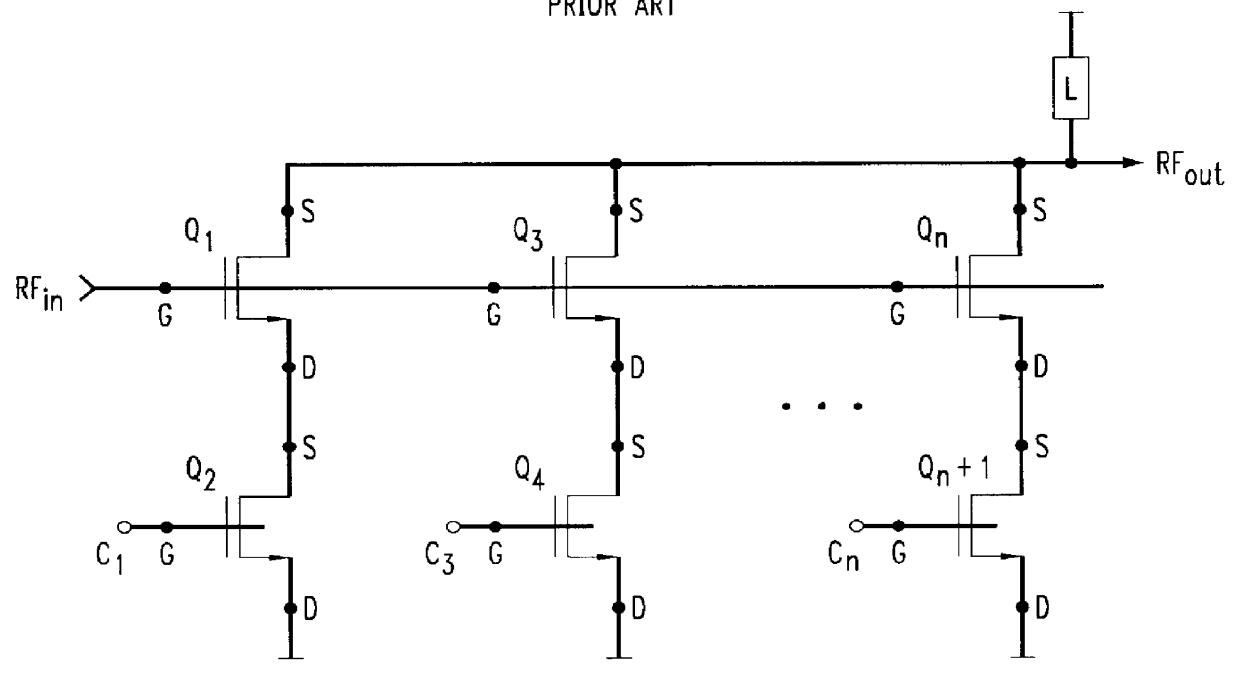
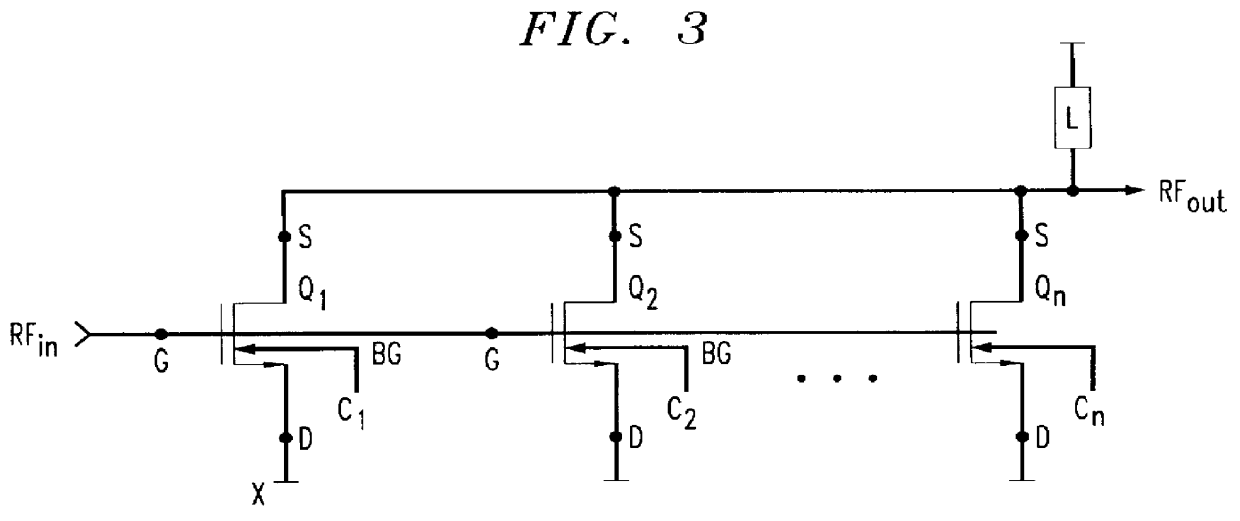
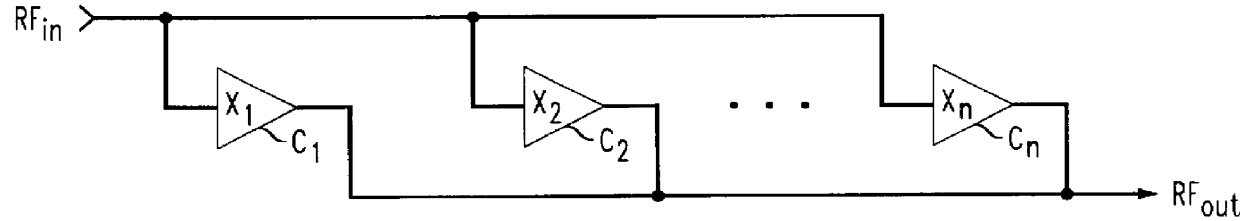
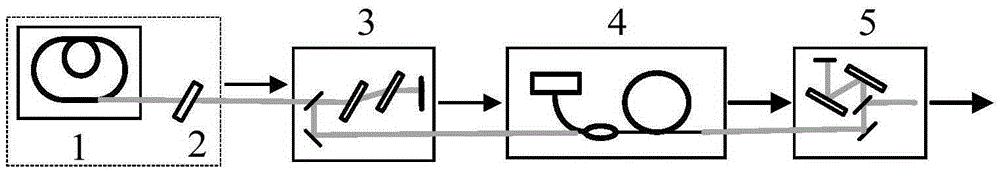
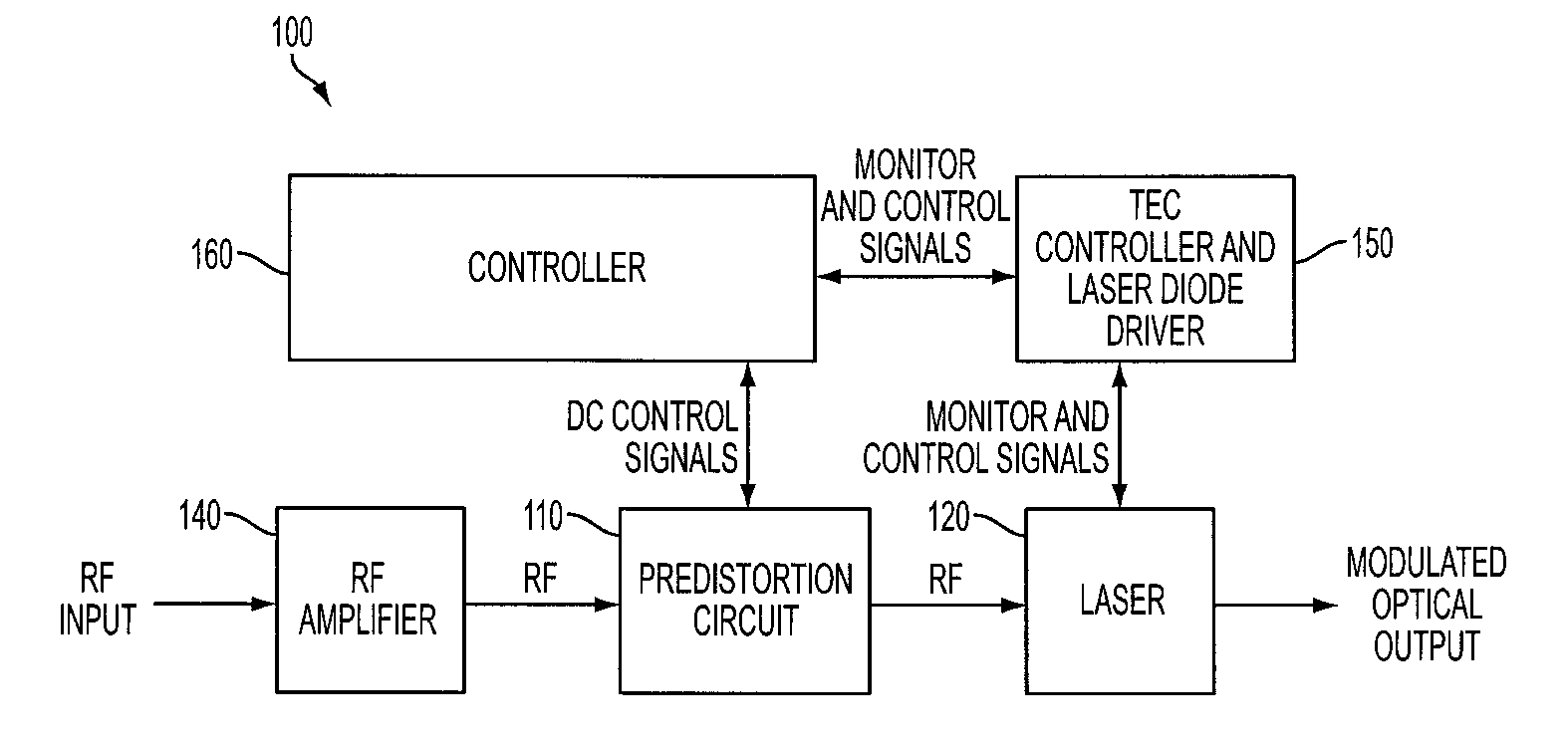
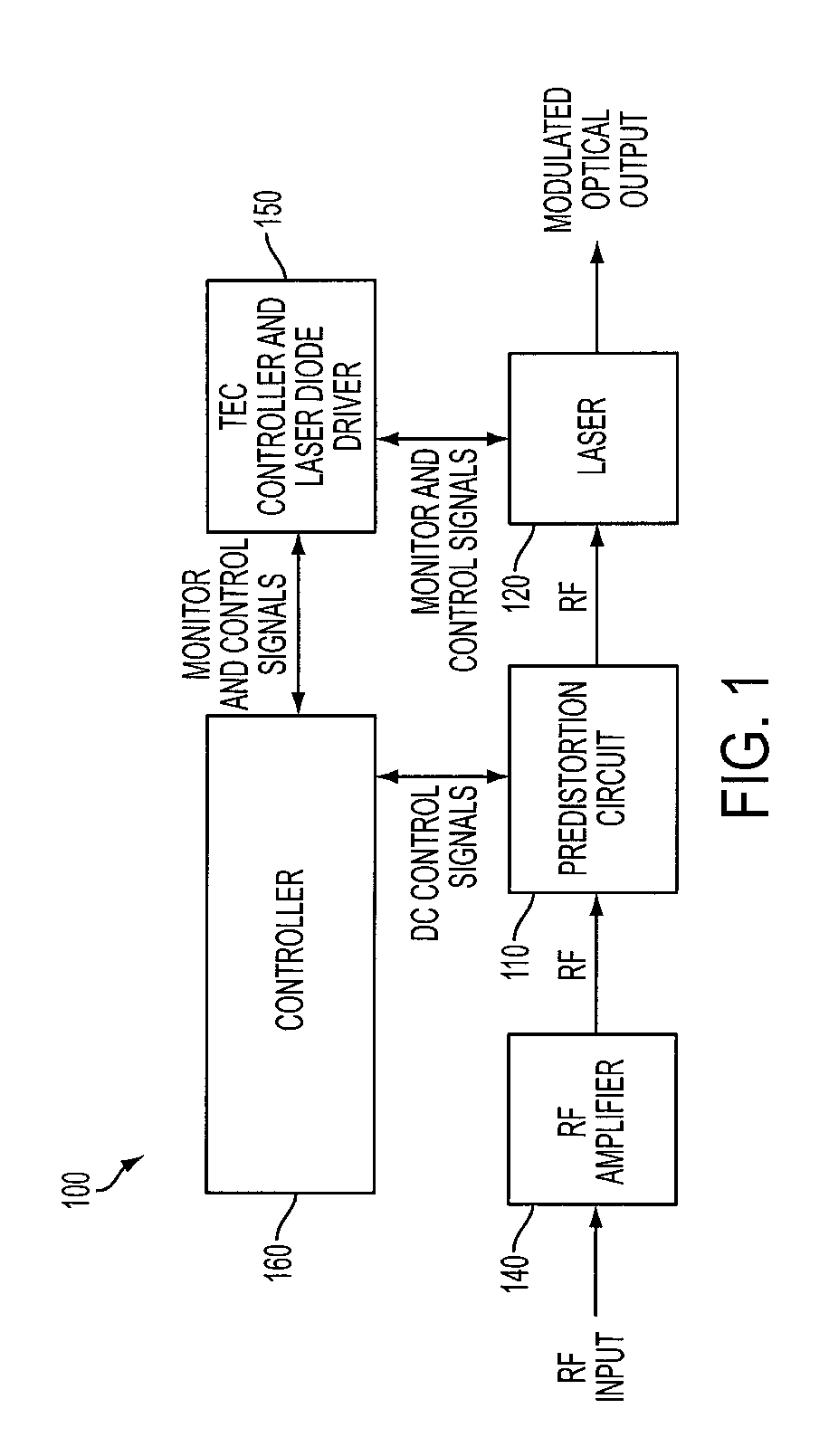
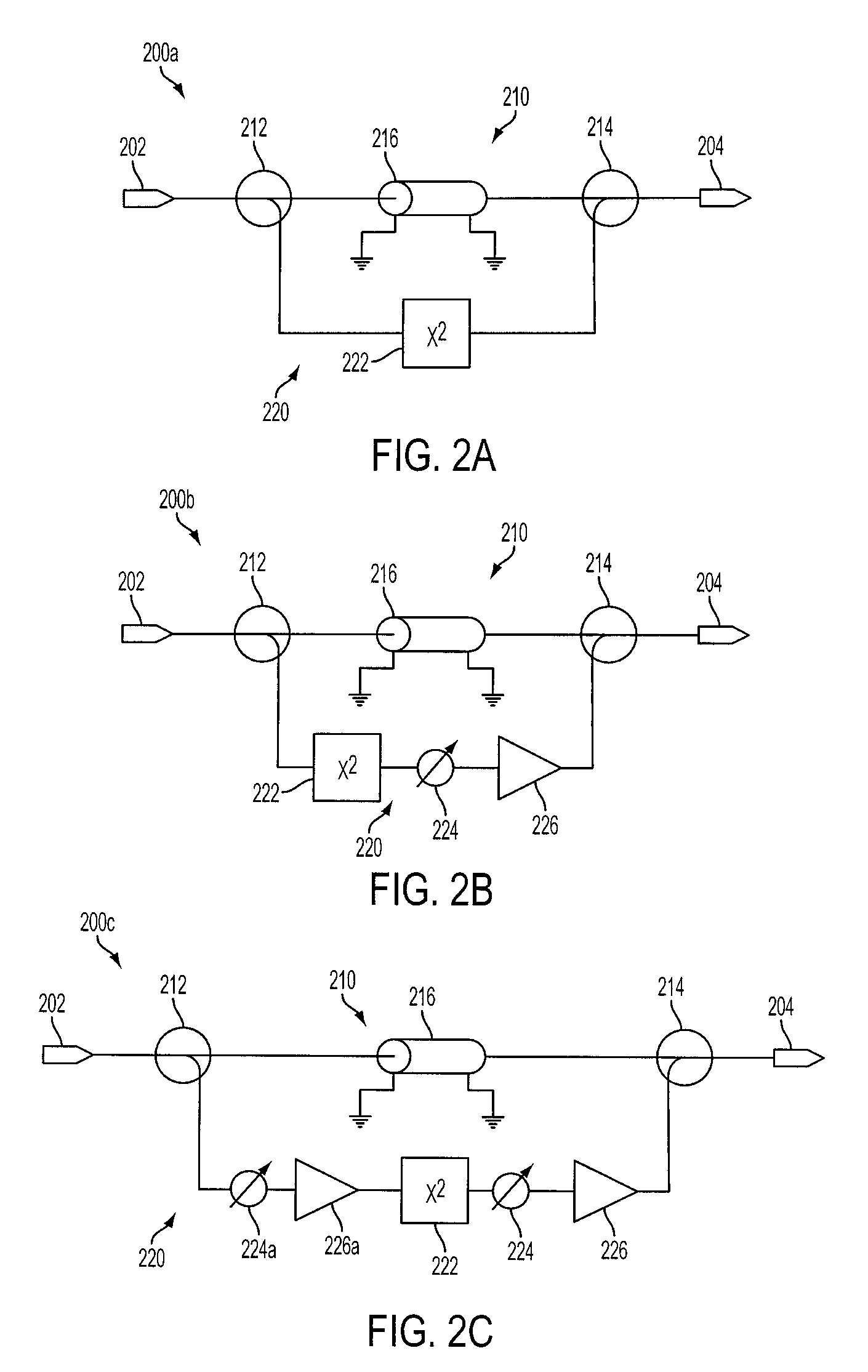
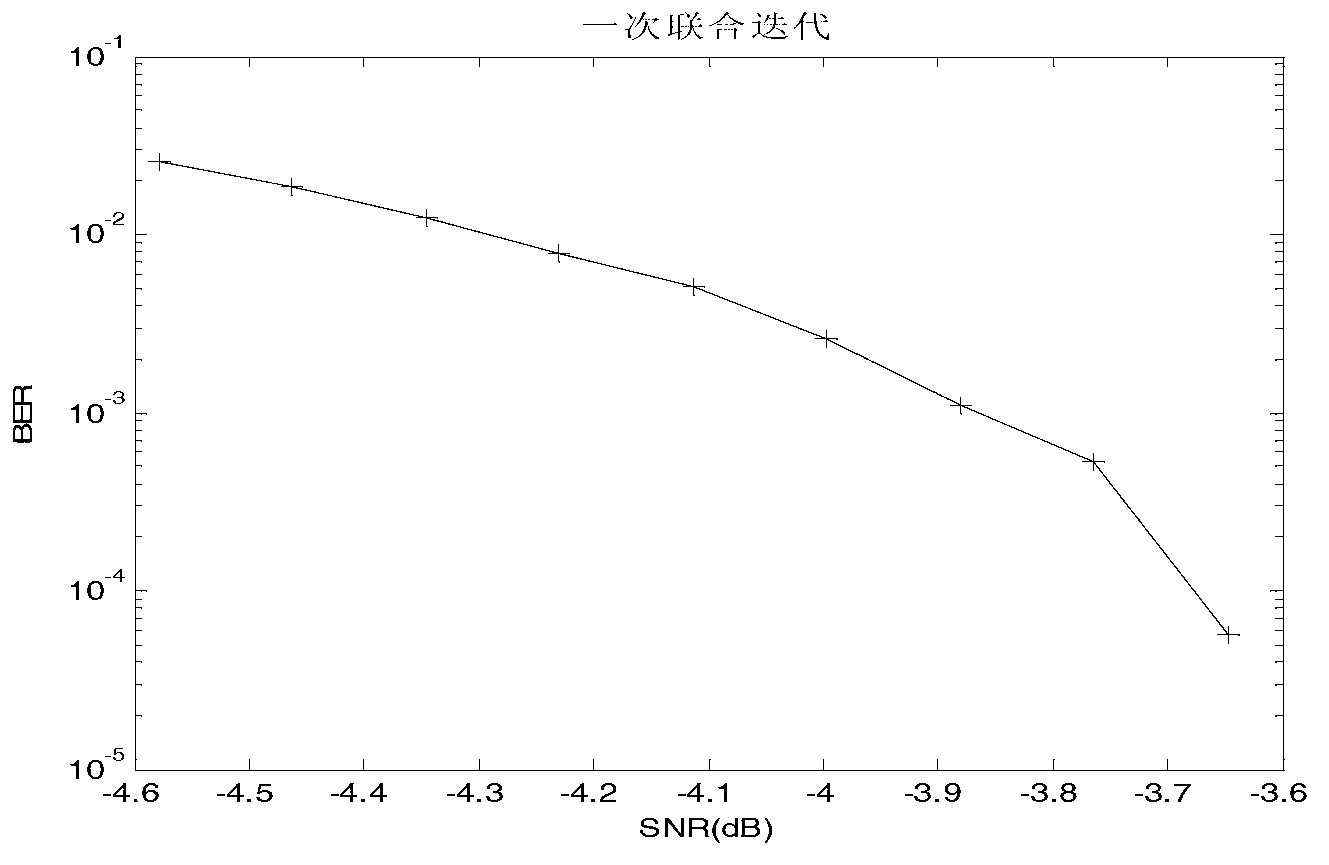
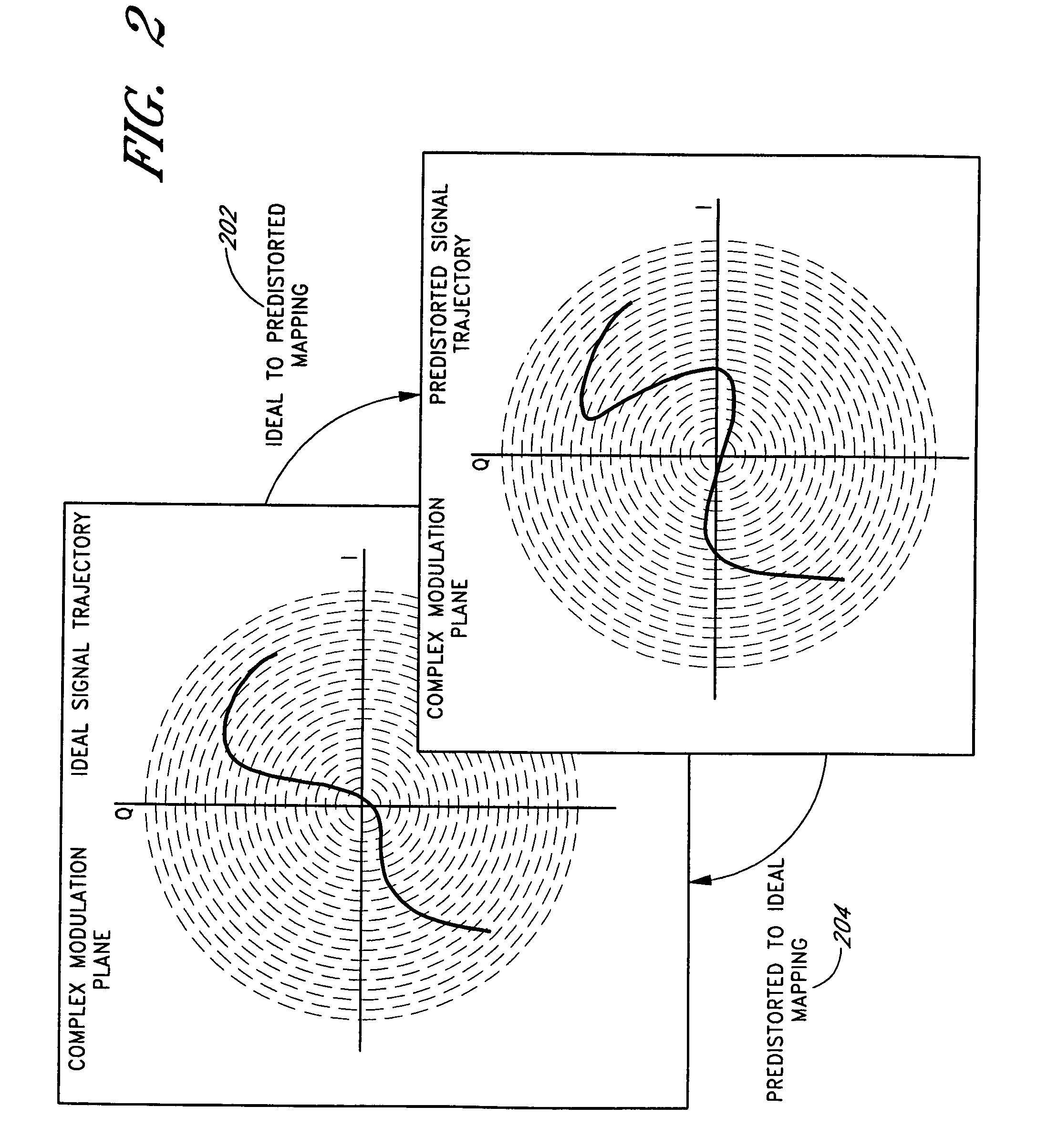
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
129 results about "Nonlinear amplifier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
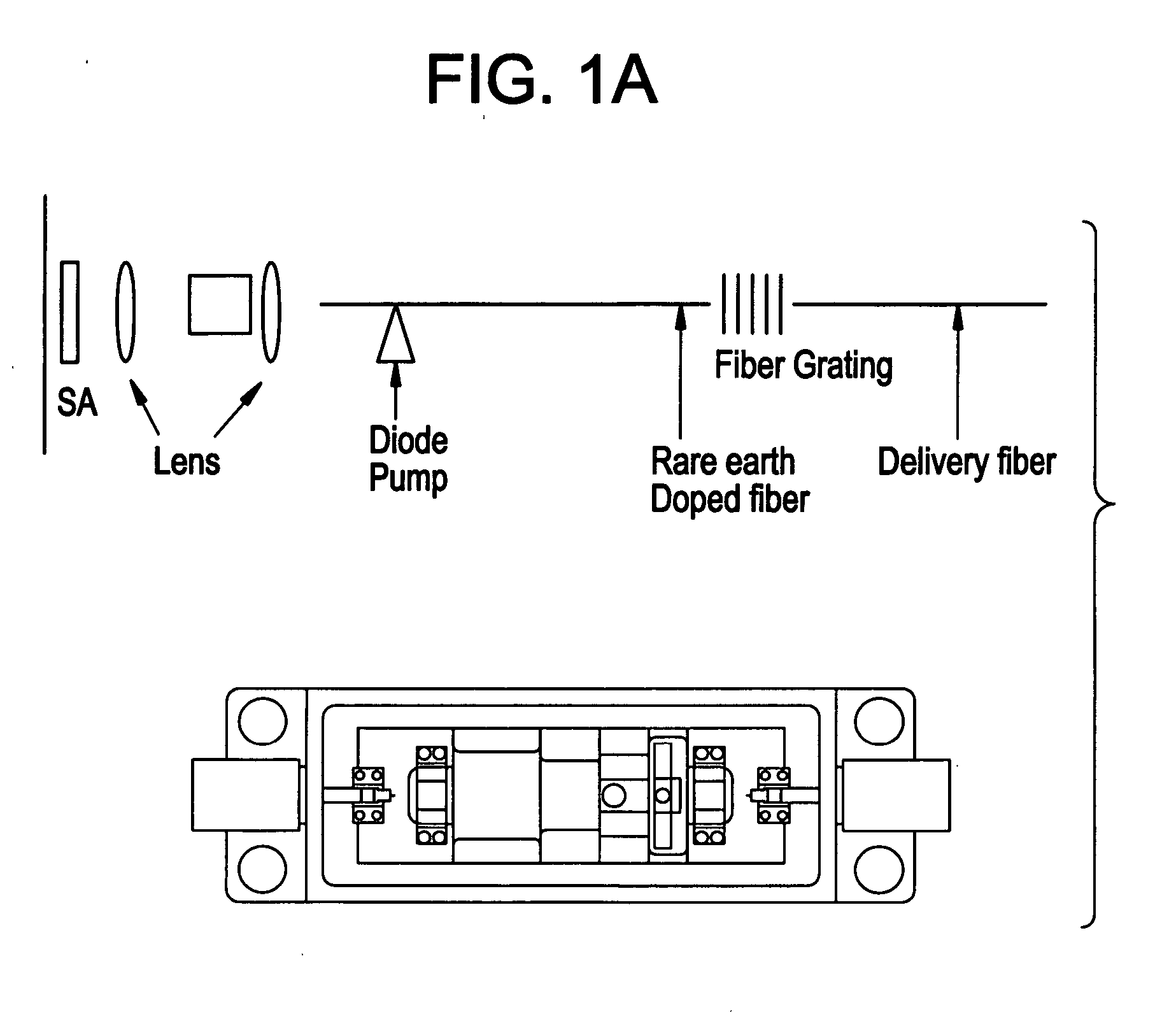
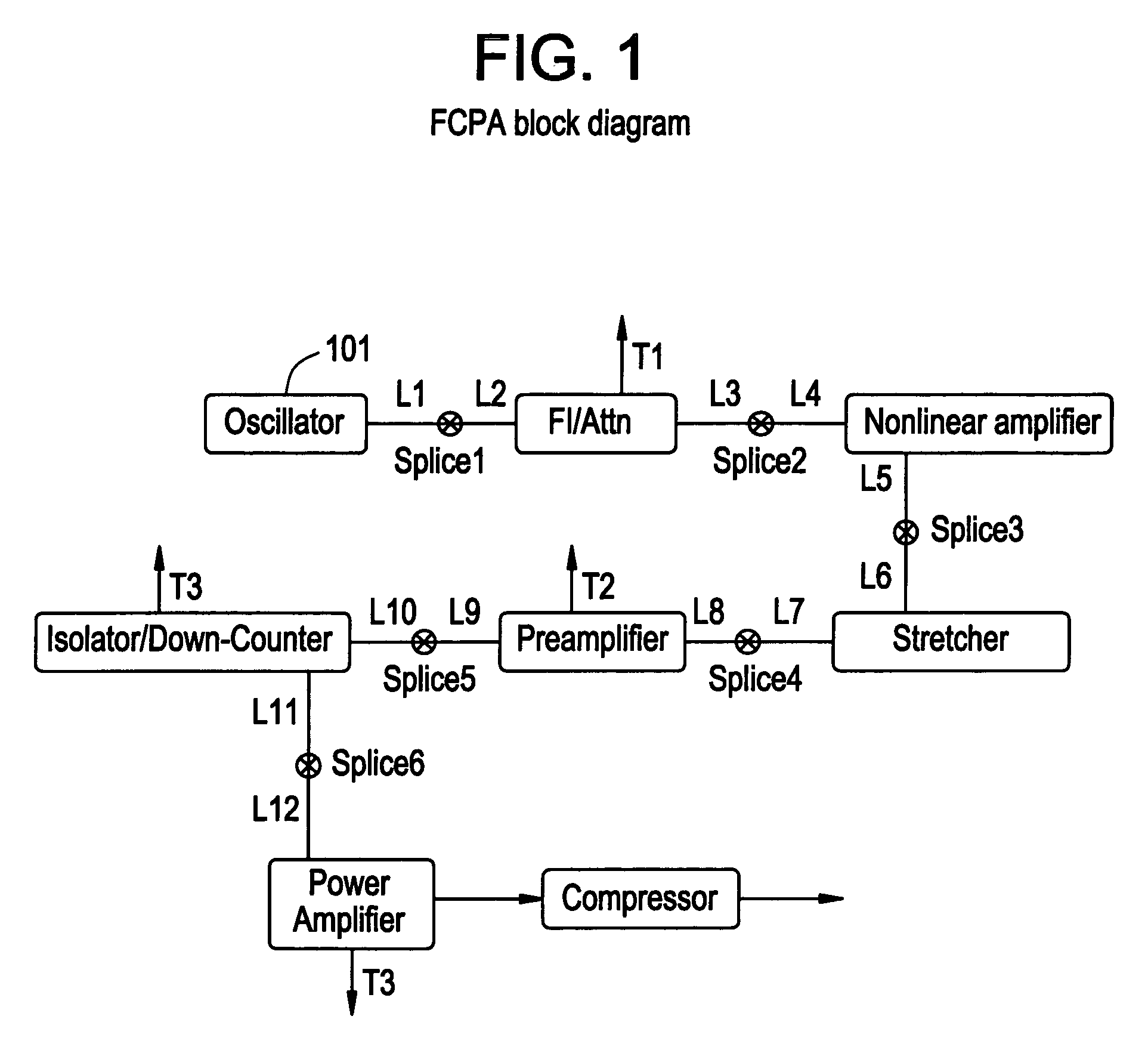
Apparatus and method for the generation of high-power femtosecond pulses from a fiber amplifier
InactiveUS6014249ALong pulse widthLow costLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsFiberDouble-clad fiber
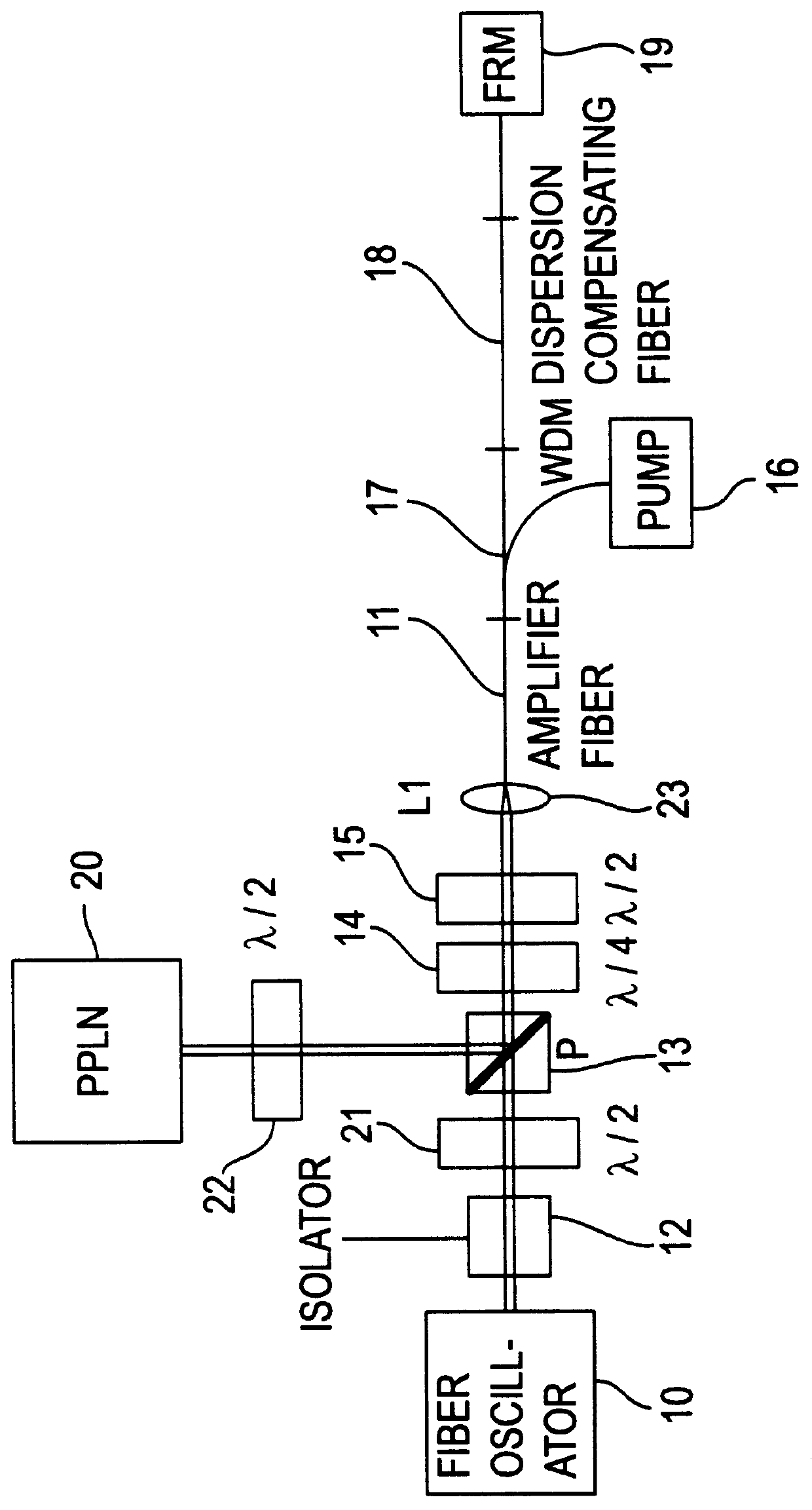
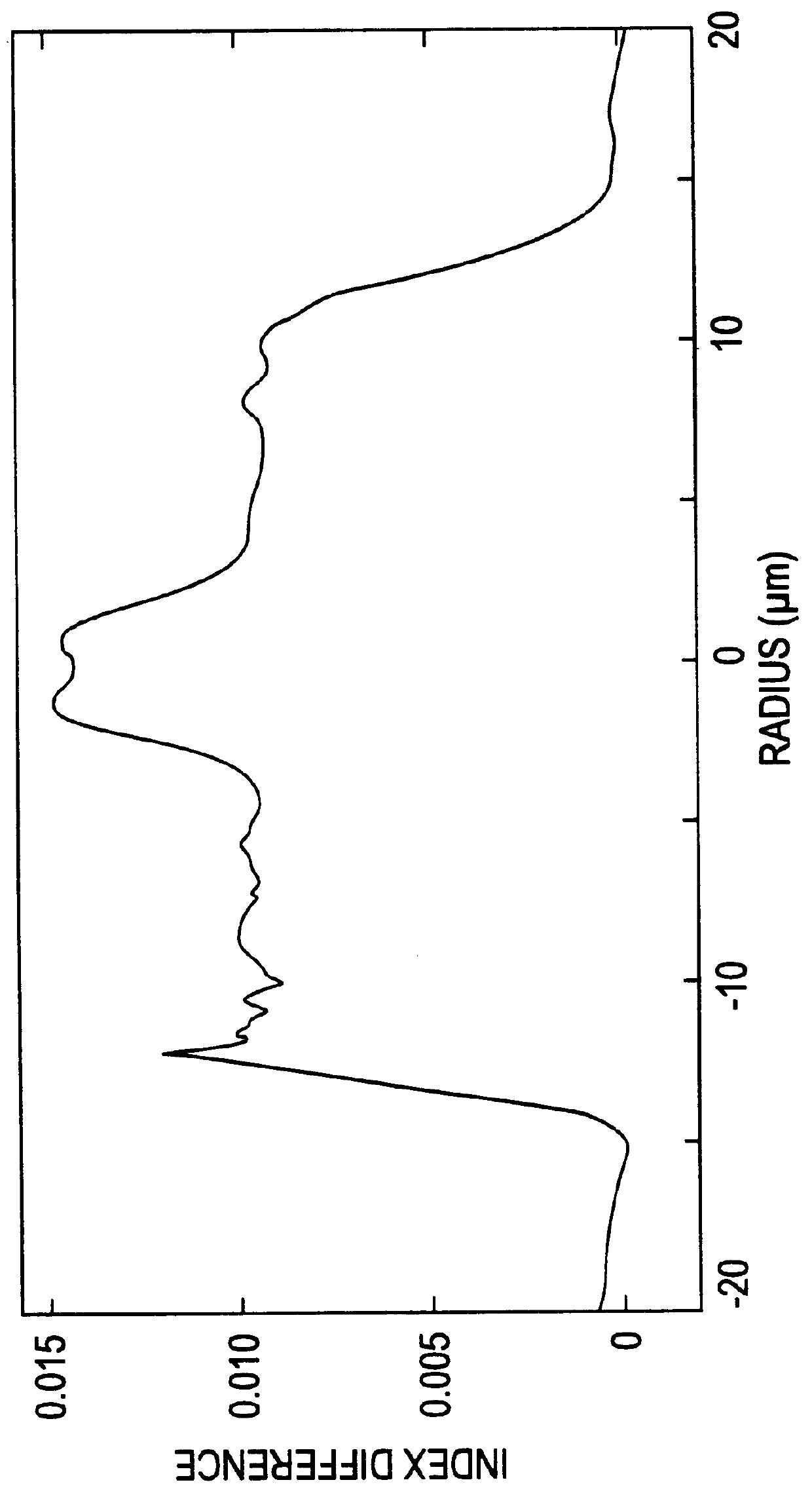
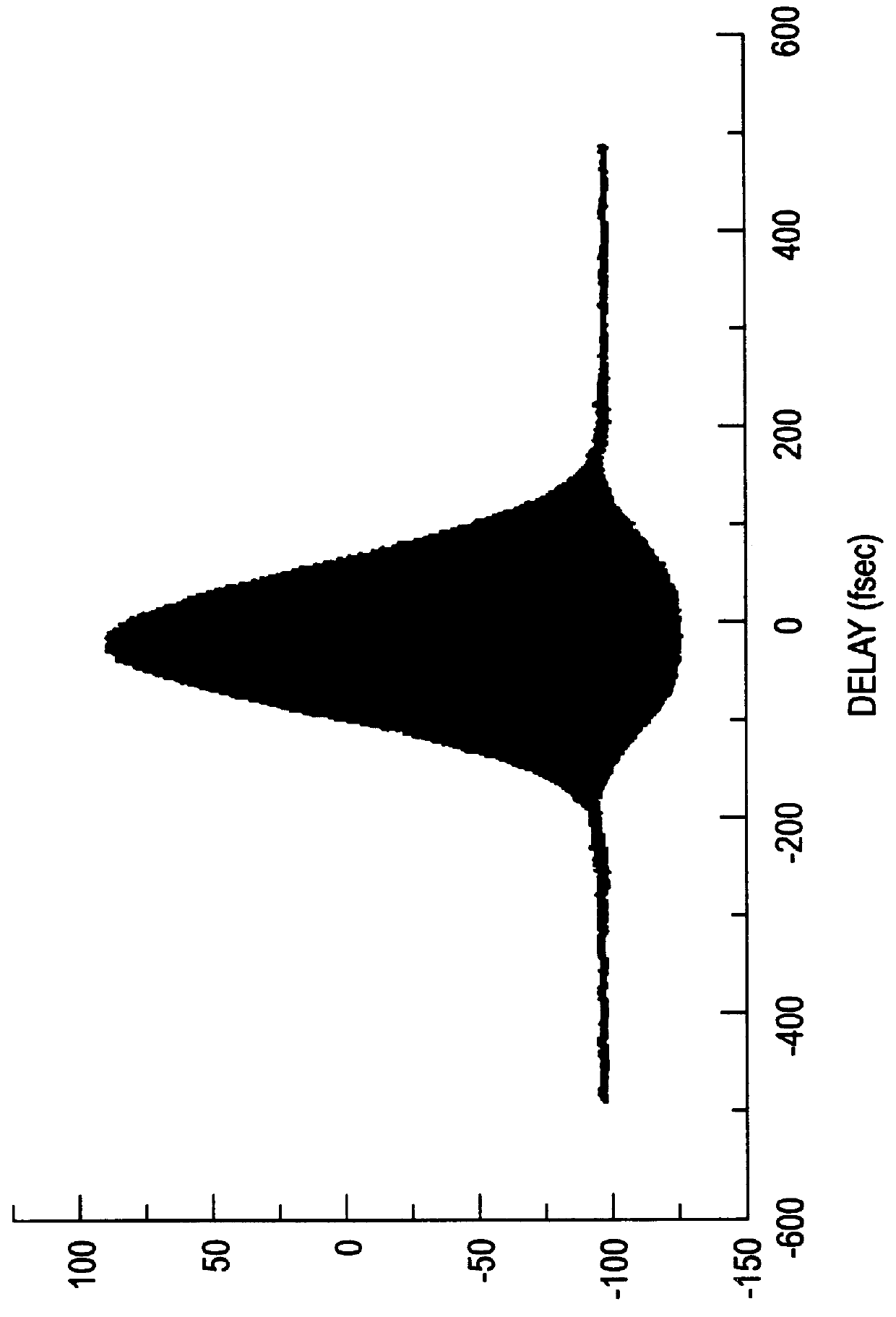
An apparatus generates femtosecond pulses from laser amplifiers by nonlinear frequency conversion. The implementation of nonlinear frequency-conversion allows the design of highly nonlinear amplifiers at a signal wavelength (SW), while still preserving a high-quality pulse at an approximately frequency-doubled wavelength (FDW). Nonlinear frequency-conversion also allows for limited wavelength tuning of the FDW. As an example, the output from a nonlinear fiber amplifier is frequency-converted. By controlling the polarization state in the nonlinear fiber amplifier and by operating in the soliton-supporting dispersion regime of the host glass, an efficient nonlinear pulse compression for the SW is obtained. The generated pulse width is optimized by utilizing soliton compression in the presence of the Raman-self-frequency shift in the nonlinear fiber amplifier at the SW. High-power pulses are obtained by employing fiber amplifiers with large core-diameters. The efficiency of the nonlinear fiber amplifier is optimized by using a double clad fiber (i.e., a fiber with a double-step refractive index profile) and by pumping light directly into the inner core of this fiber. Periodically poled LiNbO3 (PPLN) is used for efficient conversion of the SW to a FDW. The quality of the pulses at the FDW can further be improved by nonlinear frequency conversion of the compressed and Raman-shifted signal pulses at the SW. The use of Raman-shifting further increases the tuning range at the FDW. For applications in confocal microscopy, a special linear fiber amplifier is used.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
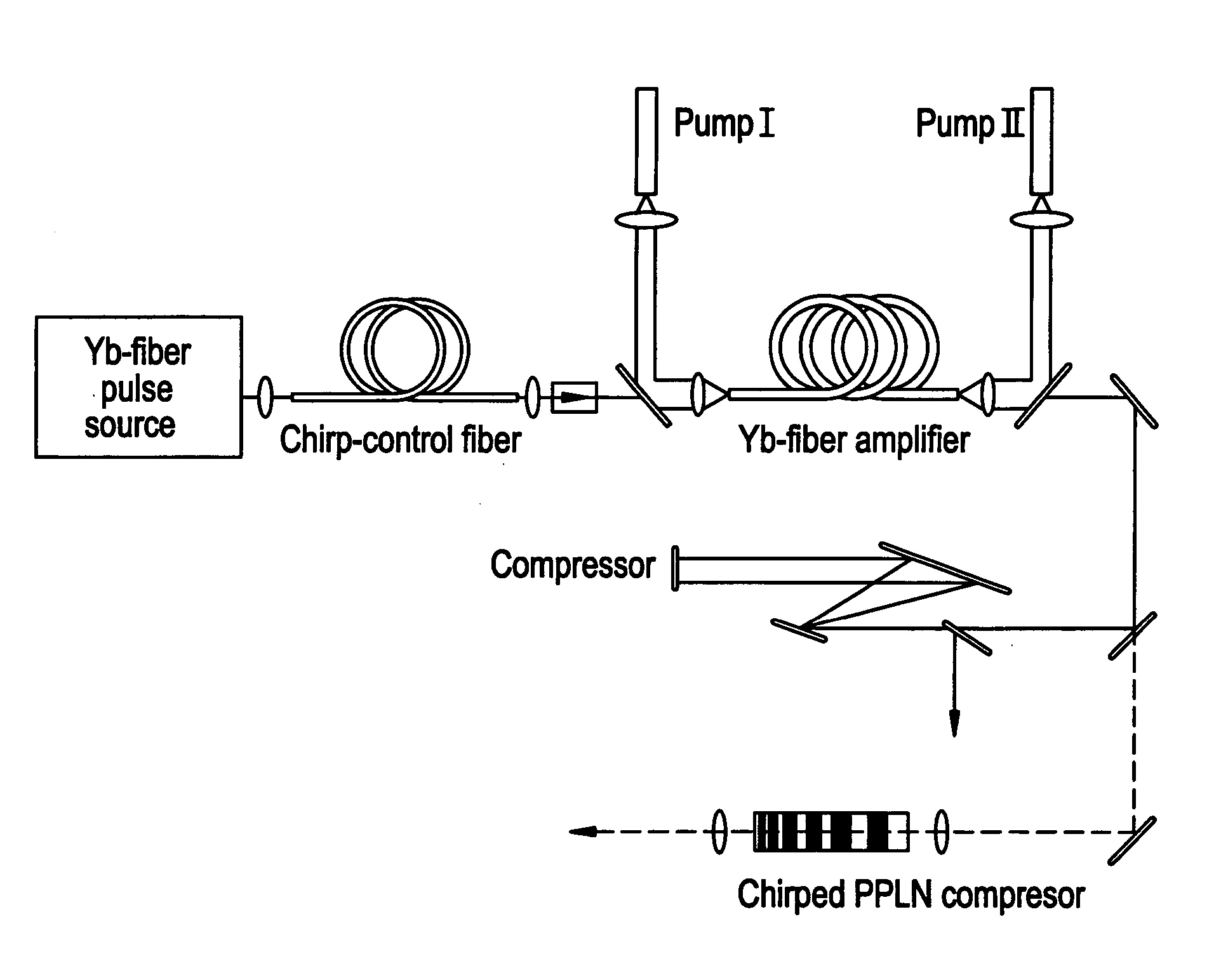
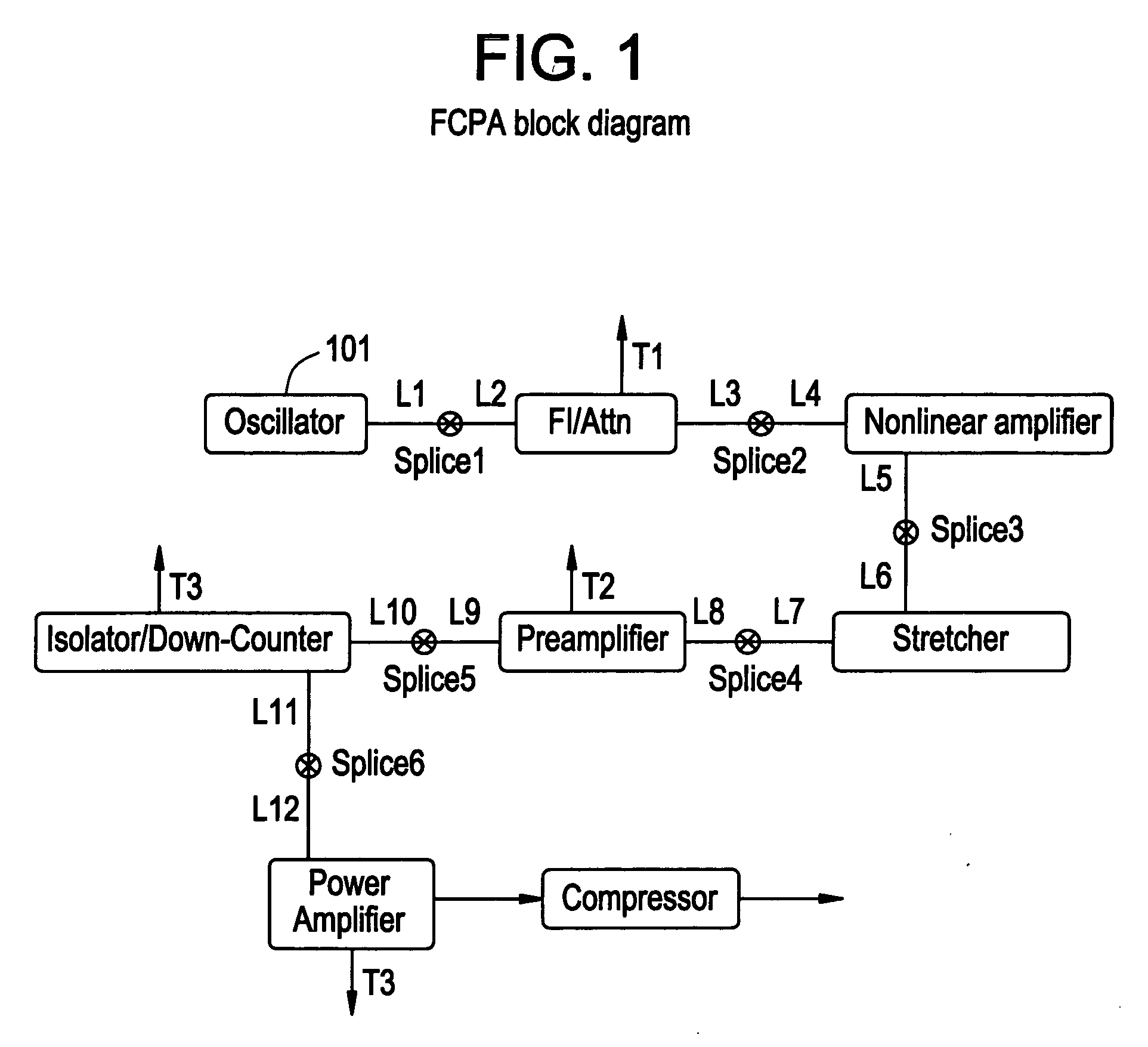
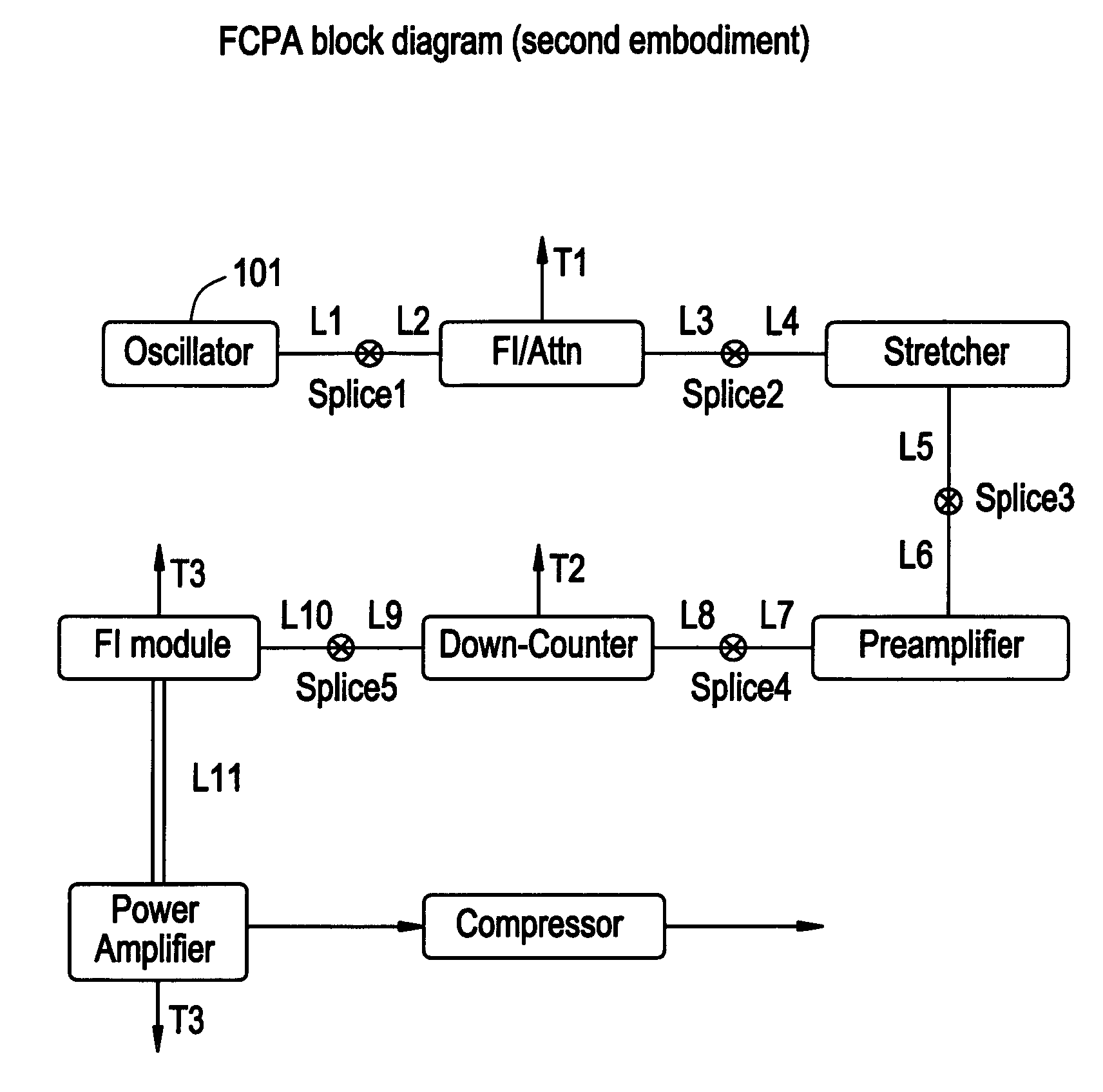
Modular fiber-based chirped pulse amplification system
InactiveUS20050226286A1Eliminate the effects ofLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsFiberAudio power amplifier
A modular ultrafast pulse laser system is constructed of individually pre-tested components manufactured as modules. The individual modules include an oscillator, pre-amplifier and power amplifier stages, a non-linear amplifier, and a stretcher and compressor. The individual modules can typically be connected by means of simple fiber splices.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
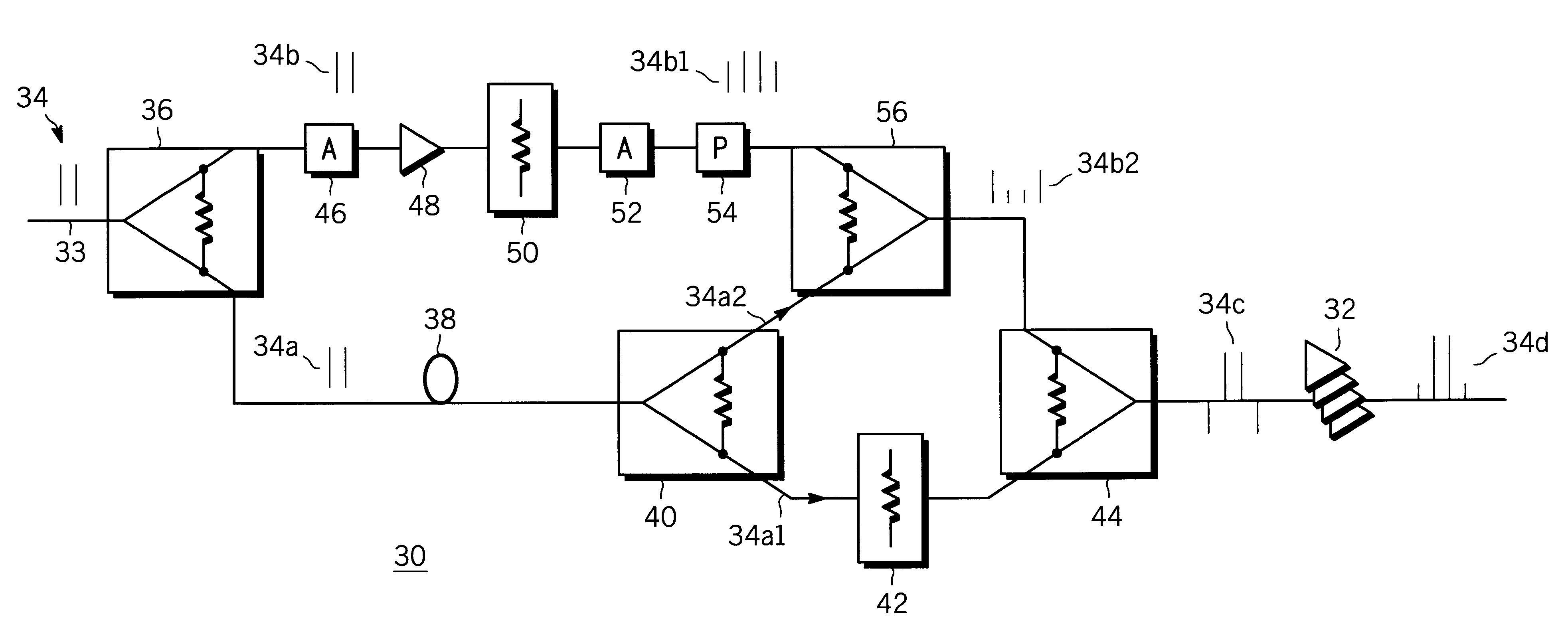
Power amplifier array with same type predistortion amplifier
InactiveUS6646505B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierCarrier signal
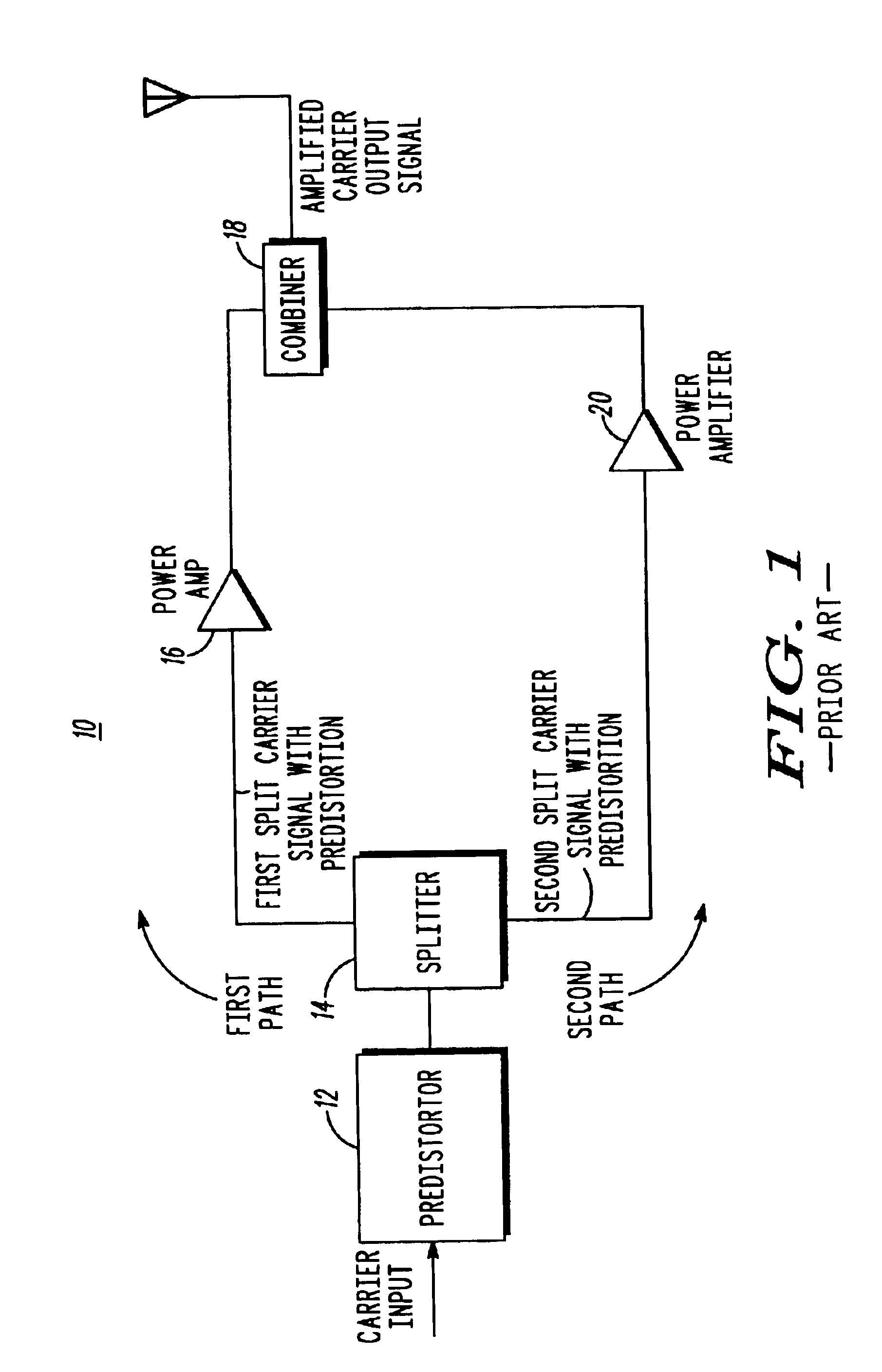
A power amplifier circuit (30, 60) improves the linearity of an amplified output signal. The power amplifier circuit (30, 60) includes an input (33, 63) for receiving a carrier signal (34, 64) and an array of combined amplifiers (32, 62) of a predetermined type for amplifying the carrier signal (34, 64). At least one amplifier (48, 78) of the predetermined type is located between the input (33, 63) and the array of combined amplifiers (32, 62) for amplifying the carrier signal (34, 64) to produce a predistorted carrier signal (34b1, 64b1) with a carrier signal component and a distortion component to condition the carrier signal (34, 64) for input into the array of combined amplifiers (32, 62), and specifically to compensate for nonlinearities produced by the array of combined amplifiers (32, 62).
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Device and method for radio transmitters
InactiveUS6047168AReduce saturationLimiting bandwidth of outputResonant long antennasGain controlLow noisePower detector
The present invention relates to a device and a method in a transmitter stage in a radio transmitter for modulating and amplifying an information signal for further transmission through a radio channel. The transmitter stage in the radio transmitter comprises a converting device (5) PCH, an amplifier control device (8) PAC, a power detector (13) and a power amplifier (2). Examples of the problems solved by the present invention are difficulties in reducing the power consumption, non-linearities in the output signal when using non-linear amplifiers in radio transmitters, and achieving a high signal-to-noise ratio in the output signal without connecting filter arrangements after such an amplifier. The solution according to the inventive method and device utilizes an information signal which has in earlier steps been divided in its polar components: a phase reference component signal (Ephr) and an amplitude component signal (Aamp). The phase reference component phase modulates a low noise high power signal source which has a constant amplitude. The amplitude of the obtained signal is then formed in an amplifier, which is controllable with the amplitude component signal (Aamp). Its current consumption is registered and compared to a control value for the current. The amplifier is controlled towards this control value.
Owner:OPTIS WIRELESS TECH LLC
Feher keying (FK) modulation and transceivers including clock shaping processors
InactiveUS20010016013A1Increase powerModulated carrier system with waveletsSynchronisation information channelsFrequency spectrumModem device
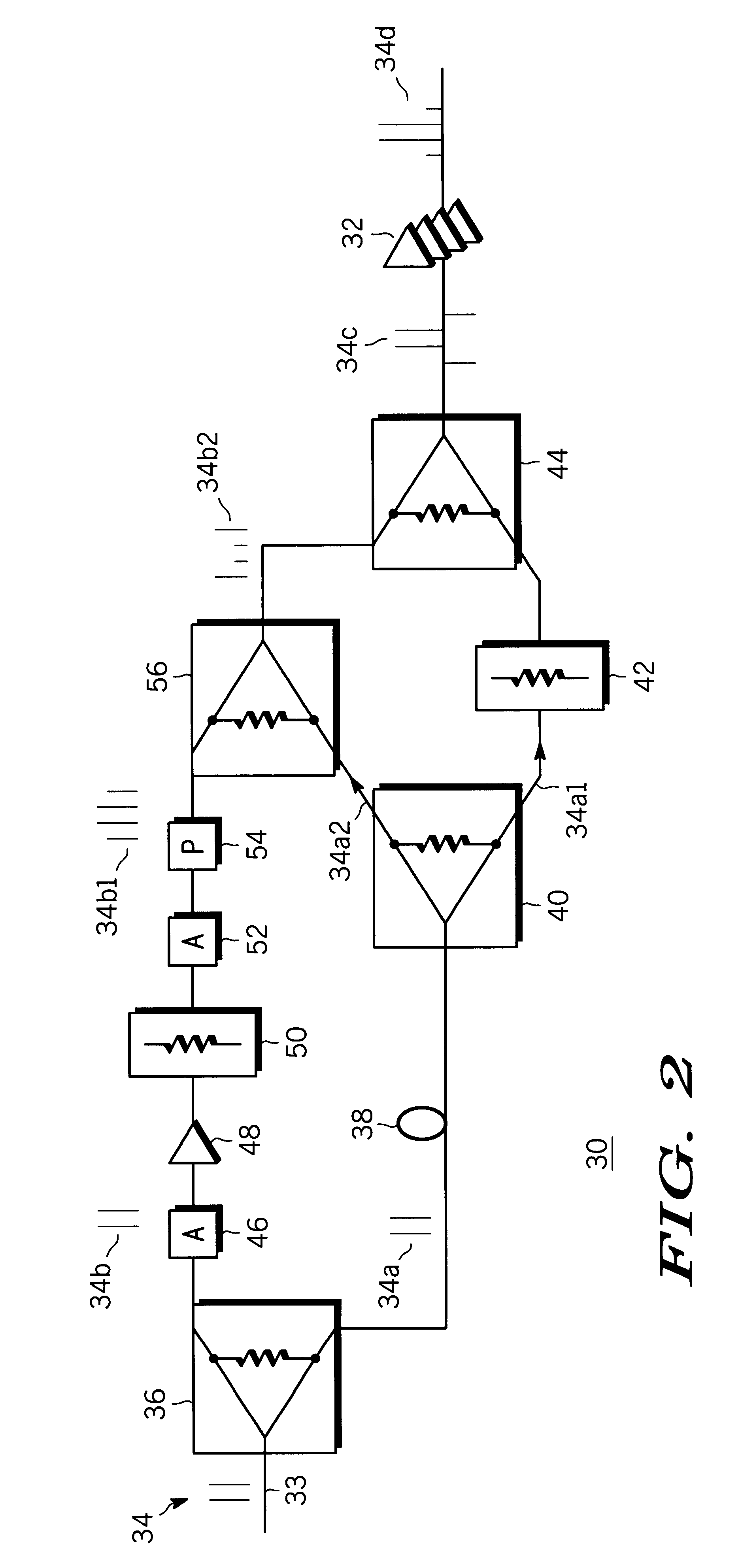
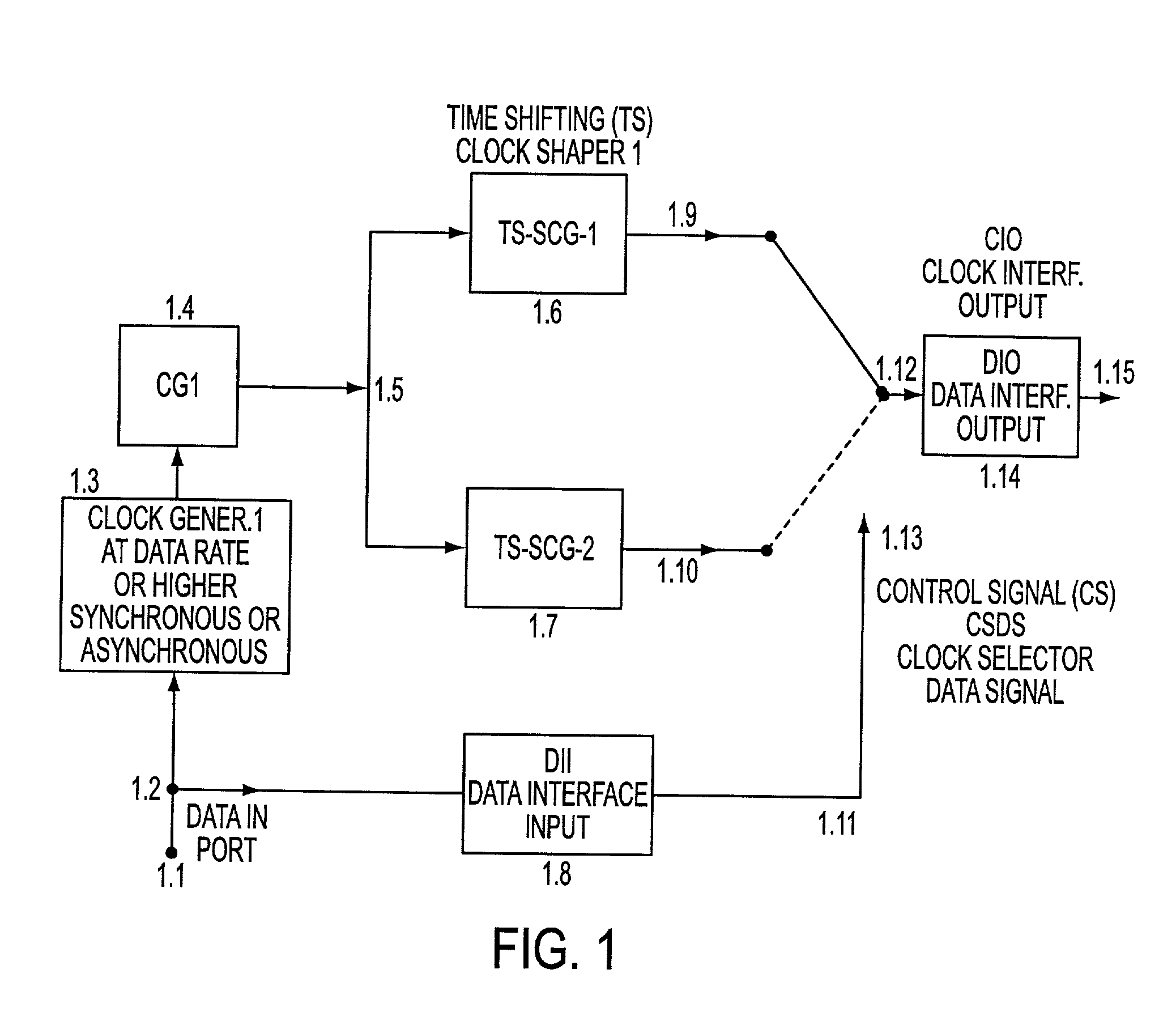
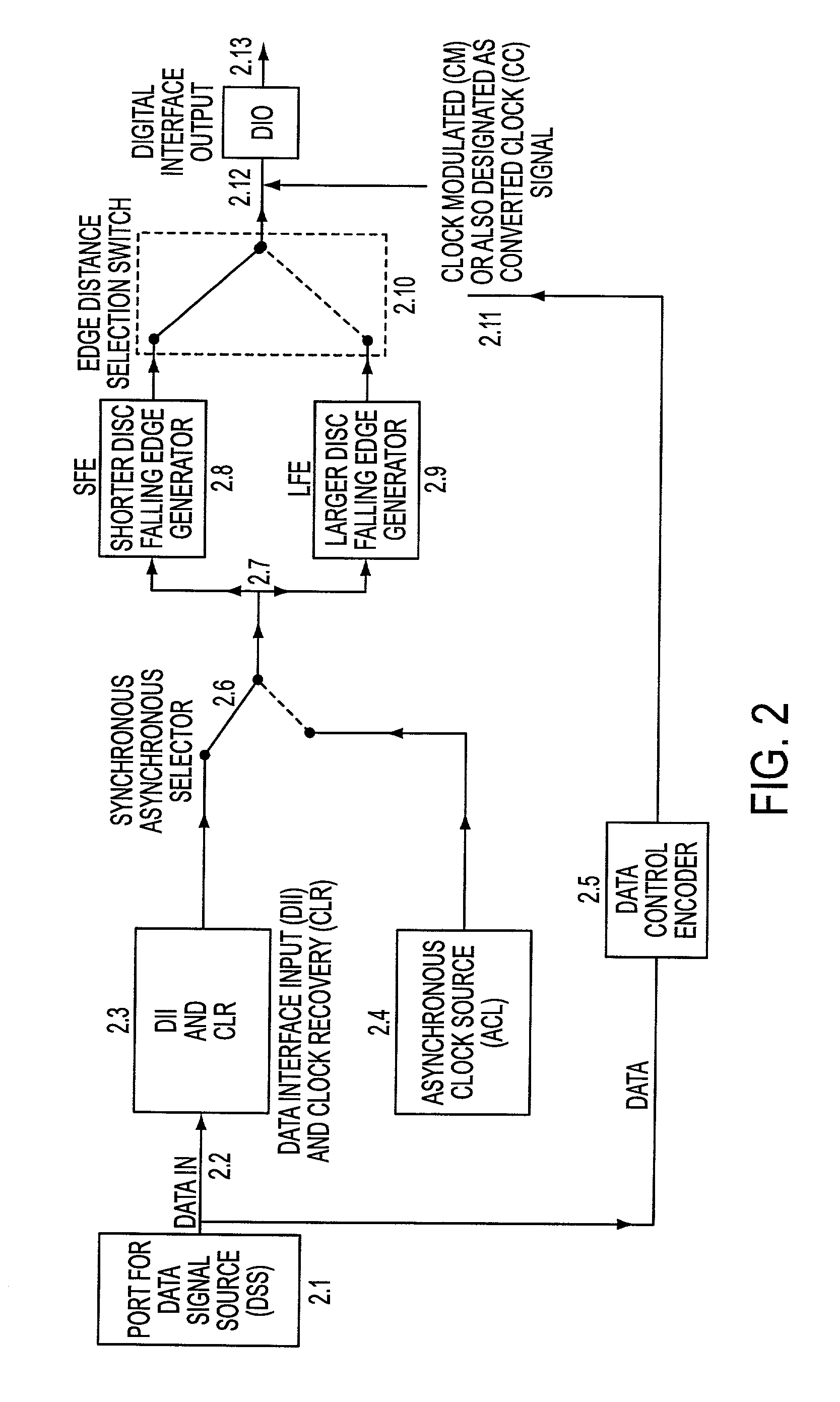
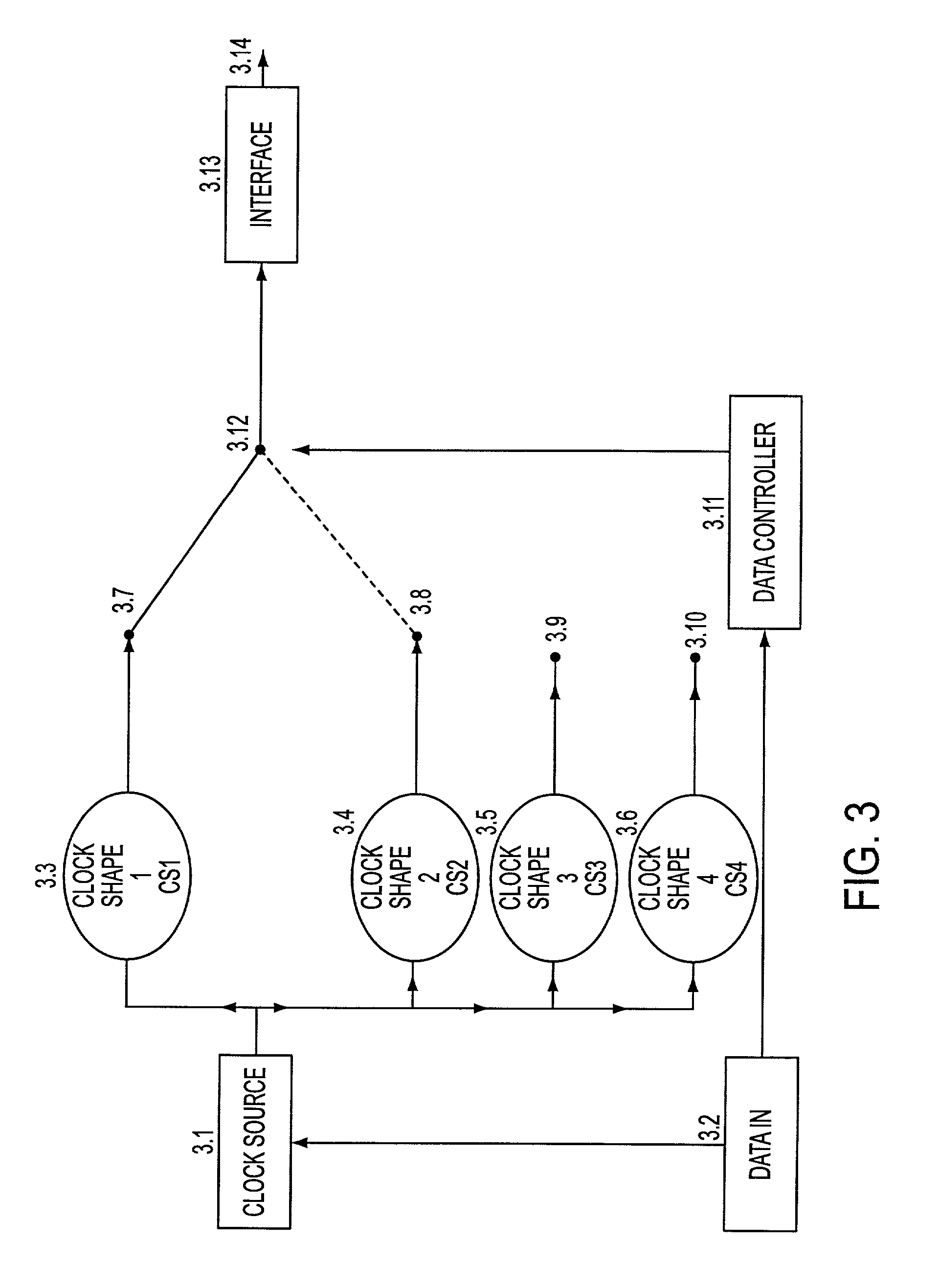
Ultra high spectral efficient Feher Keying (FK) Modulation and Demodulation (Modem), Baseband Processing (BBP), Intermediate Frequency (IF) and Radio Frequency (RF) signal generation and processing methods and implementations, including Clock Modulated (CM) and Shaped Clocked (SC) Transmitters-Receivers (transceivers) are disclosed. Additional embodiments, including Feher Quadrature Shift Keying (FQPSK) and Feher Quadrature Modulation (FQAM), in conjunction with CM and SC are also described. In the FK modulator, specified clock converted and clock shaped signal parameters are generated. These are based on the input data signal patterns and are generated by means of control signals, which are designed in the data input signal interface data signal and / or clock signal encoder units. The selectable clock signal parameters include symmetrical and non-symmetrical clock signals, shaped band-limited continuous clock signal patterns, shaped encoded clock signals, variable rise and fall time clock signals, clock signals having adjustable on and off duration, multilevel and shaped clock signals and asynchronous clock signal information transmission means, where asynchronous clocking is referenced to the incoming data source signals. The FK processors are also used in conjunction with cross-correlated FQPSK quadrature and also non quadrature modem systems as input drive signals to FM VCO based systems to SSB to VSB to DSB-SC to QAM, and FQAM and to coded systems with adaptive equalized receivers, Non Redundant Error Correction (NEC), pseudo-error monitor systems. The FK systems and FT apparatus comprises entire transceiver structures including LIN (linear) and NLA (Non Linear Amplifier) transmitter receiver, AGC, synchronization and demodulation and post demodulation signal processors.
Owner:FEHER KAMILO
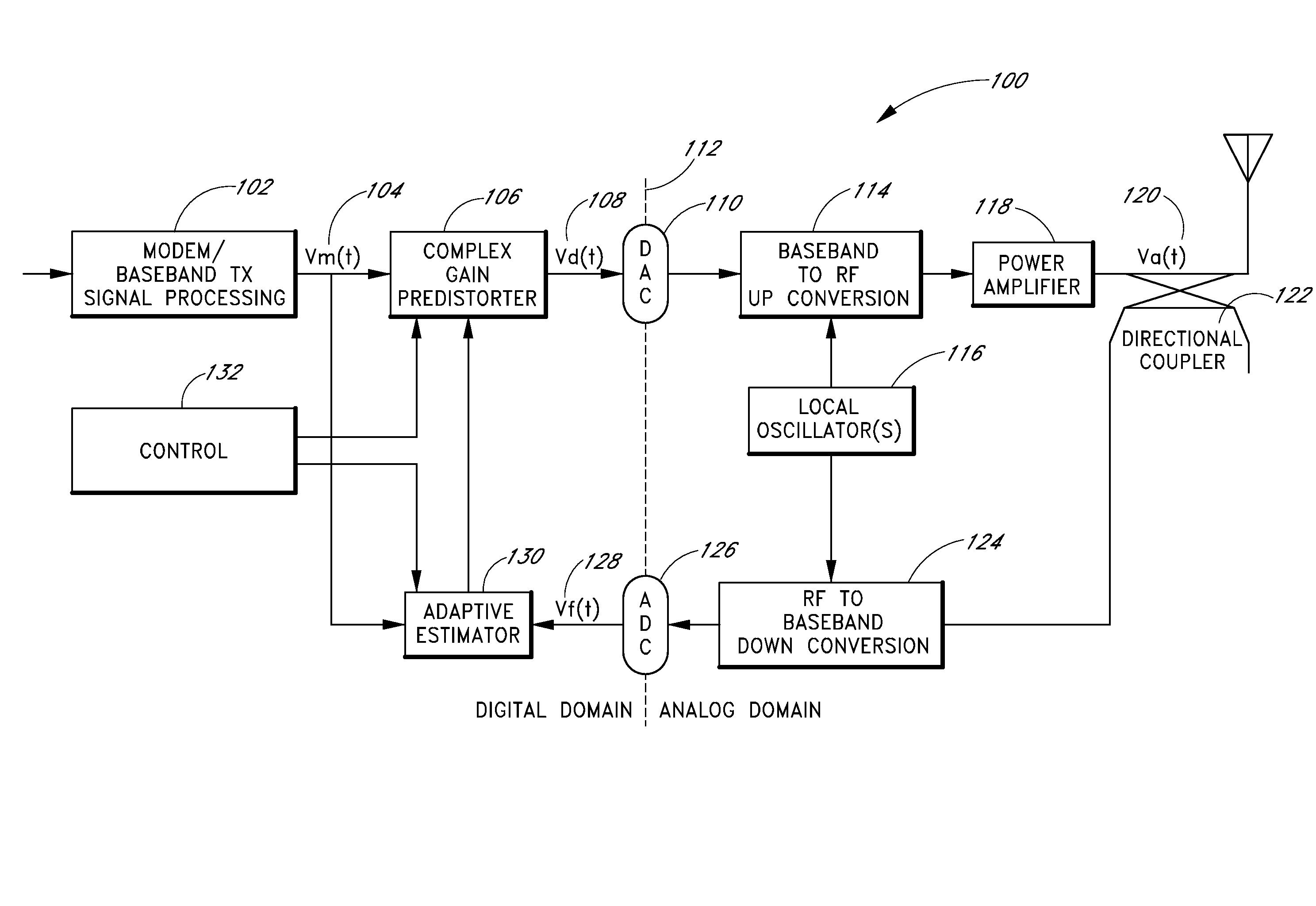
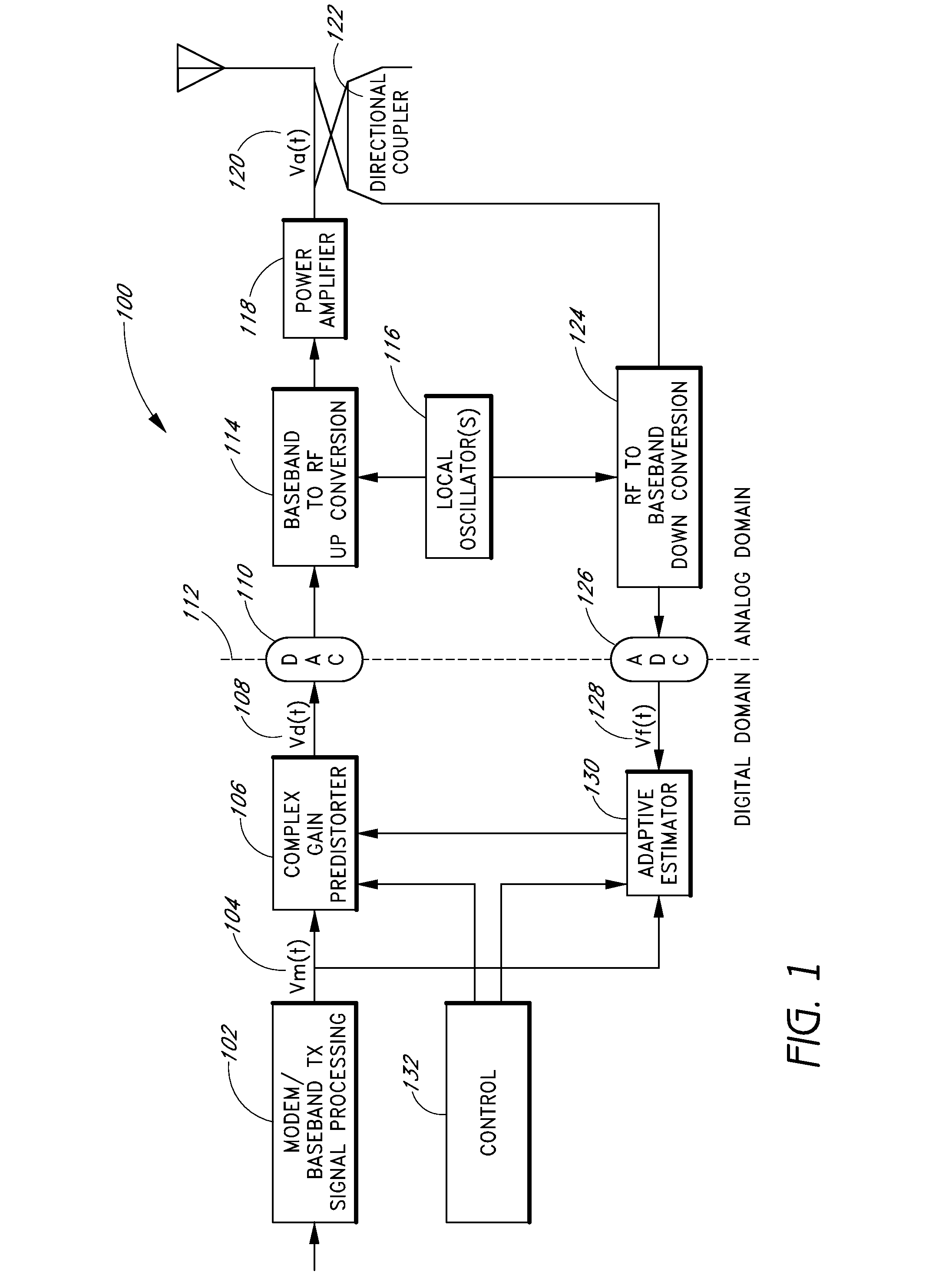
Method and apparatus of estimating non-linear amplifier response in an overlaid communication system
InactiveUS20050032472A1Eliminate biasAccurate reconstructionResonant long antennasRadio transmissionAudio power amplifierCommunications system
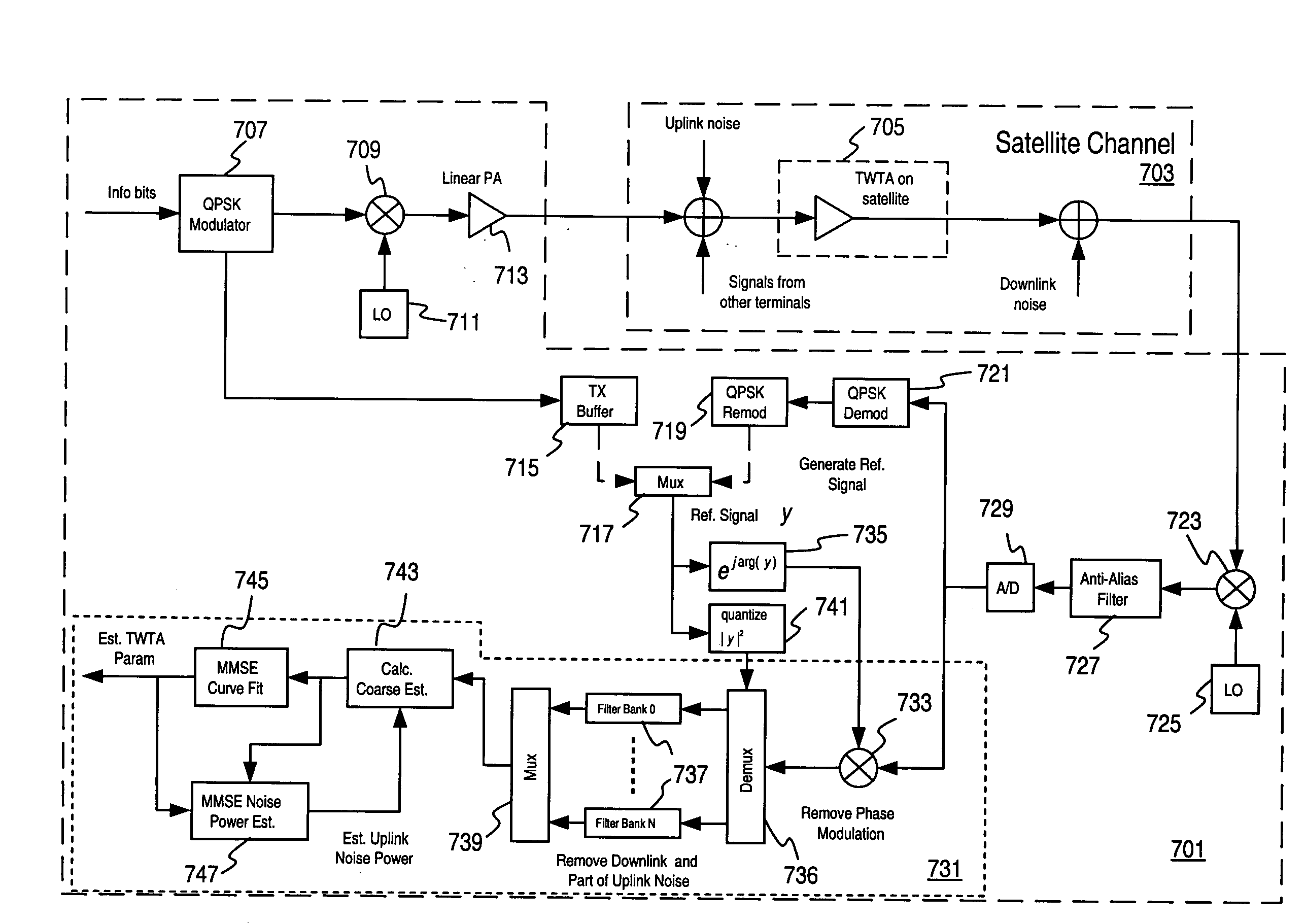
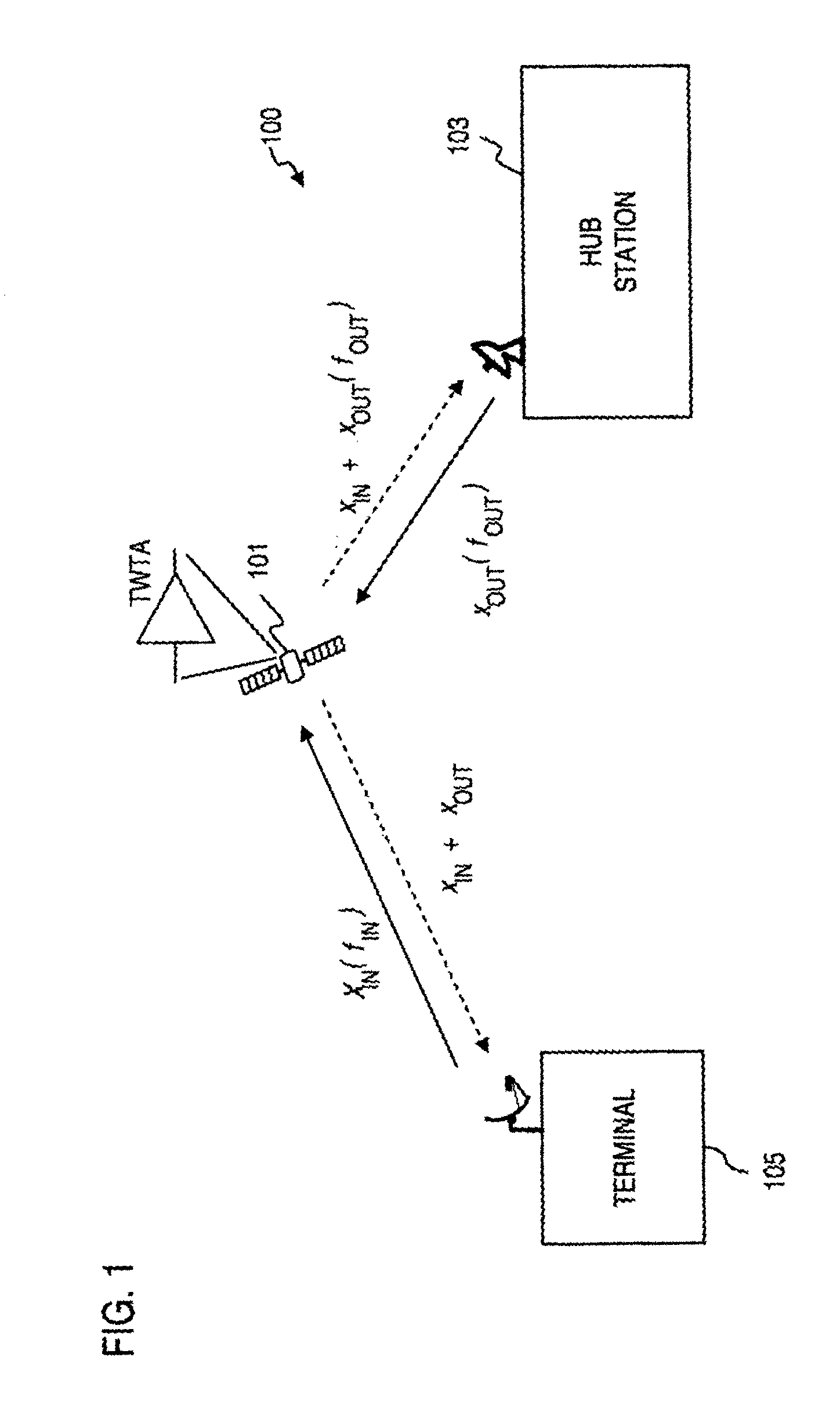
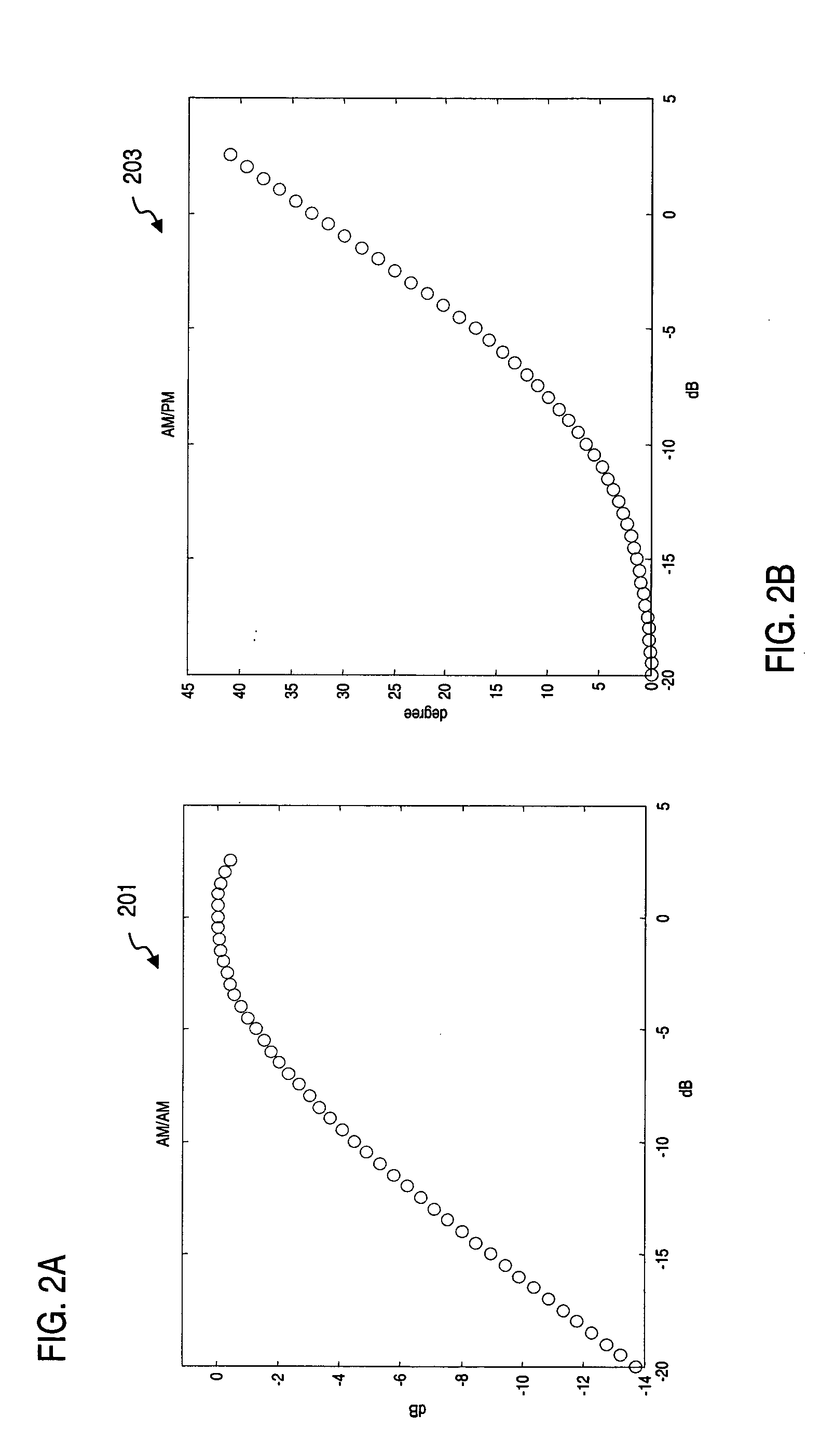
An approach is provided estimating non-linear characteristics of an amplifier (such as a Travelling Wave Tube Amplifier) used to amplify a composite signal in a radio communication system. The composite signal, which includes a plurality of inbound signals overlay on an outbound signal, is sampled. The outbound signal is utilized as a training signal. Coarse estimates of the response of the amplifier is generated based on the samples of the composite signal and the training signal. Further, the interference associated with the inbound signals are removed from the estimation of the response of the amplifier by curve-fitting and estimating interference characteristics of the composite signal. An estimated response of the amplifier is thus output, and can be utilized to provide accurate non-linearity compensation and cancellation.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
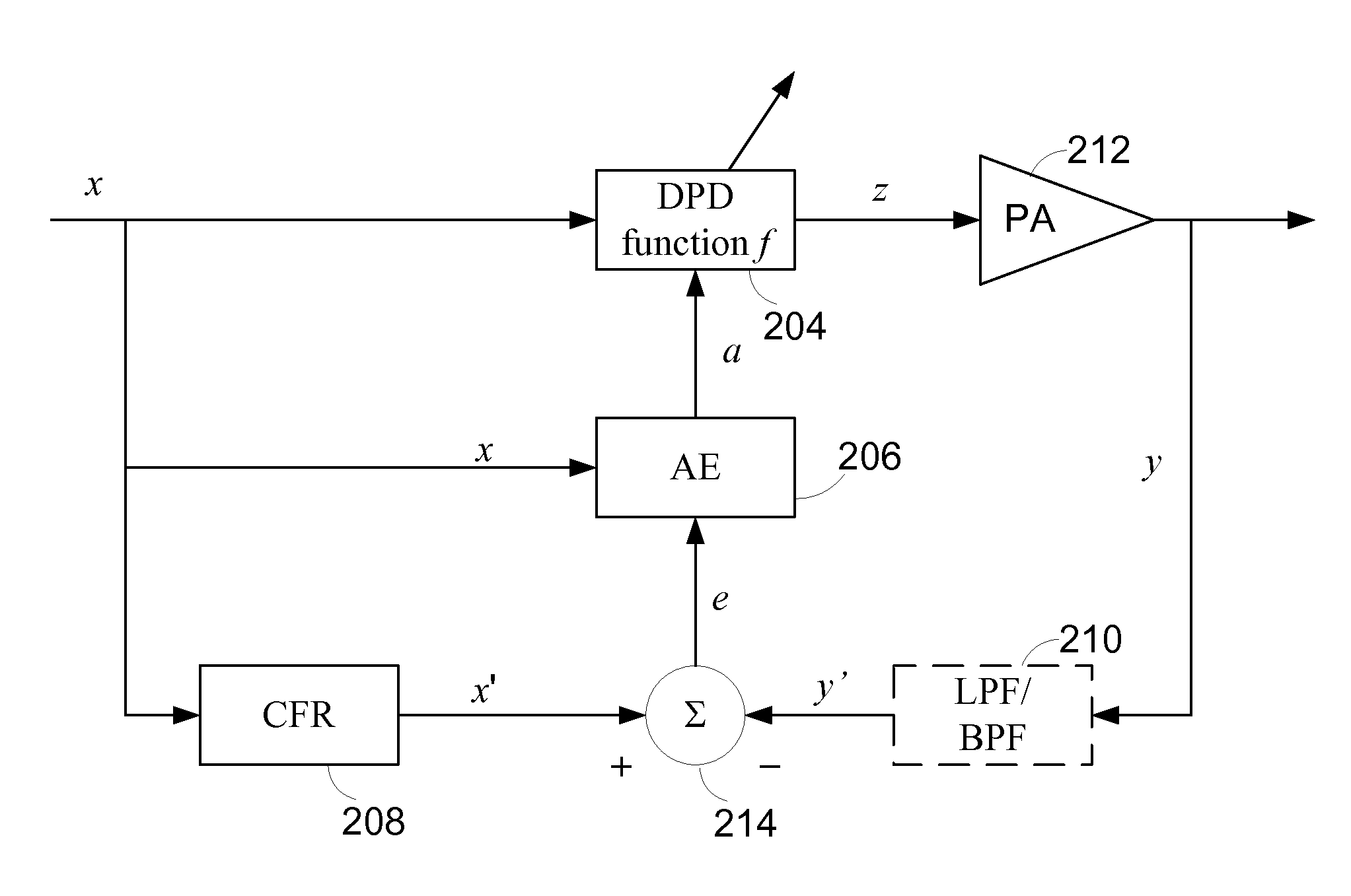
Predistortion with integral crest-factor reduction and reduced observation bandwidth
ActiveUS8446979B1Reduced observation bandwidthReduce processing requirementsResonant long antennasAmplifier with control circuitsAudio power amplifierError vector magnitude
Apparatus and methods configure digital predistortion linearizers for power amplification of bandlimited signals using non-linear amplifiers. The predistorter is configured to achieve both crest factor reduction (CFR) and predistortion for linearization. One embodiment advantageously reduces processing requirements conventionally associated with CFR by considering only the in-band component, that is, the information bearing component, of the desired signal to be reproduced for those cases in which the mitigation of in-band error vector magnitude (EVM) is preferred over the reduction of spurious out-of-band emissions.
Owner:MAXLINEAR ASIA SINGAPORE PTE LTD
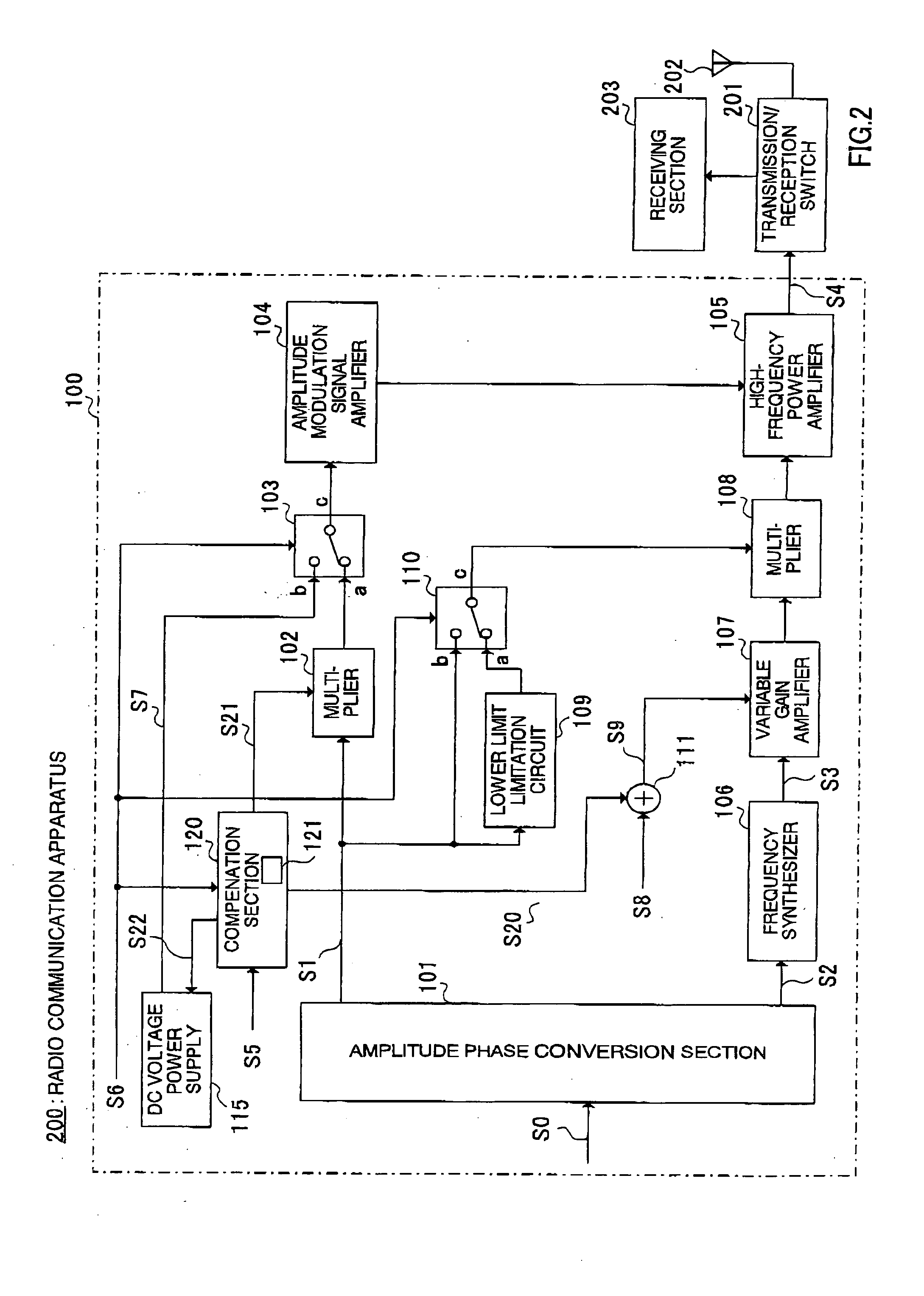
Transmitting apparatus and radio communication apparatus
InactiveUS20050245214A1Improve power efficiencyWide transmission output power control rangeResonant long antennasGain controlHigh frequency powerAudio power amplifier
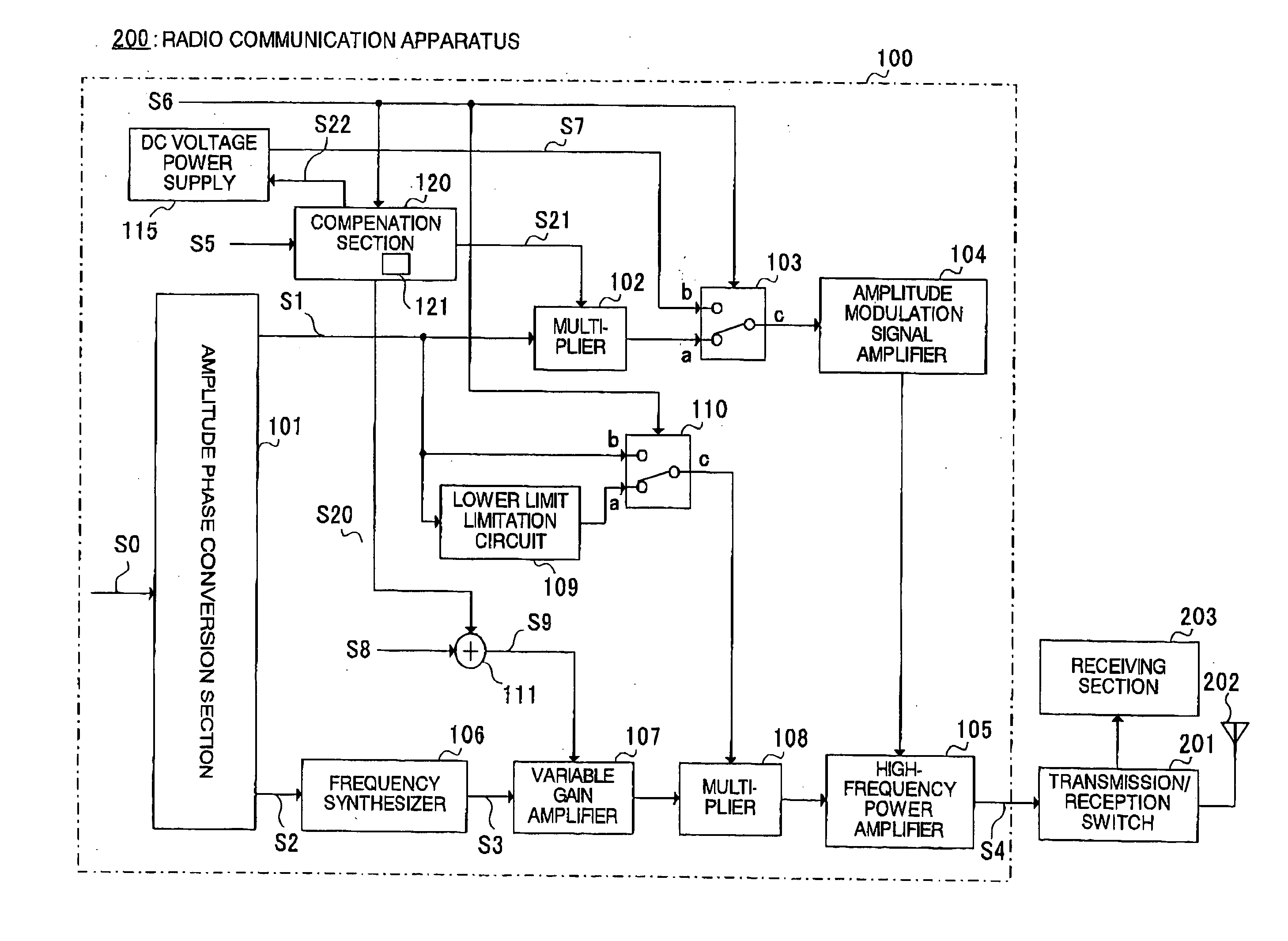
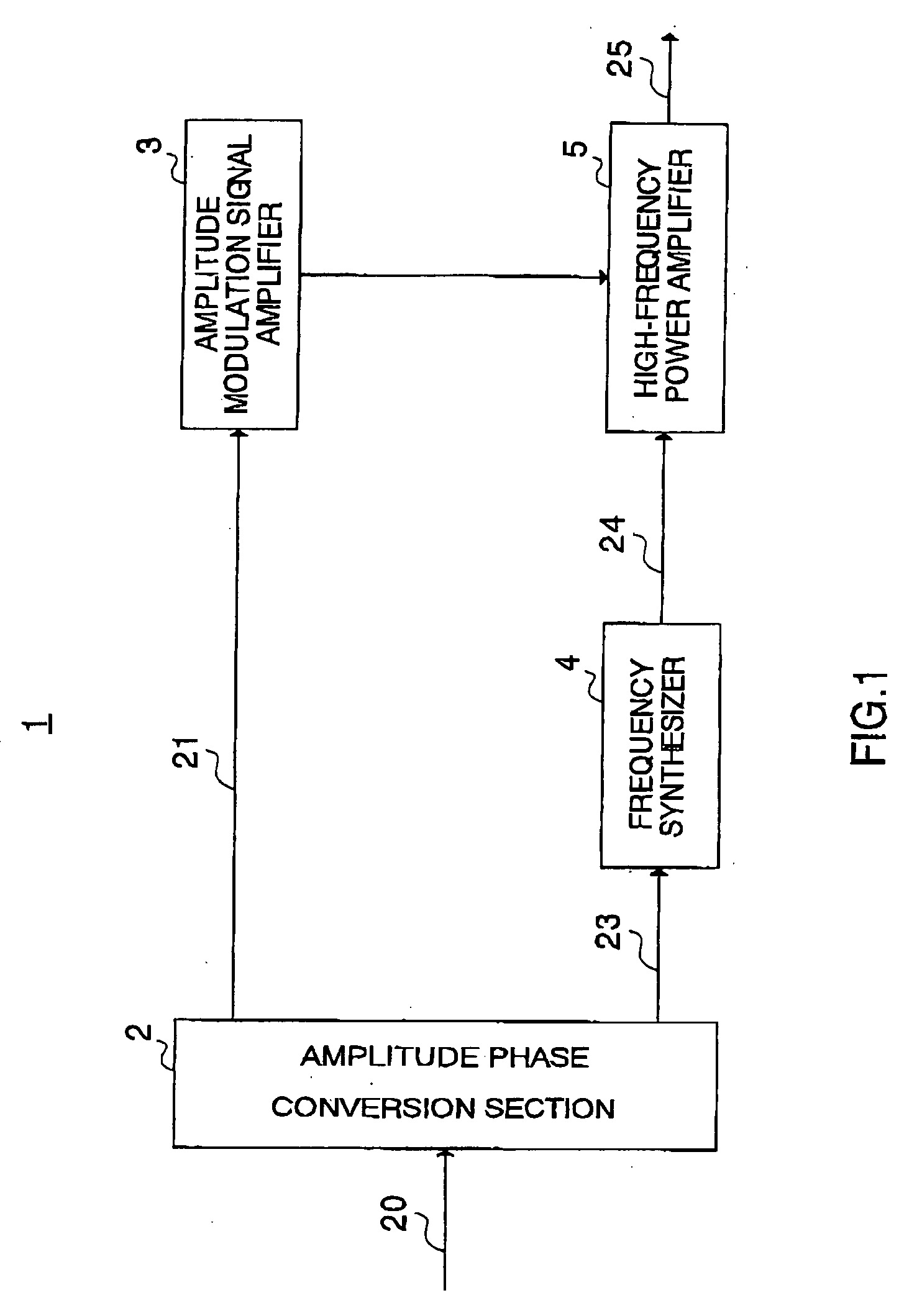
A transmitting apparatus 100 operates a high-frequency power amplifier 105 as a nonlinear amplifier in a first mode, and operates high-frequency power amplifier 105 as a linear amplifier in a second mode. When high-frequency power amplifier 105 is operated as a nonlinear amplifier, the input level of high-frequency power amplifier 105 is varied by a variable gain amplifier 107 in accordance with the average output power of a transmit signal. Transmitting apparatus 100 is also provided with a compensation table 121 for reducing error in high-frequency power amplifier 105 mode switching operations.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Adaptive predistortion of non-linear amplifiers with burst data
ActiveUS8023588B1Improve adaptabilityNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsModulated-carrier systemsAudio power amplifierEngineering
Apparatus and methods control predistortion of an RF transmitter. A base station or a mobile station can utilize predistortion to improve linearity characteristics of the RF power amplifier. When used effectively, predistortion limits spectral growth such that the amplified signal complies with regulatory requirements. With respect to bursty signals, specific improvement techniques are disclosed. A first technique is related to adaptation using only a smaller subset of samples of a burst. A second technique is related to selective application of digital predistortion, such as, only under high power conditions for a power amplifier. A third technique is directed to adaptation of less than all of the coefficients. These improvements permit the use of a smaller and less expensive amplifier for a given power class and can lengthen battery life for a mobile unit.
Owner:MAXLINEAR ASIA SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Digital predistorter for a wideband power amplifier and adaptation method
InactiveUS7333559B2Eliminate the problemRemove distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionMemory effect compensationFinite impulse responseBroadband power amplifier
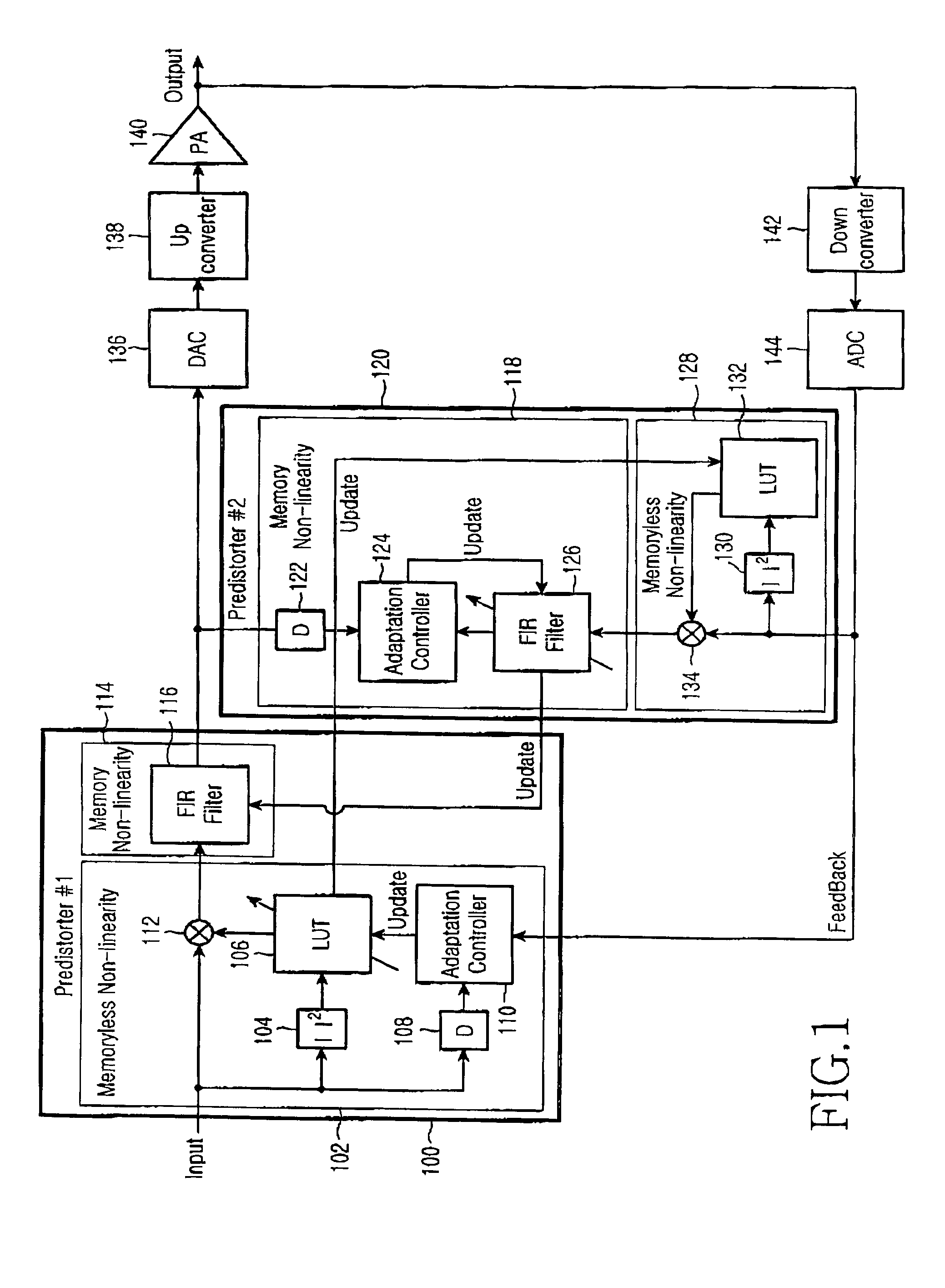
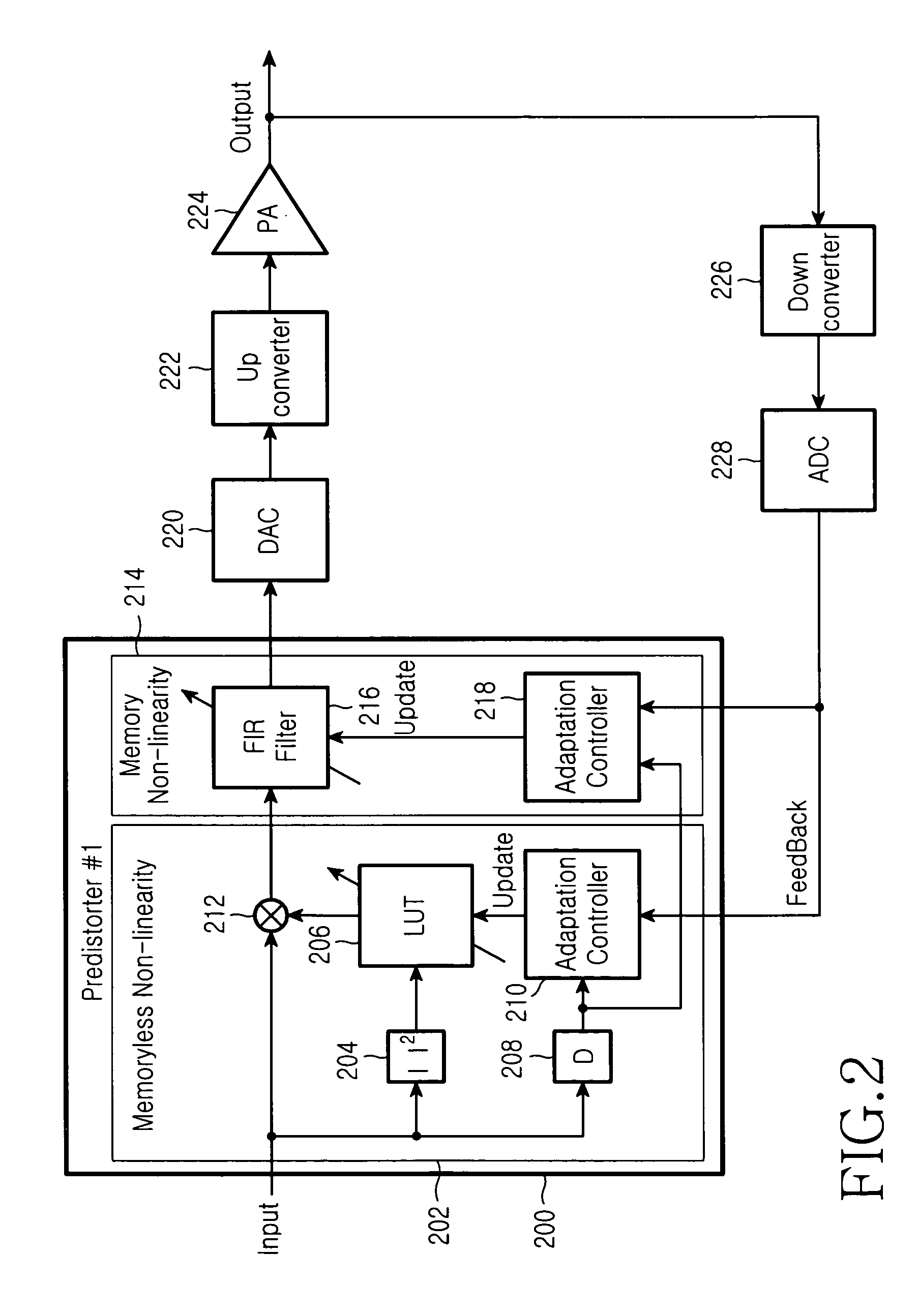
An apparatus and method for eliminating the spurious signal of a non-linear amplifier in a base station transmitter of a mobile communication system are provided. A digital predistorter includes first and second predistorters, each having a memoryless non-linearity part using a look-up table and a memory non-linearity part using an finite impulse response (FIR) filter. The first predistorter adaptively updates the look-up tables, while the second predistorter adaptively updates the filtering coefficients of the FIR filters. According to another embodiment of the present invention, a digital predistorter has a memoryless non-linearity part using a look-up table and a memory non-linearity part using an FIR filter, and adaptively updates the look-up table and the filtering coefficients of the FIR filter.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for UDP flood attack detection
ActiveUS8307430B1Easy to detectEasy to adjustMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionFrequency spectrumSystem requirements
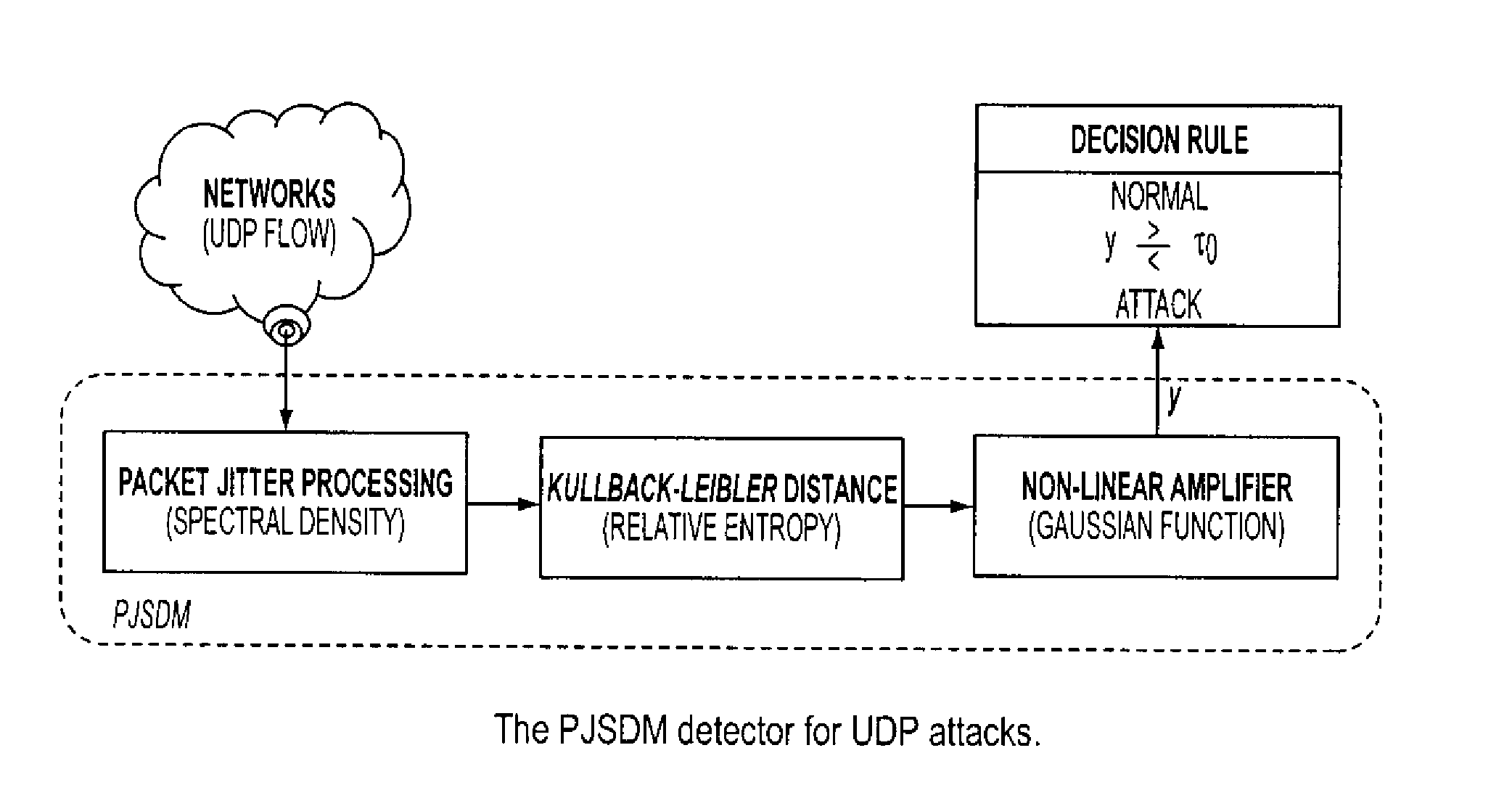
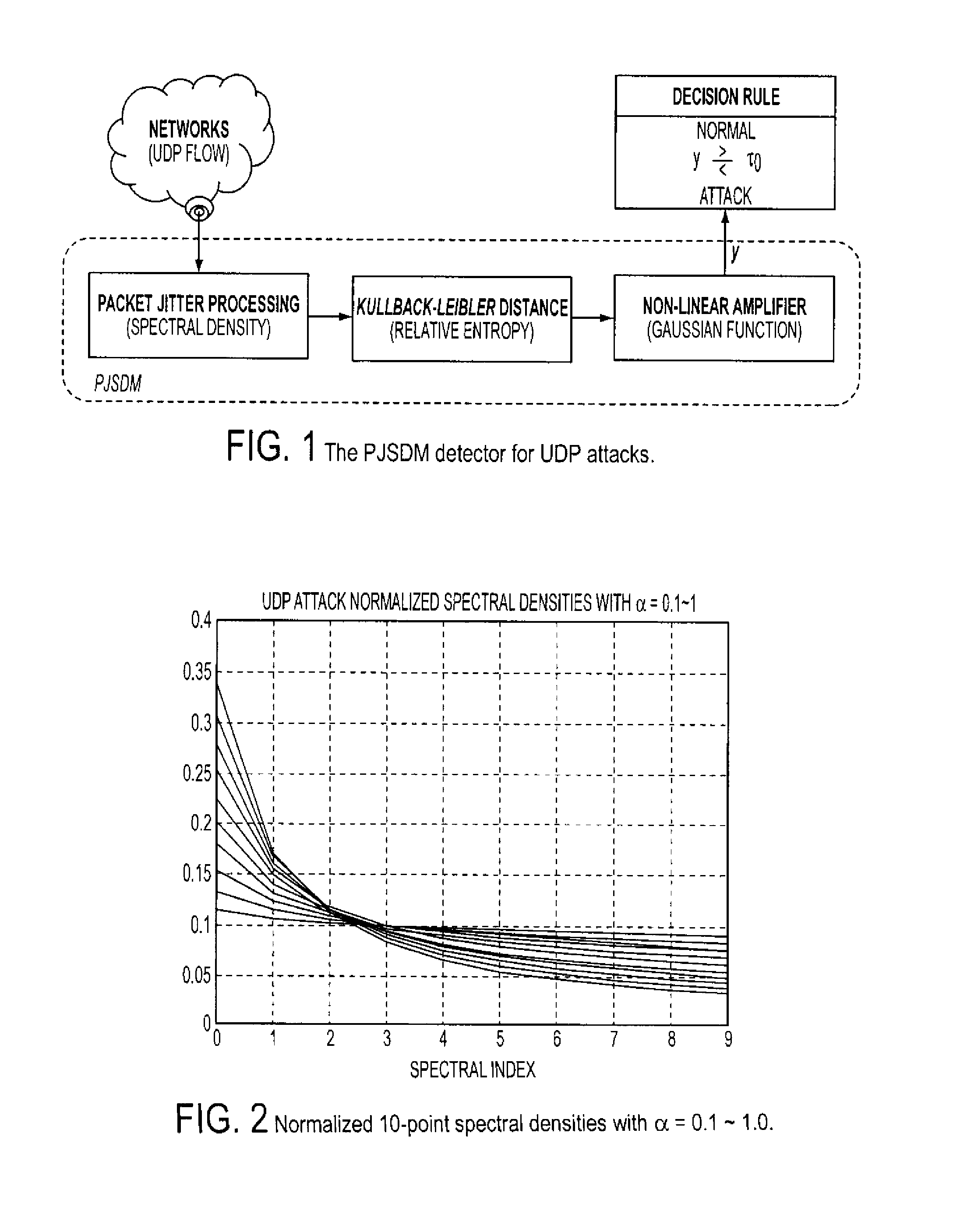
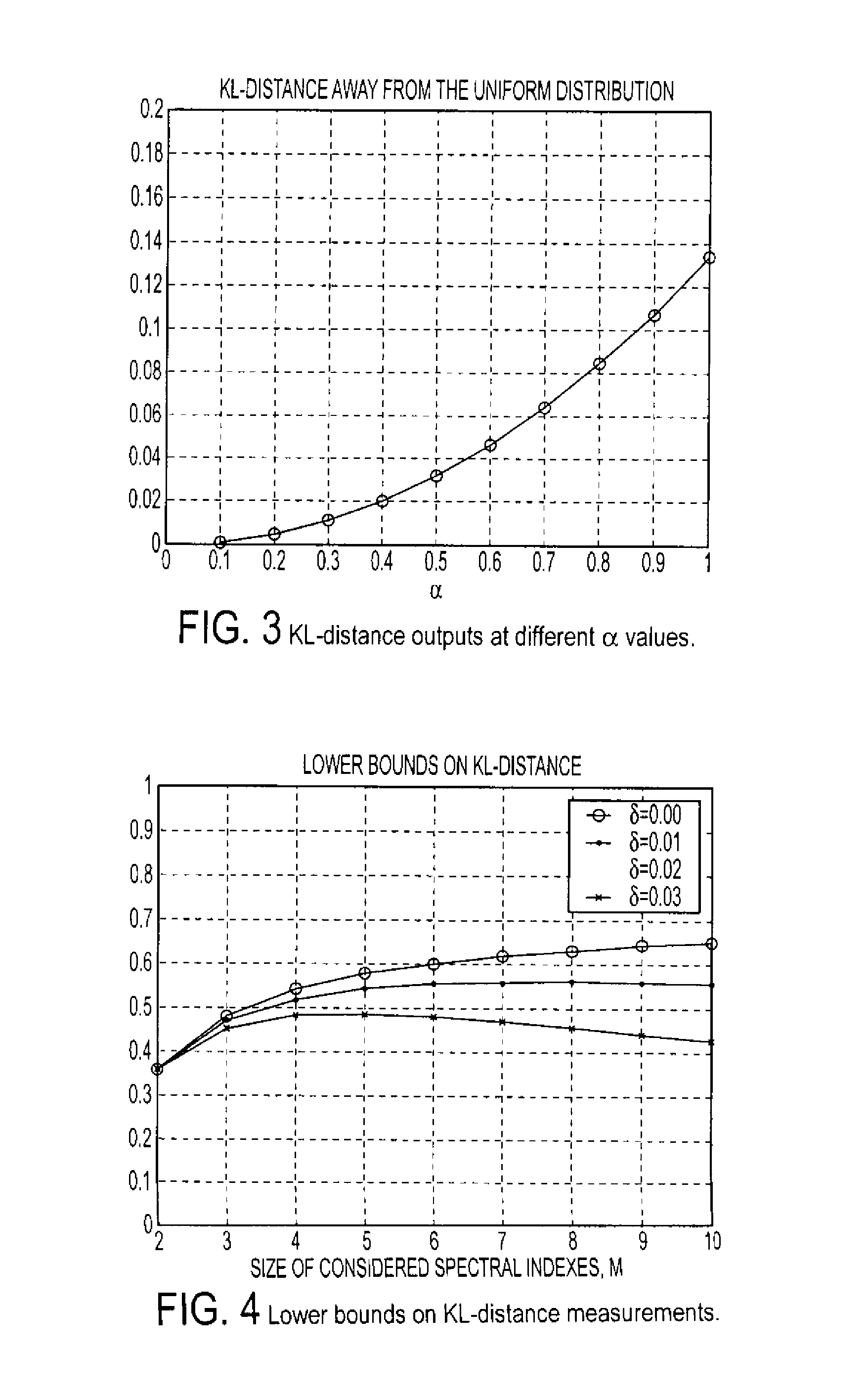
A system and method is provided to identify UDP attacks. A processor determines a spectral density of packet timing intervals, a natural distance between the spectral density and a uniform distribution, and a non-linear amplifier applying a non-linear amplification to the natural distance to detect a denial-of-service attack. It uses the concept of traffic statistics analysis, i.e., spectral densities of arrived-packet timing intervals, calculates the KL-distance measurement and makes decision based on the output of a non-linear Gaussian amplifier, with which one can easily adjust the amplifier via selecting different parameters of mean and variance to satisfy system requirements of false-positive and false-negative UDP attack detections.
Owner:RIOREY LLC
Method for the simulation of a nonlinear amplifier with envelope memory effect
InactiveUS6216100B1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionFrequency-division multiplexNonlinear amplifierDirect transfer
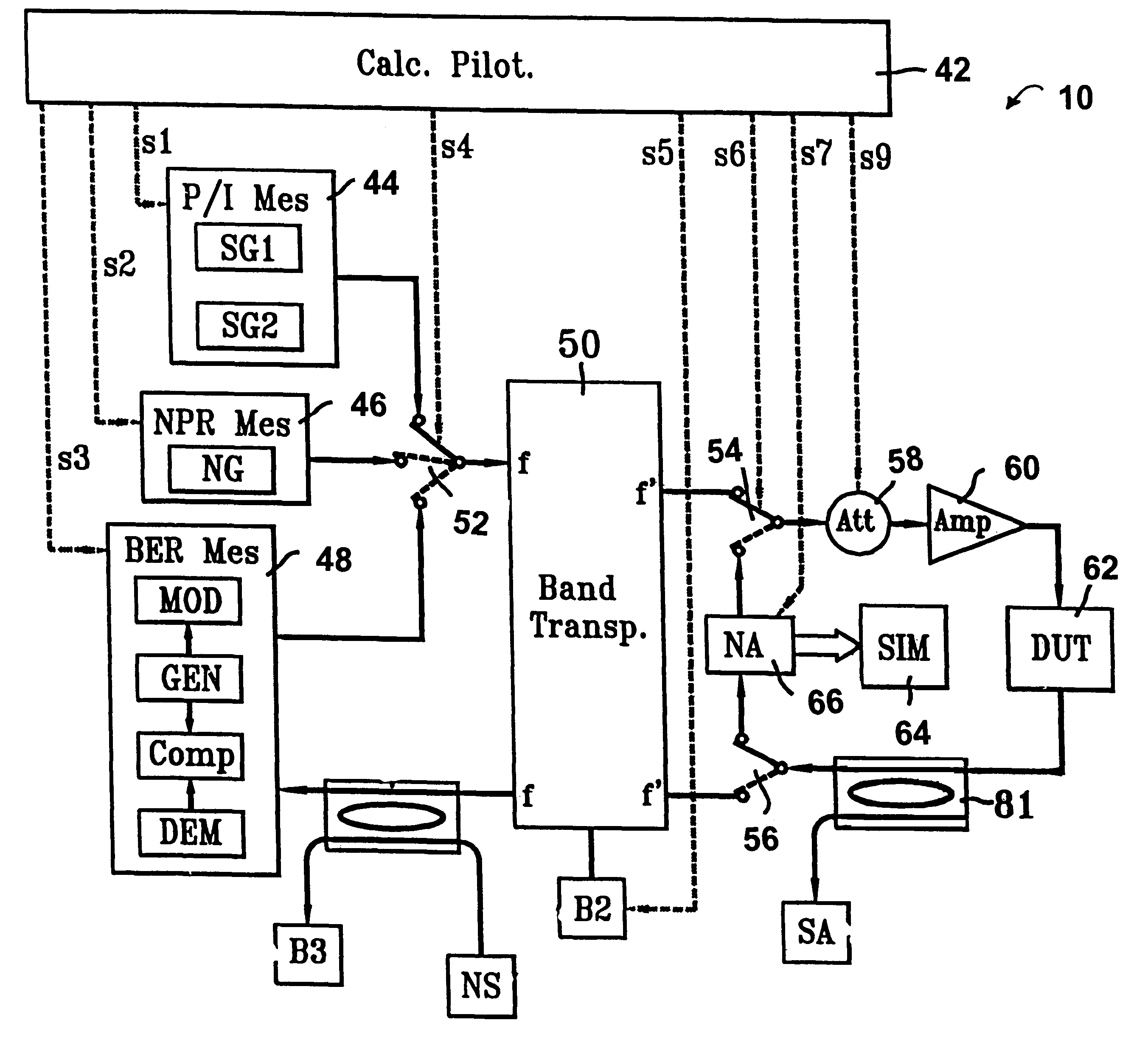
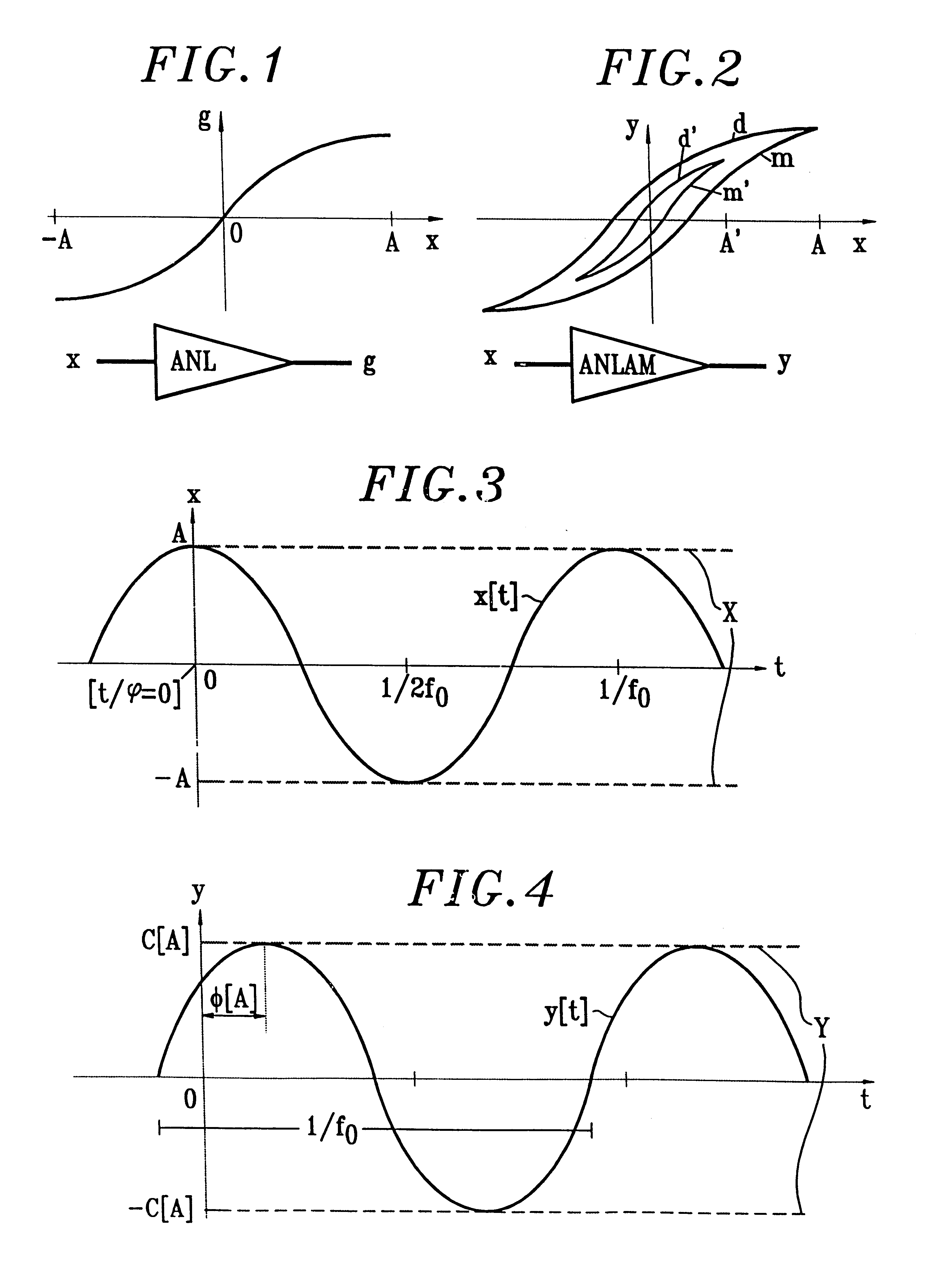
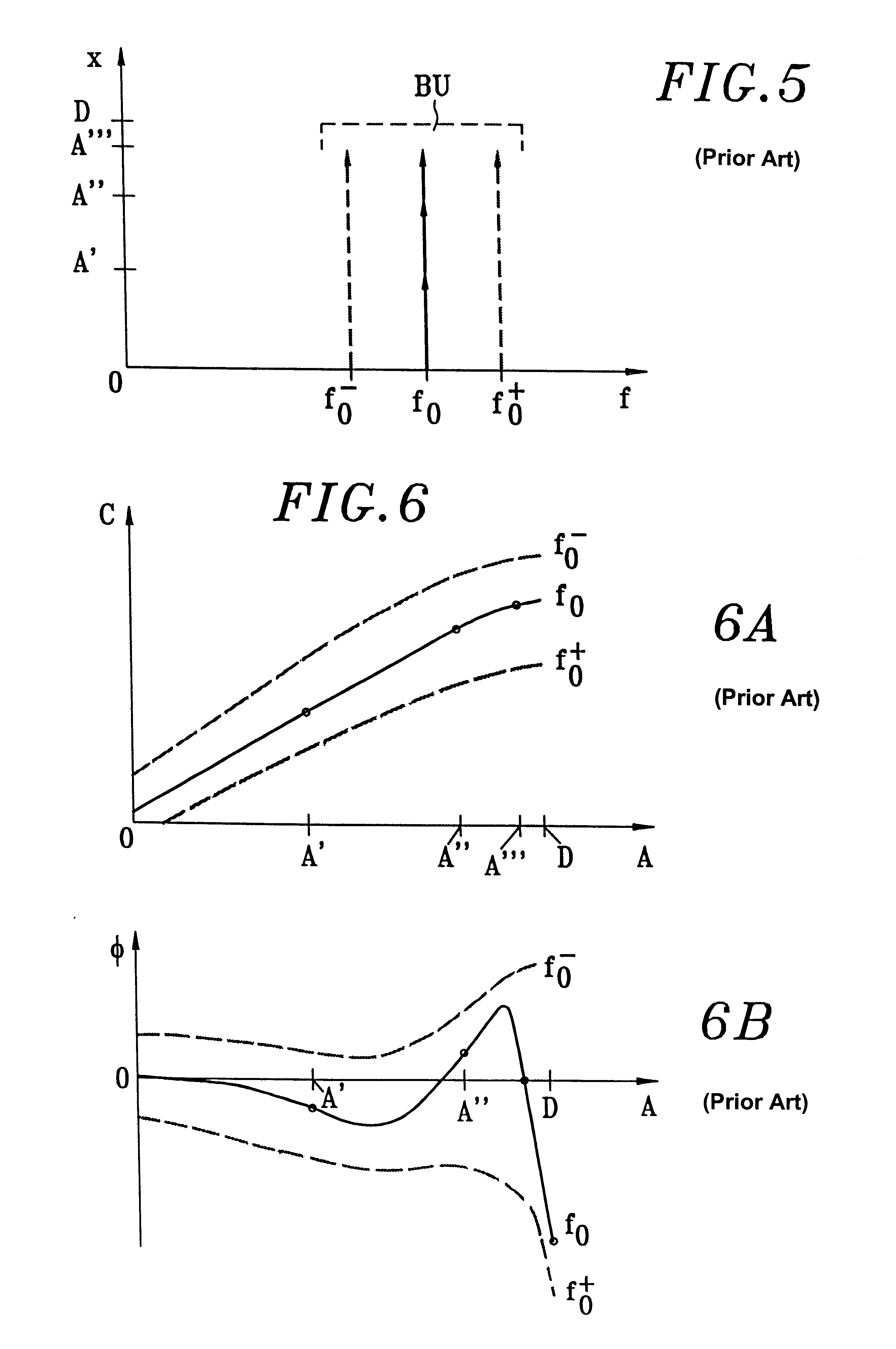
A method for the simulation of responses of a nonlinear amplifier provides for measuring characteristics of nonlinearity of amplitude and of amplitude / phase-shift conversion of the amplifier, each measurement being made at an amplitude that is constant in input. The method further includes measuring the characteristics at different frequencies, developing the characteristics in sequences of direct transfer functions, computing frequency correctors for the direct transfer functions, measuring characteristics of distortion of amplitude modulation, each measurement being performed by modulating the input amplitude, computing modulation transfer functions reproducing the distortion amplitudes at output according to the input modulation amplitudes and correcting the direct transfer functions when the input amplitude is modulated in order to simulate the envelope memory effect. There is a direct application of the invention to the field of the simulation of high efficiency microwave amplification.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC
Signal Predistortion for Non-Linear Amplifier
ActiveUS20140292406A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifiers with memory effect compensationAudio power amplifierNonlinear amplifier
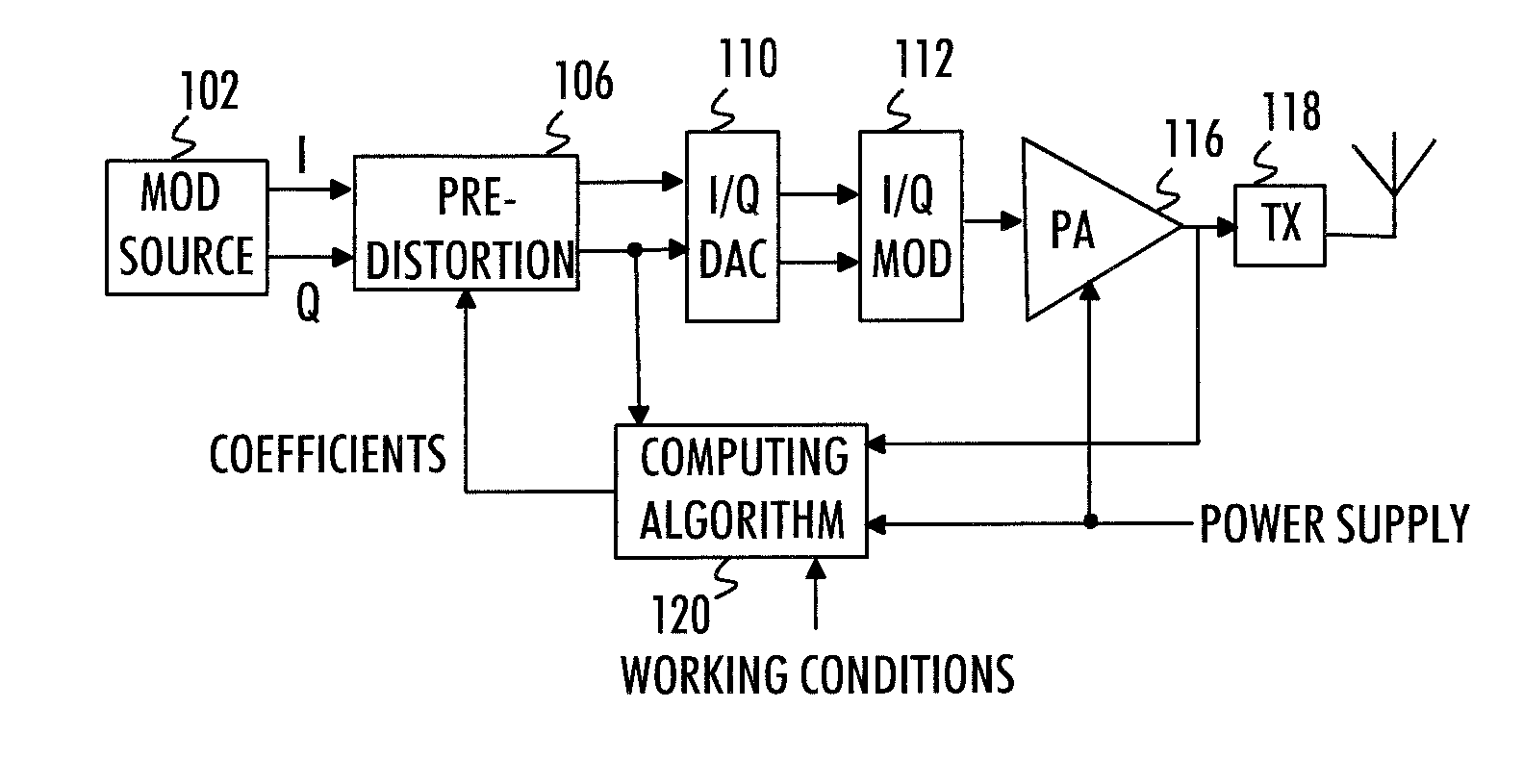
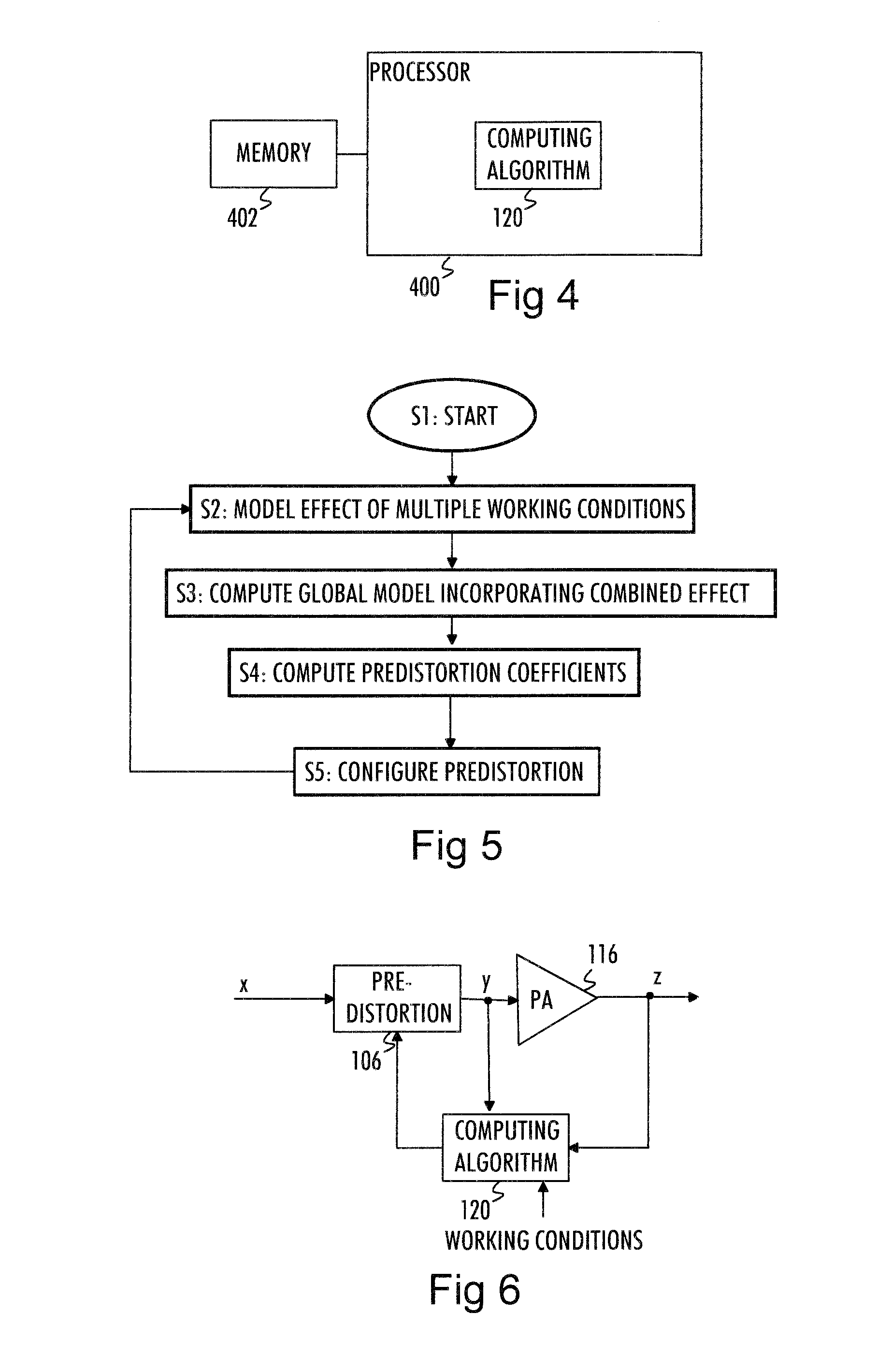
A method, apparatus, and computer program for modeling mathematically an effect of a plurality of factors on signal distortion caused by a non-linear amplifier are provided. First, there is computed a global model which incorporates a combined effect of the plurality of factors on signal distortion caused by the non-linear amplifier. Before applying the pre-distorted transmission signal to the non-linear amplifier, a transmission signal is pre-distorted with coefficients derived from the global model thus compensating for the signal distortion caused by the non-linear amplifier.
Owner:RPX CORP
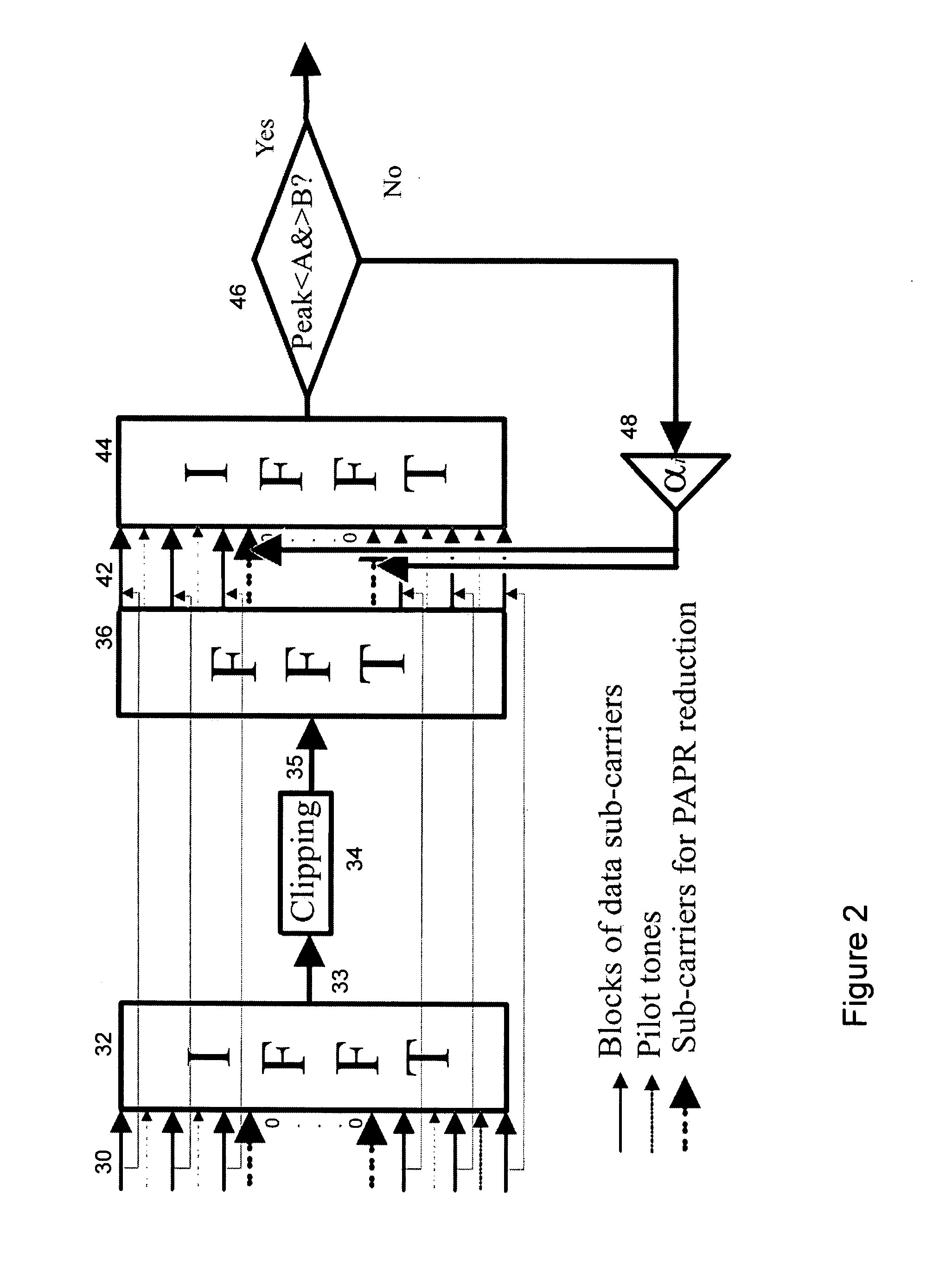
Peak-to-average-power reduction of OFDM signals
InactiveUS20080112496A1Improvement in Peak-to-Average-Power ratioEffect of clipping is minimisedAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPower amplifiersTime domainAudio power amplifier
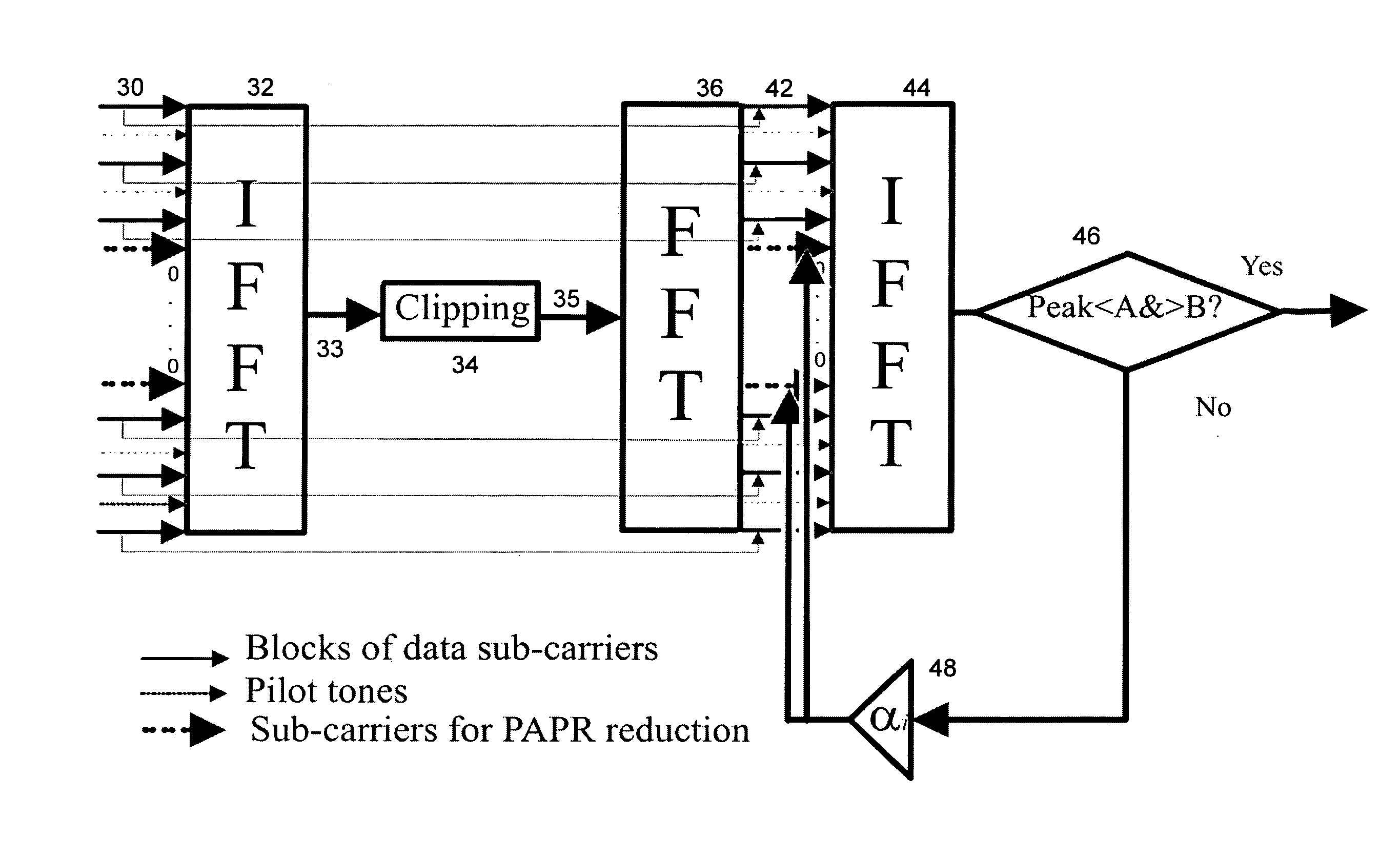
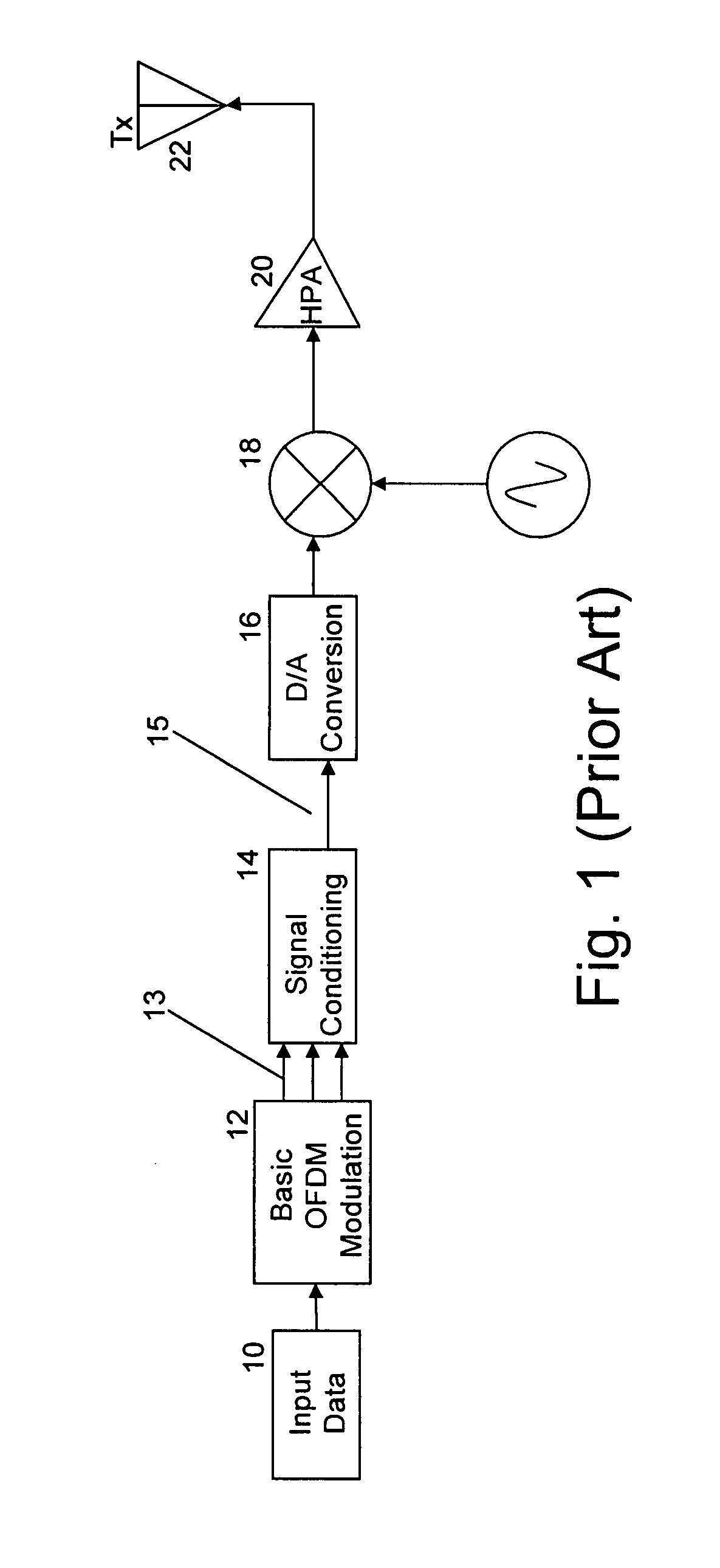
A method of processing an Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplex (OFDM) signal having a plurality of data carriers and a plurality of unused carriers is disclosed. The method comprises transforming an original frequency-domain OFDM signal into a time domain signal and simulating the effect of a non-linear amplifier on the time-domain signal to provide a potentially distorted time domain signal. The potentially distorted time domain signal is transformed into a potentially distorted frequency domain signal and at least some of any values of the data carriers in the potentially distorted frequency domain signal are restored with corresponding values from the original frequency domain signal. At least some of the unused carriers in the at least partially restored frequency domain signal are scaled with a scaling factor. The scaled frequency domain signal is transformed into a temporary time domain signal and the temporary time domain signal is analysed for the presence of a peak or near zero amplitude value that would lead to distortion by said amplifier. If the signal includes such a peak or near zero value, the scaling, transforming and analysing are repeated with an increased scaling factor.
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE DUBLIN NAT UNIV OF IRELAND DUBLIN
Modular fiber-based chirped pulse amplification system
InactiveUS7711013B2Prevent buildupEliminate the effects ofLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsFiberAudio power amplifier
A modular ultrafast pulse laser system is constructed of individually pre-tested components manufactured as modules. The individual modules include an oscillator, pre-amplifier and power amplifier stages, a non-linear amplifier, and a stretcher and compressor. The individual modules can typically be connected by means of simple fiber splices.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Backgate switched power amplifier
InactiveUS6064264AGated amplifiersAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyMOSFETAudio power amplifier
A switched power amplifier circuit employs non-linear amplifier stages including MOSFET transistors. The transistors each have source, gate, drain and backgate terminals. An input Rf signal is applied to the gate terminals and the source (or drain) terminals are connected to a load. The transistors are operated as switches by selectively applying clock signals to the backgate terminals to activate desired transistors, thus causing the transistors to turn on and allow current to flow through the load to generate power. The power to the load is increased by turning on multiple transistors at any given time.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
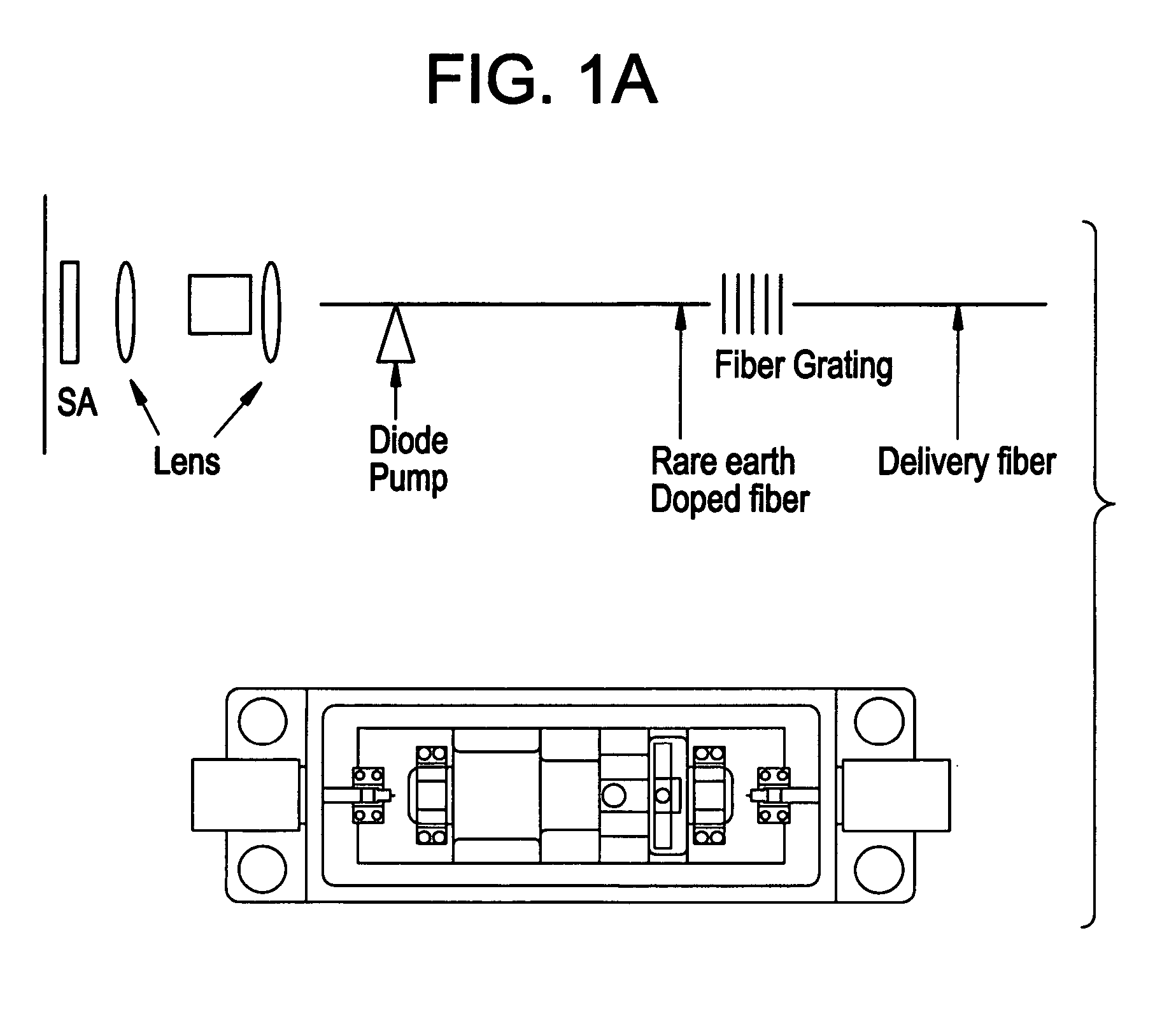
Pre-chirped management based low-noise fiber femtosecond laser amplifier
ActiveCN105390912ASuppression of High Frequency (>1kHz) NoiseLow running costActive medium shape and constructionLow noiseFiber
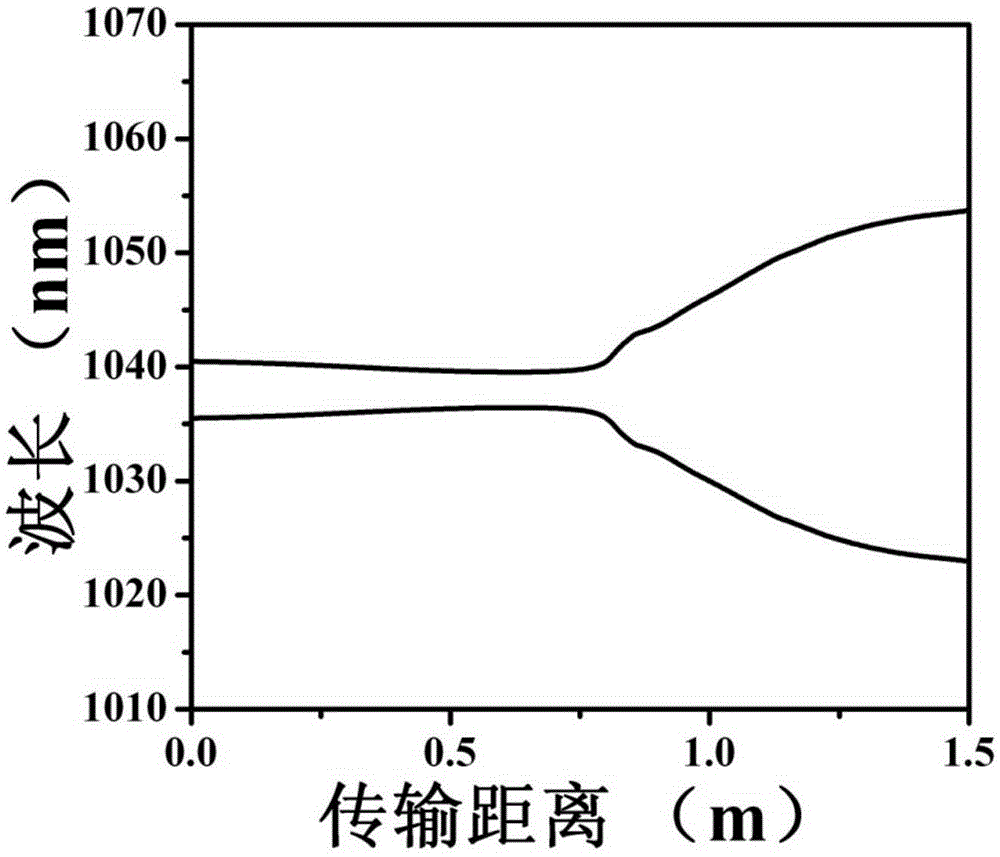
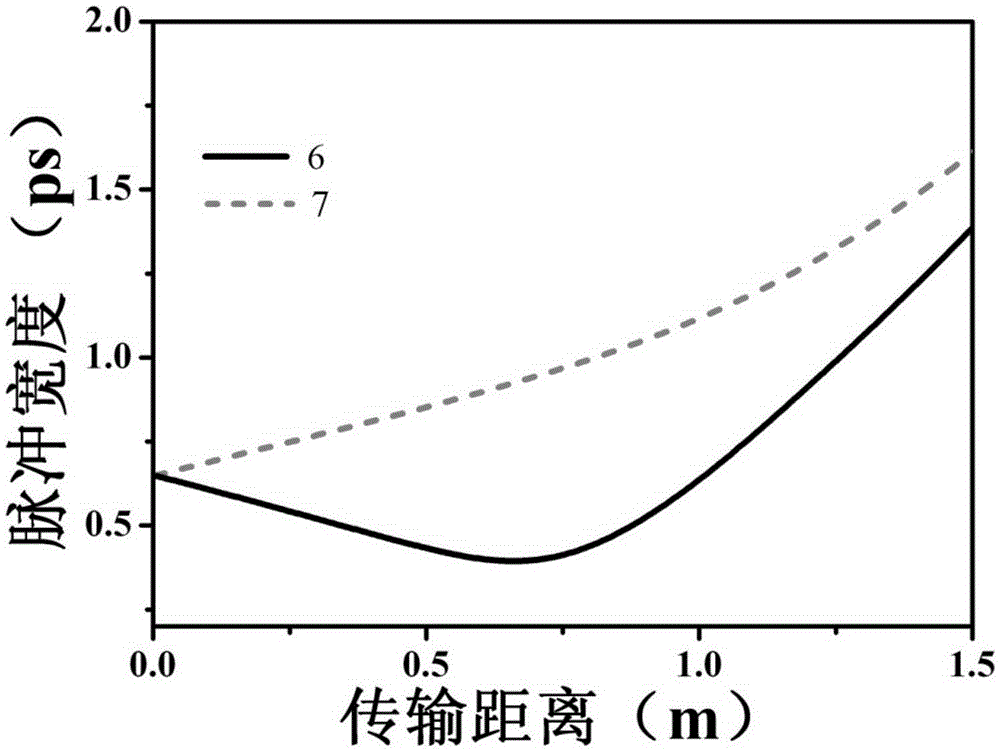
Provided a pre-chirped management based low-noise fiber femtosecond laser amplifier. The amplifier comprises an ytterbium-doped fiber dispersion management mode-locked laser (1), a spectral interference filter (2), a grating negative dispersive delay line (3), an ytterbium-doped fiber amplifier (4), and a grating pulse compressor (5). The ytterbium-doped fiber dispersion management mode-locked laser (1) generates a breathing soliton pulse sequence; the spectral interference filter (2) adjusts a center wavelength of the breathing soliton pulse sequence and enables it in the gain spectrum center of the ytterbium-doped fiber amplifier (4); the grating negative dispersive delay line (3) introduces a negative chirp into the adjusted breathing soliton pulse sequence, thereby obtaining a seed pulse; the ytterbium-doped fiber amplifier carries out self-similar amplification on the seed pulse, thereby obtaining a parabolic pulse; and the grating pulse compressor (5) compresses the parabolic pulse and generates a femtosecond laser pulse. According to the high-frequency noise of a linear amplifier effectively inhibited by the pre-chirped management based low-noise fiber femtosecond laser amplifier disclosed by the present invention, a Fourier transform-limited femtosecond laser pulse with a narrow pulse width is obtained.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
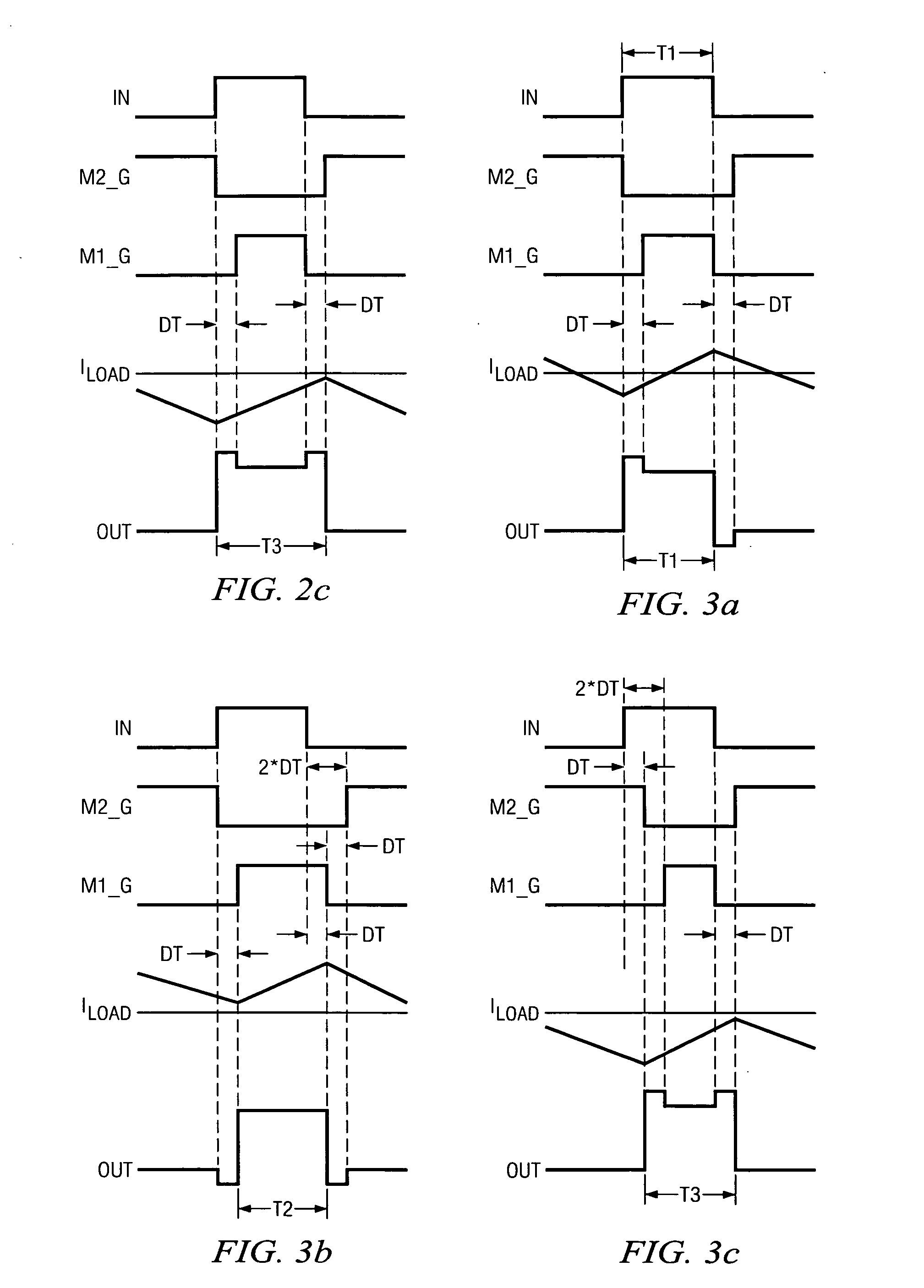
Compensation of nonlinearity introduced by dead time in switching output stage
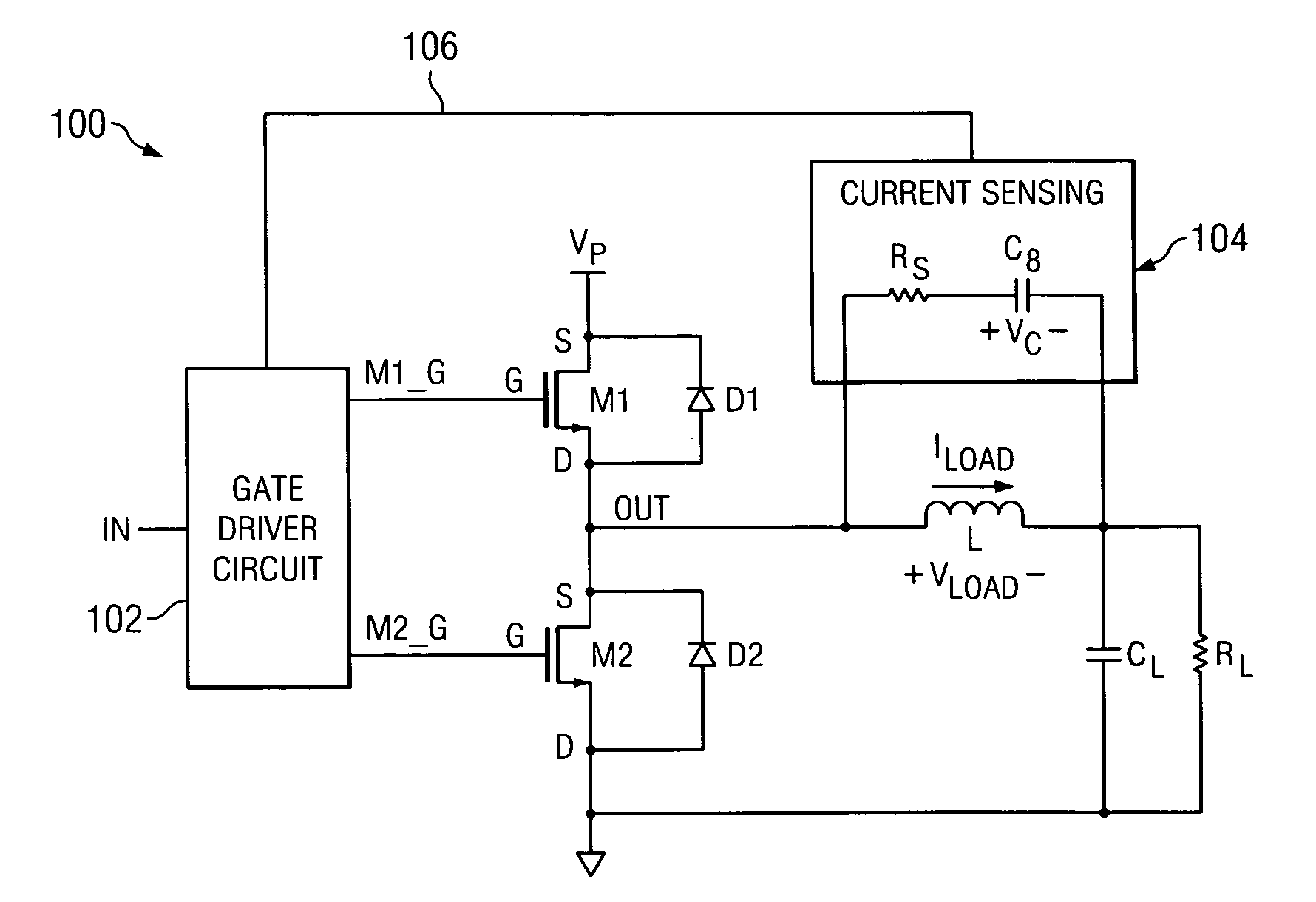
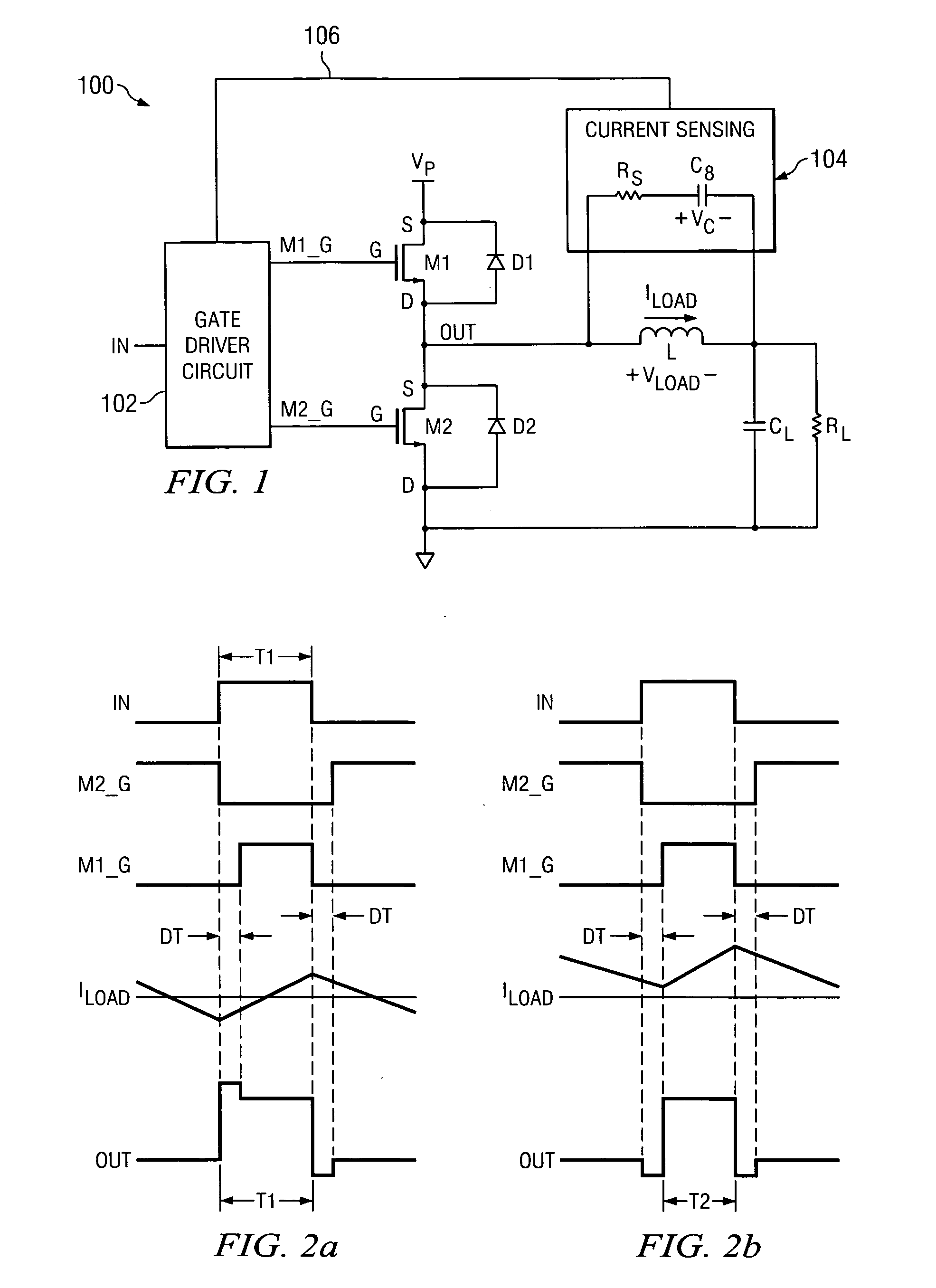
A method of operating a class D amplifier output stage that compensates for nonlinearity introduced by a residual load current during the dead time in the switching of the output stage. The amplifier output stage includes an input, a gate driver circuit, two output transistors, an output, and a current sensing circuit. The transistors are serially connected between the terminals of a power supply. A residual load current flows through the transistors when they are switched off. The gate driver circuit increases or decreases the duty cycles of signals driving the transistors based on the direction of the residual load current flowing through the transistors, thereby causing the duty cycle of the amplifier output to remain substantially constant and equal to the duty cycle of the amplifier input.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Pipelined converter systems with enhanced accuracy
ActiveUS7271750B1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersAudio power amplifierContinuous signal
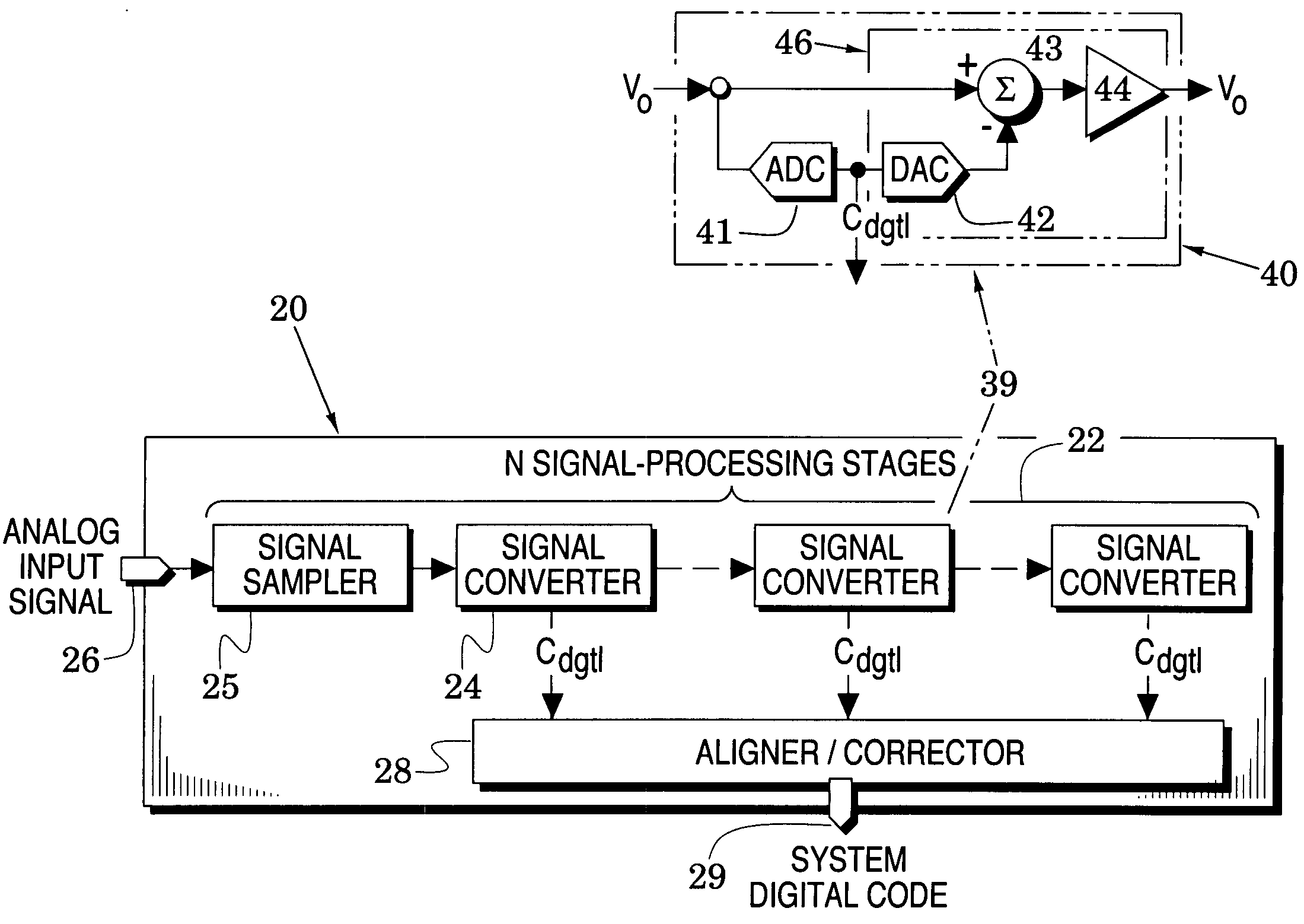
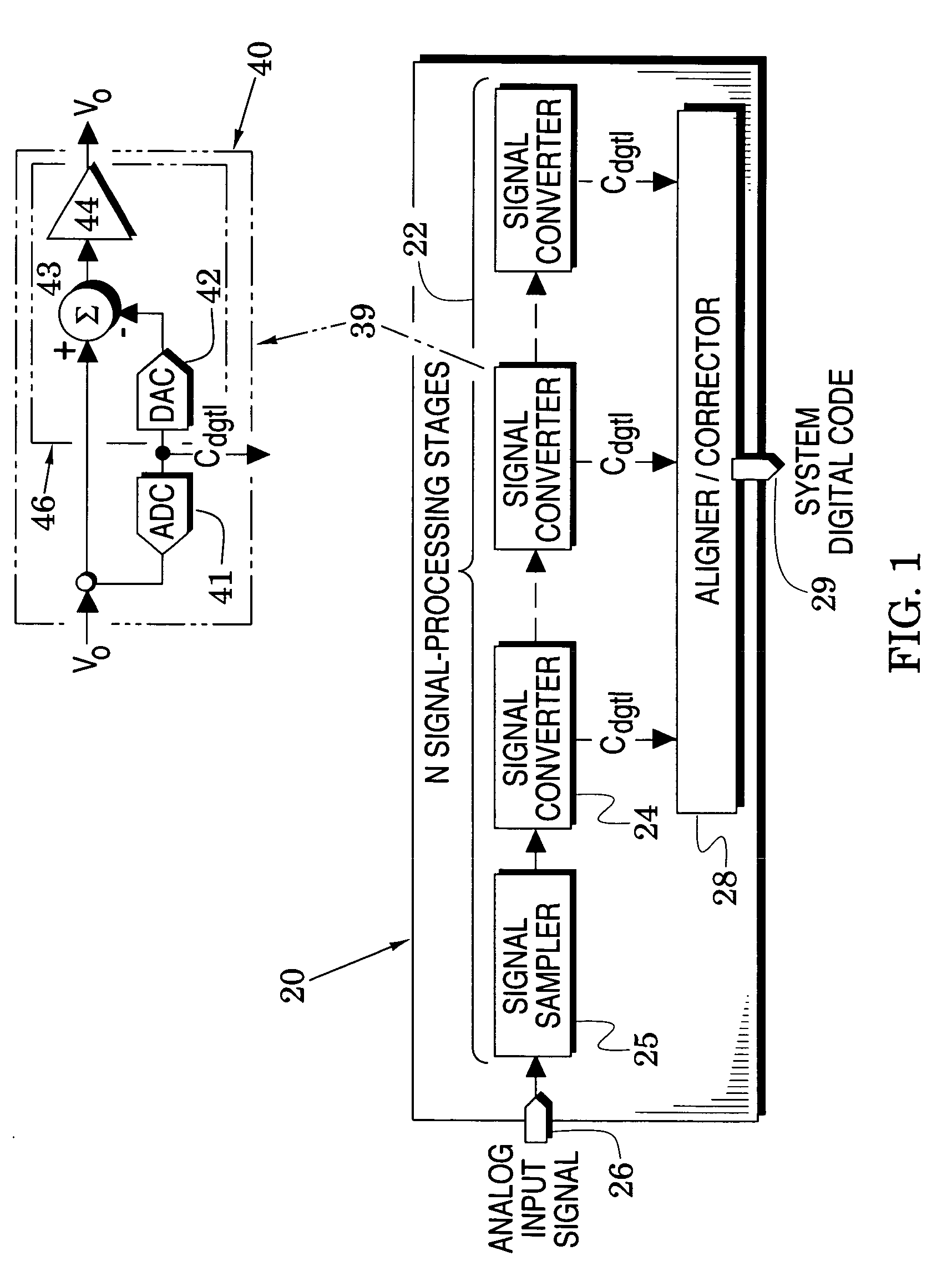
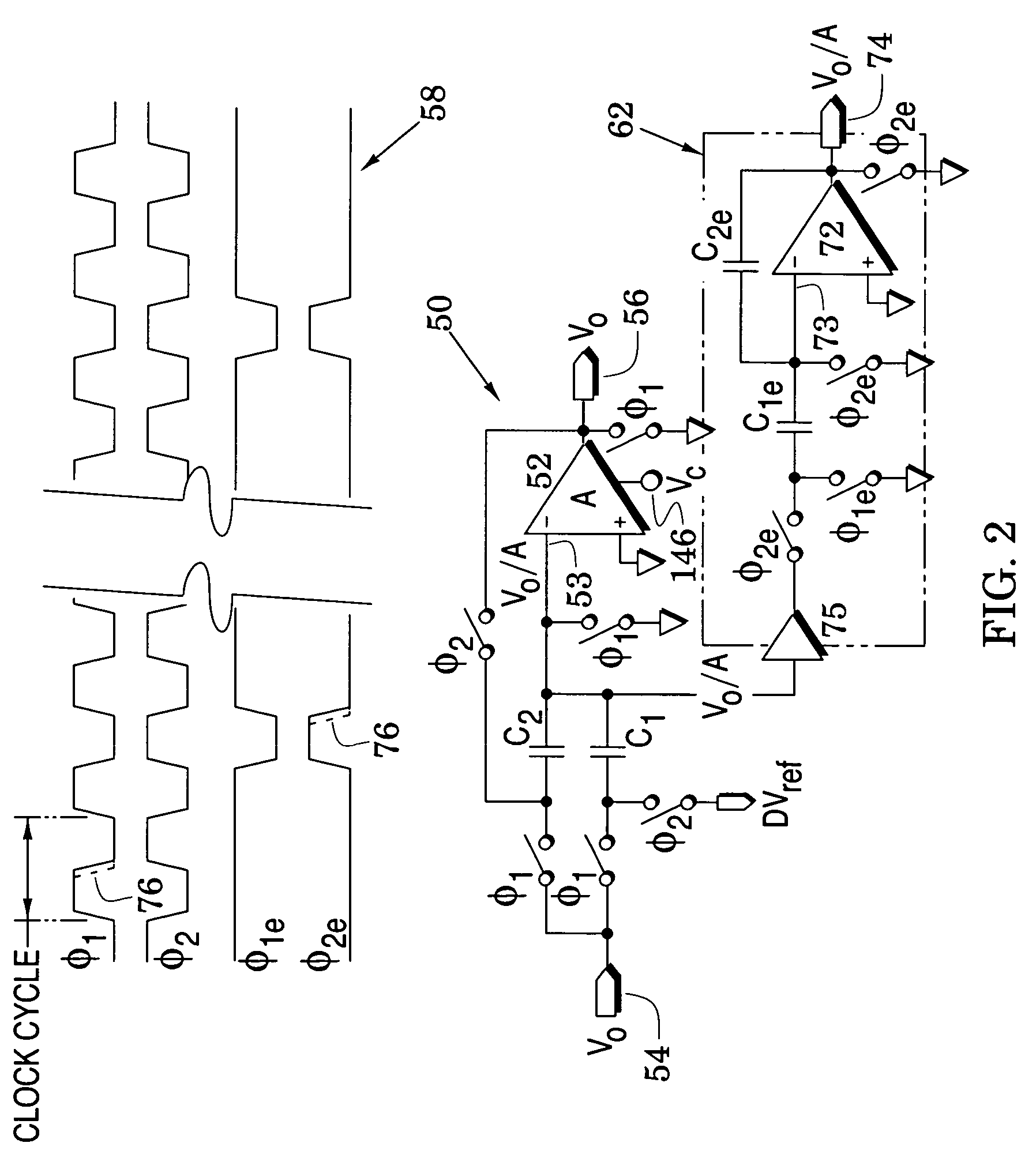
Converter system embodiments are formed with signal-processing stages which include successive signal converters and a preceding signal sampler wherein all but a last one of the stages provides an output signal to a succeeding one of the stages and all of said signal converters generate a corresponding digital code. The system embodiments generally address a selected one of the stages and include controllers which are configured to process, at a process rate less than the system's sample rate, a digital error signal and the back-end digital code of back-end ones of signal converters that succeed the selected stage to thereby adjust at least one of the back-end digital code and a control voltage in the selected stage to enhance the accuracy of the system digital code. Once the processes of these embodiments have been applied to the selected stage, they may be successively applied to preceding stages. System embodiments are also directed to nonlinear amplifier gain by including approximations (e.g., piece-wise and polynomial approximations) of amplifier gain so that they are better directed to an amplifier gain that is appropriate for the signal that is being processed through the amplifier.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Distortion compensation circuit and method based on orders of time dependent series of distortion signal
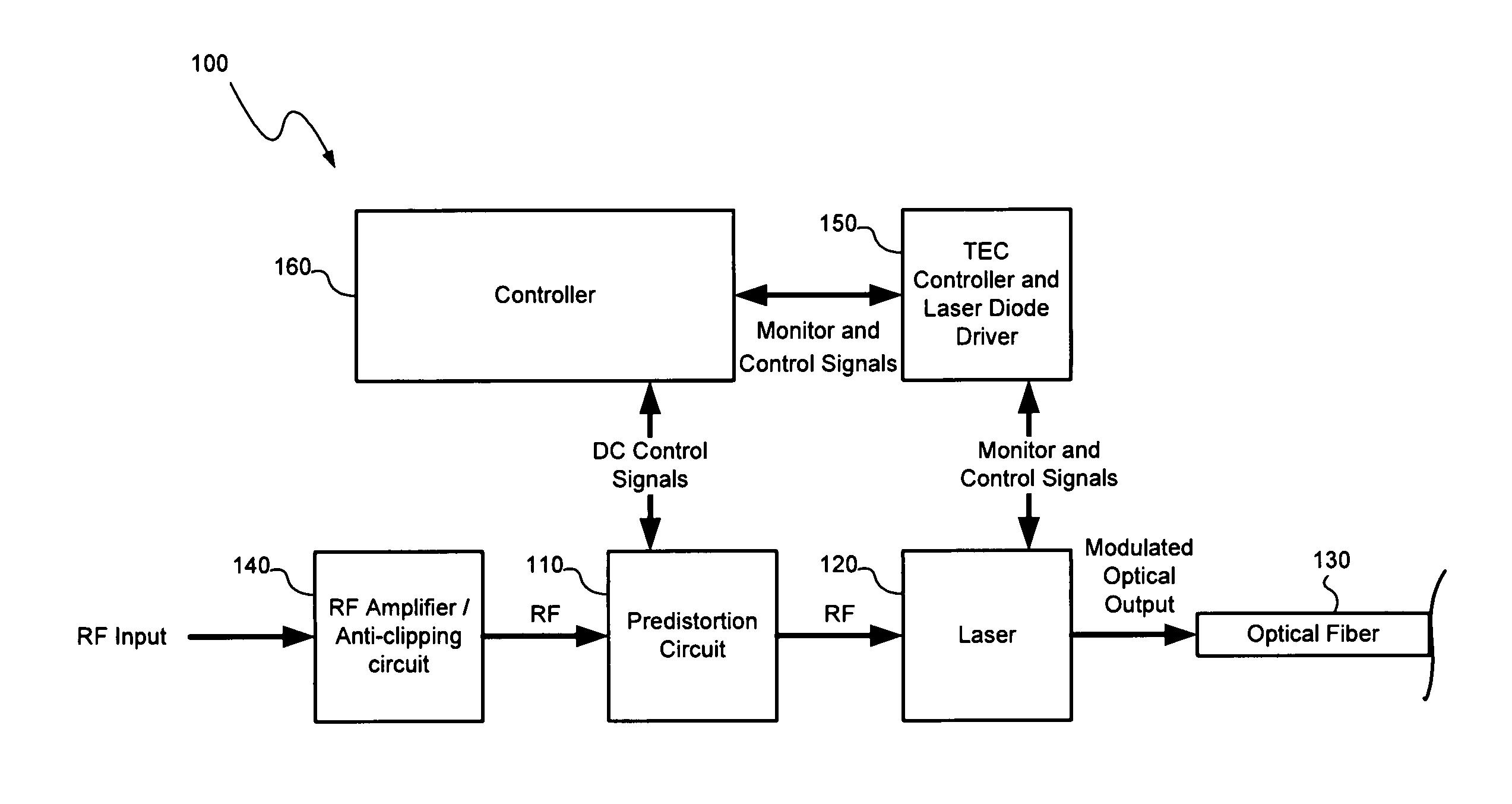
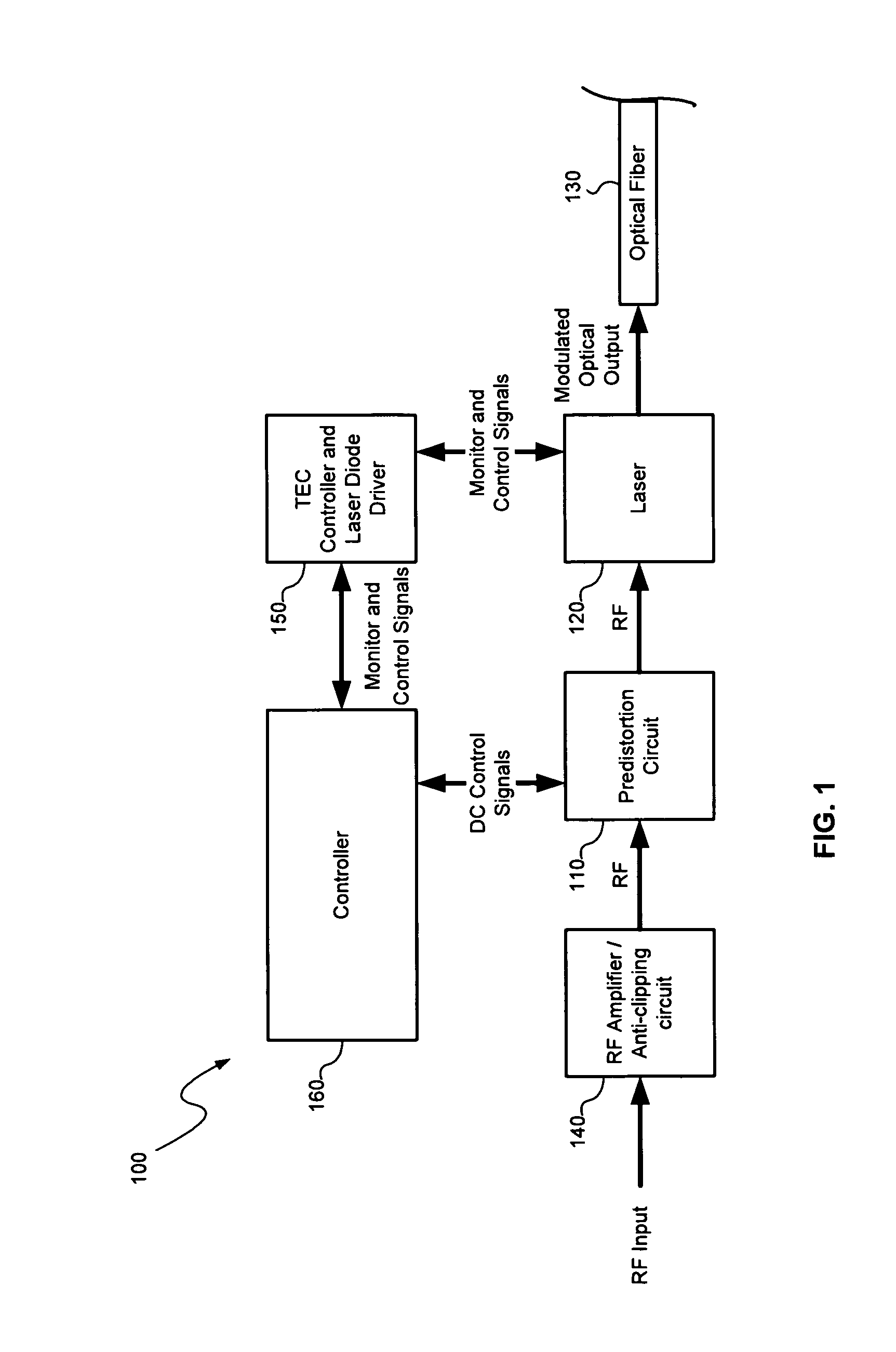
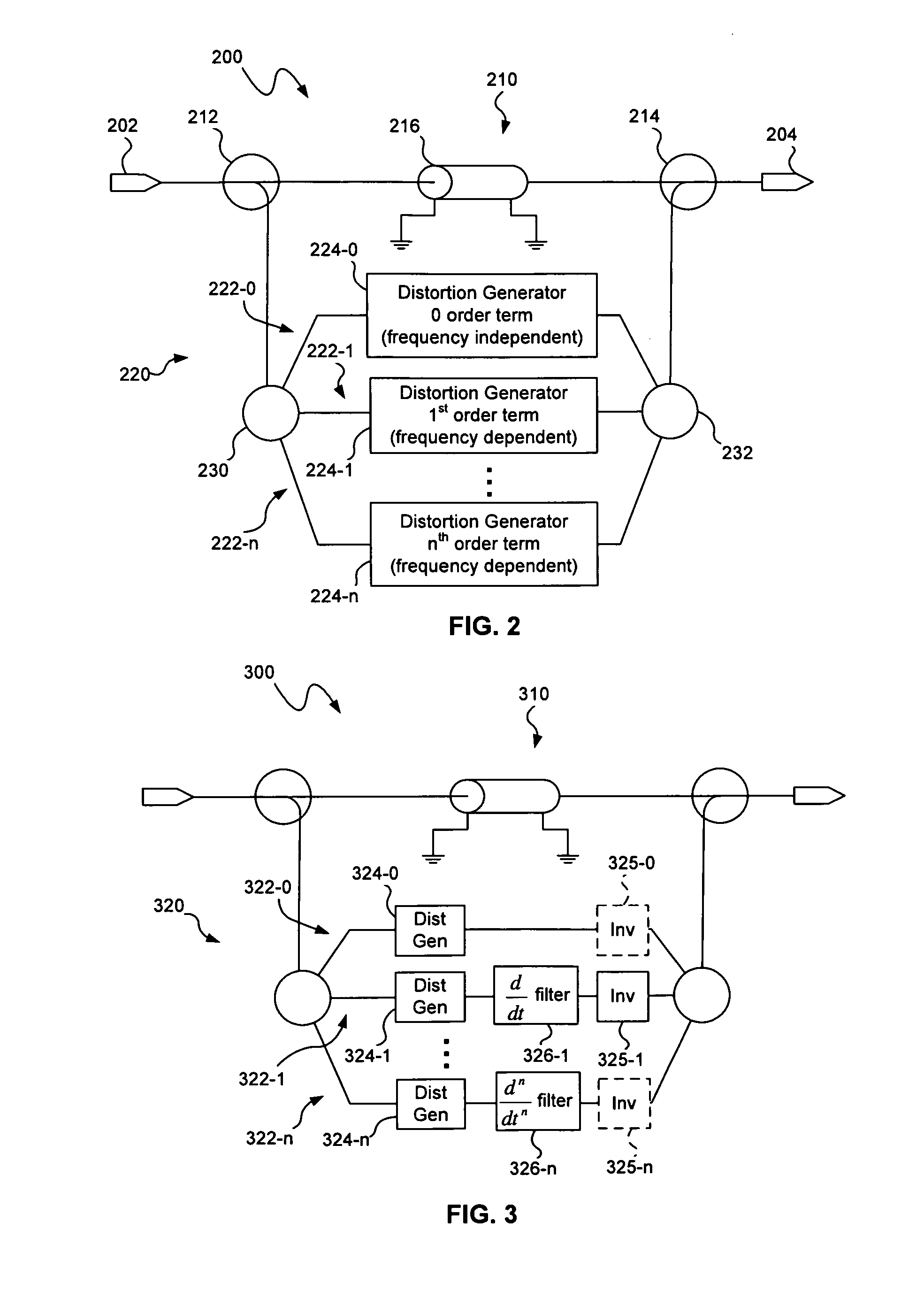
A distortion compensation circuit compensates for distortion generated by one or more non-linear elements such as a laser device. The distortion compensation circuit may be used in an optical transmitter, such as a laser transmitter used for forward path CATV applications. The distortion compensation circuit may include a primary signal path and a secondary signal path that receive an input signal. The secondary signal path produces distortion of a magnitude corresponding to the magnitude of, but at an opposite phase to, the distortion generated by the non-linear amplifier. The secondary signal path includes a plurality of distortion sub-paths with each of the distortion sub-paths configured to produce intermodulation distortion products of the same distortion order but for different frequency dependent orders in a time dependent series representative of the distortion produced by the non-linear amplifier.
Owner:APPLIED OPTOELECTRONICS
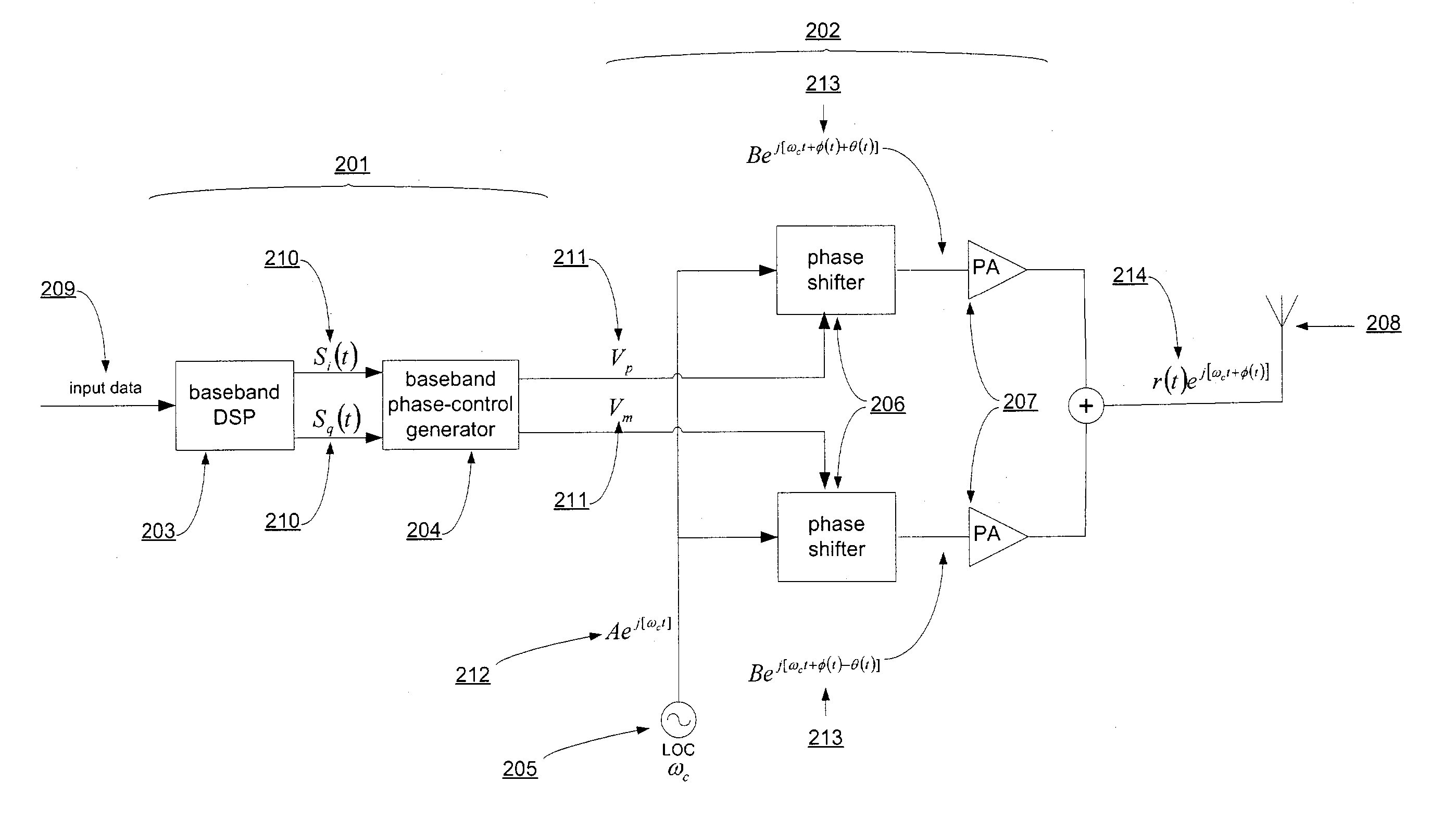
Phase shifted transmitter architecture for communication systems
InactiveUS7260157B2Improve matchHigh bandwidthSecret communicationTransmitter/receiver shaping networksCommunications systemAudio power amplifier
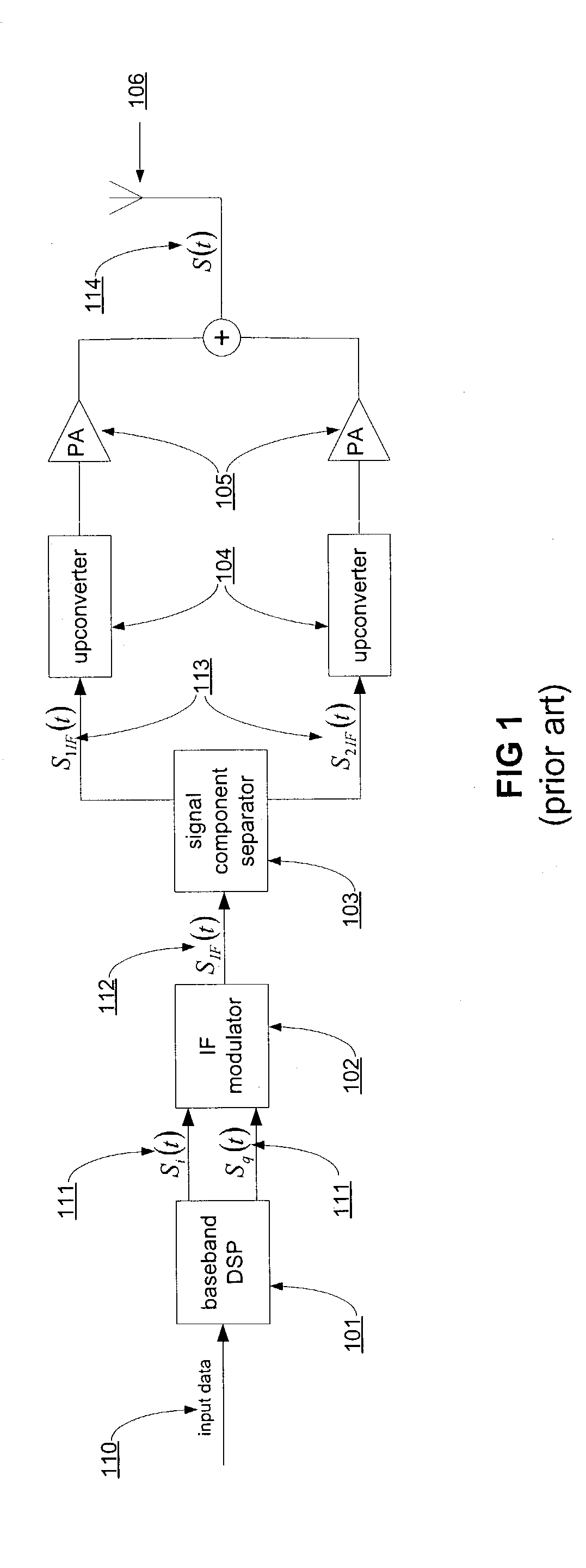
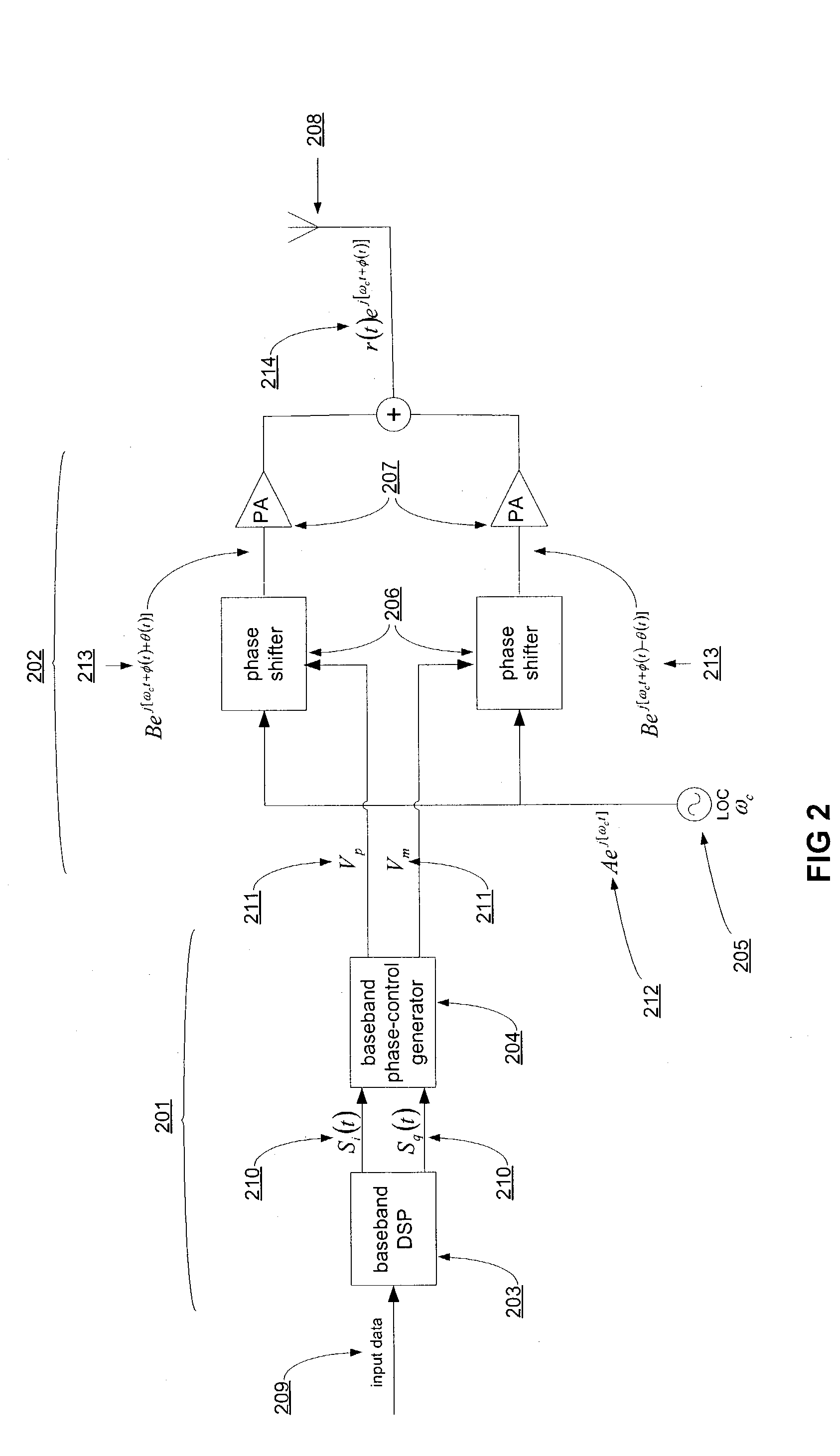
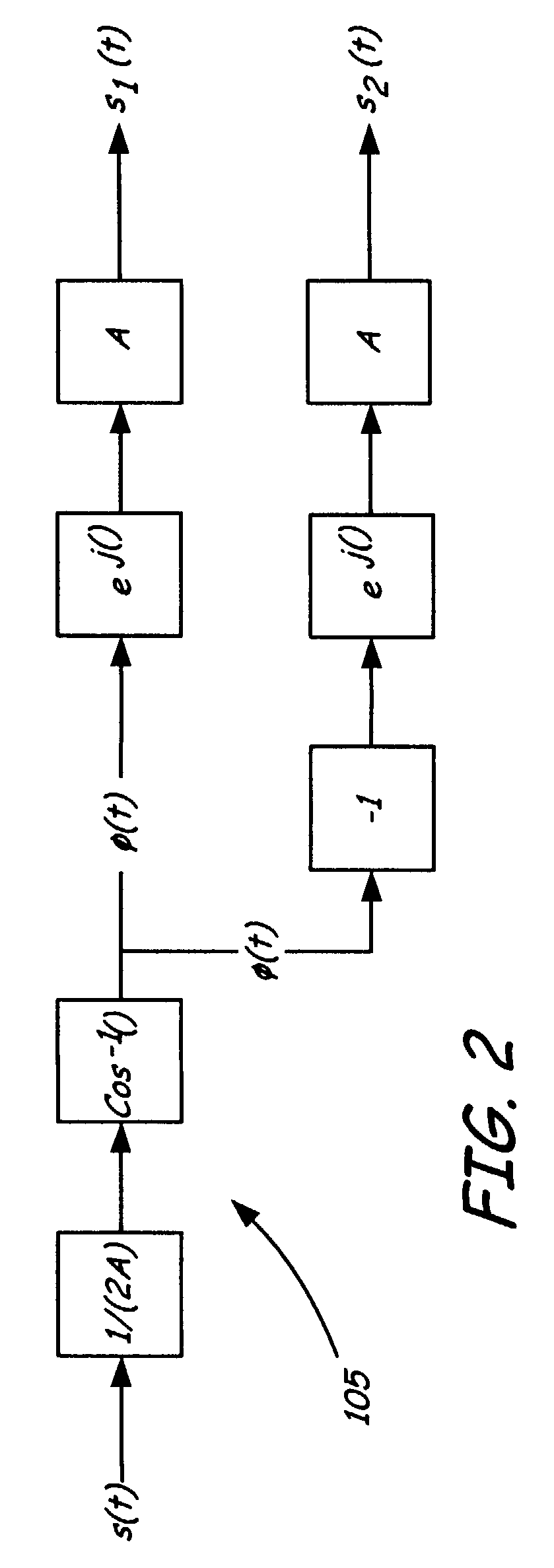
The phase shifted (PS) transmitter provides substantially linear amplification from two non-linear amplifiers by decomposing the original signal into two constant envelope signals with varying phases. The generation of the two constant envelope signals does not require the use of a signal component separator (SCS) or a reference signal generator. The phase shifted transmitter generates directly the required constant envelope, varying phase signals. This eliminates stringent requirements on the circuitry and allows the use of non-linear highly efficient power amplifiers in the transmitter. When the two above mentioned signals are combined, they constructively and destructively interfere to re-form an amplified form of the original signal, which is to be transmitted via an antenna.
Owner:HAGH SOTOUDEH HAMEDI +1
Operational amplifier arrangement
InactiveUS7042284B2Power efficient and and simpleSimple powerAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAudio power amplifierOperational amplifier
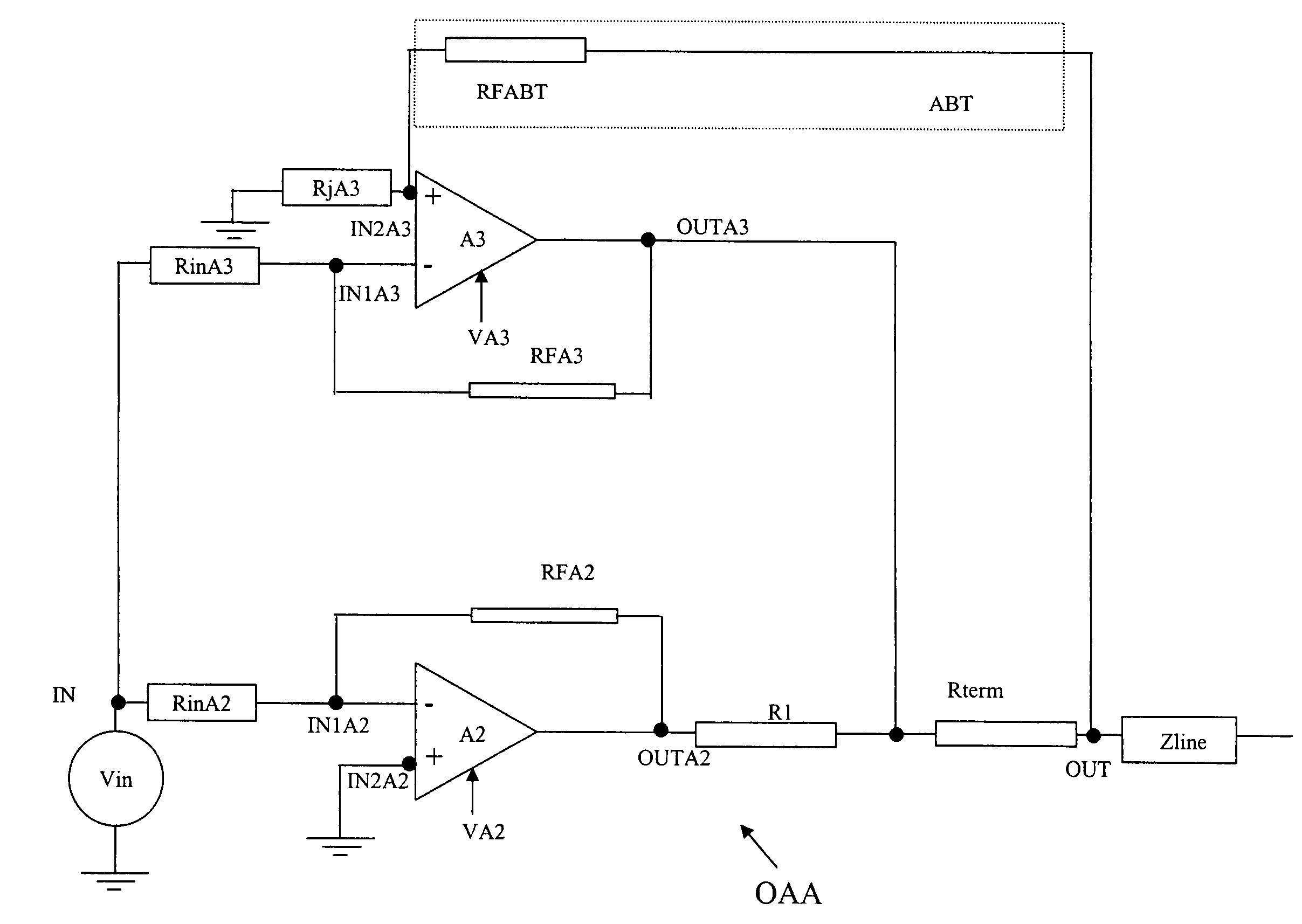
An operational amplifier arrangement having a non-linear amplifier and a linear amplifier, both having a pair of input terminals one of which is coupled to an arrangement input terminal, and both having an output terminal that is coupled to an arrangement output terminal. The output terminal of the non-linear amplifier is further coupled to the output terminal of the linear amplifier via a series impedance. The output terminal of the linear amplifier is coupled to the arrangement output terminal via a terminating impedance. The arrangement includes an active back termination arrangement coupled between the arrangement output terminal and either one of the pair of input terminals of the linear amplifier. Preferably, the linear amplifier is receiving a supply voltage that exceeds the supply voltage received by the non-linear amplifier.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Linearization of power amplifier
InactiveUS6546233B1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasFrequency spectrumLinear power amplifier
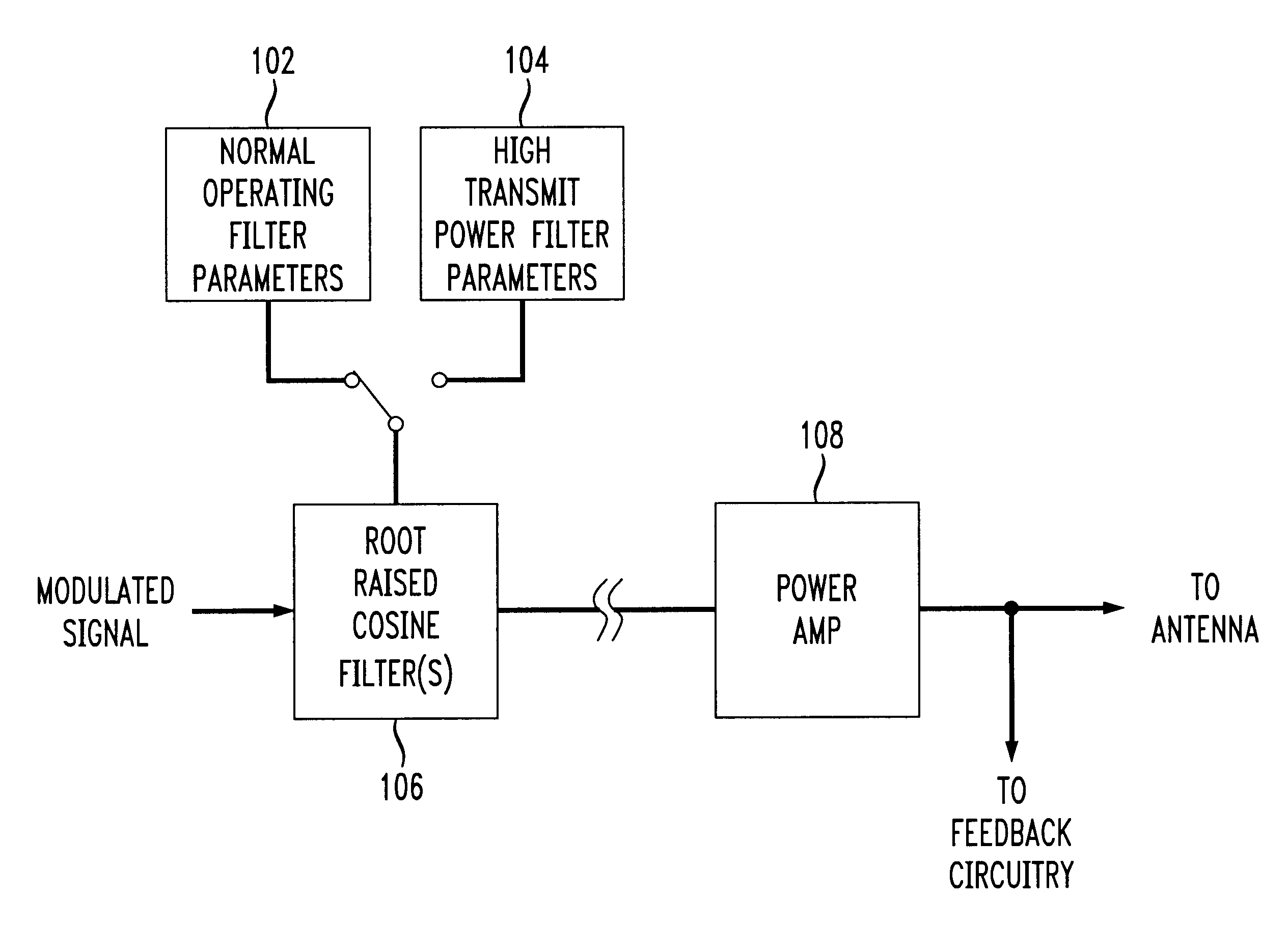
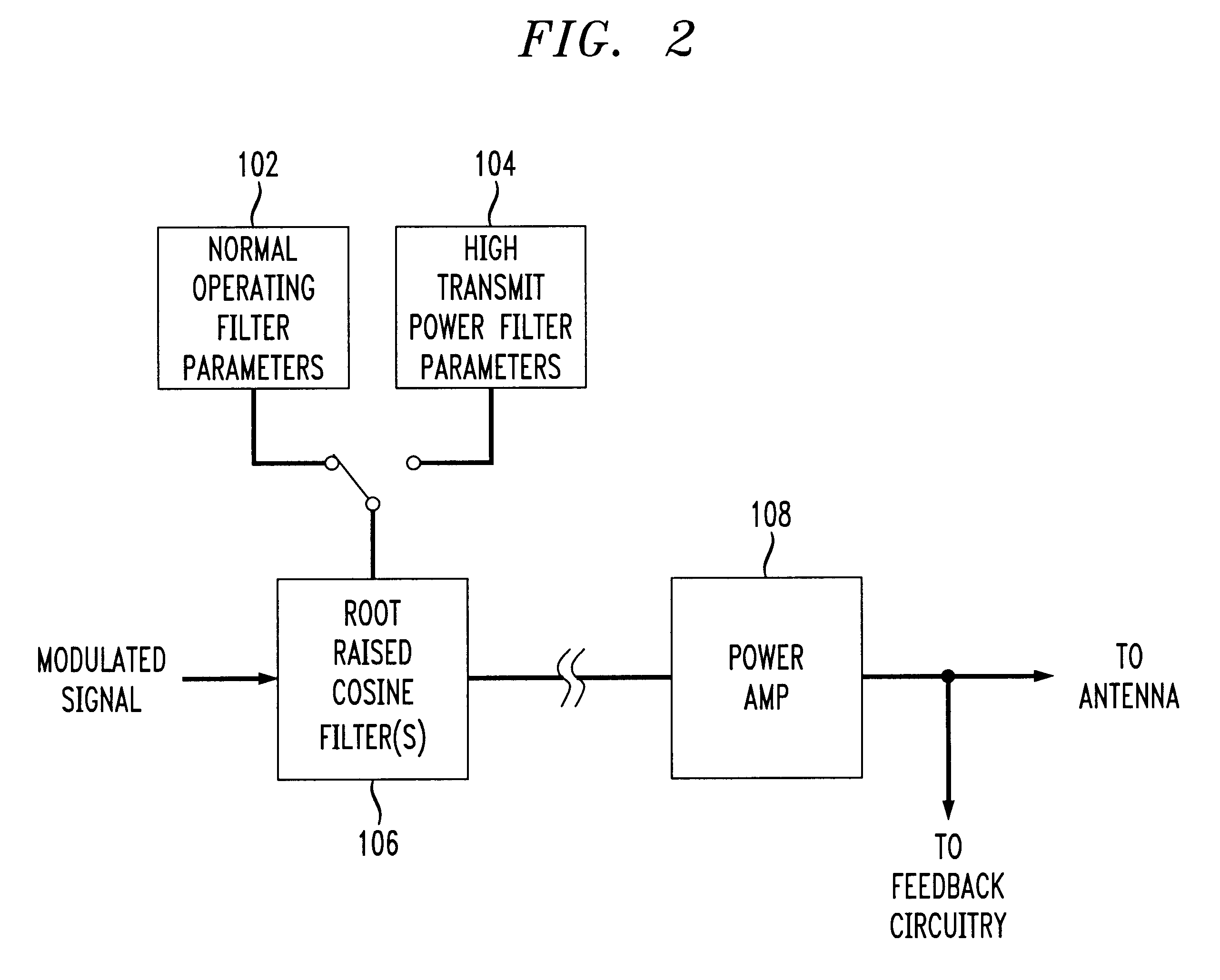
A apparatus linearizing and technique for linearizing a non-linear power amplifier used in a transmitter of, e.g., a TDMA mobile wireless telephone. Linearization of the non-linear amplifier by changing the shape of the input signal is performed when the input signal level is high, thus increasing efficiency or reducing power consumption at that time, albeit at the cost of increased inter-symbol interference (ISI). However, since the input signals at that time are at a high level, the increased ISI can be tolerated and adjacent symbols can still be distinguished from one another. The invention allows use of a non-linear power amplifier which typically enjoys a lower current consumption than that of a linear power amplifier, thus increasing the time between battery recharges and / or reducing the overall size of the wireless telephone device. The power amplifier is operated in a linear mode when transmitted power is low, thus allowing differentiation between adjacent symbols (i.e., improvement of ISI). At high input power, the power amplifier is used in its non-linear mode to reduce current consumption. The signal shape is changed by changing the parameters of the root raised cosine filters. When the input level is low, the existing, otherwise conventional filter's parameters are used. However, when the input power level is high, modified parameters are used. Switching between the two sets of filter parameters is preferably performed at baseband. Thus, a relationship between RRCF filter parameters and the amount of spectrum utilized by the transmitted signal is utilized, and RRCF filter parameters are adjusted based on a desired limitation to an output spectrum.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Digital predistortion system for linearizing a power amplifier
InactiveUS6937669B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionSecret communicationAudio power amplifierLinear power amplifier
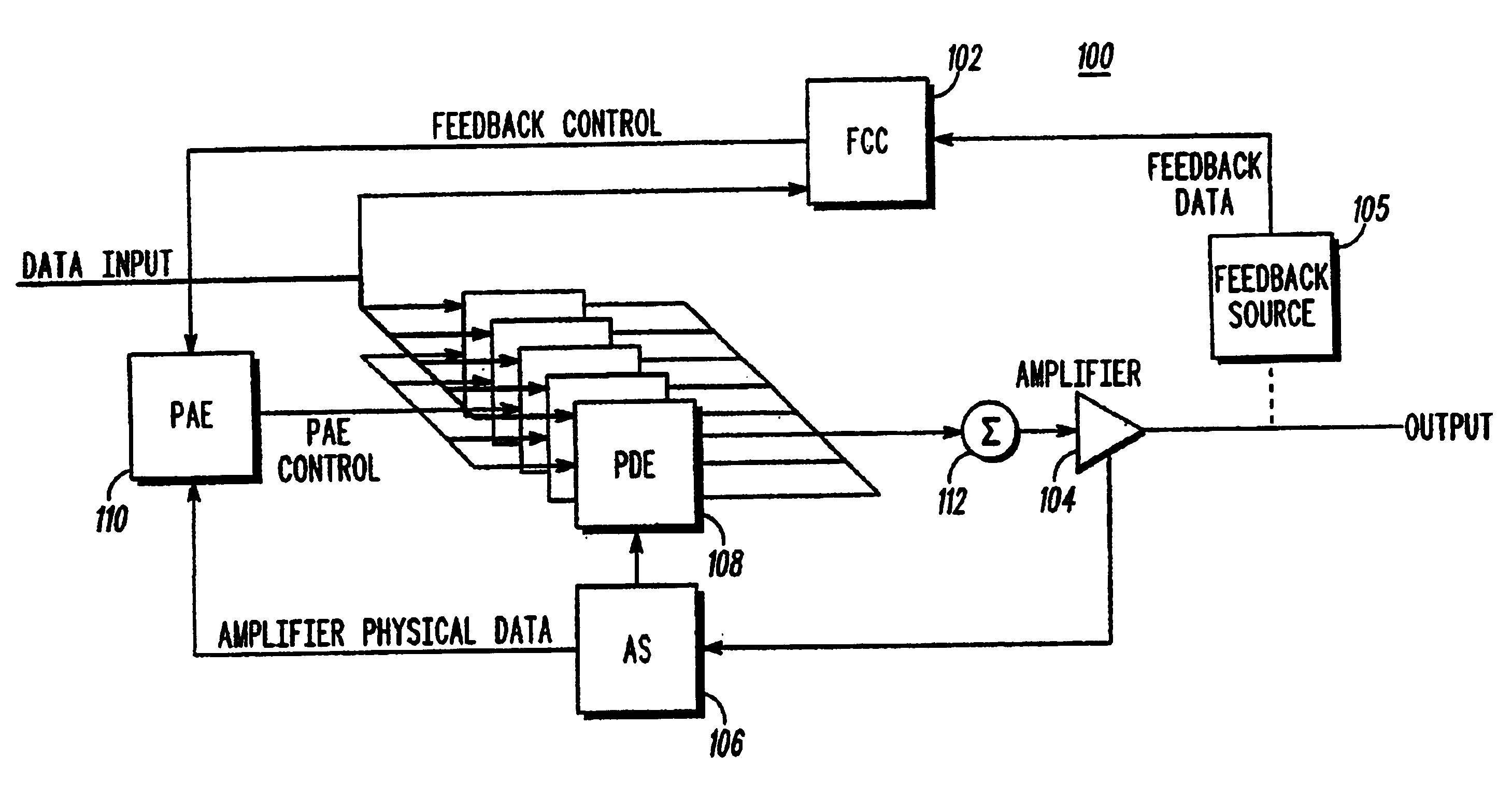
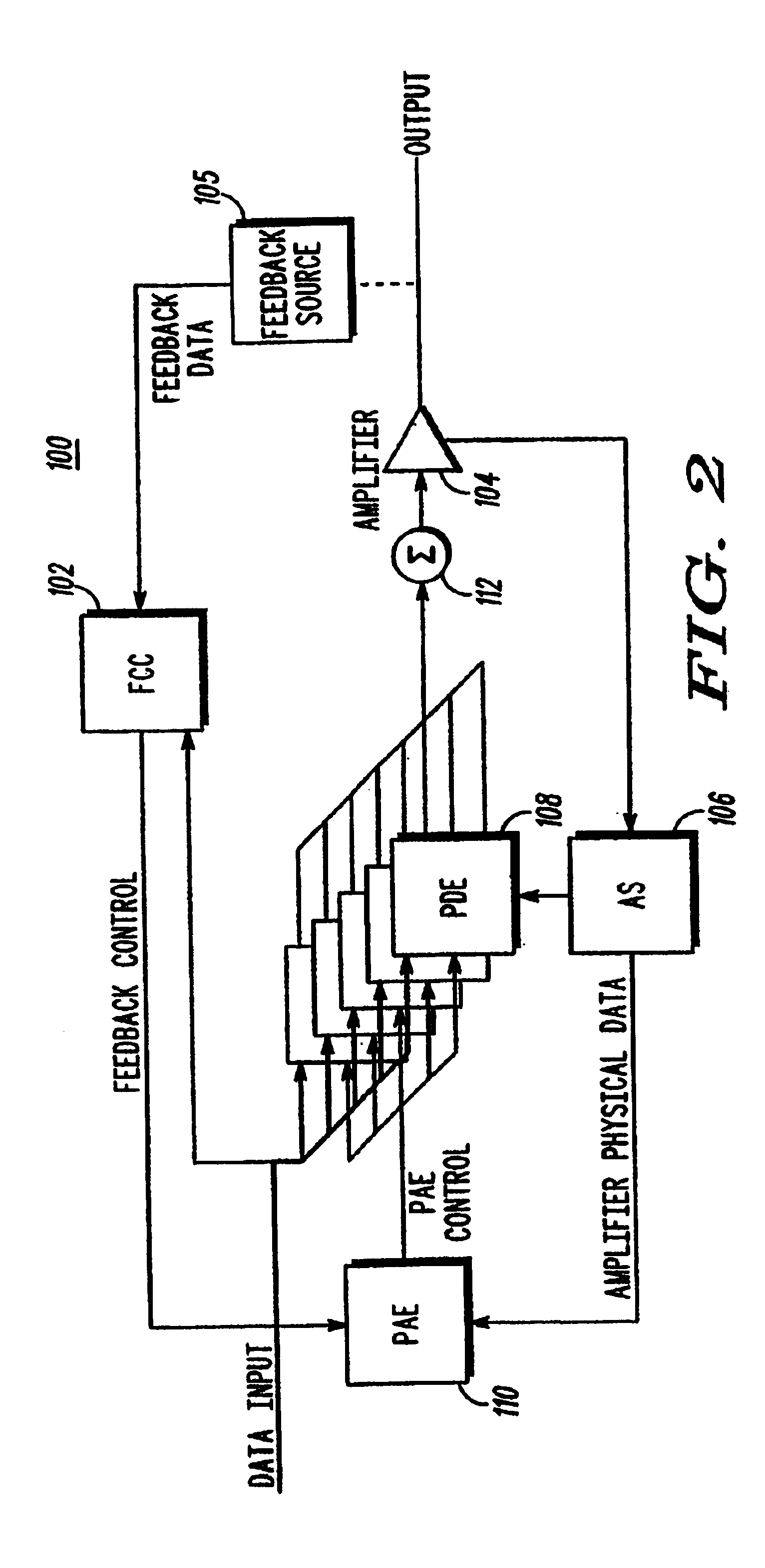
A predistortion linear power amplifier utilizes several predistortion computation engines to receive a first carrier signal. The predistortion computation engines also receive input from a predistortion algorithm engine. The predistortion algorithm engine receives its data from a predistortion amplifier sensor that monitors the operating characteristics of the amplifier and also from a feedback control circuit that provides frequency correlated input and feedback data. The processed data from the predistortion algorithm engine is then input into the predistortion computation engine along with the carrier signal. An output combiner circuit takes the output of each predistortion computation engine and generates a single correction estimate, which is then input into the nonlinear amplifier for producing a substantially linear output signal.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Predistortion circuit including distortion generator diodes with adjustable diode bias
A predistortion circuit provides a predistorted input signal that compensates for distortion generated by a non-linear amplifier such as a laser device. The predistortion circuit may be used in an optical transmitter designed for broadband applications, such as a laser transmitter used for forward path CATV applications. The predistortion circuit may include a primary signal path and a secondary signal path that receive an input signal. A second order distortion generator on the secondary signal path generates predistortion of a magnitude corresponding to the magnitude of, but at an opposite phase to, the distortion generated by the non-linear amplifier. The second order distortion generator includes diodes with an adjustable diode bias to control phase, magnitude and / or magnitude / phase versus frequency of the predistortion.
Owner:APPLIED OPTOELECTRONICS
Remote underwater sound communication method
InactiveCN103220046AOvercoming multipath interferenceReduce bit error rateError preventionPhase-modulated carrier systemsFrequency spectrumMultipath interference
The invention aims to provide a remote underwater sound communication method and belongs to the technical field of underwater sound communication. The method is based on demodulation and decoding combined iterative detection of differential encoding. A transmitter resists multi-path interference by using spread spectrum communication, the problem of phase jump and loop cycle skipping is solved by using differential modulation quadrature differential phase shift keying with high frequency spectrum utilization rate, and the transmitter adopts demodulation and decoding combined iterative technology to eliminate inter-code interference. The method has the beneficial effects that 1) the error bit rate performance of a remote underwater sound communication system is improved by the demodulation and decoding combined iterative technology; 2) the technical requirement on a non-linear amplifier is reduced by differential modulation, and differential modulation has engineering feasibility; and 3) the multi-path interference of a remote underwater sound channel is overcome by spread spectrum communication.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Quadrature LINC transmission method and apparatus
InactiveUS7570711B1Improve transmittanceLess bandwidthModulation with suppressed carrierAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAudio power amplifierDecomposition
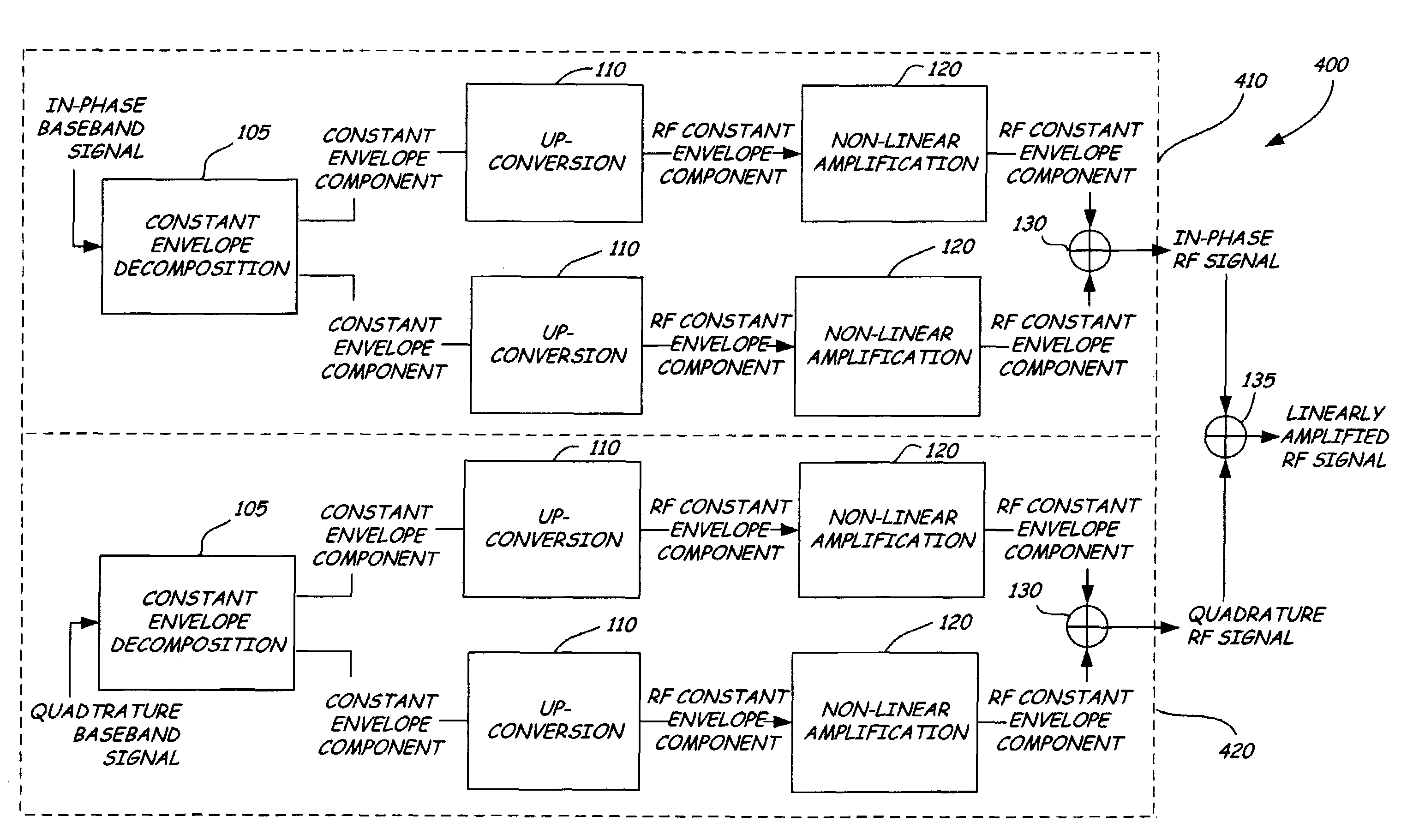
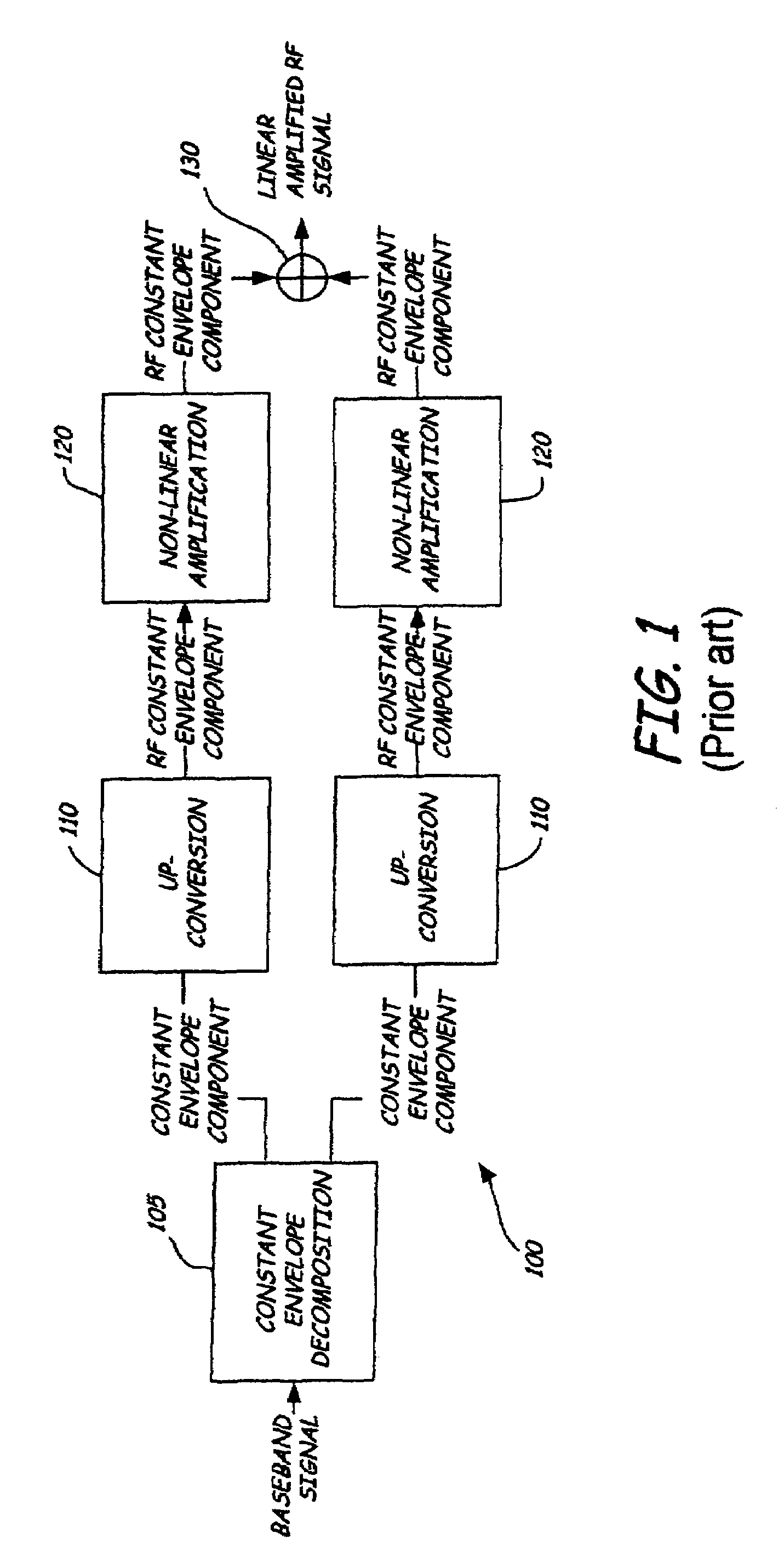
A quadrature LINC transmission system processes a baseband input signal for transmission as a linearly amplified RF signal. An in-phase LINC element processes an in-phase baseband signal into an in-phase RF signal. A quadrature LINC element processes a quadrature baseband signal into a quadrature RF signal. An output combiner combines the in-phase RF signal with the quadrature RF signal to provide the linearly amplified RF signal. The in-phase LINC element has a constant envelope decomposition block for decomposing the in-phase baseband signal into in-phase baseband constant envelope components. Two up-converters convert the in-phase baseband constant envelope components to in-phase RF constant envelope components. Two non-linear amplifiers amplify the in-phase RF constant envelope components. A combiner combines the amplified in-phase RF constant envelope components to yield the in-phase RF signal. The quadrature LINC element is similar to the in-phase LINC element and provides the quadrature RF signal.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Linear and non-linear dual mode transmitter
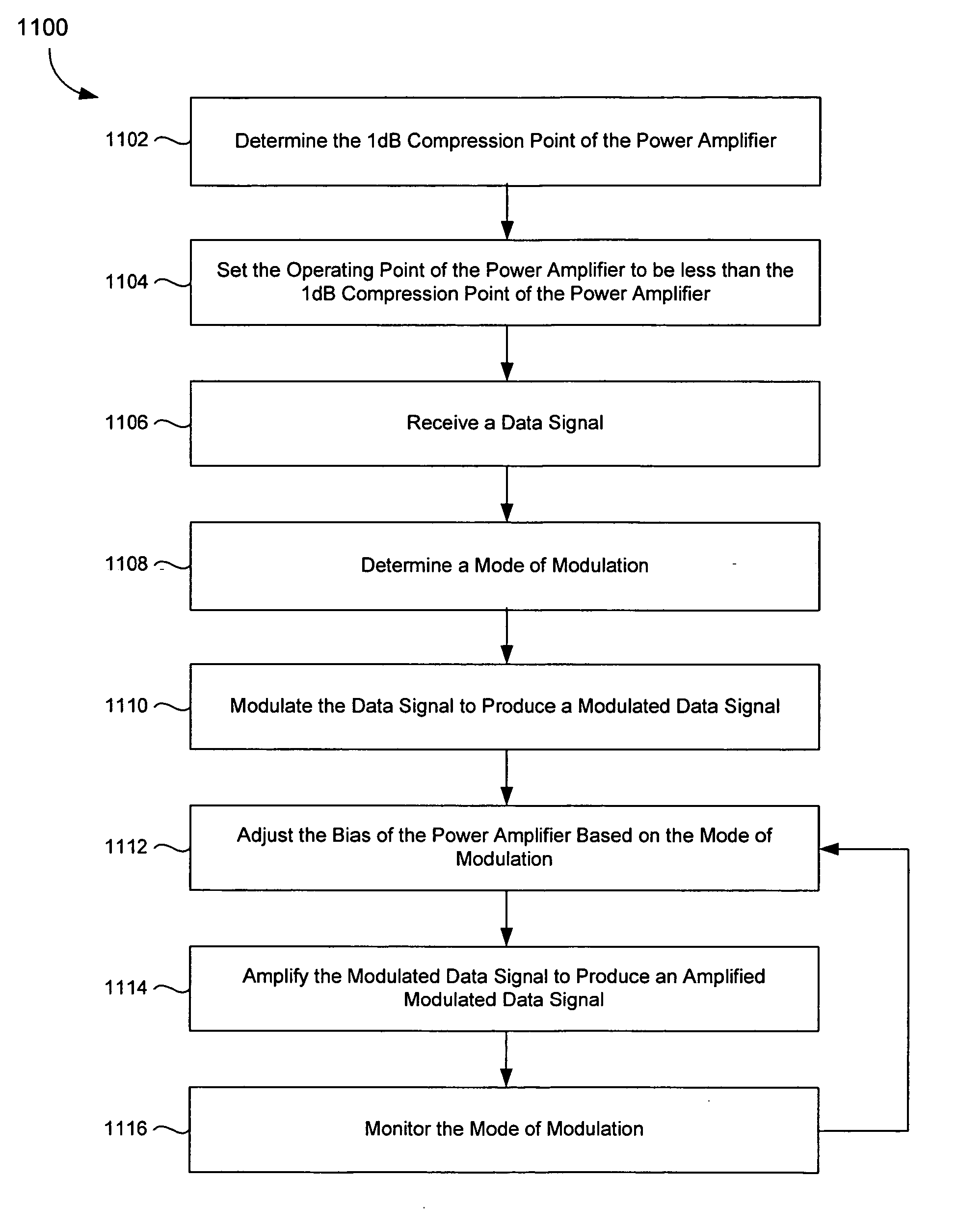
InactiveUS20060217090A1Increase powerResonant long antennasGain controlOperating pointNonlinear modulation
A transmitter includes a dual mode modulator and an amplifier coupled to the dual mode modulator. The dual mode modulator implements a linear modulation scheme during a first mode of the modulator to produce a variable envelope modulated signal. The dual mode modulator implements a non-linear modulation scheme during a second mode of the modulator to produce a constant envelope modulated signal. The amplifier is biased as a linear amplifier during the first mode of the modulator and is biased as a non-linear amplifier during the second mode of the modulator. A feed-forward connection between the dual mode modulator and the amplifier is used to indicate a change in modulation mode and to adjust the bias of the amplifier. A power of the constant envelope modulated signal is increased such that an operating point of the amplifier remains substantially constant during the first and second modes of the modulator.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Constant gain digital predistortion controller for linearization of non-linear amplifiers
InactiveUS7177603B1Improve stabilityConstant gainNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsPower amplifiersCellular radioAudio power amplifier
The invention is related to methods and apparatus for controlling and adapting a digital predistortion linearizer for amplification of bandlimited signals using non-linear amplifiers. The control method advantageously permits the predistortion function applied by a predistortion entity to provide a relatively constant gain. This attribute is advantageous for operation within cellular radio systems, which often employ digital power control systems. However, the disclosed techniques can also be applicable to virtually any type of digital predistortion for which an input signal or reference signal to be amplified is predistorted in a manner that is complementary to the distortion induced by a non-linear amplifier. Embodiments of the invention advantageously enhance the practicality of using digital linearization and predistortion amplification techniques. Embodiments of the invention can automatically adjust the characteristics of a predistorted signal so that a deviation from overall linearity is compensated and subsequently reduced while maintaining a nearly constant gain attribute.
Owner:MAXLINEAR ASIA SINGAPORE PTE LTD
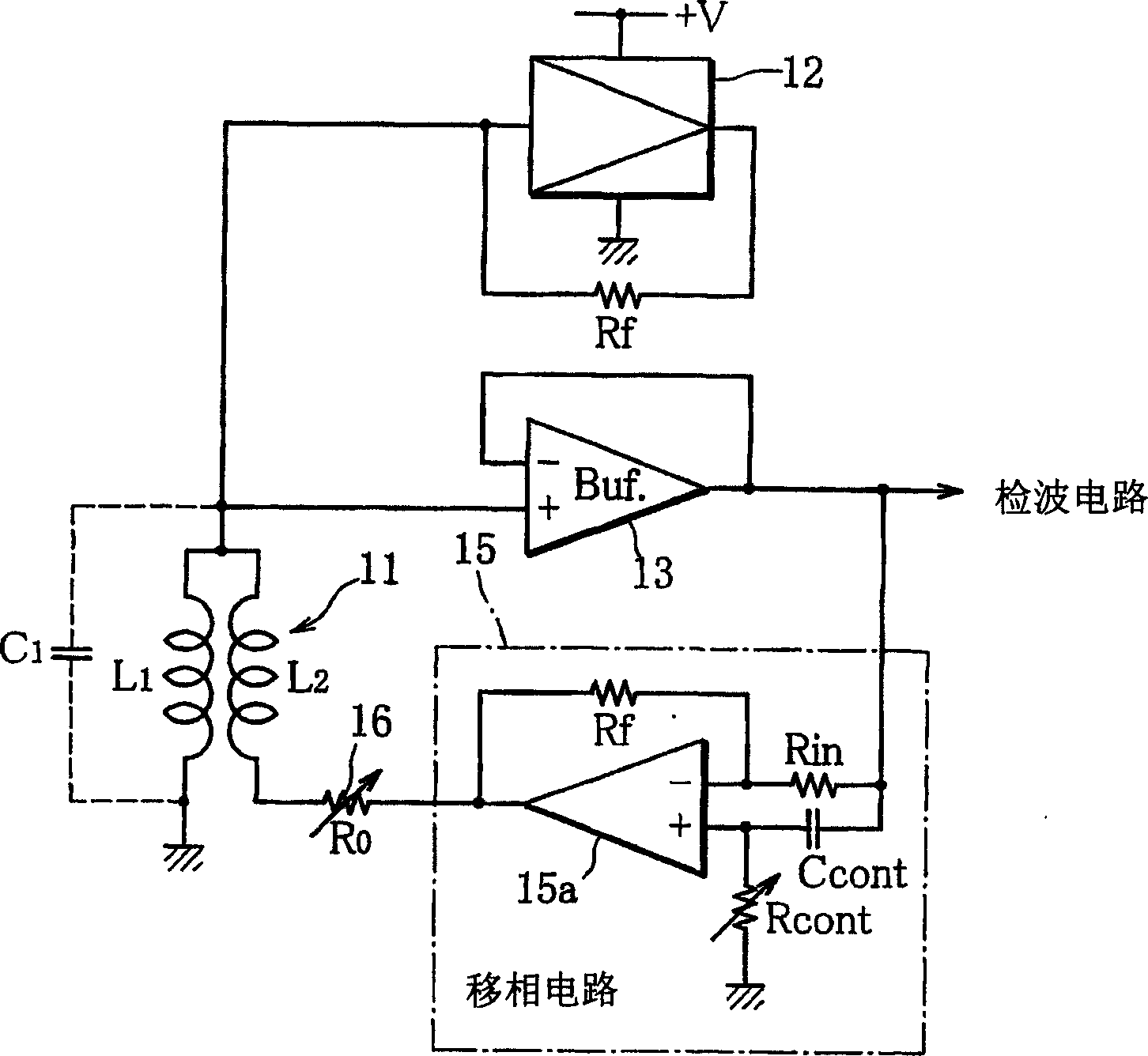
High frequency oscillation type proimity sensor
InactiveCN1516925ASimple structureHigh detection sensitivityElectronic switchingOscillations generatorsElectrical conductorProximity sensor
A high-frequency oscillation proximity sensor with an improved detection sensitivity uses, as a detection coil 11, a two-thread coil formed of substantively two coil conductors joined together at their first ends to form a joint connection end and twisted together, one of the two coil conductors being used as a resonance circuit coil L1 and the other as a copper resistance compensation coil L2, and comprises a drive circuit 12 for supplying a drive current to the joint connection end of the two-thread coil to thereby drive the detection coil to oscillate, a buffer 13 for taking out an oscillating output voltage generated at the joint connection end of the two-thread coil, and a phase shift circuit 15 for turning the phase of the oscillating output voltage taken out by the buffer by a predetermined angle and feeding it back to the copper resistance compensation coil to thereby negate the copper resistance of the two-thread coil. The drive circuit comprises a nonlinear amplifier 21 for changing the amplitude of the oscillating voltage generated at the two-thread coil in multiple stages to thereby impart a soft oscillation characteristic to a high-frequency oscillation circuit comprising the nonlinear amplifier and the two-thread coil.
Owner:YAMATAKE HONEYWELL CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com