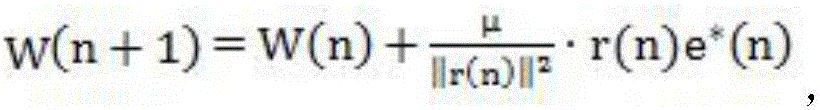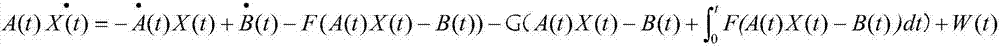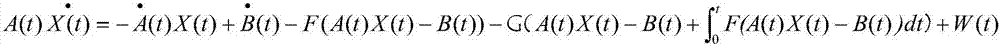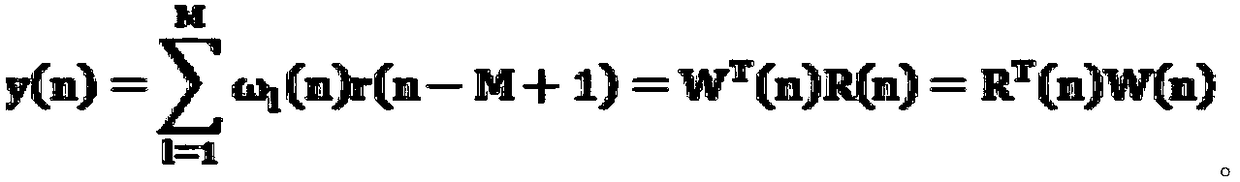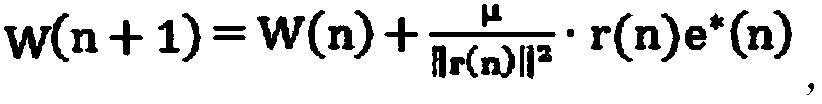Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Constant noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
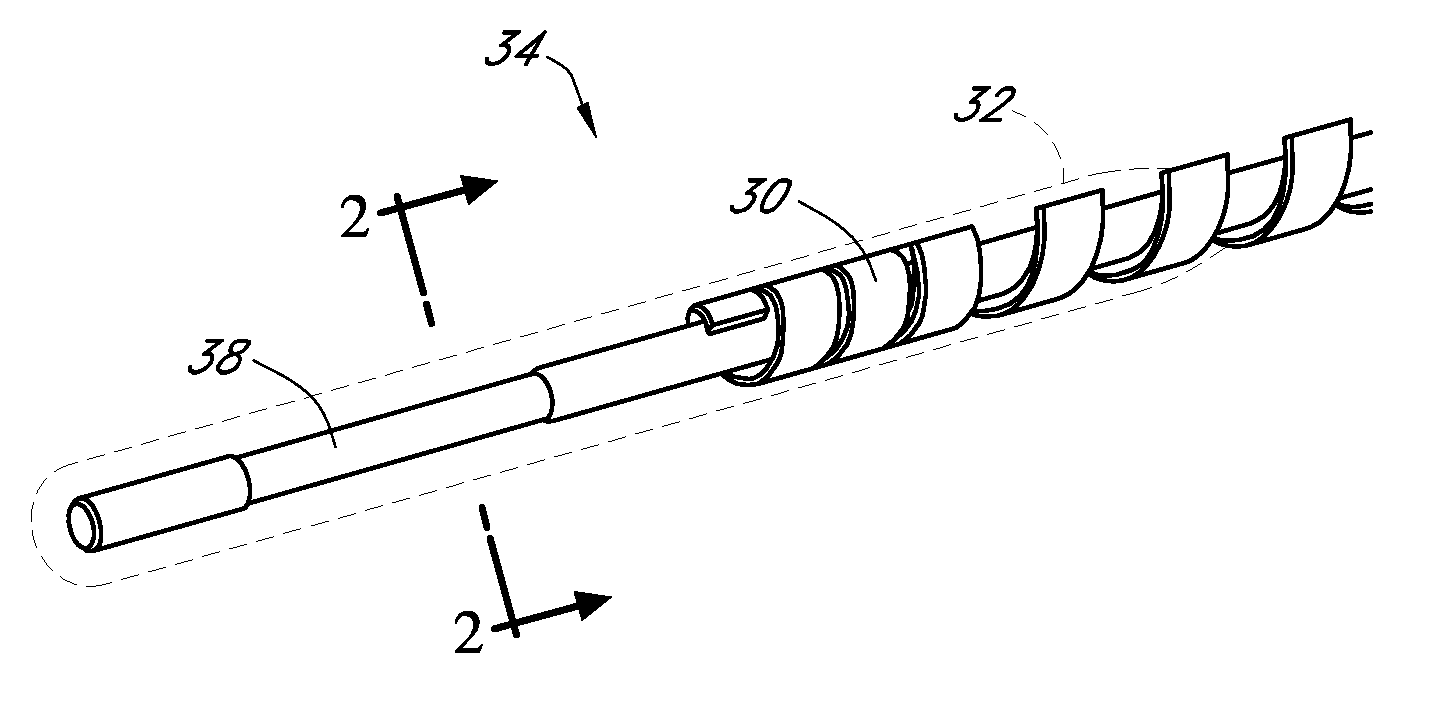
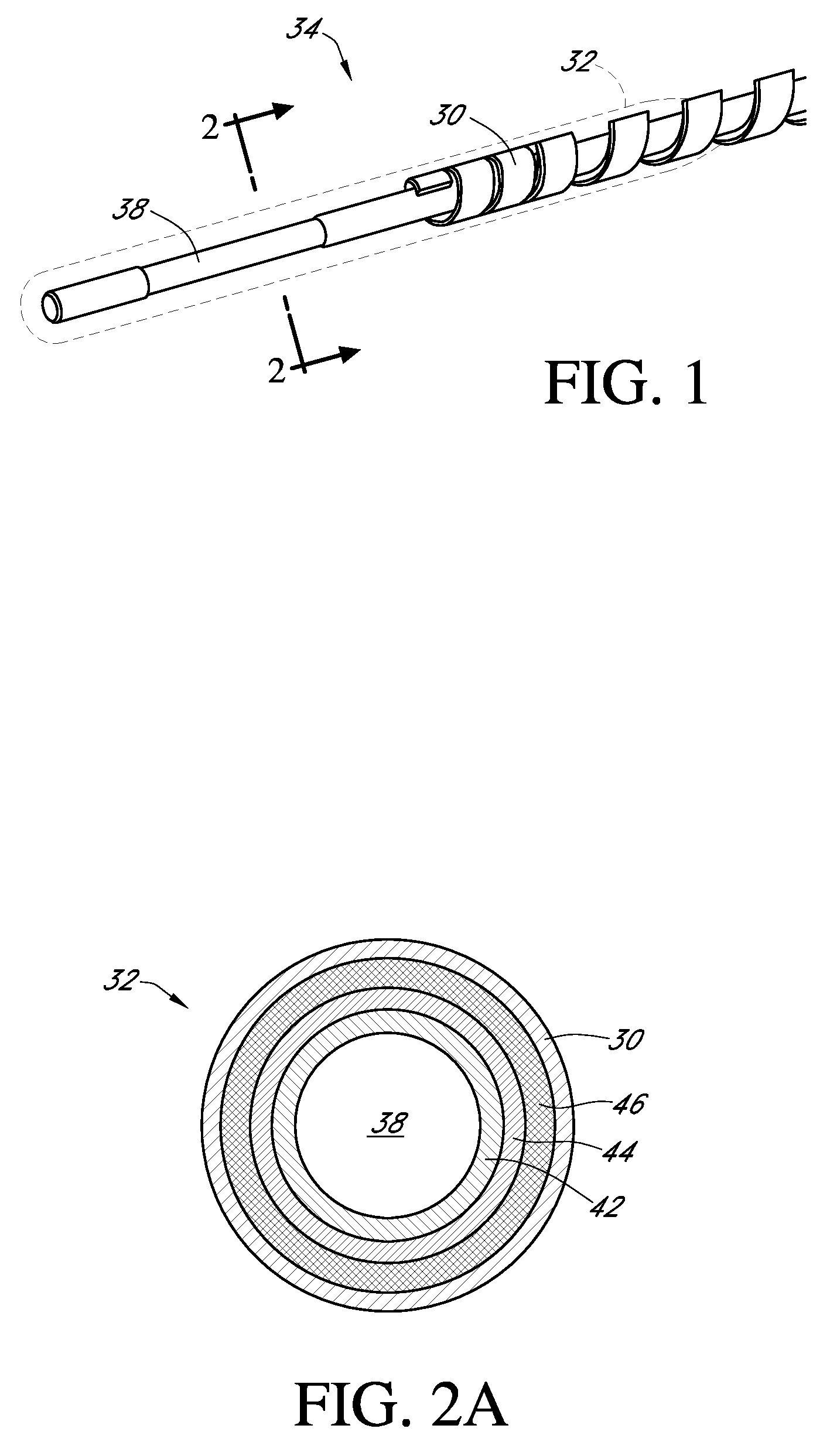
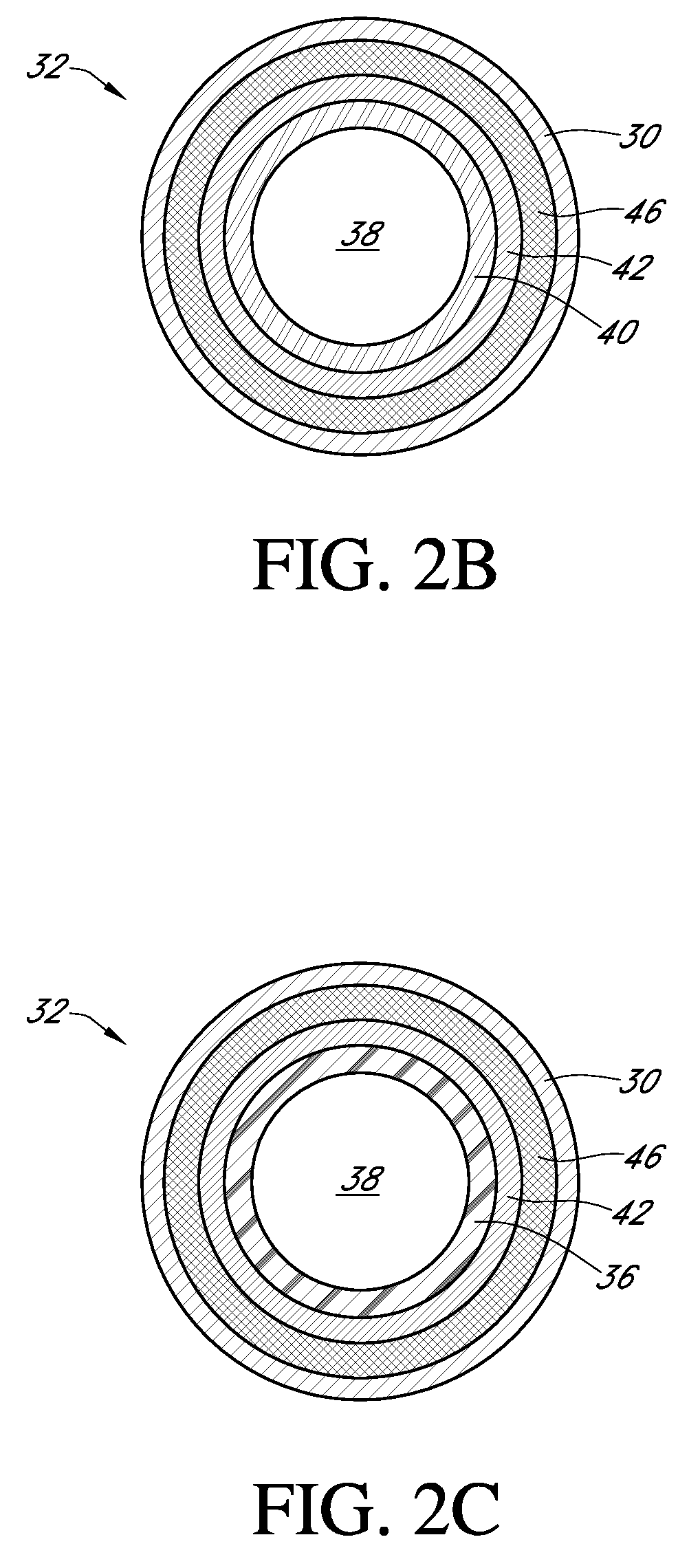
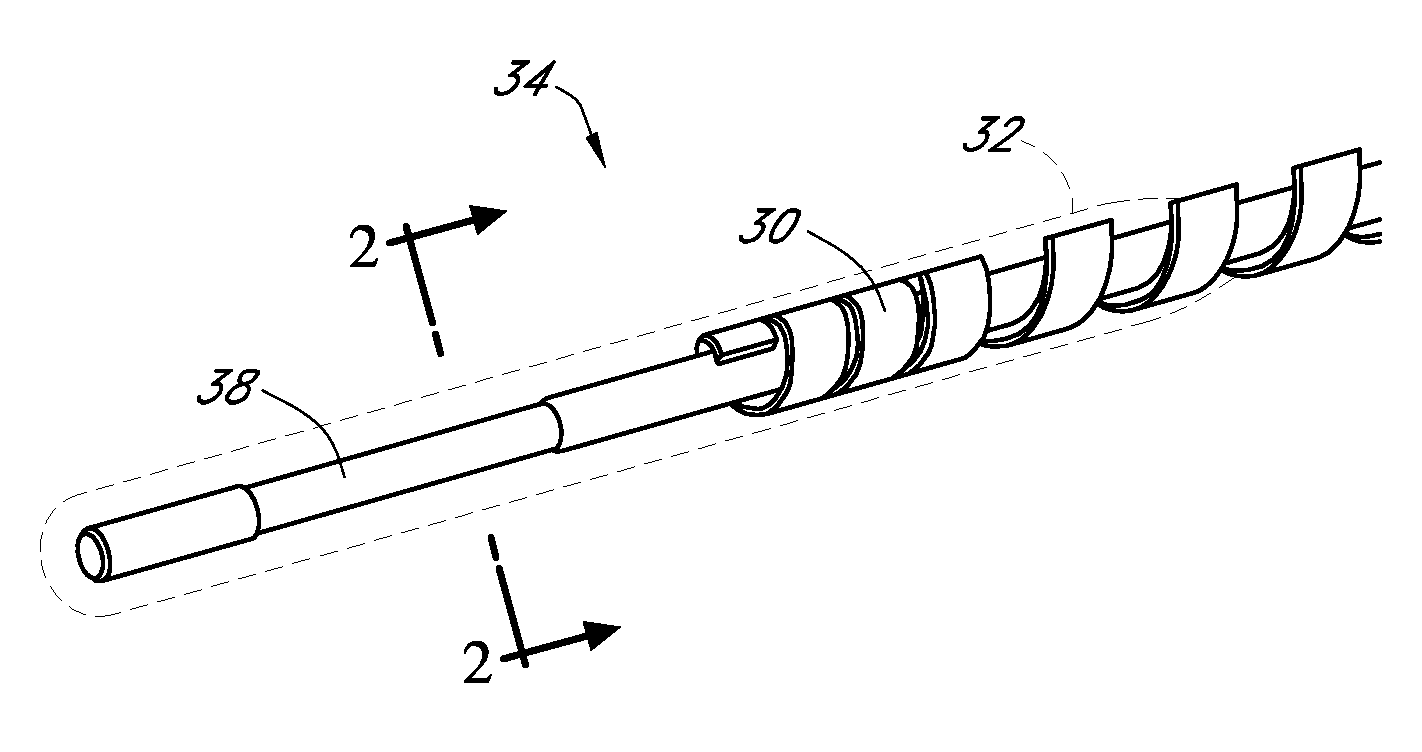
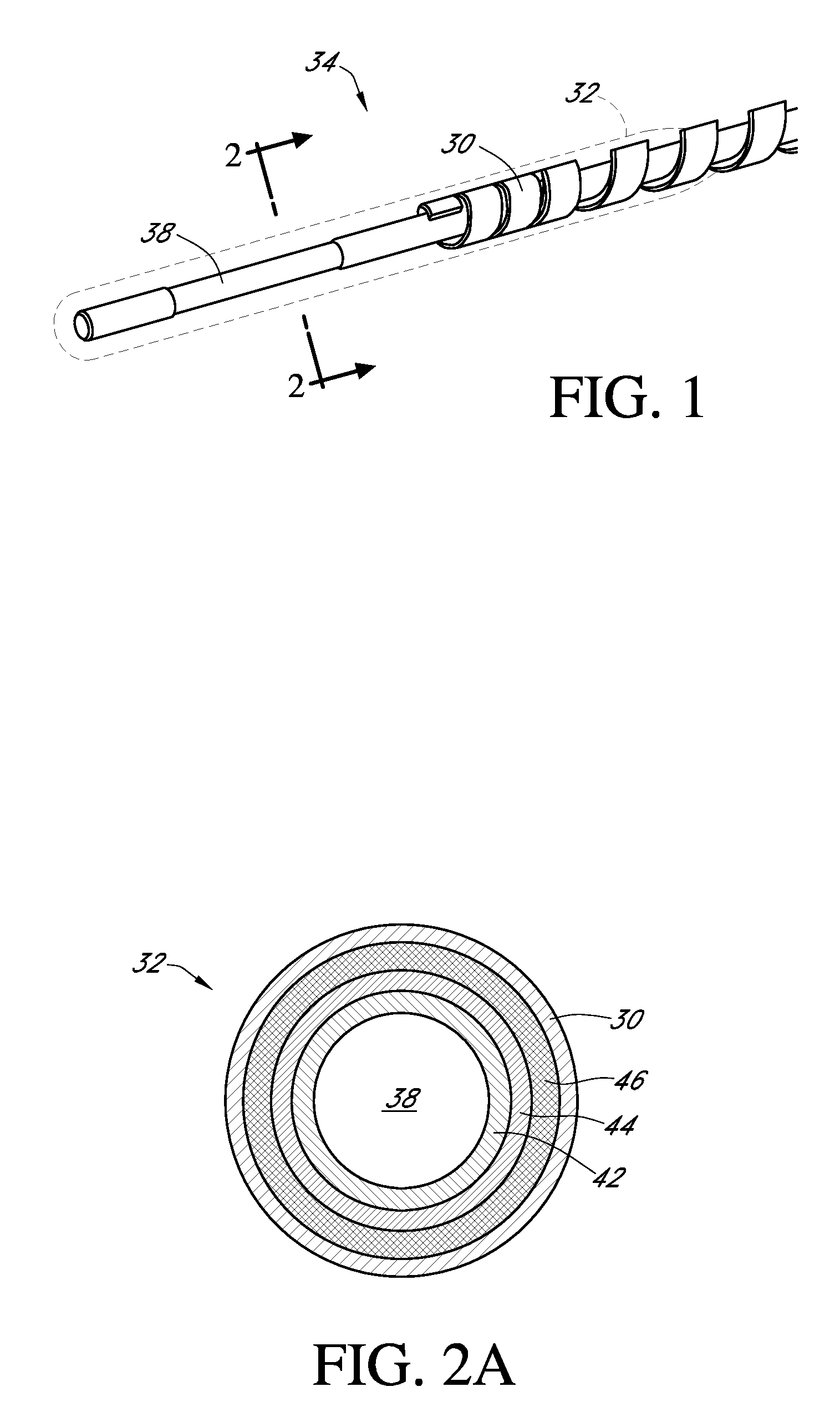
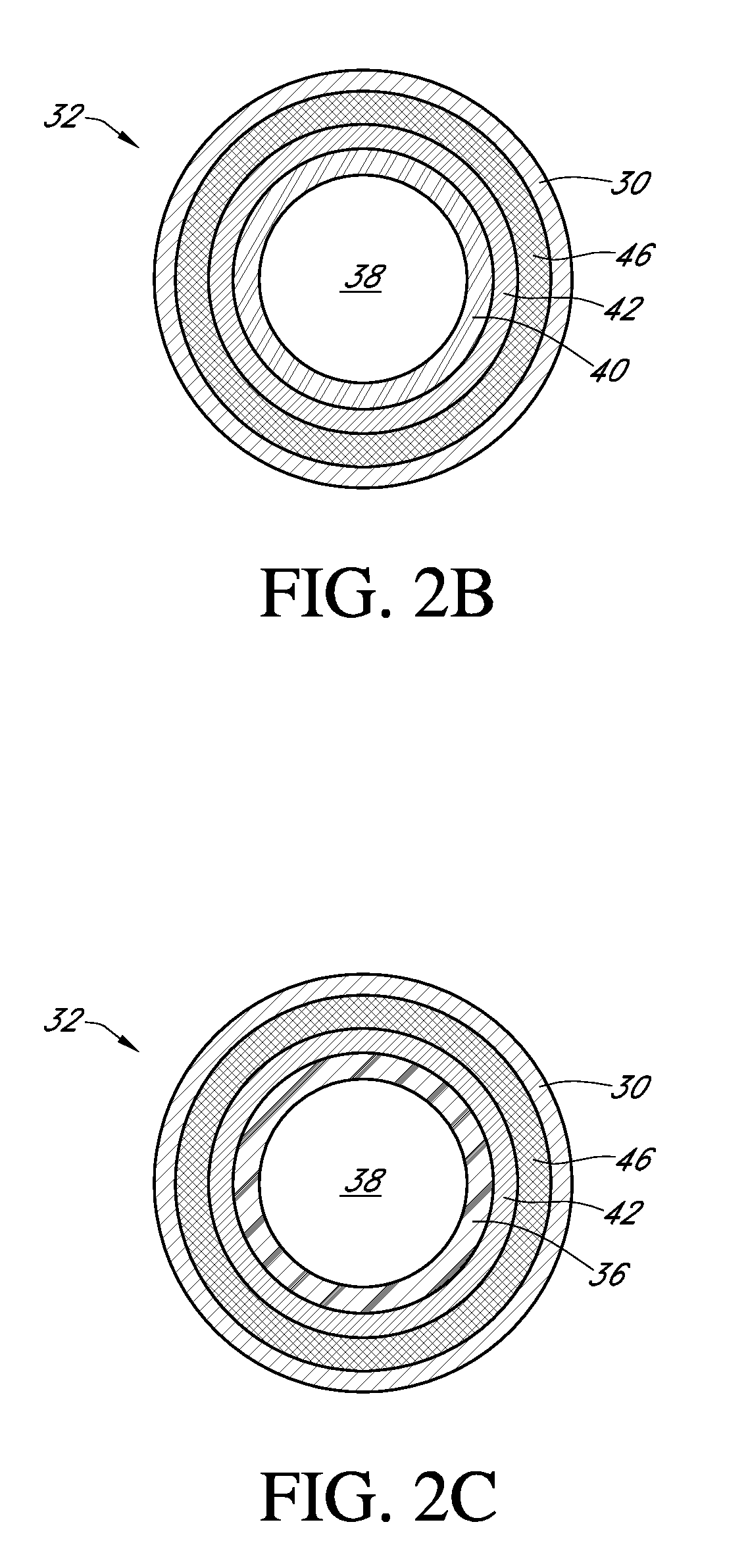
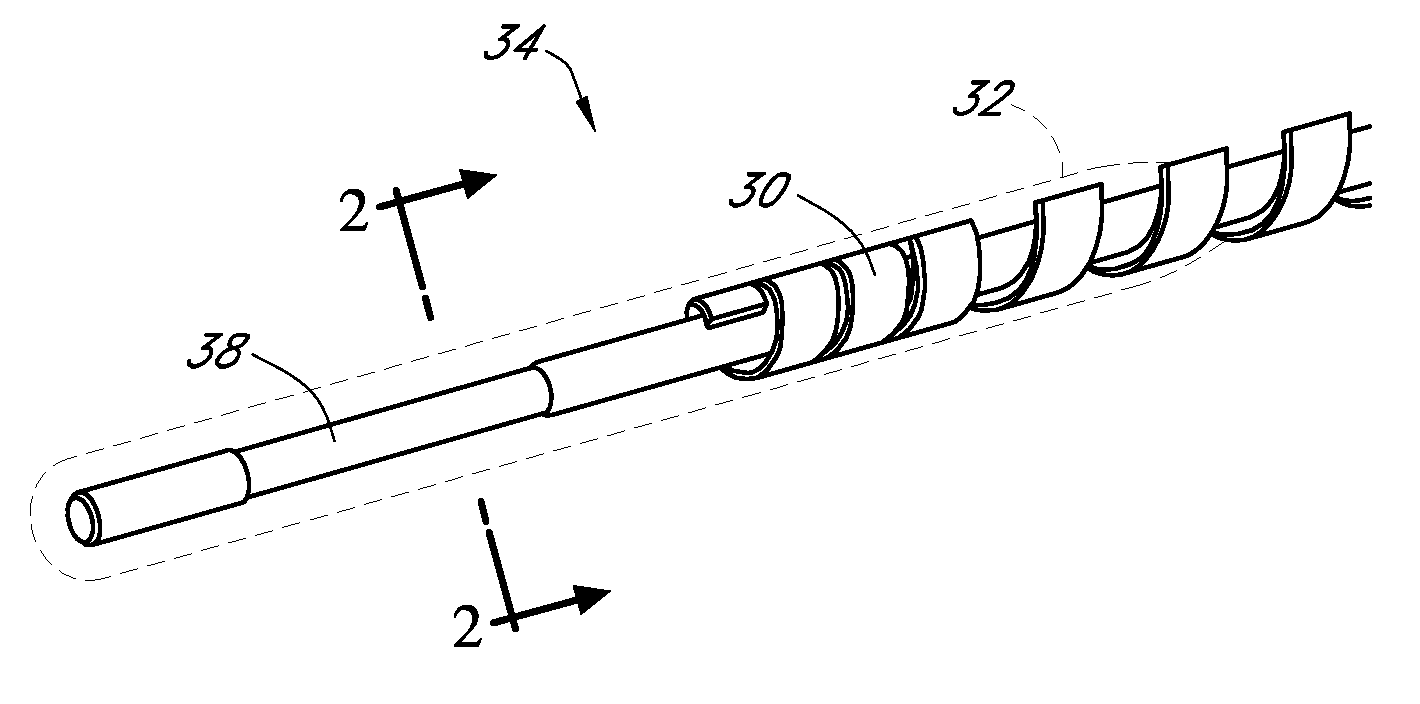
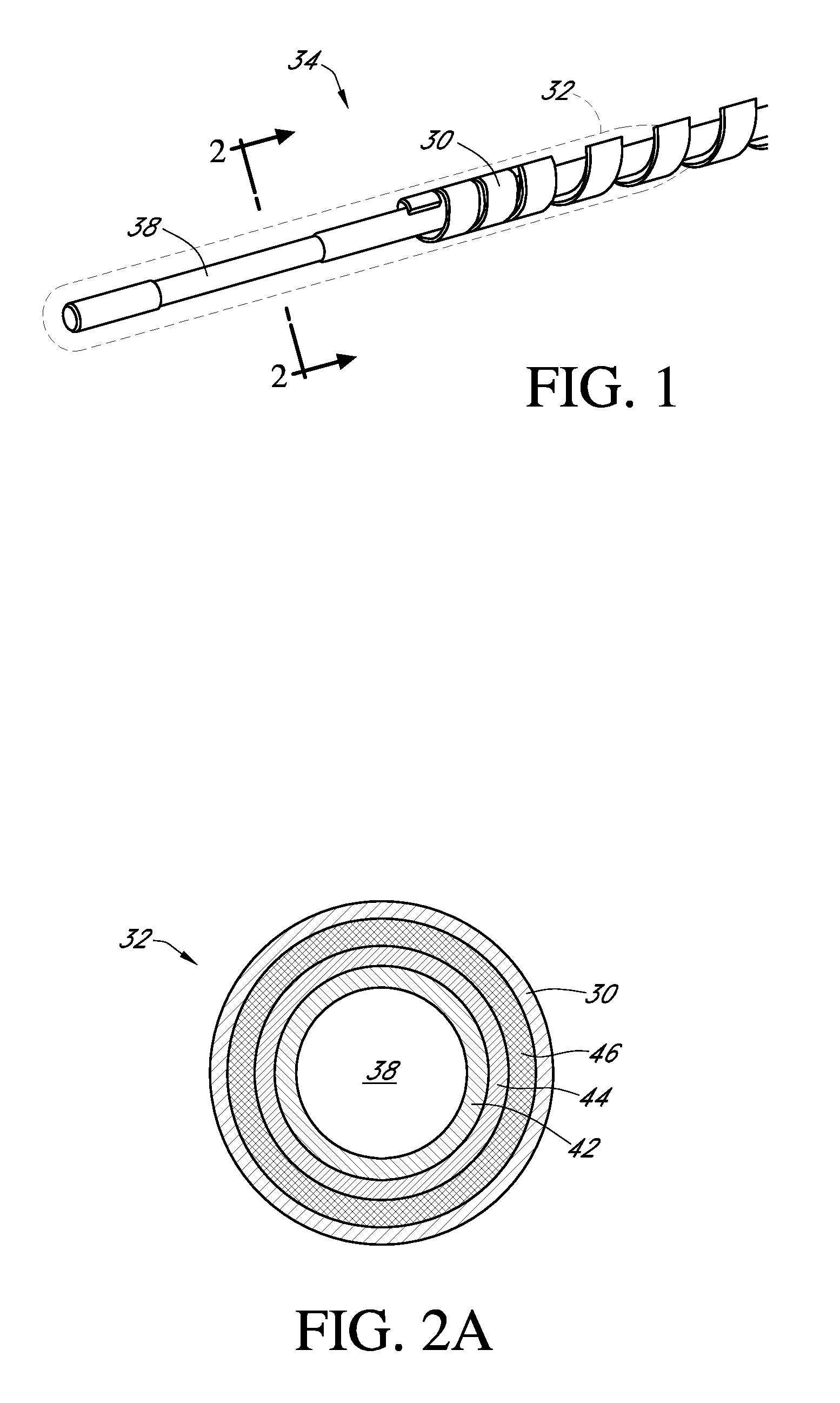
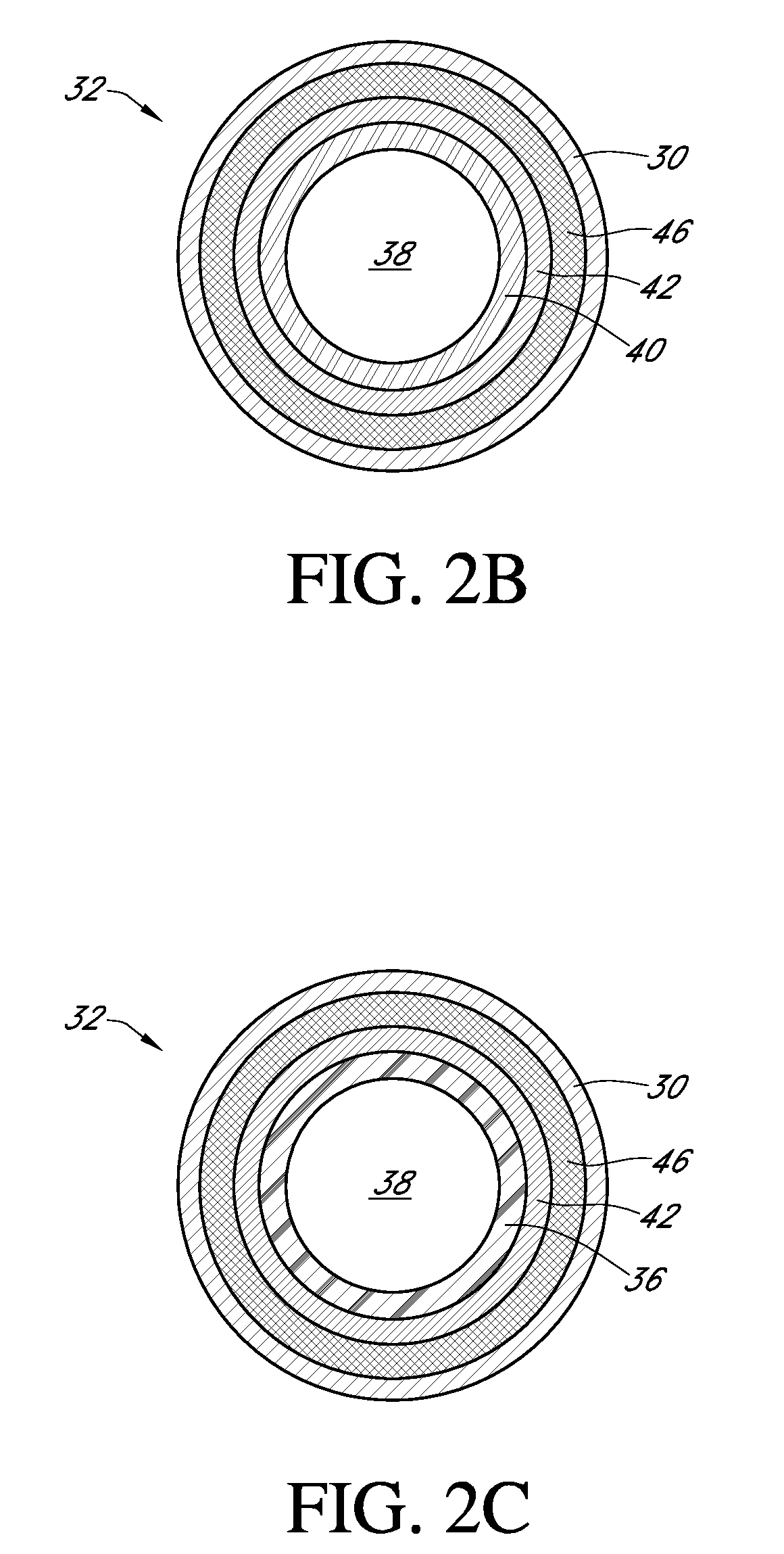
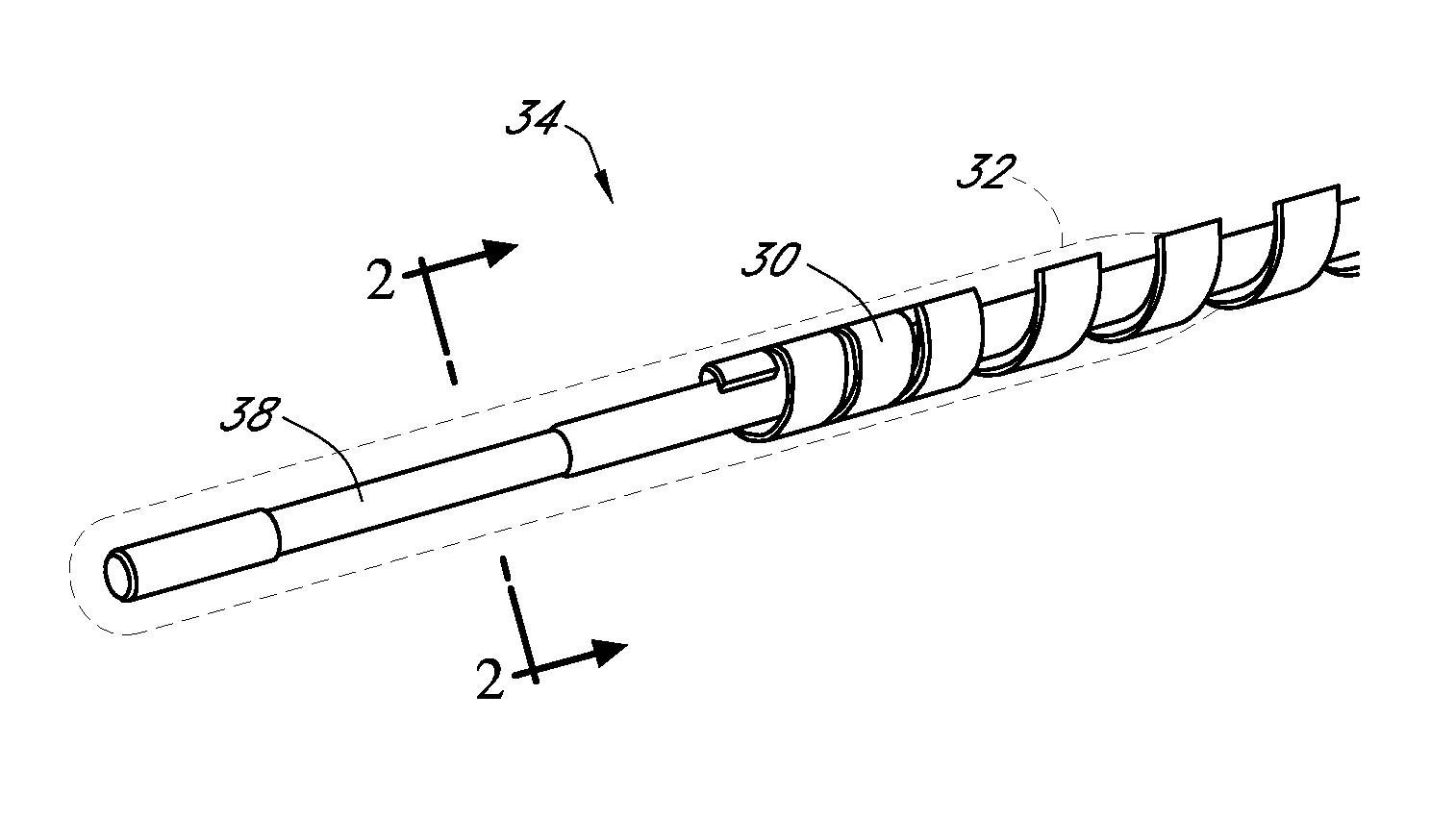
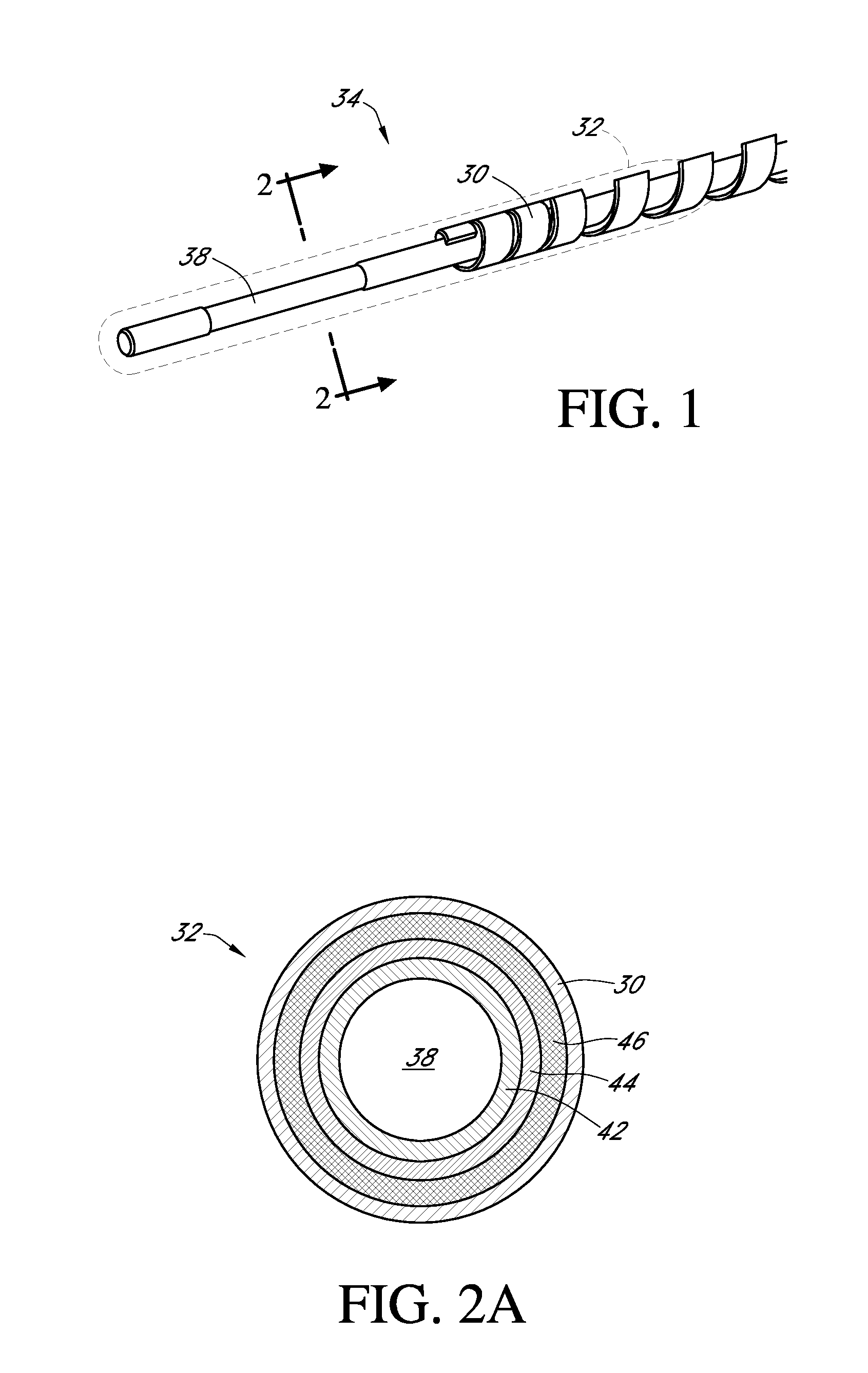
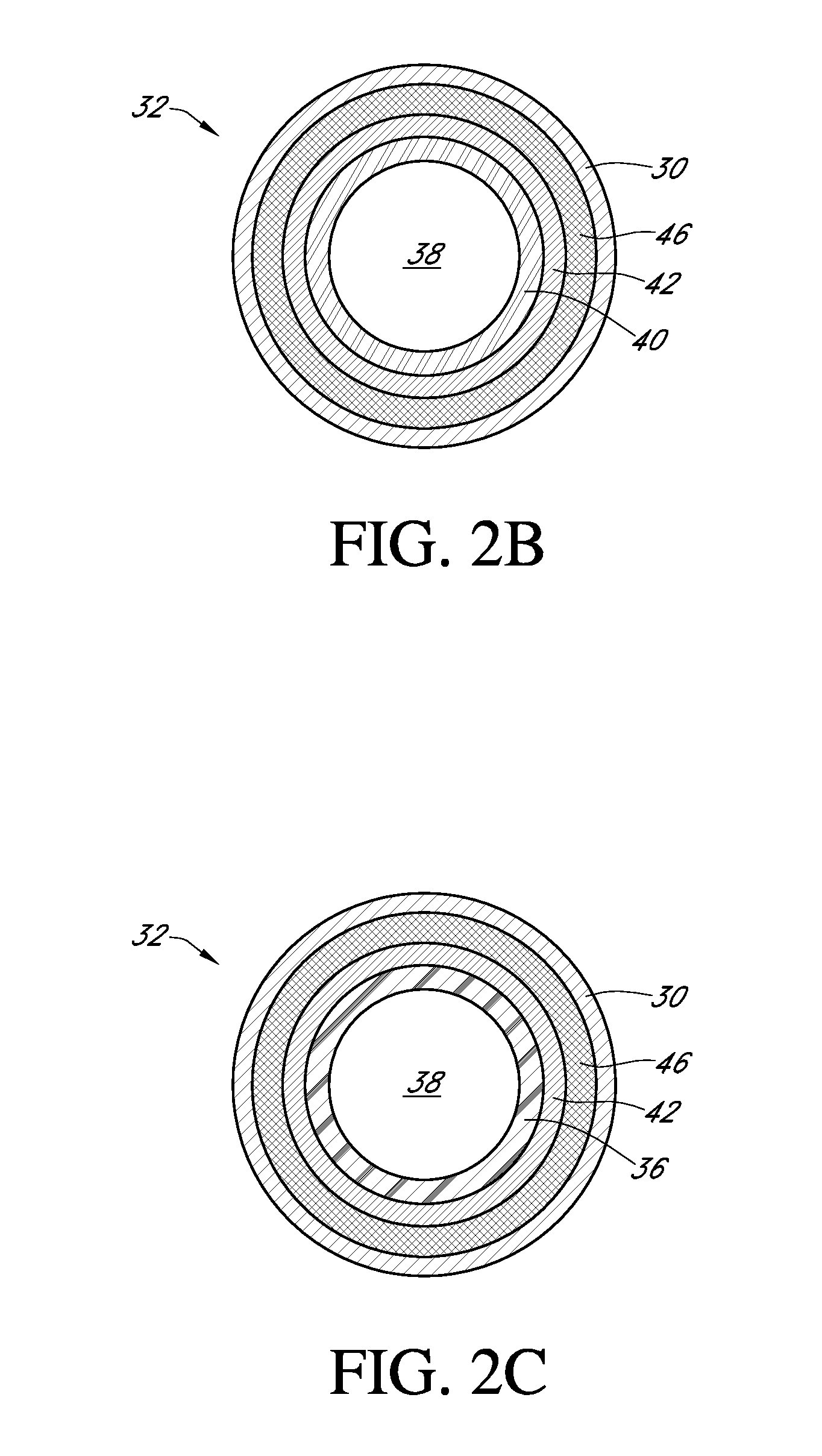
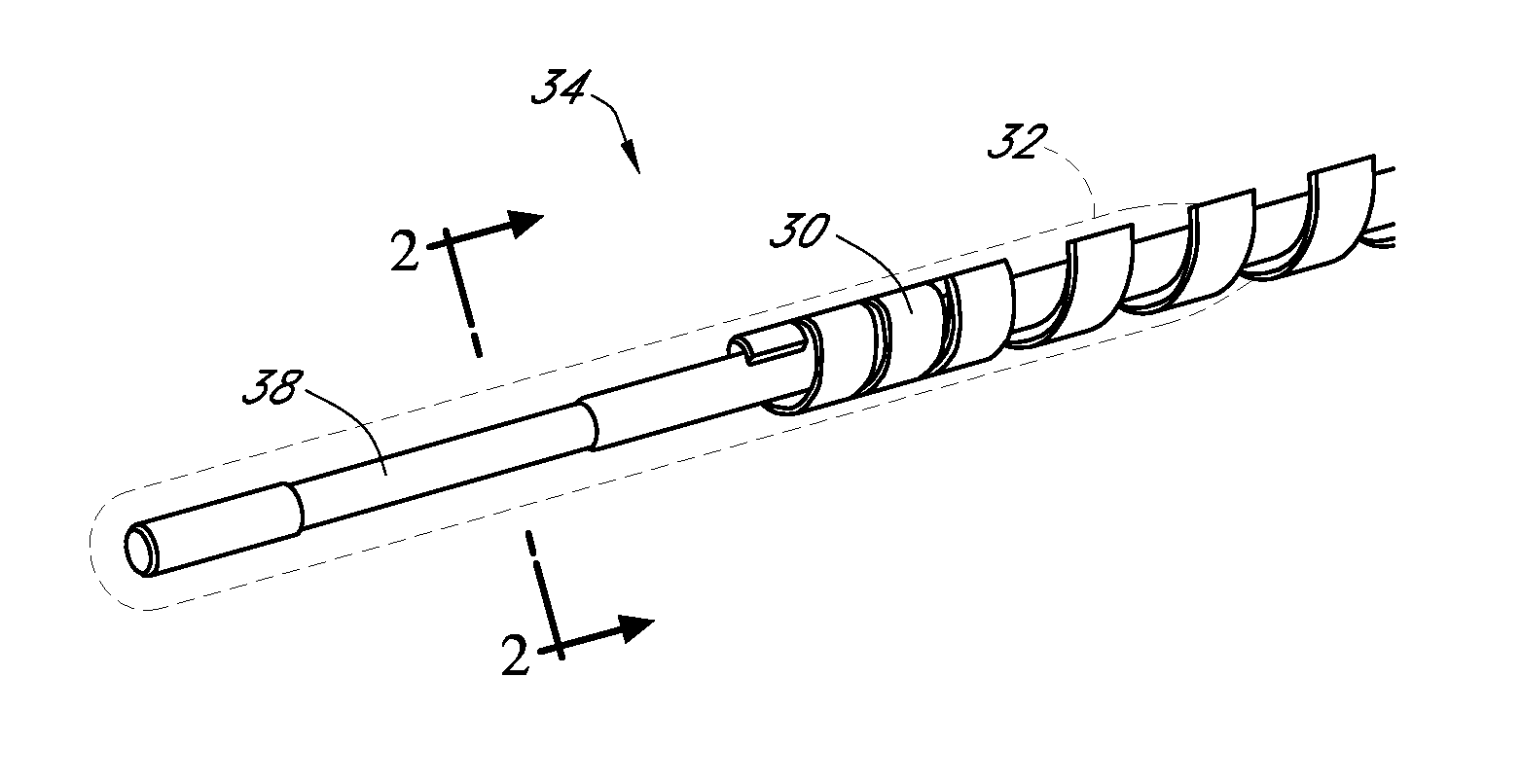
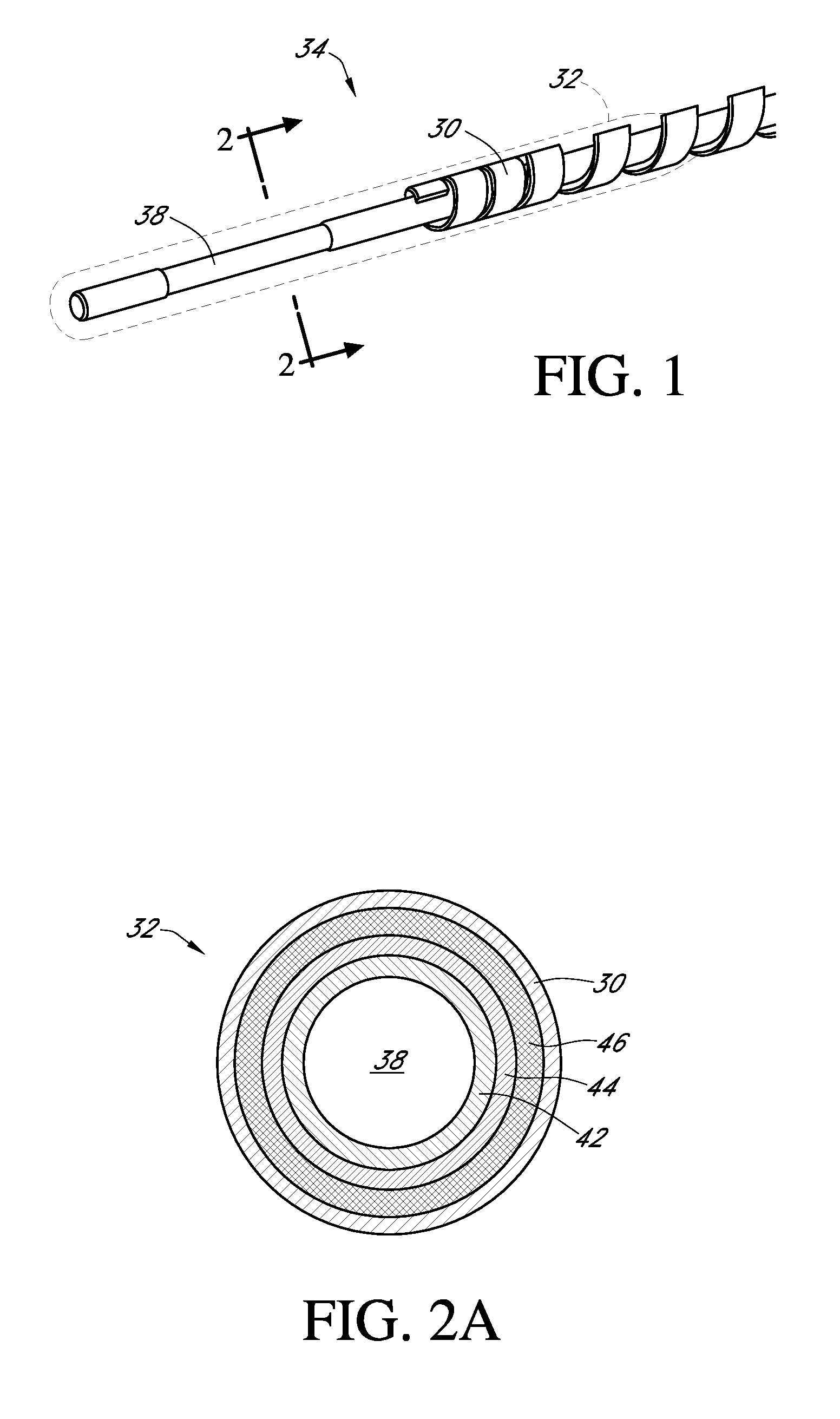
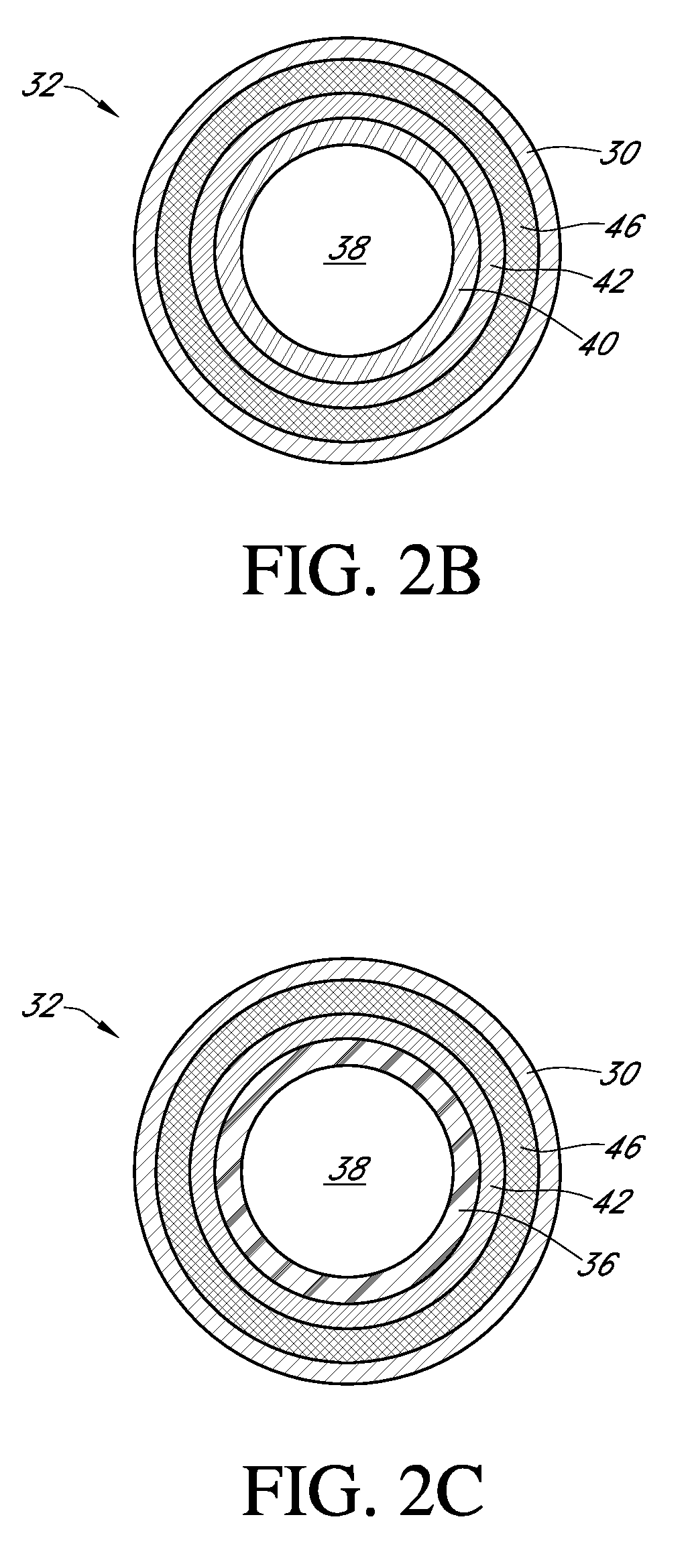
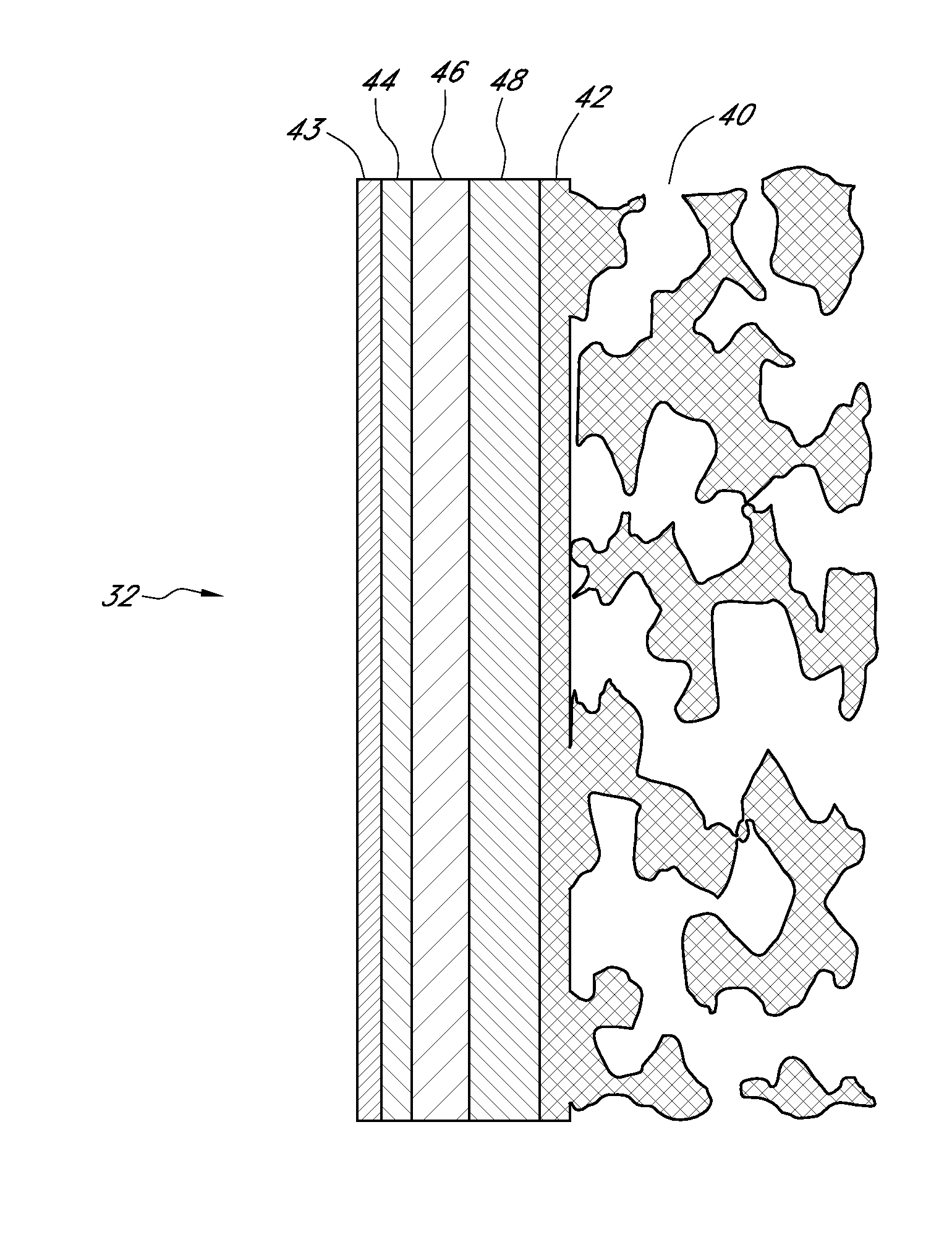
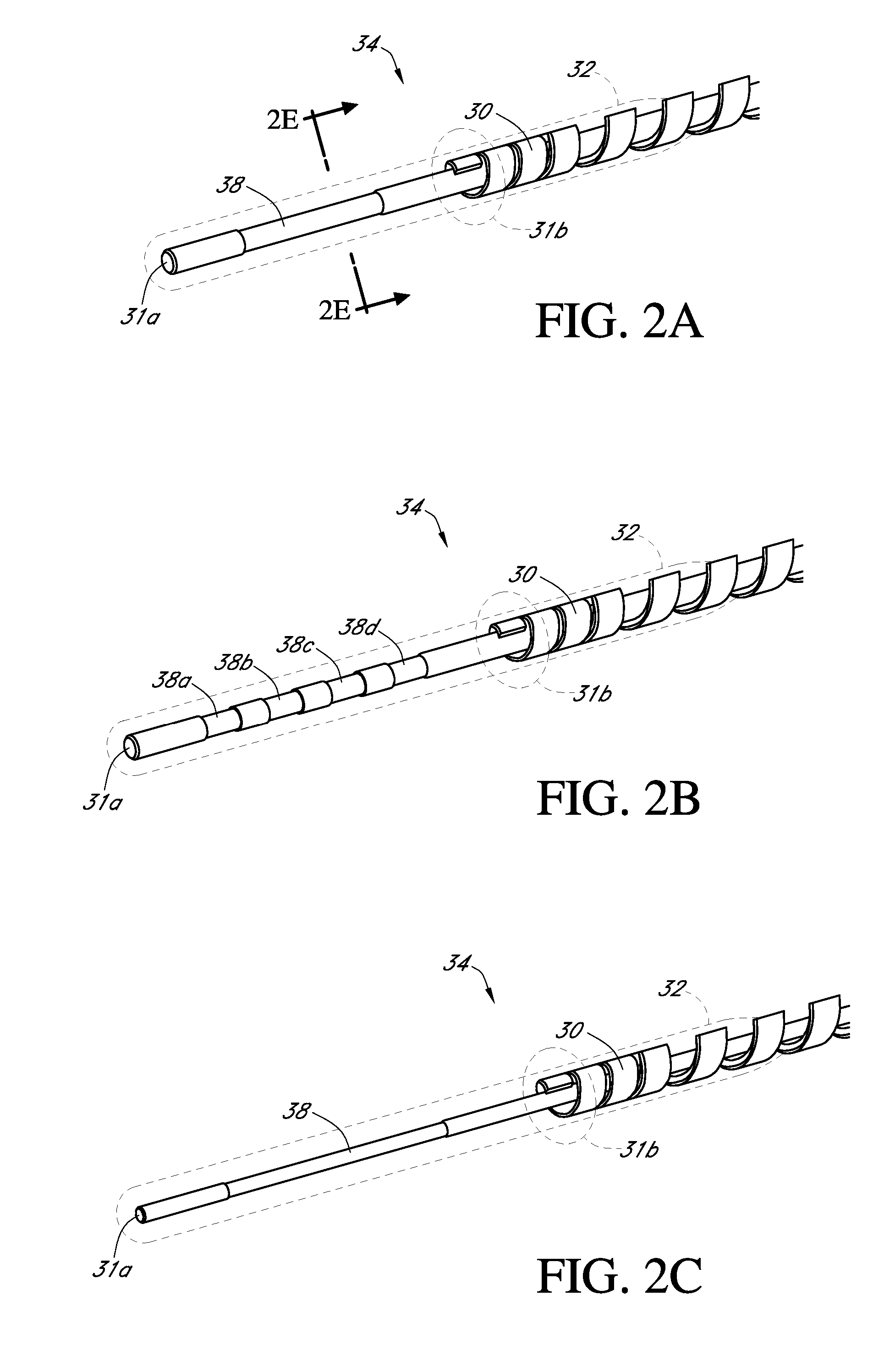
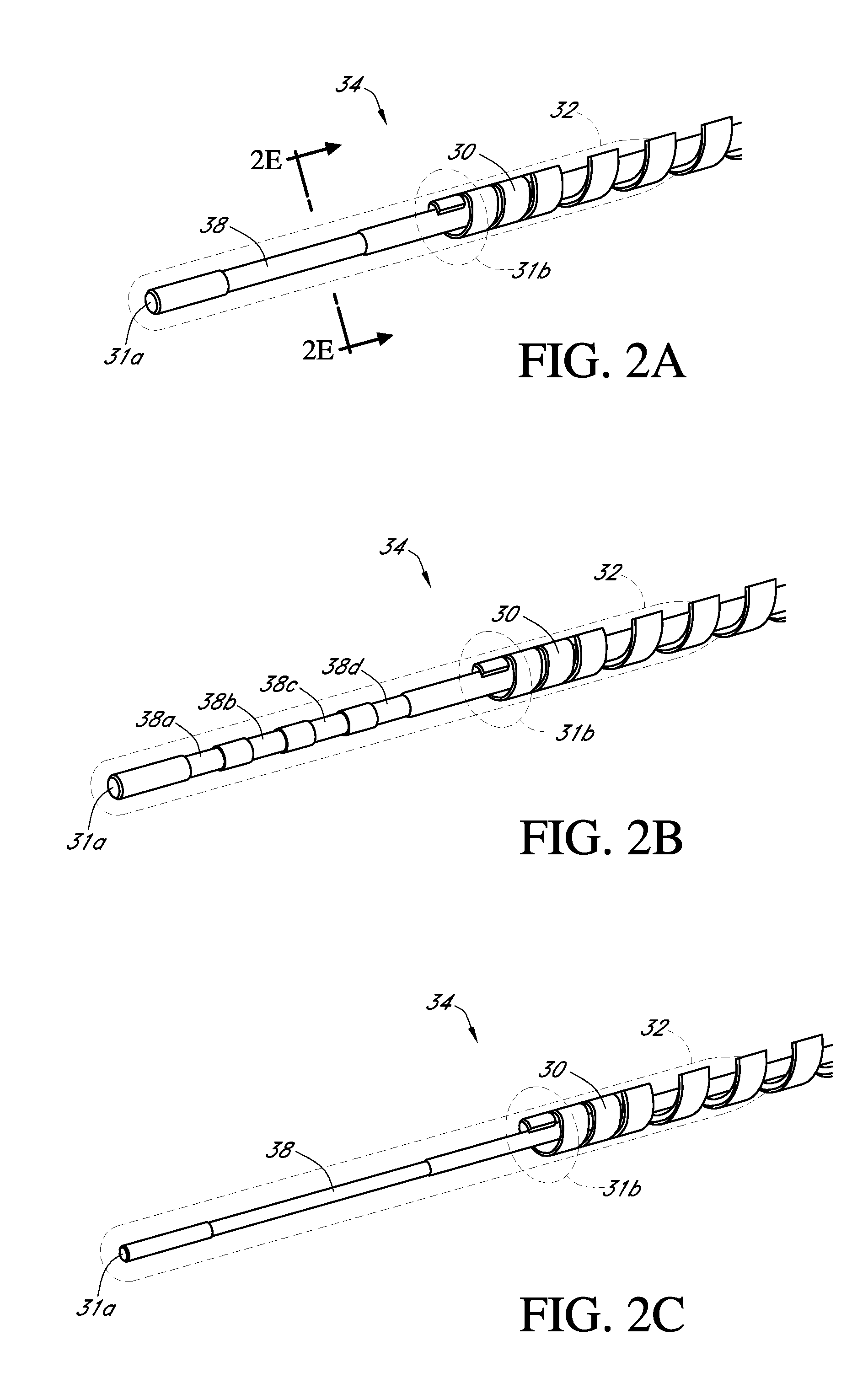
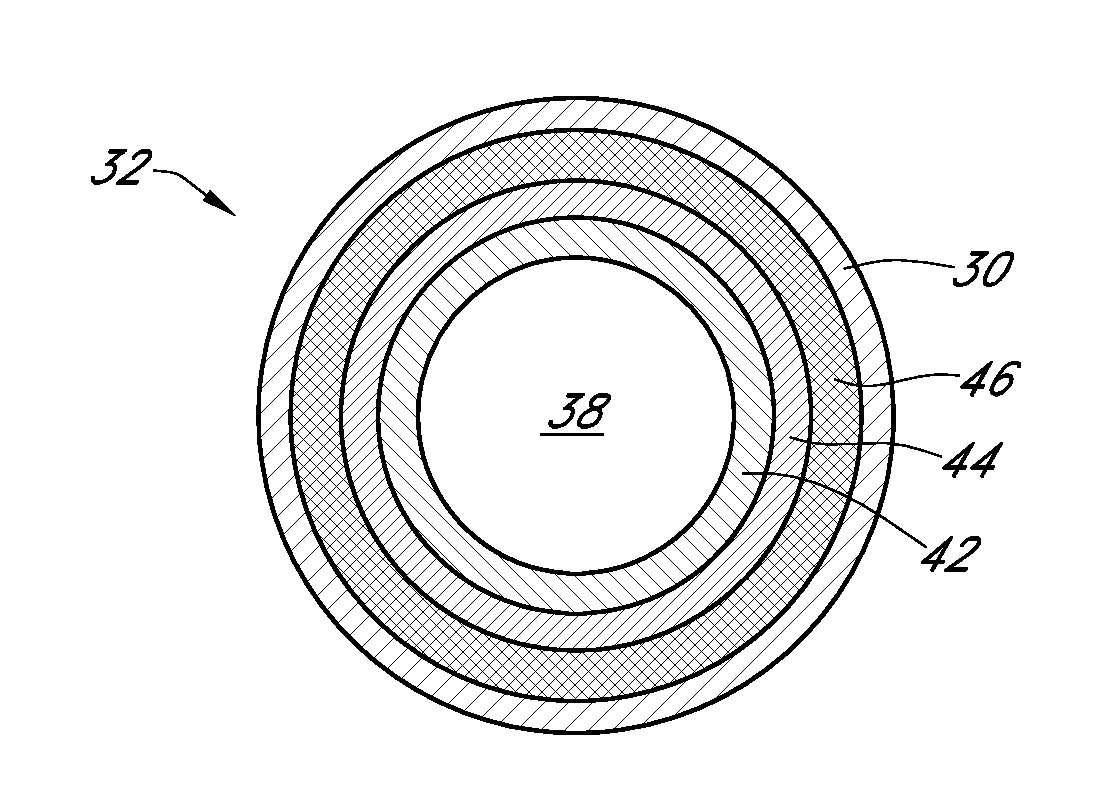
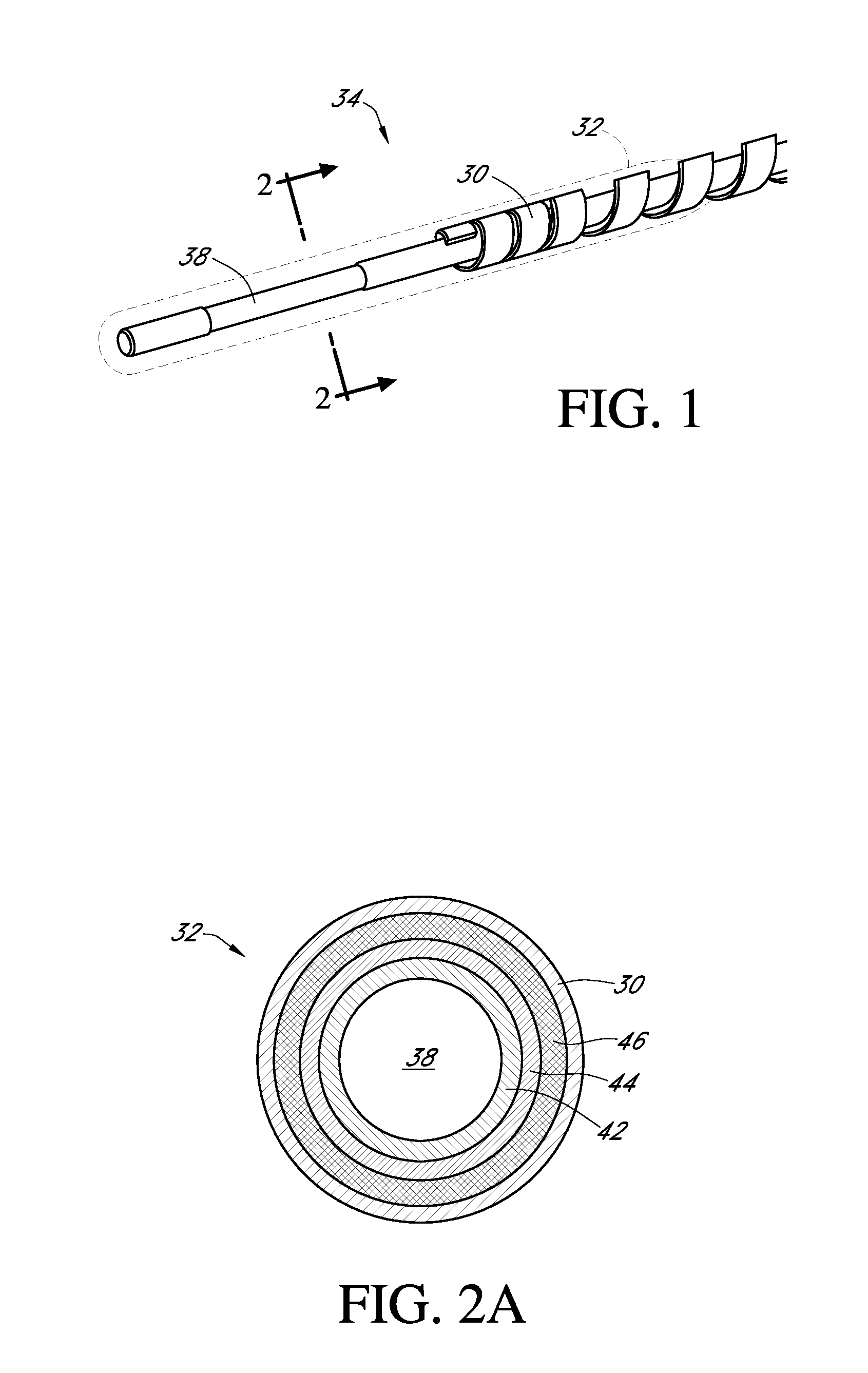
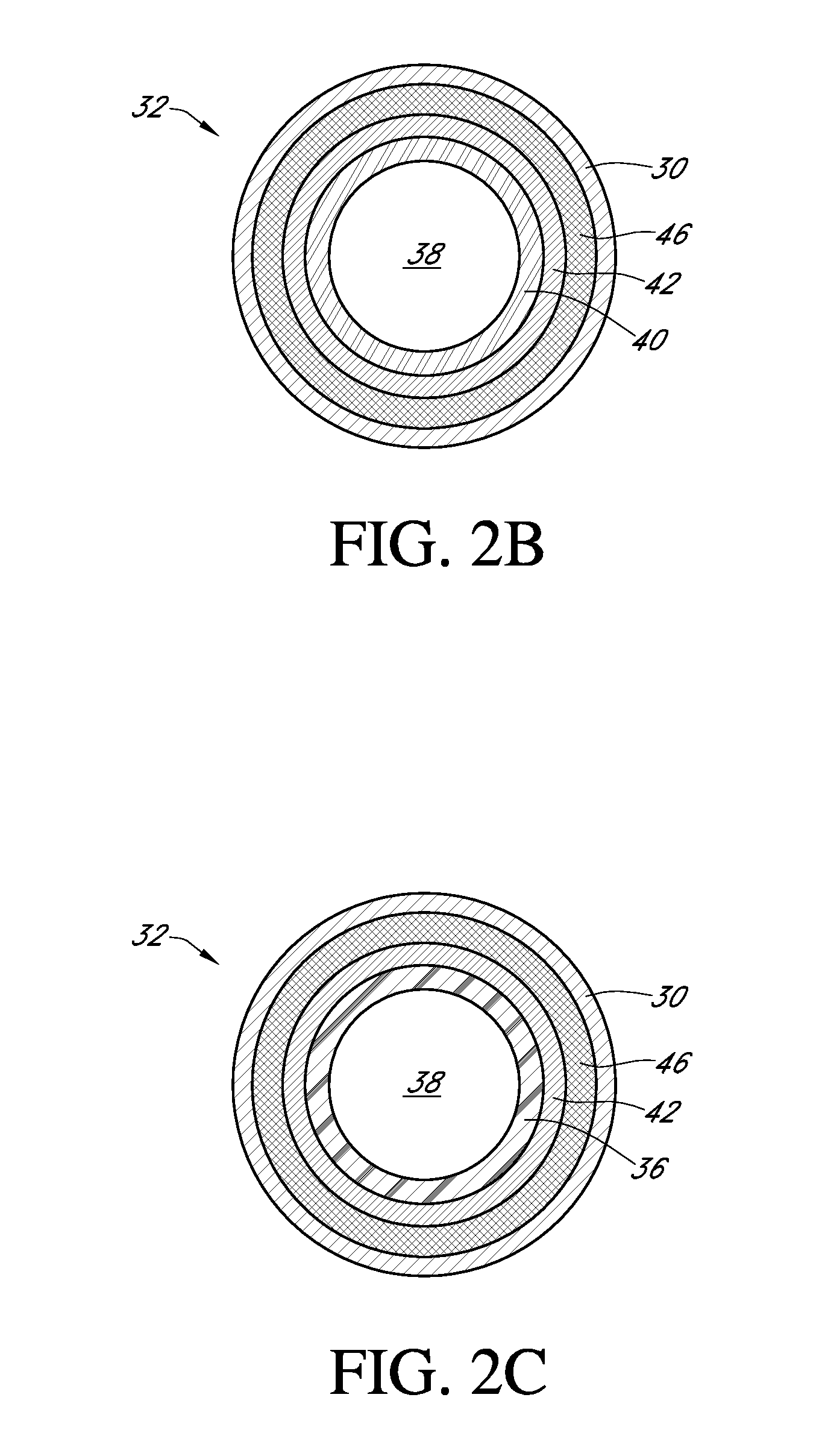
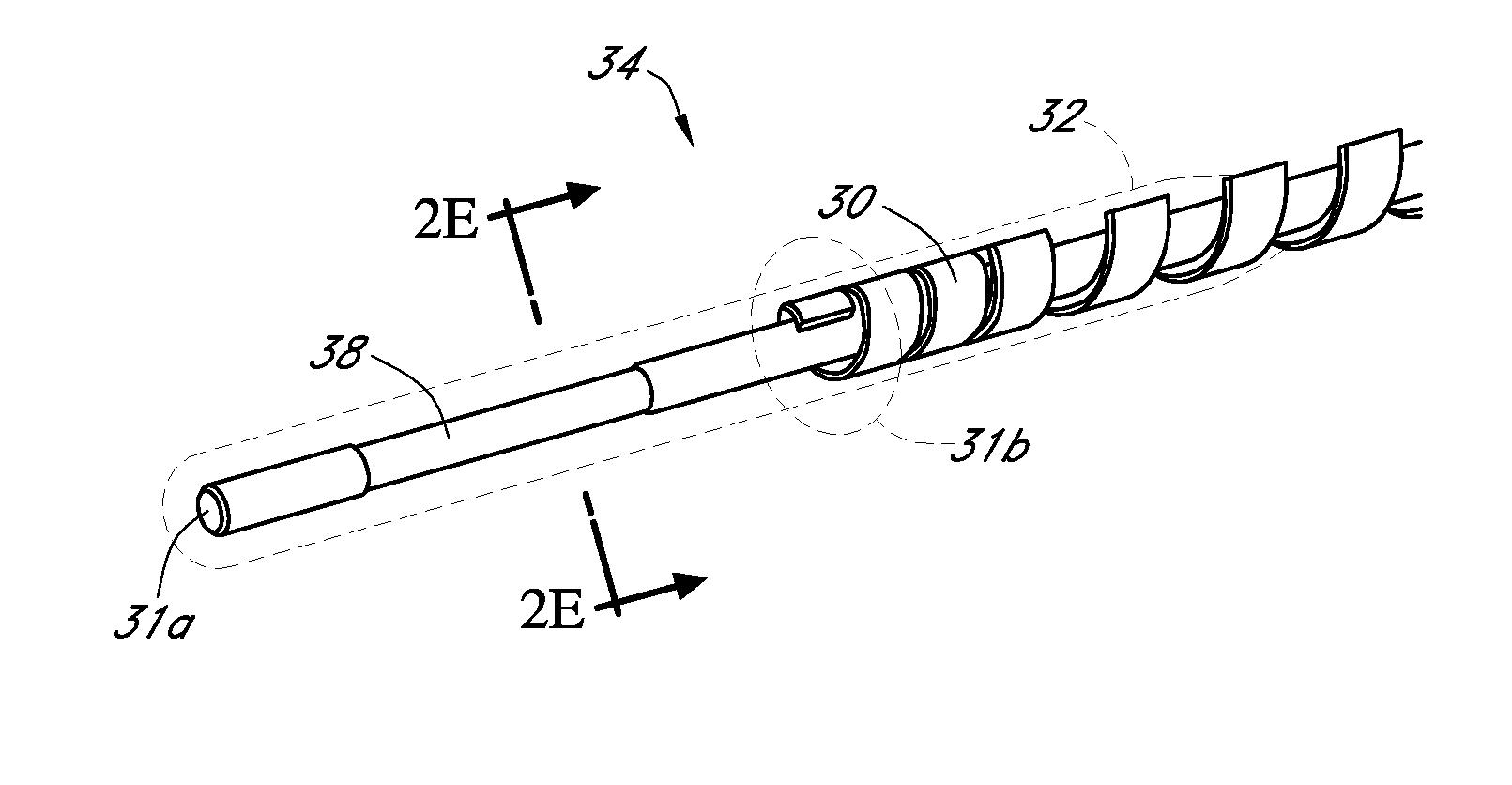
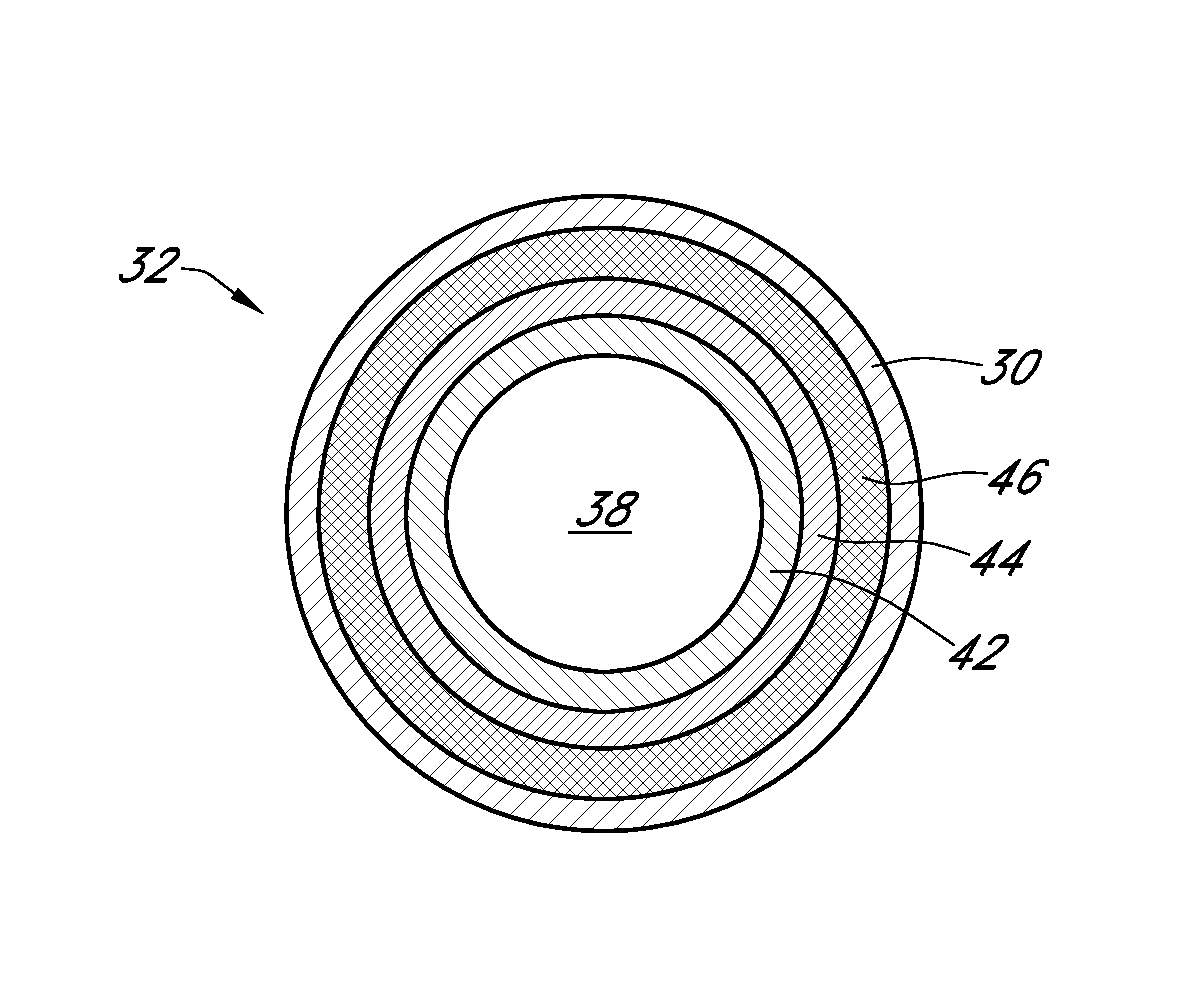
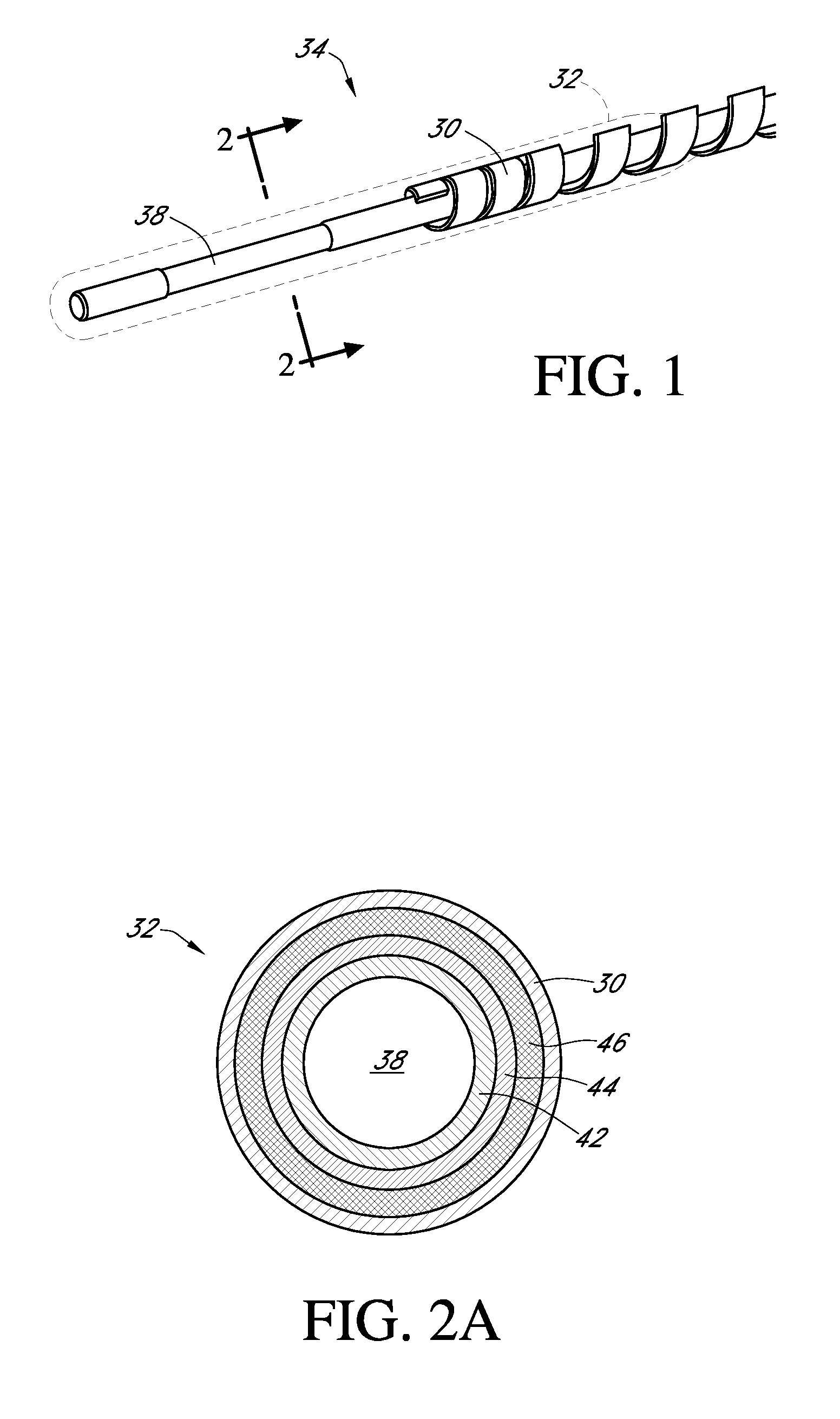
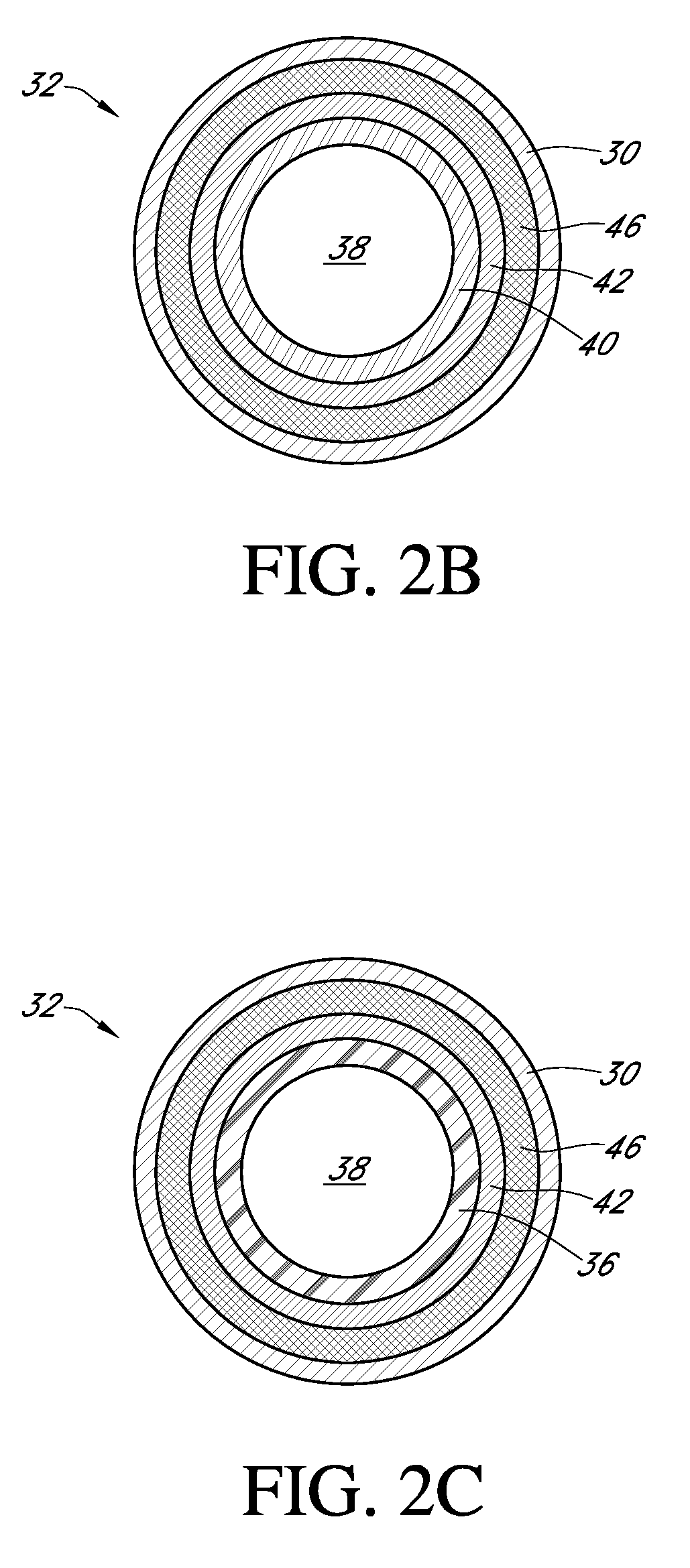
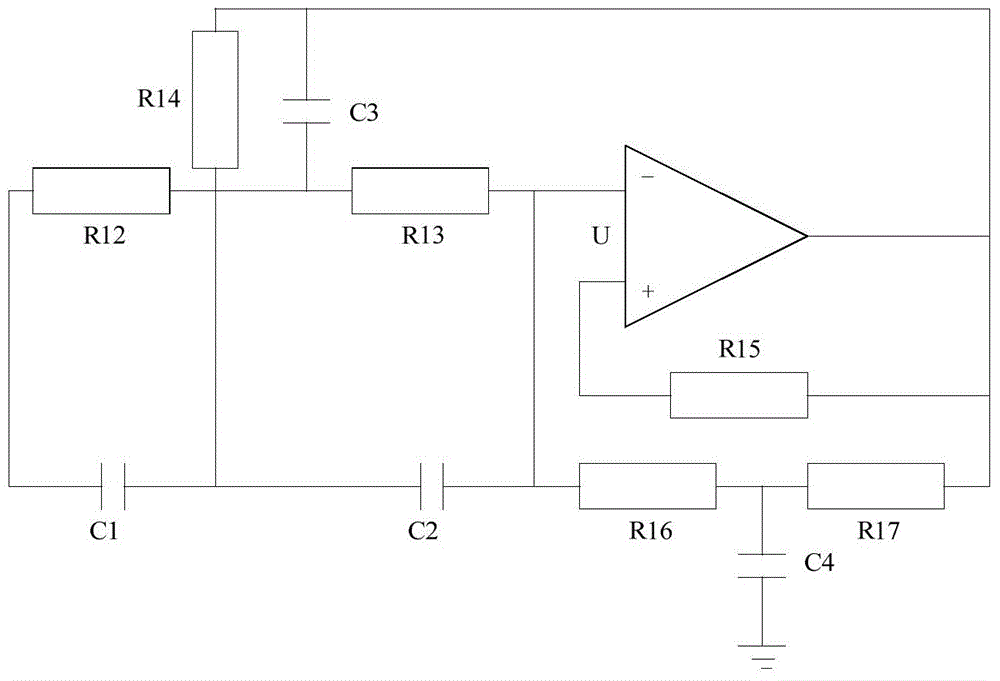
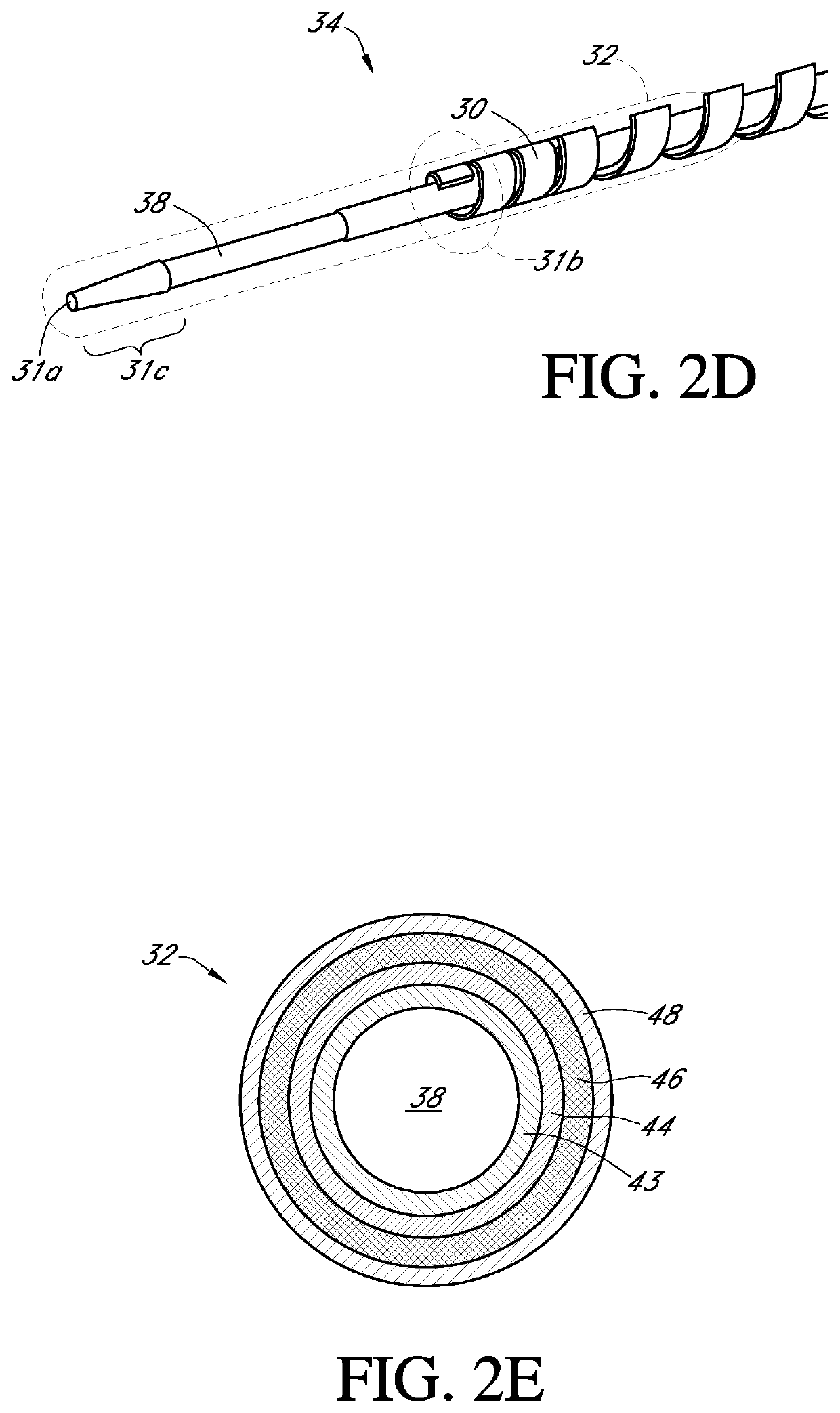
Polymer membranes for continuous analyte sensors
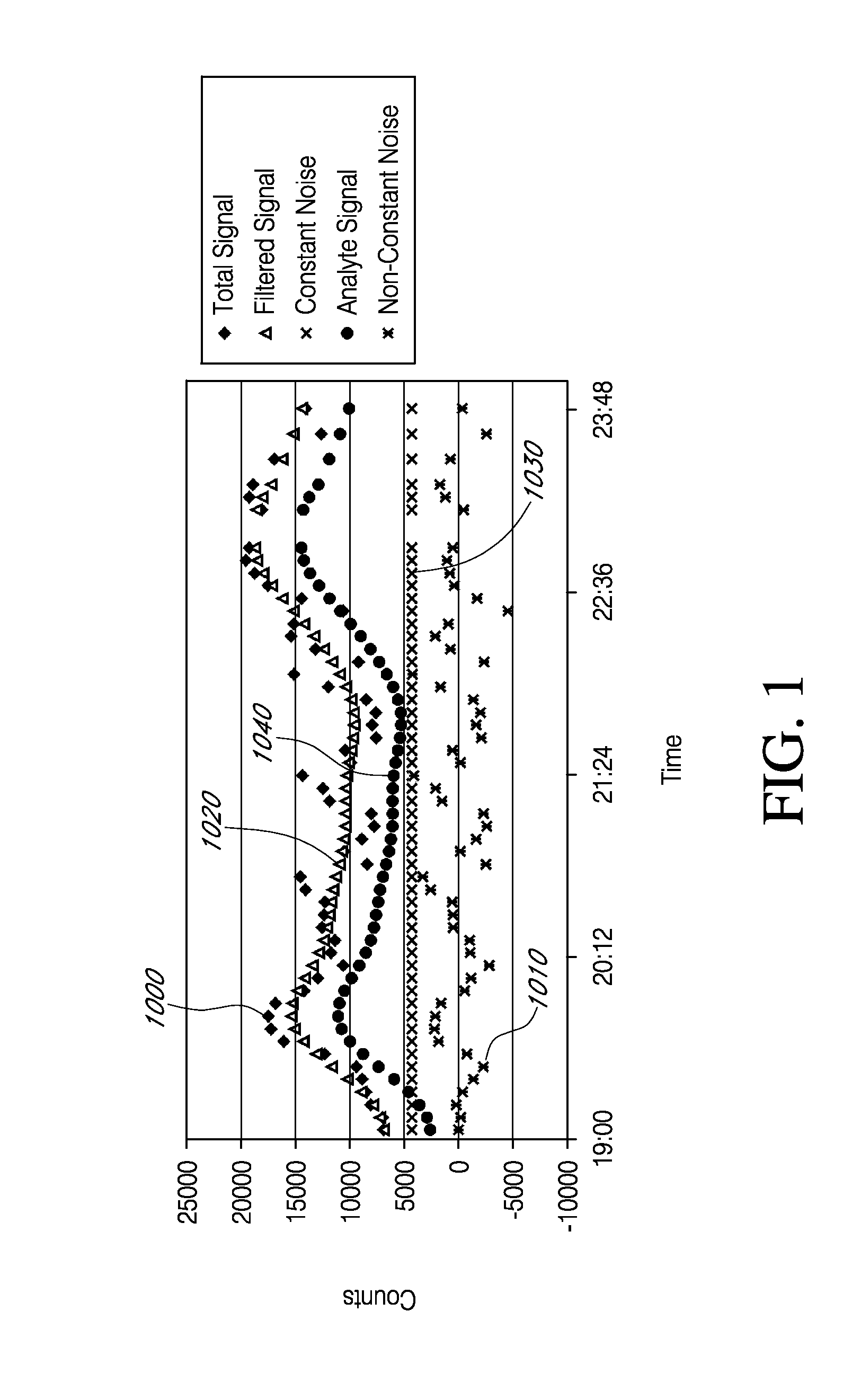
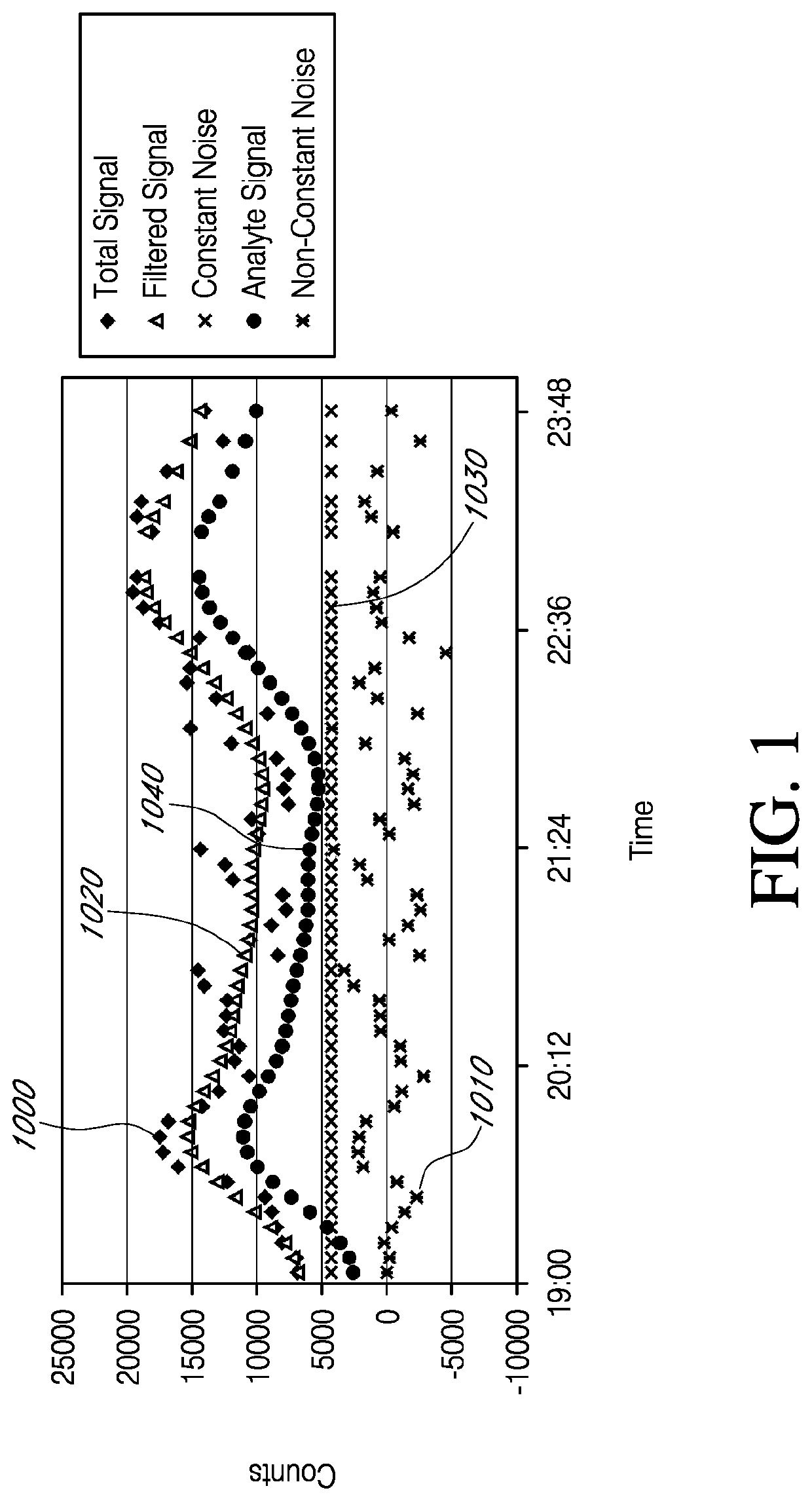
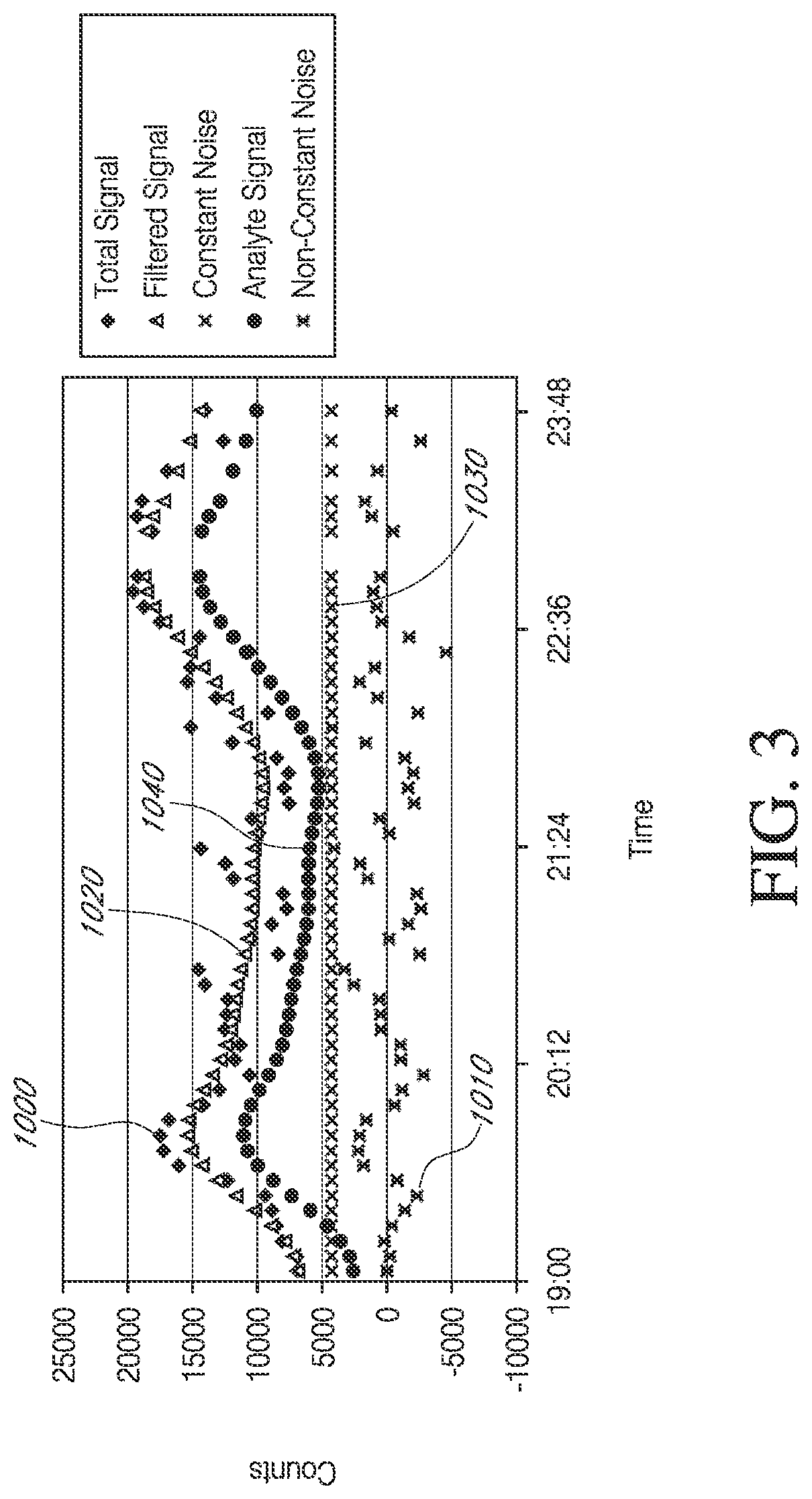
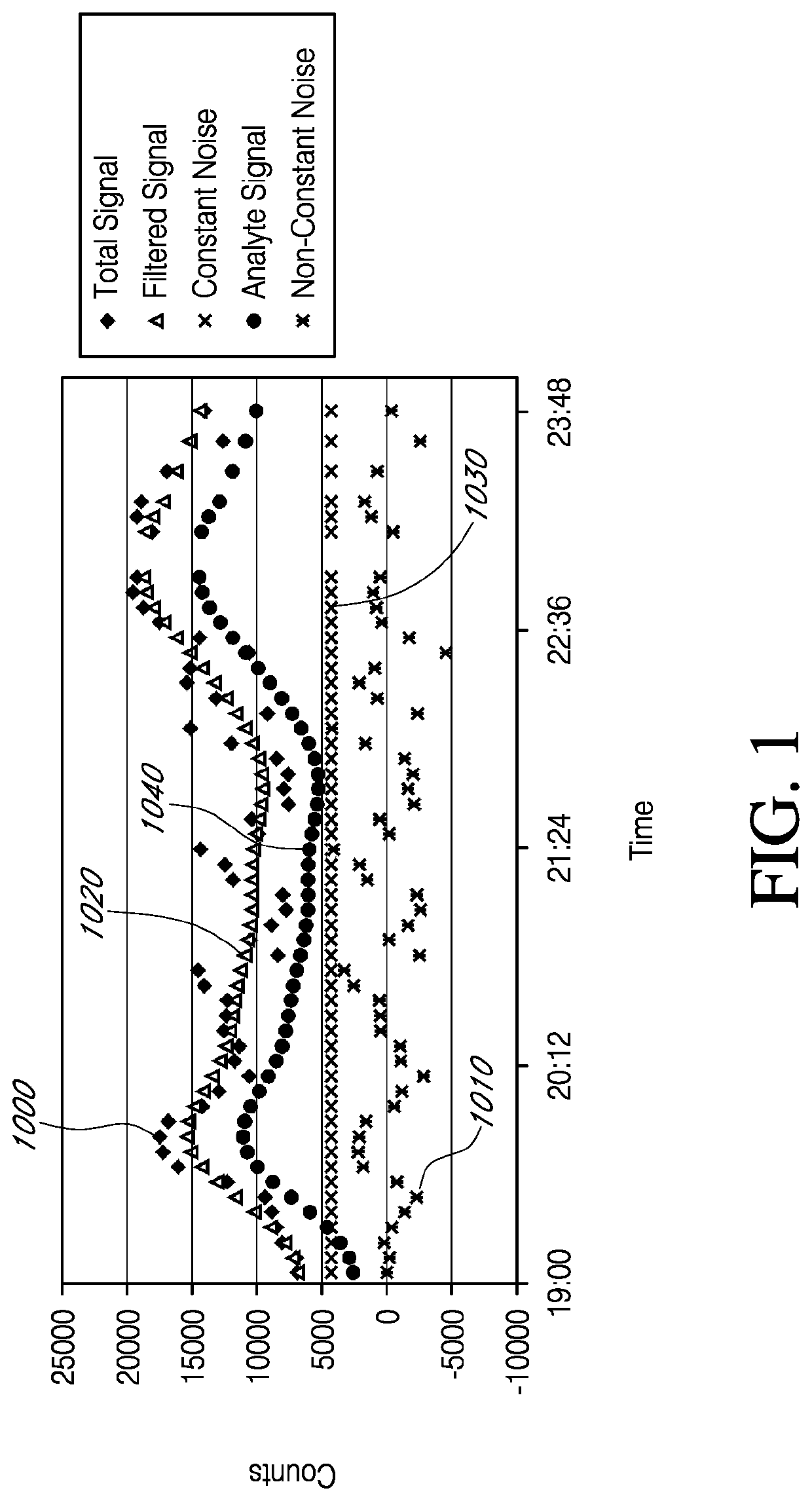
Devices and methods are described for providing continuous measurement of an analyte concentration. In some embodiments, the device has a sensing mechanism and a sensing membrane that includes at least one surface-active group-containing polymer and that is located over the sensing mechanism. The sensing membrane may have a bioprotective layer configured to substantially block the effect and / or influence of non-constant noise-causing species.
Owner:DEXCOM
Polymer membranes for continuous analyte sensors
Devices and methods are described for providing continuous measurement of an analyte concentration. In some embodiments, the device has a sensing mechanism and a sensing membrane that includes at least one surface-active group-containing polymer and that is located over the sensing mechanism. The sensing membrane may have a bioprotective layer configured to substantially block the effect and / or influence of non-constant noise-causing species.
Owner:DEXCOM
Polymer membranes for continuous analyte sensors
InactiveUS20100096259A1Machining electrodesMicrobiological testing/measurementContinuous measurementAnalyte
Devices and methods are described for providing continuous measurement of an analyte concentration. In some embodiments, the device has a sensing mechanism and a sensing membrane that includes at least one surface-active group-containing polymer and that is located over the sensing mechanism. The sensing membrane may have a bioprotective layer configured to substantially block the effect and / or influence of non-constant noise-causing species.
Owner:DEXCOM
Polymer membranes for continuous analyte sensors
ActiveUS20100274107A1Level accuracyDiagnostic signal processingMicrobiological testing/measurementContinuous measurementAnalyte
Devices and methods are described for providing continuous measurement of an analyte concentration. In some embodiments, the device has a sensing mechanism and a sensing membrane that includes at least one surface-active group-containing polymer and that is located over the sensing mechanism. The sensing membrane may have a bioprotective layer configured to substantially block the effect and / or influence of non-constant noise-causing species.
Owner:DEXCOM
Polymer membranes for continuous analyte sensors
ActiveUS20100280341A1Level accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementCatheterContinuous measurementAnalyte
Devices and methods are described for providing continuous measurement of an analyte concentration. In some embodiments, the device has a sensing mechanism and a sensing membrane that includes at least one surface-active group-containing polymer and that is located over the sensing mechanism. The sensing membrane may have a bioprotective layer configured to substantially block the effect and / or influence of non-constant noise-causing species.
Owner:DEXCOM
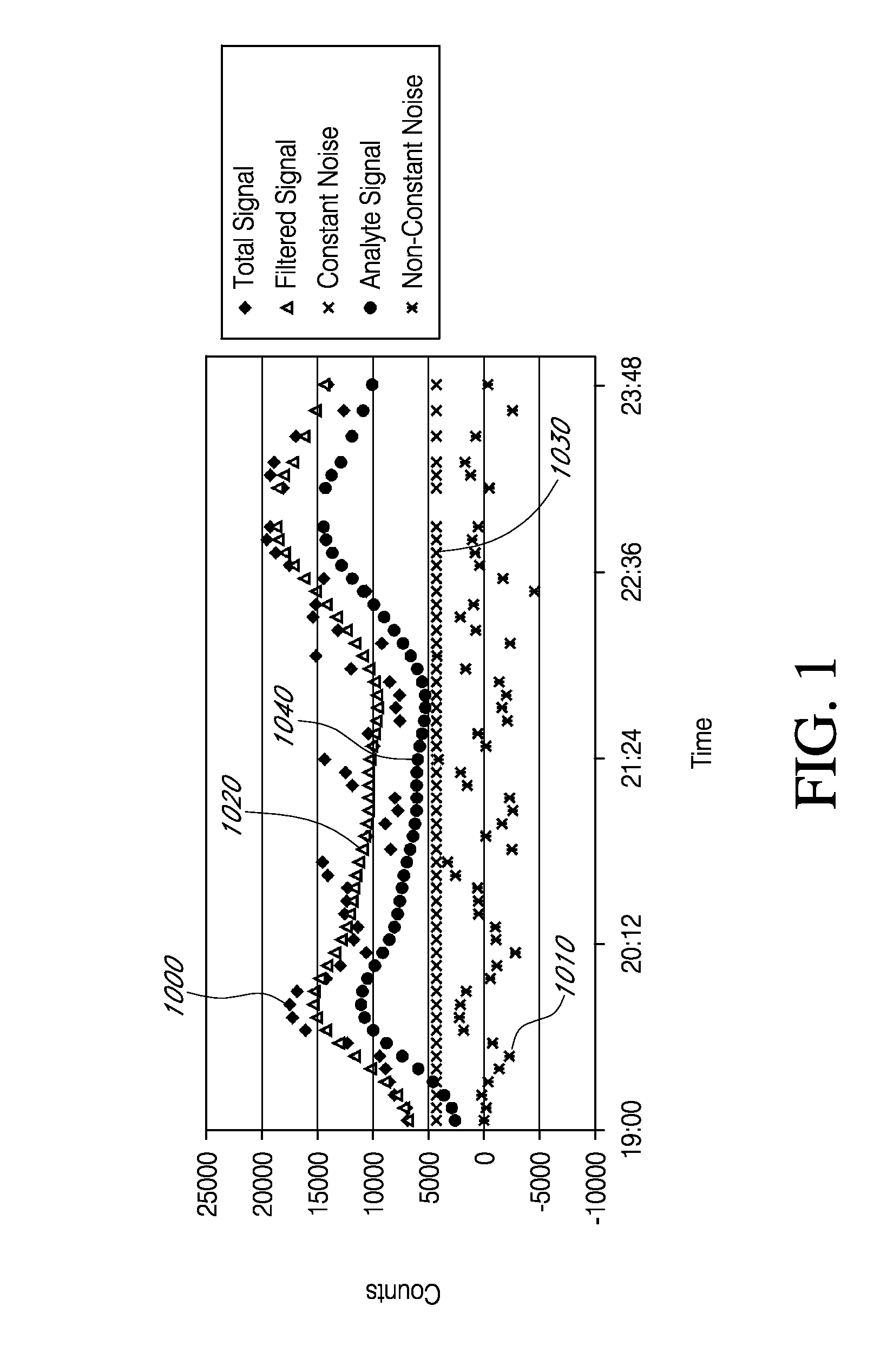
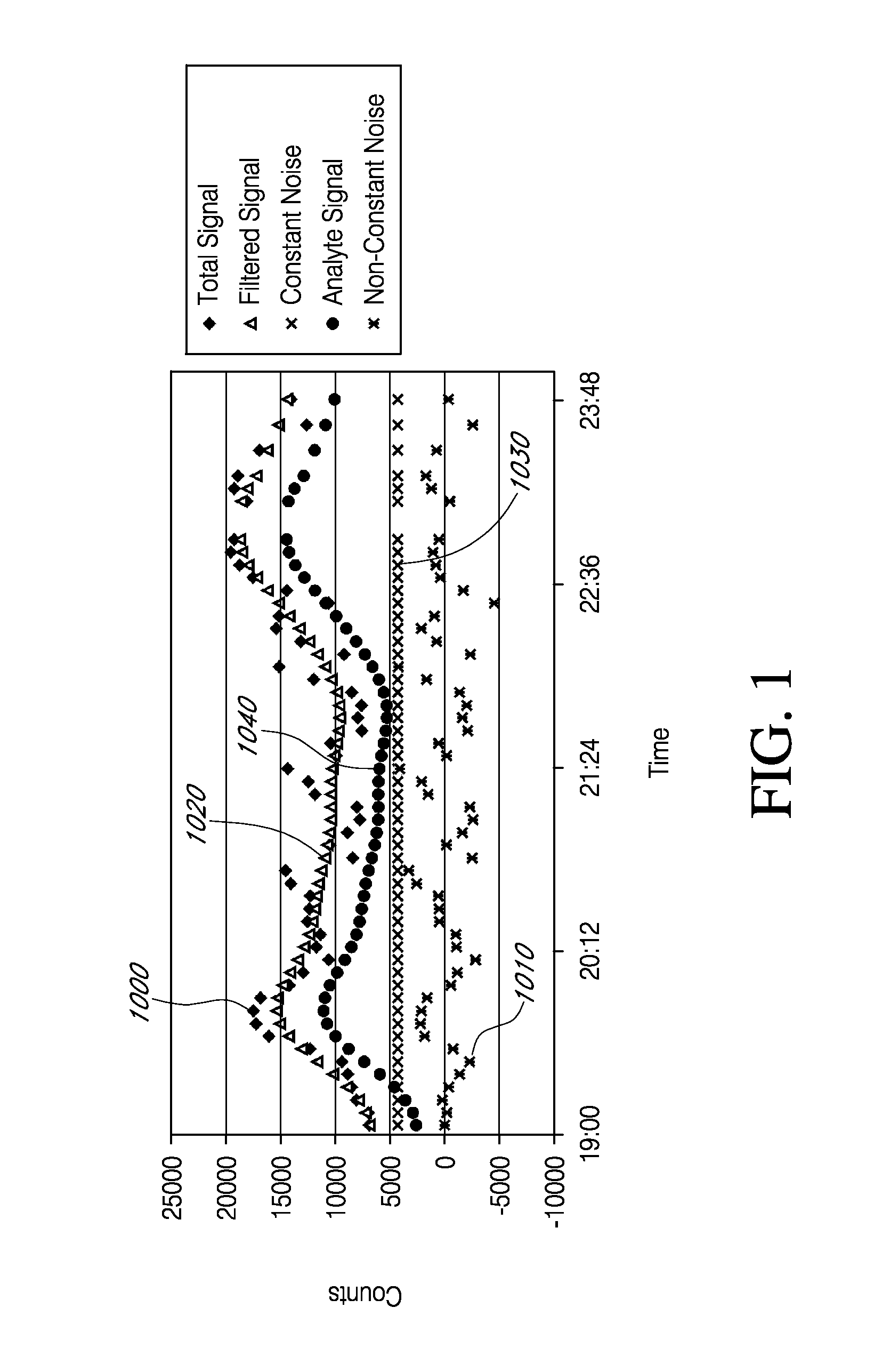
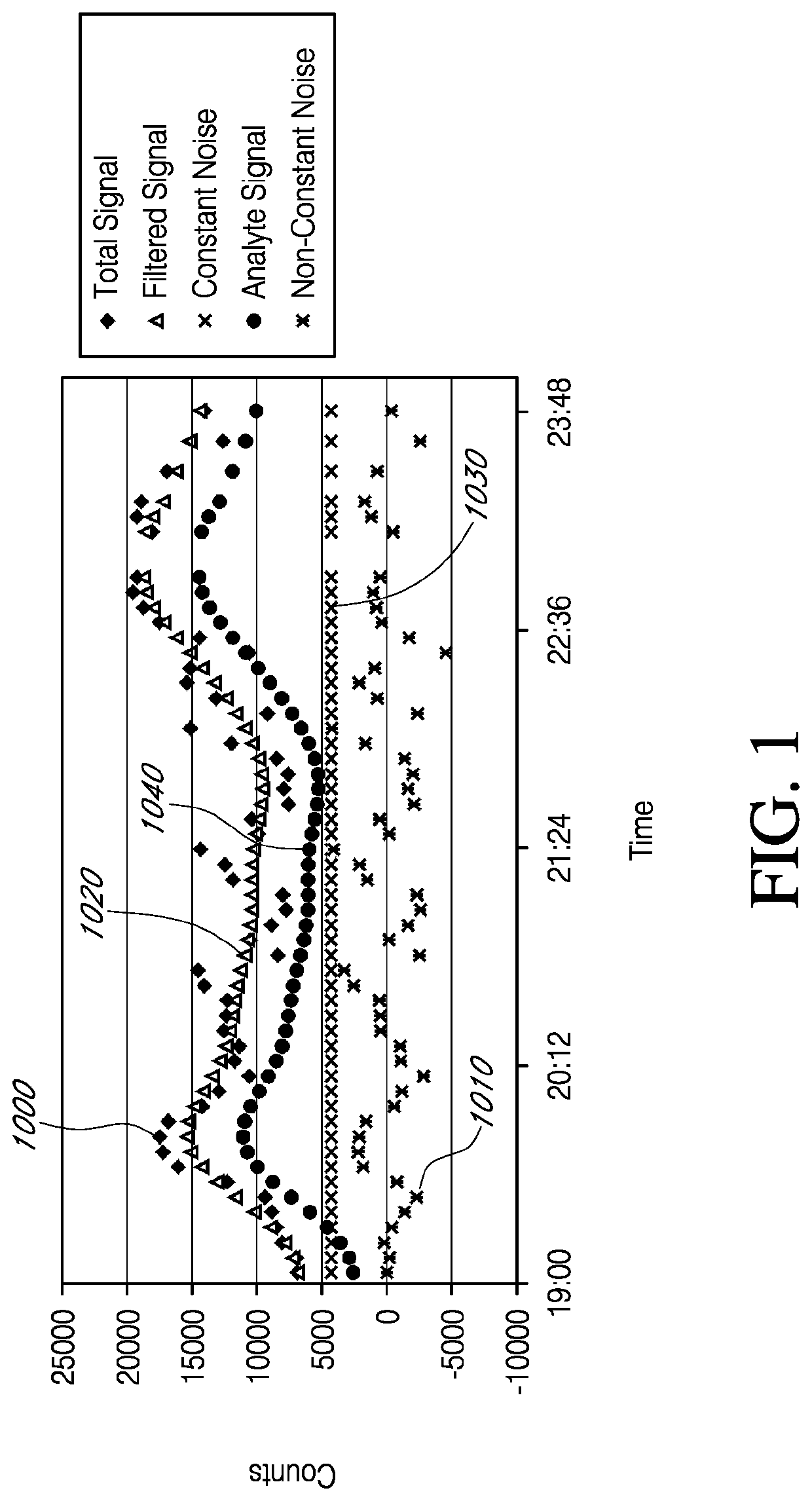
Analyte sensors having a signal-to-noise ratio substantially unaffected by non-constant noise
Systems and methods of use involving sensors having a signal-to-noise ratio that is substantially unaffected by non-constant noise are provided for continuous analyte measurement in a host. In some embodiments, a continuous analyte measurement system is configured to be wholly, transcutaneously, intravascularly or extracorporeally implanted.
Owner:DEXCOM
Analyte sensors having a signal-to-noise ratio substantially unaffected by non-constant noise
Systems and methods of use involving sensors having a signal-to-noise ratio that is substantially unaffected by non-constant noise are provided for continuous analyte measurement in a host. In some embodiments, a continuous analyte measurement system is configured to be wholly, transcutaneously, intravascularly or extracorporeally implanted.
Owner:DEXCOM
Polymer membranes for continuous analyte sensors
ActiveUS8682408B2Diagnostic signal processingMicrobiological testing/measurementContinuous measurementAnalyte
Devices and methods are described for providing continuous measurement of an analyte concentration. In some embodiments, the device has a sensing mechanism and a sensing membrane that includes at least one surface-active group-containing polymer and that is located over the sensing mechanism. The sensing membrane may have a bioprotective layer configured to substantially block the effect and / or influence of non-constant noise-causing species.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
Analyte sensors having a signal-to-noise ratio substantially unaffected by non-constant noise
Systems and methods of use involving sensors having a signal-to-noise ratio that is substantially unaffected by non-constant noise are provided for continuous analyte measurement in a host. In some embodiments, a continuous analyte measurement system is configured to be wholly, transcutaneously, intravascularly or extracorporeally implanted.
Owner:DEXCOM
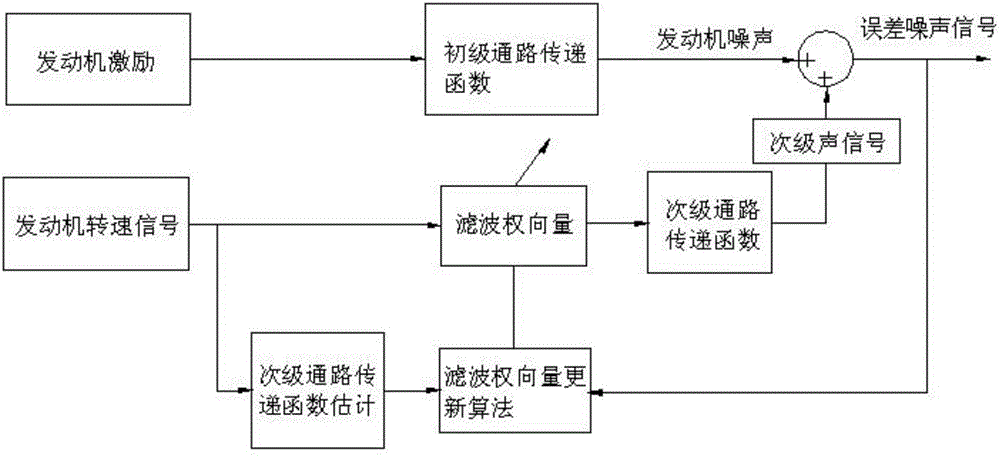
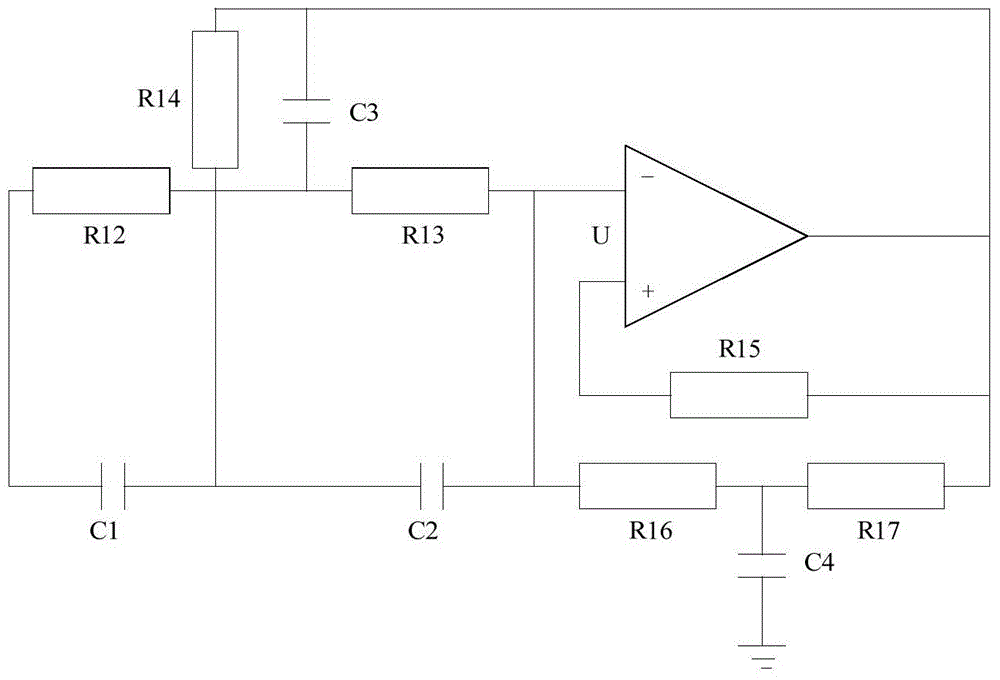
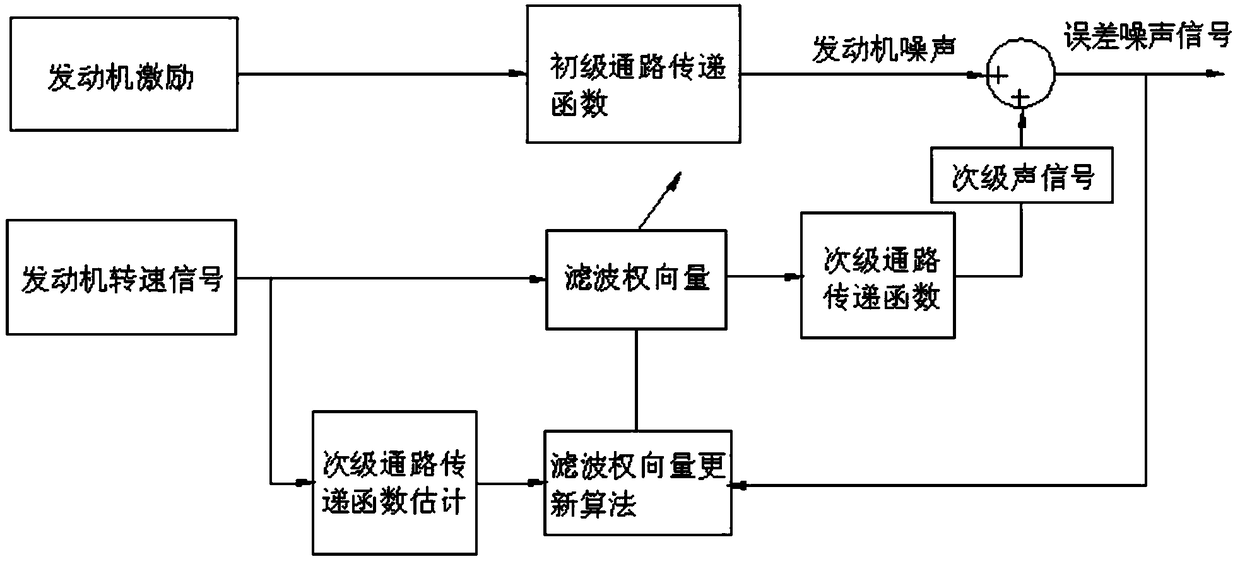
Active noise reduction system and method for engine in automobile
ActiveCN106089361ANoise impact is negligibleFast convergenceSilencing apparatusMachines/enginesSound sourcesEngineering
The invention relates to an active noise reduction system for an engine in an automobile. The system comprises two error microphones, five secondary sound source loudspeakers and one self-adaptation active controller. The two error microphones are arranged at automobile roof positions corresponding to a front row and a back row of the automobile. The five secondary sound source loudspeakers are composed of four vehicle-mounted loudspeaker boxes arranged on the automobile door sides and one secondary sound source arranged at the position of a rear row partition plate. The self-adaptation active controller comprises a DSP master control chip, an audio decoding chip, an off-chip storage unit, a CAN bus controller, a power amplifier, an error microphone signal receiving module, a secondary sound source output module and a power module. The invention further relates to an active noise reduction method for the engine in the automobile. By means of the system and method, error noise signals in active noise reduction reach the minimum value during constant noise reduction control, the noise influence caused by the error noise signals can be basically ignored, and the expected noise reduction effect can be rapidly achieved.
Owner:HEFEI CHANGAN AUTOMOBILE +1
Polymer membranes for continuous analyte sensors
Owner:DEXCOM INC
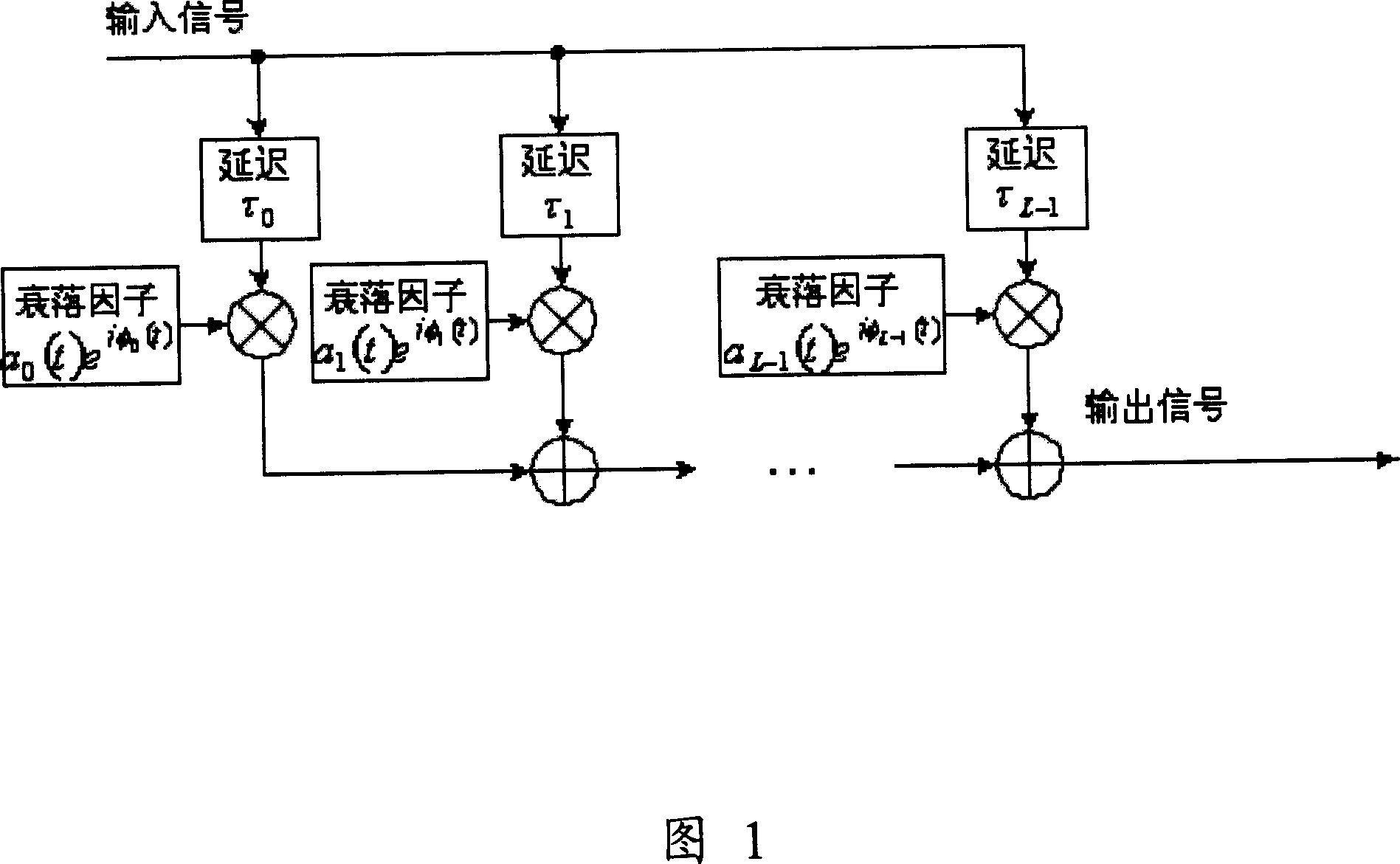
Radio channel simulating method and apparatus thereof
InactiveCN1933378AAvoid multipath fadingCost controlRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransmission monitoringEngineeringRadio channel
A simulation device of radio channel is prepared as setting said device at side of mobile station for carrying out multipath fading treatment on base band signal in order to simulate uplink and downlink channels as well as for superposing a power constant noise on multipath fading-treated signal when uplink channel is simulated.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
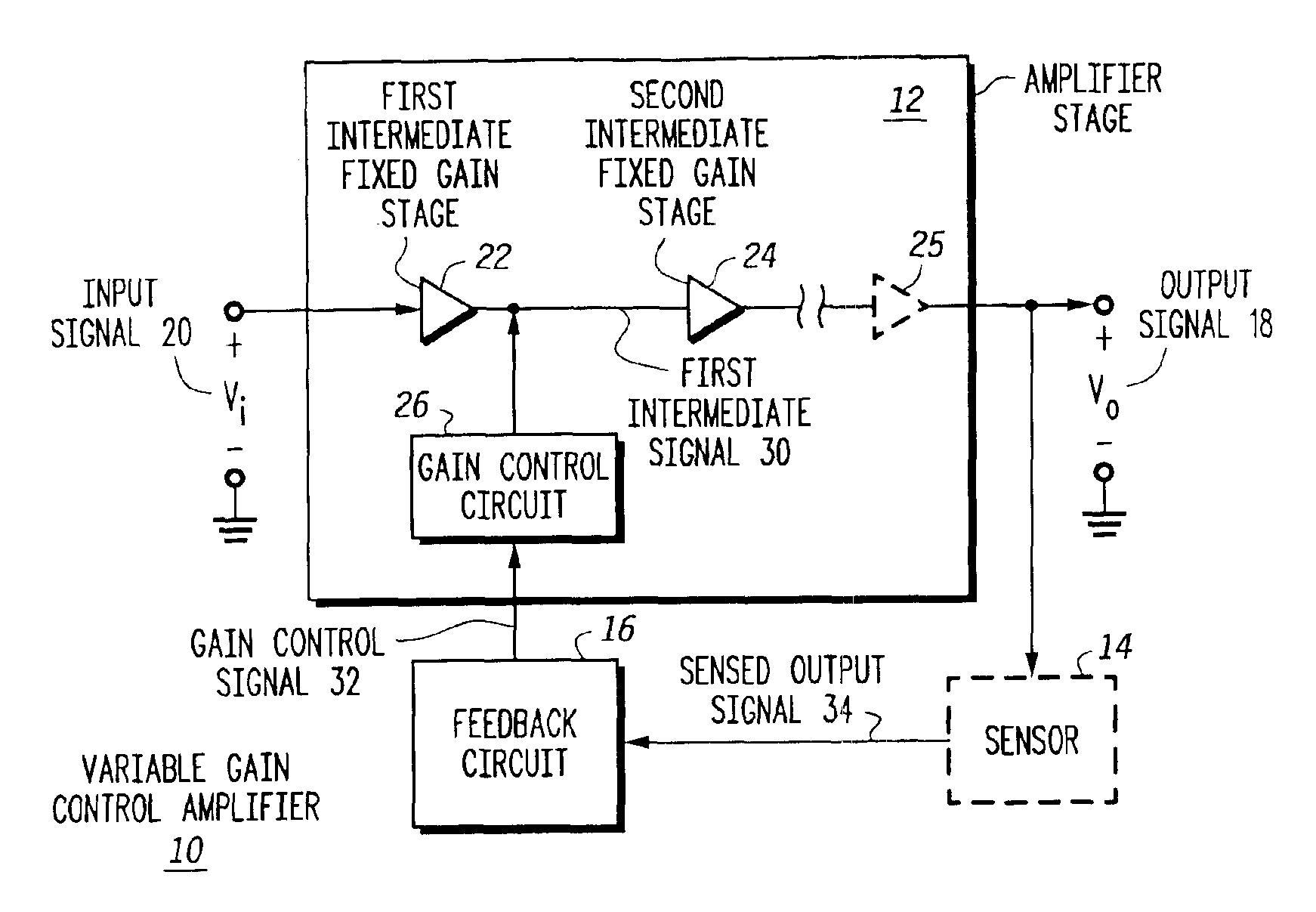
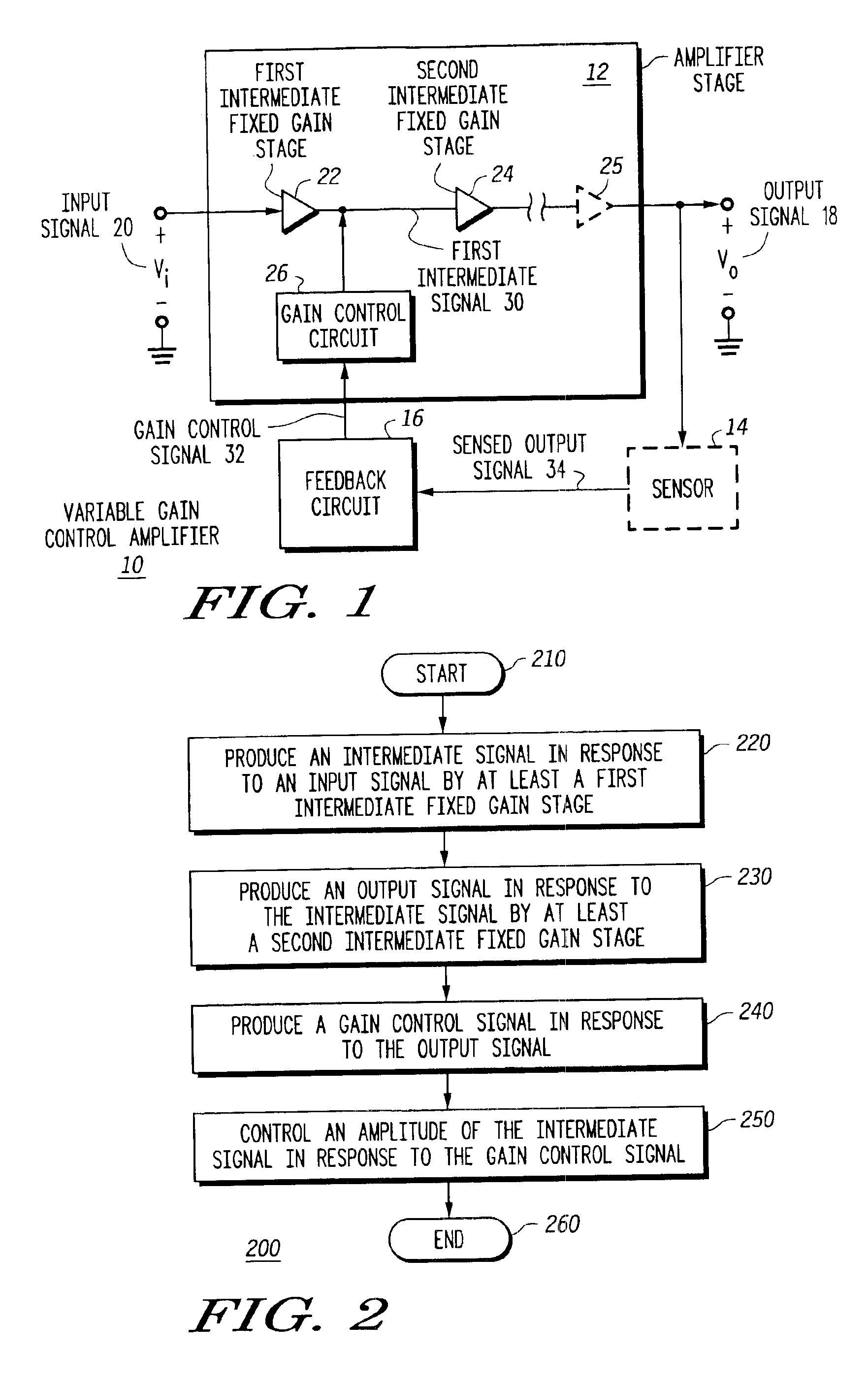
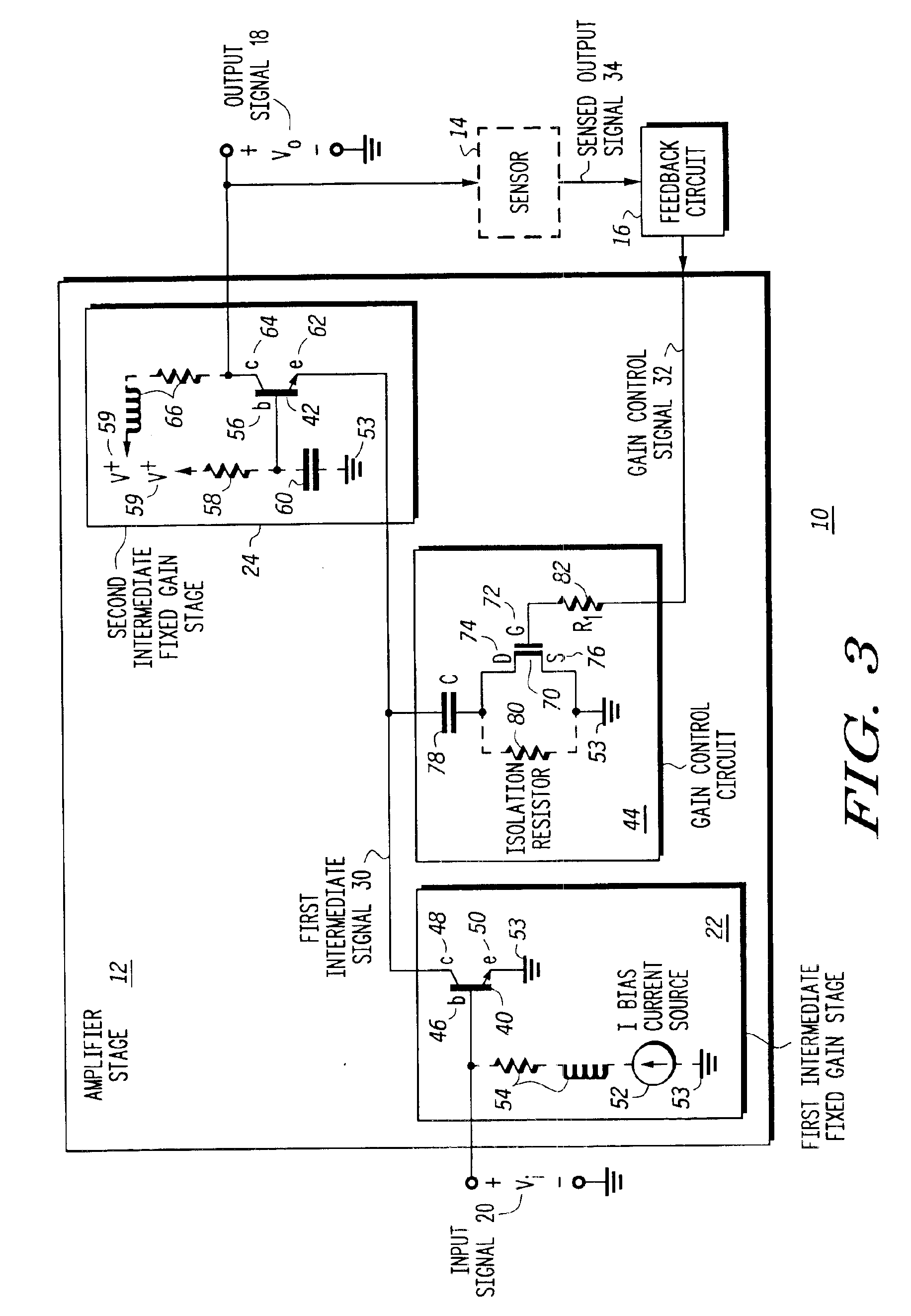
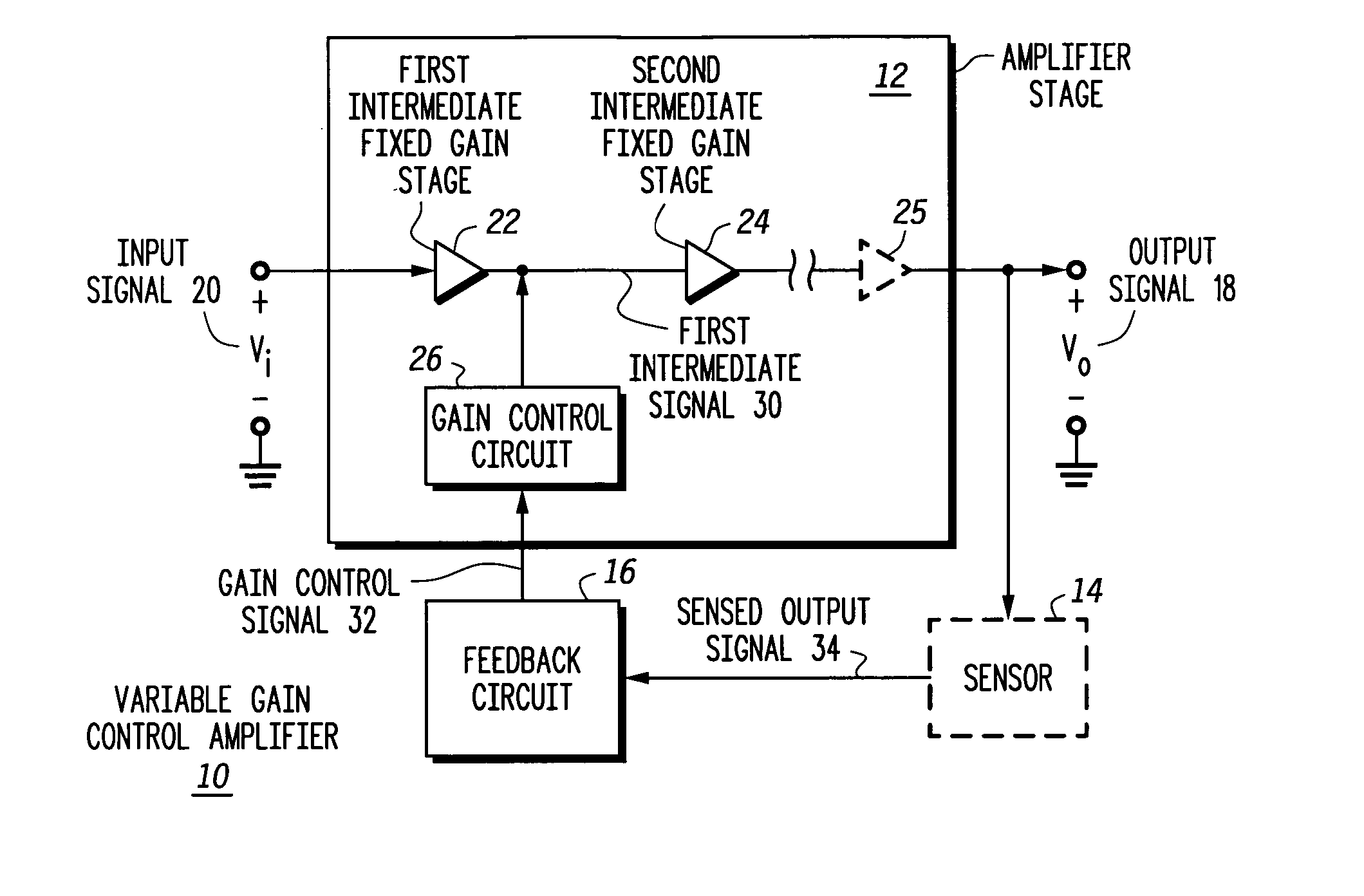
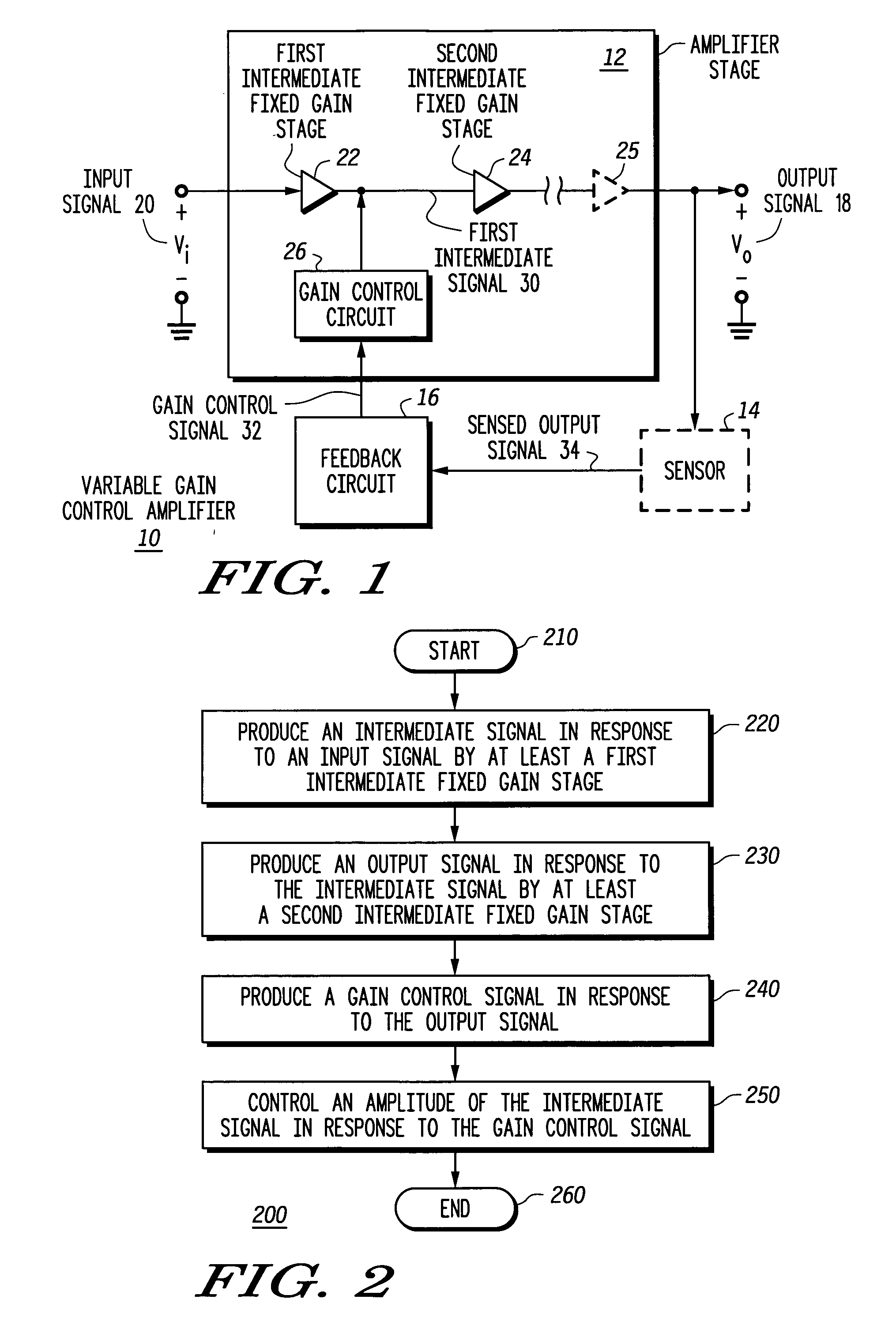
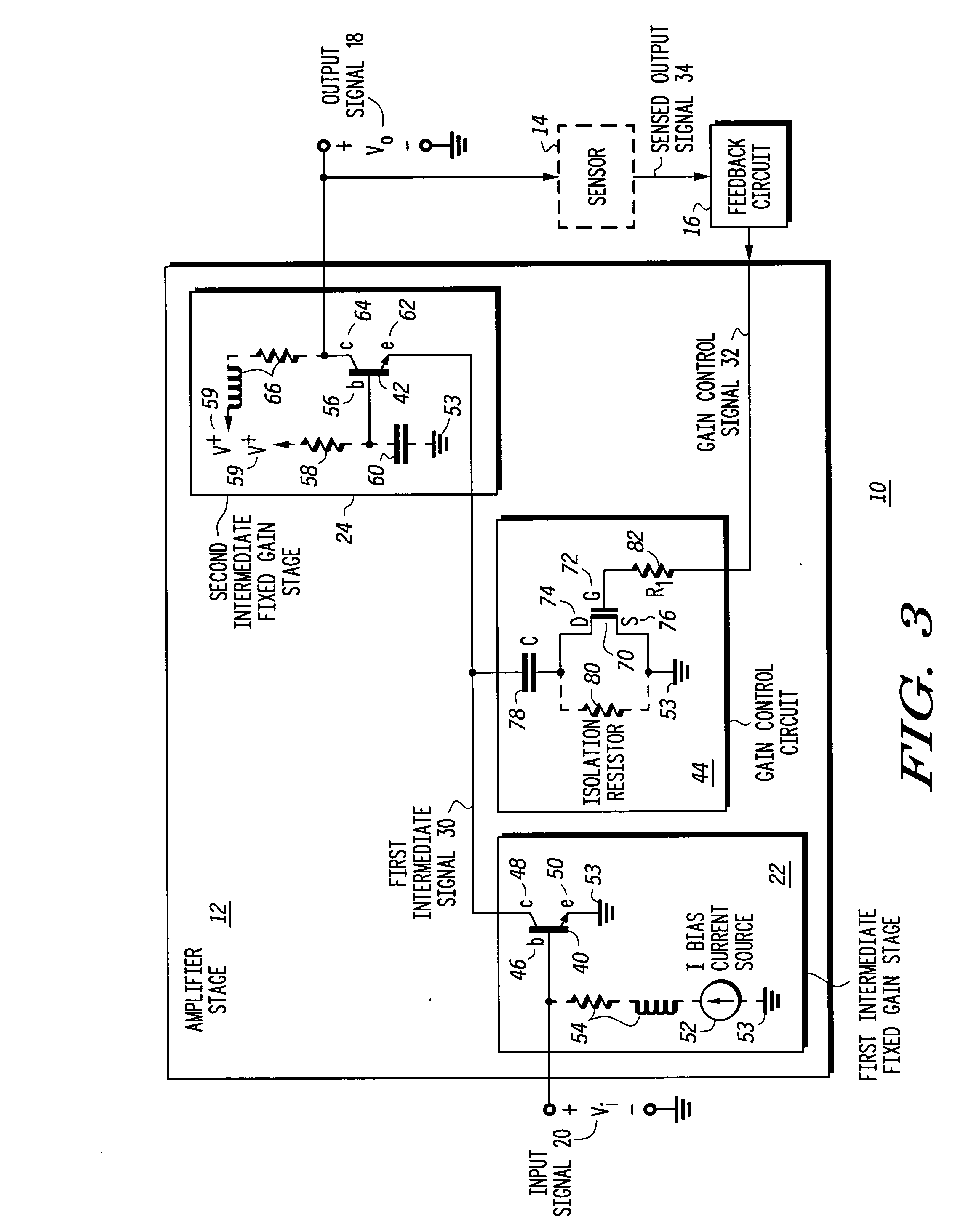
Variable gain low noise amplifier and method
A variable gain control amplifier (10) and method provides a substantially constant input impedance and output impedance, and provides a substantially constant noise figure and third order harmonic. The variable gain control amplifier (10) includes an amplifier stage including at least a first intermediate fixed gain stage (22) operative to produce a first intermediate signal (30) in response to the input signal (20). The variable gain control amplifier (10) further includes at least a second intermediate fixed gain stage (24) operative to produce an output signal (18) in response to the first intermediate signal (30). A feedback circuit (16) is operative to produce a gain control signal (32) in response to the output signal (18). A gain control circuit (26) is coupled to the at least first intermediate fixed gain stage (22) and the second intermediate fixed gain stage (24), and receives the gain control signal (32) to control an amplitude of the intermediate signal (30).
Owner:APPLE INC
Variable gain low noise amplifier and method
A variable gain control amplifier (10) and method provides a substantially constant input impedance and output impedance, and provides a substantially constant noise figure and third order harmonic. The variable gain control amplifier (10) includes an amplifier stage including at least a first intermediate fixed gain stage (22) operative to produce a first intermediate signal (30) in response to the input signal (20). The variable gain control amplifier (10) further includes at least a second intermediate fixed gain stage (24) operative to produce an output signal (18) in response to the first intermediate signal (30). A feedback circuit (16) is operative to produce a gain control signal (32) in response to the output signal (18). A gain control circuit (26) is coupled to the at least first intermediate fixed gain stage (22) and the second intermediate fixed gain stage (24), and receives the gain control signal (32) to control an amplitude of the intermediate signal (30).
Owner:APPLE INC
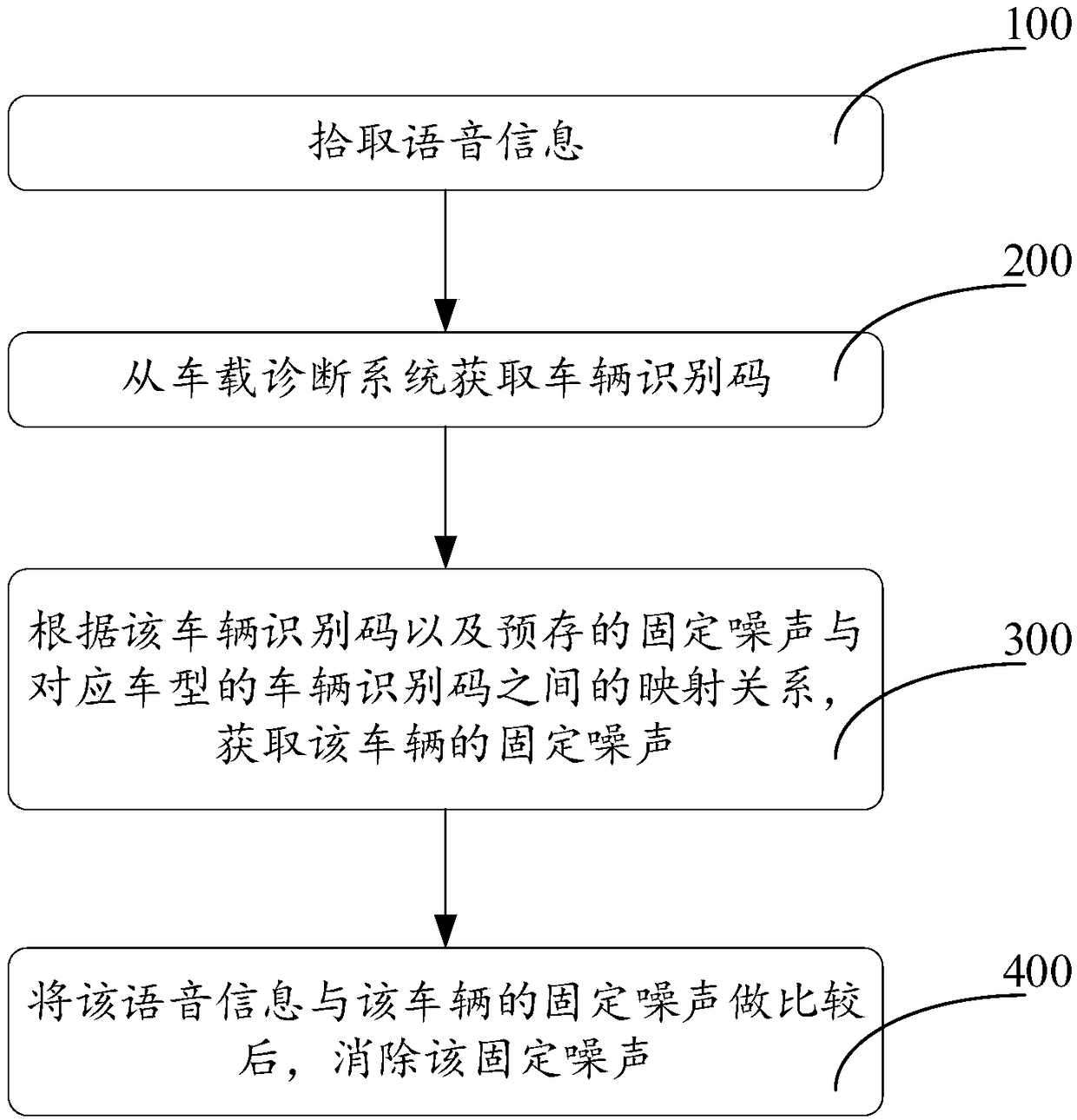
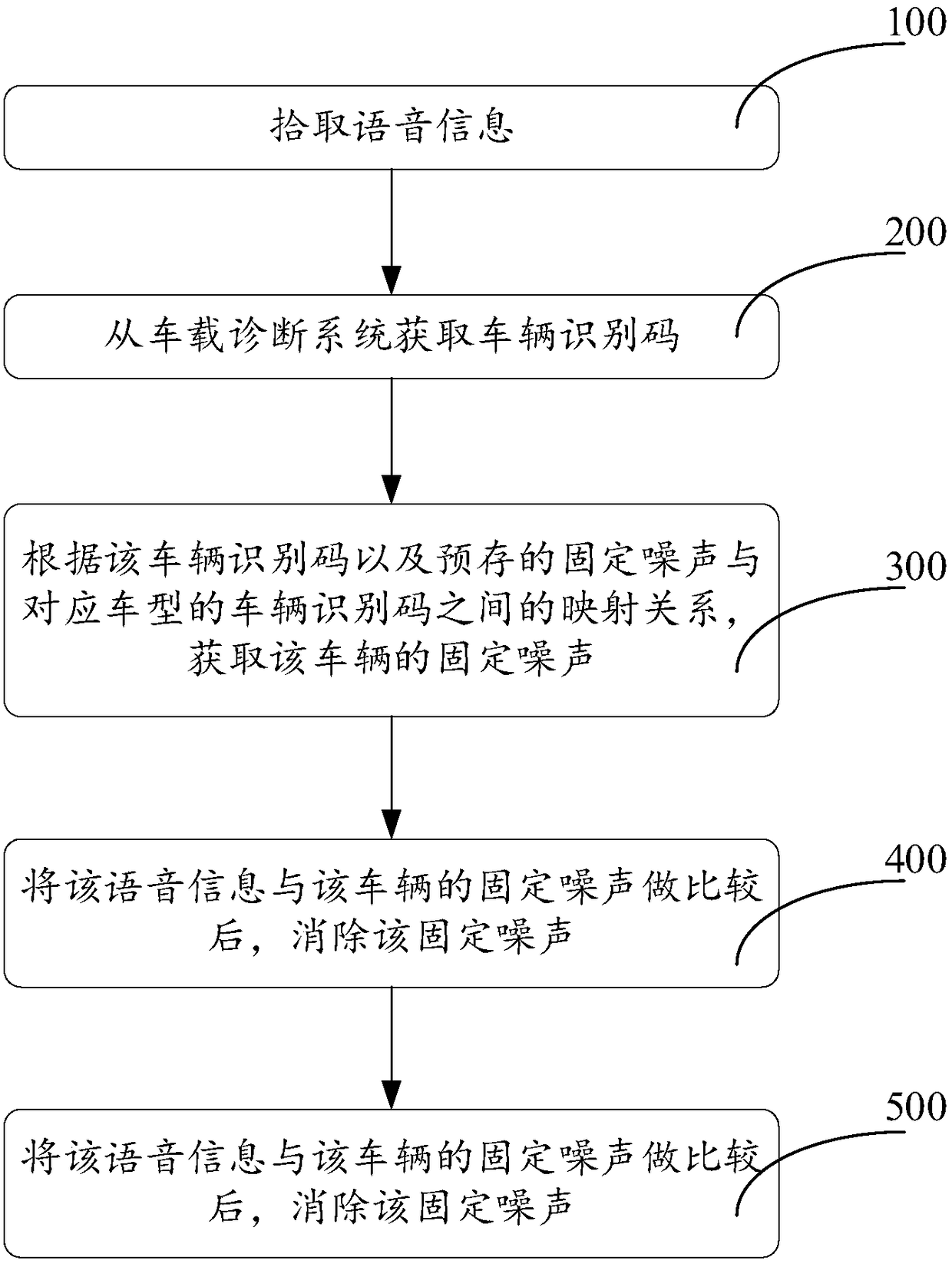
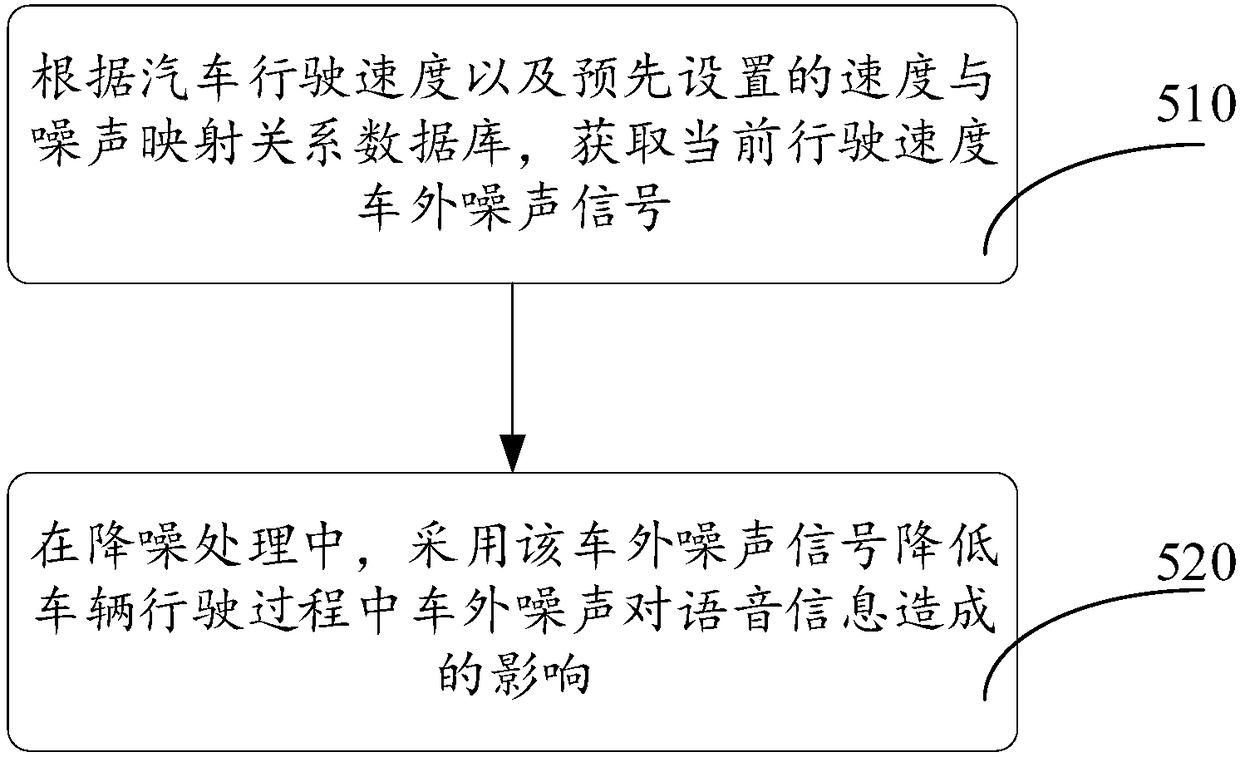
Speech signal processing method and vehicle-mounted electronic device
The invention relates to a speech signal processing method and a vehicle-mounted electronic device. The method includes the following steps that: speech information is picked up; a vehicle identification code is acquired from a vehicle-mounted diagnostic system; the constant noises of a vehicle are acquired according to the vehicle identification code and mapping relations between pre-stored constant noises and vehicle identification codes of corresponding vehicle models, wherein the mapping relations between the pre-stored constant noises and vehicle identification codes of the correspondingvehicle models include the constant noises of different vehicle models and mapping relations between the constant noises of the different vehicle models and the vehicle identification codes of the corresponding vehicle models; and after the speech information is compared with the constant noises of the vehicle, the constant noises are eliminated. Since the constant noises introduced by the vehicleare obtained in advance, the constant noises can be directly eliminated during sound processing.
Owner:ANKER INNOVATIONS TECH CO LTD
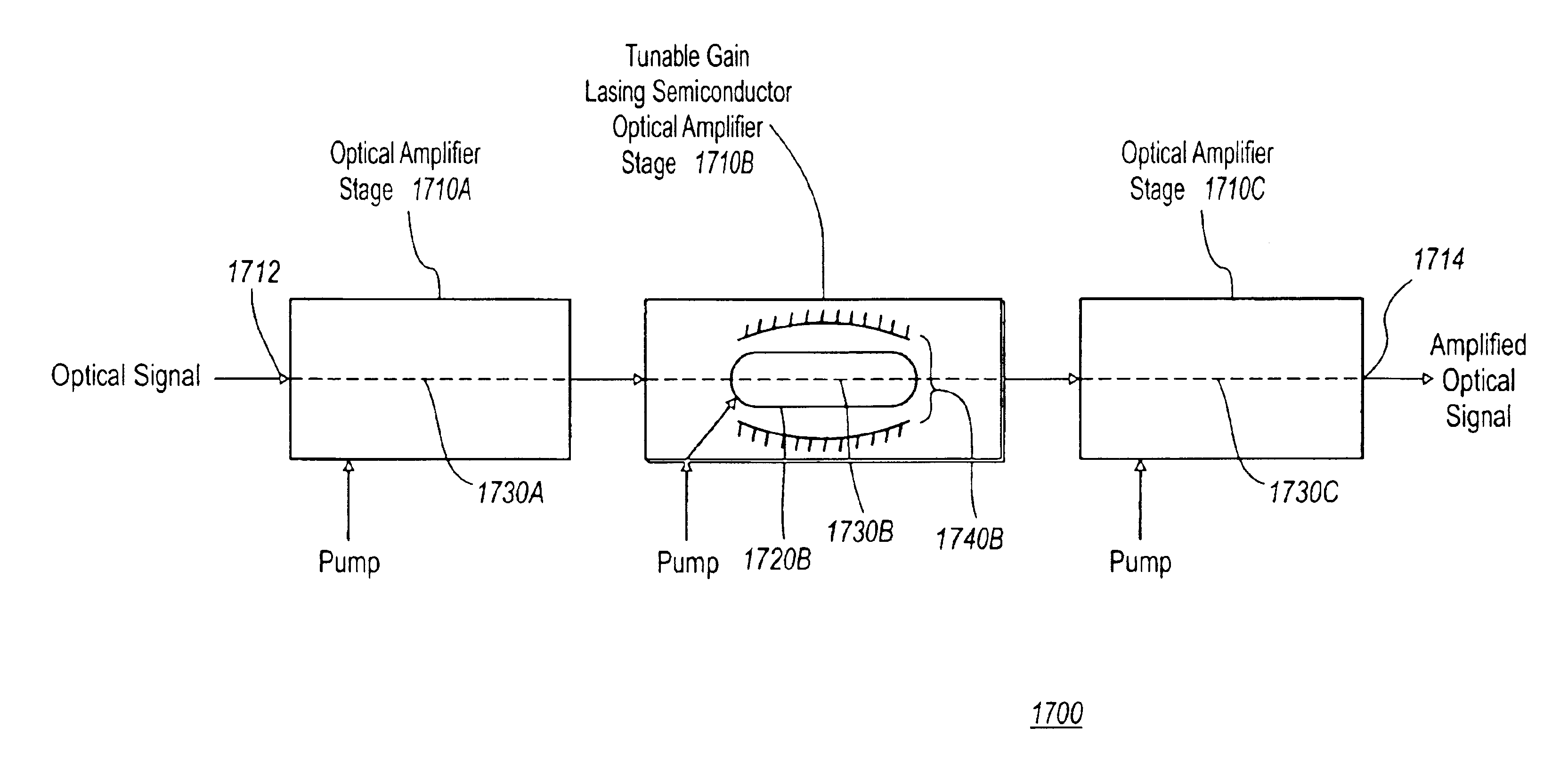
Multistage tunable gain optical amplifier
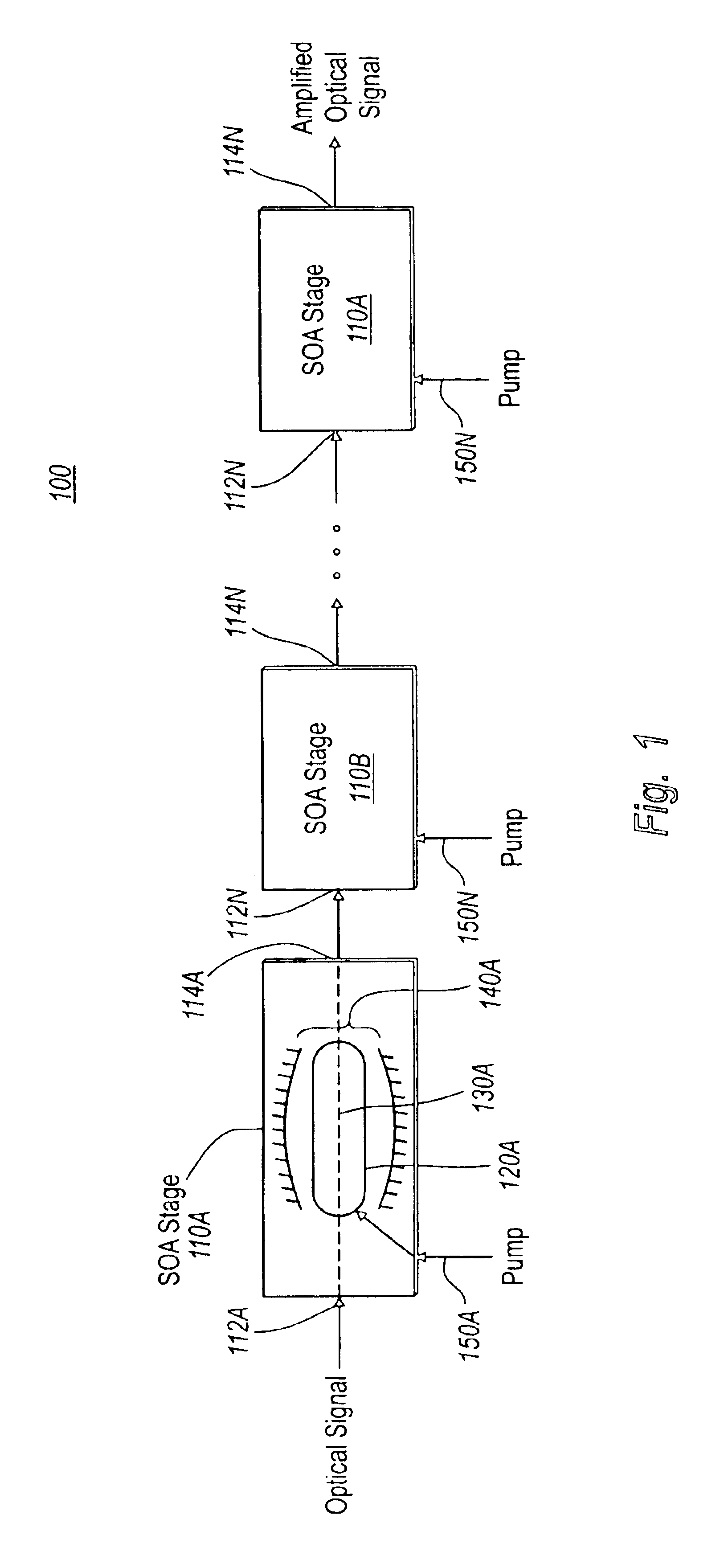
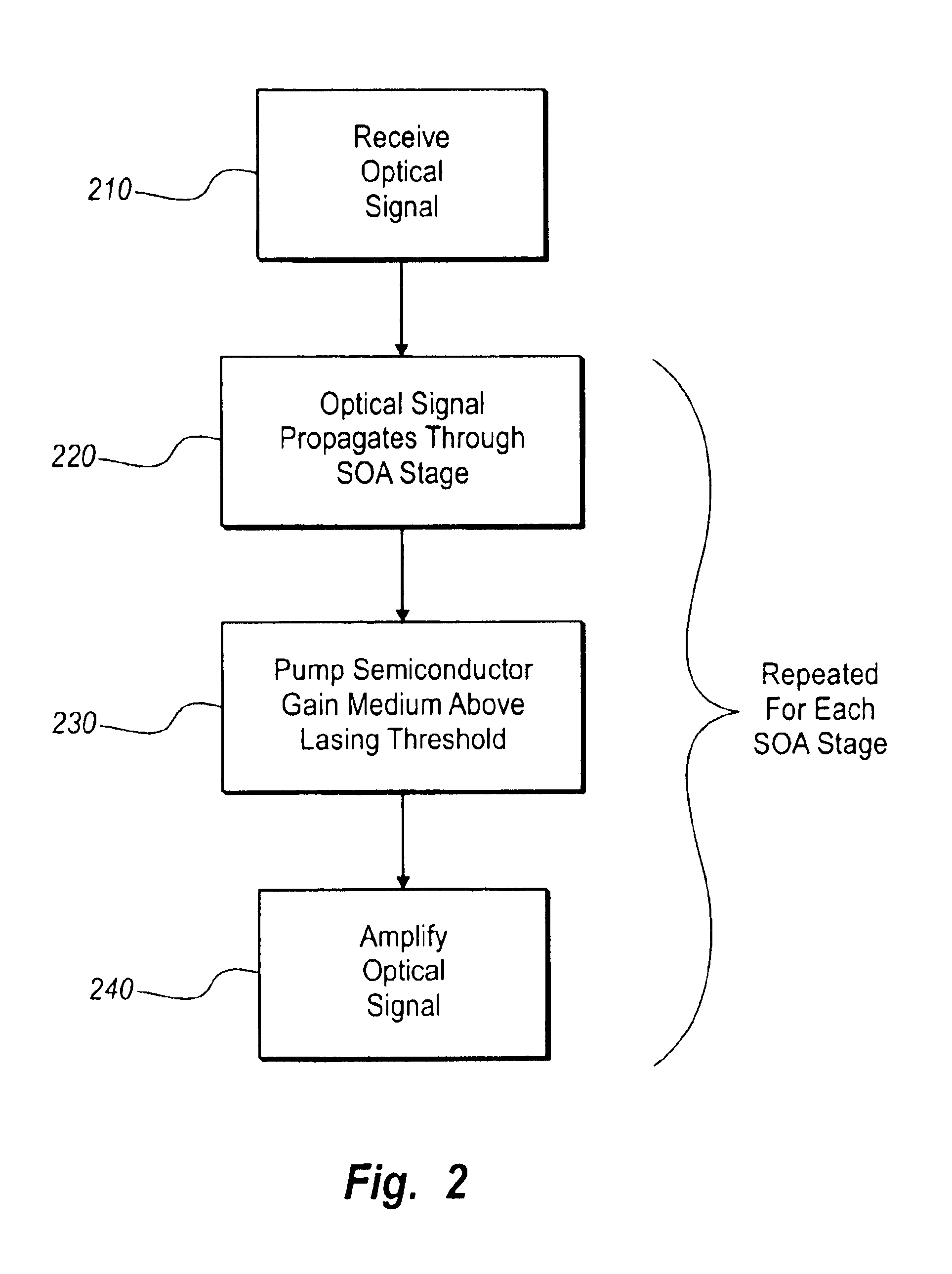
InactiveUS6891664B2Improve Noise PerformanceIncrease output powerSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser output parameters controlAudio power amplifierSingle stage
A multi-stage tunable gain optical amplifier device amplifies an optical signal by a gain amount which can be adjusted in one of the stages of the amplifier. The multi-stage amplifier includes at least two optical amplifier stages coupled in series, one of which is a tunable gain amplifier stage. The optical amplifier stages are characterized by a design parameter which varies from stage to stage. In a preferred embodiment, the design parameter includes a noise figure and a saturable power, with both parameters increasing as the optical signal propagates from stage to stage. As a result, the multi-stage tunable gain optical amplifier can achieve better noise performance and higher output power than a single stage optical amplifier with a constant noise figure and saturable power.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Noise coefficient measuring method and noise coefficient standard device
The invention discloses a noise coefficient measuring method and a noise coefficient standard device and belongs to the technical field of measurement. The noise coefficient measuring method comprises the steps that the noise coefficient standard device is provided, wherein the noise coefficients of the noise coefficient standard device at low frequency points are the constant values; a noise coefficient measurer is adopted to measure the noise coefficient standard device, and noise coefficient measurement values of the noise coefficient standard device at the low frequency points to be measured are obtained; the noise coefficient measurer is adopted to measure a device to be measured, and noise coefficient measurement values of the device to be measured at the low frequency points to be measured are obtained; the noise coefficients of the device to be measured at the low frequency points to be measured are calculated according to the constant noise coefficient values of the noise coefficient standard device at the low frequency points to be measured, the noise coefficient measurement values of the noise coefficient standard device at the low frequency points to be measured, and the noise coefficient measurement values of the device to be measured at the low frequency points to be measured. The noise coefficient measuring method and the noise coefficient standard device solve the problem that the low-frequency noise coefficients of the device cannot be measured in the prior art.
Owner:NO 722 RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND
Analyte sensors having a signal-to-noise ratio substantially unaffected by non-constant noise
Systems and methods of use involving sensors having a signal-to-noise ratio that is substantially unaffected by non-constant noise are provided for continuous analyte measurement in a host. In some embodiments, a continuous analyte measurement system is configured to be wholly, transcutaneously, intravascularly or extracorporeally implanted.
Owner:DEXCOM
Nerve computing model for solving matrix equation set
InactiveCN107391445ANeural architecturesComplex mathematical operationsActivation functionComputational model
A method for constructing a neural computing model for solving matrix equations, the formula of which is: A ( t ) X ( t ) · = - A · ( t ) X ( t ) + B · ( t ) - F ( A ( t ) X ( t ) - B ( t ) ) - G ( A ( t ) X ( t ) - B ( t ) + ∫ 0 t F ( A ( t ) X ( t ) - B ( t ) ) d t ) + W ( t ) Calculate the solved X(t) through this final formula, starting from any initial state X(0)∈Rn×m, which is equivalent to the state matrix of the time-varying theoretical solution, and each of their elements is a monotonically increasing odd activation function . The neural computing model for solving matrix equations of the present invention has the characteristics of converging to the theoretical solution of matrix equations in a limited time even under the pollution of noise (constant noise, random noise), and no matter what activation function is used, the present invention The invention can converge to the theoretical solution of matrix equations.
Owner:QUFU NORMAL UNIV
Analyte sensors having a signal-to-noise ratio substantially unaffected by non-constant noise
Systems and methods of use involving sensors having a signal-to-noise ratio that is substantially unaffected by non-constant noise are provided for continuous analyte measurement in a host. In some embodiments, a continuous analyte measurement system is configured to be wholly, transcutaneously, intravascularly or extracorporeally implanted.
Owner:DEXCOM
Electronic device for supplying power source and noise filter which having high-efficient noise reducing
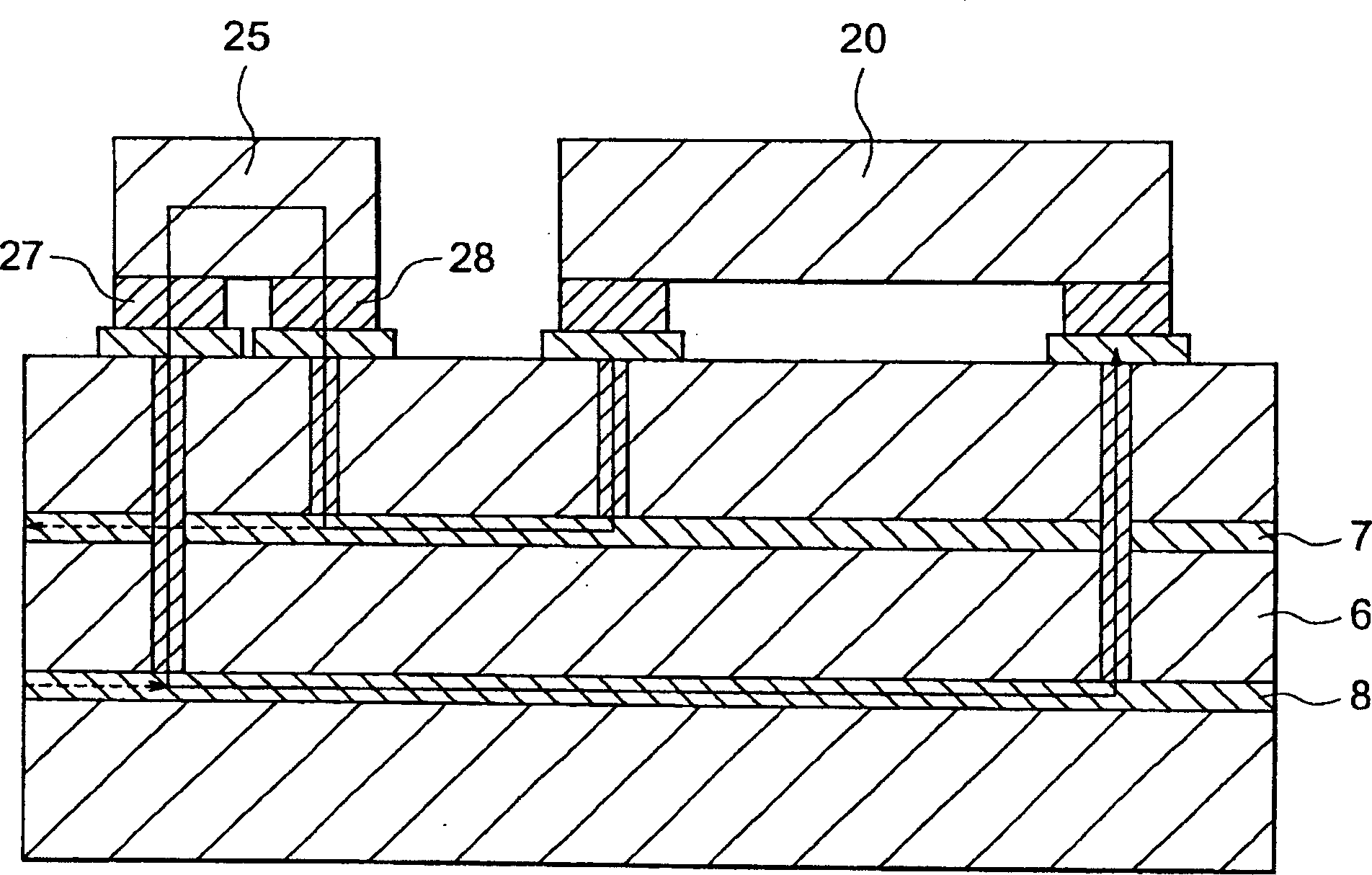
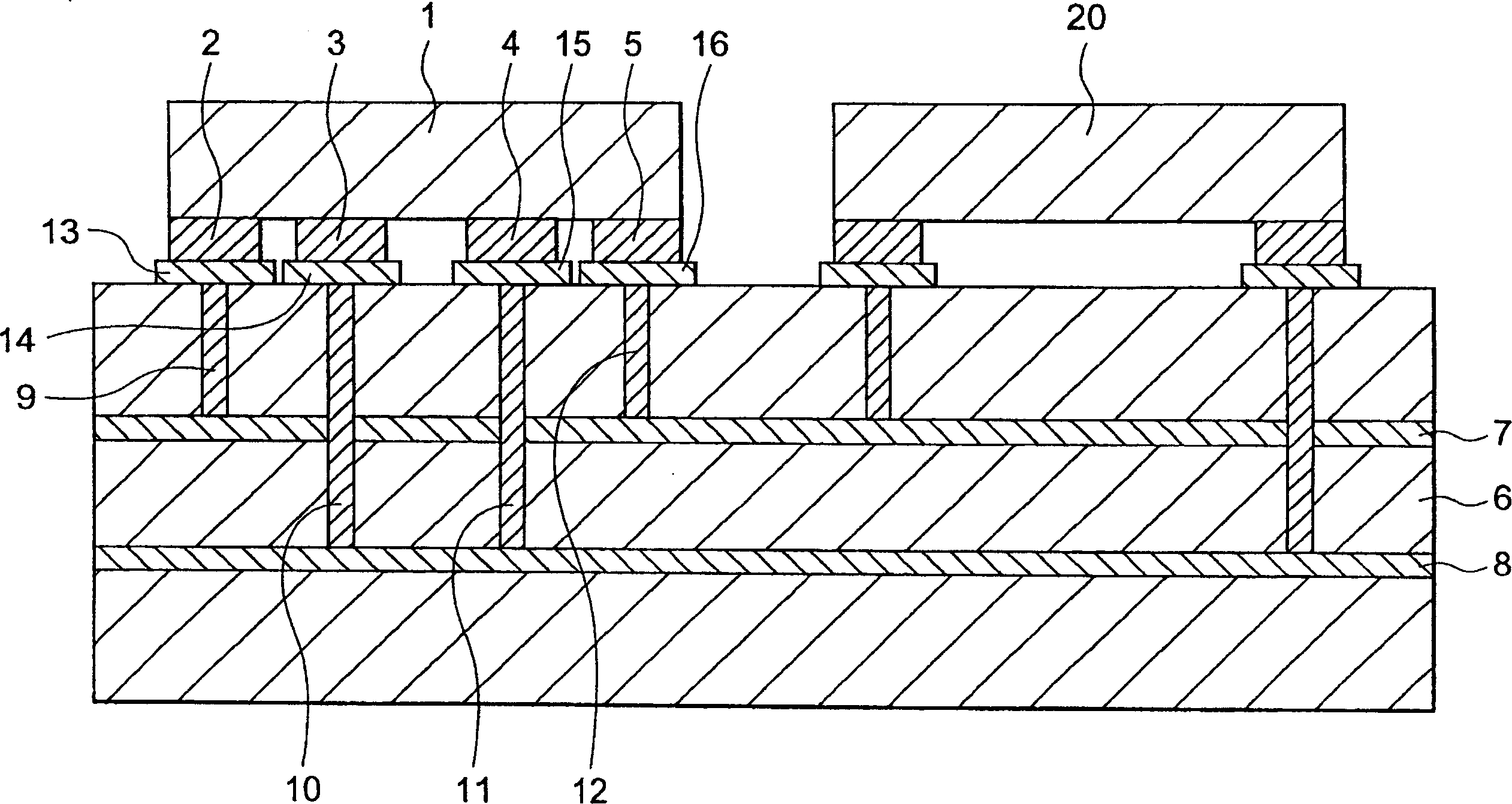
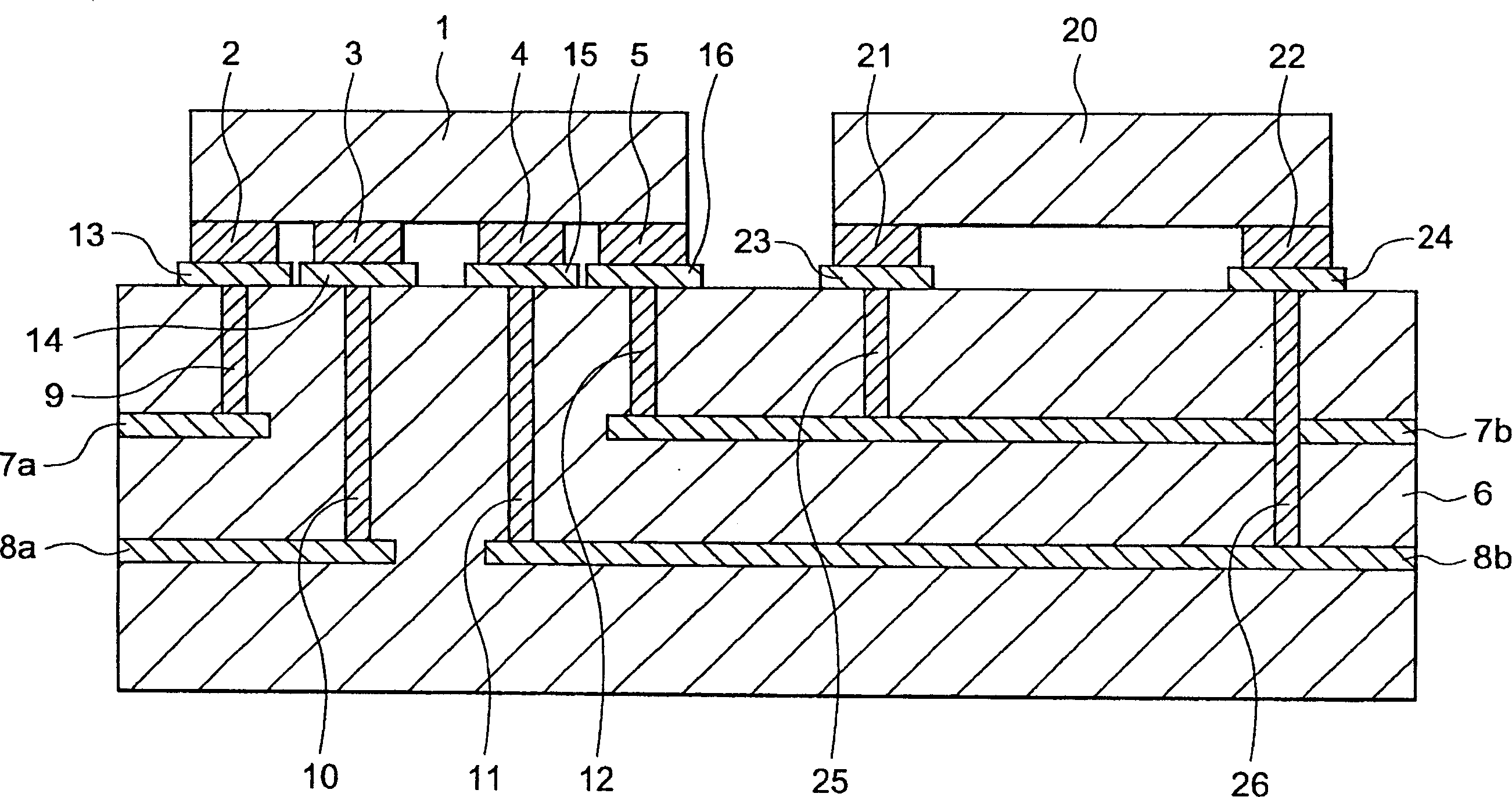
InactiveCN1446041AMultiple-port networksCross-talk/noise/interference reductionElectrical conductorConstant noise
In an electronic device for supplying DC power to an LSI chip (20), a distributed constant type noise filter (1) having an input port (2, 3) and an output port (5, 4) is fixed on a circuit board (6 )superior. The noise filter (1) reduces the ingress of high frequency noise while allowing DC power to flow through. The input ports (2, 3) are connected to a DC power line (7a) and a ground conductor (8a) on the circuit board (6). The output ports (5, 4) are connected with independent power supply conductors (7b) and independent ground conductors (8b), and the independent power supply conductors (7b) and independent ground conductors (8b) are fixed on the circuit board (6) The LSI (20) is connected. In another embodiment, the LSI (20) is fixed on another circuit board (17), and the output ports (5, 4) of the filter pass through conductor pins (18, 19) on the circuit board (6) Connect with another circuit board (17).
Owner:TOKIN CORP
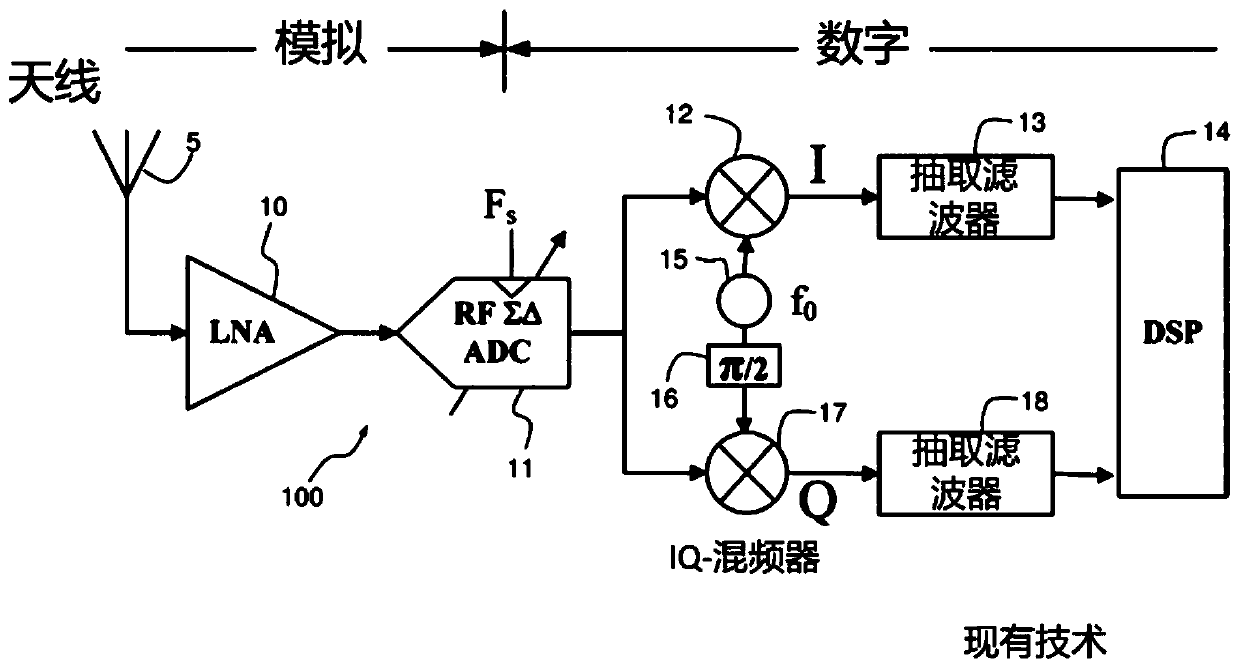
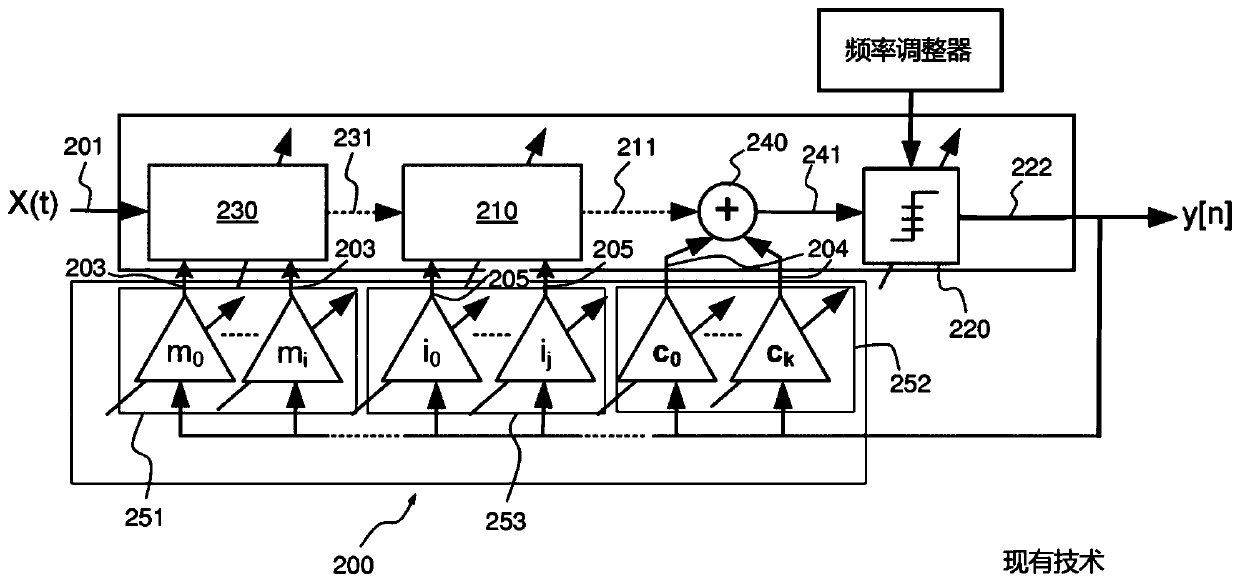
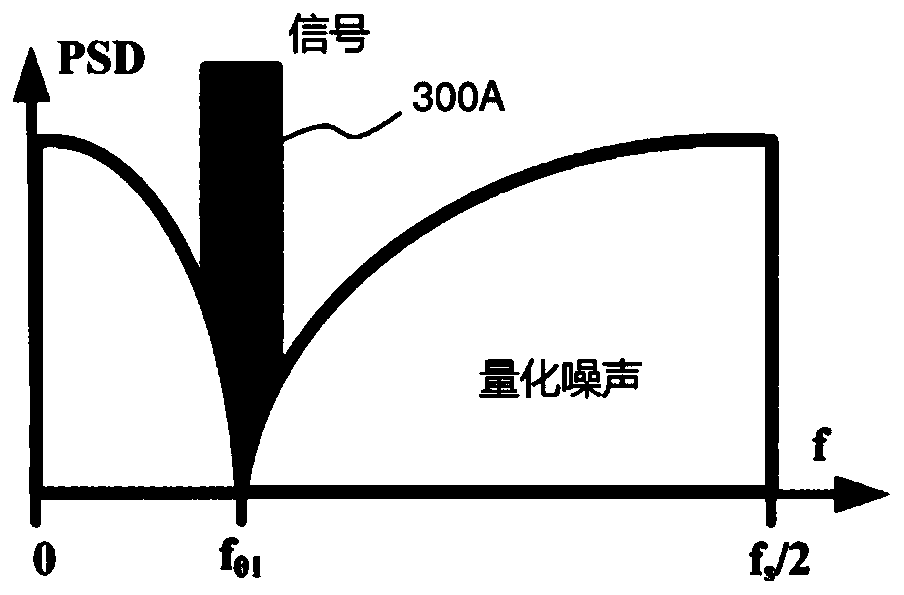
Sigma-delta modulator
A Sigma-Delta ([Sigma][Delta]) modulator for converting an analog input signal having a frequency bandwidth around a variable center frequency f 0 to a digital output signal at a sampling frequency fs . The [Sigma][Delta] modulator comprises a quantizer (420) for generating the digital output signal and a loop filter for shaping the quantization noise. The loop filter comprises at least one subfilter (430, 410) centered around a frequency f0 and constant noise shaping coefficients (451, 452, 453). The [Sigma][Delta] modulator further comprises a tunable delay element (455), a frequency adjuster (480) for adjusting the sampling frequency f s such that the normalized center frequency f0 / fs is constant, and a delay adjuster (490) for adjusting the loop delay td implemented by the quantizer and the tunable delay element (455), such that the normalized loop delay td / Ts falls in a predetermined range [tmin,tmax], where Ts=1 / fs.
Owner:SORBONNE UNIV +1
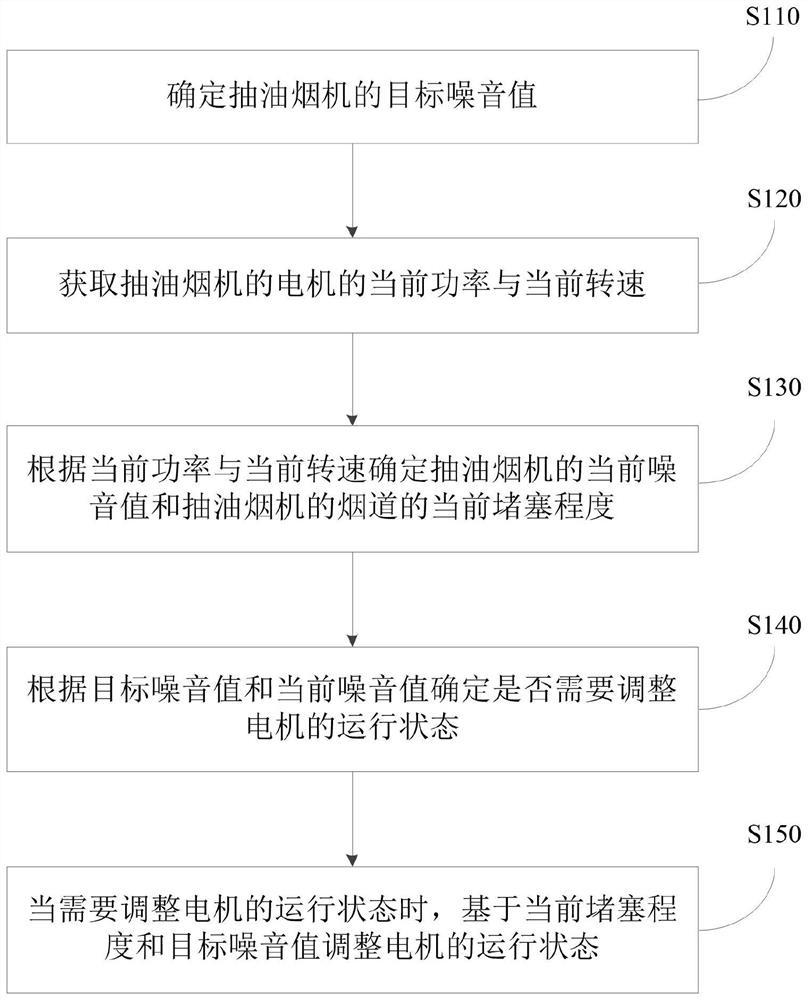
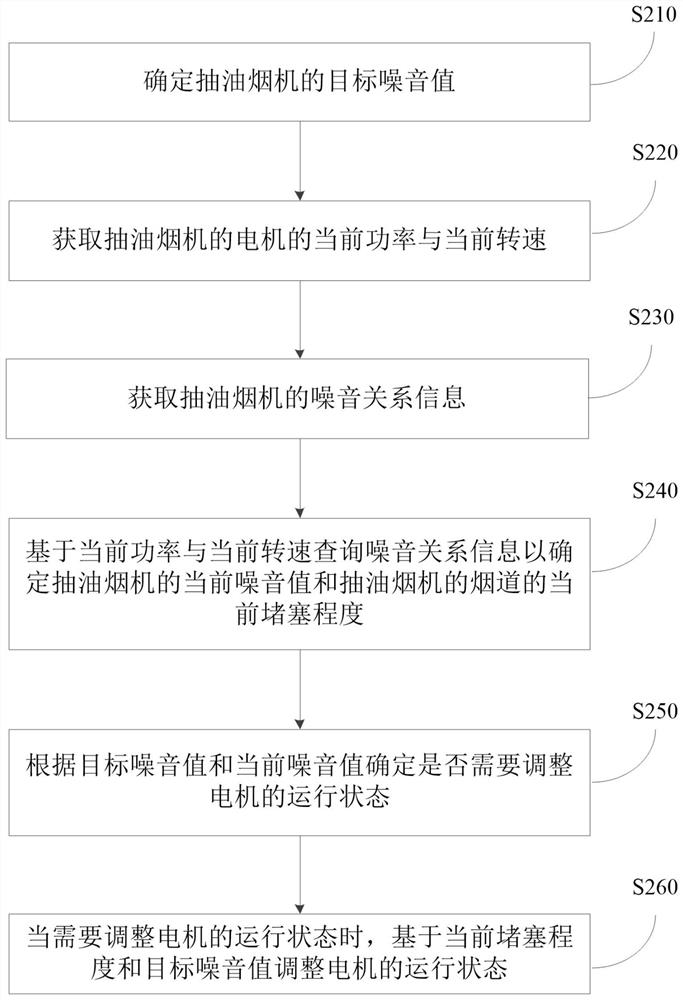
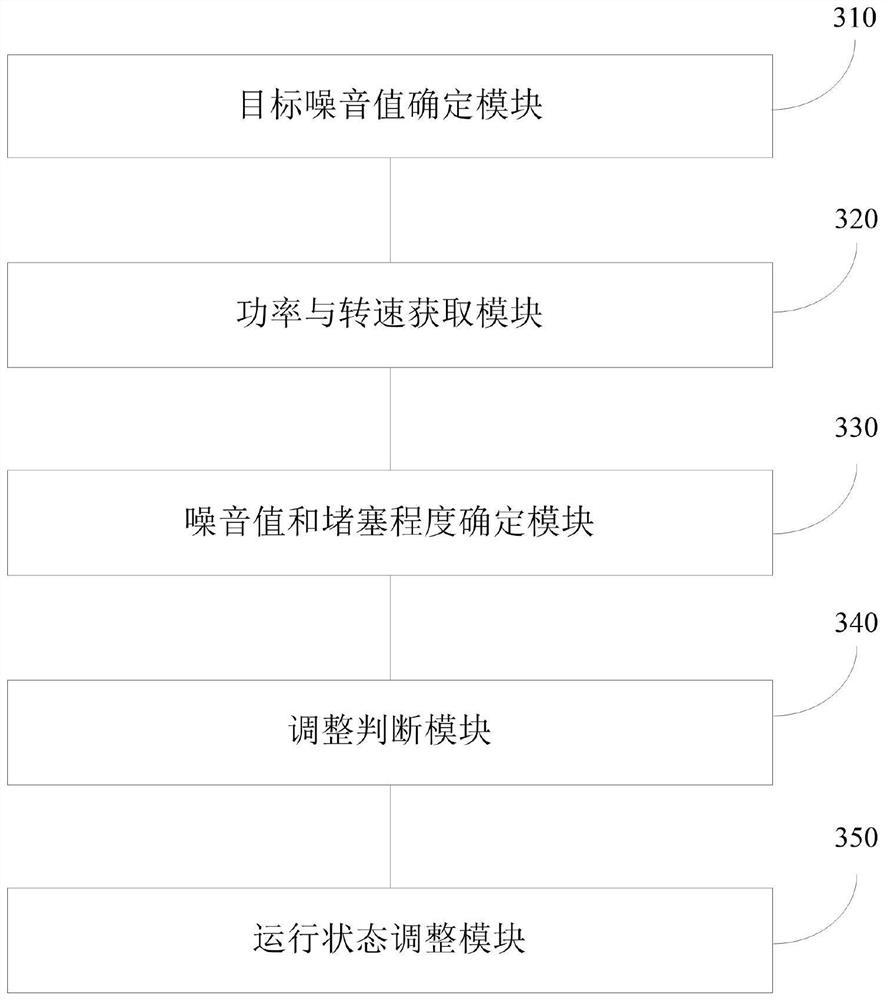
Noise control method and device of smoke exhaust ventilator, smoke exhaust ventilator and storage medium
PendingCN114322022AResolutionResolution statusDomestic stoves or rangesLighting and heating apparatusNoise controlSuction force
The invention discloses a noise control method and device of a smoke exhaust ventilator, the smoke exhaust ventilator and a storage medium. The noise control method of the range hood comprises the following steps: determining a target noise value of the range hood; acquiring the current power and the current rotating speed of a motor of the range hood; determining the current noise value of the range hood and the current blockage degree of a flue of the range hood according to the current power and the current rotating speed; determining whether the operation state of the motor needs to be adjusted according to the target noise value and the current noise value; and when the operation state of the motor needs to be adjusted, the operation state of the motor is adjusted based on the current blockage degree and the target noise value. According to the technical scheme, the problem that the range hood cannot adjust the running state of the motor in time according to the flue blocking degree is solved, and the effects that the running state of the motor is adjusted in time under the condition that the flue blocking degree is large or small, and stronger suction force is provided as much as possible under the condition that constant noise is kept are achieved.
Owner:QINGDAO HAIER WISDOM KITCHEN APPLIANCE CO LTD +1
Polymer membranes for continuous analyte sensors
PendingUS20220142532A1Level accuracyReconstruction from projectionAdditive manufacturing apparatusAnalyteConstant noise
Devices and methods are described for providing continuous measurement of an analyte concentration. In some embodiments, the device has a sensing mechanism and a sensing membrane that includes at least one surface-active group-containing polymer and that is located over the sensing mechanism. The sensing membrane may have a bioprotective layer configured to substantially block the effect and / or influence of non-constant noise-causing species.
Owner:DEXCOM
Analyte sensors having a signal-to-noise ratio substantially unaffected by non-constant noise
Systems and methods of use involving sensors having a signal-to-noise ratio that is substantially unaffected by non-constant noise are provided for continuous analyte measurement in a host. In some embodiments, a continuous analyte measurement system is configured to be wholly, transcutaneously, intravascularly or extracorporeally implanted.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
Shock absorption device for mechanical equipment
InactiveCN108953474AReduce noiseReduce harmNon-rotating vibration suppressionSteering wheelMechanical equipment
A shock absorption device for mechanical equipment comprises a workbench; a limiting fixing rack is fixedly installed on the upper surface of the workbench; a table top shock absorption device is installed below the workbench in an inlaid mode; a plurality of supporting arms are vertically installed below the table top shock absorption device; one end of each supporting arm is fixedly connected with the table top shock absorption device; the other end of each supporting arm is provided with a tyre shock absorption device, and the supporting arms are movably connected with the tyre shock absorption devices; and steering wheels are movably installed below the tyre shock absorption devices. The shock absorption device for the mechanical equipment has the beneficial effects that tyre shock absorption is conducted through the tyre shock absorption devices, noise generated by high-intensity operation is lowered, and harm of continuous noise to workers is reduced; and by adopting the table top shock absorption device for absorbing shock, the shock absorption strength of the shock absorption device for the mechanical equipment is improved, noise generated by the shock absorption device forthe mechanical equipment is reduced, and the machine service life is prolonged.
Owner:金双悦
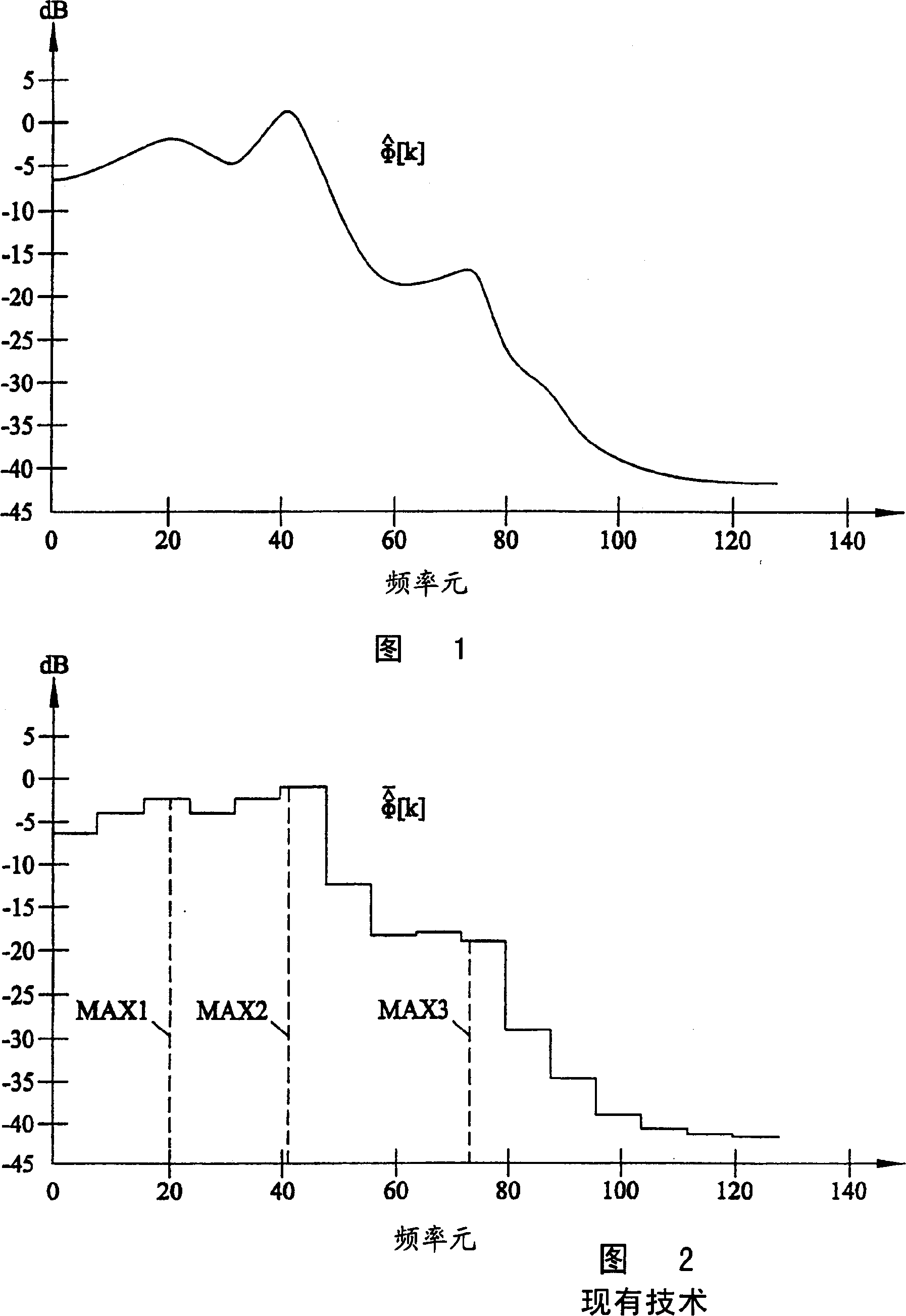
Digital filter design method and apparatus for noise suppression by spectral substraction
InactiveCN1197243CReduce complexityMinimize spectral variationDigital technique networkSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumVolumetric Mass Density
A digital filter design apparatus for noise suppression by spectral subtraction includes a first spectrum estimator for determining a high frequency resolution noisy speech power spectral density estimate from a noisy speech signal block. A second spectrum estimator determines a high frequency resolution background noise power spectral density estimate from a background noise signal block. Averaging units form a piece-wise constant noisy speech power spectral density estimate and a piece-wise constant background noise power spectral density estimate. These averaging units are controlled by devices for adapting the length of individual segments to the shape of the high frequency-resolution noisy speech power spectral density estimate and for using the same segmentation in both piecewise constant estimates. A piece-wise constant digital filter transfer function is determined using spectral subtraction-based on the piece-wise constant noisy speech power spectral density estimate and the piece-wise constant background noise power spectral density estimate.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
A Noise Figure Measurement Method and Noise Figure Standard Device
The invention discloses a noise coefficient measuring method and a noise coefficient standard device and belongs to the technical field of measurement. The noise coefficient measuring method comprises the steps that the noise coefficient standard device is provided, wherein the noise coefficients of the noise coefficient standard device at low frequency points are the constant values; a noise coefficient measurer is adopted to measure the noise coefficient standard device, and noise coefficient measurement values of the noise coefficient standard device at the low frequency points to be measured are obtained; the noise coefficient measurer is adopted to measure a device to be measured, and noise coefficient measurement values of the device to be measured at the low frequency points to be measured are obtained; the noise coefficients of the device to be measured at the low frequency points to be measured are calculated according to the constant noise coefficient values of the noise coefficient standard device at the low frequency points to be measured, the noise coefficient measurement values of the noise coefficient standard device at the low frequency points to be measured, and the noise coefficient measurement values of the device to be measured at the low frequency points to be measured. The noise coefficient measuring method and the noise coefficient standard device solve the problem that the low-frequency noise coefficients of the device cannot be measured in the prior art.
Owner:NO 722 RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND
System and method for active noise reduction of engine in vehicle
ActiveCN106089361BNoise impact is negligibleFast convergenceSilencing apparatusMachines/enginesSound sourcesEngineering
The invention relates to an active noise reduction system for an engine in an automobile. The system comprises two error microphones, five secondary sound source loudspeakers and one self-adaptation active controller. The two error microphones are arranged at automobile roof positions corresponding to a front row and a back row of the automobile. The five secondary sound source loudspeakers are composed of four vehicle-mounted loudspeaker boxes arranged on the automobile door sides and one secondary sound source arranged at the position of a rear row partition plate. The self-adaptation active controller comprises a DSP master control chip, an audio decoding chip, an off-chip storage unit, a CAN bus controller, a power amplifier, an error microphone signal receiving module, a secondary sound source output module and a power module. The invention further relates to an active noise reduction method for the engine in the automobile. By means of the system and method, error noise signals in active noise reduction reach the minimum value during constant noise reduction control, the noise influence caused by the error noise signals can be basically ignored, and the expected noise reduction effect can be rapidly achieved.
Owner:HEFEI CHANGAN AUTOMOBILE +1
Low-noise amplifying system with constant noise and linear phase during programmable attenuation
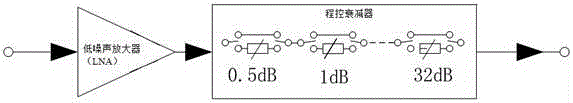
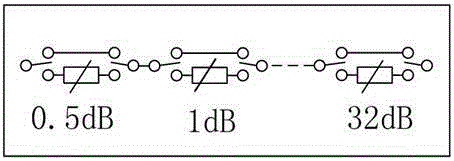
InactiveCN105187016ALinear Phase GuaranteedAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceLow noiseNoise level
The invention discloses a low-noise amplifying system with constant noise and a linear phase during programmable attenuation. A first bilateral switch, an attenuating and compensating module, a second bilateral switch and a low noise amplifier are connected in sequence between an input end and an output end of the system. The system also comprises an adaptive digital programmable attenuation control module, wherein the adaptive digital programmable attenuation control module is applied to digital programmed control of amplitude attenuation, and used for performing signal channel adaptive control according to digital attenuation at the same time in order that a programmable attenuator keeps a system noise level constant in the presence of attenuation and keeps low insertion loss of a signal channel in the absence of attenuation, and the influence of the insertion loss of a programmable attenuation radio-frequency electronic switch on a system noise coefficient is lowered; the attenuating and compensating module is used for attenuating a signal amplitude, and compensating for an electric length of a signal phase during signal attenuation through the radio-frequency electronic switch by calculation of a frequency wavelength in order to obtain the same phase difference under different attenuation situations and compensate for phase deviations caused by programmable attenuation; and the low noise amplifier is used for realizing low noise amplification of signals.
Owner:南京长江电子信息产业集团有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com