Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
409 results about "Aperture array" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An aperture array (an artist impression can be seen above) is a large number of small, fixed antenna elements coupled to appropriate receiver systems which can be arranged in a regular or random pattern on the ground.
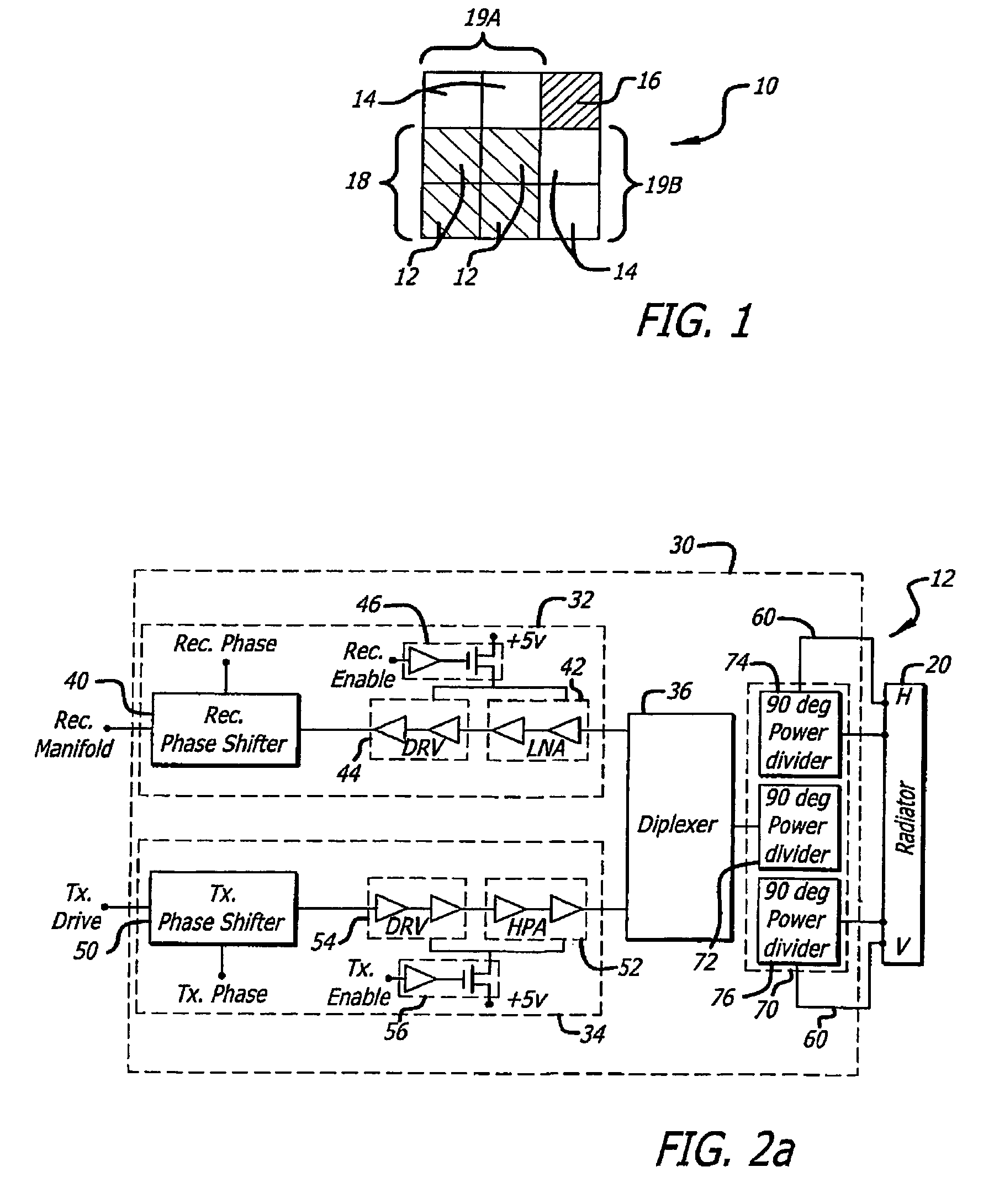
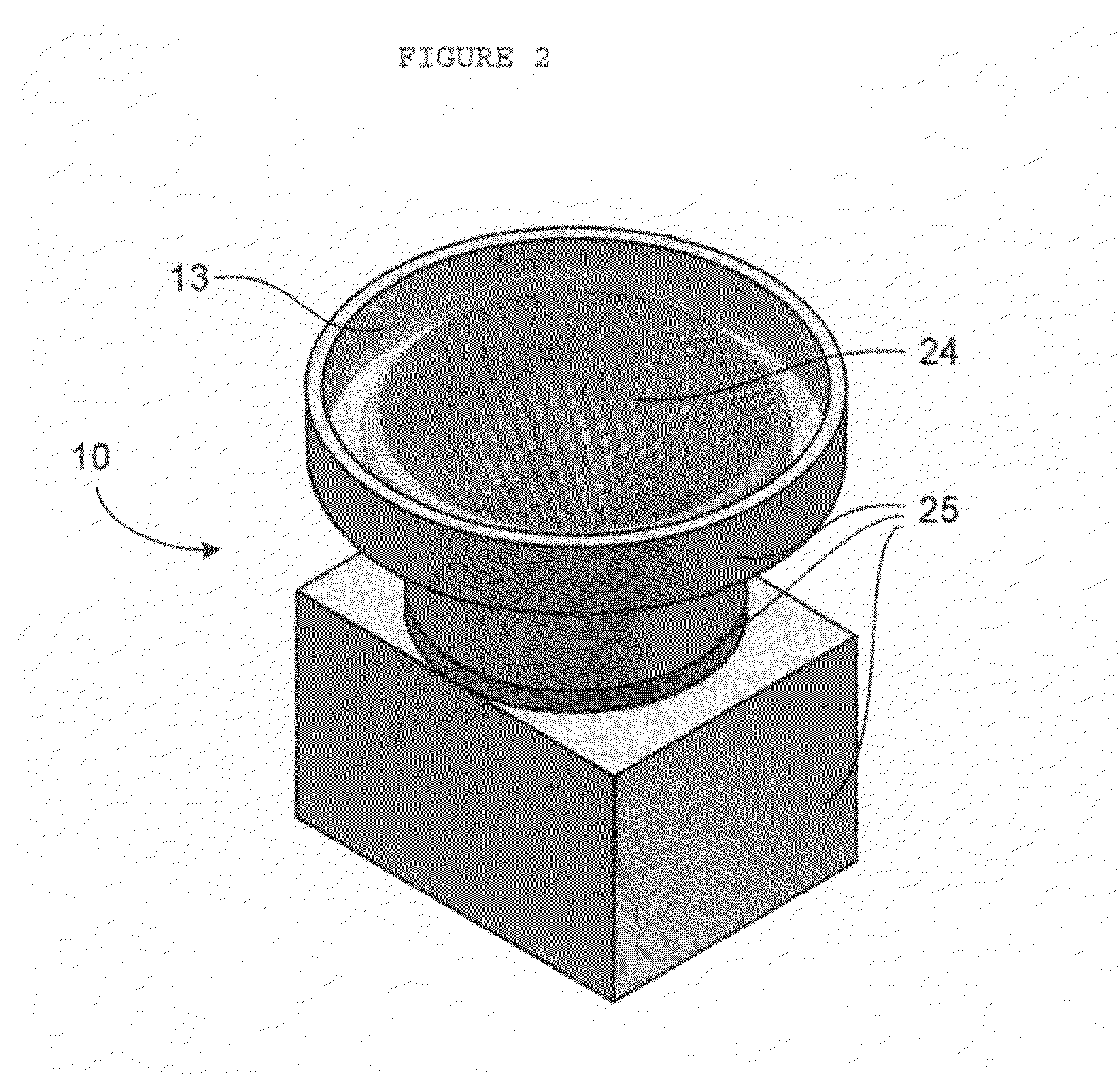
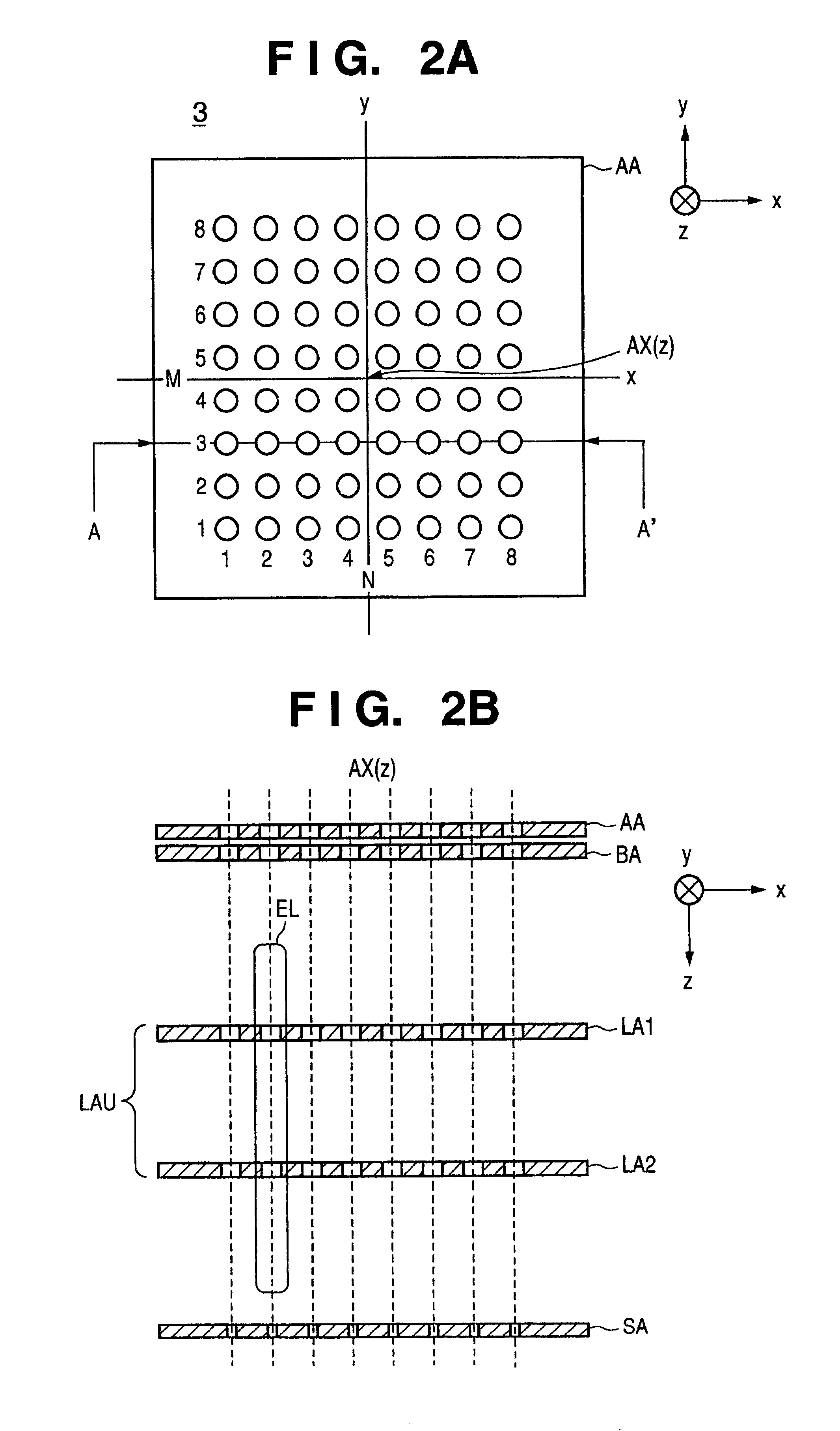
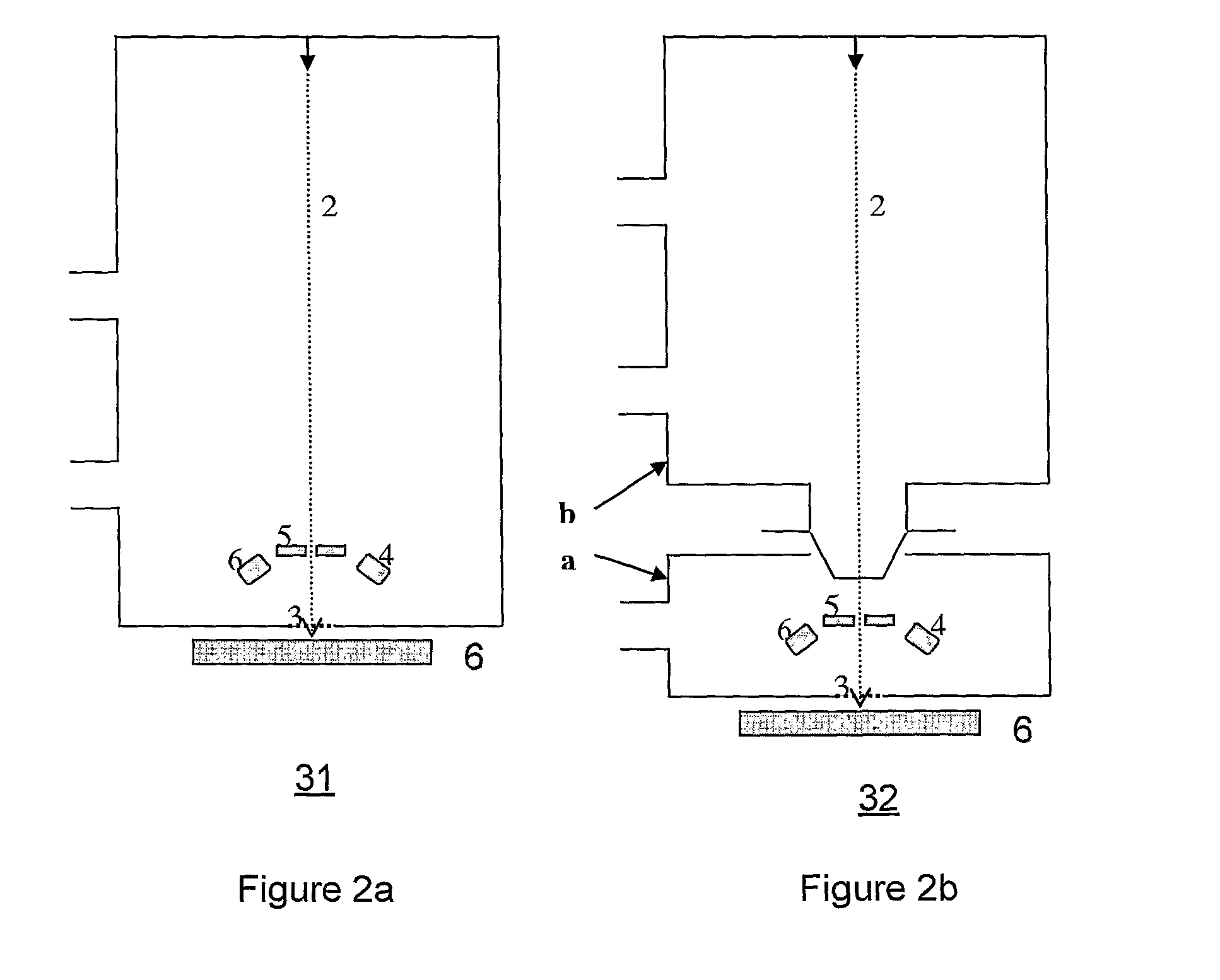
Partitioned aperture array antenna
ActiveUS8089404B2Minimize the numberExtend the antenna aperture of the receive beamSatellite radio beaconingRadio transmissionAntenna elementAperture array
A partitioned aperture array antenna. The novel antenna includes a first subarray having a first number of antenna elements equipped with transmit functionality and a second subarray having a second number of antenna elements equipped with receive functionality, wherein the first and second numbers are not equal and the first and second subarrays have at least one common antenna element. In an illustrative embodiment, the first subarray includes a transmit circuit coupled to each antenna element in the first subarray for controlling a relative transmit phase of the antenna element to steer an overall antenna transmit beam, and the second subarray includes a receive circuit coupled to each antenna element in the second subarray for controlling a relative receive phase of the antenna element to steer an overall antenna receive beam.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
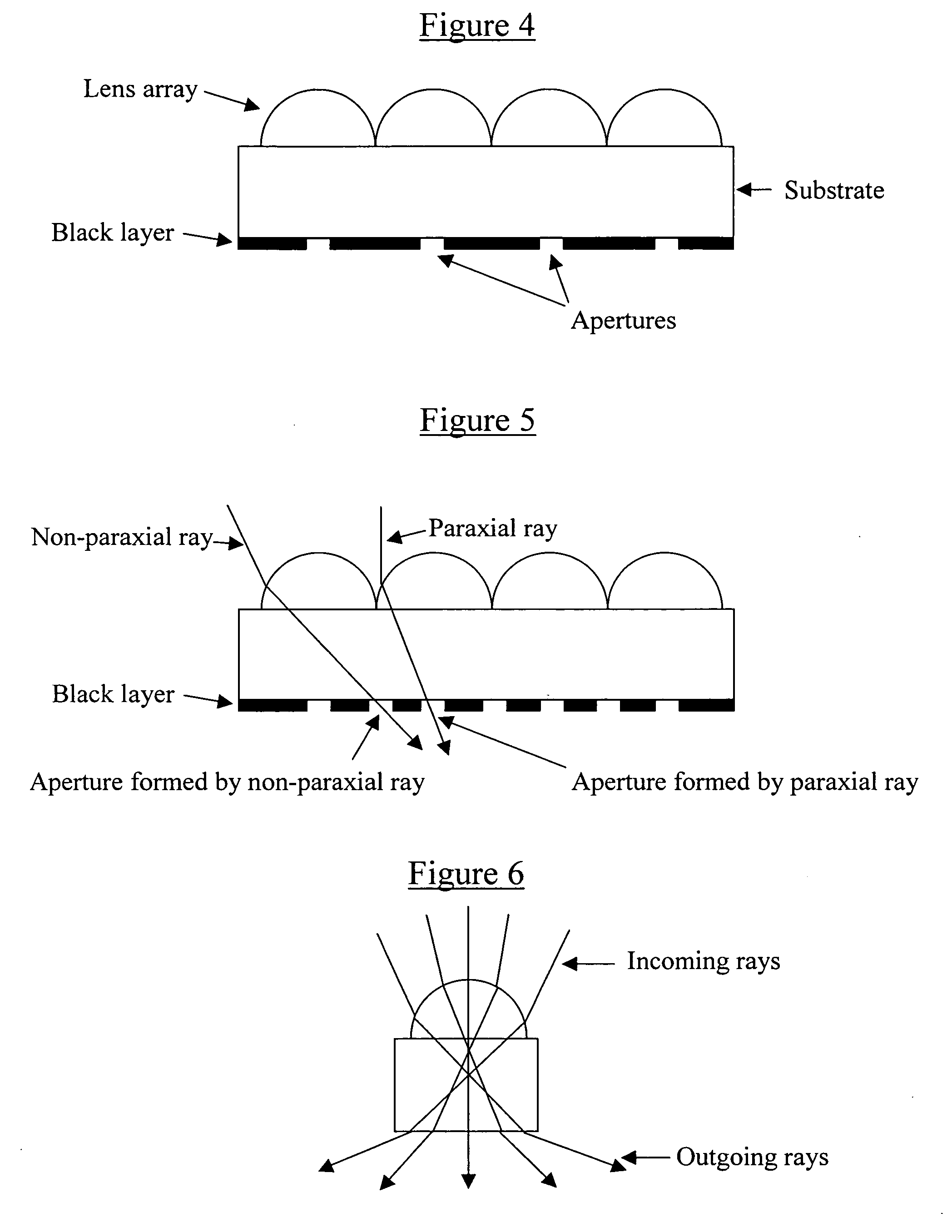
Microstructures for producing optical devices, sieves, molds and/or sensors, and methods for replicating and using same
InactiveUS20060061869A1Efficient productionPlanar/plate-like light guidesNon-linear opticsOptical axisMicro lens array
Microlens arrays include a substrate, an array of microlenses on a first side of the substrate and an aperture mask on a second side of the substrate. The aperture mask includes an array of apertures at optical axes of the lenses. A second array of apertures may be included in the aperture mask at randomized positions therein. The randomized apertures may be provided in the aperture mask by providing a diffusive layer between the aperture mask and the substrate, and directing coherent radiation through the lens array, the diffusive layer and aperture mask.
Owner:BRIGHT VIEW TECHNOLOGIES CORPORATION
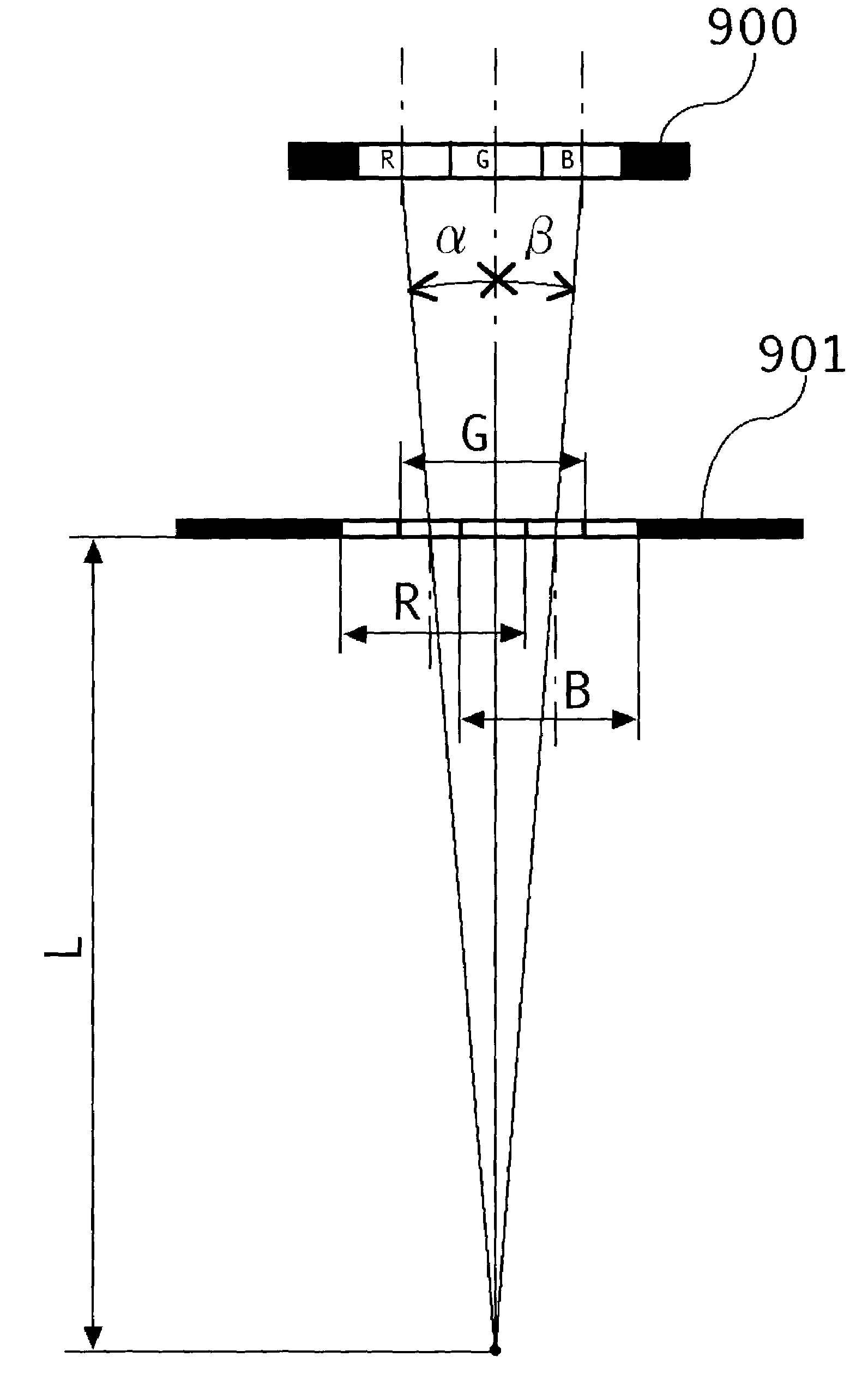
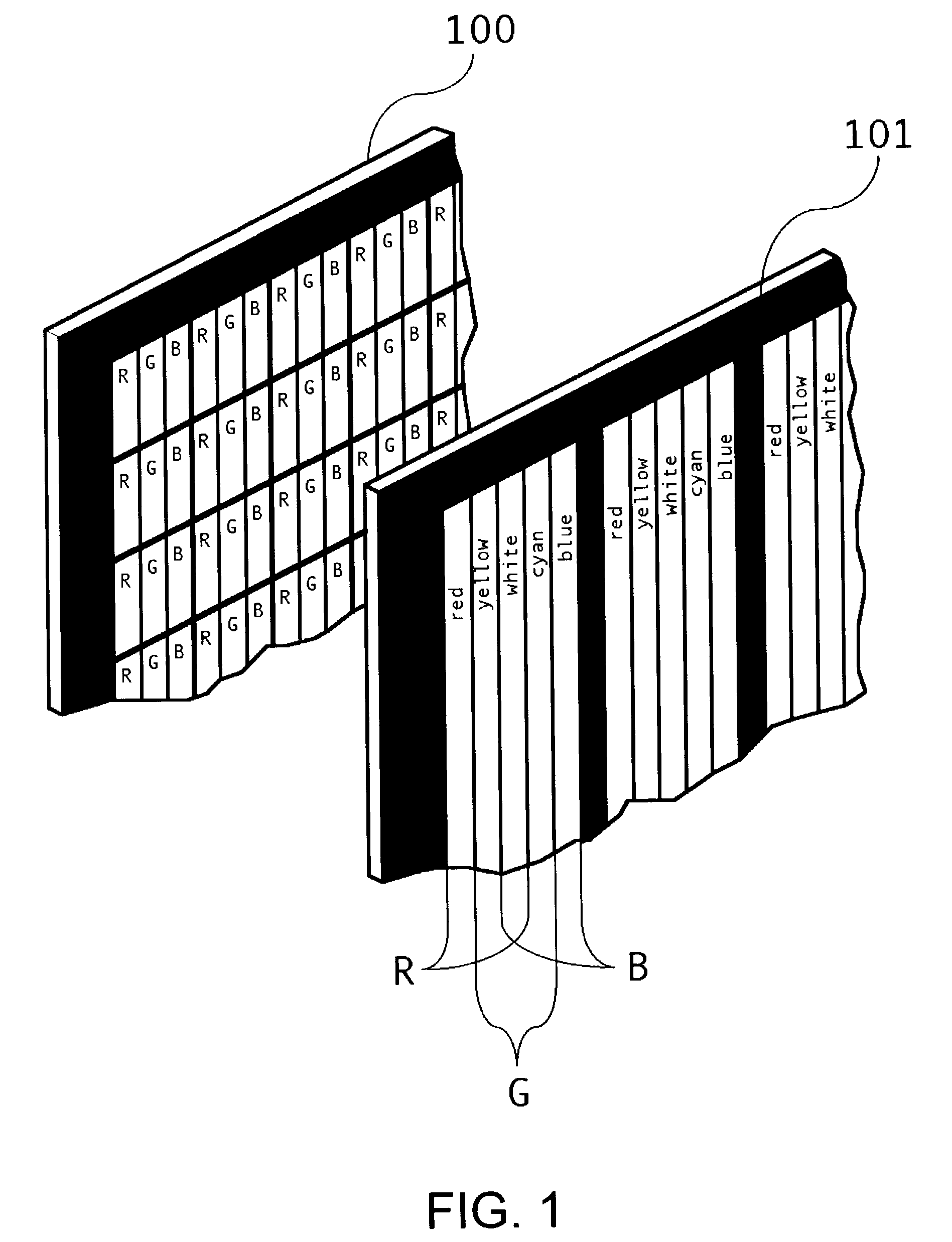
Three-dimensional image display apparatus and color reproducing method for three-dimensional image display
InactiveUS6980176B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsColor television detailsParallaxComputer graphics (images)
In a three-dimensional image display apparatus provided with a shading mask with a minute aperture array in front of a color display device, the minute apertures are provided with color filters, a setting is provided so that the visual angles between the respective centers of the red-light transmitting part, green-light transmitting part, and blue-light transmitting part of the color filters become equal, in an identical parallax image pixel region, to the visual angles between the respective centers of the red, green, and blue sub-pixels of the color display device, the respective red, green, and blue sub-pixels are made so as to be always displayed in a lighted condition at a fixed area ratio, thus color reproduction wherein brightness ratio of the three primary colors in respective parallax image pixels is maintained at an appointed value is carried out.
Owner:CANON KK
Ion enrichment aperture arrays
InactiveUS6914243B2Time-of-flight spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsAtmospheric pressure dischargeInductively coupled plasma
Improvements have been made for collecting, focusing, and directing of ions and / or charged particles generated at atmospheric or near atmospheric pressure sources, such as but not limited to, electrospray; atmospheric pressure discharge ionization, chemical ionization, photoionization, and matrix assisted laser desorption ionization; and inductively coupled plasma ionization. A multiple-aperture laminated structure is place at the interface of two pressure regions. Electric fields geometries and strengths across the laminated structure and diameters of the apertures; all of which act to optimize the transfer of the ions from the higher pressure region into the lower pressure region while reducing the gas-load on the lower pressure region. Embodiments of this invention are methods and devices for improving sensitivity of mass spectrometry when coupled to atmospheric, near atmospheric, or higher pressure ionization sources by reducing the gas-load on the vacuum system.
Owner:CHEM SPACE ASSOIATES
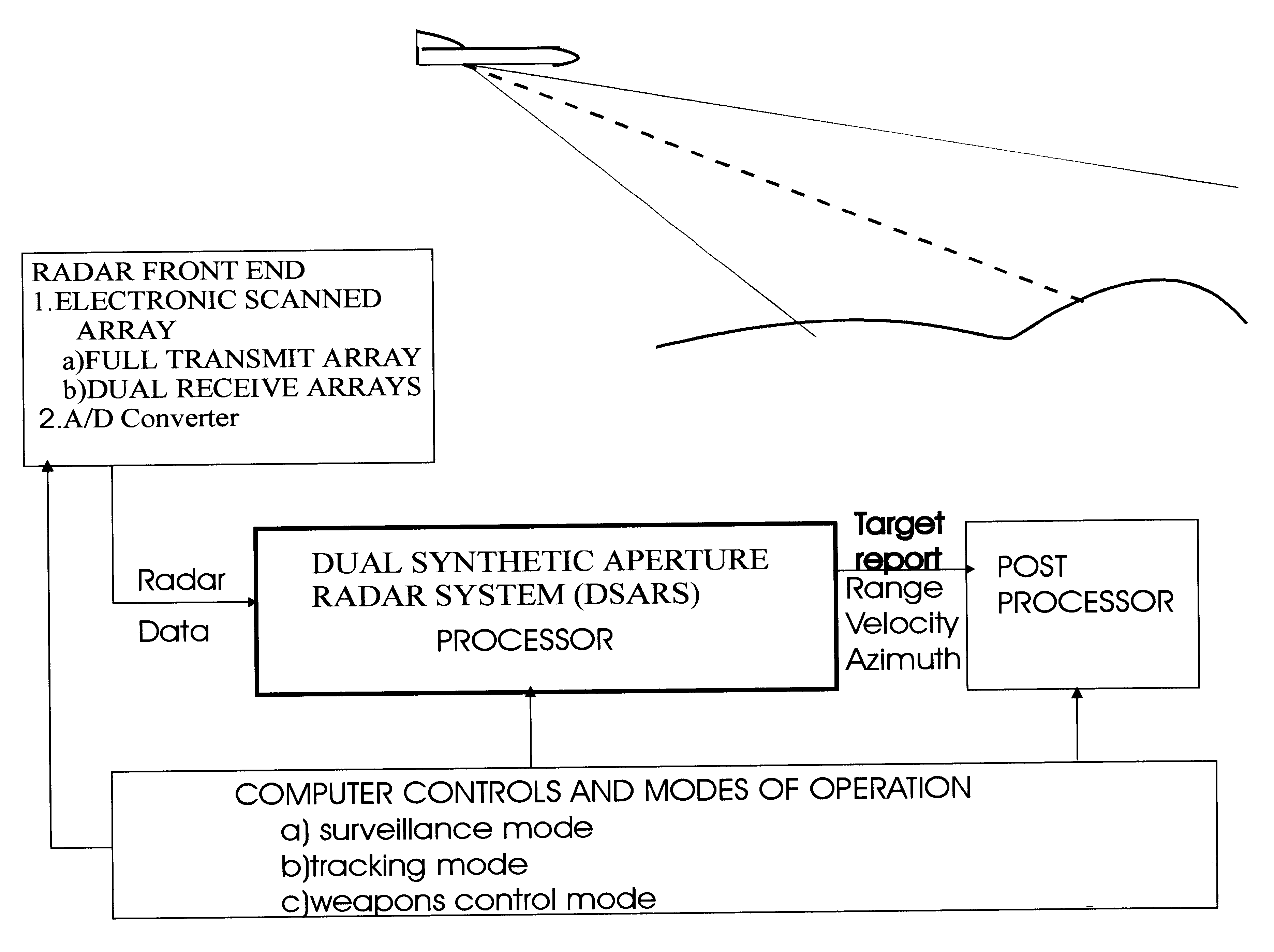
Dual synthetic aperture radar system
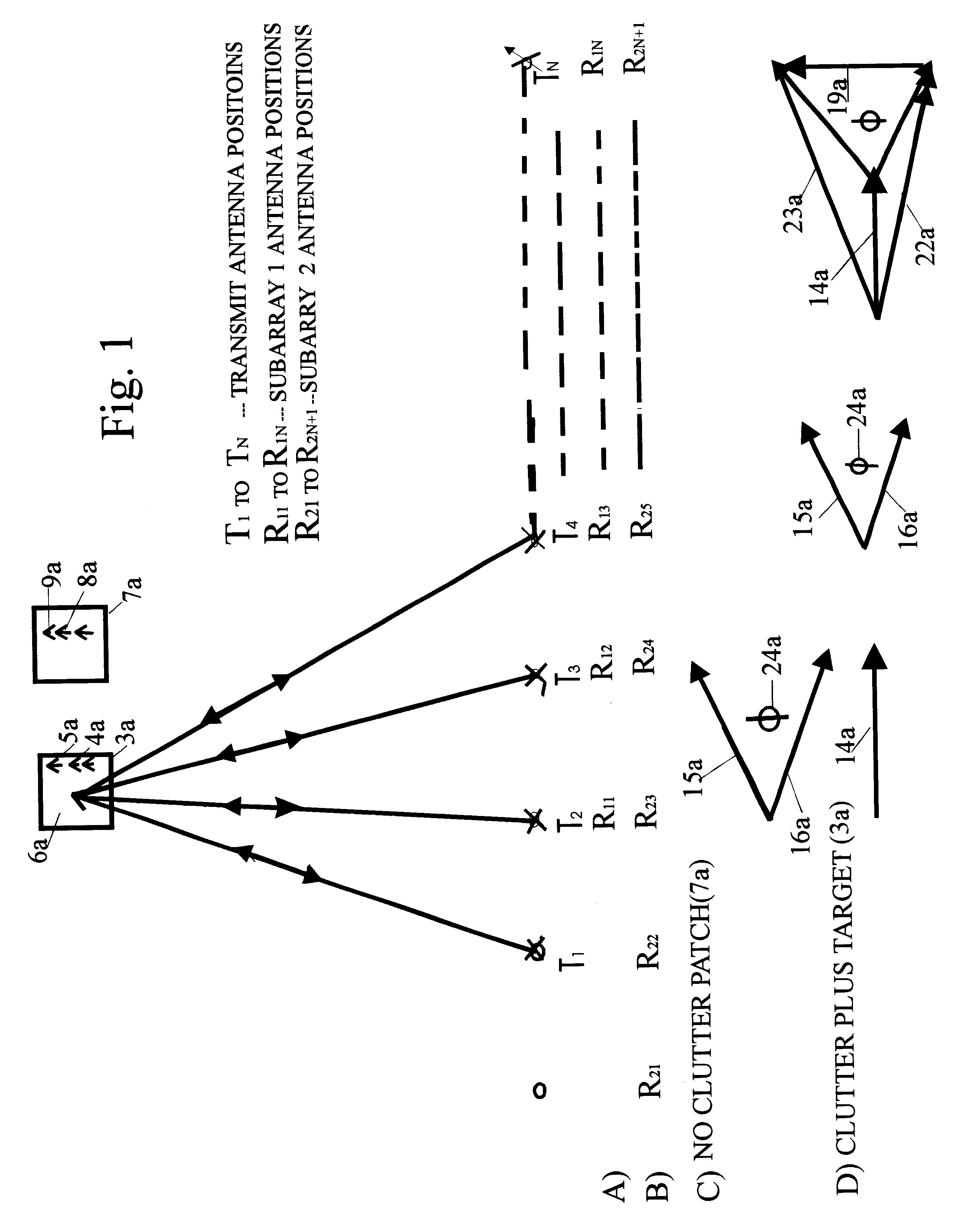
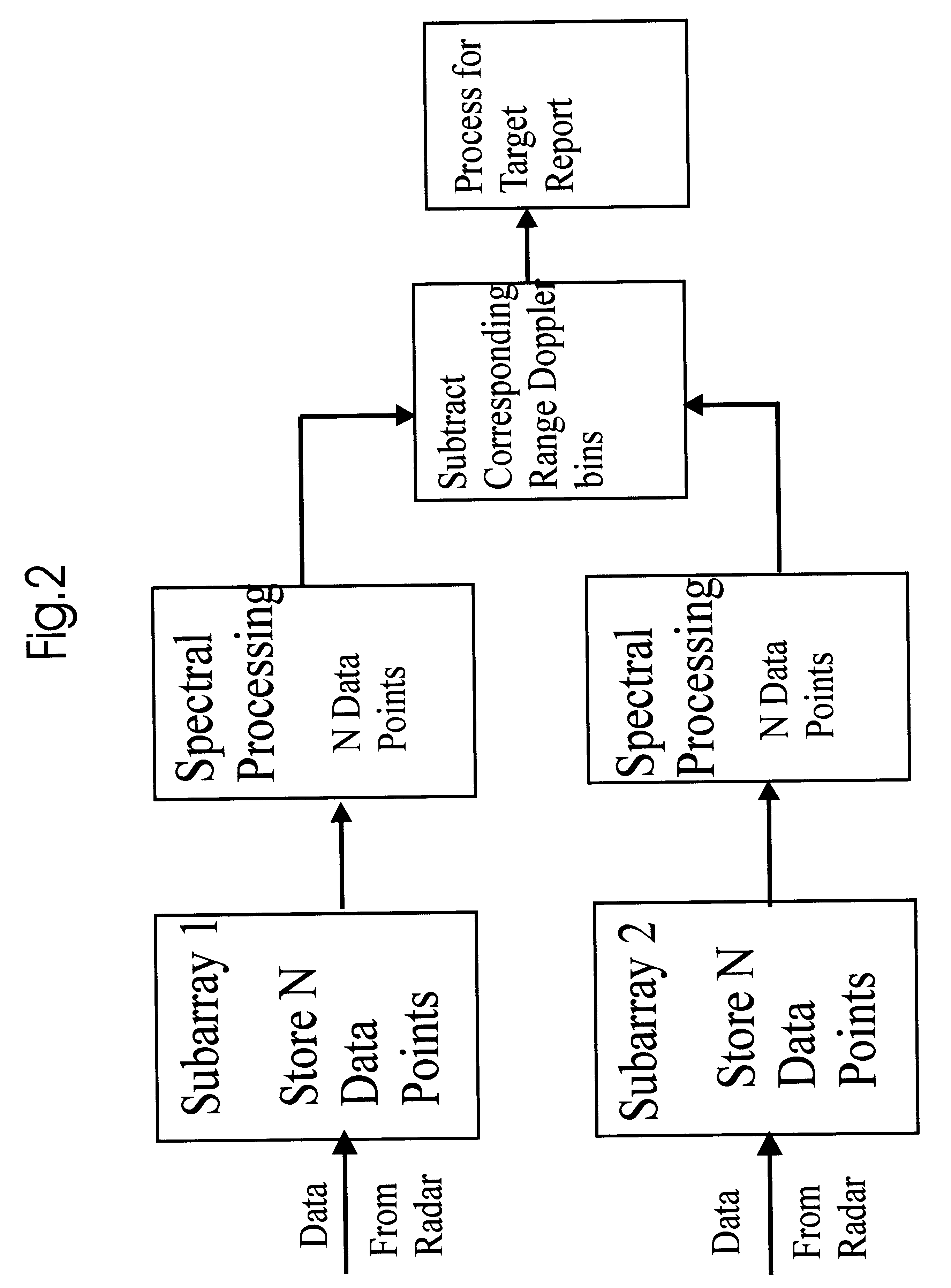
InactiveUS6633253B2Accurate angular positionAccurately radial velocityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumControl system
The dual synthetic aperture array system processes returns from the receiving arrays. The two identical receiving arrays employing displaced phase center antenna techniques subtract the corresponding spectrally processed data to cancel clutter. It is further processed that a moving target is detected and its velocity, angular position and range is measured, in or out of the presence of clutter. There are many techniques presented in the disclosure. These techniques are basically independent but are related based on common set of fundamental set of mathematical equations, understanding of radar principles and the implementations involved. These many techniques may be employed singly and / or in combination depending on the application and accuracy required. They are supported by a system that includes, optimization of the number of apertures, pulse repetition frequencies, DPCA techniques to cancel clutter, adaptive techniques to cancel clutter, motion compensation, weighting function for clutter and target, and controlling the system in most optimum fashion to attain the objective of the disclosure.< / PTEXT>
Owner:CATALDO THOMAS J
Ion enrichment aperture arrays
InactiveUS20040245458A1Maximizes transmission of ionImprove transmittanceTime-of-flight spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsAtmospheric pressure dischargeInductively coupled plasma
Improvements have been made for collecting, focusing, and directing of ions and / or charged particles generated at atmospheric or near atmospheric pressure sources, such as but not limited to, electrospray; atmospheric pressure discharge ionization, chemical ionization, photoionization, and matrix assisted laser desorption ionization; and inductively coupled plasma ionization. A multiple-aperture laminated structure is place at the interface of two pressure regions. Electric fields geometries and strengths across the laminated structure and diameters of the apertures; all of which act to optimize the transfer of the ions from the higher pressure region into the lower pressure region while reducing the gas-load on the lower pressure region. Embodiments of this invention are methods and devices for improving sensitivity of mass spectrometry when coupled to atmospheric, near atmospheric, or higher pressure ionization sources by reducing the gas-load on the vacuum system.
Owner:CHEM SPACE ASSOIATES
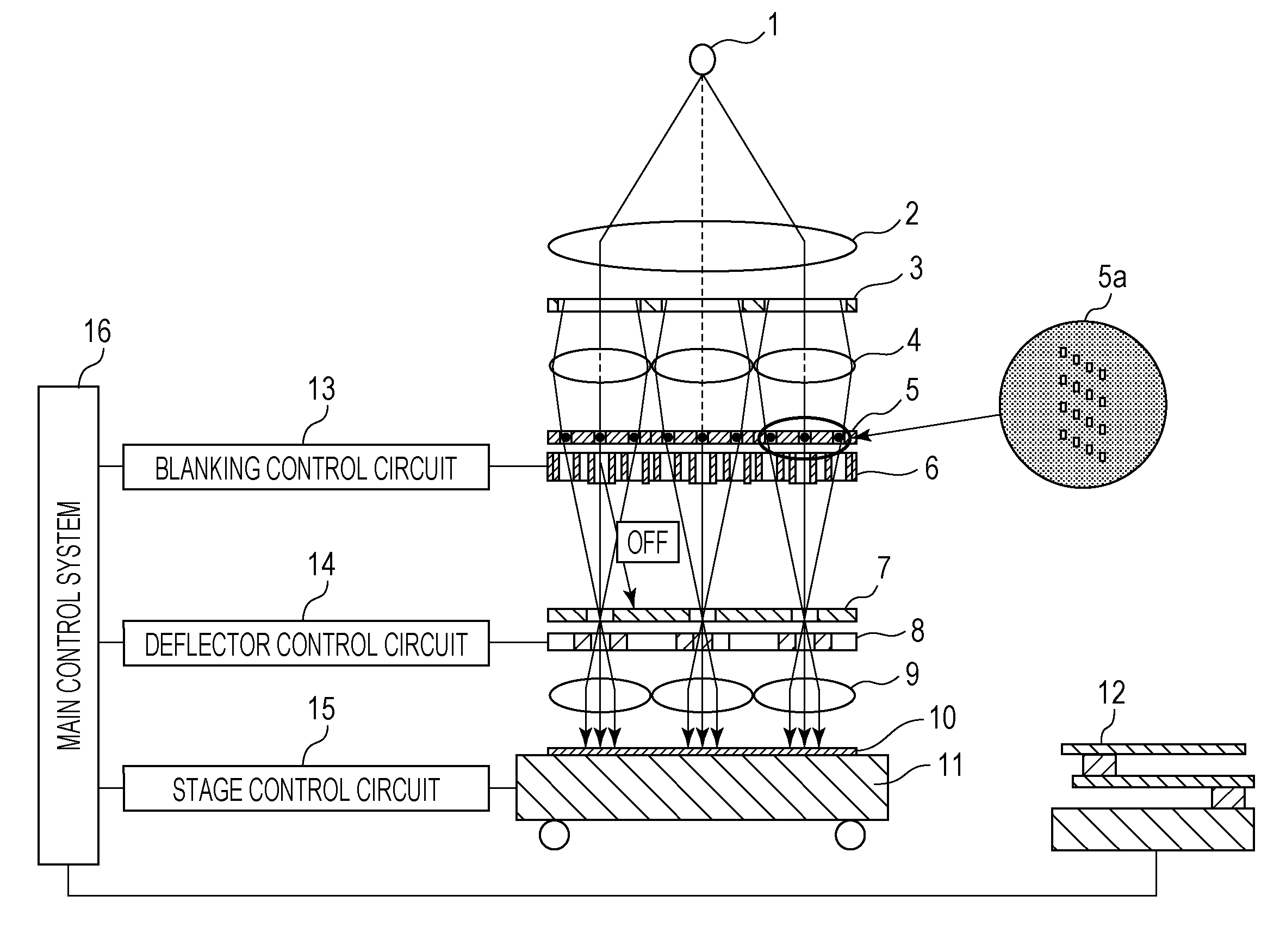
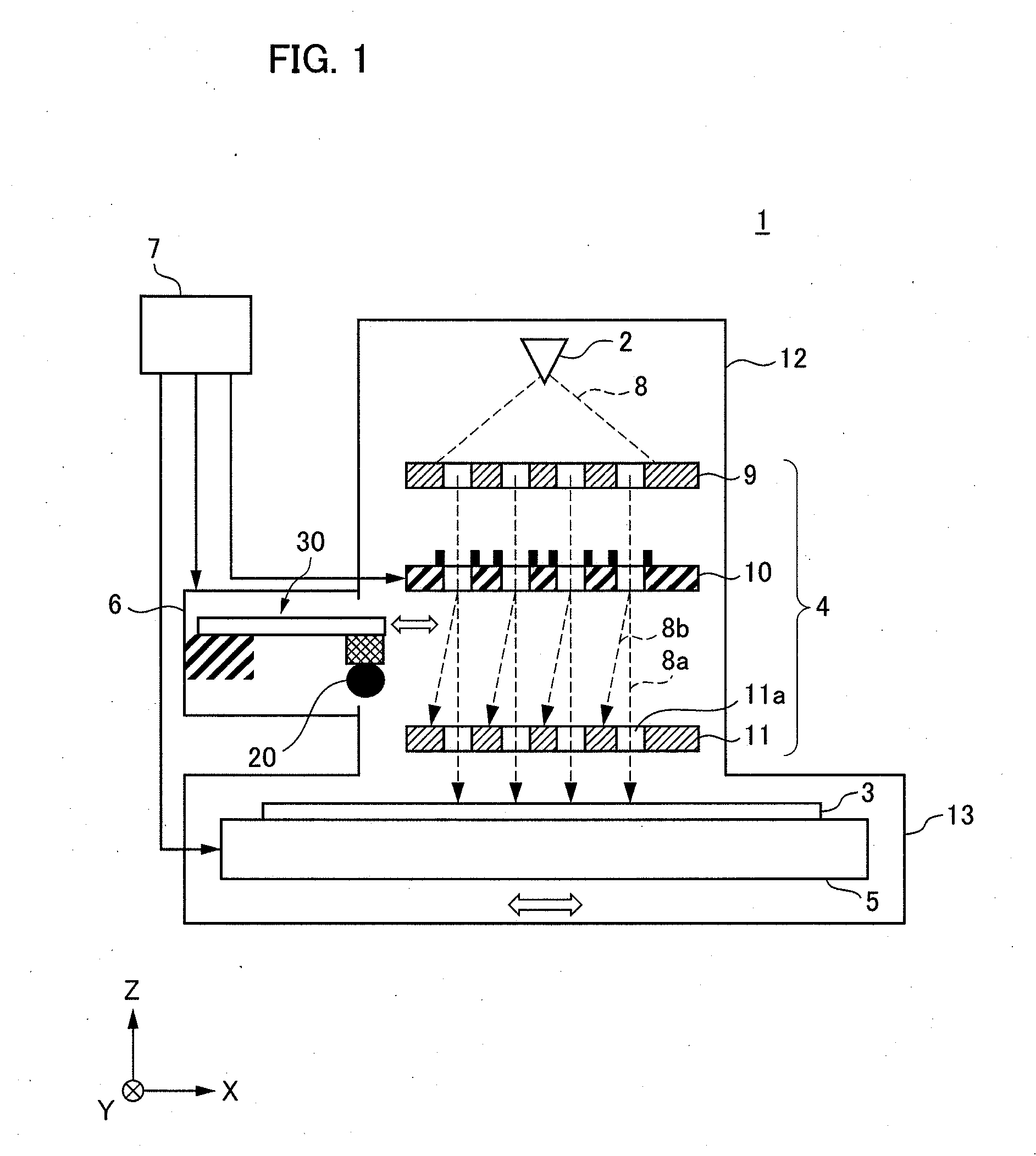
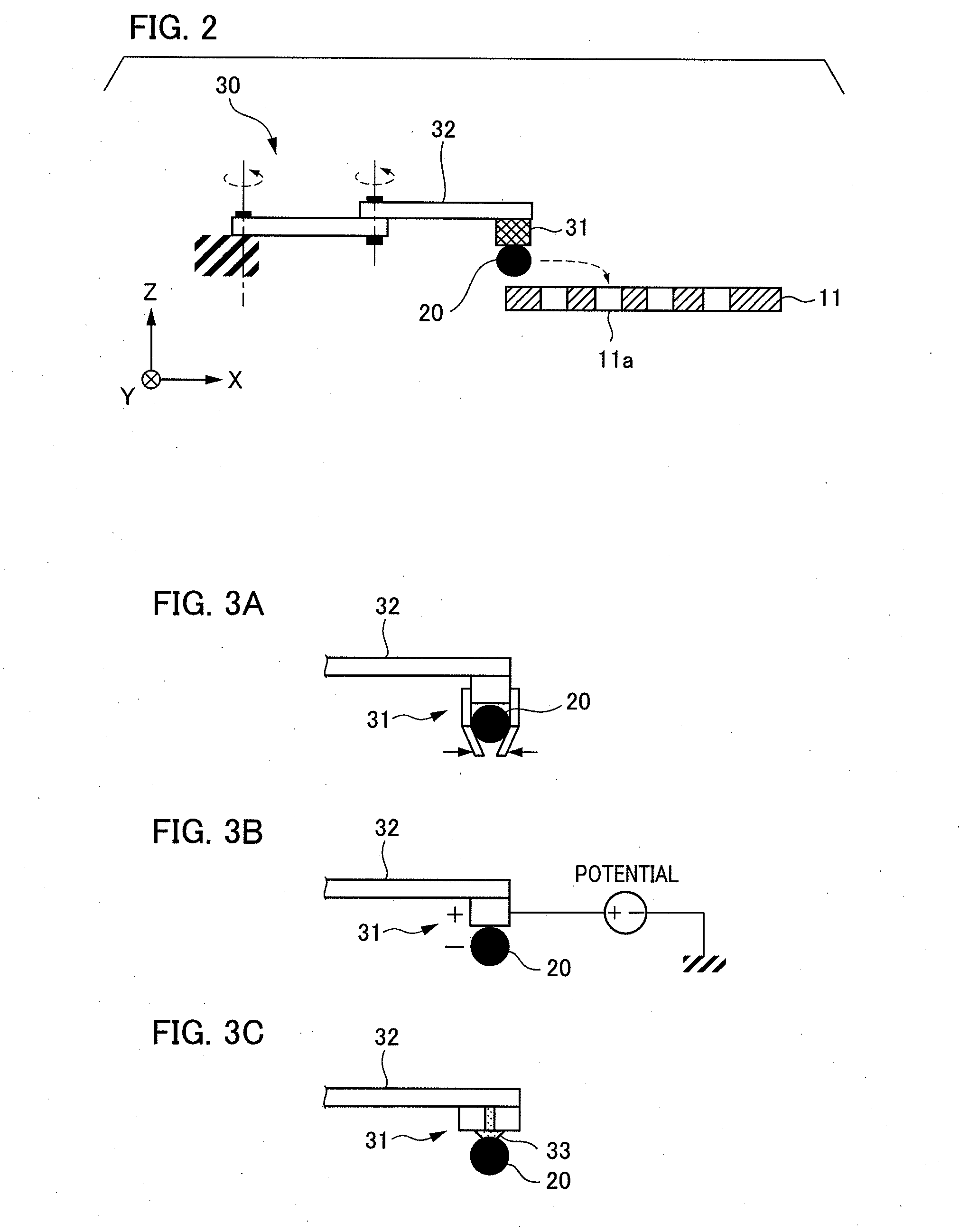
Charged particle beam applied apparatus
ActiveUS8350214B2Easy to implementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementBeam scanningSource image
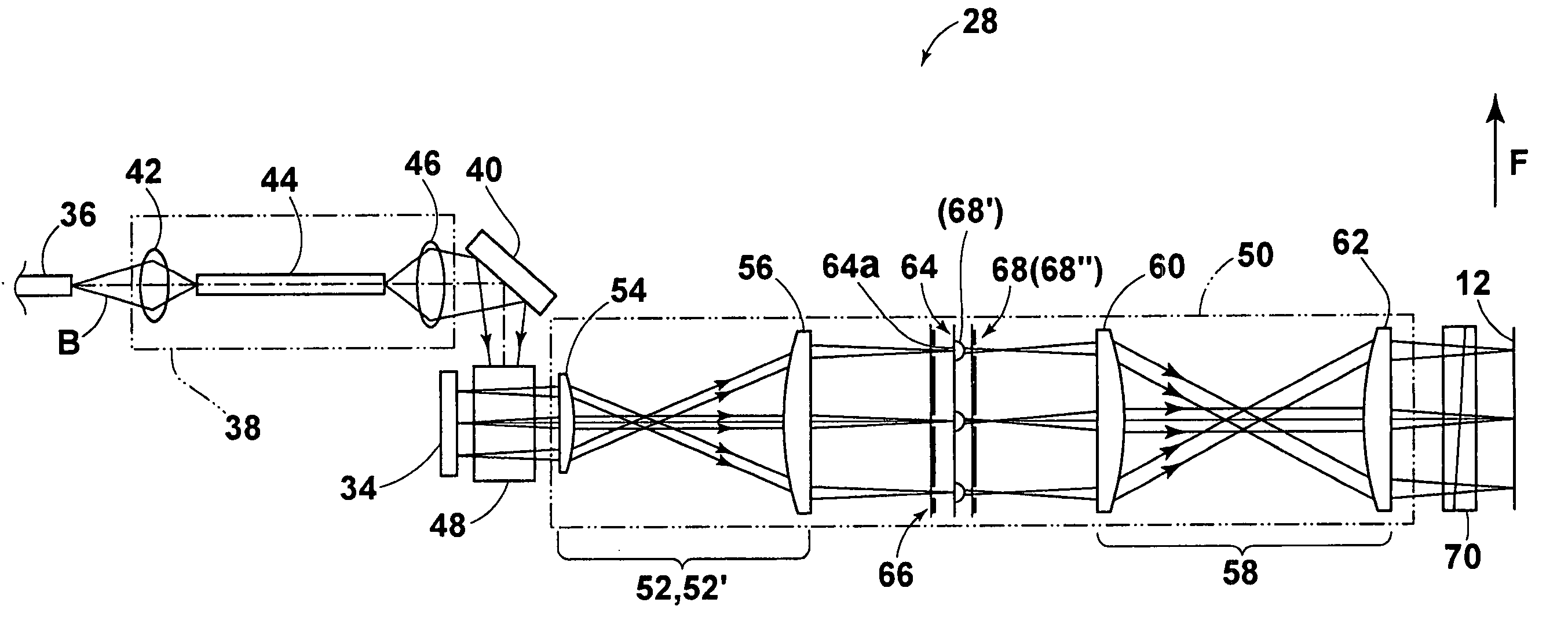
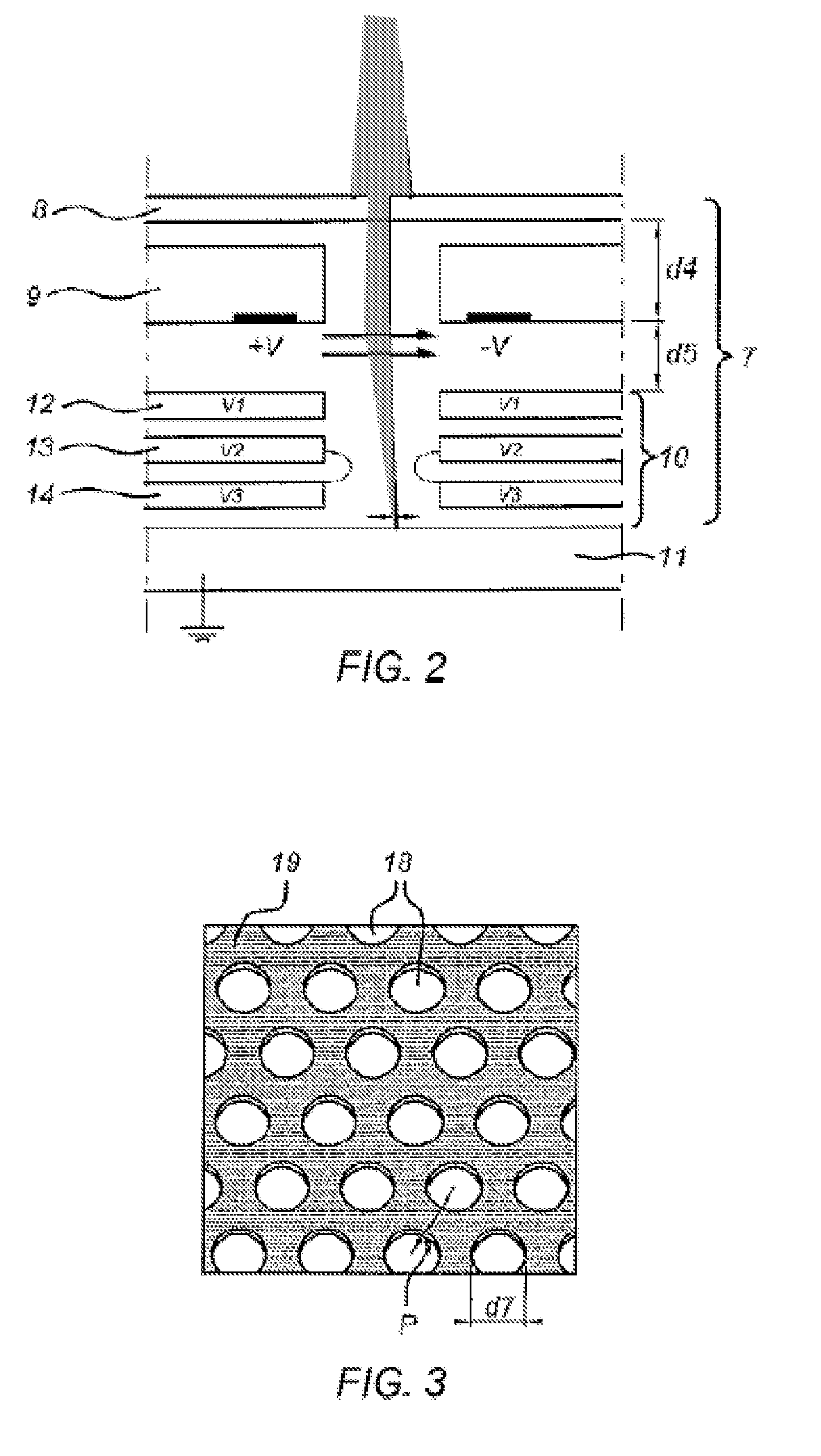
Provided is a multi-beam type charged particle beam applied apparatus in an implementable configuration, capable of achieving both high detection accuracy of secondary charged particles and high speed of processing characteristically different specimens. An aperture array (111) includes plural aperture patterns. A deflector (109) for selecting an aperture pattern through which a primary beam passes is disposed at the position of a charged particle source image created between an electron gun (102), i.e., a charged particle source, and the aperture array (111). At the time of charge-control beam illumination and at the time of signal-detection beam illumination, an aperture pattern of the aperture array (111) is selected, and conditions of a lens array (112), surface electric-field control electrode (118) and the like are switched in synchronization with each beam scanning. Thus, the charges are controlled and the signals are detected at different timings under suitable conditions, respectively.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
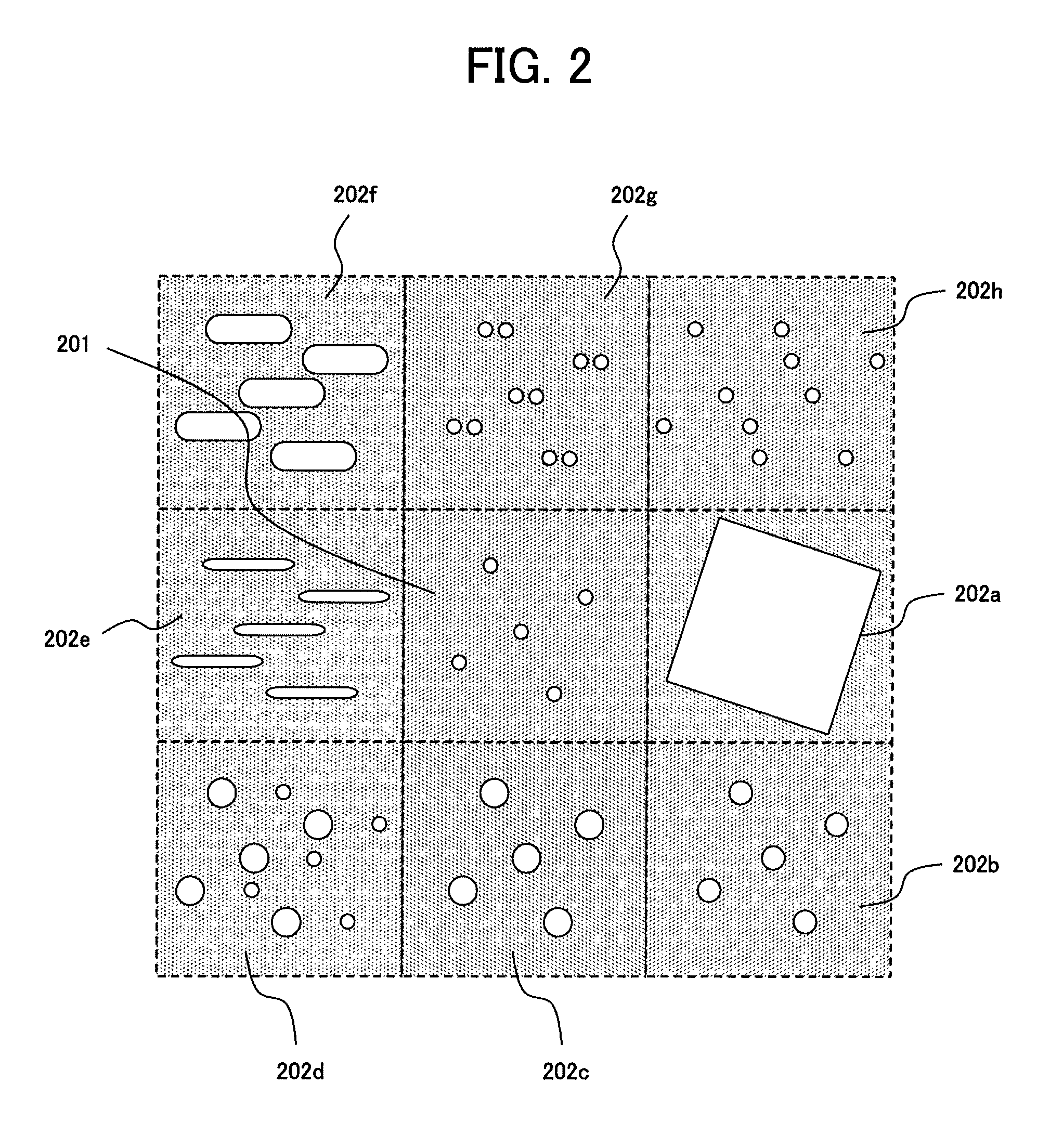
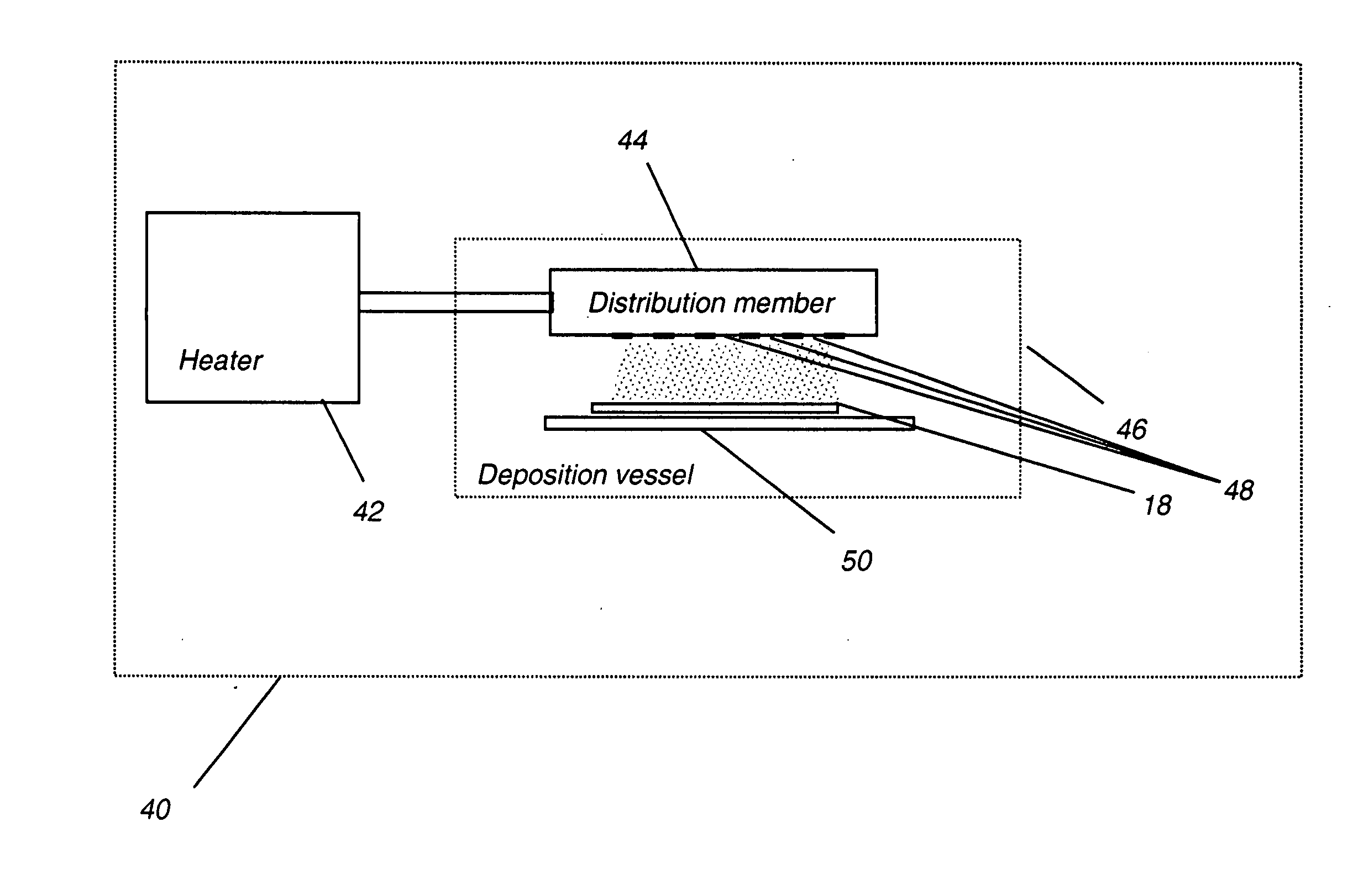
Two-dimensional aperture array for vapor deposition
ActiveUS20070163497A1High masking precisionImprove accuracyVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingGas phaseEngineering
A method for forming a layer on a surface in making a device, including providing a distribution member for receiving vaporized material, the distribution member having one or more walls defining a polygonal two-dimensional pattern of apertures is formed in a wall, which deliver vaporized material in a molecular flow onto the surface; providing the polygonal two-dimensional pattern of apertures to have at least four vertices, with a first set of apertures disposed at the vertices, a second set of edge apertures disposed between the apertures of the first set and defining the edges of the polygonal two-dimensional pattern, and a third set of interior apertures disposed within the periphery of the polygonal two-dimensional pattern defined by the first and second sets of apertures; and dimensioning the apertures to obtain a desired flow rate.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Two-dimensional light-modulating nano/micro aperture array and high-speed nano pattern recording system utilized with the array
ActiveUS7400380B2High light transmittanceIncrease motivationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanotechnologyLight beamAperture array
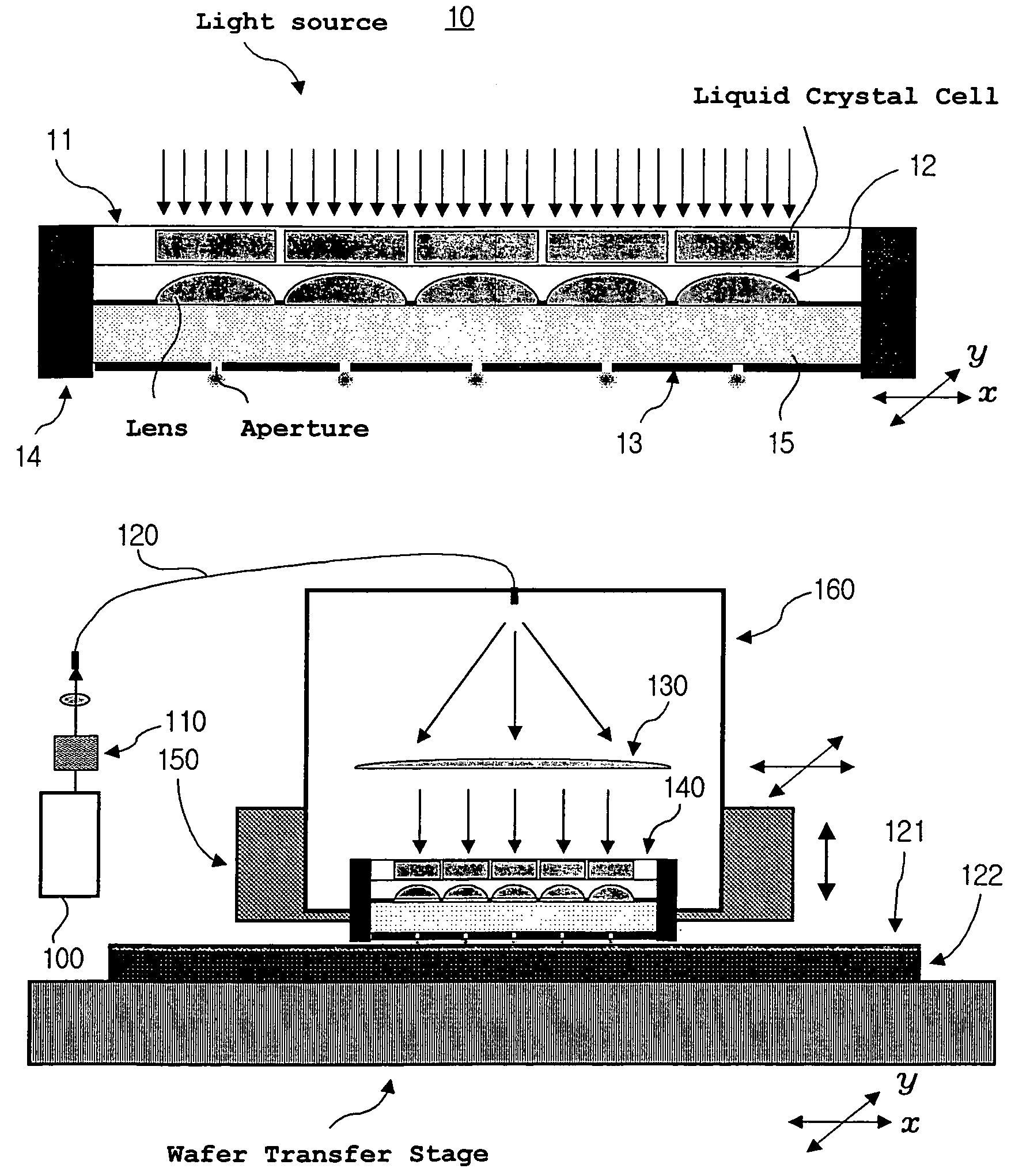
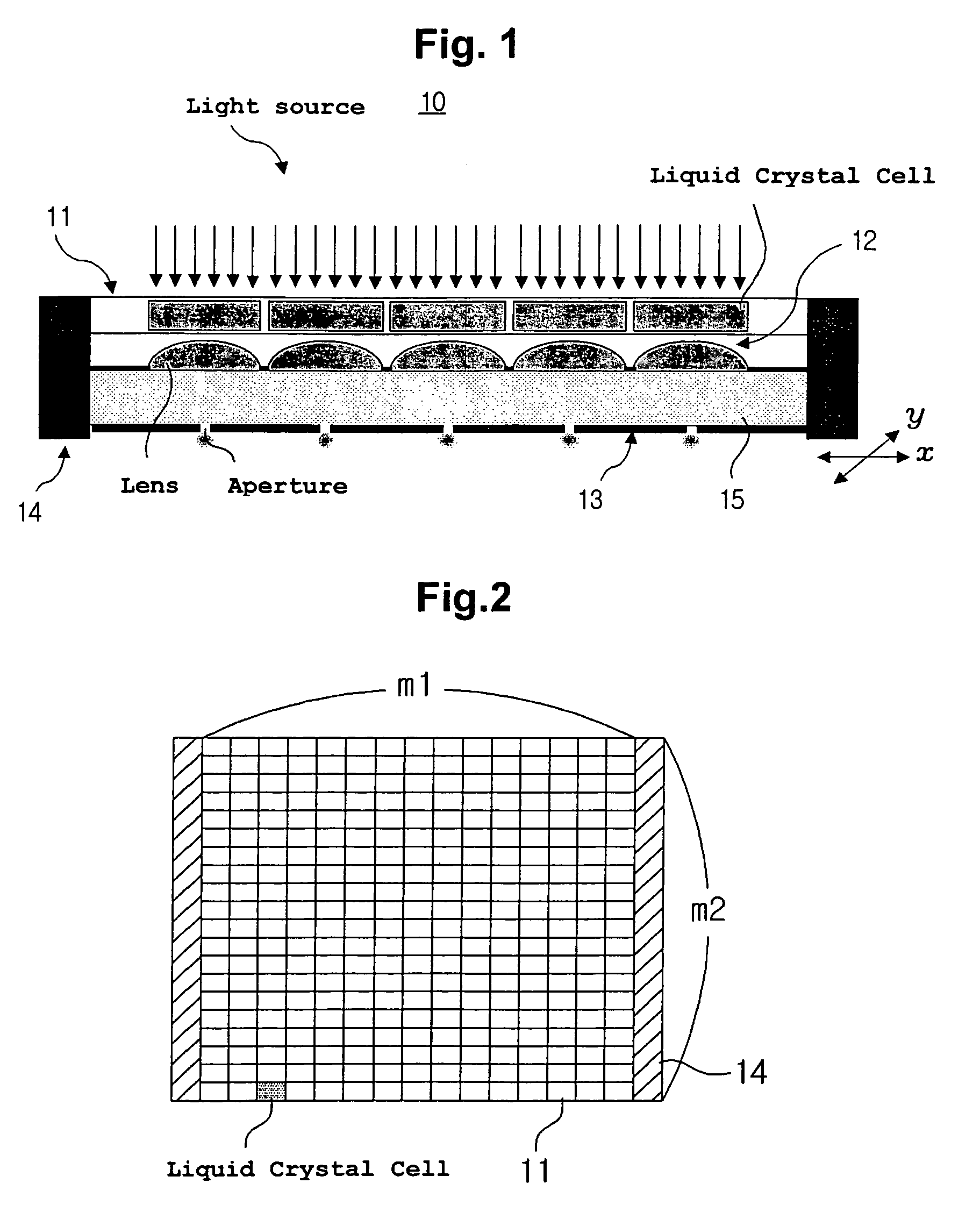
A two-dimensional light-modulating fine aperture array apparatus includes a spatial light-modulating unit for adjusting quantity of incident light by using a plurality of light amount adjusting cells (liquid crystal cells or micromirrors) arrayed in matrix form, a two-dimensional microlens array having microlenses which focus light beams passing through the light quantity adjusting cells, and a highly efficient two-dimensional fine aperture array. The light is emitted through the fine apertures by connecting the two-dimensional light-modulating fine aperture array apparatus with a light source unit. A scanning unit moves in the x and y directions to perform a scanning process on a surface of a recording medium by using the light emitted from the apertures.
Owner:YONSEI UNIVERSITY
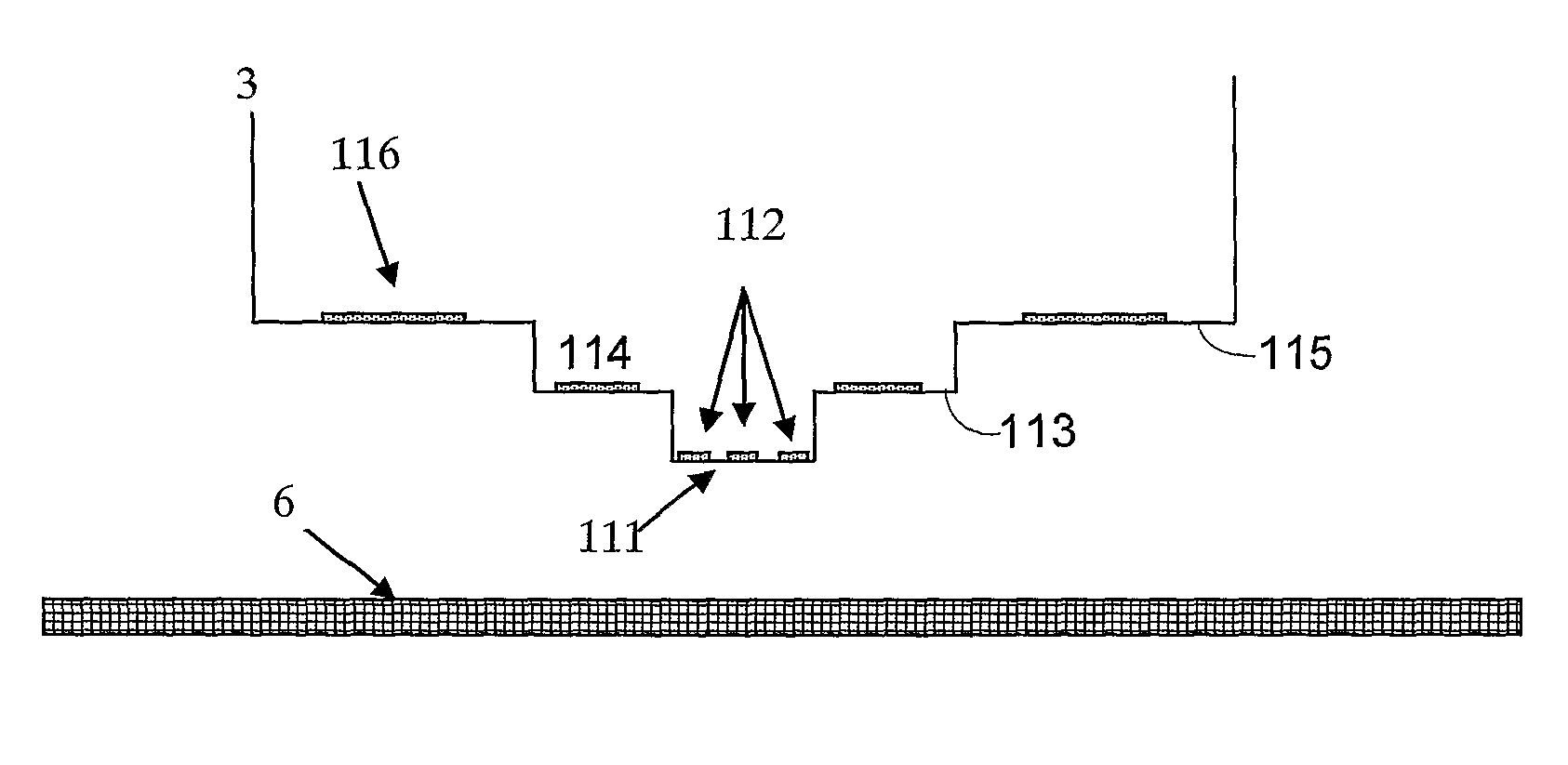
Measuring device and method that operates according to the basic principles of confocal microscopy
InactiveUS7679723B2Easy to detectAccurate analysisScattering properties measurementsMicroscopesMeasurement deviceObject point
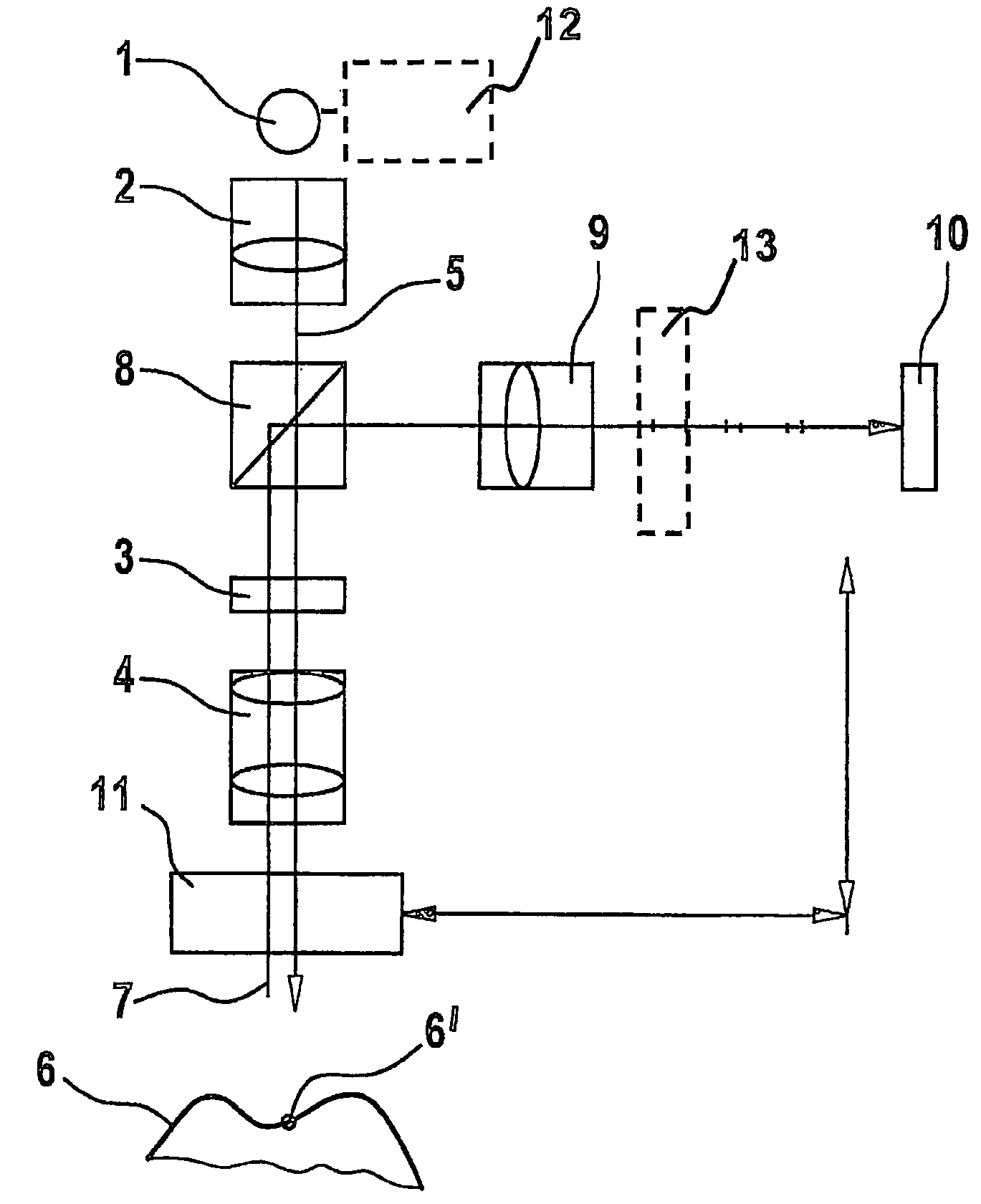
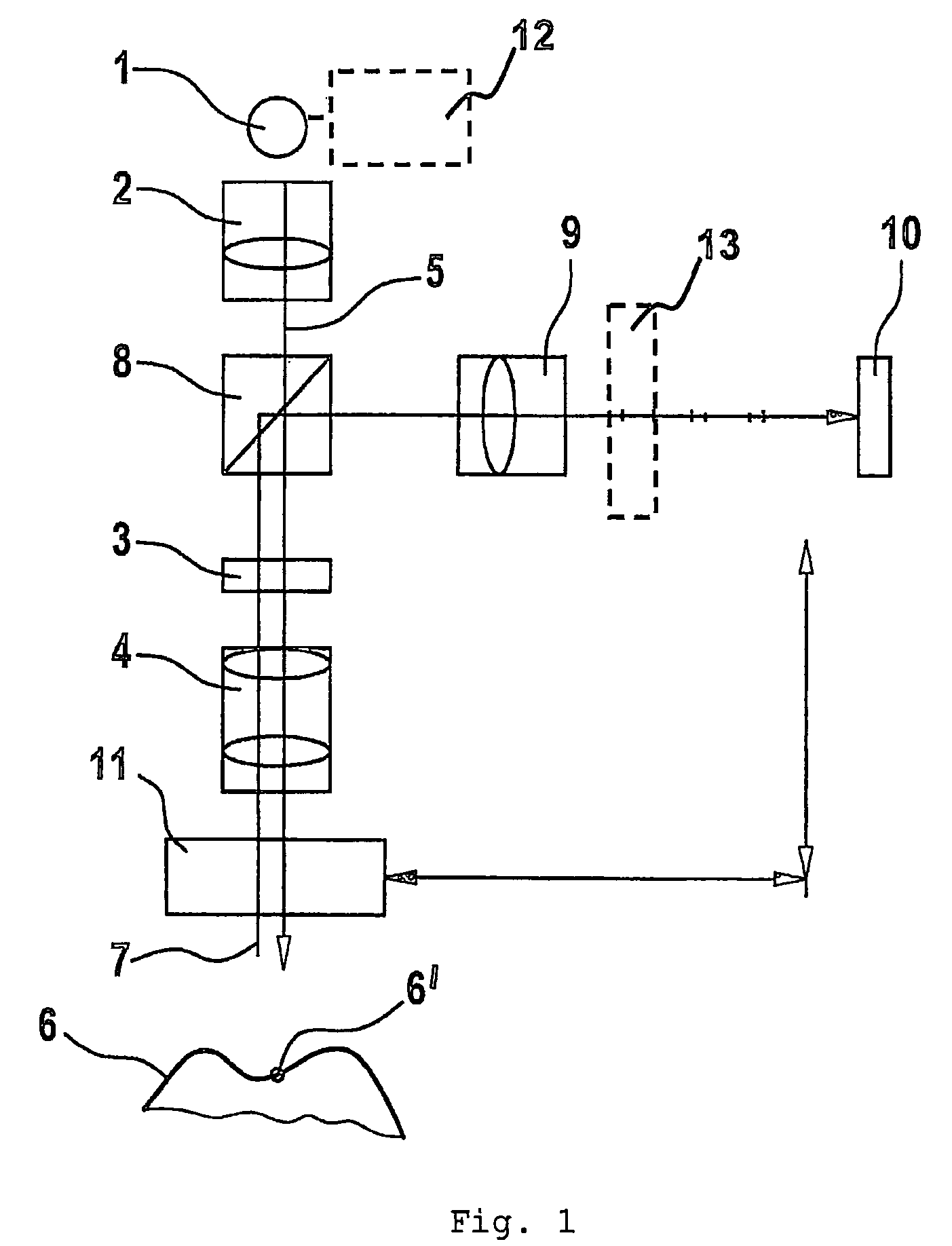
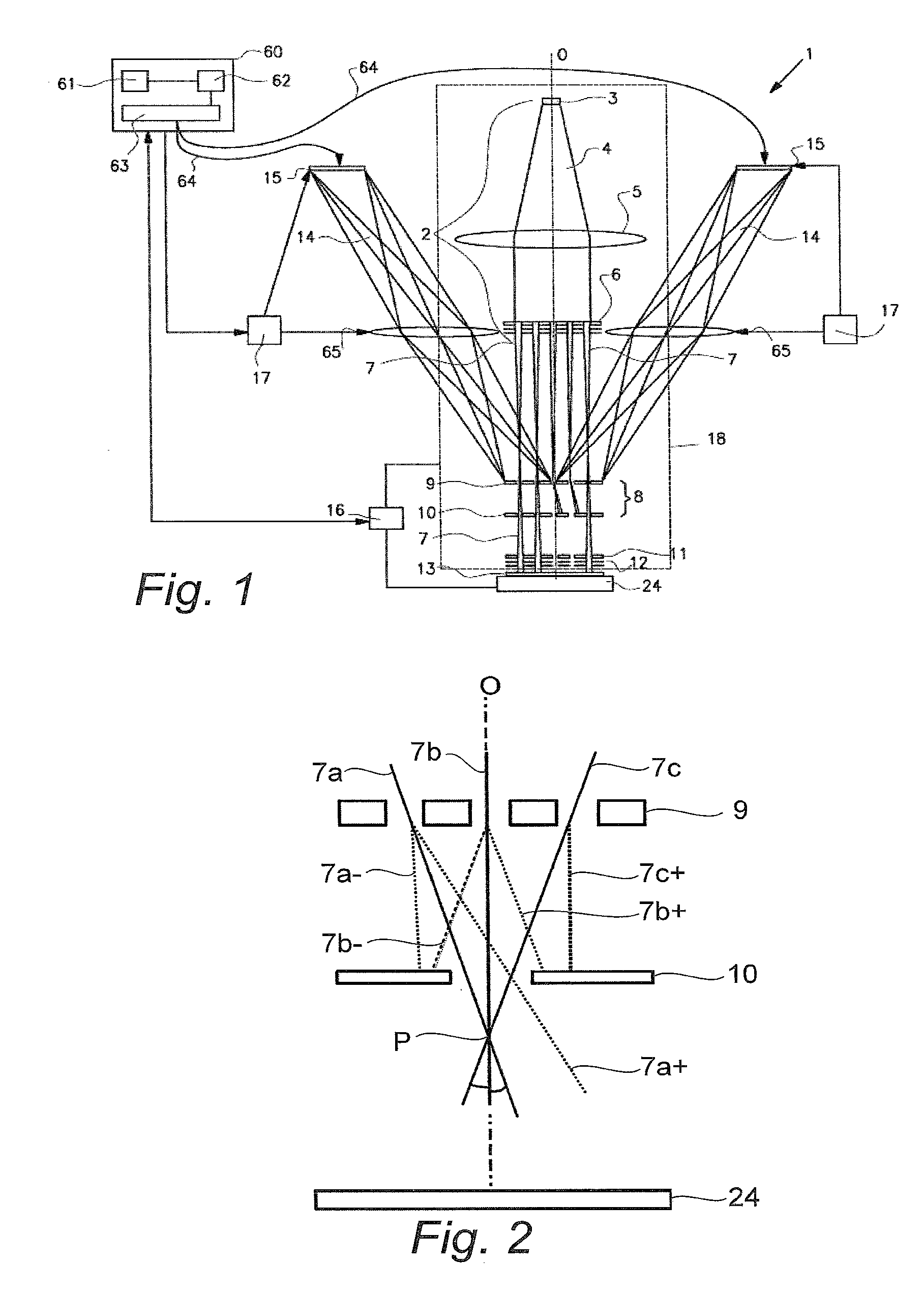
A scanning system for confocal scanning of an object, comprising a light source (1), imaging optics (4) for focusing the light (5) radiated from the light source (1) onto the object (6) to be scanned, and further comprising an image detector (10) for detecting the light (7) from an object point (6′) backscattered from the object (6) and passing through the same imaging optics (4). Means (11) for varying the length of the optical path are disposed in the optical path between the aperture array (3) and the object (6), by which means the optical distance of the image plane can be modified in a specific manner, and means are provided to influence the light (5) radiated by the light source onto the object (6) and / or the light (7) reflected from the object (6) and impinging on the sensor (10), in at least one of its characteristics, during an exposure period (tB1) for acquiring an image, and, during said exposure period (tB1), a profile holds which states a specific relationship between the characteristic of the light (5, 7) and the optical distance of the image plane from the imaging optics (4), and means (10) are provided which provide a measured value dependent on the characteristics of the light of the trajectory of observation (7) over the exposure period (tB1), a height coordinate (Zs) of the object (6) being reconstructable from the measured value achieved during said exposure period (tB1) and a reference value.
Owner:SIRONA DENTAL SYSTEMS
Multiple-Input Method And Apparatus Of Free-Space Optical Communication
An approach is provided that uses diversity to compensate fading of free-space optical (FSO) signals propagating through an environment characterized by atmospheric scintillation. One embodiment involves collecting at least one FSO beam, demultiplexing the beam by wavelength into at least two sub-beams, detecting each sub-beam to produce an electrical output therefrom, and recovering a signal using complementary information from at least two of the electrical outputs. Another embodiment involves collecting the FSO beam onto an array of spatially separated sub-apertures, detecting the light entering each sub-aperture to produce an electrical output therefrom, and recovering a signal using complementary information from at least two of the electrical outputs. This second embodiment enables both electronic adaptive processing to coherently integrate across the sub-apertures and in the case of multiple transmit apertures a free space optical Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) system.
Owner:LGS INNOVATIONS
Stereoscopic three-dimensional display based on multi-screen splicing
InactiveCN102231044ATo achieve the suspension effectStrong expandabilityProjectorsStereoscopic photographyCamera lensParallax
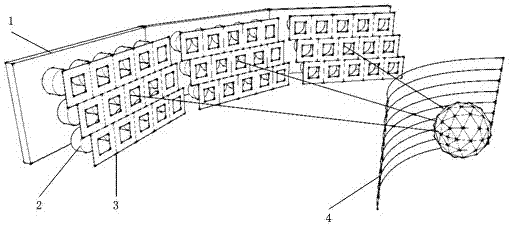
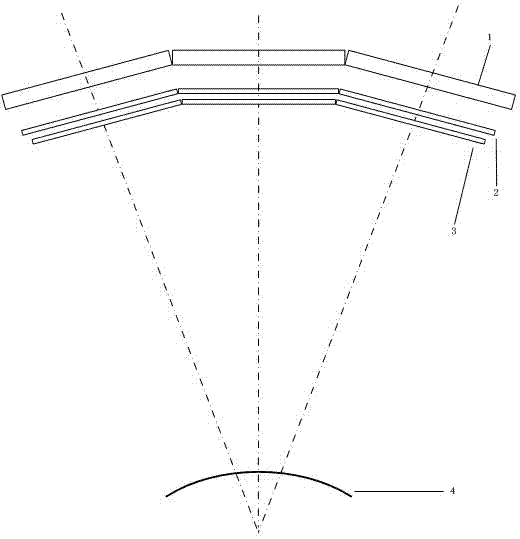
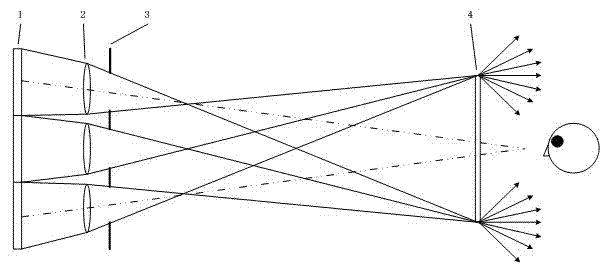
The invention discloses a stereoscopic three-dimensional display based on multi-screen splicing. The stereoscopic three-dimensional display comprises a two-dimensional display array, a projection lens array, an aperture array and a directional scattering screen. By utilizing a two-dimensional display pixel region segmentation mode and ensuring each display region of the display array to form a projector together with an aperture and a projection lens which is directly in front of the region, all projectors are staggered in vertical direction and project the images corresponding to the display regions to a same position on the directional scattering screen so as to form an image in front of an arc-shaped screen; and the images displayed in each display region are spliced by the images of a three-dimensional object from different visual angles according to a specific segmentation and recombination method. The stereoscopic three-dimensional display provided by the invention has the advantages of achieving high image resolution and high visual angle resolution and realizing observation of an exquisite three-dimensional image with a horizontal parallax. Compared with the single naked-eye display, stereoscopic three-dimensional display provided by the invention has the advantages that the multi-screen splicing settings ensures that the extension of visual angles is realized, and the spatial scale and viewing range of the three-dimensional images are increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Split aperture array for increased short range target coverage
InactiveUS7423578B1Increase the number ofEffectively double the elevation beamwidthsIndividually energised antenna arraysRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsControl signal
A phased array radar system comprising a plurality of radiating elements configured in a common array aperture for detecting and tracking targets; and a transmit and receive arrangement responsive to a first control signal for configuring the plurality of radiating elements to define a plurality of sub-apertures from the common array aperture for detecting and tracking short range targets, wherein the plurality of sub-apertures are independently steerable array apertures.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Near-field transform spectroscopy
InactiveUS6858436B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioHigh spectral resolutionSpectrum investigationComponent separationAnalyteSpectroscopy
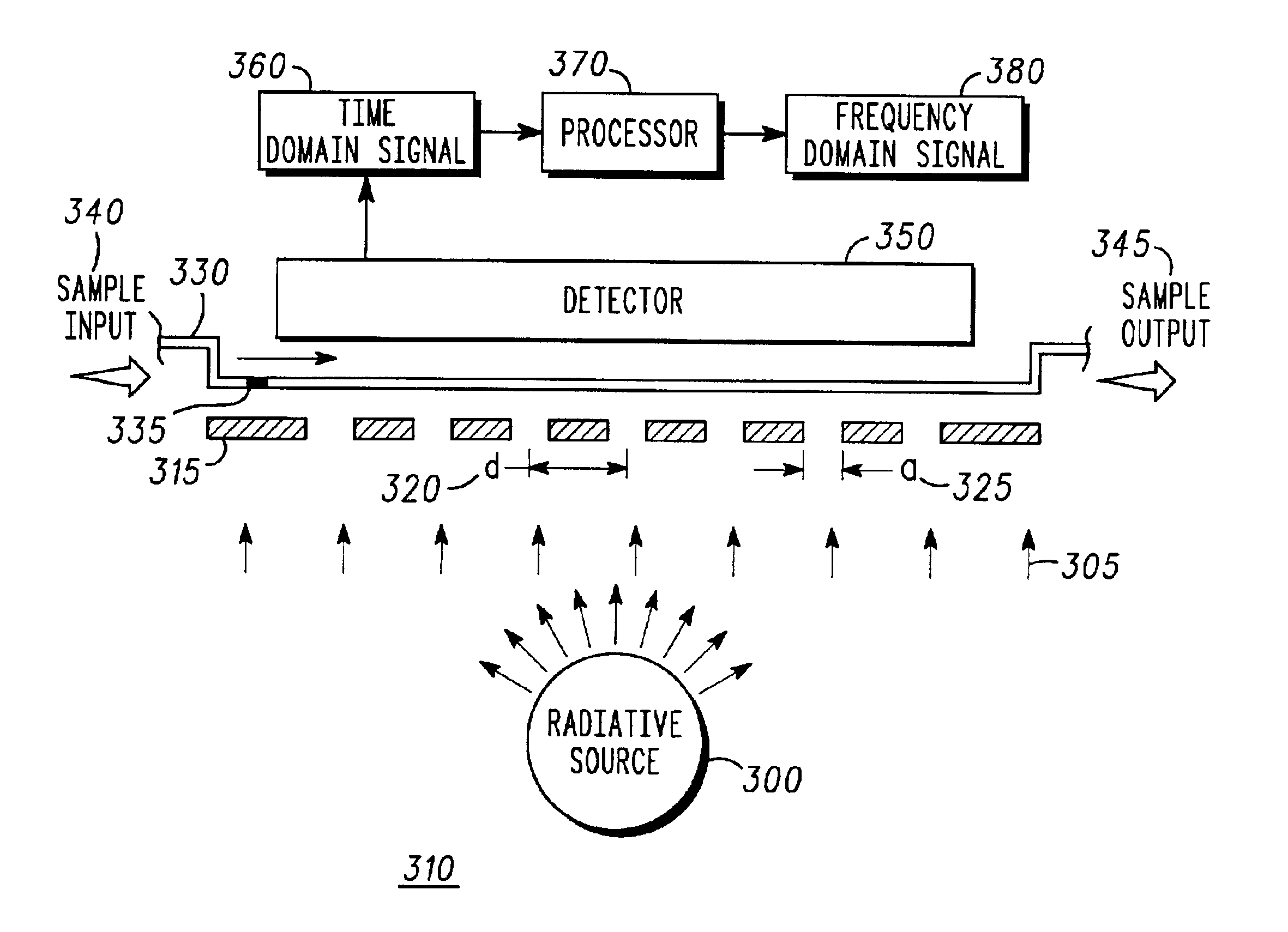
An exemplary system and method for detecting at least one analyte in a sample comprises inter alia a source of radiation (300), a near-field aperture array (315), a chromatographic field (330), a detector (350), and a data processor (370). Disclosed features and specifications may be variously controlled, adapted or otherwise optionally modified to improve detection of any sub-diffraction-limited scale phenomena. Exemplary embodiments of the present invention representatively provide for improved S / N, increased sample throughput, refined spectral resolution and enhanced detection sensitivity.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Image exposure device
InactiveUS20050213068A1Reduce sharpnessEasy alignmentPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusSpatial light modulatorLight beam
An image exposure device includes an exposure head for forming a desired pattern on a photosensitive material. The exposure head is equipped with a light source for emitting a great number of light beams, a spatial light modulator in which a great number of pixel portions are arranged for independently modulating the light beams emitted from the light source, a micro lens array in which a great number of micro lenses are arranged for individually converging the great number of light beams modulated by the pixel portions, and a total of two or more aperture arrays arranged in the stage before the micro lens array and / or the stage after the micro lens array. Each of the aperture arrays has a great number of apertures for individually restricting the light beams.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Charged particle beam applied apparatus
ActiveUS20110272576A1Easy to implementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesBeam scanningSource image
Provided is a multi-beam type charged particle beam applied apparatus in an implementable configuration, capable of achieving both high detection accuracy of secondary charged particles and high speed of processing characteristically different specimens. An aperture array (111) includes plural aperture patterns. A deflector (109) for selecting an aperture pattern through which a primary beam passes is disposed at the position of a charged particle source image created between an electron gun (102), i.e., a charged particle source, and the aperture array (111). At the time of charge-control beam illumination and at the time of signal-detection beam illumination, an aperture pattern of the aperture array (111) is selected, and conditions of a lens array (112), surface electric-field control electrode (118) and the like are switched in synchronization with each beam scanning. Thus, the charges are controlled and the signals are detected at different timings under suitable conditions, respectively.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Dipole locator using multiple measurement points
A receiver and tracking system for identifying a location of a magnetic field source. In a preferred embodiment a plurality of tri-axial antennas are positioned at three distinct points on a receiver frame. Each antenna detects a magnetic field from a source and a processor is used to determine a location of the source relative to the frame using the antenna signals. Each tri-axial antenna comprises three windings in each of three channels defined by a support structure. The windings each define an aperture area. The windings have substantially identical aperture areas and have a common center point. The receiver may to display to the operator the relative location of the field source or may direct the operator to a spot directly above the field source.
Owner:CHARLES MACHINE WORKS
Charged particle beam exposure system
ActiveUS20050269528A1Improve performanceHigh resolutionElectric discharge tubesNanoinformaticsTarget surfaceLight beam
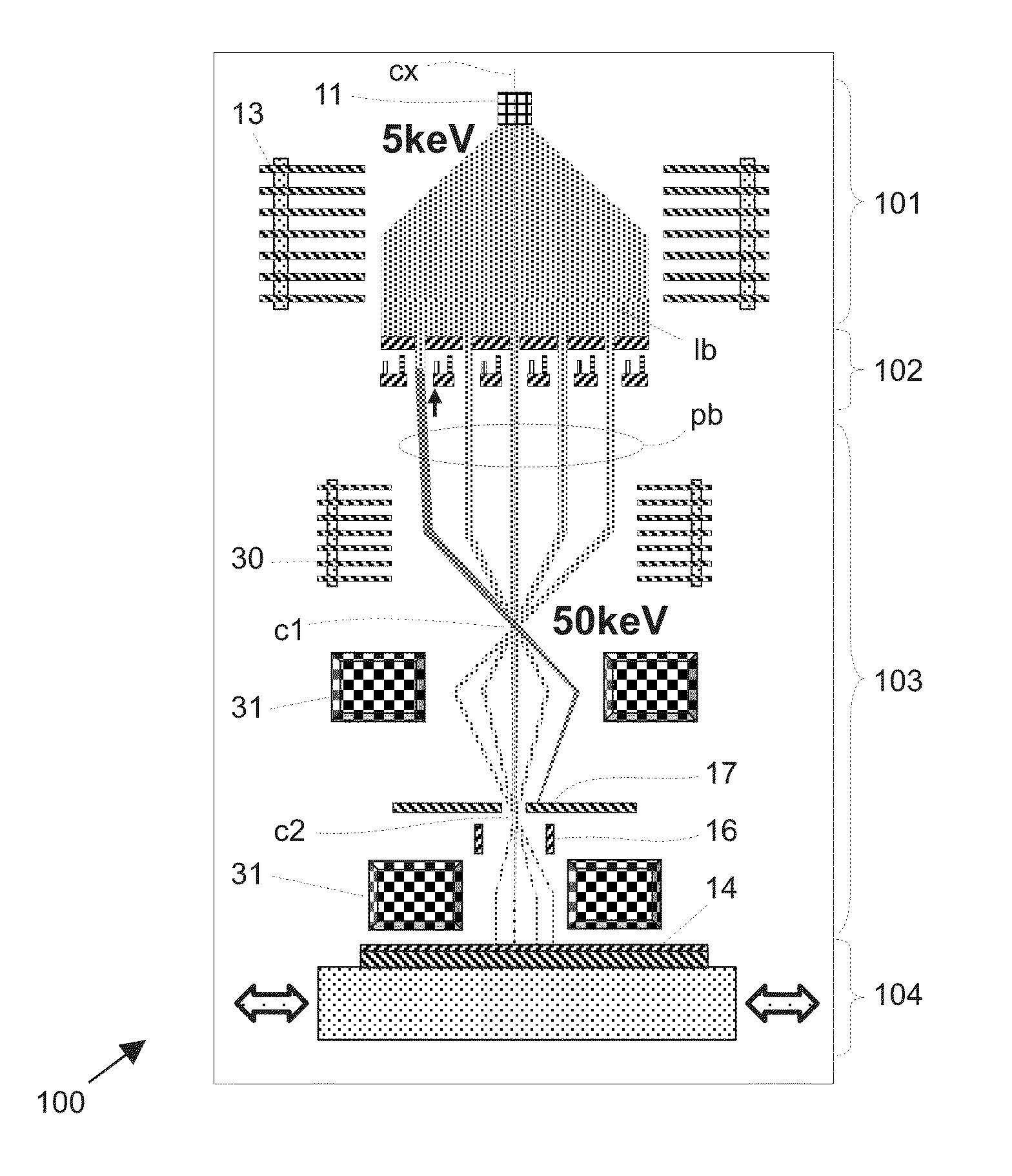
A charged particle beam exposure apparatus for transferring a pattern onto a surface of a target, comprising a beam generator comprising a plurality of n changed particle sources, substantially in one plane, each source adapted for generating a charged particle beam, a first aperture array, comprising a plurality of groups of apertures, each group of apertures aligned with one source, for splitting each beam up into a plurality of beamlets m, thus resulting in a total of nxm beamlets, and a deflector array, comprising a plurality of groups of deflectors, each group of deflectors aligned with one source and one group of apertures, each deflector in a group aligned with an aperture of the corresponding group, and each group of deflectors operable for asserting a collimating influence on its corresponding beam.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Fiber coupled artificial compound eye
InactiveUS7376314B2Sharpen imageReduce optical aberrationAdditive manufacturing apparatusCoupling light guidesDistortion freeDetector array
A multiple aperture array, wide angle imaging system incorporates compound refractive optics modeled after the eyes of insects. The system channels light through the apertures of a convex spatial filter and a pair of lenslet arrays hot press molded on a positive meniscus form. The lenslets act as afocal Keplerian telescopes to superpose light from hundreds of adjacent channels to a common point on the convex surface of a fiber optic imaging taper. The superposed light from all the channels form a curved, high intensity image that is transformed by the taper into a flat format for readout by a mosaic detector array. The image is upright and distortion free with an infinite depth of field. Ghost images are blocked by a honeycomb louver baffle positioned between the lenslets and the imaging taper. The system is conformable to the geometry of any convex mounting surface, whether spherical, aspherical, or cylindrical.
Owner:SPECTRAL IMAGING LAB
Drawing apparatus, drawing method and method of manufacturing article
InactiveUS20120219914A1Reliability advantageReliability throughputStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsComputational physicsAperture array
A drawing apparatus for drawing on a substrate by a plurality of charged particle beams includes: an aperture array, a blanker array, a scanning mechanism, and a controller. The aperture array specifies the dimension of each of the plurality of charged particle beams on the substrate. The blanker array carries out blanking of the plurality of charged particle beams independently. The scanning mechanism performs a relative scanning between the plurality of charged particle beams and the substrate in each of the first direction and a second direction which cross each other. The controller controls the blanker array at a predetermined pitch on the substrate. The dimension and the pitch are smaller in one of the first direction and the second direction than in the other.
Owner:CANON KK
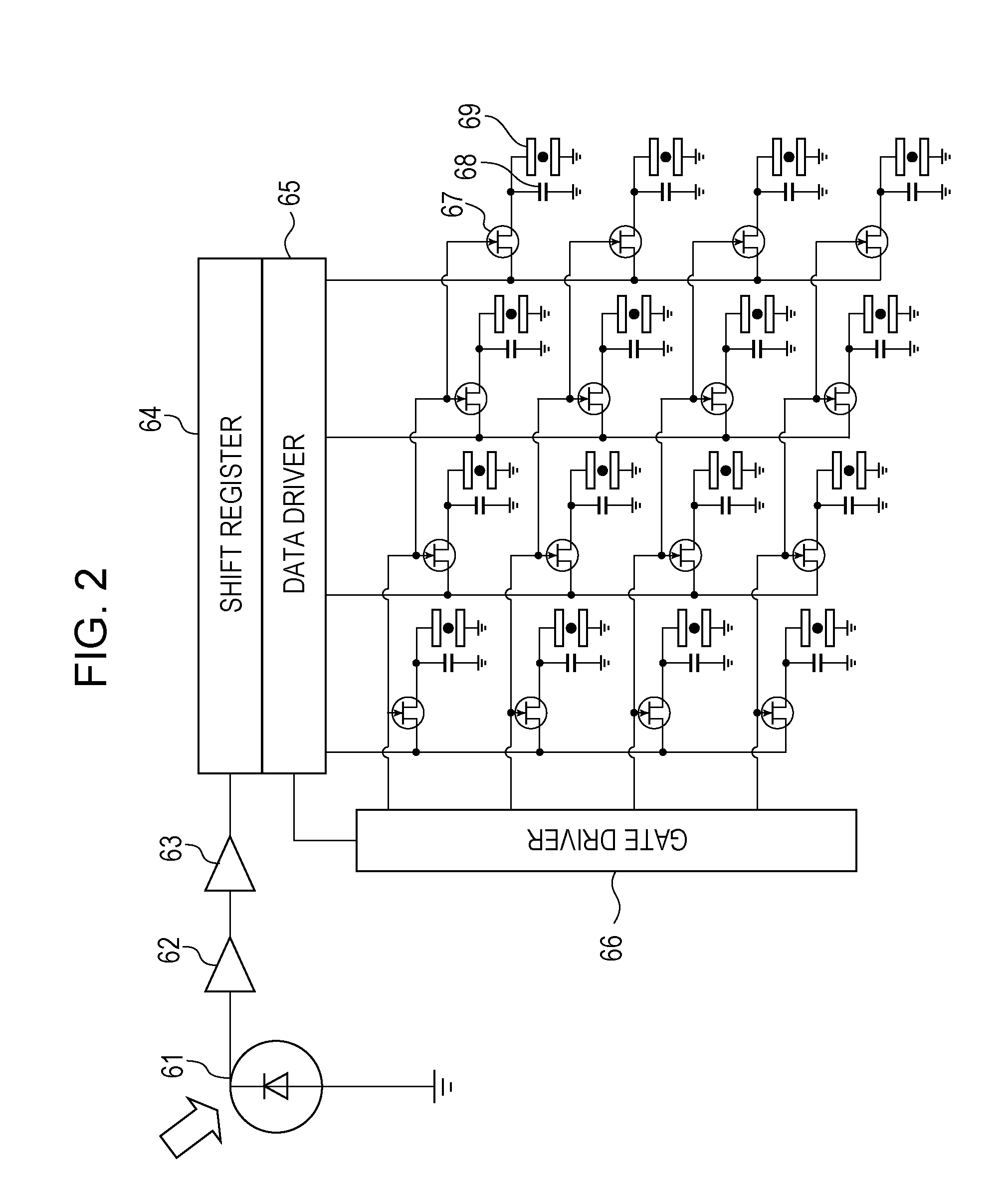
Contact-type monolithic image sensor
InactiveUS20060202104A1Reduce thicknessEasy constructionSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansCMOSIn plane
A thin monolithic image sensor of the invention is comprised of a laminated solid package composed essentially of an optical layer and an image-receiving layer placed on the top of the optical layer. The optical layer also comprises a laminated structure composed of at least an optical microlens-array sublayer and an aperture-array sublayer. The image-receiving layer is a thin flat CCD / CMOS structure that may have a thickness of less than 1 mm. The image digitized by the CCD / CMOS structure of the sensor can be transmitted from the output of the image-receiving layer to a CPU for subsequent processing and, if necessary, for displaying. A distinguishing feature of the sensor of the invention is that the entire sensor along with a light source has a monolithic structure, and that the diaphragm arrays are located in planes different from the plane of the microlens array and provide the most efficient protection against overlapping of images produced by neighboring microlenses.
Owner:MICROALIGN TECH
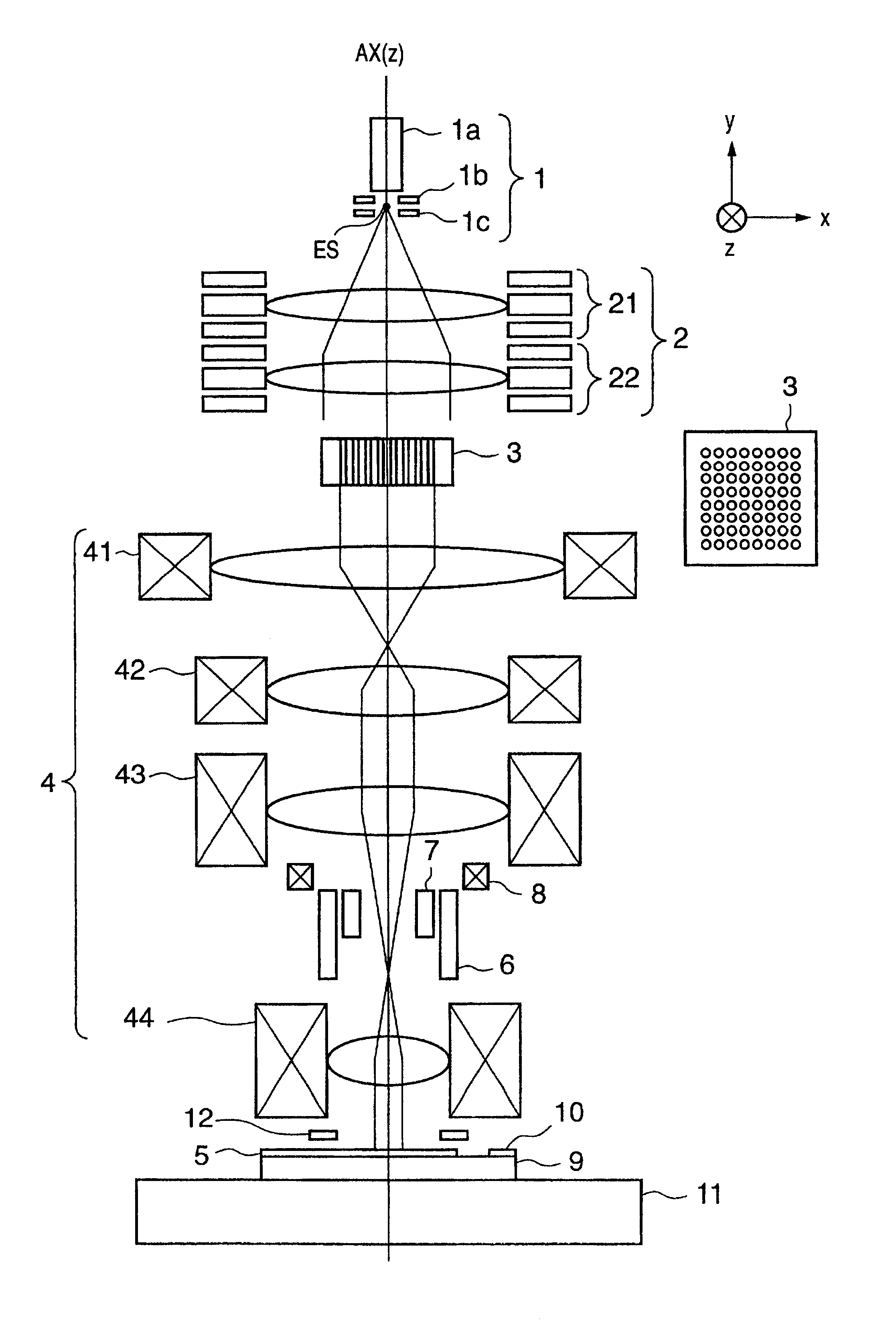
Charged particle beam exposure apparatus and method
InactiveUS7005658B2Higher-precision drawingElectric discharge tubesNanoinformaticsIntermediate imageElectron source
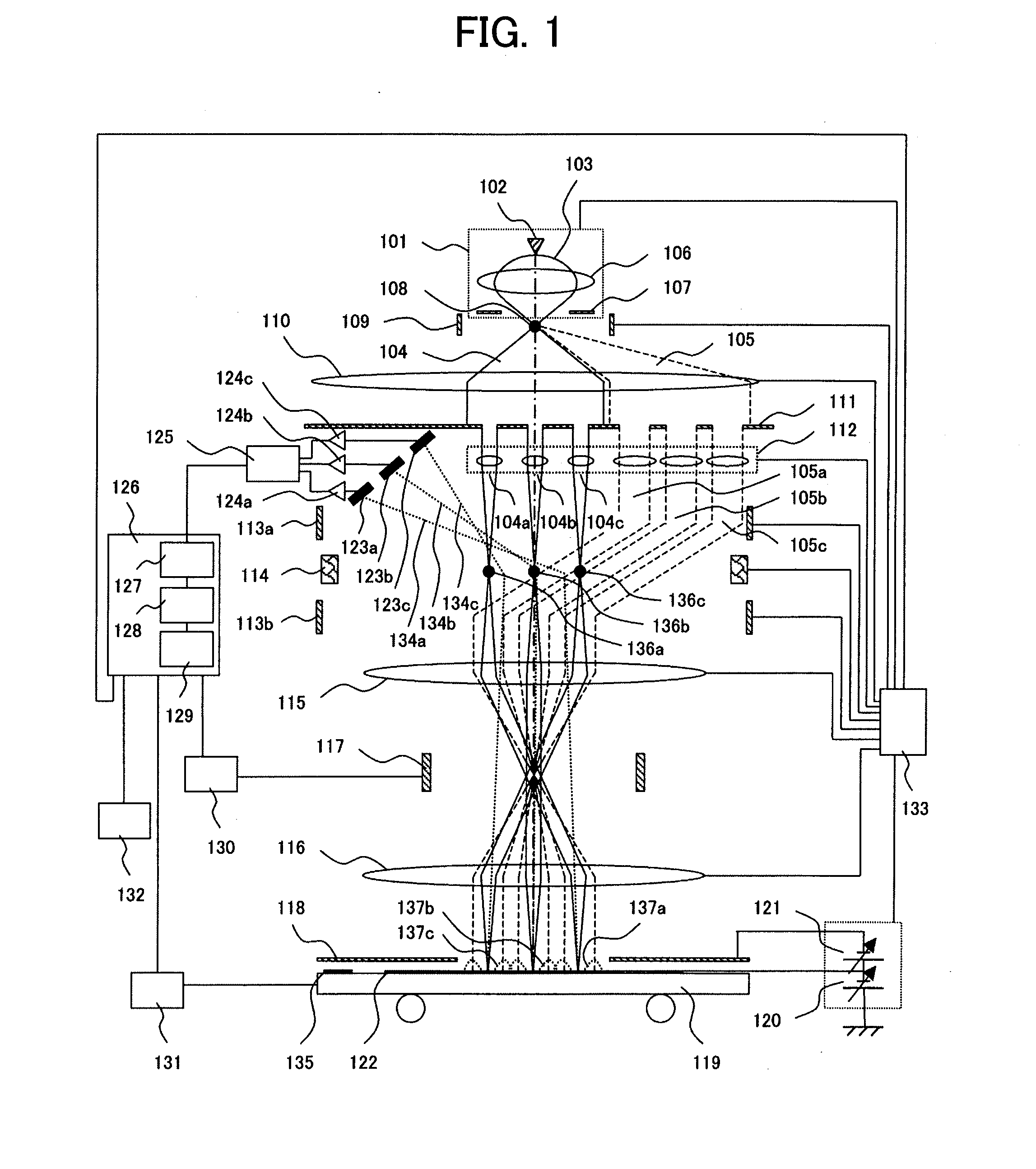
A multi-charged-particle beam drawing apparatus and method that can correct a change in positional relationship, caused by the Coulomb effect, among charged particle beams are provided. The focal lengths of two electron lenses (21, 22) that form a condenser lens (2) are adjusted individually to change a relative positional relationship between the front focal position of the condenser lens (2) and an electron source (ES). Electron beams becoming incident on an aperture array (AA) can diverge, or be focused or collimated. Therefore, positions where intermediate images (img1-img3) are to be formed can be changed, and the change in positional relationship, caused by the Coulomb effect, among the charged particle beams can be corrected.
Owner:CANON KK
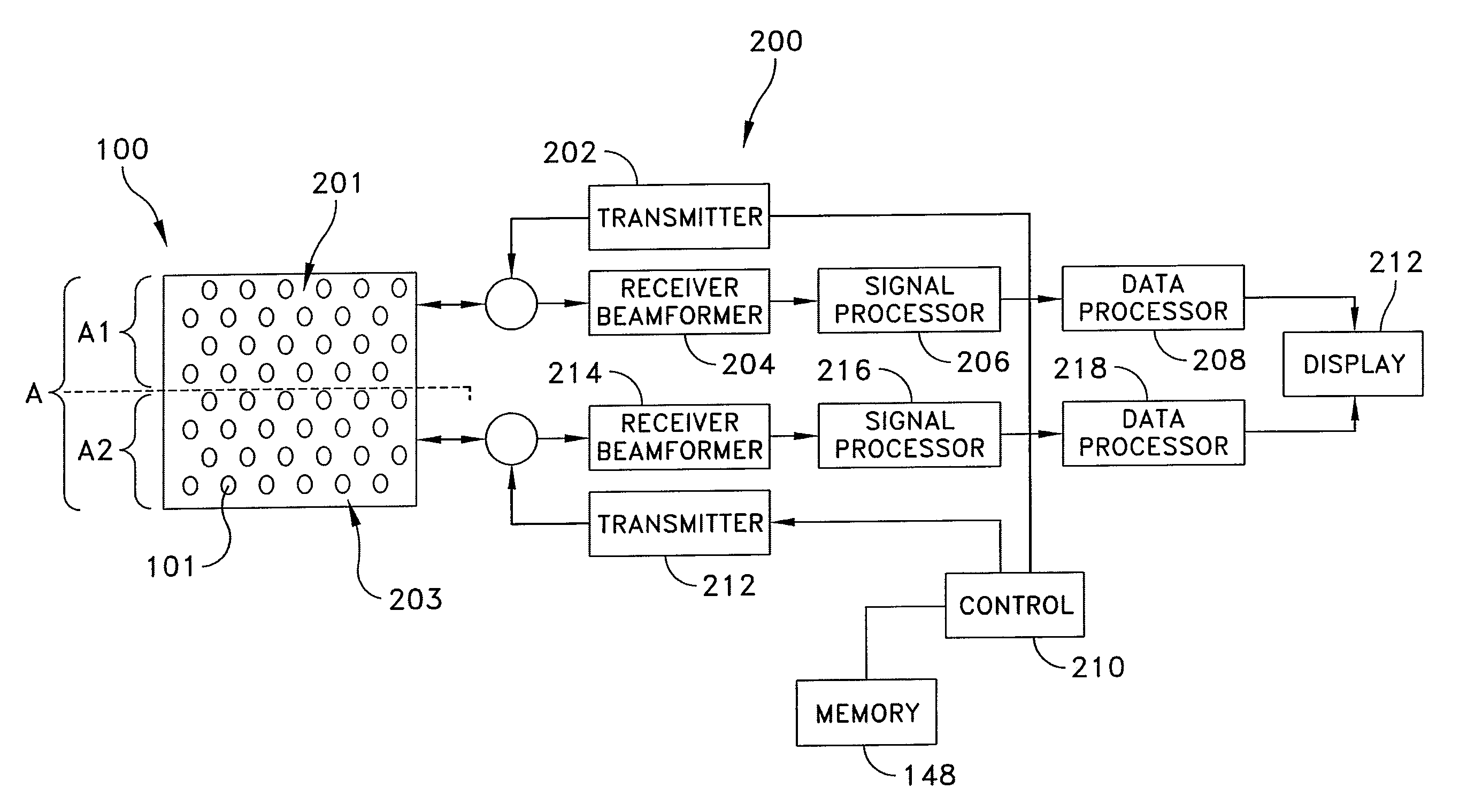
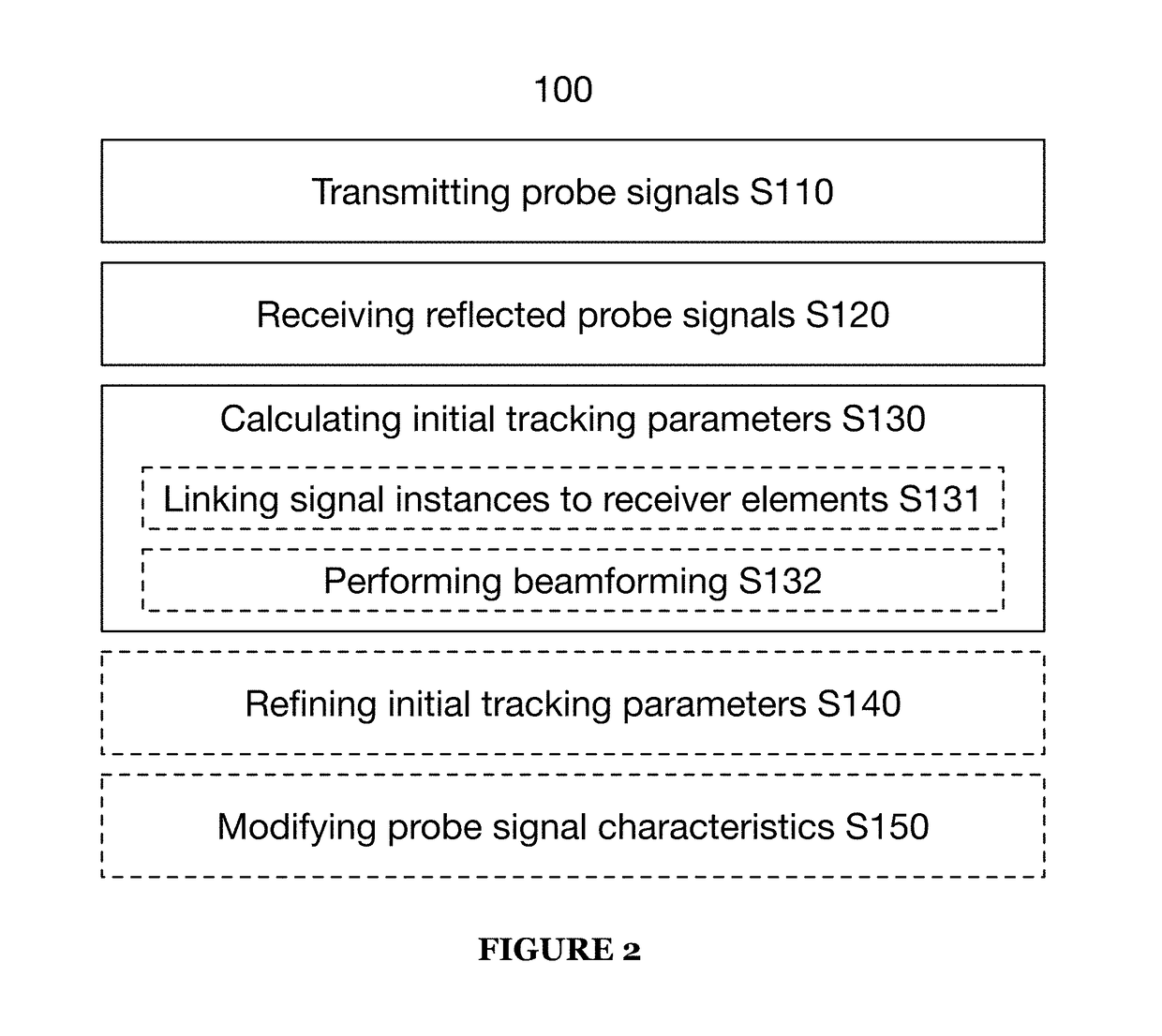
Systems and methods for virtual aperature radar tracking
A method for virtual aperture array radar tracking includes: transmitting first and second probe signals; receiving a first reflected probe signal at a radar array; receiving a second reflected probe signal at the radar array; calculating a target range from at least one of the first and second reflected probe signals; corresponding signal instances of the first reflected probe signal to physical receiver elements of the radar array; corresponding signal instances of the second reflected probe signal to virtual elements of the radar array; calculating a first target angle by performing beamforming from the signal instances of the first and second reflected probe signals; and calculating a position of the tracking target relative to the radar array from the target range and first target angle.
Owner:OCULII CORP
Interface, a method for observing an object within a non-vacuum environment and a scanning electron microscope
ActiveUS8164057B2Easy to detectHigh resolution imageEngine sealsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationScanning tunneling microscopeThin membrane
An interface, a scanning electron microscope and a method for observing an object that is positioned in a non-vacuum environment. The method includes: passing at least one electron beam that is generated in a vacuum environment through at least one aperture out of an aperture array and through at least one ultra thin membrane that seals the at least one aperture; wherein the at least one electron beam is directed towards the object; wherein the at least one ultra thin membrane withstands a pressure difference between the vacuum environment and the non-vacuum environment; and detecting particles generated in response to an interaction between the at least one electron beam and the object.
Owner:B NANO
Charged particle beam lithography apparatus and method, and article manufacturing method
InactiveUS20130164684A1Improve shielding effectStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsLithographic artistAperture array
A lithography apparatus performs writing on a substrate with a plurality of charged particle beams and includes a blanking deflector array for blanking the plurality of charged particle beams; an aperture array configured to block a charged particle beam deflected by the blanking deflector array; and a sealing mechanism configured to seal an opening of at least one of the blanking deflector array and the aperture array with a shielding material that shields a charged particle beam.
Owner:CANON KK
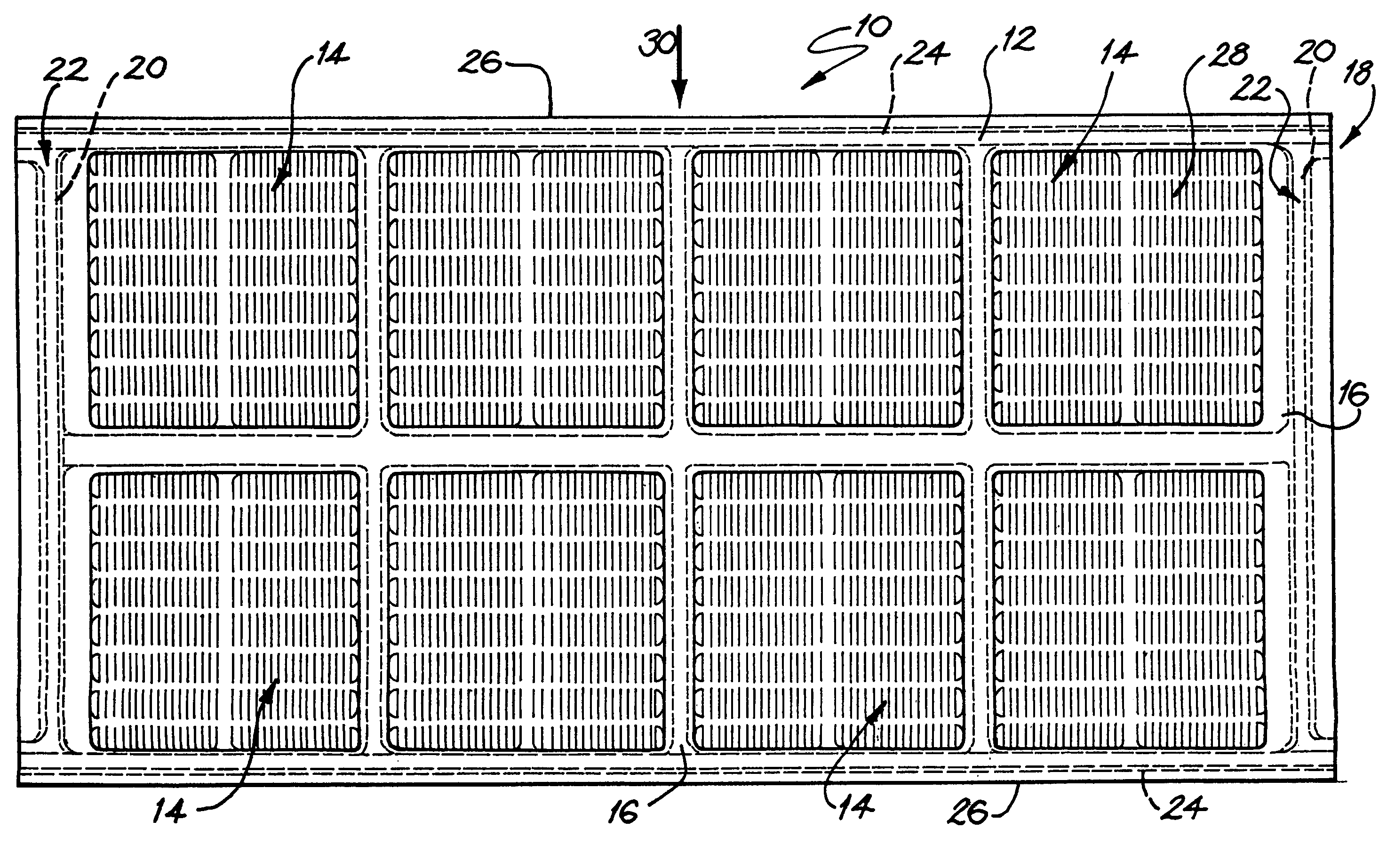
Screening module
A screening module for a screening assembly includes a panel member having a periphery defined by a pair of opposed, parallel sides and a pair of opposed parallel ends. A mounting formation is arranged about at least a part of the periphery of the panel member for mounting the panel member on an underlying frame. A plurality of discrete aperture arrays are defined in a surface of the body member. A skirt portion circumscribes each aperture array, each skirt portion depending from a lower surface of the panel member. A reinforcing arrangement is arranged beneath each aperture array, the reinforcing arrangement being bounded by its associated skirt portion.
Owner:F L SMIDTH & CO AS
Imaging system
ActiveUS20110079730A1Sufficient wafer throughputHigh resolutionStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsTarget surfaceLight beam
A charged particle multi-beamlet system for exposing a target (11) using a plurality of beamlets. The system comprises a charged particle source (1) for generating a charged particle beam (20), a beamlet aperture array (4D) for defining groups of beamlets (23) from the generated beam, a beamlet blanker array (6) comprising an array of blankers for controllably blanking the beamlets (23), a beam stop array (8) for blanking beamlets (23) deflected by the blankers, the beam stop array (8) comprising an array of apertures, each beam stop aperture corresponding to one or more of the blankers, and an array of projection lens systems (10) for projecting beamlets on to the surface of the target. The system images the source (1) onto a plane at the beam stop array (8), at the effective lens plane of the projection lens systems (10), or between the beam stop array (8) and the effective lens plane of the projection lens systems (10), and the system images the beamlet aperture array (4D) onto the target (11).
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Compensation of defective beamlets in a charged-particle multi-beam exposure tool
ActiveUS20150248993A1Improve calibration qualityExtended run timeElectric discharge tubesIrradiation devicesGraphicsLithographic artist
An exposure pattern is computed which is used for exposing a desired pattern on a target by means of a blanking aperture array in a particle-optical lithography apparatus which has a finite number of defects, said desired pattern being composed of a multitude of image elements within an image area on the target: A list of defective blanking apertures is provided, comprising information about the type of defect of the defective blanking apertures; from the desired pattern a nominal exposure pattern is calculated as a raster graphics over the image elements disregarding the defective blanking apertures; the “compromised” image elements (1105) are determined which are exposed by aperture images of defective blanking apertures; for each compromised element (1105), a set of neighboring image elements is selected as “correction elements” (1104); for each compromised element, corrected dose values are calculated for the correction elements, said corrected dose values minimizing an error functional of the deviation of the dose distribution including the defects from the nominal dose distribution, under the constraint that each of the corrected dose values falls within the allowed doses; and a corrected exposure pattern (1103) is generated by substituting the corrected dose values for the nominal dose values at the correction elements.
Owner:IMS NANOFABTION
Charged particle lithography system with intermediate chamber
ActiveUS20120293780A1Thermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationLithographic artistAmbient pressure
A charged particle lithography system for transferring a pattern onto the surface of a target, comprising a main vacuum chamber, a source chamber and an intermediate chamber, both located in the main vacuum chamber, a beam generator for generating a charged particle beam, the beam generator located in the source chamber, and a first aperture array element for generating a plurality of charged particle beamlets from the beam, the first aperture array element located in the intermediate chamber. The system is adapted for maintaining a first pressure in the main vacuum chamber, a second pressure in the intermediate chamber, and a third pressure in the source chamber, and wherein the first pressure is lower than an ambient pressure, the second pressure is lower than the first pressure, and the third pressure is lower than the second pressure.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Multiple-view directional display
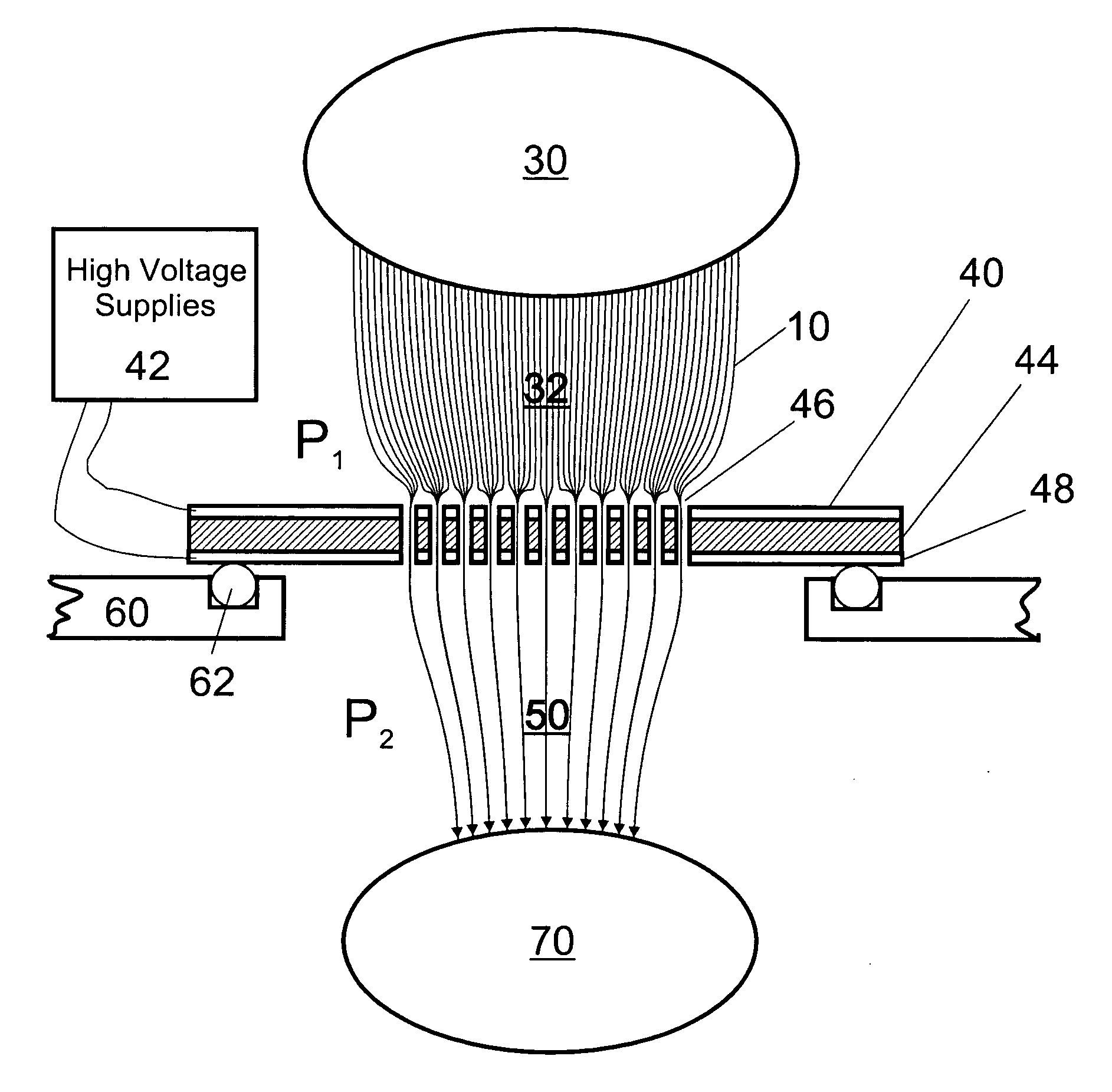
ActiveUS20090168164A1Improve display qualityReduced in angular extentAdvertisingDisplay meansParallax barrierAperture array
A multiple view directional display comprises a pixellated image display layer having a plurality of first pixels (P1) assigned to display a first image and a plurality of second pixels (P2) assigned to display a second image, and a parallax barrier aperture array (21) for directing light from the first pixels generally into a first viewing window (2) and for directing light from the second pixels generally into a second viewing window (3) not overlapping the first viewing window. The display further comprises first light directing means (31) for re-directing light emitted from a first lateral edge region (25) of each first pixel away from the second viewing window.
Owner:SHARP KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com