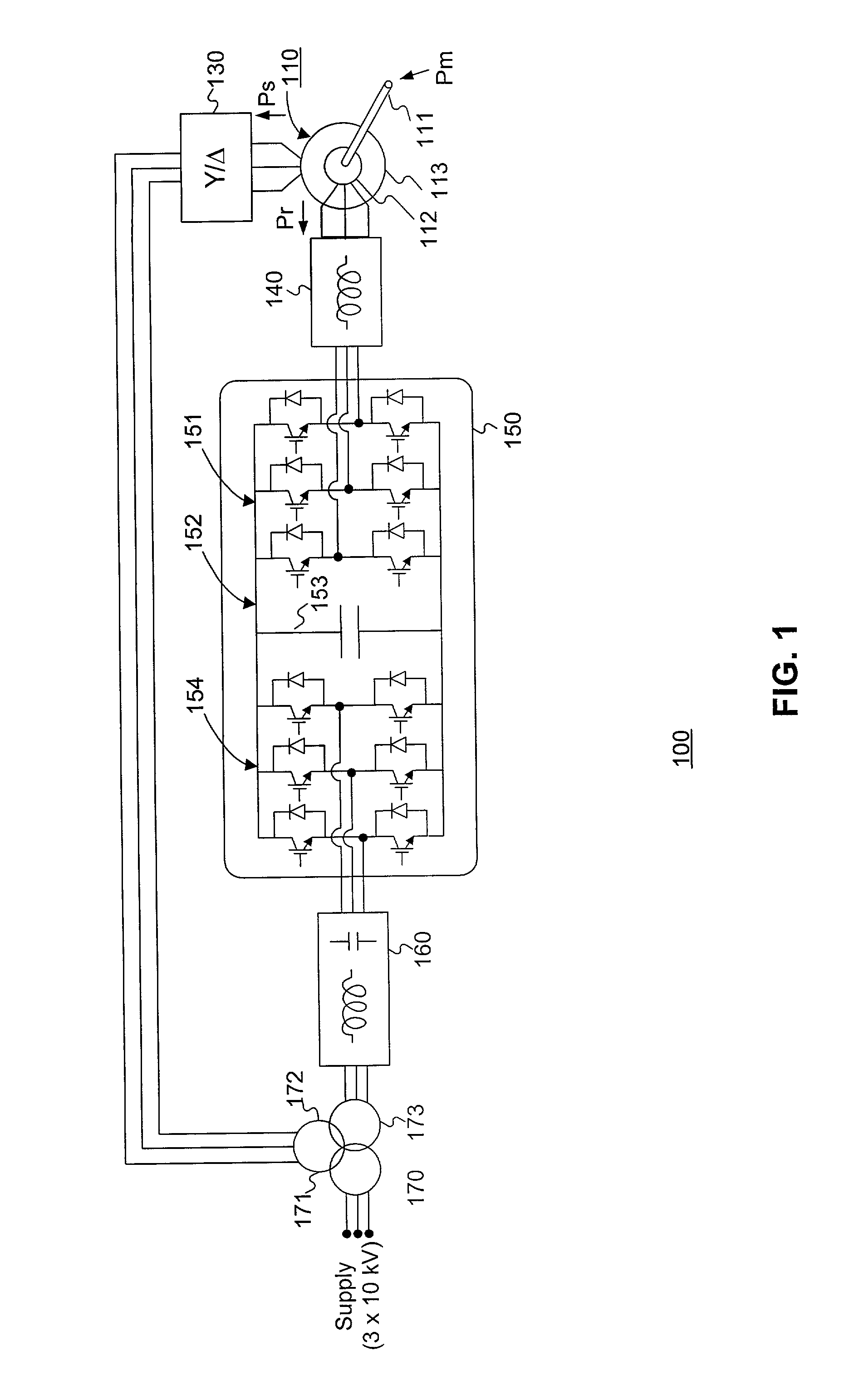
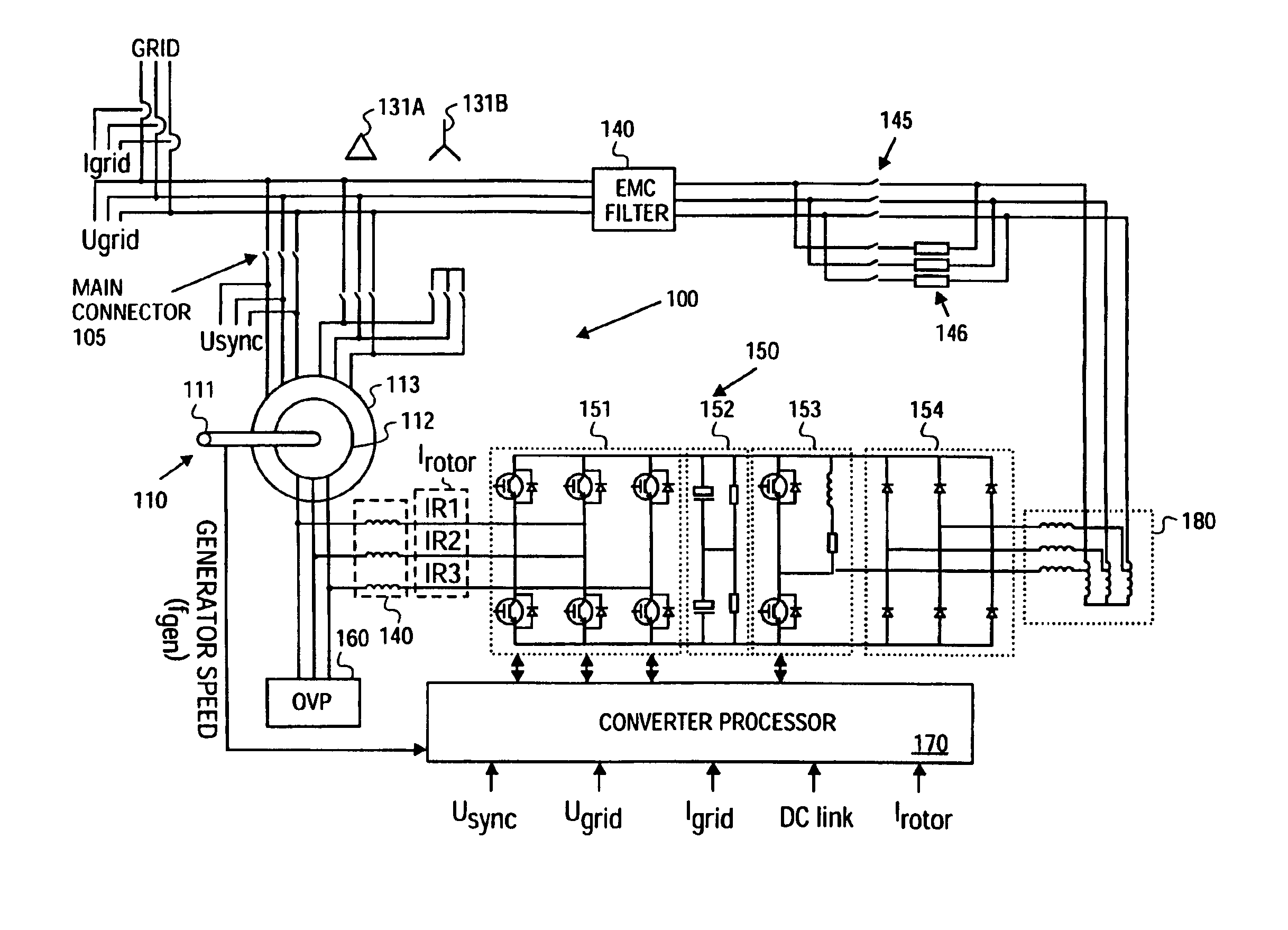
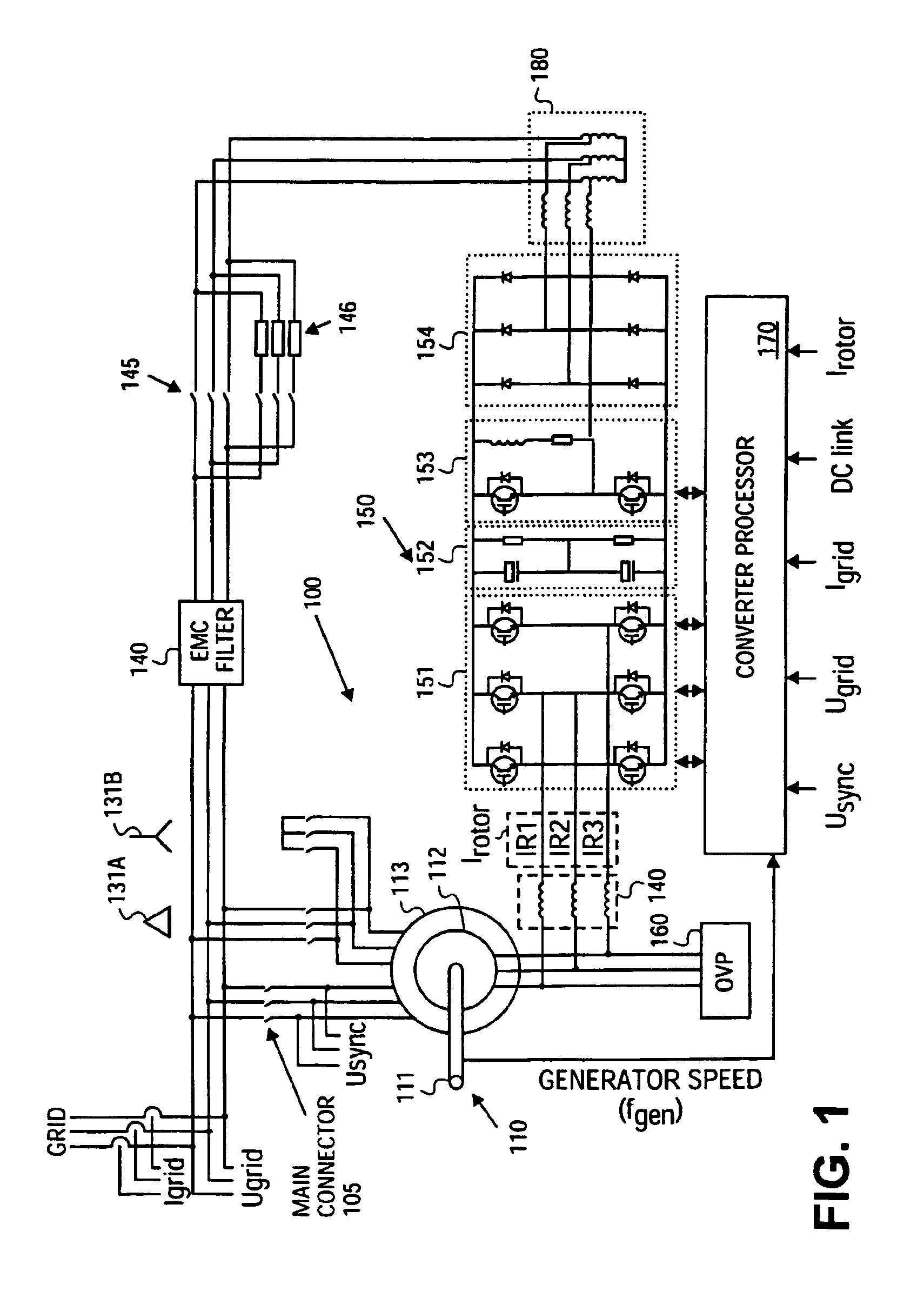
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
116results about "Variable speed operation control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
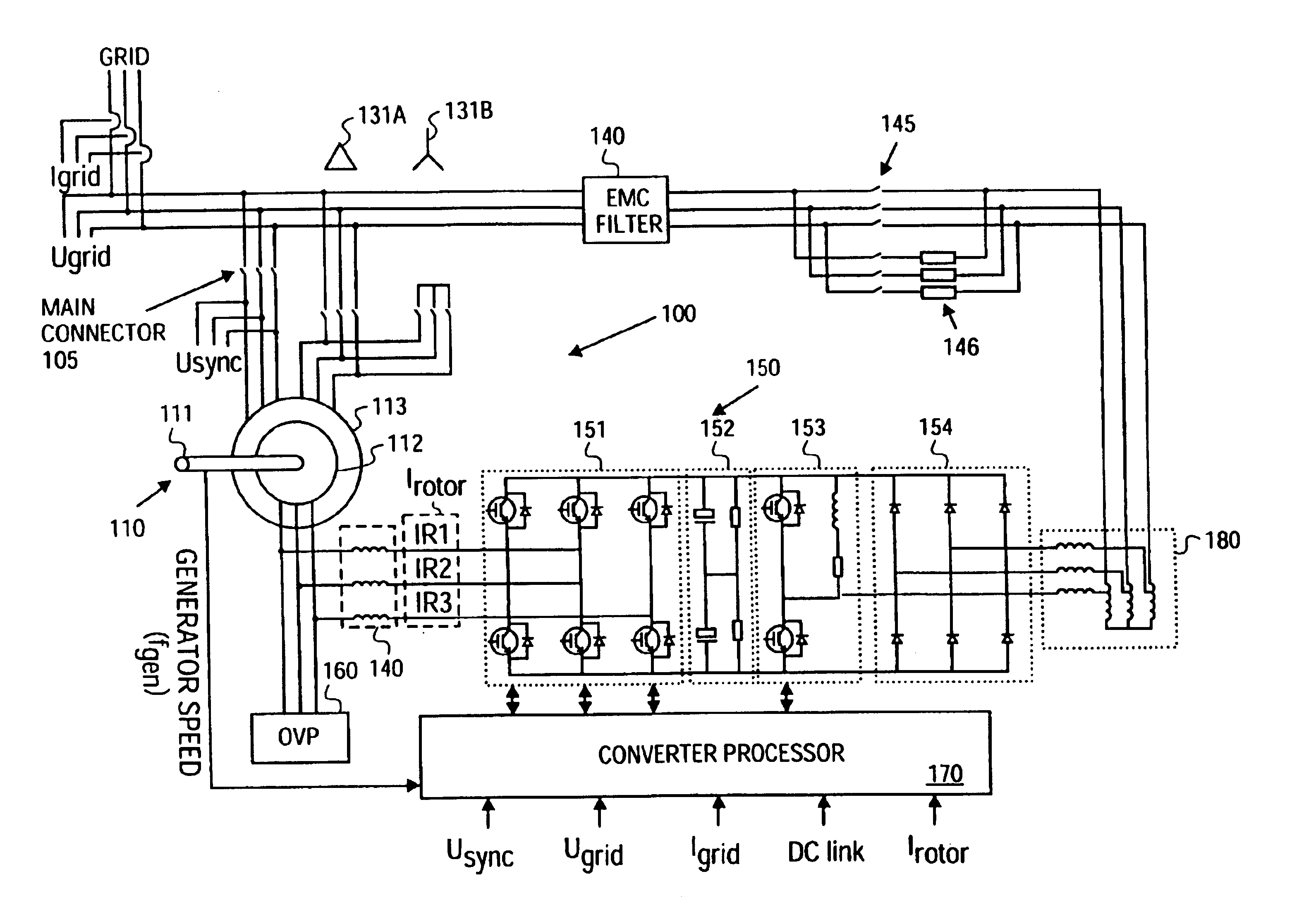
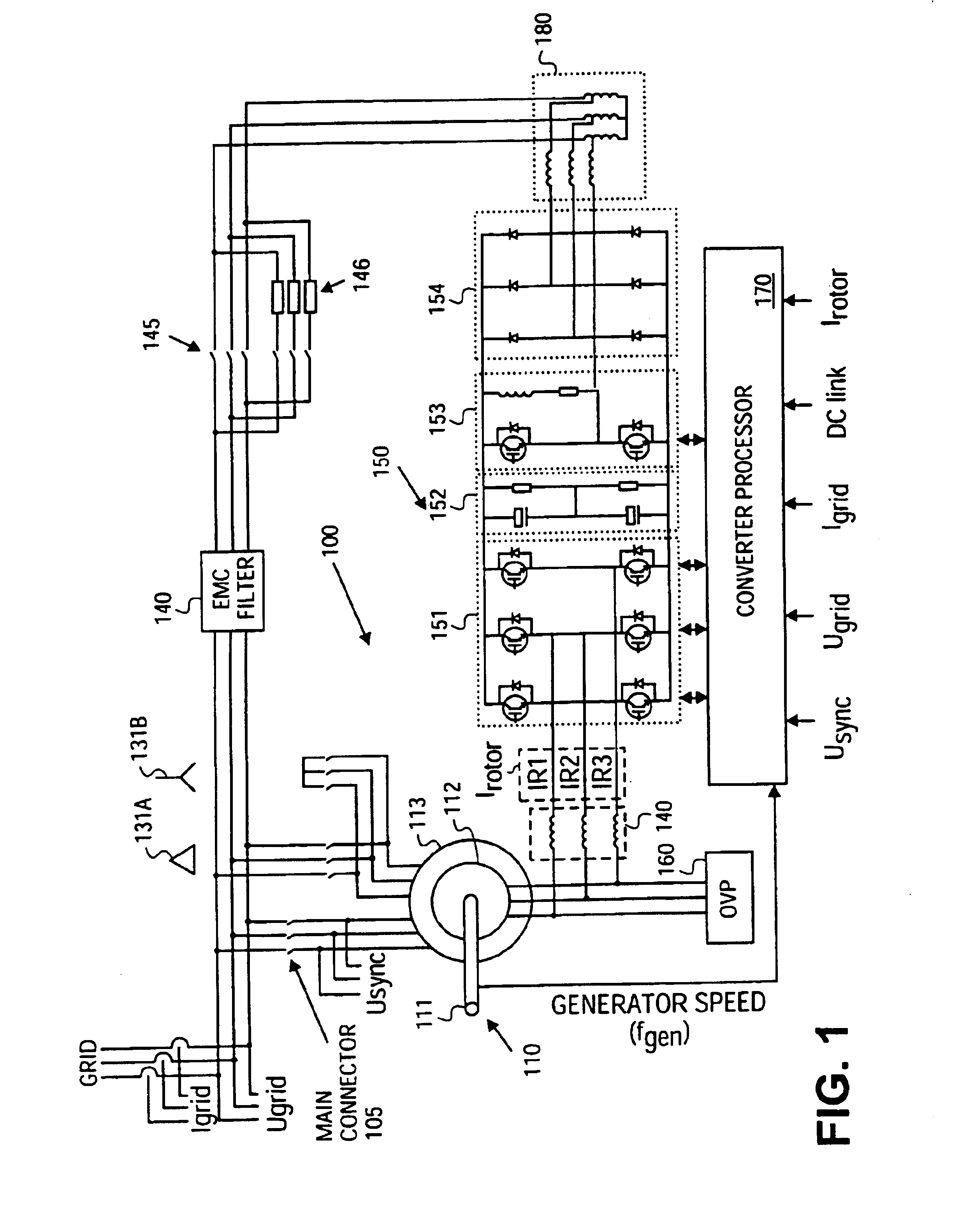
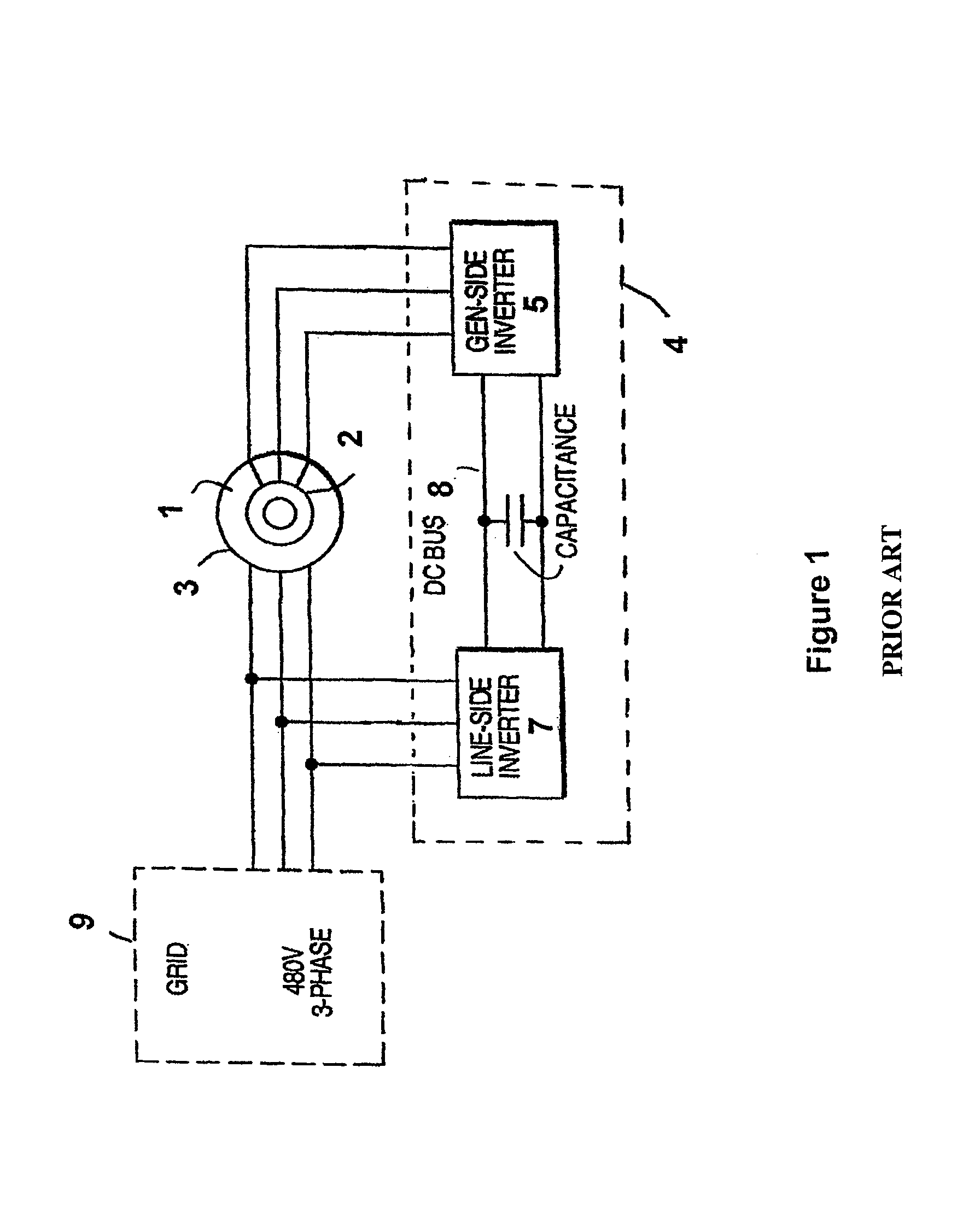
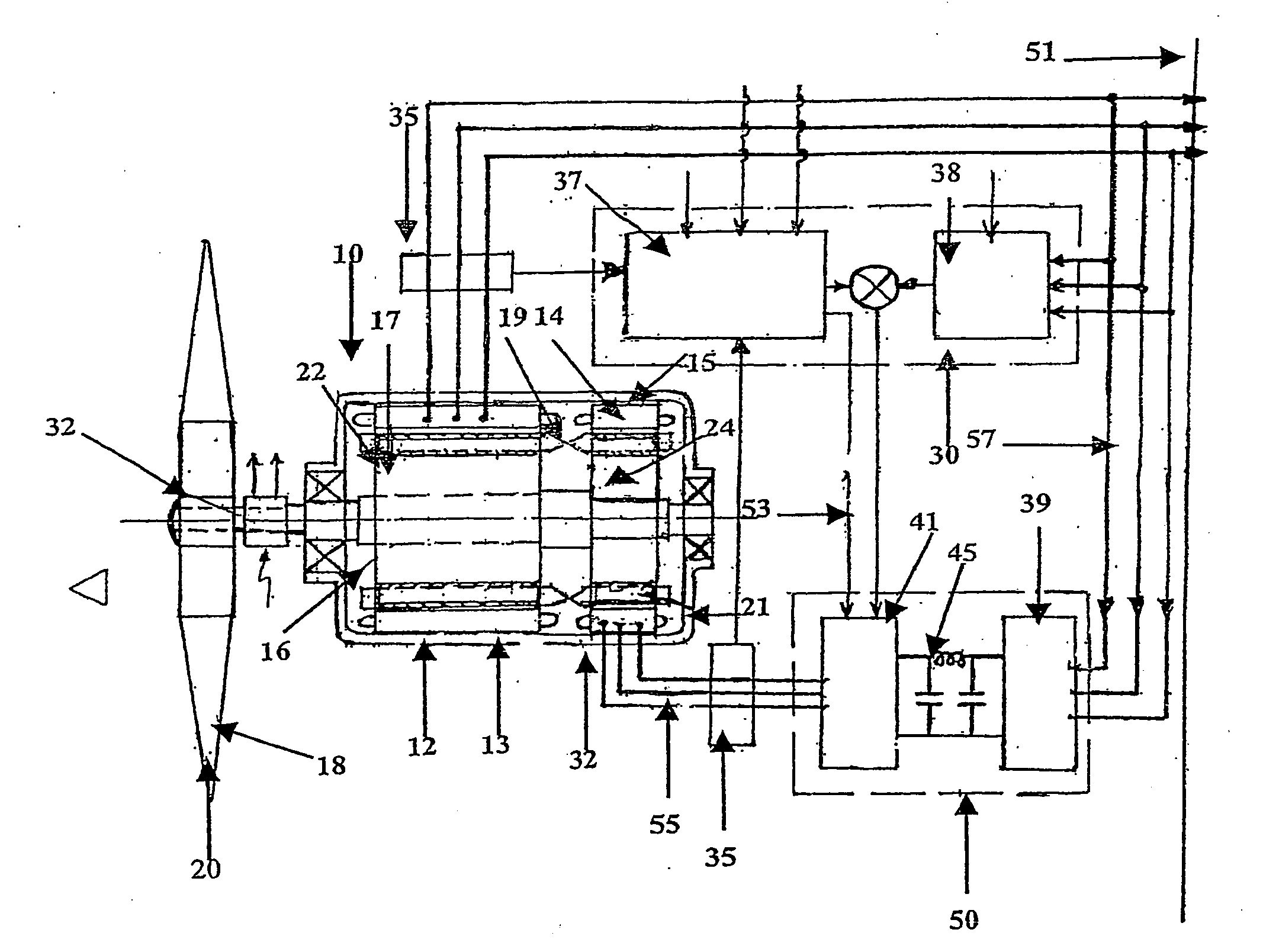
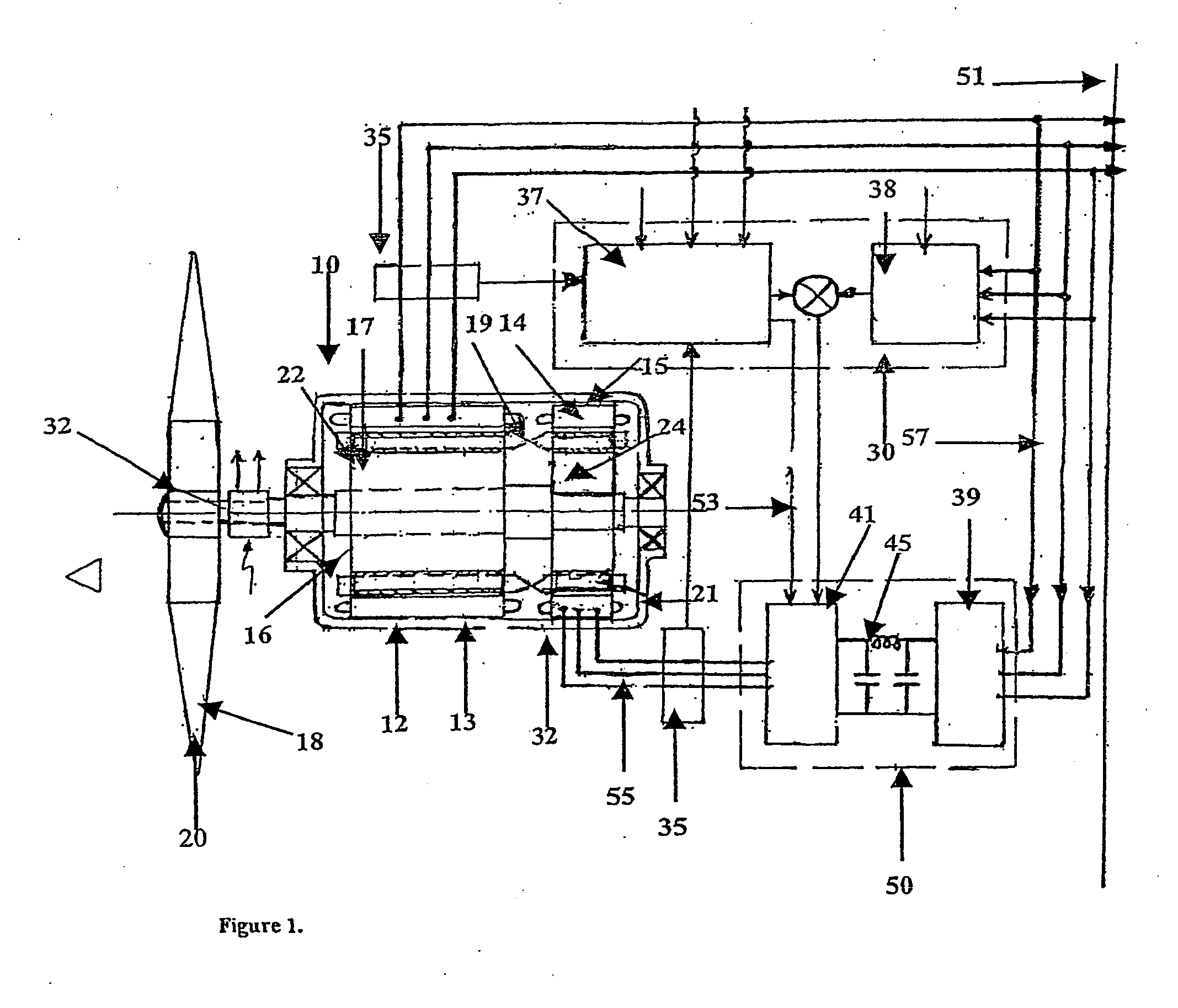
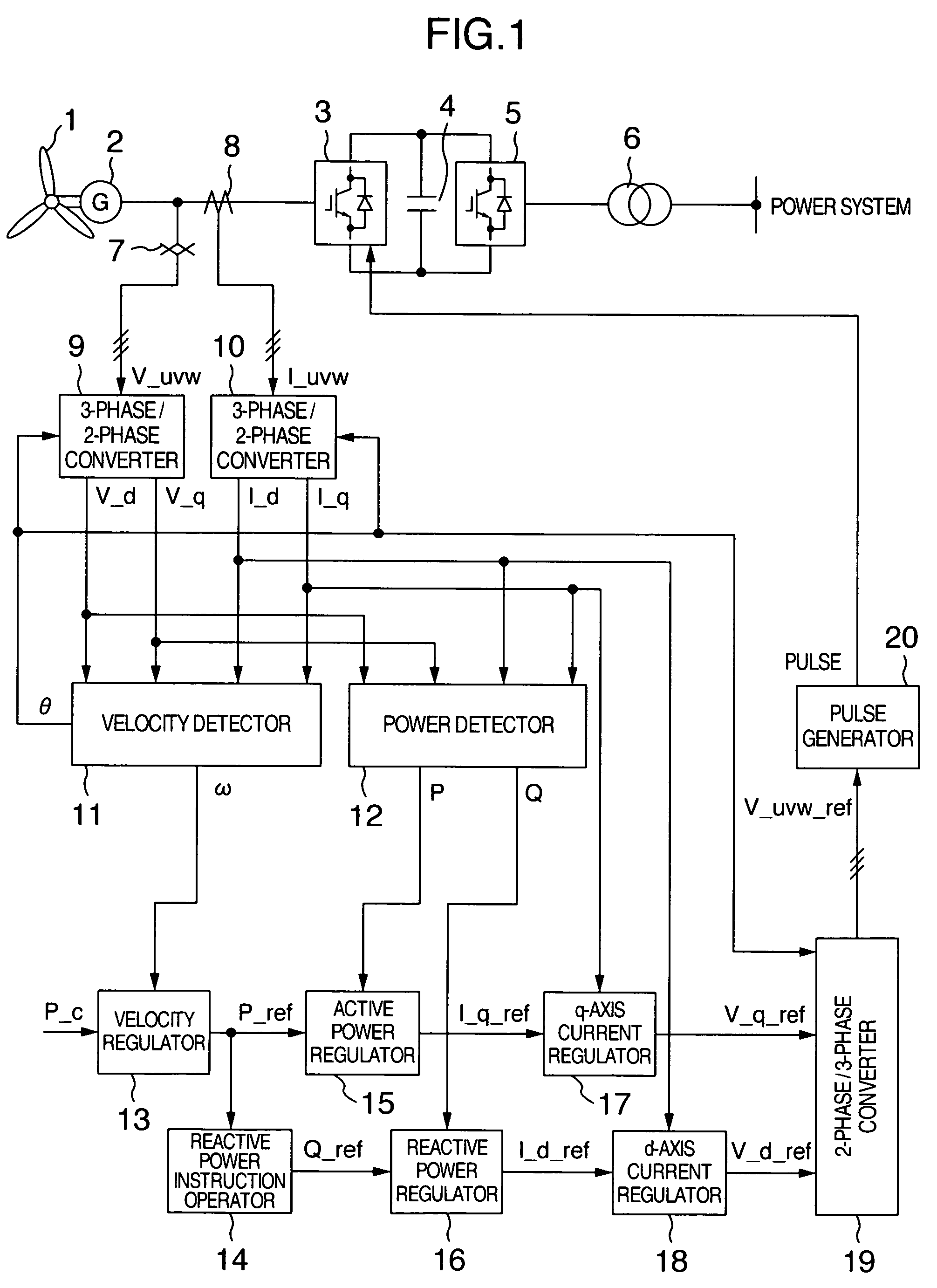
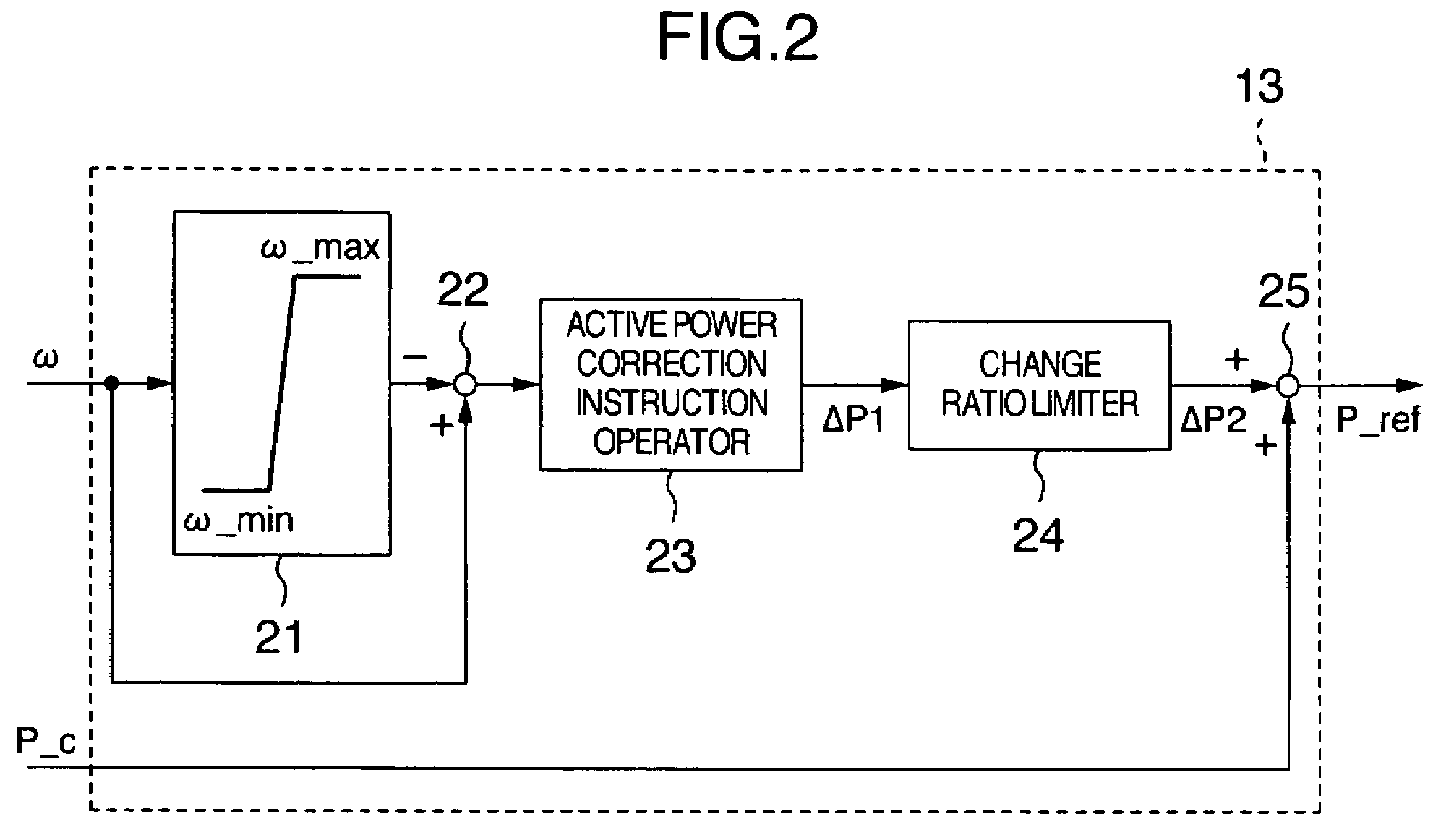
Variable speed distributed drive train wind turbine system
InactiveUS7042110B2Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityWind motor controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPermanent magnet rotorDc current
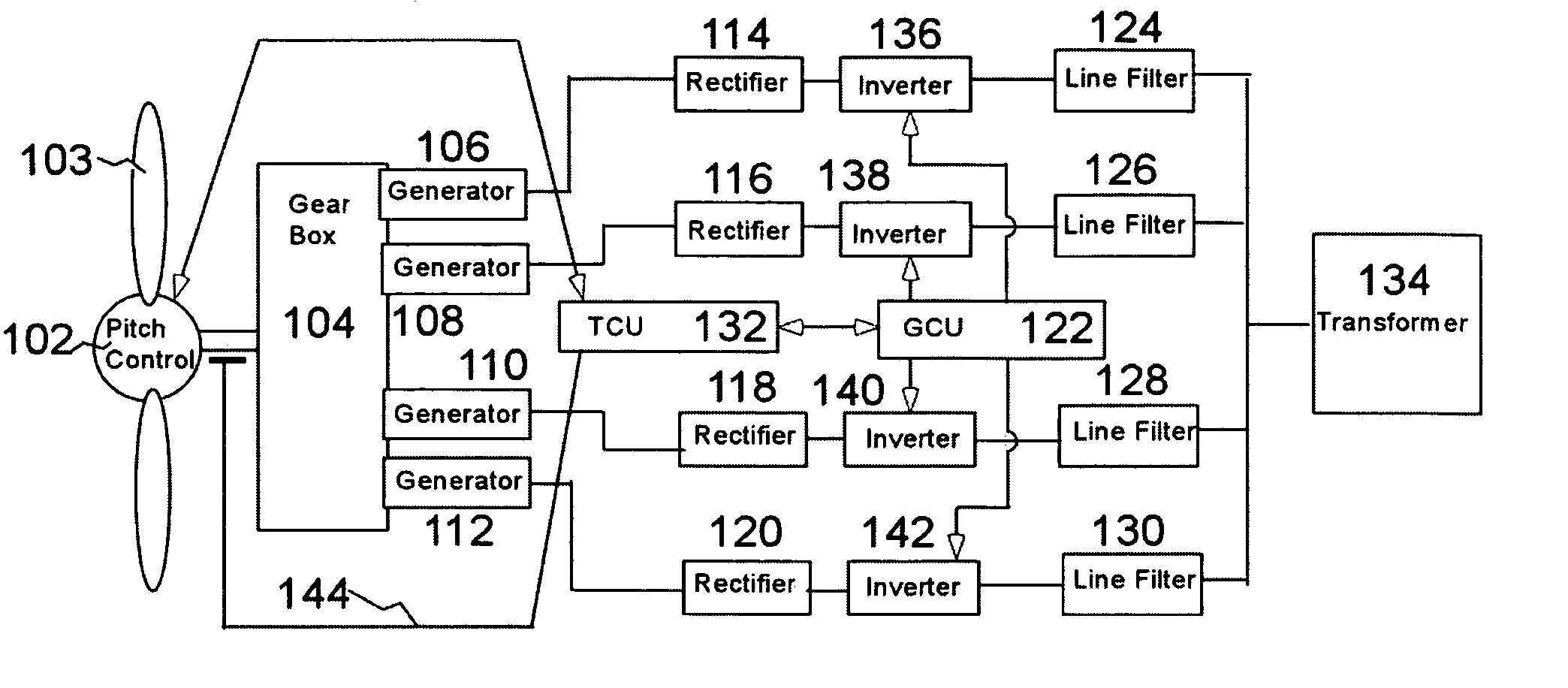
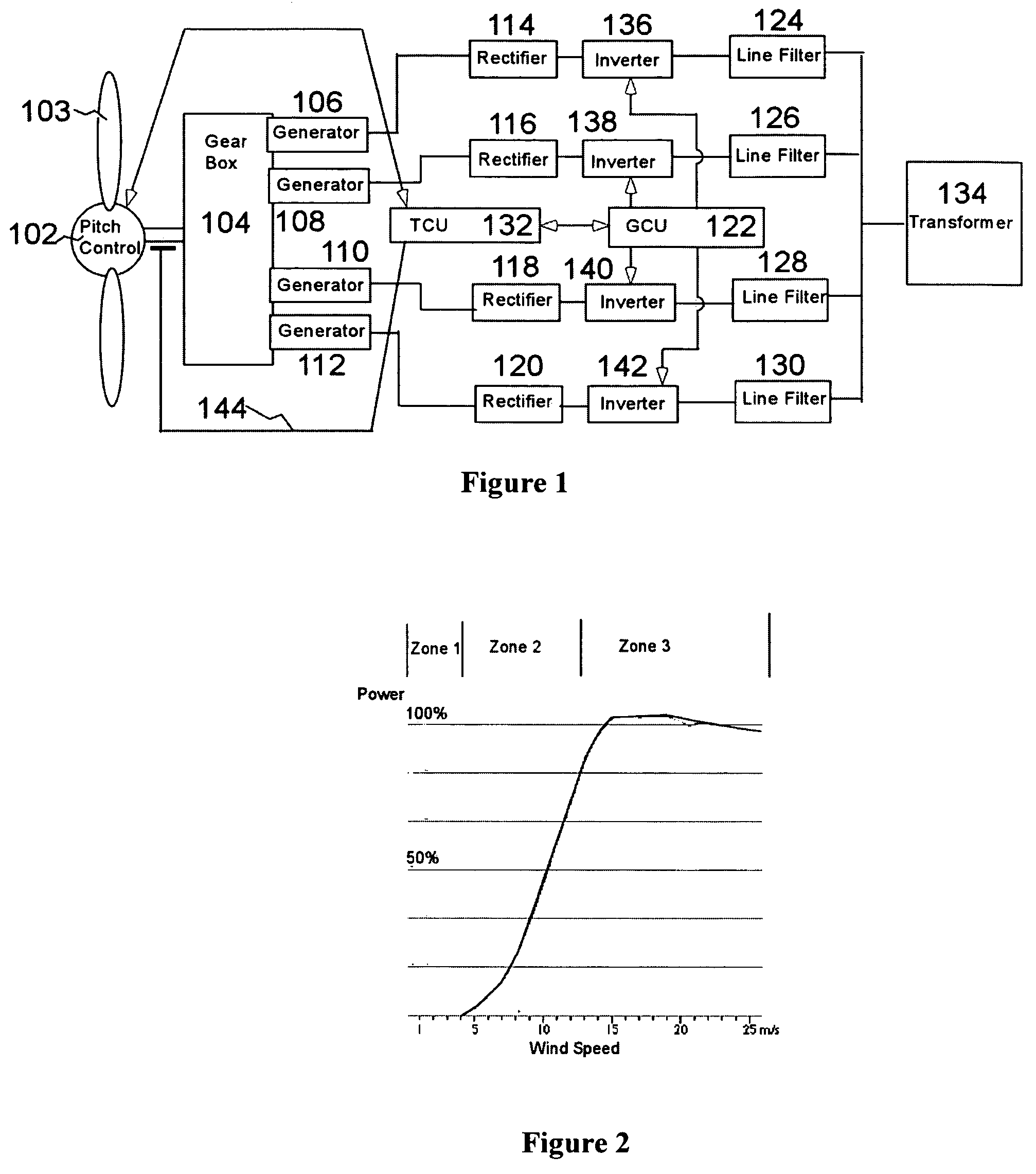
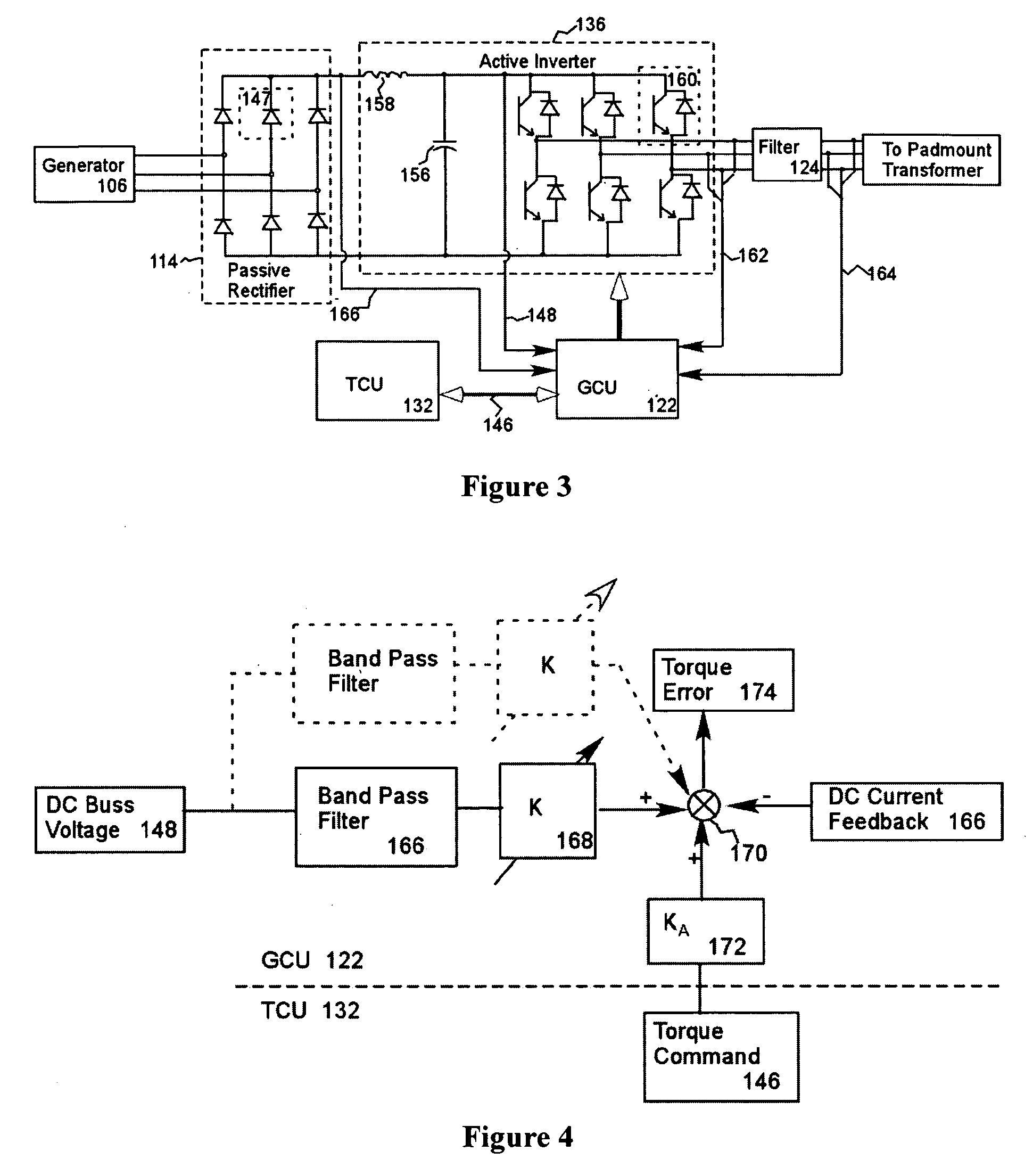
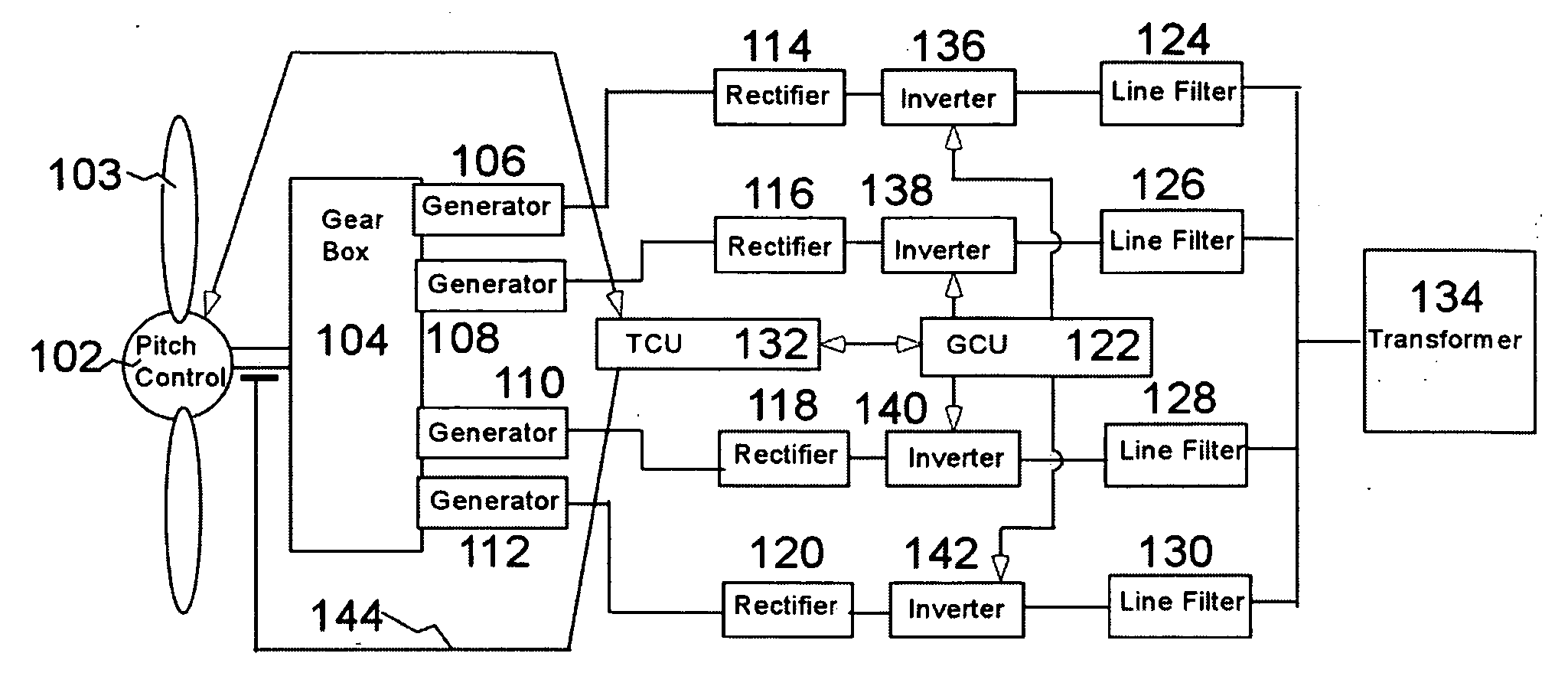
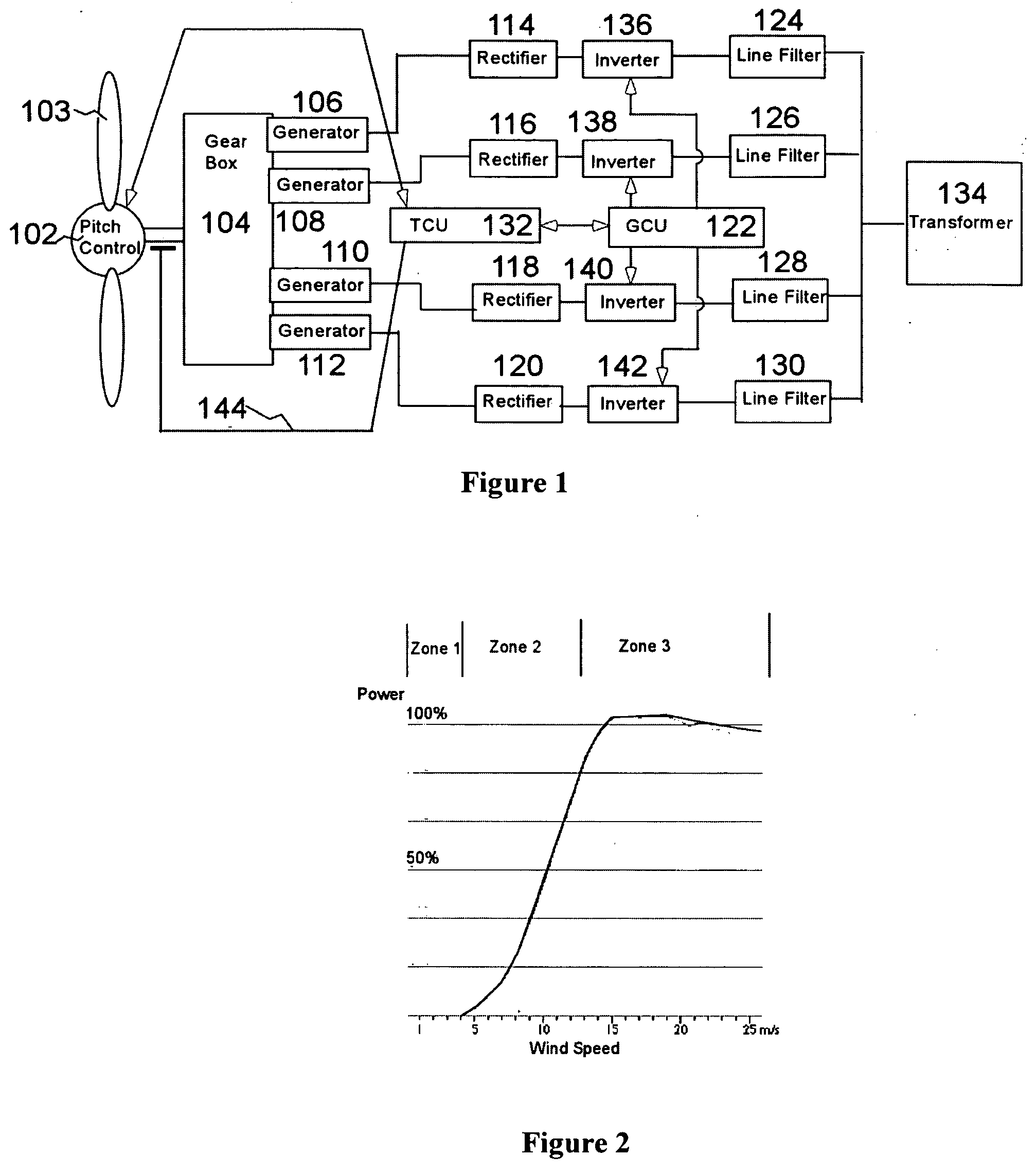
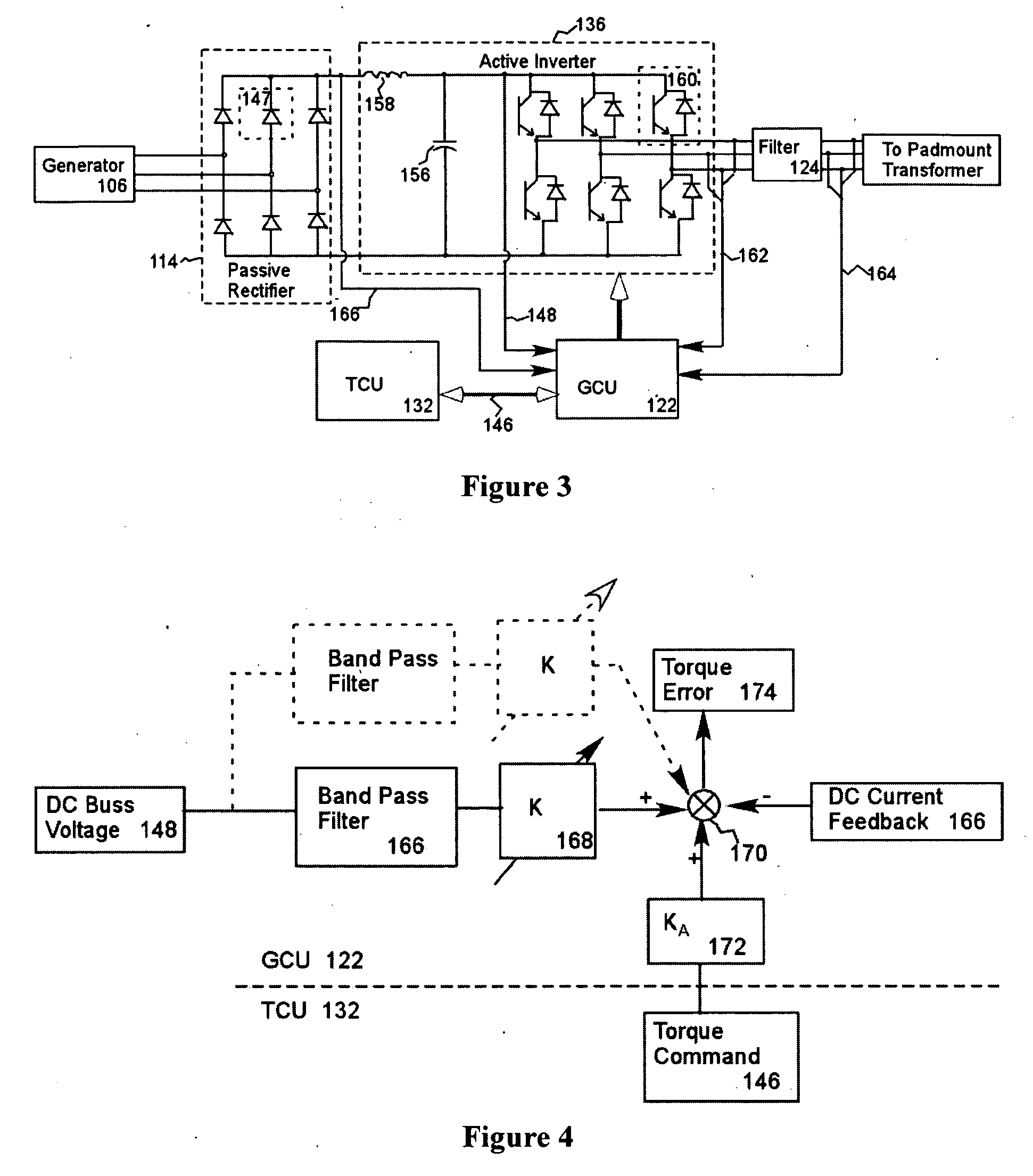
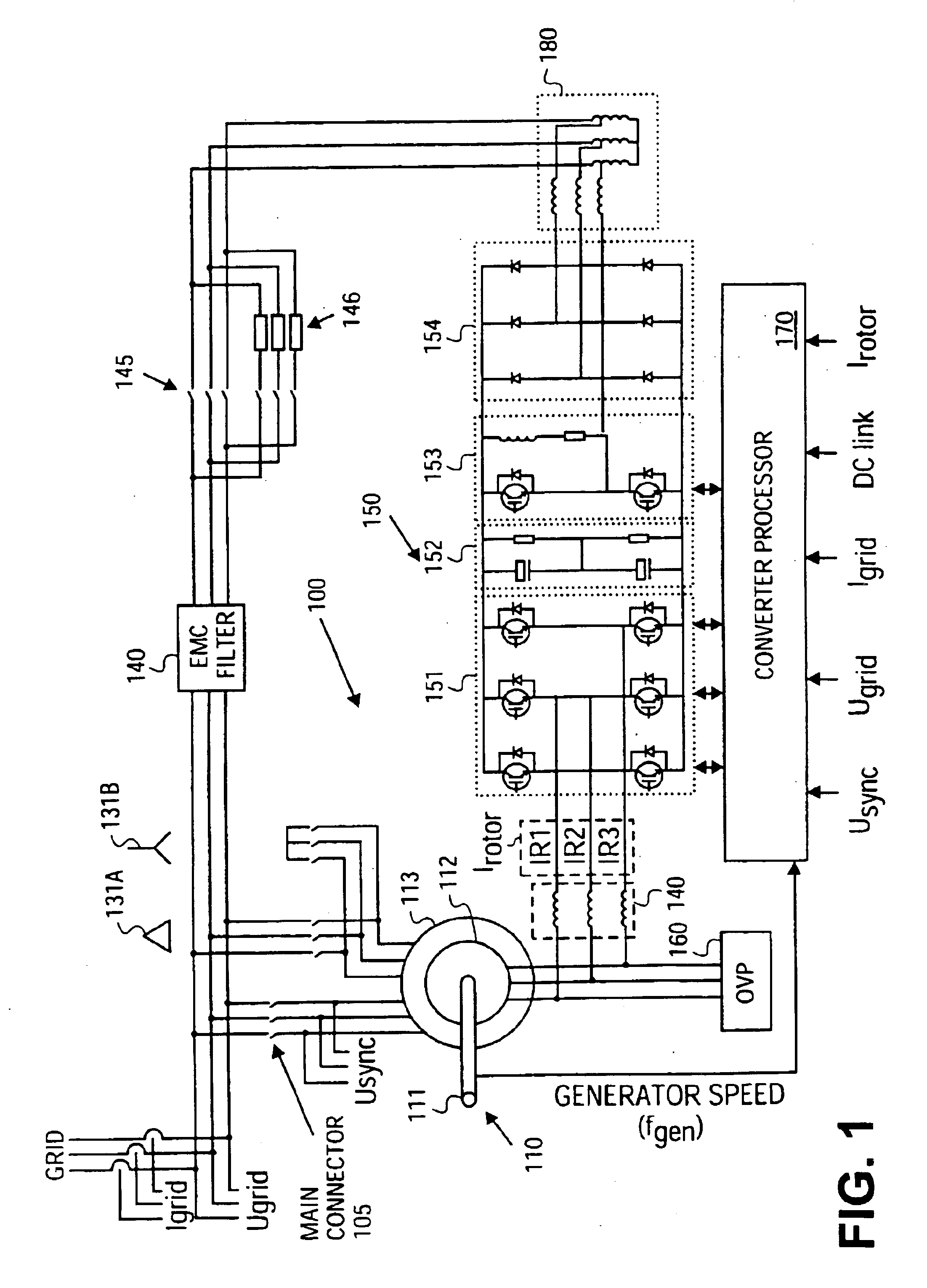
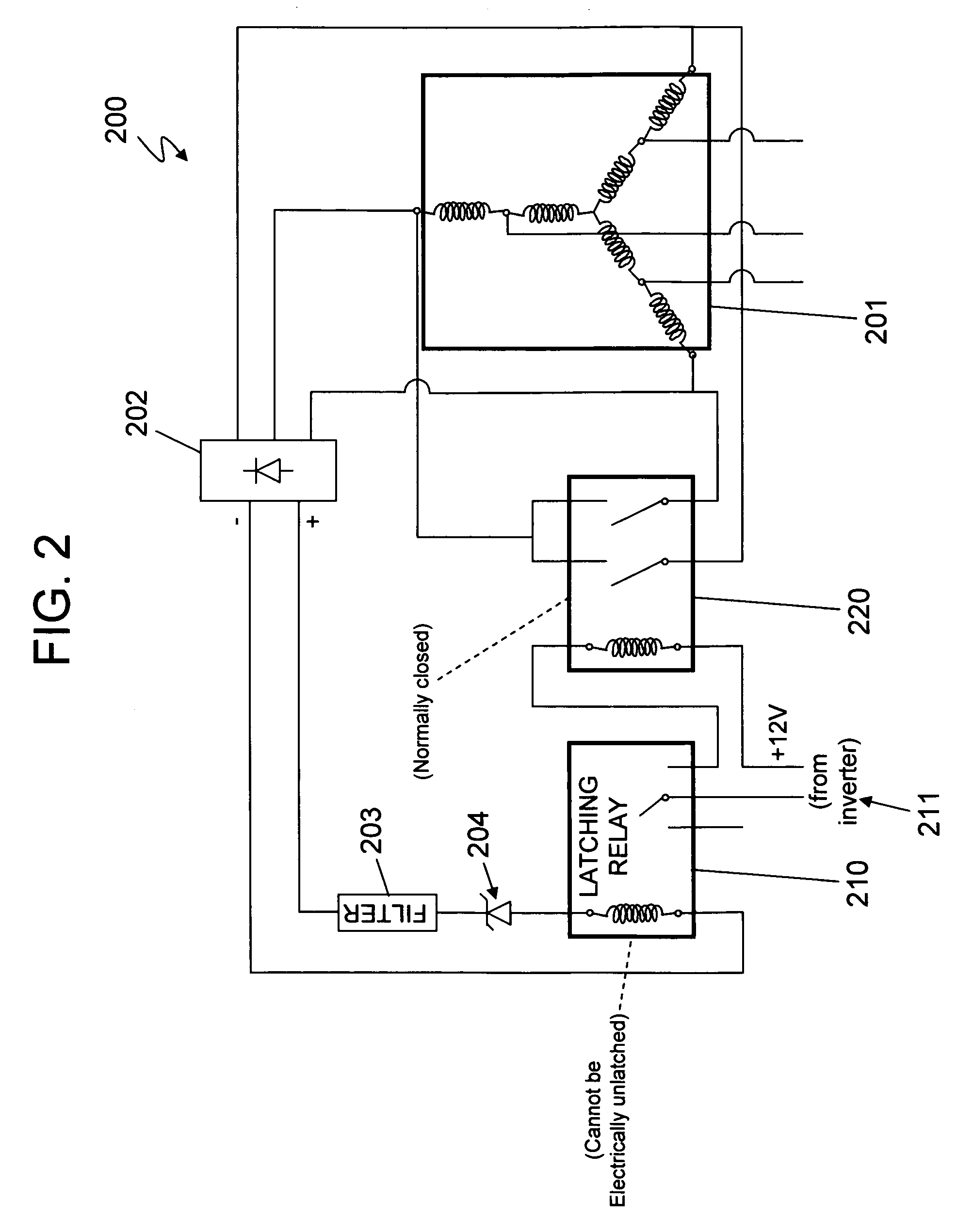
A variable speed wind turbine employing a rotor connected to a multiplicity of synchronous generators with wound field or permanent magnet rotors. A passive rectifier and an inverter are used for power transfer back to the grid. A Turbine Control Unit (TCU) commands a required generator torque based on rotor speed and power output of the turbine inverters. Torque is controlled by regulating the DC current by control of the inverter. A main-shaft-damping filter is provided by measurement of the DC bus voltage. In high winds the turbine remains at a constant average output power through a constant torque command and a varying pitch command to a rotor pitch servo system. A set point is fixed at the inverter output such that output VAR load is minimized running the turbine at very nearly unity power factor. Dynamic VAR and power factor control is provided by a separate VAR apparatus.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
Variable speed distributed drive train wind turbine system
InactiveUS20050012339A1Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityWind motor controlWorking fluid for enginesElectric power transmissionPermanent magnet rotor
A variable speed wind turbine employing a rotor connected to a multiplicity of synchronous generators with wound field or permanent magnet rotors. A passive rectifier and an inverter are used for power transfer back to the grid. A Turbine Control Unit (TCU) commands a required generator torque based on rotor speed and power output of the turbine inverters. Torque is controlled by regulating the DC current by control of the inverter. A main-shaft-damping filter is provided by measurement of the DC bus voltage. In high winds the turbine remains at a constant average output power through a constant torque command and a varying pitch command to a rotor pitch servo system. A set point is fixed at the inverter output such that output VAR load is minimized running the turbine at very nearly unity power factor. Dynamic VAR and power factor control is provided by a separate VAR apparatus.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
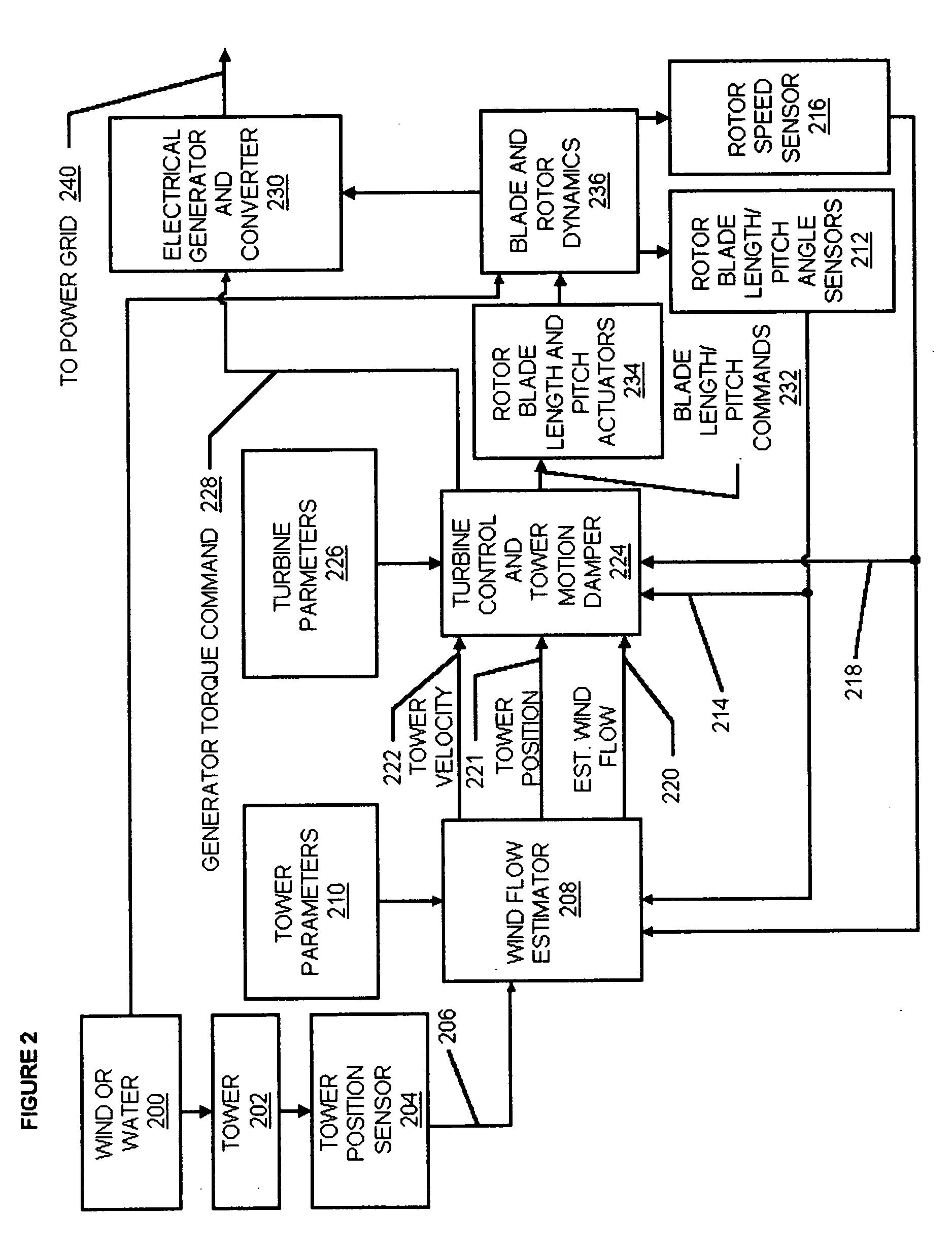
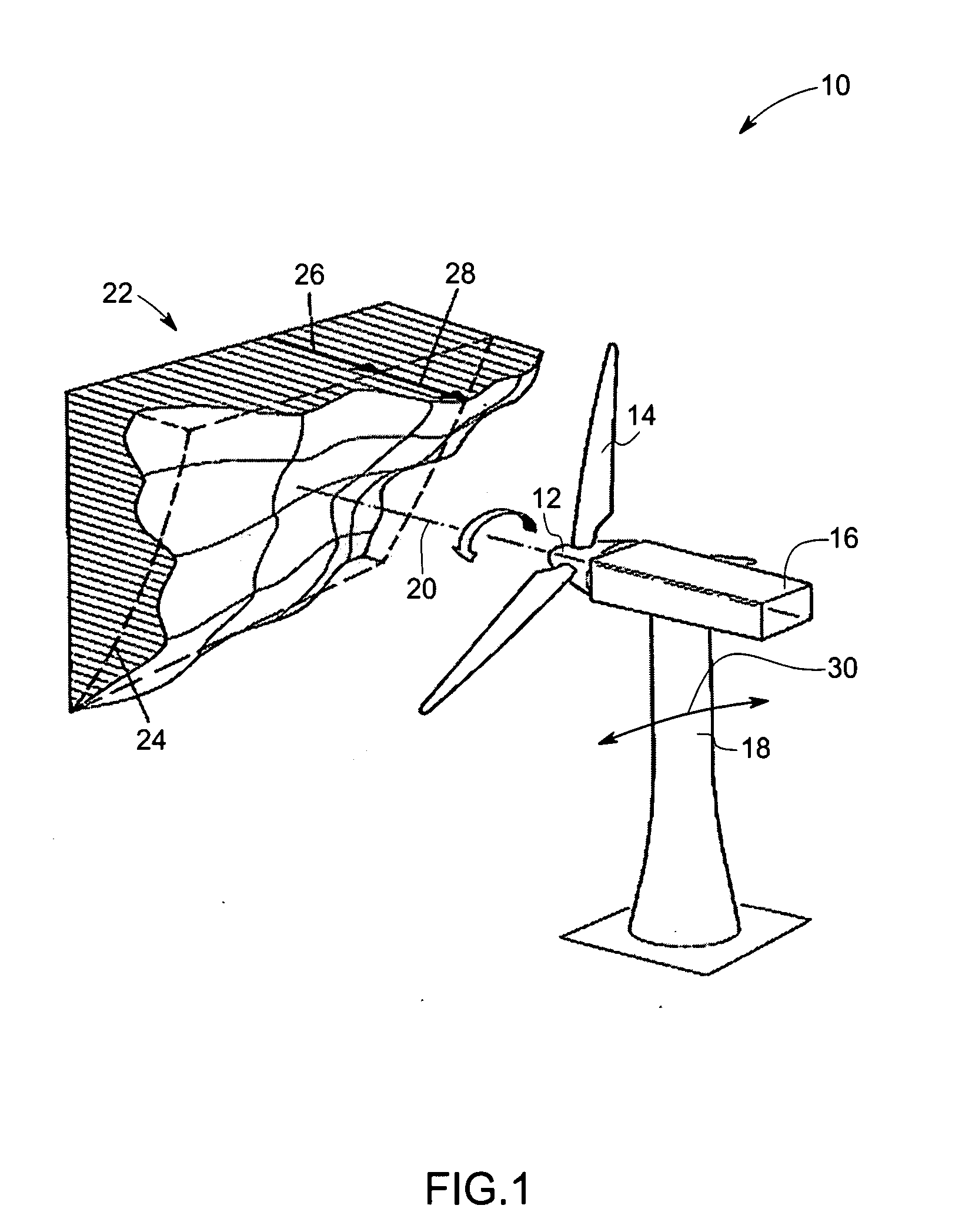
Wind flow estimation and tracking using tower dynamics
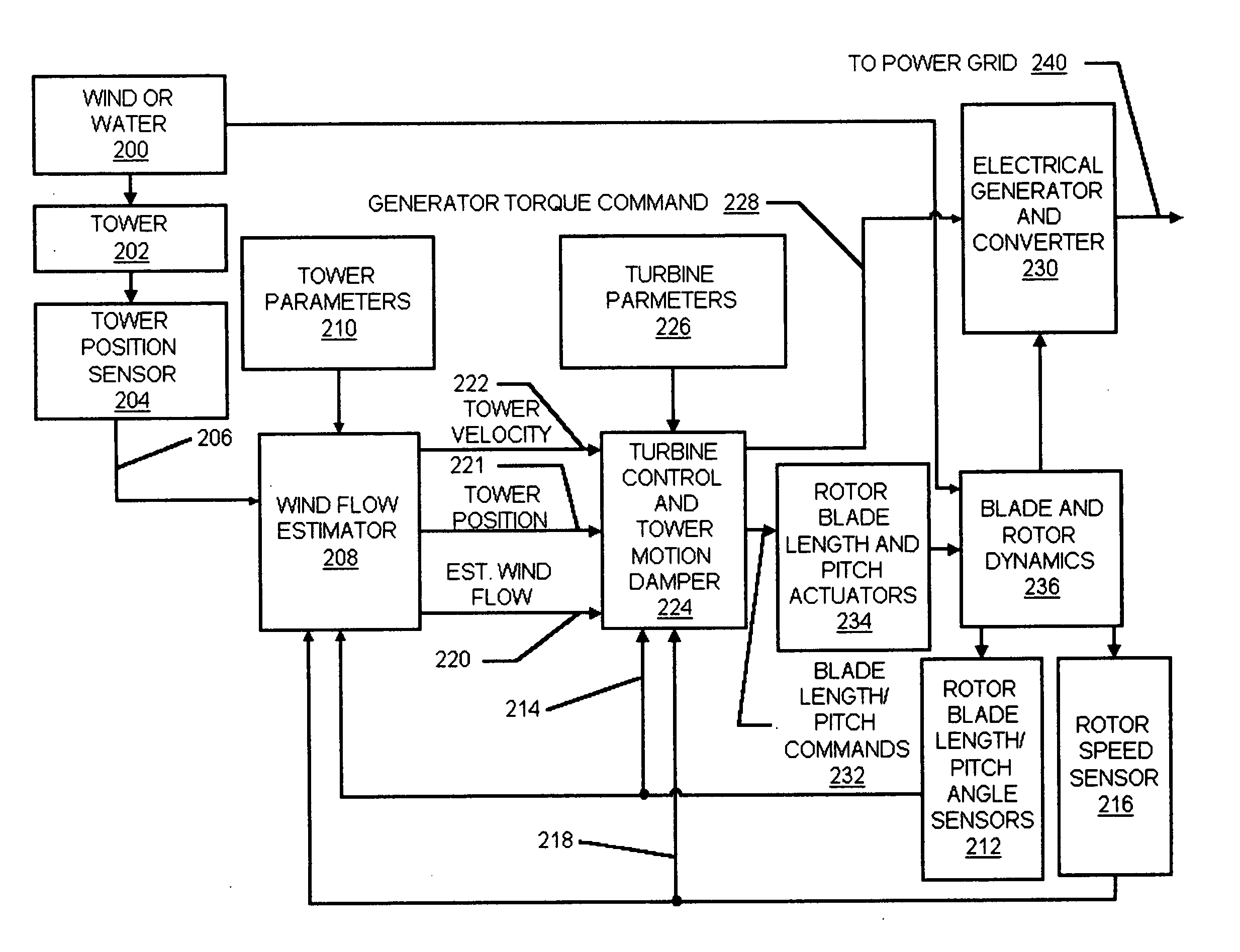
A turbine control system for a variable speed electrical generator in a wind turbine mounted atop a support tower. The wind turbine converts wind energy into a driving torque applied to the generator. The control system includes a turbine support tower position sensor and may also include other tower acceleration and velocity sensors. A wind flow estimator uses the measured motion, generator rotation rate and blade pitch angle to predict wind flow over the swept area of the turbine's rotor, and the tower motion. The predicted wind flow and motion is used in the turbine control system to properly adjust its operating point, to tune the controller, to control the rotor rotation rate, and to damp tower oscillations.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
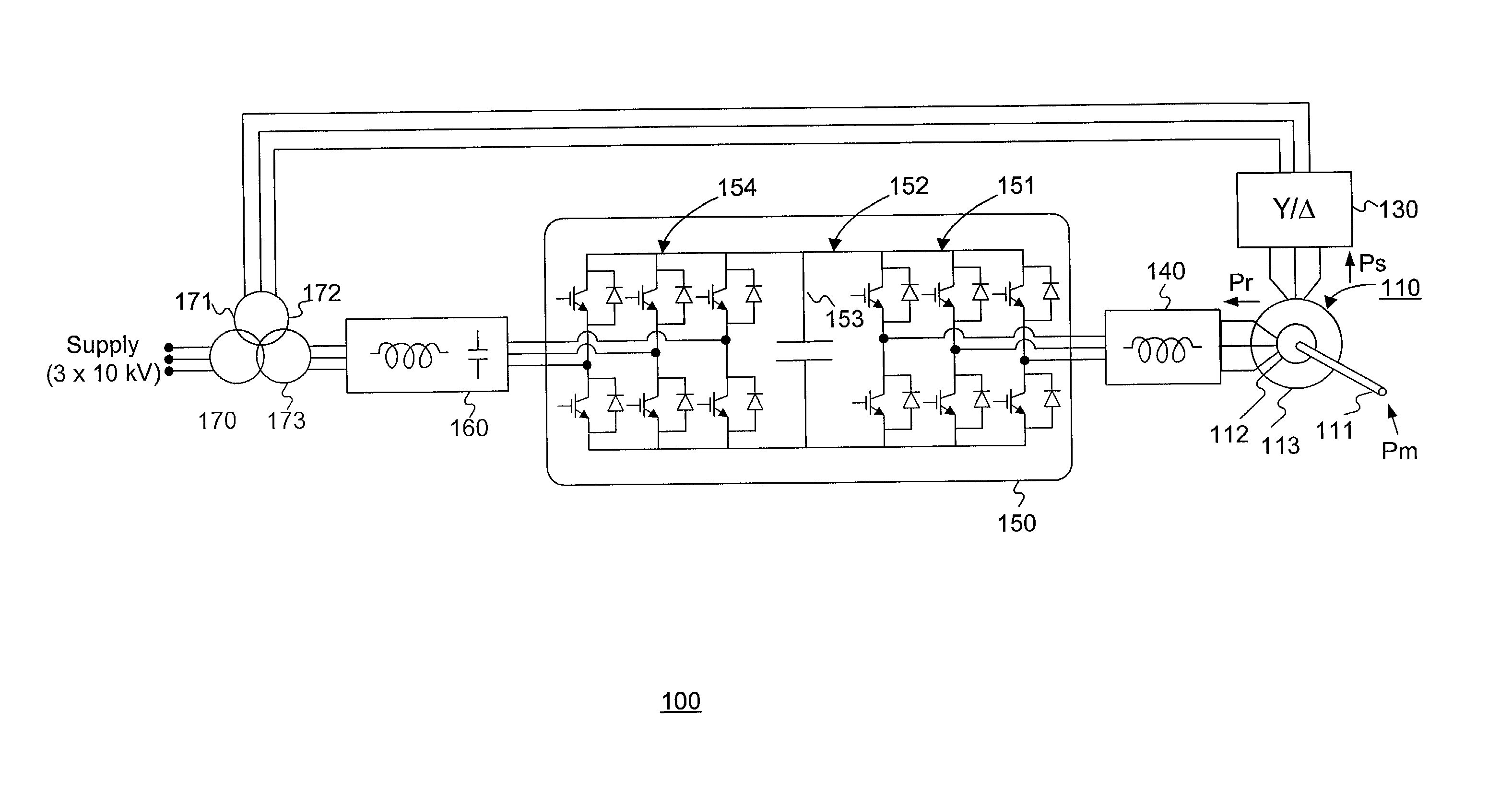
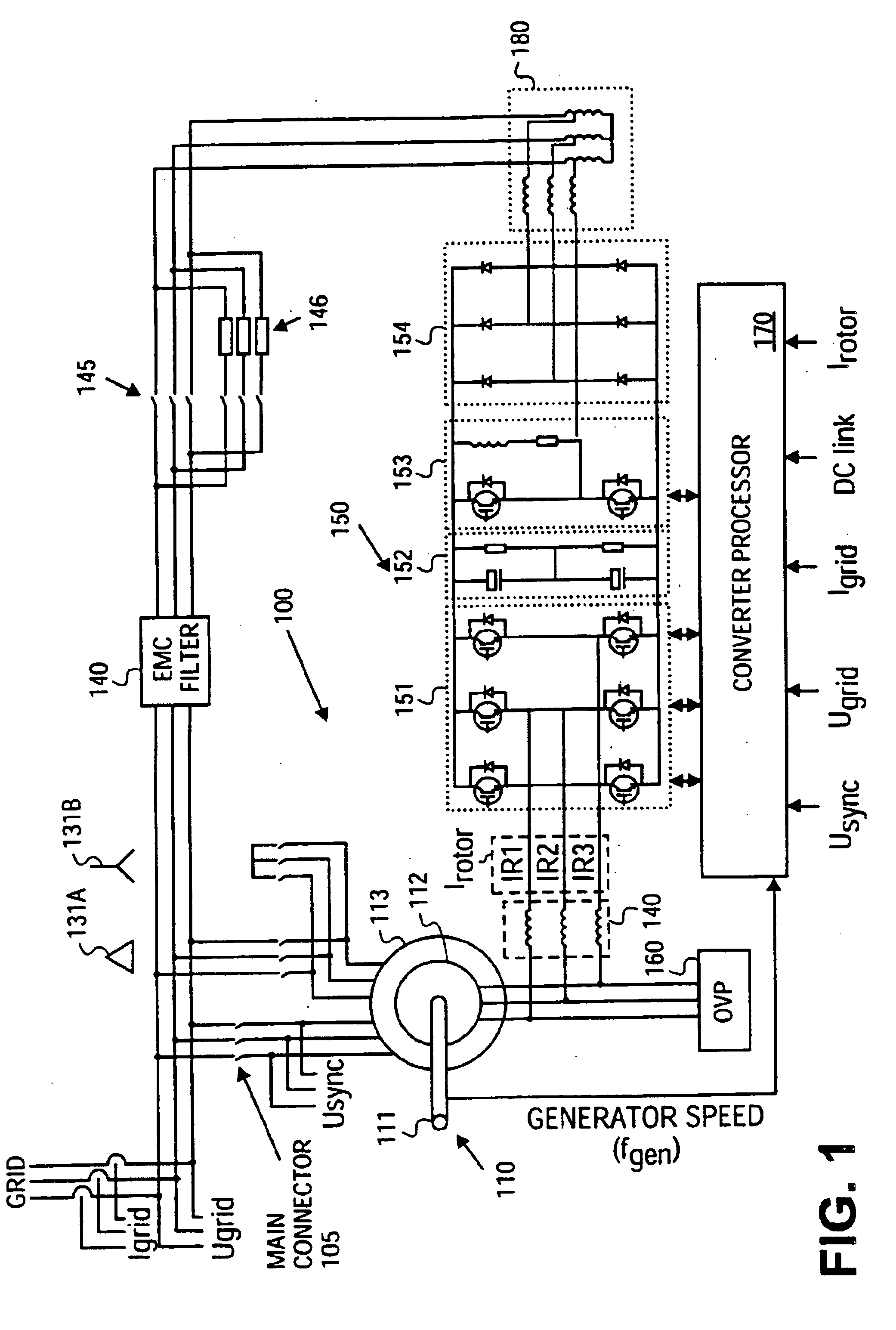
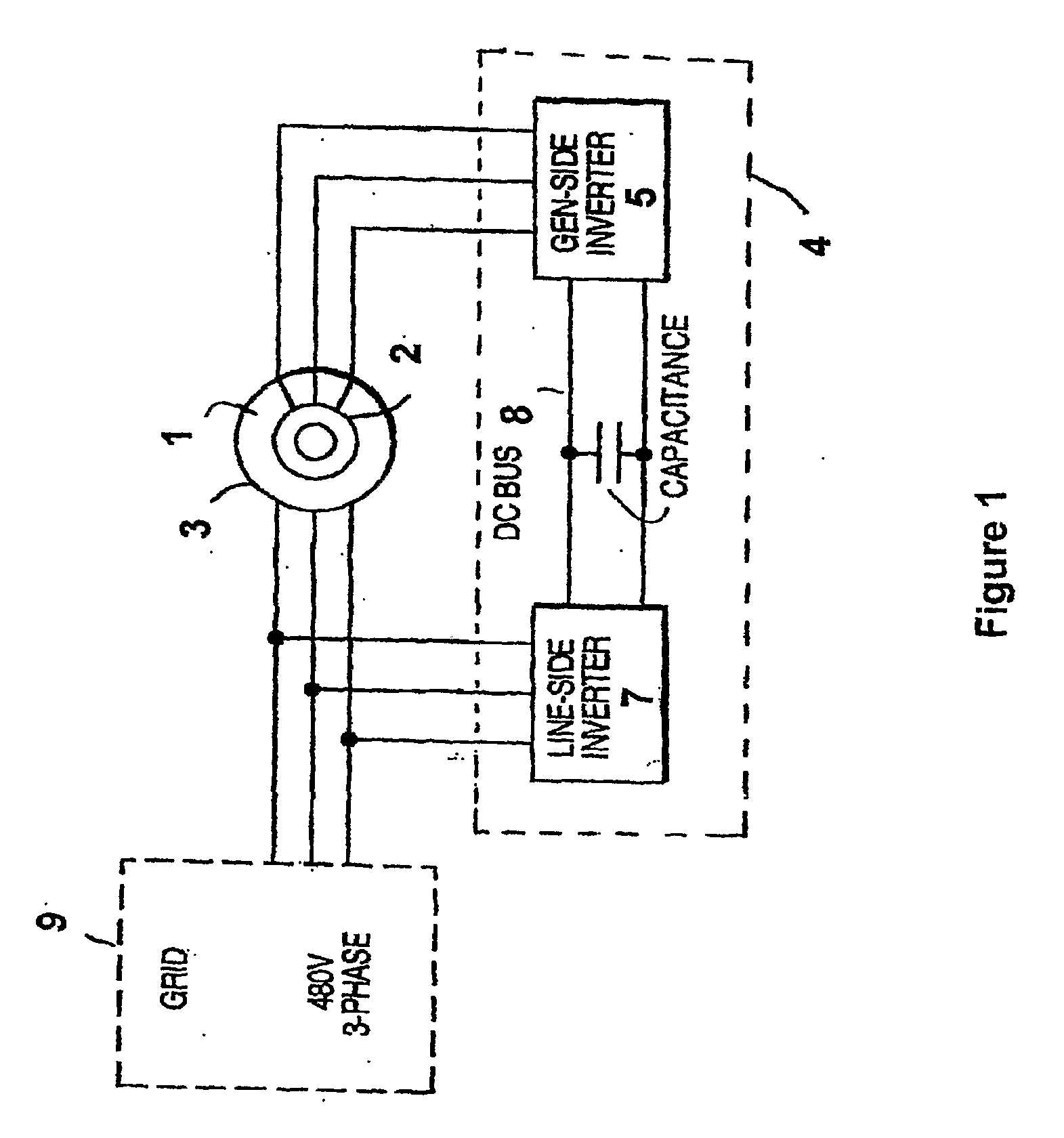
Variable speed wind turbine having a matrix converter
InactiveUS6856038B2Generator control circuitsEfficient power electronics conversionMatrix convertersConstant frequency
A variable speed wind turbine is disclosed comprising a turbine rotor that drives a doubly-fed induction generator, a matrix converter which converts variable frequency output into constant frequency output, and a control unit and a protection circuit for the matrix converter. Power is circulated in the system allowing for sensorless detection of rotor position and better output ratios of power from the system.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Variable speed wind turbine having a passive grid side rectifier with scalar power control and dependent pitch control
InactiveUS6933625B2Easy to controlImprove responsivenessOptimise machine performanceWind motor controlPower gridVariable speed wind turbine
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Variable speed wind turbine having a matrix converter
InactiveUS20020079706A1Generator control circuitsWind motor controlMatrix convertersConstant frequency
A variable speed wind turbine is disclosed comprising a turbine rotor that drives a doubly-fed induction generator, a matrix converter which converts variable frequency output into constant frequency output, and a control unit and a protection circuit for the matrix converter. Power is circulated in the system allowing for sensorless detection of rotor position and better output ratios of power from the system.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Variable speed wind turbine having a passive grid side rectifier with scalar power control and dependent pitch control
InactiveUS6856040B2Easy to controlImprove responsivenessOptimise machine performanceWind motor controlPower gridVariable speed wind turbine
A variable speed wind turbine having a passive grid side rectifier using scalar power control and dependent pitch control is disclosed. The variable speed turbine may include an electrical generator to provide power for a power grid and a power conversion system coupled to the electrical generator. The power conversion system may include at least one passive grid side rectifier. The power conversion system may provide power to the electrical generator using the passive grid side rectifier. The variable speed wind turbine may also use scalar power control to provide more precise control of electrical quantities on the power grid. The variable speed wind turbine may further use dependent pitch control to improve responsiveness of the wind turbine.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
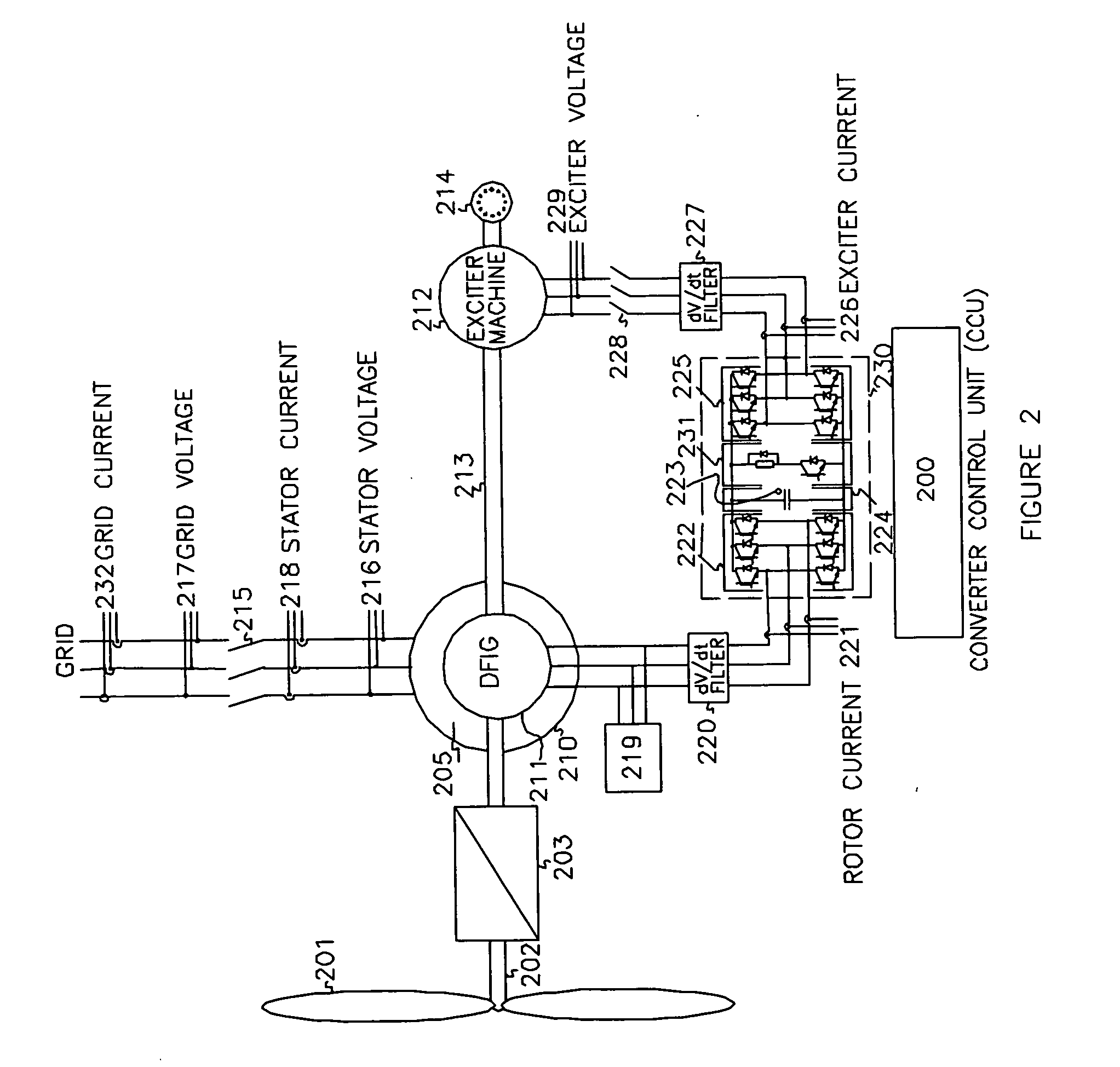
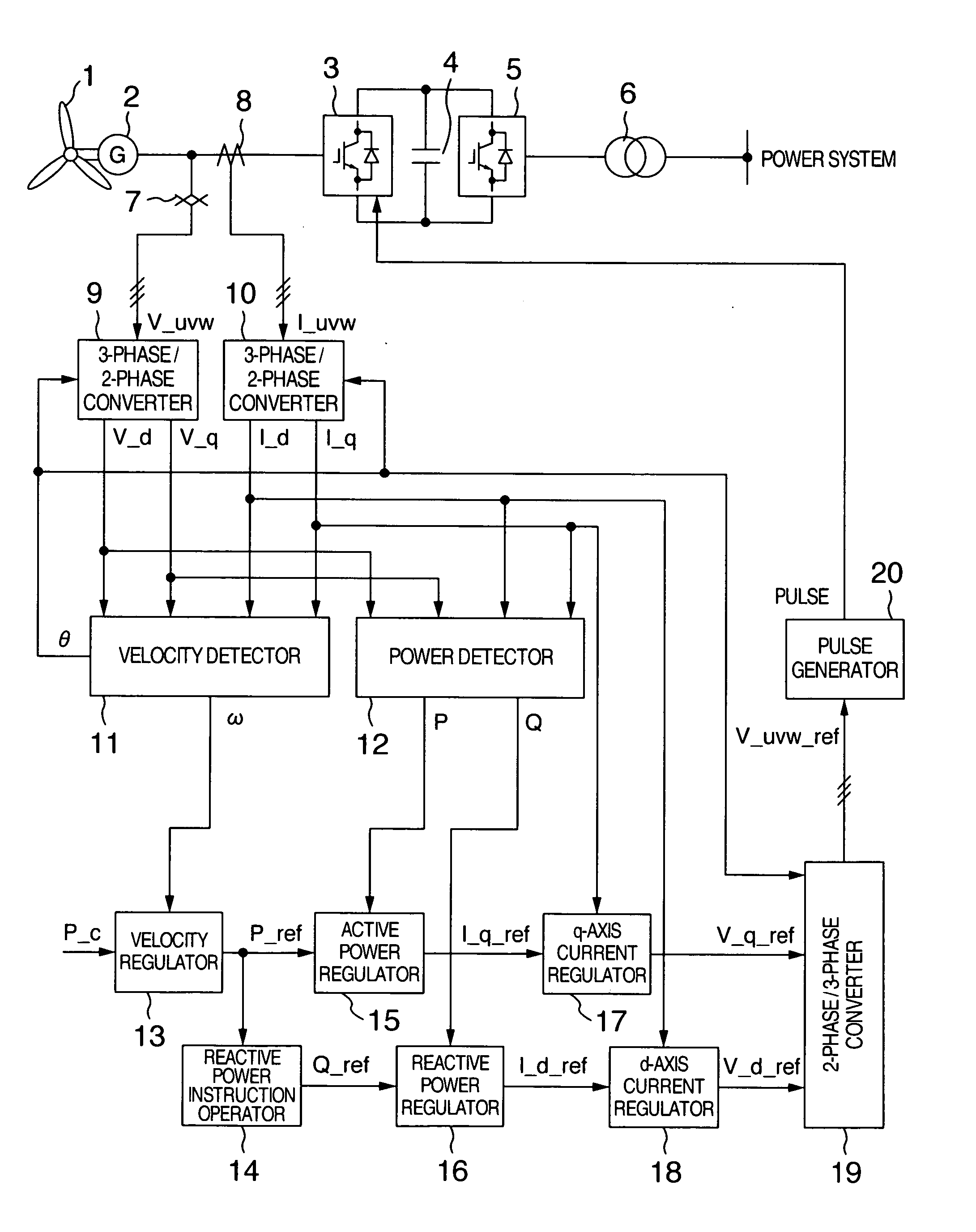
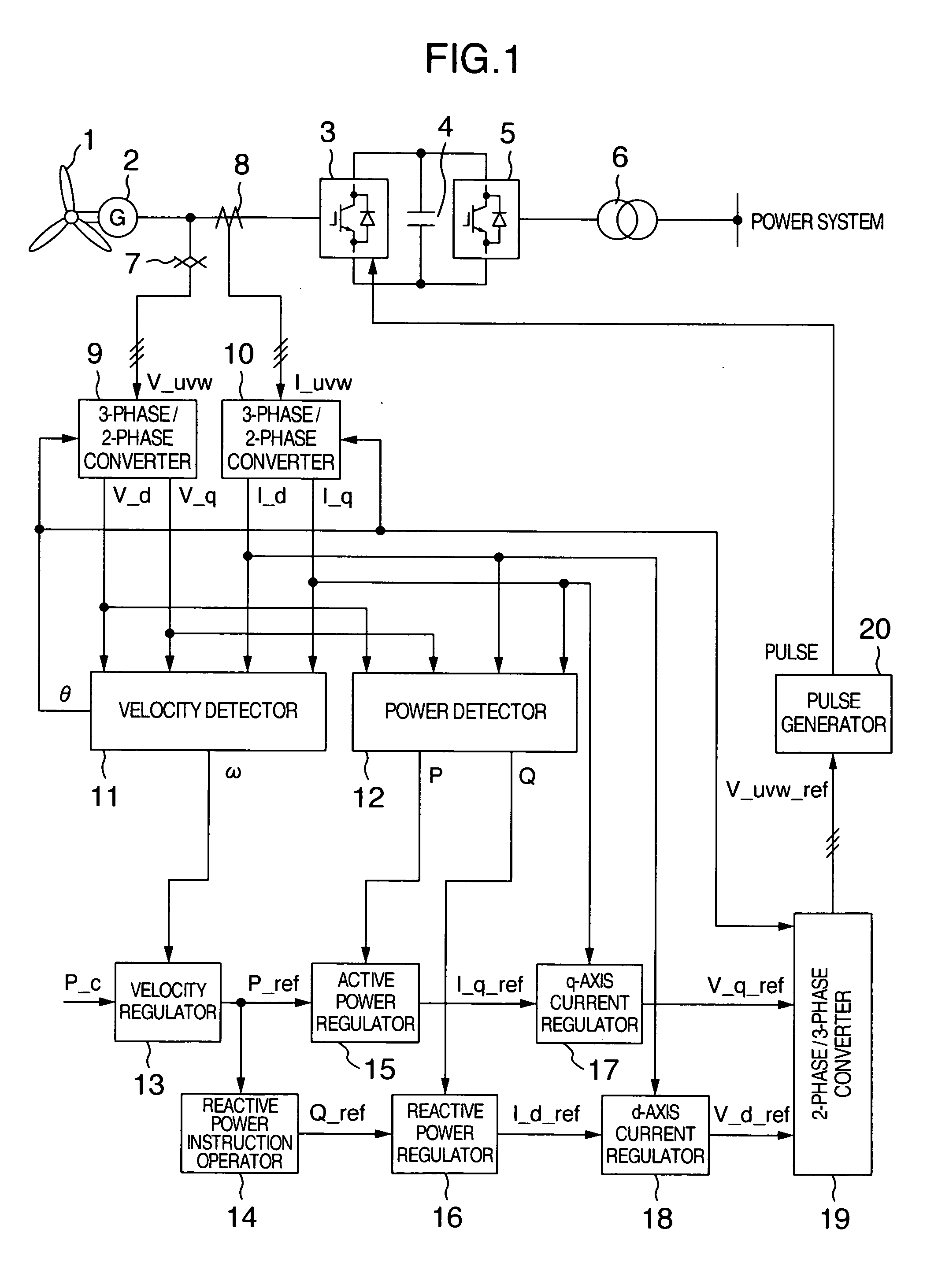
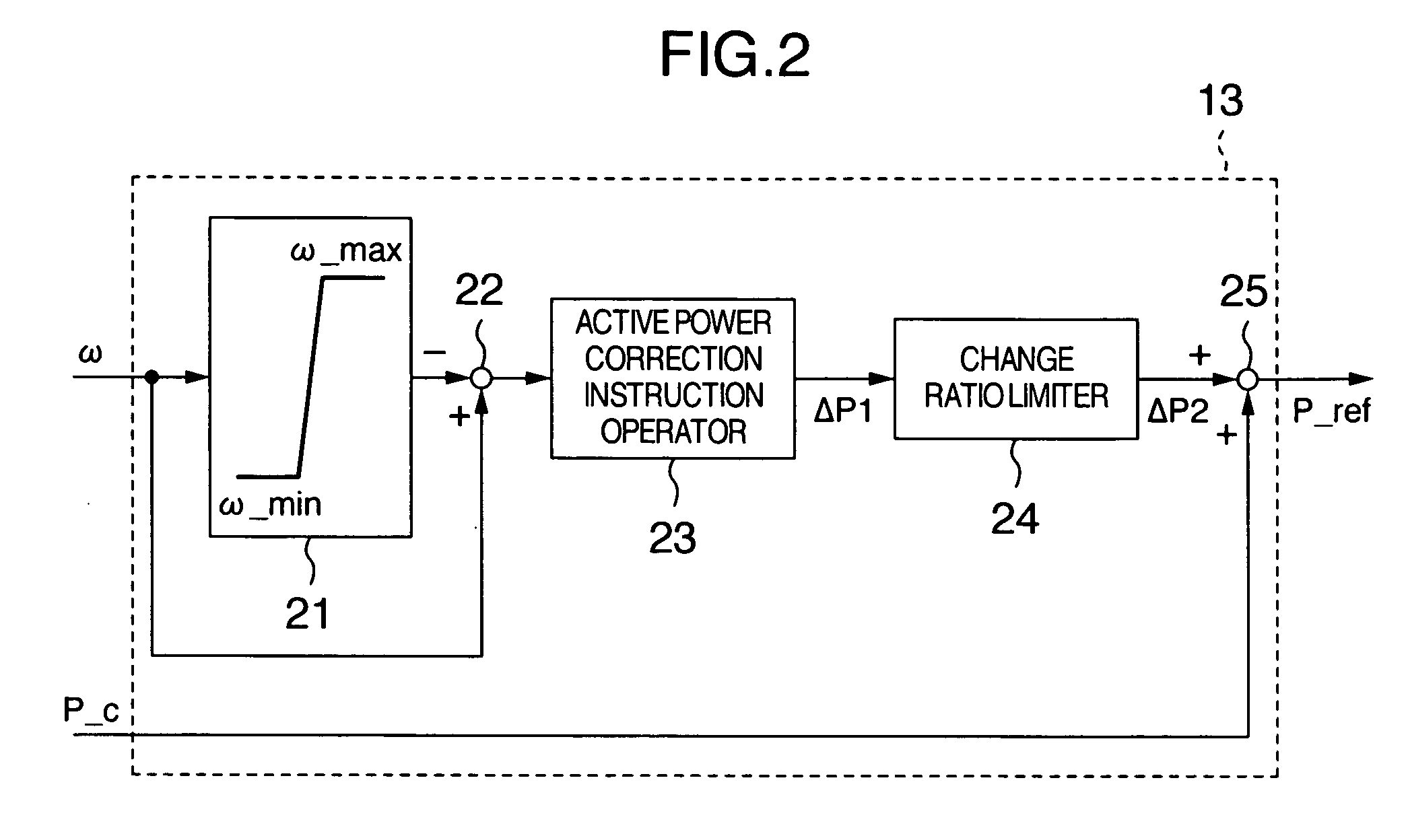
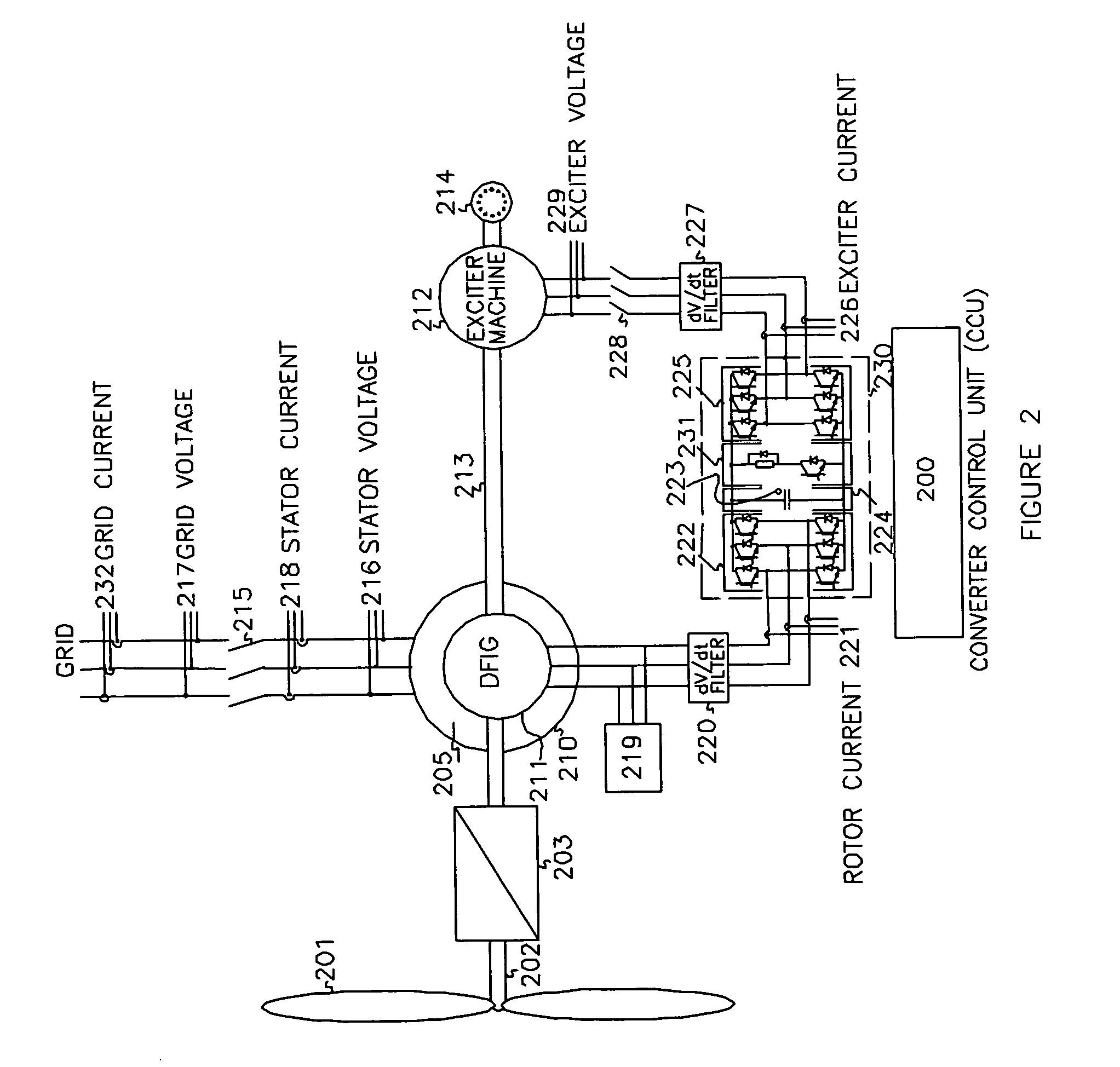
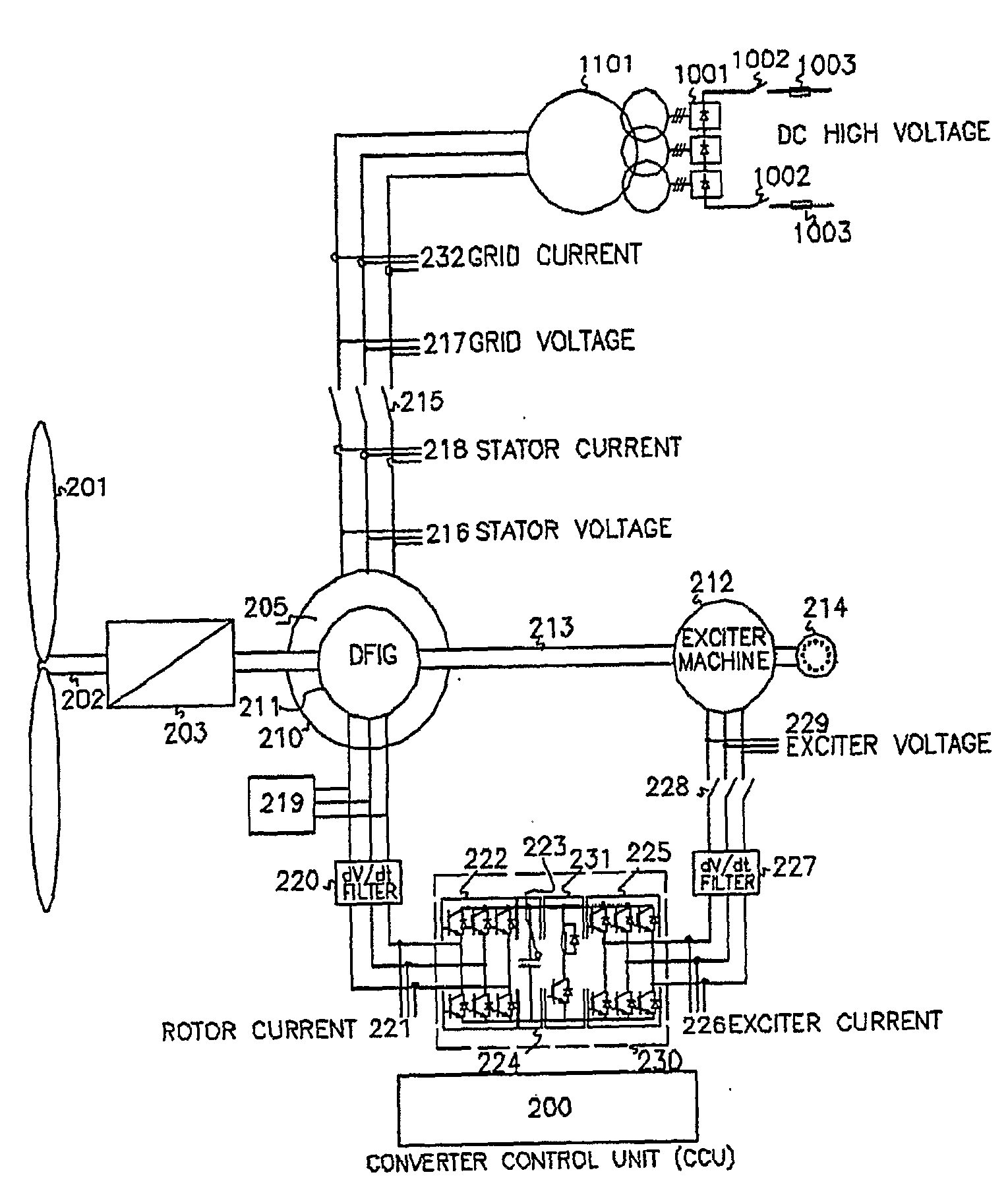
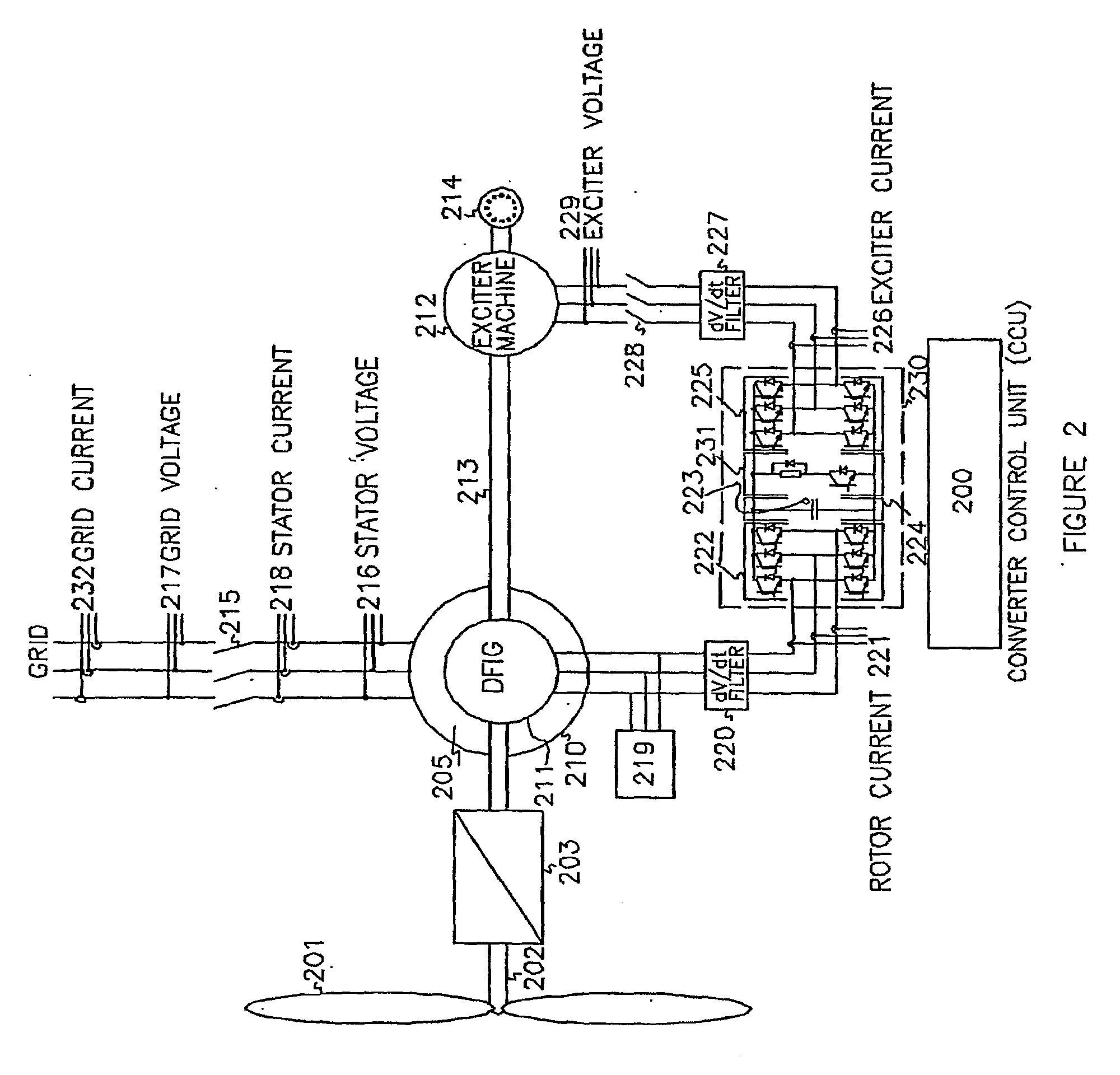
Variable speed wind turbine having an exciter machine and a power converter not connected to the grid
ActiveUS20070216164A1Avoiding undesired harmonic distortionImprove power qualityGenerator control circuitsVector control systemsPower qualityHarmonic
A variable speed wind turbine having a doubly fed induction generator (DFIG), includes an exciter machine mechanically coupled to the DFIG and a power converter placed between a rotor of the DFIG and the exciter machine. Thus, the power converter is not directly connected to the grid avoiding the introduction of undesired harmonic distortion and achieving a better power quality fed into the utility grid. Moreover, the variable speed wind turbine includes a power control and a pitch regulation.
Owner:INGETEAM POWER TECH
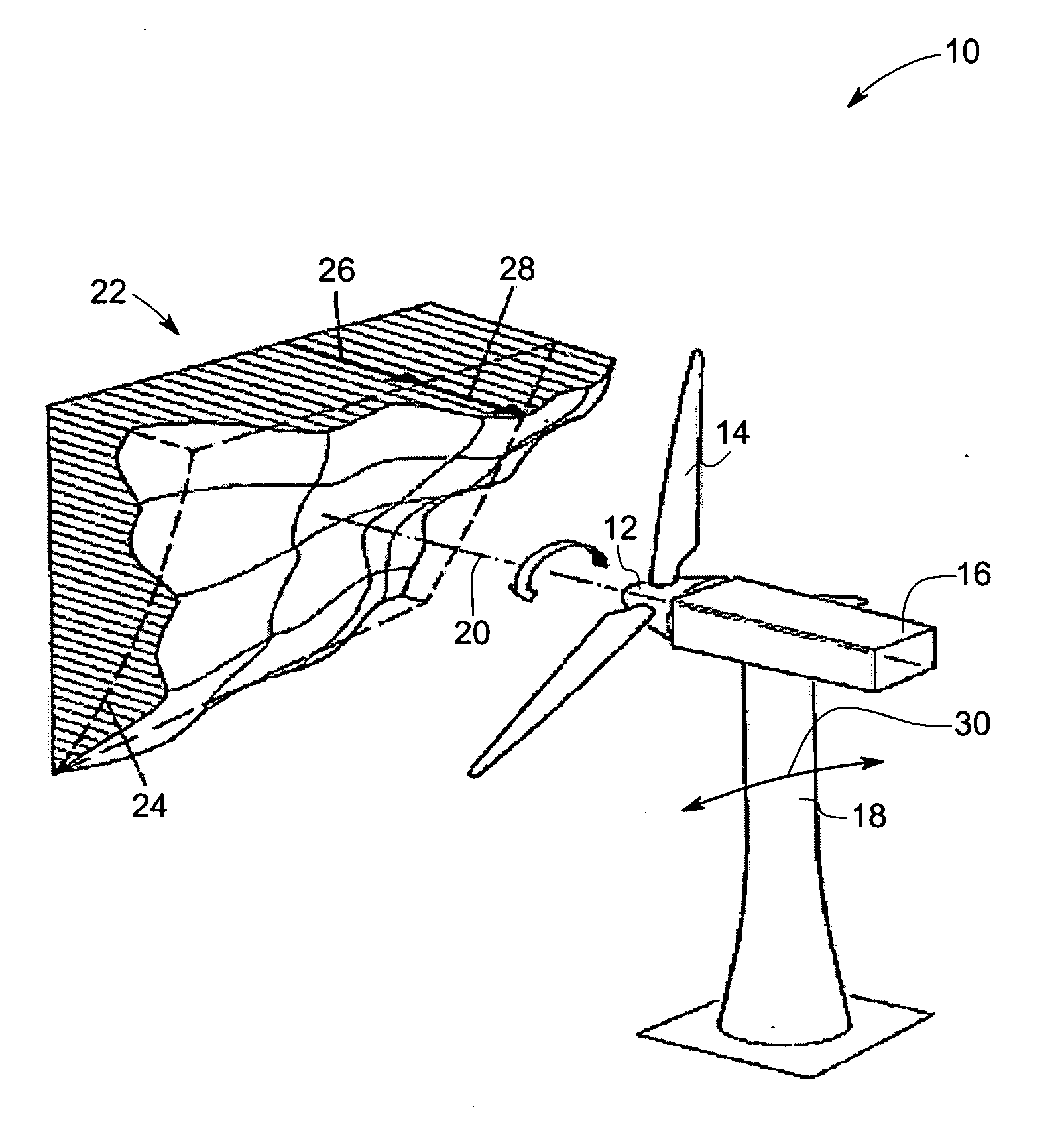
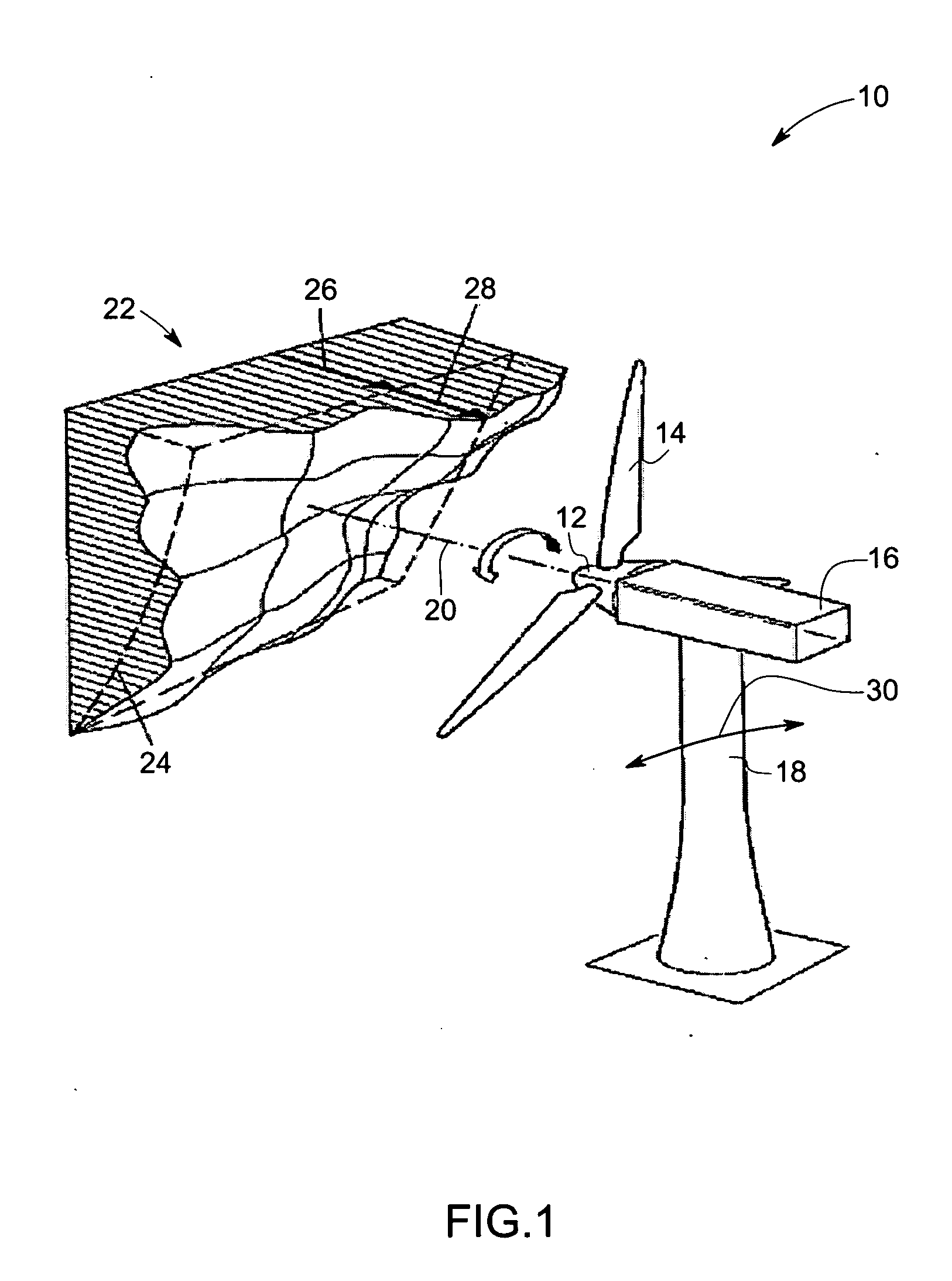
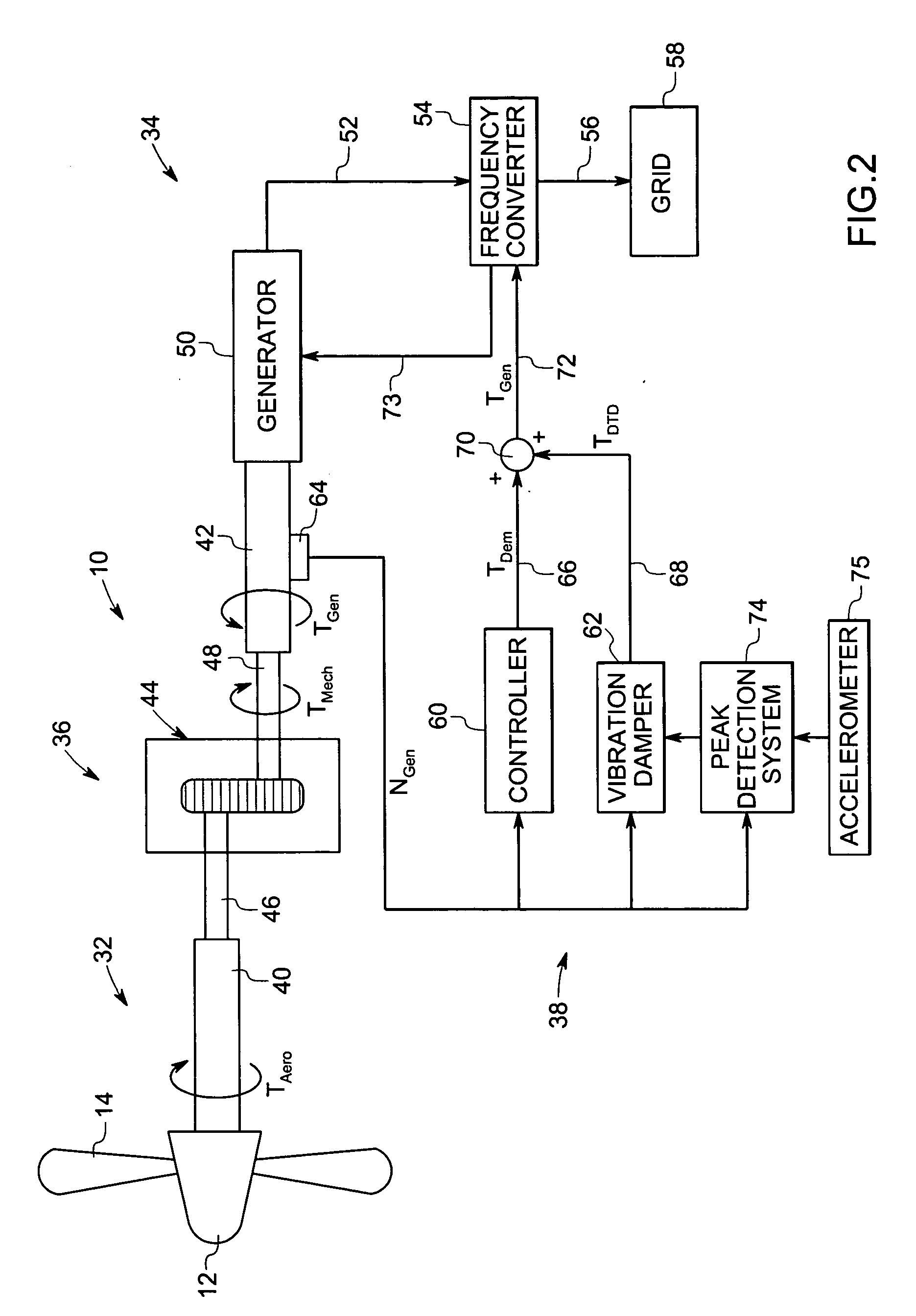
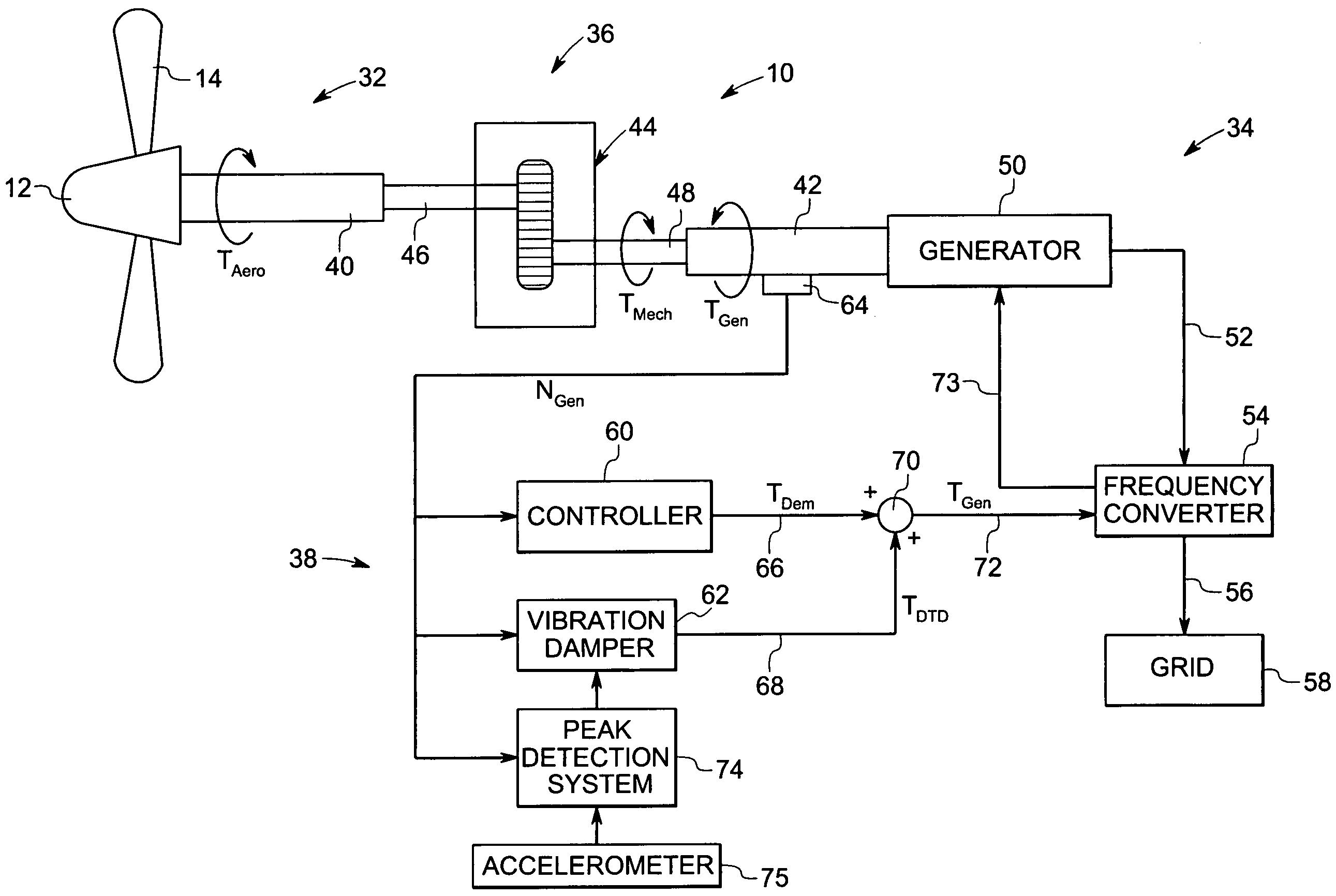
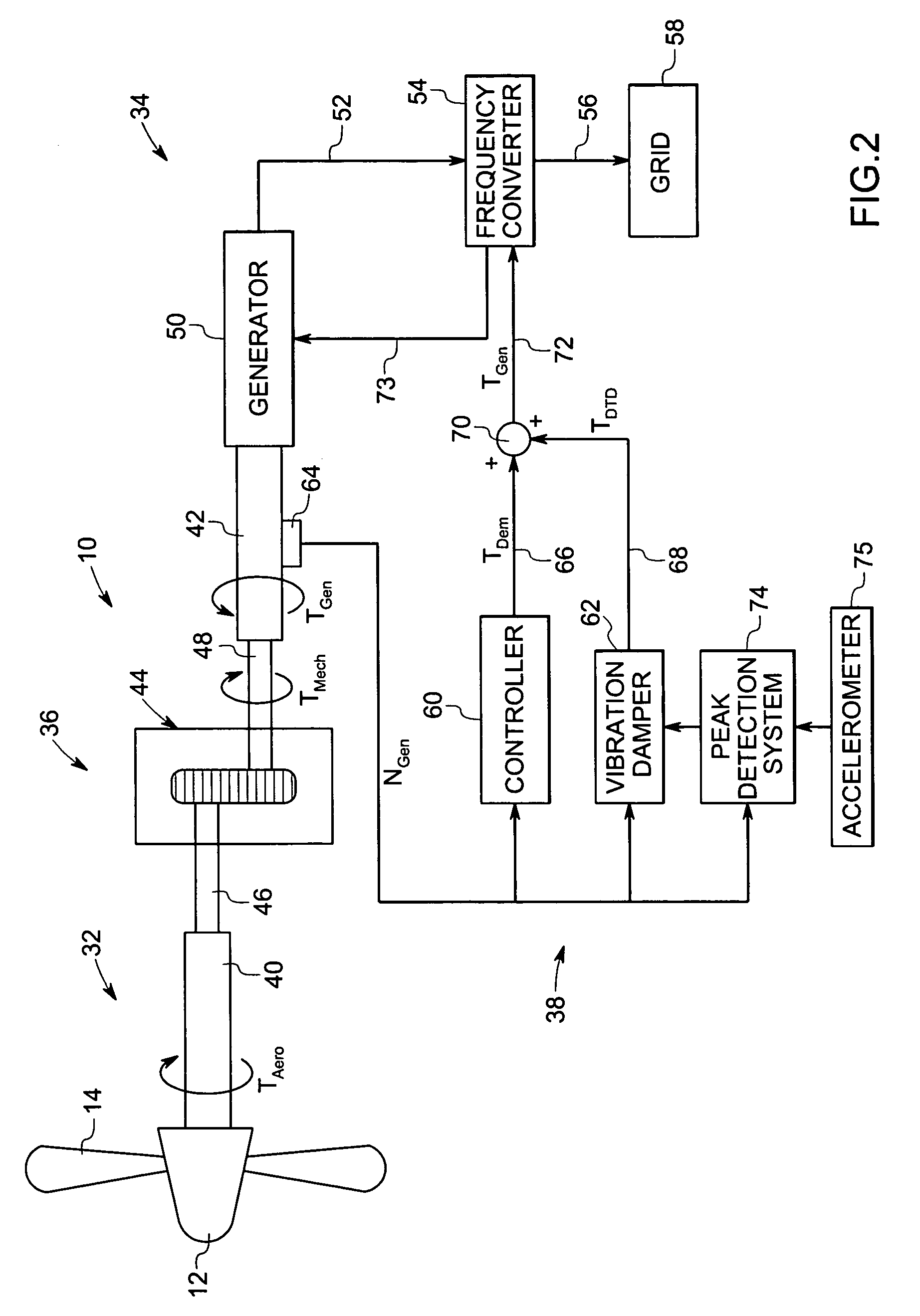
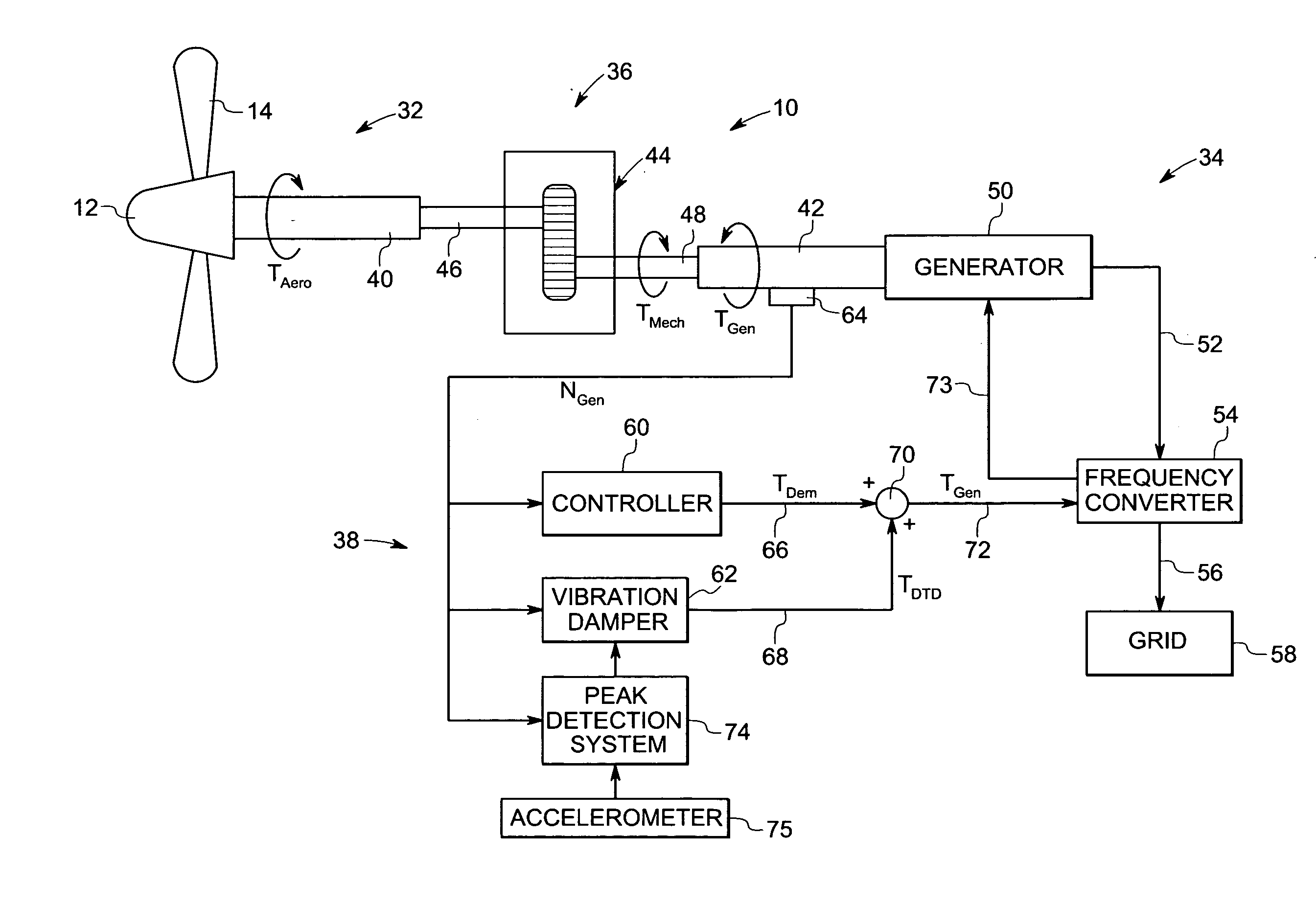
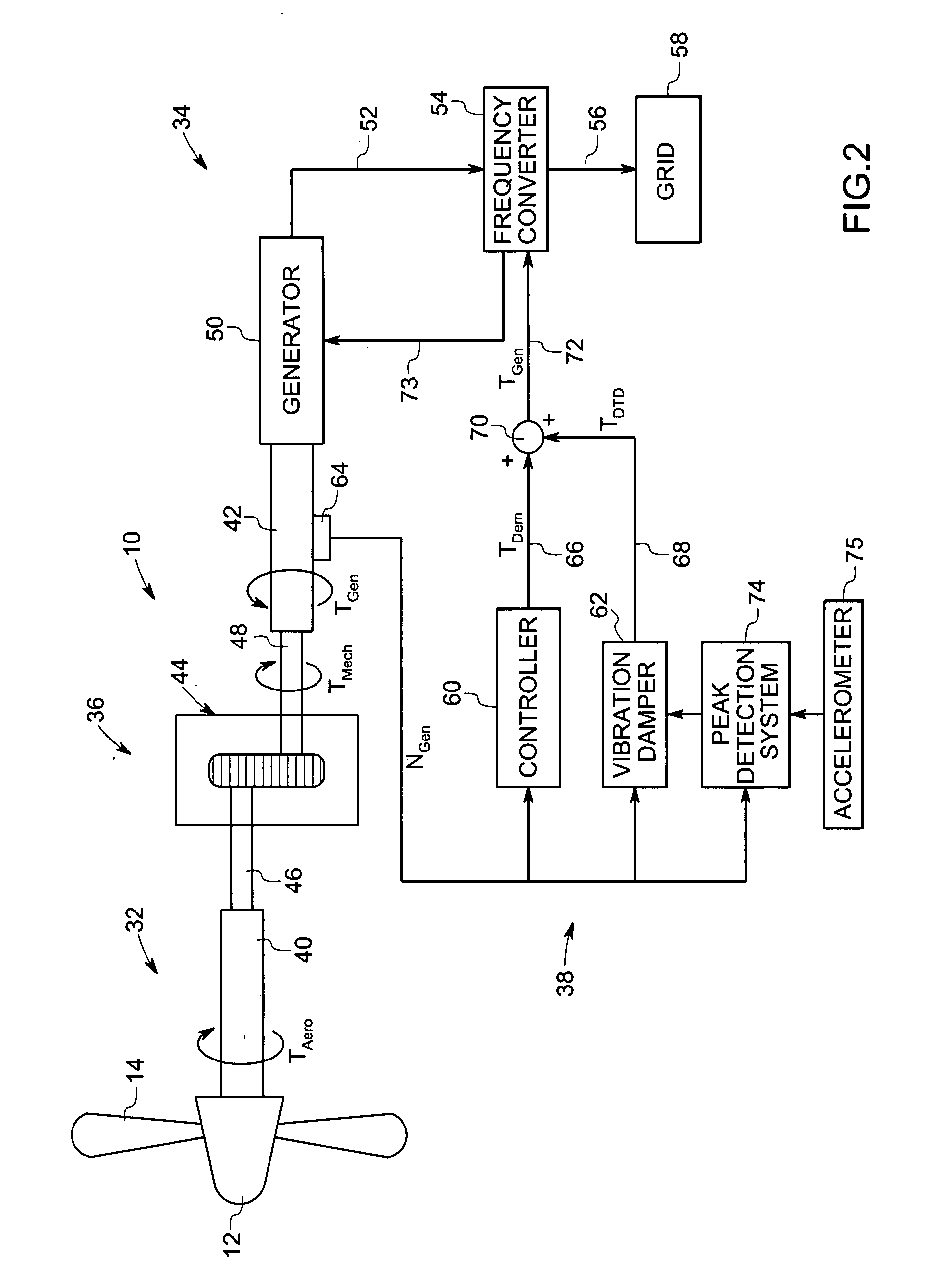
Vibration damping system and method for variable speed wind turbines
A vibration damping technique for a wind turbine system is described. The wind turbine system includes a vibration damper, which provides a variable signal to control torque produced by a generator of the wind turbine system. The variable signal is based on generator speed and has a first local peak value based on a resonant frequency of tower side-to-side oscillation.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Vibration damping system and method for variable speed wind turbines
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
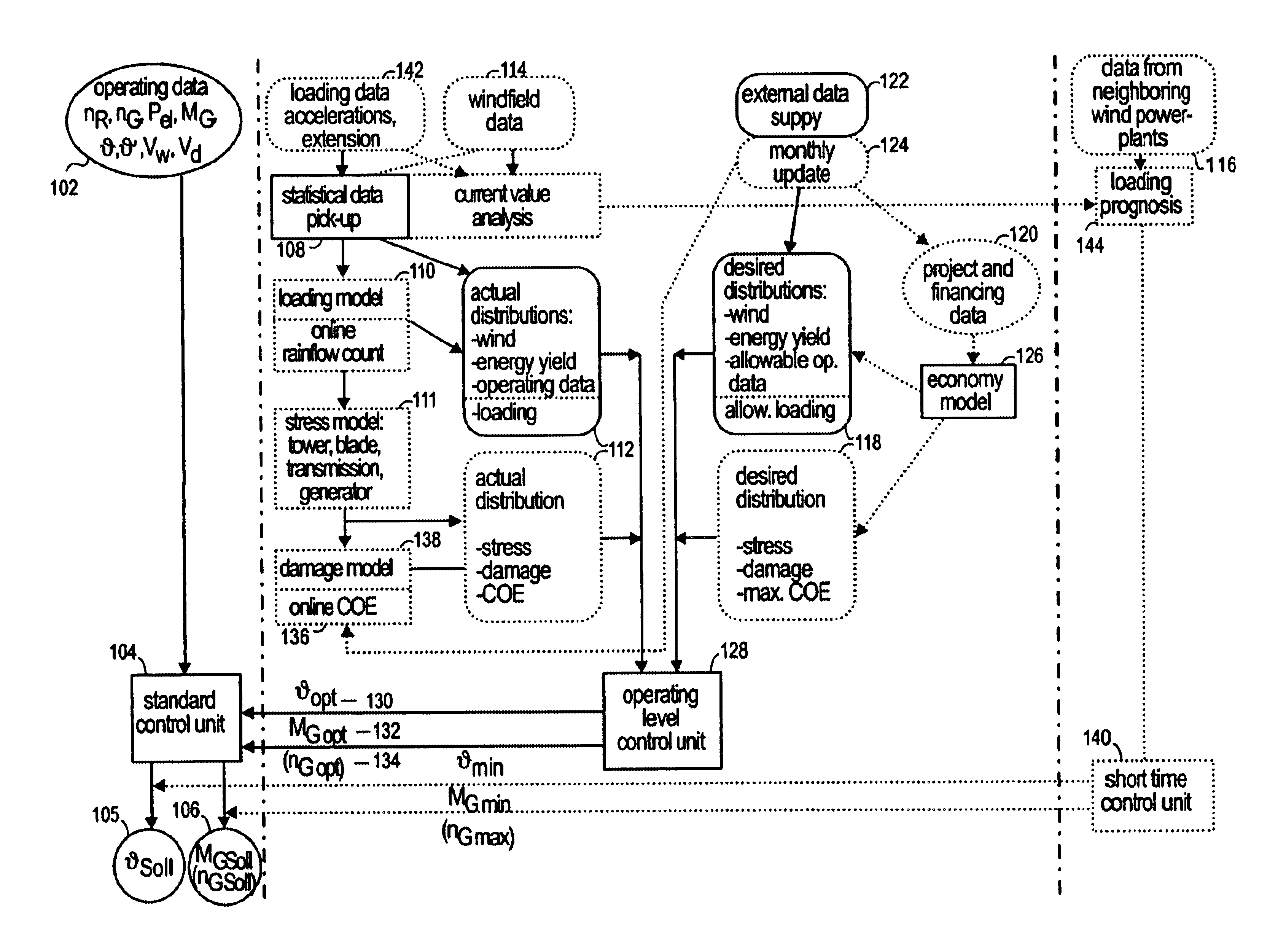
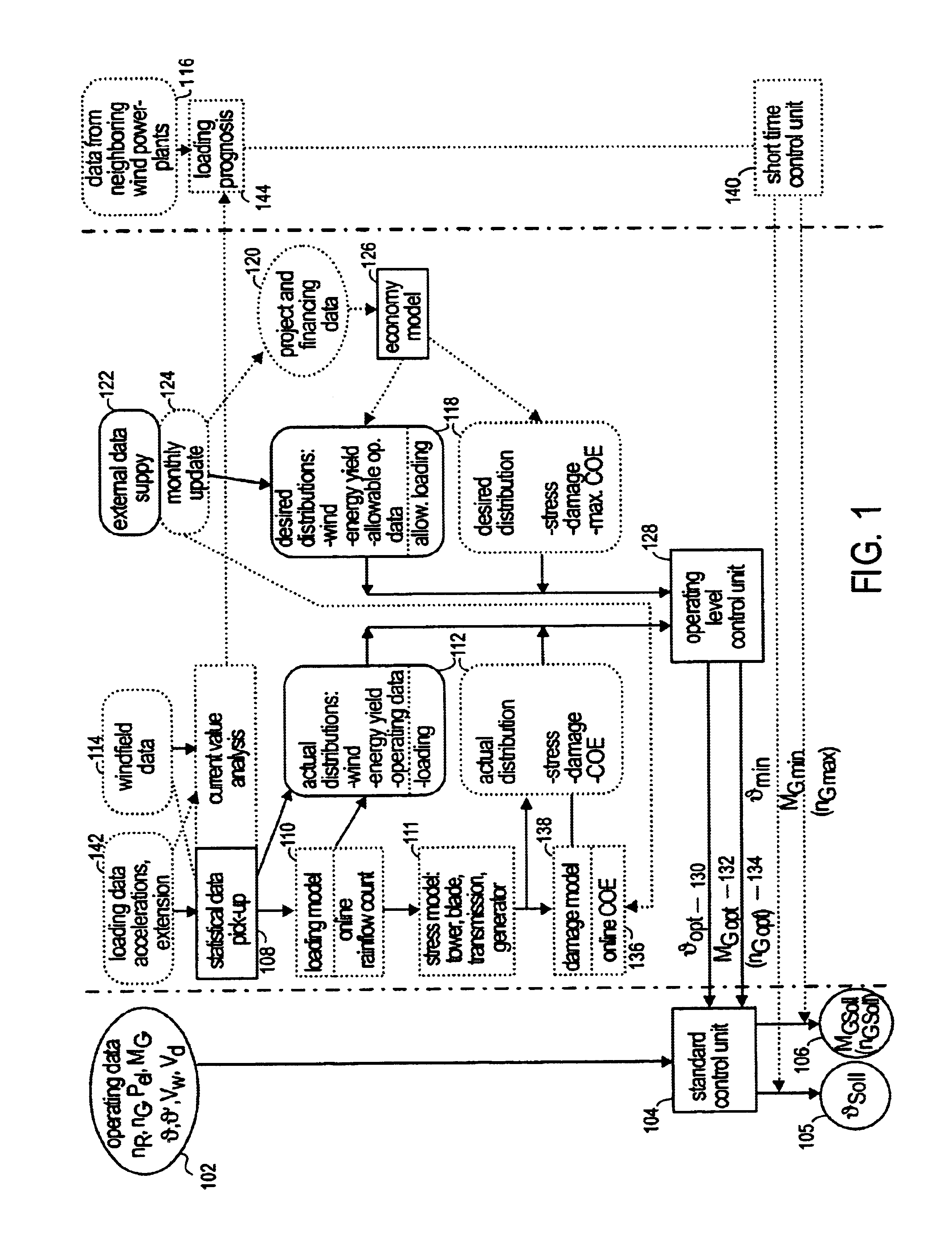
Control system for a wind power plant
InactiveUS6850821B2Raise the ratioIncrease of component fatigueLevel controlWind motor controlPeaking power plantPower station
A control system for a wind power plant that includes a damage module and a control module. The damage module compares existing stress conditions on one or more component parts of the wind power plant to current energy generating costs. The control module alters electric power generated by the wind power plant based upon the comparison.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Wind turbine generator system
ActiveUS20060028025A1Suppress rotational velocityAvoid stopWind motor controlStatic indicating devicesTurbineContinuous operation
A wind turbine generator system can regulate the rotational velocity of the wind turbine within an operation range even when the wind velocity suddenly changes and can perform continuous operation of the wind turbine. The wind turbine generator system includes a generator connected to the shaft of the wind turbine and a converter connected to the generator. When the rotational velocity of the wind turbine is within a predetermined range, power outputted from the generator is controlled so as to follow the instruction concerning the generator output given from the wind turbine to the converter. When the rotational velocity of the wind turbine is out of the predetermined range, the power outputted from the generator is controlled without following the instruction concerning generator output given from the wind turbine to the converter.
Owner:HITACHI IND PROD LTD
Variable speed wind turbine having an exciter machine and a power converter not connected to the grid
ActiveUS7425771B2Avoid distortionImprove power qualityGenerator control circuitsVector control systemsPower qualityPower grid
Owner:INGETEAM POWER TECH
Wind flow estimation and tracking using tower dynamics
A turbine control system for a variable speed electrical generator in a wind turbine mounted atop a support tower. The wind turbine converts wind energy into a driving torque applied to the generator. The control system includes a turbine support tower position sensor and may also include other tower acceleration and velocity sensors. A wind flow estimator uses the measured motion, generator rotation rate and blade pitch angle to predict wind flow over the swept area of the turbine's rotor, and the tower motion. The predicted wind flow and motion is used in the turbine control system to properly adjust its operating point, to tune the controller, to control the rotor rotation rate, and to damp tower oscillations.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
Variable speed wind turbine having a passive grid side rectifier with scalar power control and dependent pitch control
InactiveUS6856041B2Easy to controlImprove responsivenessOptimise machine performanceWind motor controlPower gridVariable speed wind turbine
A variable speed wind turbine having a passive grid side rectifier using scalar power control and dependent pitch control is disclosed. The variable speed turbine may include an electrical generator to provide power for a power grid and a power conversion system coupled to the electrical generator. The power conversion system may include at least one passive grid side rectifier. The power conversion system may provide power to the electrical generator using the passive grid side rectifier. The variable speed wind turbine may also use scalar power control to provide more precise control of electrical quantities on the power grid. The variable speed wind turbine may further use dependent pitch control to improve responsiveness of the wind turbine.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
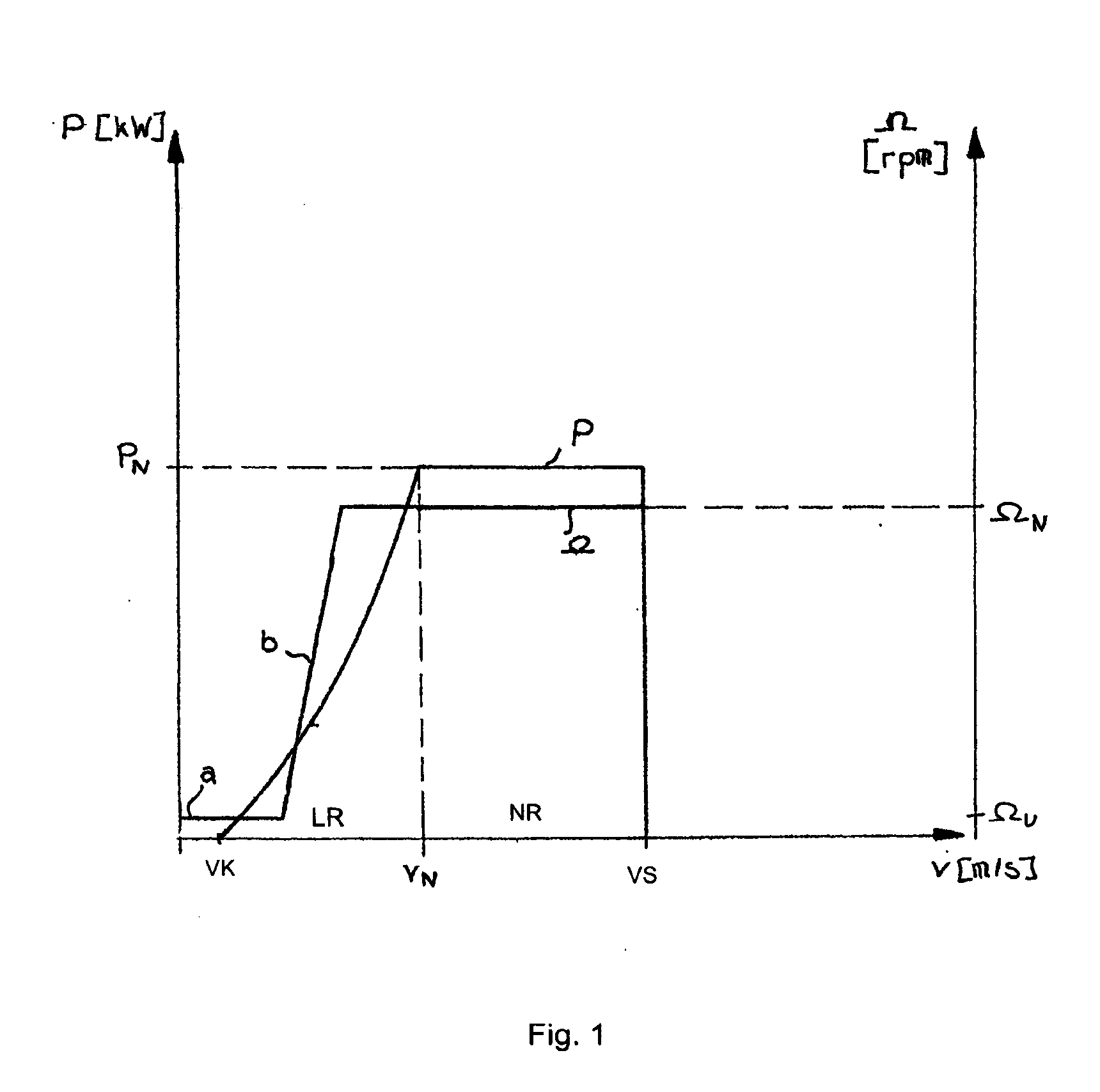
Method for controlling a wind power plant and corresponding wind power plant
InactiveUS20070216166A1Improved and reliableImprove compatibilityWind motor controlComparison table algorithmsPower stationEngineering
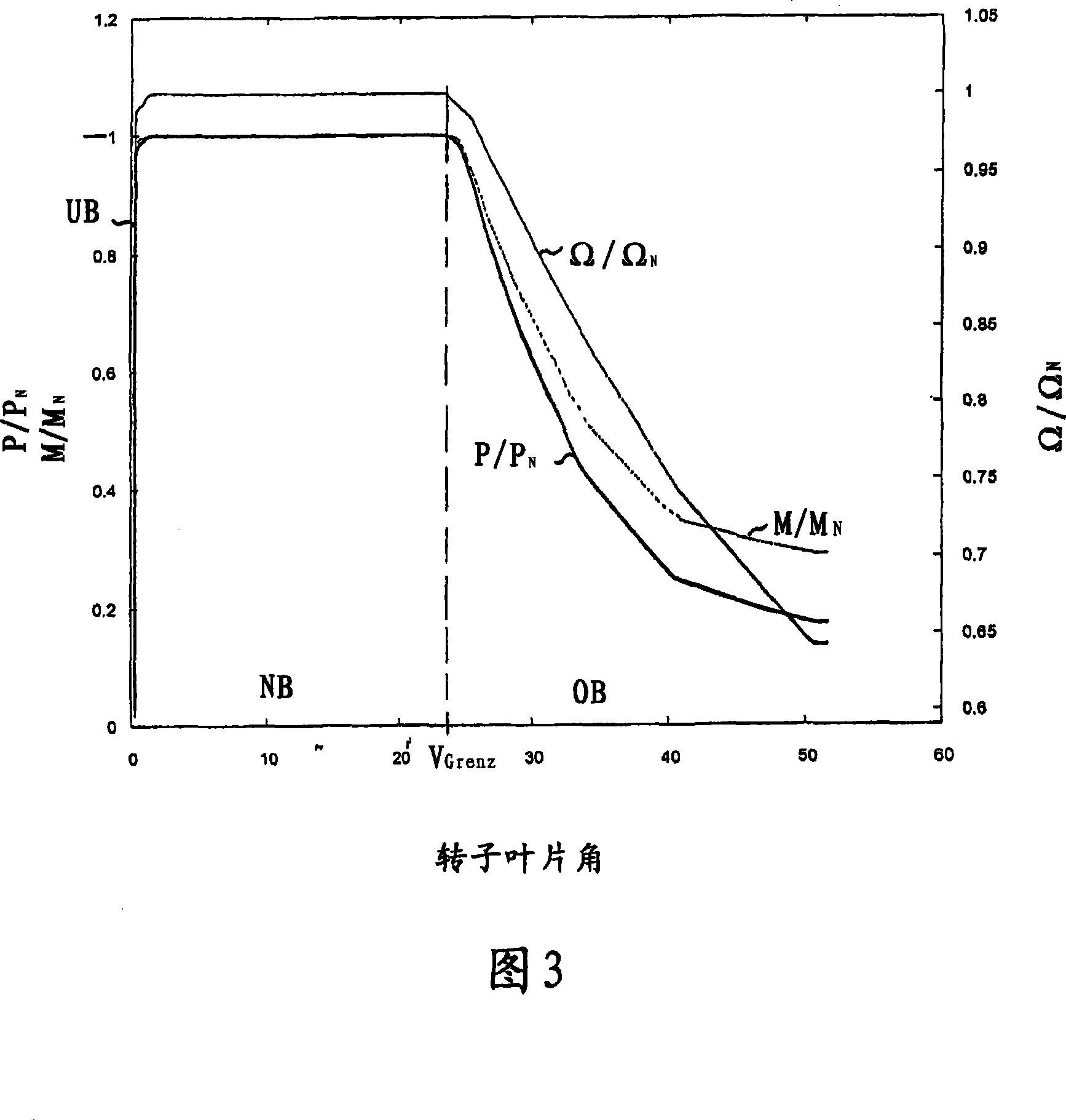
Reduction in power output or rotor speed of a wind turbine above a defined limit value, the reduction not being implemented based on the measured wind speed, but on an input value which on one hand is easily detected physically and by control technology and on the other hand is a good indicator of mechanical stresses on the wind turbine. The invention uses the rotor-blade angle as the input value in a manner that starting at the limit value, the reduction in power output or in rotor speed is adjusted as a function of the rotor-blade angle.
Owner:SENVION GMBH
Variable speed wind turbine having a passive grid side rectifier with scalar power control and dependent pitch control
InactiveUS6853094B2Easy to controlImprove responsivenessWind motor controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPower gridVariable speed wind turbine
A variable speed wind turbine having a passive grid side rectifier using scalar power control and dependent pitch control is disclosed. The variable speed turbine may include an electrical generator to provide power for a power grid and a power conversion system coupled to the electrical generator. The power conversion system may include at least one passive grid side rectifier. The power conversion system may provide power to the electrical generator using the passive grid side rectifier. The variable speed wind turbine may also use scaler power control to provide more precise control of electrical quantities on the power grid. The variable speed wind turbine may further use dependent pitch control to improve responsiveness of the wind turbine.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Wind turbine with friction drive power take off on outer rim
A wind turbine has multiple blades (10) that are mounted on a shaft (19) with a ring around a circumference of the blades. There are tires (18) that are arranged to be in contact or out of contact with the ring. The tires draw generators when the tires are in contact with the ring and the ring is rotating. A controller monitors the wind conditions and controls the turbine to produce electricity or other-energy output or to shut down if the wind falls below a predetermined level.
Owner:NEW WORLD GENERATION
High voltage direct current link transmission system for variable speed wind turbine
ActiveUS20090278351A1Avoiding undesired harmonic distortionImprove power qualityGenerator control circuitsAc-dc conversion without reversalPower qualityHigh-voltage direct current
A variable speed wind turbine having a doubly fed induction generator (DFIG), includes an exciter machine mechanically coupled to the DFIG and a power converter placed between a rotor of the DFIG and the exciter machine. Thus, the power converter is not directly connected to the grid avoiding the introduction of undesired harmonic distortion and achieving a better power quality fed into the utility grid. Moreover, the variable speed wind turbine includes a power control and a pitch regulation.
Owner:INGETEAM POWER TECH
Vibration damping method for variable speed wind turbines
A vibration damping technique for a wind turbine system is described. The wind turbine system includes a vibration damper, which provides a variable signal to control torque produced by a generator of the wind turbine system. The variable signal is based on generator speed and has a first local peak value based on a resonant frequency of tower side-to-side oscillation.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
Variable speed power generator having two induction generators on a common shaft
A variable speed power generator system, includes a primary power induction generator (12), a secondary control induction (14), each of the induction generators having a rotor (22, 24) mounted so as to be rotated by a common shaft (16) of a variable speed prime mover (20), an inverter (50) connected to the stator (15) of the secondary control induction generator, a controller (30) connected to the inverter controls the output of the inverter, output of the primary induction generator is connected to the grid (51), controller provides output signal to the inverter based on selected inputs to the controller so that the output of the primary induction generator matches the active and reactive power requirements of the grid. An induction machine which includes a rotor having laminations and insulated cage bars, the bars being electrically isolated from on another as well as electrically insulated from the laminations.
Owner:VARISPEED ELECTRIC MOTORS
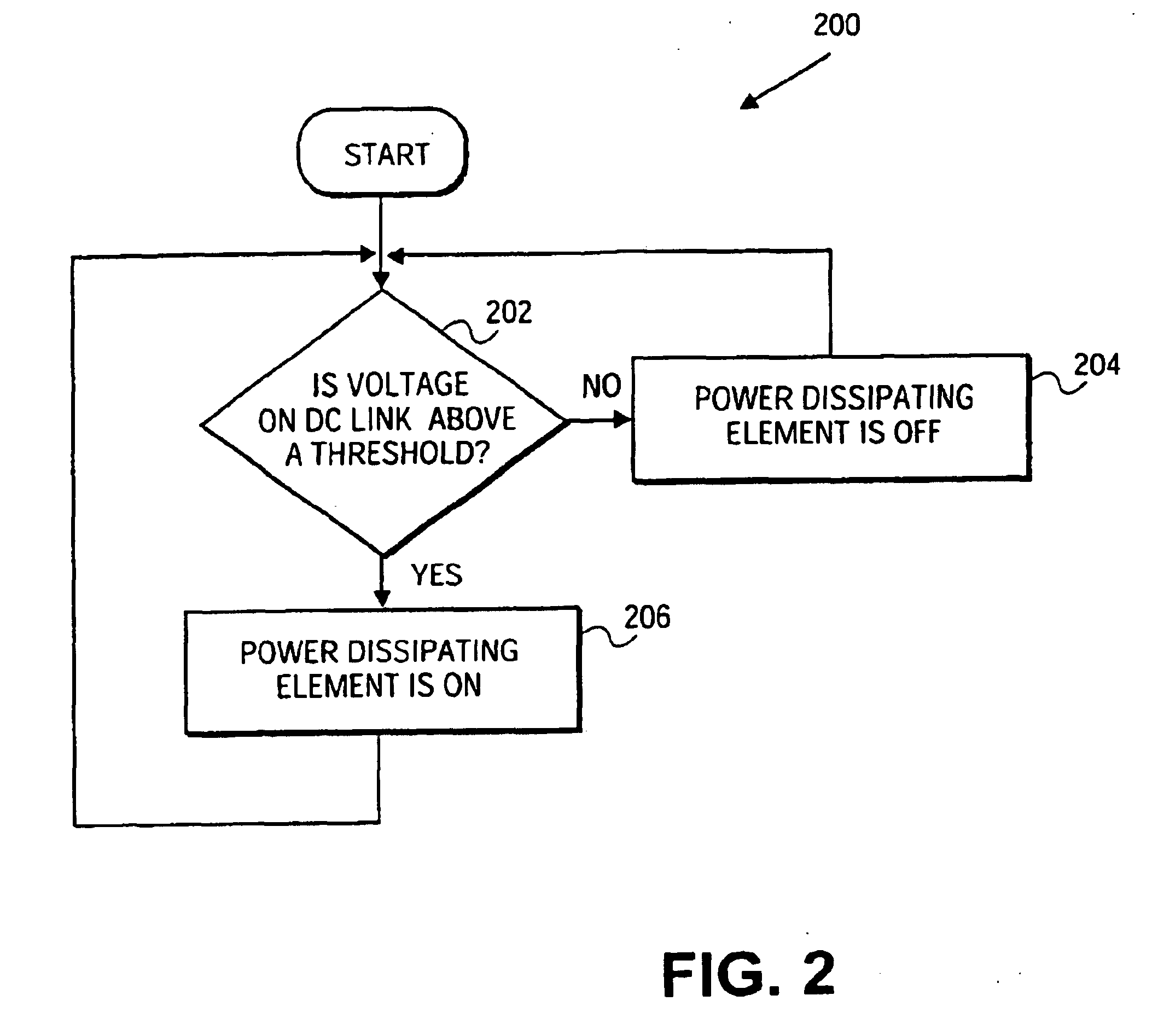
Variable speed wind turbine, and a method for operating the variable speed wind turbine during a power imbalance event
ActiveUS20120217824A1Better energy managementExcess power being dissipatedRotary current collectorWind motor controlVariable speed wind turbineTurbine
A variable speed wind turbine is provided. The wind turbine comprises a generator, a power converter for converting at least a portion of electrical power generated by the generator, an energy management arrangement coupled to the power converter, the energy management arrangement comprises an energy storage unit, and a controller. The controller is adapted to detect a power imbalance event and to transfer at least a portion of excess electrical energy generated by the generator to the energy storage unit to be stored therein when the power imbalance event is detected.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Wind turbine generator system
ActiveUS7268443B2Increase usageContinuous operationWind motor controlStatic indicating devicesRotation velocityTurbine
A wind turbine generator system can regulate the rotational velocity of the wind turbine within an operation range even when the wind velocity suddenly changes and can perform continuous operation of the wind turbine. The wind turbine generator system includes a generator connected to the shaft of the wind turbine and a converter connected to the generator. When the rotational velocity of the wind turbine is within a predetermined range, power outputted from the generator is controlled so as to follow the instruction concerning the generator output given from the wind turbine to the converter. When the rotational velocity of the wind turbine is out of the predetermined range, the power outputted from the generator is controlled without following the instruction concerning generator output given from the wind turbine to the converter.
Owner:HITACHI IND PROD LTD
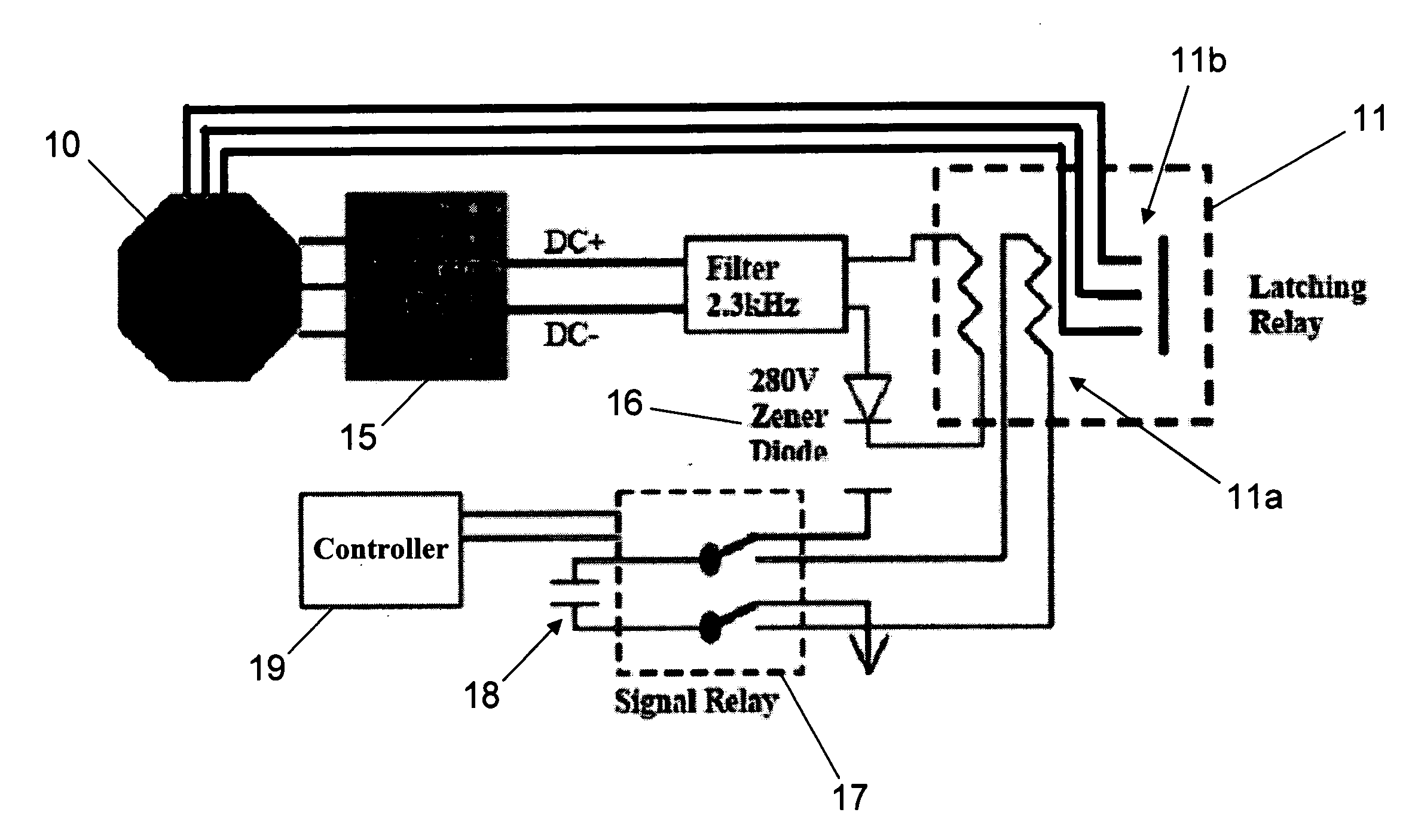
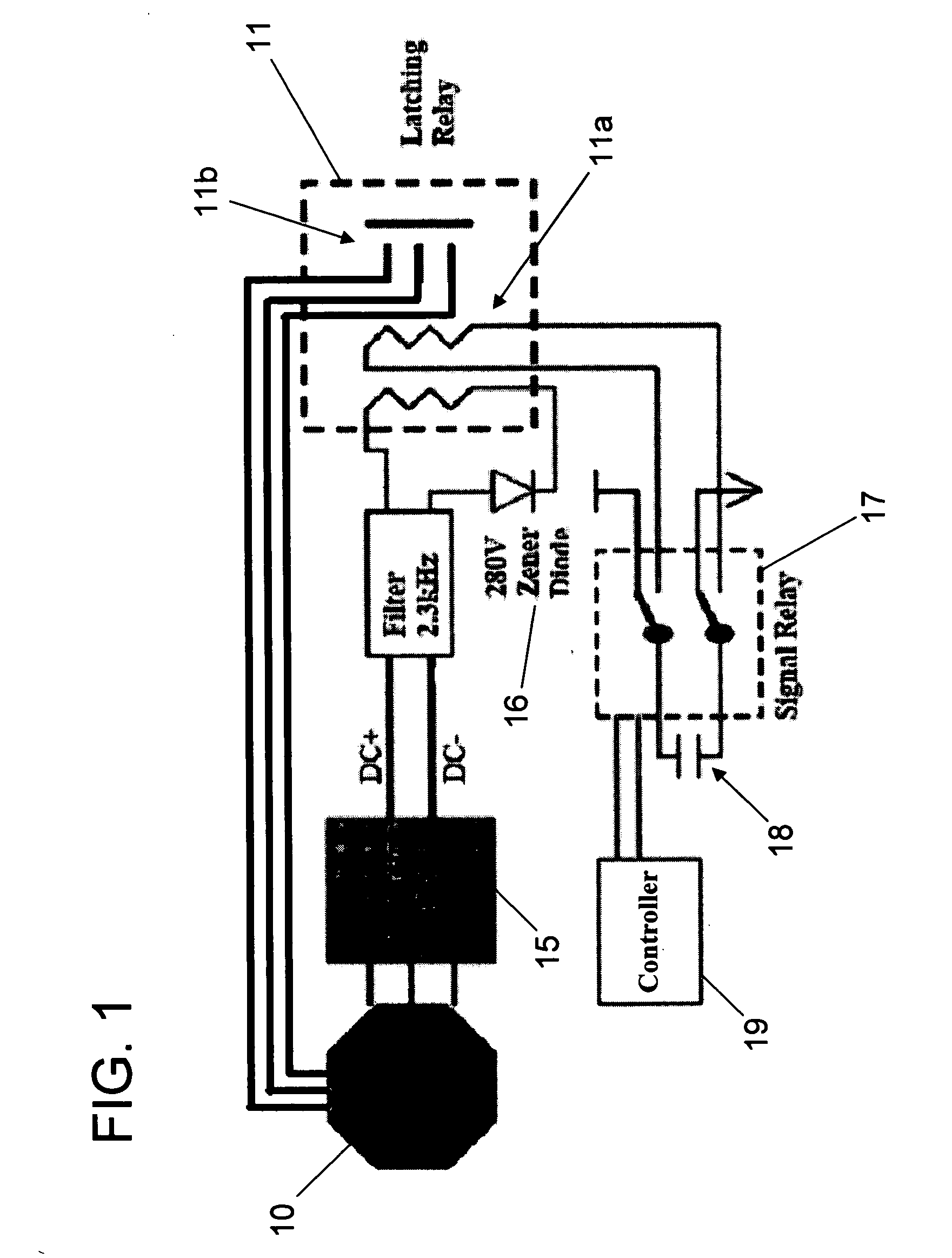
Stall controller and triggering condition control features for a wind turbine
InactiveUS20070170724A1Degraded aerodynamic performanceIncrease torqueAC motor controlWind motor controlControl theoryConductor Coil
Control features for a wind turbine that control the turbine over a range of wind speeds and under triggering conditions with reduced noise, cost, and reliability issues associated with other such controls. Control is accomplished via control electronics, which adjust the torque produced by the electrical output generation device (e.g., alternator) within the wind turbine. During normal operation, torque is adjusted for optimum aerodynamic performance and maximum output of power. In winds above rated power, the control circuit regulates torque to lower aerodynamic performance, as necessary to maintain desired power level output. In triggering conditions, such as during simultaneous control circuit failure and loss of some portion of the electrical output generation device in extreme winds, wind turbine control is accomplished by increasing torque (e.g., via a separate controller) from the electrical output generation device via shorting of windings, so as to cause retardation of blade rotation.
Owner:WIND RESOURCE LLC
Method for controlling a wind turbine and corresponding wind turbine
InactiveUS7629702B2Improved and reliableImprove compatibilityWind motor controlComparison table algorithmsEngineeringLimit value
Reduction in power output or rotor speed of a wind turbine above a defined limit value, the reduction not being implemented based on the measured wind speed, but on an input value which on one hand is easily detected physically and by control technology and on the other hand is a good indicator of mechanical stresses on the wind turbine. The invention uses the rotor-blade angle as the input value in a manner that starting at the limit value, the reduction in power output or in rotor speed is adjusted as a function of the rotor-blade angle.
Owner:SENVION GMBH
Wind Turbine Blade
ActiveUS20080206055A1Extreme and fatigue loadIncreased durabilityPropellersRotary propellersTurbine bladeSolidity
A wind turbine comprising a wind turbine blade with high lift and / or low solidity is provided. The blade is directed towards pitch regulated wind turbines, which are operated at variable rotor speed and have blades longer than about 30 meters. The blade is for example advantageous in that it may provide reduced extreme and fatigue loads at the same or near the same power production.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Wind power generation system
ActiveUS8178991B2Efficiently and optimally produceConstant generator RPM regardless of wind velocityOptimise machine performanceWind motor controlElectricityWind power system
The inventive technology described herein generally relates to the field of renewable energy production and / or more particularly wind power generation. More specifically, methods and apparatus for wind power generation utilizing perhaps multiple generators coupled through a radius adjustable coupler to at least one rotational movement element such that said coupled connection is dynamically movable across the surface the rotational movement element so as to maintain an electrical output at a constant generator rotation(s) per minute (RPM) according to the varying rotational velocity along the radius of a rotational movement element. In some embodiments such coupled generators may be sequentially loaded and disengaged to such rotational movement element to maintain an electrical output at a constant generator RPM. The inventive technology may be particularly suited to accomplishing such wind power generation across a broad range of wind and turbine rotational velocities.
Owner:SANTANGELO LAW OFFICES P C
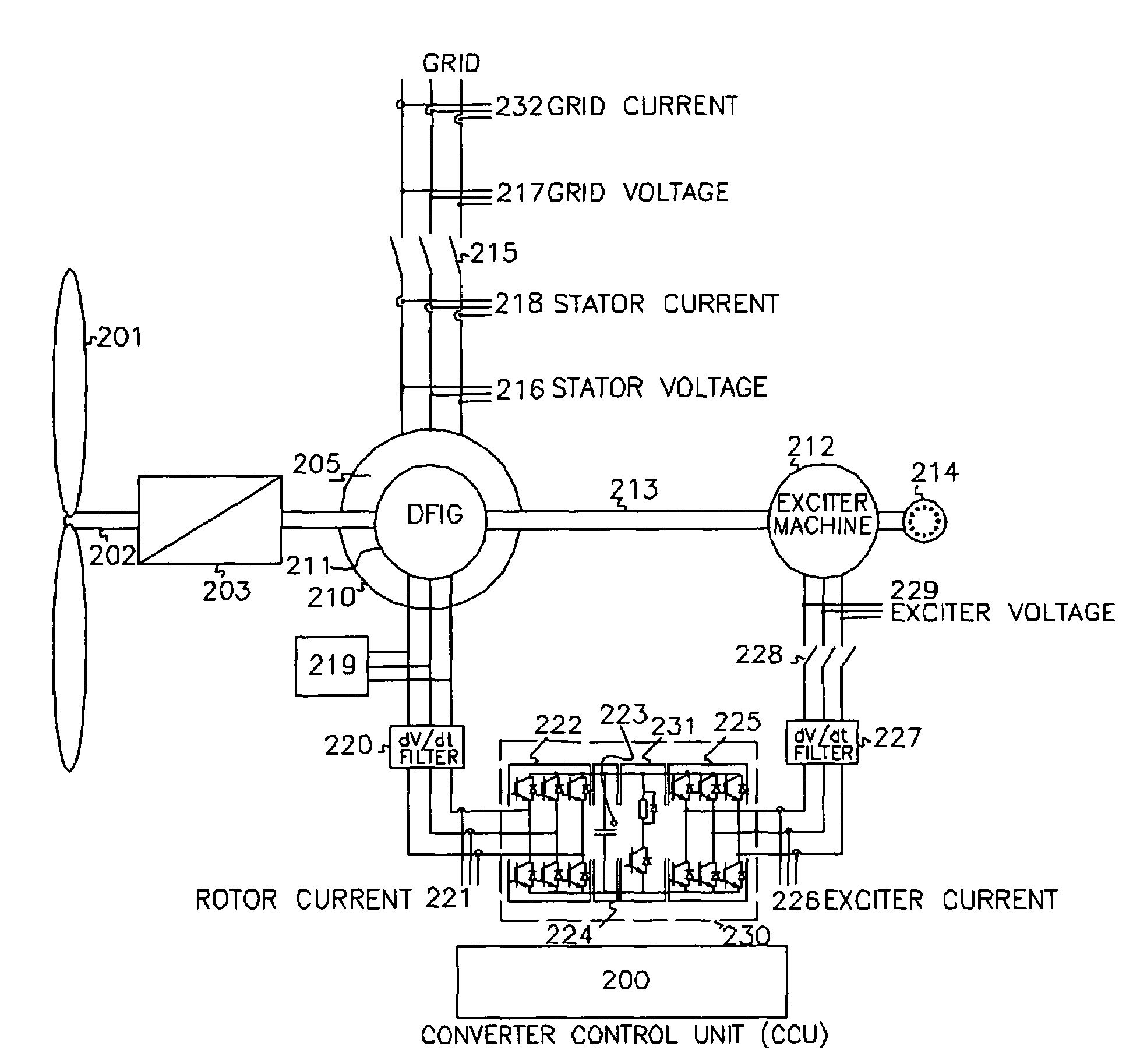
Operating method for a wind turbine with a supersynchronous cascade
InactiveUS7291937B2Improve current qualityEfficient productionGenerator control circuitsWind motor controlPhase shiftedRotation velocity
The invention relates to a wind energy system having a rotor that can be driven by the wind, preferably having one or more rotor blades that can be adjusted in angle, a generator directly or indirectly connected with the rotor, to generate electric energy, which is configured as an asynchronous generator having a super-synchronous converter cascade in the rotor circuit, for slip-variable generator operation, so that power output of the generator is possible at variable speeds of rotation of the rotor, and an operation guide system that is configured to regulate the speed of rotation of the rotor, within a predetermined wind speed range. To improve the energy yield, it is provided that the super-synchronous rectifier cascade is configured in the rotor circuit for feeding the slip power into the network. For this purpose, the super-synchronous converter cascade has a DC voltage intermediate circuit having a high-set element. These are configured to switch, as IGBT switches, with a 180 degree phase shift relative to the rotor voltage.Furthermore, the invention relates to a method for regulating the power output of the wind energy system, in that the slip is regulated, whereby the slip power is fed into the network.
Owner:DEWIND TURBINE CO
Wind turbine control methods and systems
ActiveUS20110049885A1Quick changeIncrease power generationPropellersLevel controlControl powerControl system
A method of controlling the operation of a variable speed wind turbine (11), tracking a power curve (25, 27) including a nominal operational region (3) and sub-nominal operational regions (2, 1, 0), comprising steps of: a) implementing a control strategy to follow said power curve in said nominal operational region (3) based on the use of demanded torque Td for controlling power P and on the use of demanded pitch θd for controlling demanded torque Td; b) implementing a control strategy to follow said power curve in sub-nominal operational regions (2, 1, 0) based on the use of demanded torque Td for controlling power P and on the setting of a constant optimum value for demanded pitch θd in each sub-nominal operational region (2, 1, 0). The invention also refers to a control system comprising one or more Adaptive Predictive Controllers (51, 53, 55, 59).
Owner:GAMESA INNOVATION & TECH SA
Method for controlling a wind power plant and corresponding wind power plant
InactiveCN101031720AWind motor controlComparison table algorithmsPeaking power plantMachine utilization
The power of wind energy or the revolution rate drive down to the prescribed limit value has been carried based on easily measured in physical and control technique aspect and reflect the input variable of machine utilization but not based on the metrical wind speed. For the assume of this invention, use rotor blade angle as input variable, then when arrive in the limit value adjust power and the drive down of revolution rate based on the rotor blade angle.
Owner:SENVION GMBH
Popular searches
Contigency dealing ac circuit arrangements Variable speed operation control Engine controllers Machines/engines Electric motor speed/torque regulation Wind energy generation Photovoltaic energy generation Single network parallel feeding arrangements Dynamo-electric converter control Wind motor combinations
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com