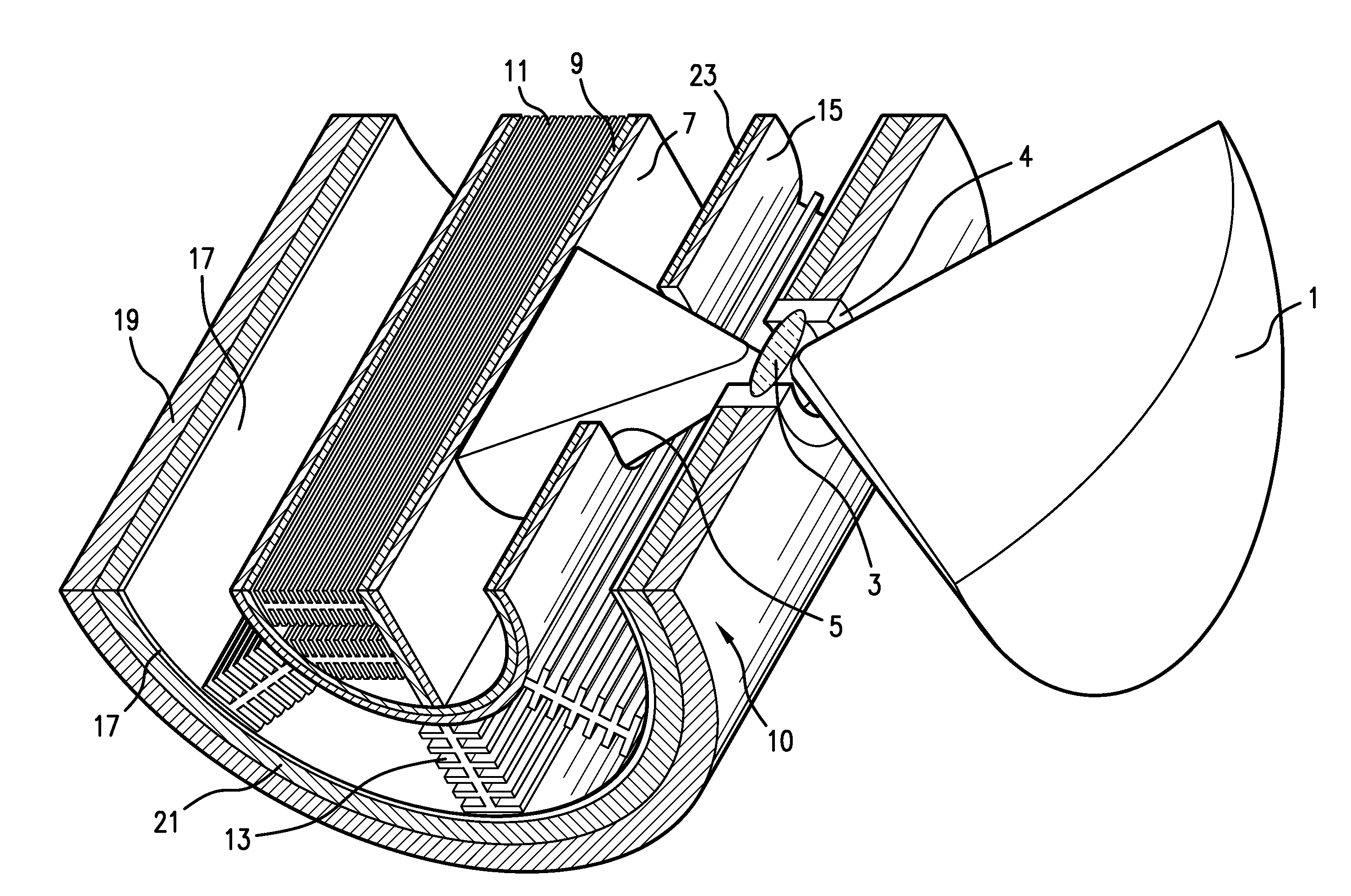
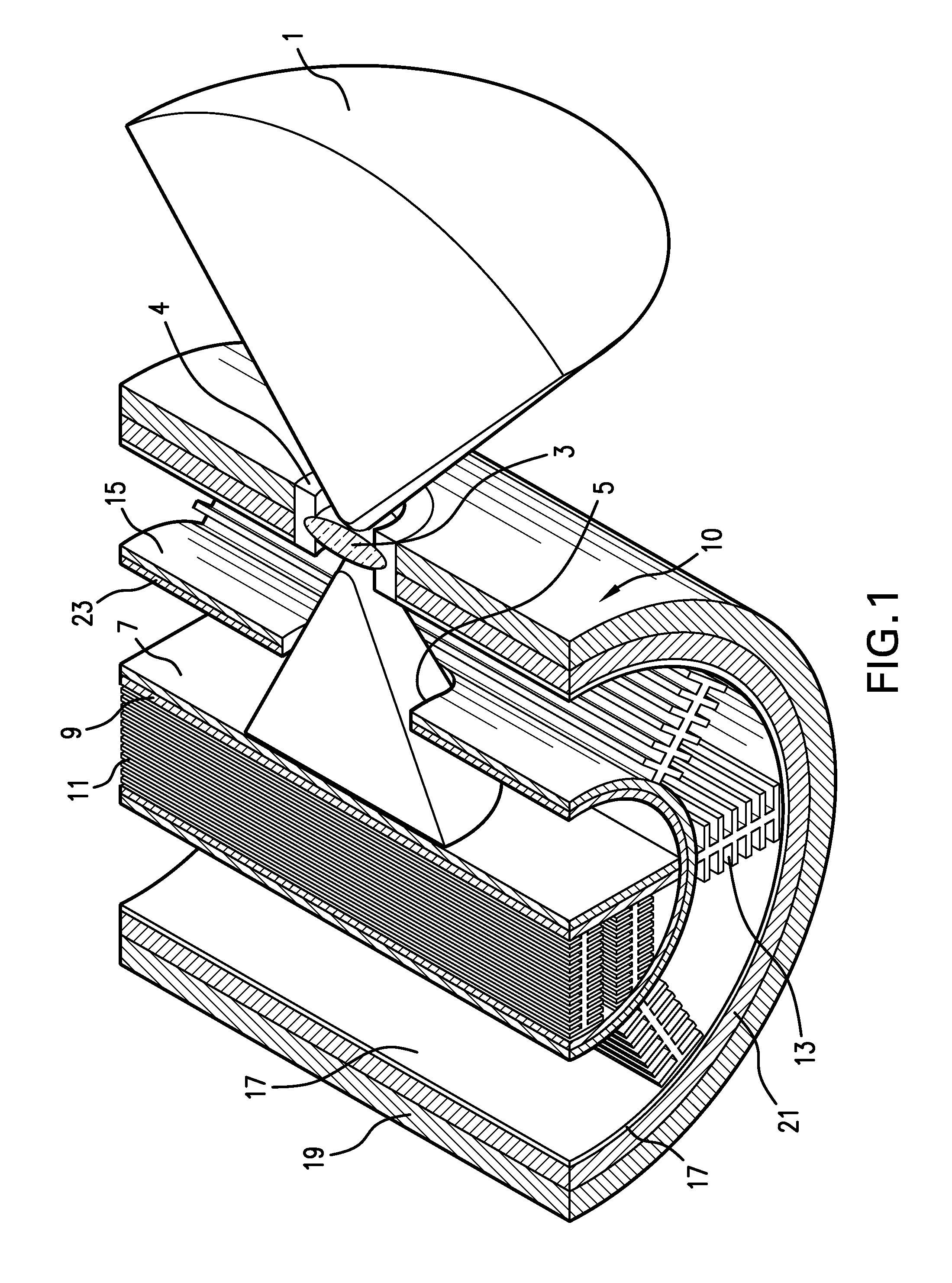
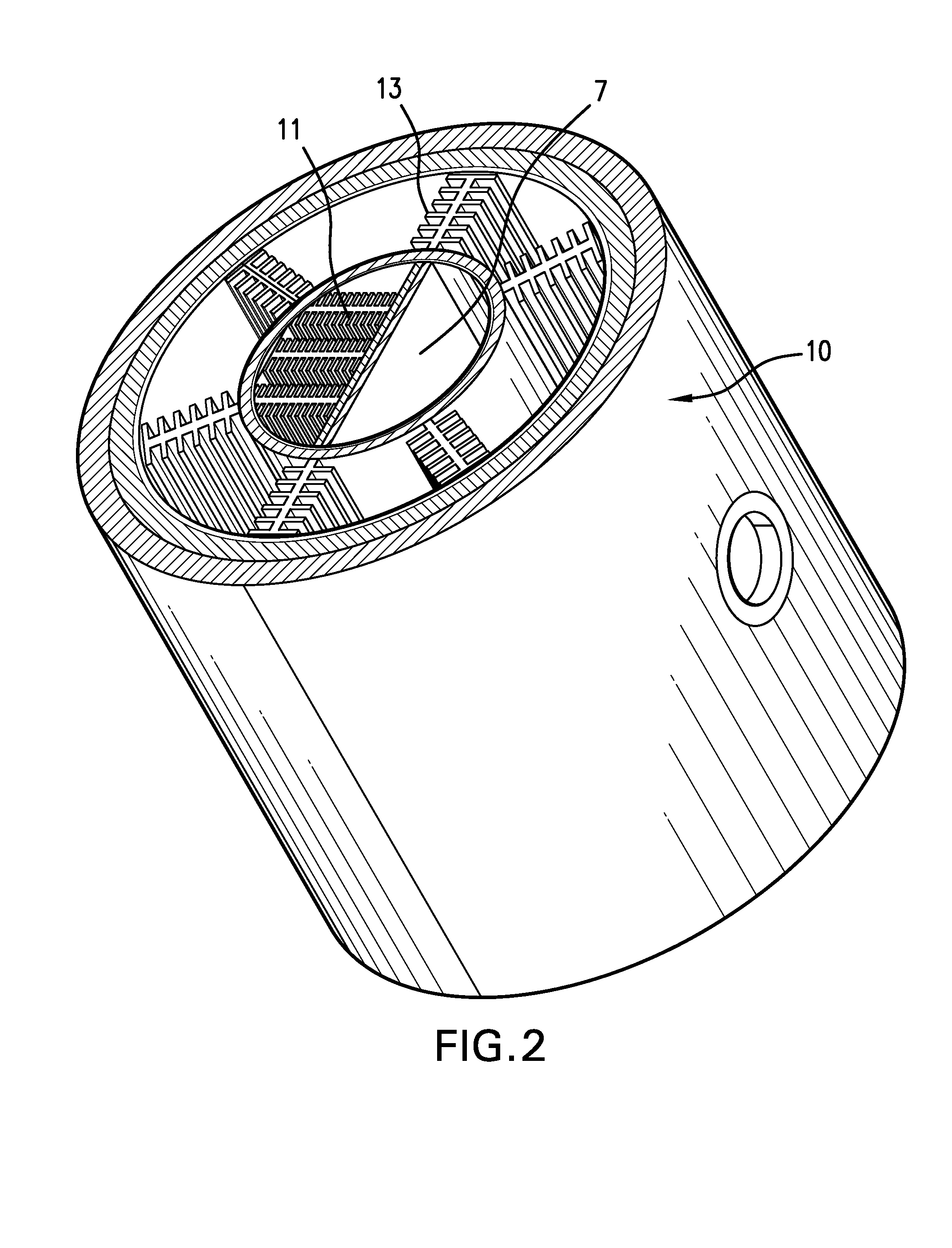
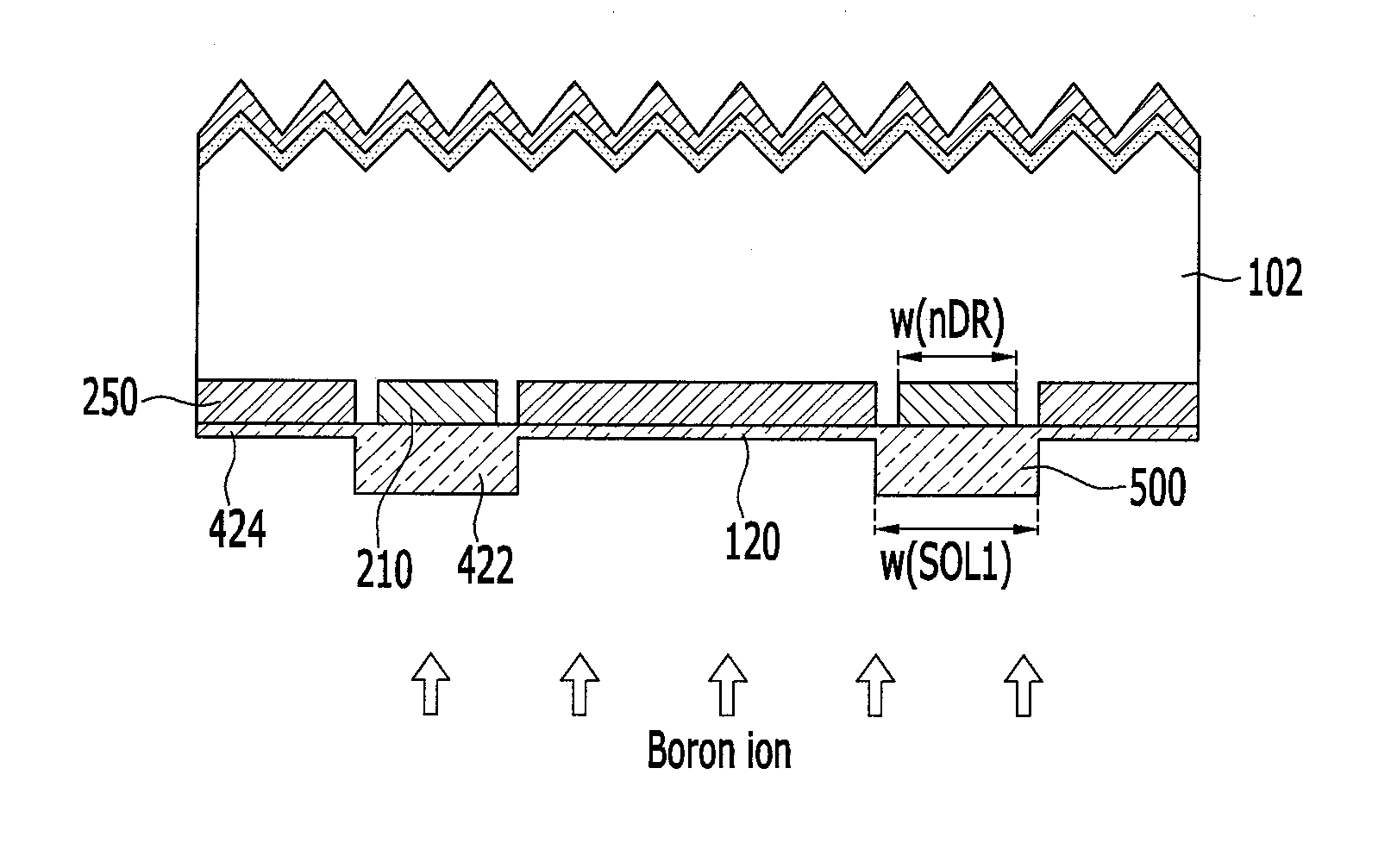
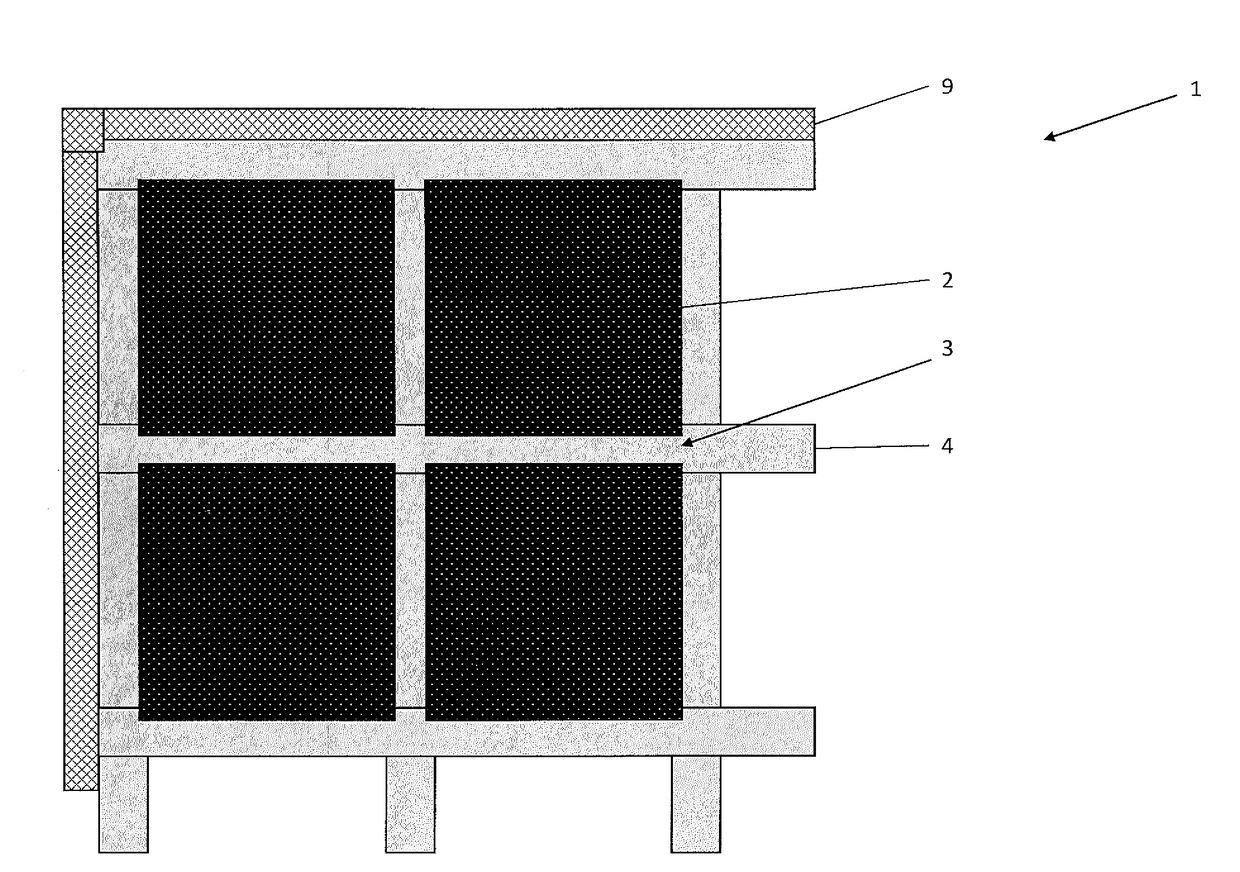
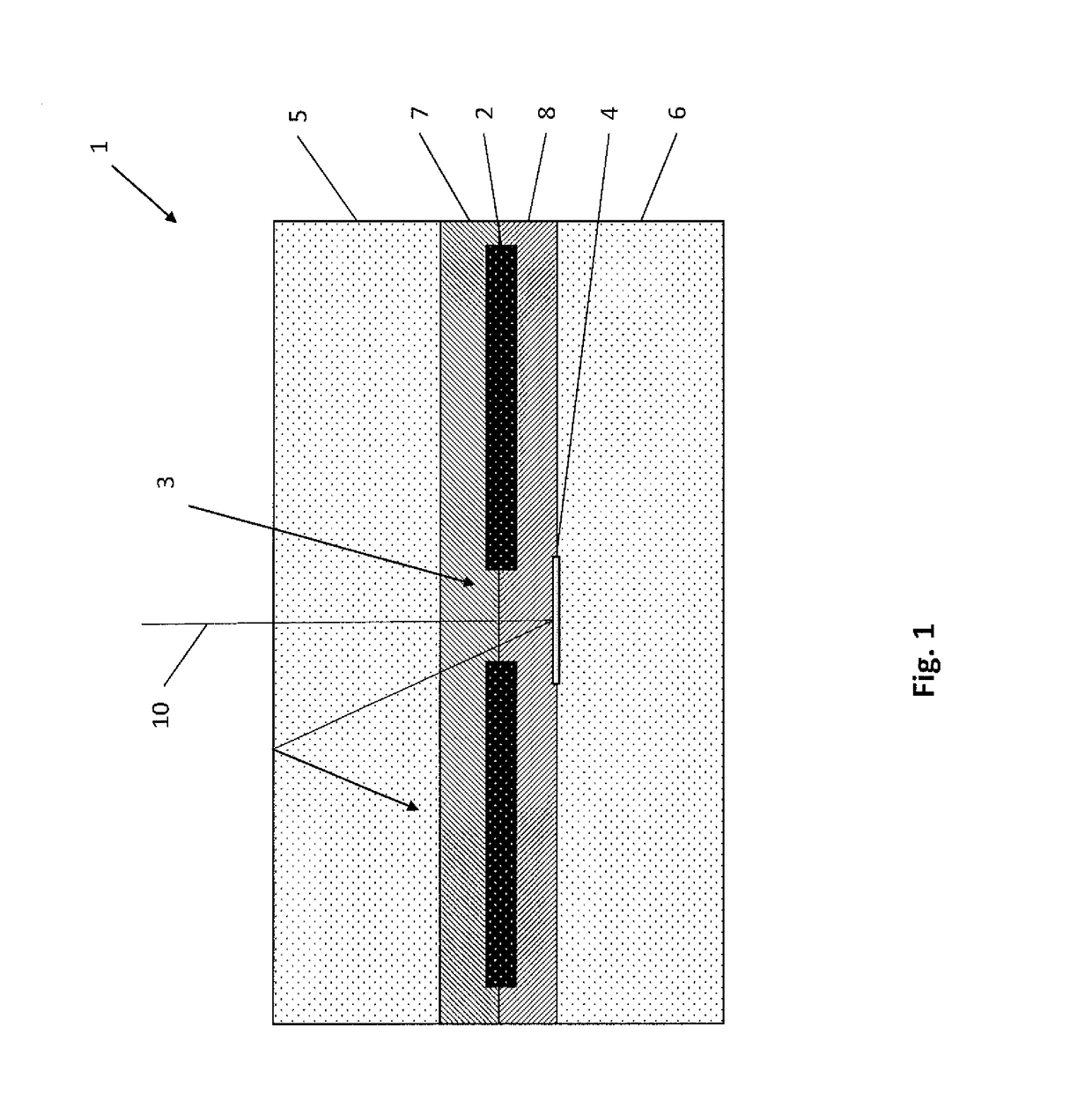
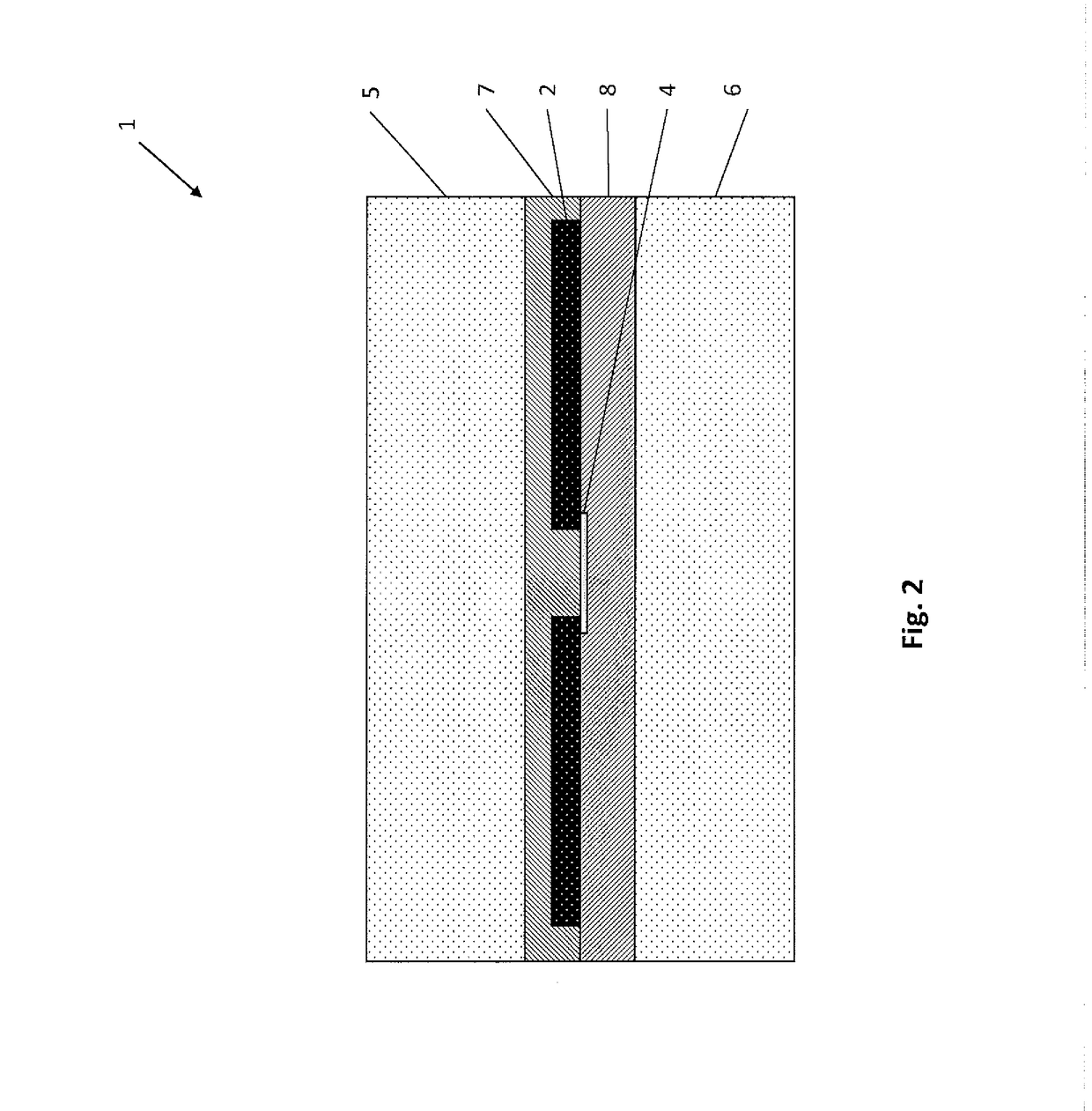
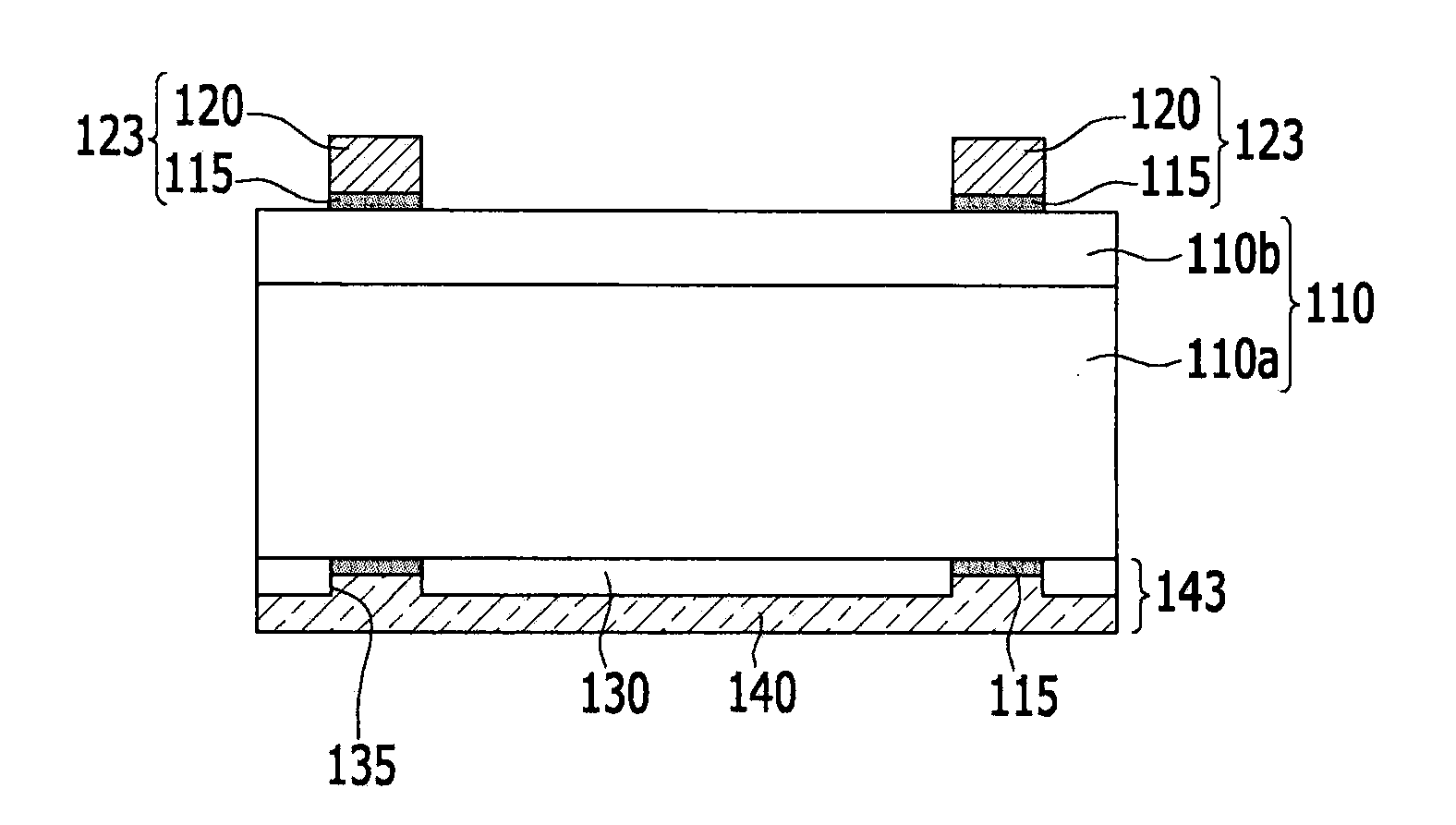
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
84results about How to "High solar efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
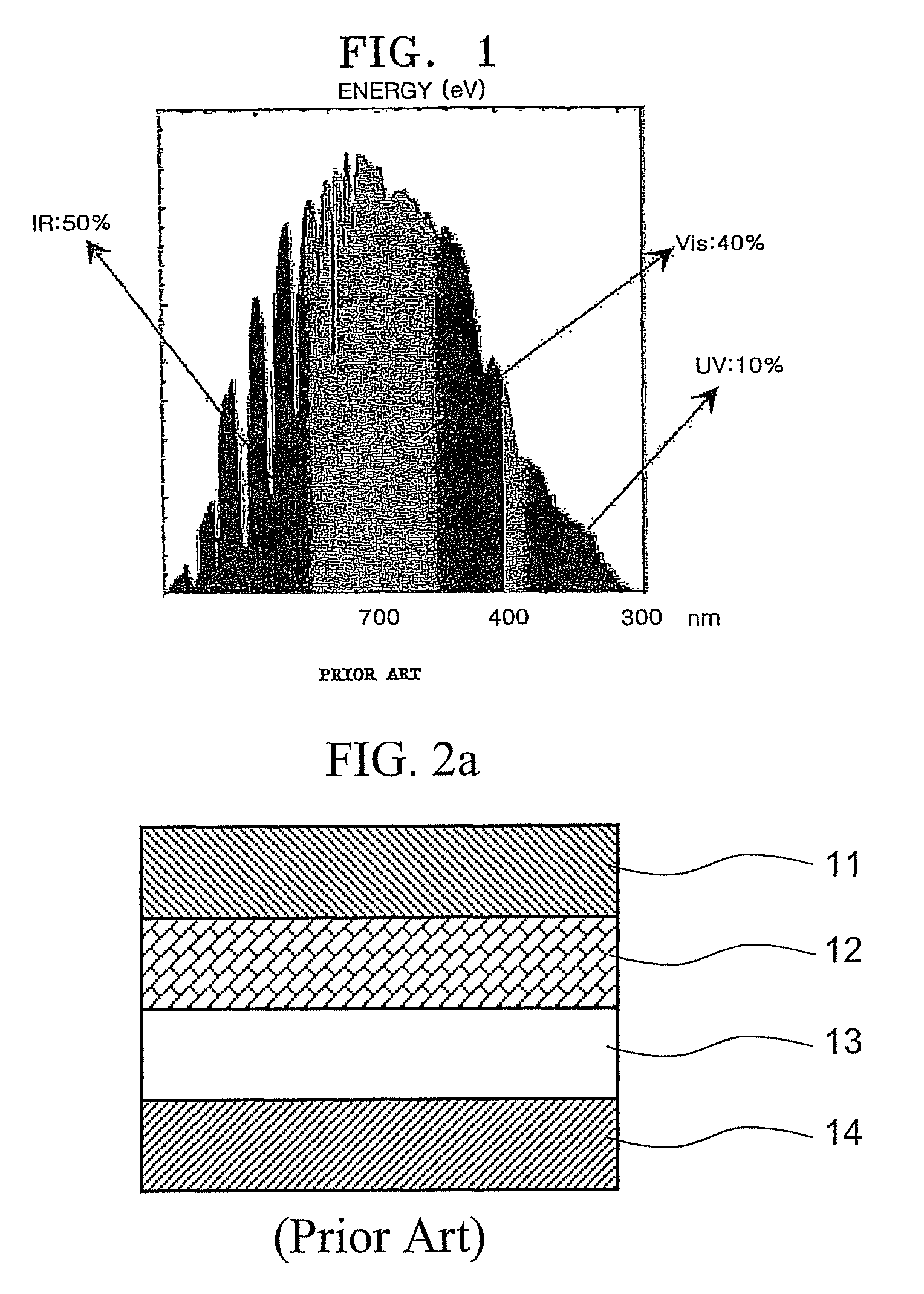
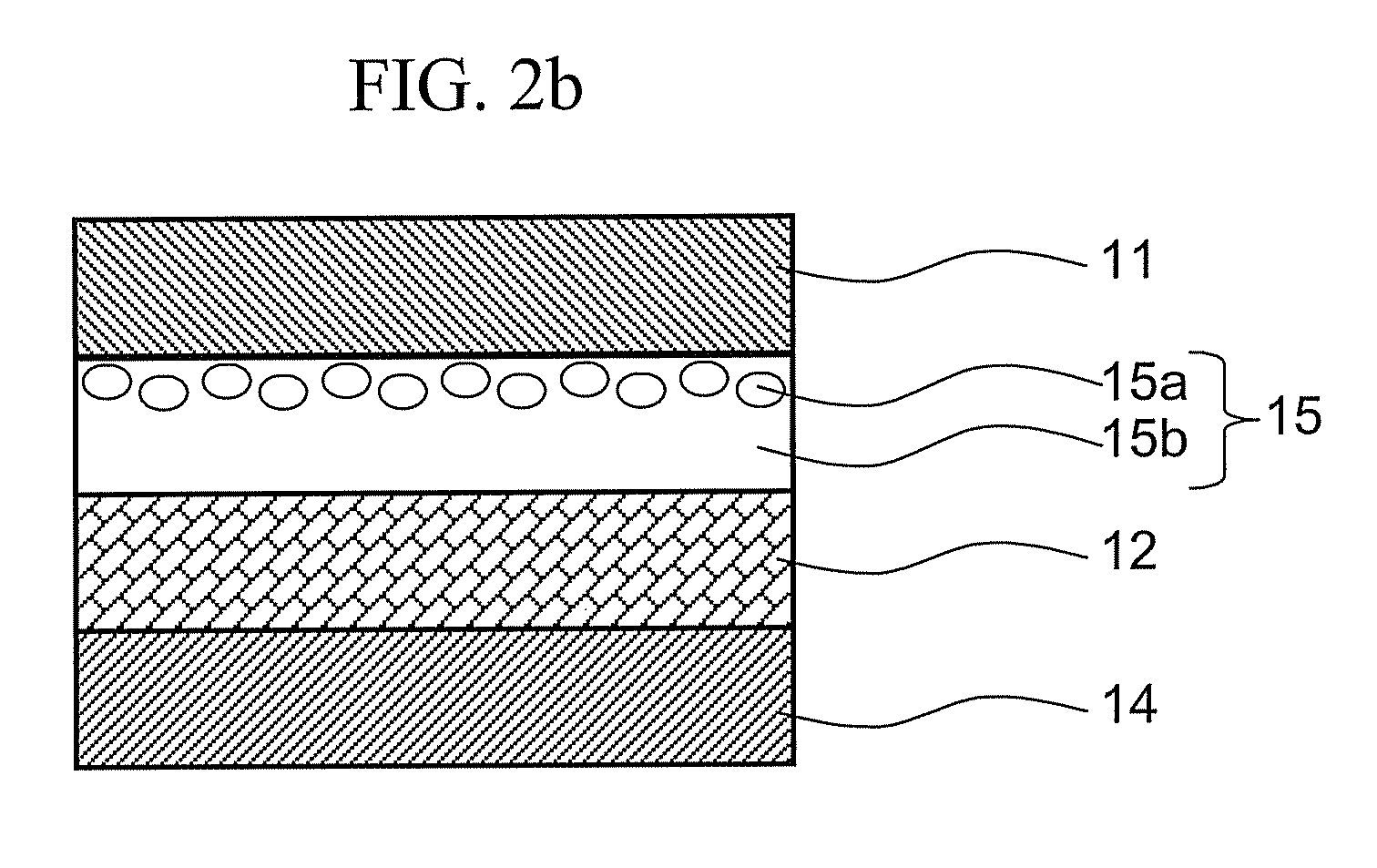
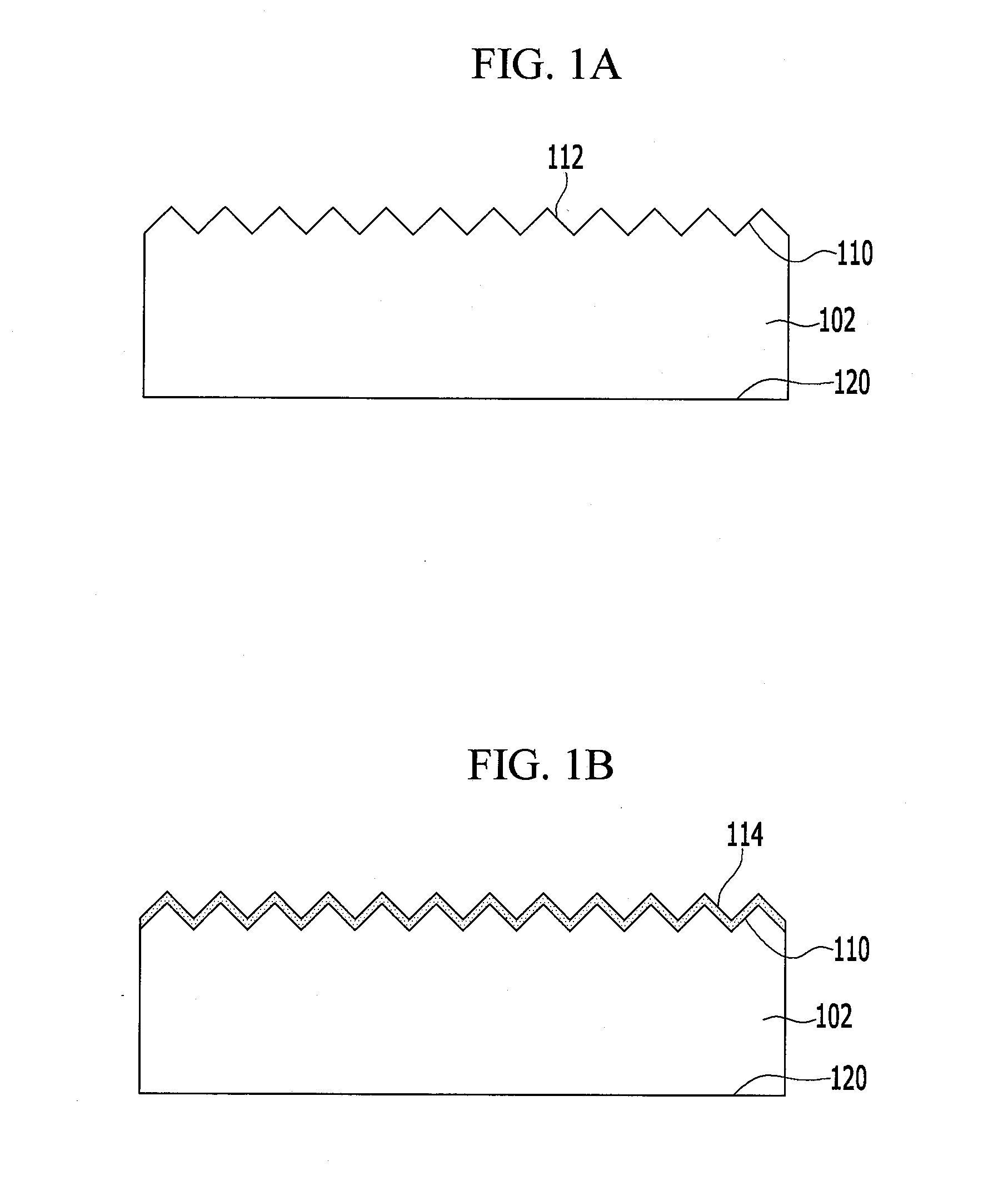
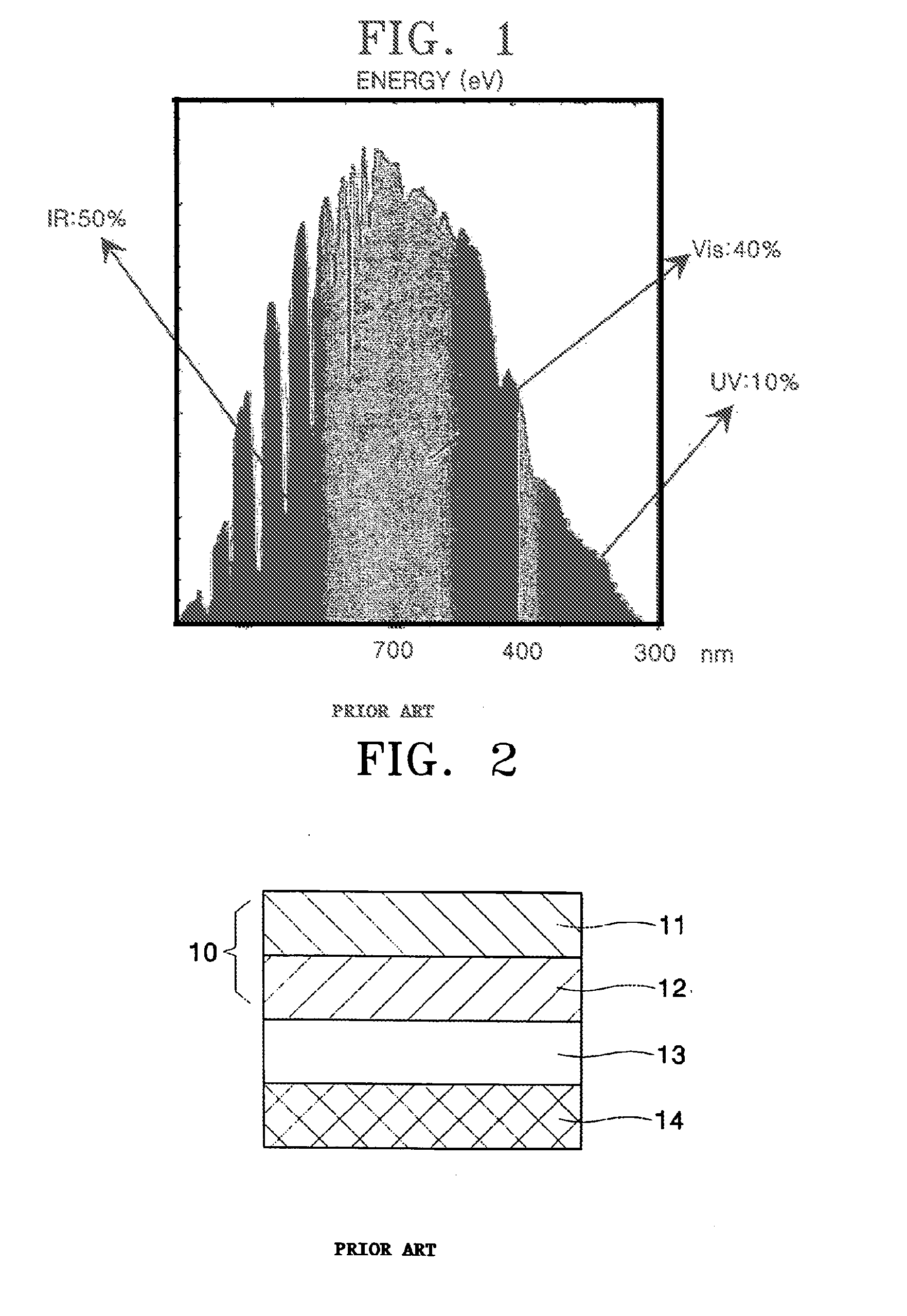
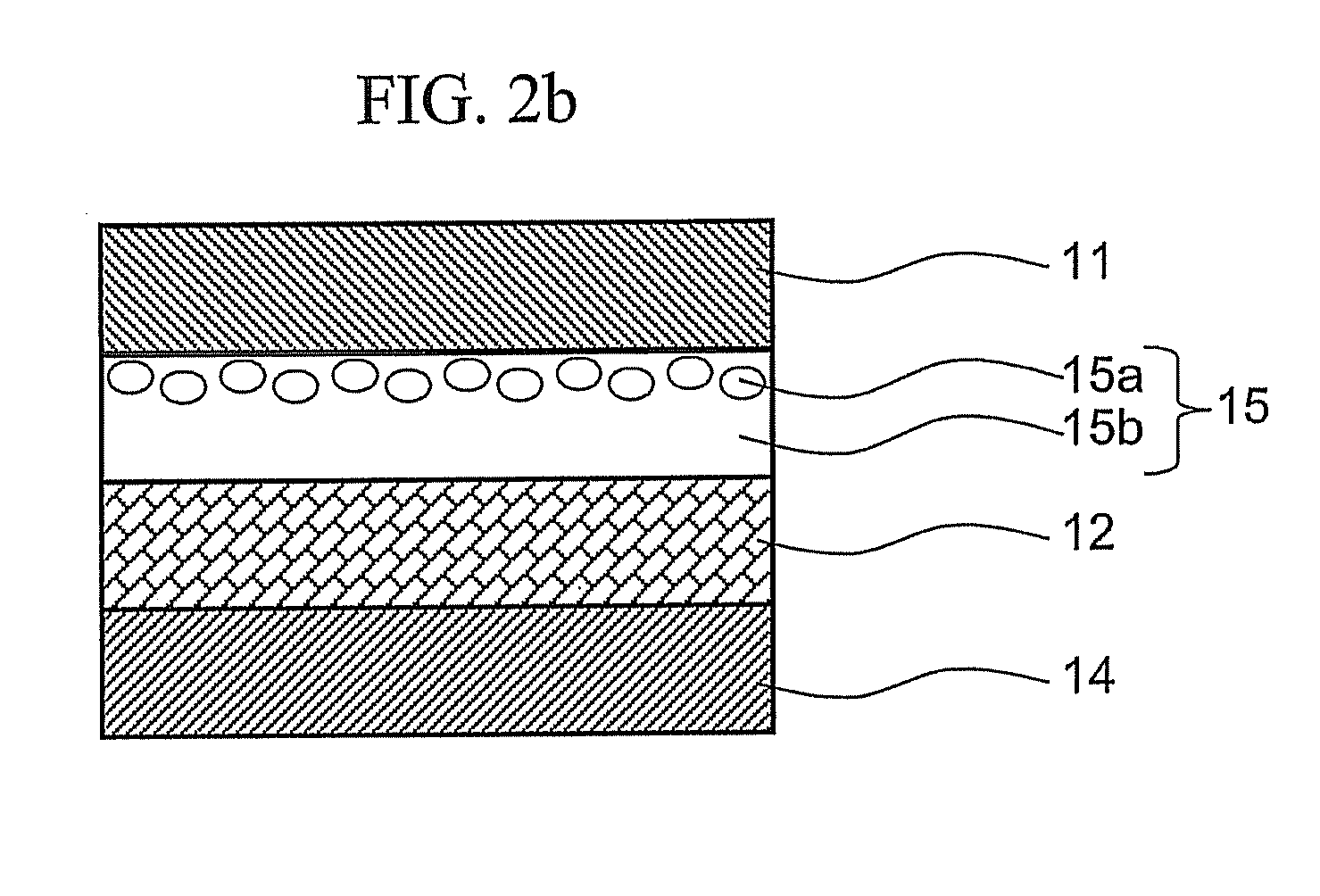
Energy conversion film and quantum dot film comprising quantum dot compound, energy conversion layer including the quantum dot film, and solar cell including the energy conversion layer
ActiveUS20060169971A1Improve energy efficiencyHigh solar efficiencyElectrolytic capacitorsFinal product manufactureHigh energySolar cell
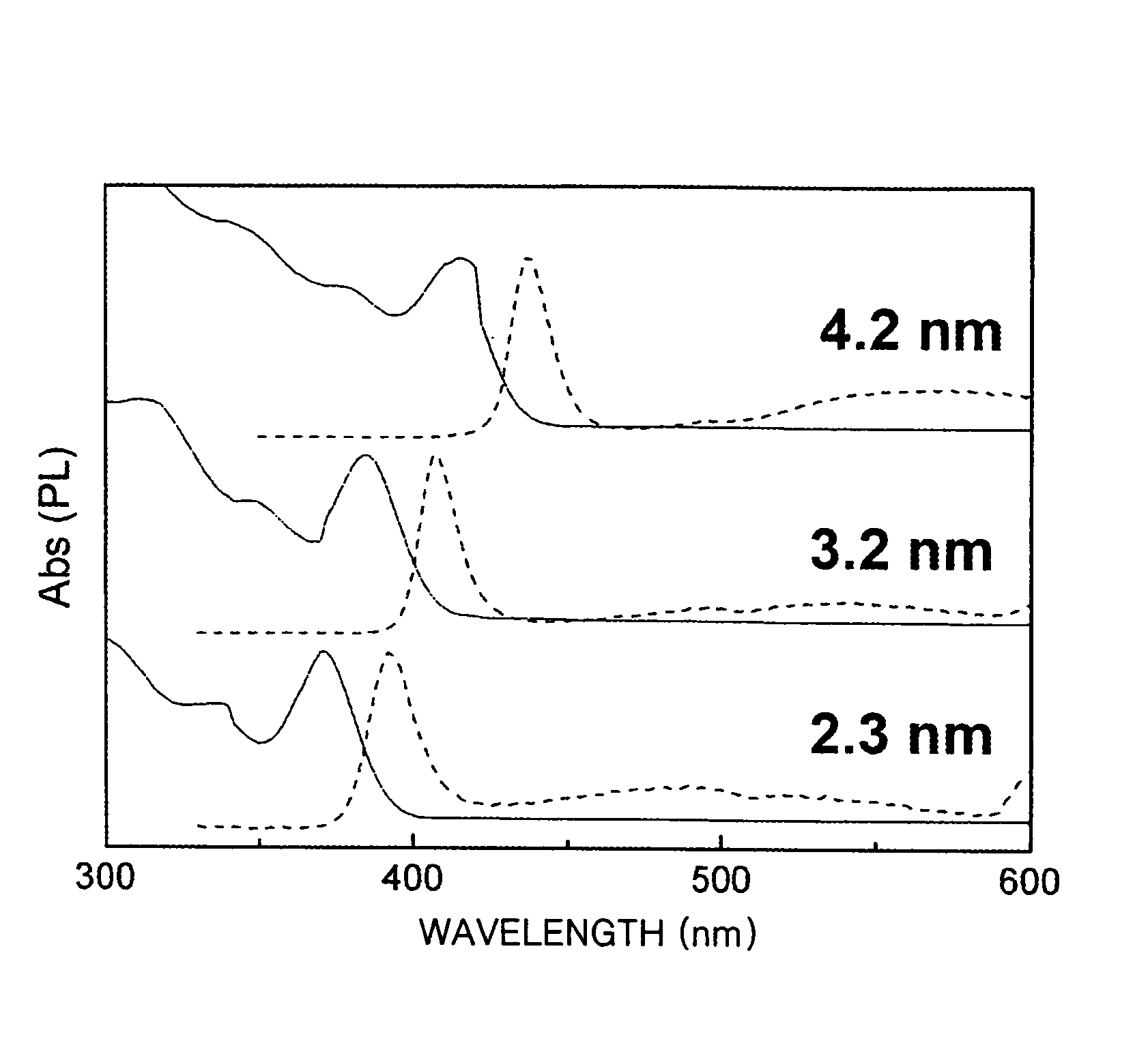
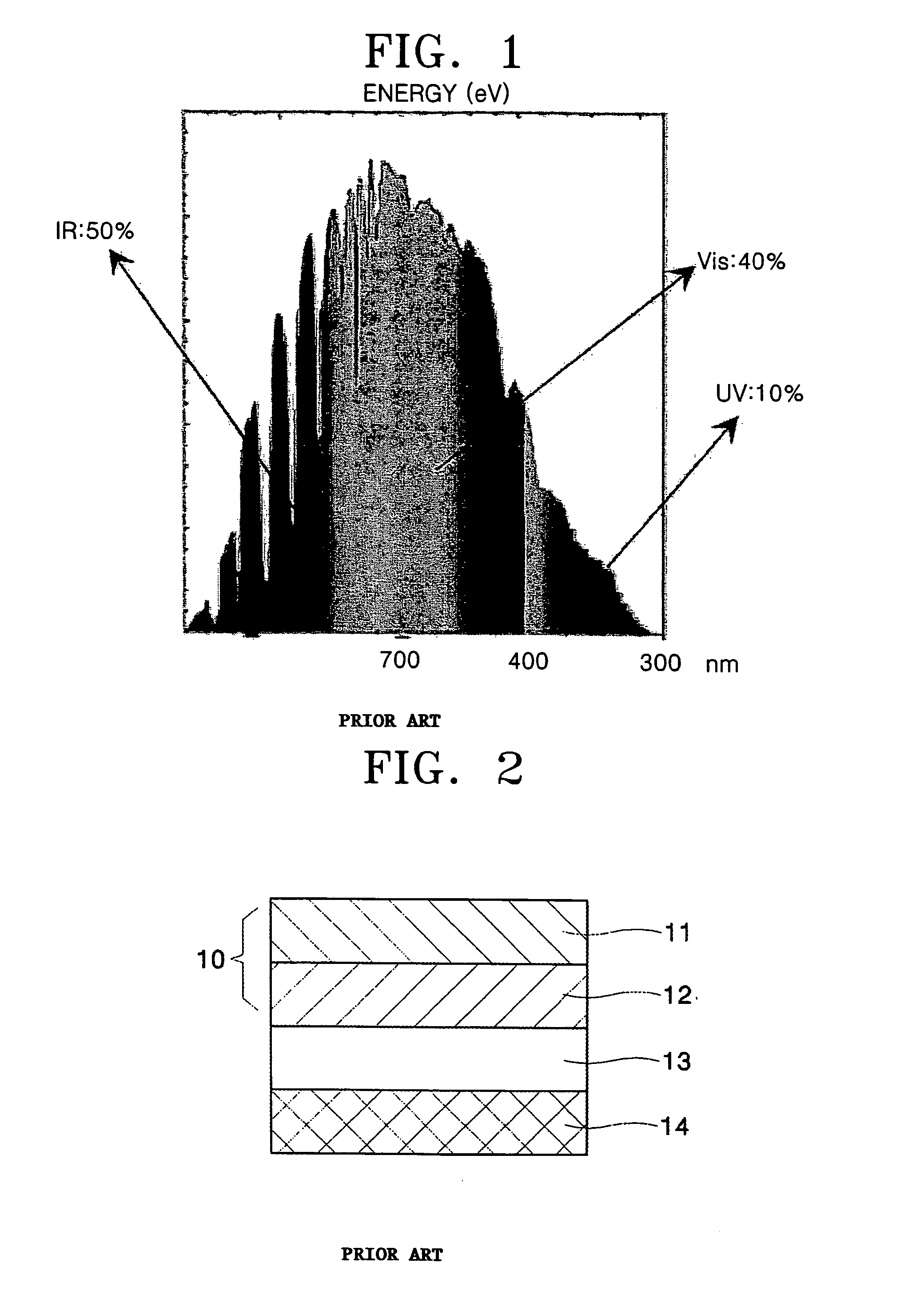
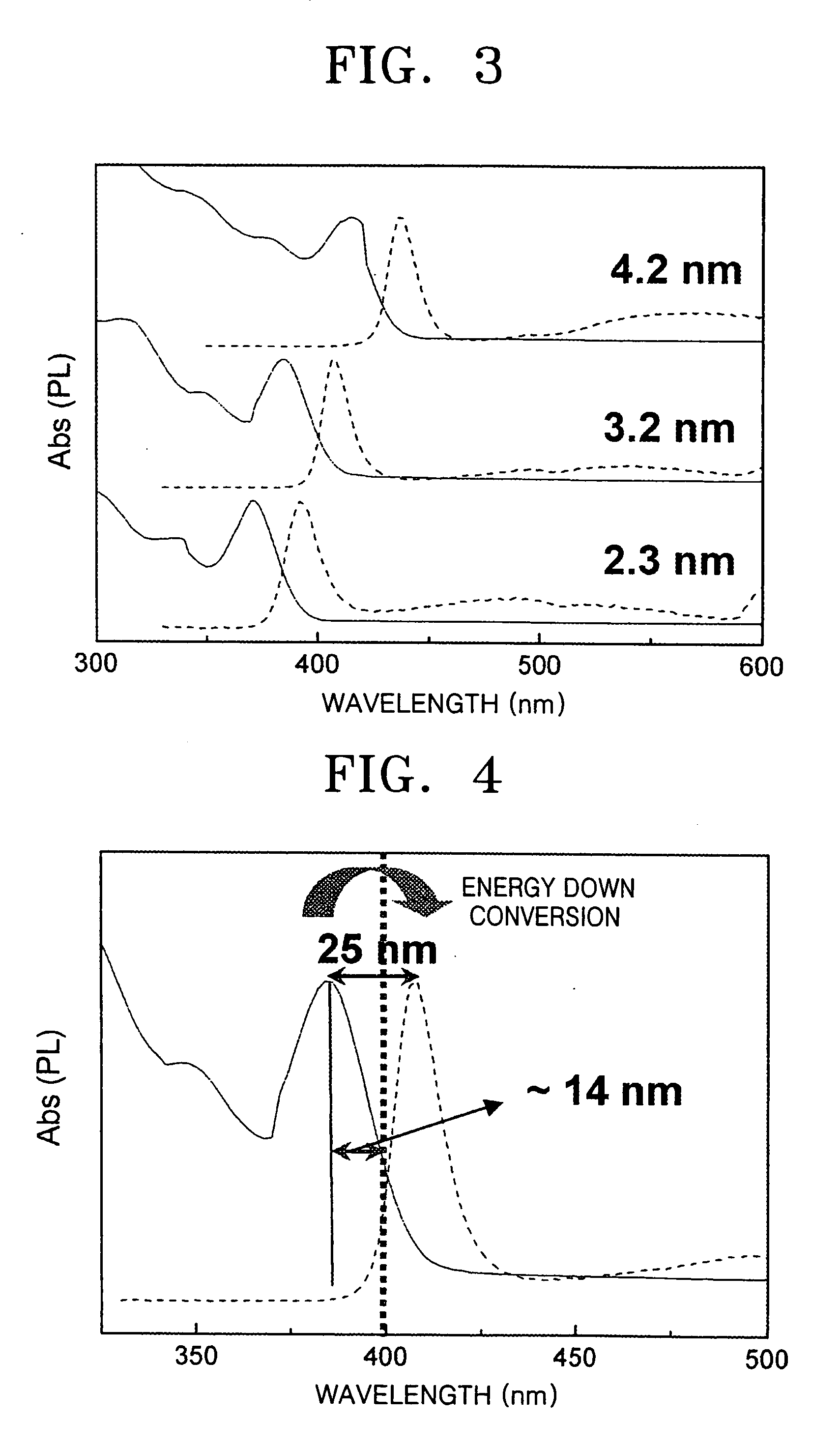
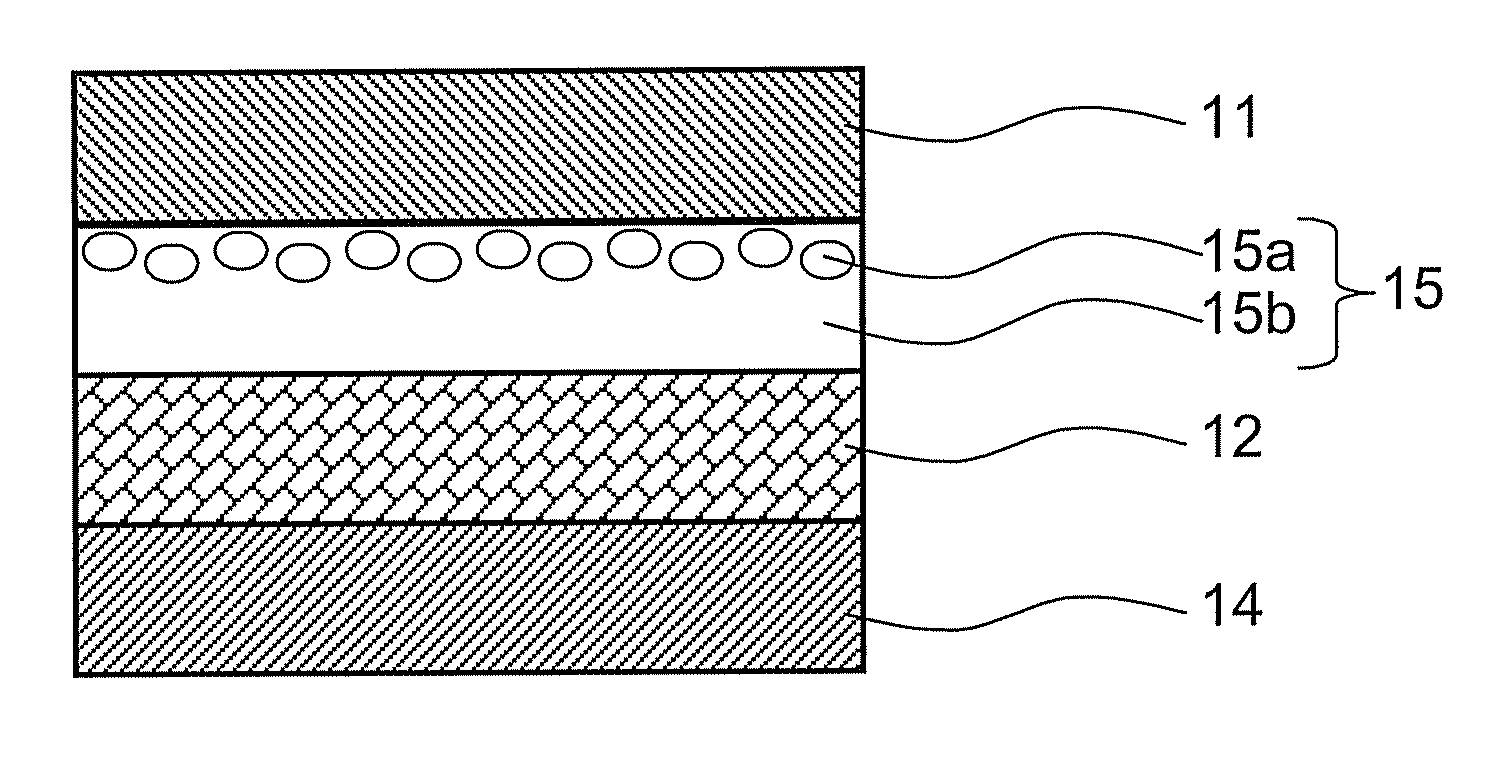
An energy conversion film and a quantum dot film which contain a quantum dot compound, an energy conversion layer including the quantum dot film, and a solar cell including the energy conversion layer. The films act as cut-off filters blocking light of a particular energy level using the light absorption and emission effects of quantum dots and can convert high energy light to low energy light. The efficiency of a solar cell may be improved by providing the cell with a film that converts light above the spectrum-responsive region to light in the cell's spectrum-responsive region. The absorption wavelength region of the films can be broadened by providing the quantum dot compound in a variety of average particle sizes, for example, by providing a mixture of a first quantum dot compound having a first average particle size and a first quantum dot compound having a second average particle size.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Energy conversion film and quantum dot film comprising quantum dot compound, energy conversion layer including the quantum dot film, and solar cell including the energy conversion layer
ActiveUS7791157B2Improve energy efficiencyHigh solar efficiencyElectrolytic capacitorsFinal product manufactureHigh energySpectral responsivity
An energy conversion film and a quantum dot film which contain a quantum dot compound, an energy conversion layer including the quantum dot film, and a solar cell including the energy conversion layer. The films act as cut-off filters blocking light of a particular energy level using the light absorption and emission effects of quantum dots and can convert high energy light to low energy light. The efficiency of a solar cell may be improved by providing the cell with a film that converts light above the spectrum-responsive region to light in the cell's spectrum-responsive region. The absorption wavelength region of the films can be broadened by providing the quantum dot compound in a variety of average particle sizes, for example, by providing a mixture of a first quantum dot compound having a first average particle size and a first quantum dot compound having a second average particle size.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
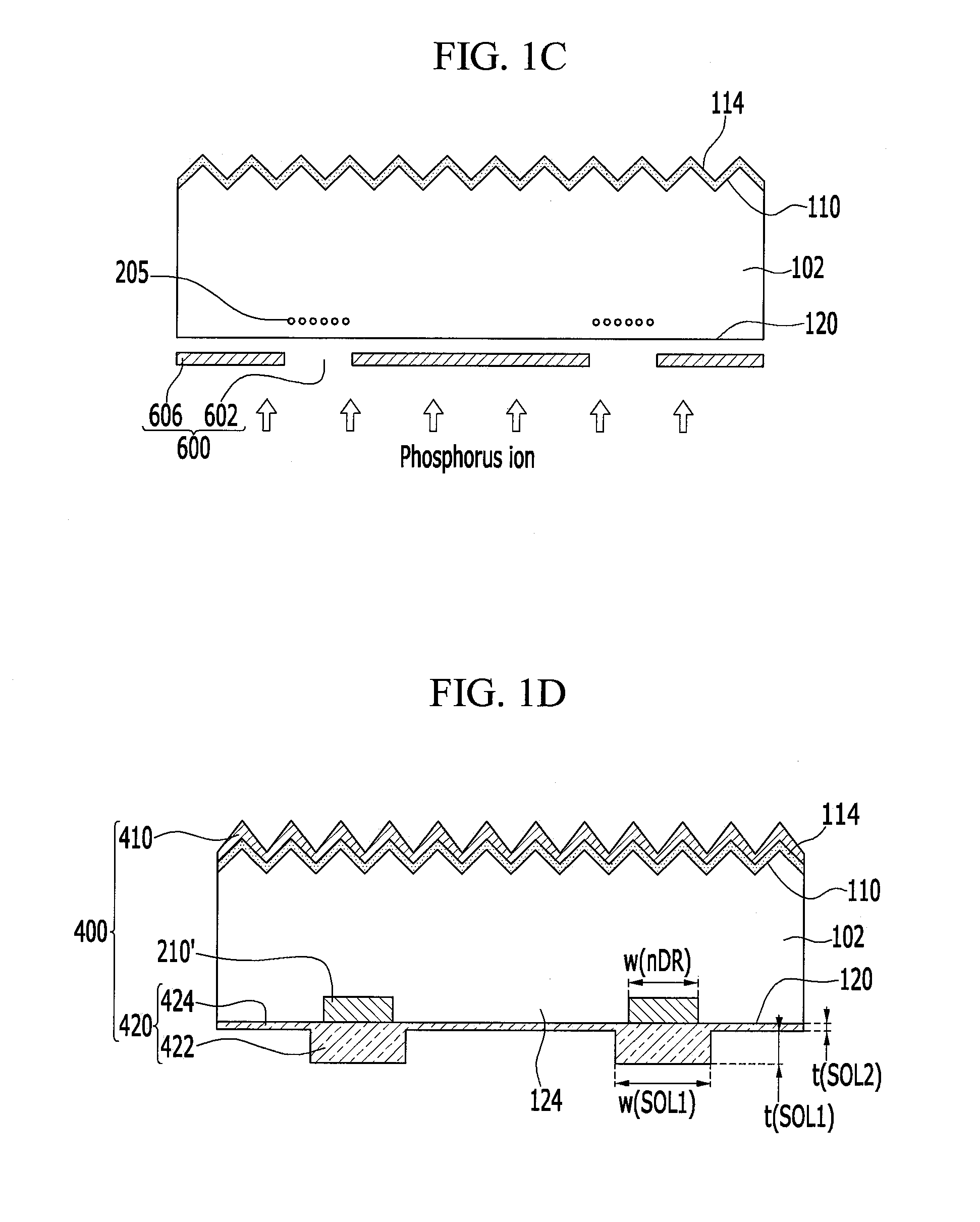
Solar cell and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20150144183A1Improve efficiencyMaximizing conversionFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBoundary regionSolar cell
A solar cell is discussed. The solar cell according to an embodiment includes a semiconductor substrate, a first conductive type region and a second conductive type region disposed on the same side of the semiconductor substrate, wherein at least one of the first and second conductive type regions includes a main region and a boundary region disposed at a peripheral portion of the main region, and the boundary region has at least one of a varying doping concentration and a varying doping depth.
Owner:SHANGRAO JINKO SOLAR TECH DEV CO LTD
Solar Light (Heat) Absorption Material and Heat Absorption/Accumulation Material and Solar Light (Heat) Absorption/Control Building Component Using the Same
InactiveUS20120017622A1Light absorbing abilityEfficient use ofSolar heating energySolar heat devicesSolar lightLiquid medium
A solar light (heat) absorption material is provided which has an excellent solar light (heat) absorbing ability and a simple structure, and may be usable as a low-cost and high-performance heat absorption / accumulation material, the inventive material being usable also as a solar light (heat) absorption / control building component that allows easy change of its solar light (heat) absorption / control ability. The material comprises particles dispersed into a liquid medium having a specific heat ranging from 0.4 to 1.4 cal / g / ° C. and a melting point of 5° C. or lower. The dispersed particles have L*value of 30 or less as determined by the CIE-Lab color system (light source D65).
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF THE RYUKYUS +1
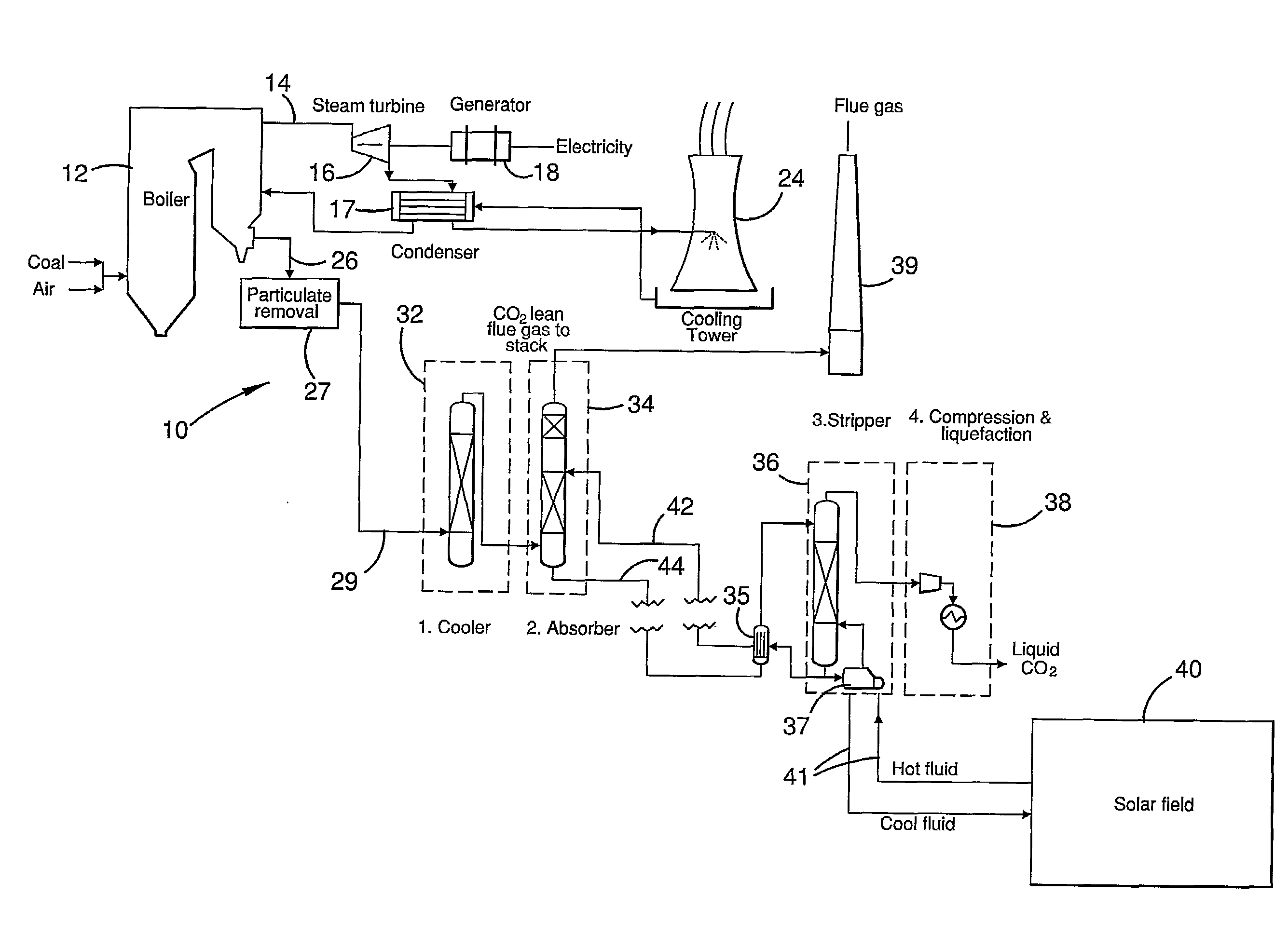
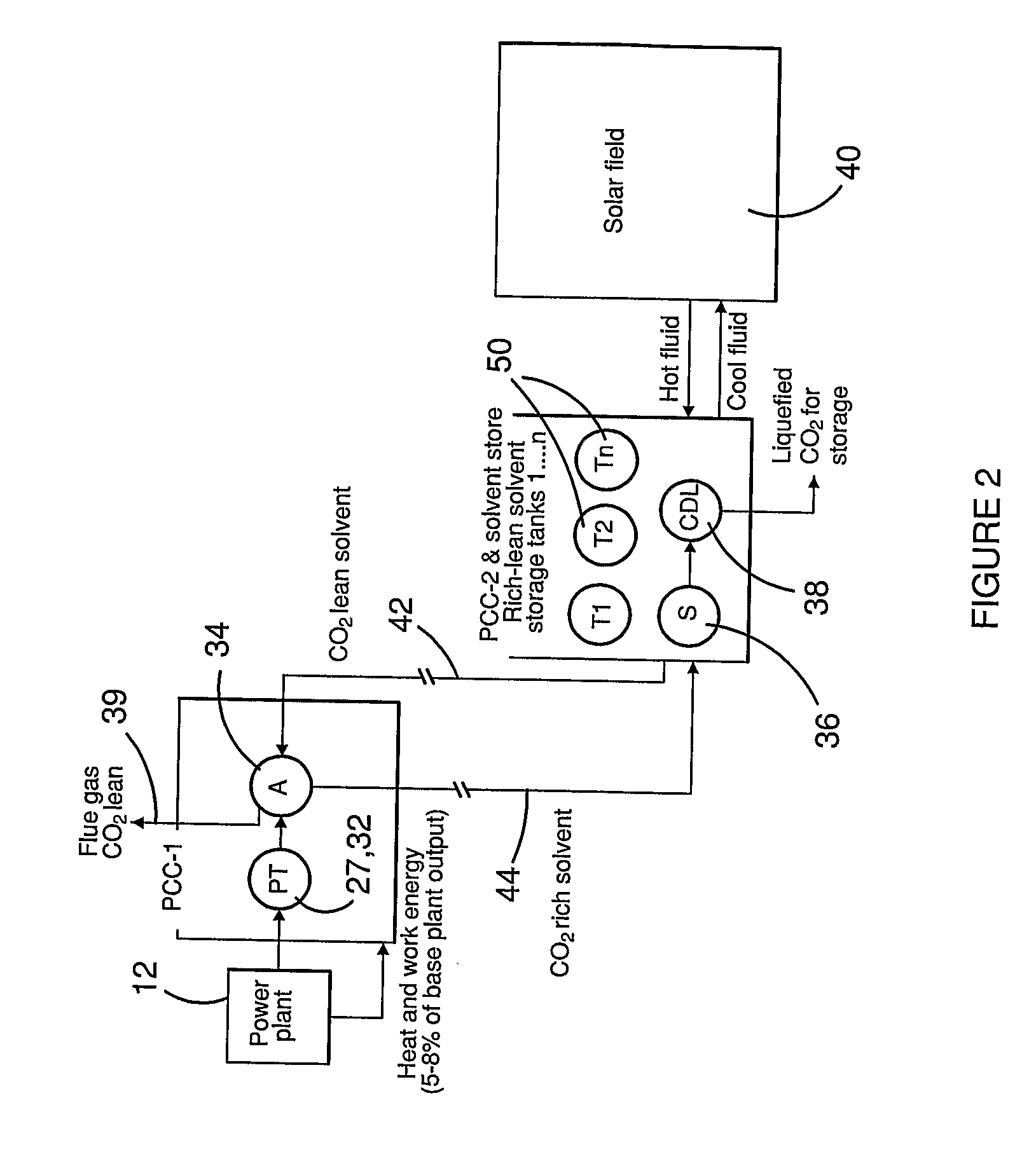
Co2 capture using solar thermal energy
InactiveUS20100005966A1Efficiently employedImprove efficiencySolar heating energyLiquid degasificationThermal energyWorking fluid
At an absorber station, CO2 is absorbed from a gas stream into a suitable solvent whereby to convert the solvent into a CO2-enriched medium, which is conveyed to a desorber station, typically nearer to a solar energy field than to the absorber station. Working fluid, heated in the solar energy field by insolation, is employed to effect desorption of CO2 from the CO2-enriched medium, whereby to produce separate CO2 and regenerated solvent streams. The regenerated solvent stream is recycled to the absorber station. The CO2-enriched medium and / or the regenerated solvent stream may be selectively accumulated so as to respectively optimise the timing and rate of absorption and desorption of CO2 and / or to provide a storage of solar energy.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
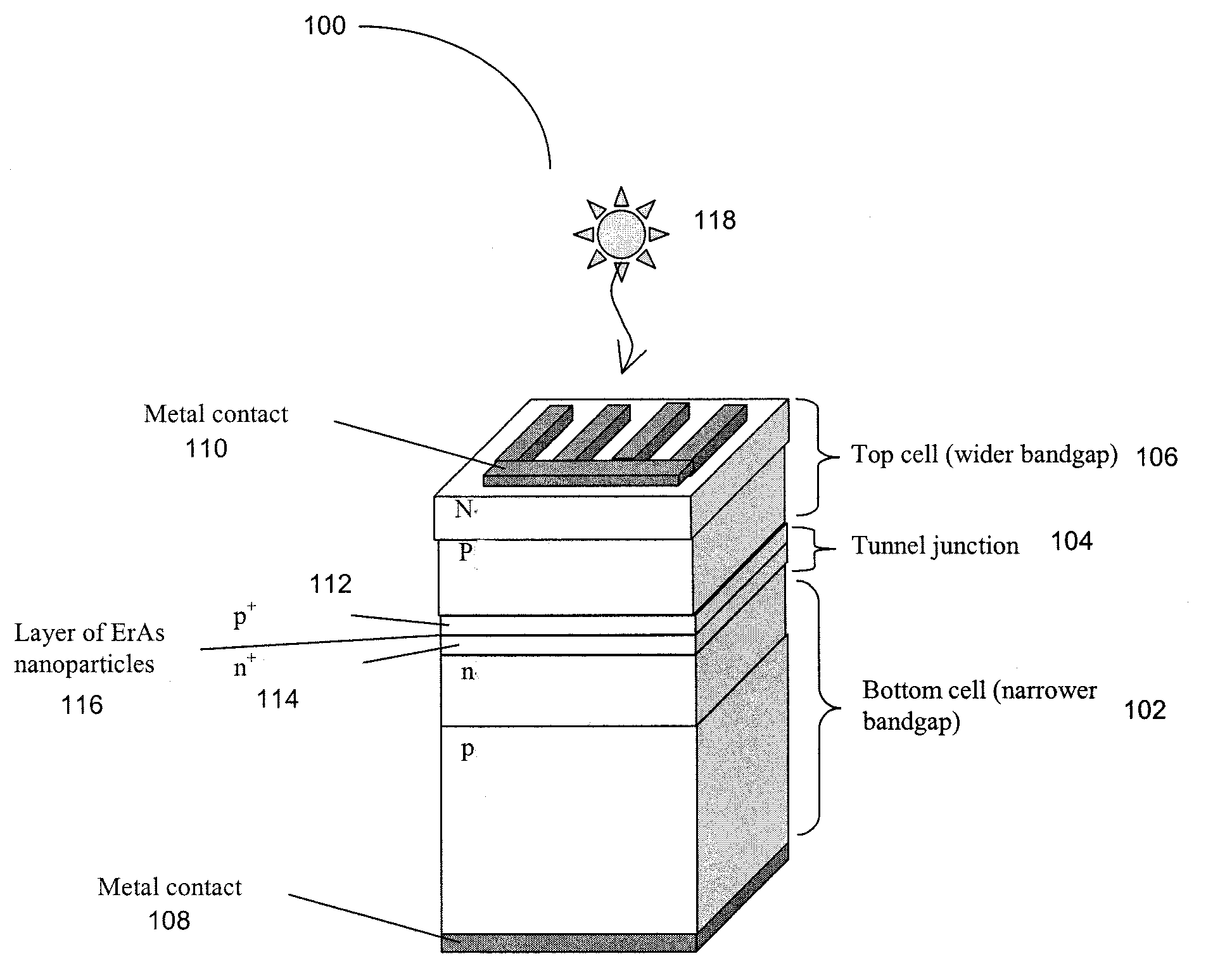
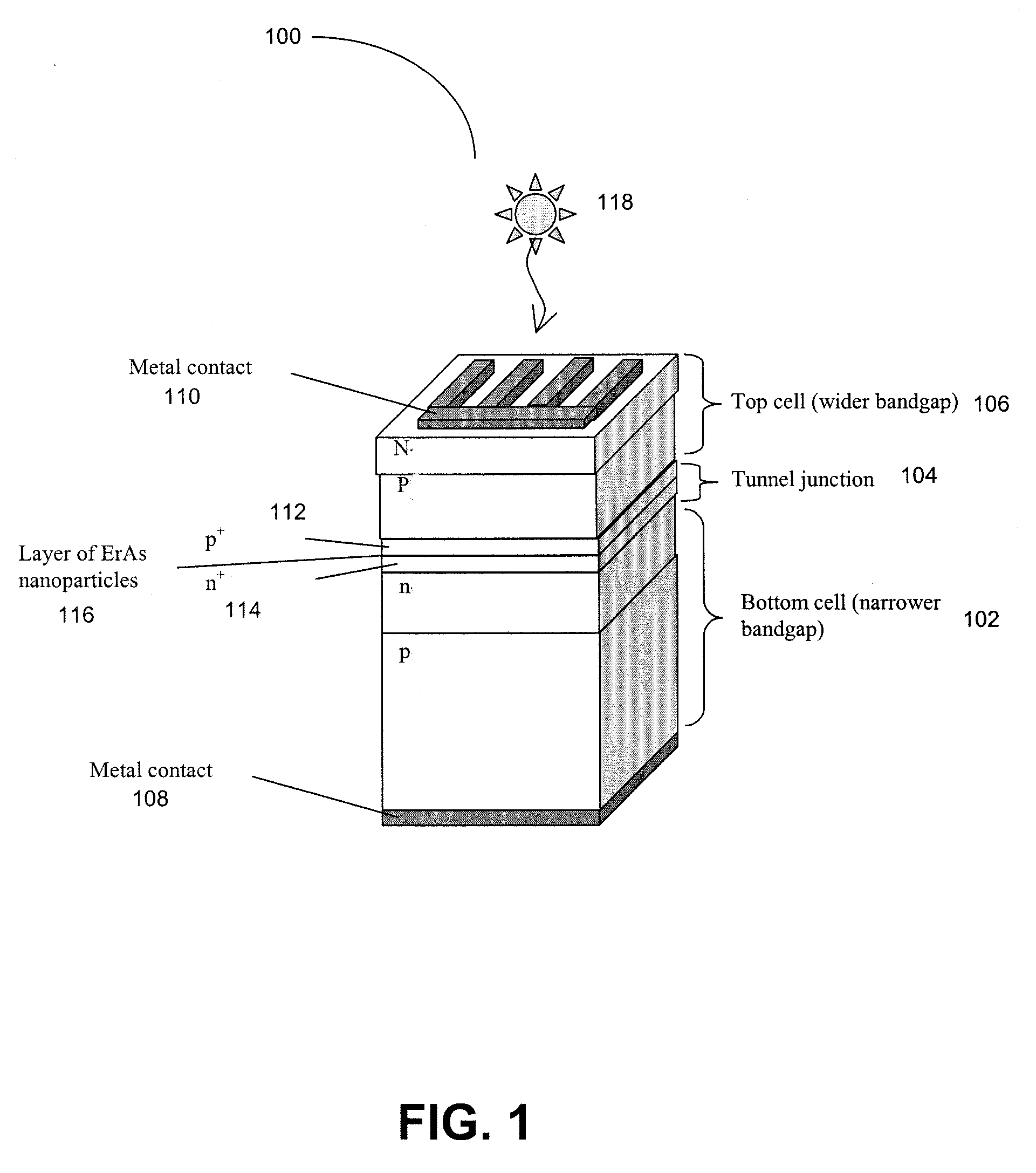
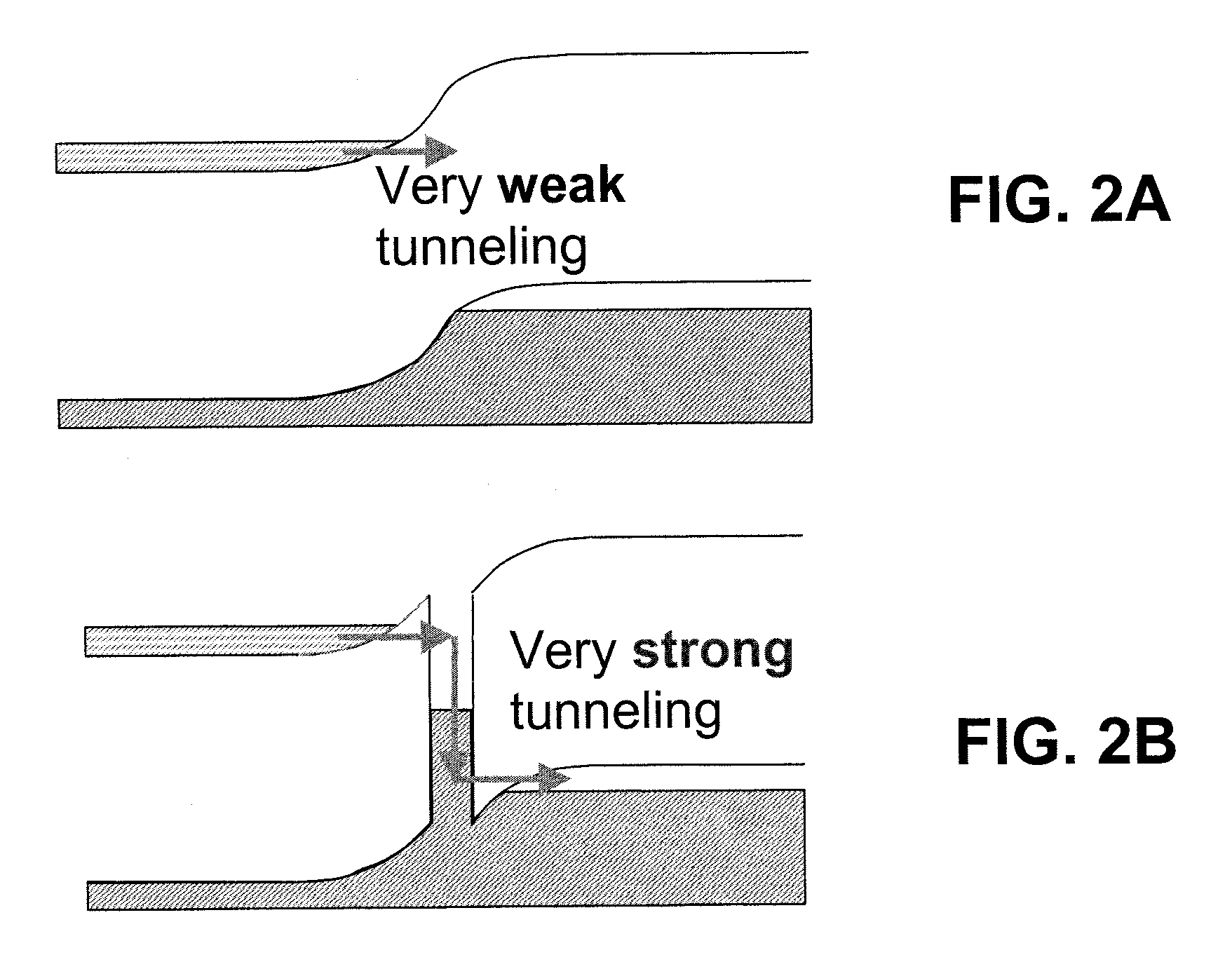
Enhanced tunnel junction for improved performance in cascaded solar cells
InactiveUS20070227588A1High densityHigh solar efficiencyFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationImproved performanceErbium
A method and device that incorporates metallic nanoparticles at the p+-n+ tunnel junction in a cascaded photovoltaic solar cell. The use of the nanoparticles enhances the tunneling current density through the tunnel junction. As such, the efficiency of the solar cell is increased. A method in accordance with the present invention comprises making a first solar cell having a first bandgap, making a tunnel junction coupled to the first solar cell, and making a second solar cell having a second bandgap, coupled to the tunnel junction opposite the first solar cell, wherein the tunnel junction comprises nanoparticles. Such a method further optionally includes the nanoparticles being a metal or a semi metal, specifically a semi-metal of erbium arsenide, the nanoparticles being deposited in an island structure within the tunnel junction, and the first solar cell being deposited on a flexible substrate. A device in accordance with the present invention comprises a tunnel junction, wherein the tunnel junction comprises nanoparticles between the n+ layer and the p+ layer of the tunnel junction. Such a device further optionally includes the device being a cascaded solar cell, the nanoparticles are a metal or semi-metal, specifically a semi-metal of erbium arsenide, and the device is fabricated on a flexible substrate.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
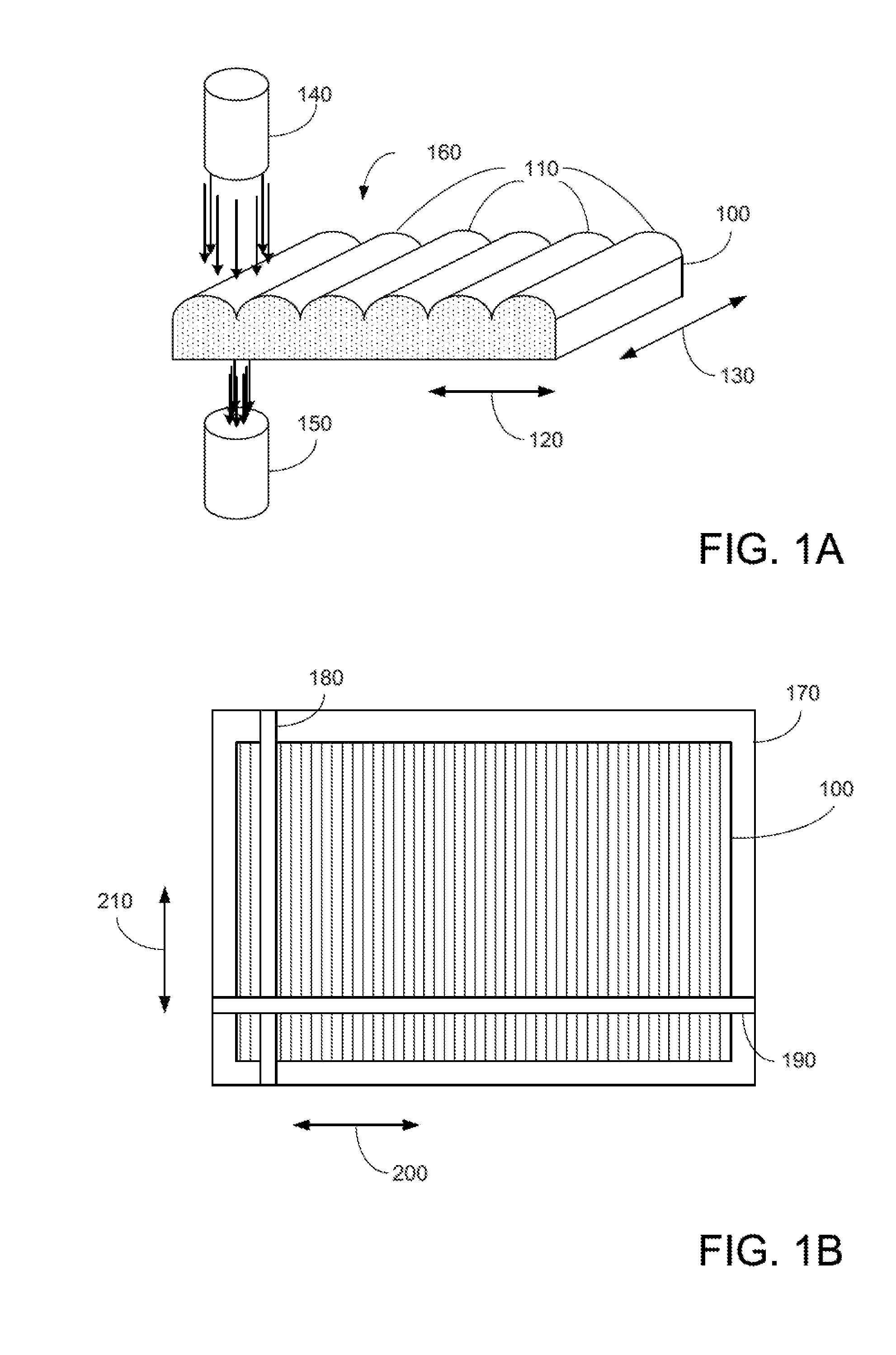
Photovoltaic strip solar modules and methods
InactiveUS20120211052A1Maximizes capturePrecise positioningPV power plantsFinal product manufactureLight energyOptoelectronics
A light energy collection device includes a glass layer having light concentrators for receiving light and for concentrating concentrated light, the light concentrators are elongated and substantially parallel manner to a first edge of the glass layer, wherein pitches of the light concentrators vary along the length generally within the range of approximately 5.5-5.8 mm, strings of multiple PV strips extending in a parallel manner to a second edge (perpendicular to the first edge) of the glass layer, wherein a string of PV strips includes: electrodes extending substantially parallel to the second edge, PV strips electrically coupled to the electrodes and extending substantially parallel to the first edge, wherein pitches of the PV strips vary along their length according to varying pitches of the light concentrators, wherein the PV strips receive concentrated light and output electrical energy in response to the concentrated light.
Owner:SOLARIA CORP
Solar chimney with internal solar collector
ActiveUS20080156315A1Useful workHigh solar efficiencySolar heating energyWind motor with solar radiationCollector deviceSolar chimney
A solar chimney includes a solar collector which heats air in the chimney, producing updrafts which can be harnessed to perform useful work. The solar collector may be located inside or outside the chimney. The device may include a reservoir for storing a heat transfer fluid, thus enabling the device to be used during both day and night. The solar chimney may be equipped with both internal and external solar collectors, operating in parallel. The solar chimney may also be equipped with multiple external solar collectors, connected in parallel to a reservoir. The solar chimney of the invention provides a convenient and practical way to convert solar energy into electrical power.
Owner:YANGPICHIT PITAYA
Solar Cell and Manufacturing Method Thereof
ActiveUS20120273040A1Simple manufacturing processLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationDopantSilicon oxide
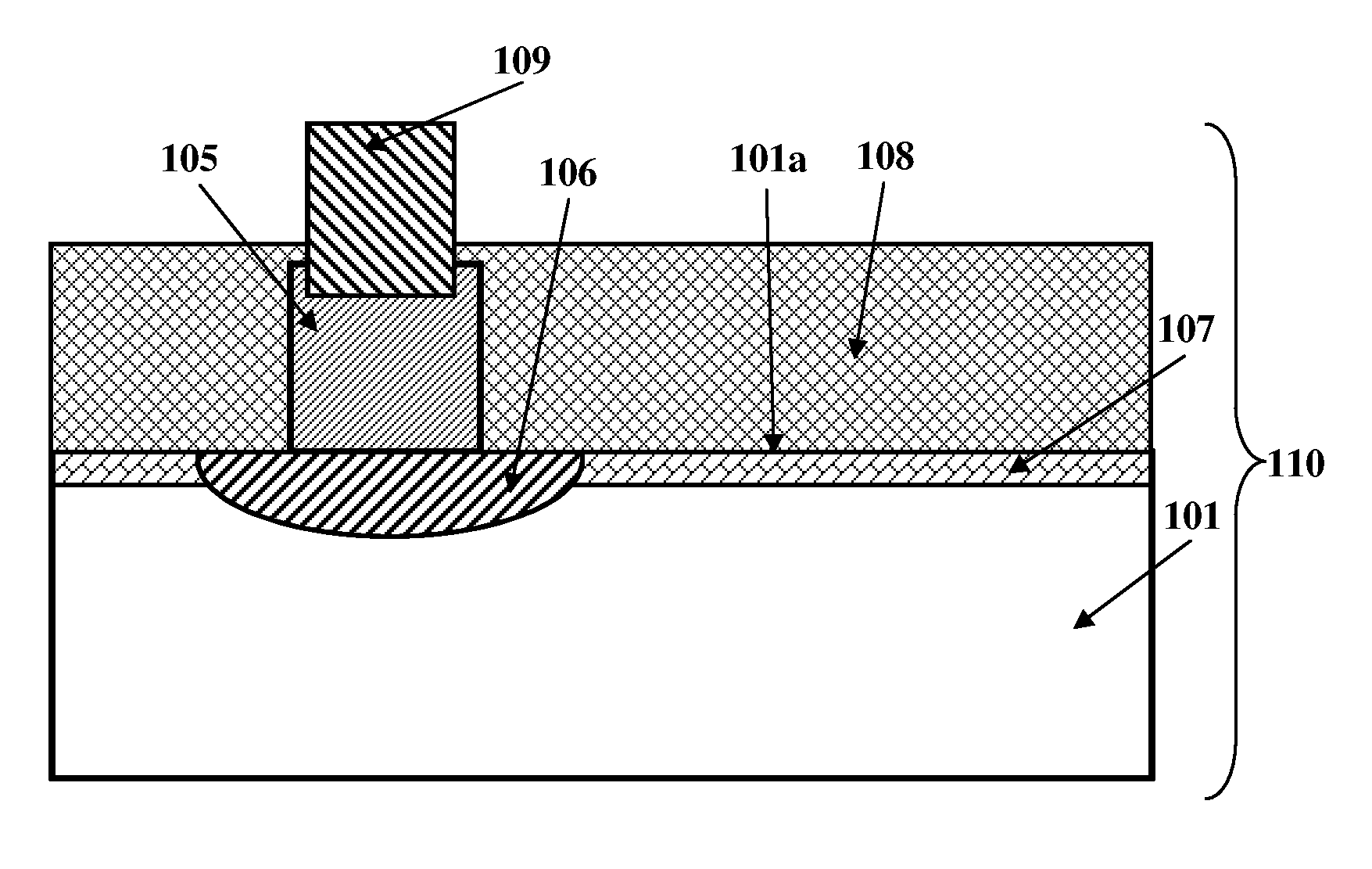
A method for forming a doped region in a solar cell includes preparing a first and second surface of a substrate, forming a first doped region doped with a first dopant in a part of the first surface, forming a silicon oxide layer on the first surface, the silicon oxide layer including a first silicon oxide layer on the first doped region and having a first thickness, and a second silicon oxide layer on a portion of the first surface undoped by the first dopant and having a second thickness that is less than the first thickness, implanting a second dopant from outside the first surface into the first silicon oxide layer and the second silicon oxide layer, and forming a second doped region adjacent the first doped region by performing heat treatment on the first silicon oxide layer, the second silicon oxide layer, and the substrate.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Polycrystalline silicon solar cell having high efficiency and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS20090178711A1Improve efficiencyHigh solar efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationAmorphous siliconOptoelectronics
Disclosed herein is a polycrystalline silicon solar cell, including: a back electrode formed on a transparent insulating substrate; an N-type polycrystalline silicon layer in which amorphous silicon is crystallized through MIC process, and in which electrons are accumulated; a light-absorbing layer which is formed by vertically crystallizing an intrinsic amorphous silicon layer using the polycrystalline silicon layer as a seed for crystallization through MIVC process, in which pairs of electrons and holes are generated in response to incident light, and which has a vertical column grain structure in which grains are arranged in the direction in which electrons and holes move; a P-type polycrystalline silicon layer which has the vertical column grain structure, and in which holes are accumulated; a transparent electrode layer; front electrodes; and an antireflection coating film, and is a method of fabricating the same.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Solar cell device
InactiveUS6593522B2Reduce manufacturing costReduce weightPV power plantsPhotovoltaic energy generationMetal foilSolar cell
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Solar cell and method for manufacturing such a solar cell
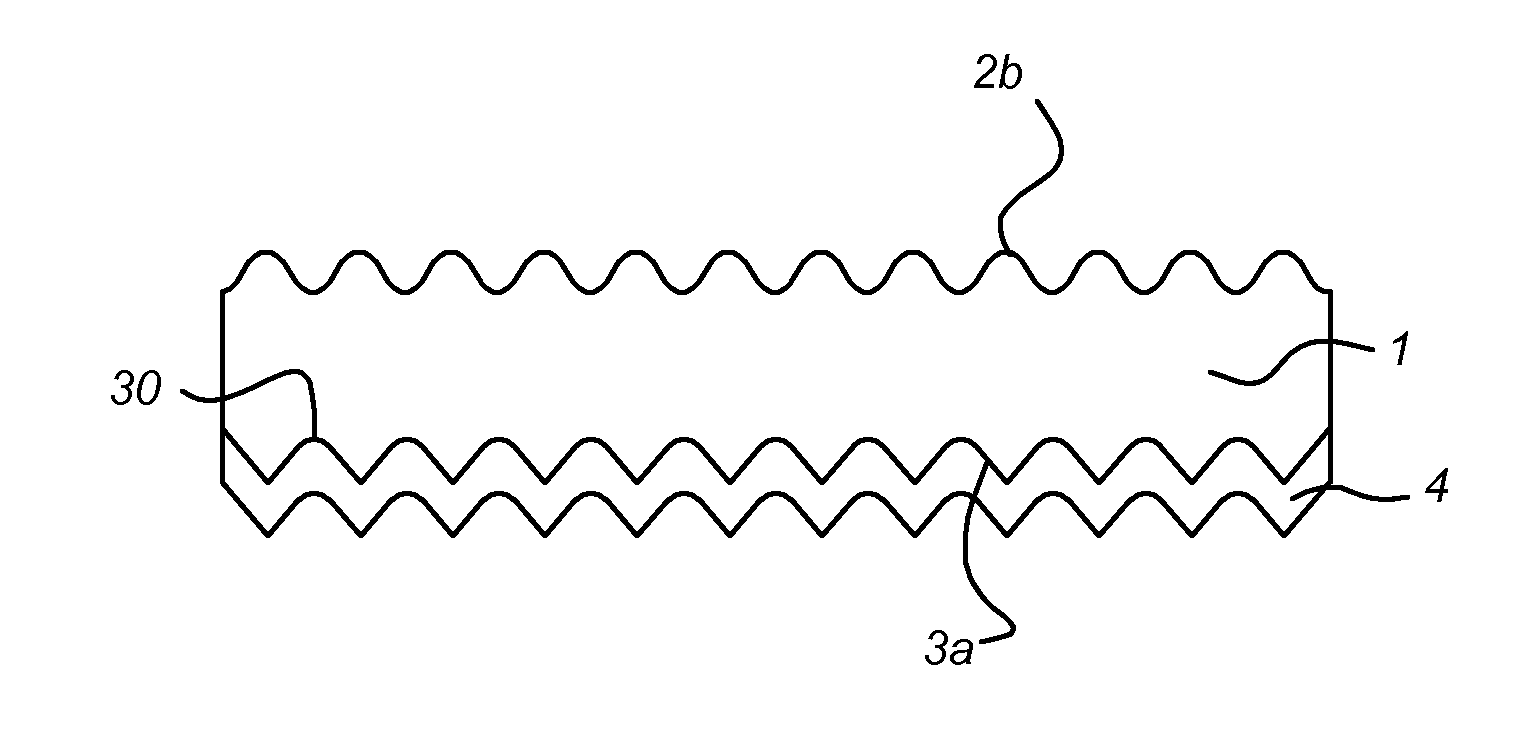
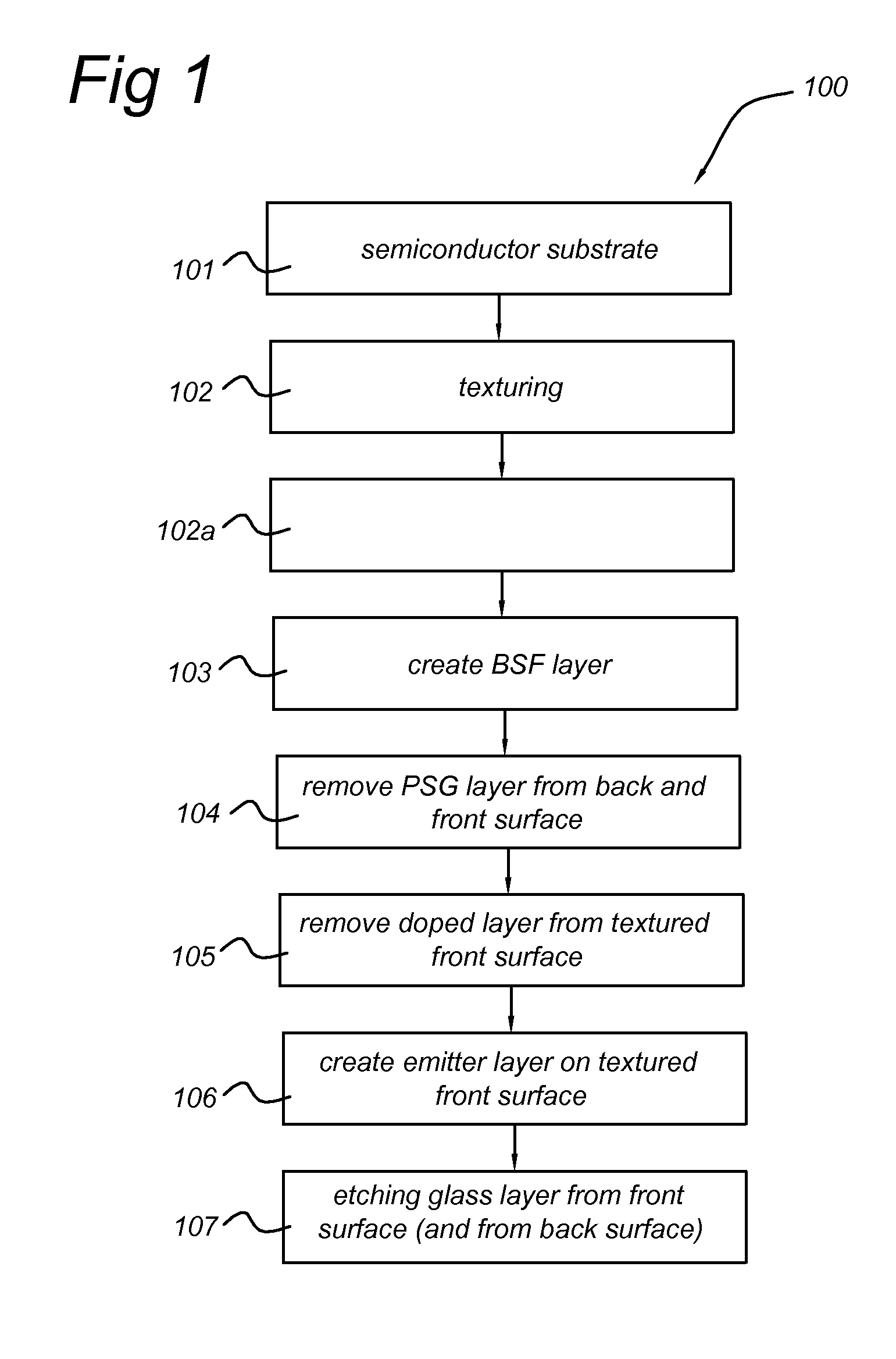
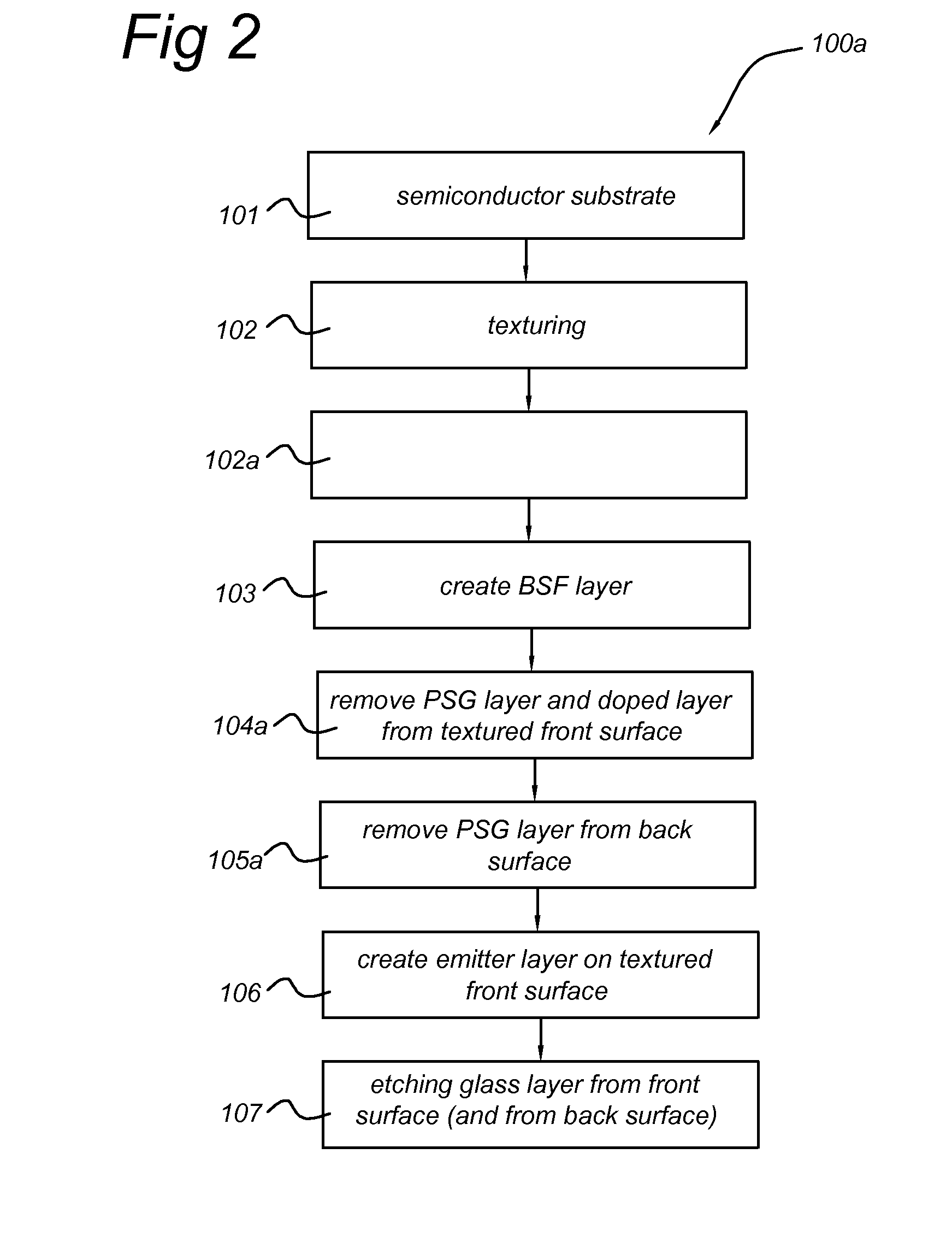
ActiveUS20120181667A1Reduce creationHigh budgetSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationDopantBack surface field
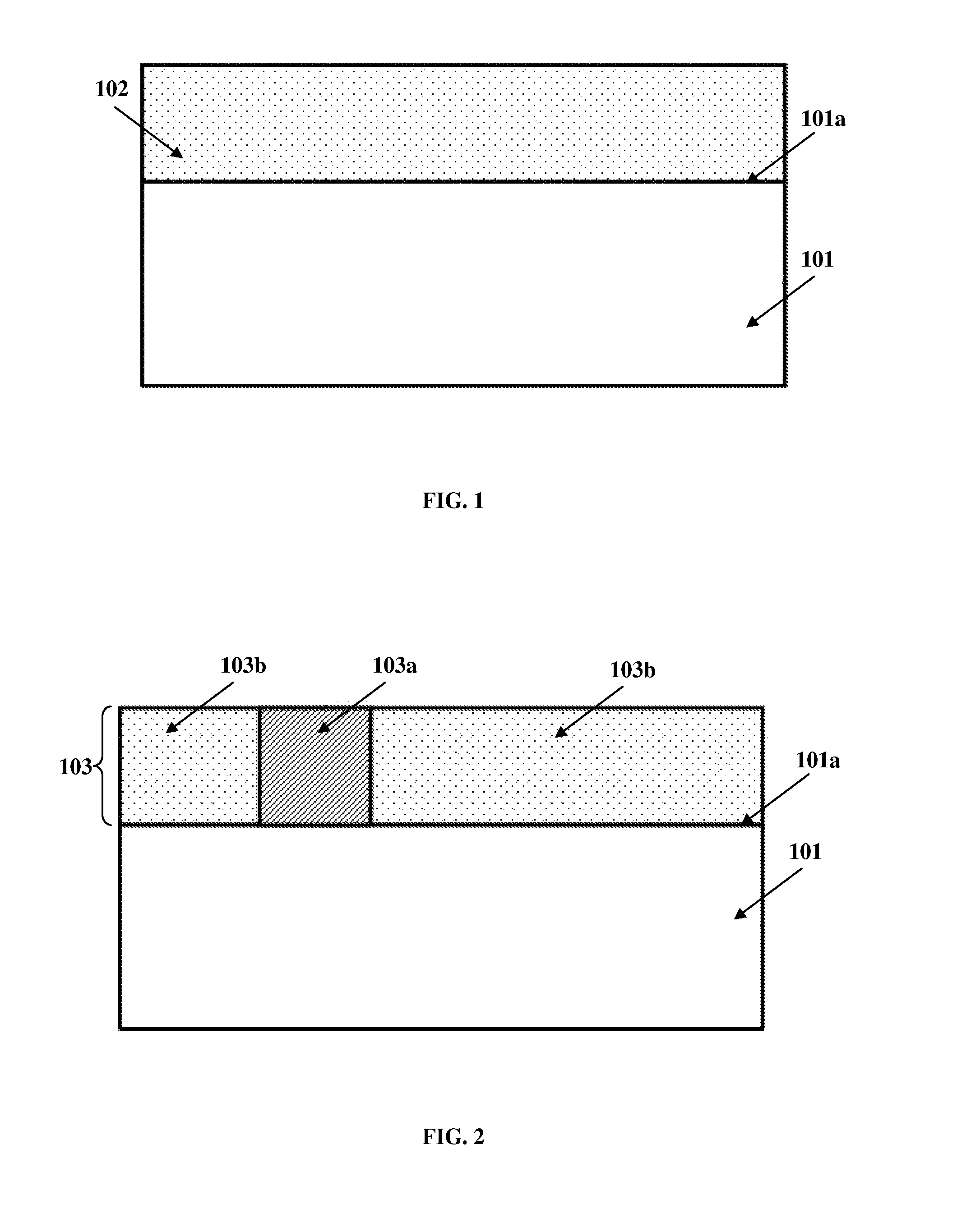
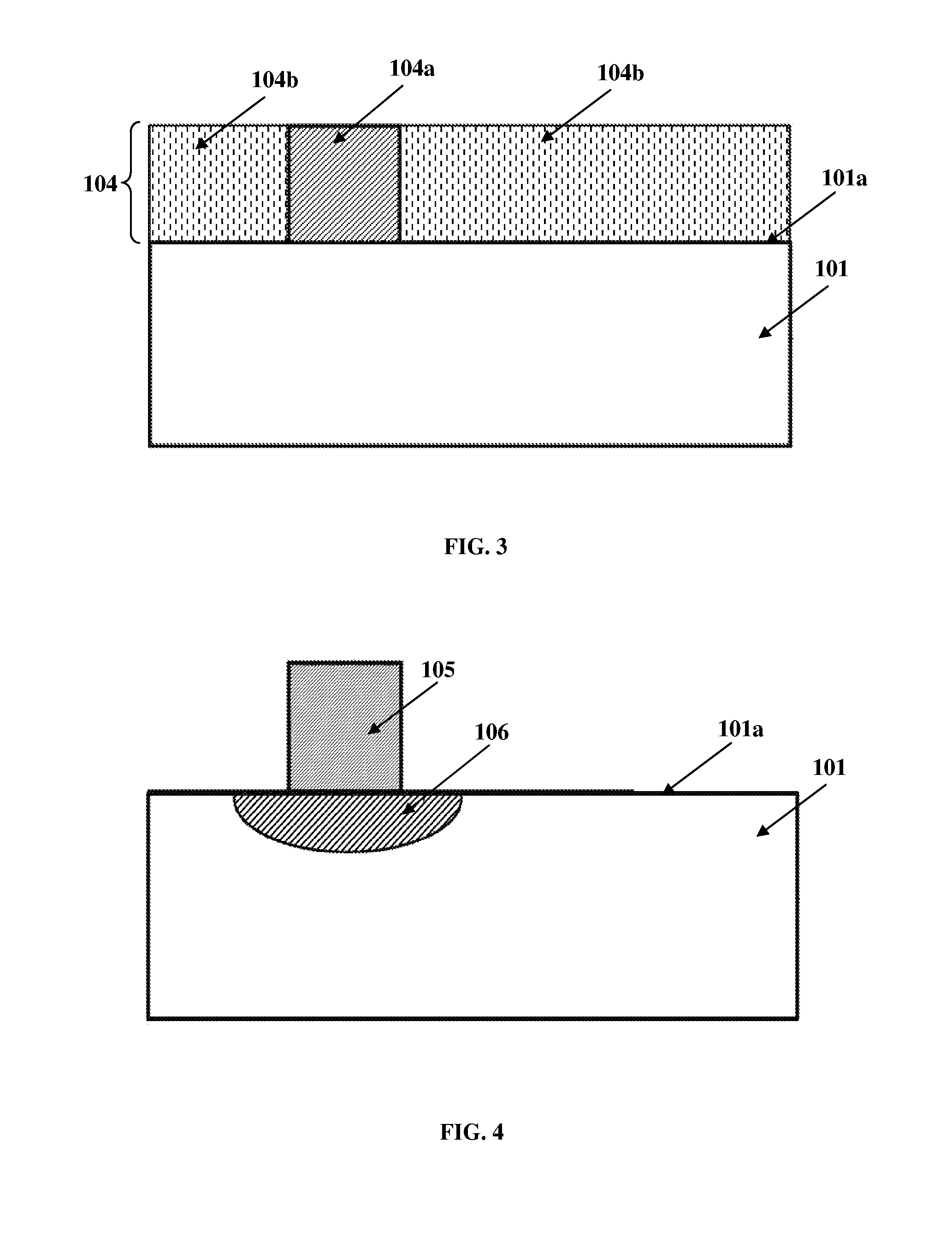
A method for manufacturing a solar cell from a semiconductor substrate (1) of a first conductivity type, the semiconductor substrate having a front surface (2) and a back surface (3). The method includes in a sequence: texturing (102) the front surface to create a textured front surface (2a); creating (103) by diffusion of a dopant of the first conductivity type a first conductivity-type doped layer (2c) in the textured front surface and a back surface field layer (4) of the first conductivity type in the back surface; removing (105; 104a) the first conductivity-type doped layer from the textured front surface by an etching process adapted for retaining texture of the textured front surface; creating (106) a layer of a second conductivity type (6) on the textured front surface by diffusion of a dopant of the second conductivity type into the textured front surface.
Owner:NEDERLANDSE ORG VOOR TOEGEPAST-NATUURWETENSCHAPPELIJK ONDERZOEK (TNO)
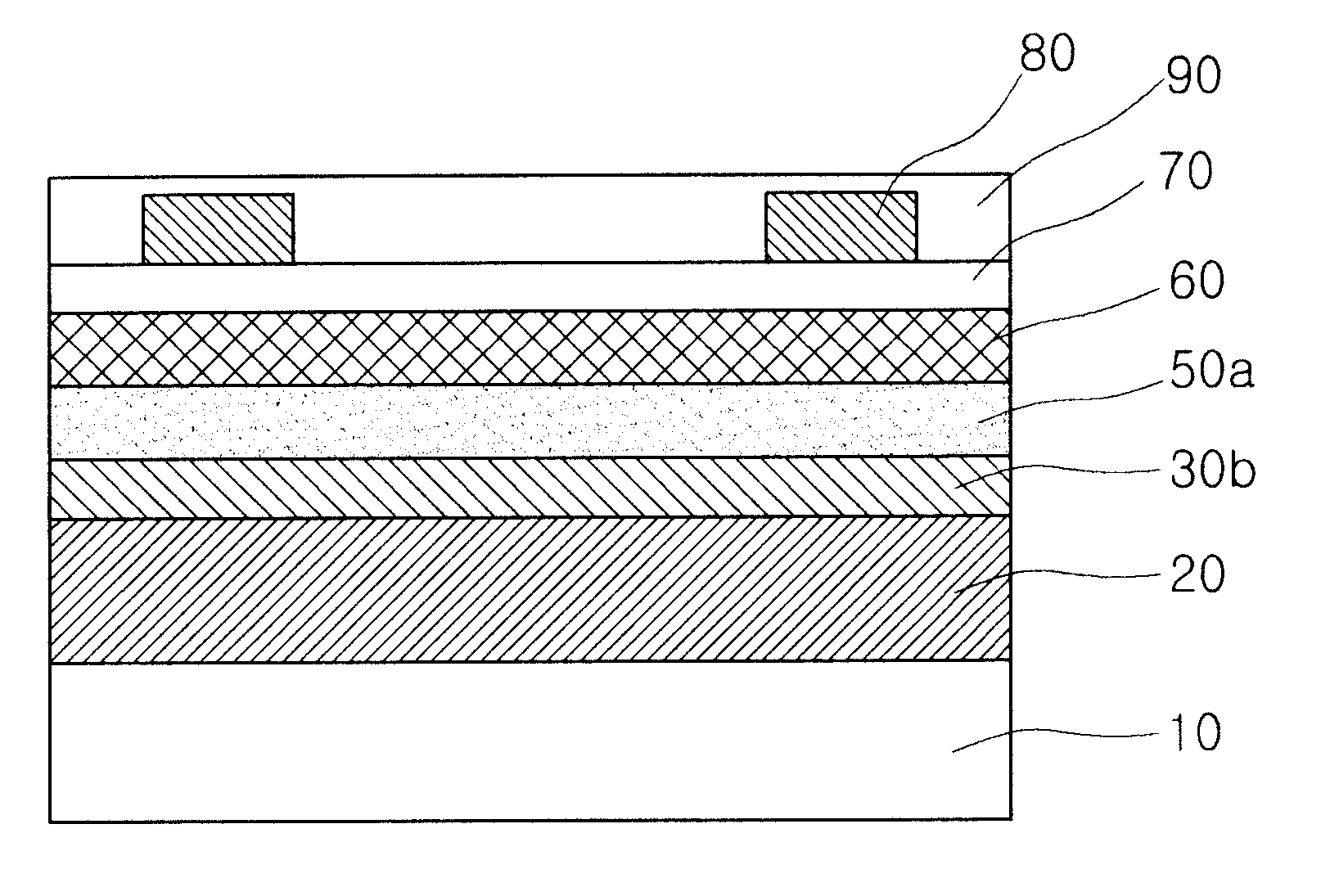
Solar cell with gradation in doping in the window layer
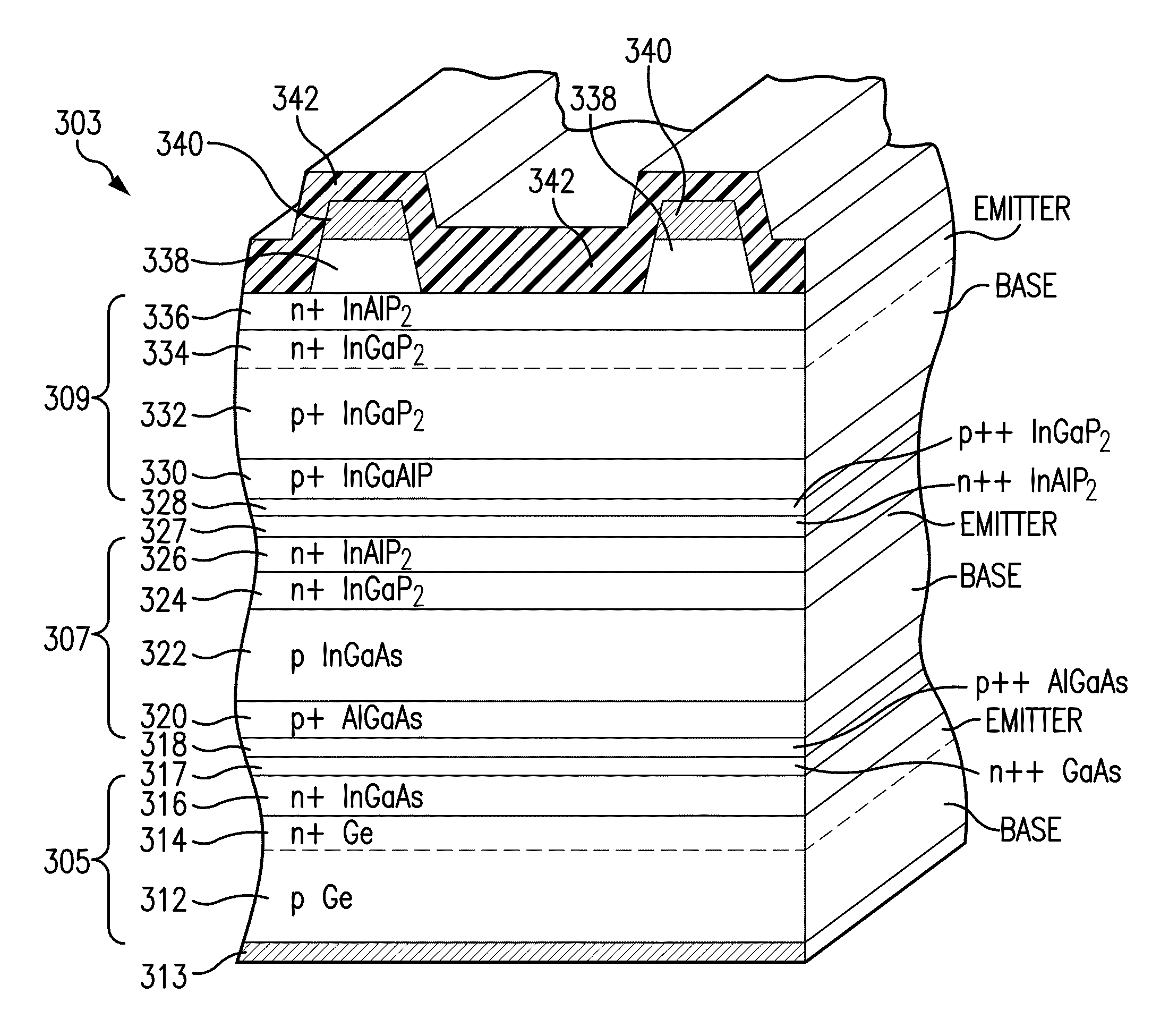
InactiveUS20130228216A1Photo-conversion efficiency can be improvedIncrease currentFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface layerElectric field
A multijunction solar cell including a window layer with a gradation in doping from the region in the window layer adjacent to the emitter region to the region in the window layer adjacent to the surface layer overlying the window layer, so that minority carriers in the window layer experience an electric field which would tend to drive them in the direction of the emitter layer, thereby increasing the efficiency of the solar cell.
Owner:SOLAERO TECH CORP
Method and system for light collection and light energy converting apparatus
ActiveUS20100078062A1Improve performanceHigh solar efficiencySolar heating energyMirrorsCollection systemLight energy
A light collection system including a light concentrating device and a reflective curving-surface device is provided. The light concentrating device receives at least a portion of an incident light and forwardly emits the portion of the incident light after concentrating and passing it through a first focal region, so as to obtain a first-stage output light. The reflective curving-surface device has an entrance aperture for receiving the first-stage output light. The reflective curving-surface device includes a reflective inner curving surface, and at least a portion of the reflective inner curving surface has a second focal region. The first focal region and the second focal region are confocal or approximately confocal within a range. As a result, at least a portion of the first-stage output light is confocally converted into a forwardly emitted second-stage output light.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Photoelectrolysis of water using proton exchange membranes
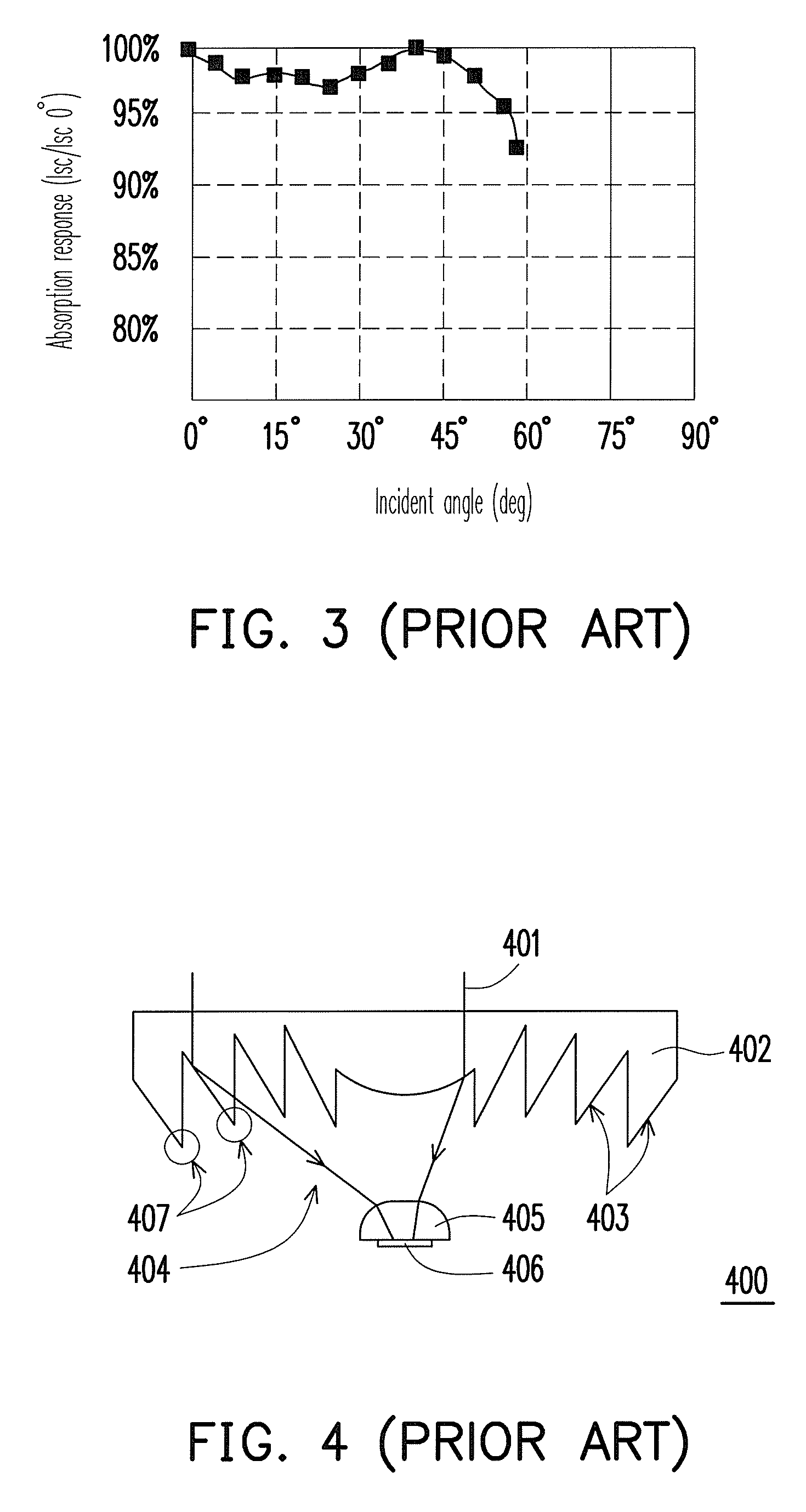
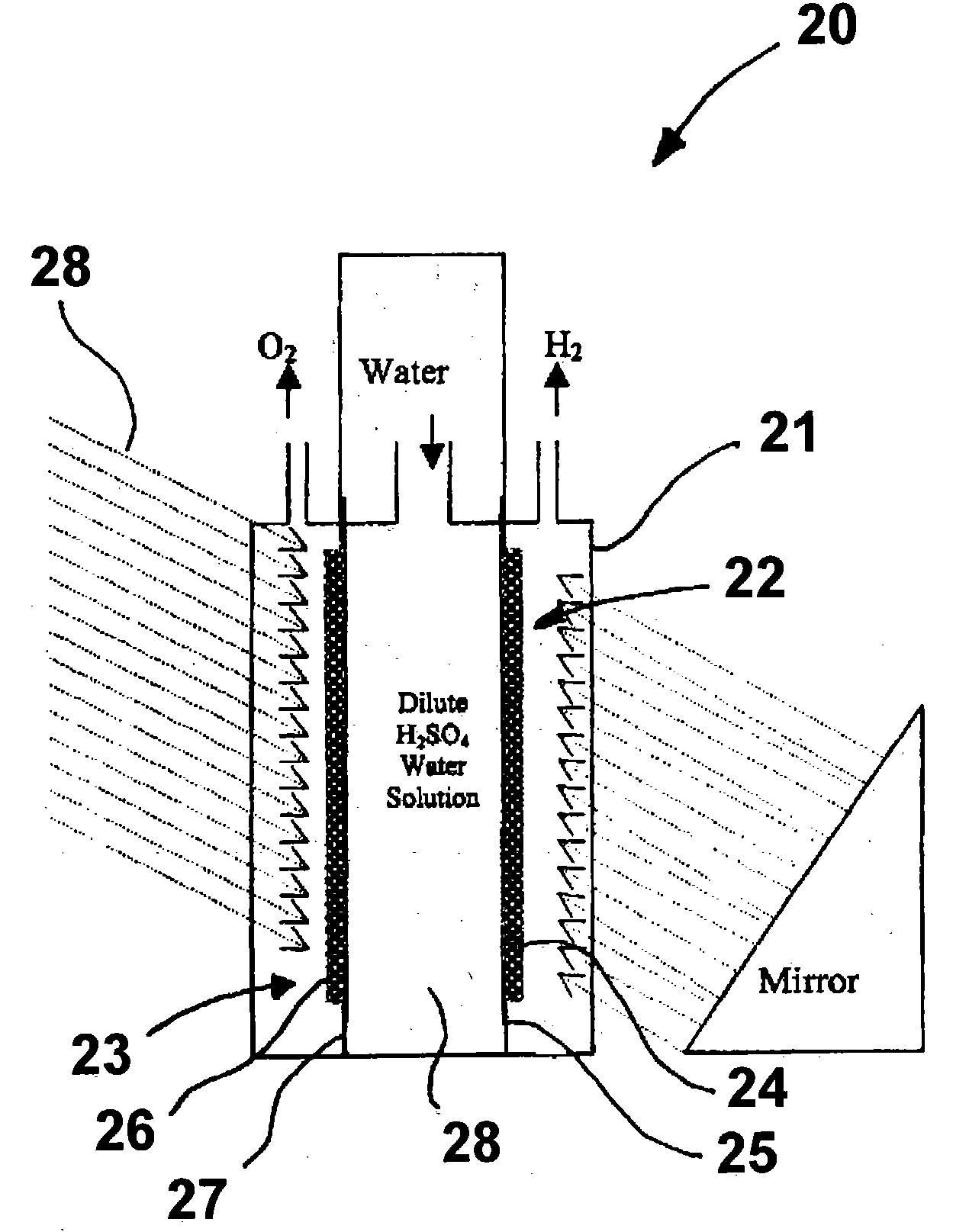
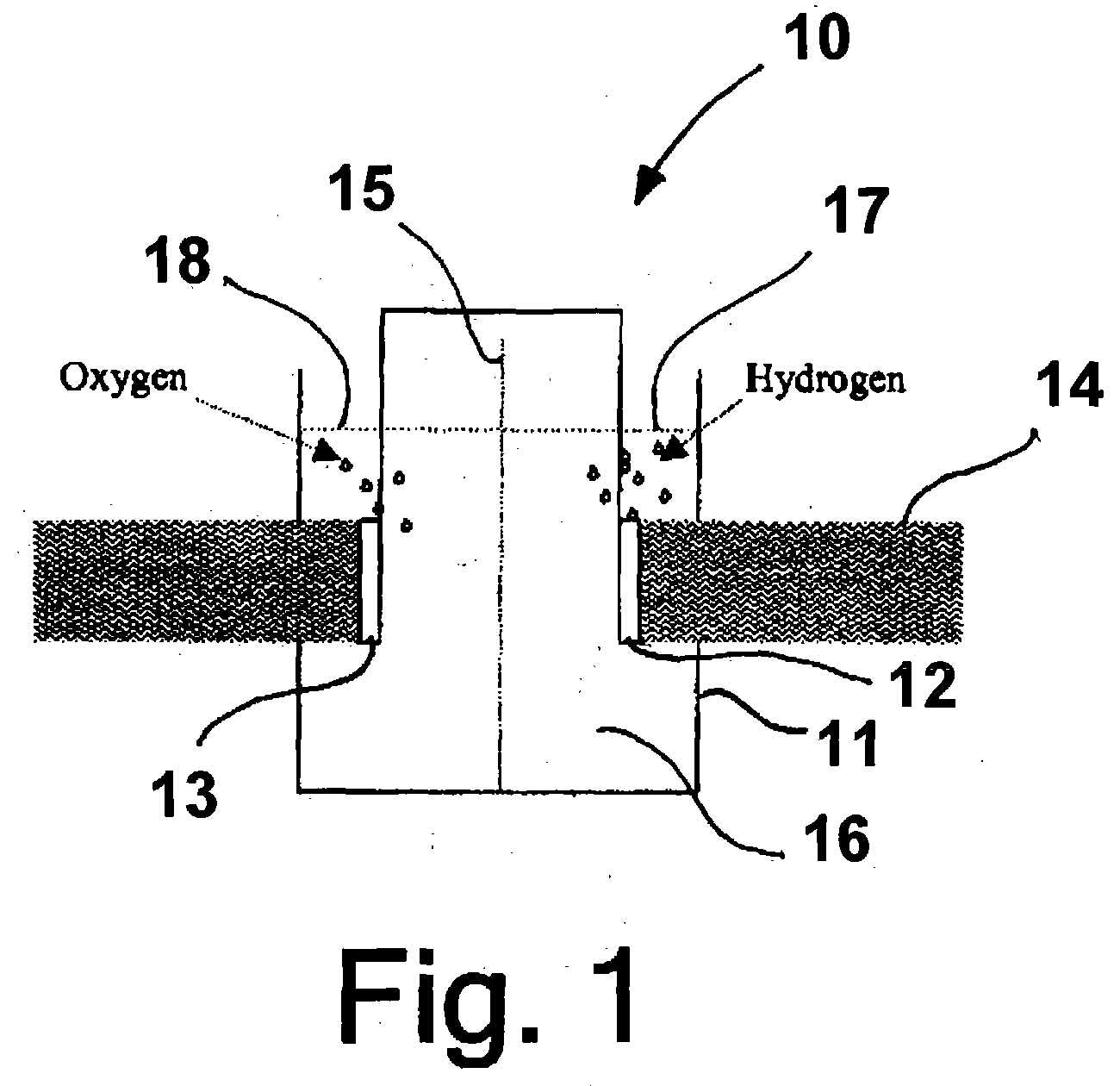
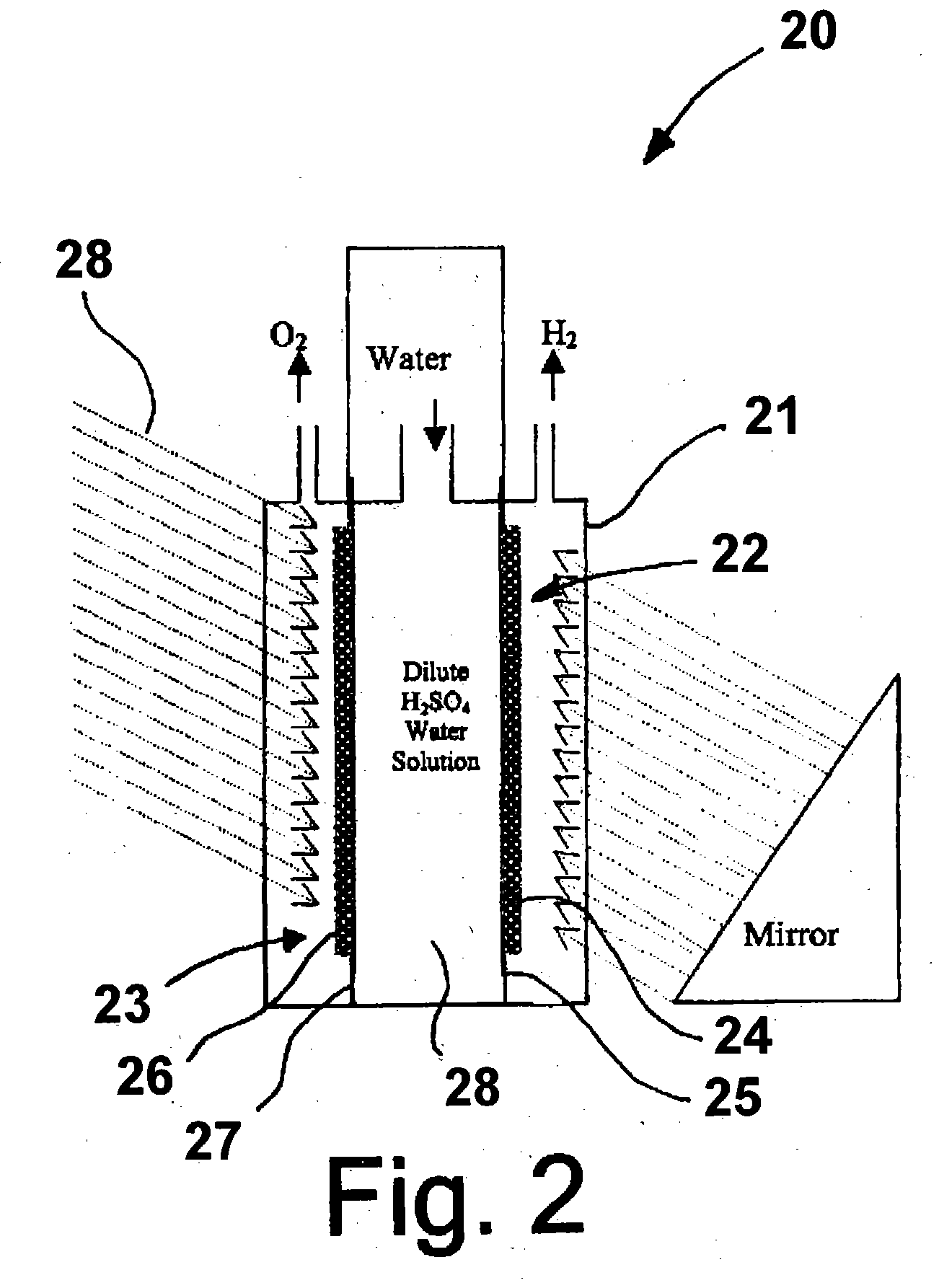
ActiveUS20050005963A1Enhanced Efficiency StabilityImprove performance stabilityMachining electrodesCellsWater useElectro catalyst
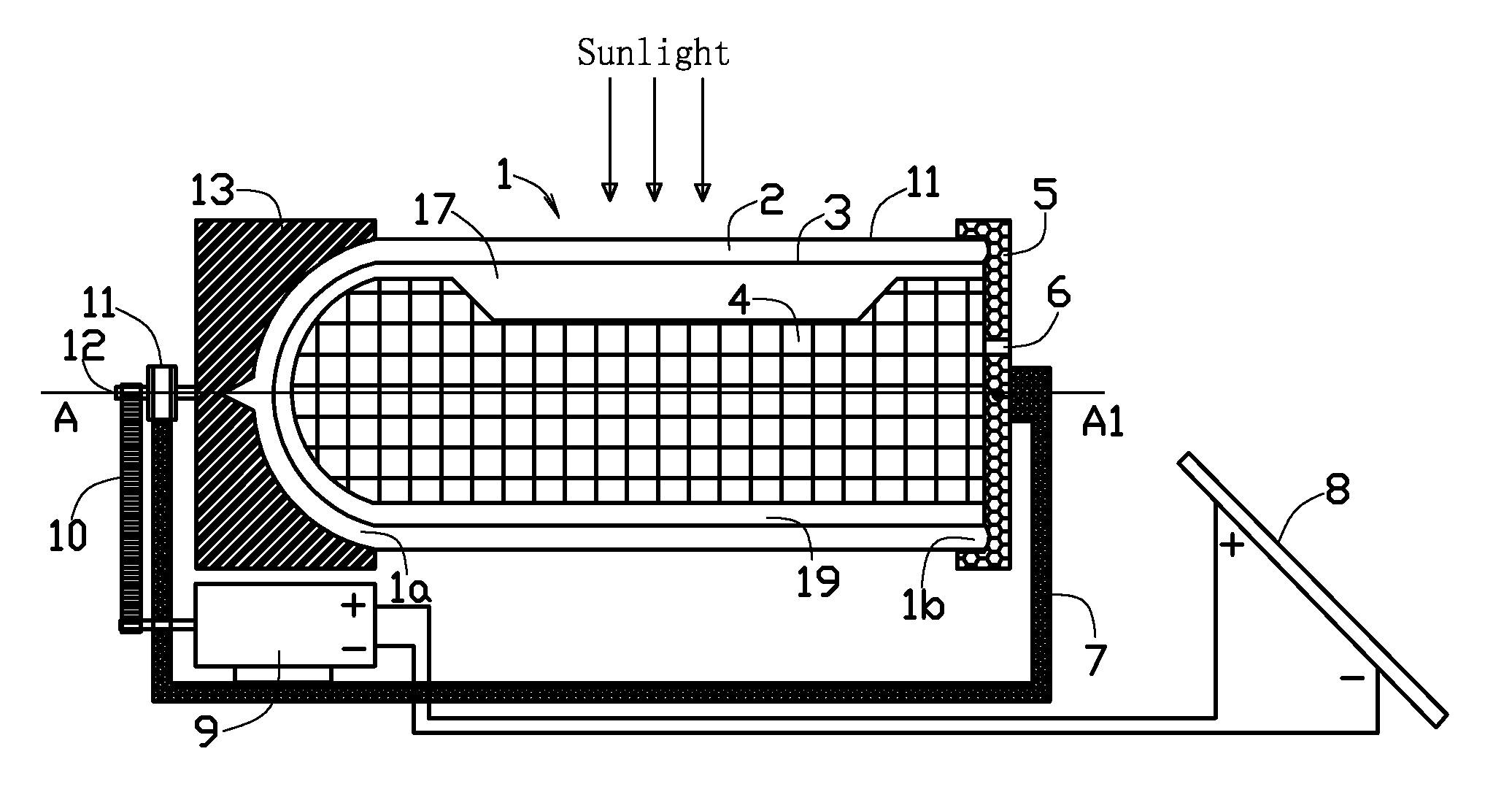
A photoelectrochemical cell which includes a light transmissive enclosure, a semiconductor photoanode disposed within the light transmissive enclosure, a semiconductor photocathode disposed within the light transmissive enclosure, and an electrolytic solution disposed entirely between the semiconductor photoanode and the semiconductor photocathode. This is achieved by the use of semiconductor photoelectrodes (photoanodes and photocathodes) which include a proton exchange membrane having an electrolyte facing surface in contact with the electrolytic solution and a light transmissive wall facing surface, and having a photo electro-catalyst disposed on the light transmissive wall facing surface.
Owner:GAS TECH INST
Diffusion Sources From Silicon Based Liquid Precursors
ActiveUS20120052618A1High solar efficiencyReduce contact resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationOligomerDopant
Methods for selectively diffusing dopants into a substrate wafer are provided. A liquid precursor is doped with dopants. The liquid precursor is selected from a group comprising monomers, polymers, and oligomers of silicon and hydrogen. The doped liquid precursor is deposited on a surface of the substrate wafer to create a doped film. The doped film is heated on the substrate wafer for diffusing the dopants from the doped film into the substrate wafer at different diffusion rates to create a heavily diffused region and a lightly diffused region in the substrate wafer. The method disclosed herein further comprises selective curing of the doped film on the surface of the substrate wafer. The selectively cured doped film acts as a diffusion source for selectively diffusing the dopants into the substrate wafer.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
Solar Cell Combination
InactiveUS20130152994A1Low costHigh solar efficiencyPV power plantsPhotovoltaic energy generationEngineeringSolar cell
A solar cell combination having at least two independent electrodes, in which at least one first electrode is formed by at least one first wire conductor that first spans a plurality of solar cells, and in which the first and the second electrodes are contacted with each other, and the first and / or second electrode is disconnected at the positions required for the connection.
Owner:SOLARWORLD INNOVATIONS
Solar chimney for daytime and nighttime use
InactiveUS20080156317A1High solar efficiencyUseful workSolar heating energyWind motor with solar radiationEngineeringSolar chimney
A solar chimney includes a solar collector which heats air in the chimney, producing updrafts which can be harnessed to perform useful work. The solar collector may be located inside or outside the chimney. The device may include a reservoir for storing a heat transfer fluid, thus enabling the device to be used during both day and night. The solar chimney may be equipped with both internal and external solar collectors, operating in parallel. The solar chimney may also be equipped with multiple external solar collectors, connected in parallel to a reservoir. The solar chimney of the invention provides a convenient and practical way to convert solar energy into electrical power.
Owner:YANGPICHIT PITAYA
Solar chimney with internal solar collector
ActiveUS7856974B2Useful workHigh solar efficiencySolar heating energyWind motor with solar radiationCollector deviceSolar chimney
A solar chimney includes a solar collector which heats air in the chimney, producing updrafts which can be harnessed to perform useful work. The solar collector may be located inside or outside the chimney. The device may include a reservoir for storing a heat transfer fluid, thus enabling the device to be used during both day and night. The solar chimney may be equipped with both internal and external solar collectors, operating in parallel. The solar chimney may also be equipped with multiple external solar collectors, connected in parallel to a reservoir. The solar chimney of the invention provides a convenient and practical way to convert solar energy into electrical power.
Owner:YANGPICHIT PITAYA
Method for manufacturing a solar cell module and solar cell module
InactiveUS20170117425A1High solar efficiencyImprove efficiencyPhotovoltaicsPhotovoltaic energy generationEngineeringSolar cell
The present invention relates to a method for manufacturing a solar cell module by the steps of: providing at least two bifacial solar cells; adjoining arrangement of the solar cells, wherein a gap is provided between the solar cells; providing a diffuse reflector in the gap area. The present invention also relates to such a solar cell module, wherein the diffuse reflector is disposed and configured such that it diffusely reflects the incident light and a portion of the diffusely reflected lights strikes on the solar cell through total reflection at the front boundary layer of the solar cell module.
Owner:SOLARWORLD IND GMBH
Conductive Paste, And Electronic Device And Solar Cell Including An Electrode Formed Using The Same
ActiveUS20120174976A1Reduce charging lossHigh solar efficiencyConductive materialNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialConductive pasteElectrical battery
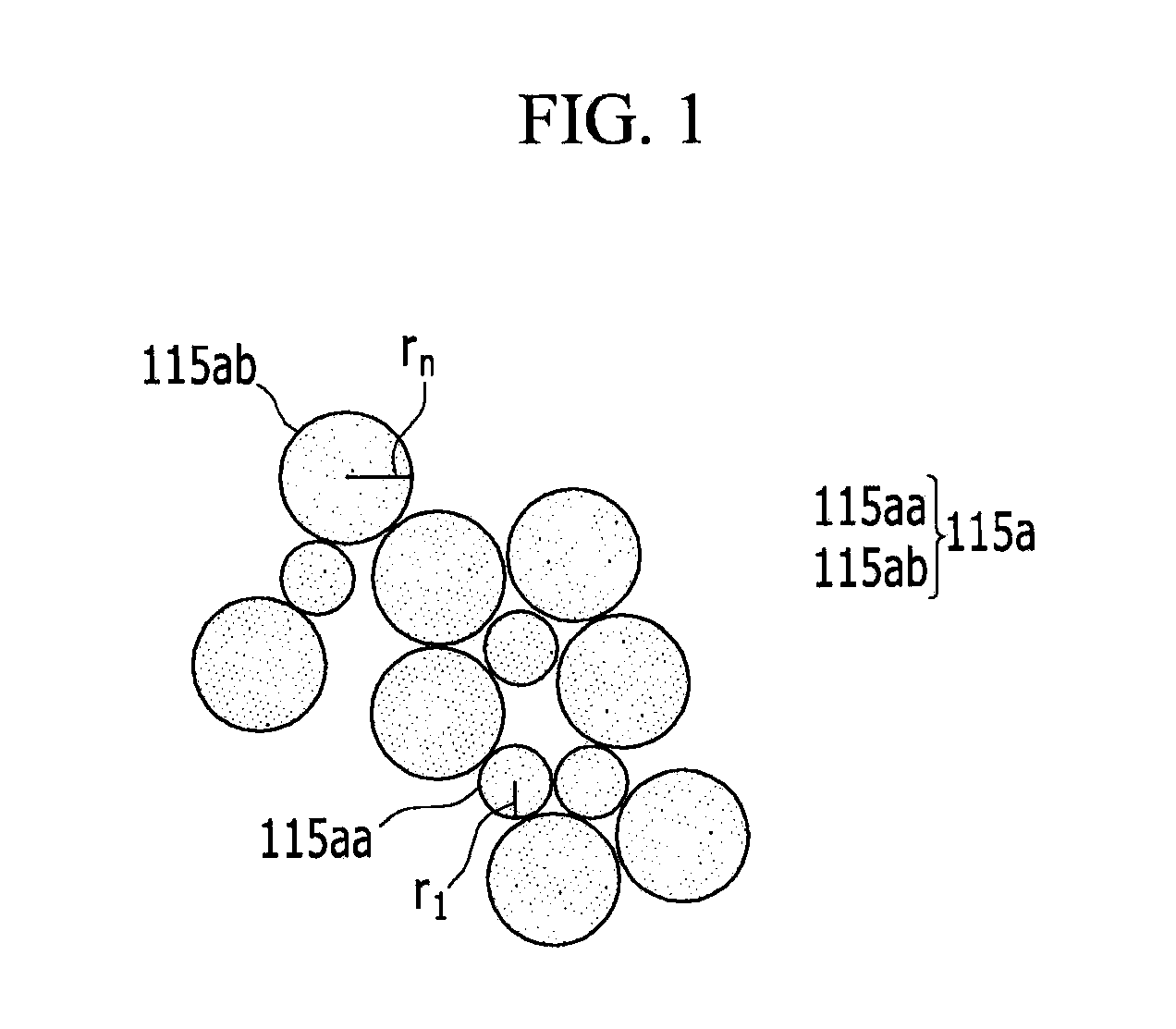
A conductive paste includes a conductive powder, a metallic glass, and an organic vehicle. The metallic glass may be an alloy including a first element with an atomic radius that satisfies the following equation: (r1−rn) / (r1+rn / 2)×100≧9% In the equation, r1 may be an atom radius of the first element, rn may be an atom radius of other elements included in the metallic glass, and n may be an integer ranging from 2 to 10.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
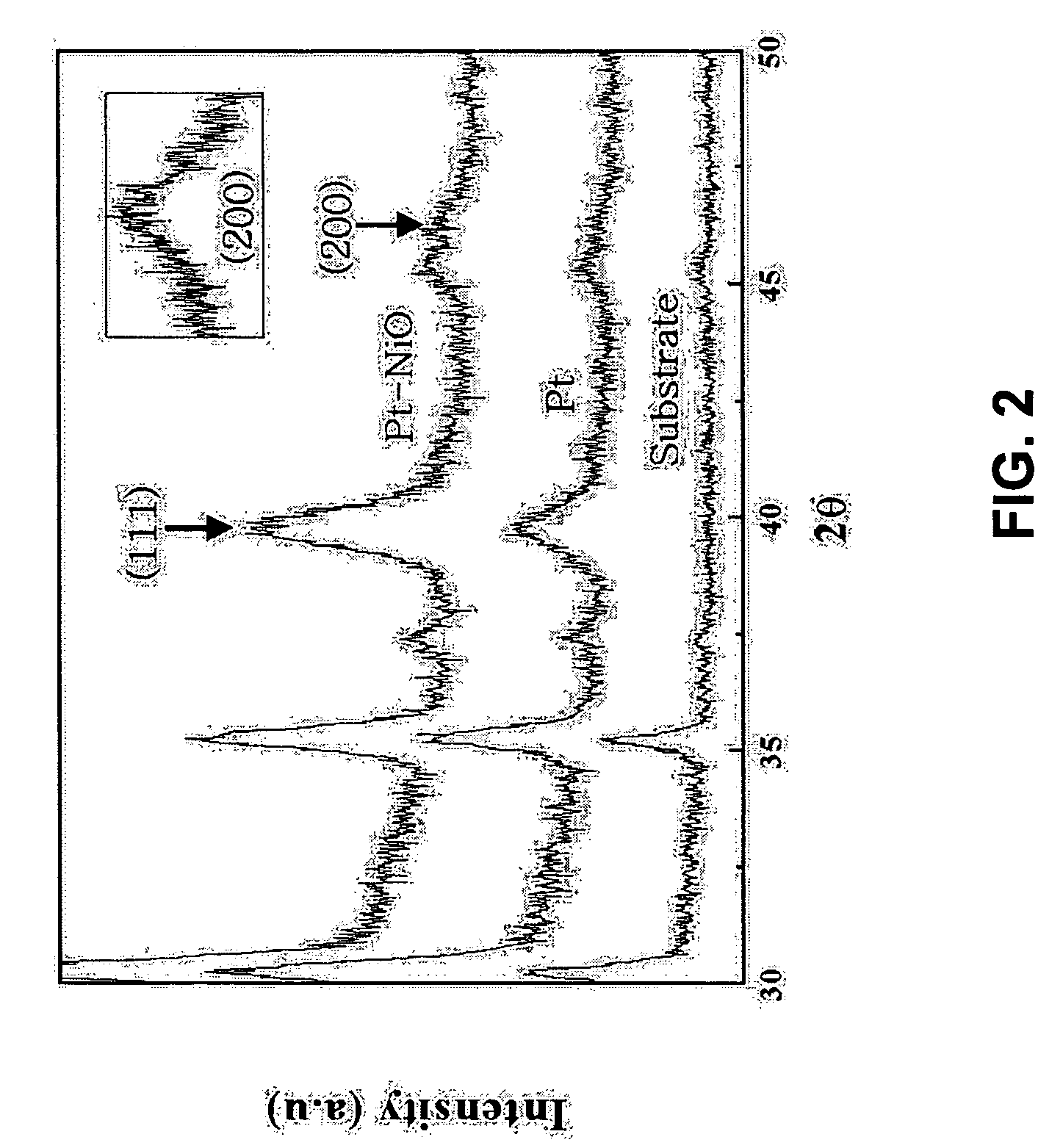
Method for fabricating Pt-MOx nanophase electrodes for highly efficient dye-sensitiized solar cell
InactiveUS20050016586A1Light increasePromote useElectrolytic capacitorsFinal product manufactureDye-sensitized solar cellOxide
A method for fabricating a counter electrode for a dye-sensitized solar cell includes co-sputtering platinum and a metal oxide as target materials to deposit nanocrystalline platinum and an amorphous metal oxide on the substrate. The counter electrode exhibits improved performances as an electro-catalyst to assist in the reduction of I3− during operation of a dye-sensitized solar cell.
Owner:GWANGJU INST OF SCI & TECH
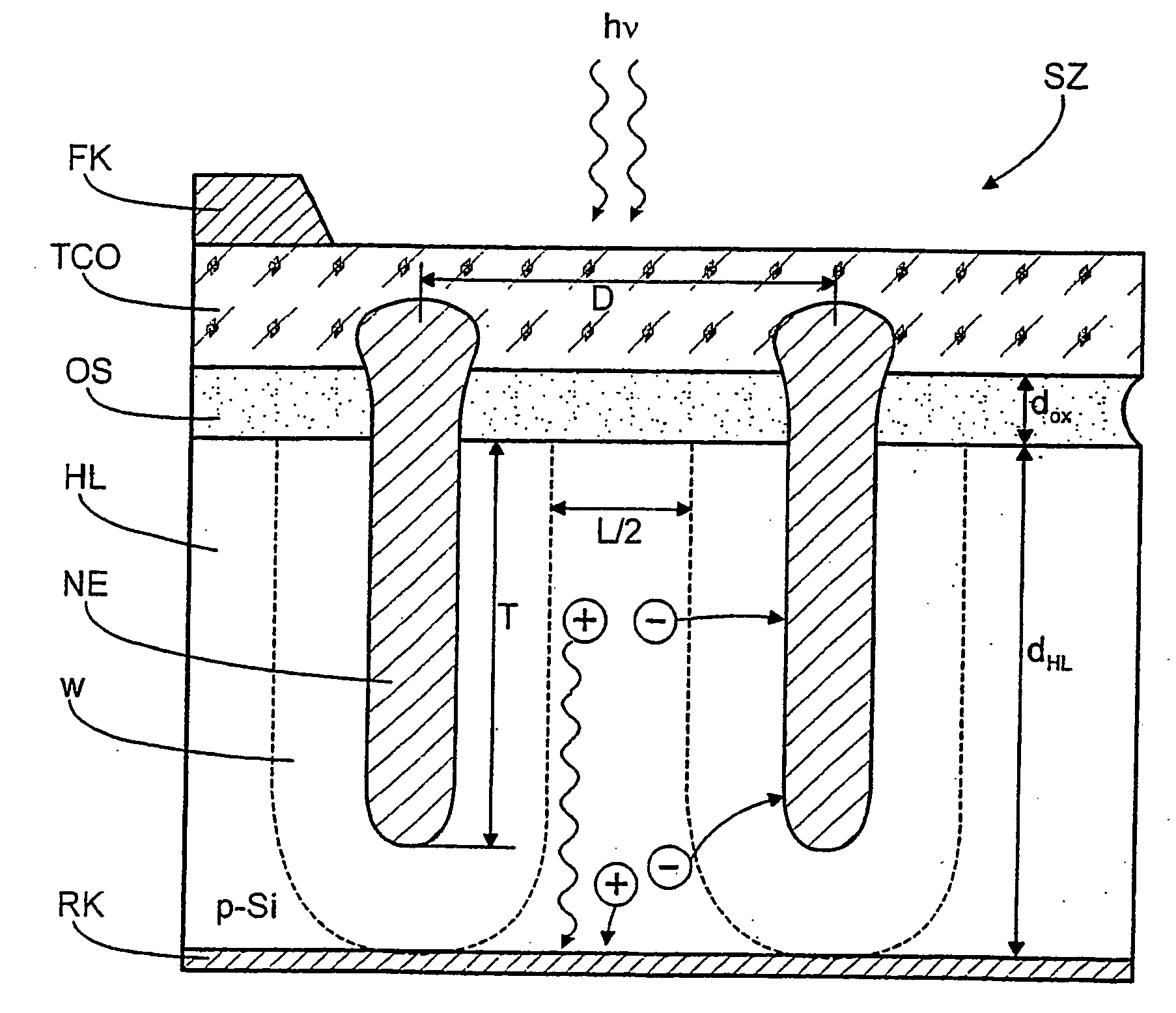
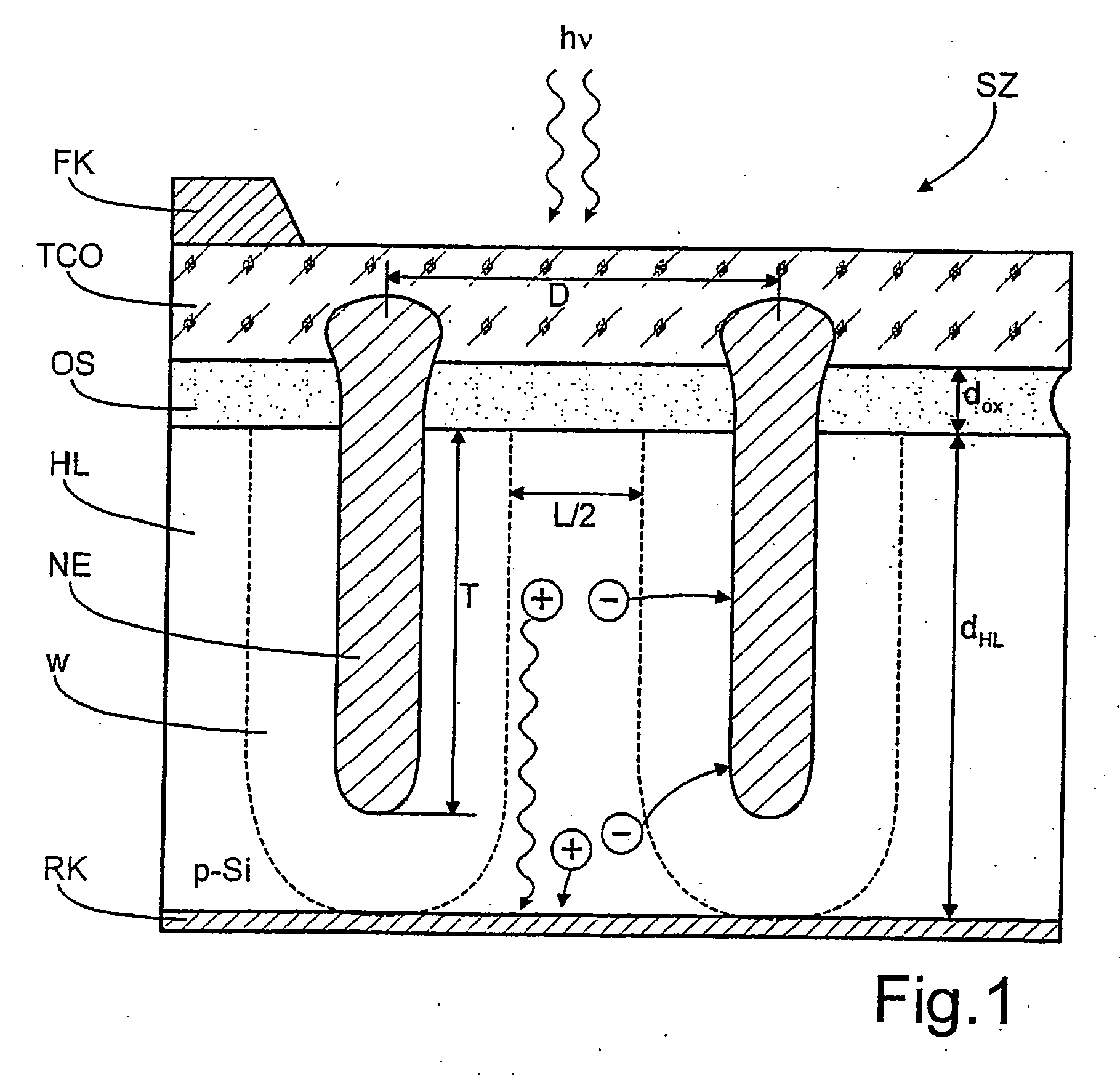
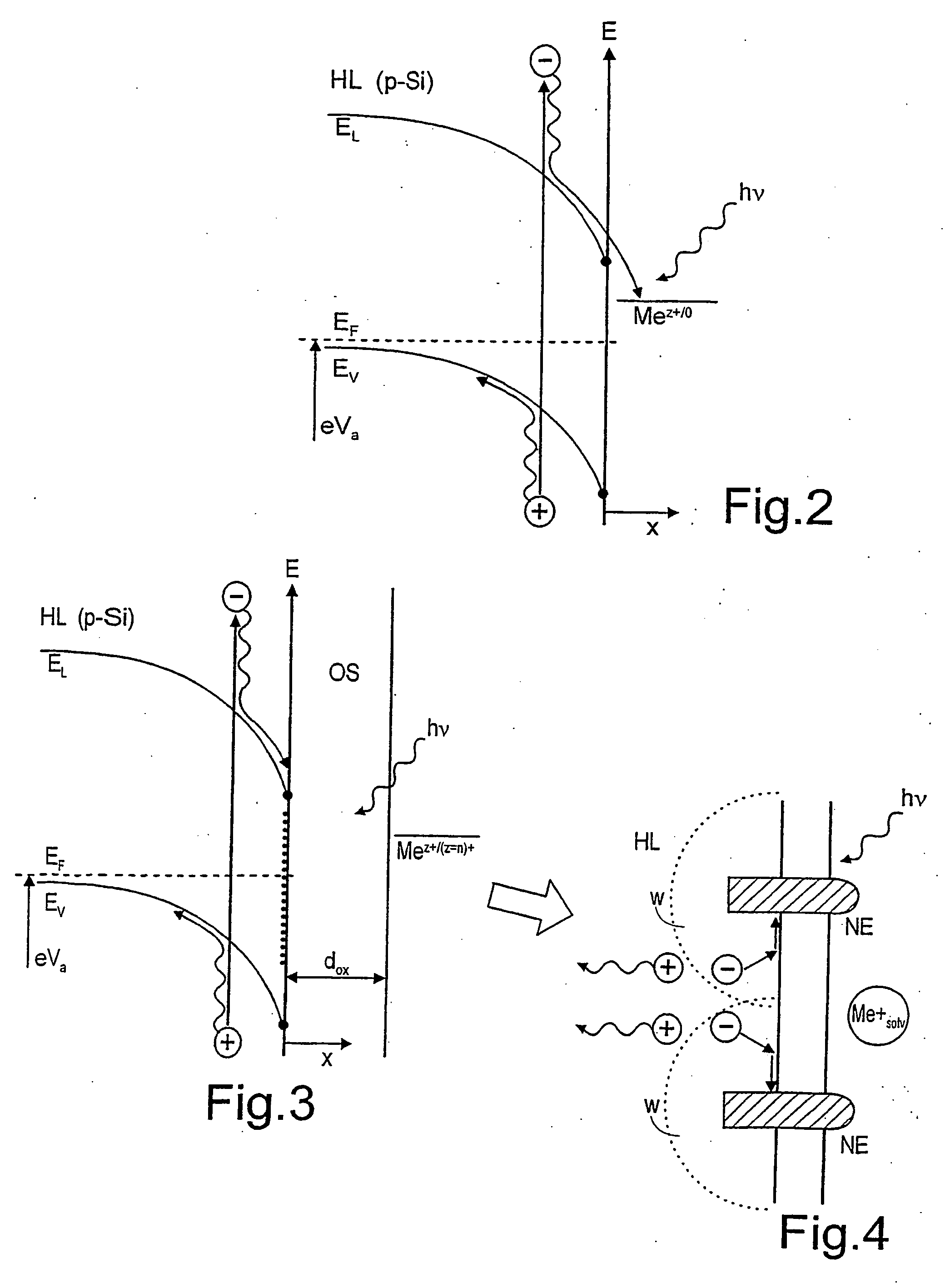
Photovoltaic solar cell...
InactiveUS20070028957A1Reduce complexityLow costPV power plantsFinal product manufactureEngineeringPhotocurrent
A photovoltaic solar cell (SZ) of improved light-to-current conversion properties is provided with nano emitters (NE) of acicular or rib-like form and are separated from each other at a uniform distance D≦√{square root over (2)}L and penetrating to a penetration depth T≥dHL-L2+winto the semiconductor layer (HL).
Owner:HELMHOLTZ ZENT BERLIN FUER MATERIALIEN & ENERGIE GMBH
Solar cell front side silver paste doped with modified grapheme and preparation method thereof
ActiveUS20180226172A1Good ohmic contactContact resistanceNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialPhotovoltaic energy generationSilver pasteOrganic solvent
A solar cell front side silver paste doped with modified graphene and its preparation method are disclosed. The solar cell front side silver paste doped with modified graphene comprises by weight 0.1-5 parts of modified graphene, 88-91 parts of silver powder, 5-15 parts of organic binder, 1-5 parts of organic solvent, 1-3 parts of glass powder, wherein the modified graphene is a surface modified graphene. A solar cell front side silver paste is developed, which is screen printed on a crystalline silicon wafer, sintered at a high temperature, penetrates the SiNx passivation layer in the crystalline silicon wafer, and thus forms a good ohmic contact.
Owner:NANTONG T SUN NEW ENERGY CO LTD
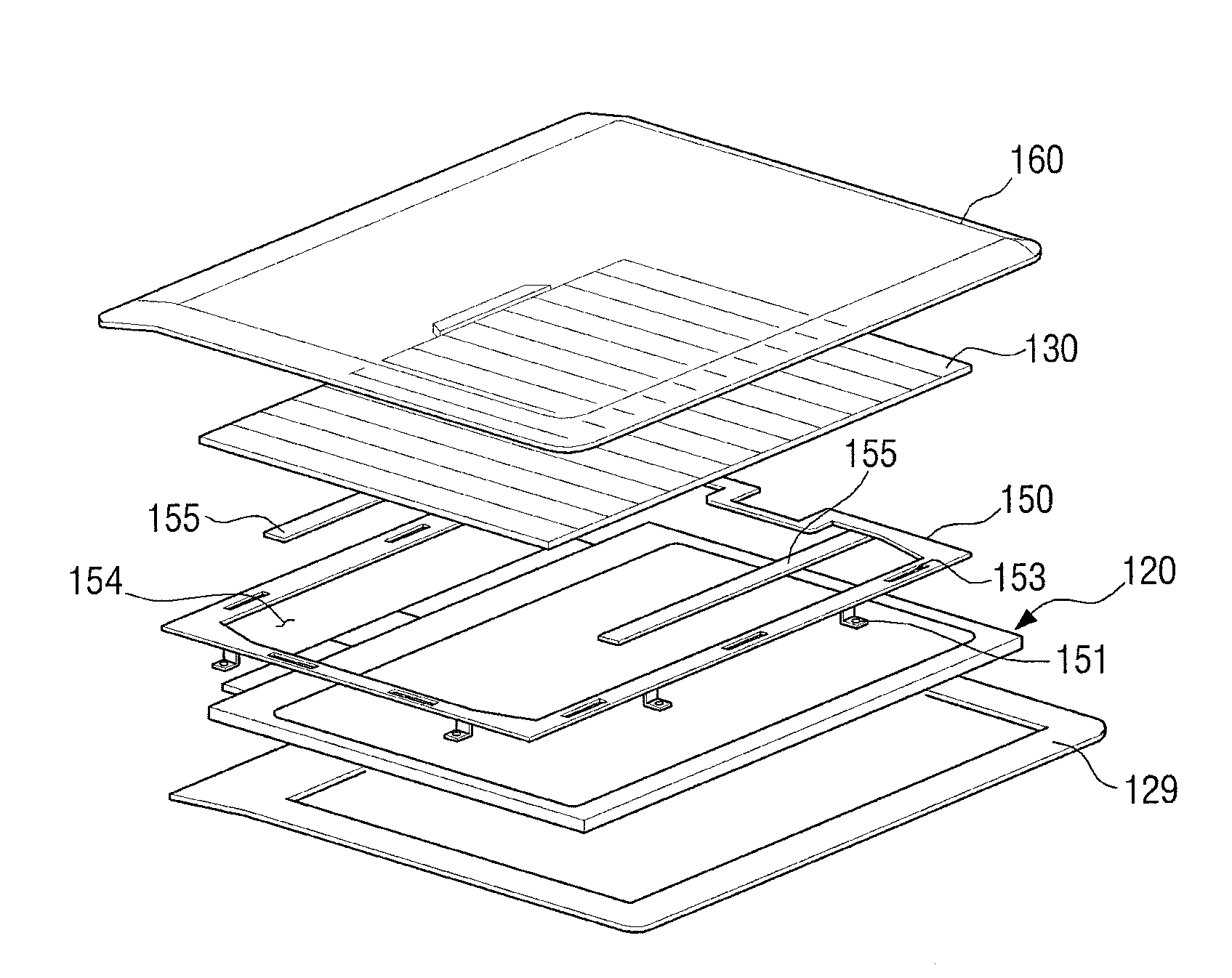
Mobile electric apparatus having solar cells
ActiveUS20130050948A1Reduce output electric power lossAvoid electromagnetic interferenceBatteries circuit arrangementsPower supply for data processingElectrical batterySolar cell
A mobile electronic apparatus includes a main body unit having a main board, a display unit disposed so as to rotate with respect to the main body unit for operating according to a control of the main board, a solar cell module disposed on a rear surface of the display unit for generating electric power by converting solar energy into electric power, and a converting circuit disposed inside the display unit for stabilizing electric power generated by the solar cell module so as to supply stable electric power.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Energy conversion film and quantum dot film comprising quantum dot compound, energy conversion layer including the quantum dot film, and solar cell including the energy conversion layer
ActiveUS20110017292A1Improve energy efficiencyHigh solar efficiencyElectrolytic capacitorsFinal product manufactureHigh energyQuantum dot
An energy conversion film and a quantum dot film which contain a quantum dot compound, an energy conversion layer including the quantum dot film, and a solar cell including the energy conversion layer. The films act as cut-off filters blocking light of a particular energy level using the light absorption and emission effects of quantum dots and can convert high energy light to low energy light. The efficiency of a solar cell may be improved by providing the cell with a film that converts light above the spectrum-responsive region to light in the cell's spectrum-responsive region. The absorption wavelength region of the films can be broadened by providing the quantum dot compound in a variety of average particle sizes, for example, by providing a mixture of a first quantum dot compound having a first average particle size and a first quantum dot compound having a second average particle size.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Solar chimney with internal and external solar collectors
ActiveUS7854224B2Useful workHigh solar efficiencyAuxillary drivesSolar heating energySolar chimneySolar energy harvesting
A solar chimney includes a solar collector which heats air in the chimney, producing updrafts which can be harnessed to perform useful work. The solar collector may be located inside or outside the chimney. The device may include a reservoir for storing a heat transfer fluid, thus enabling the device to be used during both day and night. The solar chimney may be equipped with both internal and external solar collectors, operating in parallel. The solar chimney may also be equipped with multiple external solar collectors, connected in parallel to a reservoir. The solar chimney of the invention provides a convenient and practical way to convert solar energy into electrical power.
Owner:YANGPICHIT PITAYA
Solar cell and manufacturing method thereof
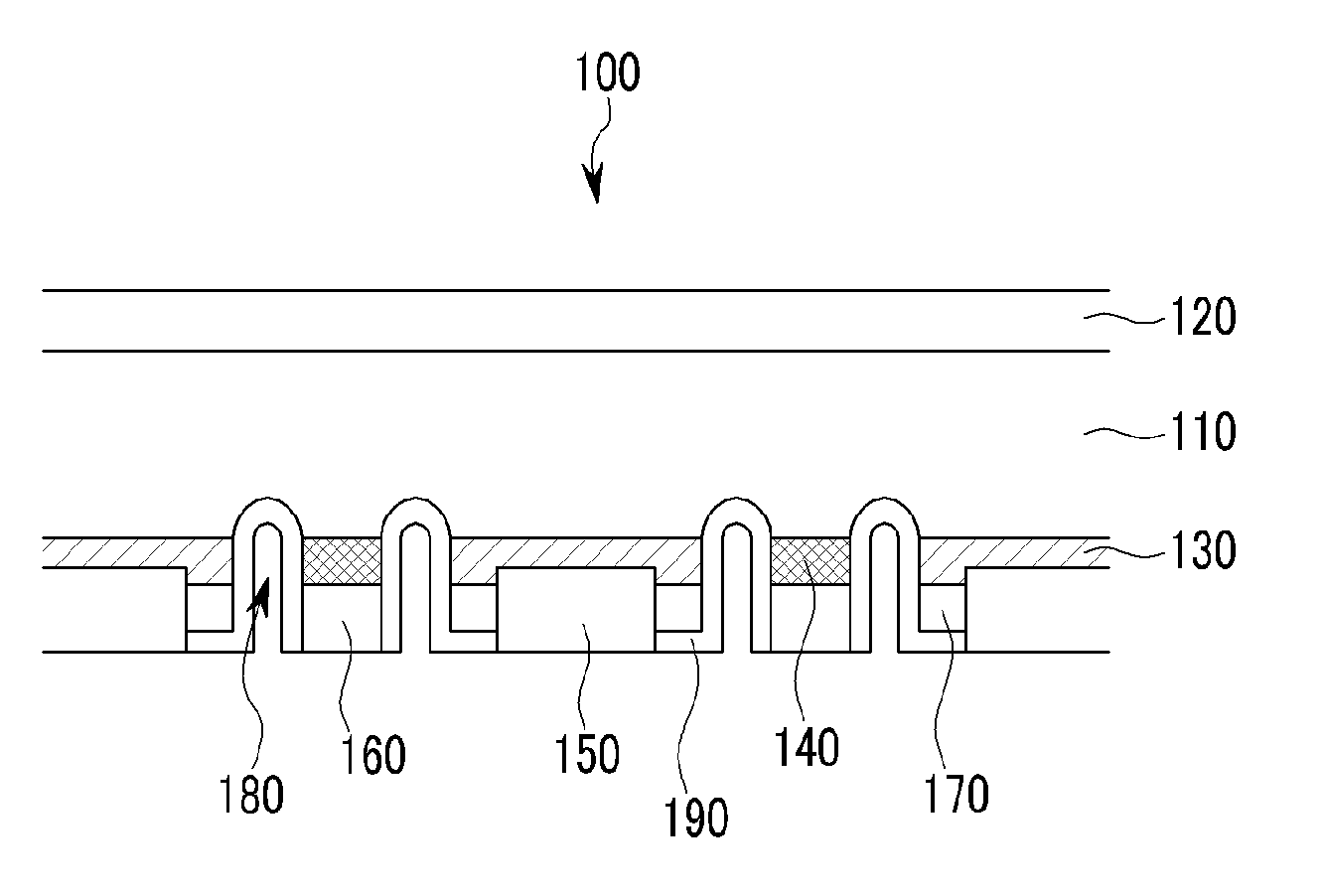
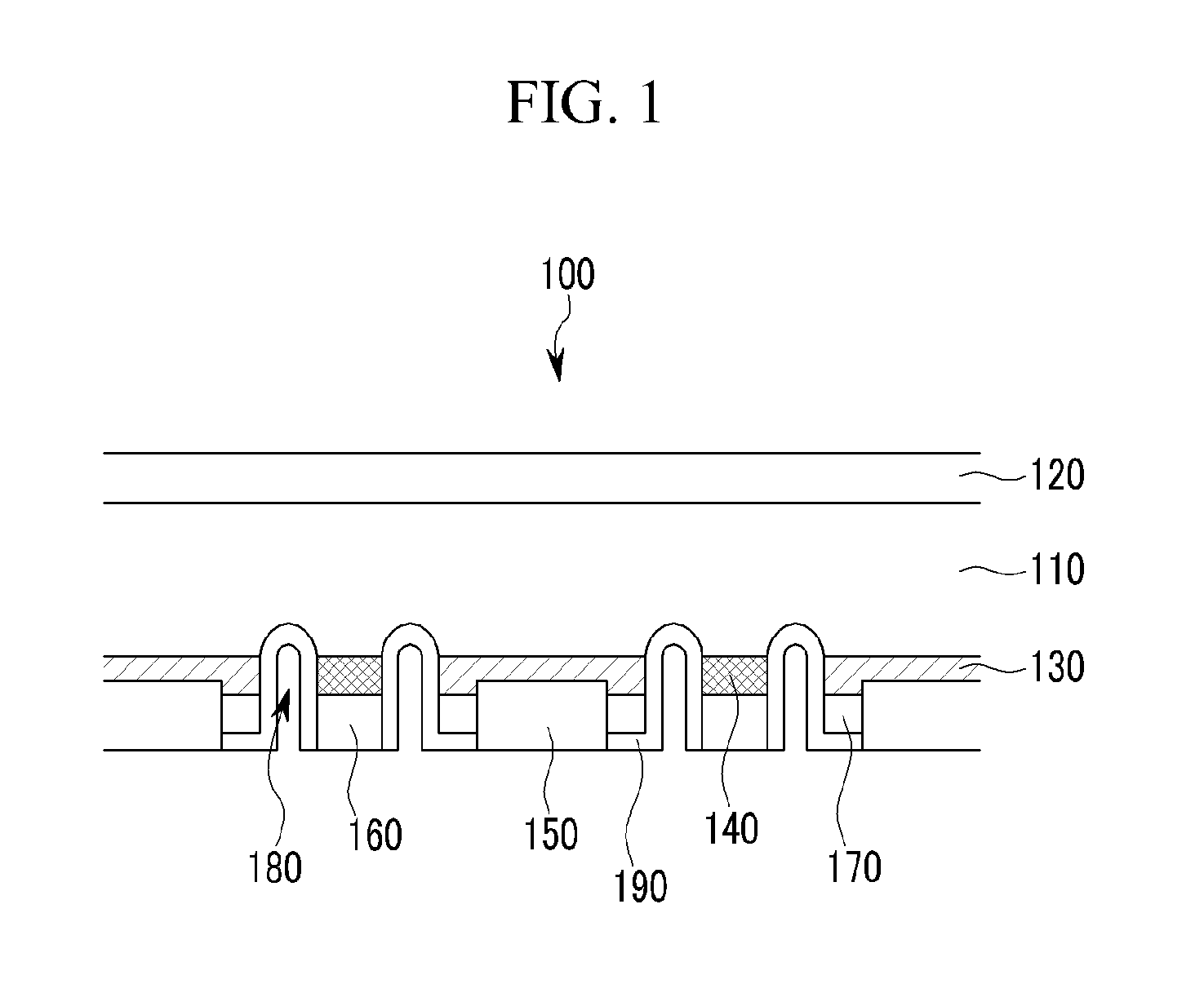
InactiveUS20110067759A1Low efficiencyHigh solar efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationEngineeringSolar cell
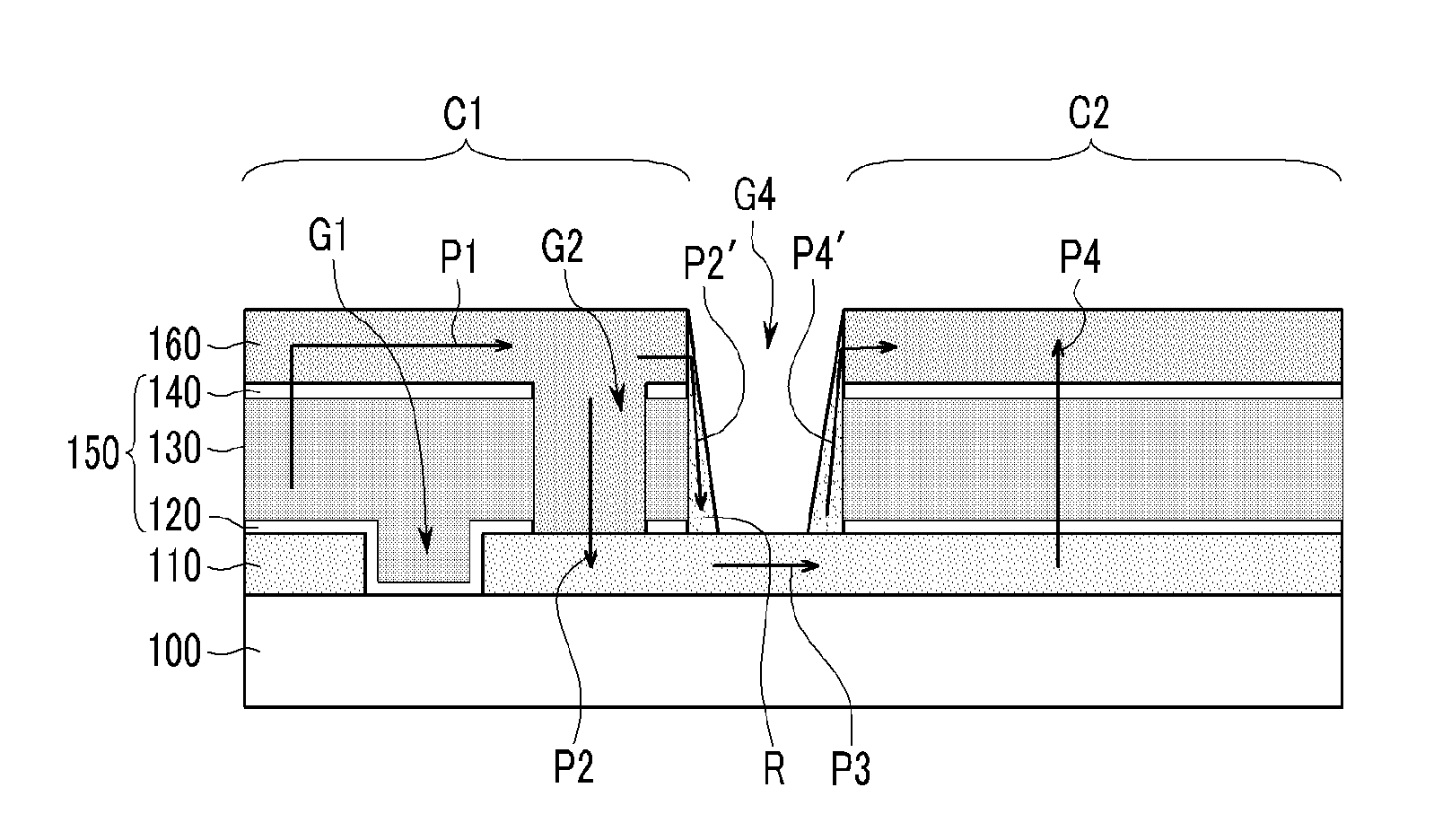
A solar cell includes; a substrate; a first electrode disposed on the substrate, and including a first groove formed therein, a semiconductor layer disposed on the first electrode, and including a second groove formed therein, and a second electrode disposed on the semiconductor layer and connected to the first electrode via the second groove, wherein a third groove passing through the first electrode, the semiconductor layer, and the second electrode is formed in a first region, a fourth groove passing through only the semiconductor layer and the second electrode is formed in a second region, and the first region and the second region are alternately disposed along a direction of extension of the third groove.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD +1
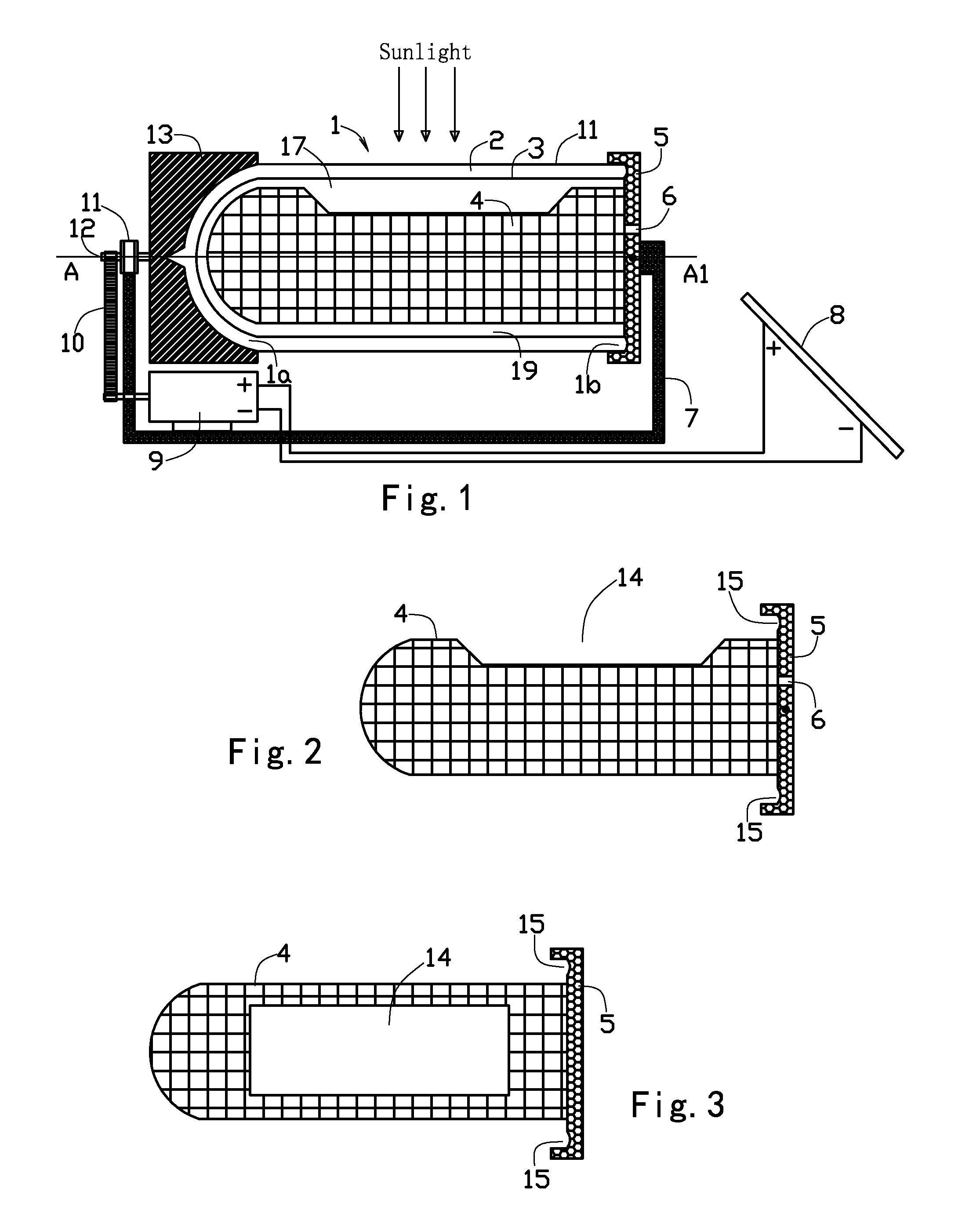
Solar Steam Cooker
InactiveUS20120263845A1High solar efficiencyShort heating timeSolar heating energySolar heat devicesCookerClose-ended
The invention provides a solar steam cooker having a solar tube enclosing an inner space and having a close end and an open end, a cover closing the open end, an inner container in the inner space of the solar tube and being rotatable with respect to the solar tube, a sleeve covering on the close end of the solar tube and having an axle, and, a strut supporting the axle of the sleeve. The solar tube is of glass and has a translucent outer layer, a blackbody inner layer and a vacuum space between the outer and the inner layer. The cover has a circular groove covering on the open end of the solar tube. The inner container has a top opening.
Owner:WANG JIANPING +1
Solar cell and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20110126906A1Improve efficiencyReduce process time and manufacturing costFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolar cellSemiconductor
A solar cell includes a semiconductor substrate, an n+ region and a p+ region disposed on the semiconductor substrate, a first electrode electrically connected to the n+ region, and a second electrode electrically connected to the p+ region. A trench formed in the semiconductor substrate separates the n+ region from the p+ region.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com