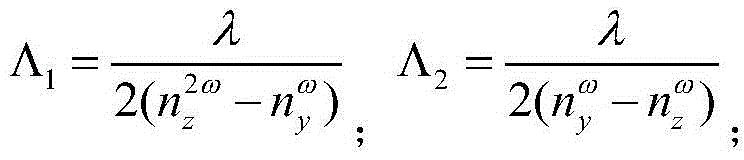Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
169 results about "Periodic poling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
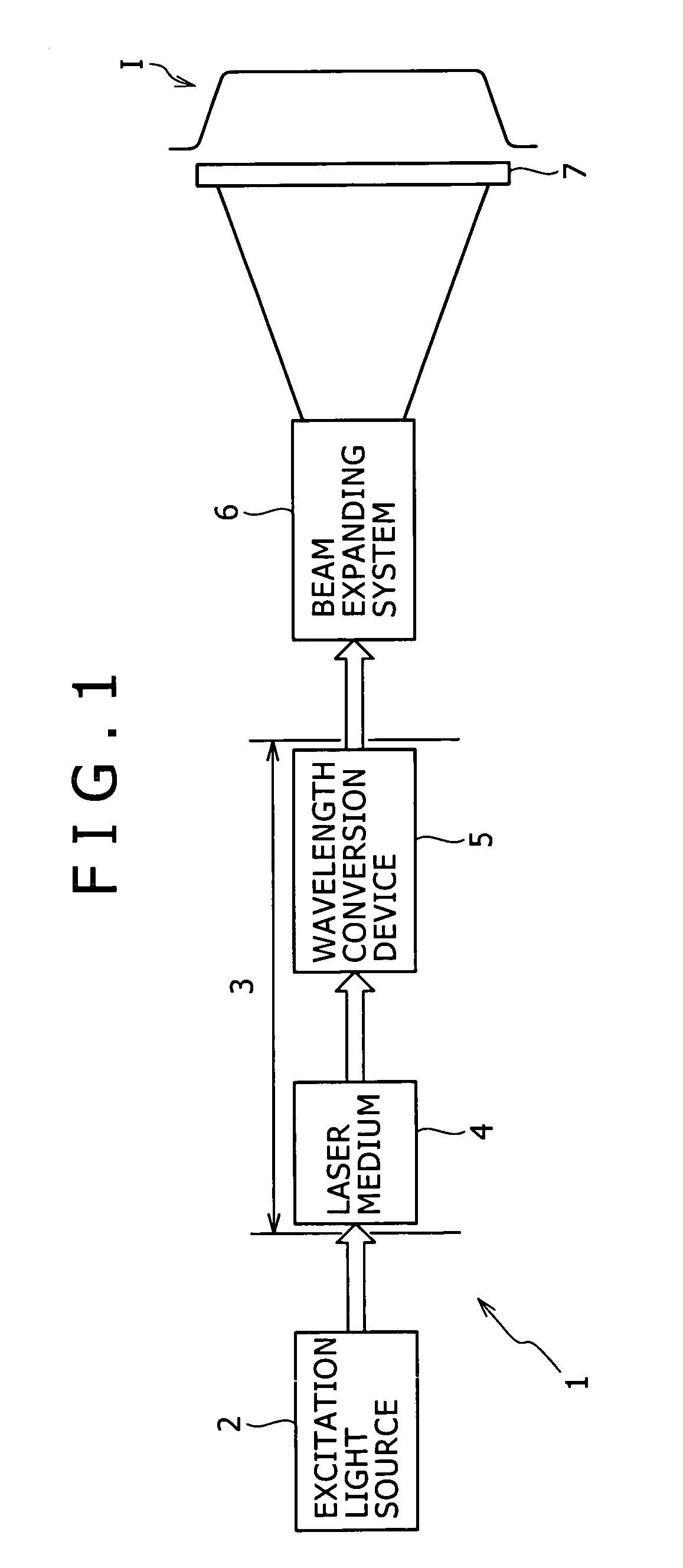
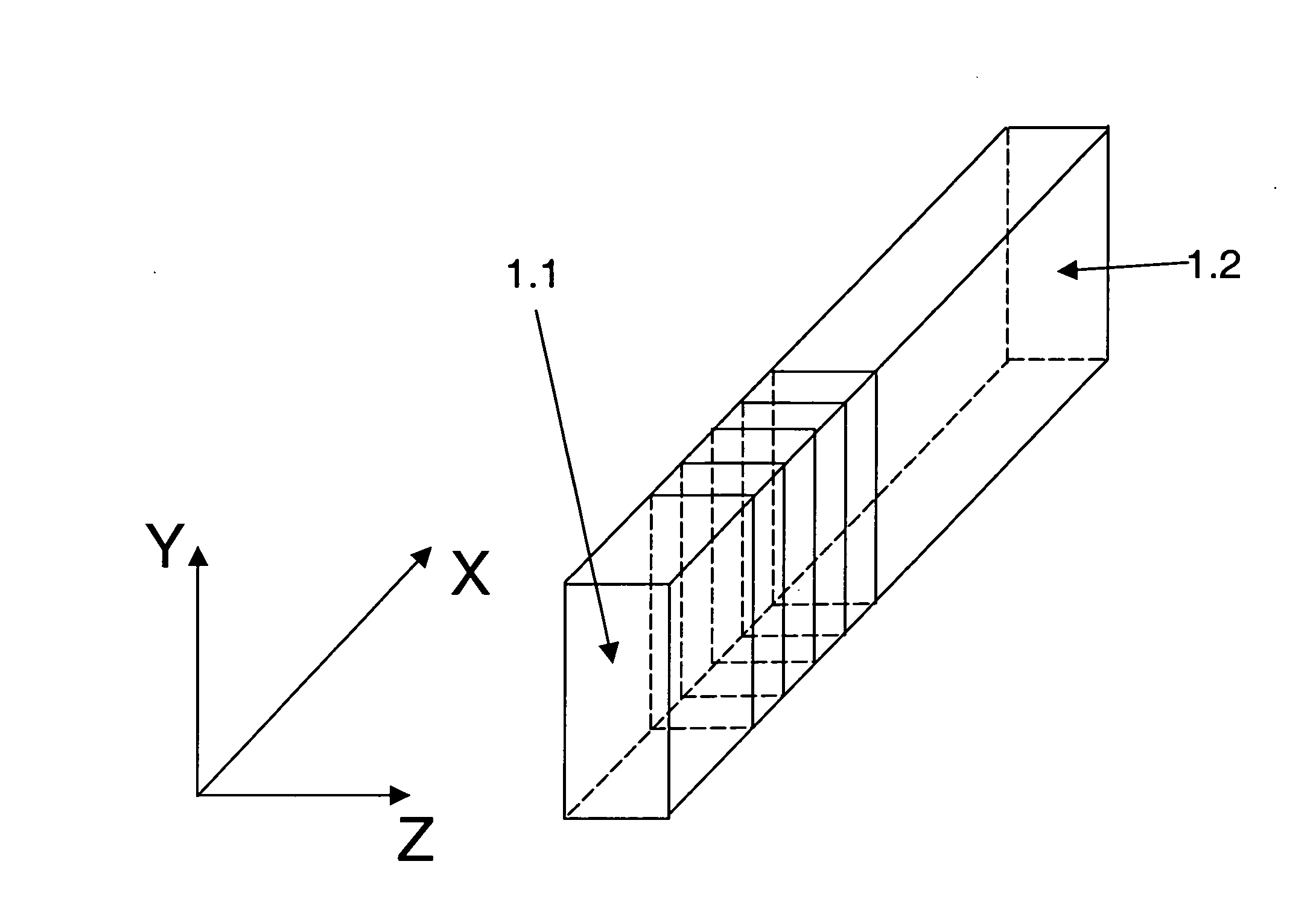
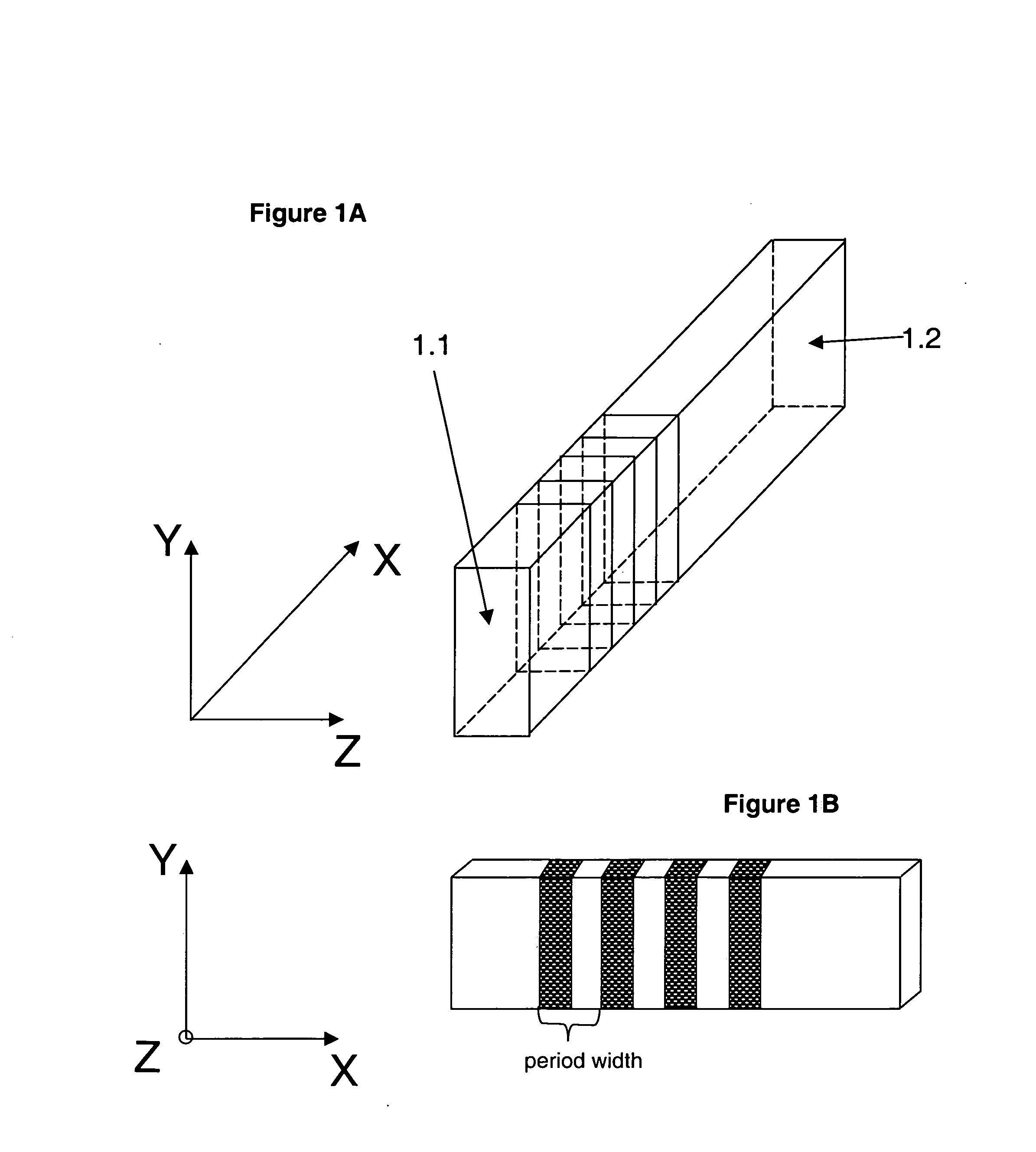
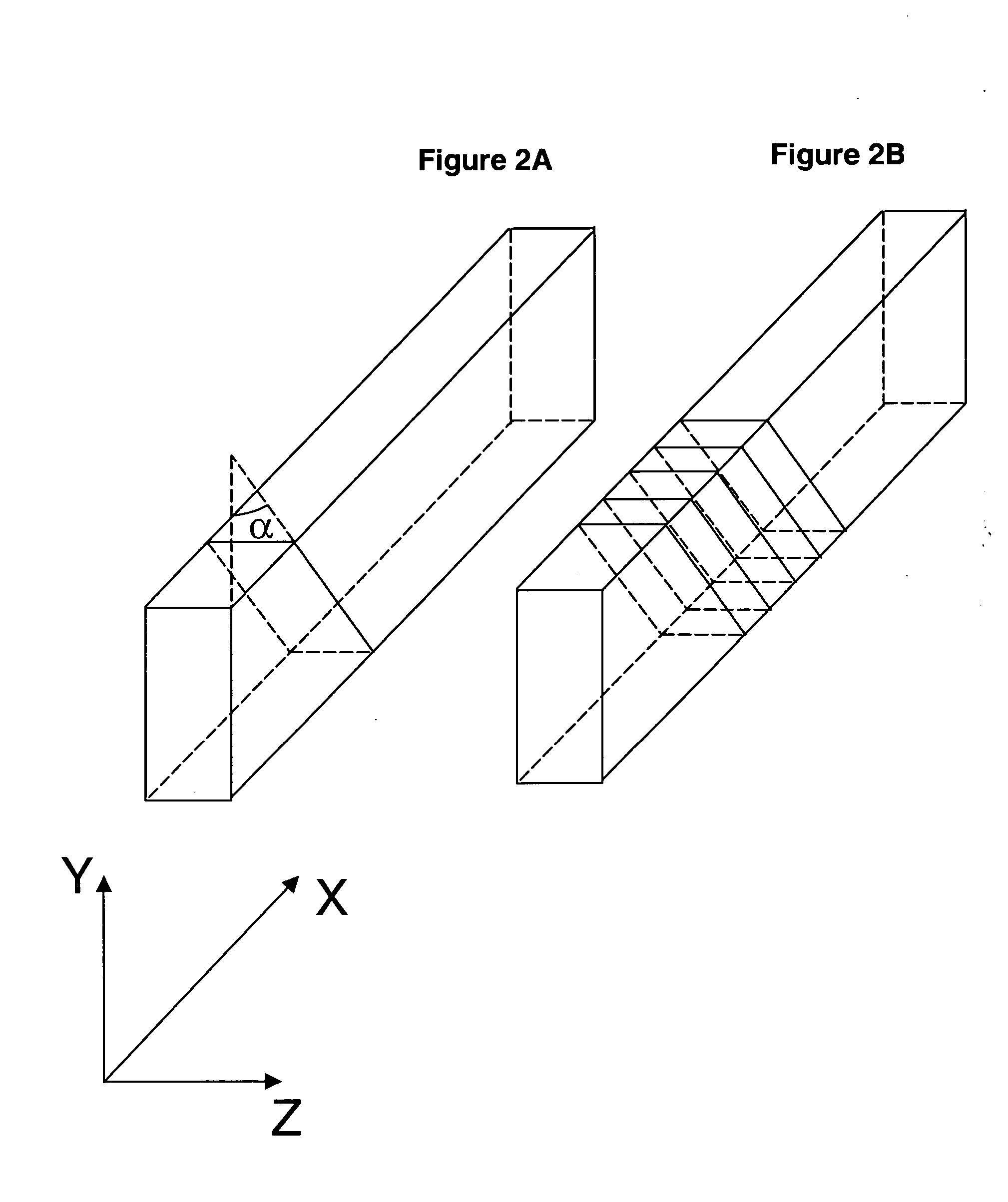
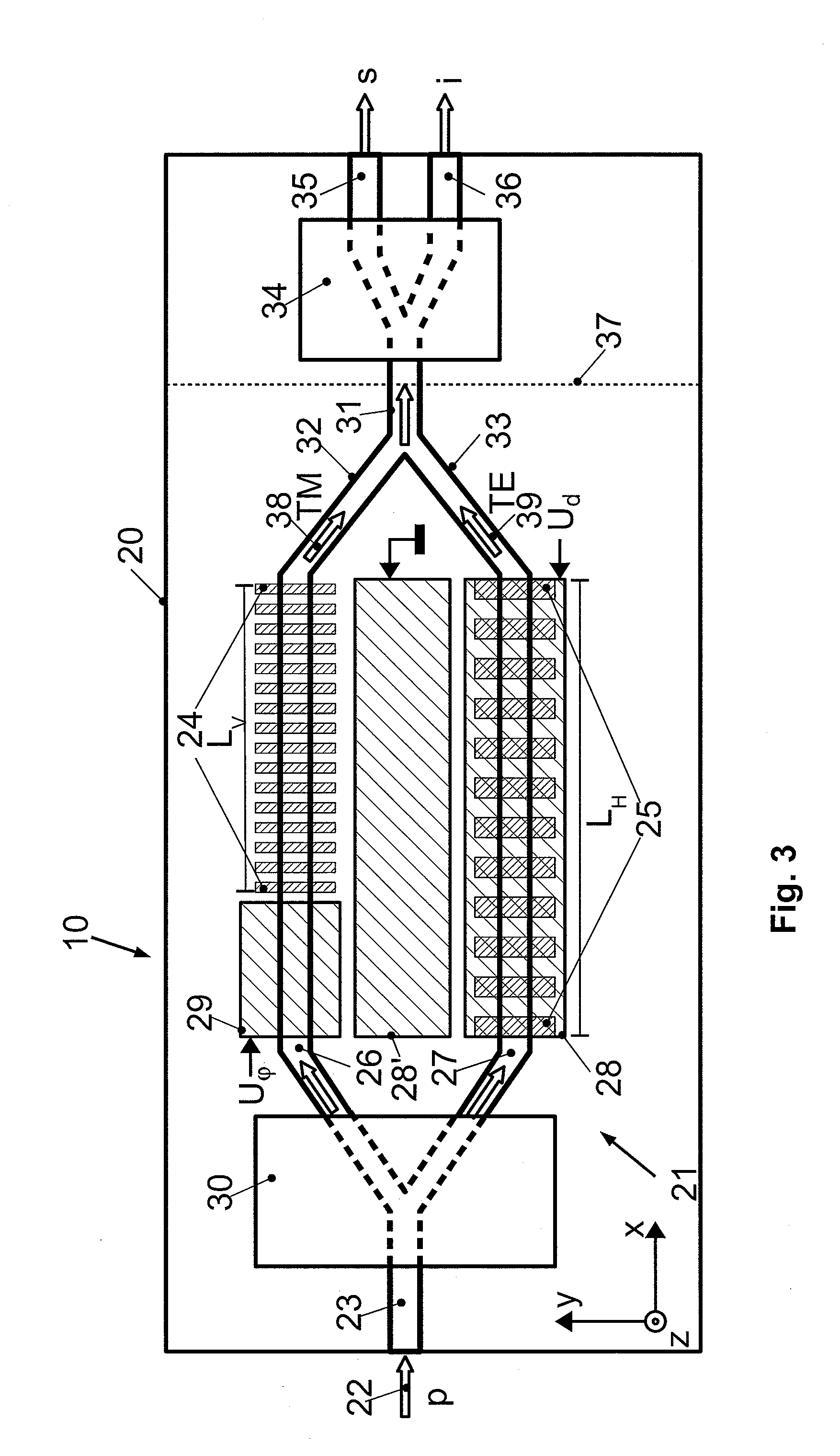
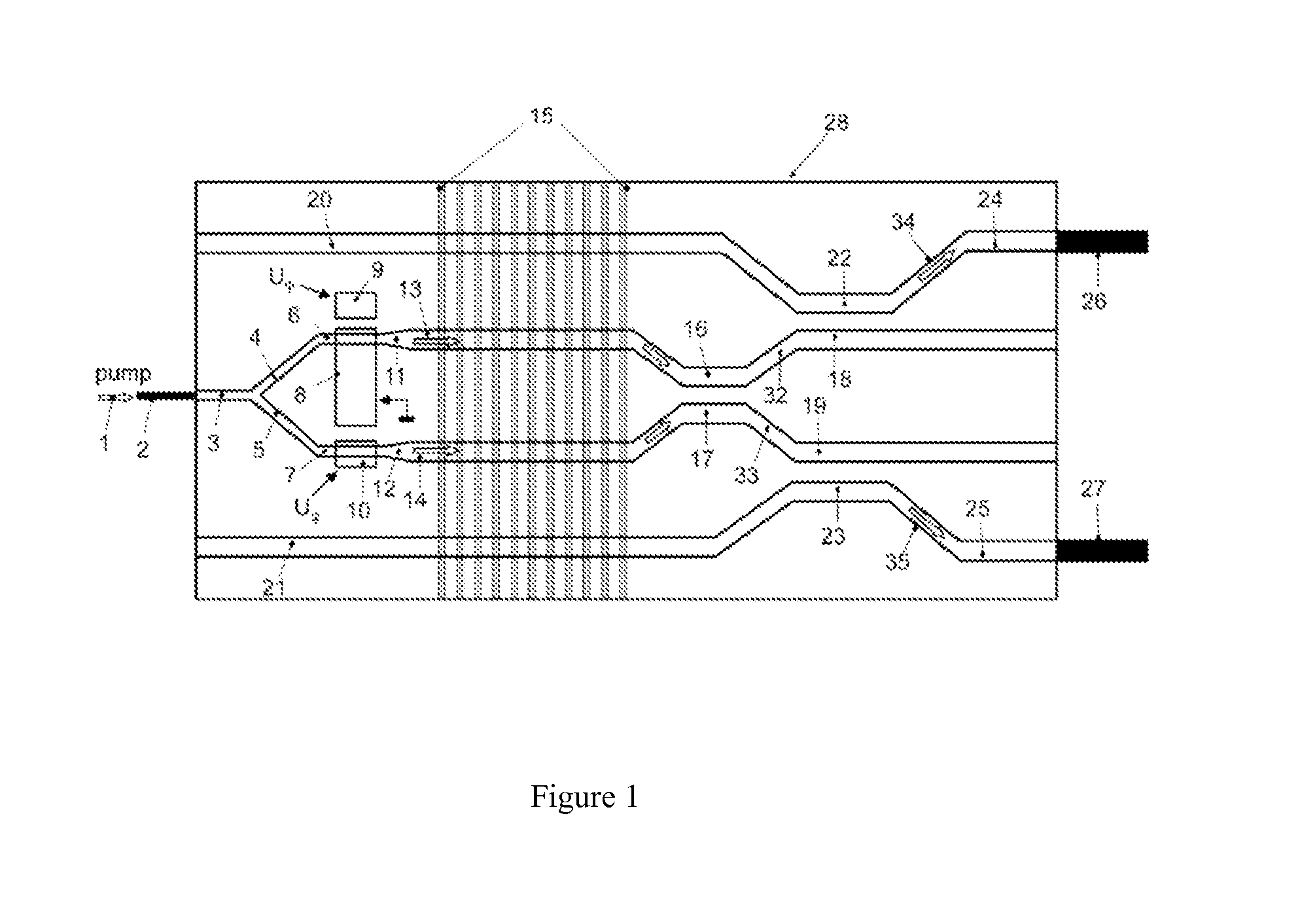
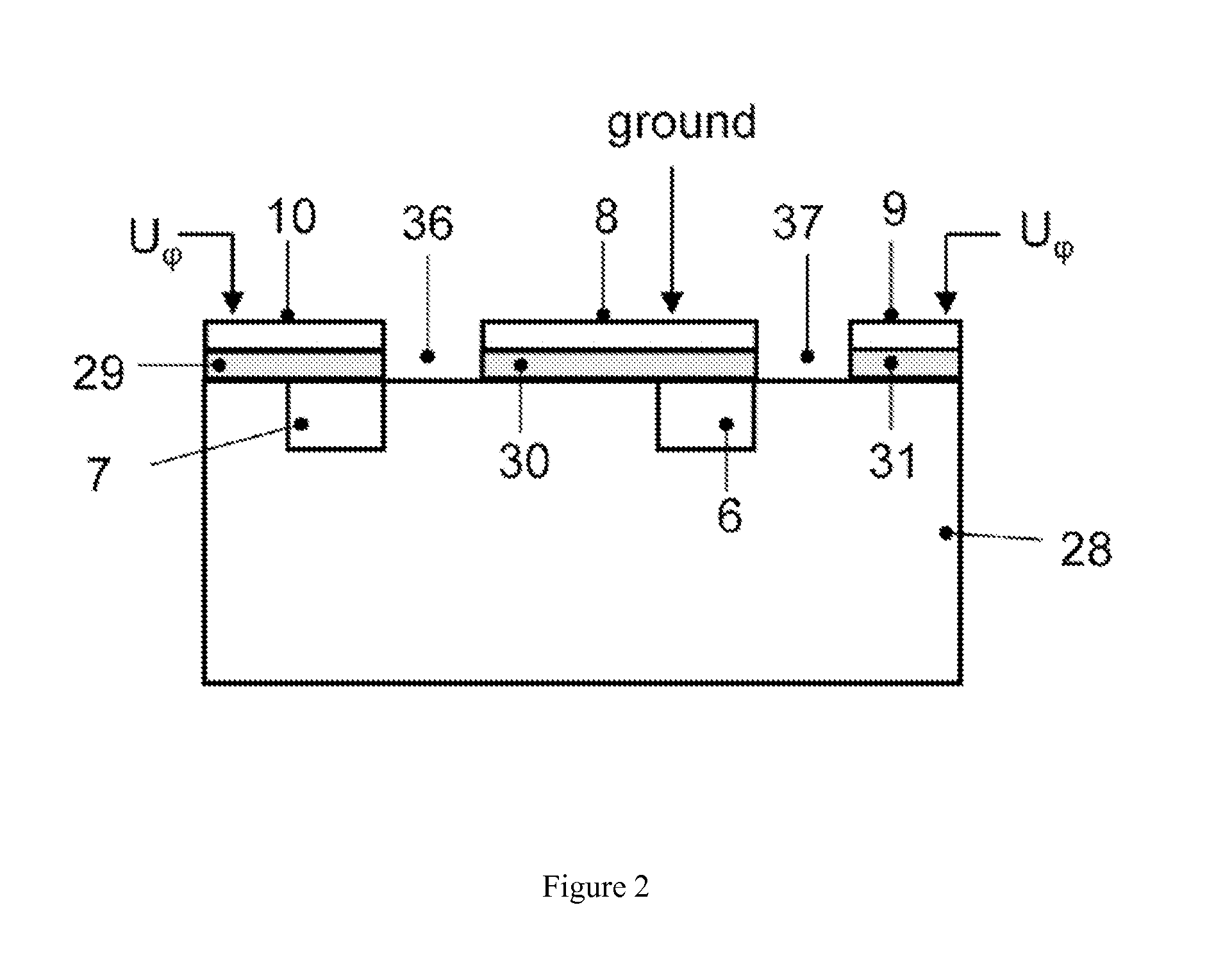
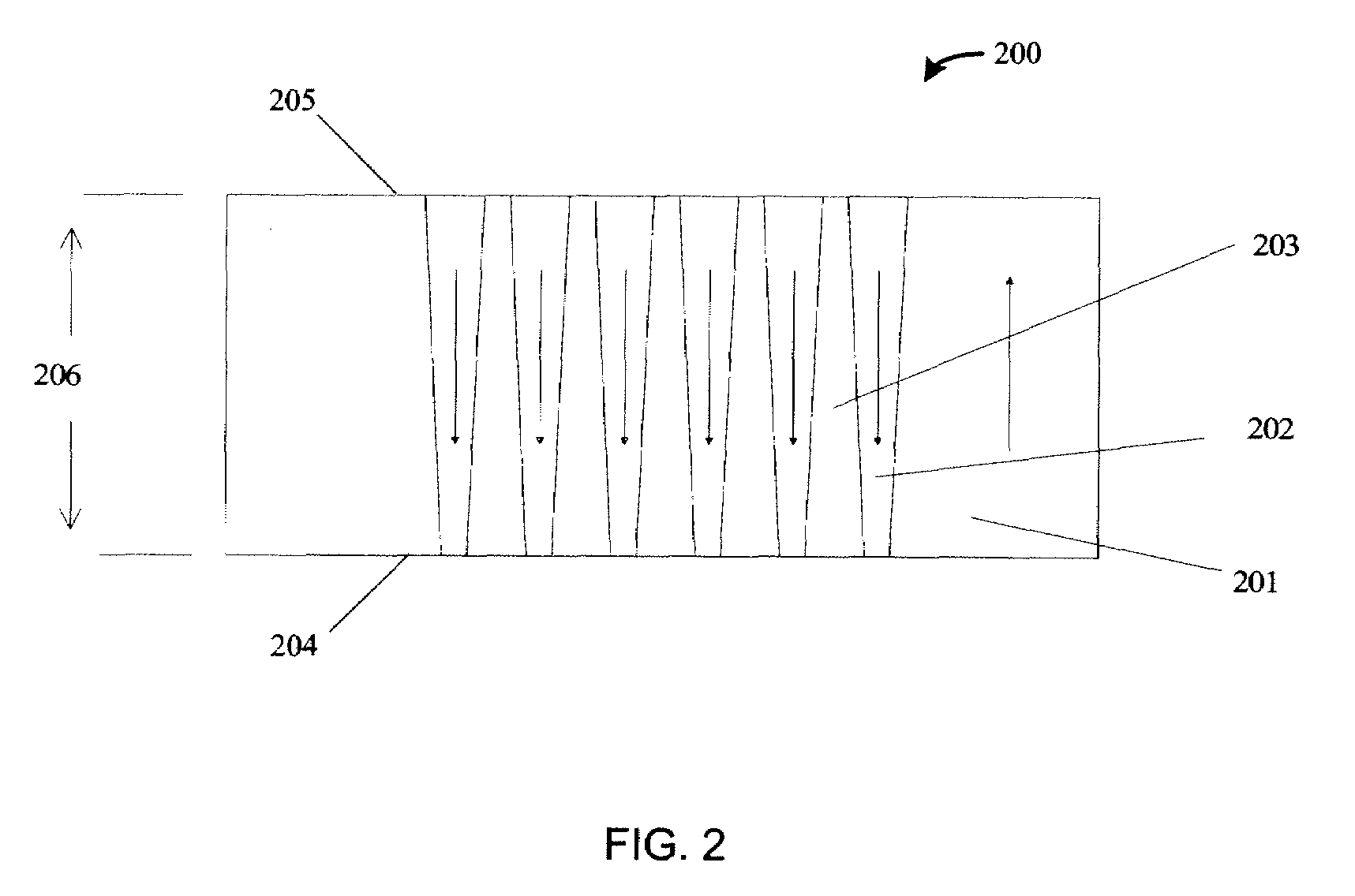
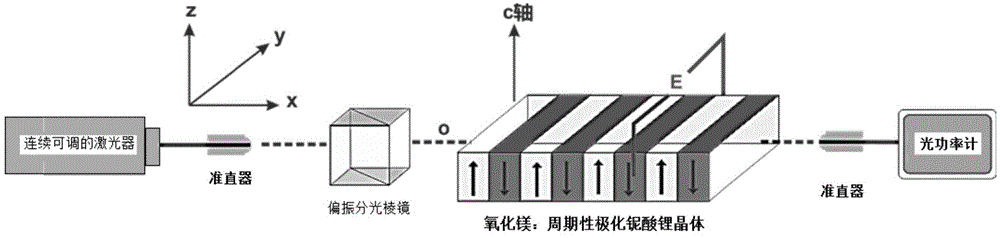
Periodic poling is a formation of layers with alternate orientation in a birefringent material. The domains are regularly spaced, with period in a multiple of the desired wavelength of operation. The structure is designed to achieve quasi-phase-matching (QPM) in the material.
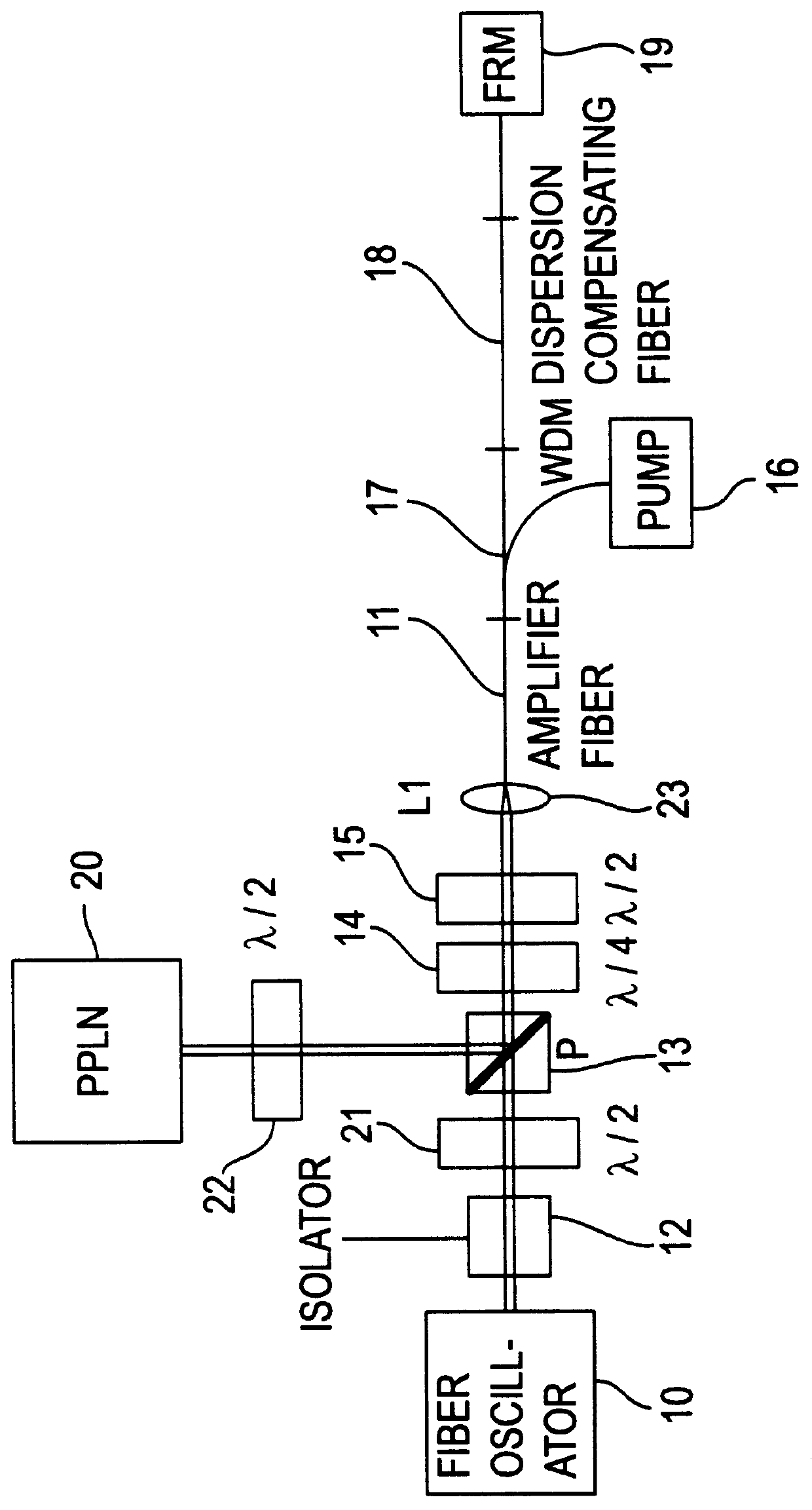
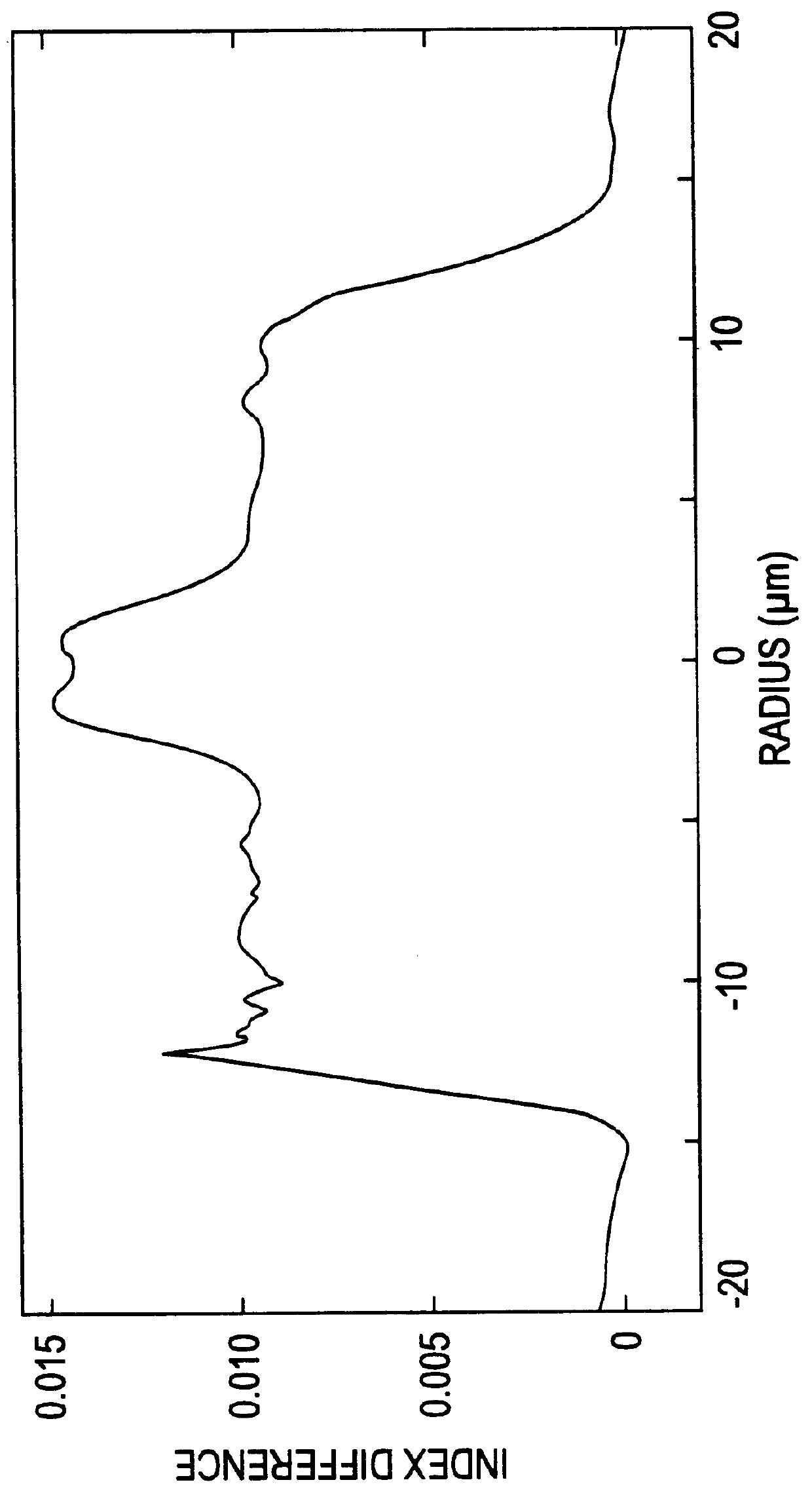
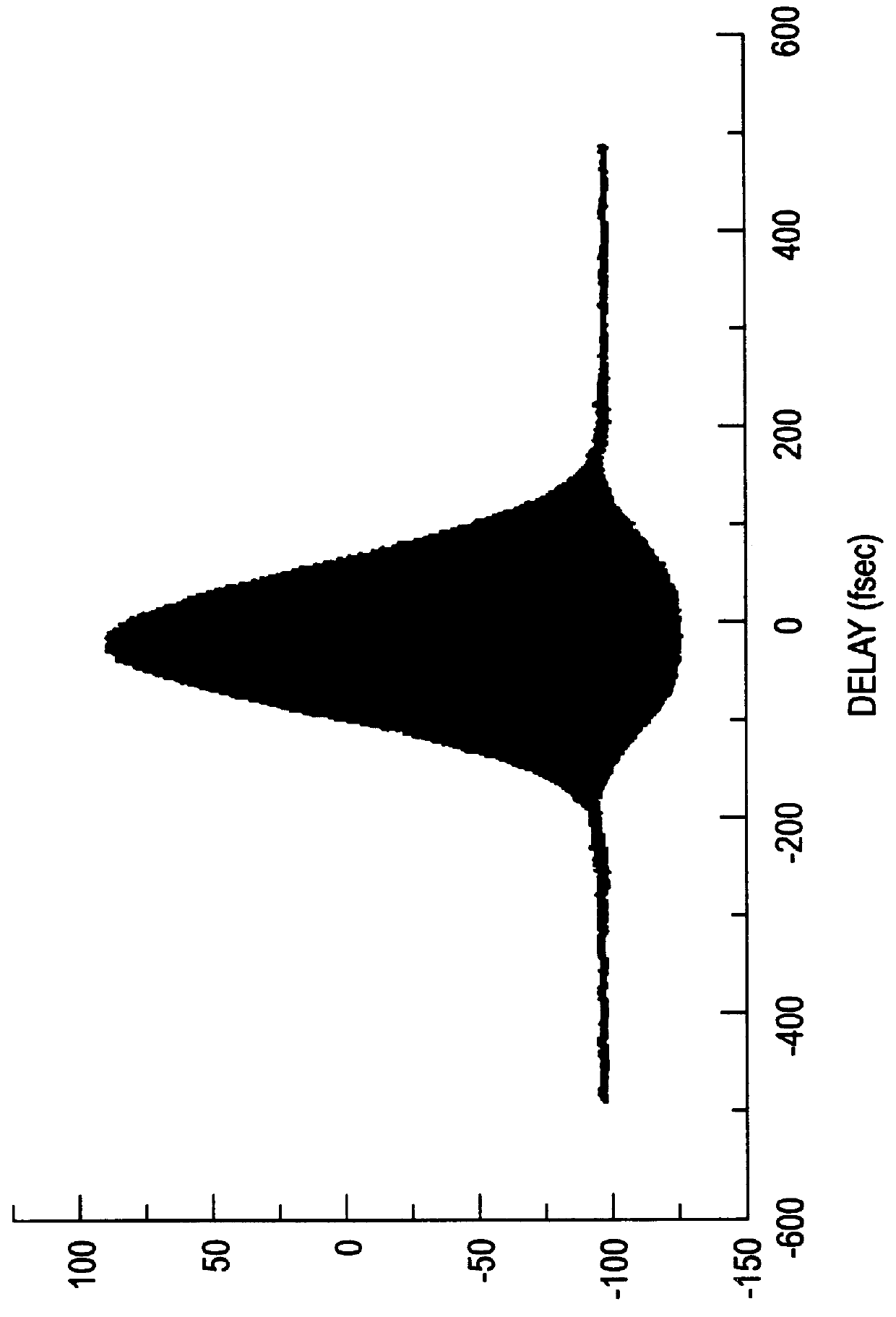
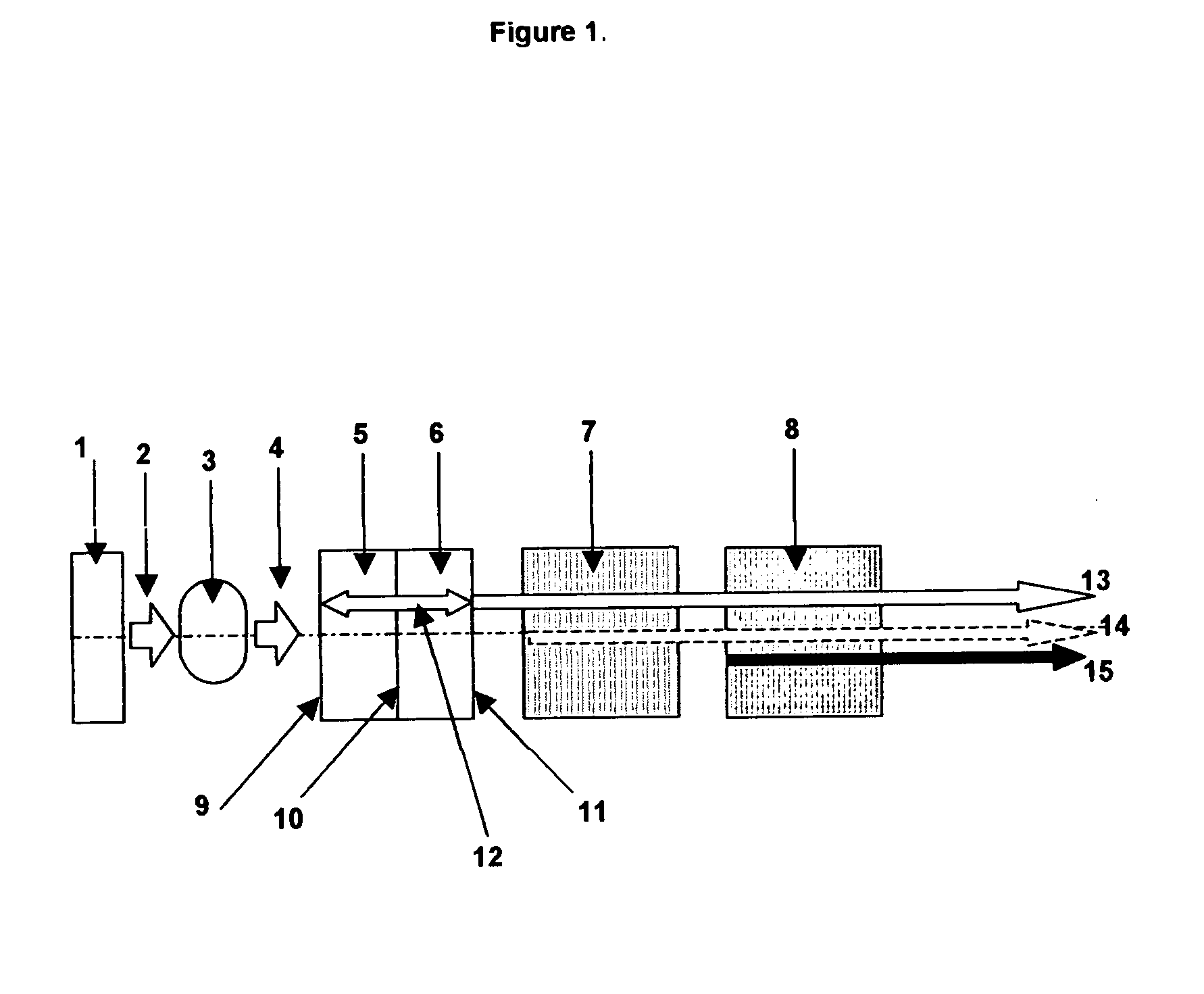
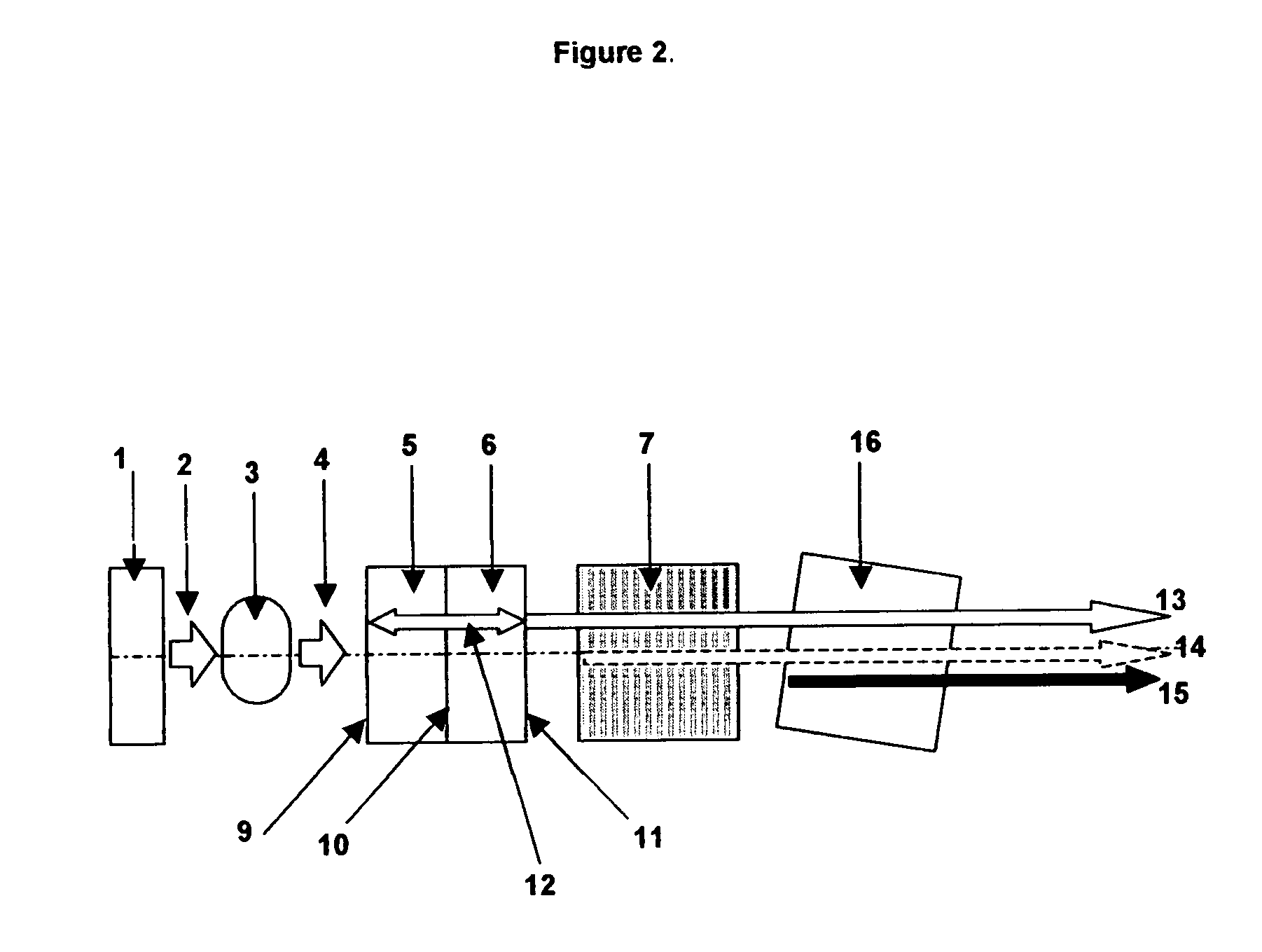
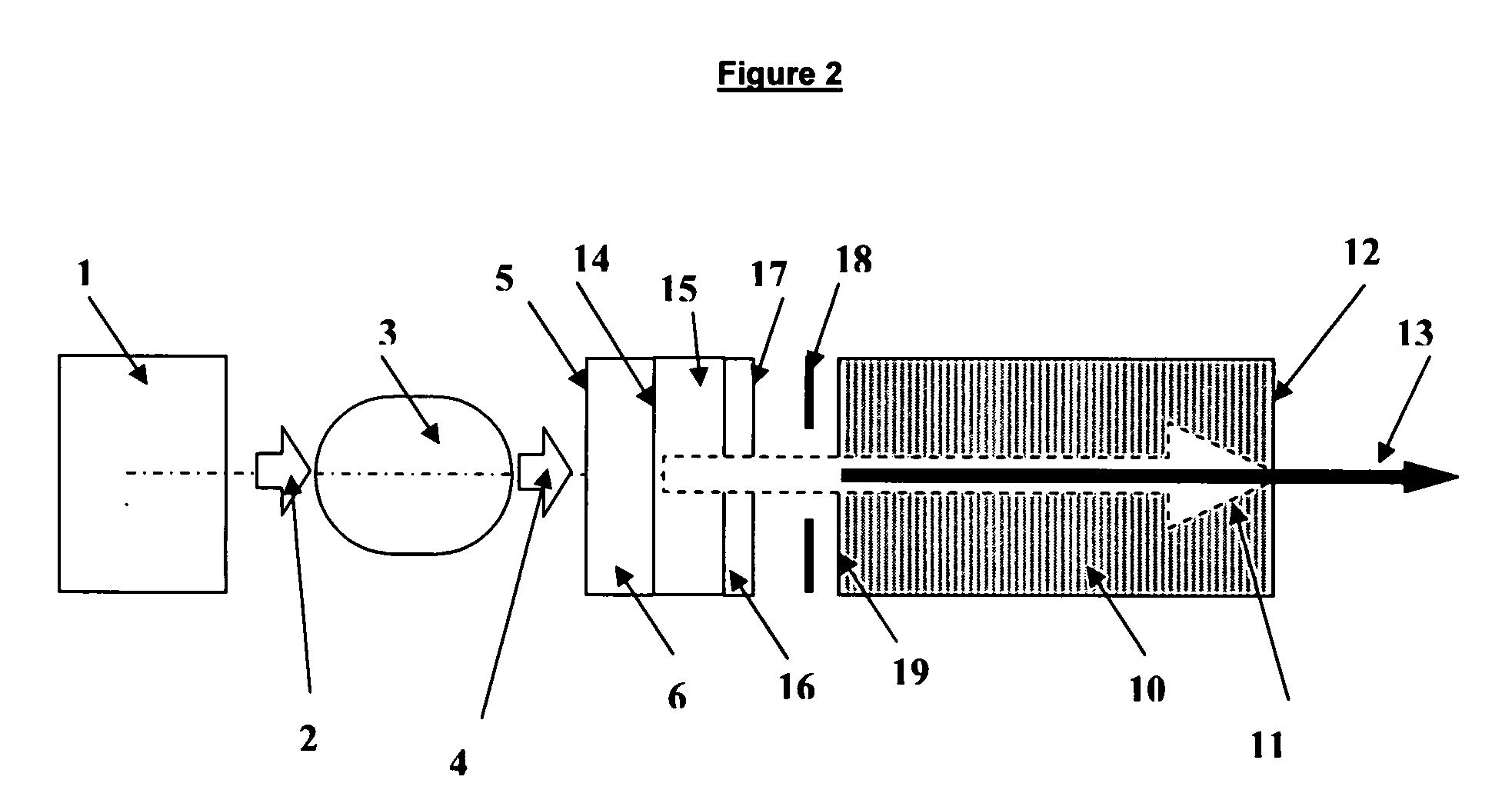
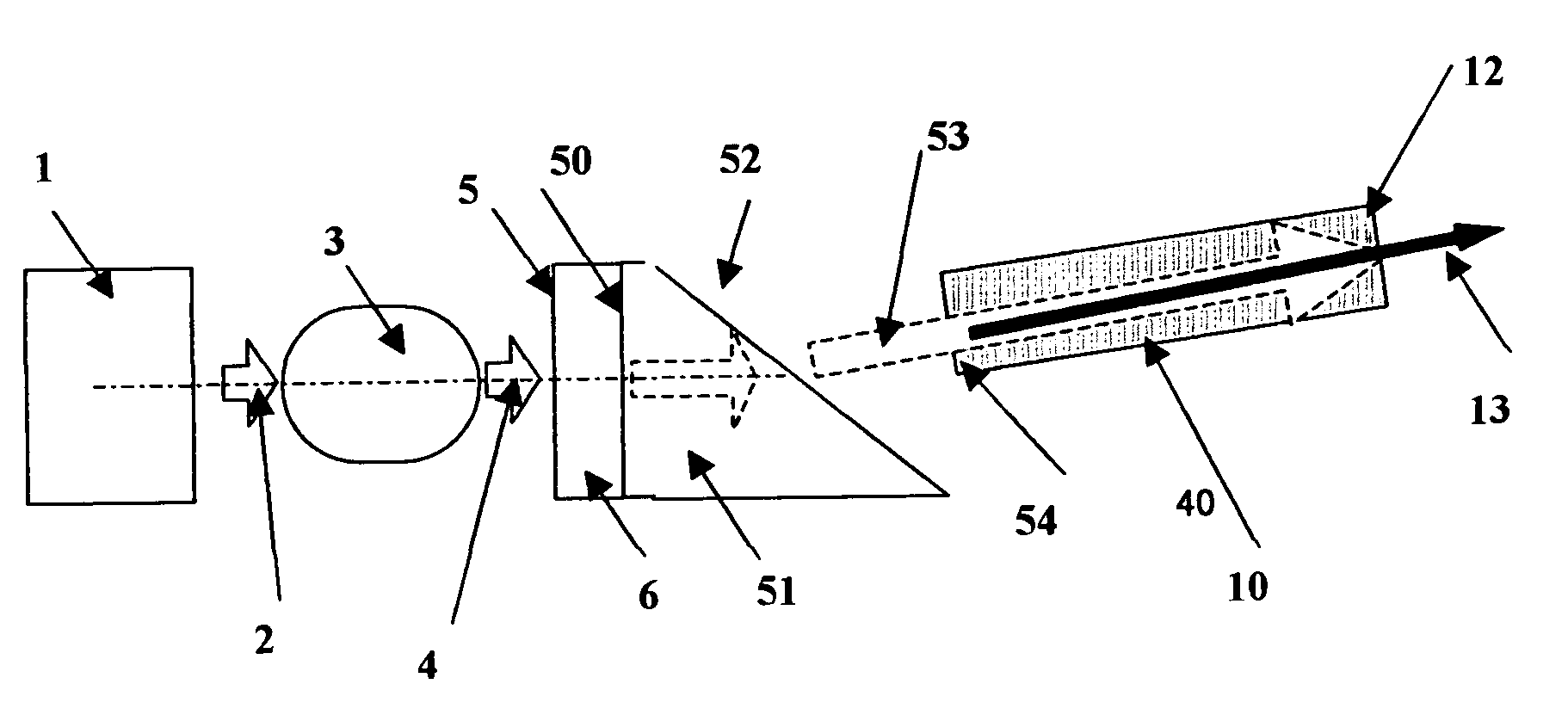
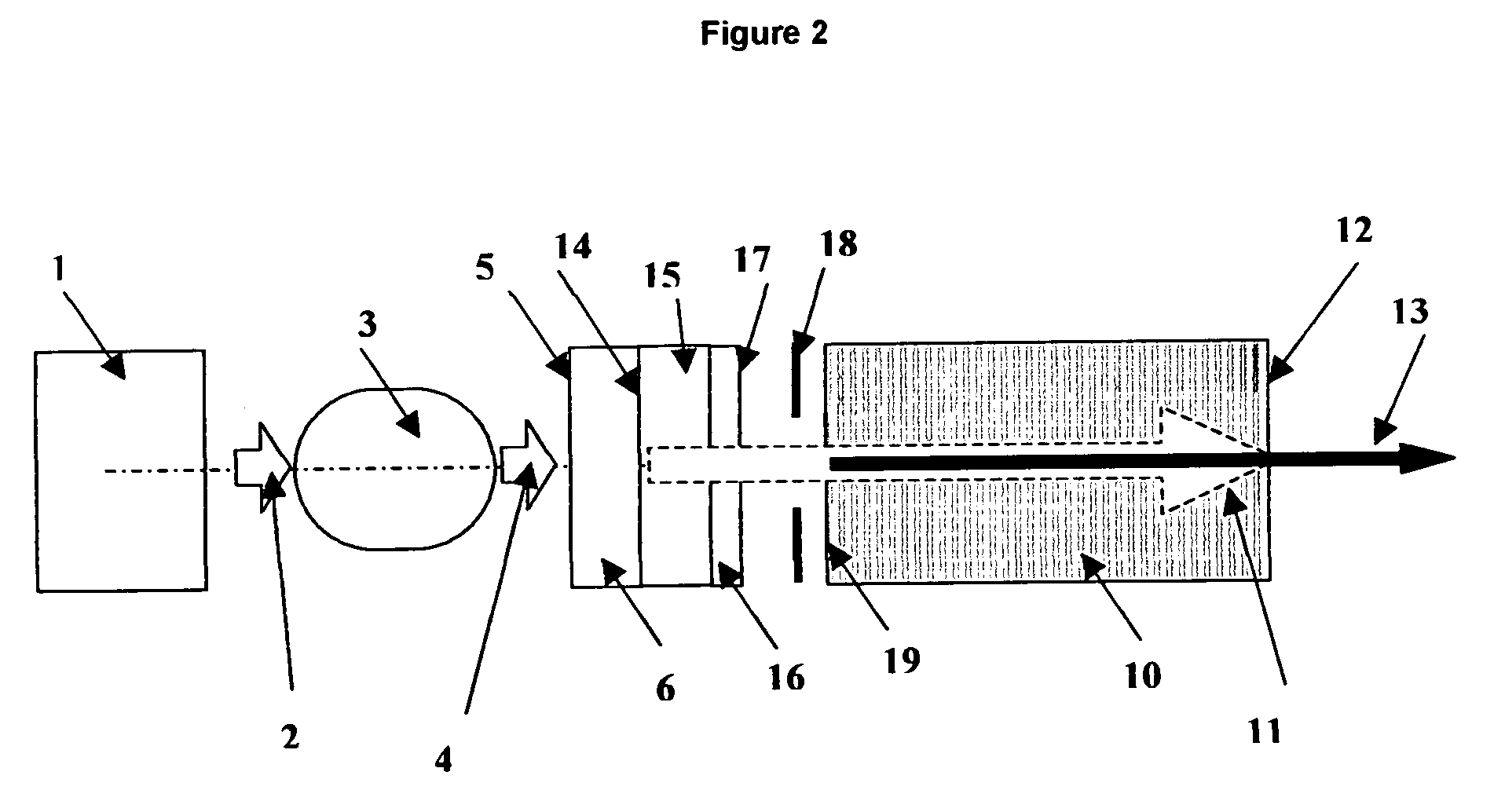
Apparatus and method for the generation of high-power femtosecond pulses from a fiber amplifier
InactiveUS6014249ALong pulse widthLow costLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsFiberDouble-clad fiber
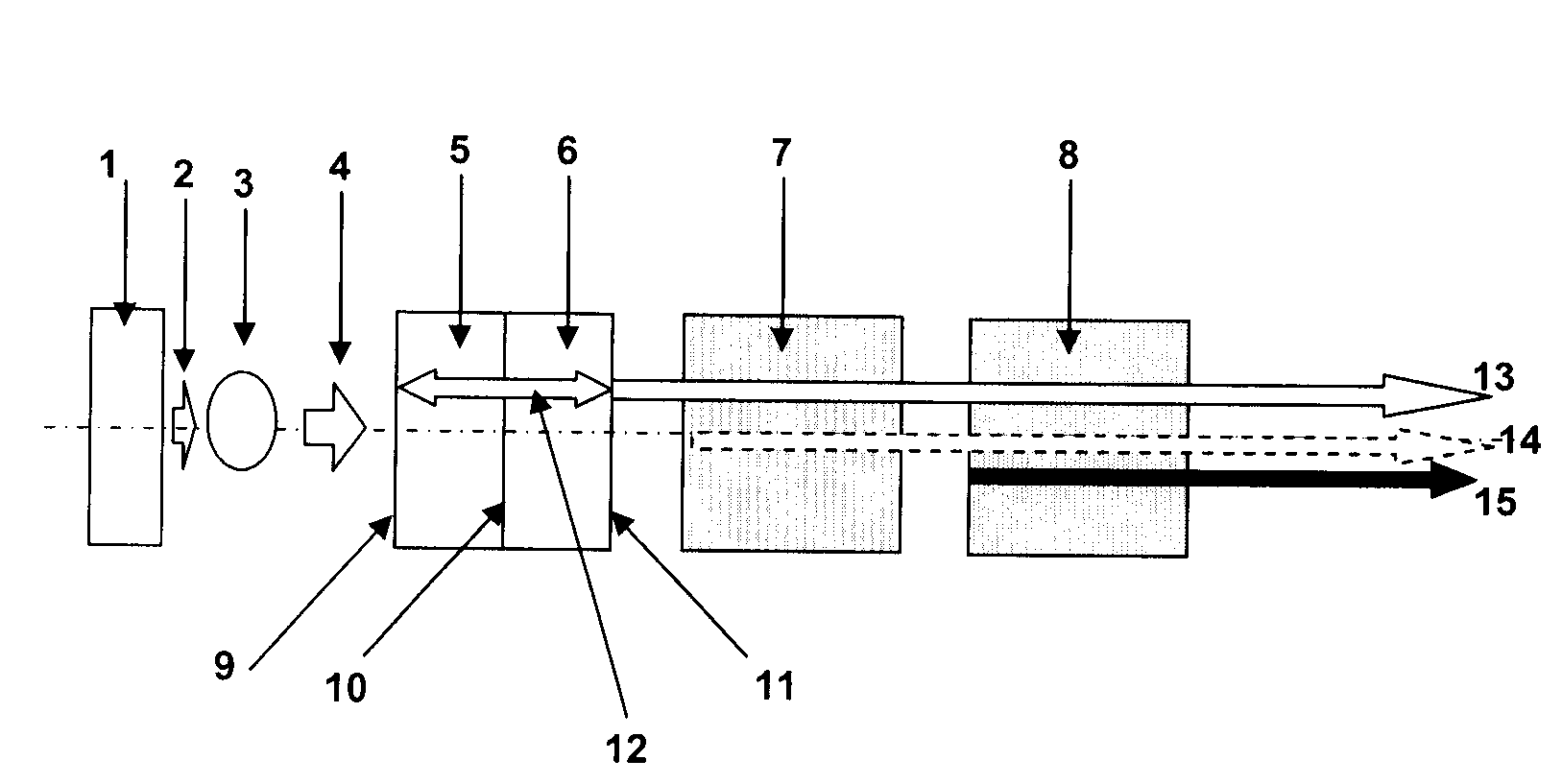
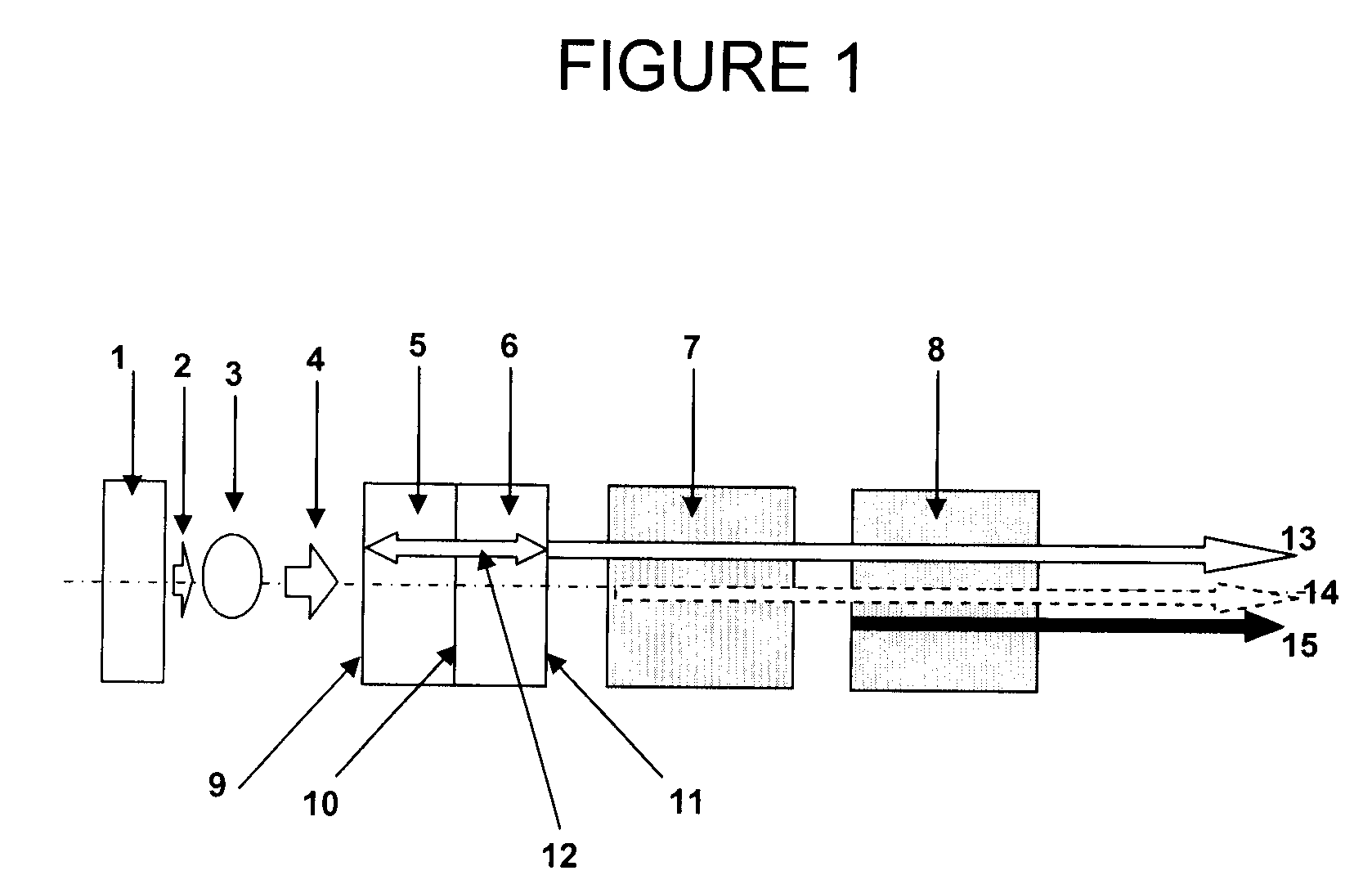
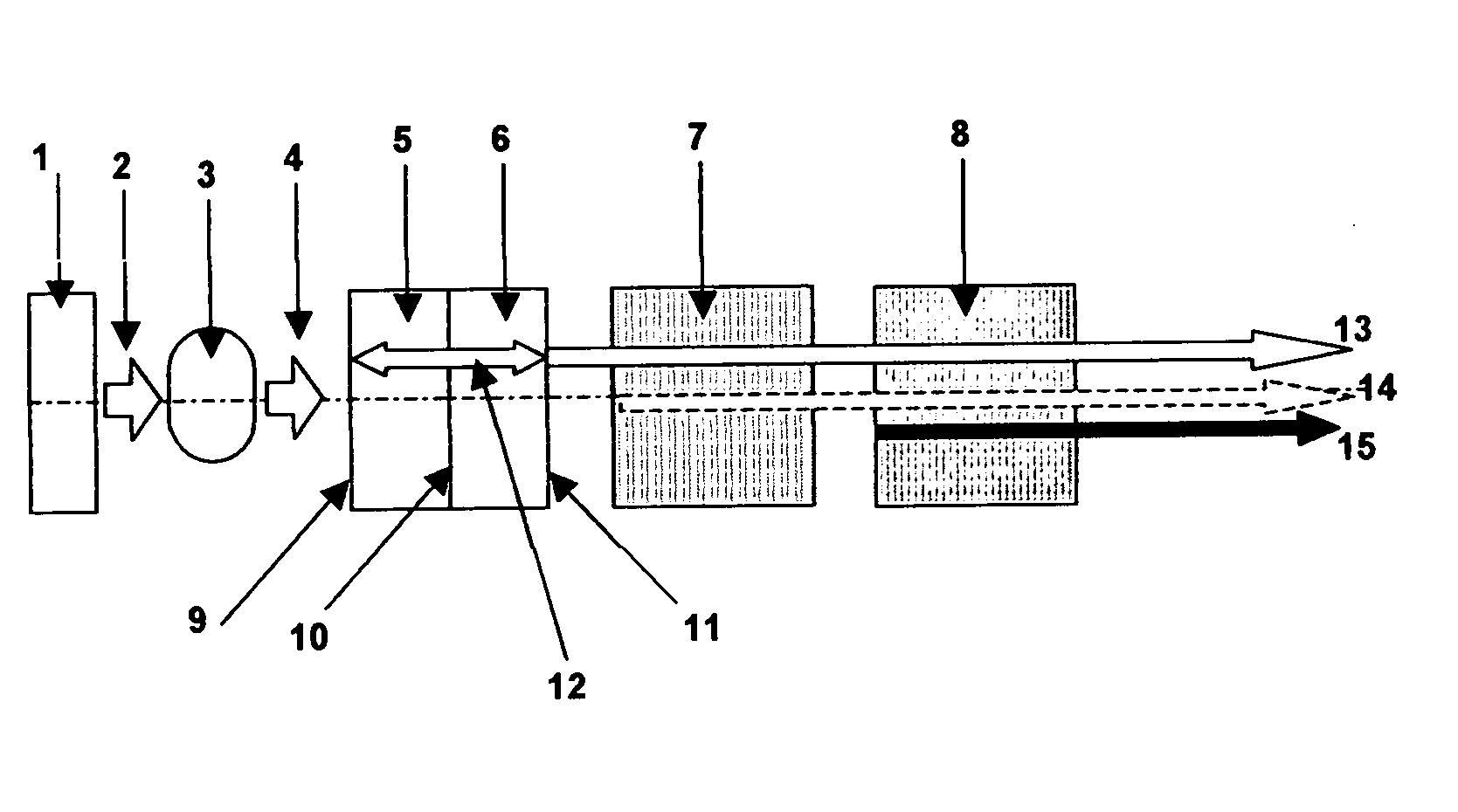
An apparatus generates femtosecond pulses from laser amplifiers by nonlinear frequency conversion. The implementation of nonlinear frequency-conversion allows the design of highly nonlinear amplifiers at a signal wavelength (SW), while still preserving a high-quality pulse at an approximately frequency-doubled wavelength (FDW). Nonlinear frequency-conversion also allows for limited wavelength tuning of the FDW. As an example, the output from a nonlinear fiber amplifier is frequency-converted. By controlling the polarization state in the nonlinear fiber amplifier and by operating in the soliton-supporting dispersion regime of the host glass, an efficient nonlinear pulse compression for the SW is obtained. The generated pulse width is optimized by utilizing soliton compression in the presence of the Raman-self-frequency shift in the nonlinear fiber amplifier at the SW. High-power pulses are obtained by employing fiber amplifiers with large core-diameters. The efficiency of the nonlinear fiber amplifier is optimized by using a double clad fiber (i.e., a fiber with a double-step refractive index profile) and by pumping light directly into the inner core of this fiber. Periodically poled LiNbO3 (PPLN) is used for efficient conversion of the SW to a FDW. The quality of the pulses at the FDW can further be improved by nonlinear frequency conversion of the compressed and Raman-shifted signal pulses at the SW. The use of Raman-shifting further increases the tuning range at the FDW. For applications in confocal microscopy, a special linear fiber amplifier is used.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
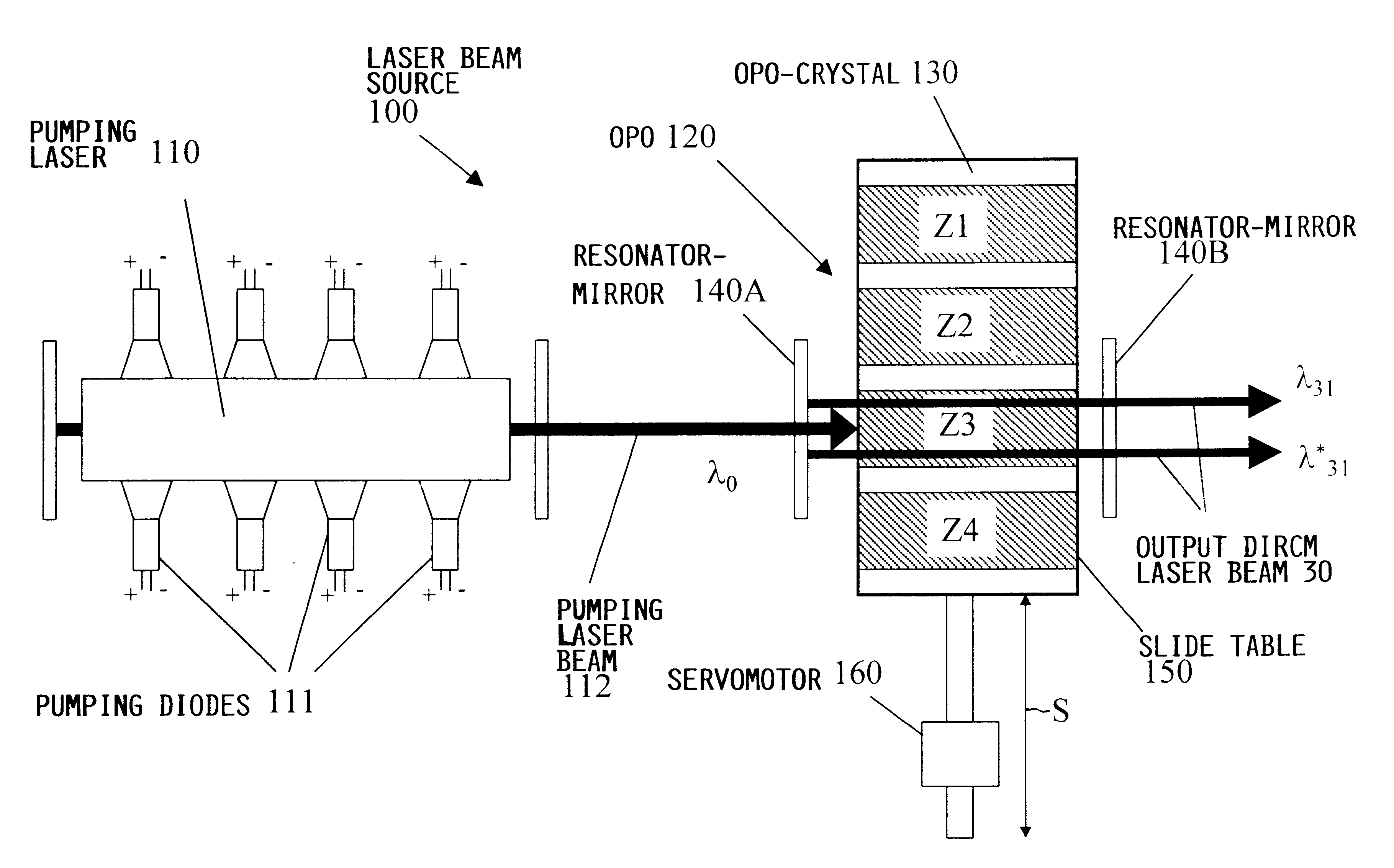
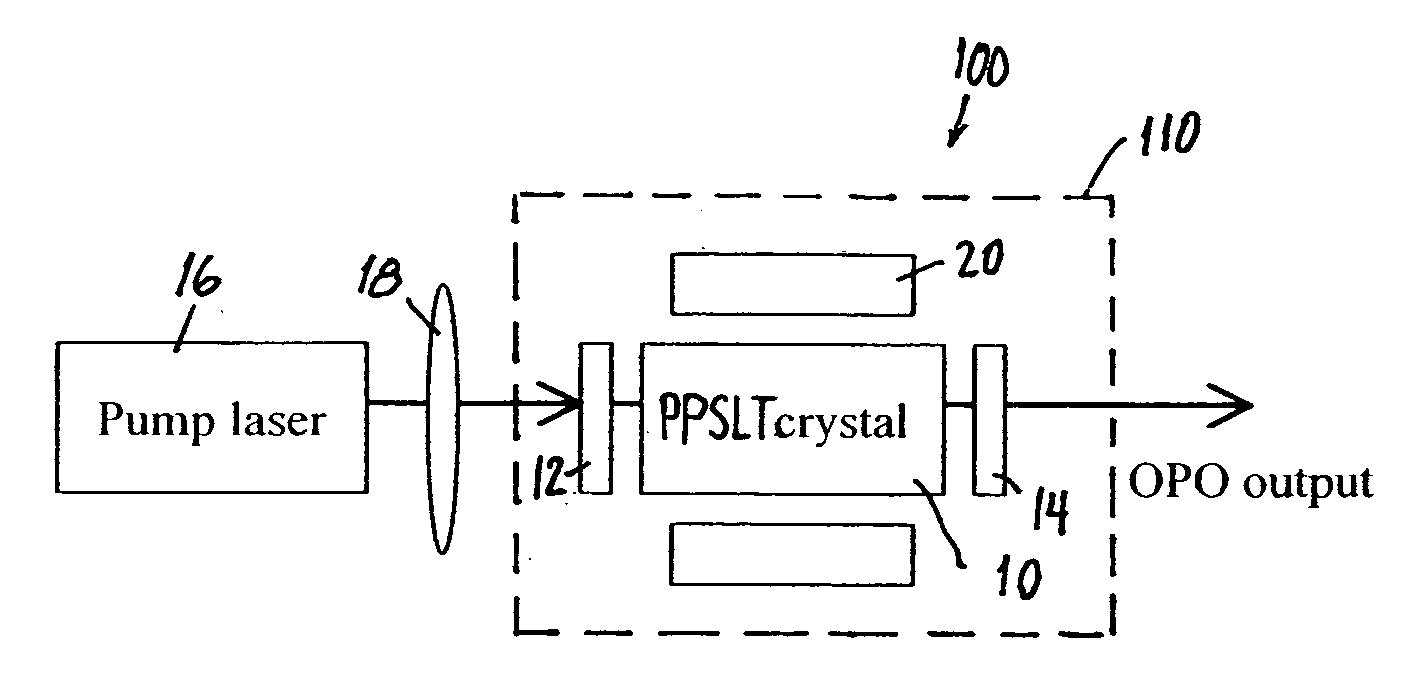
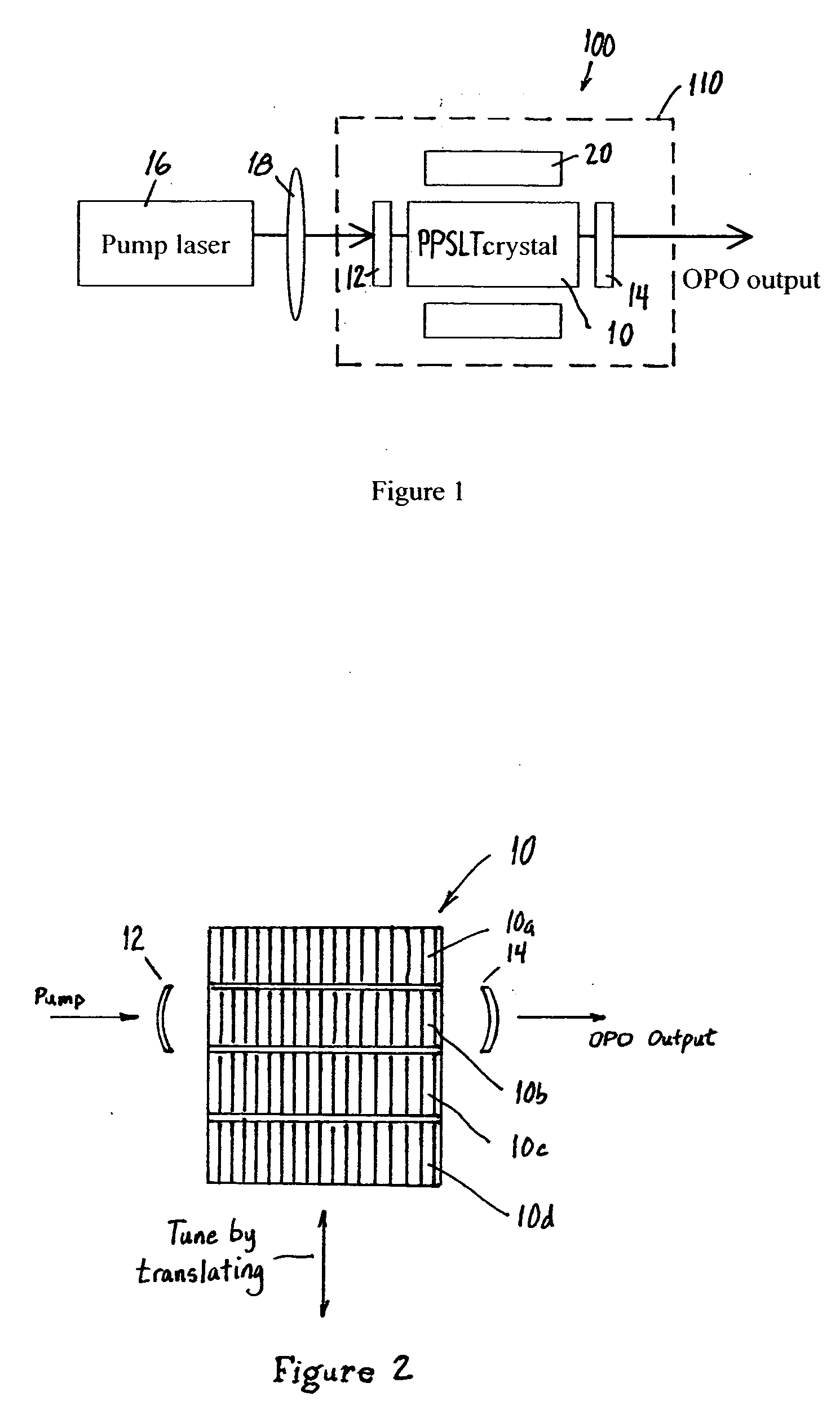
Laser beam source for a directional infrared countermeasures (DIRCM) weapon system
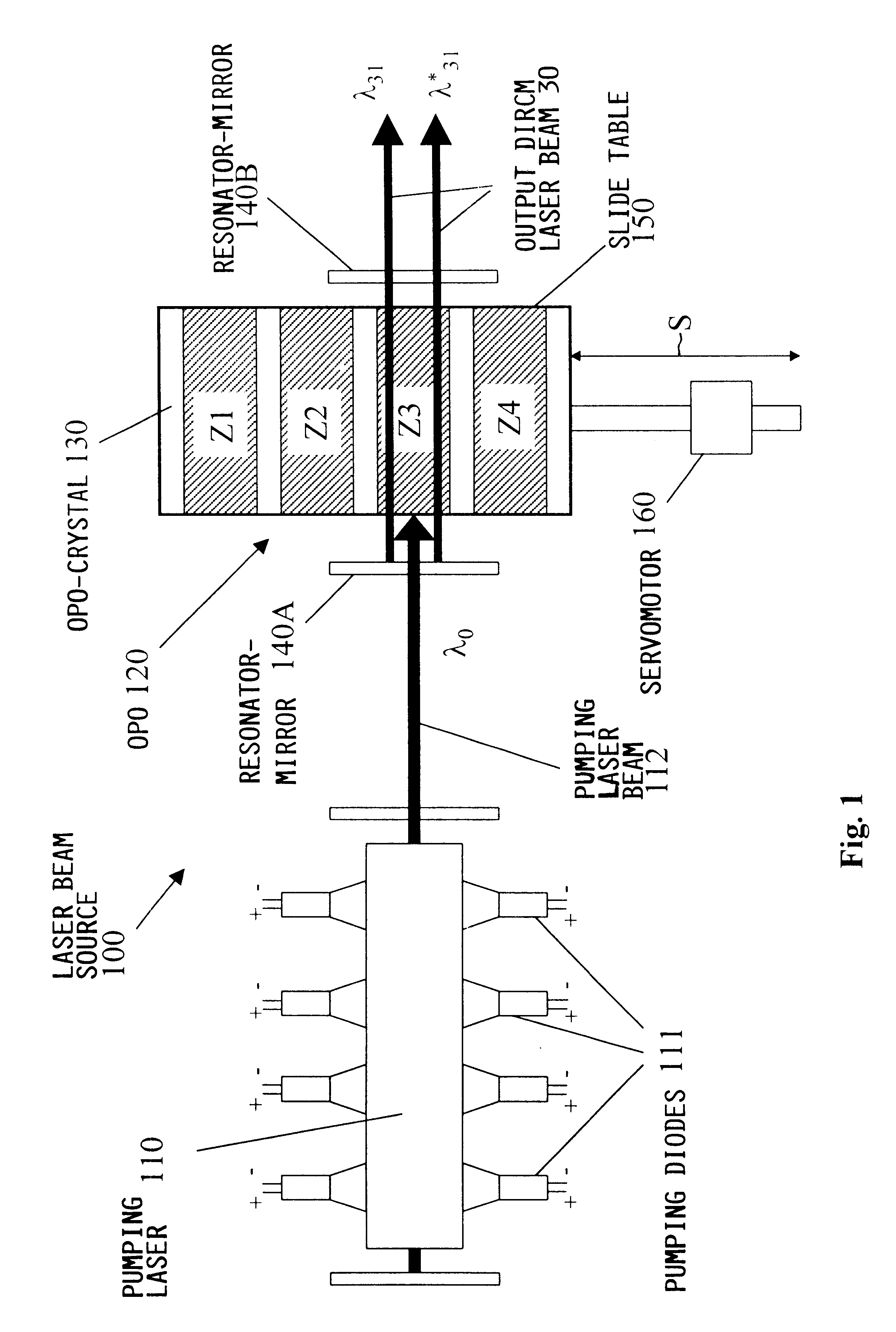
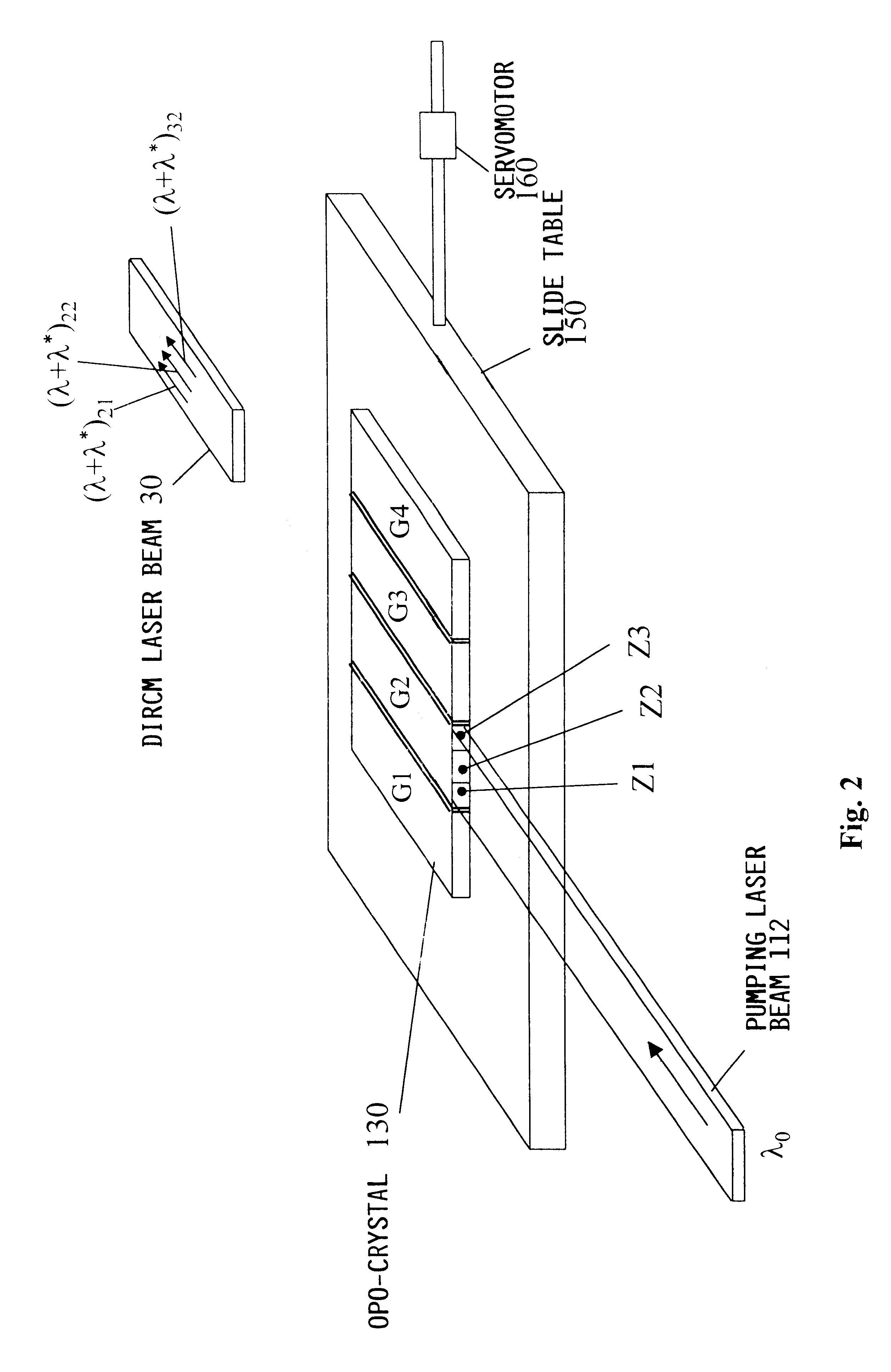
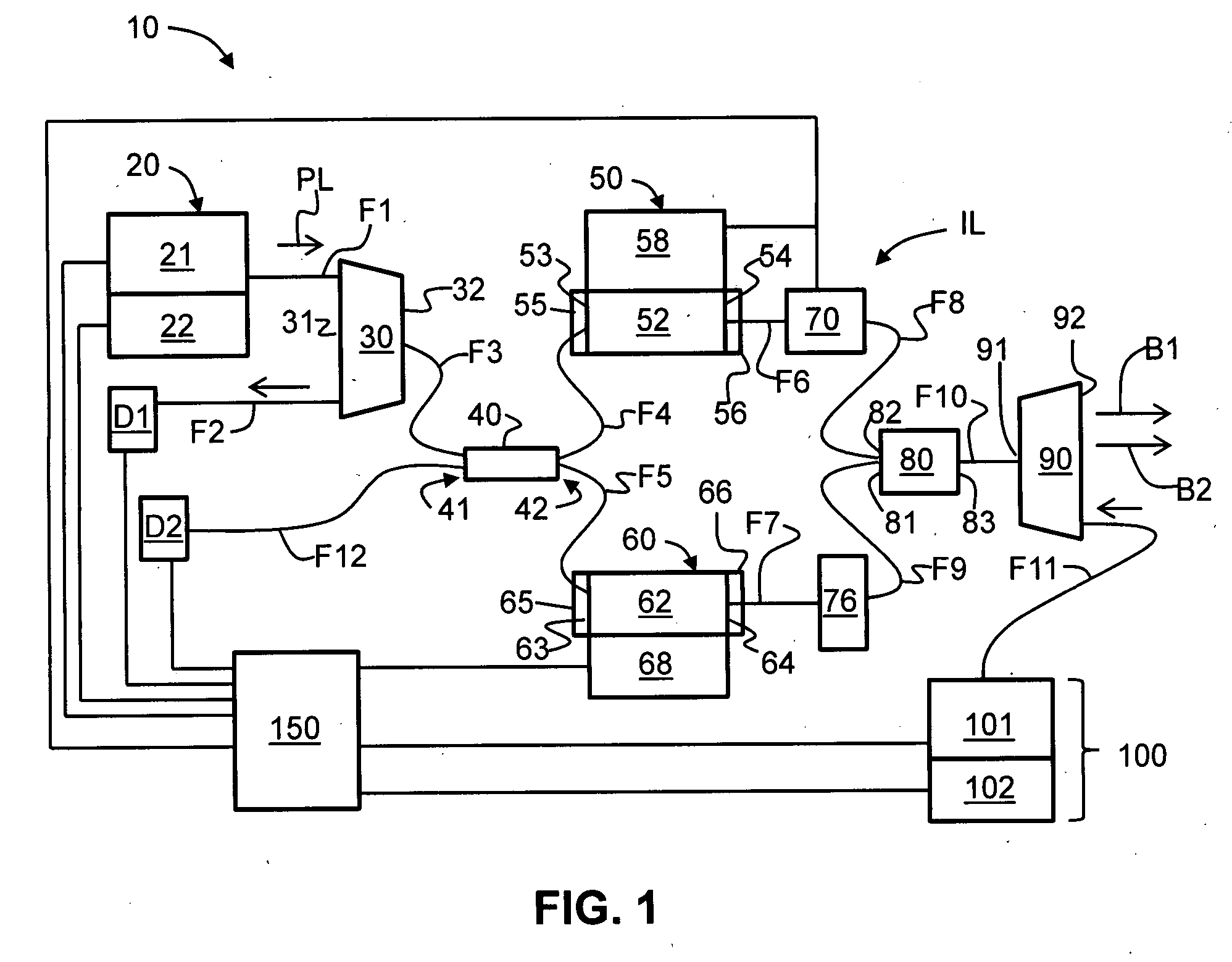
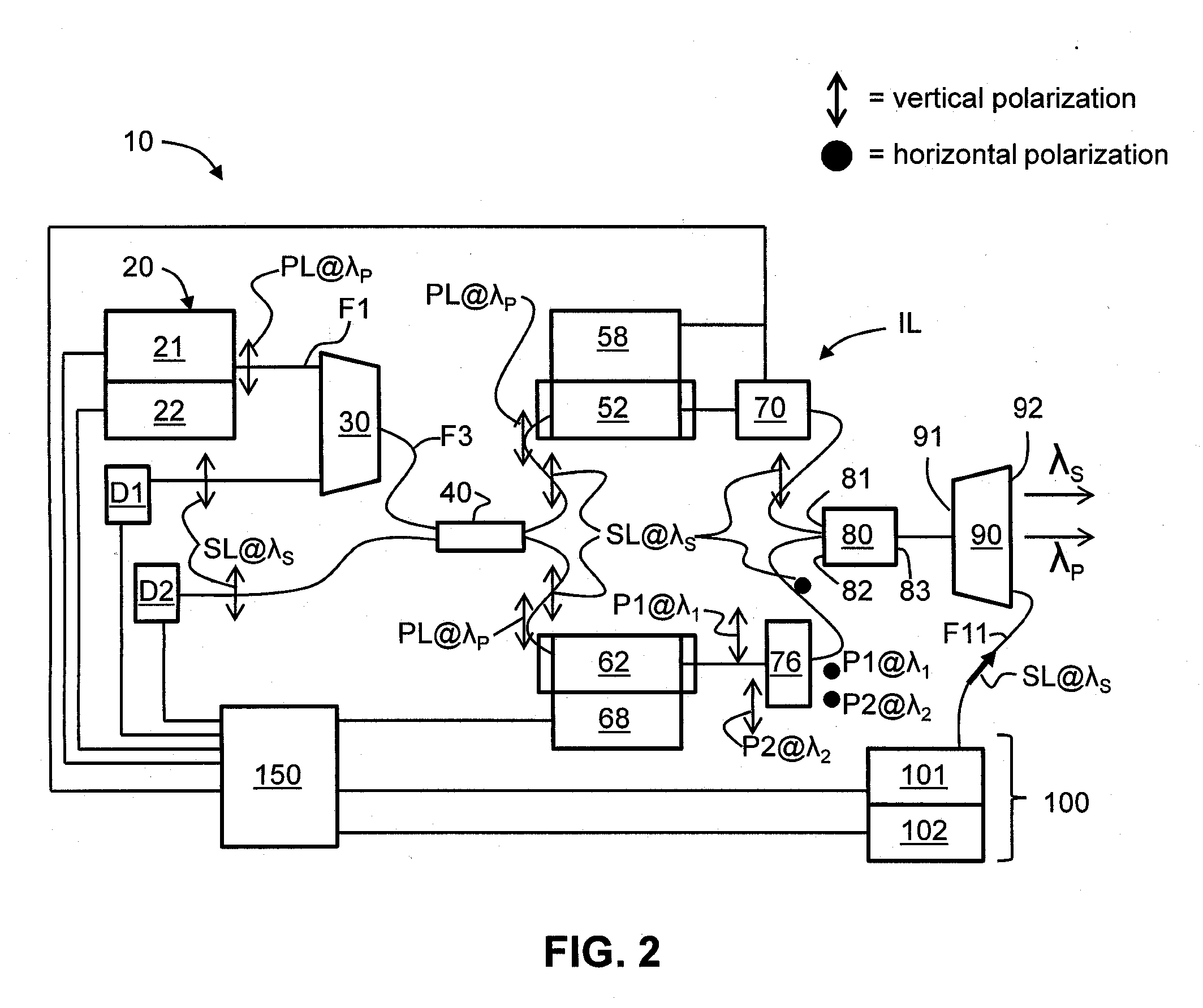
A laser beam source and an operating method thereof is provided for a directional infrared countermeasures (DIRCM) weapon system for defensively countering guided missiles having infrared seeking heads, by directing an infrared laser beam at the guided missile so as to disorient, saturate, or irreversibly destroy the IR detectors and circuitry arranged in the target seeking head. The power, pulse frequency and spectral composition of the laser beam is adjustable and selectable as required to adapt to any particular defensive engagement. To achieve this, the laser beam source comprises an Nd:YAG pumping laser and an optical parametric oscillator including an oscillator crystal arranged in a resonator cavity. The crystal includes a plurality of different periodically polarized crystal zones having different lattice constants. The adjacent zones can be grouped together into selectable crystal zone groups. The beam cross-section of the pumping laser beam corresponds to the cross-section of a single crystal zone or of a crystal zone group encompassing plural zones. The crystal is arranged on a slide table that is slidably displaceable by a servomotor, to move a selected crystal zone or group into the path of the pumping laser beam. Thereby the wavelength components and the relative intensities thereof of the output laser beam can easily be selectively adjusted.
Owner:EADS DEUT GMBH
Compact efficient and robust ultraviolet solid-state laser sources based on nonlinear frequency conversion in periodically poled materials
InactiveUS7570676B2Low costHigh peak powerOptical devices for laserNon-linear opticsNonlinear crystalsLight source
A compact and efficient ultraviolet laser source based on a optically-pumped solid-state or fiber laser that produces near-infrared output light suitable for nonlinear frequency conversion. The infrared laser output is frequency tripled or quadrupled to produce light in the ultraviolet wavelength range (200 nm to 400 nm). The novel technology is the use of highly efficient periodically poled nonlinear crystals, such as stoichiometric and MgO-doped lithium tantalate and lithium niobate. As opposed to conventional frequency-converted UV laser sources, which have high power consumption, high cost, and low efficiency, the laser sources of this invention utilize high efficiency nonlinear conversion provided by periodically poled materials and allow lower-cost architectures without additional focusing lenses, high power pump diodes, etc.
Owner:OOO SPECTRALUS
One-dimensional illumination apparatus and imaging apparatus
InactiveUS7545837B2High in output and efficiencyReduce speckle noiseSemiconductor laser arrangementsPicture reproducers using projection devicesNonlinear optical crystalLight equipment
Owner:SONY CORP
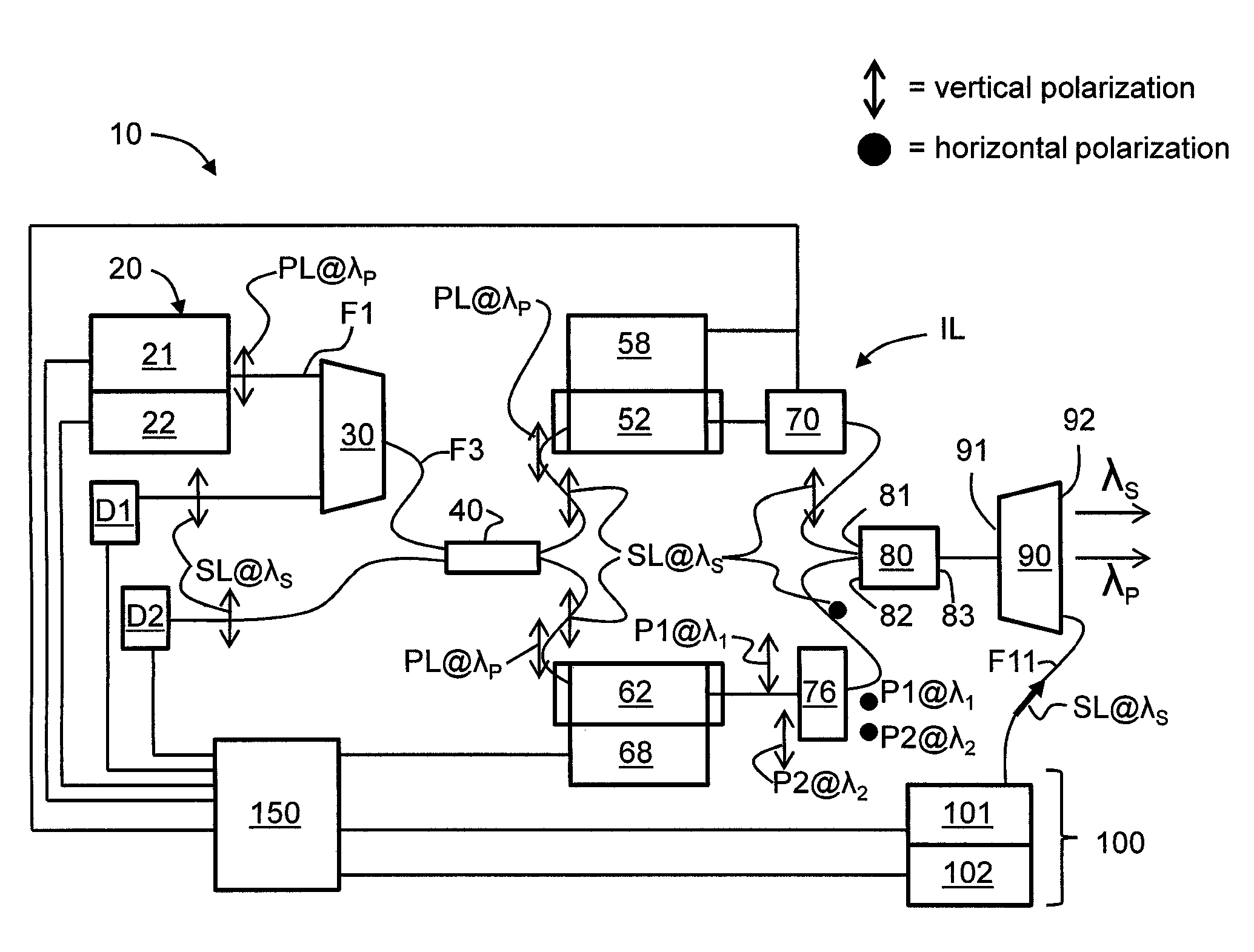
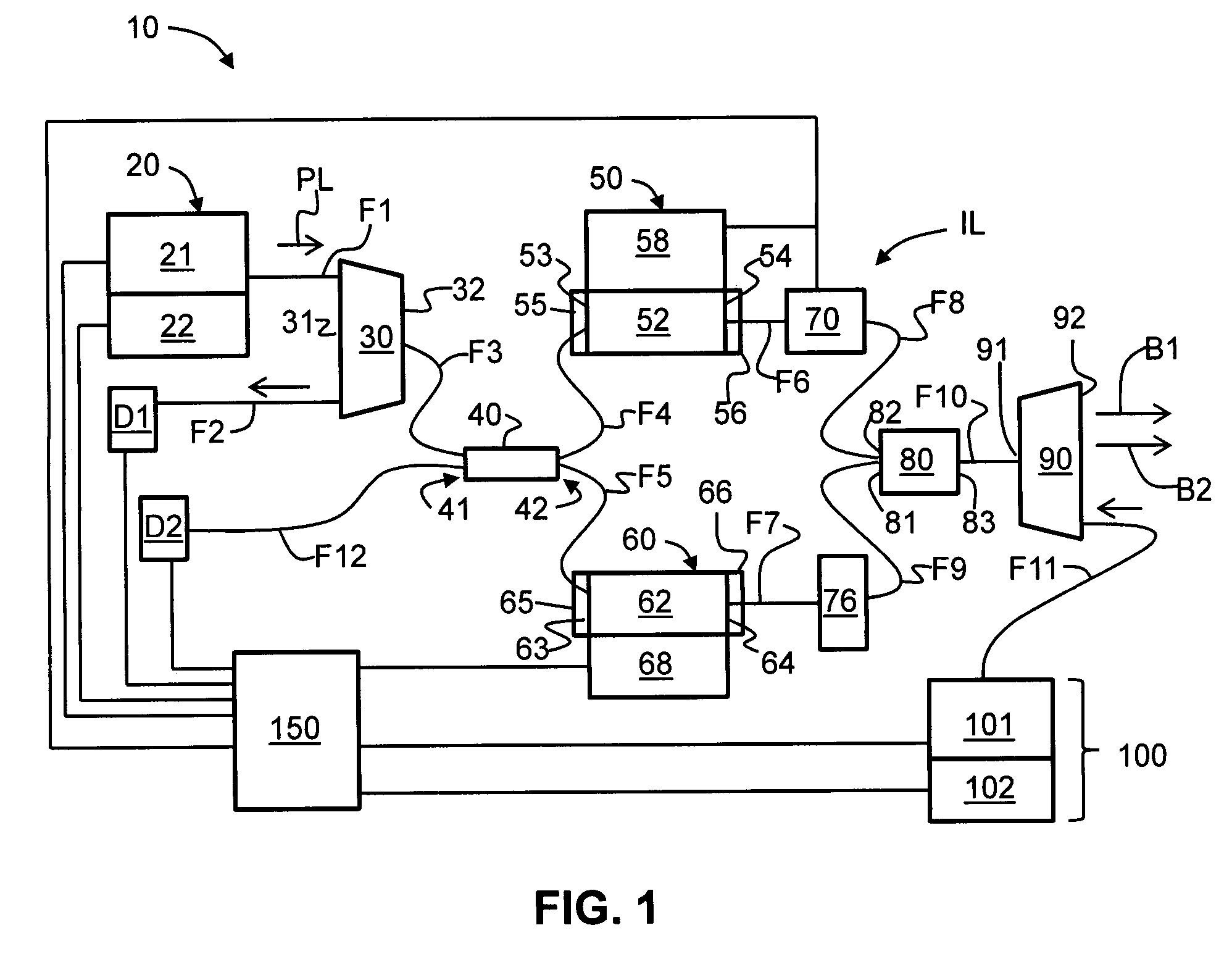
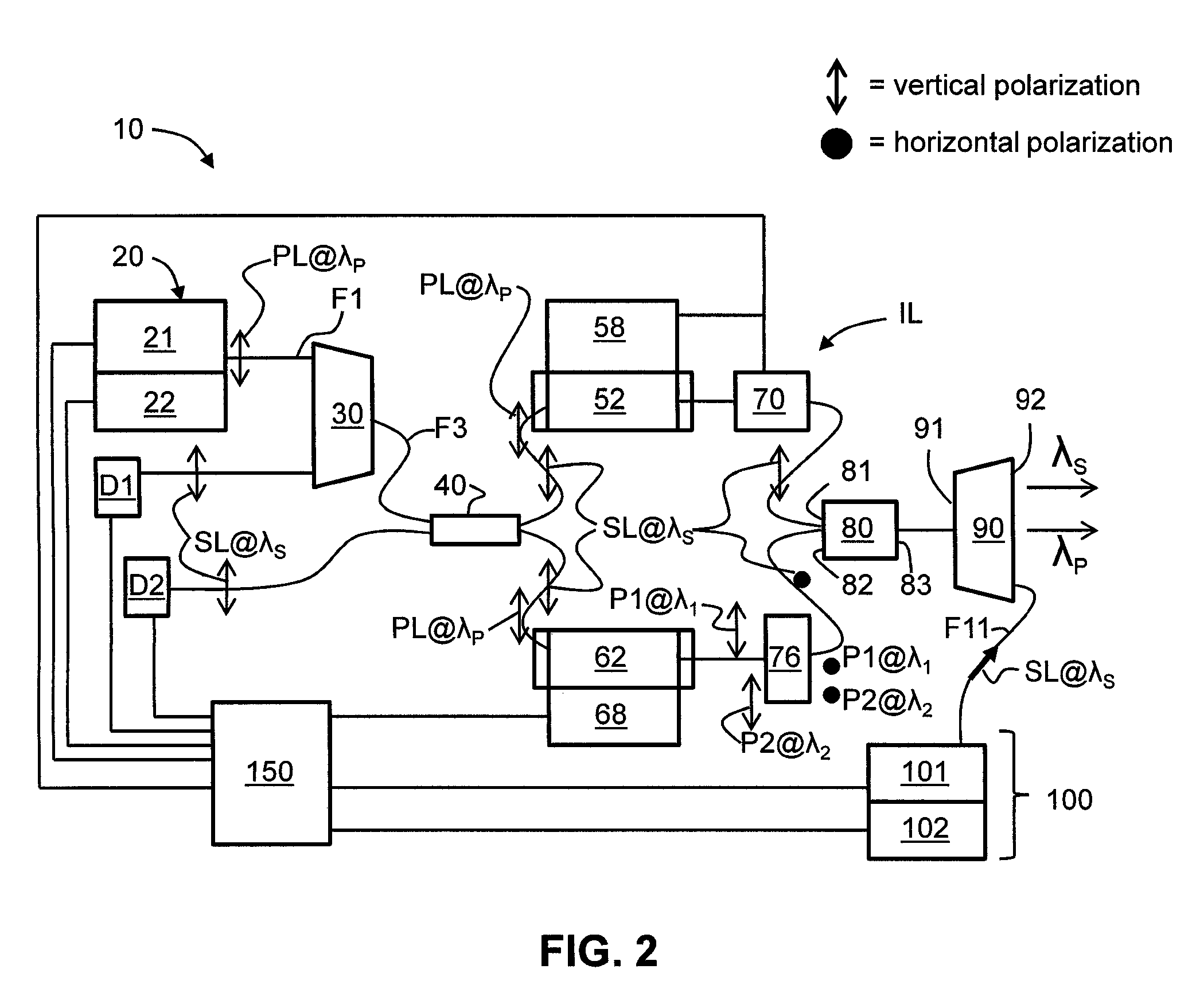
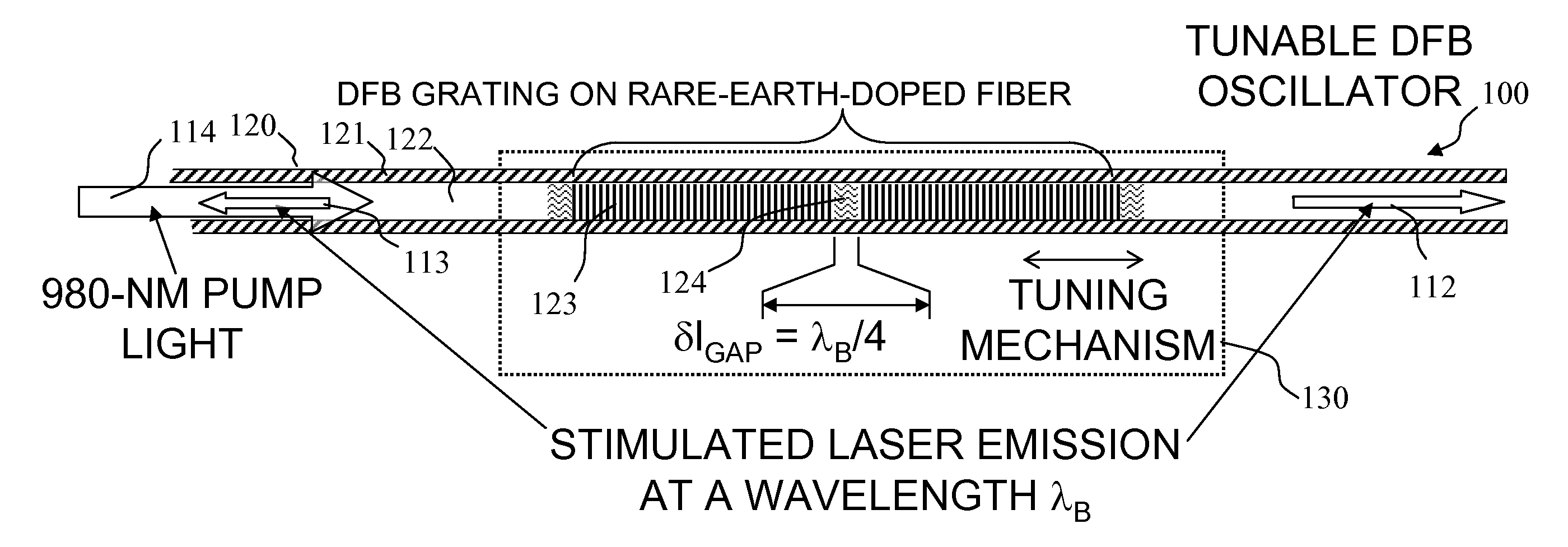
Apparatus and method for pumping and operating optical parametric oscillators using DFB fiber lasers
ActiveUS7620077B2Reduce pump powerLarge and undesirable buildupLaser using scattering effectsExcitation process/apparatusInfrared laser beamLithium niobate
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Compact efficient and robust ultraviolet
InactiveUS20070263693A1Low costHigh peak powerOptical devices for laserNon-linear opticsUltravioletLaser source
A compact and efficient ultraviolet laser source based on a optically-pumped solid-state or fiber laser that produces near-infrared output light suitable for nonlinear frequency conversion. The infrared laser output is frequency tripled or quadrupled to produce light in the ultraviolet wavelength range (200 nm to 400 nm). The novel technology is the use of highly efficient periodically poled nonlinear crystals, such as stoichiometric and MgO-doped lithium tantalate and lithium niobate. As opposed to conventional frequency-converted UV laser sources, which have high power consumption, high cost, and low efficiency, the laser sources of this invention utilize high efficiency nonlinear conversion provided by periodically poled materials and allow lower-cost architectures without additional focusing lenses, high power pump diodes, etc.
Owner:OOO SPECTRALUS
Compact solid-state laser
A compact optically-pumped solid-state laser designed for efficient nonlinear intracavity frequency conversion into desired wavelengths using periodically poled nonlinear crystals. These crystals contain dopants such as MgO or ZnO and / or have a specified degree of stoichiometry that ensures high reliability. The laser includes a solid-state gain media chip, such as Nd:YVO4, which also provides polarization control of the laser; and a periodically poled nonlinear crystal chip such as PPMgOLN or PPZnOLT for efficient frequency doubling of the fundamental infrared laser beam into the visible wavelength range. The described designs are especially advantageous for obtaining low-cost green and blue laser sources.
Owner:OOO SPECTRALUS
Compact tunable high-efficiency entangled photon source
InactiveUS20080063015A1Reduce pump powerEasy transferLaser detailsUsing optical meansWaveguidePhoton source
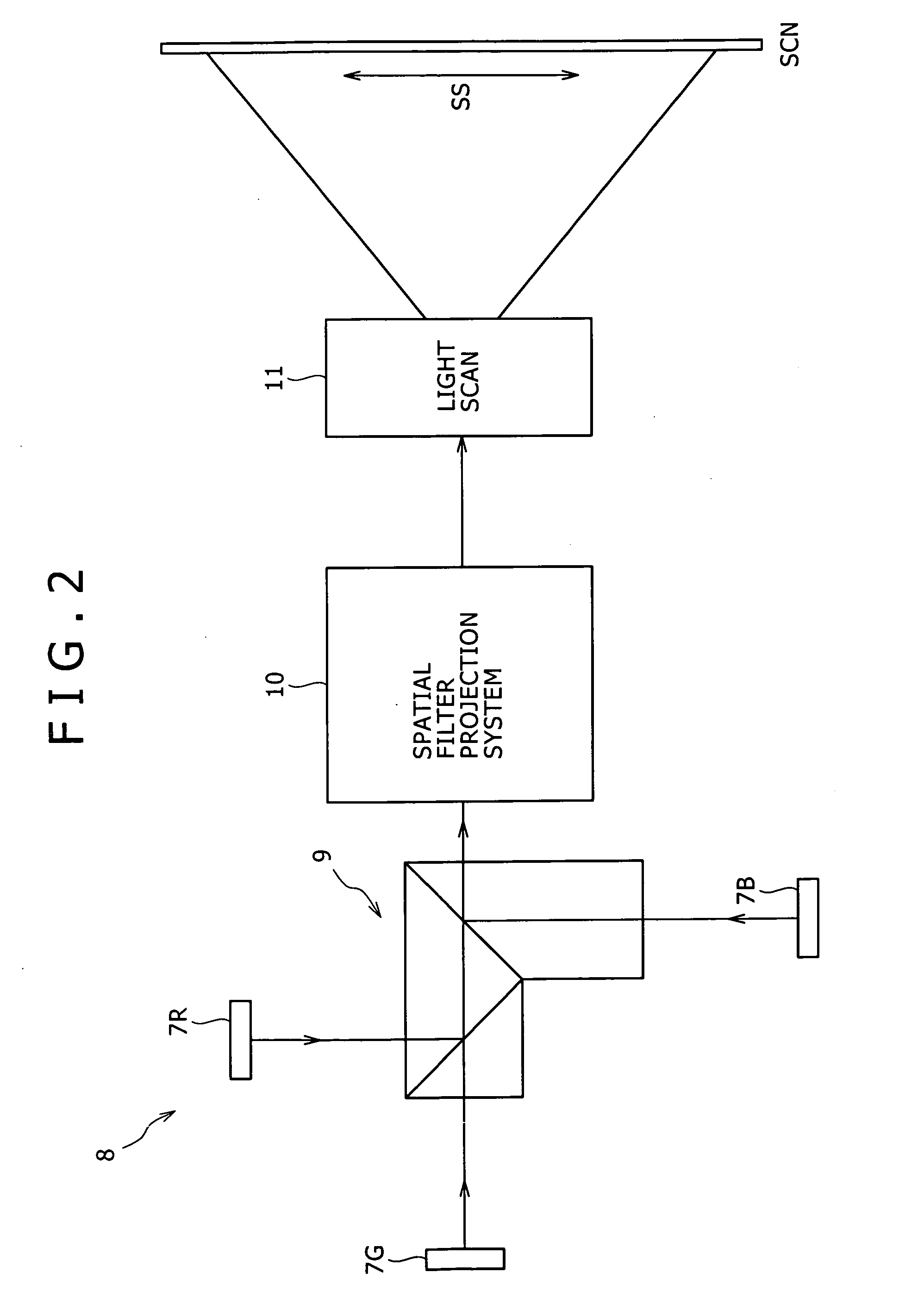
A compact, tunable, high-efficiency entangled photon source system that utilizes first and second periodically poled waveguides rather than bulk media in order to decrease the required pump power by up to several orders of magnitude. The first and second waveguides are arranged in respective arms of an interferometer. Each waveguide has partially reflecting ends, and are each placed on the Z-face of respective periodically poled KTP or LiNBO3 crystals to form respective first and second Fabry-Perot cavities. All waves (pump, idler, and signal) are co-polarized along the z-axis of the crystals. One of the waveguides is followed by a polarization rotator (shown as a half-wave-plate in the Figures) rotating the idler and signal wave polarization by 90 degrees. The outputs from two interferometer arms are combined by a polarization beam combiner and then split by a wavelength multiplexer into two spatially separated time-bin and polarization entangled beams. Another light source, a single frequency stabilized C-band laser (stabilization laser) is used to synchronize cavities spectral modes and phase-lock their outputs.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
One-dimensional illumination apparatus and imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20050238071A1High in output and efficiencyReduce speckle noiseSemiconductor laser arrangementsPicture reproducers using projection devicesNonlinear optical crystalLight equipment
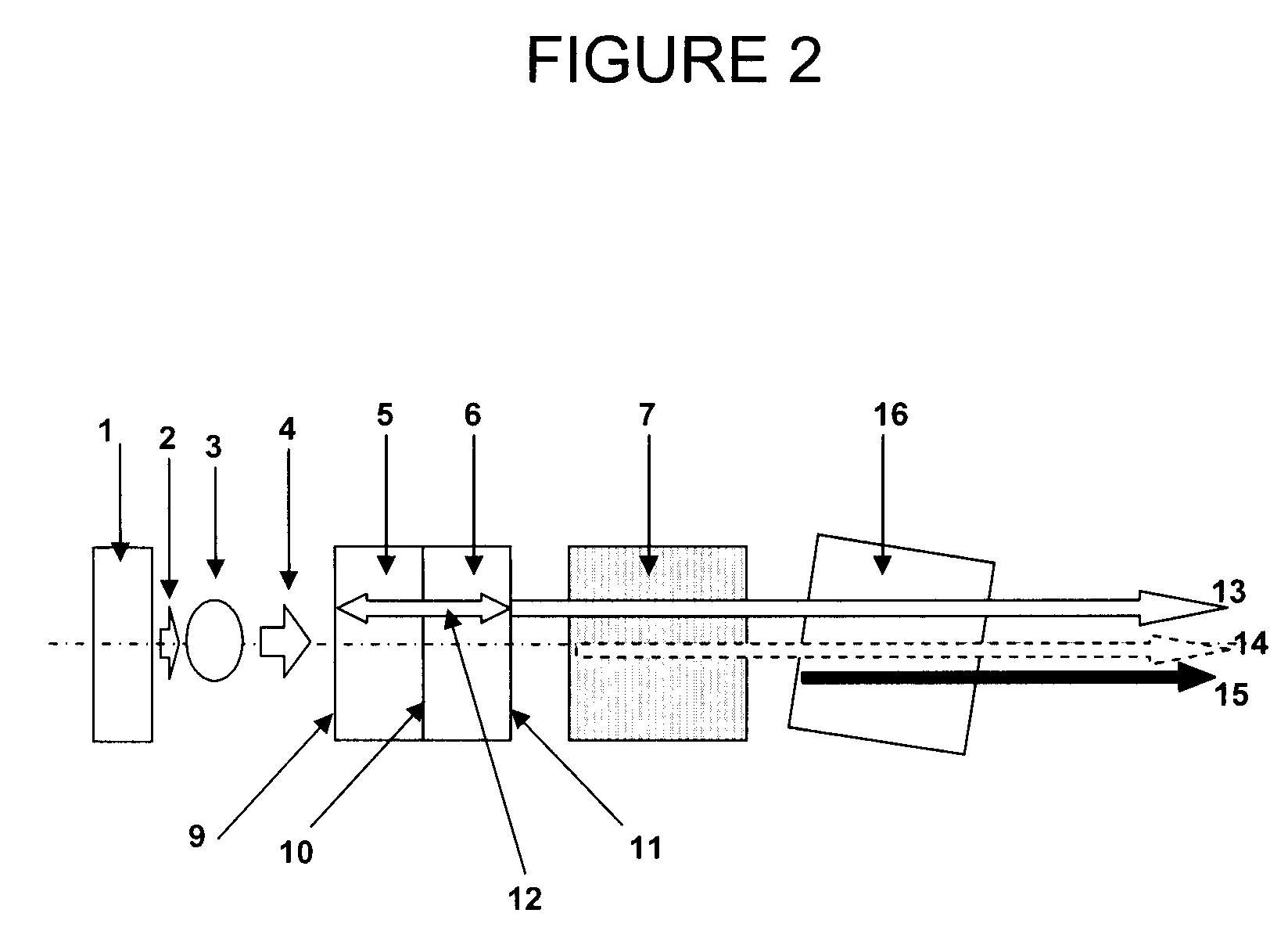
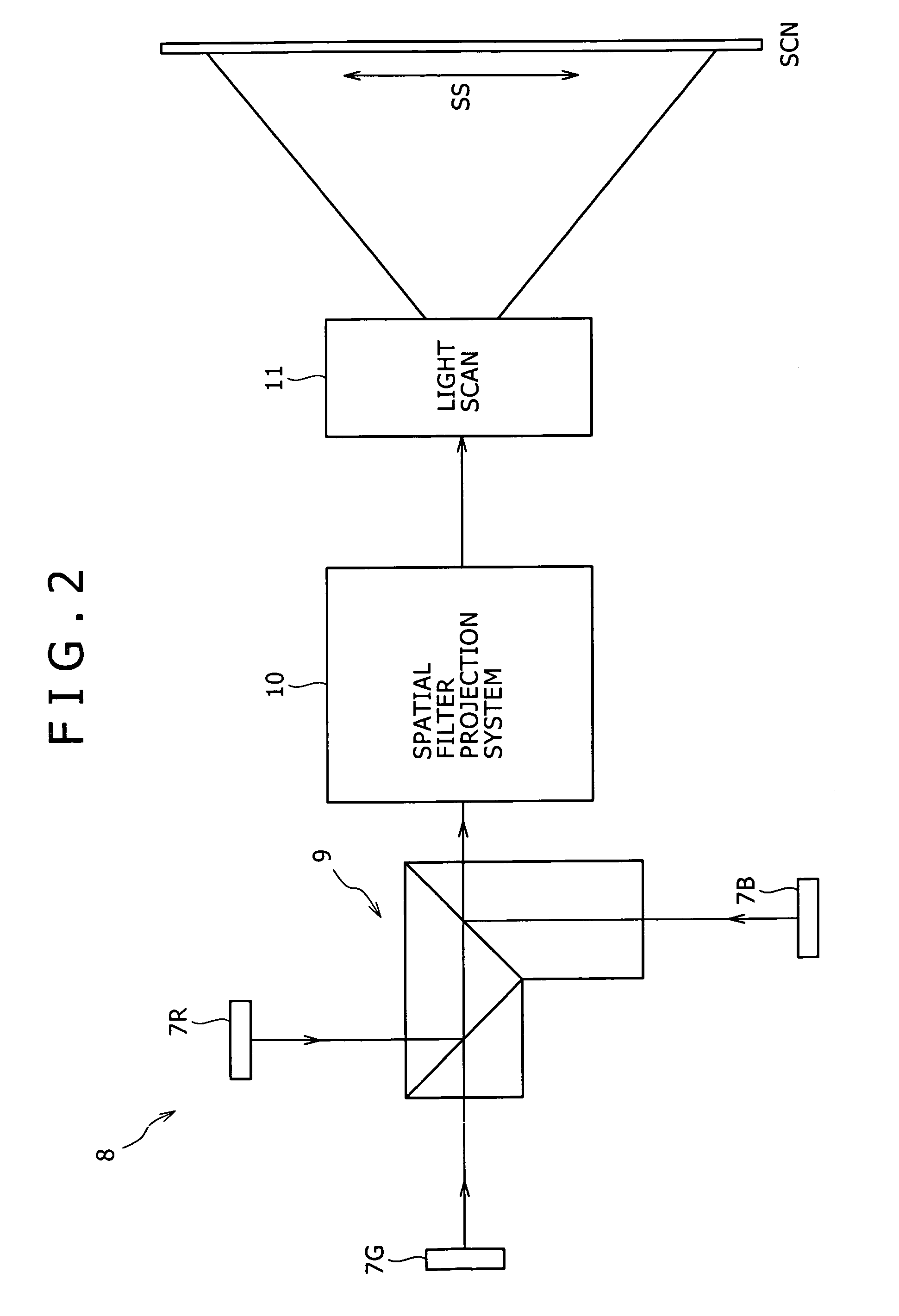
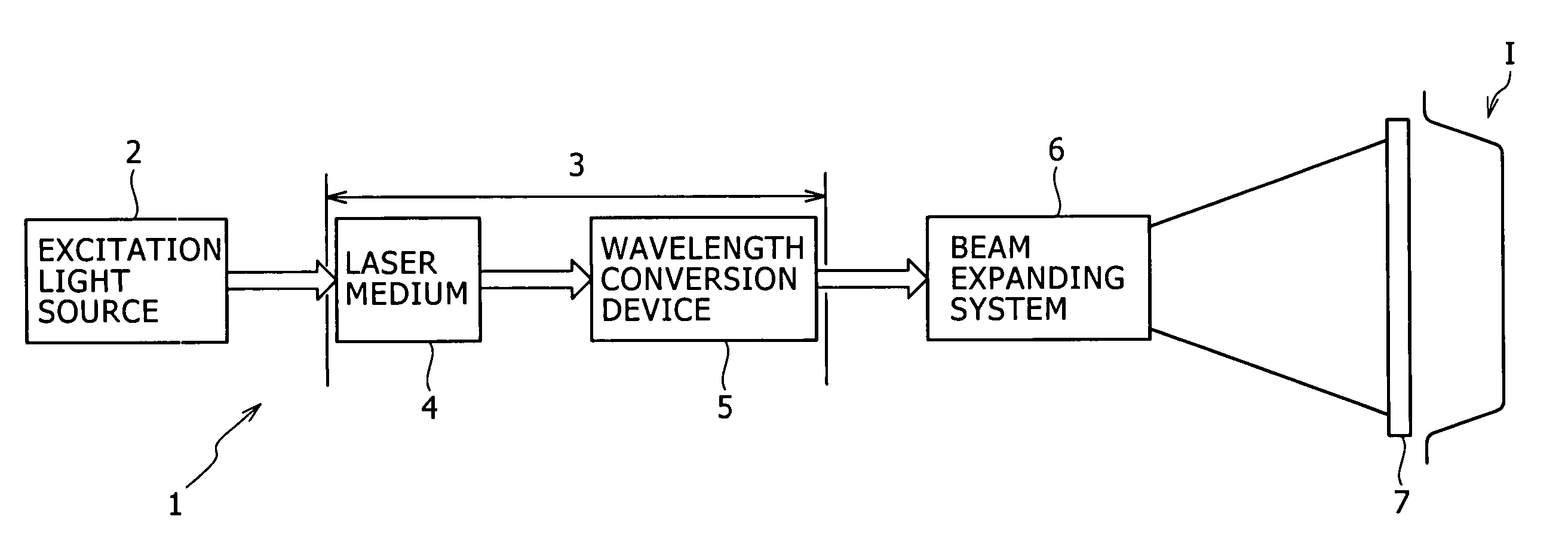
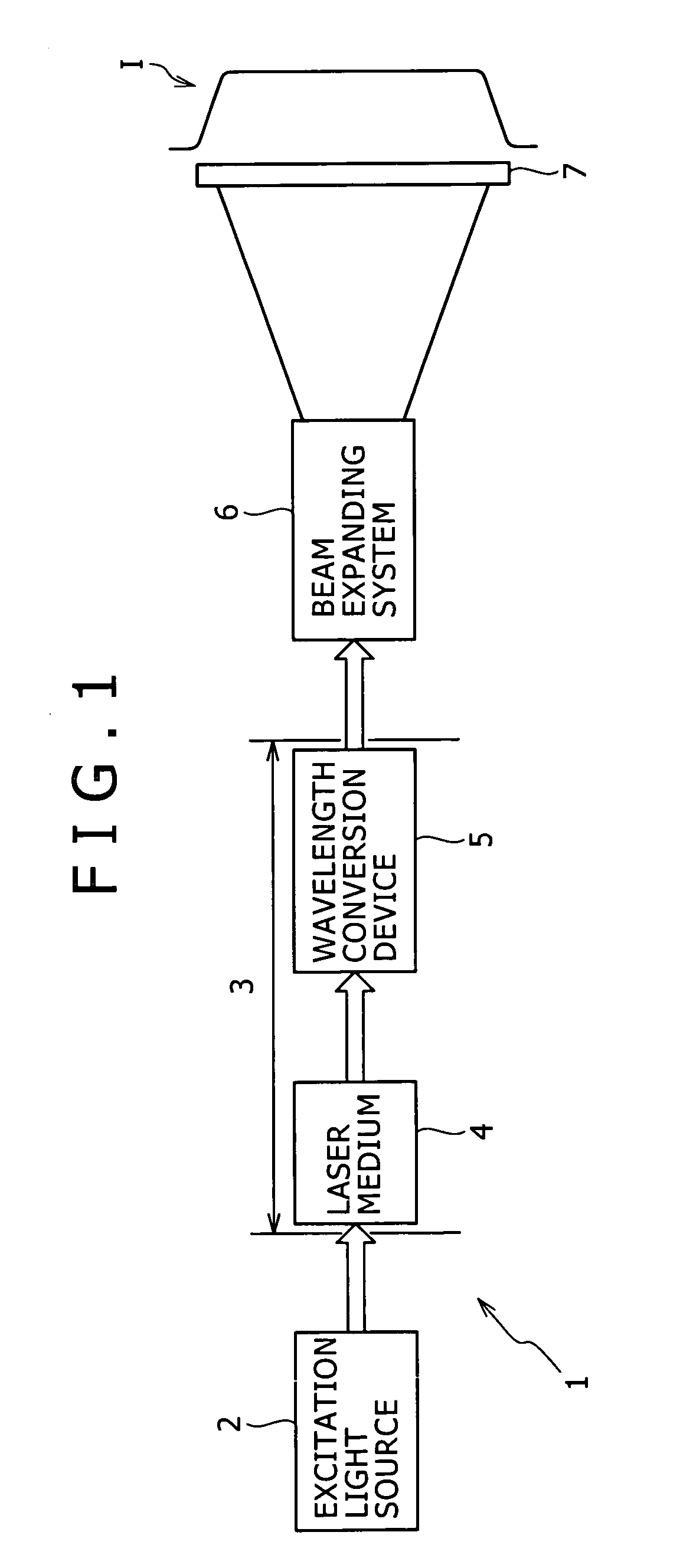
A one-dimensional transverse multiple mode laser is used for a one-dimensional illumination apparatus. A pumping light source, and a laser medium and a wavelength conversion device (nonlinear optical crystal or a nonlinear optical device) which are disposed in a resonator, are provided, and the nonlinear optical crystal or a nonlinear optical device is irradiated with a line beam obtained by exciting the laser medium in an elliptic transverse mode pattern. Then, a one-dimensional light modulation device is irradiated with the wavelength-converted line beam, and scanning with the beam modulated by the modulation device is conducted to produce a two-dimensional image. For example, in a green illumination optical system, in the case where the nonlinear optical device for obtaining visible rays through second harmonic generation from IR rays oscillated by a solid state laser medium has a periodical poling structure, stoichiometric composition periodical poling lithium tantalate having been subjected to vapor transport equilibration is used, whereby reliability is enhanced and a reduction in cost can be achieved through mass production.
Owner:SONY CORP
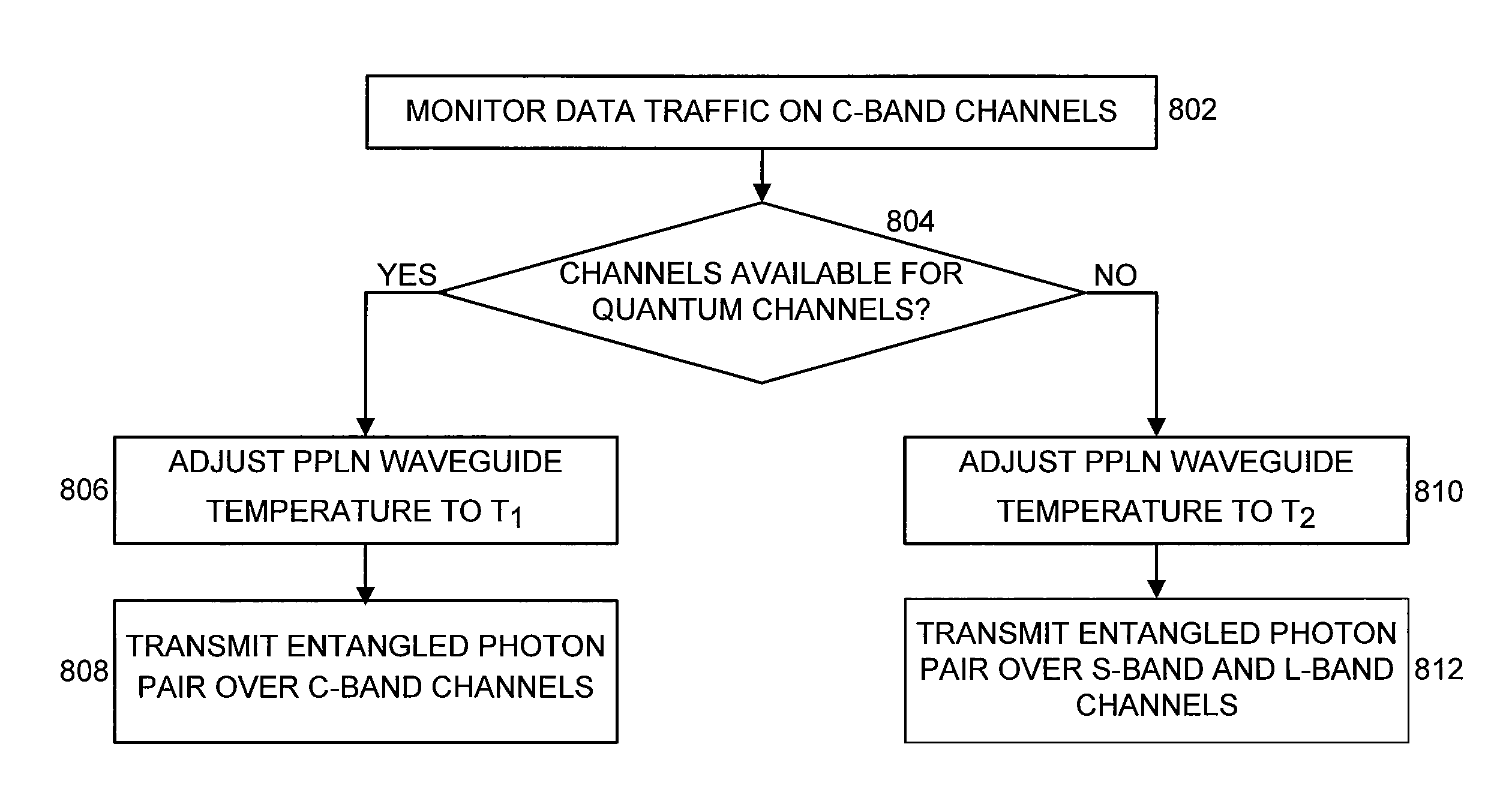
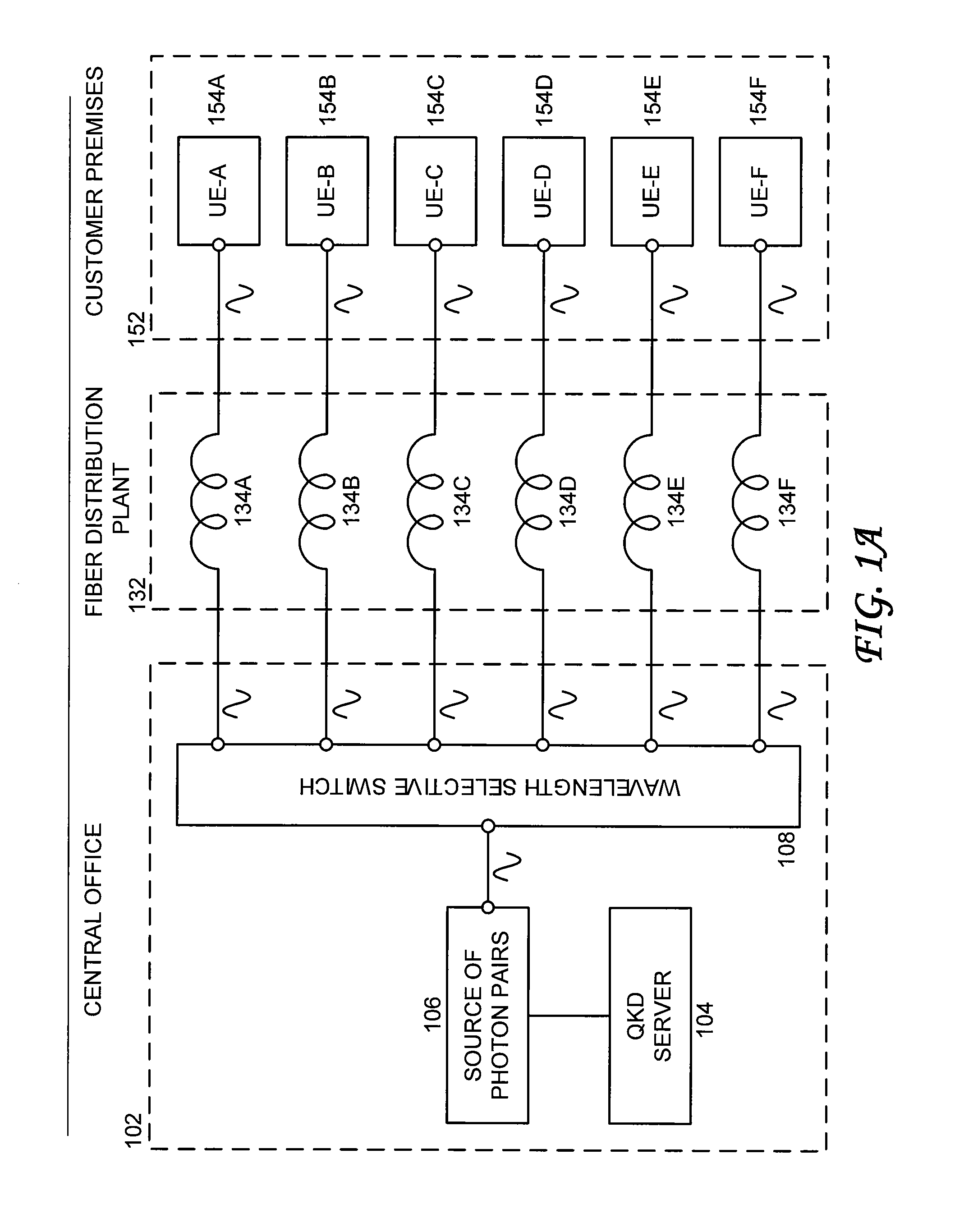
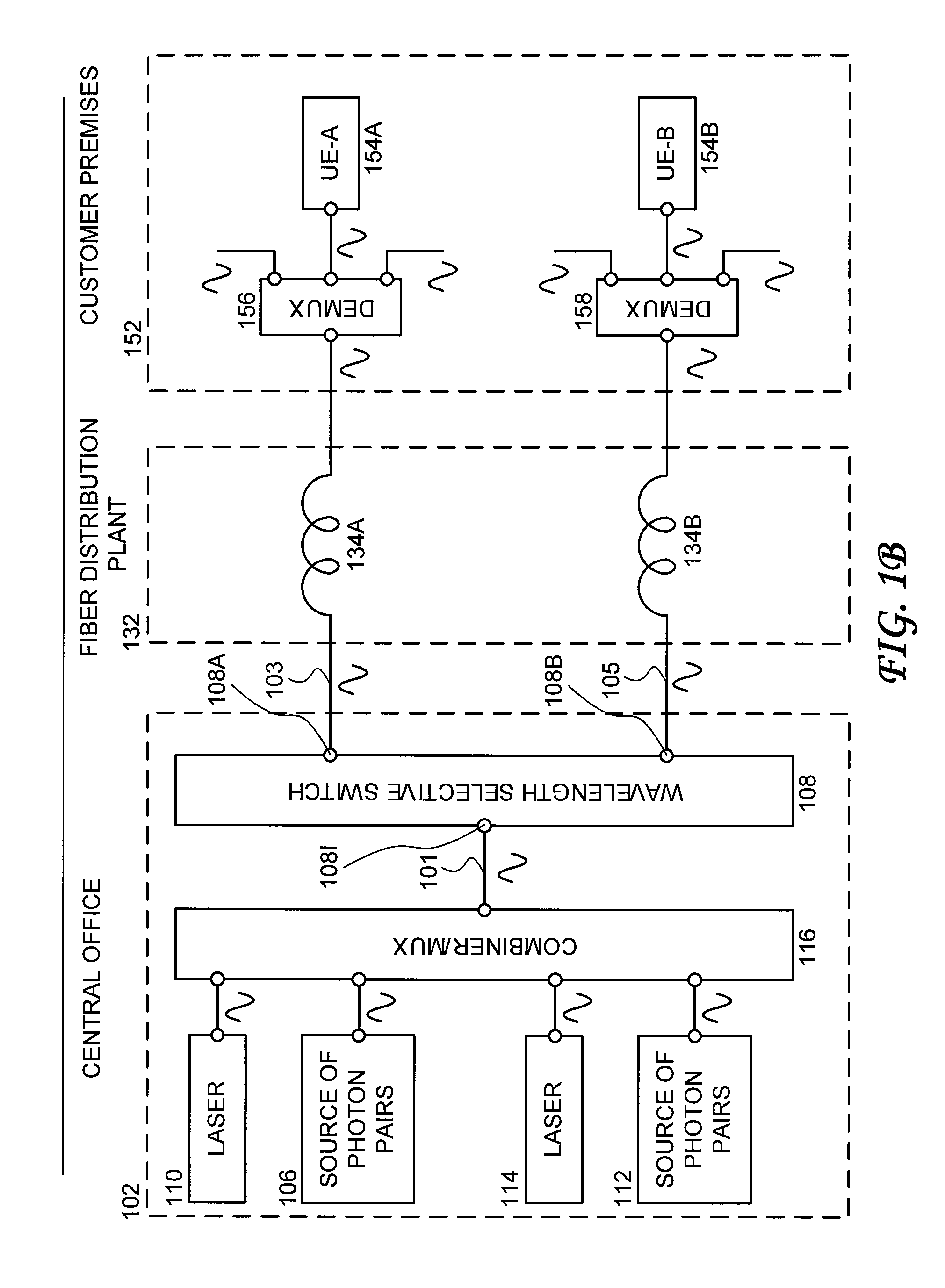
Bandwidth provisioning for an entangled photon system
ActiveUS8280250B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsC bandingFiber network
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Solid-state laser arrays using
A compact solid-state laser array for nonlinear intracavity frequency conversion into desired wavelengths using periodically poled nonlinear crystals. The crystals contain dopants such as MgO and / or have a specified stoichiometry. A preferred embodiment comprises a microchip laser cavity that includes a solid-state gain chip, such as Nd:YVO4, which also provides polarization control of the laser; and a periodically poled nonlinear crystal chip such as PPMgOLN, for efficient frequency doubling of a infrared laser pump beam into the visible wavelength range. The described designs are especially advantageous for obtaining low-cost green and blue laser sources. The use of such high-efficiency pumps and nonlinear materials allows scaling of a compact, low-cost architecture to provide high output power levels in the blue / green wavelength range.
Owner:OOO SPECTRALUS
Frequency doubling crystal and frequency doubled external cavity laser
InactiveUS20060233206A1Preserve collinearityMaximize conversion efficiencyLaser detailsNon-linear opticsExternal cavity laserHarmonic
A periodically poled second harmonic generating crystal having a long axis, said crystal comprising Magnesium Oxide doped Congruent Lithium Niobate, Magnesium Oxide doped Stoichiometric Lithium Niobate, Stoichiometric Lithium Tantalate or Potassium Titanyl Phosphate wherein the poling planes of said periodically poled crystal are canted relative to said axis and a doubled, external cavity laser utilizing said crystal, comprising an external cavity pump laser section and an extra-cavity frequency doubling section.
Owner:NEWPORT CORP
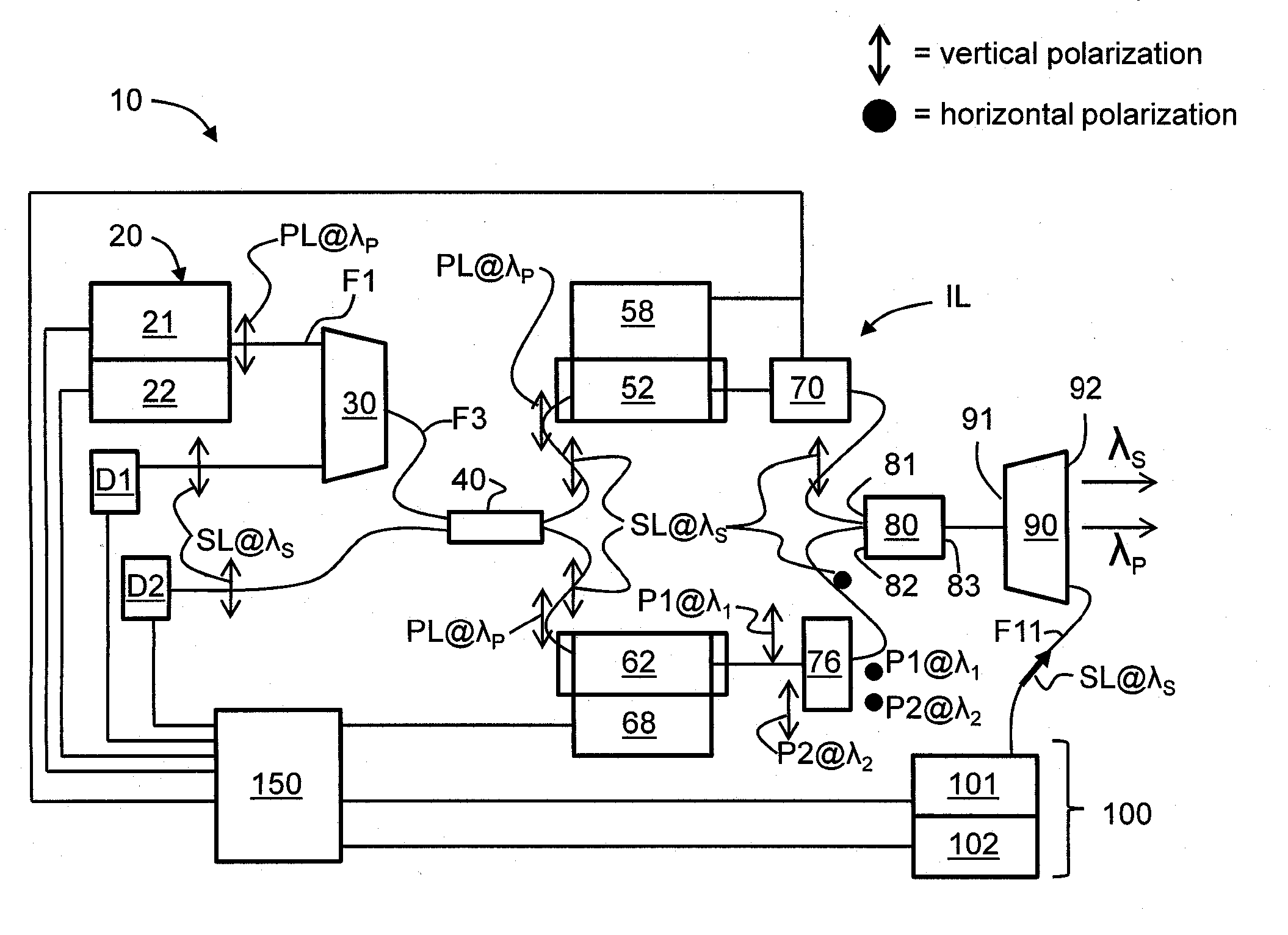
Device for Generating Polarization-Entangled Photons
InactiveUS20090103736A1Raise the possibilityEfficient electrical and thermal tuningQuantum computersKey distribution for secure communicationPeriodic polingOptical nonlinearity
A device for generating polarization-entangled photons by means of parametric down-conversion, comprising a waveguide structure formed in a substrate of an optically non-linear material with periodically poled regions, wherein, when in operation, pump photons can be supplied from a pump laser to the waveguide structure, and wherein a separating means for separating the entangled photons for the separate further conduction of signal photons and idler photons, respectively, is arranged to follow the waveguide structure.
Owner:AUSTRIAN RES CENTS GMBH ARC
Compact tunable high-efficiency entangled photon source
A compact, tunable, high-efficiency entangled photon source system that utilizes first and second periodically poled waveguides rather than bulk media in order to decrease the required pump power by up to several orders of magnitude. The first and second waveguides are arranged in respective arms of an interferometer. Each waveguide has partially reflecting ends, and are each placed on the Z-face of respective periodically poled KTP or LiNBO3 crystals to form respective first and second Fabry-Perot cavities. All waves (pump, idler, and signal) are co-polarized along the z-axis of the crystals. One of the waveguides is followed by a polarization rotator (shown as a half-wave-plate in the Figures) rotating the idler and signal wave polarization by 90 degrees. The outputs from two interferometer arms are combined by a polarization beam combiner and then split by a wavelength multiplexer into two spatially separated time-bin and polarization entangled beams. Another light source, a single frequency stabilized C-band laser (stabilization laser) is used to synchronize cavities spectral modes and phase-lock their outputs.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
Method and apparatus for pumping and operating optical parametric oscillators using dfb fiber lasers
ActiveUS20100085632A1Reduce pump powerLarge and undesirable buildupLaser using scattering effectsExcitation process/apparatusInfrared laser beamLithium niobate
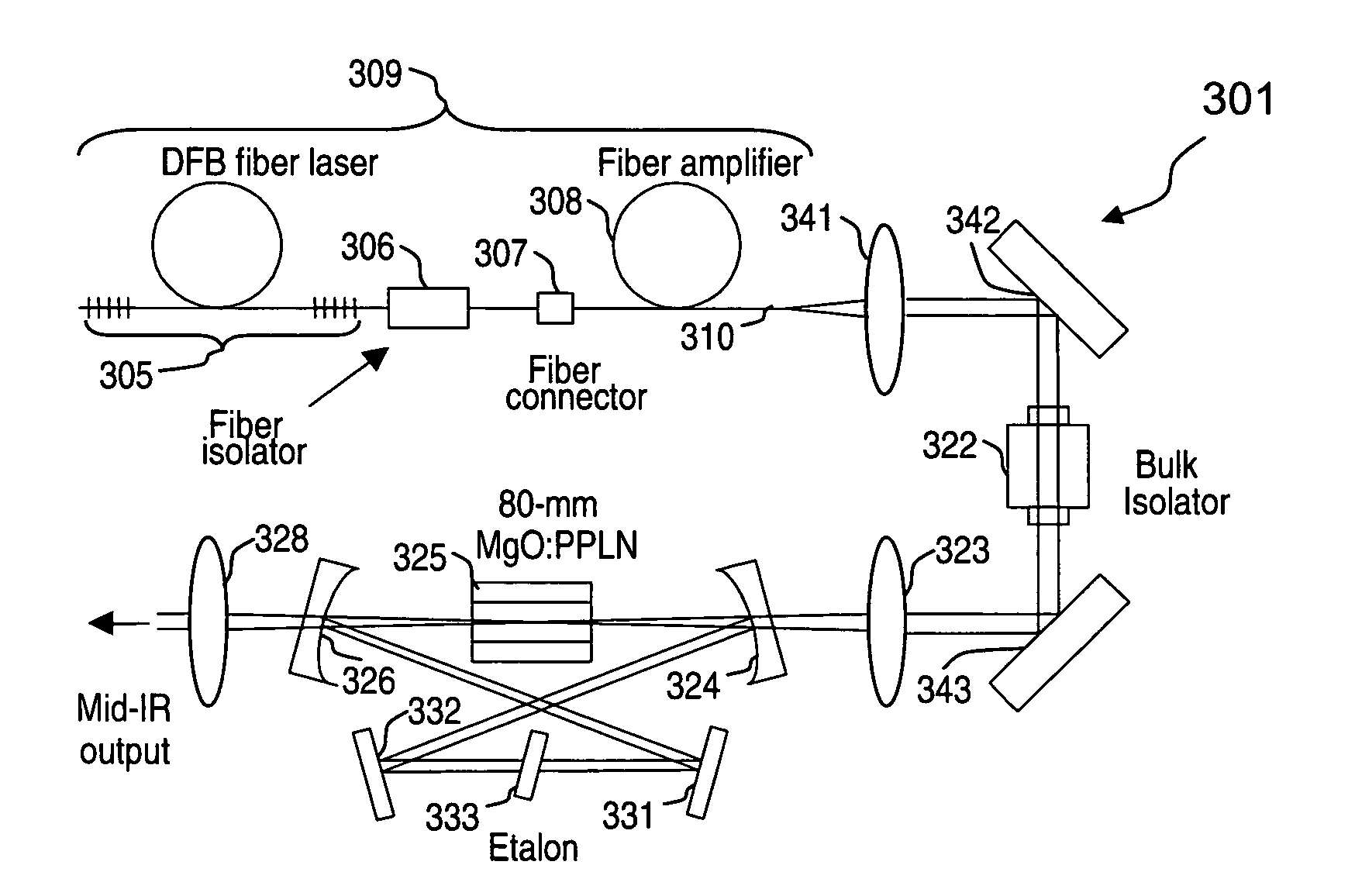
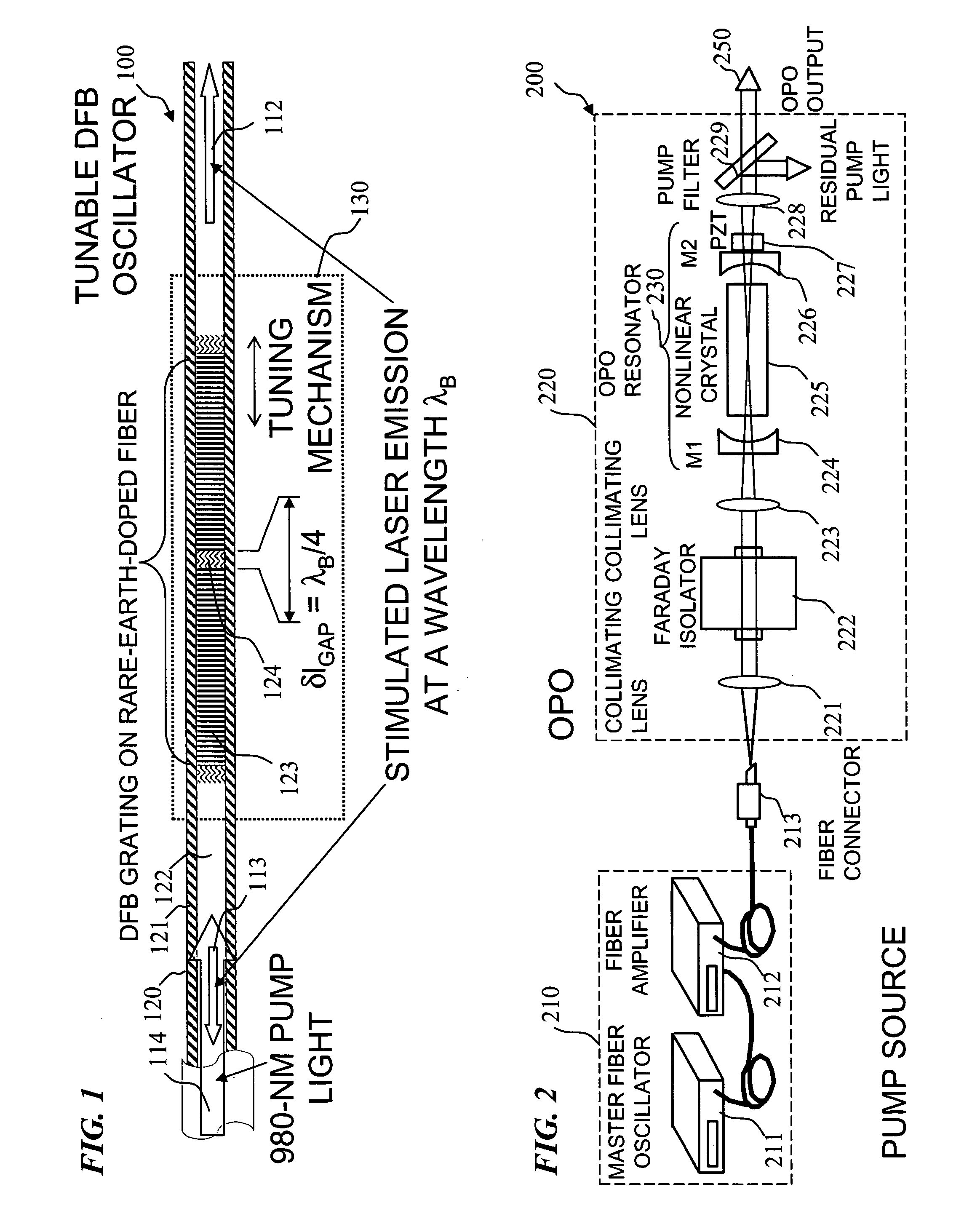
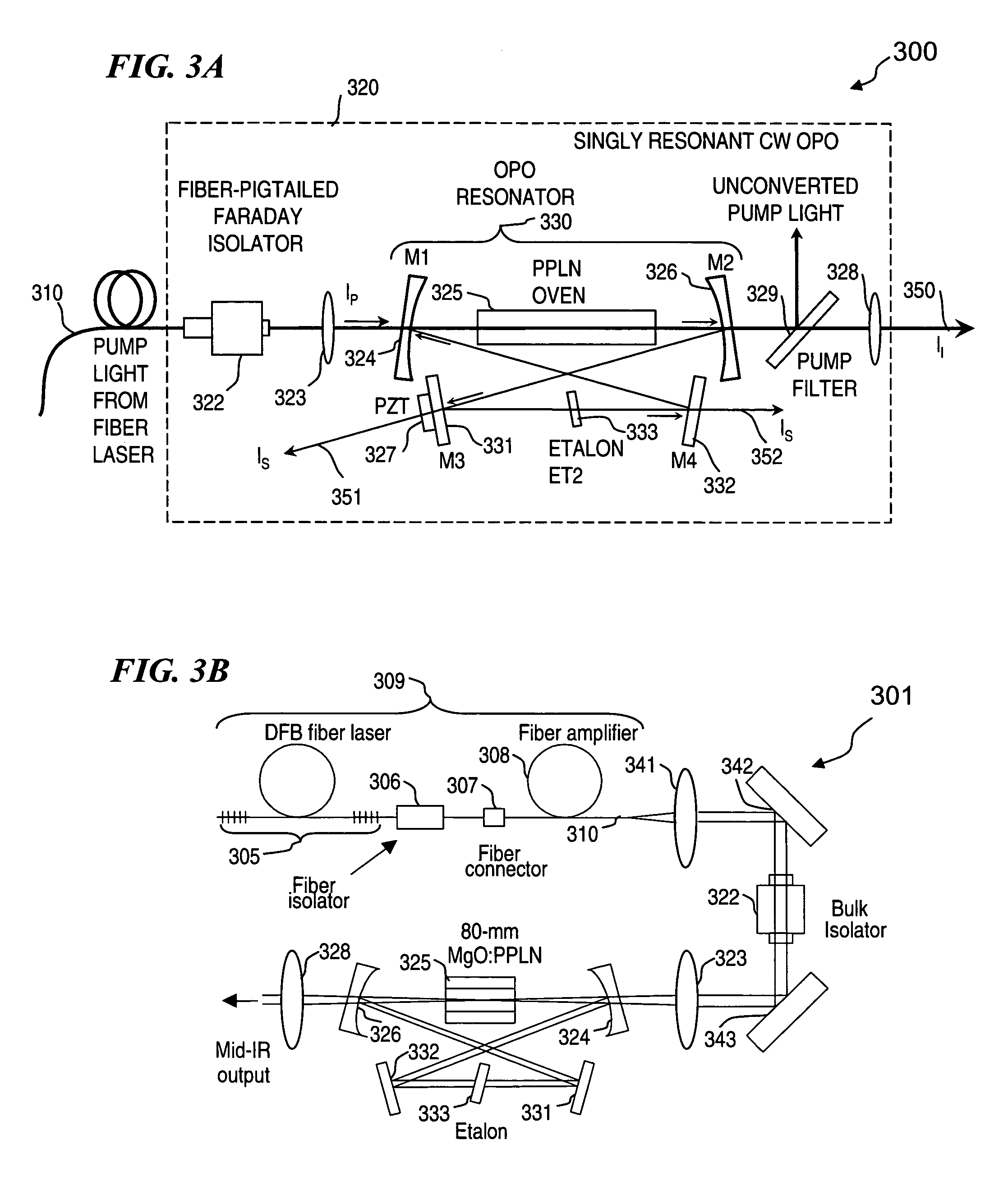
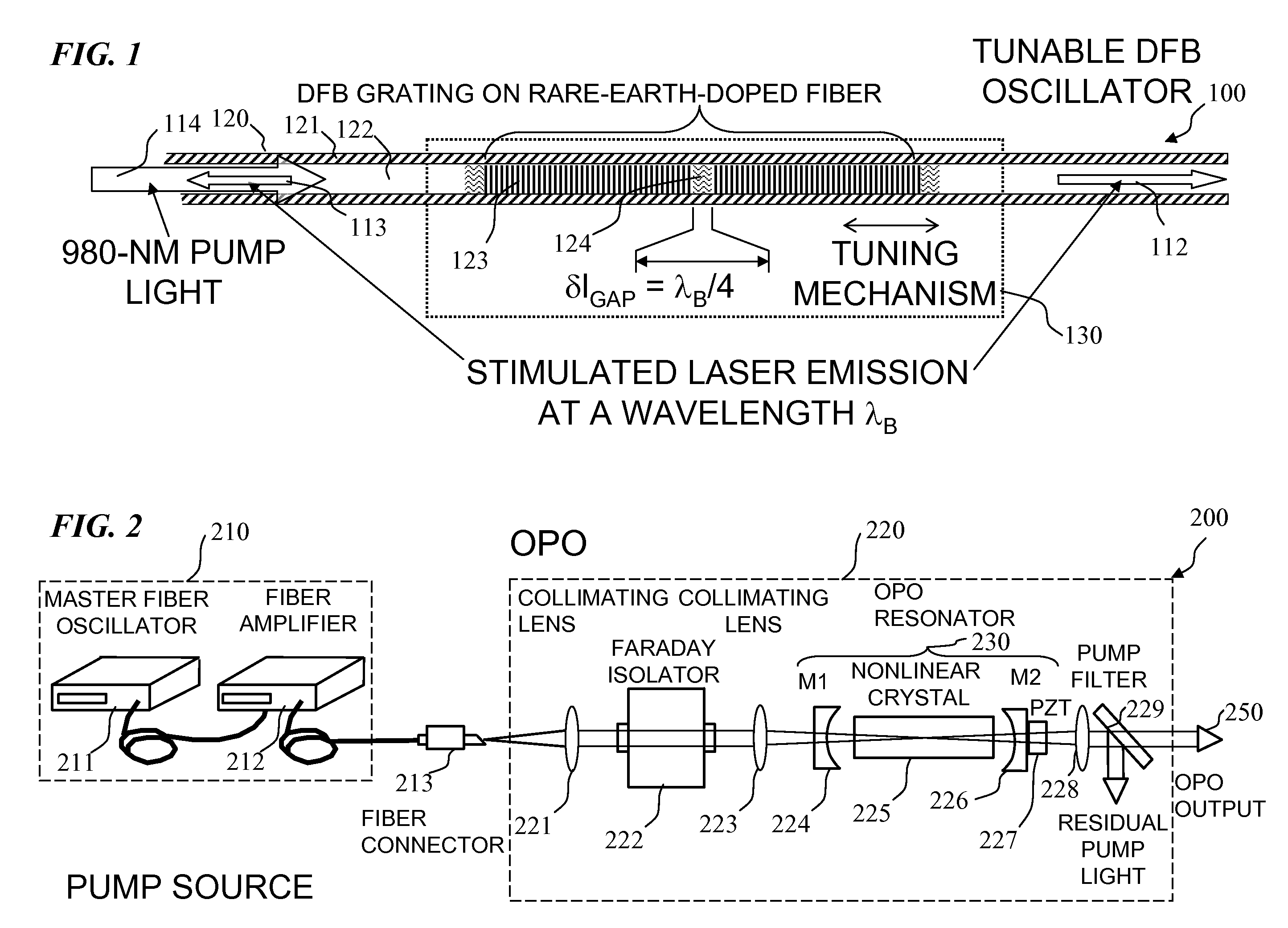
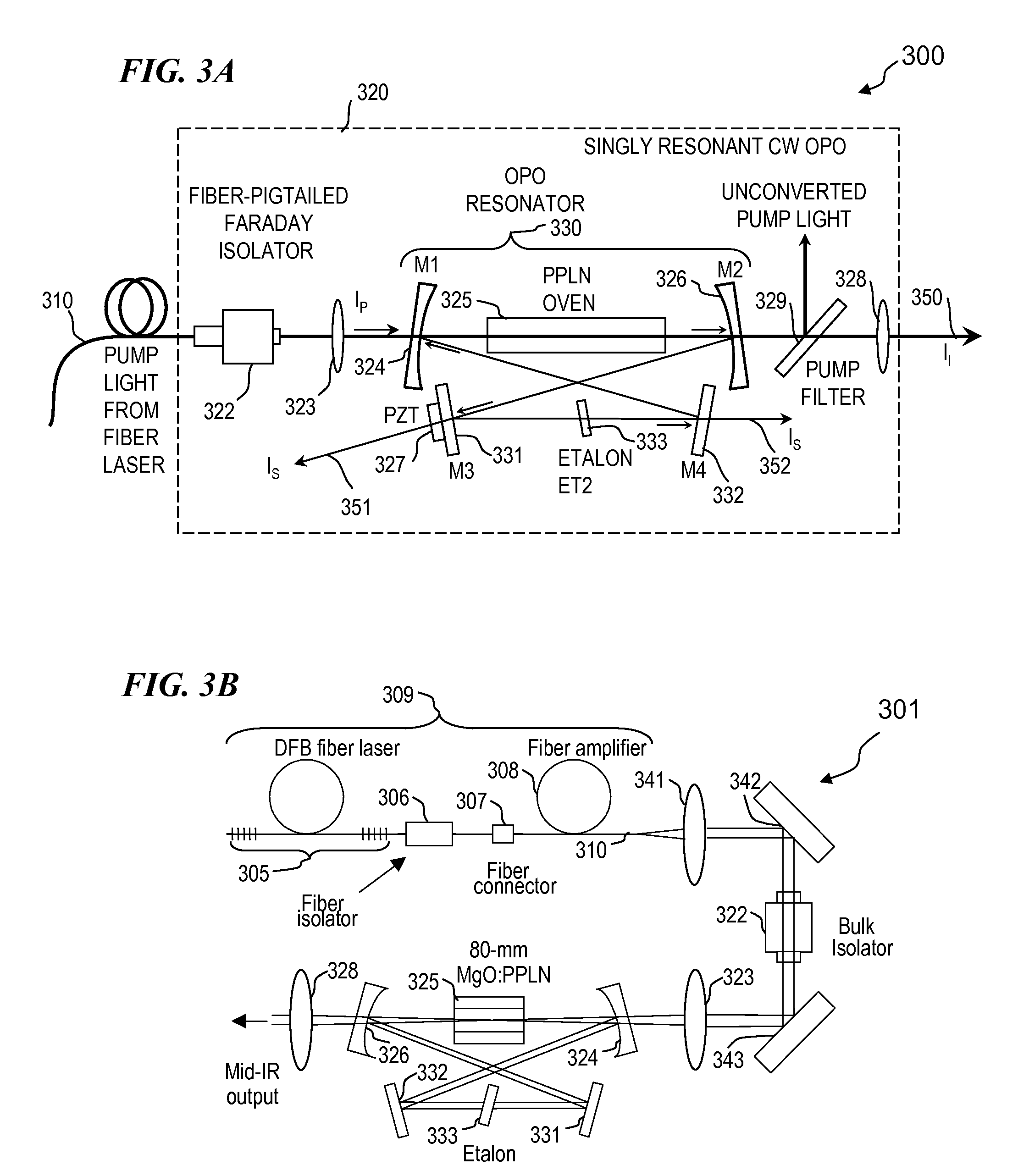
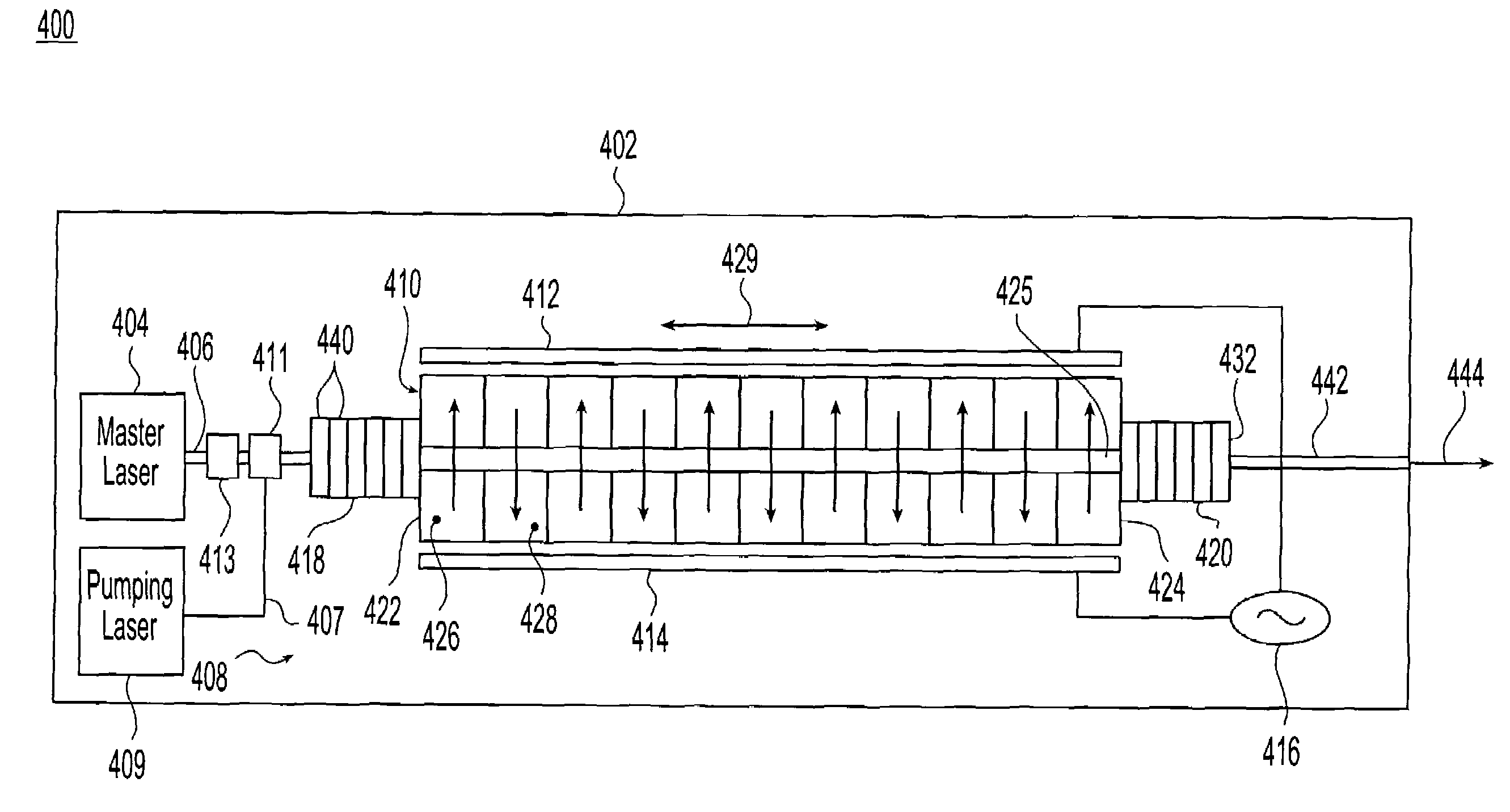
An optical parametric oscillator (OPO) is described that efficiently converts a near-infrared laser beam to tunable mid-infrared wavelength output. In some embodiments, the OPO includes an optical resonator containing a nonlinear crystal, such as periodically-poled lithium niobate. The OPO is pumped by a continuous-wave fiber-laser source having a low-power oscillator and a high-power amplifier, or using just a power oscillator. The fiber oscillator produces a single-frequency output defined by a distributed-feedback (DFB) structure of the fiber. The DFB-fiber-laser output is amplified to a pump level consistent with exceeding an oscillation threshold in the OPO in which only one of two generated waves (“signal” and “idler”) is resonant within the optical cavity. This pump source provides the capability to tune the DFB fiber laser by straining the fiber (using an attached piezoelectric element or by other means) that allows the OPO to be continuously tuned over substantial ranges, enabling rapid, wide continuous tuning of the OPO output frequency or frequencies.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN ACULIGHT CORP
Compact solid-state laser with nonlinear frequency conversion using periodically poled materials
A compact optically-pumped solid-state laser designed for efficient nonlinear intracavity frequency conversion into desired wavelengths using periodically poled nonlinear crystals. These crystals contain dopants such as MgO or ZnO and / or have a specified degree of stoichiometry that ensures high reliability. The laser includes a solid-state gain media chip, such as Nd:YVO4, which also provides polarization control of the laser; and a periodically poled nonlinear crystal chip such as PPMgOLN or PPZnOLT for efficient frequency doubling of the fundamental infrared laser beam into the visible wavelength range. The described designs are especially advantageous for obtaining low-cost green and blue laser sources.
Owner:OOO SPECTRALUS
Novel external cavity CW frequency doubling of semiconductor lasers to generate 300-600nm light
A novel control system for a simple and compact all-solid-state laser generating 300 nm to 600 nm nm light with continuously variable output power in the range from 1 mW to at least 120 mW. Single frequency radiation from an external cavity semiconductor laser is frequency doubled in a periodically poled MgO:LiNbO3 waveguide. The laser maintains a high quality TEM00 circular beam with M2<1.1 and very low noise of less than 0.06% over the entire range of output power. Less than 0.1% peak-to-peak output power variation is measured during prolonged operation. In one example, no degradation of the conversion efficiency is observed for operation at an output power of 70 mW and the laser has a small footprint of only 5×8 cm.
Owner:NEWPORT CORP
Laser light source, image display apparatus, and processing apparatus
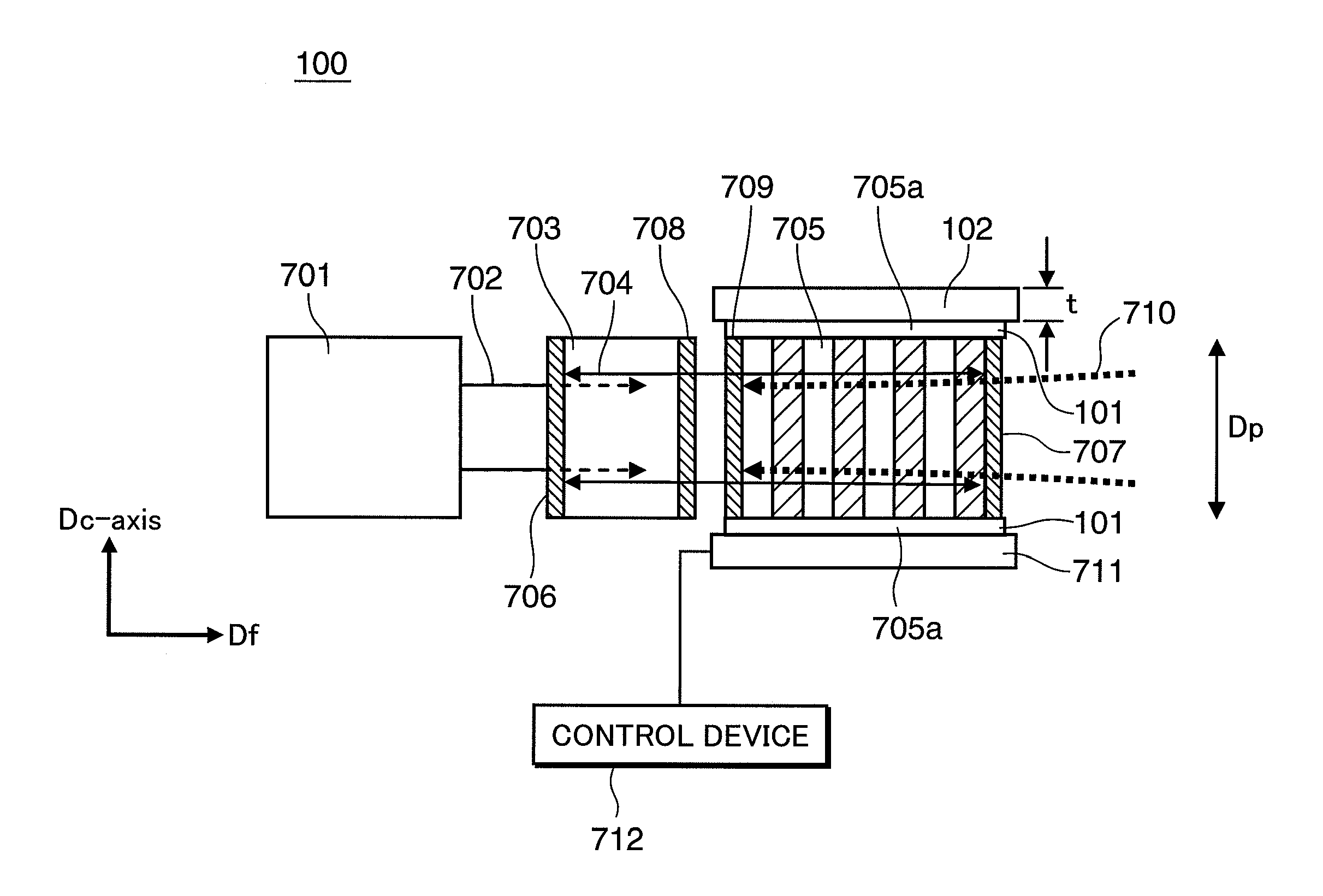
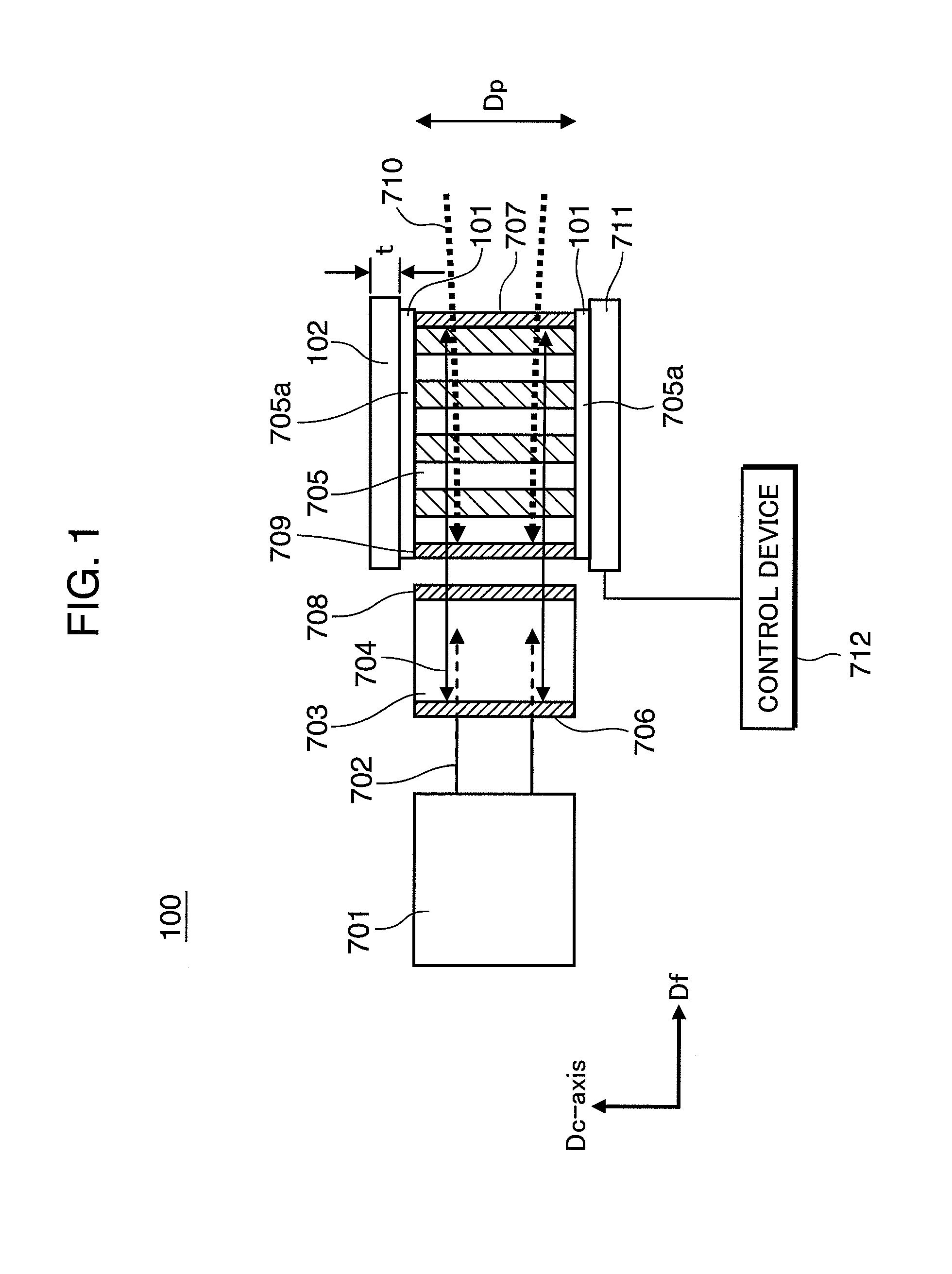
InactiveUS20090257463A1Suppress expansionSuppress contractionLaser detailsLight demodulationInsulation layerLaser light
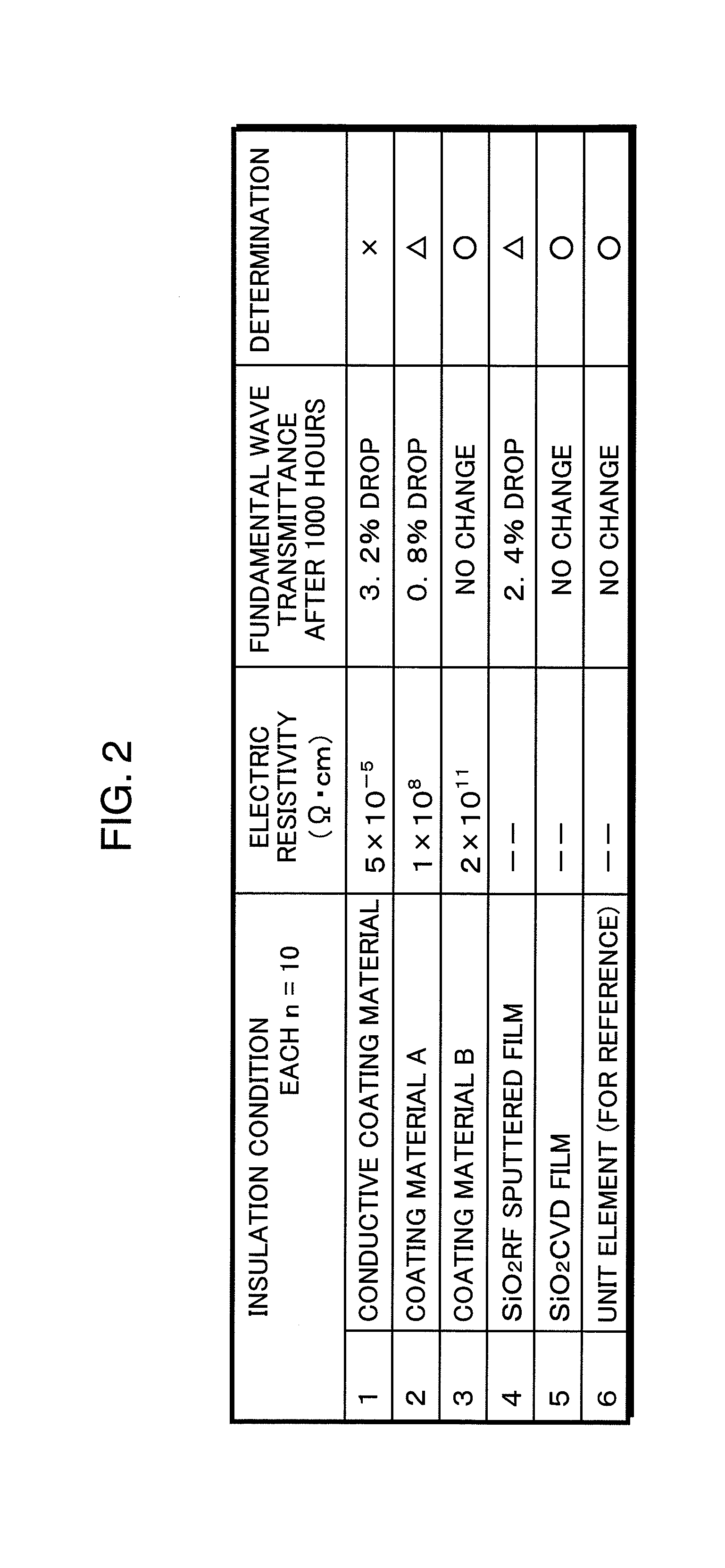
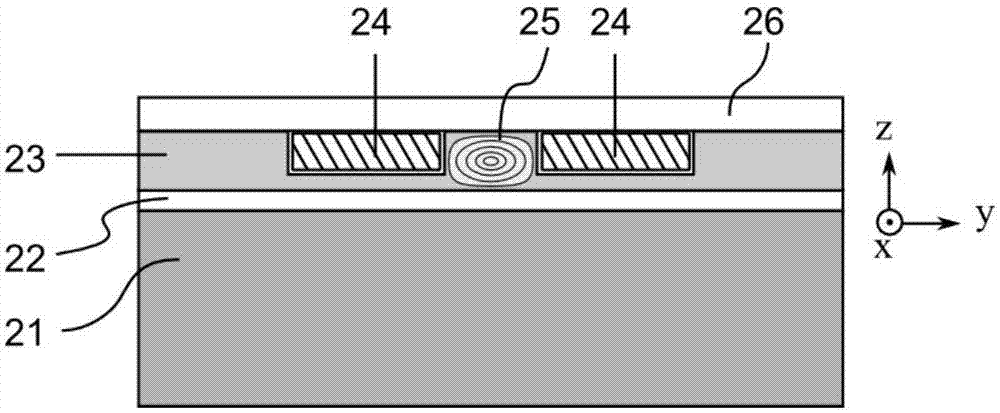
A laser light source includes a fundamental laser generator that generates a fundamental laser light, a wavelength conversion element that is made of a ferroelectric crystal with a periodically poled structure and converts the fundamental laser light to a laser light having a different wavelength, a holding member that holds at least a part of an element surface of the wavelength conversion element that crosses a polarization direction of the periodically poled structure, and an insulation layer that is provided between the holding member and the element surface. Electric resistivity of the insulation layer is 1×108 Ω·cm or higher.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Continuous-wave ultraviolet laser
ActiveUS20080240177A1Increase stability of laserEfficient frequency conversionOptical resonator shape and constructionNon-linear opticsResonant cavityUltraviolet
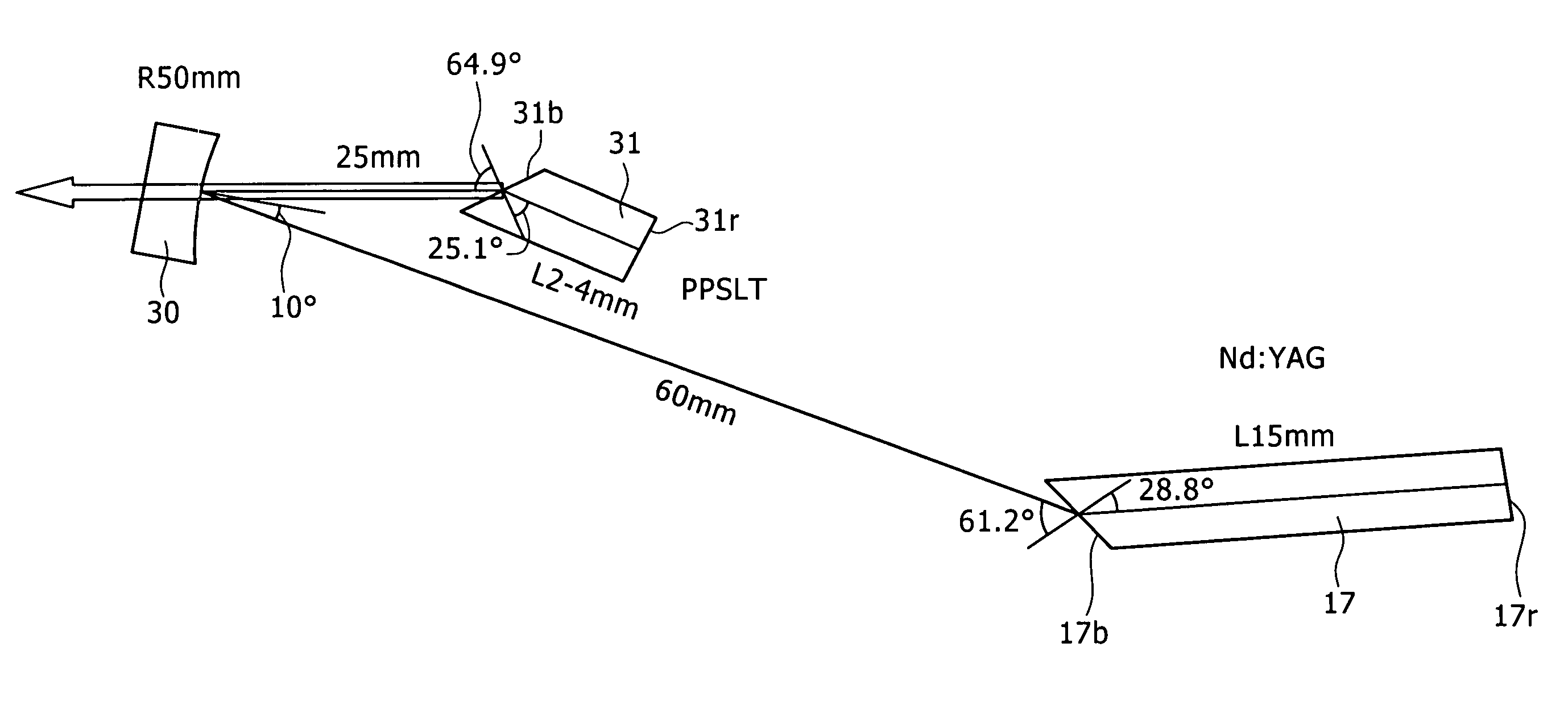
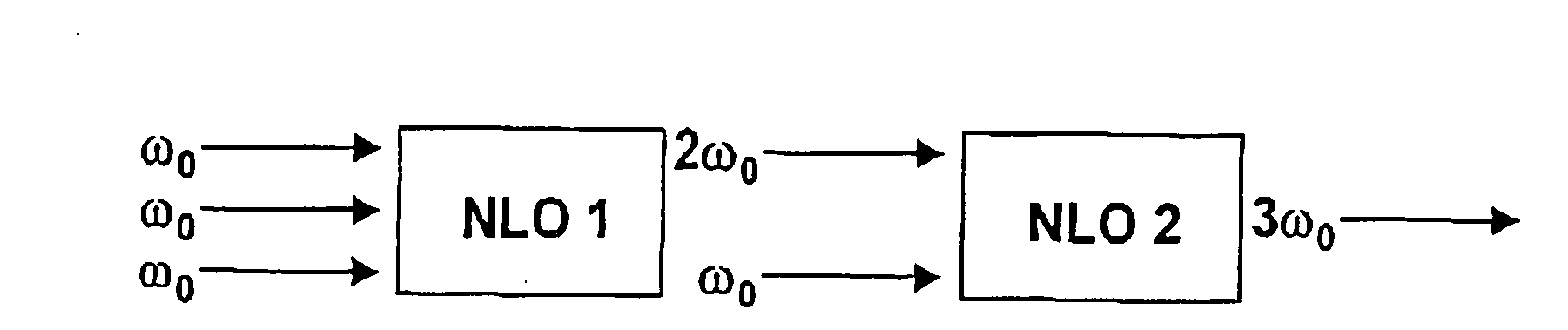
A laser is disclosed, which is suitable for efficient generation of continuous-wave laser light having a wavelength of about 400 nm or less. The short-wavelength light is generated by first frequency-doubling a fundamental wave, and then sum-frequency mixing the frequency-doubled wave and the fundamental wave. The non-linear interactions are effected by means of quasi-phasematching structures inside a resonant cavity where the fundamental wave is circulating. The sum-frequency mixing is effected using second or higher order quasi-phasematching, which allows for wider domains to be inverted for the quasi-phasematching structure compared to first order quasi-phasematching. Preferably, the sum-frequency mixing is effected using periodically poled stoichiometric lithium tantalate (PPSLT) for second or third order quasi-phasematching.
Owner:COBOLT
Wavelength converting device, laser, and method to stabilize the wavelength conversion efficiency
InactiveUS20110043895A1Improve conversion efficiencyMaximize conversion efficiencyLight demodulationNon-linear opticsNonlinear optical crystalElectrical polarity
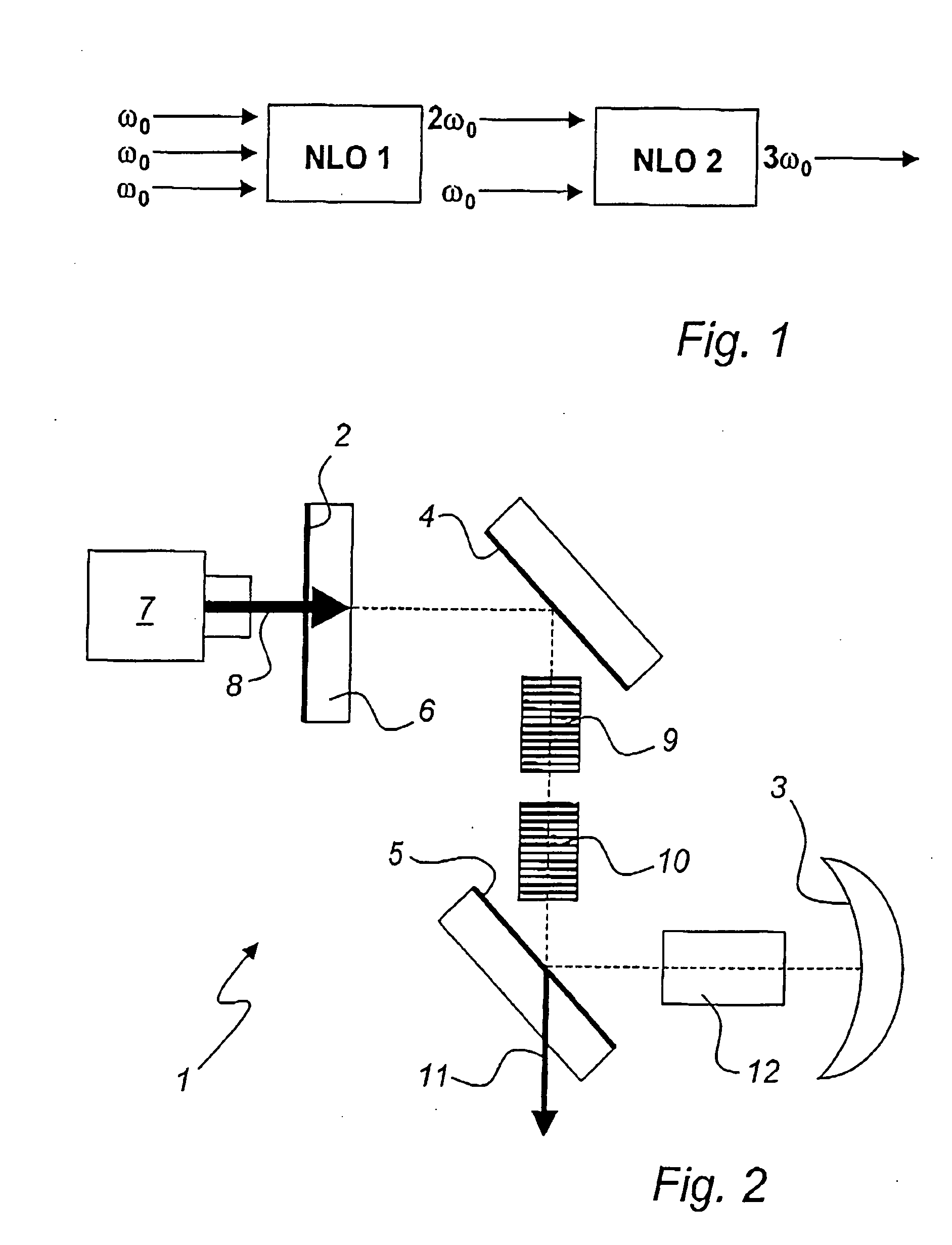
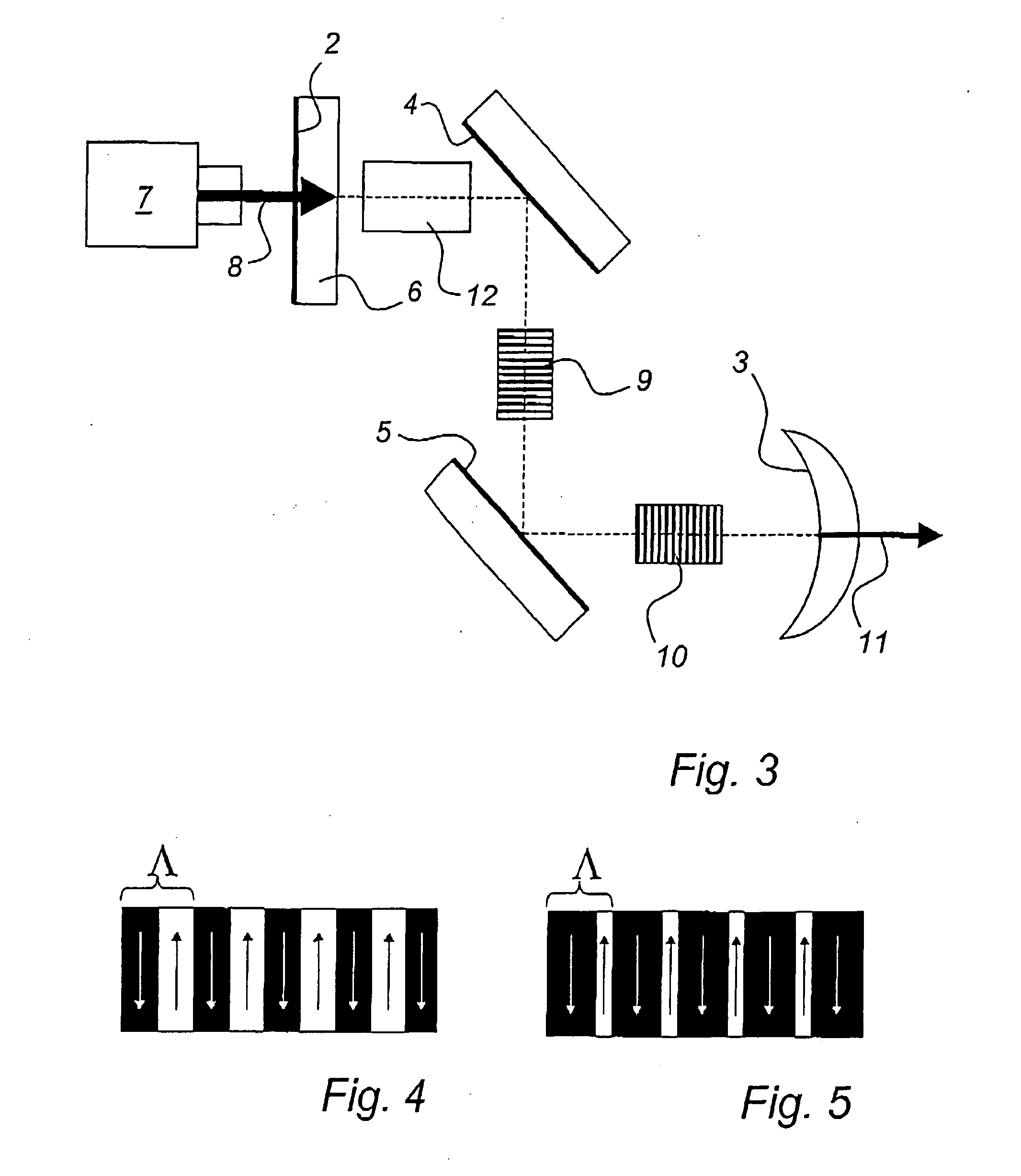
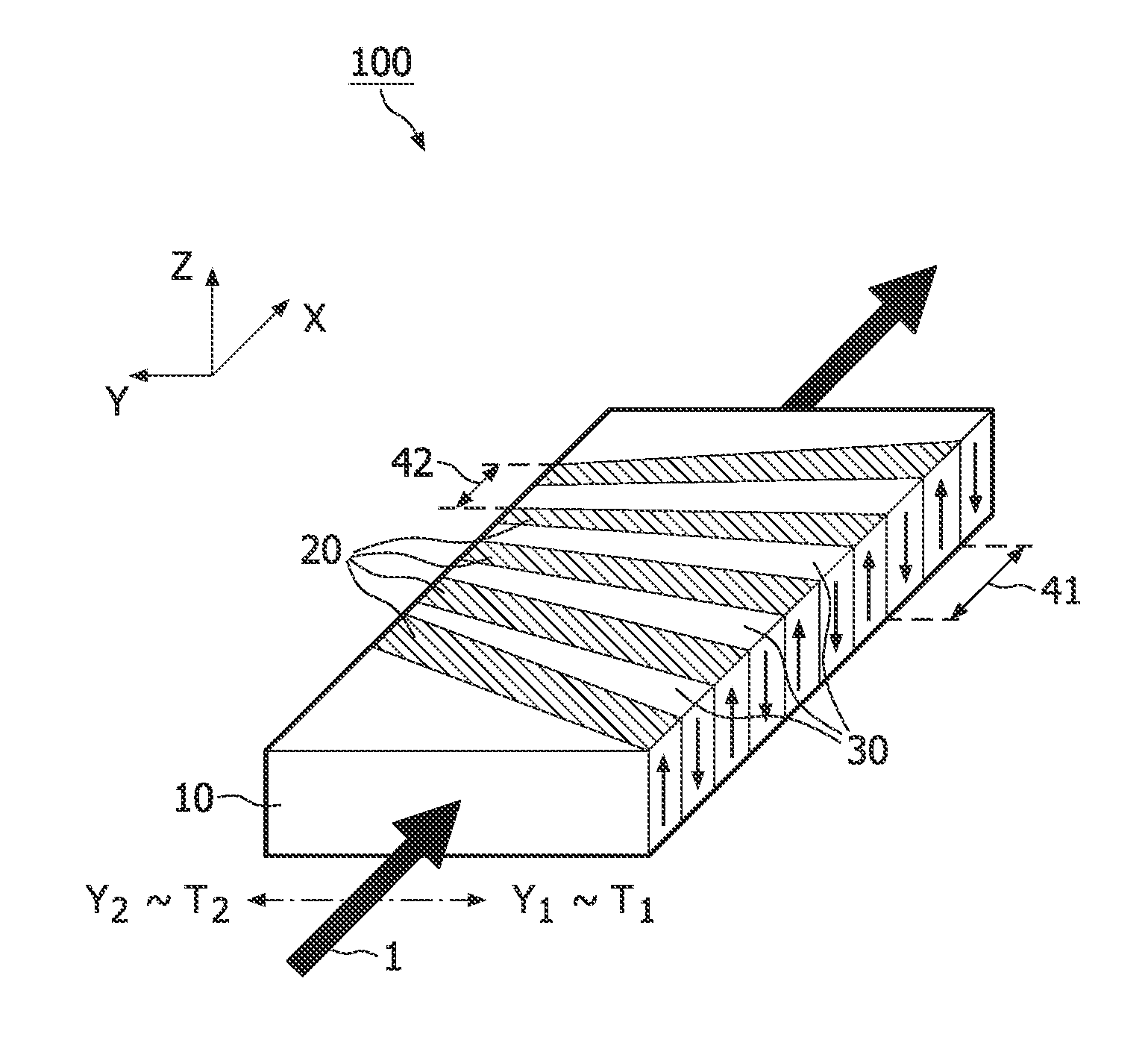
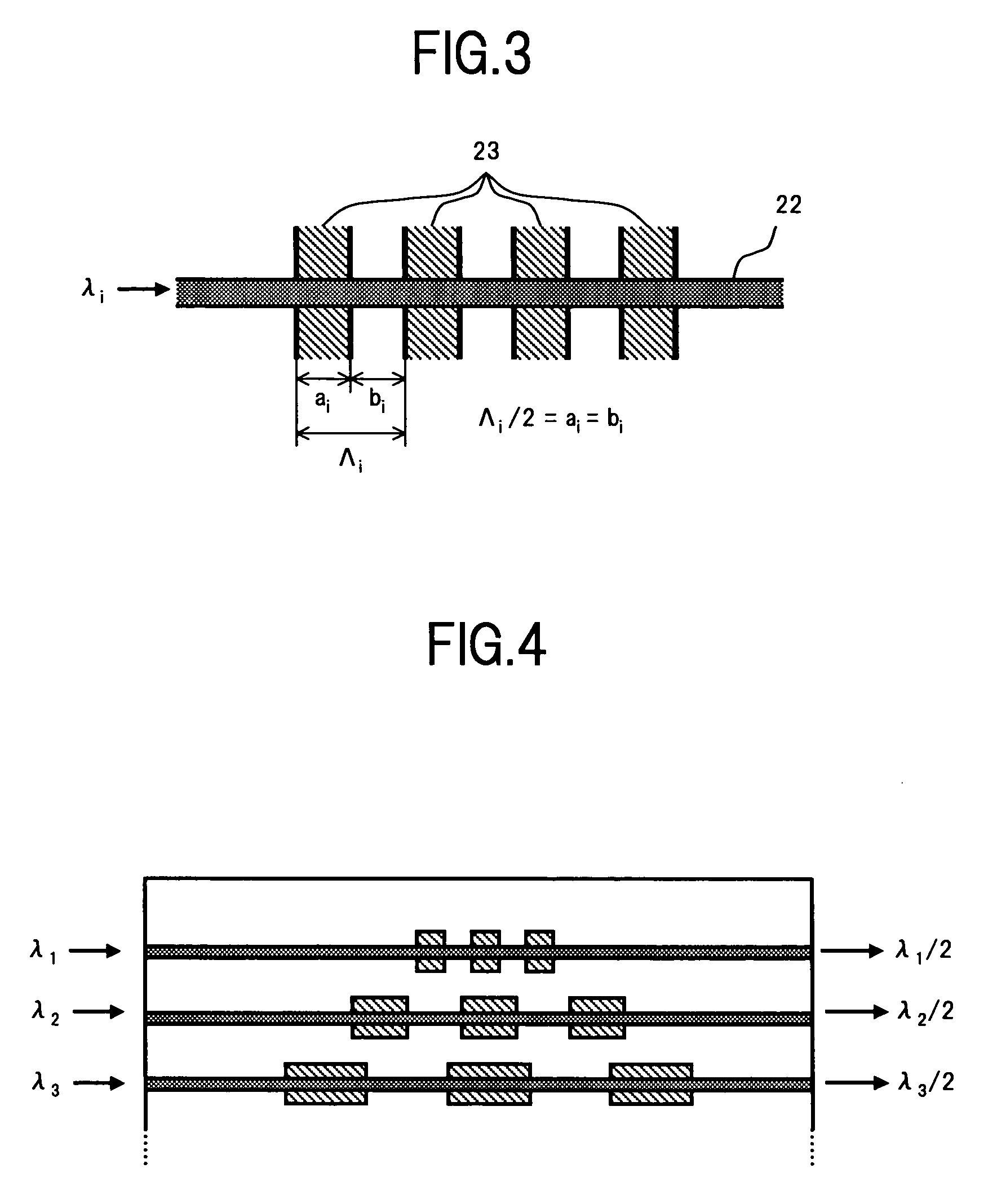
Proposed is a wavelength converting device (100) comprising a non-linear optical crystal (10) having periodically poled regions (20,30) with alternating polarity. The device (100) is characterized in that the period (41,42) of the poled regions along an axis (X) of the device vary in a direction (Y) perpendicular to the axis. The invention is based on the insight that a poling period corresponds to a given temperature. Thus, providing different poling periods along a direction in the wavelength converting device advantageously allows correlating the position of the device along that direction with a temperature.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
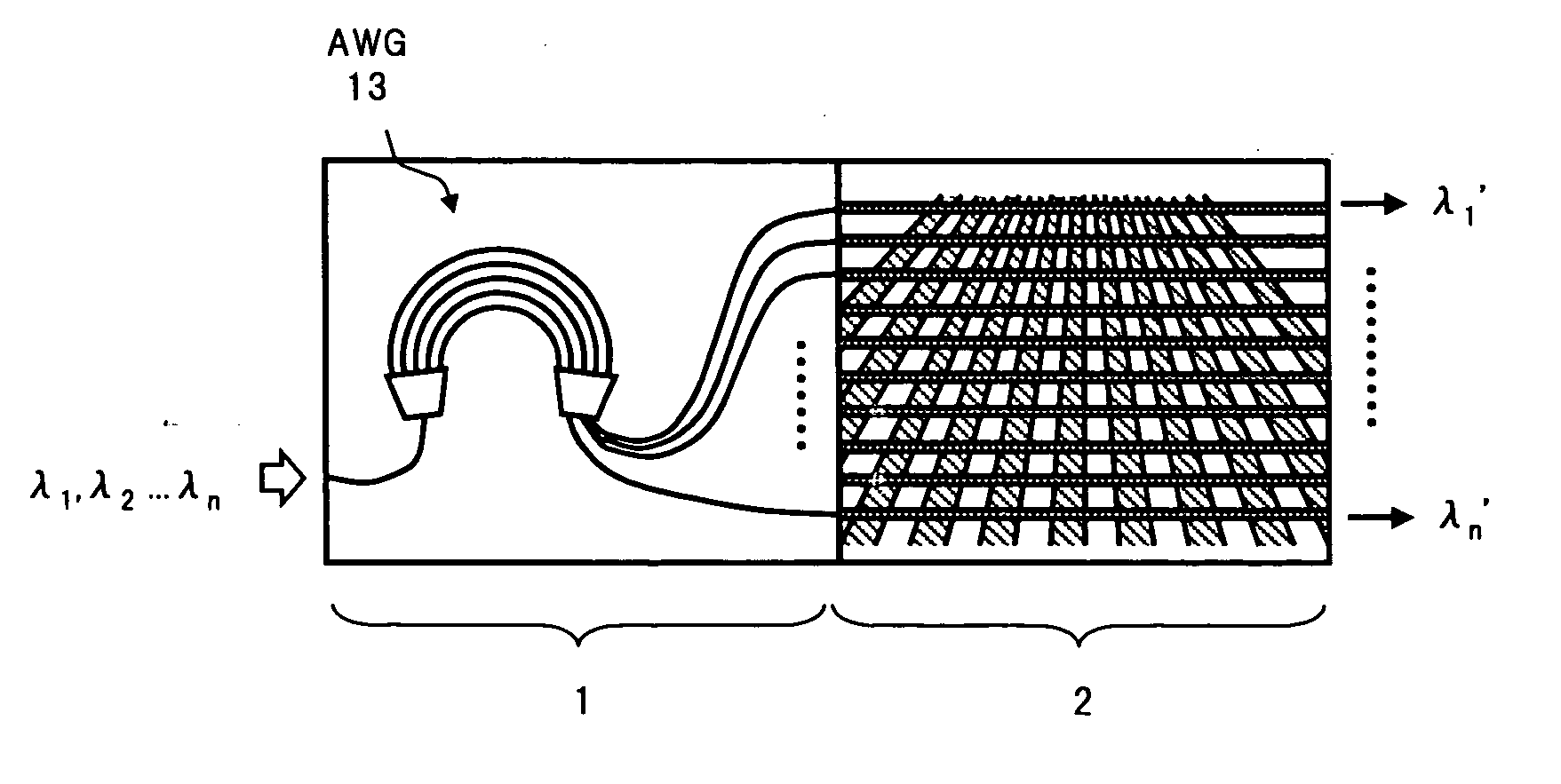
Arrayed wavelength converter
InactiveUS20050191055A1Simple structureHighly efficient wavelength conversionWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesSignal lightLength wave
An arrayed wavelength converter comprises a demultiplexing section that demultiplexes an input WDM signal light to output the demultiplexed lights, and a multiple wavelength conversion waveguide array in which the optical signals of respective wavelengths output from the demultiplexing section are given respectively to a plurality of waveguides formed in parallel on a substrate made of ferroelectric crystal. The multiple wavelength conversion waveguide array has a periodic polarization structure formed by periodically providing polarization inversion regions in which a polarization direction of the substrate is inversed, in a direction approximately perpendicular to a traveling direction of lights being propagated along the respective waveguides, and this is set such that a period of the periodic polarization structure is made different for each waveguide. As a result, it becomes possible to perform wavelength conversion of a plurality of optical signals at high efficiency with a simple structure.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
High repetition rate visible optical parametric oscillator
InactiveUS20070147443A1Increase powerRadiation pyrometryOptical resonator shape and constructionGratingCrystal structure
A tunable coherent light source includes a pump laser for generating a pump beam and an optical parametric oscillator including a crystal exhibiting an output curve for a pump beam of a defined wavelength, the output curve defining wavelengths of signal and idler outputs based on periodically poled grating periods of the crystal. The crystal has a plurality of segments associated with a plurality of grating periods of the output curve, each segment of the plurality of segments having a different crystal structure. At least one of the plurality of segments comprises a crystal structure combining at least two of the grating periods A heating device heats the crystal to an elevated operating temperature and is adjustable for adjusting the output wavelengths of each of the segments.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Polarization method for ferroelectric crystal material
InactiveCN102122105AAchieve reversalSolve the horizontal growth merge problemNon-linear opticsAfter treatmentPulse voltage
The invention relates to the technical field of after treatment on crystal materials, and discloses a polarization method for a ferroelectric crystal material. The method comprises two or more steps for preparing a short-period periodic and quasi-periodic inversion ferroelectric crystal; wherein a first step is used for applying high pulse voltage on the ferroelectric crystal to implement long-period ferroelectric crystal polarization; and a second step is used for polarizing the ferroelectric crystal again based on the first step, if the polarization is multi-step polarization, a third step is used for polarizing the ferroelectric crystal again based on the second step, and the rest is deduced from this, until the needed period is produced. With the method provided by the invention, a uniform short-period periodic polarized ferroelectric crystal body can be produced.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Frequency doubling of semiconductor lasers to generate 300-600 nm light
A novel control system for a simple and compact all-solid-state laser generating 300 nm to 600 nm nm light with continuously variable output power in the range from 1 mW to at least 120 mW. Single frequency radiation from an external cavity semiconductor laser is frequency doubled in, for example, a periodically poled MgO:LiNbO3 ridge waveguide. Our laser maintains a high quality TEM00 circular beam with M2<1.1 and a very low. noise of less than 0.06% over its range of output power. Less than 0.1% peak-to-peak output power variation is seen even during prolonged operation. In one example, no degradation of the conversion efficiency is observed for operation at an output power of 70 mW, and the laser has a small footprint of 5 cm.×8 cm.
Owner:NEWPORT CORP
Non-degenerate polarization-entangled photon pair generation device and non-degenerate polarization-entangled photon pair generation method
InactiveUS8173982B2Increase generationPromote generationSpectrum investigationNanoinformaticsQuantum entanglementSingle crystal
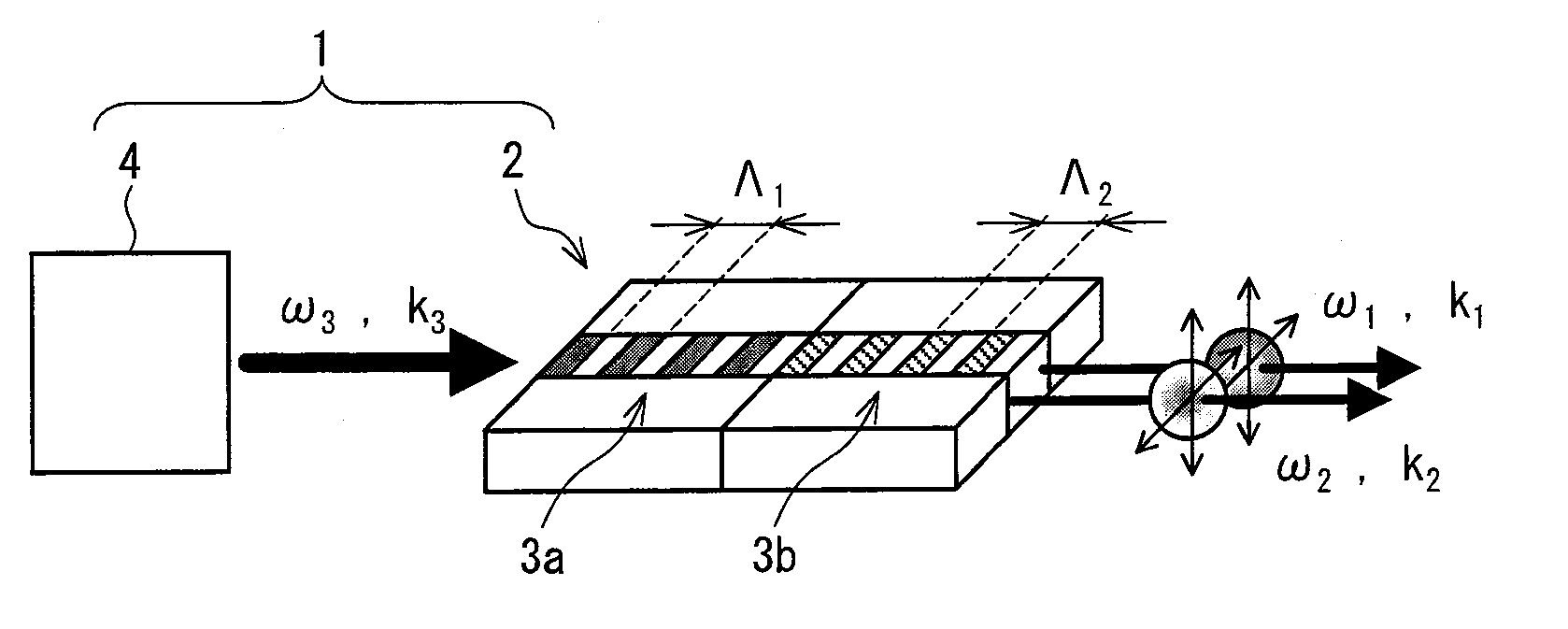
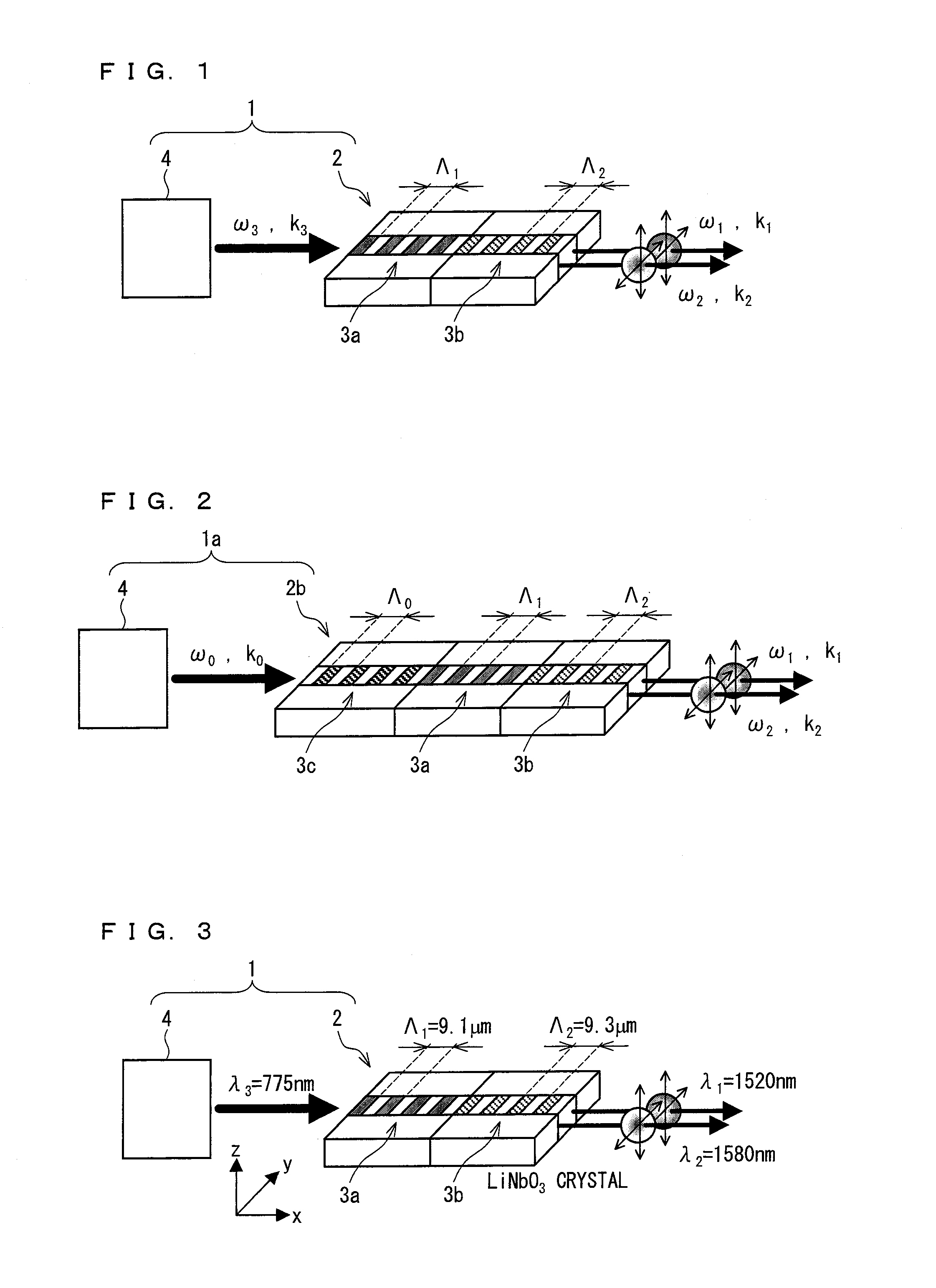
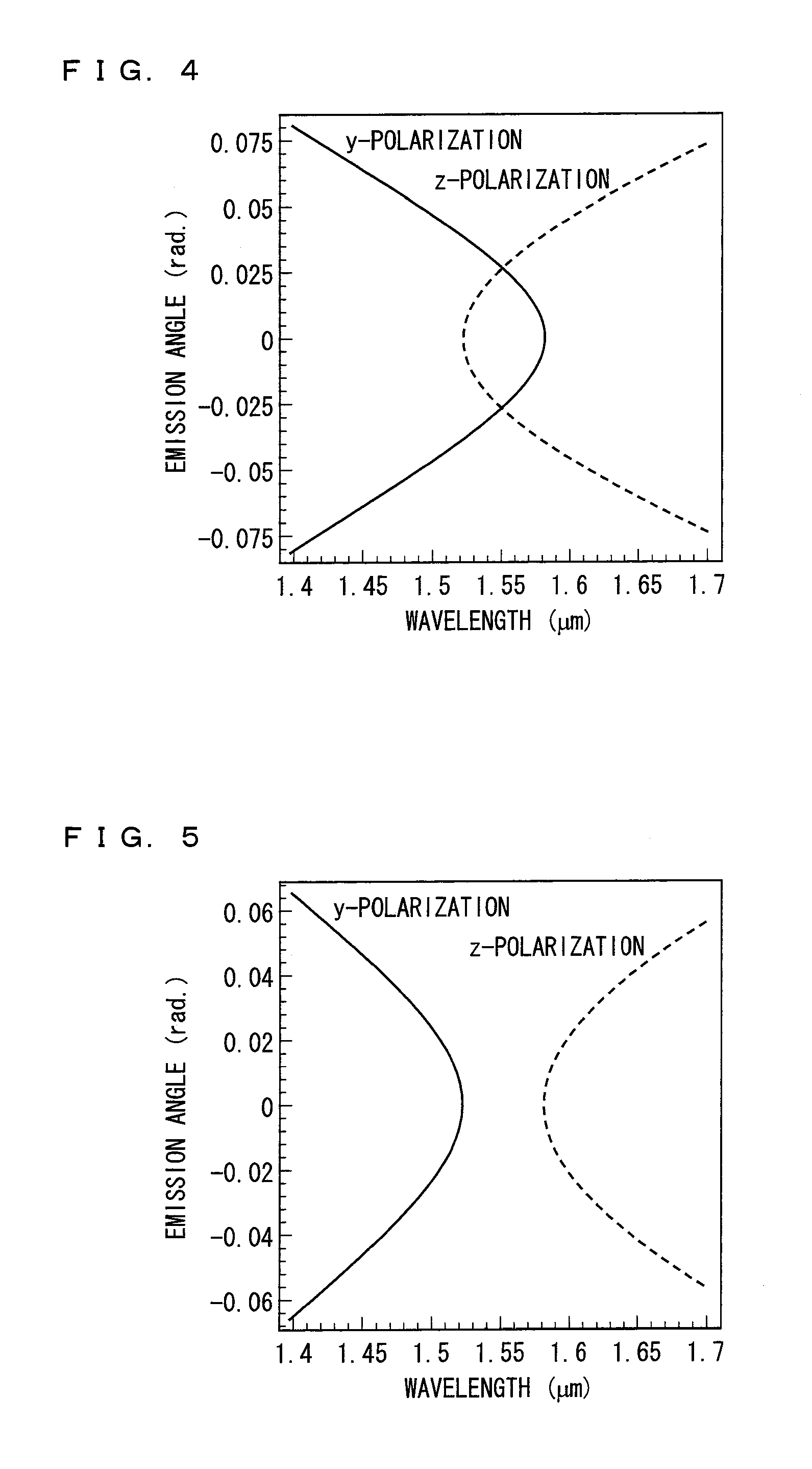
A non-degenerate polarization-entangled photon pair generation device (1) that efficiently and easily generates non-degenerate polarization-entangled photon pairs includes: a quantum-entangled photon pair generator (2) including a single crystal in which periodically poled structures (3a, 3b) having different periods are formed; and a light radiating unit (4) for entering light into the quantum-entangled photon pair generator (2) such that the light passes through the periodically poled structure (3a) and then through the periodically poled structure (3b). A period of the periodically poled structure (3a) is different from a period of the periodically poled structure (3b) such that a parabola indicative of a relation between an emission angle and a wavelength of a polarized photon emitted based on light incident on the periodically poled structure (3a) comes into contact with a parabola indicative of a relation between an emission angle and a wavelength of polarized photon emitted based on light incident on the periodically poled structure (3b), within an allowable range under a phase matching condition.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Electro-optical polarization rotator based on periodically polarized lithium niobate ridge waveguide structure
The invention discloses an electro-optical polarization rotator which comprises a silicon dioxide layer, a lithium niobate crystal film layer and an insulating medium protection layer sequentially arranged on a lithium niobate substrate, wherein a periodic lithium niobate ridge waveguide, a scribed groove and an embedded electrode arranged in the scribed groove are arranged in the lithium niobate crystal film layer; the polarized rotation of input light in the lithium niobate ridge waveguide is realized by applying an electric field in a lateral direction of the lithium niobate ridge waveguide through a transverse electro-optic effect. The electro-optical polarization rotator provided by the invention utilizes a periodically polarized lithium niobate ridge waveguide structure to have advantages of electro-optic control, small volume, low driving voltage, fast response, high polarization precision, integratability, high damage threshold and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Light source for generating an output signal having spaced apart frequencies
InactiveUS7315697B2Different widthGood periodicityWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical code multiplexFrequency spectrumRare earth
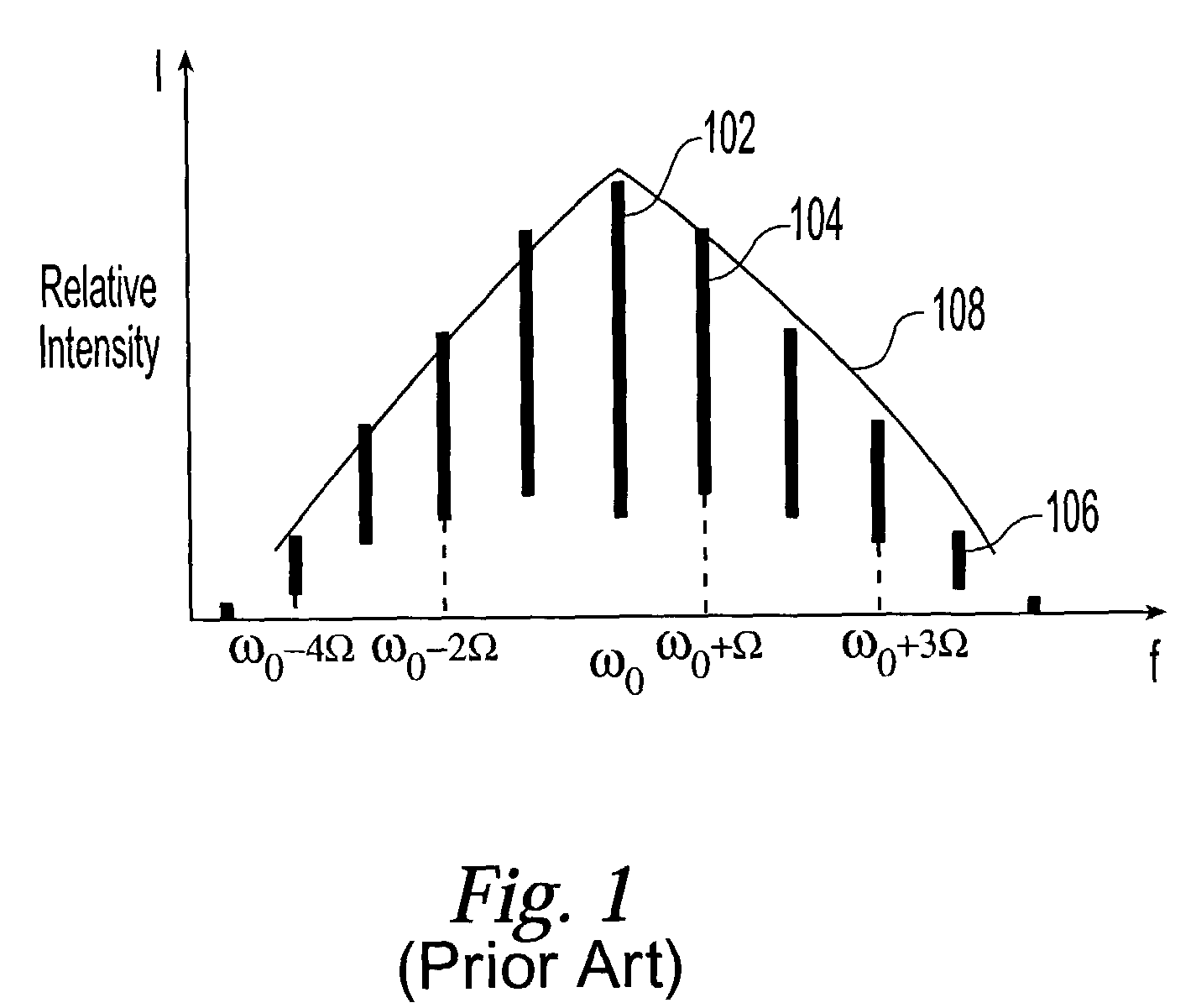
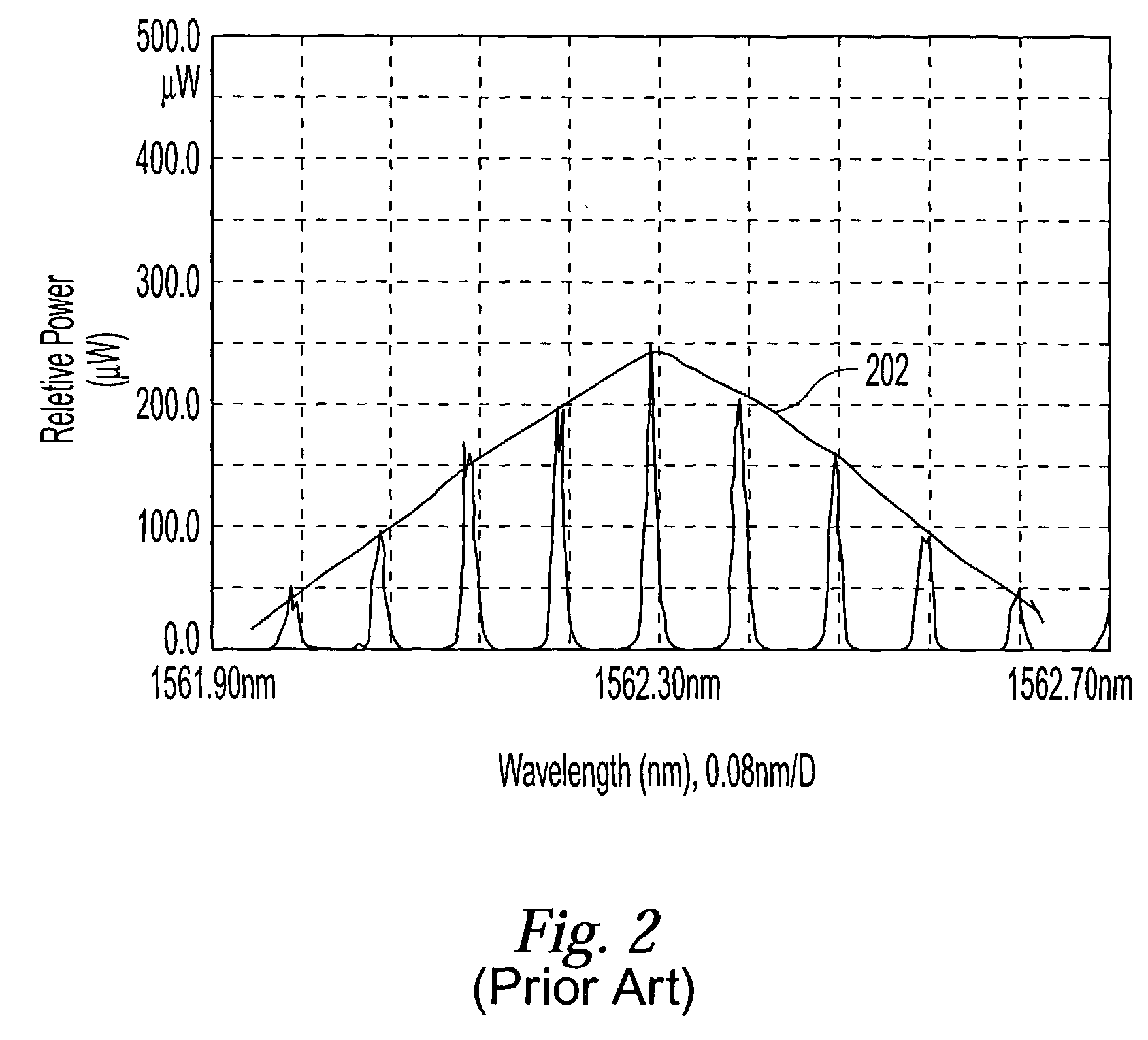
A multiple wavelength light source generates an output signal having a comb of accurately spaced apart frequencies with variable free spectral range in the C-band of optical fiber communication. The light source employs an electro-optical modulator (EOM) driven by a signal generator which modulates with EOM with multiple modulation frequencies to widen the output spectrum of signal. The EOM has a crystal provided with a waveguide. The waveguide may be doped with a rare-earth metal to impart gain properties to equalize the intensities of the comb. In one preferred embodiment, Er, Yt or other doping elements provide the gain property to waveguides. The crystal is also provided with periodically poled structure, and this may be engineered so as to form domains of unequal widths to improve the efficiency of modulation. The output signal from the light source may be split and presented to a bank of filters to create a multiple signals, each signal having one of the spaced apart frequencies. The output signals may be used as channels to be modulated by data and then combined in dense wavelength division multiplexing system, or may be used as a soliton source in time-division multiplexed communication systems.
Owner:CELIGHT
On-chip path-entangled photonic sources based on periodical poling and waveguide circuits in ferroelectric crystals
ActiveUS9274274B1Fast and precise phase controlImprove SPDC efficiencyOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsBeam splittingFerroelectric crystal
A photonic chip based on periodical poling and waveguides circuits in ferroelectric crystals, the method is based on the integration of waveguide circuits, periodical poling and electro-optic modulator (EOM). The chip is illustrated by FIG. 1. The waveguide circuits guide the photons and makes linear operations like the beam splitting, filtering etc. on the photons. The periodical poling enables the efficient spontaneous parametric down conversion (SPDC), resulting the generation of entangled photons. The EOM controls the phase of photons dynamically. The following directional coupler distributes the entangled photons and the quantum interference takes place, resulting different types of path-entangled states by controlling the voltage of EOM insides the chip.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Mobile Charge Induced Periodic Poling and Device
Devices and methods are disclosed for realizing a high quality bulk domain grating structure utilizing mobile charges that are generated by means of photo-excitation in a substrate. An effect of light exposure (UV, visible, or a combination of wavelengths) is to generate photo-induced charges. The application of a voltage across the substrate combined with the application of light exposure causes a photo-induced current to flow through the substrate. The photo-induced charges (behaving like virtual electrode inside the material) and the photo-induced current result in both reduction of the coercive field required for domain inversion in the material and improve realization of the domain inversion pattern, which previously has not been possible at room temperature.
Owner:NECSEL INTPROP
Multiplier enhancing method based on periodically poled lithium niobate
InactiveCN103605248AImprove conversion efficiencyChange cycleNon-linear opticsInformation processingSlow light
The invention provides a multiplier enhancing method based on periodically poled lithium niobate, and belongs to the technical field of optical information processing. The method includes firstly, performing room temperature electric field polarization on lithium niobate crystals, changing the polarization direction of the electric domain in a negative domain region of the +Z face of the crystals, and performing vacuum coating sputter electrode on two Y-directional sides of the crystals; then irradiated the crystals with a normal light and applying voltage of the two Y-directional sides of the lithium niobate crystals through a high voltage source simultaneously, and realizing ordinary light multiplier enhancement through produced slow light effects. According to the method, the quasi-phase matching technique (QPM) is creatively combined with effective light power enhancement resulted from the slow light effects.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com