Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
255results about "Optical code multiplex" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
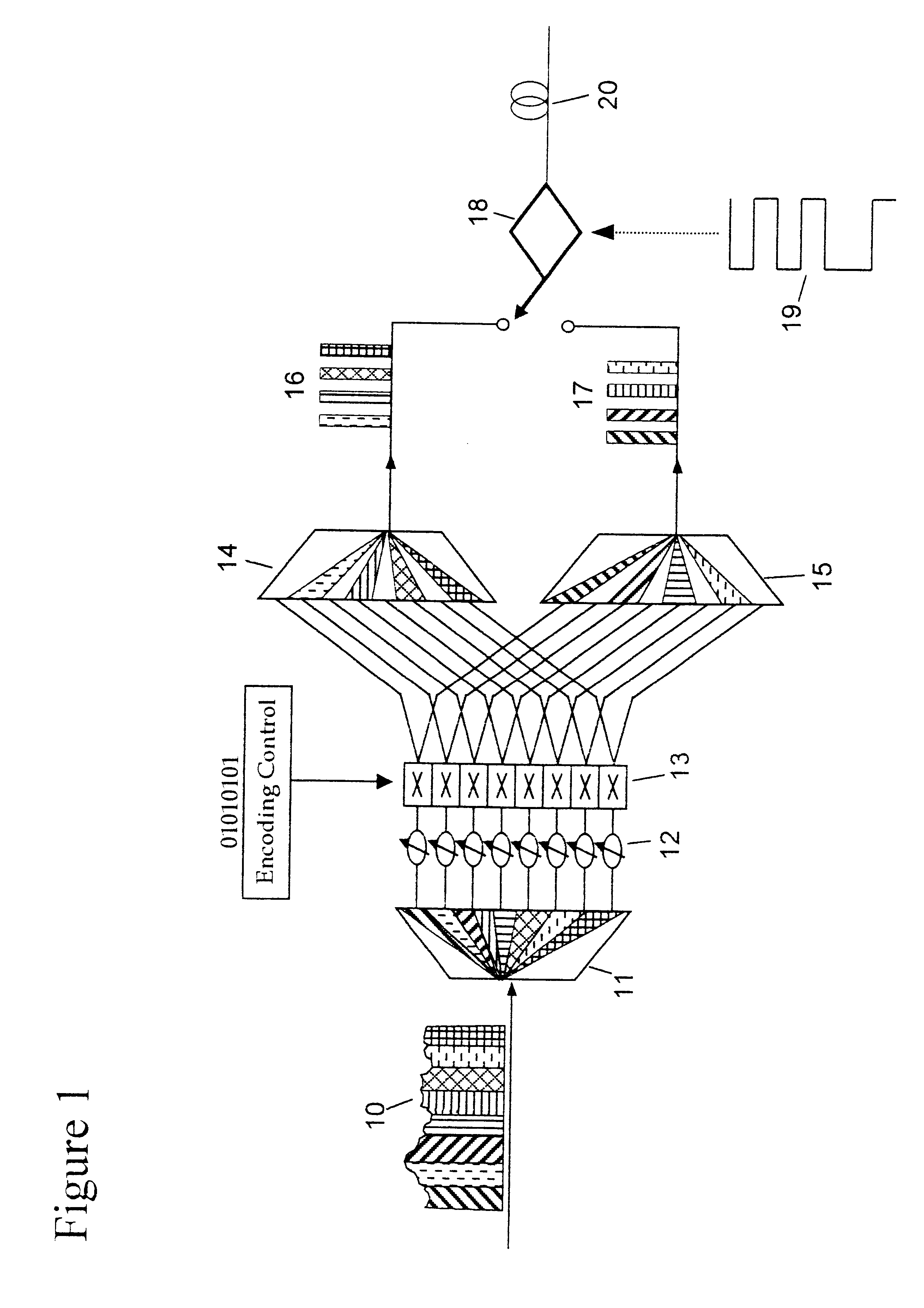
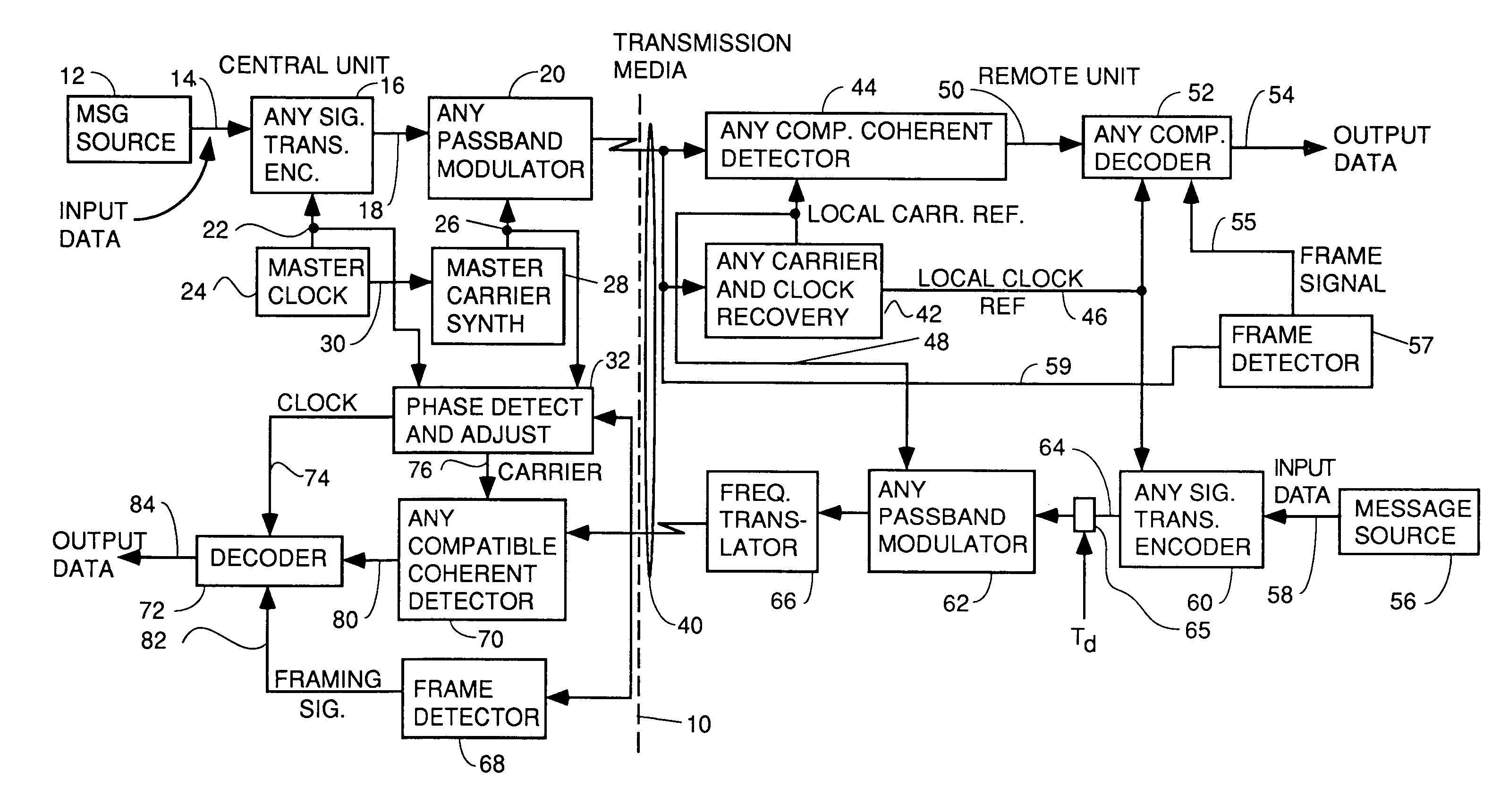
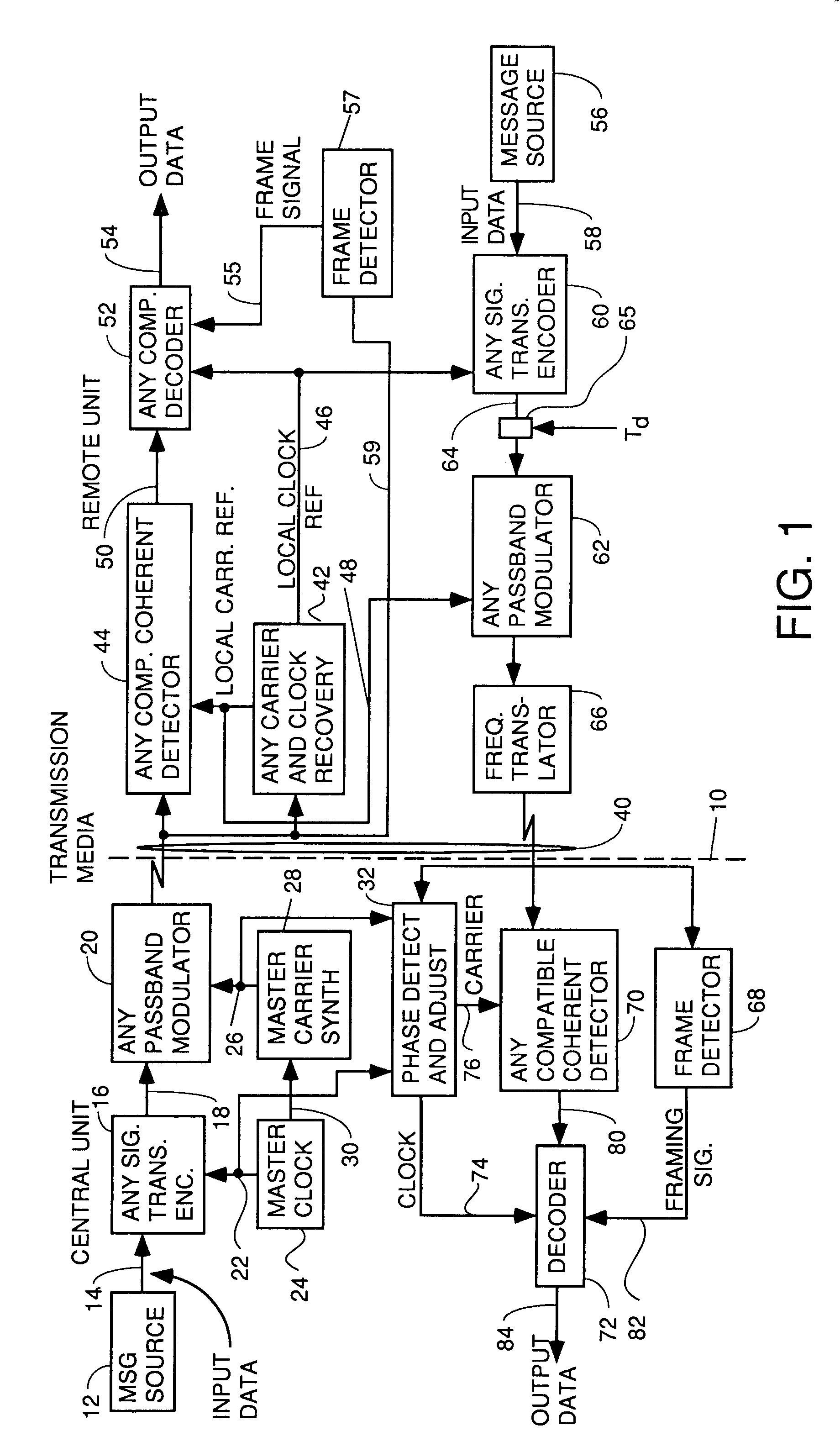
Apparatus and method for trellis encoding data for transmission in digital data transmission systems
InactiveUS6937617B2Sufficient redundancyIncorrect determinationPulse modulation television signal transmissionError preventionDigital dataPhase difference
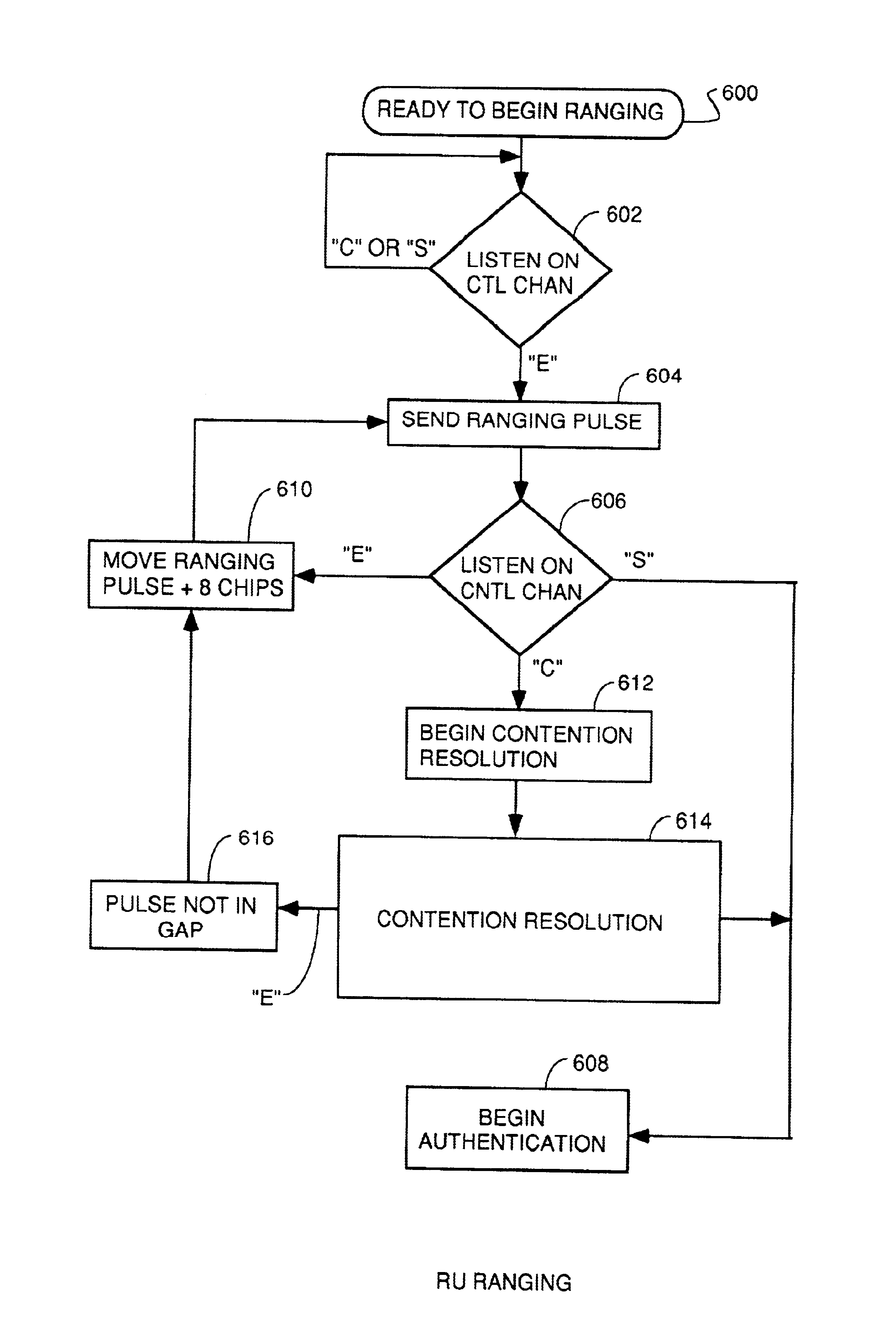
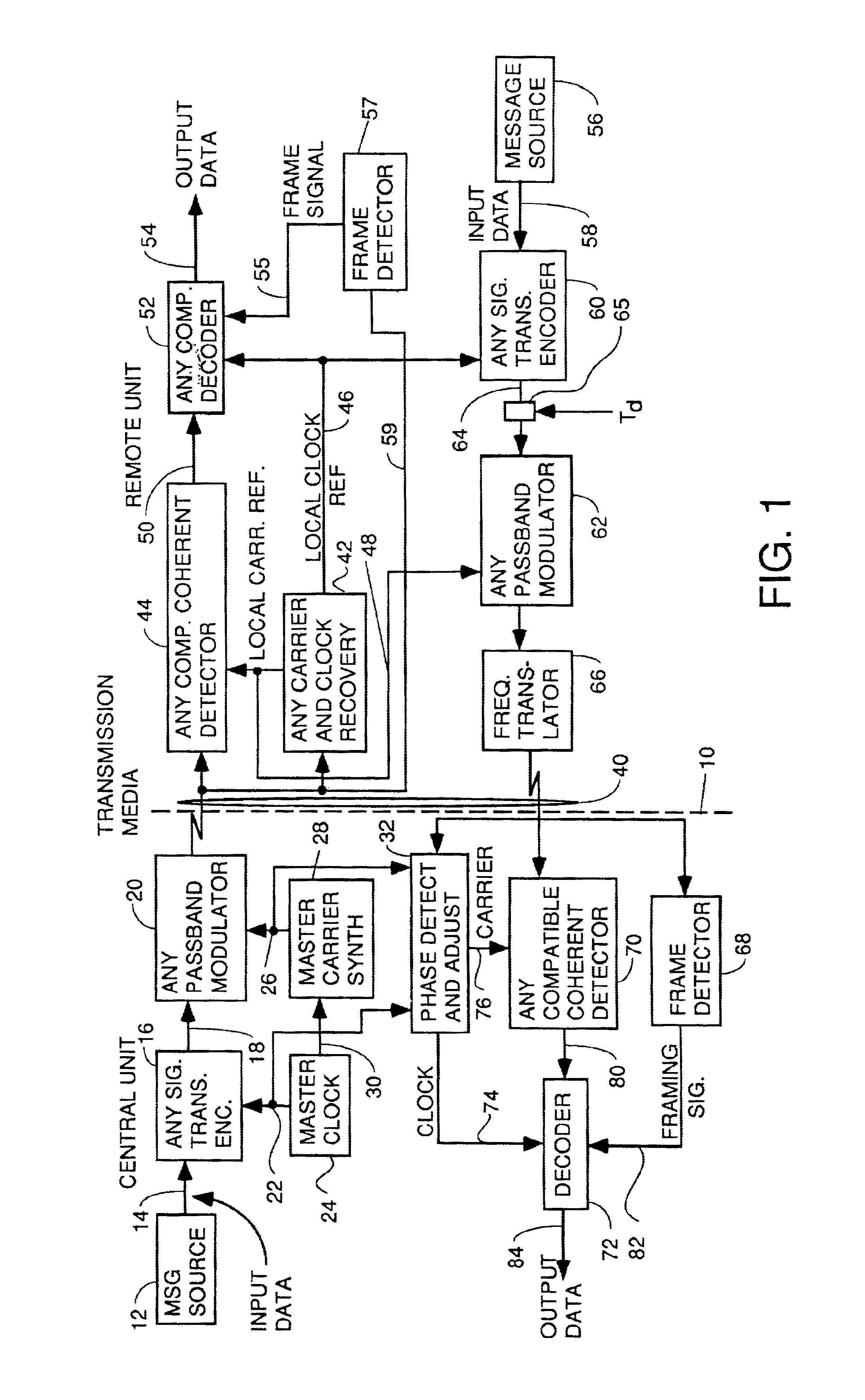
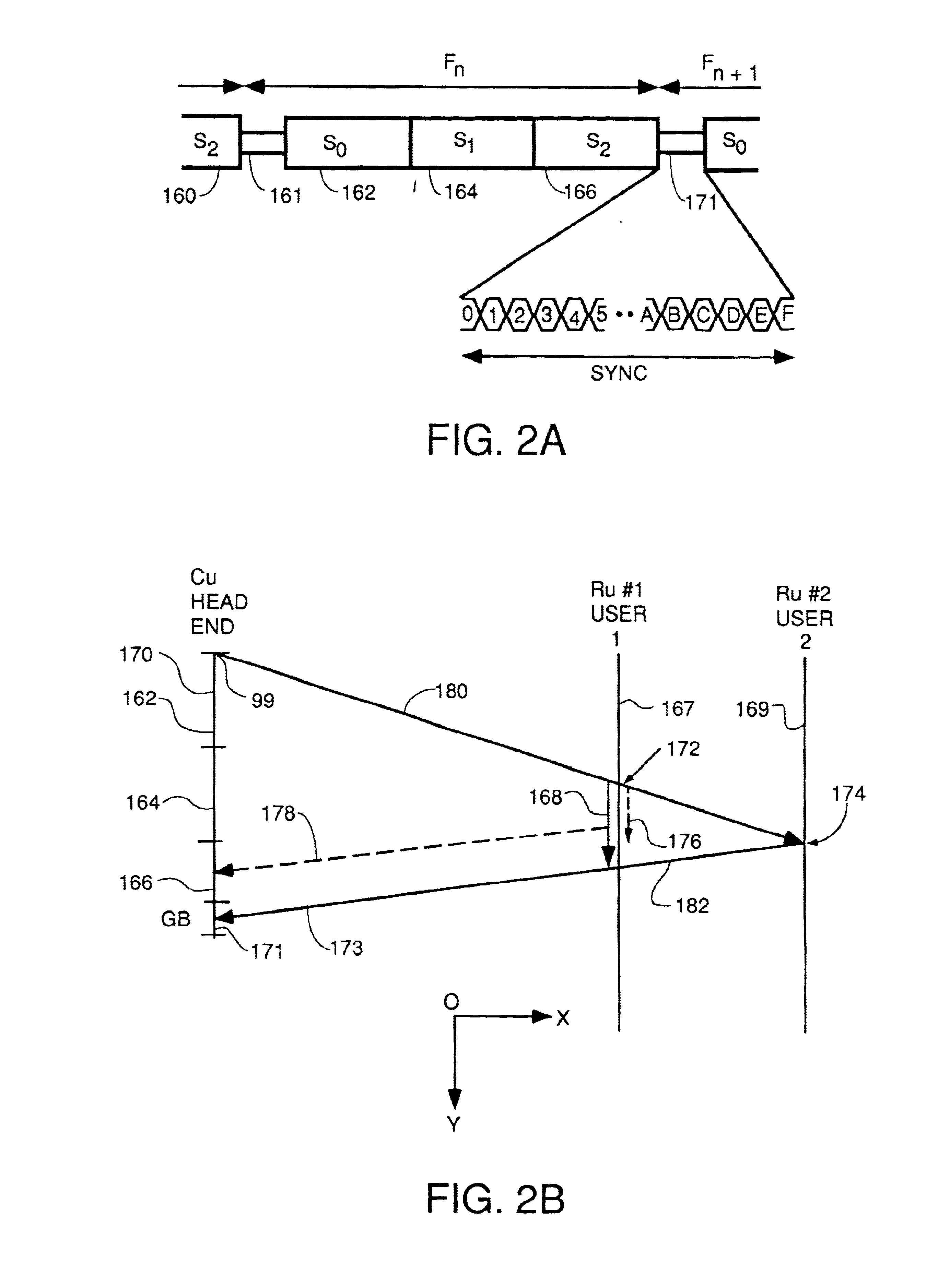
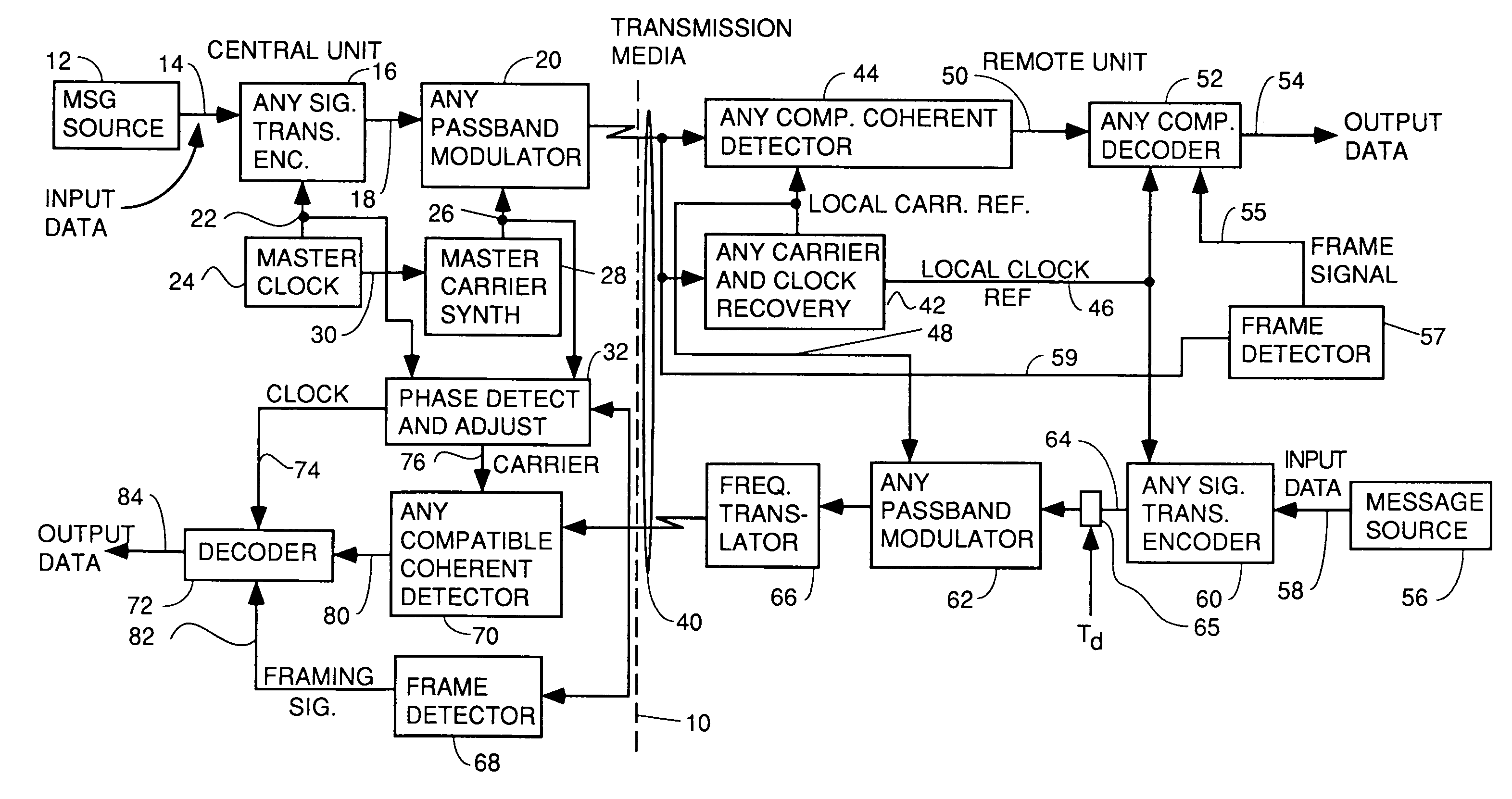
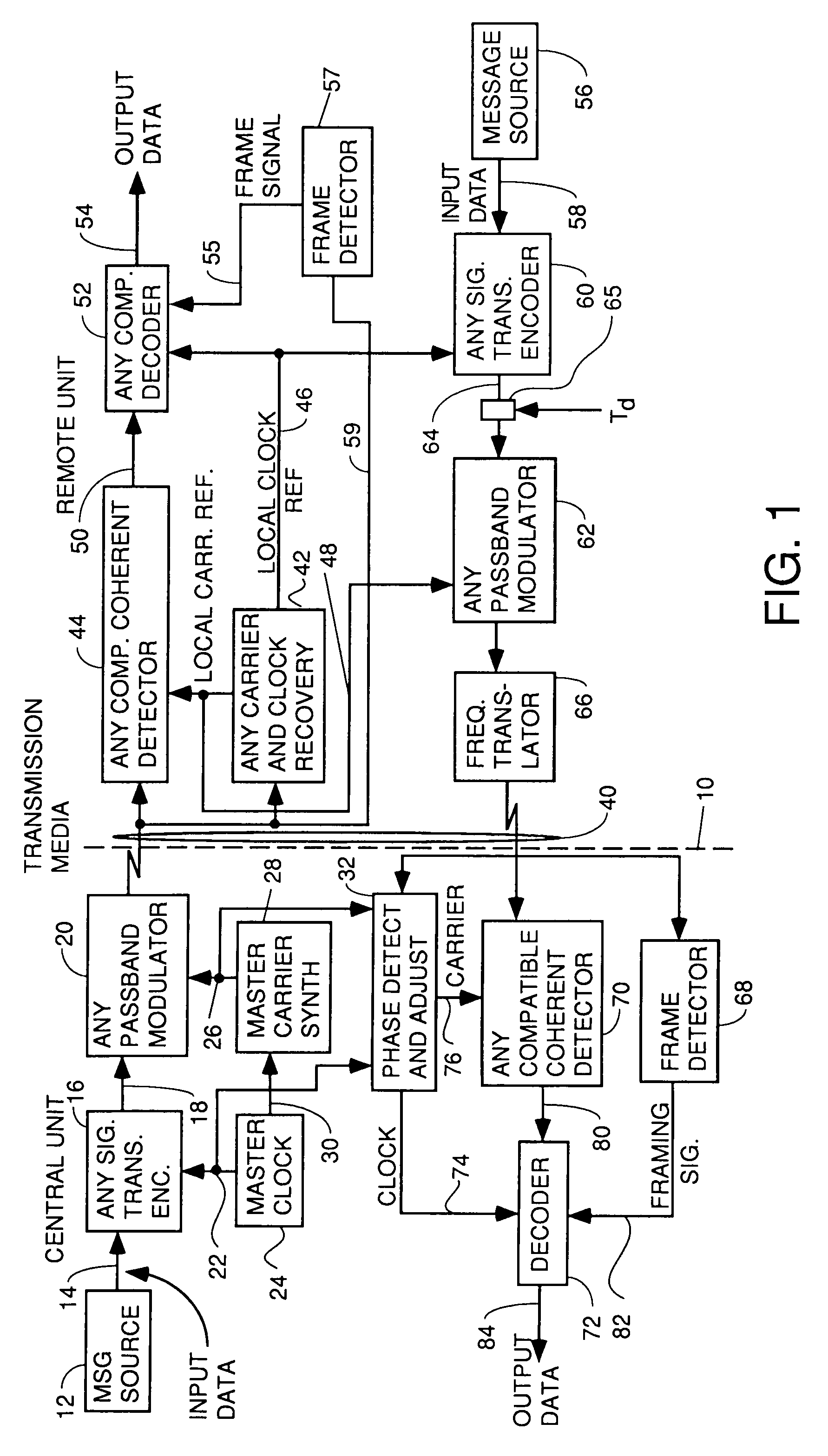
A system for bidirectional communication of digital data between a central unit and a remote unit wherein the need for tracking loops in the central unit has been eliminated. The central unit transmitter generates a master carrier and a master clock signal which are used to transmit downstream data to the remote units. The remote units recover the master carrier and master clock and synchronize local oscillators in each remote unit to these master carrier and master clock signals to generate reference carrier and clock signals for use by the remote unit receiver. These reference carrier and clock signals are also used by the remote unit transmitters to transmit upstream data to the central unit. The central unit receiver detects the phase difference between the reference carrier and clock signals from the remote units periodically and adjusts the phase of the master carrier and master clock signals for use by the central unit receiver to receive the upstream data.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Electro-optical integrated transmitter chip for arbitrary quadrature modulation of optical signals
InactiveUS7272271B2Time-division optical multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsQuadrature modulationEngineering
An optical device includes, a first Mach-Zehnder modulator that produces a first output, and a second Mach-Zehnder modulator which produces a second output. A splitter couples the first and second Mach-Zehnder modulators. A combiner combines the first and second outputs. A phase shifter is coupled to the first and second Mach-Zehnder modulators. The first Mach-Zehnder modulator, second Mach-Zehnder modulator, splitter, combiner and the phase shifter are each formed as part of a single chip made of electro-optical material. Such two similar optical device integrated together with polarization combiner provide a two-polarization performance.
Owner:CELIGHT
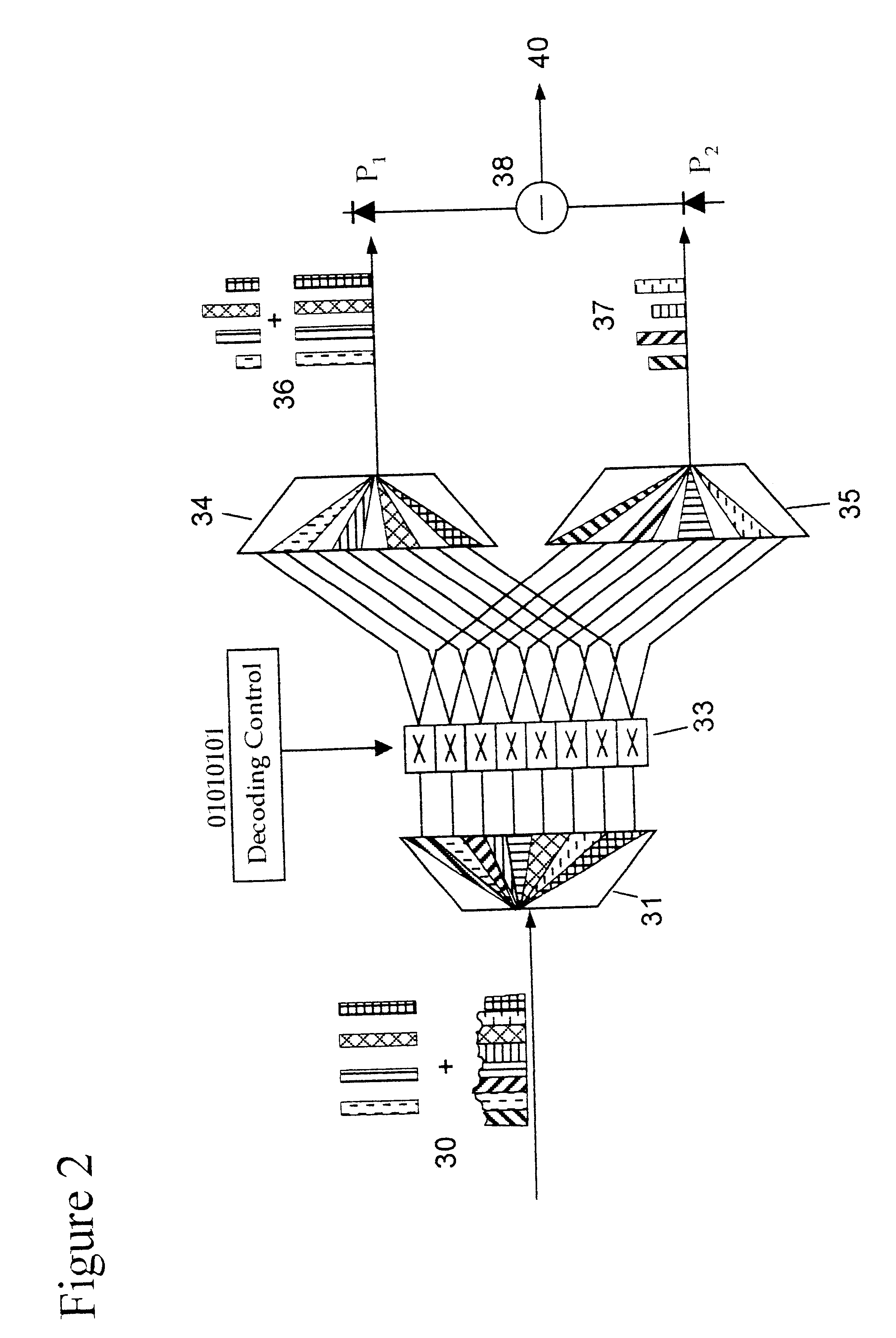
Apparatus and method for trellis encoding data for transmission in digital data transmission systems
InactiveUS7020165B2Improve throughputReduce error ratePulse modulation television signal transmissionError preventionDigital dataPhase difference
A system for bidirectional communication of digital data between a central unit and a remote unit wherein the need for tracking loops in the central unit has been eliminated. The central unit transmitter generates a master carrier and a master clock signal which are used to transmit downstream data to the remote units. The remote units recover the master carrier and master clock and synchronize local oscillators in each remote unit to these master carrier and master clock signals to generate reference carrier and clock signals for use by the remote unit receiver. These reference carrier and clock signals are also used by the remote unit transmitters to transmit upstream data to the central unit. The central unit receiver detects the phase difference between the reference carrier and clock signals from the remote units periodically and adjusts the phase of the master carrier and master clock signals for use by the central unit receiver to receive the upstream data.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
System and method for orthogonal frequency division multiplexed optical communication
InactiveUS7076169B2Eliminating artificial degradationLow costPolarisation multiplex systemsTime-division optical multiplex systemsFiberData stream
A system for optical communication send optical signals over a plurality of wavelength channels. Each wavelength channel comprises a number of orthogonal subchannel frequencies which are spaced apart from one another by a predetermined amount. Each of the subchannel frequencies is modulated with data from a data stream. The data modulation scheme splits a subchannel frequency code into H and V components, and further processes the components prior to modulation with data. The various data-modulated subchannels are then combined into a single channel for transmission. The received signals are detected and demodulated with the help of a symbol timing recovery module which establishes the beginning and end of each symbol. A polarization mode distortion compensation module at the receiver is used to mitigate the effects to polarization more distortion in the fiber.
Owner:CELIGHT
Communication system for dynamically combining power from a plurality of propagation channels in order to improve power levels of transmitted signals without affecting receiver and propagation segments
ActiveUS8111646B1Increase power levelMultiple-port networksModulated-carrier systemsMultiplexingCommunications system
The present invention relates to a communication system and method that allows a transmitter segment (ground end of uplink segment) to dynamically combine power from plurality of propagation channels (transponders) in order to improve power levels of signals being transmitted, without affecting the receiver segment (user end of downlink segment) and the propagation segment (space segment), and without modifying the configuration of the propagation apparatus (satellite). Specifically, the transmitter segment generates mixtures of input signals by using Wavefront-Multiplexing and transmits the wavefront-multiplexed (WFM) signals through propagation channels to a receiver segment that coherently separates the mixtures of received WFM signals by using adaptive equalization and Wavefront-De-Multiplexing. The WFM signal mixtures allow an operator, or automated system, at the transmitter segment to dynamically allocate equivalent channel (transponder) powers according to continuously changing market demands by dynamically including change of relative input powers into ratios of the WFM signal mixtures being transmitted.
Owner:SPATIAL DIGITAL SYST
Code-switched optical networks
InactiveUS6865344B1Analogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsCommunications systemNetwork communication
Communication systems and methods are disclosed that route, detect, and decode encoded optical signals at network nodes based on channel codes assigned to the network nodes. In an example communication system, a network hub includes a channel selector that encodes an optical signal with a channel code assigned to one or more network nodes. The channel selector is configured to encode based on a channel selection signal provided to the channel selector and can include one or more fiber Bragg coders. Code-switched communication systems can include one or more nodes configured in ring, tree, or bus architectures.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Coherent power combining for signals through multiple satellite communications channels
ActiveUS8547897B2Increase power levelMultiple-port networksModulated-carrier systemsMultiplexingCommunications system
A communication system and method that allows a transmitter segment (ground end of uplink segment) to dynamically combine power from a plurality of propagation channels (transponders) to improve power levels of signals being transmitted, without affecting the receiver segment (user end of downlink segment) and the propagation segment (space segment), and without modifying propagation apparatus configurations (satellite). Specifically, the transmitter segment generates mixtures of input signals by using Wavefront-Multiplexing and transmits wavefront-multiplexed (WFM) signals through propagation channels to a receiver segment that coherently separates the mixtures of received WFM signals by using adaptive equalization and Wavefront-De-Multiplexing. The WFM signal mixtures allow an operator, or automated system, at the transmitter segment to dynamically allocate equivalent channel (transponder) powers according to continuously changing market demands by dynamically including change of relative input powers into ratios of the WFM signal mixtures being transmitted.
Owner:CHANG DONALD C D
Optical CDMA system using sub-band coding
InactiveUS6236483B1Polarisation multiplex systemsTime-division optical multiplex systemsOptical cdmaCommunications system
An optical fiber communications system using spread spectrum code division multiple access techniques to achieve better bandwidth utilization. A transmitting user in the system encodes the optical signal using a first coding mask, and a receiving user decodes the received signal using two decoding masks, all of the masks having lengths N. The first mask is divided into two sections of lengths N / 2 each, one of the sections defining a first sub-code of length N / 2, while the other section blocks light. Each of the second and third masks is also divided into two sections, which correspond to the two sections of the first mask. The section of the second mask corresponding to the coded section of the first mask has a second code that is identical to the first code, and the section of the second mask corresponding to the blocked section of the first mask is also blocked. The section of the third mask corresponding to coded section of the first mask has a third code that is complementary to the first code, and the section of the third mask corresponding to the blocked section of the first mask is also blocked. Some users on the system have masks in which the first of the two sections are blocked and the second of the two sections are coded, while other users have masks in which the second of the two sections are blocked and the first of the two sections are coded. The first codes used to code the encoding masks are selected from a set of unipolar codes that are derived from a set of balanced bipolar orthogonal codes.
Owner:CODESTREAM TECH CORP
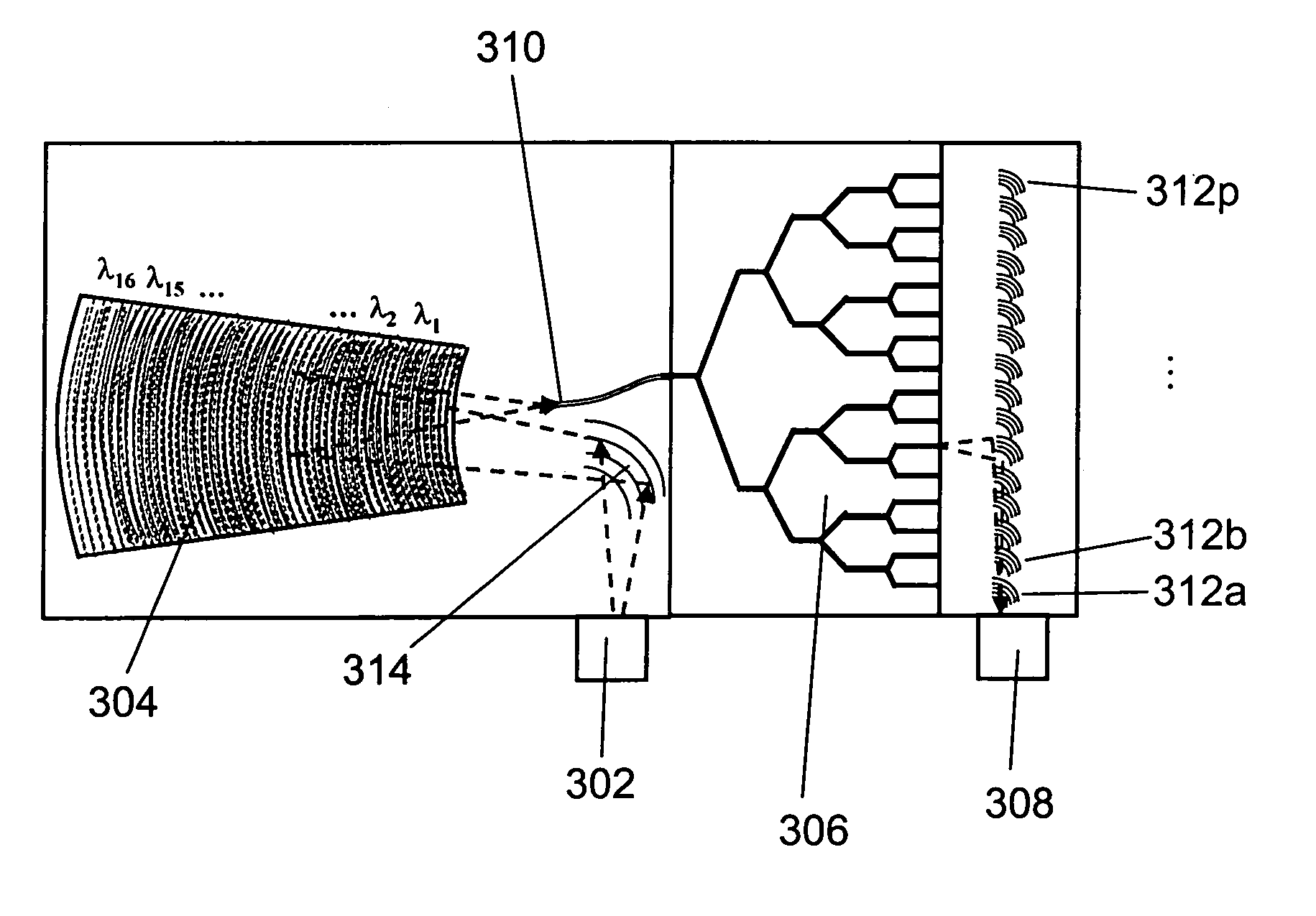
Integrated spectral encoder/decoder for optical CDMA communication system
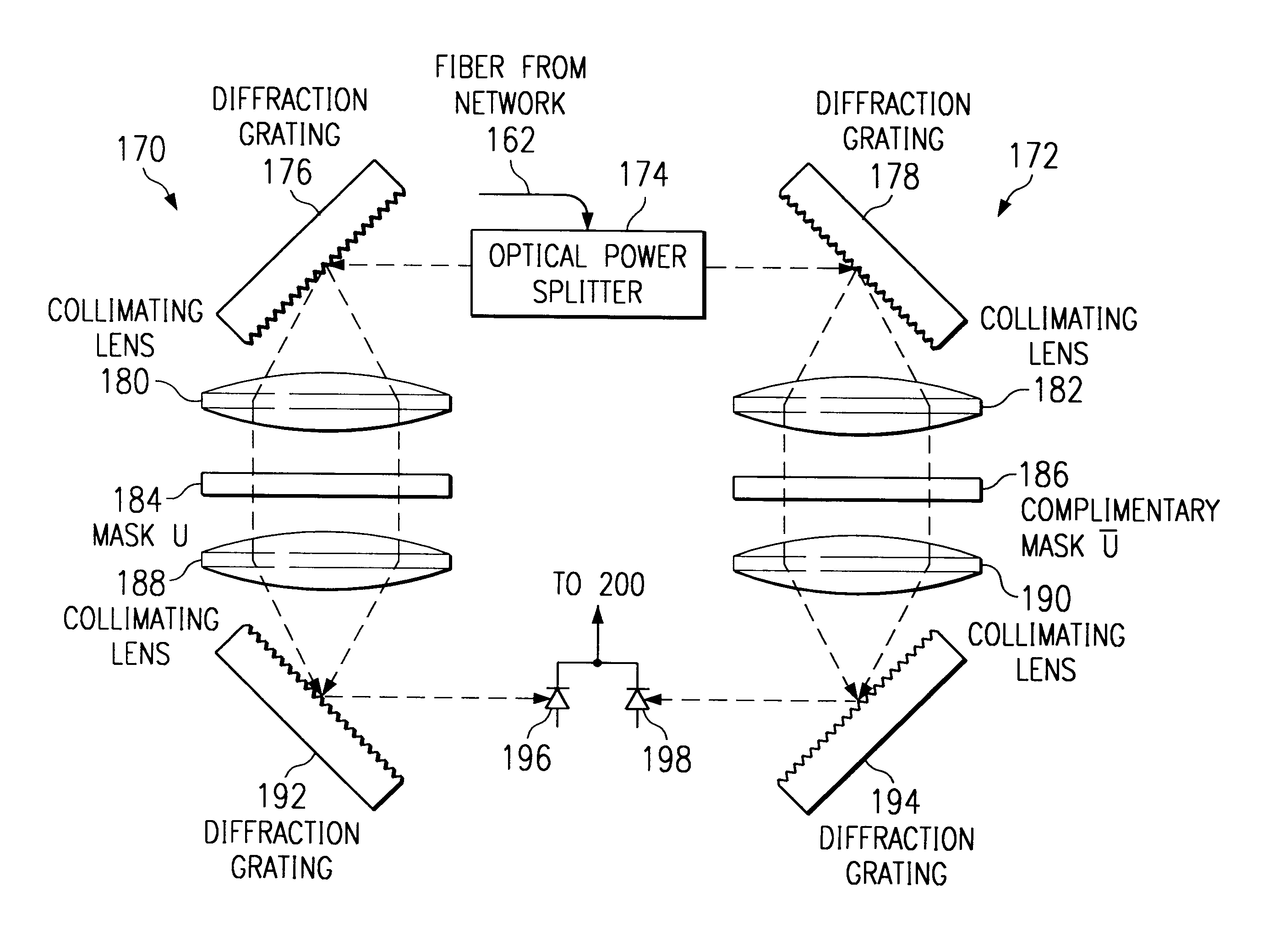
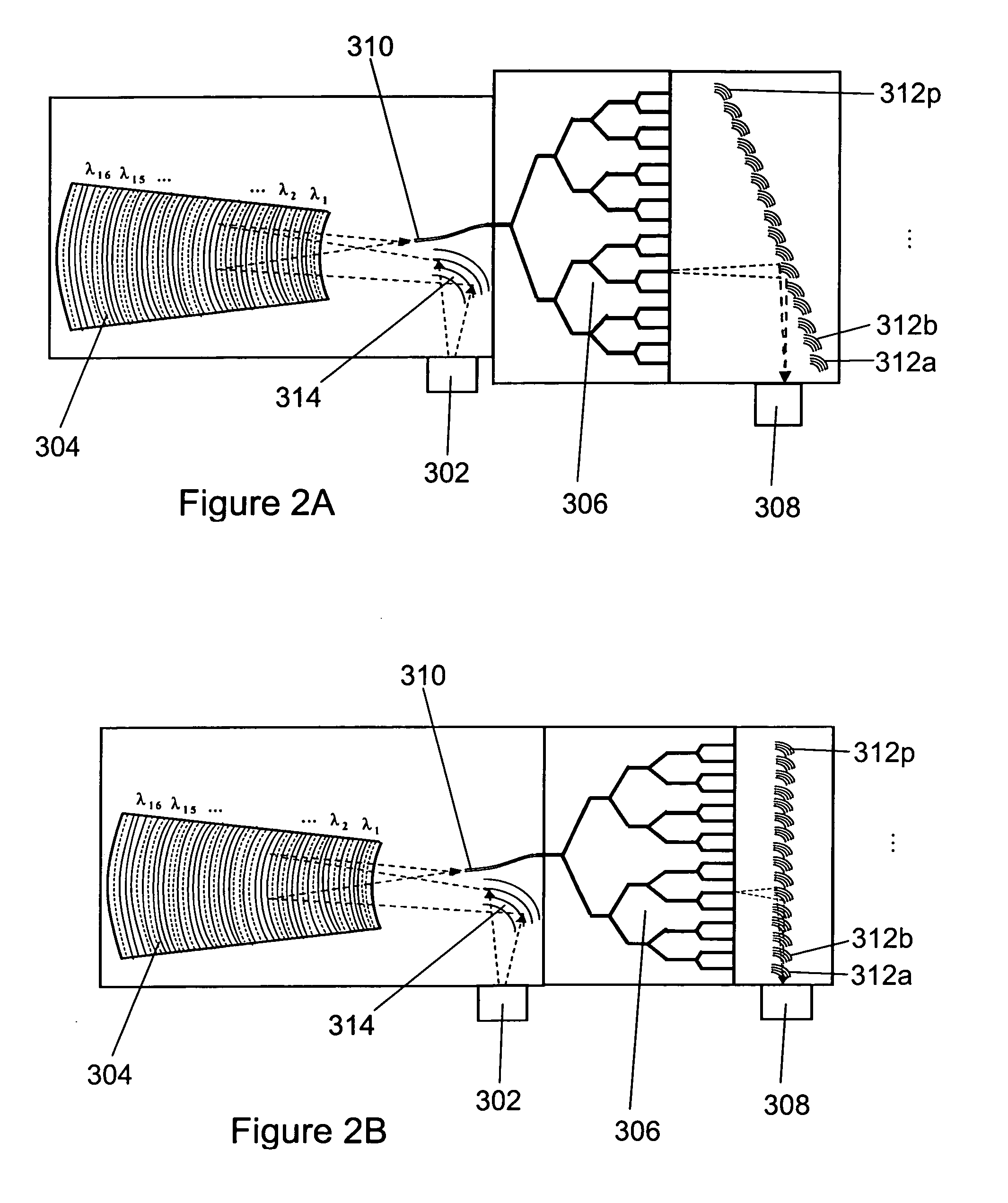
InactiveUS6807372B1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical code multiplexOptical cdmaMach–Zehnder interferometer
The encoder / decoder design for spectrum-encoded optical CDMA systems uses waveguide circuits monolithically integrated on one chip to fulfill essential encoding and decoding functions. The integrated device functions as a 1x2 wavelength selective Mach-Zehnder interferometer switch to encode the input broadband light source and to decode the transmitted spectrally encoded signals. The device comprises a frontal 3-dB coupler, a double-ended arrayed-waveguide grating (AWG), and arrays of thermooptic phase shifters and attenuators, together with their symmetric images reflected from the high-reflection coated facet, to realize all required functionality. The thermooptic phase shifters and attenuators are programmable through electronic interface to realize programmable encoding and decoding capabilities. The attenuators are used to equalize the powers and to increase the ON / OFF extinction ratio of all spectral chips.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY
Optical time delay apparatus incorporating diffractive element sets
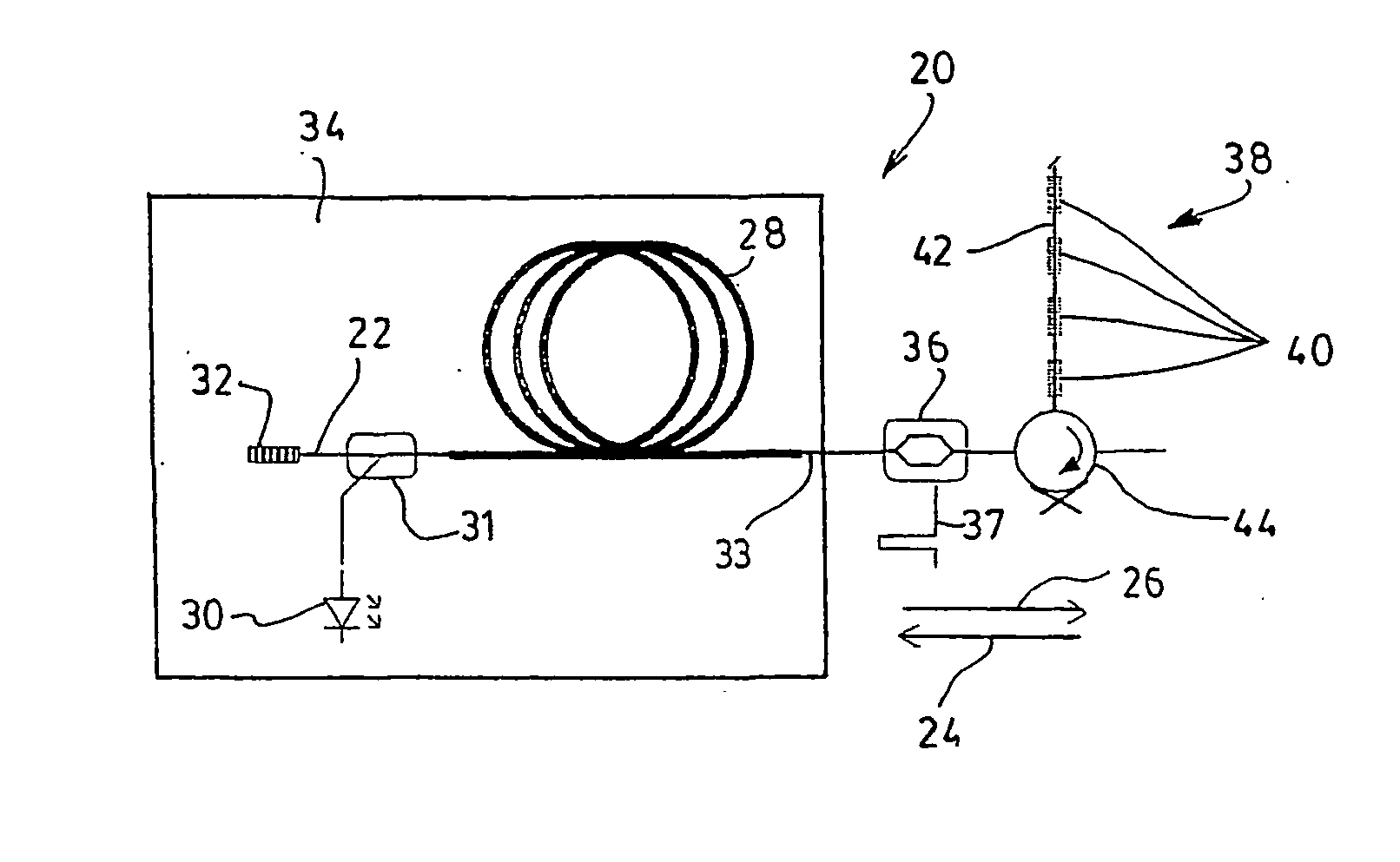
ActiveUS7190858B1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical code multiplexOptical propagationTime delays
An optical time delay apparatus comprises: a multi-wavelength optical source; a diffractive element set imparting a wavelength-dependent delay on signals routed from the source to a 1×N optical switch; and N diffractive element sets routing signals from the 1×N switch to an output port. The optical propagation delay between the source and the output port varies according to the operational state of the source and the 1×N switch. A photodetector may receive the time-delayed signal at the output port.
Owner:STEYPHI SERVICES DE
Coherent optical detector and coherent communication system and method
InactiveUS7327913B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical code multiplexCommunications systemWaveguide
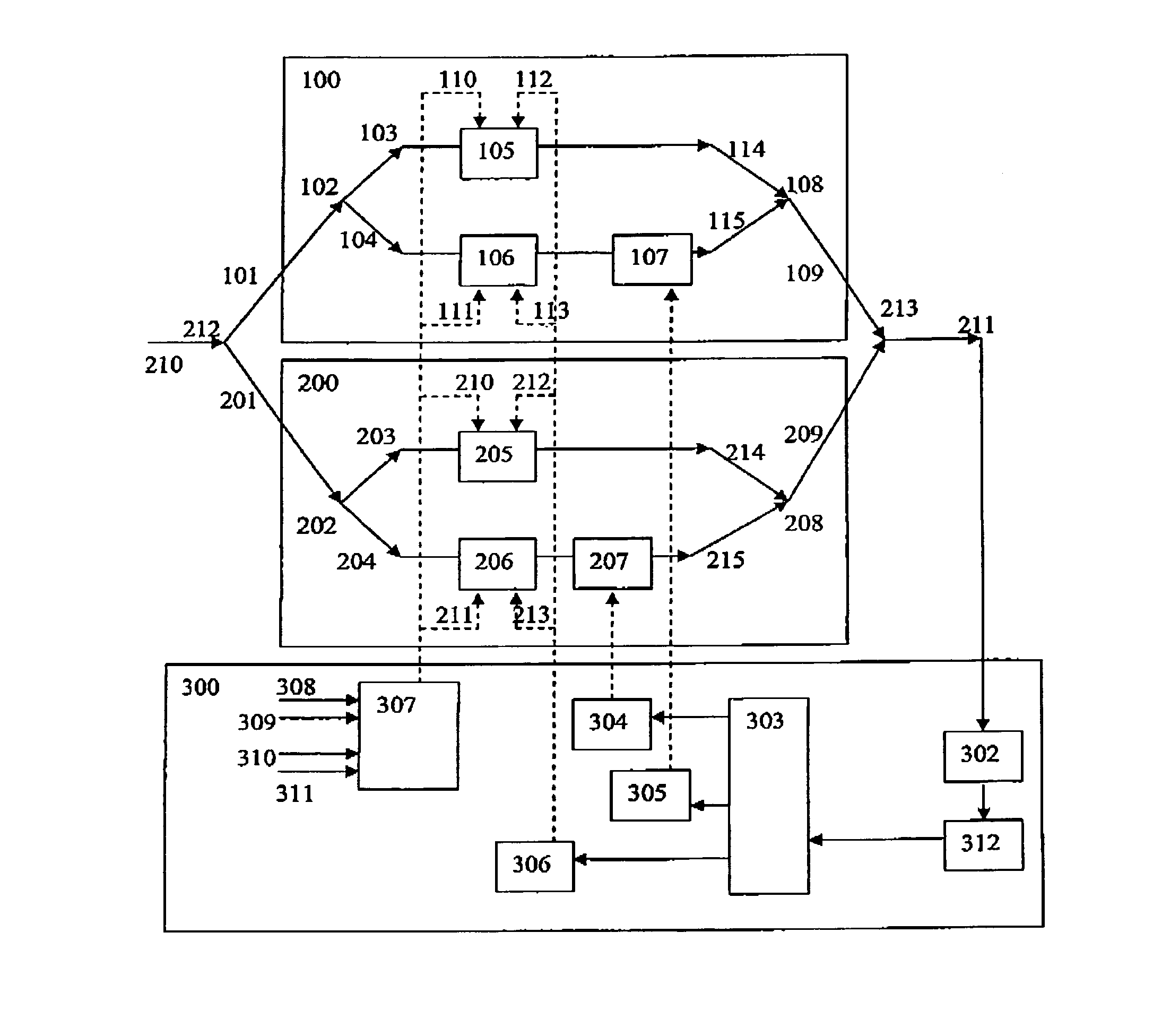
An optical device is provided with first and second inputs. A first coupler coupled is coupled to the first input and produces at least a first and second output. A second coupler is coupled to the second input and produces at least a first and second output. A third coupler is coupled to the first output of the first coupler and to the first output of the second coupler. A fourth coupler is coupled to the second output of the first coupler and to the second output of the second coupler. First and second crossing waveguides are provided with an angle selected to minimize crosstalk and losses between the first and second cross waveguides. The first crossing waveguide connects one of the first or second outputs from the first coupler with an input of the fourth coupler. The second crossing waveguide connects one of the first or second outputs from the second coupler with an input of the third coupler. A first phase shifter is coupled to the first and second waveguides. The first and second waveguides connect one of the outputs of the first or second coupler and one of the inputs of the third or fourth couplers. The first, second, third and fourth couplers, the two crossing waveguides and the phase shifter are each formed as part of a single planar chip made of an electro-optical material.
Owner:CELIGHT
Optical sources and transmitters for optical telecommunications
InactiveUS20040175188A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical code multiplexLight signalLength wave
Optical sources and transmitters for transmitting data in a spectro-temporally encoded light signal are provided. The optical source includes a pumped gain medium for generating ASE radiation. A wavelength dependent reflector is provided backward of the gain medium for reflecting wavebands adapted for spectro-temporal encoding. In one embodiment, a modulator and an encoder are provided outside of the source for embedding data into the generated signal spectro-temporally encoding this signal. In another embodiment, the wavelength dependent reflector acts as the encoder, and the modulator is provided inside the source.
Owner:ACCESSPHOTONIC NETWORKS
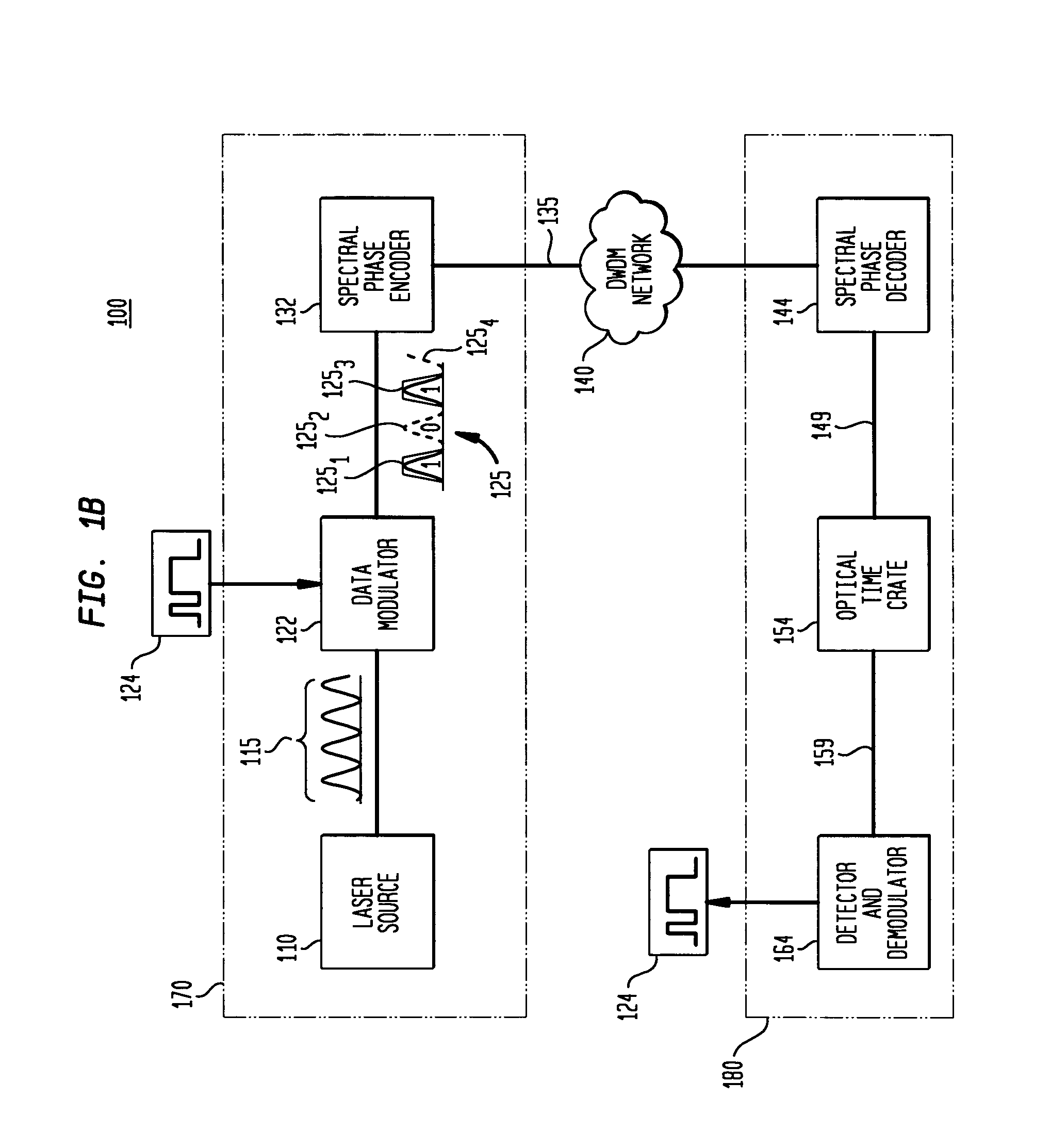
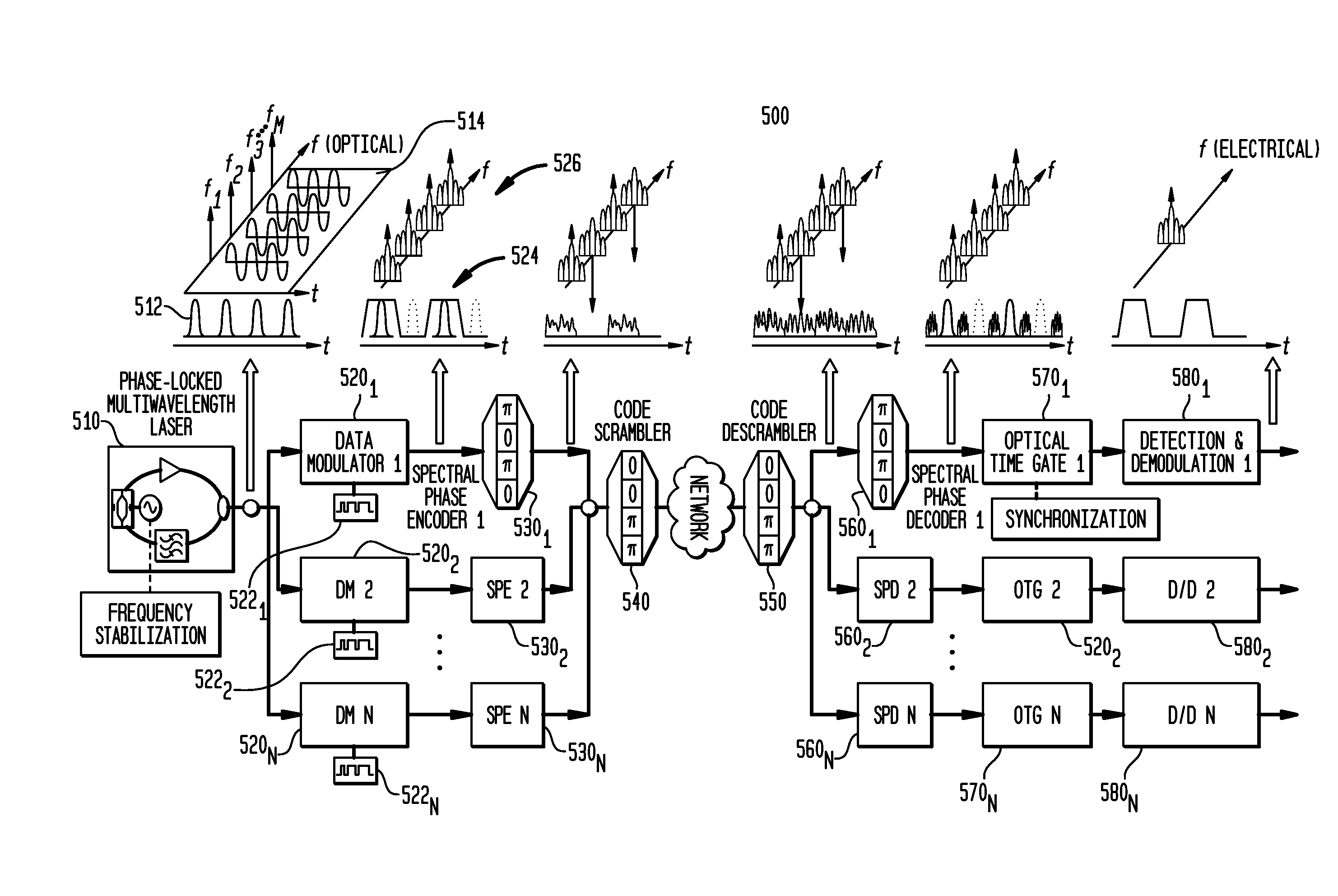
Phase chip frequency-bins optical code division multiple access
Apparatus and system for transmitting and receiving optical code division multiple access data over an optical network. The apparatus comprises a spectral phase decoder for decoding the encoded optical signal to produce a decoded signal, a time gate for temporally extracting a user signal from the decoded signal, and a demodulator that is operable to extract user data from the user signal. The system preferably comprises a source for generating a sequence of optical pulses, each optical pulse comprising a plurality of spectral lines uniformly spaced in frequency so as to define a frequency bin, a data modulator associated with a subscriber and operable to modulate the sequence of pulses using subscriber data to produce a modulated data signals and a Hadamard encoder associated with the data modulator and operable to spectrally encode the modulated data signal to produce an encoded data signal.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
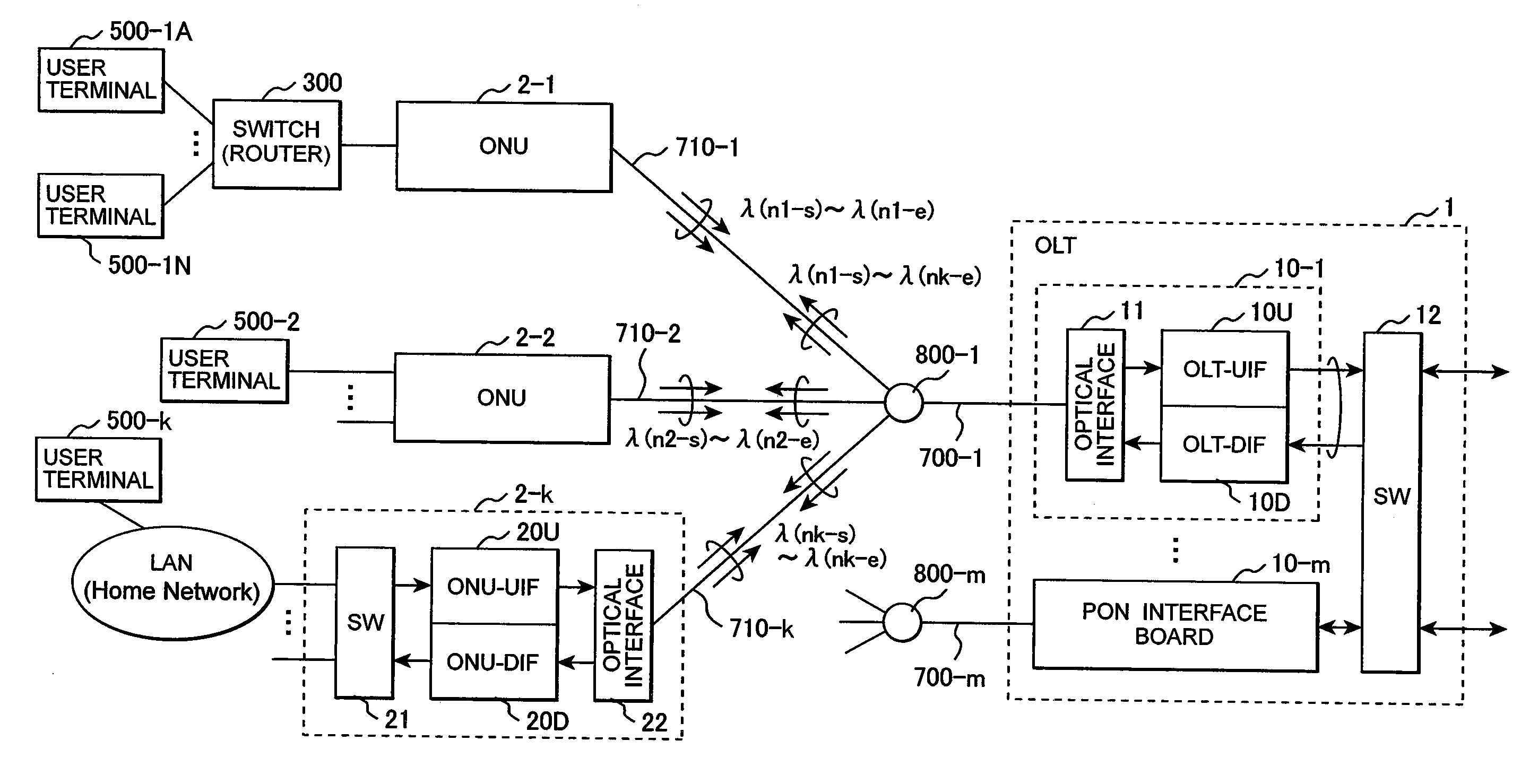
Optical transmission system, PON system, and transmission method
ActiveUS20190288777A1Avoid influenceSimple configurationWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical code multiplexTransport systemEngineering
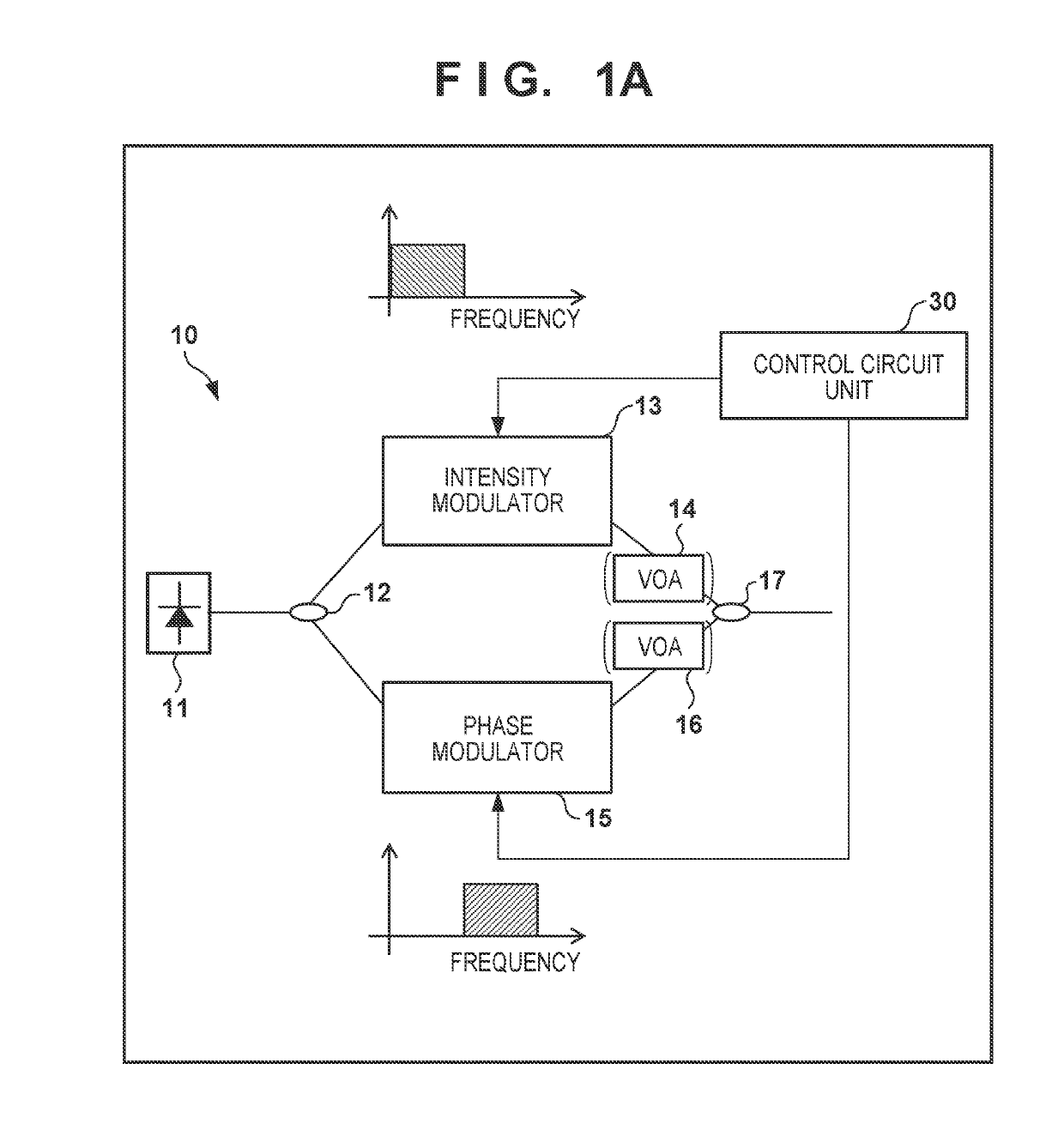
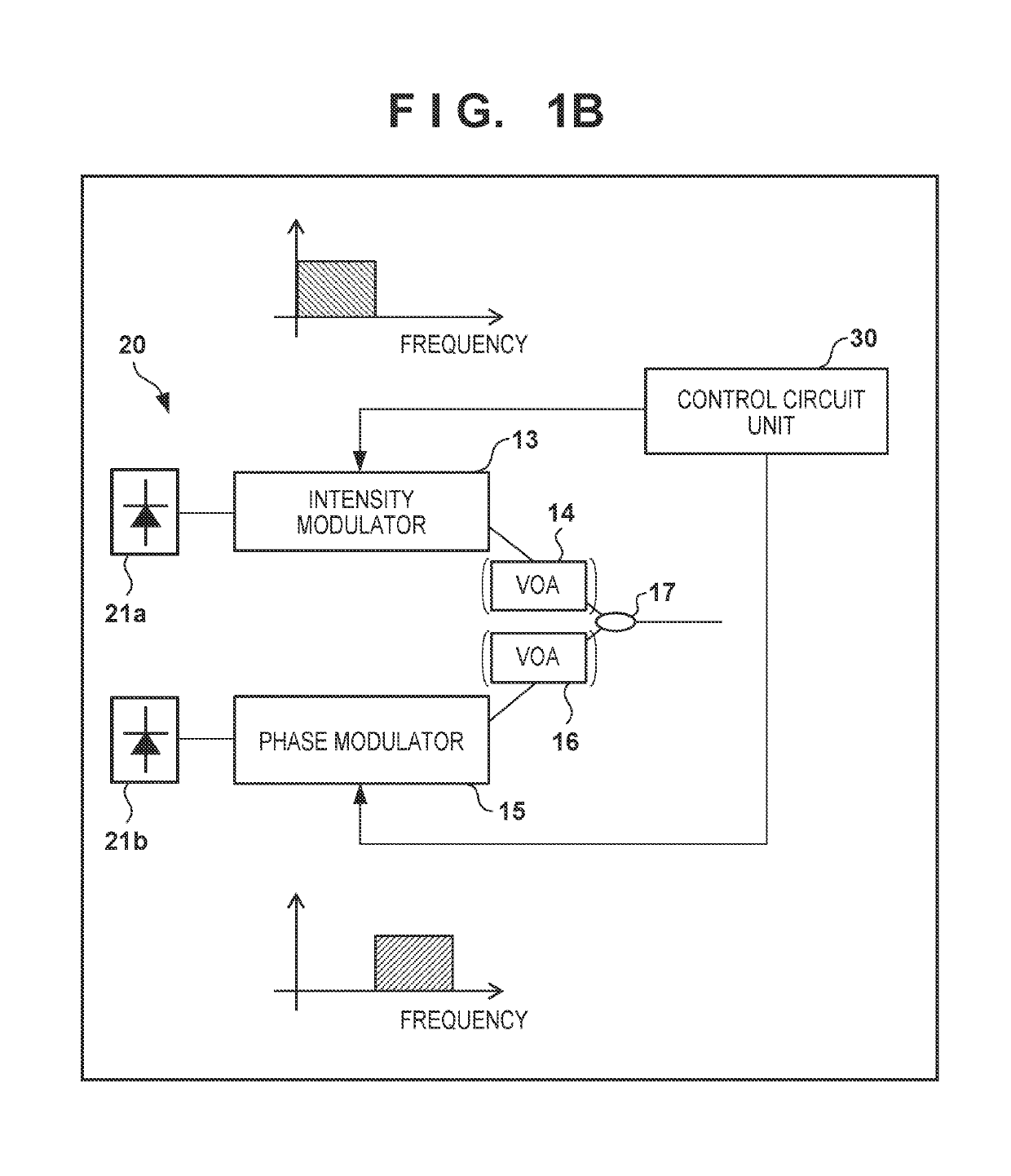
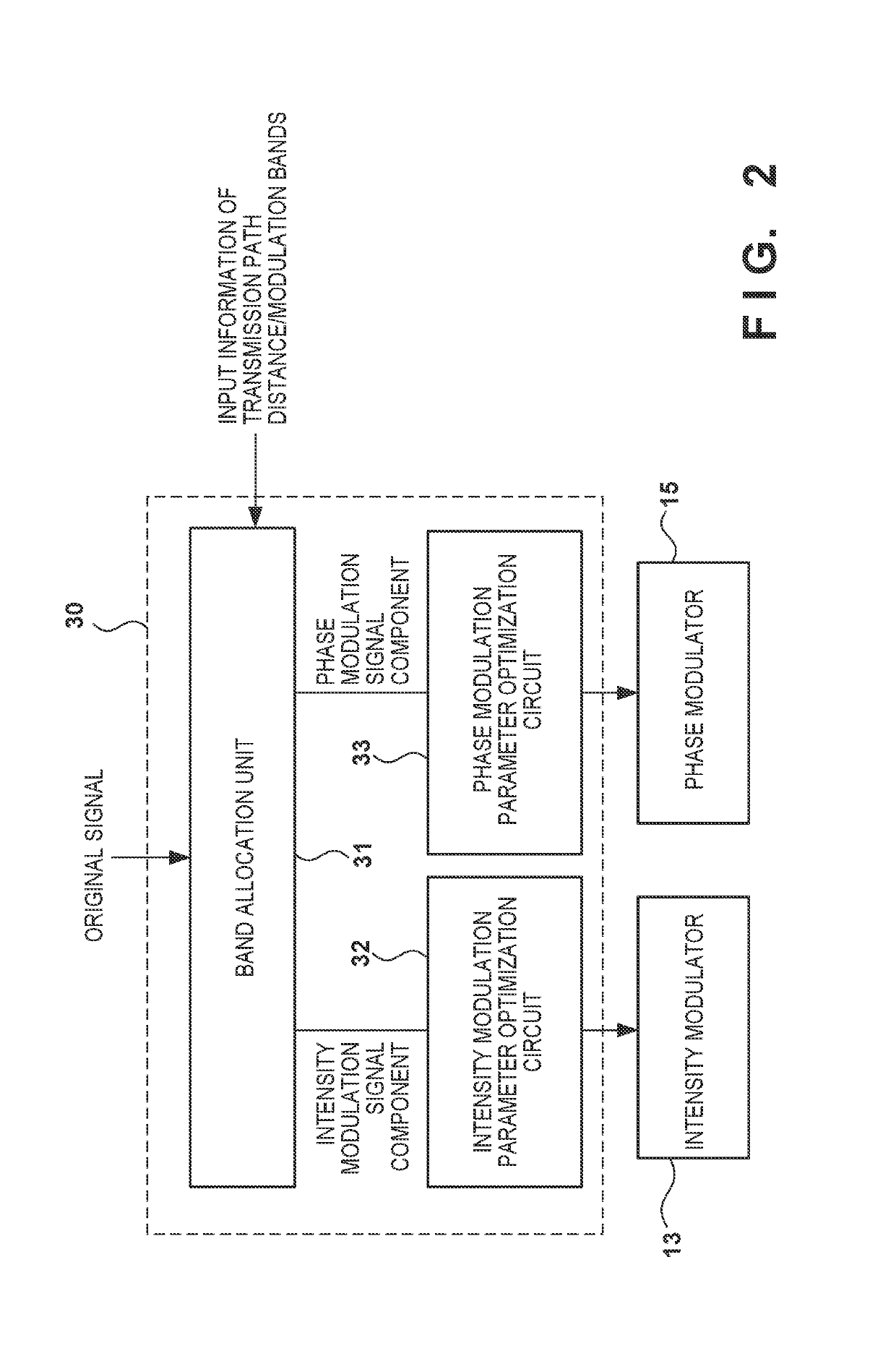
An optical transmission system in which a transmitting station and a plurality of receiving stations are connected via an optical splitter, wherein the transmitting station includes: a controller configured to determine whether to perform intensity modulation or phase modulation on optical signals based on information on transmission distances to the receiving stations and modulation bands; an intensity modulator configured to perform intensity modulation on an optical signal; and a phase modulator configured to perform phase modulation on an optical signal, and wherein one of an intensity modulation signal and a phase modulation signal is transmitted from the transmitting station to each of the receiving stations.
Owner:KDDI CORP
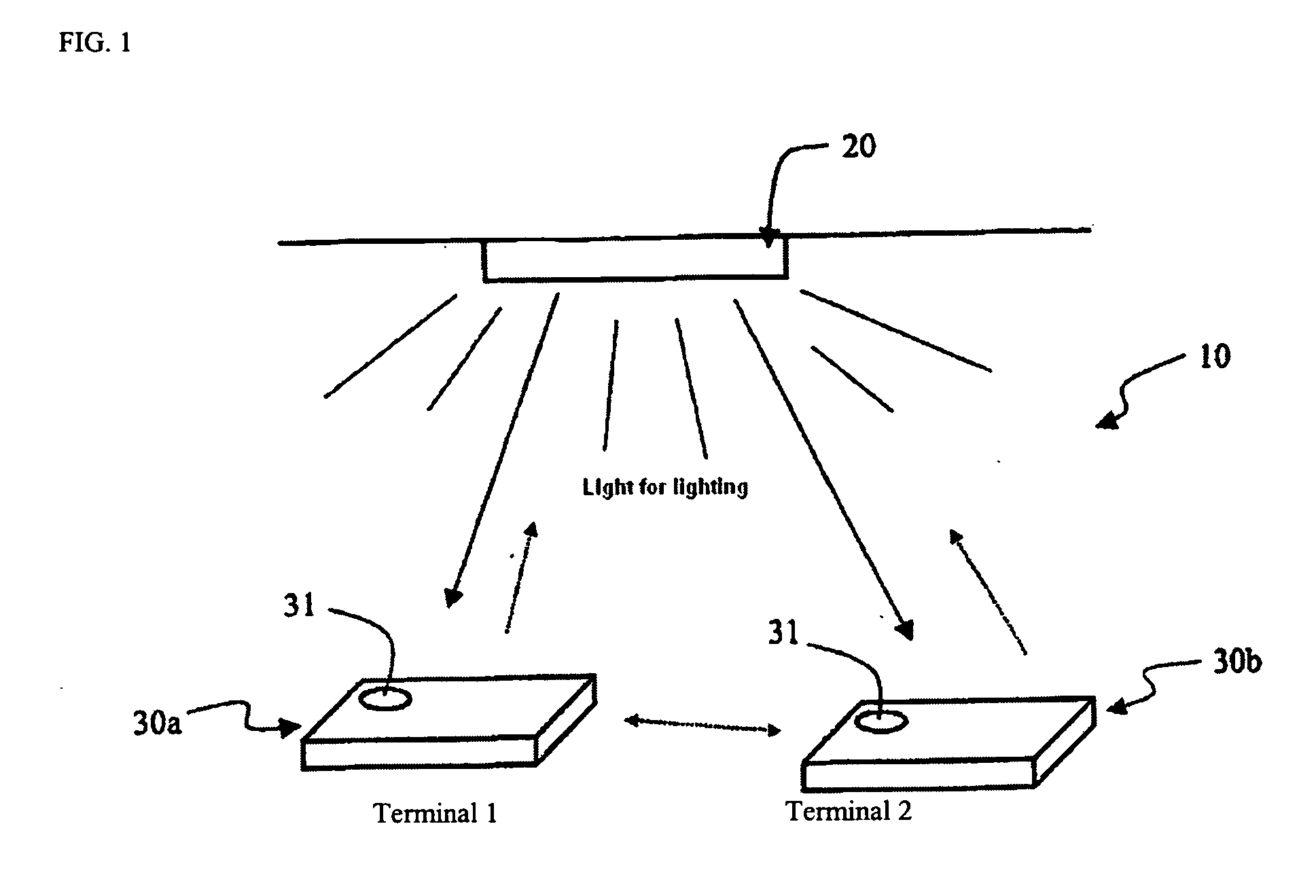
Optical communication system, lighting equipment and terminal equipment used therein
InactiveUS20070008258A1Reliable communicationSignal redundancy is increasedLaser detailsPolarisation multiplex systemsCommunications systemLight equipment
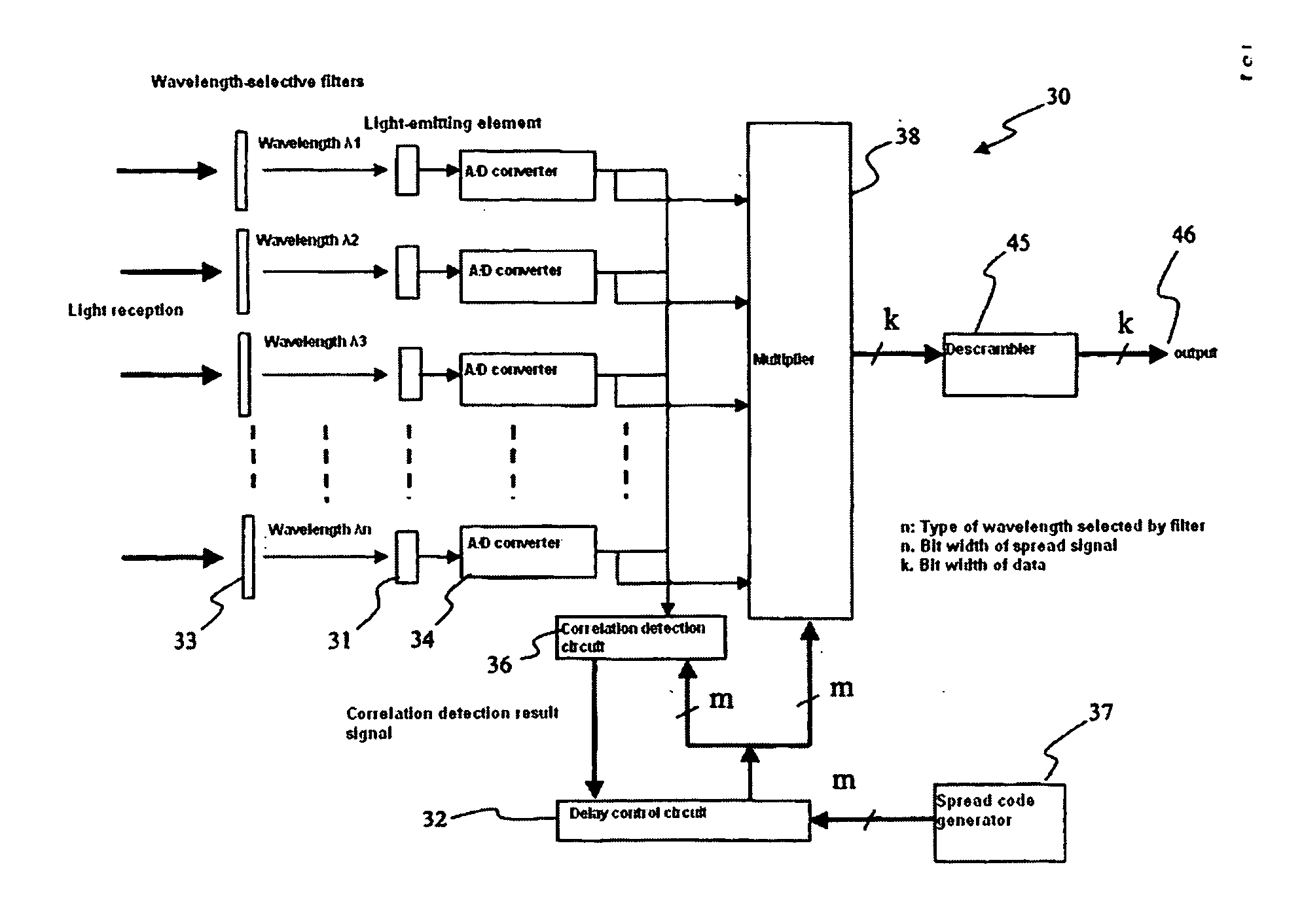
A communication system has lighting equipment that has transmitter comprising multiple light-emitting elements that each emit light of different wavelengths and terminal equipment that has light-receiver comprising multiple light-receiving elements that receive optical signals for each of the different wavelengths.
Owner:BROADCOM INT PTE LTD
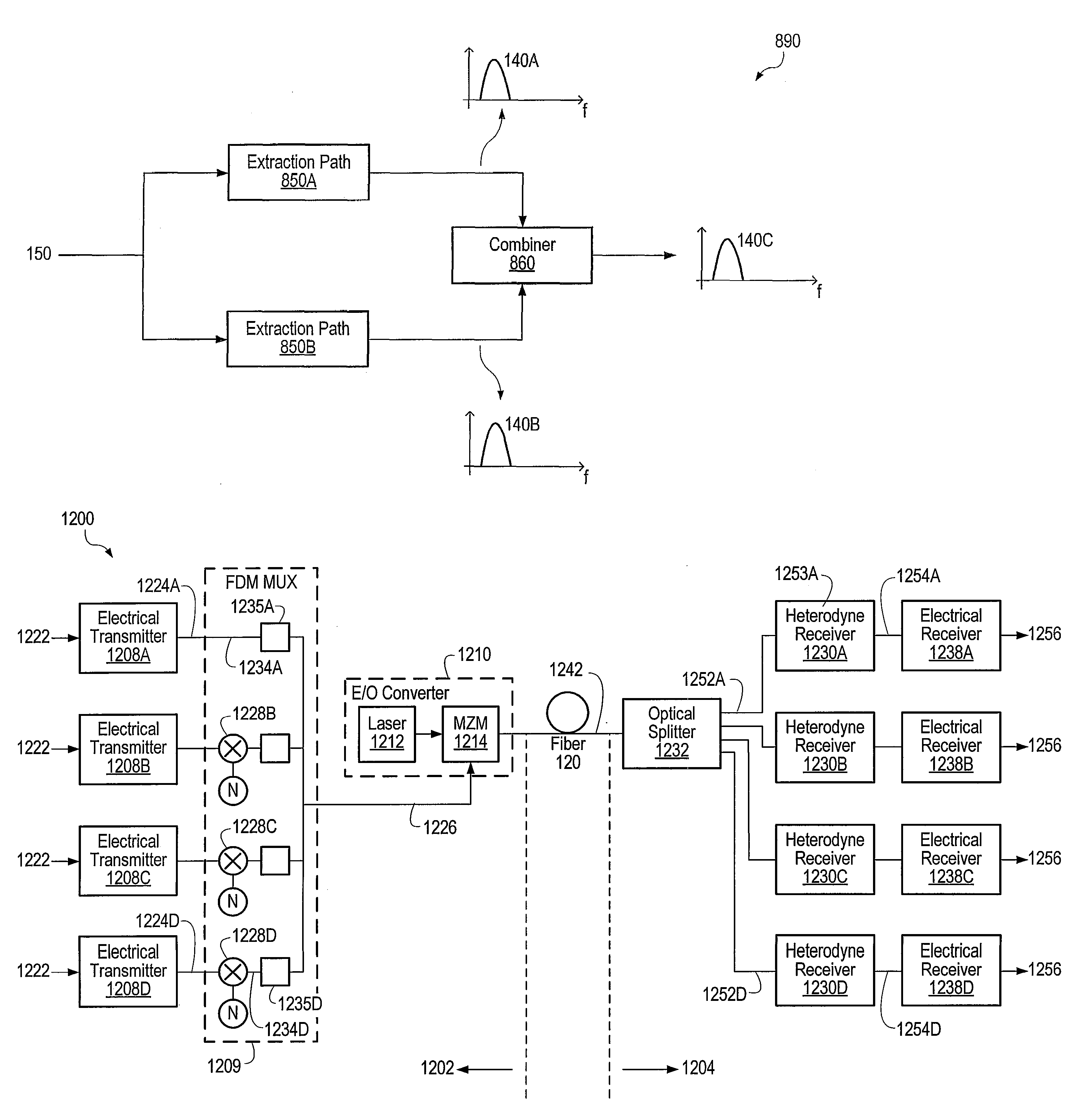
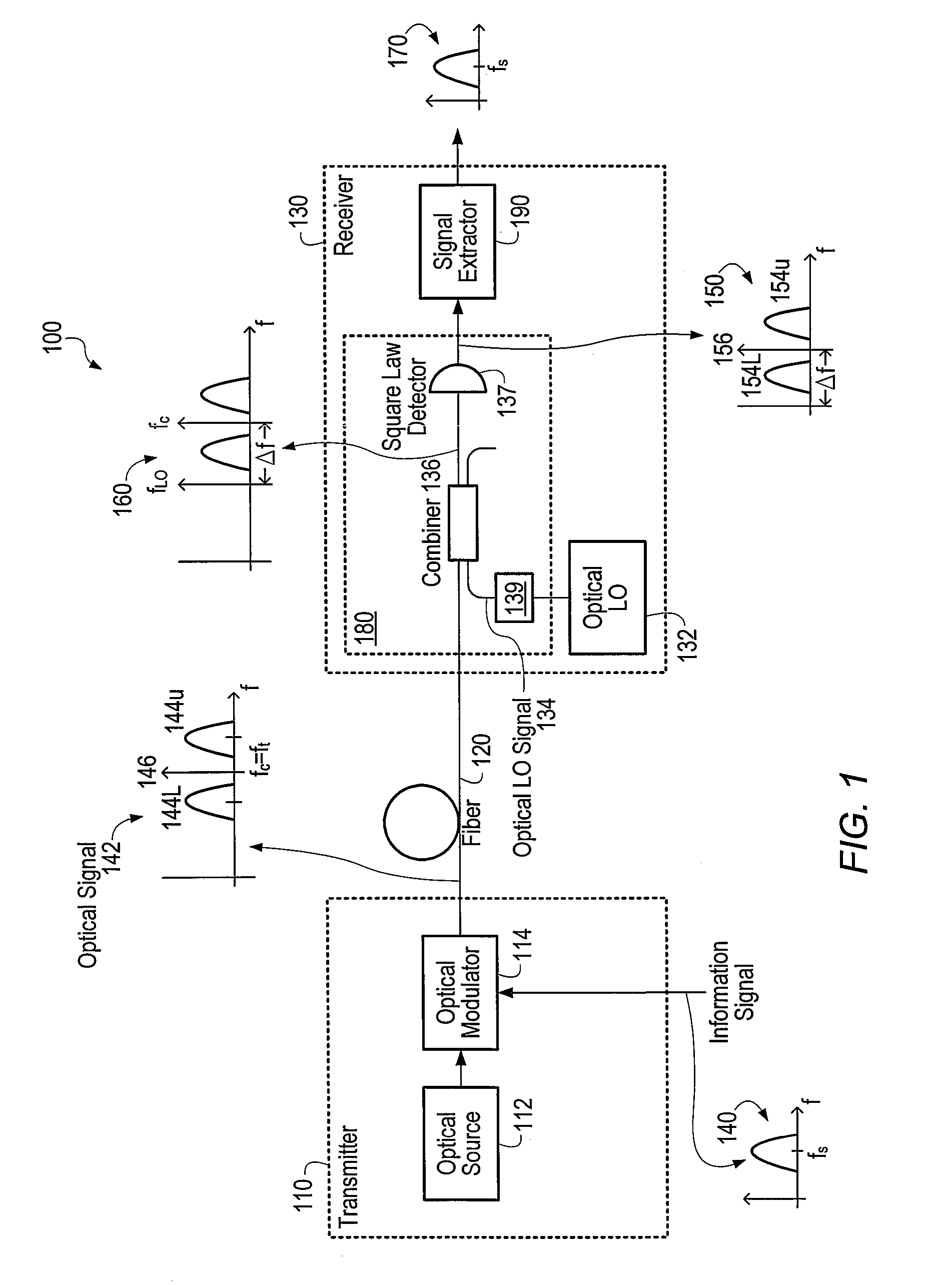
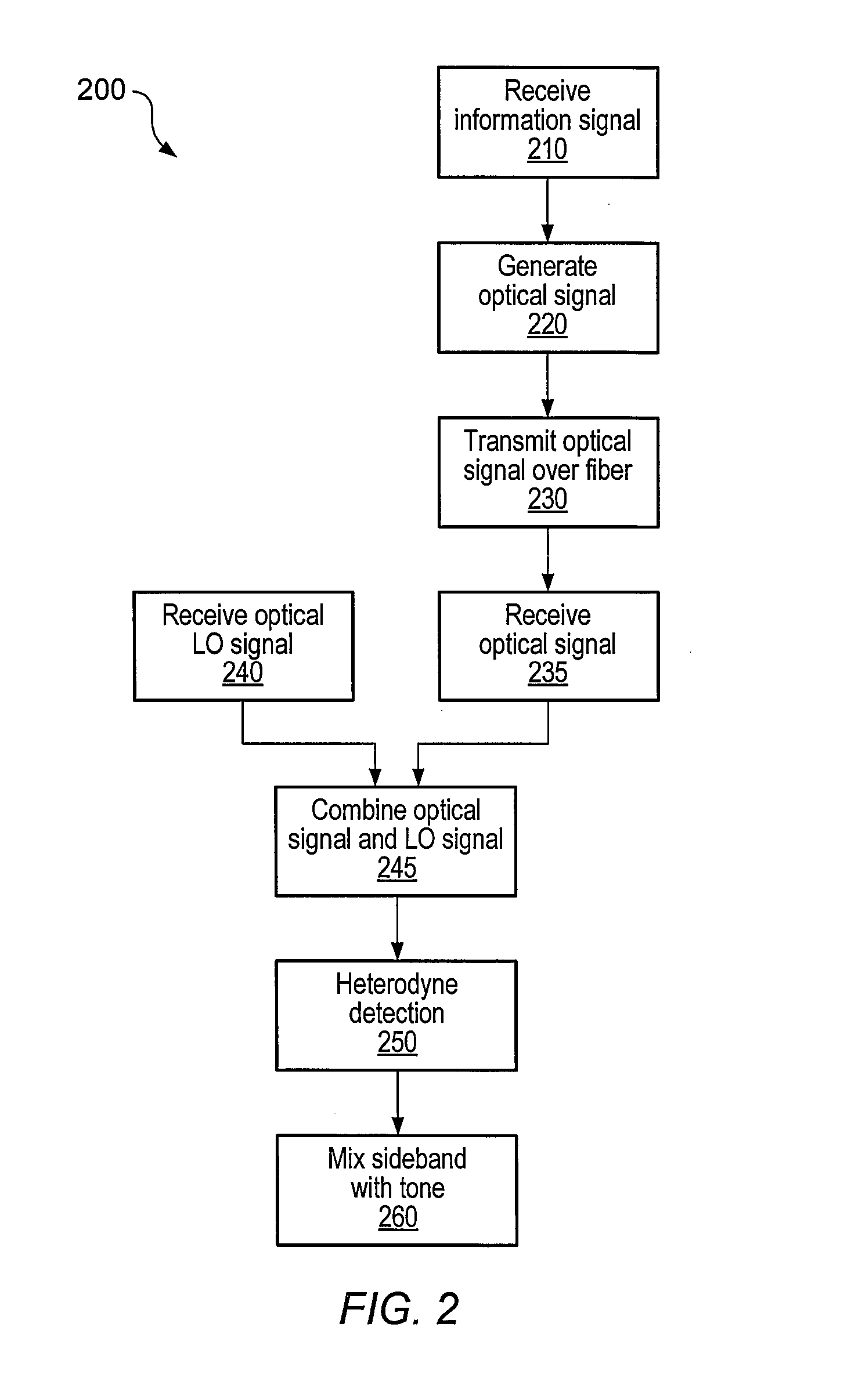
Optical communications using heterodyne detection
InactiveUS7209660B1High sensitivityGood wavelength selectivityFrequency-division multiplex detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsCommunications systemLocal oscillator
An optical communications system includes a receiver subsystem with at least two heterodyne receivers. The receiver subsystem receives a composite optical signal having two or more subbands of information and corresponding tones. An optical splitter splits the composite optical signal into optical signals. Each optical signal includes a subband(s) and corresponding tone. Each heterodyne receiver receives an optical signal. The receiver includes a heterodyne detector coupled to a signal extractor. The heterodyne detector mixes the optical signal with an optical local oscillator to produce an electrical signal which includes a frequency down-shifted version of the subband and the tone of the optical signal. The signal extractor mixes the frequency down-shifted subband with the frequency down-shifted tone to produce a frequency component containing the information.
Owner:XYLON LLC
Optical communication system using wdma and CDMA
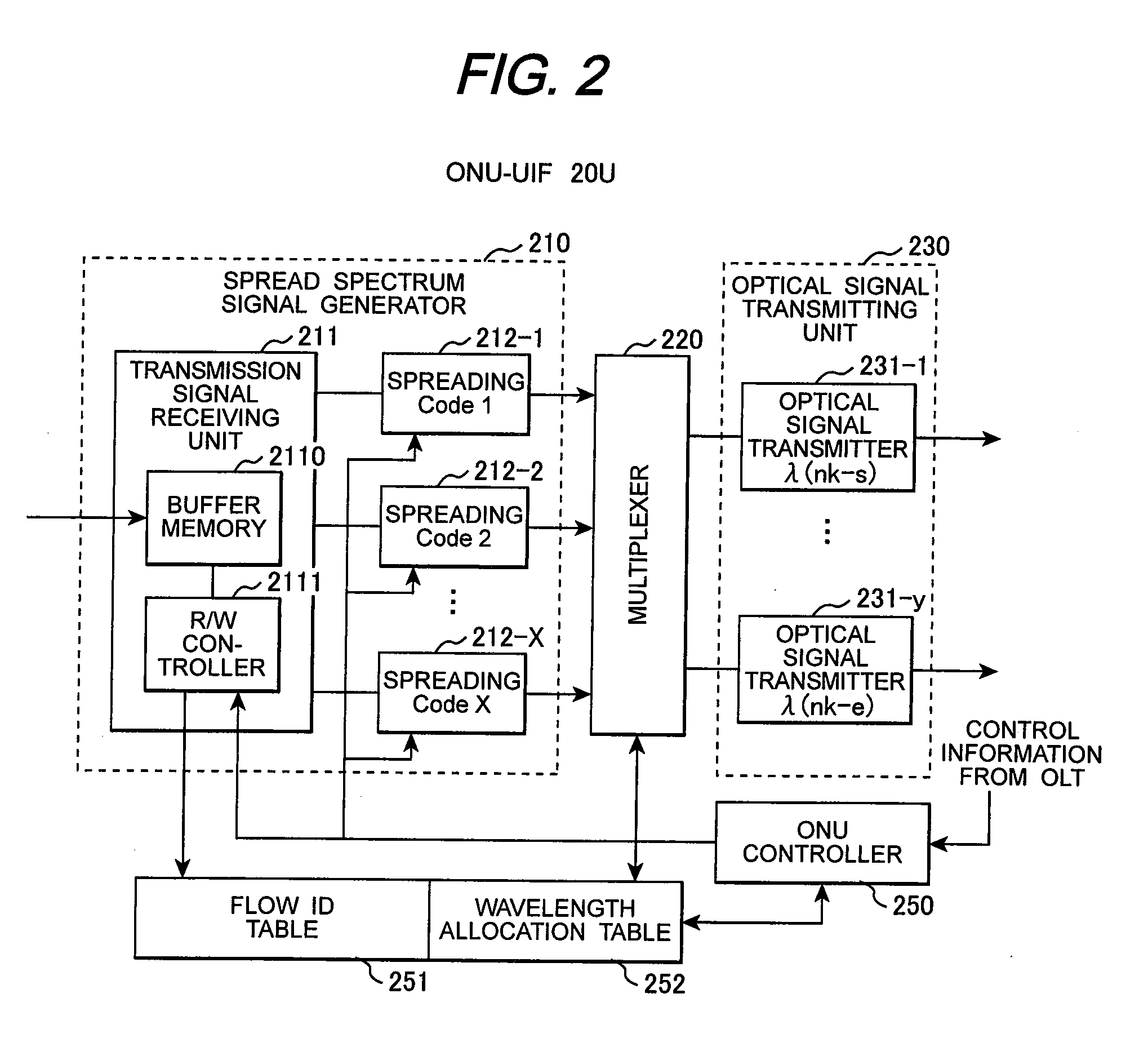
InactiveUS20100158527A1Avoid signalingInterference componentMultiplex system selection arrangementsPolarisation multiplex systemsCommunications systemResource information
In a PON system, an OLT periodically transmits a channel resource information block specifying a carrier wavelength and a spreading code on a first downstream channel to which a spread-spectrum spreader having a first spreading code is applied; one of ONUs receives the channel resource information block with a spread-spectrum despreader having the first spreading code and transmits a connection request to the OLT, using the carrier wavelength and the spreading code specified by the channel resource information block; the OLT having received the connection request transmits a new channel resource information block specifying a carrier wavelength and a spreading code to be used on an upstream data channel to the requester ONU through the first channel; and the requester ONU transmits data, using the carrier wavelength and the spreading code specified by the new channel resource information block.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Apparatus and method for SCDMA digital data transmission using orthogonal codes and a head end modem with no tracking loops
InactiveUS7031344B2Improve throughputReduce error ratePulse modulation television signal transmissionError preventionDigital dataModem device
A system for bidirectional communication of digital data between a central unit and a remote unit wherein the need for tracking loops in the central unit has been eliminated. The central unit transmitter generates a master carrier and a master clock signal which are used to transmit downstream data to the remote units. The remote units recover the master carrier and master clock and synchronize local oscillators in each remote unit to these master carrier and master clock signals to generate reference carrier and clock signals for use by the remote unit receiver. These reference carrier and clock signals are also used by the remote unit transmitters to transmit upstream data to the central unit. The central unit receiver detects the phase difference between the reference carrier and clock signals from the remote units periodically and adjusts the phase of the master carrier and master clock signals for use by the central unit receiver to receive the upstream data.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
Multiplexing of optical beams using reversed laser scanning
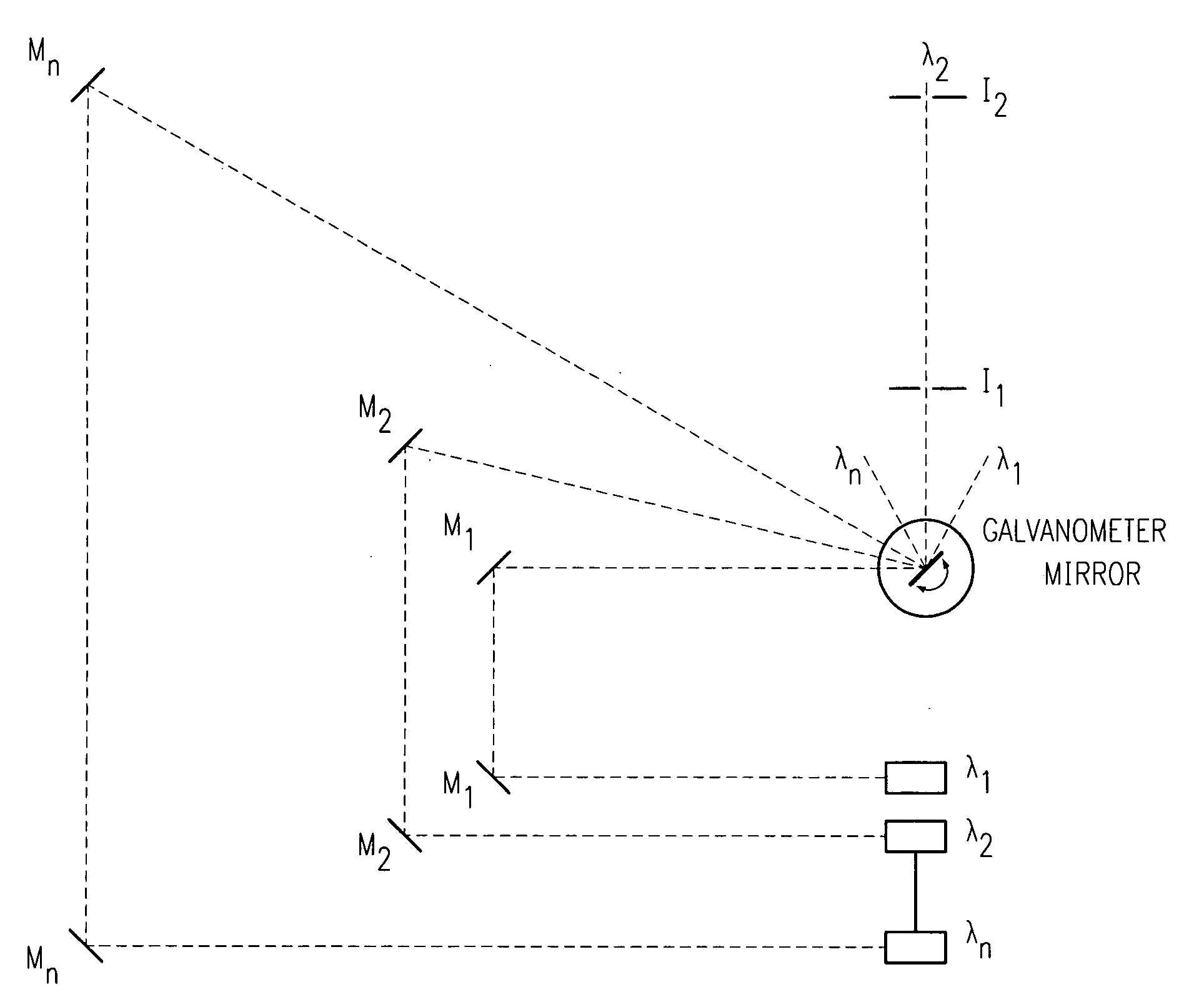
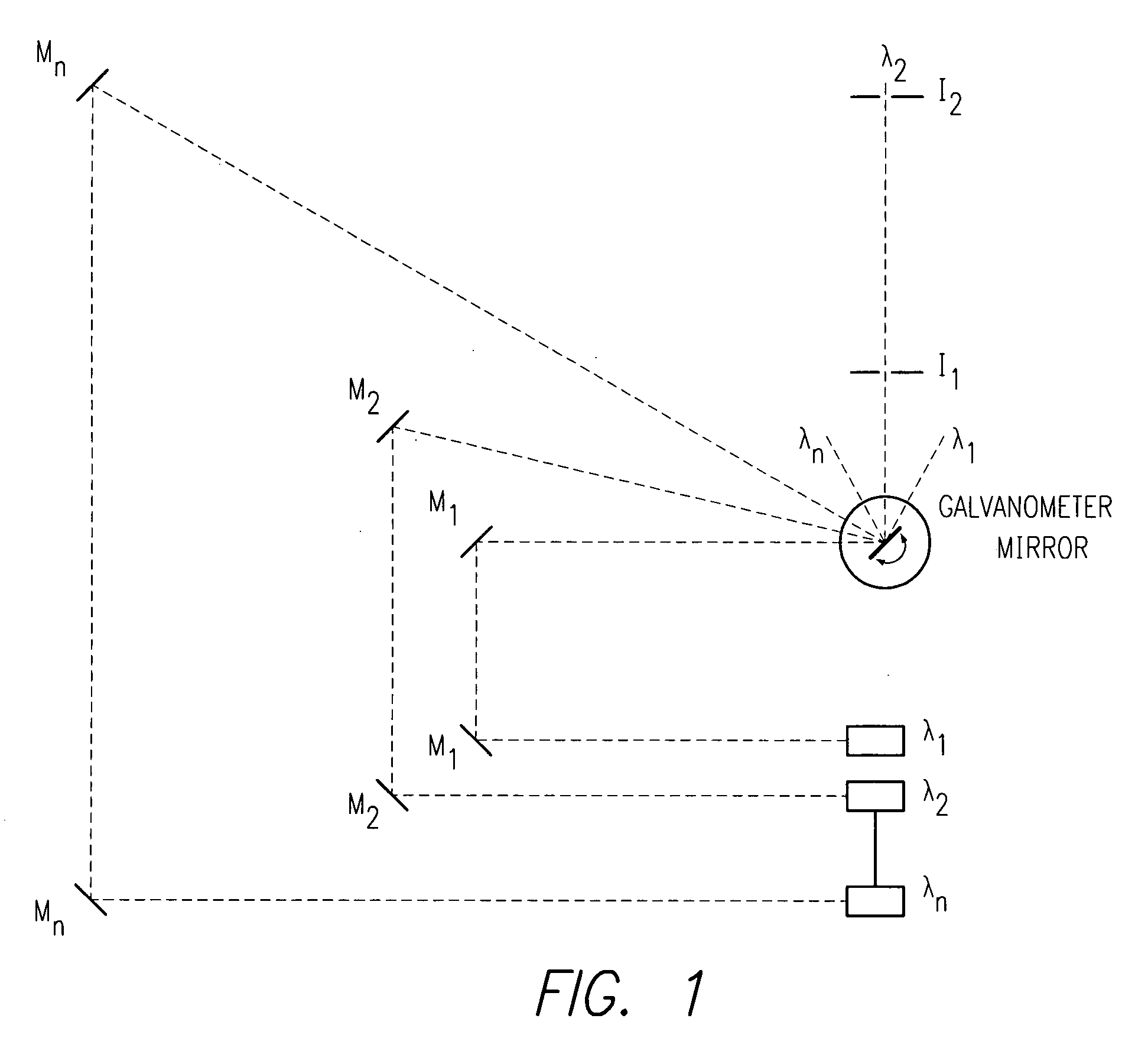
InactiveUS20090116518A1Diagnostics using lightWavelength-division multiplex systemsRotational axisCommunications system
A high efficiency, low cost, nondispersive optical multiplexing arrangement for optical beams, used a technique denominated “Reverse Laser Scanning.” In the Reverse Laser Scanning operation, different laser beams angularly meet on the rotational axis of a galvanometer-mounted mirror or the like. Upon reflection from the mirror, each of the laser beams is propagated along one defined direction by appropriate angular positioning of the galvanometer mirror. The process enables several useful deployments, including multi-chemical detection using several lasers in the same sensor, remotely operated laser switching for medical surgery and diagnosis where multiple lasers may be used, and wavelength, code, and time division multiplexing in communication systems, among others.
Owner:PRANALYTICA
Optical code division multiplexing transmission and reception method and optical code division multiplexing transceiver
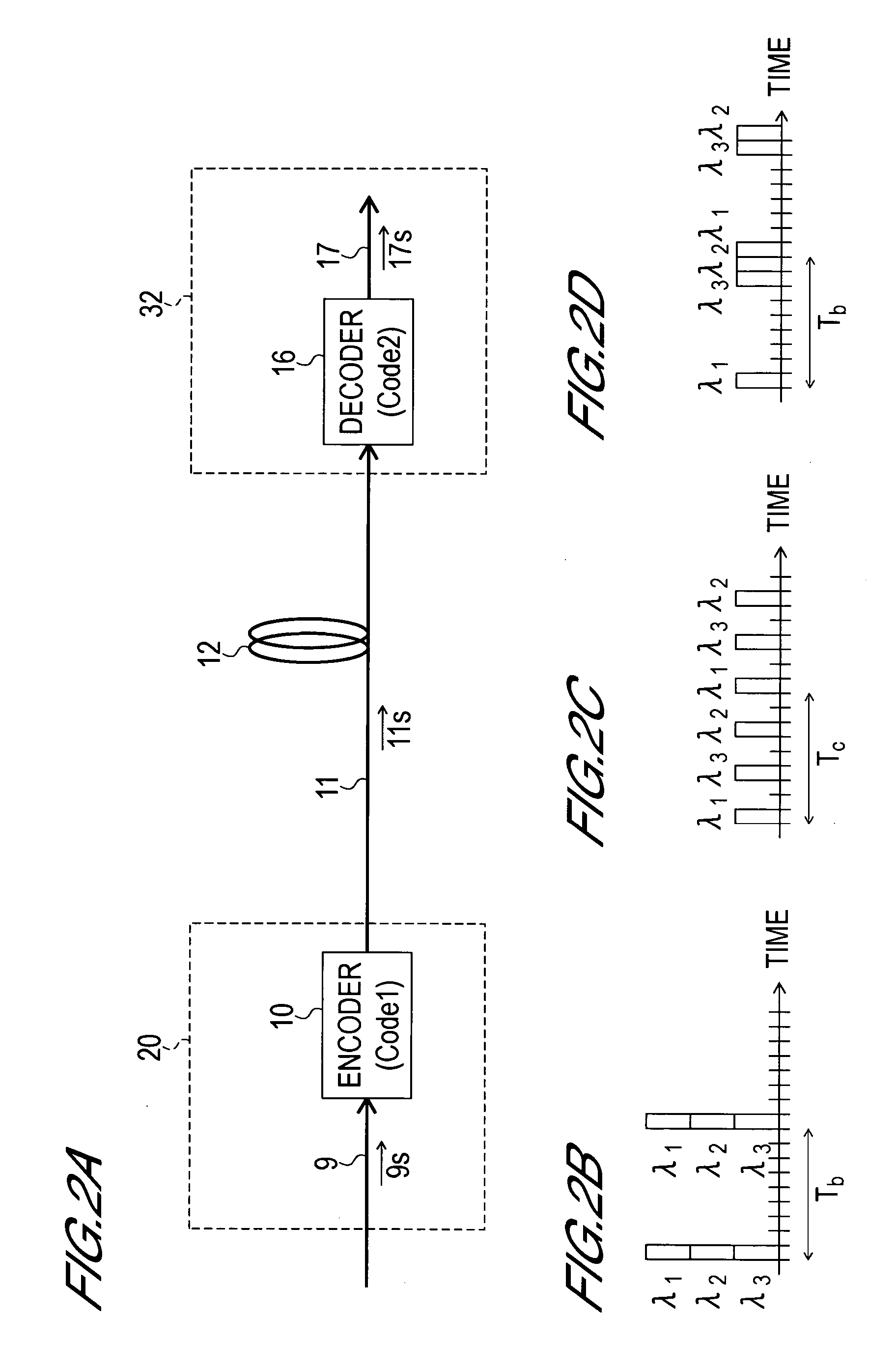
InactiveUS20060115272A1Reduce intensityReduce signal to noise ratioPolarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsTime gatingMultiplexing
An object of the present invention is to provide an OCDM transceiver with which the reduction amount of the intensity of the correlation waveform signal is smaller than that of a conventional device of the same type in the decoding step that comprises a time gate processing step. Hence, in the OCDM transceiver of the present invention that comprises an encoding portion and a decoding portion, the decoding portion is constituted comprising a decoder, clock extractor, and time gate. The decoder decodes an encoded optical pulse signal and separates the encoded optical pulse signal into a clock signal extraction signal and an optical pulse signal playback signal. The clock extractor extracts a clock signal from the clock signal extraction signal. Further, the time gate removes only the auto-correlation waveform component from the optical pulse signal playback signal. The auto-correlation waveform component is converted to an electrical signal by means of an optical receiver and generated as a reception signal.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Method and system for mitigating nonlinear transmission impairments in fiber-optic communications systems
InactiveUS7224906B2Time-division optical multiplex systemsSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansFiberReturn-to-zero
The present invention relates to a method for transmitting data. An optical pulse stream comprising a plurality of return-to-zero optical pulses is prepared by modulating a phase of light output by an optical source to thereby encode data from a data source. The light of the optical pulse stream has a wavelength. The optical pulse stream is transmitted along an optical fiber of an optical network. Optical pulse streams of the invention enhance transmission performance at least in part by reducing noise at the receiver caused by fiber non-linearities.
Owner:CELIGHT
Two-dimensional wavelength/time optical CDMA system adopting balanced-modified pseudo random noise matrix codes
A two-dimensional wavelength / time optical CDMA system employing balanced-modified pseudo random noise (PN) matrix codes is provided. Through an inverse-exclusive OR operation of a pair of modified PN code, the balanced codes are generated as optical CDMA codes in the form of a new matrix. When the codes are applied to an optical CDMA system to perform encoding and decoding, if the same number of channels as the number (M−1) of subgroups of the codes are connected, the system becomes an MAI-free system, and even if the number of channels connected is twice the number of the subgroups, an error-free system can be established. Accordingly, the number of channels that can be used simultaneously is doubled compared to the prior art method such that the economical efficiency of the optical CDMA system improves.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
System and method for scaling total client capacity with a standard-compliant optical transport network (OTN)
ActiveUS9231721B1Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTime-division multiplexFiberChannel statistics
In an Optical Transport Network (OTN) system, methods and devices are provided for communicating rate-adaptive OTUk frames. One method determines channel statistics for a fiber span connecting a transmitter to a receiver. A client input data rate is determined that is sufficient to meet a minimum communication threshold, and a rate-adaptive OTUk frame format is determined sufficient to carry the client input data rate. The format comprises a set of (n) allocated slots of client input data in a rate-adaptive OTUk frame comprising (m) slots, where (n) is less than or equal to (m). The method then fills the rate-adaptive OTUk frame, including (m−n) unallocated slots, using one of two processes. The first process fills the rate-adaptive OTUk frame with parity bits computed from client input data. The second process fills at least a portion of the rate-adaptive OTUk frame with and dummy bits.
Owner:MACOM CONNECTIVITY SOLUTIONS LLC
Optical code division multiplexing transmission/reception method and optical code division multiplexing transmission/reception device
InactiveUS20070122153A1Minimal beat noisePolarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexingEngineering
A transmission unit comprises an optical pulse train generation unit, first channel encoded optical pulse signal generation unit, second channel encoded optical pulse signal generation unit, third channel encoded optical pulse signal generation unit, and fourth channel encoded optical pulse signal generation unit; the second and fourth channels further comprise polarization controllers respectively. By means of these polarization controllers, a polarization control step is executed in which the planes of polarization of first encoded optical pulse signals of the second and fourth channels are rotated by 90°. By executing the polarization control step, the directions of the planes of polarization of the first decoded optical pulse signals of adjacent channels in the reception unit can be caused to be mutually orthogonal.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Data in motion storage system and method
ActiveUS20170280211A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsPolarisation multiplex systemsOptical cavityWaveguide
A data storage system is disclosed that includes a recirculating loop storing data in motion. The data may be carried by a signal via the loop including one or more satellites or other vessels that return, for example by reflection or regeneration, the signals through the loop. The loop may also include a waveguide, for example an optical fiber, or an optical cavity. Signal multiplexing may be used to increase the contained data. The signal may be amplified at each roundtrip and sometimes a portion of the signal may be regenerated.
Owner:NKB PROPERTIES MANAGEMENT LLC
Spectrally phase encoded optical code division multiple access system
ActiveUS20080107429A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical code multiplexFrequency spectrumTime division multiple access
System and method for transmitting and receiving encoded signals over a network along with one or more additional signals transported within a spectral gap created by the coded signals.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
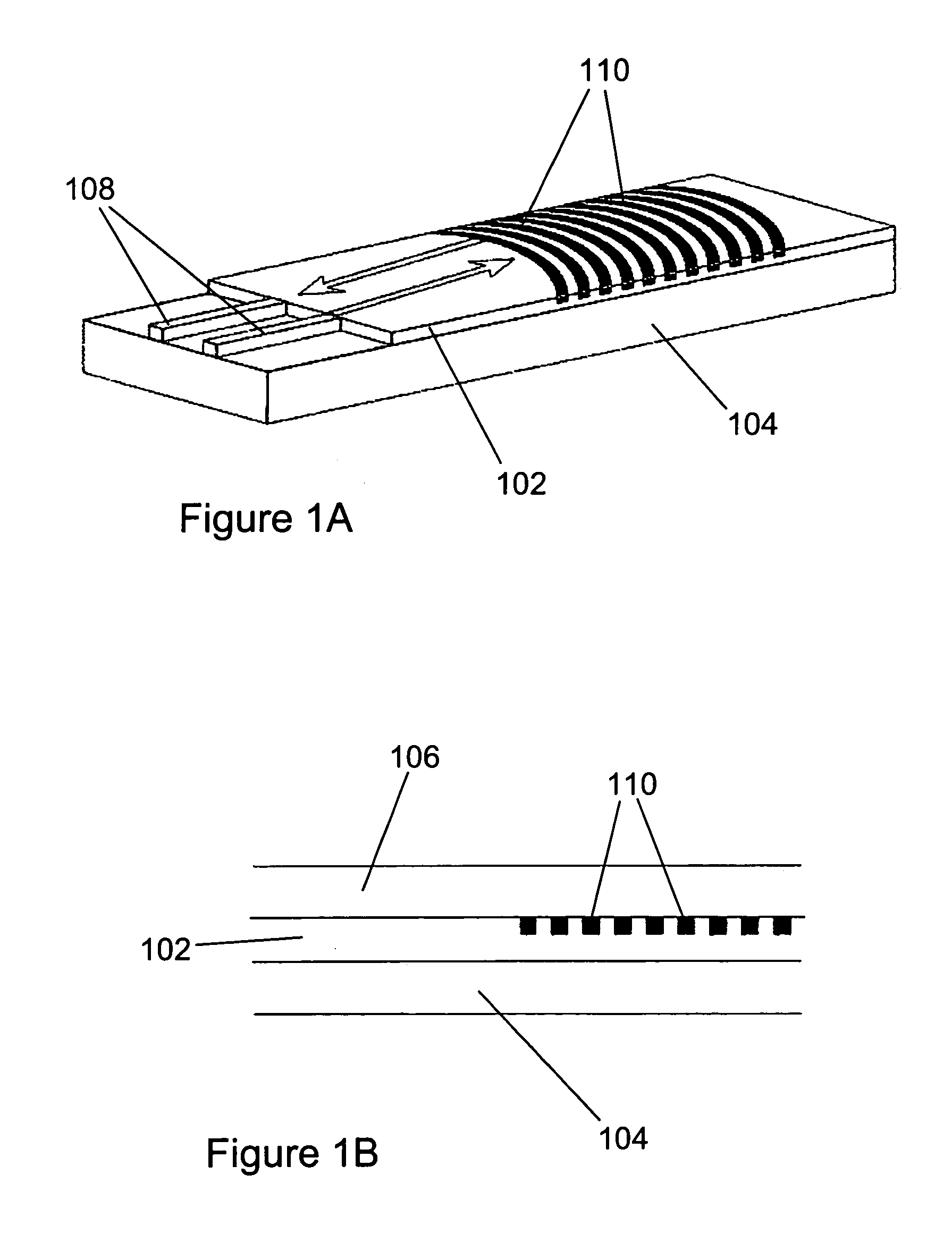
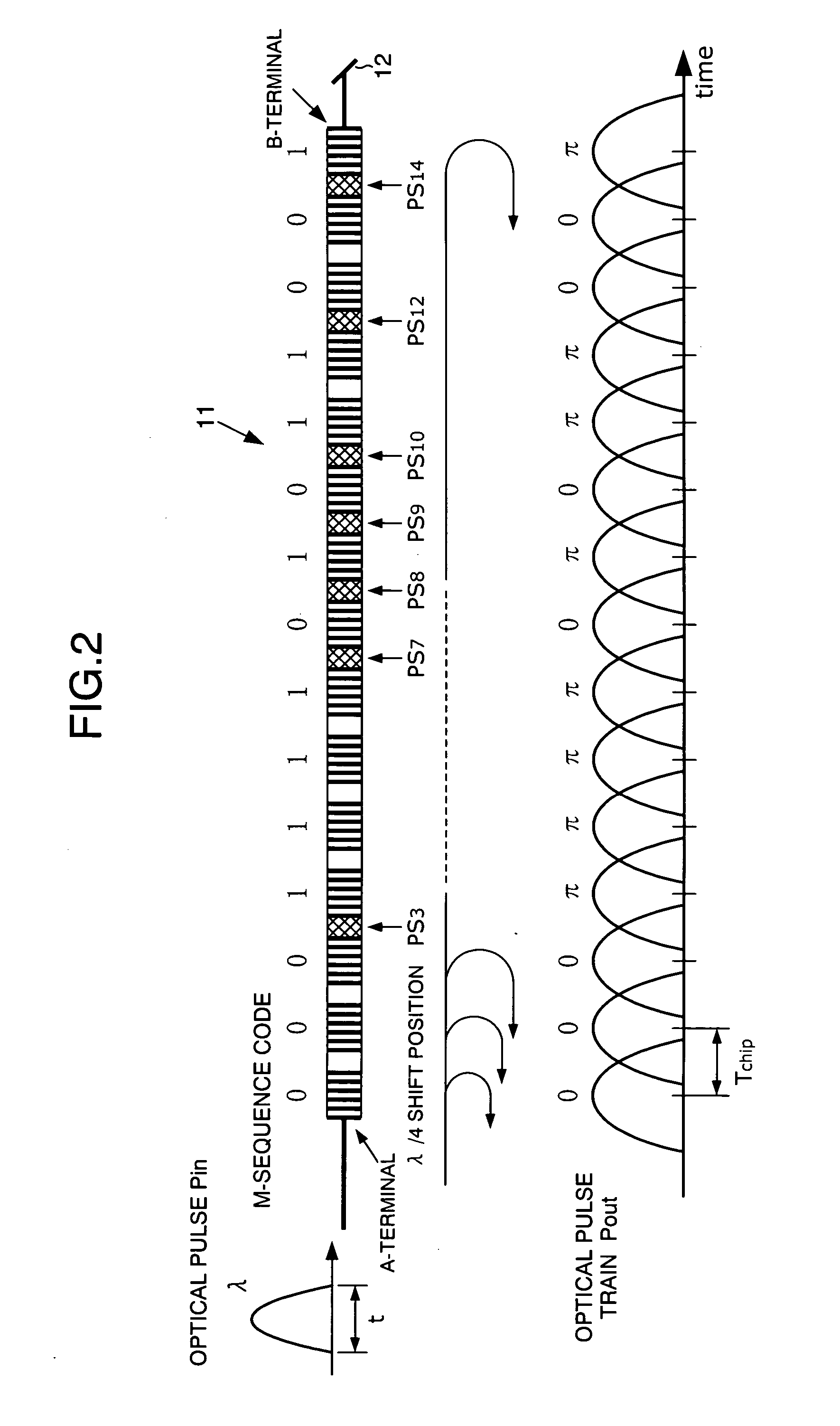
Optical signal converter, optical encoder, optical decoder, and optical code division multiplexing communication apparatus
ActiveUS20050089328A1Suppress interferenceImprove performanceOptical code multiplexElectromagnetic transmittersMultiplexingGrating
An optical signal encoder / decoder includes a grating waveguide having an identical number of uniform pitch gratings to the number of code chips of a binary phase optical code, the uniform pitch gratings being formed in a waveguide direction to reflect light of a predetermined wavelength. Here, adjacent gratings corresponding to a position at which the optical code value changes are disposed a spacing apart from each other to give a phase shift of (2m+1)π / 2 to the light, and the remaining adjacent gratings are disposed a spacing apart from each other to give a phase shift of nπ to the light (m, n: integer).
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
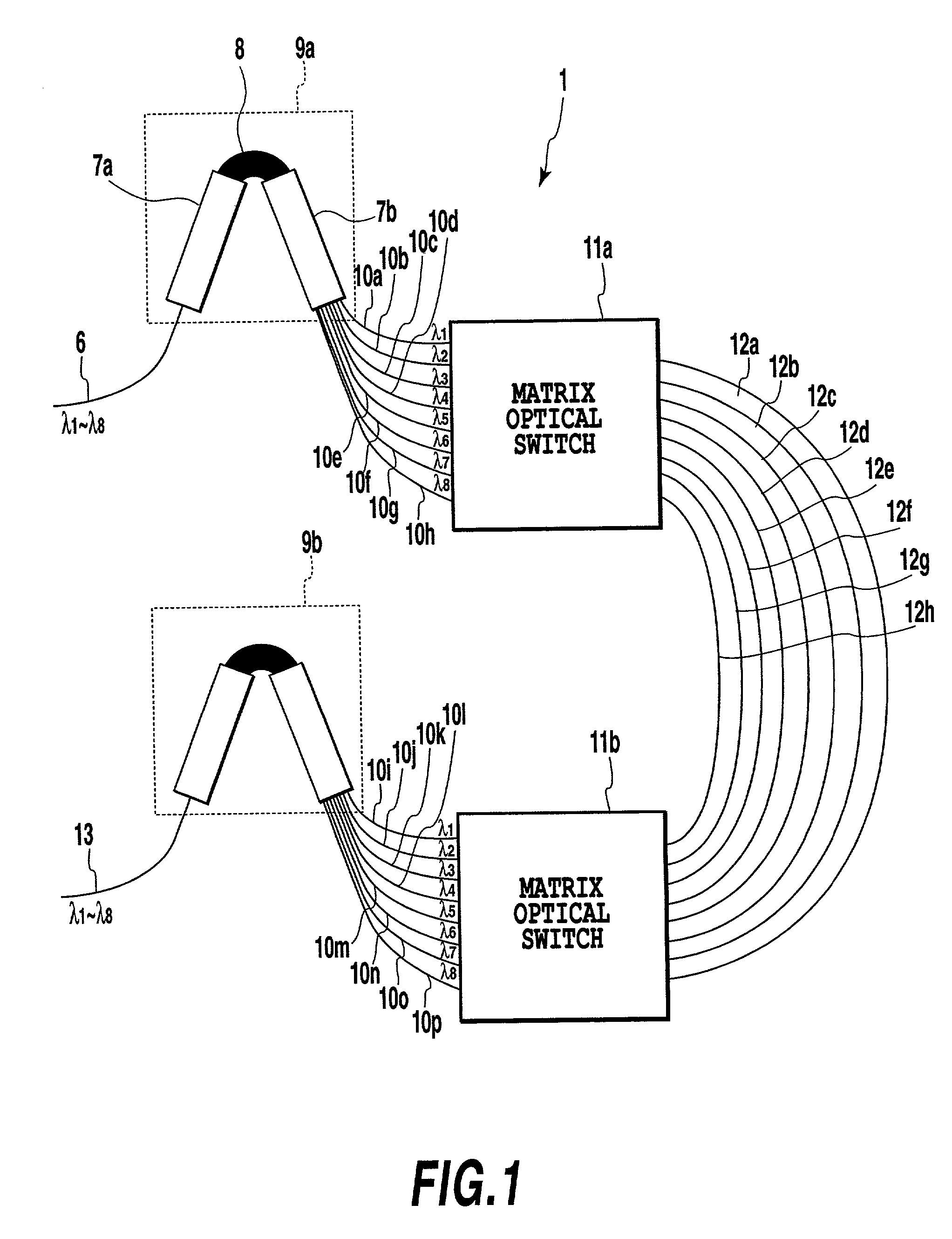
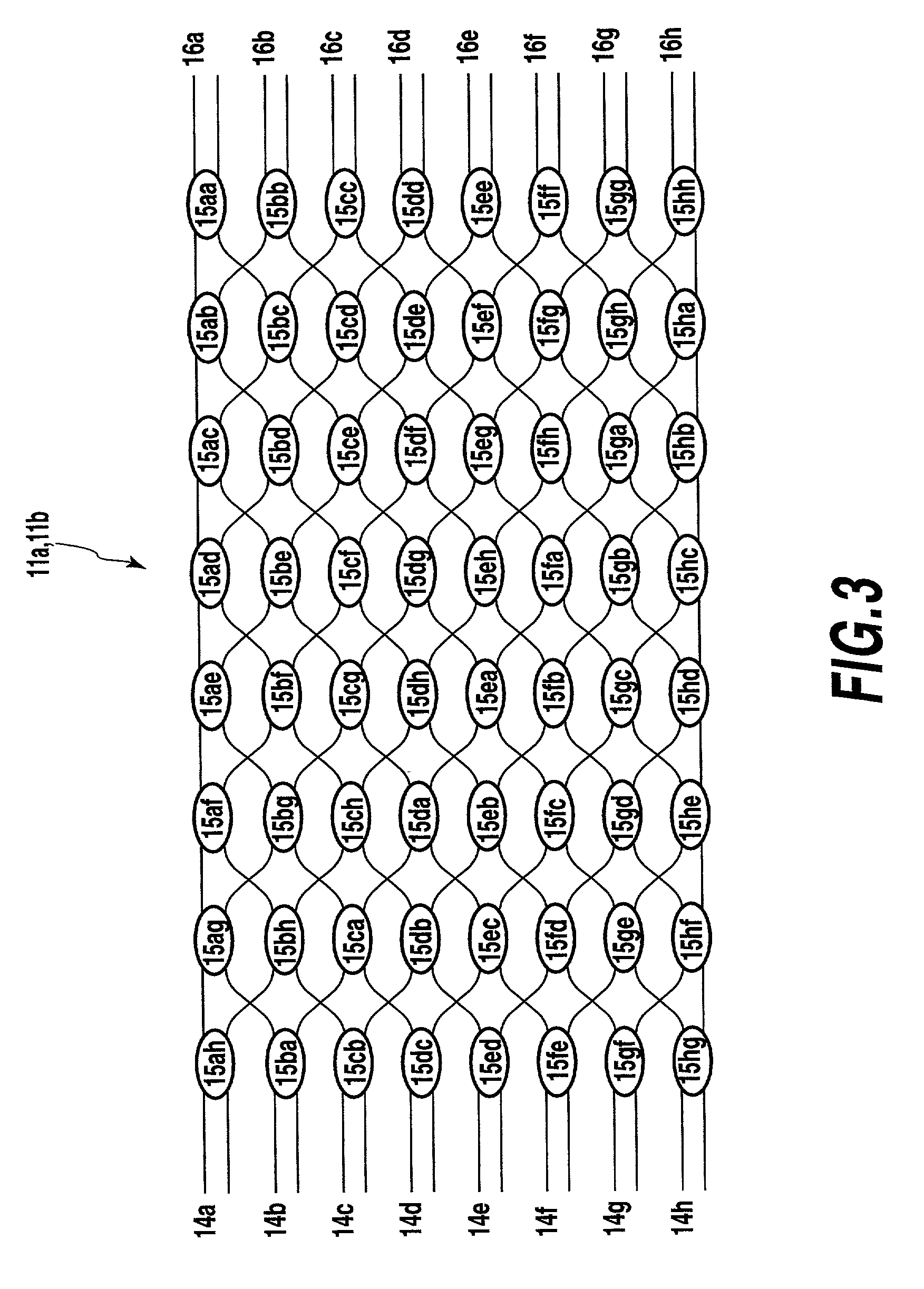
CDMA encoder-decoder, CDMA communication system, WDM-CDMA communication system
InactiveUS20010010739A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical code multiplexOptical cdmaGrating
An optical CDMA encoder-decoder is constructed by combining arrayed-waveguide gratings, matrix optical switches, and delay lines, otherwise by combining arrayed-waveguide gratings and variable delay lines, thus providing an encoding process that a wavelength change with respect to time in optical pulses.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Ocdm-based all optical multi-level security
ActiveUS20100091990A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical code multiplexMultiplexingComputer science
A high data rate optical signal is inverse multiplexed into a multitude of lower-rate tributaries, each of which is coded by its unique OCDM code, and the combined coded tributaries are injected into a common phase scrambler. Coherent summation of these optically encoded tributaries pass through a shared phase or phase and frequency scrambler before exiting the secure location. The setting of the scrambler acts as the key. The authorized recipient with the correct key retrieves the ones and zeros of the several decoded signals.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
Method and system for use in optical code division multiple access
InactiveUS20070110442A1Improve conversion efficiencyNarrow bandwidthLaser detailsOptical code multiplexOptical cdmaBroadband
A method and device are provided for automatically generating a key and a conjugate key to be used in an optical code division multiple access system. The method comprises applying a down conversion process to pump input light to thereby produce down converted broadband signal and idler fields that are complex conjugates of each other. The signal and idler fields thus serve as the key and its conjugate. Also provided according to the invention is a method for use in coding / decoding a signal in an optical code division multiple access system.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Popular searches
Other decoding techniques Broadcast transmission systems Frequency-division multiplex Radio transmission for post communication Two-way working systems Orthogonal multiplex Electrical cable transmission adaptation Error correction/detection using single space coding Baseband systems Synchronisation arrangement
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com