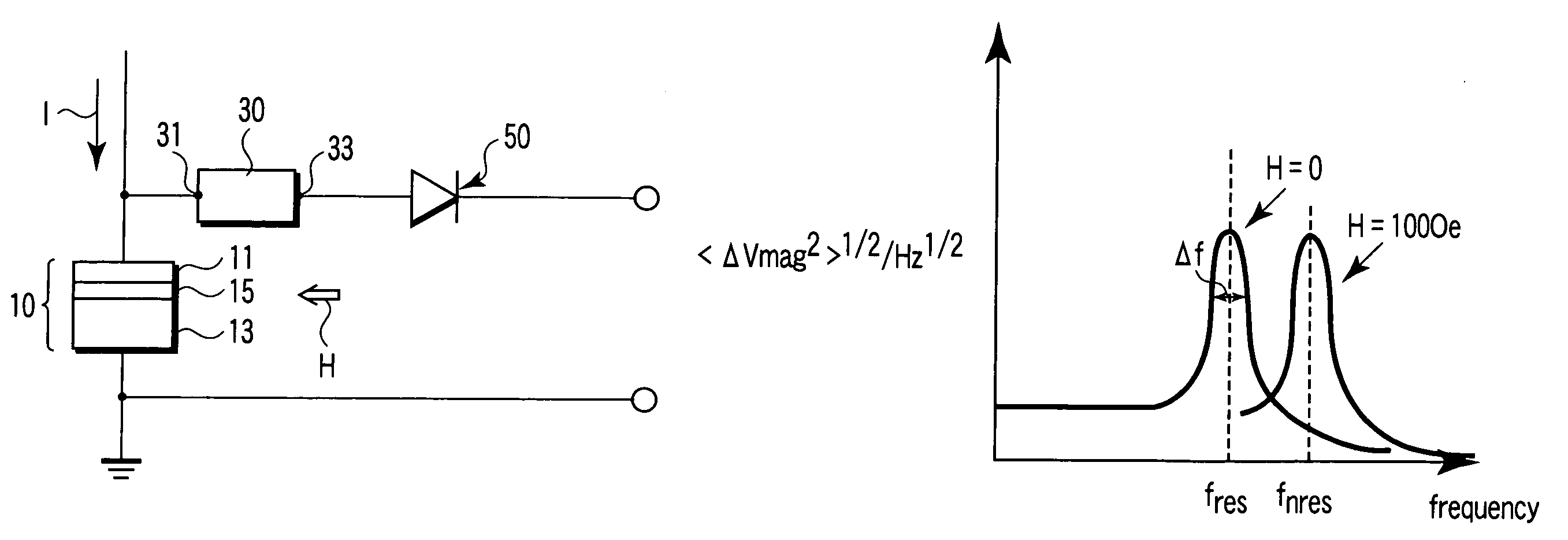Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
251results about "Signal processing for reducing noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
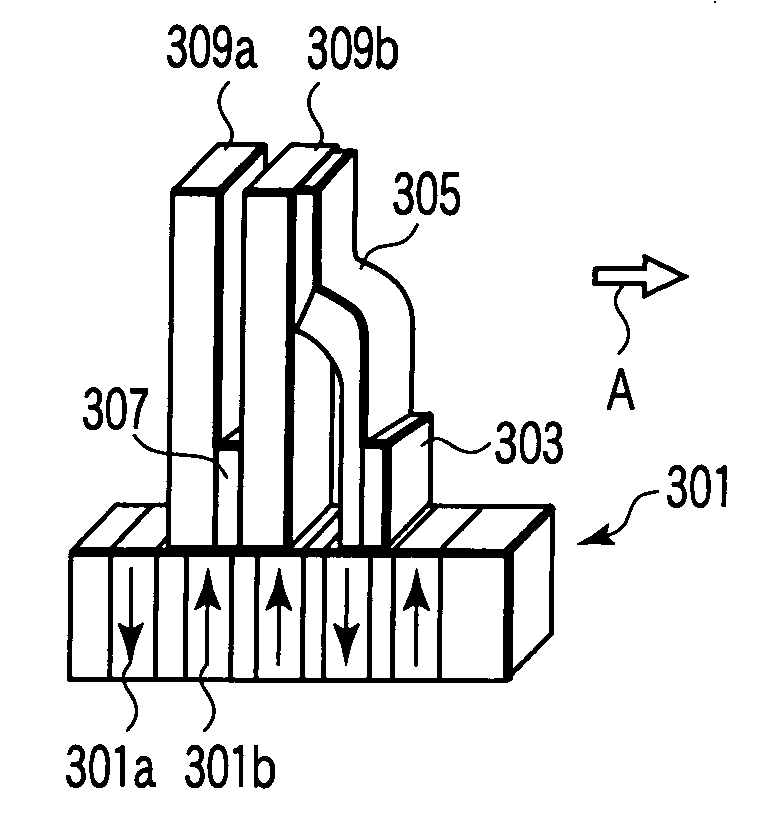
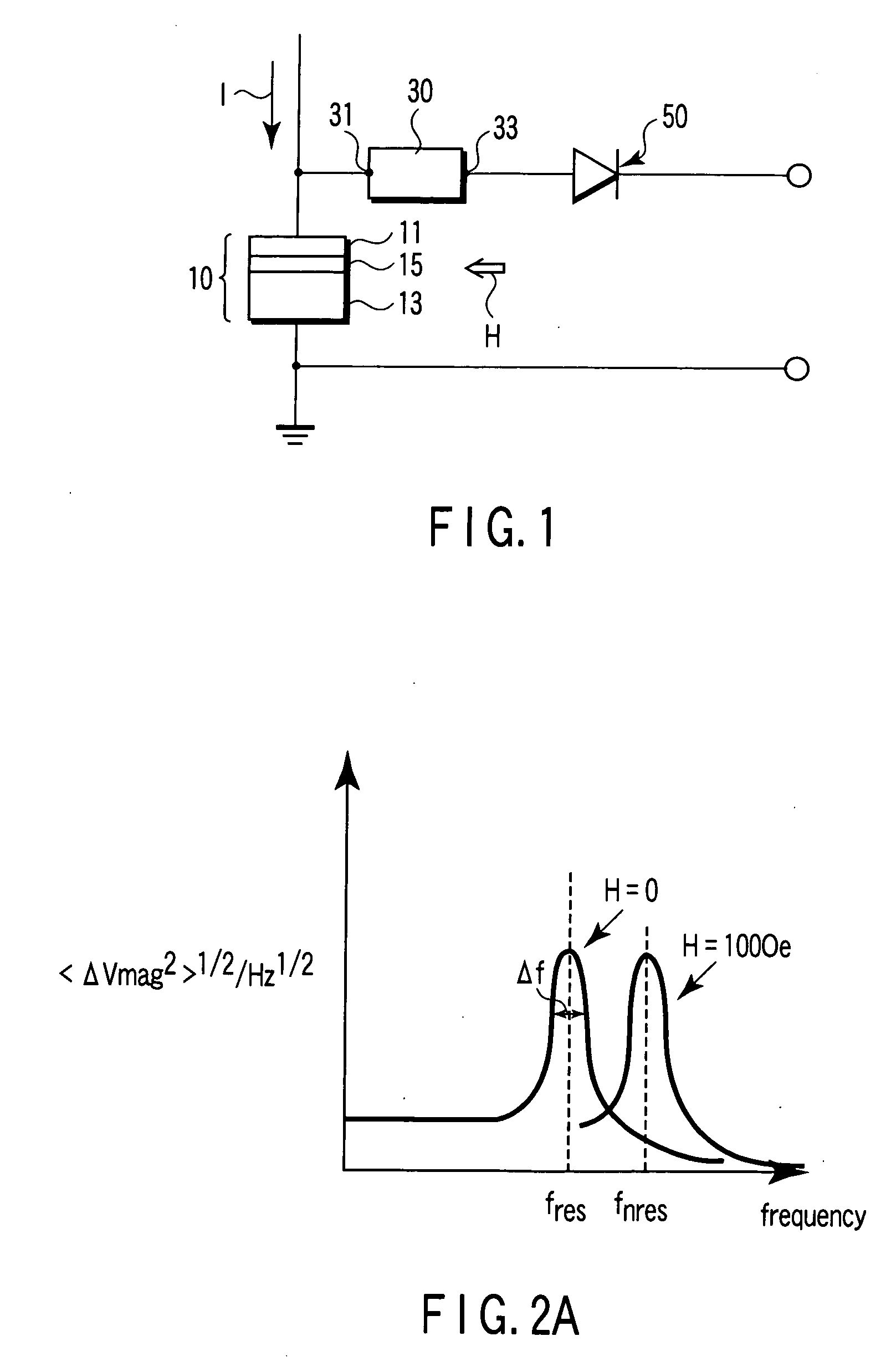
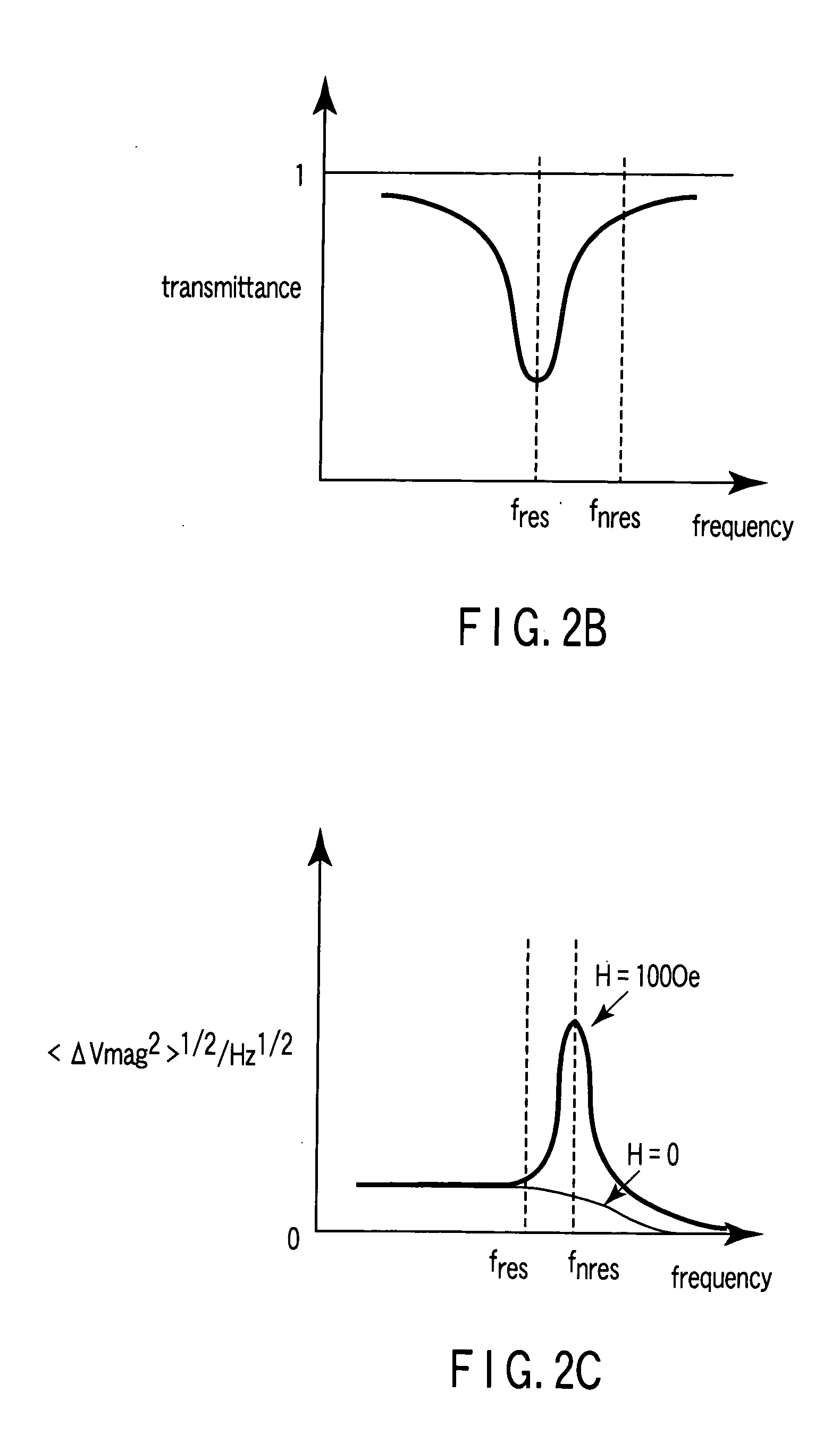
Magnetic sensor, magnetic field sensing method, semagnetic recording head, and magnetic memory device
ActiveUS20050219771A1Modification of read/write signalsNanomagnetismFrequency filteringMagnetization
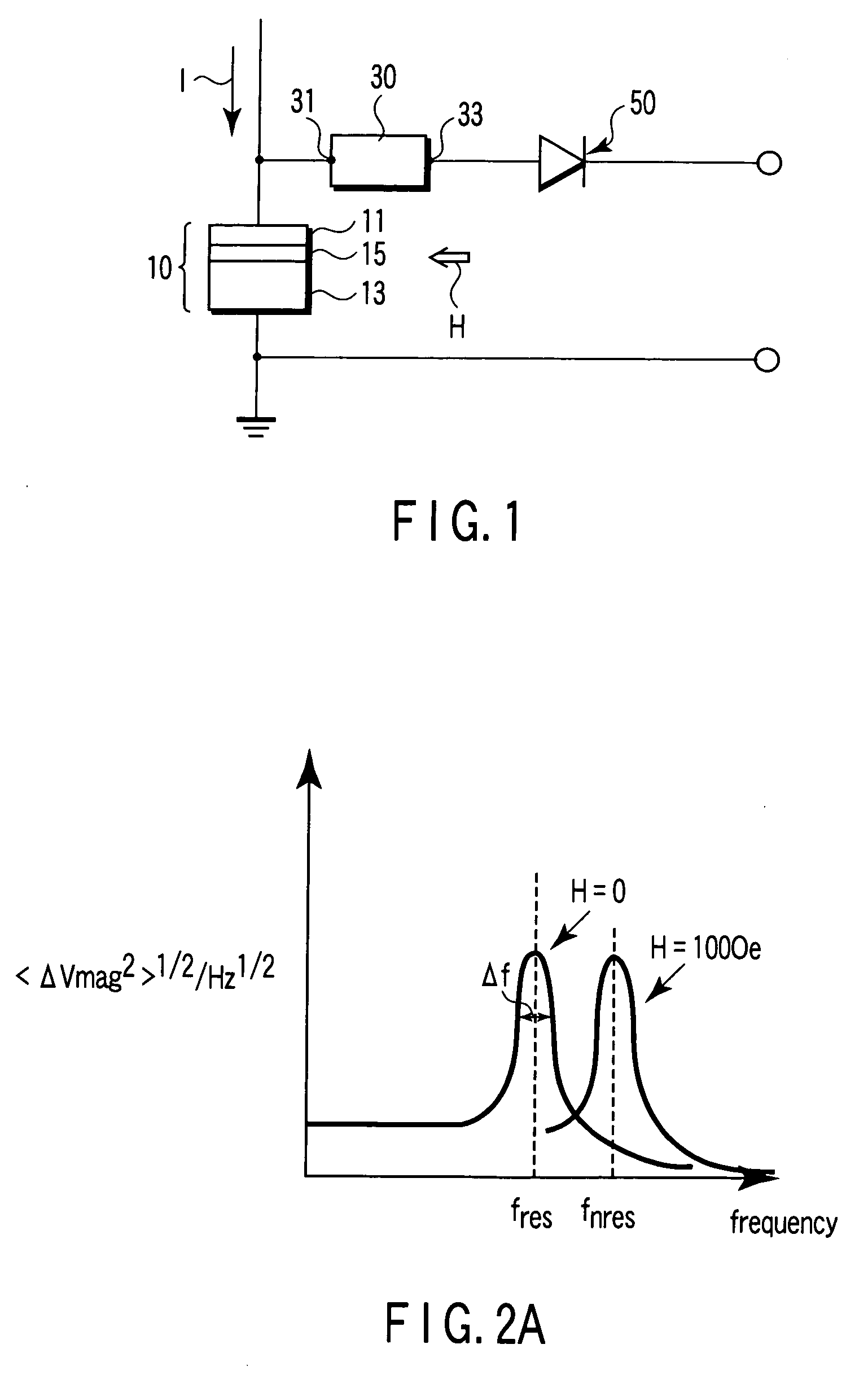
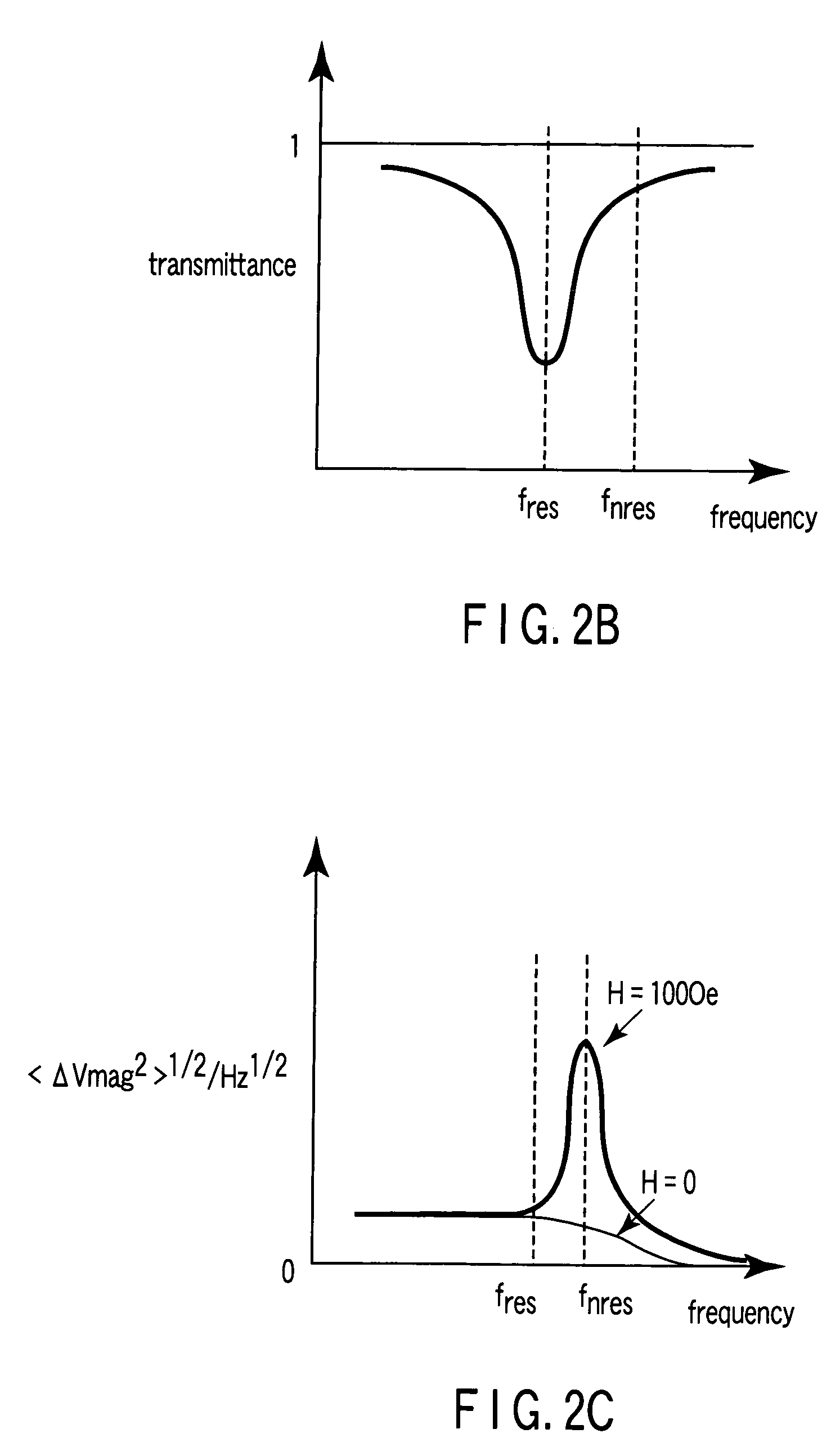
A magnetic sensor includes a magnetoresistance element having a peak of a thermal fluctuation strength of magnetization under a magnetic field having a certain frequency, a frequency filter connected to the magnetoresistance element and having its transmittance decreased or increased in substantially the frequency of the magnetic field to output a signal corresponding substantially to the peak of the thermal fluctuation strength of magnetization, and a detector connected to the frequency filter to detect the magnetic field based on the signal of the frequency filter.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
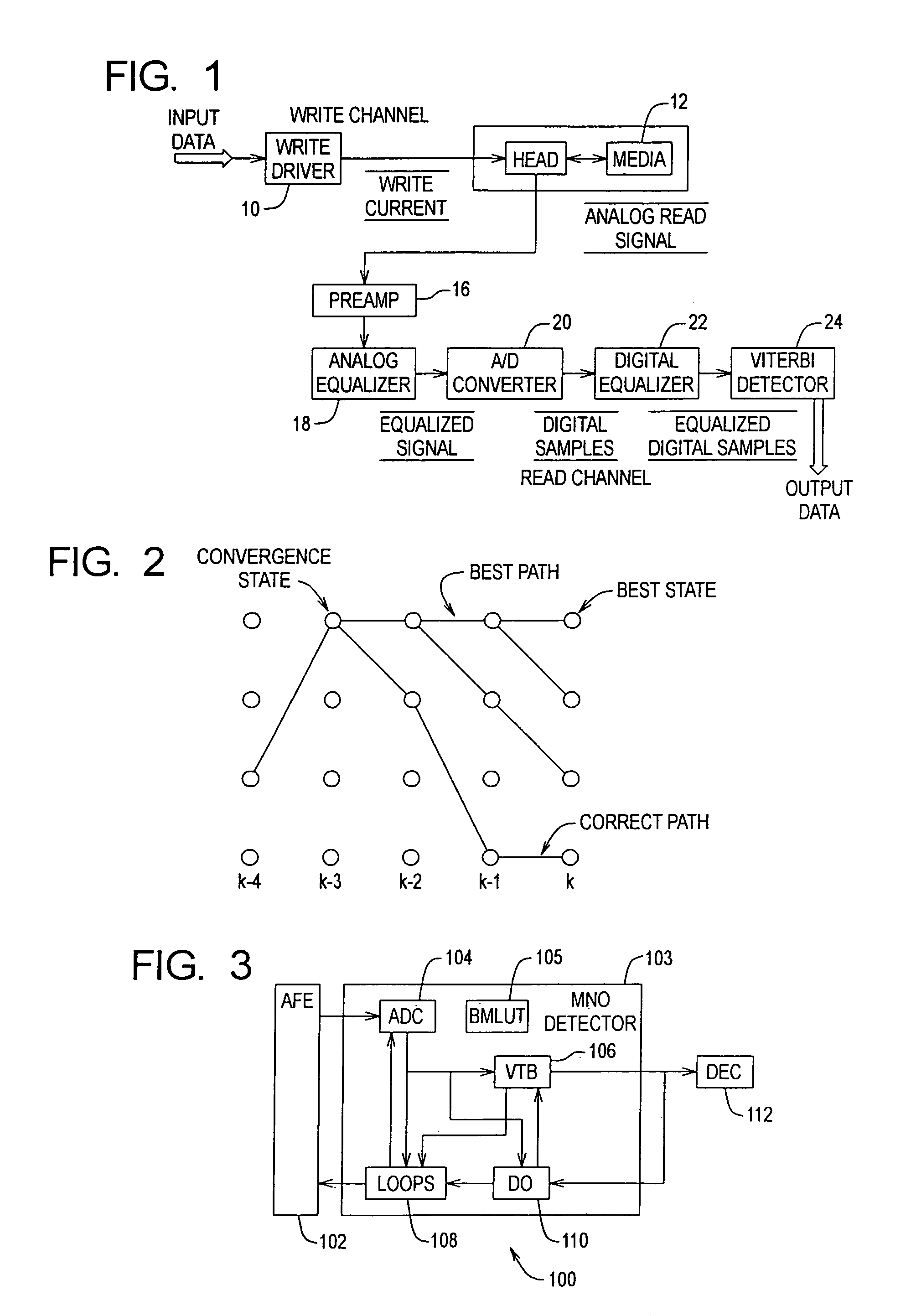
Media noise optimized detector for magnetic recording
InactiveUS7173783B1Significant disk drive yield benefitImprove reliabilityTelevision system detailsModification of read/write signalsPattern recognitionViterbi detector
A media noise optimized (MNO) detector for a read channel compensates for pattern dependent media noise, and compensates for nonlinearities from many sources such as residual MR nonlinearity, residual nonlinear transition shift, partial erasure, write-induced nonlinearity, and steady-state mis-equalization. The MNO detector is implemented by adjusting a conventional Viterbi detector branch metric so that the channel output value (ideal value) can be a nonlinear function of the state / branch bits, and the branch metric scaling factor is a function of the state / branch. For a given state / branch, the ideal value is the mean of analog-to-digital converter samples for the pattern corresponding to the state / branch, and the branch metric scaling factor is proportional to the noise variance for the pattern corresponding to that state / branch.
Owner:MAXTOR
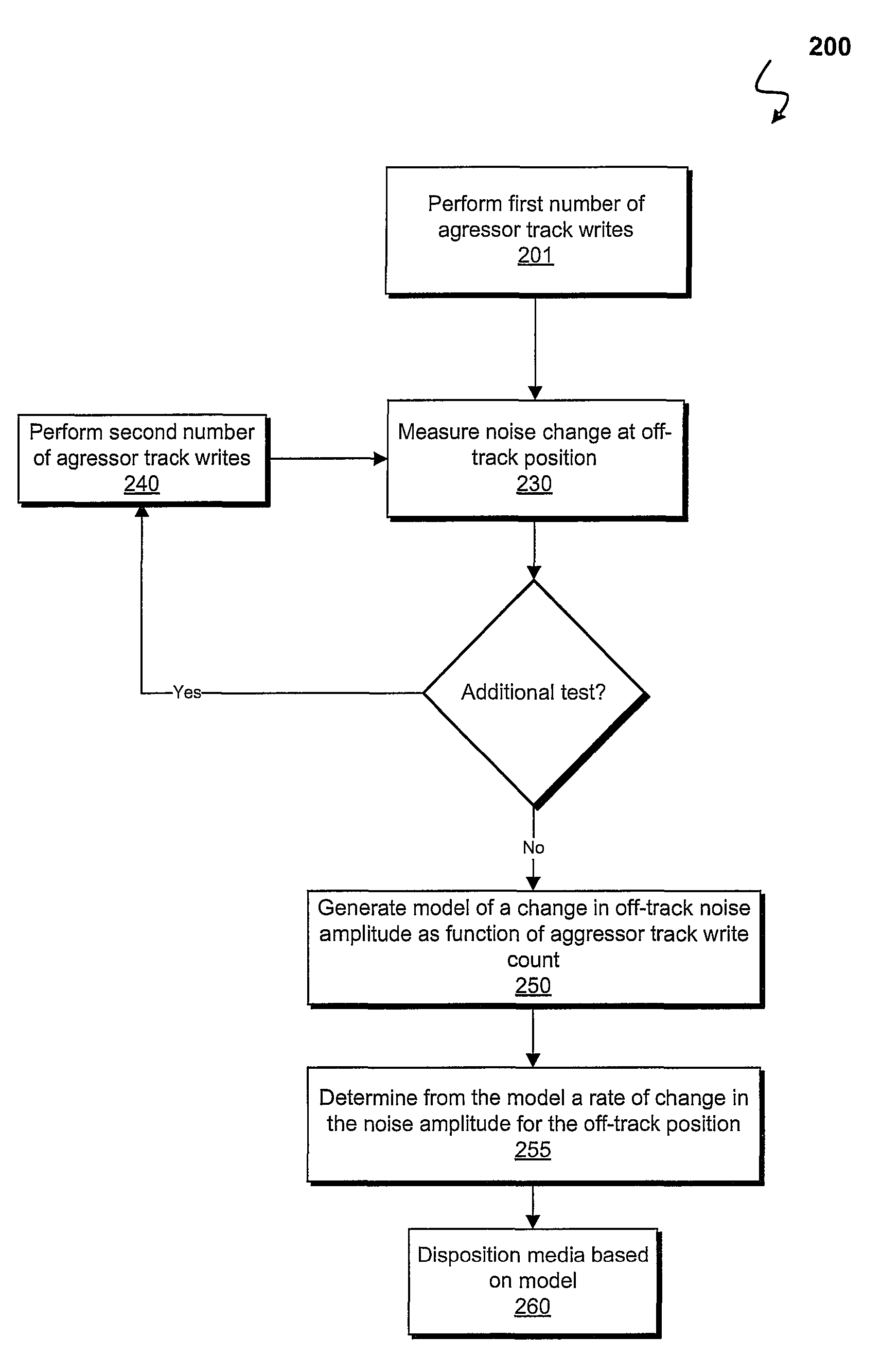
Predictive characterization of adjacent track erasure in recording media
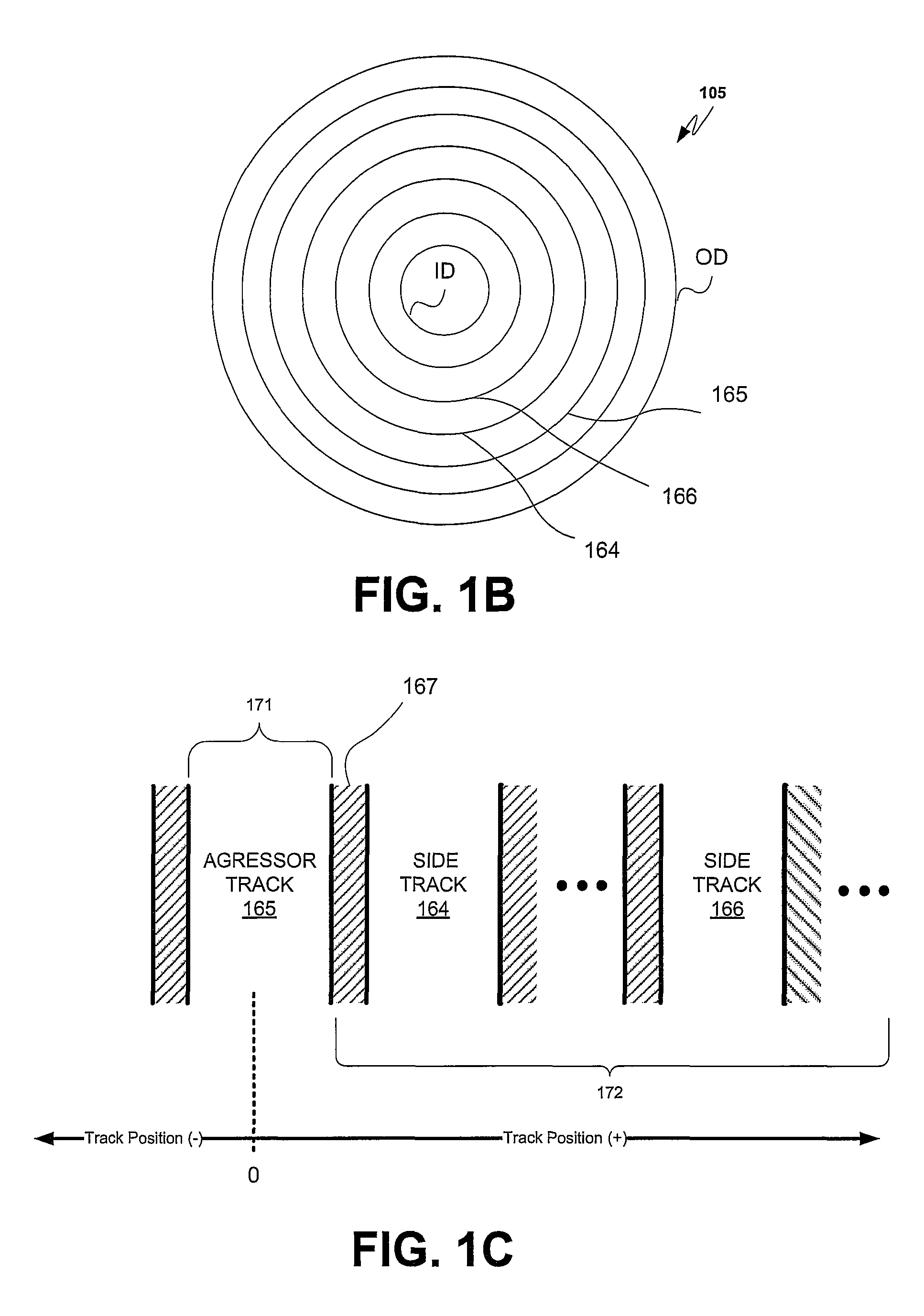
ActiveUS8125724B1Signal processing for reducing noiseErasing record carrier dataComputer scienceRecording media
A wide area track erasure (WATER) rate of change is determined from a model generated from a plurality of track erasure measurements performed on a magnetic recording media. A model of the change in noise amplitude for an off-track position as a function of the number of aggressor track writes employed in the track erasure measurements is generated. In a log-linear space a linear fit of the change in noise amplitude with respect to the number of aggressor track writes yields a rate of noise amplitude change (dB / decade) which may be utilized to rank magnetic recording media.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Magnetic sensor having a frequency filter coupled to an output of a magnetoresistance element
A magnetic sensor includes a magnetoresistance element having a peak of a thermal fluctuation strength of magnetization under a magnetic field having a certain frequency, a frequency filter connected to the magnetoresistance element and having its transmittance decreased or increased in substantially the frequency of the magnetic field to output a signal corresponding substantially to the peak of the thermal fluctuation strength of magnetization, and a detector connected to the frequency filter to detect the magnetic field based on the signal of the frequency filter.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
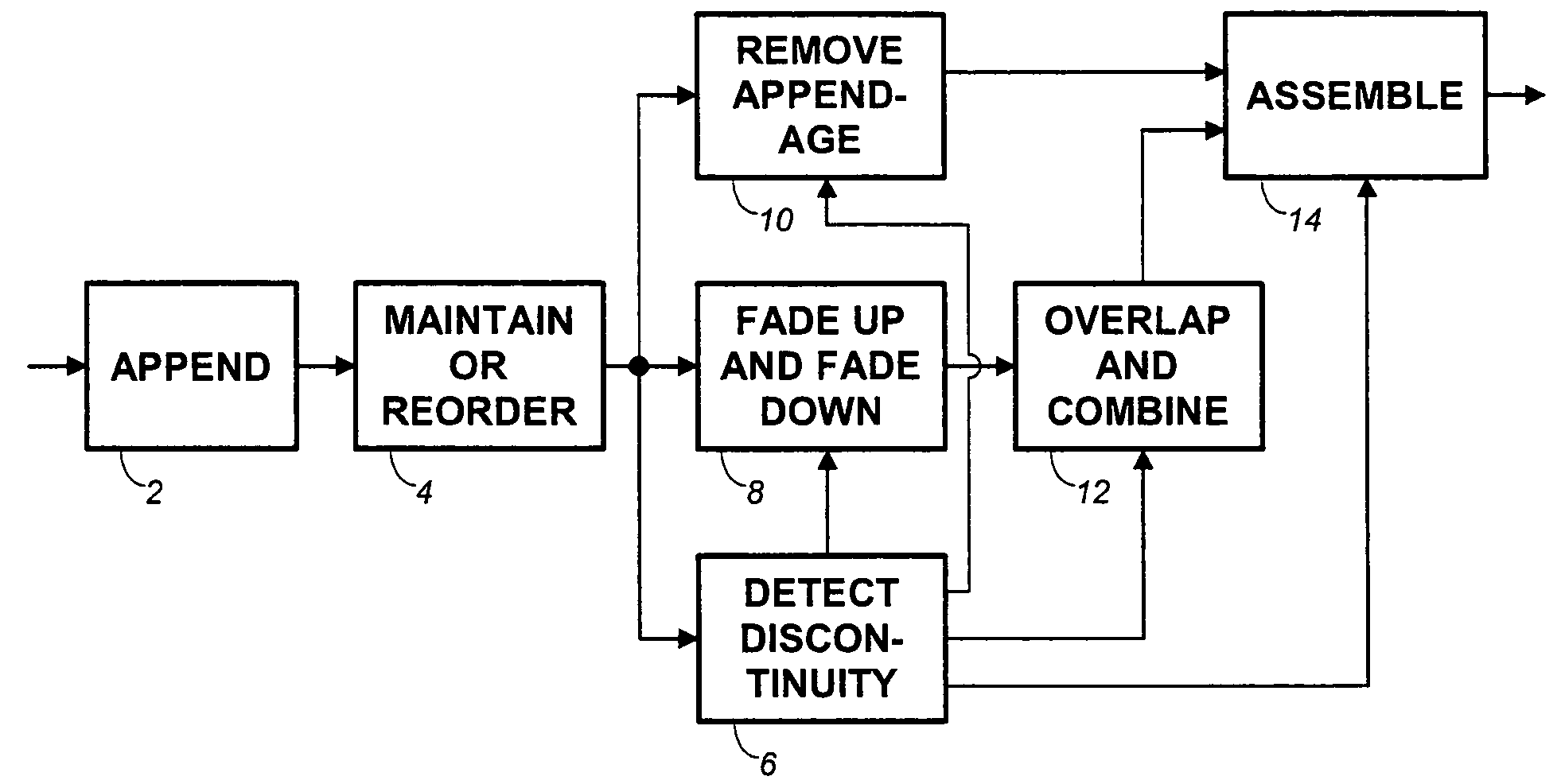
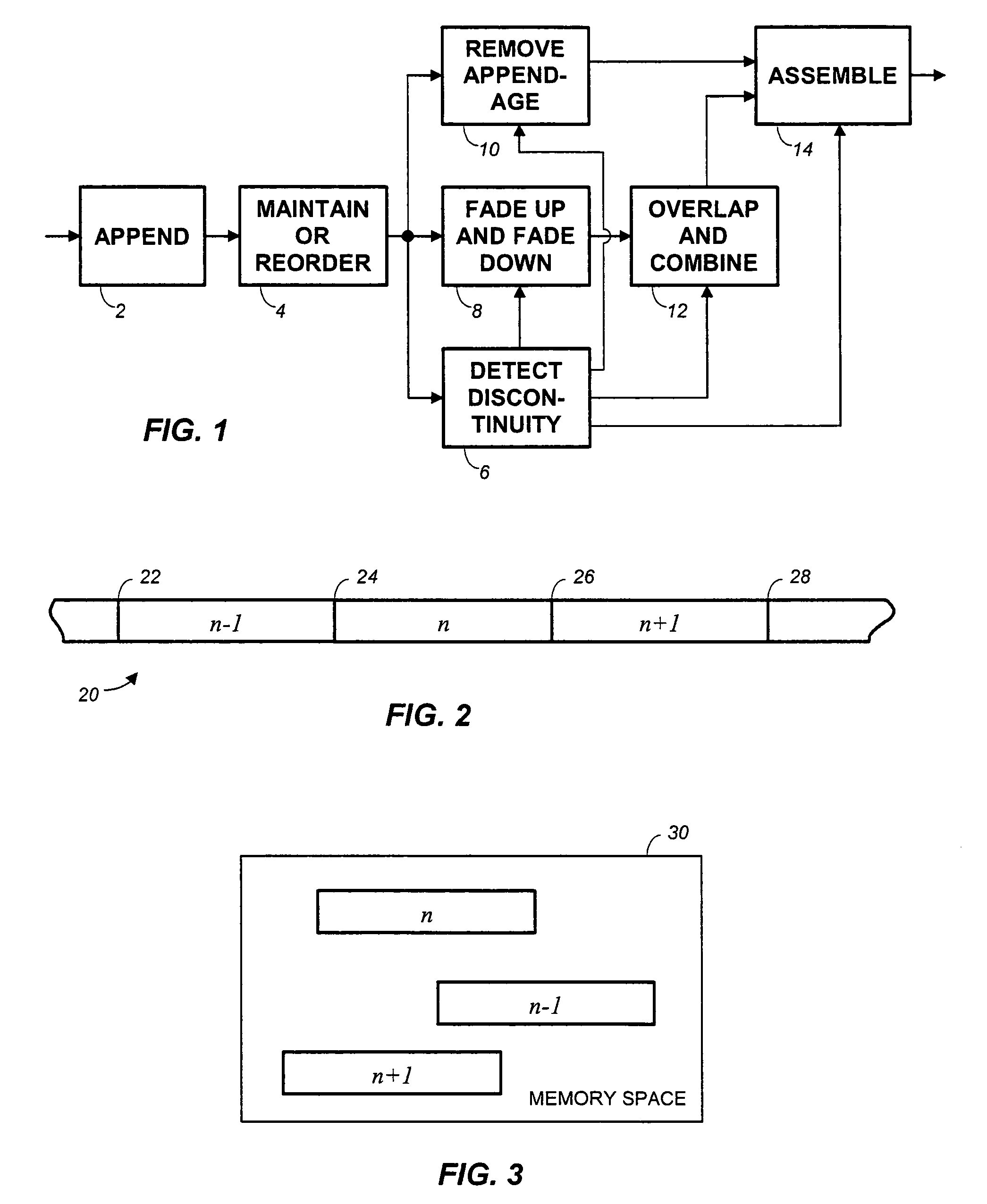
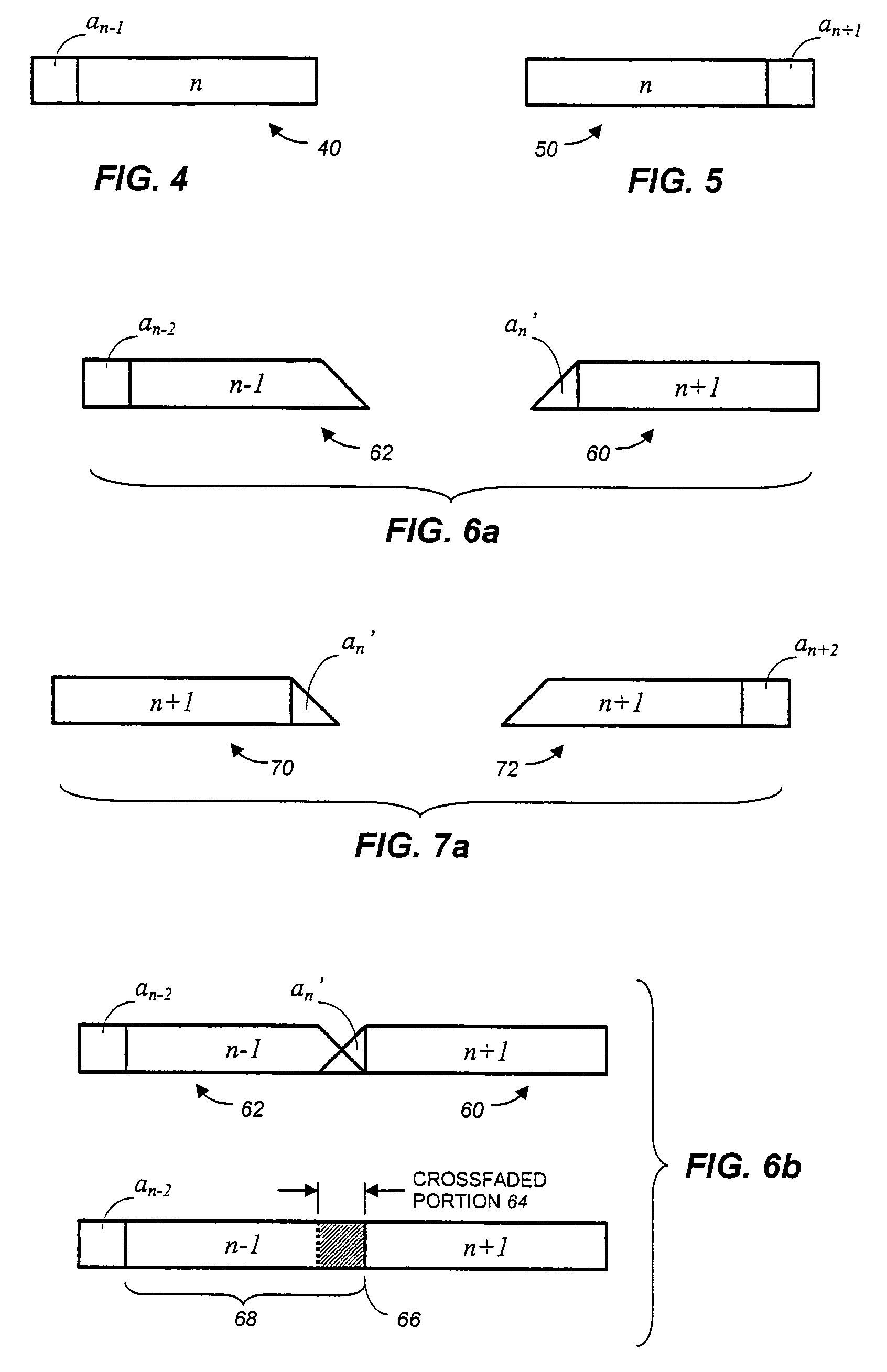
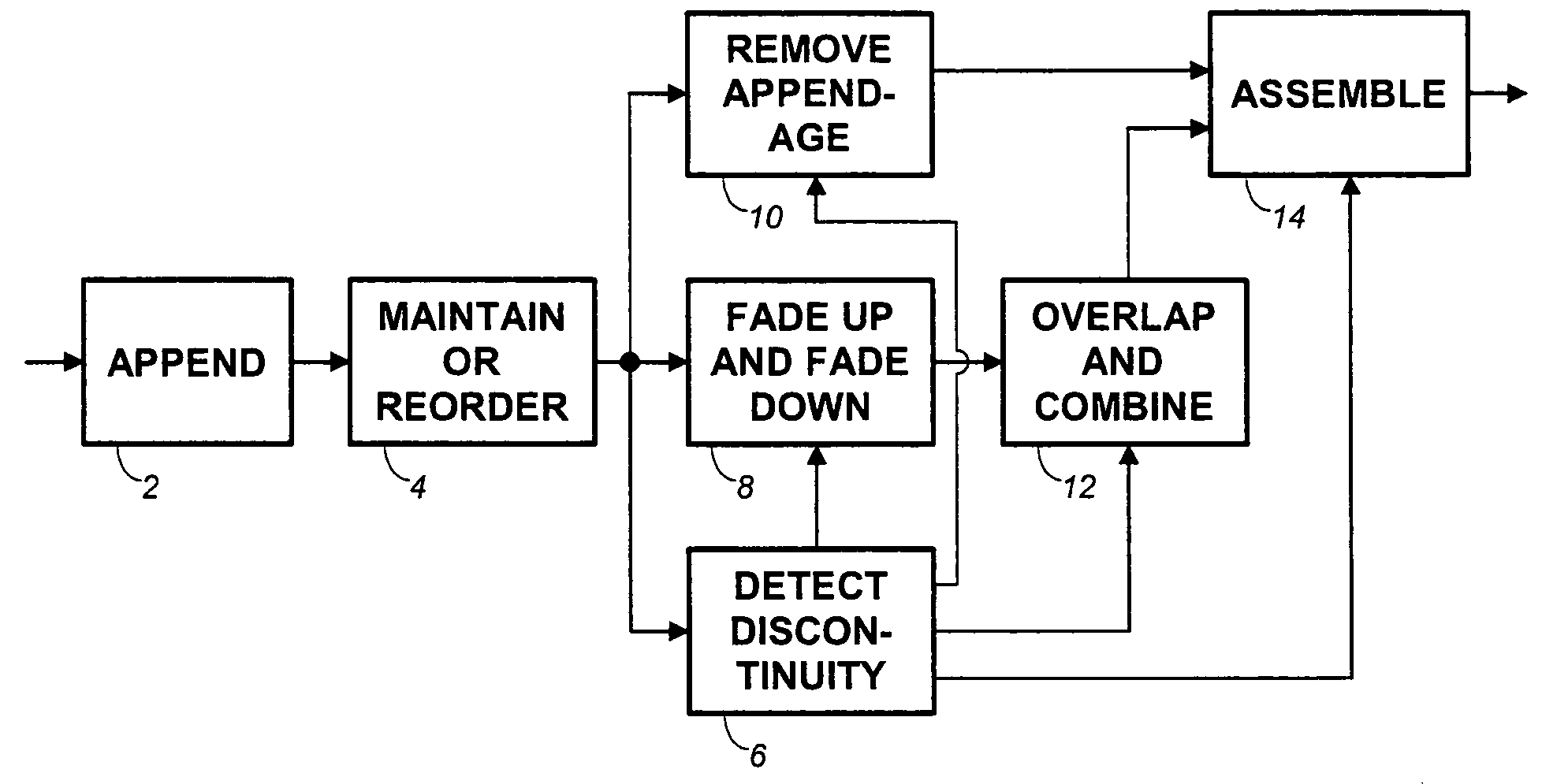
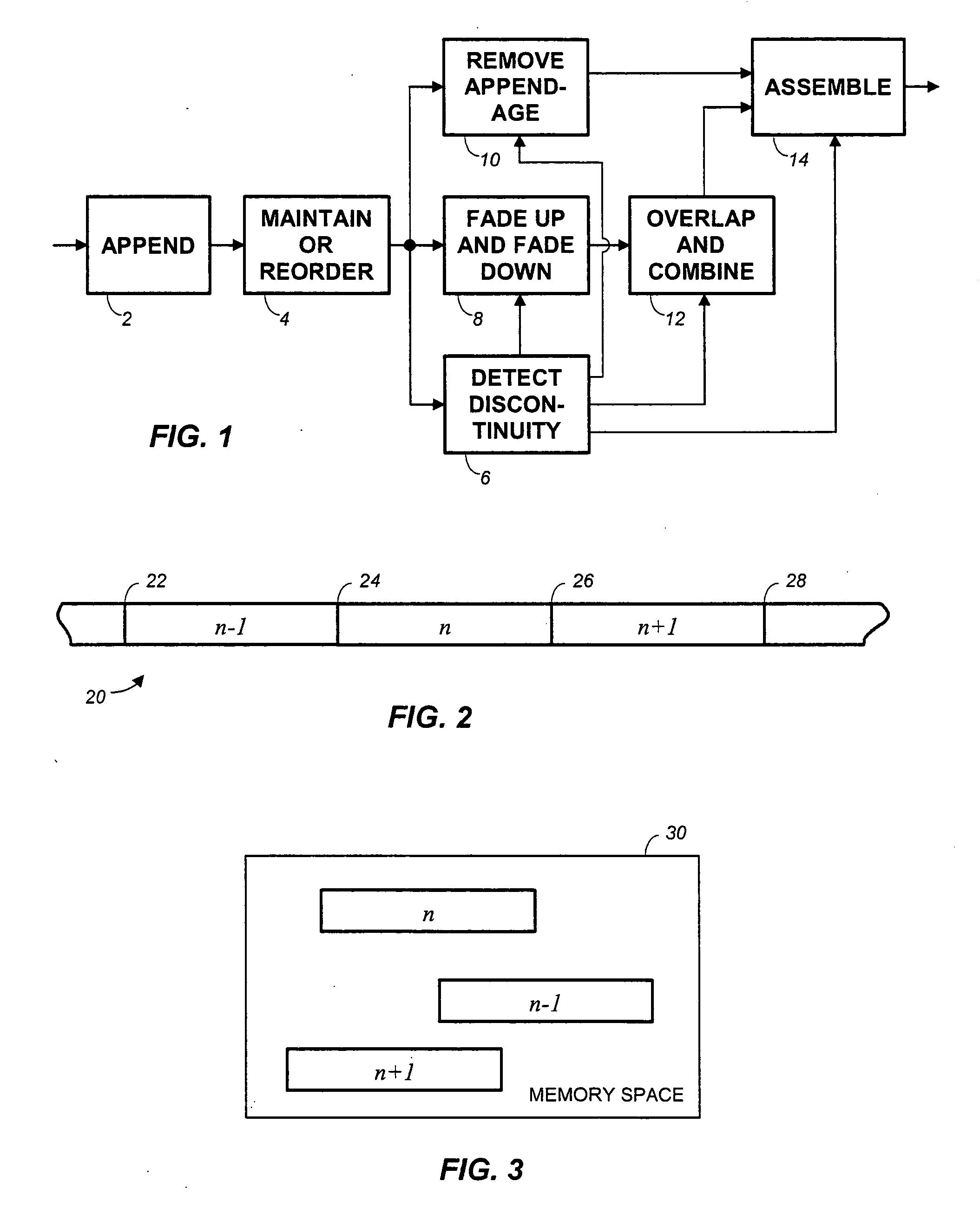
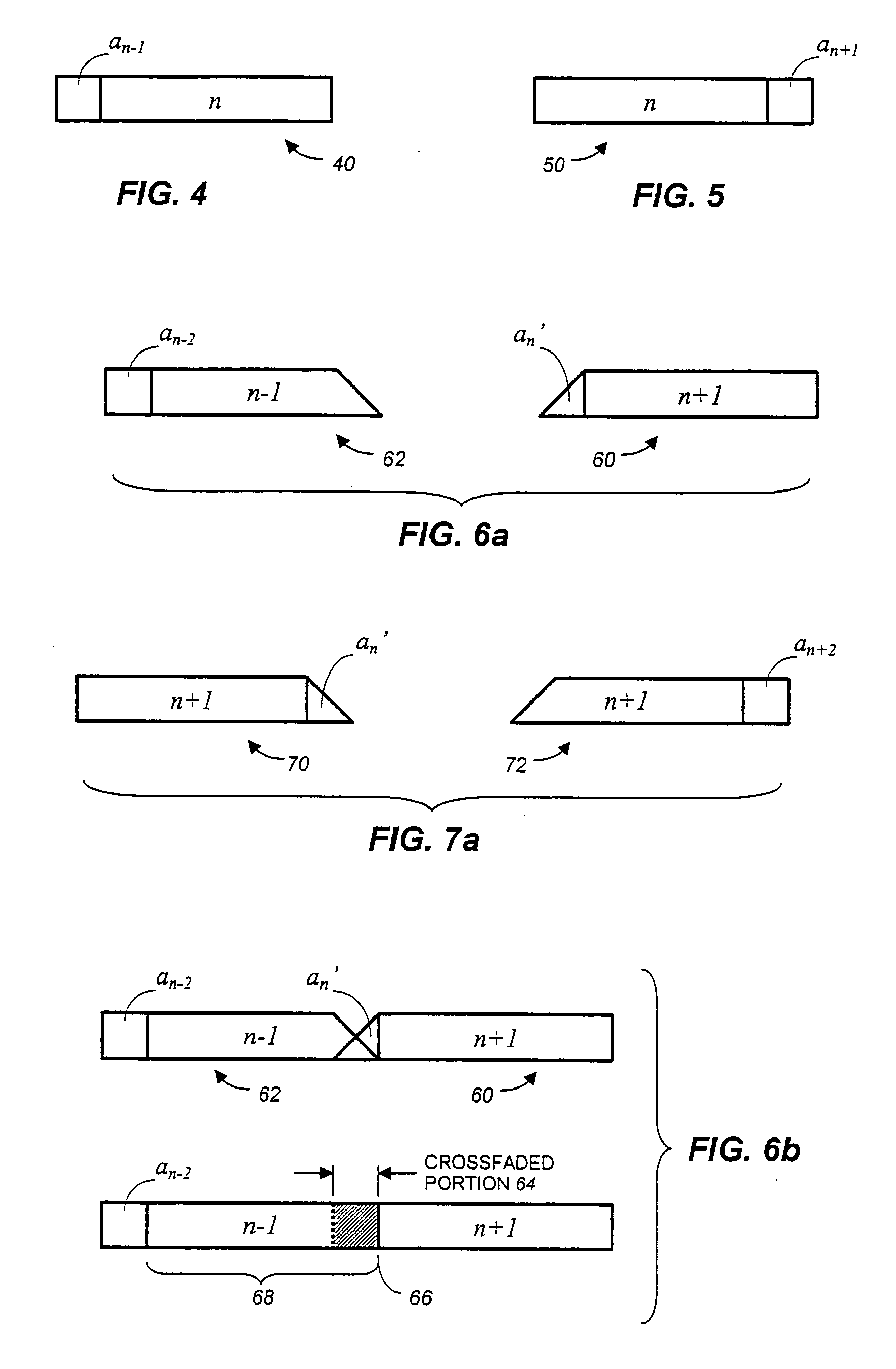
Frame-based audio transmission/storage with overlap to facilitate smooth crossfading
ActiveUS7292902B2Electrophonic musical instrumentsInput/output to record carriersFrame basedComputer graphics (images)
Methods for splicing PCM audio frames form modified frames by appending to each frame either a portion of the next preceding frame or the next following frame. According to a first approach, splices are obtained by fading up and fading down a frame end and a frame appendage only at a splice point, and overlapping and combining to provide a crossfade at the splice. Alternatively, every frame end and frame appendage is faded up and faded down, overlapped and combined. A subtractive method of providing complementary fade-up and fade-down reduces rounding errors.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
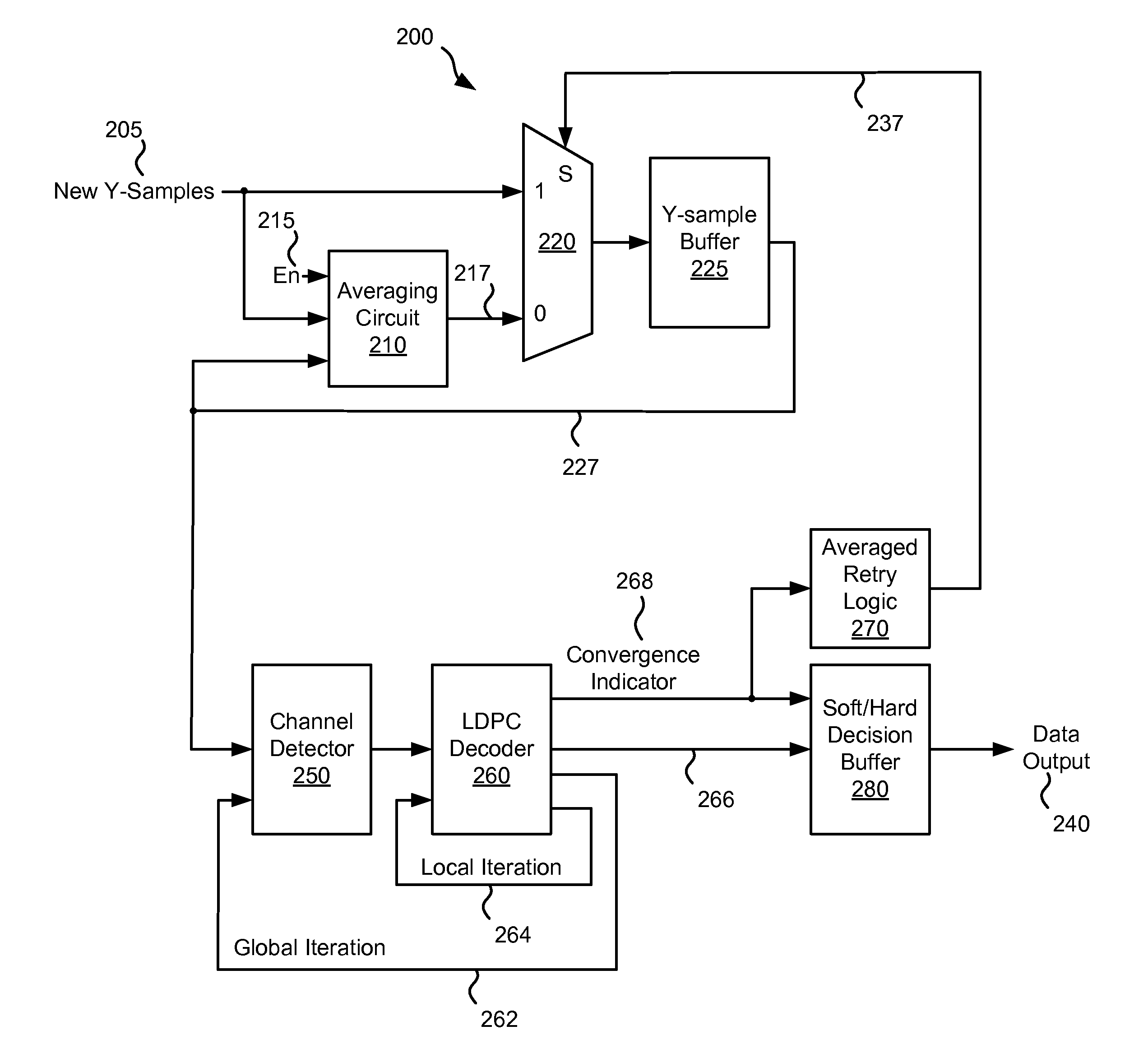
Systems and Methods for Noise Reduced Data Detection
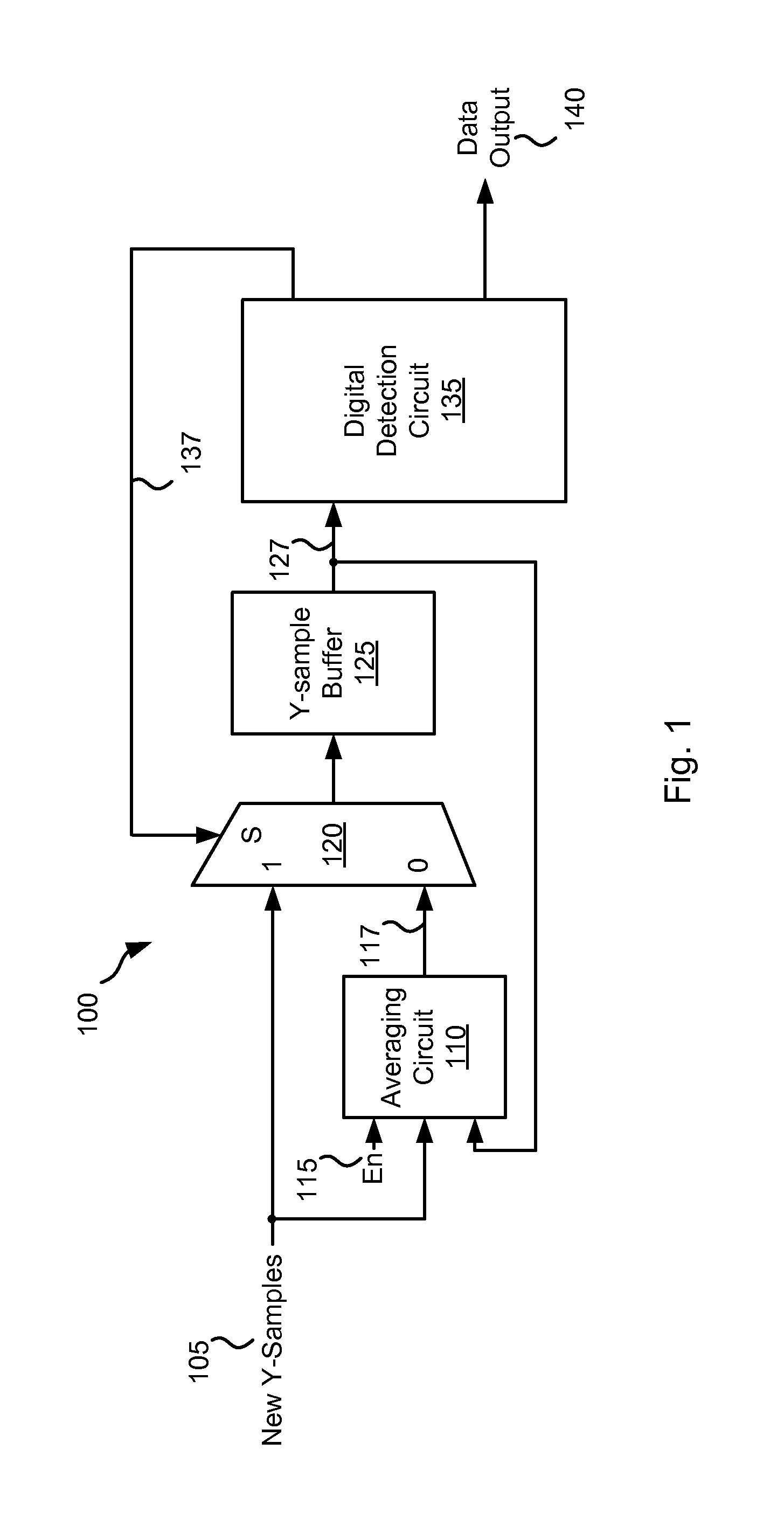
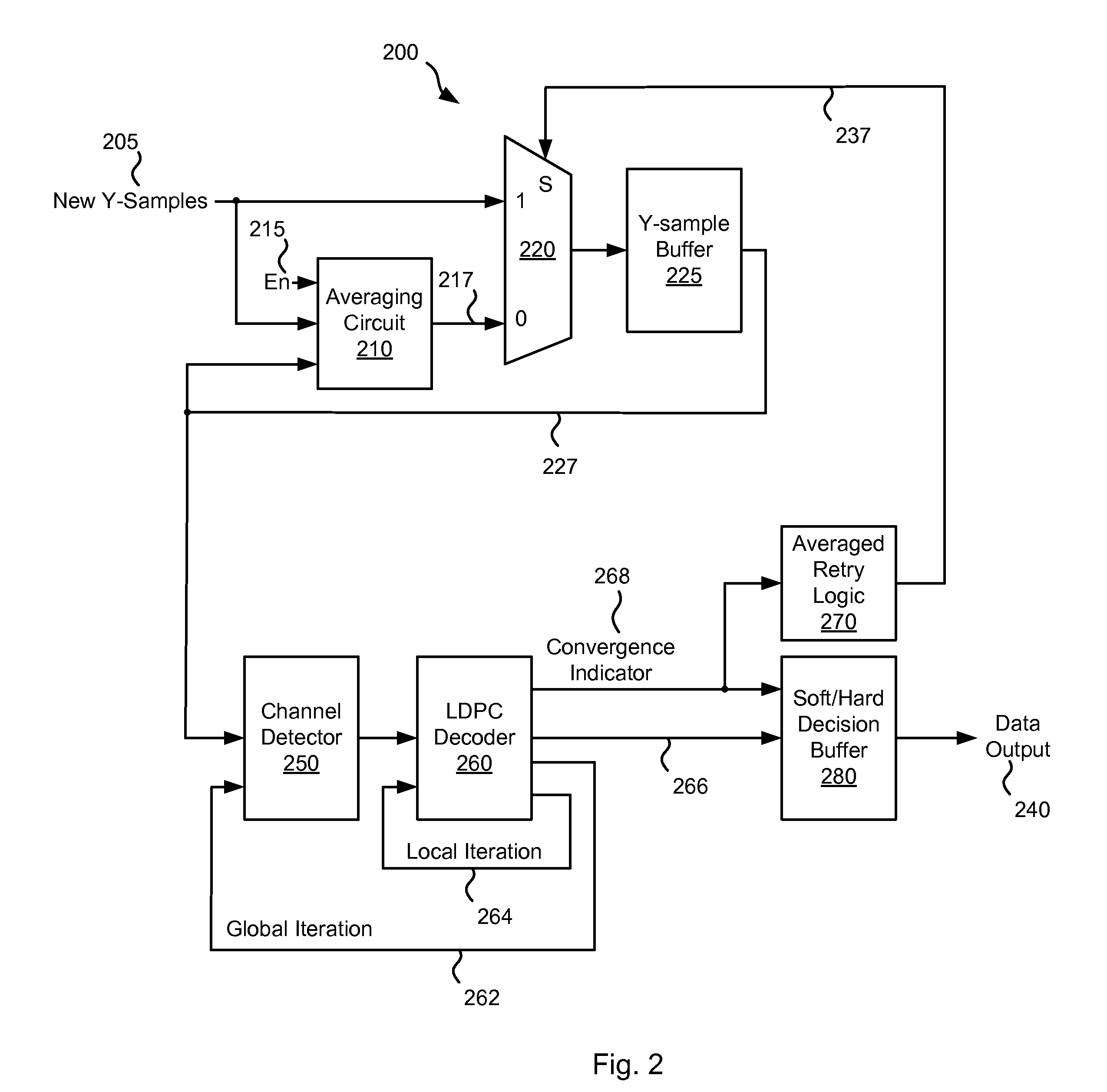
InactiveUS20110080211A1Reduce noiseData buffering arrangementsSignal processing for reducing noiseControl signalAlgorithm
Various embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for data processing. For example, some embodiments of the present invention provide noise reduced data processing circuits. Such circuits include a selector circuit, a sample set averaging circuit, and a data detection circuit. The selector circuit provides either a new sample set or an averaged sample set as a sample output based on a select control signal. The sample set averaging circuit receives the new sample set and provides the averaged sample set. The averaged sample set is based upon two or more instances of the new sample set. The data detection circuit receives the sample output, and performs a data detection algorithm on the sample output and provides the select control signal and a data output.
Owner:LSI CORPORATION
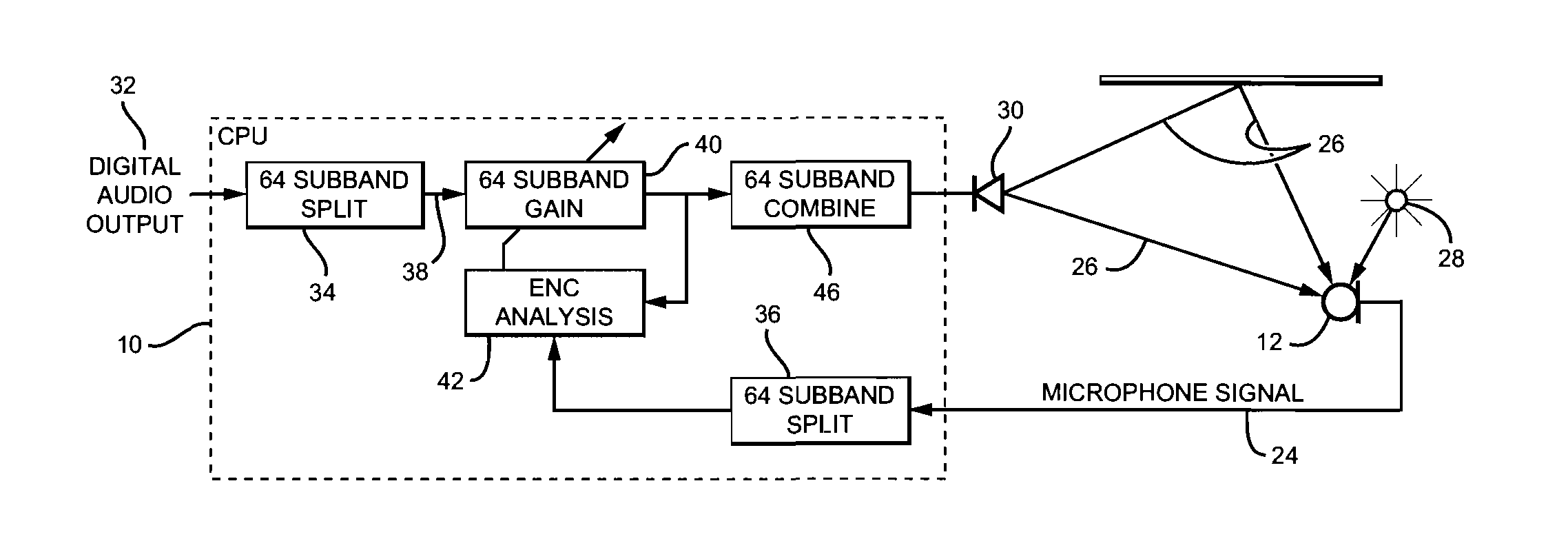
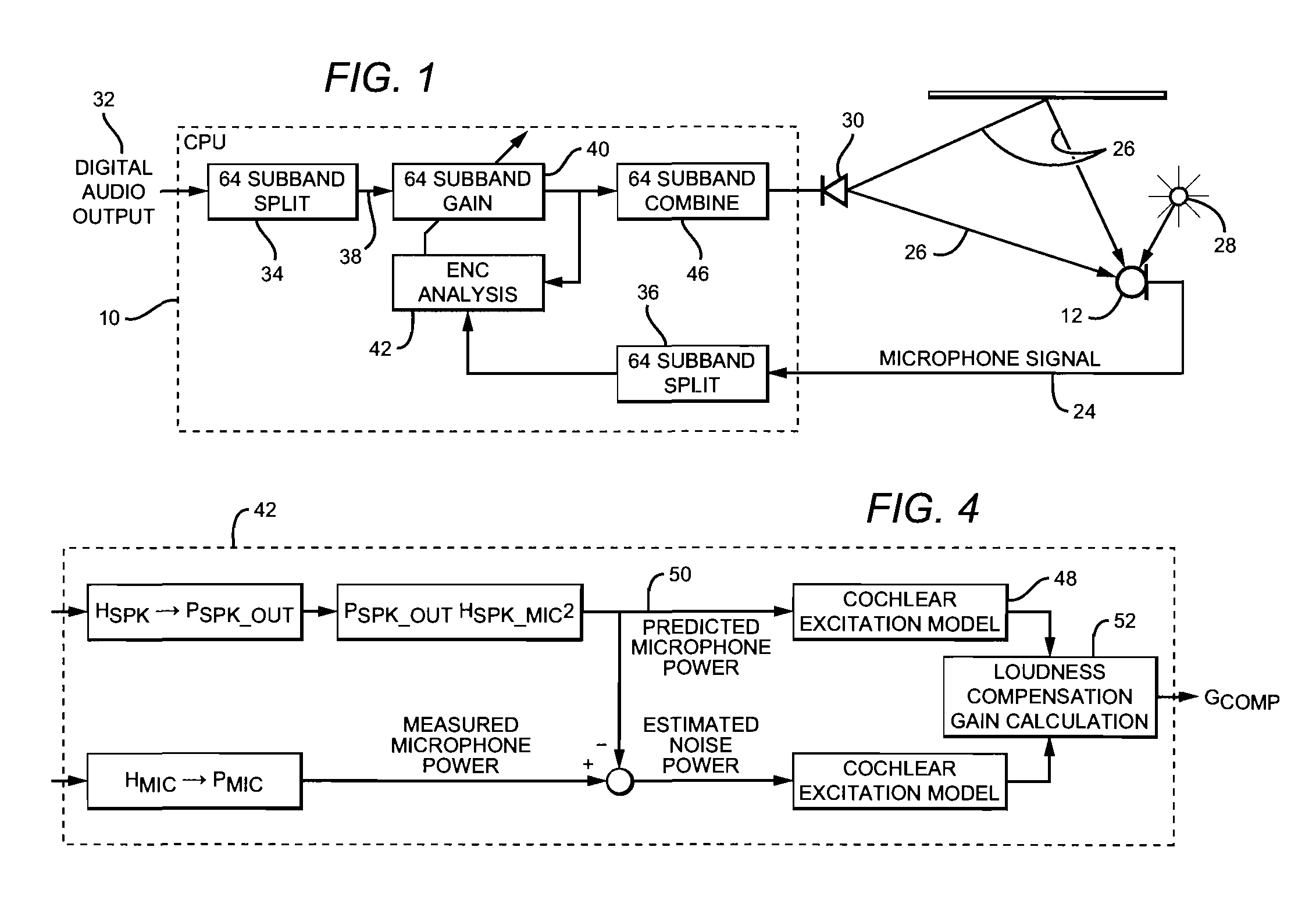
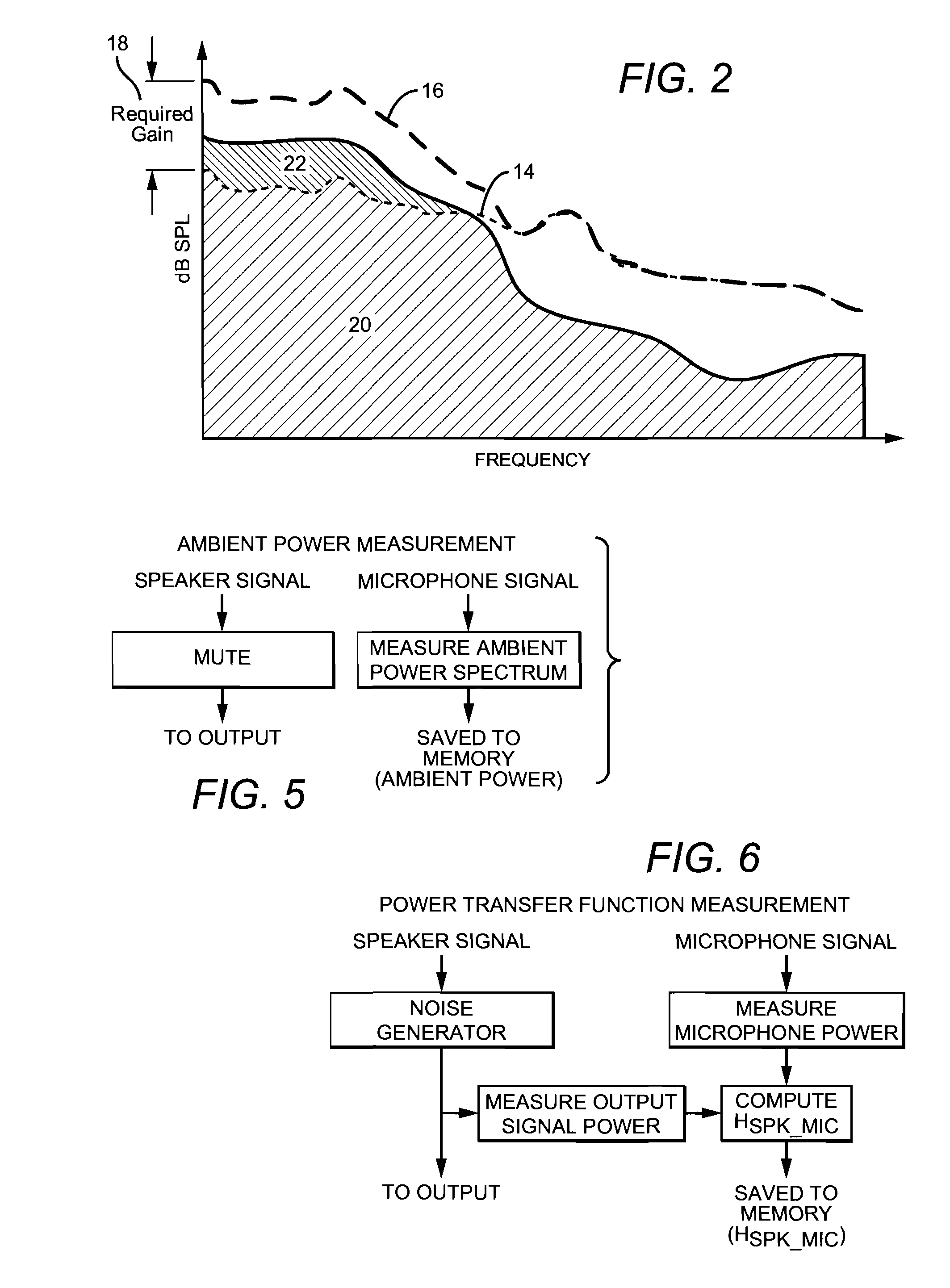
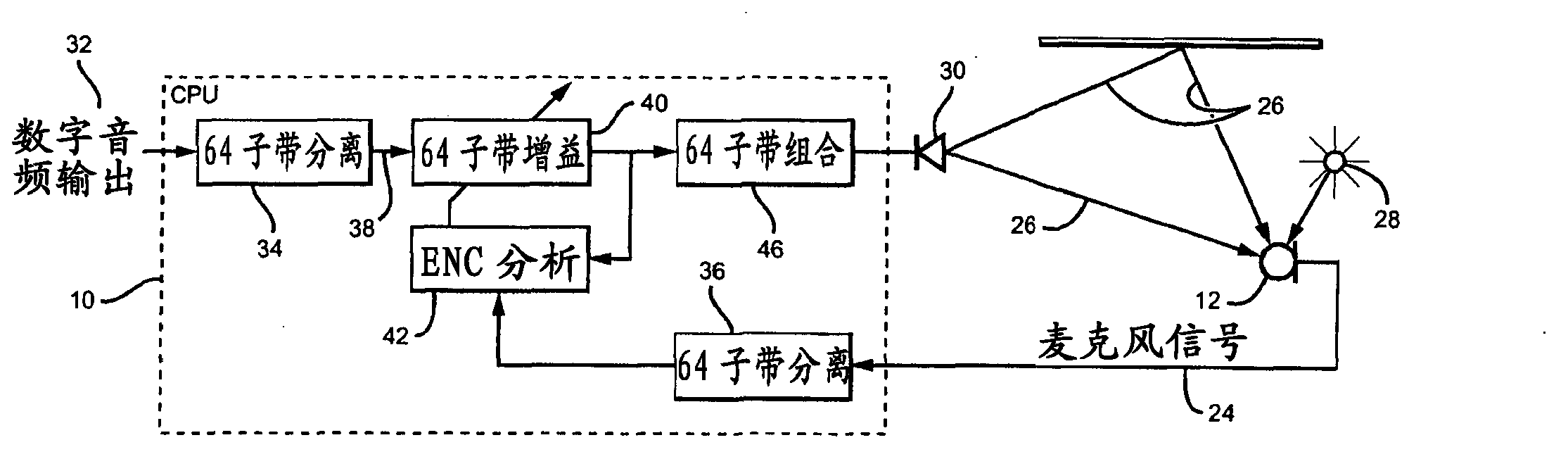
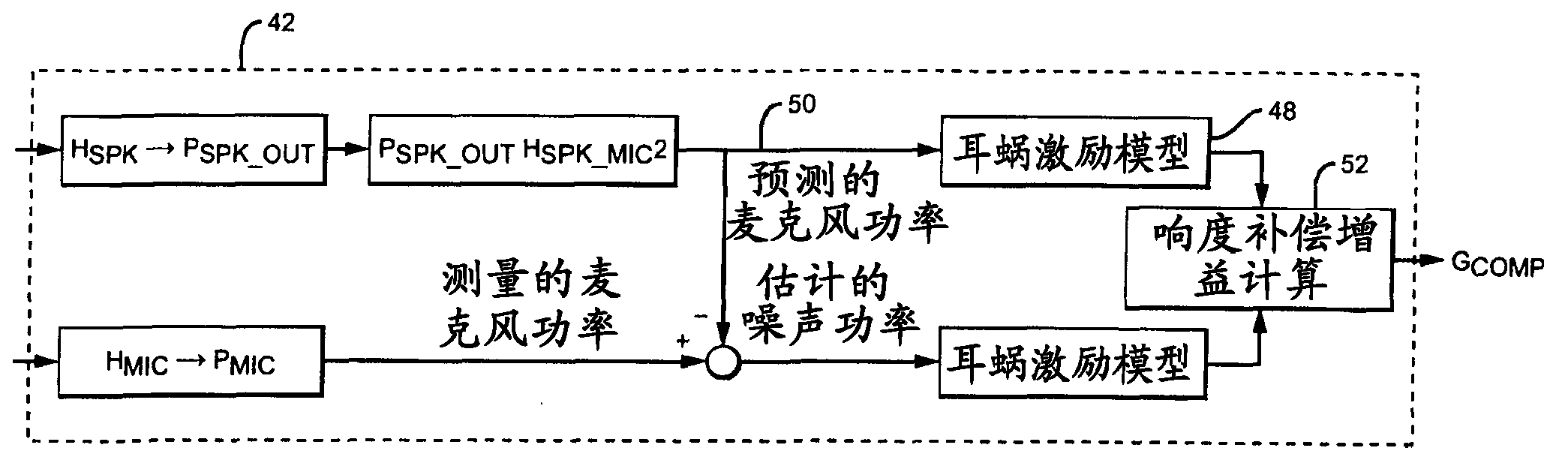
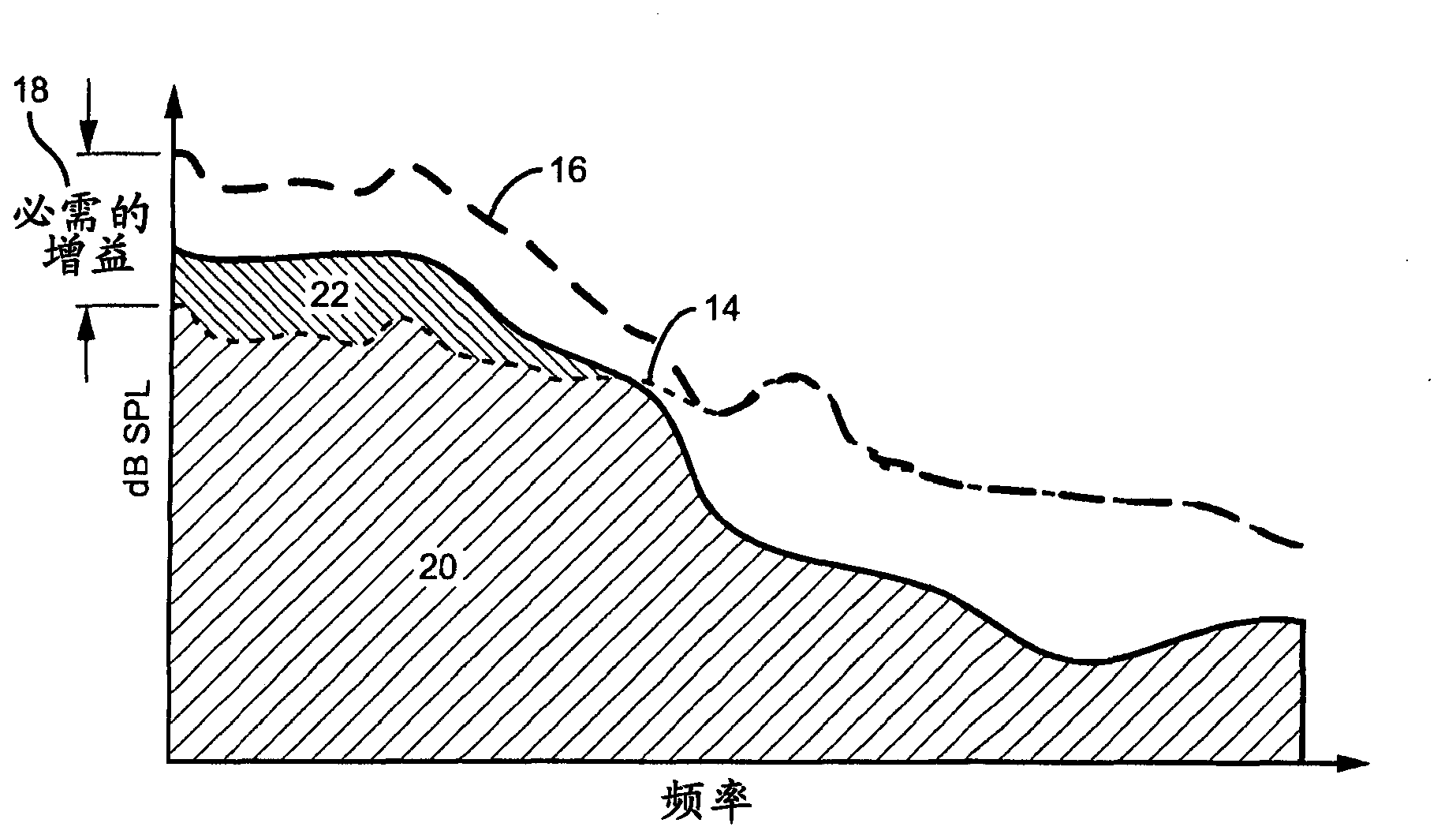
Adaptive environmental noise compensation for audio playback
InactiveUS20110251704A1Prevent maskingSignal processing for reducing noiseSpeech analysisEnvironmental noiseNoise level
The present invention counterbalances background noise by applying dynamic equalization. A psychoacoustic model representing the perception of masking effects of background noise relative to a desired foreground soundtrack is used to accurately counterbalance background noise. A microphone samples what the listener is hearing and separates the desired soundtrack from the interfering noise. The signal and noise components are analyzed from a psychoacoustic perspective and the soundtrack is equalized such that the frequencies that were originally masked are unmasked. Subsequently, the listener may hear the soundtrack over the noise. Using this process the EQ can continuously adapt to the background noise level without any interaction from the listener and only when required. When the background noise subsides, the EQ adapts back to its original level and the user does not experience unnecessarily high loudness levels.
Owner:DTS
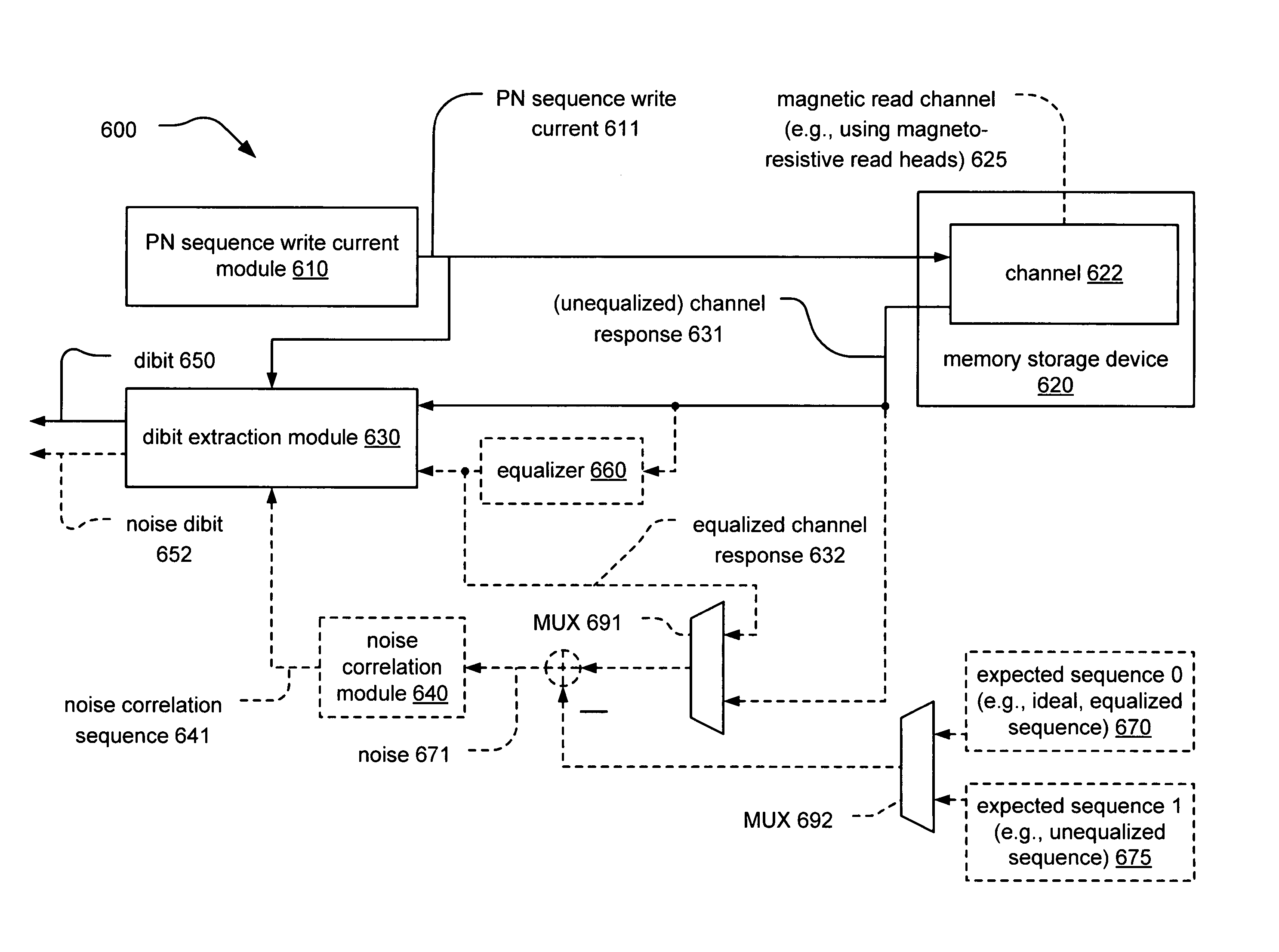
Dibit extraction
A novel means for performing dibit extraction is presented. Any one of an unequalized signal dibit, equalized signal dibit, or noise dibit can be extracted. Instead of using the correlation properties of a PN (Pseudo-Noise) sequence to approximate a PN deconvolution sequence, the use of the actual deconvolution sequence (i.e., PN sequence that includes values of +k and 0, where k is oftentimes 1) is employed so that no approximations are needed. The resulting estimate of the channel is therefore very accurate.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
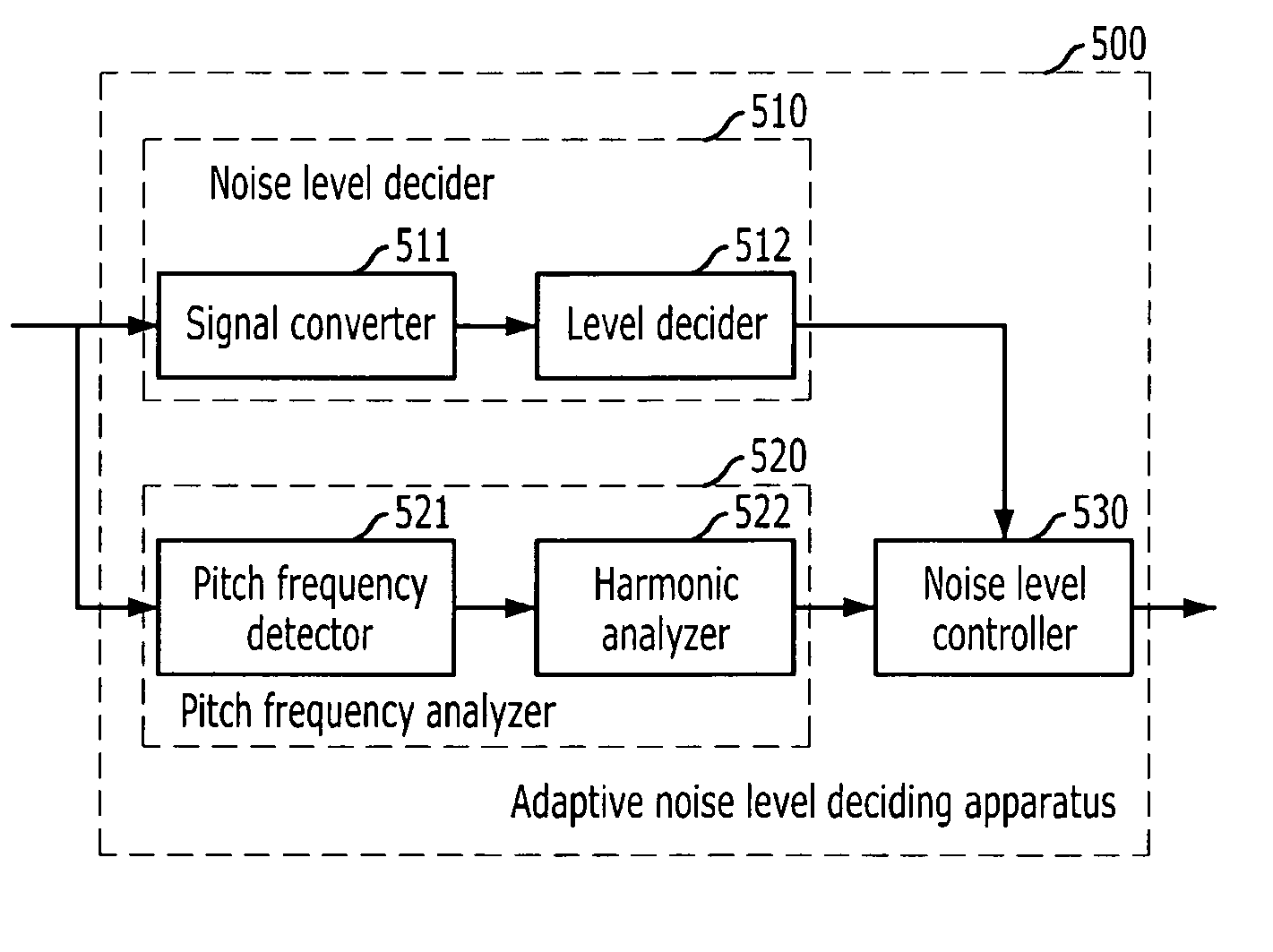
Apparatus and method for deciding adaptive noise level for bandwidth extension
InactiveUS20100094638A1Accurate measurementQuality improvementSignal processing for reducing noiseSpeech analysisBandwidth extensionNoise level
An apparatus and method for deciding an adaptive noise level for bandwidth extension are provided. The apparatus includes a noise level decider for deciding a high-band noise level for bandwidth extension according to tonality of an input signal, a pitch frequency analyzer for detecting a pitch frequency of the input signal and analyzing correlation between the detected pitch frequency and a frequency channel, and a noise level controller for adaptively controlling the decided high-band noise level based on the analyzed correlation of the pitch frequency and the frequency channel.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
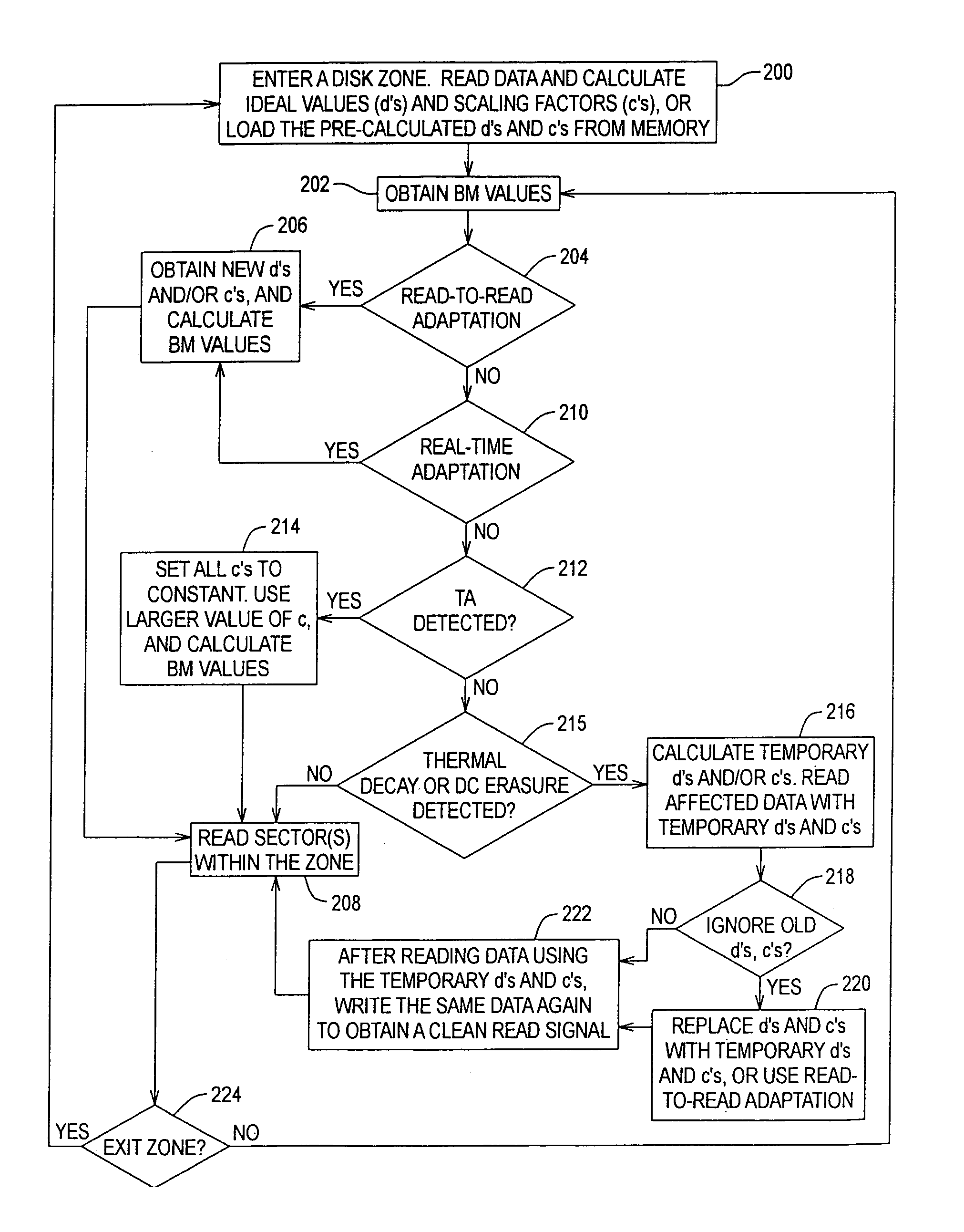
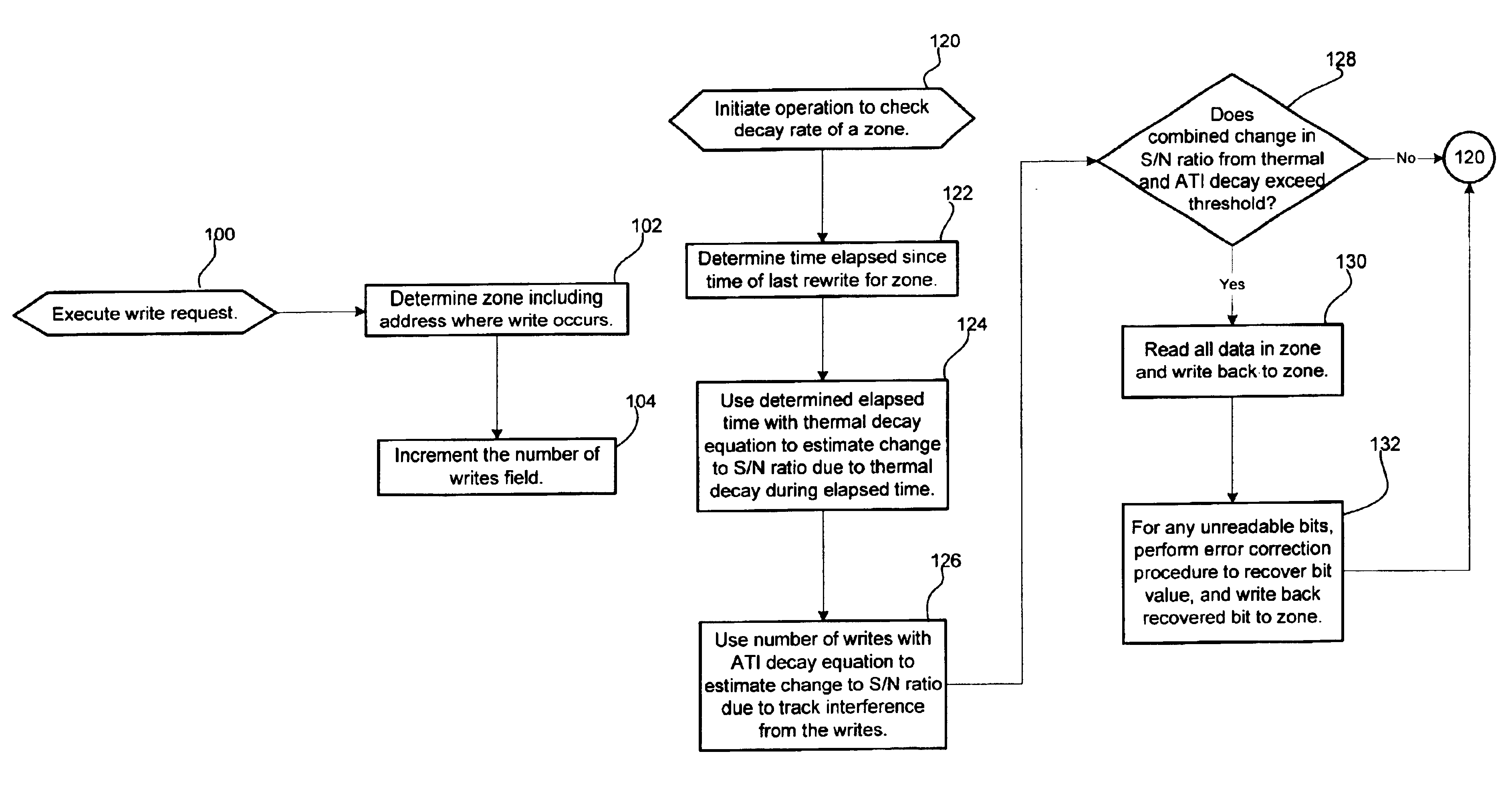
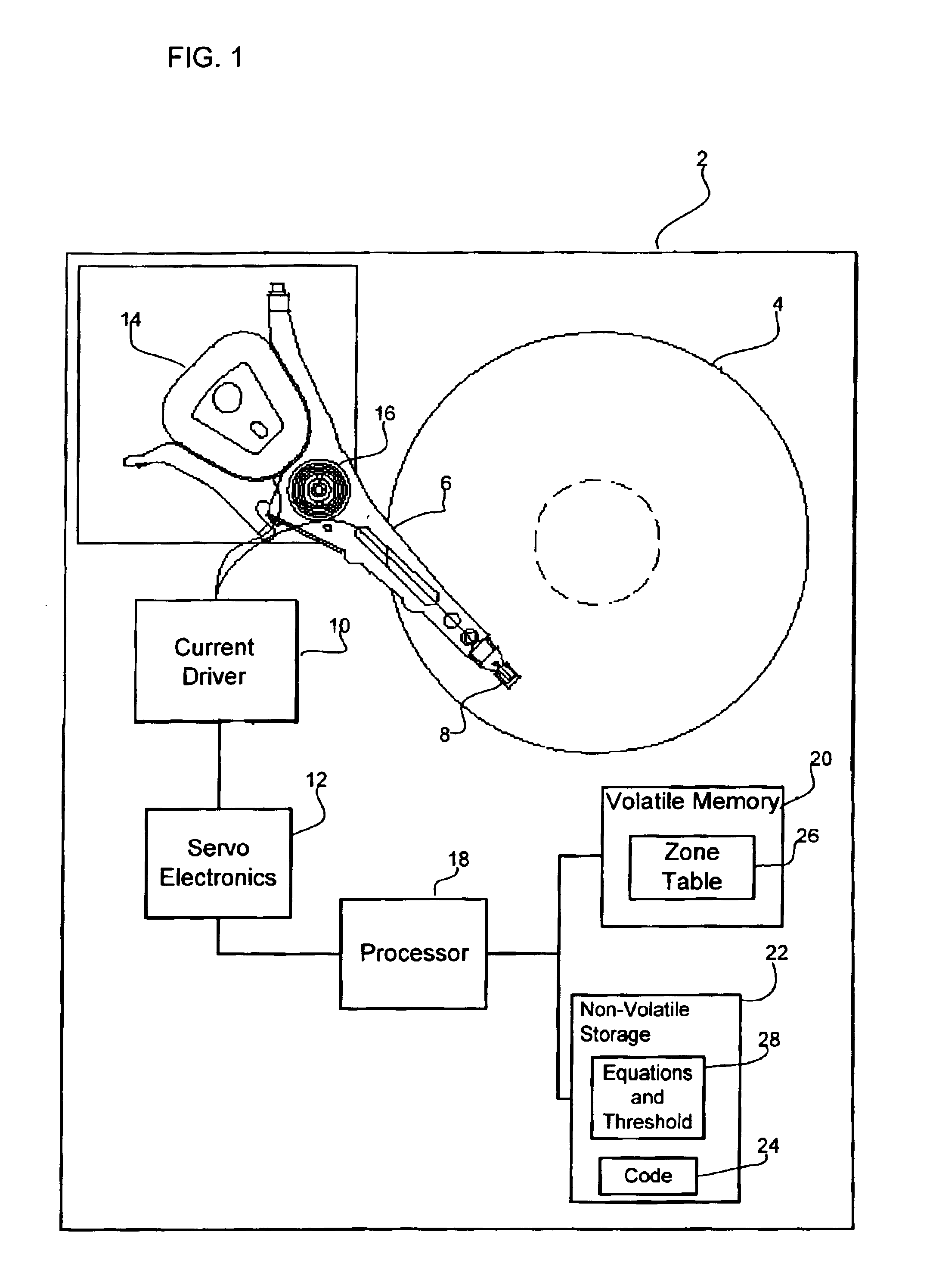
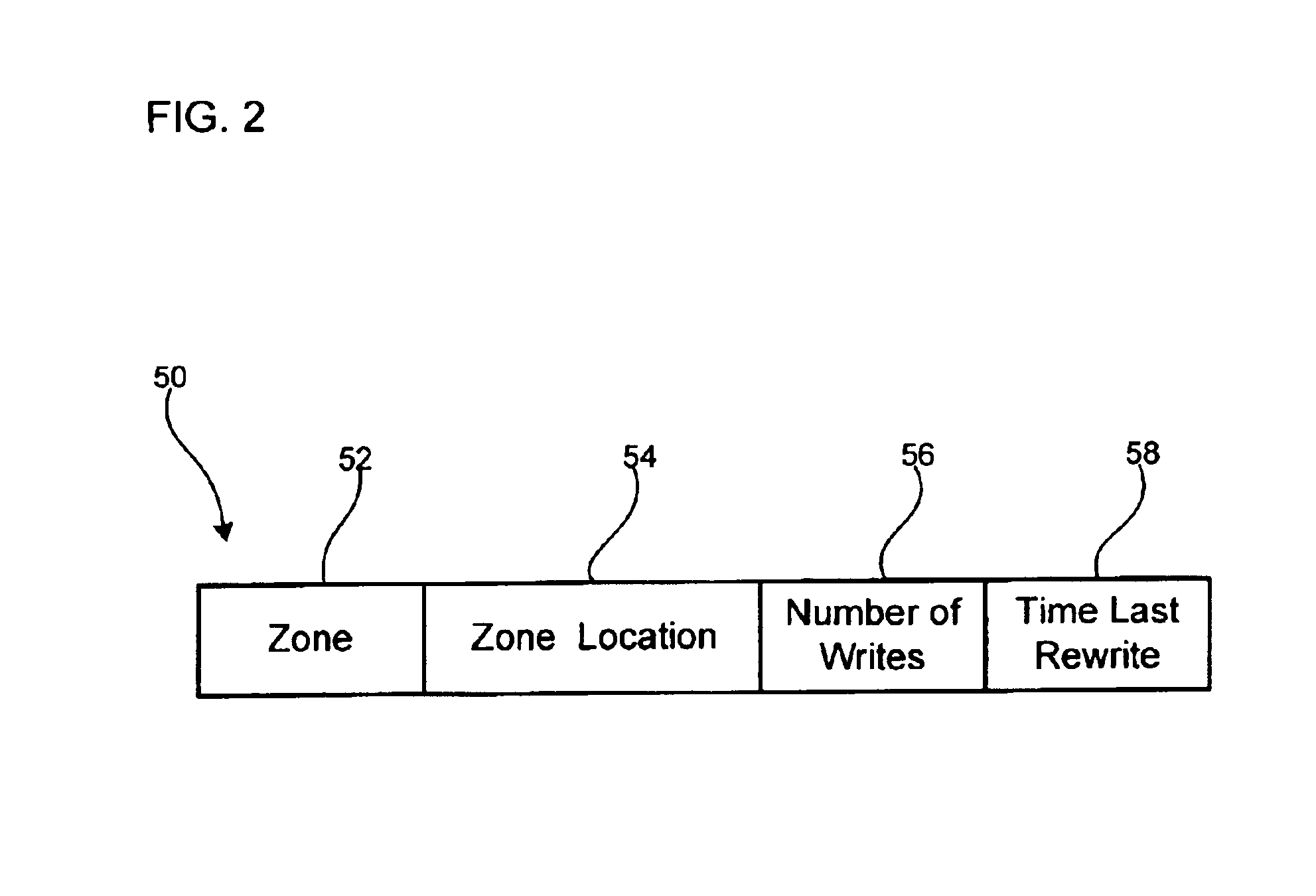
Method, system, and program for performing error correction in a storage device having a magnetic storage medium
InactiveUS6947234B2Accurately determinedDisc-shaped record carriersSignal processing for reducing noiseSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Magnetic storage
Provided are a method, system, and program for performing error correction in a storage device having a magnetic storage medium. A plurality of zones are defined in the magnetic storage medium, wherein each zone comprises a plurality of addressable locations in the magnetic storage medium. A determination is made as to whether a change of a signal-to-noise ratio for one subject zone of the plurality of zones exceeds a threshold. An operation is performed to improve the signal-to-noise ratio with respect to the subject zone of the magnetic storage medium after determining that the change of the signal-to-noise ratio exceeds the threshold.
Owner:IBM CORP
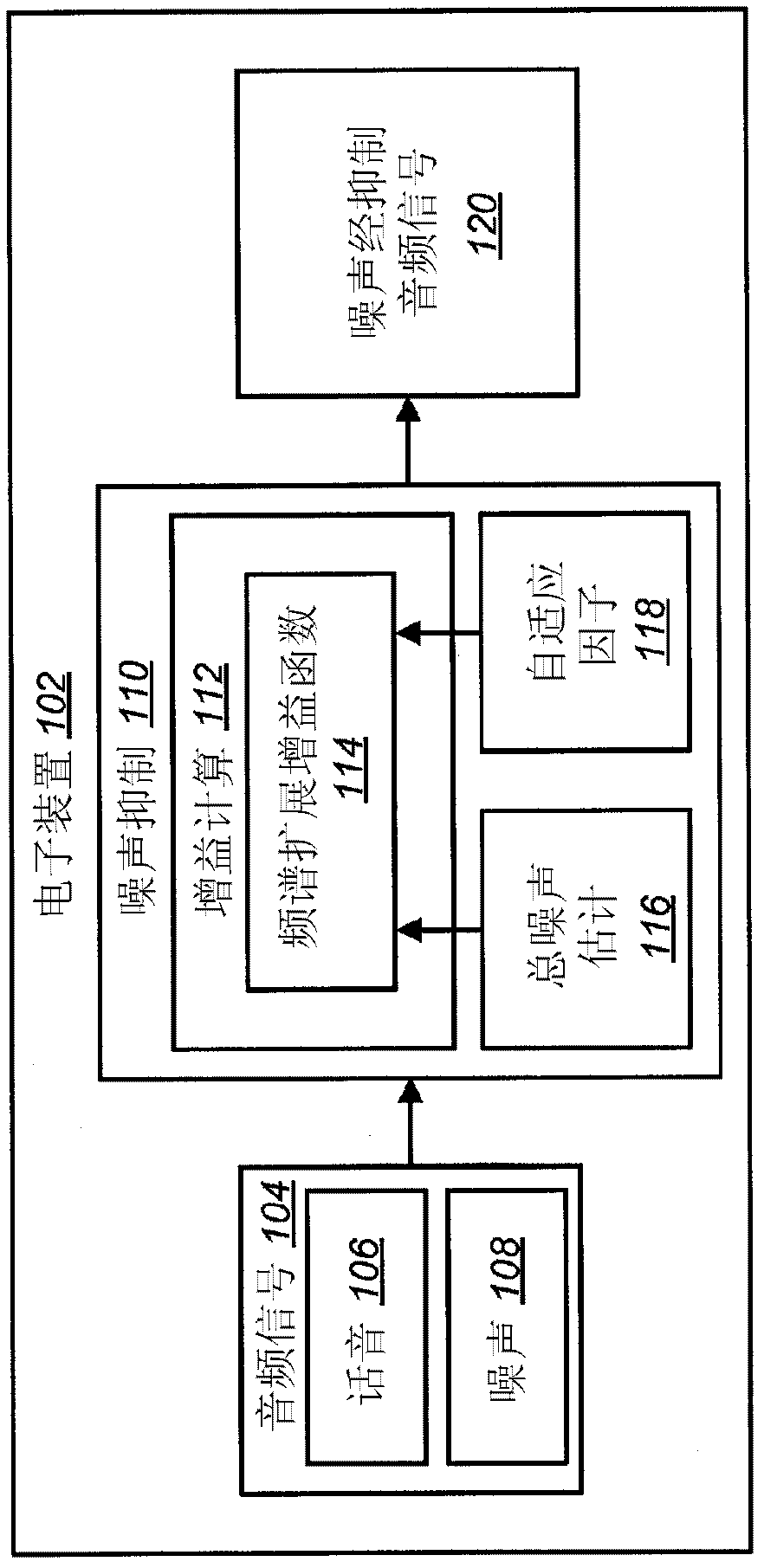
Suppressing noise in an audio signal
InactiveCN102549659ASignal processing for reducing noiseSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
An electronic device for suppressing noise in an audio signal is described. The electronic device includes a processor and instructions stored in memory. The electronic device receives an input audio signal and computes an overall noise estimate based on a stationary noise estimate, a non-stationary noise estimate and an excess noise estimate. The electronic device also computes an adaptive factor based on an input Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) and one or more SNR limits. A set of gains is also computed using a spectral expansion gain function. The spectral expansion gain function is based on the overall noise estimate and the adaptive factor. The electronic device also applies the set of gains to the input audio signal to produce a noise-suppressed audio signal and provides the noise-suppressed audio signal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and apparatus for reducing wind noise
InactiveUS20100158269A1Reduce wind noiseMinimal impactSignal processing for reducing noiseSpeech analysisComputer scienceSpeech sound
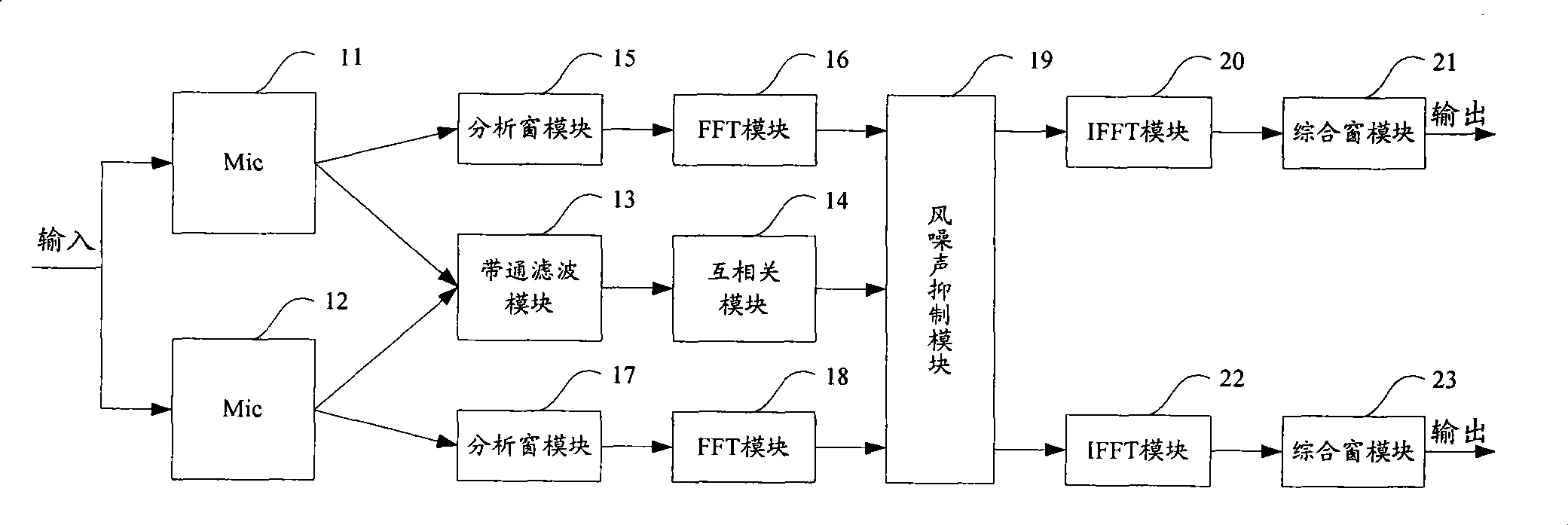
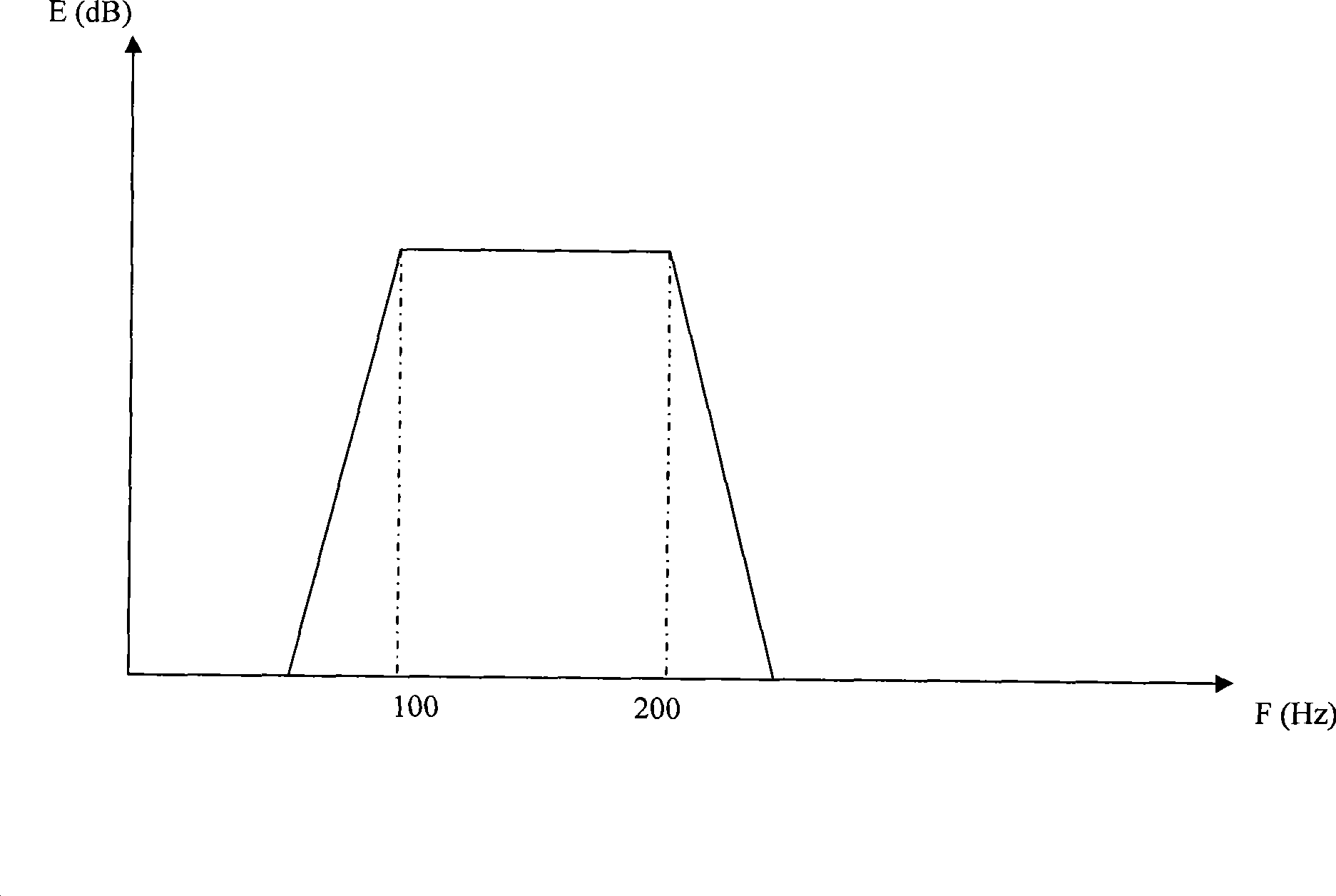
Techniques pertaining to techniques to reduce wind noises effectively in recorded signals are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, there is a strong correlation between two voice signals from target voices in the same frequency band sampled simultaneously by a pair of microphones in a common scene while there is a weak correlation between wind noises in the same frequency band of the two voice signals sampled simultaneously by the pair of microphones in the common scene. Taking advantage of this feature to provide a larger gain to the frequency band having a strong correlation and a smaller gain to the frequency band having a weak correlation, thereby the wind noise is reduced efficiently with minimum impact on the target voices.
Owner:VIMICRO CORP
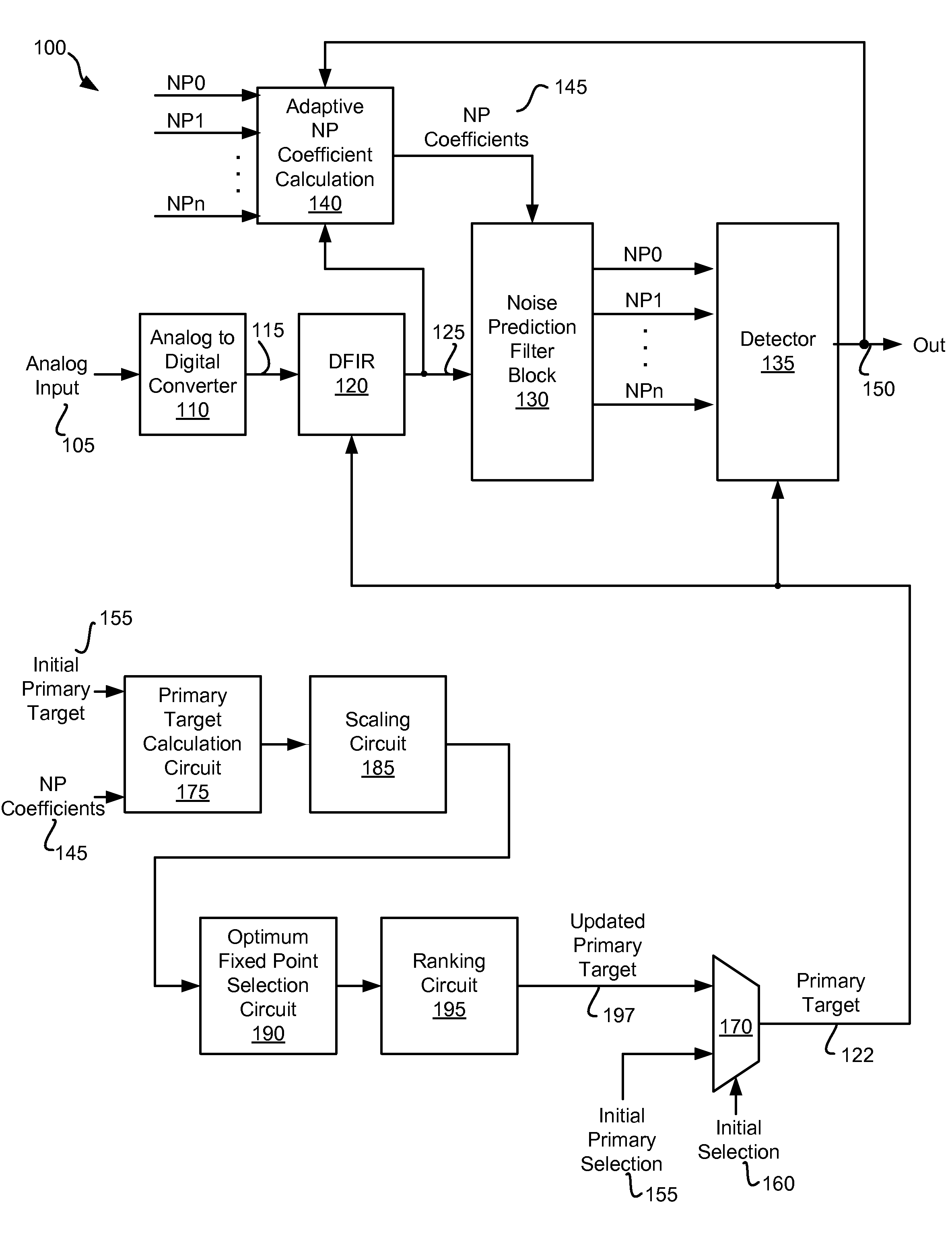
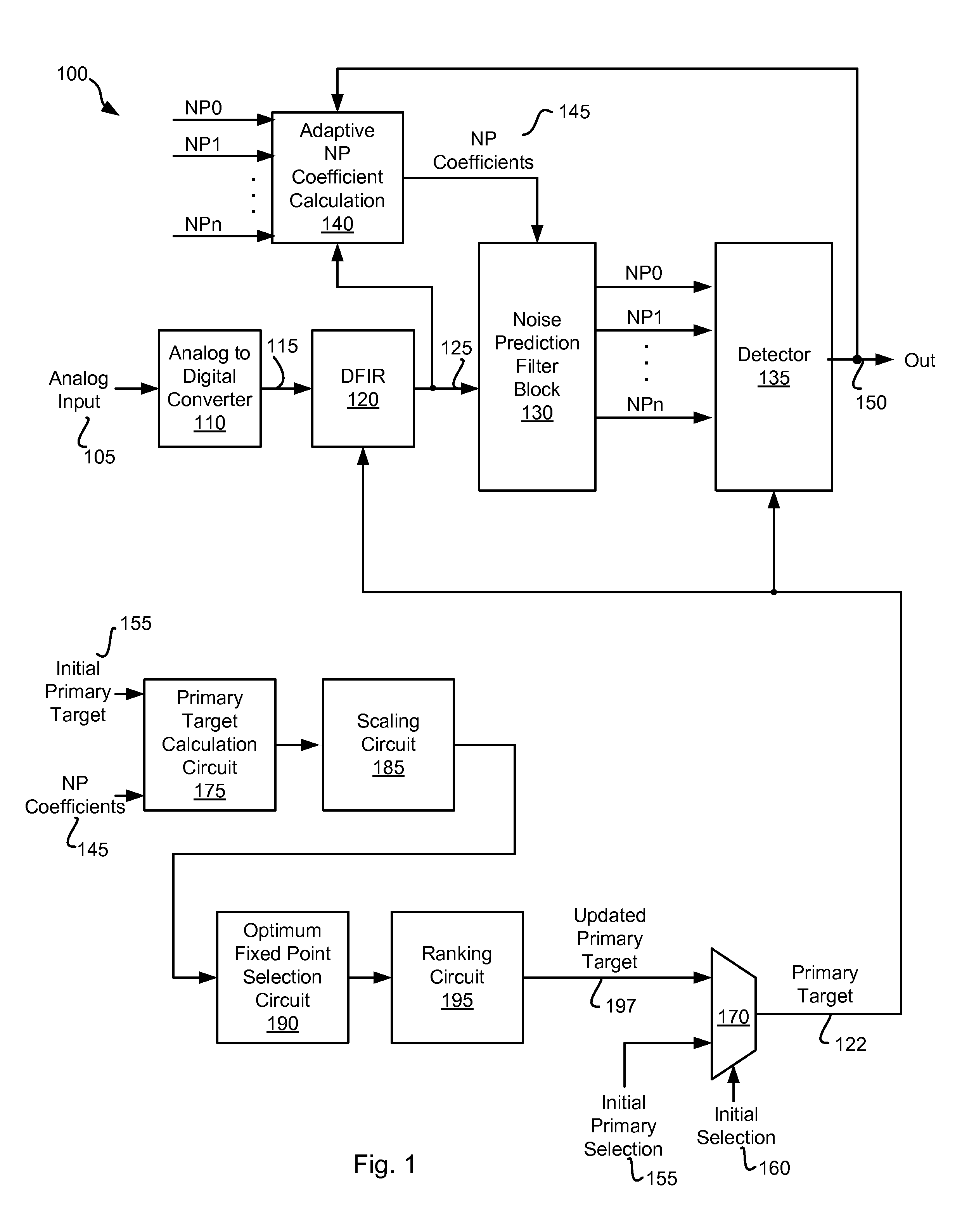
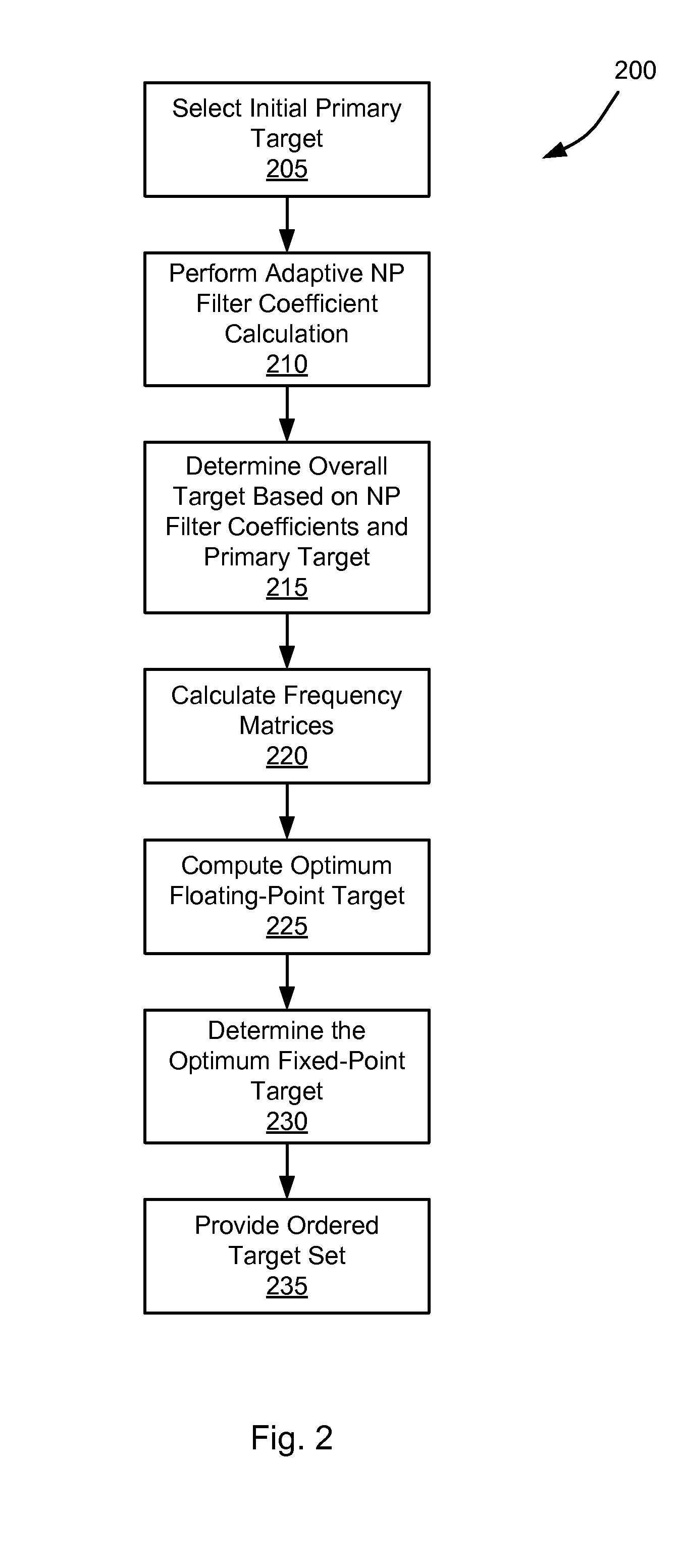
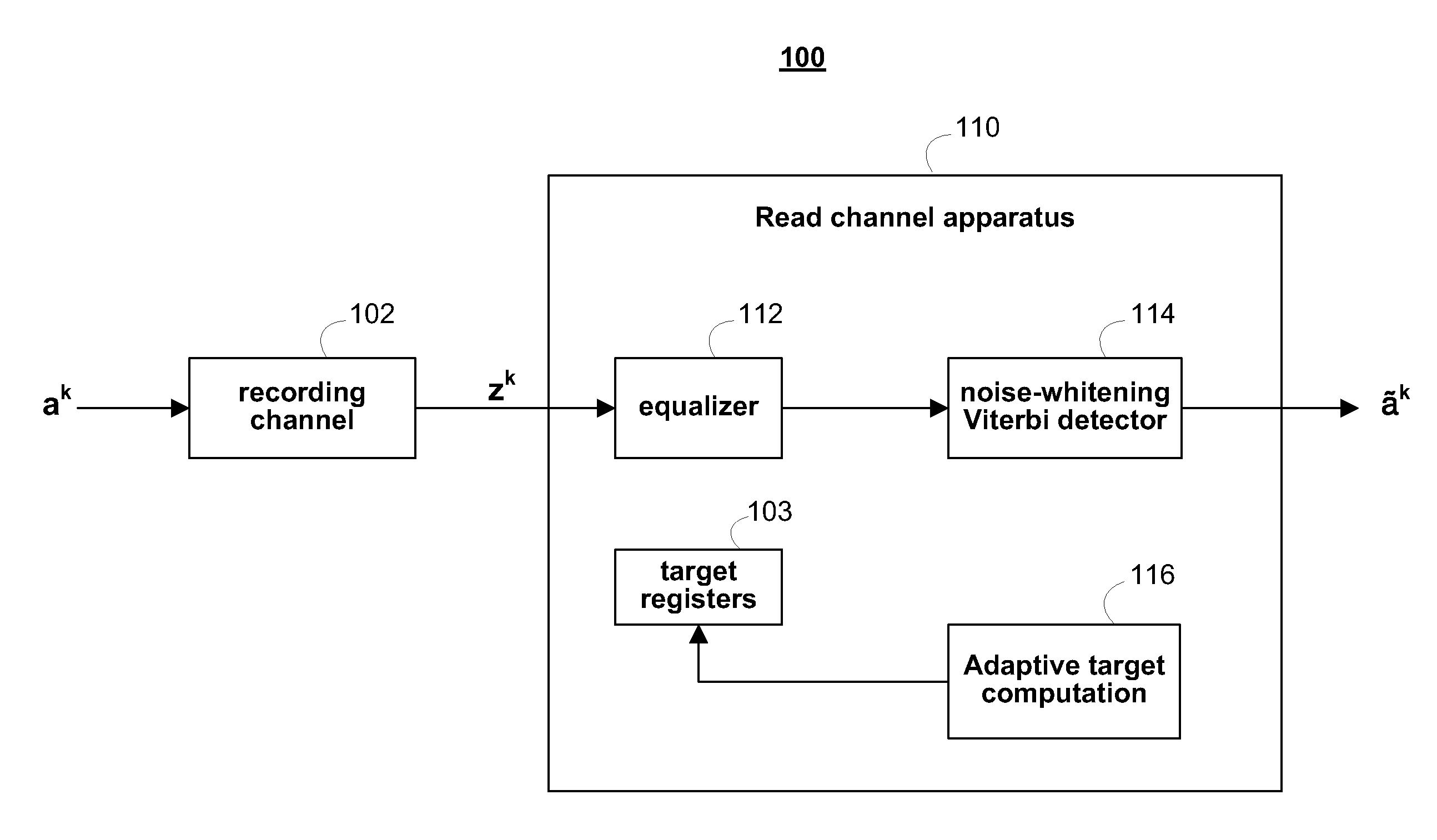
Frequency Domain Approach for Efficient Computation of Fixed-point Equalization Targets
ActiveUS20090161245A1Minimize cost functionMultiple-port networksSignal processing for reducing noiseEqualizationComputer science
Various embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for equalizing an input signal. For example, various embodiments of the present invention provide a method for performing equalization in a storage device. Such methods include providing an equalizer circuit that is governed by a target value, and a filter circuit that is governed by a filter coefficient. An initial value is provided to the equalizer circuit as the target value, and an overall target based at least in part on the initial value and the filter coefficient is calculated. An updated value is calculated based on the overall target, and the updated value is provided to the equalizer circuit as the target value.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Audio data processing apparatus and method to reduce wind noise
ActiveUS20060233391A1Reduce wind noiseImprove audio qualitySignal processing for reducing noiseTransducer protection circuitsLow frequency bandEngineering
An audio data processing apparatus and method to reduce wind noise. The apparatus includes a wind noise detecting unit to detect a wind noise section from an input audio signal, and a signal processing unit to reduce a low-frequency band signal of the input audio signal in the detected wind noise section. The apparatus determines whether wind is present and automatically reduces wind noise based on the determined result. Accordingly, the apparatus can effectively reduce wind noise.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
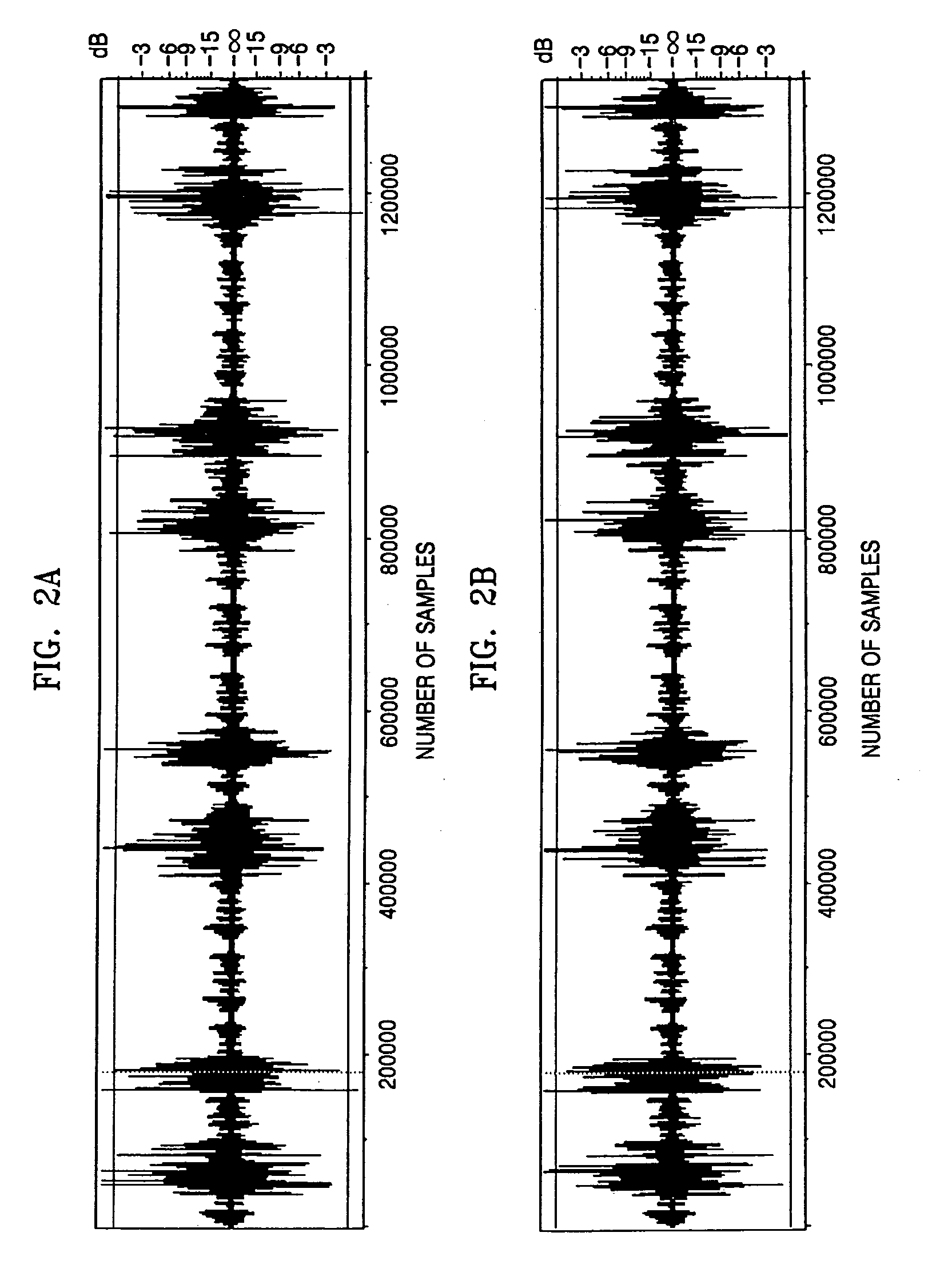
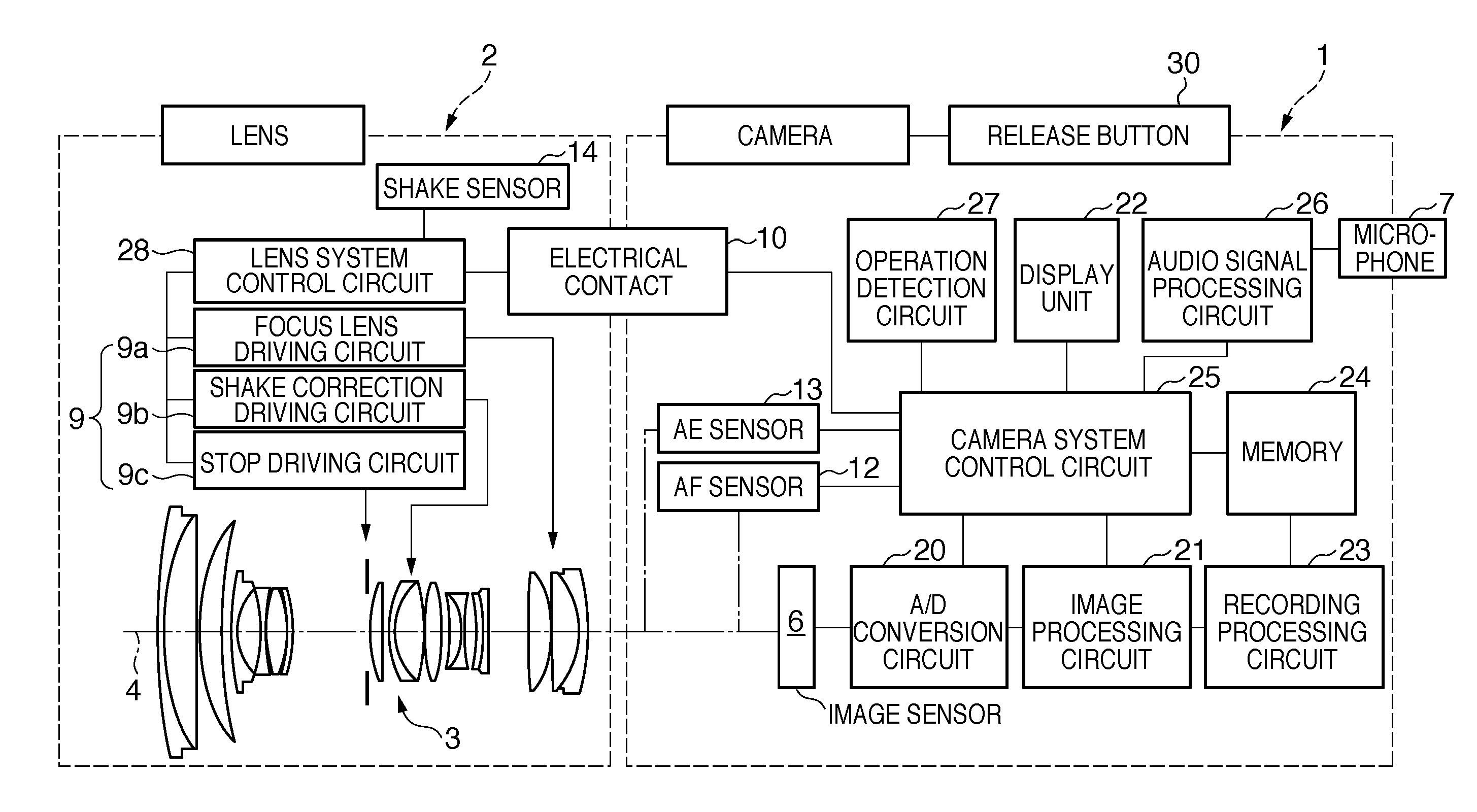
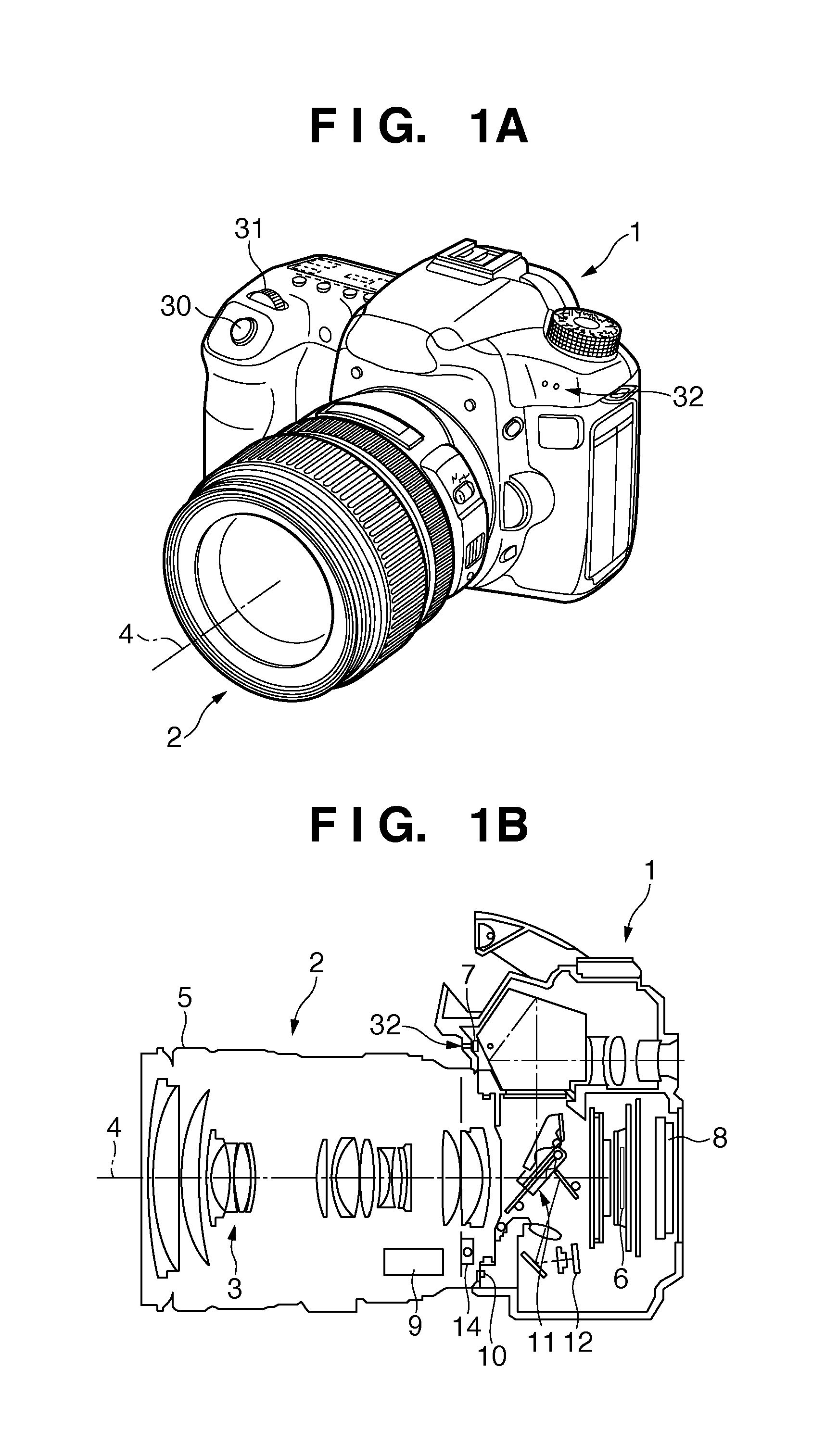
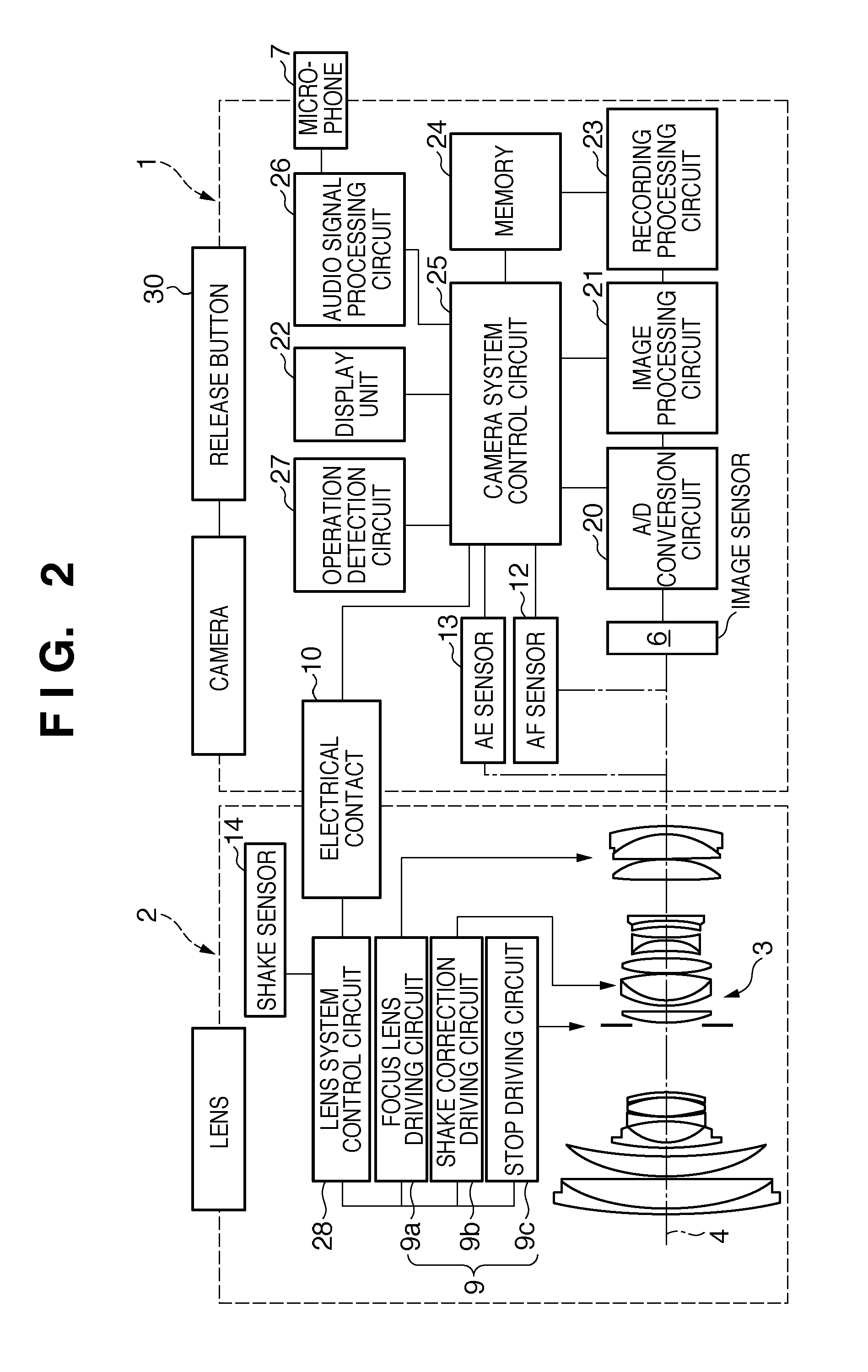
Audio signal processing apparatus and method of controlling the same
ActiveUS20110305351A1Effective noise reductionReduce operating loadSignal processing for reducing noiseProjectorsNoise reductionComputer science
When a first noise and second noise to be generated after the first noise are generated within a predetermined period, a noise reduction unit is controlled so as to execute a first noise reduction process for an audio signal in a period including the first noise and not to execute the first noise reduction process for an audio signal in a period including the second noise.
Owner:CANON KK
Noise reducing apparatus and noise reducing method
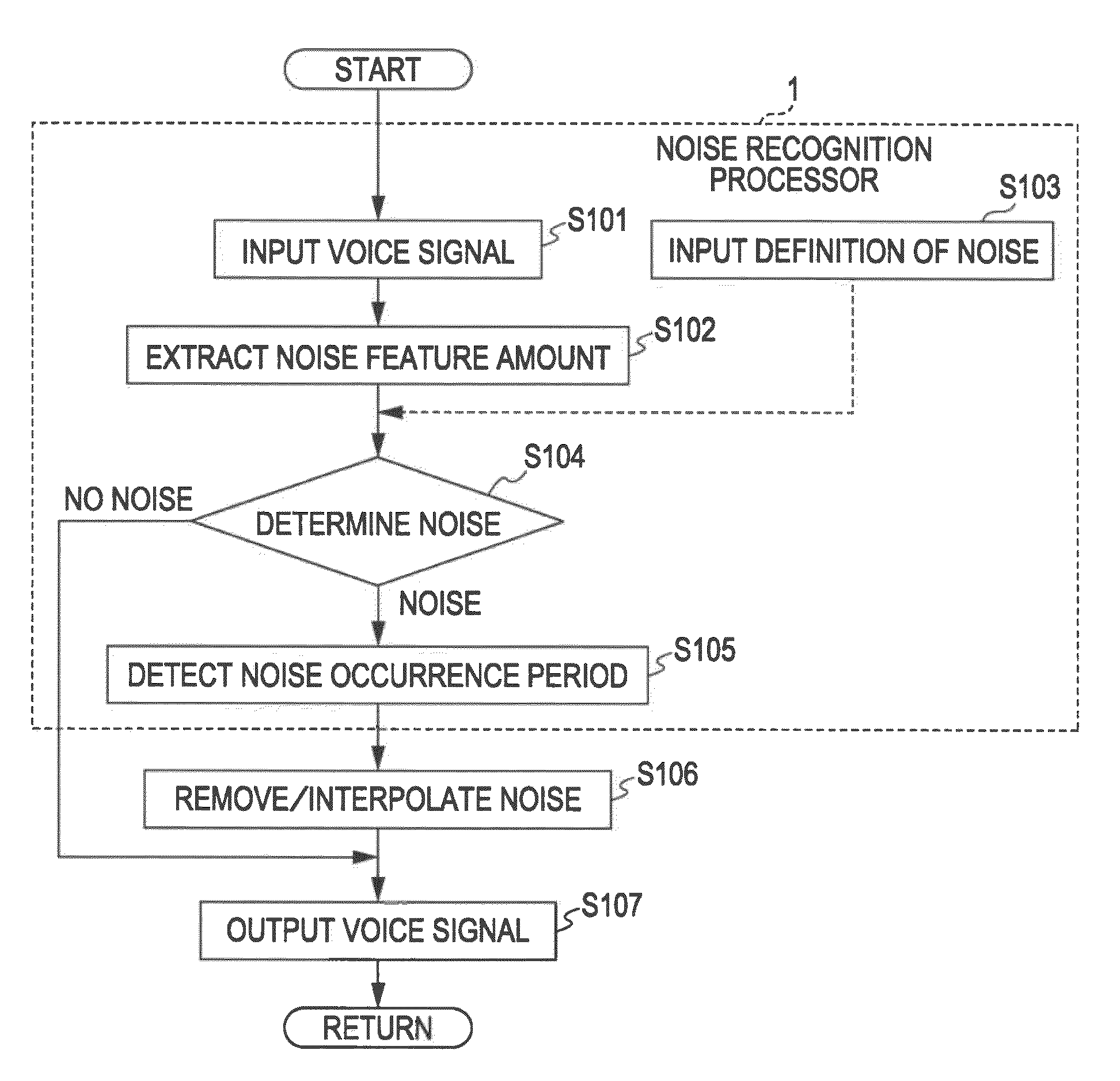
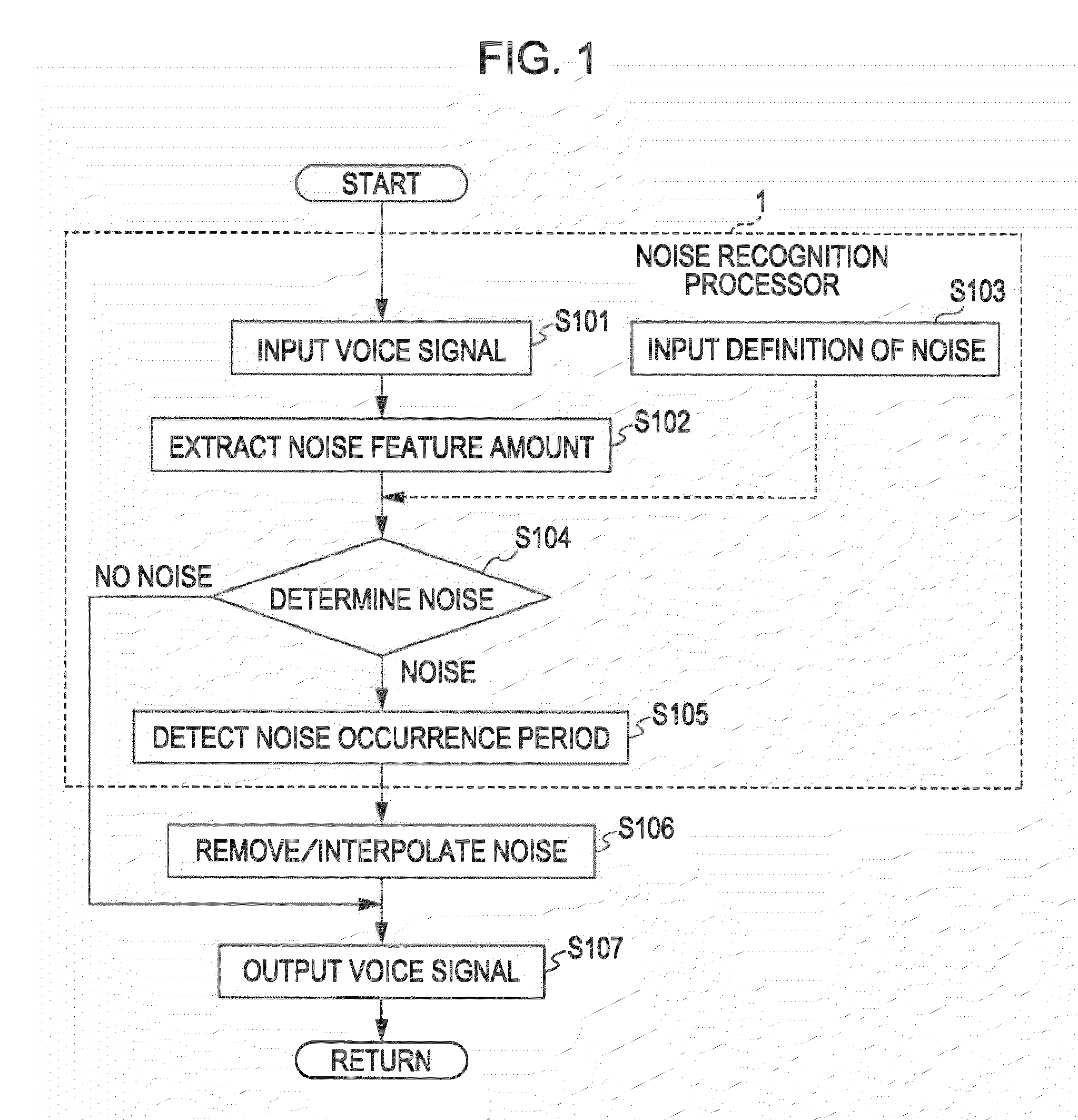
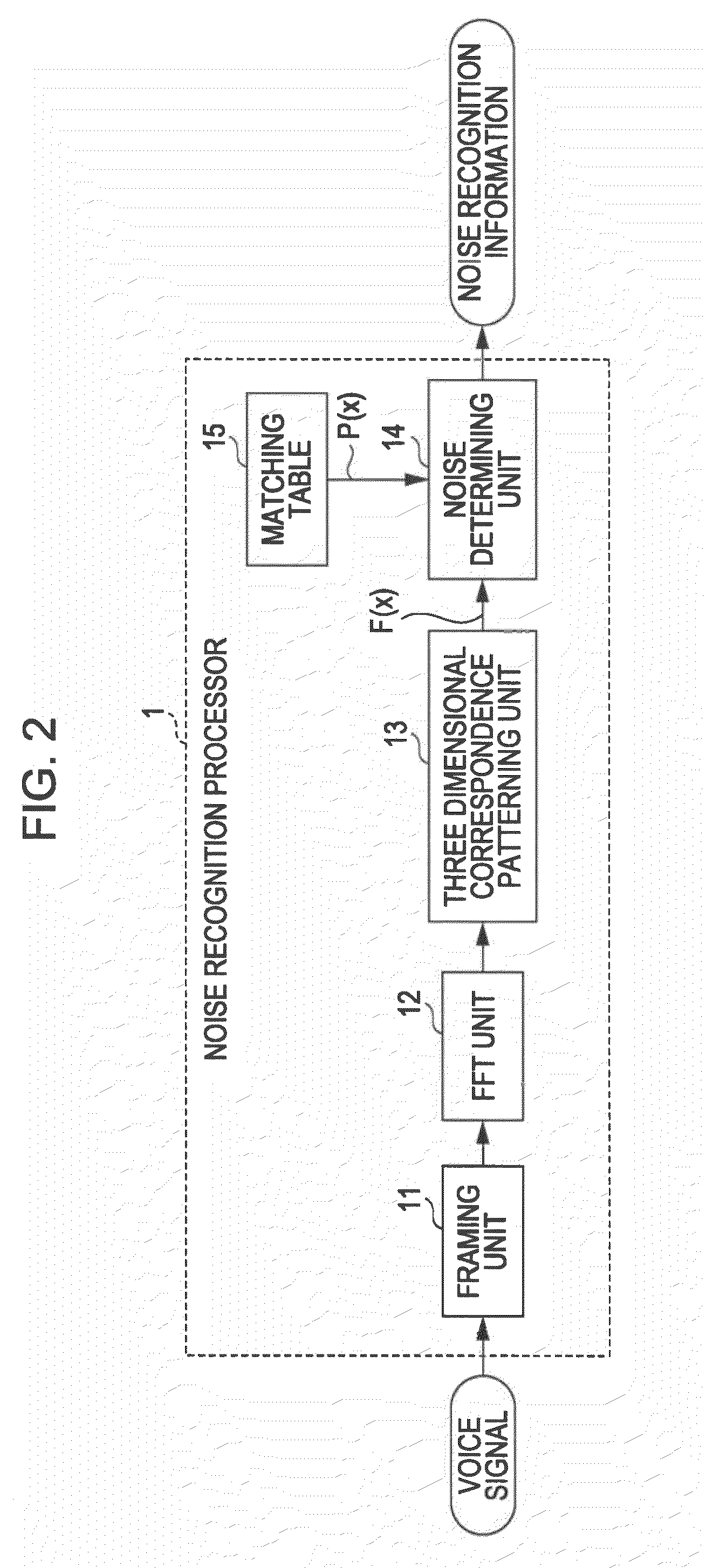
InactiveUS20100260354A1High-quality interpolation signalHigh-quality voiceSignal processing for reducing noiseSpeech analysisSpeech soundComputer science
A noise reducing apparatus includes: a voice signal inputting unit inputting an input voice signal; a noise occurrence period detecting unit detecting a noise occurrence period; a noise removing unit removing a noise for the noise occurrence period; a generation source signal acquiring unit acquiring a generation source signal with a time duration corresponding to a time duration corresponding to the noise occurrence period; a pitch calculating unit calculating a pitch of an input voice signal interval; an interval signal setting unit setting interval signals divided in each unit period interval; an interpolation signal generating unit generating an interpolation signal with the time duration corresponding to the noise occurrence period and alternately arranging the interval signal in a forward time direction and the interval signal in a backward time direction; and a combining unit combining the interpolation signal and the input voice signal, from which the noise is removed.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method and apparatus for restraining wind noise
ActiveCN101430882AWind noise suppressionRecording performance will not be reducedSignal processing for reducing noiseSpeech analysisEngineeringFrequency band
The invention discloses a method for suppressing wind noise and a device thereof, which are used for accurately suppressing the wind noise, thus ensuring that a better recording effect is achieved. The method for suppressing the wind noise comprises the following steps: performing cross-correlation operation on two channels of sound signals simultaneously acquired under a same scene to obtain a normalized cross-correlation value on each frequency band; and performing gain control on the two channels of sound signals by the normalized cross-correlation value on each frequency band to suppress the wind noise in the two channels of sound signals.
Owner:WUXI ZGMICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
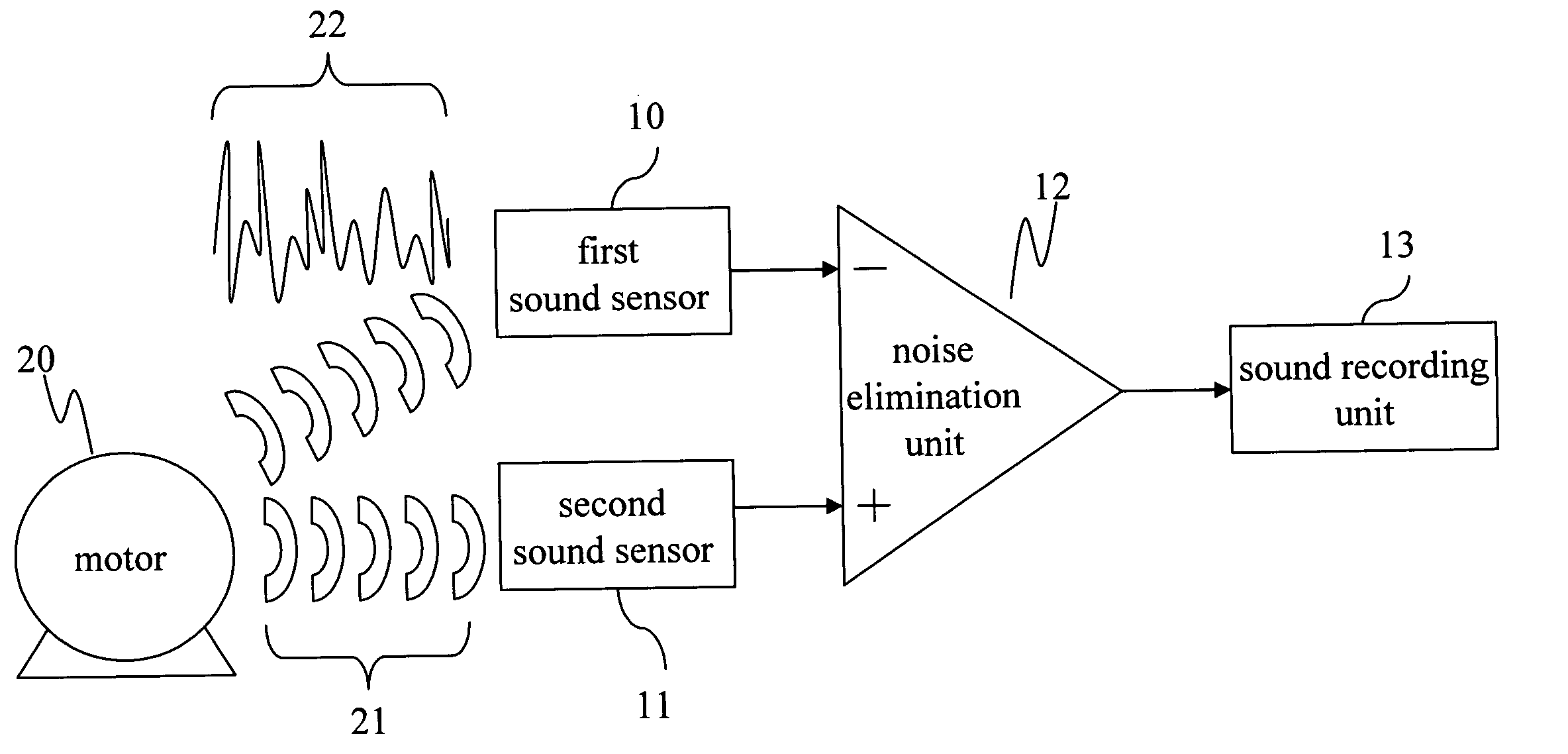
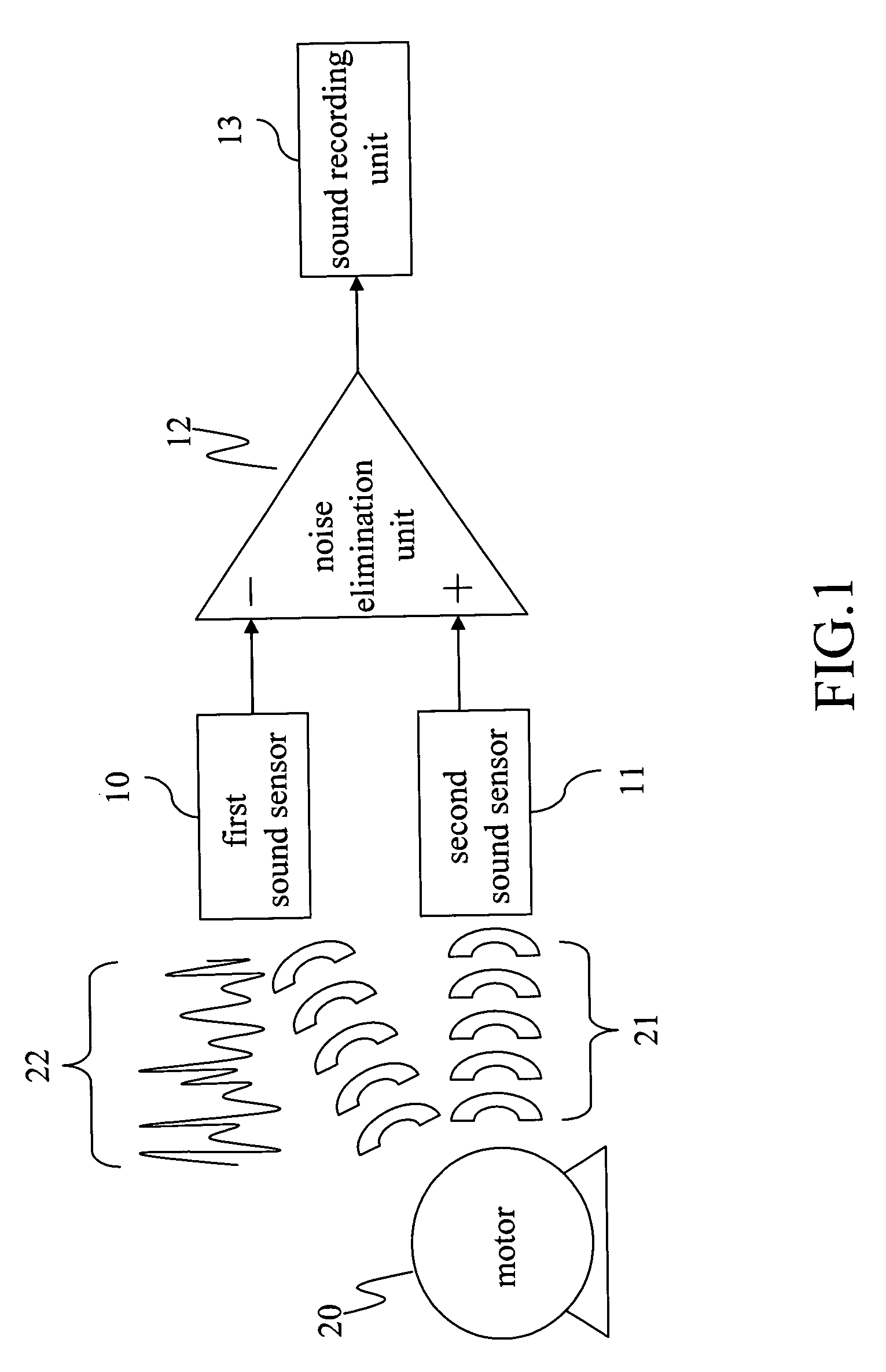
Motor operation noise elimination circuit of portable multimedia player
InactiveUS20070041588A1Cancel noiseImprove recording qualityEar treatmentSignal processing for reducing noiseEngineeringSecond sound
A motor operation noise elimination circuit of a portable multimedia player is provided, in which a first sound sensor is utilized to sense a first sound signal generated by motor operation during recording and a second sound signal input in the portable multimedia player for recording. Then the first sound signal sensed by the second sound sensor is phase-reversed in the noise elimination unit and is combined into the first and second sound signals sensed by the first sound sensor during recording, comprising: a second sound sensor, used to sense a first sound signal generated by the motor, and a noise elimination unit, used to receive the first and second sound signals sensed by the first sound sensor, and the first sound signal sensed by the second sound sensor, then a combination operation is executed, thus eliminating the first sound signal and outputting the second sound signal.
Owner:INVENTEC MULTIMEDIA & TELECOM
Combined DC restoration double detection and loops
InactiveUS8046666B2Reduce second error rateSimplify digital design processData representation error detection/correctionSignal processing for reducing noiseEngineeringNoise statistics
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Adaptive environmental noise compensation for audio playback
InactiveCN103039023ASignal processing for reducing noiseSpeech analysisEnvironmental noiseEqualization
The present invention counterbalances background noise by applying dynamic equalization. A psychoacoustic model representing the perception of masking effects of background noise relative to a desired foreground soundtrack is used to accurately counterbalance background noise. A microphone samples what the listener is hearing and separates the desired soundtrack from the interfering noise. The signal and noise components are analyzed from a psychoacoustic perspective and the soundtrack is equalized such that the frequencies that were originally masked are unmasked. Subsequently, the listener may hear the soundtrack over the noise. Using this process the EQ can continuously adapt to the background noise level without any interaction from the listener and only when required. When the background noise subsides, the EQ adapts back to its original level and the user does not experience unnecessarily high loudness levels.
Owner:DTS
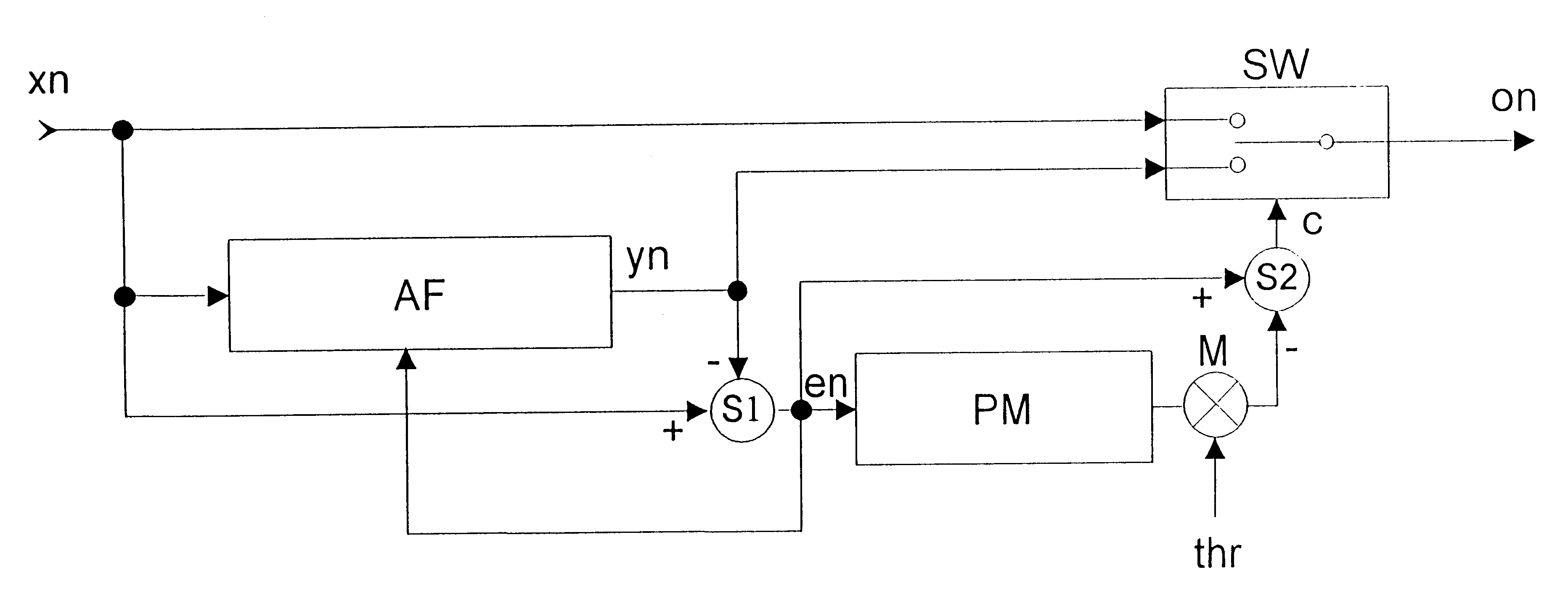
Method, equipment and recording device for suppressing pulsed interference in analogue audio and/or video signals
InactiveUS6654471B1High click densityLess complexTelevision system detailsAnalogue recording/reproducingPeak valueEngineering
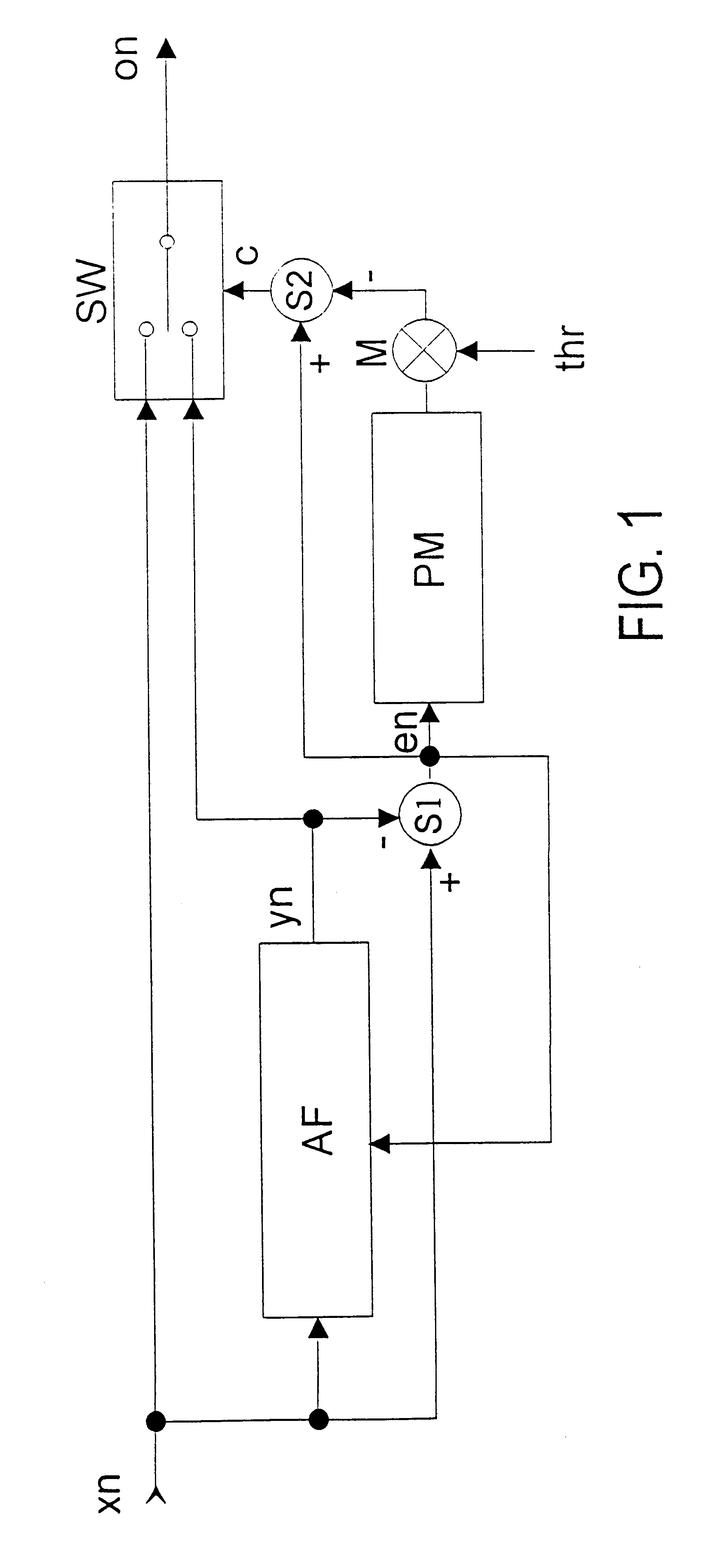
Clicks in voice and music signals are removed by detecting and interpolating the click. The use of a permanently set threshold value above the peak value of the audio signal is known for detecting the clicks, and interpolation carried out on the basis of the sample values before and after a click is known for filling them in. Disadvantages of these methods are, on the one hand, that many clicks do not have a larger amplitude than the peak signal and therefore remain undetected, and, on the other hand, interpolation is a highly complex procedure and is limited to a maximum click density. The invention provides for an error signal (en) to be determined by adaptive filtering (AF). A sample value is designated as distorted in the input signal (xn) if the absolute instantaneous value in the error signal (en) exceeds a dynamically adapted threshold value. The output signal of the adaptive filtering (yn) is used as a substitute value for the sample value designated as distorted, specifically both in the case of the signal which is output and in the input values of the adaptive filtering.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Joint fitting between members and joint structure and joining method of upper and lower floor vertical frame members
InactiveUS20070110513A1Stress transmittedEasy to placeBuilding roofsRecord information storageHorizontal orientationUpper floor
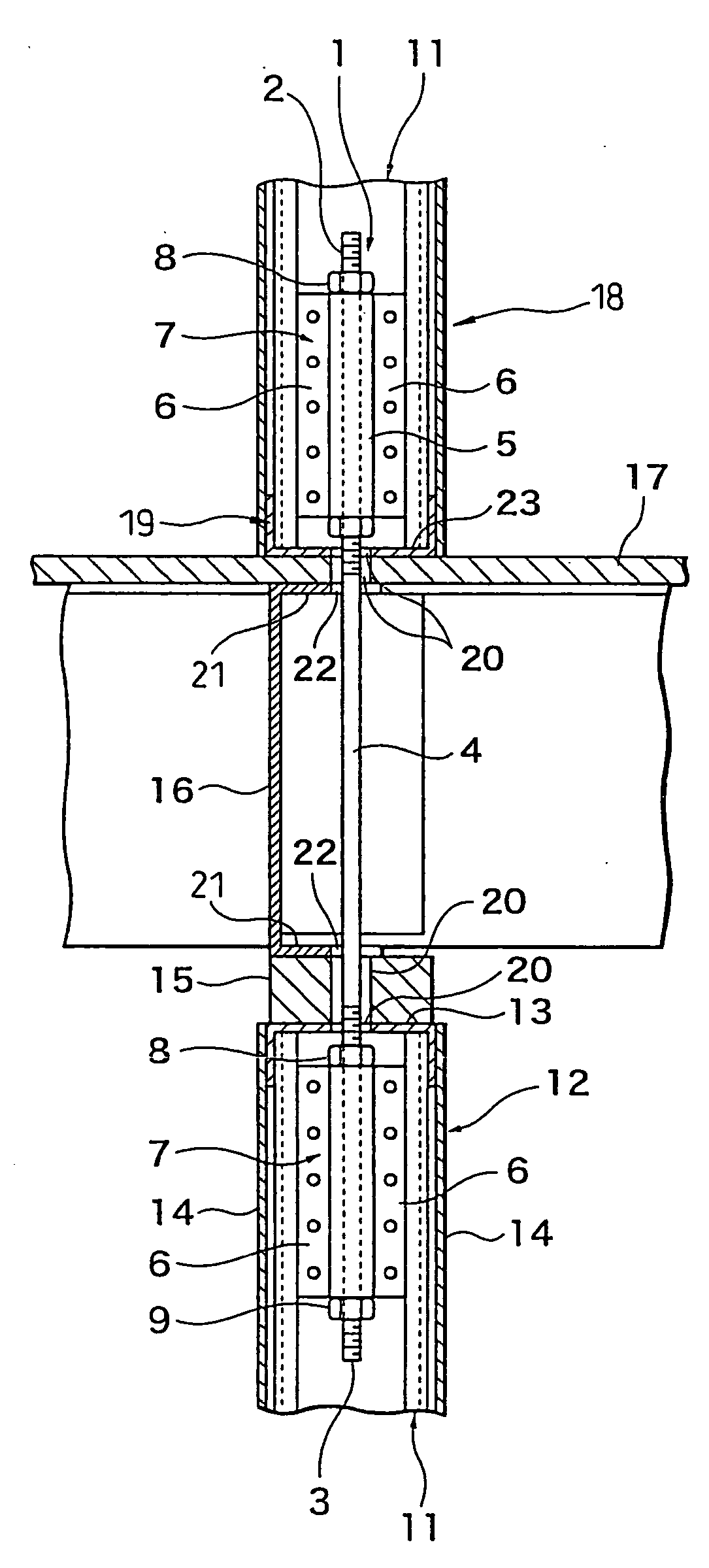
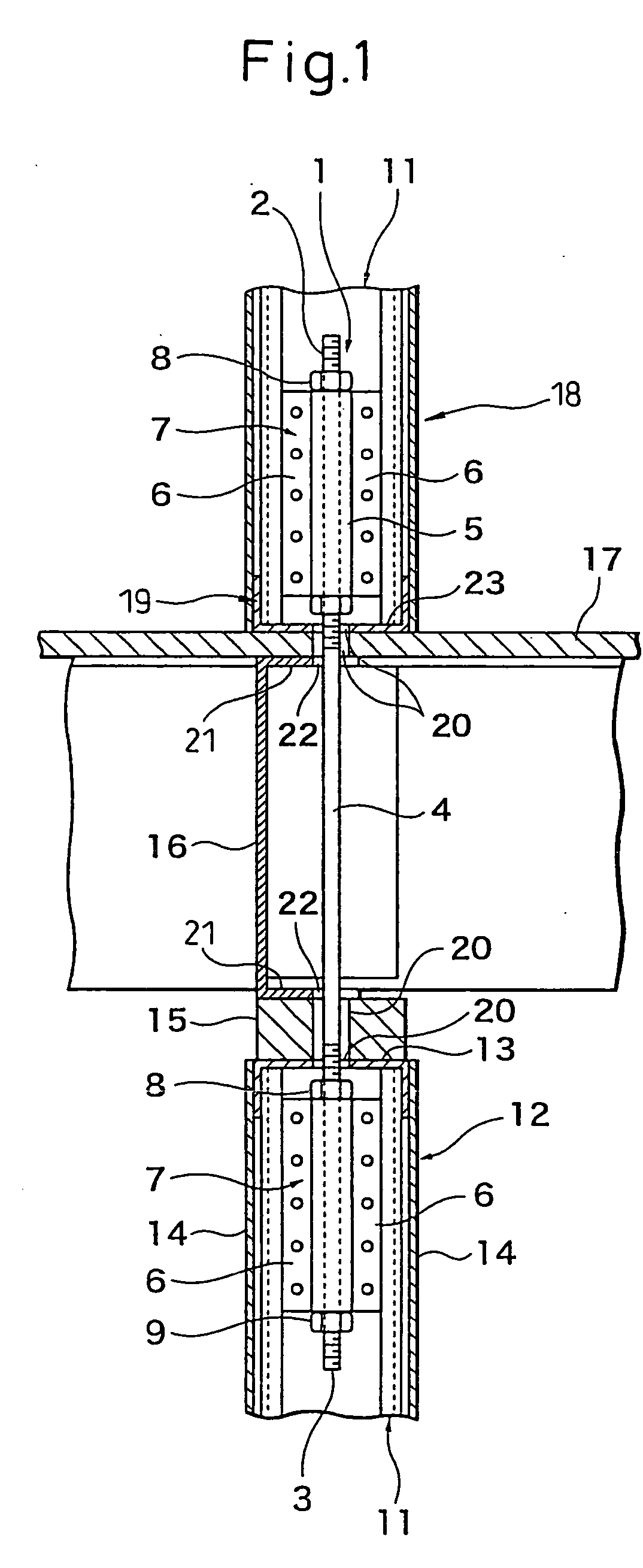
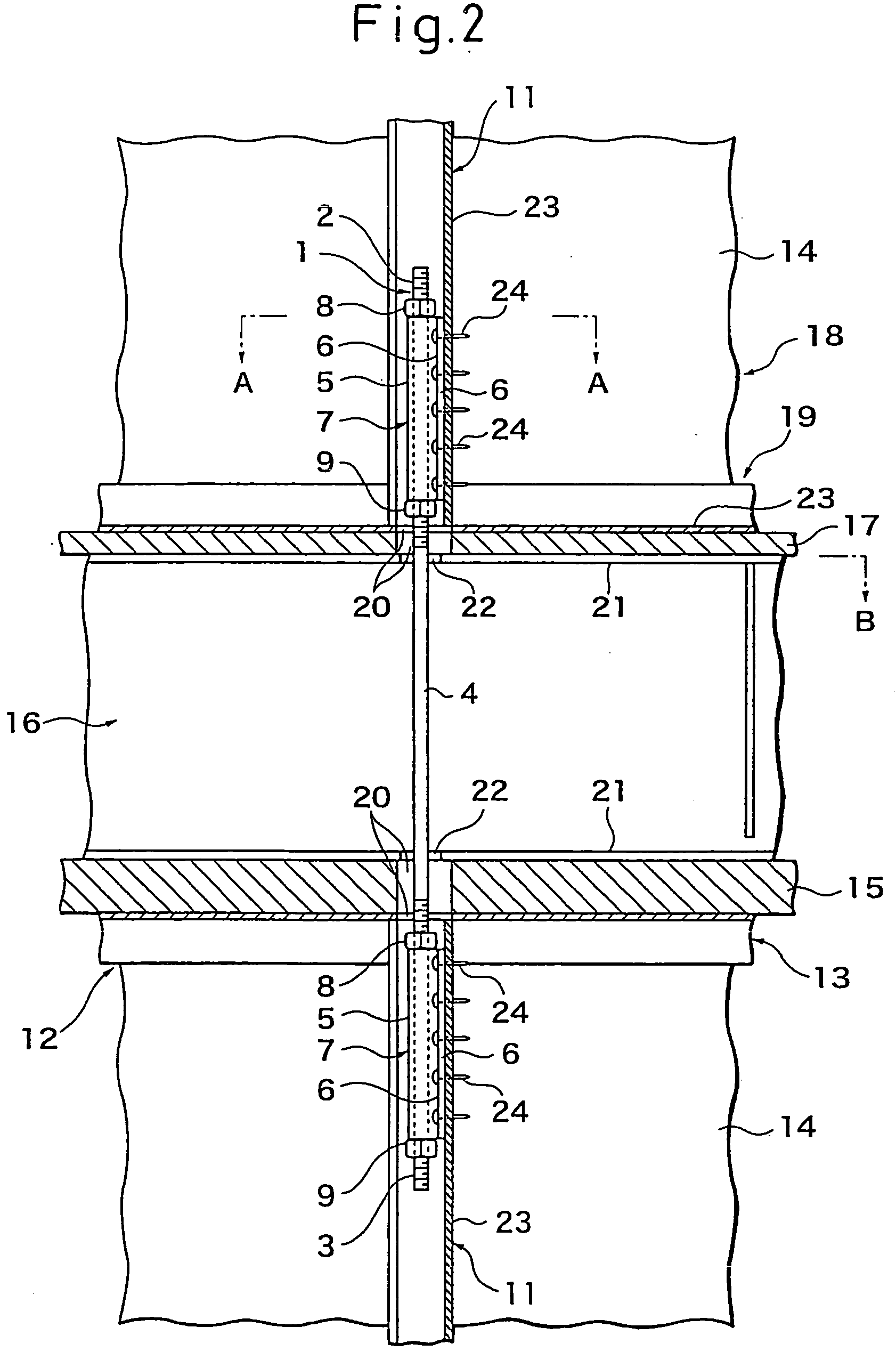
The present invention provides a joint fitting between members of a simple structure able to transmit stress of both compressive force and tensile force and a joint structure and method of joining, that is, a joint fitting 1 between members comprising a single bolt 4 having a length enabling it to be arranged vertically oriented bridging an upper floor vertical frame member and a lower floor vertical frame member at intervals along the axial direction of which bolt joint hardware 7 to be fastened to vertical frame members of the floors arranged at the upper floor side and lower floor side and having side opening groove cross-sections are arranged, the side opening grooves in the joint hardware 7 being able to detachably receive the bolt, and the joint hardware 7 being attached to be able to be fastened positioned along the longitudinal direction of the bolt 4, the joint hardware arranged at the upper and lower floors in the joint hardware being butted against vertical side surfaces of the vertical frame members 11 of the floors and fastened by drill screws 24 or other fasteners screwed in bridging the joint hardware 7 and the vertical frame members 11 in a horizontal orientation. Further, a method of joining members using the joint fitting 1 between members.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Charge/discharge control circuit for audio device
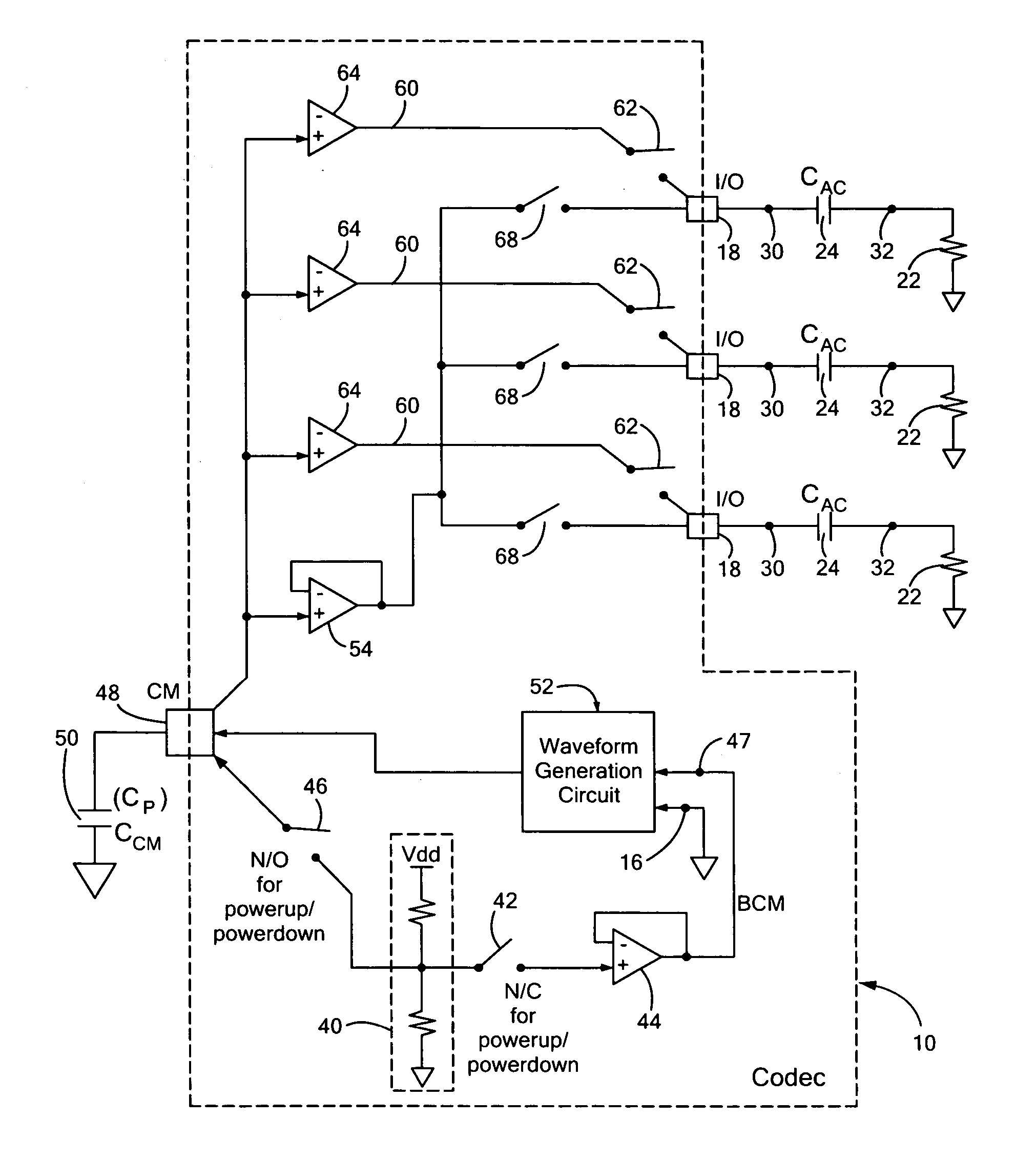
ActiveUS20070030038A1Suppressing audible artifactEasy dischargeAnalogue/digital conversionSignal processing for reducing noiseEngineeringVoltage reference
A charge / discharge control circuit for controlling current through an input / output audio device includes a first voltage reference; a second voltage reference and a waveform generation circuit responsive to the first and second voltage references for generating a multi-stage waveform profile which is approximately an inaudible waveform for suppressing audible artifacts in the input / output device.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Device for preventing pop noise in an audio output apparatus and method therefor
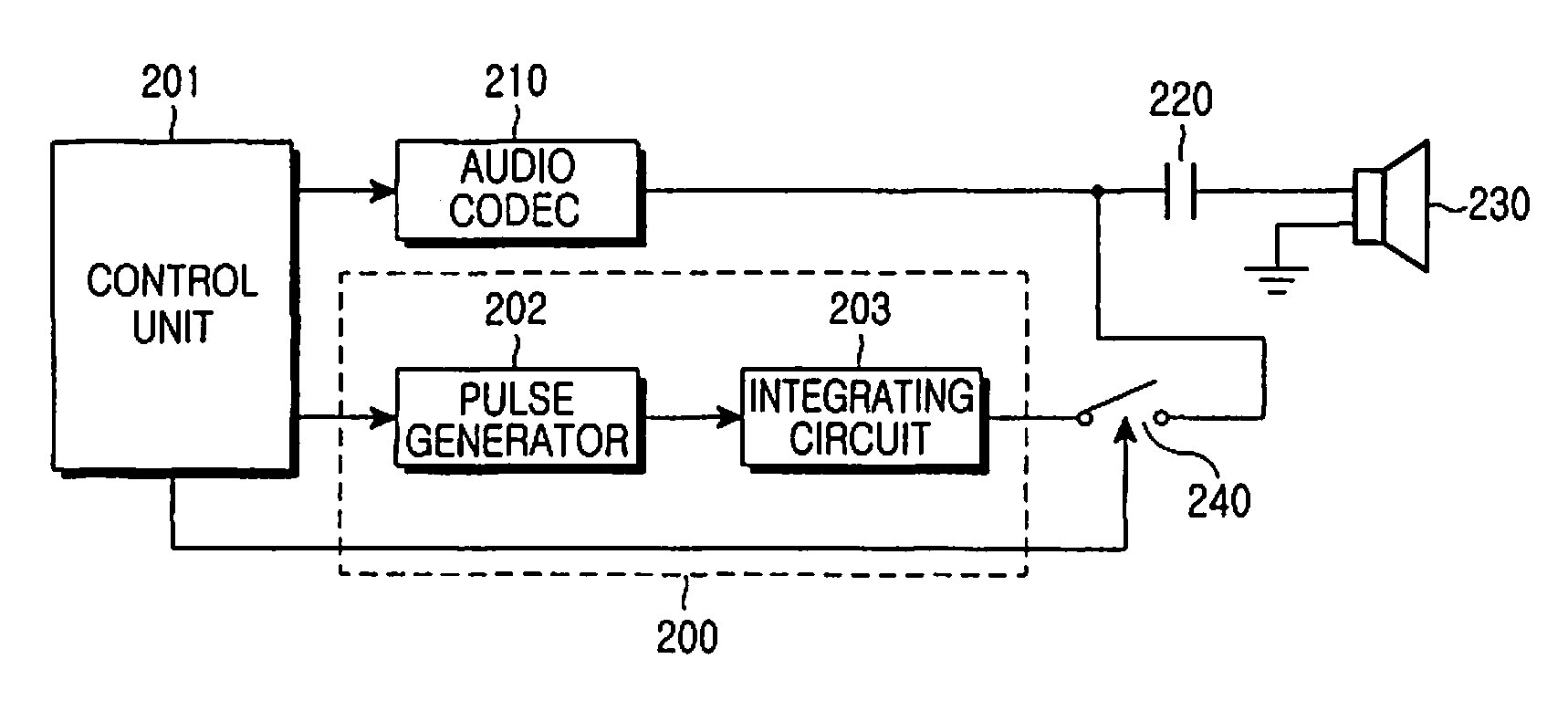
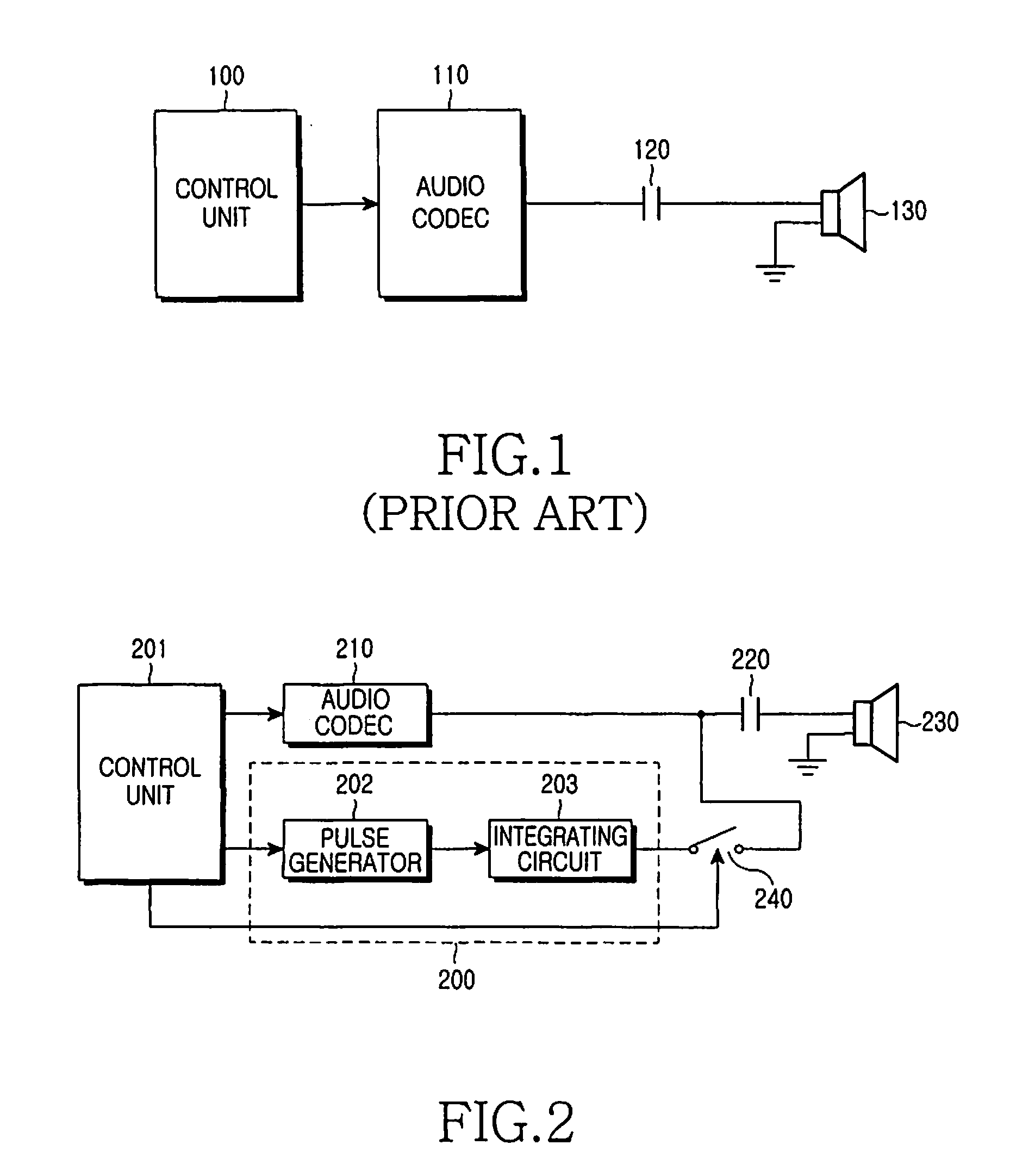
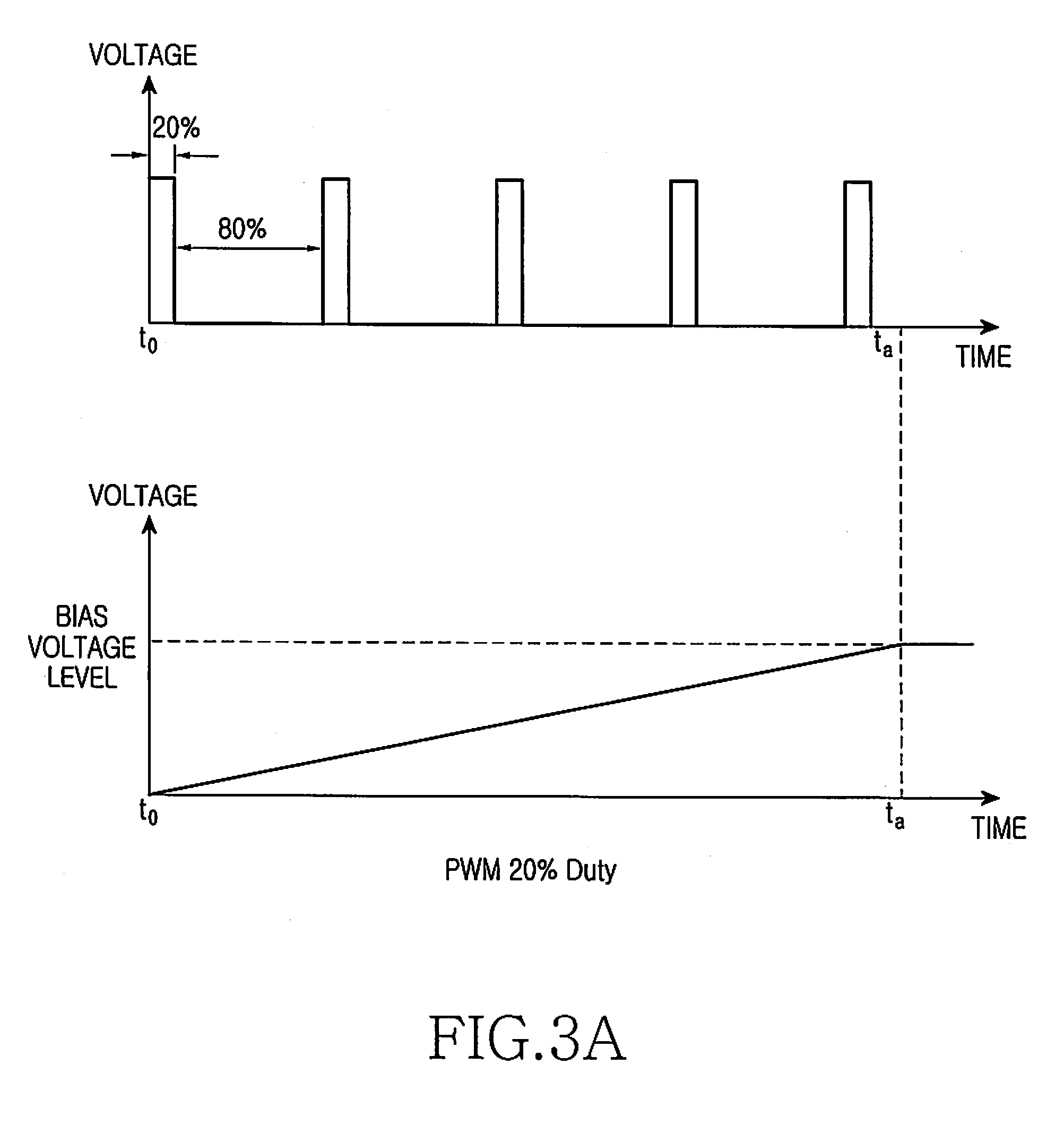
InactiveUS20080049952A1Avoid problemsAvoid noiseSignal processing for reducing noiseGain controlCapacitanceOutput device
An audio output apparatus having an audio codec for generating audio signals delivered to a speaker is provided with a device for preventing an audio pop noise caused by the bias voltage output from the audio codec, which includes a capacitor connected between an output end of the audio codec and the speaker, a capacitor charger for smoothly charging the capacitor to a predetermined voltage level, a switch arranged between the junction of the output end of the audio codec and the capacitor and the capacitor charger, and a control unit for controlling the codec, wherein the control unit turns on the switch and drives the capacitor charger before activating the audio codec, and then turns off the switch and terminates the operation of the capacitor charger if a predetermined charging time has elapsed. A method for preventing the audio pop noise caused by a bias voltage output from the audio codec includes smoothly charging the capacitor to have the same voltage level as the bias voltage of the audio codec before activating the audio codec, and activating the audio codec.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus for providing data dependent detection in a data read channel
InactiveUS7173784B2Improve detection reliabilityData representation error detection/correctionError preventionViterbi decoderComputer hardware
An apparatus for providing data dependent detection in a data read channel is disclosed. Parameters in a read channel are dynamically adjusted according to data dependent noise. For example, a comparison in an add-compare-select (ACS) unit of a Viterbi decoder may be adjusted or offset terms in error event filters may be biased to choose a Viterbi sequence with more transitions or to compensate for polarity dependent noise.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
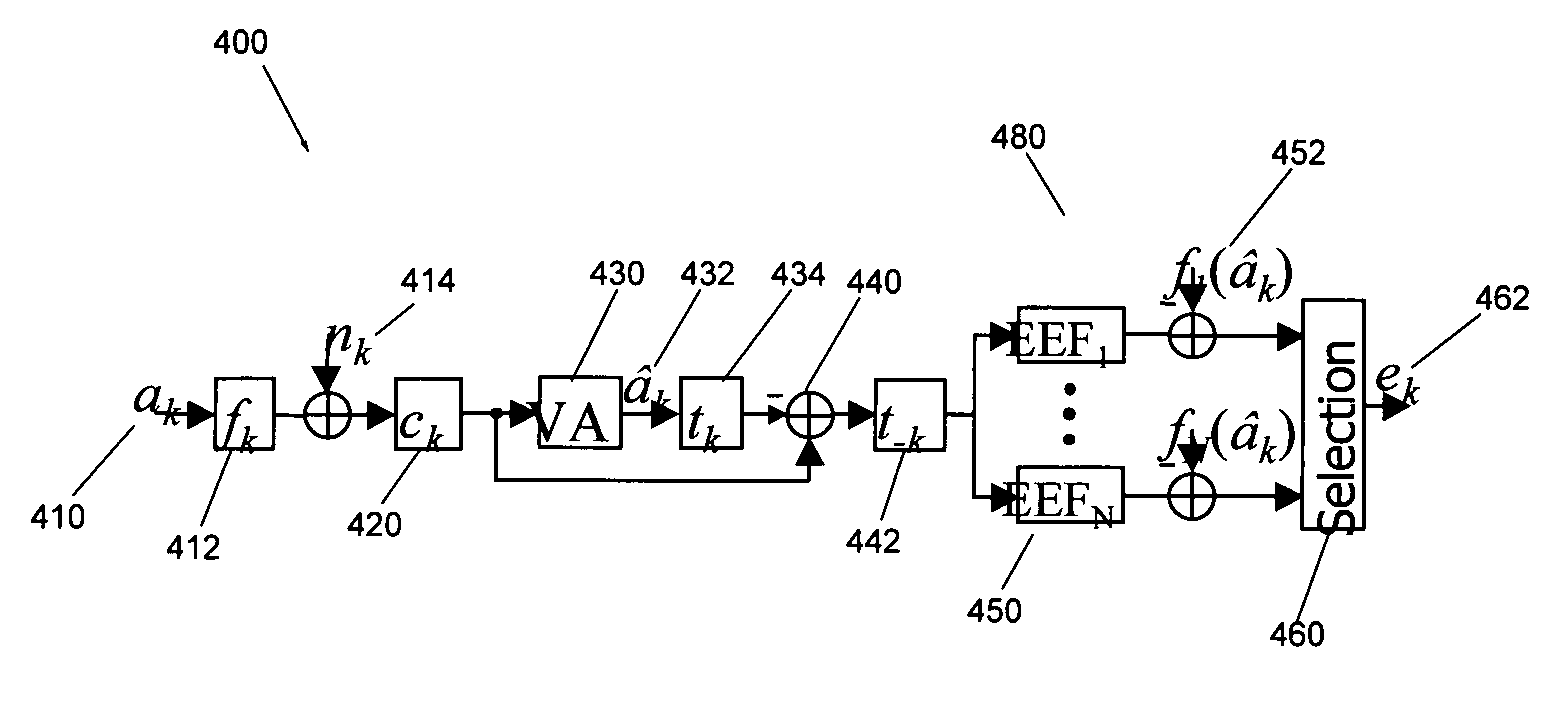
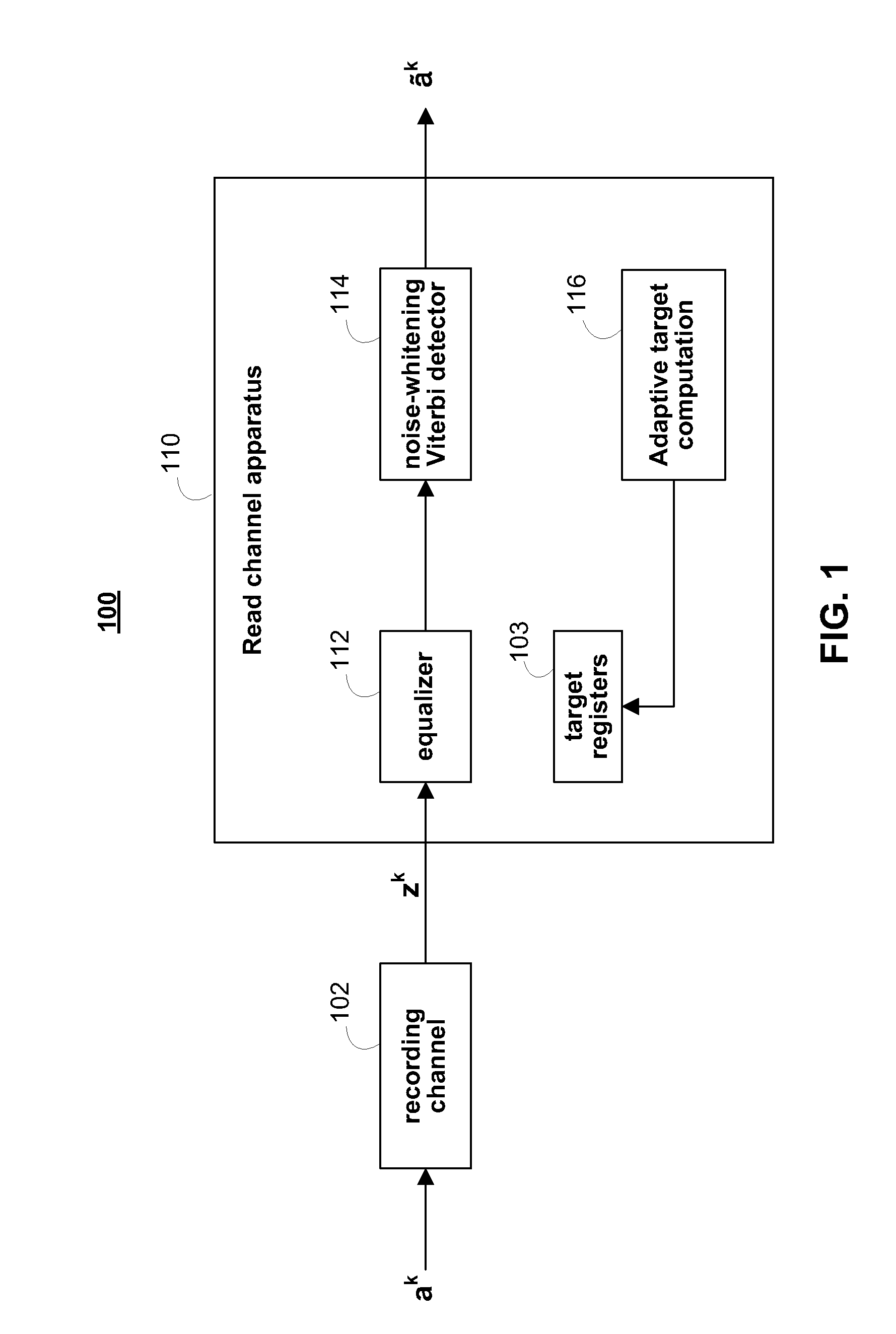
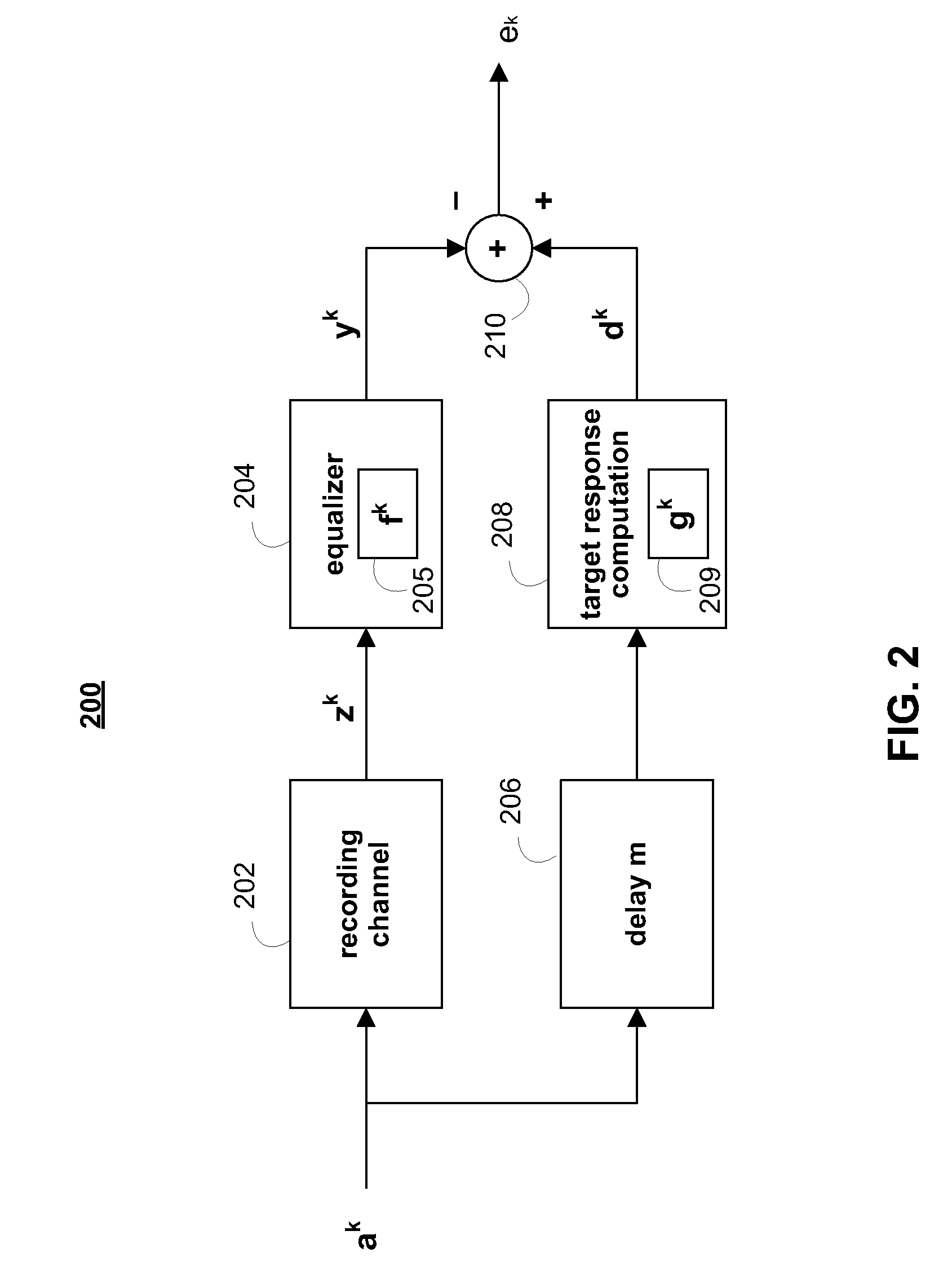
Adaptive target optimization methods and systems for noise whitening based viterbi detectors
ActiveUS7948703B1Easy to detectReduce the differenceModification of read/write signalsSignal processing for reducing noiseMean squareViterbi detector
Apparatuses and methods are provided for adaptively updating a target for a recording channel, such as a magnetic recording channel. In some embodiments, a read channel apparatus is provided which includes data path modules and adaptive path modules. The data path modules estimate user information from a recording channel, and the adaptive path modules adaptively update the target taps of the recording channel. The adaptive path modules may use a linearly constrained least-mean square (LC-LMS) algorithm to determine the amount and direction of each tap update, where the linear constraint may be a maximum phase or a mixed phase constraint. The adaptive path modules may operate independently of and be decoupled from the data path modules.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
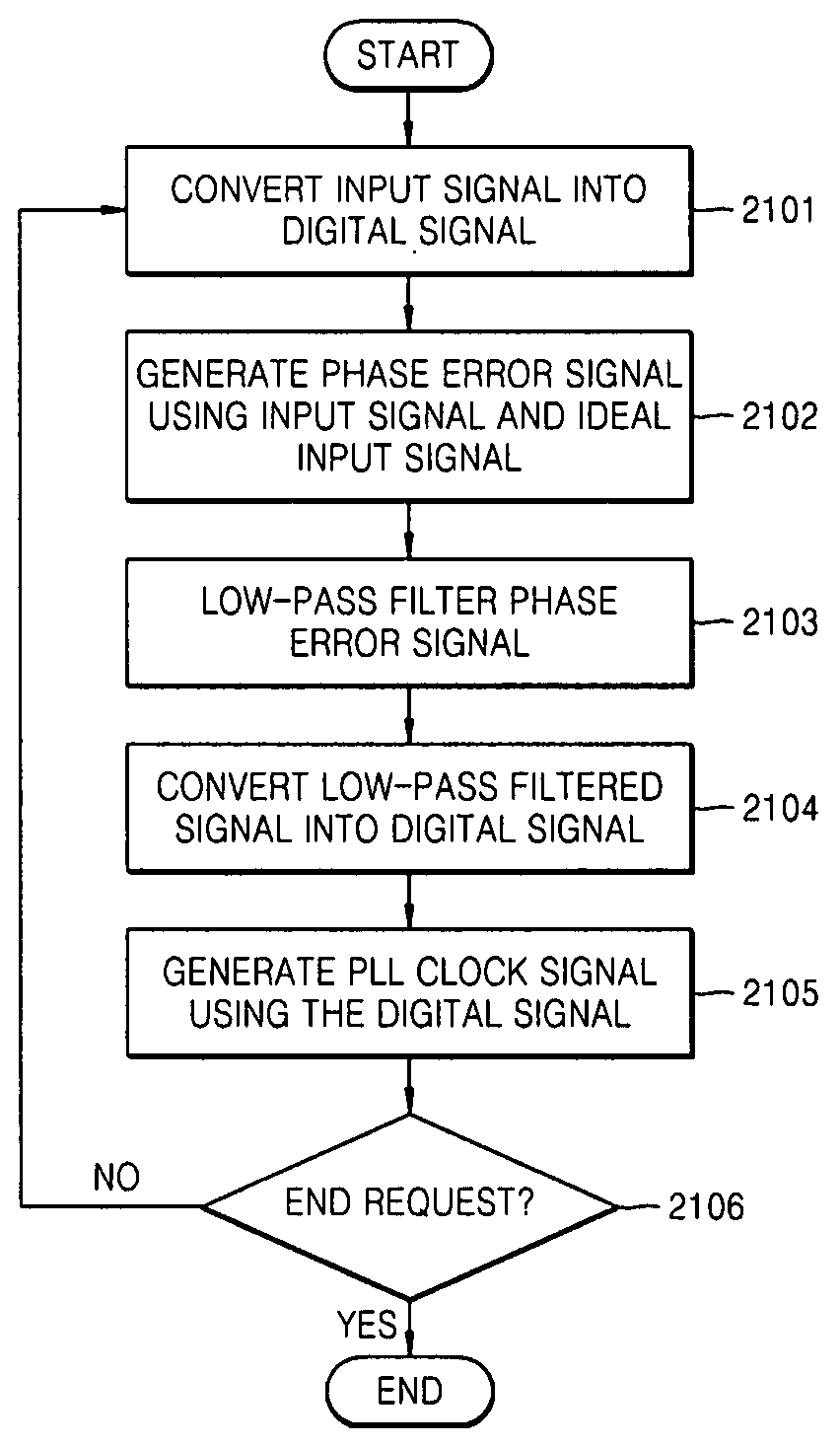
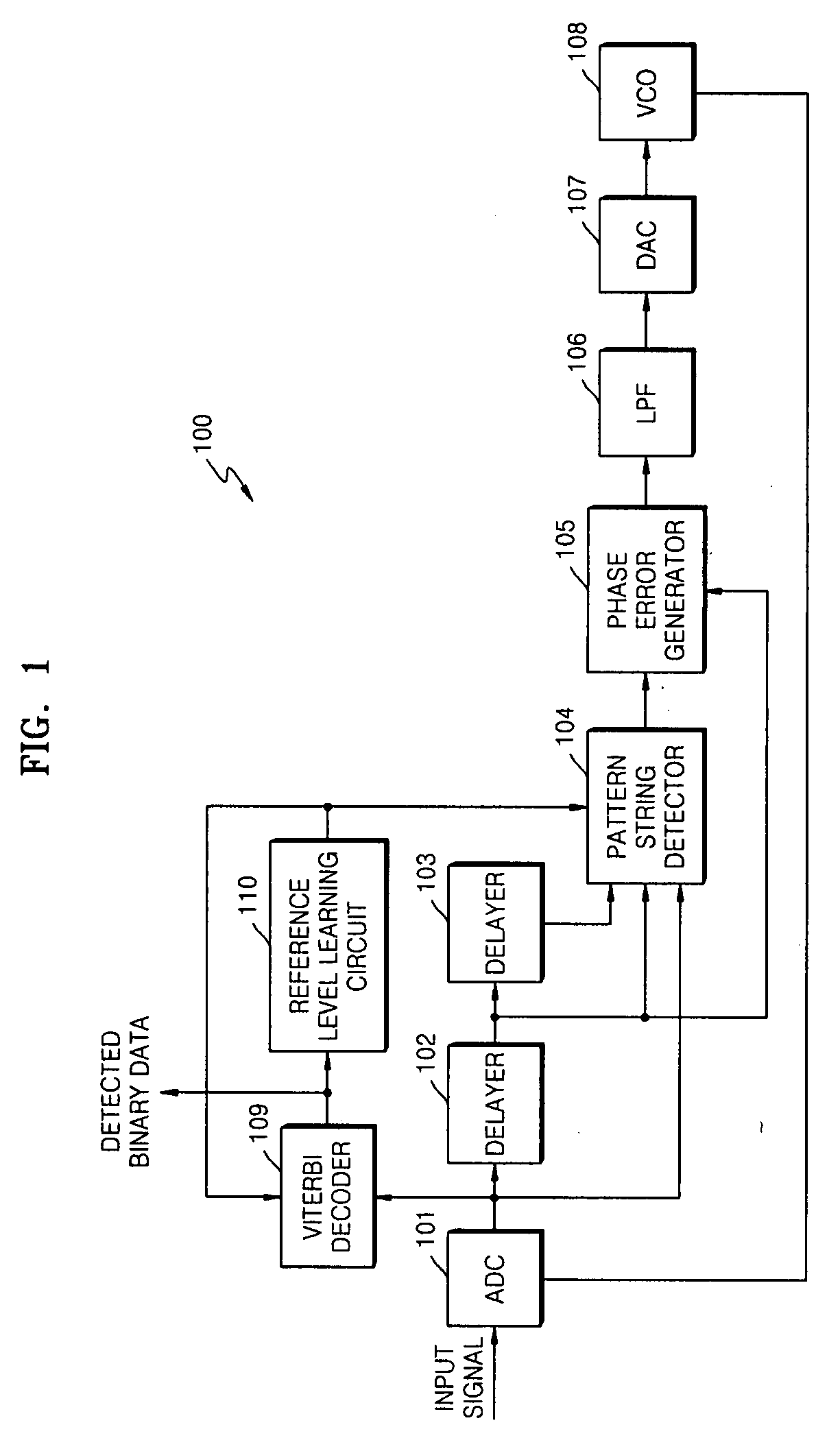
Phase detection apparatus and method, phase locked loop circuit and control method thereof, and signal reproducing apparatus and method
InactiveUS20080032652A1Hardware scale can be reducedReduce scaleAnalogue/digital conversionModification of read/write signalsPhase locked loop circuitEngineering
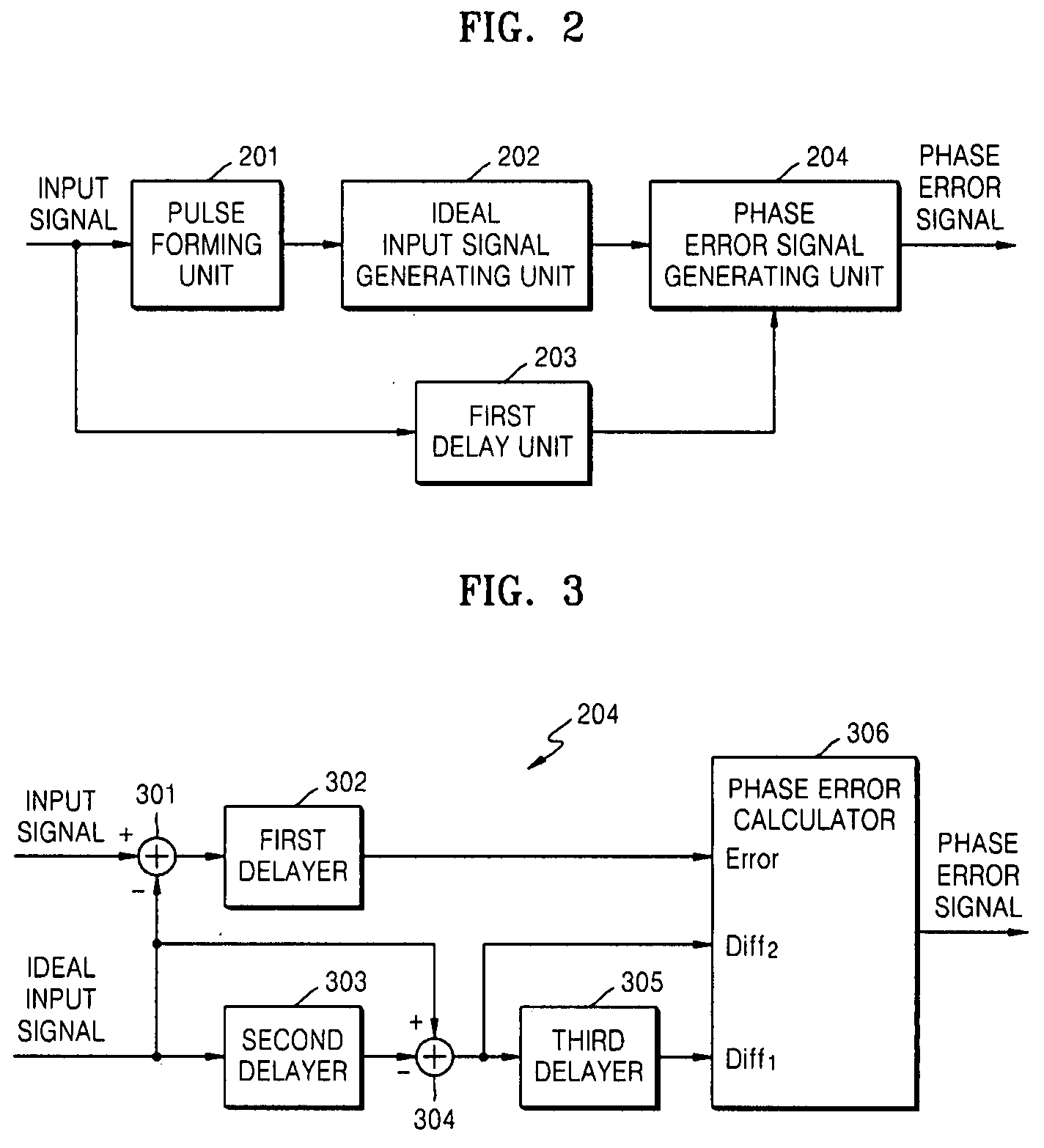
A phase detection apparatus and method, a PLL circuit and a control method thereof, and a signal reproducing apparatus and method which can provide anti-noise and anti-ISI characteristics while reducing the scale of hardware used in an optical disc reproducing system having high-ISI conditions include a pulse forming unit to detect binary data of an input signal, an ideal input signal generating unit to generate an ideal input signal based on the detected binary data, and a phase error signal generating unit to generate a phase error signal based on the input signal and the ideal input signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
A real-time digital audio signal sound mixing method and device
ActiveCN109559763ASignal processing for reducing noiseSpeech analysisComputer terminalDigital audio signals
The embodiment of the invention discloses an audio signal processing method and a terminal. According to the method, at least one frame of audio data acquired by a media playing interface and a real-time audio signal from audio input equipment are mixed in real time; and the media playing interface acquires the audio file by taking the frame as a unit, instead of acquiring the whole audio file, sothat the audio file can be flexibly switched to any frame of audio data of other audio files at any time through the media playing interface in the audio mixing process. A data path in system software is used for transmitting at least one frame of audio data, and the external environment noise is not introduced. In addition, an audio detection mechanism is introduced into the method, the volume of at least one frame of audio data participating in audio mixing can be adaptively adjusted, and the audio mixing experience is improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Frame-based audio transmission/storage with overlap to facilitate smooth crossfading
ActiveUS20050102049A1Electrophonic musical instrumentsInput/output to record carriersFrame basedComputer graphics (images)
Methods for splicing PCM audio frames form modified frames by appending to each frame either a portion of the next preceding frame or the next following frame. According to a first approach, splices are obtained by fading up and fading down a frame end and a frame appendage only at a splice point, and overlapping and combining to provide a crossfade at the splice. Alternatively, every frame end and frame appendage is faded up and faded down, overlapped and combined. A subtractive method of providing complementary fade-up and fade-down reduces rounding errors.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
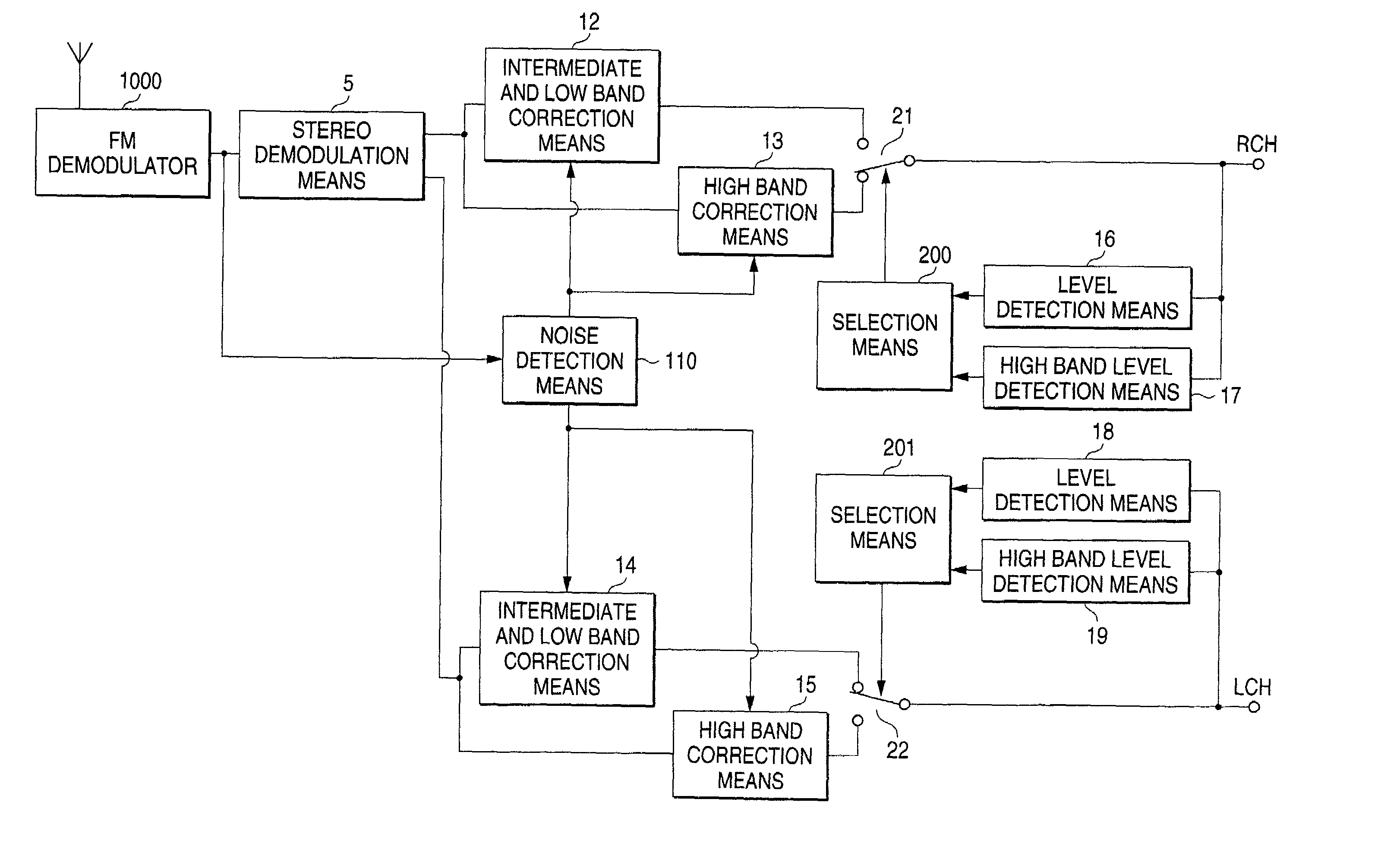
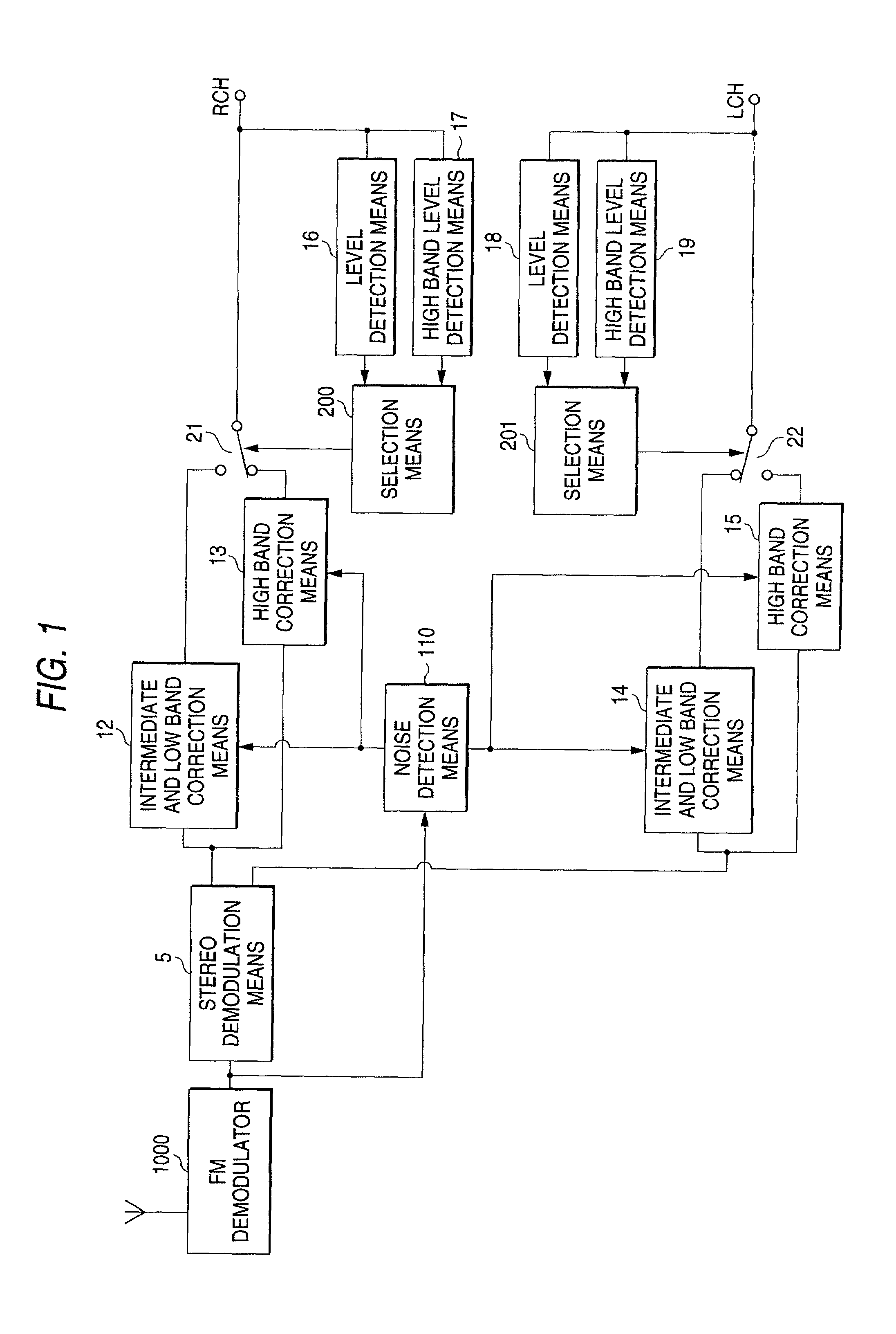
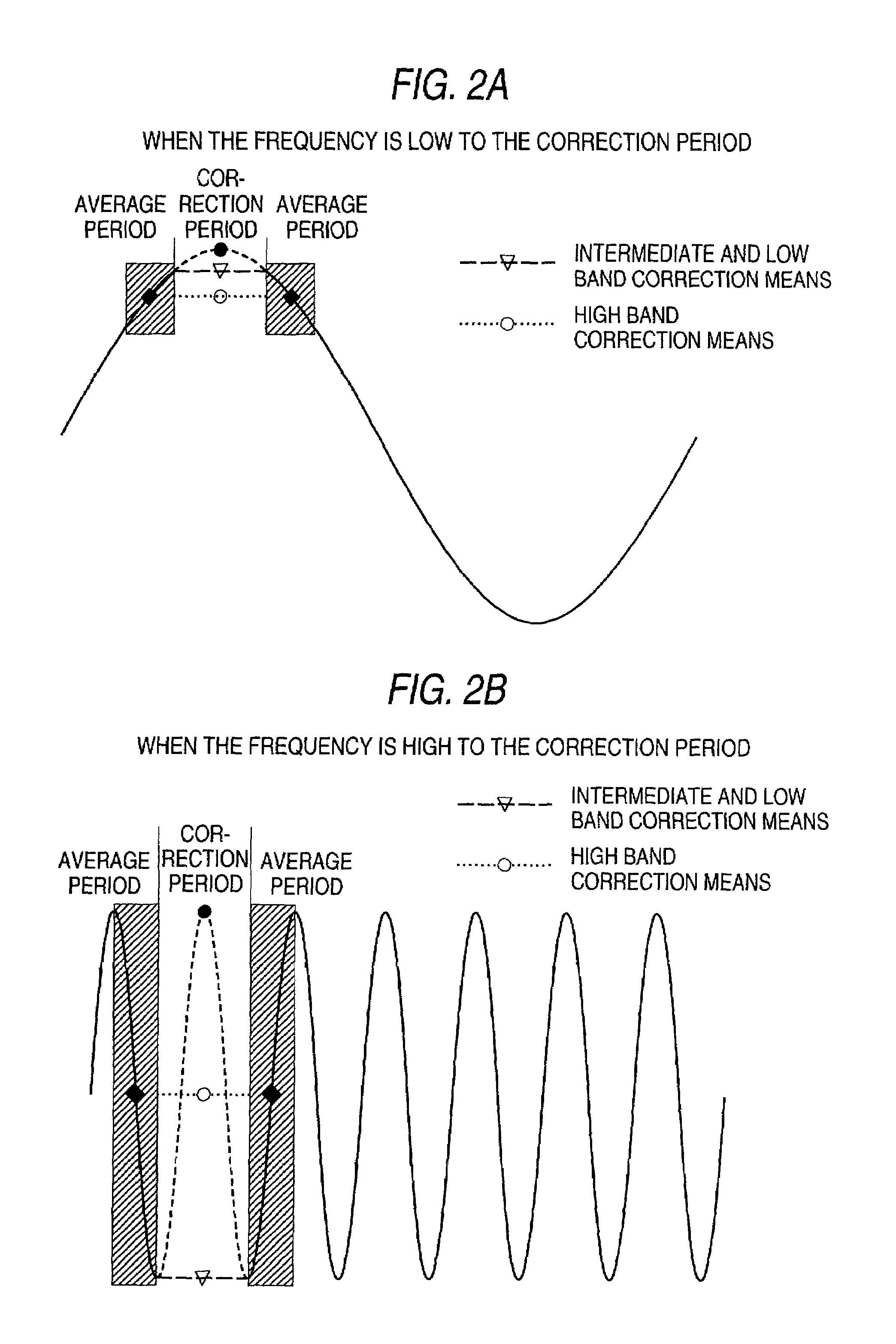
Noise reduction apparatus and audio output apparatus
InactiveUS7551743B1Correction errorNoise suppression ability is increasedSignal processing for reducing noiseBroadcast information characterisationNoise generationEngineering
The FM broadcast is received and the FM demodulated FM composite signal is stereo demodulated, and when the high band components of the demodulated signal are few, the correction is conducted by using the signals just before and just after the noise generation period, and when the high band components are large, the interpolation is conducted by using a central value calculated from the value of a predetermined period before the noise generation period, and a central value calculated from the value of a predetermined period after the noise generation period.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com