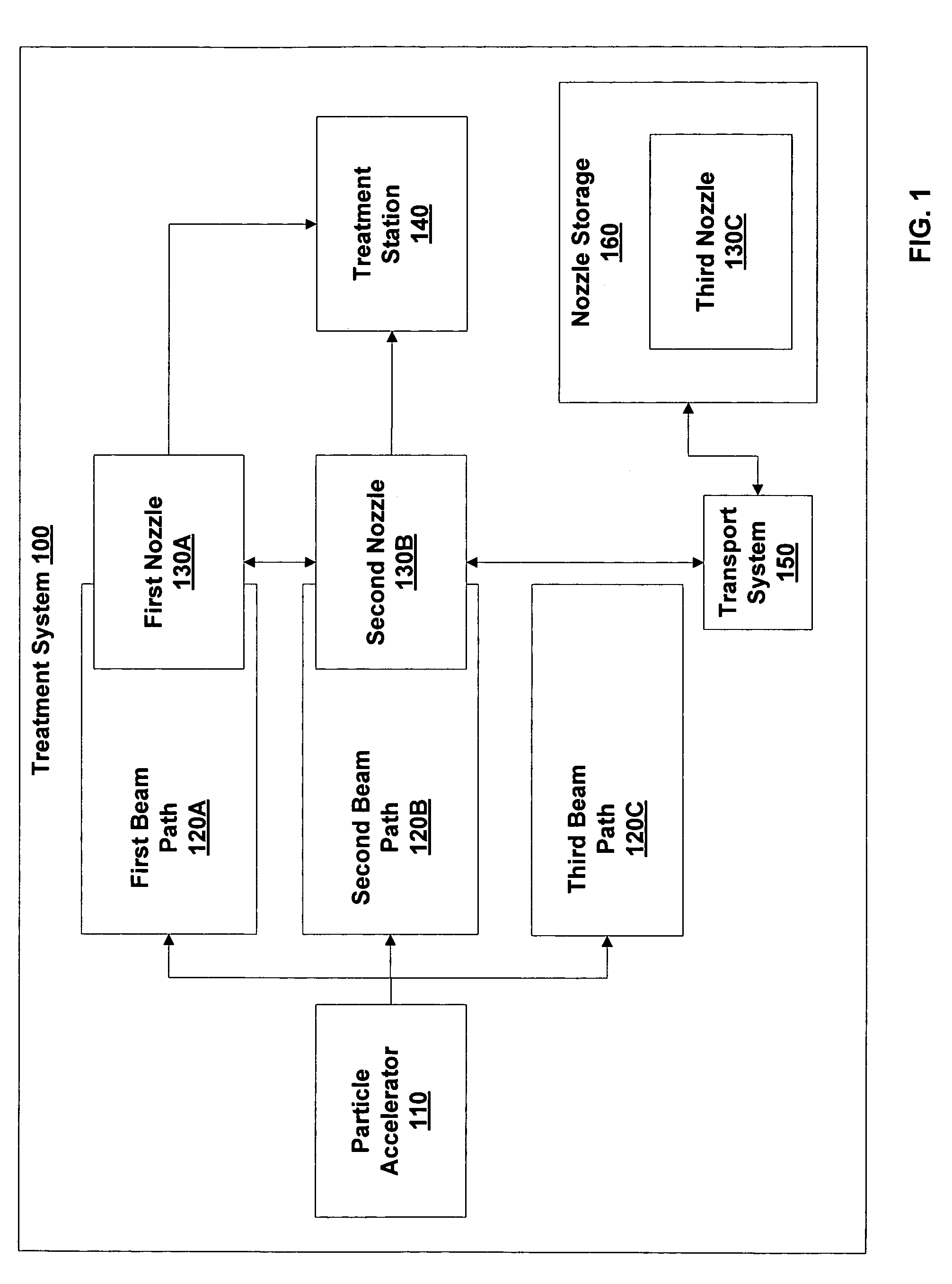
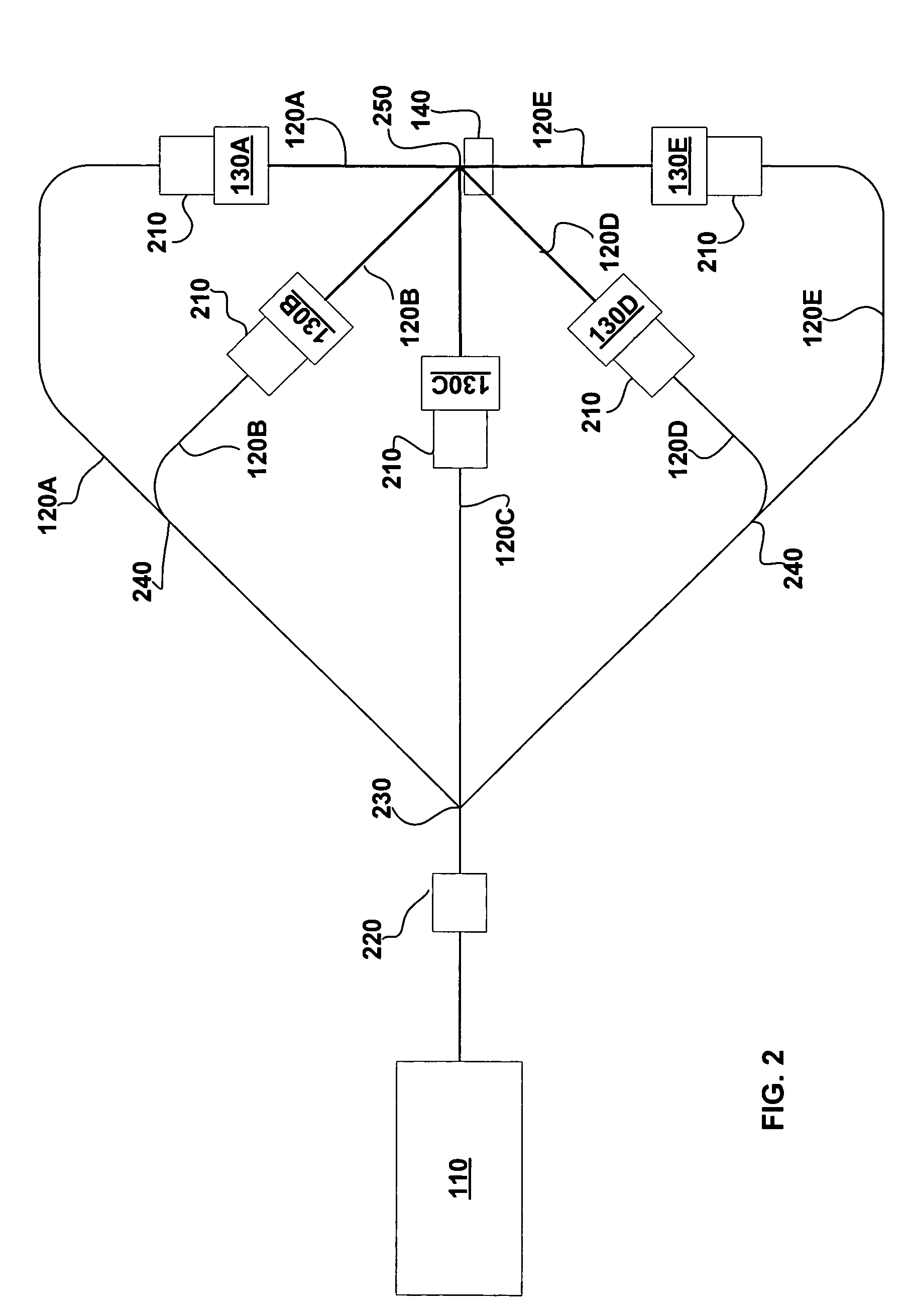
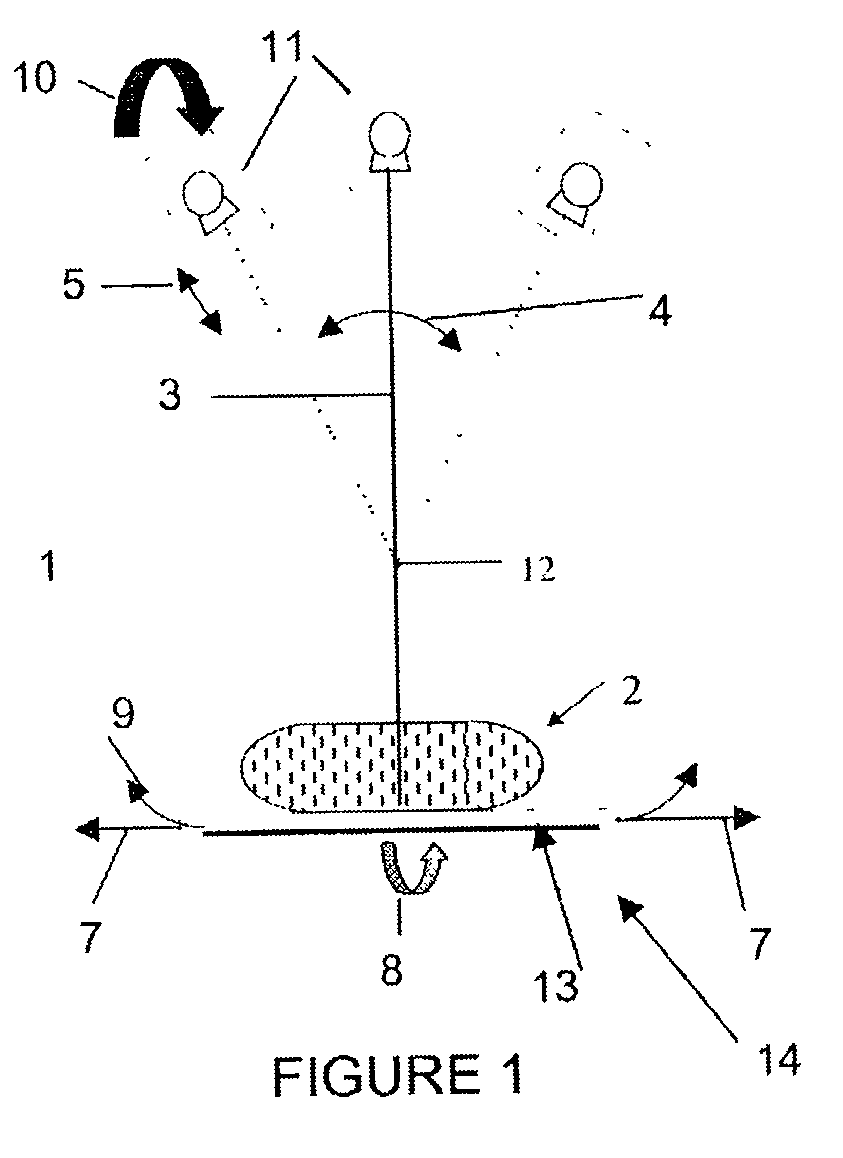
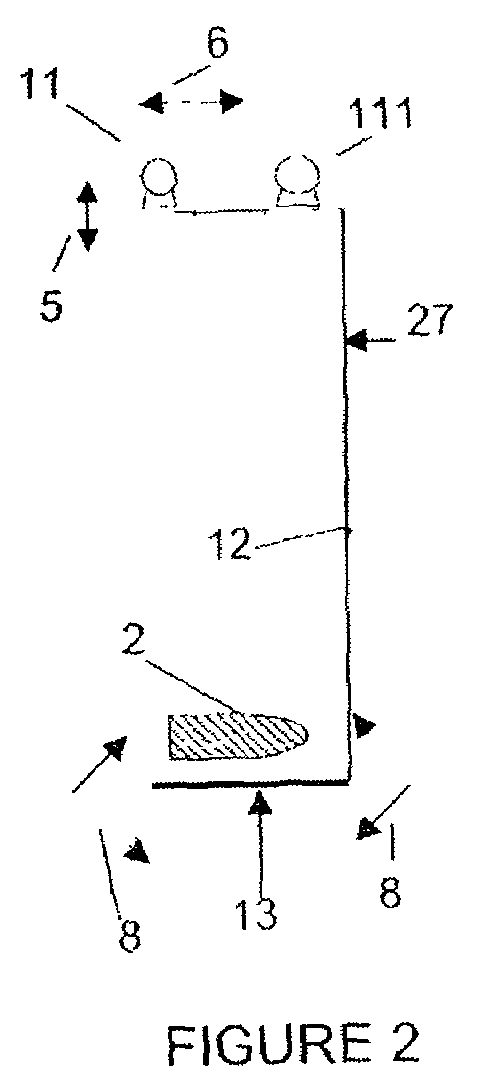
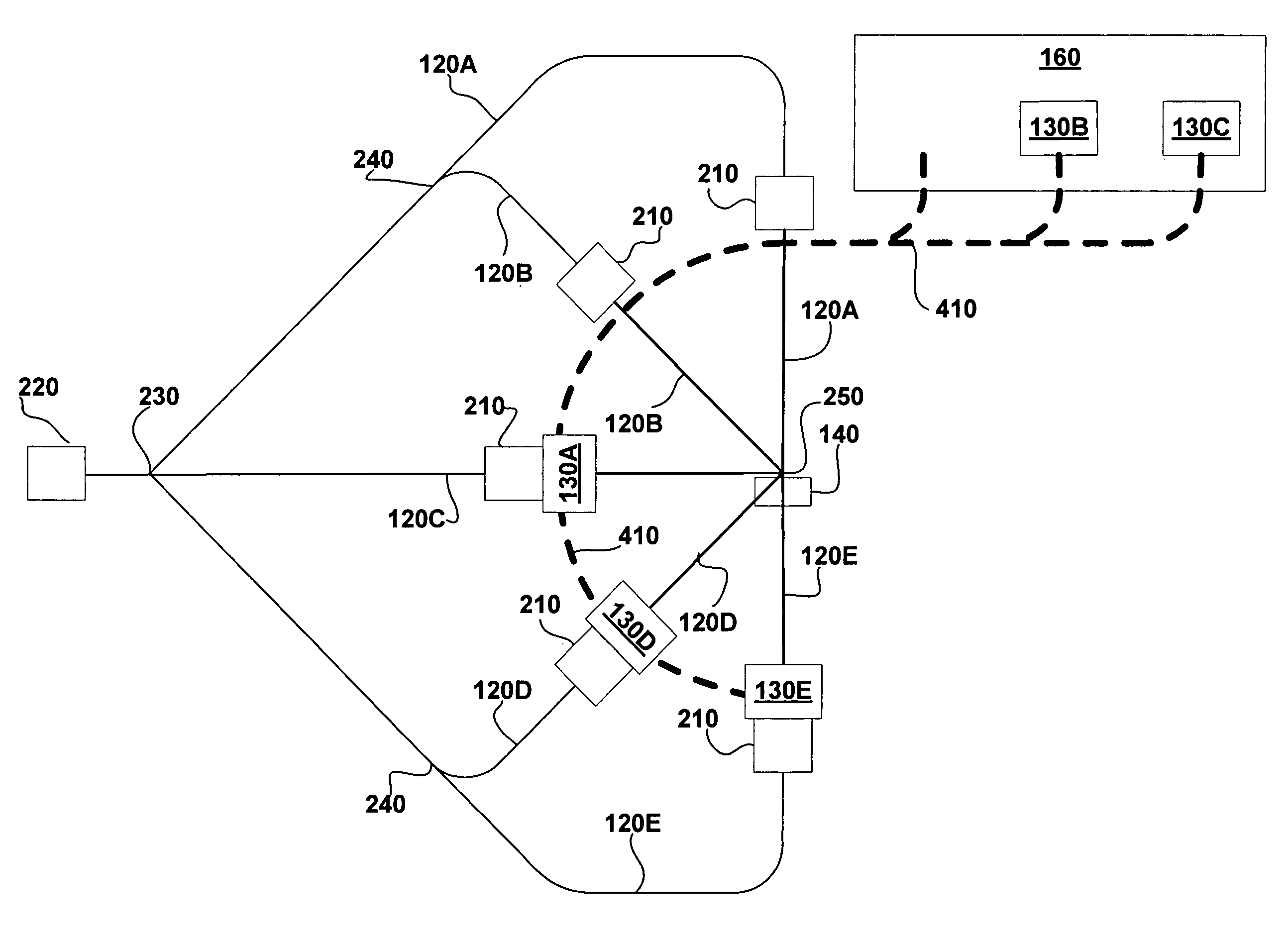
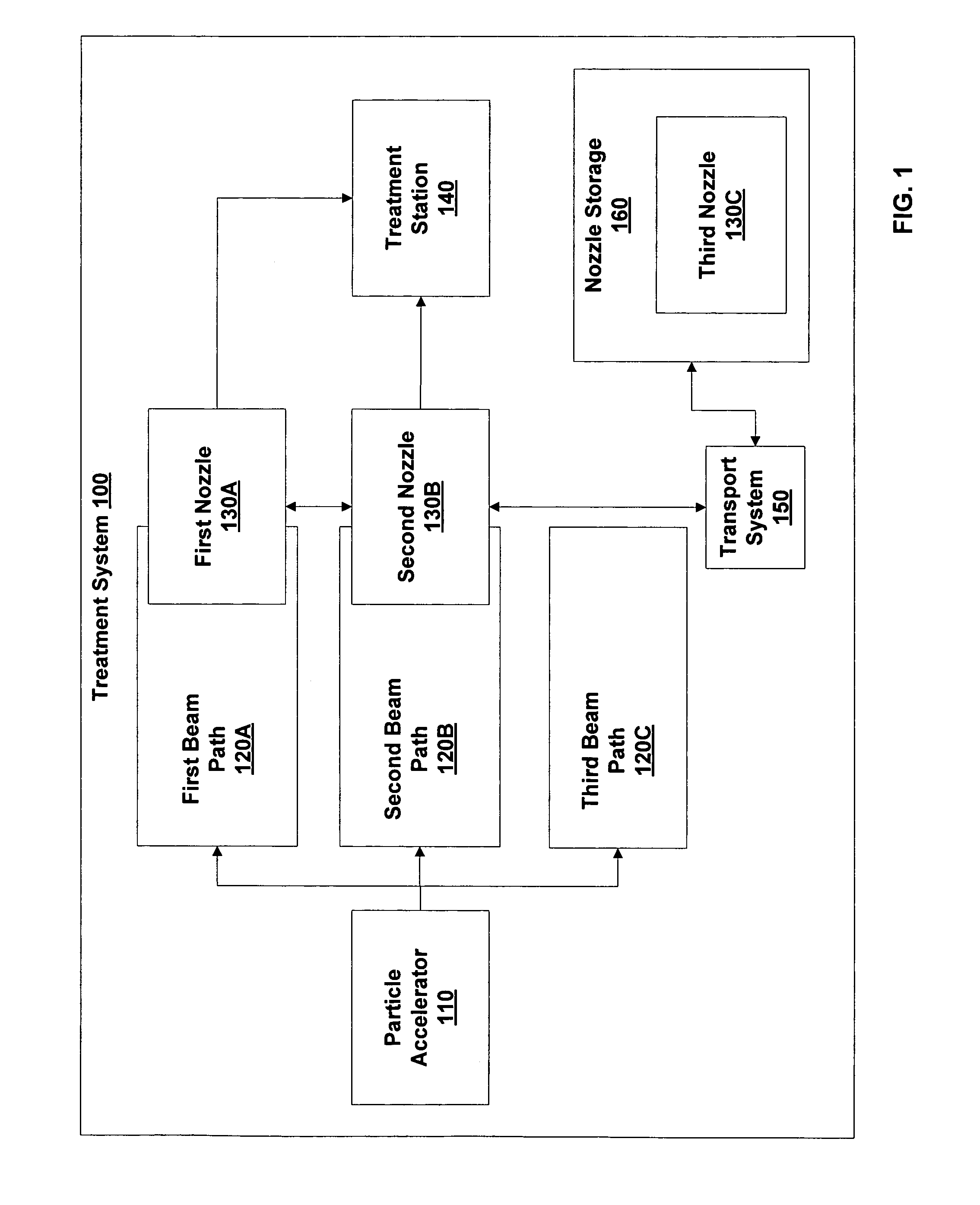
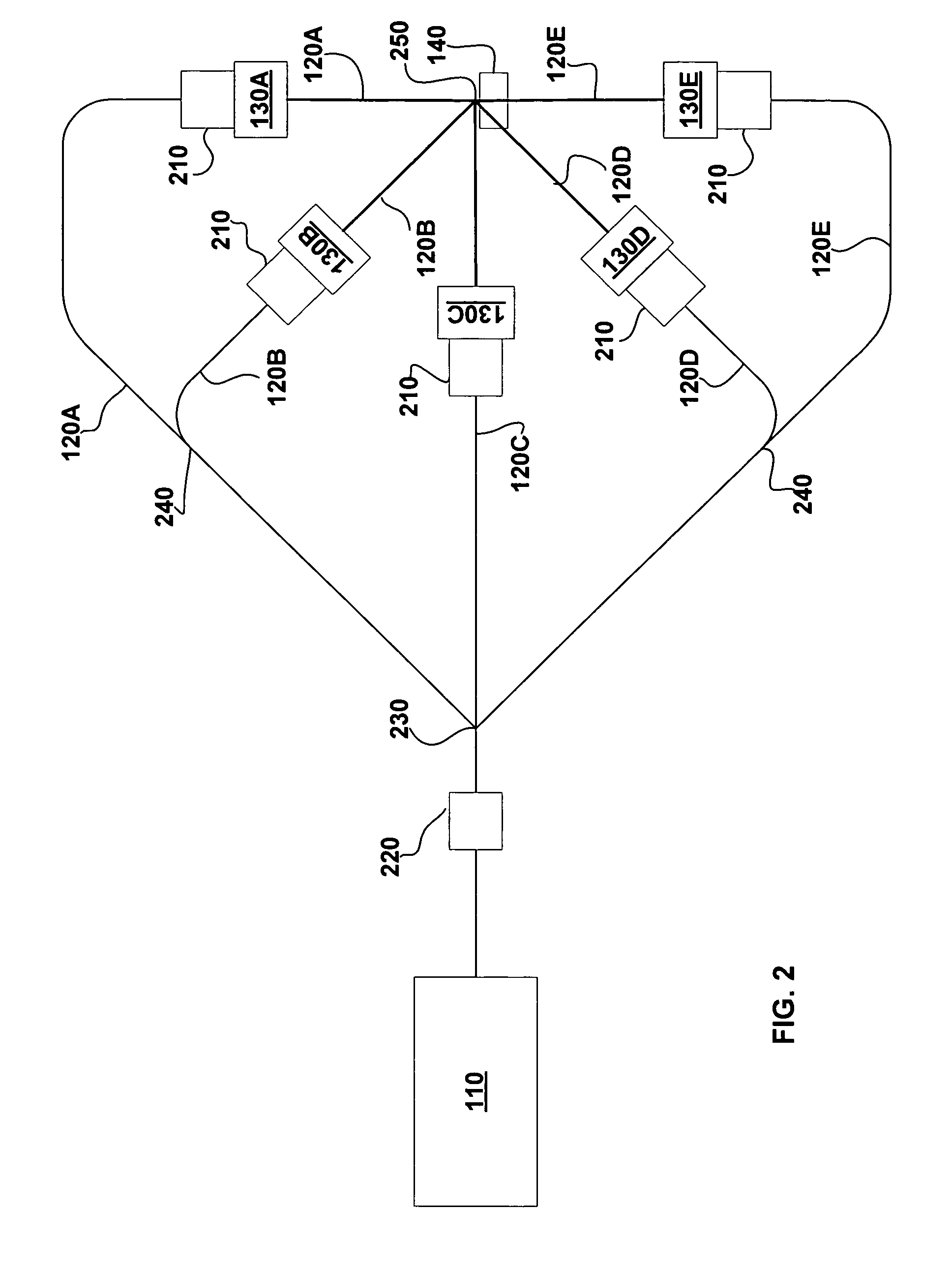
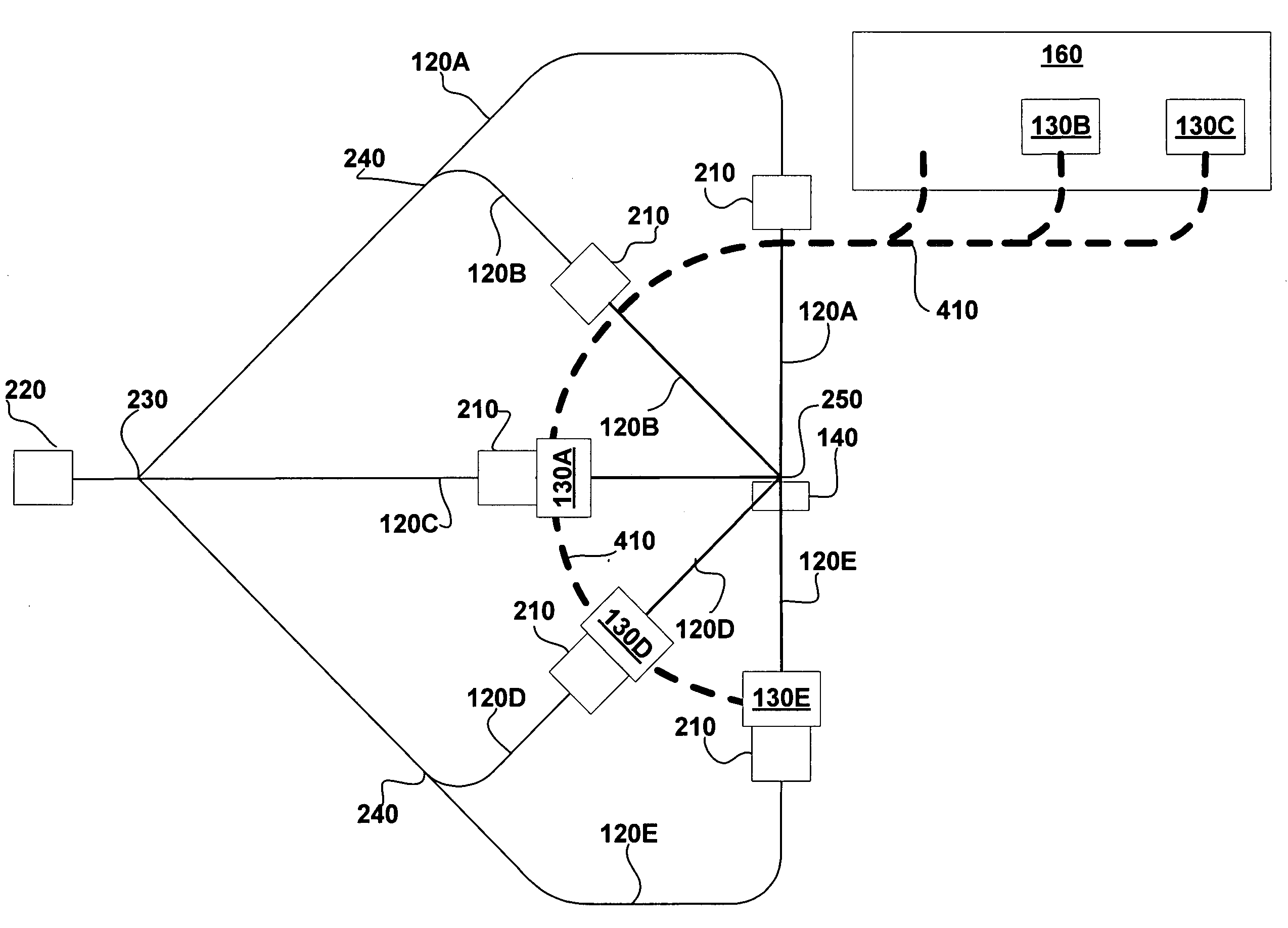
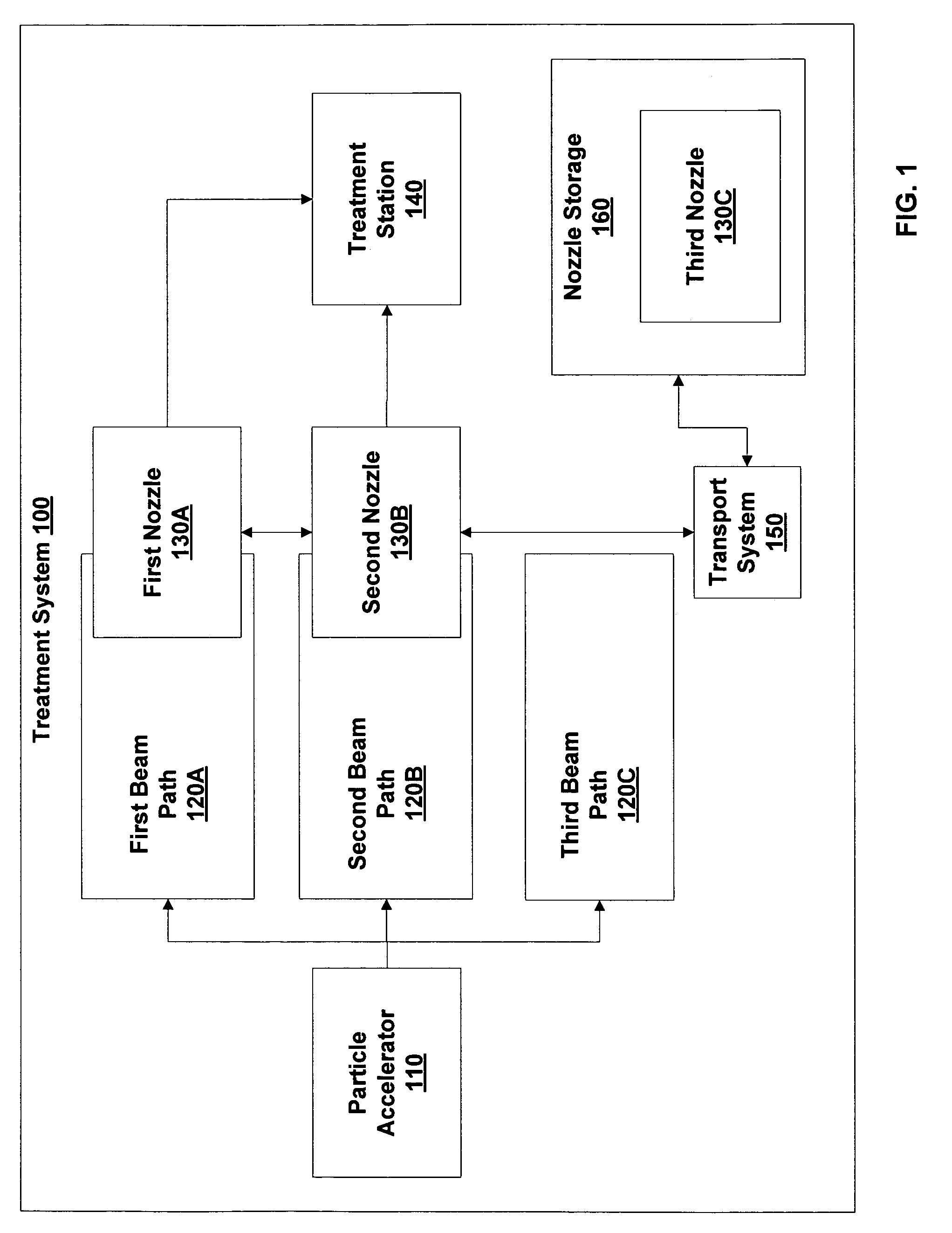
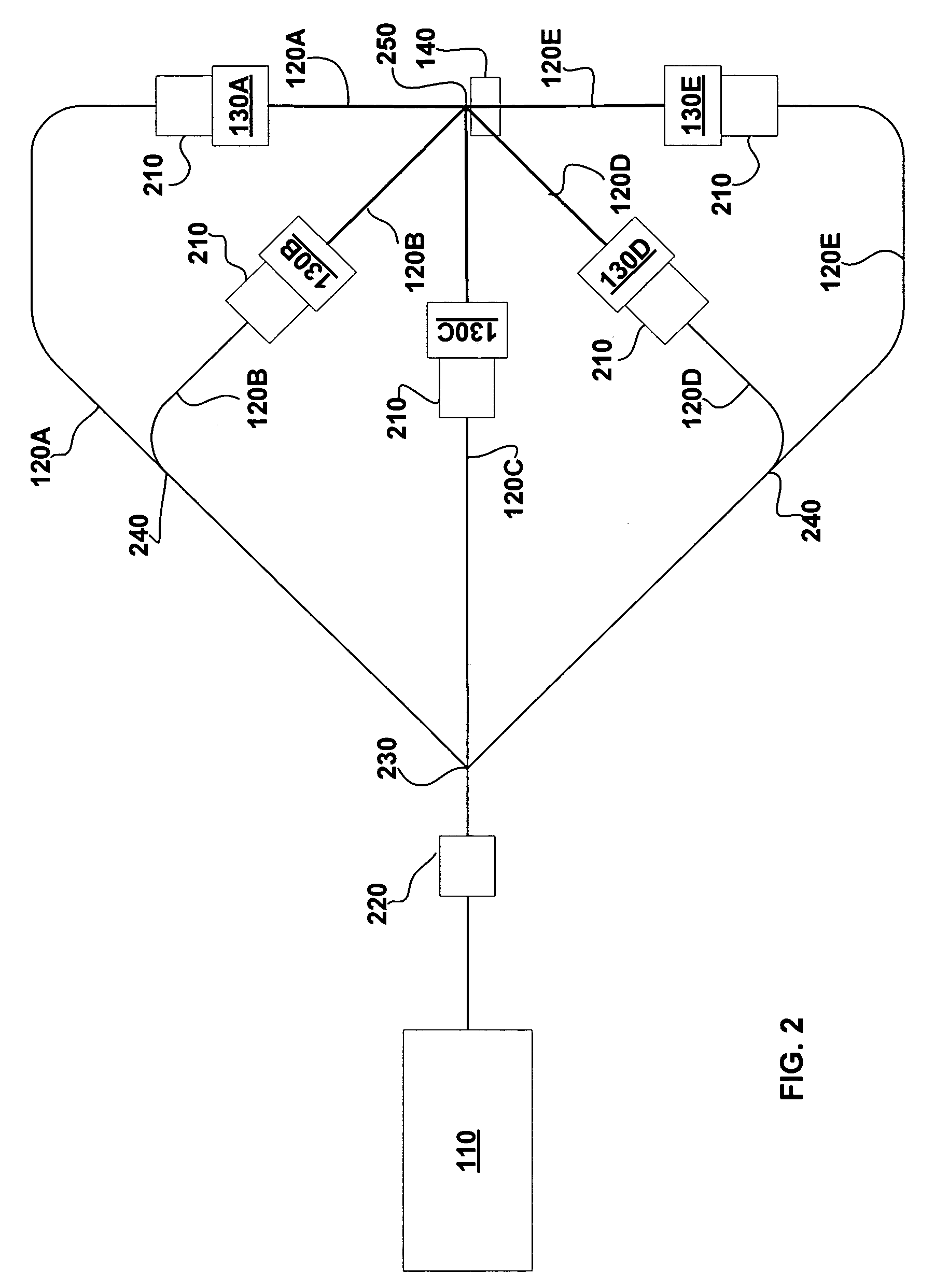
Particle beam nozzle transport system
InactiveUS7402822B2AcceleratorsChemical conversion by chemical reactionTransport systemParticle beam
An improved particle beam treatment system optionally includes exchangeable particle beam nozzles. These particle beam nozzles may be automatically moved from a storage location to a particle beam path or between particle beam paths for use in medical applications. Movement may be achieved using a conveyance, gantry, rail system, or the like. The improved particle beam treatment system optionally also includes more than two alternative particle beam paths. These alternative particle beam paths may be directed to a patient from a variety of different angles and in different planes.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Method And Software For Irradiating A Target Volume With A Particle Beam And Device Implementing Same
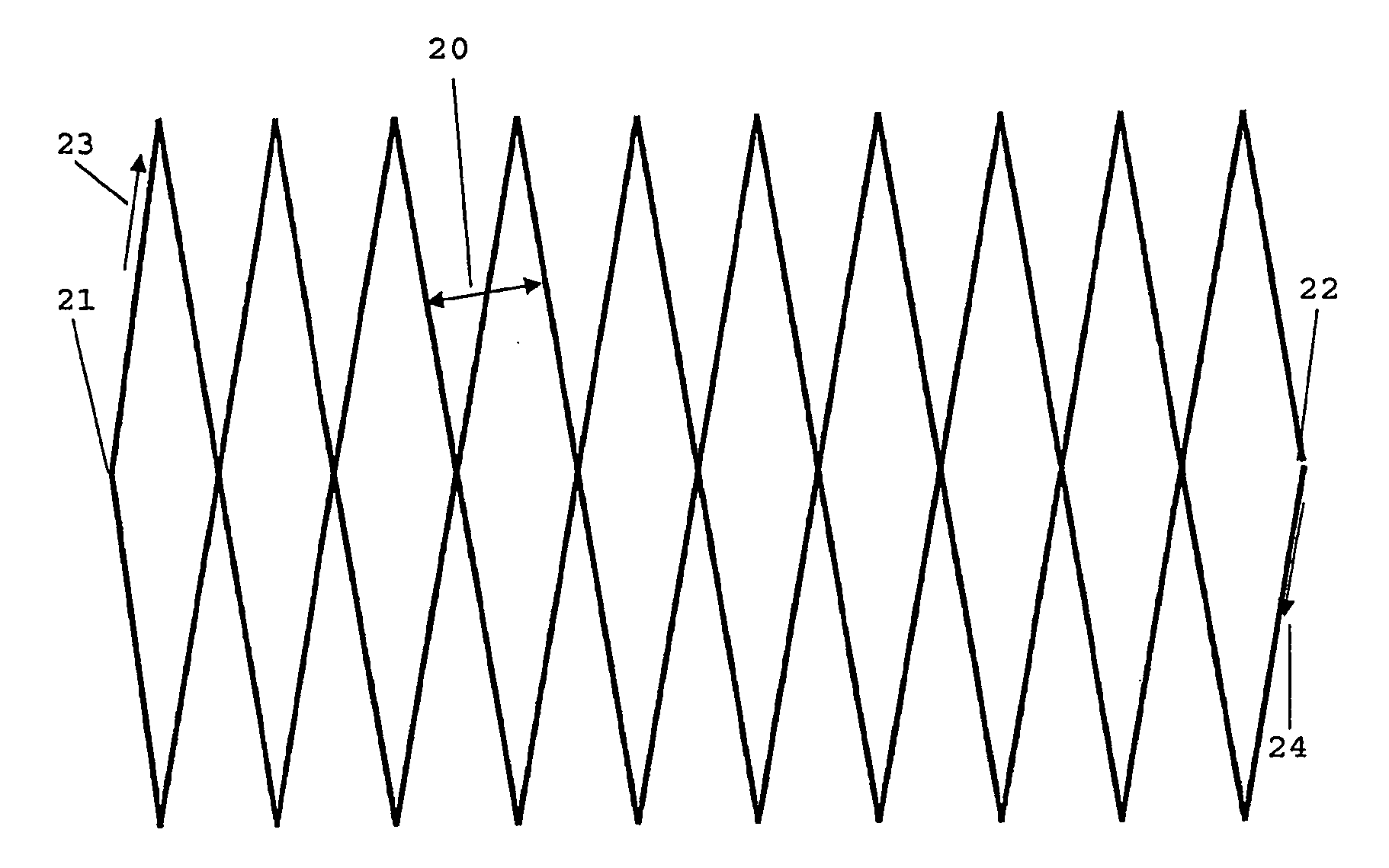
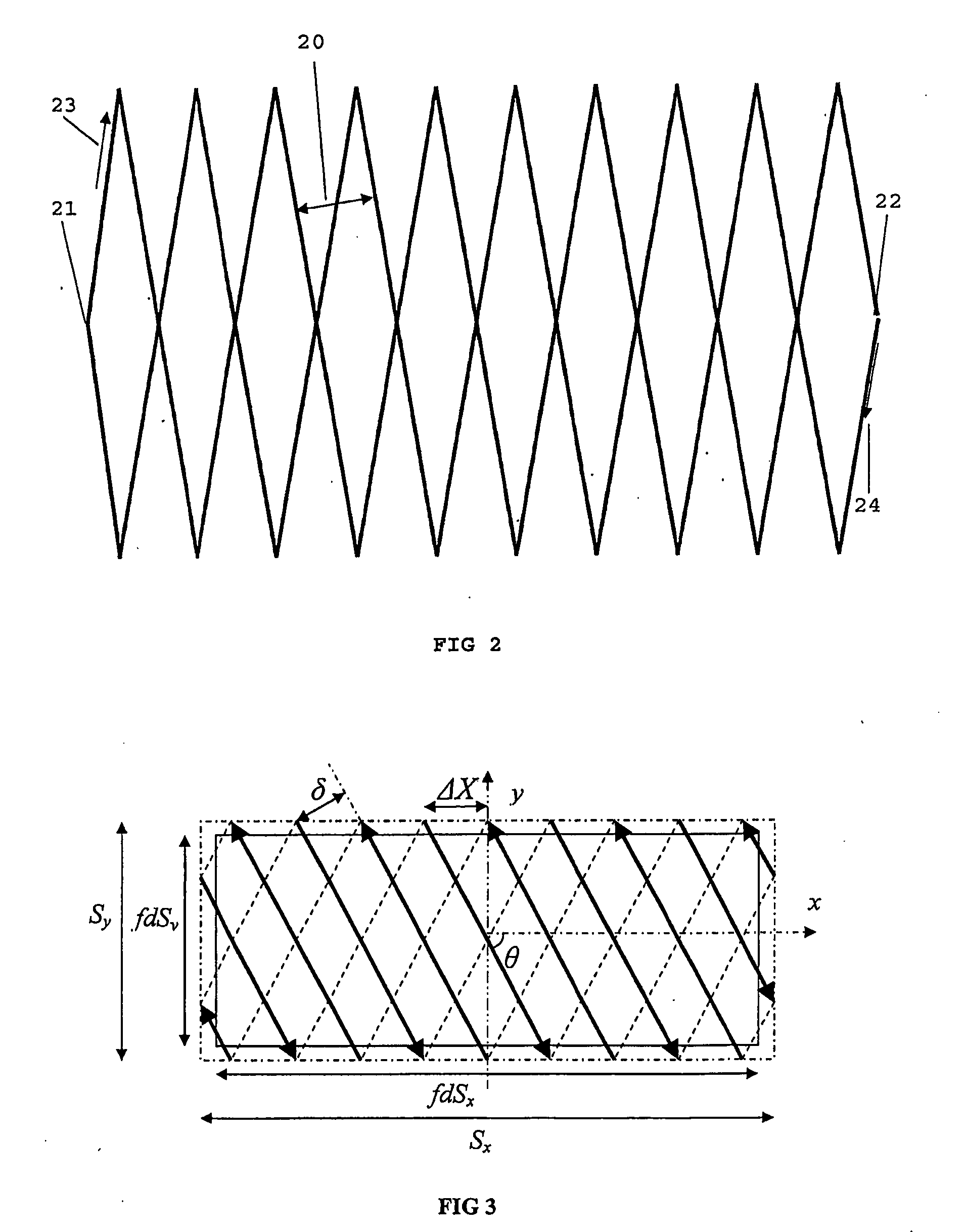
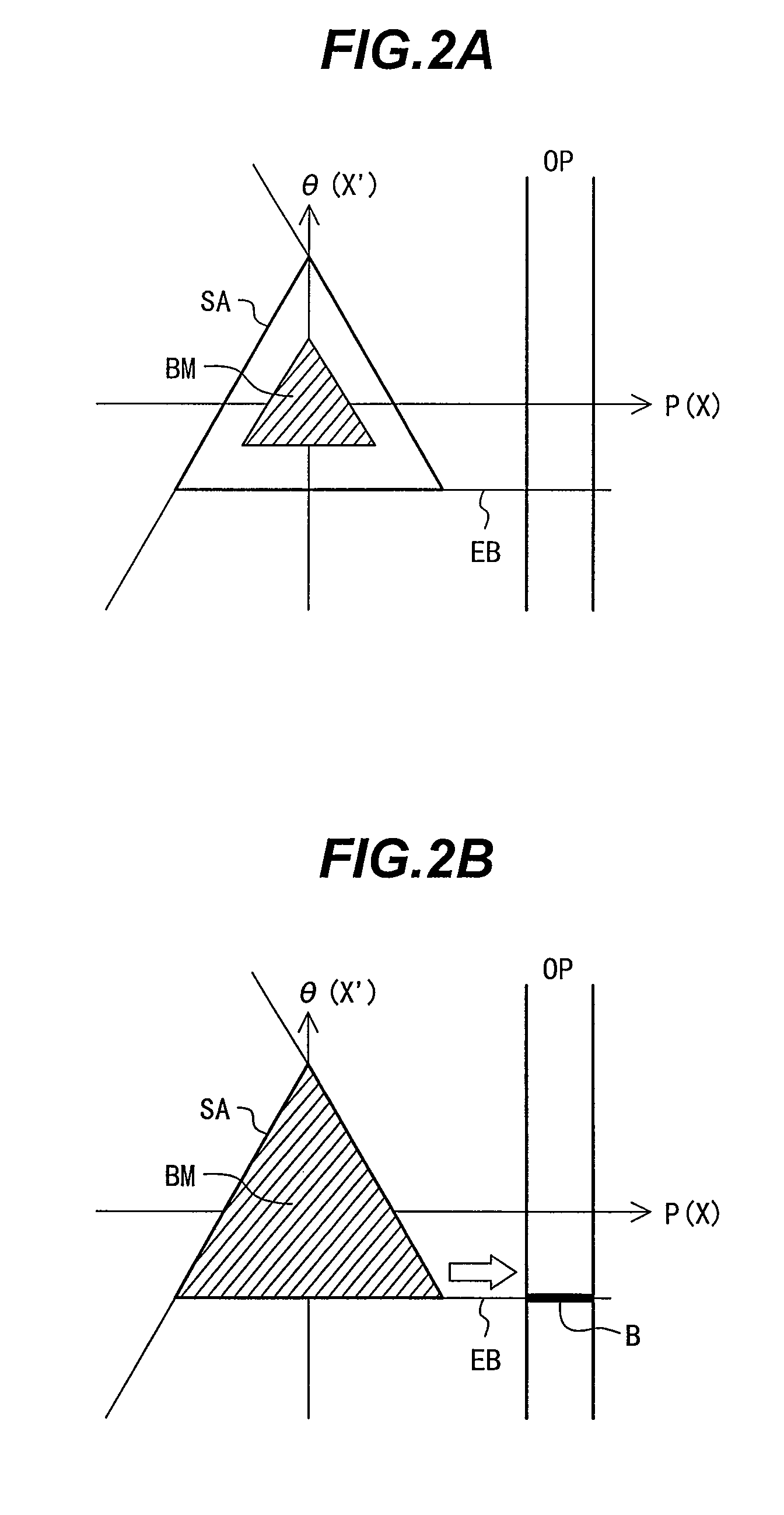
The present invention is related to a method for treating or irradiating a target volume with a particle beam produced by an accelerator, comprising the steps of: deflecting said particle beam with the help of scanning means in two orthogonal (X, Y) directions, thereby constituting an irradiation plane perpendicular to the direction (Z) of the beam, defining in the irradiation plane a scanning field which circumscribes the area of intersection of target volume and irradiation plane and scanning said scanning field by drawing scan lines which form a scan pattern comprising interleaved frames of triangle waves. The scan pattern is preferably continuous and represents contiguous rhombi figures. The invention is equally related to a device and a software program or sequencer implementing the method.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
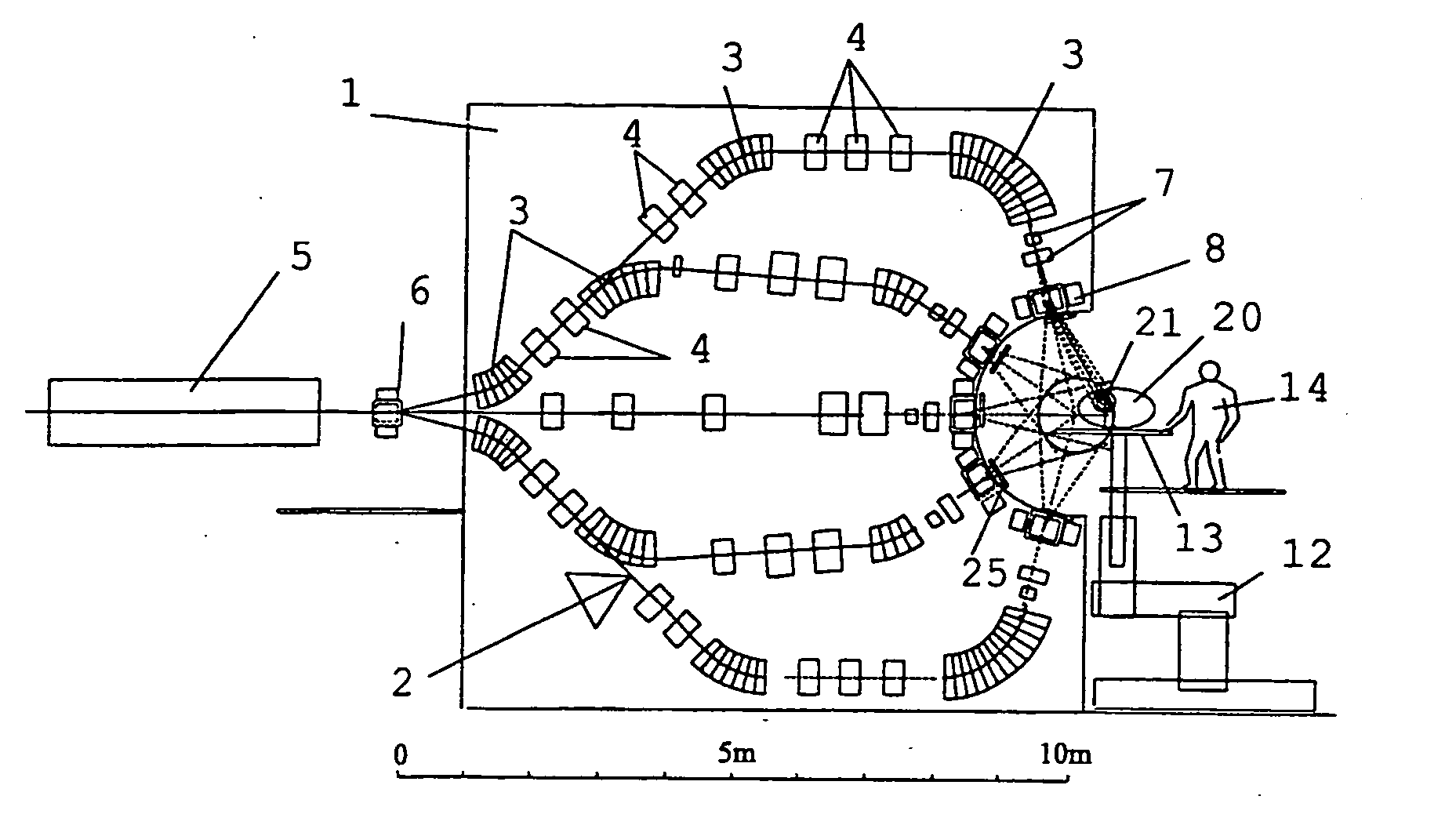
Device for irradiation therapy with charged particles
InactiveUS20060106301A1Radiation/particle handlingElectric discharge tubesVertical planeGonial angle
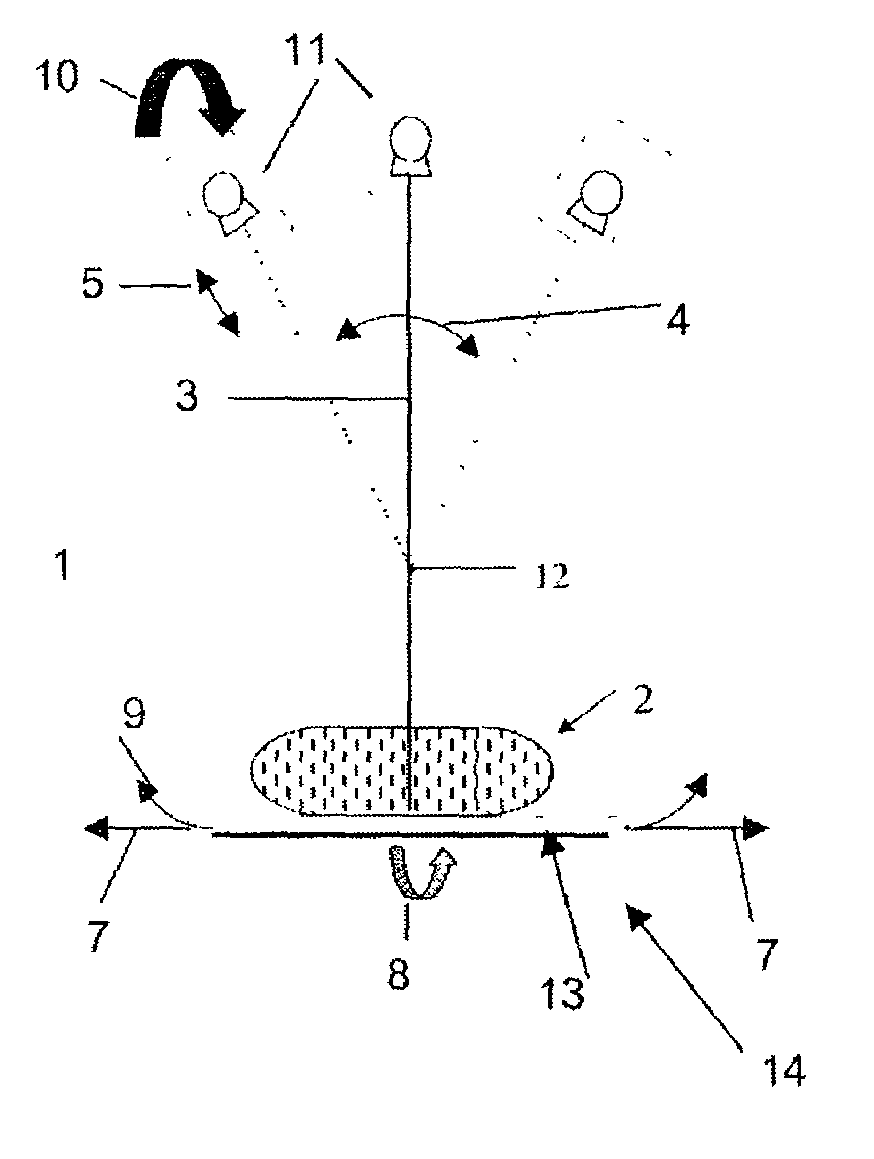
The present invention is related to a device for irradiating a patient with a charged particle beam, comprising a number of beam channels attached to a vertical wall, wherein a deflection magnet is present at the end of each channel. This deflection magnet is able to deflect the beam in the vertical plane over a given angle range. The couch whereon the patient is reclining is mobile in the vertical plane, so that the combined movement of the patient, and the variable deflection of the beam allow one point in the patient to be irradiated from several angles in the vertical plane.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
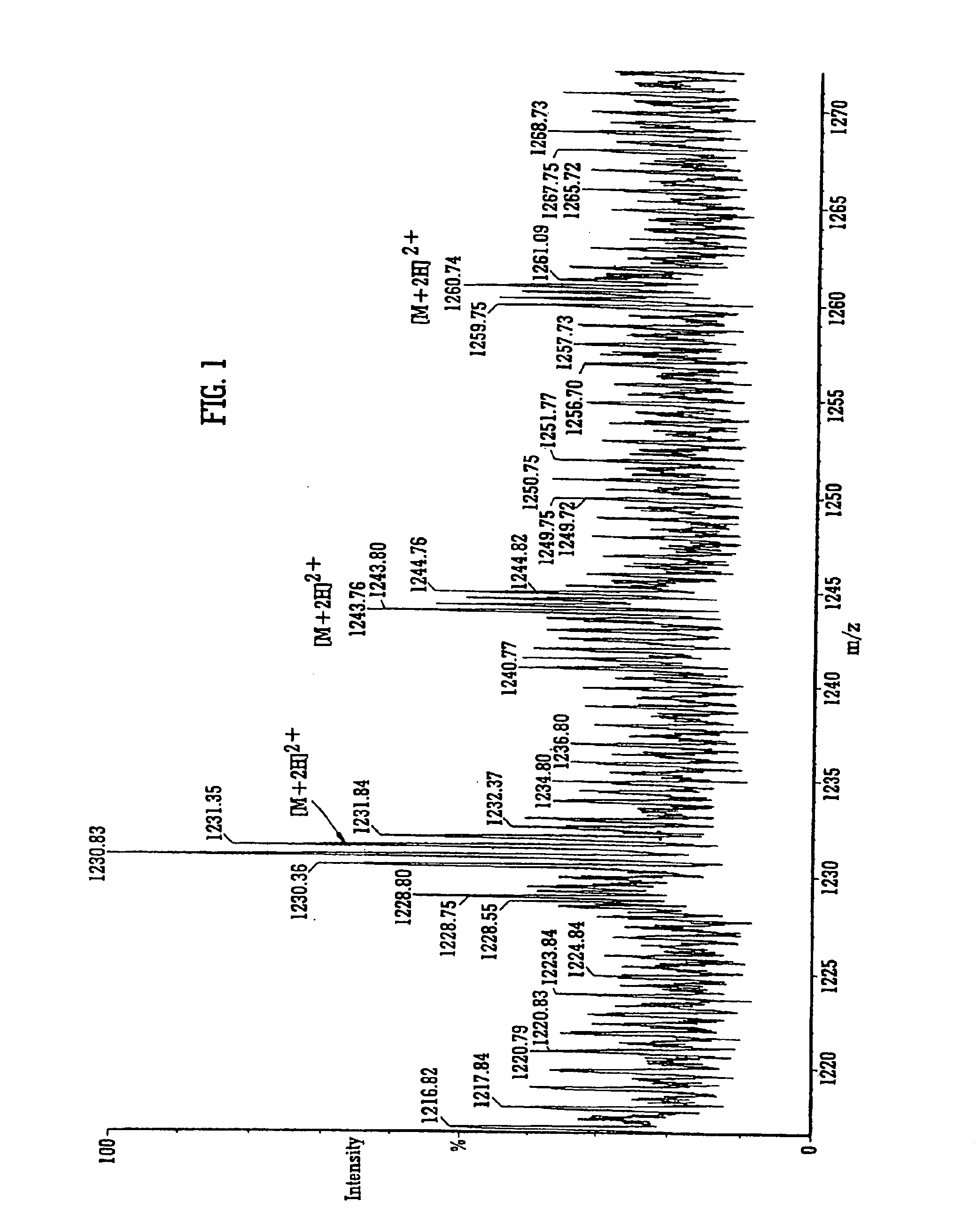
Mass spectrometer
InactiveUS6906319B2High sensitivityIncrease delay timeStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersIon trap mass spectrometryMass analyzer
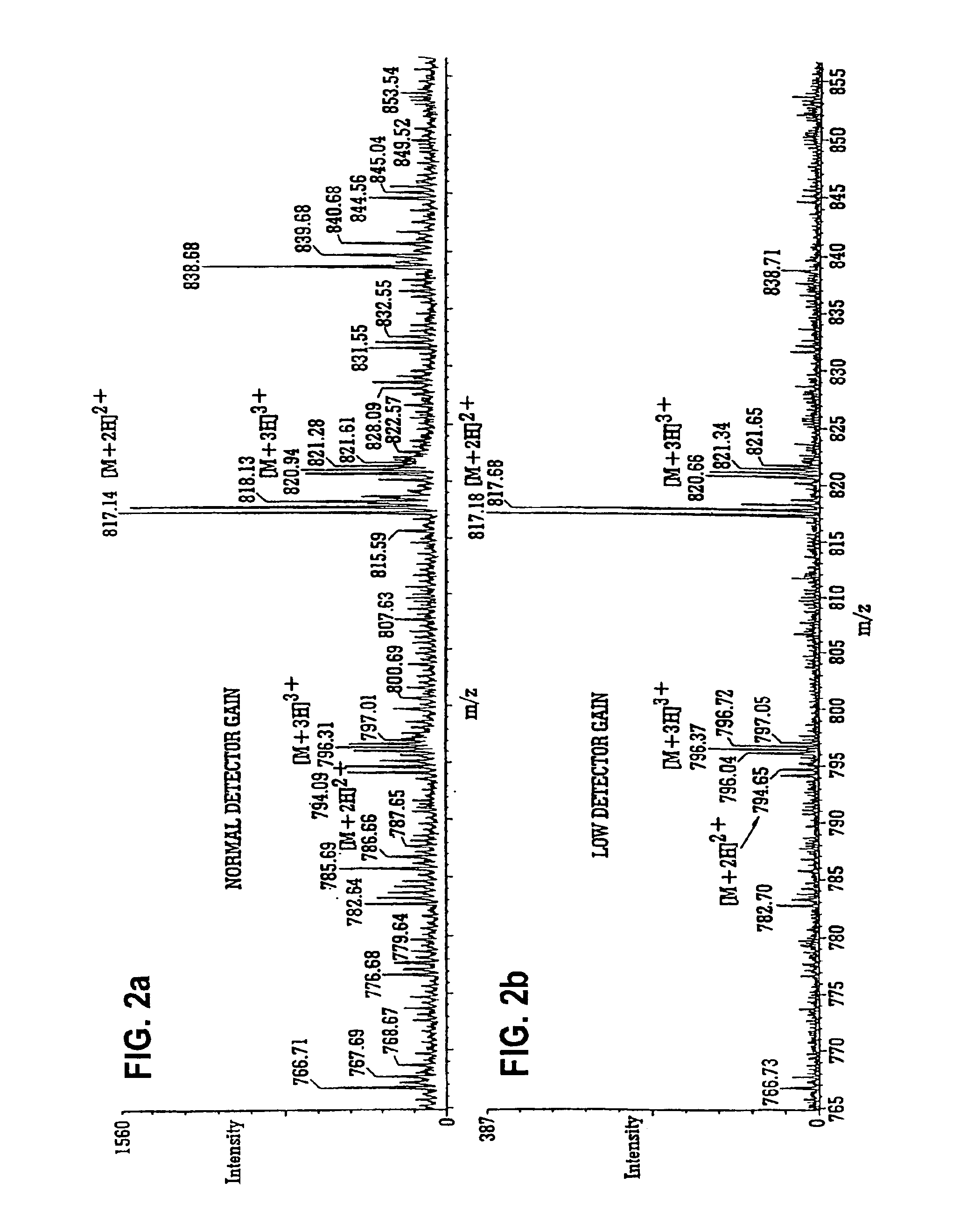
A mass spectrometer is disclosed wherein ions having a particular desired charge state are selected by operating an ion mobility spectrometer in combination with a quadrupole mass filter. Precursor ions are fragmented or reacted to form product ions in a collision cell ion trap and sent back upstream to an upstream ion trap. The fragment or product ions are then passed through the ion mobility spectrometer wherein they become temporally separated according to their ion mobility. Fragment or product ions are then re-trapped in the collision cell ion trap before being released therefrom in packets. A pusher electrode of a time of flight mass analyzer is energized a predetermined period of time after a packet of ions is released from the collision cell ion trap. Accordingly, it is possible to select multiply charged precursor ions from a background of singly charged ions, fragment them, and mass analyze the fragment ions with a near 100% duty cycle across the whole mass range.
Owner:MICROMASS UK LTD
Energy conversion film and quantum dot film comprising quantum dot compound, energy conversion layer including the quantum dot film, and solar cell including the energy conversion layer
ActiveUS20060169971A1Improve energy efficiencyHigh solar efficiencyElectrolytic capacitorsFinal product manufactureHigh energySolar cell
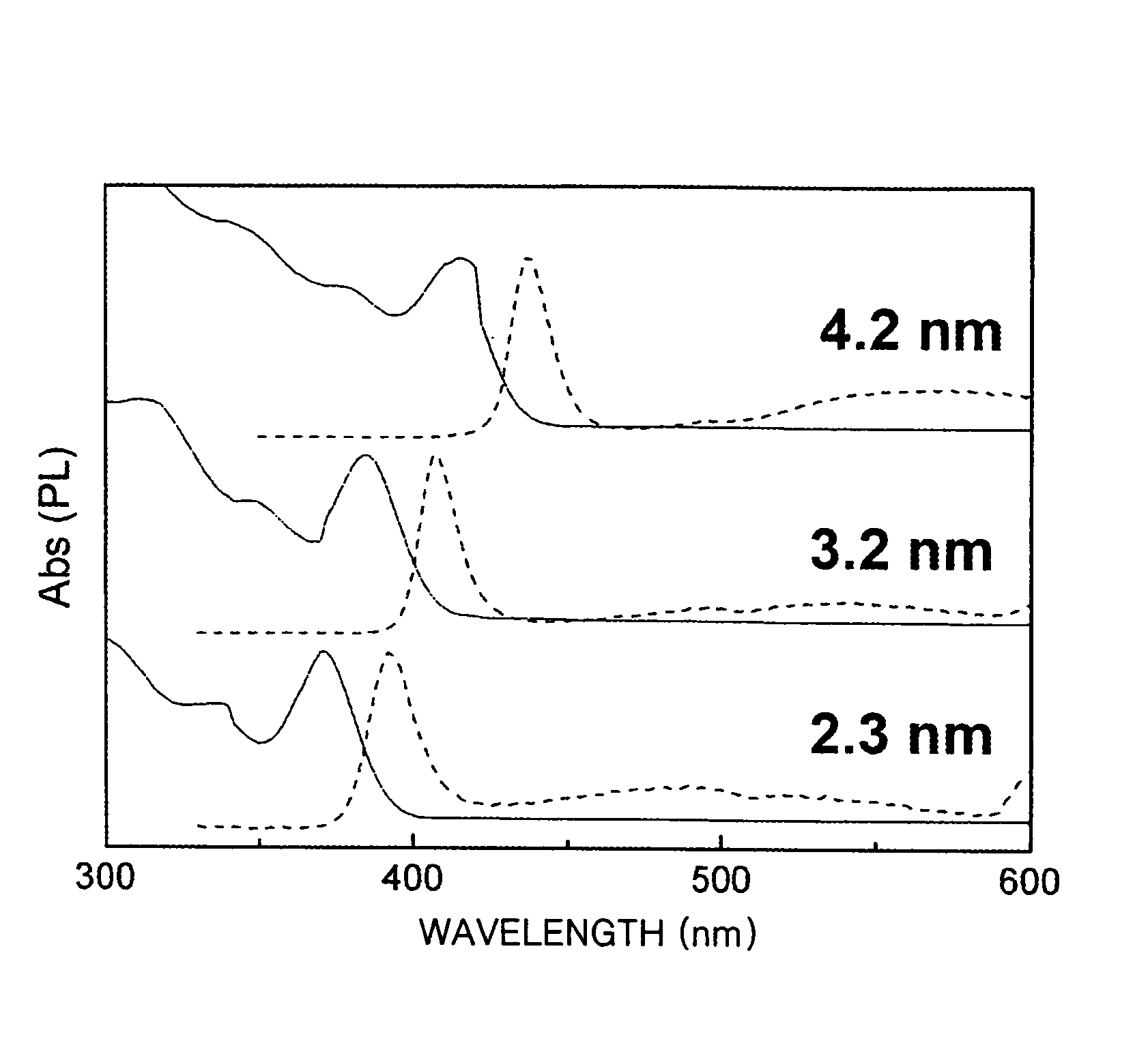
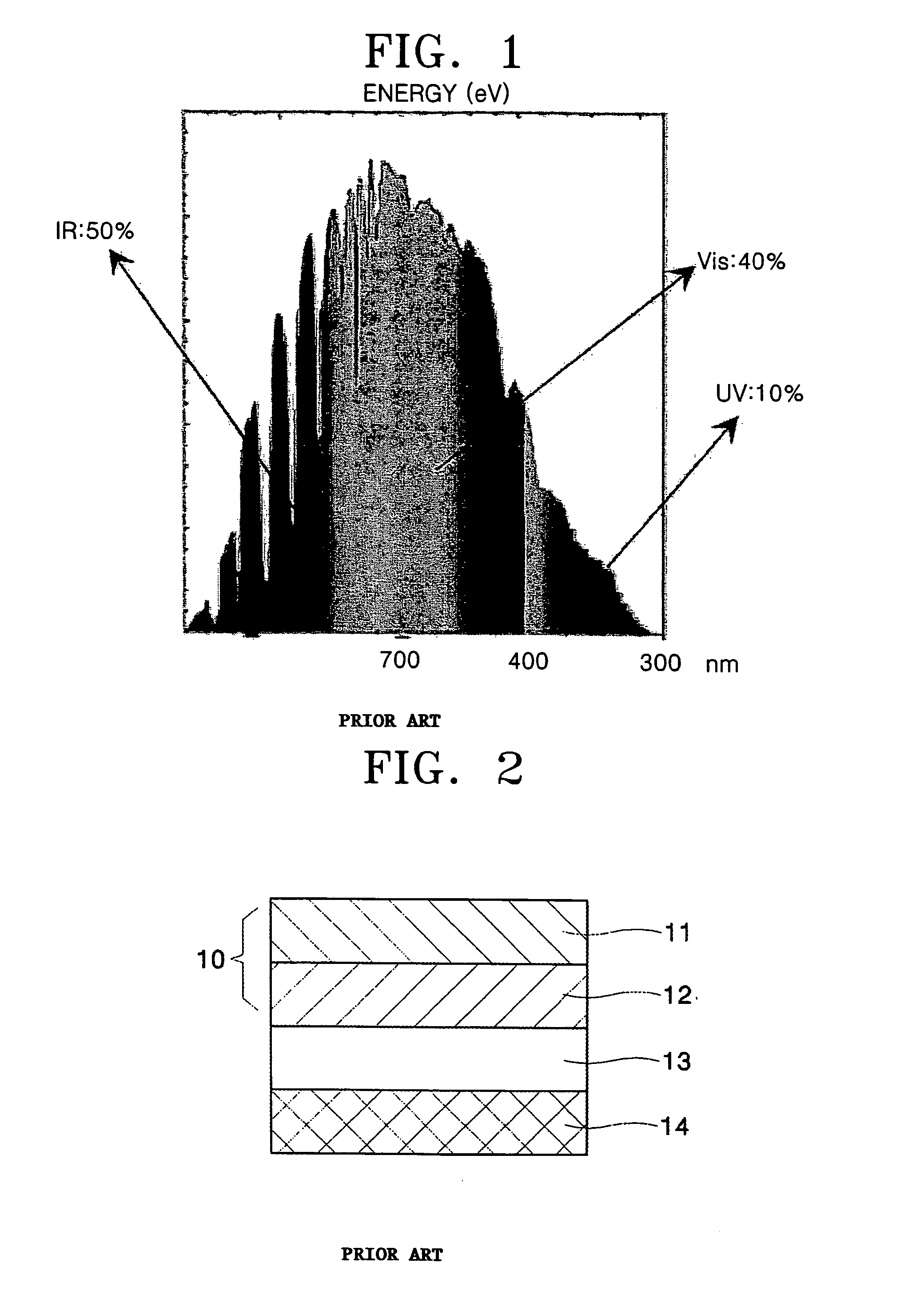
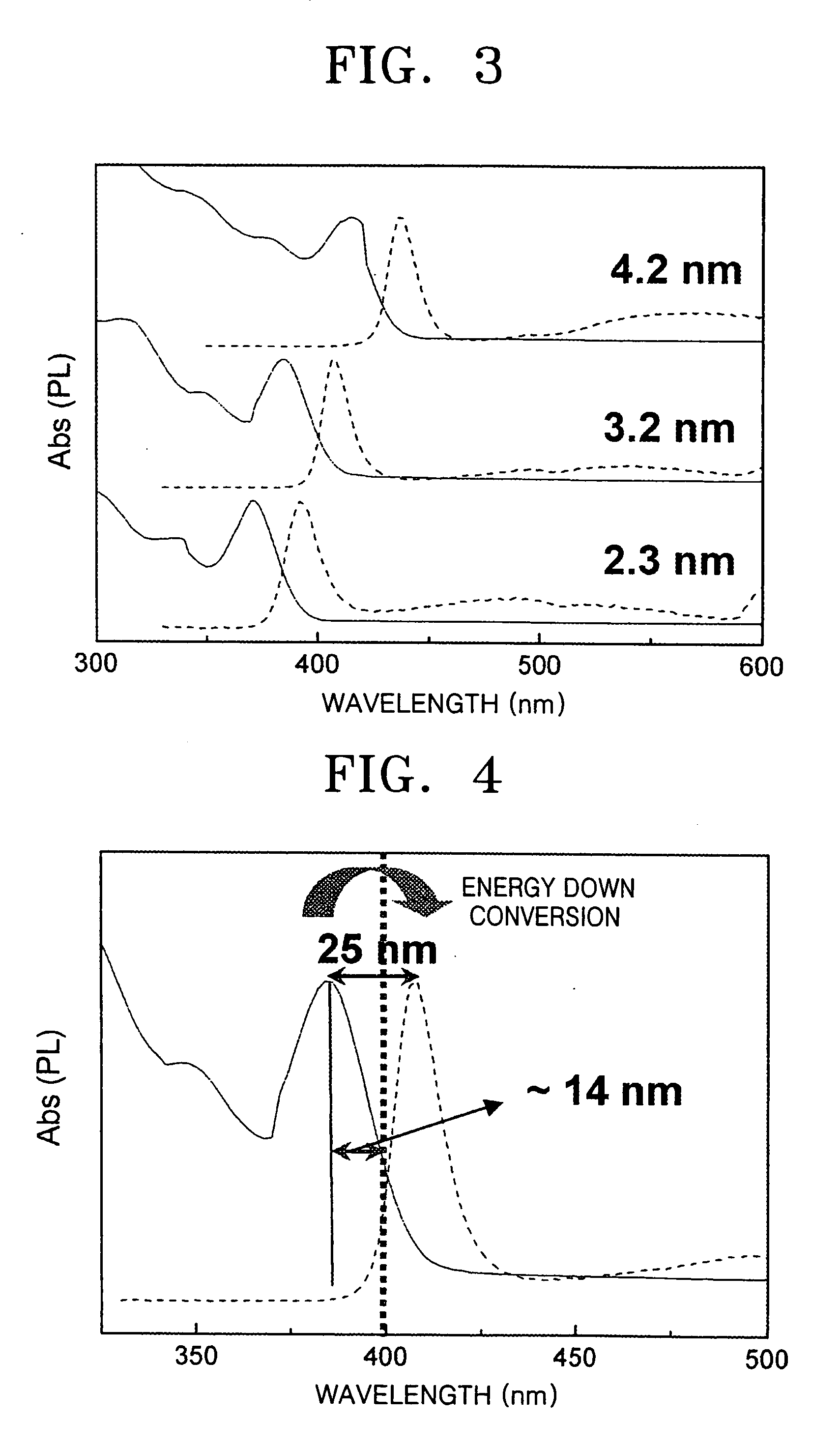
An energy conversion film and a quantum dot film which contain a quantum dot compound, an energy conversion layer including the quantum dot film, and a solar cell including the energy conversion layer. The films act as cut-off filters blocking light of a particular energy level using the light absorption and emission effects of quantum dots and can convert high energy light to low energy light. The efficiency of a solar cell may be improved by providing the cell with a film that converts light above the spectrum-responsive region to light in the cell's spectrum-responsive region. The absorption wavelength region of the films can be broadened by providing the quantum dot compound in a variety of average particle sizes, for example, by providing a mixture of a first quantum dot compound having a first average particle size and a first quantum dot compound having a second average particle size.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Particle beam therapy system
ActiveUS7772577B2Quality improvementLow costElectrode and associated part arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansTransport systemSynchrotron
A particle beam therapy system using a spot scanning method includes a synchrotron, a beam transport system, an irradiation system, and a controller. A controller is configured to turn on a radio frequency electromagnetic field to be applied to an extraction system when a charged particle beam is to be supplied to the irradiation system, and turn off the radio frequency electromagnetic field to be applied to the extraction system when the supply of the charged particle beam to the irradiation system is to be blocked by means of an electromagnet provided in the beam transport system or in the synchrotron. The controller is also adapted to turn off a radio frequency acceleration voltage to be applied to an acceleration cavity in synchronization with the turning-off of the radio frequency electromagnetic field to be applied to the extraction device.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Full field digital tomosynthesis method and apparatus
ActiveUS7110490B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTomosynthesisObject based
A tomosynthesis system for forming a three dimensional image of an object is provided. The system includes an X-ray source adapted to irradiate the object with a beam of X-rays from a plurality of positions in a sector, an X-ray detector positioned relative to the X-ray source to detect X-rays transmitted through the object and a processor which is adapted to generate a three dimensional image of the object based on X-rays detected by the detector. The detector is adapted to move relative to the object and / or the X-ray source is adapted to irradiate the object with the beam of X-rays such that the beam of X-rays follows in a non arc shaped path and / or a center of the beam of X-rays impinges substantially on the same location on the detector from different X-ray source positions in the sector.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Particle beam nozzle
An improved particle beam treatment system optionally includes exchangeable particle beam nozzles. These particle beam nozzles may be automatically moved from a storage location to a particle beam path or between particle beam paths for use in medical applications. Movement may be achieved using a conveyance, gantry, rail system, or the like. The improved particle beam treatment system optionally also includes more than two alternative particle beam paths. These alternative particle beam paths may be directed to a patient from a variety of different angles and in different planes.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Particle beam system including exchangeable particle beam nozzle
An improved particle beam treatment system optionally includes exchangeable particle beam nozzles. These particle beam nozzles may be automatically moved from a storage location to a particle beam path or between particle beam paths for use in medical applications. Movement may be achieved using a conveyance, gantry, rail system, or the like. The improved particle beam treatment system optionally also includes more than two alternative particle beam paths. These alternative particle beam paths may be directed to a patient from a variety of different angles and in different planes.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com