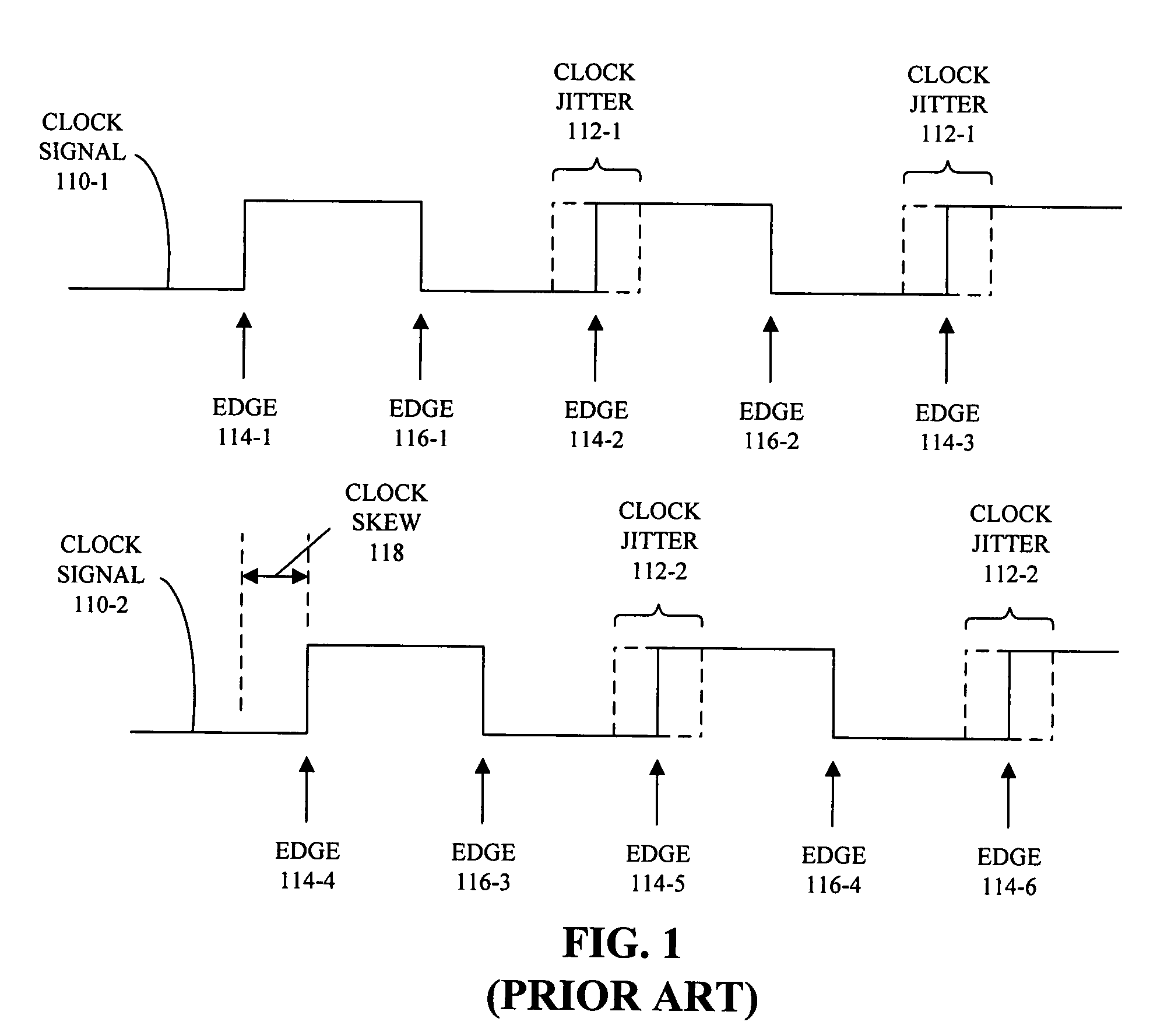
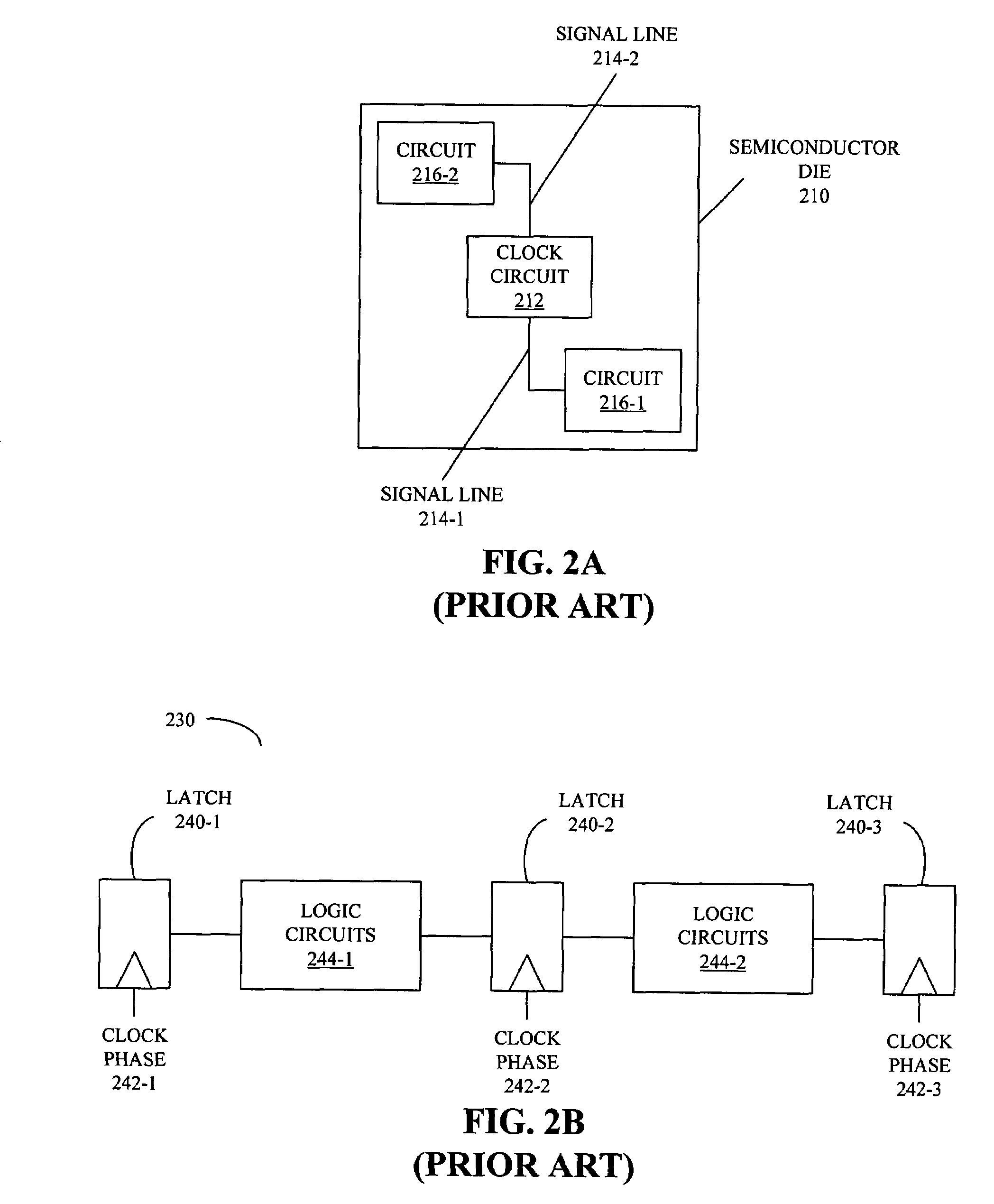
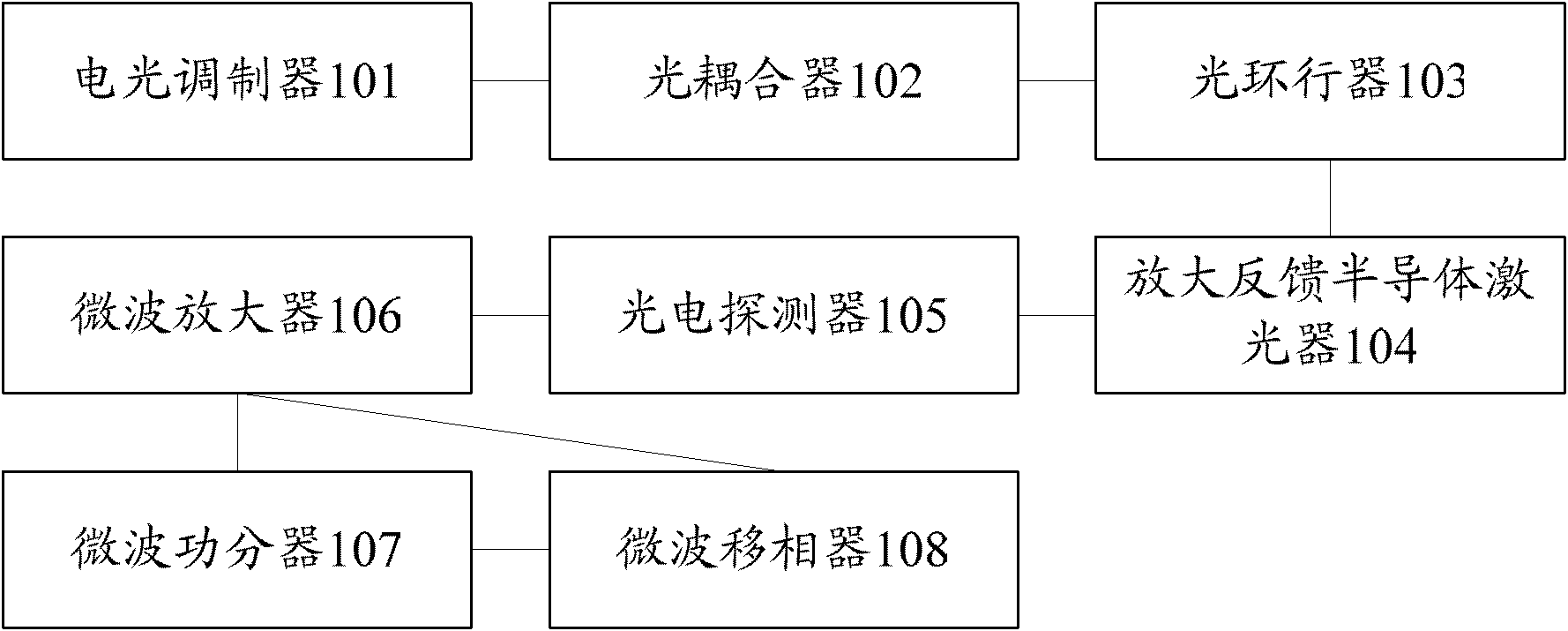
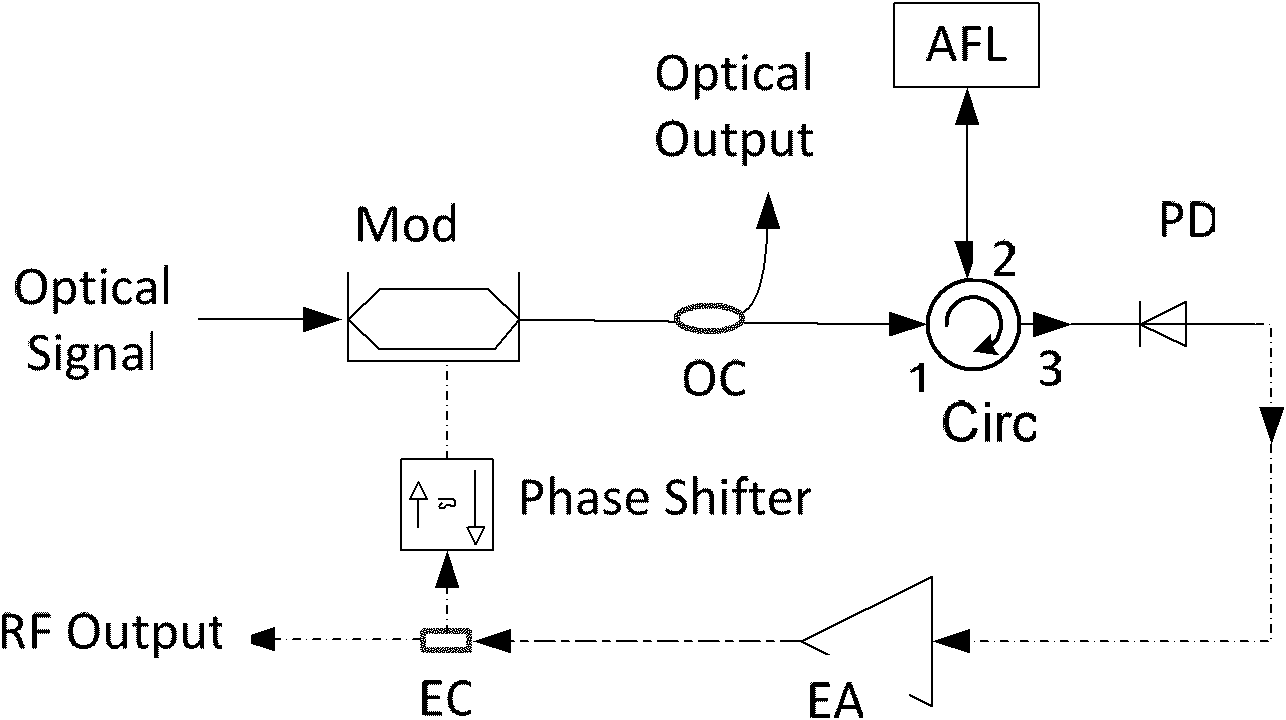
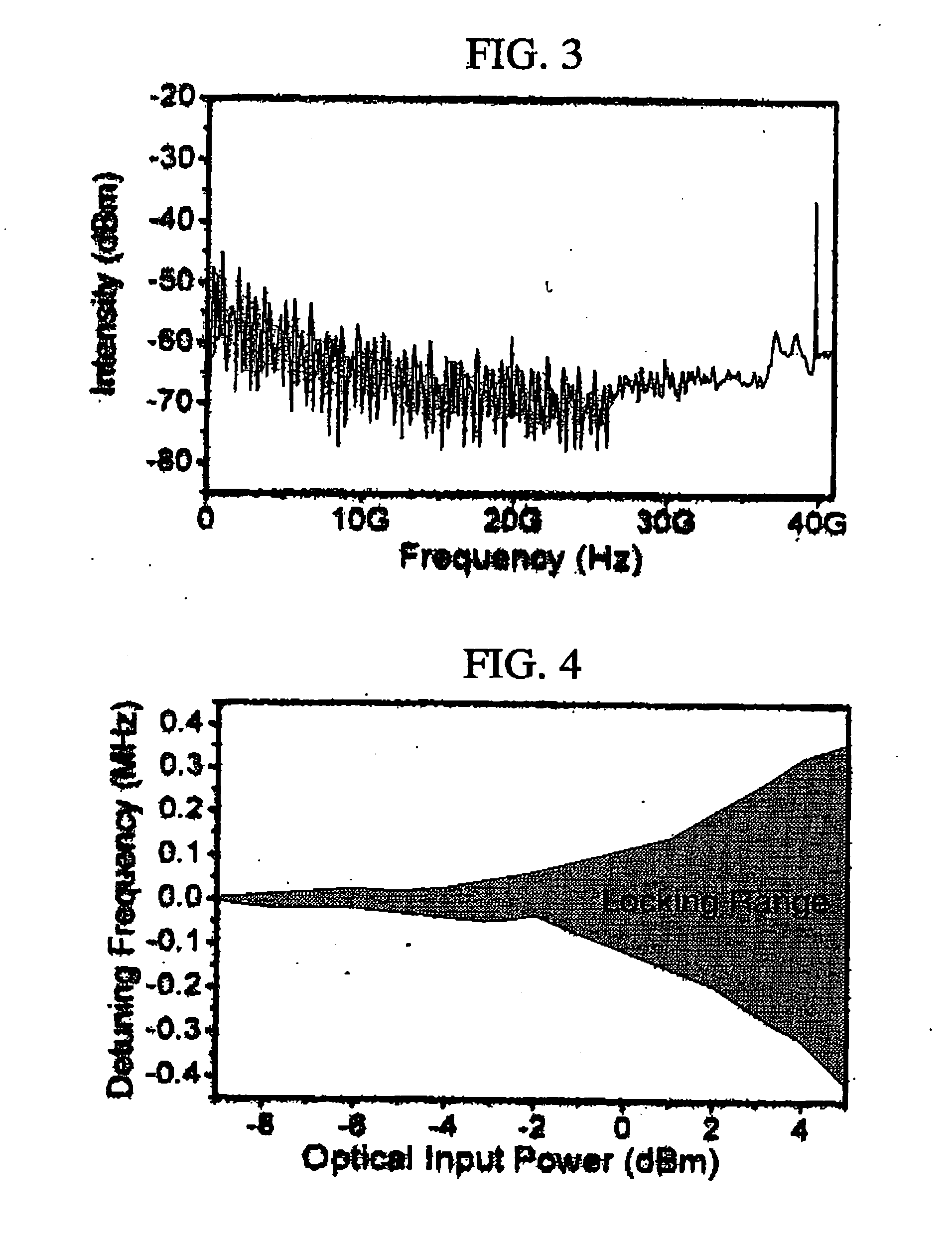
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
192 results about "Optical clock" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
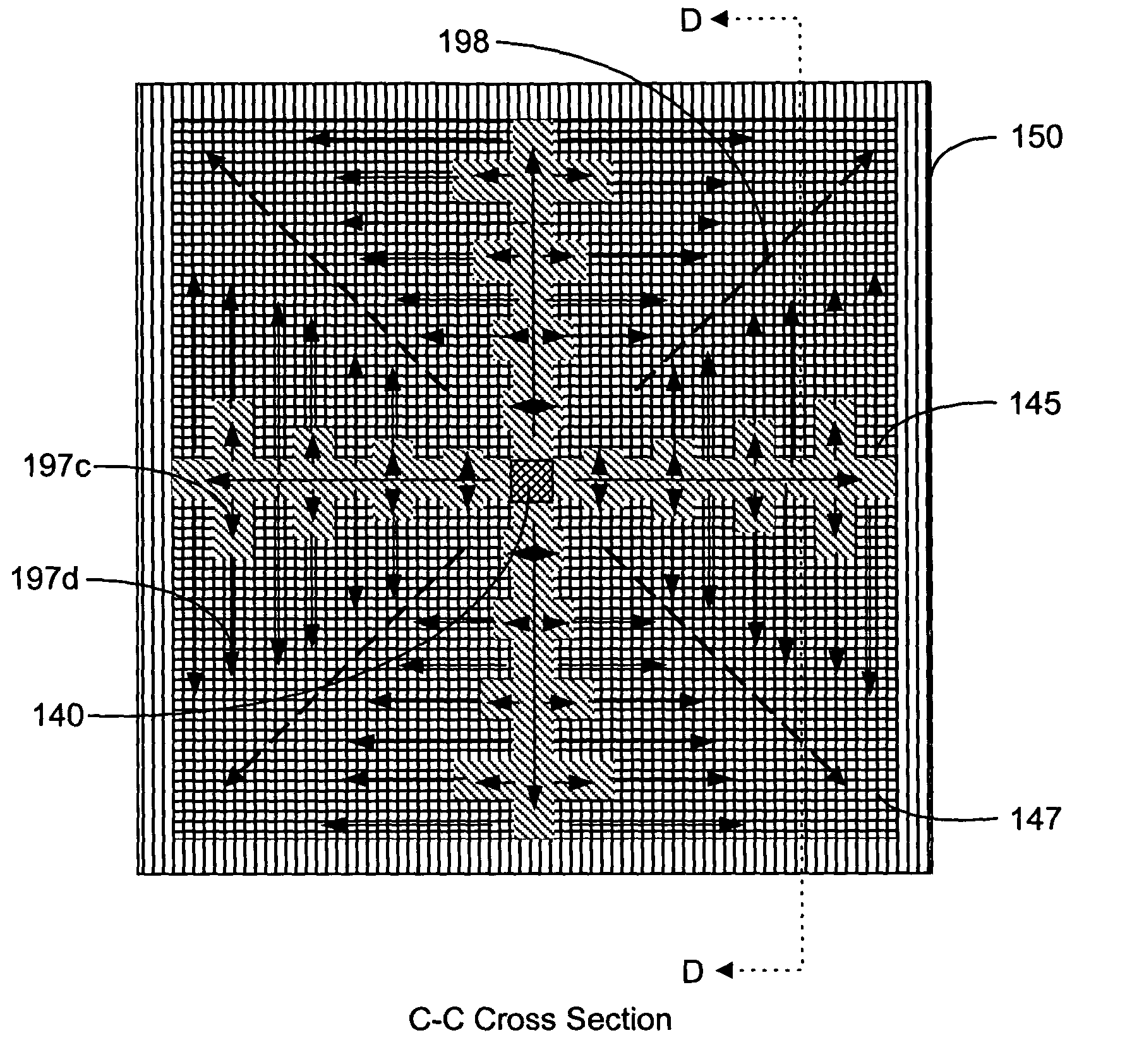
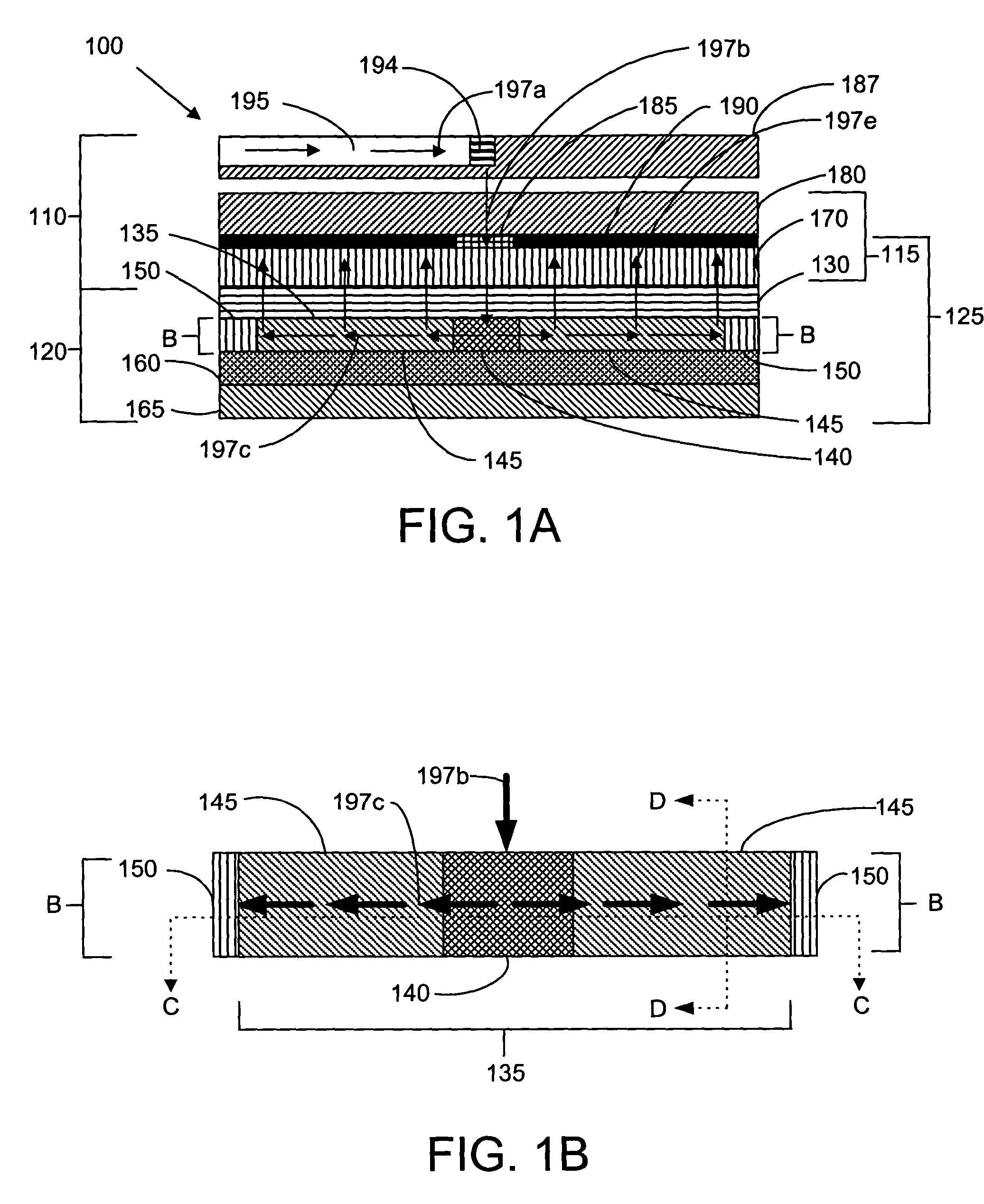
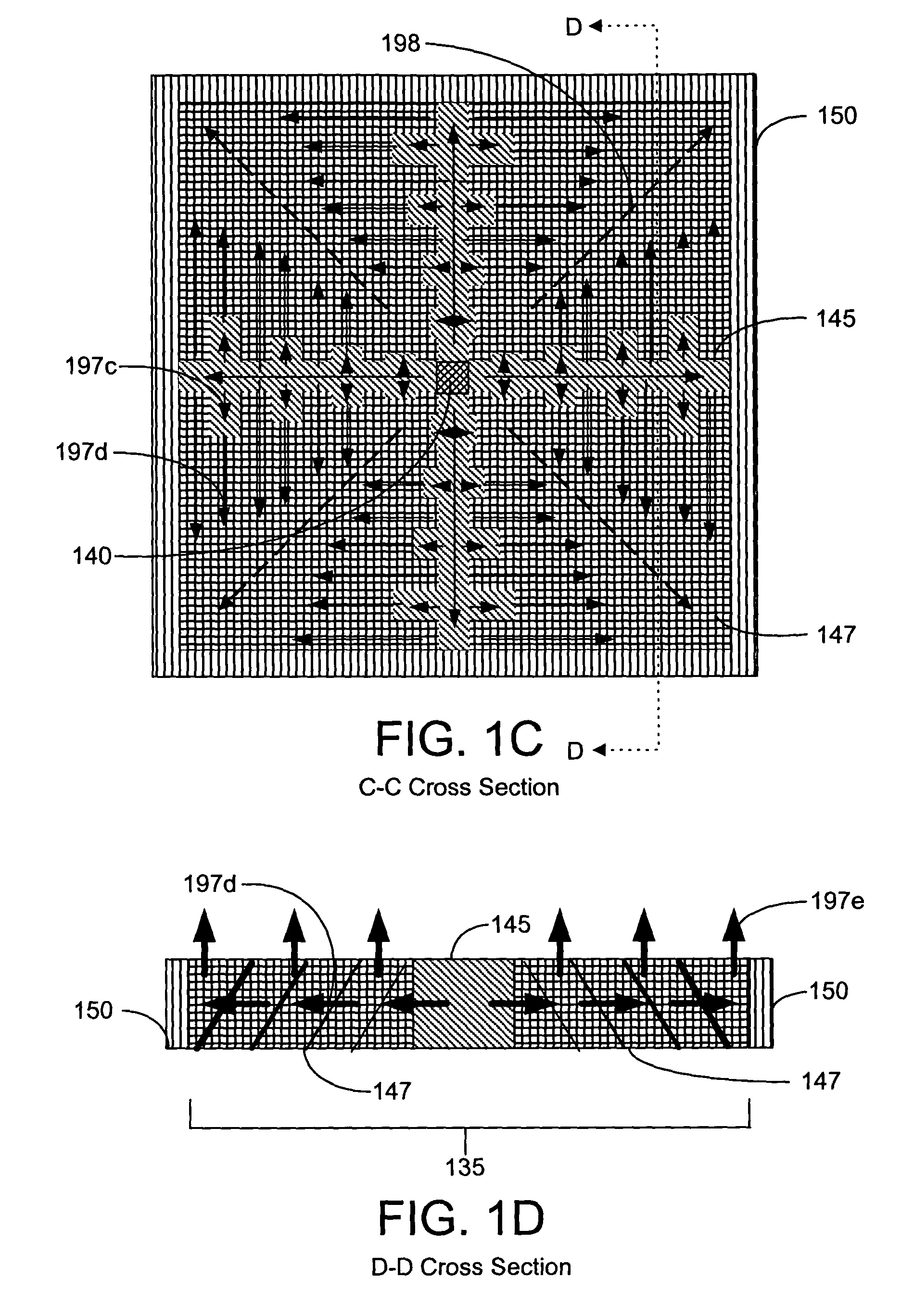
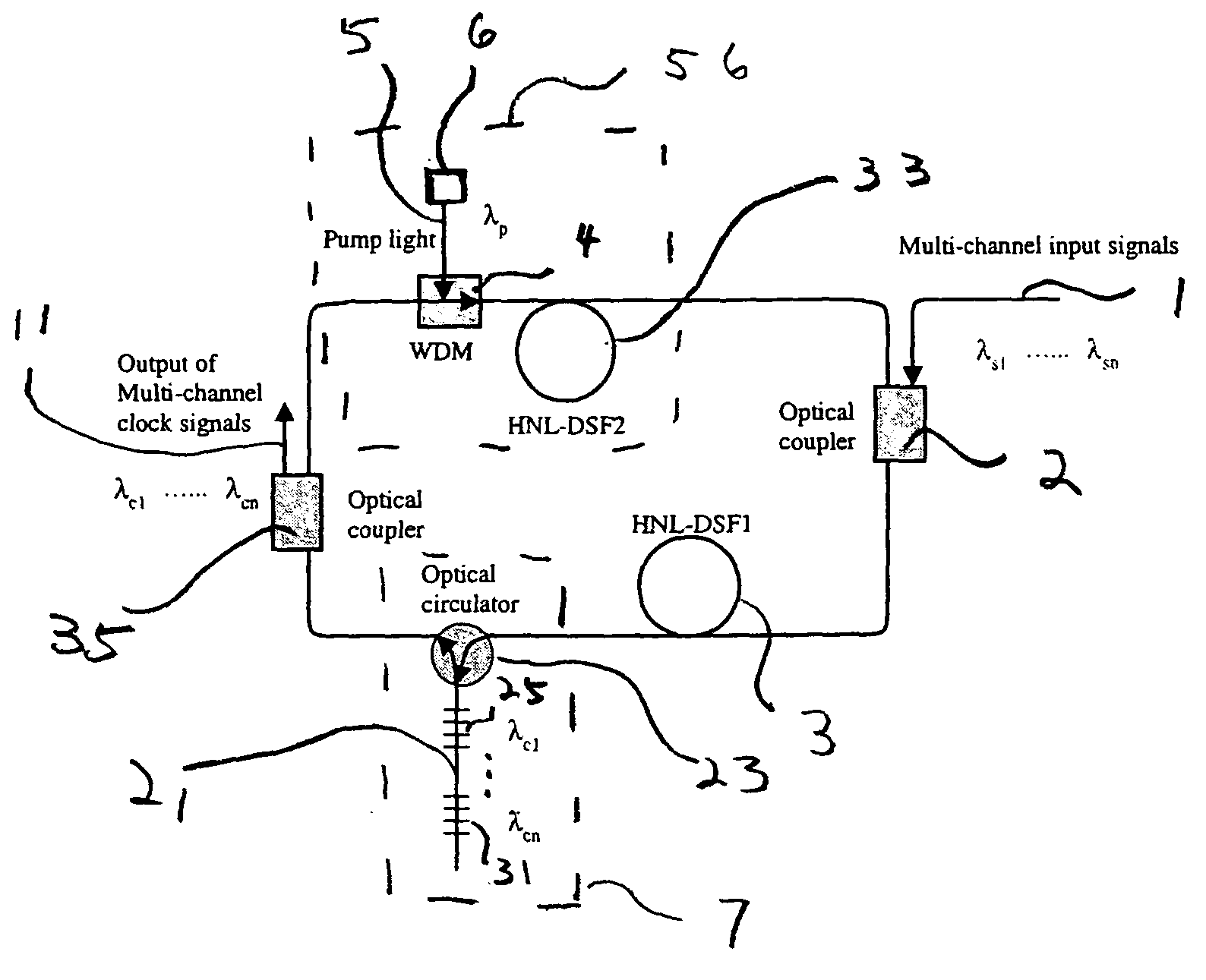
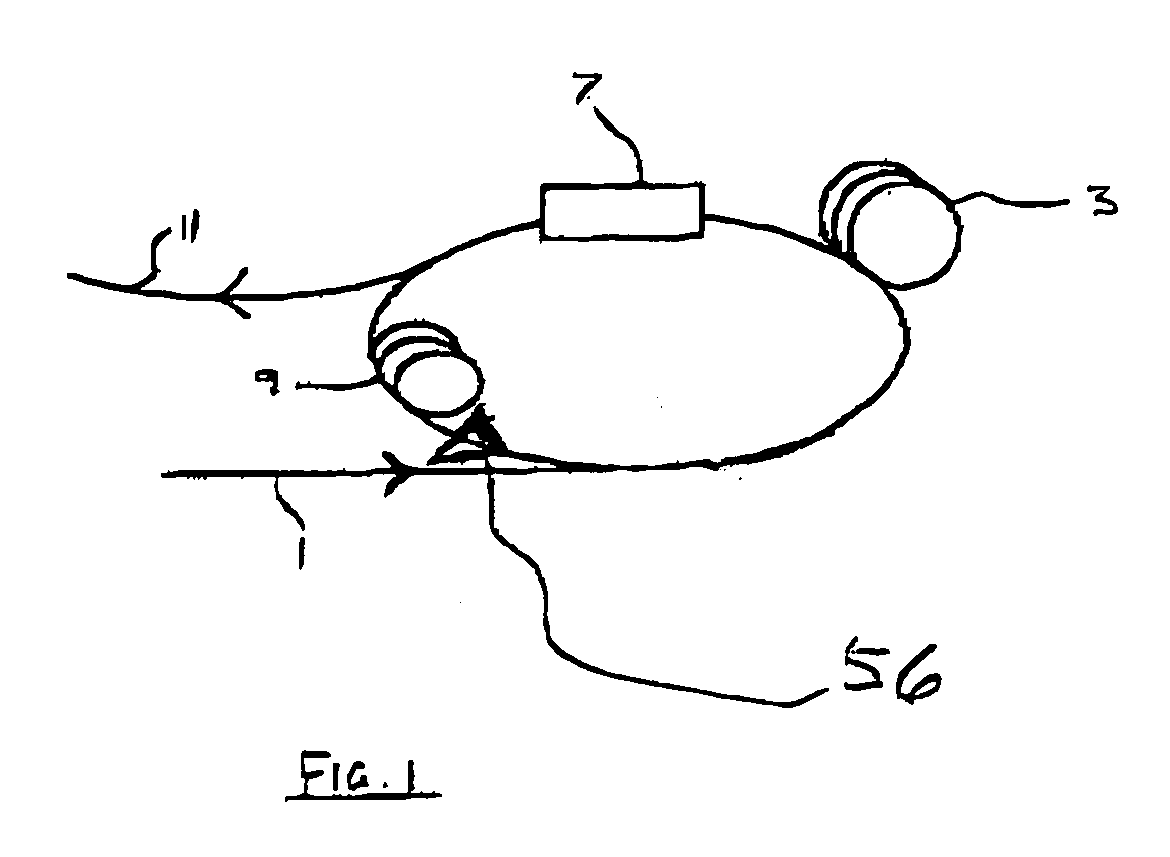
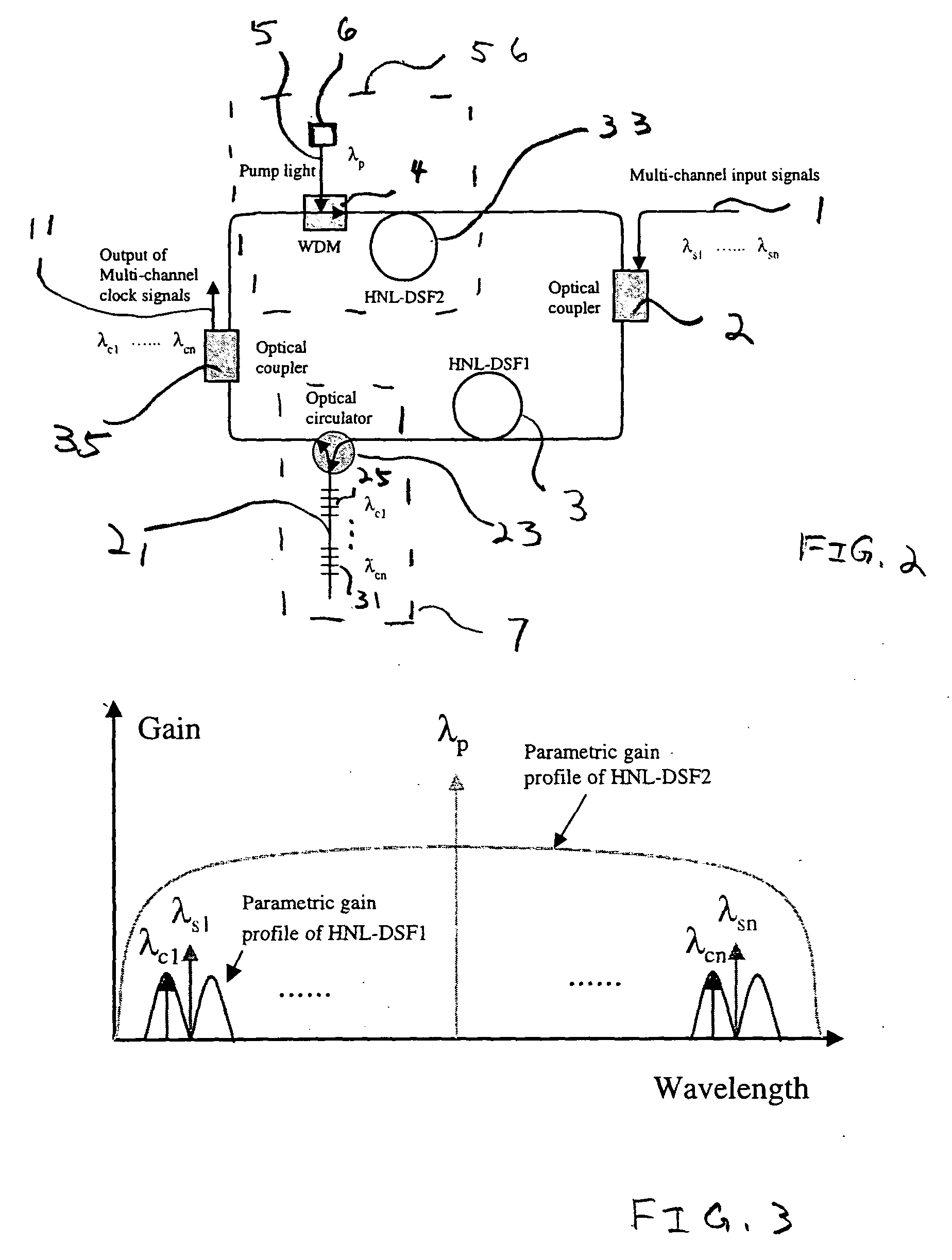
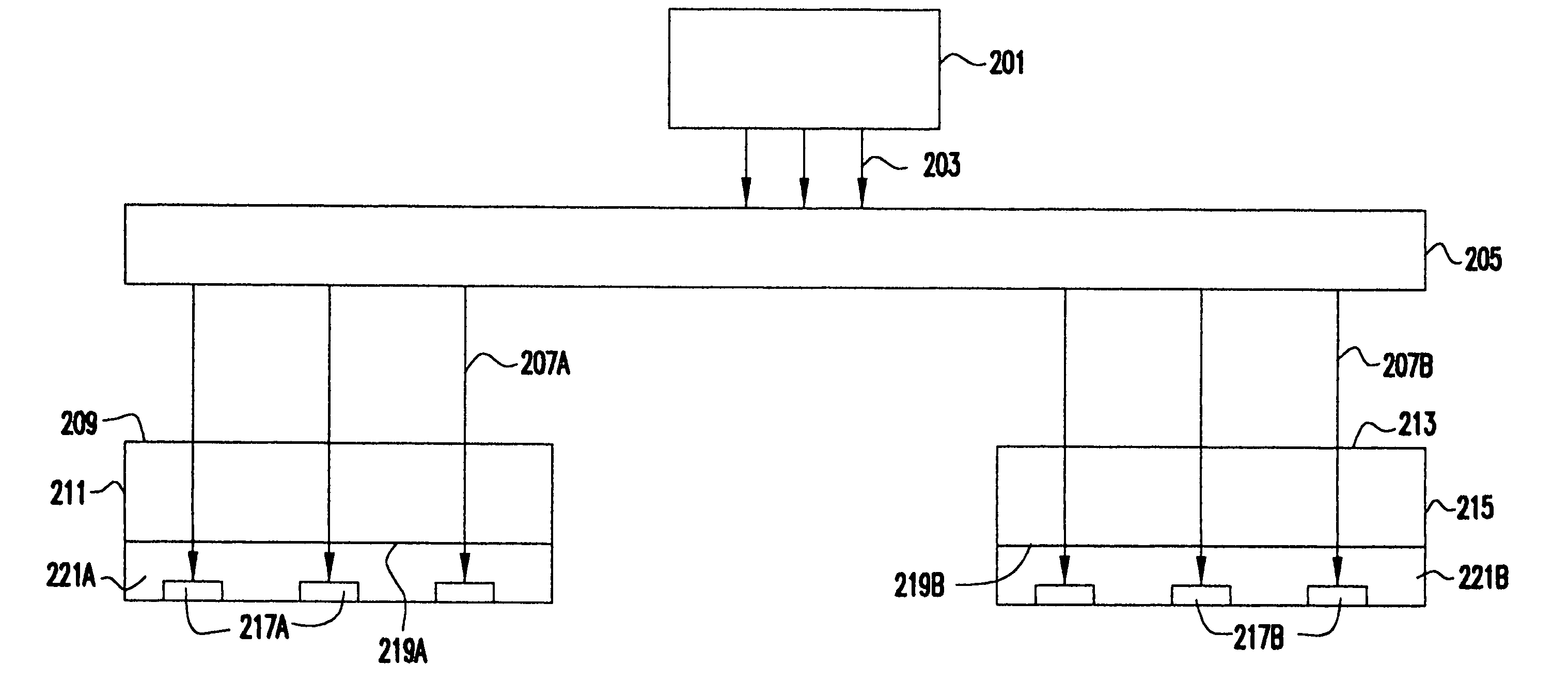
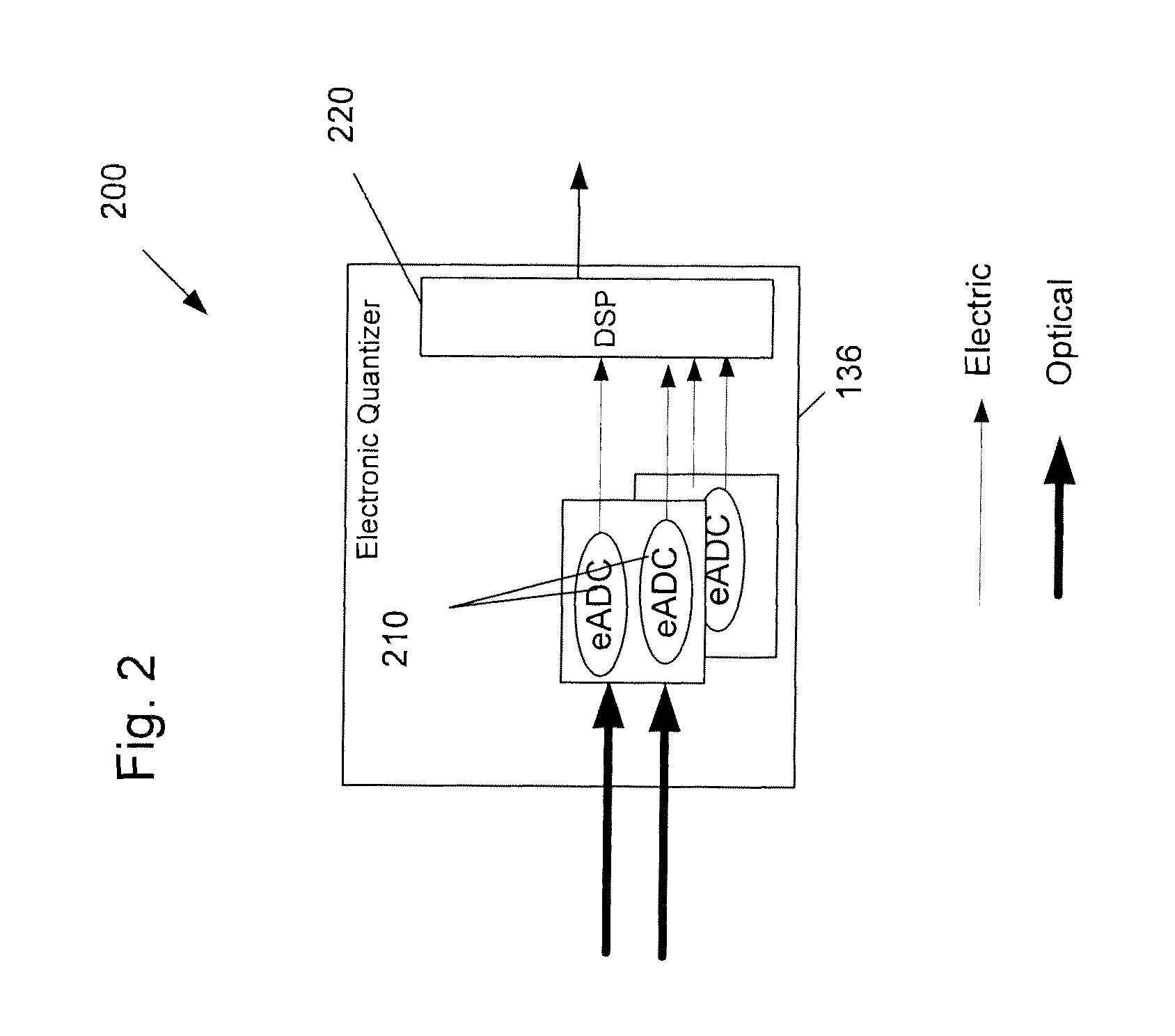
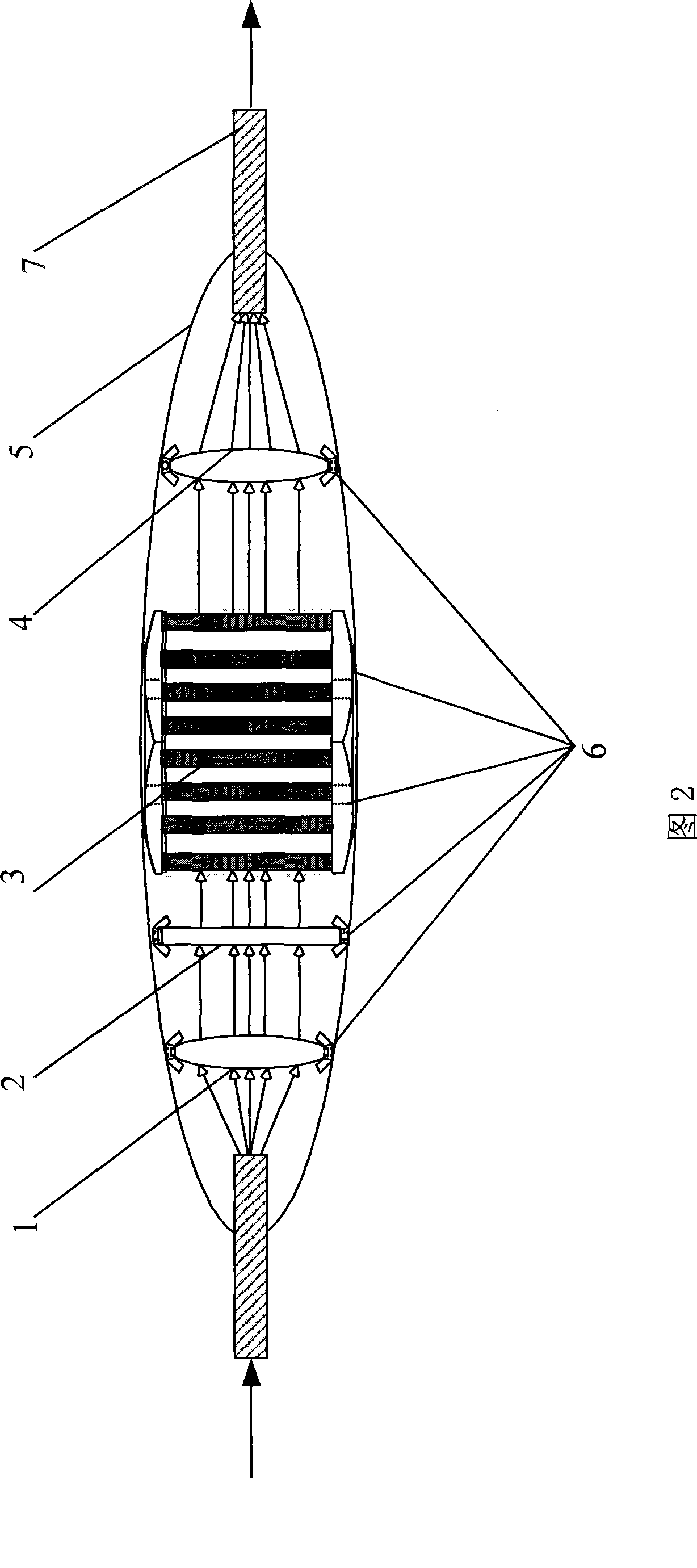
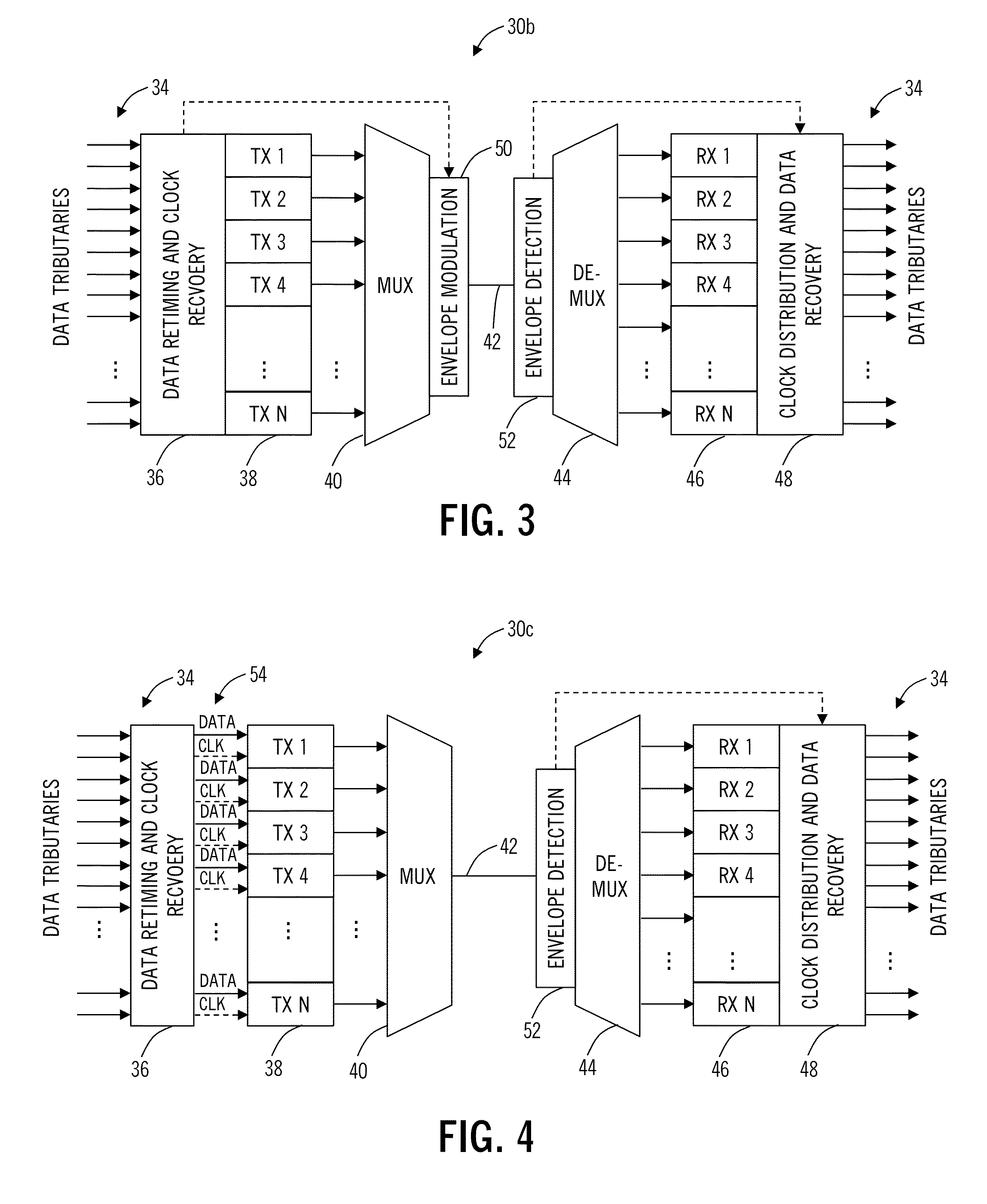
Back-side-of-die, through-wafer guided-wave optical clock distribution networks, method of fabrication thereof, and uses thereof
InactiveUS7016569B2Coupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideDistribution systemOptical clock
Systems and methods for back-of-die, through-wafer guided-wave optical clock distribution systems (networks) are disclosed. A representative back-of-die, through-wafer guided-wave optical clock distribution system includes an integrated circuit device with a first cladding layer disposed on the back-side of the integrated circuit device, and an core layer disposed on the first cladding layer. The core layer, the first cladding layer, or the second cladding layer can include, but is not limited to, vertical-to-horizontal input diffraction gratings, a horizontal-to-horizontal diffraction gratings, and horizontal-to-vertical output diffraction gratings.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
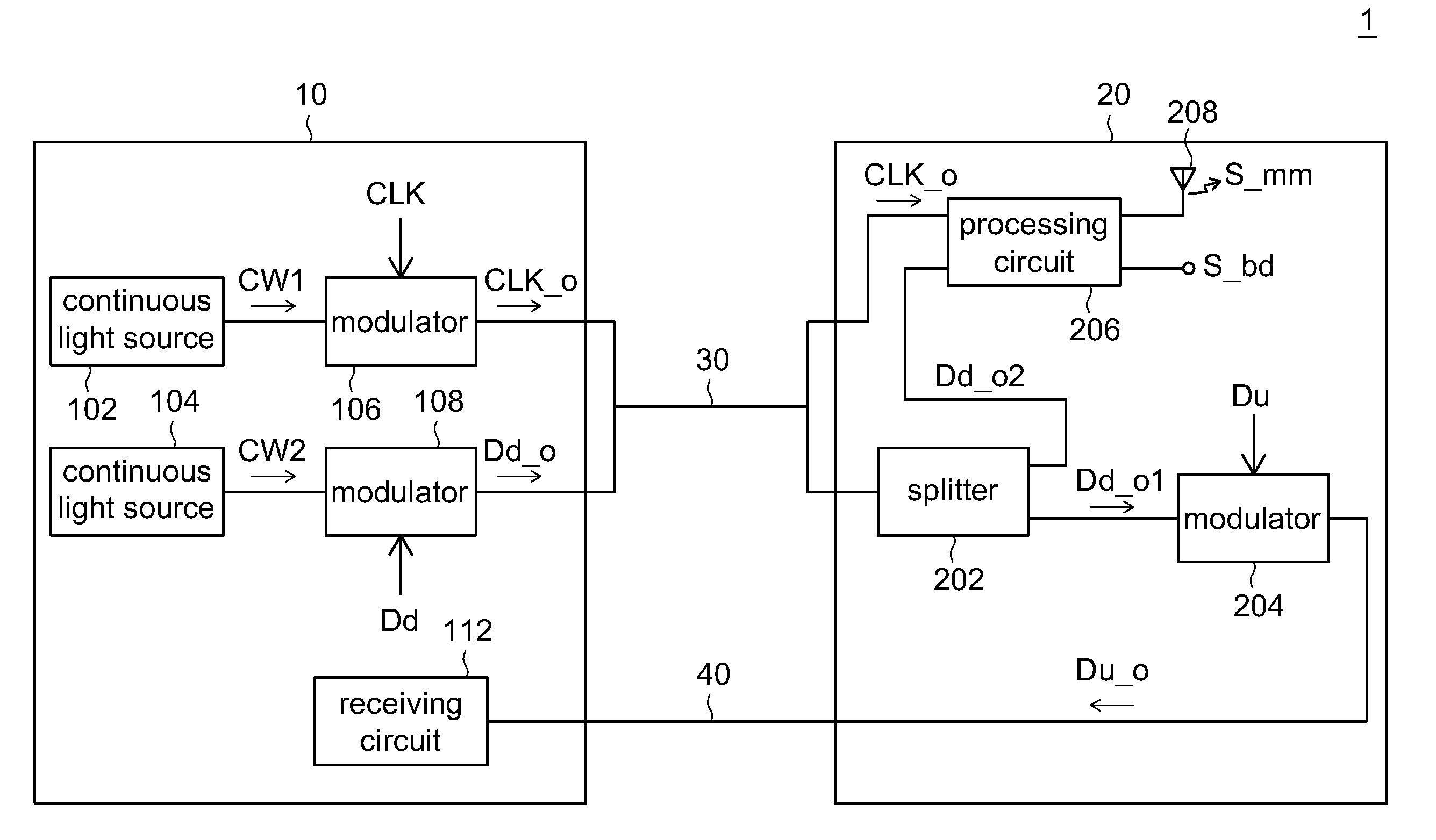
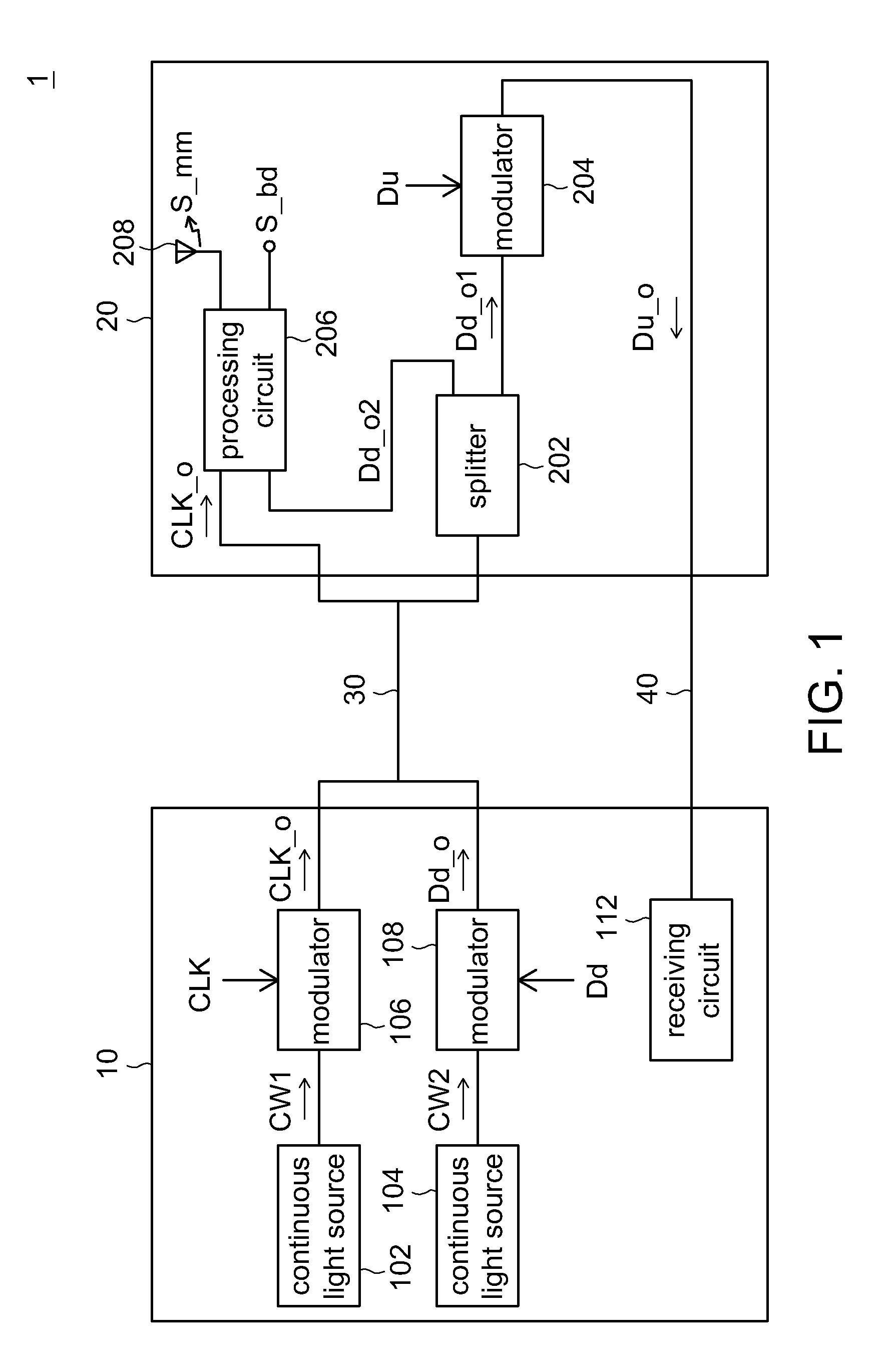
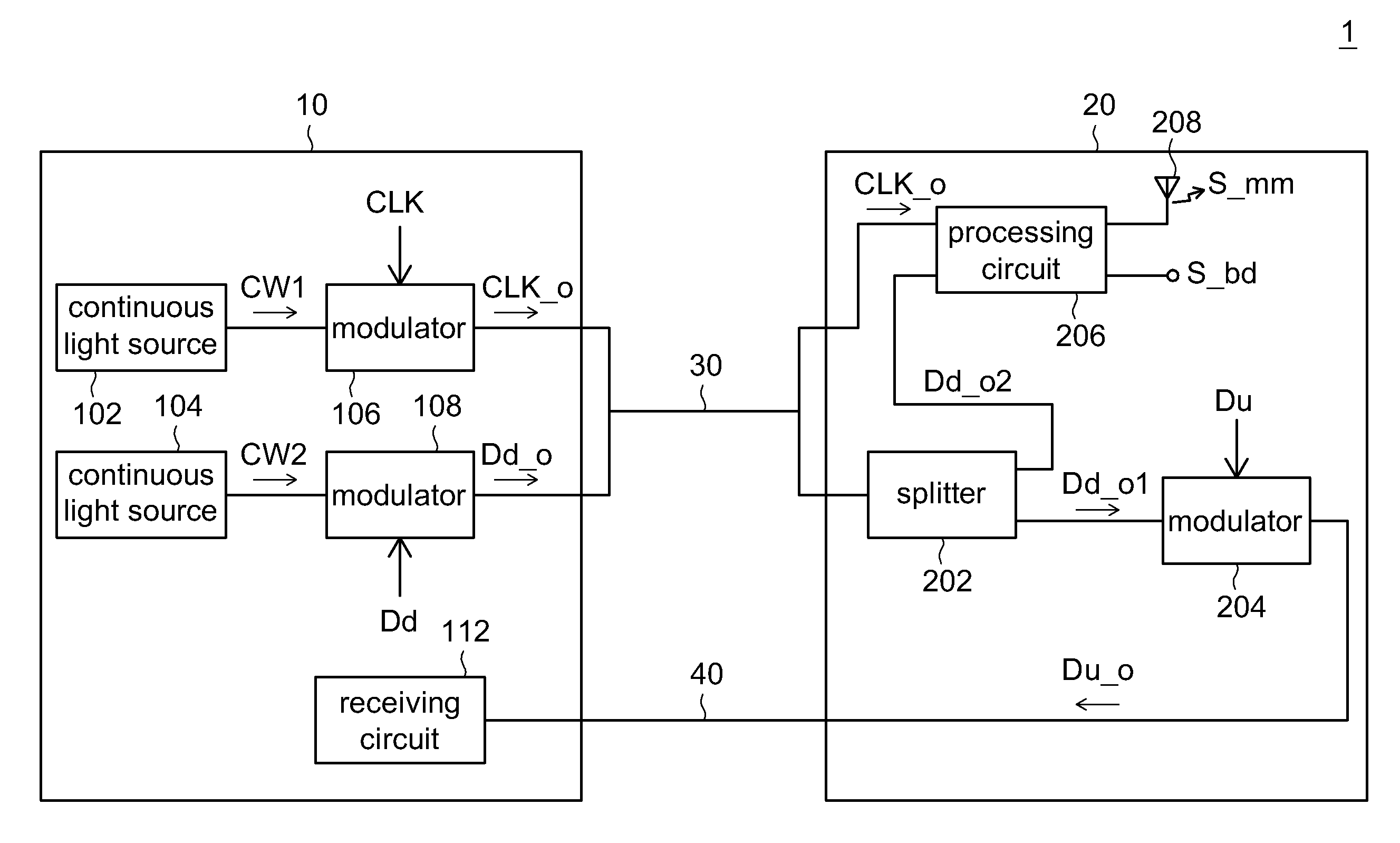
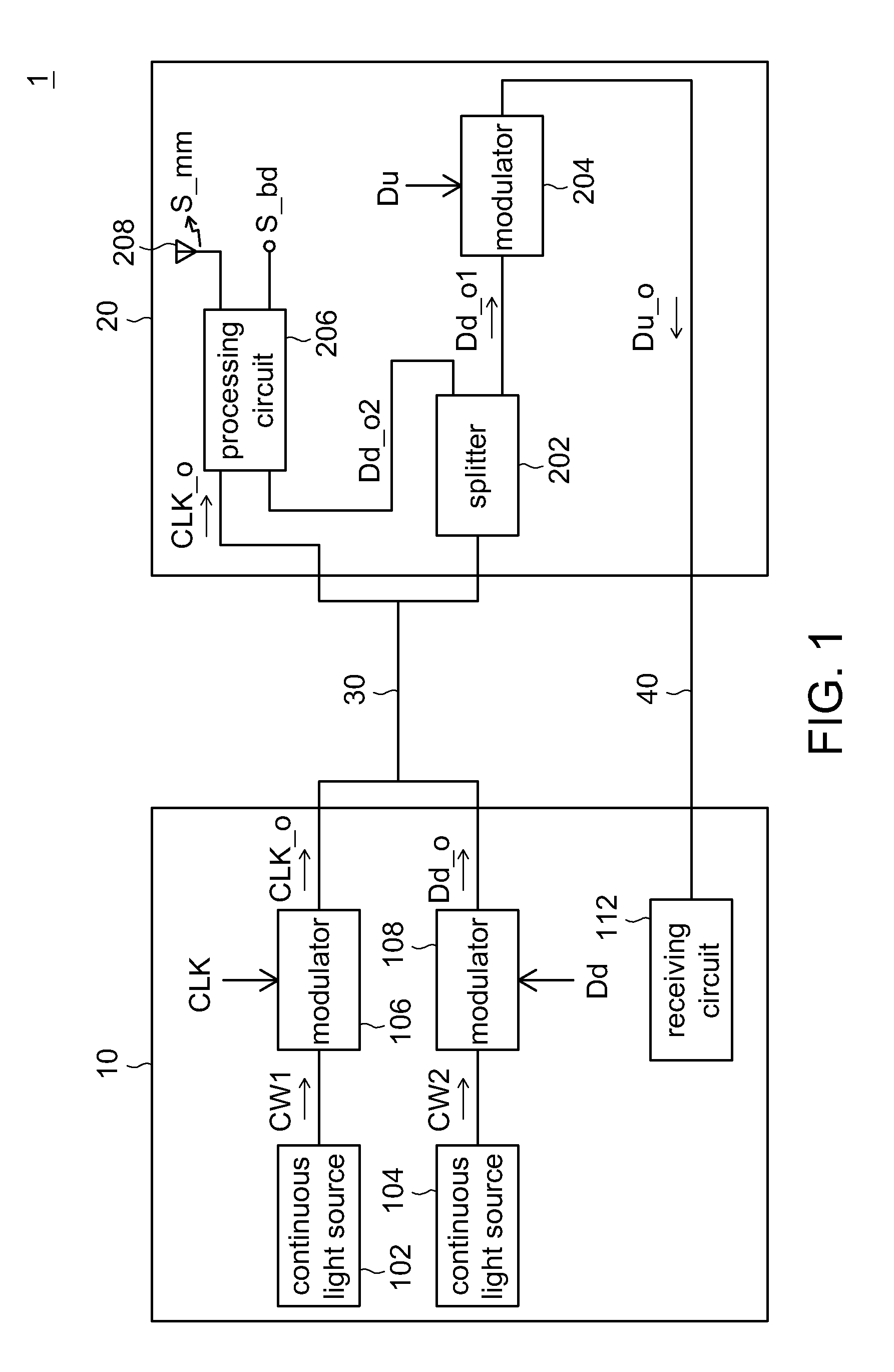
Head-End Circuit and Remote Antenna Unit and Hybrid Wired/Wireless Network System and Transceiving Method Using Thereof
A head-end circuit comprises first and second continuous light sources, first and second modulators. The first and the second continuous light sources provide first and second optical signals respectively corresponding to first wavelength and second wavelength, which is different from the first wavelength. The first modulator modulates the first optical signal based on first clock signal to generate an optical clock signal. The second modulator modulates the second optical signal based on downlink data to generate optical downlink data with the carrier of the second optical signal. The optical clock signal and the optical down link data are outputted to a remote antenna unit via first fiber path.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
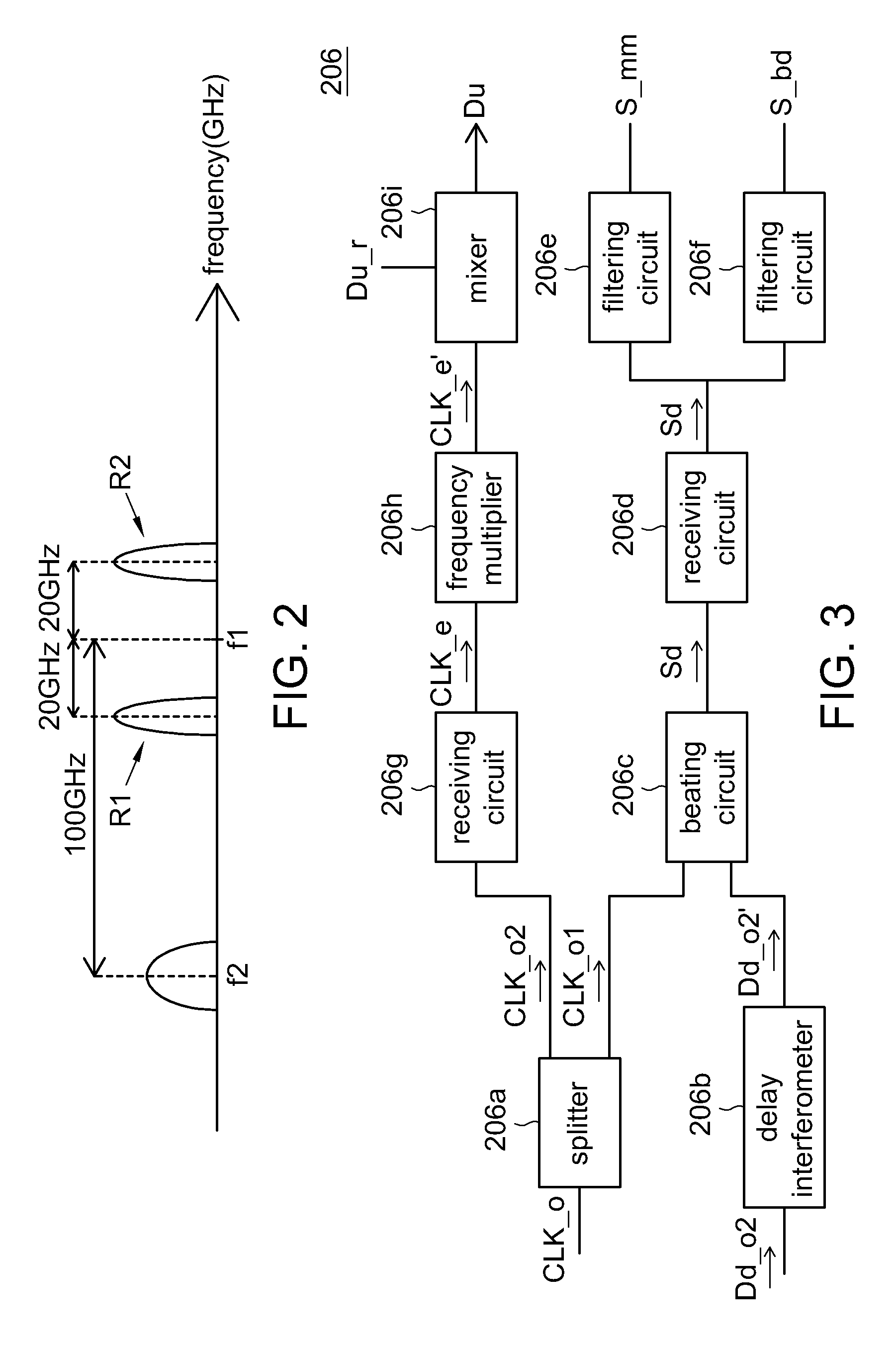
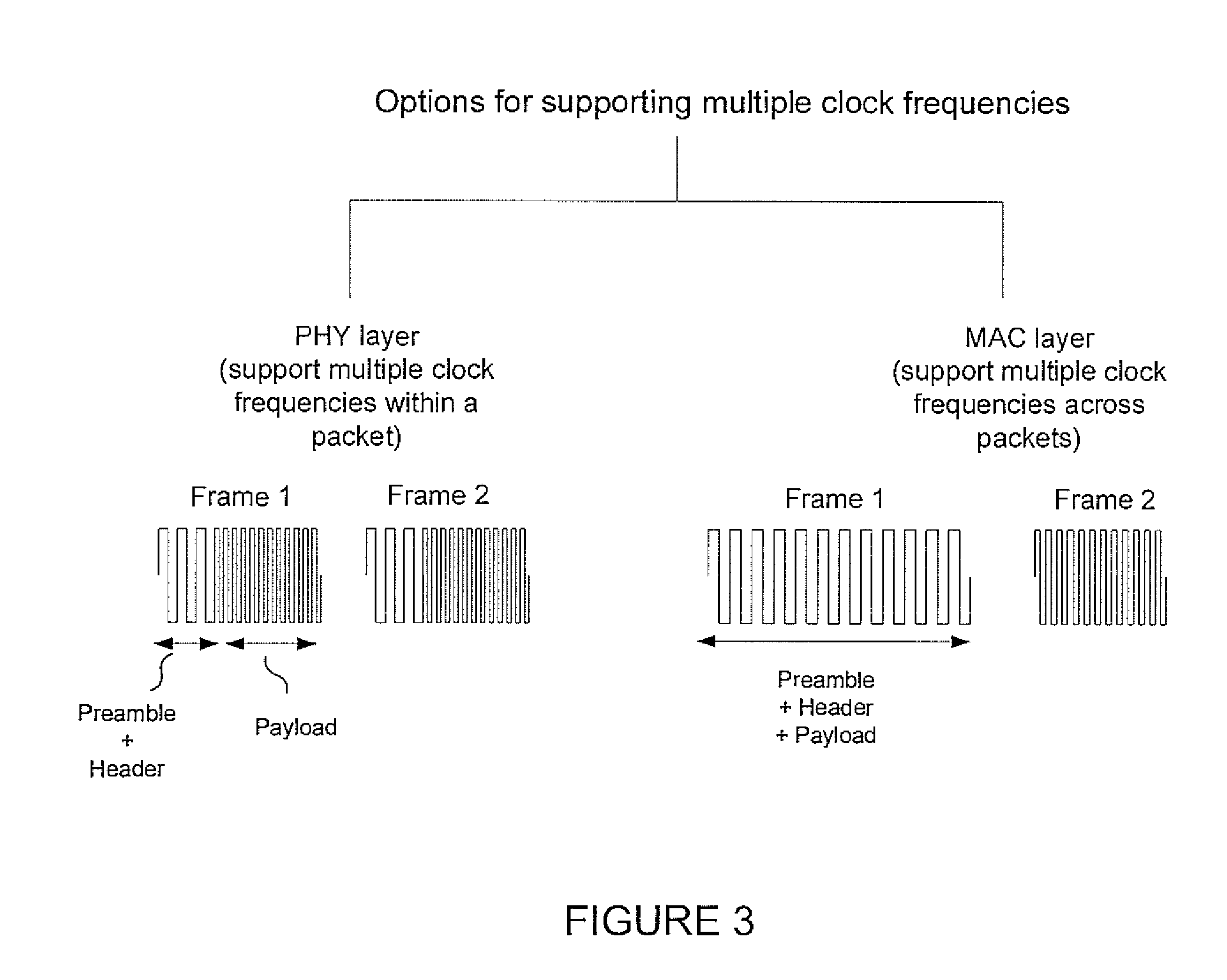
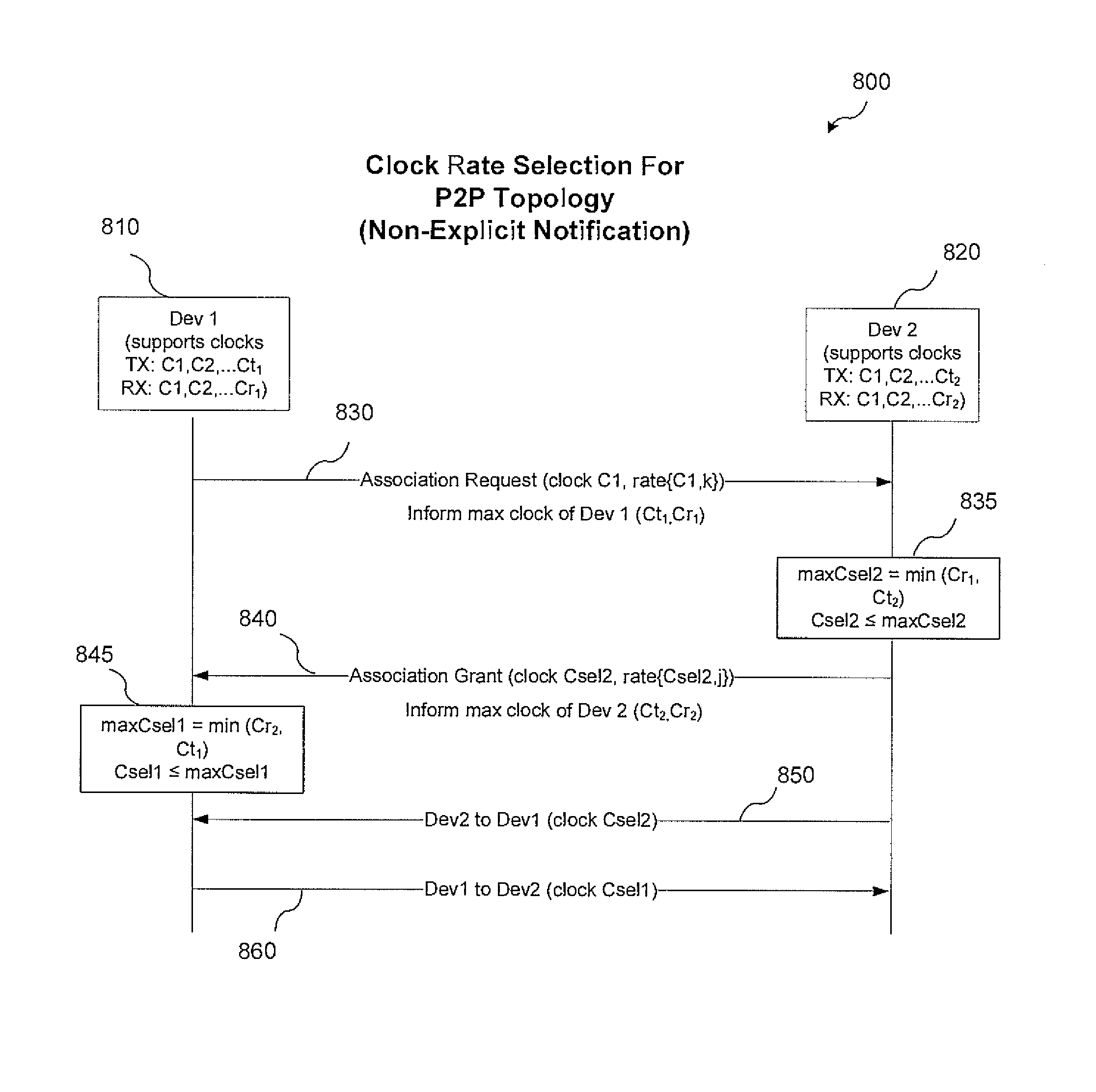
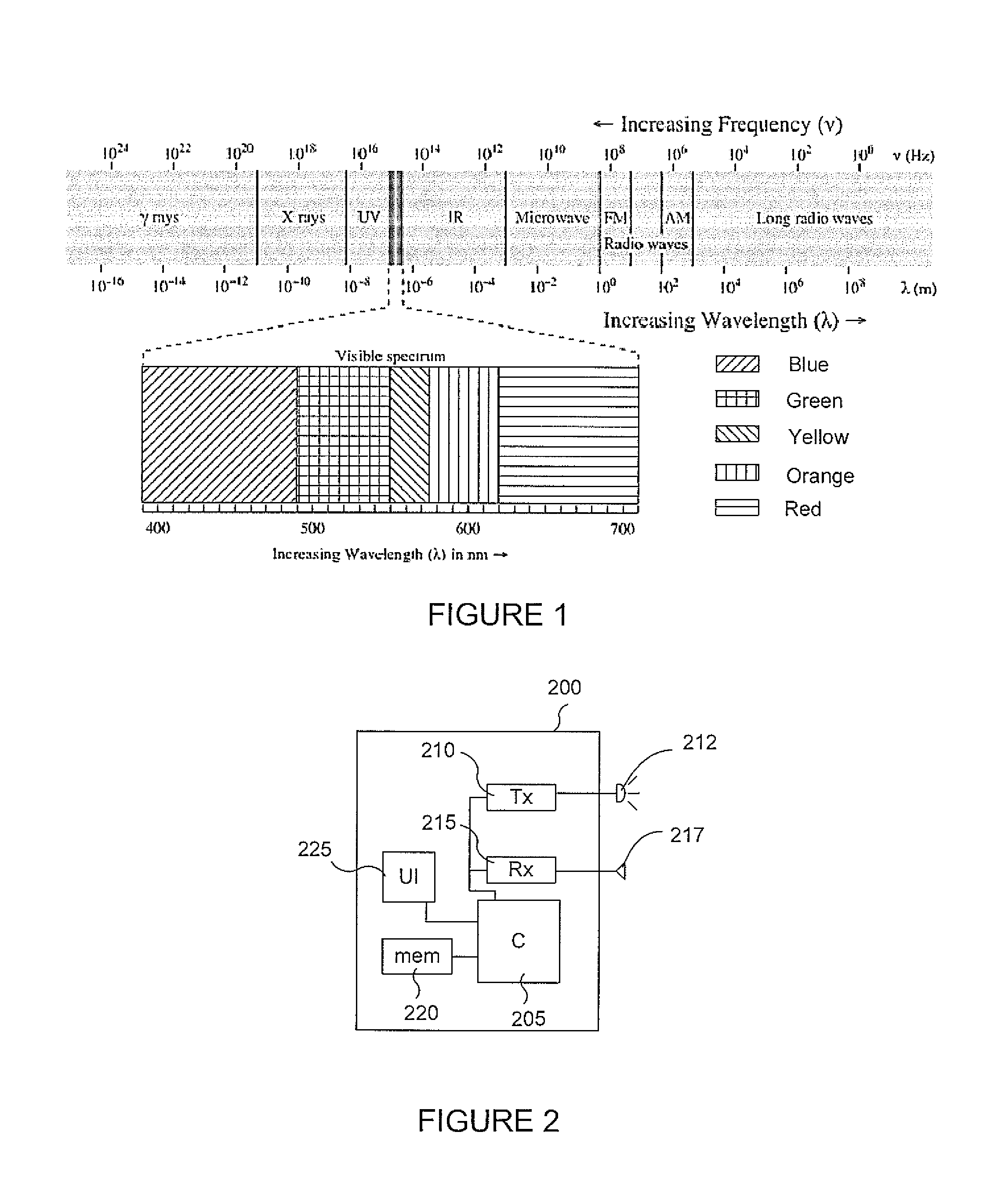
Optical clock rate negotiation for supporting asymmetric clock rates for visible light communication
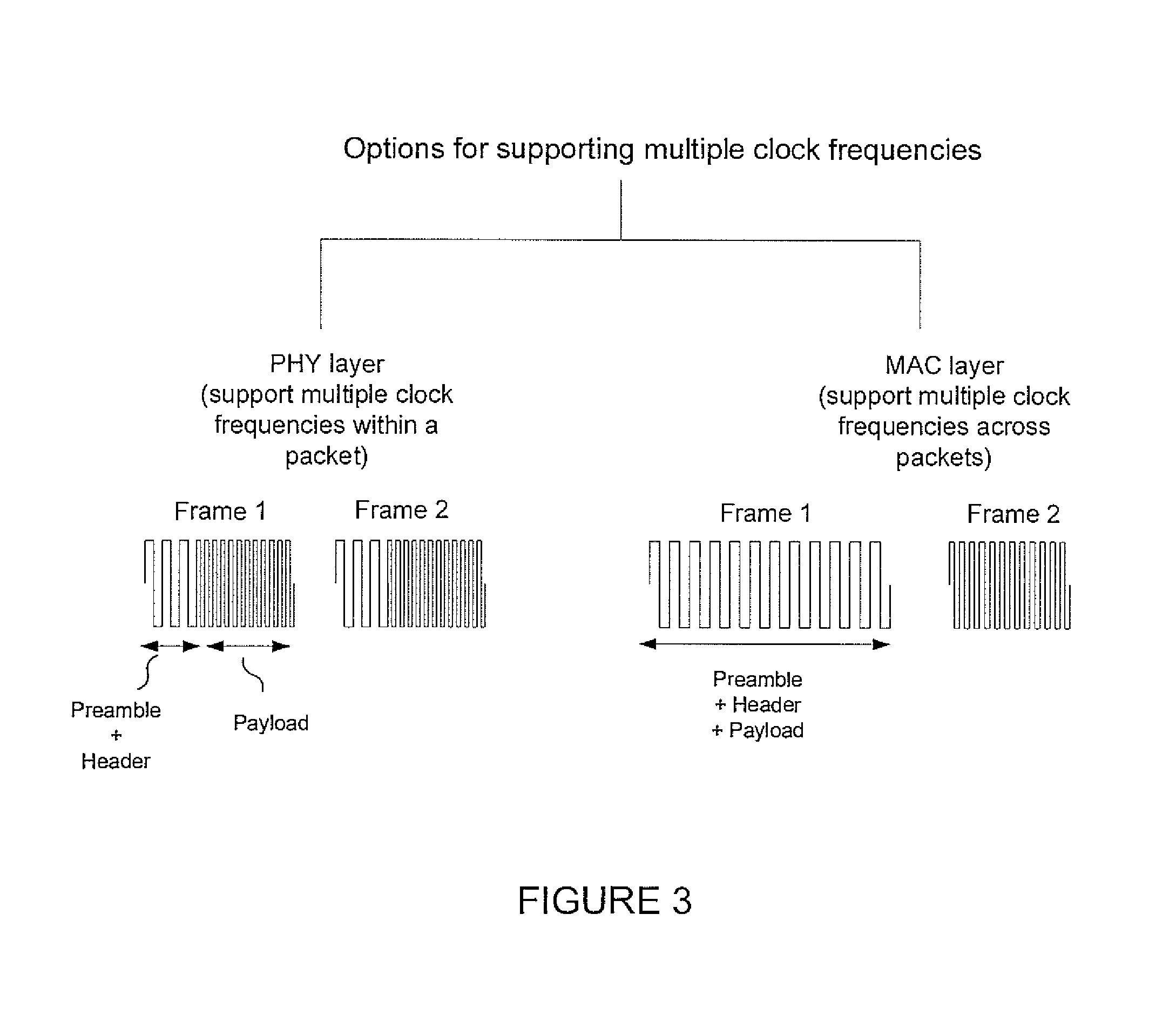
A method and apparatus conduct an optical clock rate negotiation to support asymmetric clock rates for visible light communication (VLC) in a VLC device. A first frame that includes a receiver clock rate supported by a first VLC device is transmitted at a predetermined clock rate. A response frame that includes a receiver clock rate supported by a second VLC device is received from the second VLC device. A transmission clock rate of the first VLC device is selected based on the response frame from the second VLC device. Subsequent frames for data communication are transmitted to the second VLC device at the selected transmission clock rate of the first device. Alternatively, when conducting optical clock negotiation in the PHY layer, multiple clock rates are supported within a single frame.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Phase-insensitive recovery of clock pulses of wavelength division multiplexed optical signals
InactiveUS20050063425A1Large dispersionEffective gainLaser using scattering effectsSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansMultiplexingMode-locking
An optically-pumped mode-locked fiber ring laser for optical clock recovery of multiple wavelength division multiplexed optical signals actively mode-locks a plurality of outputs of the laser as a plurality of recovered clocks for a plurality of the multiple wavelength division multiplexed optical signals. The laser cavity has a cavity length corresponding to an integer multiple of bit periods of at least one of the multiplexed optical signals for receiving a pre-amplified version of the plurality of wavelength division multiplexed optical signals to provide gain modulation through a phase-insensitive parametric amplification and recirculating a proportion of the output from the laser cavity back through the laser cavity for spatially mode-locking the output of the laser cavity as a recovered clock.
Owner:CORNING INC
Head-end circuit and remote antenna unit and hybrid wired/wireless network system and transceiving method using thereof
A head-end circuit comprises first and second continuous light sources, first and second modulators. The first and the second continuous light sources provide first and second optical signals respectively corresponding to first wavelength and second wavelength, which is different from the first wavelength. The first modulator modulates the first optical signal based on first clock signal to generate an optical clock signal. The second modulator modulates the second optical signal based on downlink data to generate optical downlink data with the carrier of the second optical signal. The optical clock signal and the optical down link data are outputted to a remote antenna unit via first fiber path.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
All-optical signal processing method and device
InactiveUS20060238866A1Polarisation multiplex systemsSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansBandpass filteringOptical clock
A method and an optical device in all-optical signal processing. It provides a novel way of taking into use the potential bandpass filtering capabilities of an optical complex one-pole resonator by, 1) excitating with at least part of the input signal an optical resonator arrangement that comprises two substantially parallel, independent, complex one-pole resonators arranged in a manner that one of the resonators is matched, and the other one is non-matched with the input signal, and 2) based on polarization separating further from the output of the optical resonator arrangement at least one optical output signal so that both the matched and non-matched resonators contribute to the formation of the output signal. The method and device can be utilized, for example, for optical signal analysis, optical clock recovery, or for producing high-frequency outputs from lower frequency input signals, like e.g. optical microwave generation.
Owner:LUXDYNE
Single optical frequency comb with high stability and high repetition frequency
InactiveCN101846861AImprove stabilityLong lock timeActive medium materialNon-linear opticsPhase noiseFrequency measurements
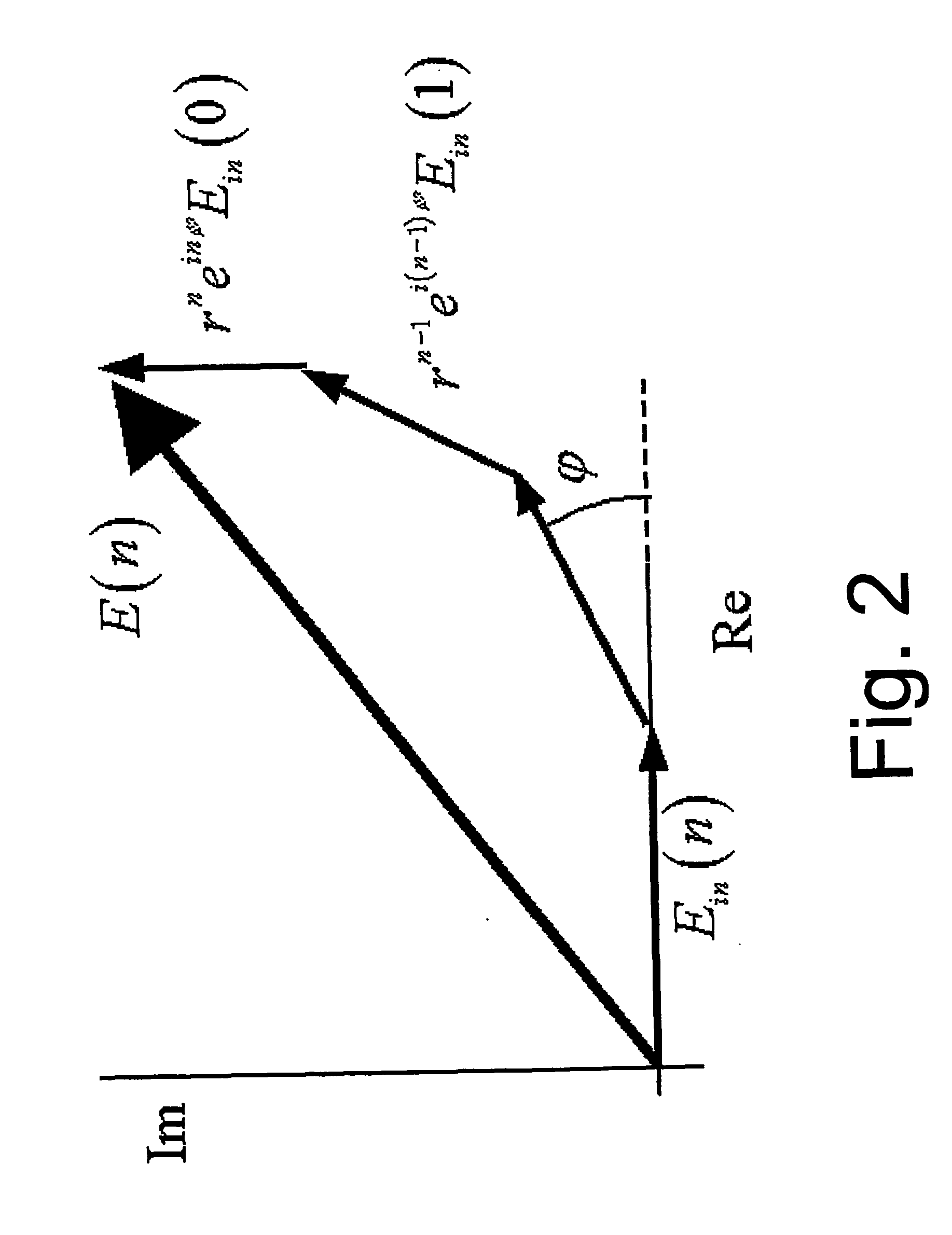
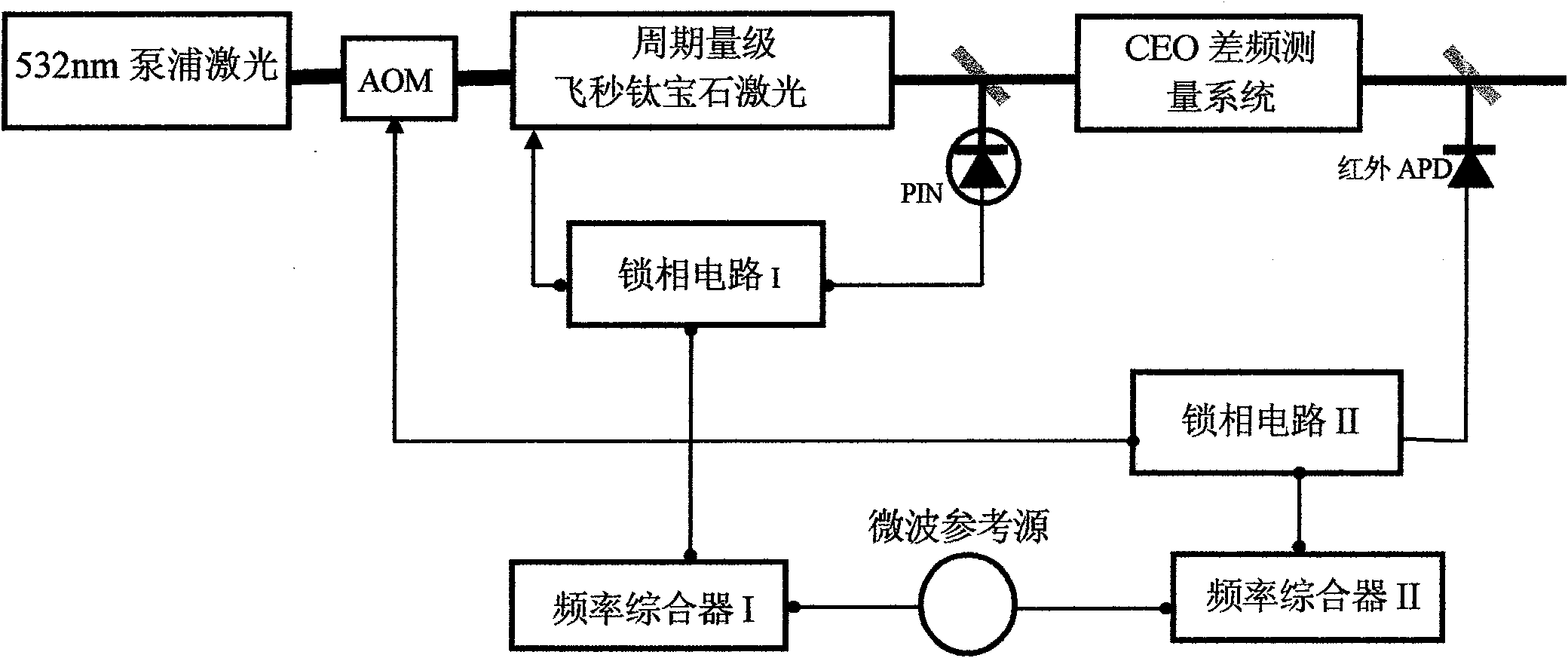
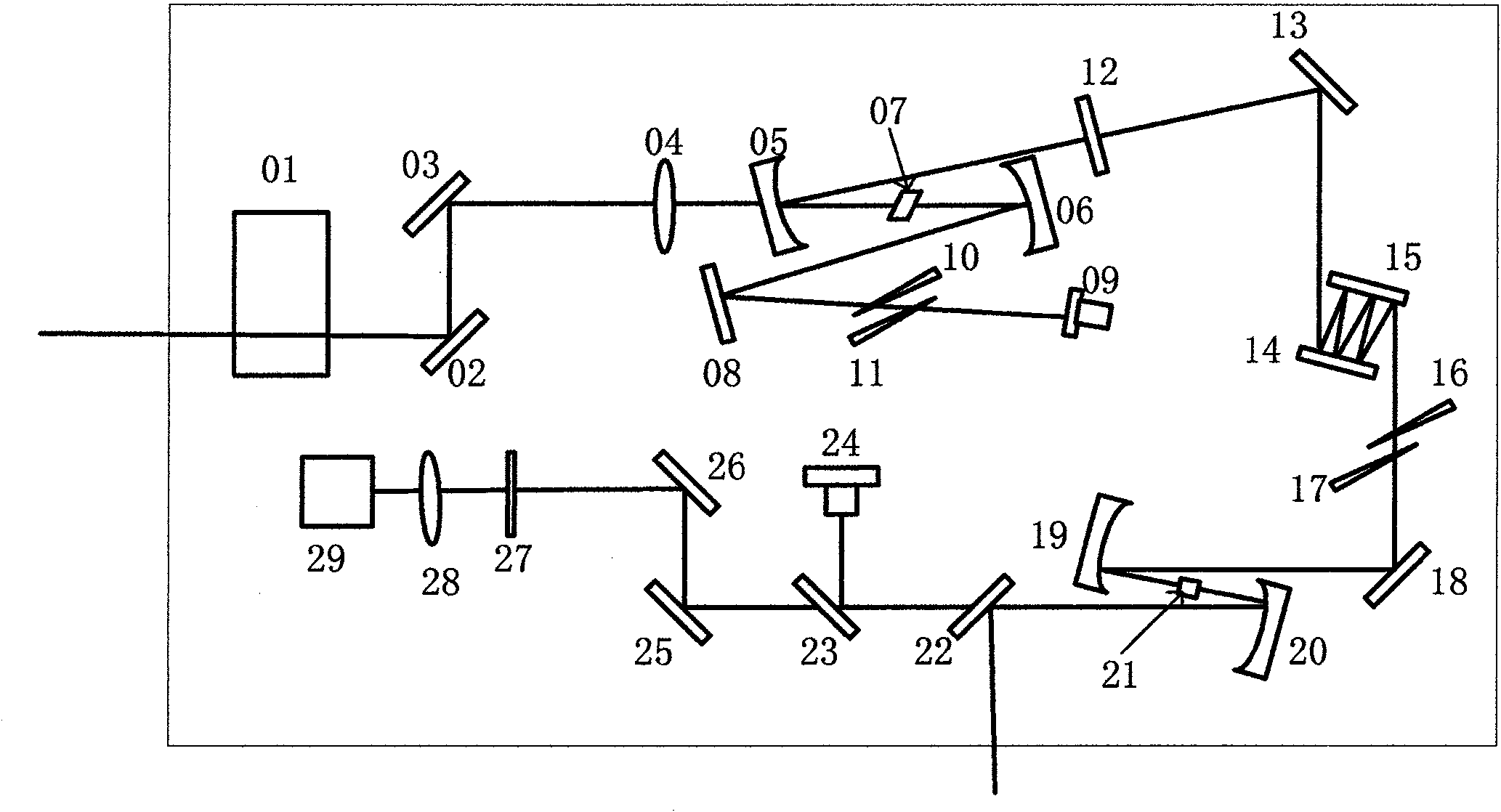
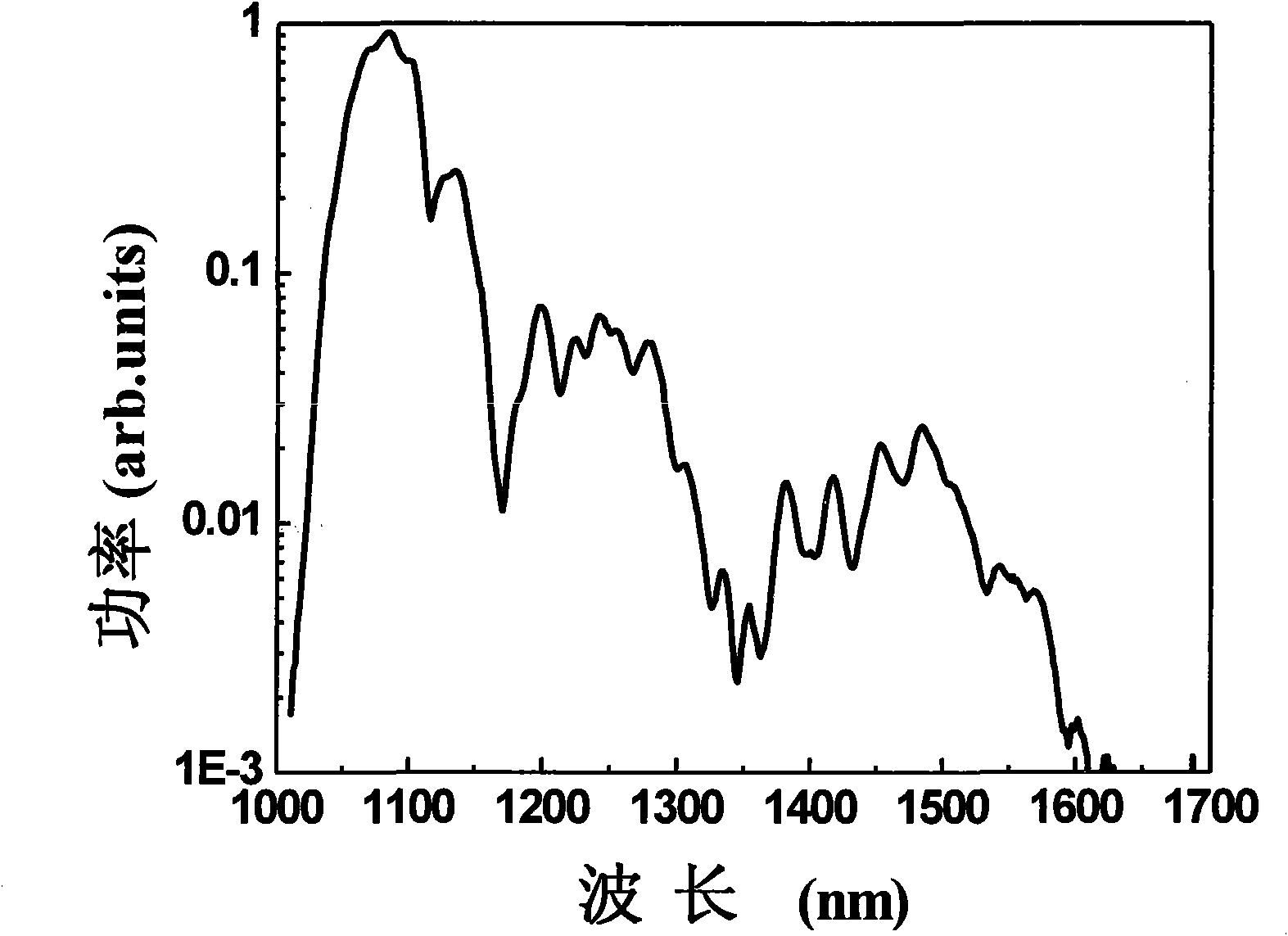
The invention discloses manufacturing method and equipment of a single optical frequency comb with high stability and high repetition frequency. The method comprises the following specific steps of: outputting femtosecond pulses with high repetition frequency, wide spectrum and pulse width less than 7 fs by using a cycle-grade femtosecond titanium sapphire oscillator; carrying out beat measurement of the CEO of the femtosecond pulses by using a single nonlinear crystal; and simultaneously locking repetition frequency and CEO frequency to a stable external microwave reference source by using a circuit feedback technology. The equipment comprises the cycle-grade femtosecond titanium sapphire oscillator, the single nonlinear crystal beat measurement fceo device and a feedback circuit device controlled on the basis of the phase lock principle. The invention has the characteristics of compact equipment structure, long locking time, high usable output power, small phase noise and the like, and is mainly applied to the scientific researches of absolute optical frequency measurement, optical clock composition, atto-second production and the like.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
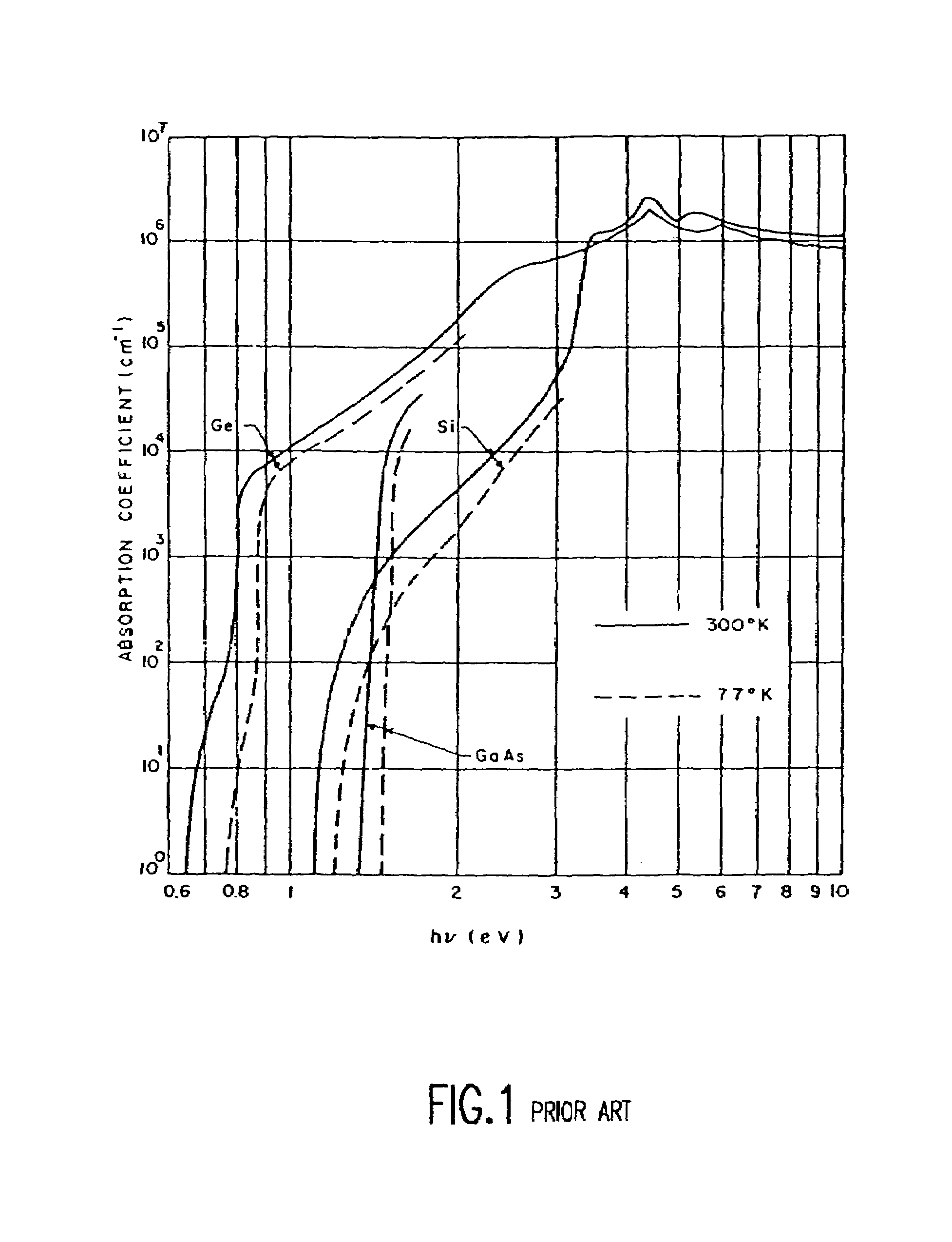
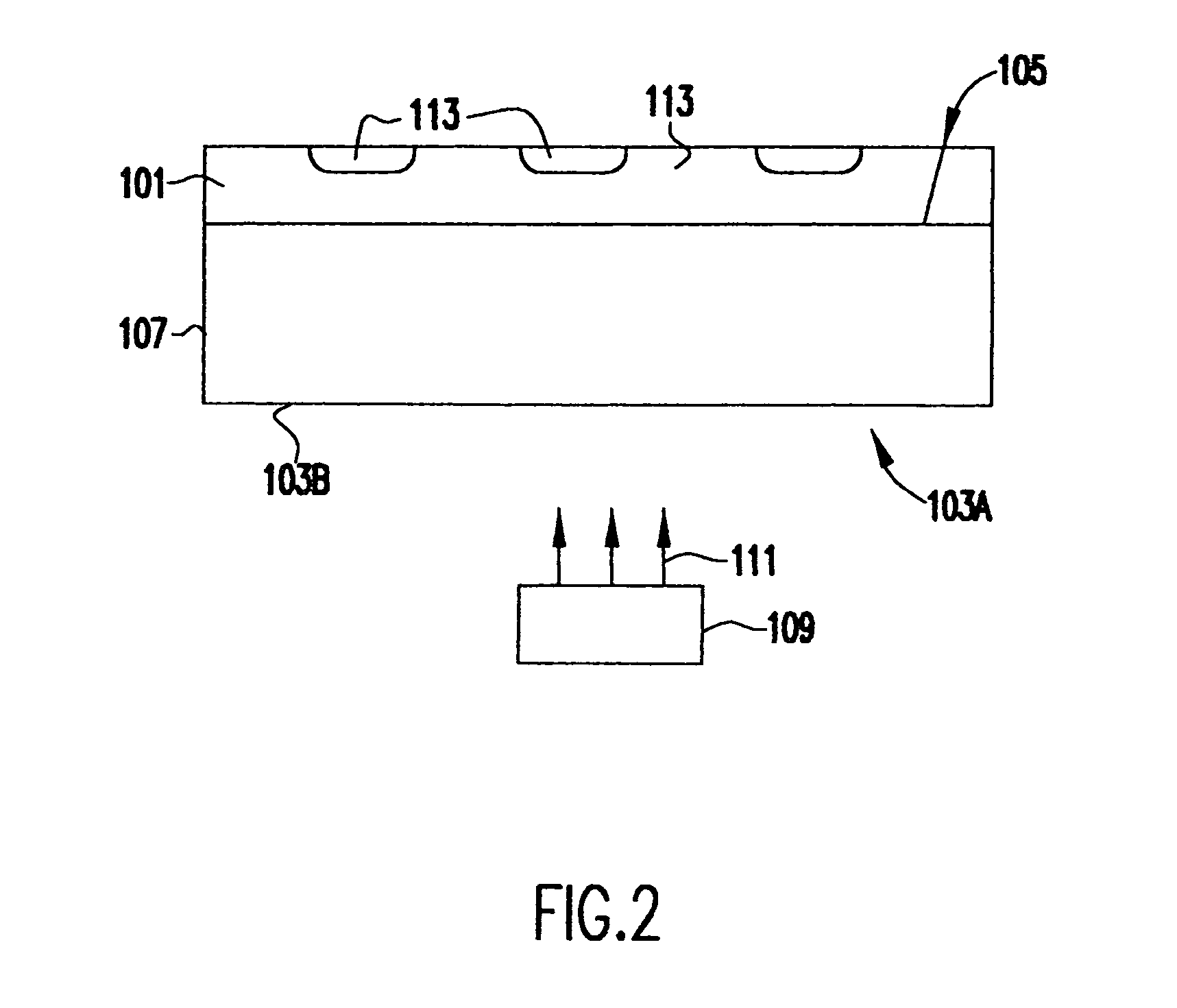
SiGe or germanium flip chip optical receiver
InactiveUS6980748B2Easy transferEasy to optimizeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHemt circuitsOptical clock
A synchronized optical clocking signal is provided to a plurality of optical receivers by providing a layer of a high absorption coefficient material, such as SiGe or Ge, on a front surface of a low absorption coefficient substrate, such as silicon. Diodes are formed in the germanium containing layer for receiving an optical signal and converting the optical signal into an electrical signal. An optical clocking signal is shined on the back surface of the silicon substrate. The light has a wavelength long enough so that it penetrates through the silicon substrate to the germanium containing layer. The wavelength is short enough so that the light is absorbed in the germanium containing layer and converted to the electrical clocking signal used for neighboring devices and circuits. The germanium concentration is graded so that minority carriers are quickly swept across junctions of the diodes and collected.
Owner:IBM CORP
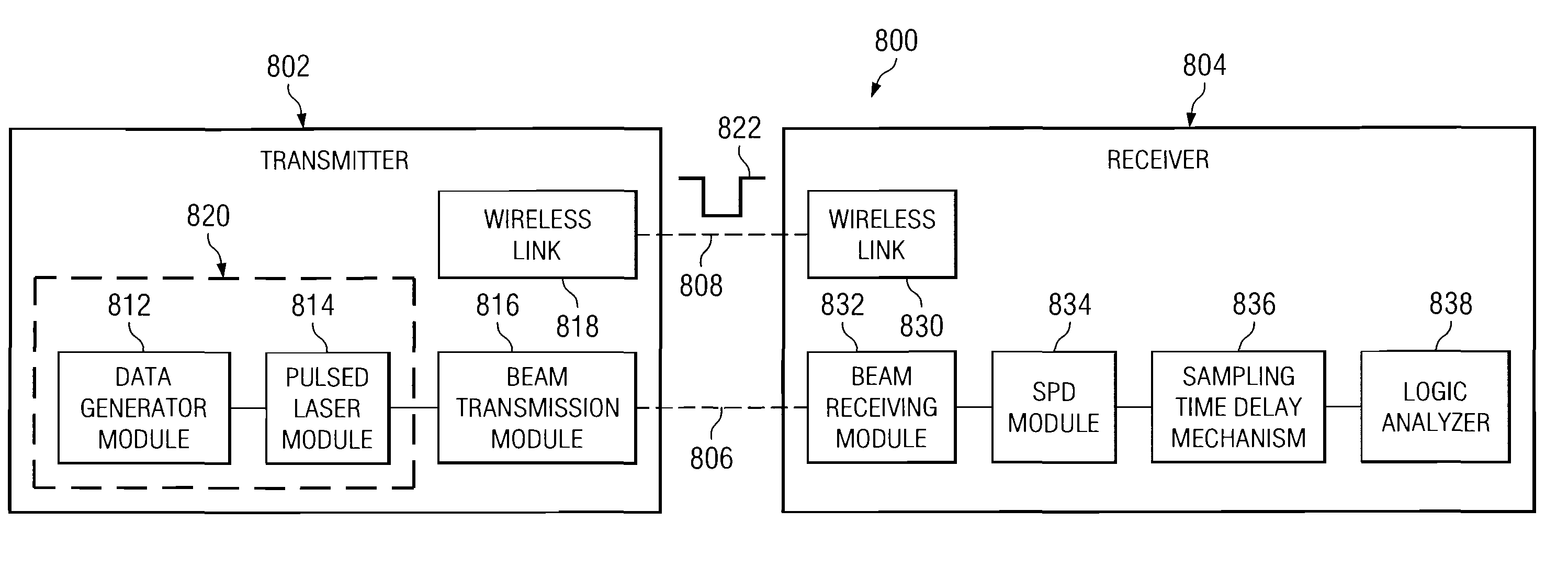
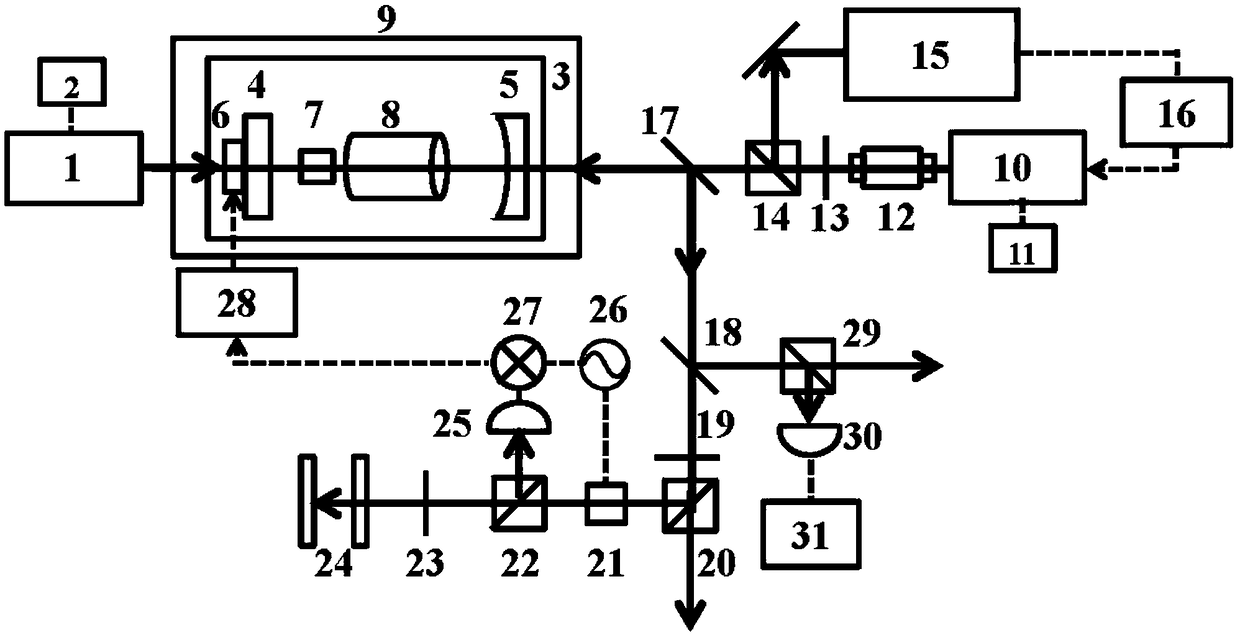
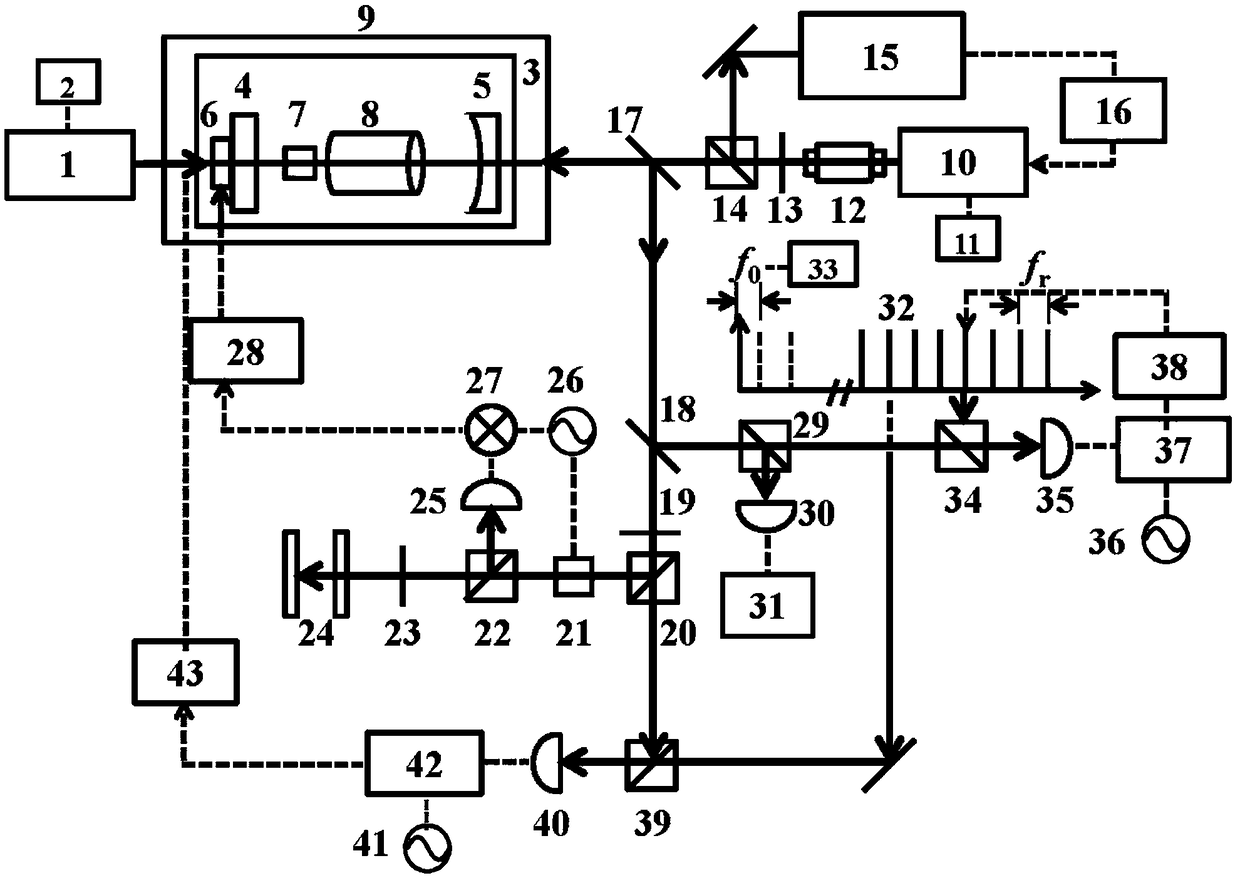
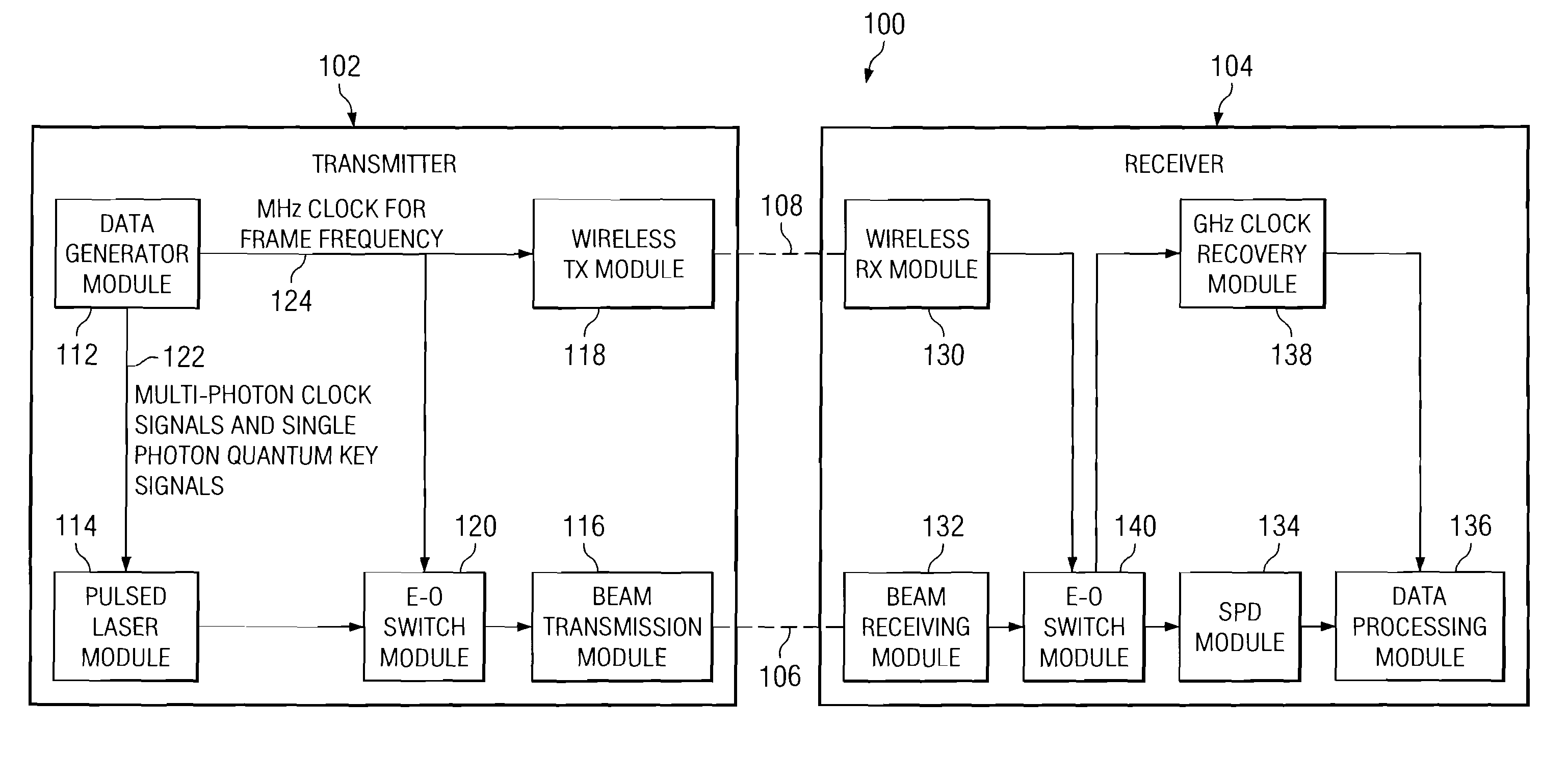
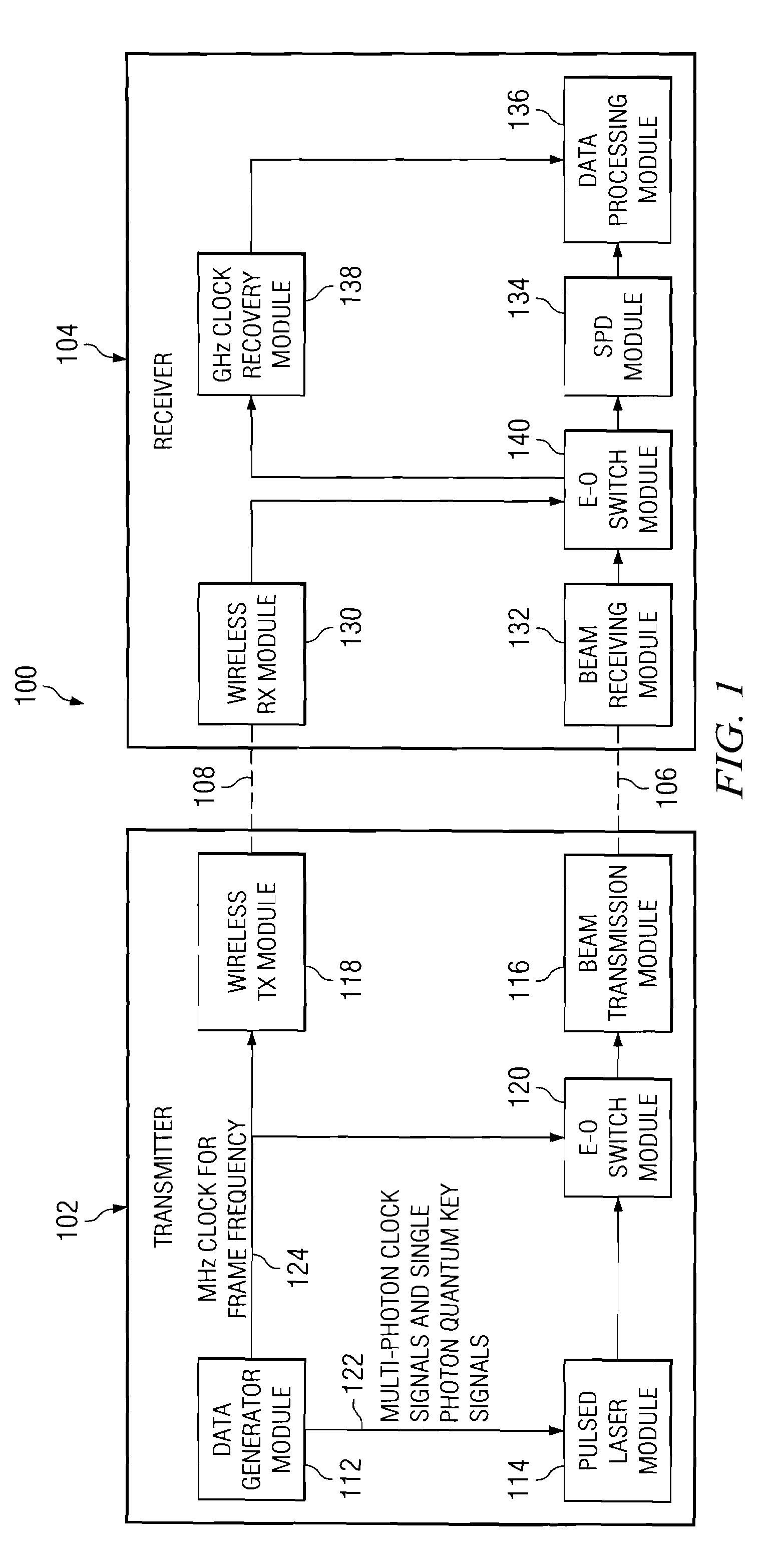
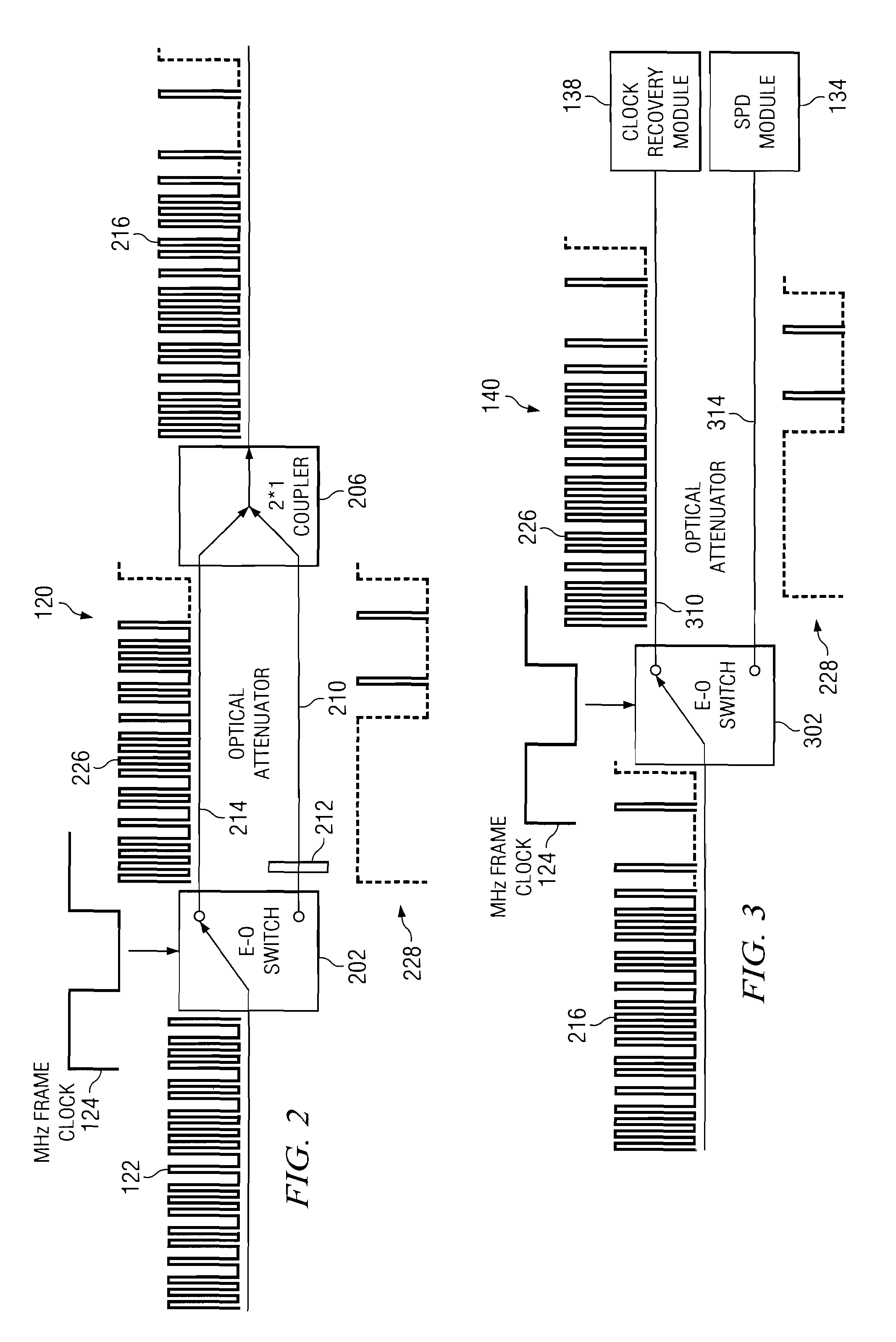
Quantum key distribution system and method
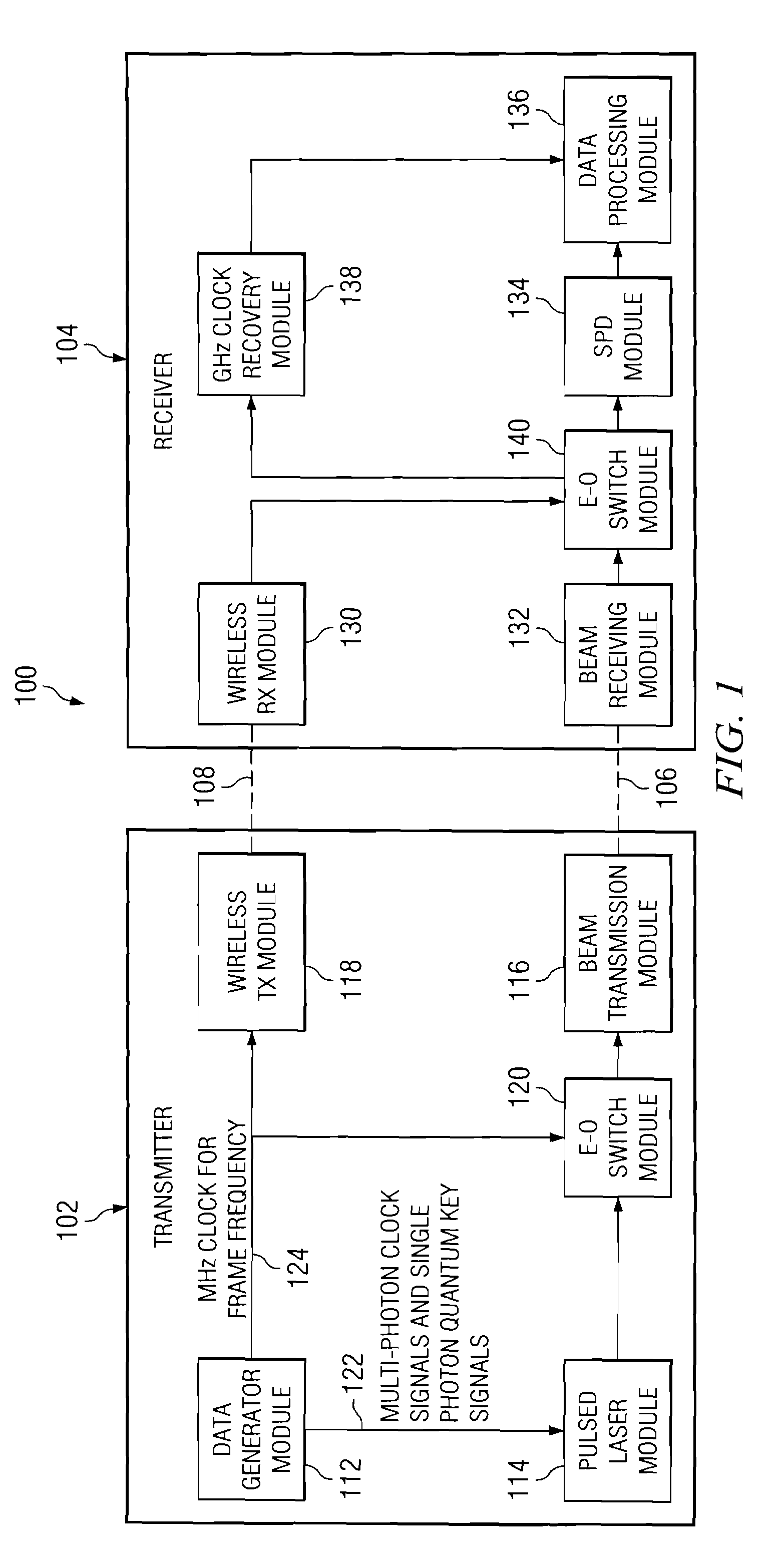
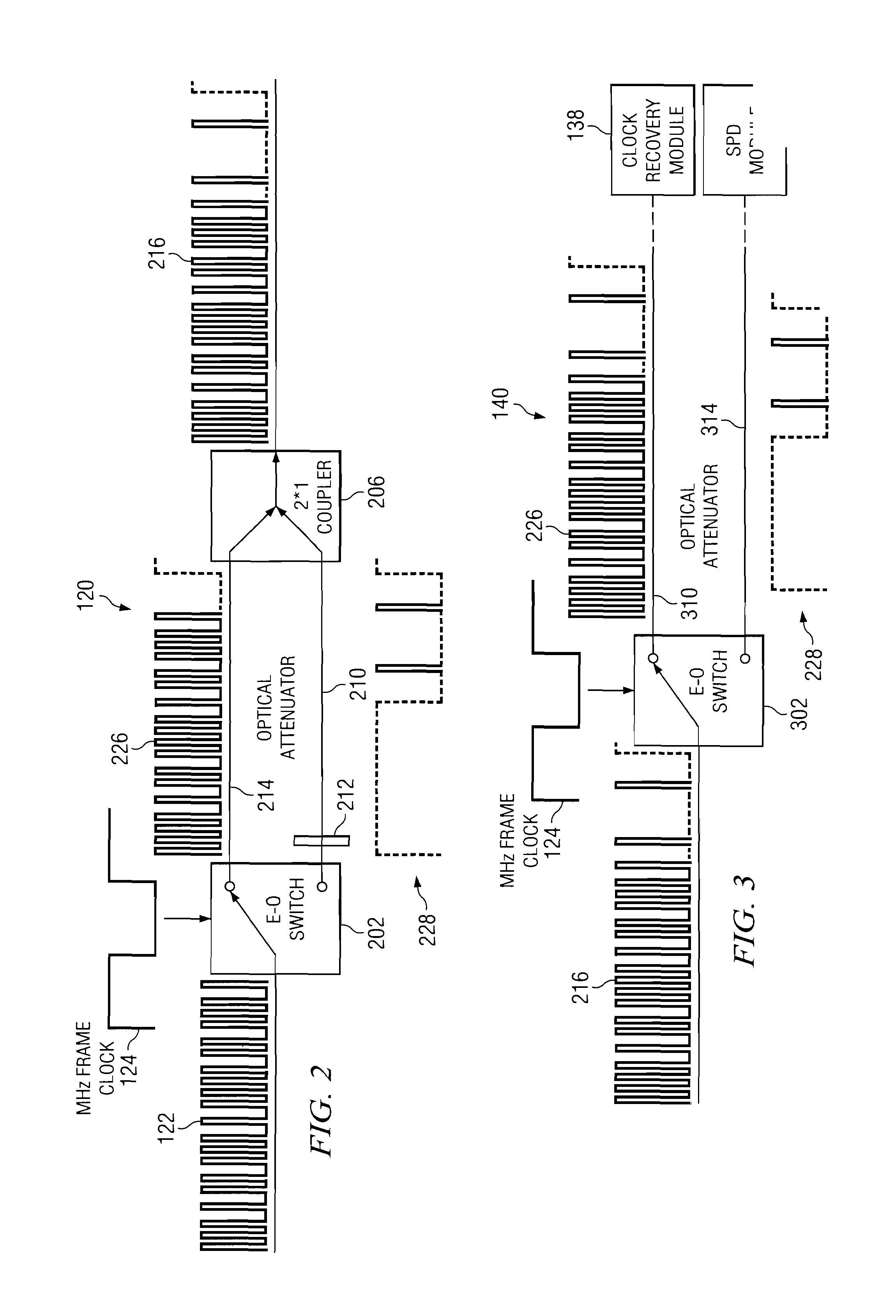
ActiveUS20080292102A1Reduce bit error rateKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesClock rateSignal on
A method and system for transmitting optical clock signals and quantum key signals on a single optical channel, and for reducing quantum bit error rate in a quantum key distribution system. The method includes receiving a multi-photon optical clock signal at an electro-optic switch at a first clock rate. The electro-optic switch may be configured for an interval defined by a second clock rate for generating a single photon quantum key signal. The multi-photon optical clock signal and the single photon quantum key signal may be combined such that the single optical channel transmits the single photon quantum key signal at a first interval and the multi-photon optical clock signal at a second interval. The quantum key signal may be transmitted from a transmitter at a first timing, and detected by a detector at a receiver. An output signal of the detector may be sampled at a second timing that is delayed relative to the first timing for reducing quantum bit error rate.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
High-precision fiber frequency transmission system
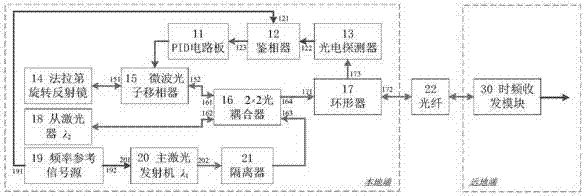
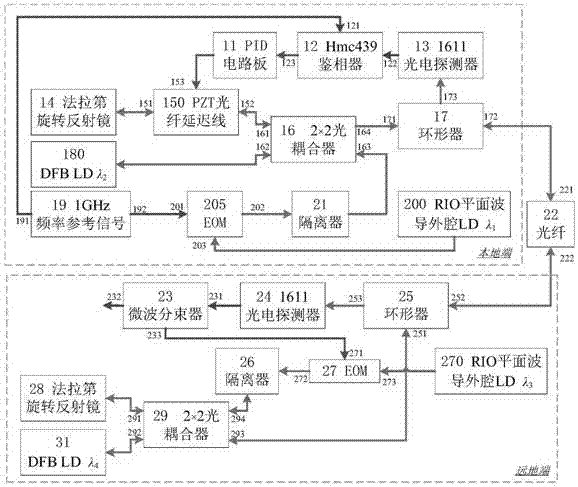
ActiveCN106877930AImprove response bandwidthImprove stabilityFibre transmissionDiscriminatorInjection locked
The invention discloses a high-precision fiber frequency transmission system, and the system comprises a PID circuit board, a phase discriminator, a photoelectric detector, a Faraday rotary reflector, a microwave photon phase shifter, a 2*2 optical coupler, a circulator, a slave laser, a frequency reference signal source, a main laser emitter, an isolator, an optical fiber link, and a time frequency receiving and transmitting module. On the basis of a single-fiber bidirectional return error signal obtaining mode, the system carries out the optical fiber link noise compensation based on injection locked coherent detection and the microwave photon phase shifter, thereby achieving the high-precision fiber frequency transmission. The system can achieve the high-precision recovery of a frequency reference signal of a local end at a far end. The system can achieve the two features, needed by phase change, on the same microwave photon phase shifter at the same time: large-bandwidth response and large dynamic range, facilitates the reduction of the complexity, and improves the stability and adaptability. The system can be used in the fields of comparison of the optical clock / atomic clock and the frequency transmission.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
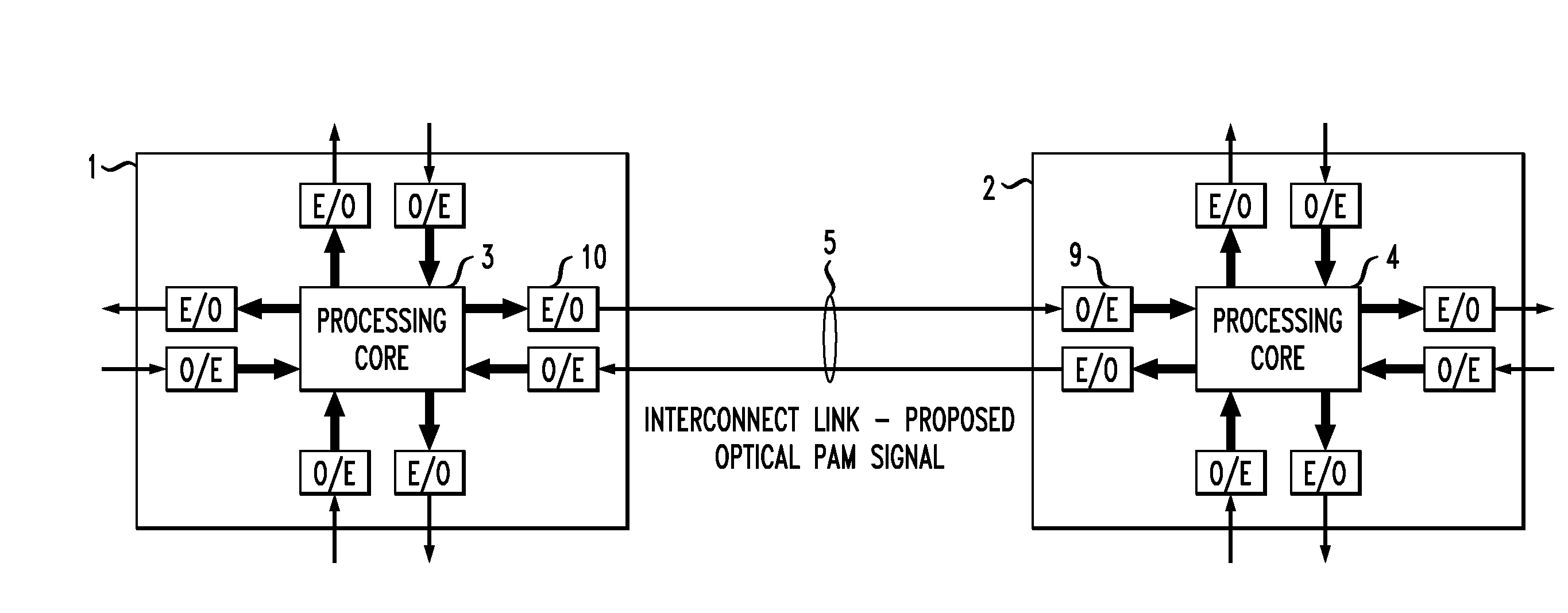
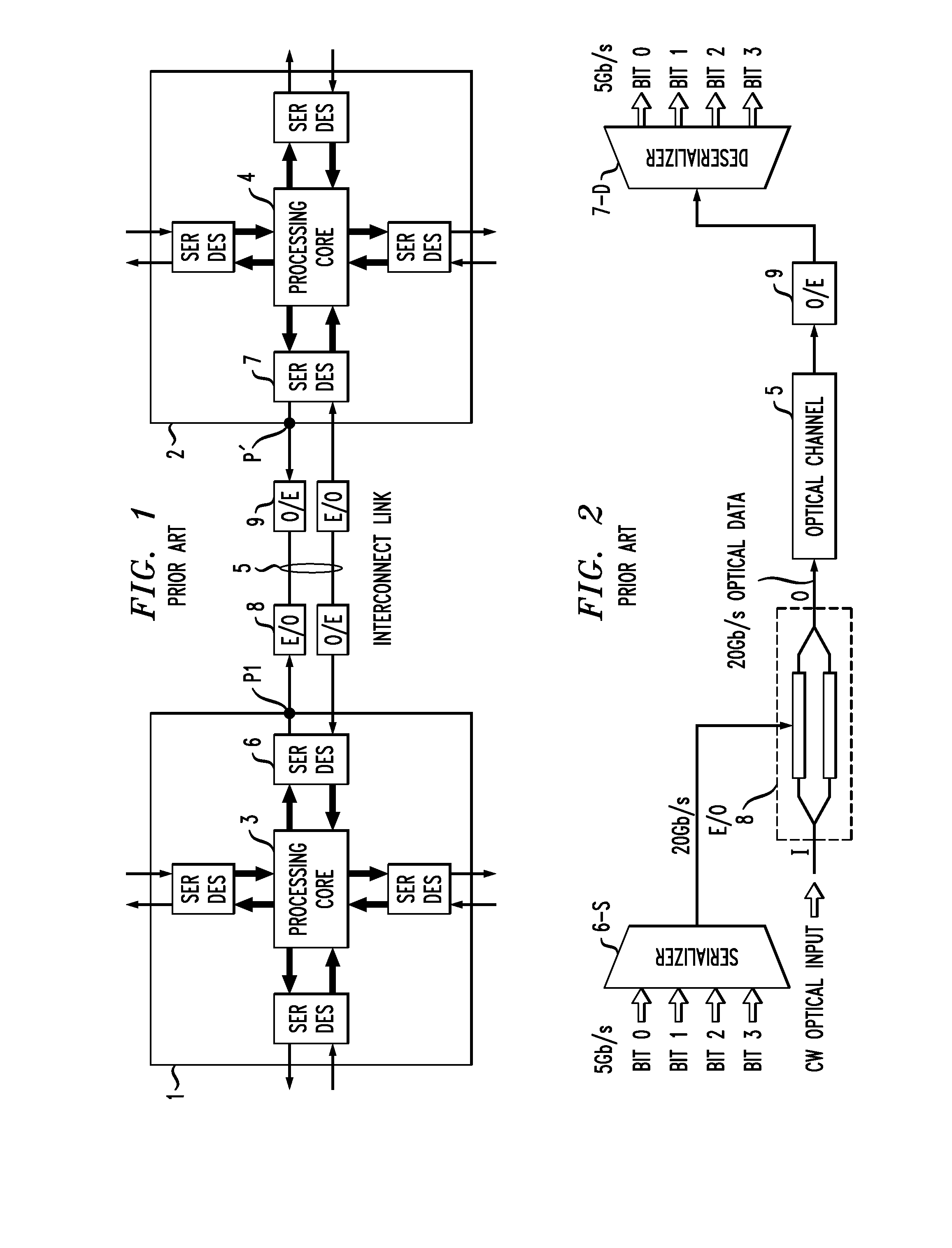
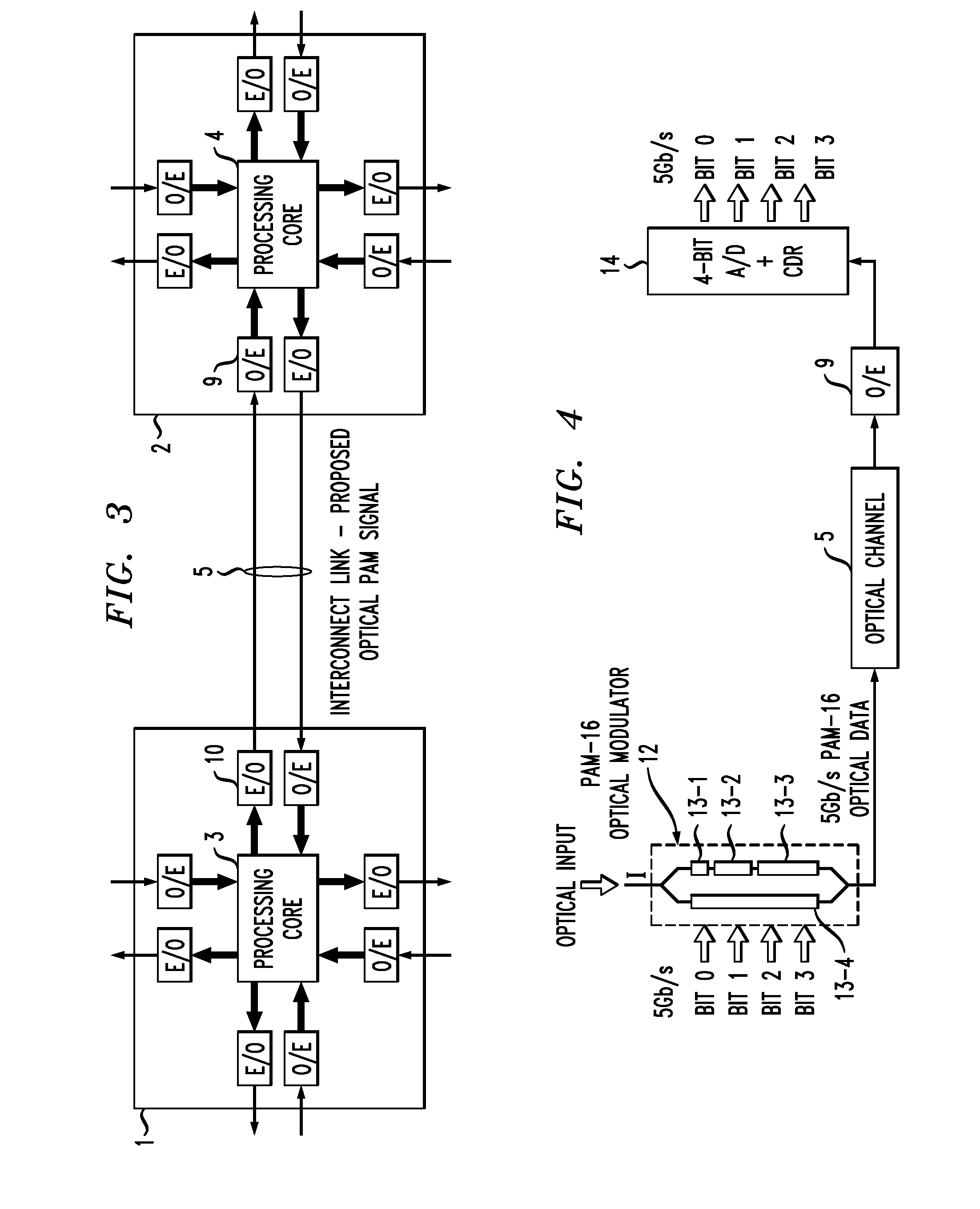
Optical Interconnection Arrangement For High Speed, High Density Communication Systems
ActiveUS20100316391A1Reduce needEliminate needSynchronisation information channelsSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansHigh densityCommunications system
An optical interconnection arrangement for use in high data applications is presented that eliminates the need for extensive serialization / de-serialization (SERDES) functionality by utilizing pulse amplitude modulation (PAM) techniques to represent the data in the optical domain while utilizing a separate channel for transmitting an optical clock signal, eliminating the need for clock recovery circuitry on the receive end of the arrangement.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Optically controlled optical PAM signal regeneration device
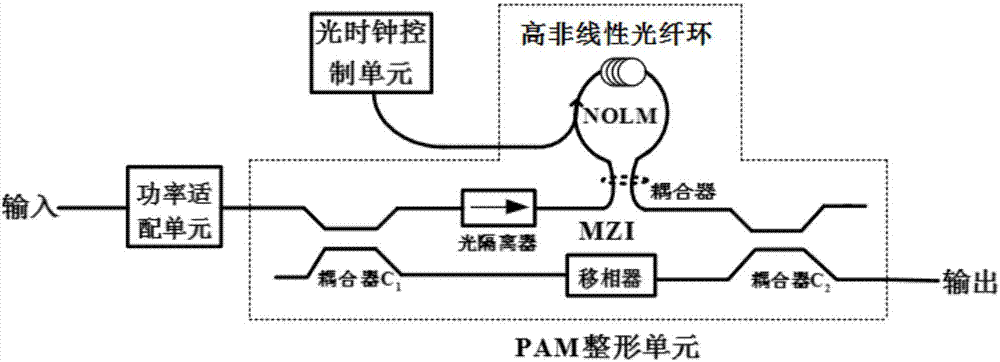
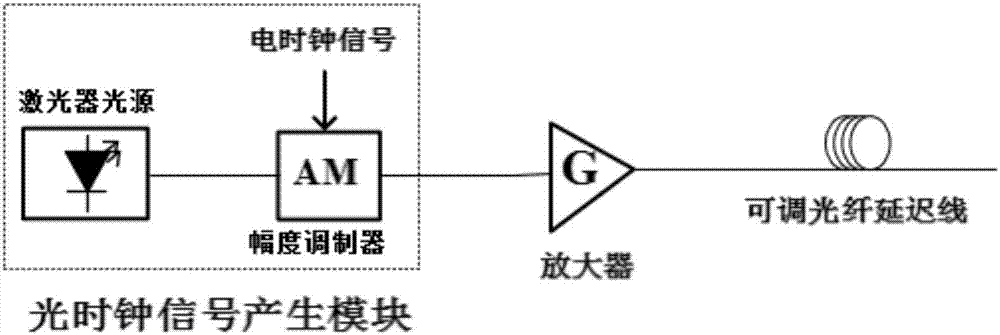
InactiveCN106972890AFlexible designTime-division multiplexElectromagnetic transmittersOptical clockSignal regeneration
The invention discloses an optically controlled optical PAM signal regeneration device comprising a power adapting unit, an optical clock control unit and a PAM reshaping unit, wherein the PAM reshaping unit is the core of a regenerator and is composed of a Mach-Zehnder interferometer MZI and a highly nonlinear fiber ring NOLM, for a to-be-regenerated degraded optical PAM signal, the level matching between the input degraded optical PAM signal and the PAM reshaping unit is accomplished by the power adapting unit, the optical clock signal power and the delay output by the optical clock control unit and a phase shifter in the MZI structure are adjusted, so that the PAM reshaping unit works normally, the loss coefficient, the optical fiber length, the nonlinear coefficient and other parameters of a highly nonlinear optical fiber in the NOLM structure, and the coupling coefficients of front and back couplers in the MZI structure are changed to design PAM reshaping units with different level numbers, and then the regeneration of the degraded optical PAM signal is accomplished. Therefore, the optically controlled optical PAM signal regeneration device disclosed by the invention can execute a reshaping and a re-timing function and has the advantages of flexible design of regeneration level numbers.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Optical clock rate negotiation for supporting asymmetric clock rates for visible light communication
A method and apparatus conduct an optical clock rate negotiation to support asymmetric clock rates for visible light communication (VLC) in a VLC device. A first frame that includes a receiver clock rate supported by a first VLC device is transmitted at a predetermined clock rate. A response frame that includes a receiver clock rate supported by a second VLC device is received from the second VLC device. A transmission clock rate of the first VLC device is selected based on the response frame from the second VLC device. Subsequent frames for data communication are transmitted to the second VLC device at the selected transmission clock rate of the first device. Alternatively, when conducting optical clock negotiation in the PHY layer, multiple clock rates are supported within a single frame.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optical deserialization with gated detectors: system and method
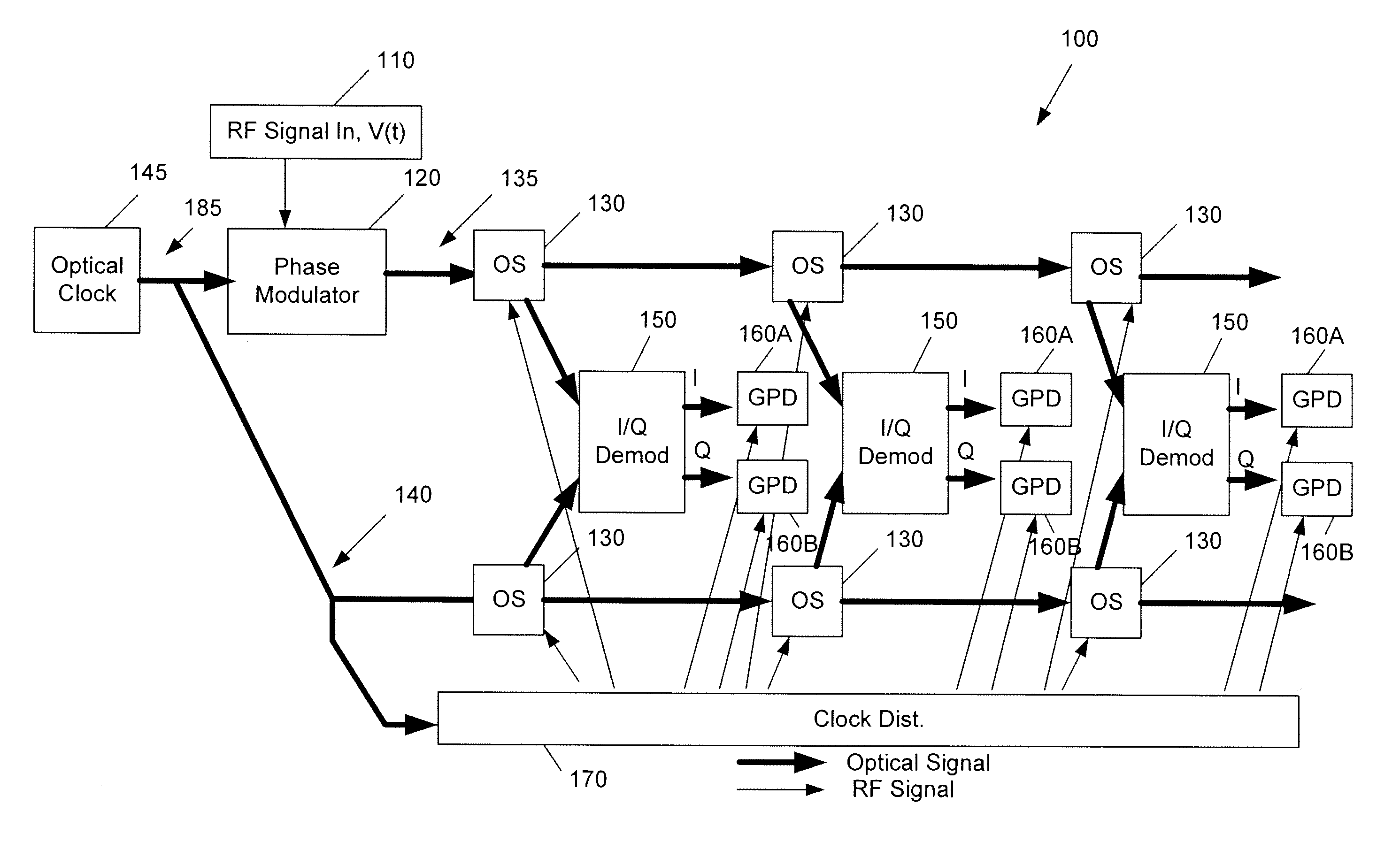
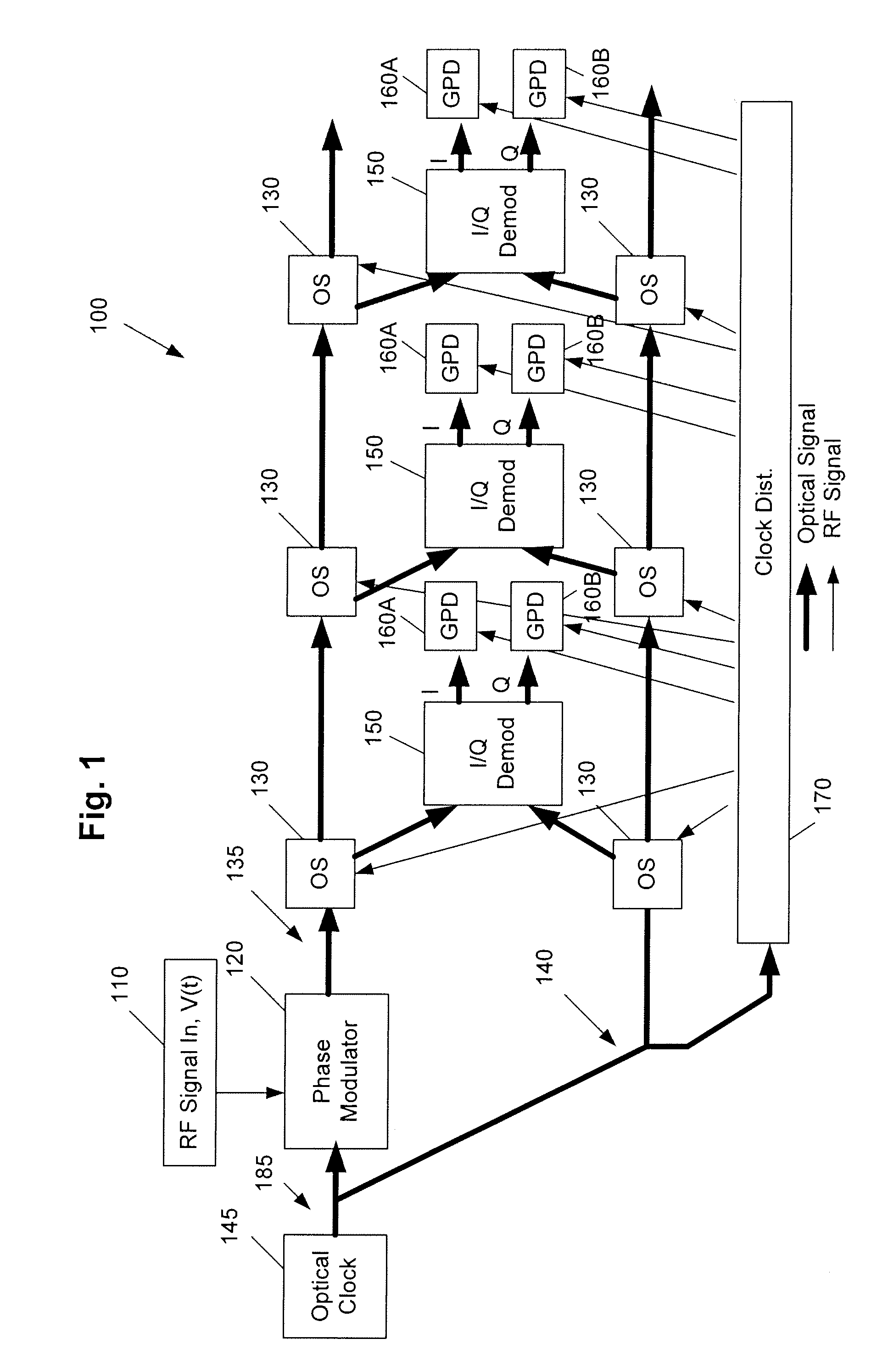
ActiveUS8456336B1Electric signal transmission systemsOptical analogue/digital convertersPulse streamOptical clock
A method of performing optical serial-to-parallel conversion of an optical signal includes performing phase modulation of the optical pulse stream and outputting a phase-modulated optical signal. Optical switching of the phase-modulated optical signal is performed by optical switches provided on a signal path. Optical switching of a reference optical clock signal is performed by optical switches provided on a reference path. I / Q demodulation of the optically switched phase-modulated optical signal respectively output by an optical switch is performed on the signal path at timings corresponding to the optically switched reference optical clock signal respectively output by an optical switch on the reference path, in which I and Q demodulated signals are output as a result thereof. Photodetection of the I and Q demodulated signals is then performed.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
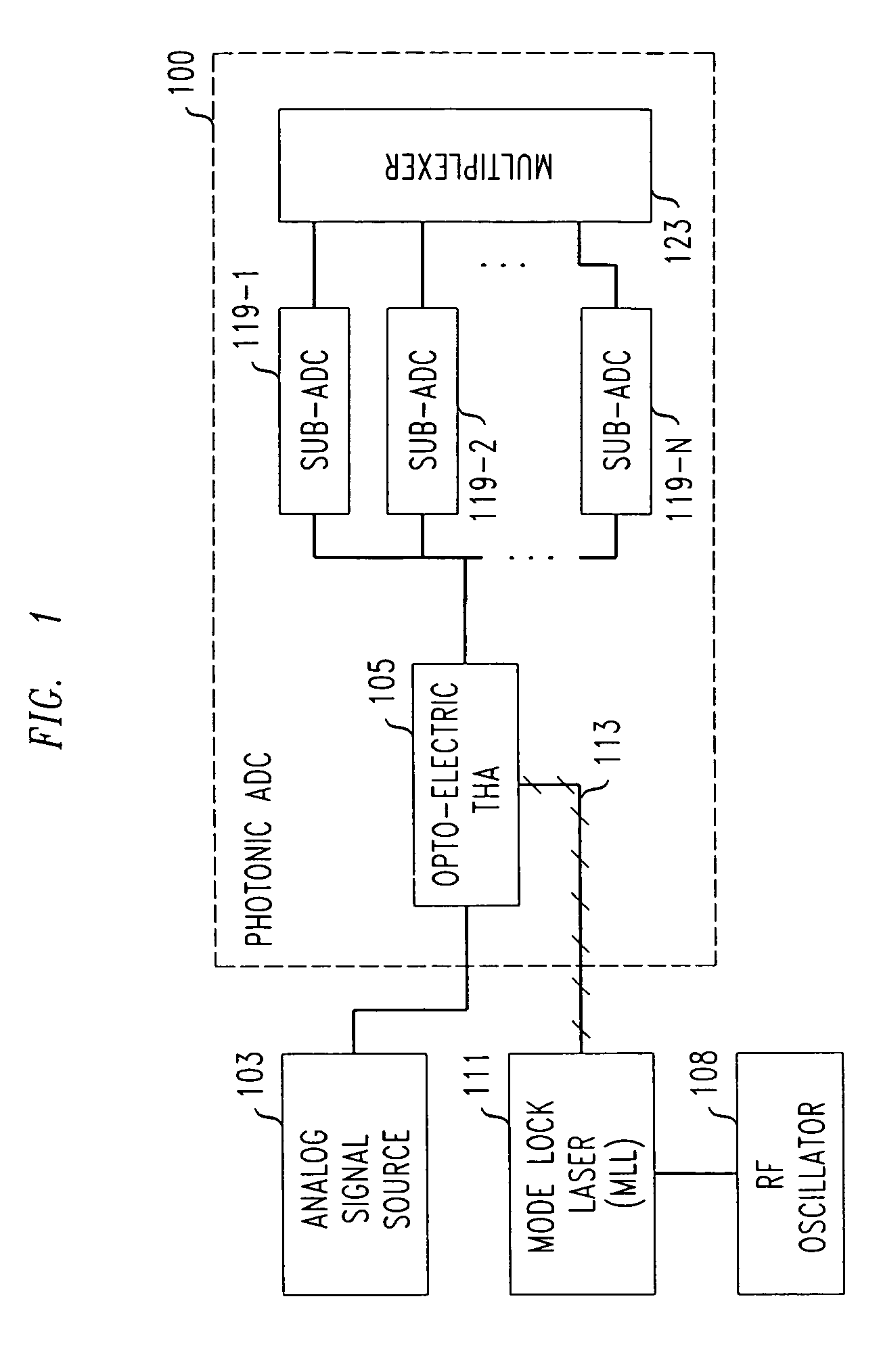
Technique for photonic analog-to-digital signal conversion
InactiveUS7956788B2Reducing the sampling jitterElectric signal transmission systemsOptical analogue/digital convertersDigital signal processingOptical clock
Owner:RPX CORP +1
Optical pulse demultiplexer
InactiveUS20050047788A1Little polarization-dependencySuppress componentTime-division optical multiplex systemsSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansOptical clockSignal light
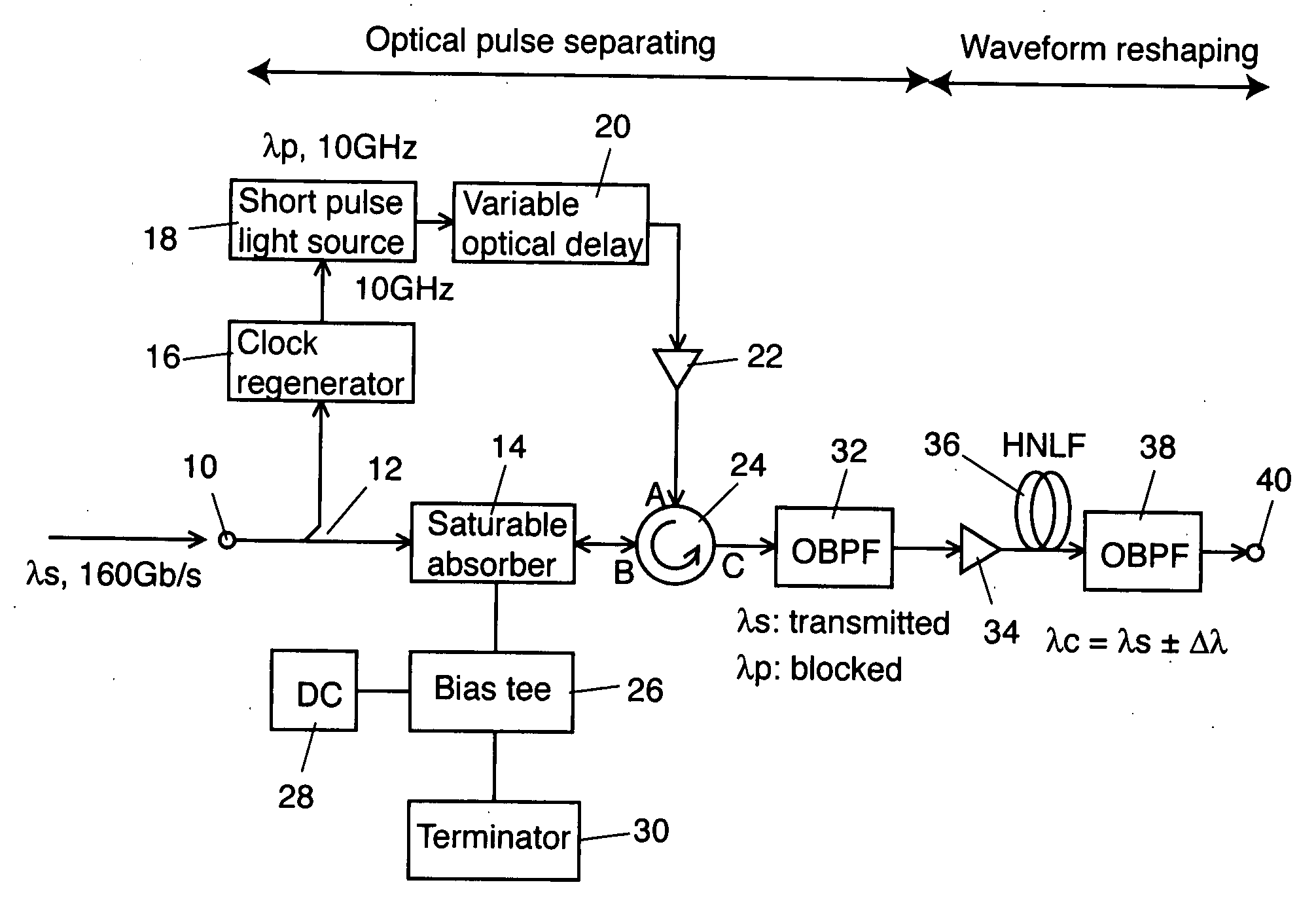
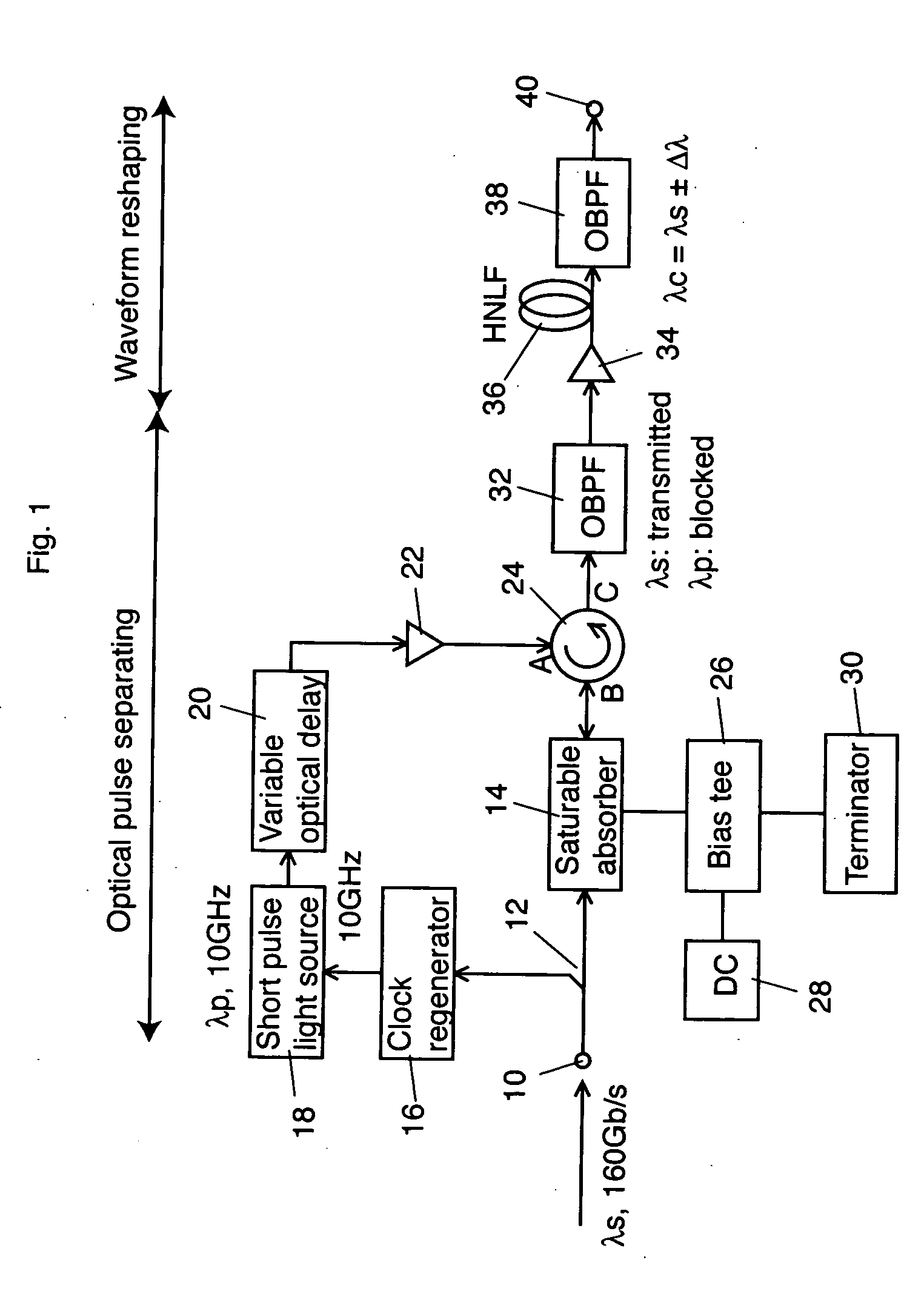
In an optical pulse demultiplexer according to the invention, an optical splitter splits an input pulse signal light having a signal wavelength into a firs portion and a second portion. An optical clock generator generates an optical clock having a clock wavelength at a predetermined frequency corresponding to 1 / n (n is integer not less than 2) of a bit rate of the input pulse signal light out of the first portion of the output lights from the optical splitter. The clock wavelength is different from the signal wavelength. A saturable absorption optical element, to which the optical clock generated by the optical clock generator and the second portion enter, separates a channel component corresponding to the predetermined frequency out of the second according to the optical clock. An optical filter extracts an optical component of the signal wavelength out of the light output from the saturable absorption optical element. A nonlinear waveform shaper suppresses a low level part of the light output from the first optical filter.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH
Clocking of integrated circuits using photonics
ActiveUS7646984B1Facilitate oversamplingDigital data processing detailsElectromagnetic transmittersOptical clockEngineering
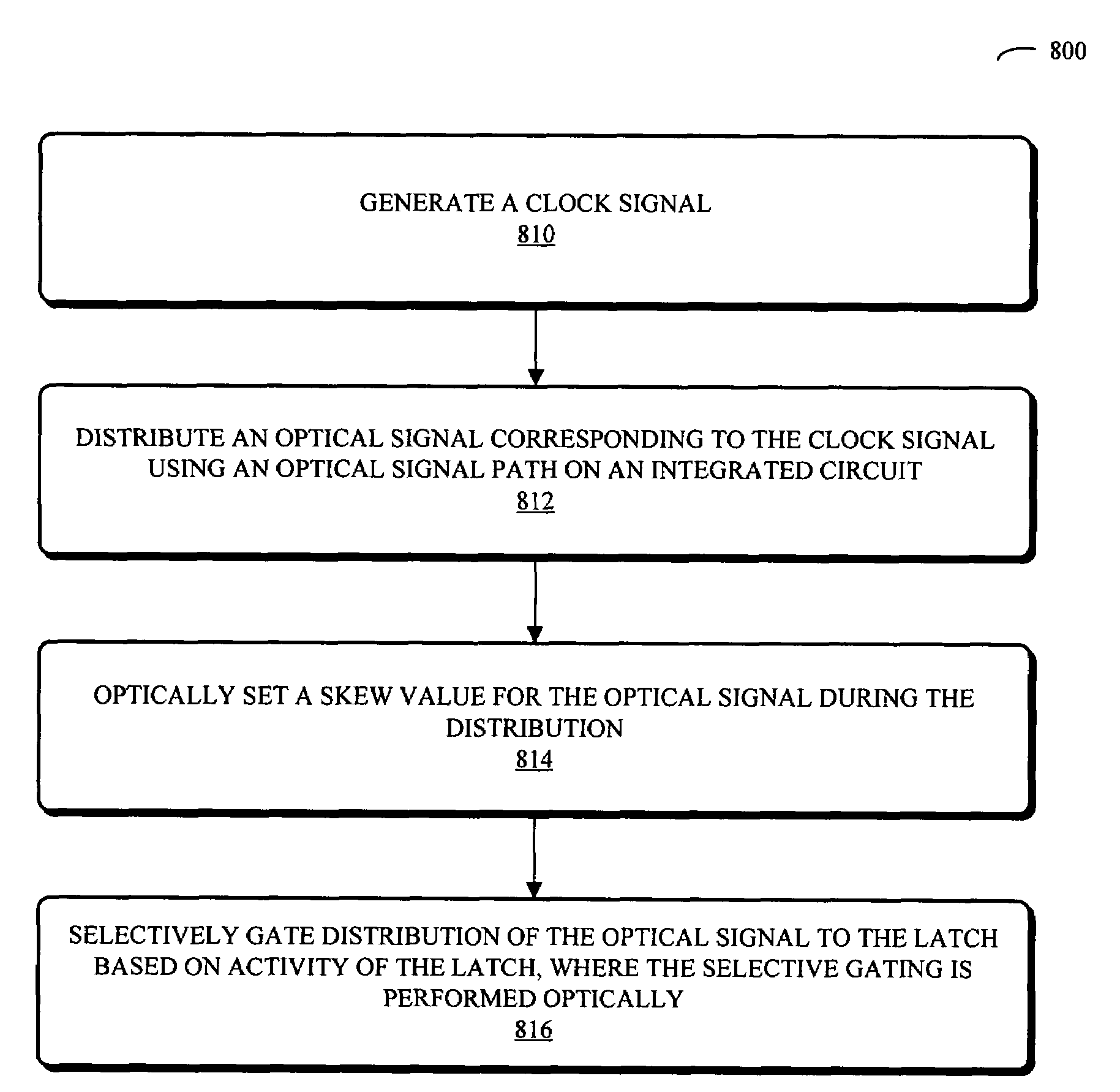
Embodiments of an integrated circuit are described. This integrated circuit includes: a clock-generator circuit configured to provide a clock signal; an optical clock path coupled to the clock-generator circuit; and a latch coupled to the optical clock path. This optical clock path is configured to distribute an optical signal corresponding to the clock signal. Furthermore, the optical clock path is configured to optically set a skew value for the optical signal, and is configured to selectively gate distribution of the optical signal to the latch based on activity of the latch. Note that the selective gating is performed optically.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
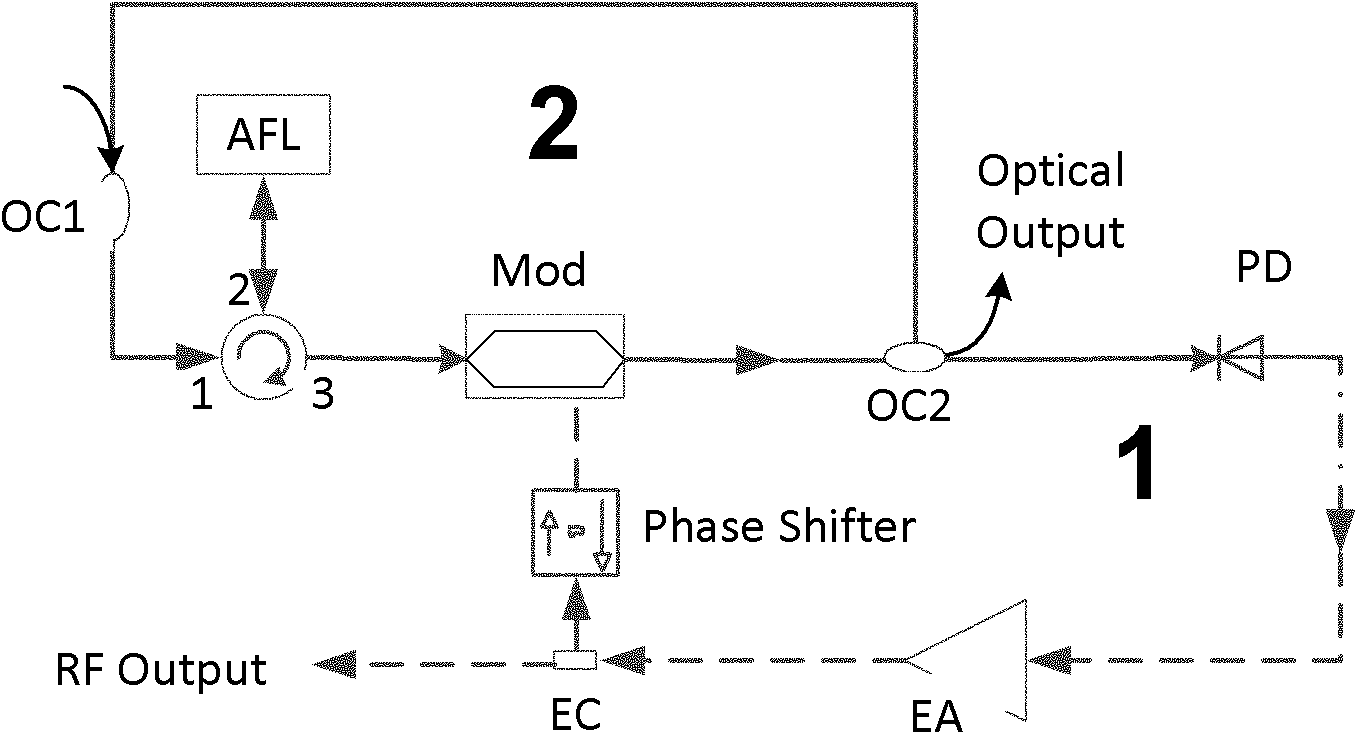
Photonic-filtering-based optoelectronic oscillator
The invention provides a photonic-filtering-based optoelectronic oscillator, which adopts an amplified feedback laser (AFL) as an optical domain filter instead of a conventional electric domain filter. A longitudinal intermode beat frequency microwave signal of the AFL serves as a drive source of a modulator for modulating laser injected into the AFL to form a self-feedback oscillatory system to further realize high-quality microwave and optical clock output functions.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method and device for synchronizing entanglement sources for a quantum communication network
ActiveUS9800399B2Low costCompensation for dispersionKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansFrequency conversionOptical clock
A device and a method for synchronizing entanglement sources with optical pump in a quantum communication network are disclosed. The device includes a pulsed optical source allowing emission of telecom wavelength optical clock pulses distributed in parallel to the entanglement sources to ensure synchronization of the entanglement sources; and for each of the entanglement sources, a frequency conversion device, allowing frequency conversion of the distributed telecom wavelength optical clock pulses to a wavelength adapted to optically pump the entanglement source. The method includes emitting and distributing in parallel, to the entanglement sources, telecom wavelength optical clock pulses; and locally, at each of the entanglement sources, frequency converting the telecom wavelength optical clock pulses to a wavelength adapted to optically pump the entanglement source.
Owner:UNIV DE NICE SOPHIA ANTIPOLIS +1
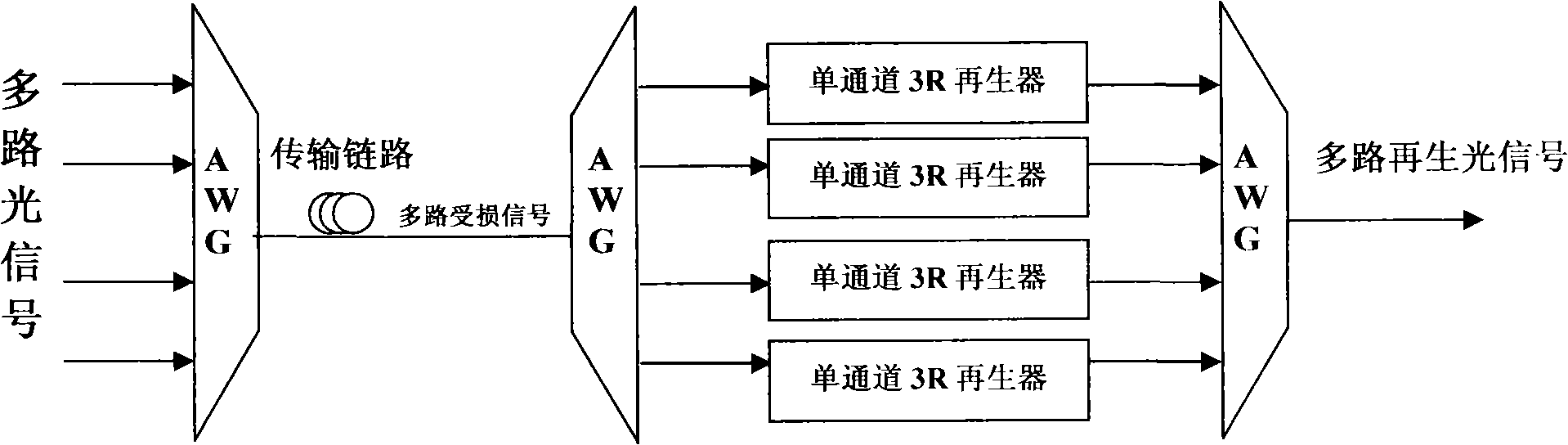
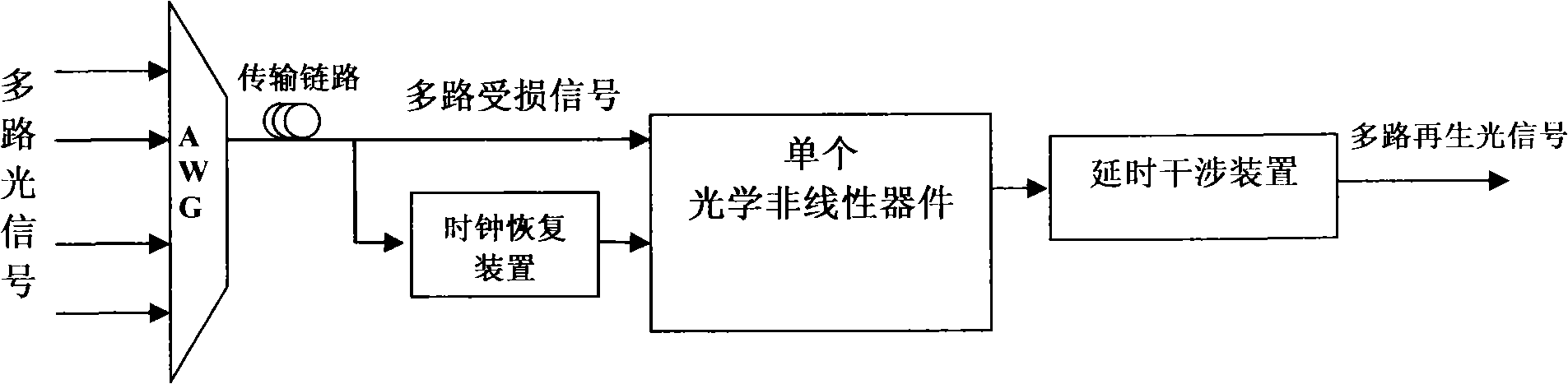
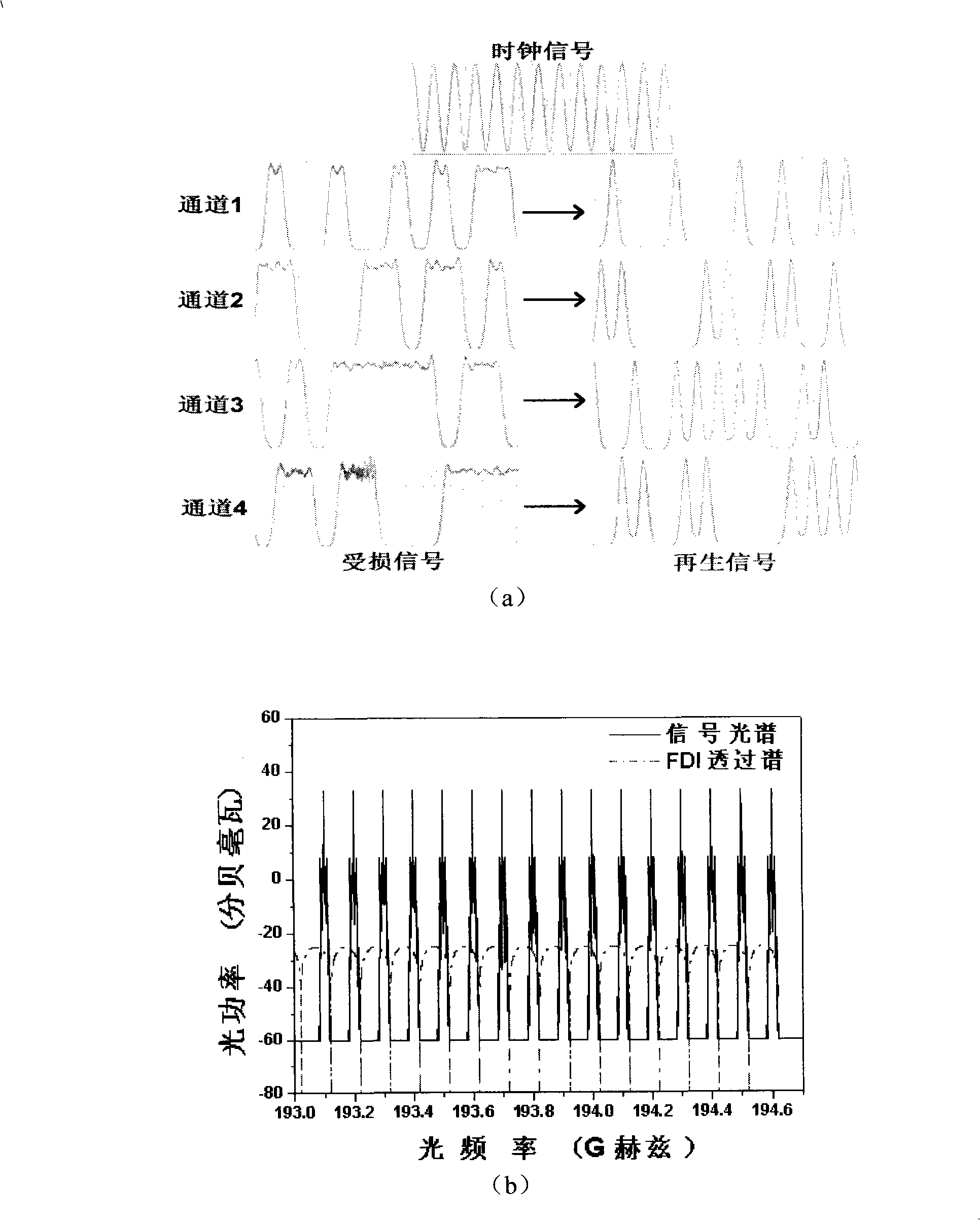
Multichannel complete light 3R regenerator
InactiveCN101304284AAvoid destructionIntegrity guaranteedElectromagnetic transmissionNetwork communicationChirp
The invention relates to an all-optical 3R regenerator with high speed and large capacity, which belongs to the technical field of an all-optical network communication. The regenerator comprises an optical clock recovery device, an optical nonlinear device and an optical delay interference device; wherein, the optical clock recovery device is used for randomly choosing a line of destroyed signals to extract synchronous optical clock signals from a plurality of lines of destroyed optical signals in a transmission link; the synchronous optical clock signals and a plurality of lines of the destroyed optical signals enter into the nonlinear optical device; the nonlinear optical device is used for realizing a cross phase modulated XPM effect among the optical clock signals and a plurality of lines of the destroyed optical signals; a plurality of optical signals produced by realizing the cross phase modulated XPM effect of the nonlinear optical device enter into the optical delay interference device; the optical delay interference device is a comb-shaped filter which is used for filtering the certain chirp part in each optical signal spectral after the XPM effect happens; meanwhile, noises and deteriorated signal parts are filtered out; a plurality of regenerated optical signals are generated. The multi-channel all-optical 3R regenerator provided by the invention can regenerate each channel in one regenerator at the same time, avoid the destroy to the original signal transmission line owing to the present multi-channel regenerated device adopts the way of separating, regenerating and then combining, keep the integrity of the original transmission line. Meanwhile, the all-optical 3R regenerator with high speed and large capacity overcomes the defects that exist in the present multi-channel 3R regeneration proposal of the complicated system, high realization cost, bad stability and uneasy integration, etc.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Dual-wavelength good-and-bad-cavity active optical clock based on secondary cavity locking technology, and implementation method thereof
ActiveCN109270825AReduce frequencyEliminate the effects ofLaser detailsApparatus using atomic clocksResonant cavityOptical clock
The invention discloses a dual-wavelength good-and-bad-cavity active optical clock based on the secondary cavity locking technology, and an implementation method thereof. The dual-wavelength good-and-bad-cavity active optical clock and the implementation method thereof have the advantages that a solution based on the secondary cavity locking technology is provided, the cavity traction suppressioneffect of bad cavity lasers in a dual-wavelength good-and-bad-cavity laser system is utilized twice, the influences of the residual cavity traction effect on the long-term stability of an active optical frequency standard are eliminated, the cavity traction suppression effect is amplified to squared times of the bad cavity coefficient of a main resonant cavity, the length of the main resonant cavity is locked twice by a servo feedback system, and the immunity of the active optical frequency standard in the dual-wavelength good-and-bad-cavity system to cavity mold jittering is achieved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Quantum key distribution system and method
ActiveUS7881473B2Reduce bit error rateSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesUser identity/authority verificationSignal onClock rate
Owner:THE BOEING CO
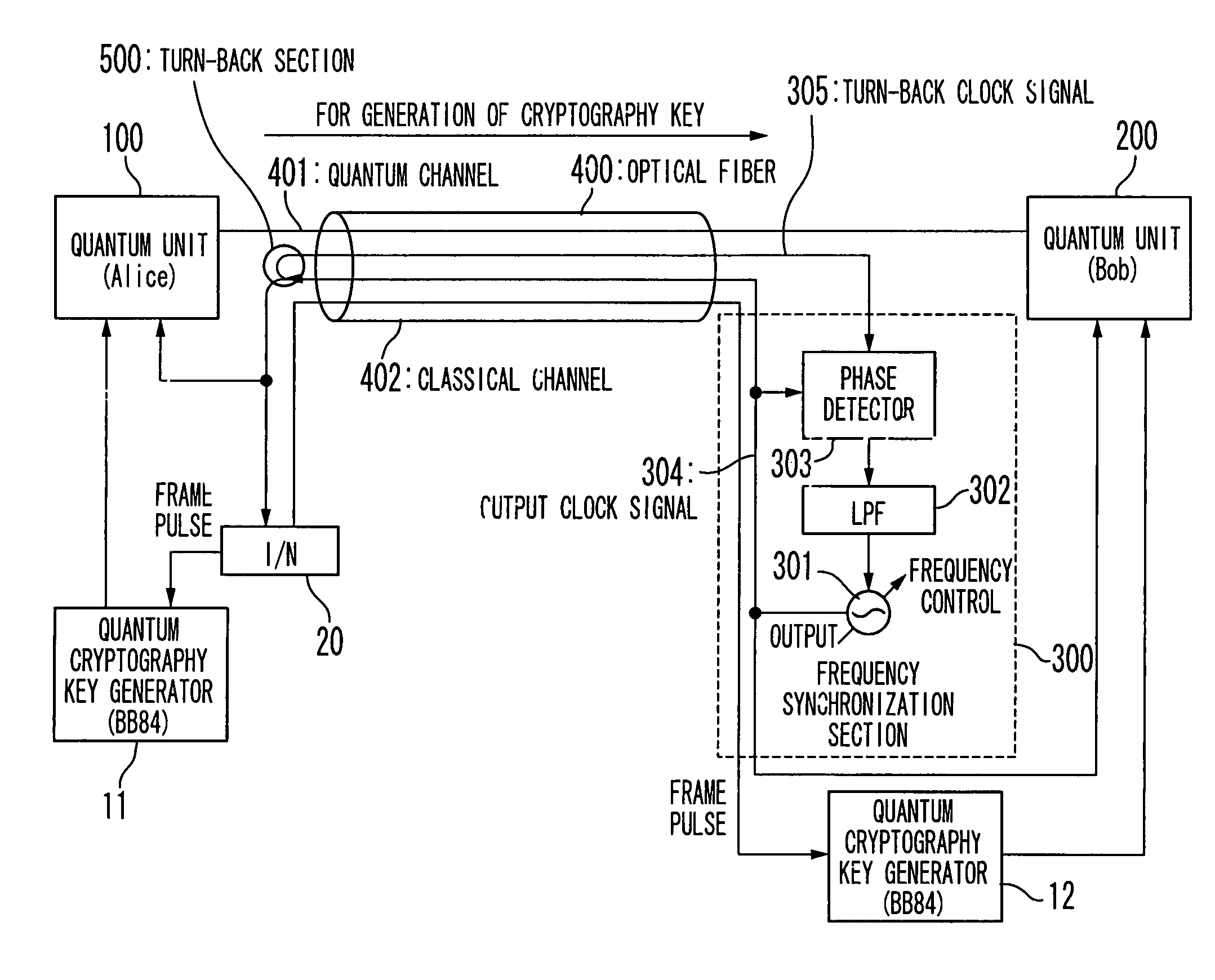
Quantum cryptography key distributing system and synchronizing method used in the same
ActiveUS7869599B2Key distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesOptical clockPhase modulation
A quantum cryptography key distributing system includes an optical fiber; a transmission unit and a reception unit. The transmission unit is connected with the optical fiber, generates a transmission optical pulse signal from an optical pulse signal based on a first data in synchronism with an optical clock signal and transmits the transmission optical pulse signal to the reception unit via the optical fiber. Polarization of the transmission optical pulse signal is different from that of the optical pulse signal. The reception unit is connected with the optical fiber, transmits the optical pulse signal to the transmission unit via the optical fiber, phase-modulates a part of the transmission optical pulse signal based on a second data in synchronism with the optical clock signal, and detects a reception data corresponding to the first data based on the transmission optical pulse signal in synchronism with the optical clock signal.
Owner:NEC CORP
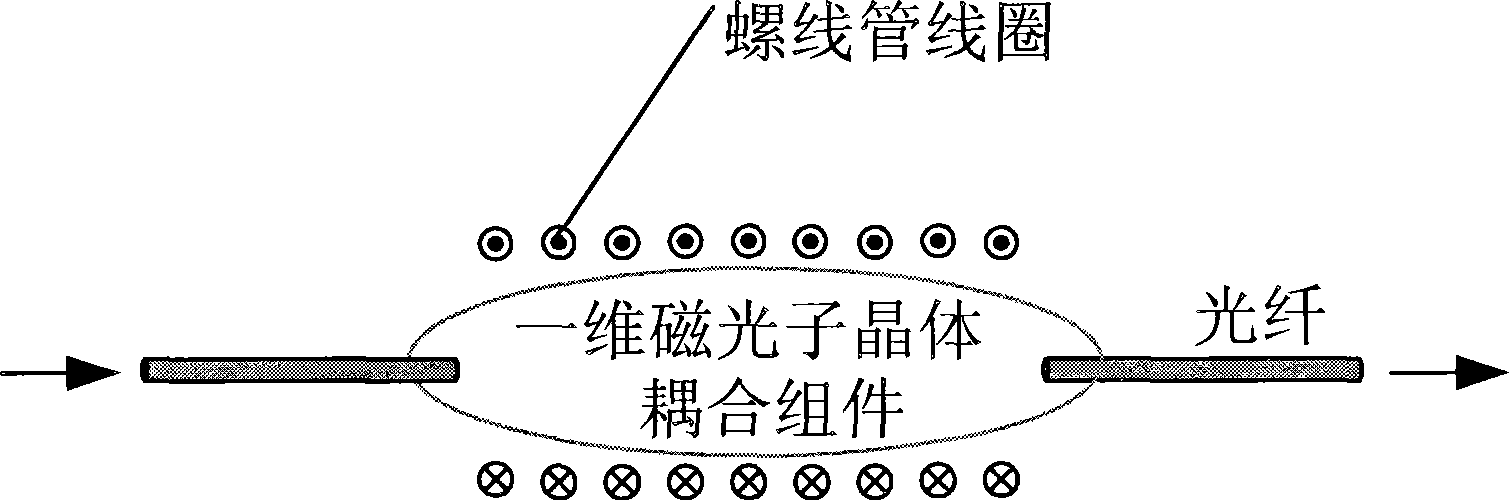
Device and method for extracting light clock
InactiveCN101436907APower balanceAdjust duty cycleCoupling light guidesFibre transmissionTransfer procedureOptical clock
The invention discloses an optical clock extractor, which belongs to the technical field of optical communication and solves the problems that in the prior art, the optical clock extractor is complex and the extractable clock range thereof is limited. The optical clock extractor comprises a one-dimensional magnetic photonic crystal optical fiber coupler module and an adjustable off-set magnetic field unit for providing an applied magnetic field for the one-dimensional magnetic photonic crystal optical fiber coupler module, wherein the one-dimensional magnetic photonic crystal optical fiber coupler module comprises a collimating lens, a polarizer, a one-dimensional magnetic photonic crystal and a self-focusing lens. The invention also provides a method for performing optical clock extraction by using the extractor, which can achieve the adjustment of the spacing between transmission harmonic peaks to finally realize the optical clock extraction and process optical clock signals into the required forms. The optical clock extractor and the method not only achieve the optical clock extraction, but also can inhibit the jitter of the optical clock signals in the transmission process, and have the characteristics of simple realization, low cost, convenient operation, and automatic recognition of optical signal clocks.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
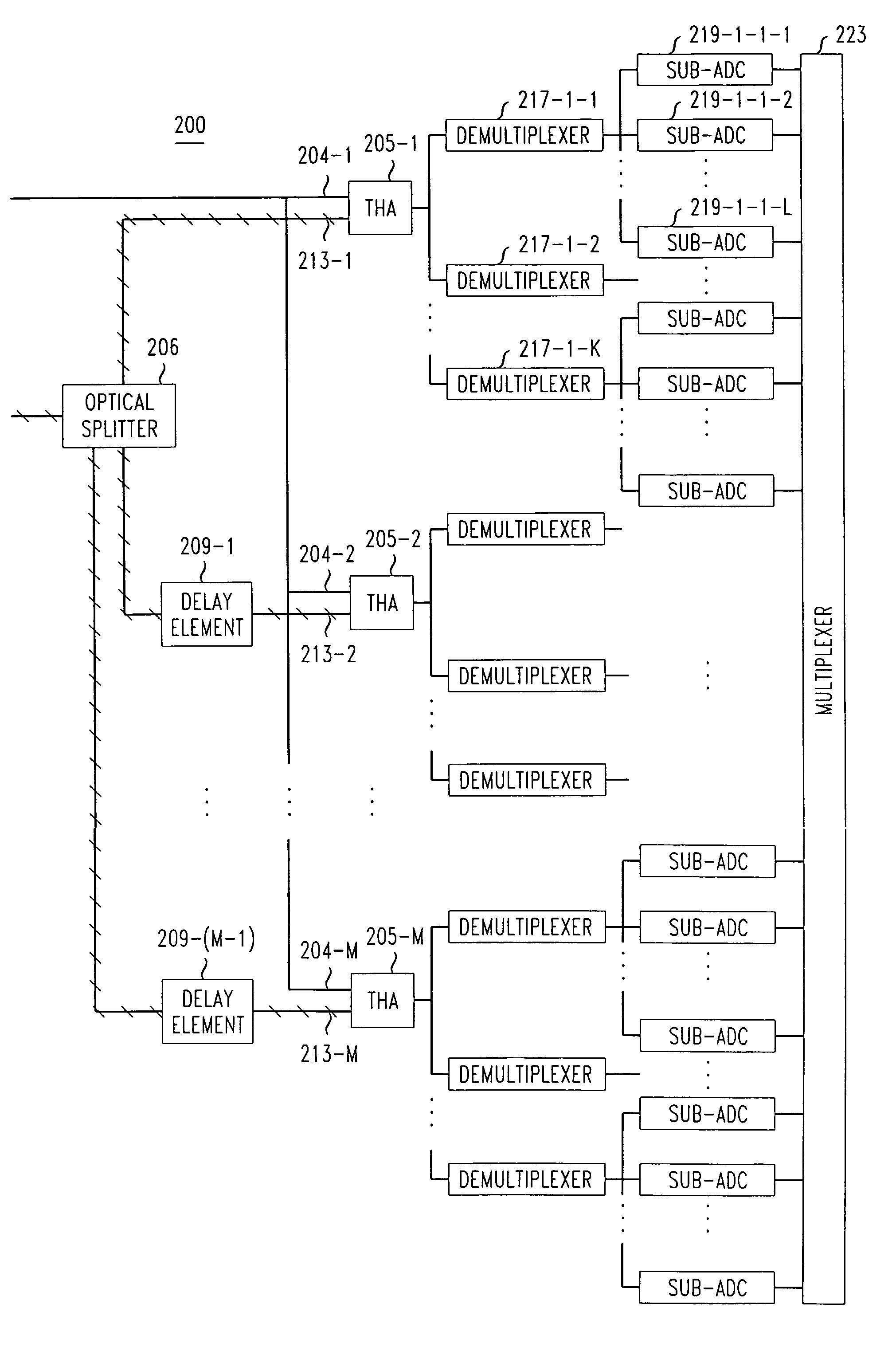
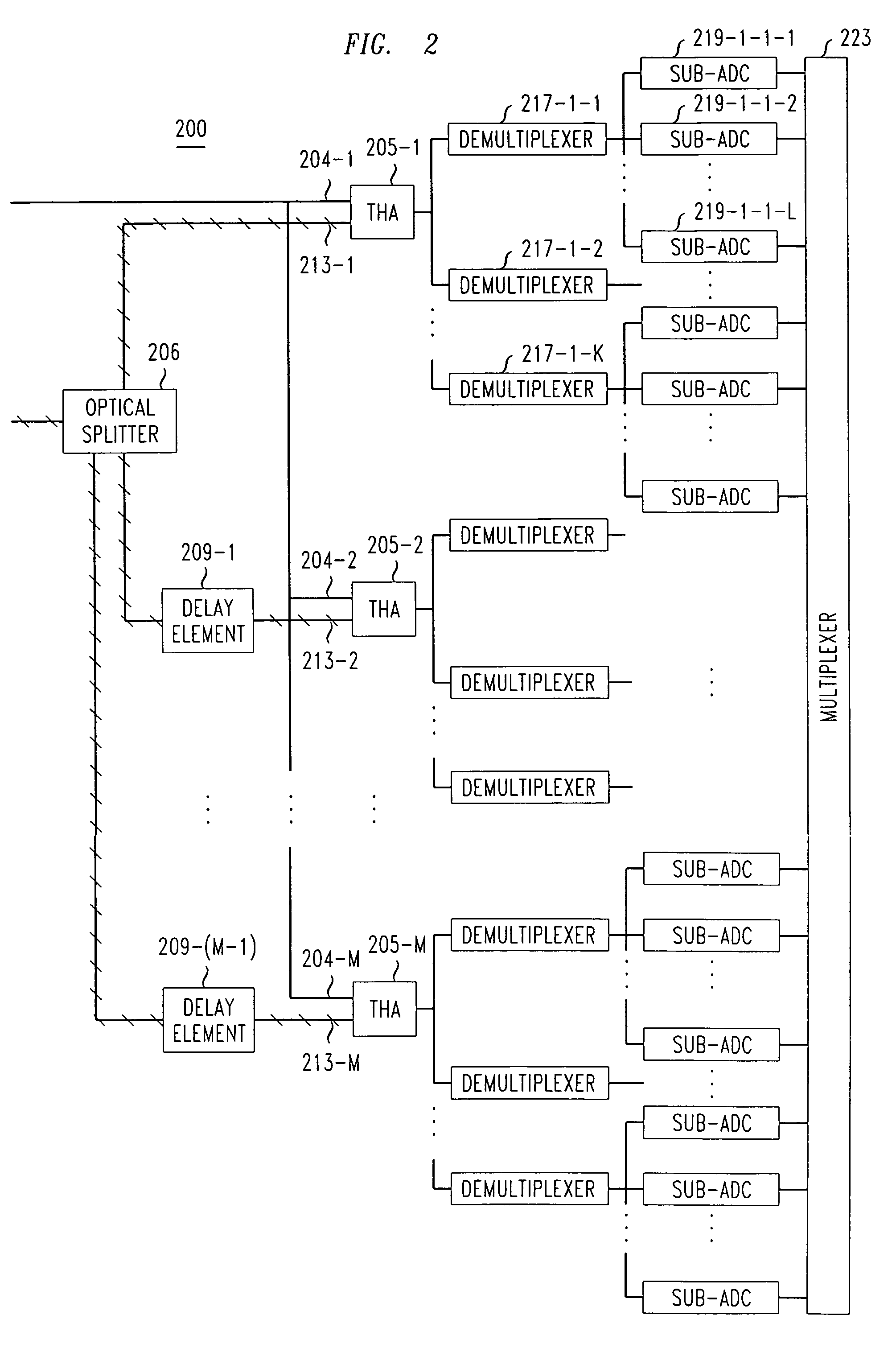
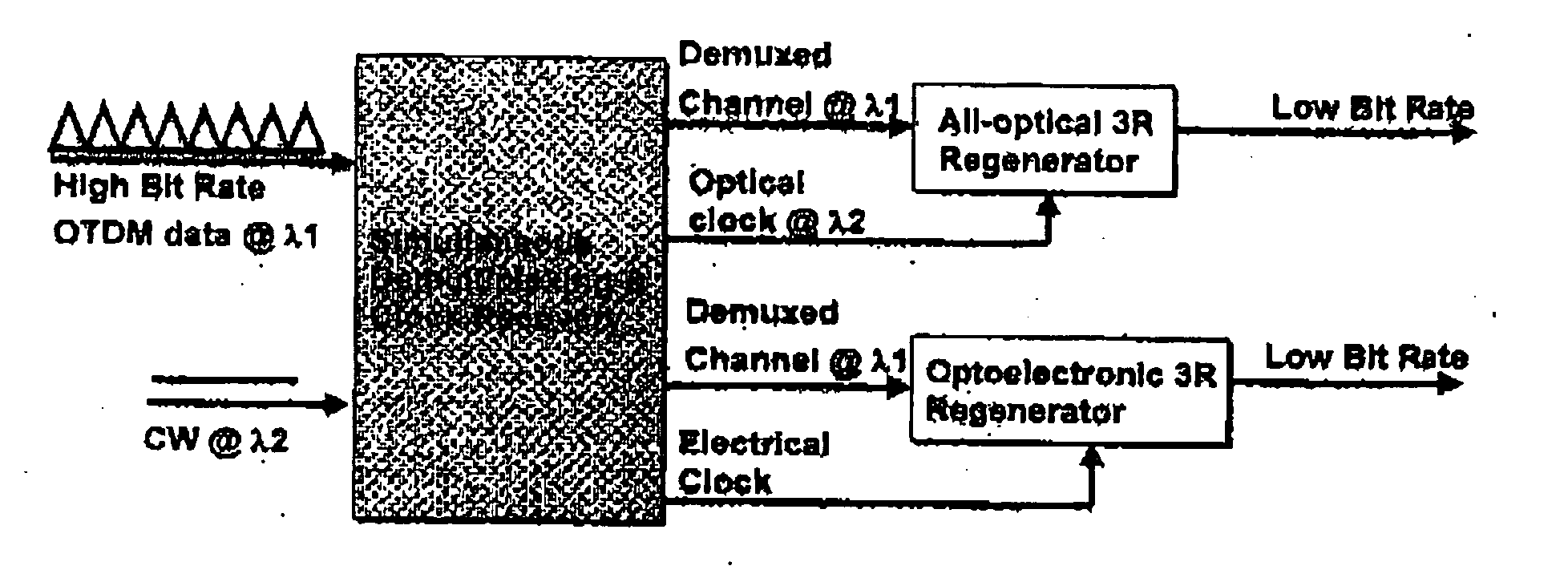
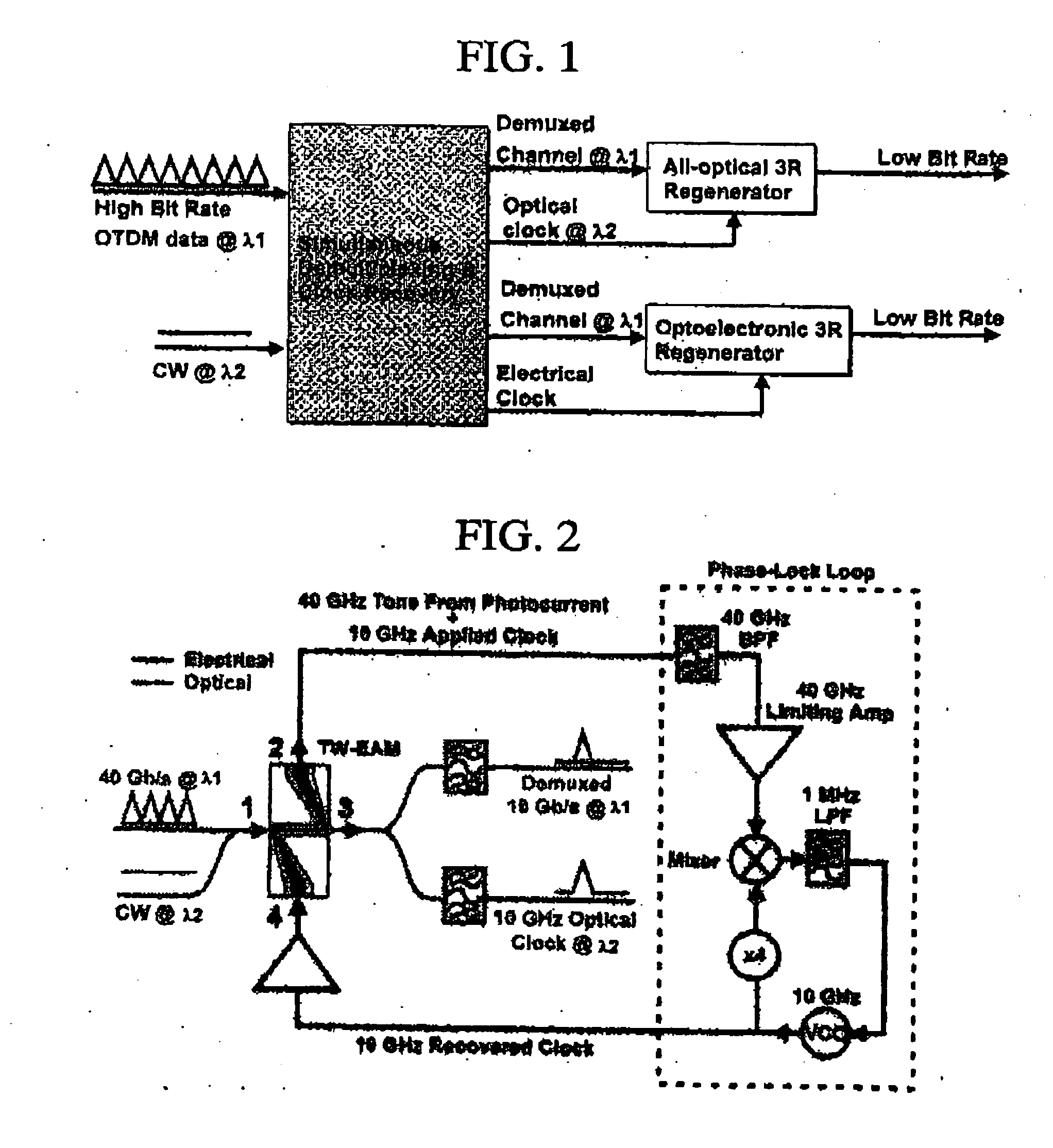
Apparatus for simultaneous OTDM demultiplexing, electrical clock recovery and optical clock generation, and optical clock recovery
InactiveUS20050018271A1Improve reliabilityLow costTime-division optical multiplex systemsElectromagnetic receiversElectricityElectro-absorption modulator
An apparatus for simultaneous OTDM demultiplexing, electrical clock recovery and optical clock generation, and optical clock recovery using a traveling-wave electroabsorption modulator. The apparatus includes a TW-EAM and a PLL coupled thereto. The TW-EAM includes a first, a second, a third, and a fourth. The first port is used for an optical input and the third port is used for optical output. The second port is coupled to an input, and the fourth port is coupled to an output, of the PLL. When the first port receives optical input, the second port produces a photocurrent to be applied to the PLL, and the fourth port receives a recovered clock produced by the PLL, and the third port produces demultiplexed data and an optical clock. Using the same configuration, the apparatus produces a recovered optical clock signal.
Owner:KDDI R&D LAB INC +1
Clock synchronization method and device
ActiveCN104092528AShorten convergence timeImprove stabilitySynchronising arrangementOptical clockNetwork topology
The invention provides a clock synchronization method. The method comprises the steps of sending Topology messages to other clock node devices through ports on two sides according to a preset low sending frequency; receiving Topology messages sent by the other clock node devices through the ports on two sides; constructing a network topology table according to the received Topology messages, wherein the network topology table contains the priority vector of each port through which the Topology messages are sent; determining whether the device is an optimal clock node device according to the priority vector of each port; if yes, releasing synchronous clocks to the other clock node devices through a main port; if not, determining the main port and a slave port from the ports on two sides according to the network topology table, and receiving the synchronous clock released by the optical clock node device through the slave port to achieve the updating of a local clock; forwarding the synchronous clock to a next hop of node device through the main port. By the adoption of the clock synchronization method, convergence time of port role calculation can be reduced, and the stability of a system can be improved.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
Apparatus and method for wavelength conversion and clock signal extraction using semiconductor optical amplifiers
ActiveUS20070070493A1High extinction ratioLaser detailsCoupling light guidesReturn-to-zeroOptical clock
Provided is an apparatus and method for simultaneous optical wavelength conversion and optical clock signal extraction using semiconductor optical amplifiers (SOAs). The apparatus includes: a wavelength converter receiving a pump beam having input information and a probe beam having a different wavelength from the pump beam, and outputting the pump beam with an overshoot shifted to a red wavelength and an undershoot shifted to a blue wavelength due to non-linear characteristics and self-phase modulation of semiconductor optical amplifiers (SOAs) and the probe beam delivered the input information from the pump beam; an optical divider dividing output paths of the probe beam to which the input information has been delivered and the pump beam having the overshoot and the undershoot; a converted-wavelength extractor filtering the probe beam received from the optical divider; and a clock data regenerator obtaining a pseudo return-to-zero (PRZ) signal from the pump beam received from the optical divider and extracting a clock signal from the PRZ signal. The apparatus and method can simultaneously perform wavelength conversion and optical clock signal extraction on an NRZ signal using an optical method, without converting the NRZ signal into an electrical signal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Optical clock recovery device for recovering the clock from an optical signal
ActiveUS7209666B2Improved stability of amplitudeImprove frequency stabilityLaser detailsSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansTelecommunications networkClock recovery
An all-optical clock recovery system for recovering the clock from a received optical signal with a short response time and without patterning effects includes a first optical clock recovery device adapted to supply a first optical clock signal in response to the received optical signal and a second optical clock recovery device adapted to supply a second optical clock signal in response to the first optical clock signal. Applications include regenerating optical packets in asynchronous optical packet-switched telecommunication networks.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
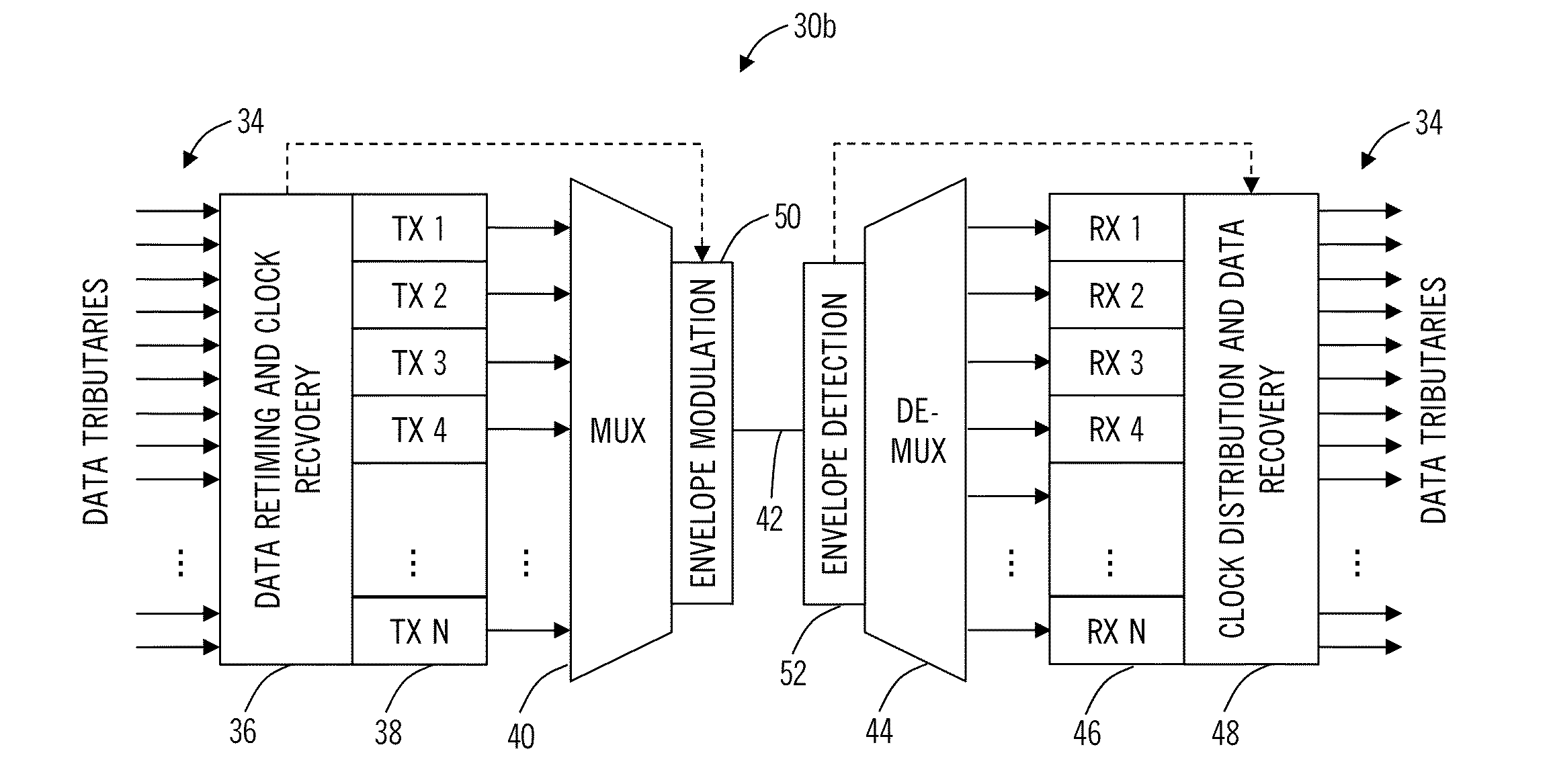
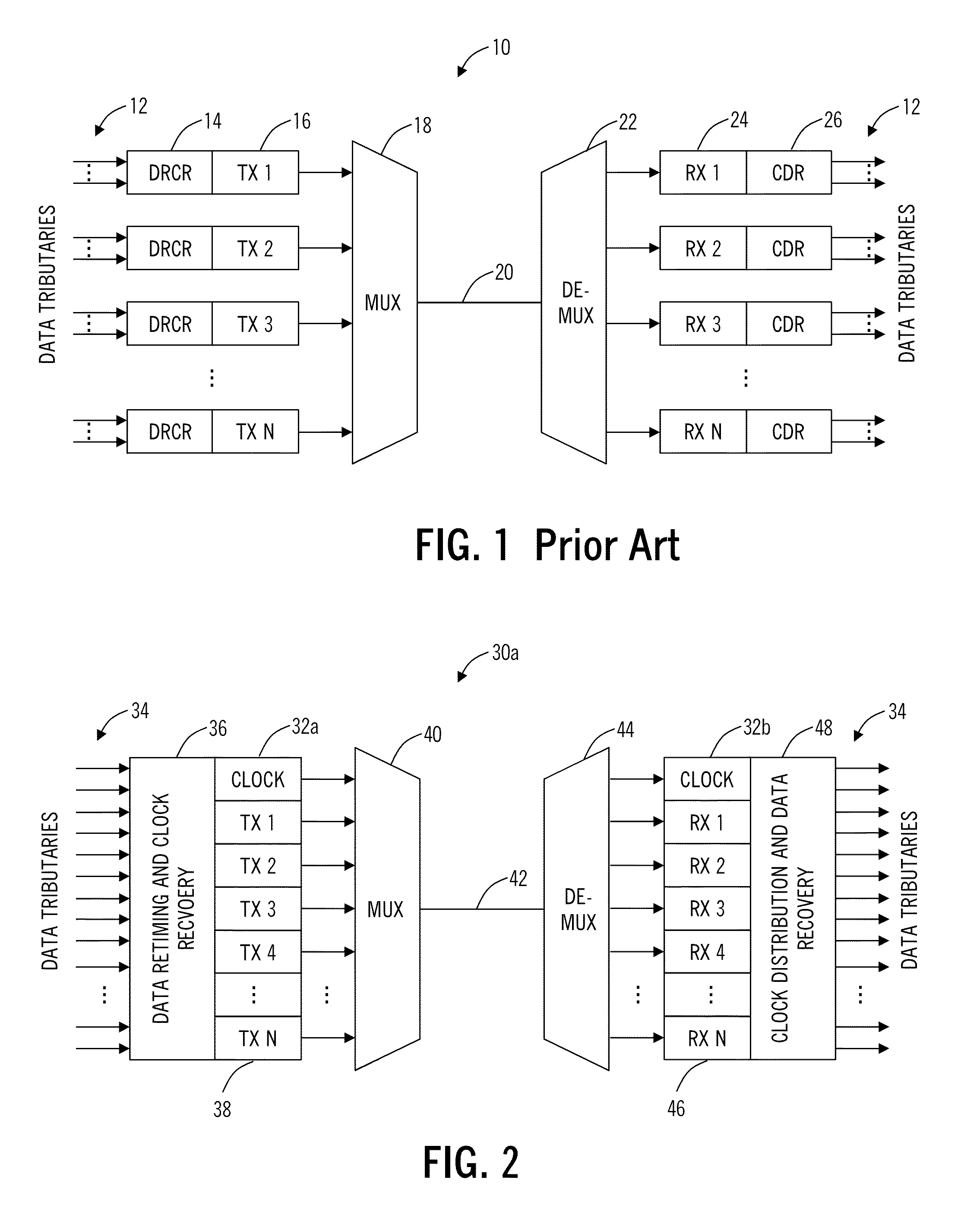
Optical transceiver and method with channel binding, clock forwarding, and integrate-and-dump receivers
ActiveUS20150172040A1Simplifying clocking architectureImprove receiver sensitivityChannel dividing arrangementsSynchronisation information channelsSystems designTransceiver
An optical transceiver includes N transmitters each transmitting one of N transmitted optically bound channels; a clock forwarding mechanism to transmit a transmitted optical clock signal to an opposing optical receiver; N receivers each receiving one of N received optically bound channels; and a clock recovery mechanism to receive a received optical clock signal from the opposing optical transmitter. A method and photonically integrated system are also disclosed. The optical transceiver, method, and system optimize system design of WDM highly parallelized transceivers with optical bound channels, a simplified clocking architecture, and boosted receiver sensitivity. The optical transceiver, method, and system include clock recovery followed by data recovery and can utilize integrate-and-dump optical receivers with a recovered clock.
Owner:CIENA
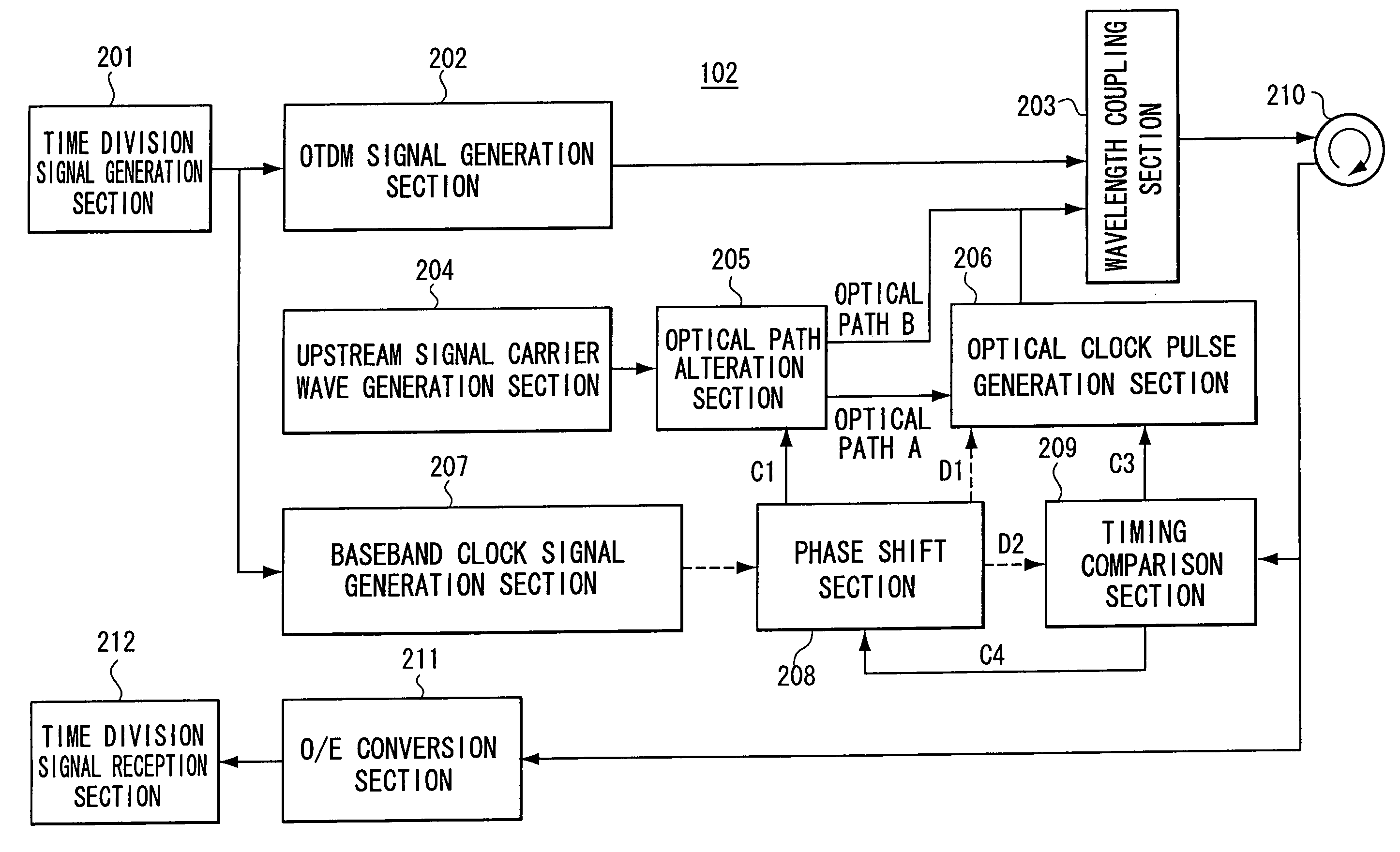
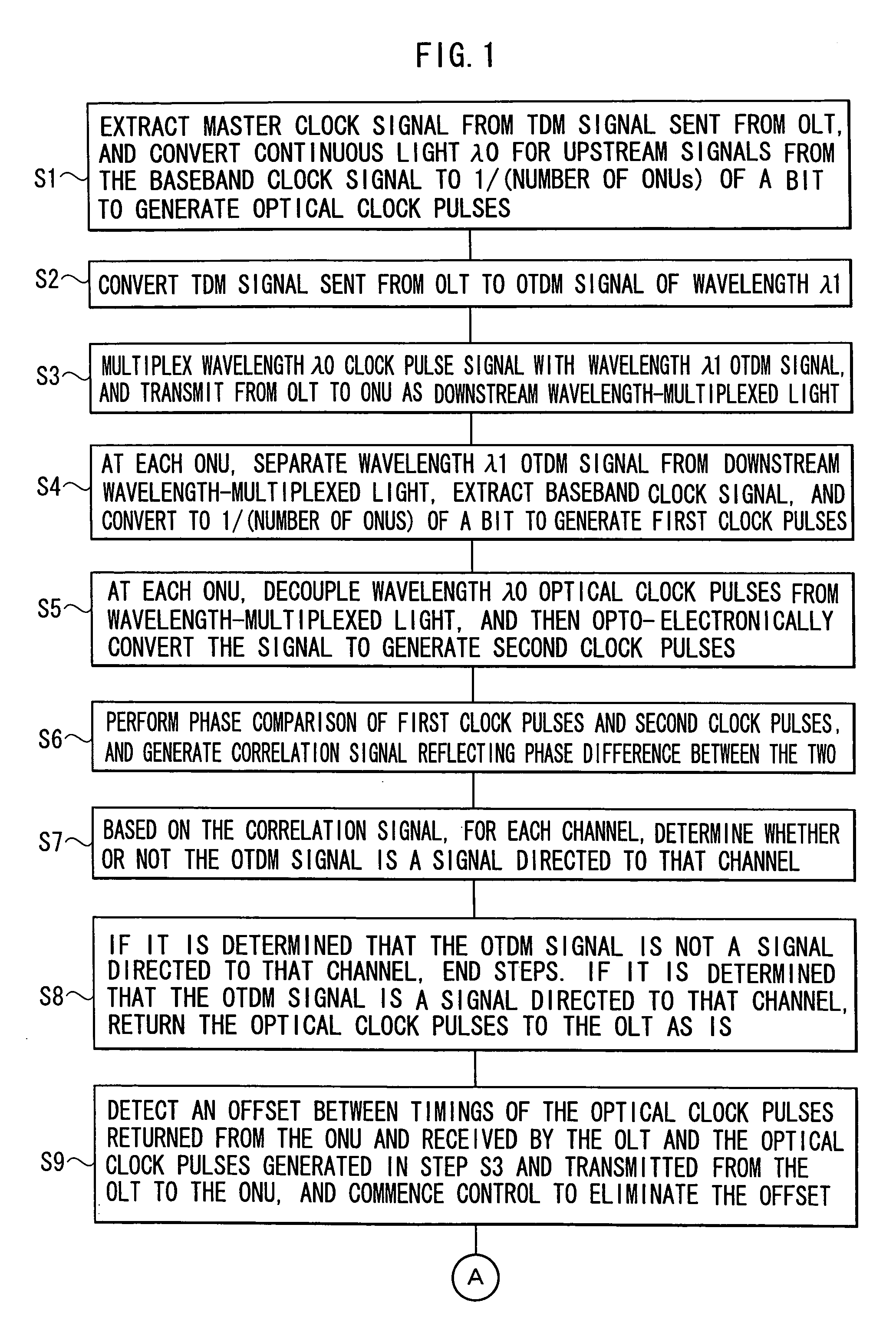
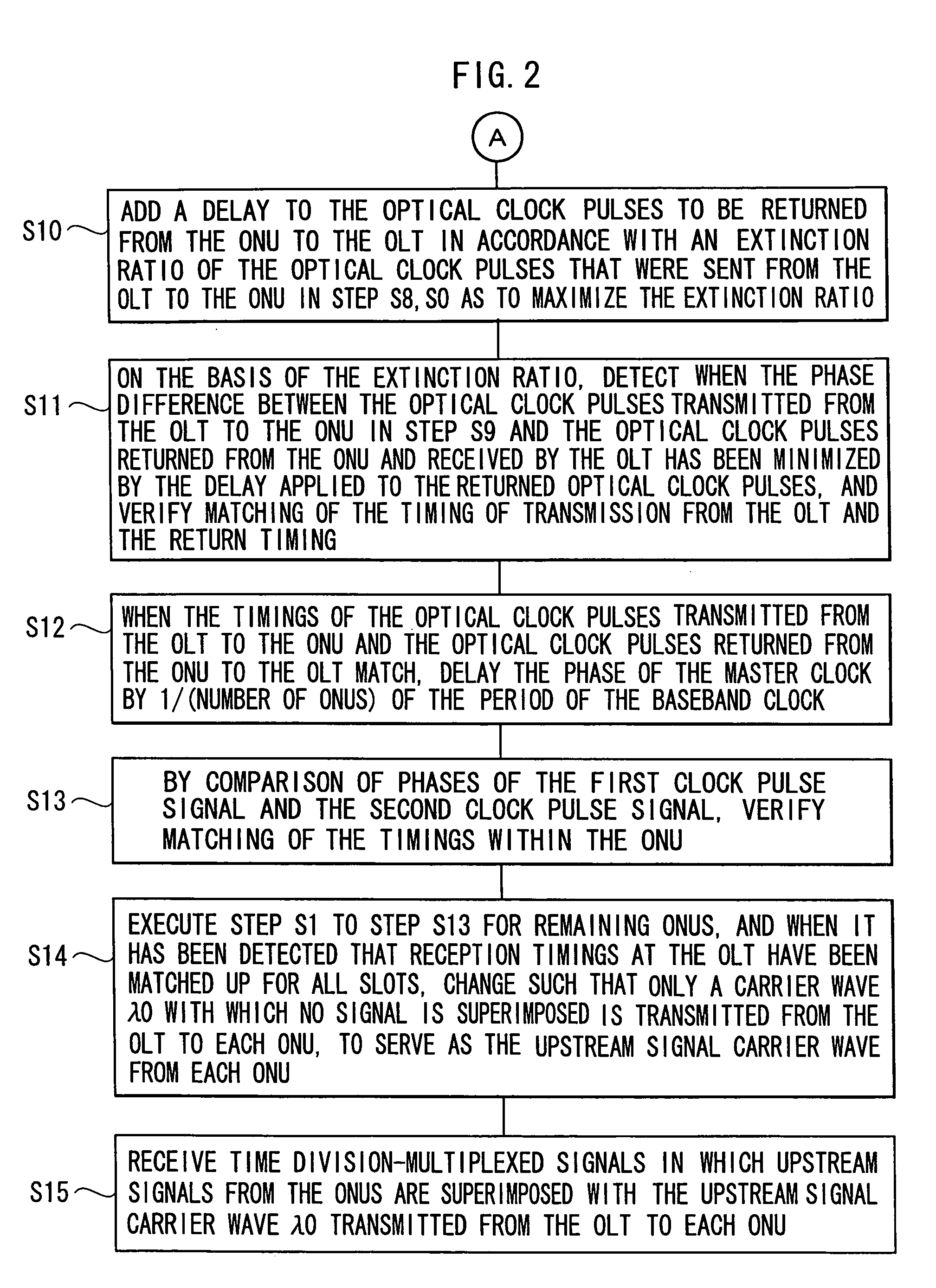
Terminal device, center device, optical communication network system and upstream signal timing control method
InactiveUS20080240720A1Time-division optical multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsTerminal equipmentOptical clock
An upstream signal timing control method which controls a timing of an upstream optical signal, from a terminal device to a center device, to a timing that the center device intends. Optical clock pulses synchronized with the timing that the center device intends are sent from the center device to the terminal device. The terminal device delay-controls the optical clock pulses and retransmits them to the center device. The center device detects an offset between the timing and a timing of the returned optical clock pulses, and applies timing offset information to the transmitted optical clock pulses. The terminal device performs the delay control in accordance with the timing offset information applied to the received optical clock pulses. When the offset between the timing and the returned optical clock pulse timing is at or below a threshold, the center device verifies completion of timing control of the upstream optical signal.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com