Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
777results about "Generator control circuits" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
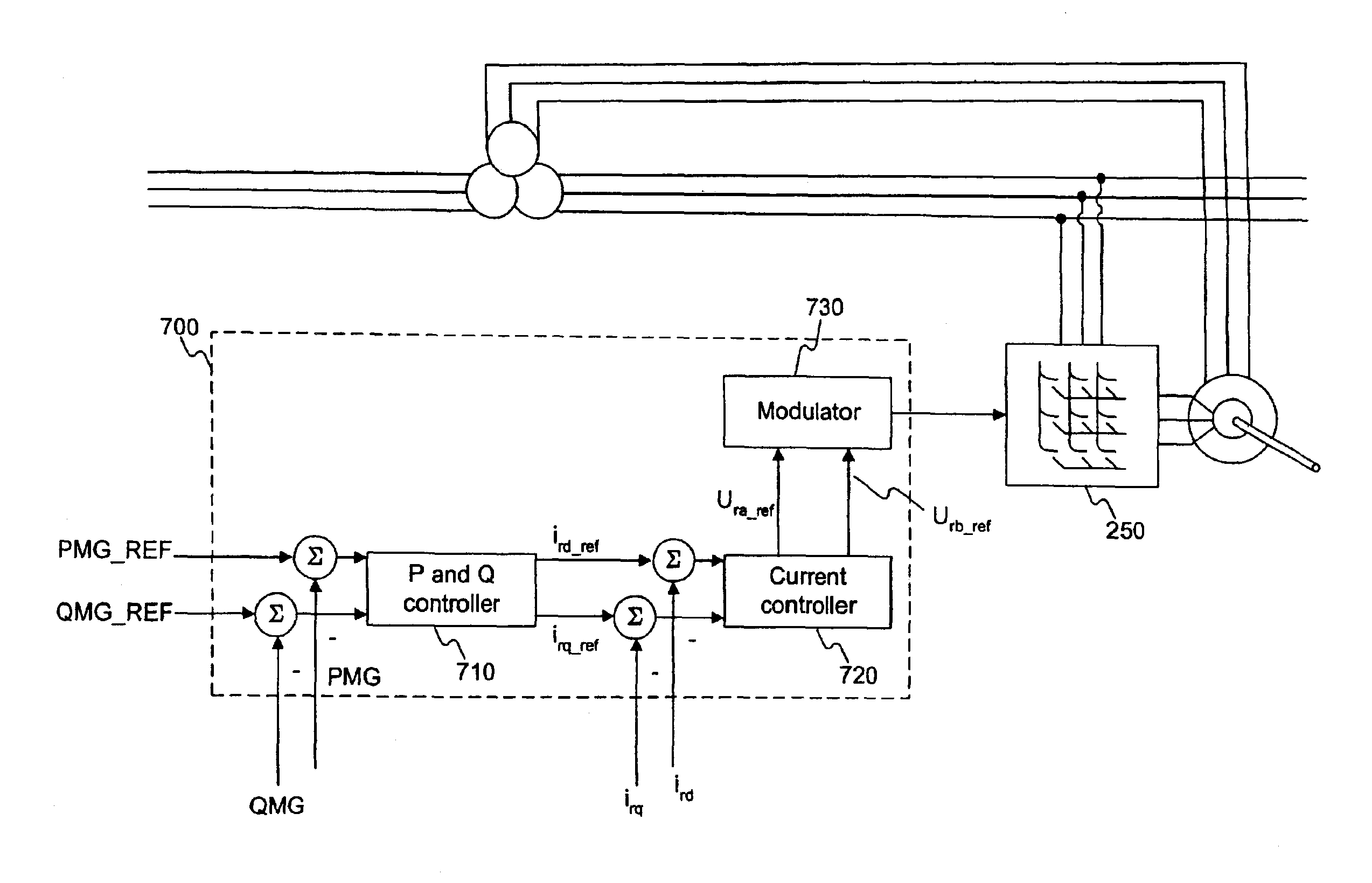
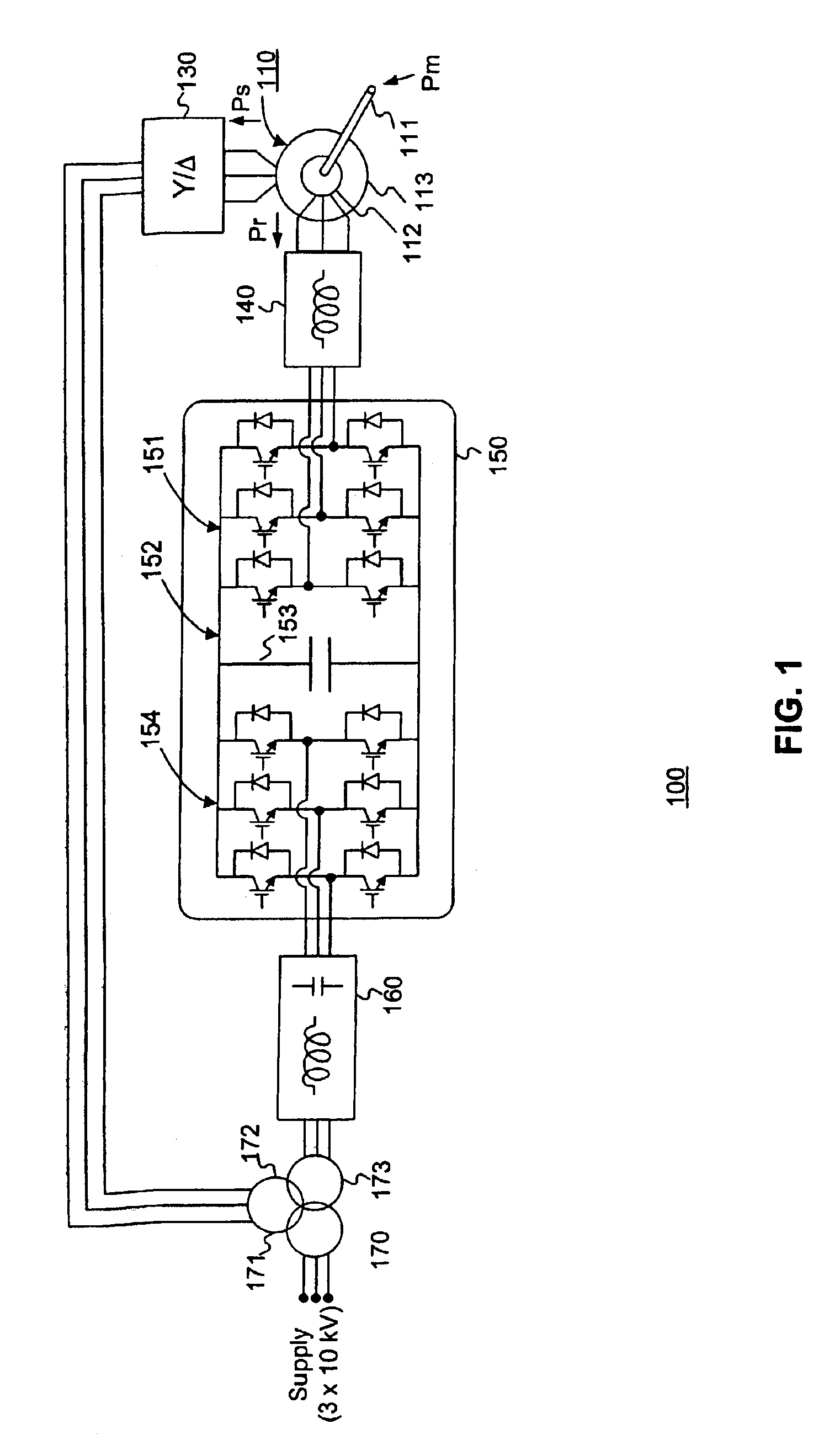
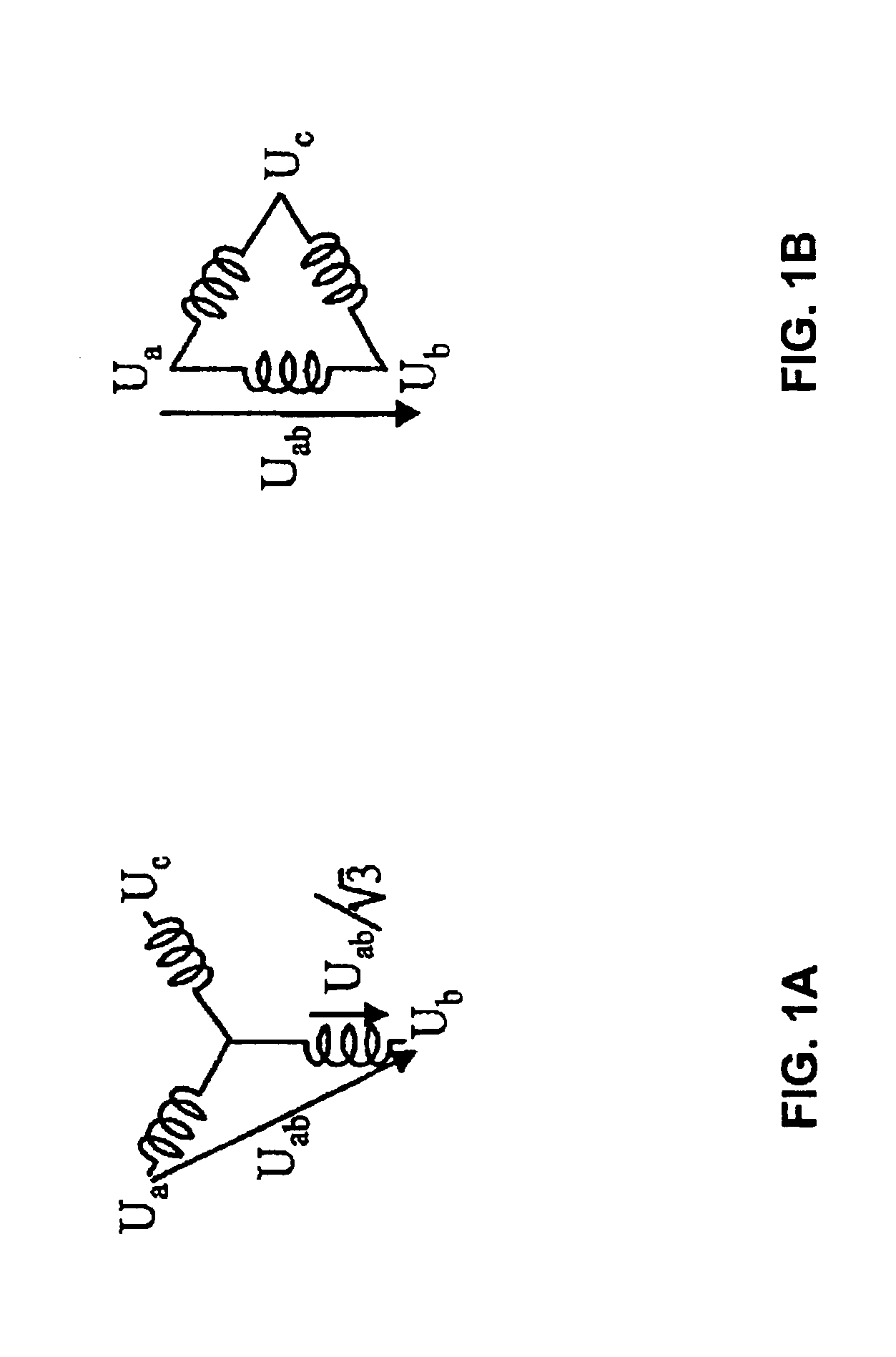
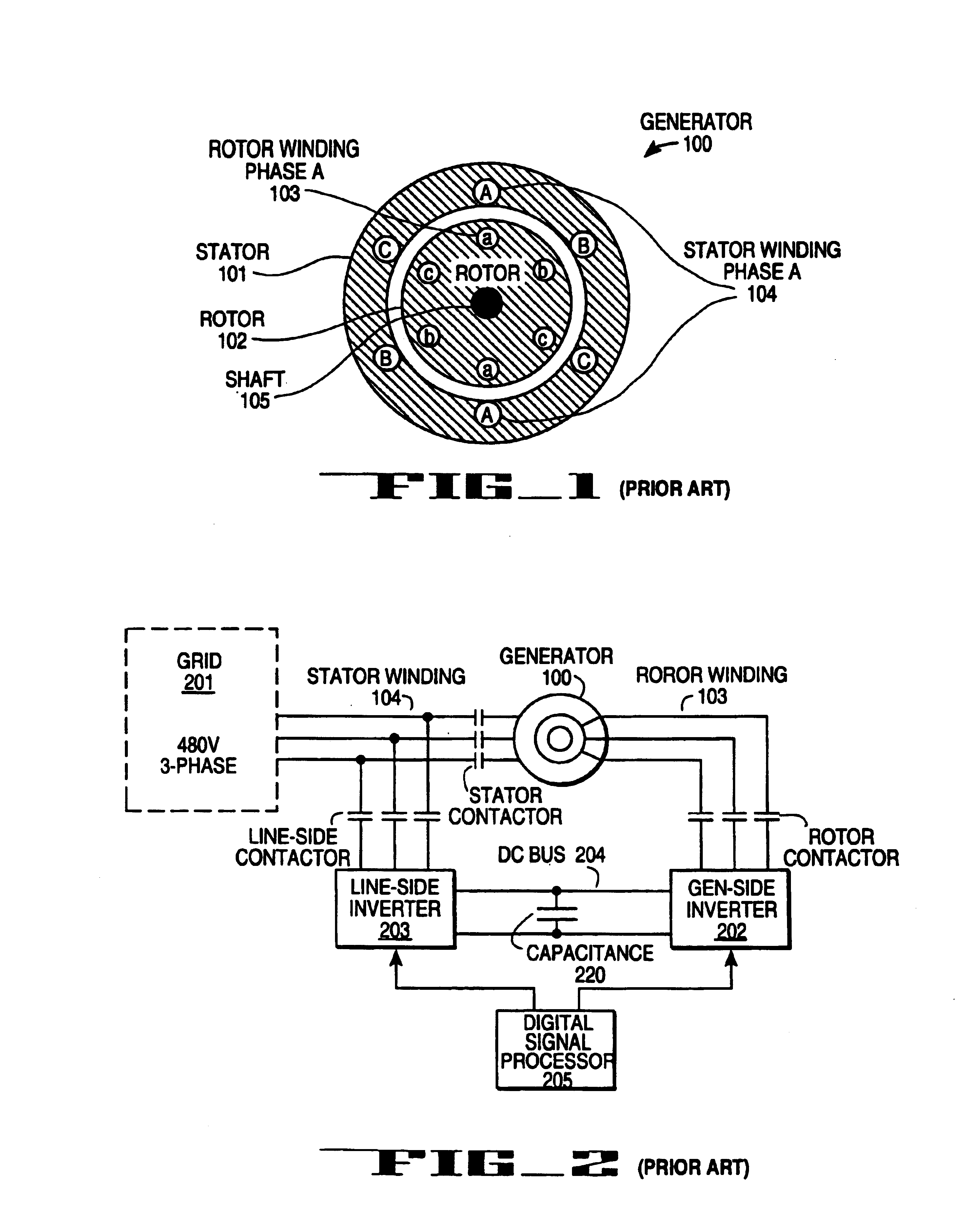
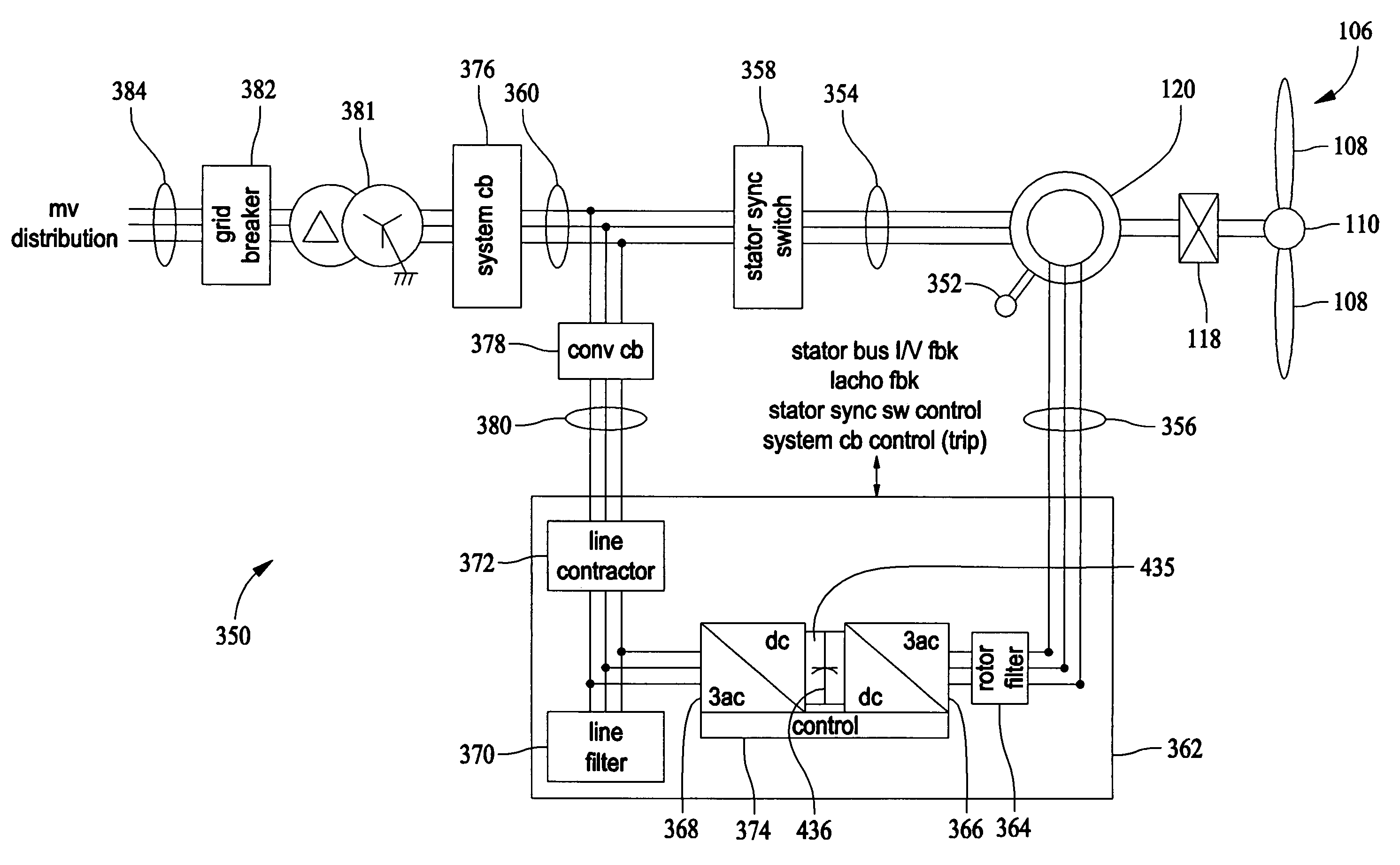
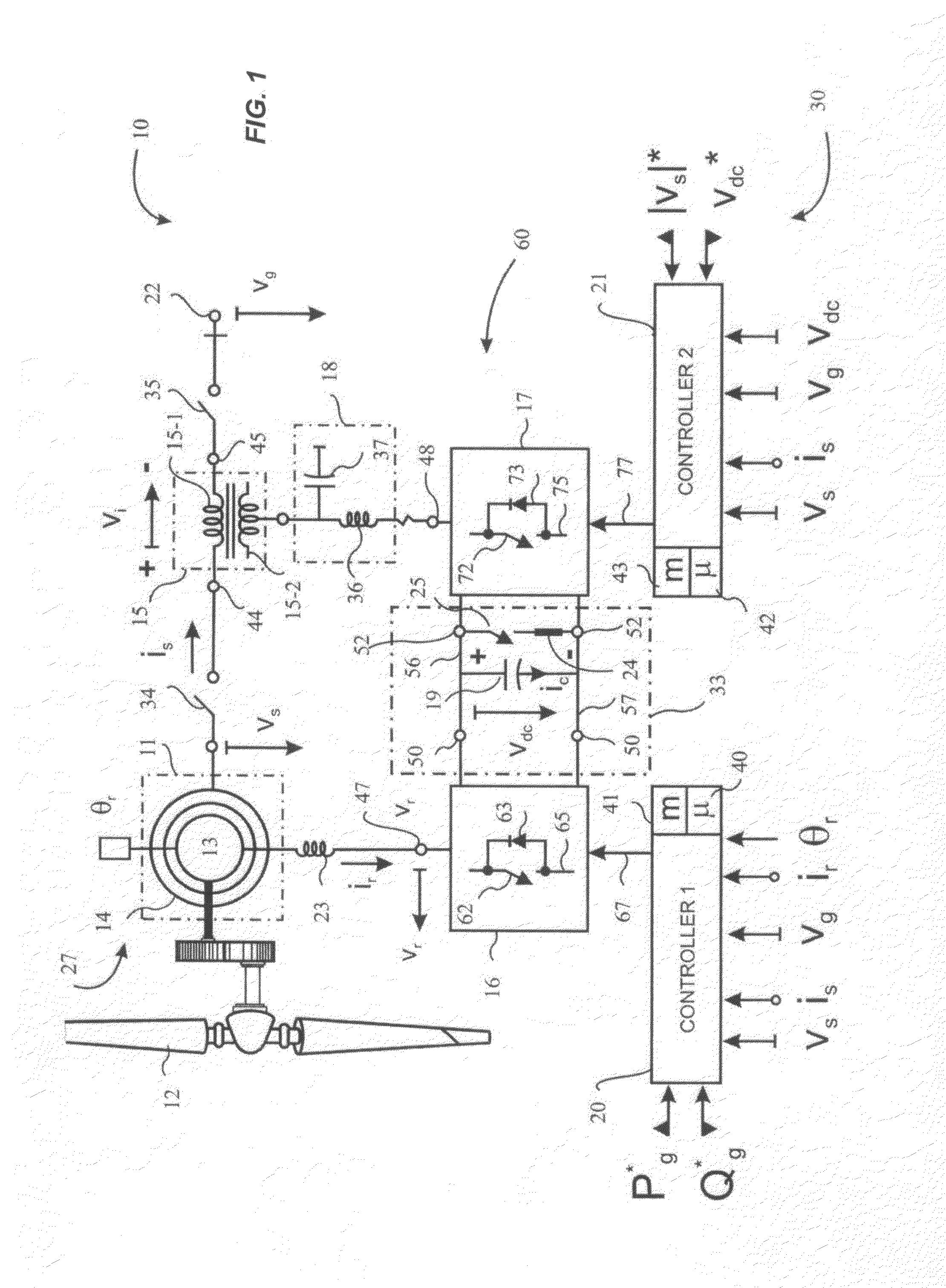
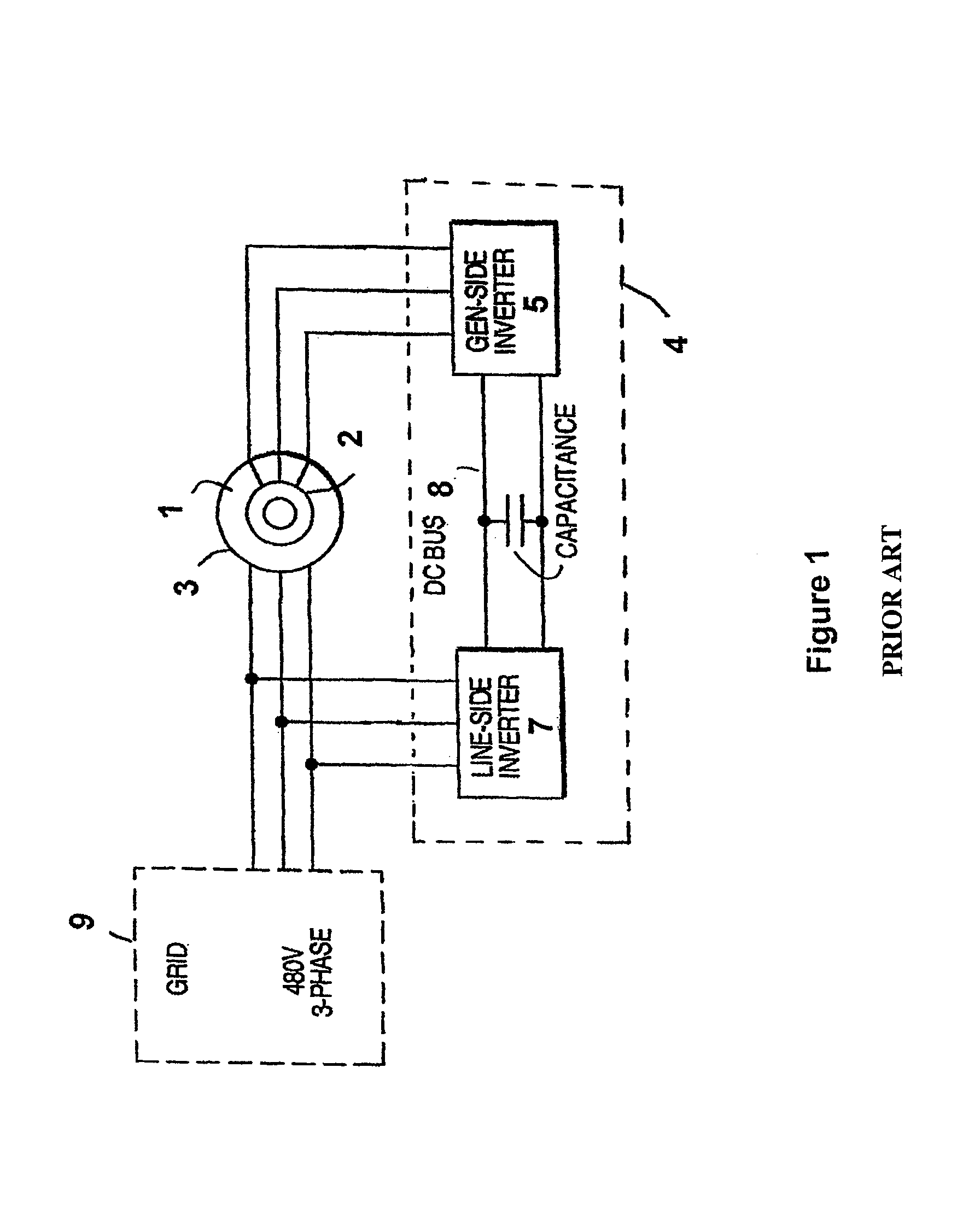
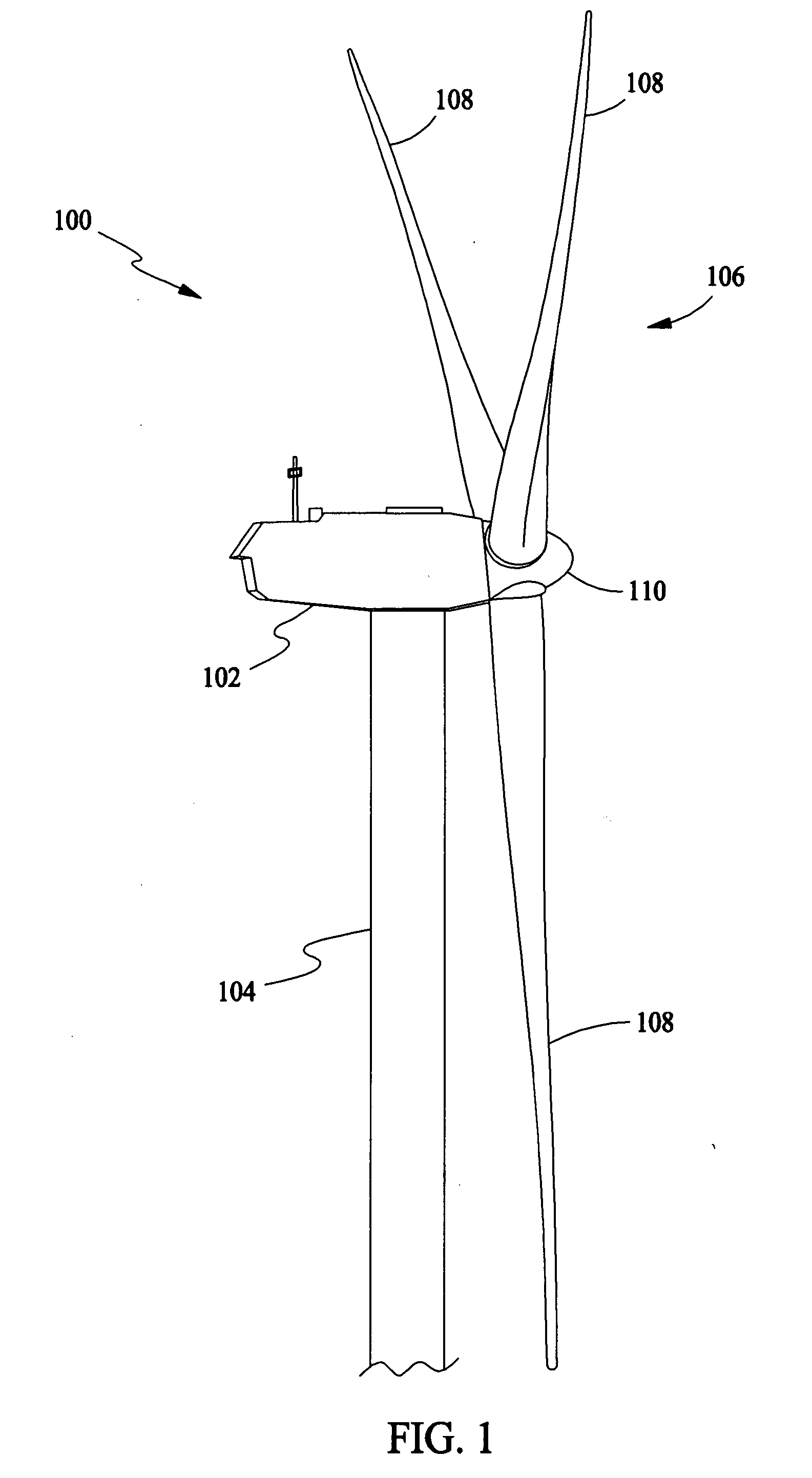
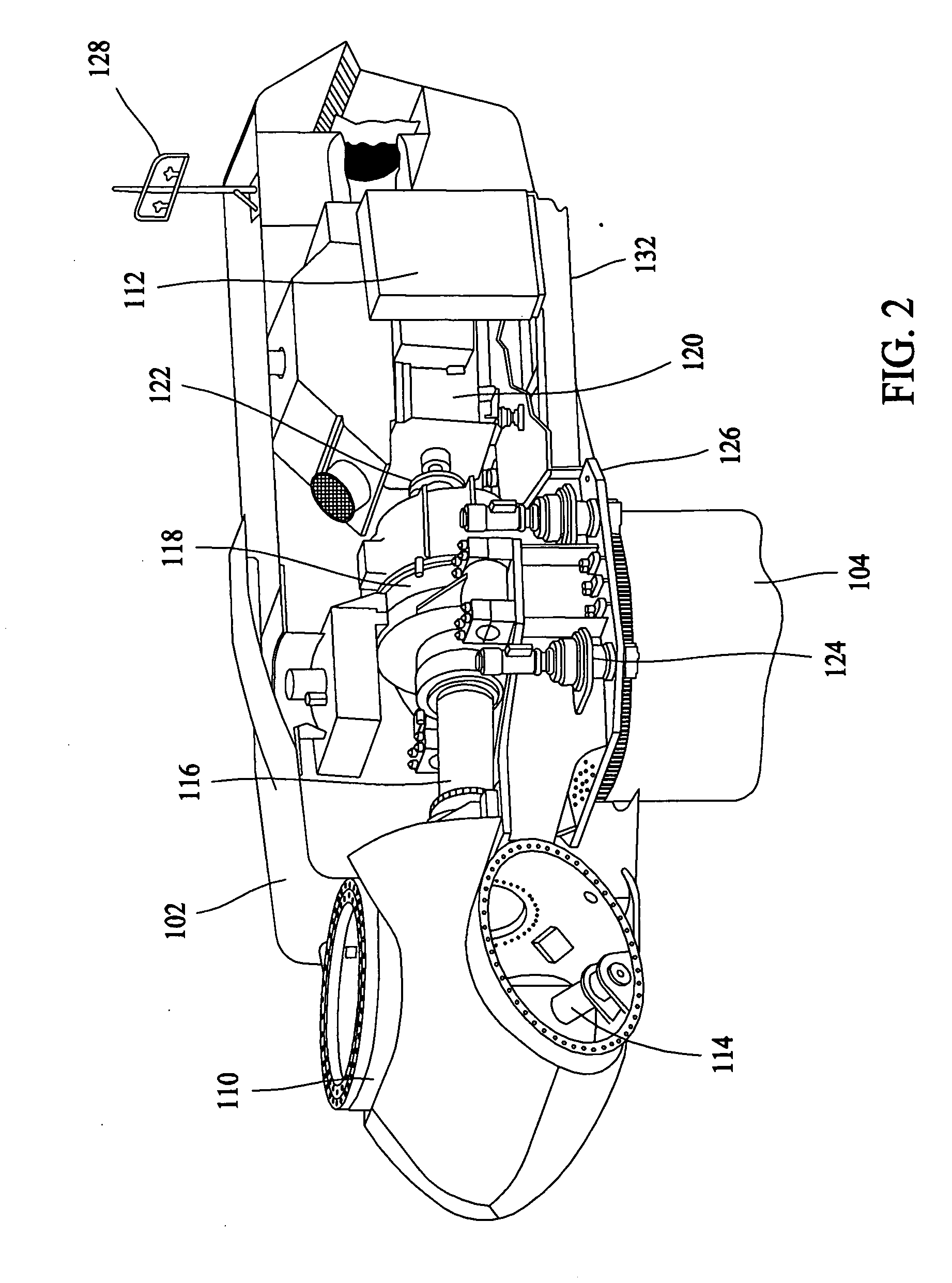
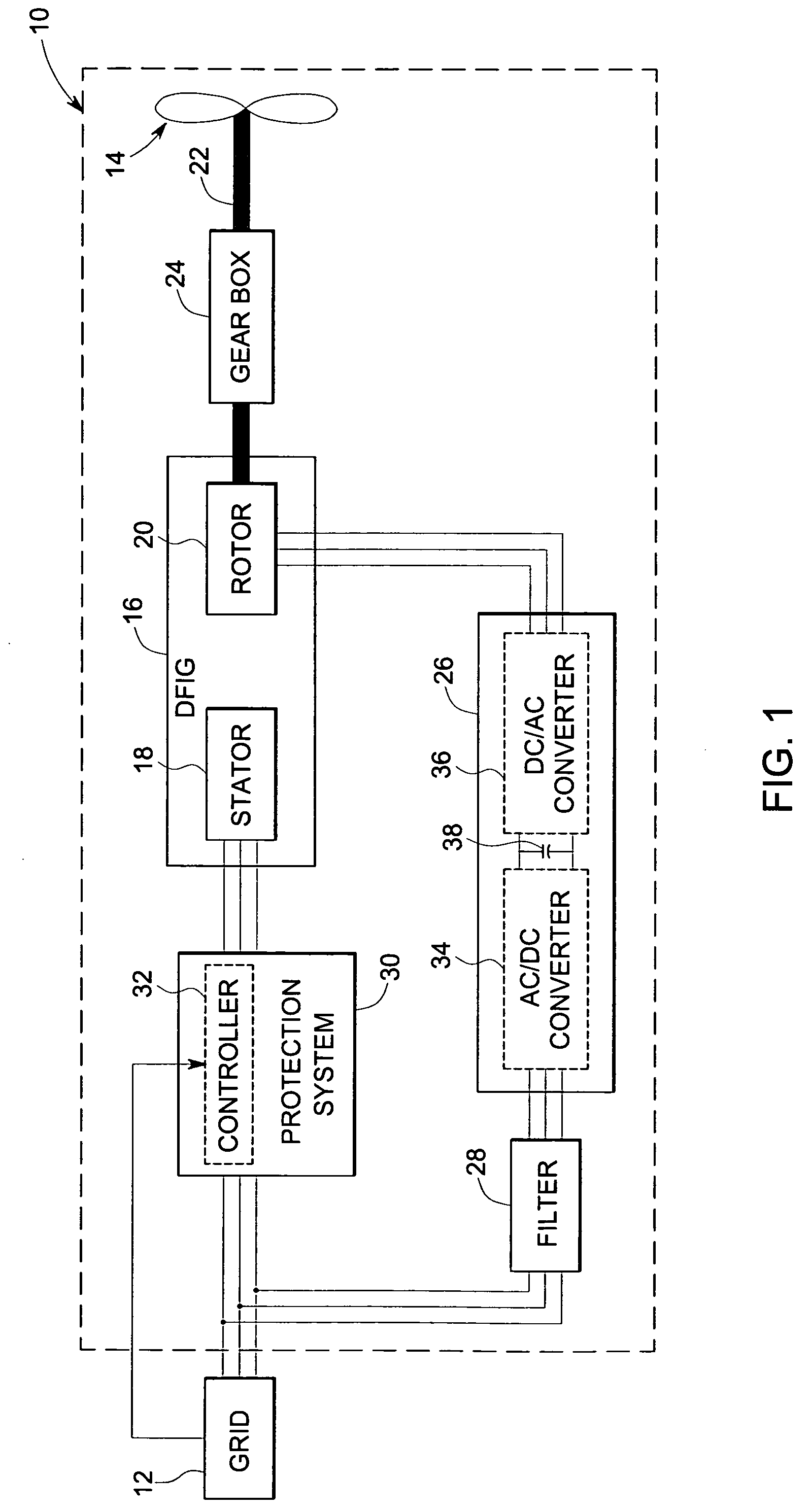
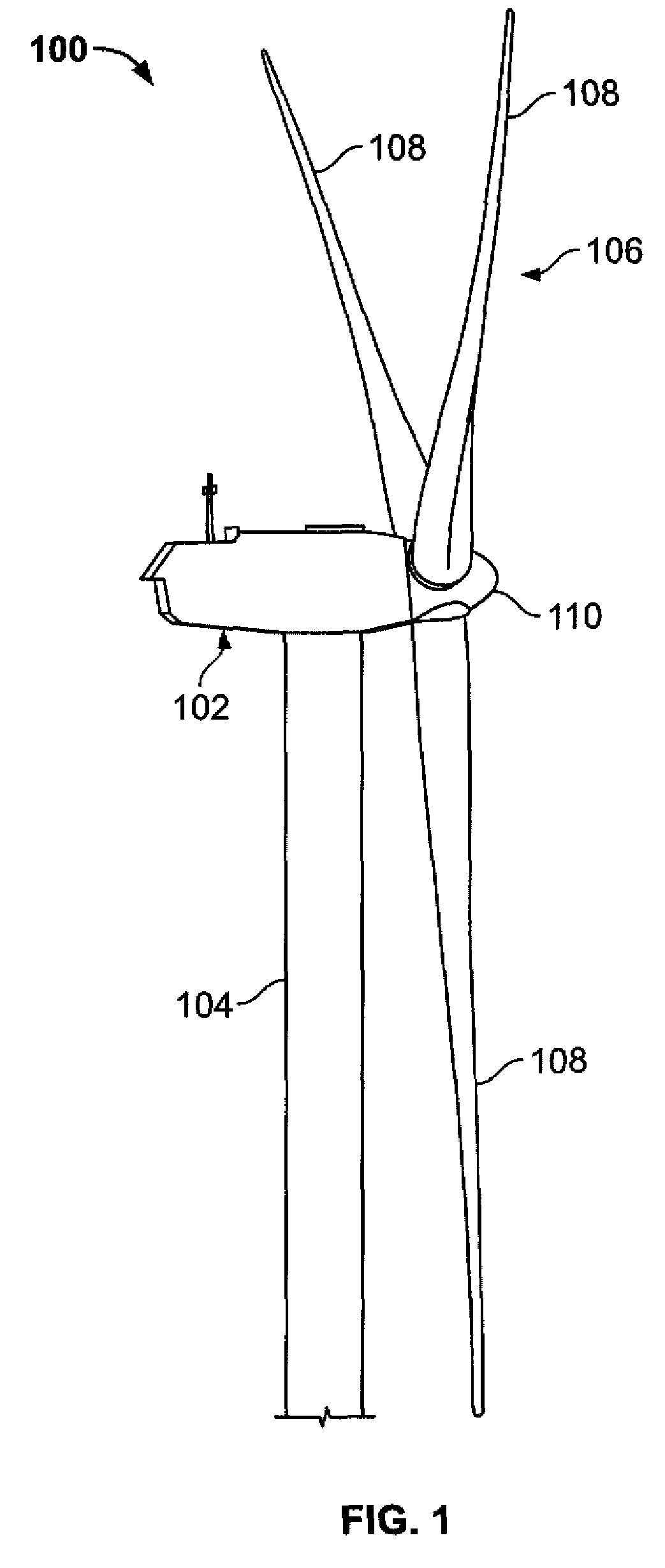
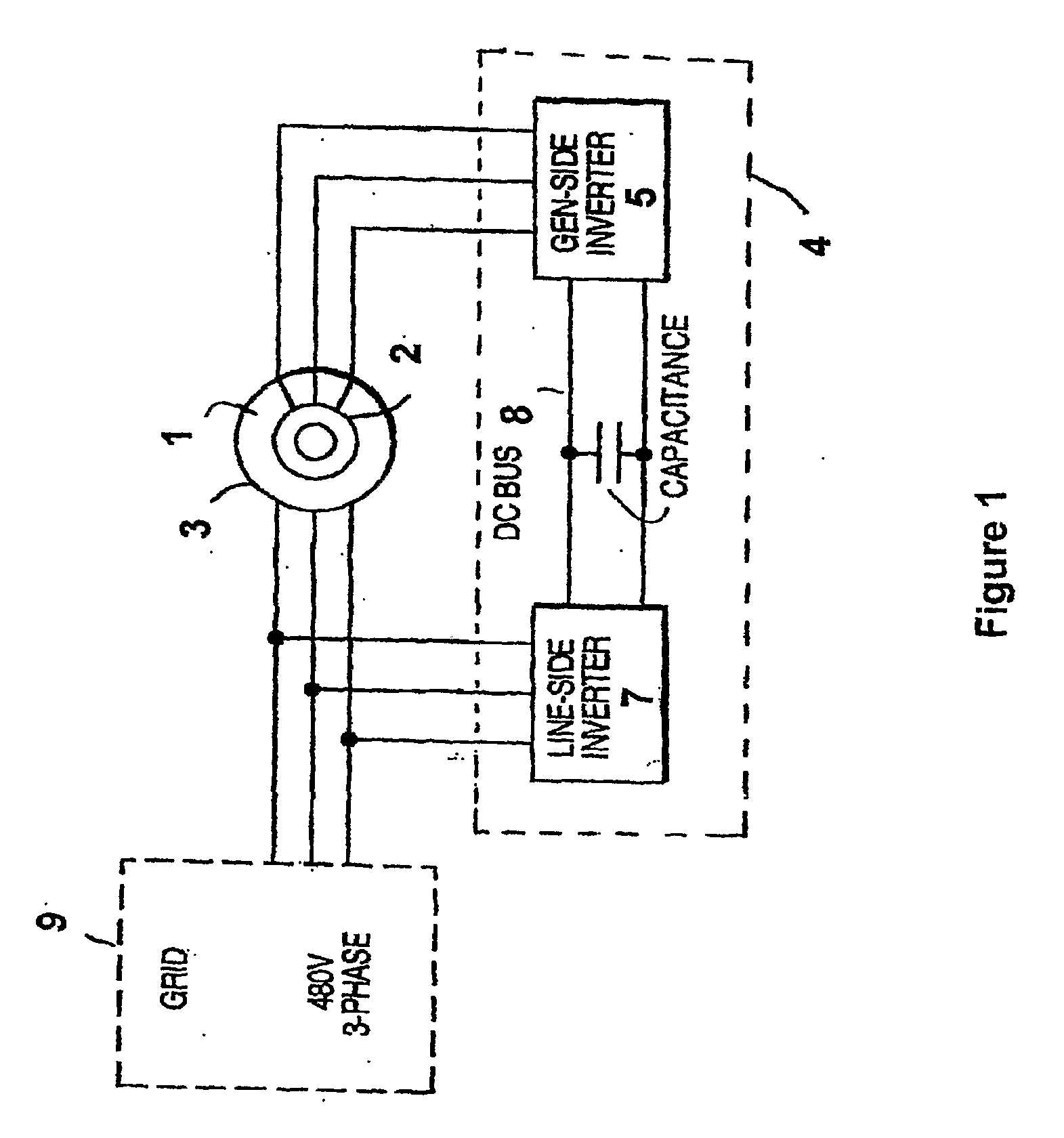
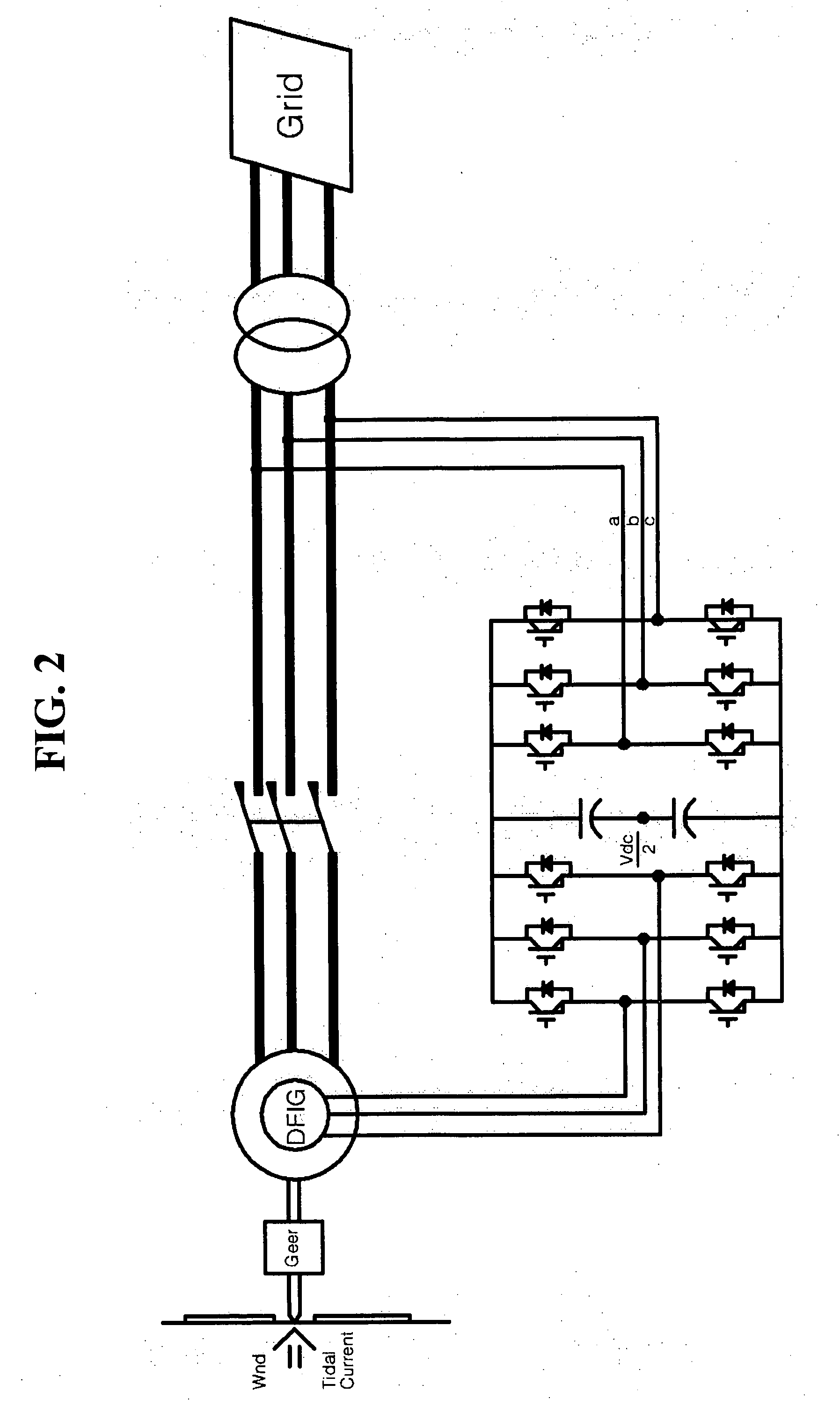
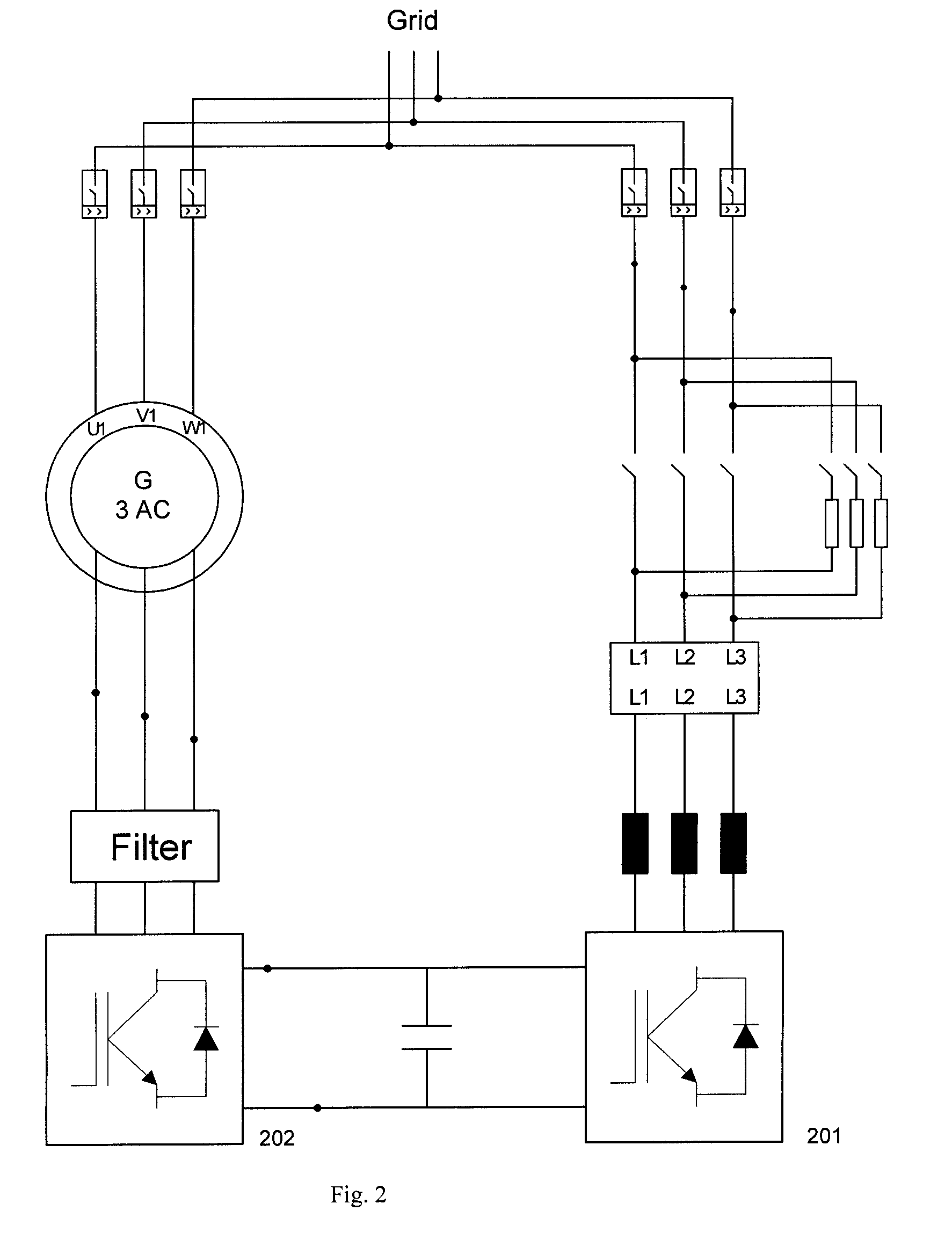
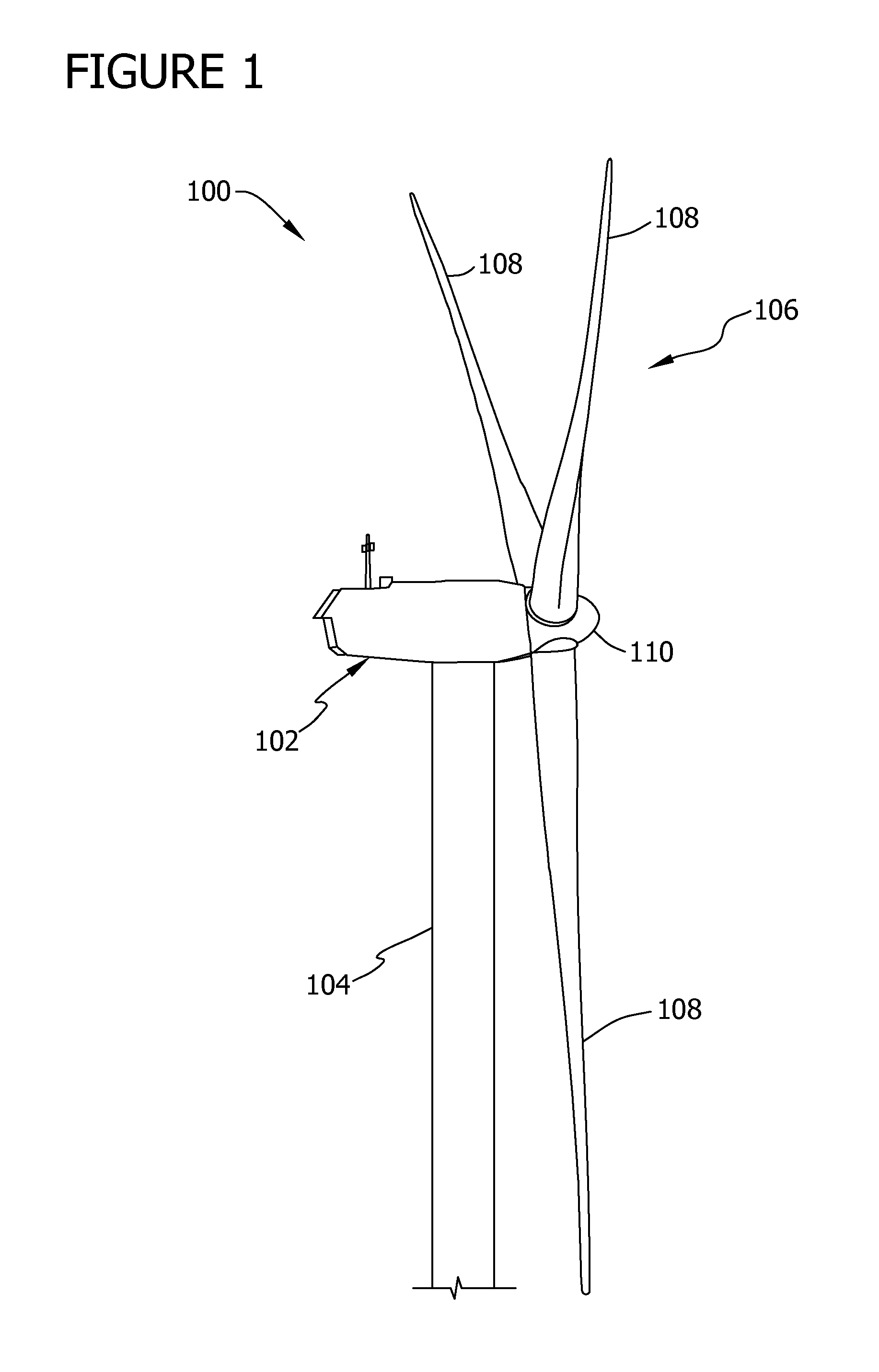
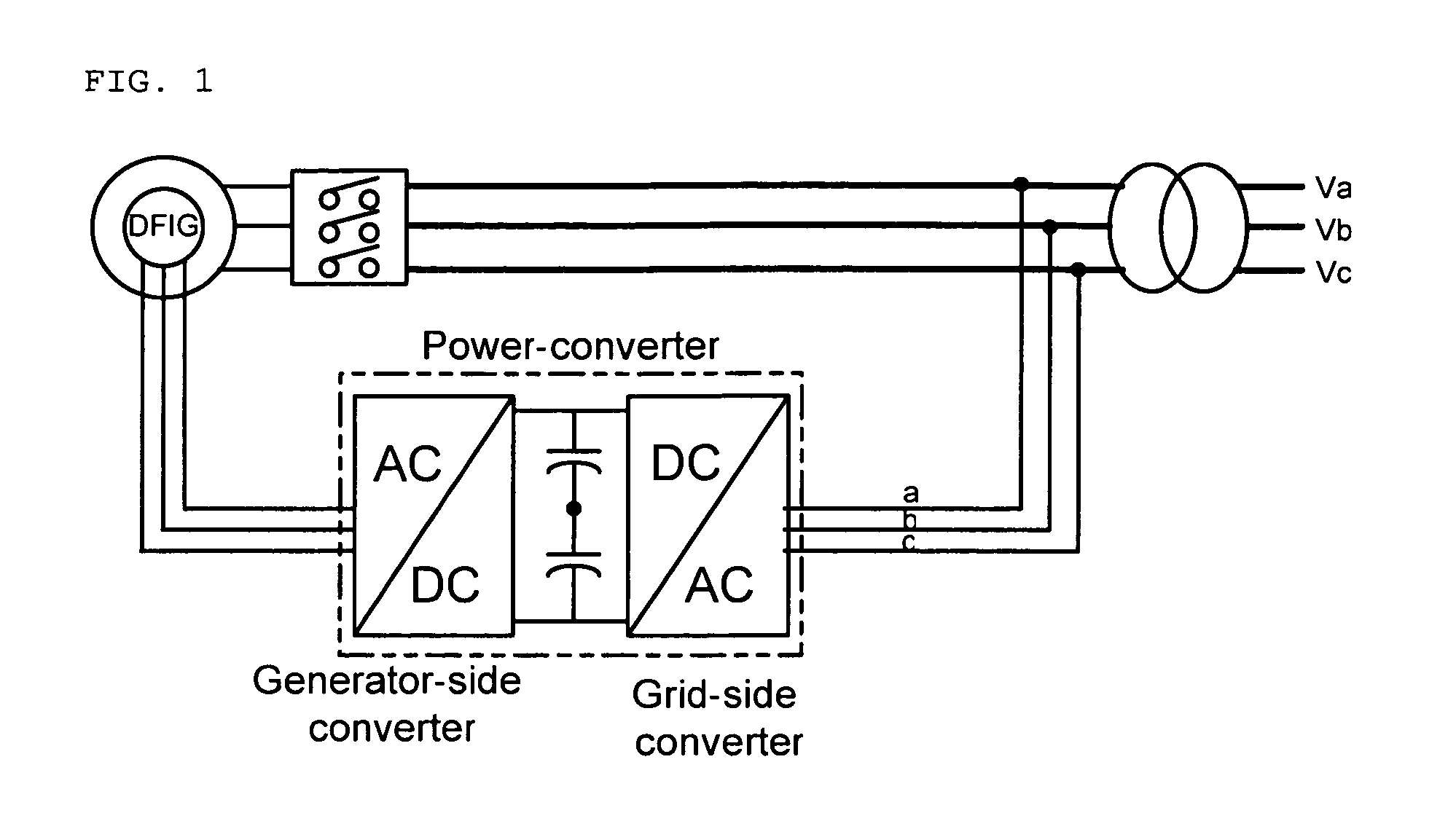
Variable speed wind turbine having a matrix converter
InactiveUS6856038B2Generator control circuitsEfficient power electronics conversionMatrix convertersConstant frequency
A variable speed wind turbine is disclosed comprising a turbine rotor that drives a doubly-fed induction generator, a matrix converter which converts variable frequency output into constant frequency output, and a control unit and a protection circuit for the matrix converter. Power is circulated in the system allowing for sensorless detection of rotor position and better output ratios of power from the system.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Variable speed wind turbine generator
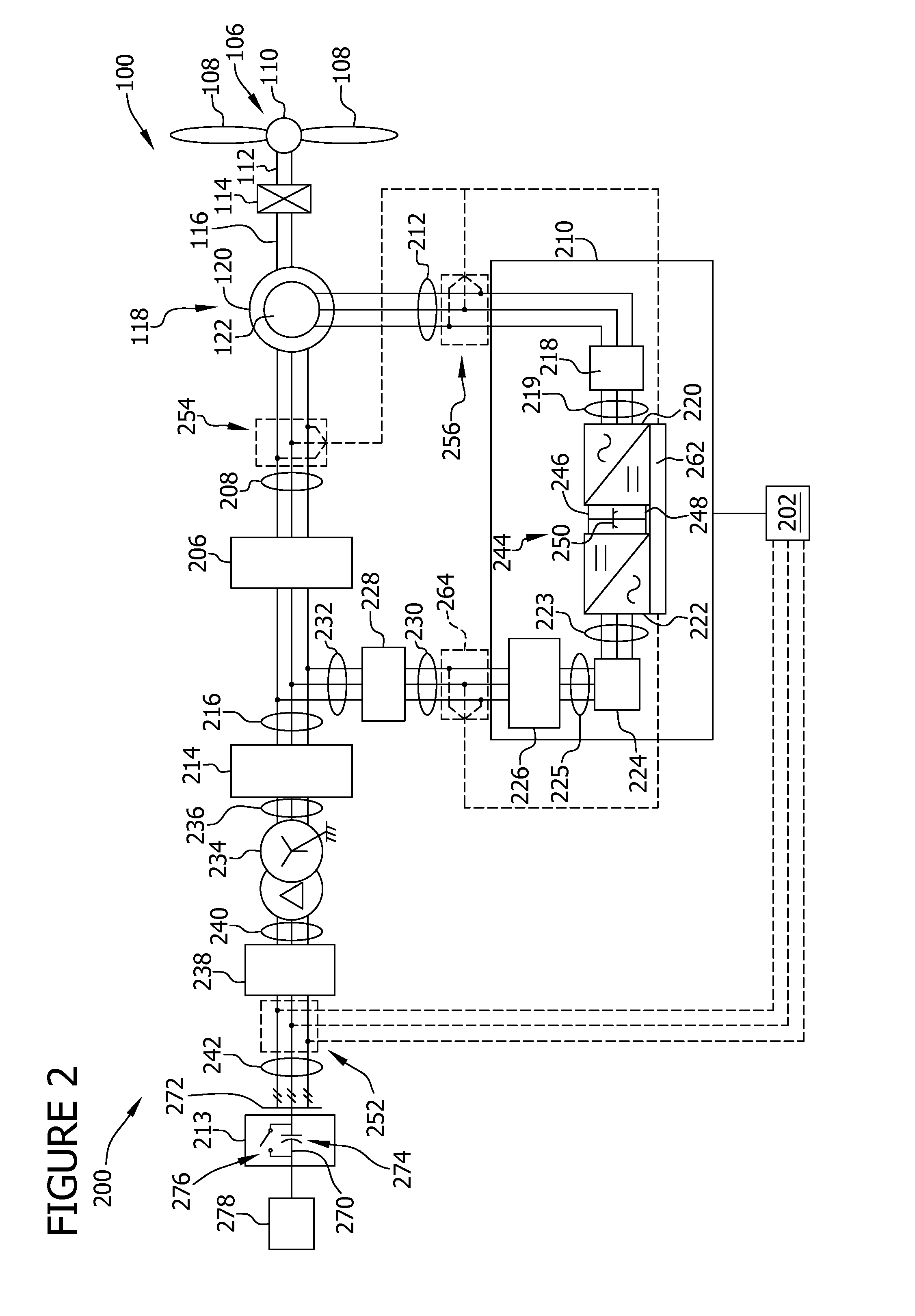
InactiveUS6856039B2Generator control circuitsWind motor controlVariable speed wind turbineControl theory
A variable speed system for use in systems, such as, for example, wind turbines, is described. The system comprises a wound rotor induction generator, a torque controller and a proportional, integral derivative (PID) pitch controller. The torque controller controls generator torque using field oriented control, and the PID controller performs pitch regulation based on generator rotor speed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Variable speed wind turbine having a matrix converter
InactiveUS20020079706A1Generator control circuitsWind motor controlMatrix convertersConstant frequency
A variable speed wind turbine is disclosed comprising a turbine rotor that drives a doubly-fed induction generator, a matrix converter which converts variable frequency output into constant frequency output, and a control unit and a protection circuit for the matrix converter. Power is circulated in the system allowing for sensorless detection of rotor position and better output ratios of power from the system.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
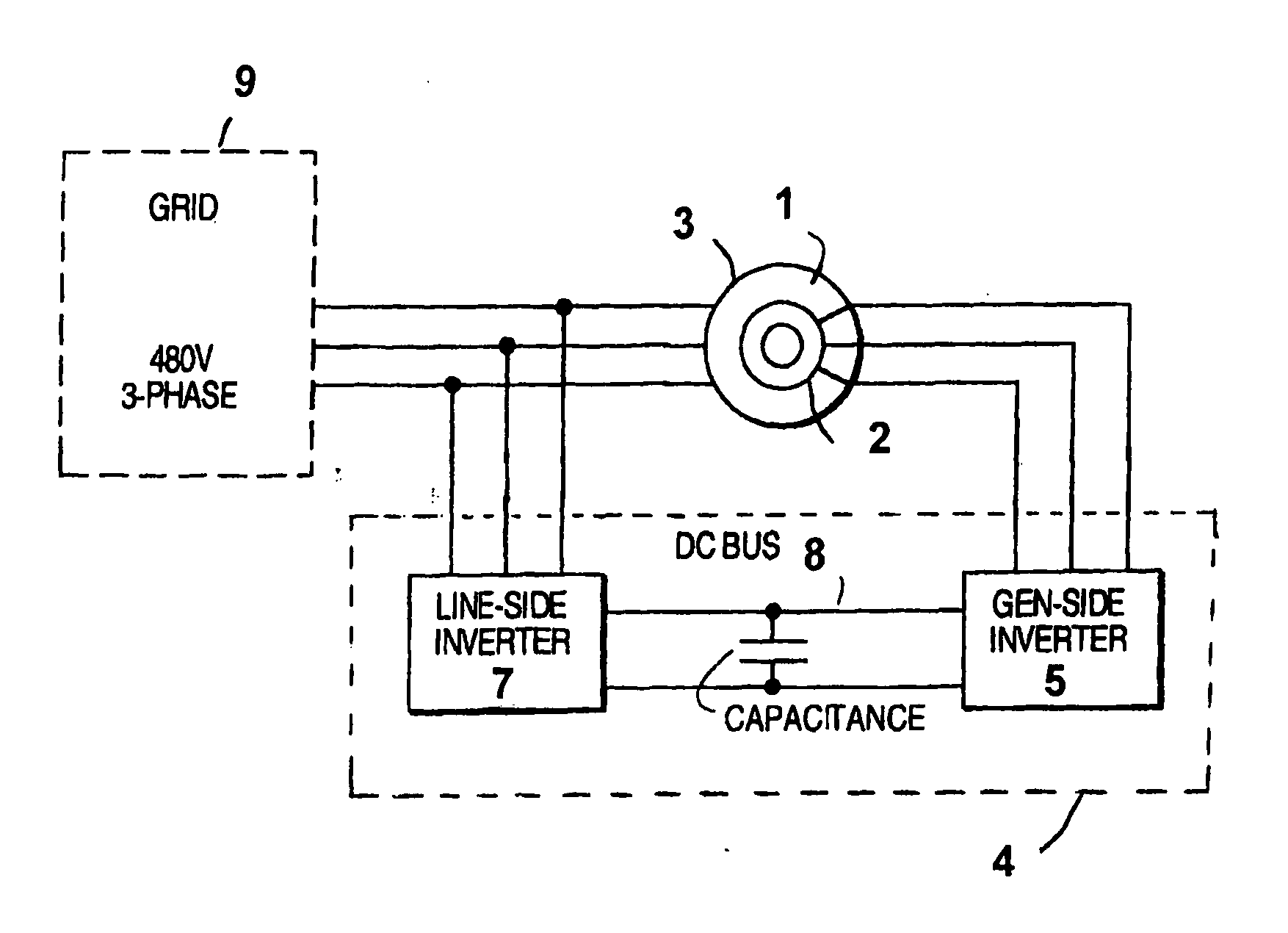
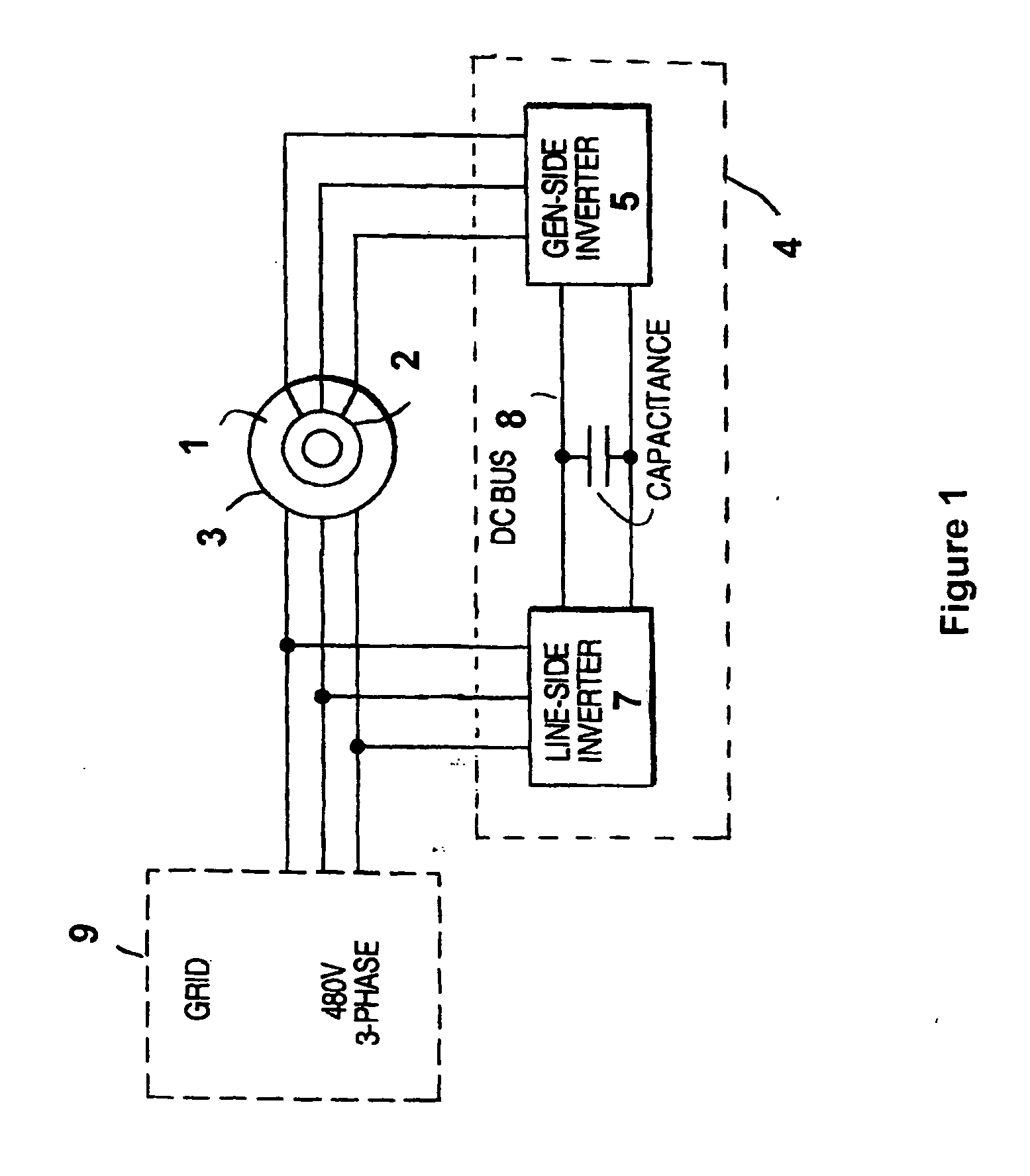
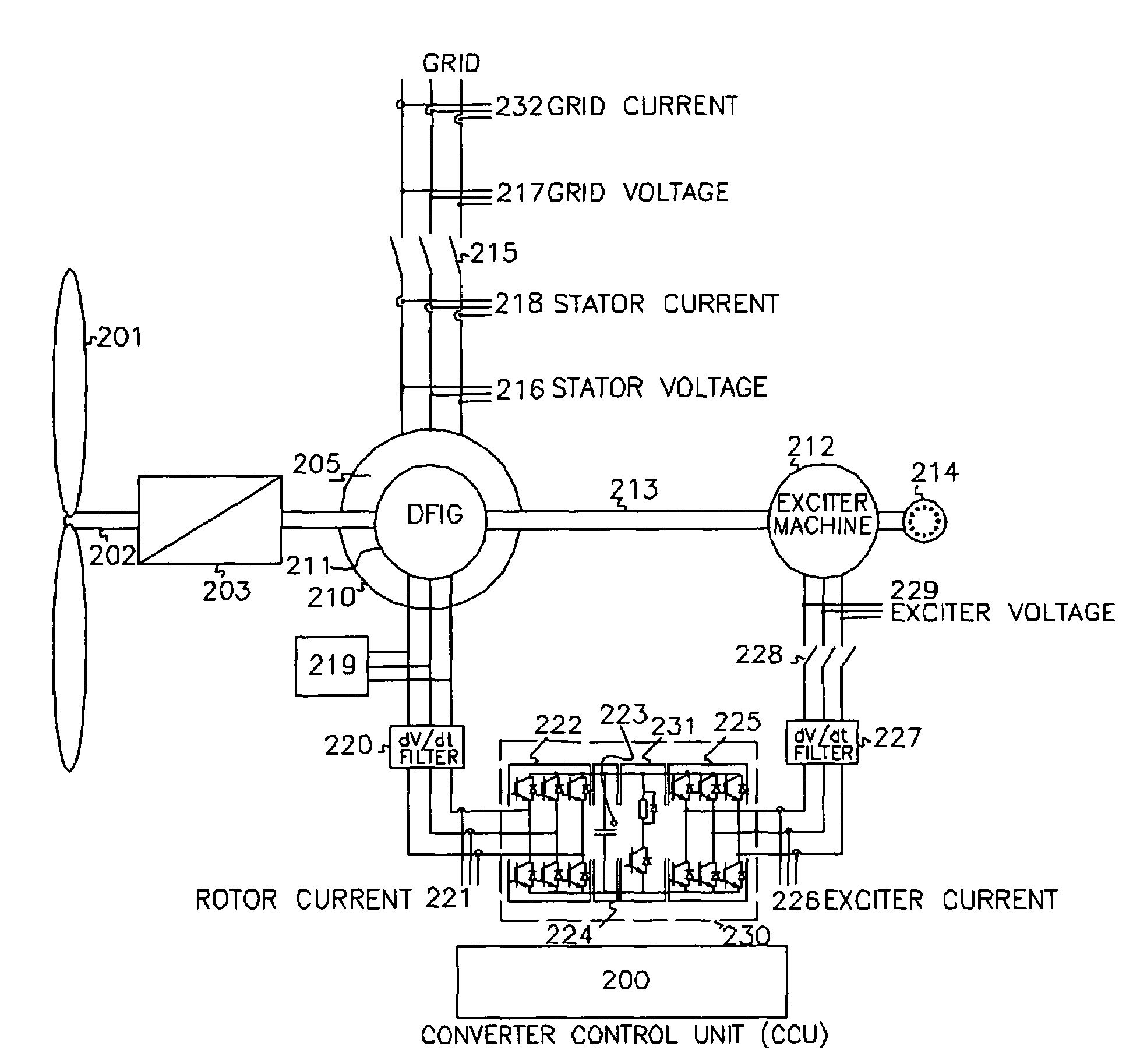
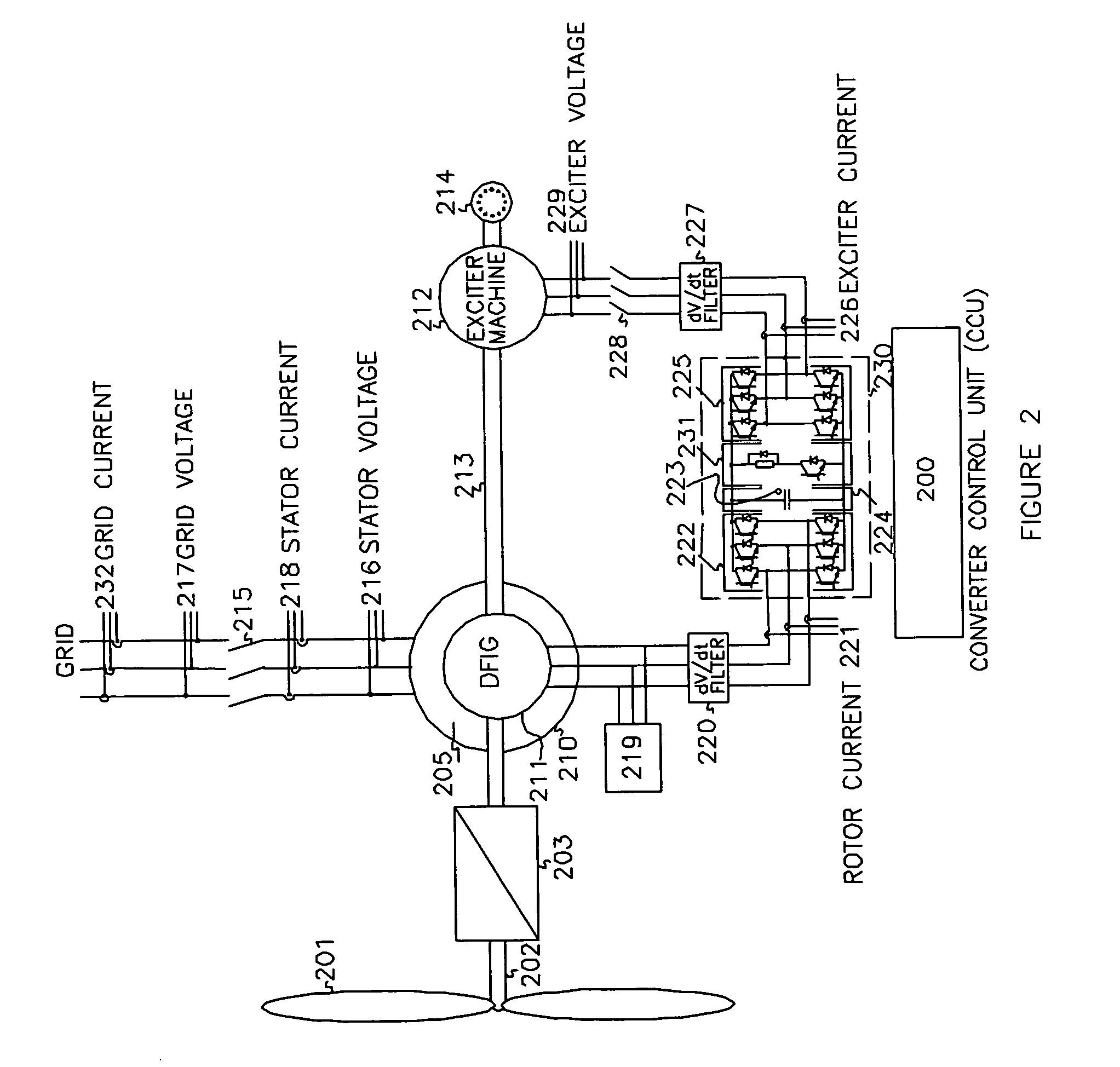
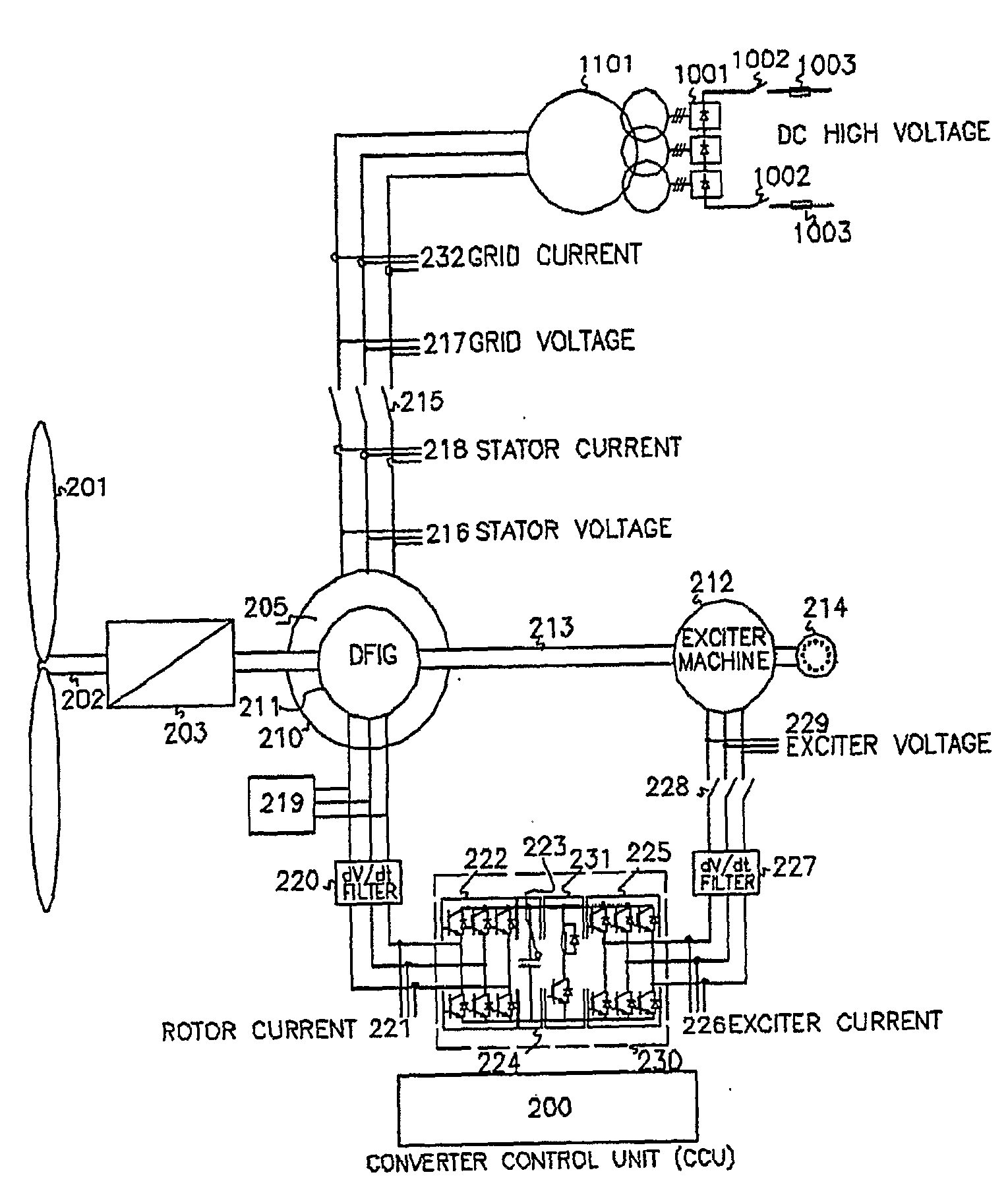
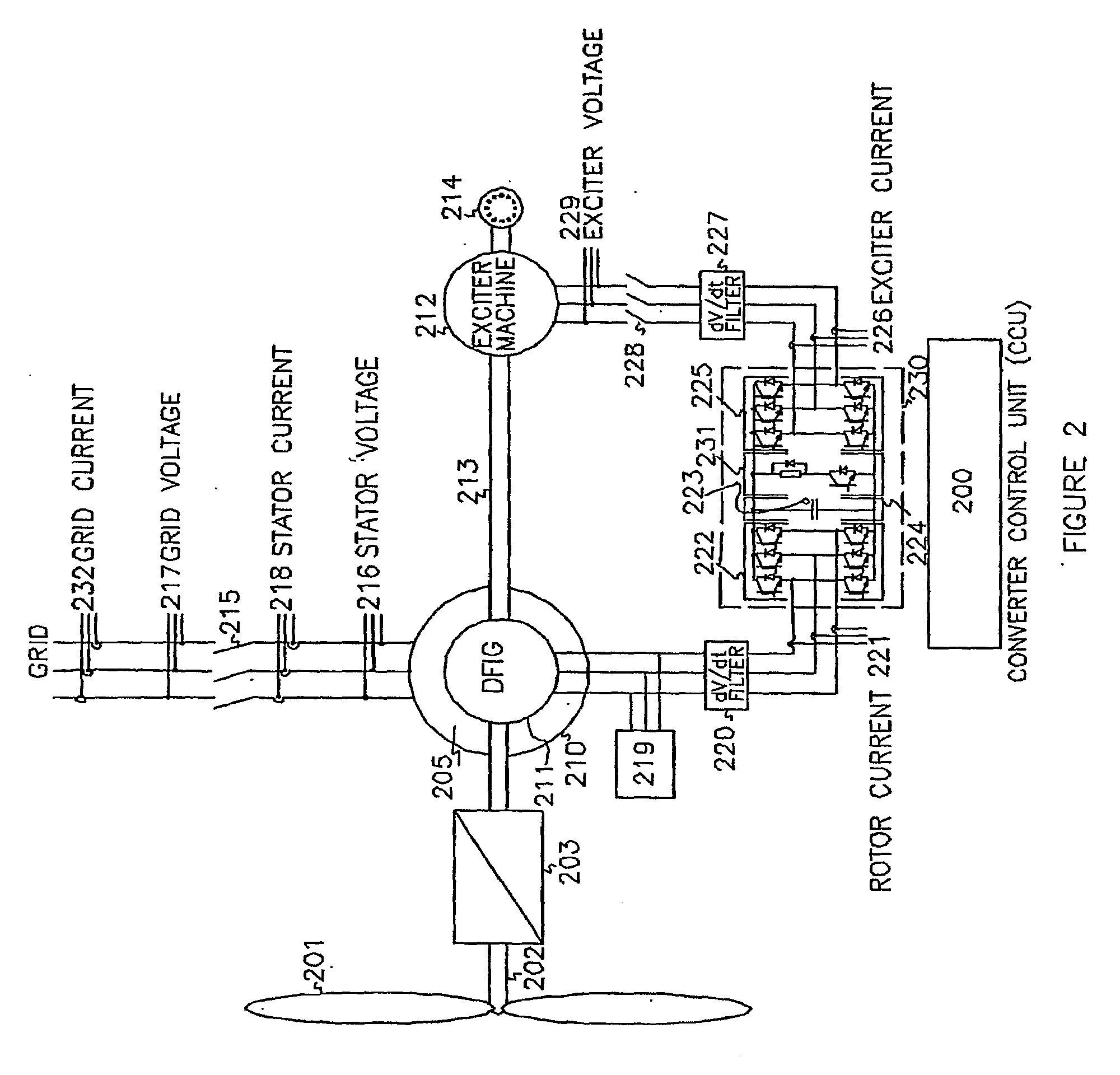
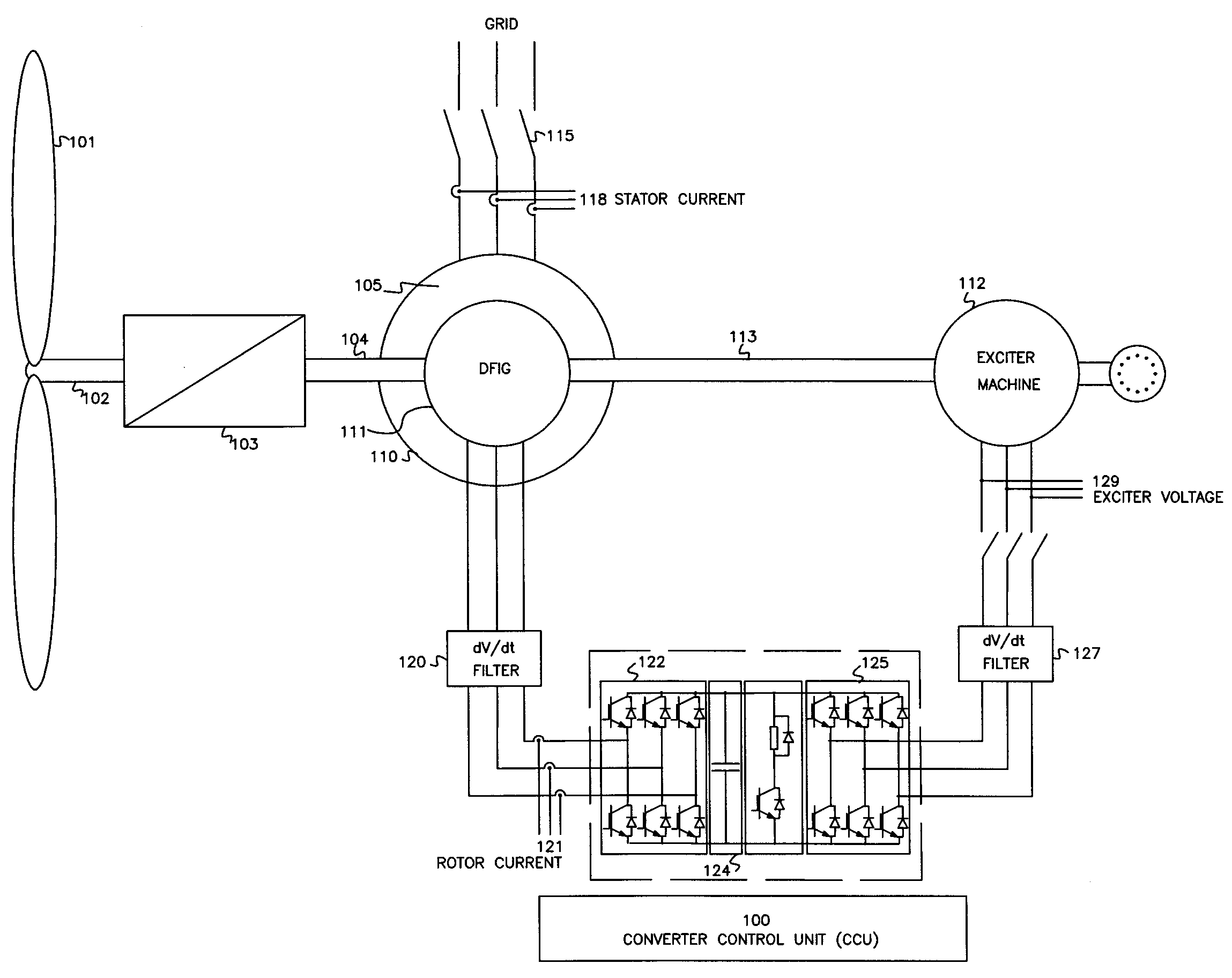
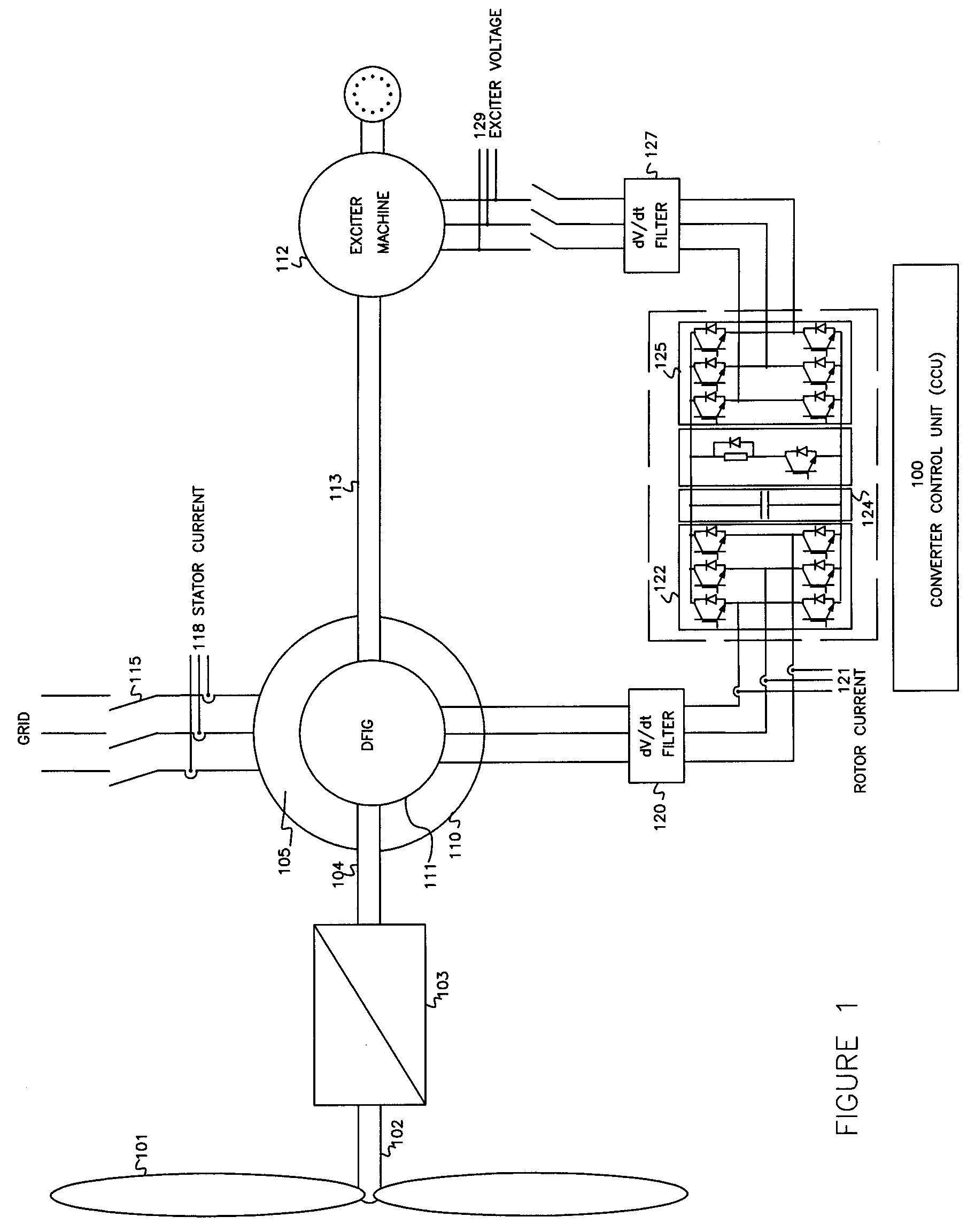
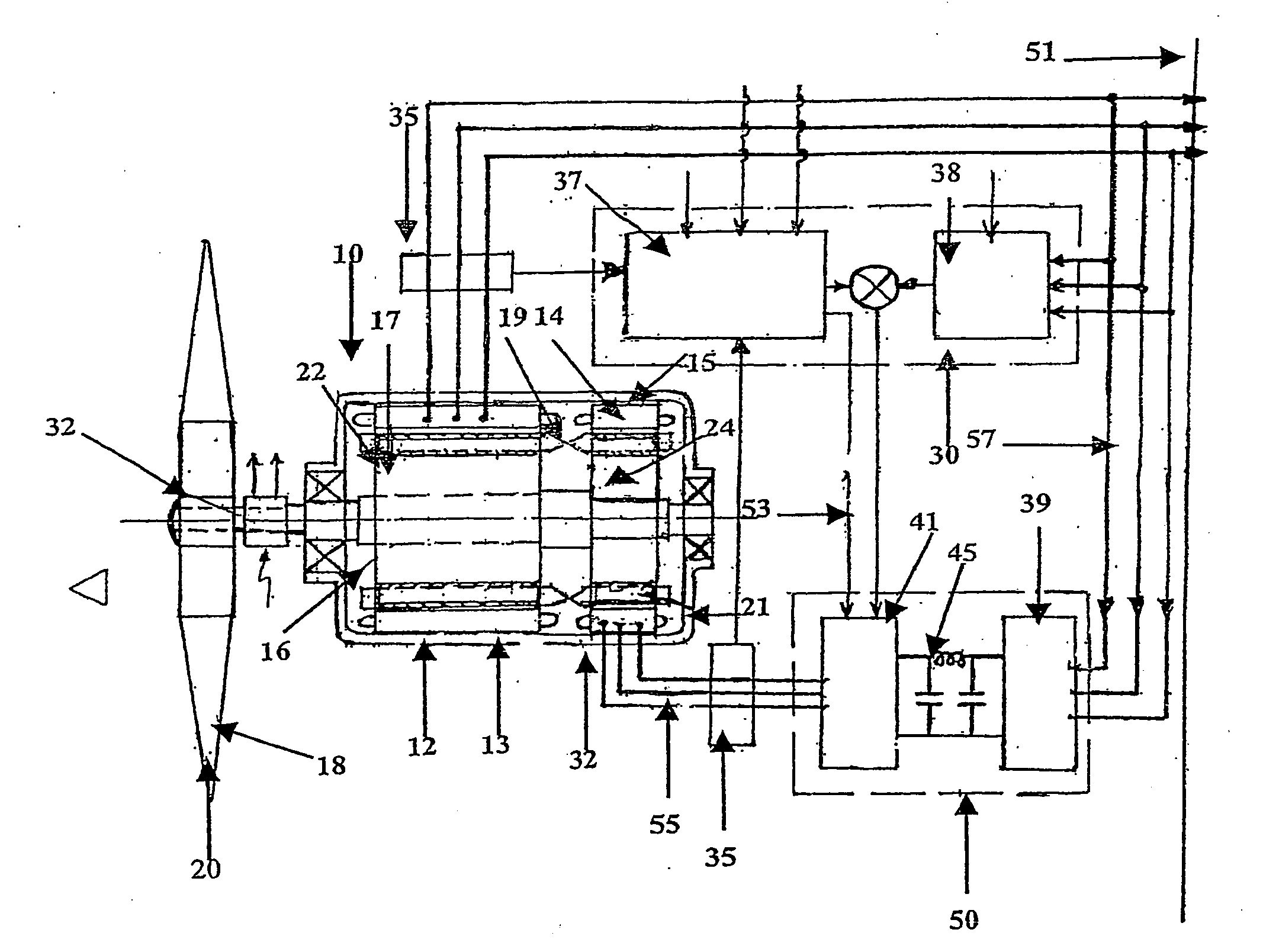
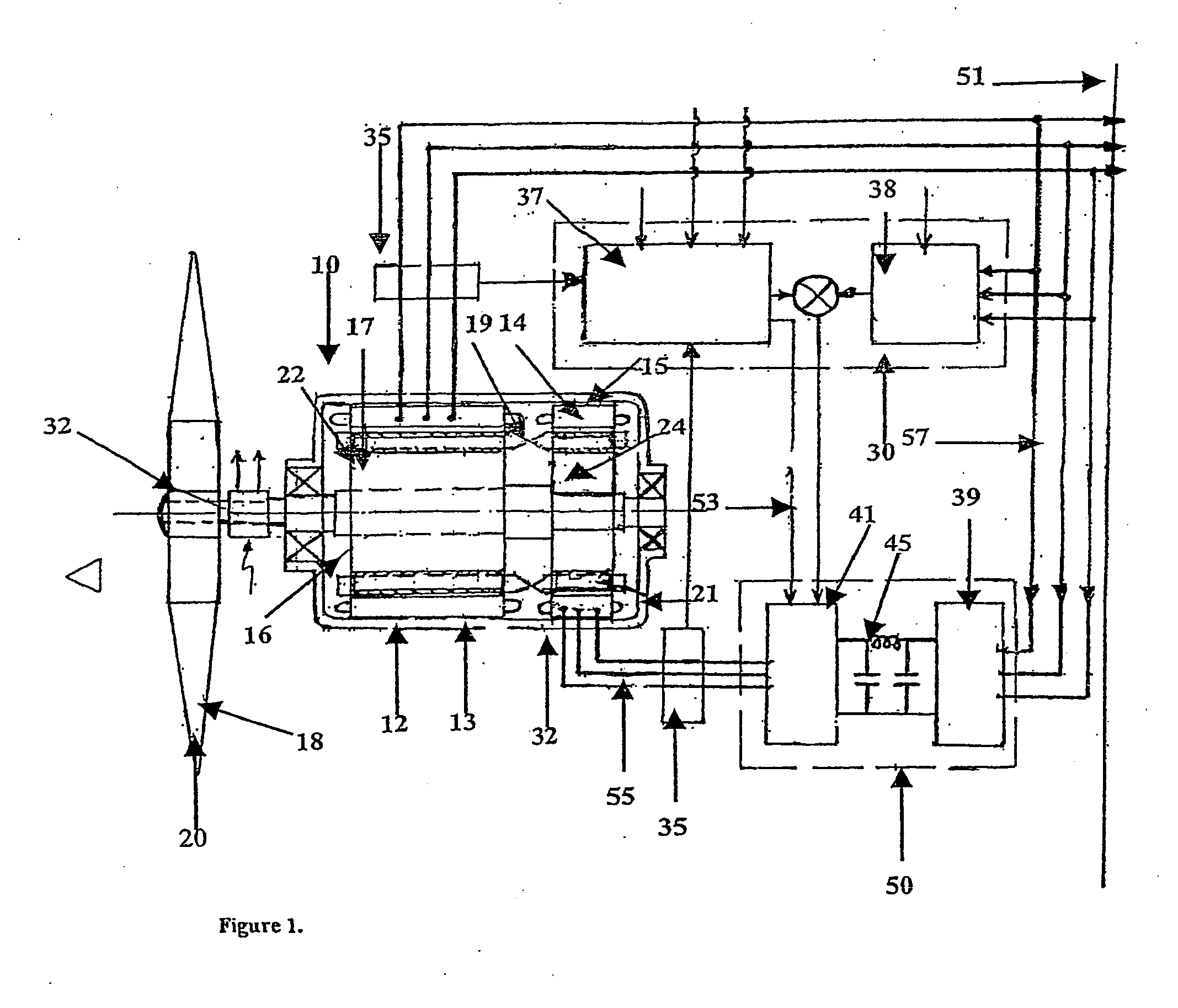
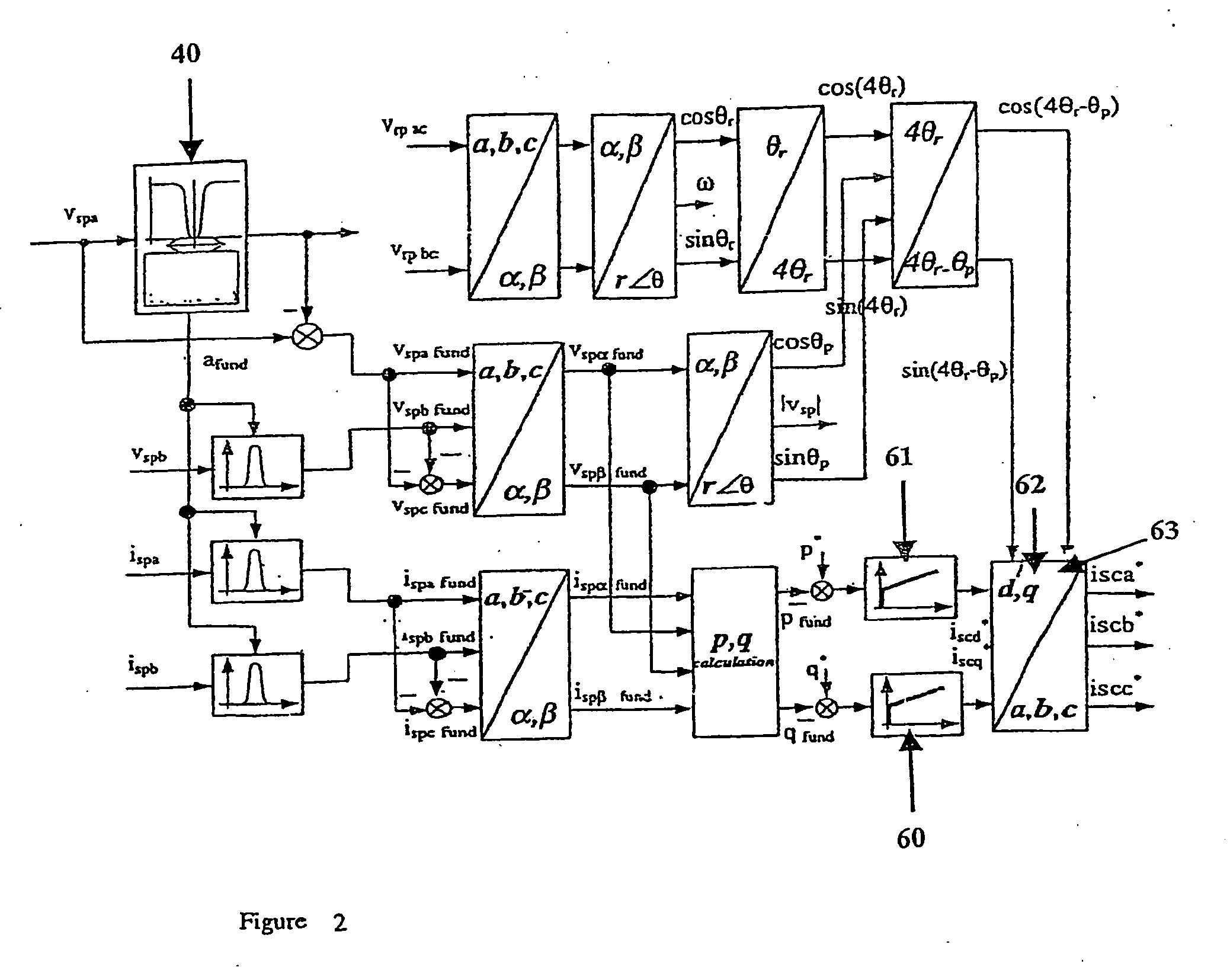
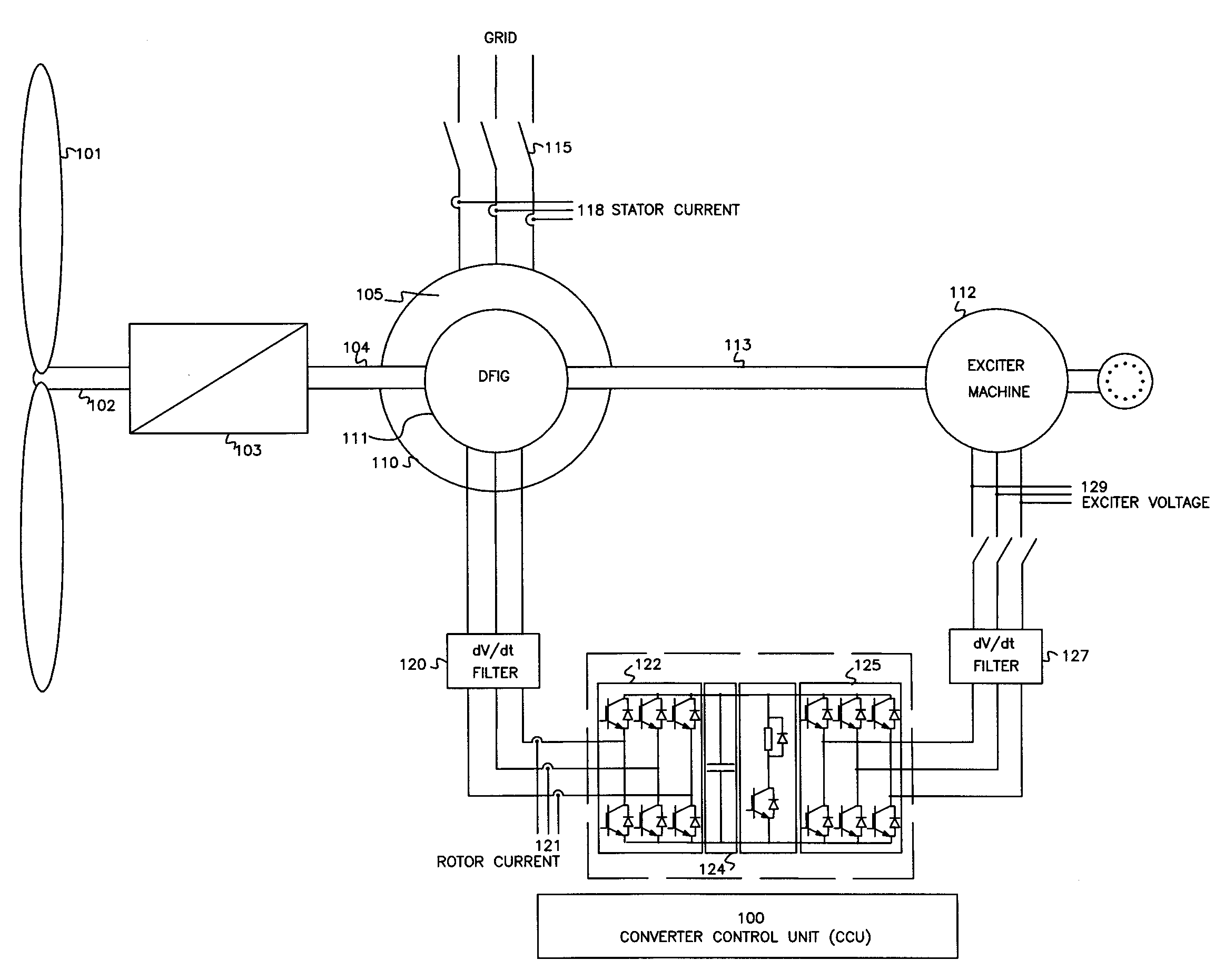
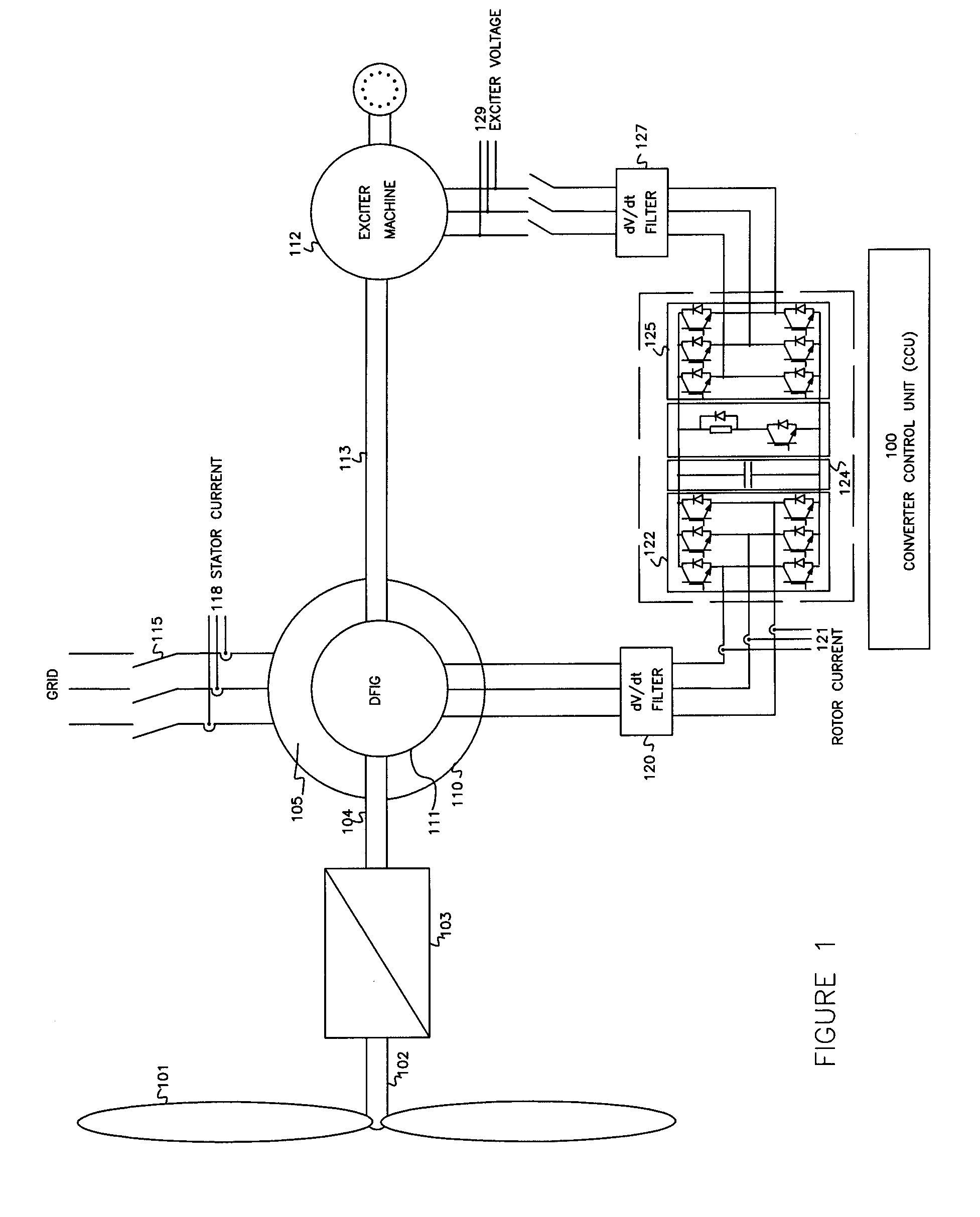
Variable speed wind turbine having an exciter machine and a power converter not connected to the grid
ActiveUS20070216164A1Avoiding undesired harmonic distortionImprove power qualityGenerator control circuitsVector control systemsPower qualityHarmonic
A variable speed wind turbine having a doubly fed induction generator (DFIG), includes an exciter machine mechanically coupled to the DFIG and a power converter placed between a rotor of the DFIG and the exciter machine. Thus, the power converter is not directly connected to the grid avoiding the introduction of undesired harmonic distortion and achieving a better power quality fed into the utility grid. Moreover, the variable speed wind turbine includes a power control and a pitch regulation.
Owner:INGETEAM POWER TECH
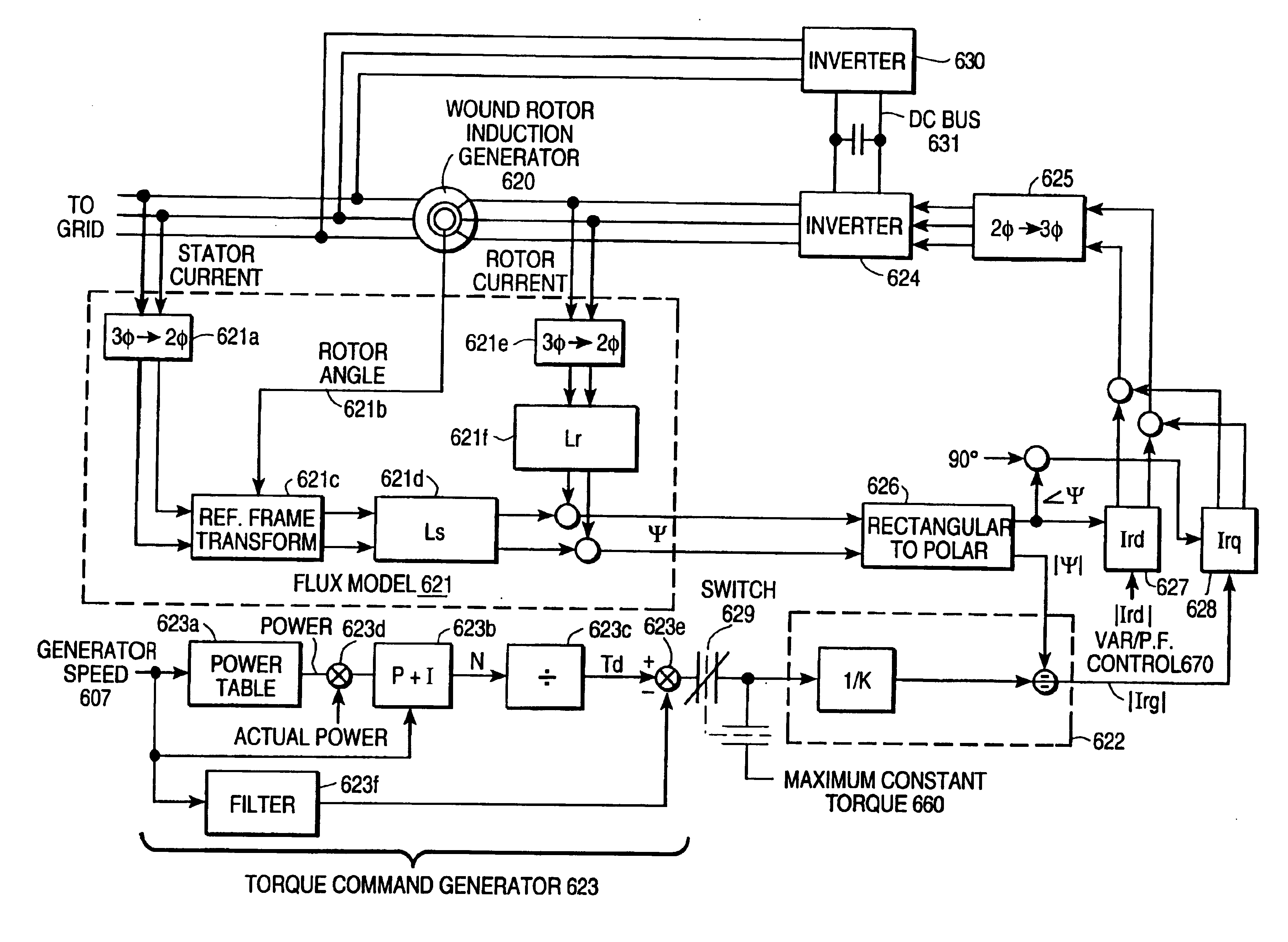
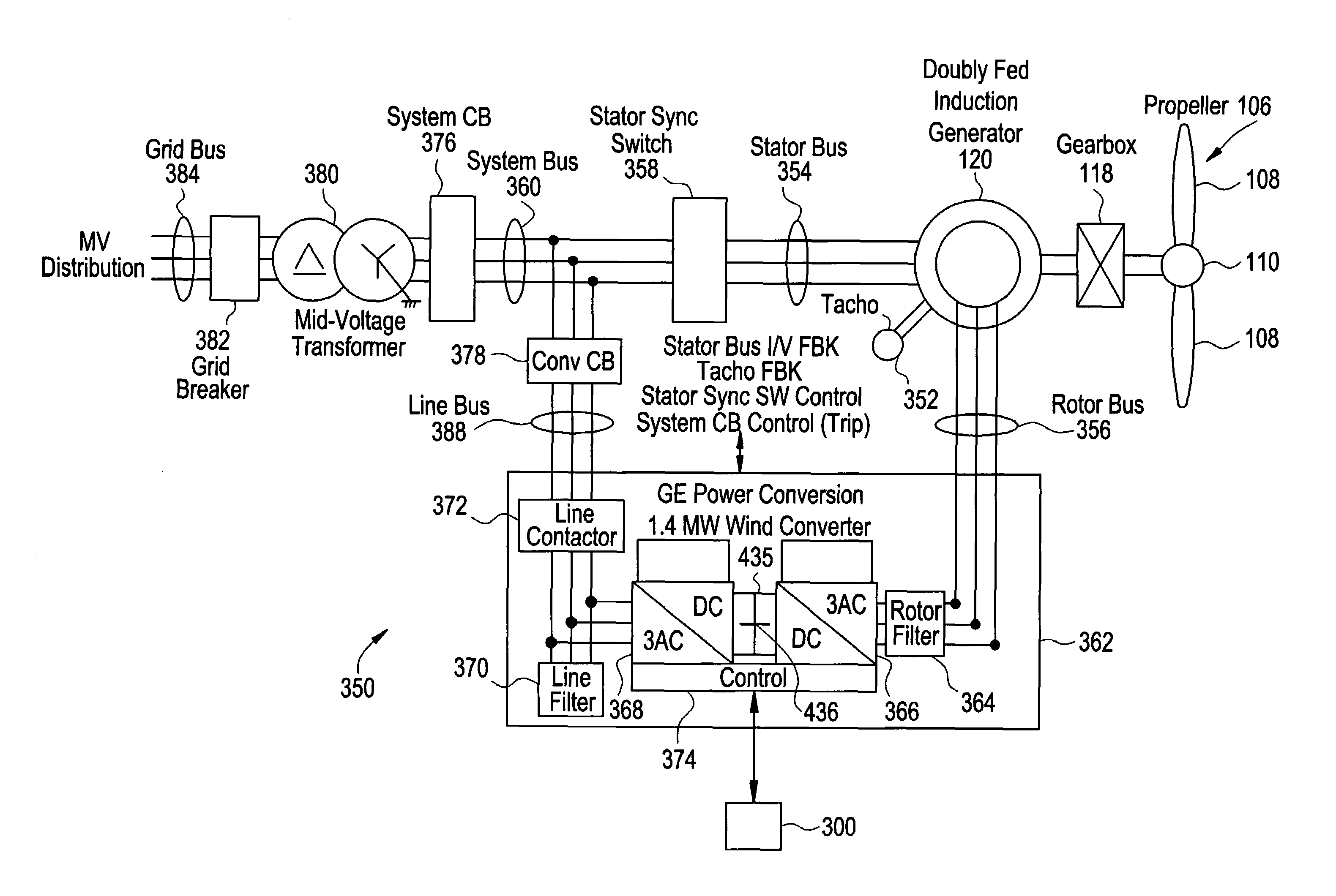
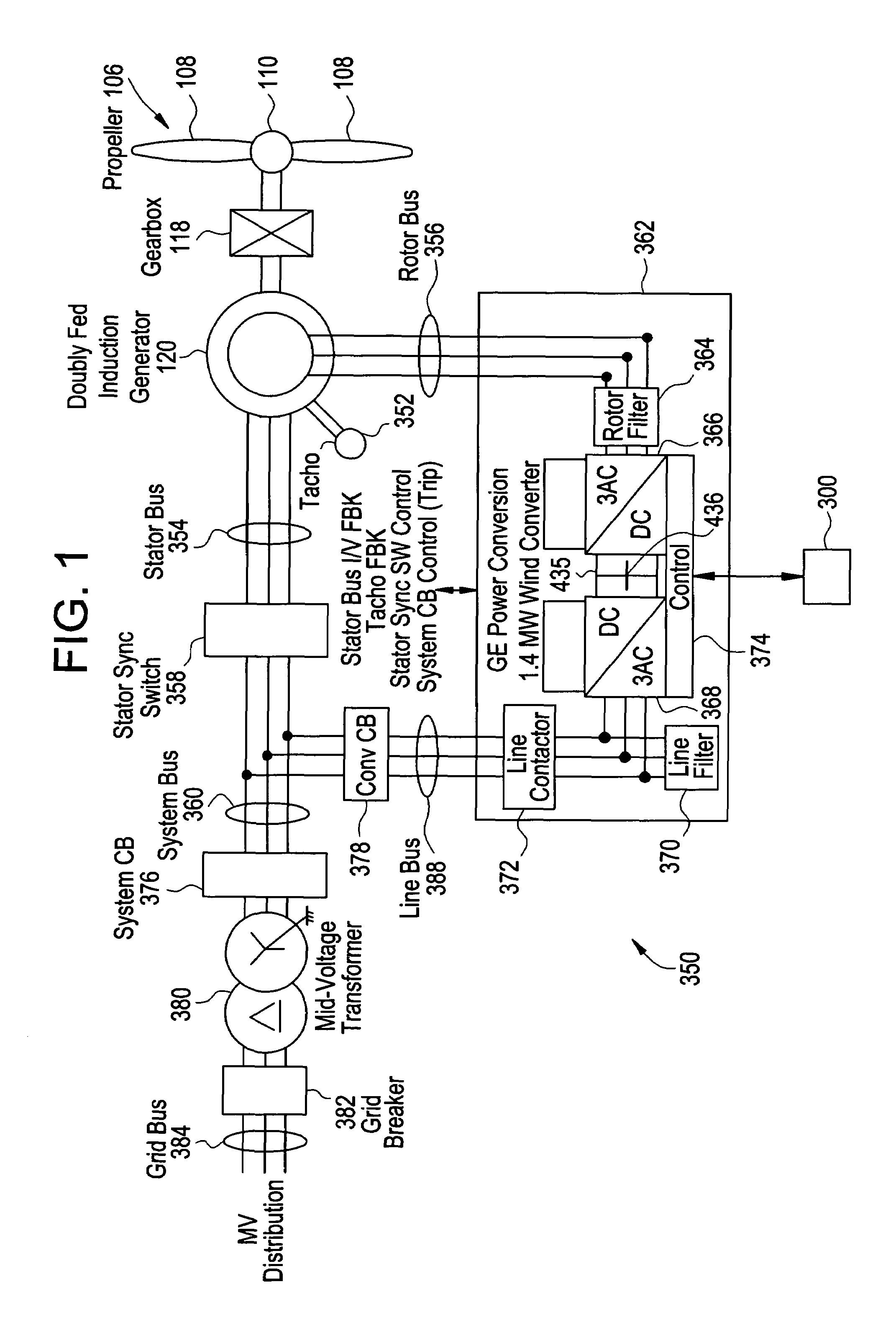
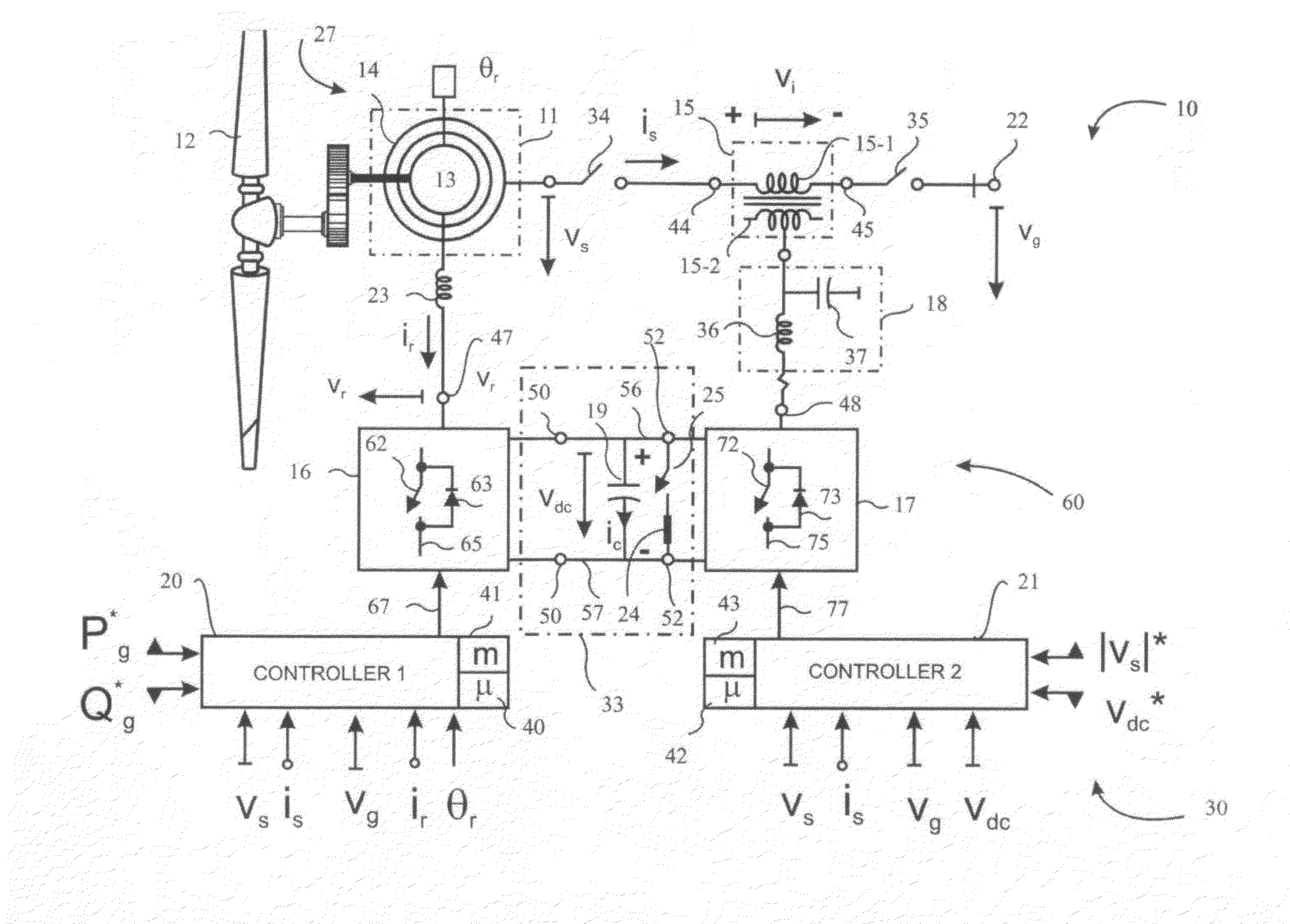
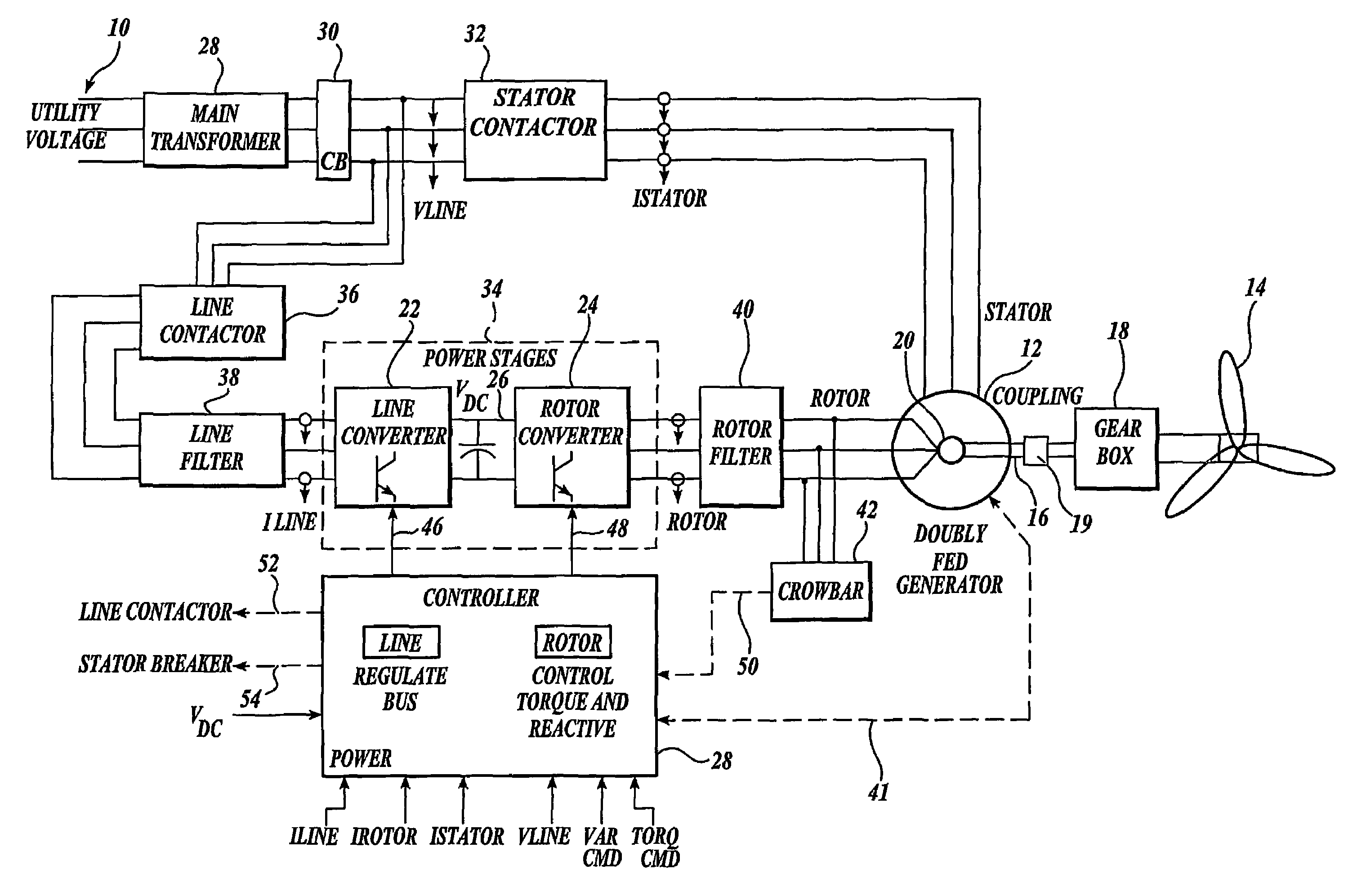
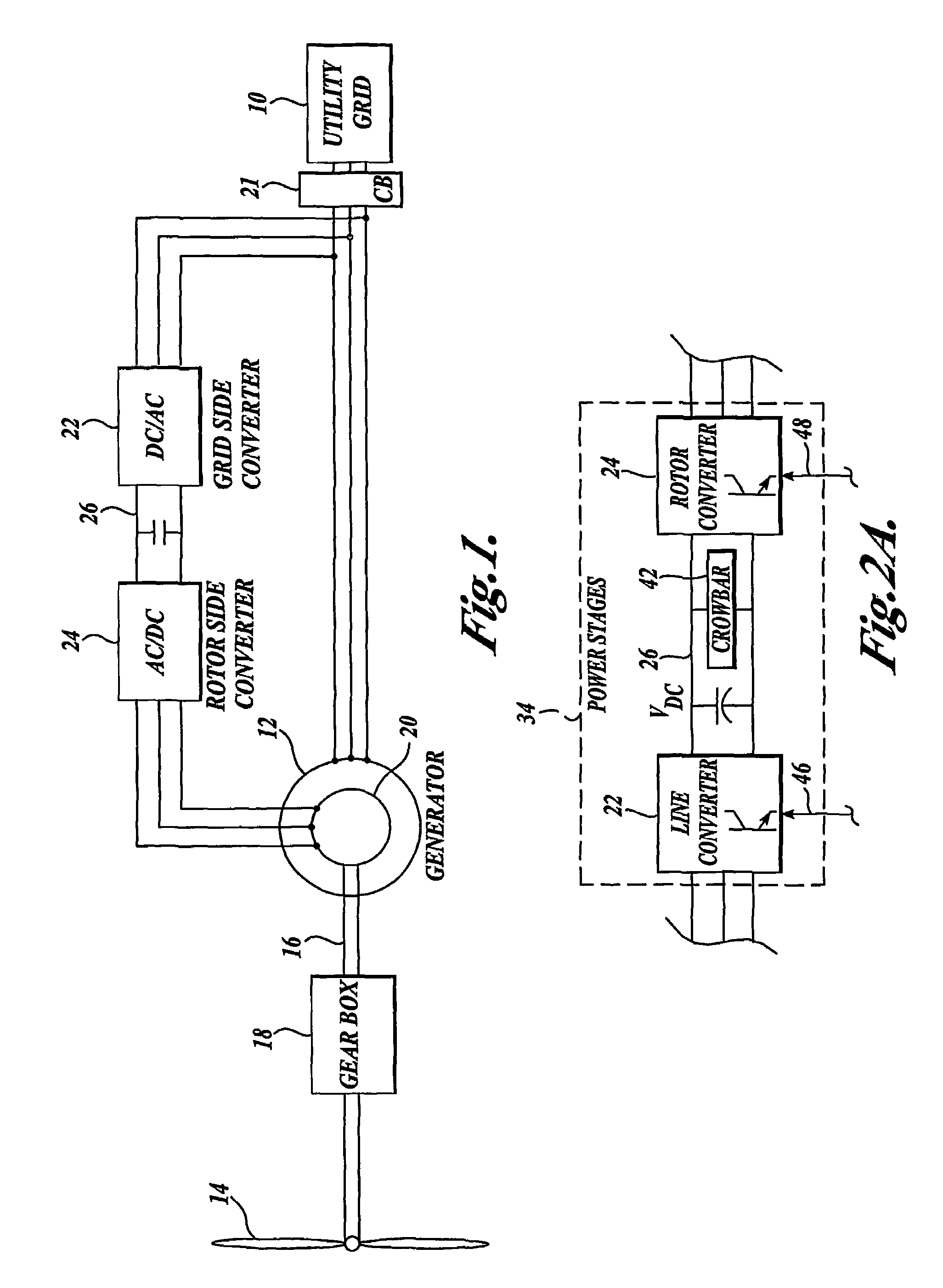
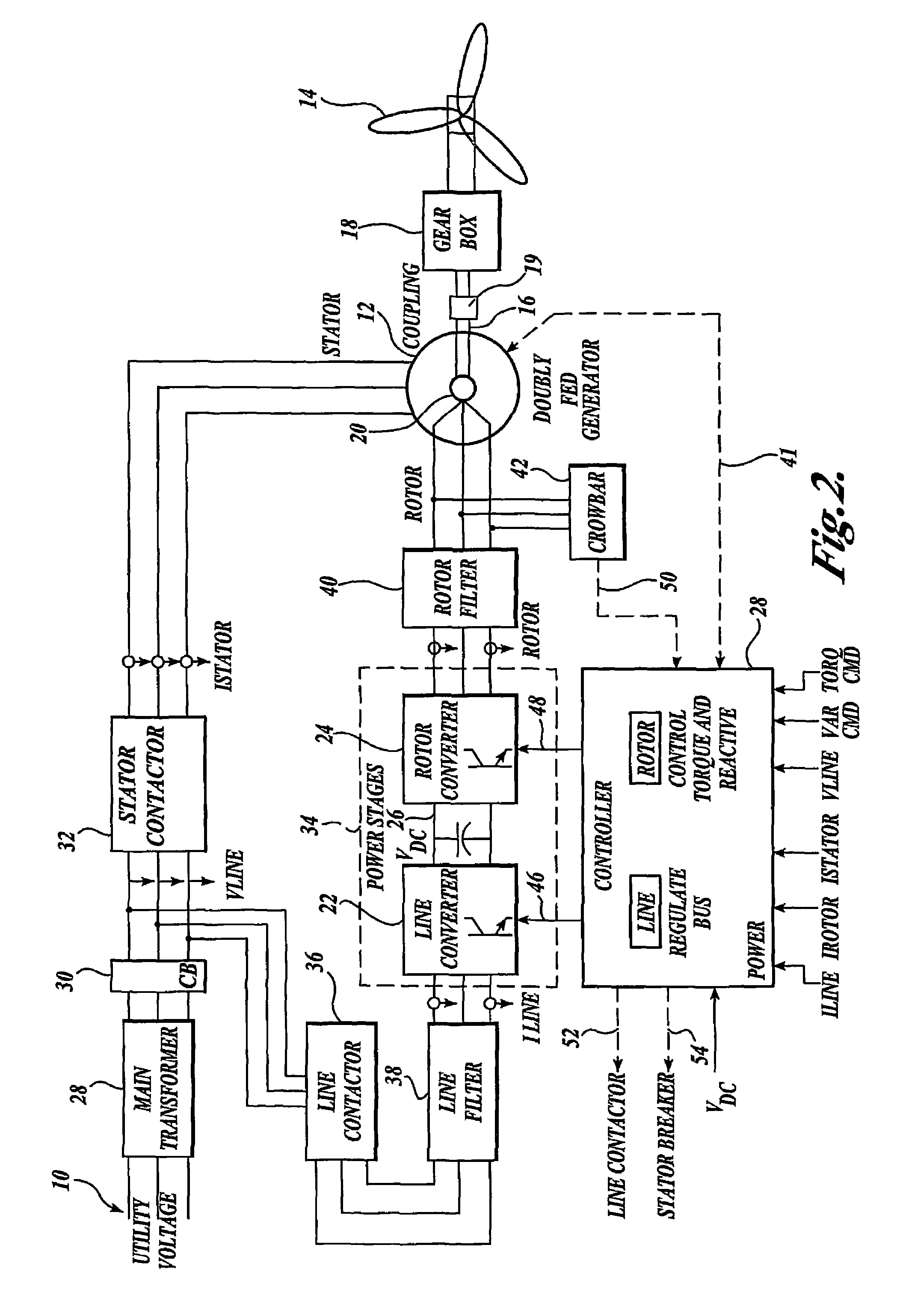
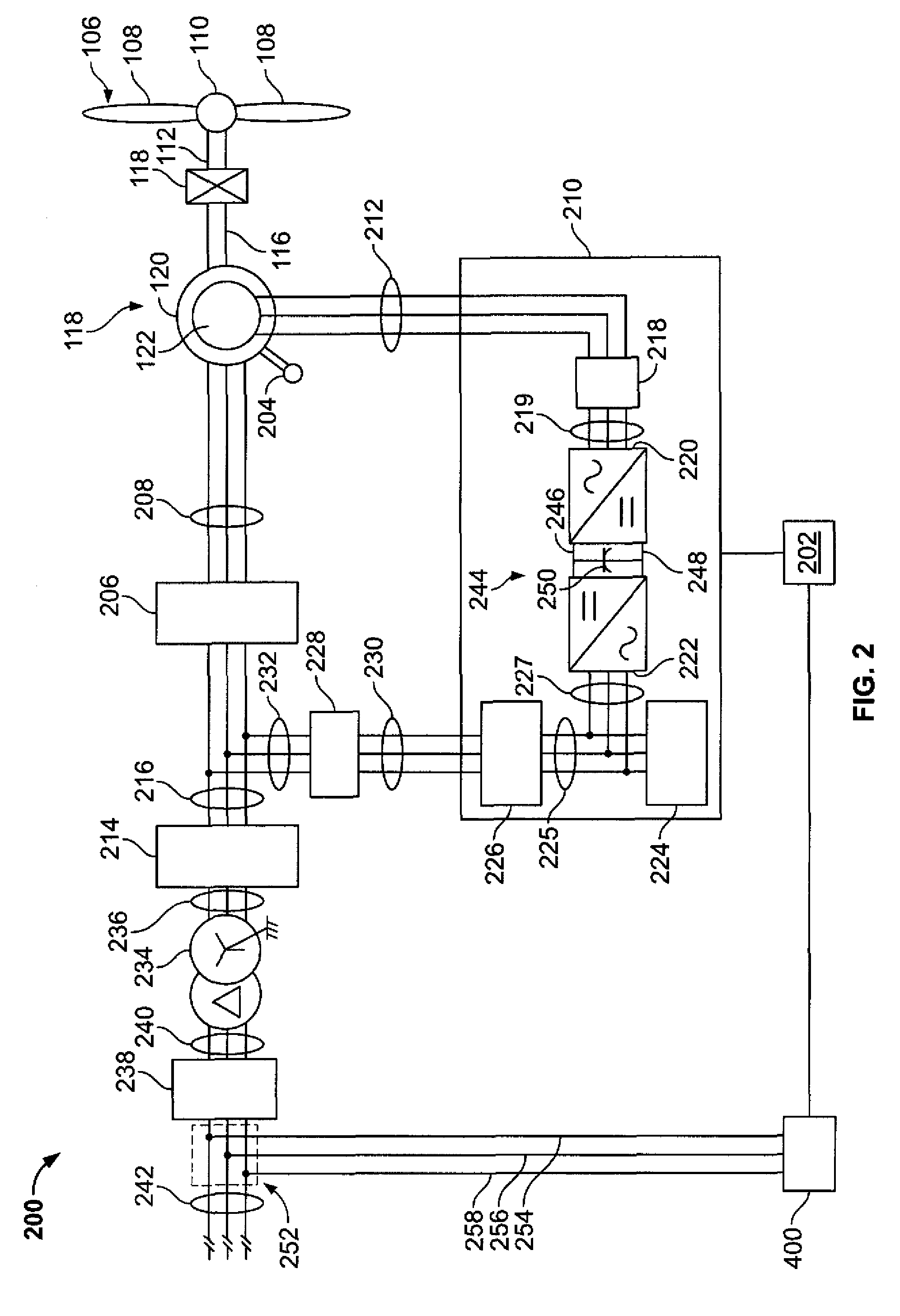
Control system for doubly fed induction generator
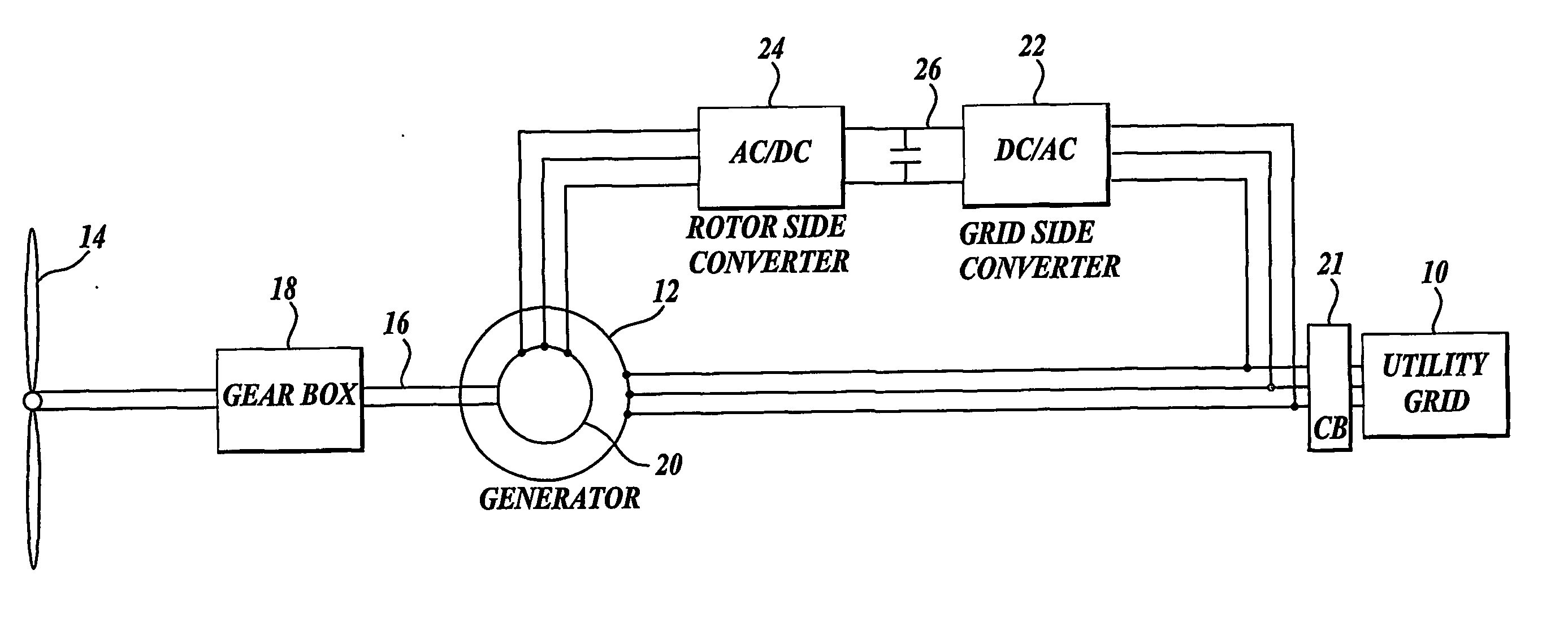
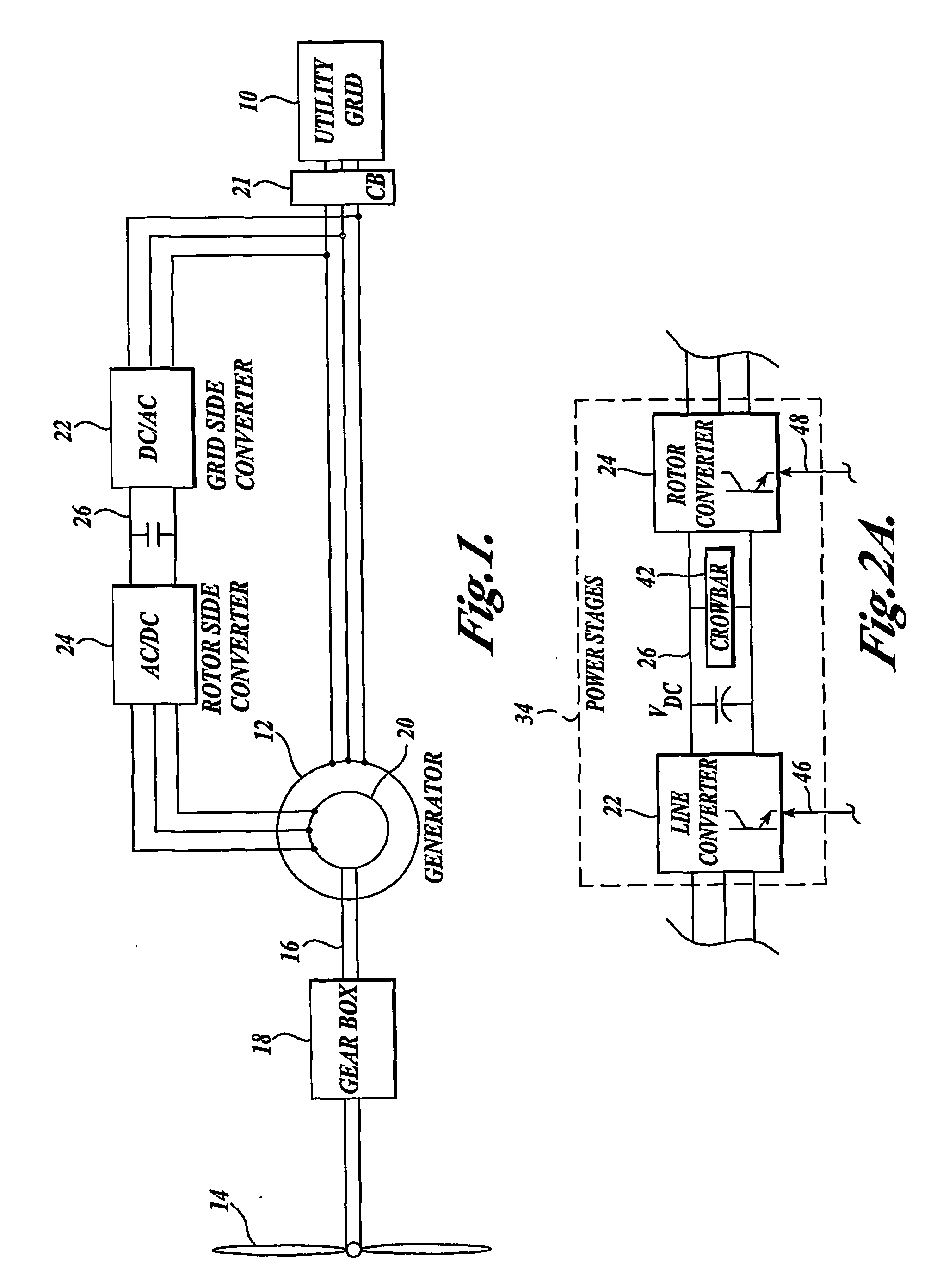
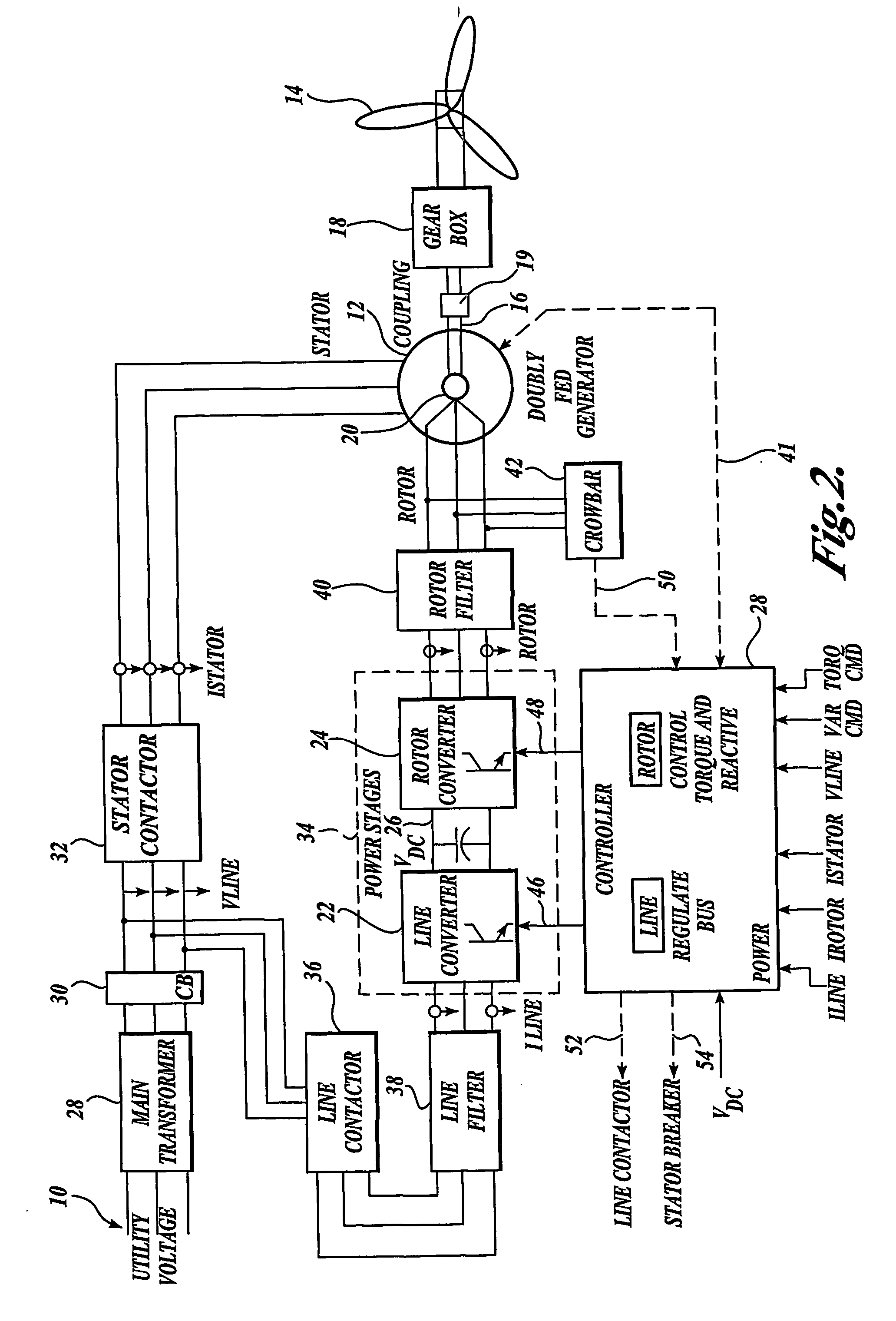
ActiveUS20070052244A1Reducing rotor currentMaintain balanceGenerator control circuitsAC motor controlControl systemControl signal
A controller (28) for a doubly fed induction generator (12,20) adjusts control signals to a rotor side converter (24) and line side converter (22) to adjust rotor current when a voltage transient on a utility grid (10) occurs, so that the doubly fed induction generator can ride through the transient. The controller can also turn off the transistors of the rotor side converter (24) to reduce rotor current and / or activate a crowbar (42) to reduce the voltage of the DC link (26) connecting the converters (22, 24) when significant voltage transients occur on the grid (10). This permits continued operation of the DFIG system without disconnecting from the grid.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC SOLAR INVERTERS USA
Variable speed wind turbine generator
InactiveUS6847128B2Generator control circuitsWind motor controlVariable speed wind turbineControl theory
A variable speed system for use in systems, such as, for example, wind turbines, is described. The system comprises a wound rotor induction generator, a torque controller and a proportional integral derivative (PID) pitch controller. The torque controller controls generator torque using field oriented control, and the PID controller performs pitch regulation based on generator rotor speed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method, apparatus and computer program product for injecting current
Method and apparatus that provide a response to the negative sequence current demands during a disturbance of the grid system connected to power-generating equipment, such as a wind turbine system, provide for tracking components in the grid signal, orienting at least a portion of the signal, and injecting the oriented portion. Controlled injection of negative sequence current provides for extending small-signal control response, and also provides for modifications of the apparent impedance to the grid interconnect of the power conversion equipment.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
Variable Speed Wind Turbine Configured For Wind Farm Operation
InactiveUS20090206606A1Easy to controlGood effectGenerator control circuitsOptimise machine performancePower gridVariable speed wind turbine
The present invention relates to an improved wind turbine, of the type which employs doubly fed induction generators (DFIG), and a wind park including the same, which permits the use of lighter weight turbines, with the ability to have greater energy capture, more precise control of asymmetrical phases and enhanced maintenance and support of the grid during fault conditions.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
System and method for power control in wind turbines
A system and method for power control in wind turbines are provided. The method includes switching a plurality of switching devices in a power conversion component of the wind turbine system in a normal switching mode to provide power flow through the power conversion component. The method further includes switching the plurality of switches devices in the power conversion component of the wind turbine system in a short circuit switching mode to prevent power flow through the power conversion component.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
Doubly-controlled asynchronous generator
InactiveUS20080150285A1Avoid problemsReduce settingsGenerator control circuitsWind motor controlTransformerElectric power distribution
An electric power generator system or a motor comprising a doubly-fed asynchronous generator or motor comprising a stator and a rotor, a transformer having a first winding and a second winding, the first winding having a first end and a second end; and wherein the stator and the transformer are connectable in series with an electric power distribution grid.
Owner:WIND TO POWER SYST
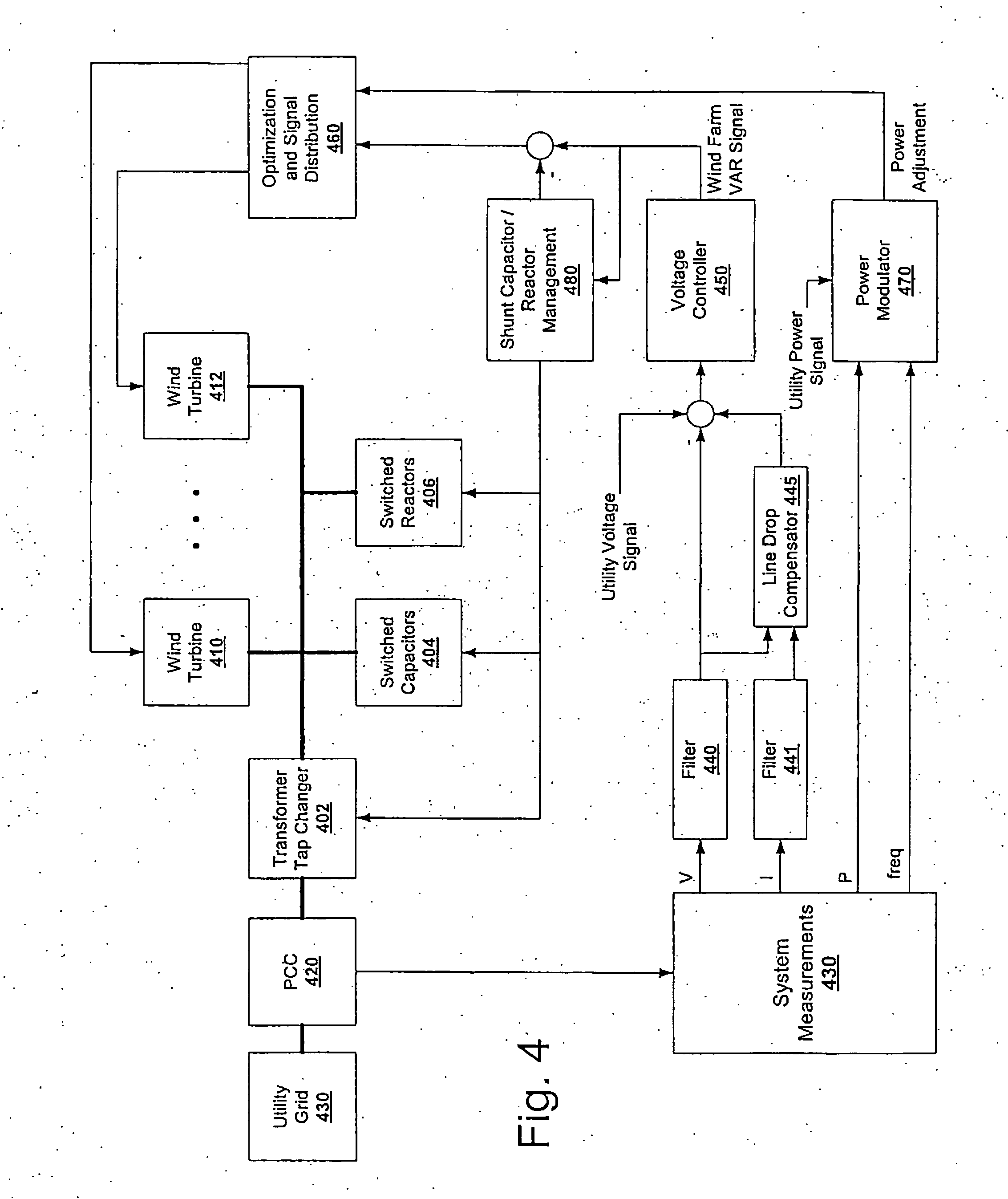
Continuous reactive power support for wind turbine generators
Real and reactive power control for wind turbine generator systems. The technique described herein provides the potential to utilize the total capacity of a wind turbine generator system (e.g., a wind farm) to provide dynamic VAR (reactive power support). The VAR support provided by individual wind turbine generators in a system can be dynamically varied to suit application parameters.
Owner:WILKINS THOMAS ALEXANDER +1
Variable speed wind turbine having an exciter machine and a power converter not connected to the grid
ActiveUS7425771B2Avoid distortionImprove power qualityGenerator control circuitsVector control systemsPower qualityPower grid
Owner:INGETEAM POWER TECH
Power conditioning architecture for a wind turbine
ActiveUS20070278797A1Small sizeIncrease generationGenerator control circuitsWind motor controlPower gridVoltage sag
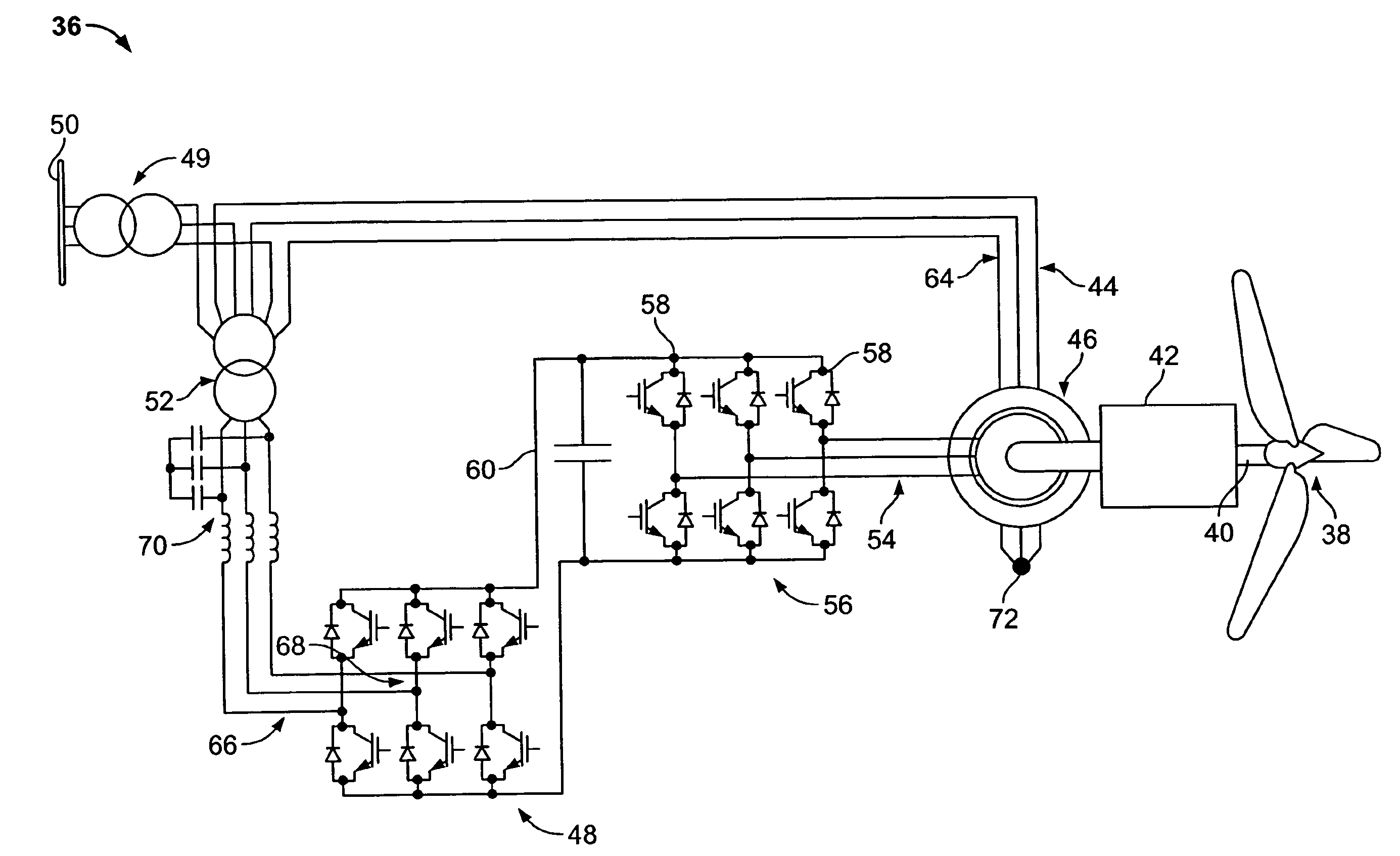
A wind turbine 36 has a back-to-back AC / DC / AC power electronic converter chain in which the grid side converter 48 is connected in series with DFIG stator windings 64. The machine side converter 56 is fed from the rotor windings 54 of the DFIG 44. Series connection of the grid side converter 48 enables voltage sag ride-through capability via control of the stator flux.In the event of a grid voltage sag, the series converter allows for a controlled response in the stator flux and electromagnetic shaft torque, protects the machine side converter and enables continued power delivery to the grid.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
System and method for power control in wind turbines
A system and method for power control in wind turbines are provided. The method includes switching a plurality of switching devices in a power conversion component of the wind turbine system in a normal switching mode to provide power flow through the power conversion component. The method further includes switching the plurality of switches devices in the power conversion component of the wind turbine system in a short circuit switching mode to prevent power flow through the power conversion component.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Control system for doubly fed induction generator
ActiveUS7411309B2Total current dropGuaranteed uptimeGenerator control circuitsAC motor controlControl systemControl signal
A controller (28) for a doubly fed induction generator (12,20) adjusts control signals to a rotor side converter (24) and line side converter (22) to adjust rotor current when a voltage transient on a utility grid (10) occurs, so that the doubly fed induction generator can ride through the transient. The controller can also turn off the transistors of the rotor side converter (24) to reduce rotor current and / or activate a crowbar (42) to reduce the voltage of the DC link (26) connecting the converters (22, 24) when significant voltage transients occur on the grid (10). This permits continued operation of the DFIG system without disconnecting from the grid.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC SOLAR INVERTERS USA
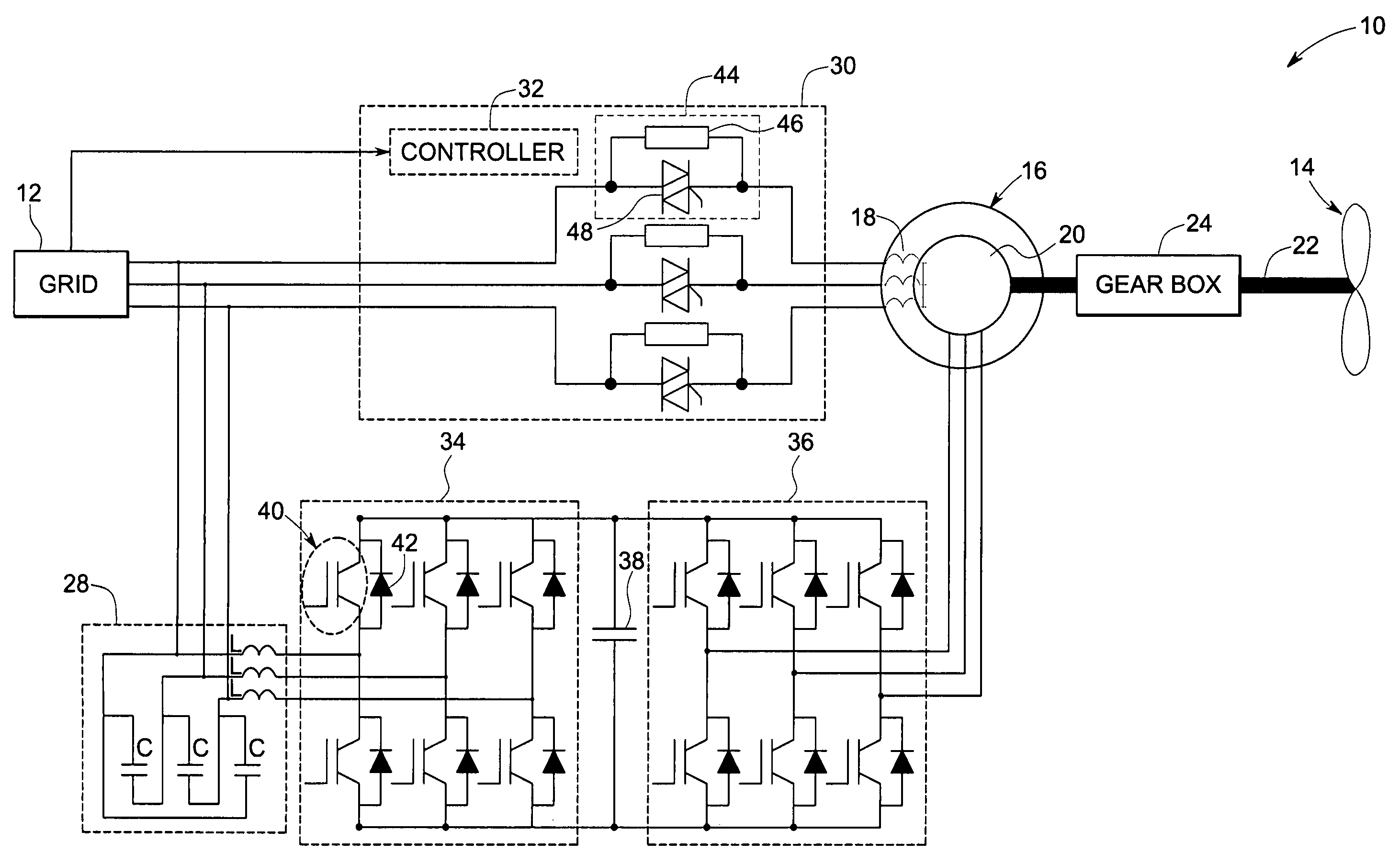
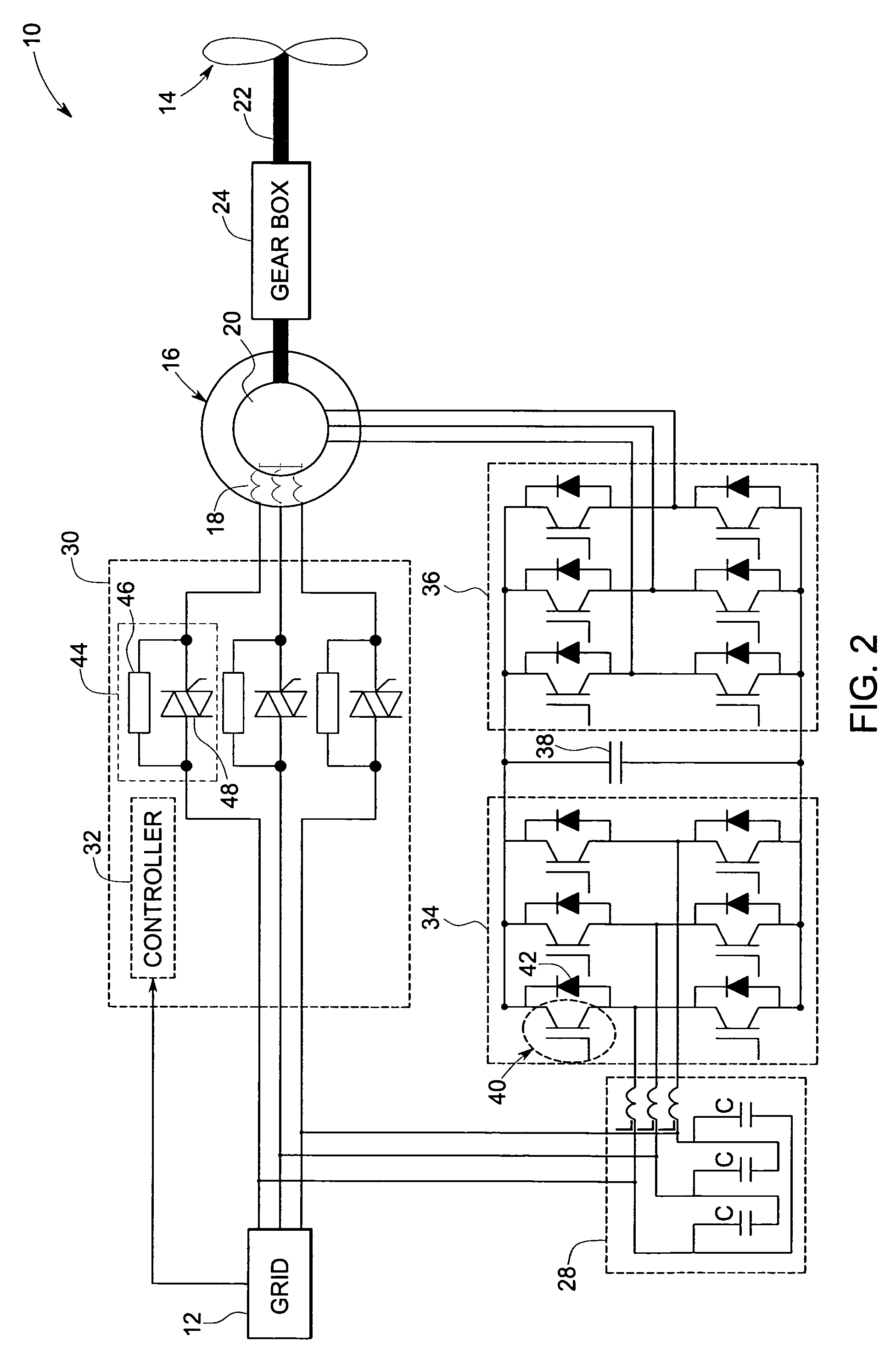
System and method of operating double fed induction generators
ActiveUS7253537B2Generator control circuitsGeneration protection through controlGrid faultPower grid
A protection system and a protection method are provided for protecting a double fed induction generator and a gearbox during a grid fault. The protection system includes a plurality of controlled impedance devices. Each of the controlled impedance devices is coupled between a respective phase of a stator winding of the double fed induction generator and a respective phase of a grid side converter. The protection system also includes a controller configured for coupling and decoupling impedance in one or more of the plurality of controlled impedance devices in response to changes in at least one of a utility grid voltage and a utility grid current.
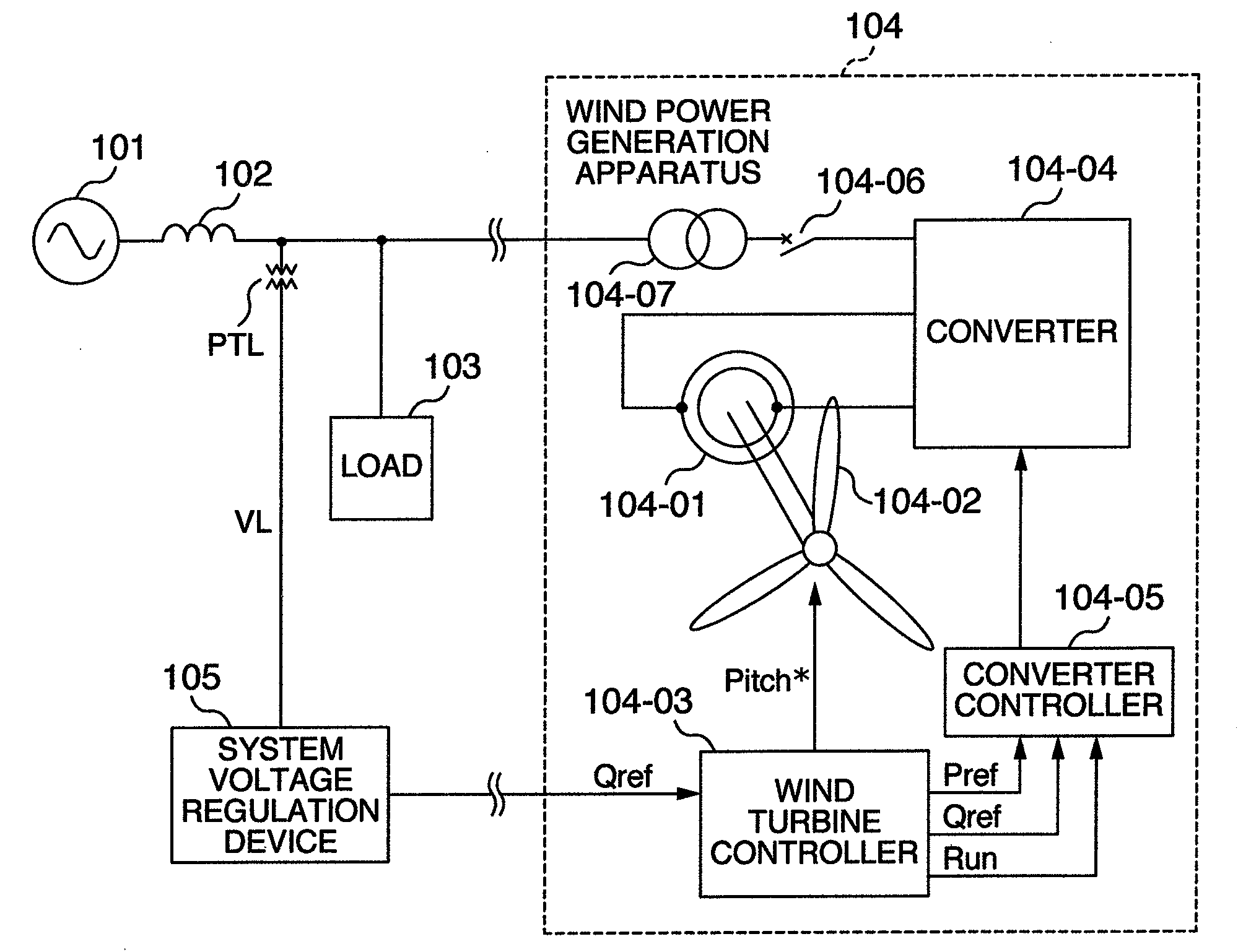
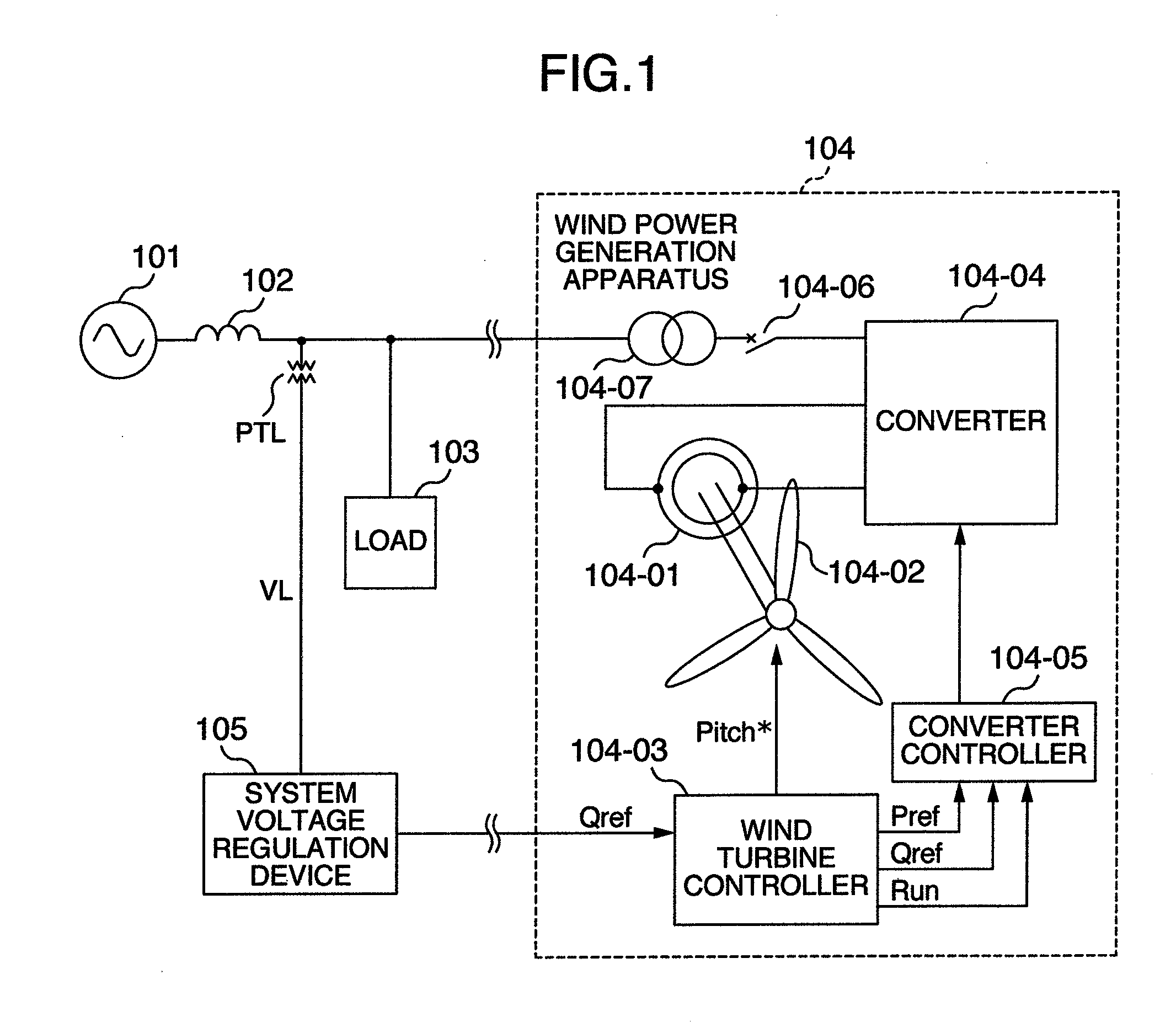
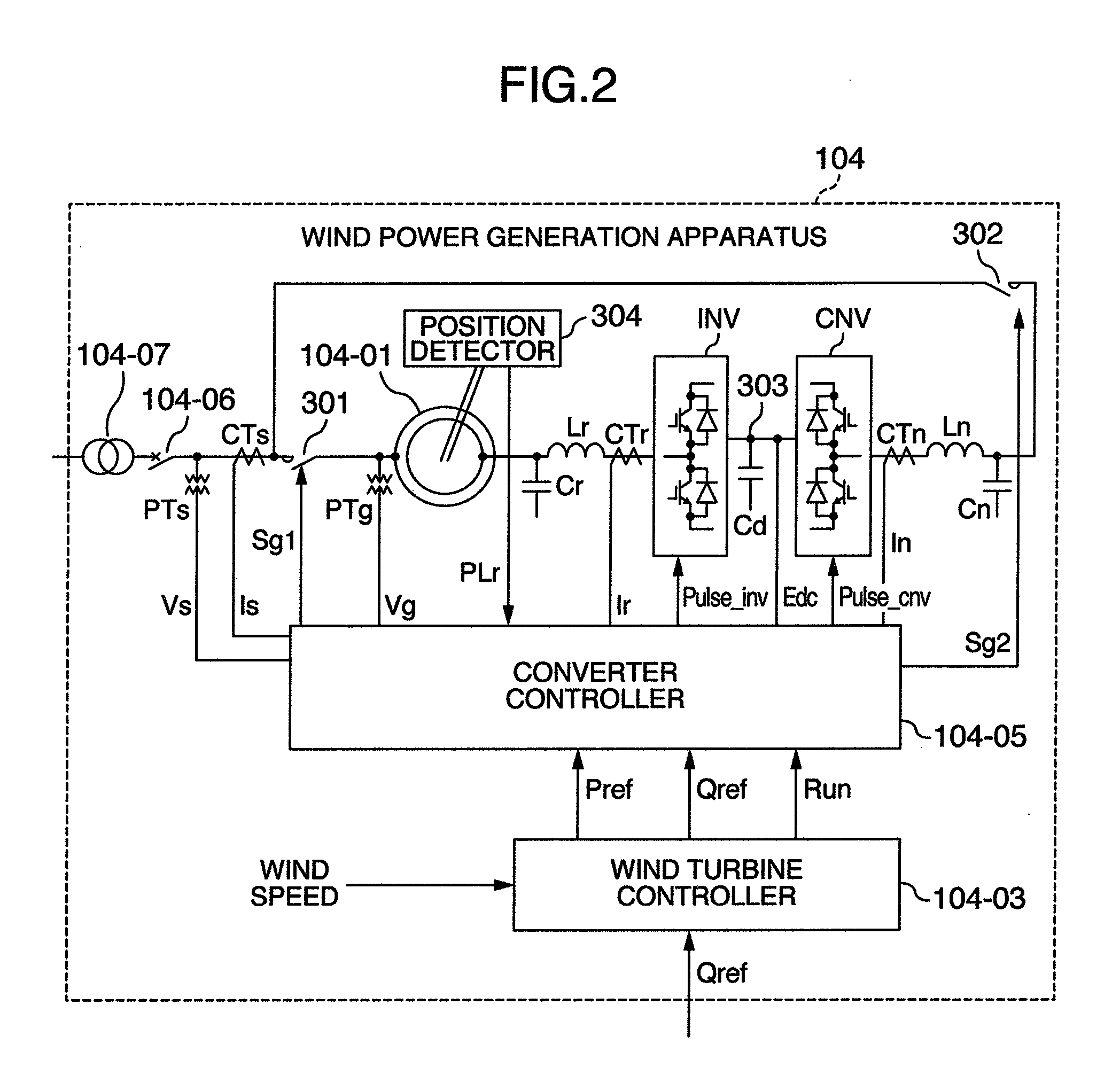
Wind Power Generation Apparatus, Wind Power Generation System and Power System Control Apparatus
ActiveUS20080106099A1Suppresses voltage fluctuationsHigh output fluctuationGenerator control circuitsWind motor controlElectricityElectric power system
An interface device transmits a reactive power command depending on a power system from a voltage regulation device of the power system to a wind power generation apparatus electrically connected to the power system, and the wind power generation apparatus receives the reactive power command. Then, the wind power generation apparatus outputs reactive power according to a value obtained by adding, to a reactive power command, another reactive power command for suppression of voltage fluctuation caused by output power of the wind power generation apparatus.
Owner:HITACHI IND PROD LTD
Method and apparatus for operating electrical machines
ActiveUS7629705B2Generator control circuitsWind motor controlElectric power transmissionVoltage amplitude
A method for operating an electrical machine includes coupling the electrical machine to an electric power system such that the electric power system is configured to transmit at least one phase of electric power to and from the electrical machine. The method also includes configuring the electrical machine such that the electrical machine remains electrically connected to the electric power system during and subsequent to a voltage amplitude of the electric power system operating outside of a predetermined range for an undetermined period of time.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
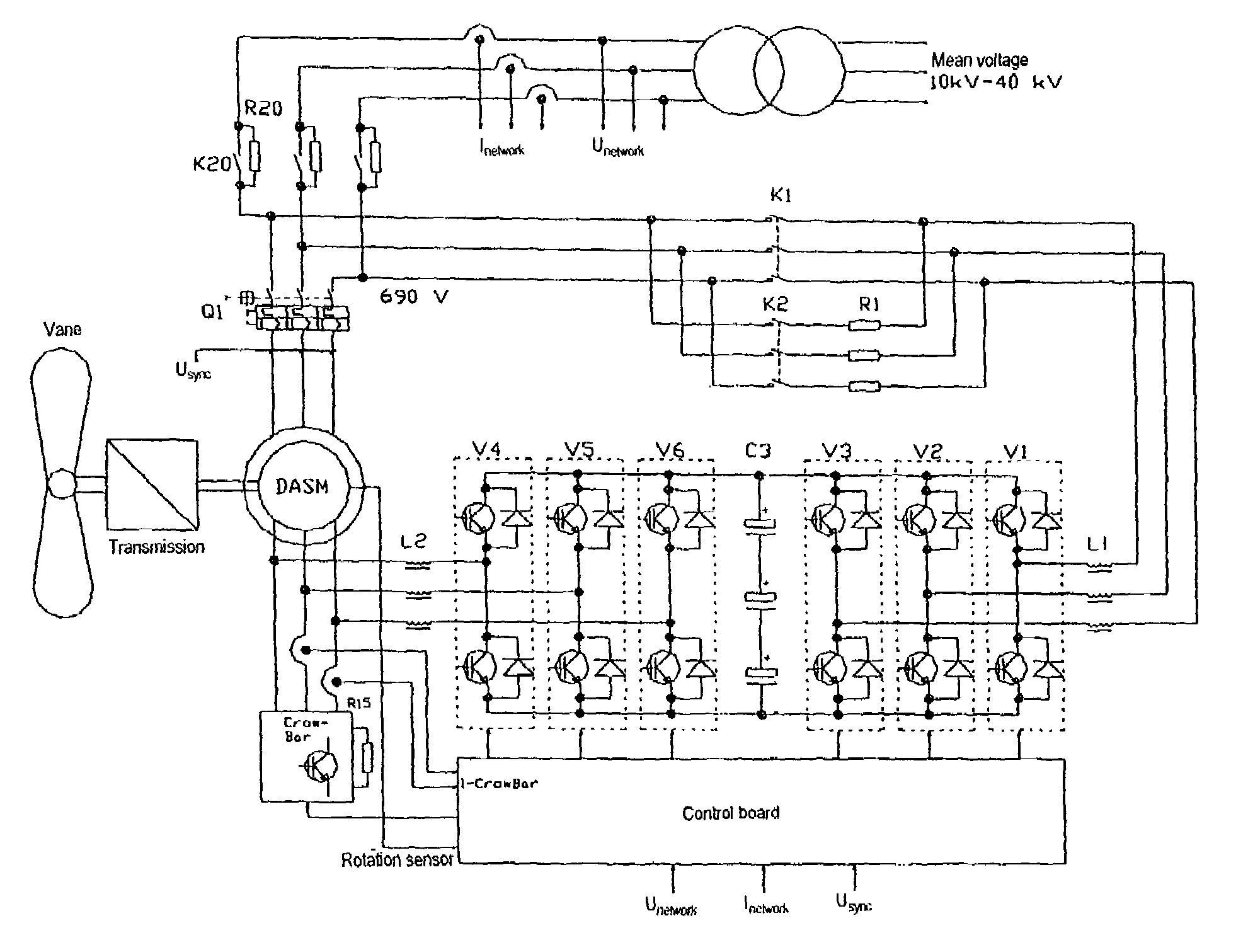
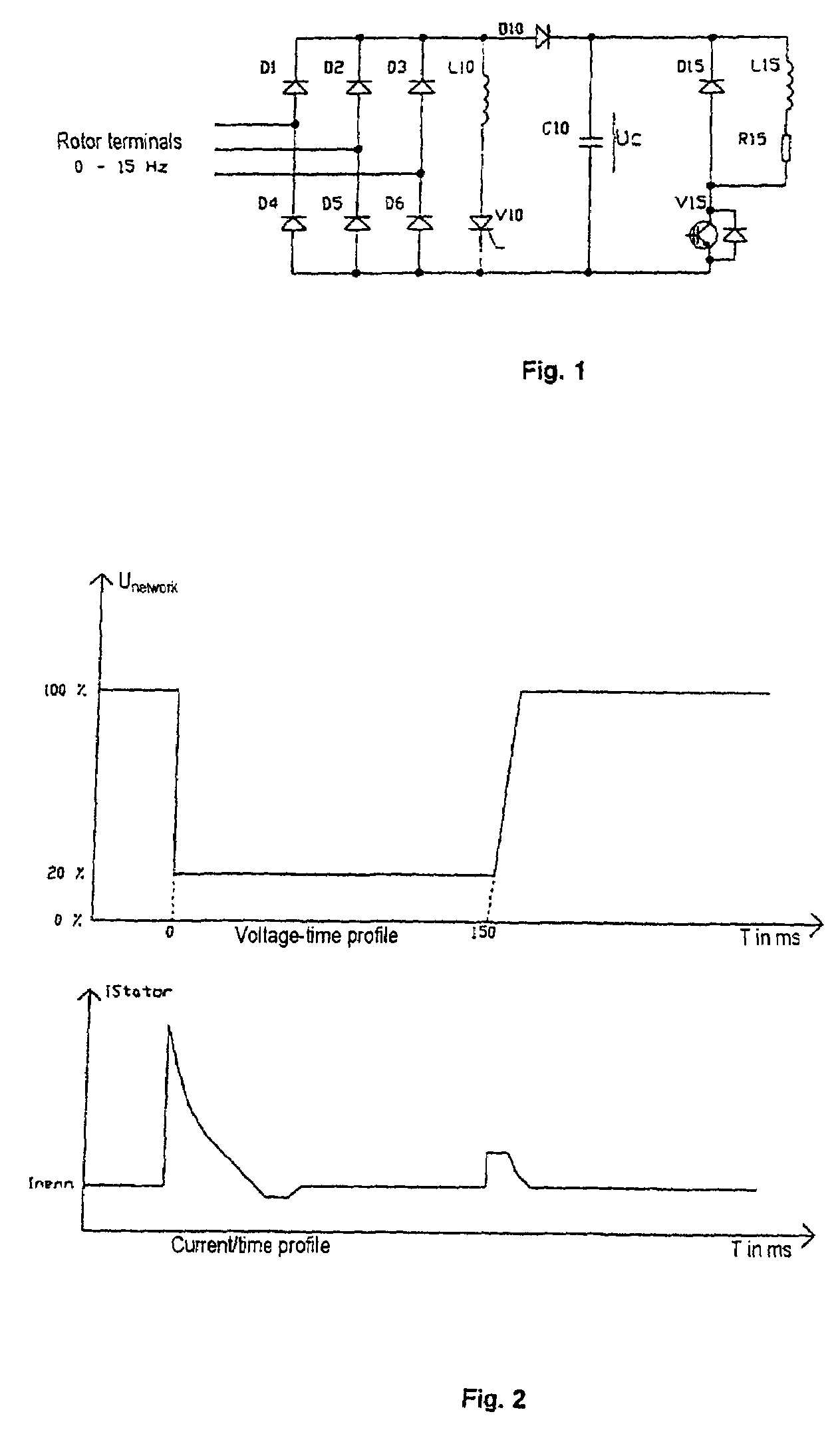
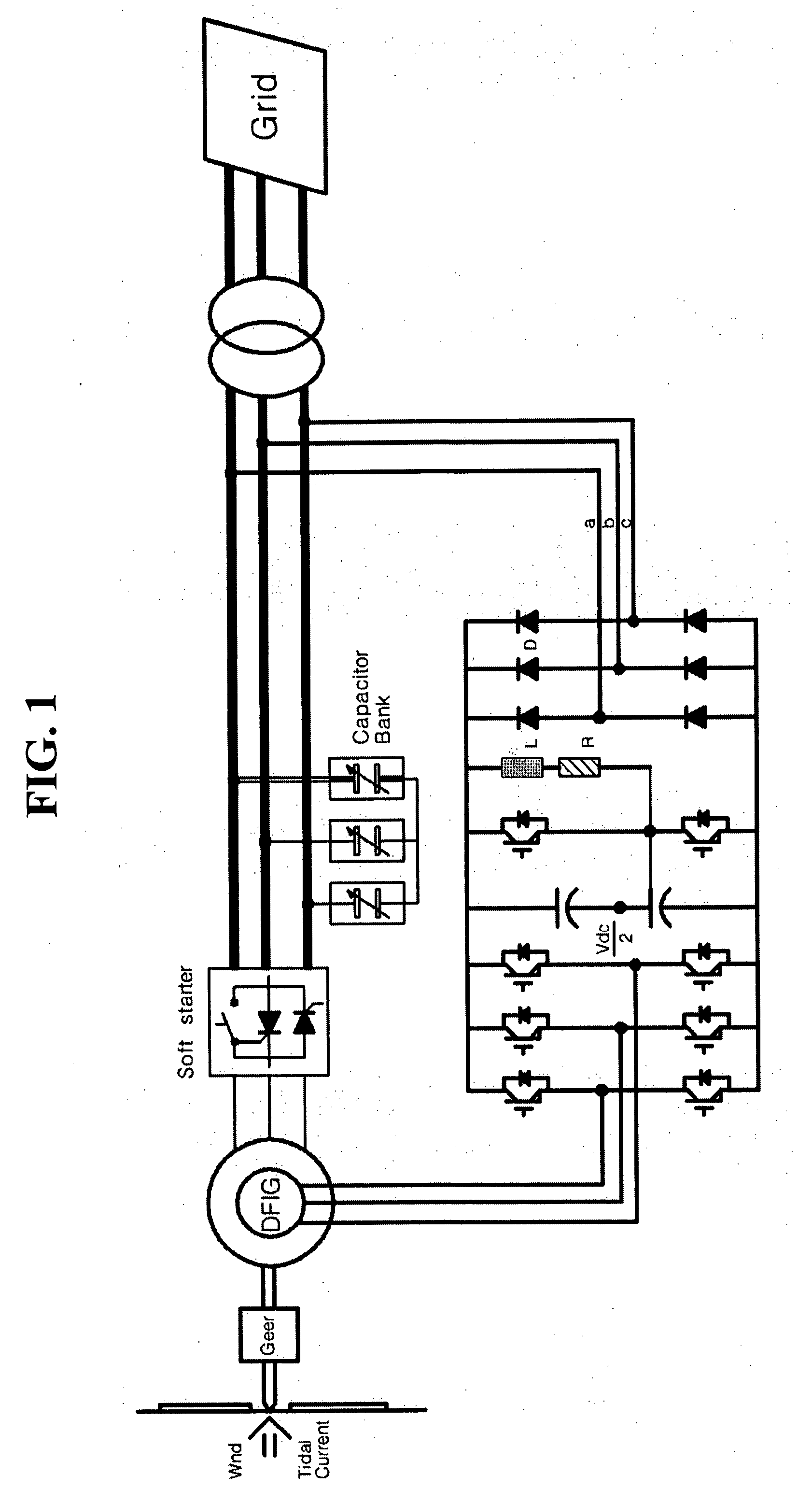
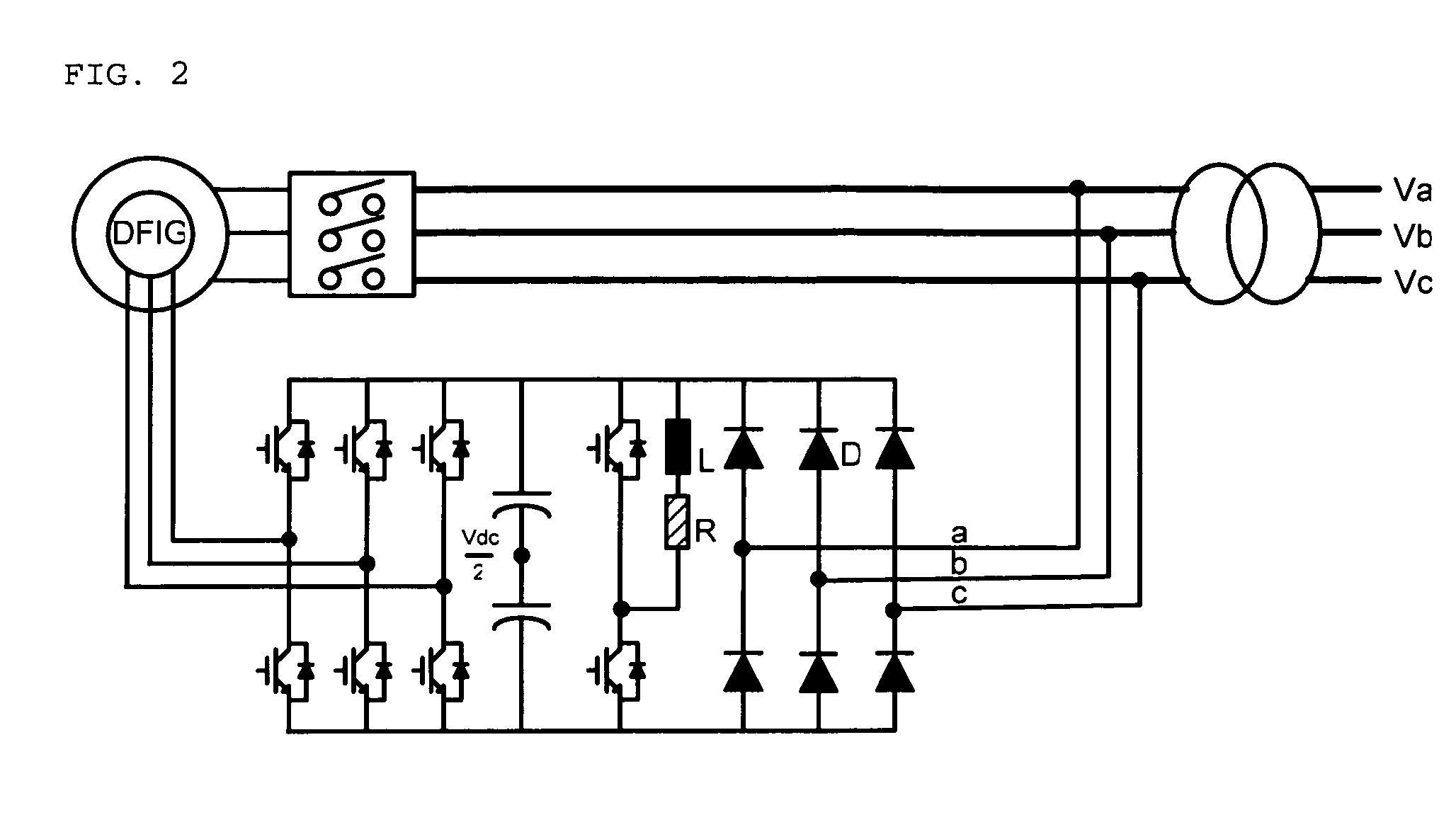
Circuit arrangement and methods for use in a wind energy installation
InactiveUS7102247B2Simple and high-speed and robust controlGenerator control circuitsWind motor controlWind forcePower station
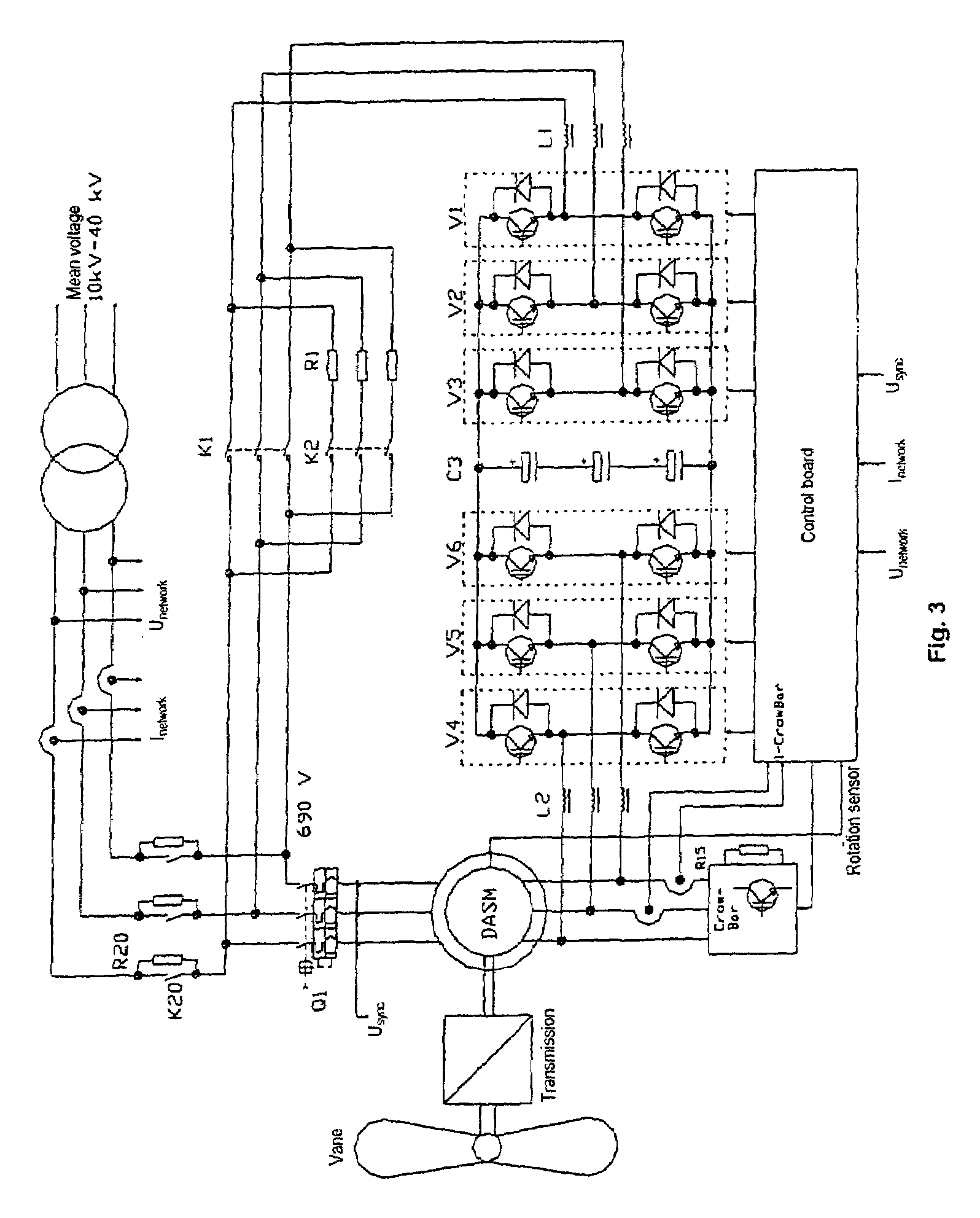
The invention relates to a circuit with a variable rotational speed to be used particularly in a wind power plant, comprising a double fed asynchronous generator (DASM), a crow-bar, an additional resistor (R15) and a converter. In order to meet the requirements of the network provider, whereby a particularly permanent coupling to the network should be ensured so that the wind power plant can start up and stabilize the network during and after medium voltage short circuit in the network, the additional resistor can be regulated with the aid of a fast switch in such a way that the converter can be provisionally disconnected at least partly in case of a short circuit in the network. The rotor current is momentarily assumed by the additional resistor and disconnected after the rotor short circuit current dies out so that the converter can be subsequently connected once again and so that it can supply the desired active short circuit current to the network.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Apparatus and method for controlling the reactive power from a cluster of wind turbines connected to a utility grid
The present invention relates to a method for increasing a total reactive power capability of a cluster of wind turbines operationally connected to a grid. The method comprises the steps of generating a voltage value representative of a grid voltage level, determining a total required reactive power value based on the voltage value, and activating at least one wind turbine in said cluster to increase the total reactive power capability from a present value to the required total reactive power value by a predetermined amount. Moreover, the present invention relates to a system suitable for carrying out the before-mentioned method.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
High voltage direct current link transmission system for variable speed wind turbine
ActiveUS20090278351A1Avoiding undesired harmonic distortionImprove power qualityGenerator control circuitsAc-dc conversion without reversalPower qualityHigh-voltage direct current
A variable speed wind turbine having a doubly fed induction generator (DFIG), includes an exciter machine mechanically coupled to the DFIG and a power converter placed between a rotor of the DFIG and the exciter machine. Thus, the power converter is not directly connected to the grid avoiding the introduction of undesired harmonic distortion and achieving a better power quality fed into the utility grid. Moreover, the variable speed wind turbine includes a power control and a pitch regulation.
Owner:INGETEAM POWER TECH
Low voltage ride through system for a variable speed wind turbine having an exciter machine and a power converter not connected to the grid
InactiveUS7622815B2Improve variable performanceReduce capacityGenerator control circuitsMachines/enginesPower gridVariable speed wind turbine
A variable speed wind turbine having a doubly fed induction generator (DFIG) includes an exciter machine mechanically coupled to the DFIG and a power converter placed between a rotor of the DFIG and the exciter machine which guarantees a stable voltage to the power converter. Thus, the power converter is not directly connected to the grid allowing the continuous operation of the system during a low voltage event in the grid.
Owner:INGETEAM POWER TECH
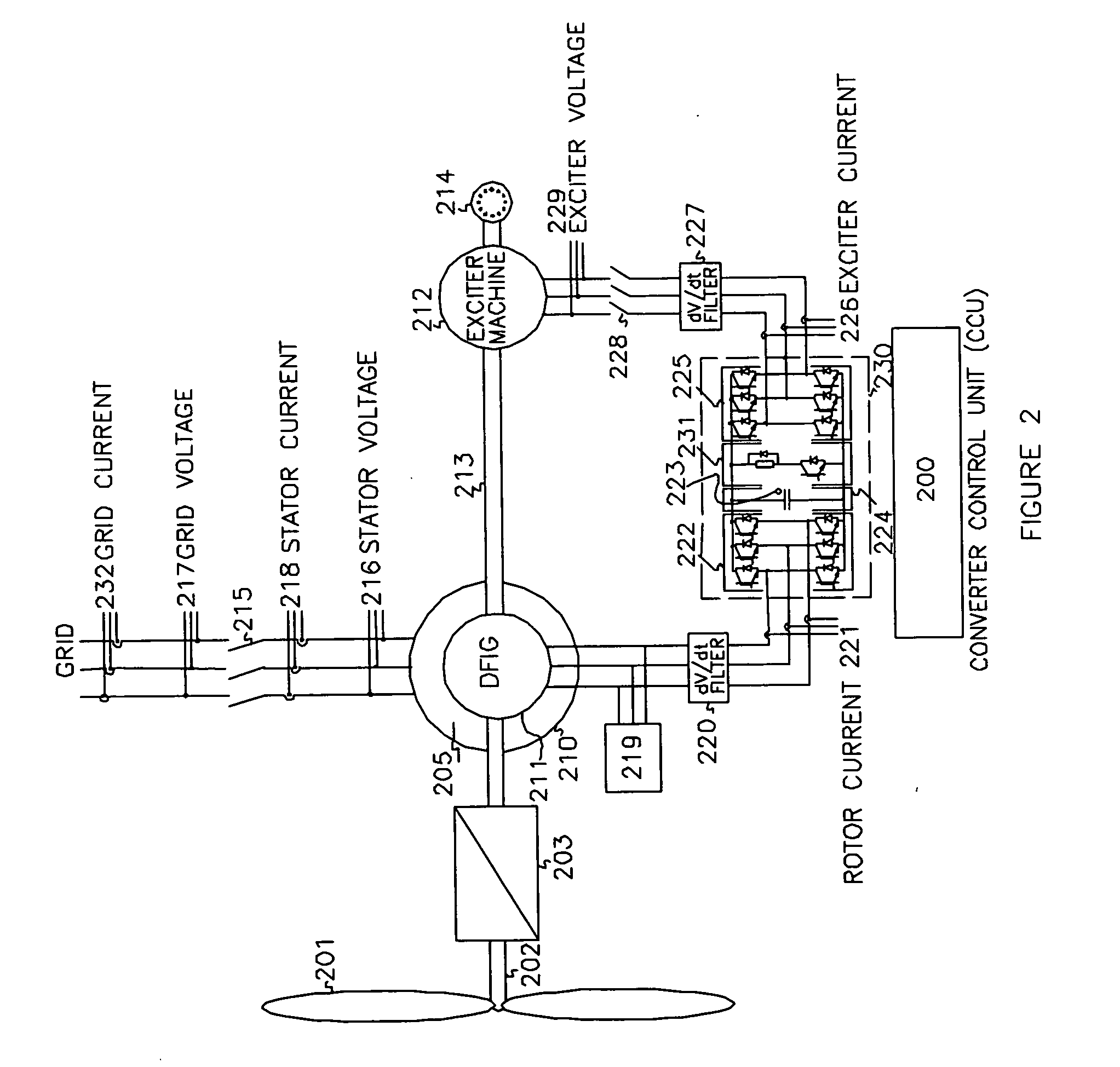
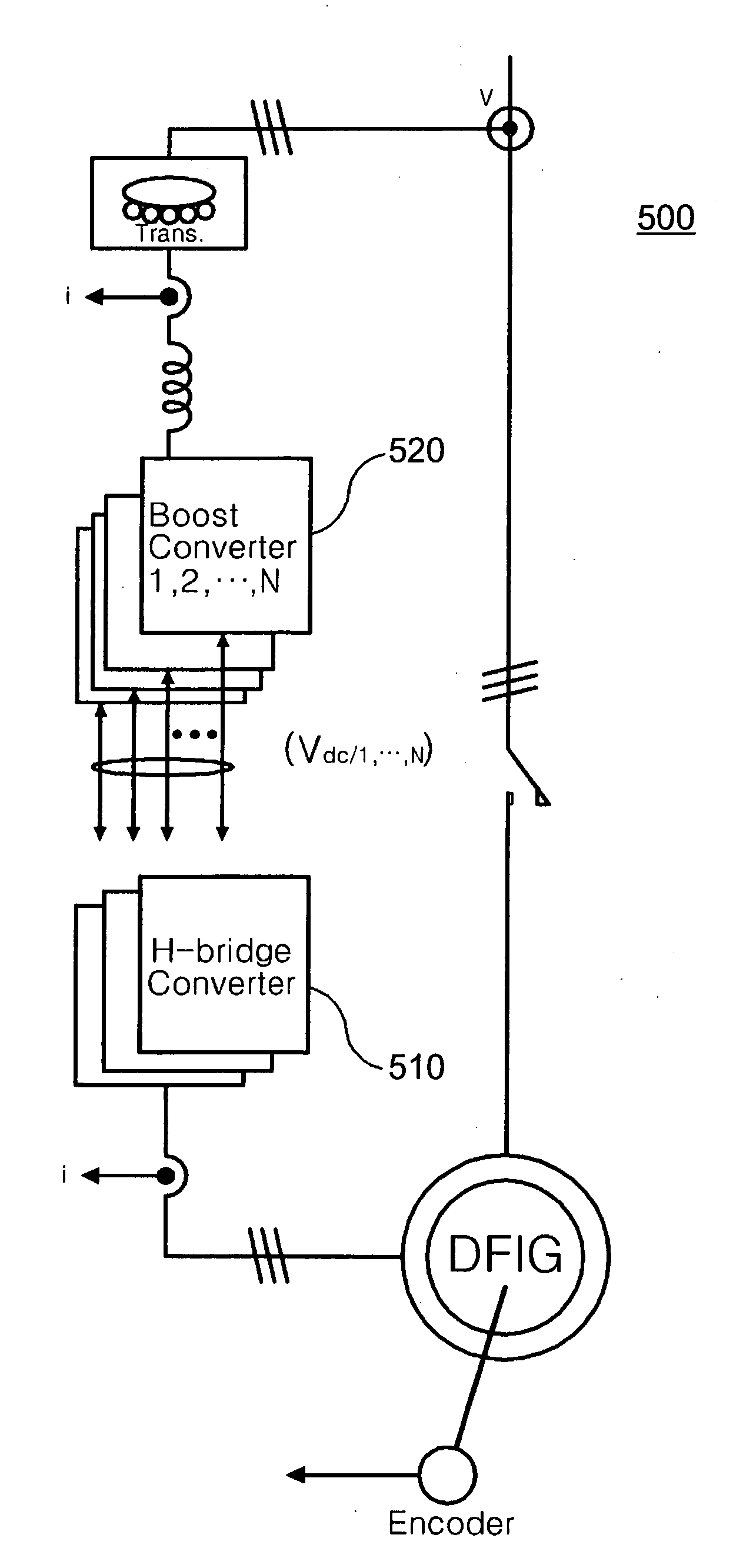
Controller of doubly-fed induction generator
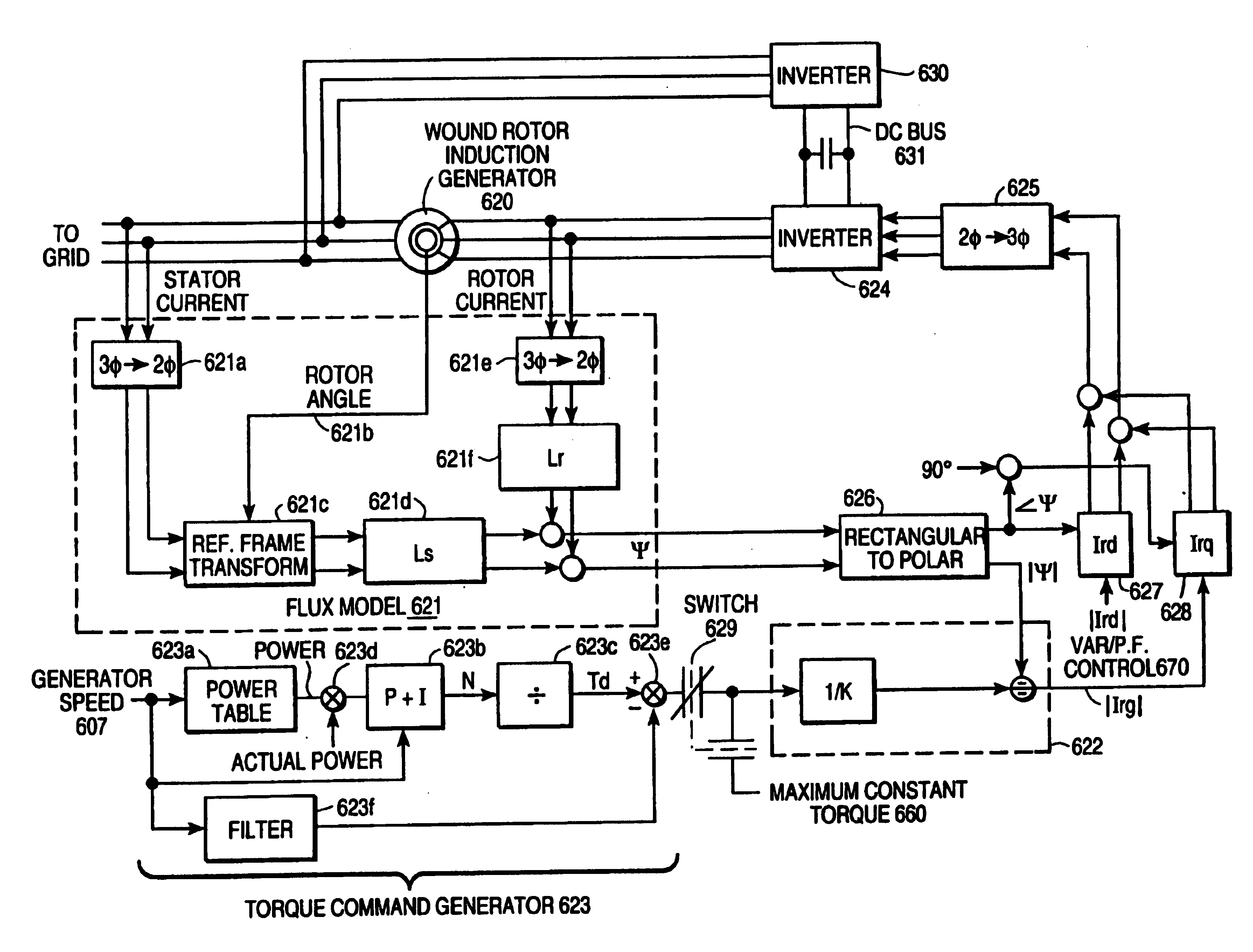
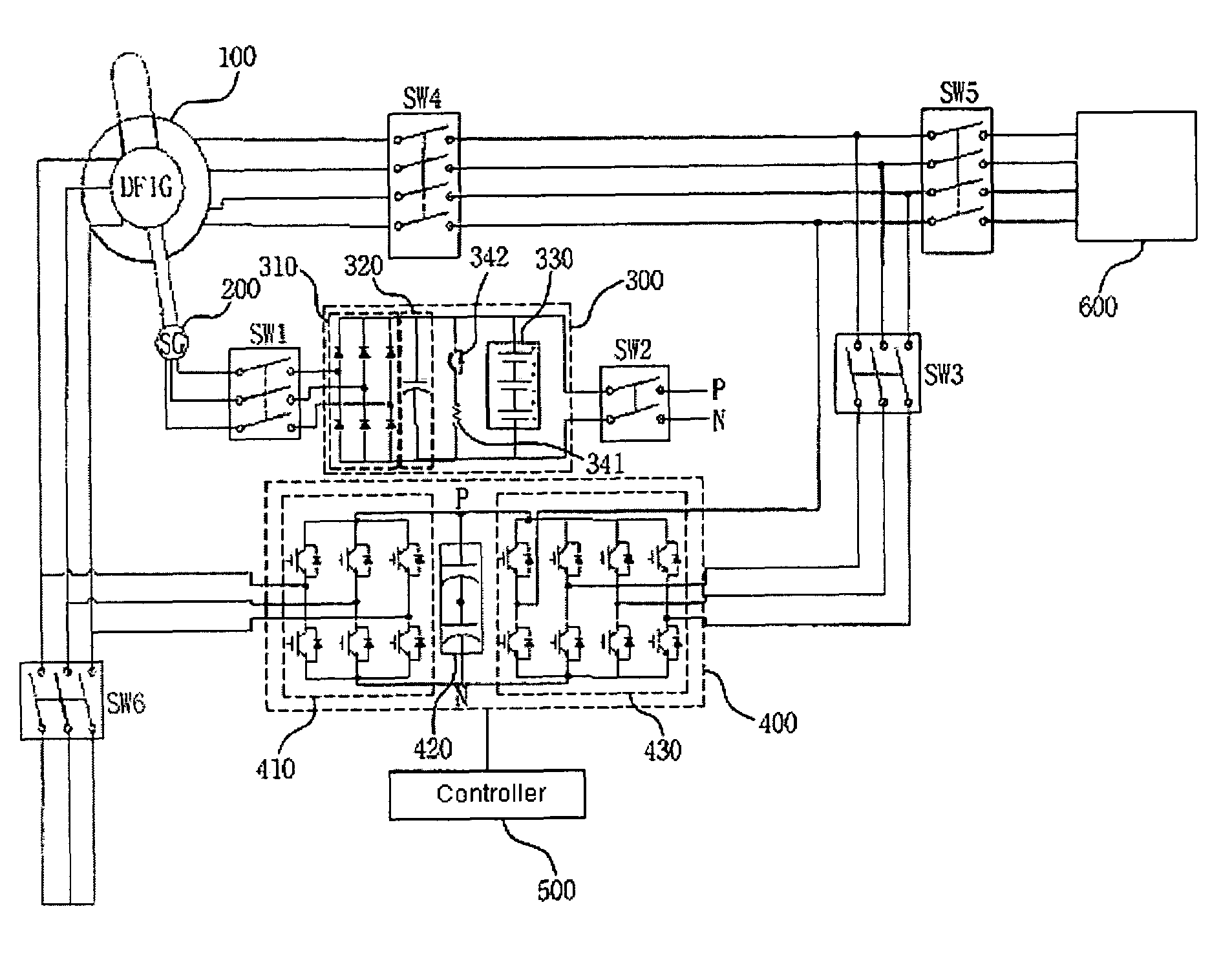
ActiveUS20080303489A1Easy to detectProblem can be overcome fastGenerator control circuitsElectric motor controlHigh voltageDouble fed induction generator
Disclosed is a controller of a grid coupled type doubly-fed induction generator having a multi-level converter topology, which can control the doubly-fed induction generator having a high voltage specification and can perform a fault ride-through function, an anti-islanding function and a grid voltage synchronization function required for a dispersed power generation facility. The controller makes a H-bridge multi-level converter generate a three-phase voltage waveform resulted from the structure that single-phase converters each being composed of a 2-leg IGBT are stacked in a serial manner, and controls a rotor current so as to make the rotor coil of the doubly-fed induction generator in charge of a slip power only. The boost converter is composed of a 3-leg IGBT and a boost inductor generating a direct current voltage of its source required for the H-bridge multi-level converter.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
Variable speed power generator having two induction generators on a common shaft
A variable speed power generator system, includes a primary power induction generator (12), a secondary control induction (14), each of the induction generators having a rotor (22, 24) mounted so as to be rotated by a common shaft (16) of a variable speed prime mover (20), an inverter (50) connected to the stator (15) of the secondary control induction generator, a controller (30) connected to the inverter controls the output of the inverter, output of the primary induction generator is connected to the grid (51), controller provides output signal to the inverter based on selected inputs to the controller so that the output of the primary induction generator matches the active and reactive power requirements of the grid. An induction machine which includes a rotor having laminations and insulated cage bars, the bars being electrically isolated from on another as well as electrically insulated from the laminations.
Owner:VARISPEED ELECTRIC MOTORS
Low voltage ride through system for a variable speed wind turbine having an exciter machine and a power converter not connected to the grid
InactiveUS20080157529A1Improve variable performanceReduced power capacityGenerator control circuitsMachines/enginesPower gridEngineering
A variable speed wind turbine having a doubly fed induction generator (DFIG) includes an exciter machine mechanically coupled to the DFIG and a power converter placed between a rotor of the DFIG and the exciter machine which guarantees a stable voltage to the power converter. Thus, the power converter is not directly connected to the grid allowing the continuous operation of the system during a low voltage event in the grid.
Owner:INGETEAM POWER TECH
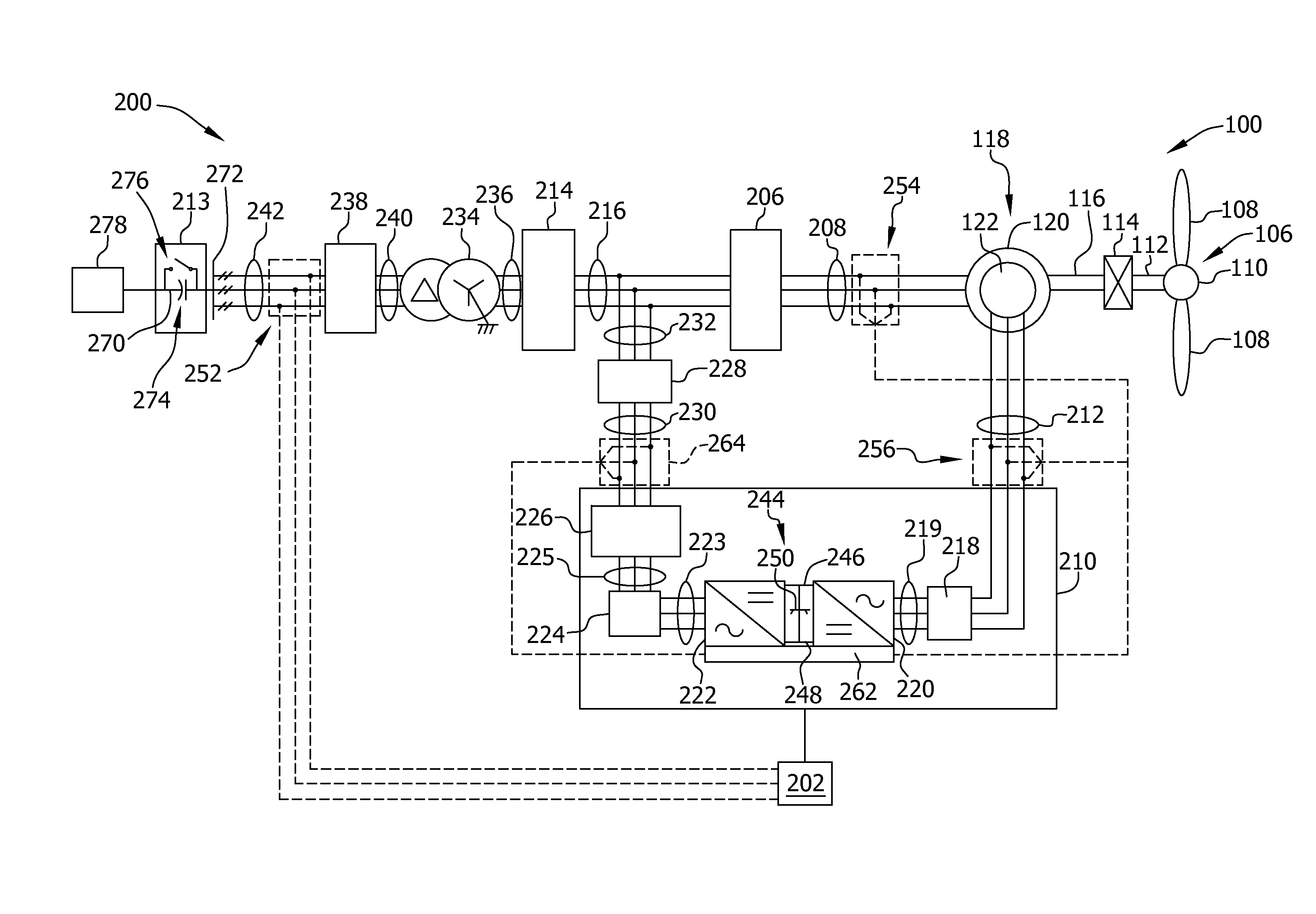
Method and apparatus for generating power in a wind turbine
ActiveUS20110101689A1Reduce the amplitudeGenerator control circuitsElectric motor controlTurbineElectrical and Electronics engineering
A power converter for a wind turbine including an array of switching devices and a control module having a current damping device. The control module is configured to control a switching behavior of the array of switching devices and to receive a current having a first frequency component from the wind turbine. The current damping device is configured to reduce an amplitude of the first frequency component.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
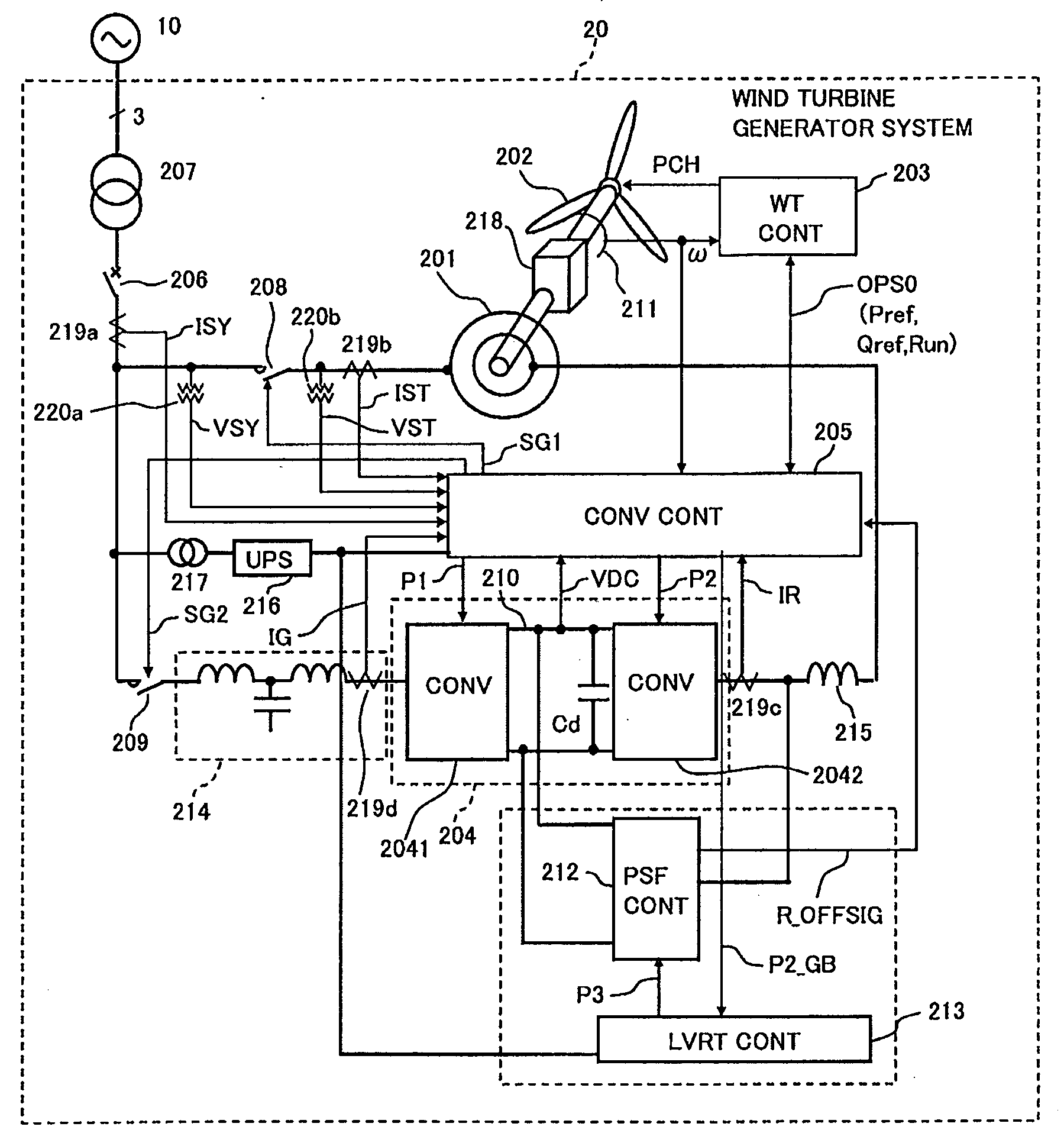
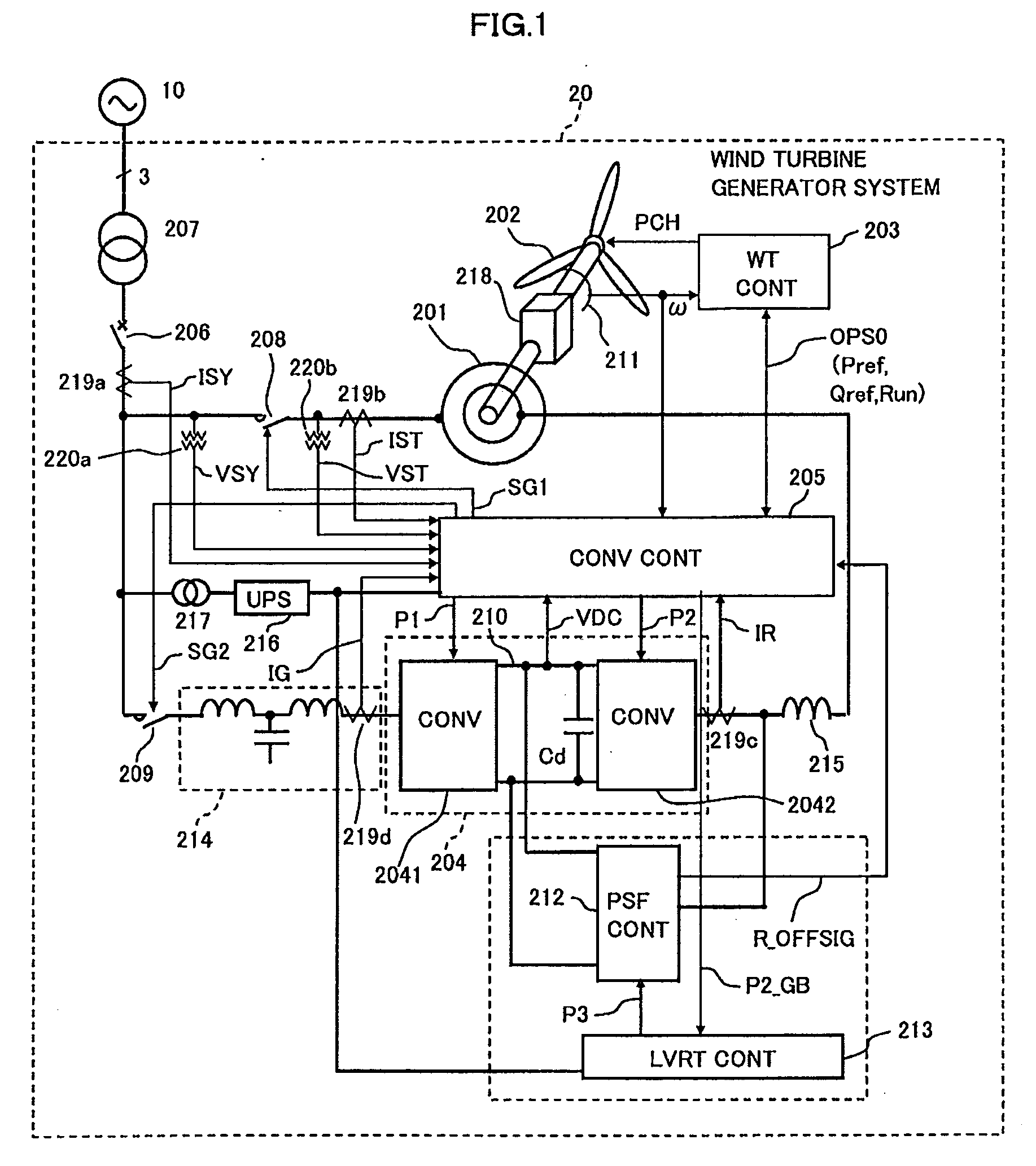
Wind turbine generator system
In a wind turbine generator system including an AC exciting converter a grid side converter, and a controller configured to control the AC-exciting converter and the grid side converter, the controller operates a short-circuiting circuit when decrease in the grid voltage and increase in the DC voltage are detected.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Variable speed wind power generation system
A variable speed wind power generation system including a wind turbine, generation power command means for generating a generation power command value based on a state quantity of the wind turbine and generator control means for controlling the power converter for controlling electric power of the generator, wherein the generator control means operates to regulate the generation power of the generator in order to change the generation power amount according to the generation power command value.
Owner:HITACHI IND PROD LTD
Electric power converting device and power converting method for controlling doubly-fed induction generator
ActiveUS7579702B2Generator control circuitsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectricityStator voltage
Disclosed herein is an electric power converting device and power converting method for controlling doubly-fed induction generators, which provides a synchronous generator for generating auxiliary electric power independently of a doubly-fed induction generator so as to generate electricity even in a system power-free environment, a grid-side converter is composed of a three-phase four-wire converter so as to generate a balanced voltage even in an unbalanced load condition and automatically synchronize a stator voltage of a doubly-fed induction generator and a system voltage with each other.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
Method and apparatus for operating electrical machines
ActiveUS20080093853A1Generator control circuitsWind motor controlVoltage amplitudeElectric power transmission
A method for operating an electrical machine includes coupling the electrical machine to an electric power system such that the electric power system is configured to transmit at least one phase of electric power to and from the electrical machine. The method also includes configuring the electrical machine such that the electrical machine remains electrically connected to the electric power system during and subsequent to a voltage amplitude of the electric power system operating outside of a predetermined range for an undetermined period of time.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com